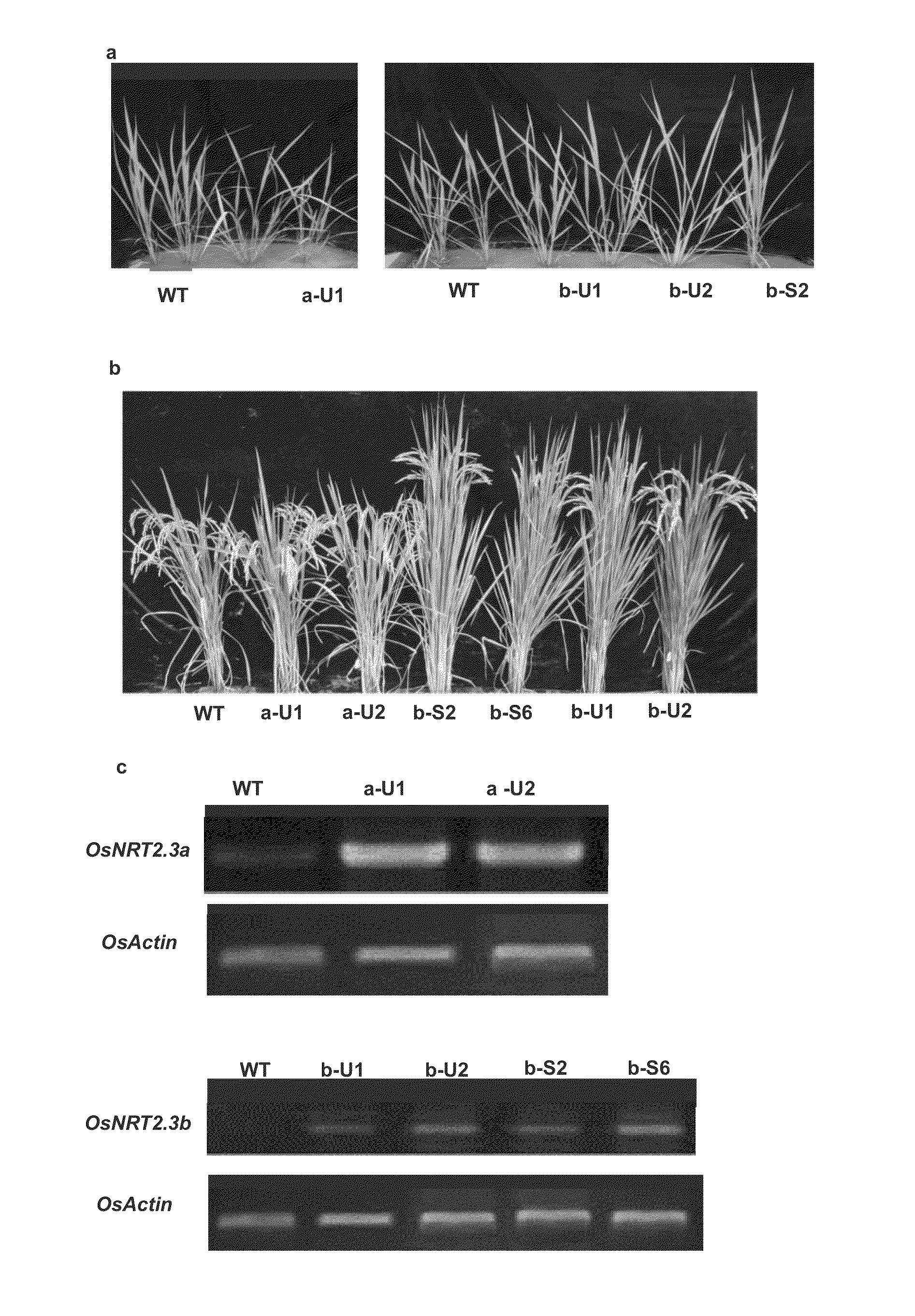
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Nitrate transporters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
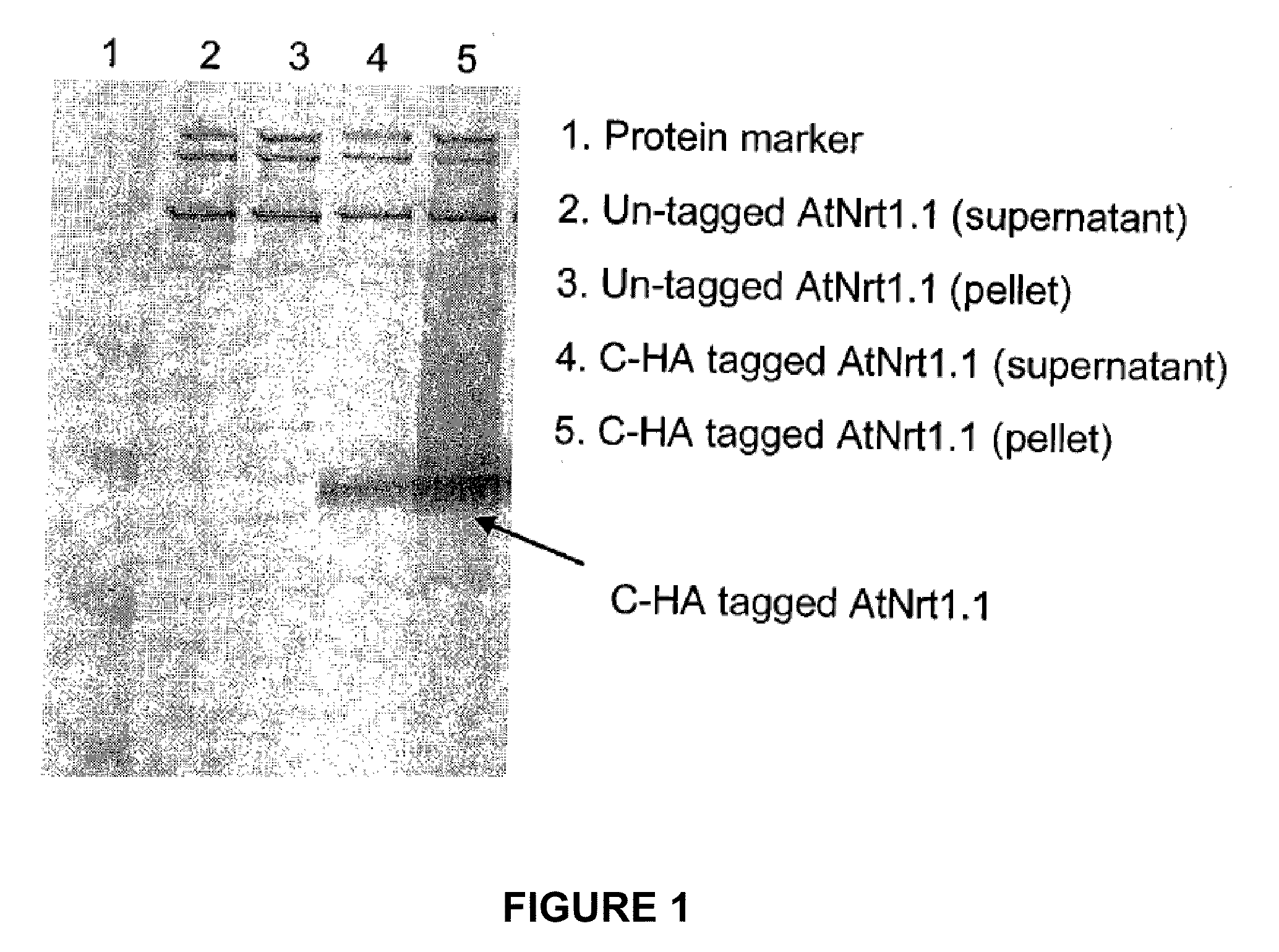
Nitrate transporters belonging to two different families (the NNP and the PTR families) have now been identified in plants, each of which is represented by multiple genes that are differentially regulated and which may encode transporters with different regulatory or kinetic properties.
Application of rice nitrate transporter NRT1.1B in enhancing nitrogen utilization efficiency of plants
ActiveCN104277101AIncreased nitrate levelsClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesNitrate transportNitrogen fertilization
The invention discloses application of a rice nitrate transporter NRT1.1B in enhancing nitrogen utilization efficiency of plants. The protein NRT1.1B is disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table, and can be used for enhancing nitrate content of plants or enhancing nitrate transport capacity of plants, thereby enhancing the nitrogen utilization efficiency of the plants. The experimental result proves that when the nitrate transporter NRT1.1B in the rice is overexpressed to obtain the transgenic strain, the nitrate content is obviously enhanced, which indicates that the nitrate transporter NRT1.1B has important application potential in enhancing nitrogen utilization efficiency. The invention provides a new way for culturing crops with high nitrogen fertilizer utilization ratio.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
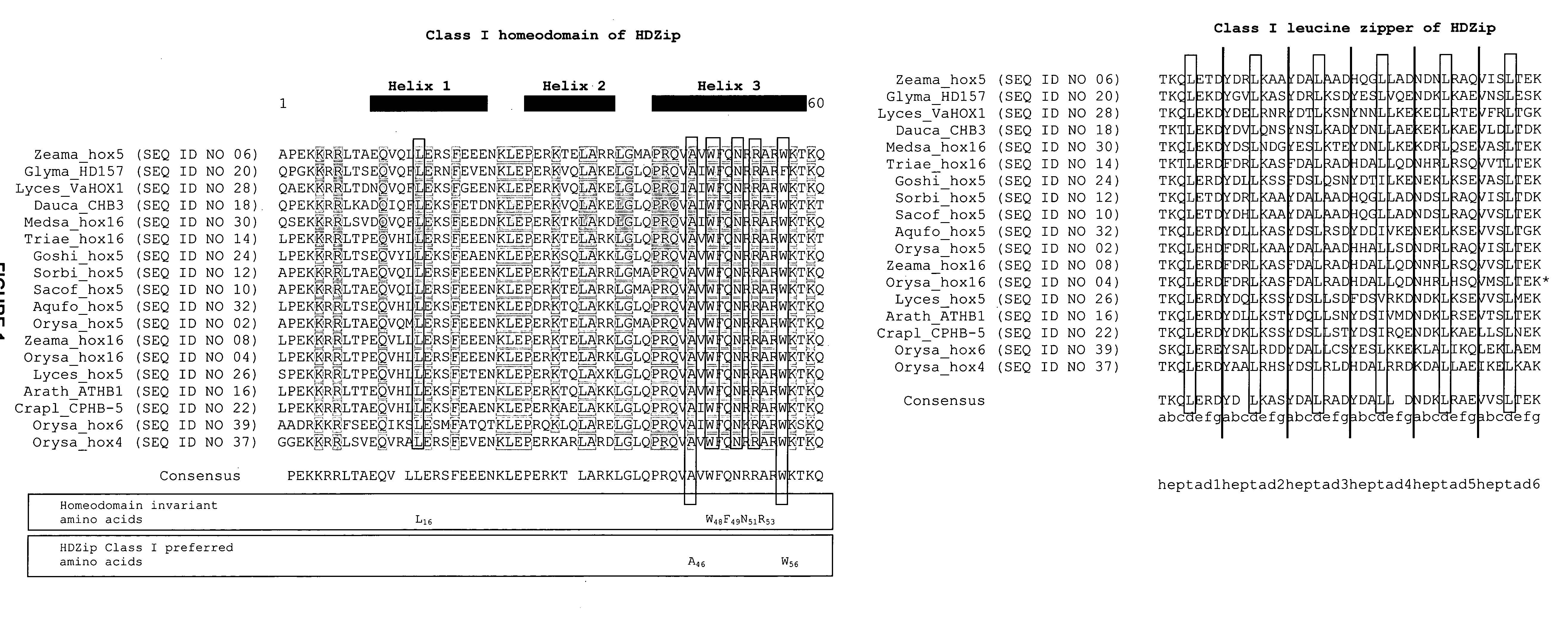
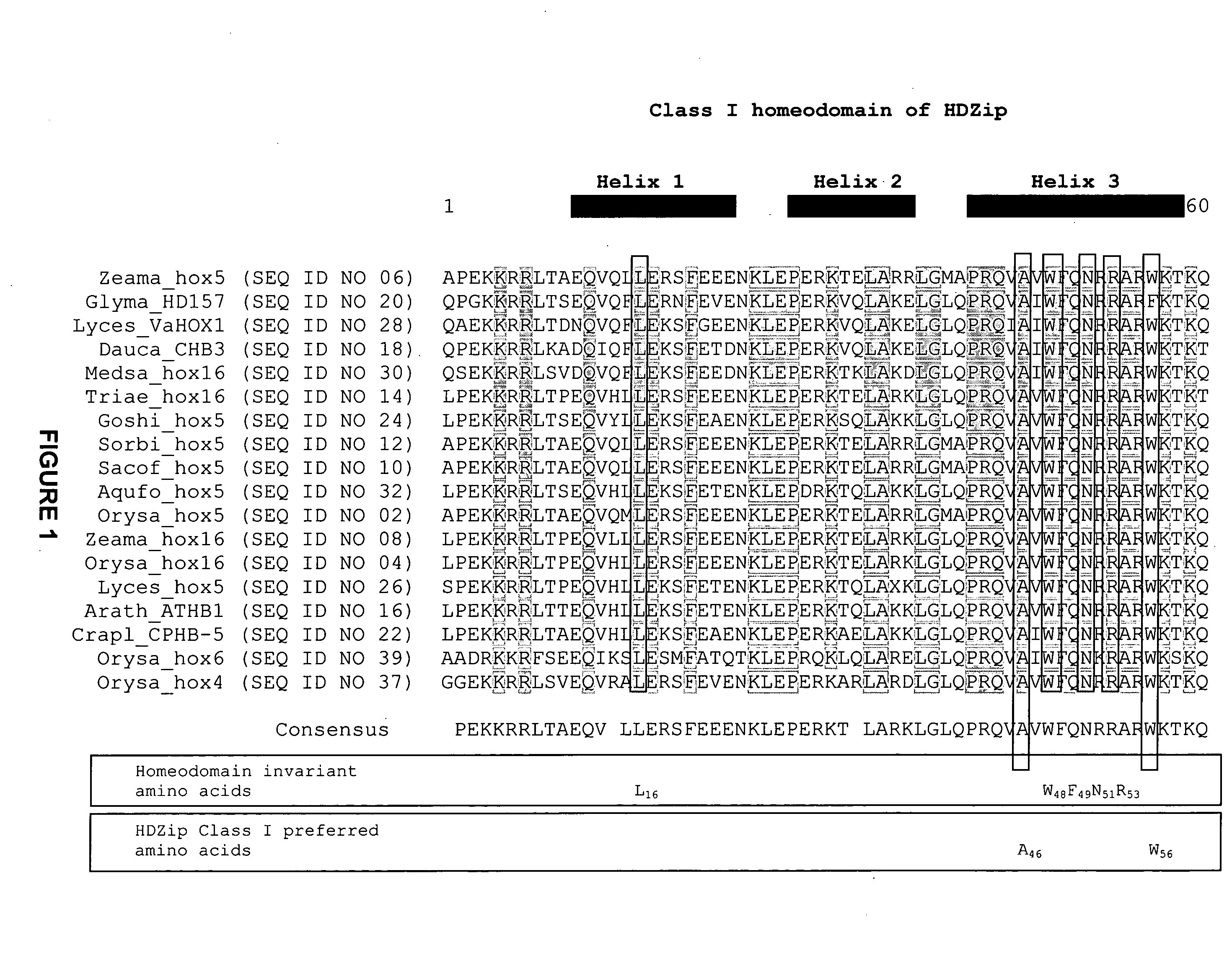
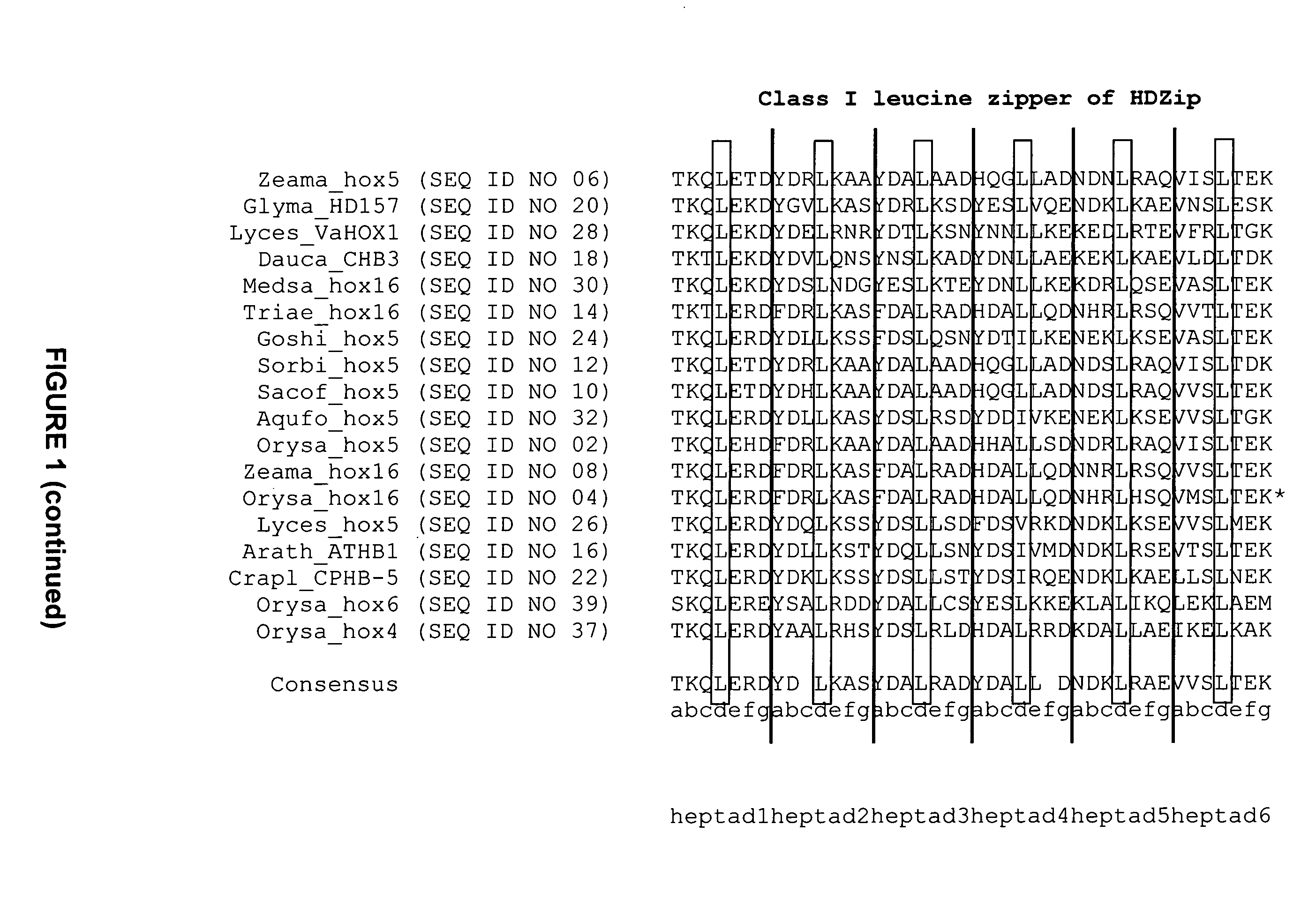
InactiveUS20080127365A1Improve featuresSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGlycogen synthase I
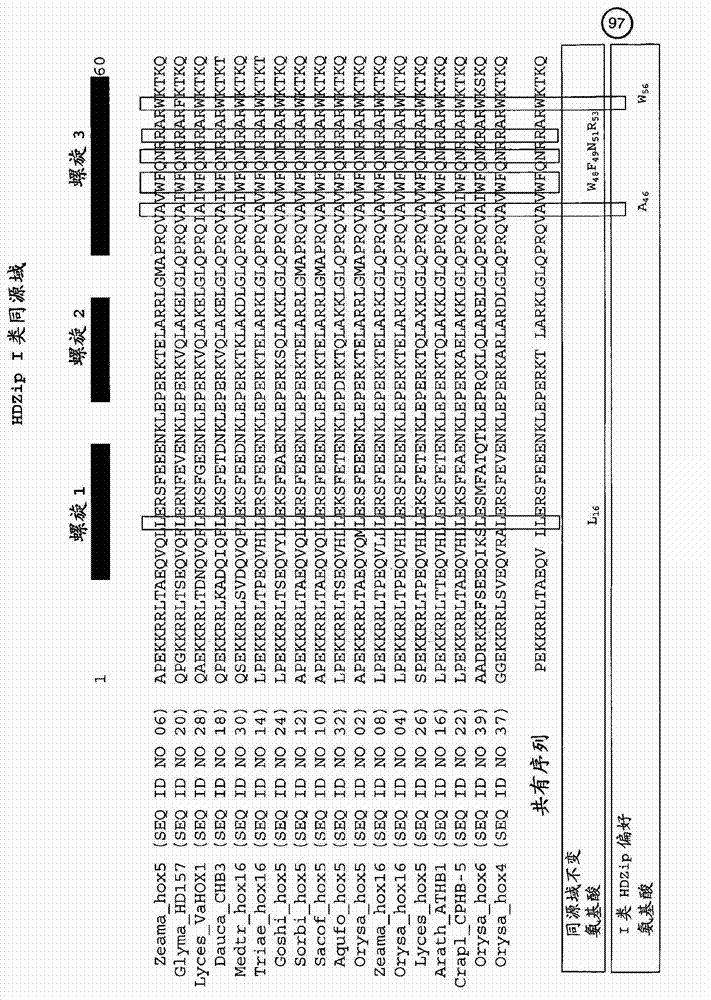
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I HDZip hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a NRT protein or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted YEP16; or having modulated expression of a Group I shaggy-like kinase or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
