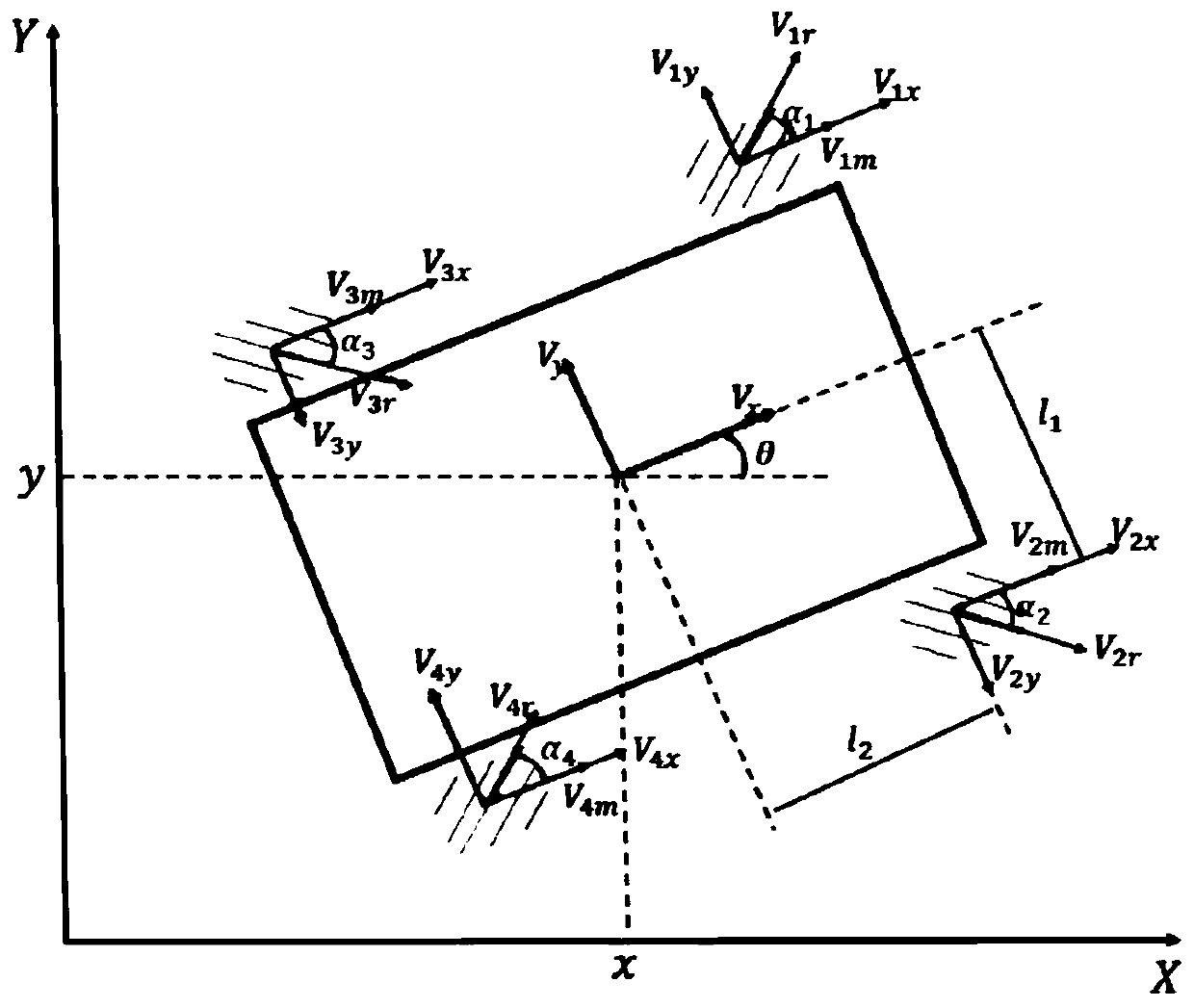
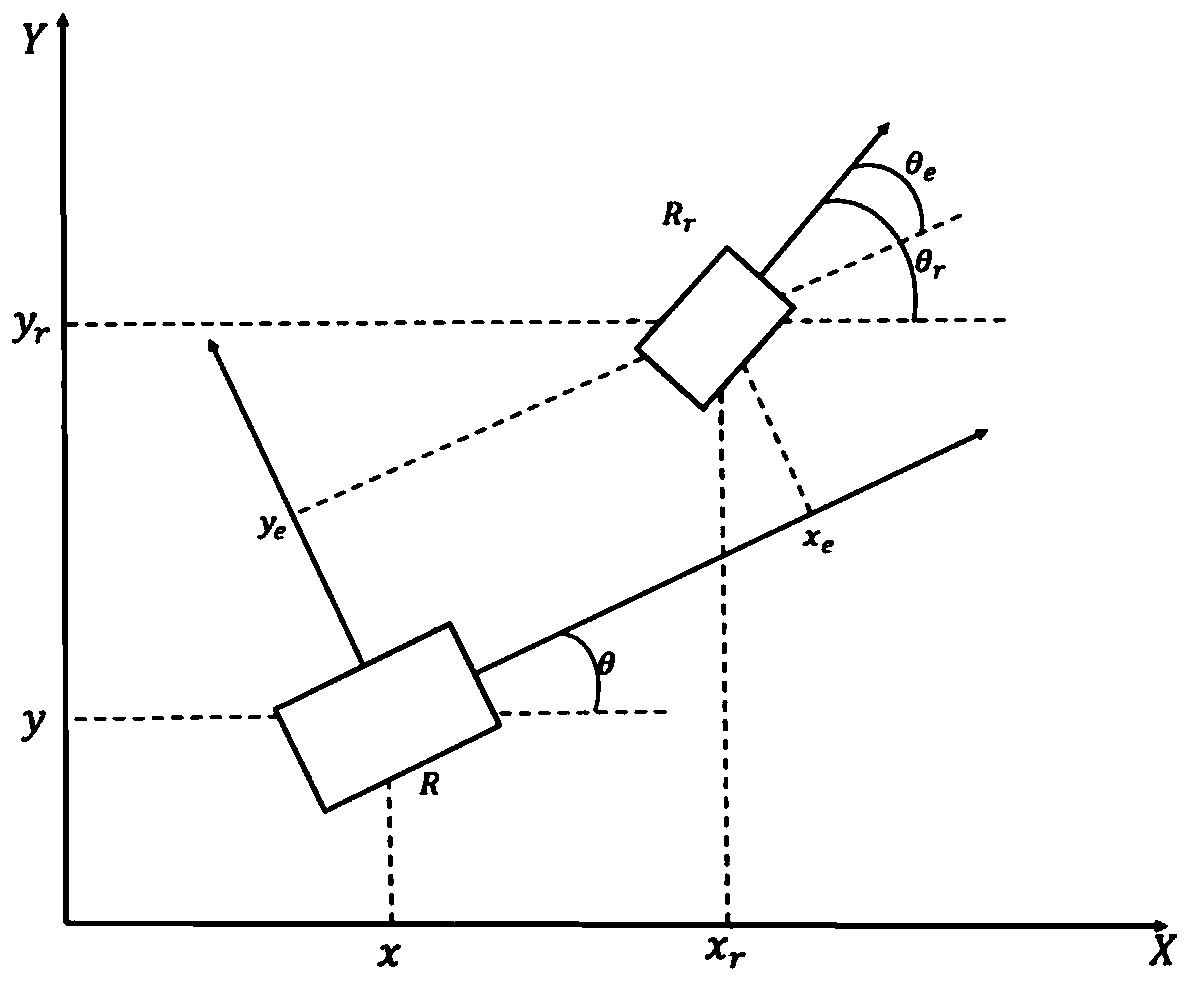
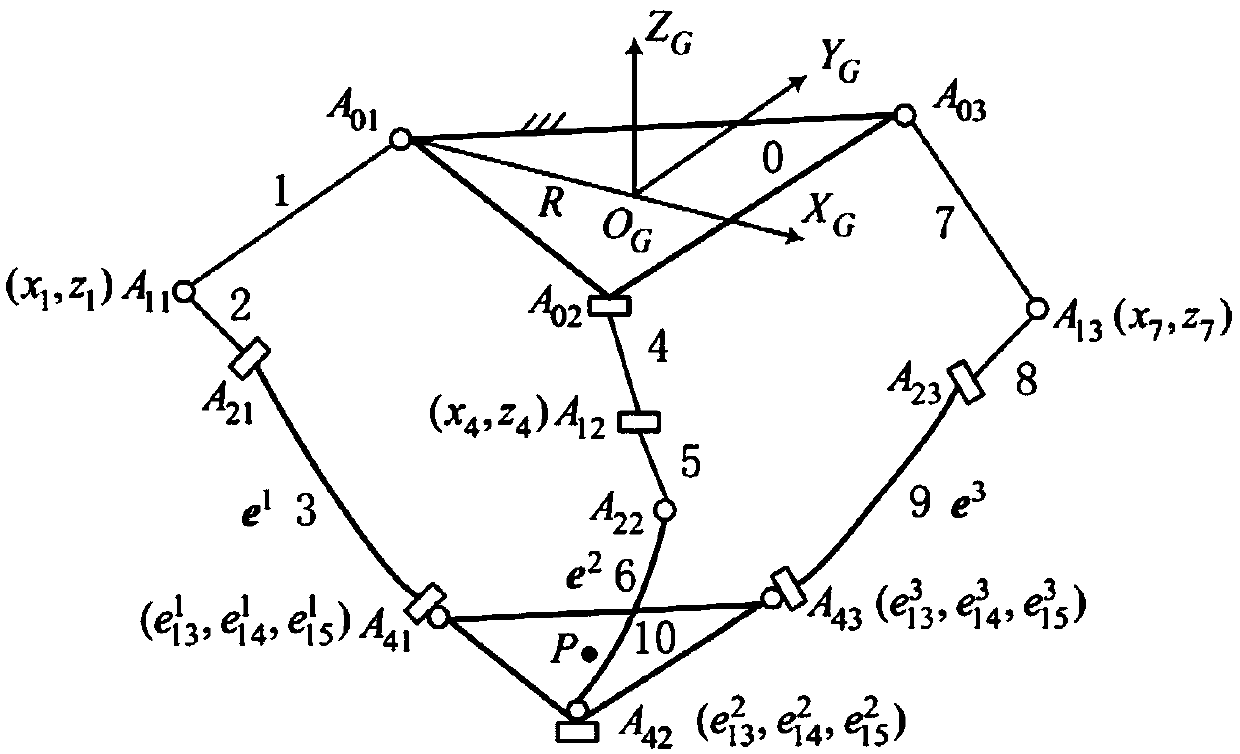
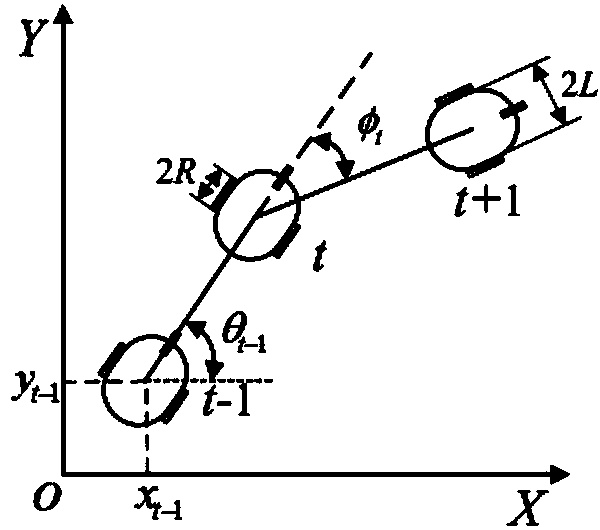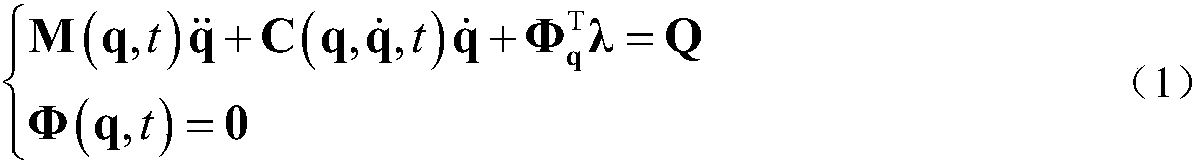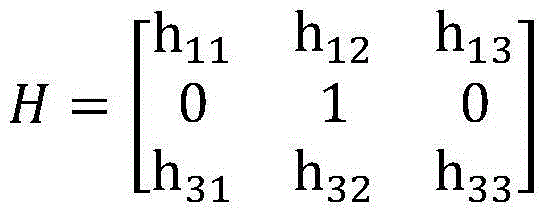Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Holonomic constraints" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
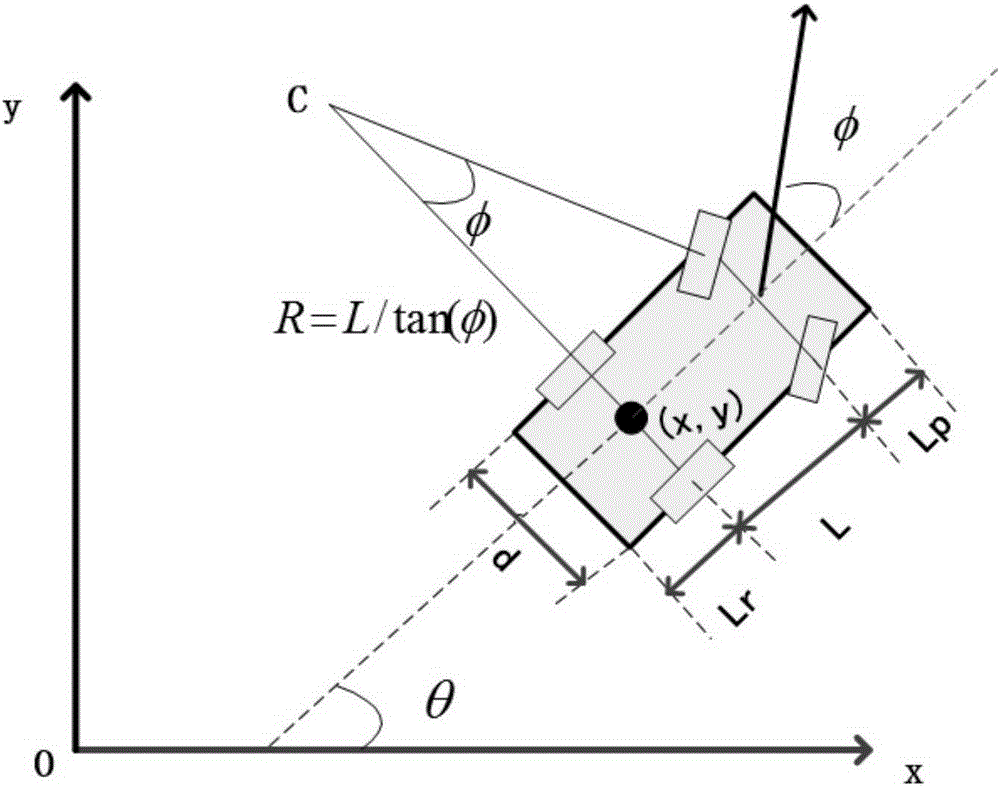
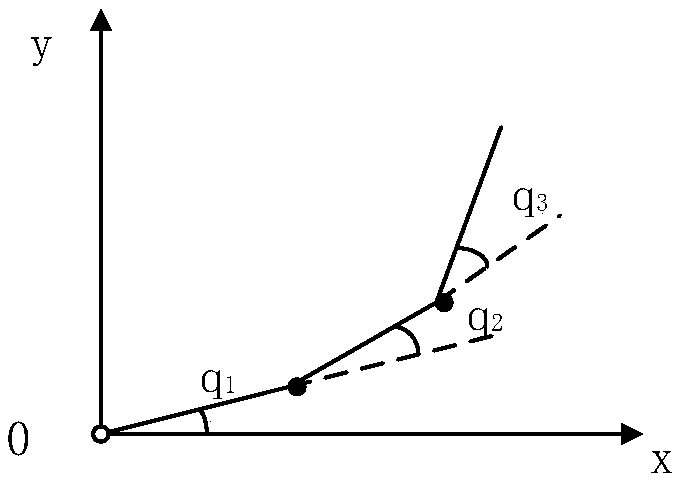
In classical mechanics, holonomic constraints are relations between the position variables (and possibly time) which can be expressed in the following form: f(q₁,q₂,q₃,…,qₙ,t)=0 where {q₁,q₂,q₃,…,qₙ} are the n coordinates which describe the system. For example, the motion of a particle constrained to lie on the surface of a sphere is subject to a holonomic constraint, but if the particle is able to fall off the sphere under the influence of gravity, the constraint becomes non-holonomic.
