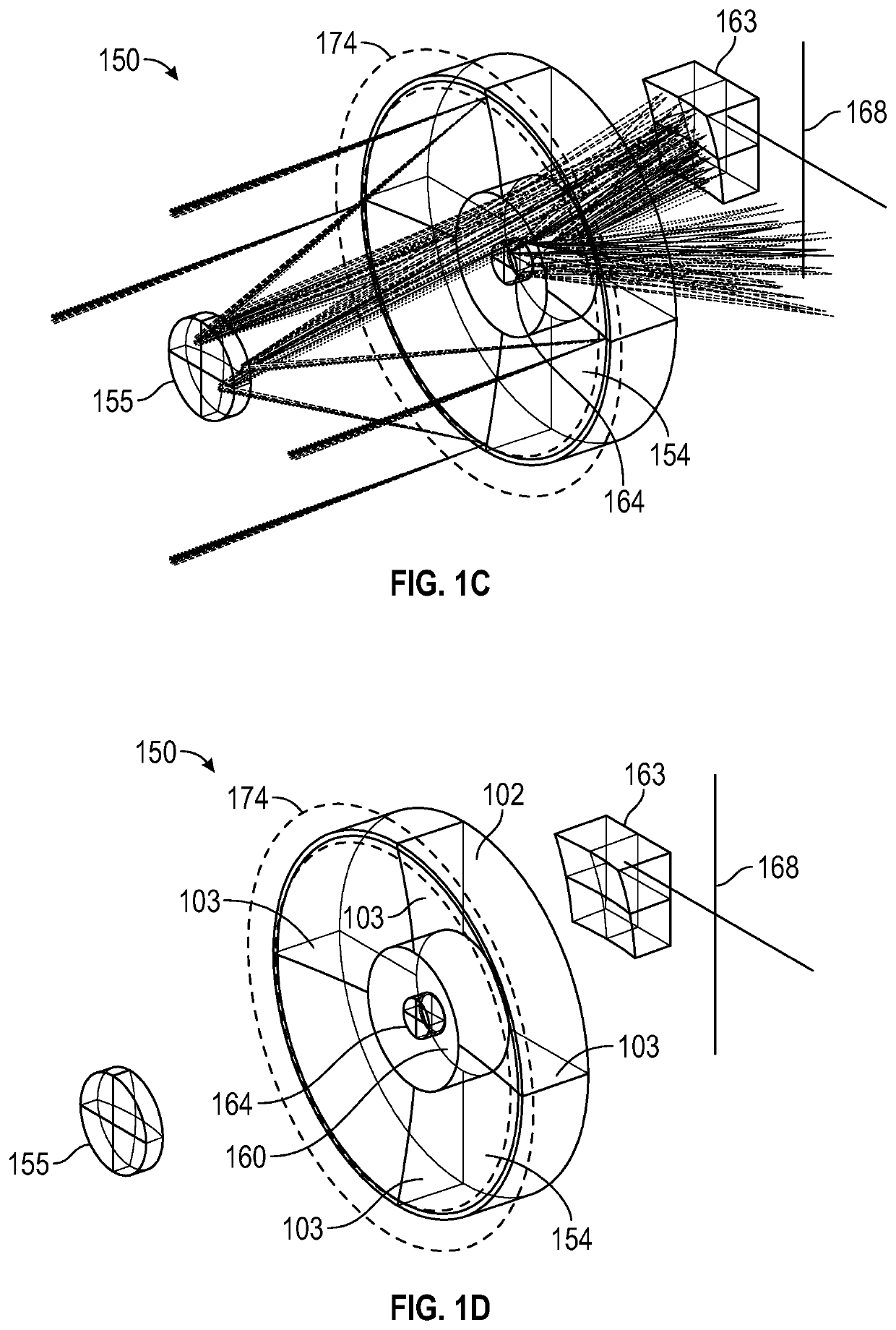
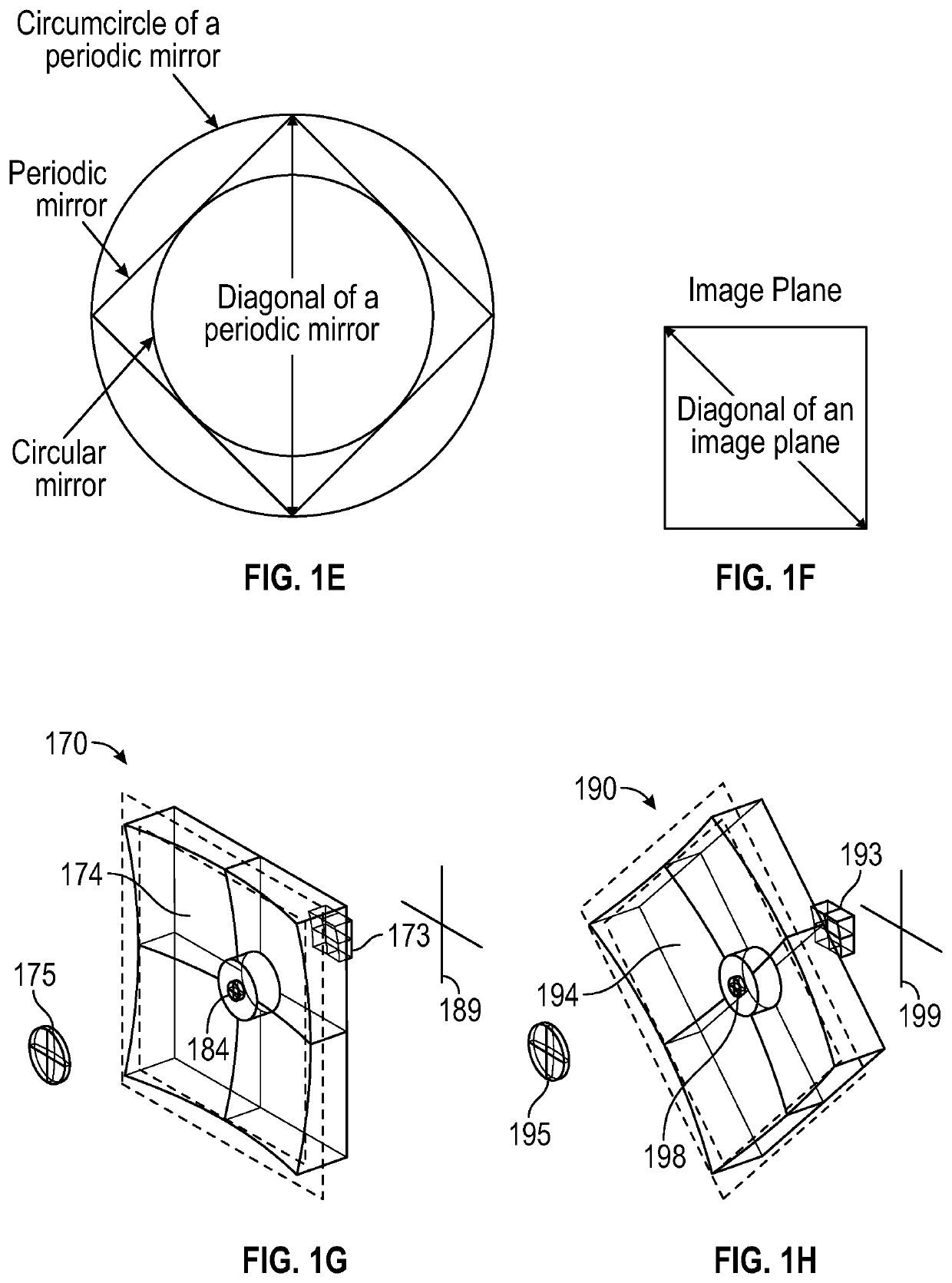
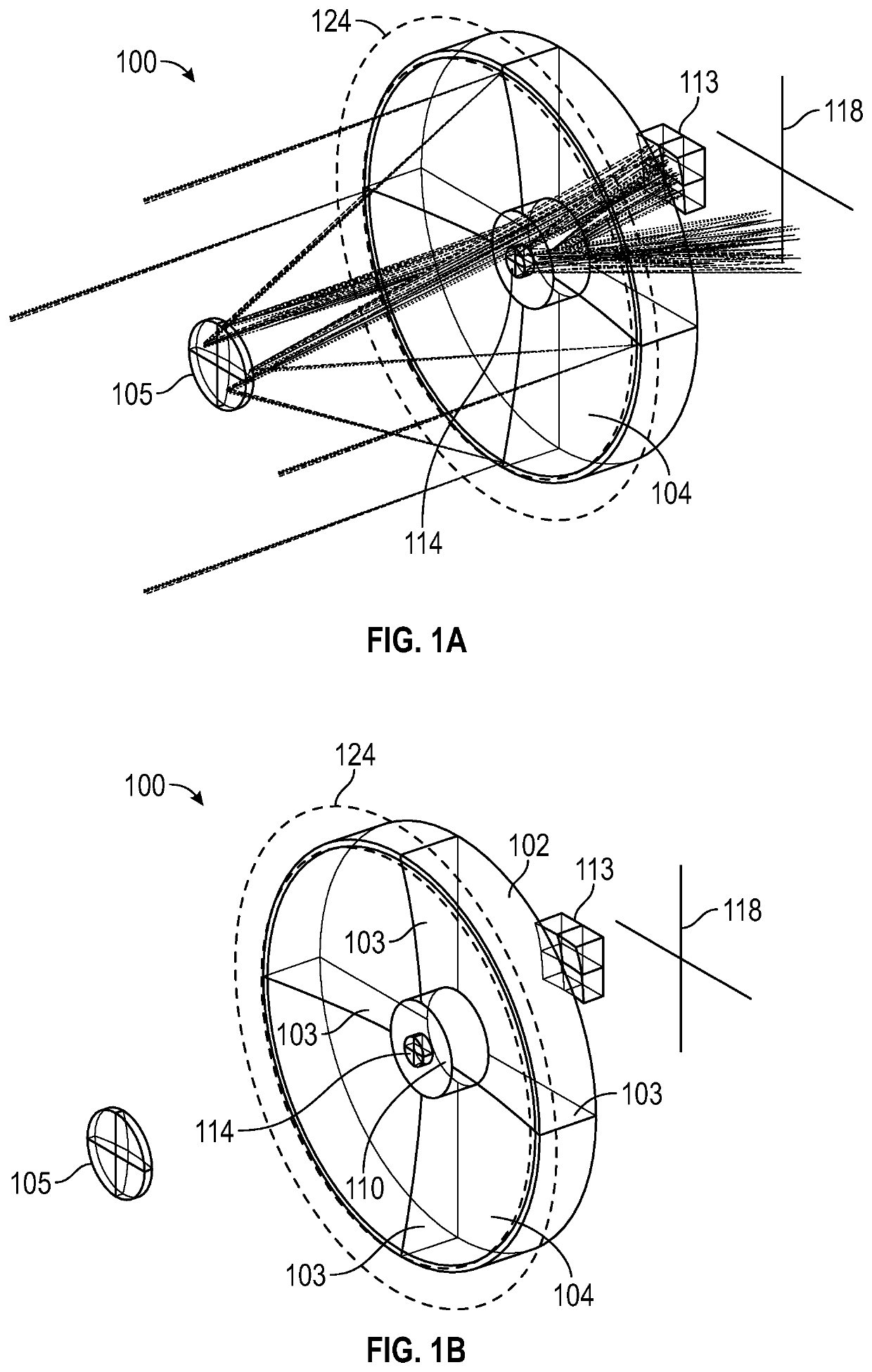
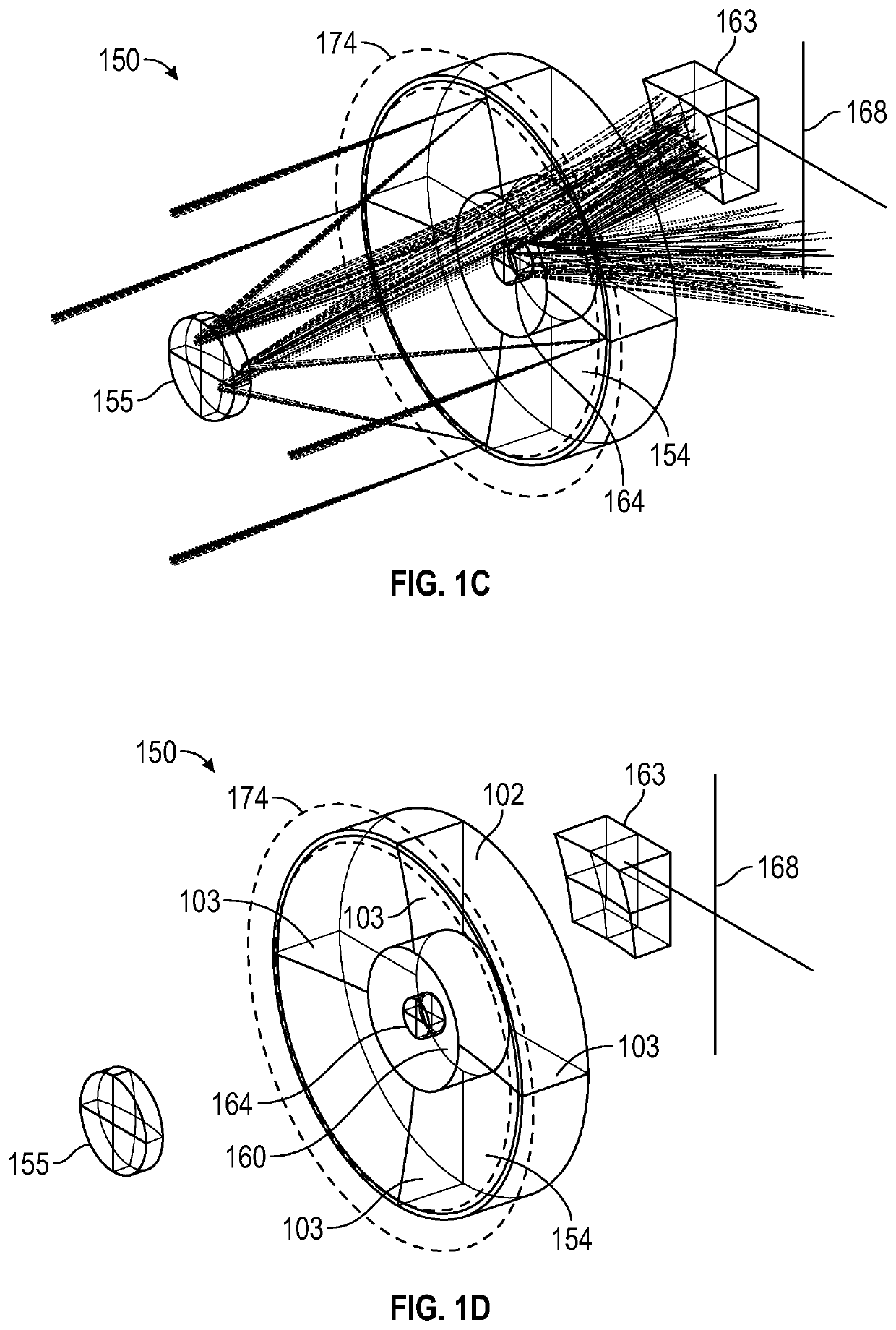
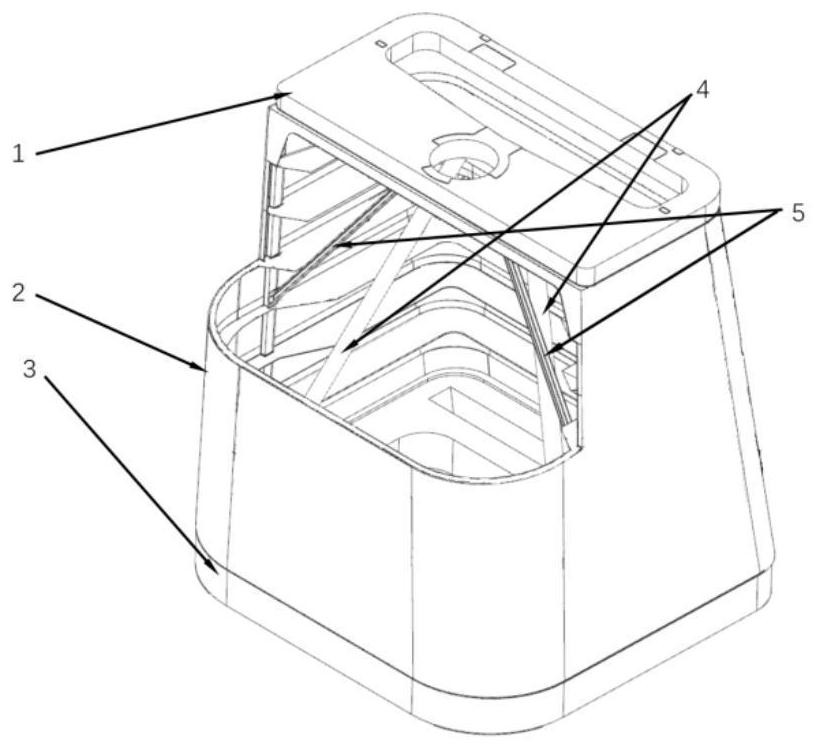
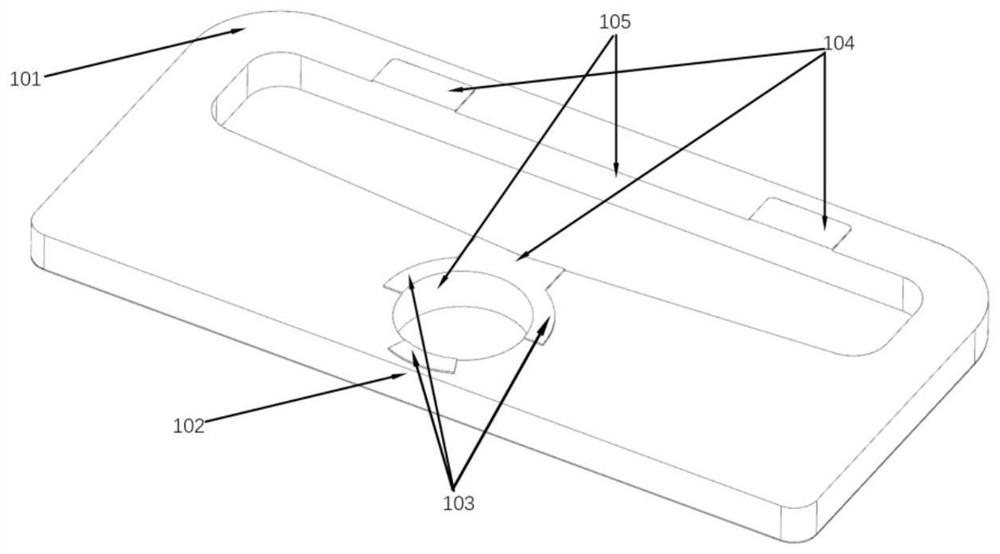
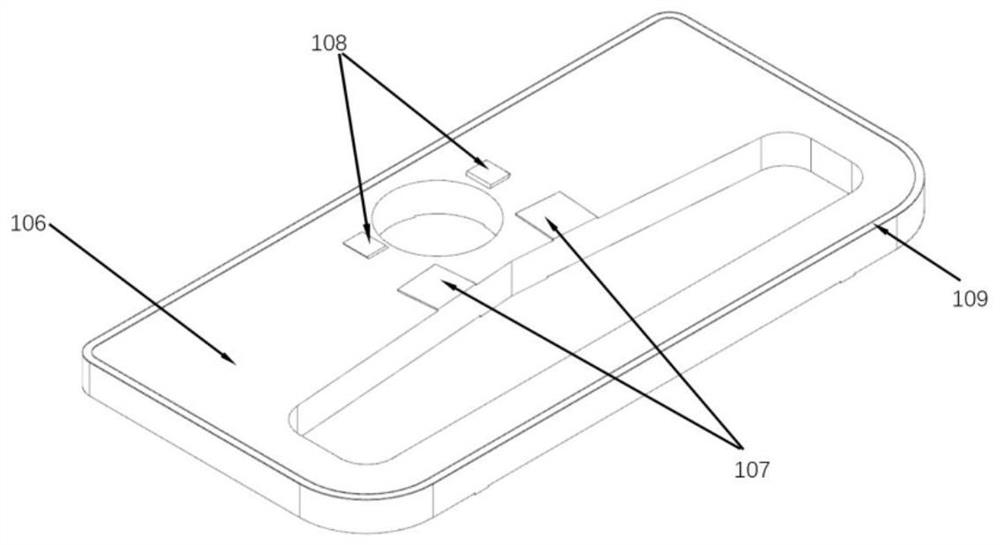
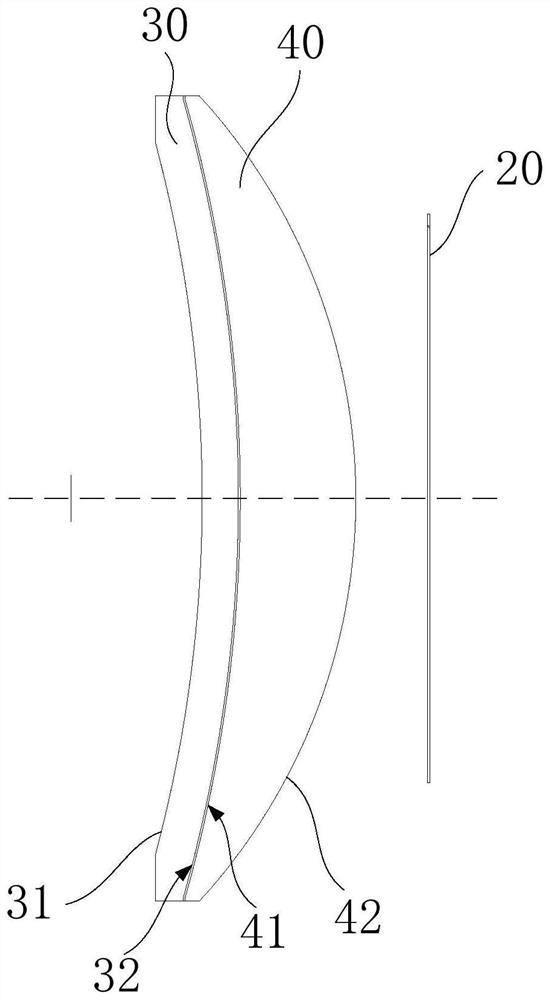
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Foldscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
