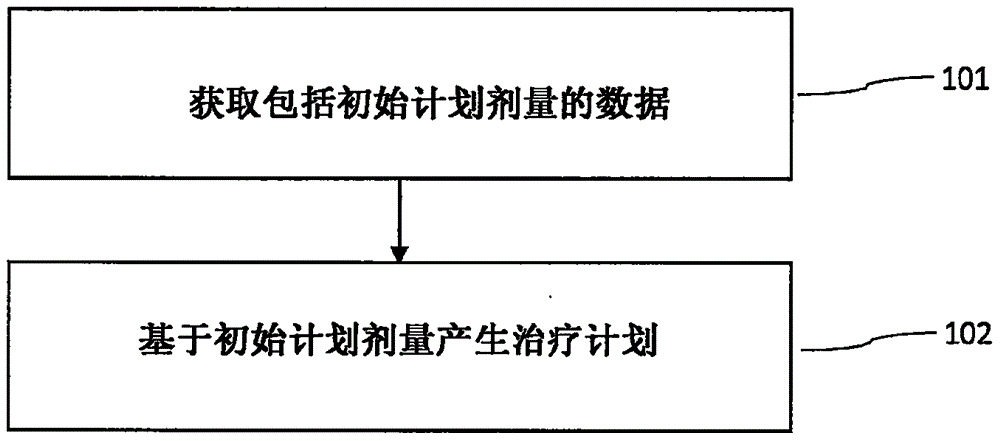
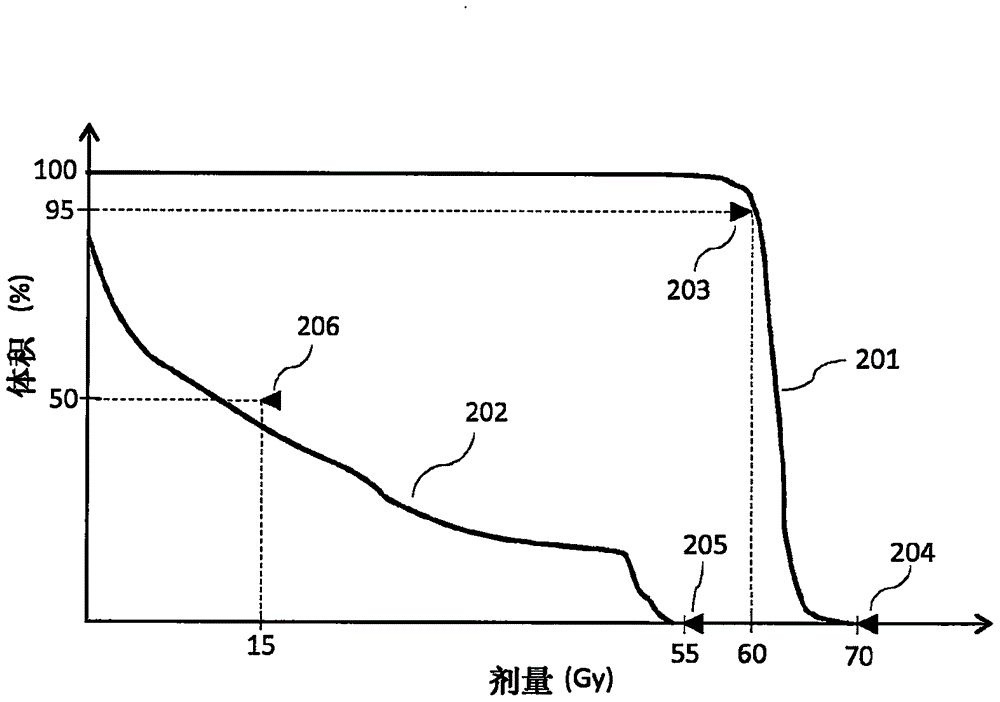
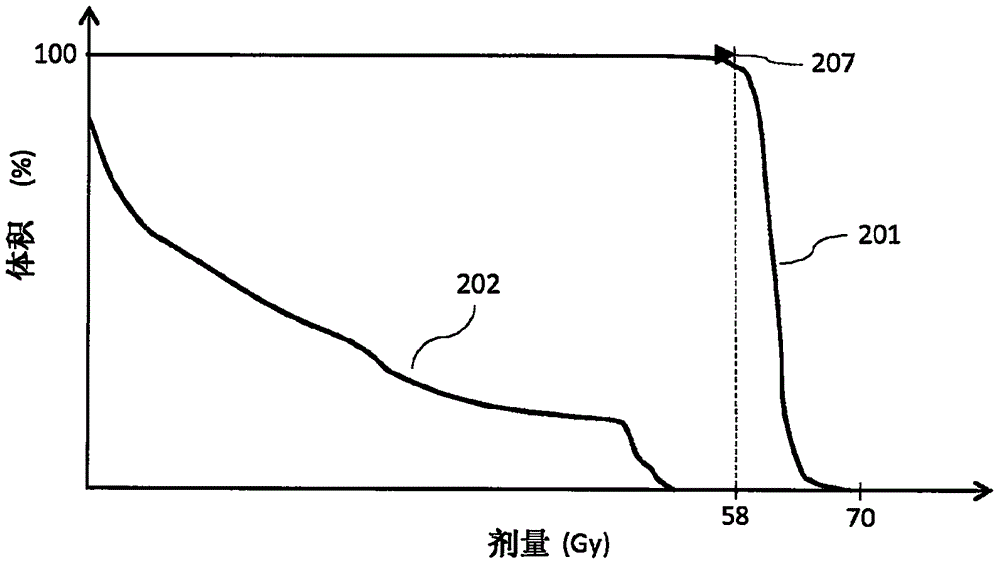
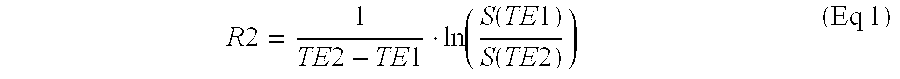Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Planned Dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The proposed dosage of the treatment.
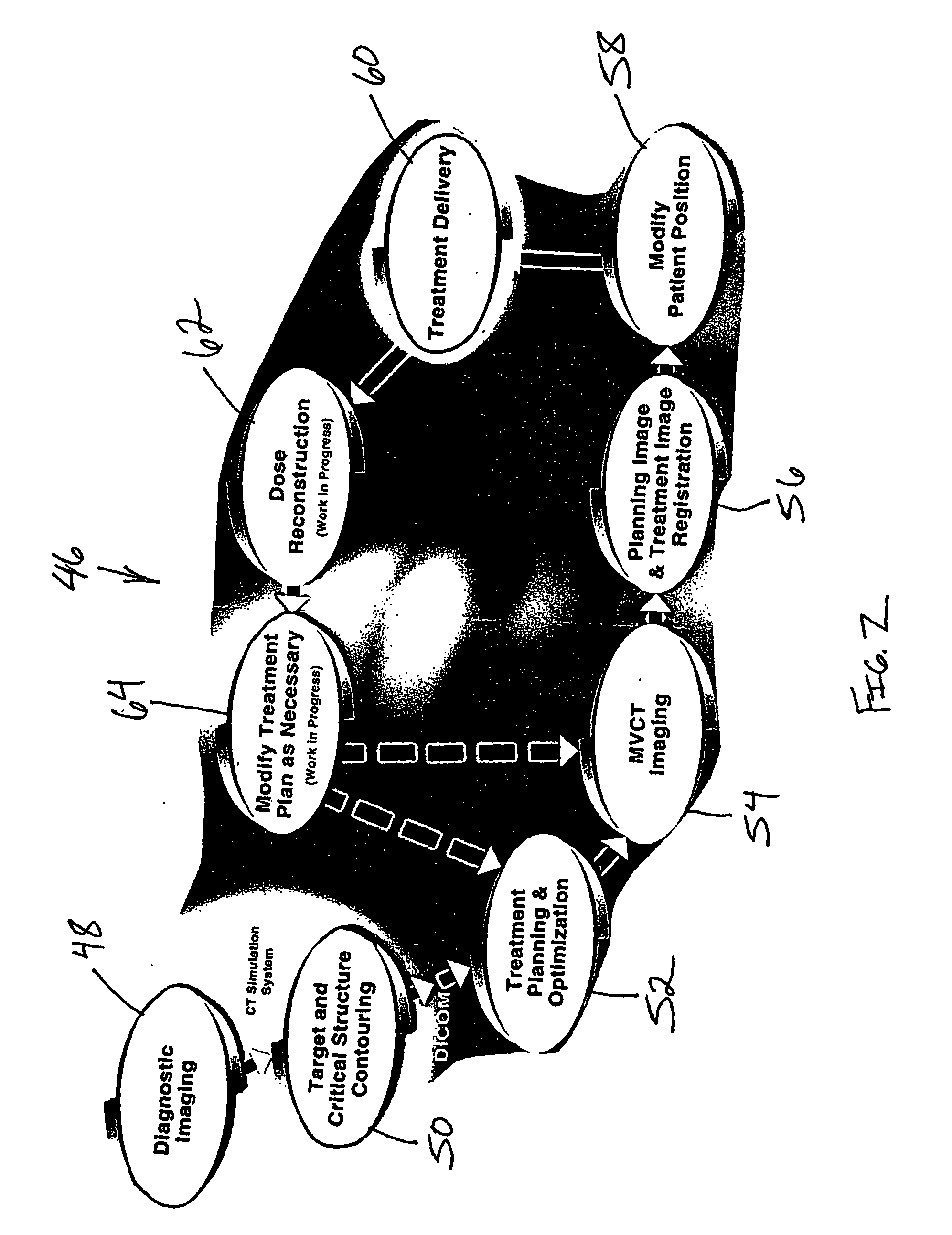
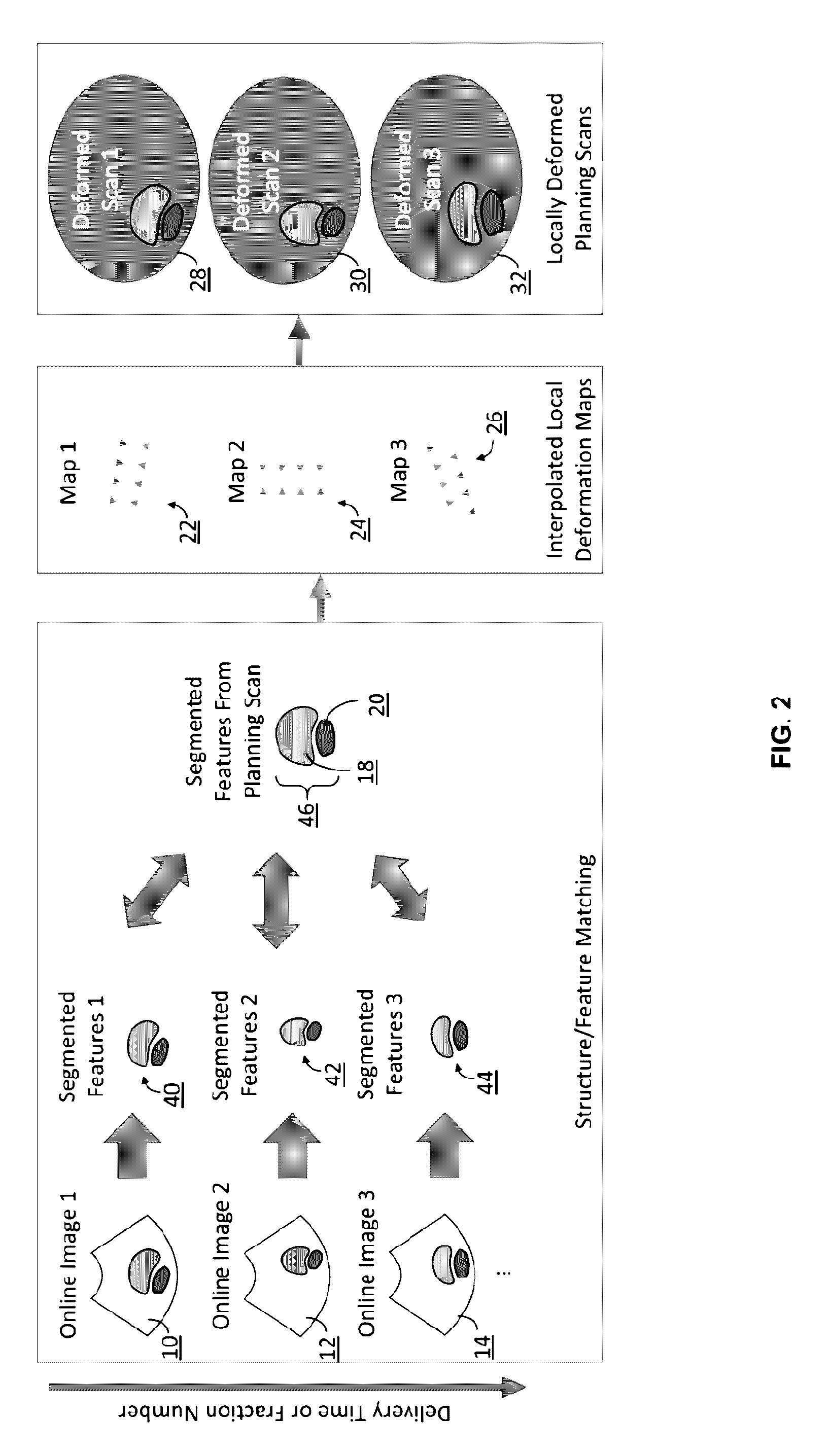
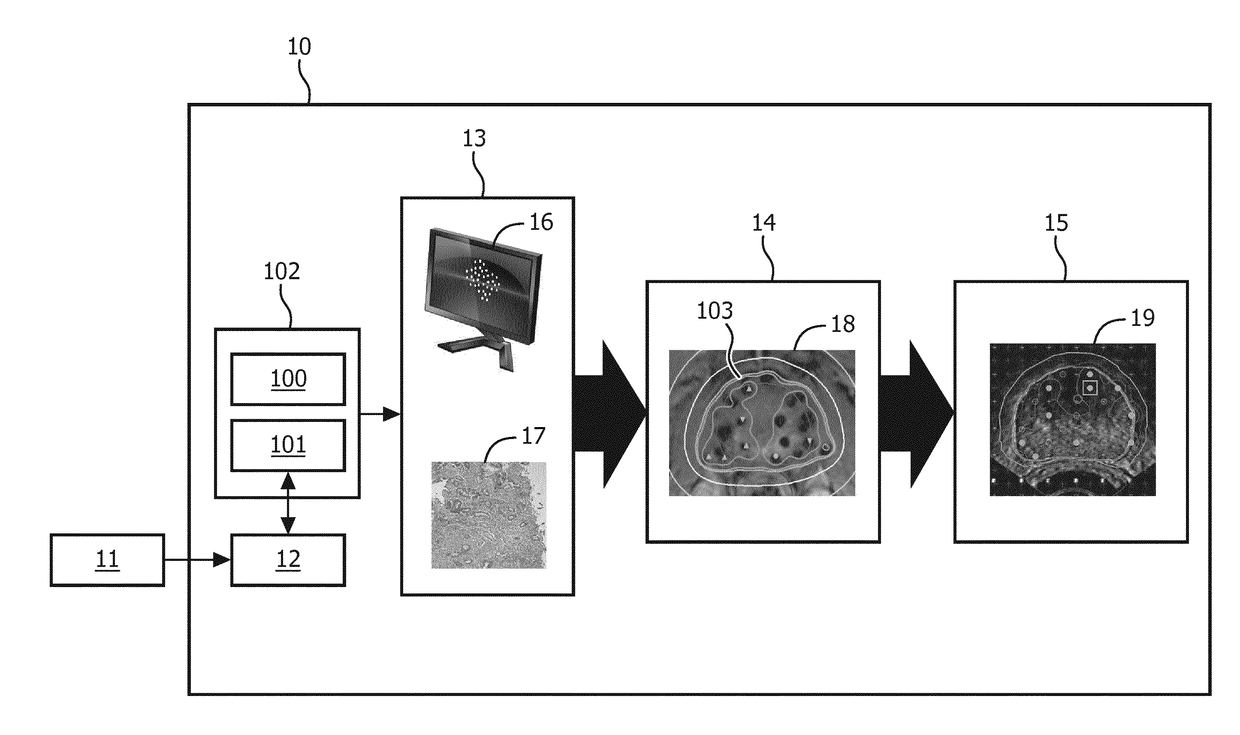
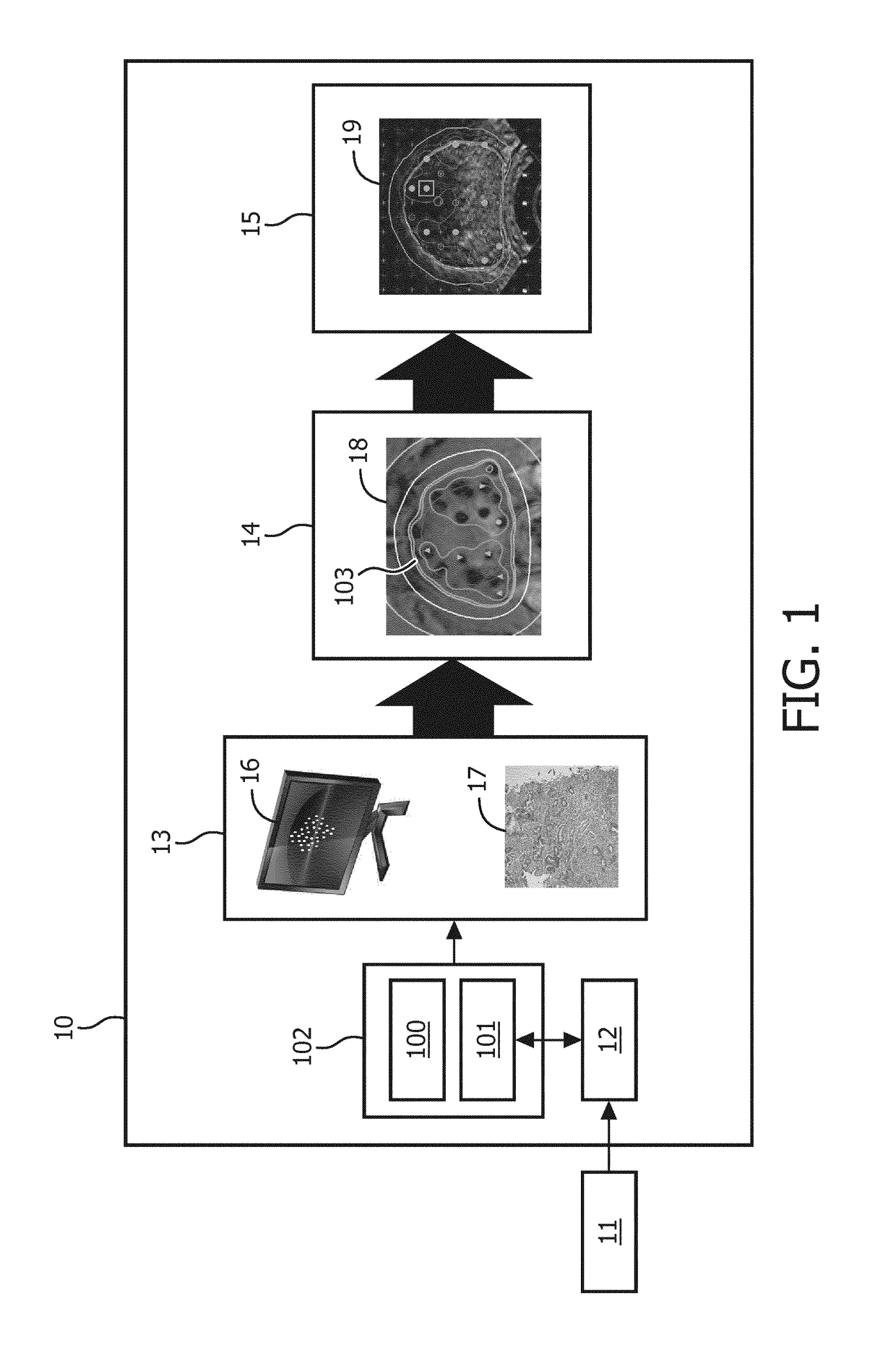
Method for modification of radiotherapy treatment delivery
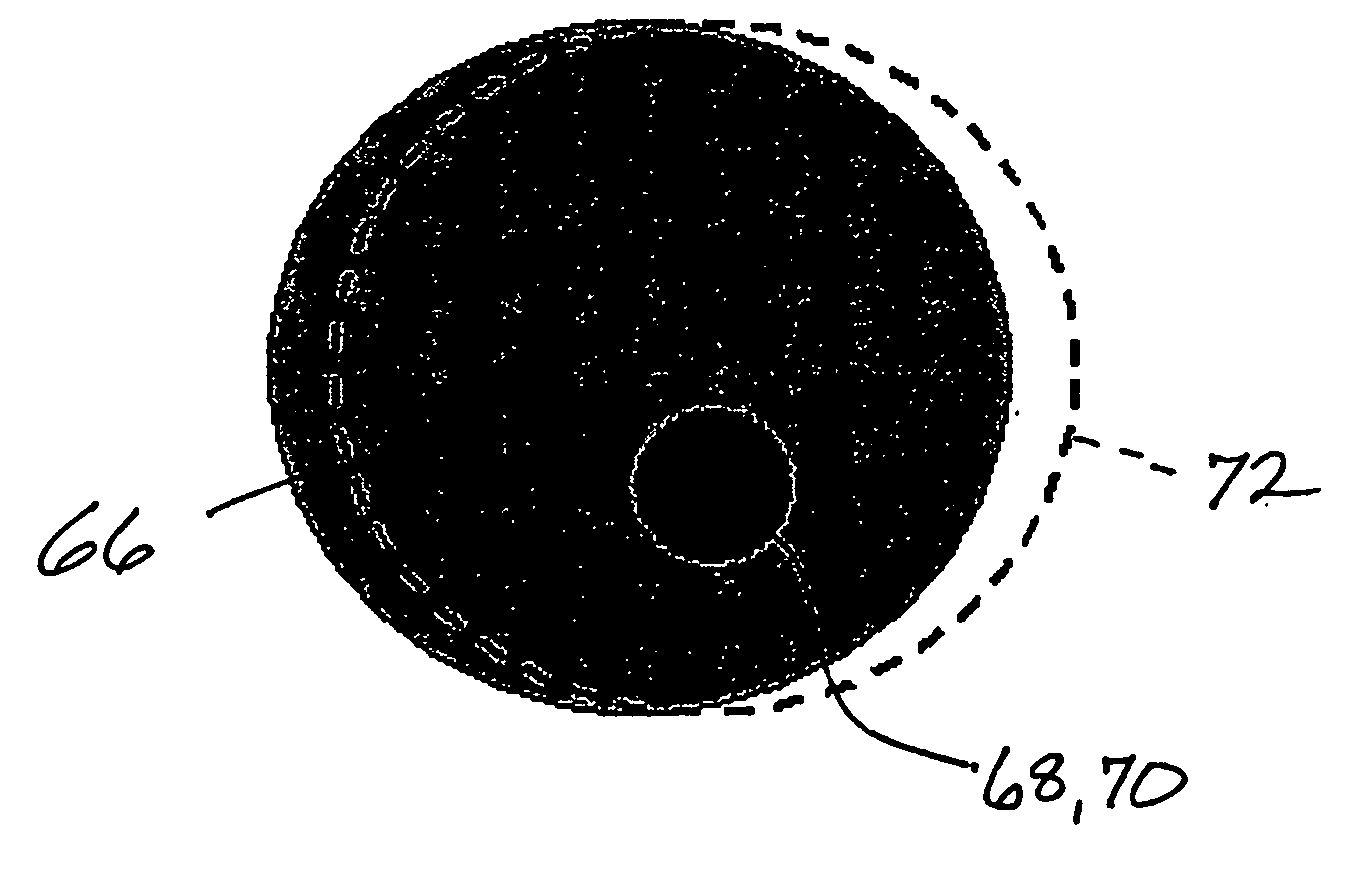
ActiveUS20050201516A1Improve harmConvenience to workElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical physicsPlanned Dose
The present invention provides a novel method of contoured-anatomy dose repositioning (CADR) as a means to automatically reposition a patient to better recover the planned dose distribution without reoptimize the treatment plan. Specifically, CADR utilizes planning CT images, the planned dose distribution, and on-line images for repositioning dose distribution on a given day. Contours are also placed upon the images using manual, automatic, template-based, or other techniques. CADR then optimizes the rigid-body repositioning of the patient so that the daily dose distribution closely matches the planned dose distribution. The present invention also provides a method of multiple-margin optimization with daily selection (MMODS) to improve radiation delivery without reoptimization. During the initial optimization procedure, plans are optimized for several margins of various contours (e.g., tight, medium, loose, etc.), or with different objectives (e.g., aggressive treatment, sensitive structure sparing, etc.). Similarly, if multiple patient image sets are available, plans can be optimized for the different anatomical layouts, either using current information, or accumulated information regarding the superposition of organ locations in the combination of images. A user can then choose in real time from a variety of optimized plans, generally with different margins, during the treatment process, and thereby compensate for a recognized change in size or position of the tumor or neighboring tissue.
