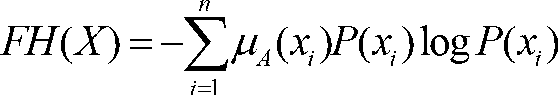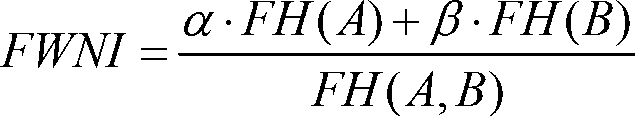Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Image guided radiotherapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
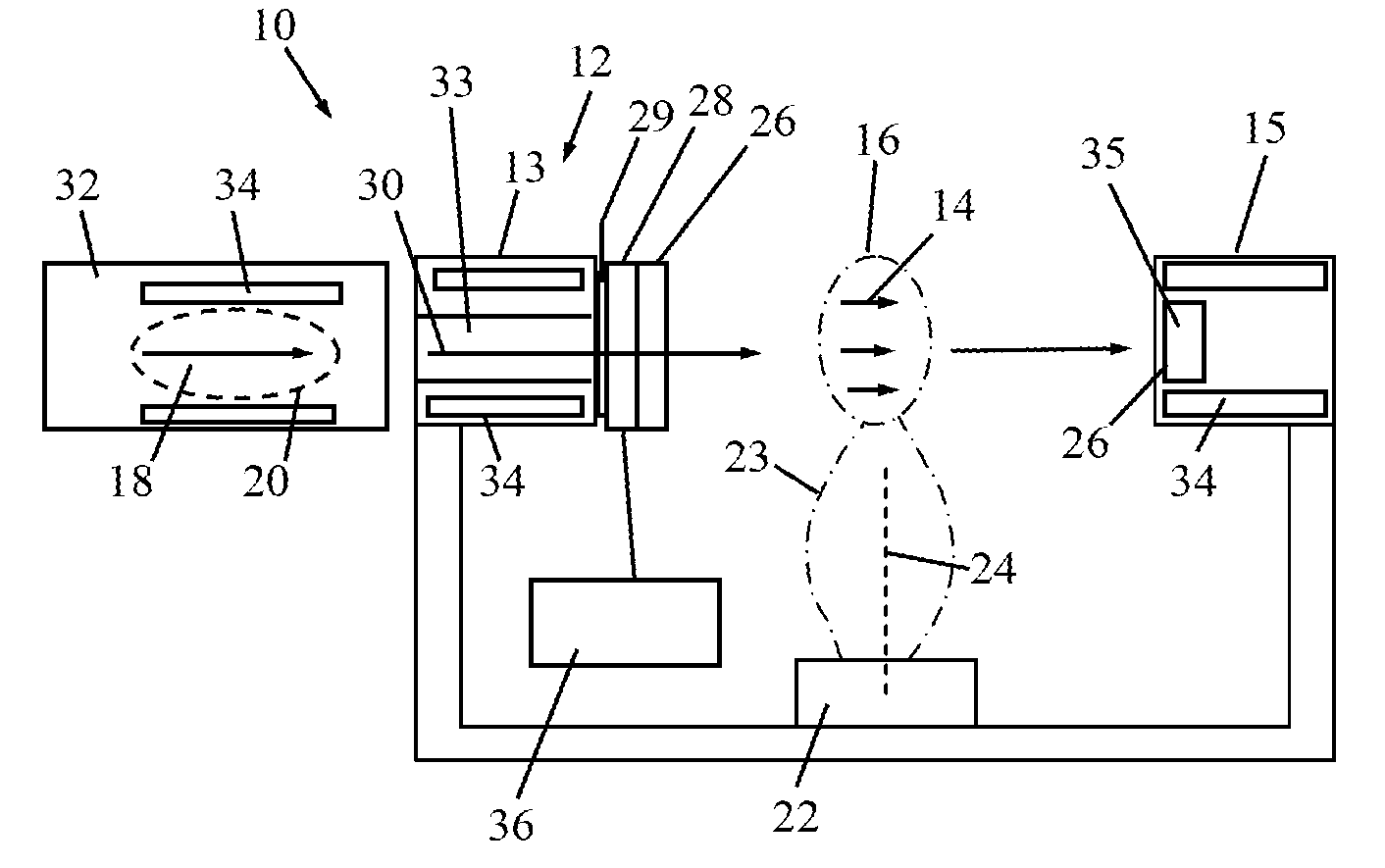
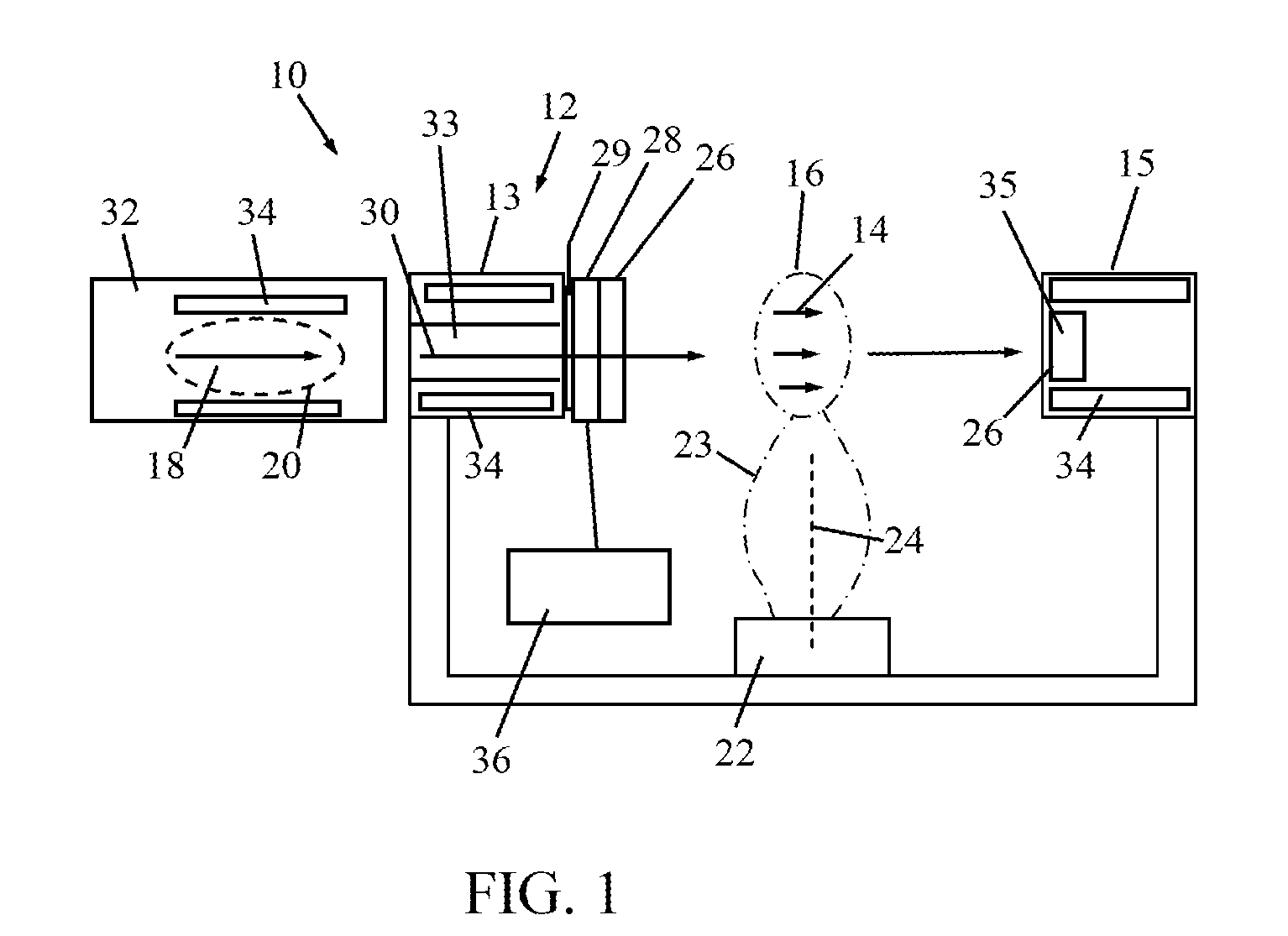
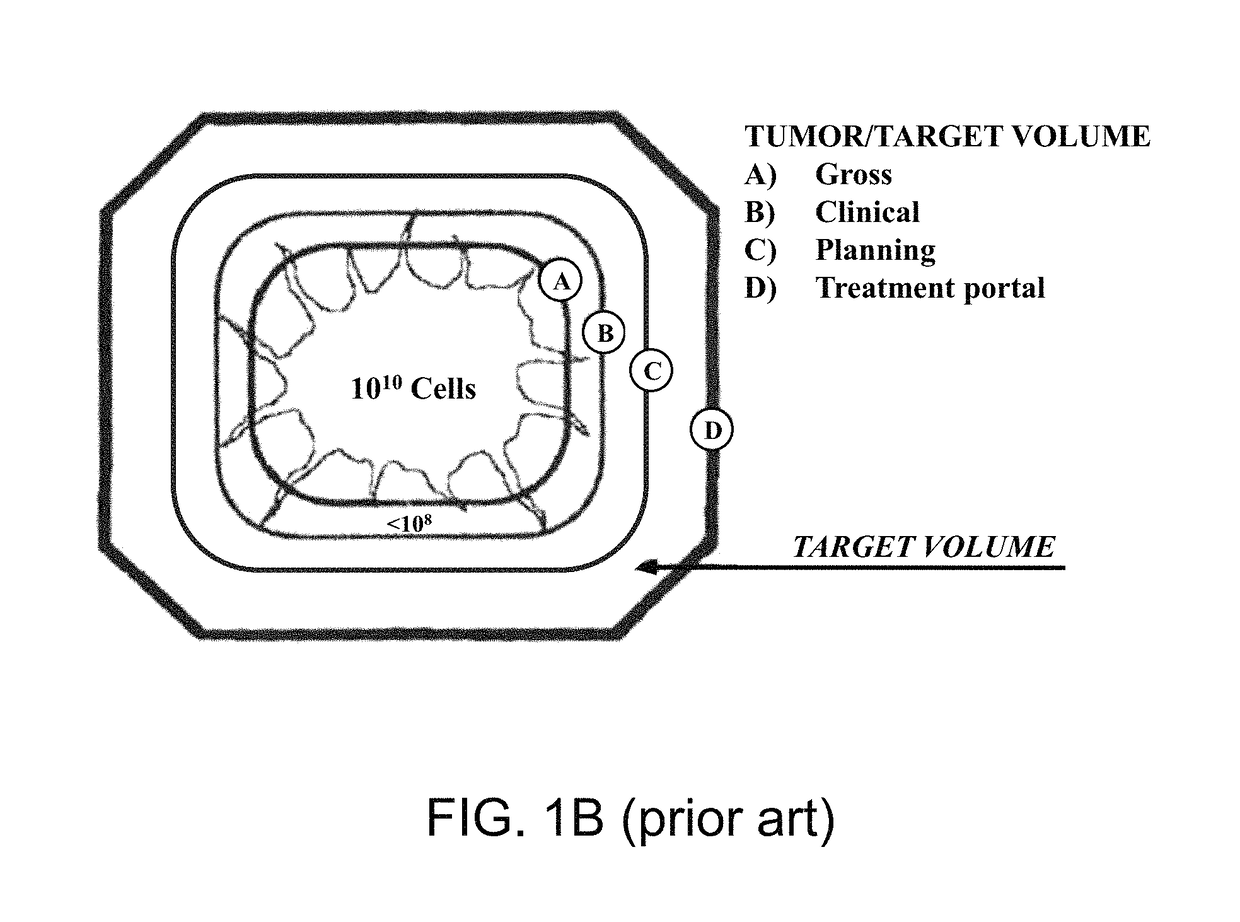
Image-guided Radiation Therapy (IGRT) Image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) is the use of imaging during radiation therapy to improve the precision and accuracy of treatment delivery. IGRT is used to treat tumors in areas of the body that move, such as the lungs.
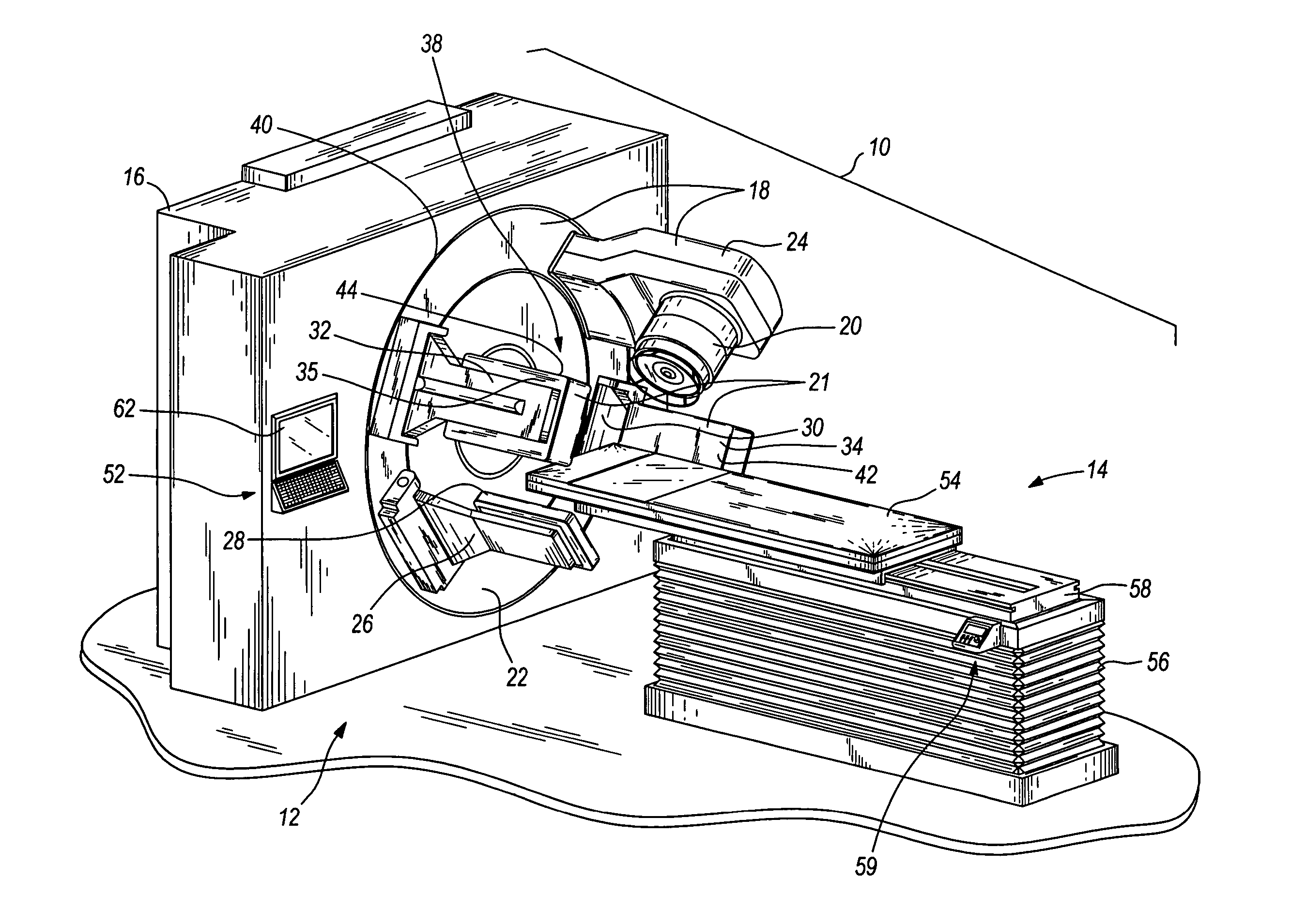
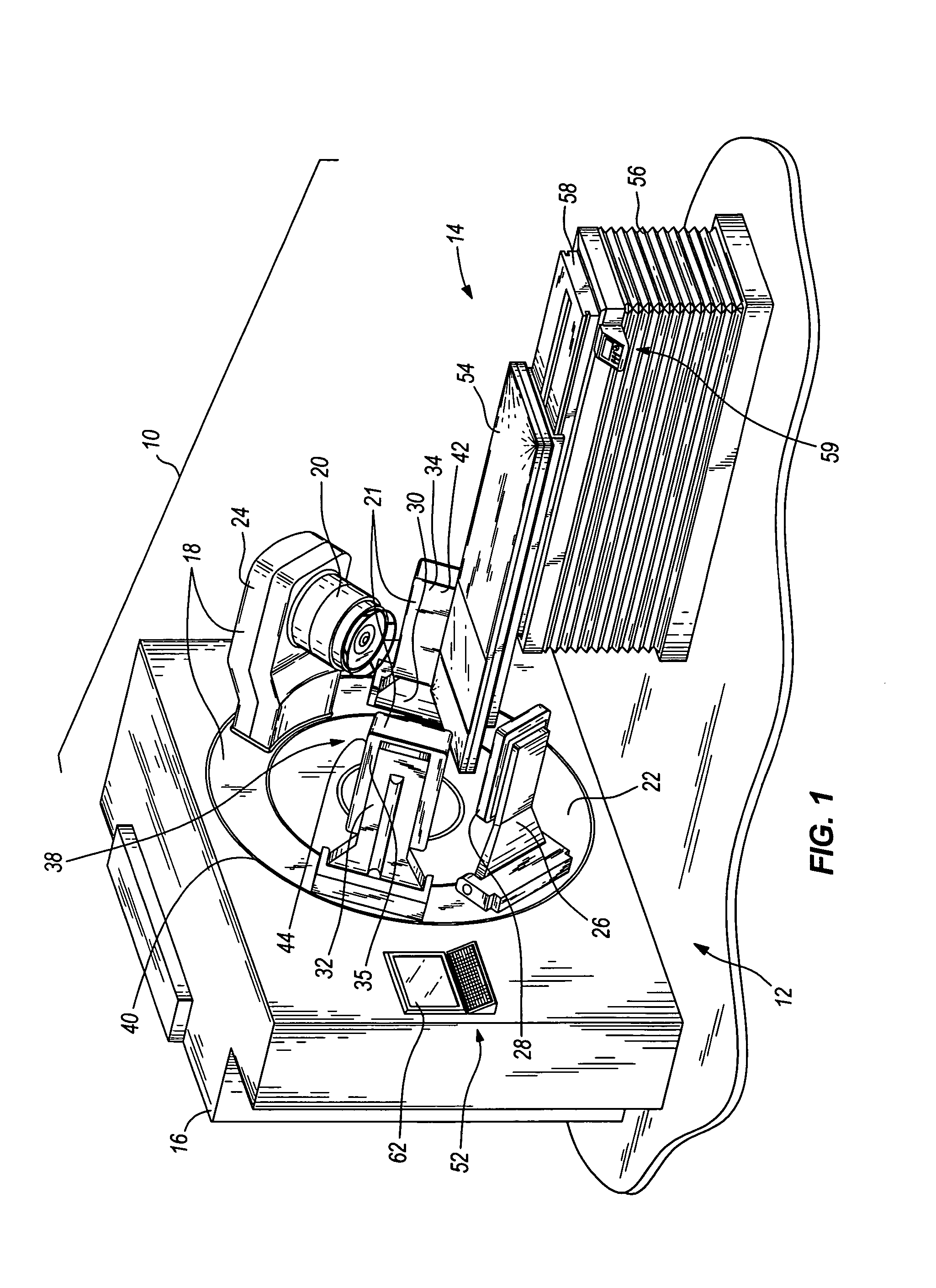
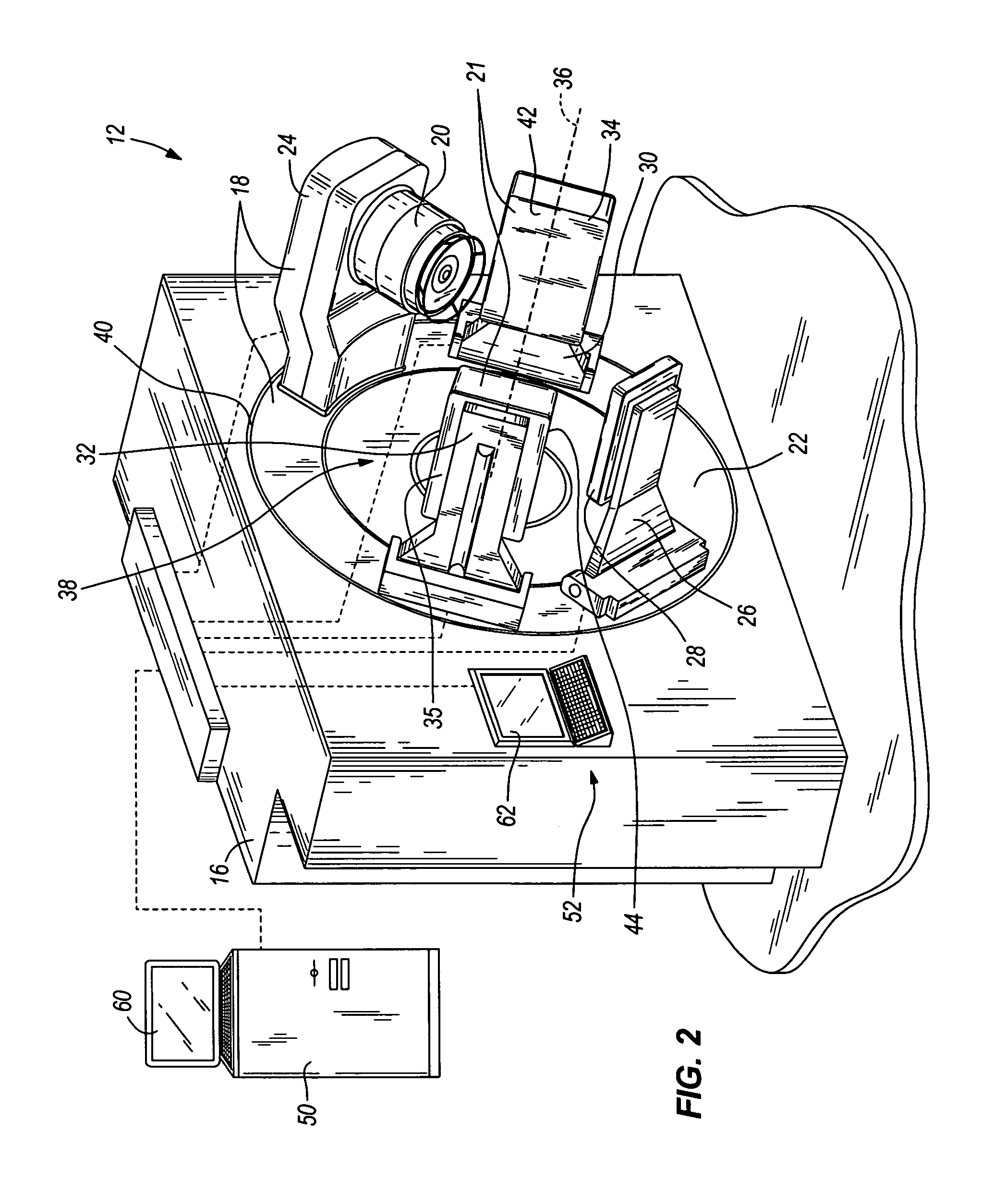
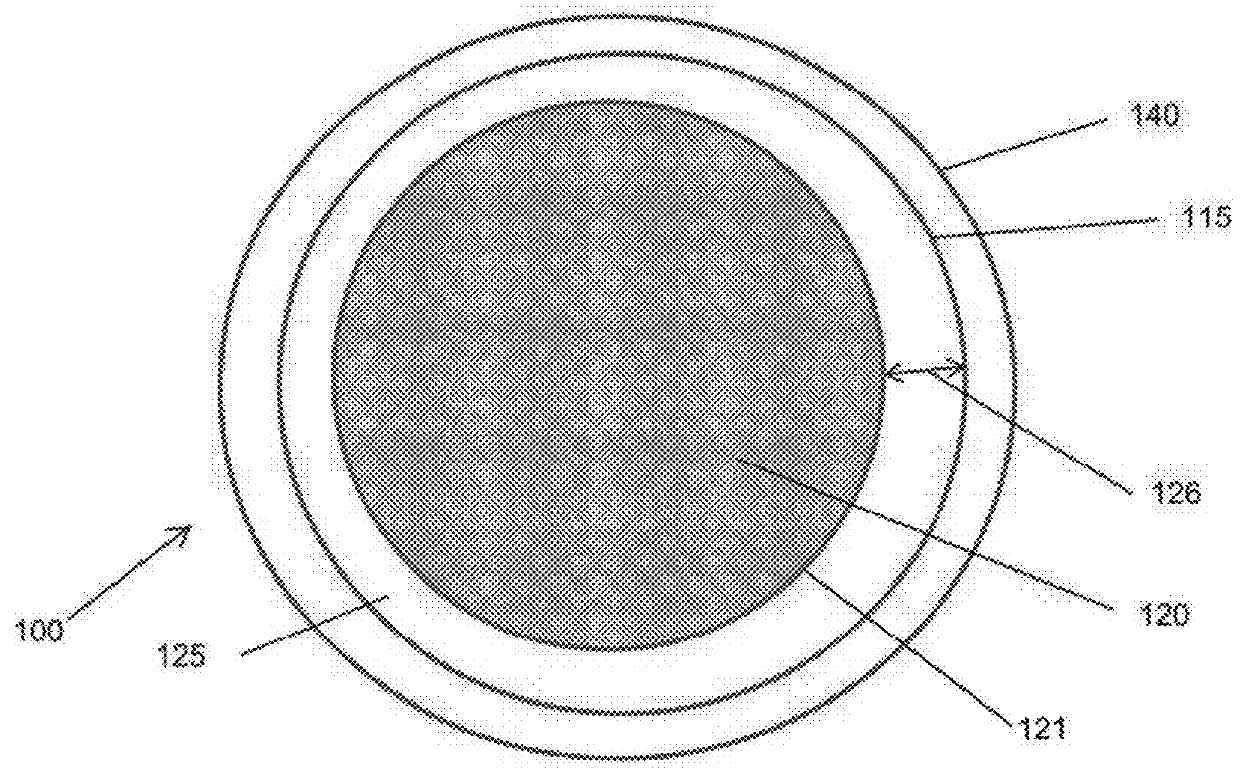
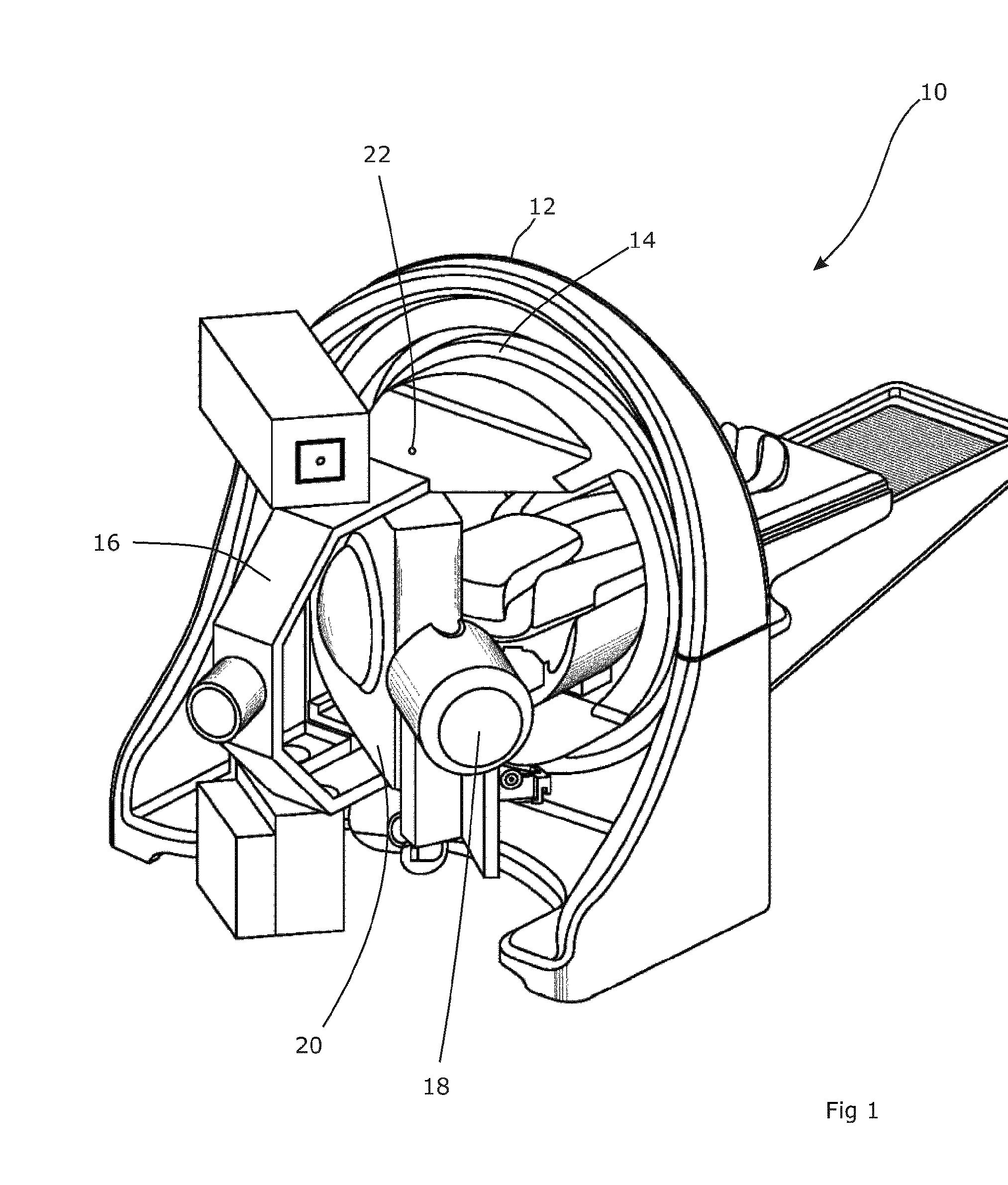
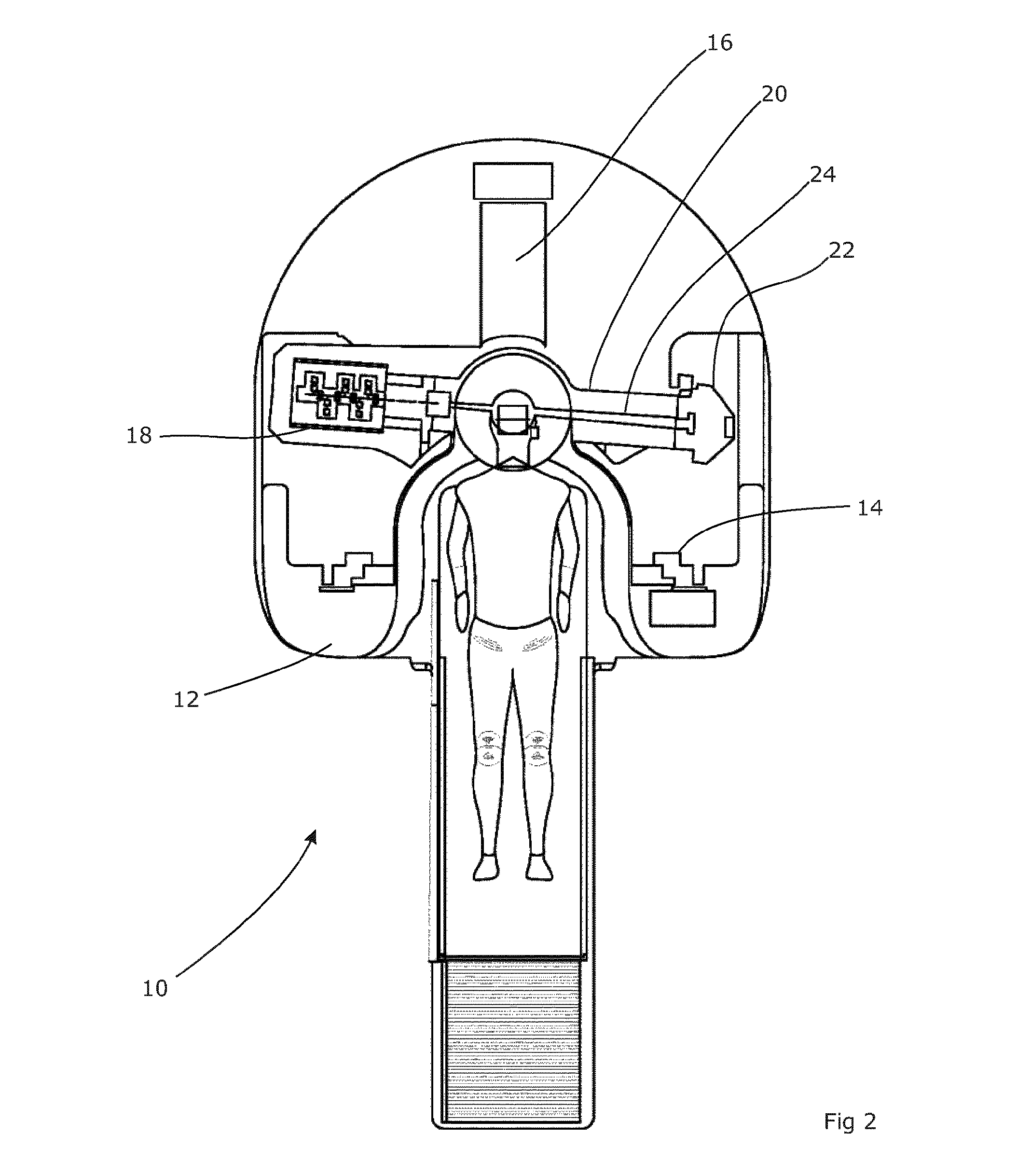
Image-guided medical intervention apparatus and method
ActiveUS20060113482A1Image is differentSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma rayImaging equipment
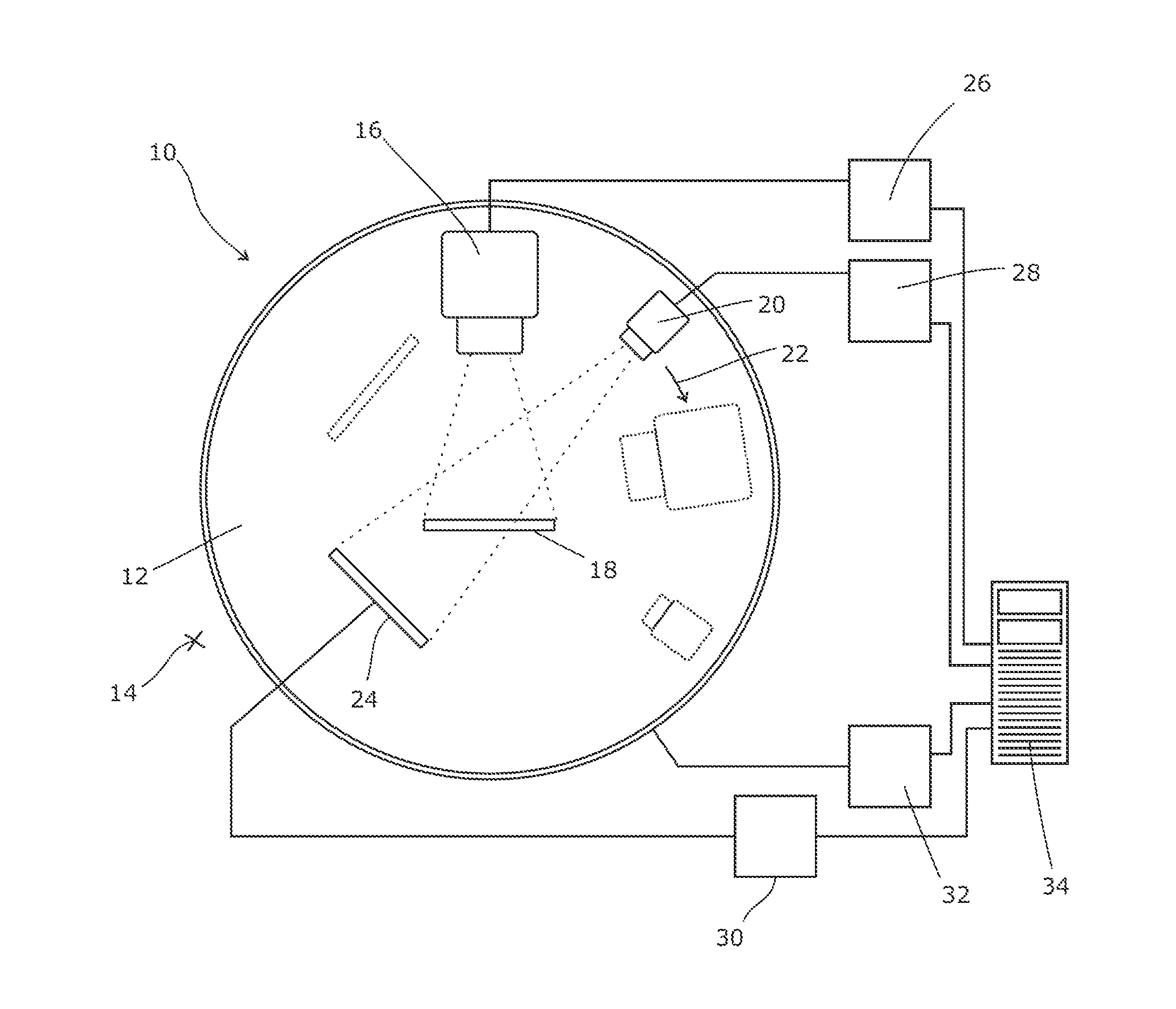
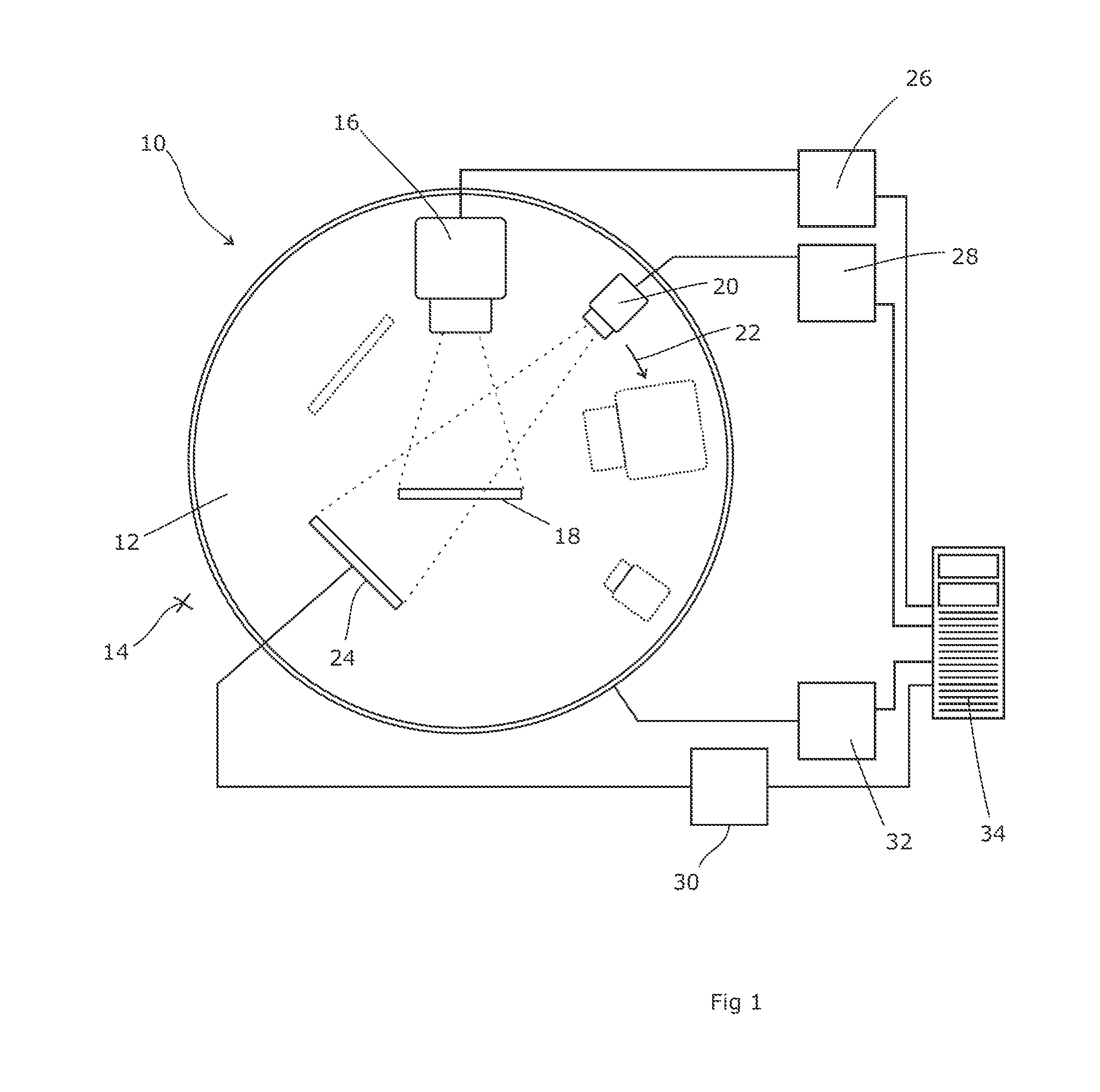
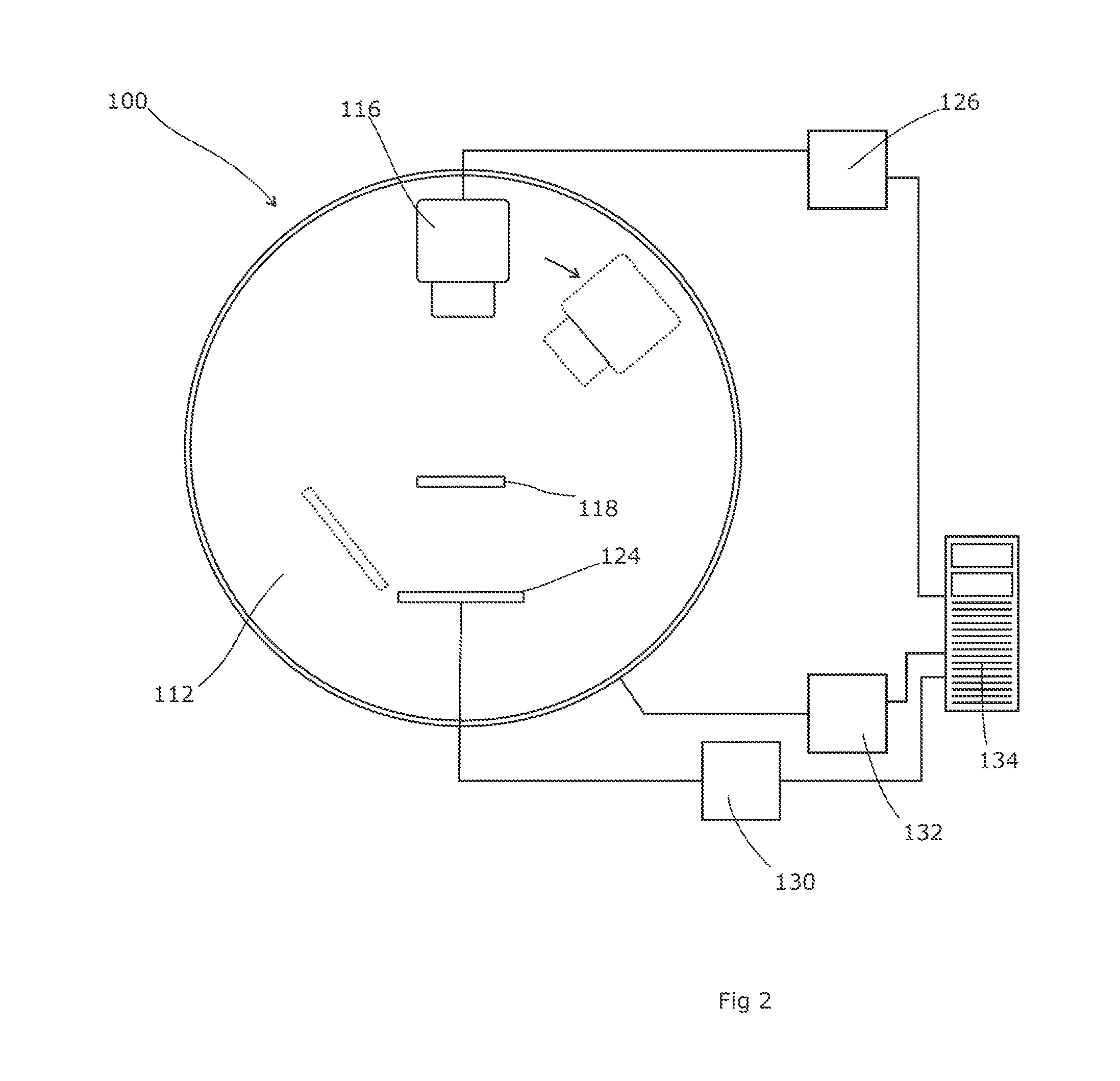
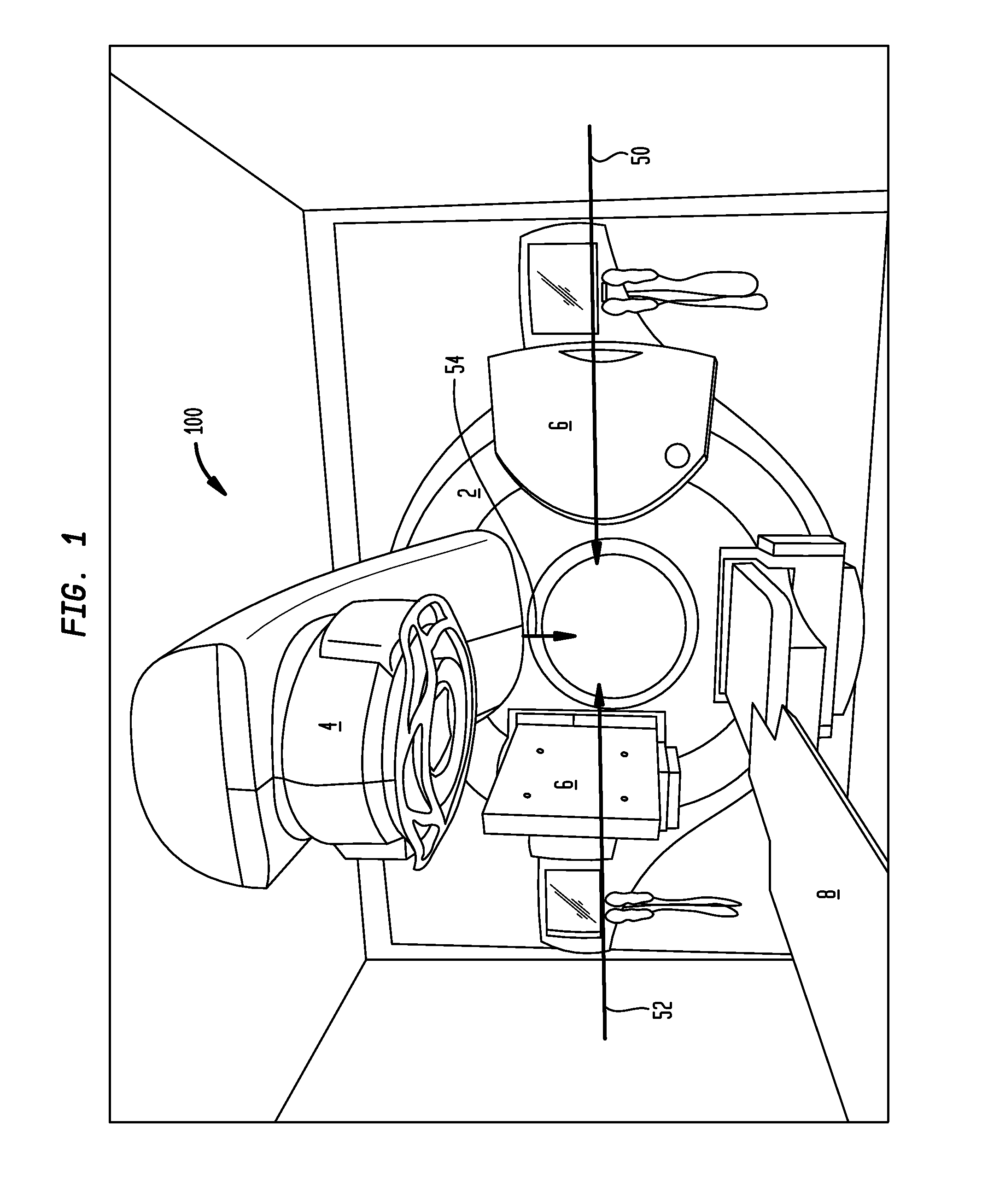
In some embodiments, an image-guided radiotherapy apparatus and method is provided in which a radiotherapy radiation source and a gamma ray photon imaging device are positioned with respect to a patient area so that a patient can be treated by a beam emitted from the radiotherapy apparatus and can have images taken by the gamma ray photon imaging device. Radiotherapy treatment and imaging can be performed substantially simultaneously and / or can be performed without moving the patient in some embodiments. The gamma ray photon imaging device can be coupled and movable with respect to any part of a building structure, can be located on a portable frame movable to and from the radiotherapy radiation source and patient, or can take other forms. In some embodiments, the gamma ray photon imaging device can be used for imaging in connection with other types of medical interventions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Image-guided medical intervention apparatus and method
ActiveUS7265356B2Image is differentSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansGamma rayNuclear medicine
In some embodiments, an image-guided radiotherapy apparatus and method is provided in which a radiotherapy radiation source and a gamma ray photon imaging device are positioned with respect to a patient area so that a patient can be treated by a beam emitted from the radiotherapy apparatus and can have images taken by the gamma ray photon imaging device. Radiotherapy treatment and imaging can be performed substantially simultaneously and / or can be performed without moving the patient in some embodiments. The gamma ray photon imaging device can be coupled and movable with respect to any part of a building structure, can be located on a portable frame movable to and from the radiotherapy radiation source and patient, or can take other forms. In some embodiments, the gamma ray photon imaging device can be used for imaging in connection with other types of medical interventions.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