Plant nitrate transporters and uses thereof
PendingCN107208100AImprove qualityClimate change adaptationStable introduction of DNANitrogenTransgene
Methods and compositions that affect yield and other agronomic characteristics in plants are disclosed. Methods of transgenic modulation and marker-assisted breeding by expressing NRT1.1 B are also disclosed, thereby improving the nitrogen utilization and grain yield in rice and other crops.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Trangenic plants
InactiveUS20140223603A1Low costReduce negative environmental effectsClimate change adaptationFused cellsTransgeneGMO Plants
The invention relates to transgenic plants with improved growth and nitrogen use efficiency expressing nitrate transporter gene, methods of making such plants and methods for improving growth and nitrogen use efficiency.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD +1
Functional Expression of Higher Plant Nitrate Transporters in Pichia Pastoris
InactiveUS20080311612A1Eliminate disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesIn vivoBiology
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Nitrate transport protein of diatom and its coding gene and application
InactiveCN1887903ANormal growthImprove nitrogen absorption capacityAlgae/lichens peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The present invention is kind of nitrate transport protein of diatom and its coding gene and application in transgenic plant. The nitrate transport protein has one of the following amino acid residue sequence: 1. SEQ ID No. 1 in the sequence list; and 2. the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 through substitution, deletion or addition of 1-10 amino acid residues and coding protein possessing nitrate transport function. The transgenic tobacco, rice or lawn grass with the gene of the present invention NAT3 can grow normally on the culture medium with nitrogen element content only 1 / 32 normal value, and this proves the capacity of NAT3 in raising the nitrogen absorption. The present invention may have wide application foreground in plant nitrogen fertilizer absorption and breeding low nitrogen resisting plant variety.
