Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
87 results about "Process control network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
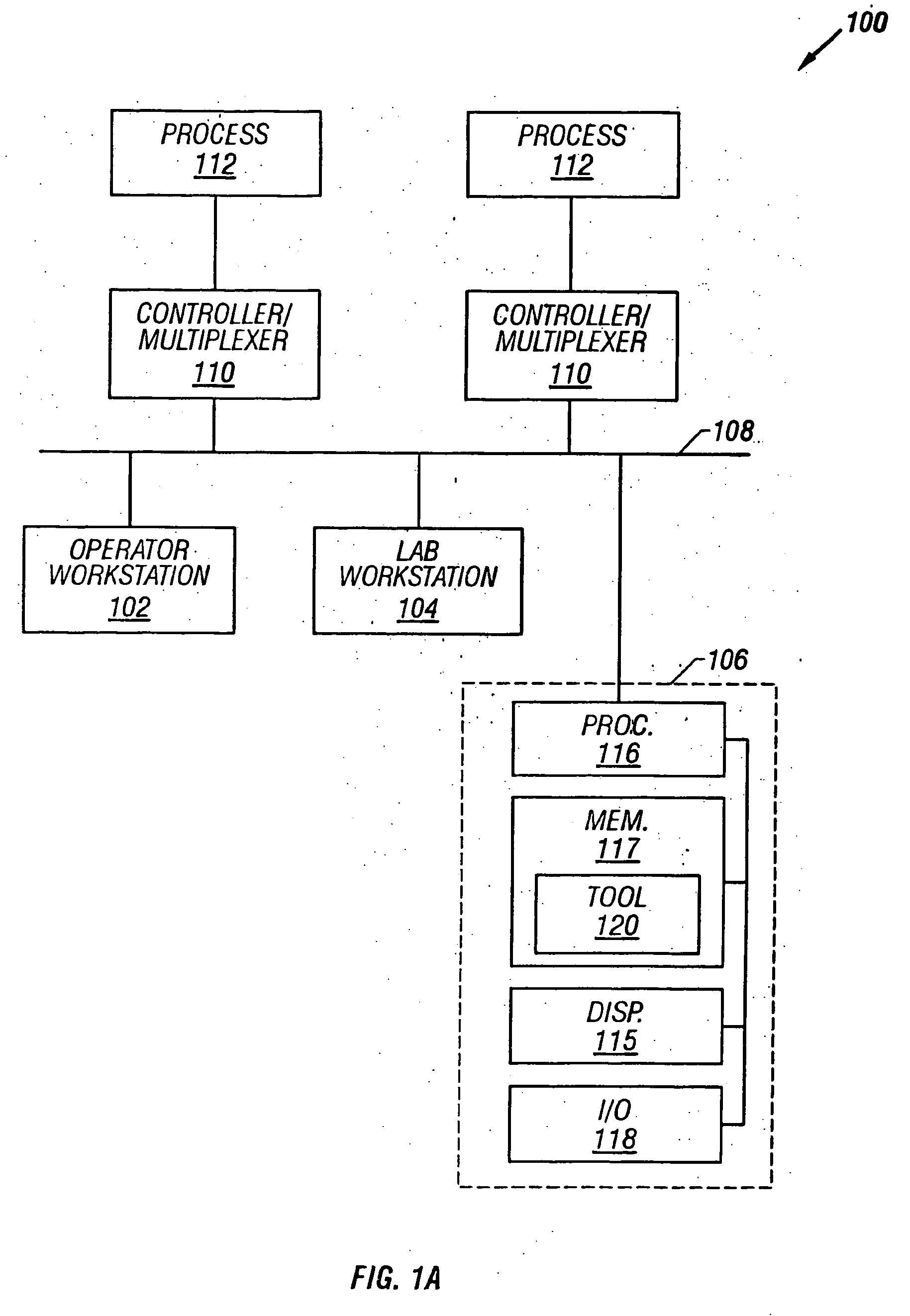
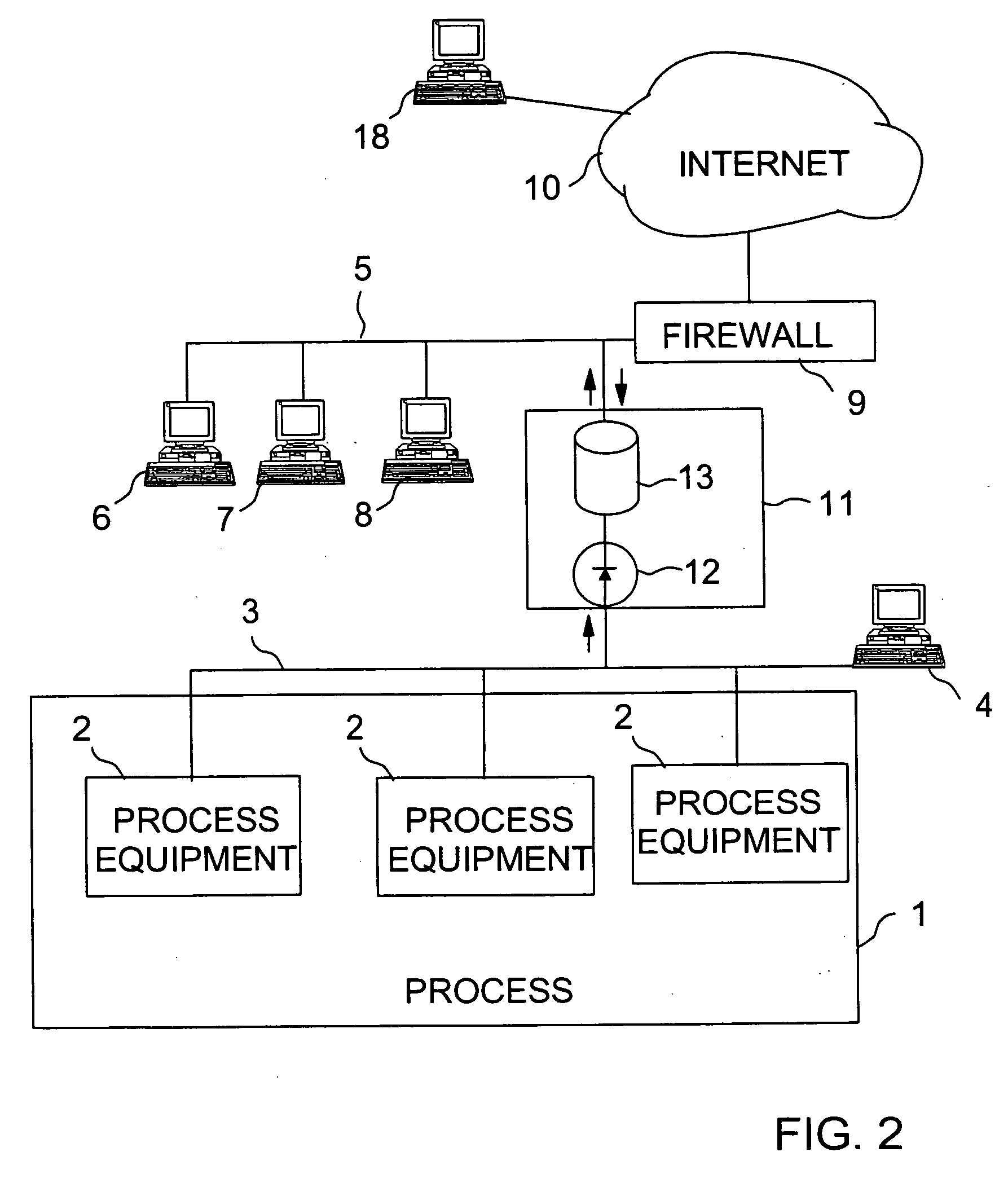
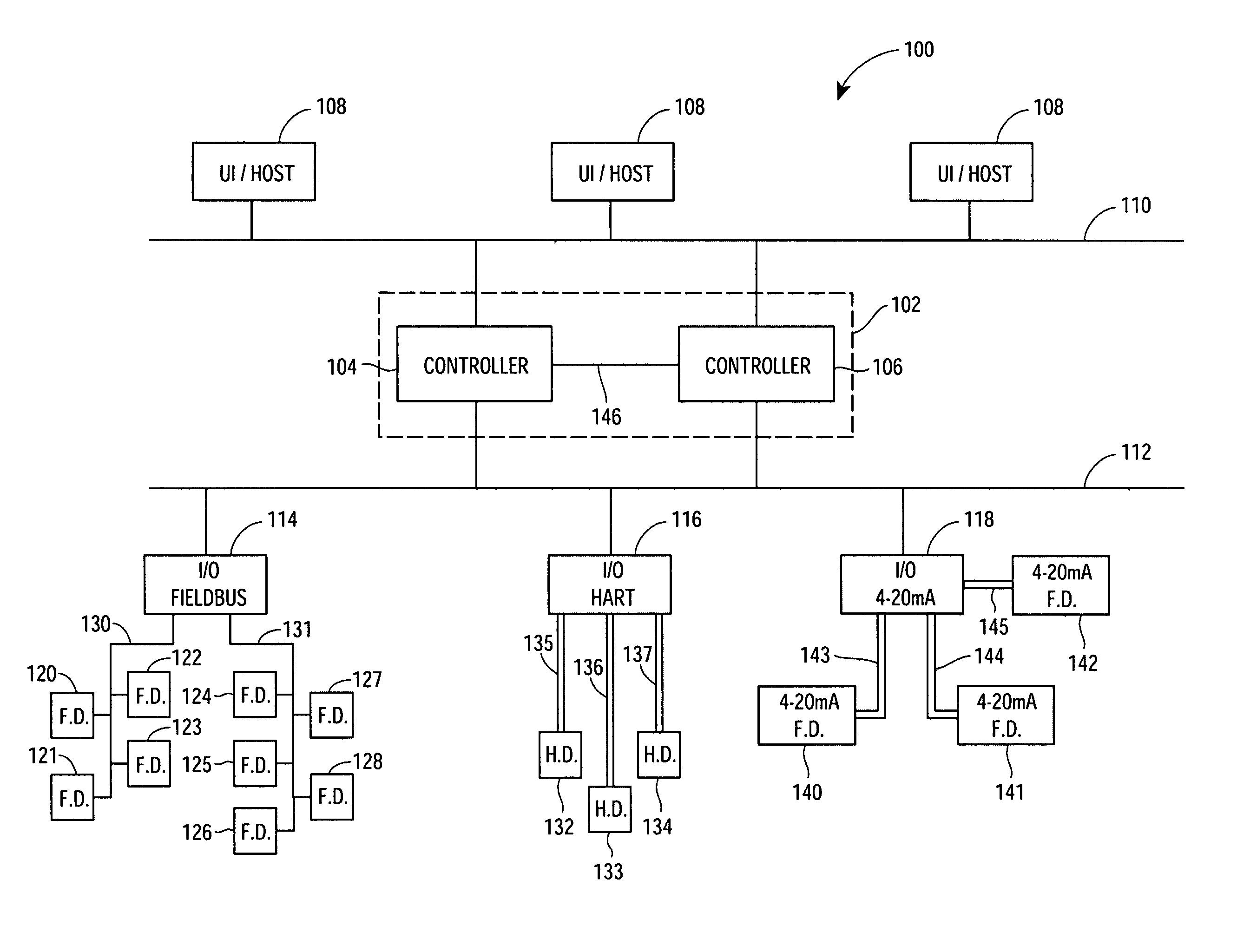
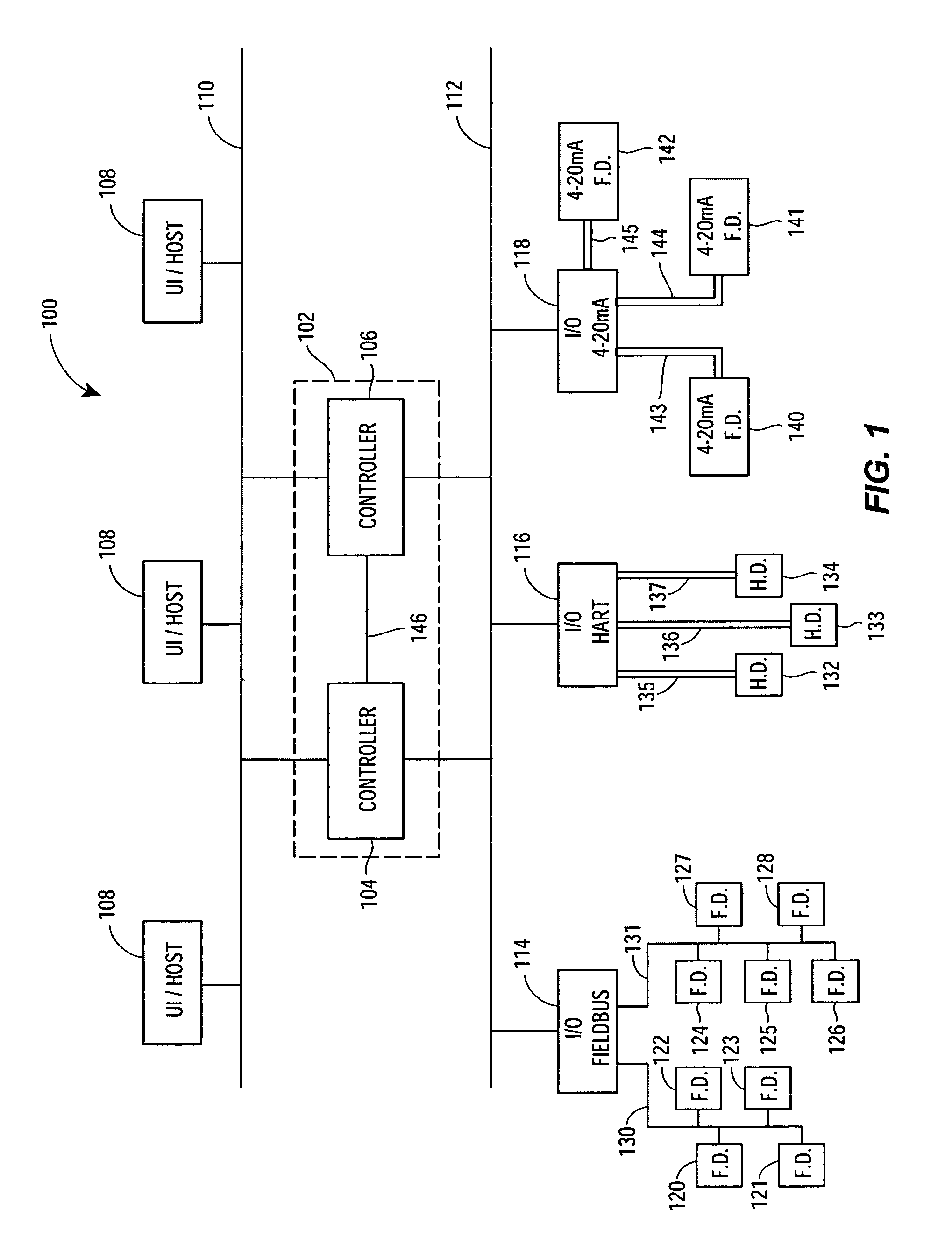
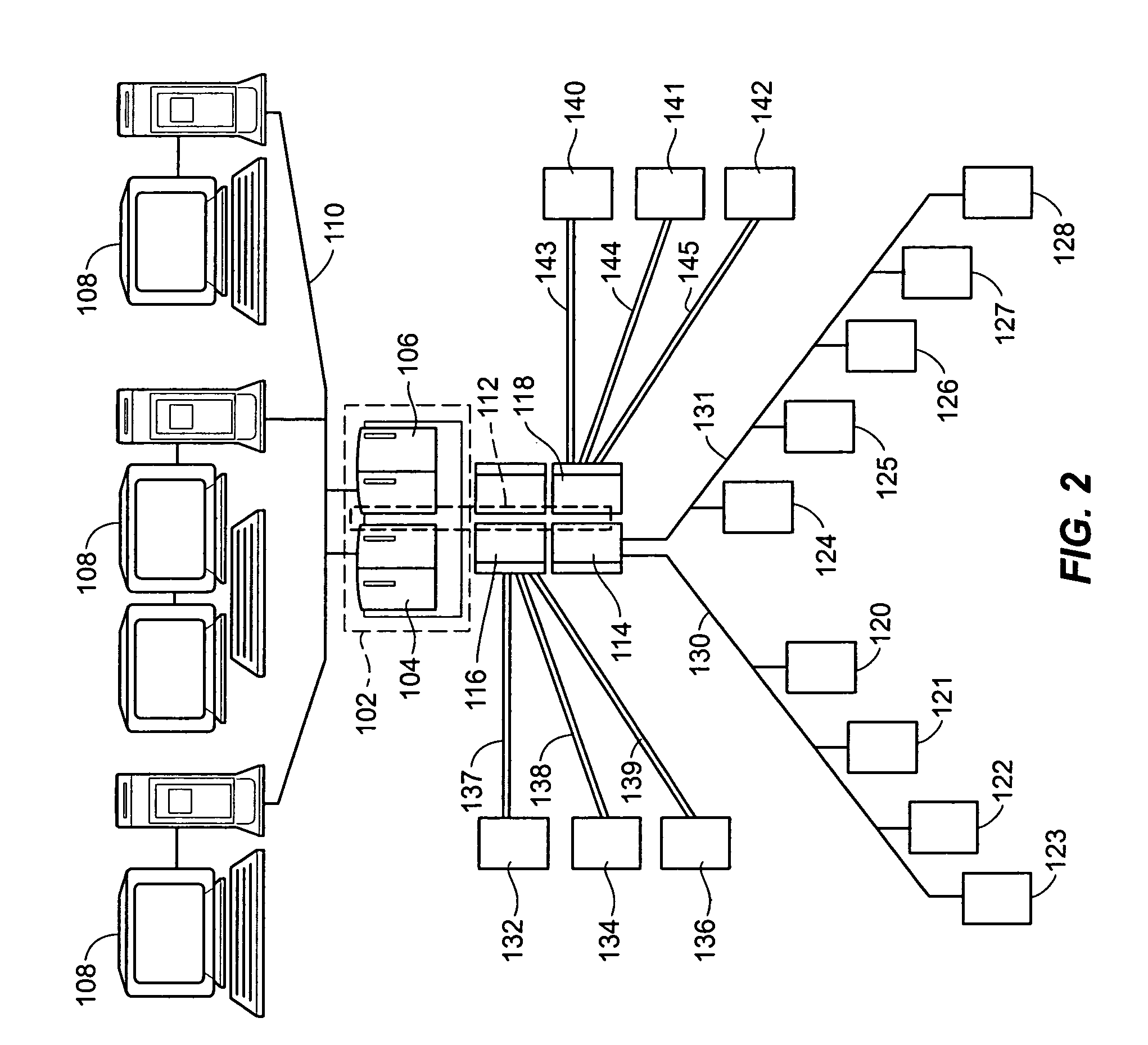
A Process Control Network (PCN) is a communications network layer that is a part of the Industrial Automation networks in Process Industries. This network is used to transmit instructions and data between control and measurement units and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) equipment.
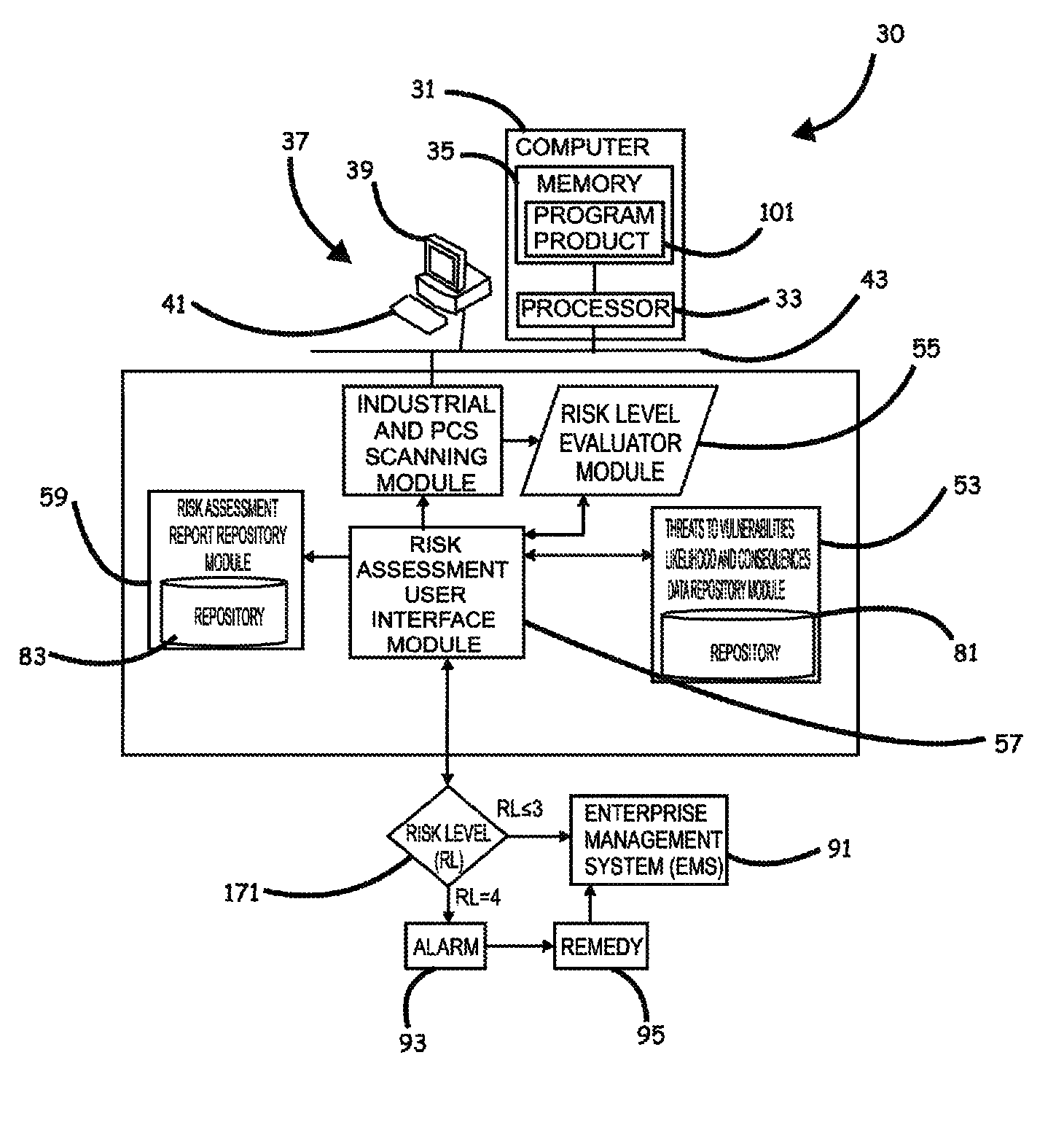
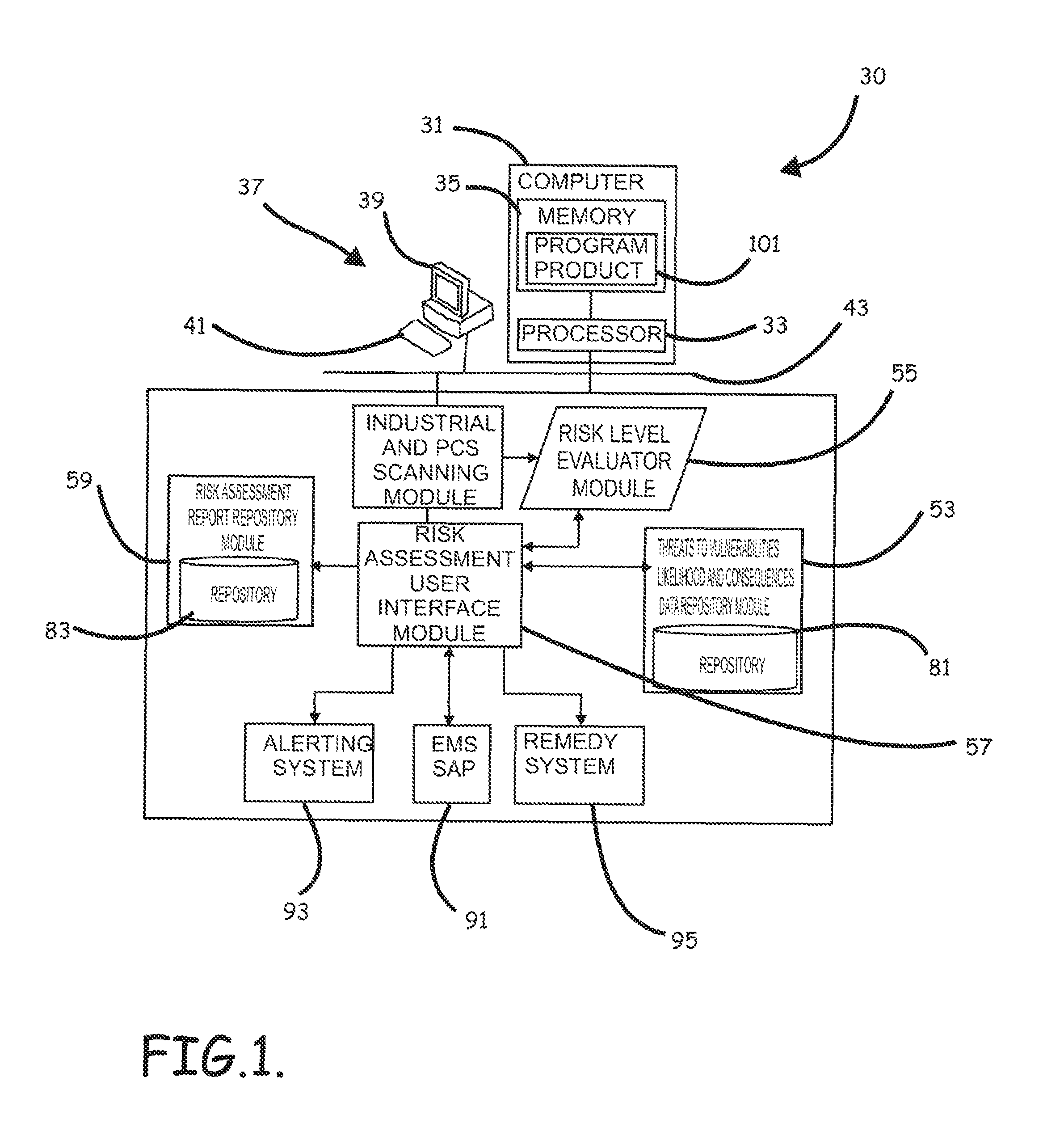
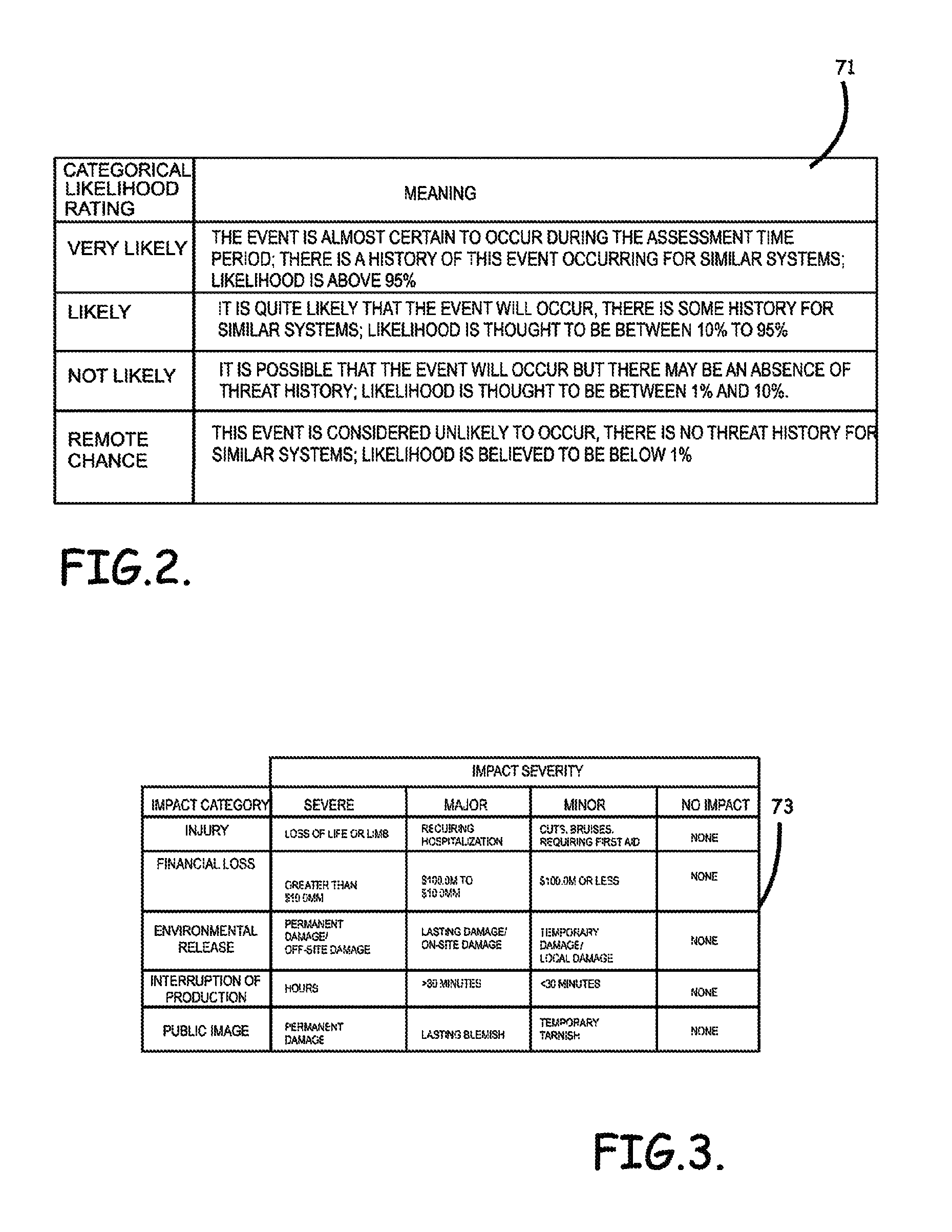
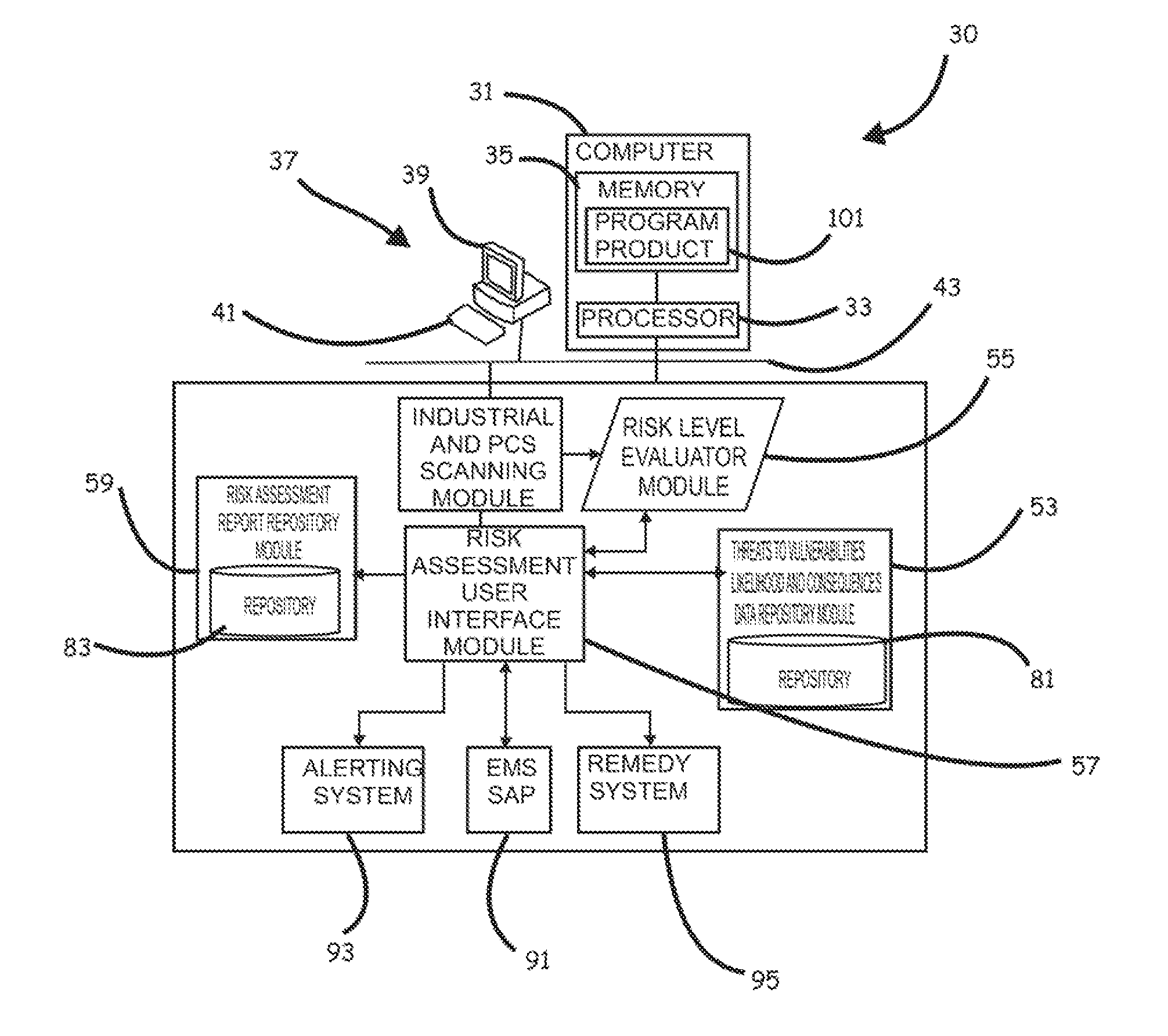
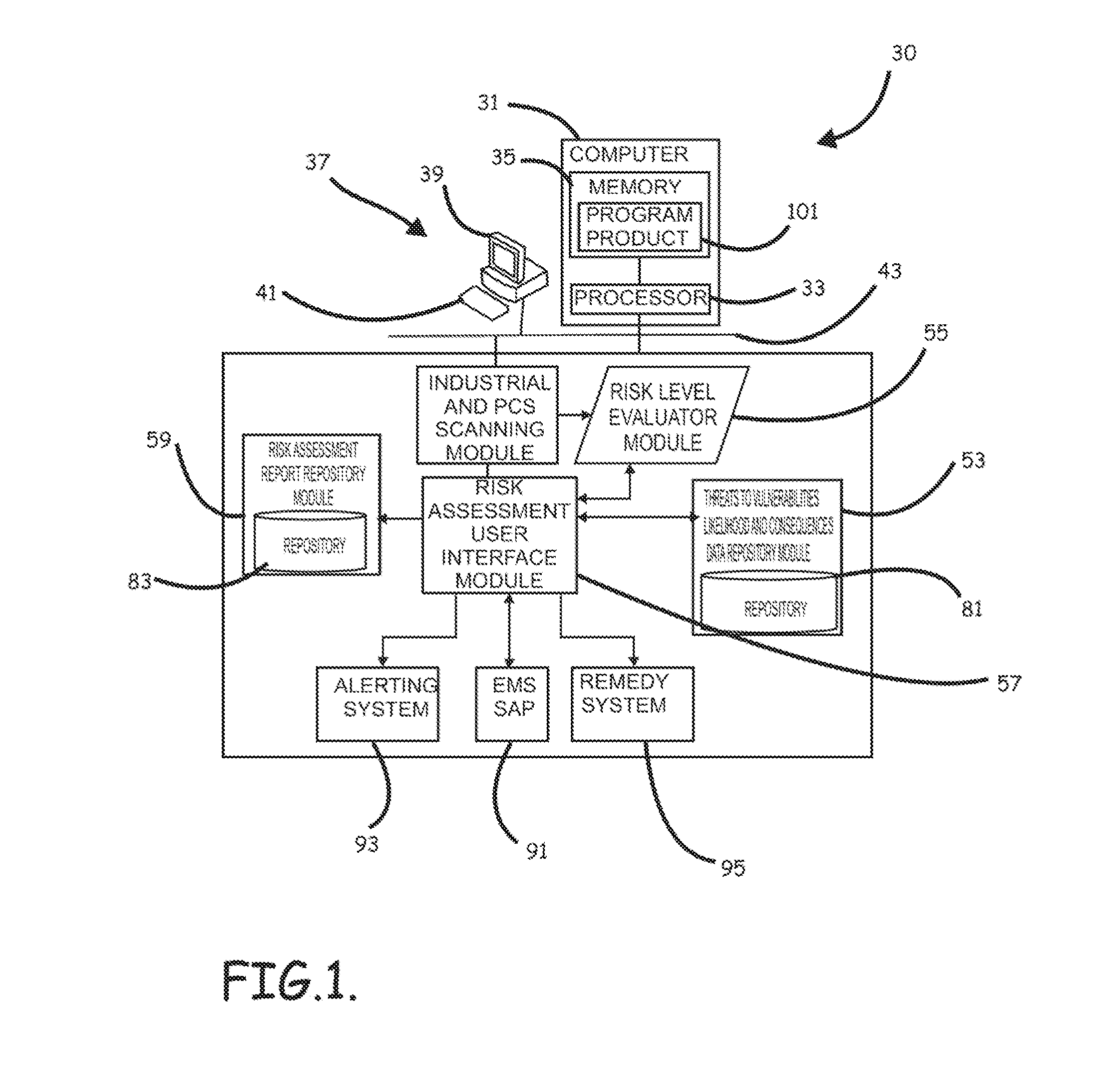
Systems, program product and methods for performing a risk assessment workflow process for plant networks and systems
ActiveUS8621637B2Minimizing human interactionEasy to implementProgramme controlMemory loss protectionRisk levelProcess control network
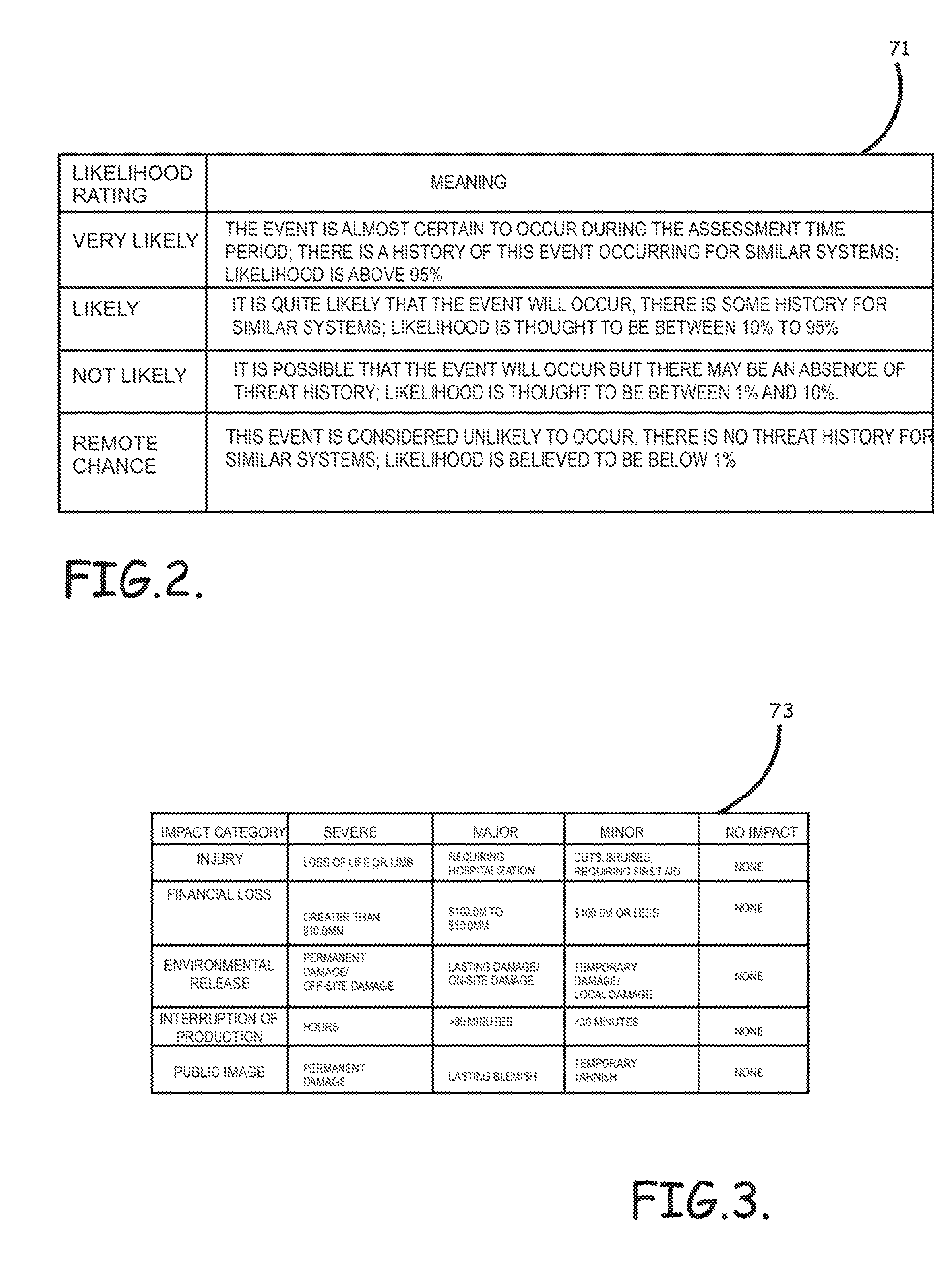
Systems, methods, and program product to perform a cyber security risk assessment on a plurality of process control networks and systems comprising a plurality of primary network assets at an industrial process facility, are provided. An example of a system and program product can include an industrial and process control systems scanning module configured to identify networks and systems topology and to execute system and network security, vulnerability, virus, link congestion, node congestion analysis to thereby detect susceptibility to know threats to define potential vulnerabilities; a threats to vulnerabilities likelihood and consequences data repository module configured to determine a likelihood of each of a plurality of known threats exploiting identified vulnerabilities and to identify consequences of the exploitation to individual impacted systems and to overall plant operation; and a risk level evaluator module configured to determine a risk level rating for any identified vulnerabilities and provide recommended corrective actions.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
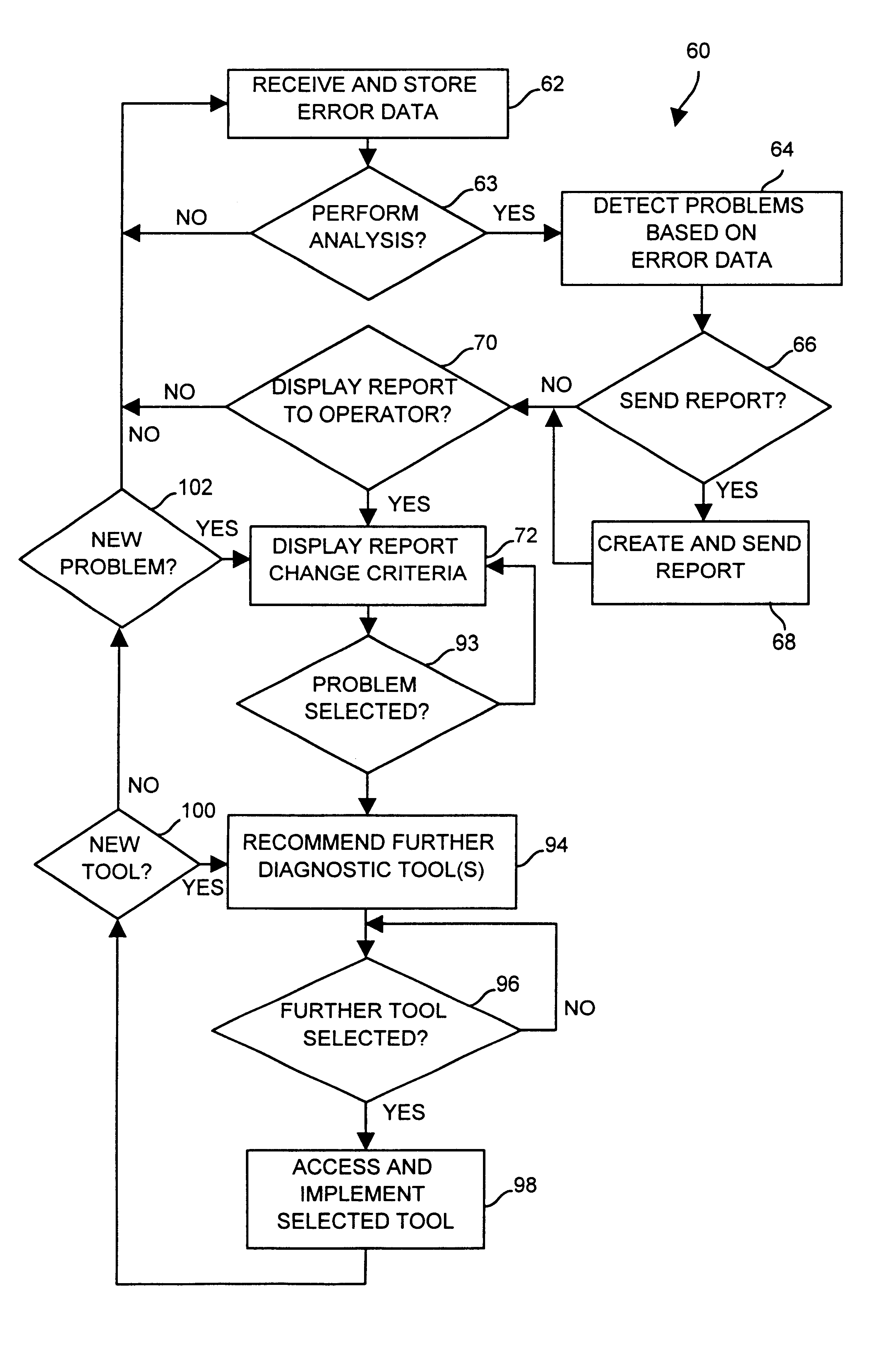
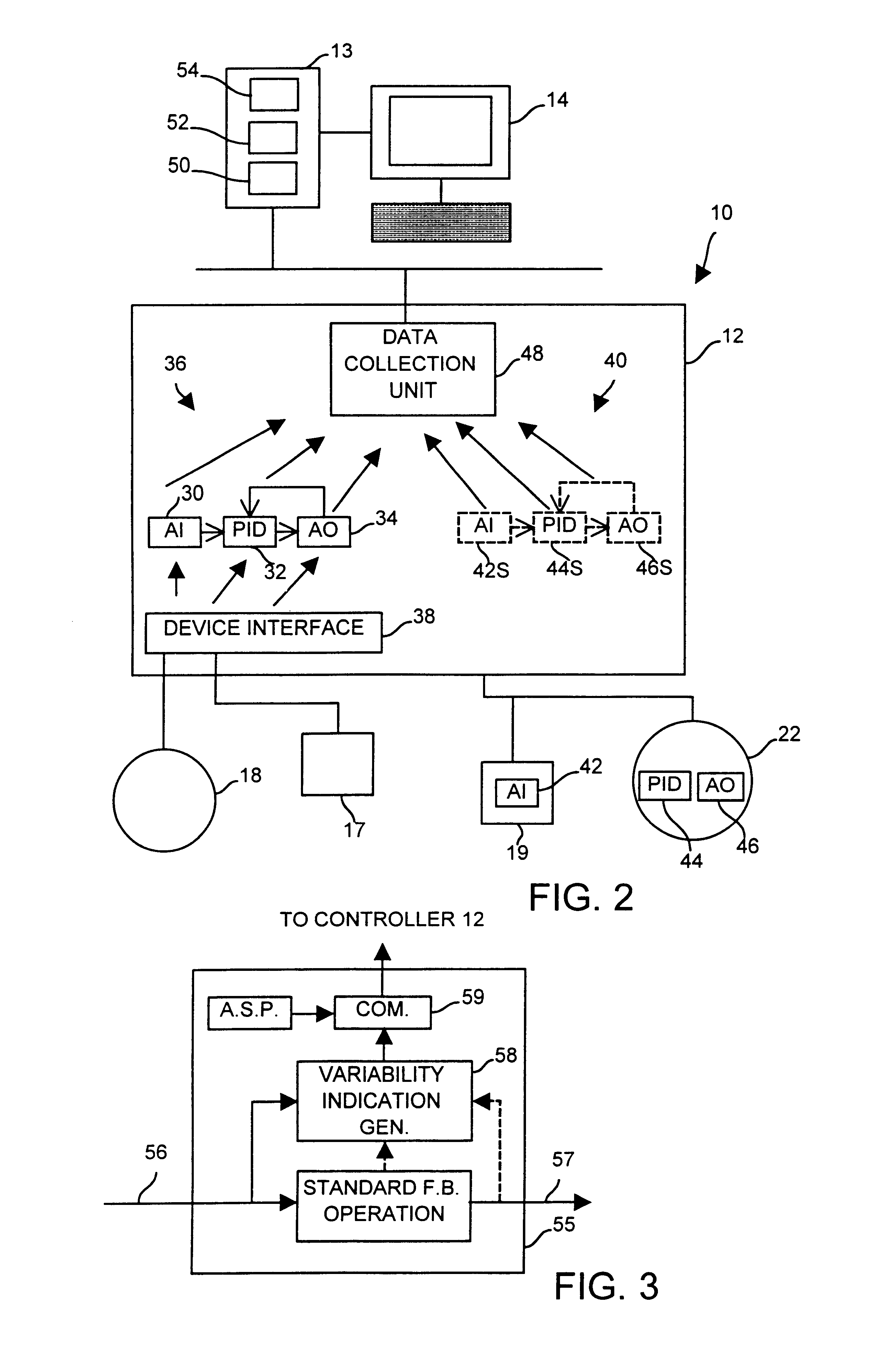
Diagnostics in a process control system which uses multi-variable control techniques
InactiveUS6615090B1Shorten the timeReduce the burden onNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsProcess control networkState parameter
A diagnostic tool automatically collects and stores data indicative of a variability parameter, a mode parameter, a status parameter and a limit parameter for a multi-variable function block associated with one or more devices or loops within a process control system, processes the collected data to determine which devices, loops or function blocks have problems that result in reduced performance of the process control system, displays a list of detected problems to an operator and then suggests the use of other, more specific diagnostic tools to further pinpoint or correct the problems. When the diagnostic tool recommends and executes a data intensive application as the further diagnostic tool, it automatically configures a controller of the process control network to collect the data needed for such a tool.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