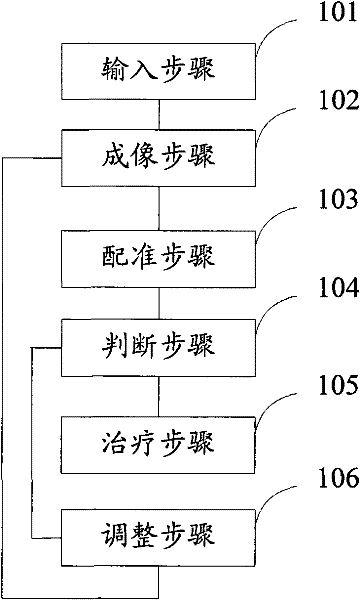
Positioning method for use in image-guided radiotherapy
InactiveCN102232835AReflect postural errorAccurately determineRadiation diagnosticsX-rayComputer science
The invention provides a positioning method for use in image-guided radiotherapy, which comprises the following: a step of input, which is to input a radiotherapy plant image; a step of imaging, which is o acquire the image data of a patient by using KV-grade X-rays and acquire the image of a patient according to the image data; a step of registering, which is to register the image of the patient with the radiotherapy plant image; a step of judging, which to judge whether the positions of the two images are consistent according to the registration results, and execute a step of treatment if the positions of the two images are consistent or execute a step of regulation if the positions of the two images are inconsistent; a step of treatment, which is to treat the patient by using an MV-grade X-rays, wherein the KV-grade X-rays and the MV-grade X-rays are from the same accelerating tube; and the step of regulation, which is to regulate the position of a patient according to the registration result and return to the step of imaging. The positioning method is used for improving the positioning accuracy of image-guided radiotherapy.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Target Tissue Locator for Image Guided Radiotherapy
InactiveUS20080177179A1Enhanced radiationEliminate requirementsSurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical deviceRadiography
The present invention relates to different methods of delineating target tissue from non-target tissue using differences in radiographic properties of a medical device.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
MRI system for upright radiotherapy
InactiveUS20100174172A1Eliminate distractionsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRotational axisResonance
An image-guided radiotherapy system including a magnet assembly operable to produce a horizontal imaging field in an imaging region, and a non-imaging field in a non-imaging region, a positioner operable to rotate an object in the imaging region about a generally vertical rotational axis, a magnetic resonance (MR) imager in communication with the horizontal imaging field, a collimator operable to collimate a generally horizontal radiation beam directed towards the object, and a radiation source operable to produce a radiation beam of charged particles substantially parallel to the non-imaging field in the non-imaging region.