Owner:北京优利康生物农业技术有限公司
Fast-growing aquatic plant nitrate transport protein GeNRT2.1 and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105481955AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyGrow fastMicroorganism based processesPlant peptidesNitrate transportProtein C
The invention discloses a fast-growing aquatic plant nitrate transport protein GeNRT2.1 and a coding gene and application thereof. The protein is the protein a or the protein b or the protein c, wherein the protein a is provided with an amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 5 in a sequence table; the protein b is a fusion protein obtained by connecting labels to the end N and / or the end C of the protein shown in the sequence 5 in the sequence table; the protein c has the same function and is the protein obtained through substitute and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues for the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 5 in the sequence table. A test proves that the protein GeNRT2.1 has the function of a nitrate transport protein and can improve the plant nitrogen utilization efficiency, so that the plant grows rapidly.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in plants
InactiveUS20110010797A1Promote plant growthImproved nitrate remobilizationImmunoglobulinsFermentationNitrogenArabidopsis
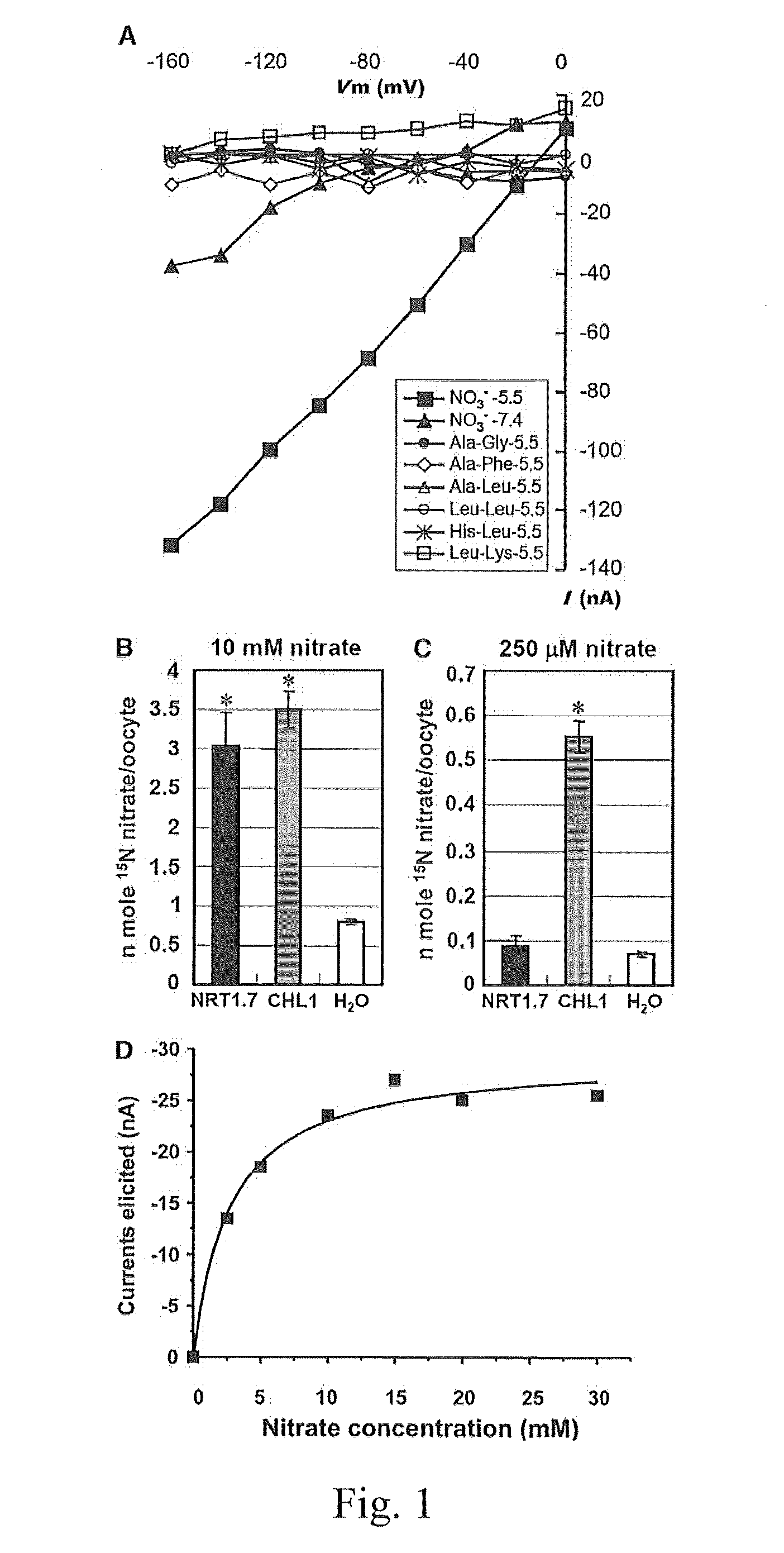
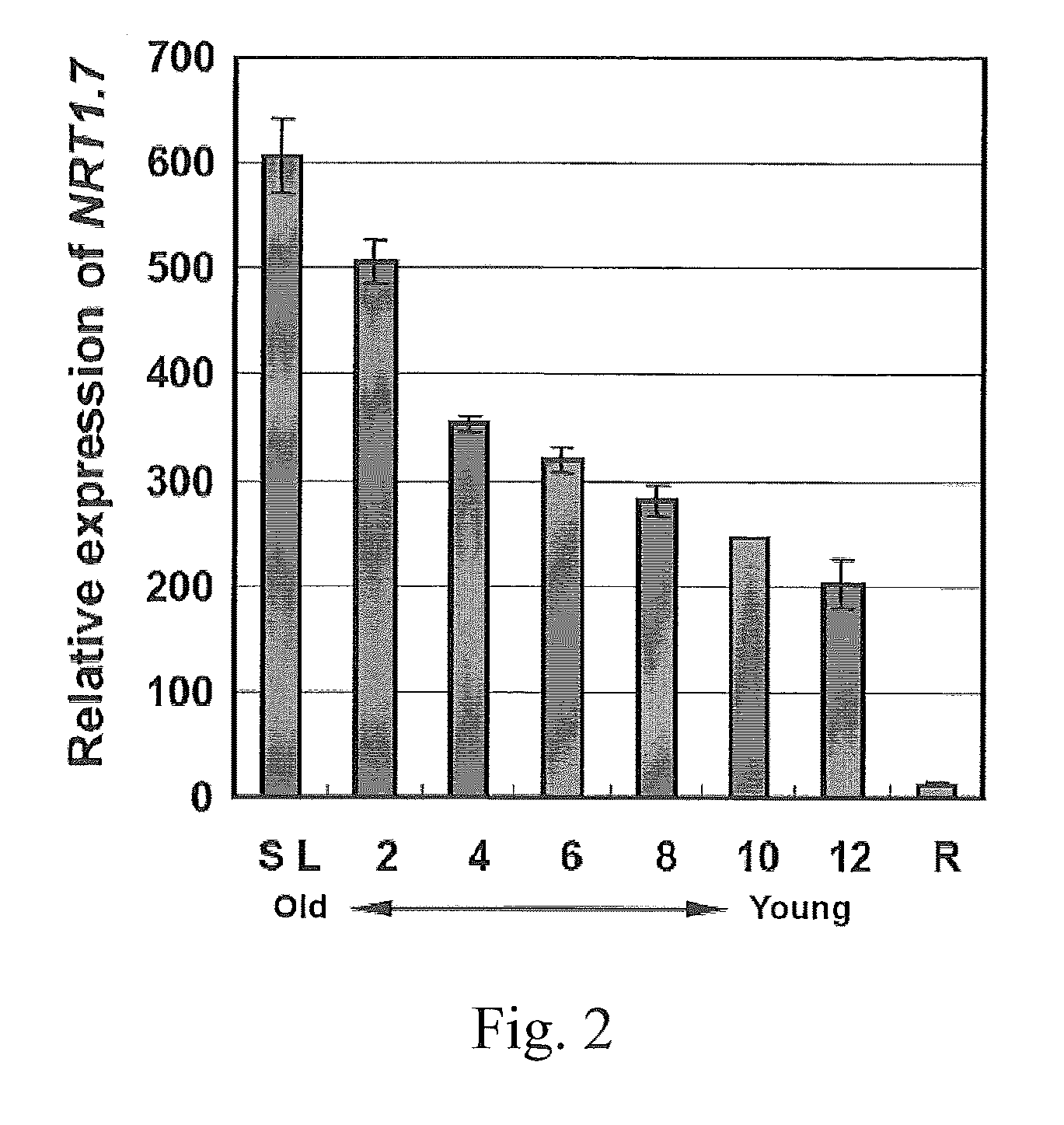
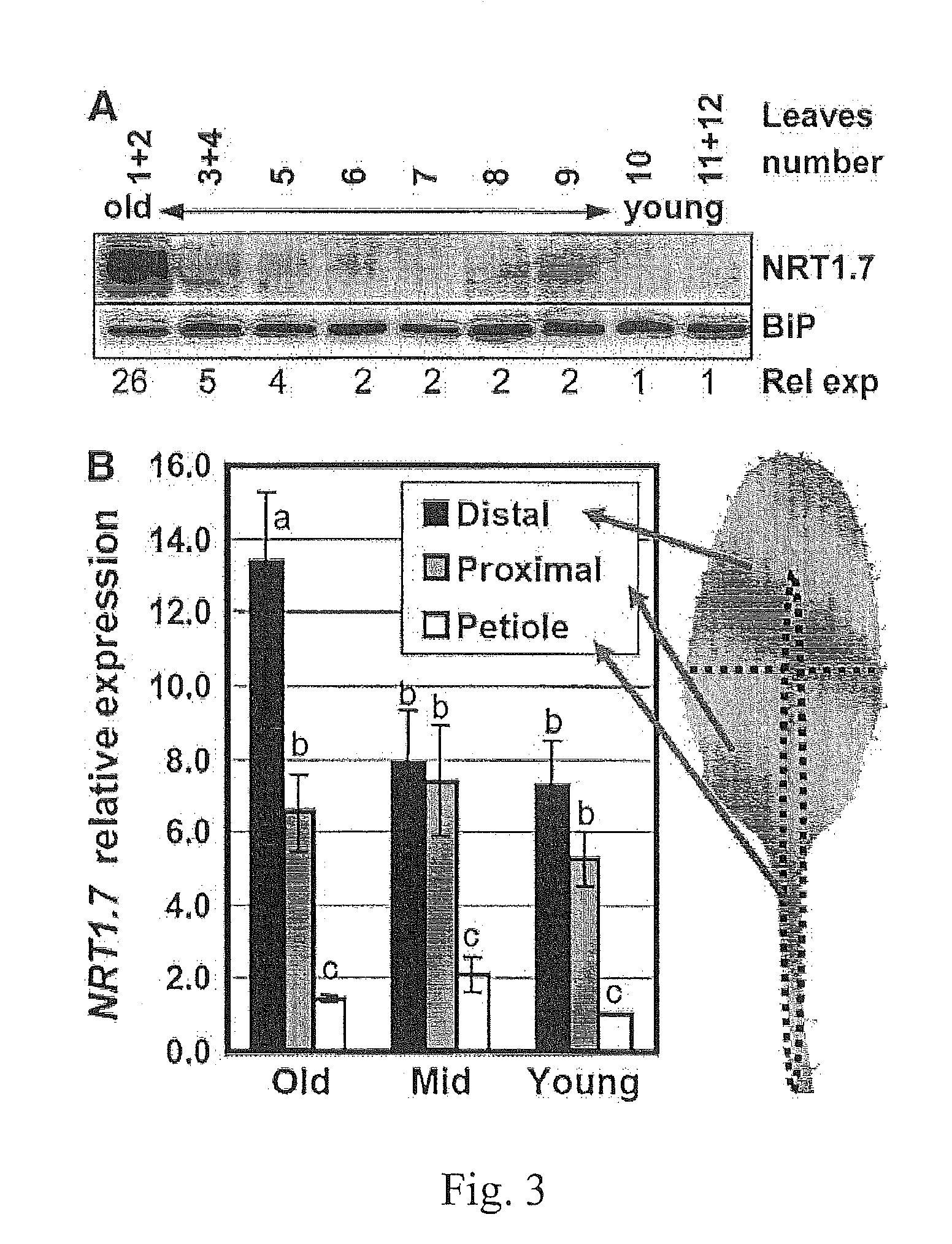
The present invention provides a method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in a plant comprises regulating the expression of Arabidopsis NRT 1.7 or an orthologue thereof so that the nitrate remobilization from older leaves to young leaves in the plant is regulated, thereby the nitrogen utilization efficiency is changed. The present invention also provides a transgenic plant obtainable by transforming a plant with an expression construct with a high or low level of expression of NRT 1.7. On the other hand, the present invention yet provides a chimera nitrate transporter, a DNA molecule coding for this chimera transporter and an expression vector thereof.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
InactiveCN102925455AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGrowth plantWild type
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (referred to as YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (hereinafter referred to as YEP16); or having modulated expression of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
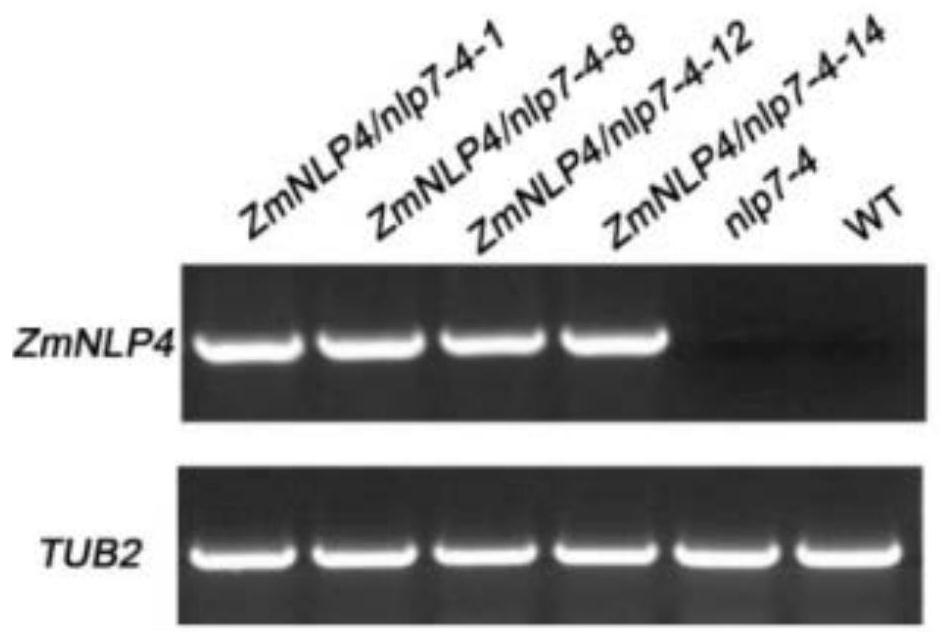
Transcription factor ZmNLP4 derived from corn and application thereof