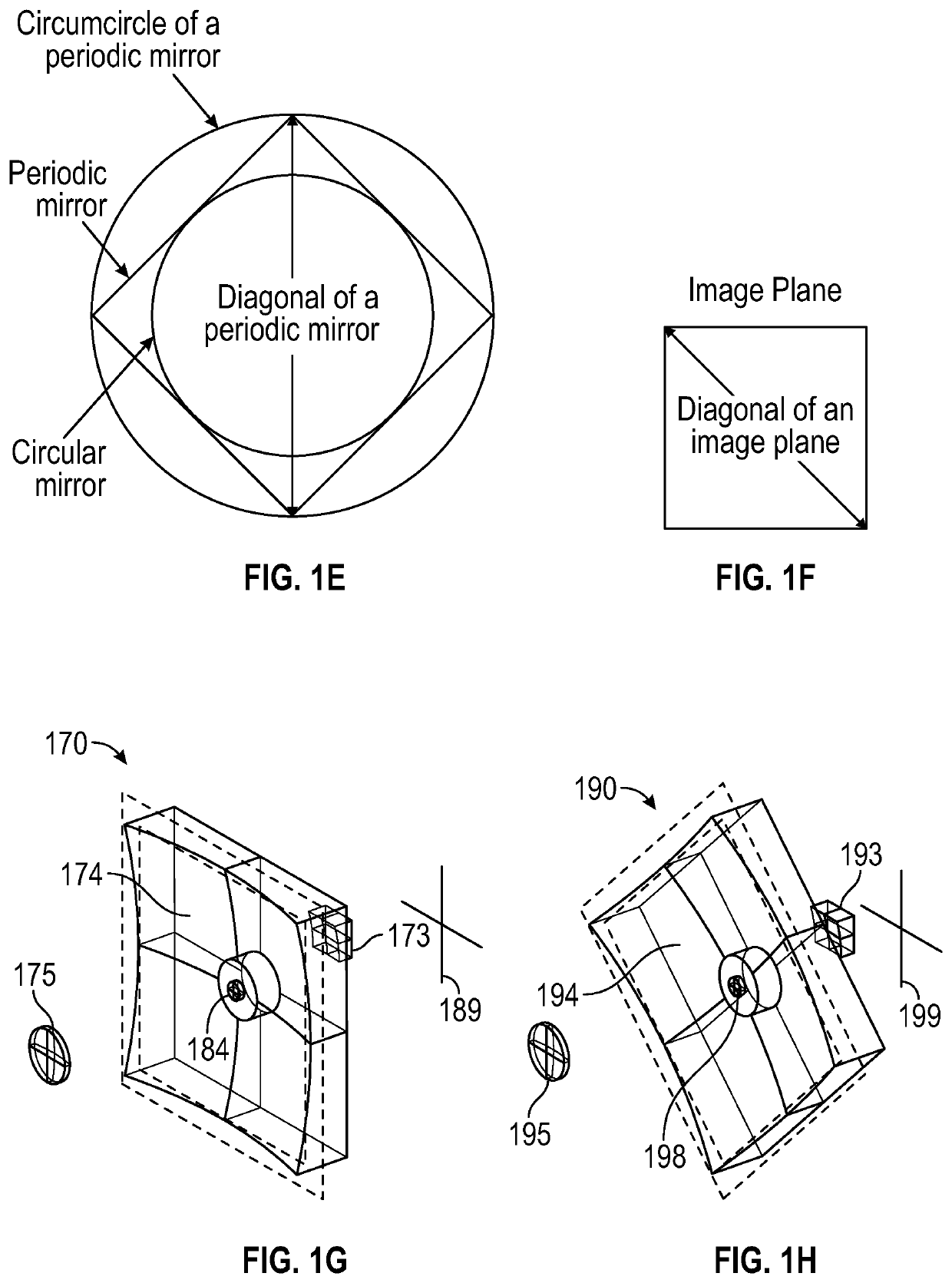
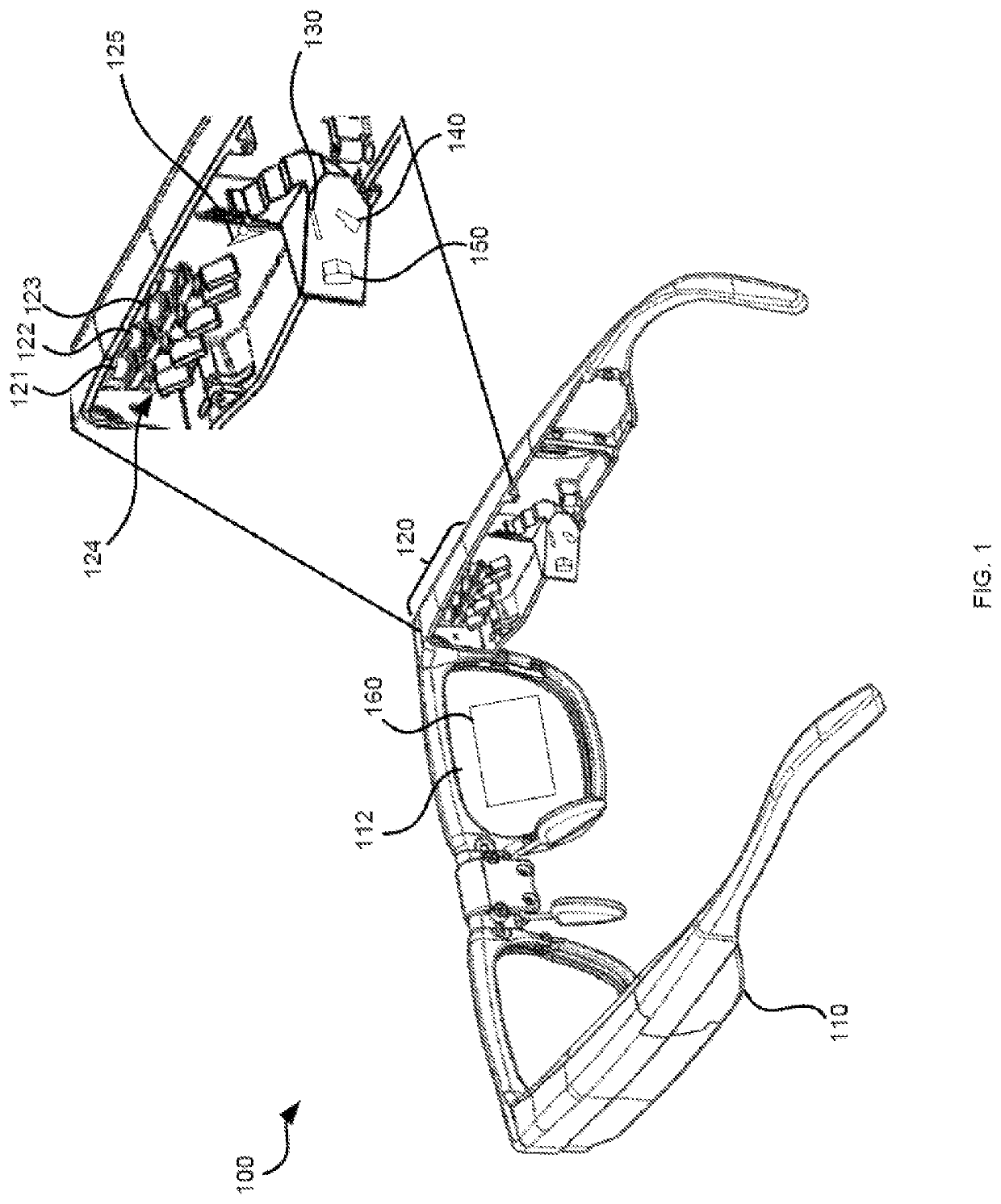
A Foldscope is an optical microscope that can be assembled from simple components, including a sheet of paper and a lens. It was developed by Manu Prakash and designed to cost less than US$1 to build. It is part of the "frugal science" movement which aims to make cheap and easy tools available for scientific use in the developing world.
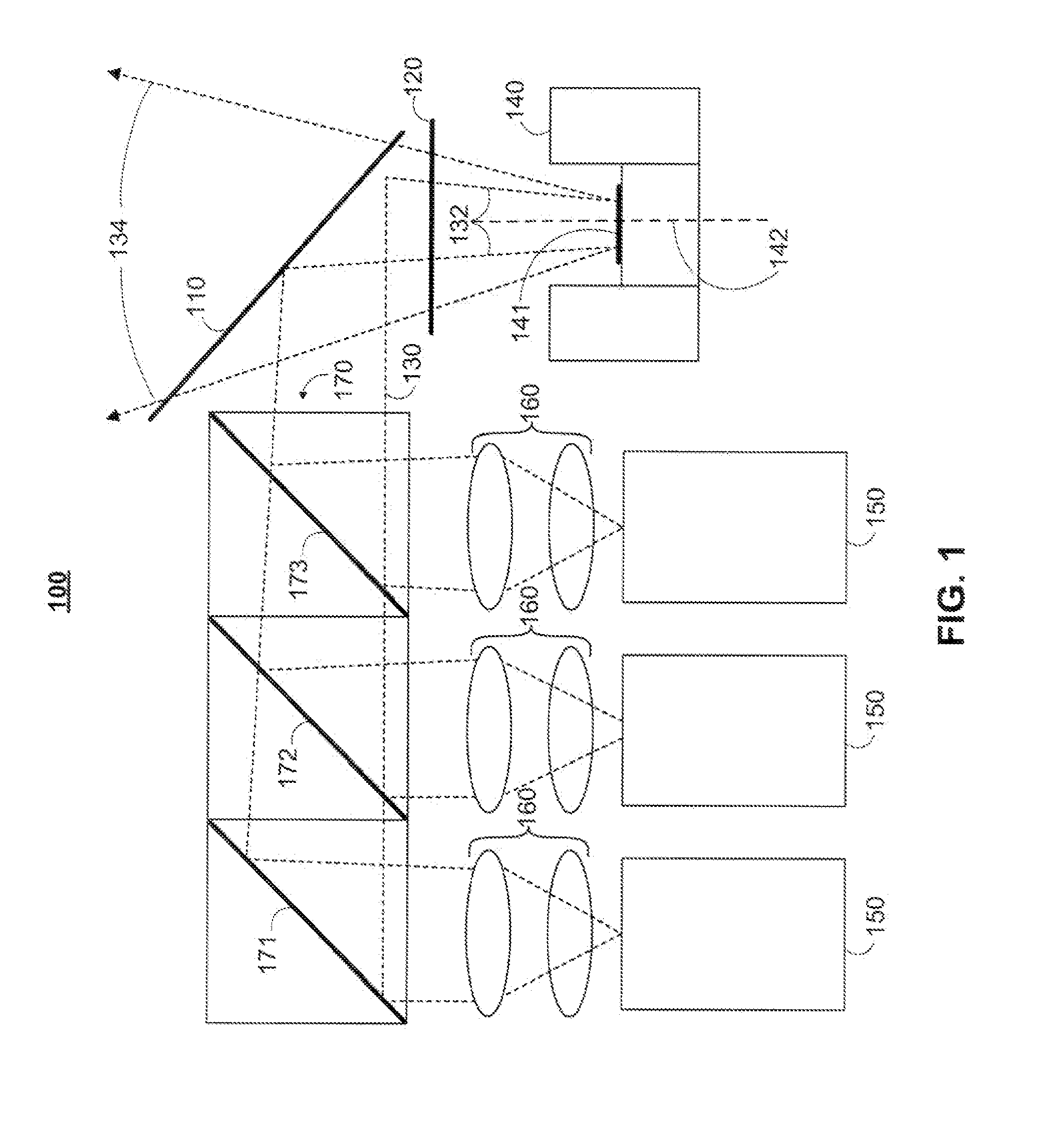
