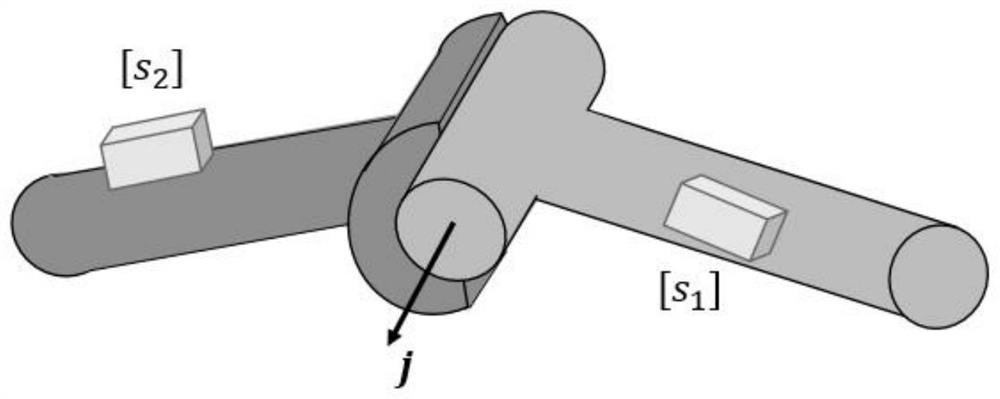
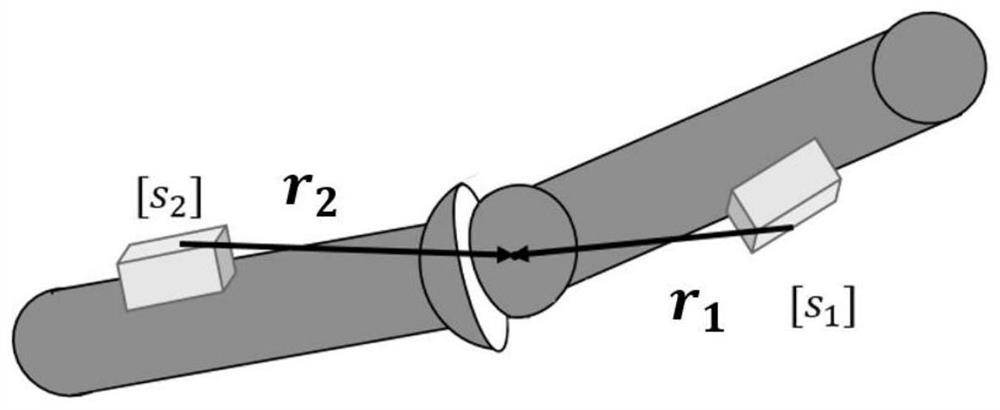
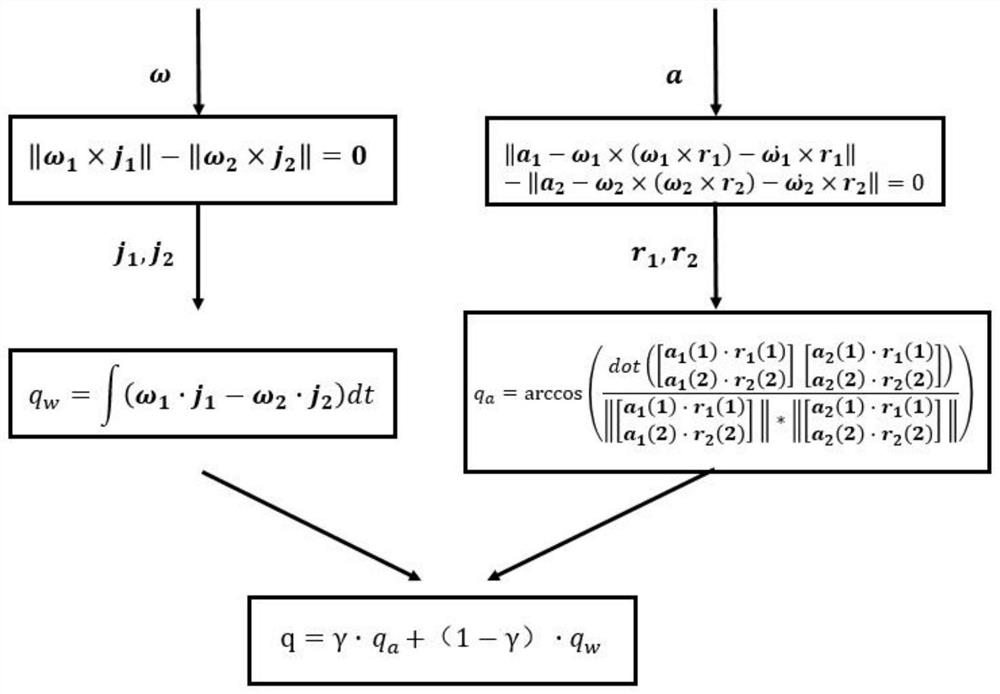
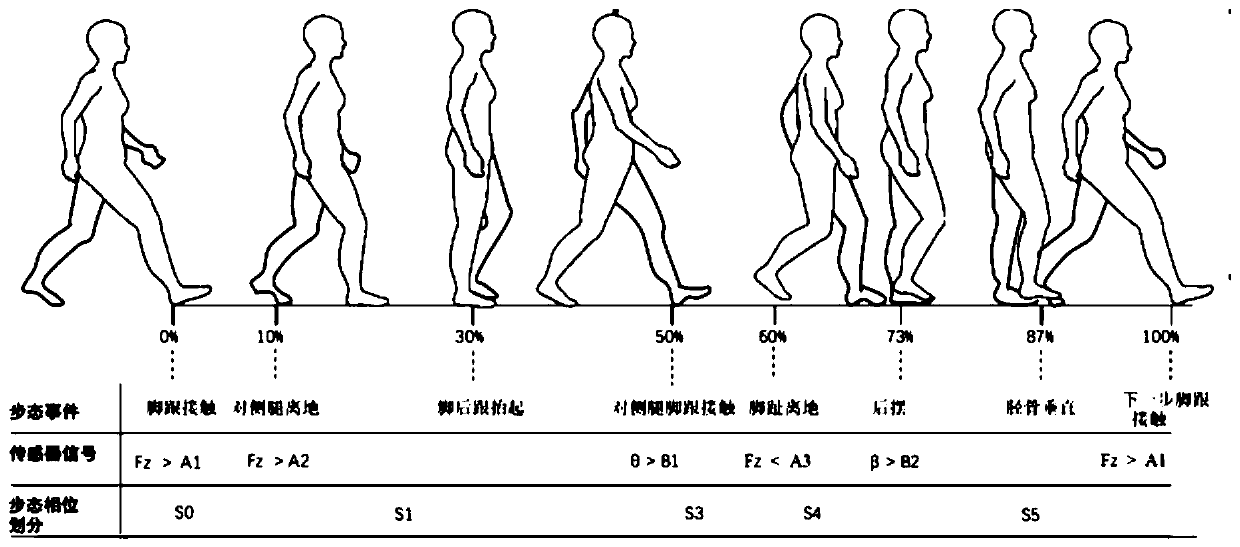
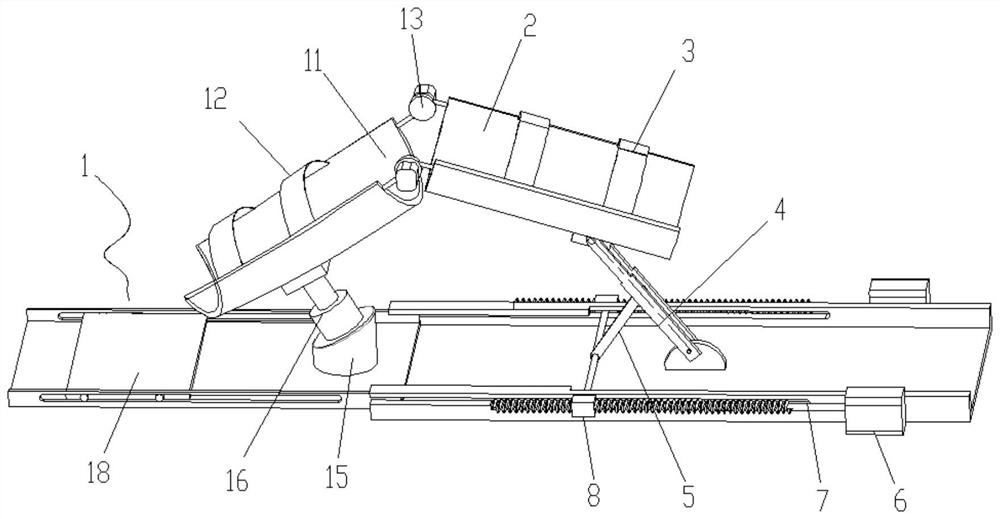
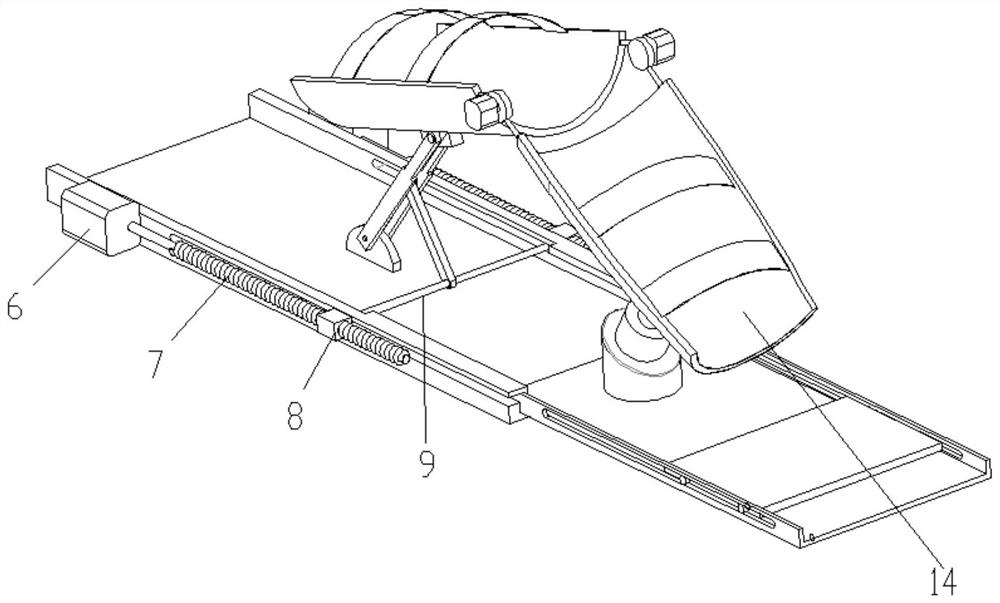
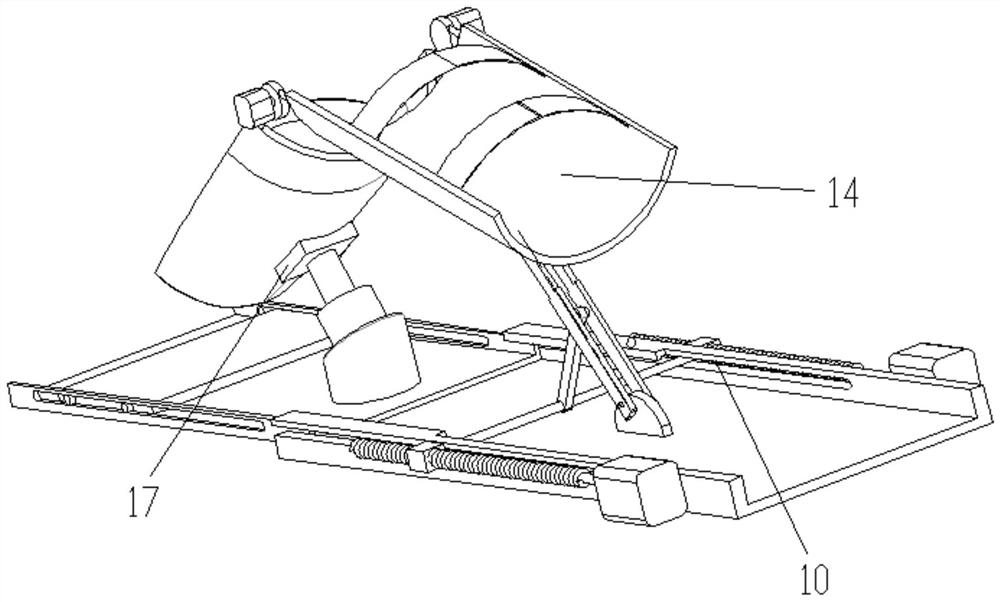
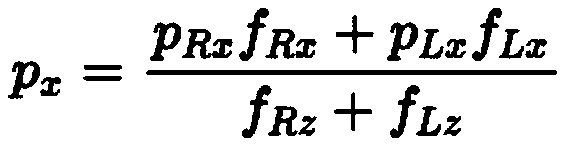Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
99 results about "Joint angulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
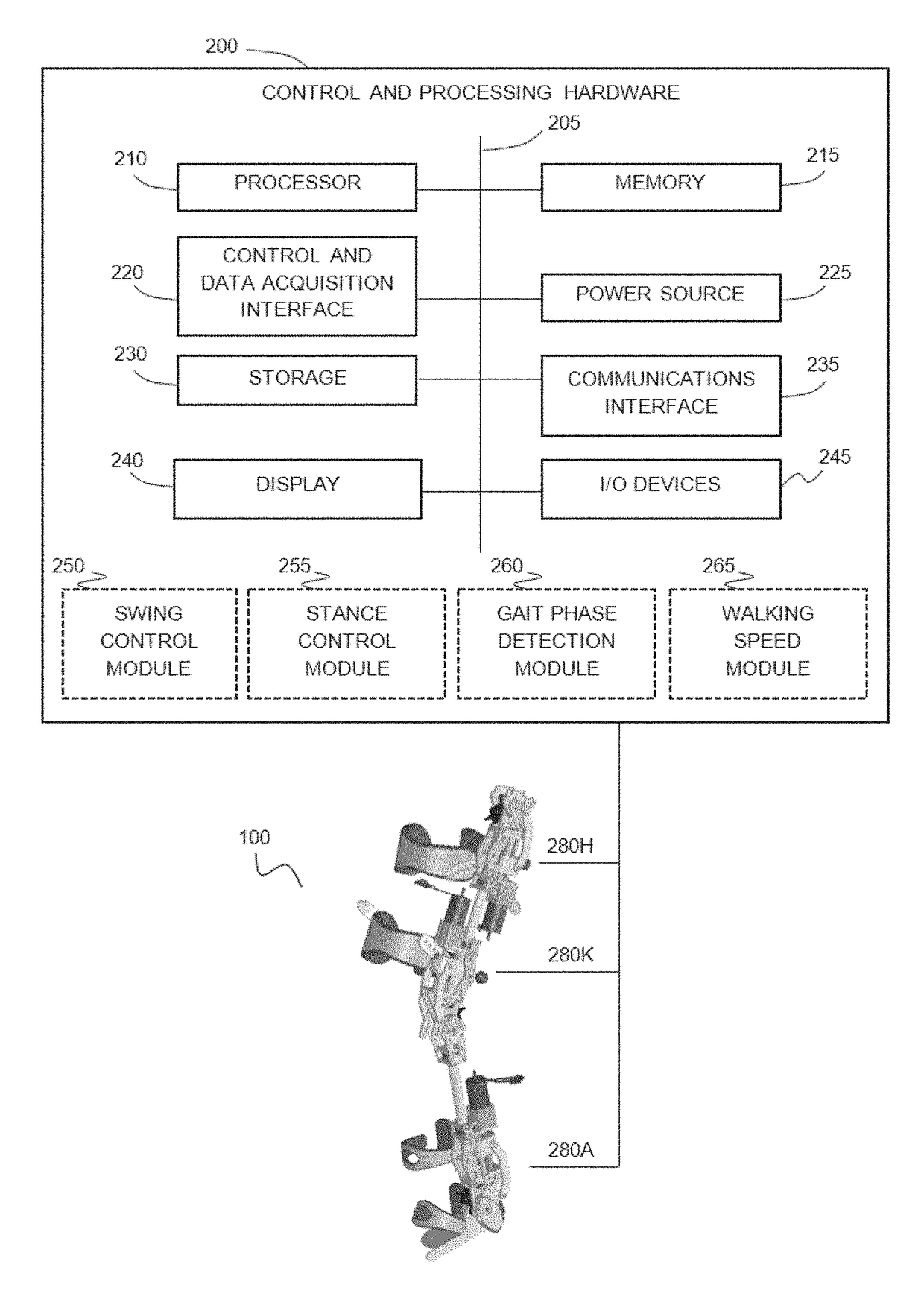
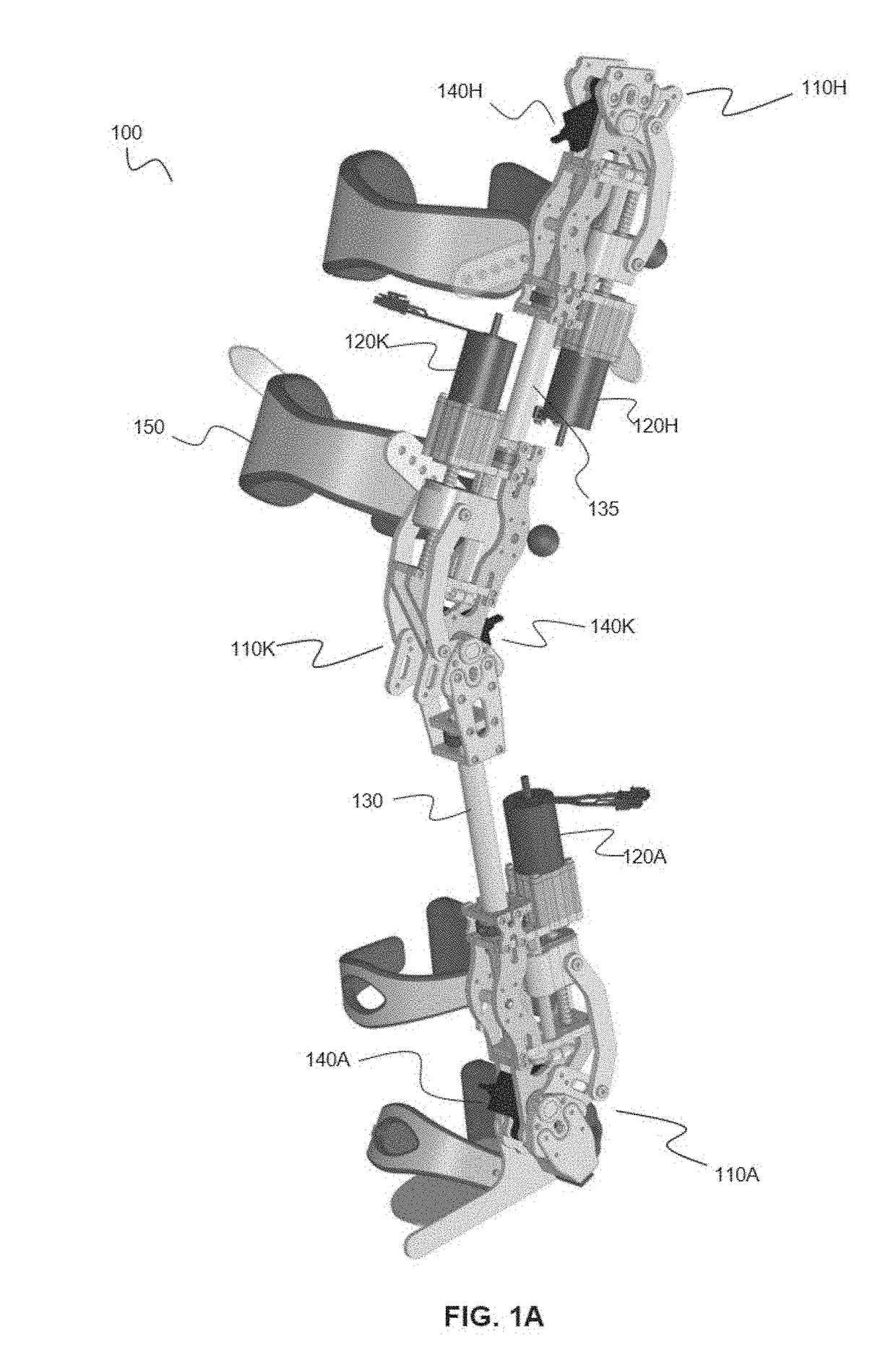
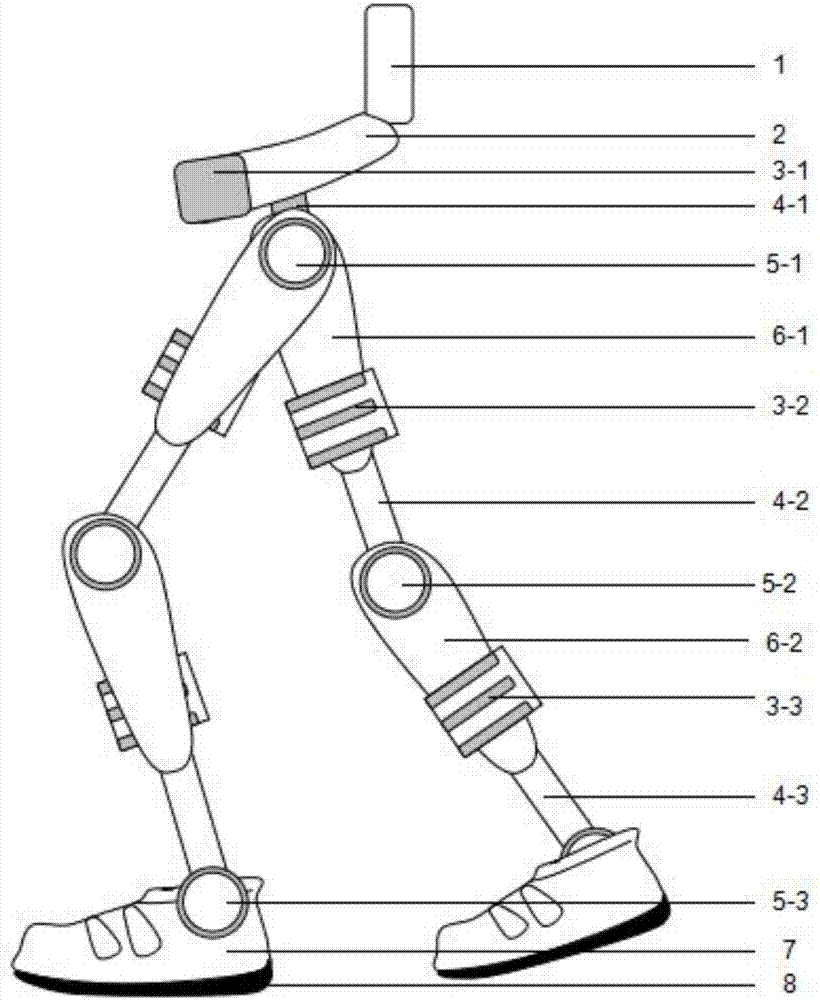
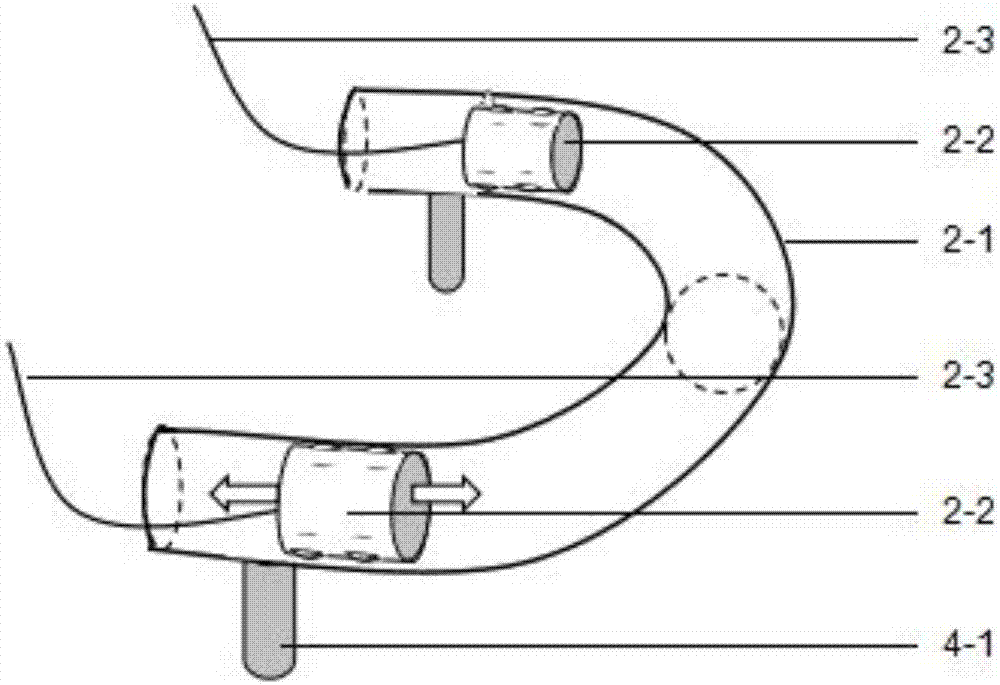
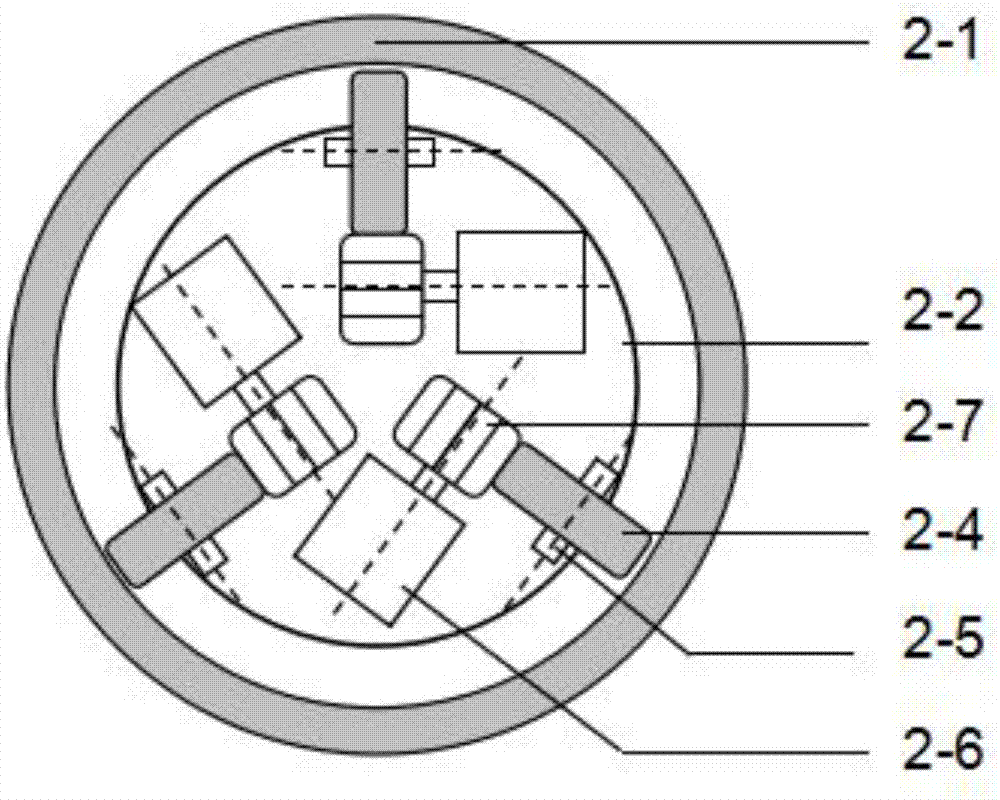
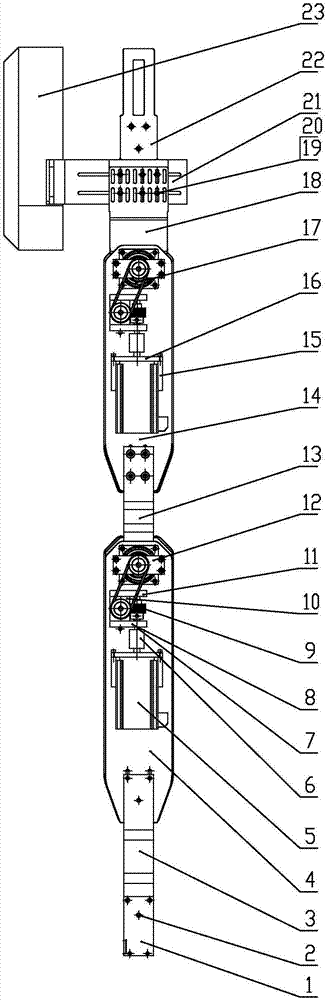
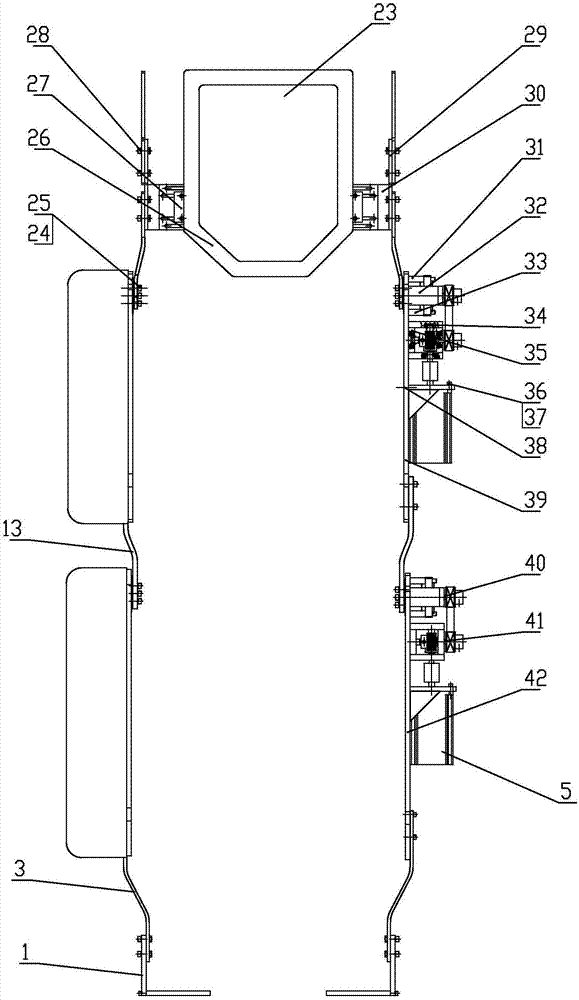
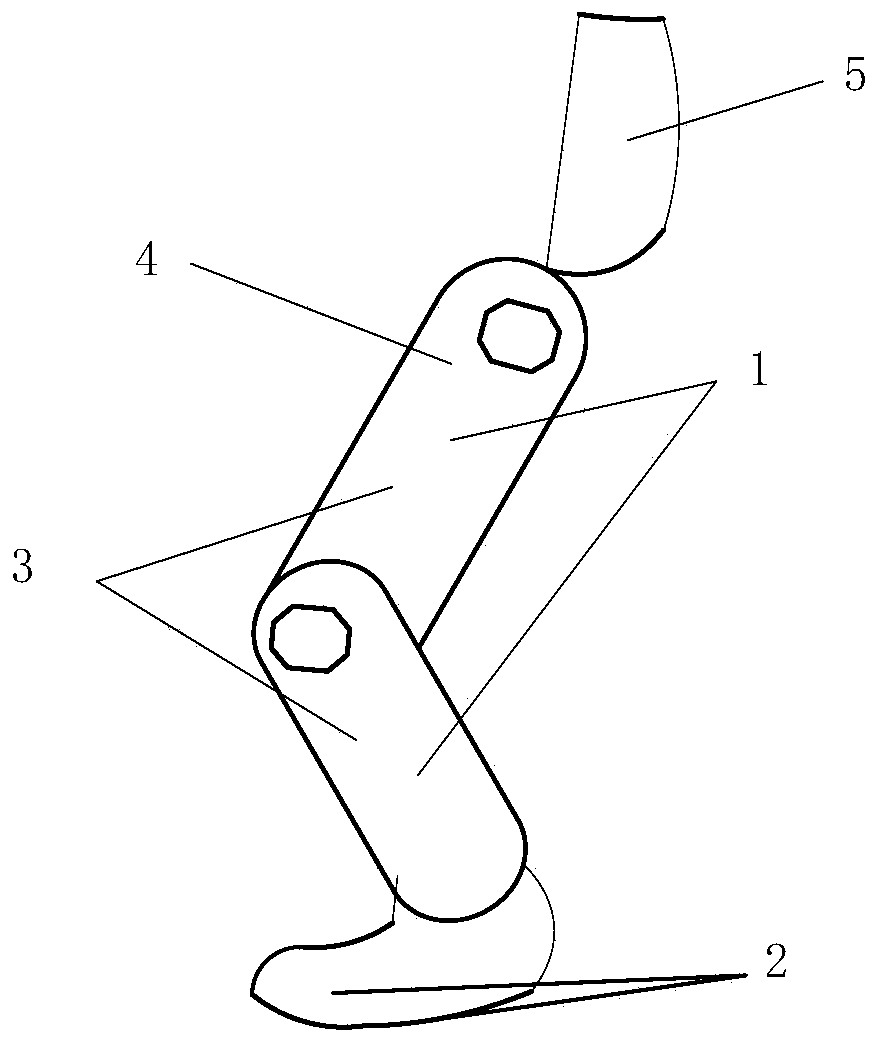
Powered lower limb devices and methods of control thereof
In some aspects, methods are provided for controlling a powered lower limb device. A stance phase control method is disclosed in which the required joint torque is determined based on the difference between two joint angles, such as the knee joint and the ankle joint. A swing control method is also disclosed that employs feedback-based minimum jerk trajectory control. In other embodiments, a joint assembly for use in modular lower limb device is provided. The joint assembly includes a reconfigurable slider-crank mechanism that is configurable to provide a plurality of different ranges of rotational travel, rotational speeds, and torques, for customization according to different anatomical joints. The joint assembly may include a compact coupling device for coupling a ball screw of the slider-crank mechanism to an output shaft of a motor. When employed to form a modular orthosis, the joint assembly may be adapted for self-alignment as its length adjustment method during setup.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
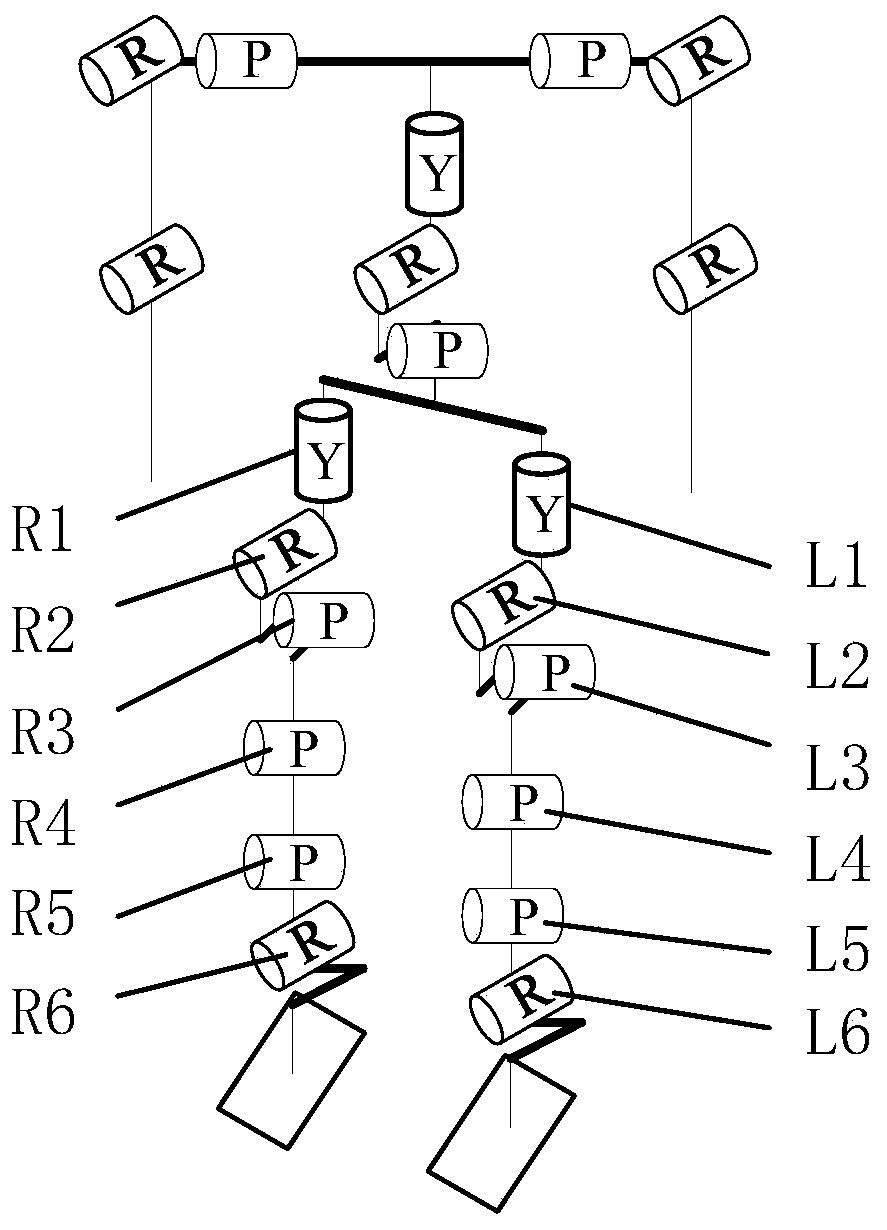
Actively and passively hybrid-driven lower limb-assisted exoskeleton robot and control method
PendingCN112060060AGuaranteed load capacityImprove motor performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorExoskeleton robotEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of exoskeleton robots and in particular relates to an actively and passively hybrid-driven lower limb-assisted exoskeleton robot and a control method. The robot comprises a waist-hip bracket and two thigh mechanisms. The waist-hip bracket is passively driven and comprises an adjustable waist rack and a hip joint assisted coil spring mechanism. The hip joint assisted coil spring mechanism achieves flexion / extension of two hip joints. Each thigh mechanism comprises a knee joint driving motor, a harmonic reducer, a knee joint angle sensor, an ankle joint spherical hinge and a foot. The knee joint driving motor and the harmonic reducer achieve flexion / extension of the knee joint. The ankle joint spherical hinge achieves dorsal extension / plantar flexion, introversion / extroversion and rotation of the ankle joint. The thigh waist-hip joint achieves passive drive of the hip joint through the coil spring mechanism and active drive of the knee joint through themotor. On the premise of guaranteeing a loading capacity of a wearer, the complexity of a lower limb-assisted exoskeleton robot system is reduced, and the lower limb-assisted exoskeleton robot systemis simple in structure and easy to control.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Limb spasticity evaluating and testing method and device for achieving method
ActiveCN105726039AEasy to implementEasy to operateDiagnostic signal processingSensorsHuman bodyEngineering
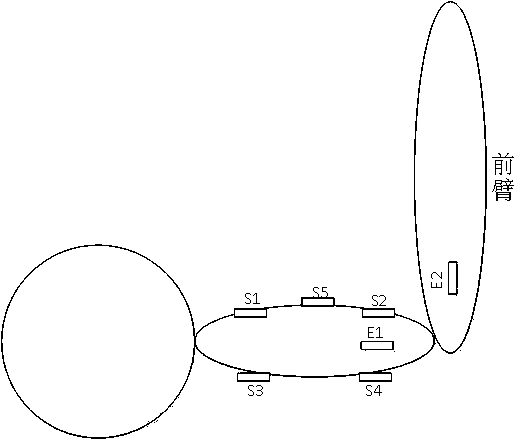
The invention discloses a limb spasticity evaluating and testing method and a device for achieving the method. The limb spasticity evaluating and testing method comprises the following steps: measuring change data of elbow joint angle acceleration or linear acceleration of any point of a front arm in the process that an elbow joint of a human body stretches at different angle speeds, and joint angle values corresponding to the acceleration change, processing measured angles, speeds and acceleration signals, displaying in real time, and storing; and evaluating the upper limb spasticity degree according to elbow joint angle acceleration of upper and lower limbs at different angle speeds or elbow joint angles corresponding to sudden linear speed change of any point of the front arm and elbow joint angle acceleration or acceleration change data of any point of the front arm. Spasticity can be objectively and quantitatively tested and evaluated, the difficulty that current spasticity testing is relatively large in objectiveness can be solved, and the method is simple in design and low in cost.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
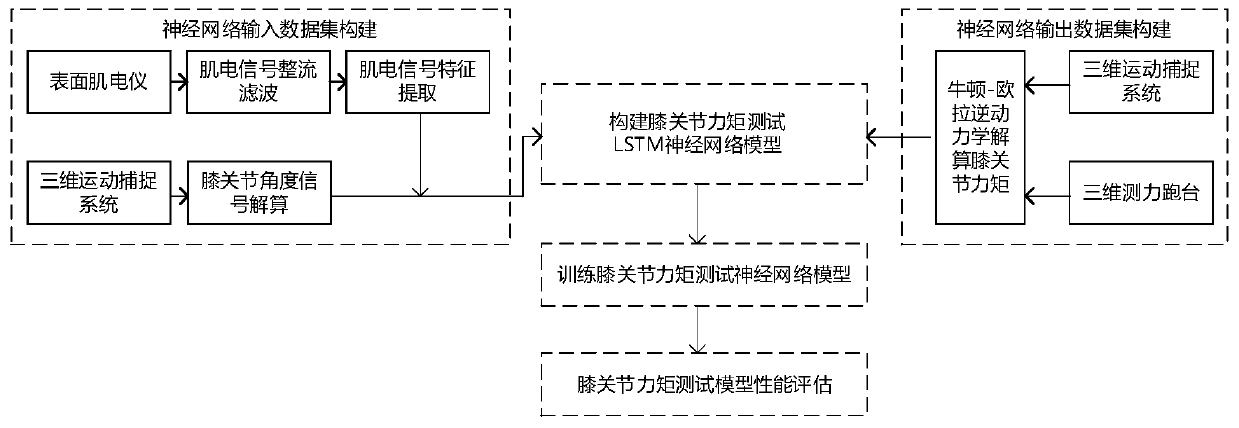
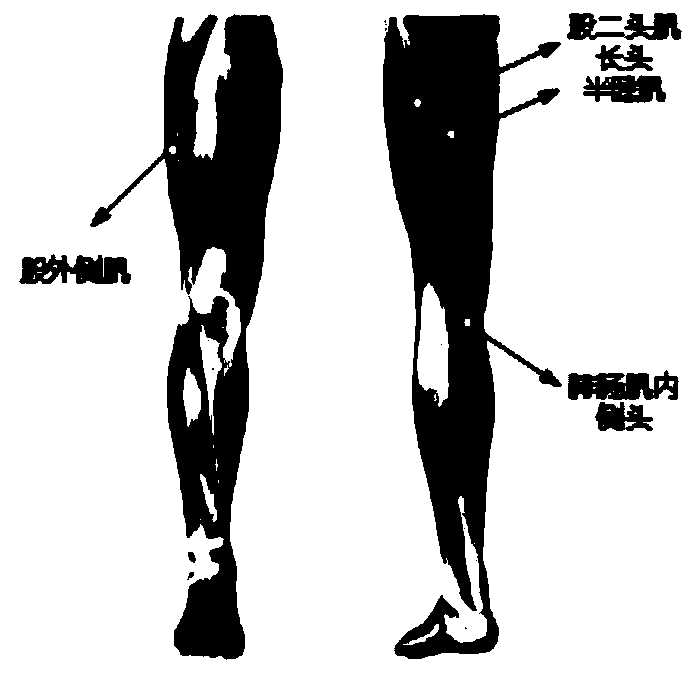
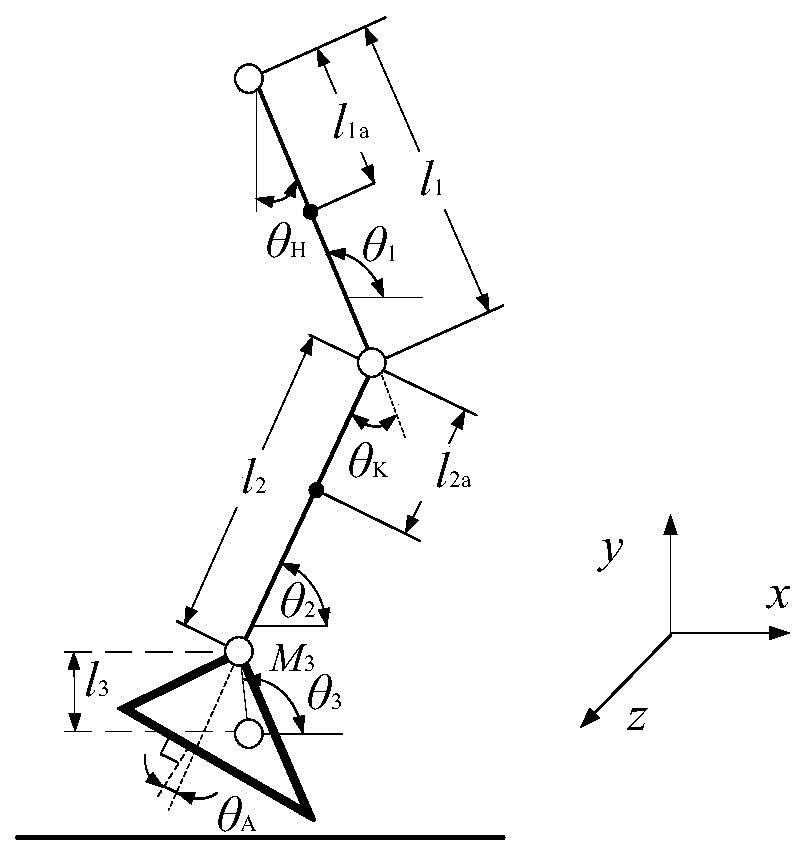
Human body knee joint force moment testing system and method based on surface electromyogram signals, and application
PendingCN110801226AIncrease sampling rateAccurate collectionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodySimulation
The invention relates to a human body knee joint force moment testing system and method based on surface electromyogram signals, and an application. The method comprises the following steps of step 1,collecting electromyogram signals of four muscles of vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, biceps femoris long head and gastrocnemius muscle of lower limbs of a user, and performing feature extraction; step 2, synchronously collecting leg kinematics data of the user in the walking process through a three-dimensional movement acquiring system, computing knee joint angles of the user, besides, synchronously collecting the insole pressure of feet of the user in the walking process through a force measuring treadmill, constructing a simplified dynamics model of legs of the user, and performing inverse dynamics solving to obtain the calculated force moment of knee joints of the user; and step 3, constructing a training dataset and a test dataset of a knee joint force moment testing long-term and short-term memory (LSTM) neural network, and completing the training of the knee joint force moment test neural network model through data obtained in the step 1 and the data obtained in the step 2. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being wide in application range and high in test precision.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Real-time detecting method for knee joint angles and device
ActiveCN102551995AImprove mental qualityFrequent detection experimentWalking aidsDiagnostic recording/measuringInternal memoryKnee Joint
The invention discloses a real-time detecting method for knee joint angels and a device. The method includes that an ultrasonic detecting device is mounted on the inner side of the front of a walking aid robot platform, multiple channels of ultrasonic range-finding sensors detect distance data among thigh detected surfaces and shank detected surfaces of lower limbs on both sides and the detecting platform, and information of bent angels of knee joints in a walking process of a testee is obtained. The device is an ultrasonic detecting system erected on the basis of the walking aid robot platform and comprises the multiple channels of ultrasonic range-finding sensors, a single chip microcomputer data acquisition and transmission device, a data processing unit for a portable computer and an internal memory, and a knee joint bent angle calculating and analyzing unit. The detecting device is mounted on a walking aid robot, devices are not mounted on the body of the testee, the testee is not limited in a walking process, the information of the bent angels of the knee joints can be obtained, and the detecting system is convenient in installation, simple in structure and low in cost.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
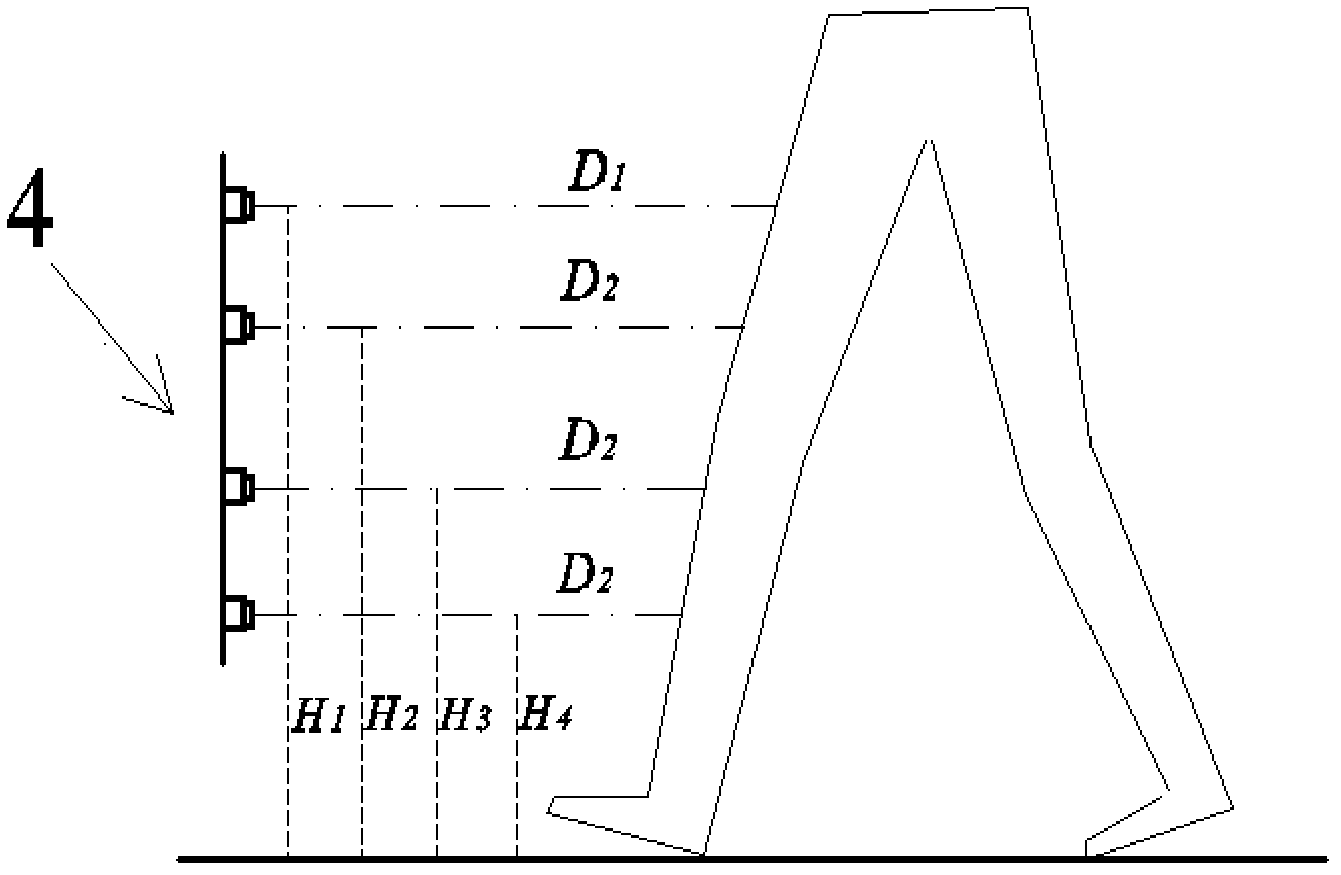
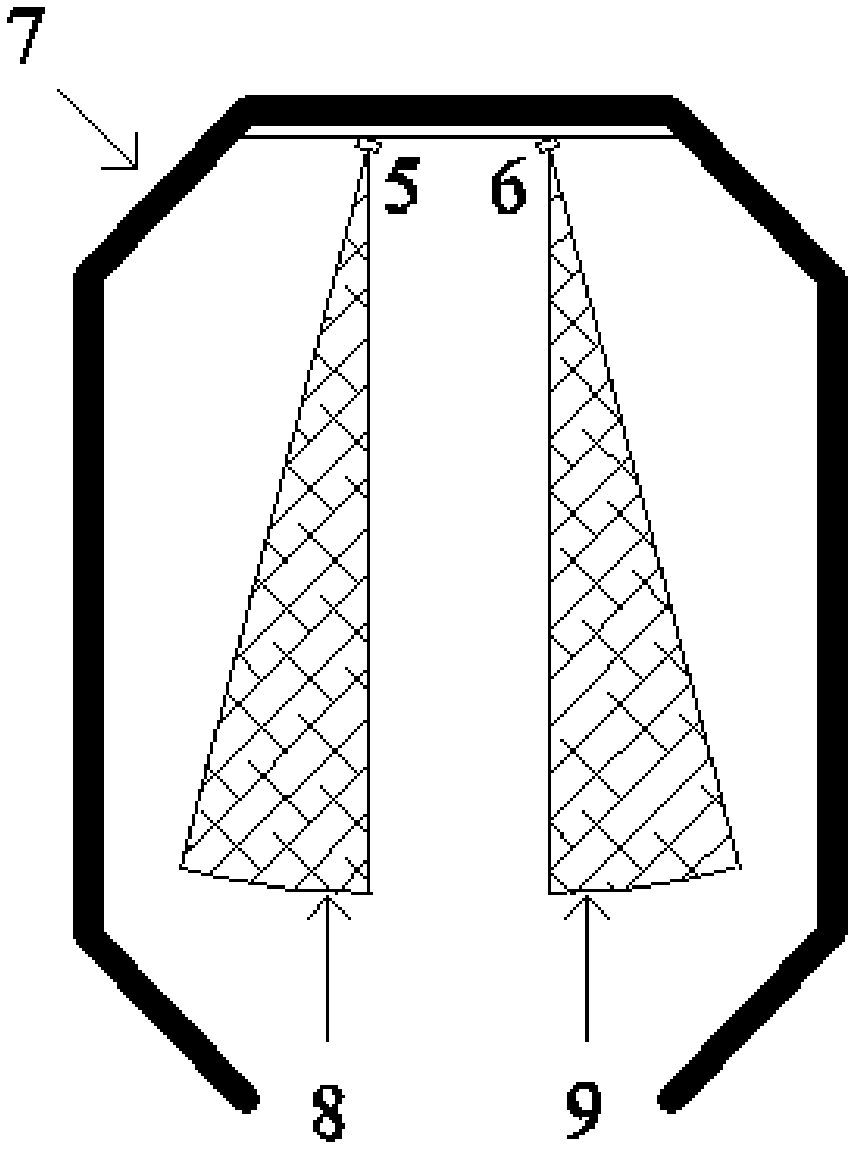
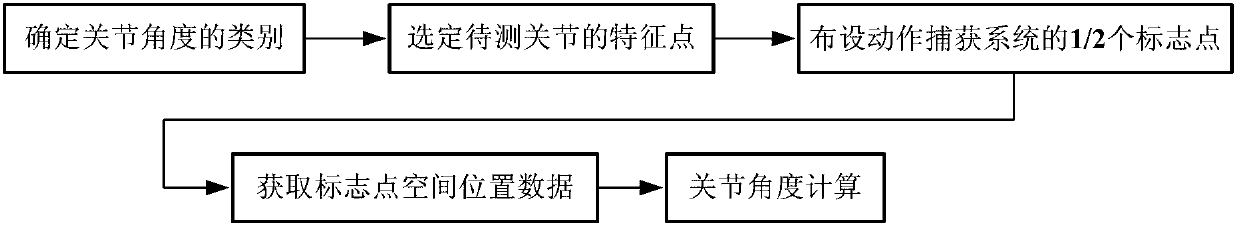
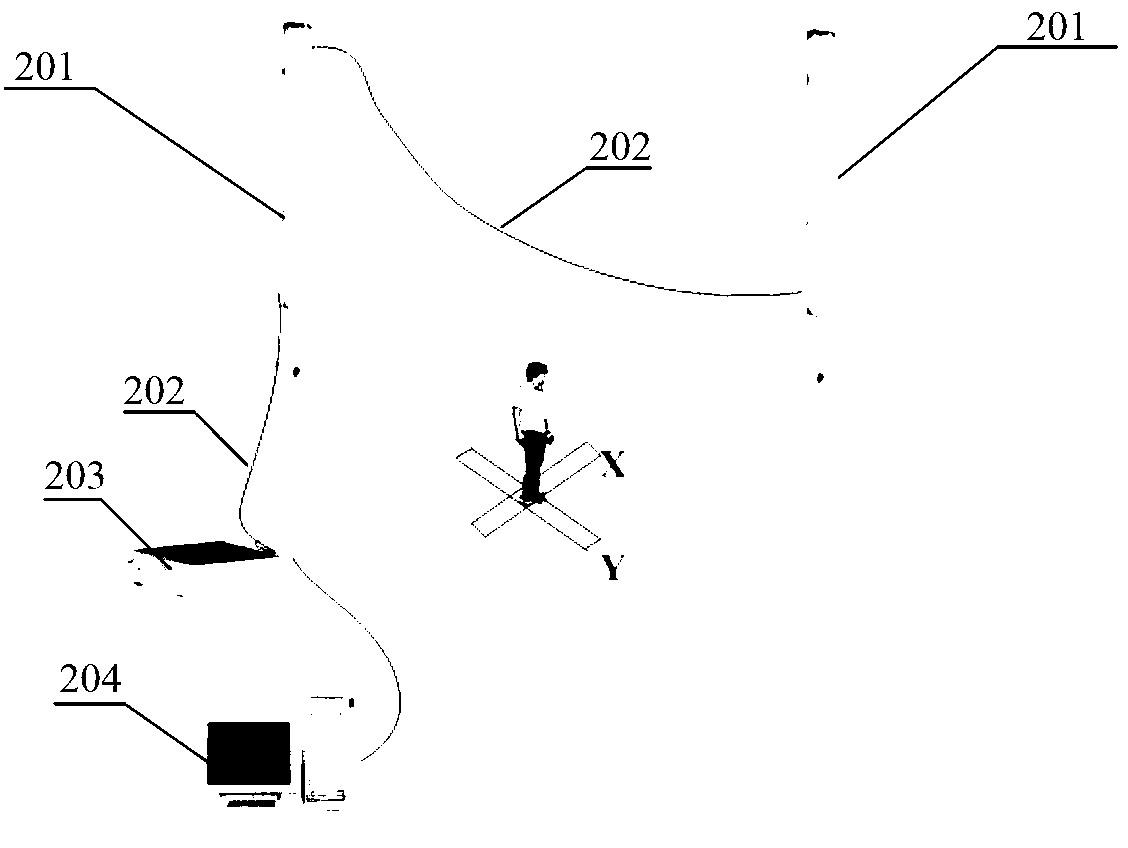
Human joint angle measuring method based on feature point space position
InactiveCN103340632AAchieve recordGood repeatabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCrowdsEngineering
The invention provides a human joint angle measuring method based on a feature point space position. According to the human joint angle measuring method based on the feature point space position, human joint motion can be tracked so that a space track of a joint mark point can be collected. On the basis, joint motion angle values of the portions of neck, elbow, wrist, hip and the like are measured through least squares fit and the Newton interpolation method, descriptive statistical analysis can be further conducted on the joint angle values, and therefore the requirements that position accuracy is better than 2mm and the measuring accuracy of joint angles is better than 0.2 degree are satisfied. According to the human joint angle measuring method based on the feature point space position, the problems that manual measurement is slow, a person to be measured is prone to fatigue, and a measuring result is poor in accuracy in the prior art are solved, the problems that when three dimension scanning measurement is used, required data volume is large, calculation speed is low, and auxiliary work amount of the measurement is large are solved. The joint motion angles of large sample crowd can be measured and calculated rapidly, accurately and automatically.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
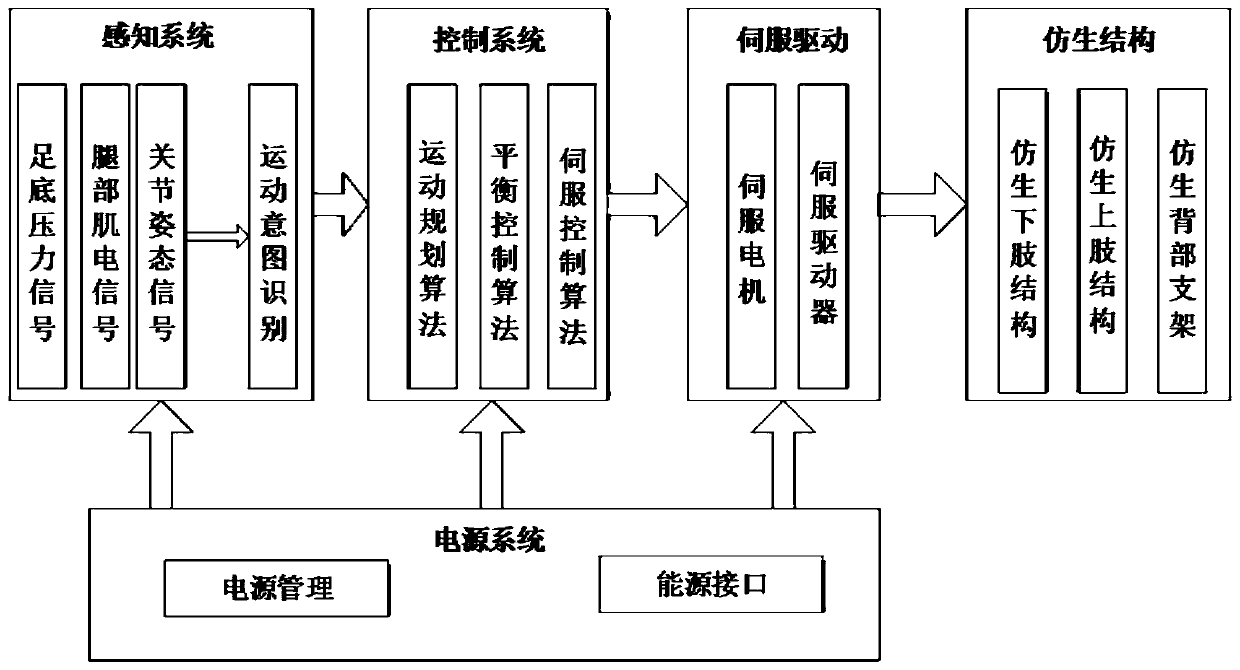
Lower-limb brain-like intelligent mechano-electronic exoskeleton and integrated control system thereof
PendingCN107468486ASolve the problem of slow recovery effectGuaranteed stabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorChiropractic devicesEngineeringGravity center