ActiveCN107602683AIncrease biomassIncrease the content of amino acidsPlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideLateral root
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and provides a transcription factor ZmNLP4 derived from corn and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a coded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with a receptor Arabidopsis, the Arabidopsis in which the transcriptionfactor is transferred has the advantages that the total biomass is obviously increased, the content of in-vivo amino acids and total nitrogen is increased, the main root length and quantity of lateral roots are obviously increased, the yield per plant is obviously increased, and the expressions of nitrate transporters, nitrate reductase genes and nitrite reductase genes are obviously increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
InactiveUS8853492B2Improve featuresSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGlycogen synthase I
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I HDZip hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a NRT protein or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted YEP16; or having modulated expression of a Group I shaggy-like kinase or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
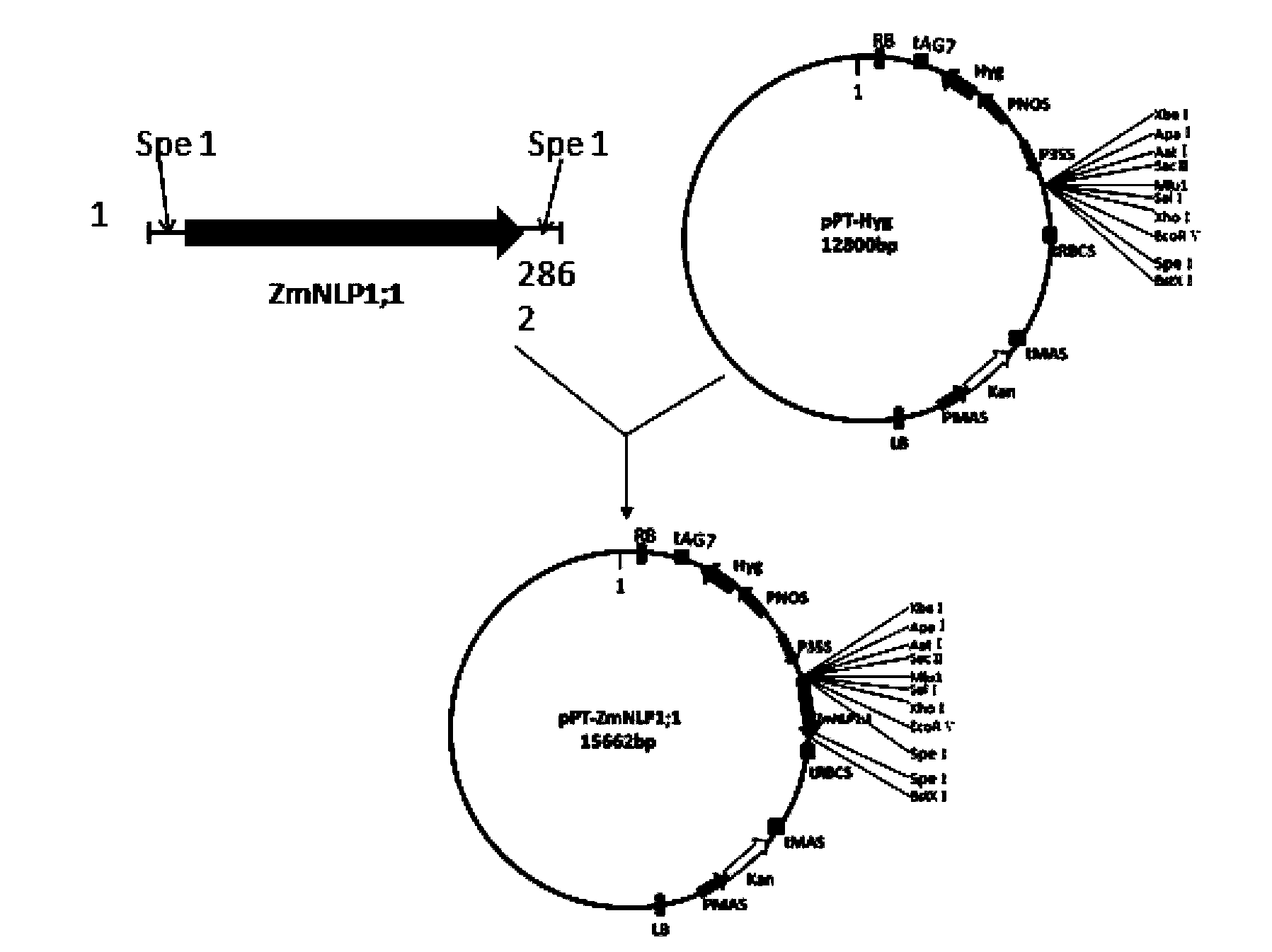
Transcription factor derived from corn and new use of coding gene thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor derived from corn and new use of a coding gene thereof. The new use provided by the invention is a method using a coding nucleic acid molecule of ZmNLP1;1 to cultivate a transgenic plant. The method is a method for cultivating the transgenic plant with at least one characters of the following 1)-4): 1) aboveground biomass is higher than that of a receptor plant; 2) after induction of a nitrate, the nitrate transport protein gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; 3) after induction of the nitrate, nitrate reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and 4) after induction of the nitrate, nitrite reductase gene expression is higher than that of the receptor plant; and the method comprises a step for introducing a ZmNLP1;1 gene into the receptor plant; and the ZmNLP1;1 gene codes a protein shown in SEQ ID No.2. Experiments show that, in the condition of using nitric nitrogen (NO<3->) as a sole nitrogen source, the aboveground biomass and the total biomass of arabidopsis transgenic with the ZmNLP1;1 gene are increased significantly compared with that of receptor arabidopsis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
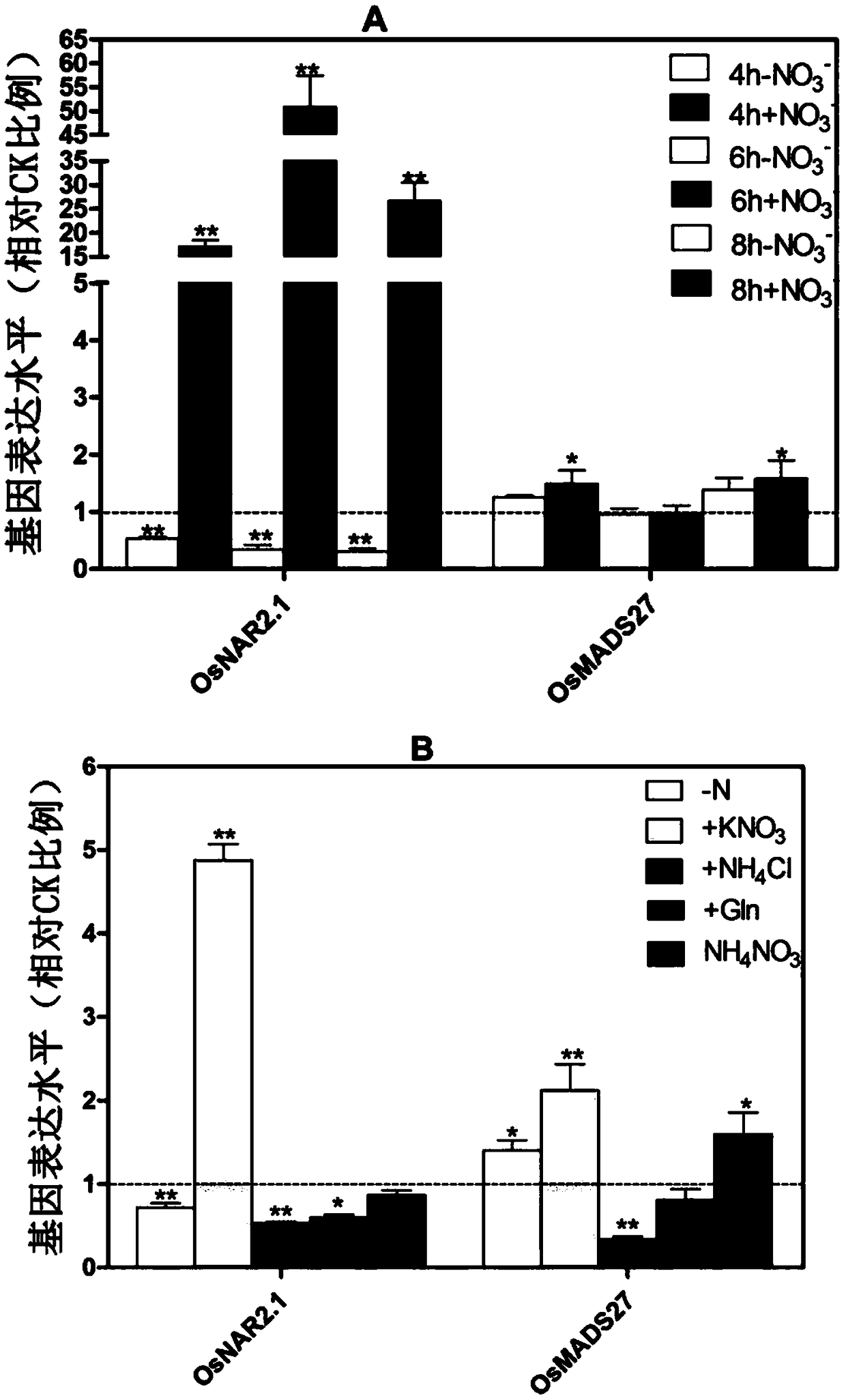
Application of rice OsMADS27 gene and protein in improving nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency of rice