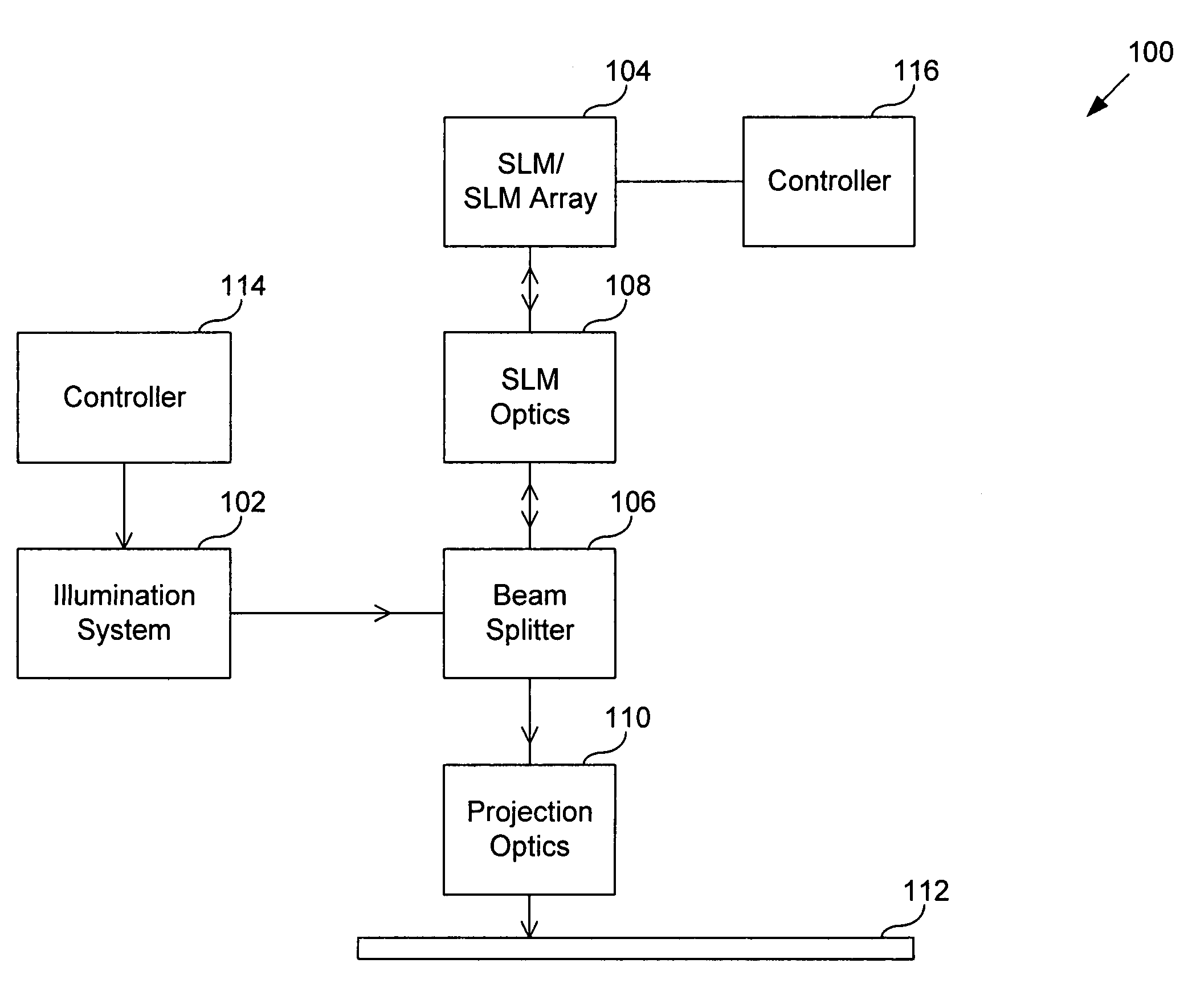
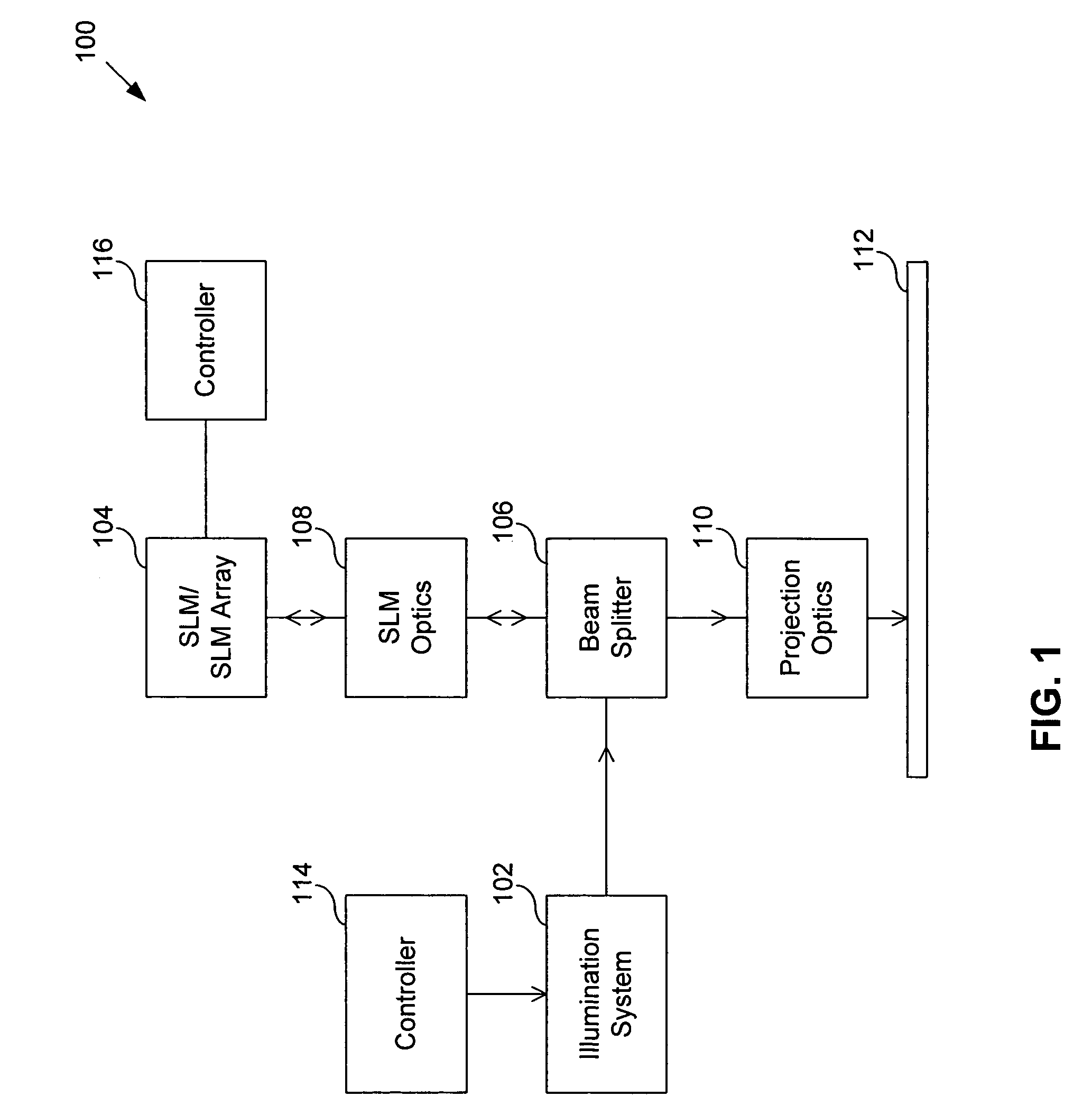
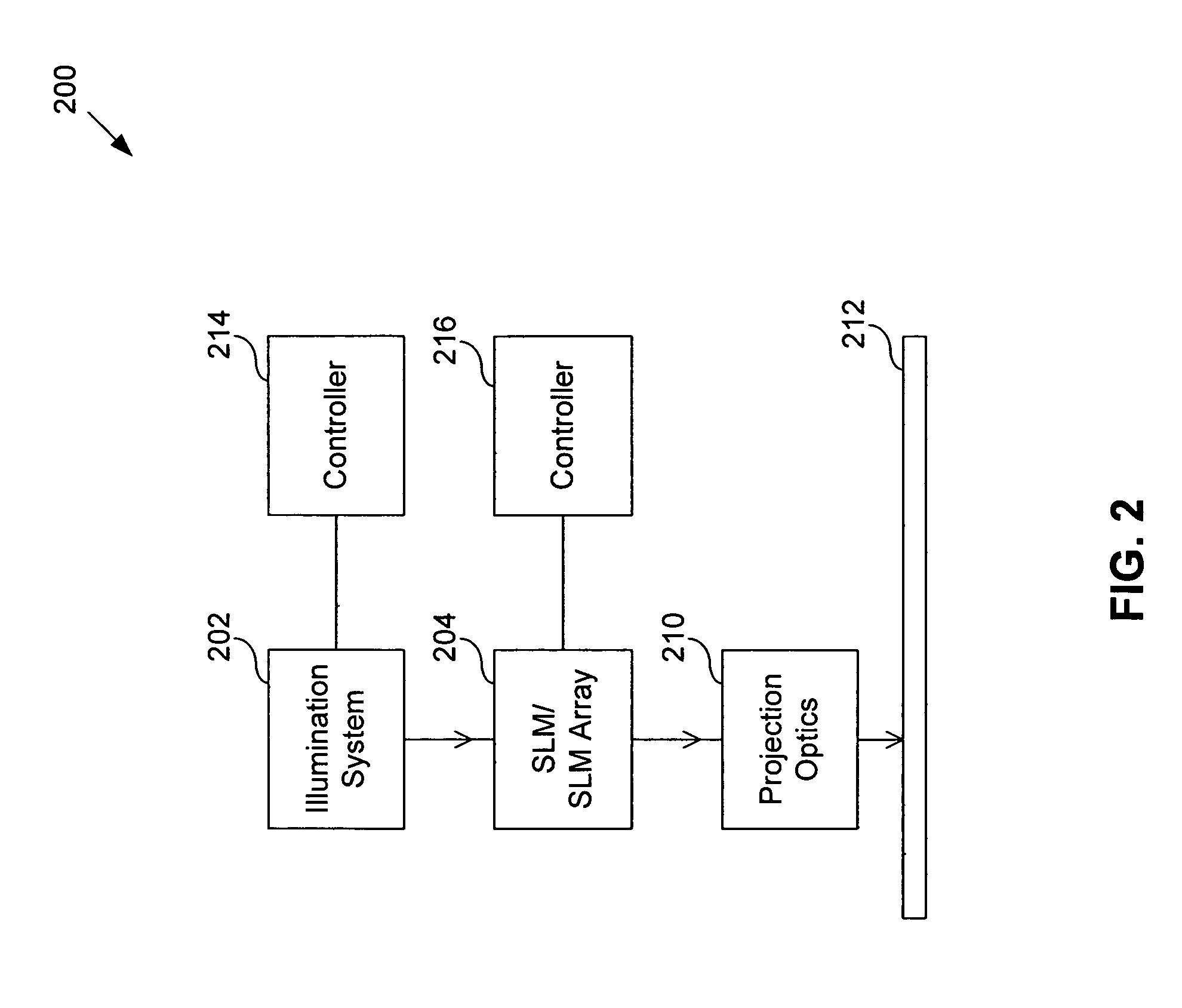
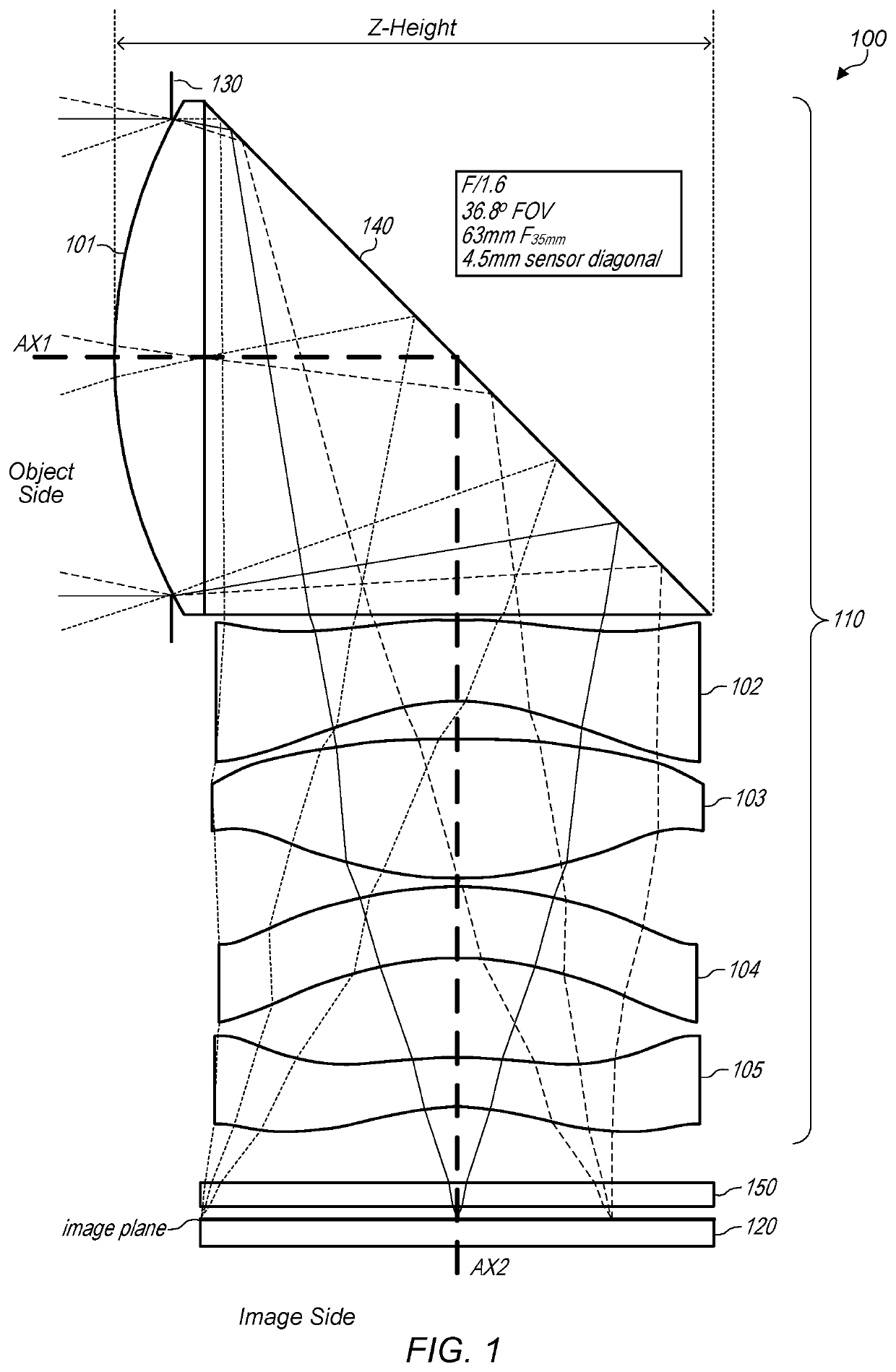
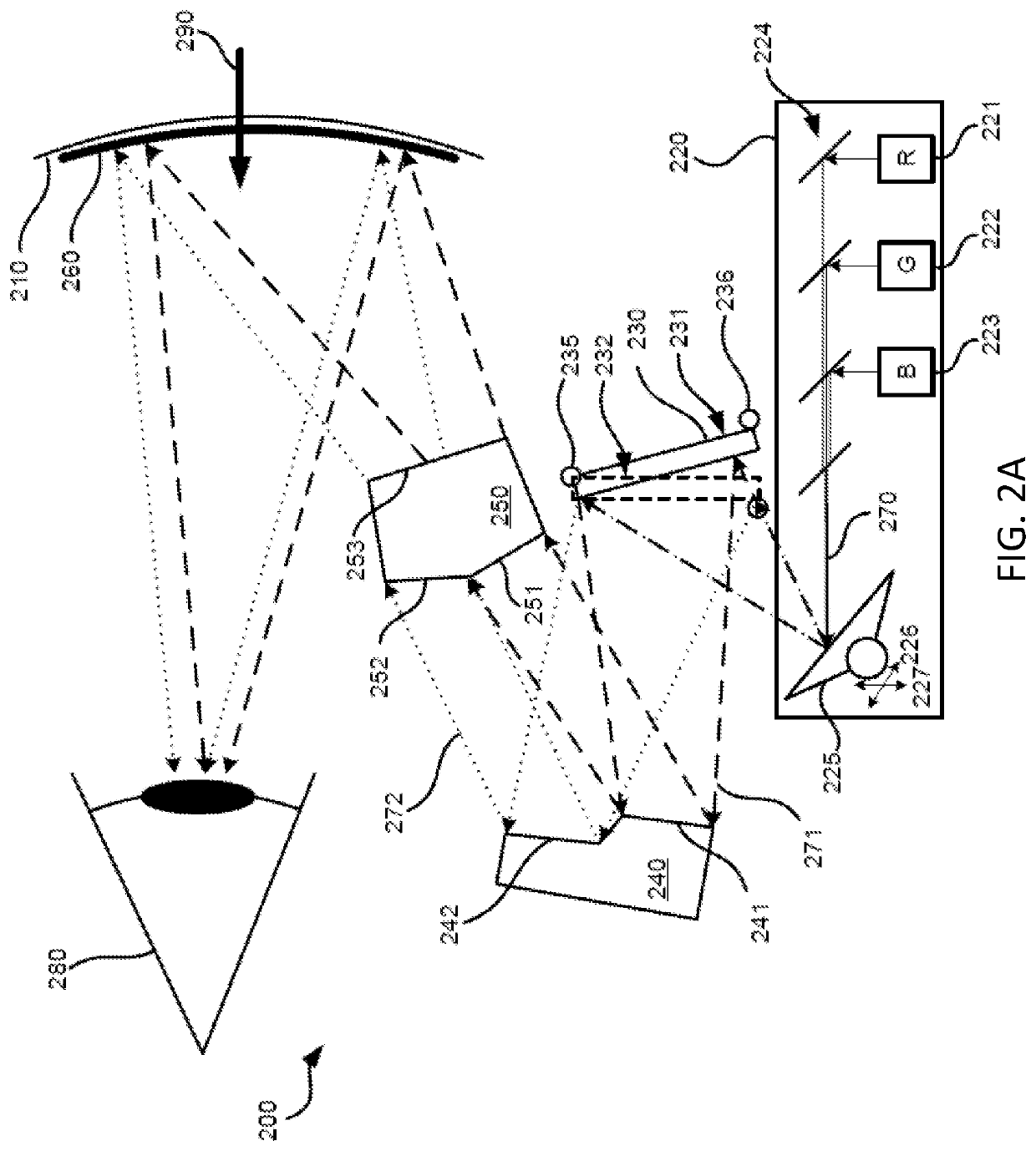
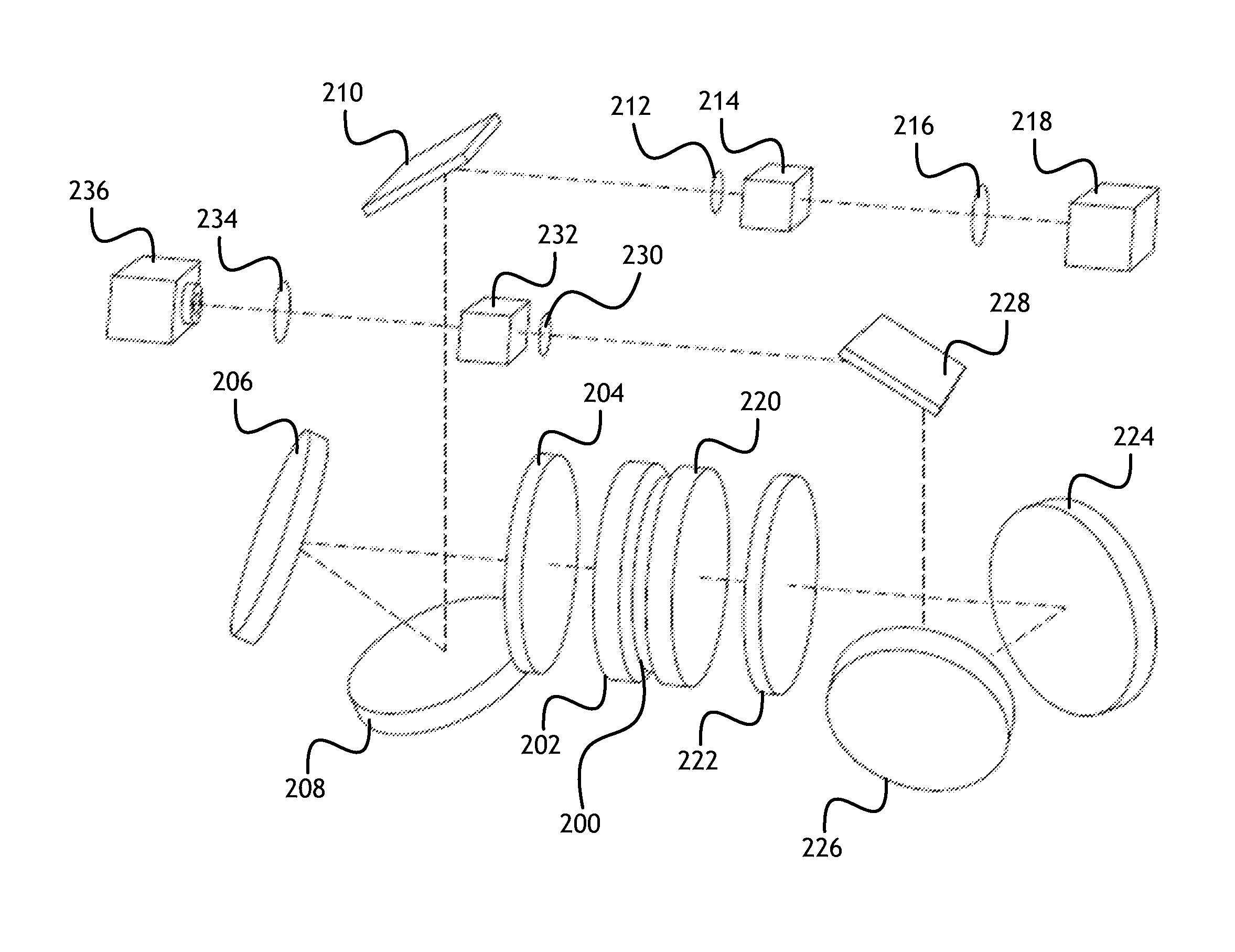
Mems-based projector suitable for inclusion in portable user devices
InactiveUS20080037090A1Reduce the overall heightReduce in quantityColor television detailsOptical elementsMultiple componentPrism
A MEMS-based projector may be included in various user devices. A selective fold mirror, a MEMS-based projector, and a polarization rotator may be oriented to reflect a beam within the device for external projection. Alternatively, a total internal reflection prism may take the place of a selective fold mirror or a polarization rotator and may reduce the number of necessary components in the user device. Various optical components may be placed in the MEMS-based projector and arranged in different positions to reflect a light beam in a desired direction for external projection. The components that make up the MEMS-based projector may depend on the available footprint in the device and the direction in which the light beam is to be projected. Some optical components may provide multiple functionalities which would otherwise require multiple components and may reduce the size of the projector.