Unmanned path planning method, system and device thereof
ActiveCN107702716ASatisfy the requirements of non-integrity constraintsReduce storage space requirementsInstruments for road network navigationNavigational calculation instrumentsExtensibilityCollision detection
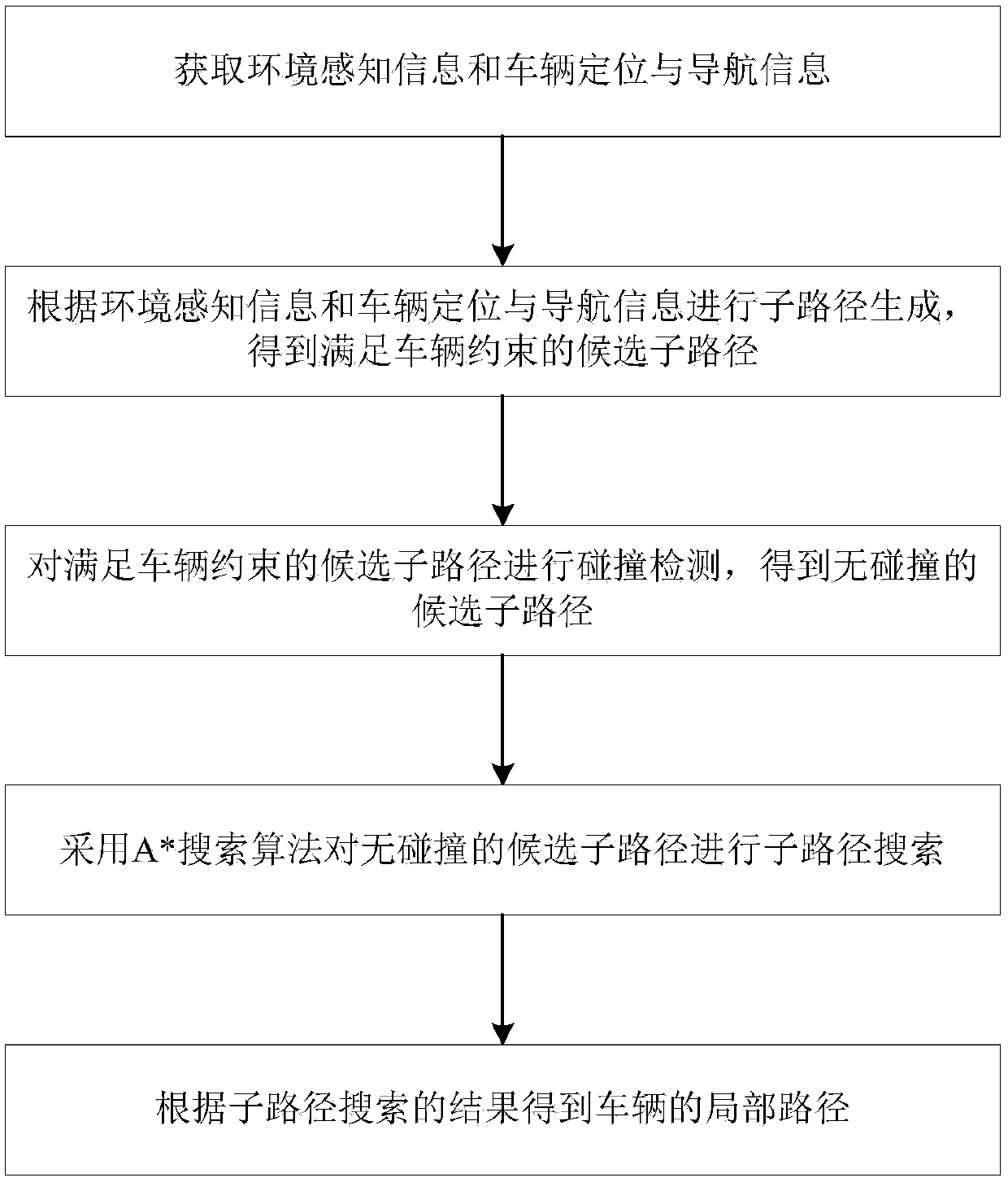
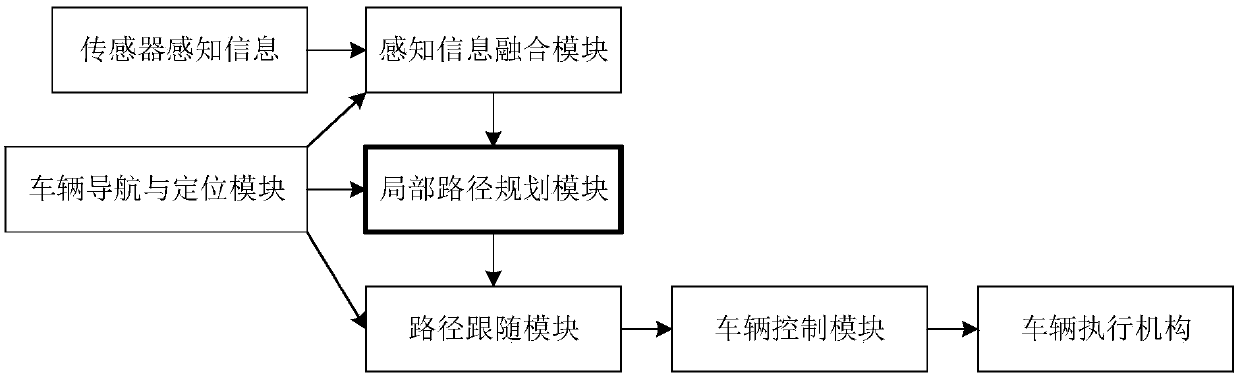
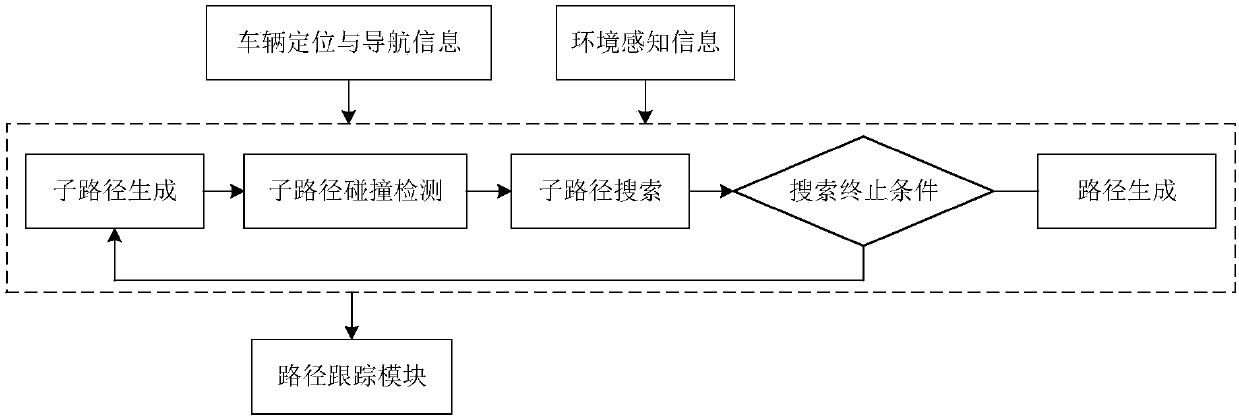
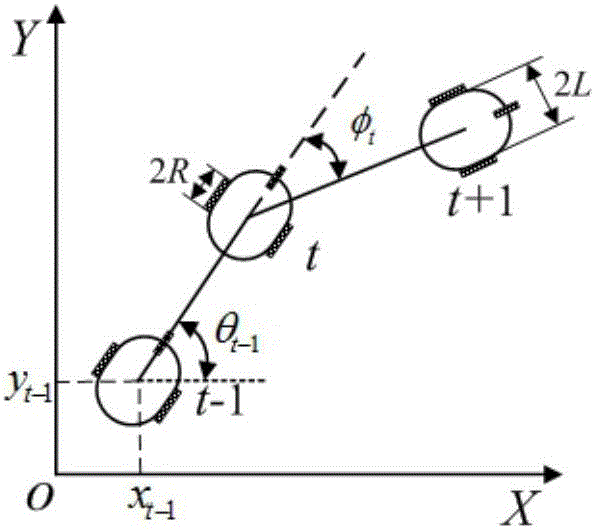
The invention discloses an unmanned path planning method, a system and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring environment perception information and vehicle positioningand navigation information, wherein the environment perception information contains barrier information, curb information and lane line information, and the vehicle positioning and navigation information contains vehicle pose and a target path; conducting subpath generation according to the environment perception information and the vehicle positioning and navigation information to obtain a candidate subpath which satisfies vehicle constraints; conducting collision detection on the candidate subpath which satisfies vehicle constraints, so as to obtain a collisionless candidate subpath; conducting subpath search on the collisionless candidate subpath by A* search algorithm; and obtaining a vehicle local path according to the subpath search result. The requirement on storage space is low, and the requirement on nonholonomic constraints of vehicles can be met. The method of the invention has advantages of good adaptability and good extensibility, and can be widely applied in the field ofautomatic drive.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XIAOPENG MOTORS TECH CO LTD
Method for planning optimal path for incremental environment information sampling of indoor mobile robot
ActiveCN106444769AImprove efficiencyGood obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesCollision detectionSimulation
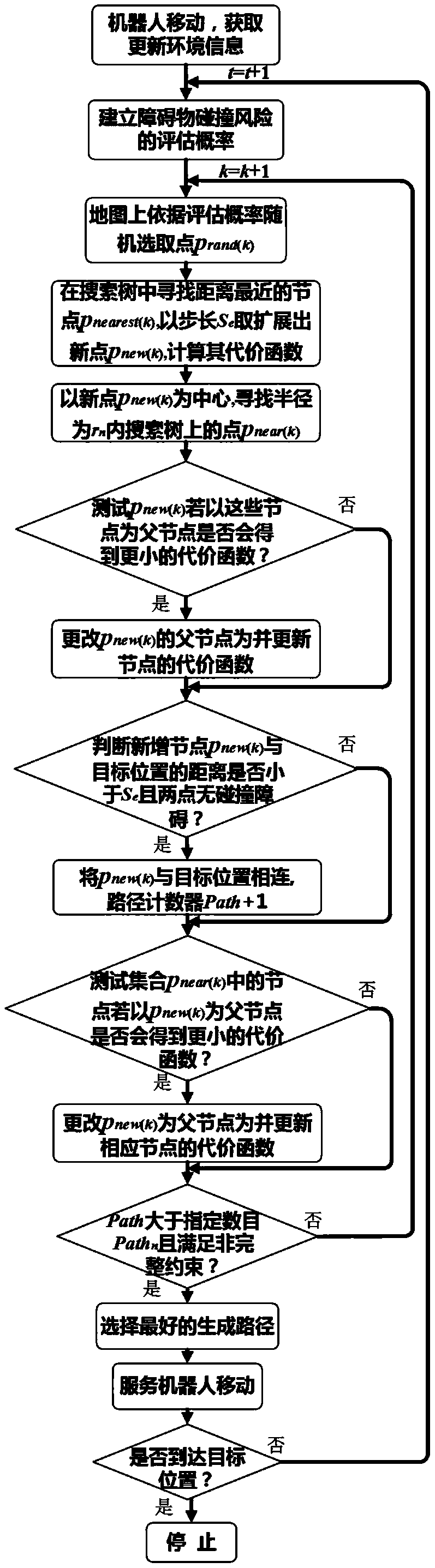
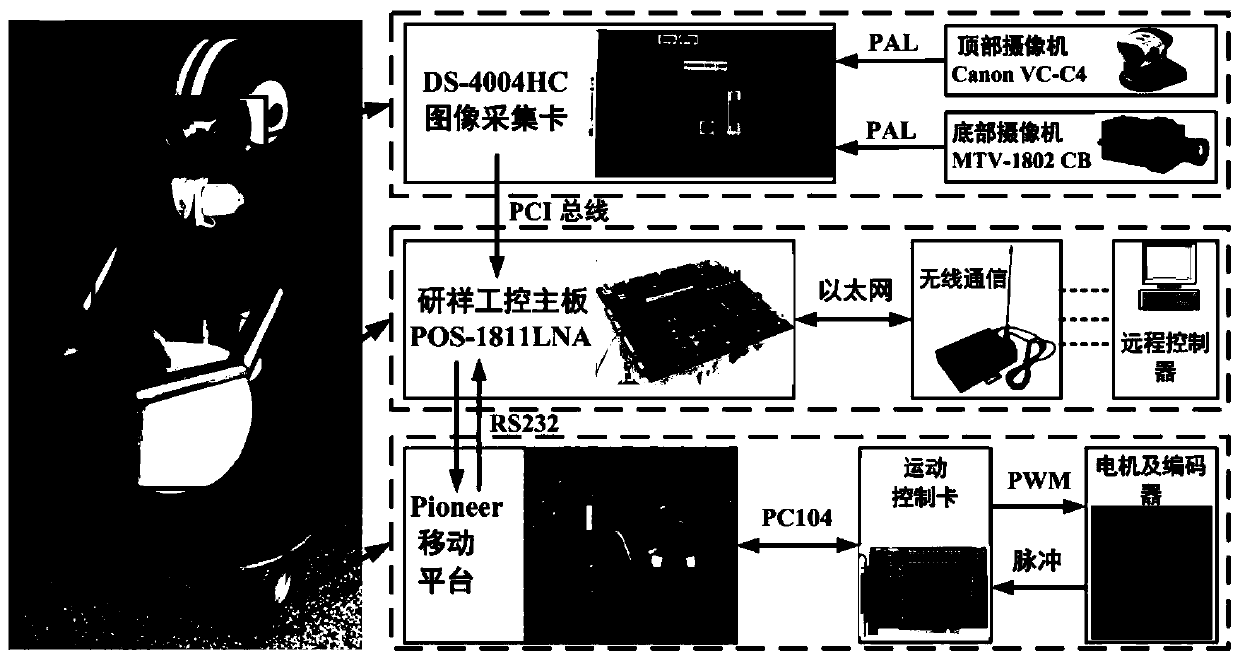
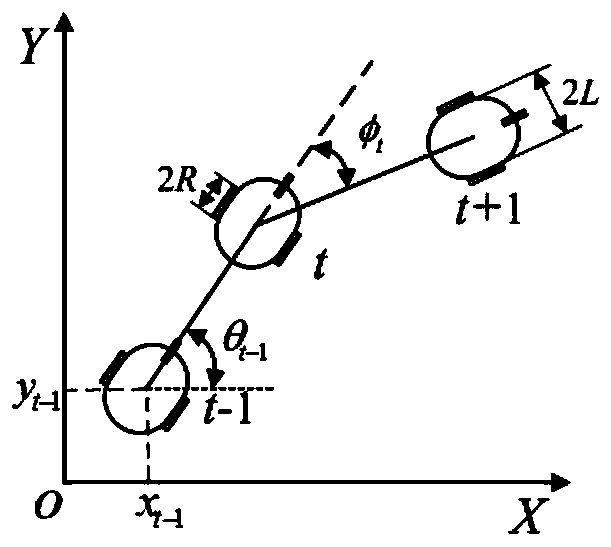
The invention discloses a method for planning an optimal path for incremental environment information sampling of an indoor mobile robot. The method comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring surrounding environment information, and establishing obstacle collision risk-based evaluation probability; (2) planning a path by utilizing an optimal path planning algorithm for the incremental environment information sampling; (3) enabling the indoor mobile robot to select the path and enter a new path planning process. By adopting the optimal path planning algorithm for the incremental environment information sampling, the current optimal path can be planned in real time according to the current conditions of the indoor mobile robot and the inherent nonholonomic constraints of the robot; meanwhile, a collision detection environment in a search tree extension process is optimized; the planning efficiency is improved; the indoor mobile robot can reach a specified position quickly and safely.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
