Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Front-side bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
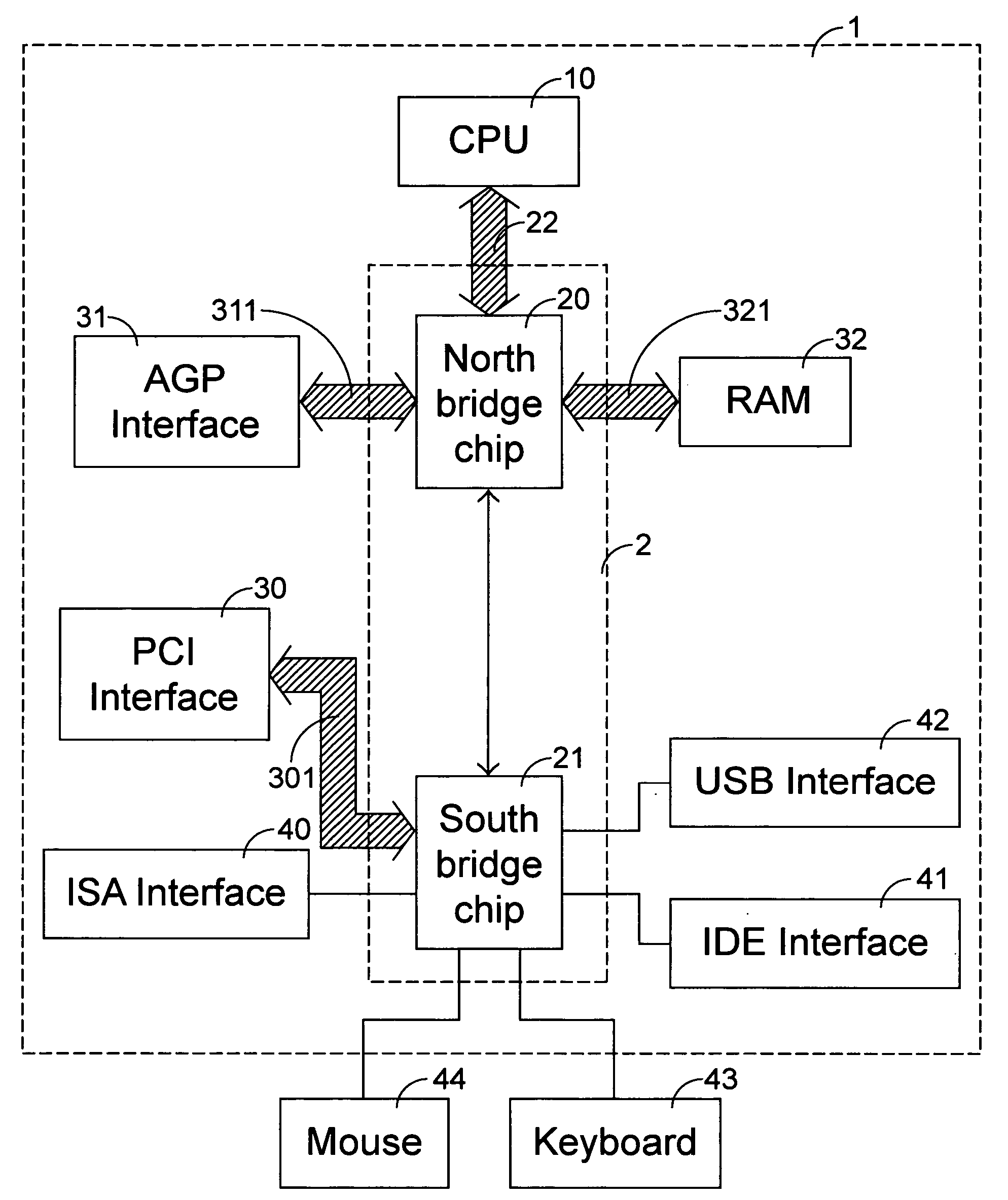
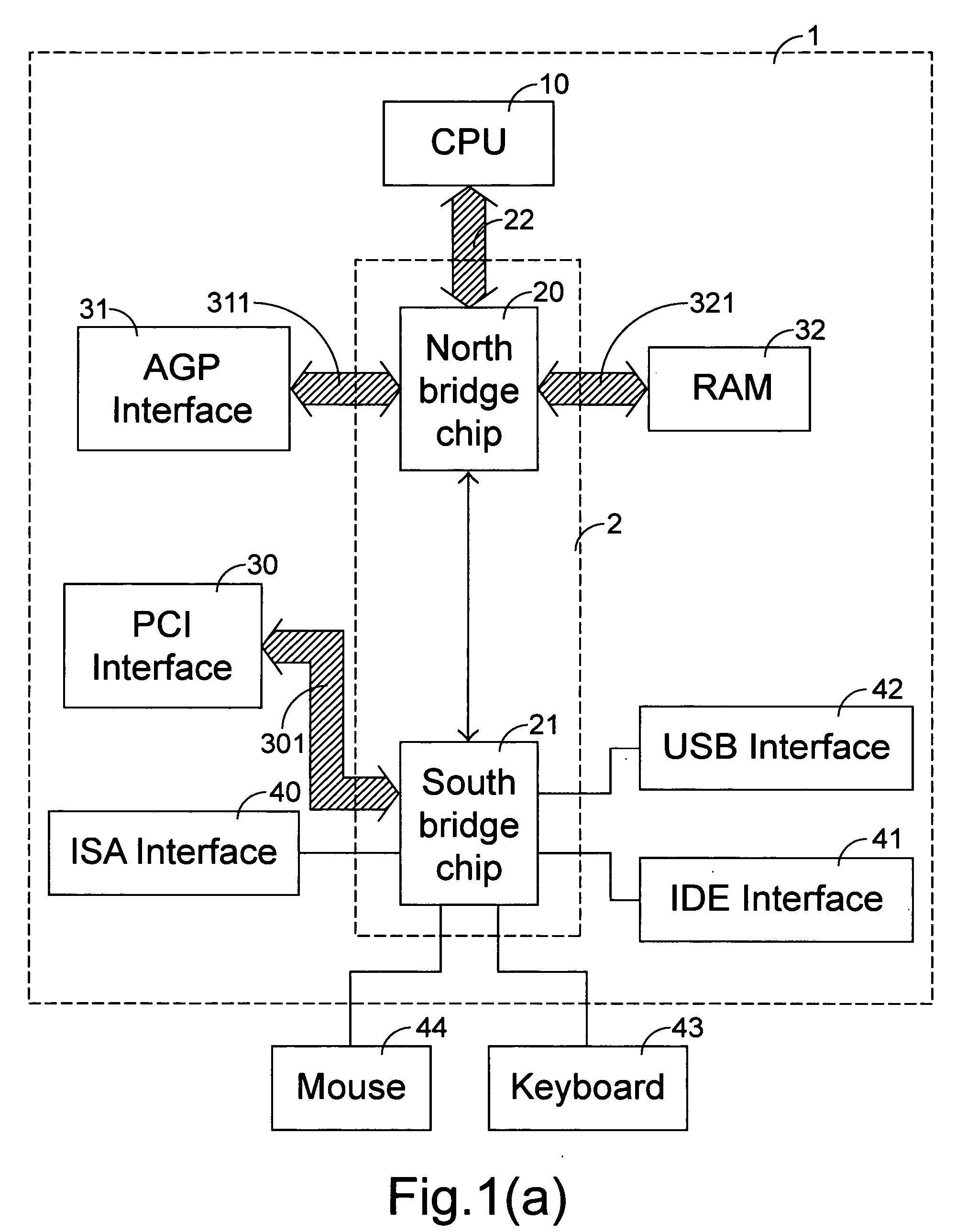
A front-side bus (FSB) is a computer communication interface (bus) that was often used in Intel-chip-based computers during the 1990s and 2000s. The EV6 bus served the same function for competing AMD CPUs. Both typically carry data between the central processing unit (CPU) and a memory controller hub, known as the northbridge.
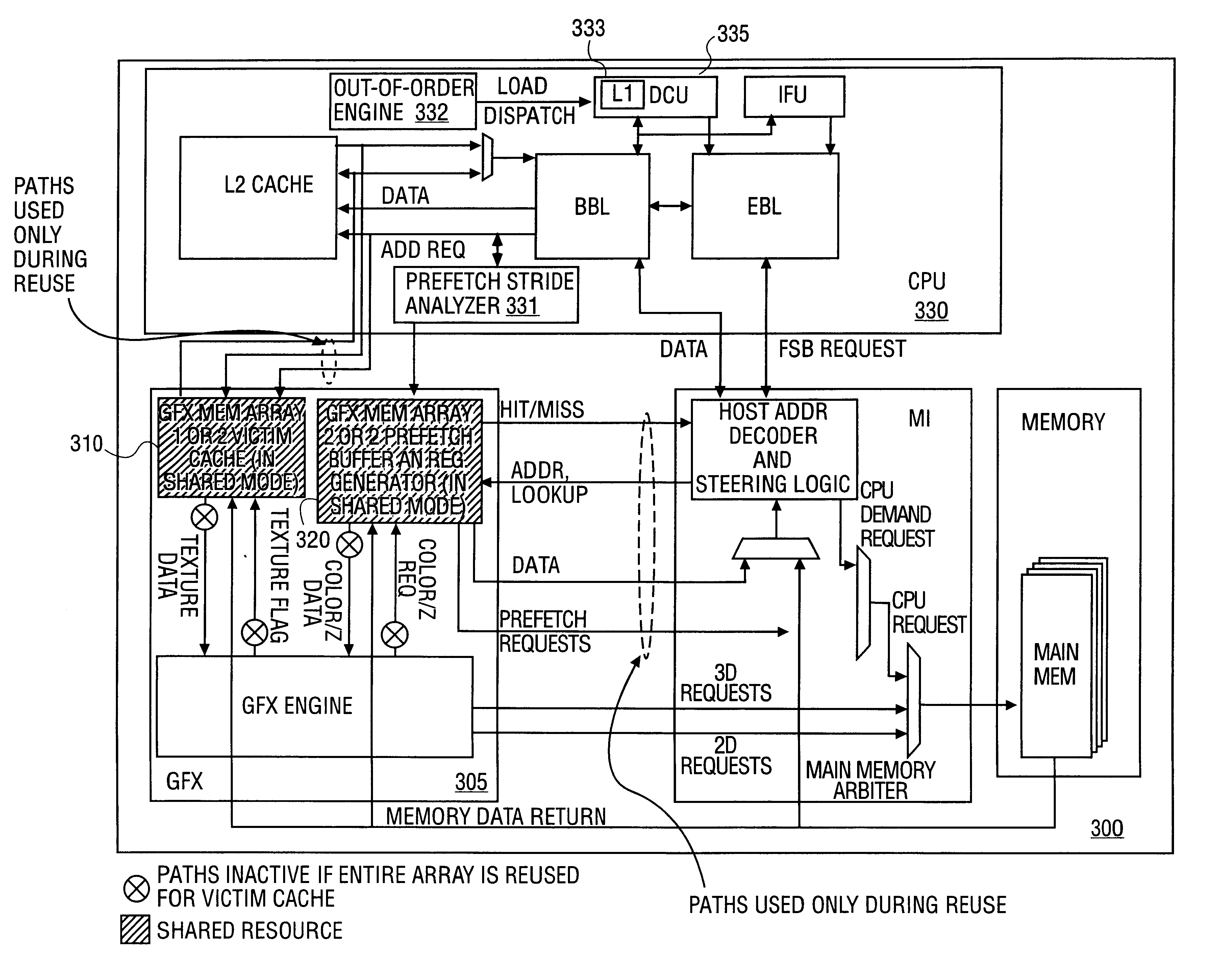
Opportunistic sharing of graphics resources to enhance CPU performance in an integrated microprocessor
InactiveUS6842180B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGraphicsAddress decoder
An electronic device that has an integrated central processing unit (CPU) including a pre-fetch stride analyzer and an out-of-order engine is provided. The electronic device also has a graphics engine, having graphics memory, that is coupled to the integrated CPU. A main memory that is coupled to a memory controller is provided. The memory controller is also coupled to the CPU and the graphics engine. The device has a host address decoder coupled to the integrated CPU. A front side bus (FSB) is provided that is coupled to the integrated CPU and the host address decoder. Also provided is a plurality of memory components. Accordingly, either the plurality of memory components or the graphics memory can be shared to perform alternate memory functions. Additionally, a method is provided that determines allocation availability between memory components in an integrated computer processing unit. The method also shares an available memory component as a pre-fetch buffer and another available memory component as a victim cache.
Owner:INTEL CORP
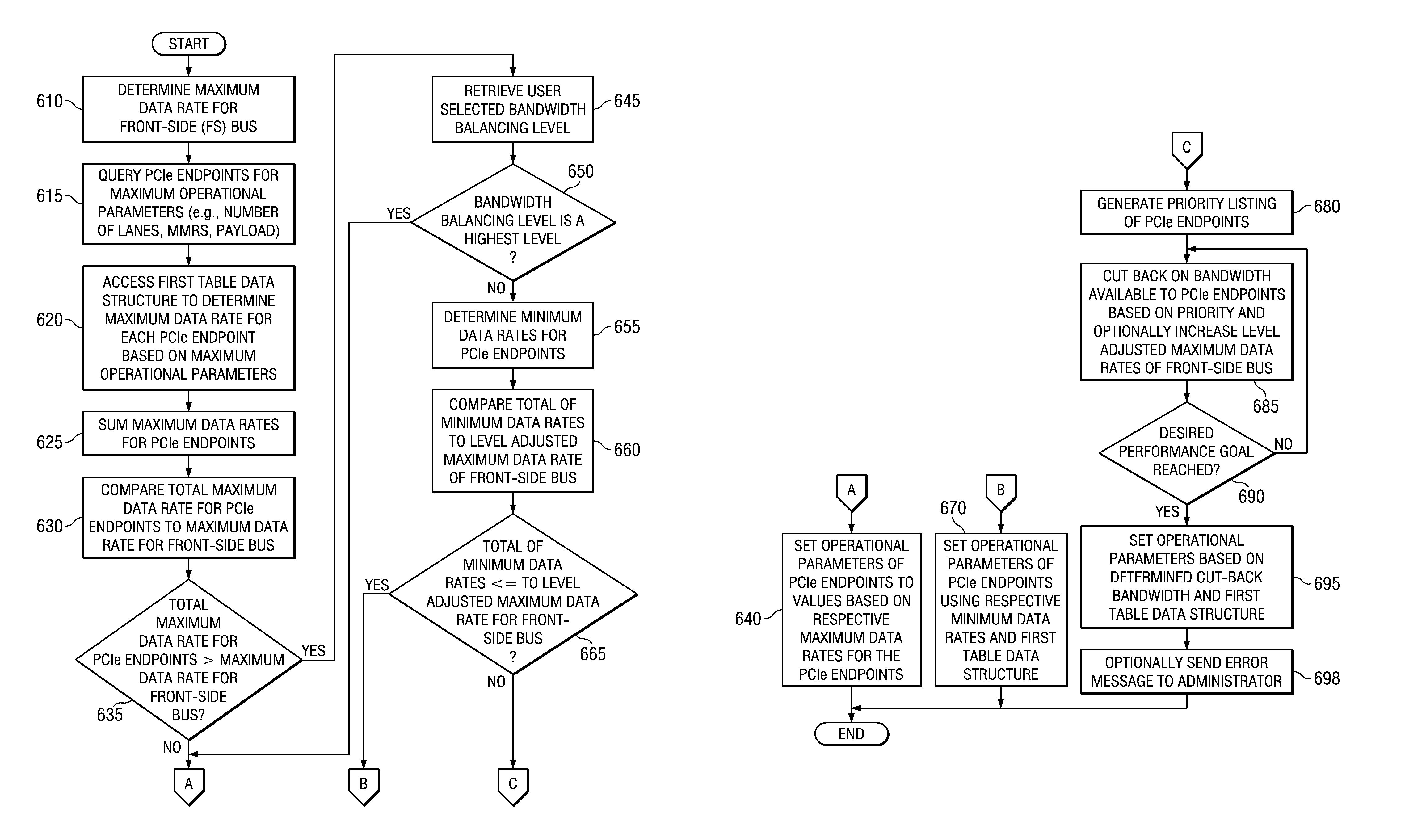
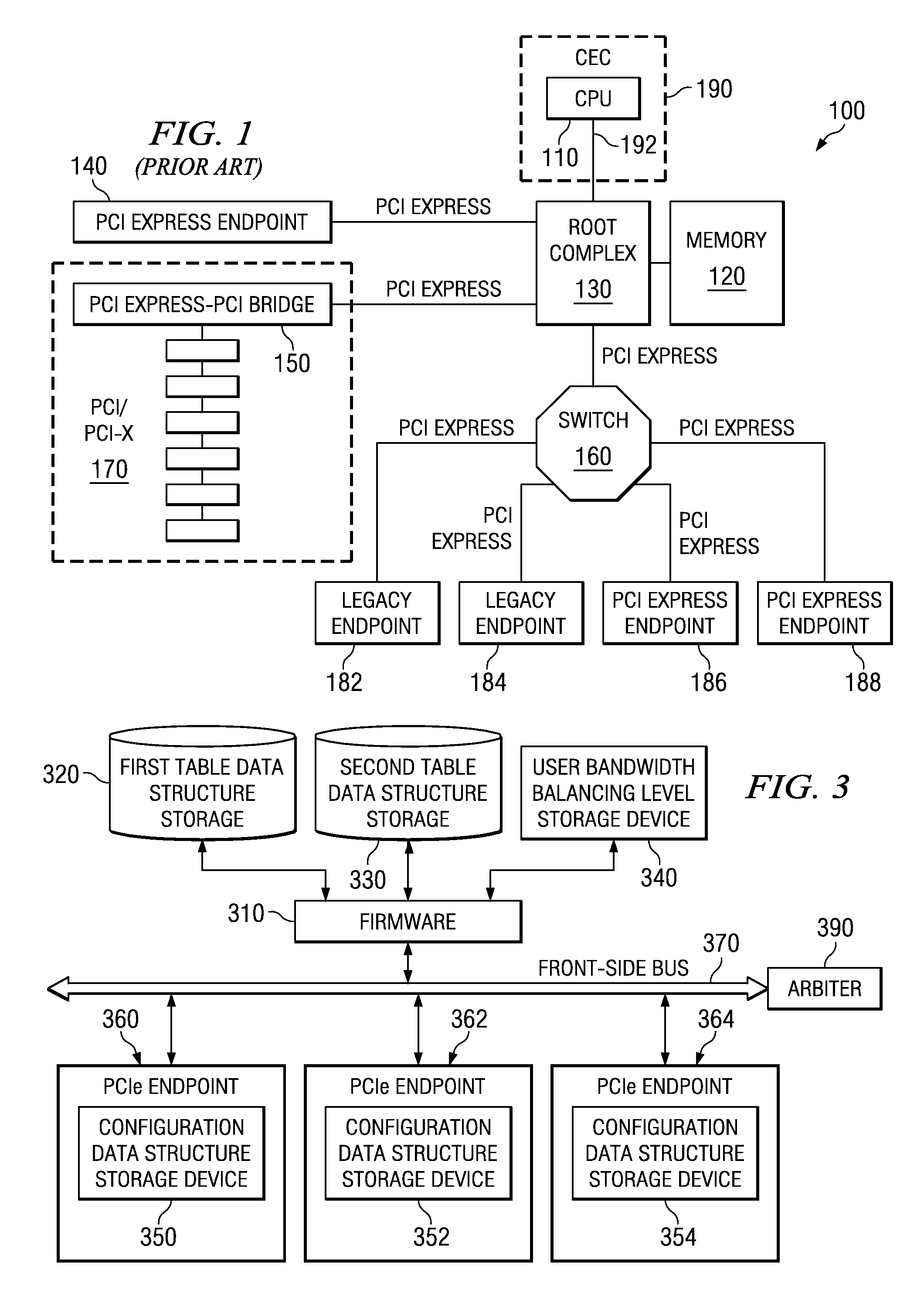
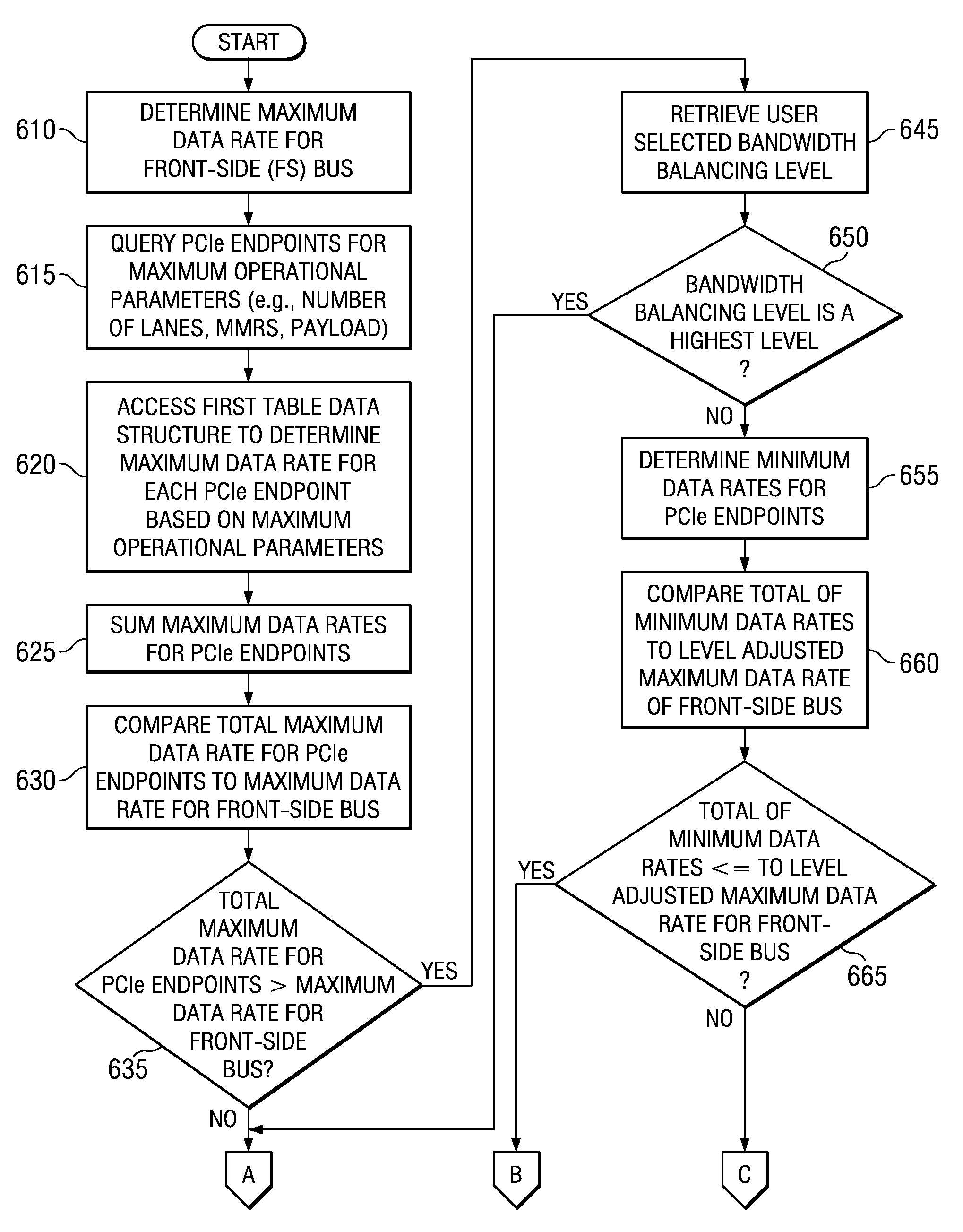
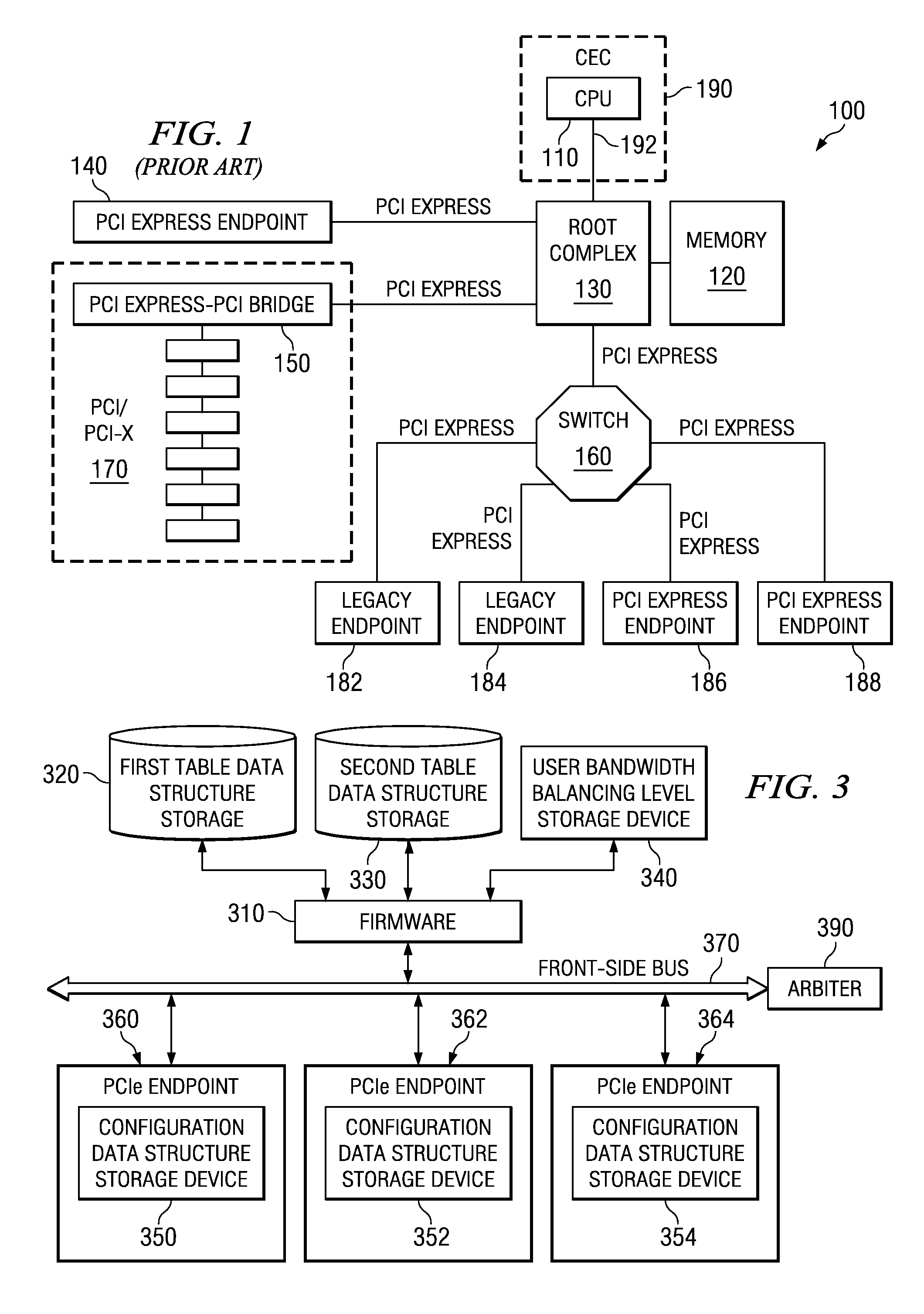
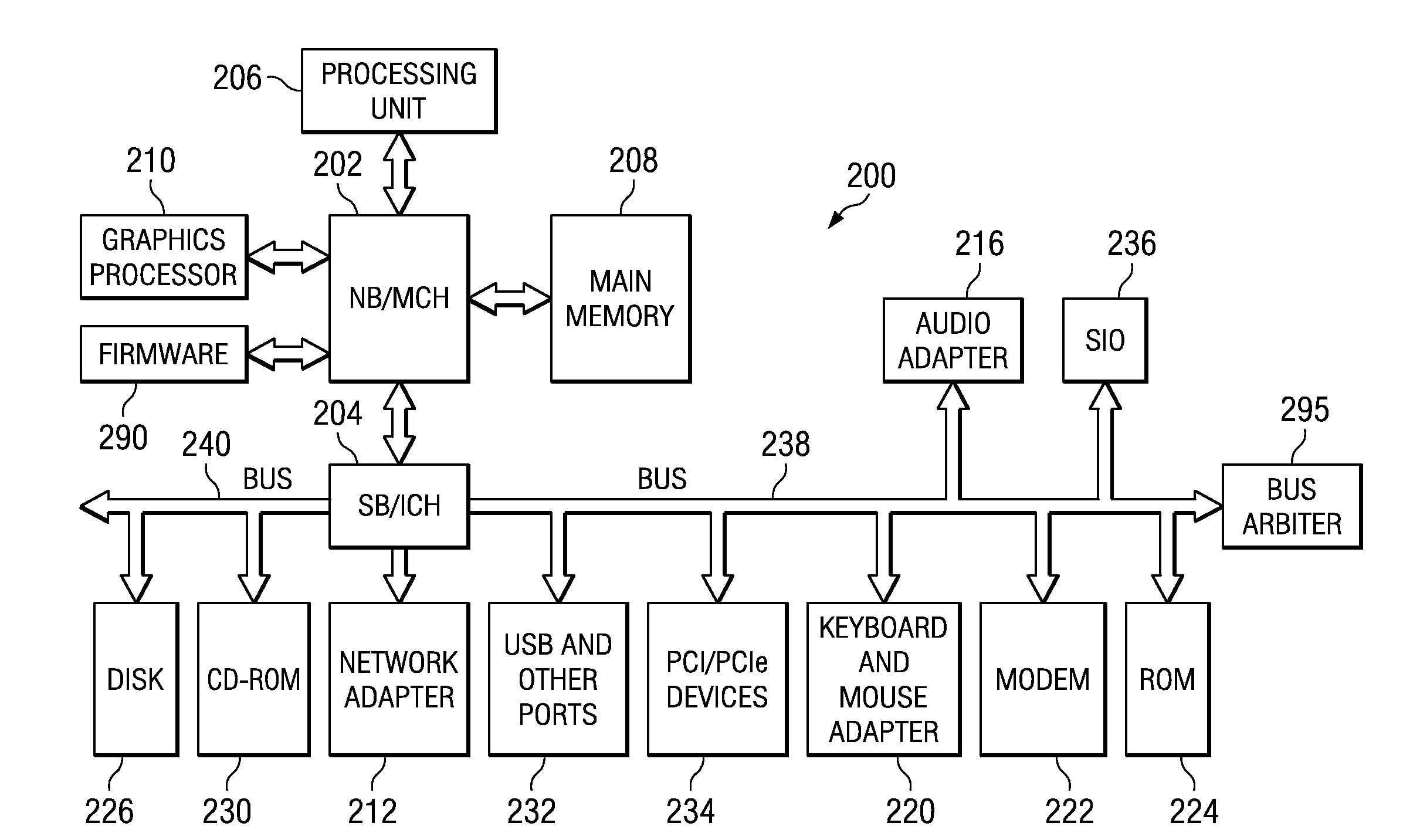
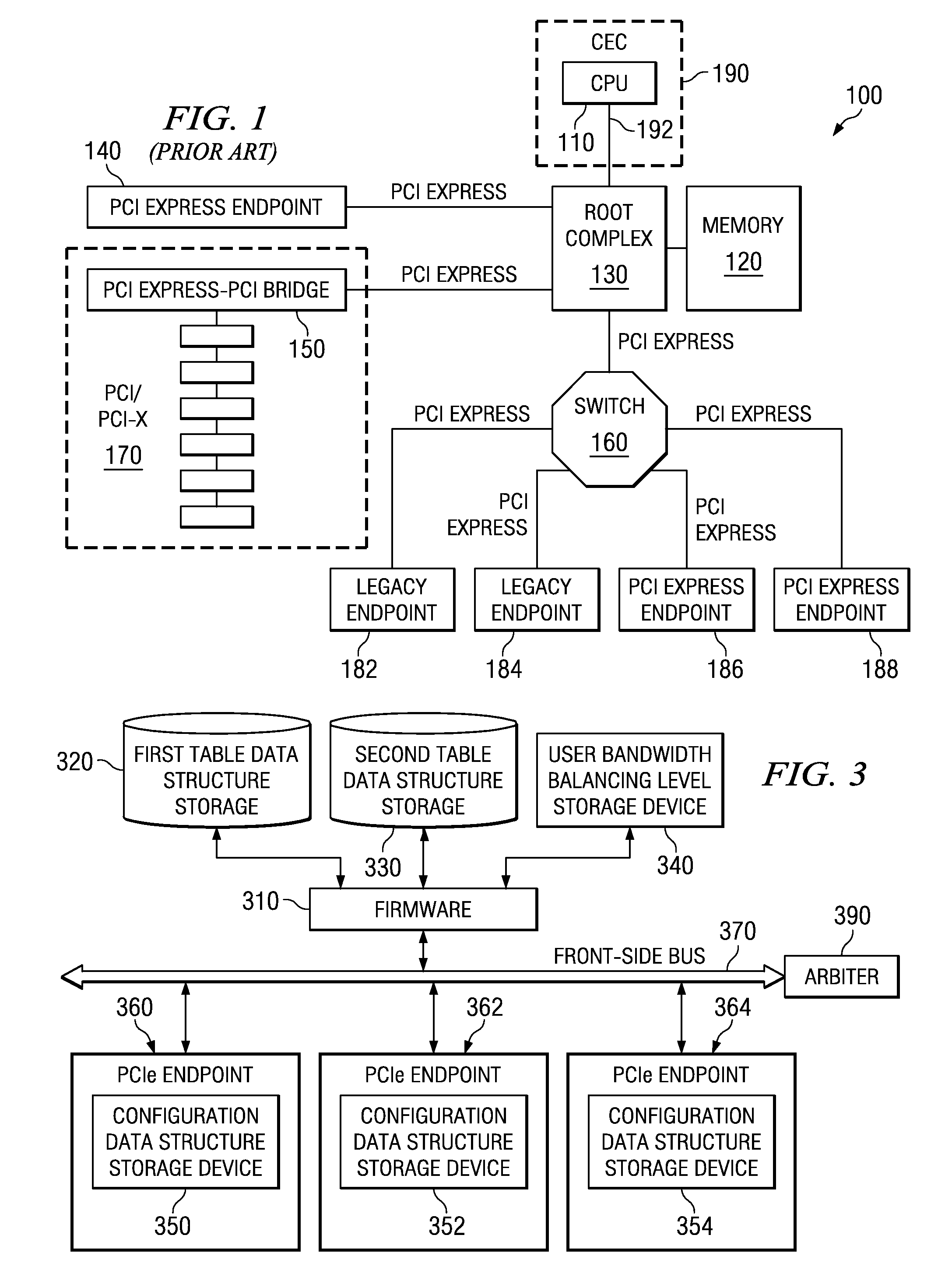
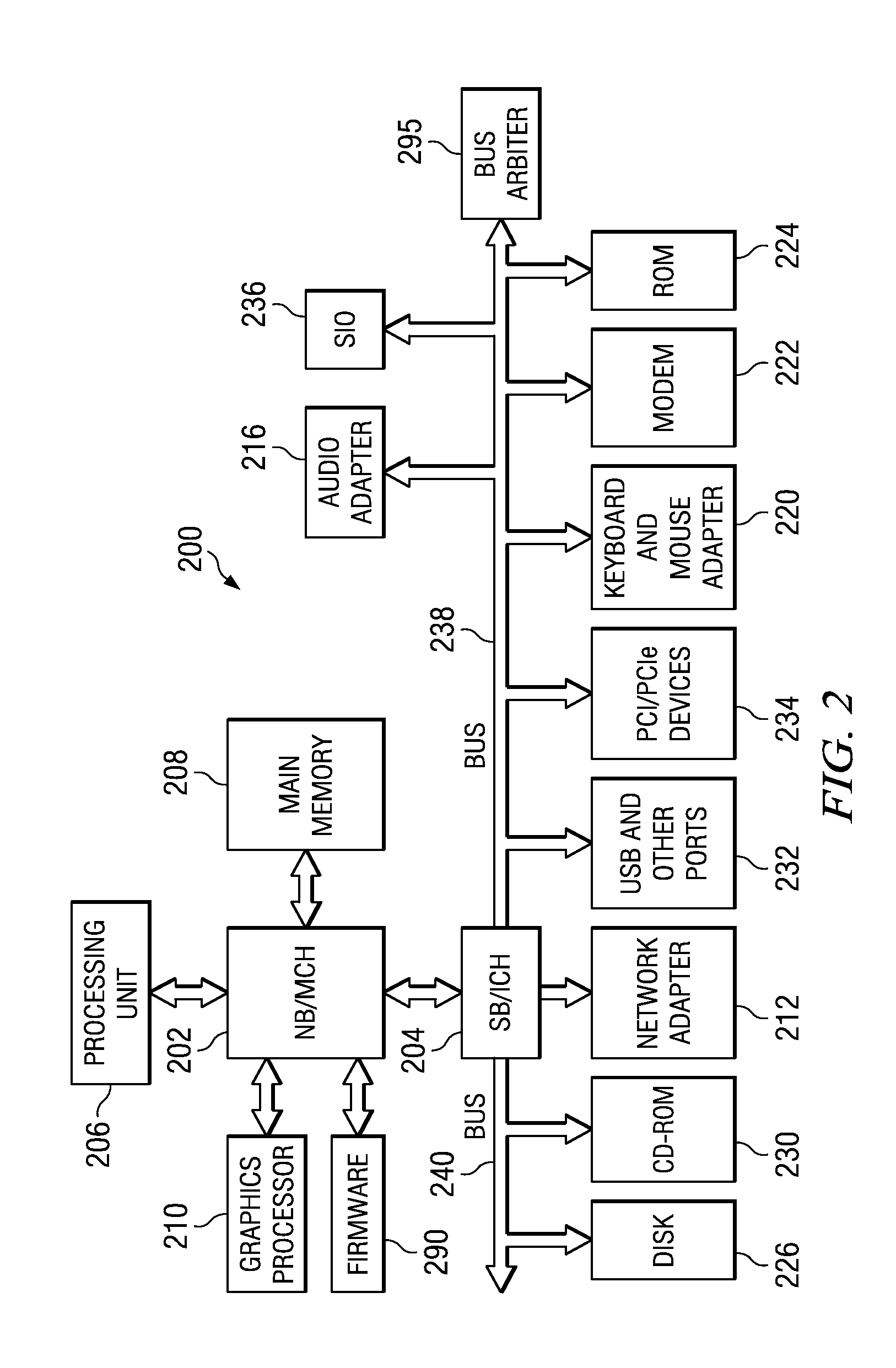
System and Method for Balancing PCI-Express Bandwidth
InactiveUS20080263246A1Maximize useMinimize the possibilityElectric digital data processingData processing systemControl data
A system and method for balancing bus bandwidth across a plurality of PCI-Express (PCIe) endpoints are provided. Firmware automatically operates in concert with established data structures to set operational parameters of the PCIe endpoints so as to maximize usage of the available bandwidth of a front-side bus while minimizing isochronous issues and the likelihood that the performance of the PCIe endpoints cannot be guaranteed. A first table data structure comprises various combinations of operational parameter settings for controlling bandwidth usage of each of the endpoints of the data processing system. A second table data structure contains a listing of the endpoints that the data processing system supports with their associated minimum data rates, priorities, and whether the endpoints have isochronous requirements. A setting of the desired bandwidth balancing level is used along with these data structures to determine how to adjust the operating parameters of the PCIe endpoints.