Owner:EIN GAL MOSHE
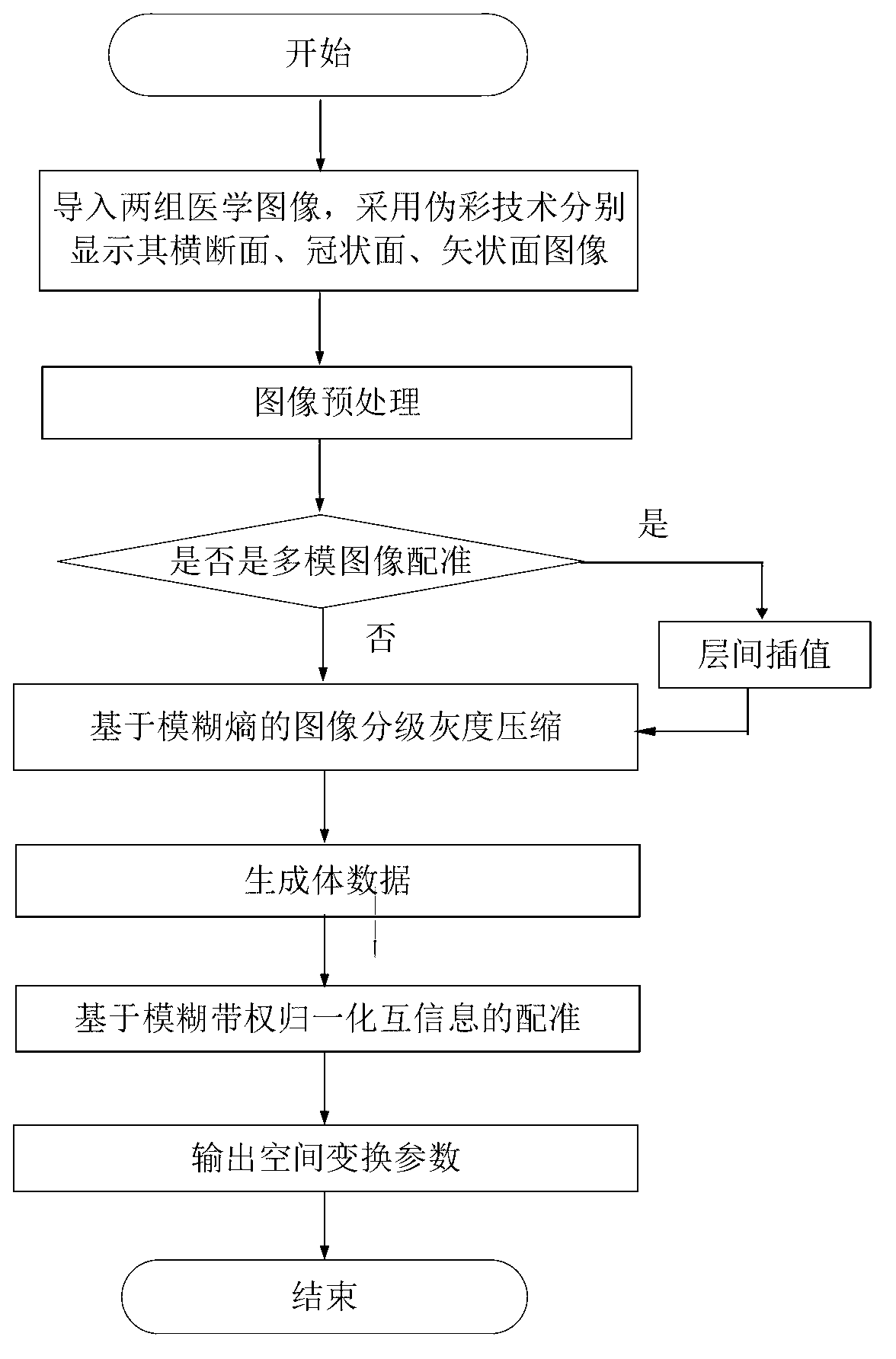
Method and system for registering three-dimensional medical images on basis of weighted fuzzy mutual information
ActiveCN103020976ACalculation speedHigh speedImage analysisNormalized mutual informationCoronal plane
The invention provides a method and a system for registering three-dimensional medical images on the basis of weighted fuzzy mutual information, and relates to the technical field of image-guided radiotherapy and medical image analysis. The method mainly includes steps of 1, guiding the medical images; 2, displaying the medical images; 3, processing the medical images; and 4, registering the medical images. In the step of guiding the medical images, single-mode image registration and multi-mode image registration are supported; in the step of displaying the medical images, cross section, coronal plane and sagittal plane images of the medical images to be registered are colored differently by a pseudo-color technology; in the step of processing the medical images, grayscales of the medical images are classified and compressed on the basis of a concept of fuzzy entropy, and mutual information calculation is reduced; and in the step of registering the medical images, normalized mutual information measures are modified on the basis of the fuzzy entropy, and the robustness of medical image registration is improved. The method and the system have the advantages that the measure method on the basis of the mutual information is adopted, the method and the system are applicable to single-mode image registration, and a good effect can also be realized for multi-mode image registration.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanoparticle-guided radiotherapy
The present invention relates to a method and nano-sized particles for image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) of a target tissue. More specifically, the invention relates to nano-sized particles comprising X-ray-imaging contrast agents in solid form with the ability to block x-rays, allowing for simultaneous or integrated external beam radiotherapy and imaging, e.g., using computed tomography (CT).
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Image-Guided Radiotherapy
ActiveUS20140321615A1Limited cross sectional areaTomographyMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationLight beamTherapeutic radiation
A radiotherapy apparatus comprises a rotatable gantry, supporting a source of therapeutic radiation and a source of diagnostic radiation, the two sources being rotationally (or angularly) spaced apart around a rotation axis of the gantry, with at least one collimator associated with the source of therapeutic radiation and arranged to limit the cross-sectional area of a beam produced by that source, a control means arranged to conduct a treatment fraction using the apparatus by causing the apparatus to i. acquire images of a patient using the source of diagnostic radiation, ii. retain those images at least temporarily, iii. subsequently, after further rotation of the gantry, select a retained image acquired when the source of diagnostic radiation was at a rotational position corresponding to the instantaneous rotational position of the source of therapeutic radiation, and iv. control the beam relative to the patient using information derived from the selected image. The corresponding rotational position is ideally one in which the source of therapeutic radiation is at the same or substantially the same rotational position as was the source of diagnostic radiation at the point in time when the image was acquired. An alternative a radiotherapy apparatus comprises a rotatable gantry supporting a source of therapeutic radiation and a source of diagnostic radiation, at least one collimator associated with the source of therapeutic radiation and arranged to limit the cross-sectional area of a beam produced by that source, a reconstruction means arranged to i. obtain two-dimensional images of a patient using the source of diagnostic radiation, ii. retain those images at least temporarily, iii. apply a recency threshold to the retained images thereby to exclude images less recent than the threshold, iv. select at least three such retained images meeting the recency threshold and reconstruct a CT volume or tomographic image using the selected images, and a control means arranged to conduct a treatment fraction or treatment session using the apparatus, controlling the collimator using information derived from the CT volume.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
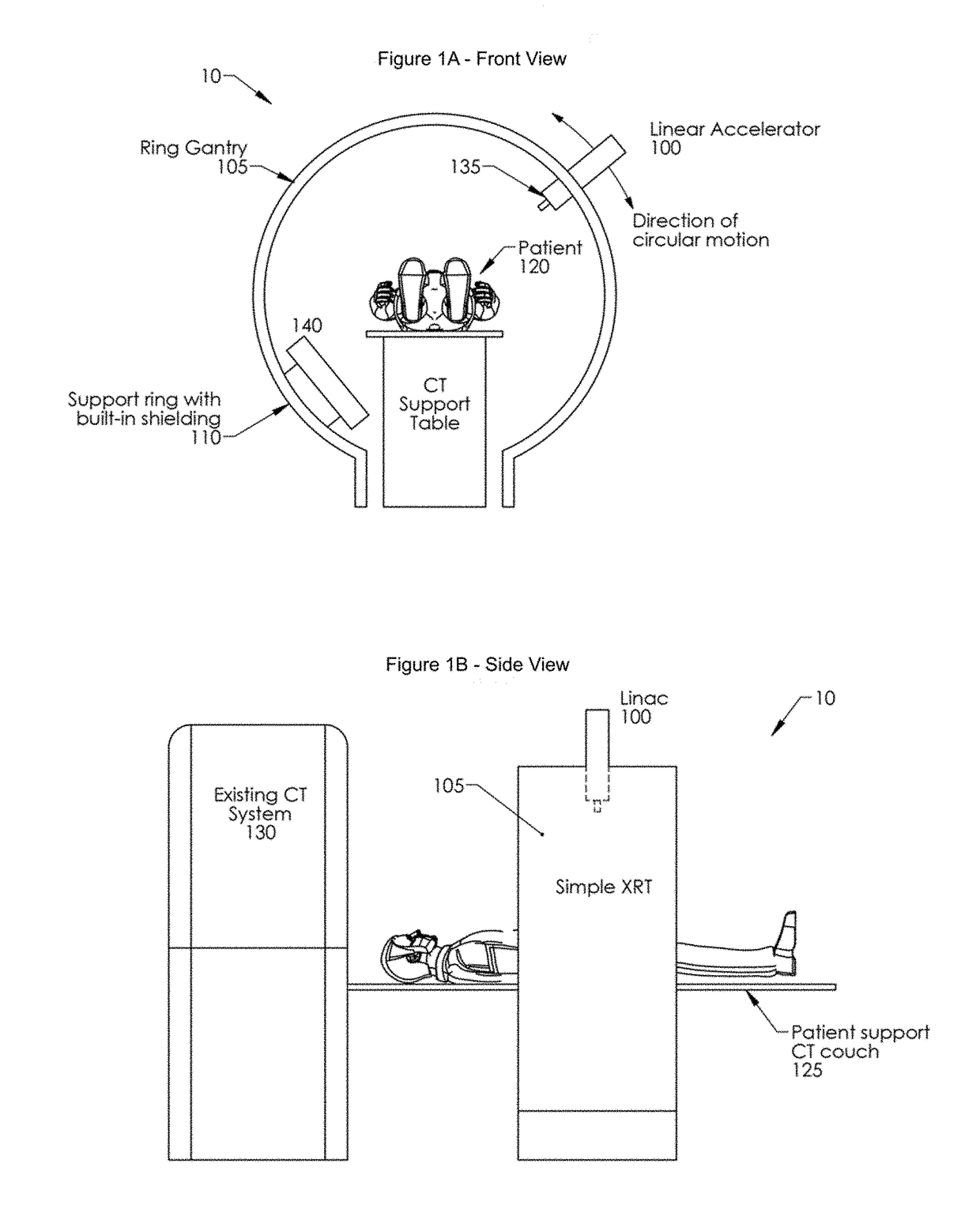
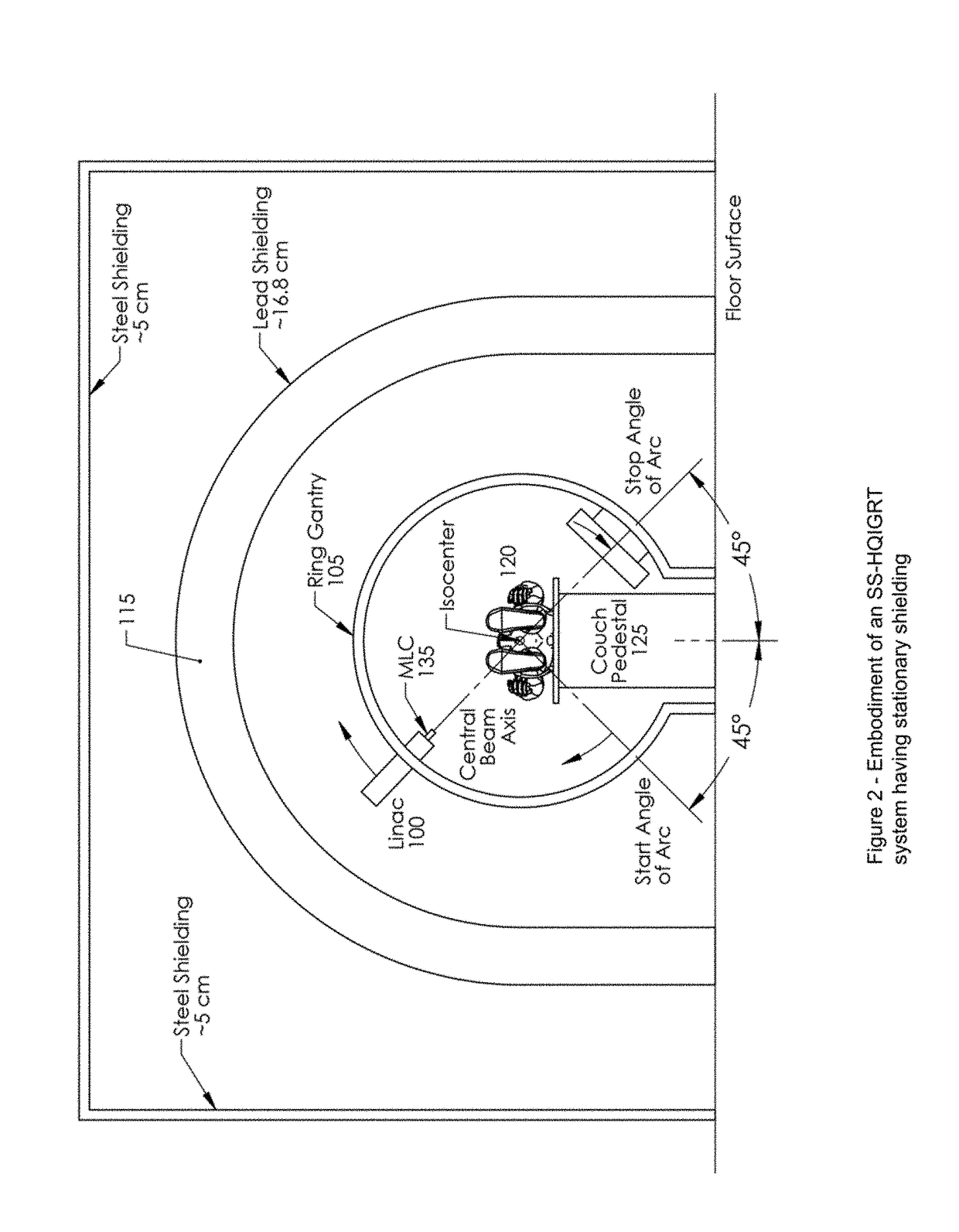
Self-Shielded Image Guided Radiation Oncology System
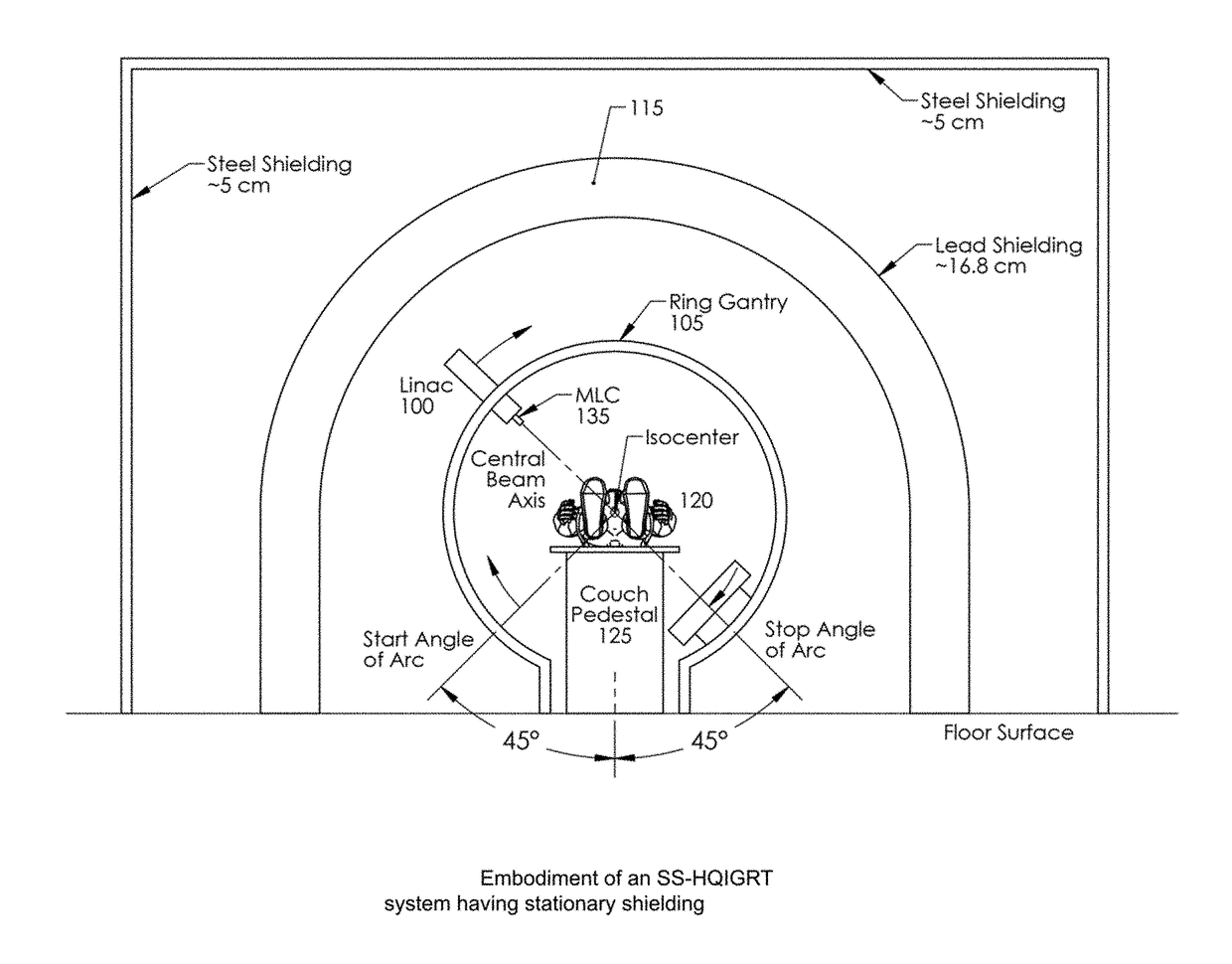
ActiveUS20180280733A1Utilization factor is loweredReduce thicknessRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsTomographyCt scannersEngineering
An image-guided radiotherapy system adapted to be juxtaposed adjacent a CT scanner comprises a frame having an orifice adapted to permit passage therethrough of a couch on which a patient is positioned, together with a gantry assembly rotatably mounted on the frame in which the gantry assembly comprises a shielding cylinder having an orifice therethrough in alignment with the orifice in the frame. The shielding cylinder has affixed thereto a linac-based treatment head configured to provide radiotherapy, and a beamstop positioned angularly opposite the treatment head to absorb radiation from the treatment head. The shielding cylinder provides sufficient shielding of radiation scattered from the patient and the remainder of the system to not require a conventional vault. In some embodiments an arch may be used instead of a cylinder.