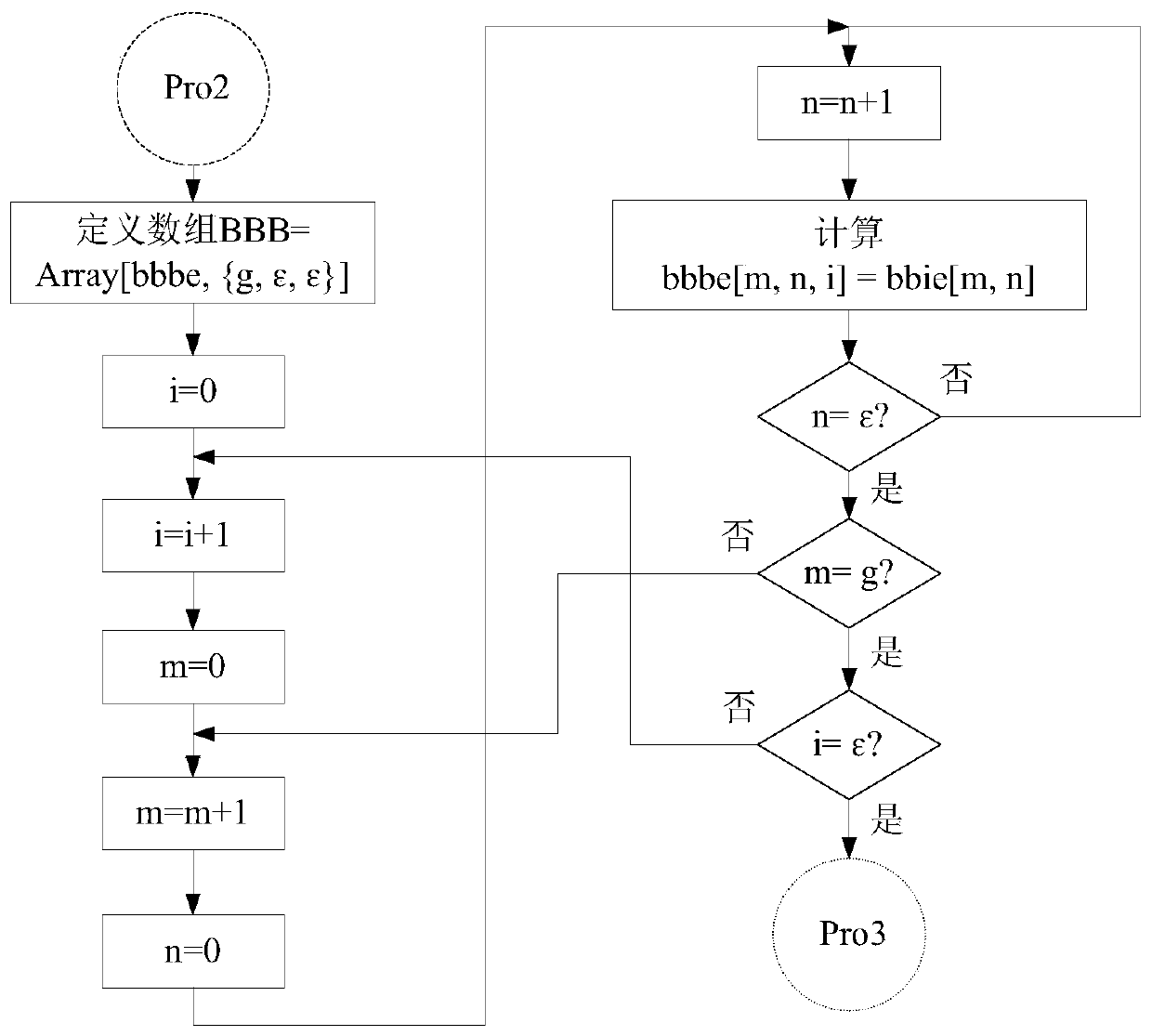
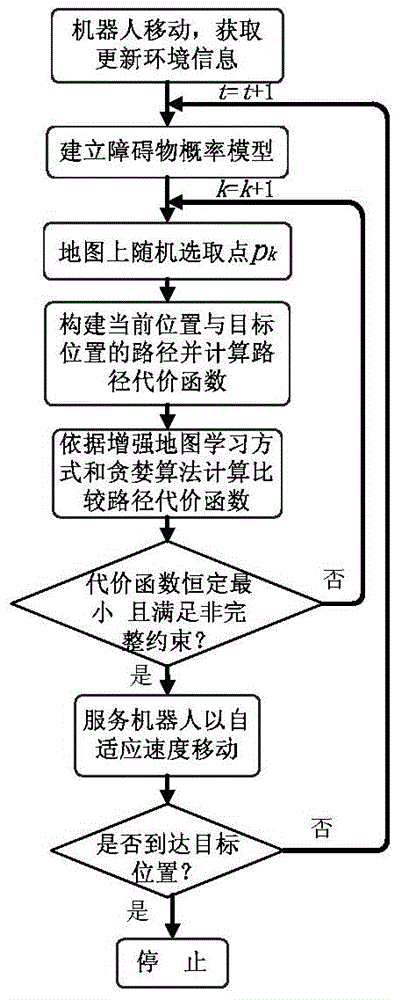
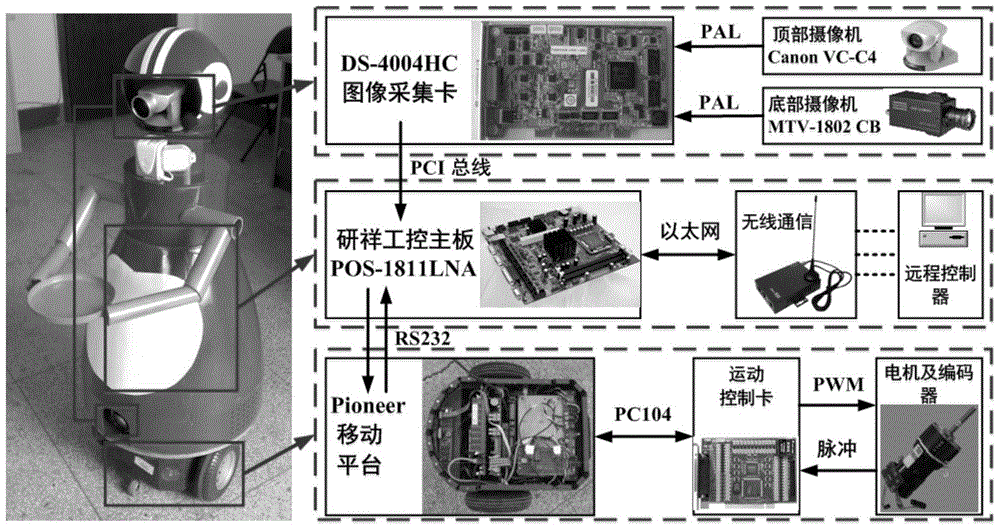
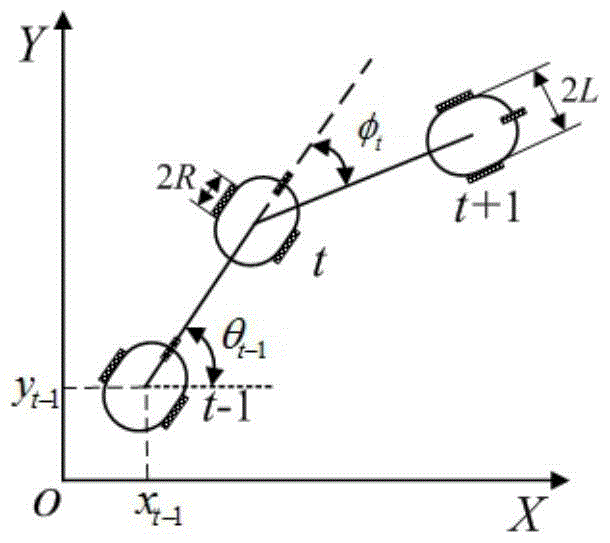
Enhanced map learning path planning method for indoor mobile robot
ActiveCN104298239AGood planning pathSolve practical system application problemsAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsGreedy algorithmPlanning approach
The invention discloses an enhanced map learning path planning method for an indoor mobile robot. The method includes the steps that (1) ambient environment information is acquired, and an obstacle probability density model is established; (2) path planning is carried out through a greedy algorithm and an enhanced map learning method; (3) path selection and self-adaptation speed strategy adjustment are conducted on the indoor mobile robot. By the adoption of the enhanced map learning path planning method, a current optimal path can be planned in real time according to the current condition of the indoor mobile robot and the inherent non-holonomic constraint of the robot, meanwhile, the obstacle crossing ability, the target point convergence ability and the planning efficiency of the indoor mobile robot can be considered through the self-adaptation speed strategy adjustment, and therefore the indoor mobile robot can arrive at a specific location safely and effectively.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
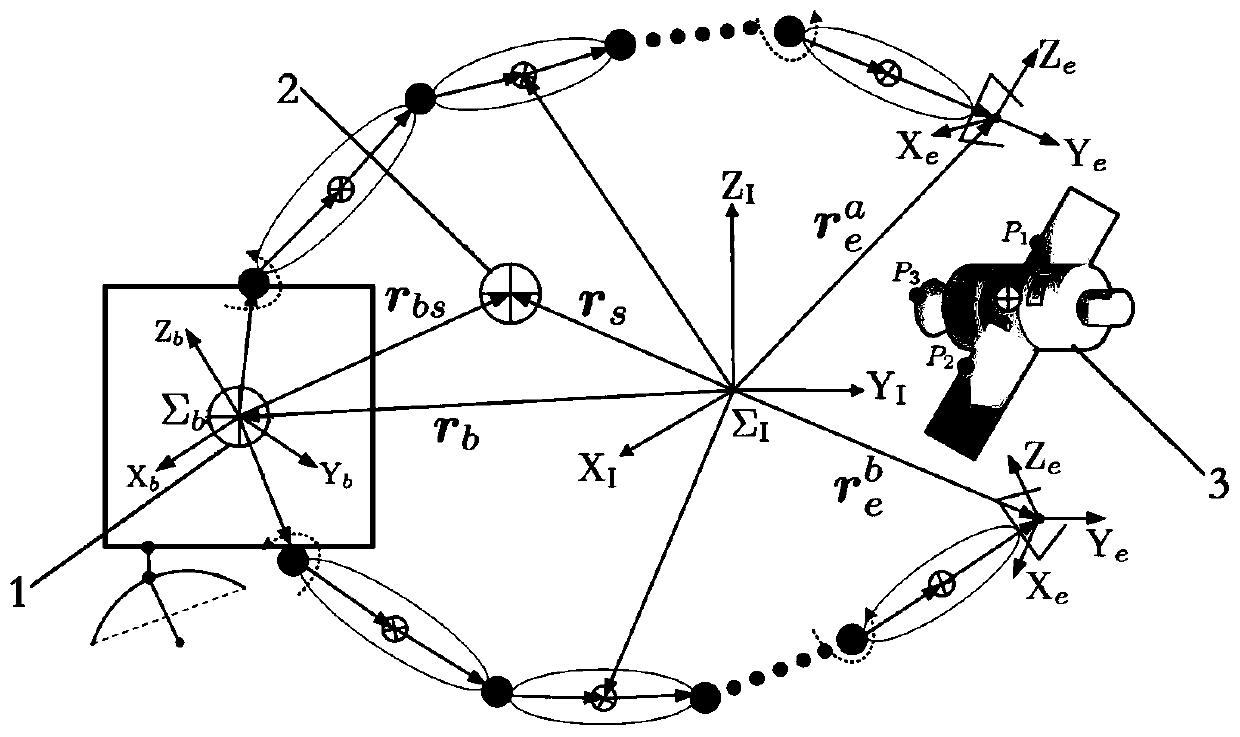
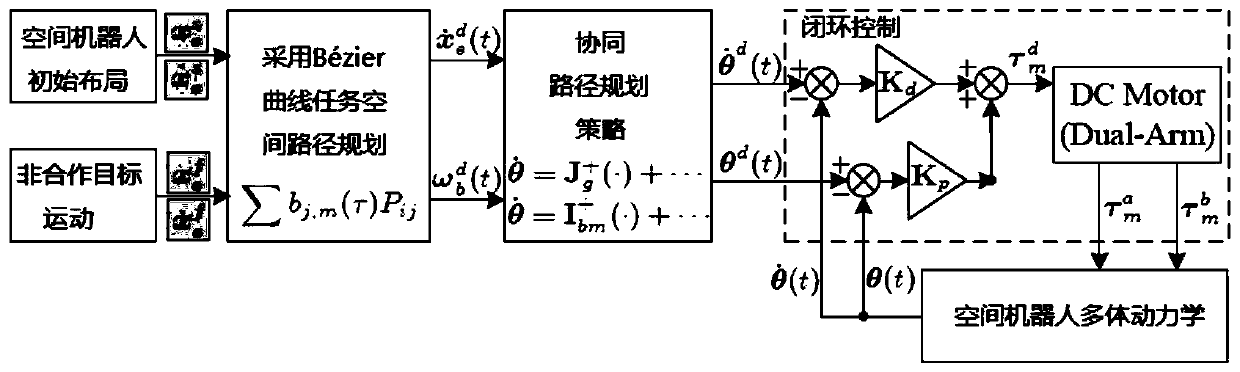
Collaborative path planning method for kinematic redundant two-arm space robot
ActiveCN110104216AImplementing a collaborative path planning methodSmall attitude disturbanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorCosmonautic vehiclesKinematics equationsDynamic balance
The invention discloses a collaborative path planning method for a kinematic redundant two-arm space robot. The collaborative path planning method for the kinematic redundant two-arm space robot comprises the following steps that a dynamic equation and a kinematic equation of a space robot system are established; a redundant solution of an inverse kinematics equation of an end-effector is solved,and a system non-holonomic constraint equation is obtained through a momentum conservation equation; a task space constraint equation of the relationship between the end-effector motion and the attitude of a base is obtained through the system non-holonomic constraint equation; the path planning of the end-effector in a task space is obtained by using a quintic bezier curve, and path execution time is determined by the velocity and acceleration boundary of the end-effector; and the joint motion trajectory planning corresponding to different task priorities is obtained through the end-effectormotion equation and the task space constraint equation. The collaborative path planning method of the space two-arm robot is implemented, various tasks can be performed according to the priorities ofthe tasks such as a multi-arm collaborative task and a dynamic balancing task, and the operation ability of a space manipulator is greatly expanded.