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
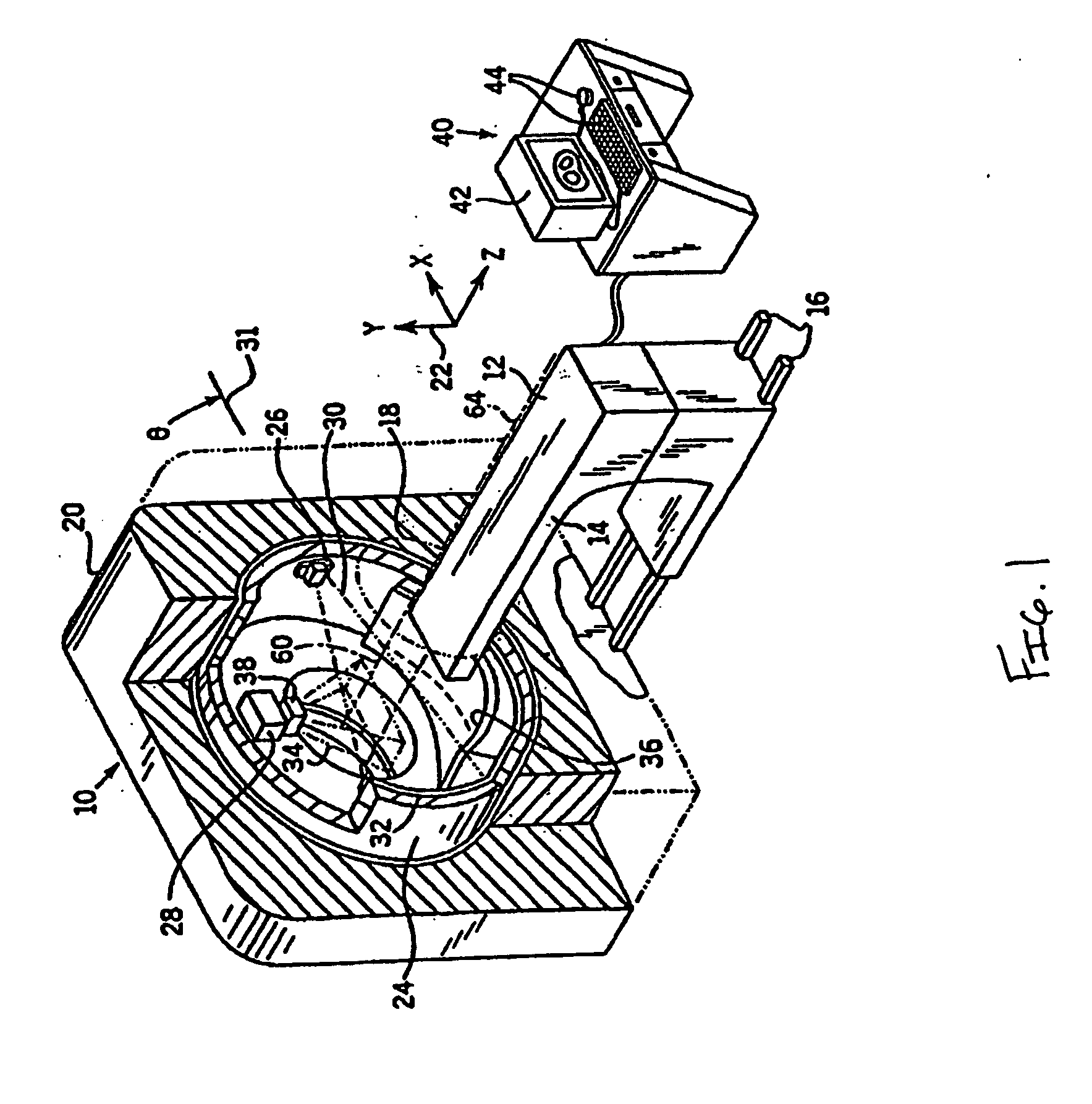
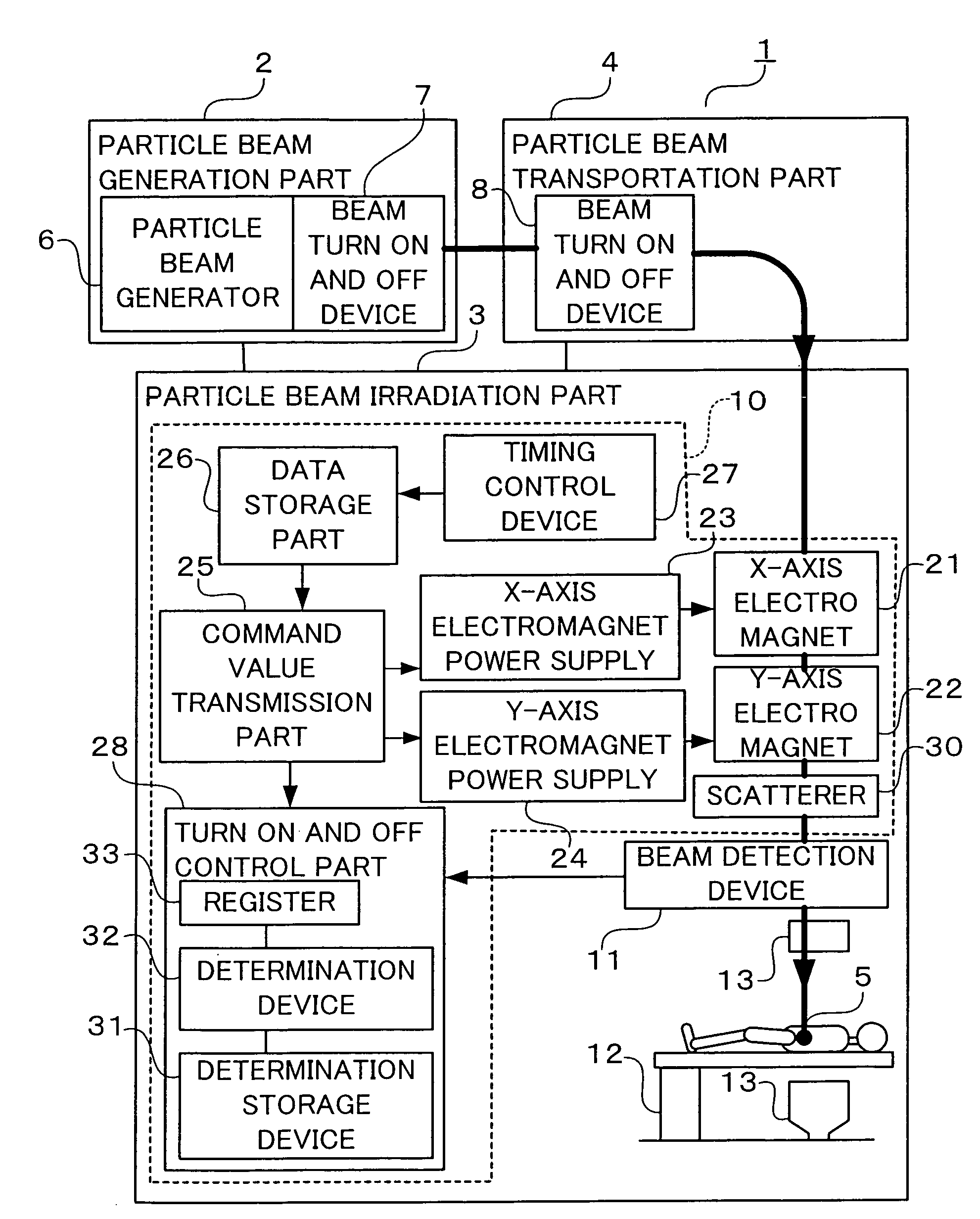
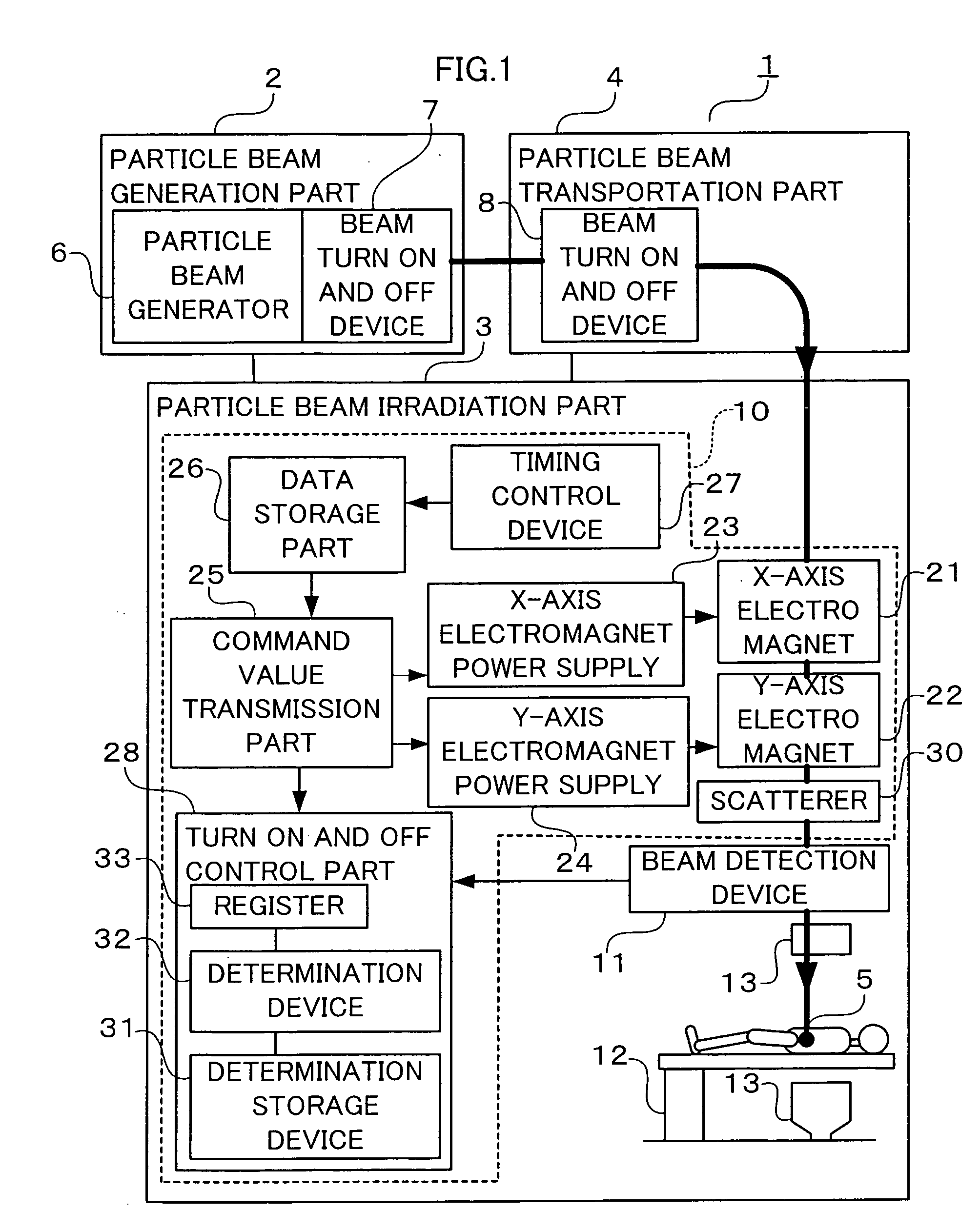
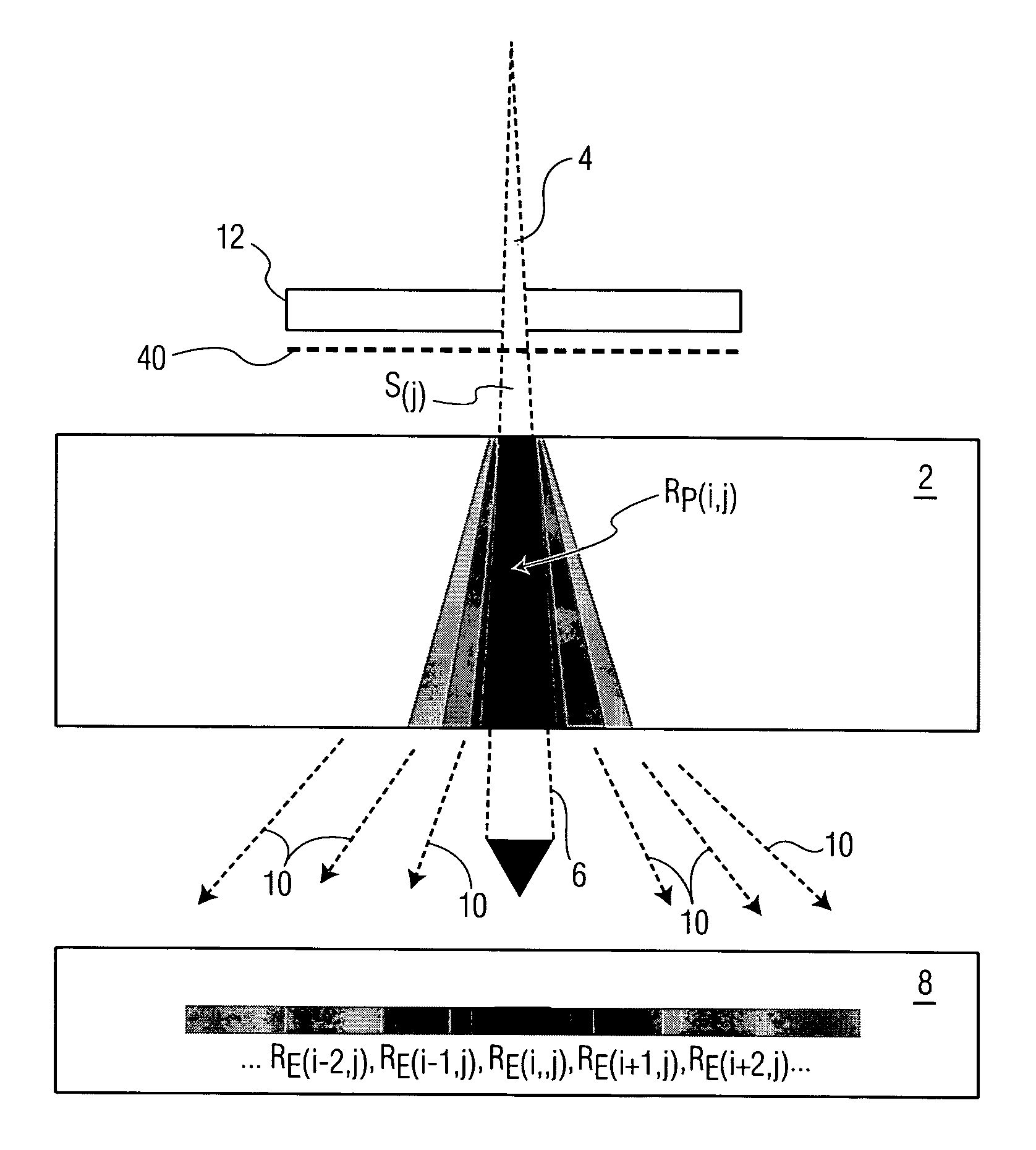
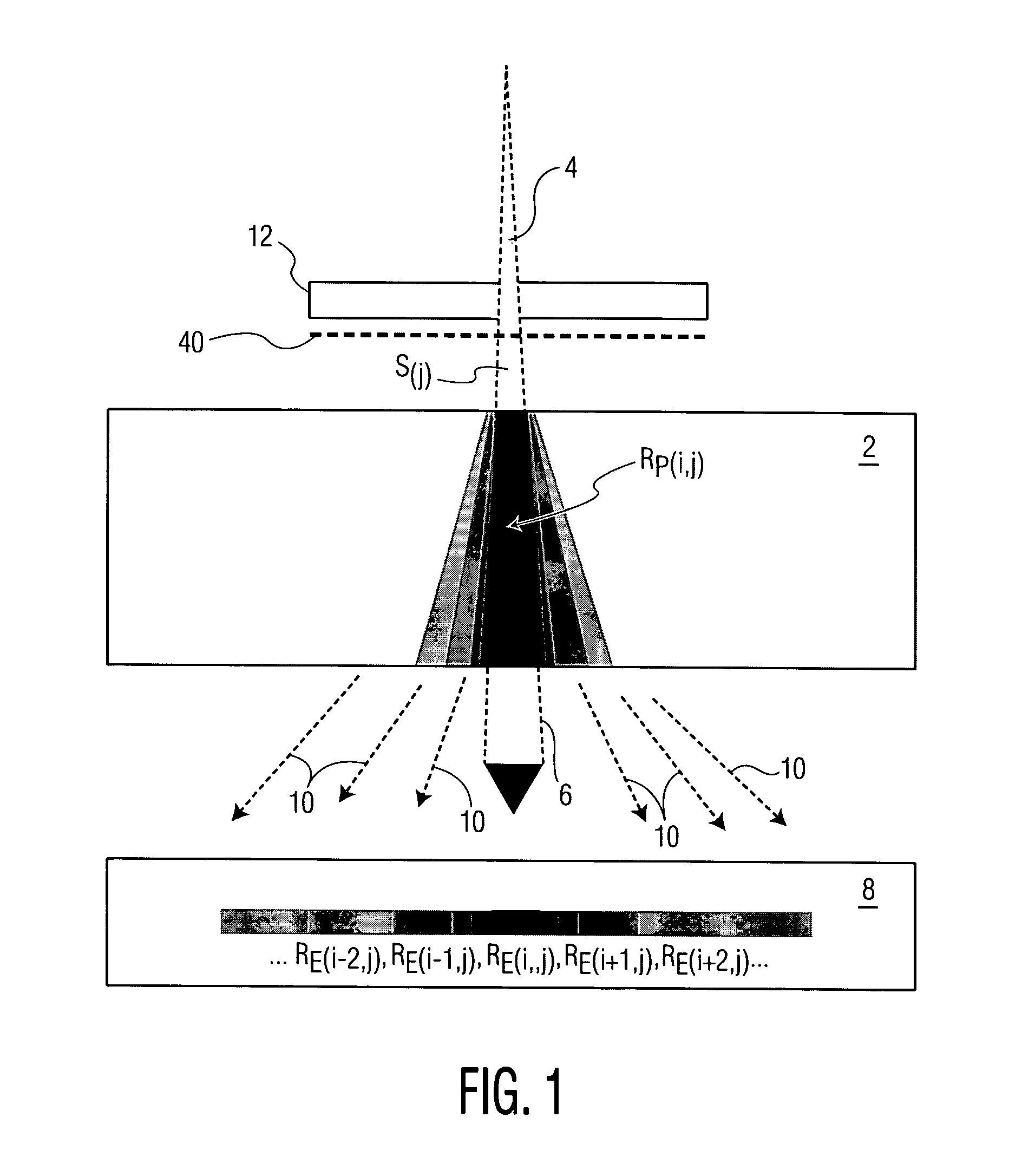
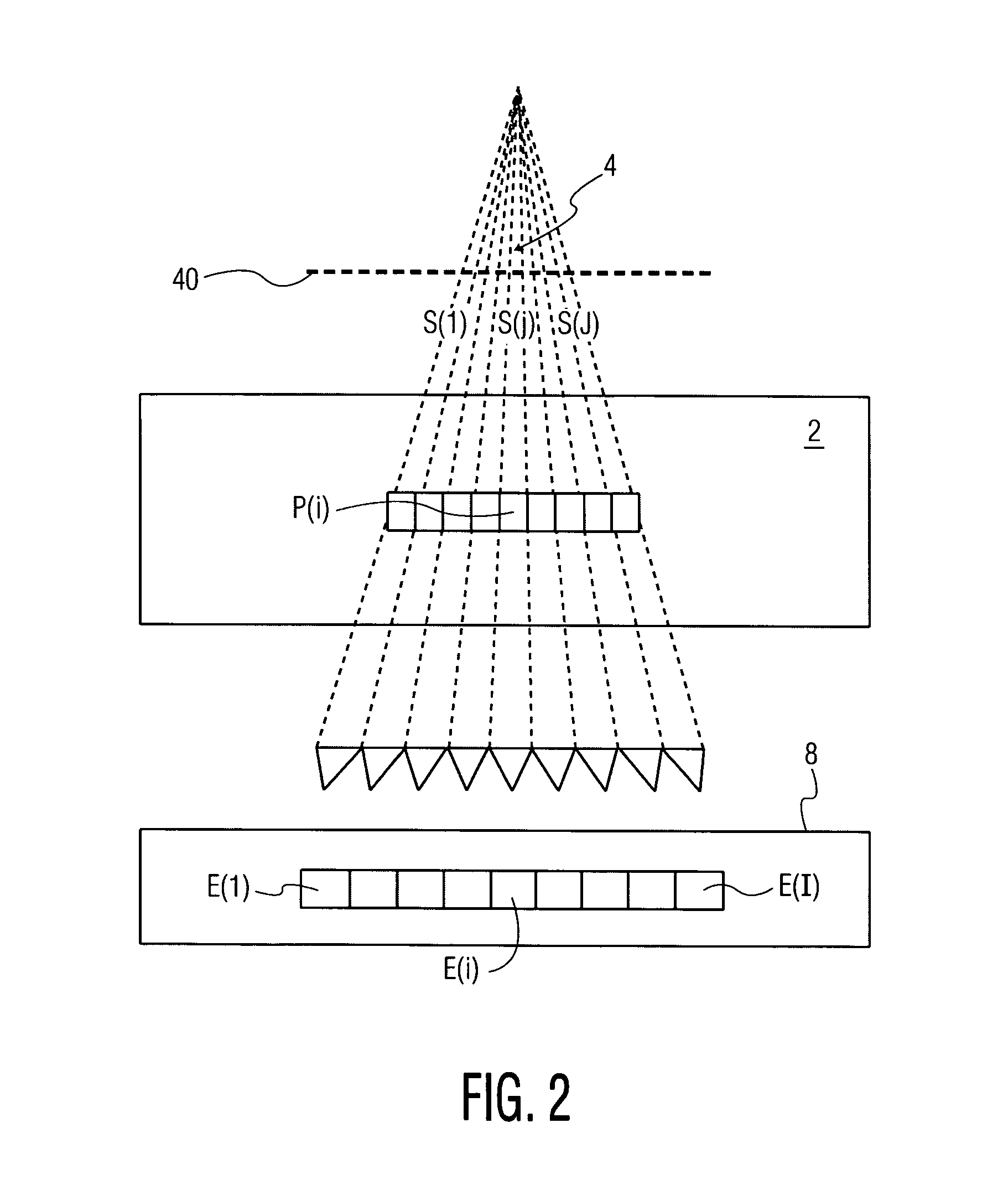
Particle beam therapeutic apparatus
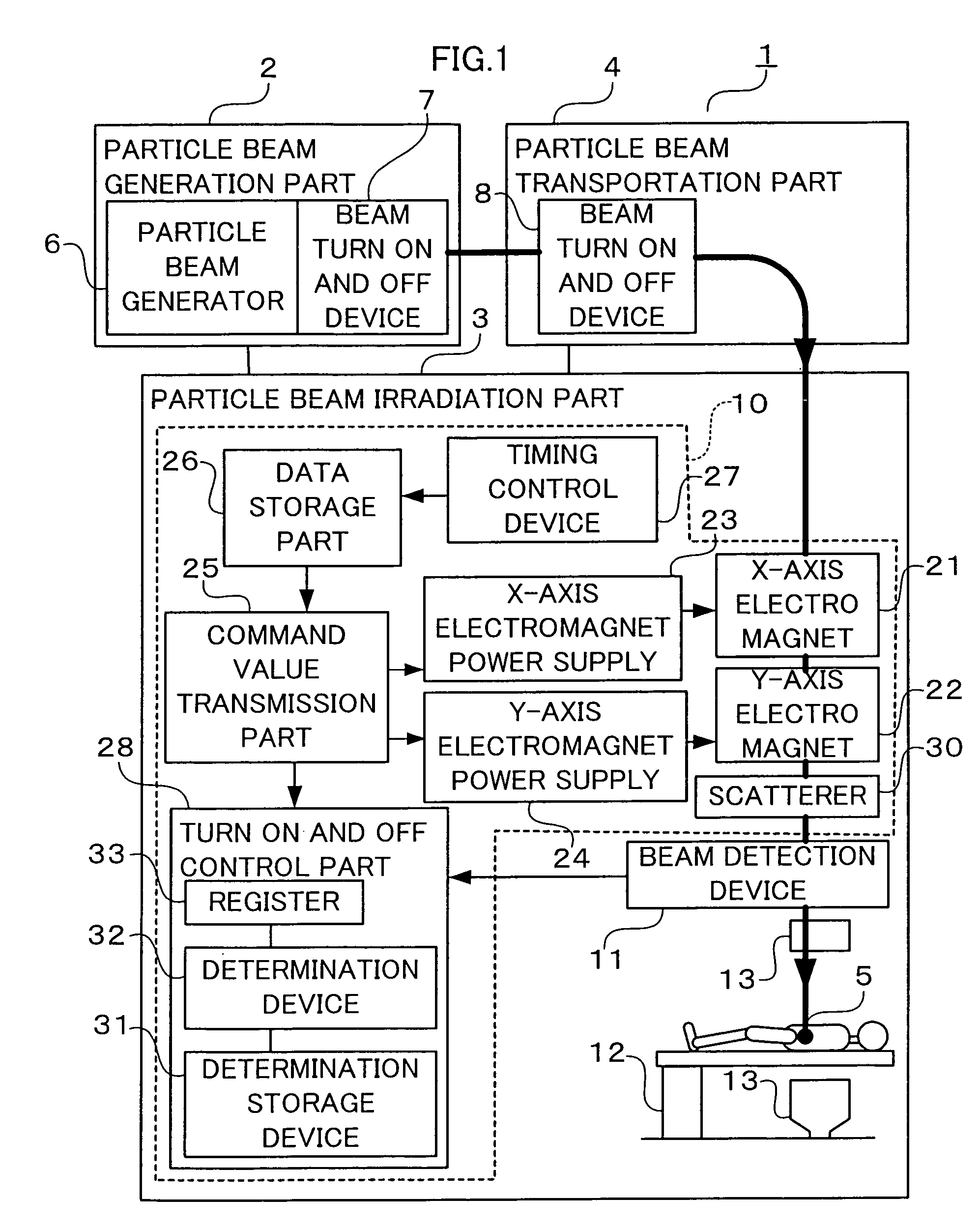
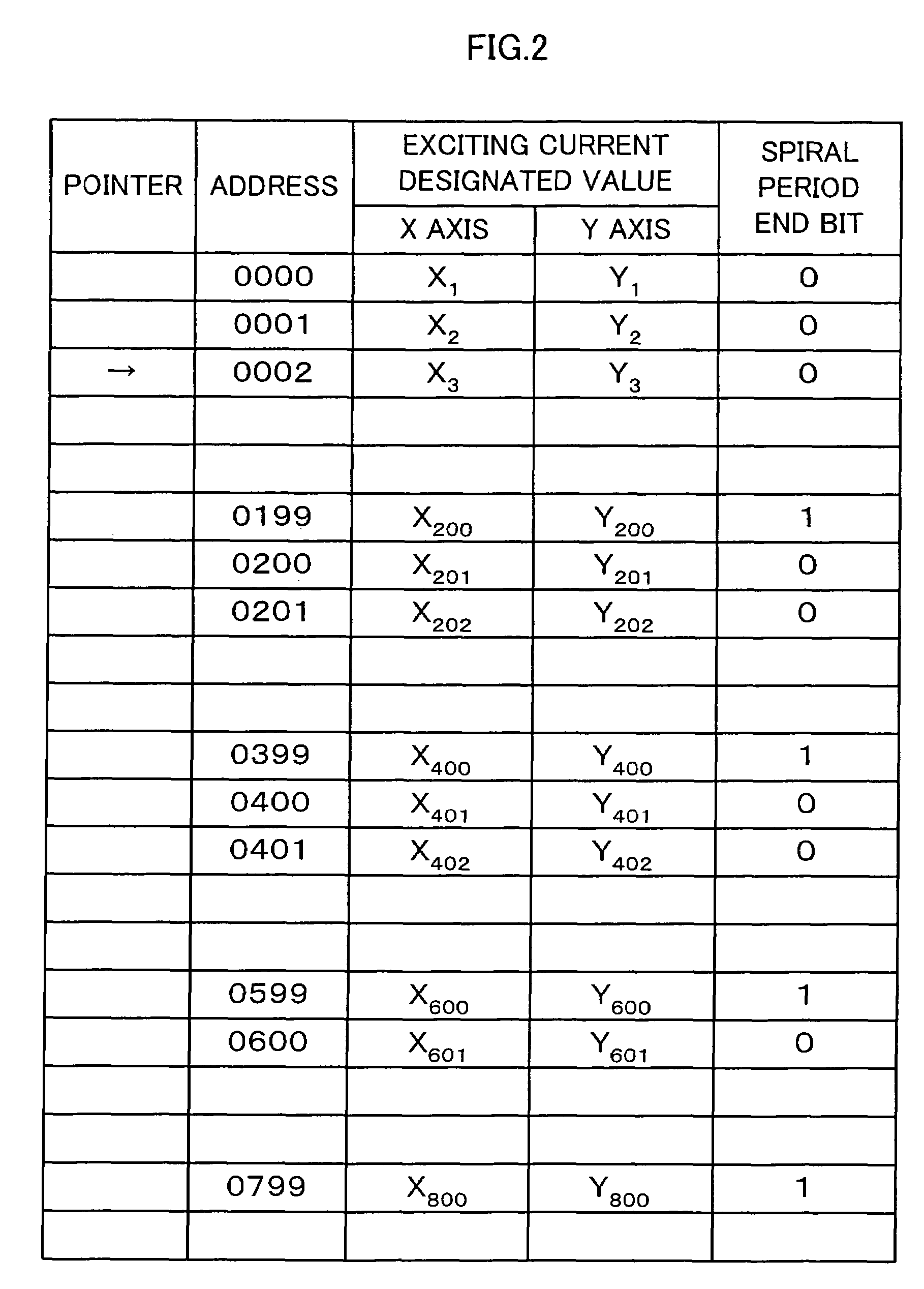
ActiveUS7378672B2Shorten the timeReduce stepsElectrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle beamParticle physics
A particle beam therapeutic apparatus can ensure the uniformity of dose distribution by overlapping the desired loci of the irradiation of a particle beam a reduced number of times. A flow of a particle beam transported so as to be irradiated to a diseased part is caused to deflect in two mutually orthogonal directions perpendicular to the direction of travel of the particle beam. The irradiation position of the particle beam is scanned, upon each period, in a manner to return to a position of irradiation located at the start of the period, whereby a plurality of loci drawn within one period are overlapped with one another thereby to irradiate a desired planned dose to the diseased part. The particle beam can be interrupted only at the end of the period.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for modification of radiotherapy treatment delivery
ActiveUS8406844B2Reduce deliveryAvoid structureElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringTemplate basedPlanned Dose
Owner:TOMOTHERAPY INC
Method for verification of intensity modulated radiation therapy
InactiveUS20070071169A1Improve accuracyAccurate calculationX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyDose levelIntensity-modulated radiation therapy
An accurate method for inversely verifying a therapeutic radiation dose delivered to a patient via an x-ray delivery system without involving any computational iteration was developed. The usage of it includes detecting the transmitted radiation dose image after passage through the patient, imaging the patient during treatment to anatomically record information of the patient, followed by inversely verifying through use of both the detected radiation image and the imaging data, the actual radiation dose delivered to the patient, and comparing the level of the dose delivered to a previously planned dose to determine whether the planned dose was delivered, or whether an overdose or underdose occurred.