InactiveCN109355305AImprove nitrogen use efficiencyEasy to transportPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceNitrate
The invention discloses application of rice OsMADS27 gene and protein in improving the nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency of rice. According to the application, it is found according to research thatthe rice OsMADS27 protein can interact with nitrate translocator cofactors OsNAR2.1, overexpression OsMADS27 gene can significantly promote the expression of nitrate translocator, thereby promoting the transfer and absorption of the rice to nitrate, and improving the nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency. The application of the rice OsMADS27 gene and protein in improving the nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency of the rice is helpful for researching key regulatory genes related to the nitrogen absorption of the rice, is of great significance for screening and breeding of nutrient efficient plant varieties, can also provide a theoretical basis and technical support for explaining a physiological mechanism of nitrogen utilization of the rice, improving the nitrogen utilization efficiency of the rice and genetic improvement of rice varieties, and has important theoretical significance and potential application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
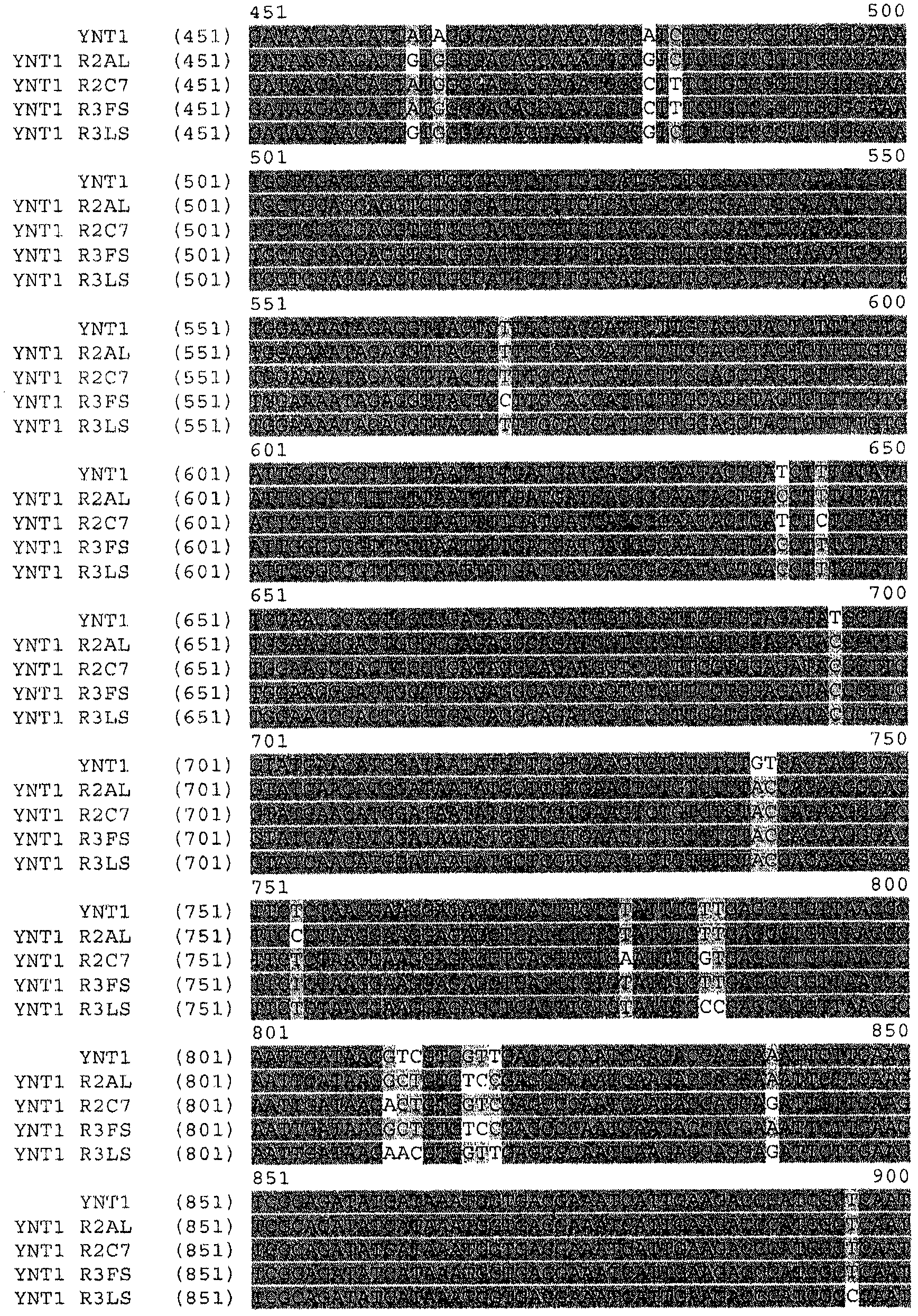
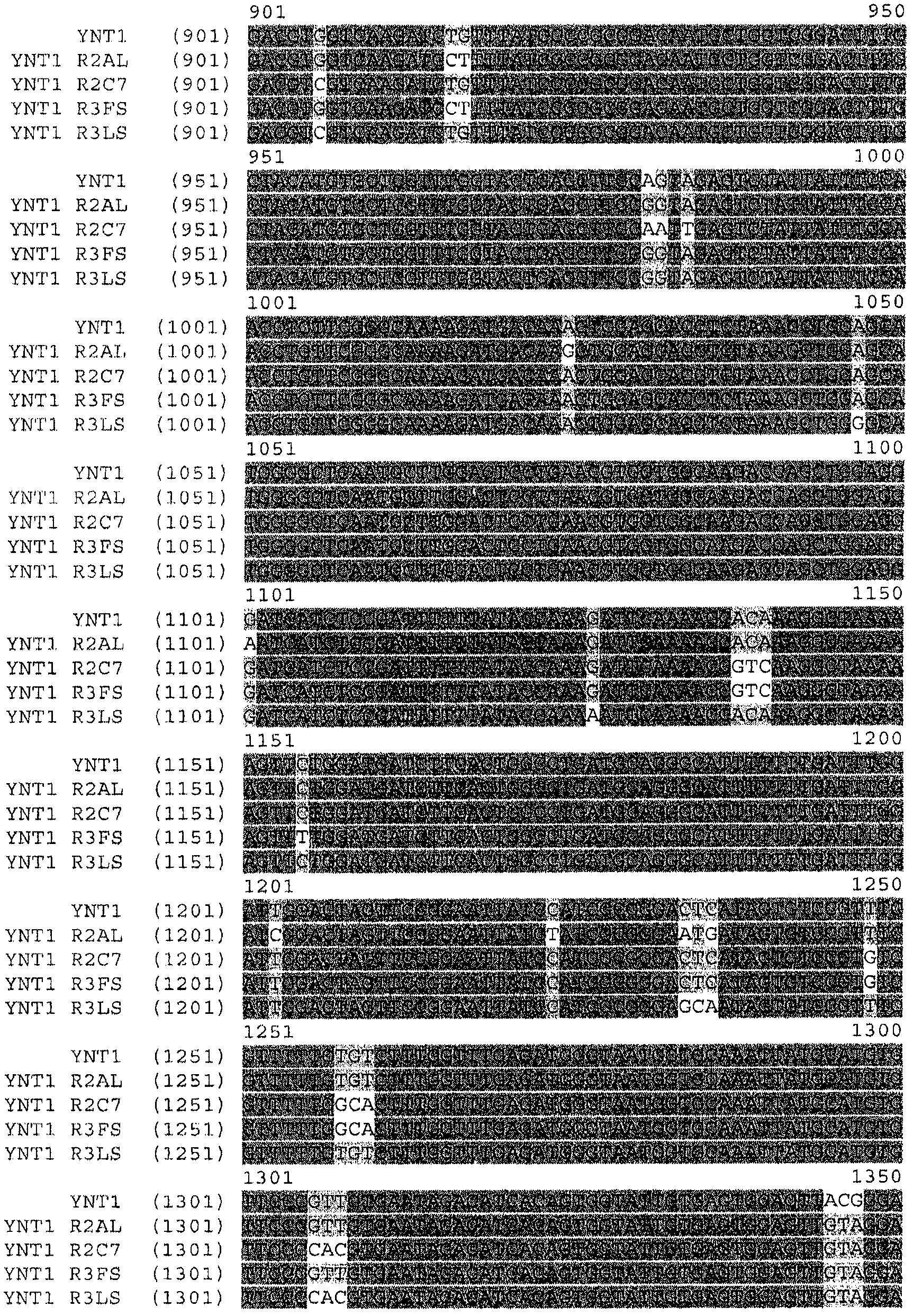
Functional expression of shuffled yeast nitrate transporter (YNT1) in maize to improve nitrate uptake under low nitrate environment
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering NT activity, nitrogen utilization efficiency and / or uptake in plants. The invention relates to a method for the production of plants with maintained or increased yield under low nitrogen fertility. The invention provides isolated nitrate transporter variant (NT variant) nucleic acids and their encoded proteins. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, and transgenic plants. Plants transformed with nucleotide sequences encoding the NT variant enzyme show improved properties, for example, increased yield.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
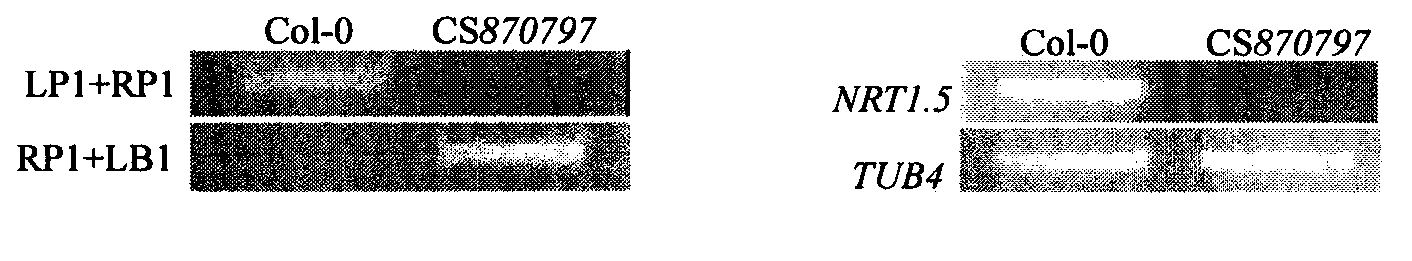
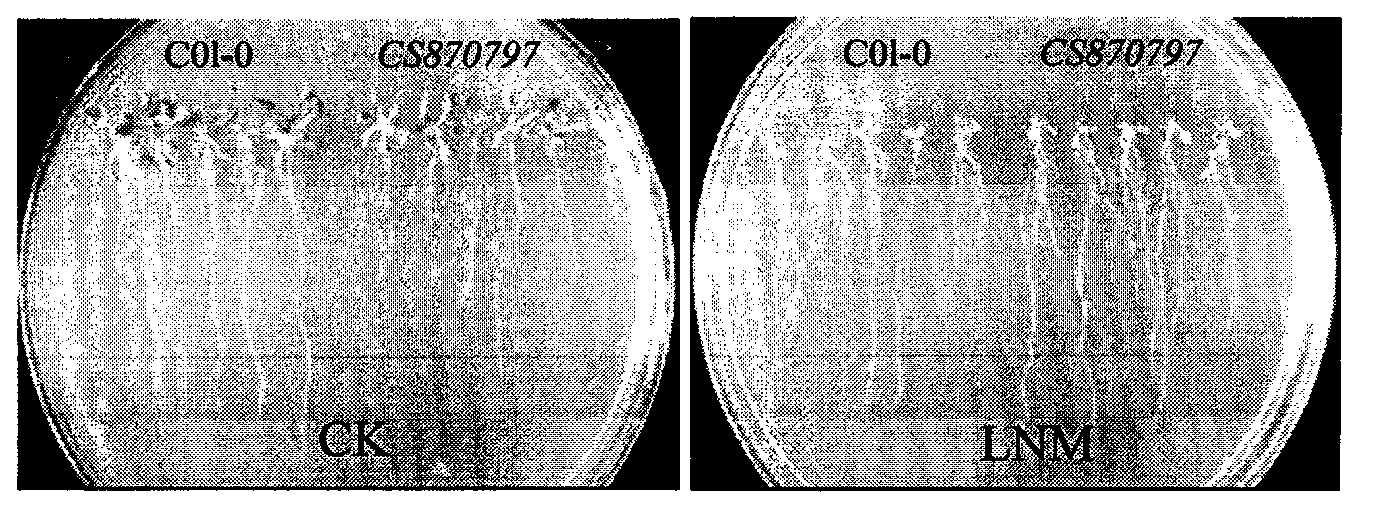
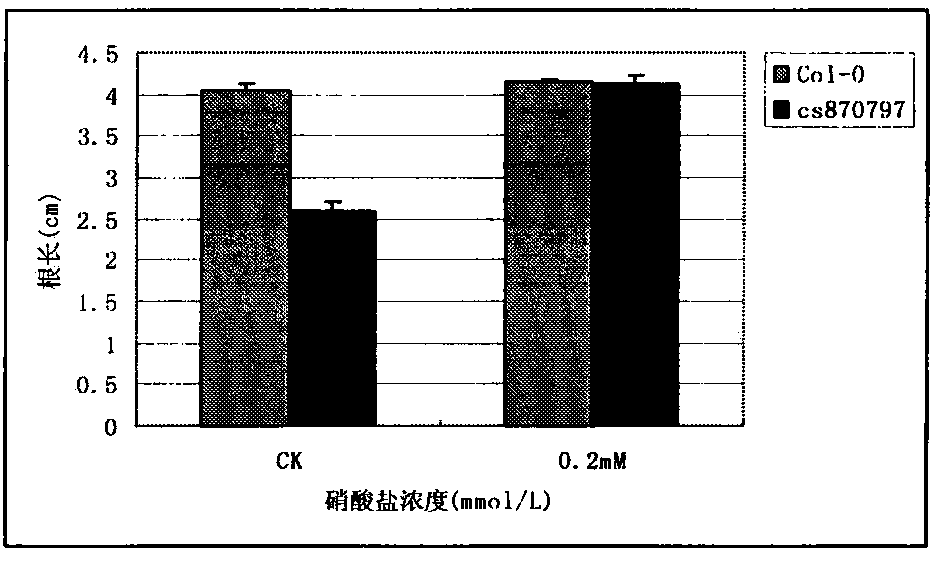