Owner:RES & DEV INST OF NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV IN SHENZHEN +1
Improved method for planning paths of driverless vehicles by aid of rapidly random-exploring trees
ActiveCN108196536AShort pathContinuous and smooth direct followable pathPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPlanning approachRandom tree
The invention relates to an improved method for planning paths of driverless vehicles by the aid of rapidly random-exploring trees. The improved method is characterized by particularly comprising steps of 1), searching and acquiring an initial path from a starting point to an end point by the aid of RRT (rapidly random-exploring tree) algorithms; 2), pruning the initial path by the aid of one-waypruning processes to obtain preliminary pruned paths; 3), further reducing the lengths of the preliminary pruned paths by the aid of bidirectional pruning processes; 4), removing sharp included angleson the paths by the aid of peak clipping processes; 5), carrying out smoothing processing on the paths without clipped peaks to obtain follow paths of the driverless vehicles. Compared with the priorart, the improved method has the advantages that the paths are short, non-holonomic constraints are taken into consideration, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Automatic parking locus optimization method based on full-simultaneous dynamic optimization framework
The invention discloses an automatic parking locus optimization method based on a full-simultaneous dynamic optimization framework, and brings forward a vehicle-environment integrated modeling dynamic optimization framework based on full-simultaneous solution strategy, for the purposes of solving the problem of safe parking at a narrow parking space within shortest time due to fast rhythm of cities, effectively eliminating influences exerted by different parking space shapes on locus planning strategies and optimizing a safe bump-free locus which has nonholonomic constraints and satisfies low-speed parking of vehicles within the shortest time. The method provided by the invention is crucially characterized in that vehicle-parking space obstacle avoidance integrated modeling is realized by use of an MPCC mathematic optimization technology, and at the same time, can optimize correlation indexes of vehicle kinetics and dynamics. According to the method, control information such as the speed, the front-wheel corner, the accelerated speed, the front-wheel angular velocity and the like of a vehicle tracking optimization locus can be directly obtained, and actual parking assistance is facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots
ActiveCN109885052ASolve the speed constraint problemFull rangePosition/course control in two dimensionsPosition/direction controlPredictive controllerOmnidirectional mobile robot
The invention discloses an error model predictive control method based on kinematics modeling of omnidirectional mobile robots. The error model predictive control method comprises the following stepsthat S11, a velocity constraint kinematics model is established between FM-OMR four Mecanum wheels; S12, a tracking error kinematics model of a FM-OMR is established; S13, aiming at the trajectory tracking problem of the FM-OMR and the tracking error kinematics model, an error model predictive controller combined with a velocity constraint equation is designed; and S14, according to the error model predictive controller, effective trajectory tracking parameters between the omnidirectional mobile robots are controlled so as to enable tracking errors between the omnidirectional mobile robots toremain unchanged. According to the error model predictive control method based on the kinematics modeling of the omnidirectional mobile robots, the error model predictive control method based on the trajectory tracking error kinematics modeling is provided aiming at the omnidirectional mobile robots with the four Mecanum wheels, the non-holonomic constraint problem of the effective trajectory tracking control is solved, and the accuracy and the validity are realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A flexible multi-body robot modeling and solving method based on multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction
ActiveCN109543264AAccurate descriptionAvoid the phenomenon of wrong iterative solutionsProgramme-controlled manipulatorDesign optimisation/simulationCorrection algorithmState parameter
The invention discloses a flexible multi-body robot modeling and solving method based on multi-dimensional reconstruction correction, This method is successively performed by: A mathematical model ofrigid component and a flexible component are respectively constructed and parameters are set, the holonomic constraint conditions of a flexible multi-body robot system are established, the static anddynamic equations of flexible multi-body robot system with holonomic constraints are obtained, According to the known state parameters of t-time, the state parameters of t + h-time are obtained by iterative solution of dynamic equations under complete constraints using multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction method, and the state parameters of t + h-time are obtained by repeated iterativeprocess until the end of the algorithm. The forward and inverse dynamic models of flexible multi-body robot with holonomic constraints are established by the modeling and solving method, and the dynamic equations are solved iteratively by using the multi-dimensional reconstruction and correction algorithm. The modeling is complete and the solving scale is small. Compared with the traditional solving method, the convergence condition is easier to be satisfied, and the efficiency of calculation and solution is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
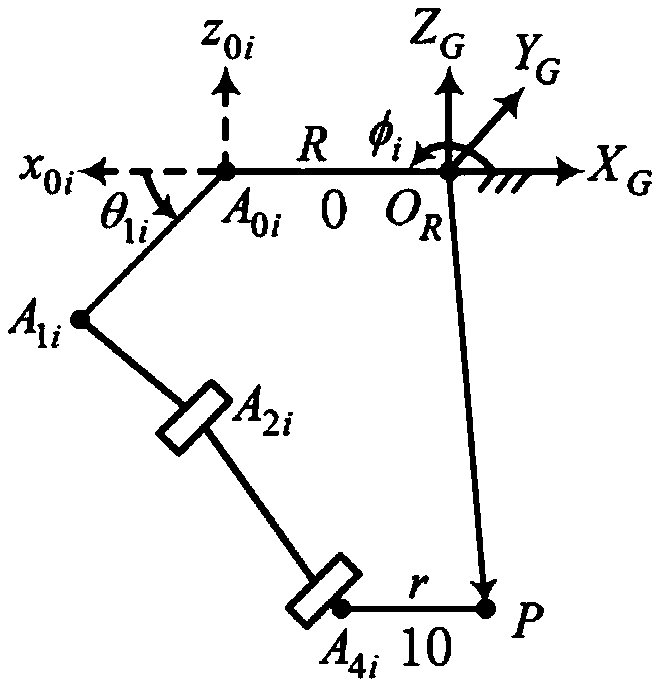
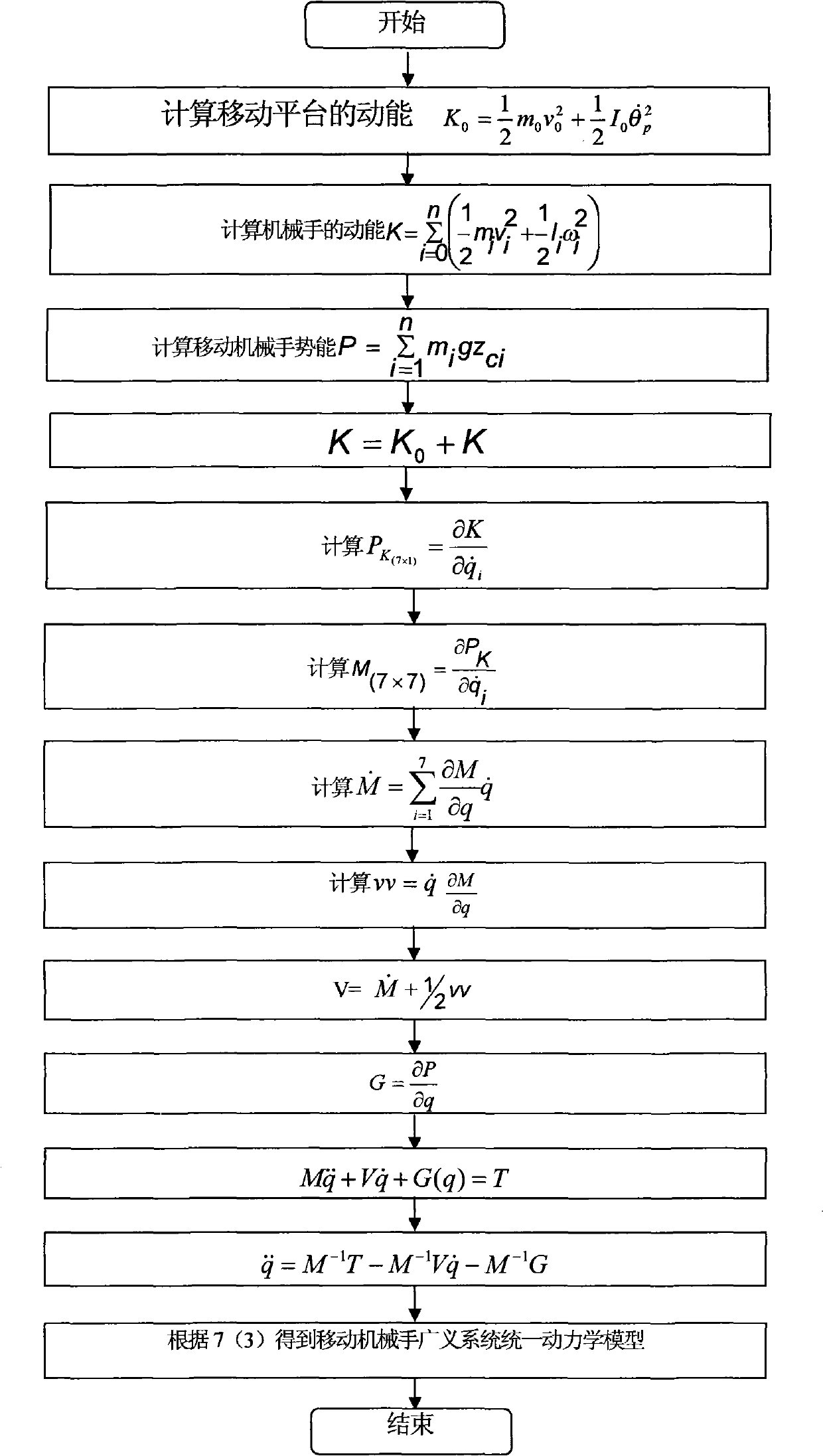
Unified dynamic modeling method of generalized system of crawler-type mobile manipulator
InactiveCN101526801AAvoid control errorOvercoming control difficultiesSimulator controlManipulatorDynamic methodSimulation
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Orbit expansion based multi-robot tracing formulation control method
InactiveCN102073320AGuaranteed normal movementHigh precisionVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlDifferential coefficientRange of motion
The invention discloses an orbit expansion based multi-robot tracing formulation control method, comprising the following steps of: a) for a group of target orbit in a plane, expanding vectors of the target orbit, which point to each point on the orbit along the center of the target orbit, into an orbital cluster equivalent to an orbital function, and determining the movable range of robots; b) calculating tracing error by virtue of the orbital function, and designing the virtual angular velocity of the robots to ensure the tracing error to meet design requirements; c) calculating the generalized arc length and differential coefficient of the generalized arc length when the robots move along the orbit, by virtue of the orbital function and the target orbit, and designing the control force of the robots by virtue of neighbor information obtained by communication to realize formulation; d) calculating the error between the real angular velocity and the virtual angular velocity, and designing the control moment of force of the robot to complete tracing; and e) completing motion control on the robots by virtue of a servo system. The orbit expansion based multi-robot tracing formulation control method disclosed by the invention is especially applicable to nonholonomic constraint dynamic robots and simple and convexly- closed orbits. The method is simple and reliable, has higher accuracy and can be applied to multi-robot optimized information acquisition and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
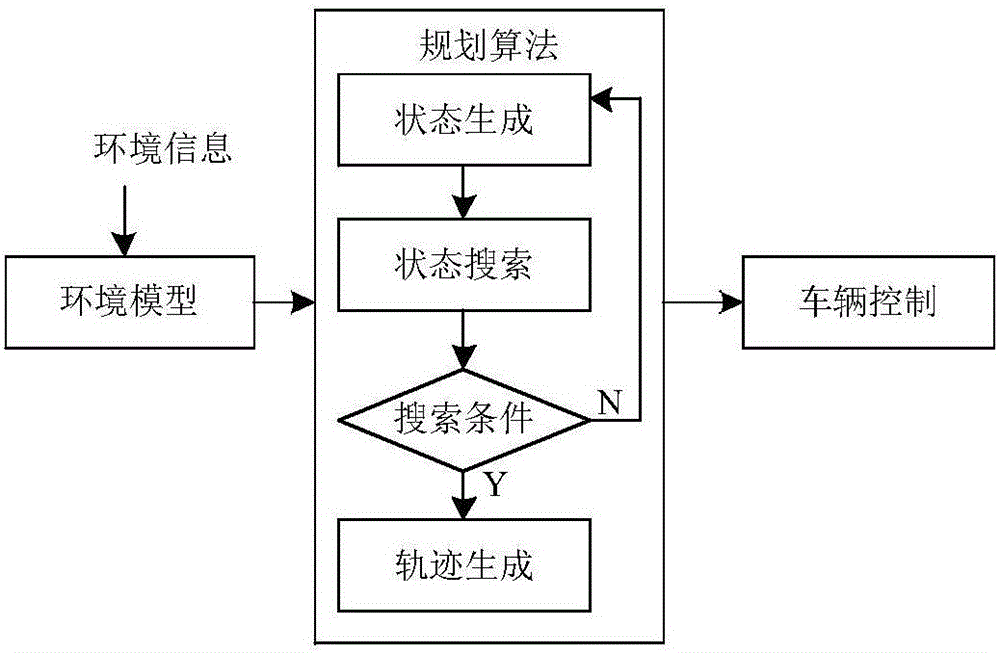
Unified automatic driving transverse planning method and system
ActiveCN106371439ASimplify the upper-level behavior decision-making moduleAvoiding the local minima problemPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesPerformance indexLocal environment