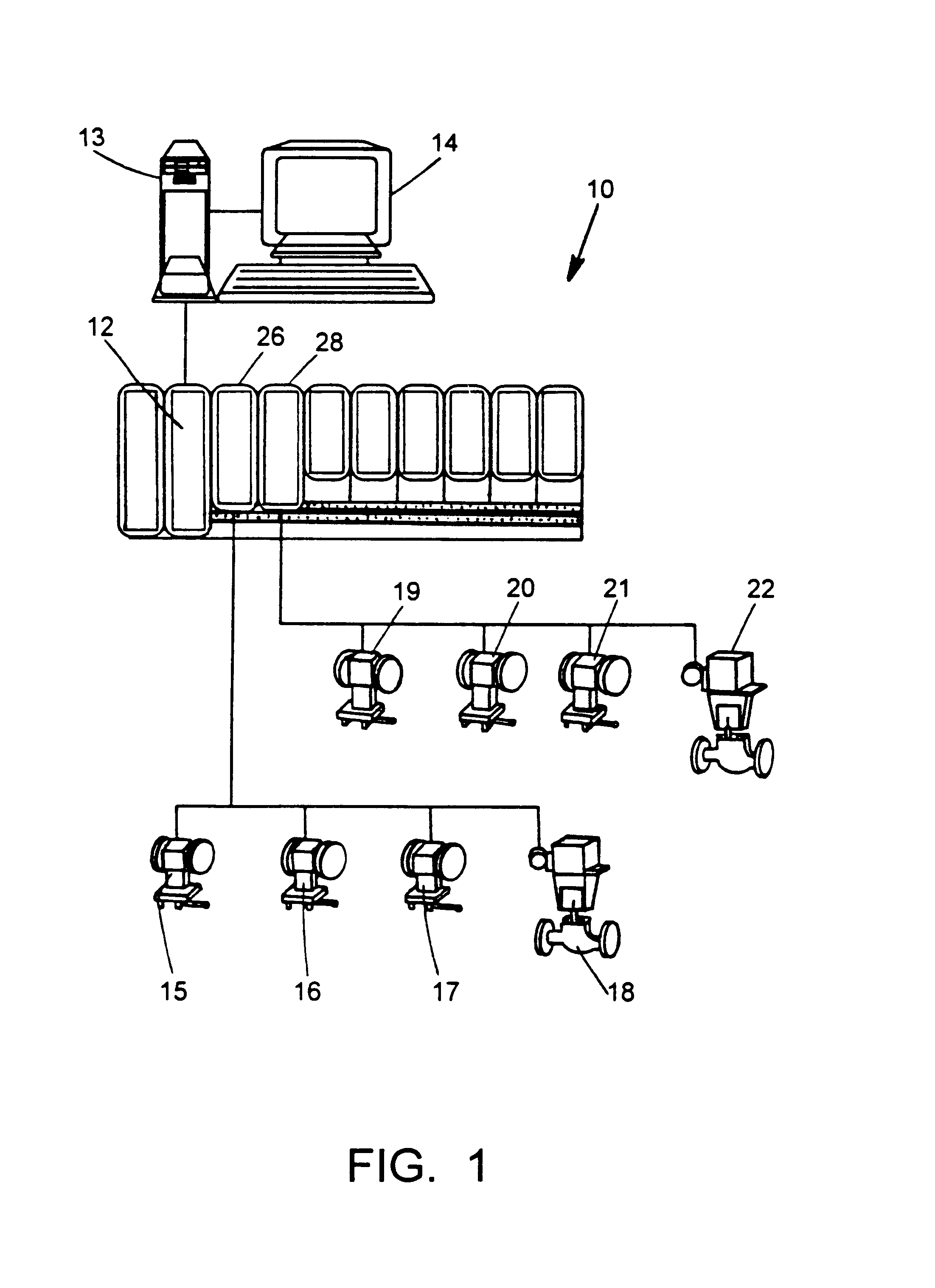
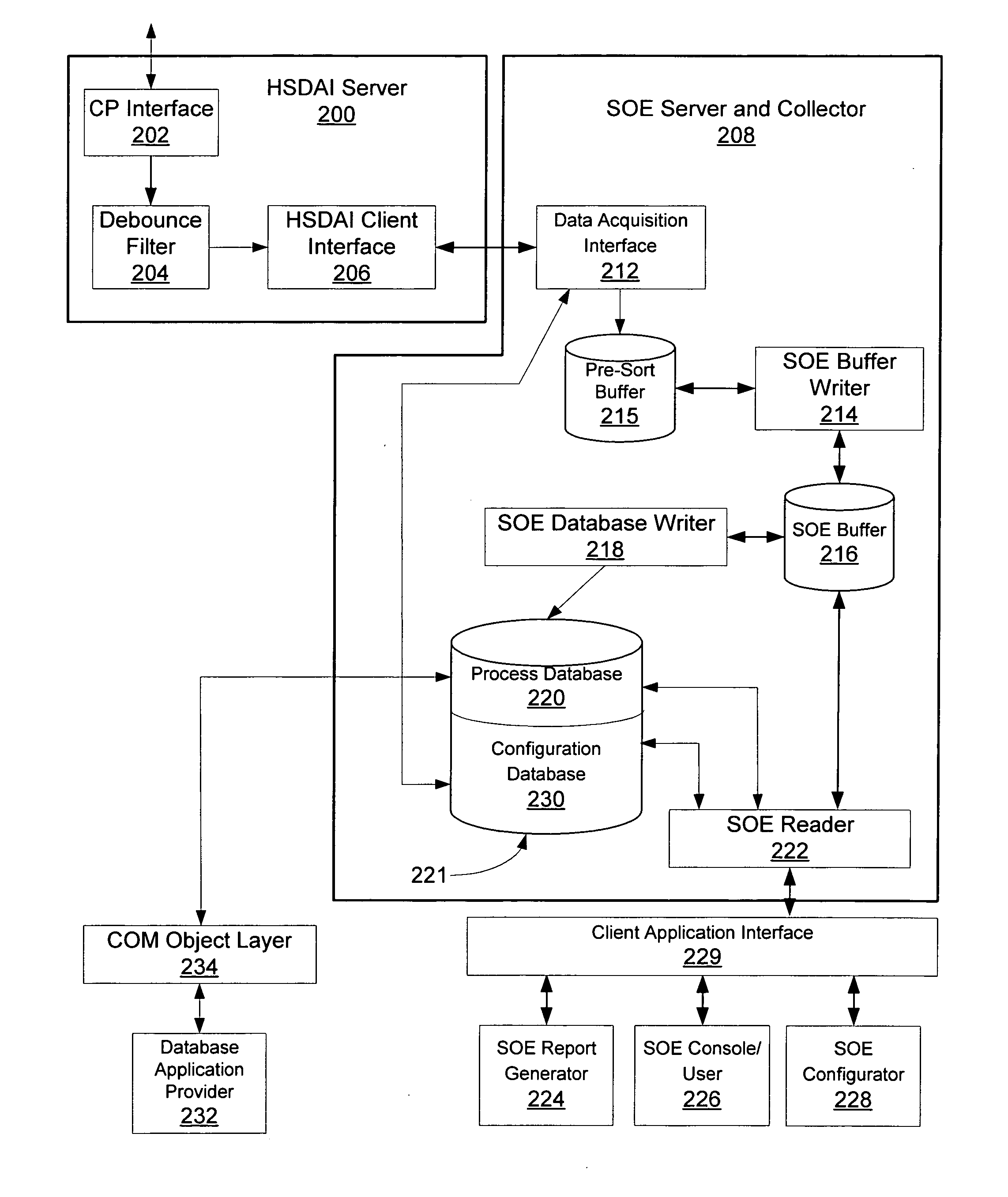
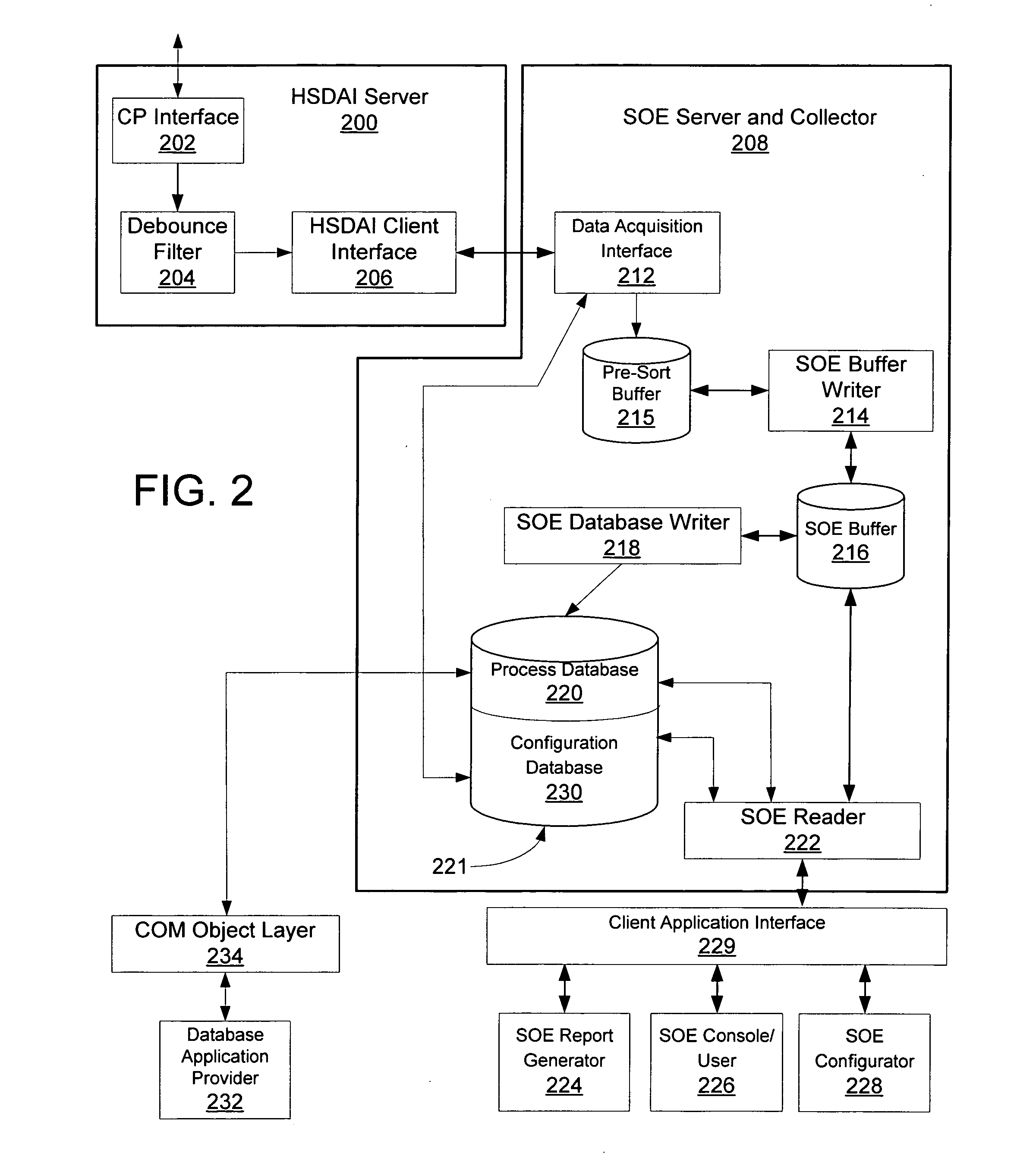
Sequence of events recorder facility for an industrial process control environment
ActiveUS20070244571A1Facilitate carrying out recited stepProgramme controlComputer controlDigital dataProcess control network
A sequence of events (SOE) recorder facility in a process control network environment is described herein. The SOE recorder facility is hosted by a networked node that receives digital signal status change (event) data from a networked controller. The sequence of events recorder facility receives a configured set of digital data signals from the controller, temporarily buffers the events in chronological order according to timestamps assigned to the events by their sources (e.g., fieldbus modules). The data is thereafter copied / removed from the buffer and provided to multiple destinations including: a process database that maintains an archival copy of the received event data for rendering event reports, and an SOE client user interface for rendering event logs to printers and / or graphical user interface displays.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC SYST USA INC
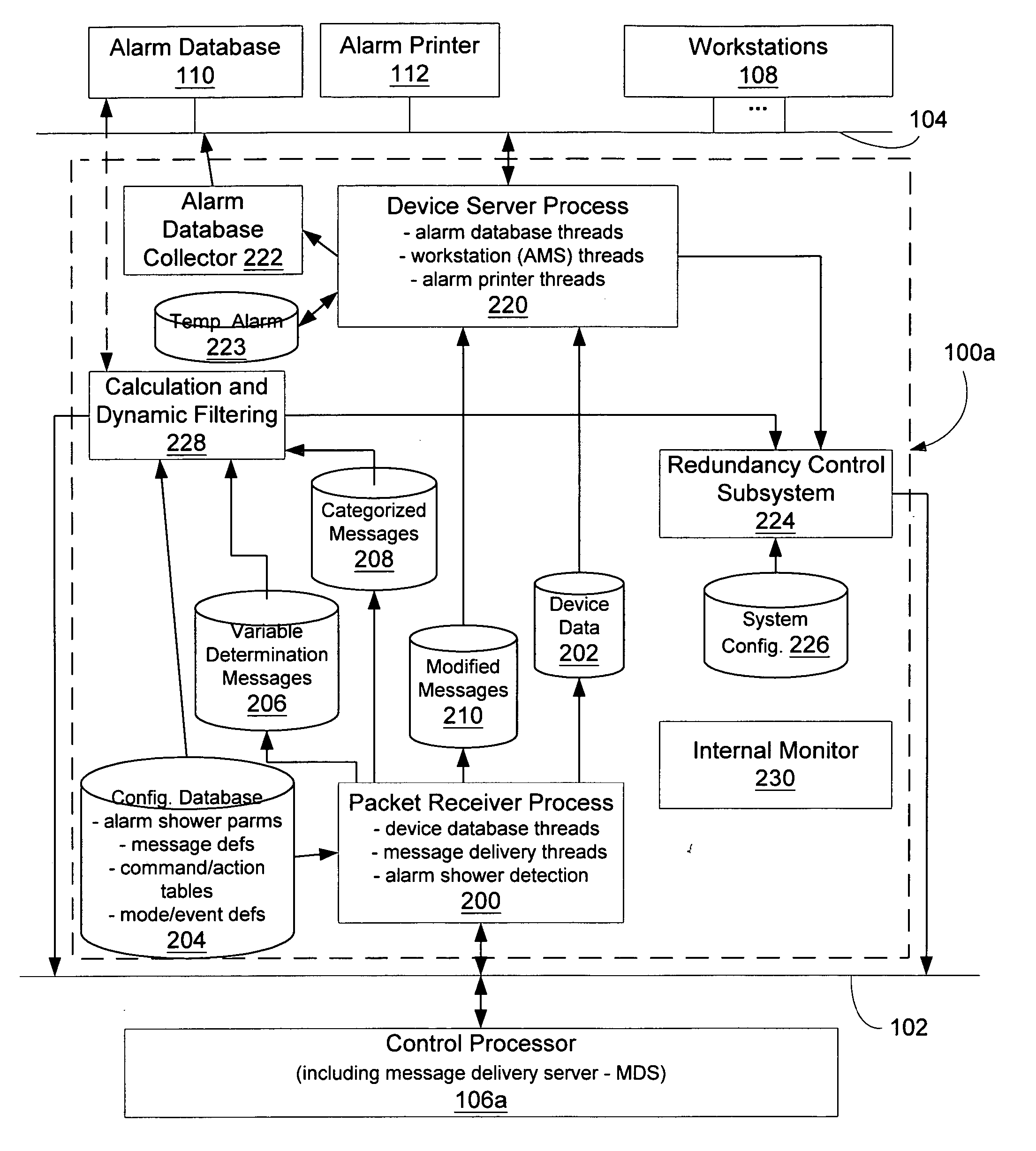
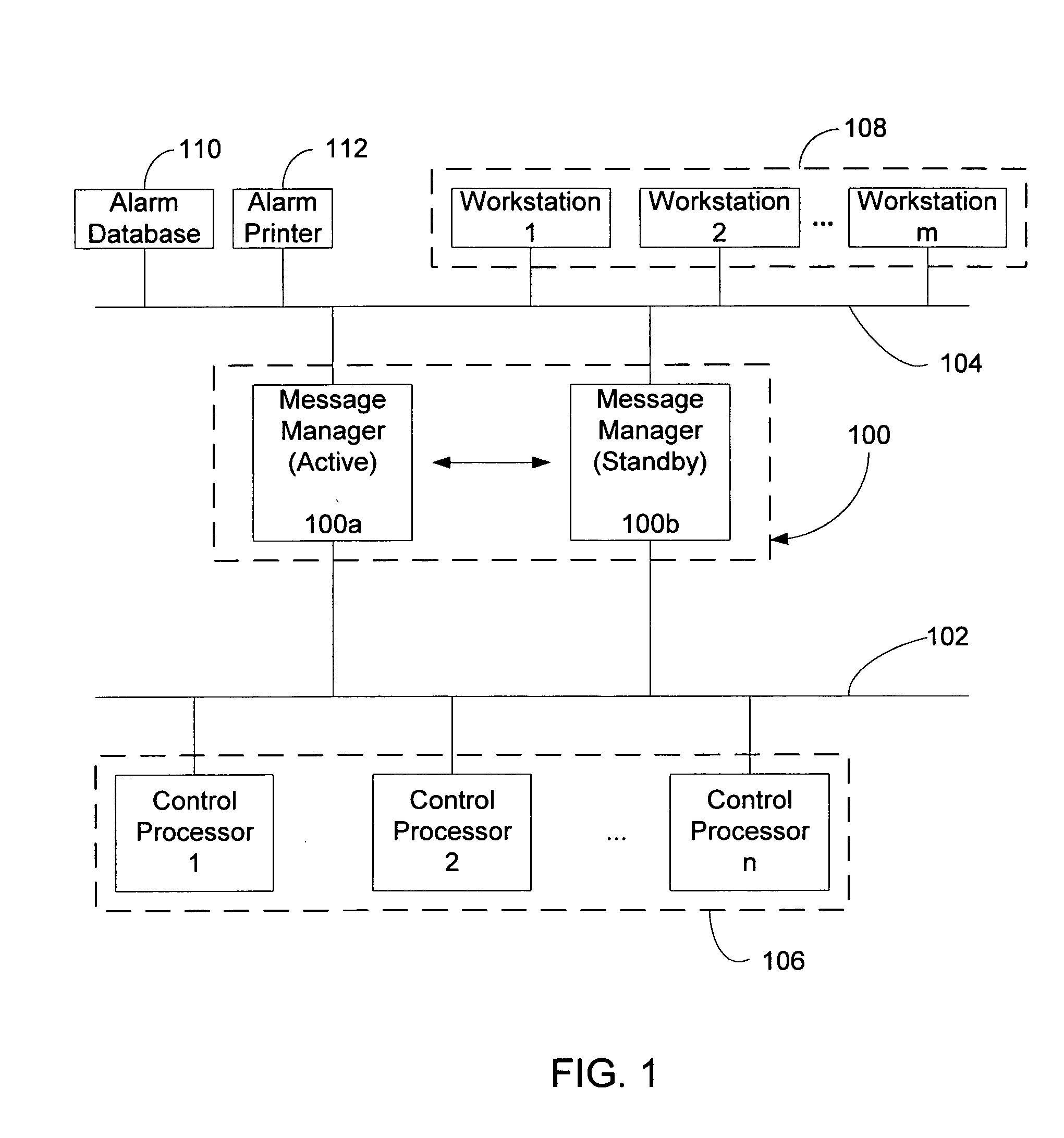
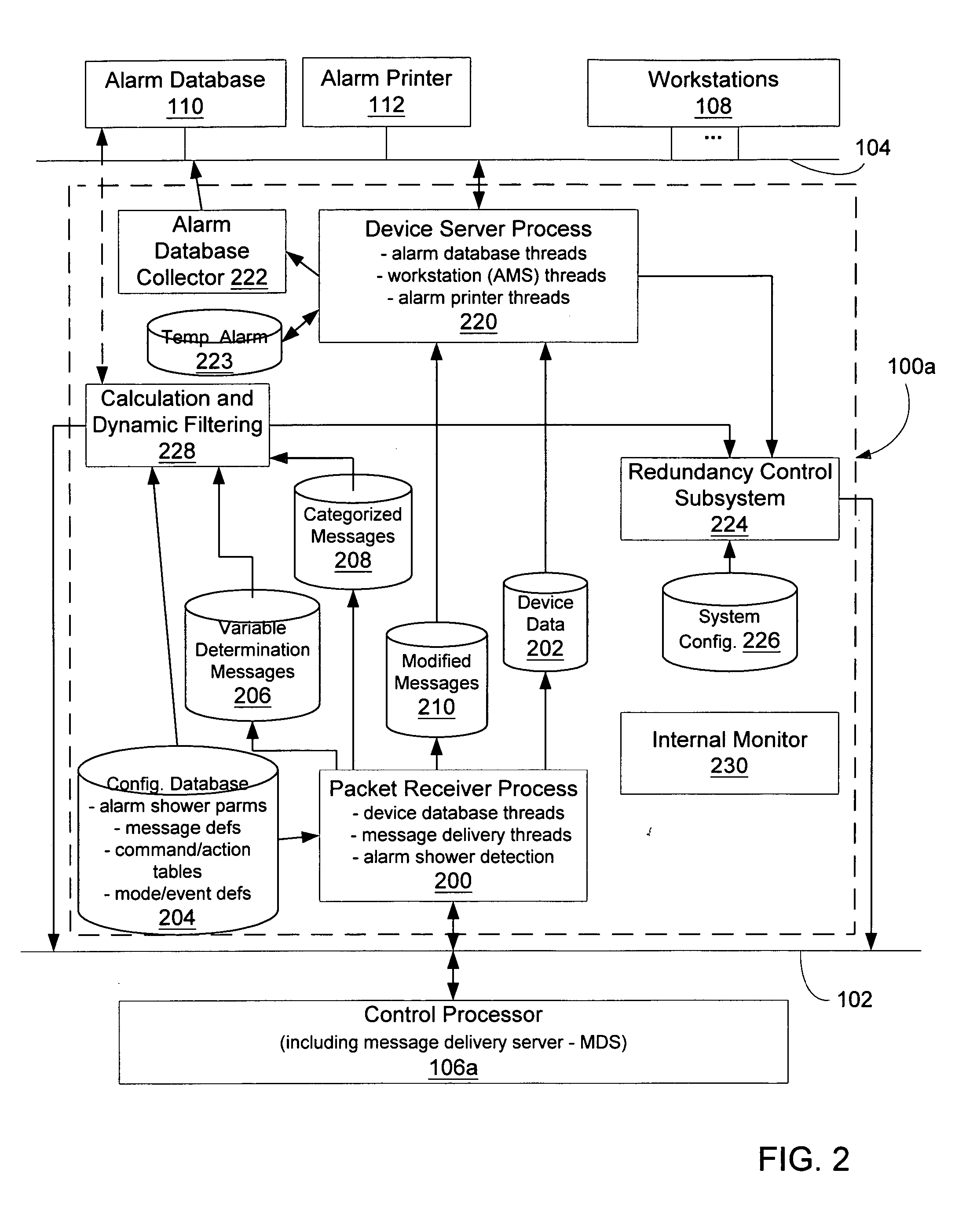
Message management facility for an industrial process control environment
InactiveUS20060168013A1Easy to implementProgramme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsAlarm messageProcess control network
A message management facility is described herein that is hosted by a networked node, in a process control network environment, that is separate from a control processor. The message management facility routes a stream of messages received from the control processor to a set of destinations on a supervisory network. By interposing the message management facility on a node that is interposed, in a message steam, between alarm message sources (control processors) and alarm message sinks (workstations, printers, historians), a number of additional functions can be implemented to carry out a number of advanced functions. Examples of such functions include: table-based routing of a single alarm to a number of destinations on an application network, suppressing alarm showers by applying a criterion to received messages when shower conditions have been sensed, invoking commands based upon a configured category assigned to particular identified messages prior to delivery of the message to its final destination, and invoking actions in response to event / mode status changes (including re-prioritizing alarms).