The invention relates to a lower-limb brain-like intelligent mechano-electronic exoskeleton and an integrated control system thereof. The lower-limb brain-like intelligent mechano-electronic exoskeleton is characterized by comprising a gravity center adjusting device, a plurality of mechano-electronic joints, a plurality of connecting rods, a plurality of exoskeleton bodies, foot fixing shoes and pelma sensors; the gravity center adjusting device is installed on the waist connecting rod, and the waist connecting rod, the hip mechano-electronic joint, the thigh exoskeleton bodies, the thigh connecting rods, the knee mechano-electronic joints, the shank exoskeleton bodies, the shank connecting rods and the ankle mechano-electronic joints are connected in sequence; the mechano-electronic joints are internally provided with joint angle and damping sensors respectively and driven by corresponding mechanical joint driving devices to generate actions. The lower-limb brain-like intelligent mechano-electronic exoskeleton is reasonable in design, various actions can be precisely sensed, and on this basis, the corresponding control functions are achieved. Meanwhile, the balance of the lower limbs is automatically adjusted through the gravity center adjusting device, the walking stability and reliability are ensured, and the problem that the rehabilitation effect of a patient who loses the lower limb functions is slow can be effectively solved.
Owner:臧大维 +1
Regeneration power mechanical skeleton system
PendingCN107457766AReasonable structural designEasy to assembleProgramme-controlled manipulatorHuman bodyData acquisition
The invention relates to a regeneration power mechanical skeleton system. The regeneration power mechanical skeleton system is designed to solve the technical problems that existing like products are in shortage of data signal pre-catching and collecting, real-time monitoring, restoration gait position information and feedback compensation amount. The regeneration power mechanical skeleton system comprises a mechanical system and a data collection system. The mechanical system comprises a lower limb servo mechanism and a connection mechanism. The regeneration power mechanical skeleton system is characterized in that according to the mechanical system, a rotational joint between a hip joint connection plate and a thigh plate and a rotational joint between the thigh plate and a shank plate are each provided with a hall angle sensor; the hall angle sensors are used for collecting ground angle signals of the lower limbs and the waist of the human body and obtaining angle values of all the joints through foot angle difference calculation, the joint angles and torque signals of the human body are pre-caught and stored in a control system of the mechanical skeleton system, and a user independently selects a control pattern; and the posture of the human body is monitored in real time through the control system, and limb position information and the feedback compensation amount are provided for the human body gait restoration control process.
Owner:张翔宇 +2
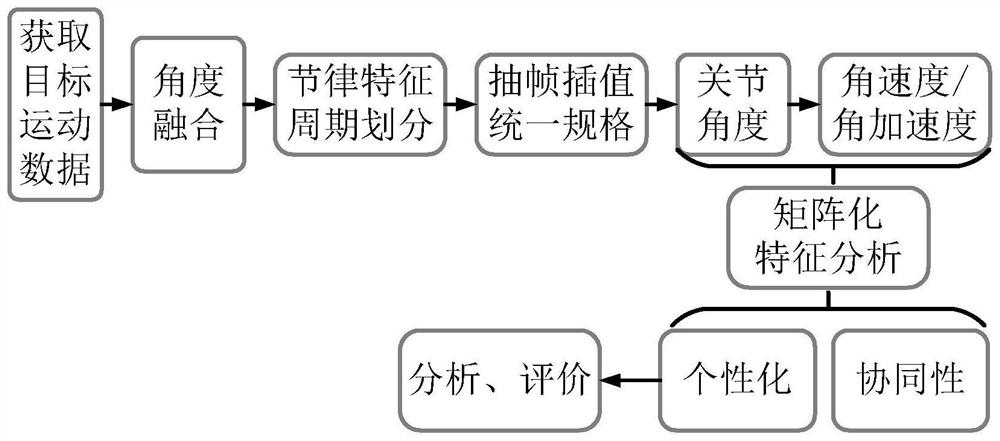
Joint angle-based rhythm motion collaborative analysis method
PendingCN111950383AEfficient extractionEfficient analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsPattern recognitionHuman body
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
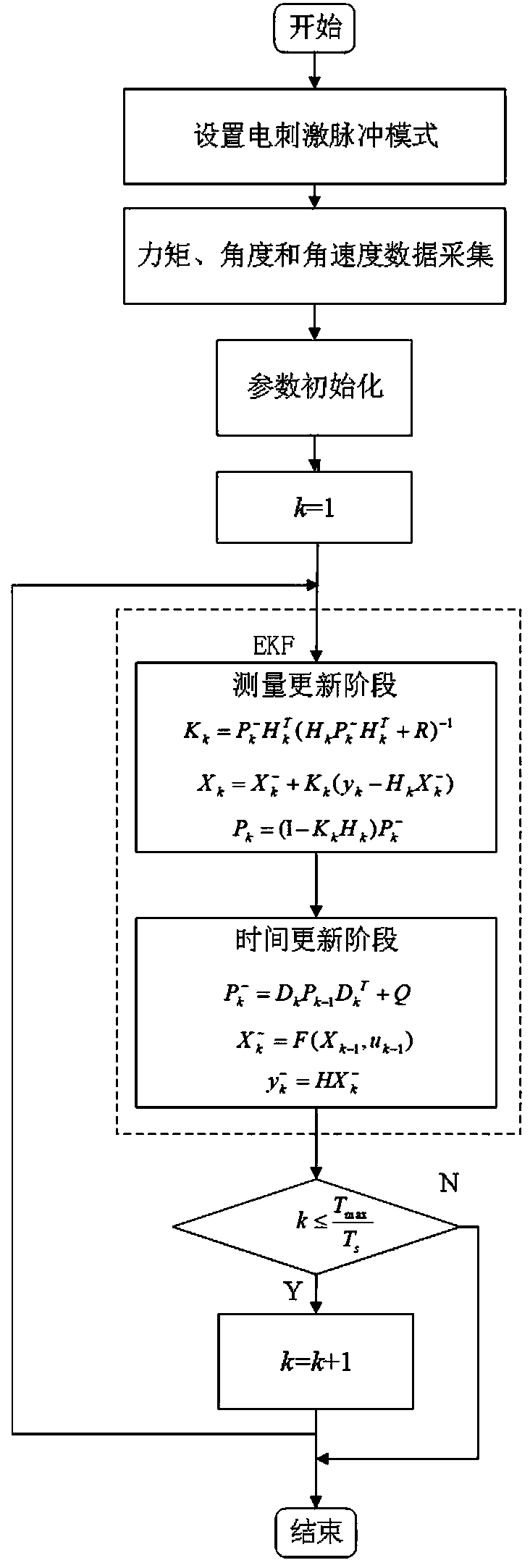
On-line estimation method of elbow joint torque under functional electrical stimulation
InactiveCN109106339ARealize online estimationSafe and reliable controlDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityEstimation methods
The invention relates to an on-line estimation method of elbow joint torque under functional electrical stimulation, the musculoskeletal model is pre-modeled by off-line acquisition of joint torque, angle and angular velocity data, and then real-time acquisition of joint angle and angular velocity signals, real-time adaptive updating of the parameters of the pre-modeling musculoskeletal model system, so as to achieve online estimation of torque. The invention realizes on-line estimation of torque through real-time acquisition of joint angle and angular velocity signals.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
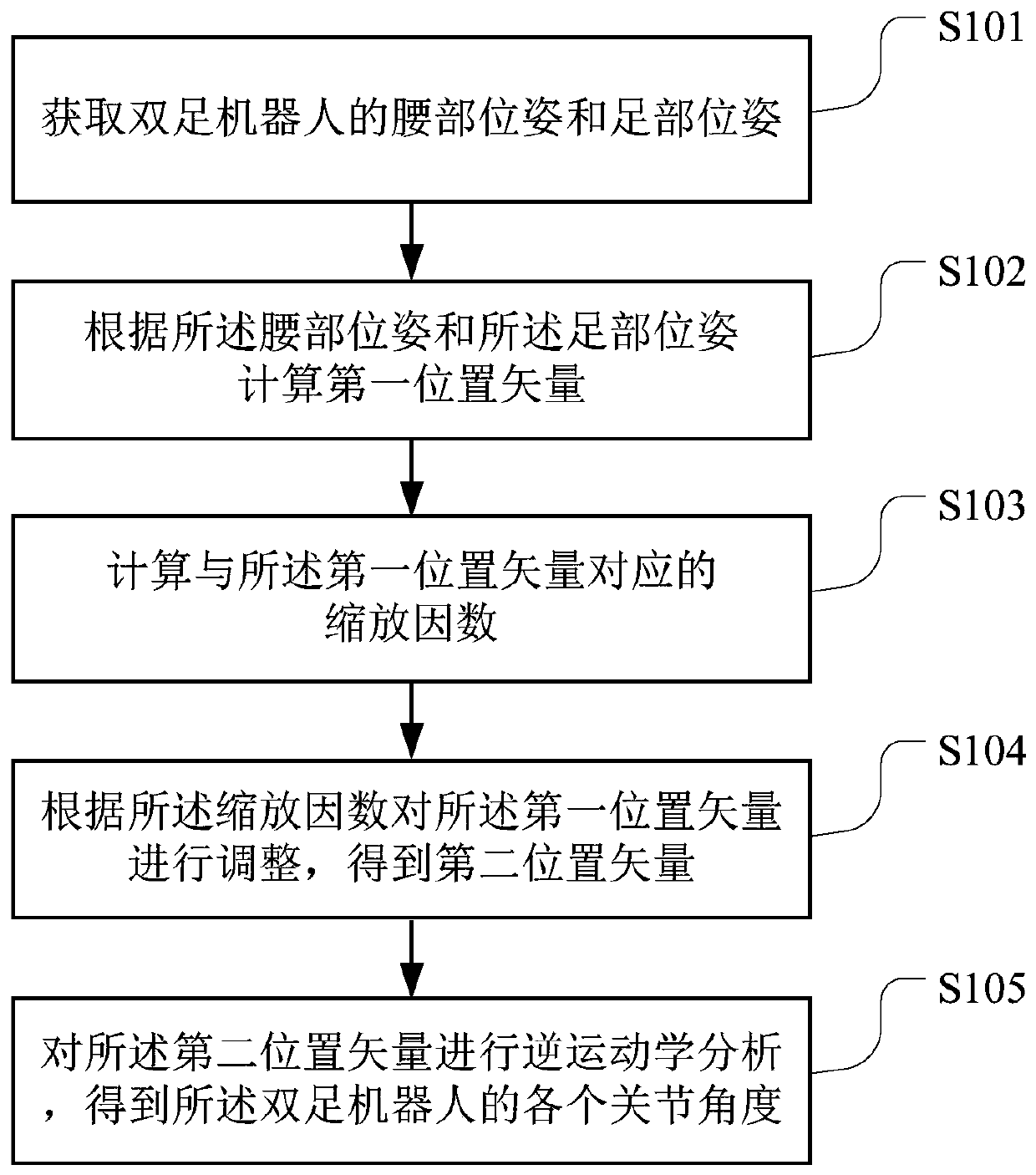
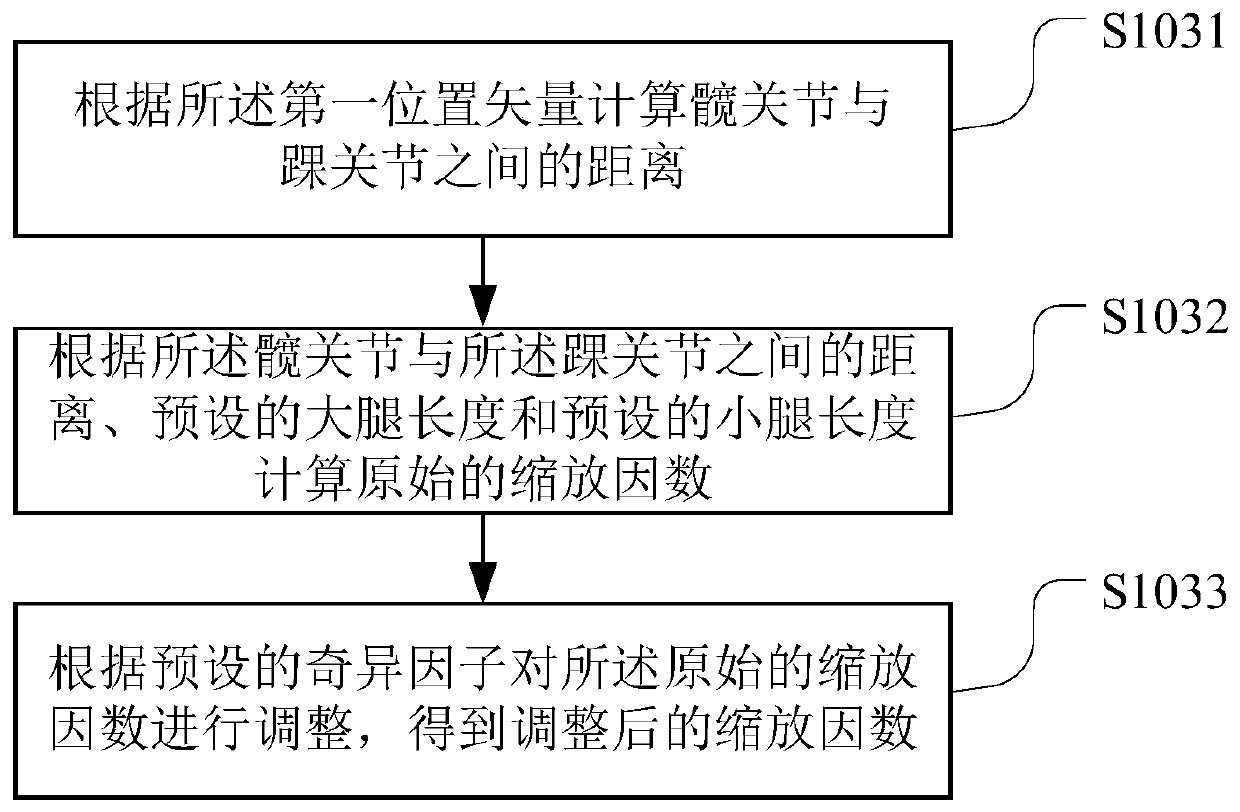
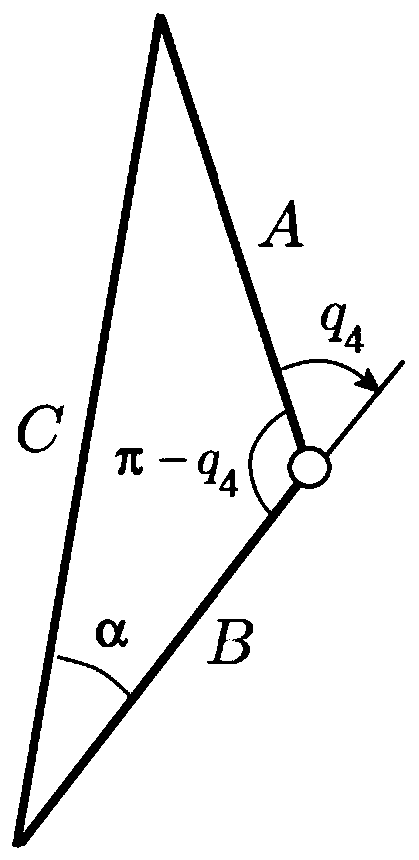
Singular-avoiding gait planning method and device, readable storage medium and robot
PendingCN110989585AAvoid singularity problemsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesGait planningSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of computers, and particularly relates to a singularity-avoiding gait planning method and device, a computer readable storage medium and a robot. The method comprises the steps of acquiring the waist posture and the foot posture of the biped robot; calculating a first position vector according to the waist pose and the foot pose, wherein the first position vector is a hip joint position vector in an ankle joint coordinate system; calculating a scaling factor corresponding to the first position vector; if the scaling factor meets a preset singularityjudgment condition, adjusting the first position vector according to the scaling factor to obtain a second position vector; and performing inverse kinematics analysis on the second position vector toobtain each joint angle of the biped robot. According to the embodiment of the invention, on the basis of the prior art, the consideration of a singular problem is added, and the possible singular problem is effectively avoided through the adjustment of the hip joint position vector.