Disclosed is a unified automatic driving transverse planning method. The method comprises the following steps: describing vehicle surrounding environment information in a unified mode; based on the unifiedly described vehicle surrounding environment information, planning an executable locus in real time in a driving process of a vehicle; executing the executable locus to guide the vehicle to run transversely; and through the previous three steps, realizing optimal local locus planning based on various constraints, performance indexes and driving behaviors. Disclosed is also a unified automatic driving transverse planning system. The system comprises an environment model sub-module, a planning algorithm sub-module and a vehicle control sub-module, wherein the environment model sub-module, according to environment perceiving information, in accordance with traffic rules and properties of traffic participants, constructs a unified local environment model, describes the vehicle surrounding environment information in a unified mode and reflects a potential dangerous degree around the vehicle; and the planning algorithm sub-module takes vehicle nonholonomic constraints and safety and comfortableness requirements into consideration, and based on the environment model, planning the executable locus in real time in the driving process of the vehicle.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Point calm increment intelligent control method of two-wheeled robot
InactiveCN102023569ASolve the stability problem of the point stabilization controlIncrease Increment ControlAdaptive controlProportional controlSimulation
The invention provides a point calm increment intelligent control method of a two-wheeled robot. In the control method, an increment controller containing a task adaption level and an operation control level is provided, and an expected wheel speed as ratio controller output in the prior art is used as an expected wheel speed adaptive value of the task adaption level output in the increment controller provided by the invention, thereby solving the problem of stability of point calm control caused by the non-holonomic constraints problem of the robot; and the operation control level is added to carry out further increment wheel speed following control on the expected wheel speed adaptive value, thereby solving the stability problem of the point calm control caused by acceleration and speed constraint limitation which necessarily exist in a motion execution system, ensuring that the motion curve of the good robot is obtained, and effectively improving the rapidity of the motion of the robot simultaneously.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
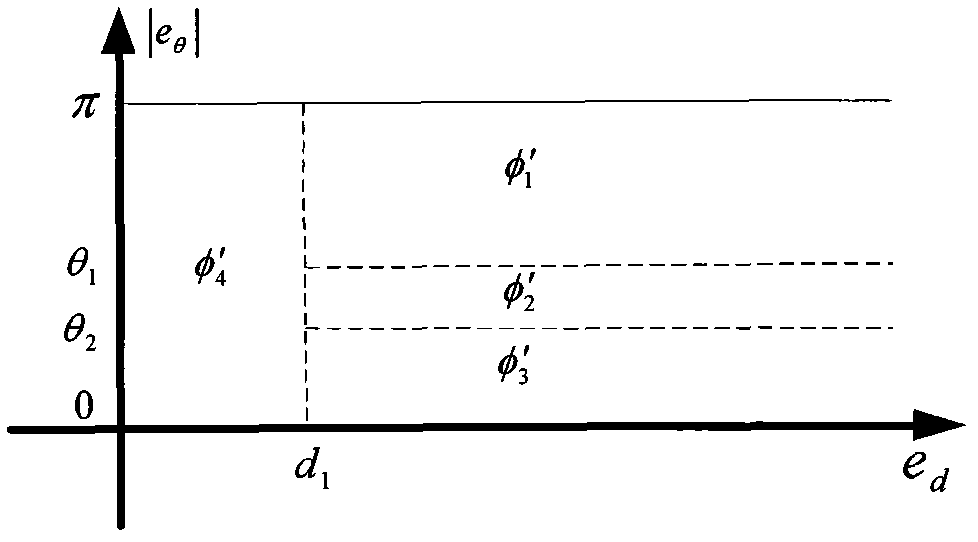
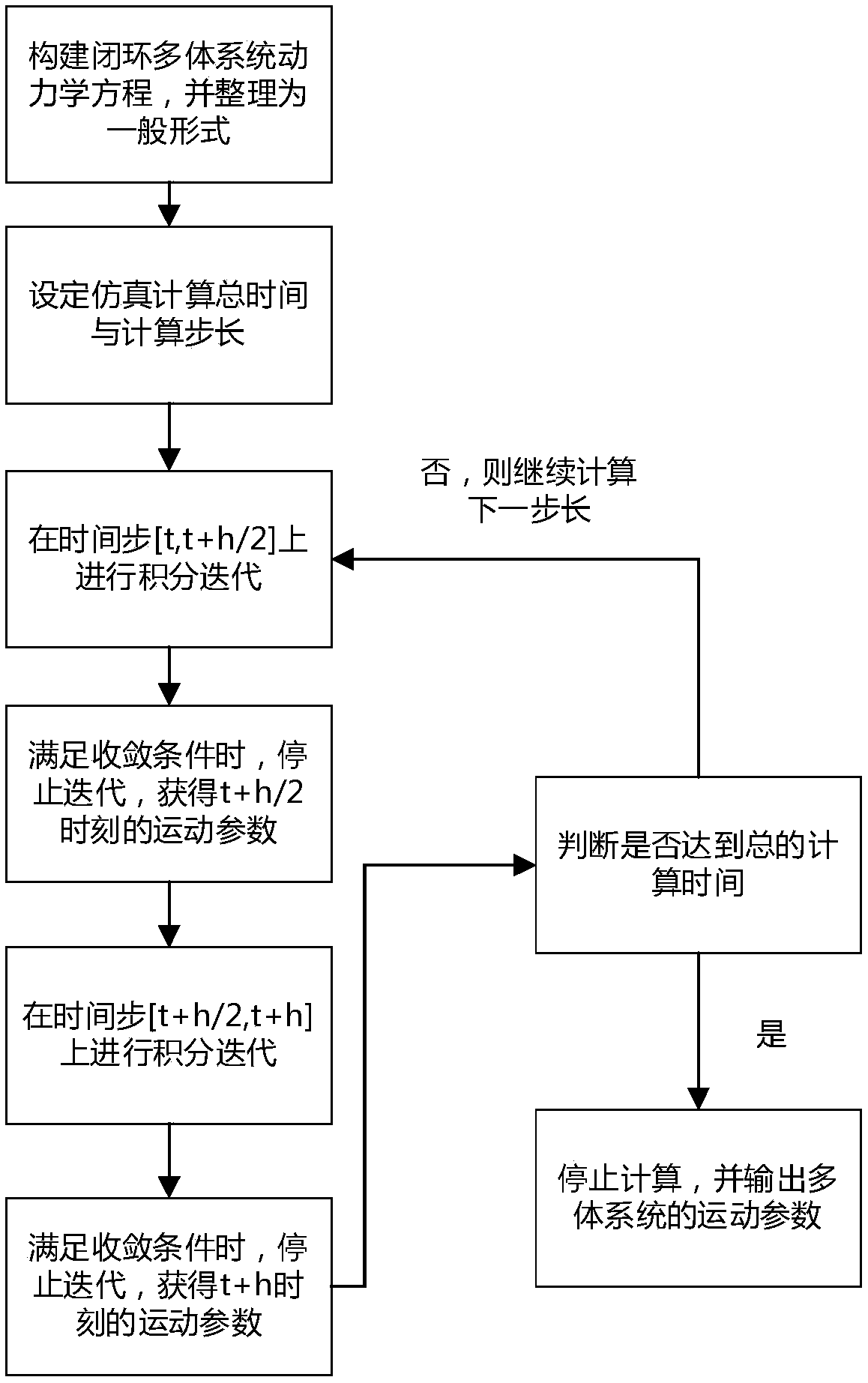
Multi-body-dynamics-equation solving method based on Bathe integration strategy
ActiveCN107943748AGood precisionSolve for stabilityComplex mathematical operationsAlgebraic equationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a multi-body-dynamics-equation solving method based on a Bathe integration strategy. The method includes: establishing a corresponding coordinate system in a multi-body dynamics system, and using a relative-coordinate method and a Lagrangian-multiplier method to obtain dynamics equations according to a virtual-power principle; seeking a second derivative of a constraint equation with respect to time to obtain differential-algebraic equations of an index -1, and adding constraint stability terms to form a general form of the dynamics equations with complete constraints;carrying out integration iteration solving on the general form of the dynamics equations with the complete constraints on a time step [t, t+h / 2] to obtain motion parameters of a moment t+h / 2; carryingout integration iteration solving on a time step [t+h / 2, t+h] to obtain the motion parameters of a moment t+h; and carrying out repeated iteration calculation, outputting values of generalized displacement, velocity and acceleration, which are of a system and are changed over time, when calculation time reaches set total simulation time, and thus analyzing motion status of the multi-body process-closed-loop dynamics system in certain time. The method can also achieve better precision in a case of larger integration step length.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Homography matrix based visual servo control method for shortest path
InactiveCN104950893AImprove robustnessReduce usagePosition/course control in two dimensionsMatrix decompositionThree stage
The invention discloses a homography matrix based visual servo control method for a shortest path. The method comprises steps as follows: motion of a robot is decomposed into three stages, firstly, the robot is rotated to face a position point where a target image is located, the position point where the target image is located is called a target point for short, then the robot is horizontally moved to the target point, finally, the robot is rotated to an angle of a target pose, and the robot motion can be controlled according to corresponding control laws at each stage. According to the method, elements in a homography matrix are directly utilized to constitute error functions, homography matrix decomposition is not required, robustness for camera parameters and image noise is better, and meanwhile, the problems about unknown depth information of a monocular camera and nonholonomic constraint of a tracked robot are solved, so that the robot reaches the target pose stably through the shortest path.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods and apparatus for blind separation of multichannel convolutive mixtures in the frequency domain
A method and apparatus is disclosed for performing blind source separation using frequency-domain normalized multichannel blind deconvolution. The multichannel mixed signals are formed as frames of N samples, which consist of r consecutive blocks of M samples. The frames of mixed signals are separated using separating filters in the frequency domain in an overlap-save manner using a discrete Fourier transform(DFT). The separated signals are then converted back into the time domain using the inverse DFT to be applied to a nonlinear function. The cross-power spectra between separated signals and nonlinear-transformed signals are computed and are normalized by the power spectra of separated signals and the power spectra of nonlinear-transformed signals to have flat spectra. The invention then applies the time domain constraint to preserve the first L cross-correlations. These alias-free normalized cross-power spectra are further constrained by nonholonomic constraints. The invention then computes natural gradient by convolving alias-free normalized cross-power spectra with separating filters. After the length of separating filters is constrained to L, separating filters are updated using the natural gradient and normalized to have unit norm. The terminating conditions are checked to see if separating filters converged.
Owner:南 承铉
Wheeled mobile robot point stabilization rolling optimization control method
The invention discloses a wheeled mobile robot point stabilization rolling optimization control method which comprises the following steps of: based on a dynamic model of a mobile robot of a global coordinate system, combining control constraint and state constraint into design of a point stabilization controller by using a state feedback model prediction control method; finally designing a smooth stabilization control rule expression equation of a mobile robot control system through variable substitution. Therefore, the problem of point stabilization control stability caused by incomplete constraint of the mobile robot self, the problem of point stabilization control stability caused by inevitable acceleration and speed constraint of a movement execution system of the mobile robot self, and the problem of point stabilization control stability caused by uncertainty of various external environments can be solved, and movement rapidness and accuracy can be effectively improved while good mobile robot movement tracks are ensured.