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Systems, Program Product and Methods For Performing a Risk Assessment Workflow Process For Plant Networks and Systems
ActiveUS20120180133A1Easy to editEasy to customizeProgramme controlMemory loss protectionProcess control networkRisk level
Systems, methods, and program product to perform a cyber security risk assessment on a plurality of process control networks and systems comprising a plurality of primary network assets at an industrial process facility, are provided. An example of a system and program product can include an industrial and process control systems scanning module configured to identify networks and systems topology and to execute system and network security, vulnerability, virus, link congestion, node congestion analysis to thereby detect susceptibility to know threats to define potential vulnerabilities; a threats to vulnerabilities likelihood and consequences data repository module configured to determine a likelihood of each of a plurality of known threats exploiting identified vulnerabilities and to identify consequences of the exploitation to individual impacted systems and to overall plant operation; and a risk level evaluator module configured to determine a risk level rating for any identified vulnerabilities and provide recommended corrective actions.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
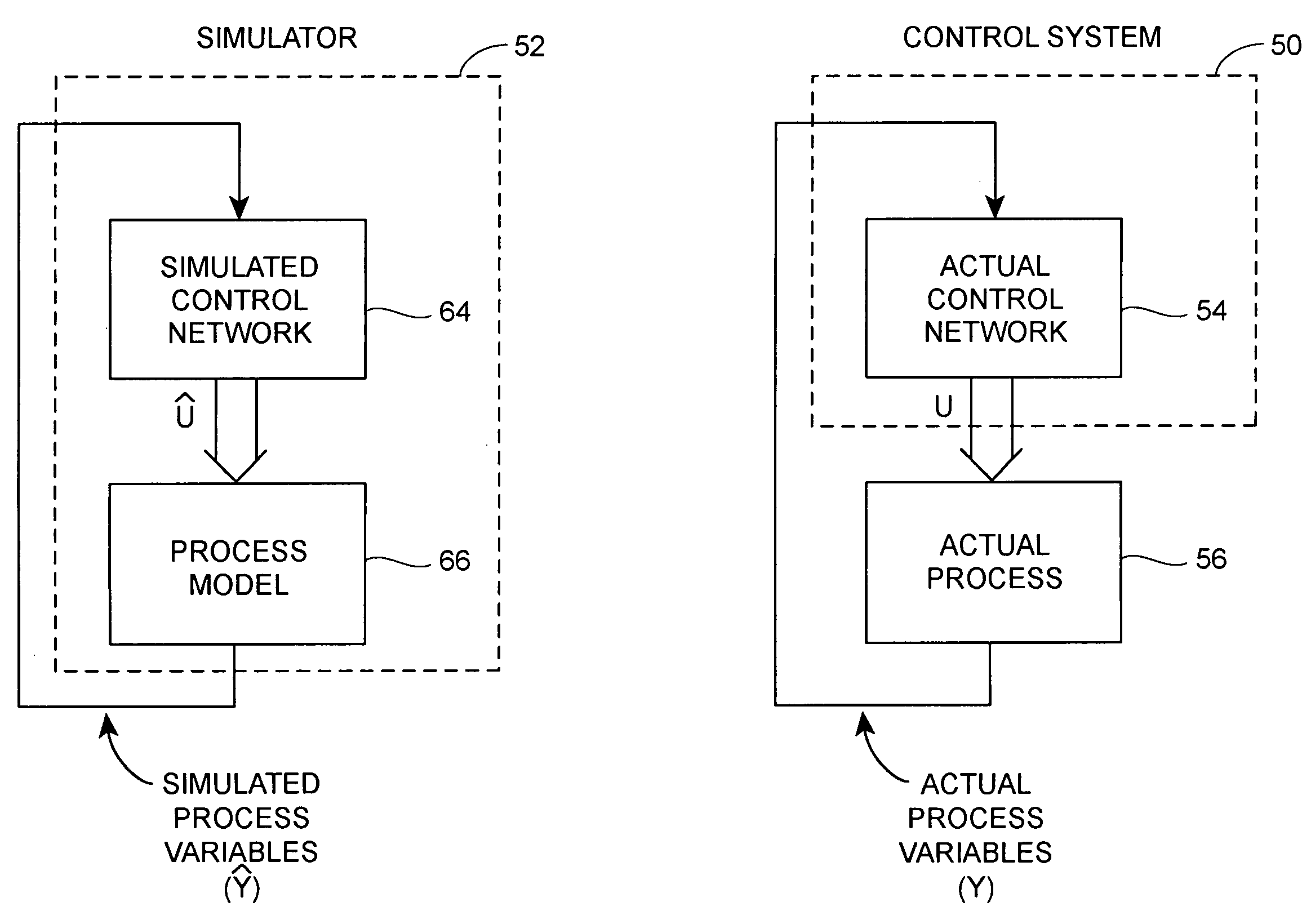
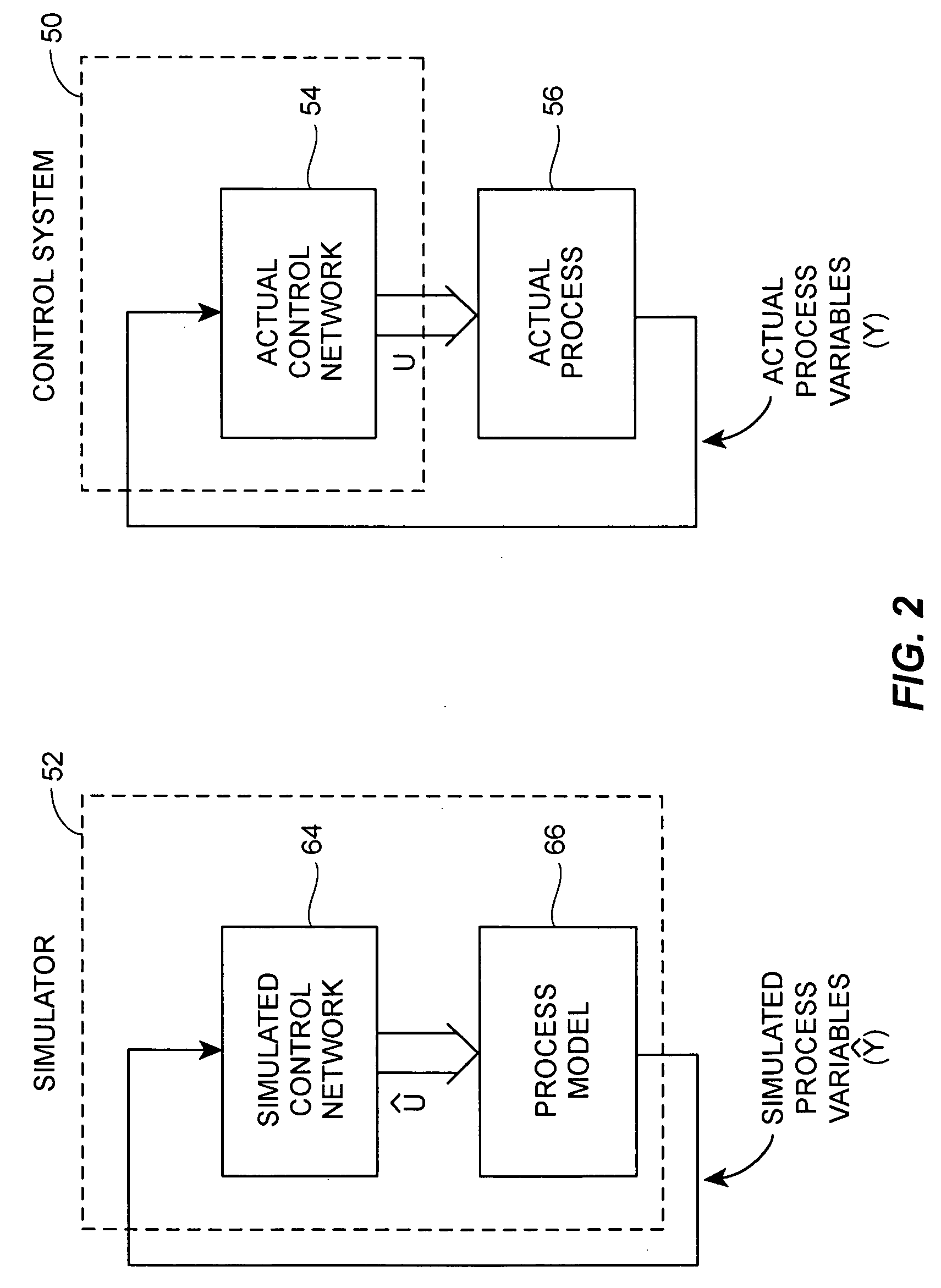
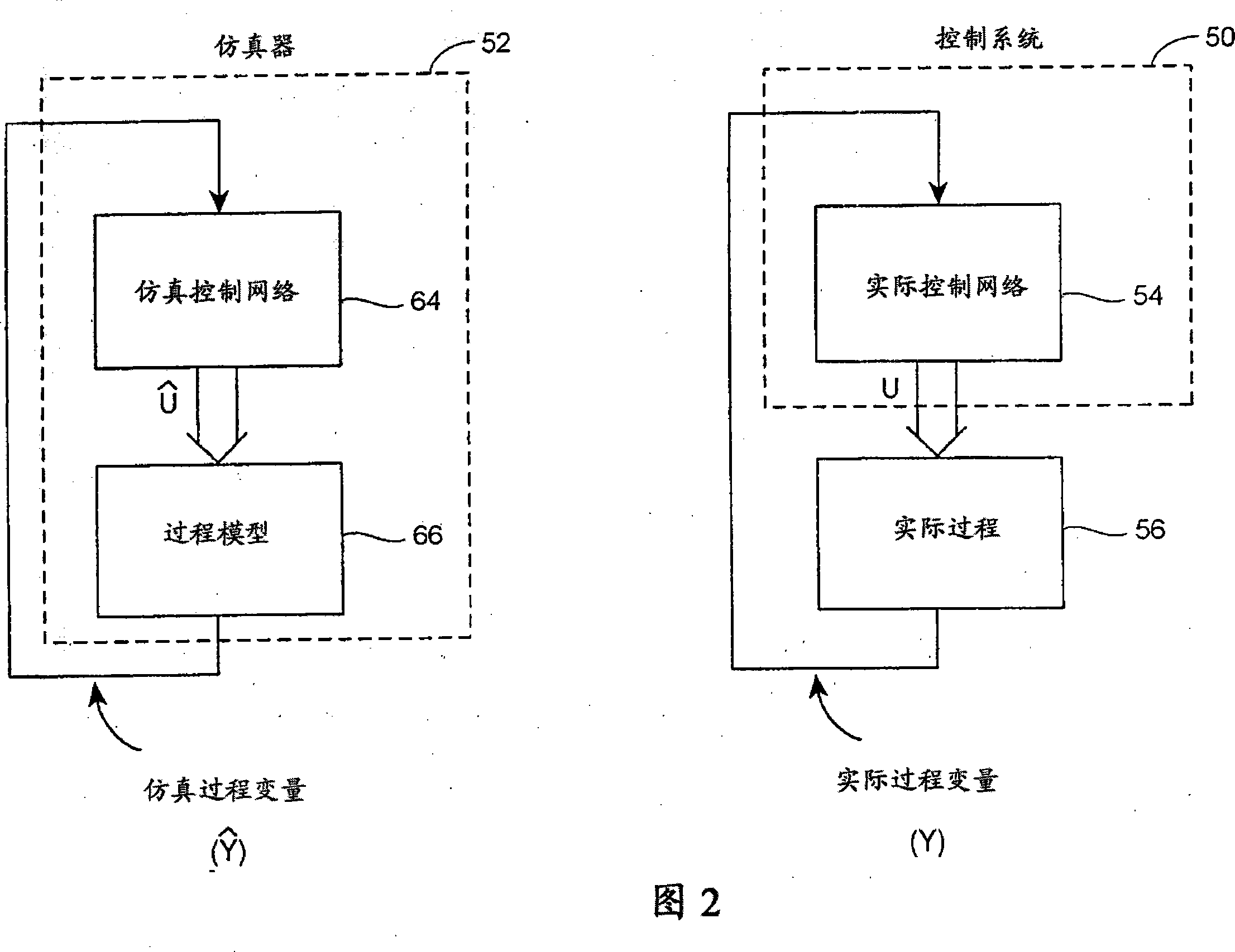
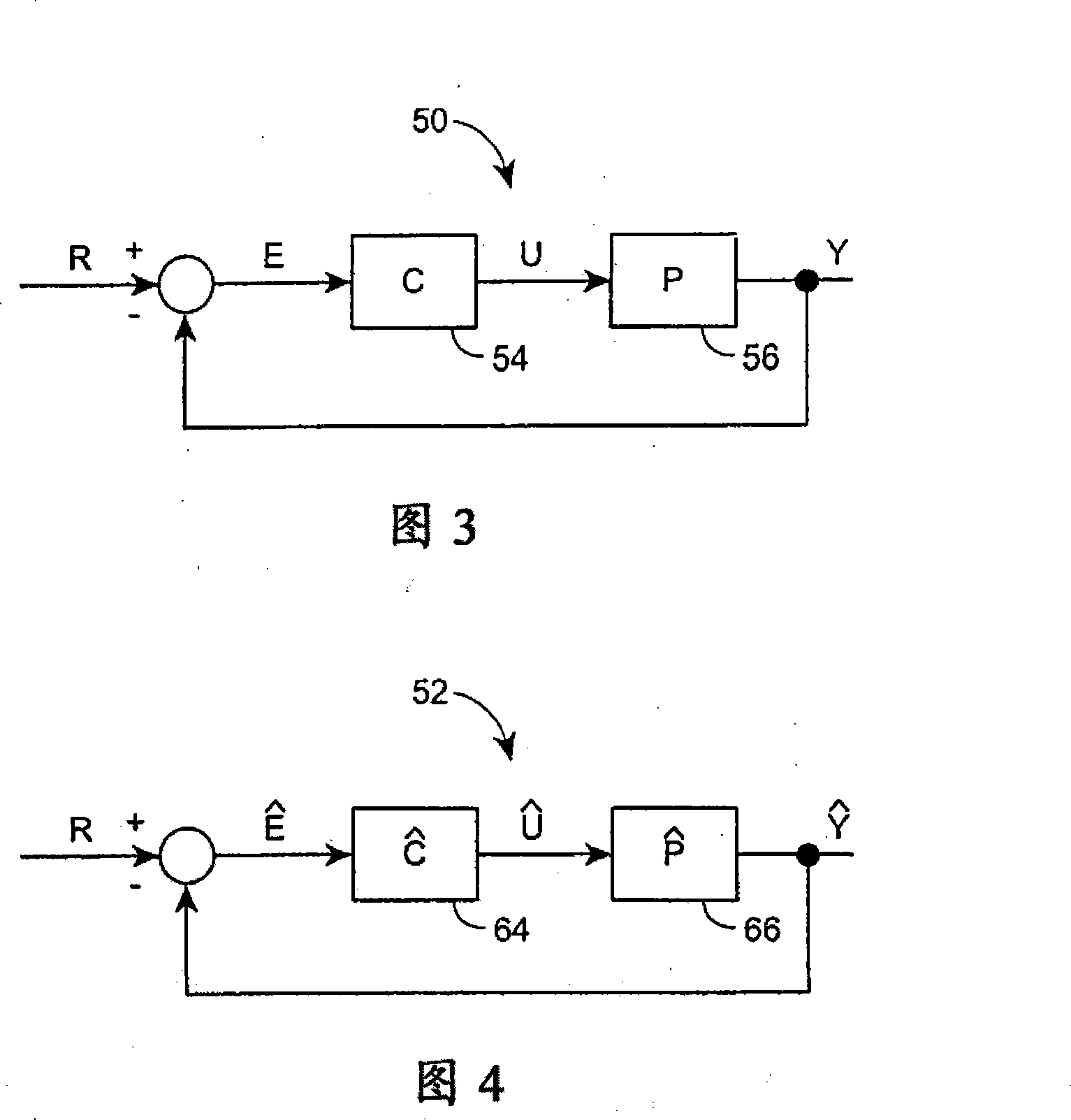
Real-time synchronized control and simulation within a process plant
ActiveUS20080027704A1Easy to useEasy to understandProgramme controlAnalogue computers for electric apparatusProcess control networkReal-time simulation
A process control system simulation technique performs real-time simulation of an actual process control network as that network is running within a process plant in a manner that is synchronized with the operation of the actual process control network. This real-time, synchronized simulation system includes a simulation process control network and a process model which are automatically updated periodically during the operation of the actual process control network to reflect changes made to the process control network, as well as to account for changes in the plant itself, i.e., changes which require an updated process model. The disclosed simulation system provides for more readily accessible and usable simulation activities, as the process control network and the process models used within the simulation system are synchronized with and up-to-date with respect to the current process operating conditions. Moreover, this simulation system is more accurate as it uses process models developed from the current state of the process whenever the simulation system beings to perform a simulation. Still further, the disclosed simulation system is easy to operate, as it uses the same user interface applications as the actual process control network and can be initialized and used at any time during operation the process plant without any significant configuration or set-up activities.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
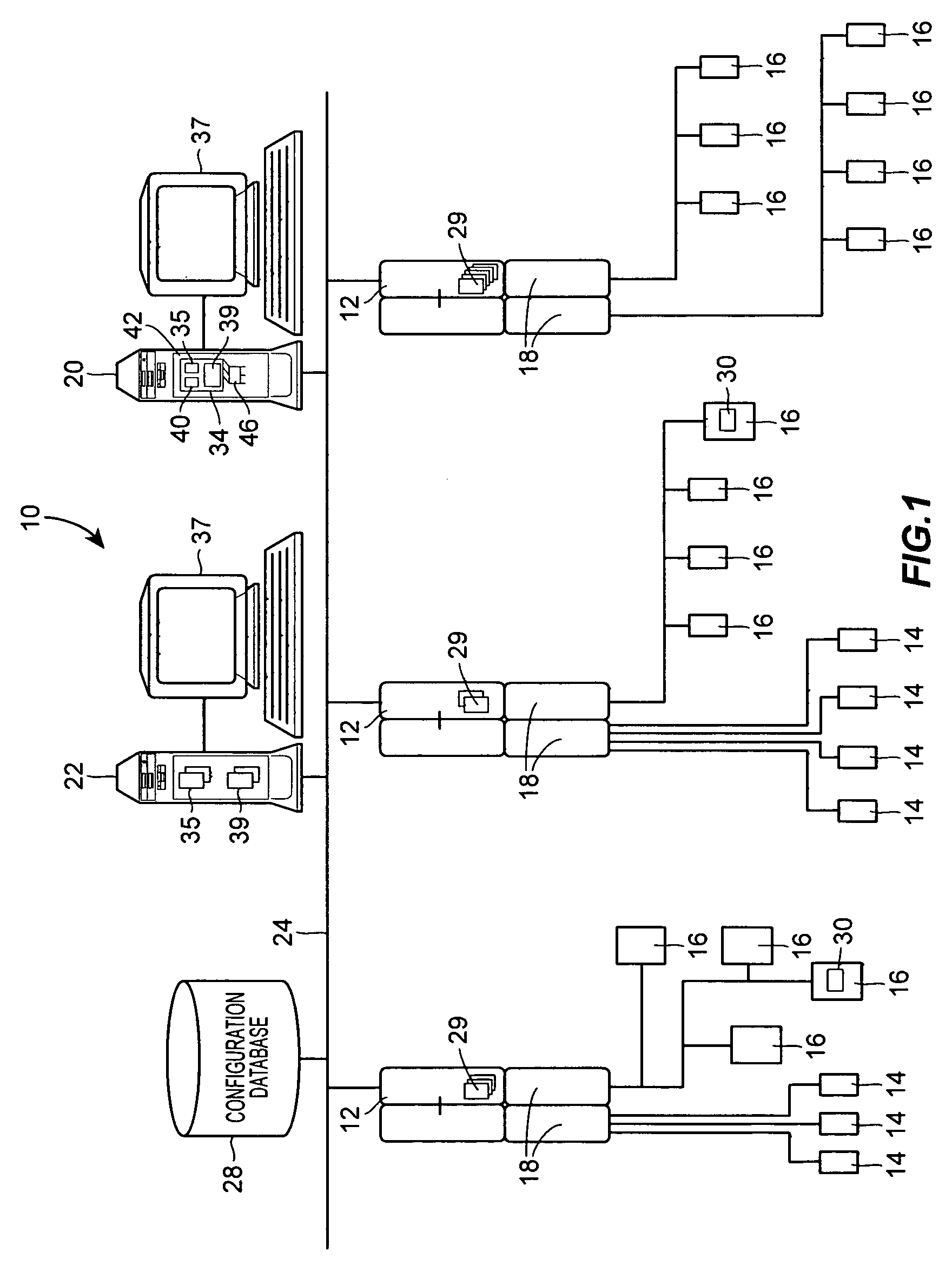
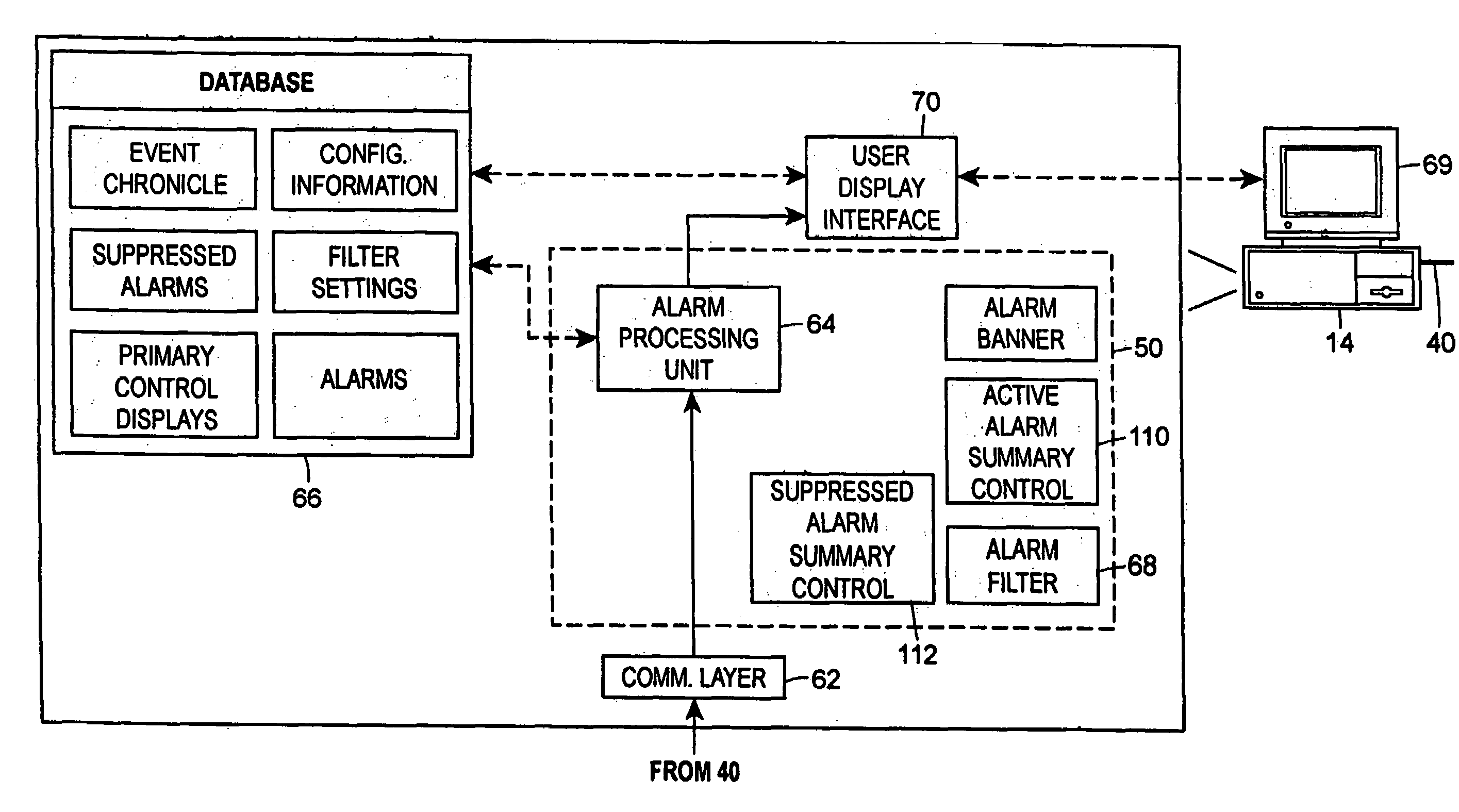
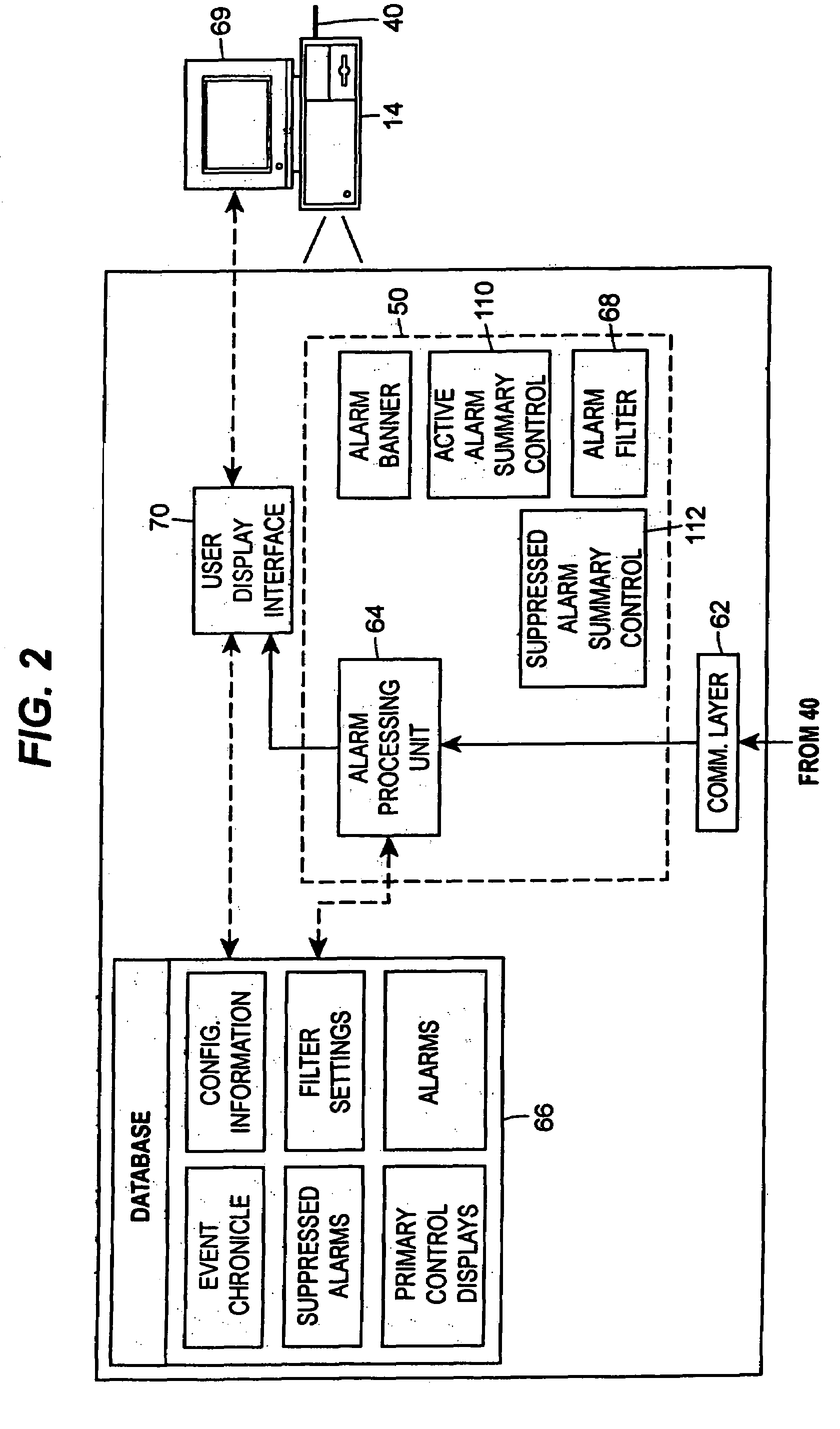
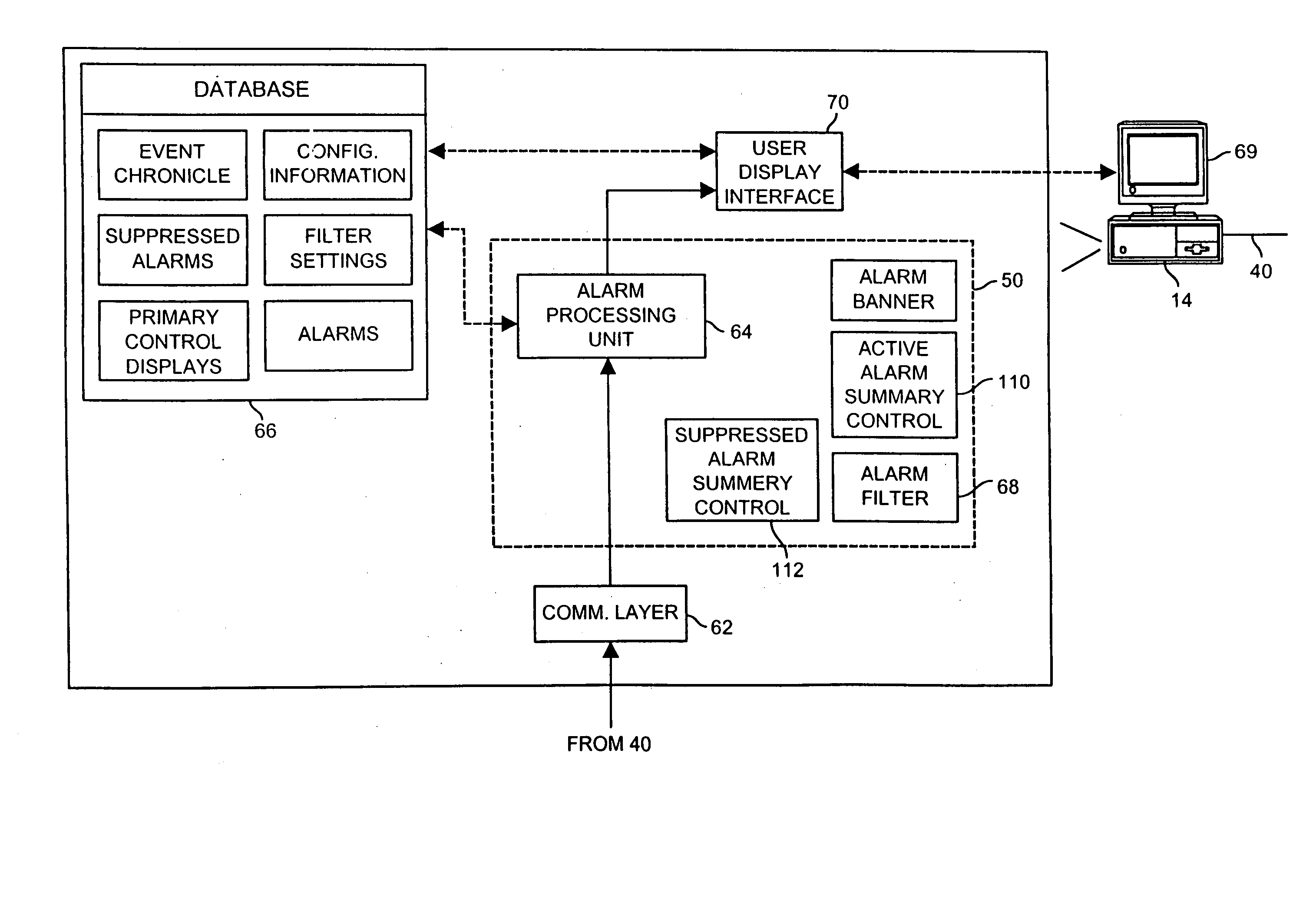
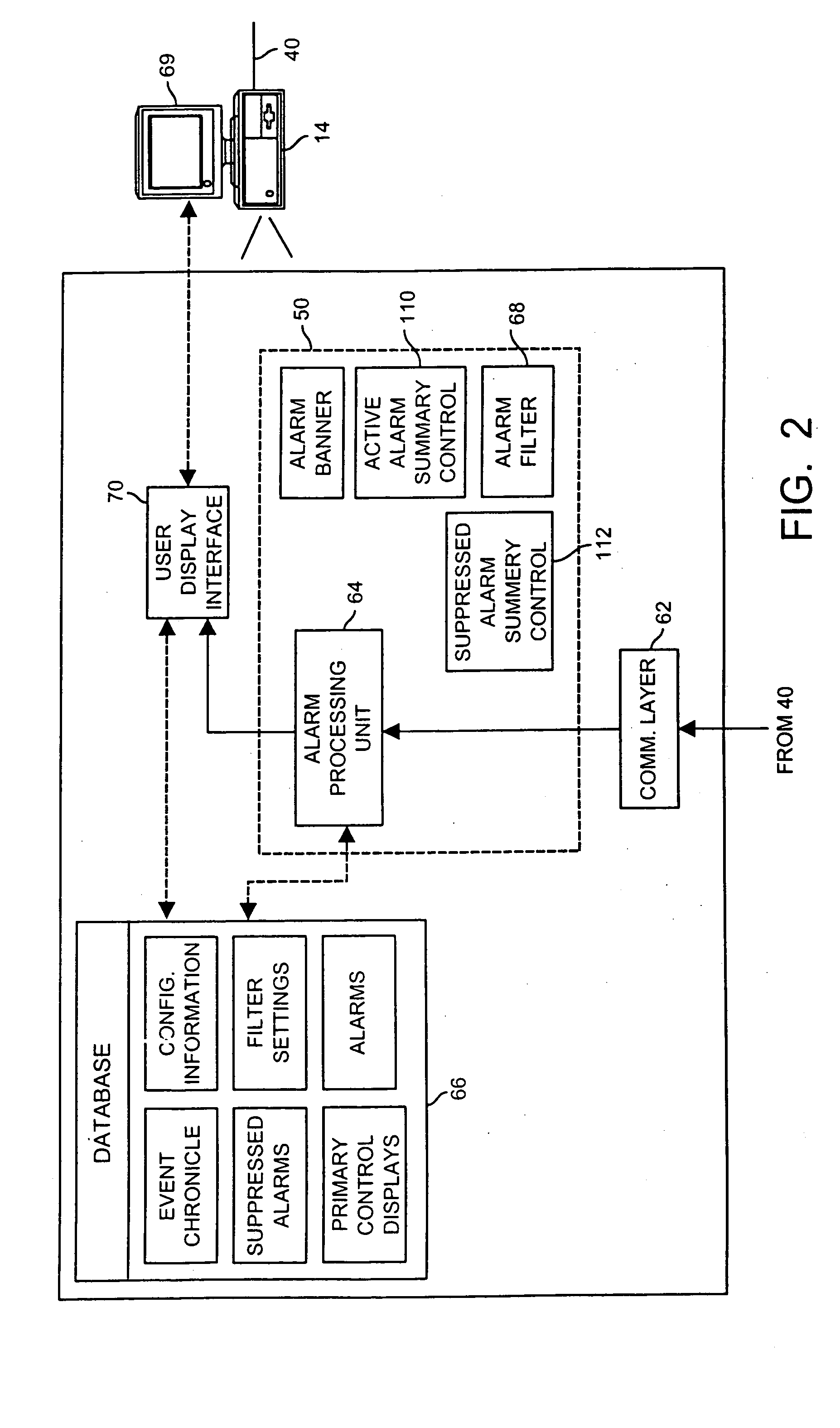
Integrated alarm display in a process control network
An alarm display and interface tool for use in a process control system receives and displays different categories of alarms, including for example, device alarms and hardware alarms as well as traditional process alarms, on a single display to enable an operator or other user to view and have access to these different categories of alarms. The display and interface tool may be used to filter the alarms that are displayed according to any number of categories, including the category of the alarm, the priority of the alarm, the status of the alarm, etc. so as to alternatively segregate or combine the tasks typically associated with operator, maintenance and engineer personnel. The tool may also be used to access each of the displayed alarms to obtain more information about any individual alarm.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
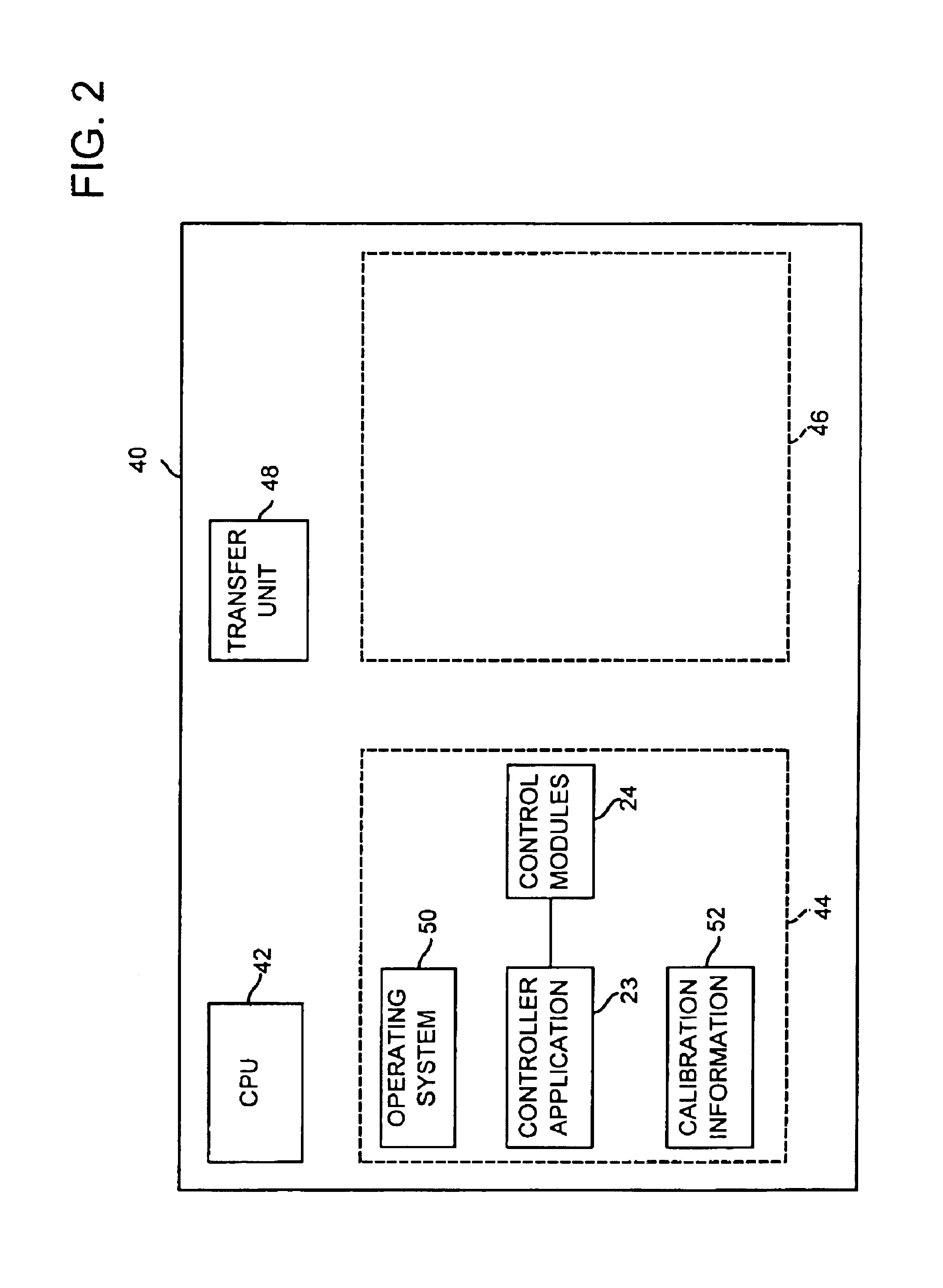
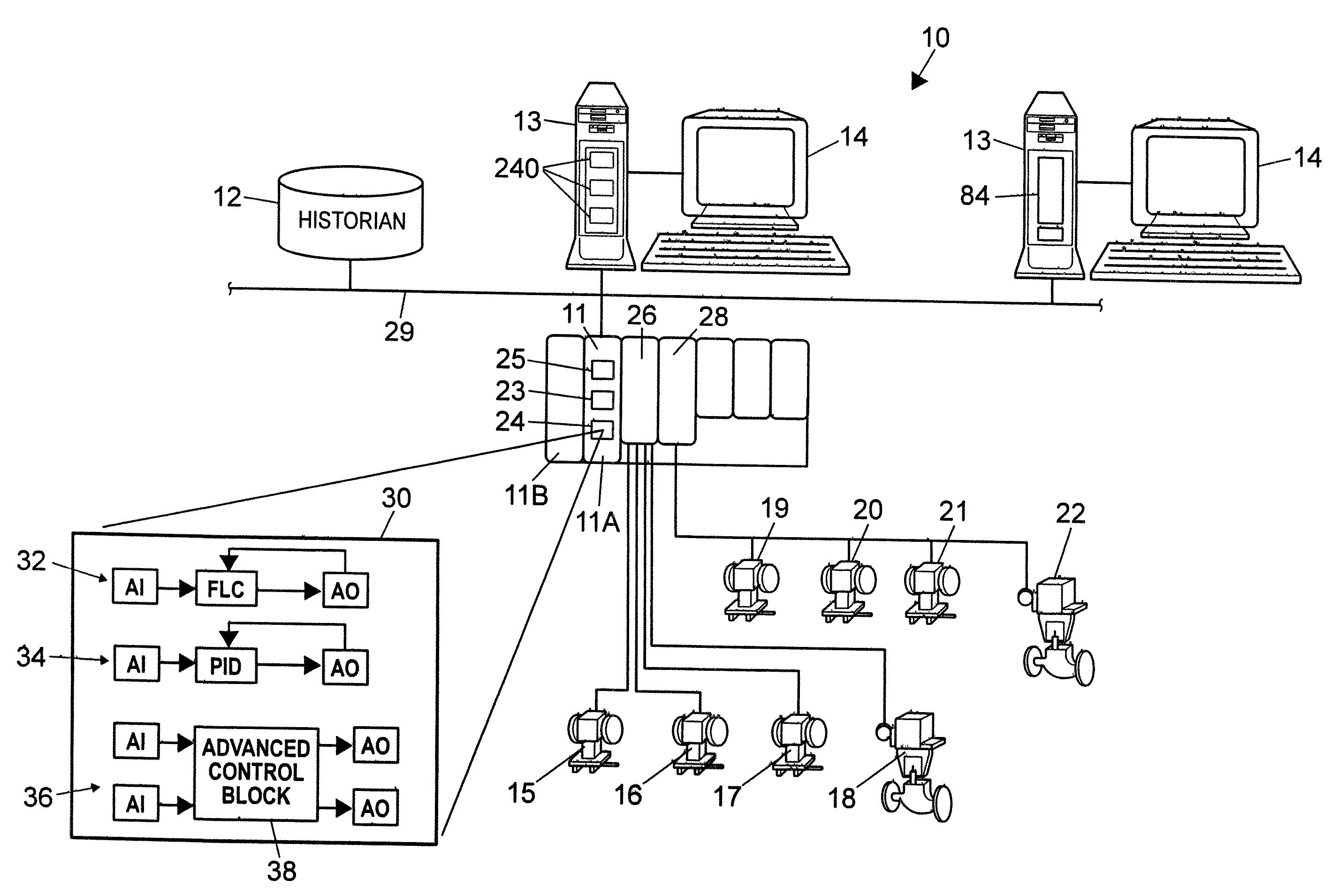
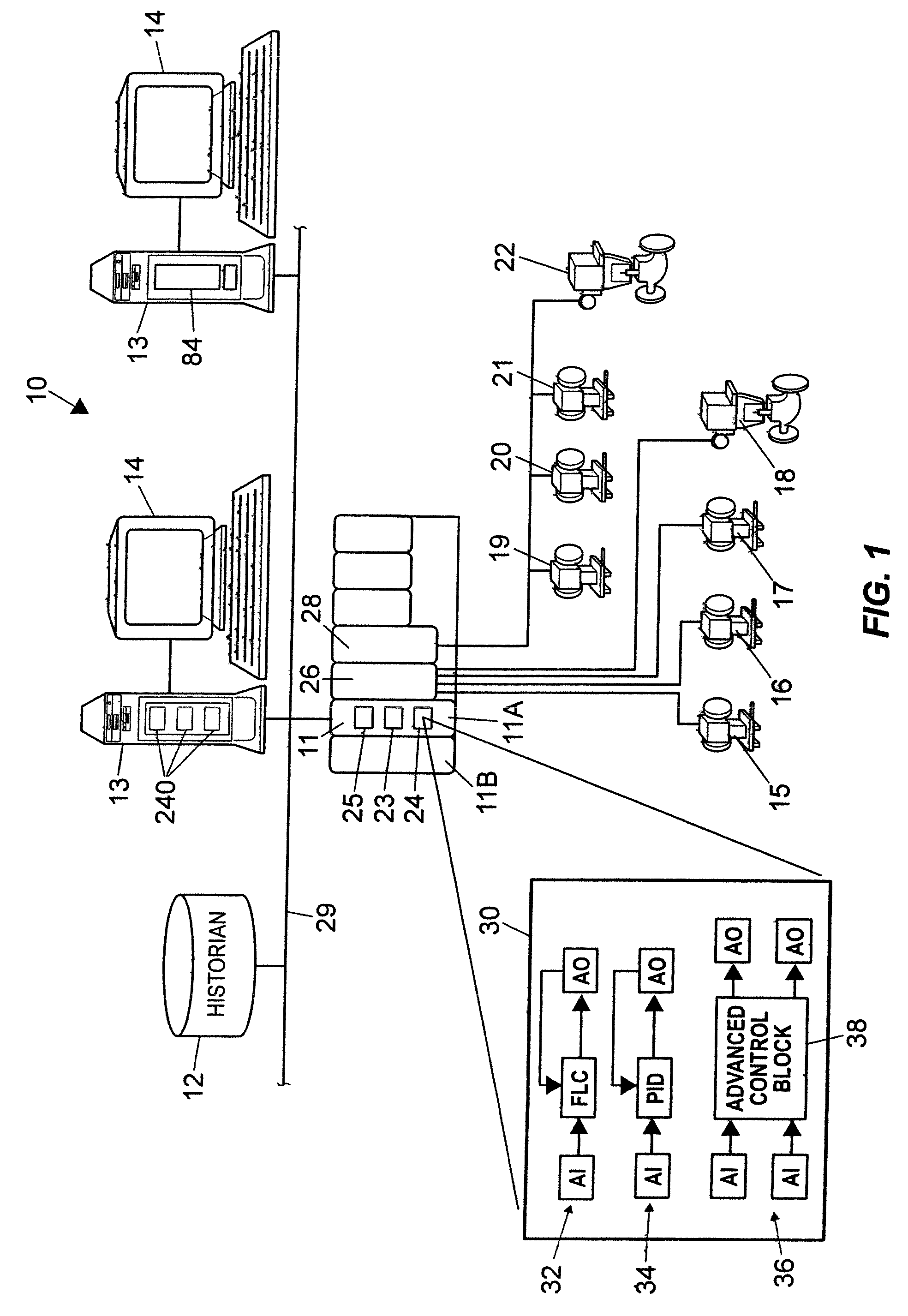
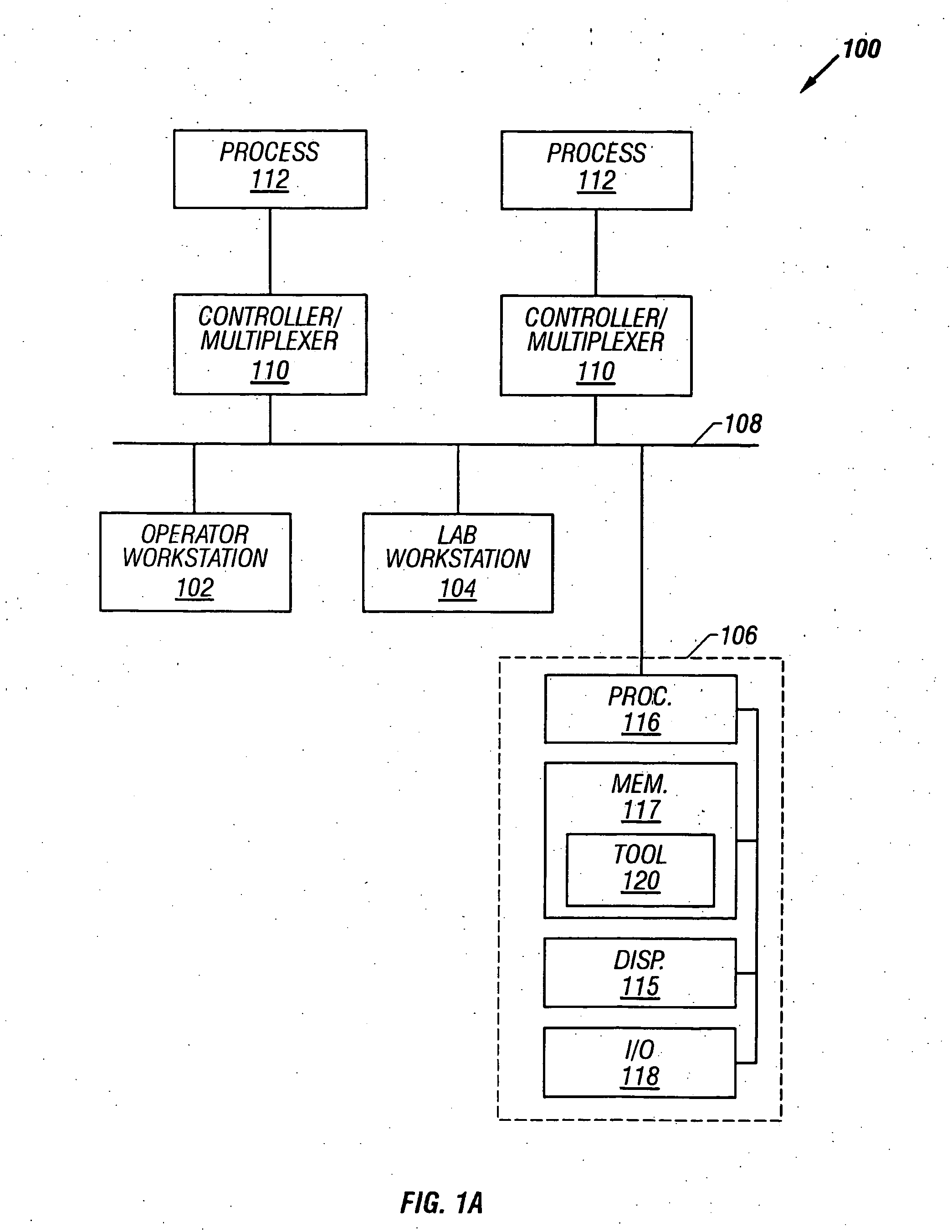
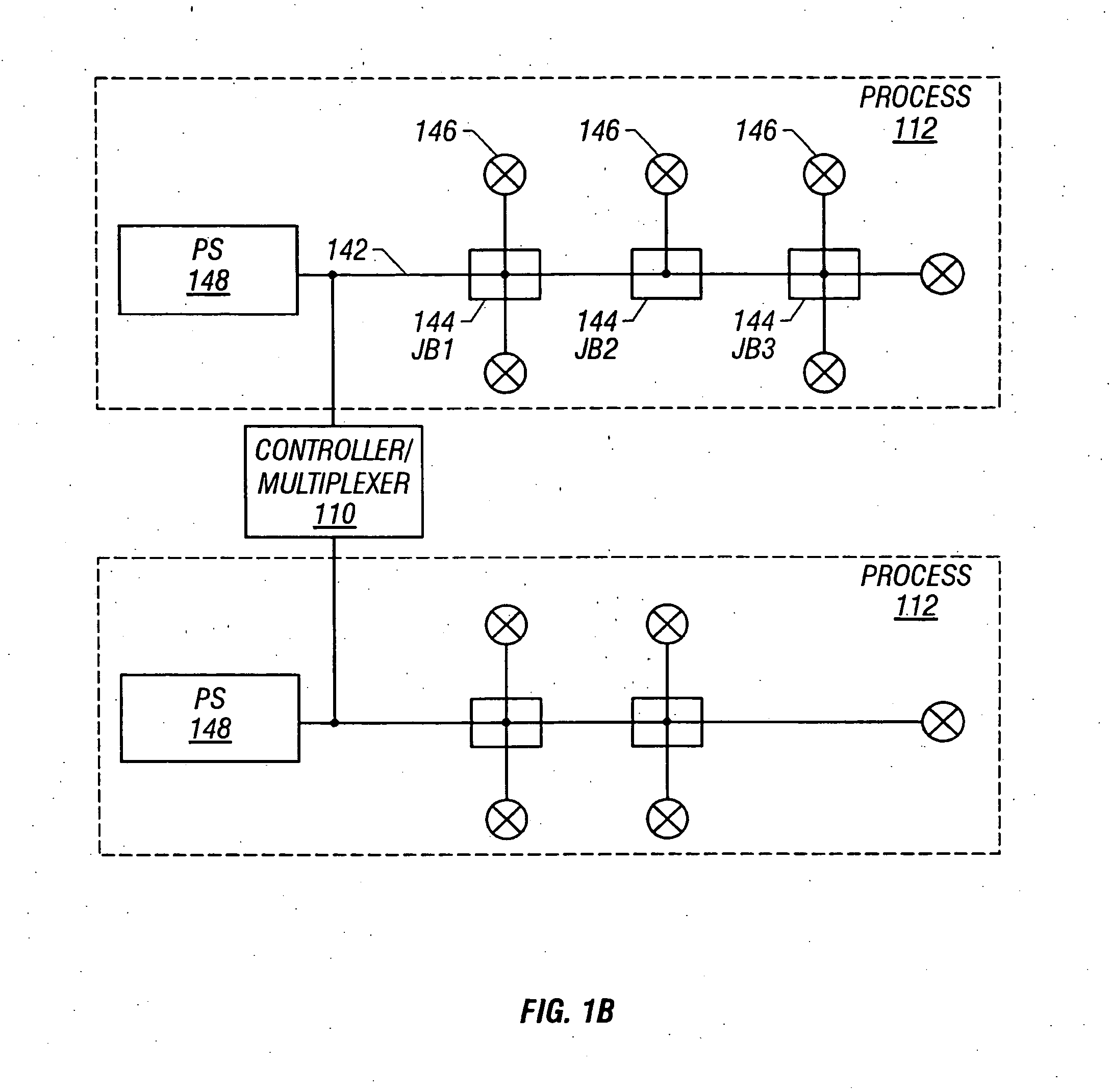
Process control system using a process control strategy distributed among multiple control elements
InactiveUS20020013629A1Easy to implementFlexible allocationComputer controlSimulator controlProcess control networkWorkstation