Nitrate transporter gene AtNRT1.5, and coding protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of plant molecular biology, and specifically relates to functional verification of arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene AtNRT1.5. A function of the gene in efficient utilization of plant nitrogen is studied by inserting T-DNA of the AtNRT1.5 gene into a homozygous line of a mutant CS870797. Experimental results show that the growth of the mutant on a high-nitrogen (MS) medium is inhibited; the root system of the mutant is obviously shorter than that of the wild type; and in a low nitrogen condition, the growths of the root systems of the mutant and the wild type have no difference, but dry weight of the mutant is lower than that of the wild type. Determination results of nitrogen content show that the nitrogen content in the root system of the mutant is higher than that of the wild type while the nitrogen content in the shoot is significantly lower than that of the wild type; and the difference is more obvious on the high nitrogen (MS) medium. The results demonstrate that after mutation of the ATNRT1.5 gene, nitrogen uptake capacity of the root system is not affected significantly while transportation capacity of the nitrogen from roots to shoots is reduced significantly. Over-expression of the gene is expected to improve the nitrogen utilization capability of plants and has relatively large economic value in plant nitrogen nutrition efficient molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
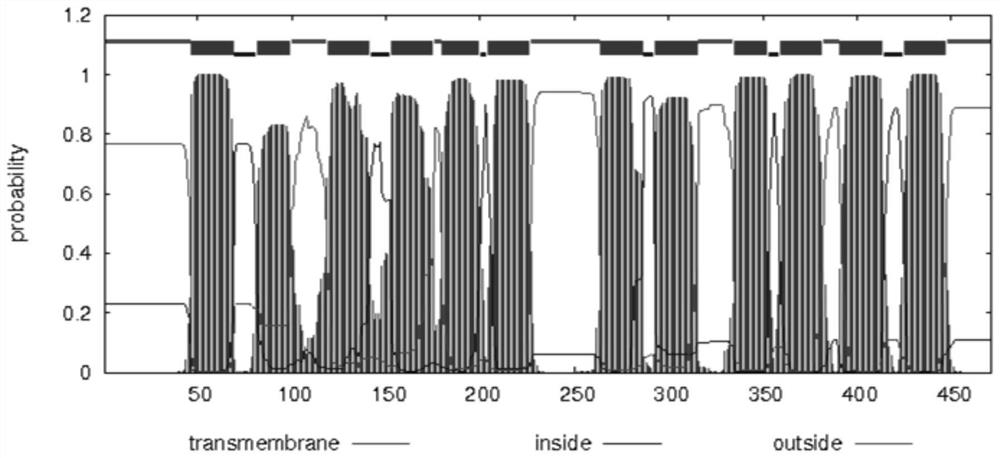
Tea tree NRT1 gene, protein and gene expression method
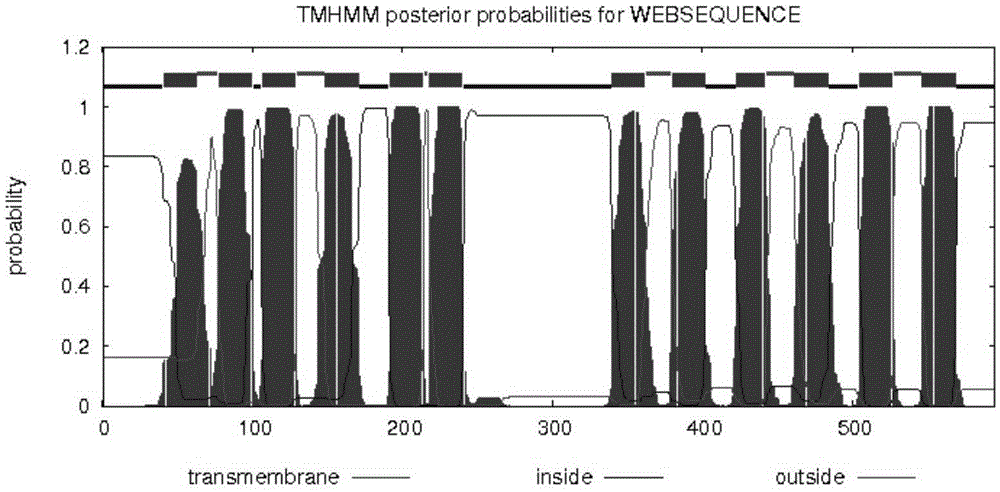
The invention discloses a tea tree NRT1 gene, a sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses a tea tree NRT1 protein, a sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The invention also discloses a gene expression method of the tea tree NRT1. A total length of the tea tree NRT1 gene sequence is 1880bp, 594 amino acids are encoded, the protein molecular weight is 65.92kD, and a theoretic isoelectric point is 9.07043. 12 transmembrane helical regions are contained, wherein a large hydrophilic ring exists between a sixth transmembrane helical region and a seventh transmembrane helical region. The protein is a hydrophilic protein, and the tea tree NRT1 is a constitutive gene. The mechanism for absorbing and assimilating NO3<-> in different tissue parts of a tea tree is shown to be possibly different, and the NRT1 is not only used as a nitrate transfer protein, but also is a signal acceptor sensing the nitrate.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Salt Du's algal nitrate transfer protein and its code sequence
A novel salt resistance associated protein-Du's saline alga nitrate transporter, the polynucleotide for coding it, the process for preparing said protein by recombination, the application of said polynucleotide, and the method for improving the salt resistance of plant by use of said transporter are disclosed.