Owner:IBM CORP
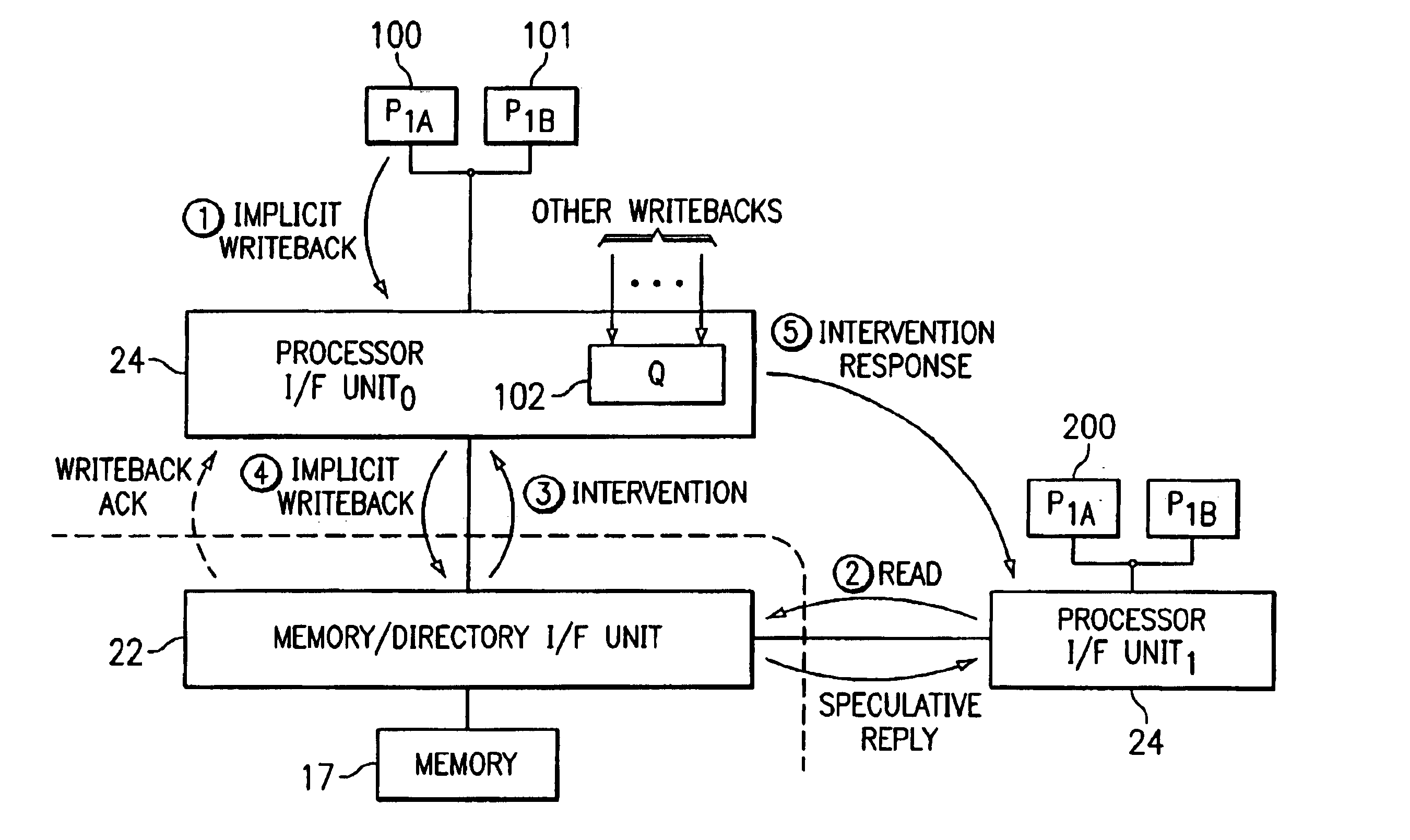
System and method for handling updates to memory in a distributed shared memory system
InactiveUS6915387B1Readily apparentEliminate and reduce disadvantageMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingComputerized system
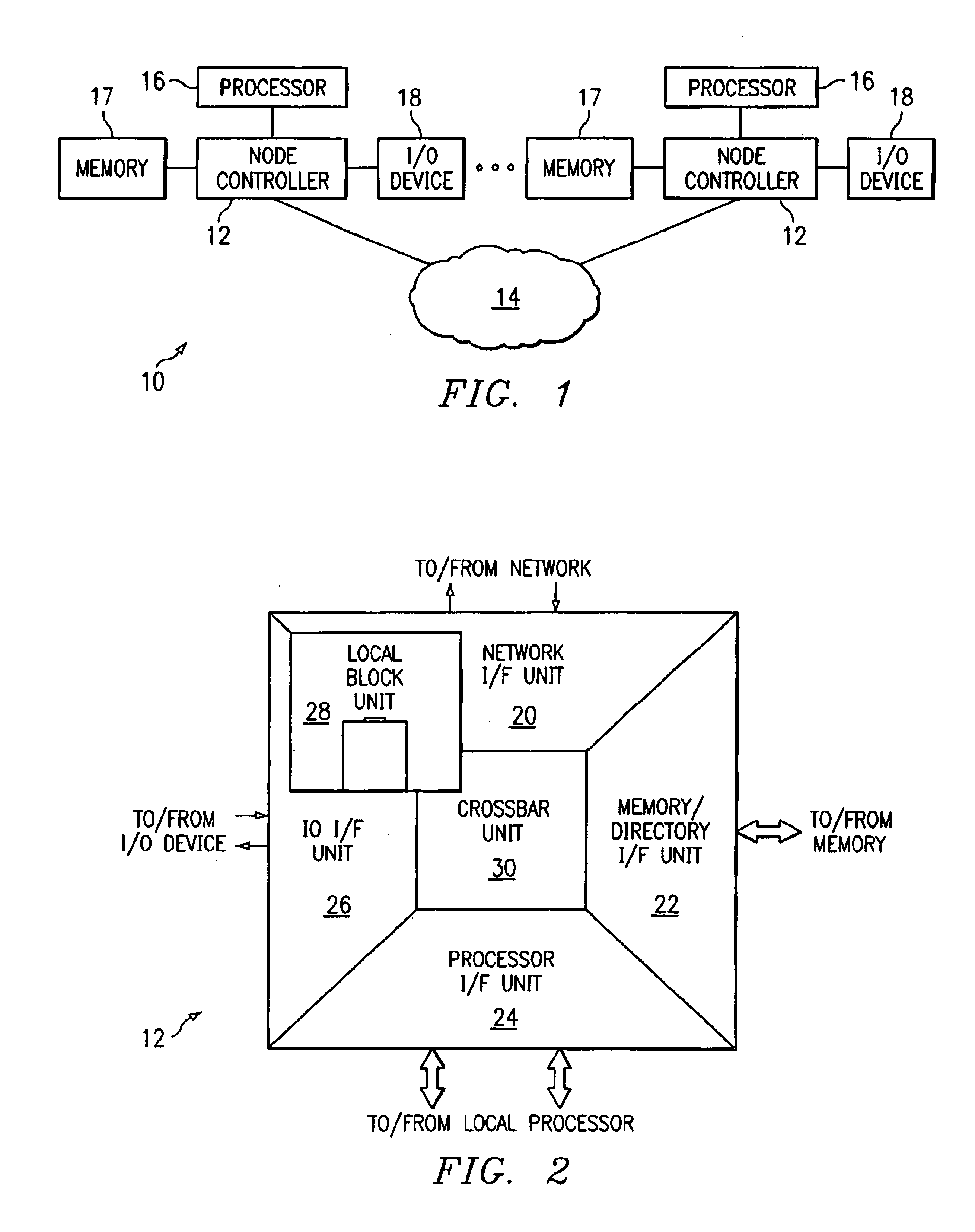
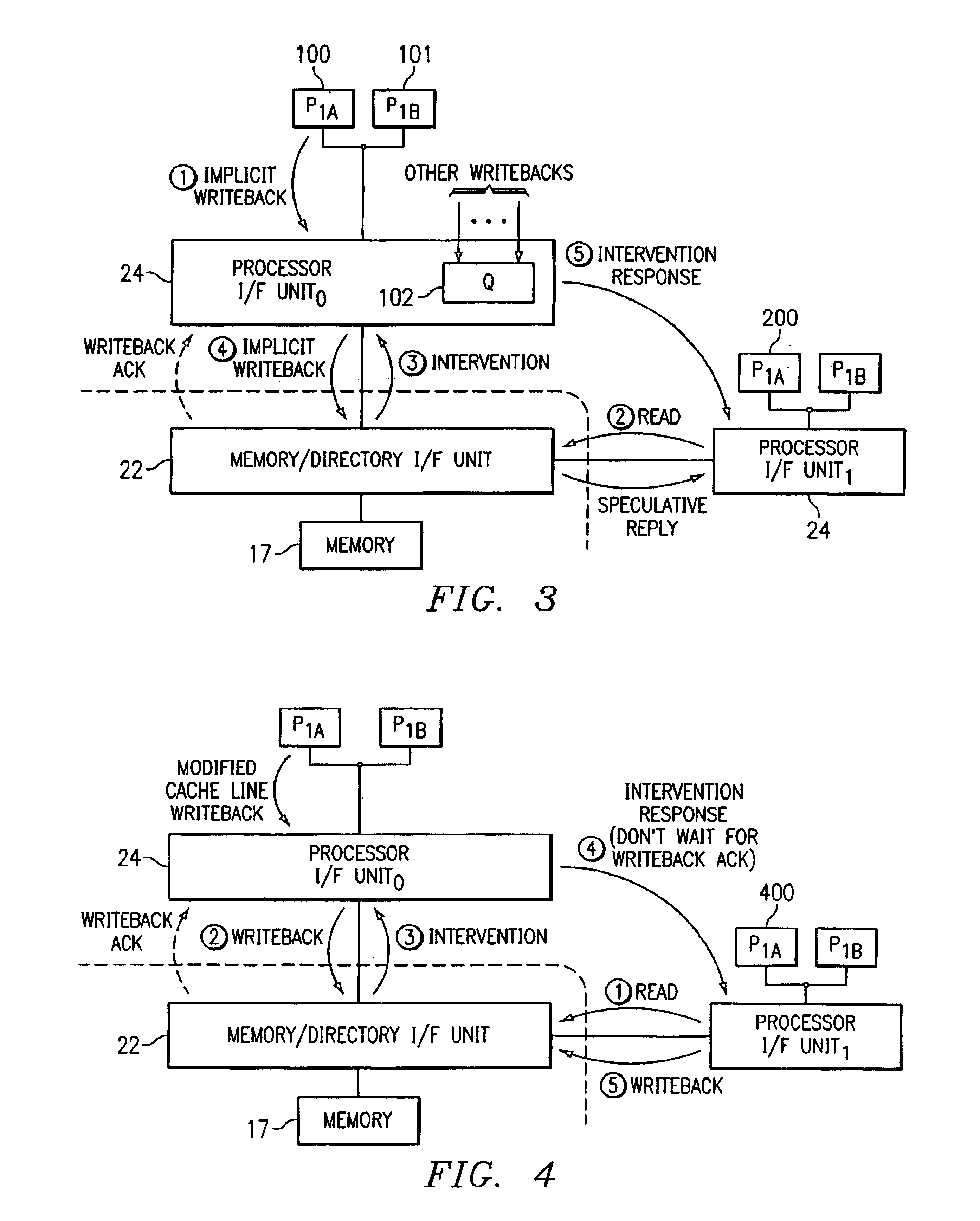
A processor (100) in a distributed shared memory computer system (10) receives ownership of data and initiates an initial update to memory request. A front side bus processor interface (24) forwards the initial update to memory request to a memory directory interface unit (22). The front side processor interface (24) may receive subsequent update to memory requests for the data from processors co-located on the same local bus. Front side bus processor interface (24) maintains a most recent subsequent update to memory in a queue (102). Once the data has been updated in its home memory (17), the memory directory interface unit (22) sends a writeback acknowledge to the front side bus processor interface (24). The most recent subsequent update to memory request in the queue (102) is then forwarded by the front side bus processor interface (24) to the memory directory interface unit (24) for processing.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
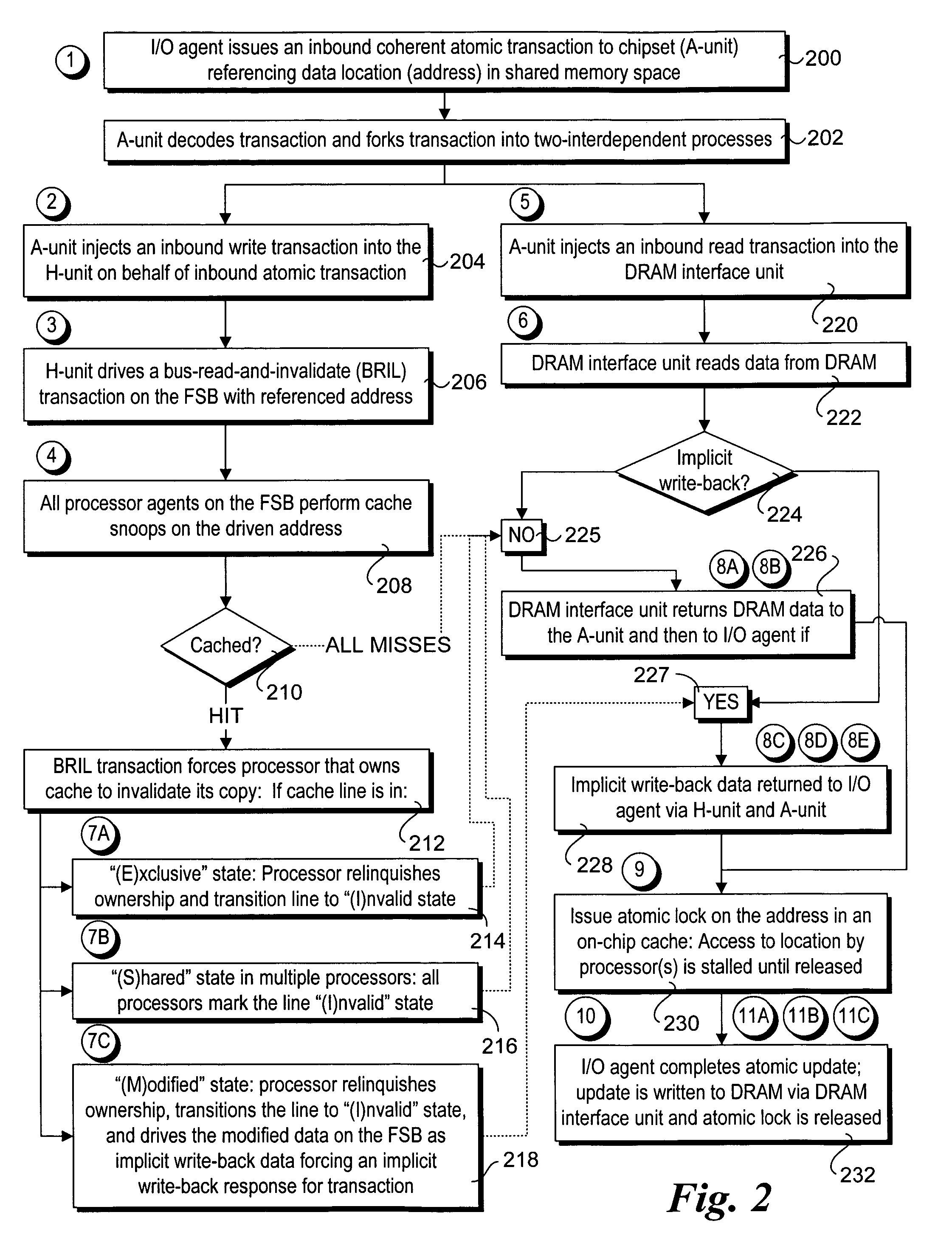
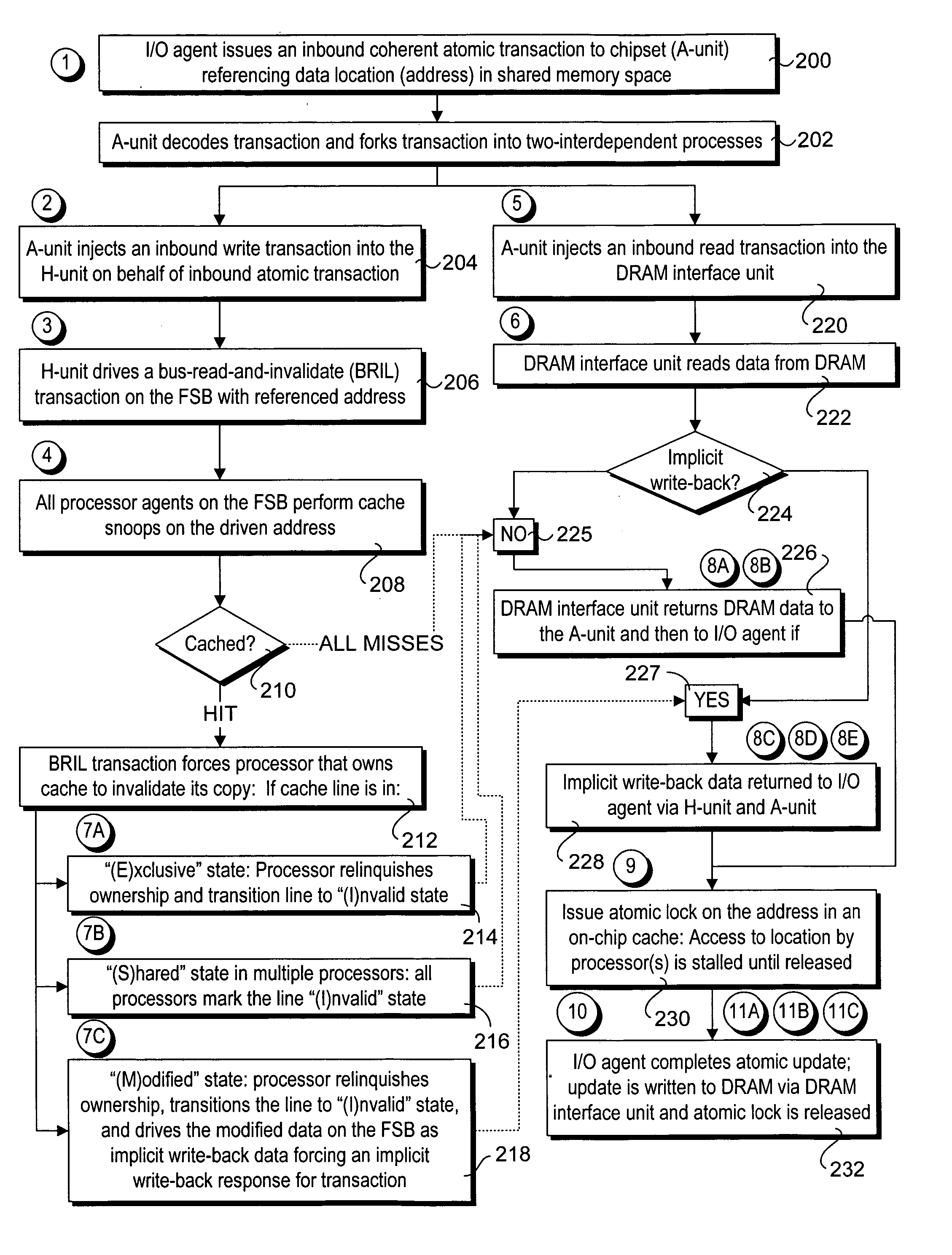
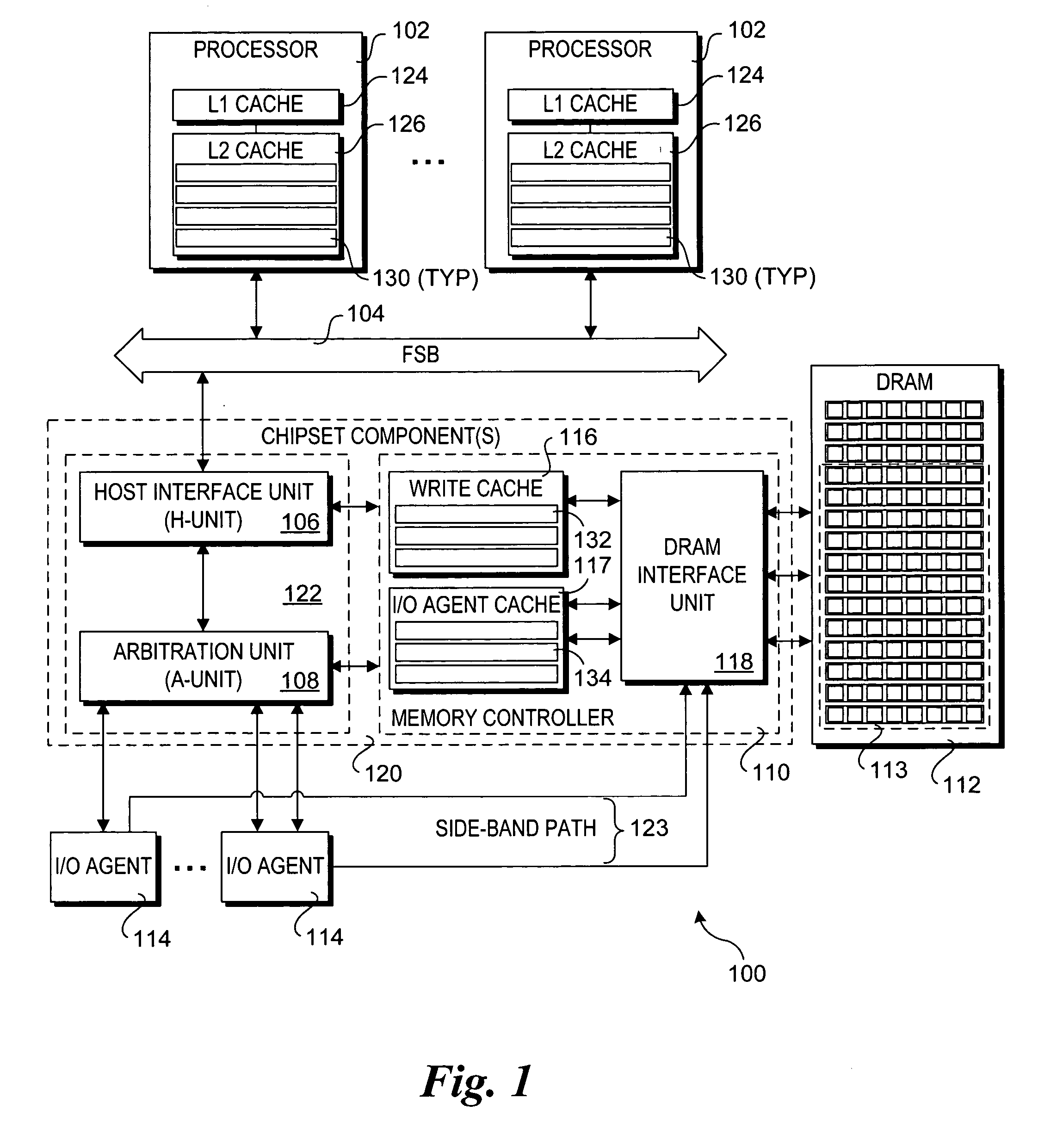
Method and apparatus to enable I/O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces
Method and apparatus to enable I / O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces. The apparatus includes an arbitration unit, a host interface unit, and a memory interface unit. The arbitration unit provides an interface to one or more I / O agents that issue atomic transactions to access and / or modify data stored in a shared memory space accessed via the memory interface unit. The host interface unit interfaces to a front-side bus (FSB) to which one or more processors may be coupled. In response to an atomic transaction issued by an I / O agent, the transaction is forked into two interdependent processes. Under one process, an inbound write transaction is injected into the host interface unit, which then drives the FSB to cause the processor(s) to perform a cache snoop. At the same time, an inbound read transaction is injected into the memory interface unit, which retrieves a copy of the data from the shared memory space. If the cache snoop identifies a modified cache line, a copy of that cache line is returned to the I / O agent; otherwise, the copy of the data retrieved from the shared memory space is returned.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System for Dynamically Balancing PCI-Express Bandwidth
ActiveUS20090094401A1Maximize useMinimize the possibilityEnergy efficient ICTTransmissionData ratePCI Express