A process controller implements an overall, user-developed control strategy in a process control network that includes distributed controller and field devices, such as Fieldbus and non-Fieldbus devices. A user defines the control strategy by building a plurality of function blocks and control modules and downloading or installing user-specified portions of the control strategy into the Fieldbus devices and the non-Fieldbus devices. Thereafter, the Fieldbus devices automatically perform the downloaded portions of the overall strategy independently of other portions of the control strategy. For example in a process control system that includes distributed field devices, controllers and workstations, portions of the control strategy downloaded or installed into the field devices operate independently of and in parallel with the control operations of the controllers and the workstations, while other control operations manage the Fieldbus devices and implement other portions of the control strategy.
Owner:NIXON MARK +6
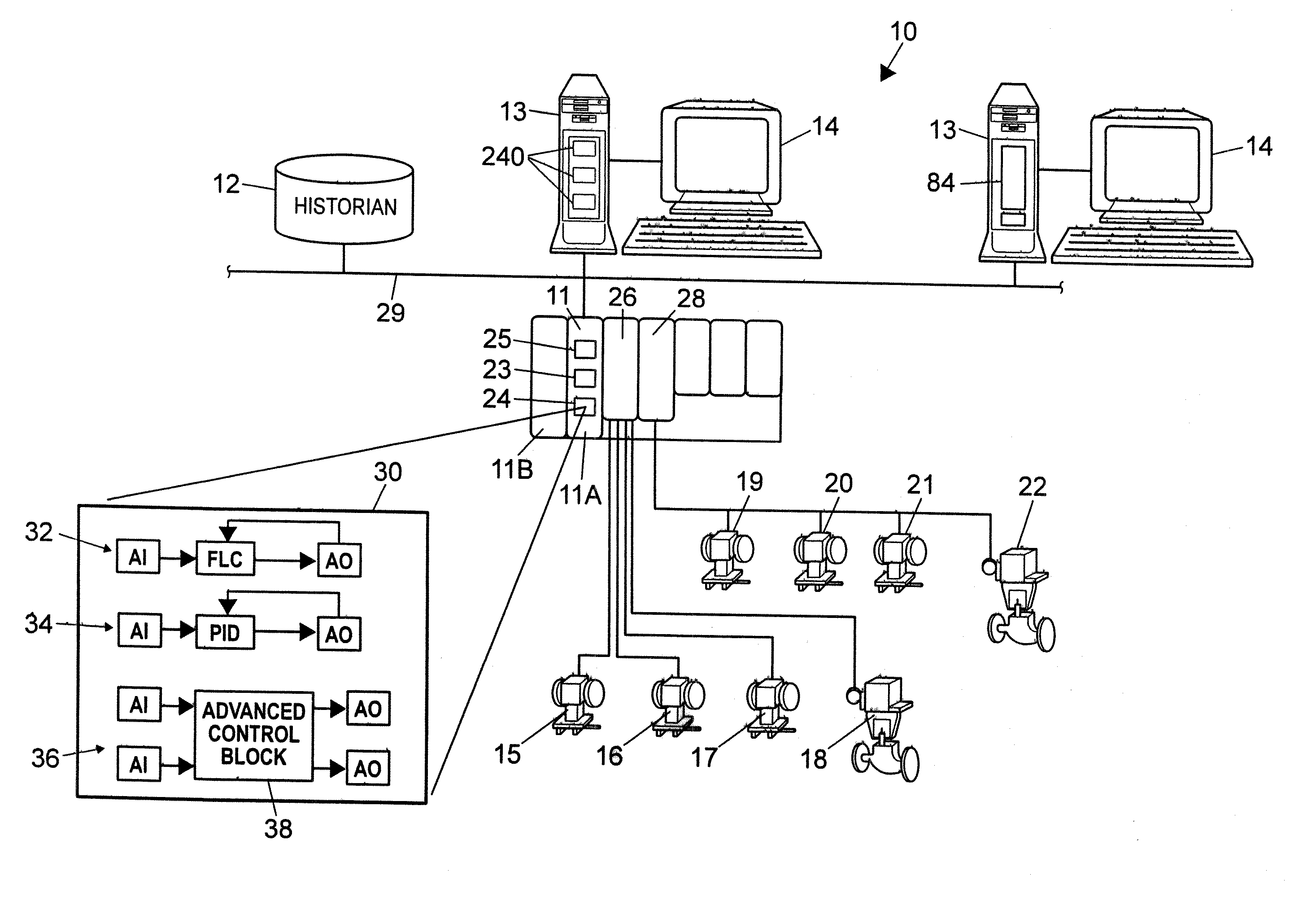
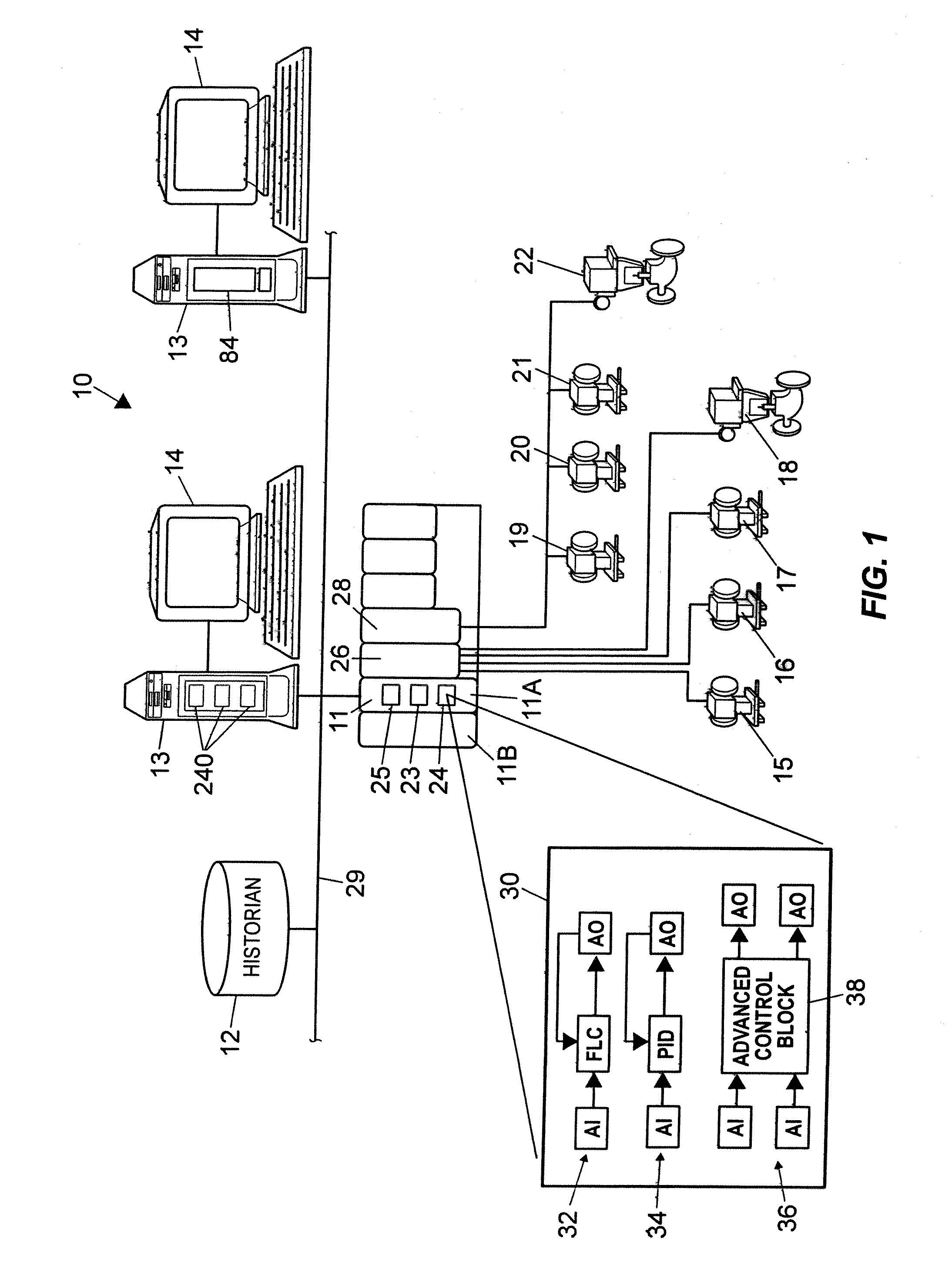
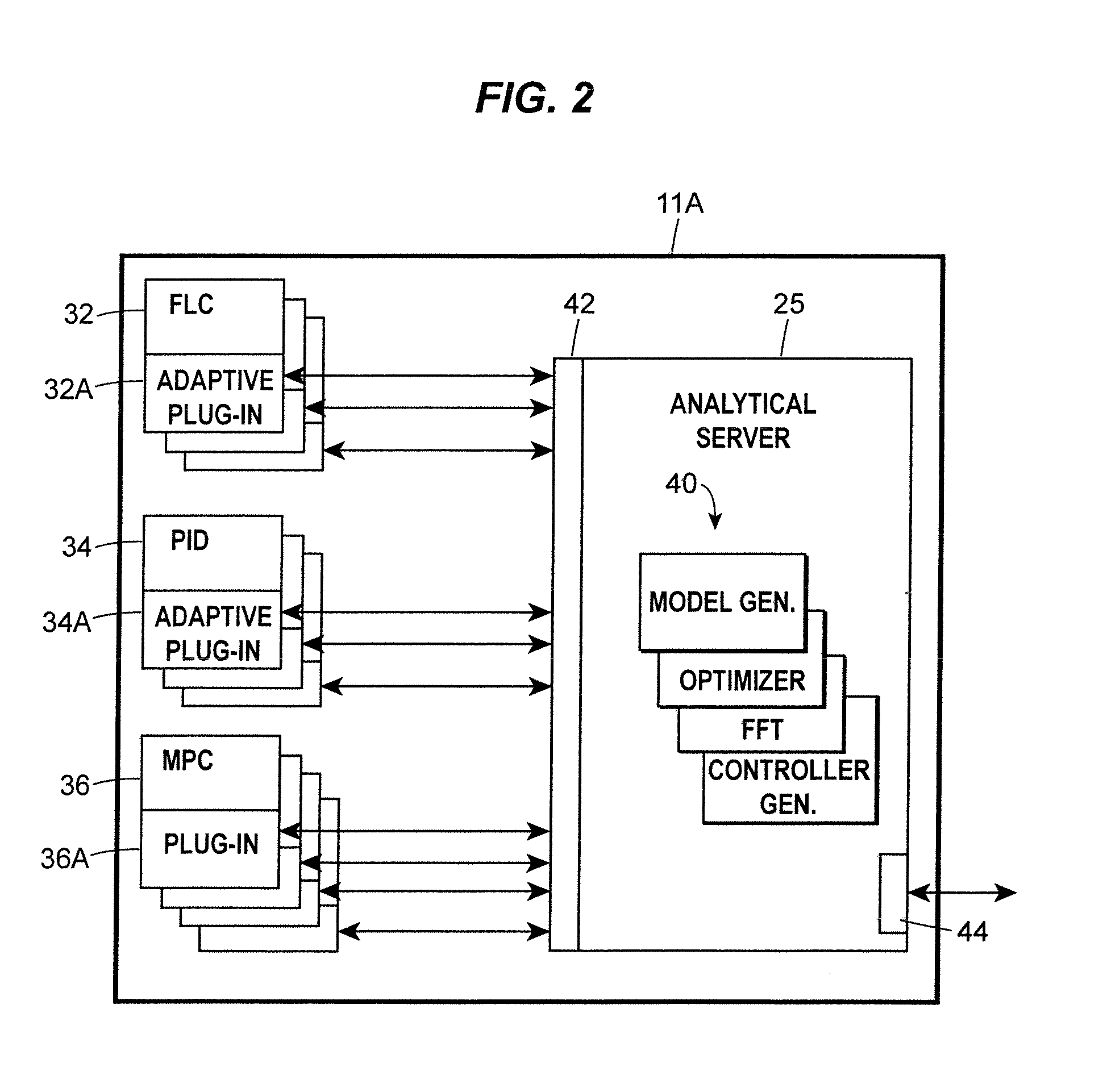
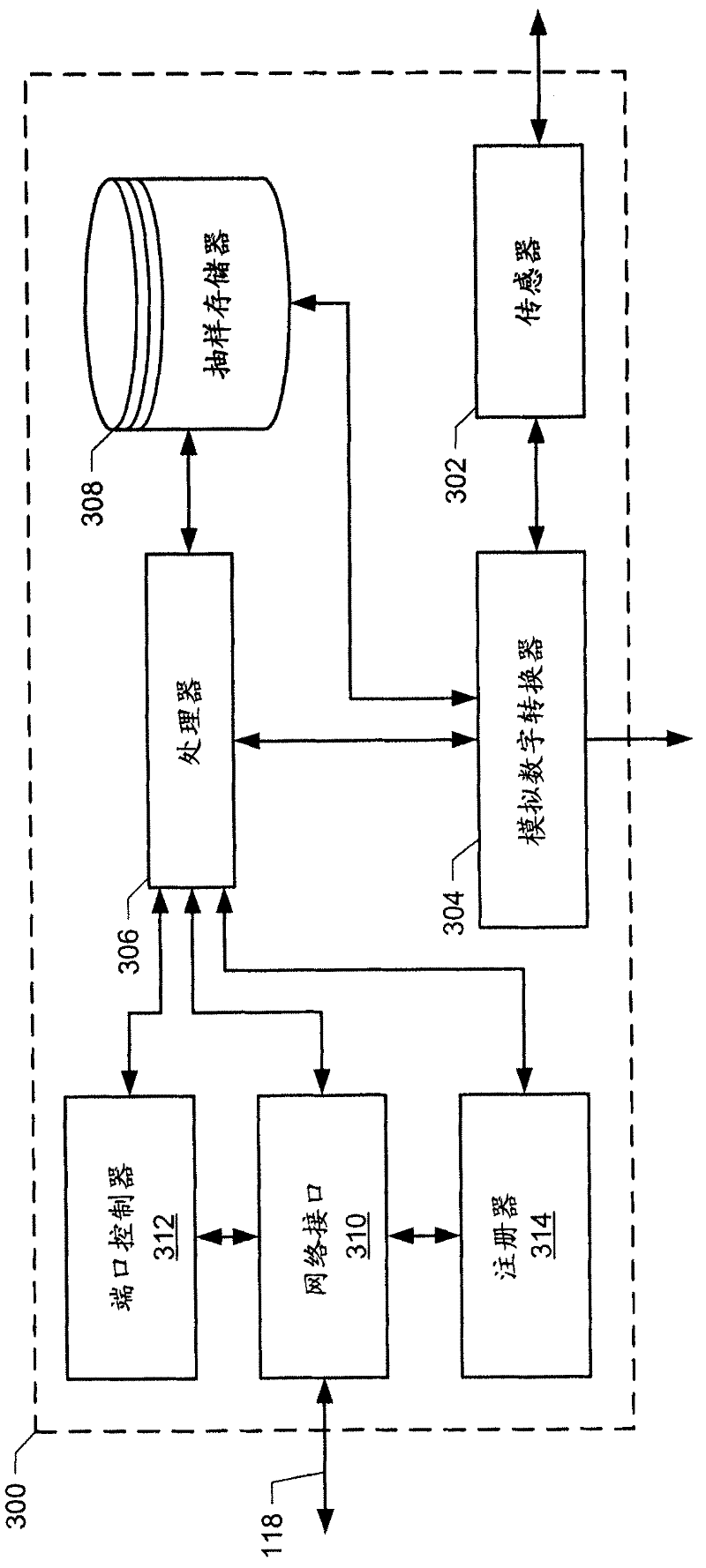
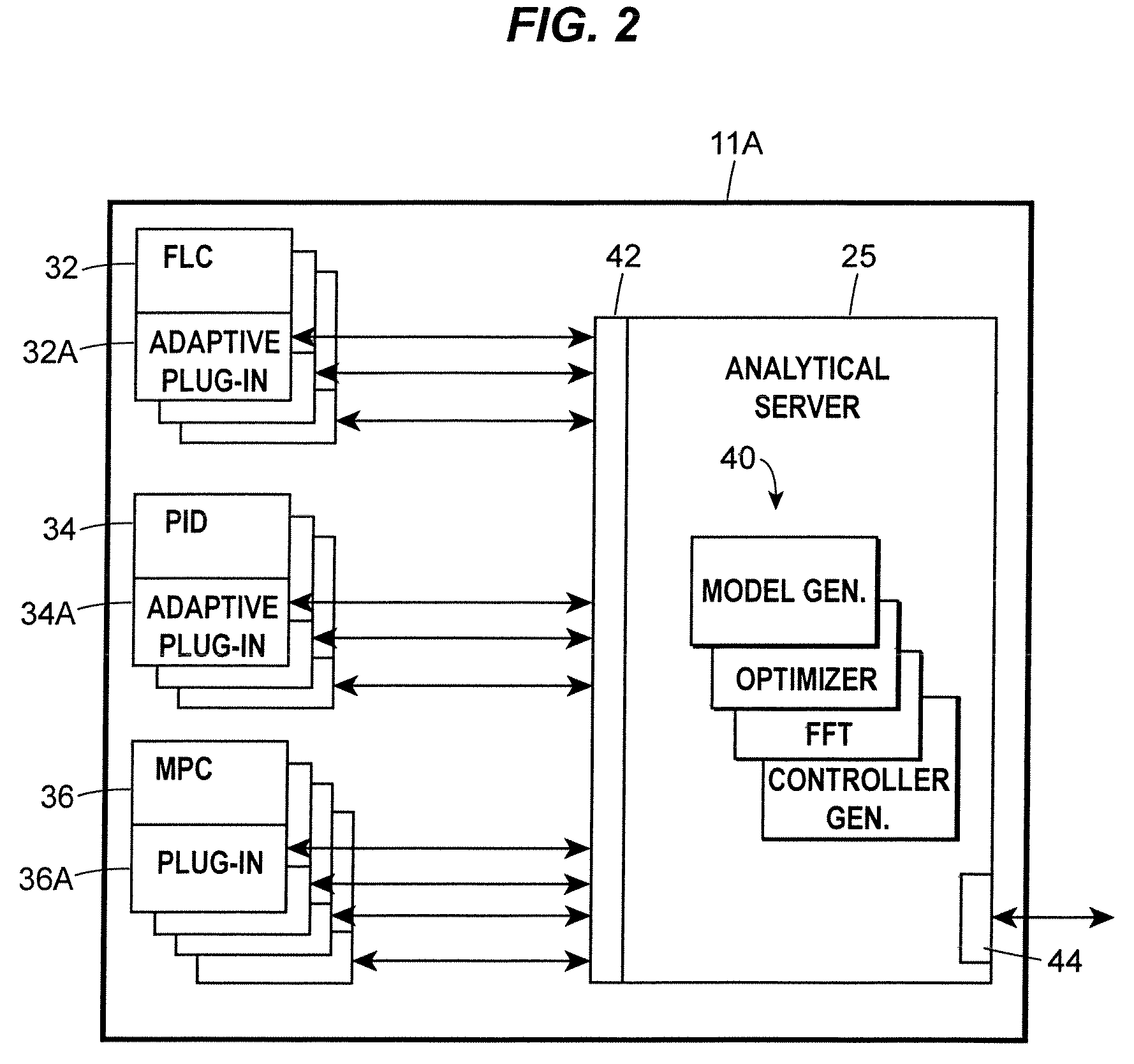
Analytical Server Integrated in a Process Control Network
ActiveUS20070142936A1Faster and efficient supportComputer controlTechnology managementProcess control networkLoop control
A process control system integrates the collection and analysis of process control data used to perform certain computationally expensive process control functions, like adaptive model generation and tuning parameter generation, in the same control device in which one or more of the process control routines are implemented, to thereby provide for faster and more efficient support of the process control routines. This system replaces a layered approach using multiple processing devices by integrating an analytical server which performs computationally expensive analyses used by one or more control routines directly into the real-time control device in which the one or more control routines are located. This integration provides the ability to analyze large quantities of data for multiple process loops controlled by a particular device in a fast and efficient manner.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
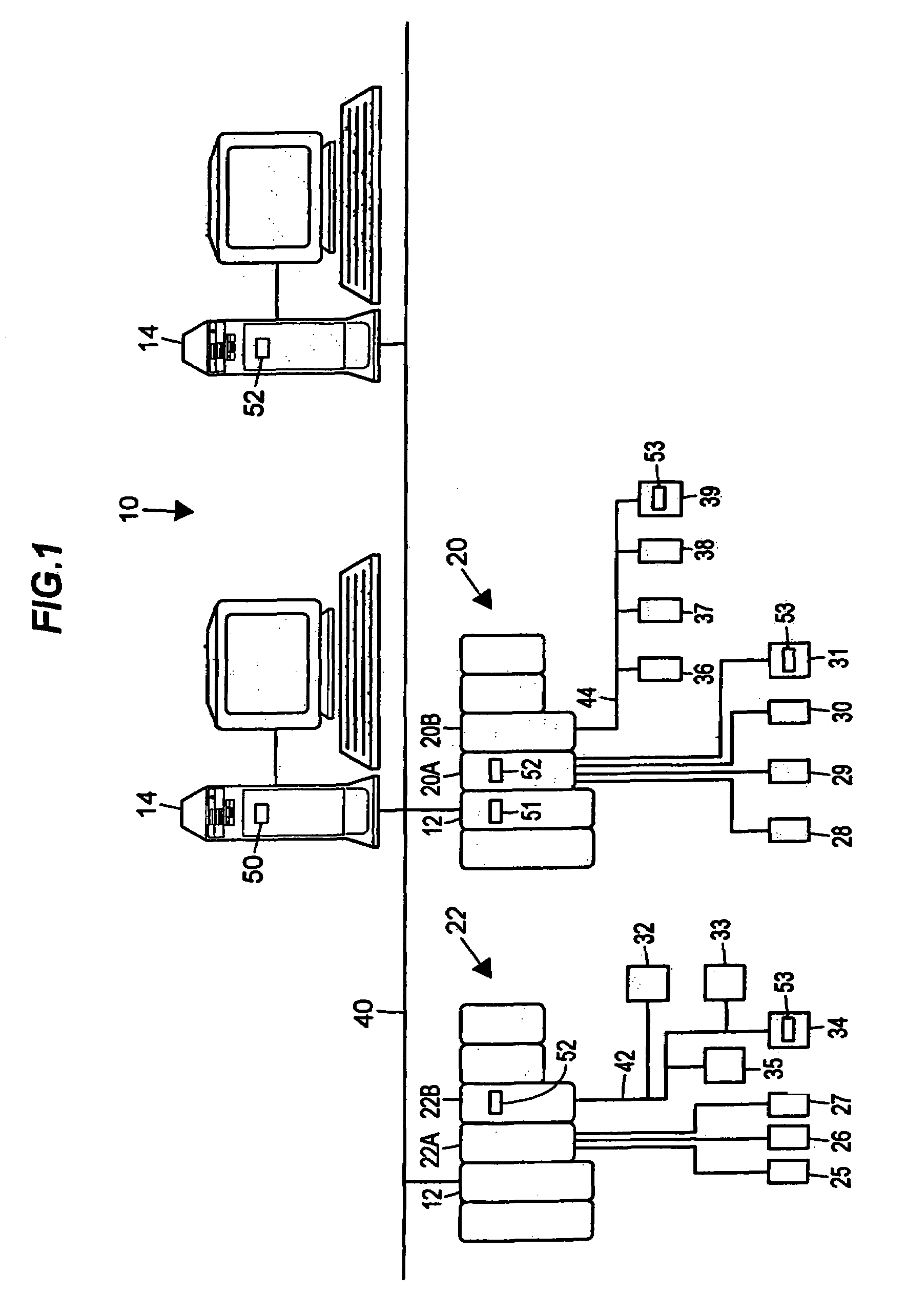
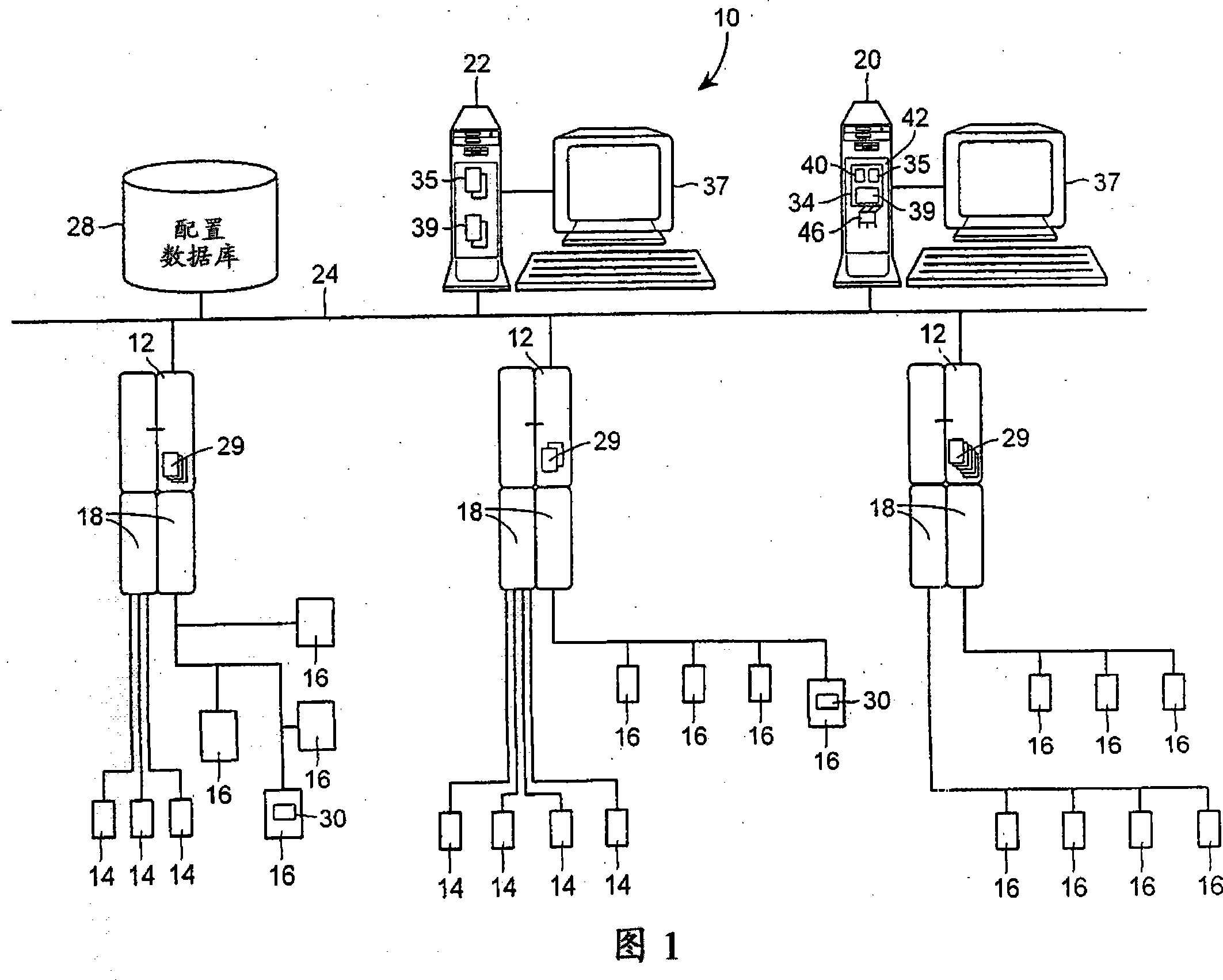
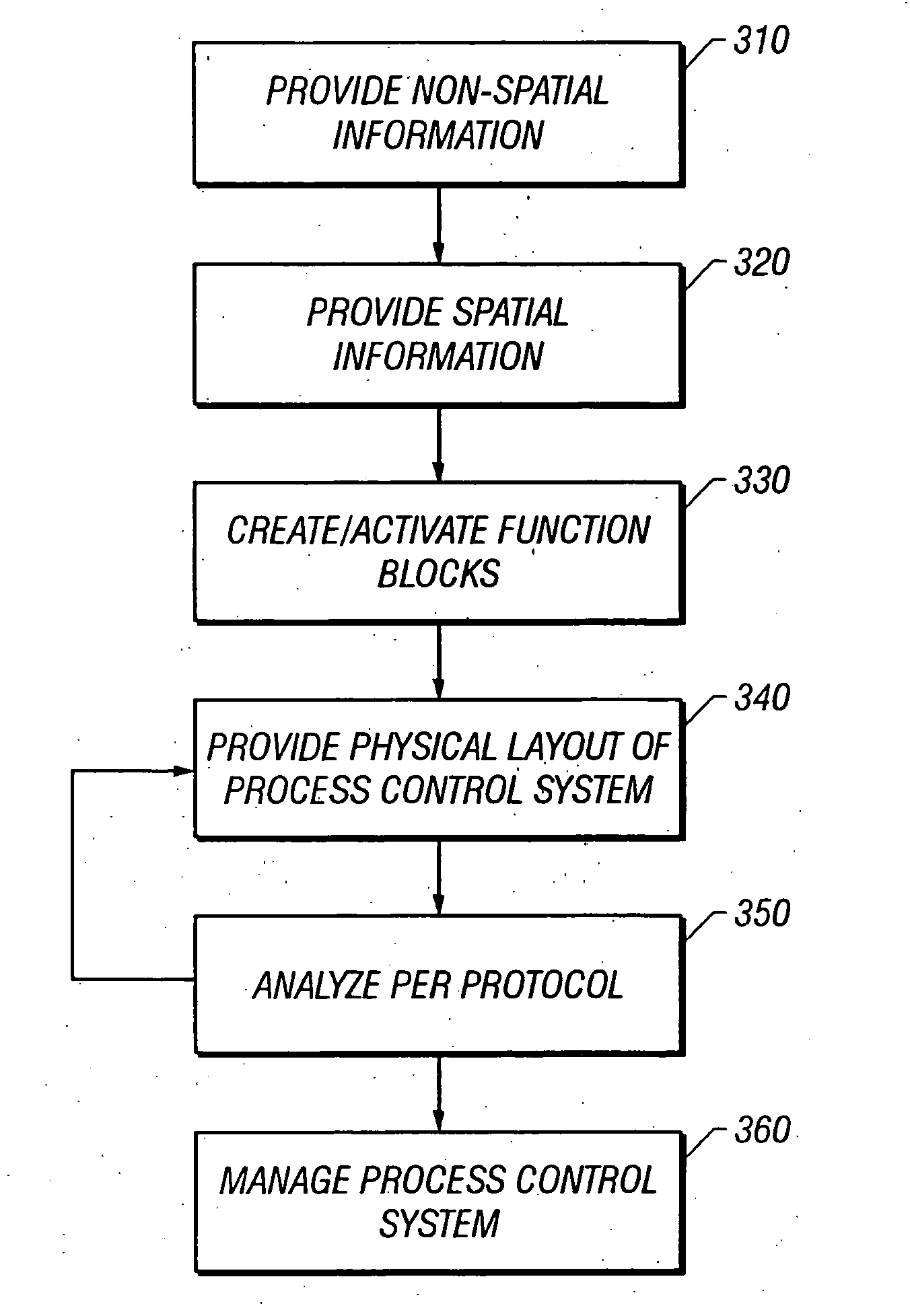
Enhanced tool for managing a process control network
InactiveUS20070179645A1Efficient designEfficient use ofSampled-variable control systemsComputer controlProcess control networkControl system
A process control configuration and management system provides a plurality of function blocks representing a plurality of devices in relation to a spatial layout of a facility in which the process control system is implemented. The configuration and management system also provides process control information and process simulation information related to each of the plurality of devices in relation to the spatial layout of the facility. The configuration and management system may be implemented on a handheld device and it may include a geographic positioning system providing geographic positioning data related to the handheld device and various devices in relation to the spatial layout of the facility.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
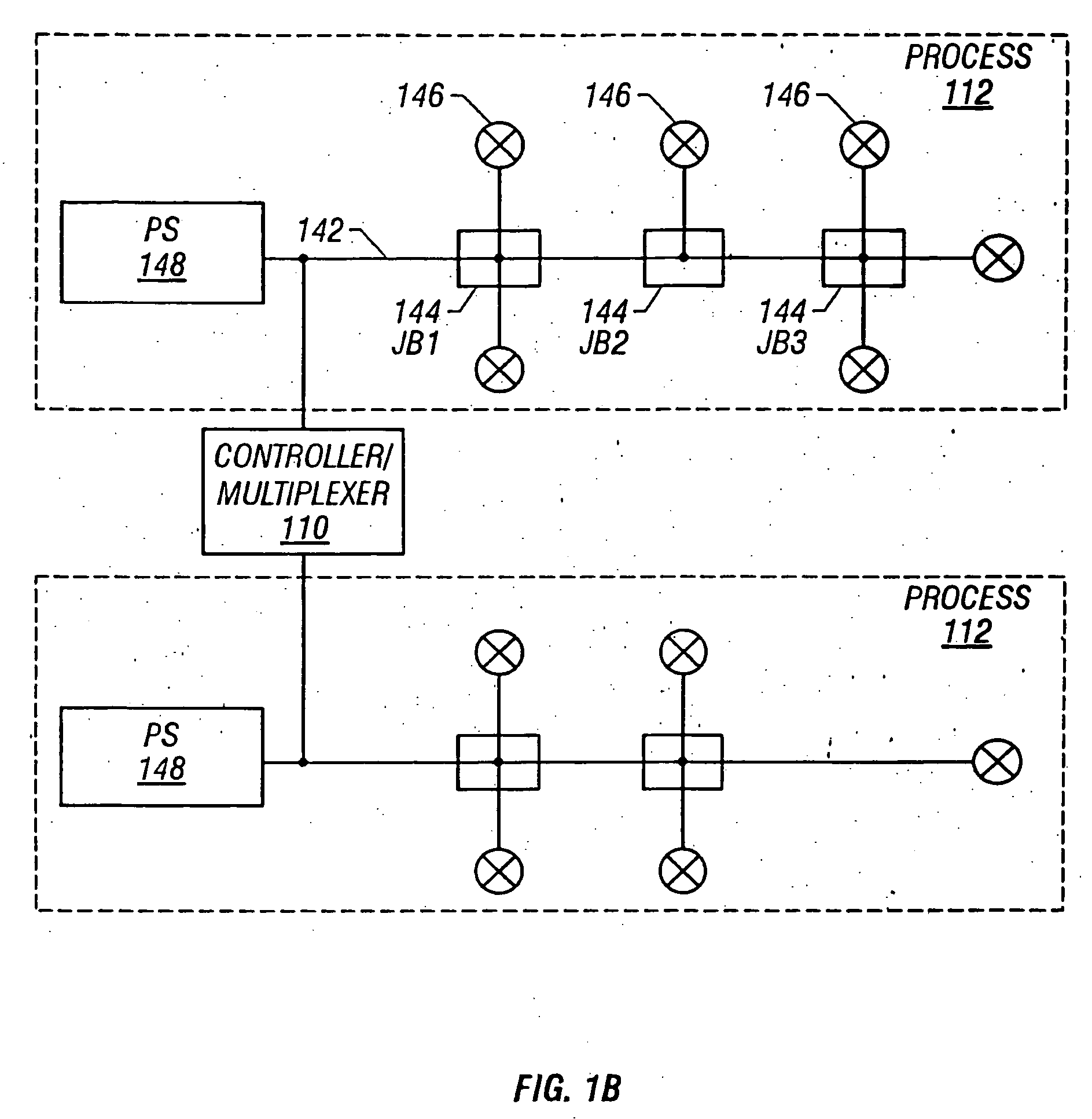
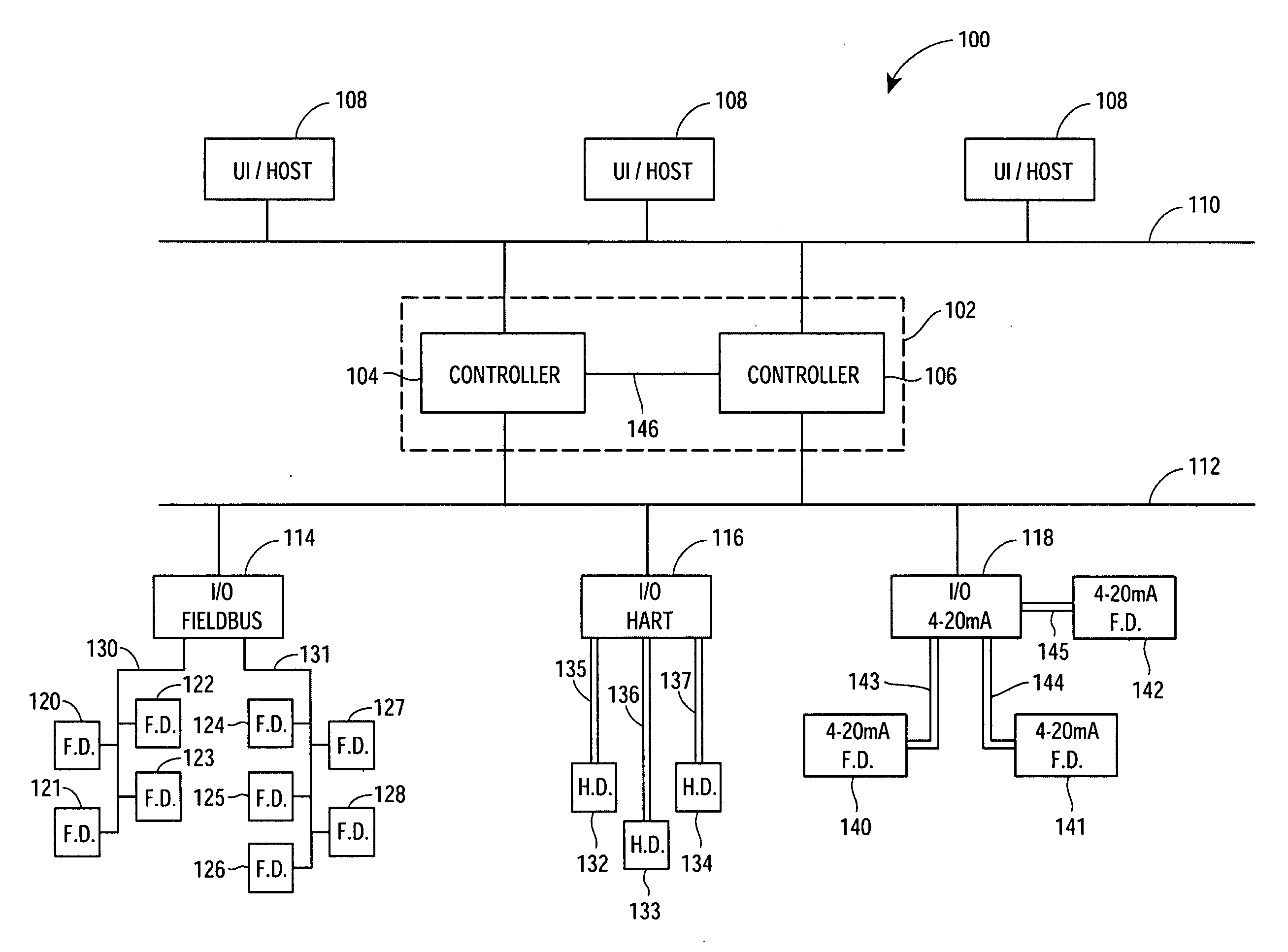
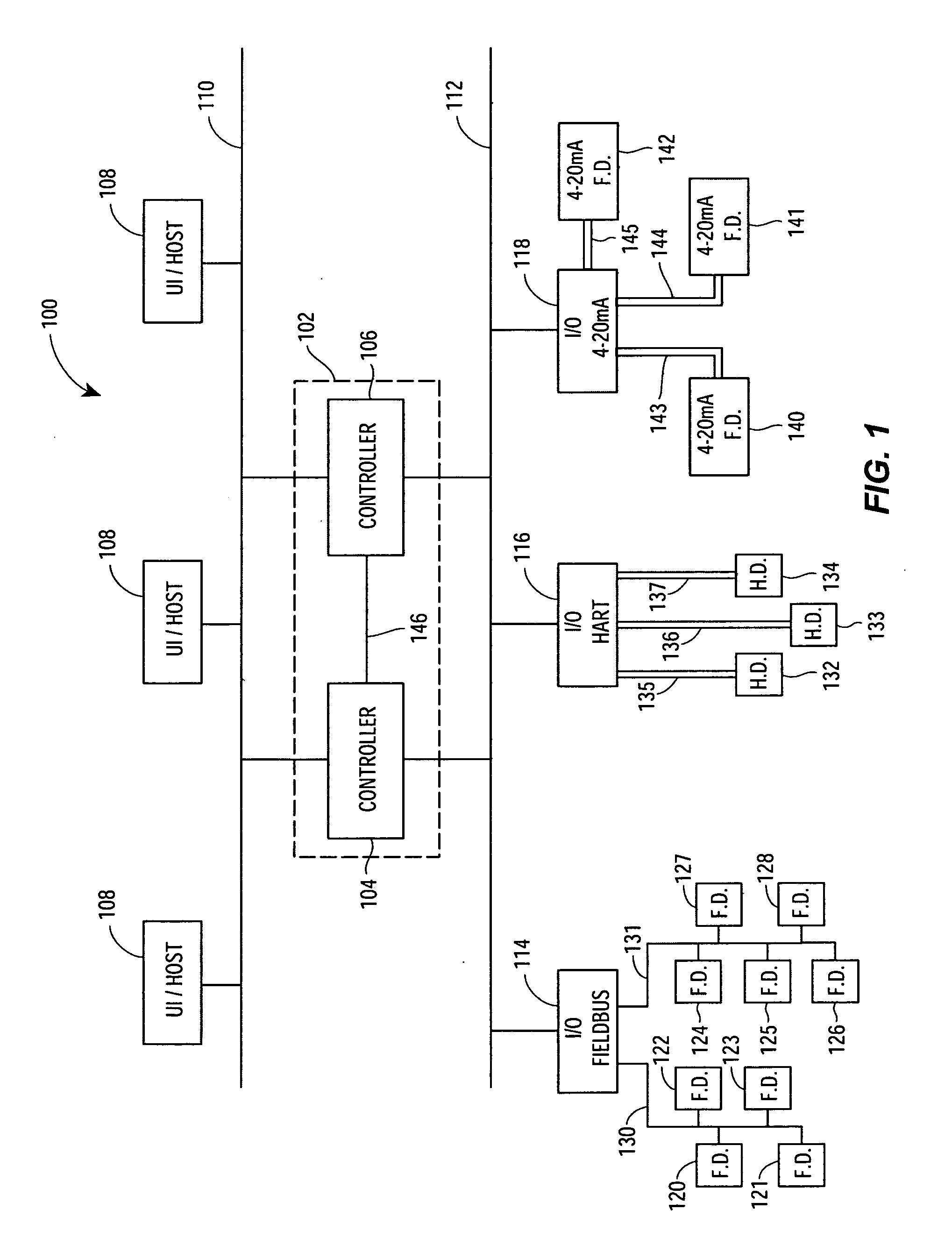
Method for redundant controller synchronization for bump-less failover during normal and program mismatch conditions
The present invention relates generally to process control systems and devices and, more particularly, to an apparatus for and a method of implementing redundant controller synchronization for bump-less failover during normal and mismatch conditions at the redundant controllers. The redundant controllers are configured to transmit state information of the process control areas of the primary controller to the backup controller that is necessary for synchronizing the redundant controllers but is not typically transmitted to other devices during the performance of process control functions. Synchronization messages are transmitted from the primary controller to the backup controller each time one of the control areas executes to perform process control functions. In other aspects, the redundant controllers are configured to determine state information at the backup controller from other process control network information during a fallover of the primary controller where a mismatch condition exists between the control areas of the two controllers during the downloading of reconfigurations, and to initialize the backup controller at startup when the mismatch condition exists.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
Automatic Configuration of Synchronous Block Execution for Control Modules Run in Fieldbus Networks
ActiveUS20080249641A1Easy and optimal useFaster rateComputer controlSimulator controlProcess control networkAuto-configuration