Owner:MICROVISION
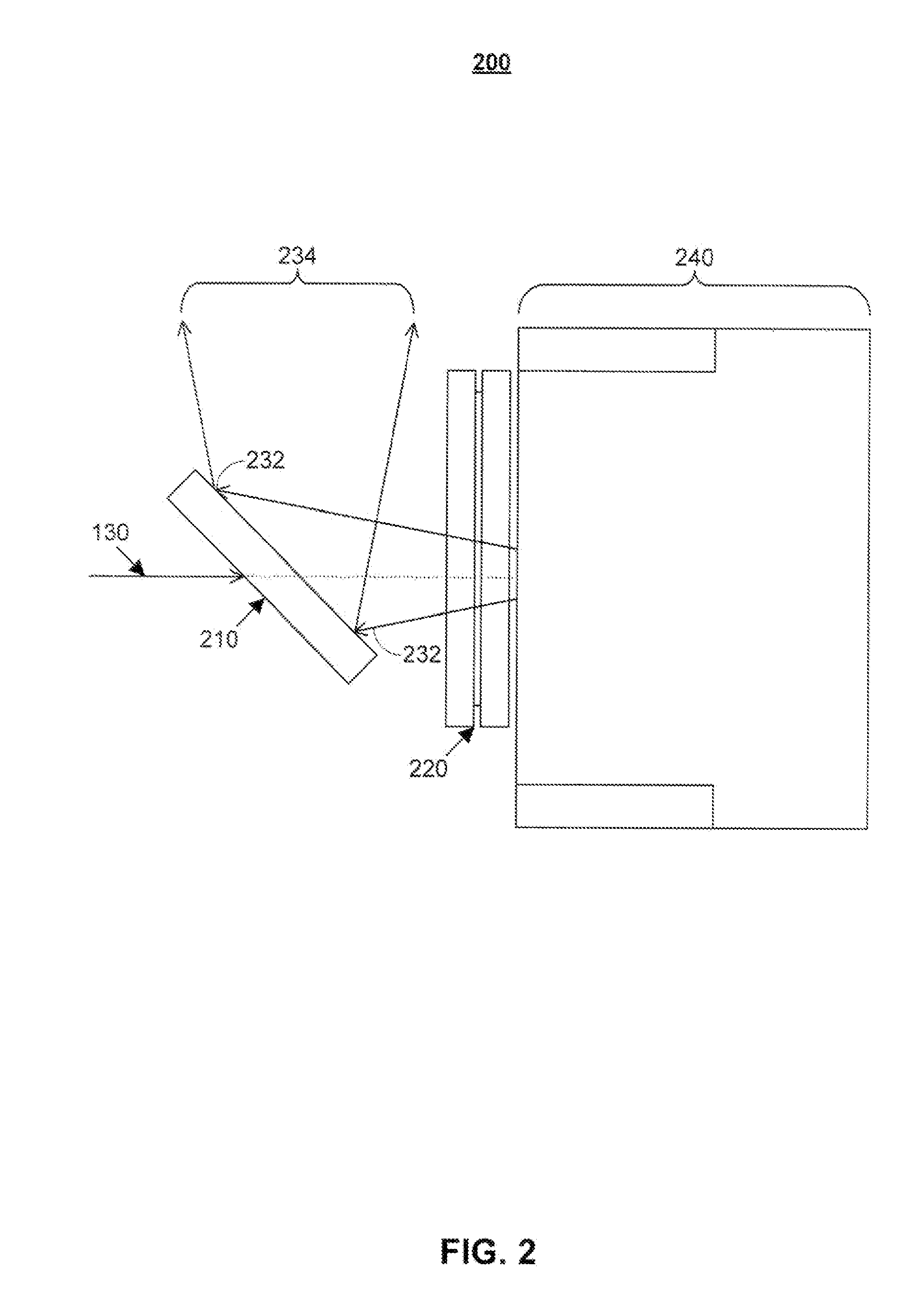
Image-based code reader for acquisition of multiple views of an object and methods for employing same
ActiveUS8322621B2Visual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationDepth of fieldCard reader
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
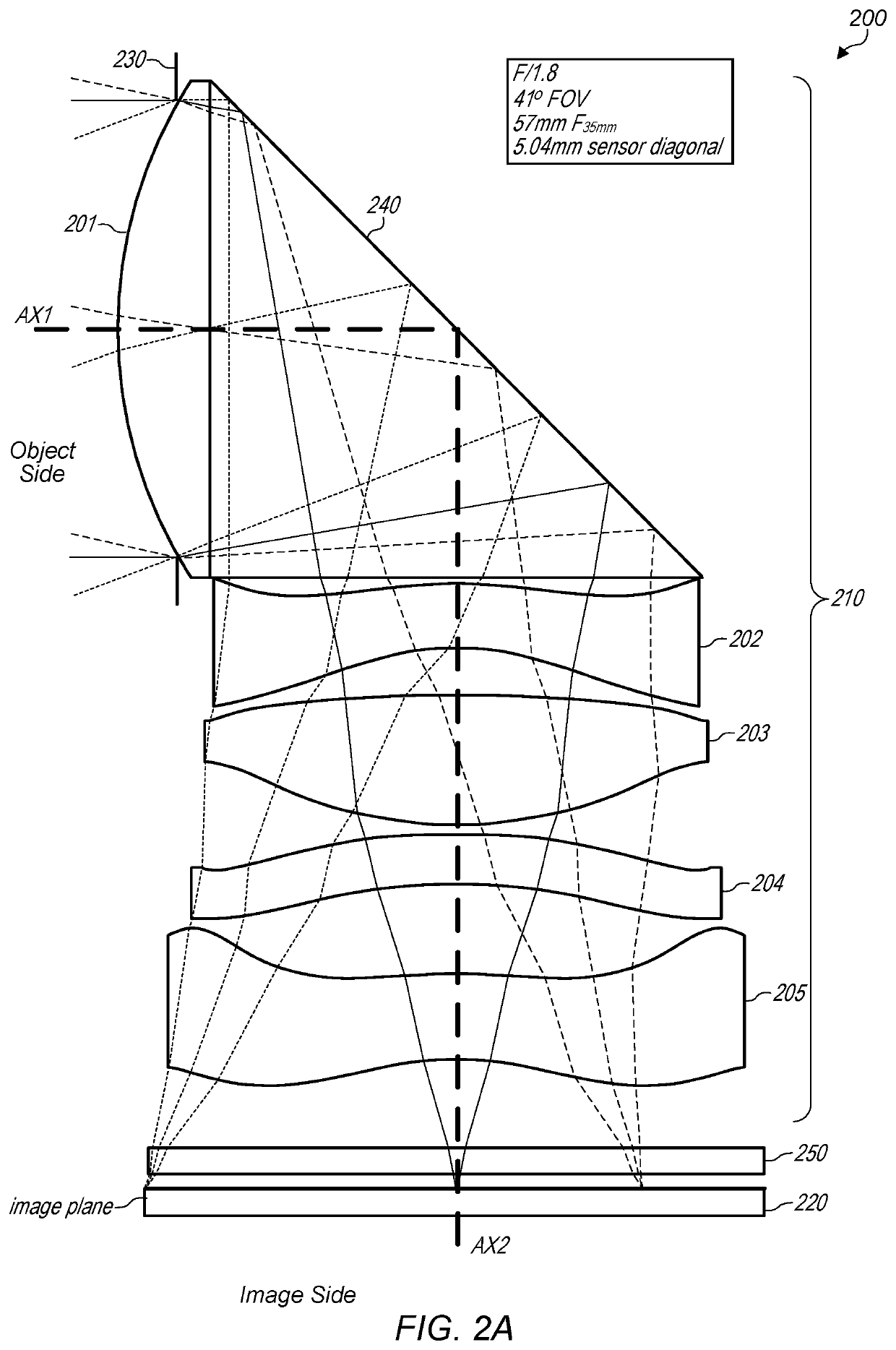
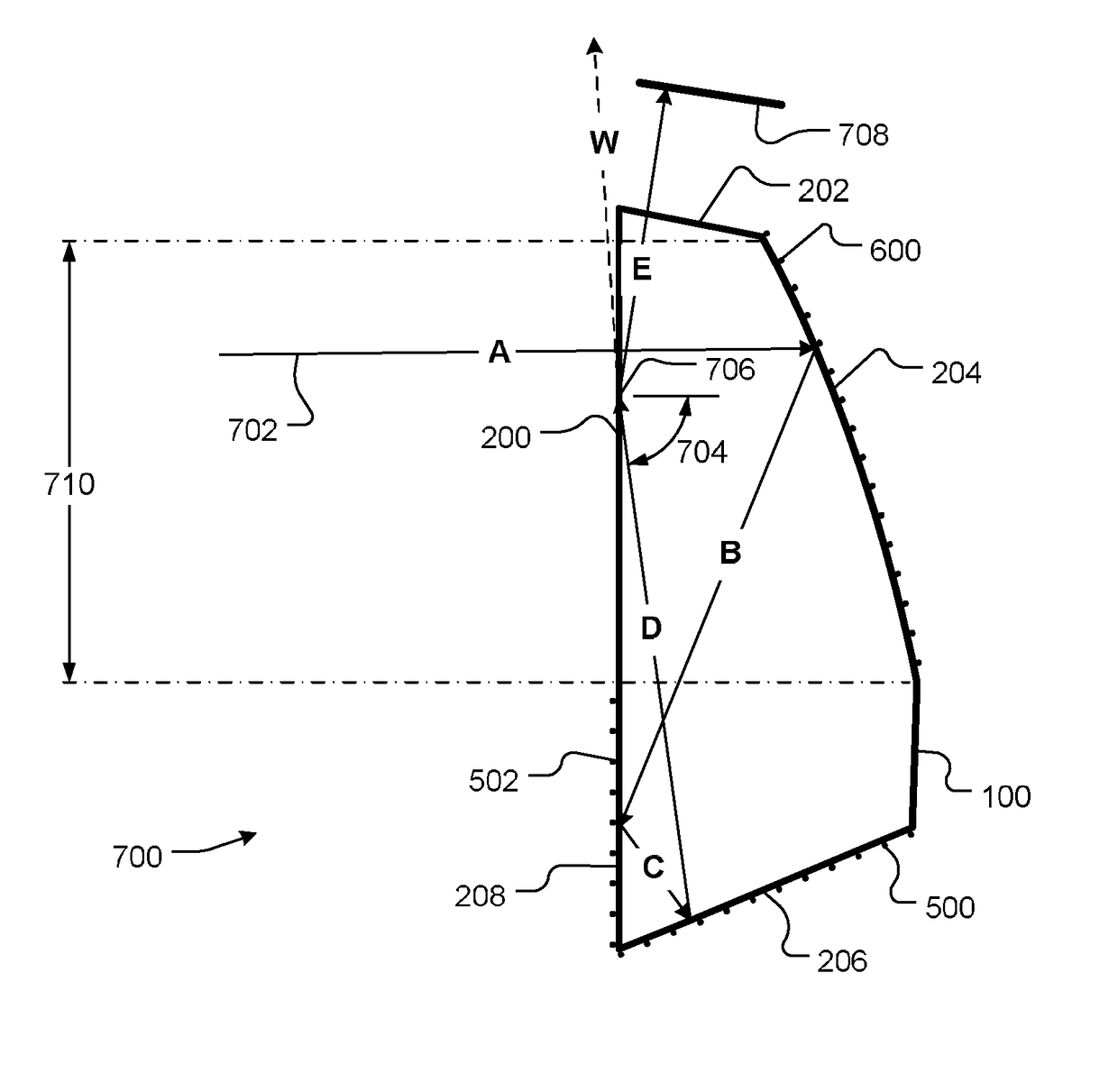
Folded lens system
ActiveUS20190196148A1Reduce and eliminate interferenceProvide functionalityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPhysicsPrism
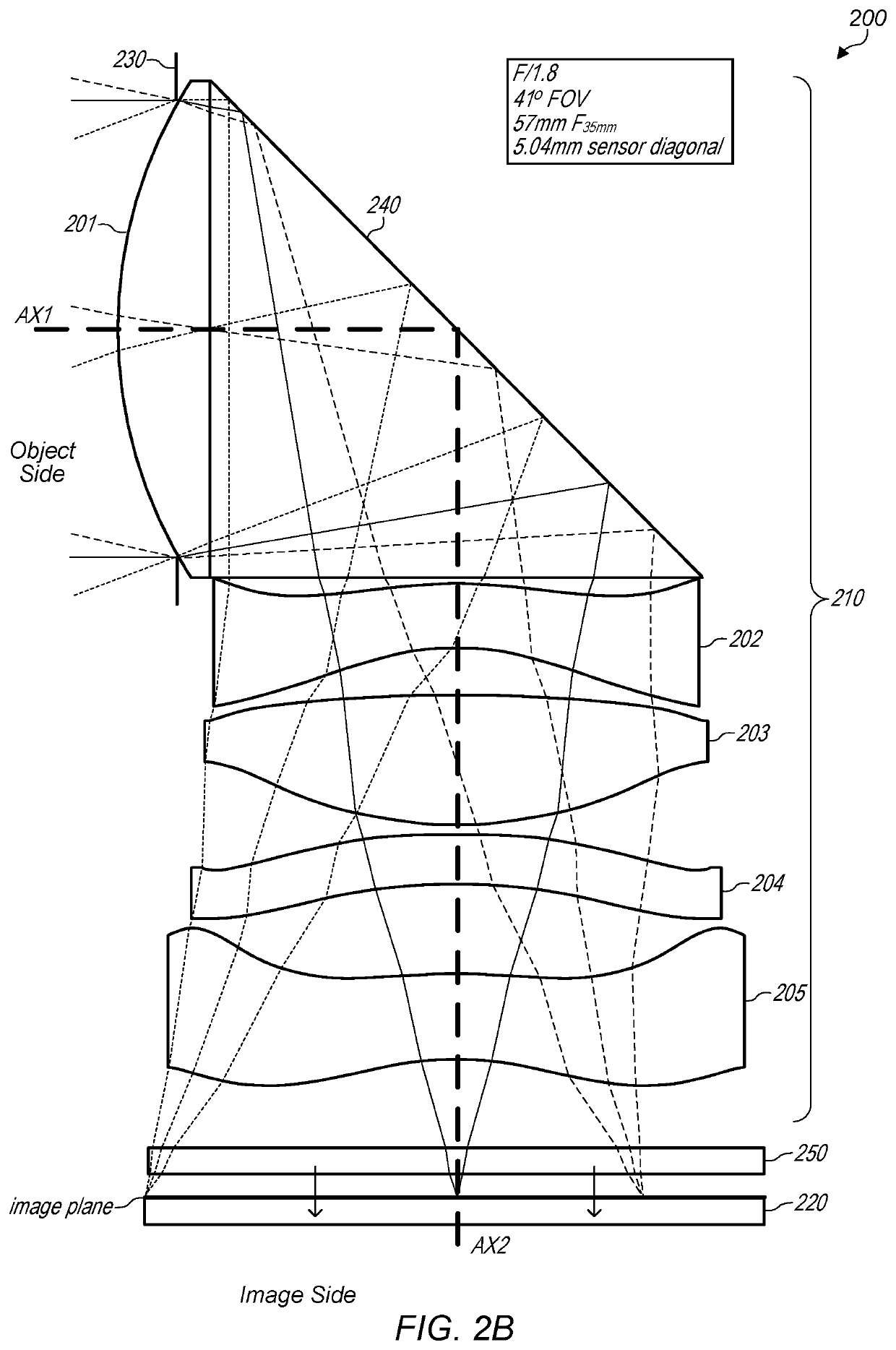
A folded lens system that includes lenses with refractive power and two light folding elements such as prisms. A first lens on a first axis refracts light to a first folding element. The first folding element redirects the light from the first axis onto a second axis on which one or more lenses are arranged. The lenses on the second axis refract the light to a second folding element. The second folding element redirects the light onto a third axis on which a sensor is disposed. The lens system may include a front aperture. The sensor may be moved on the third axis to provide autofocusing, or alternatively the lens system may include one or more optical actuators that provide autofocusing. The lens system may have a low F-number (<=2.8), and may have a 35 mm equivalent focal length in the medium to long telephoto range.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for calibrating a spatial light modulator array using shearing interferometry
InactiveUS6965436B2Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansSpatial light modulatorGrating
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Optical lens and electronic device
InactiveCN110764232AShorten the lengthEasy to placeCamera body detailsOptical elementsMedicineEngineering
The application discloses an optical lens and an electronic device, and the optical lens comprises a first reflector, a lens module, a second reflector and an image sensor, wherein the light incidentfrom the outside is reflected by the first reflector and then enters the lens module, the light emitted from the lens module is incident to the second reflector, the light reflected by the second reflector is converged to the image sensor, and the image sensor is used for converting the focused light into an electrical signal for imaging. The optical lens and the electronic device according to theembodiment of the application fold the optical path between the lens module and the image sensor through the second reflector to reduce the length of the optical lens, which facilitates the placementof components on the main board of the electronic device, facilitates layout, and at the same time, is beneficial to achieve a long focal length optical lens.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