Owner:ETM ELECTROMATIC
Method to estimate 3D abdominal and thoracic tumor position to submillimeter accuracy using sequential x-ray imaging and respiratory monitoring
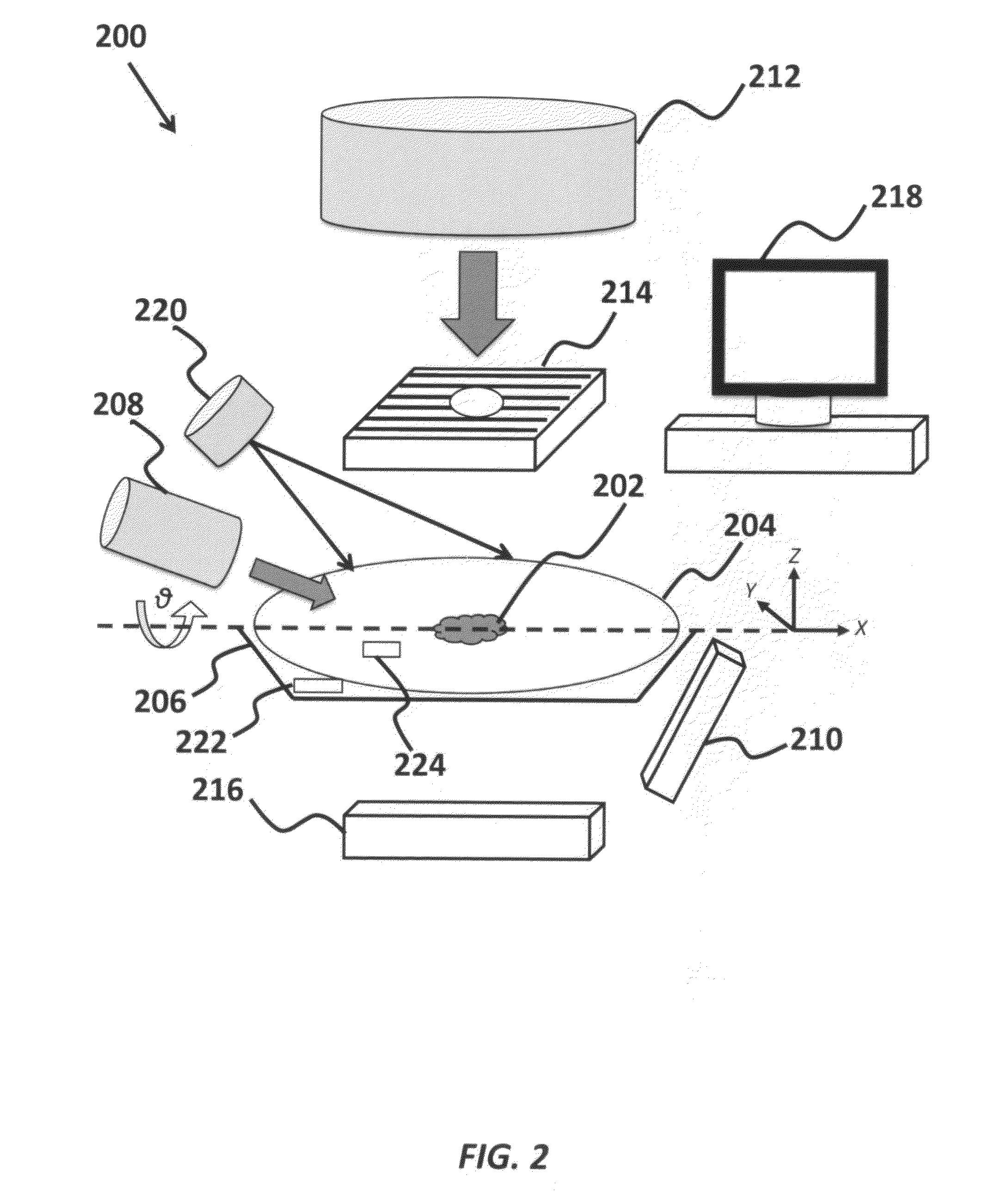
A method of estimating target motion for image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) systems is provided. The method includes acquiring by a kV imaging system sequential images of a target motion, computing by the kV imaging system from the sequential images an image-based estimation of the target motion expressed in a patient coordinate system, transforming by the kV imaging system the image-based estimation in the patient coordinate system to an estimate in a projection coordinate system, reformulating by the kV imaging system the projection coordinate system in a converging iterative form to force a convergence of the projection coordinate system to output a resolved estimation of the target motion, and displaying by the kV imaging system the resolved estimation of the target motion.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
CBCT image reconstruction method based on compressed sensing
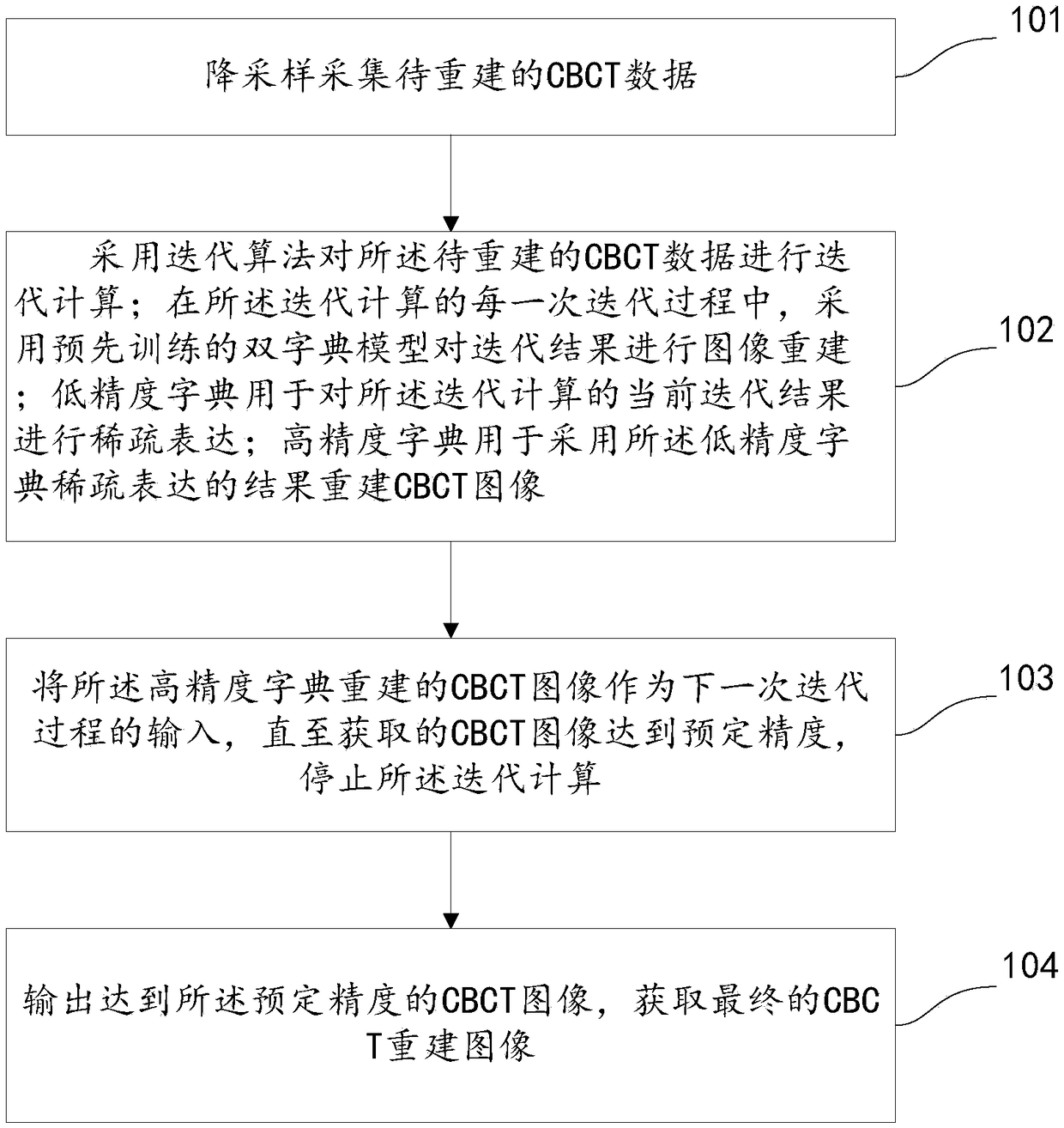
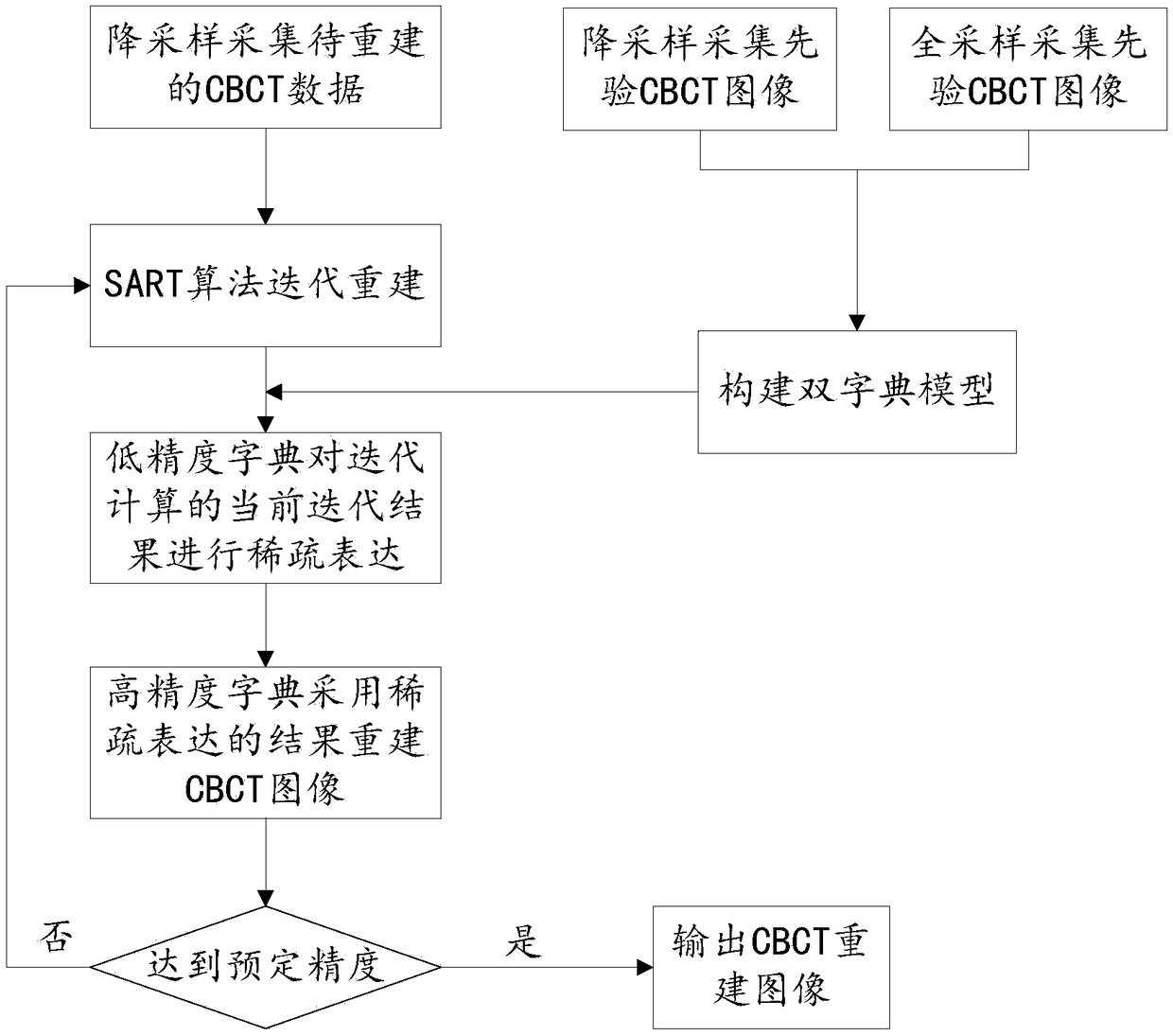
PendingCN109035360AReduce scan doseQuality improvementImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionAlgorithmX ray dose
The invention discloses a CBCT image reconstruction method based on compression sensing. The CBCT data to be reconstructed are iteratively computed by using iterative algorithm. In each iteration of the iterative computation, the pre-trained dual dictionary model is used to reconstruct the image of the iterative result. The dual dictionary model includes: low-precision dictionary, high-precision dictionary; a low precision dictionary is used to sparsely express the current iterative results of the iterative computation. High-precision dictionary is used to reconstruct CBCT images using the results of low-precision dictionary sparse representation. The CBCT image reconstructed by high-precision dictionary is used as the input of the next iterative process until the acquired CBCT image reaches the predetermined accuracy, and the iterative calculation is stopped to obtain the final CBCT reconstructed image. The technical proposal provided by the invention can remarkably reduce the X-ray dose received by a patient during a single CBCT scan in image-guided radiotherapy on the premise of ensuring the clinical application of the CBCT reconstructed image, and reduce the CBCT scan time.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
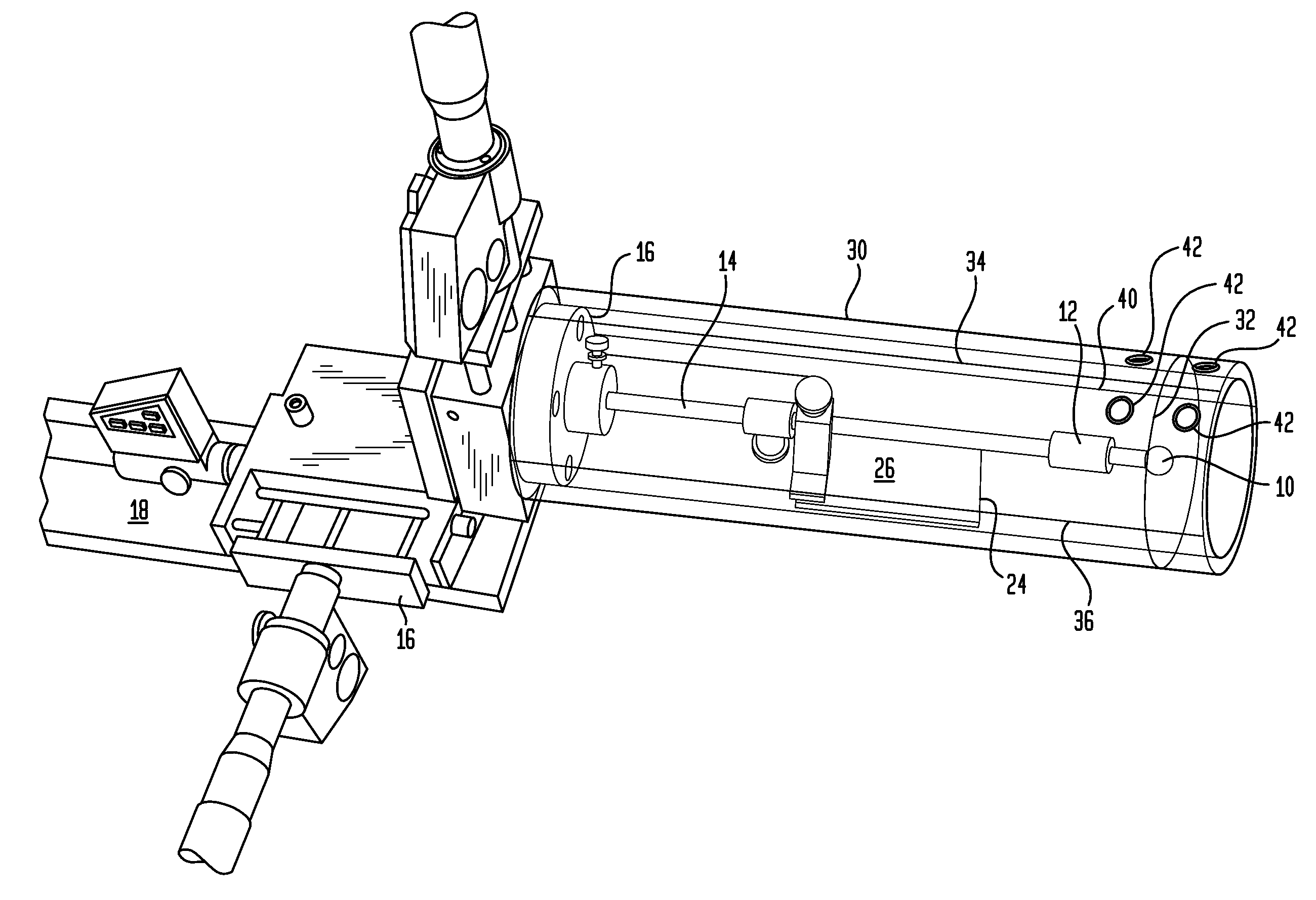
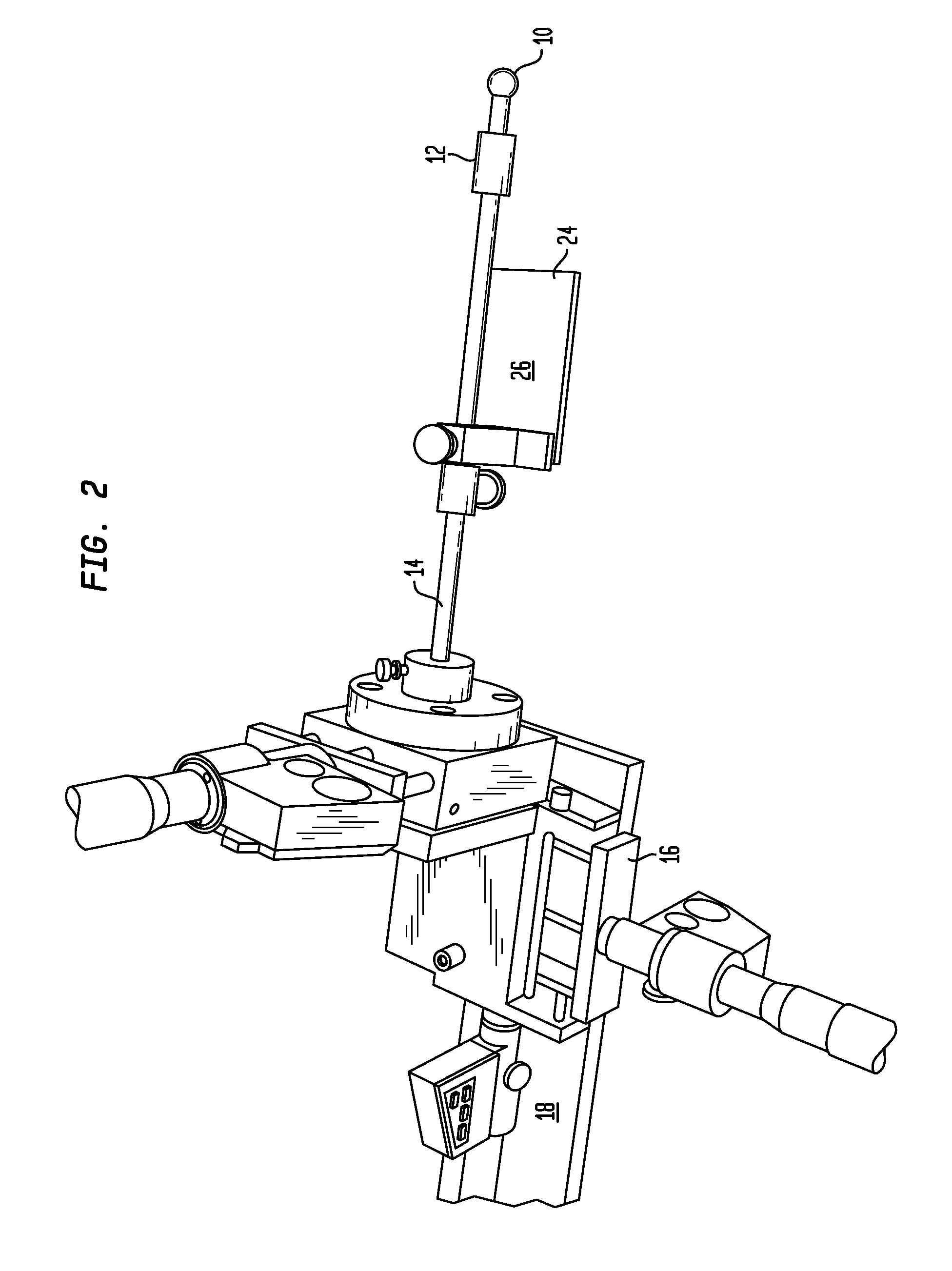
Quality-control jig for use with radiotherapy apparatus
A jig for calibrating an image-guided radiotherapy apparatus is disclosed. The jig includes a ball bearing and a three-axis positioner. Once the ball bearing has been moved to the calculated radiation isocenter of the apparatus, other calibration procedures can be performed by directing light onto the jig.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
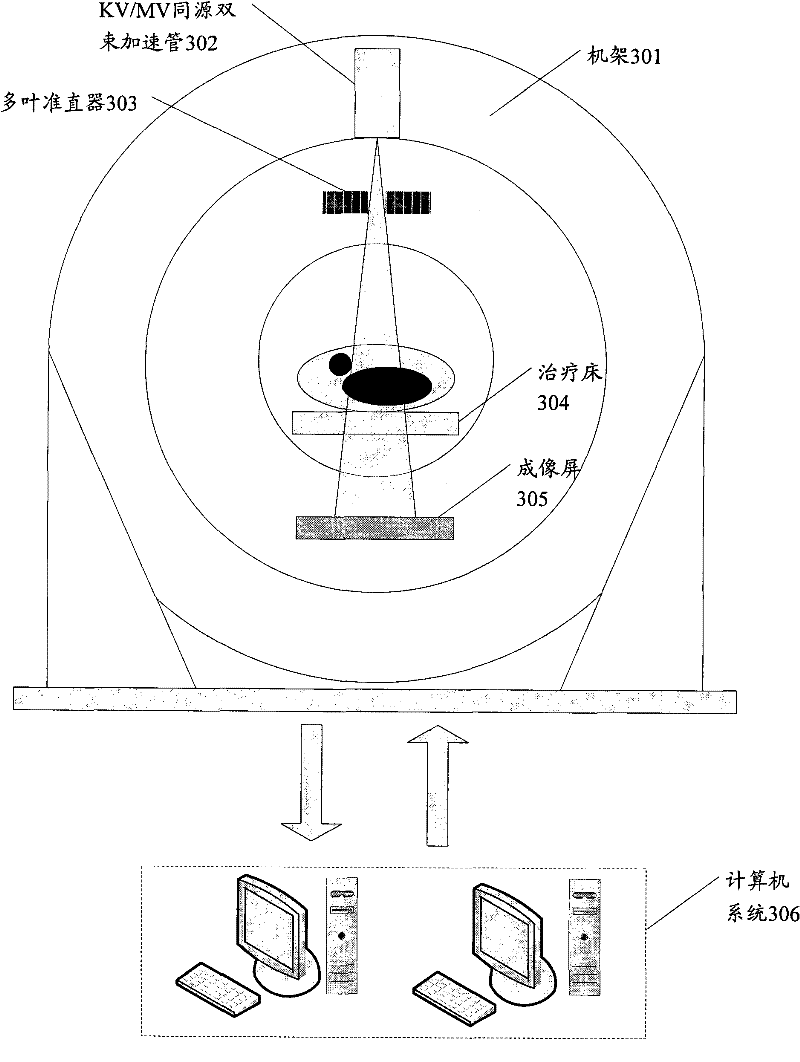
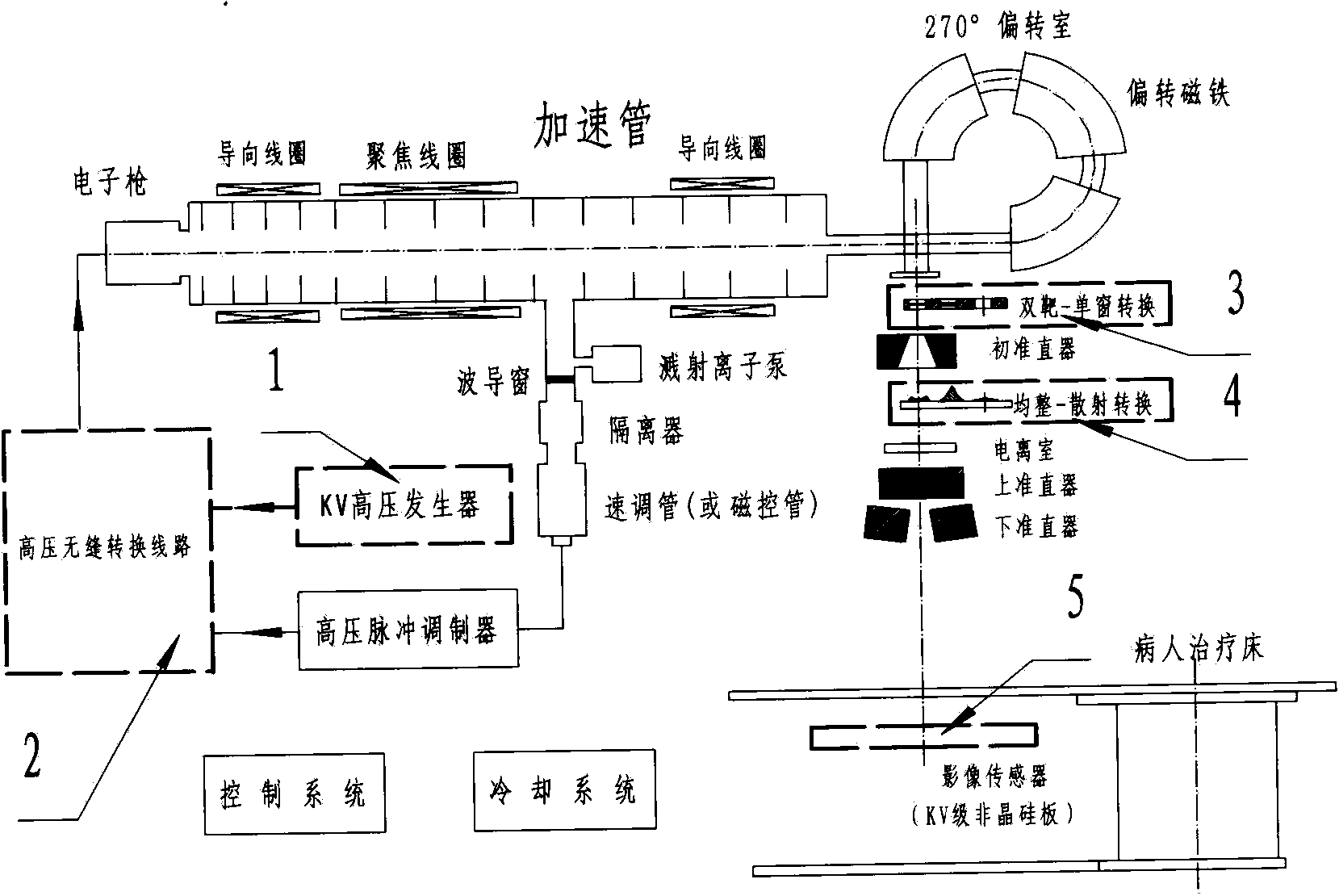
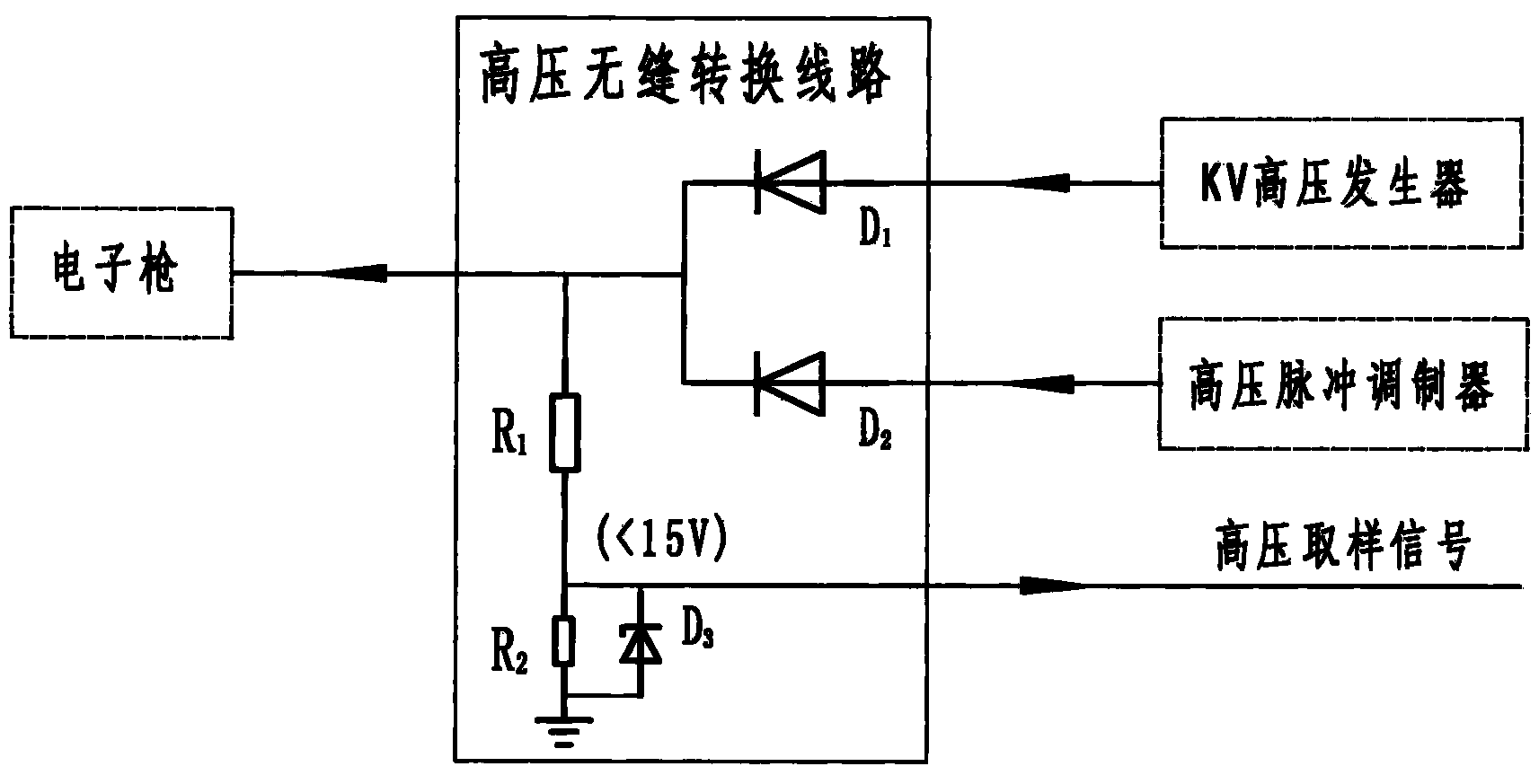
Medical linear accelerator KV/MV coaxial X ray image system