Owner:UBTECH ROBOTICS CORP LTD
Lower limb rehabilitation robot based mirror training method for lower limb rehabilitation
InactiveCN111759672AAchieve the purpose of reproductionAvoid Accuracy ImpactDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationElectric machinery
The invention discloses a lower limb rehabilitation robot based mirror training method for lower limb rehabilitation. The method includes the following steps: 1, initializing each joint angle of a lower limb rehabilitation robot; 2, collecting an initial pose when a patient sits on the lower limb rehabilitation robot at an initial state; 3, controlling, by the lower limb rehabilitation robot, motors to rotate to the initial pose; 4, collecting real-time dynamic data during the rehabilitation training of the patient; 5, processing the real-time dynamic data through an industrial personal computer, and obtaining the actual moment required by the rotation of each joint; and 6, adjusting the rotating angles of the motor of each joint, detecting the positions of the motors in real time to obtain the current position information of each joint, and feeding the information back to the industrial personal computer to inspect until the mirror position on the healthy side of the patient is achieved. The method can control the lower limb rehabilitation robot to drive the affected side of the patient to complete mirror motion according to the motion track of the healthy side of the patient, sothat reliability can be provided for the lower limb rehabilitation training of the patient.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Man-machine interaction intelligent control method of load maneuvering exoskeleton and exoskeleton system
ActiveCN113001540AAccurate trackingSimplified position calculationProgramme-controlled manipulatorHuman bodyKinetics equation
The invention discloses a man-machine interaction intelligent control method of a load maneuvering exoskeleton and an exoskeleton system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, modeling a human body and the load maneuvering exoskeleton into a five-connecting-rod model consisting of a trunk, a left thigh, a right thigh, a left shank and a right shank; dividing the five-connecting-rod model into a supporting leg model and a swinging leg model, and respectively establishing kinetic equations of the two models by utilizing a Lagrange motion equation; and then designing a hybrid control method combining position control and AIA control based on a tracking differentiator, applying the position control to the supporting leg model in a gait period, enabling the joint angle of an exoskeleton to track the joint angle of the human body in real time, applying the AIA control based on the tracking differentiator to the swinging leg model, enabling the exoskeleton to adapt to the human body movement and environment of a wearer by self, achieving the two control methods alternately according to a supporting phase and a swinging phase of the gait cycle, so that the exoskeleton tracks the position of the human body in real time. Coordinated movement of the exoskeleton and the human body can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Self-stabilization control method, system and device of wheel-legged robot
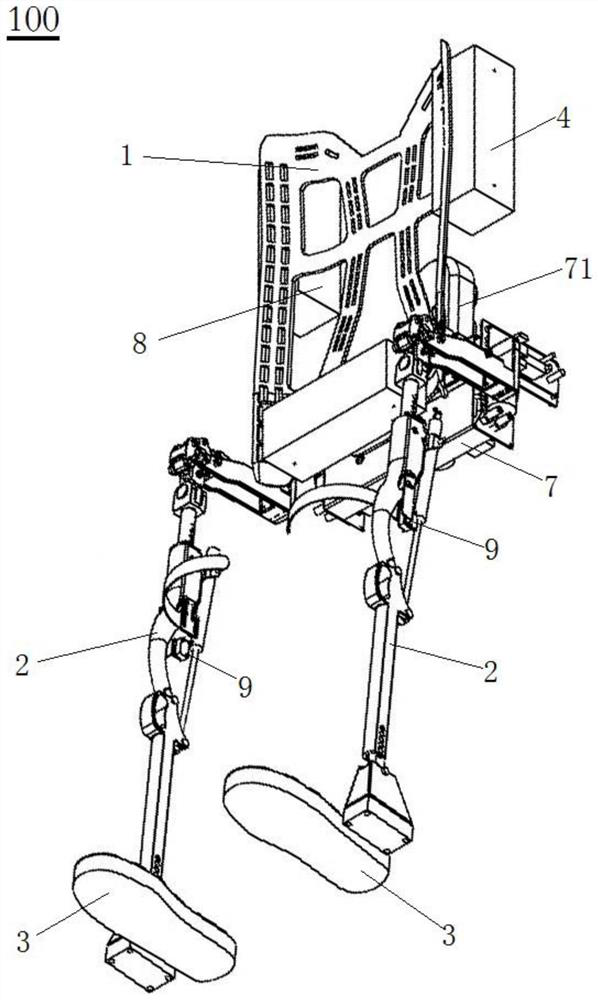
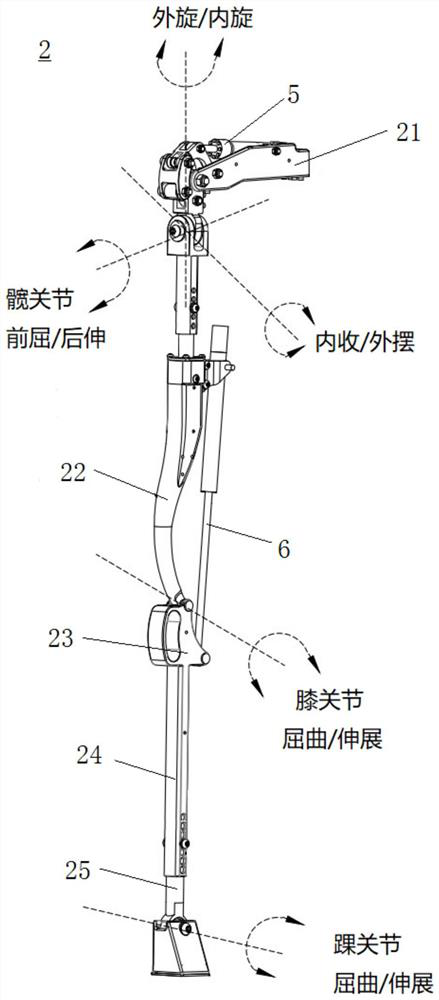
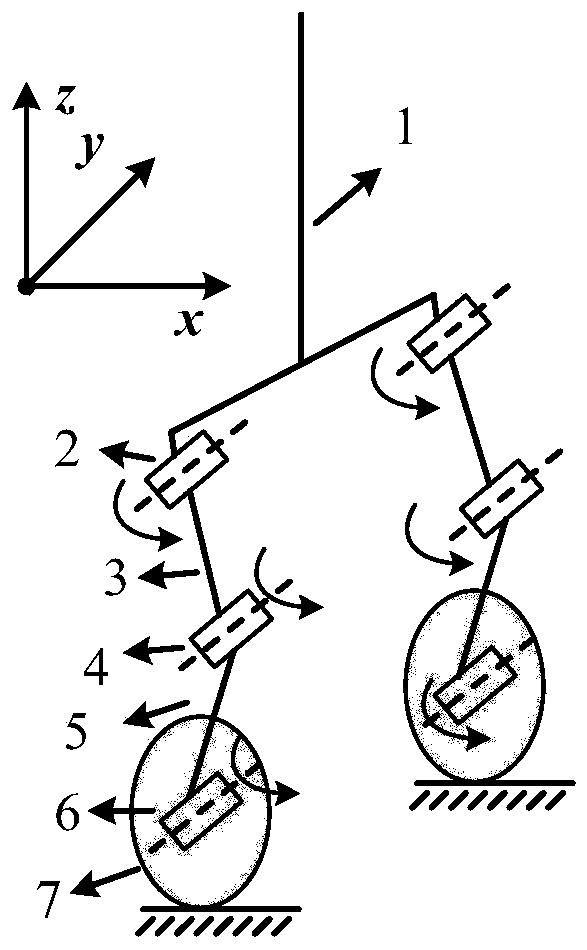
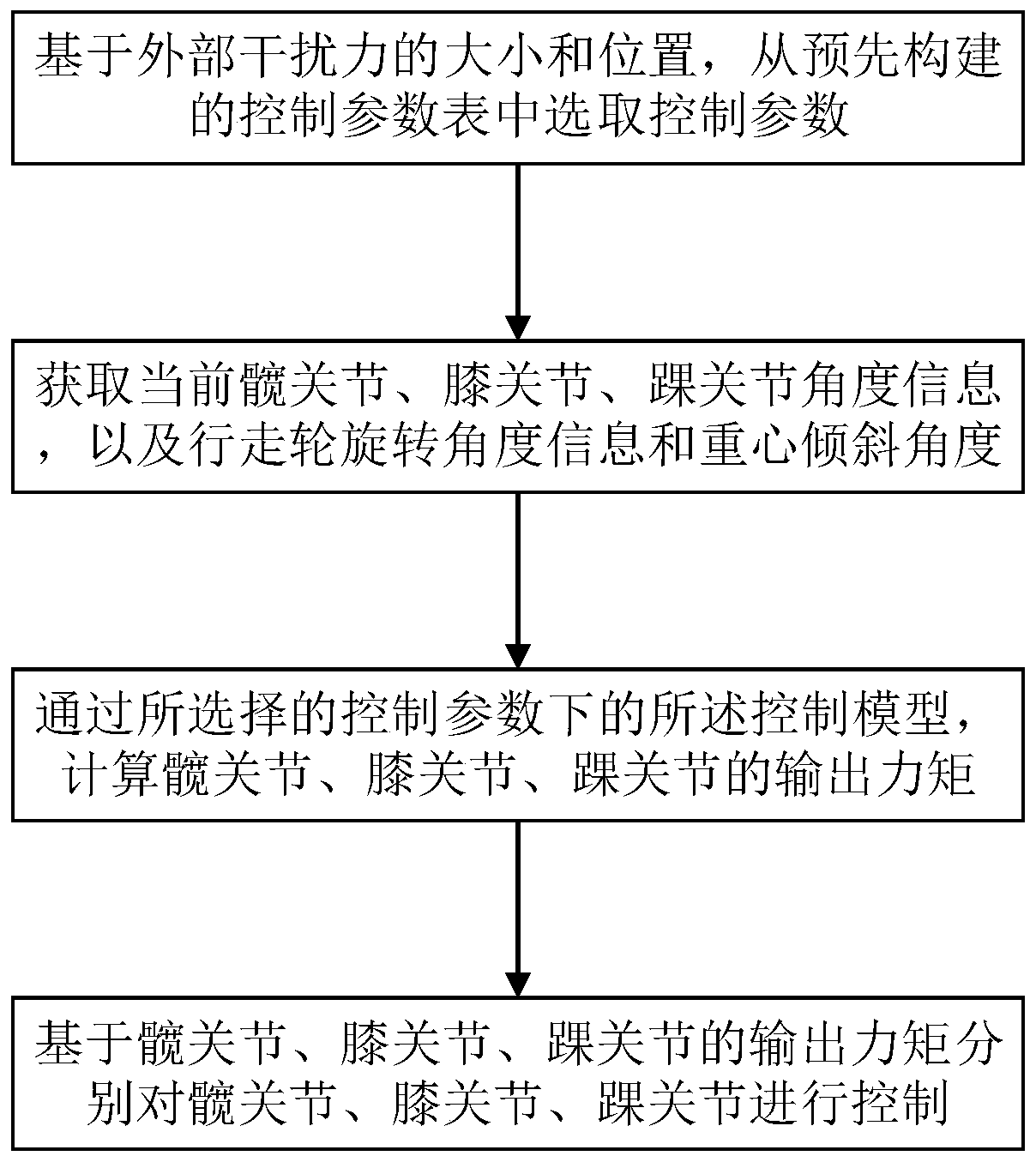
ActiveCN110764413AStable stateQuickly return to the initial stateAdaptive controlVehiclesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationStabilization control
The invention belongs to the field of robot control, and specifically relates to a self-stabilization control method, system and device of a wheel-legged robot, aiming to enable the wheel-legged robotto keep stable even facing external disturbance and to return to the initial state. The method comprises steps of selecting control parameters from a pre-established control parameter table based onsize and position of external interference force, wherein the control parameters are control parameters of a preset control model; acquiring angle information of a hip joint, a knee joint and an anklejoint at the moment, rotating angle information of a traveling wheel and angle of inclination of a center of gravity, and calculating output torques of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint according to the control model with the selected control parameters; and controlling the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint based on the output torques of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint. The wheel-legged robot can keep stable even facing external disturbance and can return to the original state rapidly.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
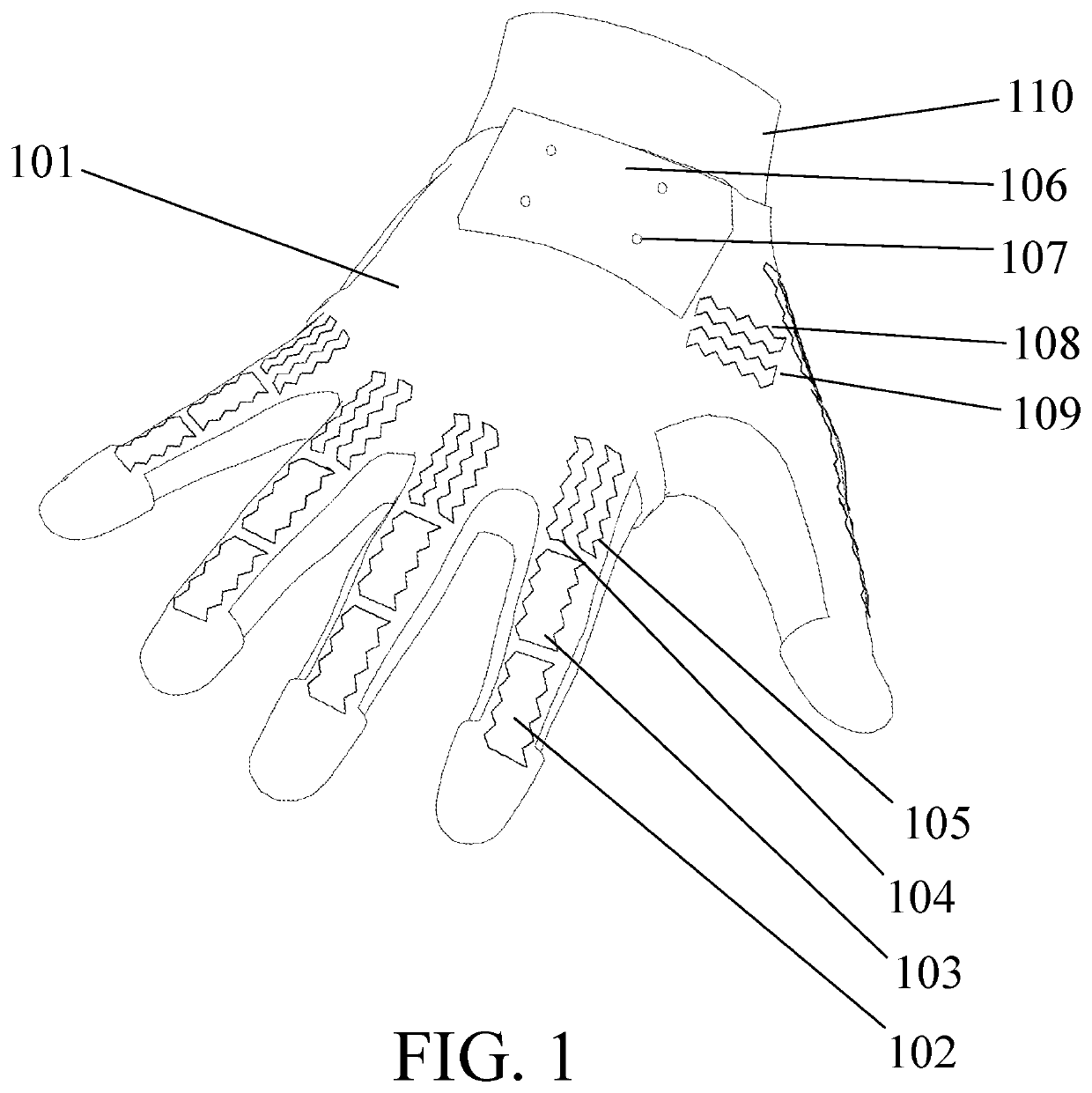
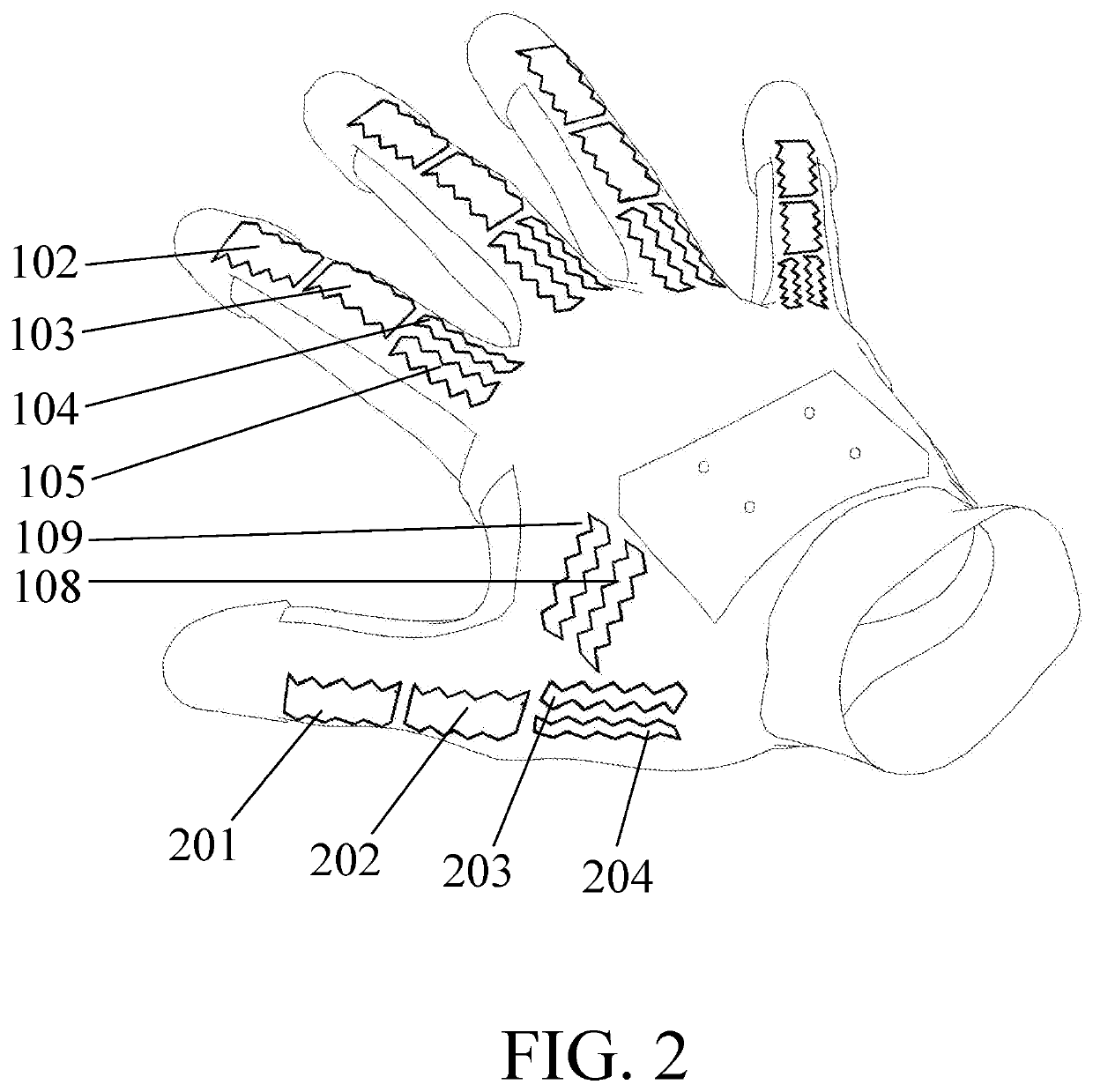
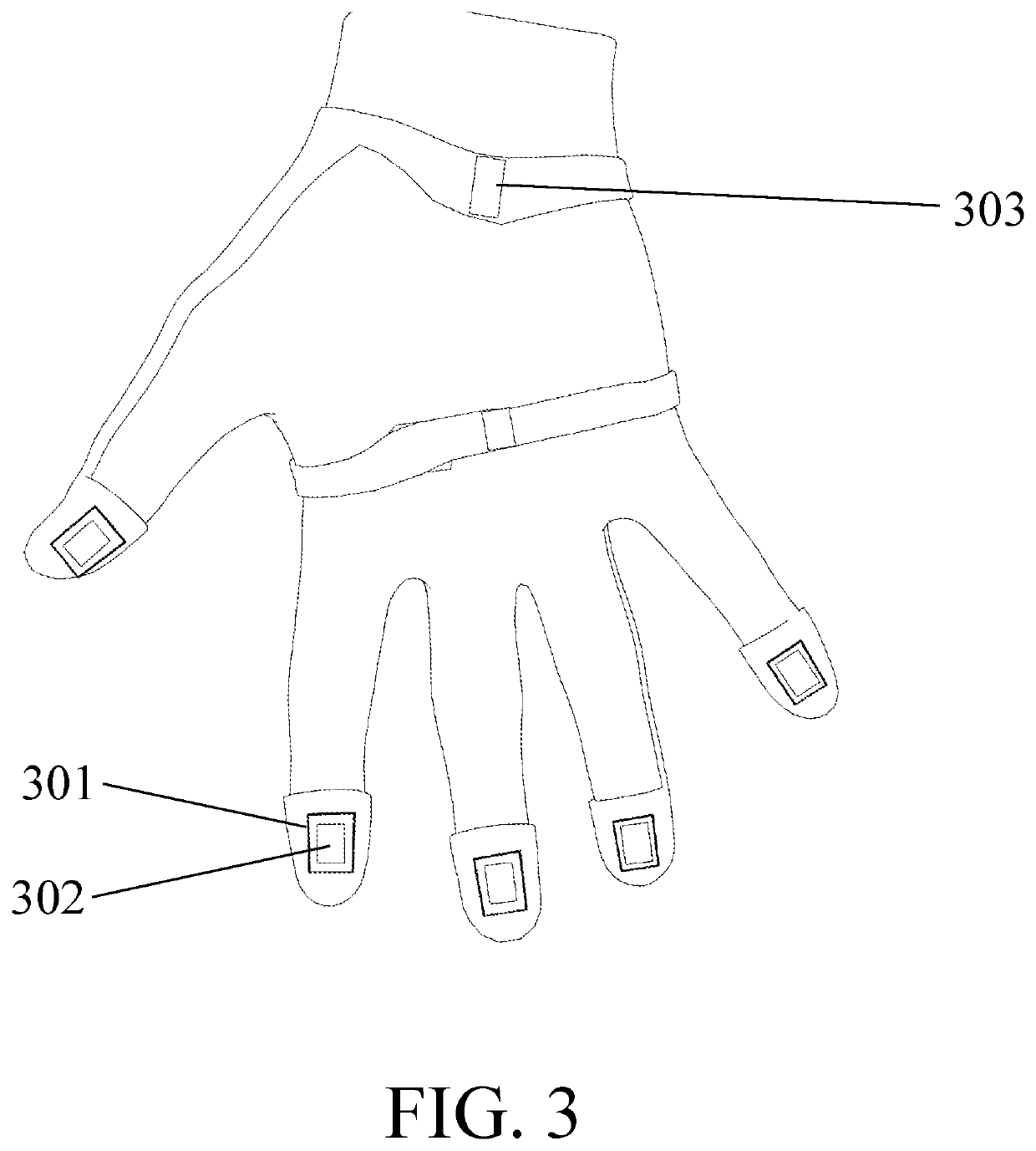
Hand worn interface device
PendingUS20200150761A1Input/output for user-computer interactionInductance measurementsEngineeringCurrent driver
A wearable device comprises a flexible substrate carrying multiple conducting loops which are formed into a zig zag pattern so as to be able to accommodate a stretching of the substrate. The substrate is formed into a glove and the loops positioned such that they are aligned with the anatomical joints. As the anatomical joints move, the loops change shape and accordingly change their inductance—this is measured by the electronics in the glove and used to calculate the joint angles in a processor which transmits the angles to an external computer system. Some of the loops are attached to current drivers in the electronics module, and a magnet positioned close to the loop, providing means for a force to be generated between magnet and loop when the current driver passes current through the loop, thereby providing tactile feedback to the user.