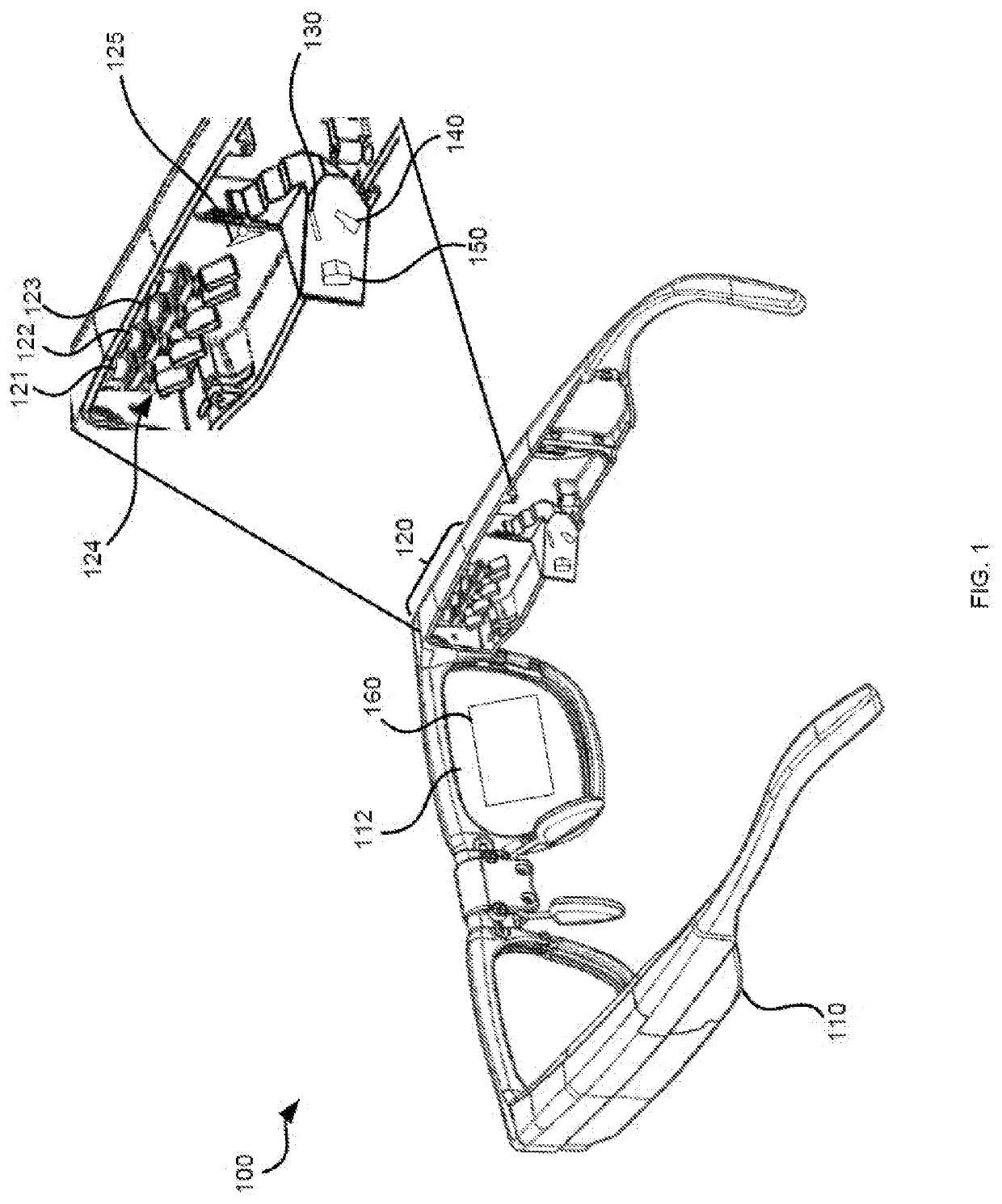
Systems, devices, and methods for increasing resolution in wearable heads-up displays
Systems, devices, and methods for increasing resolution in wearable heads-up displays (WHUD) are described. A WHUD includes a support structure, a scanning laser projector (SLP), a fold mirror, a split mirror, an optical splitter, and an optical combiner. When the WHUD is worn on the head of a user, the optical combiner is positioned in a field of view of the user. The SLP scans light signals onto the fold mirror which reflects light onto one of at least two reflective surfaces of the split mirror, based on a state of the fold mirror. The split mirror redirects the light signals onto the optical splitter, which, in turn, redirects the light signals towards the optical combiner. The optical combiner redirects the light signals to the eye at exit pupils containing the full usable resolution of the SLP.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
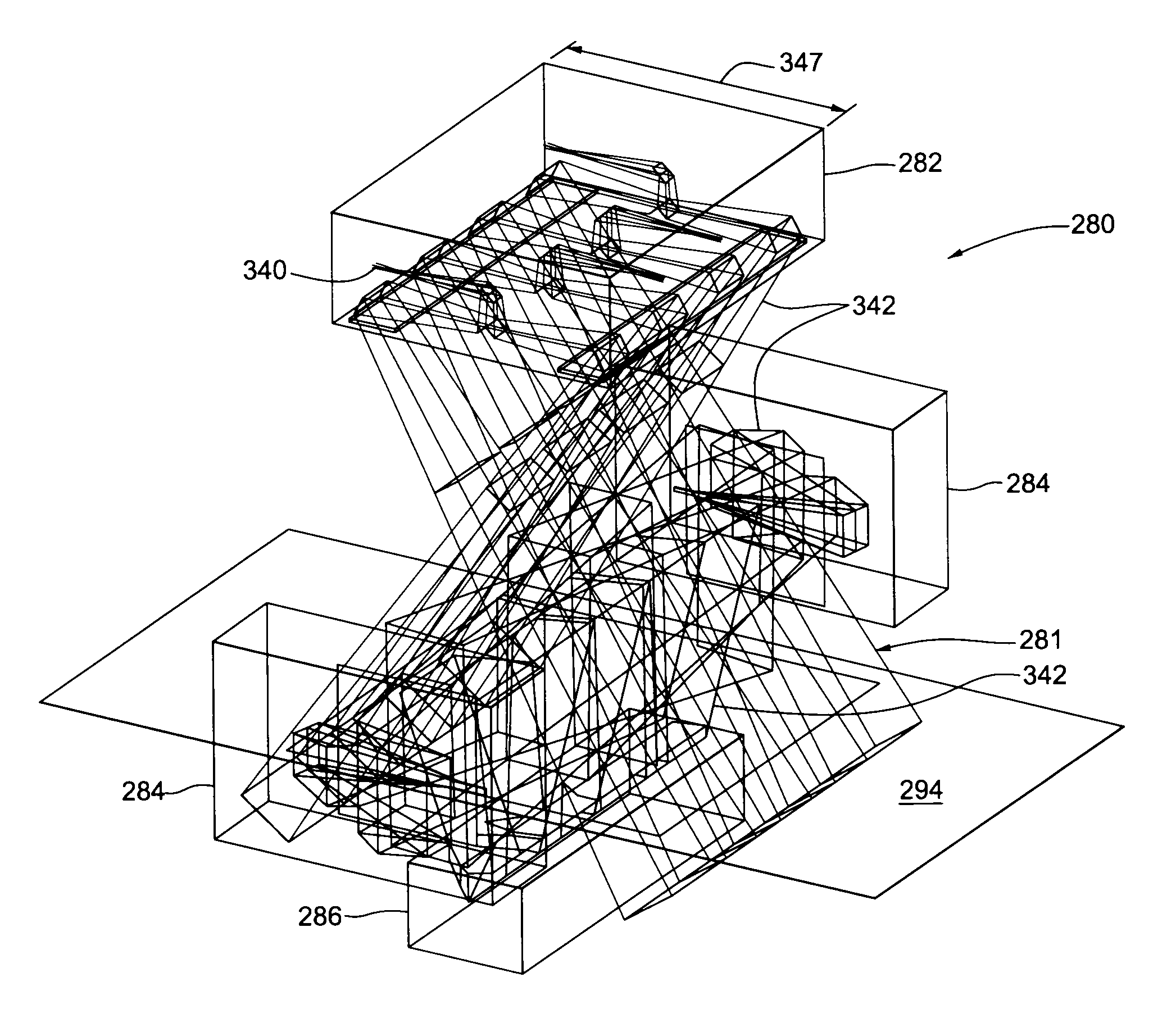
Small form factor, multispectral 4-mirror based imaging systems
An all-reflective or reflective and cata-dioptric optical system is described including a concave primary mirror having a central aperture and a radius, the primary mirror having one of a parabolic, non-parabolic conical, or aspherical surface, a convex secondary mirror facing the primary mirror, the secondary mirror having an aspherical surface, where an optical axis extends from a vertex of the primary mirror to a vertex of the secondary mirror, a concave tertiary mirror arranged behind the primary mirror, the tertiary mirror having one of a parabolic, non-parabolic conical or aspherical surface, a concave quaternary mirror arranged in the central aperture of the primary mirror or behind the primary mirror, the quaternary mirror having one of a spherical, parabolic, non-parabolic conical or aspherical surface, and / or at least one image plane having one or more aggregated sensors. Additional multispectral imaging may utilize beam splitter(s), folding mirror(s), focal length optimizer(s) and / or additional image planes.