A method or apparatus automatically configures a control module for synchronous execution on a Fieldbus segment of a process control network by determining if all of the critical function blocks of a particular control module can be assigned to FOUNDATION® Fieldbus field devices or to the I / O device associated with a particular Fieldbus segment. If so, the method or apparatus automatically assigns the function blocks of the control module, which would otherwise be scheduled to execute in a controller, to the I / O device for the Fieldbus segment. This technique enables all of the critical or necessary function blocks within the control module to execute in one macrocycle of the Fieldbus segment, thereby executing synchronously on a Fieldbus segment. This operation, in turn, increases the overall execution rate of the control module with respect to control modules that have function blocks split between a controller and field devices on a Fieldbus segment, which has been the traditional manner of configuring control modules implemented using devices on a Fieldbus segment.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
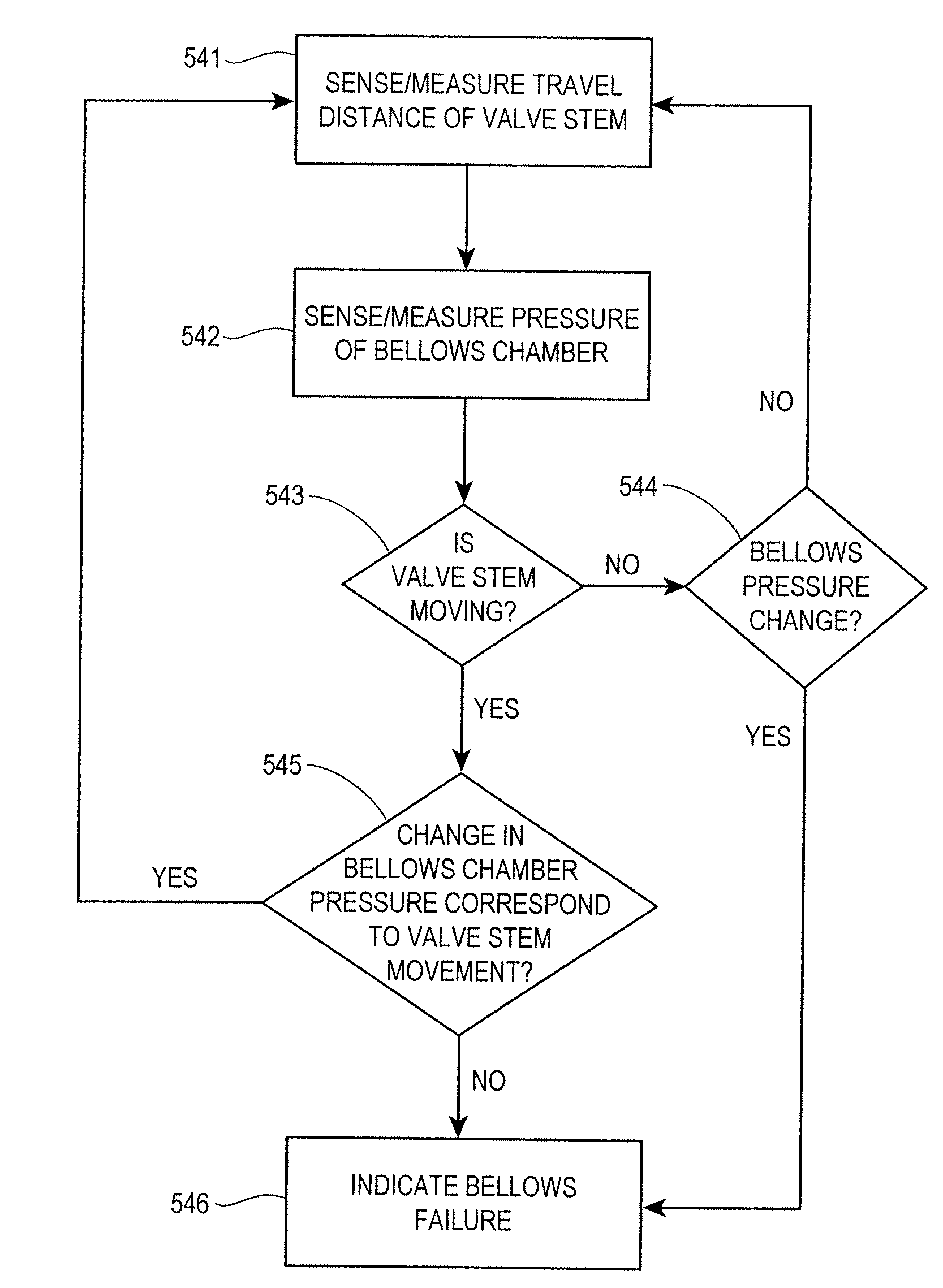
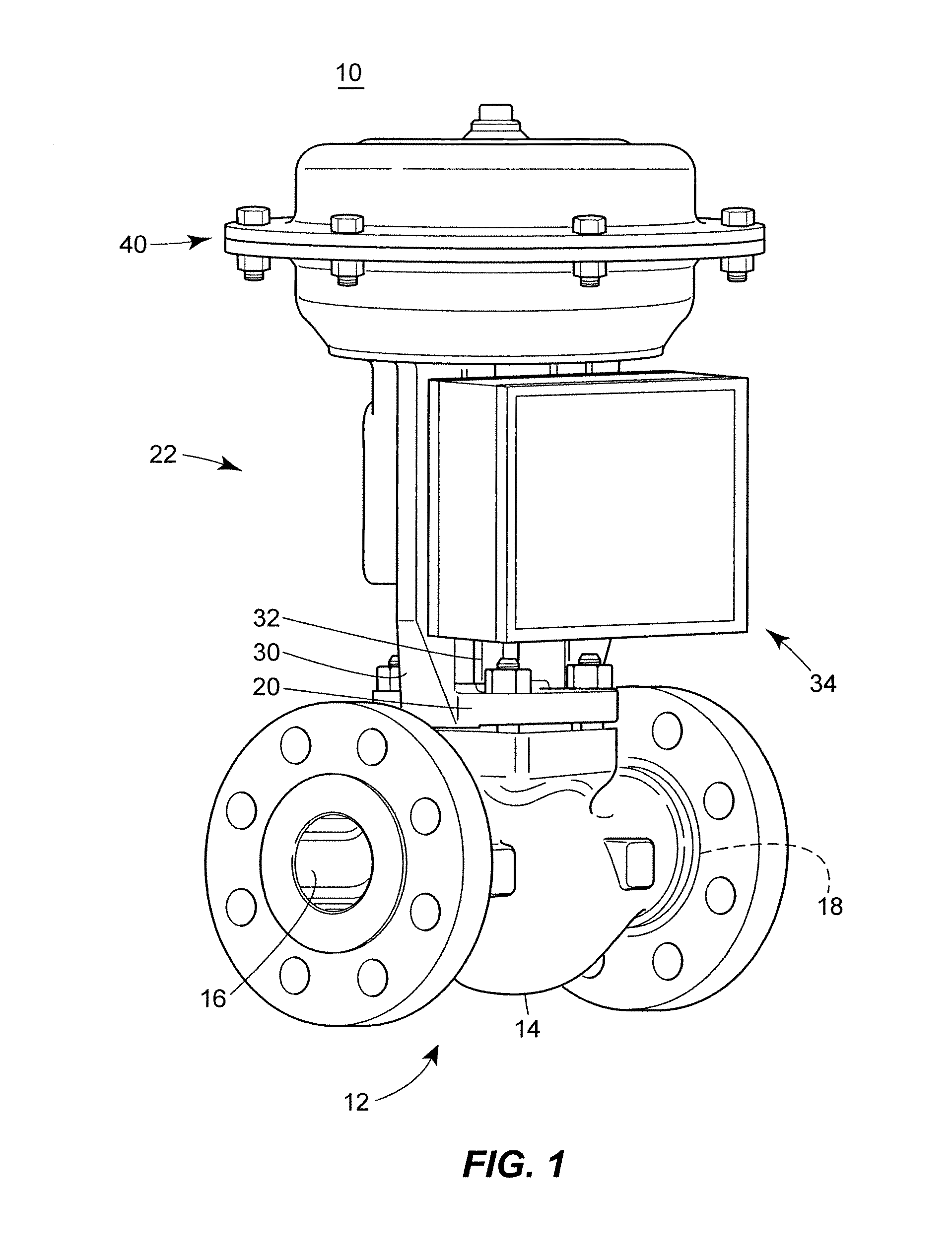
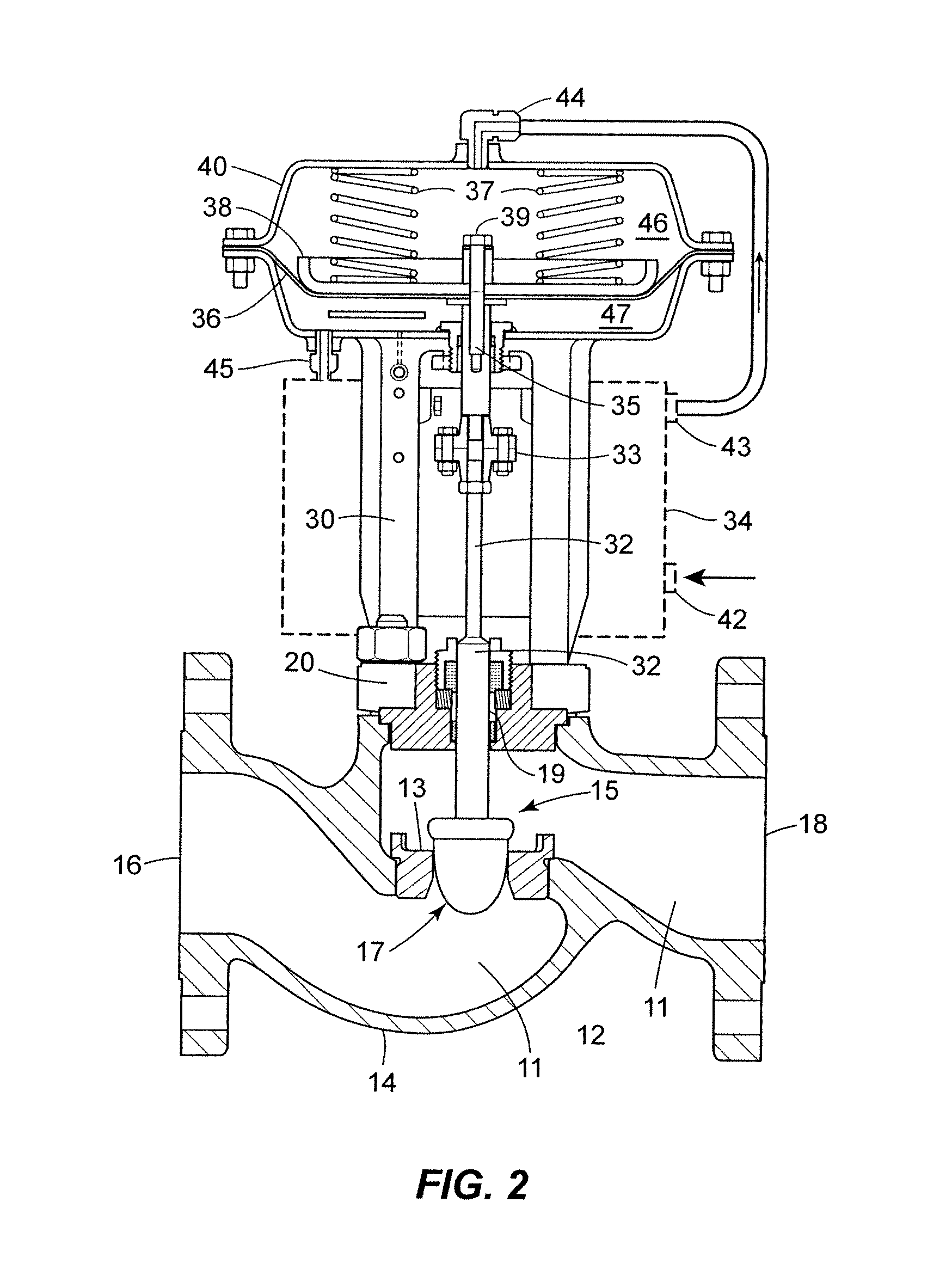
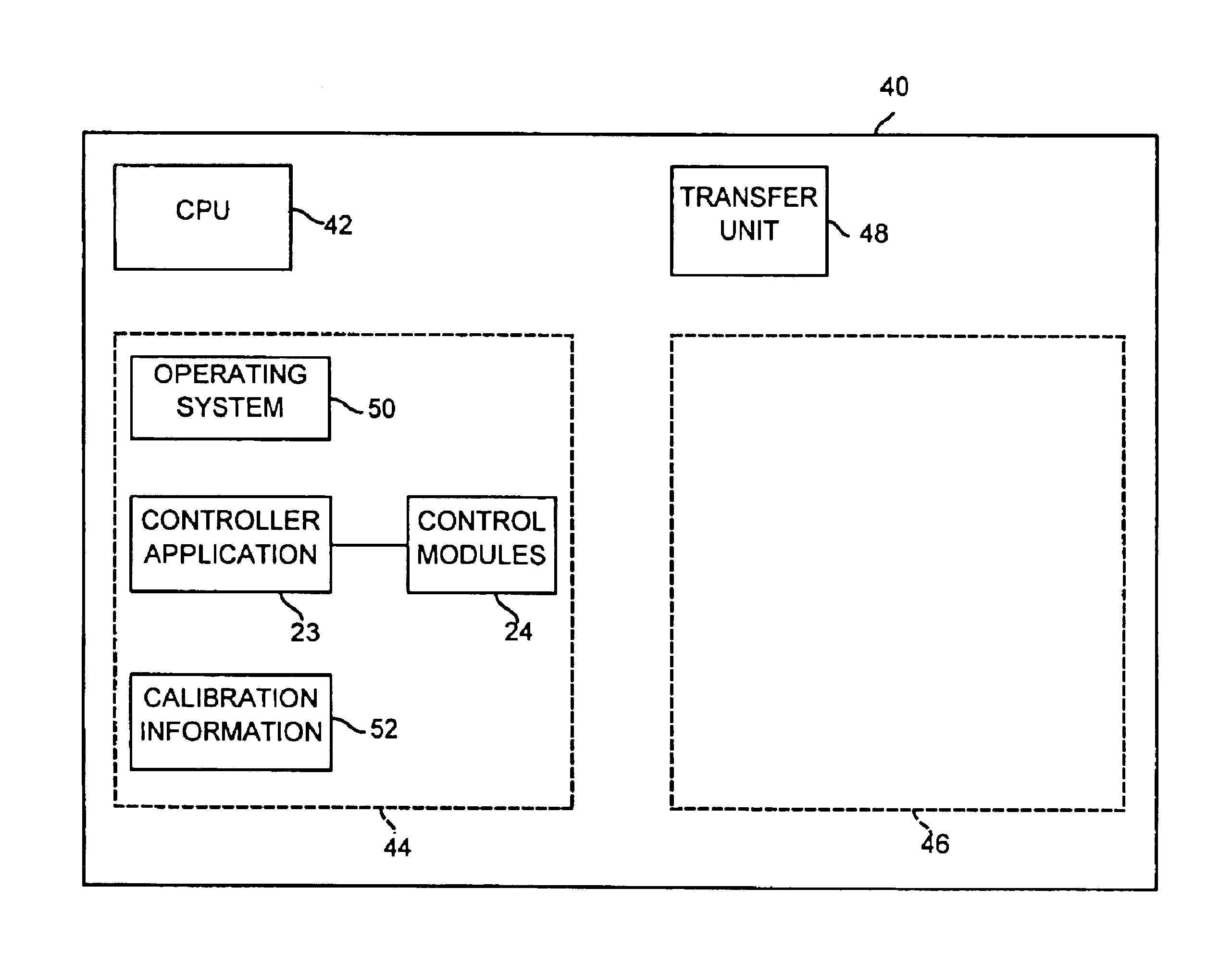
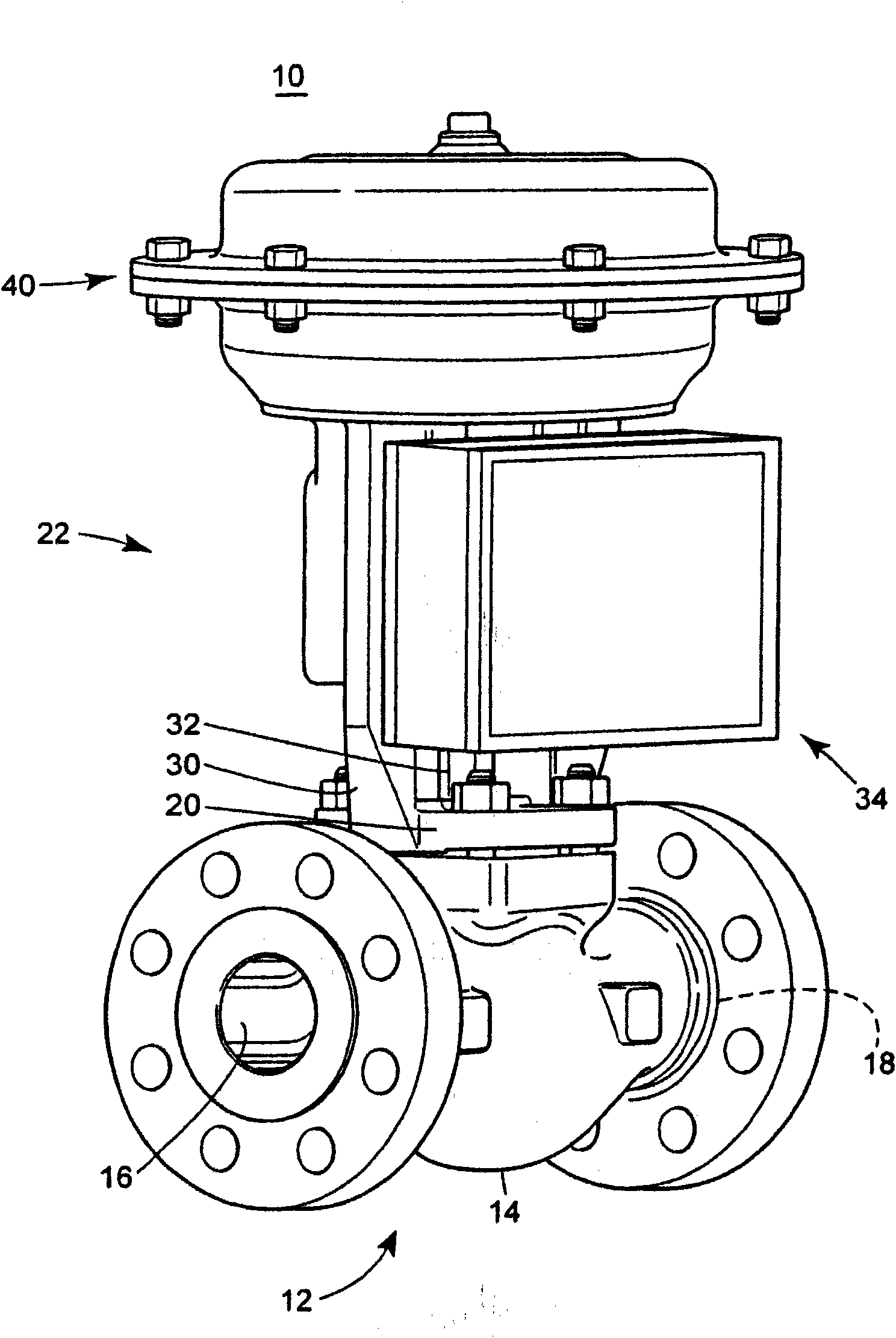
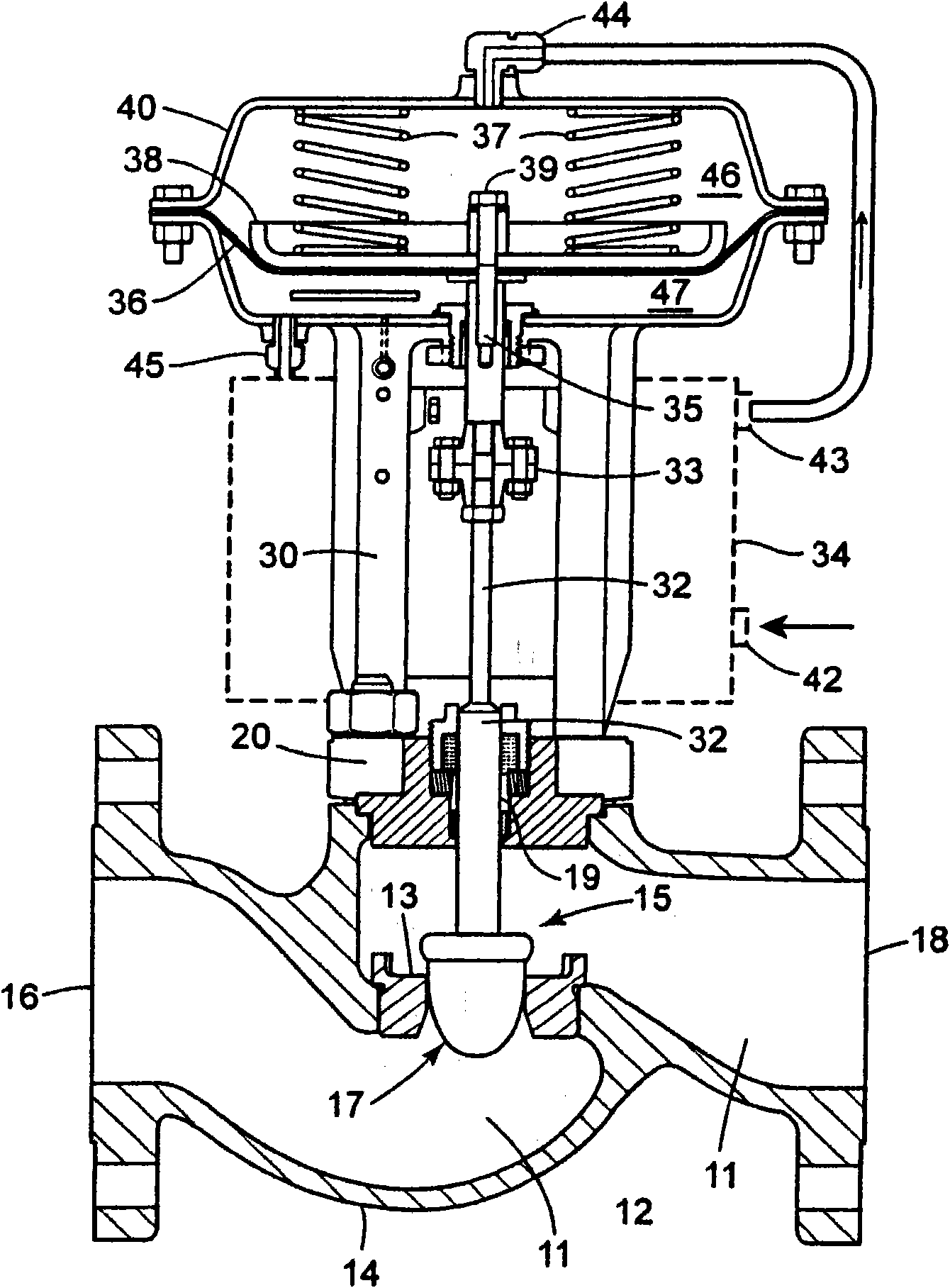
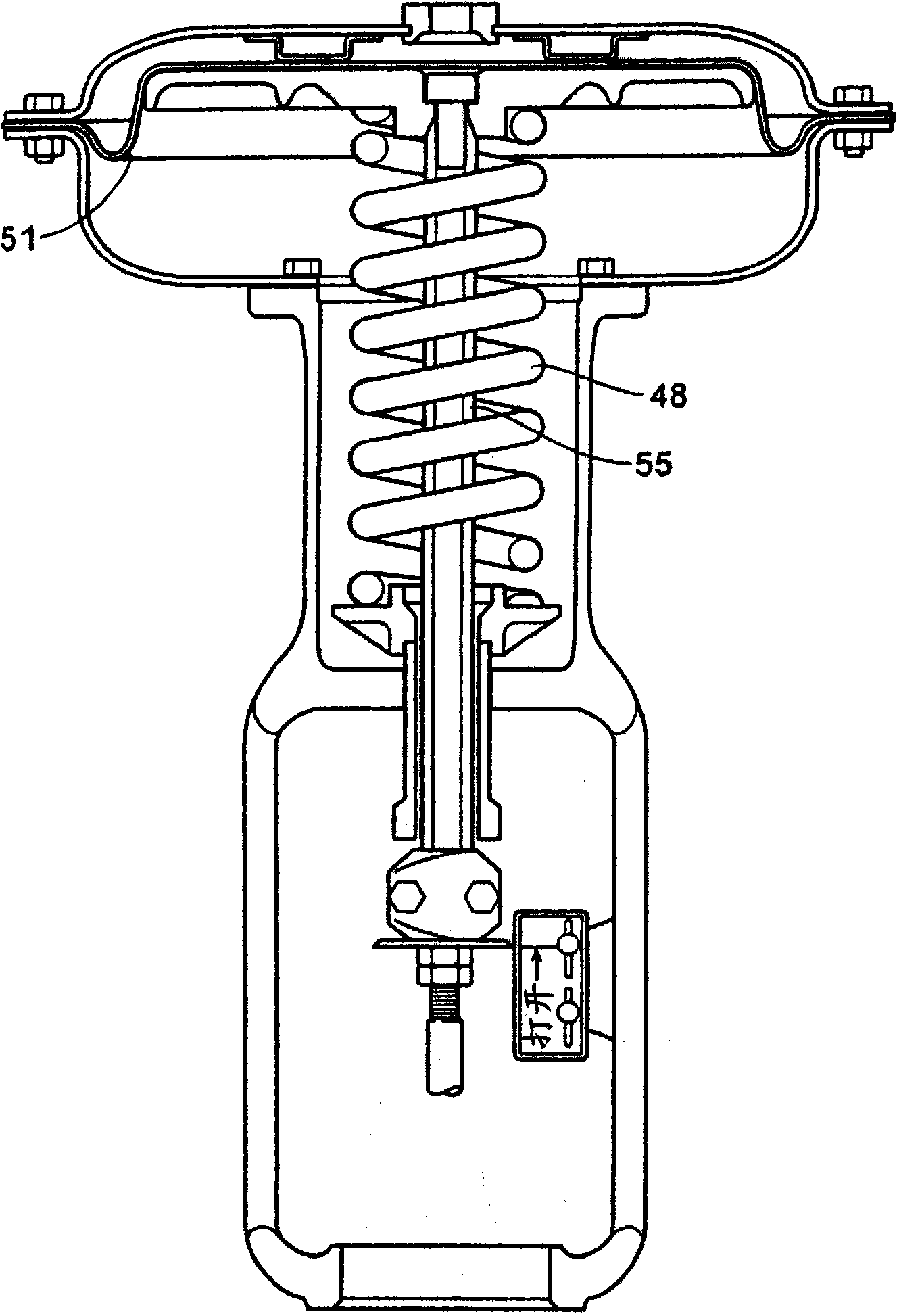
Diagnostic method for detecting control valve component failure
The claimed method and system identifies faults and / or deterioration of components in a process control valve. The system may use different sensor combinations to provide the necessary data to compute irregular component integrity. Alerts may be generated to indicate potential component integrity problems. In particular, the system may detect potential deterioration and / or faults in actuator springs, pneumatic tubing and piping, and bellows seals. The claimed system may be communicatively coupled to a process control network to provide a more elaborate alarm system. Moreover, additional statistical methods may be used to refine the detection accuracy of the system.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
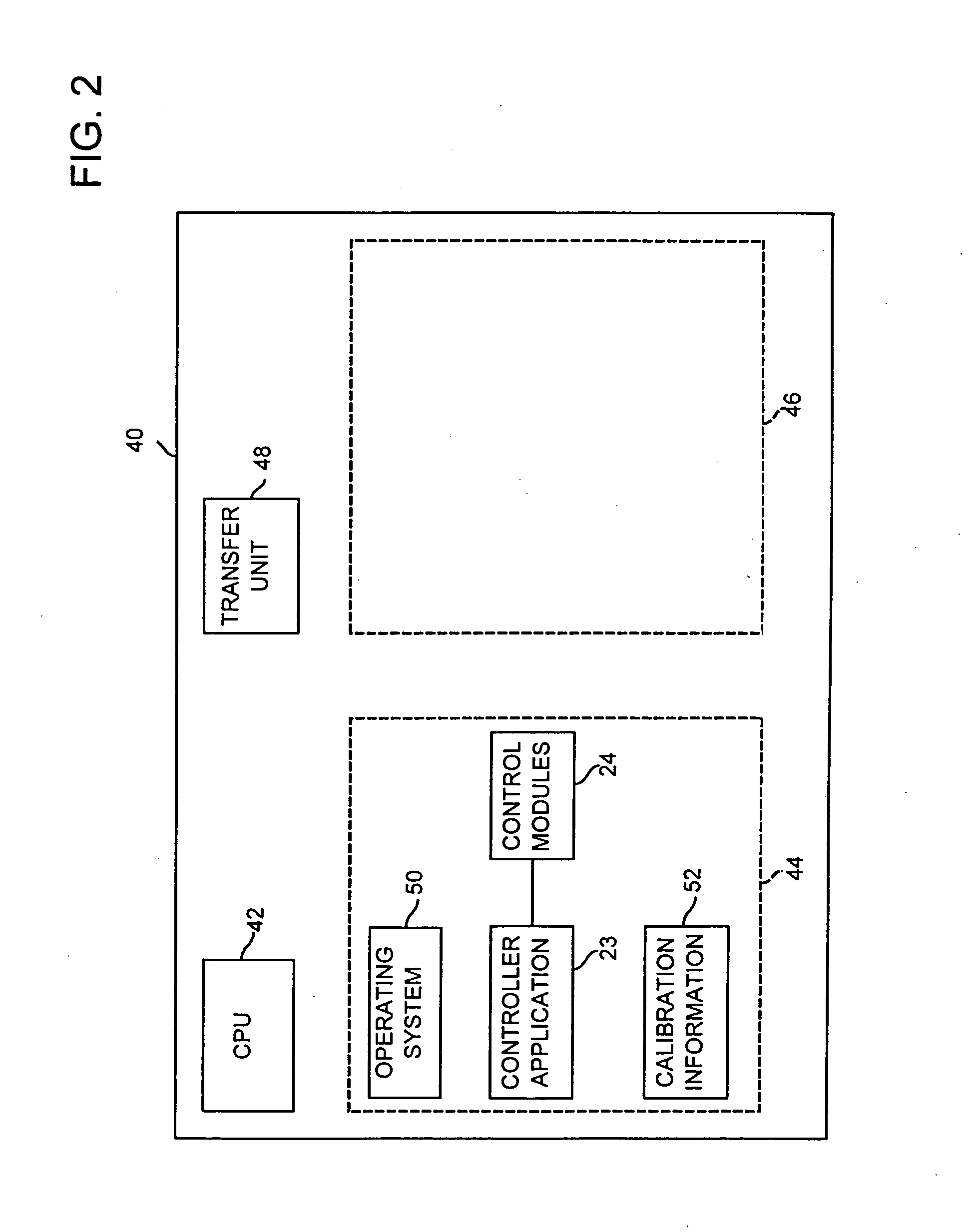
Downloadable code in a distributed process control system
InactiveUS6850973B1Shorten the timeReduce disruptionComputer controlError detection/correctionProcess control networkControl system
A method of reprogramming a field device in a process control network using the standard communications protocol for the network, and a reprogrammable field device in the process control network adapted for being reprogrammed using the standard communications protocol for the network. The method and device of the present invention use the standard communications protocol to transmit the downloaded code to the field device and store the downloaded code in the field device while the device is enabled to perform process control. Once the new code is downloaded and stored in the field device, the field device is disabled from performing process control, reprogrammed to execute the downloaded code, and reenabled to perform process control.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
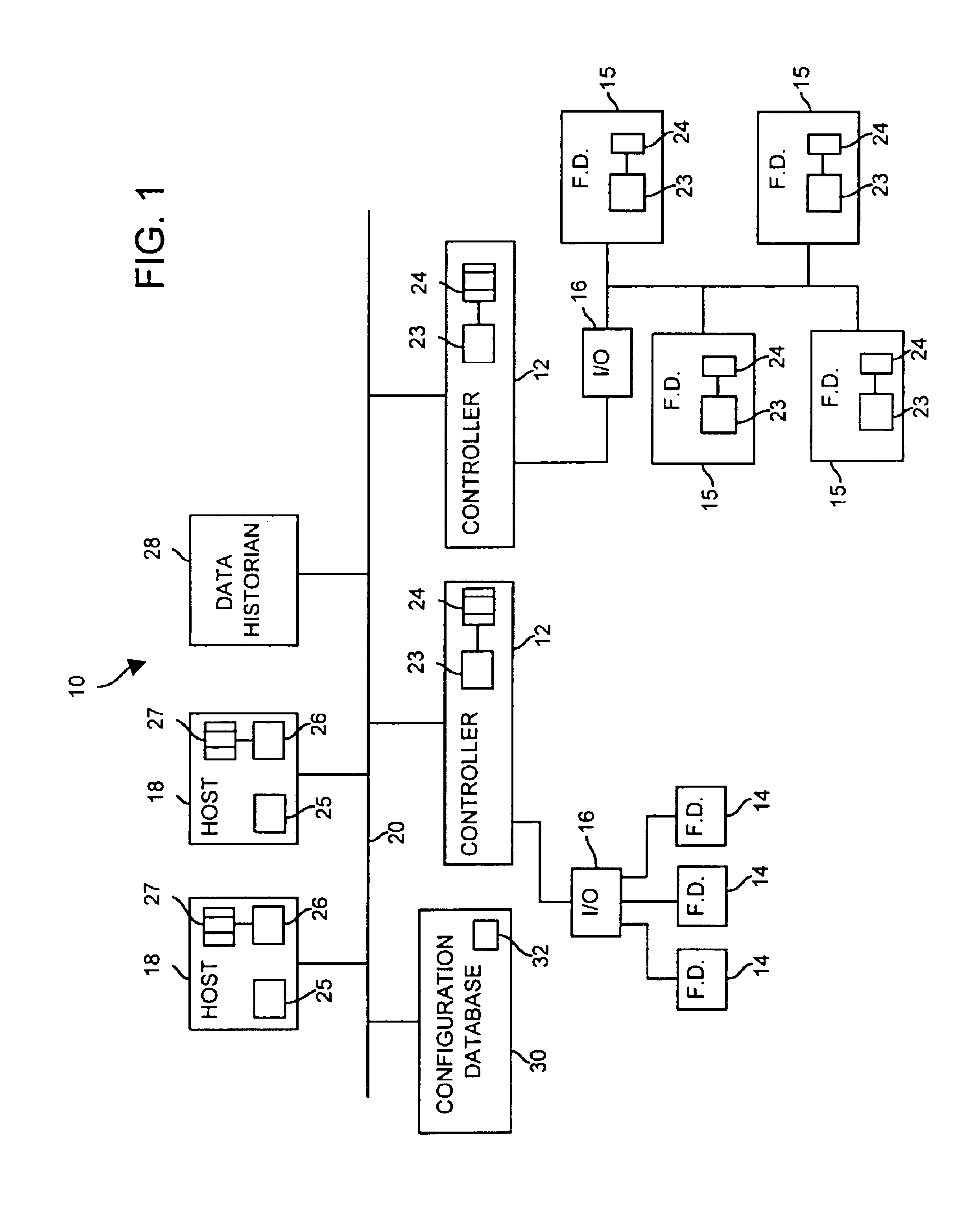
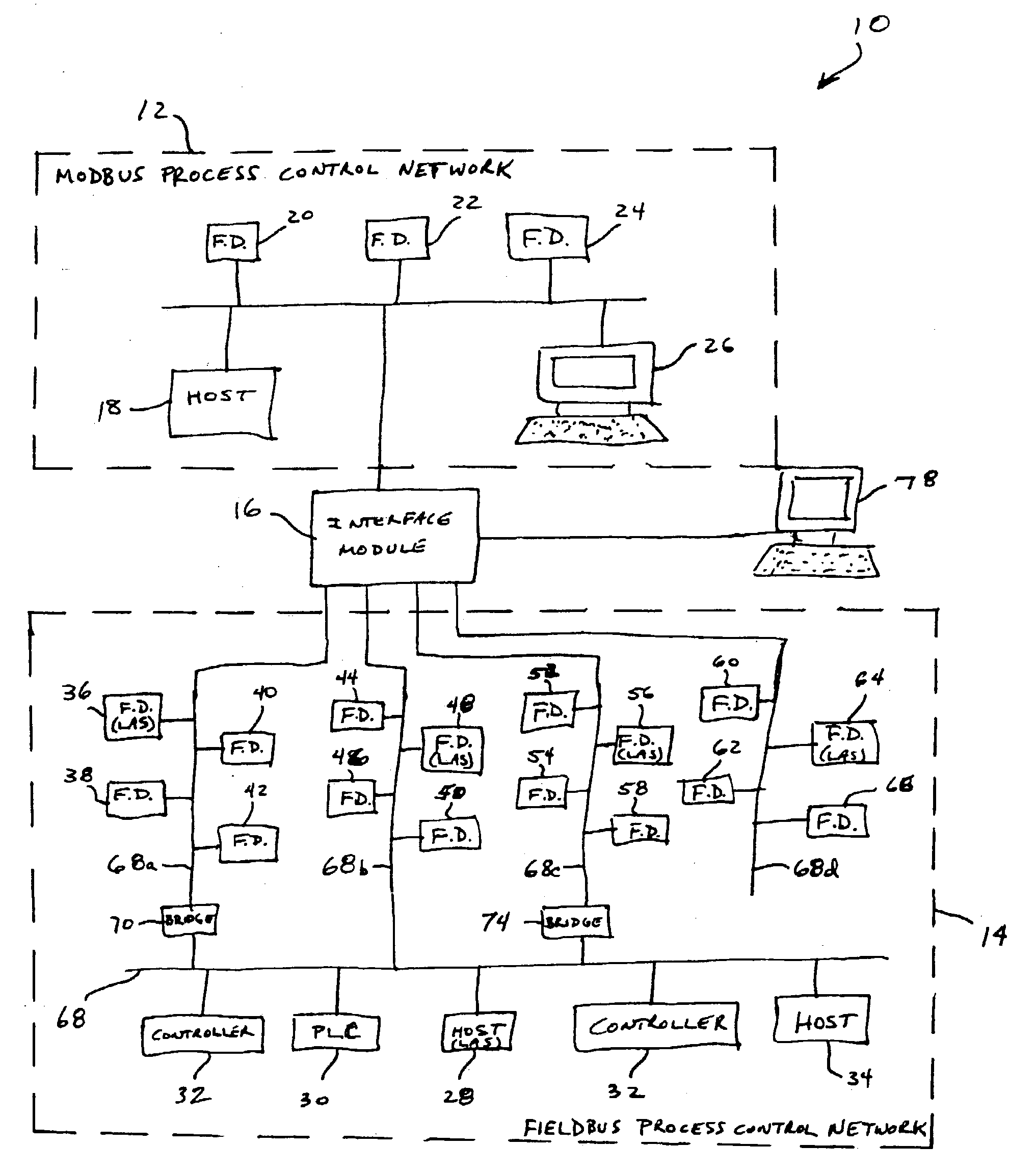
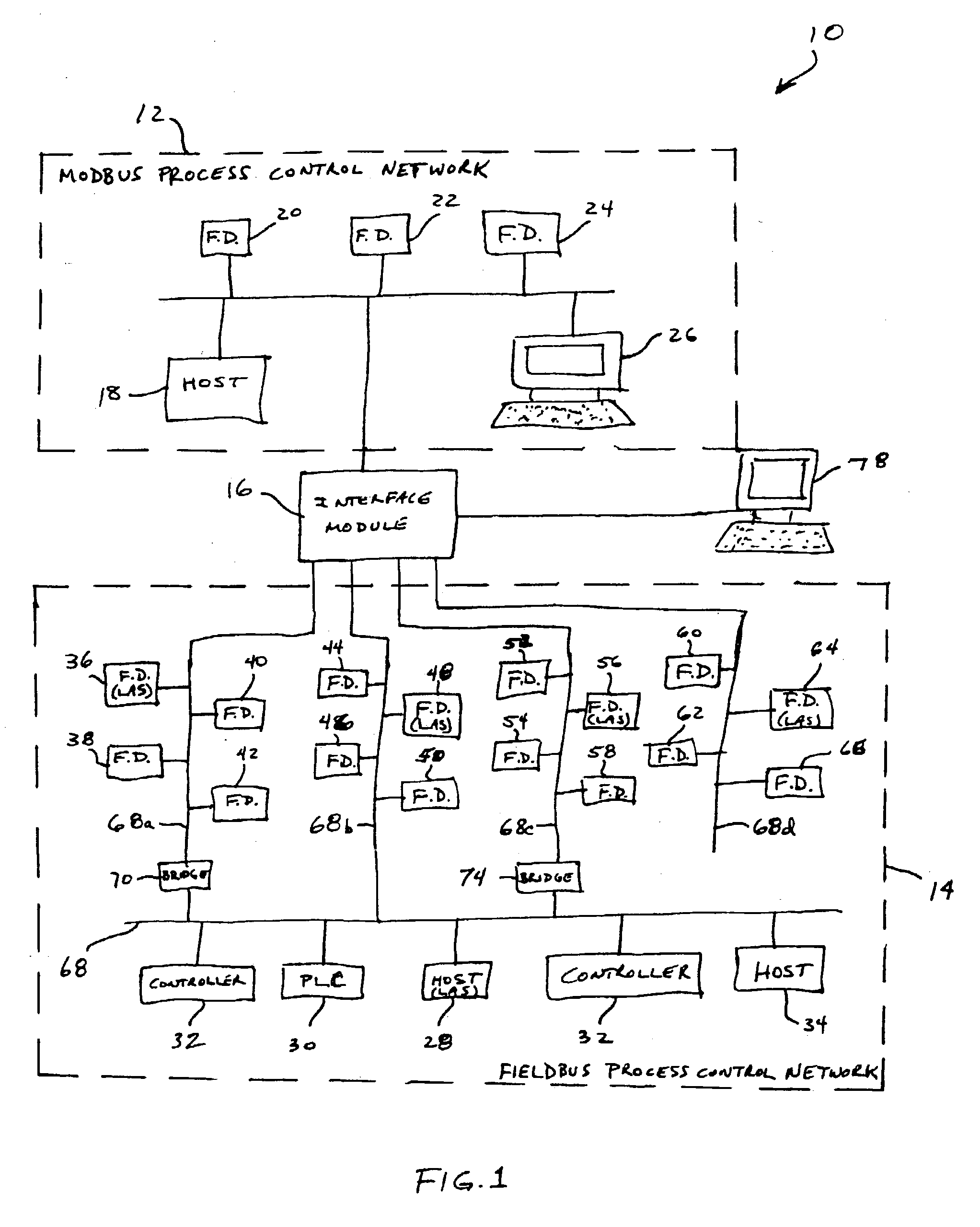
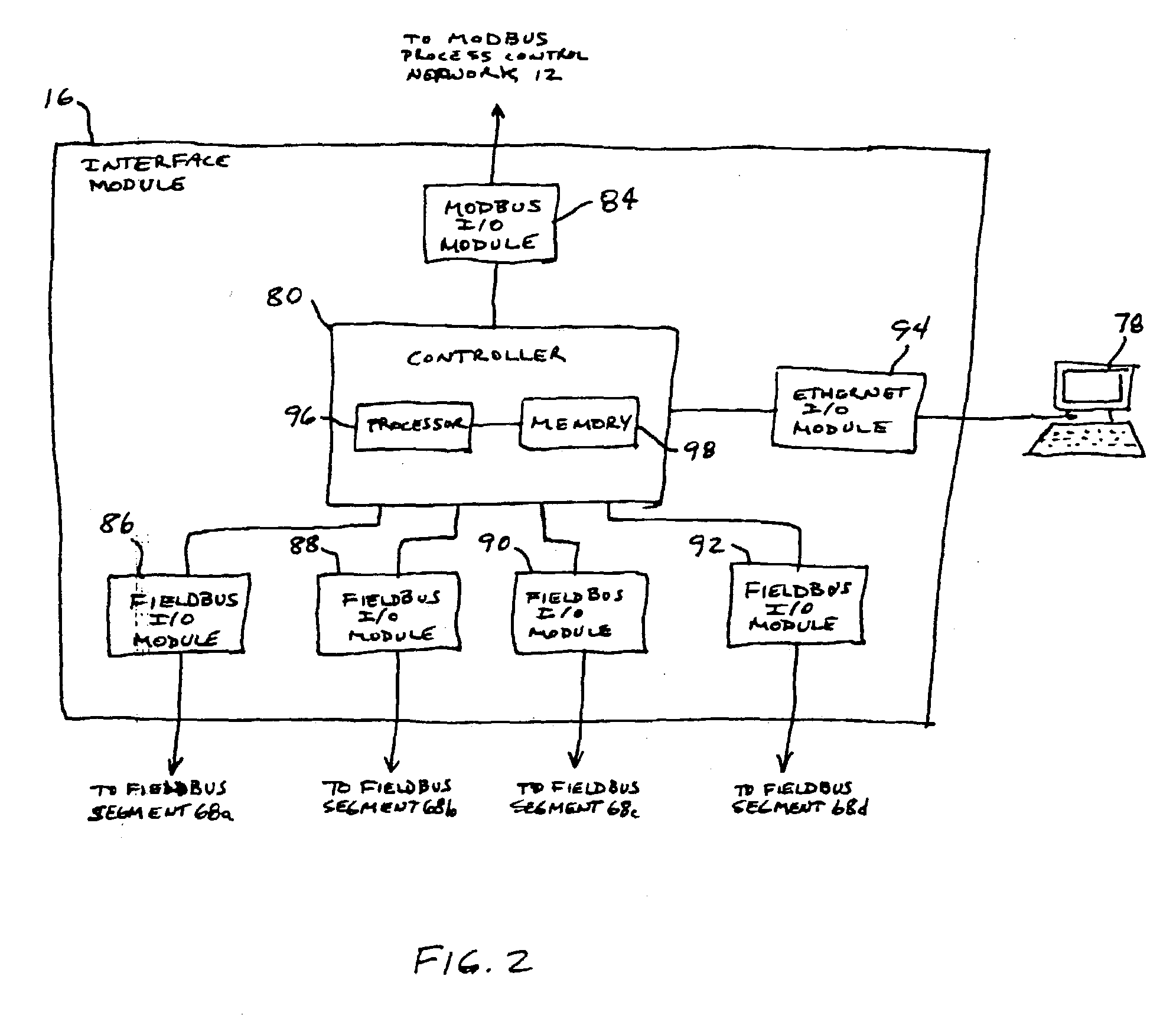
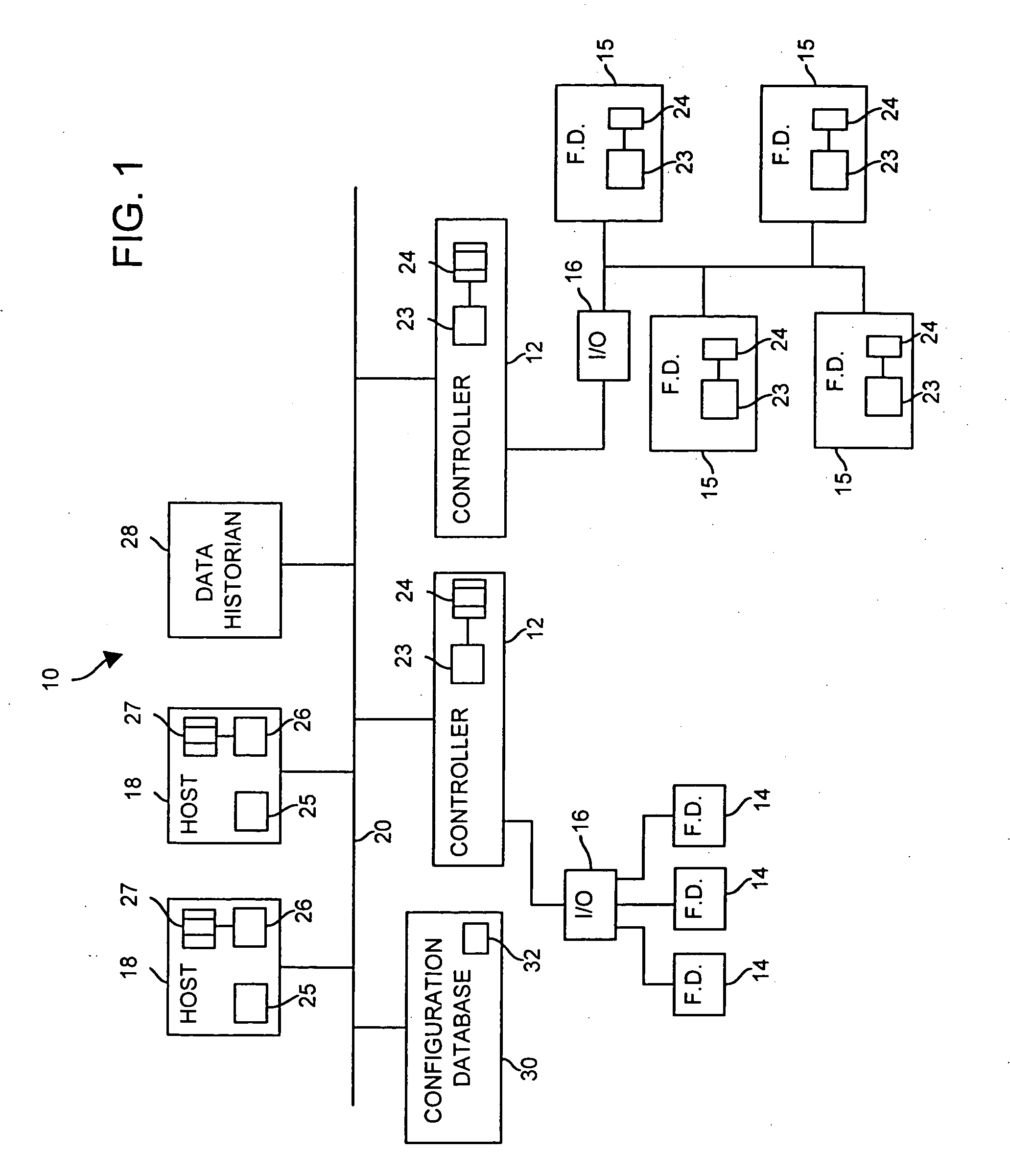
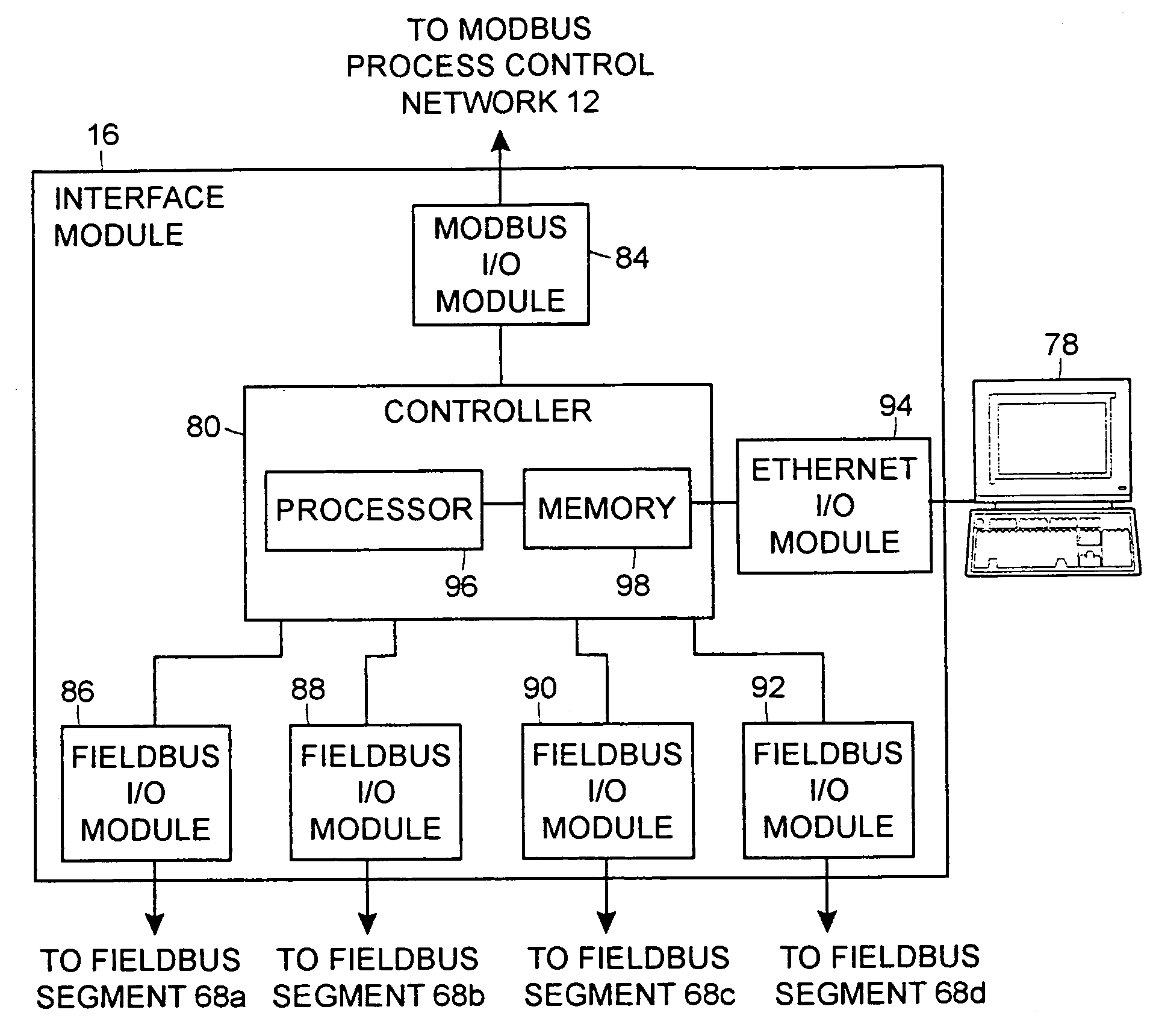
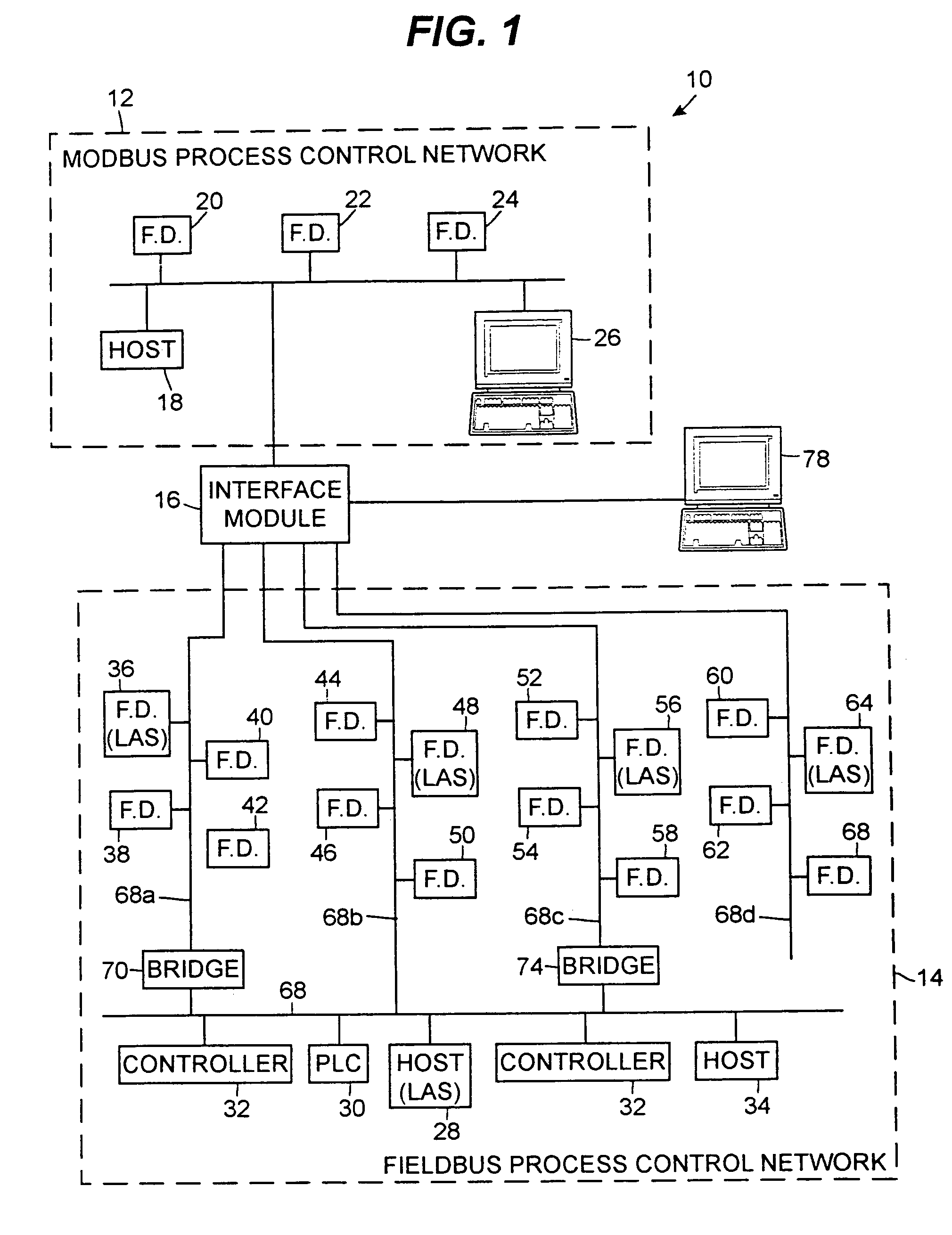
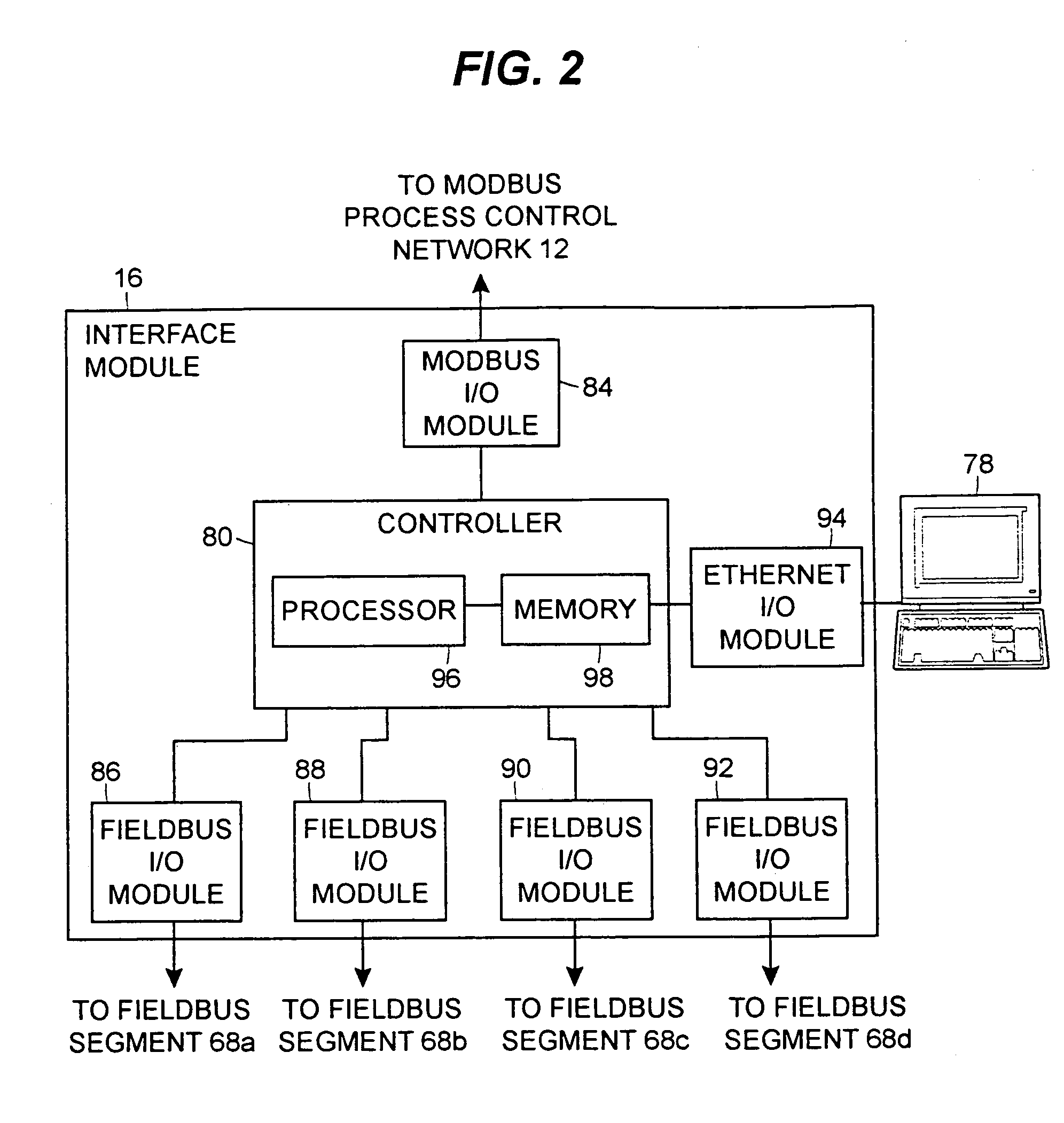
Interface module for use with a Modbus device network and a Fieldbus device network
An interface module is operatively coupled to a Fieldbus process control network and a Modbus process control network to facilitate the exchange of process control information between the networks. The interface module stores a register map database in which the process control parameters of the function blocks in the field devices of the Fieldbus process control network are mapped to register numbers of the Modbus process control network. Once the Fieldbus process control parameters are mapped to the Modbus registers, the interface module is adapted to transmit request messages on the Fieldbus process control network to the Fieldbus field devices for the current values of the process control parameters, receive response messages from the Fieldbus field devices, and store the current values of the process control parameters in the register map database.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
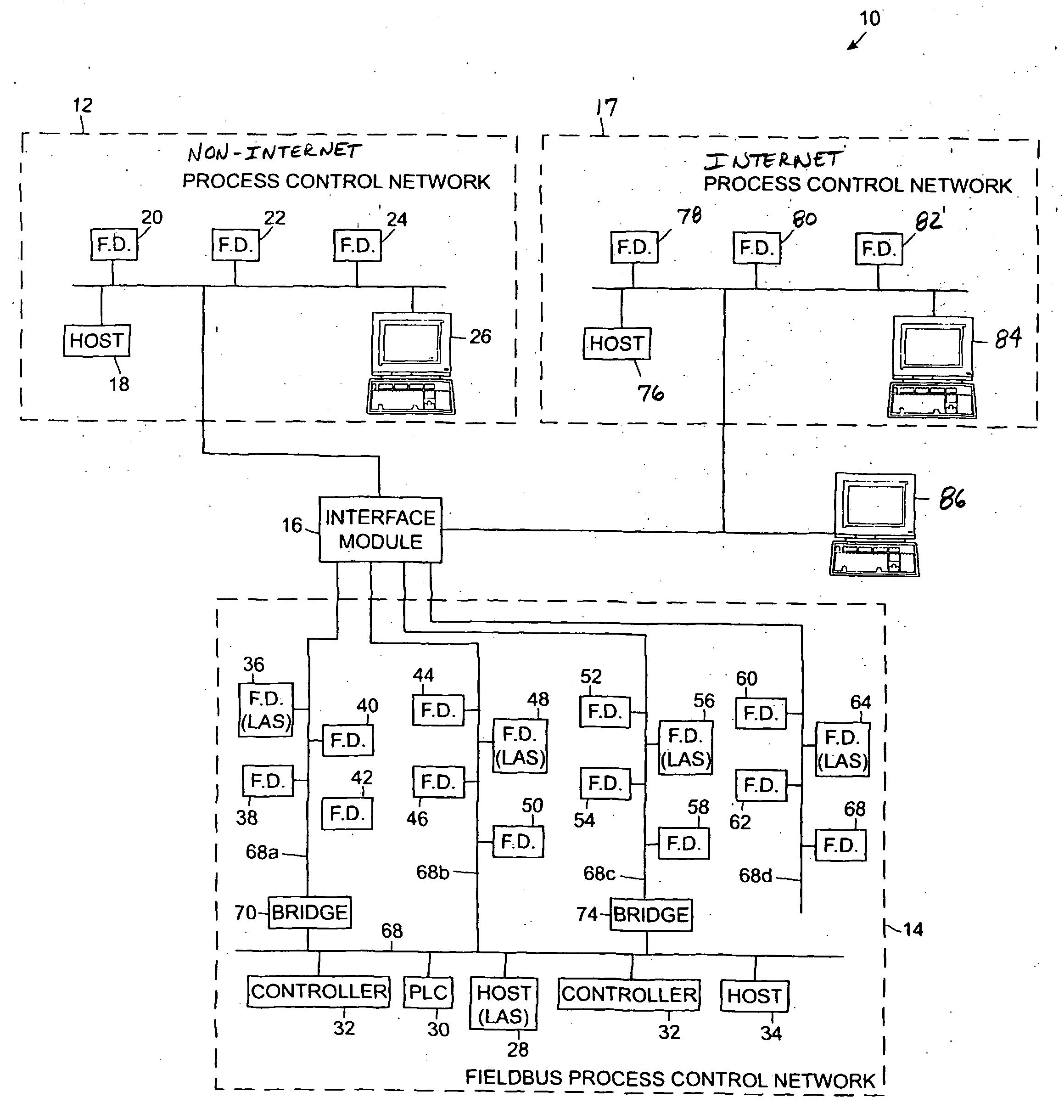
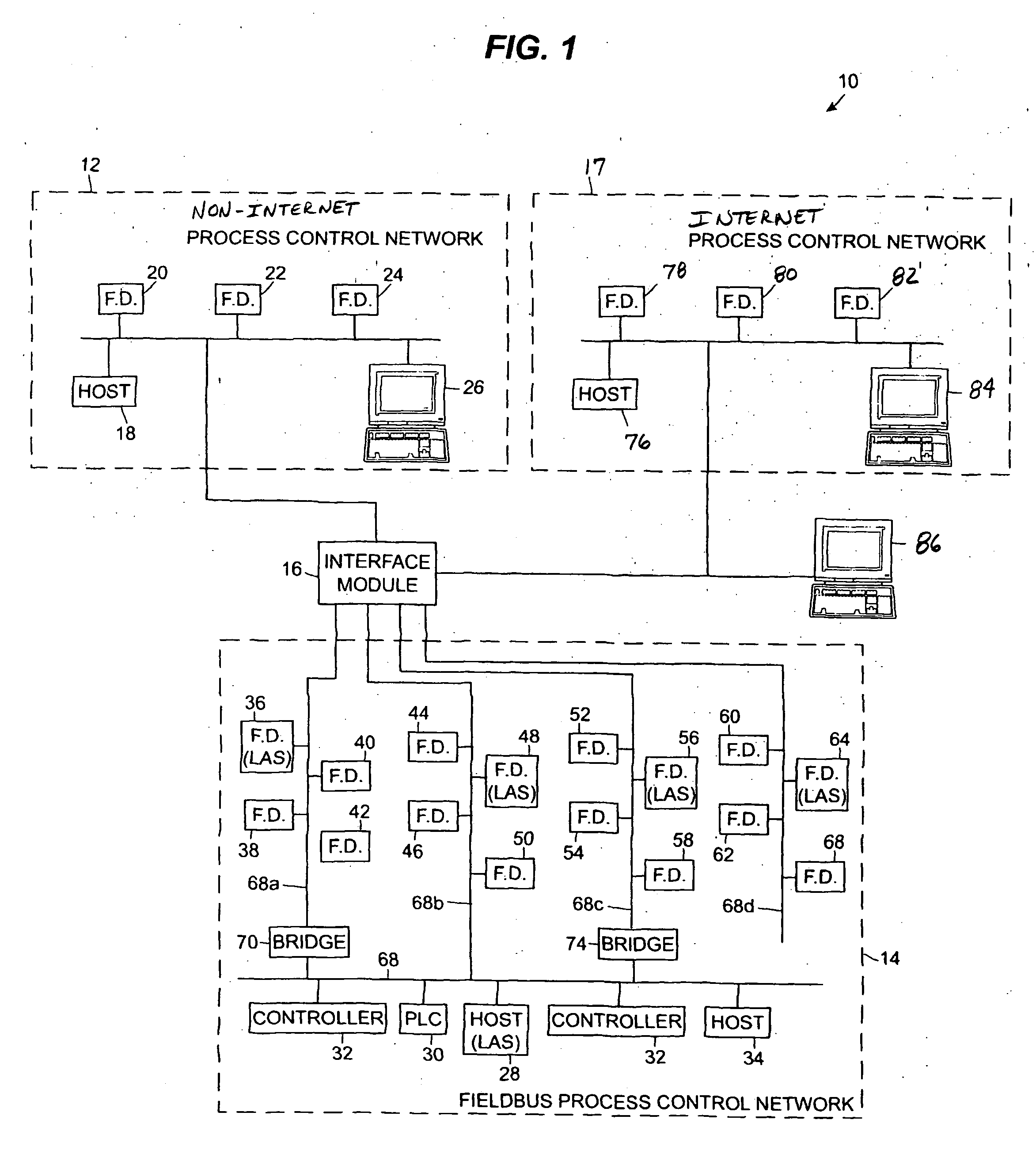
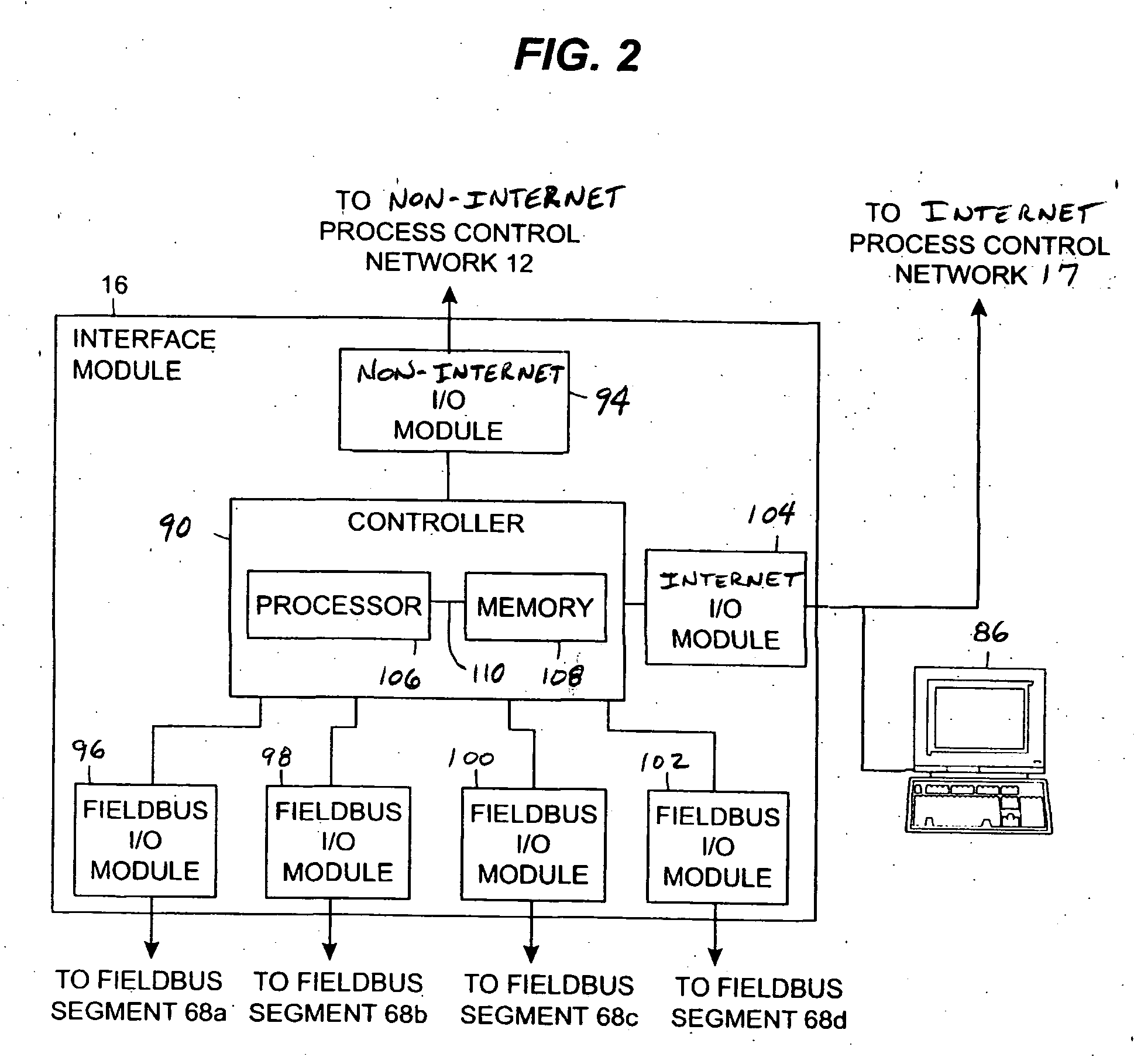
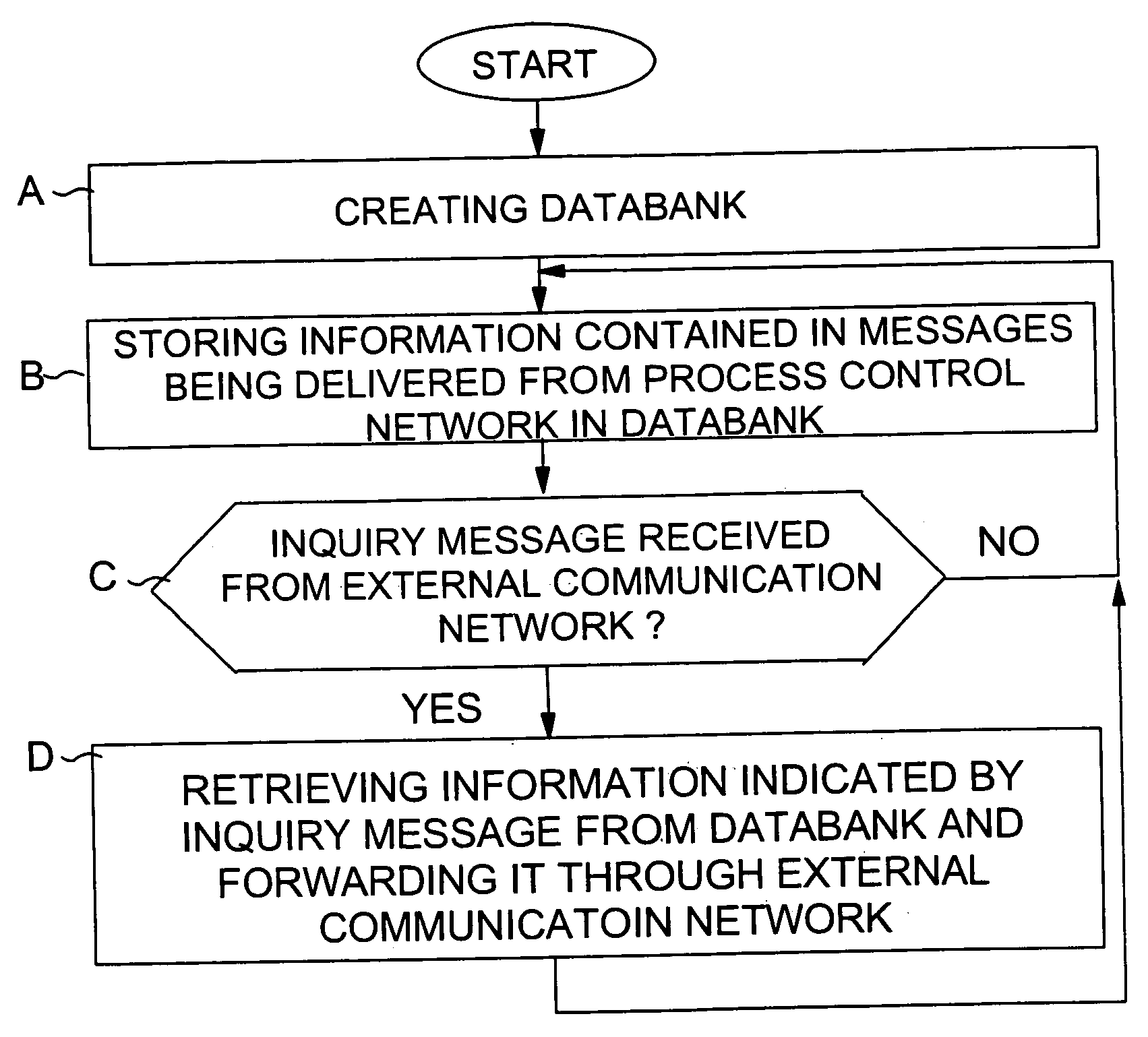
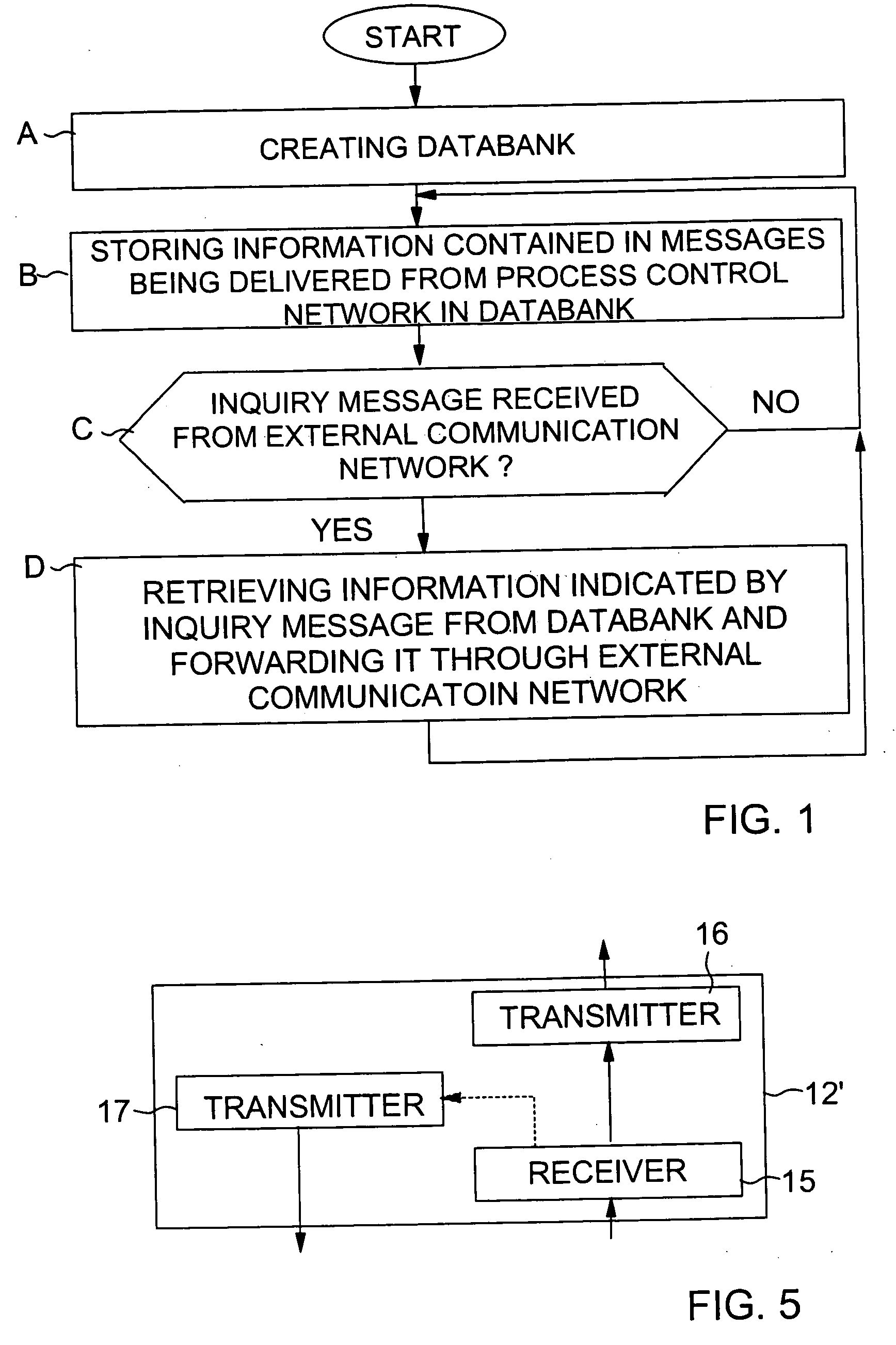
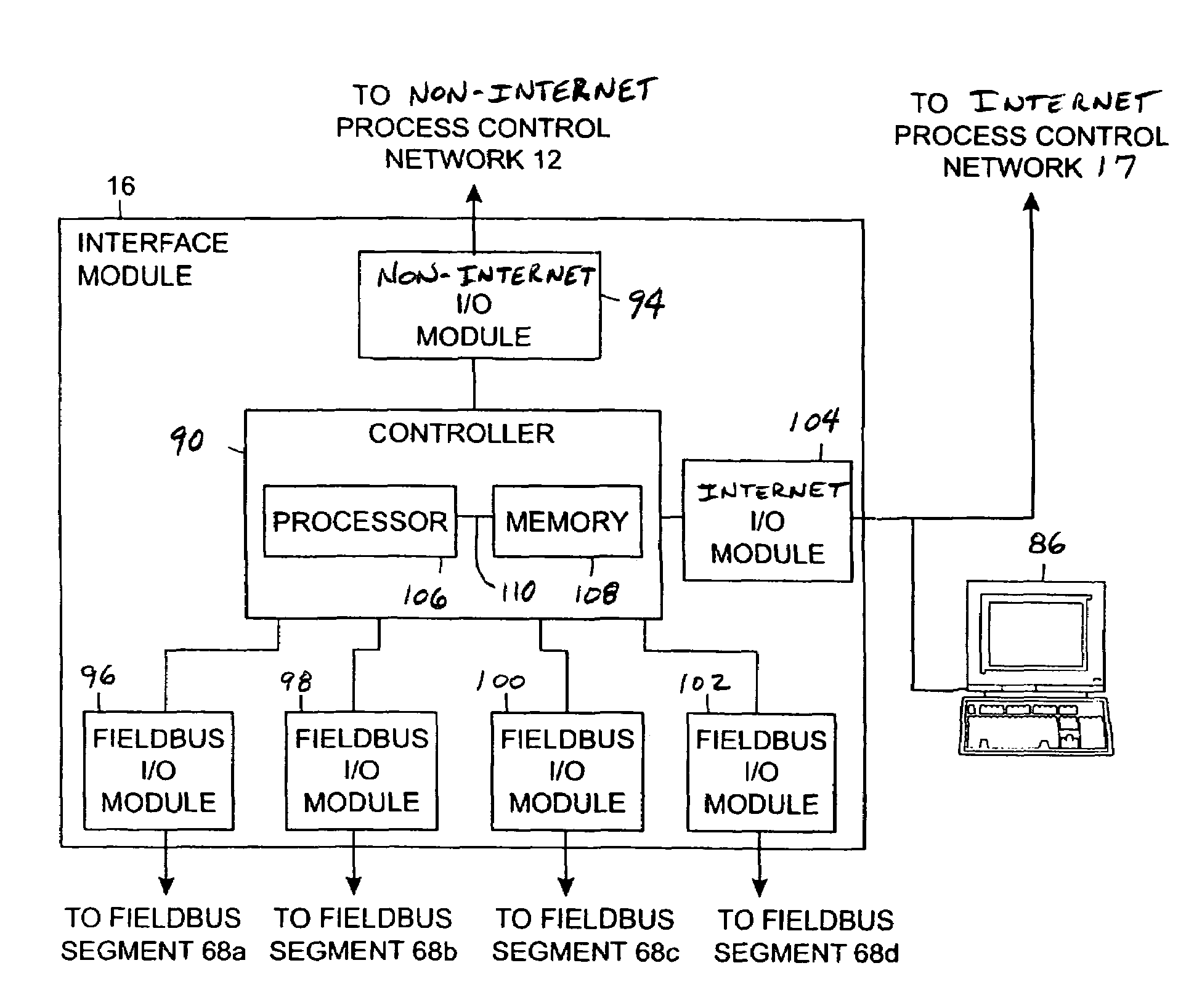
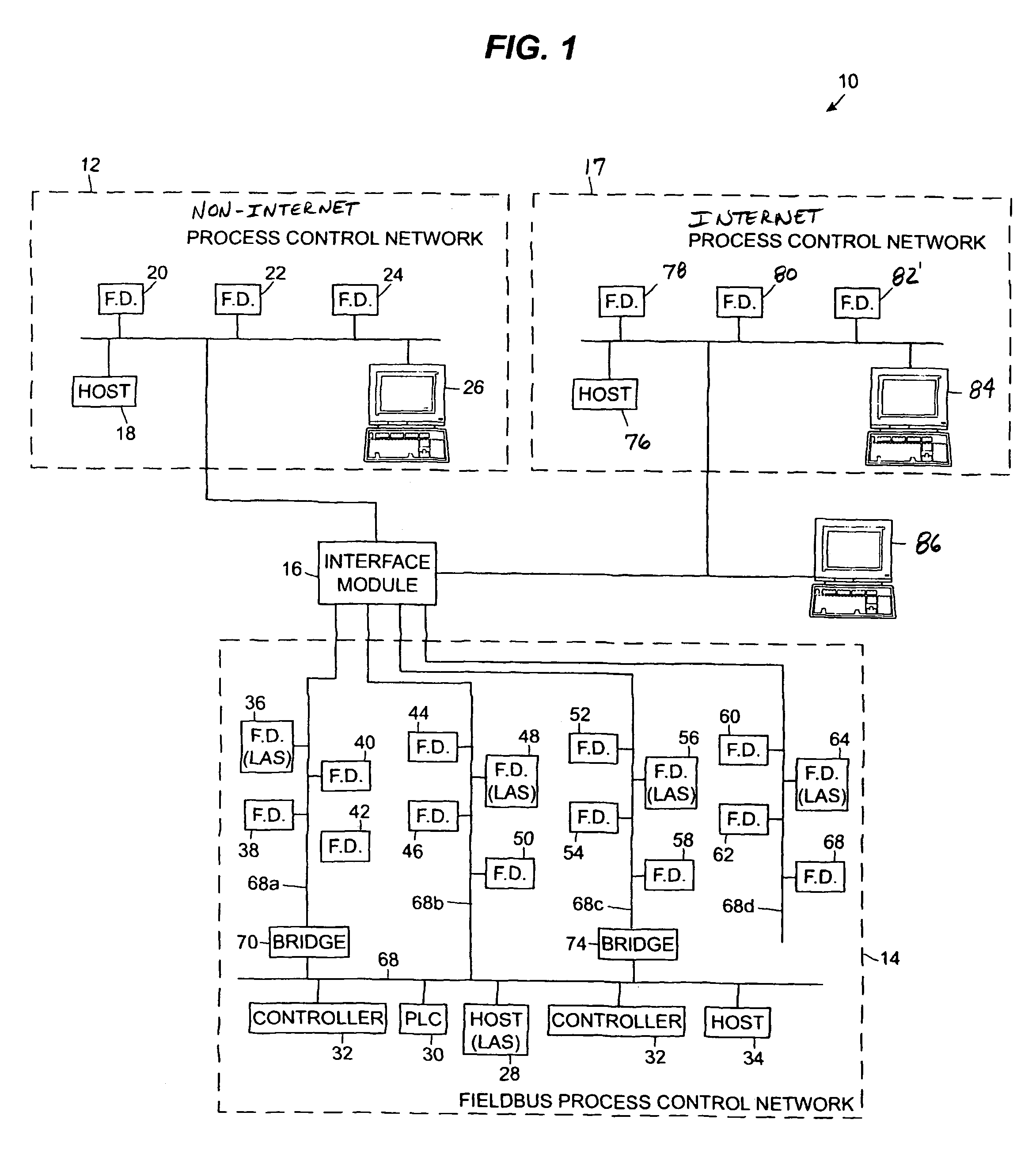
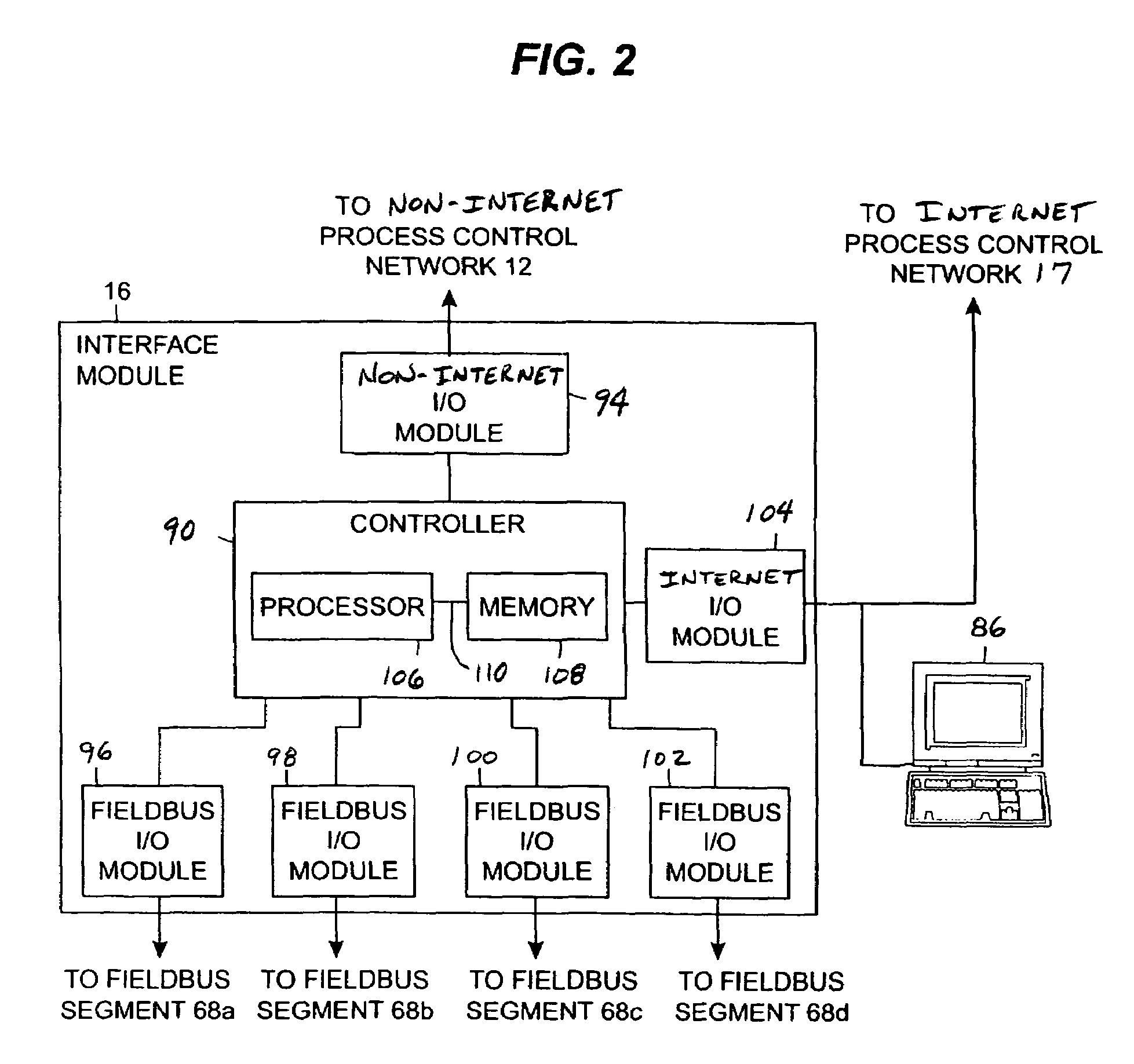
Interface module for use with a fieldbus device network and with internet and non-internet based process control networks
InactiveUS20050066104A1Facilitate communicationData switching networksTotal factory controlProcess control networkTTEthernet