Owner:PLEXUS IMMERSIVE CORP
Human body action acquisition method based on inertial sensor without standard posture correction
ActiveCN111895997ARealize automatic calculationAngle measurementNavigational calculation instrumentsHuman bodyKnee Joint
The invention discloses a human body action acquisition method based on an inertial sensor without standard posture correction. The method comprises the steps that 1, an IMU is arranged, and joint physiological kinematics constraints are established; 2, by utilizing the IMU in the step 1, when the number of sampling points of the IMU exceeds 100, an optimization program runs according to a constraint equation, and a joint axis and a joint position vector are estimated by utilizing a Gauss-Newton method; 3, two groups of joint angles are respectively solved through acceleration information andangular velocity integration by utilizing the solved joint axis and joint position vector; and 4, weighted average of the two joint angles in the step 3 is solved through complementary filtering, andthe joint angles are solved. The method aims to decode IMU signals of lower limbs of a human body and calculate angles of hip joints, knee joints and ankle joints of the lower limbs in real time according to a kinematic model of the lower limbs of the human body.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
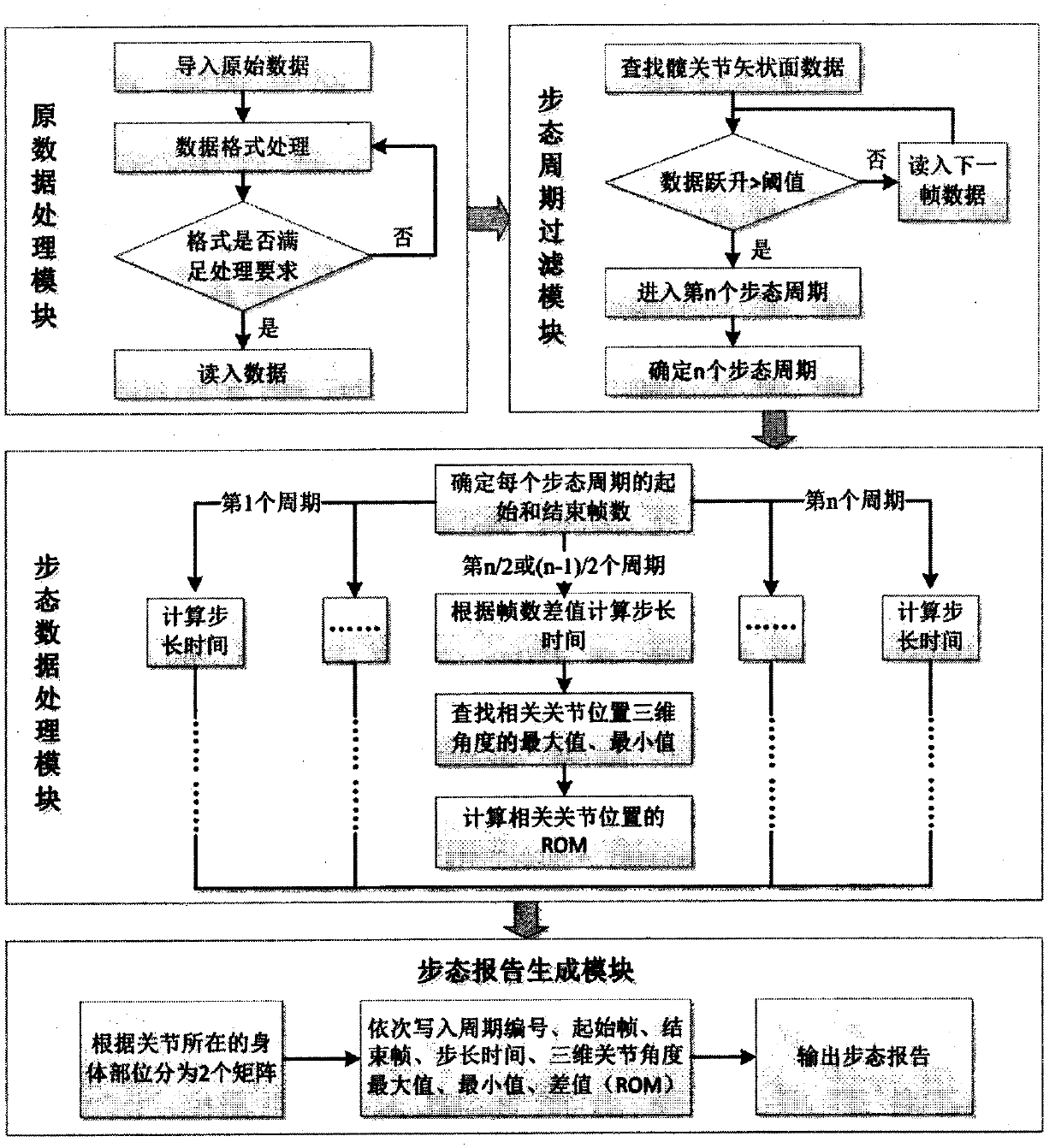
Python-based gait cycle and three-dimensional limb motion angle algorithm
InactiveCN107609523AEasy to handleImprove general performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyVertical plane
The invention provides a Python-based gait cycle and three-dimensional limb motion angle algorithm. The algorithm comprises the following steps of: butting a three-dimensional motion capture system, and formatting original data according to body parts where vital joints are located and joint names; setting a rise threshold value according to gait cycle features, and determining all the gait cyclesin a database on the basis of an angular variation law of hip joint vertical plane; determining a step length time on the basis of a data recording frequency and start and end frames of the gait cycles, searching maximum values and minimum values of three-dimensional joints in each gait cycle by utilizing Python, and calculating a three-dimensional limb motion angle; and generating two data matrixes according to joint positions and respectively writing a gait and a limb motion index of each gait cycle. The algorithm is capable of rapidly and effectively processing a large number of real-timejoint angle data, is suitable for various three-dimensional motion capture systems, different loads of human body and different clothing equipment conditions, and is strong in generality, high in flexibility and good in expandability.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
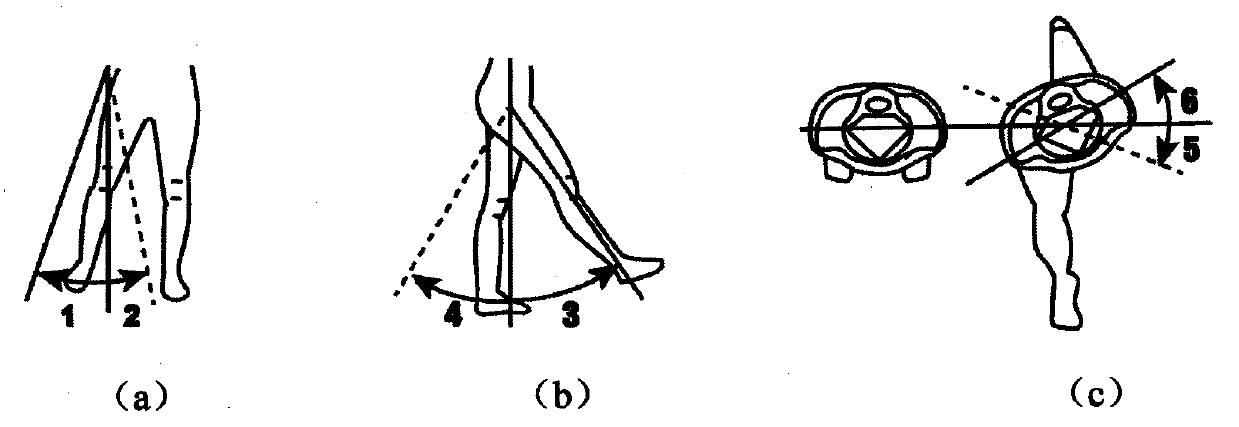
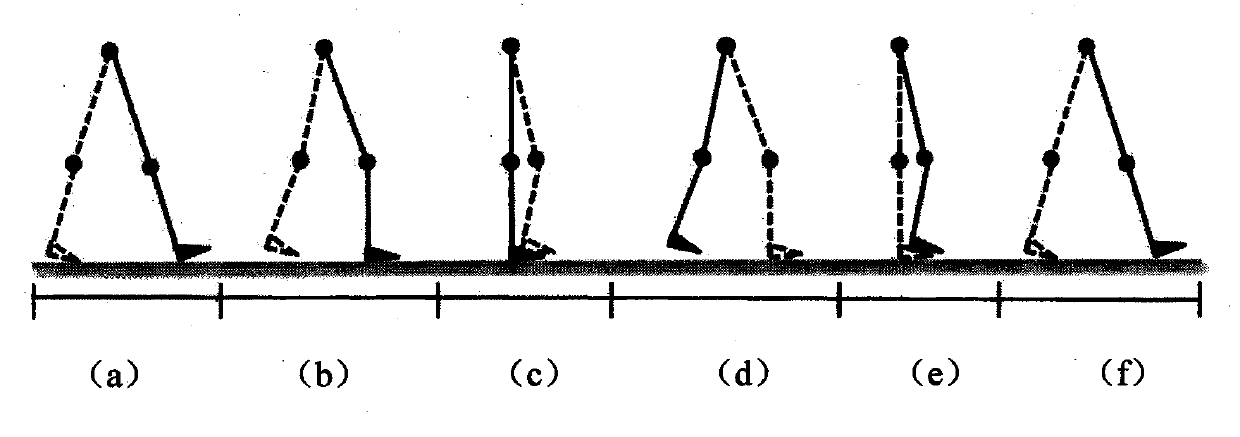
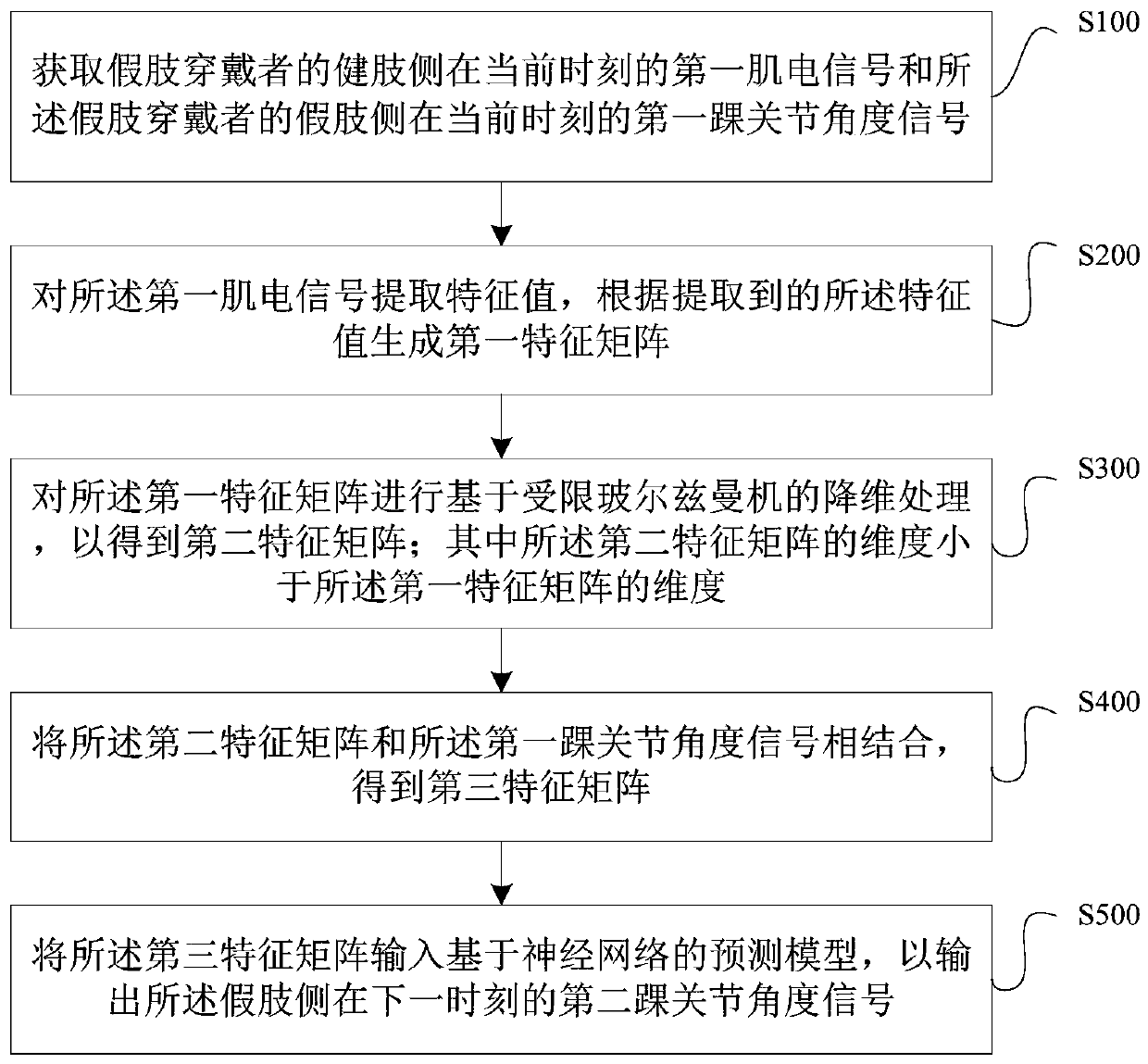
Method and device for predicting angle of ankle joint of artificial limb
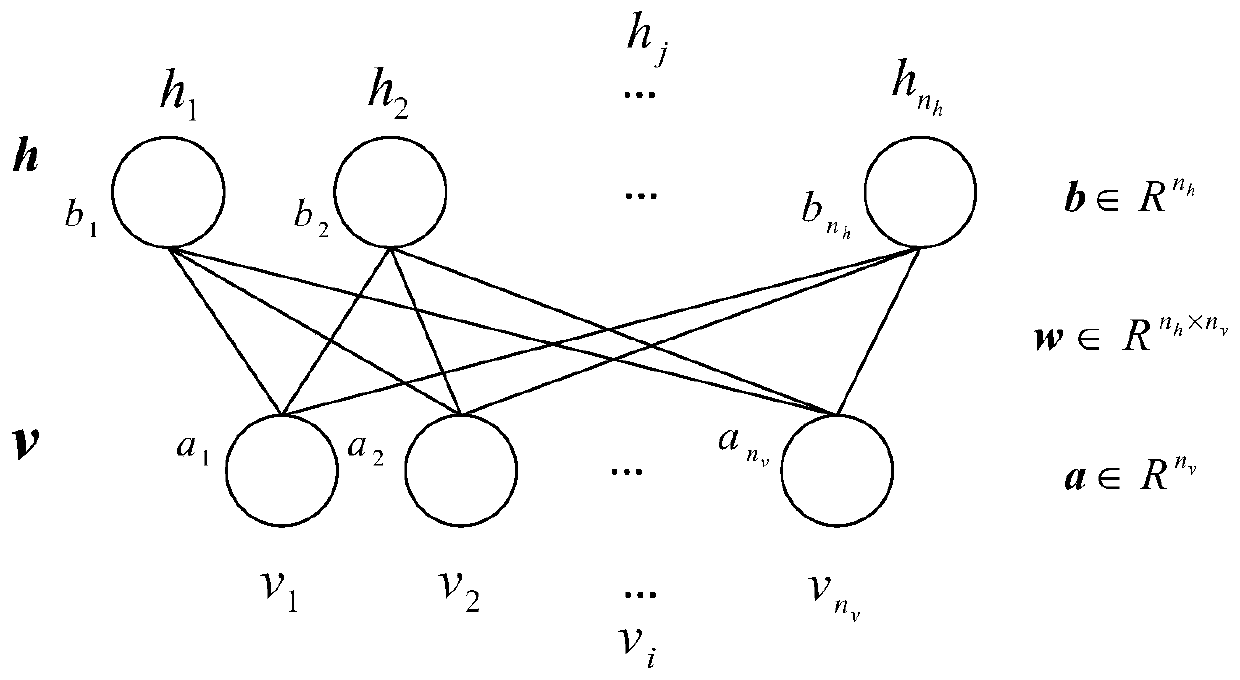
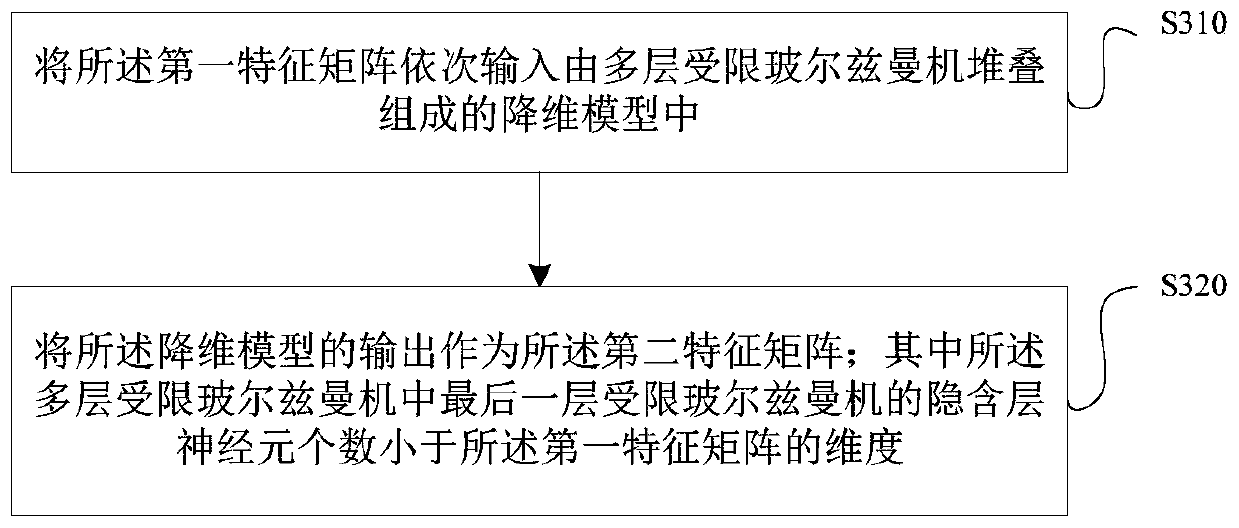
ActiveCN111476204AReduce the amount of data calculationReduce dimensionalityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesRestricted Boltzmann machinePhysical therapy
The invention discloses a method and a device for predicting the angle of an ankle joint of an artificial limb. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a first electromyographic signal ofthe healthy limb side of an artificial limb wearer at the current moment and a first ankle joint angle signal of the artificial limb side of the artificial limb wearer at the current moment; extracting a feature value of the first electromyographic signal, and generating a first feature matrix according to the extracted feature value; performing dimension reduction processing based on a restrictedBoltzmann machine on the first feature matrix to obtain a second feature matrix of which the dimension is smaller than that of the first feature matrix; combining the second feature matrix with the first ankle joint angle signal to obtain a third feature matrix; and inputting the third feature matrix into a prediction model based on a neural network so as to output a second ankle joint angle signal of the artificial limb side at the next moment. According to the method, the prediction result of the ankle joint track of the artificial limb has relatively high accuracy.