Owner:NJ UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF +1
Radiotherapy planning method and device, radiotherapy dose determining method and device and radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device
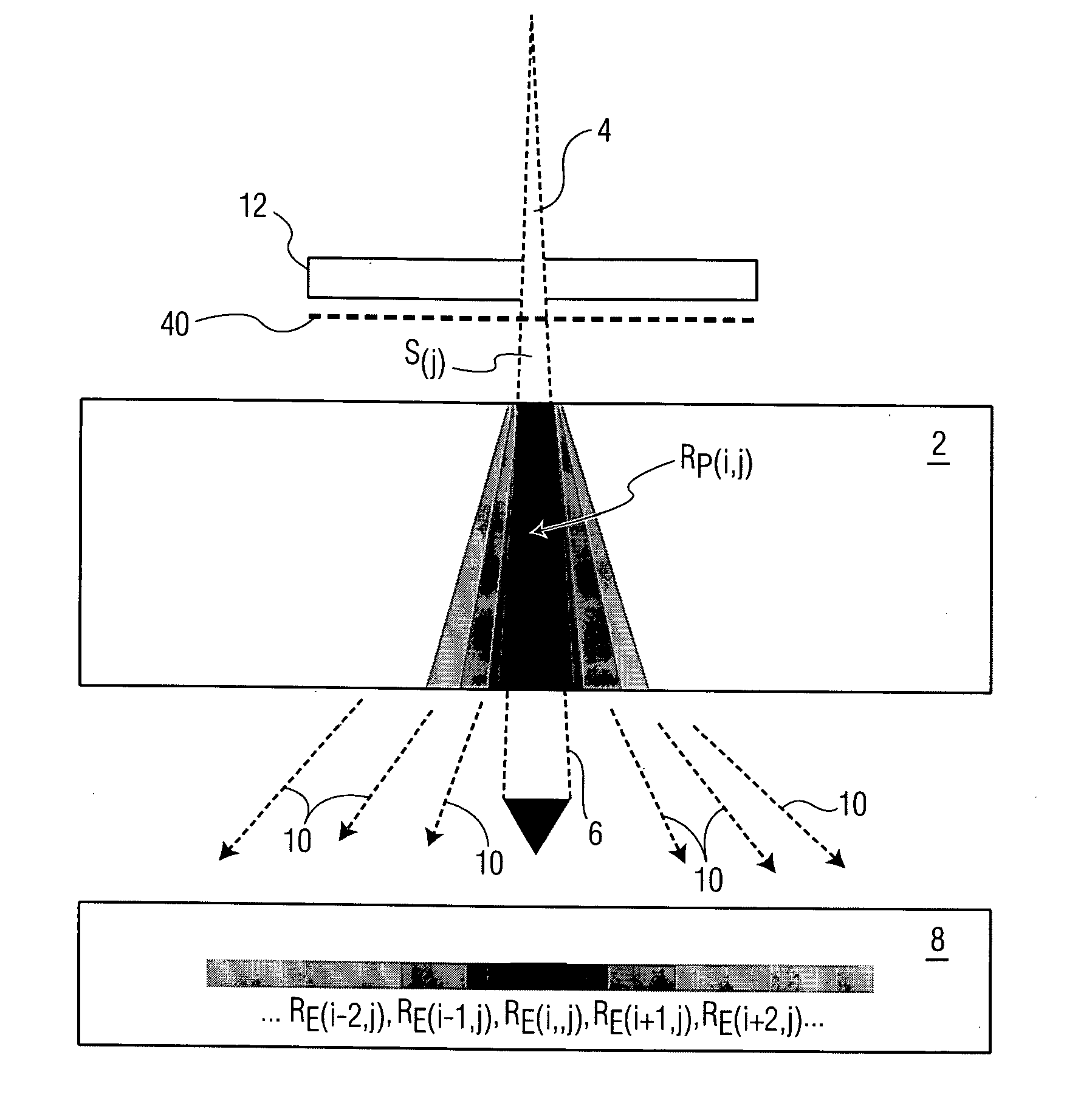
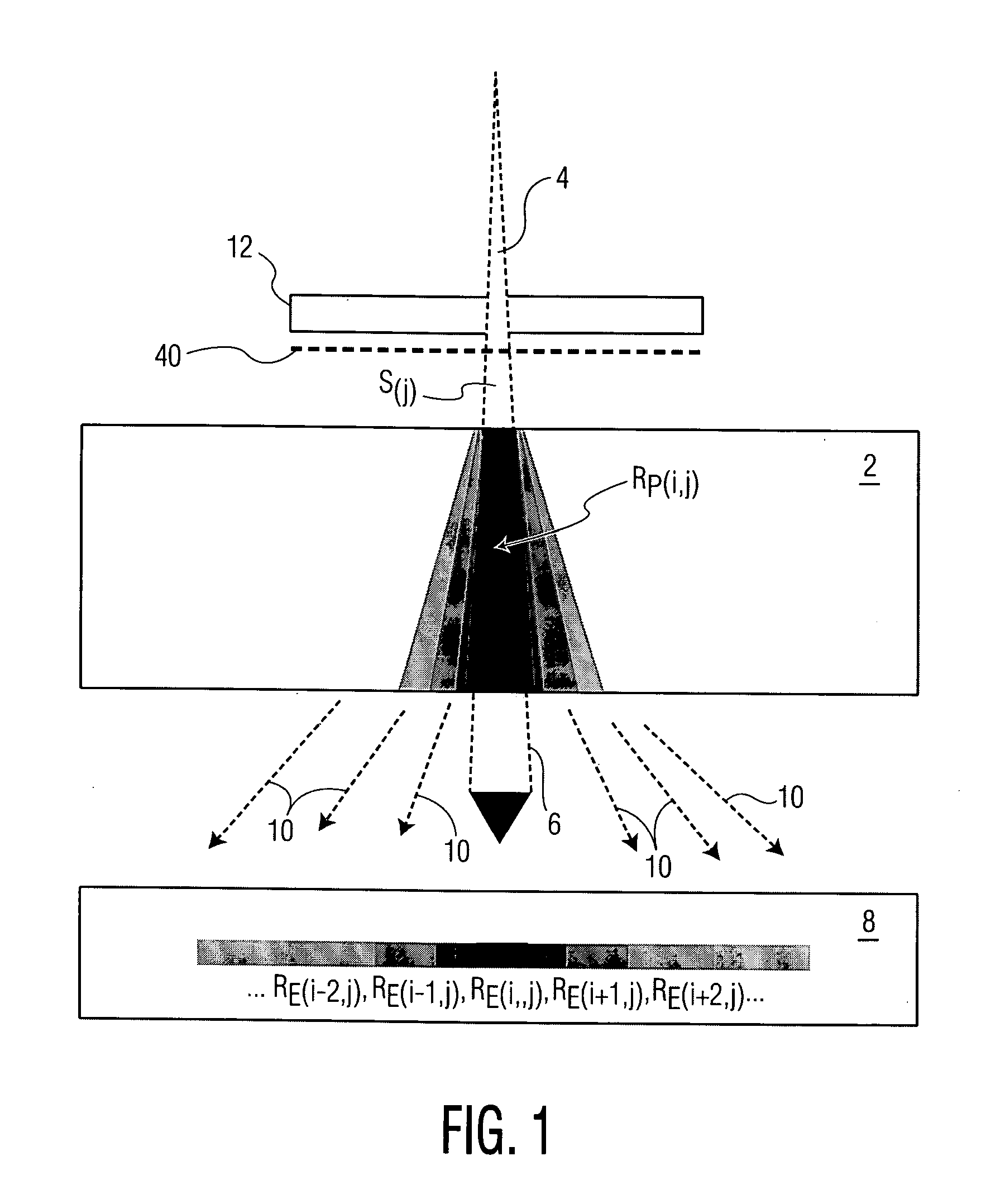
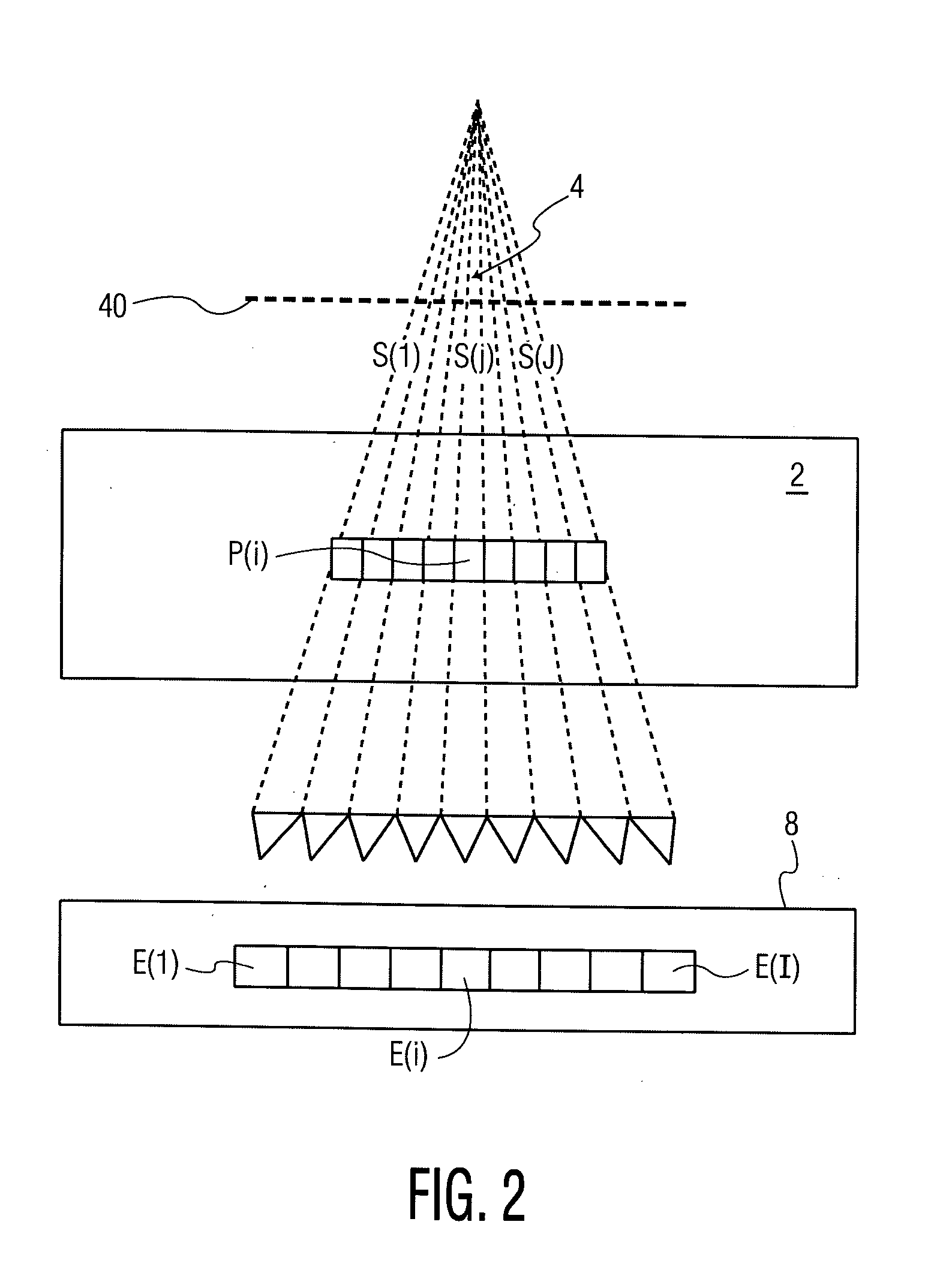
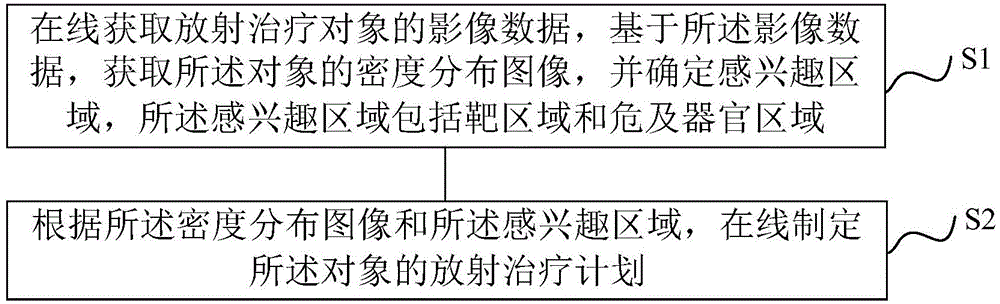
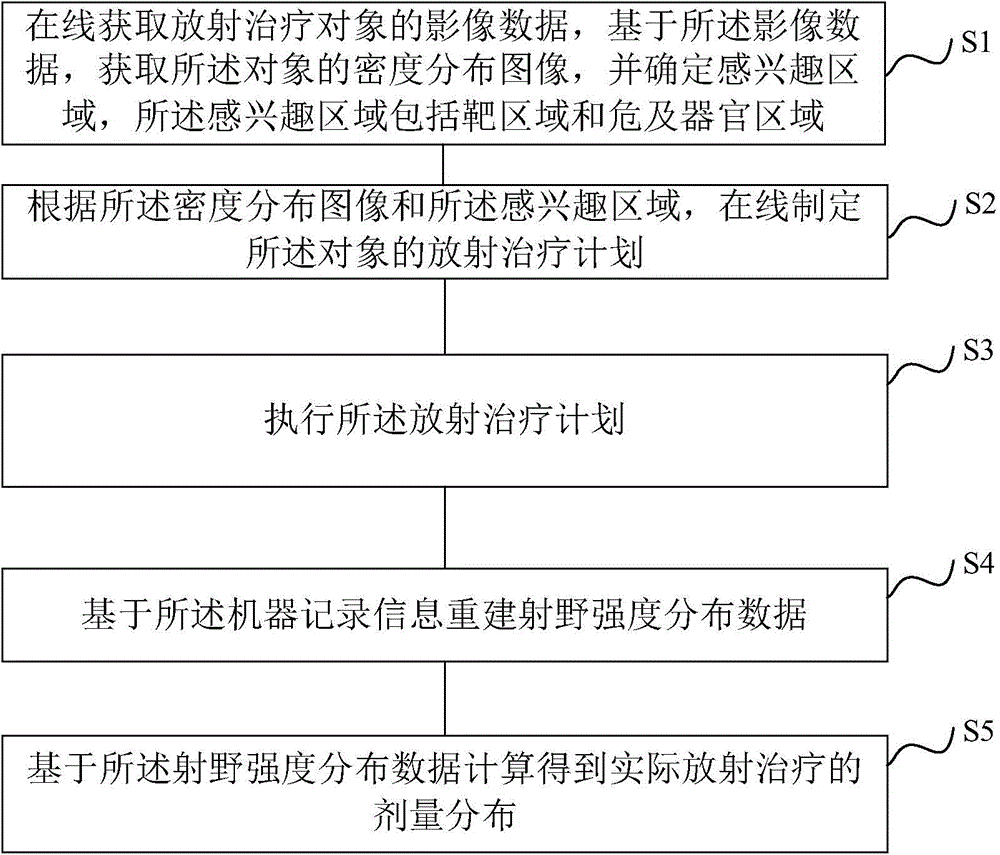
ActiveCN104548372AHigh precisionReduce repetitive setup errorsRadiation therapyObject basedDensity distribution
The invention discloses a radiotherapy planning method and device, a radiotherapy dose determining method and device and a radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method and device. The radiotherapy dose determining method includes the steps of online obtaining image data of a radiotherapy object, obtaining a density distribution image of the object based on the image data, determining a region of interest, and online making a radiotherapy plan of the object according to the density distribution image and the region of interest; executing the radiotherapy plan; rebuilding radiation field intensity distribution data based on information recorded by machines; carrying out calculation based on the radiation field intensity distribution data to obtain practical radiotherapy dose distribution. As the online-obtained image data are adopted, the accuracy of the image data is improved; as the radiation field intensity distribution data are rebuilt based on the information recorded by the machines, the dose distribution accuracy is higher. In the radiotherapy quality guaranteeing method, when deviation exists between the practical dose distribution result and a main plan dose, a sub-plan is modified, it is guaranteed that the use total dost is coincident with the plan dose, and the radiotherapy quality is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Particle beam therapeutic apparatus
ActiveUS20060231775A1Shorten the timeReduce stepsElectrode and associated part arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansParticle beamParticle physics
A particle beam therapeutic apparatus can ensure the uniformity of dose distribution by overlapping the desired loci of the irradiation of a particle beam a reduced number of times. A flow of a particle beam transported so as to be irradiated to a diseased part is caused to deflect in two mutually orthogonal directions perpendicular to the direction of travel of the particle beam. The irradiation position of the particle beam is scanned, upon each period, in a manner to return to a position of irradiation located at the start of the period, whereby a plurality of loci drawn within one period are overlapped with one another thereby to irradiate a desired planned dose to the diseased part. The particle beam can be interrupted only at the end of the period.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
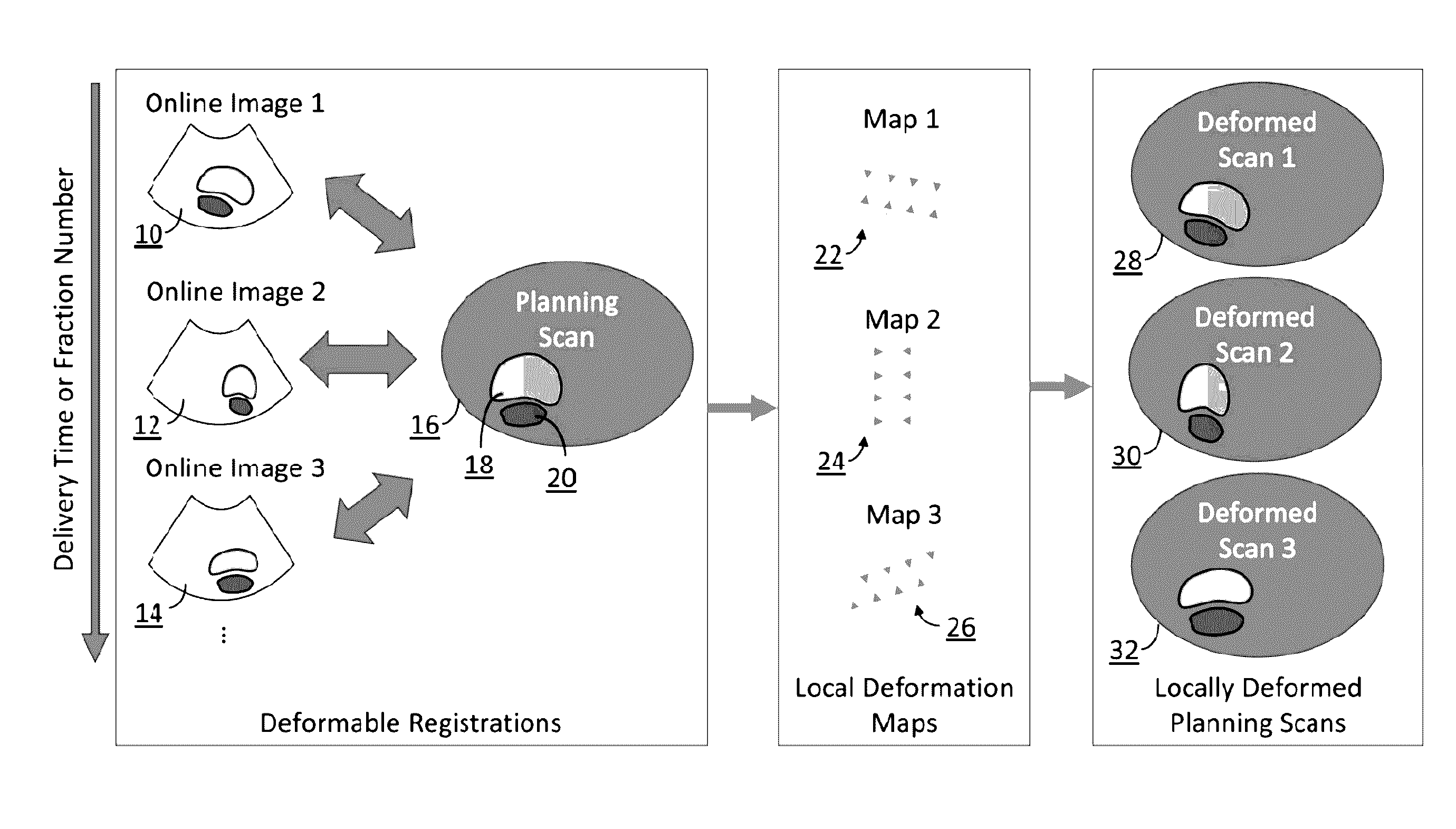
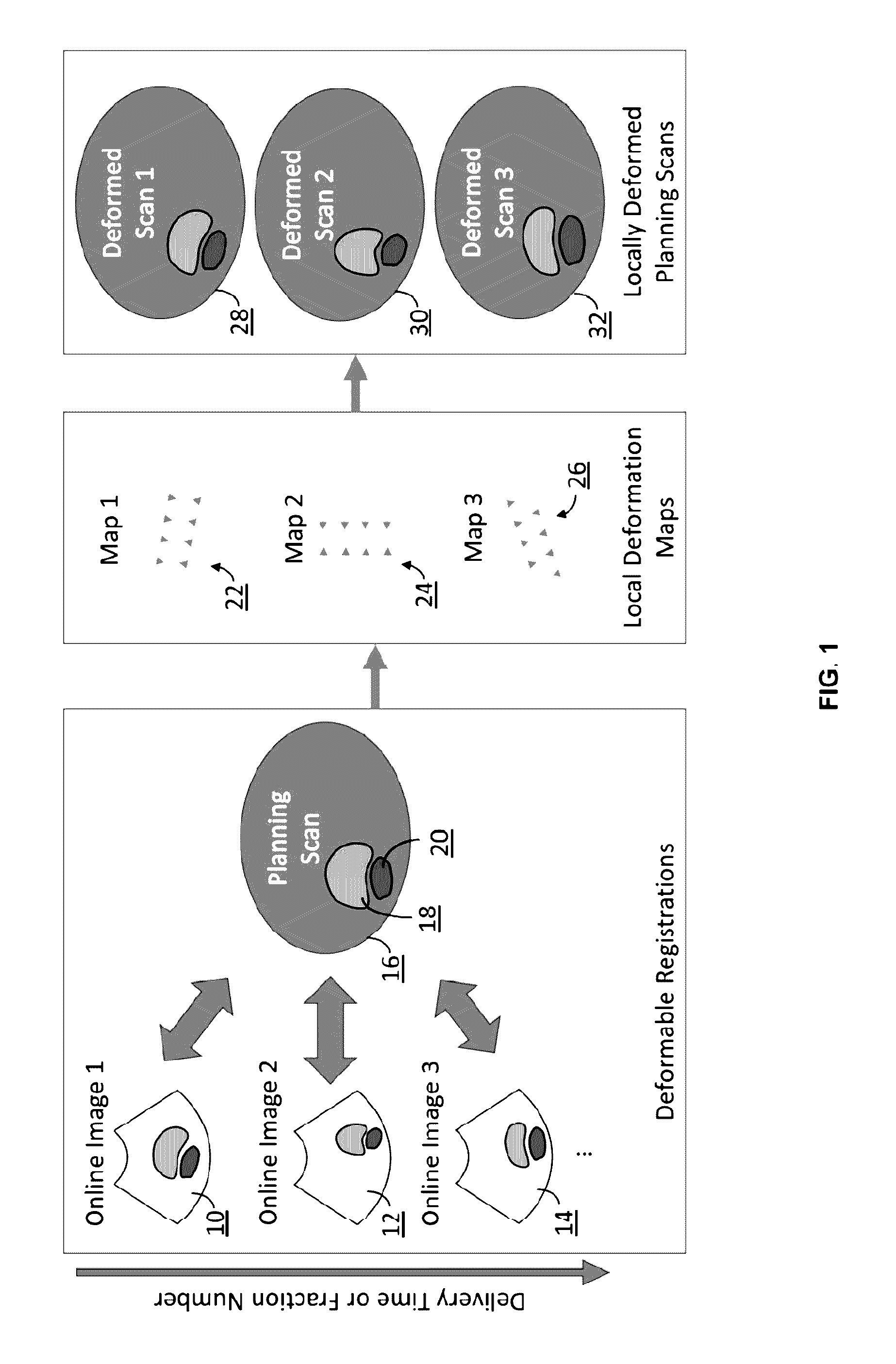
Radiotherapy dose assessment and adaption using online imaging
InactiveUS20160279444A1Improve representationUltrasound therapySurgical instruments for heatingTreatment deliveryPlanned Dose
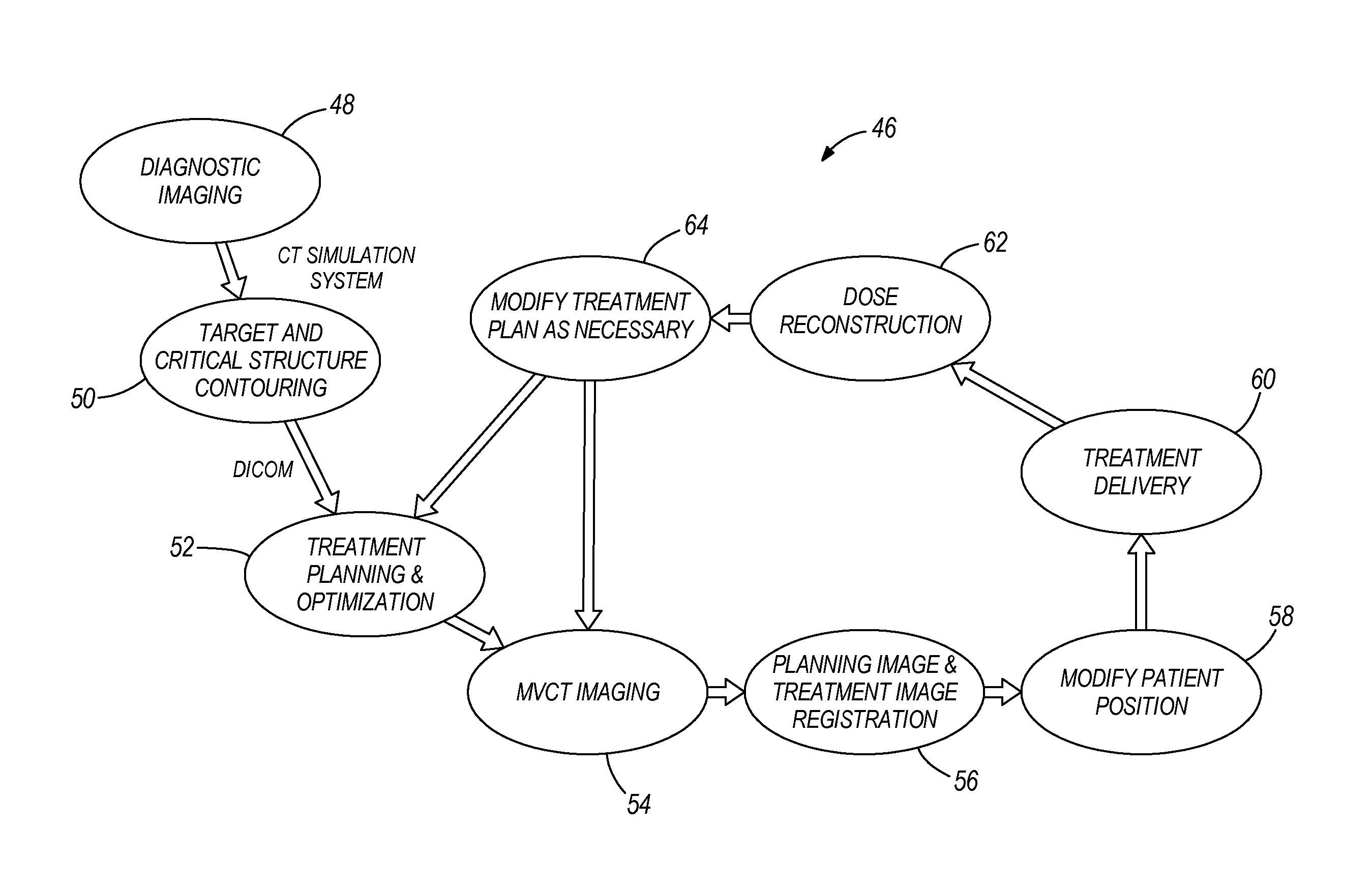
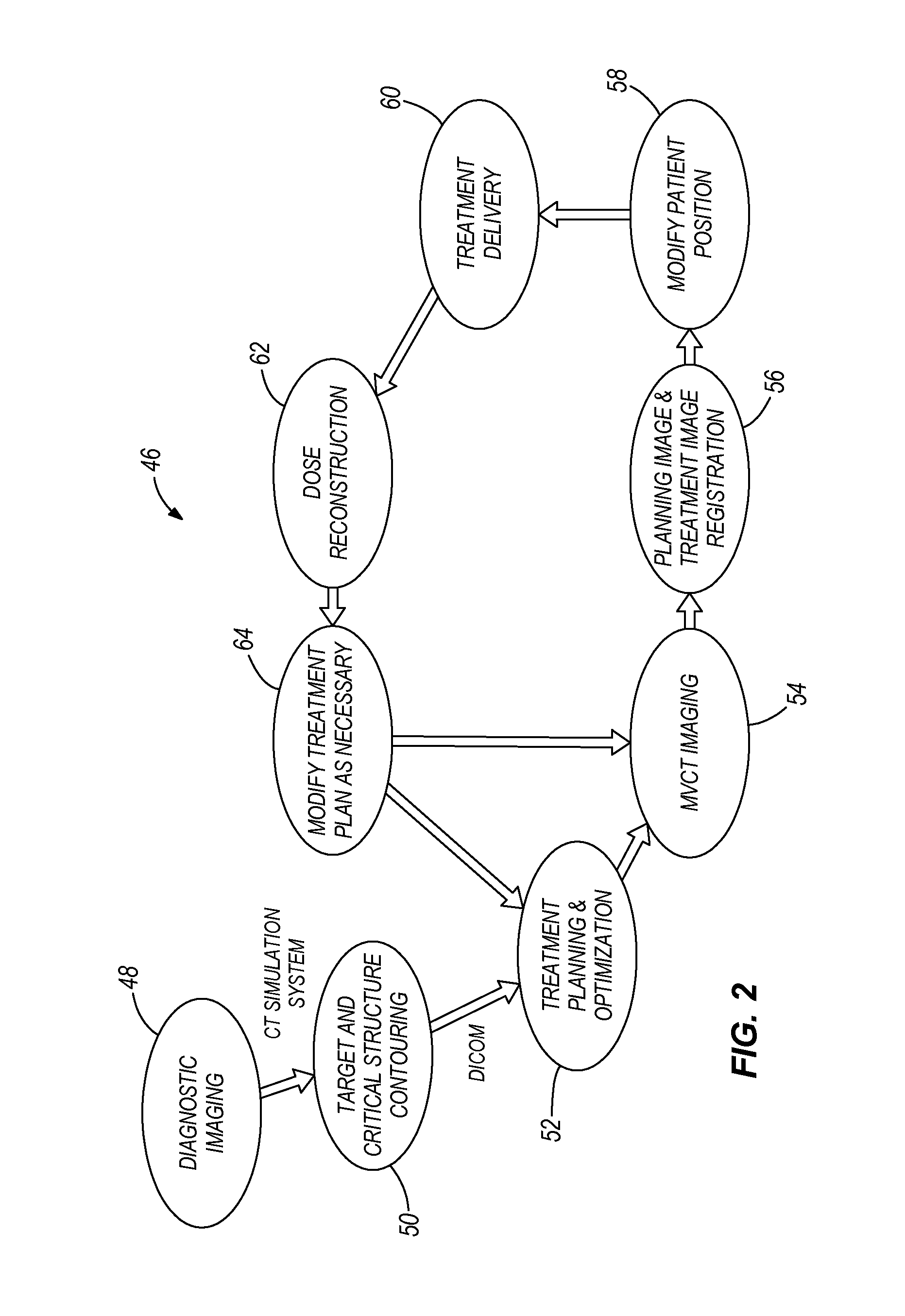
In external beam radiation therapy, a planning image (scan) of the patient is obtained prior to treatment as a basis for constructing a radiation delivery plan. However, since the planning scan is obtained prior to treatment (potentially days or weeks prior), it does not necessarily represent the state of the patient's anatomy as it presents at the time of treatment beam delivery. The potential mismatch between the patient's anatomy in the planning scan and anatomy at the time of treatment can result in dose discrepancies between the planned dose and the actual delivered dose. The methods herein describe the use of online images taken immediately before or during treatment delivery in order to predict, assess, and adapt to such discrepancies.