An interface module is operatively connected to a Fieldbus process control network and to at least one non-Fieldbus process control network to facilitate the exchange of process control information between the networks. The interface module stores a database in which the process control parameters of the function blocks in the field devices of the Fieldbus process control network are mapped to corresponding process control parameters of the non-Fieldbus process control network. Once the Fieldbus process control parameters are mapped to the non-Fieldbus process control parameters, the interface module is adapted to transmit request messages on the Fieldbus process control network to the Fieldbus field devices for the current values of the process control parameters, receive response messages from the Fieldbus field devices, and store the current values of the process control parameters in the database. The interface module may also function in the other direction to map non-Fieldbus process control parameters to corresponding Fieldbus process control parameters.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Integrated alarm display in a process control network
InactiveUS20050012608A1More informationComputer controlElectric testing/monitoringProcess control networkControl system
An alarm display and interface tool for use in a process control system receives and displays different categories of alarms, including for example, device alarms and hardware alarms as well as traditional process alarms, on a single display to enable an operator or other user to view and have access to these different categories of alarms. The display and interface tool may be used to filter the alarms that are displayed according to any number of categories, including the category of the alarm, the priority of the alarm, the status of the alarm, etc. so as to alternatively segregate or combine the tasks typically associated with operator, maintenance and engineer personnel. The tool may also be used to access each of the displayed alarms to obtain more information about any individual alarm.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
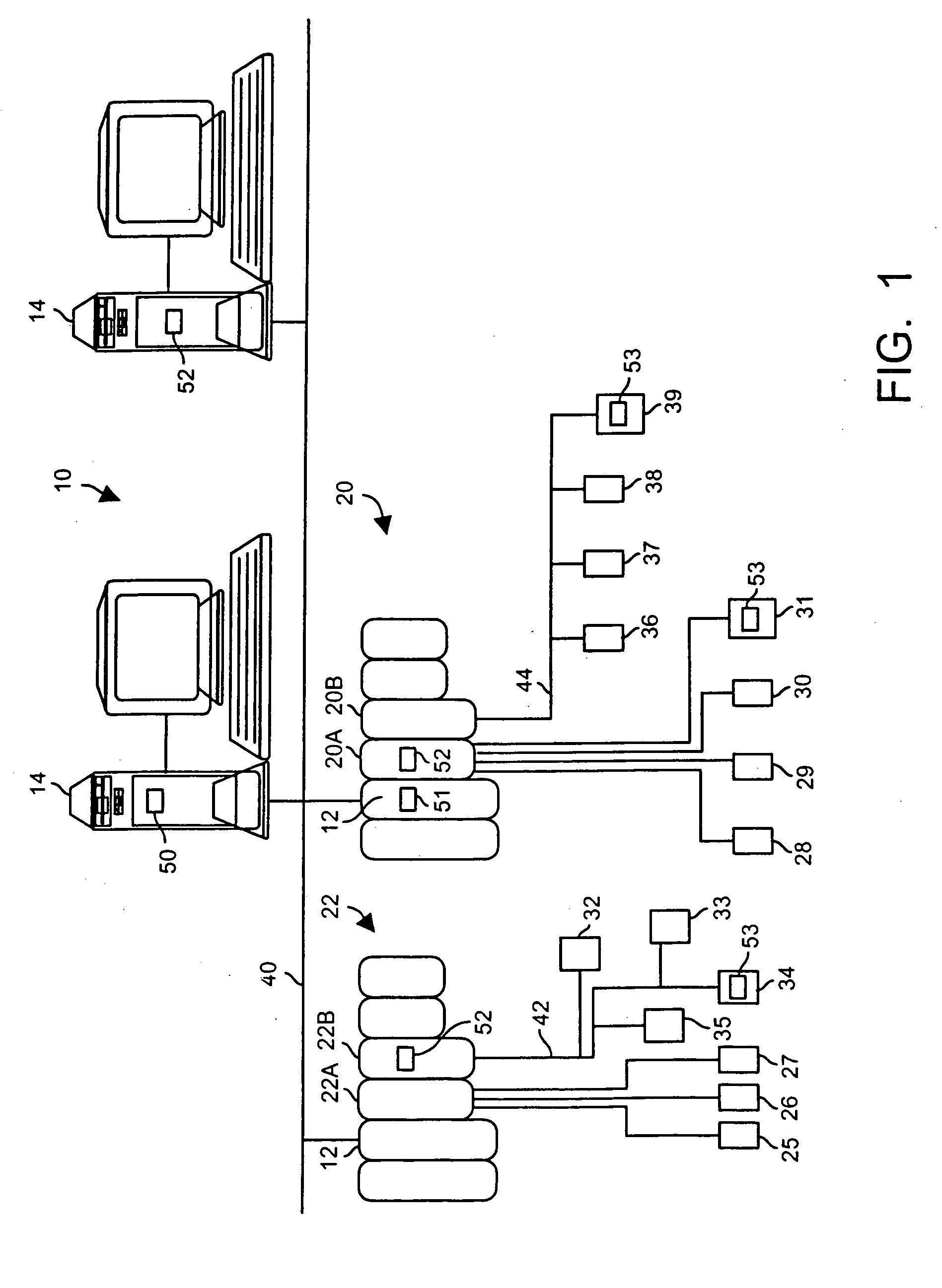
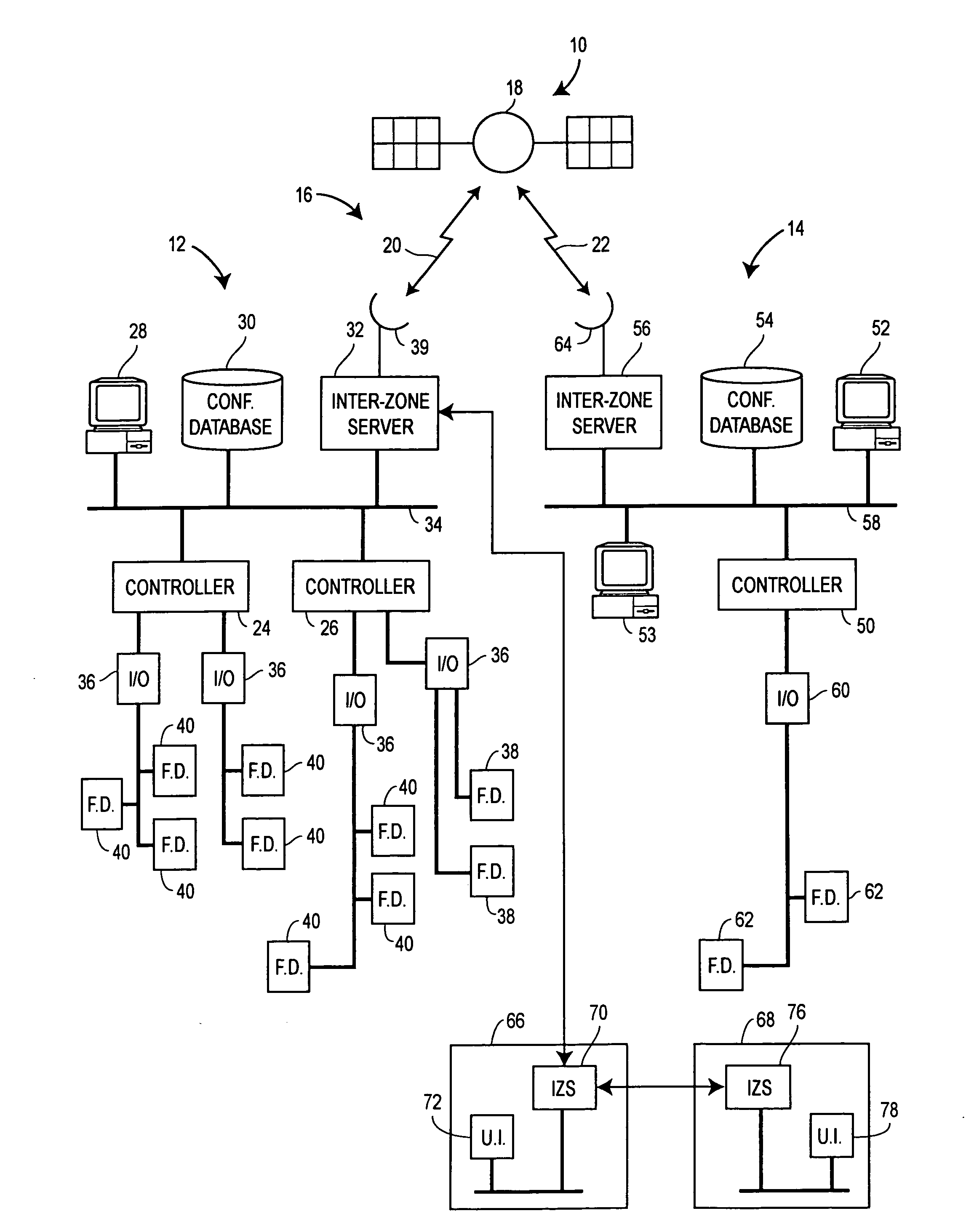
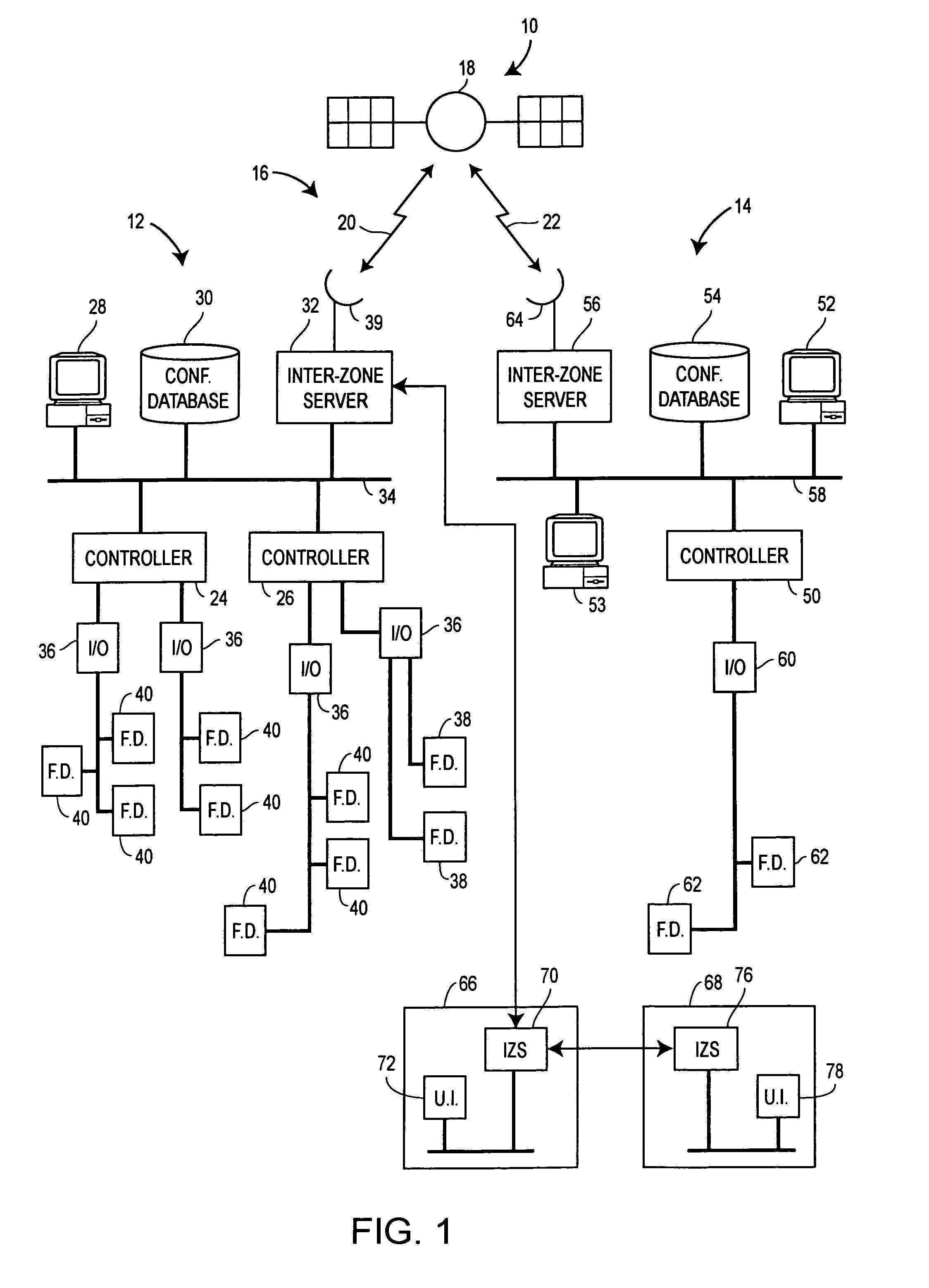
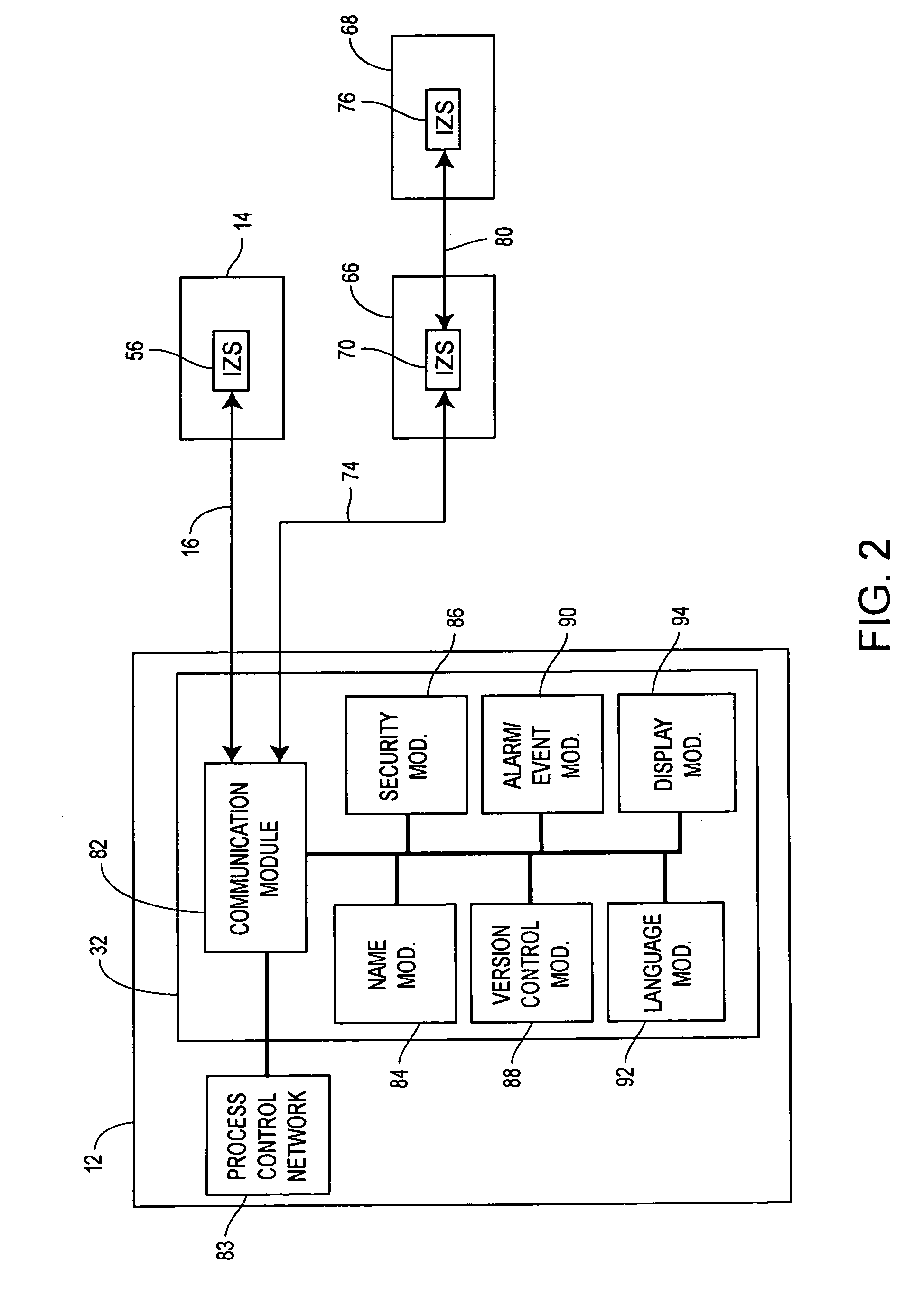
Interconnected zones within a process control system
InactiveUS7289994B2Facilitate communicationDatabase management systemsComputer controlProcess control networkTelecommunications link
A process control system includes multiple zones containing process control network communicatively interconnected to exchange information necessary to monitor the system and to perform process control. Each zone may include an inter-zone server that controls the exchange of information between the zones via communication links. In addition to controlling the routing of information between the zones, the inter-zone servers may perform additional processing on the information being exchanged, such as security monitoring, language translation and version control.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Real-time synchronized control and simulation within a process plant
ActiveCN101114160AEasy to useEasy to operateProgramme controlSimulator controlProcess control networkReal-time simulation
A process control system simulation technique performs real-time simulation of an actual process control network as that network is running within a process plant in a manner that is synchronized with the operation of the actual process control network. This real-time, synchronized simulation system includes a simulation process control network and a process model which are automatically updated periodically during the operation of the actual process control network to reflect changes made to the process control network, as well as to account for changes in the plant itself, i.e., changes which require an updated process model. The disclosed simulation system provides for more readily accessible and usable simulation activities, as the process control network and the process models used within the simulation system are synchronized with and up-to-date with respect to the current process operating conditions. Moreover, this simulation system is more accurate as it uses process models developed from the current state of the process whenever the simulation system beings to perform a simulation. Still further, the disclosed simulation system is easy to operate, as it uses the same user interface applications as the actual process control network and can be initialized and used at any time during operation the process plant without any significant configuration or set-up activities.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
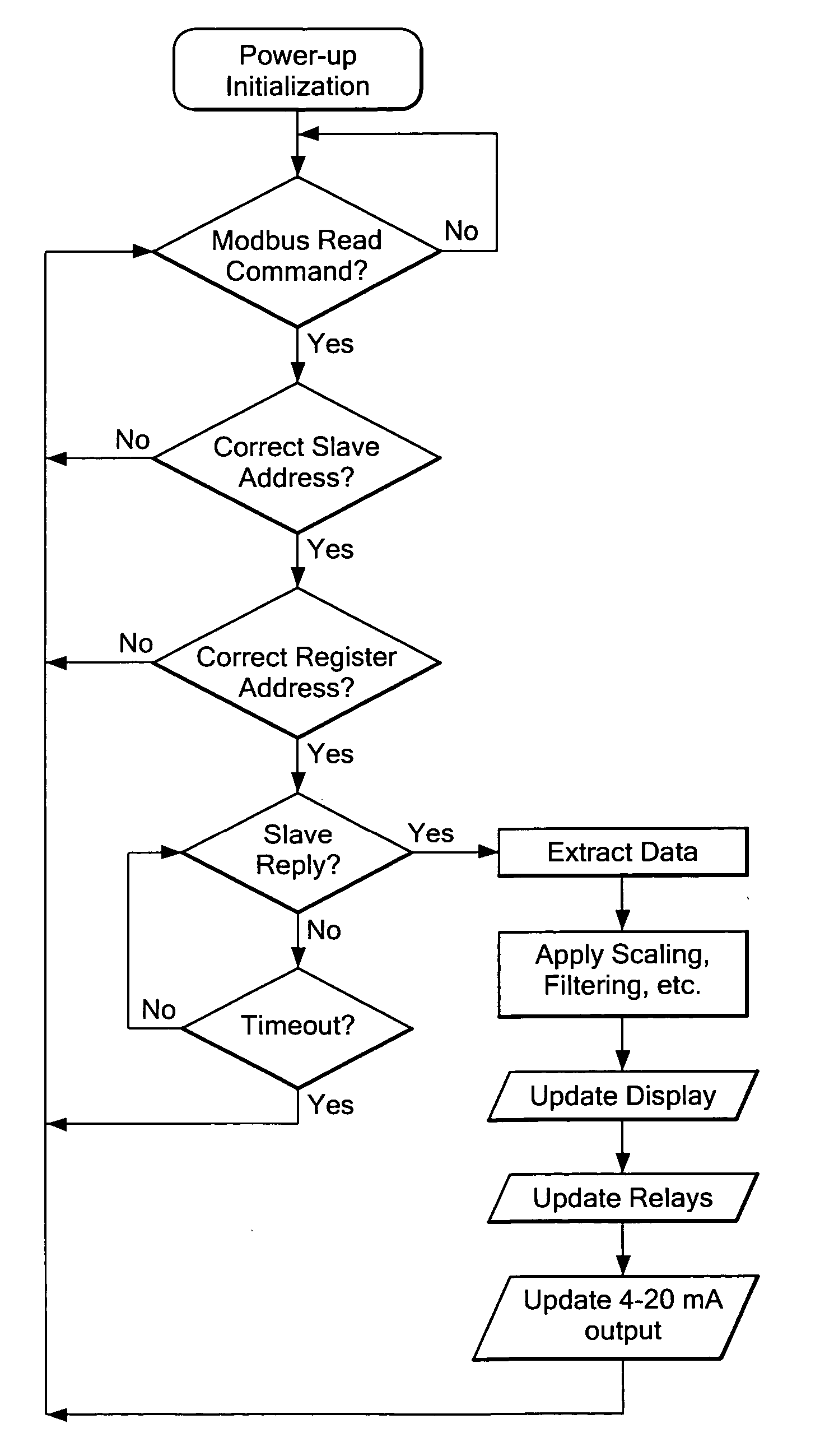
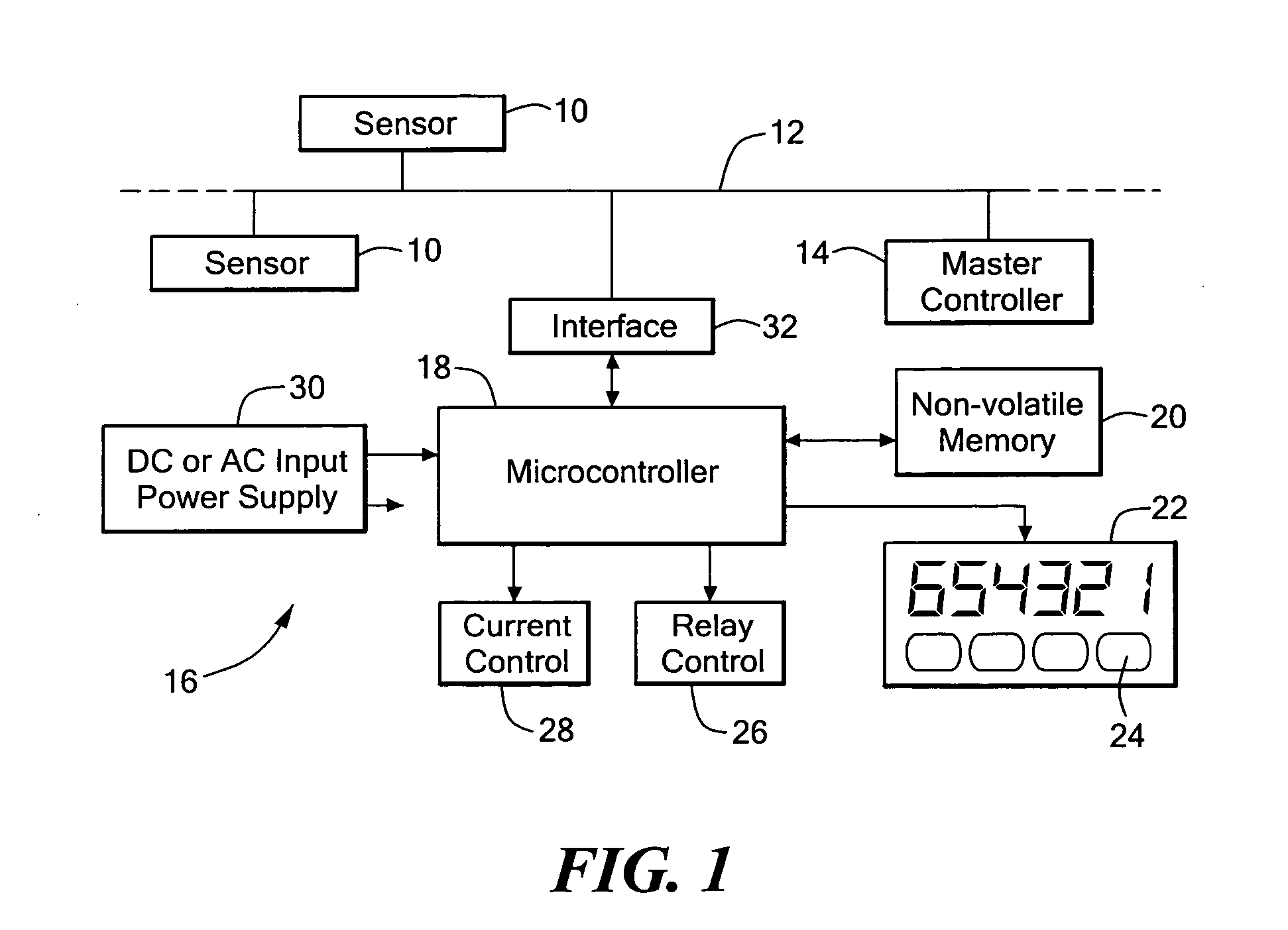
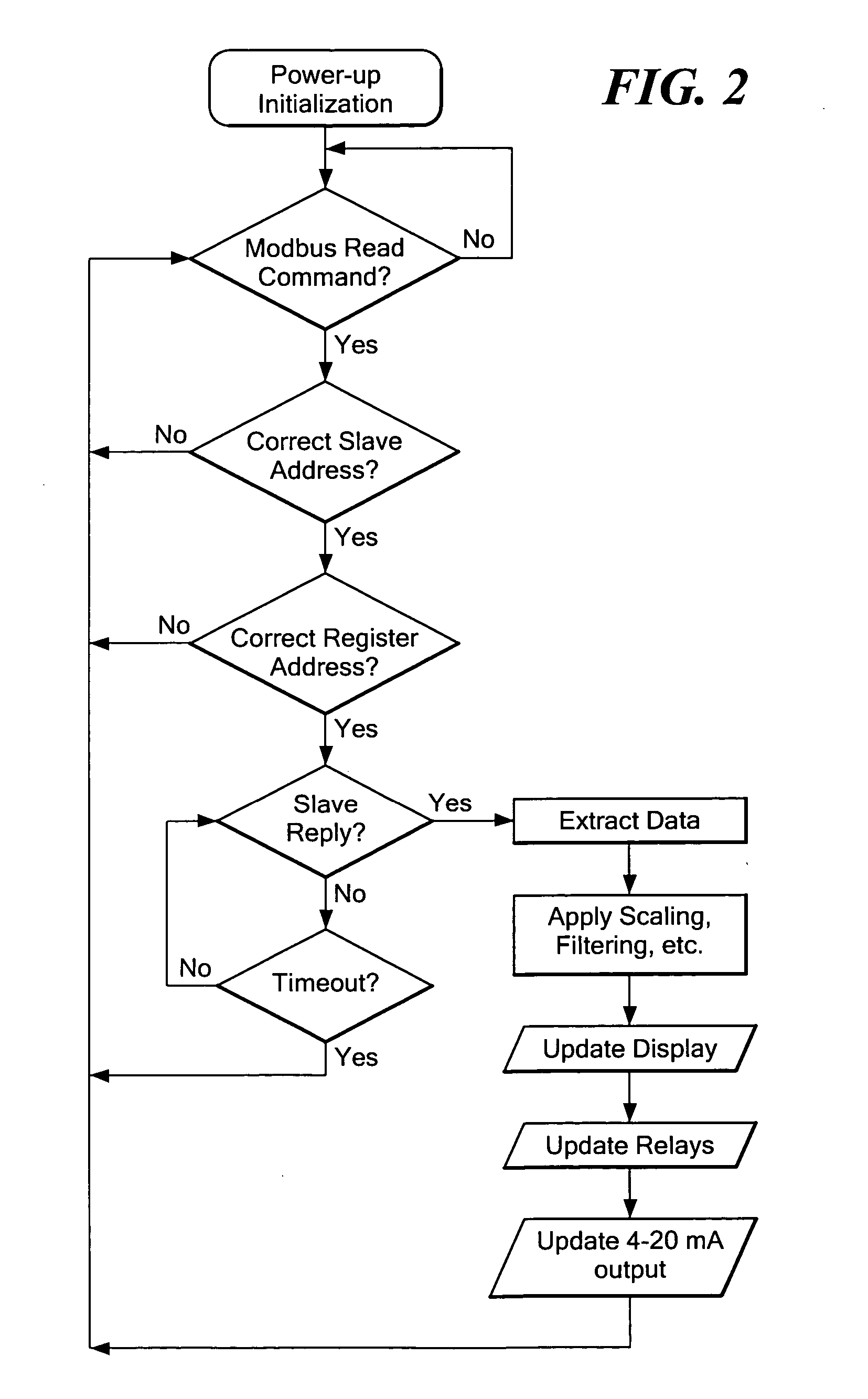
System for monitoring and display of process control data
A data monitoring system is provided which is coupled to a data bus and which responds to identified data to cause the display of data from one or more designated sensors. The system can also provide outputs to activate and deactive relays and to control other devices. The programming and operation of a master controller does not have to be altered for use of the present system. The system operates to monitor one or more designated sensors and data from such sensors and to utilize the received data for display and / or operational purposes. The invention is especially useful in a process control network in which a large number of sensors is distributed throughout a facility and in which it is desirable to be able to read sensor data from one or more remote locations within a facility. The invention is also useful for other circumstances wherein data on a bus is to be monitored at a remote position.