In a dynamic mode, firmware sets a threshold of errors that may occur within a predetermined period of time. If the threshold is exceeded, the firmware queries the front-side bus performance counters to determine whether the front-side bus is operating at its maximum data rate. If the front-side bus is not running at the maximum data rate, then the firmware bumps the data rate settings for the endpoint that exceeds the threshold by one step. If the front-side bus is running at its maximum data rate, then the firmware queries all the endpoints to determine which endpoints are active. The firmware then determines whether there are any active endpoints that are lower priority than the complaining endpoint. The mechanism drops the lower priority endpoints by one step and raises the complaining endpoint by one step.
Owner:IBM CORP
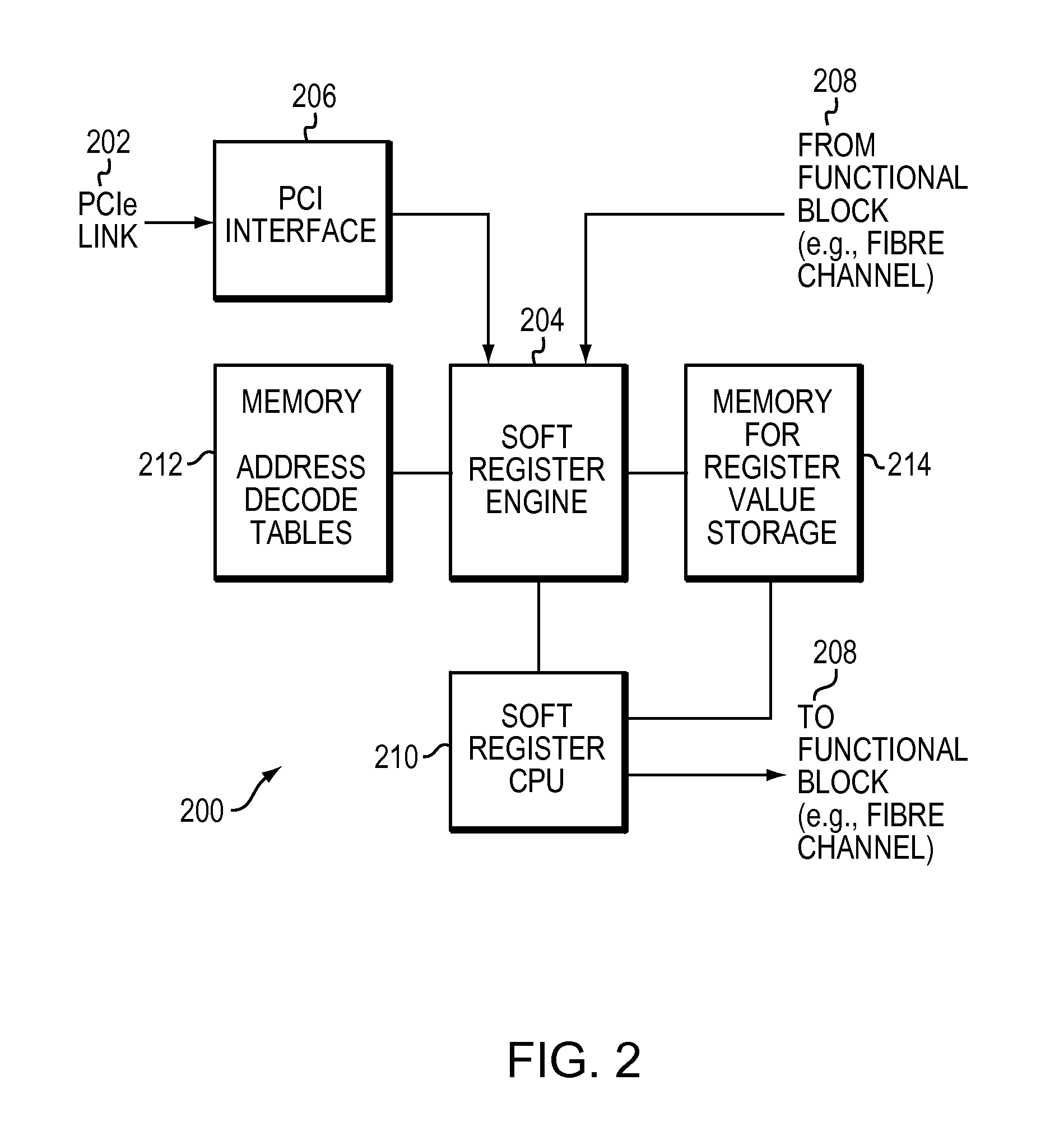
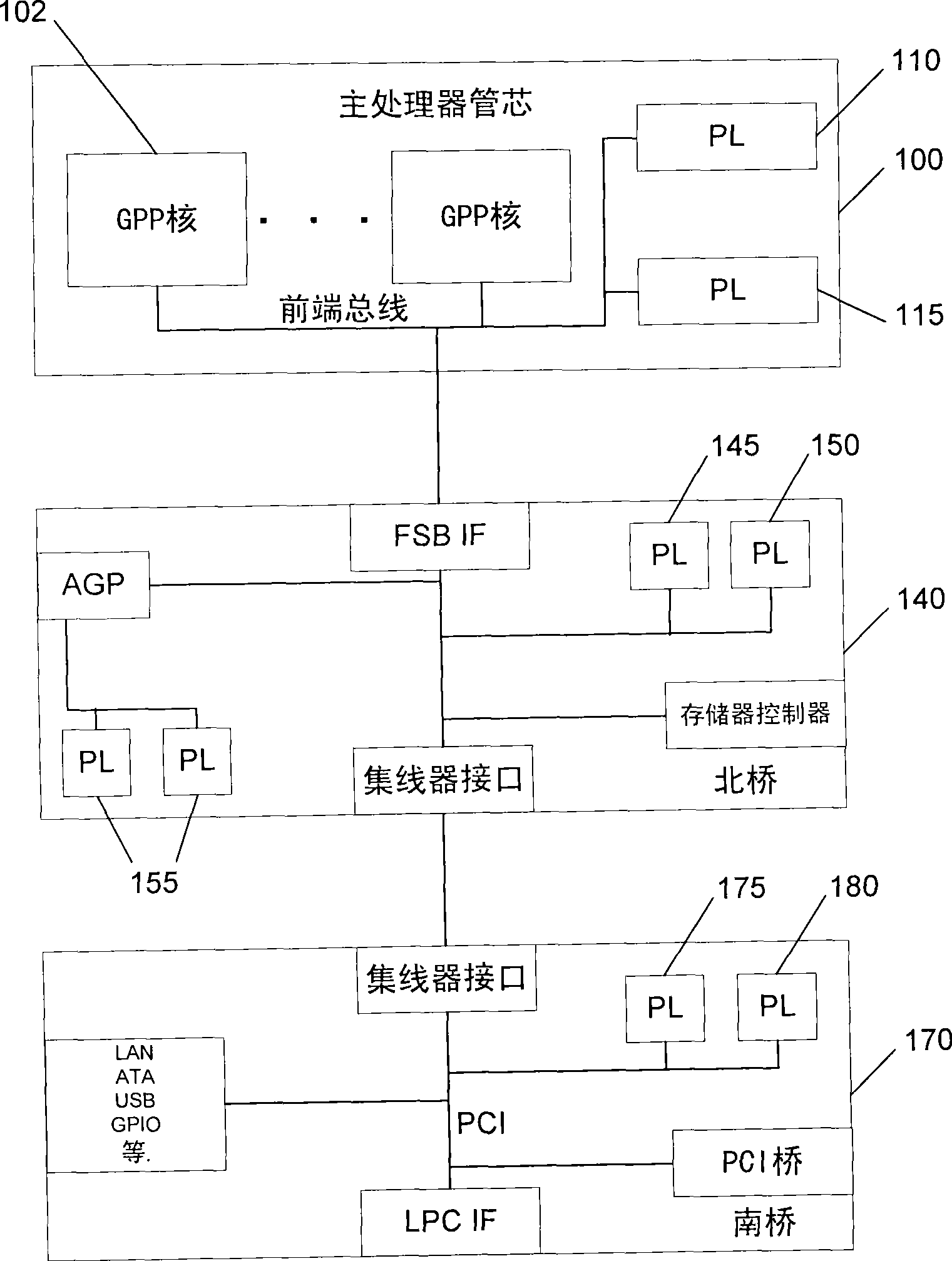
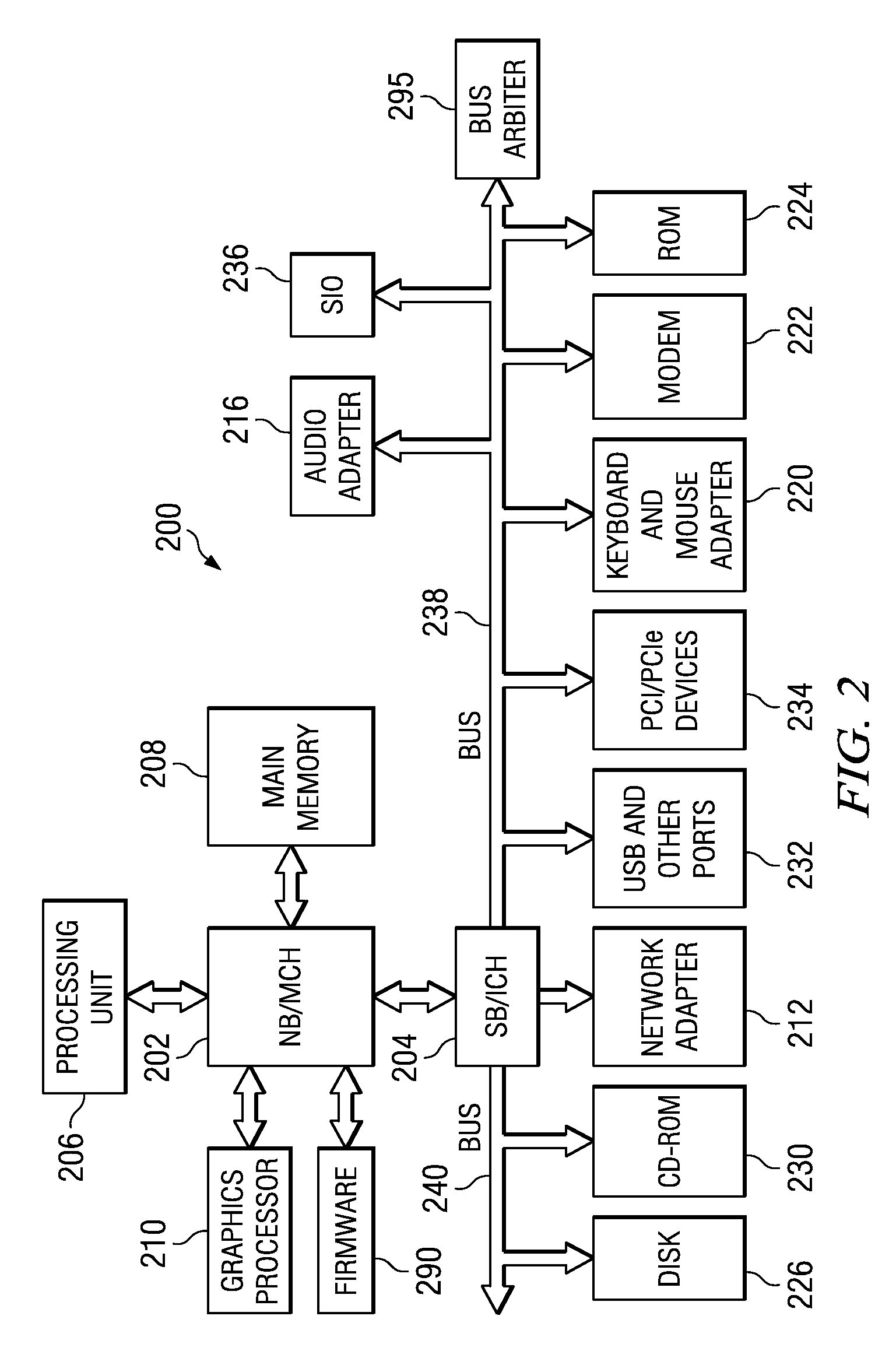
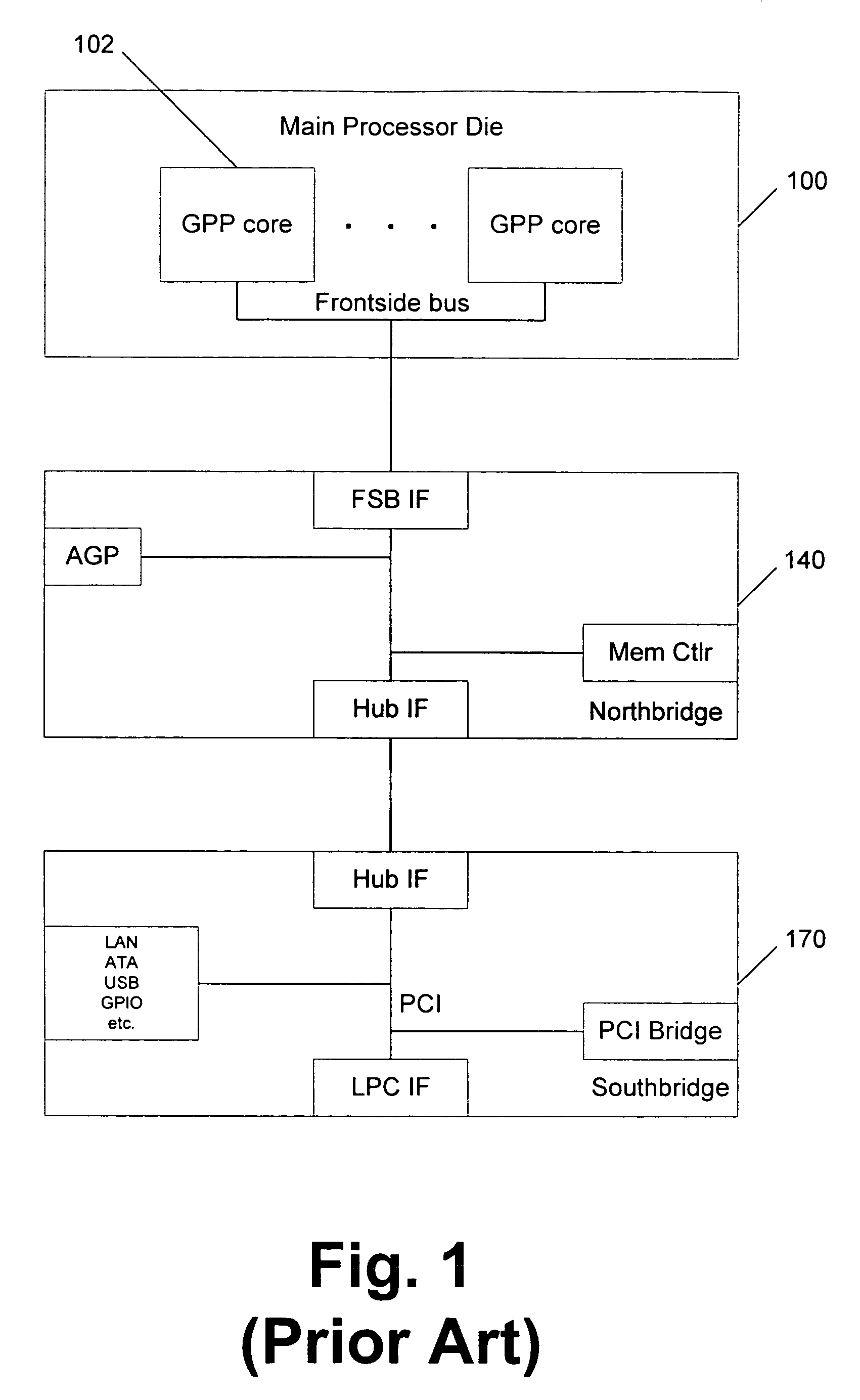
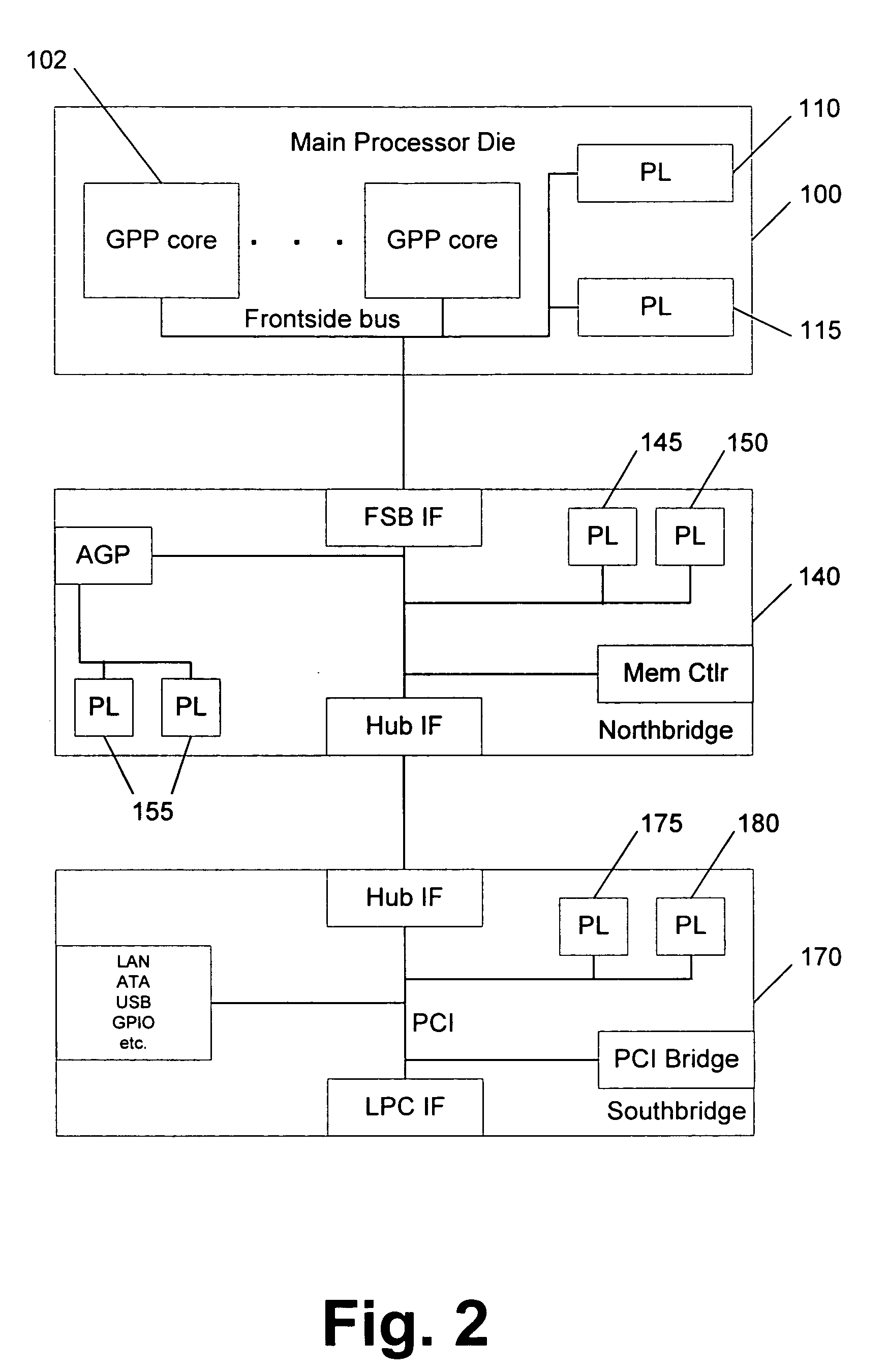
Integrating programmable logic into personal computer (PC) architecture
InactiveUS20060242611A1Improve abilitiesExtends the capability of the processor coreEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeCoprocessor
A portion of chip die real estate is allocated to blocks of programmable logic (PL) fabric. These blocks can be used to load special purpose processors which operate in concert with the general purpose processors (GPPs). These processors, implemented in PL, may integrate with a PC system architecture. Blocks of PL are integrated with fixed blocks of logic interfaces connecting, for example, to a system's front side bus. This facilitates configuration of the PL as coprocessors or other devices that may operate as peers to GPPs in the system. Moreover, blocks of PL may be integrated with fixed logic interfaces to existing IO buses within a system architecture. This facilitates configuration of the PL as soft devices, which may appear to the system as physical devices connected to the system. These soft devices can be handled like physical devices connected to the same or similar IO buses.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
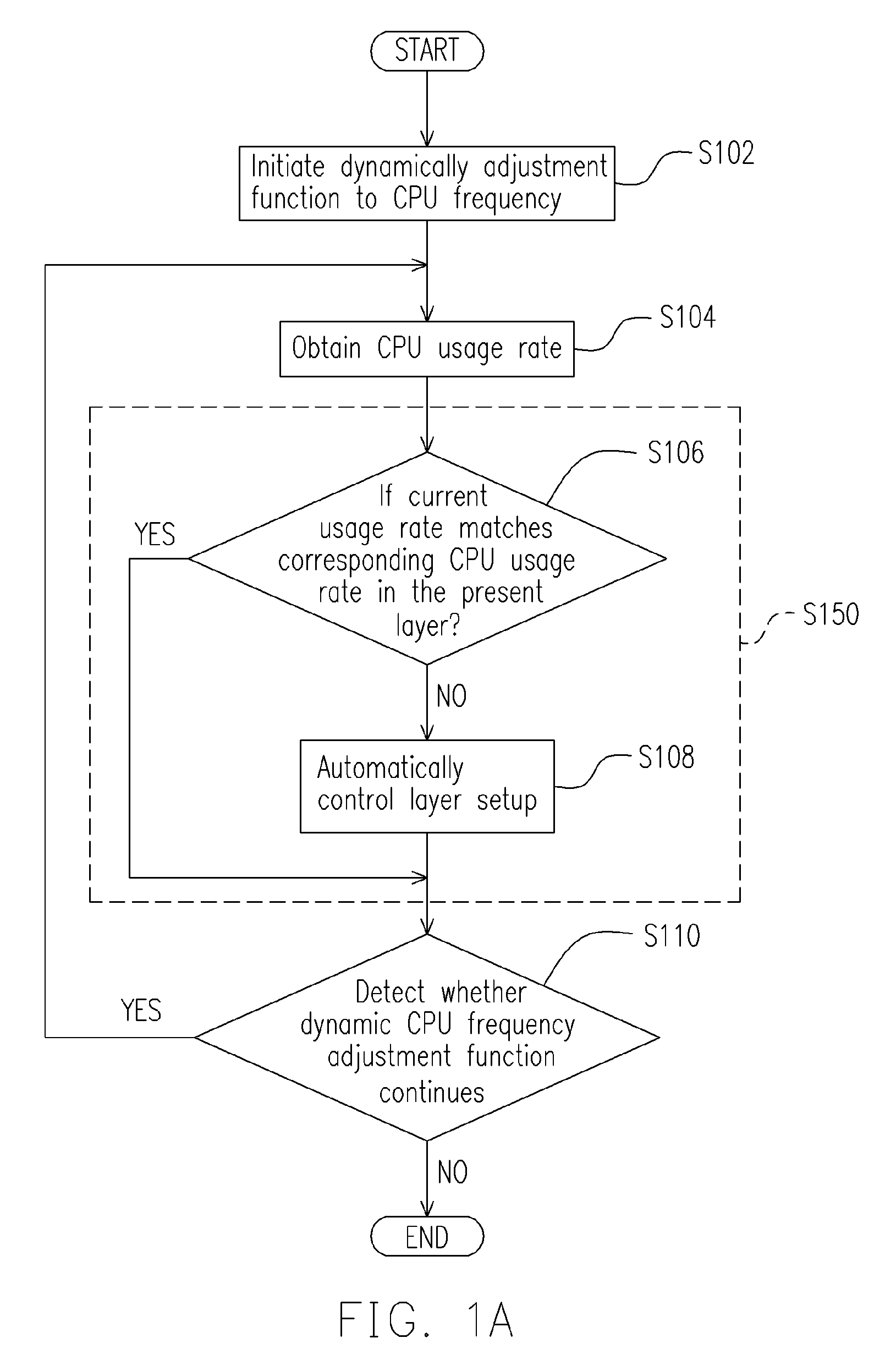
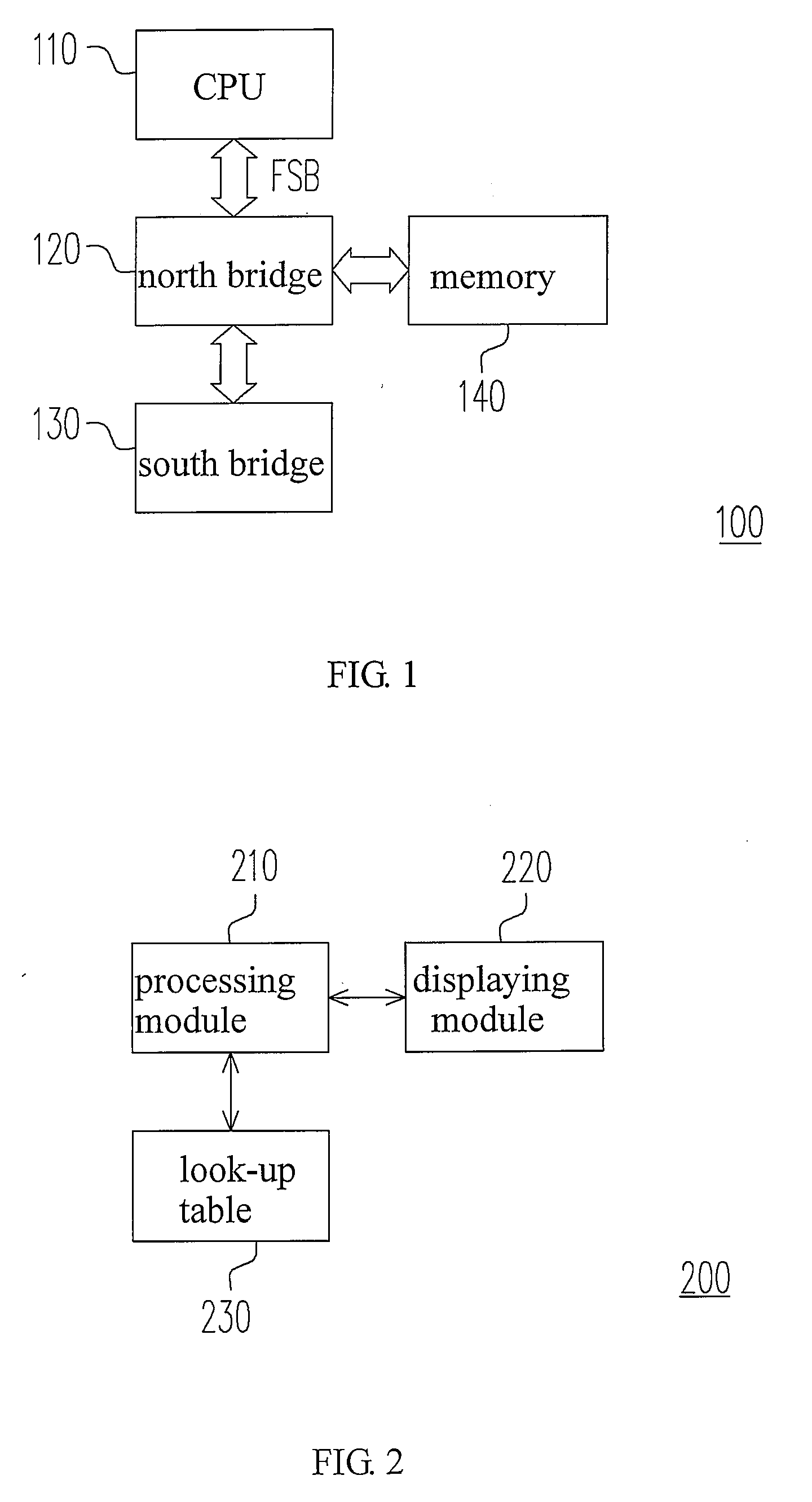
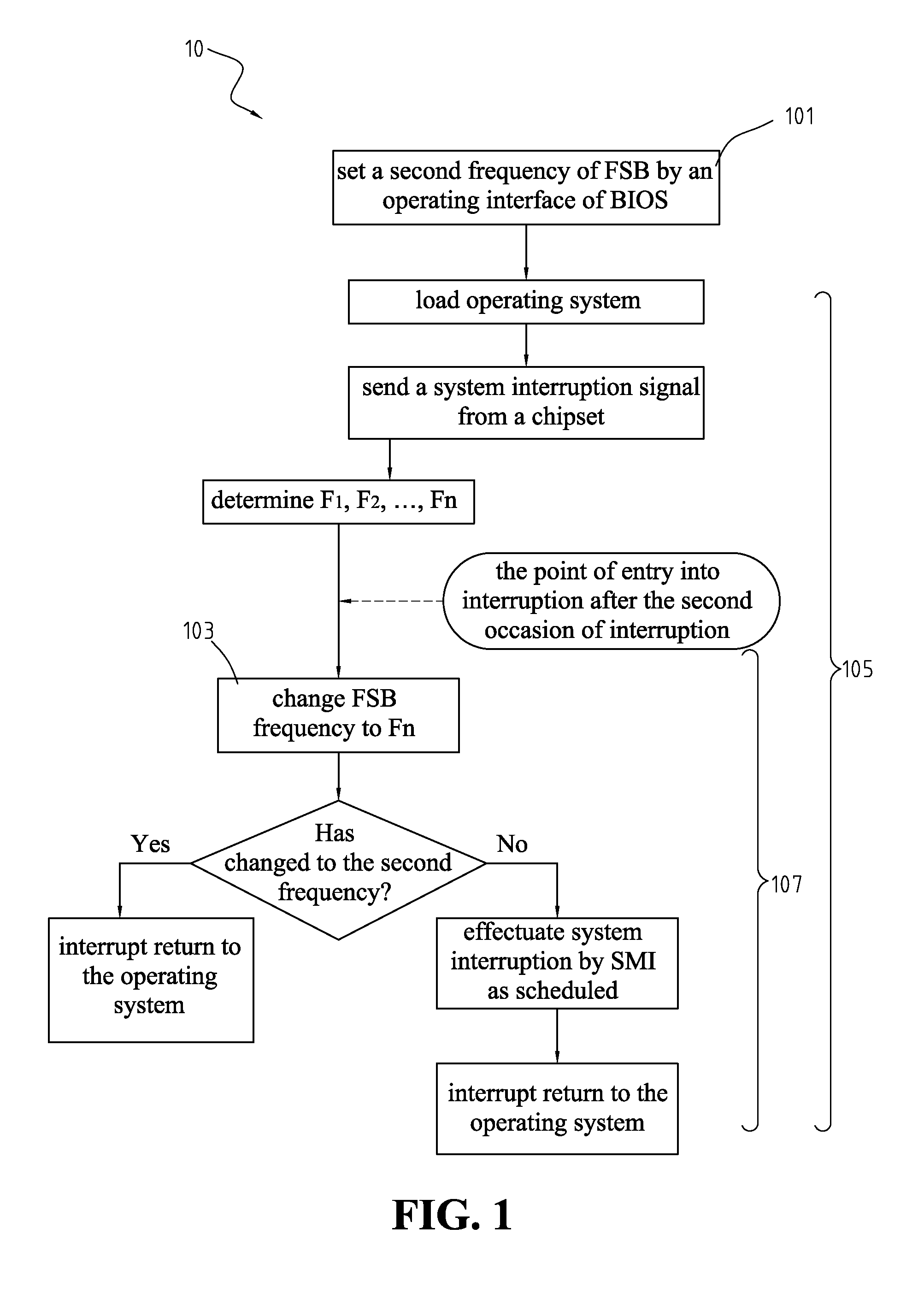
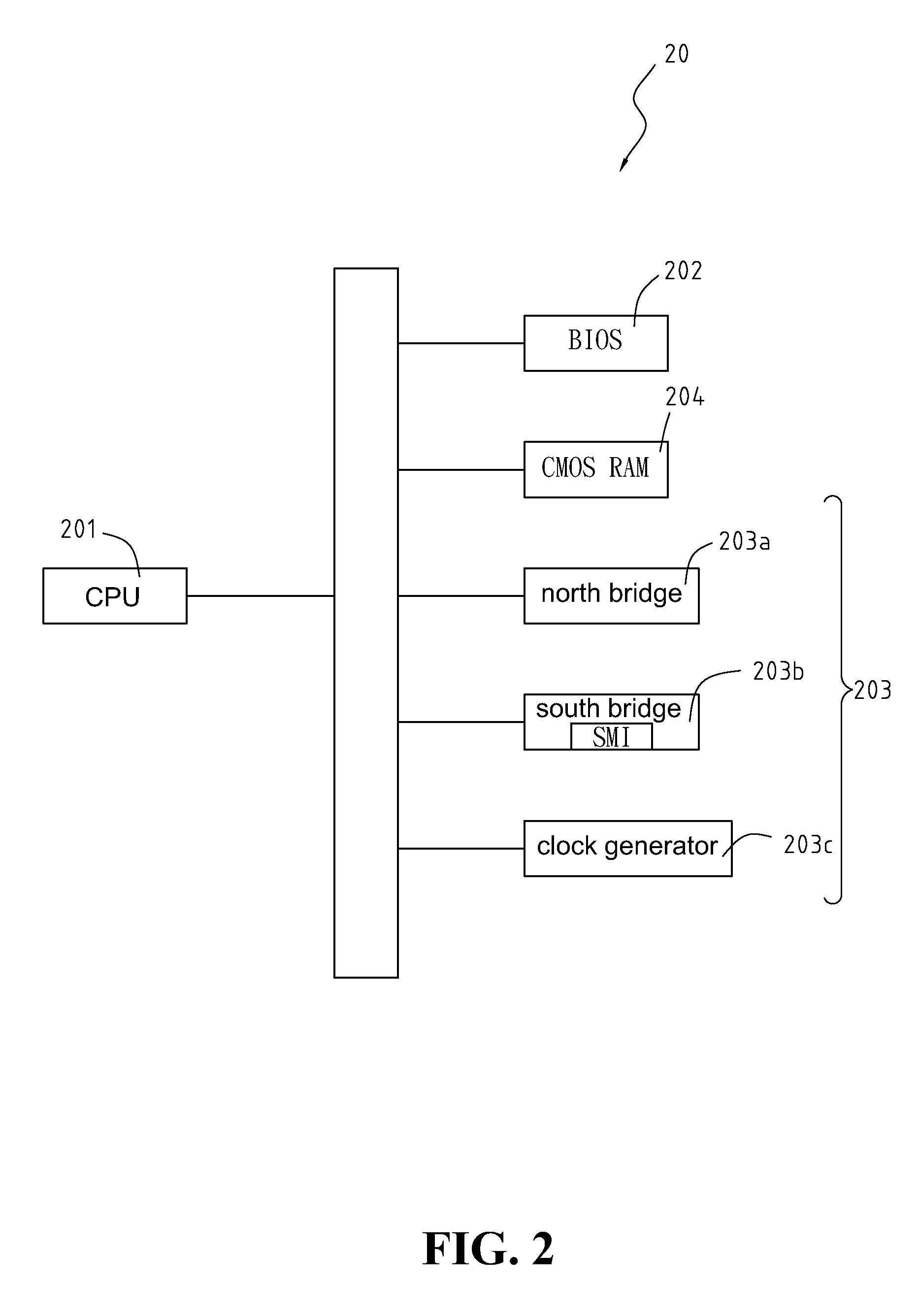
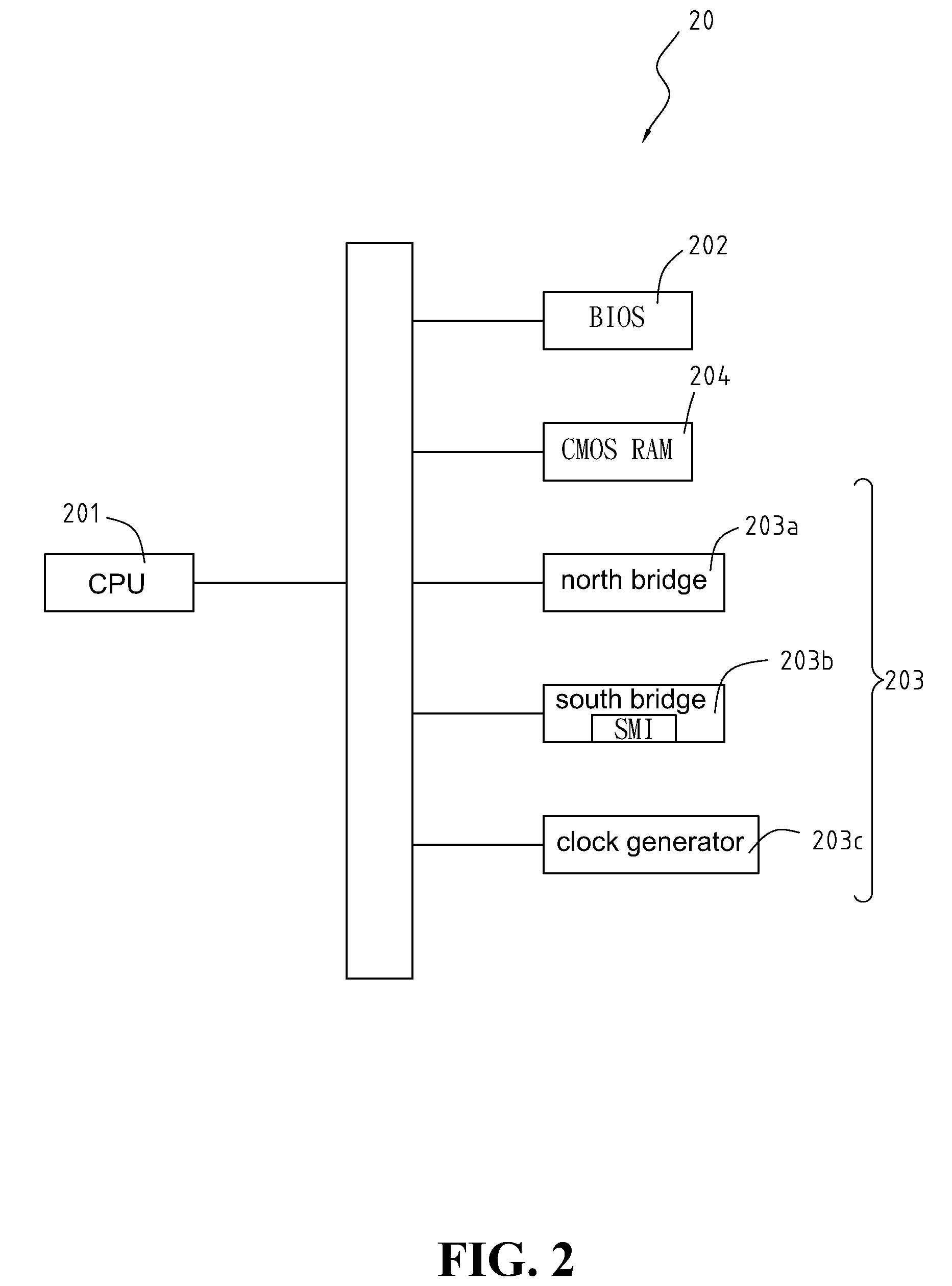
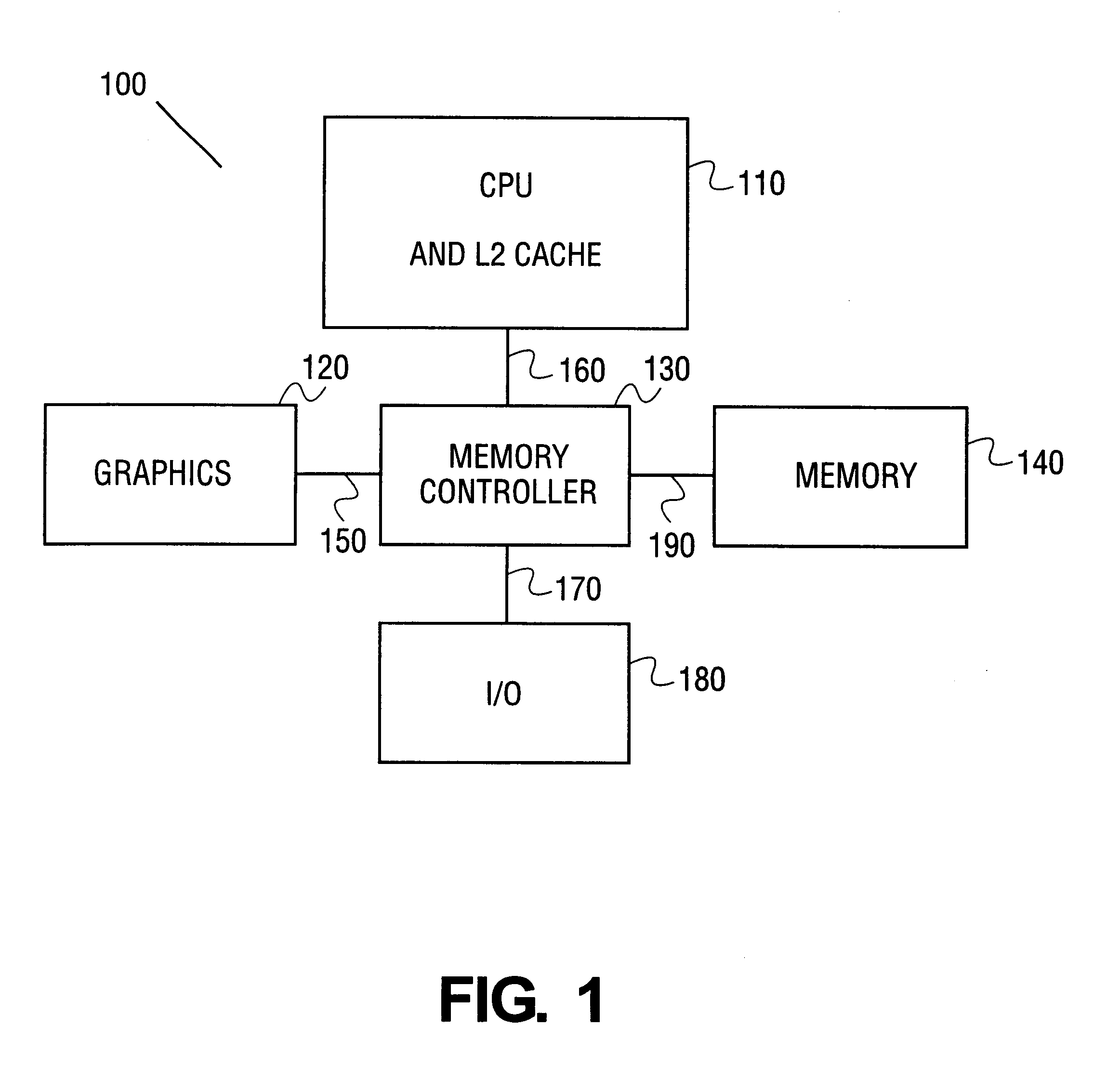
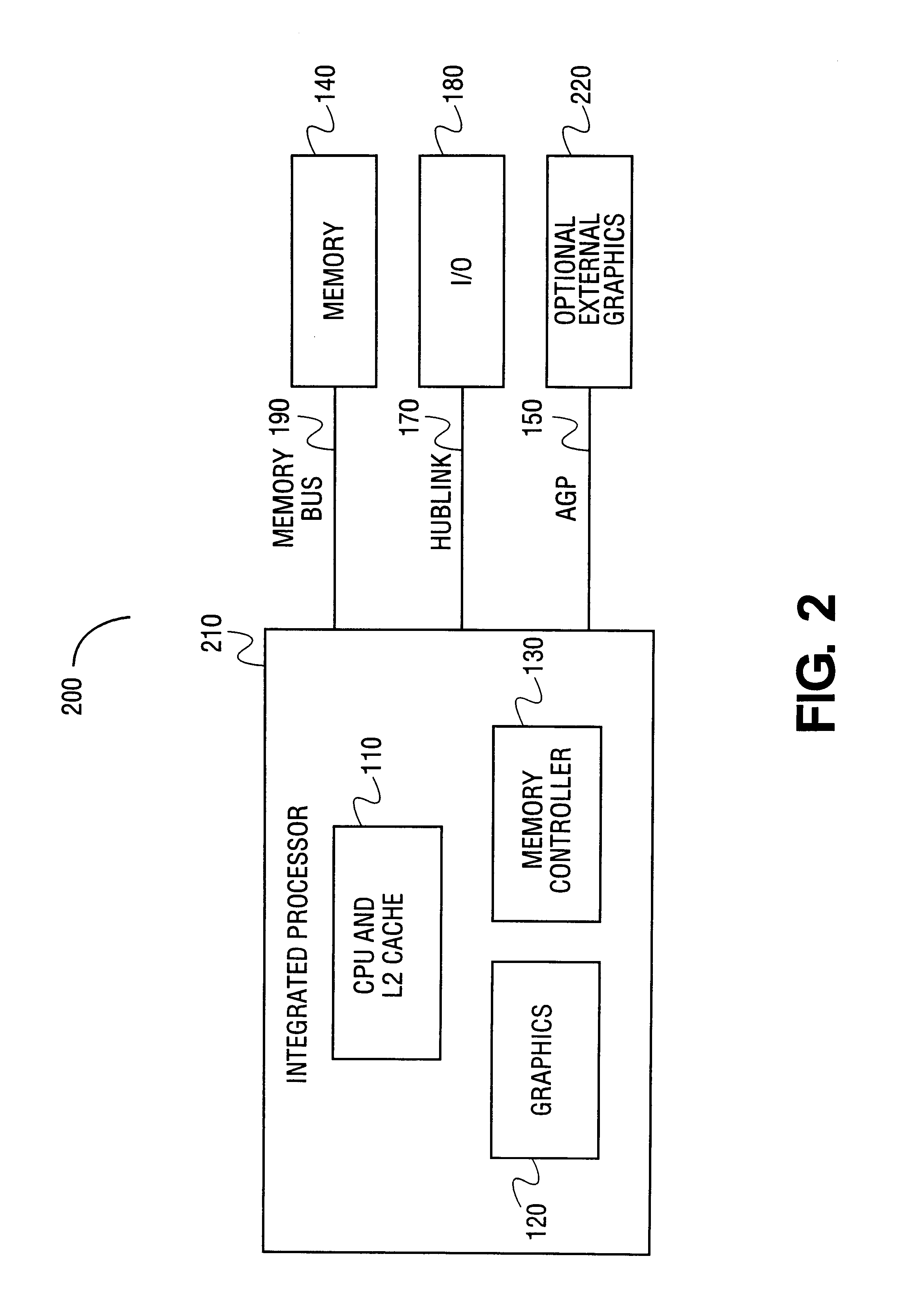
[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]
ActiveUS20050125705A1Save power consumptionProlong system operation timeEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementProcessor frequencyTranslation table
A method for dynamically adjusting central processing unit (CPU) frequency. Firstly, a translation table is provided between multilayer of CPU usage percentage and front-end bus operation frequency. Secondly, a current usage percentage of the CPU is obtained. Lastly, the operation frequency of the front-end bus is adjusted to a corresponding layer according to the current usage rage, so that the current usage rage is located within the range of CPU usage percentage that is defined by corresponding layer.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
Inline PCI-IOV Adapter