Owner:四川川大光耀生物工程有限公司
Methods for improving rice grain yield
The present invention relates to methods for increasing rice grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency by increasing the expression of a nitrate transporter gene, as well as transgenic plants expressing increased expression of the gene and methods of making such plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Functional expression of yeast nitrate transporter (ynt1) in maize to improve nitrate uptake
InactiveCN102549149AInput unchangedLow costClimate change adaptationOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to altering NT activity, nitrogen utilization and / or uptake in plants. The invention relates to a method for the production of plants with maintained or increased yield under low or normal nitrogen fertility. The invention provides isolated nitrate transporter (NT) nucleic acids and their encoded proteins. The invention further provides recombinant expression cassettes, host cells, and transgenic plants. Plants transformed with nucleotide sequences encoding the NT enzyme show improved properties, for example, increased yield.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
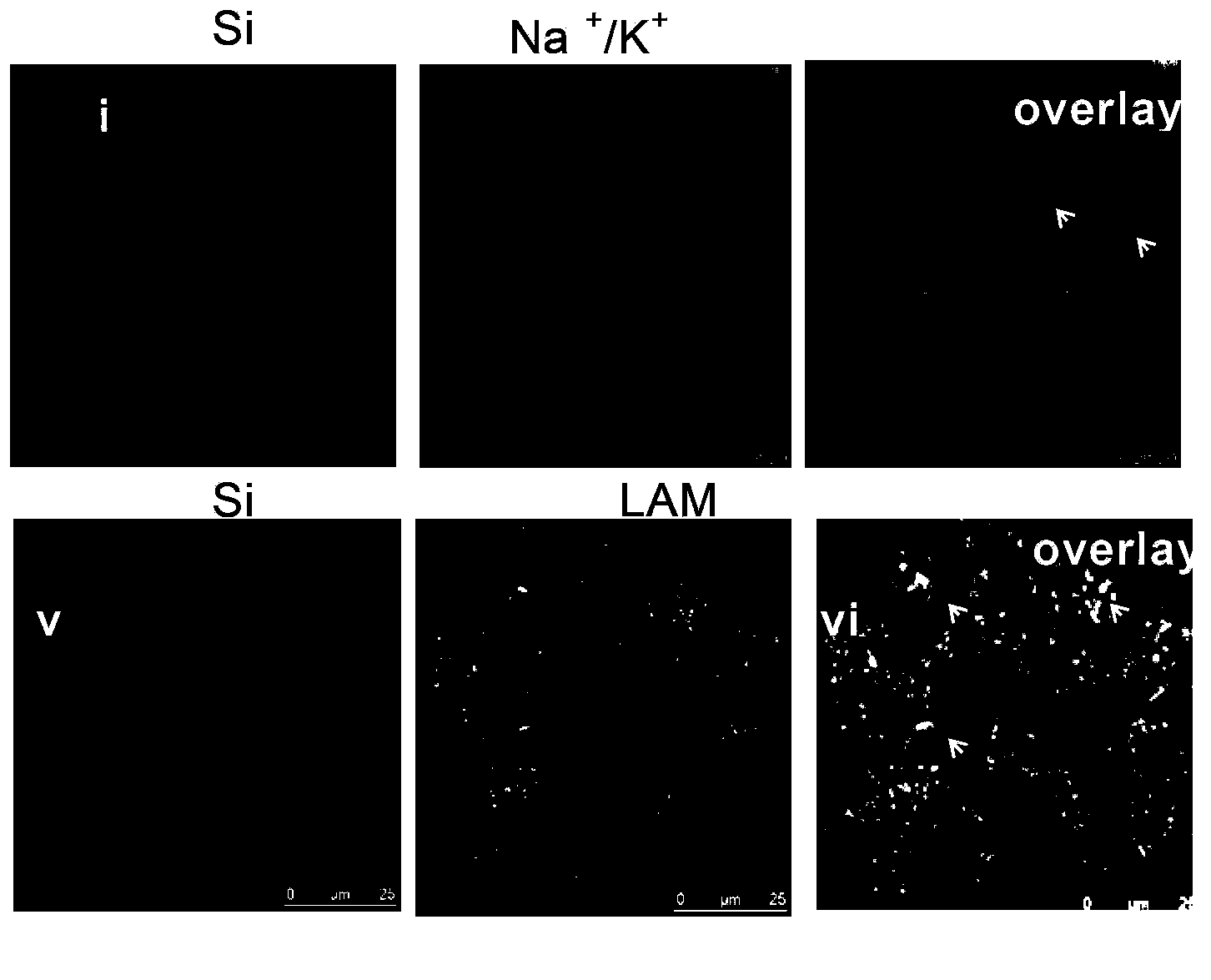
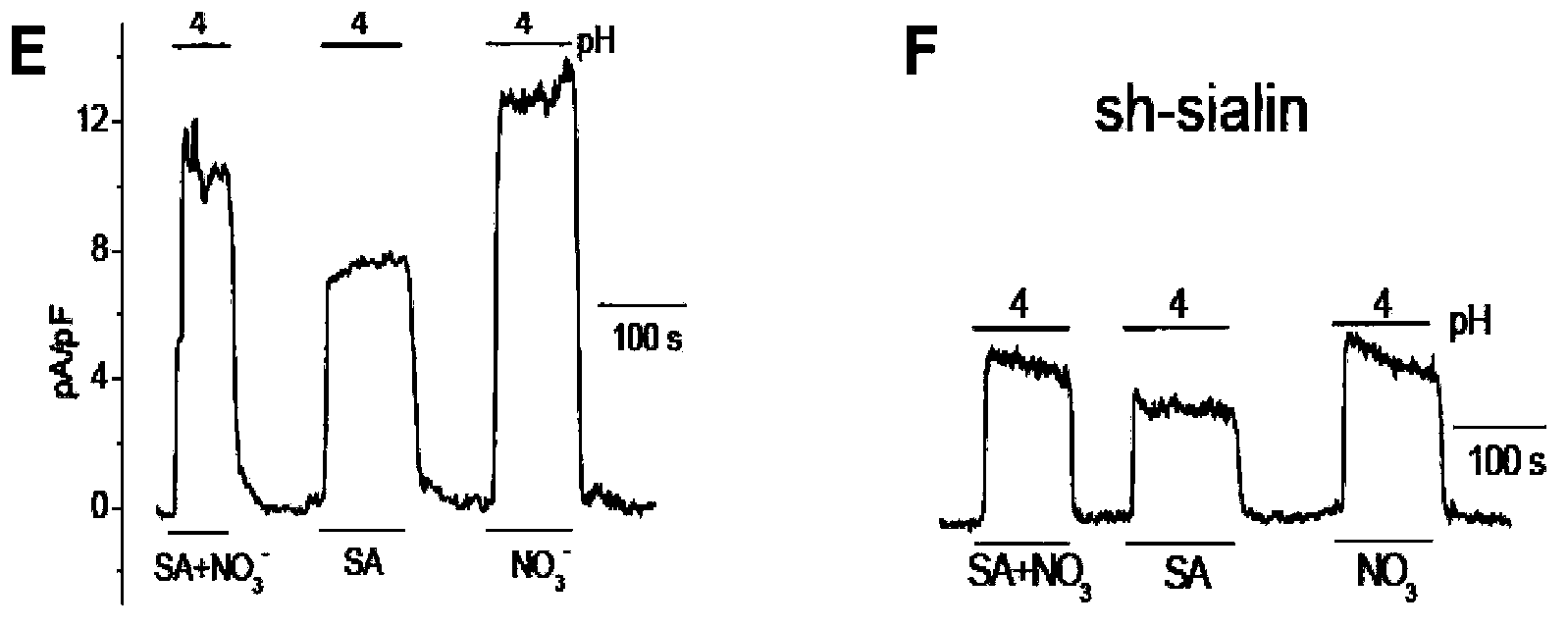
Use of SLC17A5 gene and coded protein thereof in preparing medicines for treating or diagnosing nitrate transfer or metabolic block or disorder related diseases
The invention discloses use of an SLC17A5 gene and a coded protein thereof in preparing medicines for treating or diagnosing nitrate transfer or metabolic block or disorder related diseases. According to the use disclosed by the invention, a mass of experiments finally confirm that the SLC17A5 gene coded protein (Sialin protein) is a mammal nitrate transfer protein, and the SLC17A5 gene or the coded protein thereof can be used for preparing medicines for treating in vivo nitrate transfer and metabolic block related diseases as well as anti-hypertension and antishock medicines and medicines for treating myocardial infarction and preventing gastric ulcer and the like.
Owner:王松灵
Primer group and kit for detecting rice nitrate transport protein gene, and detection method and application thereof
InactiveCN110129480AAccurate identificationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerAgricultural science
Owner:JIANGSU XUHUAI DISTRICT HUAIYIN AGRI SCI RES INST
Functional expression of higher plant nitrate transporters in Pichia Pastoris
InactiveUS20100175147A1Eliminate disadvantagesFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementPichia pastorisIn vivo
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene NRT3.1, and encoding protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the fields of plant molecular biology and transgenic correlation techniques, and particularly relates to verification of low-nitrogen-resistance function of Arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene NRT3.1 and application of the gene in culture of new species of low-nitrogen-resistance nitrogen nutrition high-efficiency plants. By using the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana as the material, the homozygous strain system of the NRT3.1 gene T-DNA insertion mutant CS876661 is utilized to research the functions of the NRT3.1 gene in the plant low-nitrogen high-efficiency aspect. The experimental result shows that the dry weight of the above-ground part of the NRT3.1 gene knockout mutant is obviously lower than that of the wild type (P=0.002) under low-nitrogen culture conditions (0.1mM NO3<->), and the nitrogen contents of the root and above-ground part are respectively obviously lower than those of the wild type (P=0.045, P=0.01), which indicates that the NRT3.1 gene has important functions in signal transmission paths under plant response low-nitrogen stress. The overexpression of the gene is estimated to enhance the low nitrogen resistance of the plant and has great economic value in plant nitrogen nutrition high-efficiency molecule breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene NRT2.1, encoding protein and applications thereof
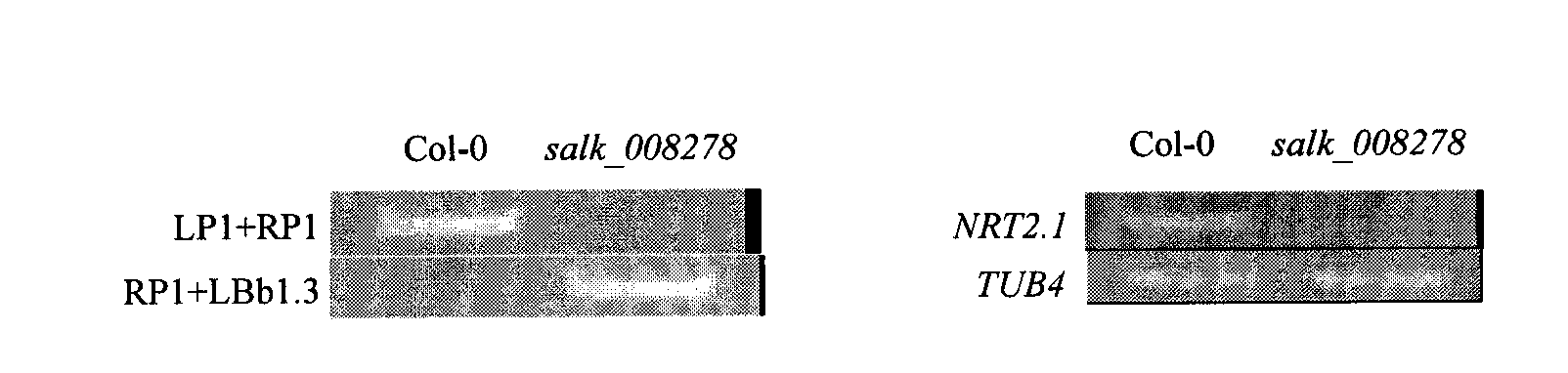
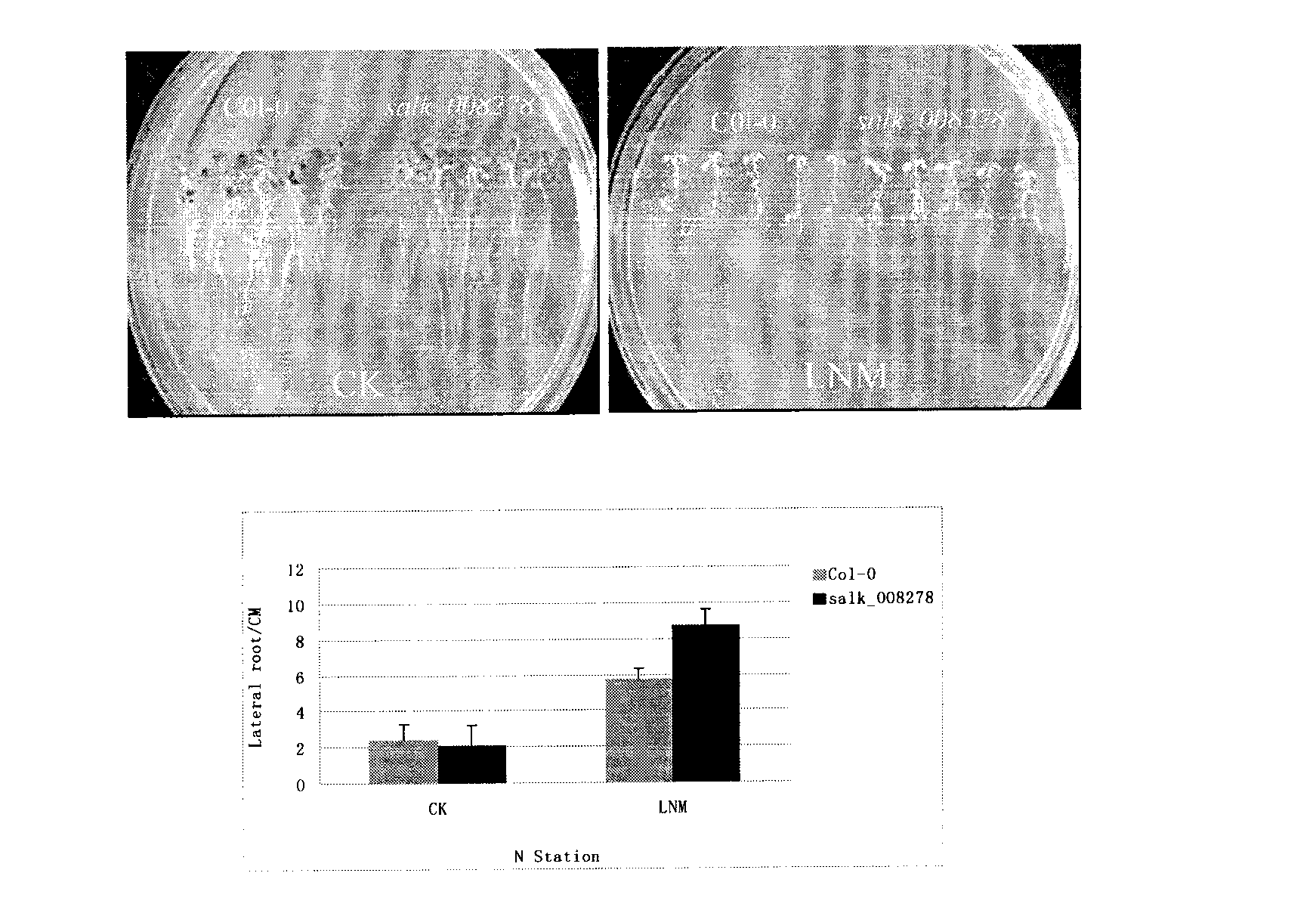
The invention belongs to the plant molecule biology and transgenic related technical field, and specifically relates to verification of low nitrogen resistance of arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene NRT2.1 and applications of the arabidopsis thaliana nitrate transporter gene NRT2.1 in breeding of new low nitrogen resistance and nitrogen nutrition efficiency plant varieties. According to the present invention, a model plant arabidopsis thaliana is adopted as a material, and NRT2.1 gene T-DNA is adopted to insert into a mutant salk_008278 homozygosis line so as to research functions of the NRT2.1 gene in the field of plant low nitrogen efficiency, wherein experiment results show that lateral roots of the NRT2.1 knocked out mutant is significantly more than lateral roots of the wild-type (P=0.044) under a high sucrose / low nitrogen (7.5% sucrose, 0.1 mM NH4NO3) culture condition, such that the NRT2.1 gene provides important effects in a signal transduction pathway of the plant response to low nitrogen stress, and it can be predicted that overexpression of the gene can increase low nitrogen resistance of the plant and can provide high economic values in plant nitrogen nutrition efficiency molecule breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
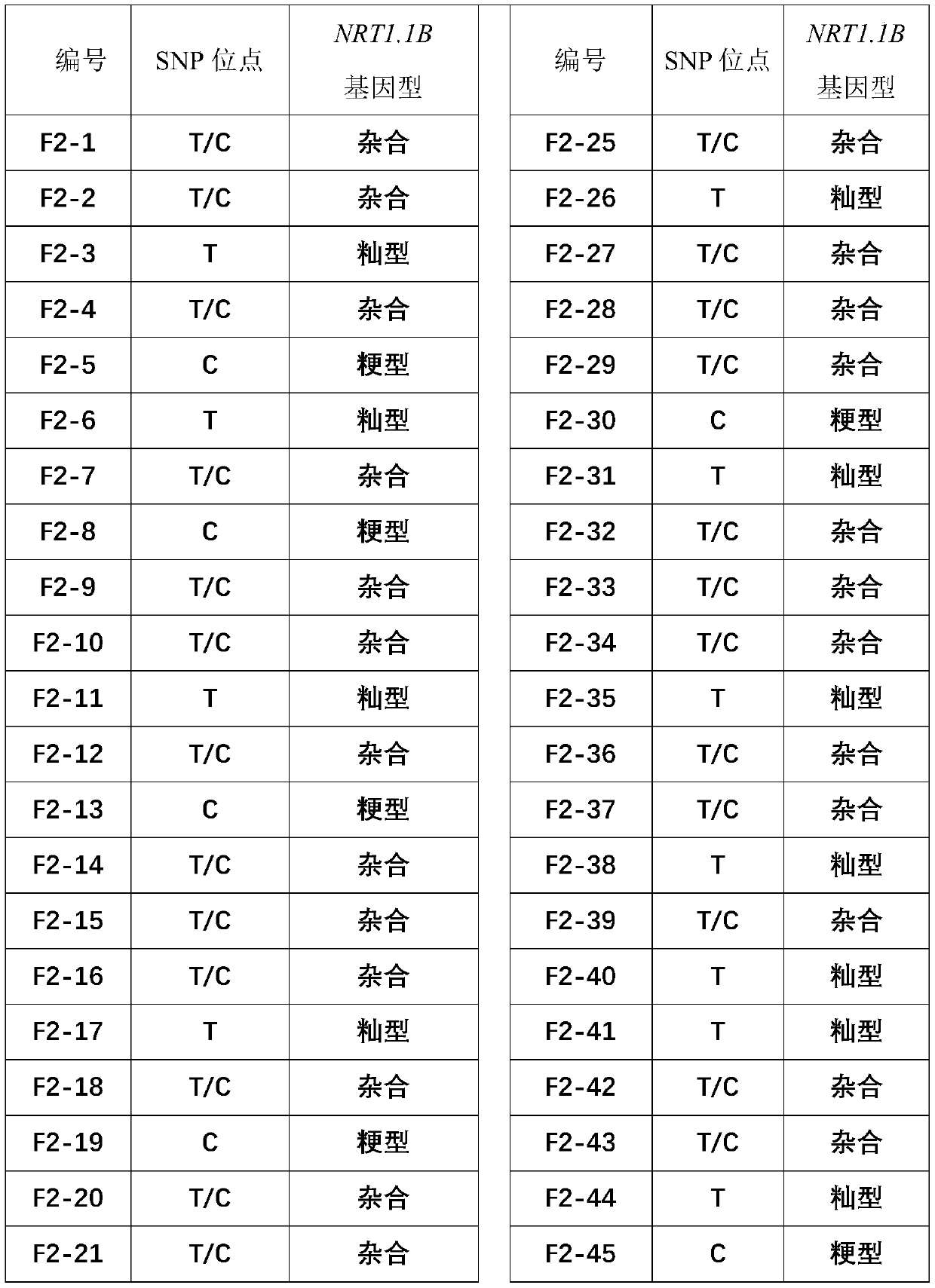
PCR/ LDR (polymerase chain reaction/ ligase detection reaction) molecular marker and method for authenticating Oryza sativa L. nitrate transport protein gene NRT1. 1B genotype