Owner:国家康复辅具研究中心秦皇岛研究院
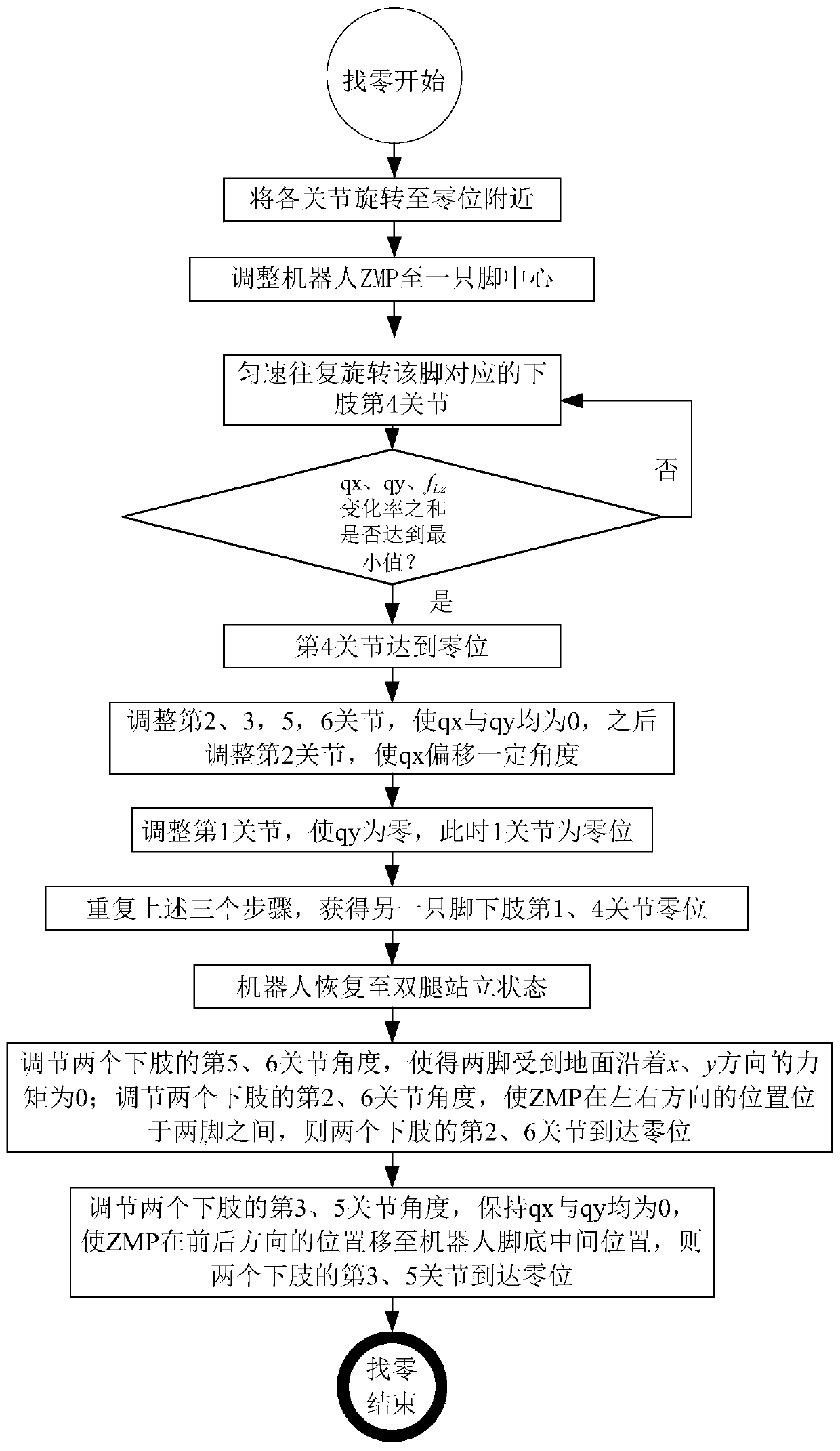
Humanoid robot lower limb joint zero position calibration method
ActiveCN110802593AFast motion controlPrecise motion controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLower extremity joint
The invention discloses a humanoid robot lower limb joint zero position calibration method. The humanoid robot lower limb joint zero position calibration method comprises the following steps that whether or not a fourth joint reaches a zero position is judged according to whether or not the sum Sv of the square of change rates of qx, qy and f<z> reaches a minimum value firstly, after the fourth joint reaches the corresponding zero position, the angle of a first joint is adjusted to enable the first joint to reach the corresponding zero position; and then a second joint, a sixth joint, a thirdjoint and a fifth joint are adjusted to enable the second joint, the sixth joint, the third joint and the fifth joint to reach the corresponding zero positions. Parameters qx, qy and f<z> in the calibration method are acquired through an attitude sensor mounted on a trunk and a six-dimension force / torque sensor fixed to an ankle joint correspondingly, other devices are not needed for assistance, moreover, zero position calibration is completed by the robot itself, the effects of being rapid and accurate are achieved, and the cost is saved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
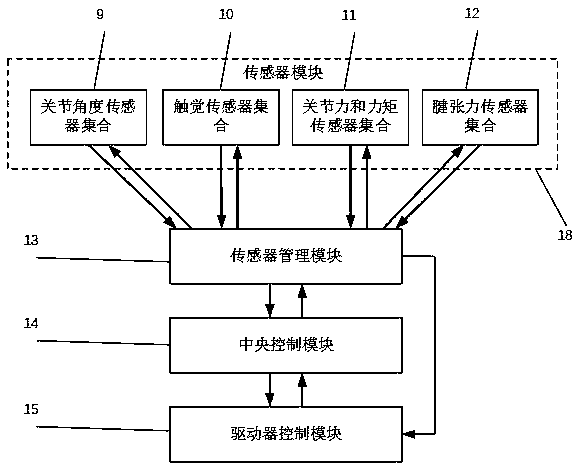
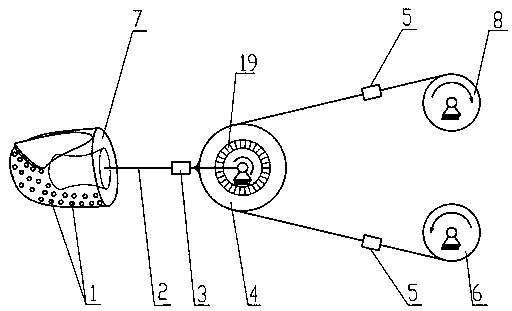
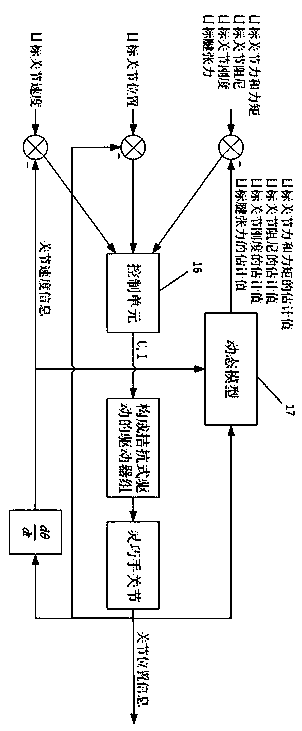
Multi-sensor based dexterous hand antagonistic type control system
ActiveCN110842952AReduce power consumptionReduce feverProgramme-controlled manipulatorGripping headsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTactile perception
The invention discloses a multi-sensor and antagonistic drive based dexterous hand control system. The system comprises an antagonistic driven dexterous hand in tendon transmission, a joint angle sensor, a touch sensor in bionic skin, a joint force and torque sensor, a tendon tension sensor, a sensor management module, a driver control module and a central control module. According to the system,perception modes of different levels of force and touch are effectively decoupled, various sense information can be flexibly and comprehensively analyzed under different operating tasks, the control difficulty is simplified, and design complexity and cost of each type of sensor (and the bionic skin with touch) are reduced; and through the central control module of the system, the dexterous hand can avoid excessive relaxation or tensioning of the tendon, joint damping and joint rigidity of each joint can be controlled, the compliance operation and the anti-interference performance and robustness can be taken into account, and the system can still work reliably when the joint force and torque sensor or the tendon tension sensor is partially or completely lacked or works abnormally.
Owner:NEUROCEAN TECH INC
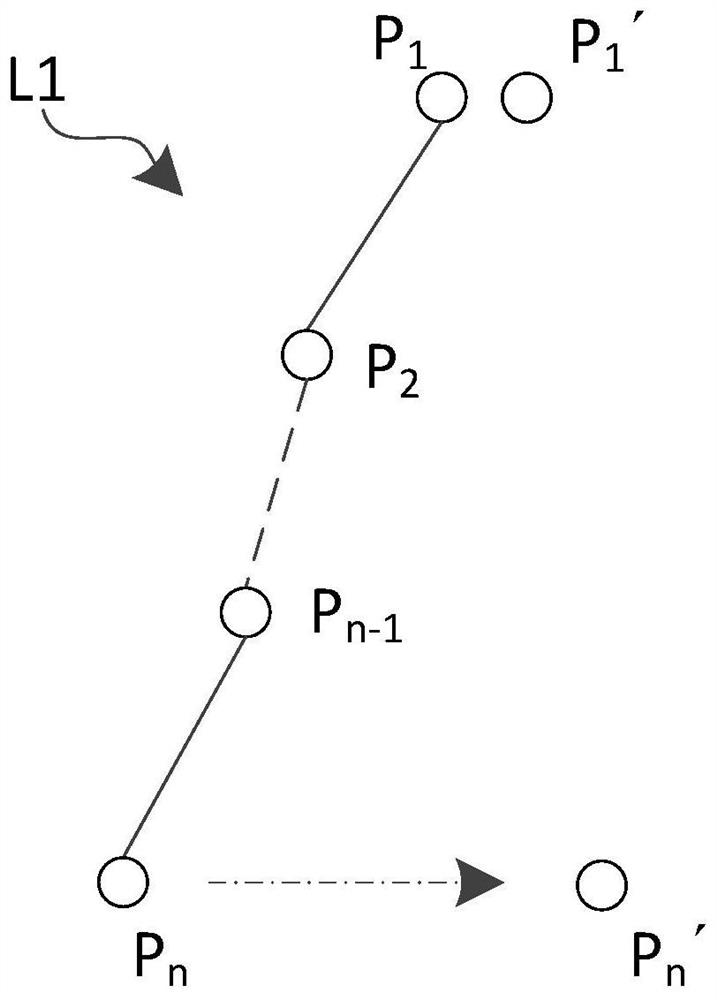
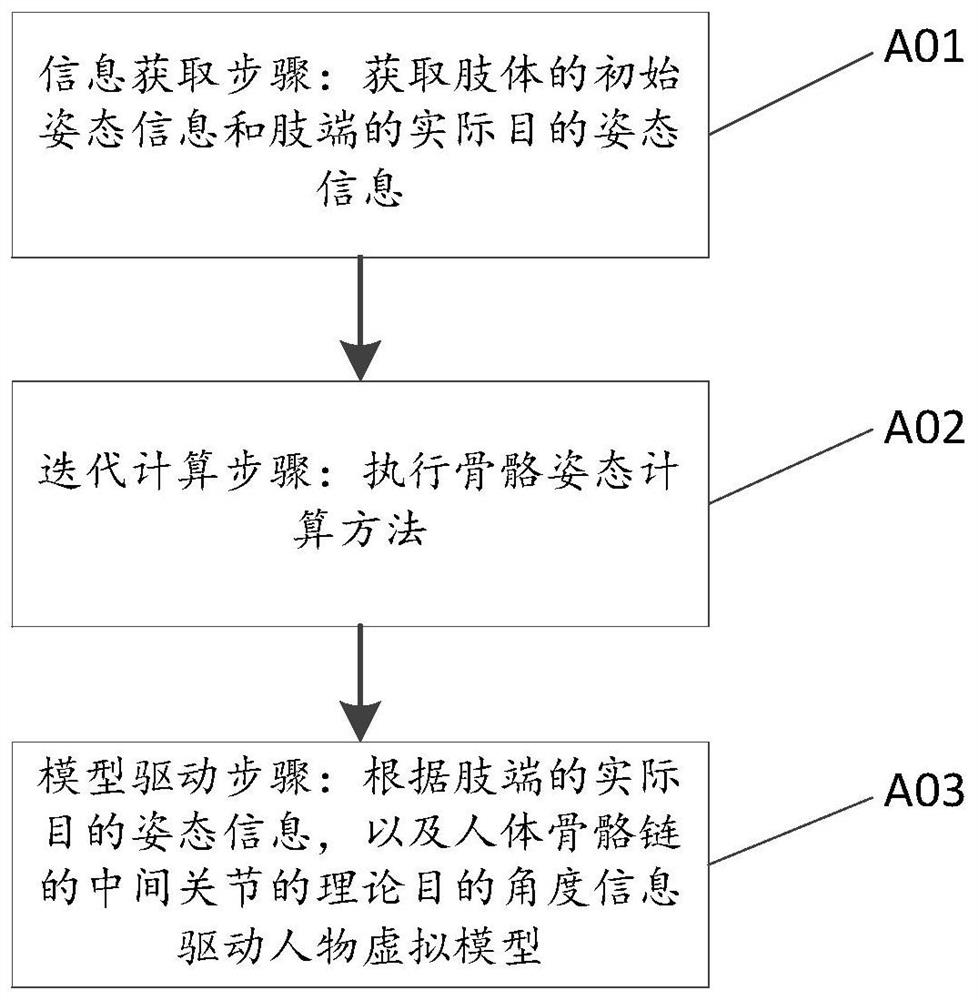
Skeleton attitude calculation method, character virtual model driving method and storage medium
ActiveCN108876815BGuaranteed smooth gradient effectMeet application needsImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyGonial angle
A bone pose calculation method, a figure virtual model driving method and a storage medium. The bone pose calculation method is the key step of the figure virtual model driving method, and comprises: based on a bone pose iterative calculation process of inverse kinematics, reversely calculating the joint angle change of an intermediate joint of a human bone chain according to the pose information change of a limb end, so that after each iteration, various joint angles are close to the best value, thereby effectively guaranteeing a smooth graduated effect when a body movement is simulated, and meeting the application requirement of realistically simulating body movement. In addition, multiple judgment mechanisms are used during an iterative calculation process, so that various joint angle changes and the pose information change of a limb end can be updated for the next iterative calculation in time, thereby simplifying the judgment process, guaranteeing the effectiveness of an iterative loop, improving the calculation speed of a system while ensuring that the calculation result is accurate, and enhancing the time relevancy of a body movement capturing process.
Owner:SHENZHEN REALIS MULTIMEDIA TECH CO LTD
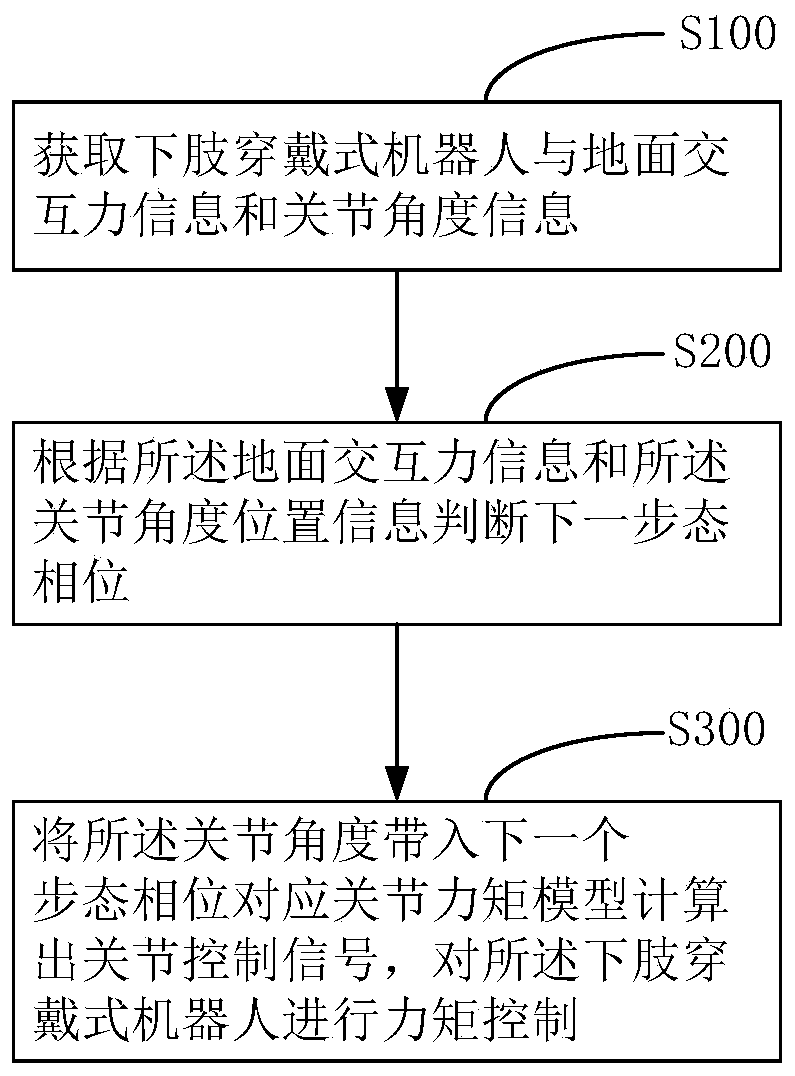
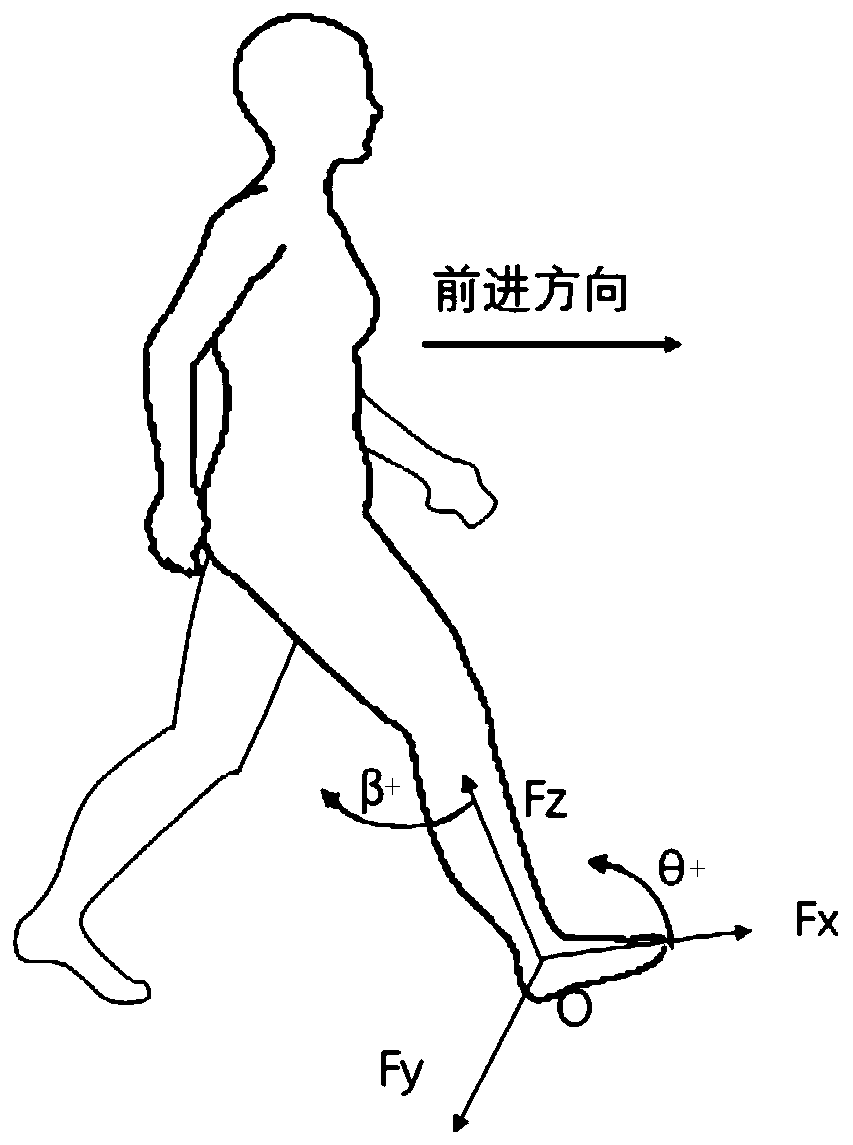
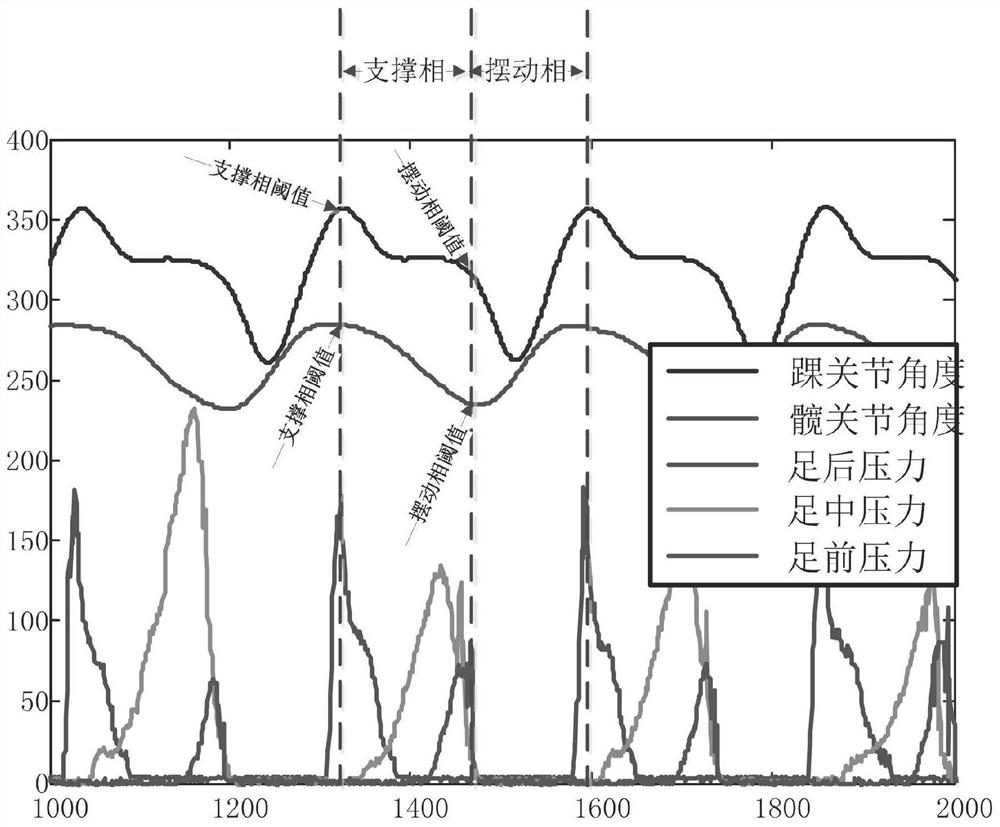
Gait control method, device and equipment for lower limb wearable robot
InactiveCN111568700ALow costSimple control methodDiagnosticsWalking aidsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationControl signal
The invention discloses gait control method, device and equipment for a lower limb wearable robot. The method comprises the steps of obtaining ground interaction force information and joint angle information of the lower limb wearable robot; judging a next gait phase according to the ground interaction force information and the joint angle position information; and substituting a joint angle intoa joint torque model corresponding to the next gait phase to calculate a joint control signal, and performing torque control on the lower limb wearable robot. The next gait phase is judged according to the ground interaction force information and the joint angle information of the lower limb wearable robot, the ground interaction force information and the joint angle information can be collected through a sensor, the cost is low, control signals are calculated according to joint torque models corresponding to different gait phases, and the control method is simple.