A system for enabling input / out virtualization for a device is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes a plurality of host CPUs; a multi-root switch connected to each of the plurality of host CPUs via respective buses; and an inline PCI virtualizing device connected to the multi-root switch via a front-side bus and the device via a back-side bus, the inline PCI virtualizing device including a plurality sets of registers, each of the plurality sets of registers accessible by a corresponding host CPU of the plurality of host CPUs and implementing functionalities of the device.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus to enable I/O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces
Method and apparatus to enable I / O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces. The apparatus includes an arbitration unit, a host interface unit, and a memory interface unit. The arbitration unit provides an interface to one or more I / O agents that issue atomic transactions to access and / or modify data stored in a shared memory space accessed via the memory interface unit. The host interface unit interfaces to a front-side bus (FSB) to which one or more processors may be coupled. In response to an atomic transaction issued by an I / O agent, the transaction is forked into two interdependent processes. Under one process, an inbound write transaction is injected into the host interface unit, which then drives the FSB to cause the processor(s) to perform a cache snoop. At the same time, an inbound read transaction is injected into the memory interface unit, which retrieves a copy of the data from the shared memory space. If the cache snoop identifies a modified cache line, a copy of that cache line is returned to the I / O agent; otherwise, the copy of the data retrieved from the shared memory space is returned.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Balancing PCI-express bandwidth
InactiveUS7660925B2Maximize usePerformance of was minimizedElectric digital data processingData processing systemControl data
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
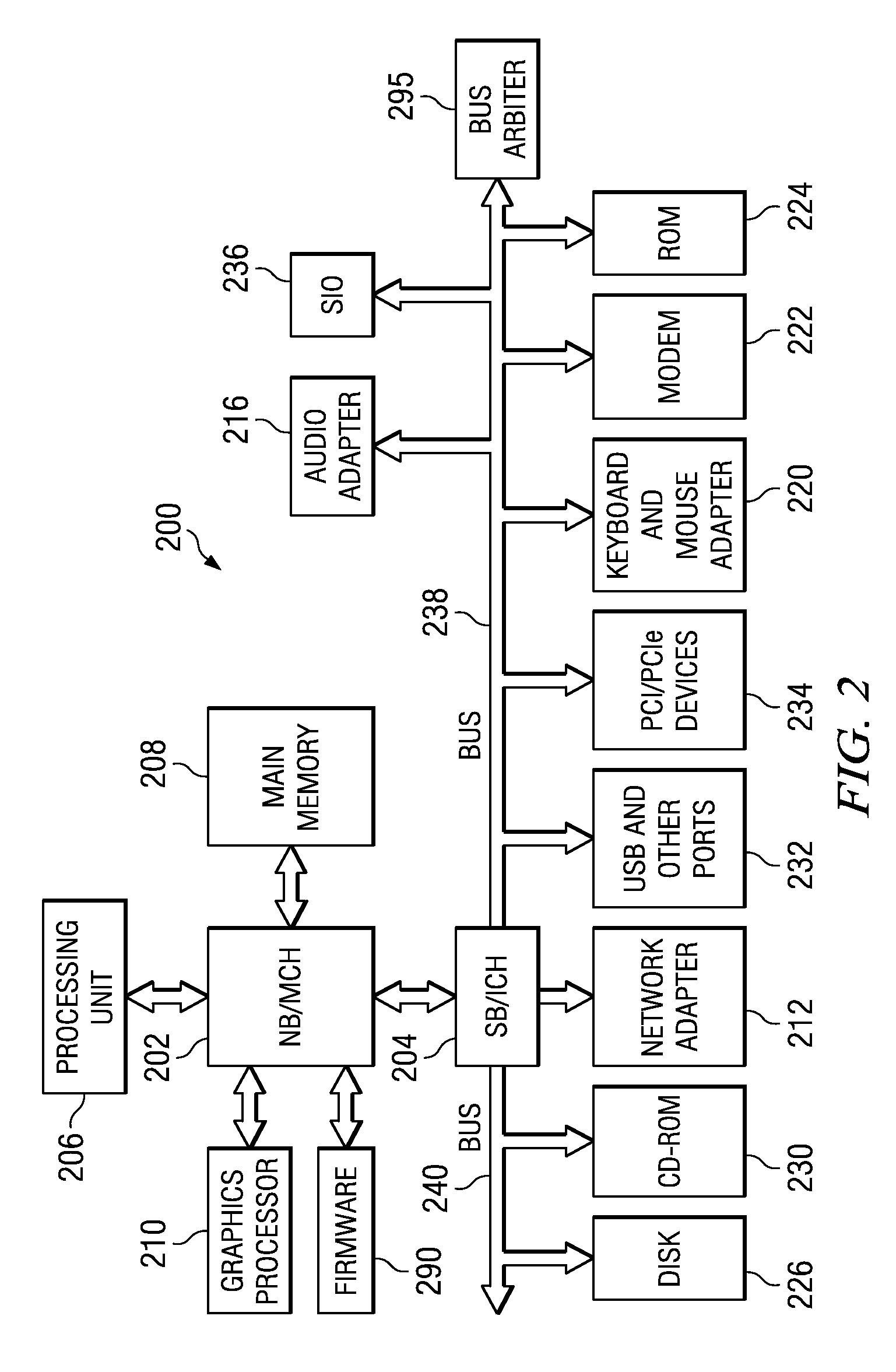
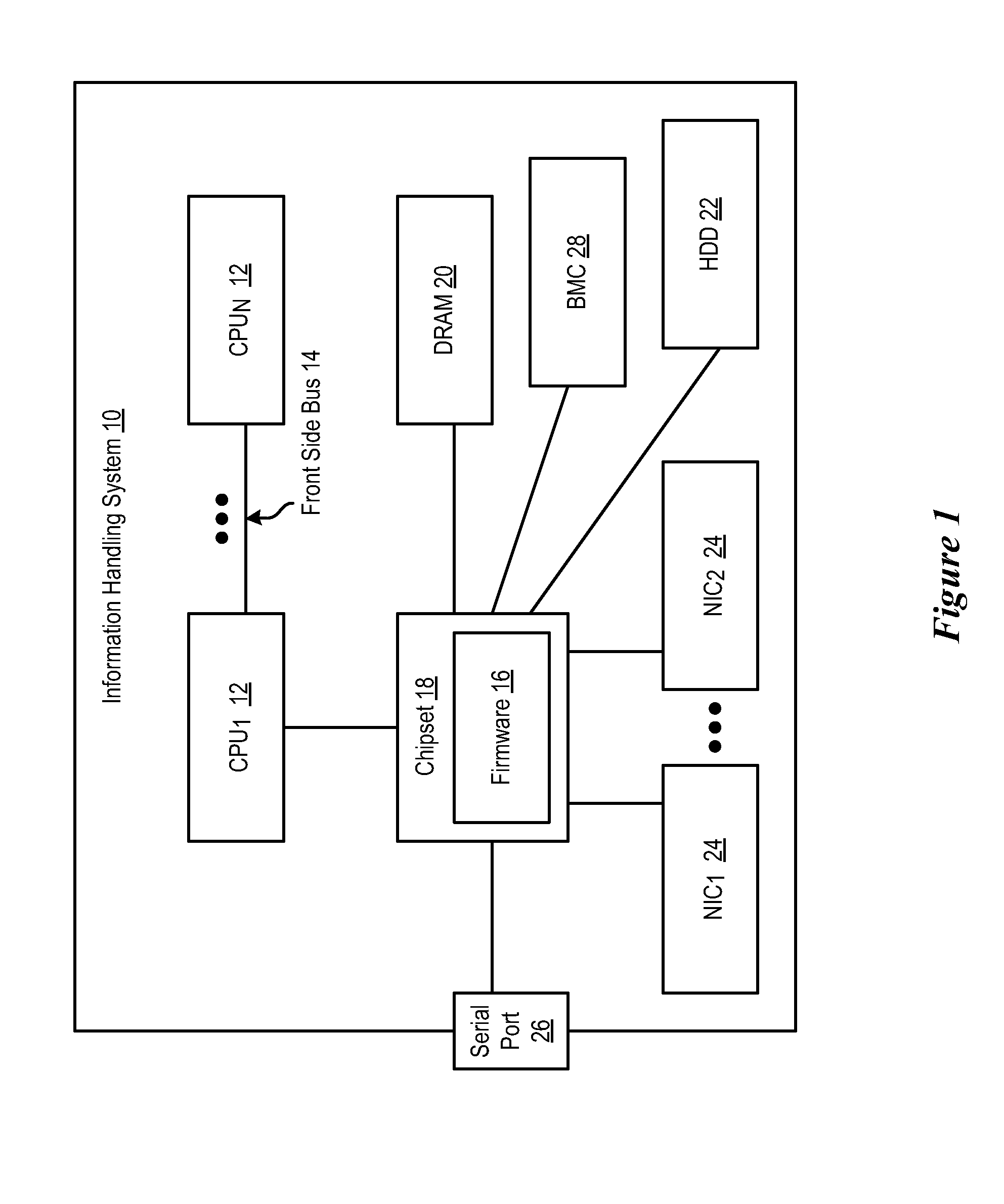
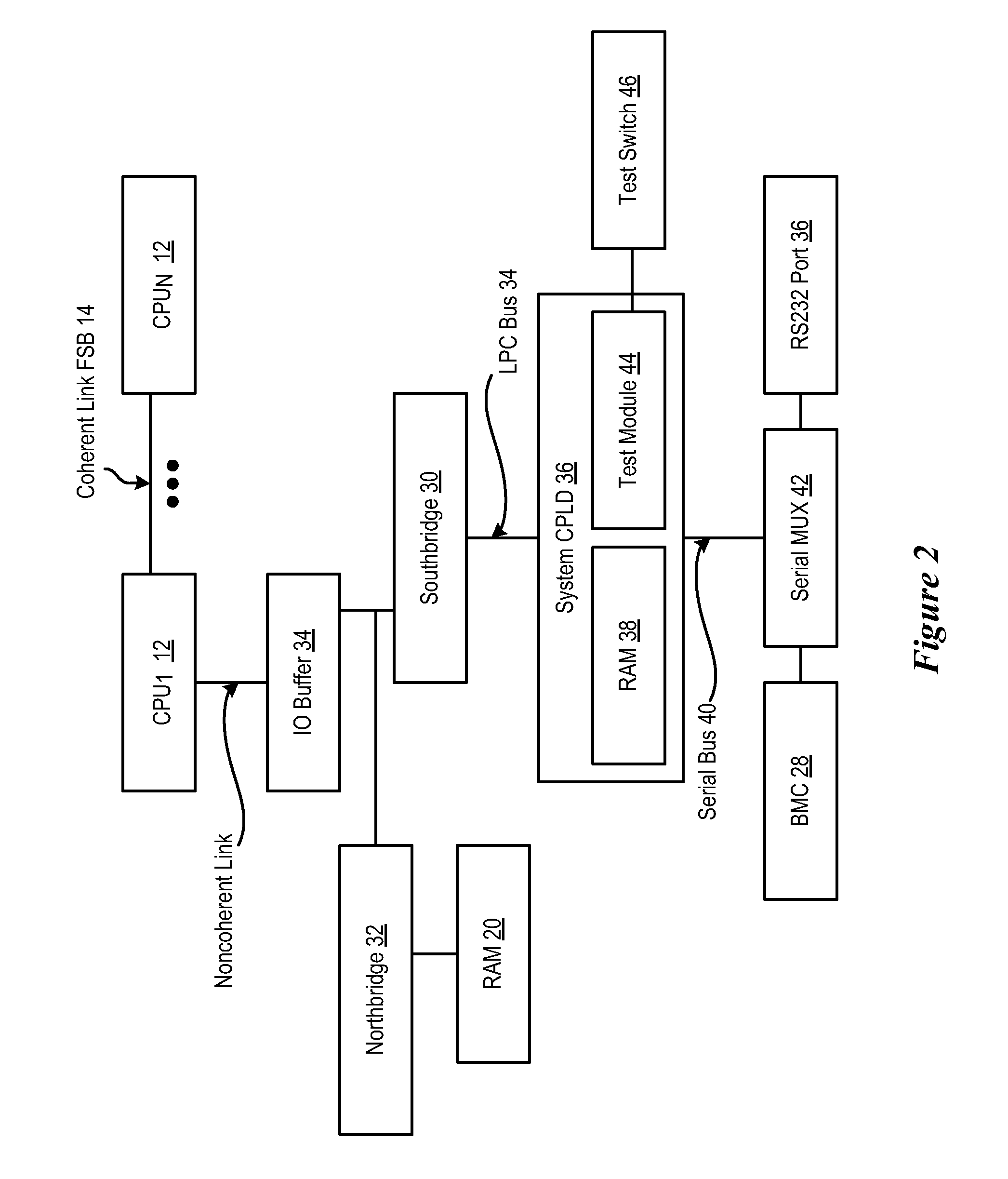
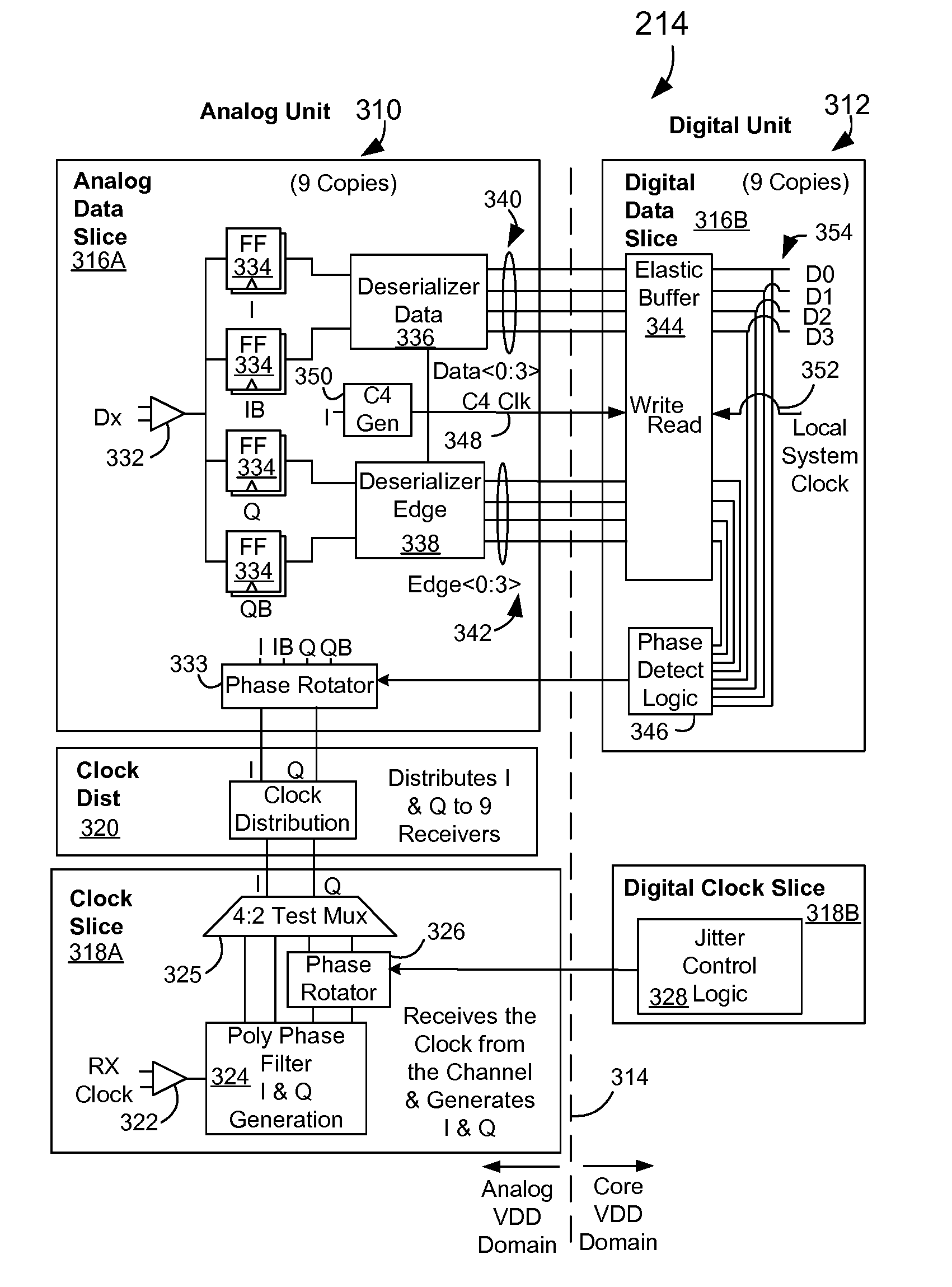
System and method for analyzing CPU performance from a serial link front side bus
ActiveUS20090077365A1Maintain powerReduce disadvantagesError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsMulti processorHandling system
Monitoring of boot progress for a multiprocessor information handling system is performed with a test module running on a CPLD. RAM integrated in the CPLD stores boot progress information passed through an I / O buffer located between the processors and the firmware that boots the processors. Downloading of the boot progress from the RAM to an external device, such as through a serial port, provides a processor trace that is analysis and debugging of the firmware by recording processor operations through the boot progress.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
CPIC signal processing board
InactiveCN101122892AEasy accessImprove communication efficiencyMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingMulti sliceSoftware development