Owner:浙江天甘科技有限公司
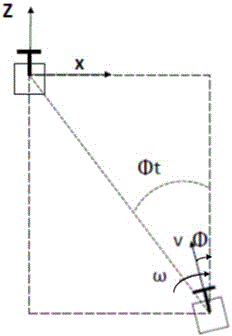
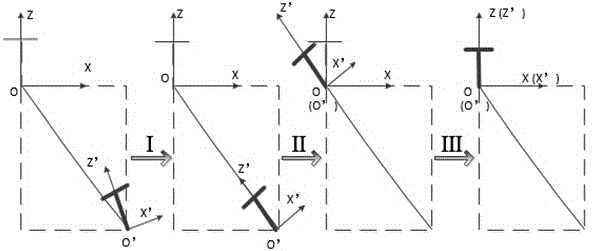
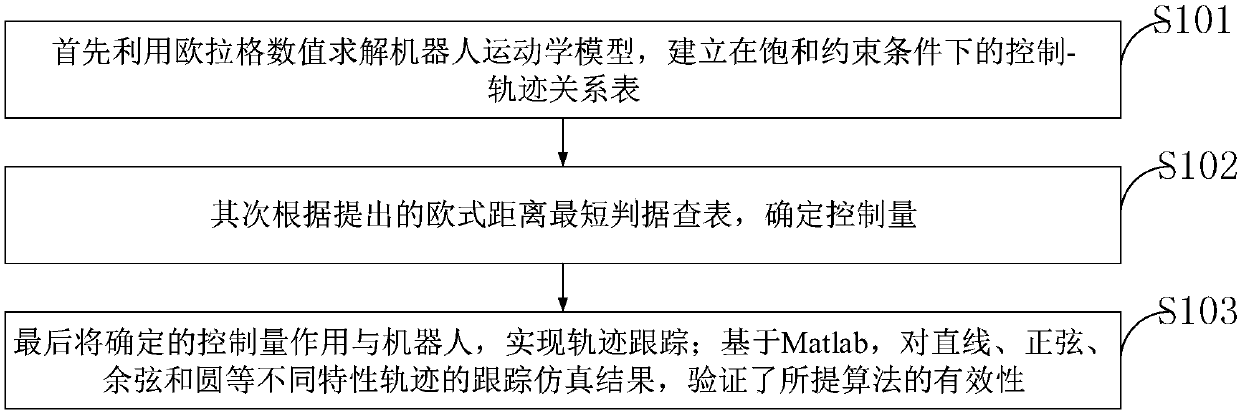
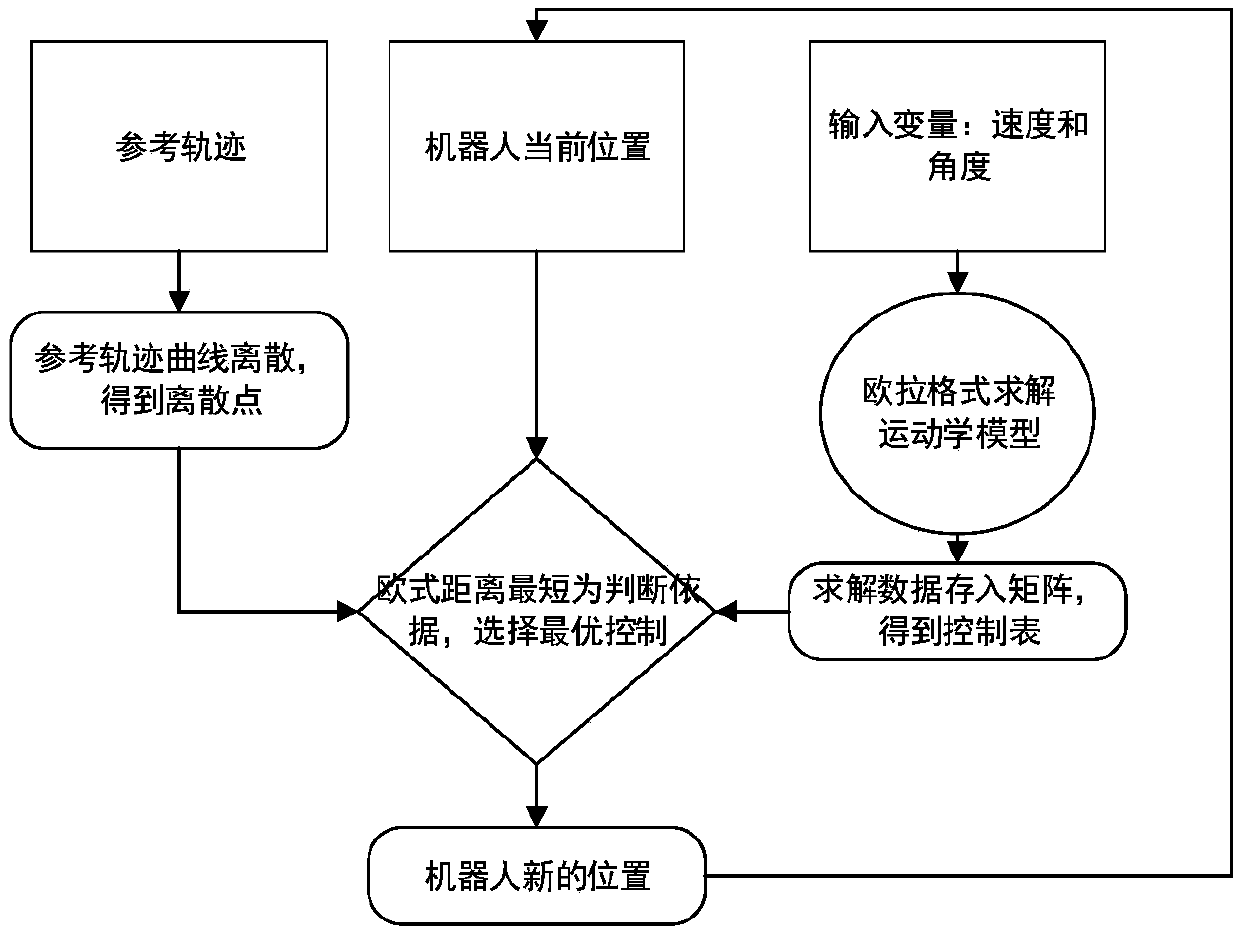
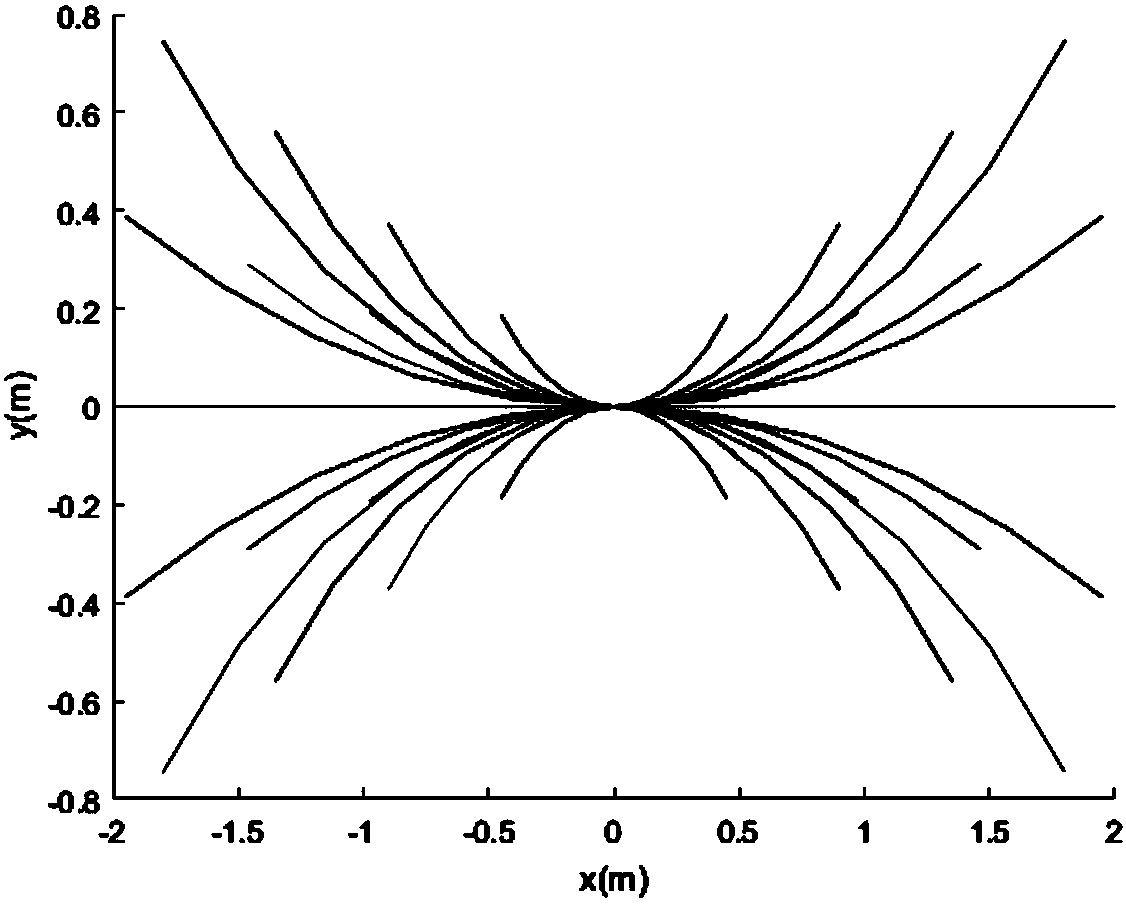
Incomplete constraint wheeled robot locus tracking control method based on look-up table method
ActiveCN107943056AVerify validityRealize trajectory trackingPosition/course control in two dimensionsKinematicsSimulation
The invention belongs to the technical field of robots, and discloses an incomplete constraint wheeled robot locus tracking control method based on a look-up table method. The method comprises the steps: solving a robot kinematic model through an Euler numerical value, and building a movement locus (x, y) relation table between system input (v, omega) and the robot under the condition of saturation constraint; determining a control input quantity according to a proposed shortest Euclidean distance criterion look-up table; finally employing the determined control input quantity for the robot, and enabling the movement locus of the robot to be tracked to a specific reference locus. The effectiveness of the method provided by the invention is verified based on Matlab through the tracking simulation results of linear, sine, cosine and circular loci.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Novel under-actuated robot wrist device based on nonholonomic constraint
InactiveCN105598996ALess joint degrees of freedomReduce volumeJointsControl systemHolonomic constraints
The invention relates to a novel under-actuated robot wrist device based on nonholonomic constraint. The novel under-actuated robot wrist device based on nonholonomic constraint comprises a fixed platform, a movable platform, two branch mechanism chains, two drive power sources and a middle constraint device. The fixed platform is connected with the movable platform through the two branch mechanism chains. The two branch mechanism chains are driven by the two drive power sources for transmission through two branch mechanisms, the nonholonomic constraint is formed by the middle constraint device, and then three-freedom-degree motion of the movable platform is achieved. A three-freedom-degree parallel mechanism driven by the two power sources is adopted for three-freedom-degree motion, power sources are fewer, a wrist is small in size, low in weight and low in cost, and only a low control system is needed. The device is simple in structure and reliable in work, can serve as a joint of a robot, and is used for driving more arm joint freedom degrees through a few power sources.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method based on complex operation tasks
ActiveCN105904458ARelieve pressureFlexible operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationConstraint control
The invention discloses a non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method based on complex operation tasks. The complex operation tasks are decomposed by calculating the constraint matrix CVF, and a constraint controller is designed finally. Compared with a general mechanical arm control method, the non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method has two beneficial effects on the aspects of the task level and control method for complex space control tasks, specifically, the control tasks which a mechanical arm needs to complete in the space include approaching the target, tracing the path, avoiding obstacles and the like, and since proper movement spinor collections are selected according to the different operation tasks so as to establish the constraint matrix, the method has a better capacity of adapting to the complex tasks compared with prior methods; and besides, by means of the non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method, operation is more flexible, an operator can control the mechanical arm to move only in the horizontal motion direction or rotation direction, no extra constraint is needed, and accordingly the stress of the operator is relieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
State estimation method and system under heading constraint
ActiveCN108871365ATake advantage ofAvoid wastingInstruments for road network navigationEstimation methodsAlgorithm
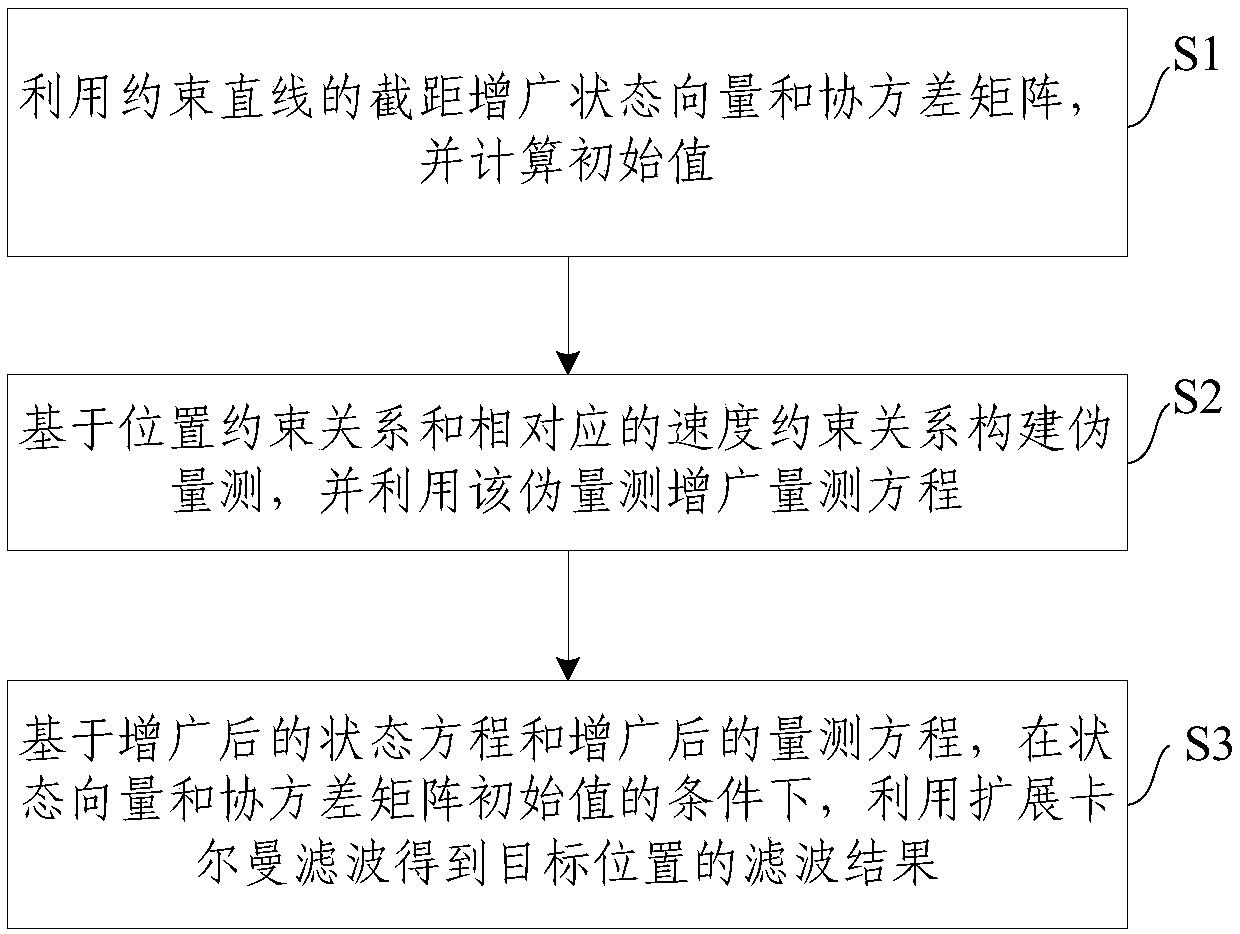
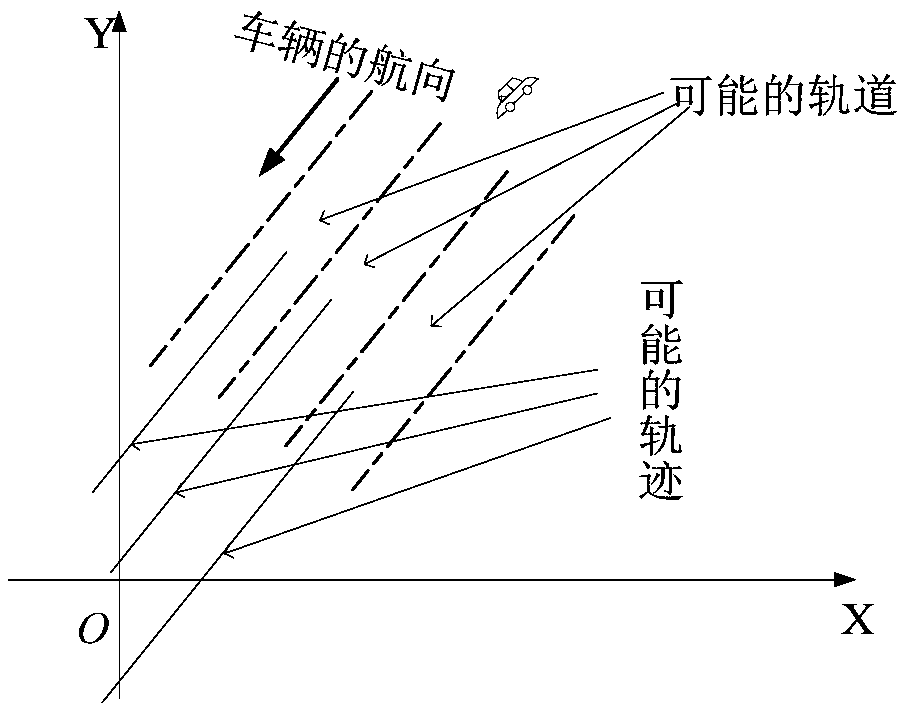
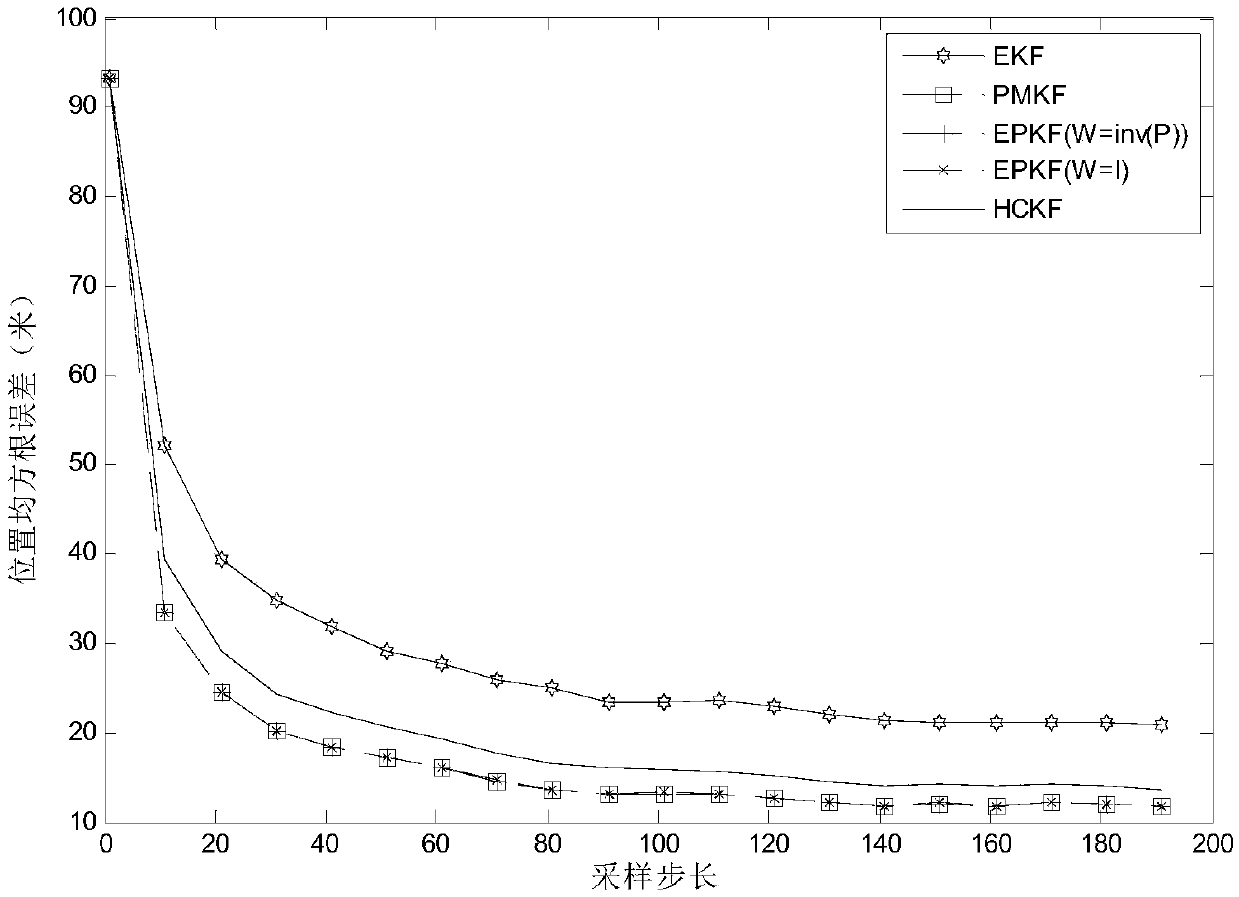
The invention provides a state estimation method and system under heading constraint. The method comprises the following steps: under the condition that heading is known, augmenting a state vector anda covariance matrix by utilizing nodal increment of a constraint straight line, and augmenting an original state equation; calculating an initial value; constructing pseudo measurement based on a position constraint relation and a corresponding speed constraint relation; augmenting a measurement equation by utilizing the pseudo measurement; based on the augmented state equation and the augmentedmeasurement equation, and initial values of the state vector and the covariance matrix, carrying out extended Kalman filtering to obtain a filtering result of a target position. By adopting the stateestimation method and system under the heading constraint, the state estimation problem under incomplete constraint conditions is solved; prior known information is sufficiently utilized and wastes ofthe information are avoided.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
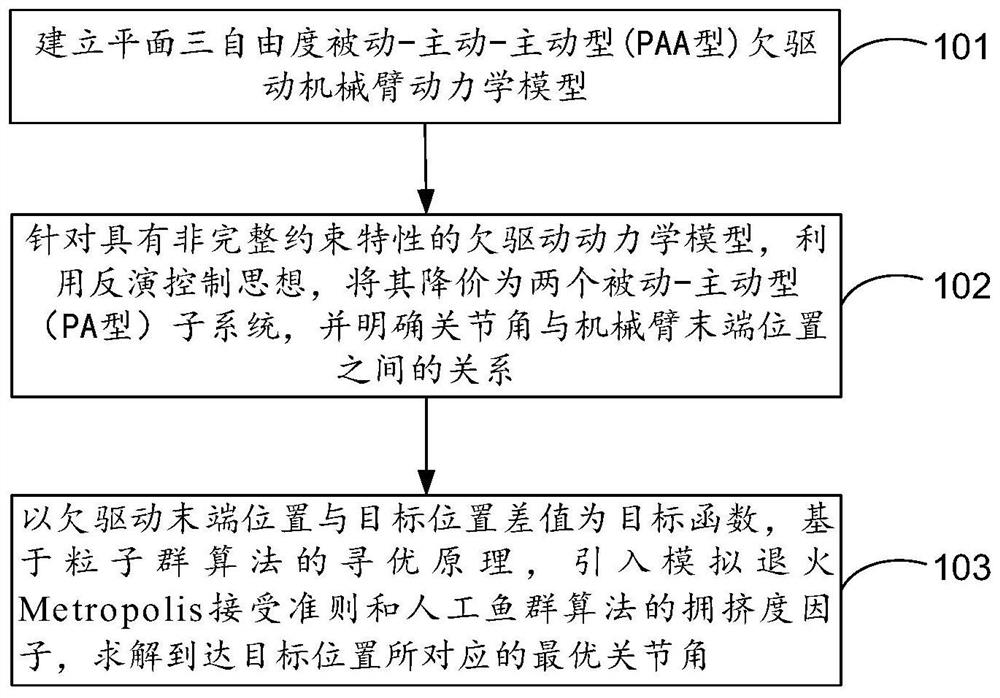
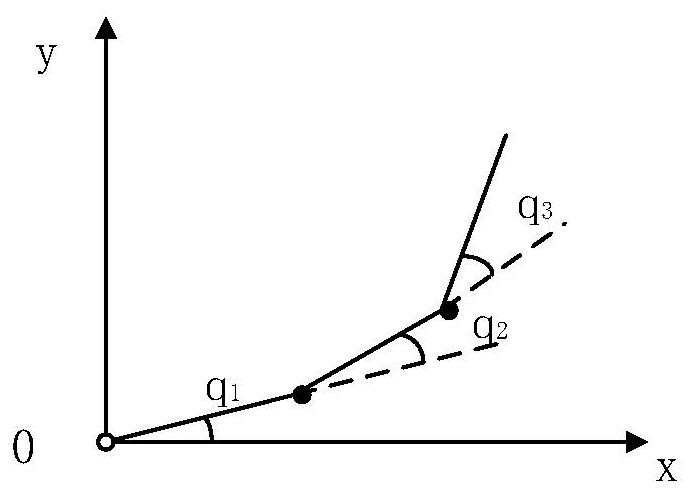
Method for optimizing joint angles of under-actuated mechanical arms on basis of improved particle swarm algorithms
ActiveCN109262612AAvoid cases of premature convergenceImprove global search performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal optimumEngineering
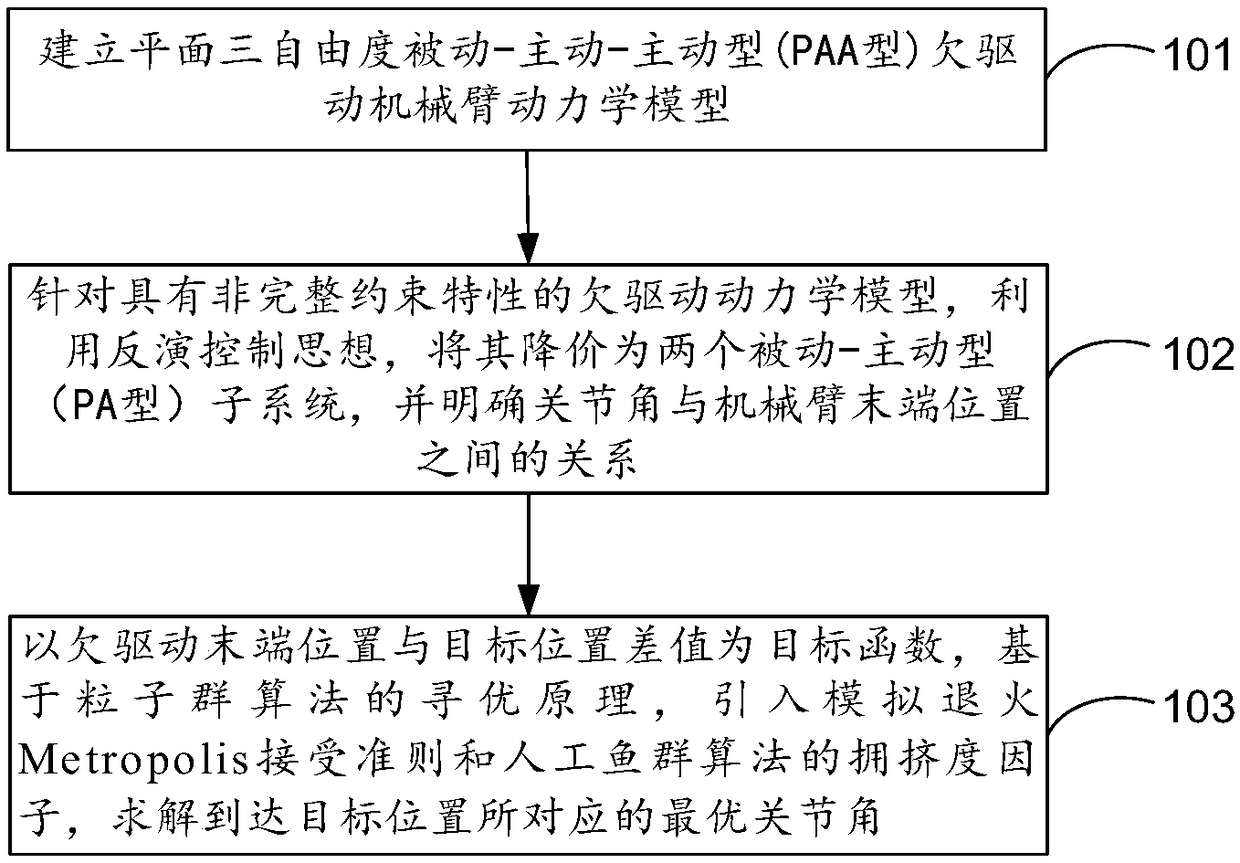