Owner:PRECISION DIGITAL CORP
System, communication network and method for transmitting information
InactiveUS20050165939A1Control safetyProgramme controlComputer controlProcess control networkProcess equipment
Owner:METSO AUTOMATION OY
Interface module for use with a fieldbus device network and with internet and non-internet based process control networks
An interface module is operatively connected to a Fieldbus process control network and to at least one non-Fieldbus process control network to facilitate the exchange of process control information between the networks. The interface module stores a database in which the process control parameters of the function blocks in the field devices of the Fieldbus process control network are mapped to corresponding process control parameters of the non-Fieldbus process control network. Once the Fieldbus process control parameters are mapped to the non-Fieldbus process control parameters, the interface module is adapted to transmit request messages on the Fieldbus process control network to the Fieldbus field devices for the current values of the process control parameters, receive response messages from the Fieldbus field devices, and store the current values of the process control parameters in the database. The interface module may also function in the other direction to map non-Fieldbus process control parameters to corresponding Fieldbus process control parameters.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Methods and apparatus to collect process control data
ActiveCN102402215ASampled-variable control systemsElectric testing/monitoringProcess control networkElectric equipment
The present invention discloses a method and apparatus to collect process control data, and a product. The method to collect process control data includes registering an electronic device description such as using Electronic Device Description Language (EDDL) describing a parameter to be measured and a measurement sampling rate, measuring the parameter based on the measurement sampling rate, storing data, preferably using an any one of an array object, a matrix object, a class object or a struct object, representative of the measured parameter in a data structure, and transferring data in the data structure to a first process control device via a process control network in response to at least one of a request for the data, a condition associated with the data, or an event associated with the data.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Analytical server integrated in a process control network
ActiveUS7738975B2Faster and efficient supportComputer controlTechnology managementProcess control networkLoop control
A process control system integrates the collection and analysis of process control data used to perform certain computationally expensive process control functions, like adaptive model generation and tuning parameter generation, in the same control device in which one or more of the process control routines are implemented, to thereby provide for faster and more efficient support of the process control routines. This system replaces a layered approach using multiple processing devices by integrating an analytical server which performs computationally expensive analyses used by one or more control routines directly into the real-time control device in which the one or more control routines are located. This integration provides the ability to analyze large quantities of data for multiple process loops controlled by a particular device in a fast and efficient manner.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
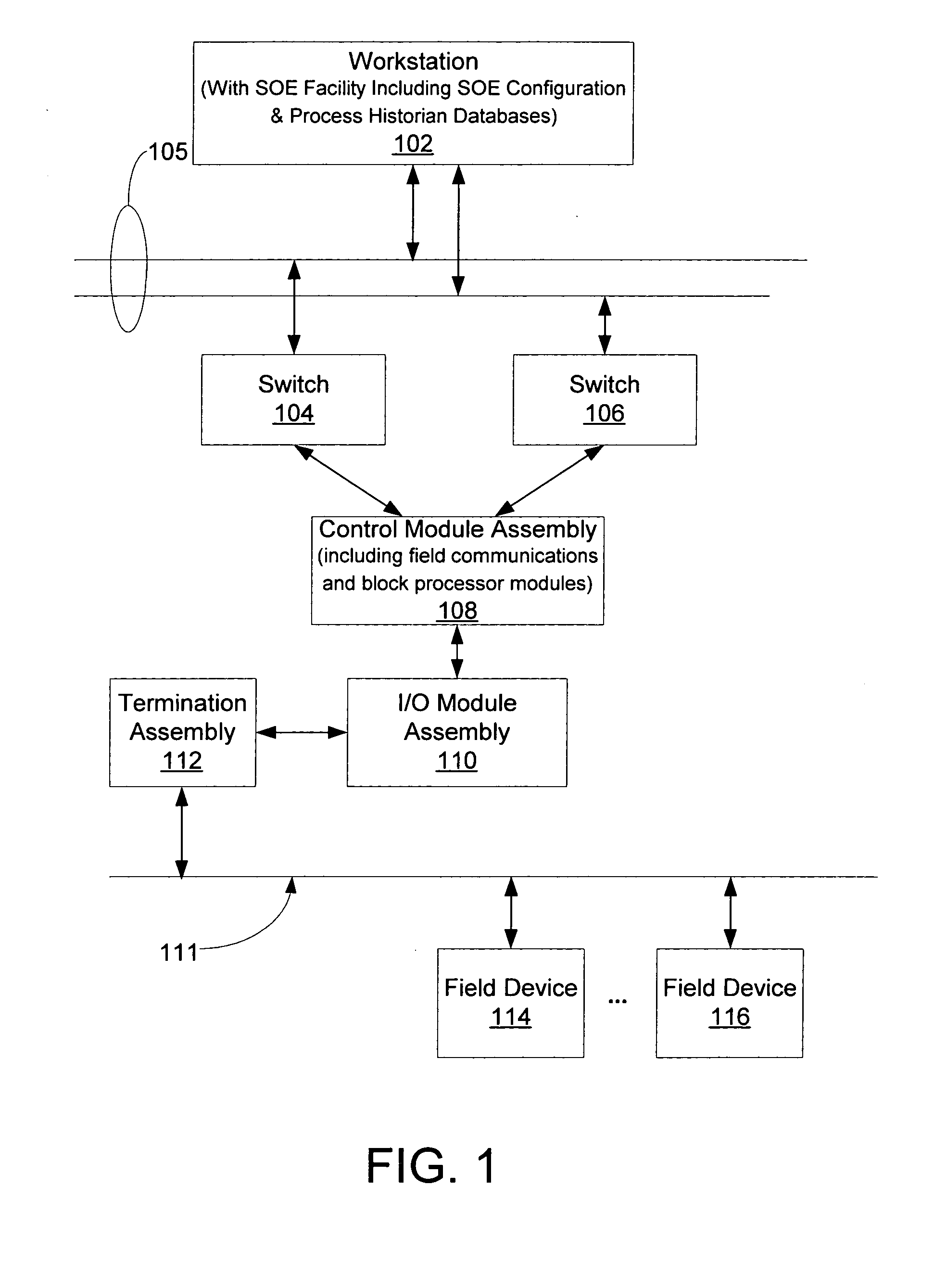
Tool for configuring and managing a process control network including the use of spatial information
InactiveUS20050010307A1Efficient designEfficient use ofMultiple digital computer combinationsTotal factory controlProcess control networkControl system
The present invention is directed to a tool which includes spatial information for configuring and managing a process control system which conforms to a standard protocol. Such a tool advantageously allows the efficient design and use of a process control system while ensuring that the physical characteristics of the system conform to the standard. In addition, the tool provides for more efficient diagnostics, on-line debugging, alarm monitoring and device maintenance.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
Downloadable code in a distributed process control system
InactiveUS20050097194A1Shorten the timeConvenient amountComputer controlError detection/correctionProcess control networkControl system