Owner:SONITRACK SYST
Method for verification of intensity modulated radiation therapy
InactiveUS7450687B2Improve accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyIntensity-modulated radiation therapyTherapeutic radiation
An accurate method for inversely verifying a therapeutic radiation dose delivered to a patient via an x-ray delivery system without involving any computational iteration was developed. The usage of it includes detecting the transmitted radiation dose image after passage through the patient, imaging the patient during treatment to anatomically record information of the patient, followed by inversely verifying through use of both the detected radiation image and the imaging data, the actual radiation dose delivered to the patient, and comparing the level of the dose delivered to a previously planned dose to determine whether the planned dose was delivered, or whether an overdose or underdose occurred.
Owner:NJ UNIV OF MEDICINE & DENTISTRY OF +1
Cloud-computing based dose verification system and method of tumor radiotherapy
InactiveCN104933652ARealize remote controlLow costData processing applicationsTransmissionDose verificationDosimeter
The invention discloses a cloud-computing based dose verification system and method of tumor radiotherapy. The system comprises a user terminal equipment, a cloud computing server, a local therapy planning system, a computer, an HDFS data storage server and a medical linear accelerator. According to the system and method, EPID information collection is separated from dose analysis and comparison, and part which needs computing and analyzing is transferred to the server based on cloud computer; the equipment at the user end only makes therapy plans, collects, pre-processes and transmits EPID images and receives and display analysis results; and Gamma analysis between to-be-compared dose distribution and reference dose distribution is accelerated. The parallel operation mechanism of cloud computing is used, so that planning dose verification of tumor radiotherapy can be greatly accelerated, time of clinical dosimeter verification is reduced, and the efficiency of radiotherapy is improved.
Owner:苏州动影信息科技有限公司
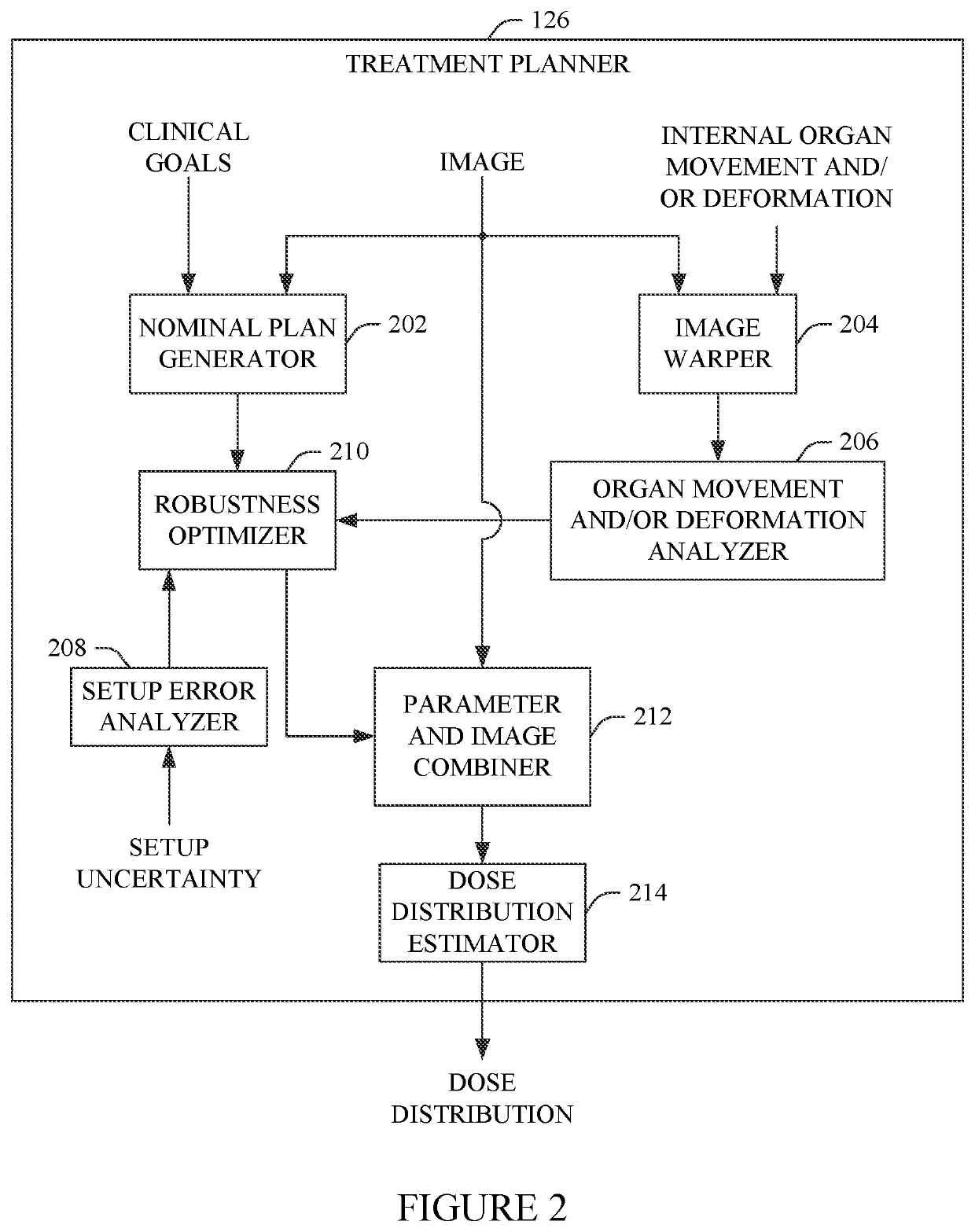
Intensity modulated proton therapy (IMPT) plan optimization based at least on internal organ anticipated movement and/or expected deformation
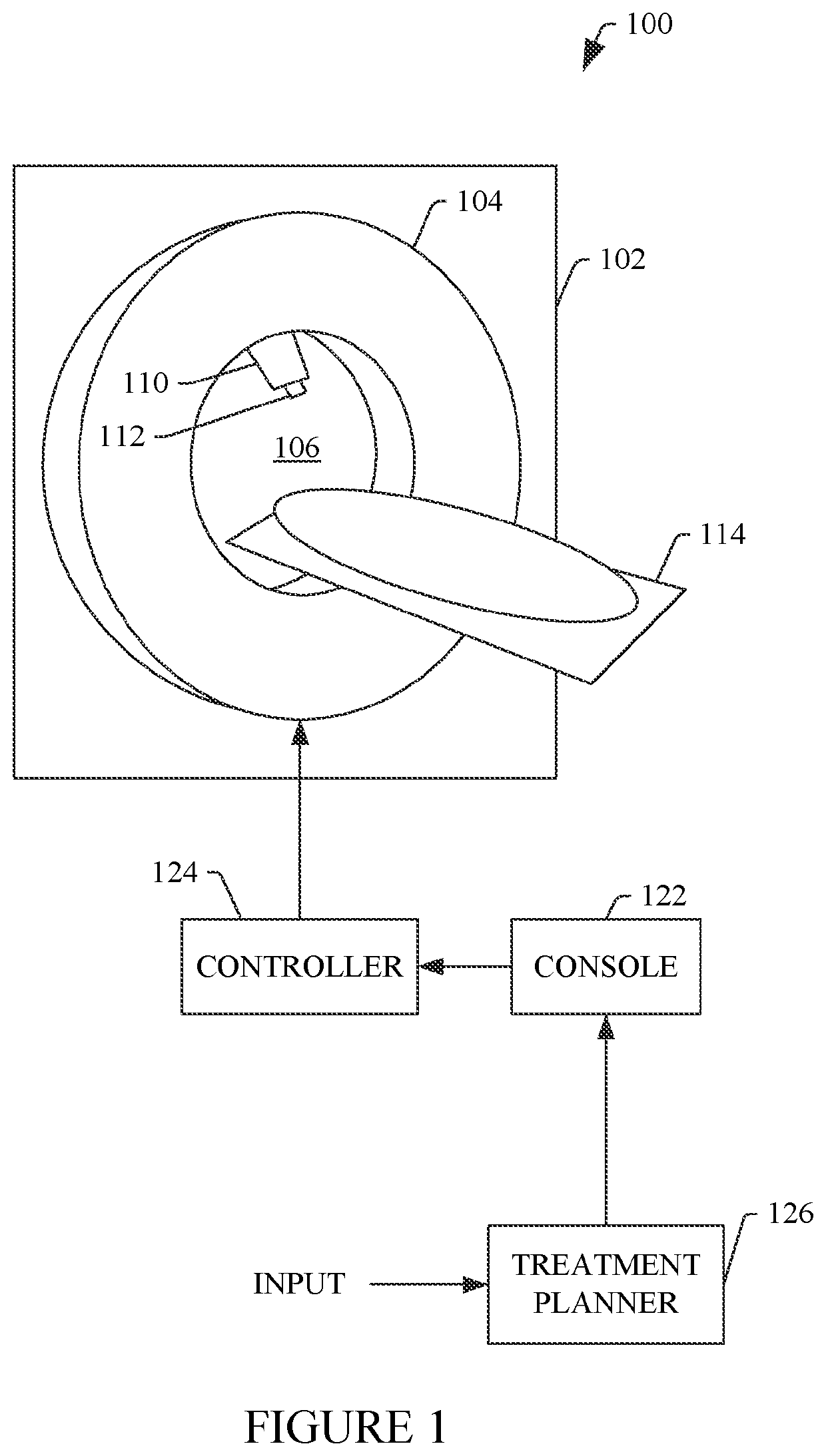
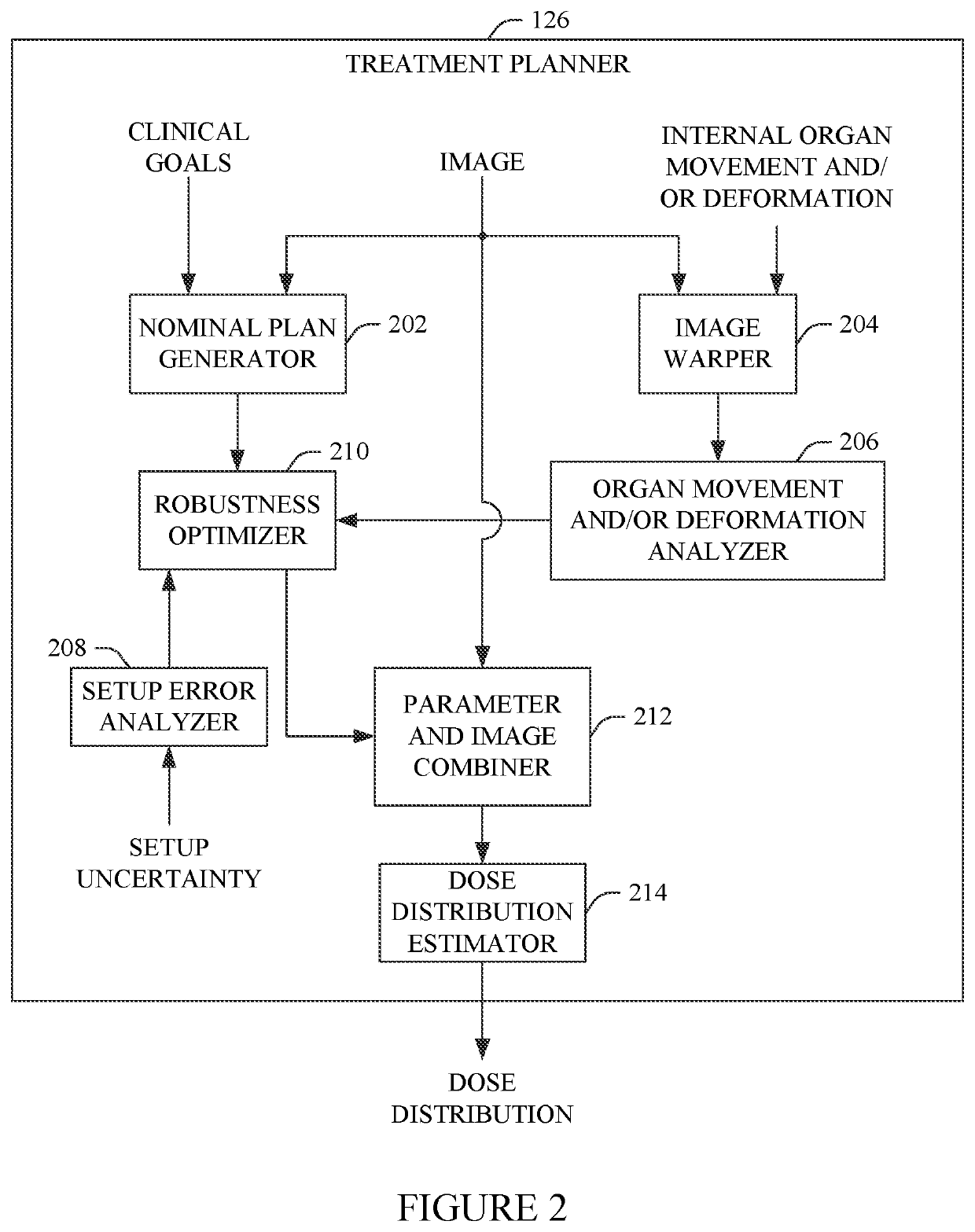
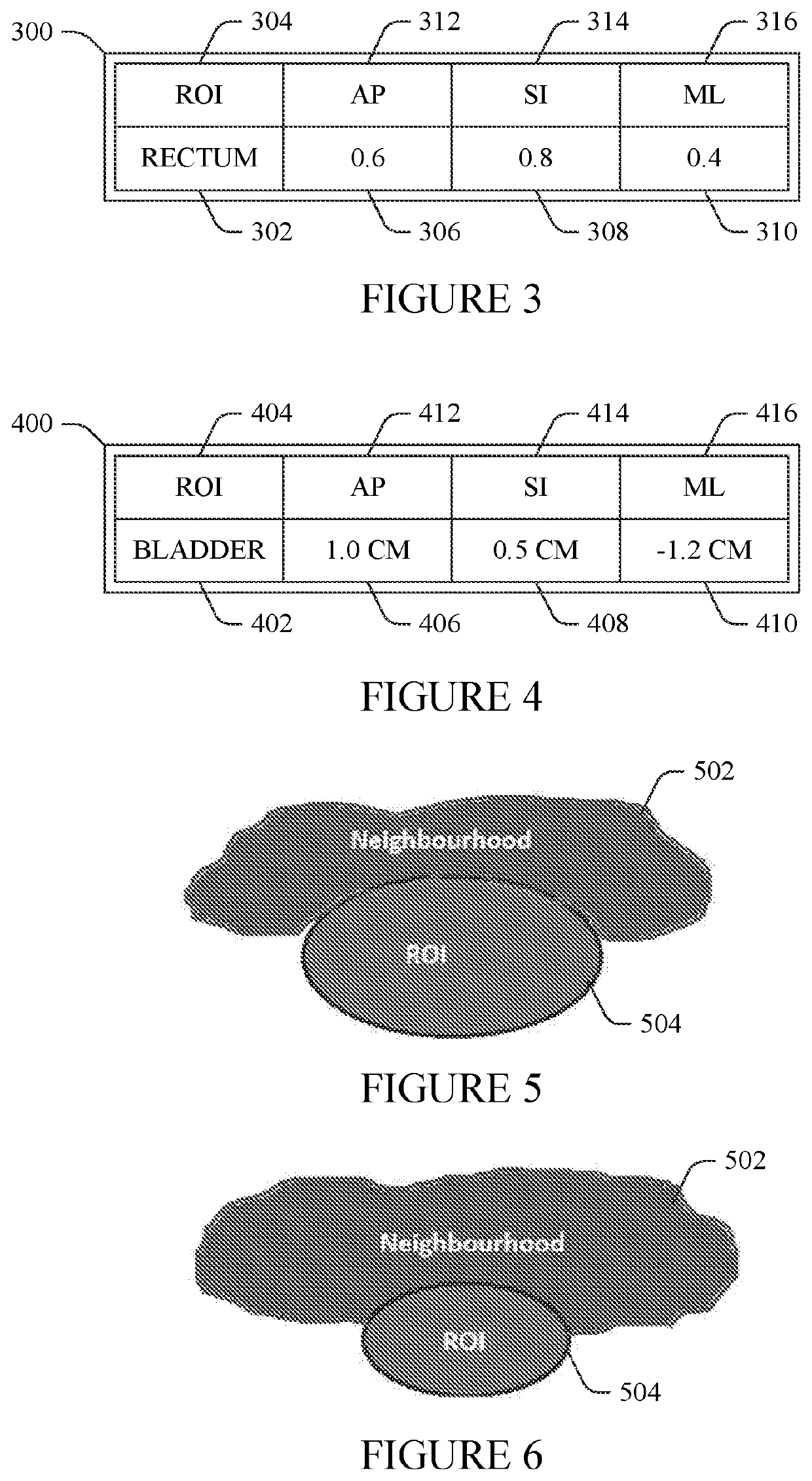
A method includes generating a nominal dose distribution based on an image and clinical goals. The method further includes generating a setup error dose distribution based on range and setup uncertainties. The method further includes generating a dose distribution for a parameter of an internal organ. The method further includes optimizing a planned dose distribution of an intensity modulated proton therapy plan by minimizing a total objective value including the nominal dose distribution, the setup error dose distribution dose distribution, and the dose distribution for the internal organ. The method further includes generating a final dose distribution for the intensity modulated proton therapy plan based on beam parameters of the optimized planned dose distribution. The method further includes controlling a proton therapy apparatus configured to deliver proton therapy based on the intensity modulated proton therapy plan with the optimized planned dose distribution.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Evaluation of dose accuracy of radiation therapy treatment plans
ActiveUS10765891B2Verified and reliableReduce the numberMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringNuclear medicine
The invention relates to a system and a method for evaluating a treatment plan for an external radiation therapy treatment, the treatment plan comprising parameters for controlling an external radiation therapy apparatus during the treatment. The system comprises a database storing historic treatment plans and storing for each historic treatment plan a quality parameter indicative of whether a deviation between a planned dose distribution and a measured dose distribution resulting from an execution of the treatment plan is within an acceptable limit. An evaluation unit determines a threshold value for each of a plurality of treatment plan metrics based on the historic treatment plans and the associated quality parameters. Further, the evaluation unit calculates a value of each of the metrics for the treatment plan and compares the value of each of the metrics with the threshold value determined for the respective metric.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dose-guided precise radiotherapy real-time verification system
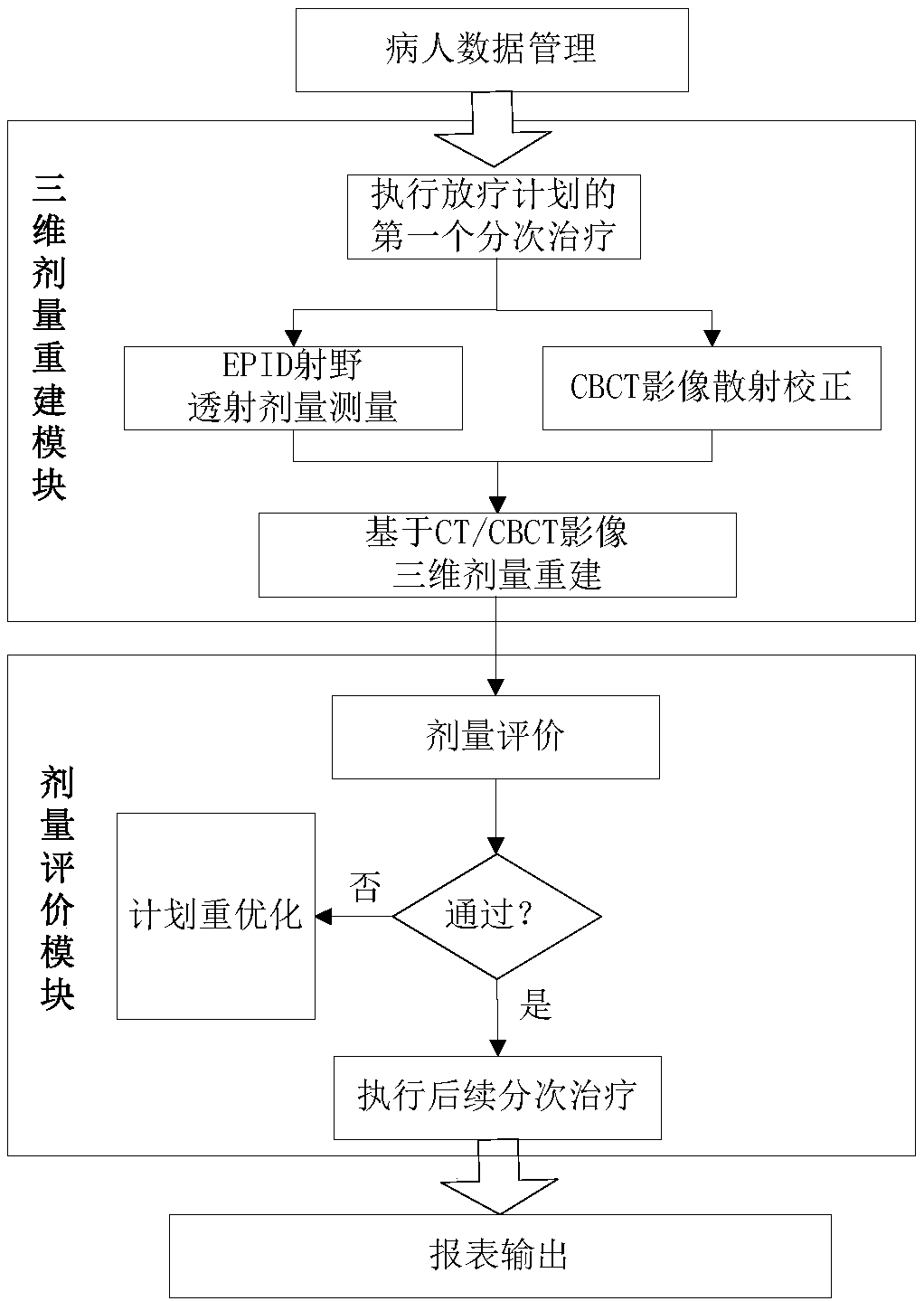
InactiveCN108404302AExact fitReal-time quality control treatmentX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPatient dataPlanned Dose
The invention discloses a dose-guided precise radiotherapy real-time verification system, which mainly comprises a patient data management module, a three-dimensional dose reconstruction module and adose evaluation module which are connected successively; the patient data management module is used for obtaining a radiotherapy patient data set from a radiotherapy information management system andproviding data input for the functional module of the system; the three-dimensional dose reconstruction module implements the scattering correction of a patient cone beam CT image, field transmissionimage acquisition, real-time dose calibration, and three-dimensional dose reconstruction functions; the dose evaluation module provides a dose assessment method and a result visualization function, and a user selects a two-dimensional dose assessment or a three-dimensional dose assessment as needed to provide decision-making data for a radiation therapist to perform subsequent fractional treatmentand plan correction. The dose-guided precise radiotherapy real-time verification system uses modular design, and uses a dose-guided radiotherapy plan to perform precise and real-time quality controltreatment, thereby achieving a precise coincidence of the therapeutic dose and the planned dose.