Owner:SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY OF CHINA
Hip and knee bending angle adjusting device and method
The invention discloses a hip and knee bending angle adjusting device and method, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments, the hip and knee bending angle adjusting device comprises a base, a hip joint angle adjusting assembly and a knee joint angle adjusting assembly, the hip joint angle adjusting assembly comprises a thigh fixing part and a hip joint adjusting part, the hip joint adjusting part comprises a supporting rod, an angle adjusting rod and a driving mechanism, one end of the supporting rod is rotatably arranged on a base, the other end of the supporting rod is fixed to a thigh fixing plate, one end of the angle adjusting rod is rotatably arranged on the supporting rod, the other end of the angle adjusting rod is arranged on the driving mechanism, the knee joint angle adjusting assembly comprises a shank fixing part and a knee joint adjusting part, one end of the shank fixing plate is movably arranged on the thigh fixing plate, and the knee joint adjusting part comprises a rotary driving mechanism. The hip bending angle is adjusted through the hip joint angle adjusting assembly, and the knee bending angle is adjusted through the knee joint angle adjusting assembly, so that the needed accurate angle is achieved, and a patient is in a comfortable posture and rapidly recovered.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
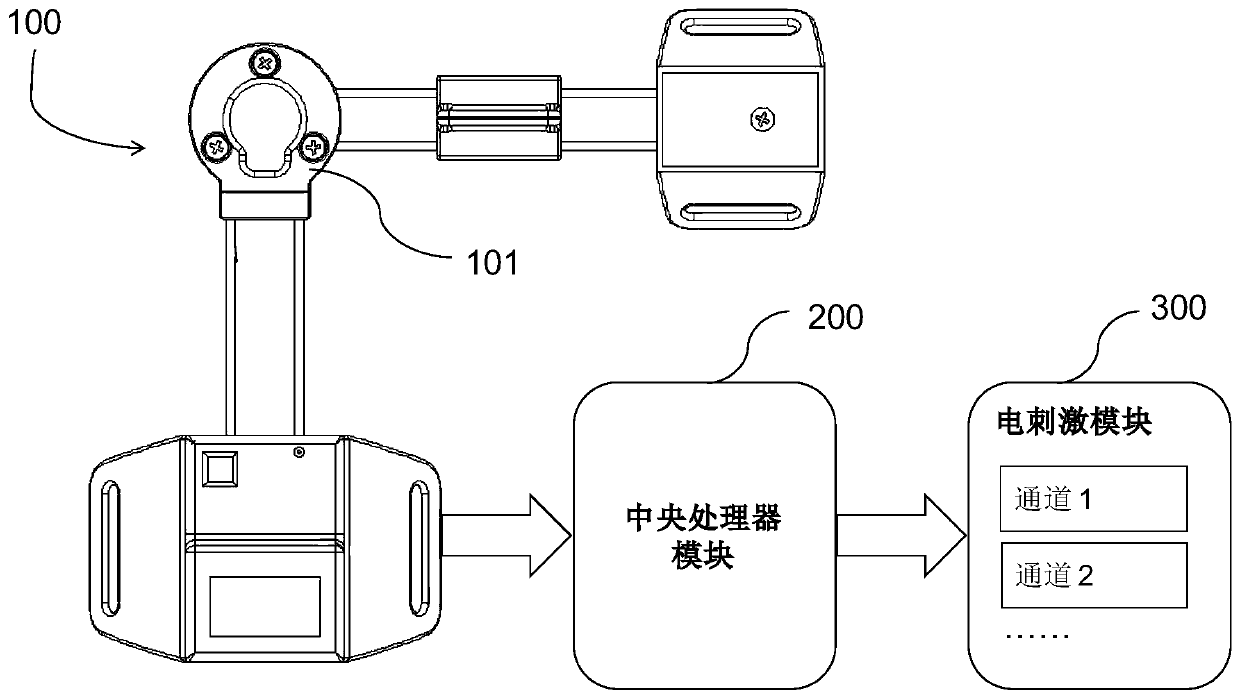
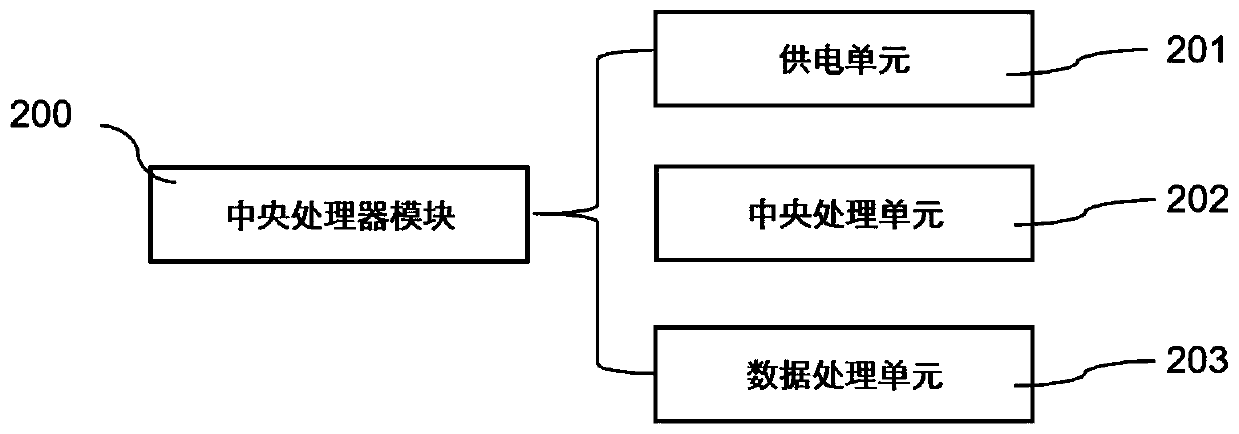
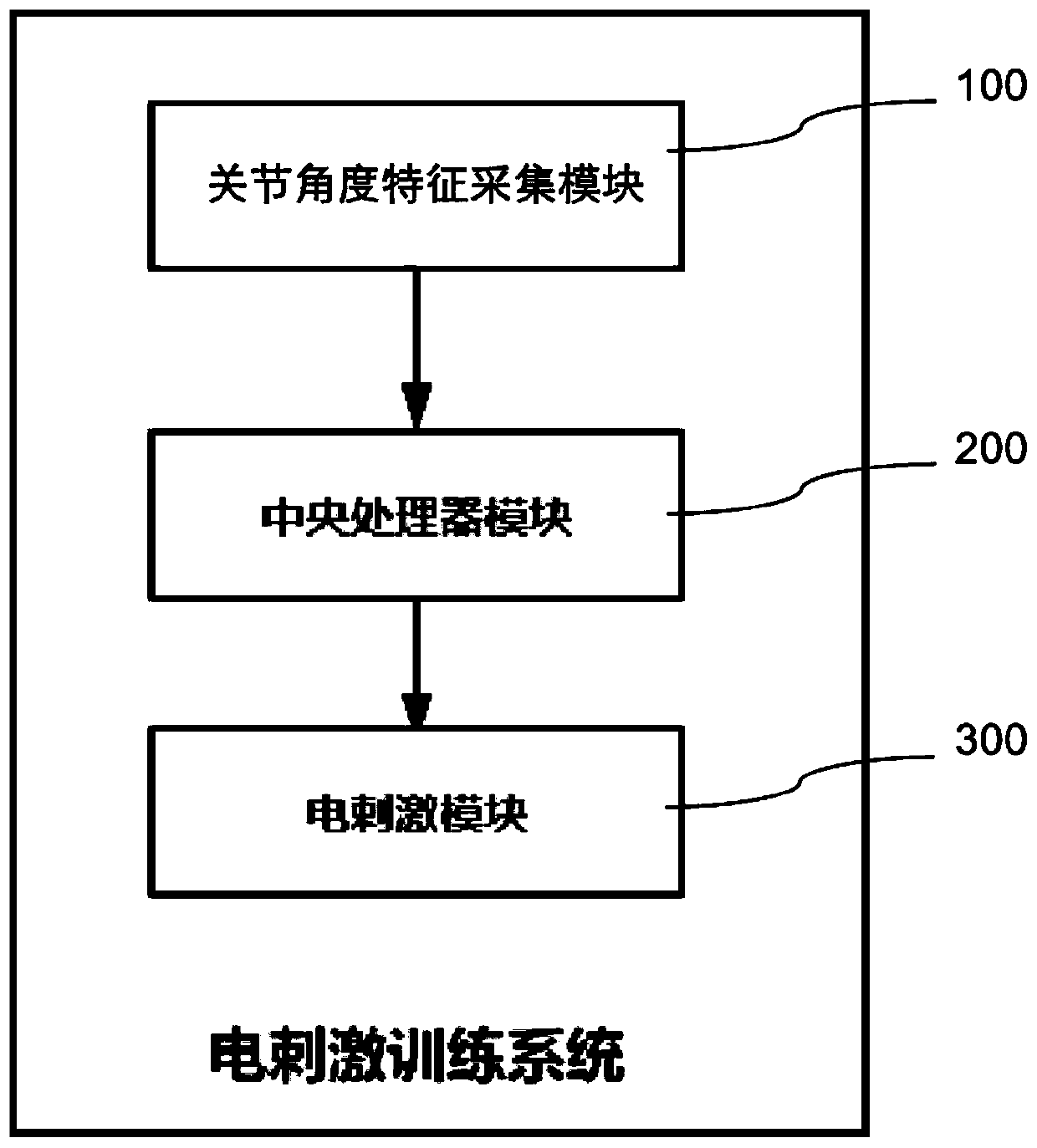
Limb electrical stimulation training system based on joint angle feedback
PendingCN111388863AAchieve targetedElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringControl signalElectrical stimulations
The invention provides a limb electrical stimulation training system based on joint angle feedback, and relates to the technical field of rehabilitation therapy. The limb electrical stimulation training system comprises a joint angle feature acquisition module used for collecting angle parameters of joints in a motion process, a central processor module connected with the joint angle feature acquisition module and used for identifying joint angle characteristics and sending out a control signal, and an electrical stimulation module connected with the central processor module and used for generating an electrical stimulation signal acting on a joint motion muscle group. According to the system, a limb muscle group of motion obstacle is electrically stimulated when a rehabilitation person actively moves to a joint obstacle point, so that the rehabilitation person is helped to go through the obstacle point, the joint motion angle reaches an angle as a normal person, and rehabilitation training is carried out.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
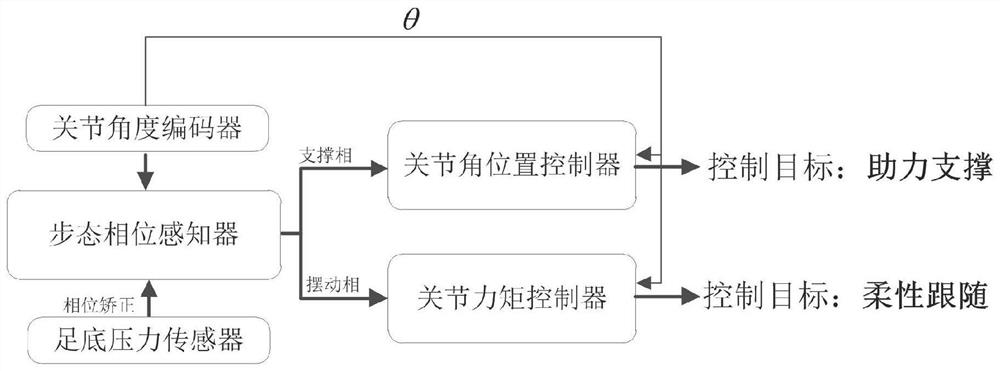
Sensing and control system and method for lower limb joint assisting exoskeleton system
ActiveCN112192570ASimple configurationImprove reliabilityProgramme-controlled manipulatorControl systemMachine
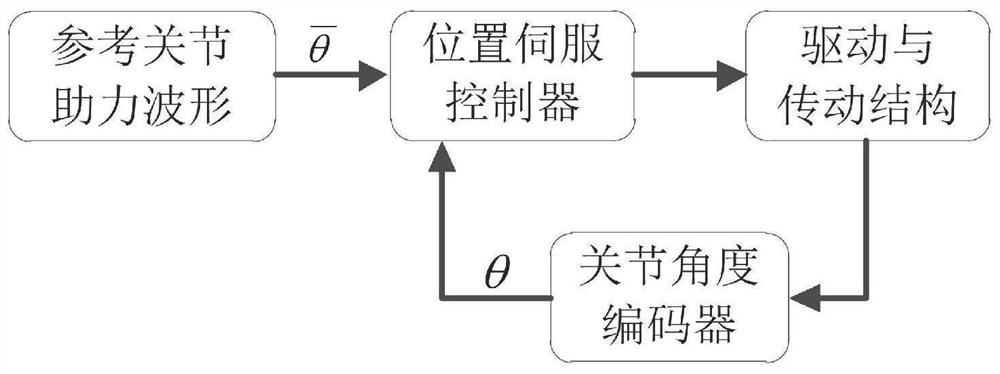
The invention discloses a sensing and control system and method for a lower limb joint assisting exoskeleton system. The system comprises a joint angle encoder, a gait phase sensor, a joint angle position controller, and a joint torque controller, wherein the joint angle encoder measures a joint angle position, and transmits an output signal to the gait phase sensor, the joint angle controller andthe joint torque controller; the gait phase sensor performs gait phase judgment according to the joint angle signal and divides the gait phase into a support phase and a swing phase; when the gait phase sensor judges that a robot is currently in the support phase, a joint angle position control mode is adopted; and when the gait phase sensor judges that the robot is currently in the swing phase,a joint torque control mode is adopted. According to the sensing and control system, sensor configuration is simplified, reliability and rapidity of the sensing system are improved, wearable performance of other fittings is not influenced, active assistance is realized, and the man-machine following performance can be improved.
Owner:中国船舶集团有限公司第七零七研究所九江分部
A motion intention recognition and device method for lower extremity exoskeleton
ActiveCN110141239BEnsure safetyGuaranteed efficiencyProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnostic recording/measuringExoskeleton robotLower extremity joint
A movement intention recognition and device method for lower limb exoskeleton, belonging to the field of lower limb exoskeleton robot sensing technology. The movement intention recognition device includes a lower limb electromyographic signal acquisition module, a plantar pressure acquisition module, a lower limb inertial information measurement module, a data acquisition and transmission module and a central controller. The method uses one-to-one SVM multi-classification to obtain an offline database gait trajectory based on plantar pressure signals, uses a CNN online joint angle estimation model to obtain a real-time prediction trajectory of joint angles based on myoelectric signals, and combines the two types of gait trajectories based on the degree of muscle fatigue. The trajectory is fused with variable gain information to provide an accurate desired motion trajectory for the lower limb joint drive of the exoskeleton robot. The invention effectively combines the advance of the electromyographic signal and the stability of the plantar pressure signal, greatly improves the accuracy and real-time performance of movement intention recognition, and provides sufficient guarantee for the safety and power-assisted efficiency of the exoskeleton robot. ensure.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
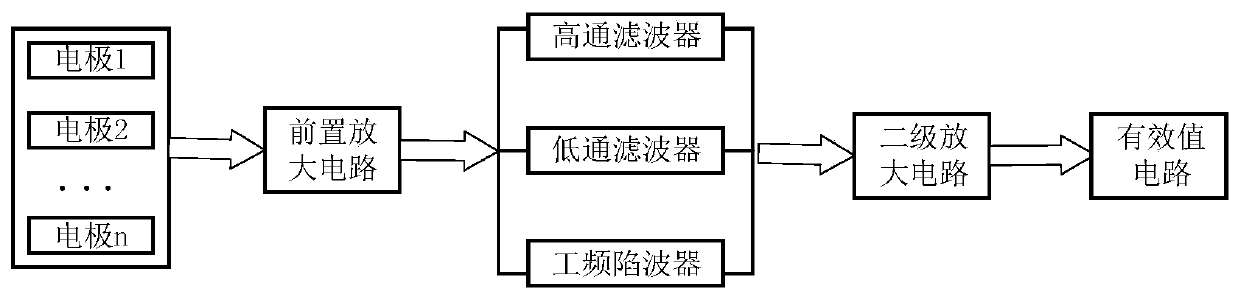
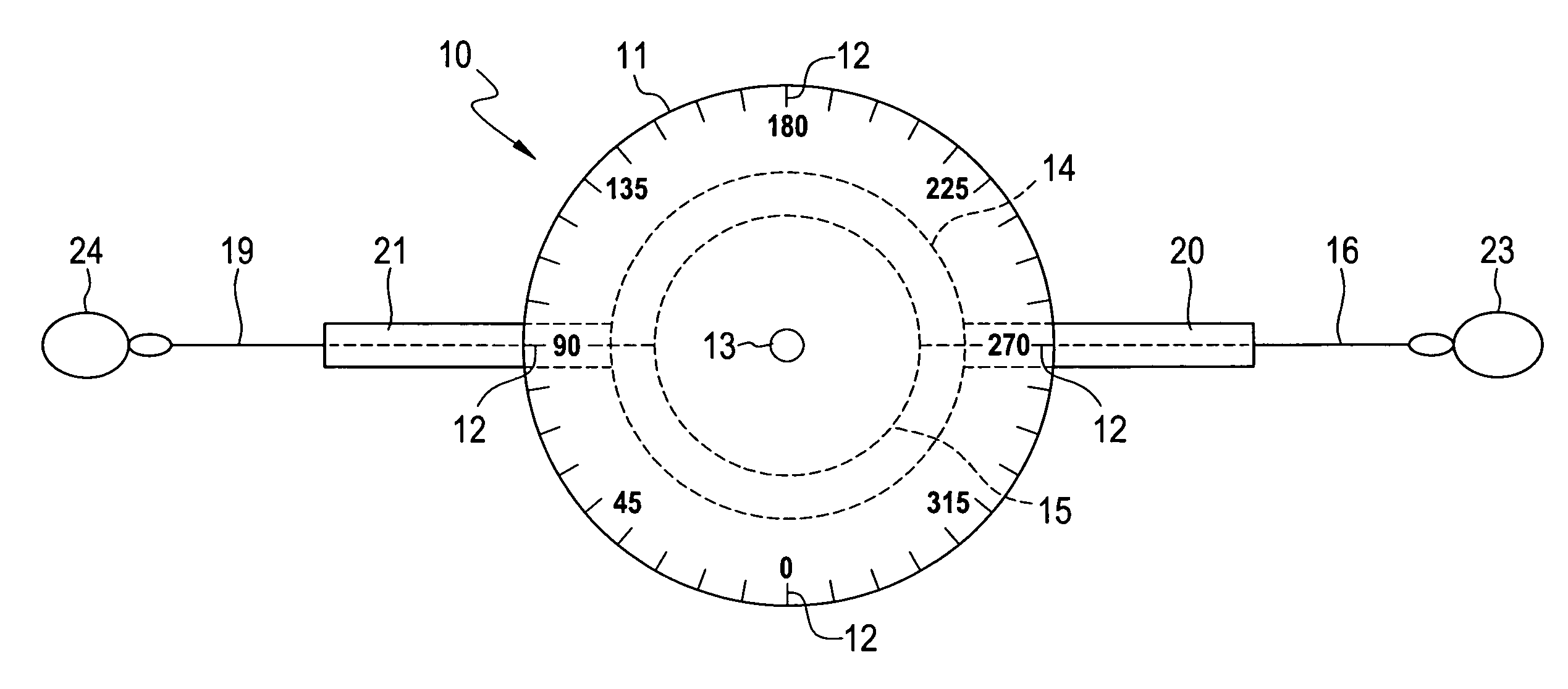
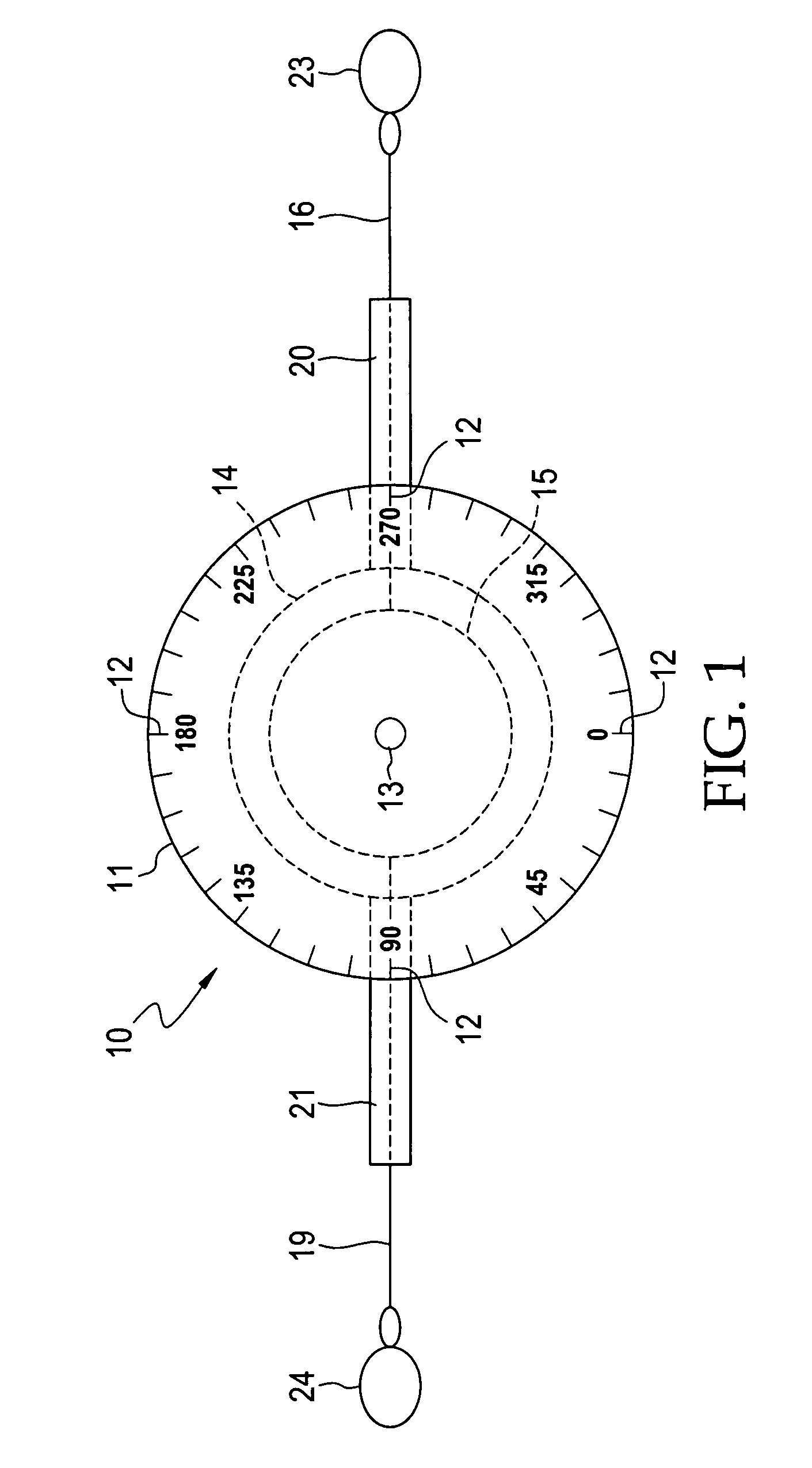
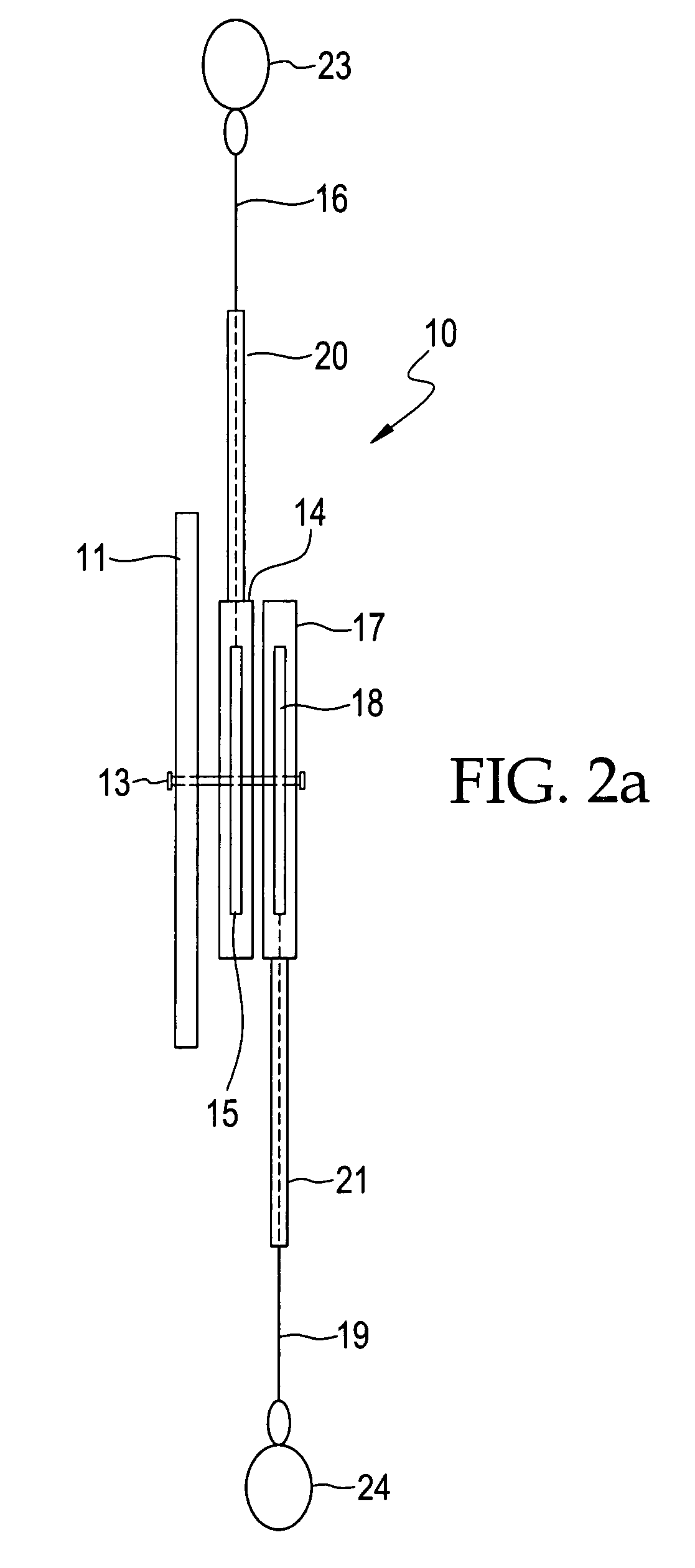
Dual line protractor for biometric measurements
InactiveUS7404256B1Improve accuracyGood precisionAngles/taper measurementsSurgeryAnatomical landmarkProtractor
A dual line protractor fixed to a central axis which has two housings, each housing having a spool with retractable lines, the housings and spools being rotatably attached to the central axis. The spools and housings rotate independently of each other on the central axis. The lines can be extended from the spools and the tips of the lines are attached to anatomical landmarks on first and second body members. The protractor is placed on a joint between the first and second body members. The lines extend from the spools and housings over degree marks on the protractor. The difference between the degree marks provide the angle between the body members at the joint. The application of the dual line protractor for these measurements is simple and rapid, requiring only a few minutes, so that the range of motion of several joints with several repeat measurements can be performed in a relatively short period of time. Placing the tips of the lines on anatomical landmarks produces remarkable accuracy and precision in the measurement of joint angles. Because string-like lines are used to indicate the degree marks, the dual line protractor does not interfere with the natural motion of the body member being measured, allowing accurate dynamic joint angle measurement.