The present invention provides a CPCI signal processing board, including at least two general processors, which mutually connect through a front-end bus, a north bridge chip, which connects with the processor through the front-end bus and with a shared memory and a CPCI bus, which connects the north bridge chip through a PCI bridge. The present invention is equipped with the following technology effects: the application of multi-slice general processors can compute parallel data in large scale and at the same time provide developers with a general software developing platform. The multi-slice general processor connects with the north bridge chip bu sharing the front-end bus and the north bridge chip connects with a shared memory, improving communication efficiency greatly and reducing communication delay.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
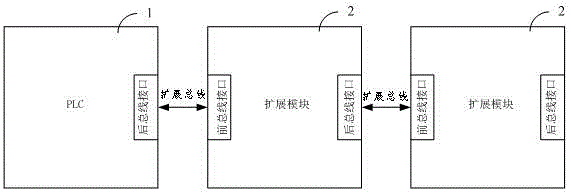
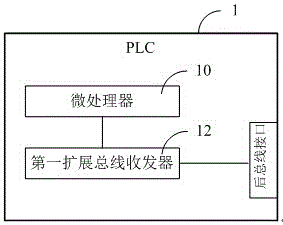
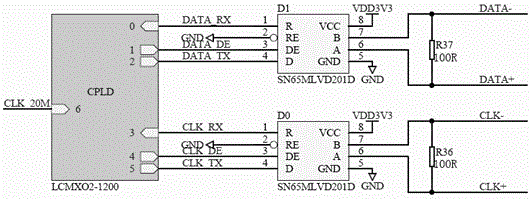
PLC control system and PLC extension bus implementation method
ActiveCN105116830AImplement multi-point samplingStable samplingProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersTransceiverControl system
The invention discloses a PLC control system, which comprises a PLC and a plurality of extension modules, wherein the PLC is cascaded with the plurality of extension modules by adopting extension buses; the PLC comprises a microprocessor and a first extension bus transceiver, the microprocessor is used for controlling communication between the PLC and the plurality of extension modules, and the first extension bus transceiver is used for exchanging data with the first stage extension module through a PLC rear bus interface; and each extension module comprises an extension microprocessor and a second extension bus transceiver, the extension microprocessor is used for controlling communication between the extension module and the PLC, and the second extension bus transceiver is used for exchanging data with the previous stage extension module or the PLC through a corresponding stage front bus interface and exchanging data with the next stage extension module through a corresponding stage rear bus interface. The invention further discloses a corresponding PLC extension bus implementation method. Through implementing the technical scheme of the invention, the speed of a PLC extension bus can be increased, the cost is reduced, and the anti-interference capability in the sampling process is high.
Owner:深圳市合信自动化技术有限公司
Method for adjusting a front-side bus frequency based on a processor usage rate stored in a translation table and generating the translation table if it does not exist
ActiveUS7296169B2Save power consumptionExtended operating timeEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingTranslation tableFront-side bus
A method for dynamically adjusting central processing unit (CPU) frequency. Firstly, a translation table is provided between multi-layer of CPU usage percentage and front-side bus operation frequency. Secondly, a current usage percentage of the CPU is obtained. Lastly, the operation frequency of the front-side bus is adjusted to a corresponding layer according to the current usage rage, so that the current usage rage is located within the range of CPU usage percentage that is defined by corresponding layer.