Owner:中科超精(南京)科技有限公司
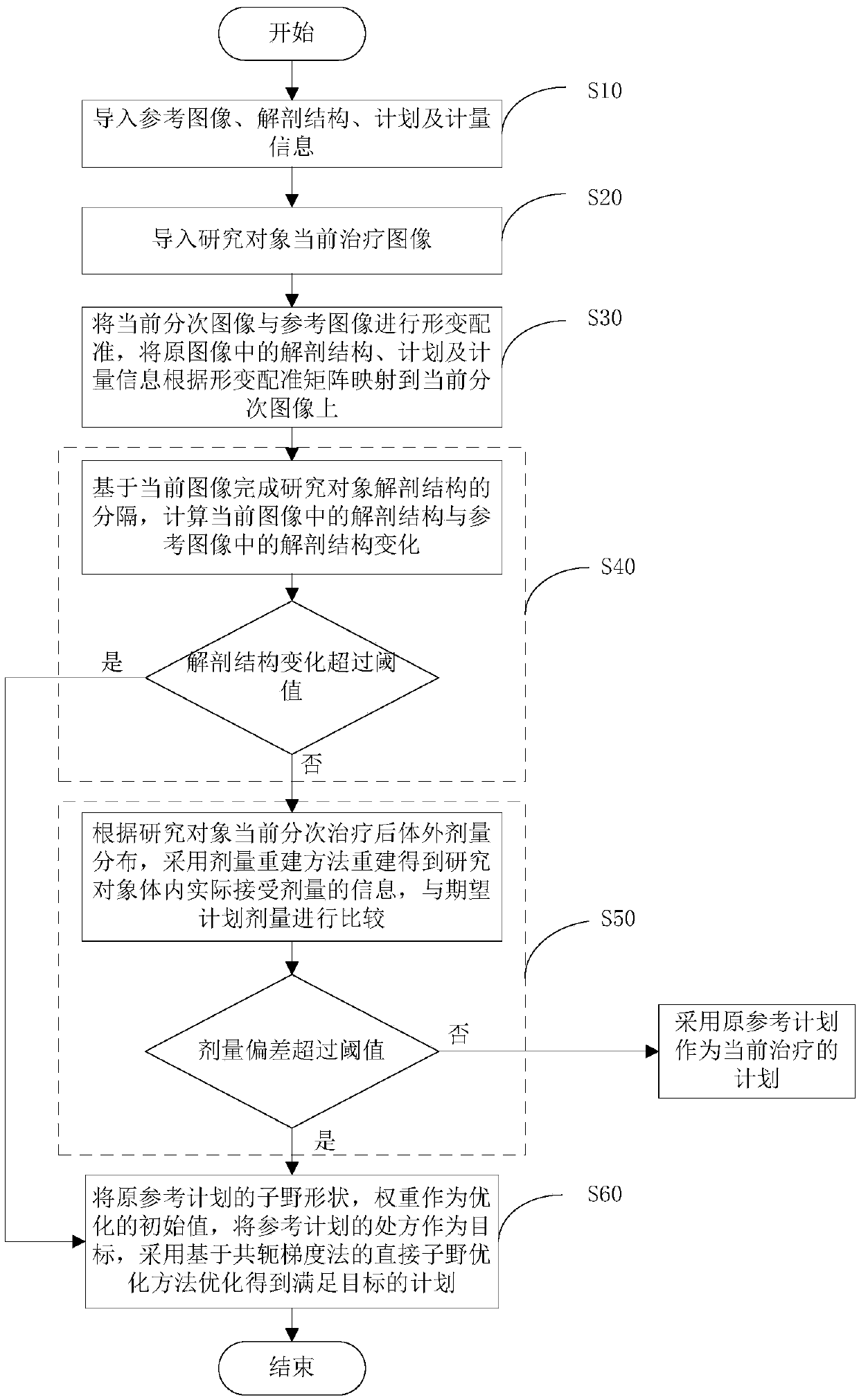
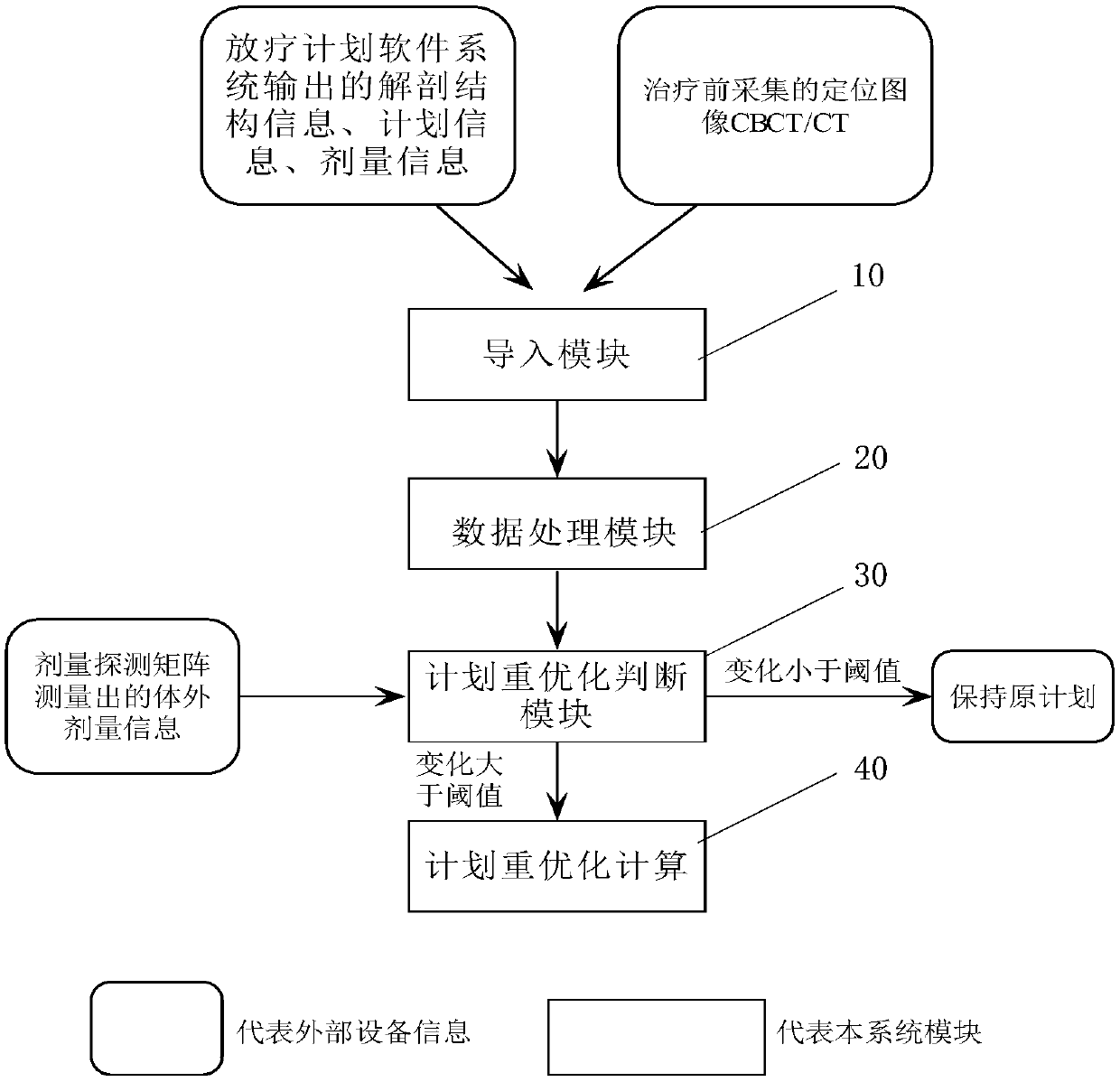
Dose-guided self-adaptive radiotherapy planning re-optimization system and method
The invention discloses a dose-guided self-adaptive radiotherapy planning re-optimization system and method. The system includes a guide module, a data processing module, a plan re-optimization judgment module and a plan re-optimization module. The guide module is used for guiding the reference image, anatomical structure, planning and dose information of a research object, and an image for guiding precise positioning during current fractional treatment; the data processing module is used for calculating the anatomical structure of the current image and the anatomical structure of a referenceimage; the plan re-optimization judgment module is used for judging whether to enter the plan re-optimization module or not according to the anatomical structure change, the actual dose received by patients is compared with the planned dose if the anatomical structure change is within the threshold, re-optimization is needed if there are great difference between the actual dose and the planned dose, otherwise, an original reference plan is used as the current treatment plan. The plan re-optimization not only considers the difference between the current anatomical structure and the original anatomical structure, but also uses the fast conjugate gradient algorithm to automatically optimize the plan according to the actual dose received by the research object.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Incremental treatment planning
ActiveCN106029170AReduce computing timeReserved dose-volume statisticsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyProgram planningInverse treatment planning
A method for generating a radiotherapy treatment plan for a patient is provided. The treatment plan is optimized by using an optimization objective which is at least partly based on an initially planned dose to the patient.
Owner:RAYSEARCH LAB
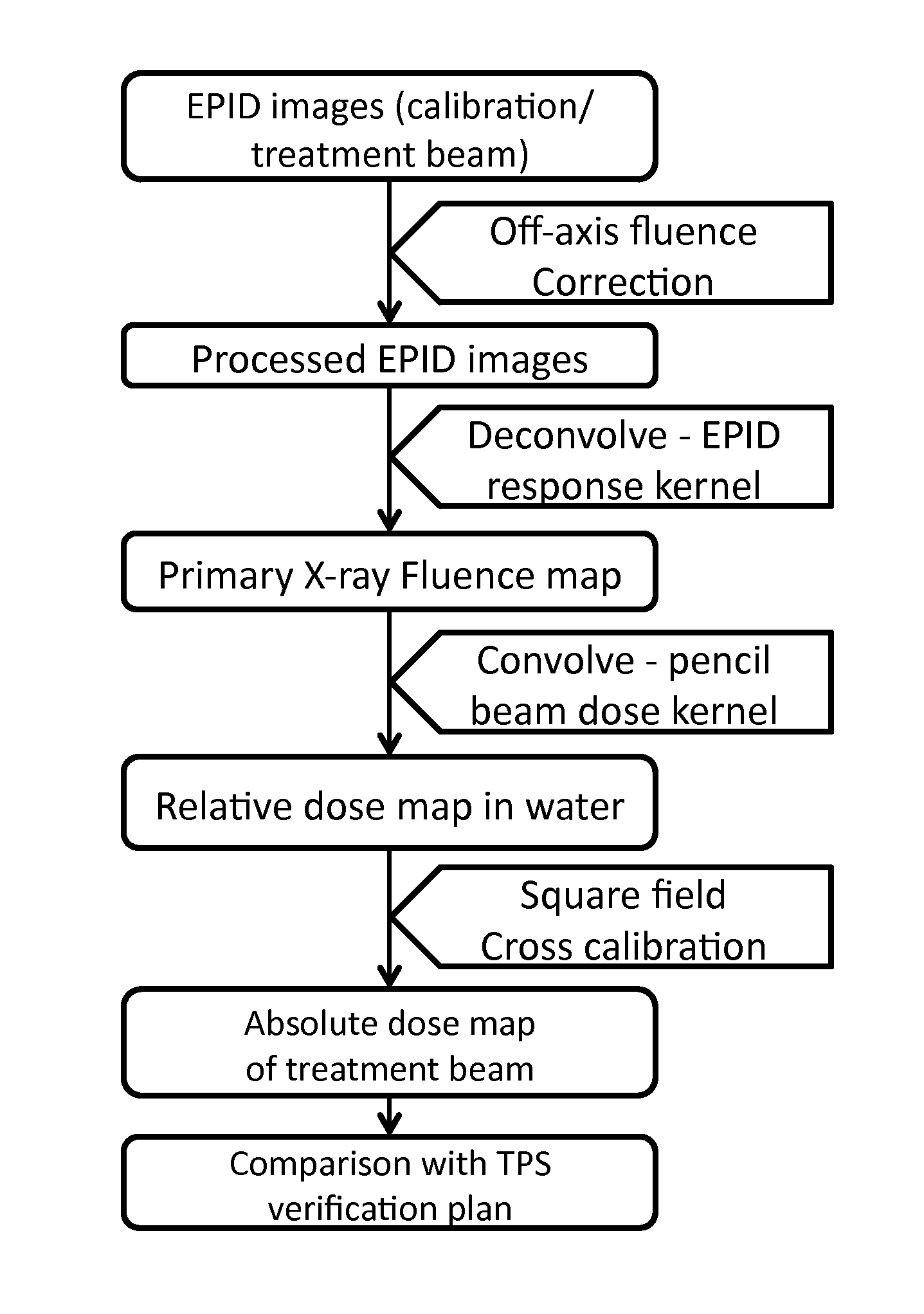
Novel EPID dosimetry method and system for radiation therapy
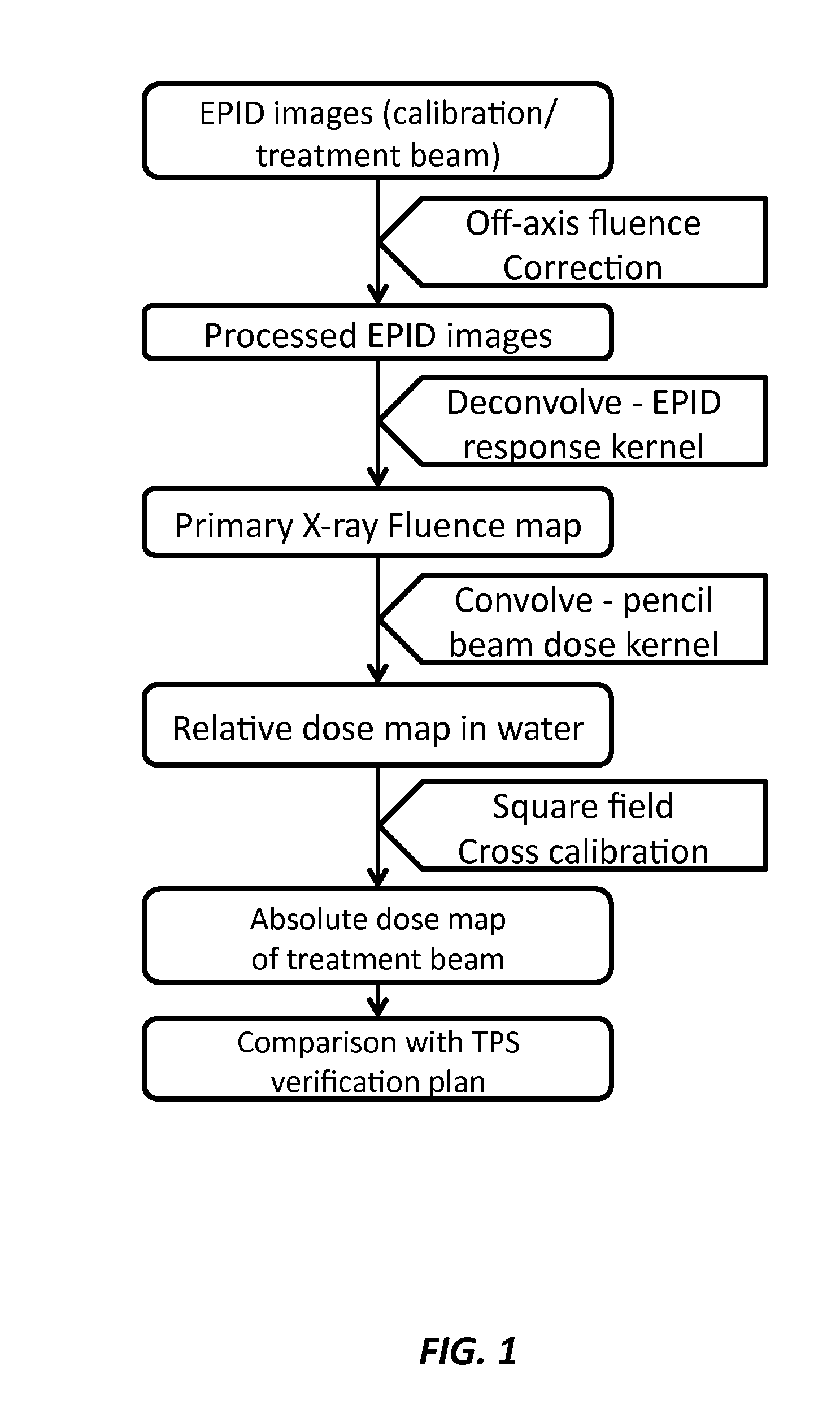
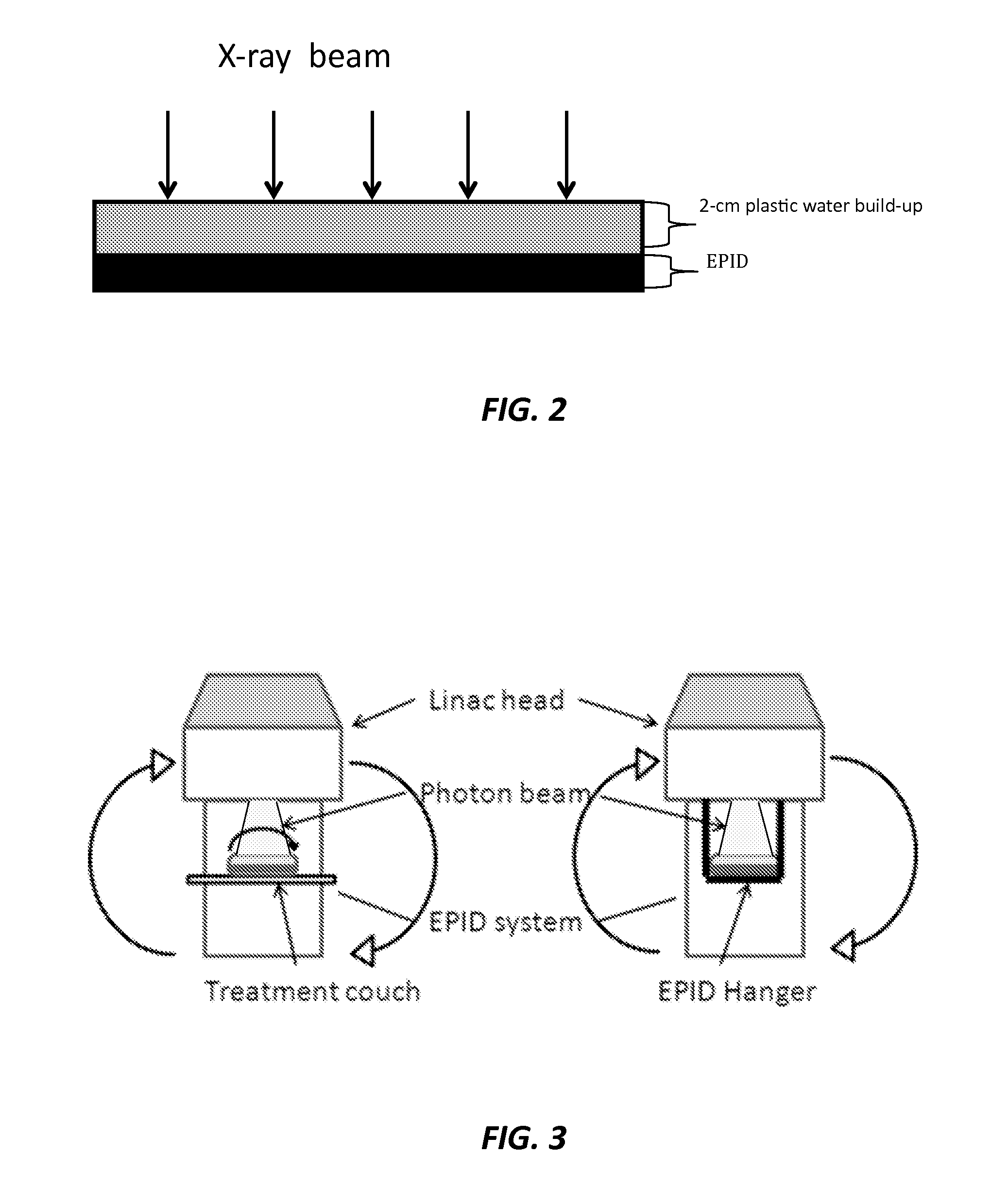
A method of electronic portal imaging (EPID) for radiation dosimetric measurement and quality assurance (QA) in radiation therapy is provided that includes imaging a calibration photon beam and a treatment beam using an EPID imager disposed between a plastic water build-up phantom and a plastic water back-scatter phantom that is thicker than the plastic water build-up phantom, correcting the EPID images using an off-axis correction map that takes into account a horn-shape of a photon fluence profile, deconvolving the corrected EPID images using a Monte Carlo simulated EPID response kernel, the deconvolved corrected EPID images provide a primary photon fluence map, reconstructing a relative dose map using the primary photon fluence map convolving with a Monte Carlo simulated pencil-beam dose distribution kernel, and generating an absolute dose map using cross calibration to a 10x10 cm2 square field that is compared with a planned dose distribution for QA analysis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Real time adaptive controller medication dosing
ActiveUS10255412B2Managing respiratory diseaseImprove adhesionDrug and medicationsMedical devicesApplication serverMedicine
Systems and methods for monitoring accurate, real-time medicament device events, performing analytics on that data, and providing notifications are described. In various embodiments, an application server receives controller medication events, analyzes the events, associated event times, and controller medication dosage plans to characterize event times and send notifications for future doses. The controller medication dosage plan may specify a dose time for a planned dose, a narrow time window comprising the dose time, and an expanded time window comprising the narrow time window and longer in duration than the narrow time window, and the events may be characterized based on their time relative to the dose time, the time windows, and other events.