The invention discloses a medical linear accelerator KV / MV coaxial X ray image system, belonging to the medical linear accelerator research and manufacture field. The invention provides a medical linear accelerator KV / MV coaxial X ray image system which guarantees a KV level image system to be in a same coordinate axis with MV level radiotherapy ray while collecting images with quality equivalent to the quality of images obtained through a conventional medical X ray image device, which is an image guiding radiotherapy goal pursued by industries at home or aboard and still not finished. The main points of the invention are that a KV level high voltage generator which is exclusive for a regular X ray image device is provided for the medical linear accelerator, and original pulse high voltage or adjustable KV level image high voltage can be freely switched for the electronic emission system through the "high voltage seamless converting circuit" so as to realize the technology of accuracy radiotherapy therapy under coaxial high definition image guiding.
Owner:宫良平
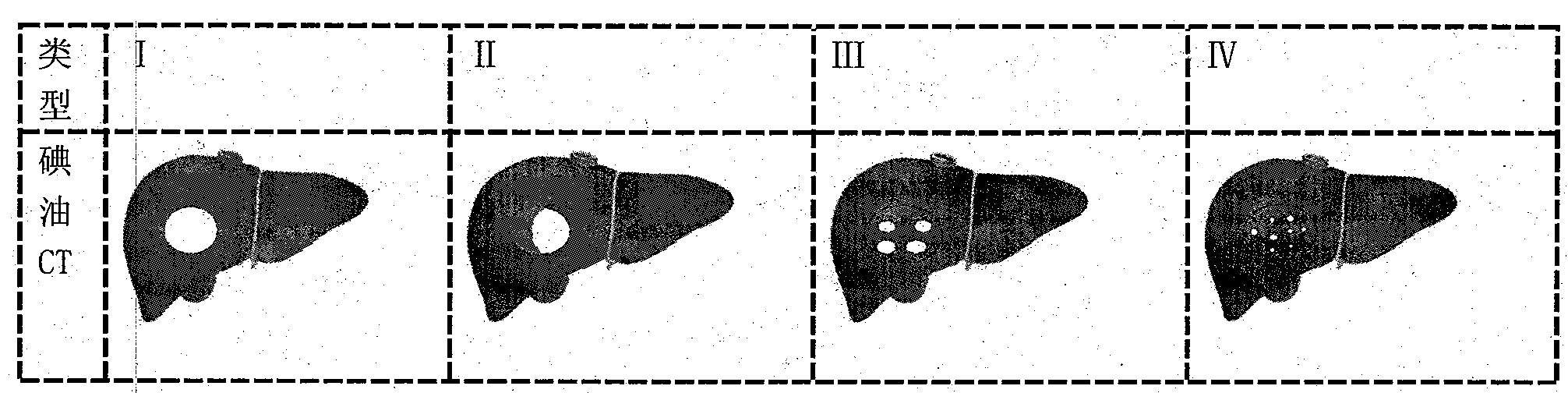
United autonomous respiration control on-line alignment technique using iodized oil image to guide image-guided radiotherapy
InactiveCN101559256AGood clinical efficacyAvoid damageRadiation therapyAutonomous breathingIodized oil
The invention provides a united autonomous breath control on-line alignment technique using iodized oil image to guide image-guided radiotherapy, wherein, the autonomous breath control technique (ABC) is employed to control the liver to move with the breath in the process of radiation treatment, meanwhile, the iodized oil image is employed to carry out 3-D-registration-based image-guided on-line alignment positioning errors between a planned CT and a conical beam CT (CBCT); in addition, strengths of both aspects are combined to maximize accuracy in the radiation treatment in the liver cancer, thus overcoming the defect of depending on the musculus diaphragm, the vertebral body and the liver to conduct 2-D registration to indirectly reflect movement of liver neoplasm and providing a novel radiation treatment technology with high accuracy which can improve radiation treatment dosage for liver neoplasm while reducing harm caused by normal liver organization radiation treatment for liver cancer patients who are not suitable for operations.
Owner:SHANDONG RES INST OF TUMOUR PREVENTION TREATMENT
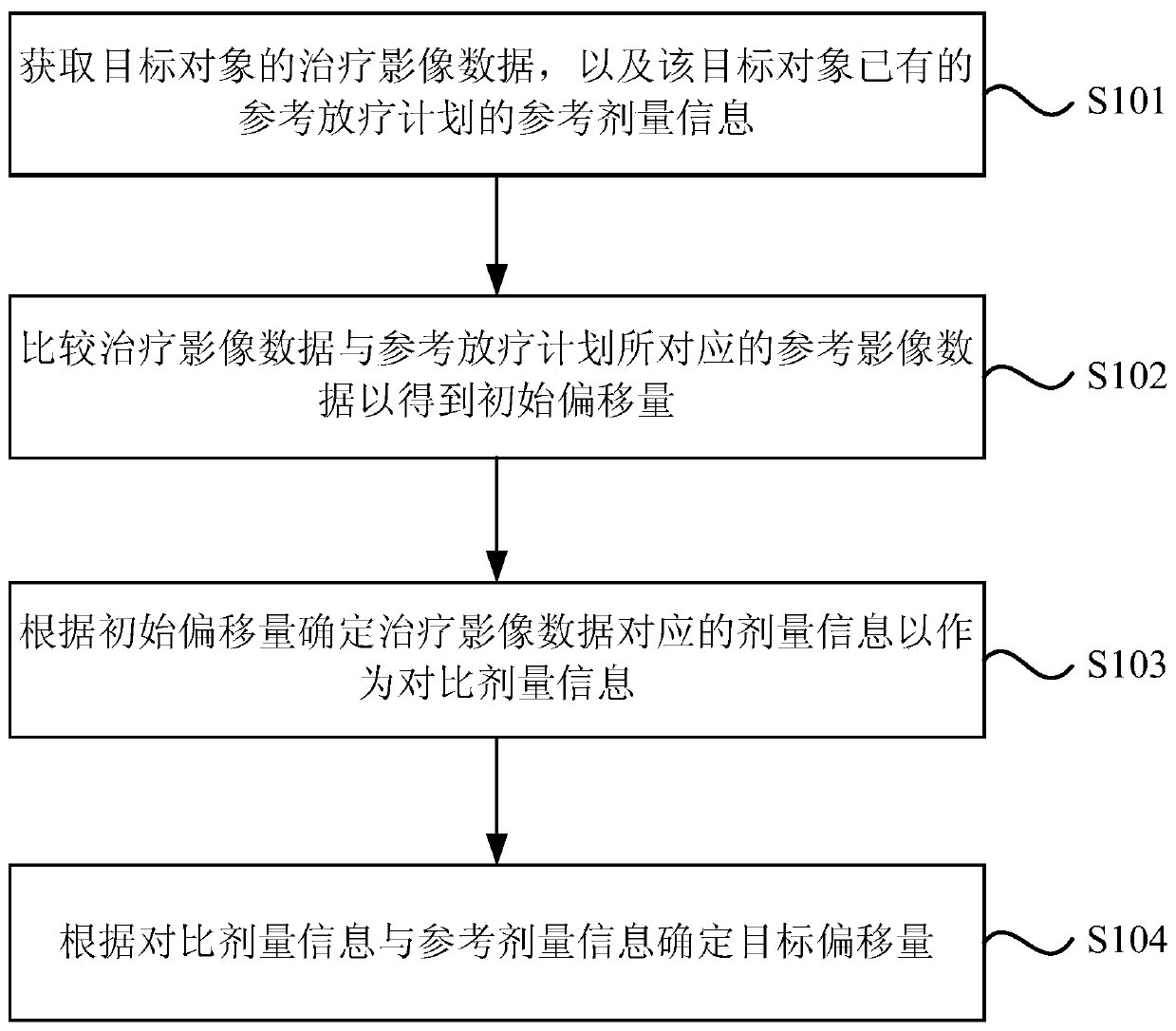
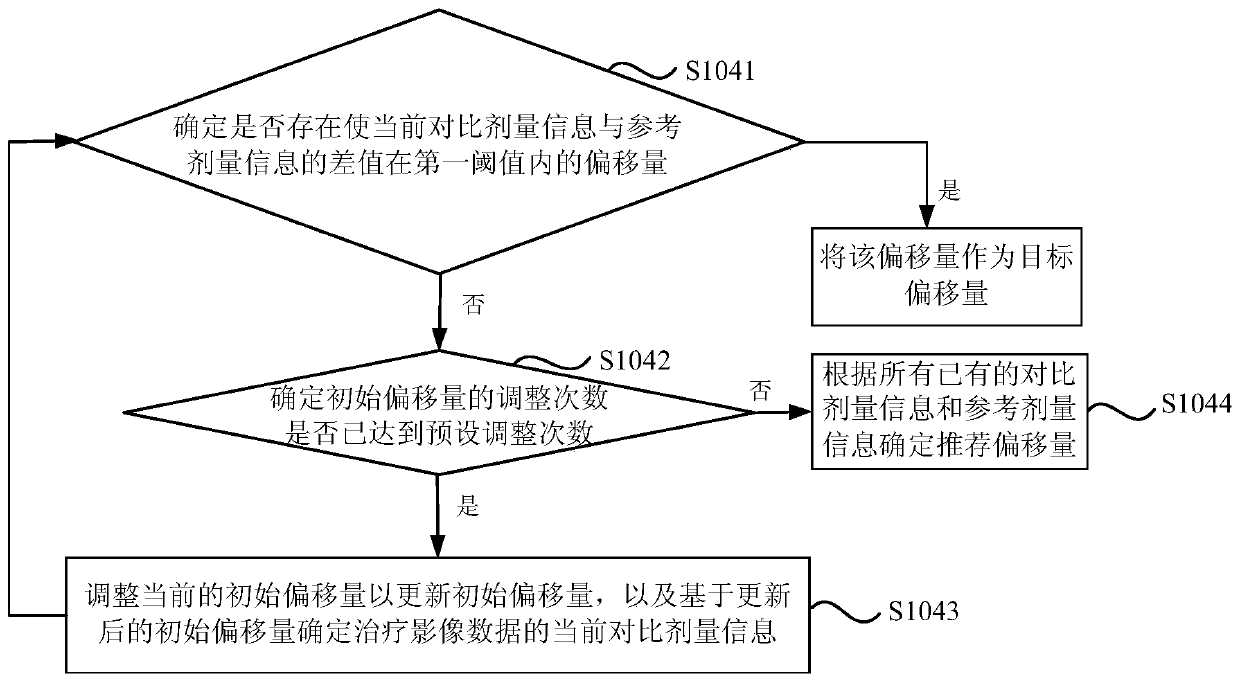
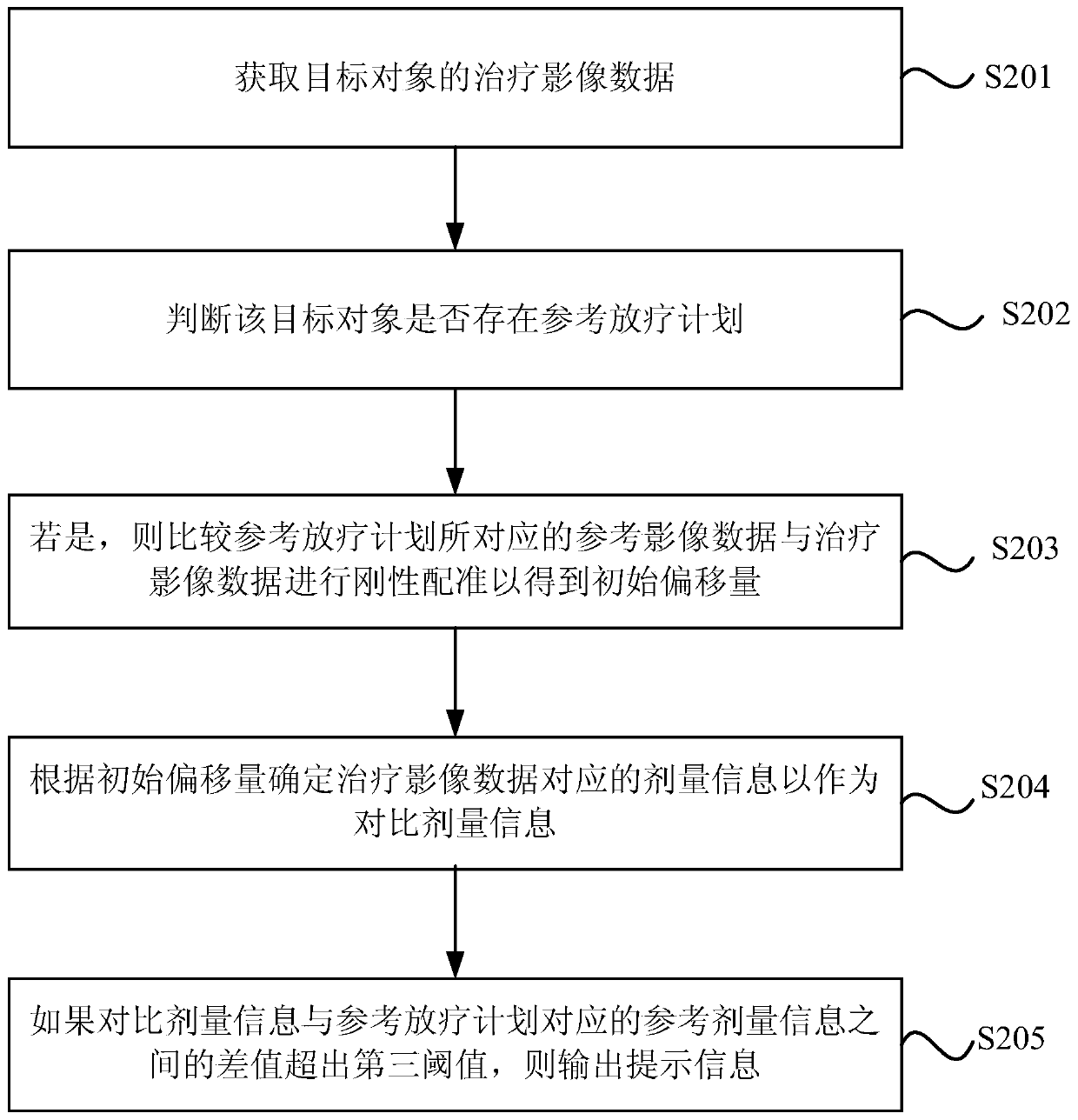
Dosage-guided positioning device, dosage monitoring device, radiotherapy system and medium
ActiveCN110292723ASimplify workImprove accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyReference imageComputer science
The embodiment of the invention discloses a dosage-guided positioning device, a dosage monitoring device, a radiotherapy system and a medium. The dosage-guided positioning device comprises a processor, wherein the processor is used for acquiring therapeutic image data of a target object and reference dosage information of an existing reference radiotherapy plan of the target object, comparing thetherapeutic image data with reference image data corresponding to the reference radiotherapy plan to obtain an initial offset, determining dosage information corresponding to the therapeutic image data as contrast dosage information according to the initial offset, and determining a target offset according to the contrast dosage information and the reference dosage information. The problem that the accuracy of image-guided radiotherapy positioning in the prior art excessively depends on the experience of a physicist or a technician is solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