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method for optimizing joint angles of under-actuated mechanical arms on the basis of improved particle swarm algorithms. The method includes building planarthree-degrees-of-freedom passive-active-active type (PAA type) under-actuated mechanical arm kinetic models; reducing order of each under-actuated mechanical arm kinetic model with non-holonomic constraint characteristics by the aid of back-stepping control thoughts to obtain two passive-active type (PA type) subsystems, and making relations between the joint angles and the locations of the tail ends of mechanical arms definite; utilizing difference values of the locations of the tail ends of the under-actuated mechanical arms and target locations as target functions, leading in simulated annealing Metropolis acceptance criteria and congestion degree factors of artificial fish school algorithms and solving the corresponding optimal joint angles for reaching the target locations. Accordingto the technical scheme, the method has the advantages that the local optimization trapping probability of optimization algorithms can be lowered during under-actuated mechanical arm location control,and the solving precision can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Mechanical modeling method for nonholonomic constraint system
ActiveCN106383973AAvoid double countingReduce computing timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationArray data structureReverse order
The invention discloses a mechanical modeling method for a nonholonomic constraint system. The mechanical modeling method comprises the steps of introducing an intermediate variable to describe a nonholonomic constraint relation according to the complexity of nonholonomic constraints when constraint analysis is carried out; revealing independent generalized velocity information included in kinetic energy through the constraint analysis, extracting a coefficient of a product item of independent generalized velocity and defining the coefficient as the intermediate variable, and changing the kinetic energy into a new form of expression; in a modeling process, calculating partial derivatives of some function variables to generalized coordinates or total derivatives of the function variables to time massively, establishing a function-variable implication relation table and introducing composite derivation to solve by analyzing a variable subordinate structure; and defining several structural arrays to store calculation results since the calculation of the influence of the nonholonomic constraints on the system is more complex. In order to avoid a model expansion problem caused by back substitution of the intermediate variable, the calculation expression of the model needs to be outputted in a reverse order.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Online optimization calmness control method for wheel type movable stage robot
ActiveCN107168064AMeet the real-time requirements of fast controlSimple designAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime limit
An online optimization calmness control method for a wheel type movable stage robot aims at a requirement for realizing calmness controlling of the wheel type movable stage robot in a non-complete restraining condition. Firstly, through defining a discrete time three-order dynamics model of the wheel type movable stage robot and a randomly selected initial time limited time window control sequence, a calmness control error sequence in a time window and gradient of the error sequence relative to a controlled input sequence are calculated. Then a Newton's method is utilized for establishing an updating mechanism for each sampling time control sequence. Furthermore according to a rolling optimization control principle, a controlled input amount at each sampling time point is calculated, thereby realizing calmness controlling to the wheel type movable stage robot. The online optimization calmness control method according to the invention has advantages of easy understanding, small number of setting parameters, high versatility and simple online calculation. Furthermore the online optimization calmness control method satisfies a requirement for high real-time performance in quick calmness controlling of the wheel type movable stage robot.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
An Optimal Path Planning Method for Incremental Environmental Information Sampling of Indoor Mobile Robots
ActiveCN106444769BImprove efficiencyGood obstacle avoidancePosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesCollision detectionSimulation
The invention discloses an optimal path planning method for incremental environmental information sampling of indoor mobile robots. The steps are: (1) Obtain the surrounding environment information and establish an evaluation probability based on the obstacle collision risk; (2) Use the incremental The optimal path planning algorithm based on environmental information sampling is used for path planning; (3) the indoor mobile robot performs path selection and enters a new path planning process. The optimal path planning algorithm using incremental environmental information sampling can plan the current best path in real time based on the current situation of the indoor mobile robot and the inherent non-holonomic constraints of the robot. At the same time, the collision detection environment during the search tree expansion process is optimized. , improves planning efficiency and enables indoor mobile robots to reach designated locations quickly, safely and effectively.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
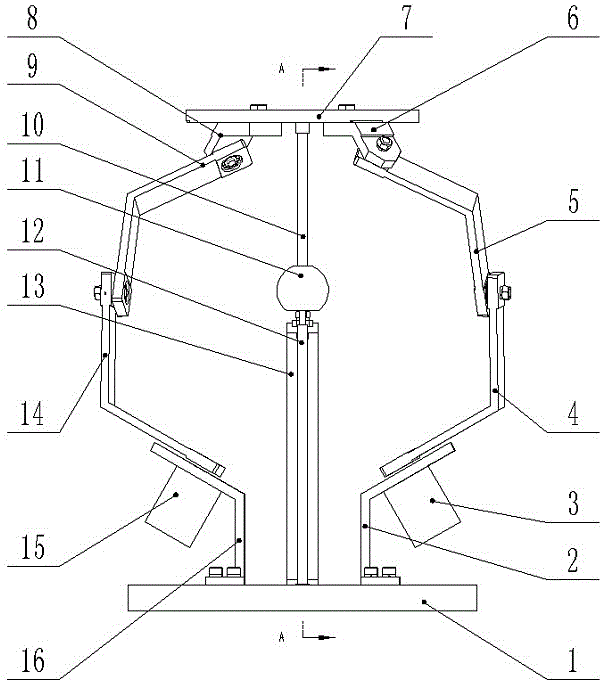
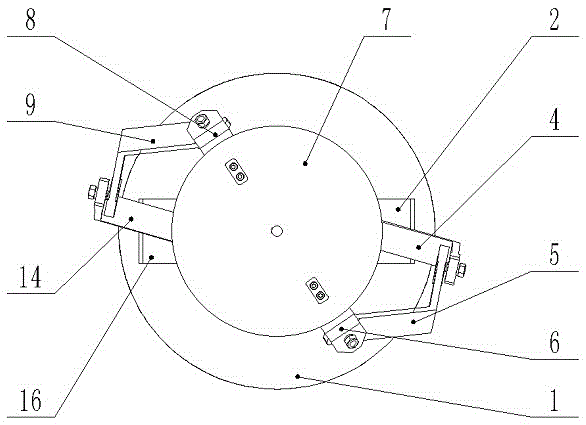
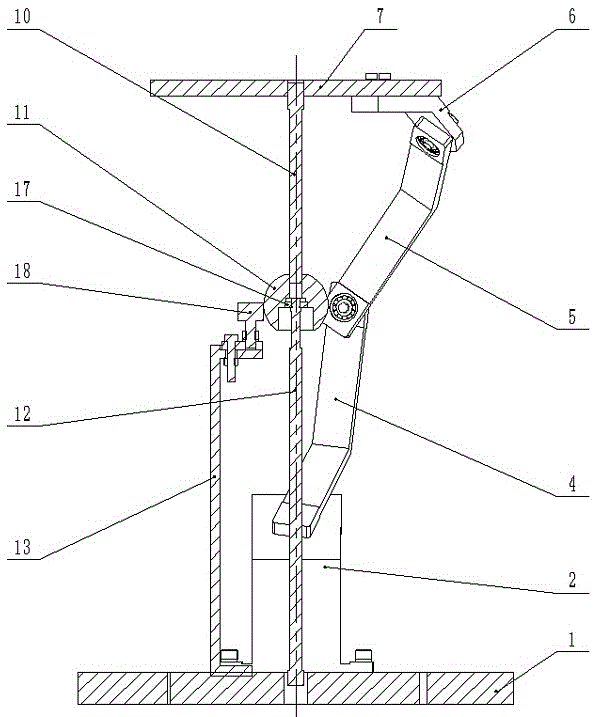
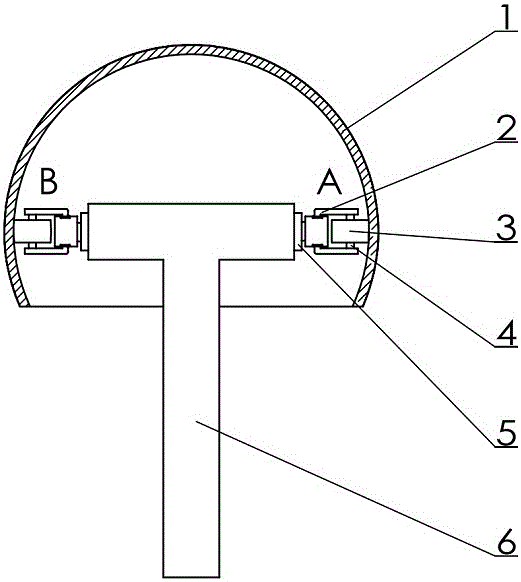
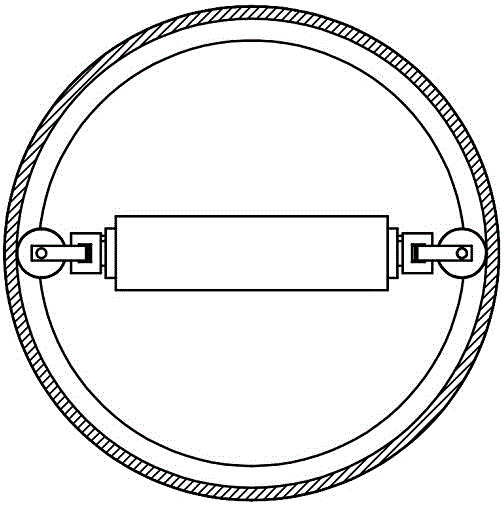
Built-in Nonholonomic Spherical Constraint Structure