Owner:PARKER EMMETT L
Real-time human body posture recognition method under complex environment based on bidirectional LSTM
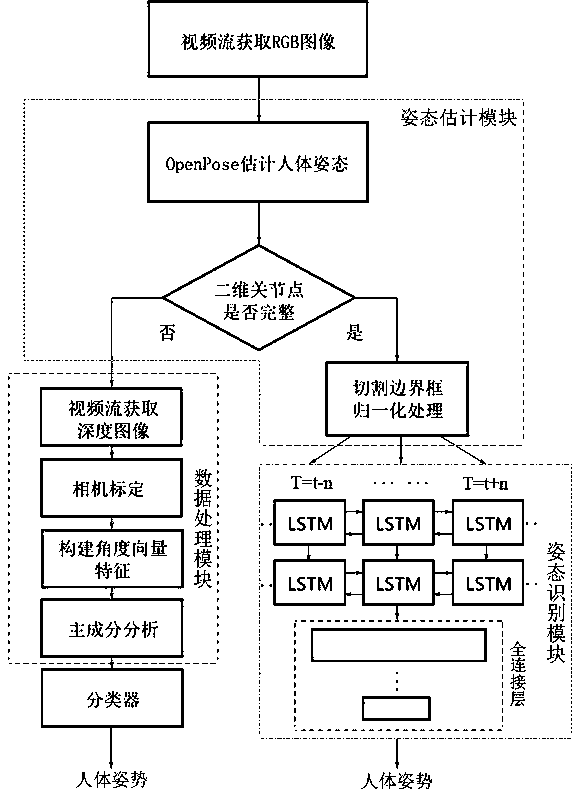
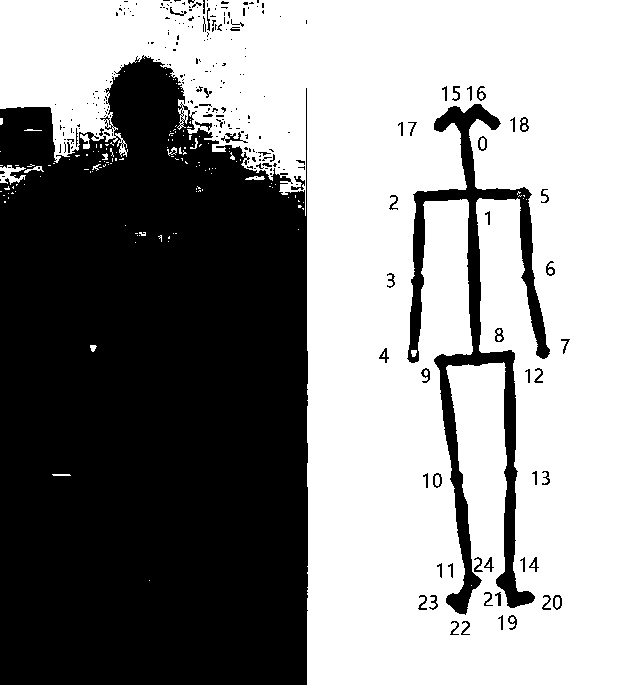
PendingCN111259749AImprove accuracyBiometric pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsHuman bodyMedicine
The invention discloses a real-time human body posture recognition method in a complex environment based on bidirectional LSTM. OpenPose is used as a human body posture estimation module to obtain two-dimensional joint point data of a human body. And judging whether the human body is in a shielded state or not according to the data missing condition. For a non-occlusion condition, constructing a classifier based on bidirectional LSTM, and sending the initial two-dimensional joint point information to the classifier to obtain a human body posture of the non-occlusion condition; and for a shielding state, performing three-dimensional mapping by using internal parameters of a depth camera, constructing a trunk vector and a joint angle, processing the high-dimensional features by using principal component analysis, and sending the processed high-dimensional features to a classifier to obtain a human body posture of the shielding condition. According to the method, the human body posture can be accurately recognized in a complex environment.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Auxiliary system and method applied to joint rehabilitation, and storage medium
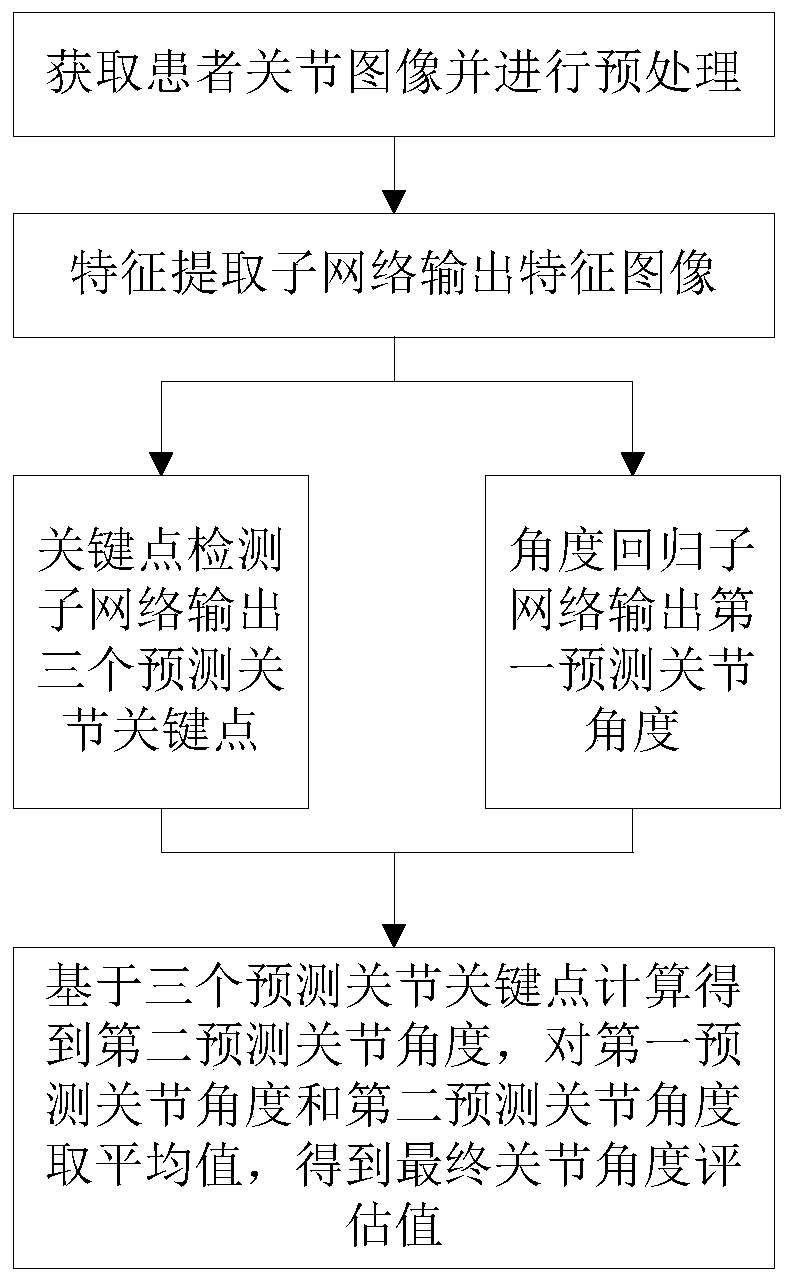
ActiveCN111481208AImprove medical complianceReduce cumbersome stepsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationSimulation
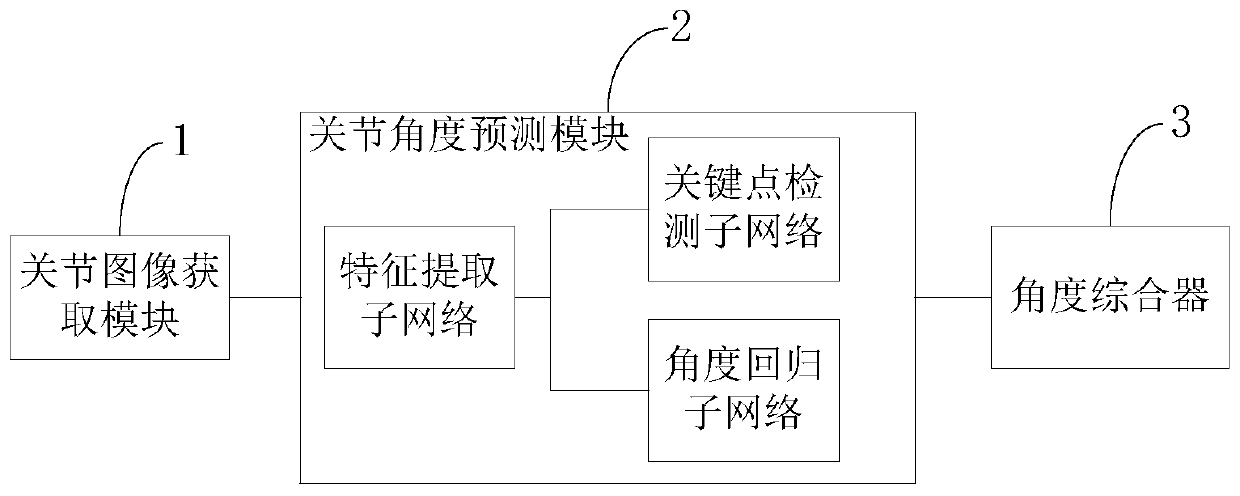
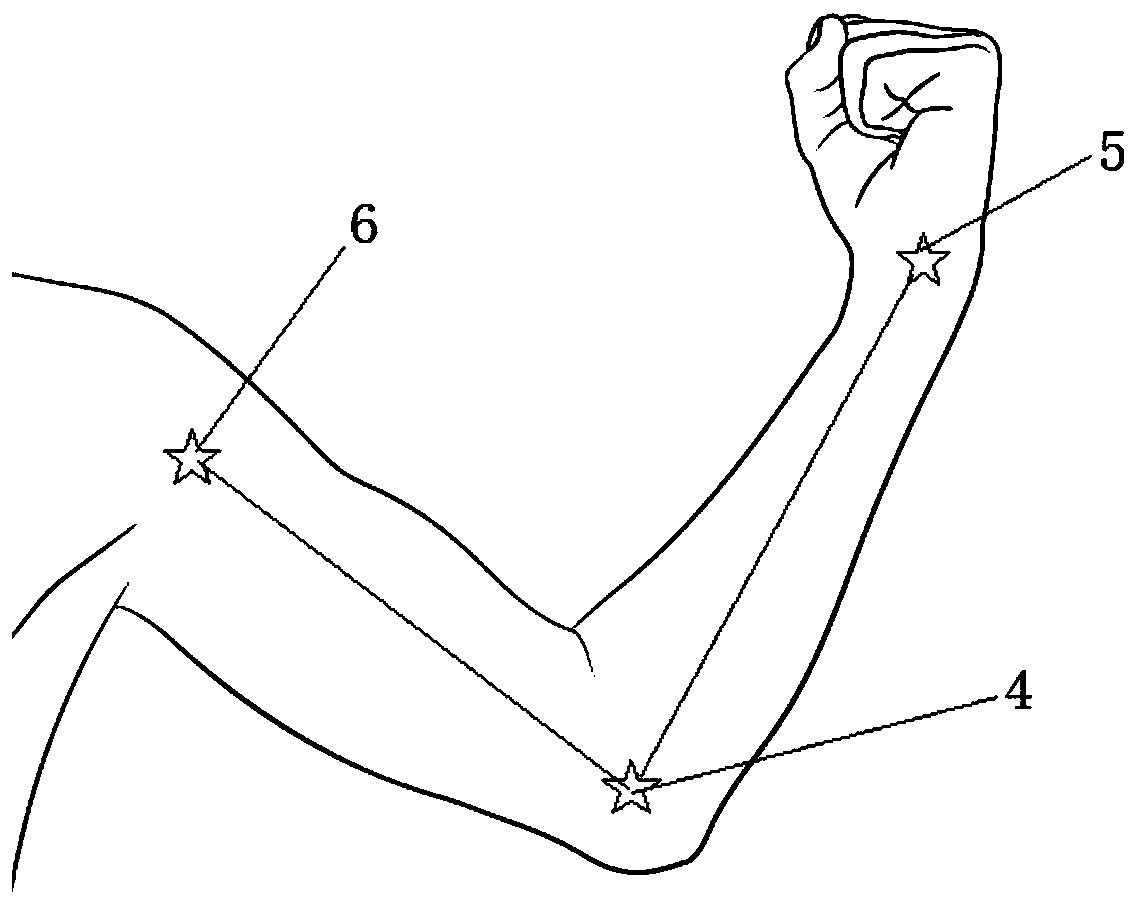
The invention discloses an auxiliary system and method applied to joint rehabilitation, and a storage medium, and the system comprises a joint image obtaining module which is used for obtaining a joint image of a patient and carrying out the preprocessing of the joint image; a joint angle prediction module which is used for predicting a first predicted joint angle and three predicted joint key points through a joint rehabilitation evaluation model based on the preprocessed patient joint image; and an angle synthesizer which is used for calculating to obtain a second predicted joint angle basedon the three predicted joint key points, and averaging the first predicted joint angle and the second predicted joint angle to obtain a final joint angle evaluation value. Only the joint image of thepatient needs to be acquired; therefore, the joint rehabilitation evaluation model can be utilized to calculate and predict the angle of the joint, so that the activity of the joint is directly sentto an operator or a rehabilitative apparatus, the tedious steps of manual measurement and joint rehabilitation angle calculation are omitted, the medical compliance of a patient is improved, and the operator or the rehabilitative apparatus can know the rehabilitation situation of the patient at the first time.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Action data analysis method, device and system and computer readable storage medium
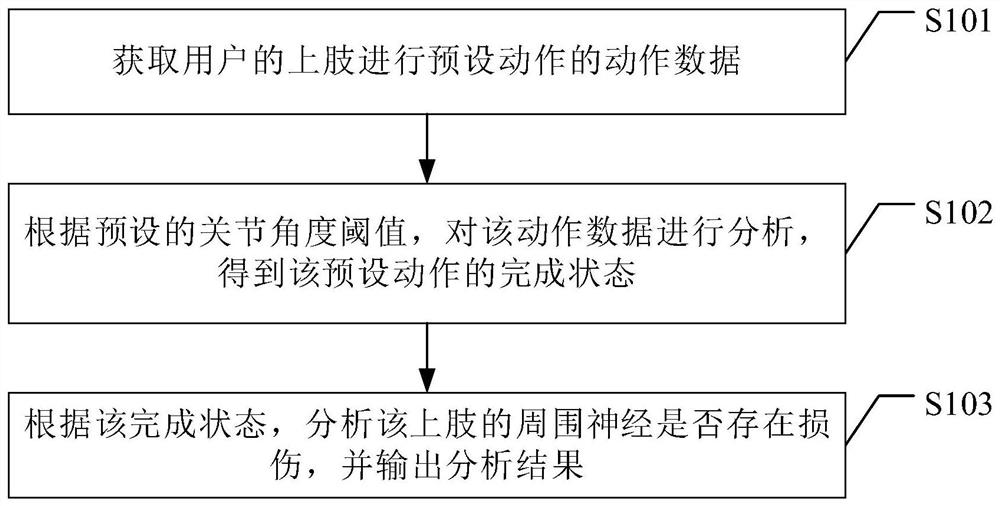
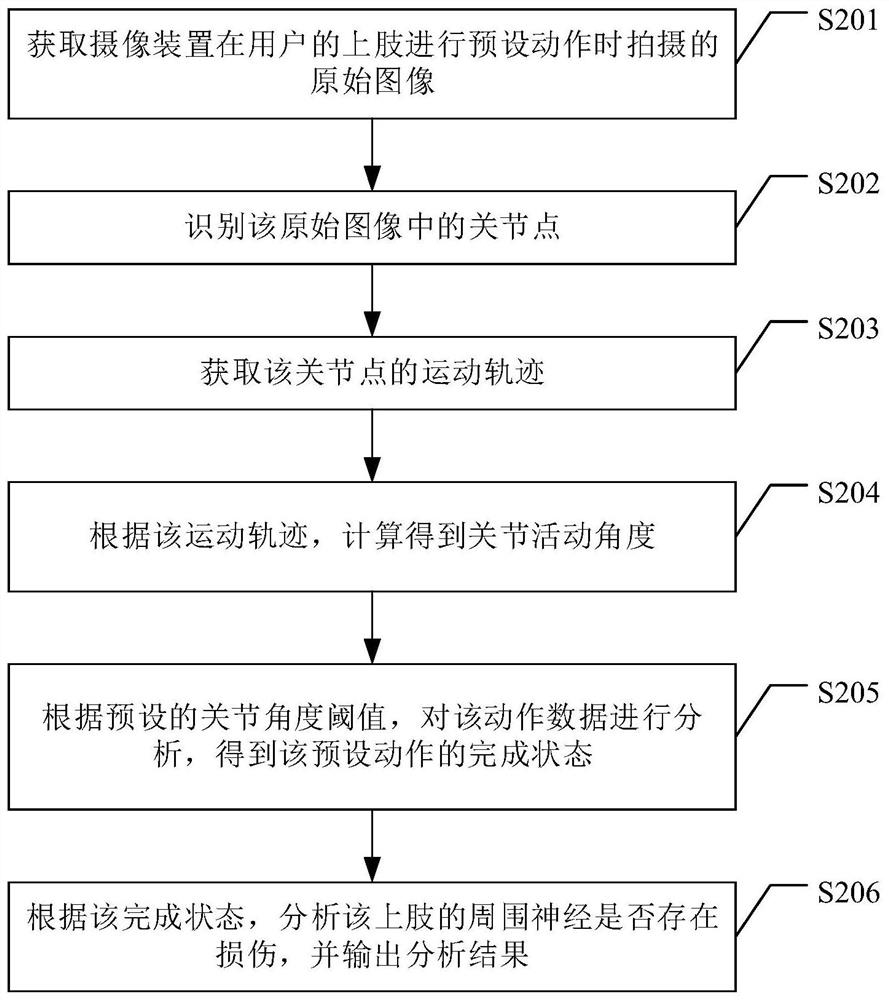
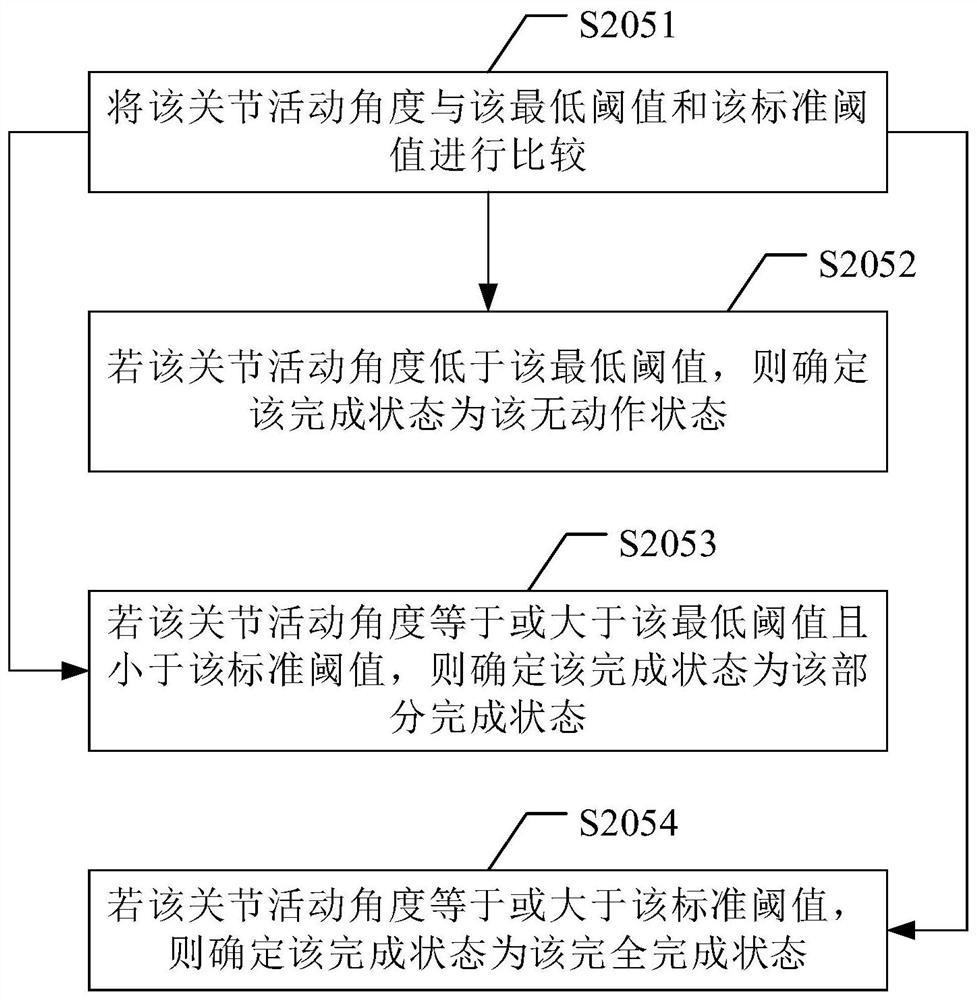
PendingCN113113108AImprove objectivityImprove accuracyPhysical therapies and activitiesMedical data miningSimulationPeripheral neuron
The embodiment of the invention provides an action data analysis method, device and system and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring action data of preset actions of upper limbs of a user; according to a preset joint angle threshold value, analyzing the action data, and obtaining the completion state of the preset action; according to the completion state, analyzing whether the peripheral nerve of the upper limb is injured, and outputting an analysis result. According to the invention, upper limb peripheral nerve injury assessment based on user action data analysis can be realized, the objectivity and accuracy of assessment are improved, and the purpose of saving labor cost is achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com