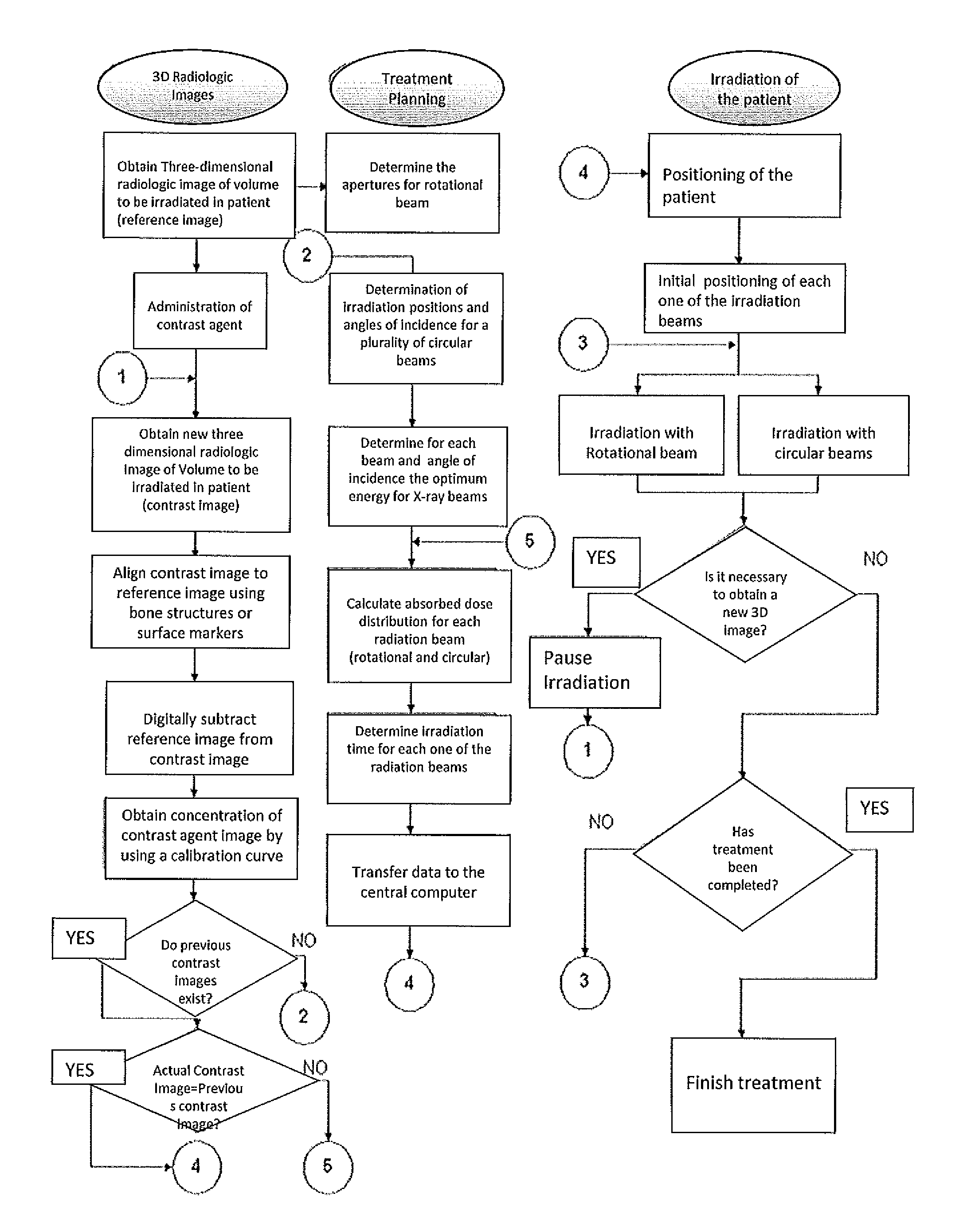
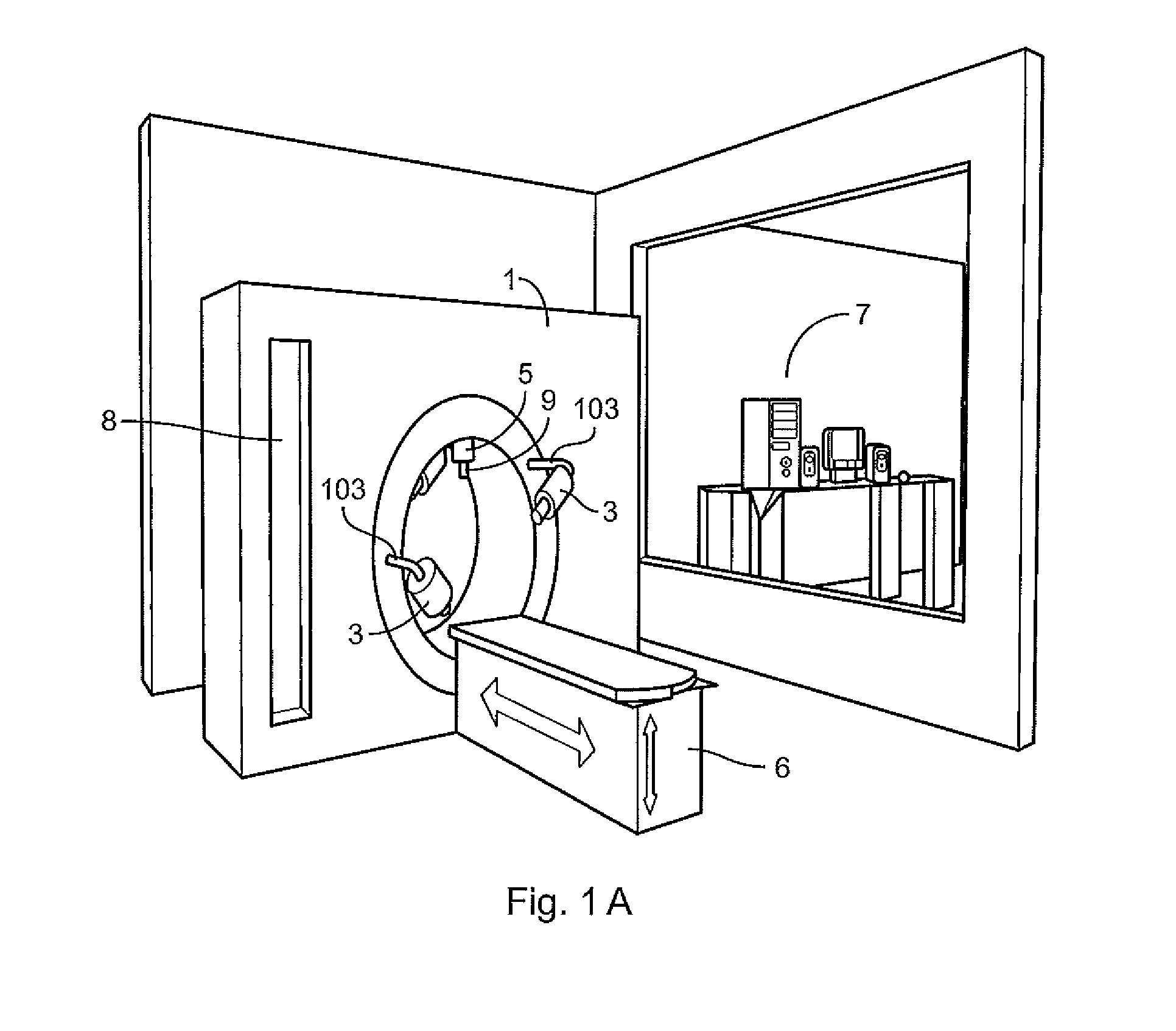
Apparatus and method to carry out image guided radiotherapy with kilo-voltage x-ray beams in the presence of a contrast agent
InactiveUS20120027162A1Reduce decreaseNecessary flexibilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer control systemX-ray
The present invention is related to an apparatus and method to carry out image-guided radiotherapy or radiosurgical treatments using Kilovoltage X-ray beams; one of the problems with the clinical application of this treatment consists in the absorbed dosage imparted unto a point within the subject to be irradiated depends on the local concentration of the contrast agent at that point, and the lack of properly quantifying the presence of the contrast agent at each point of the tumor or malformation to be irradiated results in a significant decrease in the quality of the treatment; the method and apparatus of the present invention resolve this and other problems. The Method consists of the following steps: a) determining the geometry of the patient and the concentration of the contrast agent at each point of the same, b) planning of treatment, and c) irradiating of the tumor or malformation; the apparatus includes a system to obtain three-dimensional images of the patient, a plurality of X-ray generating sources, a system to automatically position said X-ray generating sources in such a way that the radiation produced is directed towards the site to be irradiated in the patient, and a computer controlled system.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION & DE ESTUDIOS AVANZADOS DEL INST POLITECNICO NACIONAL
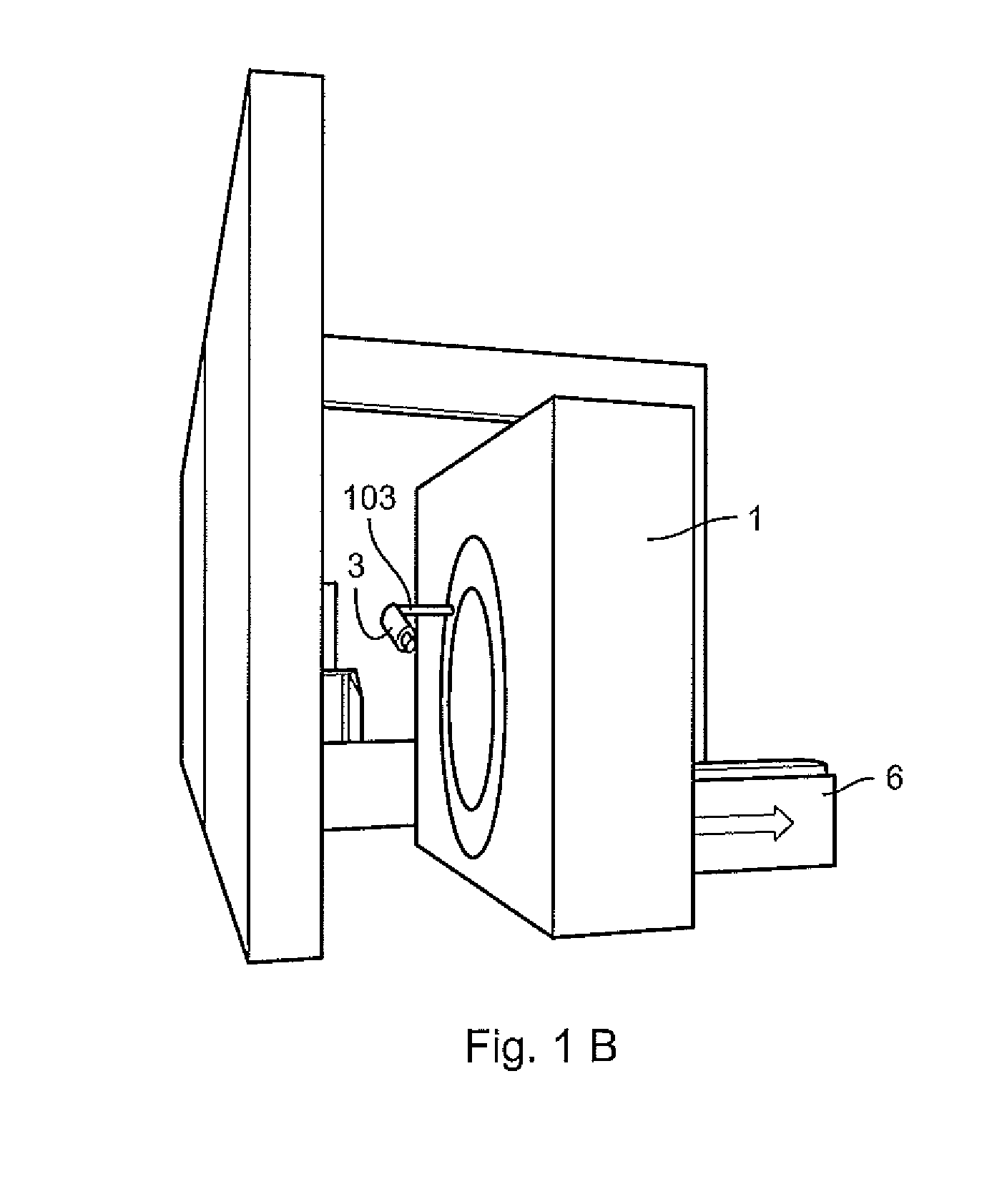
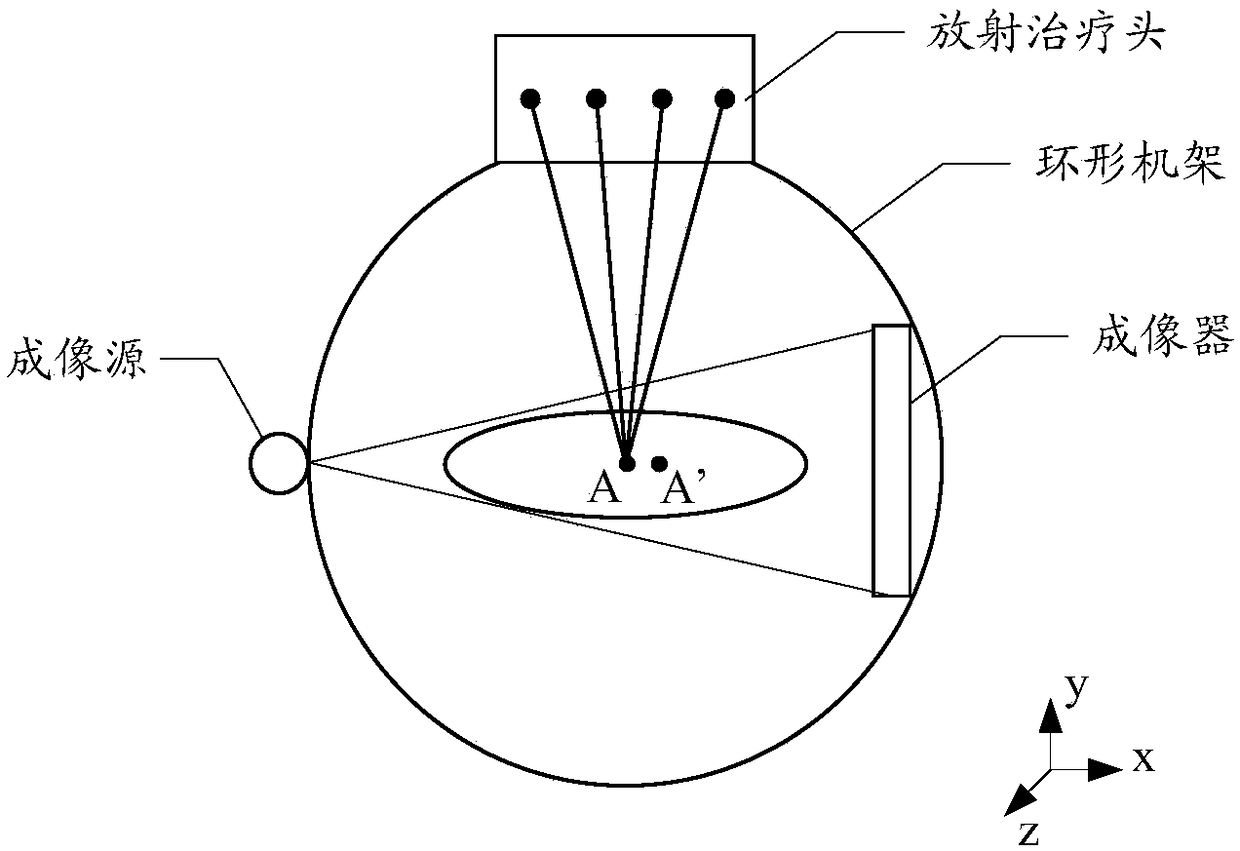
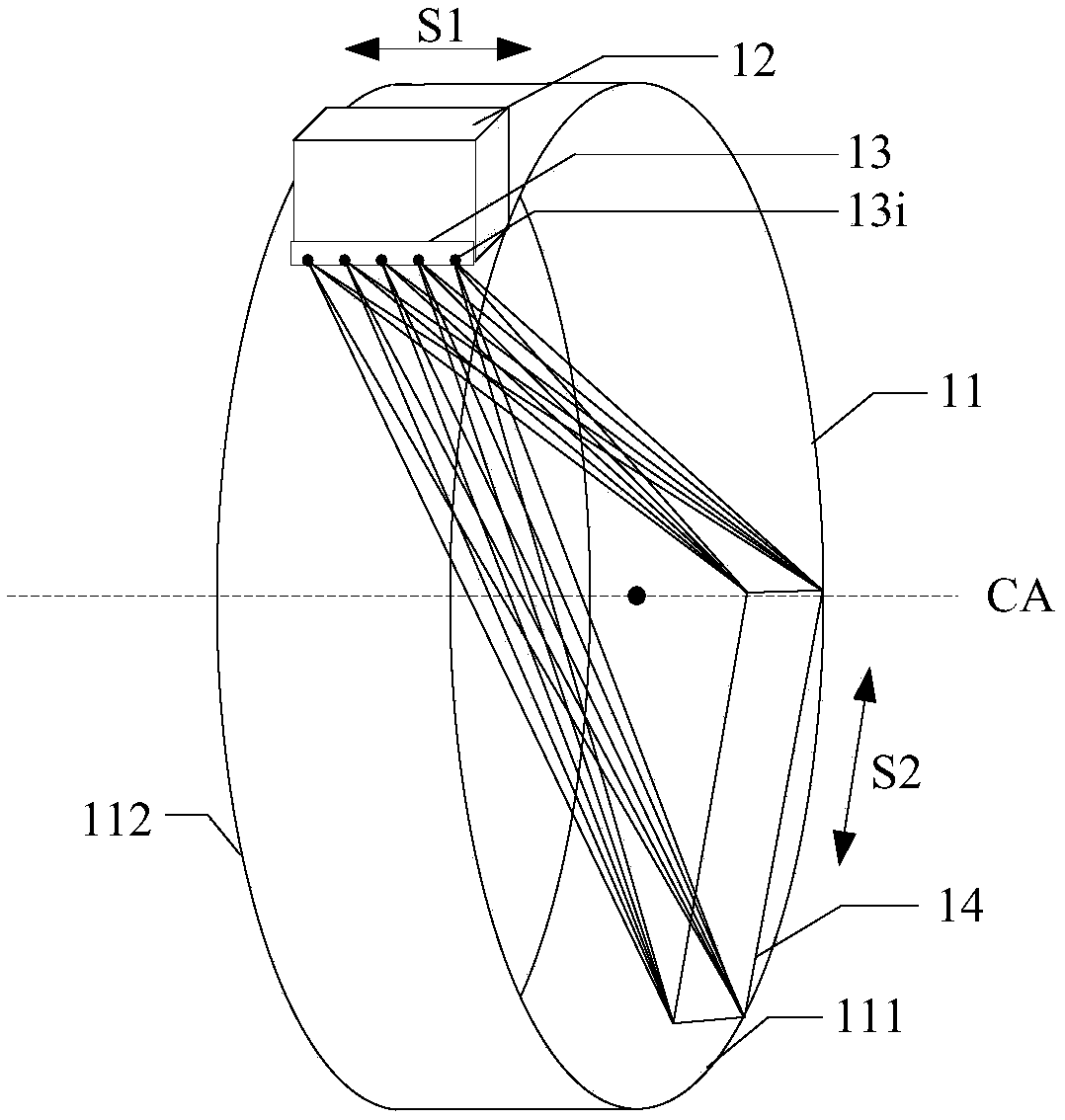
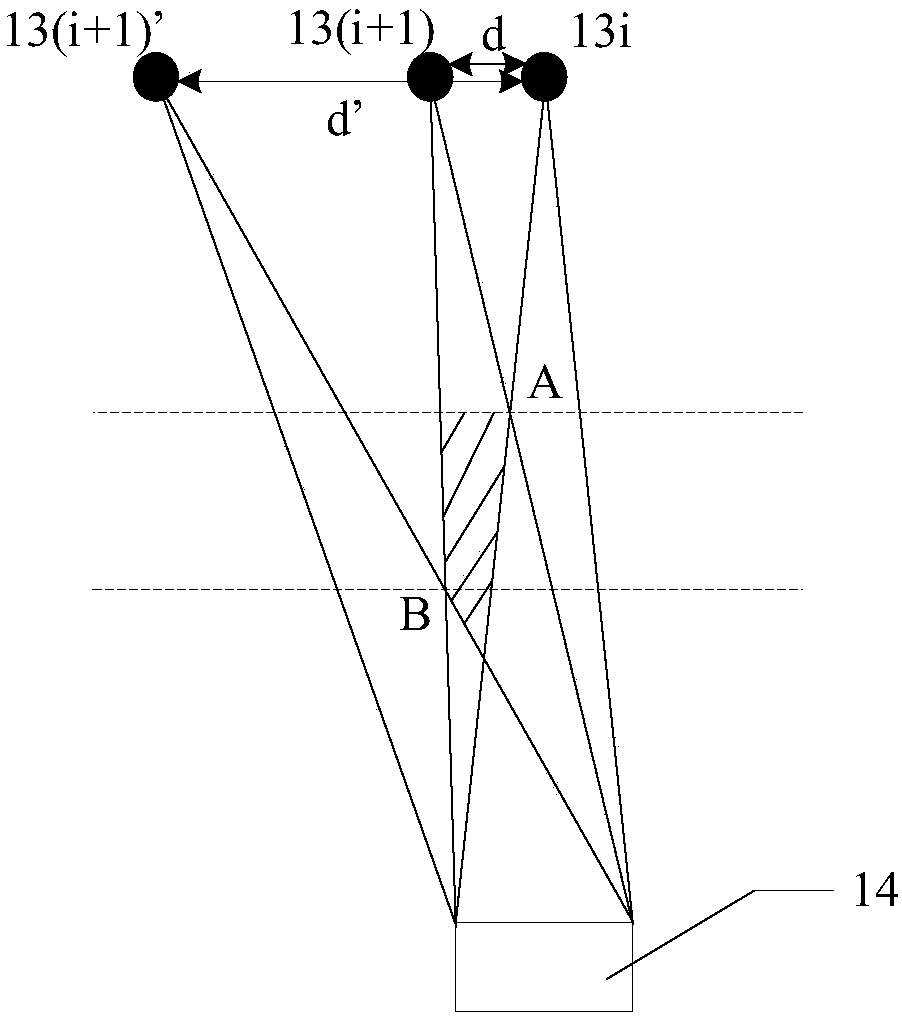
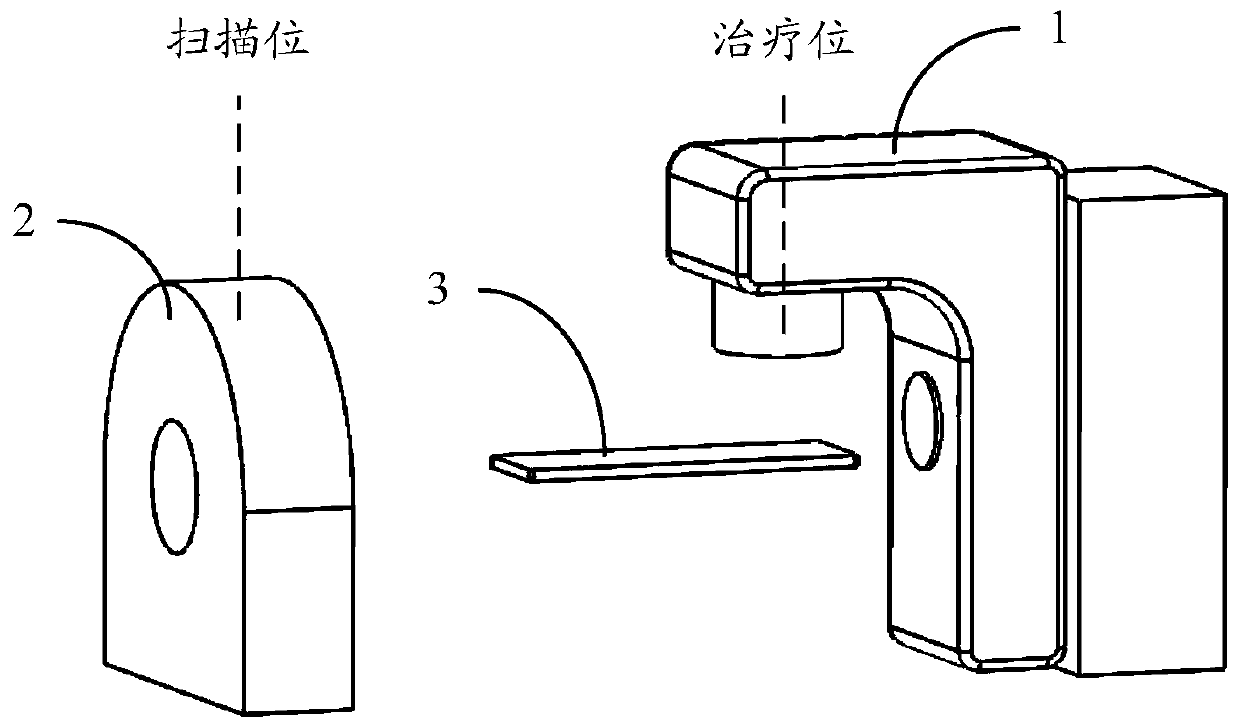
Image-guided radiotherapy equipment
PendingCN108310684AHigh precisionExact hitX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyEngineeringImage guided radiotherapy
The embodiment of the invention discloses image-guided radiotherapy equipment. The image-guided radiotherapy equipment comprises an annular rack, a radiotherapy head, a strip-shaped imaging source anda strip-shaped imager, wherein the annular rack can rotate around a central shaft; the radiotherapy head is arranged on the annular rack and is used for emitting treatment beams; the strip-shaped imaging source comprises a plurality of imaging sub-sources and is capable of respectively emitting imaging beams; the plurality of imaging sub-sources are arranged at positions close to the radiotherapyhead in a first direction; the strip-shaped imager is arranged on an opposite side of the strip-shaped imaging source in a second direction intersecting with the first direction and is used for receiving imaging beams passing through an affected part of a patient and converting the imaging beams into a three-dimensional imaging signal so as to generate a three-dimensional image of the affected part of the patient.