Owner:RECIPROCAL LABS CORP D B A PROPELLER HEALTH
Interpolation algorithm for intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data based on gradient features
InactiveCN105389476AReduce generationReduced dose data distribution characteristicsComputer-assisted medicine prescription/deliverySpecial data processing applicationsIntensity-modulated radiation therapyPlanned Dose
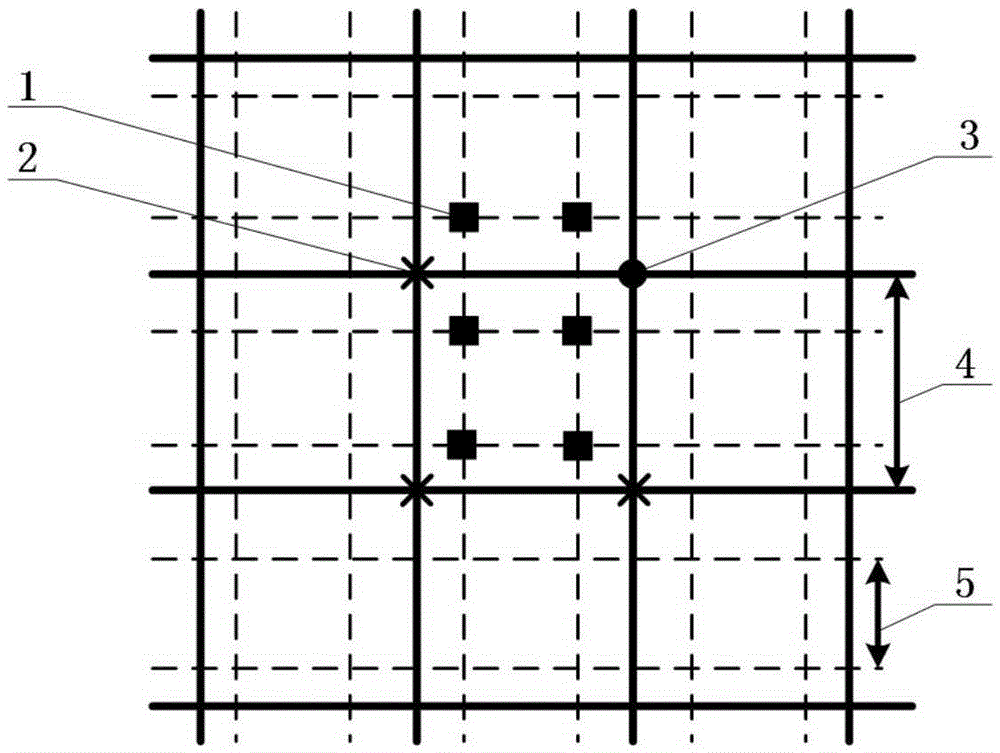
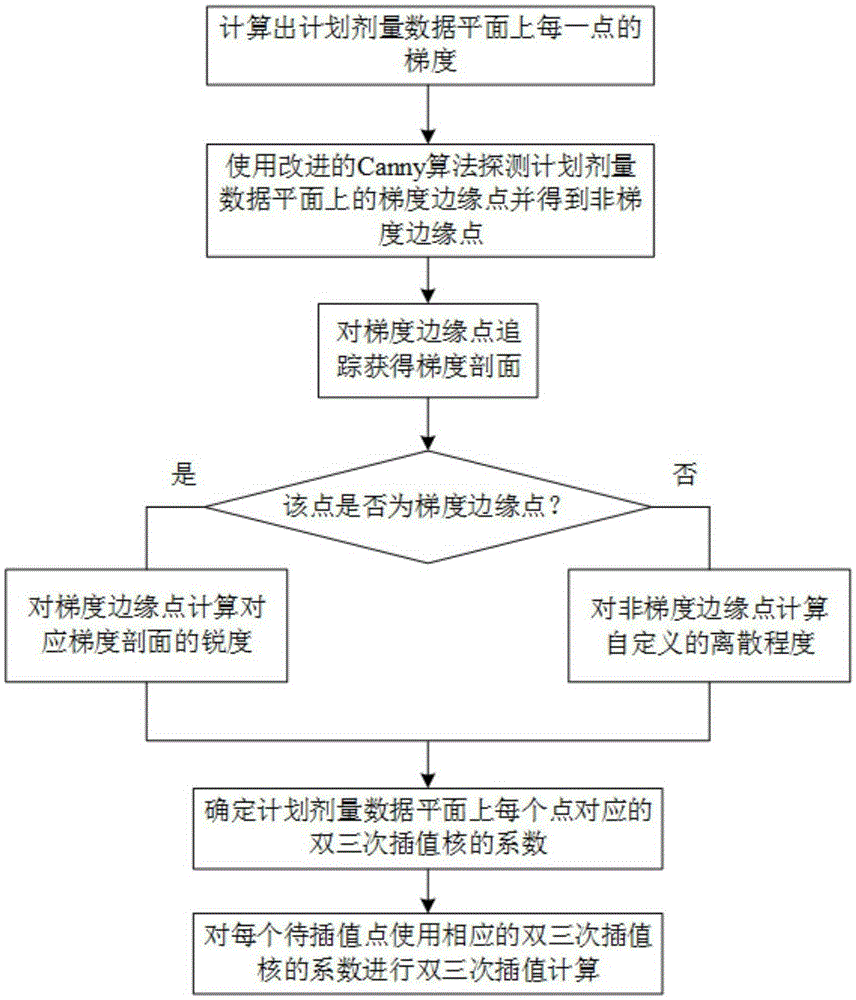
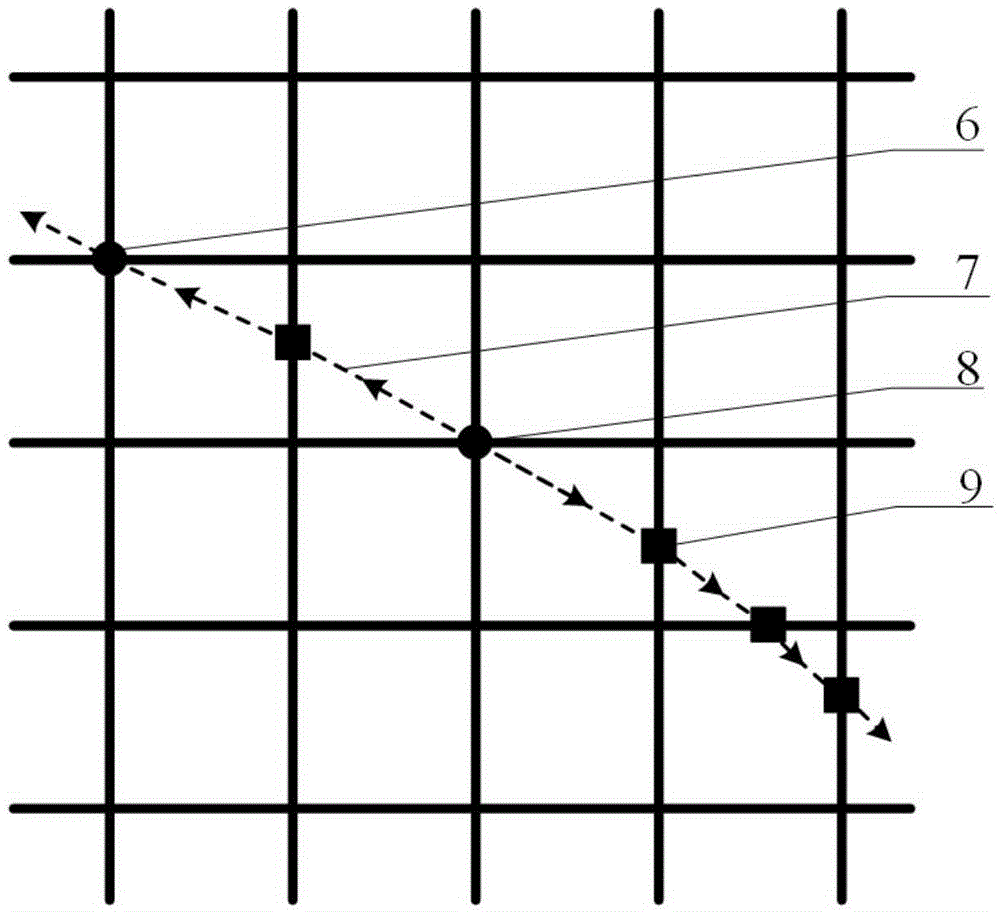
The invention relates to an interpolation algorithm for intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data based on gradient features, belonging to the technical field of intensity-modulated radiation therapies. The interpolation algorithm comprises the following steps: obtaining various gradient edge points and non-gradient edge points on an intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data plane by adopting an improved traditional Canny algorithm according to gradient features of the intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data plane; obtaining a coefficient of a bicubic interpolation kernel corresponding to each point on the intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data plane according to the acutance of a gradient profile corresponding to the obtained gradient edge points and the deviation coefficient corresponding to the non-gradient edge points; and performing bicubic interpolation of each point to be interpolated by using the coefficient of the bicubic interpolation kernel so as to obtain the intensity-modulated radiation therapy plan dose data of each point to be interpolated. The interpolation algorithm disclosed by the invention overcomes the smoothing effect of the traditional bilinear interpolation while the error is reduced; and the original gradient information is reserved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for reducing diagnostic radiation dose in image guided radiotherapy
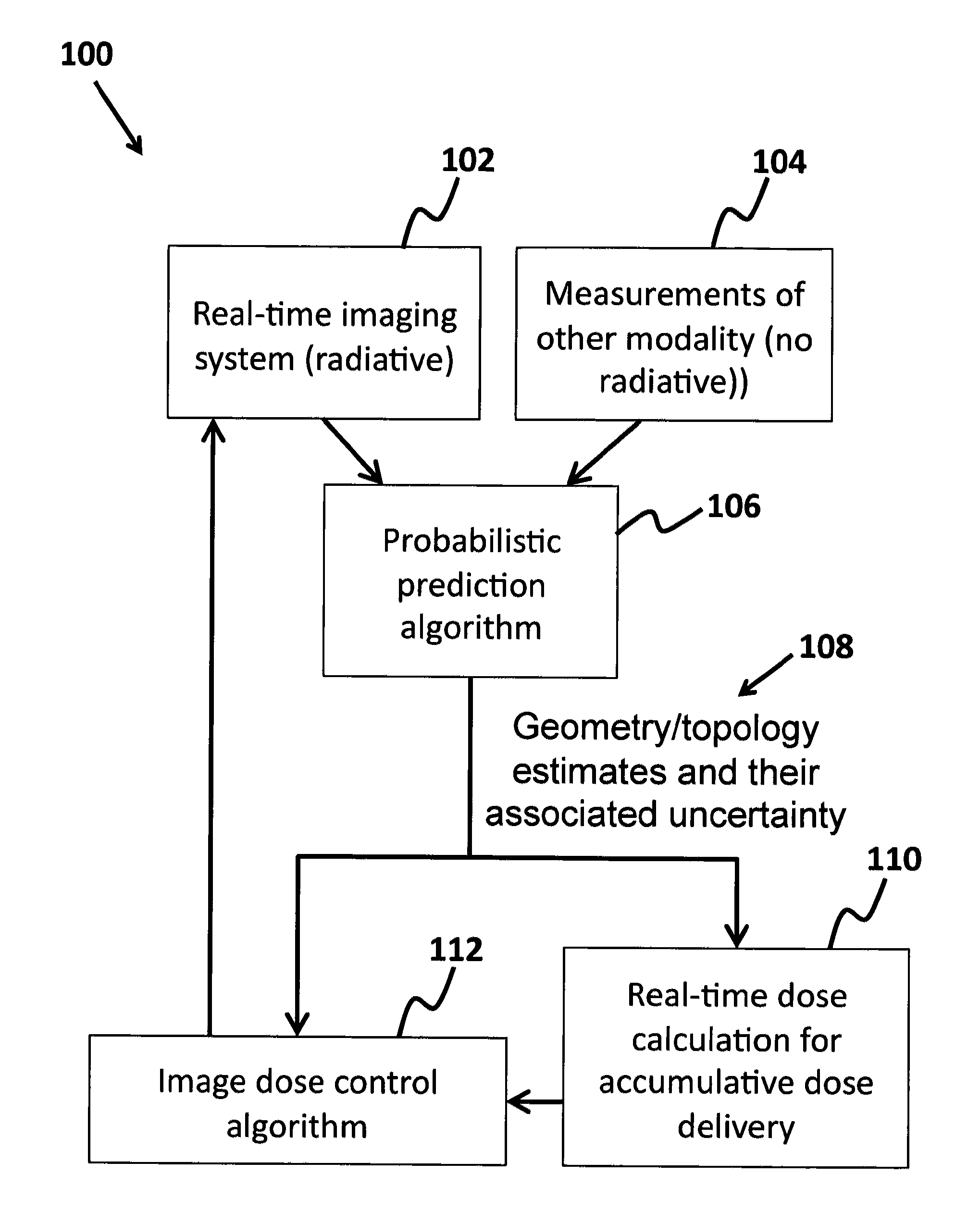
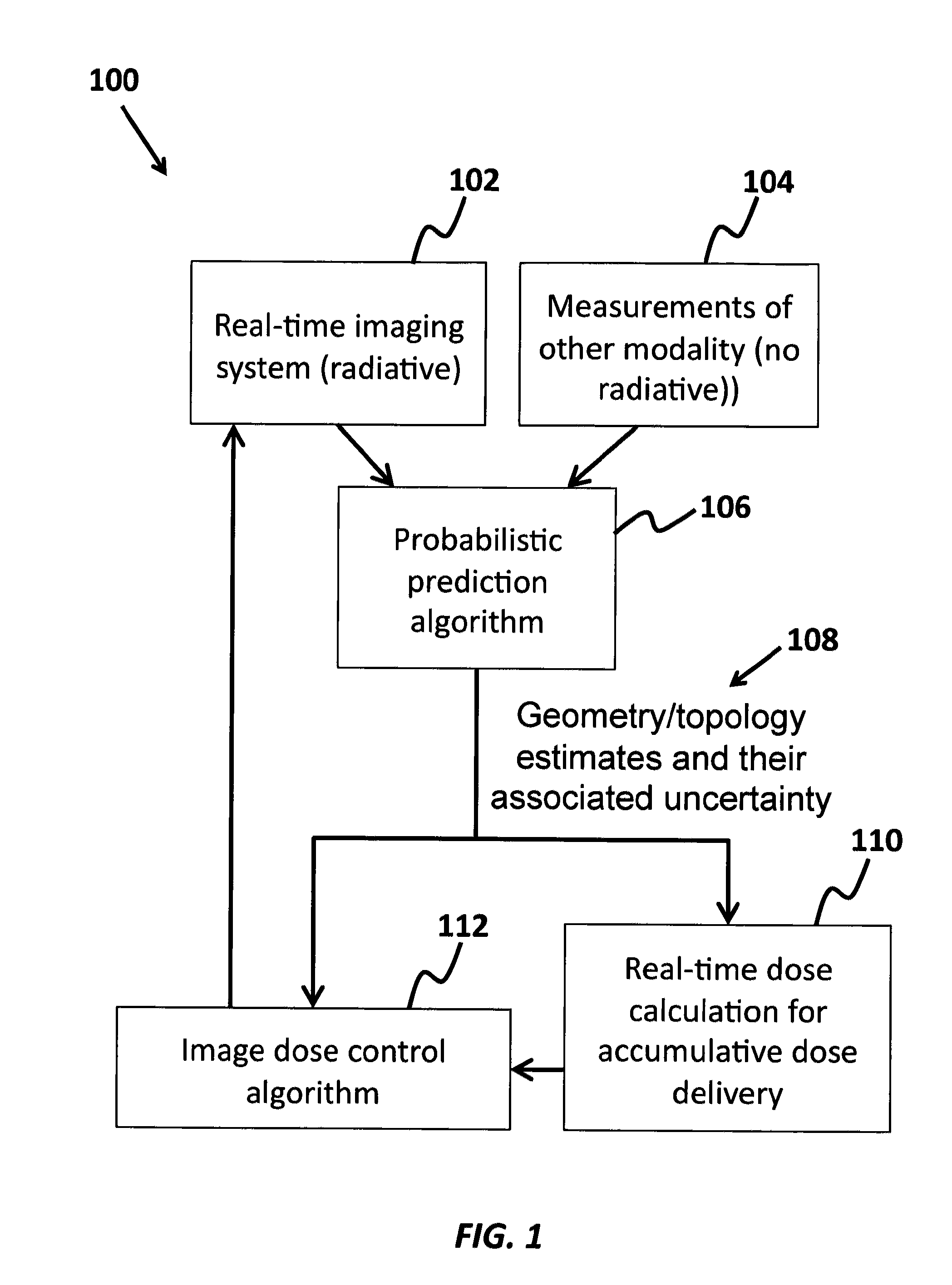
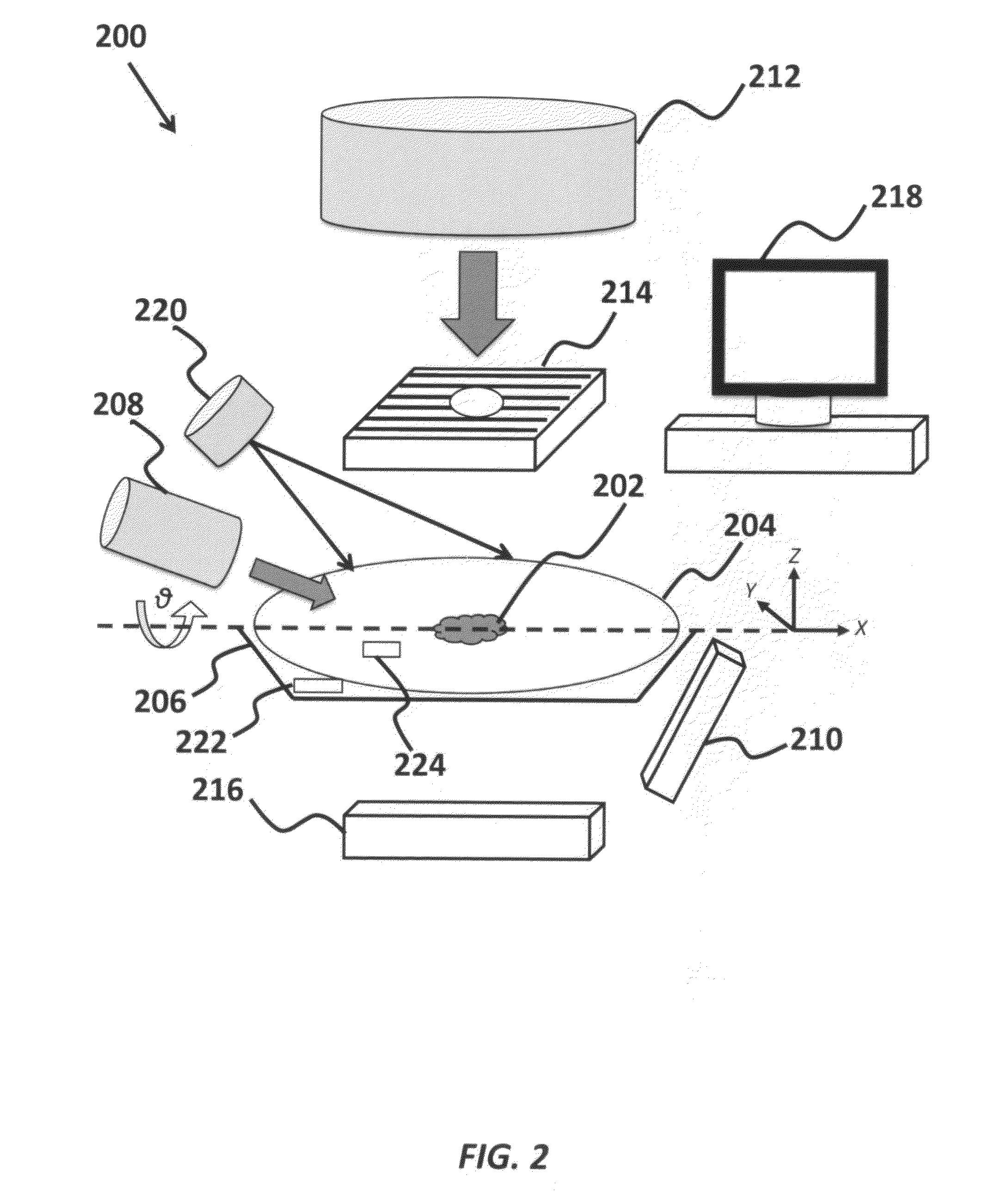
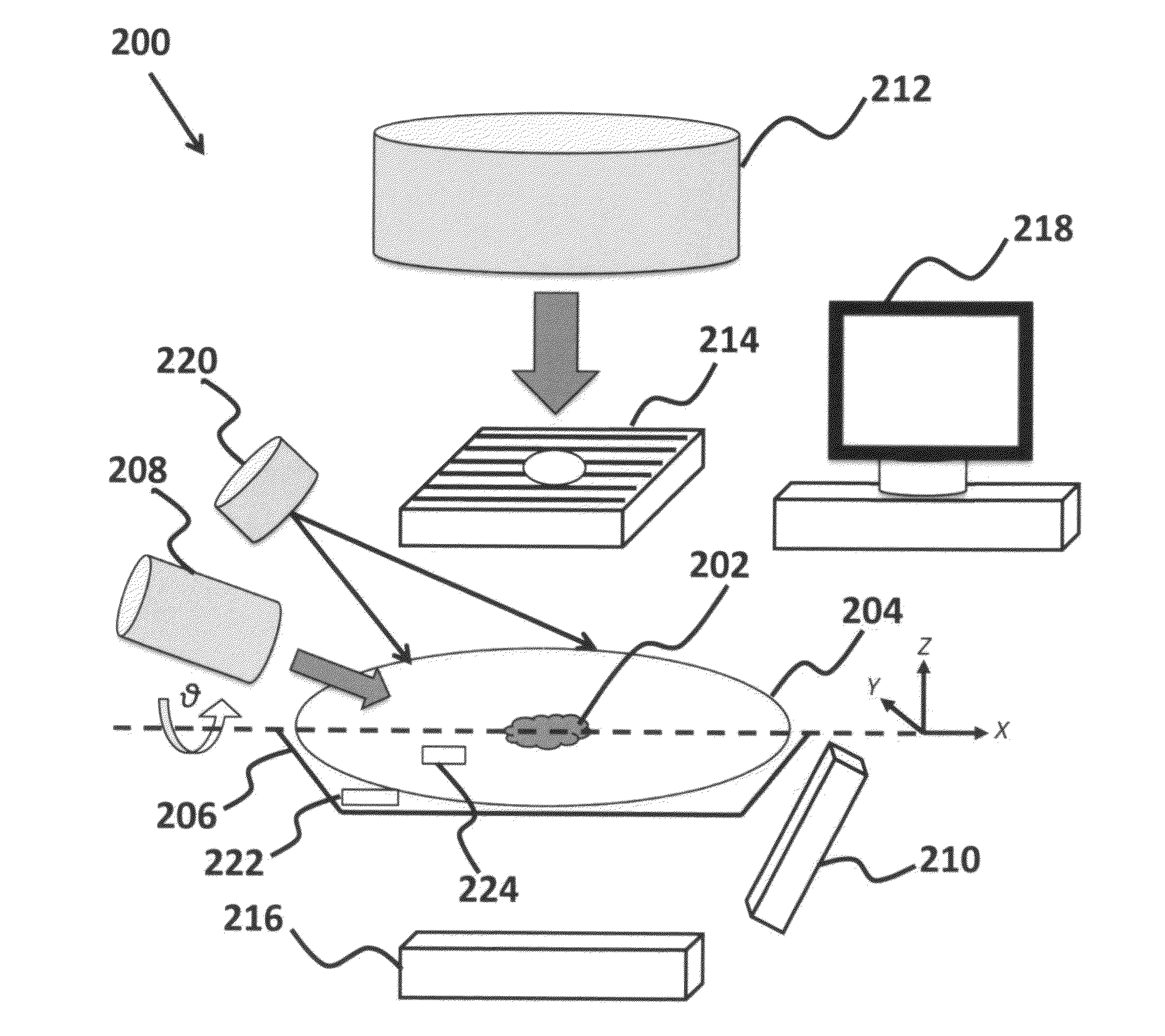
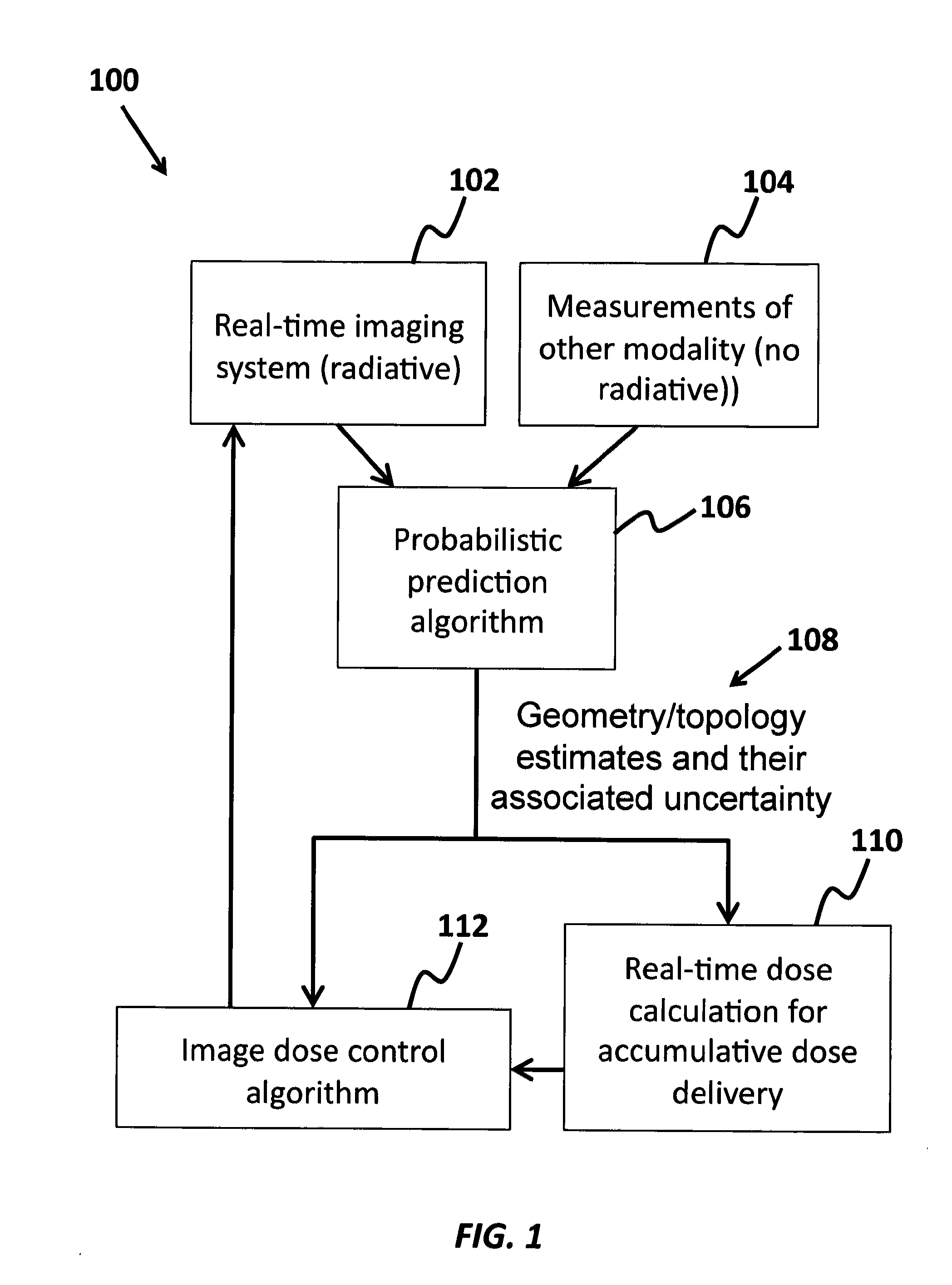
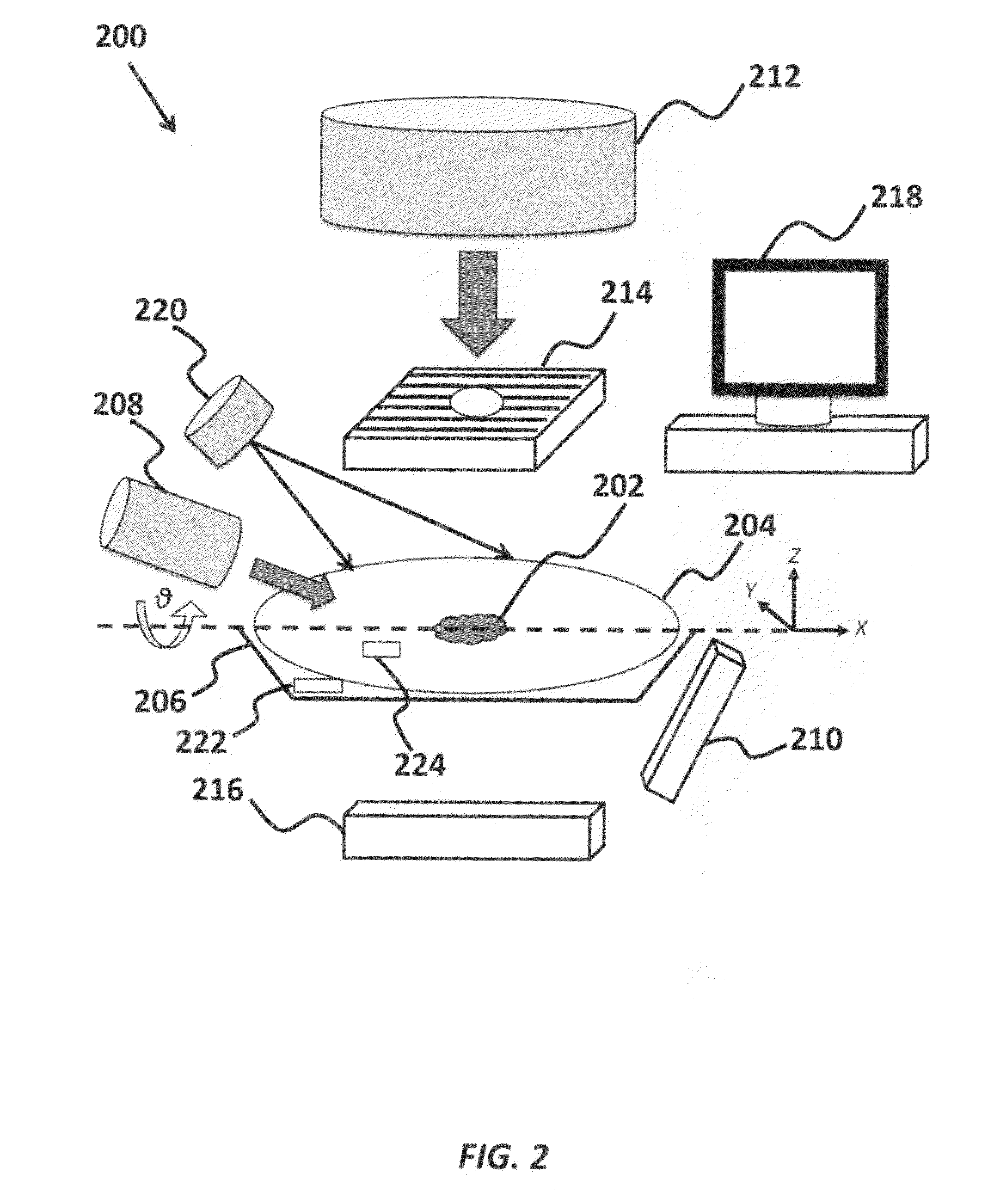
InactiveUS8837674B2Minimize ToxicityIncrease agreementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsAdaptive imaging
A method of minimizing radiation toxicity in image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is provided that includes using a probabilistic prediction algorithm that is operated on a suitably programmed computer and includes multimodality inputs and provides real-time geometric and topological target estimates to compensate for system latency, using an online adaptive imaging system that provides radiographic images of the target when the geometric and topological target estimates are in a region of predefined uncertainty, and using an image dose control algorithm, operating on a suitably programmed computer, that includes parameters for controlling dose per image, where instances for image acquisition are optimized according to a planned dose pattern and delivery result.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for reducing diagnostic radiation dose in image guided radiotherapy
InactiveUS20120076270A1Minimizing radiation toxicityMinimize ToxicityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsAdaptive imaging
A method of minimizing radiation toxicity in image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is provided that includes using a probabilistic prediction algorithm that is operated on a suitably programmed computer and includes multimodality inputs and provides real-time geometric and topological target estimates to compensate for system latency, using an online adaptive imaging system that provides radiographic images of the target when the geometric and topological target estimates are in a region of predefined uncertainty, and using an image dose control algorithm, operating on a suitably programmed computer, that includes parameters for controlling dose per image, where instances for image acquisition are optimized according to a planned dose pattern and delivery result.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
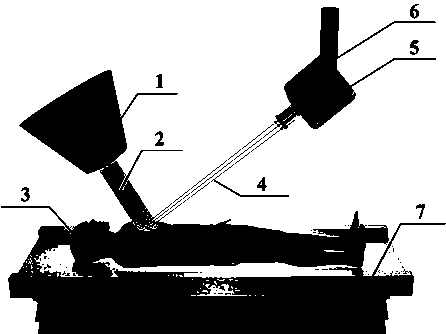
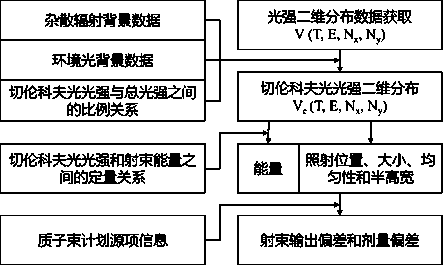
Real-time monitoring method for particle radiotherapy beam
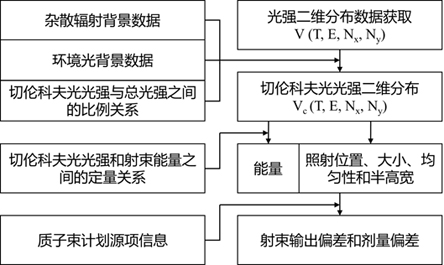
ActiveCN109893778AGuaranteed protective effectEnsure safetyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle radiotherapyPlanned Dose
The invention discloses a real-time monitoring method for a particle radiotherapy beam. The monitoring method comprises the following steps: the irradiation position, size, shape, uniformity and half-height width of a proton beam can be monitored in real time according to two-dimensional distribution of Cherenkov light intensity; actual output energy of the proton beam can be determined on the basis of the quantitative relationship between Cherenkov light intensity and the energy of the proton beam; the dose deviation value can be calculated according to the real-time deviation information ofbeam output. The novel method is simple, practical, stable and reliable and capable of comprehensively monitoring beam information (including energy, irradiation position, size, uniformity and half-height width) in the proton radiotherapy process in real time, and accurate supply of the planned dose can be effectively ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Evaluation of dose accuracy of radiation therapy treatment plans