Owner:COMPAL ELECTRONICS INC
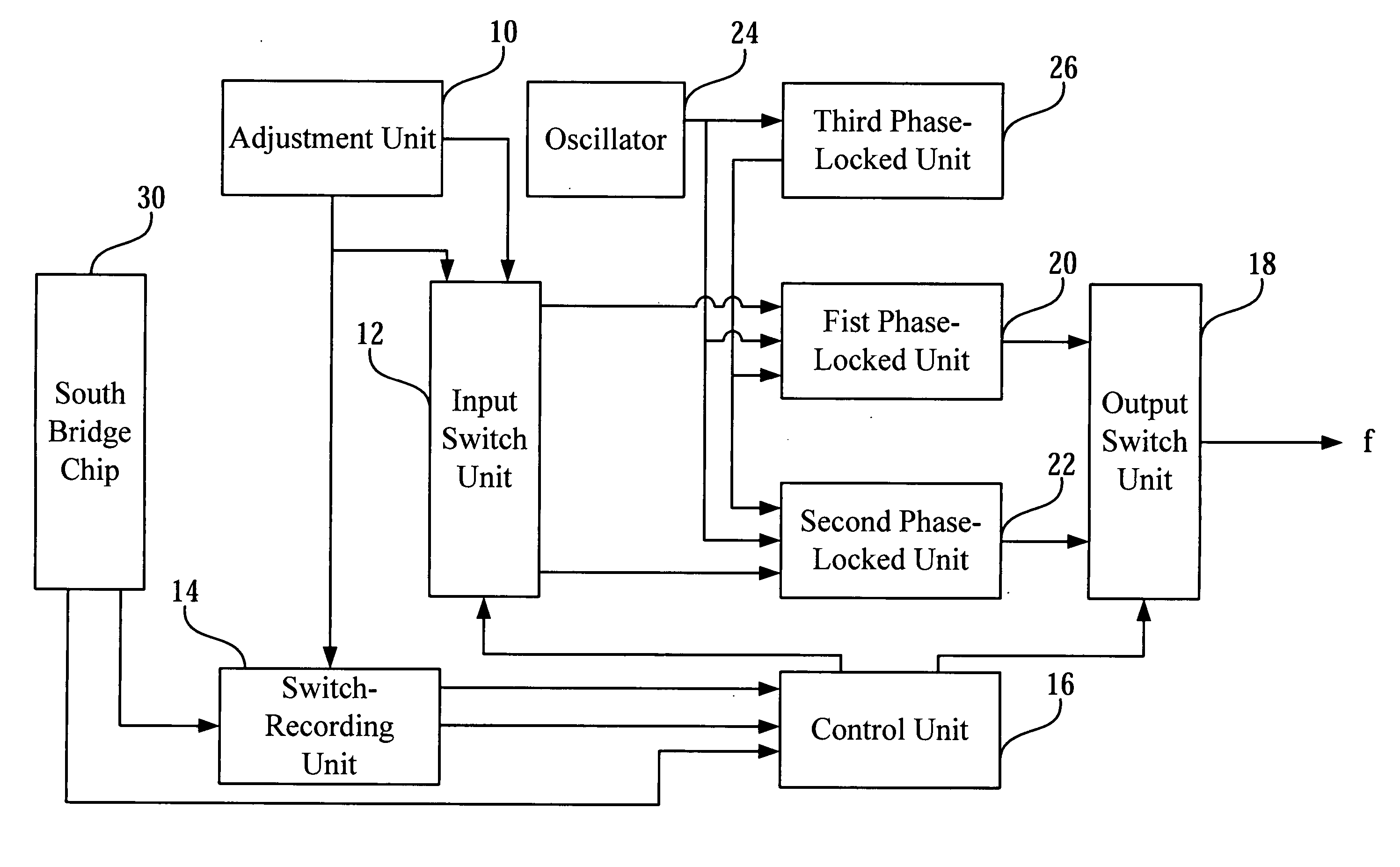
Switching circuit and method thereof for dynamically switching host clock signals
ActiveUS20070174649A1Stabilizing adjustment of operating frequencyEnergy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringFront-side bus
A switching circuit located in a computer system is disclosed in the present invention. The switching circuit comprises a first phase-locked loop generating a first host clock signal, a second phase-locked loop generating a second host clock signal and an output switch unit coupled to the first PLL and the second PLL. When the computer system operates in a first mode, the output switch unit chooses the first host clock signal to be a fundamental clock signal of the front side bus. In the other hand, when the computer system operates in a second mode, the output switch unit chooses the second host clock signal to be a fundamental clock signal of the front side bus.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
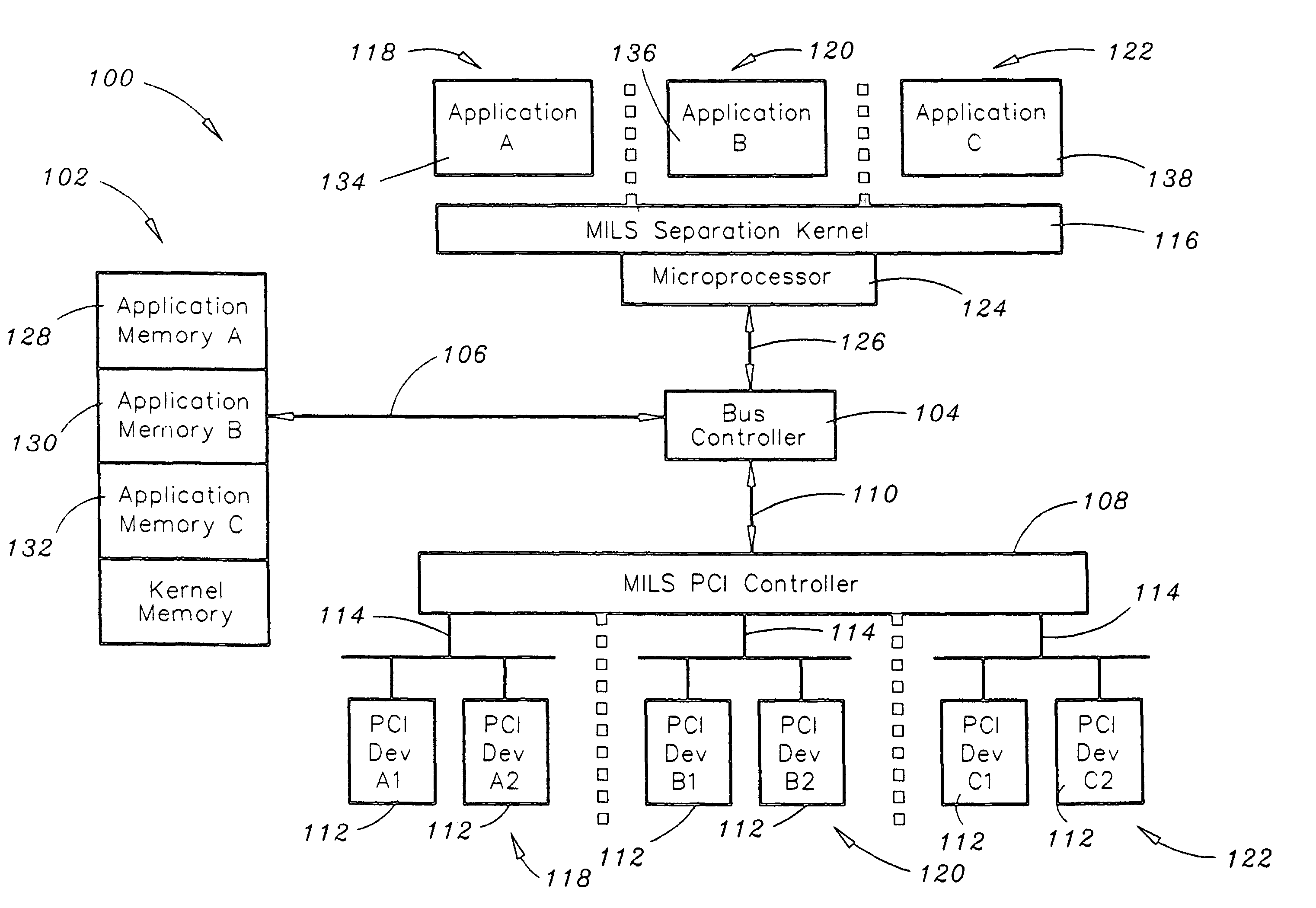
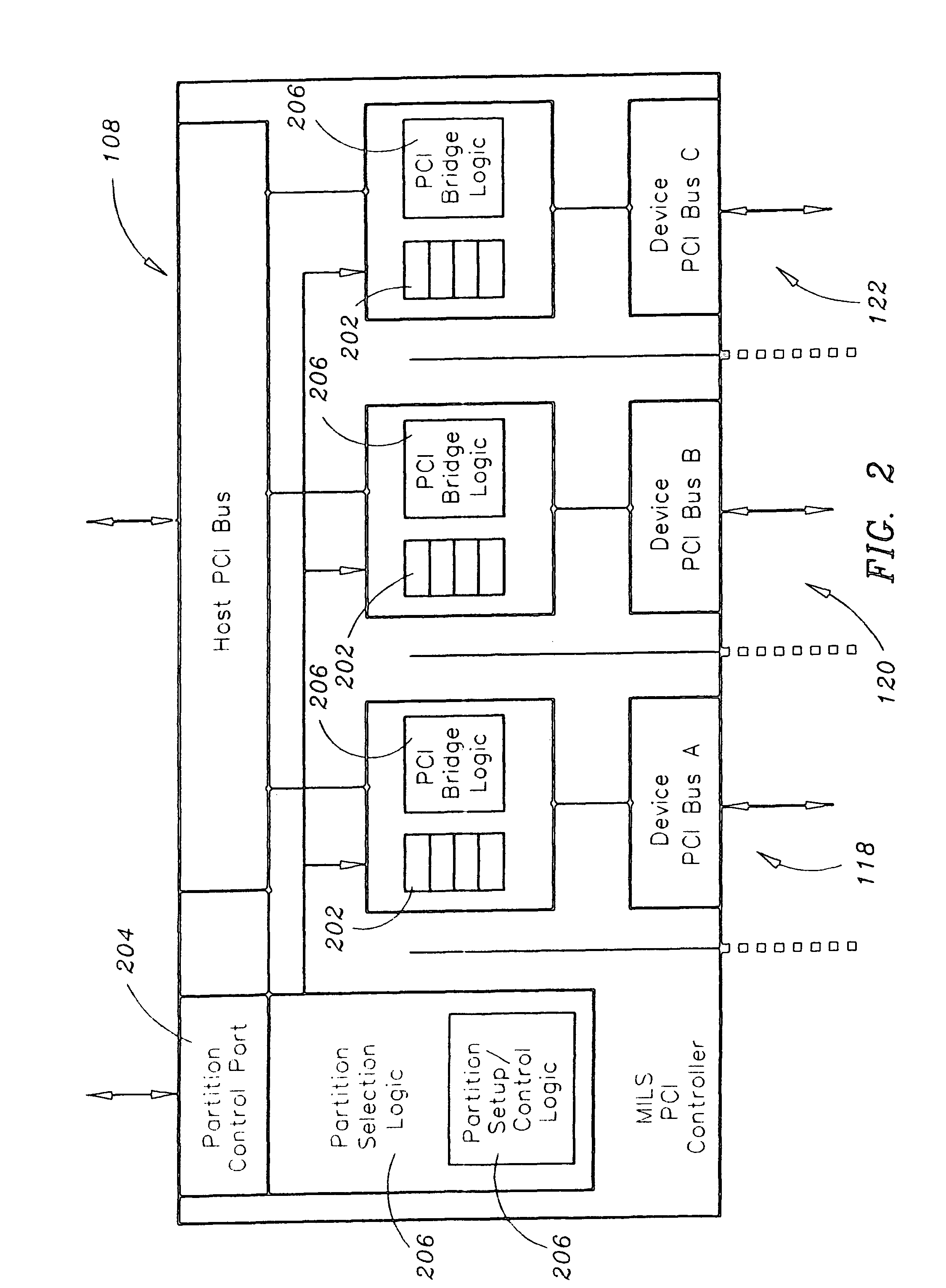
System for extending Multiple Independent Levels of Security (MILS) partitioning to input/output (I/O) devices
ActiveUS7676608B1Digital computer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionControl systemMemory bus
The present invention is a system for providing Multiple Independent Levels of Security (MILS) partitioning. The system includes a memory, a bus controller communicatively coupled to the memory via a memory bus, and a MILS controller communicatively coupled to the bus controller via a host-side bus, the MILS controller configured for monitoring and controlling system transactions. The system further includes a plurality of input / output (I / O) devices communicatively coupled to the MILS controller via a plurality of corresponding device-side buses. The system further includes a MILS separation kernel configured for mapping regions of the memory to a plurality of user partitions. Each I / O device included in the plurality of I / O devices is allocated to a partition included in the plurality of partitions and is isolated from MILS separation kernel space. The MILS separation kernel is configured for guaranteeing isolation of the partitions of the memory. The system further includes a processor connected to the bus controller via a processor front-side bus. The MILS controller is configured for extending MILS partitioning to the plurality of I / O devices.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
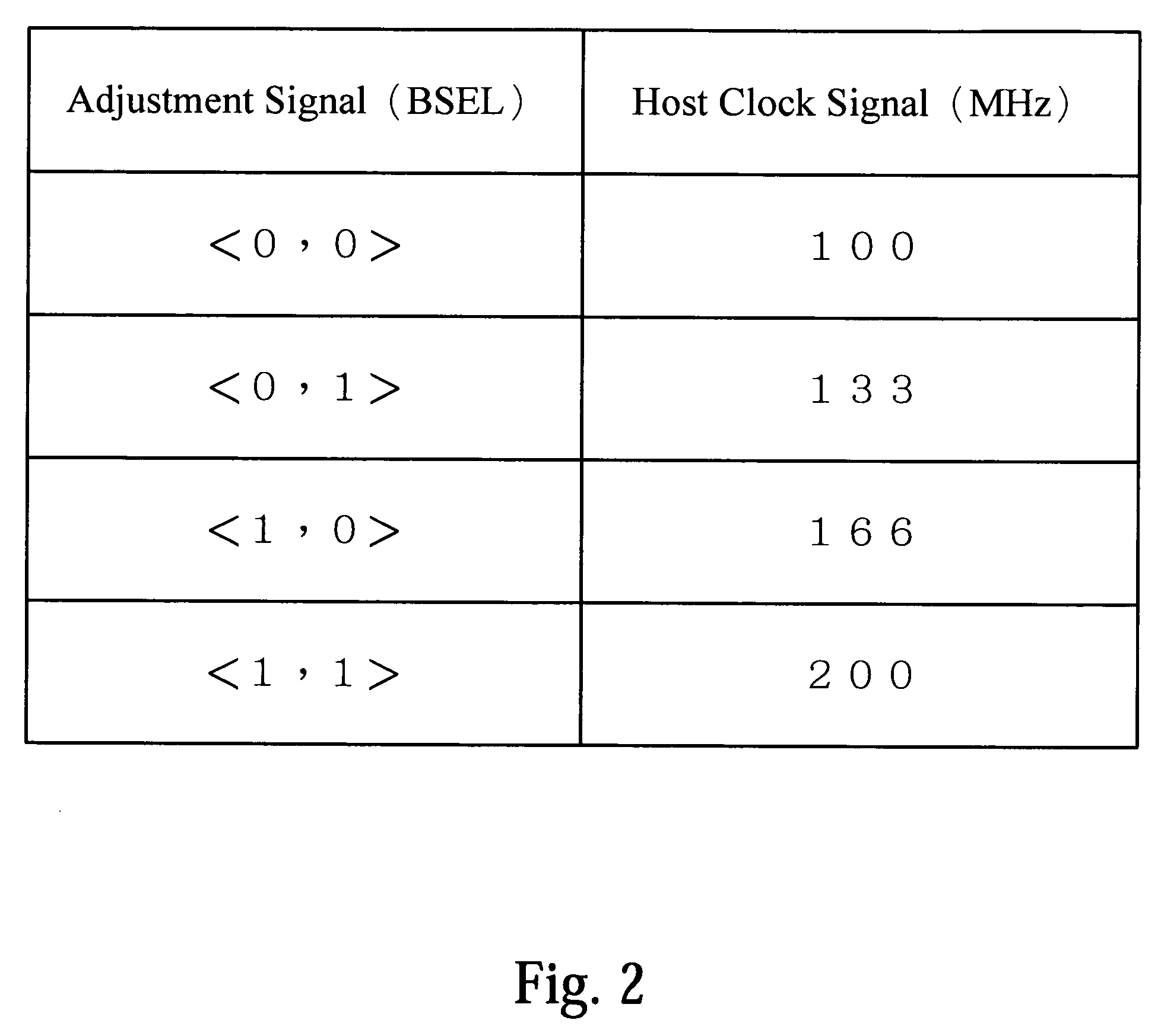
Method for setting actual opertation frequency of memory and setting module thereof
InactiveUS20090077410A1Easy to doSimple processGenerating/distributing signalsData conversionTransformation ratioFront-side bus
A method for setting an actual operation frequency of a memory is provided. The method includes the following steps. First, a memory model list is provided for selecting a memory model. Then, an estimation operation frequency of the memory is obtained according to the selected model. Finally, the operation frequency of a front side bus (FSB) is adjusted and cooperated with a frequency transformation ratio to generate the actual operation frequency of the memory according to the estimation operation frequency.
Owner:ASUSTEK COMPUTER INC
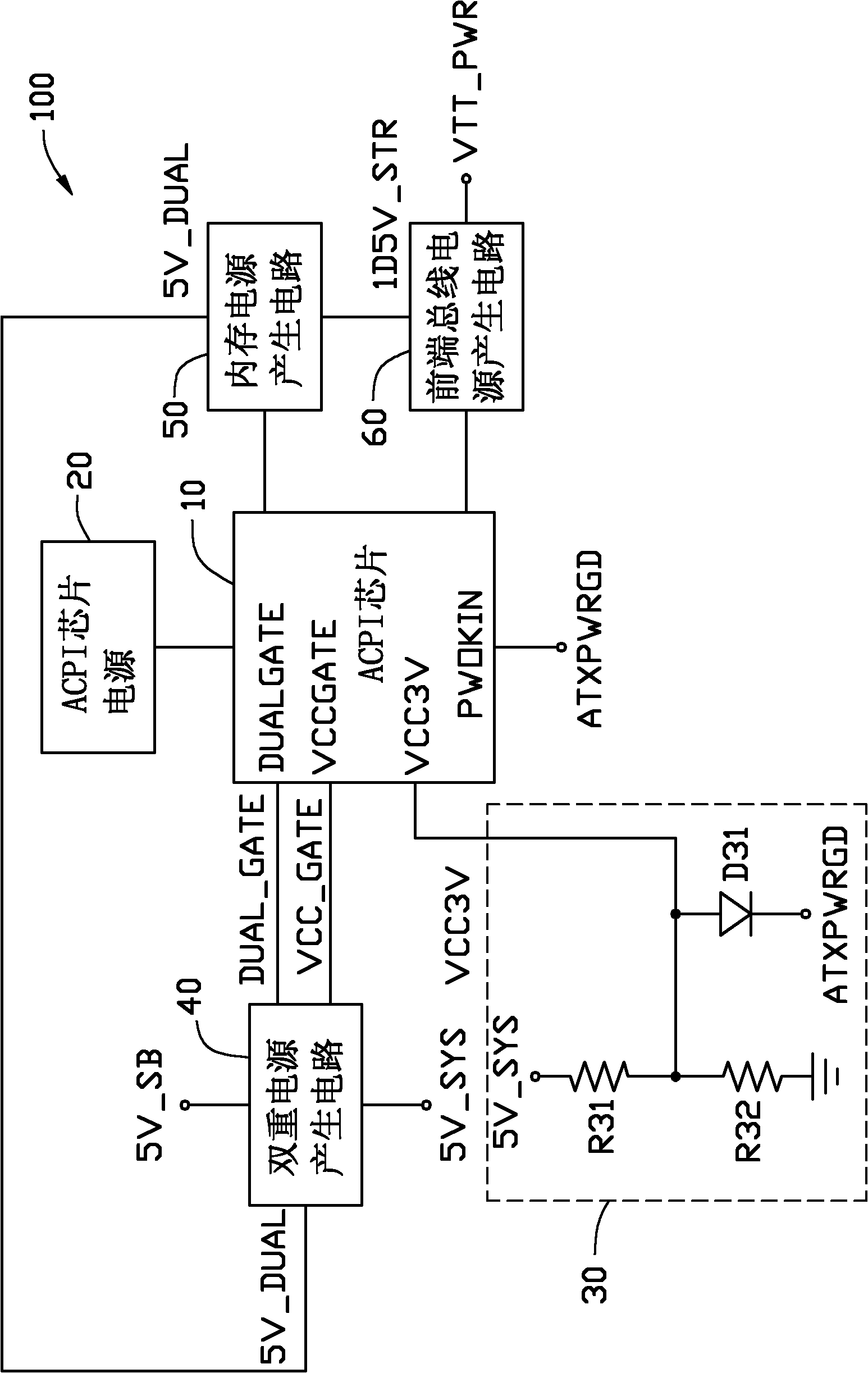
Time sequence control circuit and front-end bus power supply with time sequence control circuit
ActiveCN102213971AVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingElectrical resistance and conductanceControl signal
Owner:SHENZHEN DONGZHOU NEW ENERGY TECH
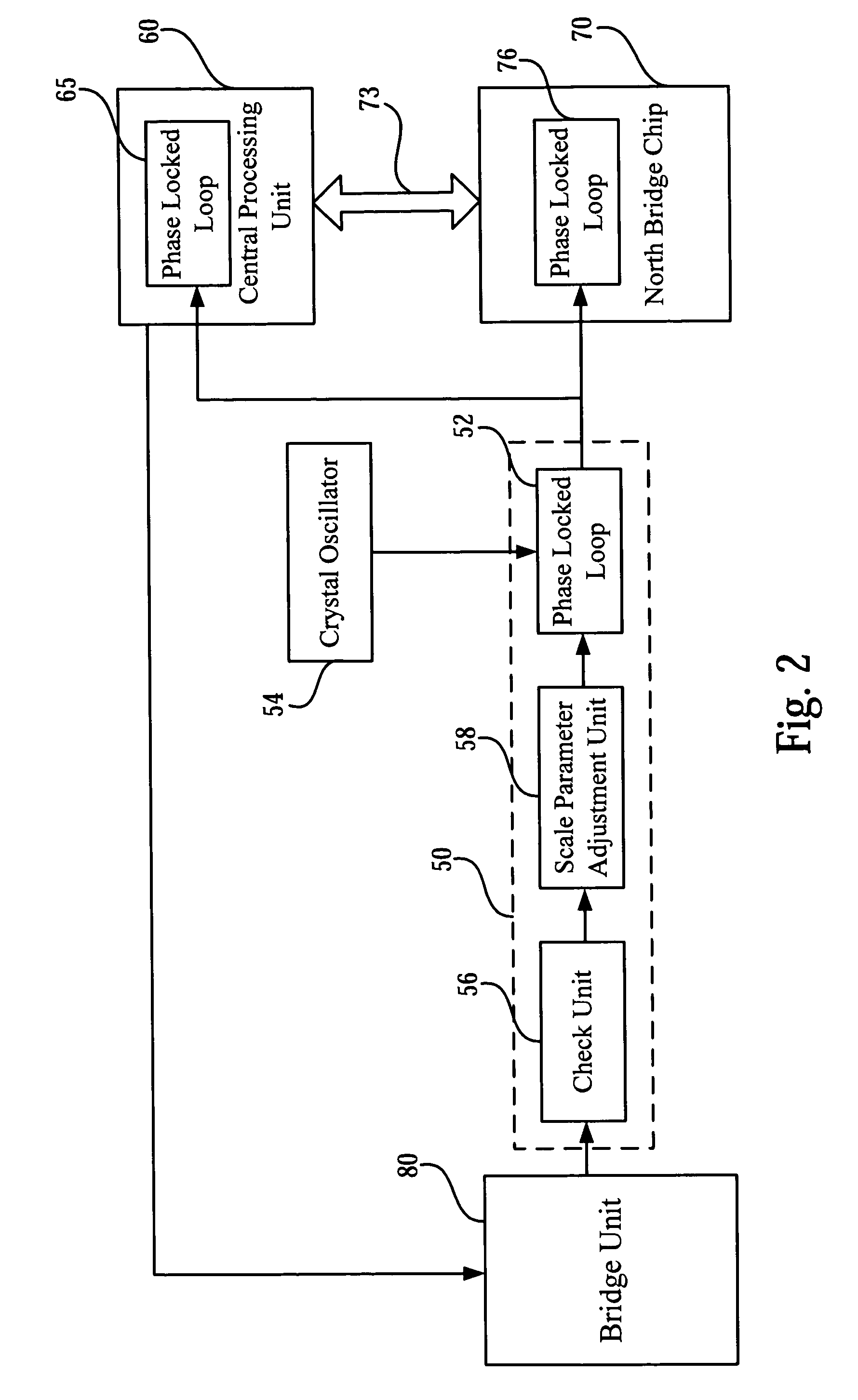
Dynamic adjusting circuit for basic clock signal of front-side bus and method thereof
ActiveUS7549073B2Easy to adjustEfficient powerPulse automatic controlVolume/mass flow measurementEngineeringFront-side bus
By adjusting a scale factor of a phase locked loop in computers for generating a basic clock signal of a front-side bus, the frequency of the basic clock signal is modulated when the central processing unit of computers operates. By a bridge unit of the present invention, a selecting signal is received so as to output a corresponding adjustment signal to a check unit and then the check unit checks the adjustment signal for outputting a checking signal to a scale parameter adjustment unit. According to the checking signal, the scale parameter adjustment unit adjusts a first scale parameter of the scale factor that the phase locked loop uses now and outputs this parameter to the phase locked loop. Thus after receiving a fixed clock signal for generating the basic clock signal, the phase locked loop generates the basic clock signal of the front-side bus in accordance with the adjusted first scale parameter and further the frequency of the basic clock signal is adjusted.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