Owner:CYBERMED TECH XIAN +1
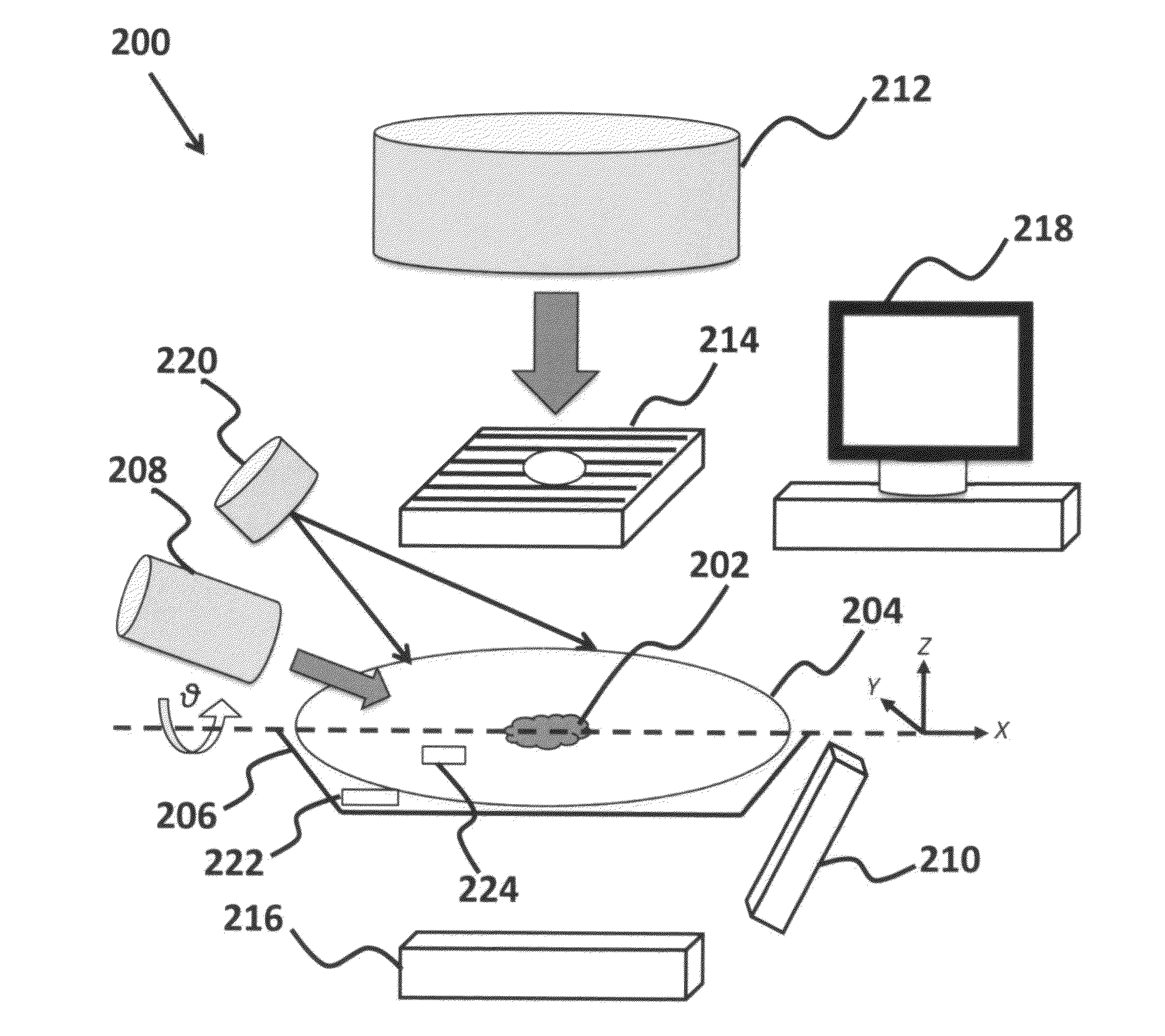
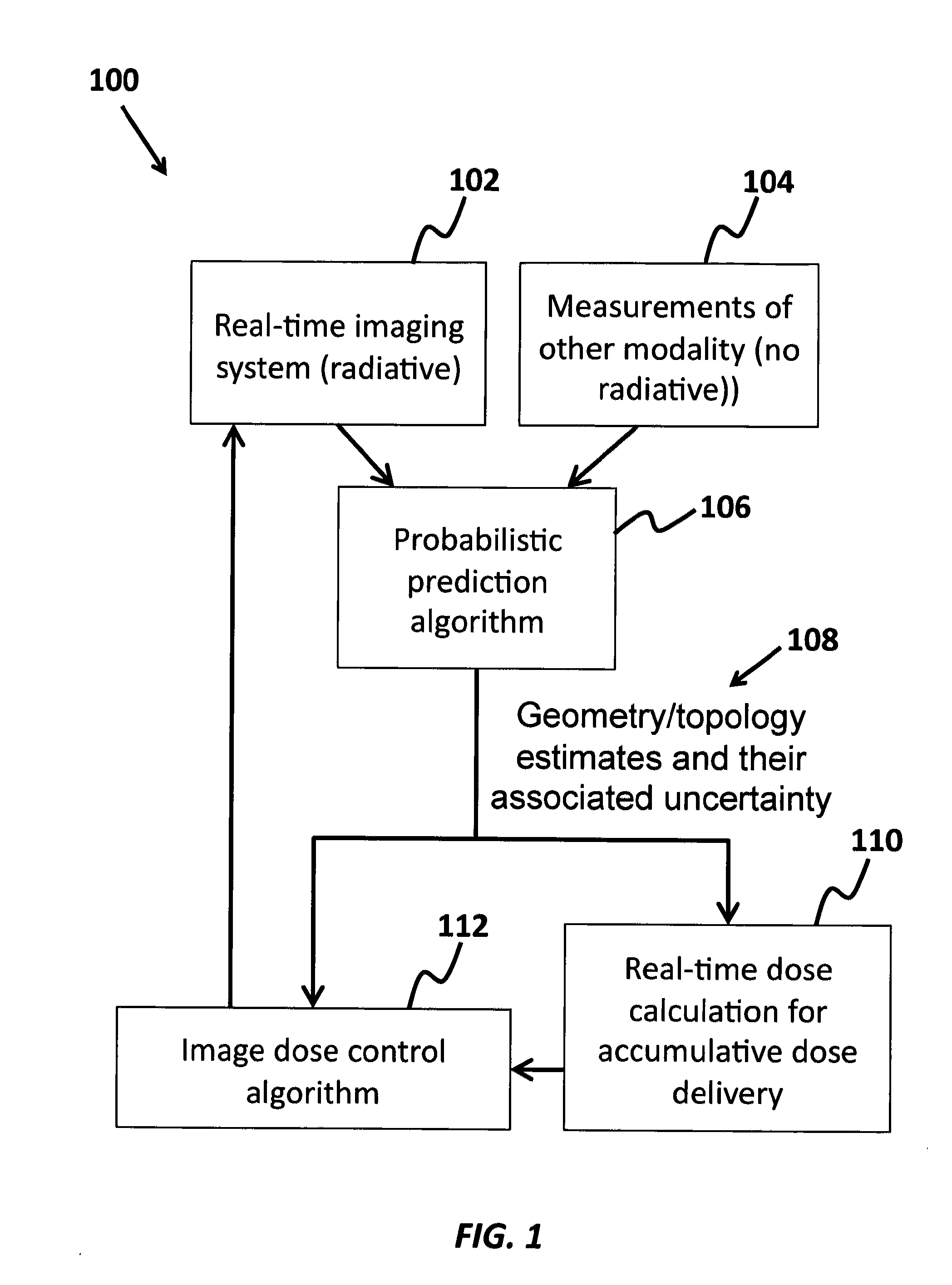
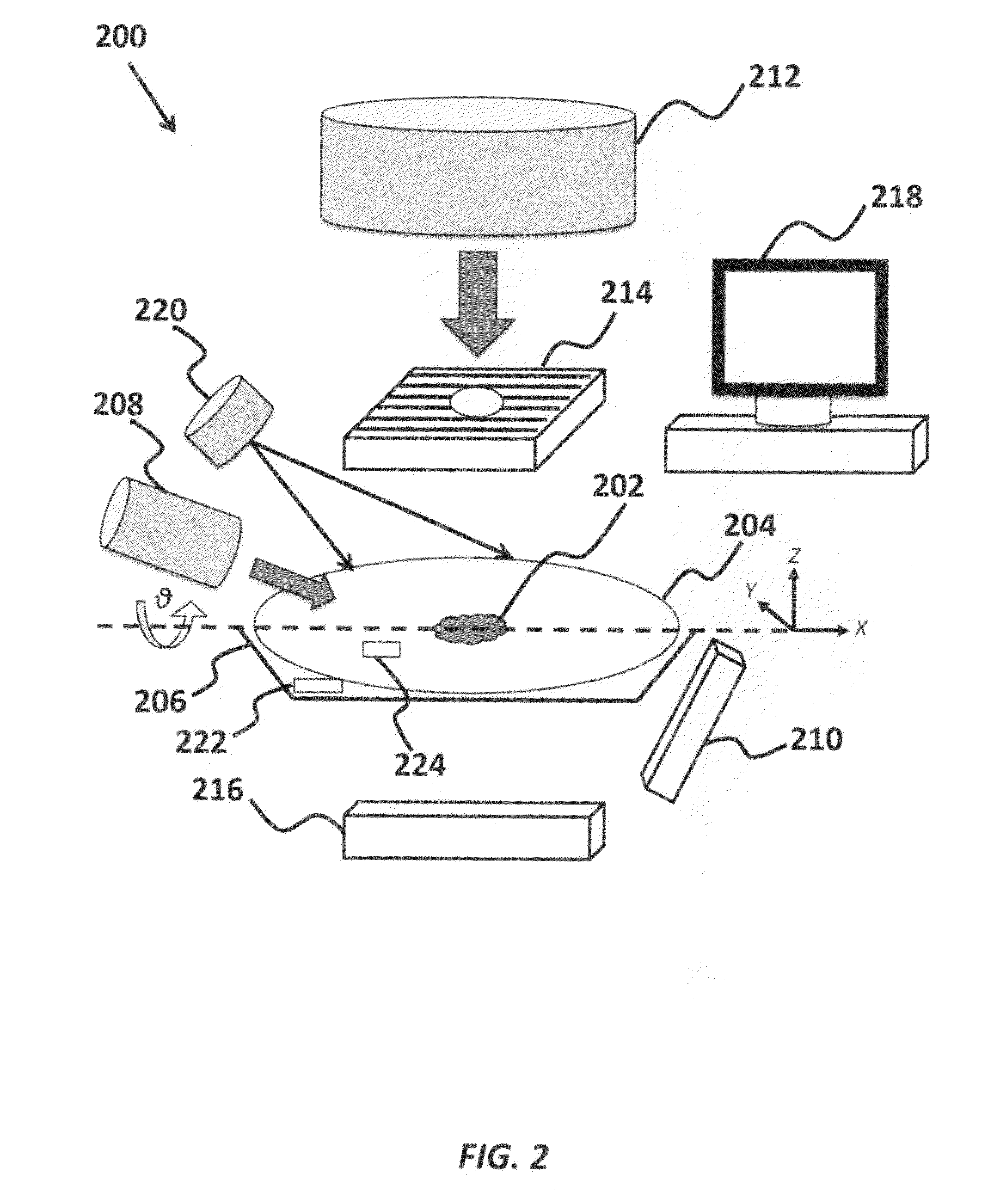
Method for reducing diagnostic radiation dose in image guided radiotherapy
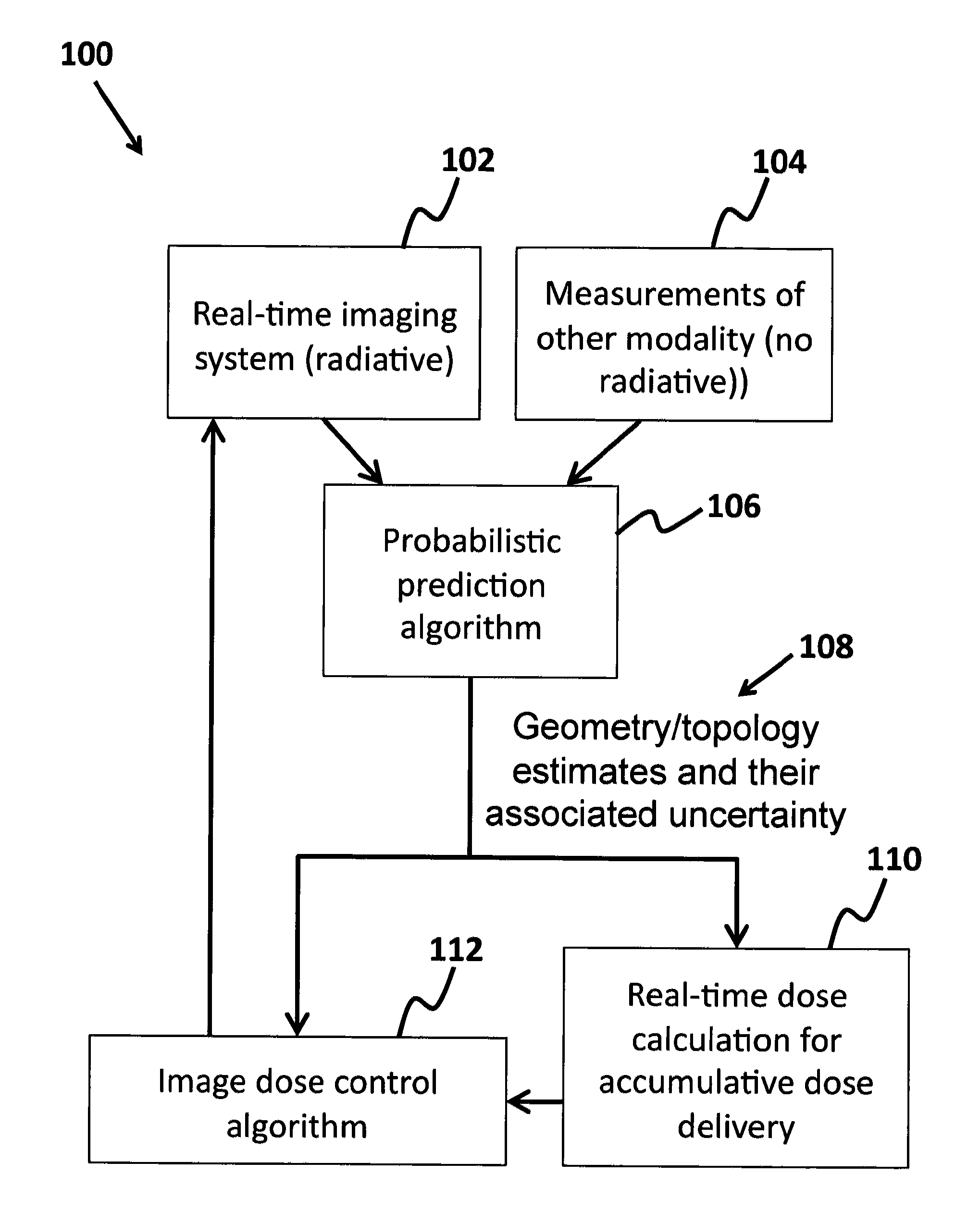
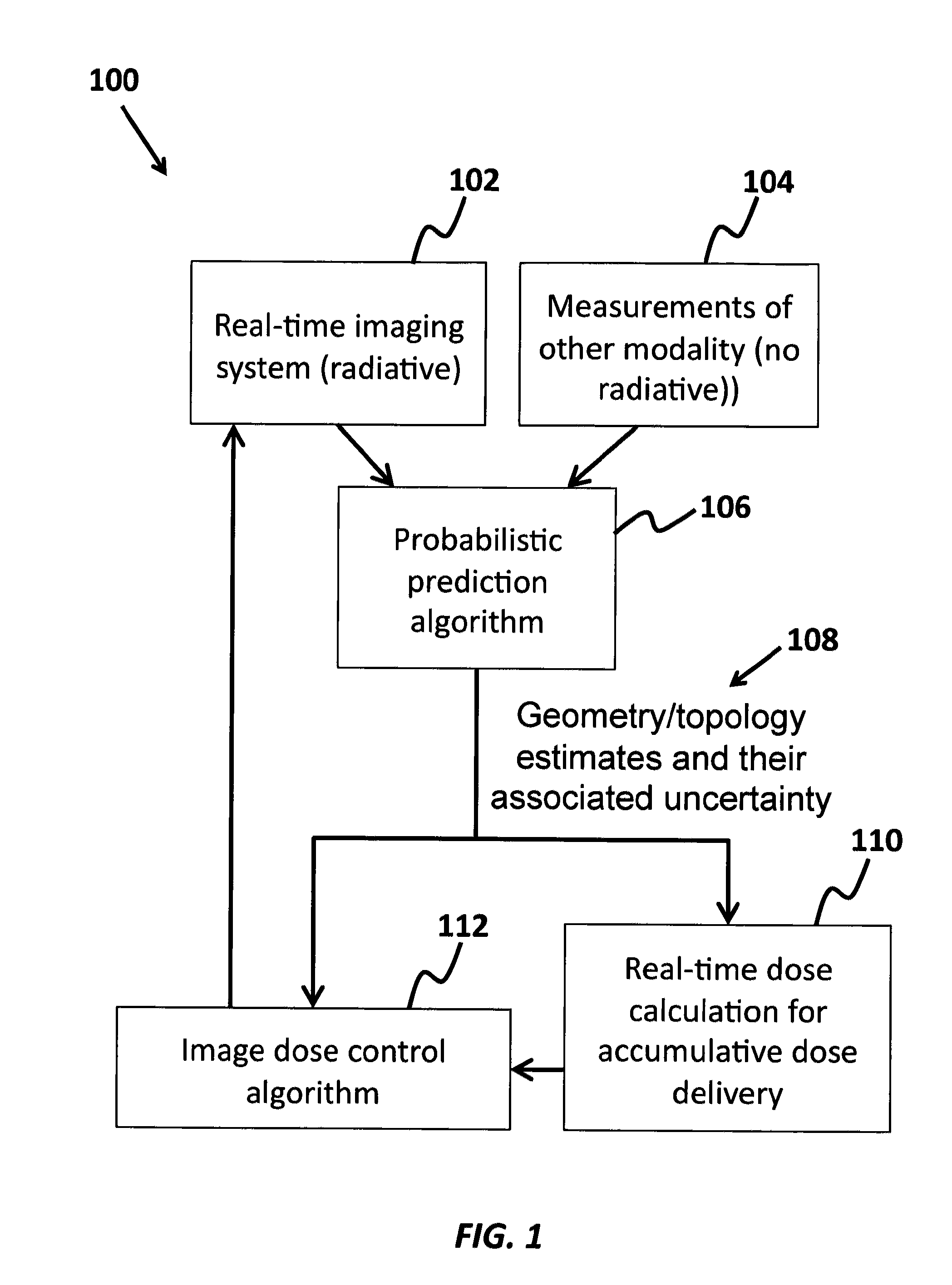
InactiveUS8837674B2Minimize ToxicityIncrease agreementX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsAdaptive imaging
A method of minimizing radiation toxicity in image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is provided that includes using a probabilistic prediction algorithm that is operated on a suitably programmed computer and includes multimodality inputs and provides real-time geometric and topological target estimates to compensate for system latency, using an online adaptive imaging system that provides radiographic images of the target when the geometric and topological target estimates are in a region of predefined uncertainty, and using an image dose control algorithm, operating on a suitably programmed computer, that includes parameters for controlling dose per image, where instances for image acquisition are optimized according to a planned dose pattern and delivery result.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Positioning deviation determining method and device
ActiveCN110038233AEliminate displacement in the height directionImprove irradiation accuracyX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyComputer sciencePosition bias
The invention discloses a positioning deviation determining method and device and belongs to the technical field of image-guided radiotherapy. The method can avoid errors in a positioning deviation acquisition process and comprises the steps as follows: acquiring first space coordinates of a treatment table in a therapy position and the distance between the isocenter and the upper surface of the treatment table; controlling the treatment table to move to a scanning position according to preset second space coordinates, and acquiring a reset scanning image of an object, wherein the reset scanning image comprises an image of the upper surface of the treatment table; determining the position aligning to the isocenter with the image of the upper surface of the treatment table as a reference inthe reset scanning image according to the first space coordinates, the second space coordinates and the distance; and determining position deviation between a treatment plan center and the isocenteraccording to a positioning scanning image and the reset scanning image, and determining the positioning deviation according to the position deviation.
Owner:SHENYANG NEUSOFT ZHIRUI RADIOTHERAPY TECH CO LTD
Image-Guided Radiotherapy For Internal Tumor Boost
ActiveUS20160051841A1X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMethod of imagesPrescribed radiation dose
A method of image-guided radiotherapy for treatment of a radio-resistant or radio-sensitive tumor. A three-dimensional visualized tumor image is obtained and the boundary of the tumor is identified. A boosted radiation dose of treatment is designated and applied to a boost region within the tumor boundary. A predetermined prescribed radiation dose is simultaneously applied with the boosted radiation dose within the tumor boundary and in a planning target volume region, which is outside of the tumor boundary. The boosted radiation dose outside of the boost region decreases at a boost dose decreasing rate such that the boosted radiation dose is equal to the predetermined prescribed radiation dose at the tumor boundary.
Owner:NGUYEN NAM
Method for reducing diagnostic radiation dose in image guided radiotherapy
InactiveUS20120076270A1Minimizing radiation toxicityMinimize ToxicityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyPrediction algorithmsAdaptive imaging
A method of minimizing radiation toxicity in image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) is provided that includes using a probabilistic prediction algorithm that is operated on a suitably programmed computer and includes multimodality inputs and provides real-time geometric and topological target estimates to compensate for system latency, using an online adaptive imaging system that provides radiographic images of the target when the geometric and topological target estimates are in a region of predefined uncertainty, and using an image dose control algorithm, operating on a suitably programmed computer, that includes parameters for controlling dose per image, where instances for image acquisition are optimized according to a planned dose pattern and delivery result.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Quality-control jig for use with radiotherapy apparatus
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method to estimate 3D abdominal and thoracic tumor position to submillimeter accuracy using sequential x-ray imaging and respiratory monitoring
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for acquiring magnetic resonance image data for image-guided radiotherapy
ActiveUS20190290932A1Improve comparabilityGood reproducibilityMagnetic measurementsSurgeryResonanceMri image
In a method for acquiring magnetic resonance raw data for image-guided radiotherapy, a number of imaging goals are provided to a computer. For each imaging goal, a magnetic resonance imaging protocol is selected. For each selected magnetic resonance imaging protocol, a number of parameters for that protocol are adjusted according to the respective imaging goal. The resonance raw data are acquired with the magnetic resonance imaging protocol and their parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Apparatus and method to carry out image guided radiotherapy with kilo-voltage X-ray beams in the presence of a contrast agent
InactiveUS8681937B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer control systemTreatment use
The present invention is related to an apparatus and method to carry out image-guided radiotherapy or radiosurgical treatments using Kilovoltage X-ray beams; one of the problems with the clinical application of this treatment consists in the absorbed dosage imparted unto a point within the subject to be irradiated depends on the local concentration of the contrast agent at that point, and the lack of properly quantifying the presence of the contrast agent at each point of the tumor or malformation to be irradiated results in a significant decrease in the quality of the treatment; the method and apparatus of the present invention resolve this and other problems. The Method consists of the following steps: a) determining the geometry of the patient and the concentration of the contrast agent at each point of the same, b) planning of treatment, and c) irradiating of the tumor or malformation; the apparatus includes a system to obtain three-dimensional images of the patient, a plurality of X-ray generating sources, a system to automatically position said X-ray generating sources in such a way that the radiation produced is directed towards the site to be irradiated in the patient, and a computer controlled system.