ActiveUS20190143147A1Reduce in quantityVerified and reliableMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMass parameterPlanned Dose
The invention relates to a system and a method for evaluating a treatment plan for an external radiation therapy treatment, the treatment plan comprising parameters for controlling an external radiation therapy apparatus during the treatment. The system comprises a database storing historic treatment plans and storing for each historic treatment plan a quality parameter indicative of whether a deviation between a planned dose distribution and a measured dose distribution resulting from an execution of the treatment plan is within an acceptable limit. An evaluation unit determines a threshold value for each of a plurality of treatment plan metrics based on the historic treatment plans and the associated quality parameters. Further, the evaluation unit calculates a value of each of the metrics for the treatment plan and compares the value of each of the metrics with the threshold value determined for the respective metric.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Dose planning system
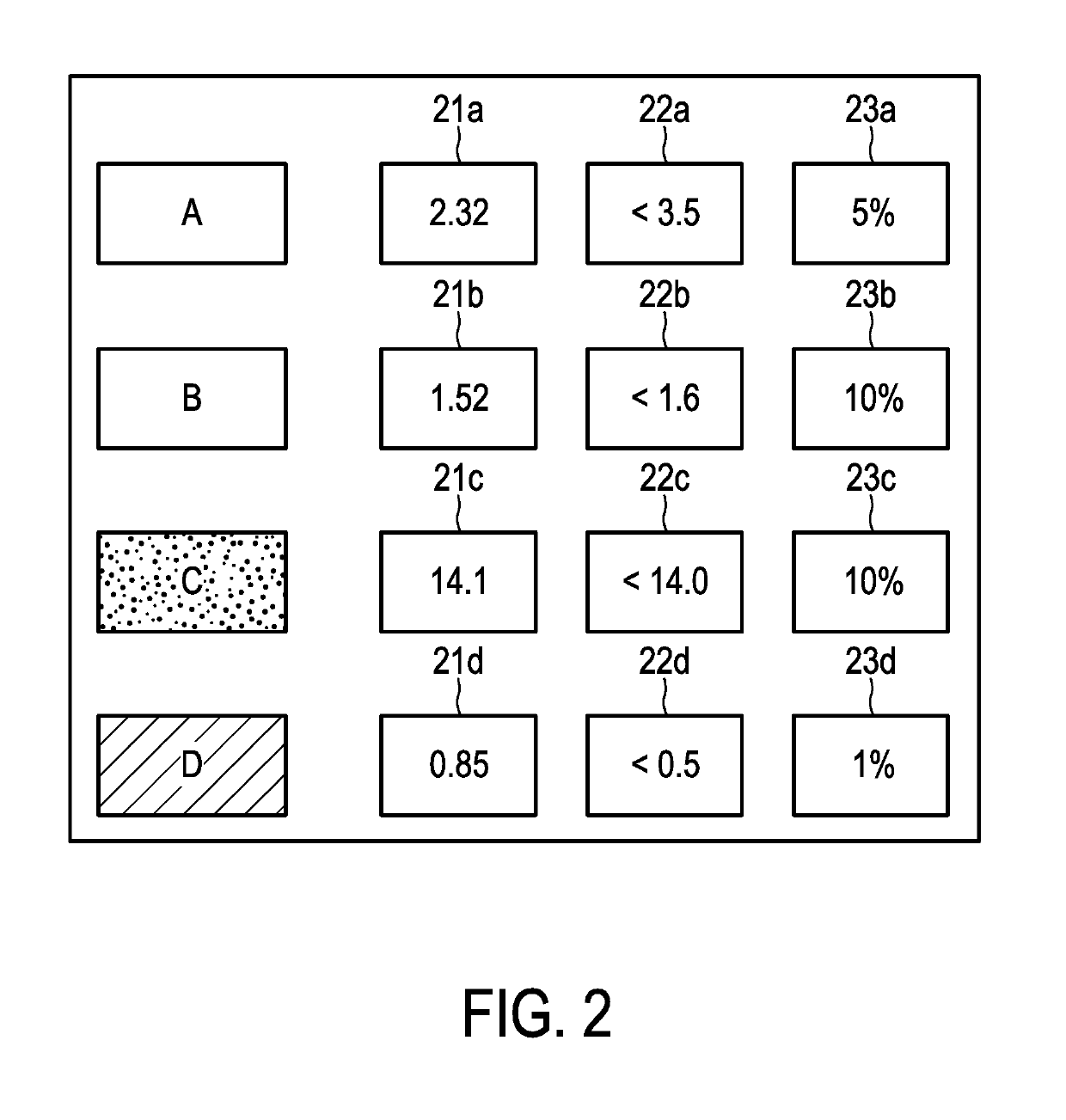
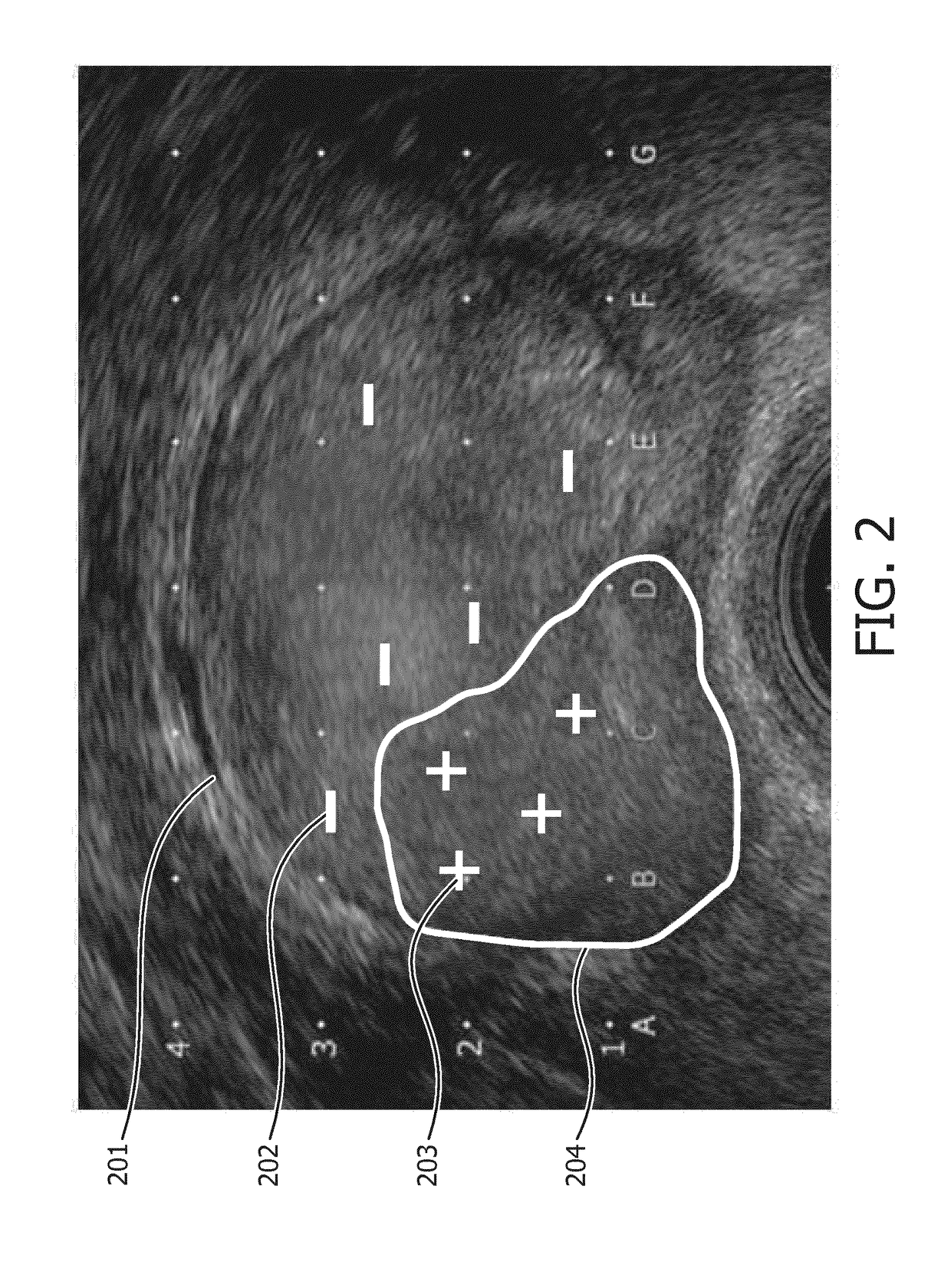
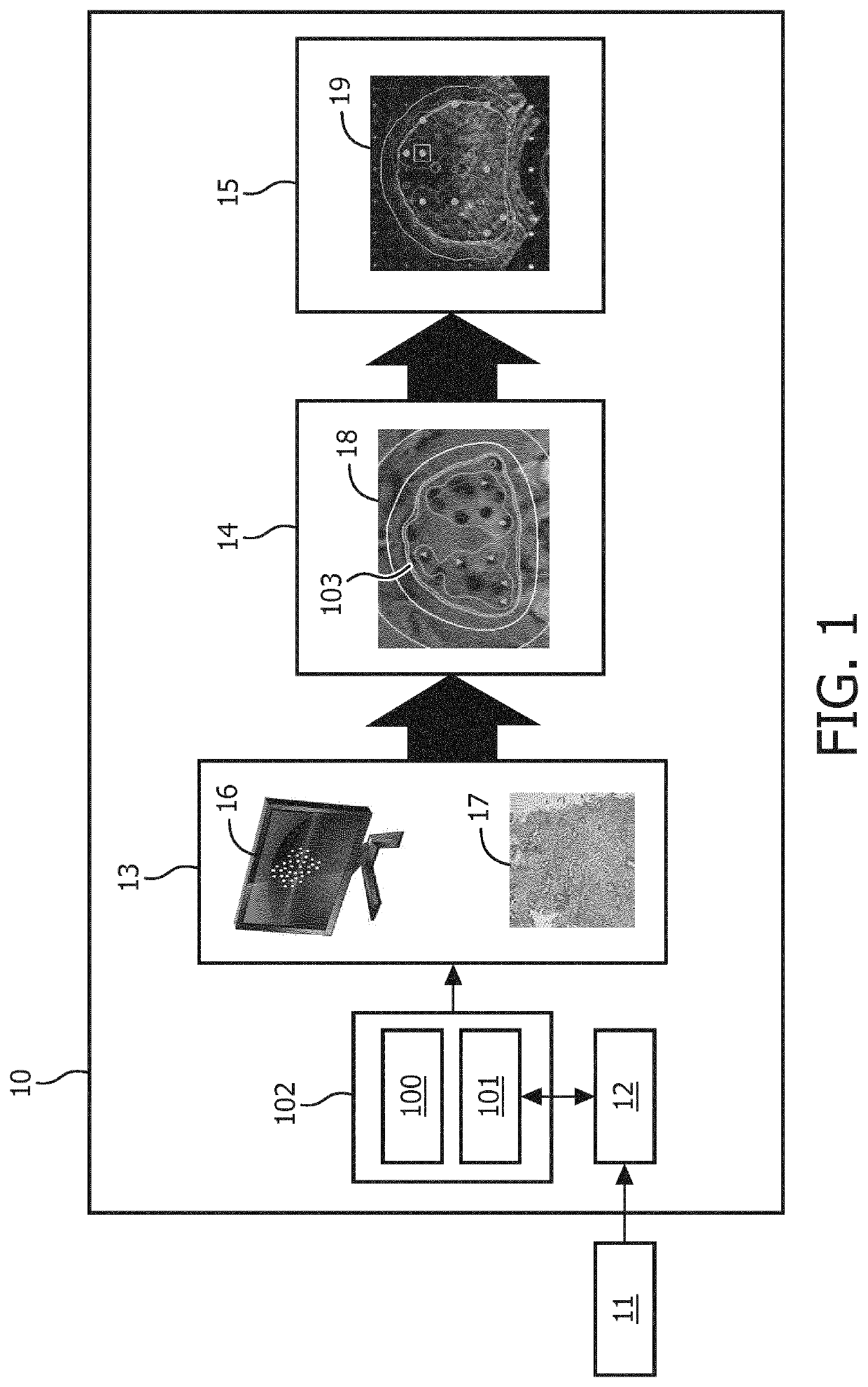
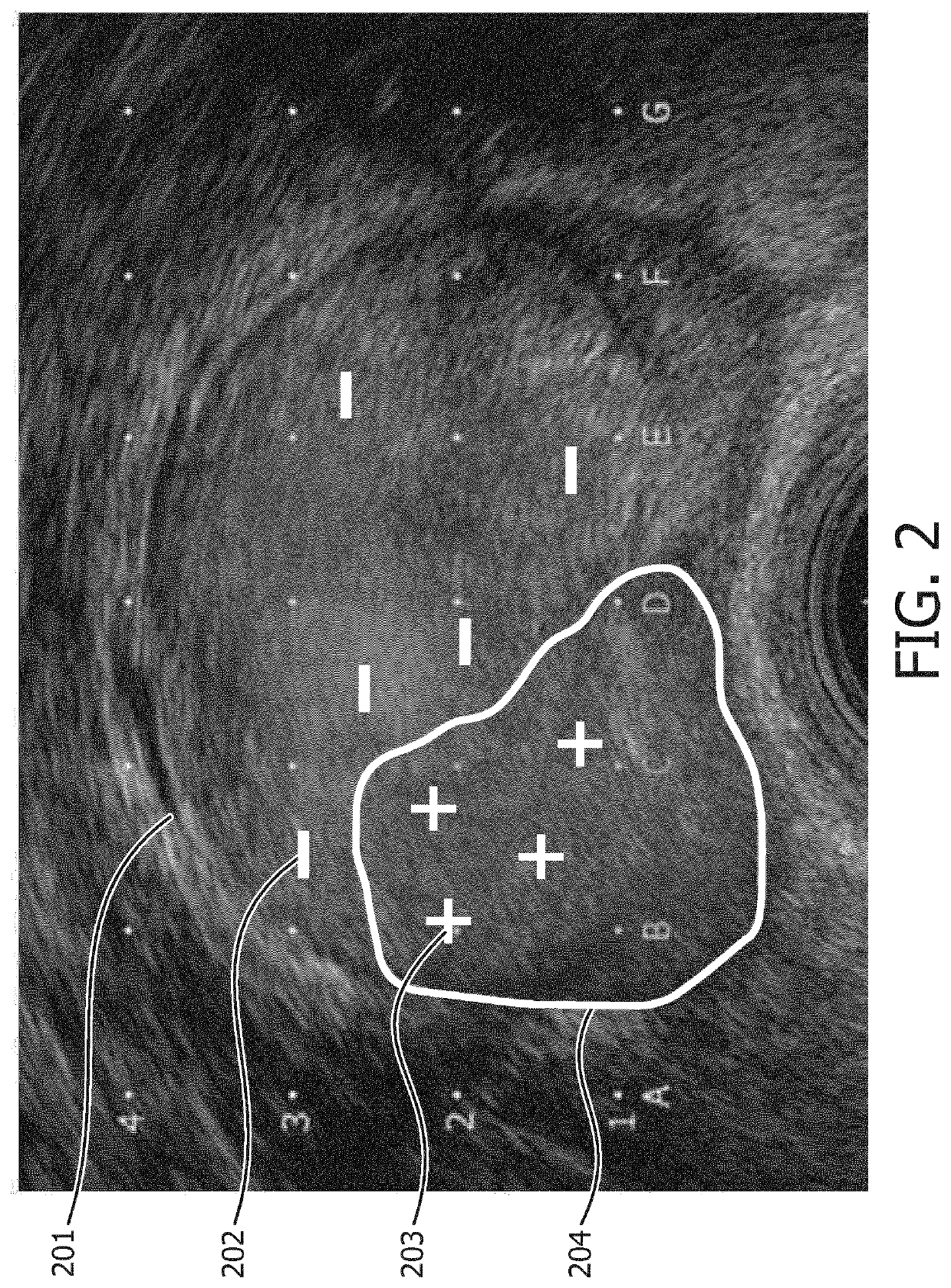
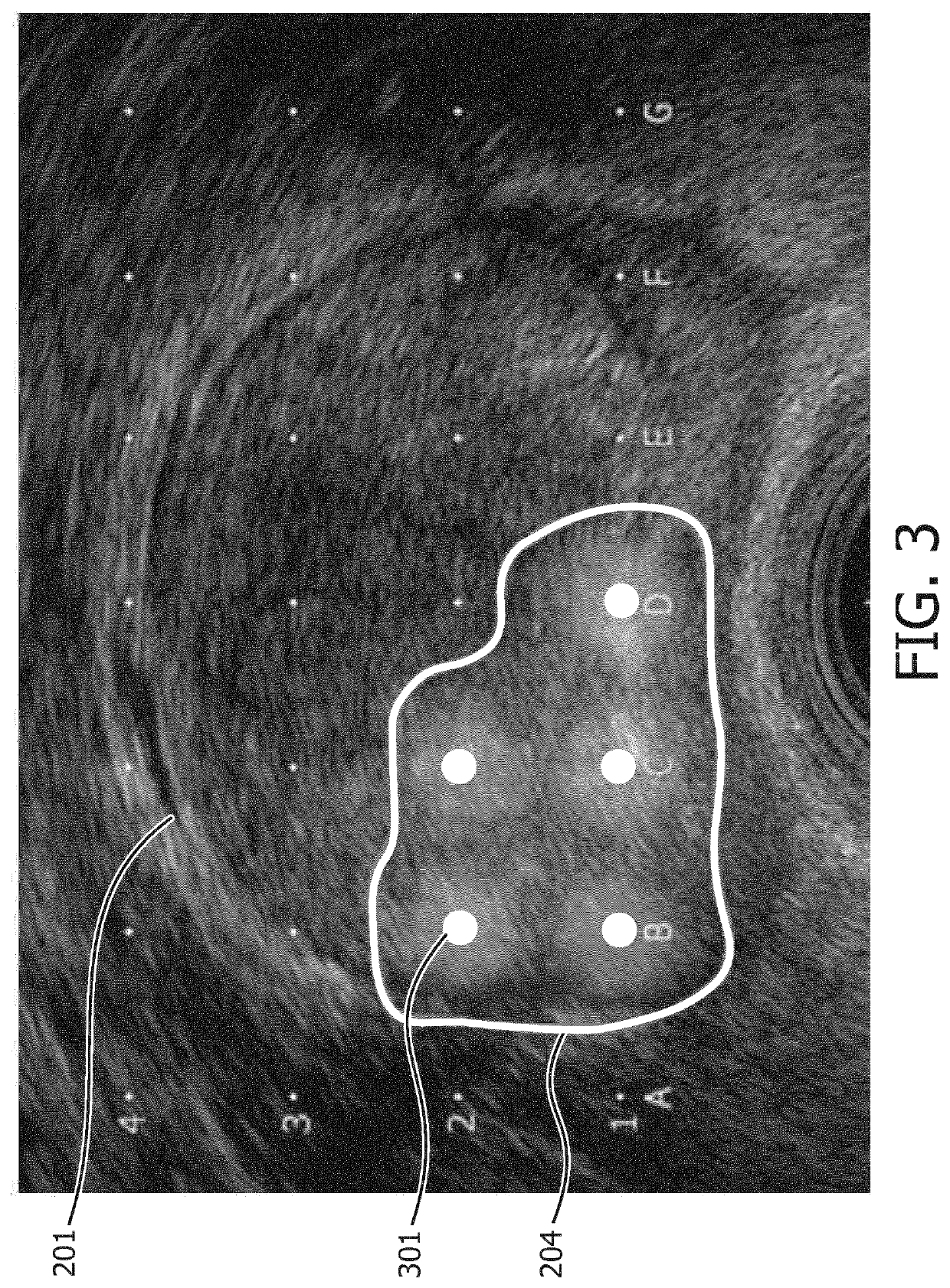
ActiveUS20180153619A1Speed up diagnosis to treatment processPrecise delineation of tumour tissue may be complicatedDrug and medicationsSurgical needlesTissue characterizationDose planning
It is an object of the invention to improve treatment planning. This object is achieved by a dose planning system comprising a biopsy map creation module configured for receiving biopsy information for an organ of interest regarding biopsy locations and tissue characteristics of tissue found at the biopsy locations, wherein the biopsy map creation module is further configured for creating a spatially annotated biopsy map for the organ, by linking the spatial information on the biopsy locations to the tissue characteristics of tissue found at the corresponding biopsy locations. The dose planning system further comprises a probability map calculation module configured for creating a tumour probability map by calculating a tumour probability for locations in the organ from which no biopsy was taken by using the tumour and / or tissue characteristics from the biopsy locations and a dose planning module configured for creating a dose plan based on the tumour probability map, wherein planning constraints are such that on average a higher tumour probability results in a higher planned dose and a lower tumour probability results in a lower planned dose.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
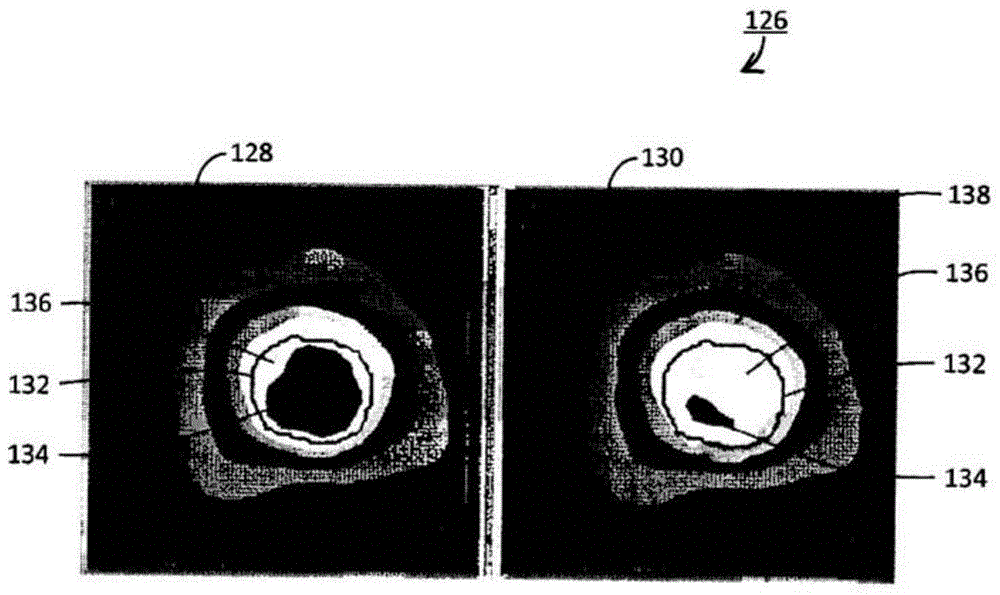
Method of using the novel polymer gel for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) validation
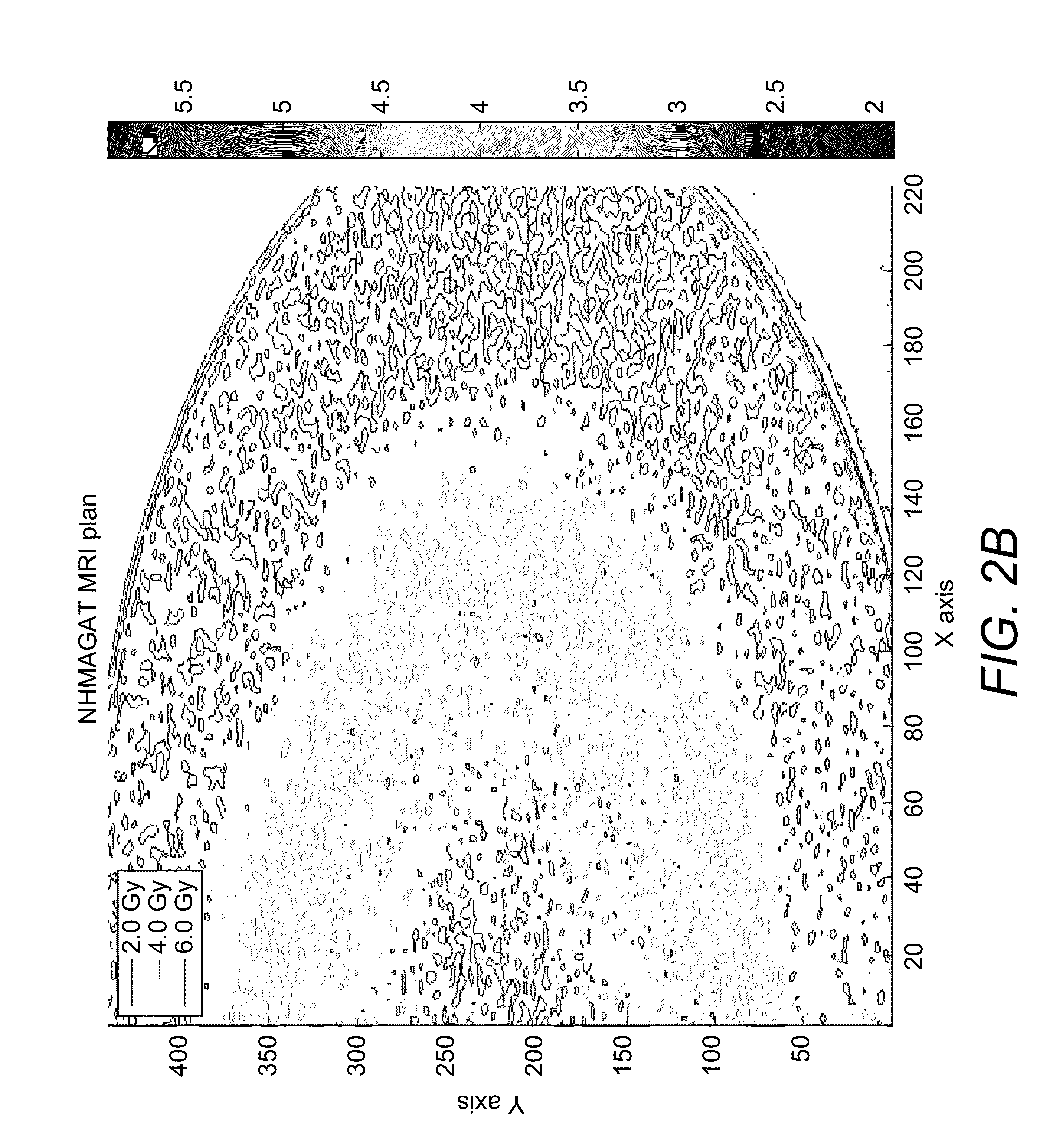
Novel normoxic N-(Hydroxymethyl) acrylamide (NHMAGAT) polymer gel dosimeters for MRI scanning are introduced for radiotherapy planning system. The composition of the NHMAGAT polymer gel and method of making the NHMAGAT polymer gel dosimeter are disclosed. The dosimeters are irradiated with Varian Rapid Arc linear systems at different absorbed doses. The results show that the percent depth dose and 2D plan dose distribution of NHMAGAT polymer gel dosimeters are in a good agreement with the ionization chamber measurements and CT planned dose distribution, respectively.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Mitigation of interplay effect in particle radiation therapy
ActiveUS20180280729A1Reduce impactTreatment safetyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle radiotherapyMedicine
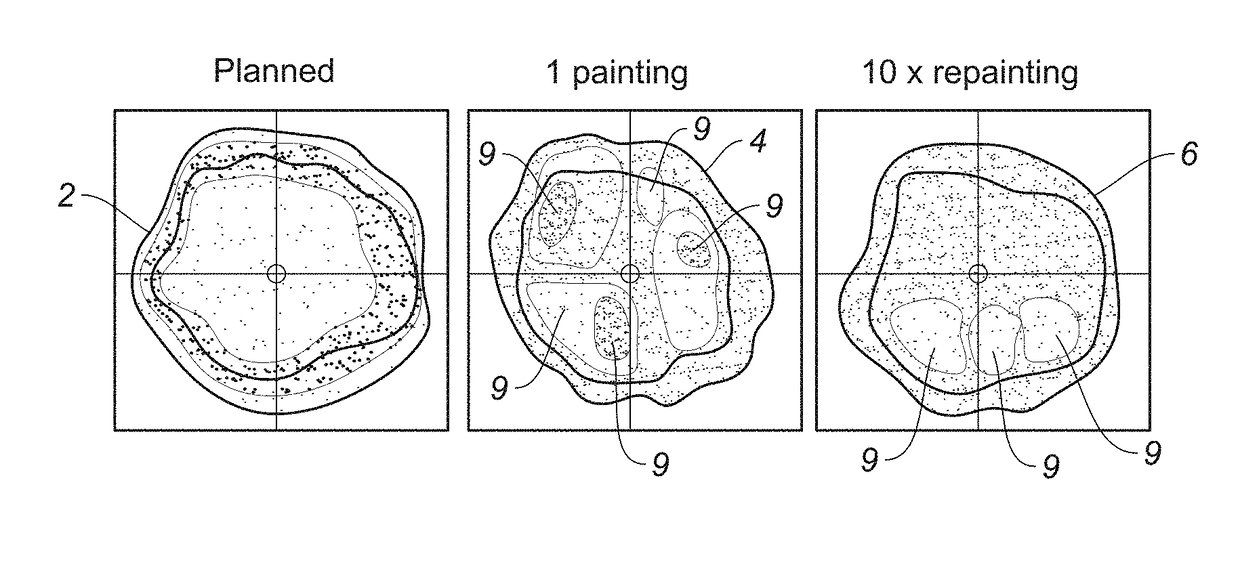
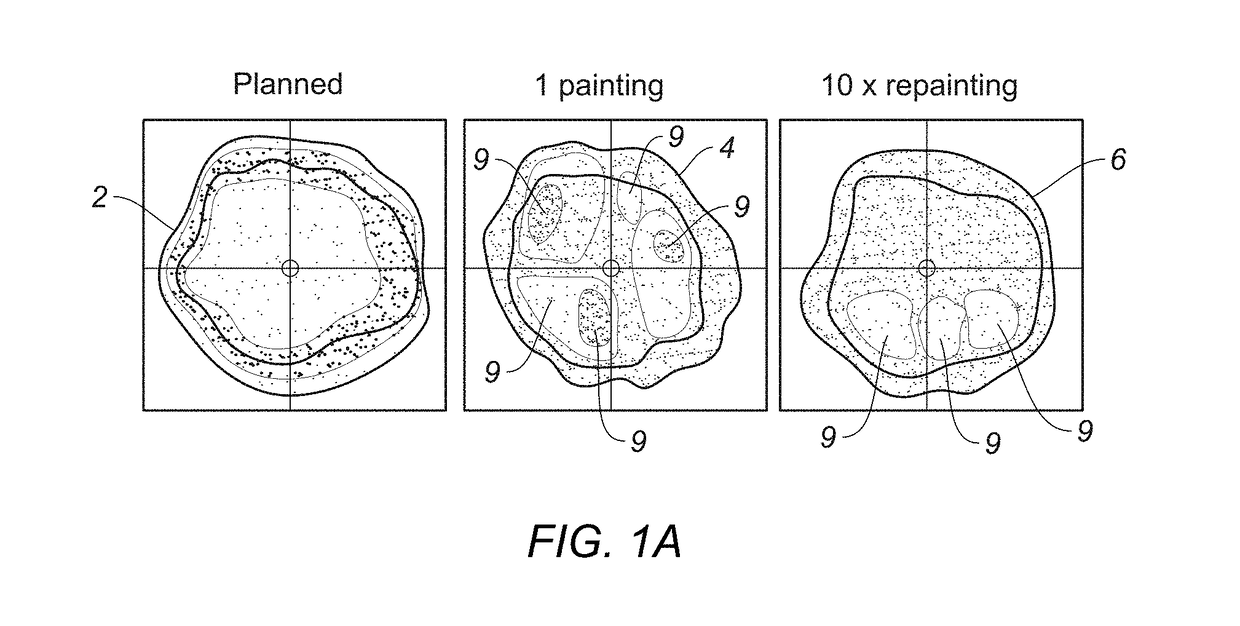
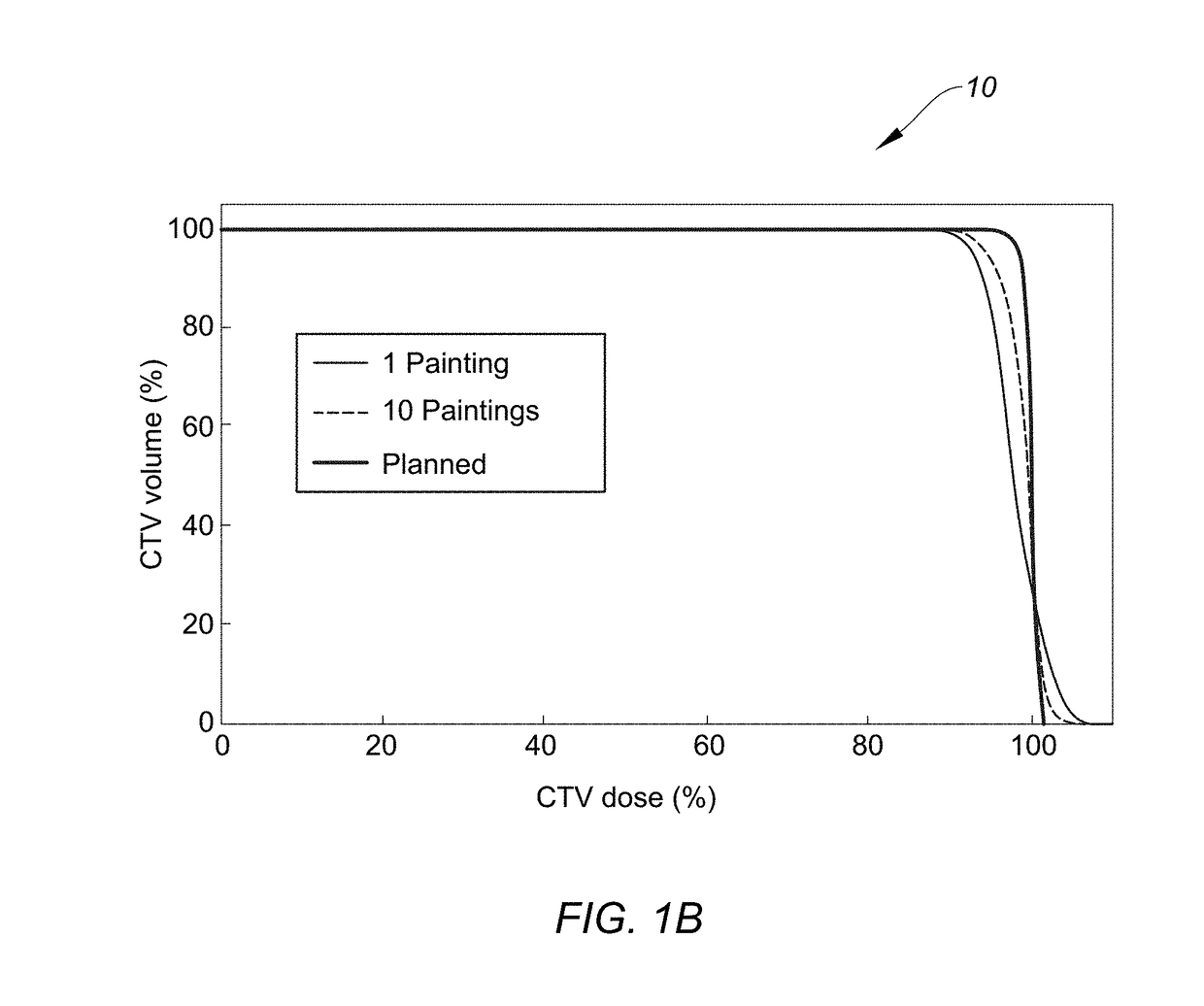
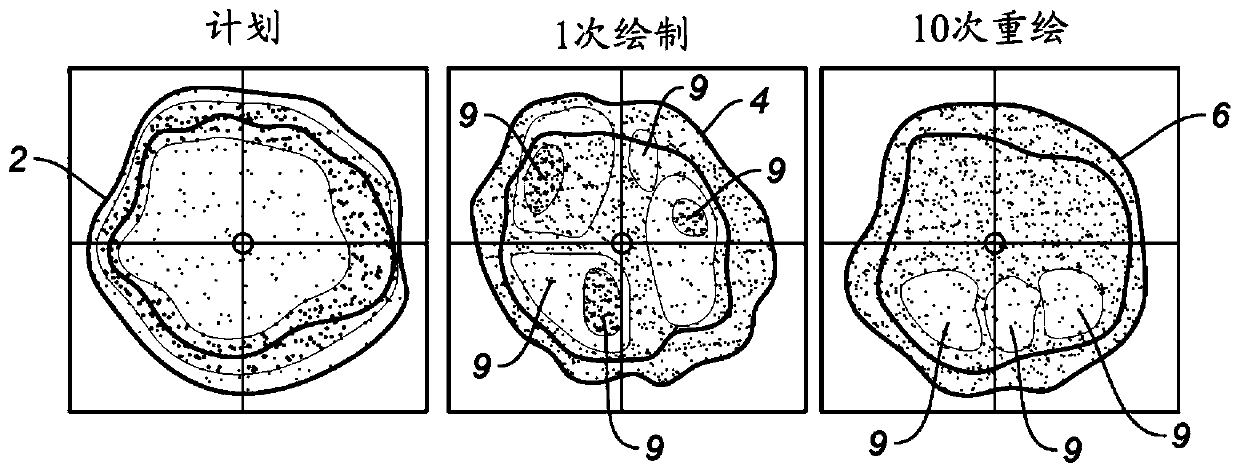
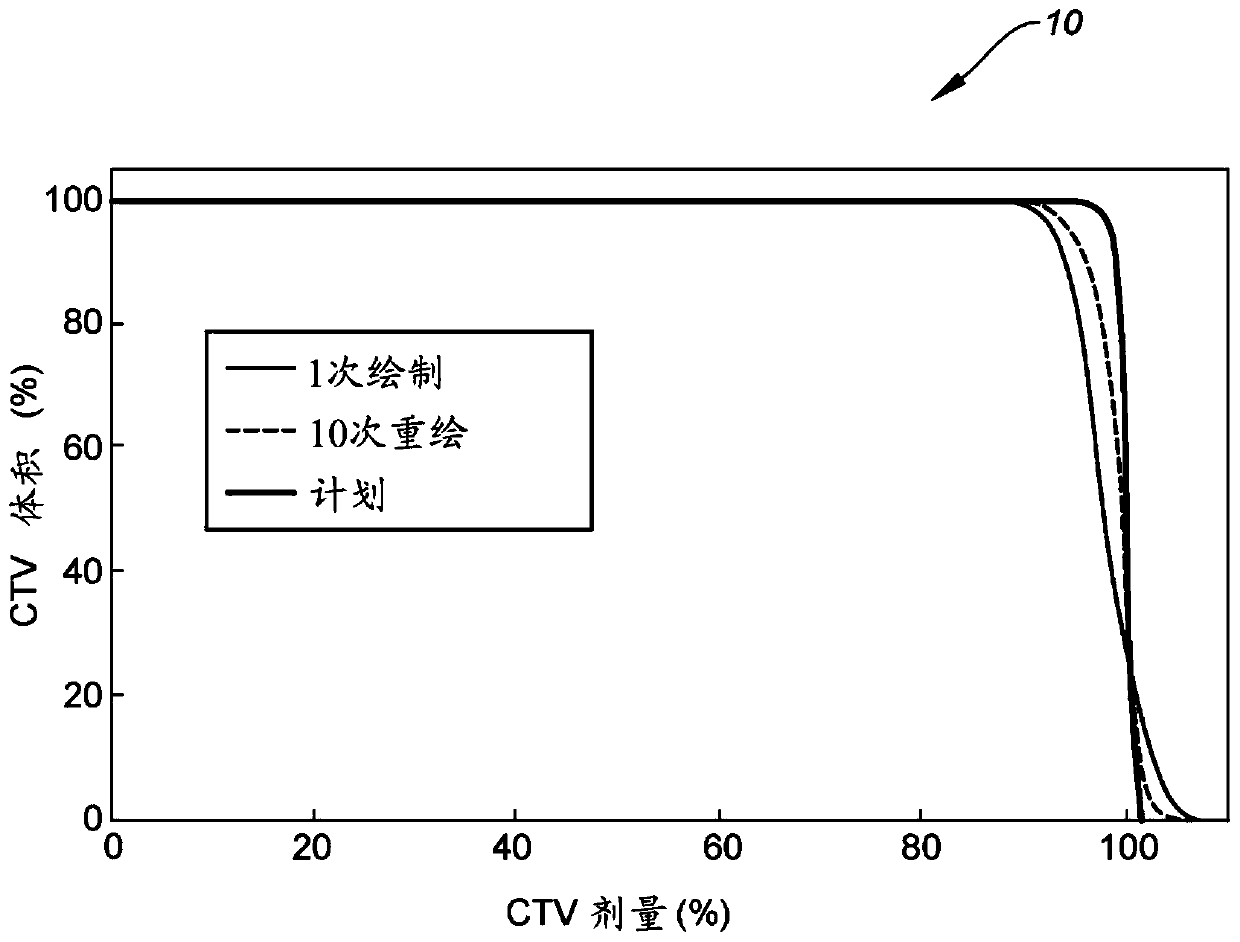
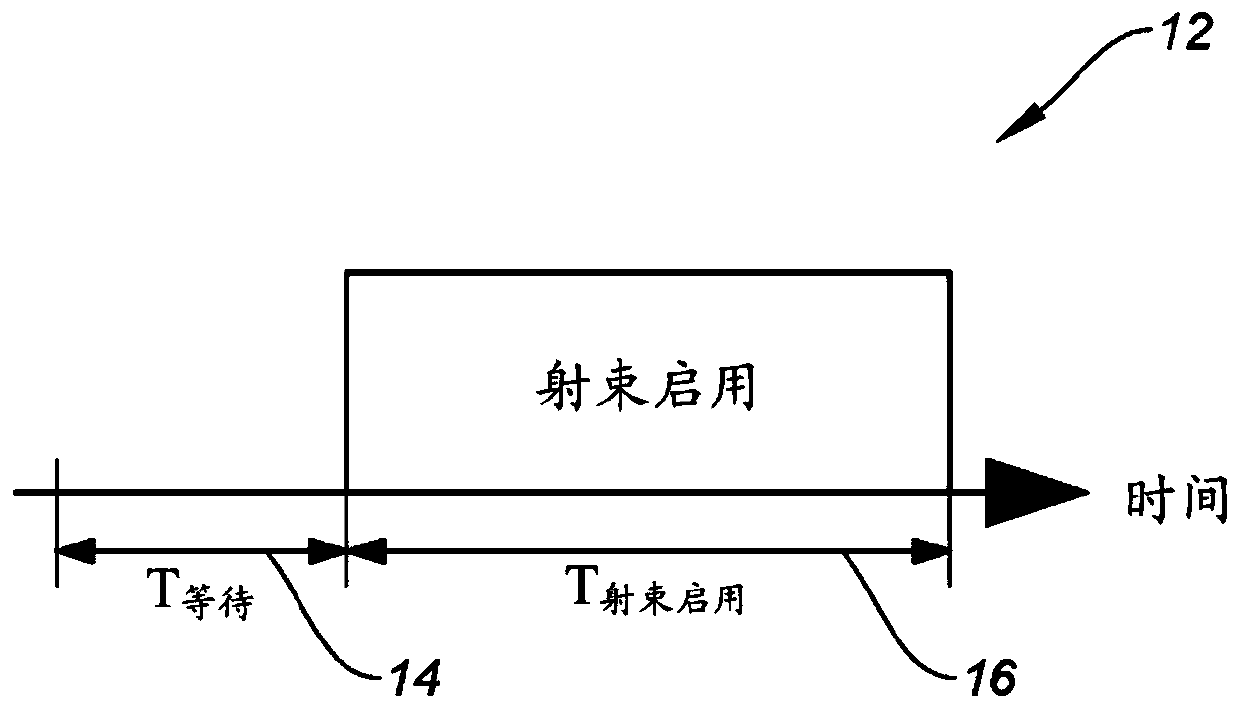
The present disclosure relates to a new scan technique for particle radiation therapy that may be used for cancer treatment. One embodiment relates to a method of mitigating interplay effect in particle radiation therapy in a moving target including a period of movement, where the particle radiation therapy defines a planned dose in each spot of each layer of the moving target. The method comprising dividing the planned dose in each spot into a number of spot repaintings; and generating a scan pattern for each layer by defining a beam-on time at each spot for each spot repainting, and calculating a wait time between consecutive beam-on times to distribute the spot repaintings for each spot of a respective layer are distributed over a duration of an integer number of periods of movement.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Mitigation of interplay effect in particle radiation therapy
The present disclosure relates to a new scan technique for particle radiation therapy that may be used for cancer treatment. One embodiment relates to a method of mitigating interplay effect in particle radiation therapy in a moving target including a period of movement, where the particle radiation therapy defines a planned dose in each spot of each layer of the moving target. The method comprising dividing the planned dose in each spot into a number of spot repaintings; and generating a scan pattern for each layer by defining a beam-on time at each spot for each spot repainting, and calculating a wait time between consecutive beam-on times to distribute the spot repaintings for each spot of a respective layer are distributed over a duration of an integer number of periods of movement.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST PARTICLE THERAPY GMBH & CO KG +1