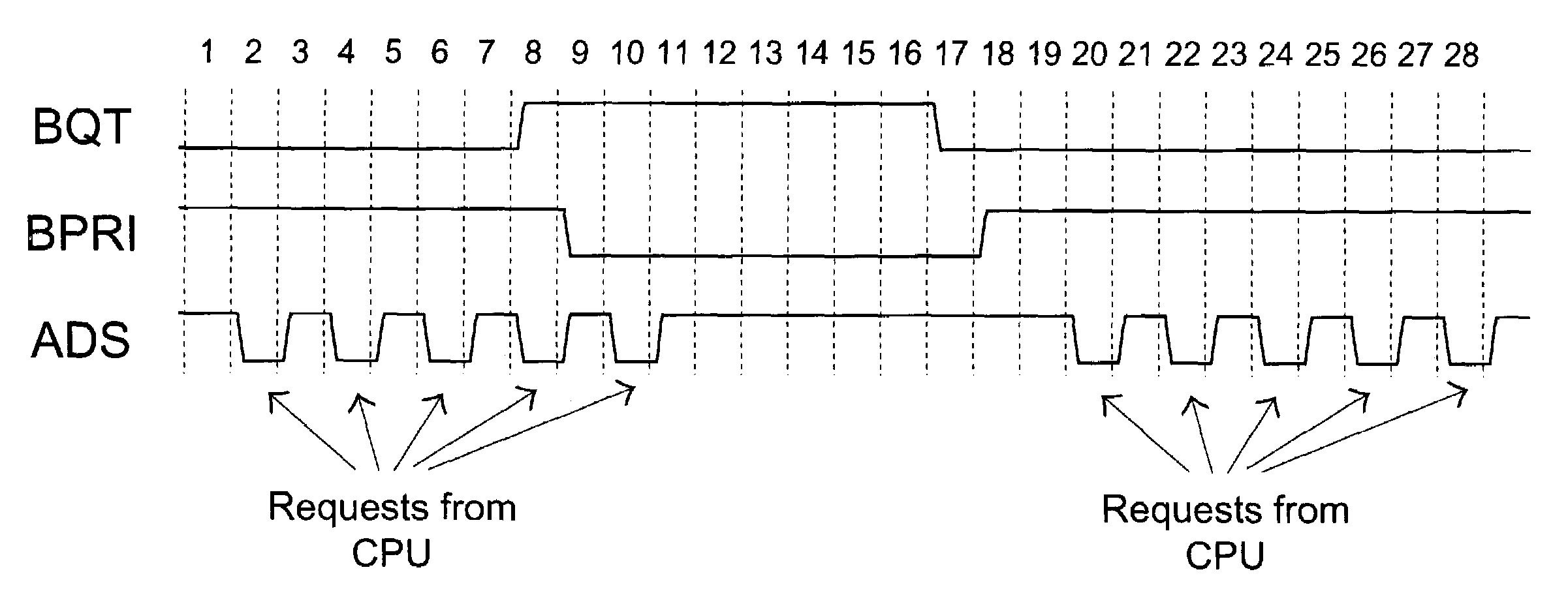
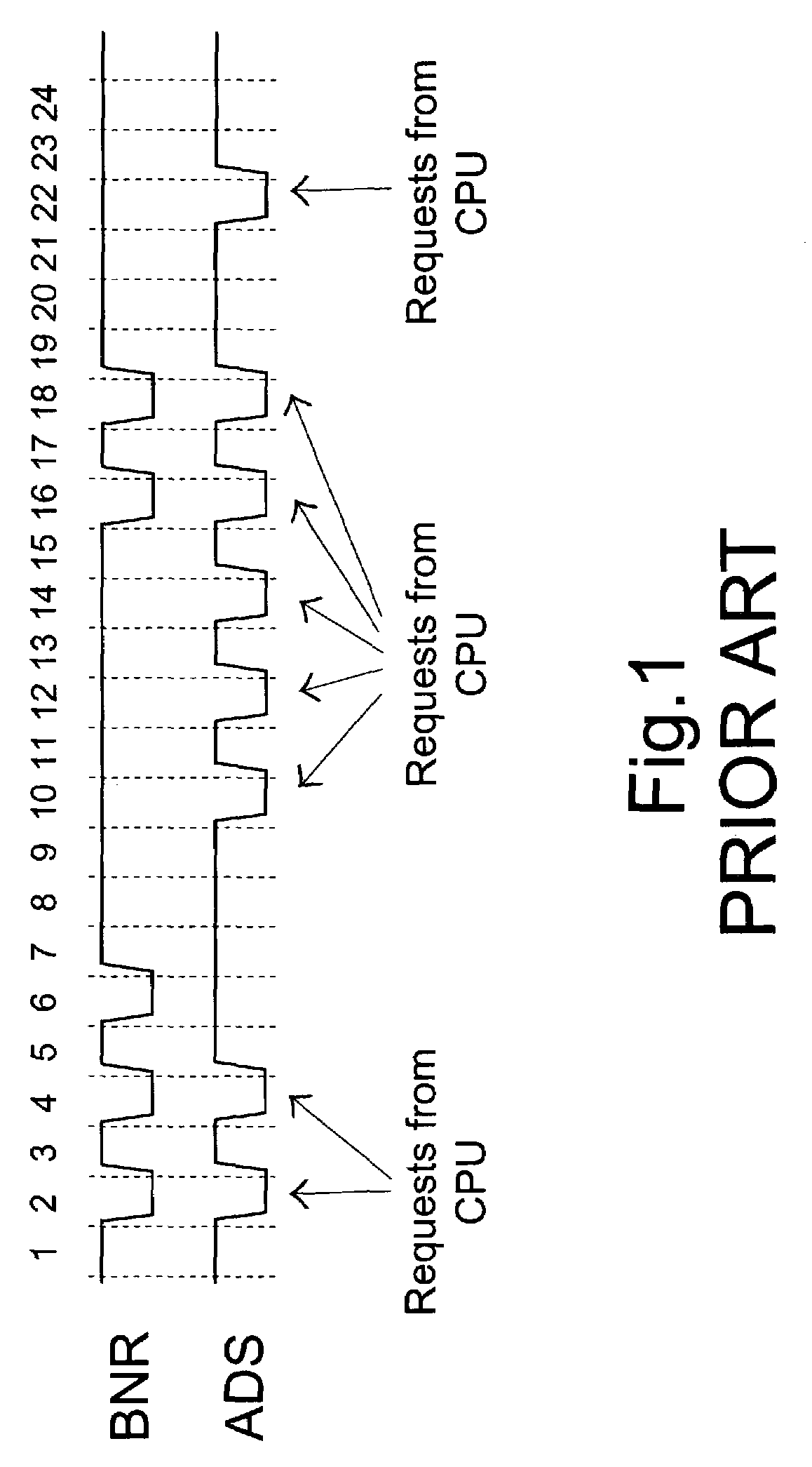
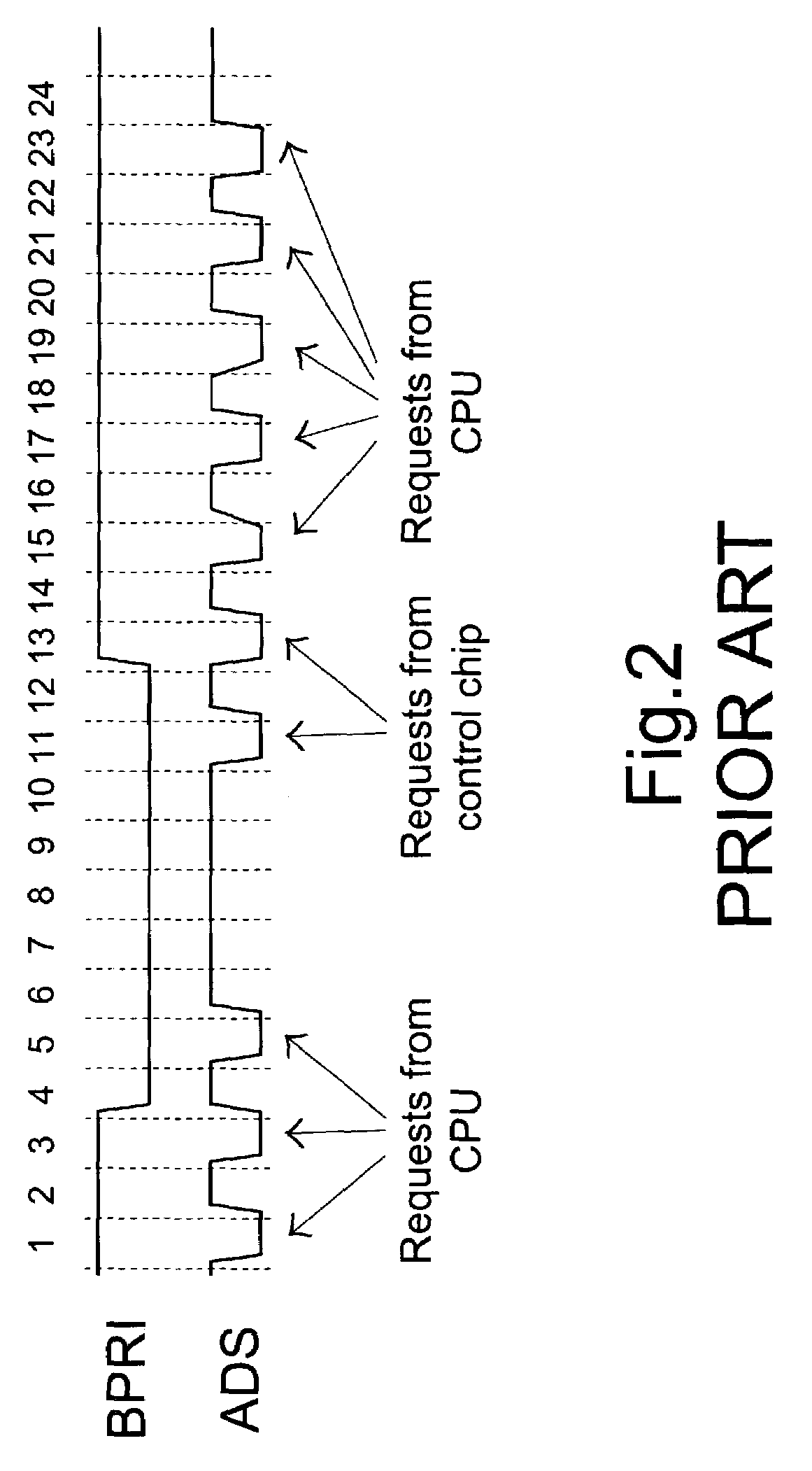
Method for blocking request to bus
InactiveUS7047336B2Prevent overloadEnergy efficient ICTUnauthorized memory use protectionFront-side busBus priority
A method for blocking a request to a front side bus interconnected between a central processing unit (CPU) and a control chip includes the following steps. First, a bus ownership of the control chip is assigned via a bus priority signal line. Any request from the CPU to the front side bus is blocked when the control chip owns the bus ownership. Meanwhile, any request from the control chip to the front side bus is inhibited when the CPU is blocked from outputting any request to the front side bus.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Switching circuit and method thereof for dynamically switching host clock signals
ActiveUS7565564B2Stabilizing adjustment of operating frequencyEnergy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringFront-side bus
A switching circuit located in a computer system is disclosed in the present invention. The switching circuit comprises a first phase-locked loop generating a first host clock signal, a second phase-locked loop generating a second host clock signal and an output switch unit coupled to the first PLL and the second PLL. When the computer system operates in a first mode, the output switch unit chooses the first host clock signal to be a fundamental clock signal of the front side bus. In the other hand, when the computer system operates in a second mode, the output switch unit chooses the second host clock signal to be a fundamental clock signal of the front side bus.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
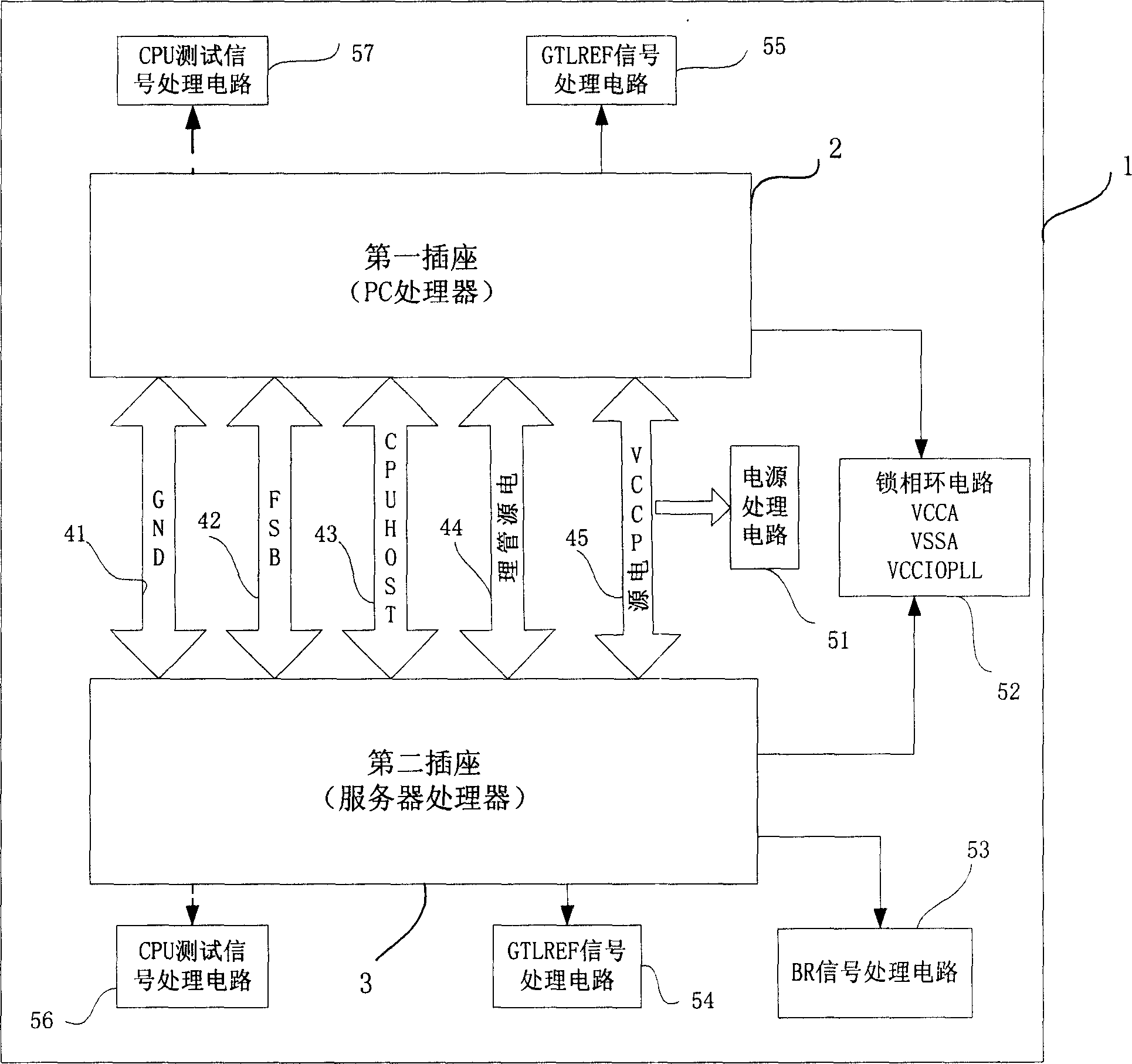
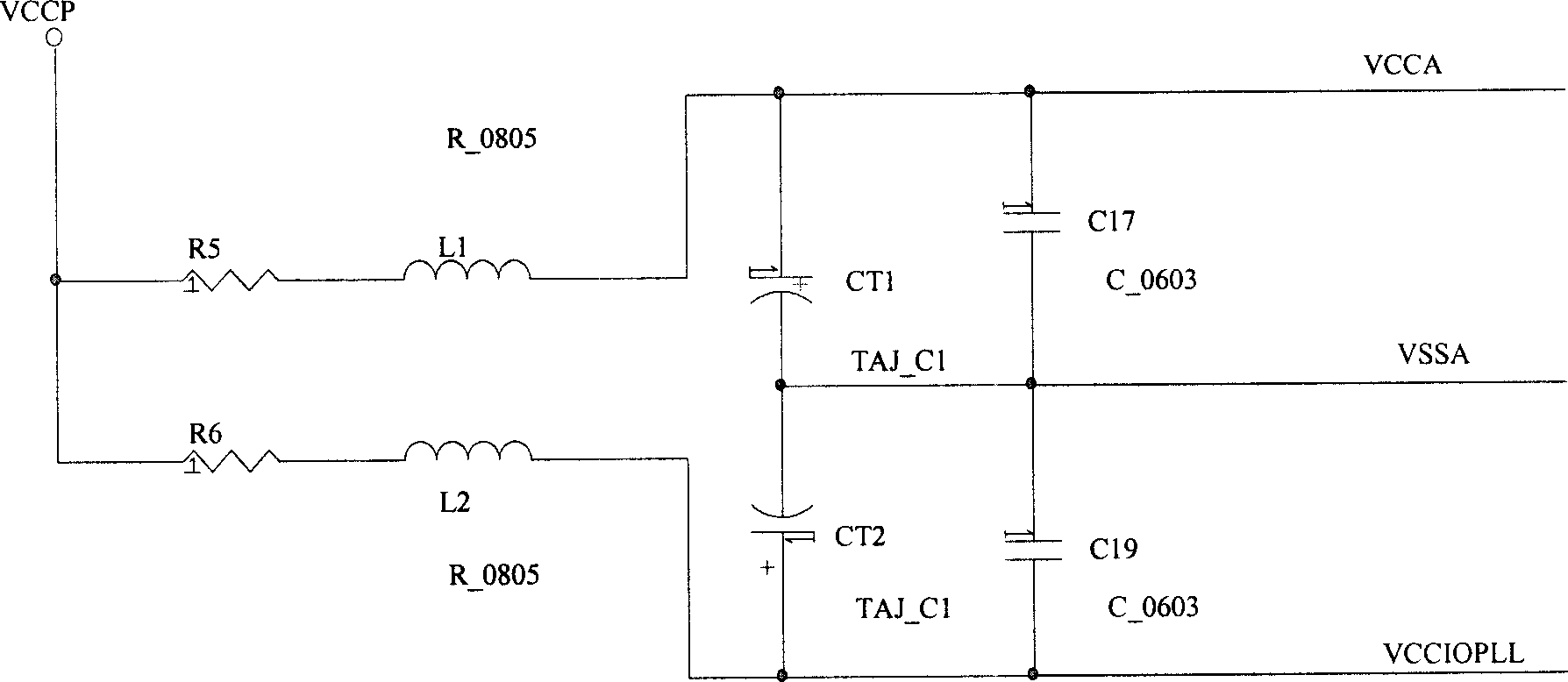
Switching device
InactiveCN1635440ALow costEasy to operateDigital data processing detailsElectricityPhase locked loop circuit
This invention relates to a switch device used in PC processor and service processor, which comprises the following steps: base plate; first and second plugs located on the base plate, wherein the earth legs, front bus legs, CPY HOST legs, power legs and power management legs are electrically connected between the two plugs; locking phase circuit to process the VCCA, VSSA and VCCIOPLL signals in the processor to provide the double frequency to the processor and servo; GTLREF signal process circuit to lower the interference to the processor; BR signal process circuit to match the bus require signal impedance in the processor; power process circuit to make the filter and energy storing of the power signals in the processor supply.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
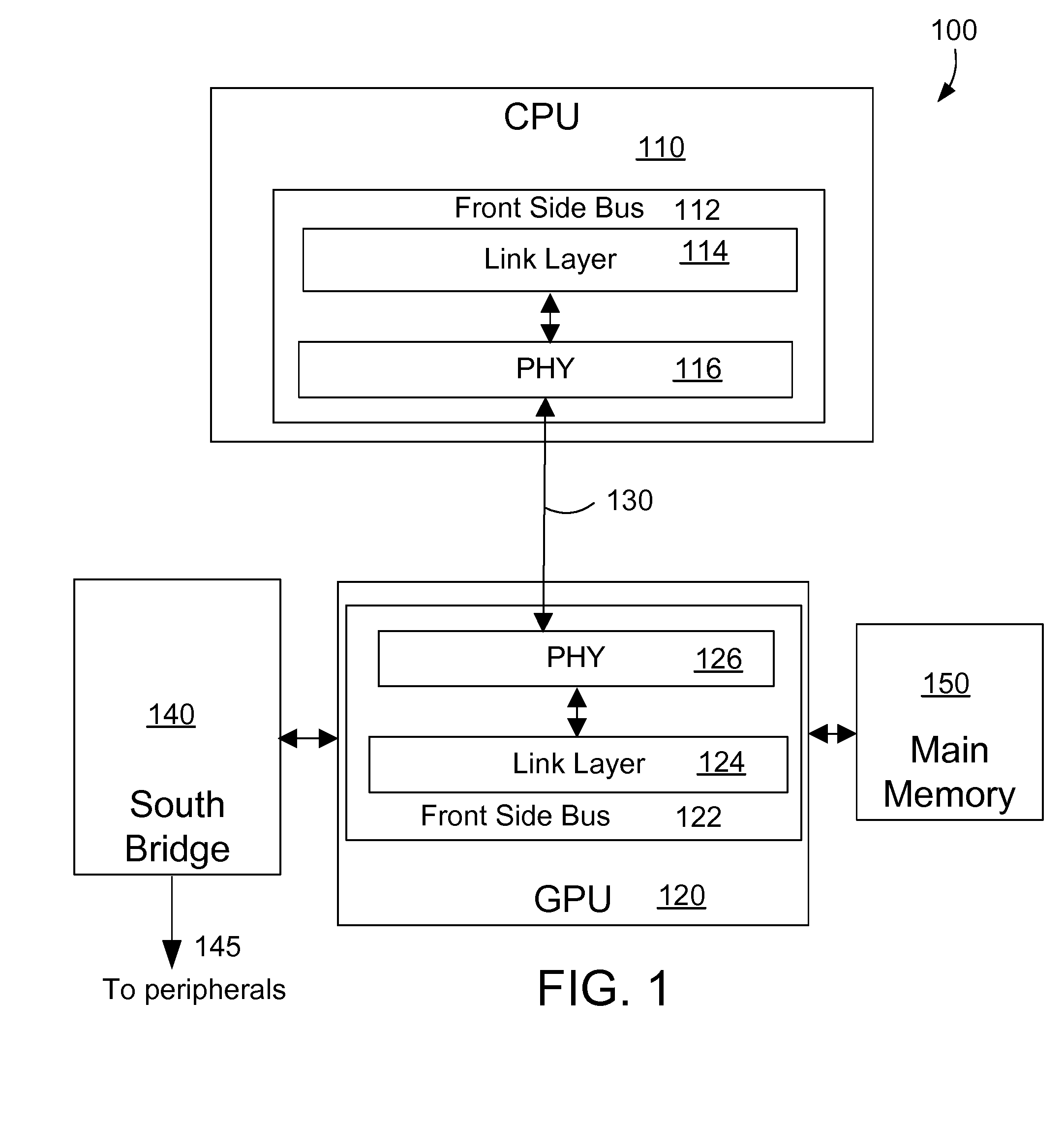
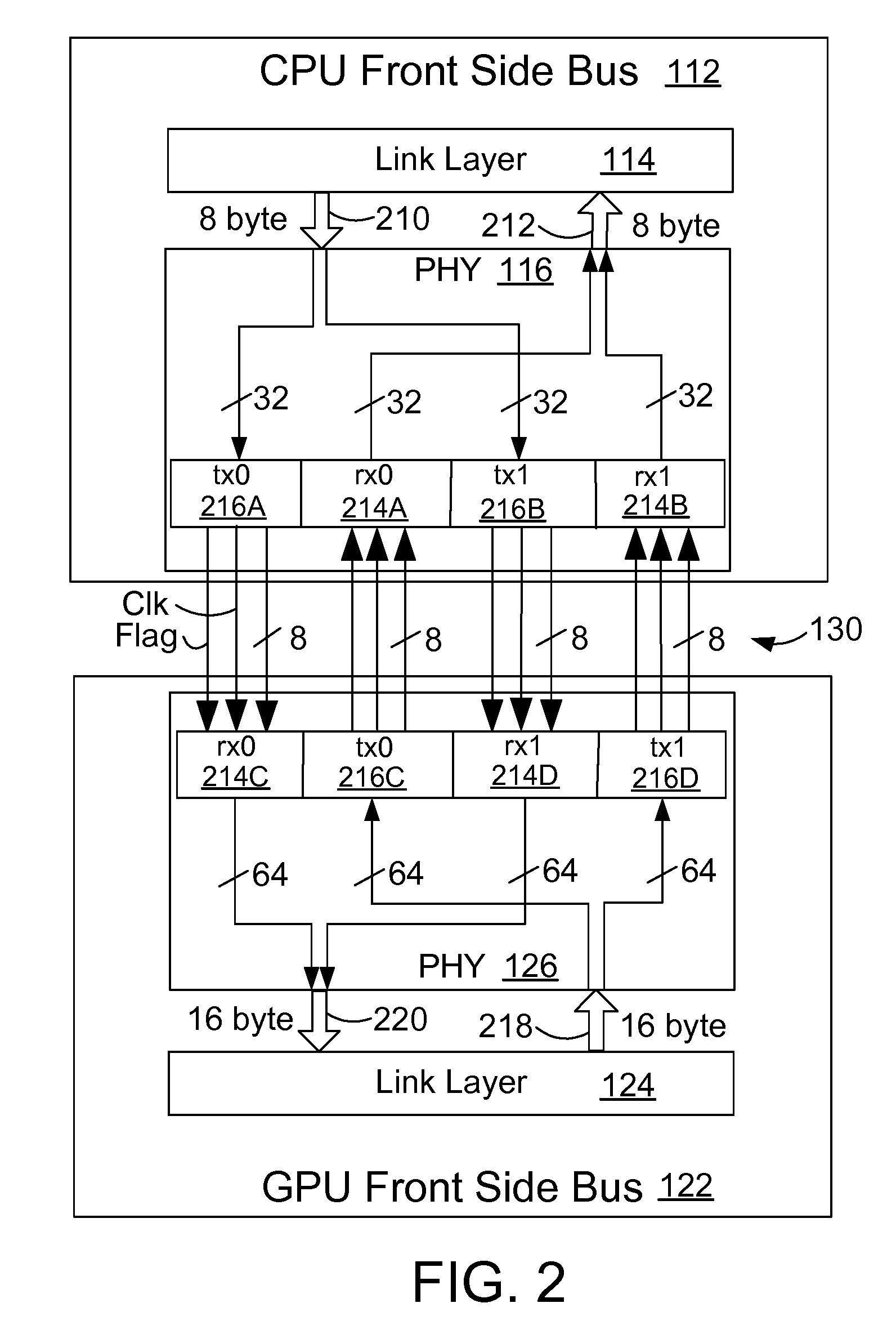
Architecture for a Physical Interface of a High Speed Front Side Bus
InactiveUS20080147952A1Simple interfaceEnergy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsGraphicsFront-side bus
A high speed computer processor system includes a high speed interface for a graphics processor. In a preferred embodiment, the high speed interface includes a front side bus (FSB) that interfaces to a similar high speed interface on the graphics processor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamically balancing bus bandwidth
ActiveUS7653773B2Improve performanceMaximize useEnergy efficient ICTTransmissionData rateEngineering
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data transmission coordinating method
A data transmission coordinating method is used between a central processing unit and a bridge chip of a computer system. By entering the computer system into a coordinating state, the data transmission coordinating method is executed. The bridge chip and the CPU are informed of maximum bit numbers of each other for data transmission therebetween via the front side bus. Then, a commonly operable maximum bit number for data transmission between the CPU and the bridge chip can be coordinated according to the first and second maximum bit numbers. Once the commonly operable maximum bit number is determined, the CPU is reset to operate with the commonly operable maximum bit number. The maximum bit numbers are those of bus transmission bandwidth or bus transmission speed.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
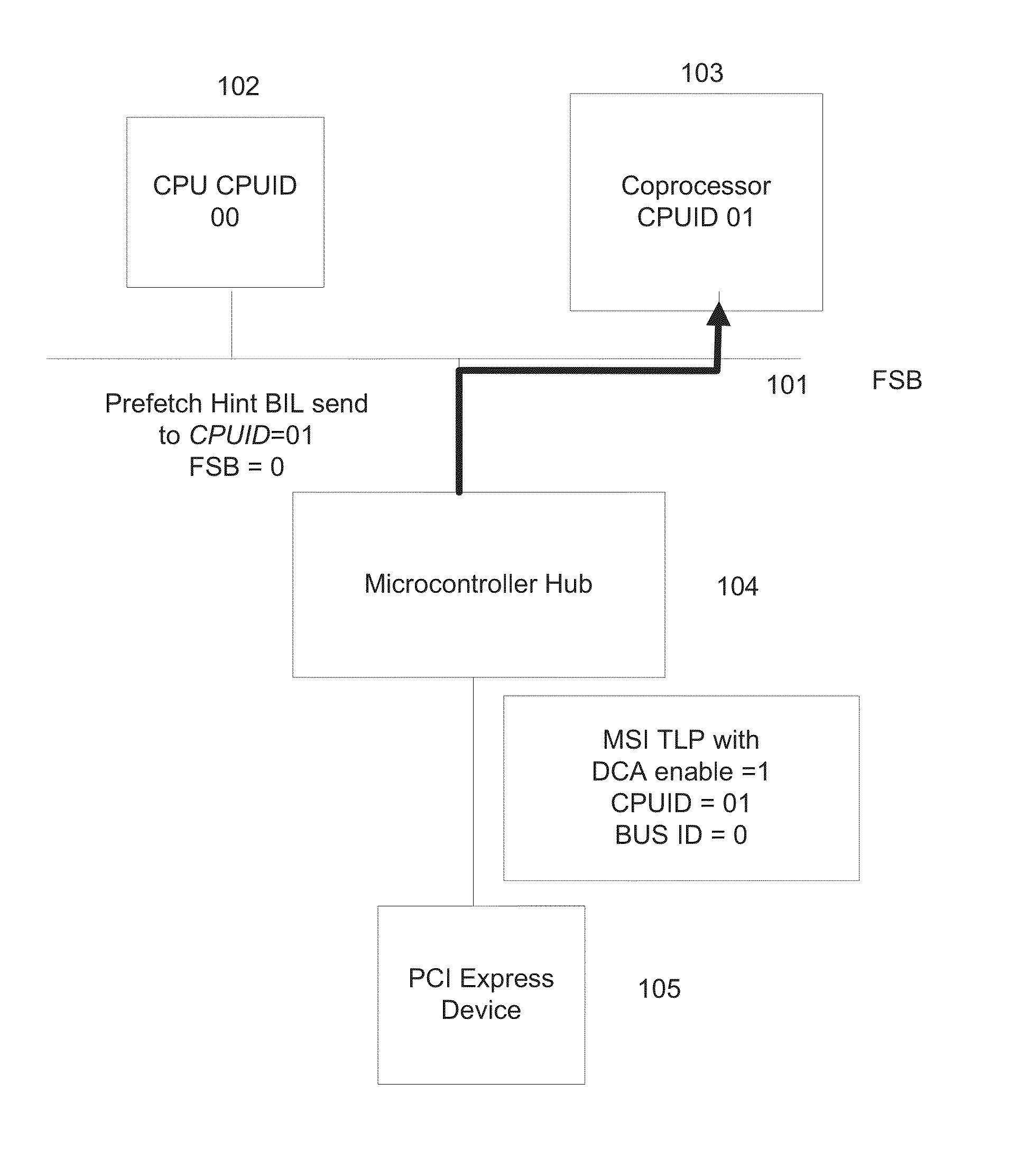
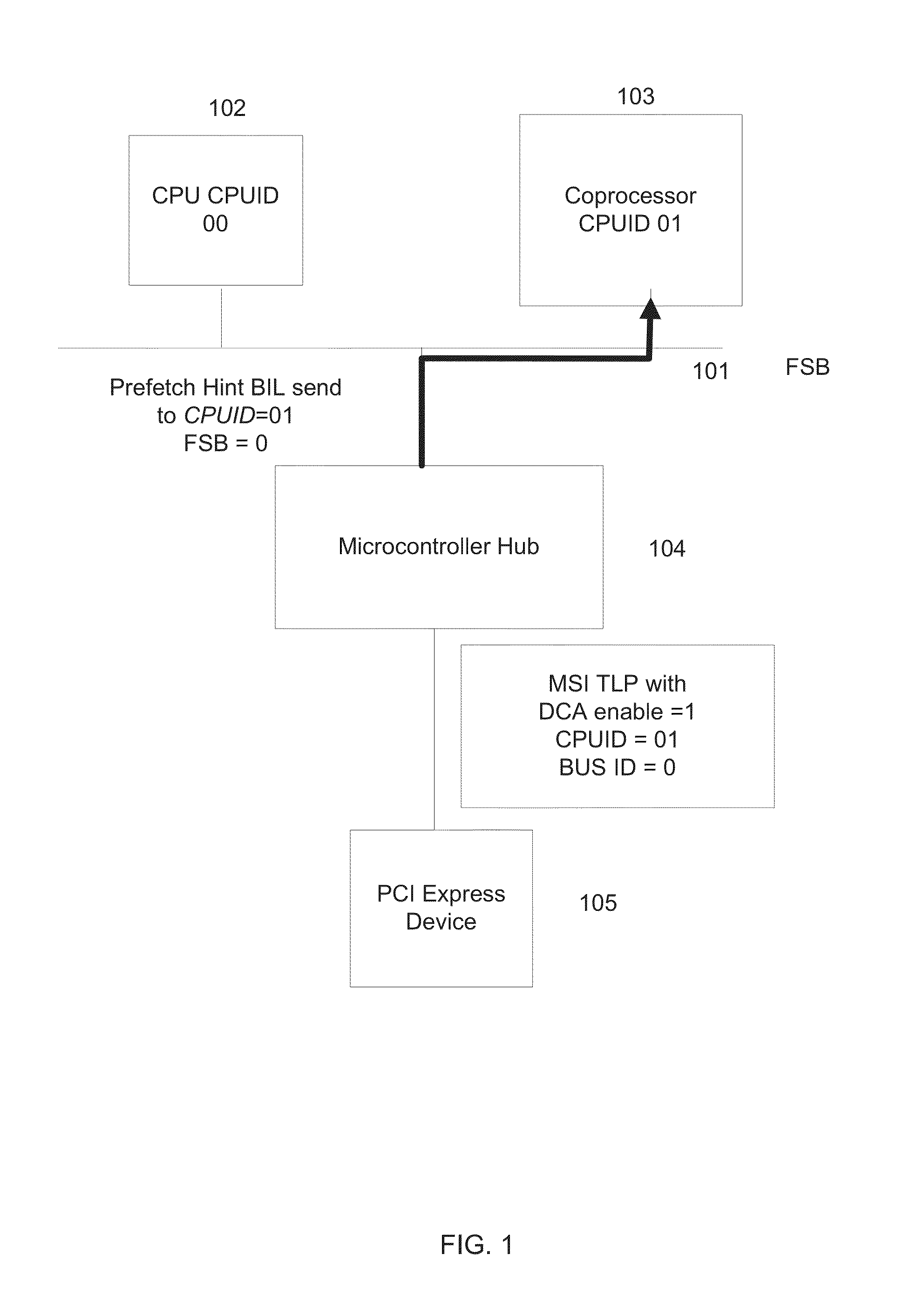