InactiveCN111363843ASuitable for high-throughput detectionReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerNitrate transport
The invention relates to a PCR / LDR (polymerase chain reaction / ligase detection reaction) molecular marker and a method for authenticating an Oryza sativa L. nitrate transport protein gene NRT1. 1B genotype, and belongs to the technical field of Oryza sativa L. breeding. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention comprises one pair of PCR primers and three LDR probes, wherein the forward primer sequence of the PCR primer pair is disclosed in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the reverse primer sequence of the PCR primer pair is disclosed in SEQ ID NO. 2; and the LDR probes include a fluorescence labeling probe Probe-FAM of which the sequence is disclosed in SEQ ID NO. 3, an indica type allele specific probe Probe-ind of which the sequence is disclosed in SEQ ID NO. 4 and a japonica-type allele specific probe Probe-jap of which the sequence is disclosed in SEQ ID NO. 5. According to the method, an Oryza sativa L. variety or the nitrate transport protein gene NRT1. 1B genotype in each strain in abreeding population can be accurately and quickly authenticated, and in addition, the high-throughput detection of multiple samples can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in plants
ActiveUS20140201863A1Improve utilization efficiencyImprove efficiencySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNitrogenArabidopsis
The present invention provides a method for changing nitrogen utilization efficiency in a plant comprises regulating the expression of Arabidopsis NRT 1.7 or an orthologue thereof so that the nitrate remobilization from older leaves to young leaves in the plant is regulated, thereby the nitrogen utilization efficiency is changed. The present invention also provides a transgenic plant obtainable by transforming a plant with an expression construct with a high or low level of expression of NRT 1.7. On the other hand, the present invention yet provides a chimera nitrate transporter, a DNA molecule coding for this chimera transporter and an expression vector thereof.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Transgenic plants with improved growth and nitrogen use efficiency
InactiveUS9012721B2Low costEliminate the effects ofSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationNitrogenGMO Plants
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD +1
A transcription factor zmnlp4 derived from maize and its application
ActiveCN107602683BIncrease biomassIncrease the content of amino acidsPlant peptidesFermentationReceptorLateral root
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and provides a transcription factor ZmNLP4 derived from corn and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a coded amino acid sequence of the transcription factor is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with a receptor Arabidopsis, the Arabidopsis in which the transcriptionfactor is transferred has the advantages that the total biomass is obviously increased, the content of in-vivo amino acids and total nitrogen is increased, the main root length and quantity of lateral roots are obviously increased, the yield per plant is obviously increased, and the expressions of nitrate transporters, nitrate reductase genes and nitrite reductase genes are obviously increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
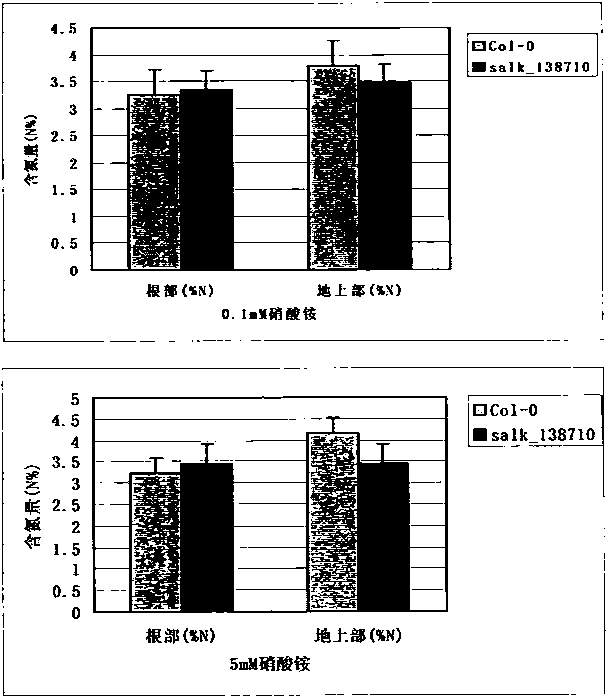
Nitrate transporter gene AtNRT1.1, coding protein and applications
The invention provides a nitrate transporter gene AtNRT1.1, a coding protein and applications, and belongs to the plant molecular biology and transgenosis related technology fields. Through insertion of arabidopsis AtNRT1.1 gene T-DNA into a homozygous strain of a mutant salk_138710, functions of the AtNRT1.1 gene at aspects of plant low-nitrogen tolerance and efficient utilization of nitrogen are researched. Experiment results show that, a AtNRT1.1 gene knockout mutant has greener leaf color than wild type and slightly longer roots and shows a low nitrogen tolerance phenotype without any addition of exogenous nitrogen element. Under treatment condition of else addition of 0.1 nM and 5 mM of ammonium nitrate, the nitrogen content of the mutant root is higher than that of the wide type but the nitrogen content of the overground part is obviously lower than that of the wide type (P is equal to 0.0001), which shows the AtNRT1.1 gene has important regulation and control effects on nitrogen element absorption and transportation under different concentrations, and predicts that the silencing of the gene can raise plant low-nitrogen tolerance ability and has great economic value in plant nitrogen nutrition efficient molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hongyan strawberry nitrate transporter gene FaNRT2.7 and application thereof
PendingCN114561398AIncreased nitrate levelsPromote maturityPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyFragaria
The invention relates to the technical field of plant genes, in particular to a Hongyan strawberry nitrate transporter gene FaNRT2.7 and application thereof, and provides cloning and analysis of the gene and a promoter of the Hongyan strawberry nitrate transporter gene FaNRT2.7 and application of analysis on response modes of different nitrogen forms, nitrate nitrogen, hormones and other abiotic stresses. Therefore, the method can be applied to screening germplasm materials, cultivating high-quality varieties and coping with abiotic stress according to different response states.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com