Intensity modulated proton therapy (IMPT) plan optimization based at least on internal organ anticipated movement and/or expected deformation
ActiveUS20200261743A1Minimizes valueX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyNuclear medicinePlanned Dose
A method includes generating a nominal dose distribution based on an image and clinical goals. The method further includes generating a setup error dose distribution based on range and setup uncertainties. The method further includes generating a dose distribution for a parameter of an internal organ. The method further includes optimizing a planned dose distribution of an intensity modulated proton therapy plan by minimizing a total objective value including the nominal dose distribution, the setup error dose distribution dose distribution, and the dose distribution for the internal organ. The method further includes generating a final dose distribution for the intensity modulated proton therapy plan based on beam parameters of the optimized planned dose distribution. The method further includes controlling a proton therapy apparatus configured to deliver proton therapy based on the intensity modulated proton therapy plan with the optimized planned dose distribution.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
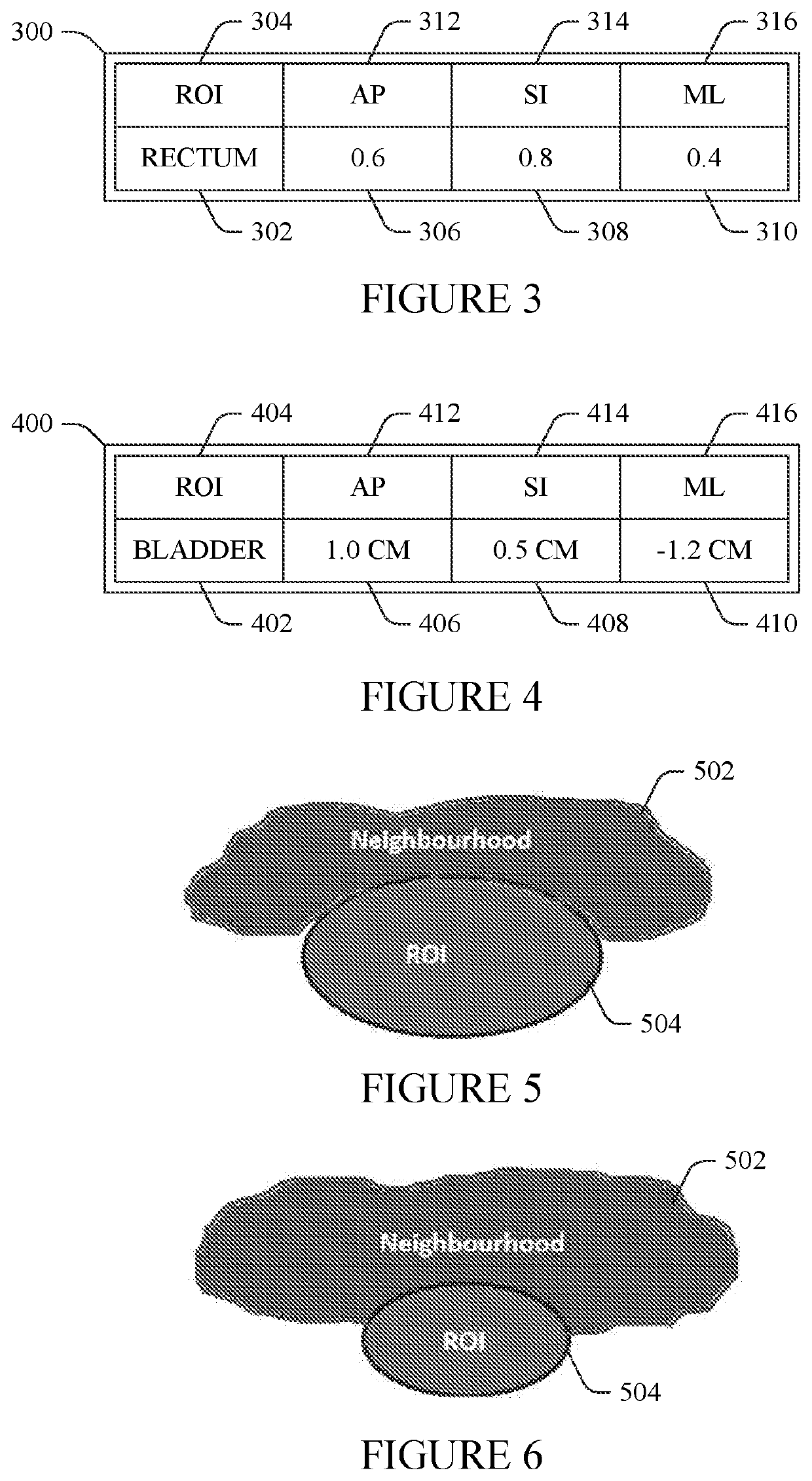
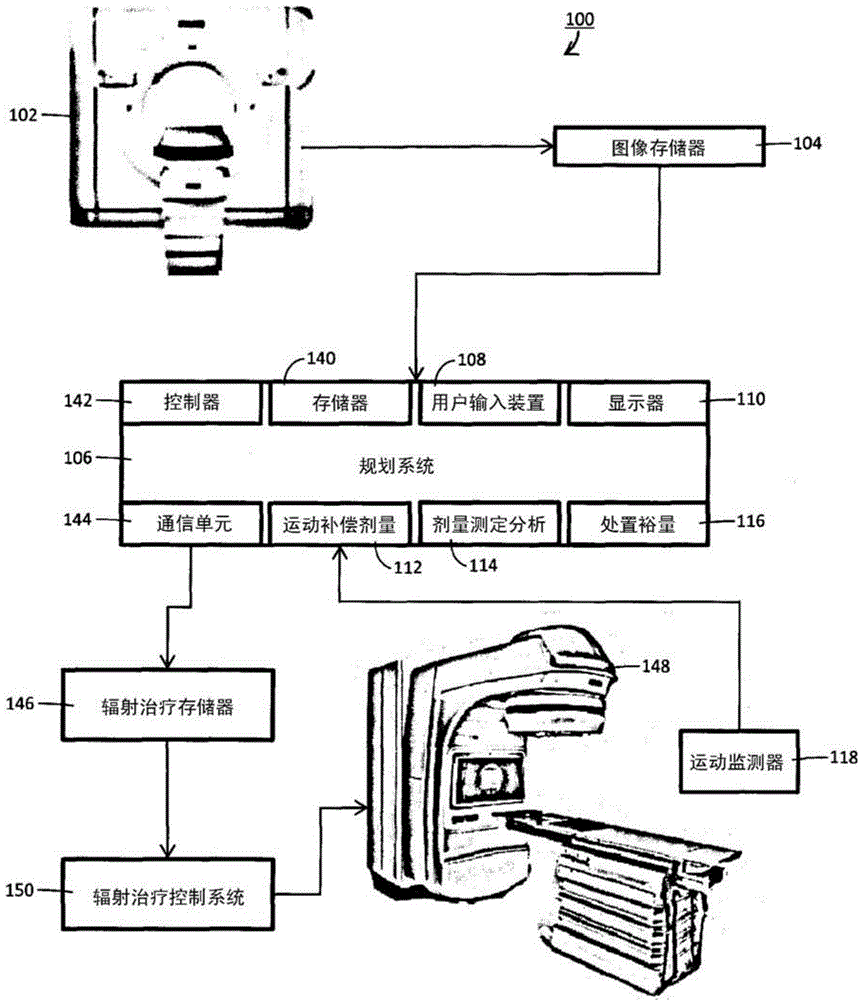
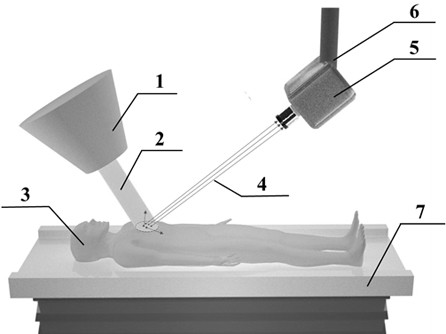
Studying the dosimetric impact of exercise to generate adapted patient-specific margins in EBRT planning
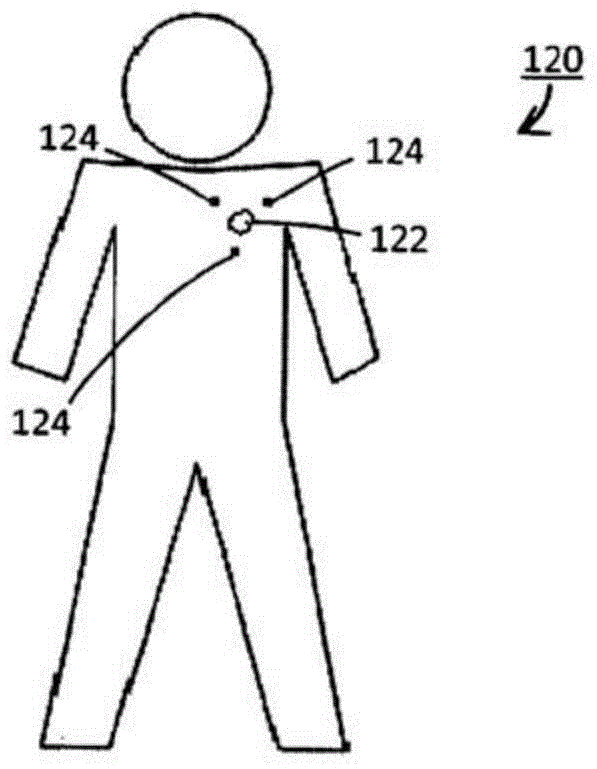
ActiveCN103687649BAccurately determineImproving the radiation therapy treatment planning processOrgan movement/changes detectionSpeech analysisPlanned DosePatient Motion
A treatment planning system (106) for generating a patient-specific treatment margin. The system (106) includes one or more processors (142). The processor (142) is programmed to receive a radiation treatment plan (RTP) for irradiating a target (122) during one or more treatment segments. The RTP includes one or more treatment margins around the target (122), and a planned dose distribution for the target (122). The processor (142) is further programmed to receive motion data for at least one treatment segment of the RTP from one or more target surrogates (124), use the motion data and the planned dose distribution to calculate a motion-compensated dose distribution of the target (122), comparing the motion-compensated dose distribution with the planned dose distribution, and based on a dosimetry between the motion-compensated dose distribution and the planned dose distribution difference to adjust the disposition margin.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV +1
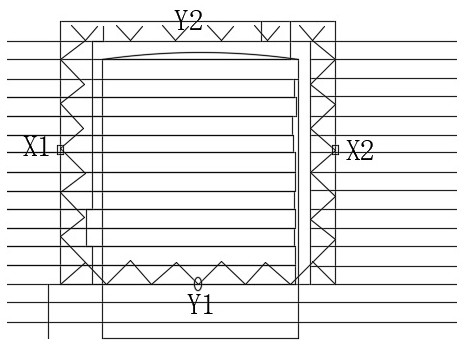
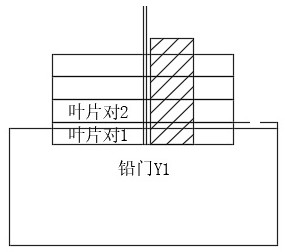
A method to reduce the influence of fixed lead door and wild lead door position error on planned dose
ActiveCN112245817BIn place precision solutionX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for reducing the influence of the in-position error of the fixed lead gate and the wild lead gate on the planned dose. ; S2, select the range of possible values for the coordinates of the fixed lead door and the shooting field lead door; S3, customize a blade below the lead door as a static closed blade, so that the blade blocking the fixed lead door and the wild lead door is statically closed; S4, set The reduction of the fixed jaw shot field in the planning system is an option system that affects the planned dose due to the in-position error of the fixed jaw field. The virtual coordinates are used as the actual jaw coordinates, which effectively solves the problem that the in-position error of the fixed jaw shooting field may cause the change of the target dose to block the moving projection blades.
Owner:靖江市人民医院
Dose planning system
ActiveUS10695130B2Precise delineation of tumour tissue may be complicatedIncrease probabilityDrug and medicationsSurgical needlesTissue characterizationComputer vision
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
A method for real-time monitoring of particle radiotherapy beams
ActiveCN109893778BGuaranteed protective effectEnsure safetyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle radiotherapyNuclear engineering
The invention discloses a real-time monitoring method for a particle radiotherapy beam. The monitoring method comprises the following steps: the irradiation position, size, shape, uniformity and half-height width of a proton beam can be monitored in real time according to two-dimensional distribution of Cherenkov light intensity; actual output energy of the proton beam can be determined on the basis of the quantitative relationship between Cherenkov light intensity and the energy of the proton beam; the dose deviation value can be calculated according to the real-time deviation information ofbeam output. The novel method is simple, practical, stable and reliable and capable of comprehensively monitoring beam information (including energy, irradiation position, size, uniformity and half-height width) in the proton radiotherapy process in real time, and accurate supply of the planned dose can be effectively ensured.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com