The invention relates to a structure with an incomplete spherical constraint added inside. The structure with the incomplete spherical constraint added inside comprises a spherical shell, a idler wheel supports, idler wheels, idler wheel shafts, a servo motor and a big support, wherein the big support is in a T shape, one end of a cross rod of the big support is fixedly connected with the servo motor, the idler wheel supports are fixedly connected with the servo motor through keys, the idler wheel shafts are fixedly connected with the idler wheel supports, and the idler wheels are connected with the idler wheel supports in a rotary mode; the same structure is connected to the other end of the cross rod of the big support, and the structures at the two ends of the cross rod of the big support are distributed symmetrically relative to a vertical rod shaft of the big support; the spherical shell makes contact with the idler wheels in a purely sliding mode, in other words, the idler wheels can only roll along the spherical shell and can not slide, and the directions of the axes of the idler wheels at the two ends are in the parallel and symmetrical state all the time. According to the structure with the incomplete spherical constraint added inside, the incomplete constraint is directly added into a spherical surface, an internal compete spherical constraint is omitted, space is saved, and meanwhile precision is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
A Nonholonomic Teleoperation Constrained Control Method Based on Complex Manipulation Tasks
ActiveCN105904458BRelieve pressureFlexible operationProgramme-controlled manipulatorSimulationConstraint control
The invention discloses a non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method based on complex operation tasks. The complex operation tasks are decomposed by calculating the constraint matrix CVF, and a constraint controller is designed finally. Compared with a general mechanical arm control method, the non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method has two beneficial effects on the aspects of the task level and control method for complex space control tasks, specifically, the control tasks which a mechanical arm needs to complete in the space include approaching the target, tracing the path, avoiding obstacles and the like, and since proper movement spinor collections are selected according to the different operation tasks so as to establish the constraint matrix, the method has a better capacity of adapting to the complex tasks compared with prior methods; and besides, by means of the non-integrate teleoperation constraint control method, operation is more flexible, an operator can control the mechanical arm to move only in the horizontal motion direction or rotation direction, no extra constraint is needed, and accordingly the stress of the operator is relieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A joint angle optimization method of underactuated manipulator based on improved particle swarm optimization
ActiveCN109262612BAvoid cases of premature convergenceImprove global search performanceProgramme-controlled manipulatorLocal optimumDynamic models
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Orbit expansion based multi-robot tracing formulation control method
InactiveCN102073320BHigh precisionEfficient use ofVehicle position/course/altitude controlPosition/direction controlDifferential coefficientRange of motion
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A Mechanized Mechanics Modeling Method for Nonholonomic Constrained Systems
ActiveCN106383973BAvoid double countingReduce computing timeGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationComputational physicsRelational table
The invention discloses a mechanized mechanics modeling method of a non-holonomic constraint system. During the constraint analysis, intermediate variables are introduced to describe the non-holonomic constraint relationship according to the complex situation of the non-holonomic constraint; the independent generalized velocity contained in the kinetic energy is revealed through the constraint analysis Information, extract the coefficient of the independent generalized velocity product term and define it as an intermediate variable, and rewrite the kinetic energy into a new form of expression; The total derivative of , can be solved by analyzing the subordination structure of variables, establishing a function-variable implication relationship table and introducing compound derivatives; calculating the influence items of non-holonomic constraints on the system is more complicated, and several structure arrays can be defined to store calculation results. In order to avoid the problem of model expansion caused by the back substitution of intermediate variables, the calculation expressions of the model need to be output in reverse order.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
A Path Planning Method for Indoor Mobile Robot Enhanced Map Learning
ActiveCN104298239BGood planning pathSolve practical system application problemsAdaptive controlPosition/course control in two dimensionsGreedy algorithmSimulation
The invention discloses an enhanced map learning path planning method for an indoor mobile robot. The method includes the steps that (1) ambient environment information is acquired, and an obstacle probability density model is established; (2) path planning is carried out through a greedy algorithm and an enhanced map learning method; (3) path selection and self-adaptation speed strategy adjustment are conducted on the indoor mobile robot. By the adoption of the enhanced map learning path planning method, a current optimal path can be planned in real time according to the current condition of the indoor mobile robot and the inherent non-holonomic constraint of the robot, meanwhile, the obstacle crossing ability, the target point convergence ability and the planning efficiency of the indoor mobile robot can be considered through the self-adaptation speed strategy adjustment, and therefore the indoor mobile robot can arrive at a specific location safely and effectively.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com