Owner:CENT DE INVESTIGACION & DE ESTUDIOS AVANZADOS DEL INST POLITECNICO NACIONAL
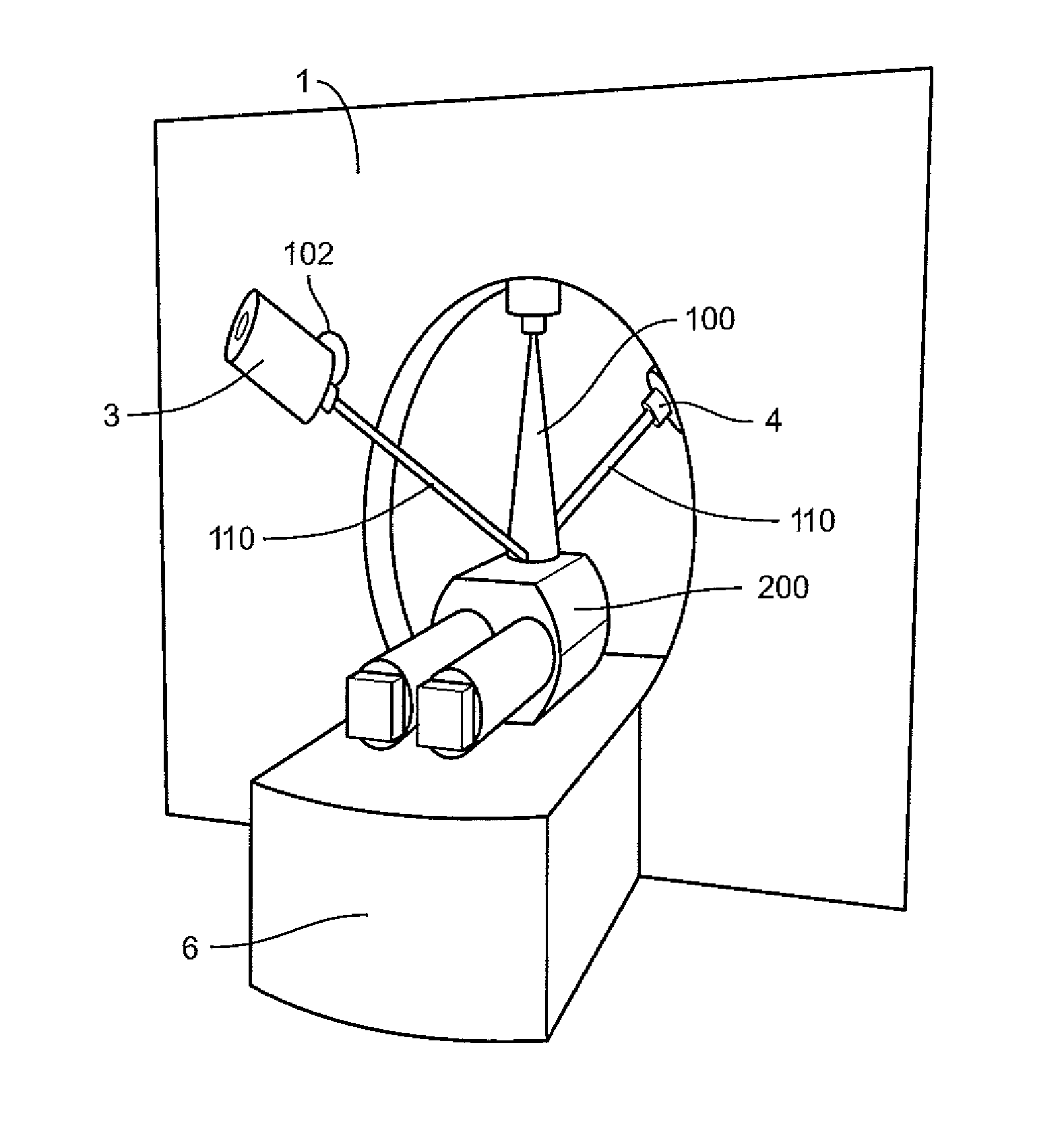
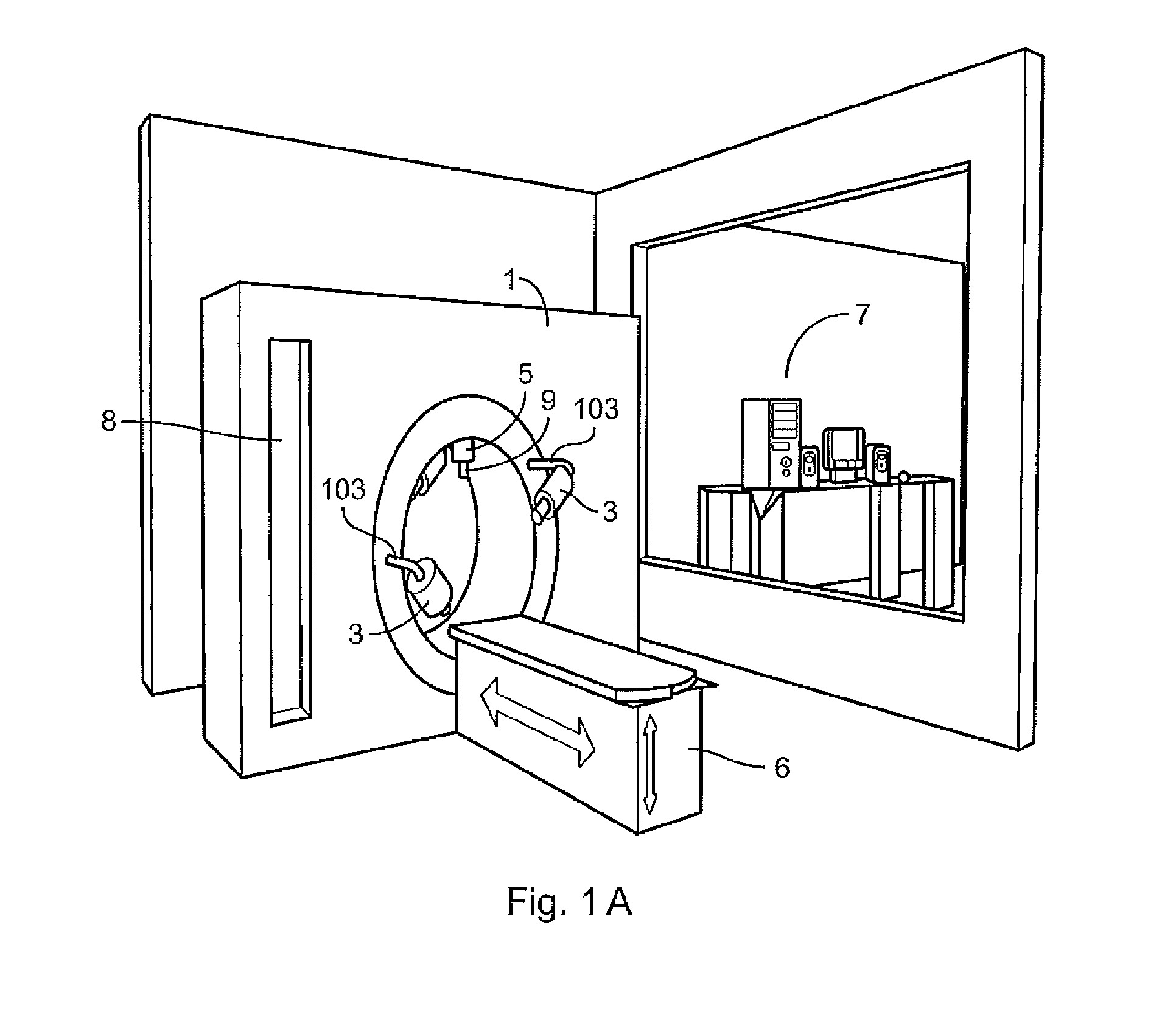
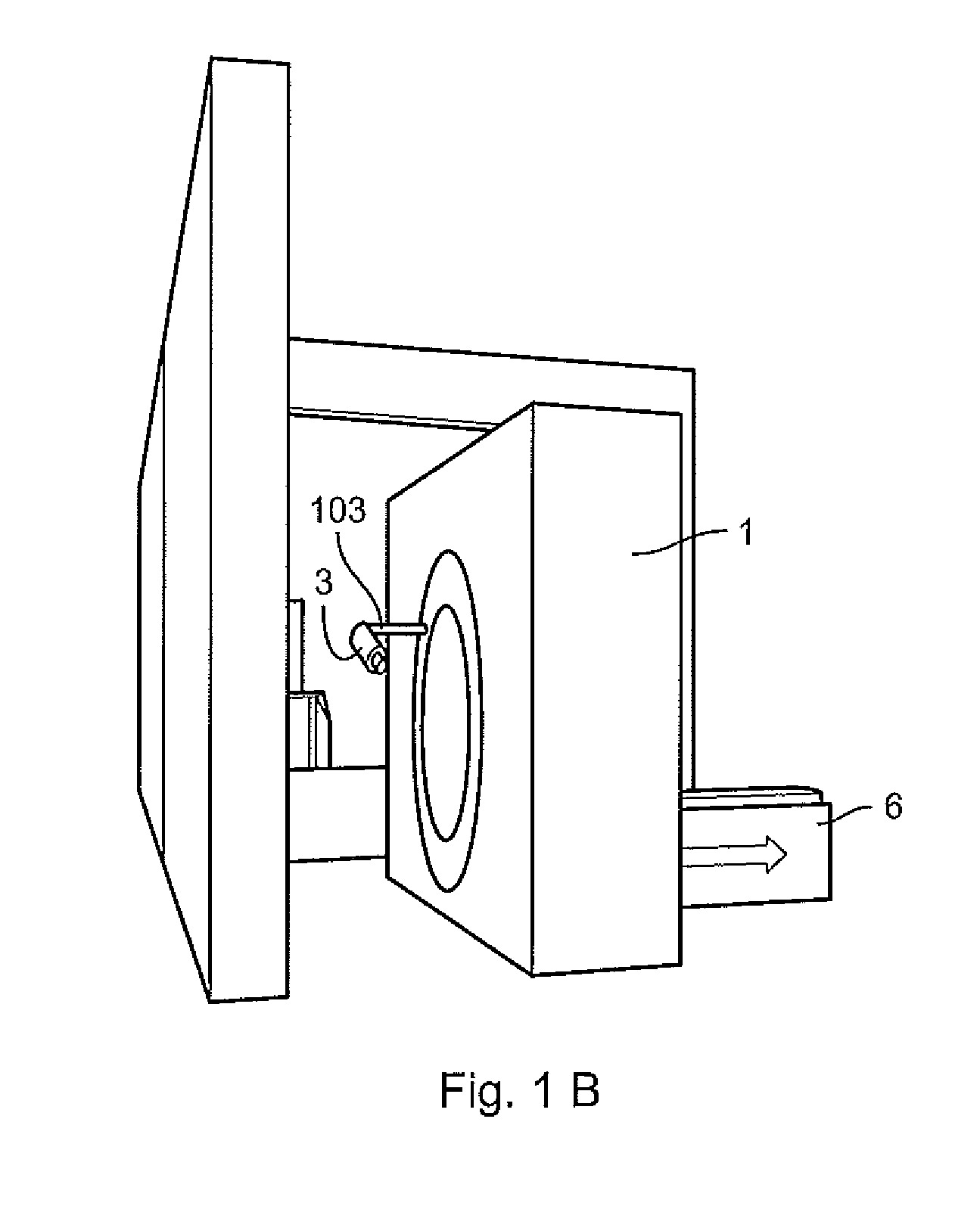
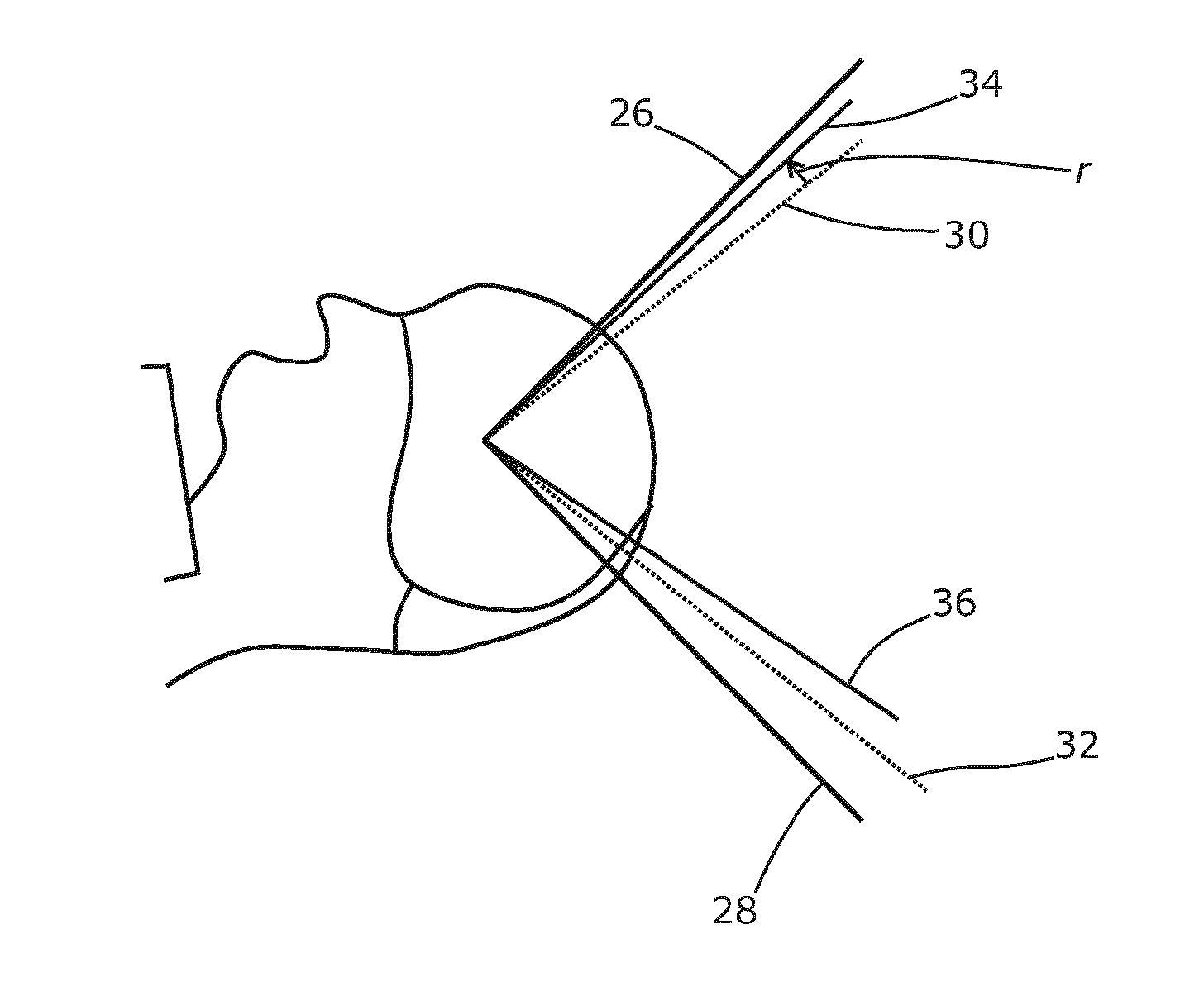
Image guided radiotherapy
An apparatus is disclosed, which comprises a radiotherapy delivery apparatus having a radiation source for emitting a beam of radiation and rotatable around an axis intersecting the beam through a range of at least x degrees, an imaging device, and a control unit for controlling the source and imaging device. The apparatus further comprises a treatment planning computer configured to receive a first image of a patient, and receive parameters defining the operations of the radiotherapy delivery apparatus. The parameters include an available range of rotation for the source defined as x-e, where e>0. The treatment planning computer is further configured to generate a treatment plan for the patient based on the received image and parameters. The control unit determines a patient position using the imaging device, determines a rotation r of the patient around the axis relative to the first image, and compensates for the rotation by offsetting the source by a rotation equal to r when r<e.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Nanoparticle-guided radiotherapy
The present invention relates to a method and nano-sized particles for image guided radiotherapy (IGRT) of a target tissue. More specifically, the invention relates to nano-sized particles comprising X-ray-imaging contrast agents in solid form with the ability to block x-rays, allowing for simultaneous or integrated external beam radiotherapy and imaging, e.g., using computed tomography (CT).
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Image-guided radiotherapy for internal tumor boost
ActiveUS10166405B2X-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMethod of imagesPrescribed radiation dose
A method of image-guided radiotherapy for treatment of a radio-resistant or radio-sensitive tumor. A three-dimensional visualized tumor image is obtained and the boundary of the tumor is identified. A boosted radiation dose of treatment is designated and applied to a boost region within the tumor boundary. A predetermined prescribed radiation dose is simultaneously applied with the boosted radiation dose within the tumor boundary and in a planning target volume region, which is outside of the tumor boundary. The boosted radiation dose outside of the boost region decreases at a boost dose decreasing rate such that the boosted radiation dose is equal to the predetermined prescribed radiation dose at the tumor boundary.
Owner:NGUYEN NAM
Device for installing image guidance radiotherapy device detection screen
The invention provides a device for installing an image guidance radiotherapy device detection screen, and belongs to the technical field of auxiliary medical instruments. The device comprises a lifting mechanism arranged on the left side of the device and used for driving the device to ascend and descend vertically, a telescopic mechanism arranged on the upper side of the device and used for driving the device to conduct telescopic motion forwards and backwards, and a folding mechanism arranged on the rear side of the device and used for driving the device to be unfolded and folded. The lifting mechanism comprises a first motor, a first coupler, a first lead screw, a first lead screw sliding nut, a first lead screw sliding nut seat and the like. The telescopic device comprises a third motor, a third coupler, a third lead screw, a third lead screw sliding nut, a third lead screw sliding nut seat and the like. The folding device comprises a second motor, a second coupler, a second lead screw, a second lead screw sliding nut, a second lead screw sliding nut seat and the like. In the using process, the ascent and descent motion, the telescopic motion and the folding motion are independent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
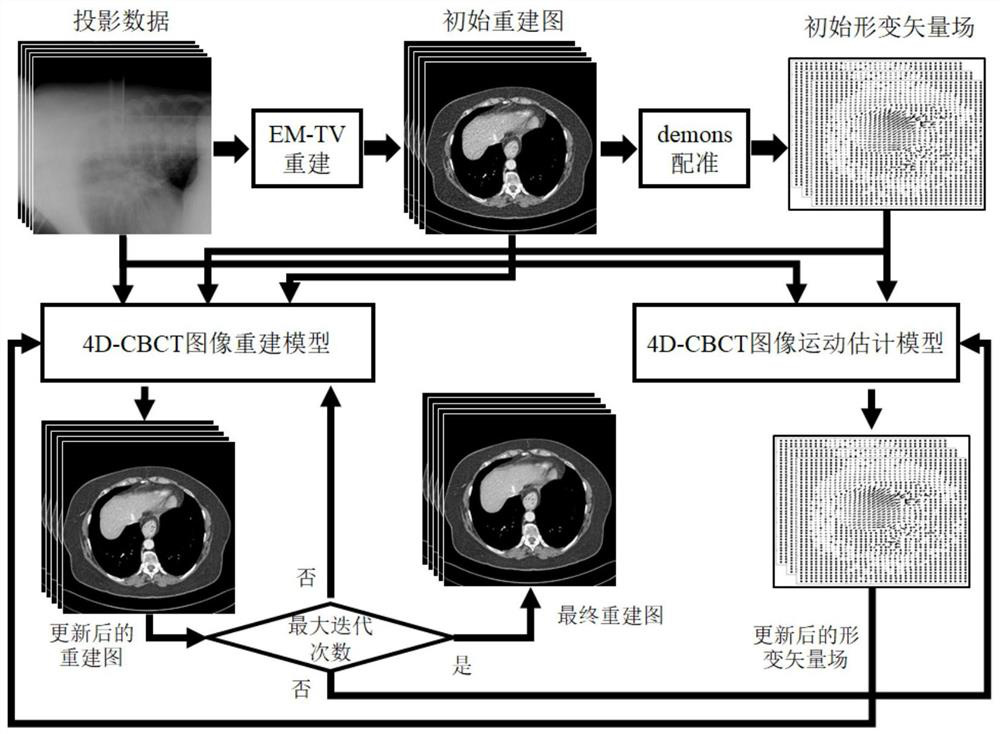
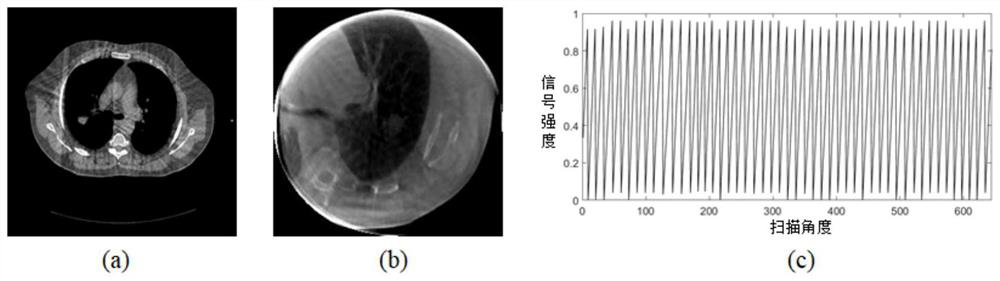
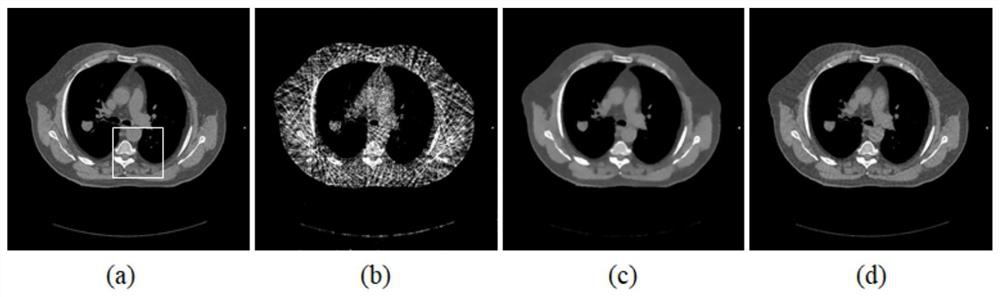
4D-CBCT reconstruction method combining motion estimation and space-time tensor enhanced representation
PendingCN111951346AReduce blurPrecise positioningImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionComputed tomography
The invention discloses a 4D-CBCT reconstruction method combining motion estimation and space-time tensor enhancement representation, and belongs to the technical field of computed tomography. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out phase division on 4DCBCT projection data of a patient by utilizing a respiration signal, reconstructing by adopting an EMTV algorithm to obtainan initial image, and estimating an initial deformation vector field by utilizing the initial image; then, introducing the space-time tensor enhancement representation into an image reconstruction model, constraining the reconstructed image after deformation vector field processing, and obtaining an updated reconstructed image; then, establishing a symmetrical motion estimation model by utilizingthe updated reconstructed image and the projection data to obtain a new deformation vector field; and finally, alternately updating the reconstructed image and the deformation vector field through iteration to obtain a high-quality reconstructed image. Motion blur and aliasing artifacts in 4D-CBCT reconstruction can be effectively relieved, more details are reserved, the contrast ratio of the reconstructed image is improved, and the 4D-CBCT is promoted to be used in the field of image guided radiotherapy.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com