The present invention is directed to a method of reprogramming a field device in a process control network using the standard communications protocol for the network, and a reprogrammable field device in the process control network adapted for being reprogrammed using the standard communications protocol for the network. The method and device of the present invention use the standard communications protocol to transmit the downloaded code to the field device and store the downloaded code in the field device while the device is enabled to perform process control. Once the new code is downloaded and stored in the field device, the field device is set to a steady state condition and / or disabled from performing process control, reprogrammed to execute the downloaded code, and reenabled to perform process control.
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Interface module for use with a Modbus device network and a Fieldbus device network
An interface module is operatively coupled to a Fieldbus process control network and a Modbus process control network to facilitate the exchange of process control information between the networks. The interface module stores a register map database in which the process control parameters of the function blocks in the field devices of the Fieldbus process control network are mapped to register numbers of the Modbus process control network. Once the Fieldbus process control parameters are mapped to the Modbus registers, the interface module is adapted to transmit request messages on the Fieldbus process control network to the Fieldbus field devices for the current values of the process control parameters, receive response messages from the Fieldbus field devices, and store the current values of the process control parameters in the register map database.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT INC
Diagnostic method for detecting control valve component failure
Owner:FISHER CONTROLS INT LLC
Method for redundant controller synchronization for bump-less failover during normal and program mismatch conditions
The present invention relates generally to process control systems and devices and, more particularly, to an apparatus for and a method of implementing redundant controller synchronization for bump-less failover during normal and mismatch conditions at the redundant controllers. The redundant controllers are configured to transmit state information of the process control areas of the primary controller to the backup controller that is necessary for synchronizing the redundant controllers but is not typically transmitted to other devices during the performance of process control functions. Synchronization messages are transmitted from the primary controller to the backup controller each time one of the control areas executes to perform process control functions. In other aspects, the redundant controllers are configured to determine state information at the backup controller from other process control network information during a failover of the primary controller where a mismatch condition exists between the control areas of the two controllers during the downloading of reconfigurations, and to initialize the backup controller at startup when the mismatch condition exists.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
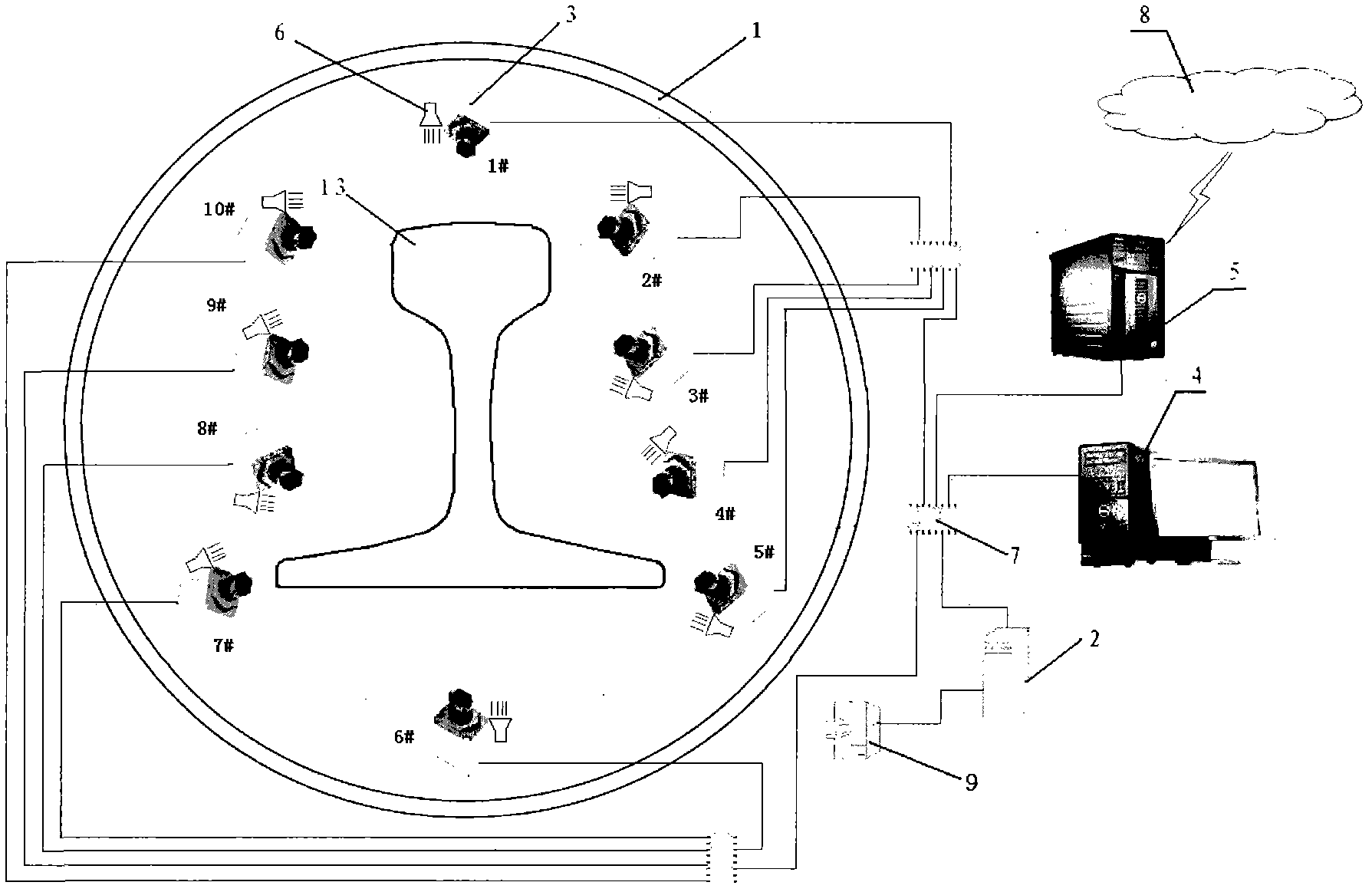
Surface defect automatic detecting device for section bars
InactiveCN102384910ARun at high speedAutomatic identification and strong adaptabilityOptically investigating flaws/contaminationInformation processingEngineering
The invention relates to a surface defect automatic detecting device for production process of a section bar rolling mill production line, which comprises a fixing device, a control device, video cameras, an image collecting computer, an information processing server, a light-emitting diode (LED) light source, a local area network, a process control network system, a spraying device, a pinch roll, a conveying roller way, stripper rubber and compressed air. The surface defect automatic detecting device for production process of the section bar rolling mill production line is characterized in that the number of the video cameras is determined according to the maximum number of the video cameras needed in the most complex surfaces of all varieties of the section bars to be detected. The surface defect automatic detecting device achieves automatic detection of surface defect of section bars (including varieties of heavy rails, H-shaped steel, joint steel, channel steel, steel angle and the like) by controlling and adjusting focal distance and angle of the video camera and the number of the video cameras. The surface defect automatic detecting device for production process of the section bar rolling mill production line is strong in adaptability, the same configuration can be applied to heavy rail processing lines and profile steel finishing lines, and accordingly software, hardware and spare parts of the device are universal, and manufacture and maintenance cost of equipment can be saved.
Owner:魏卿轩
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com