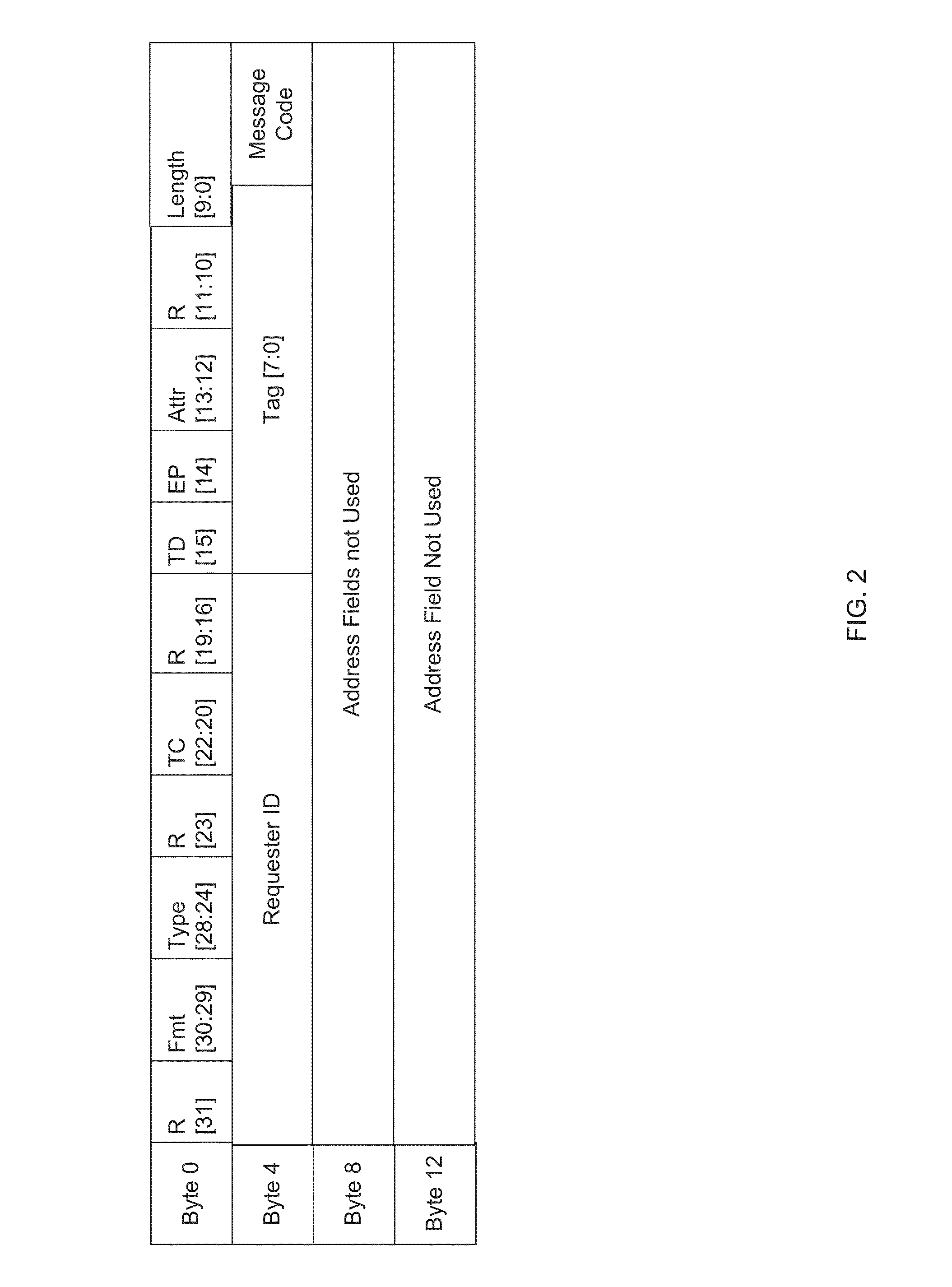
System and deterministic method for servicing MSI interrupts using direct cache access
A system and method for creating a guaranteed MSI latency by coupling a coprocessor, which may be a dedicated agent, to the existing front side bus (“FSB”) in a processor (e.g., Intel® Atom™ processor) to handle deterministic interrupts. MSI interrupts may be automatically forwarded to the coprocessor using the existing DirectCache Access field. Users may control the handling time and methodology of MSI interrupts.
Owner:INTEL CORP
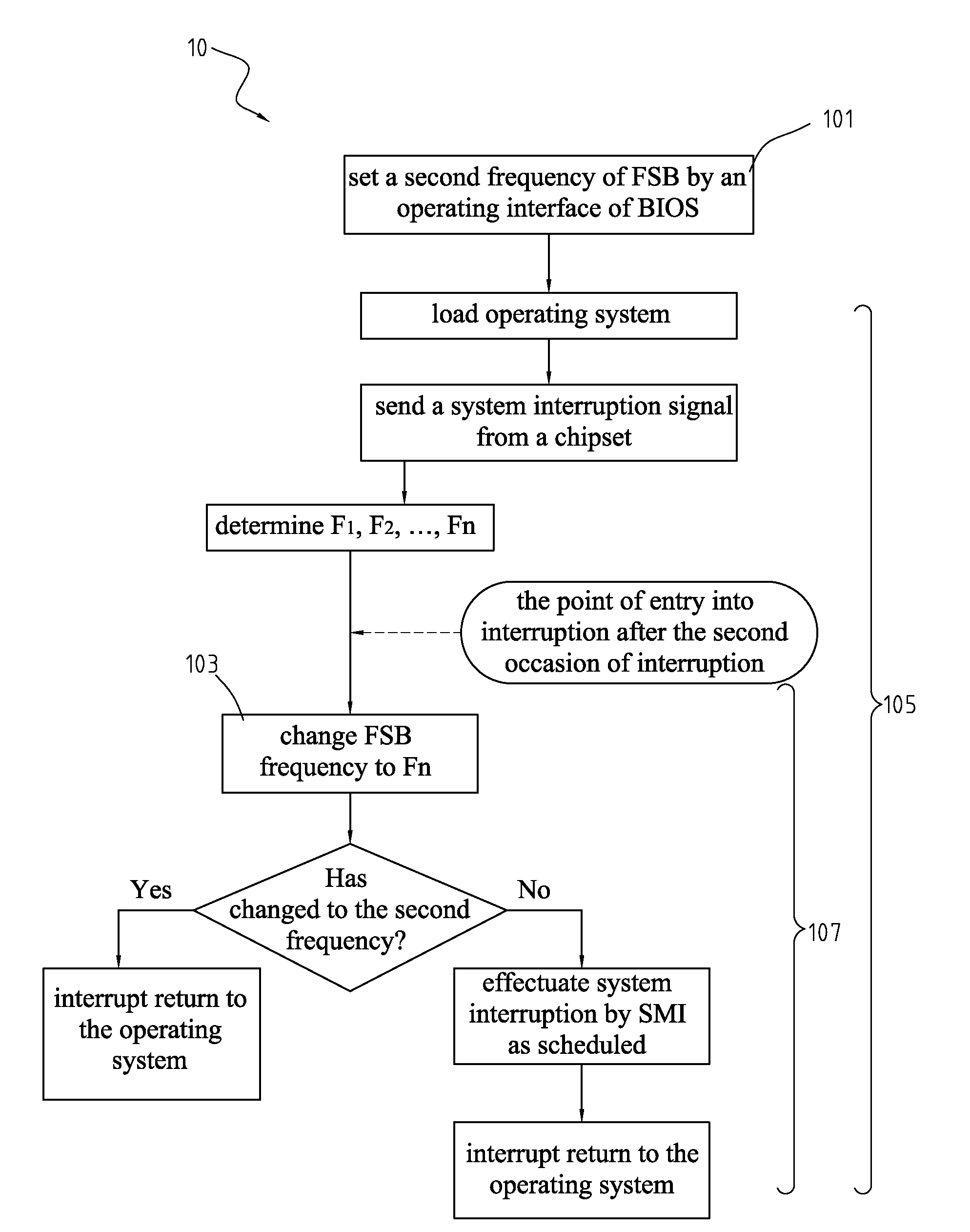
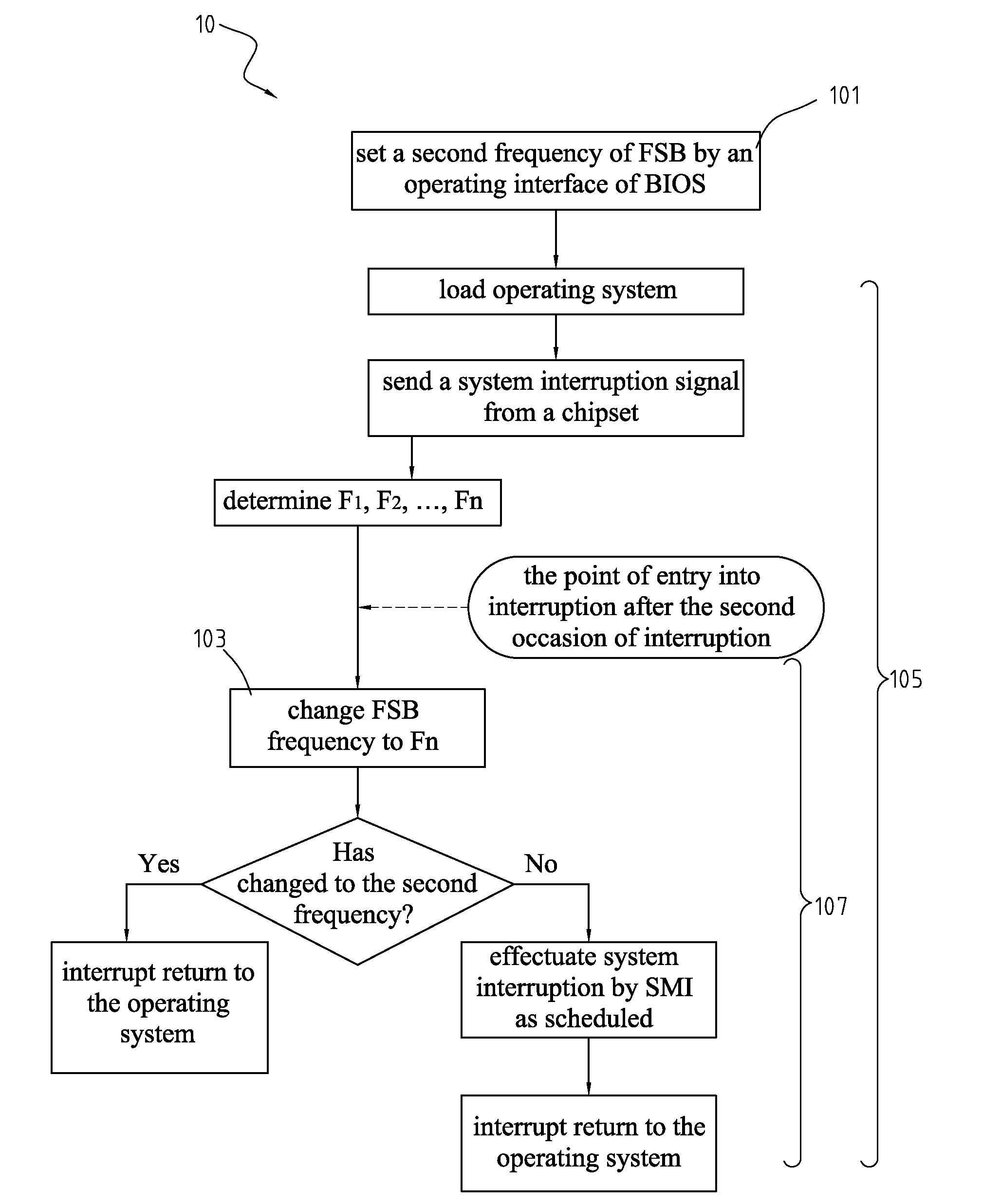
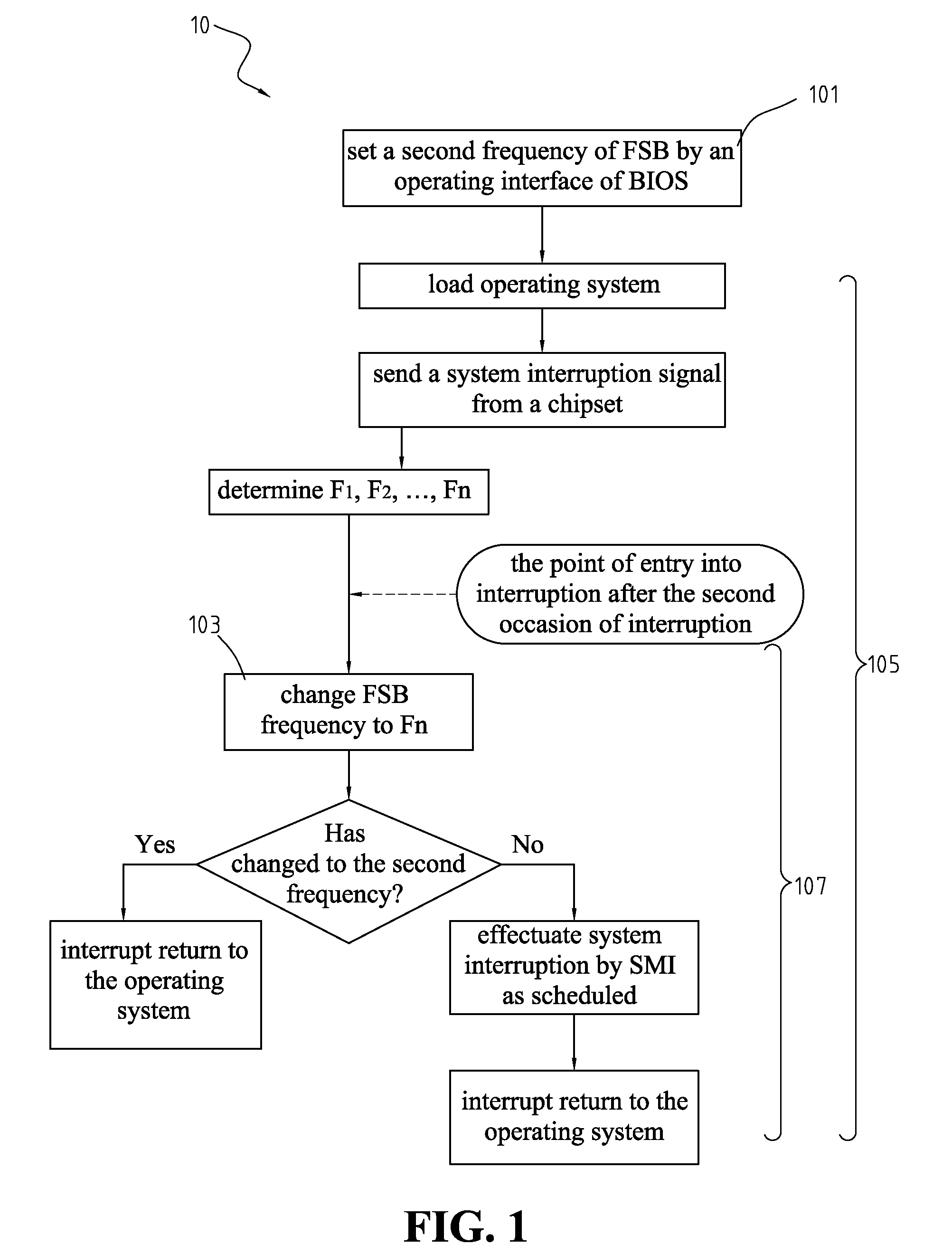
Method for overclocking central processing unit of computer motherboard
A method for overclocking a central processing unit (CPU) of a computer motherboard is disclosed. Step A is to set a second frequency of front side bus (FSB) by an operating interface of BIOS. Step B is to determine FSB frequency Fn at each of N stages according to a difference between a first frequency and the second frequency. Step C is to load the CPU with an operating system by booting the CPU at the first frequency of FSB, and send an interruption signal to the CPU from a chipset at predetermined intervals upon completion of the loading of the operating system so as to allow the BIOS to gain control over the CPU, and execute step D by the CPU on each of N occasions of interruption until the FSB frequency of the CPU is changed to the second frequency. Step D is to execute the BIOS by the CPU on the nth occasion of interruption such that the CPU operates at the FSB frequency Fn, and allow the operating system to resume control over the CPU.
Owner:MSI COMP SHENZHEN
Architecture for a physical interface of a high speed front side bus
A high speed computer processor system includes a high speed interface for a graphics processor. In a preferred embodiment, the high speed interface includes a front side bus (FSB) that interfaces to a similar high speed interface on the graphics processor.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Integrating programmable logic into personal computer (pc) architecture
InactiveCN101427217AComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionEnergy efficient computingGeneral purposeCoprocessor
A portion of chip die real estate is allocated to blocks of programmable logic (PL) fabric. These blocks can be used to load special purpose processors which operate in concert with the general purpose processors (GPPs). These processors, implemented in PL, may integrate with a PC system architecture. Blocks of PL are integrated with fixed blocks of logic interfaces connecting, for example, to a system's front side bus. This facilitates configuration of the PL as coprocessors or other devices that may operate as peers to GPPs in the system. Moreover, blocks of PL may be integrated with fixed logic interfaces to existing IO buses within a system architecture. This facilitates configuration of the PL as soft devices, which may appear to the system as physical devices connected to the system. These soft devices can be handled like physical devices connected to the same or similar IO buses.
Owner:MICROSOFT CORP
Overclocking CPU with stepwise increase in frequency by BIOS gaining control upon interrupt generated at predetermined intervals
A method for overclocking a central processing unit (CPU) of a computer motherboard is disclosed. Step A is to set a second frequency of front side bus (FSB) by an operating interface of BIOS. Step B is to determine FSB frequency Fn at each of N stages according to a difference between a first frequency and the second frequency. Step C is to load the CPU with an operating system by booting the CPU at the first frequency of FSB, and send an interruption signal to the CPU from a chipset at predetermined intervals upon completion of the loading of the operating system so as to allow the BIOS to gain control over the CPU, and execute step D by the CPU on each of N occasions of interruption until the FSB frequency of the CPU is changed to the second frequency. Step D is to execute the BIOS by the CPU on the nth occasion of interruption such that the CPU operates at the FSB frequency Fn, and allow the operating system to resume control over the CPU.
Owner:MSI COMP SHENZHEN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00000.png)
![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00001.png)
![[method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency] [method for dynamically adjusting CPU requency]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/5c651547-426c-417b-b45c-ce0a92af810f/US20050125705A1-20050609-D00002.png)