Owner:CHOI YOUNGWAN
Dioptric telescope for high resolution imaging in visible and infrared bands
ActiveUS20210325648A1Unwanted motionHigh transfer functionTelescopesBeam splitterHigh resolution imaging
A cata-dioptric optical system for high resolution imaging in visible and infrared bands. The system includes a concave primary mirror, a convex secondary mirror, at least one beam splitter, a first folding mirror, a first group of lenses, a second group of lenses, and at least two image planes. The image planes have one or more aggregated sensors, where a first image plane receives rays from the first group of lenses and a second image plane receives rays from the second group of lenses, and at least one image plane is positioned behind the primary mirror and at a radial distance from the optical axis that is no more than the radius of the primary mirror.
Owner:CHOI YOUNGWAN
Projection device for changing imaging effect through light refraction
The invention relates to the technical field of projection equipment. The invention further discloses a projection device for changing the imaging effect through light refraction. The device comprisesa shell, a telescopic rod is movably connected to the surface of the shell, a folding mirror is movably connected to the surface of the telescopic rod, a flexible screen is fixedly connected to the surface of the folding mirror, a toothed plate is movably connected to the interior of the shell, an extrusion plate is movably connected to the surface of the toothed plate, an elastic cover is movably connected to the surface of the extrusion plate, and a compression spring is movably connected to the interior of the elastic cover. If the range of the video projected at the moment is too small, the extrusion plate can be pushed to move towards two sides, and the extrusion plate meshes the toothed plate to push the shell to rotate away, and drives the folding mirror to rotate to the state shown in the figure 8. When the folding mirror is unfolded, the spring rod pushes the lamp source to move in the direction close to the folding mirror. In the moving process, it is known that the maximumprojection picture is enlarged from the maximum projection picture, and therefore the effect of changing the shape of the convex lens and the focal length to enlarge the projection picture is achieved.
Owner:杭州新五板全息科技有限公司
Long-focal-length large-view-field miniaturized active athermalization optical system
PendingCN113805325AHigh resolutionWide temperature range operationOptical elementsImaging lensOptic system
The invention discloses a long-focal-length large-view-field miniaturized active athermalization optical system which comprises a Cassegrain reflection primary mirror, a reflection secondary mirror, a field lens, a collimating mirror, a first folding mirror, a second folding mirror, a first imaging mirror group, a third folding mirror, a second imaging mirror group, a fourth folding mirror, an imaging lens and a detector focal plane. The Cassegrain reflection primary mirror and the reflection secondary mirror form a Cassegrain imaging system, the field lens is arranged between the Cassegrain reflection primary mirror and the reflection secondary mirror, and the field lens is used for compressing the field angle of the collimating mirror and correcting the field curvature of the imaging system; and the collimating lens, the first folding lens, the second folding lens, the first imaging lens group, the third folding lens, the second imaging lens group, the fourth folding lens, the imaging lens and the detector focal plane are sequentially connected through light paths. The system can work in a wide temperature range, the cost of the system is reduced, meanwhile, the space structure of the system is optimized through the turning mirror, and miniaturization is achieved.
Owner:AEROSPACE SCI & IND MICROELECTRONICS SYST INST CO LTD
Optical turbulence sensor and method for combining multi-aperture glitter and differential image motion
InactiveCN103335816AConvenient on-site adjustmentImprove reliabilityAerodynamic testingInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsEyepieceExit pupil
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Catadioptric projection objective
ActiveUS8446665B2Reduce contrastReduce stray lightMirrorsOptical filtersAnti-reflective coatingIntermediate image
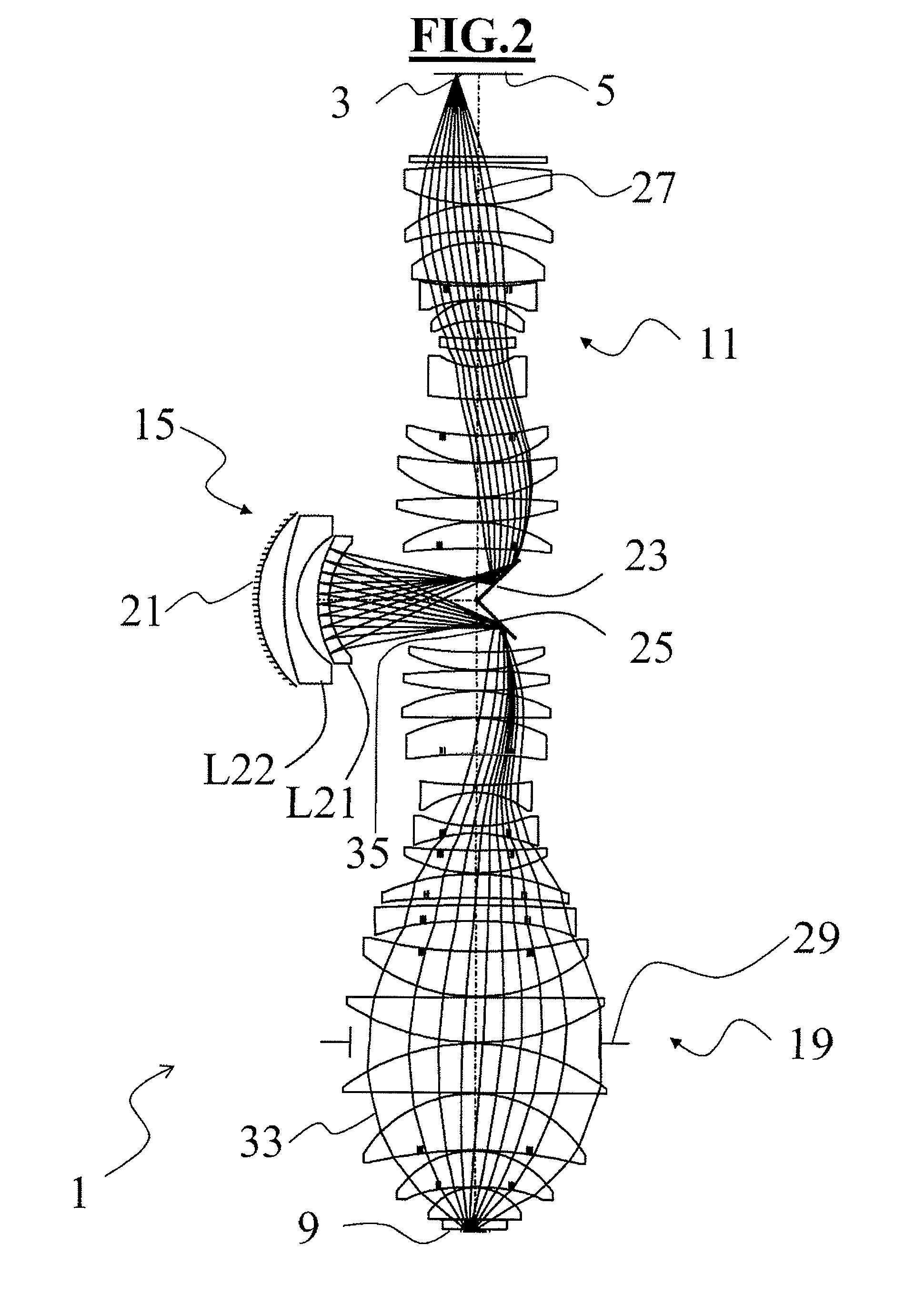
Catadioptric projection objective (1) for microlithography for imaging an object field (3) in an object plane (5) onto an image field (7) in an image plane (9). The objective includes a first partial objective (11) imaging the object field onto a first real intermediate image (13), a second partial objective (15) imaging the first intermediate image onto a second real intermediate image (17), and a third partial objective (19) imaging the second intermediate image onto the image field. The second partial objective is a catadioptric objective having exactly one concave mirror and having at least one lens (L21, L22). A first folding mirror (23) deflects the radiation from the object plane toward the concave mirror and a second folding mirror (25) deflects the radiation from the concave mirror toward the image plane. At least one surface of a lens (L21, L22) of the second partial objective has an antireflection coating having a reflectivity of less than 0.2% for an operating wavelength of between 150 nm and 250 nm and for an angle-of-incidence range of between 0° and 30°. As an alternative or in addition, all the surfaces of the lenses of the second partial objective are configured such that the deviation from the marginal ray concentricity is greater than or equal to 20°.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Optical remote sensor using structural deformation amount to compensate misalignment rate of optical system
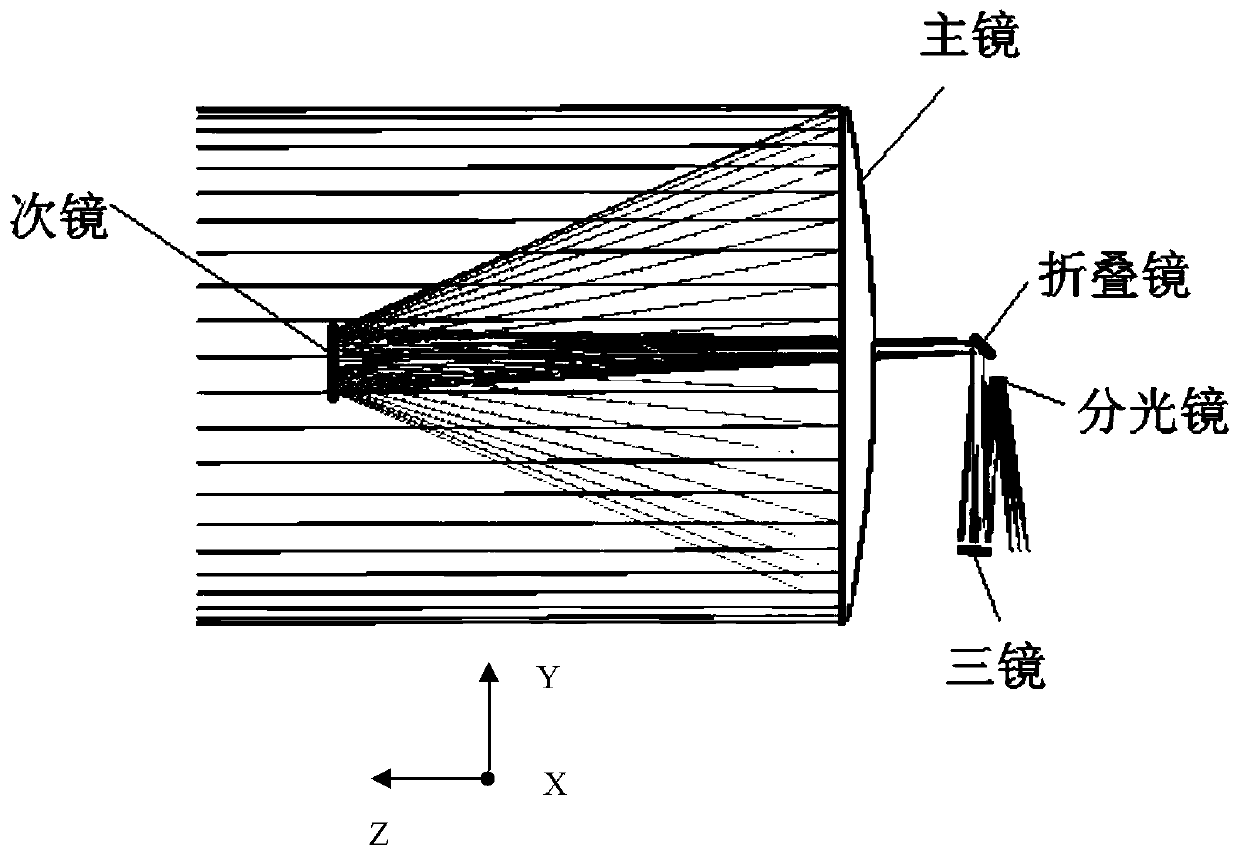
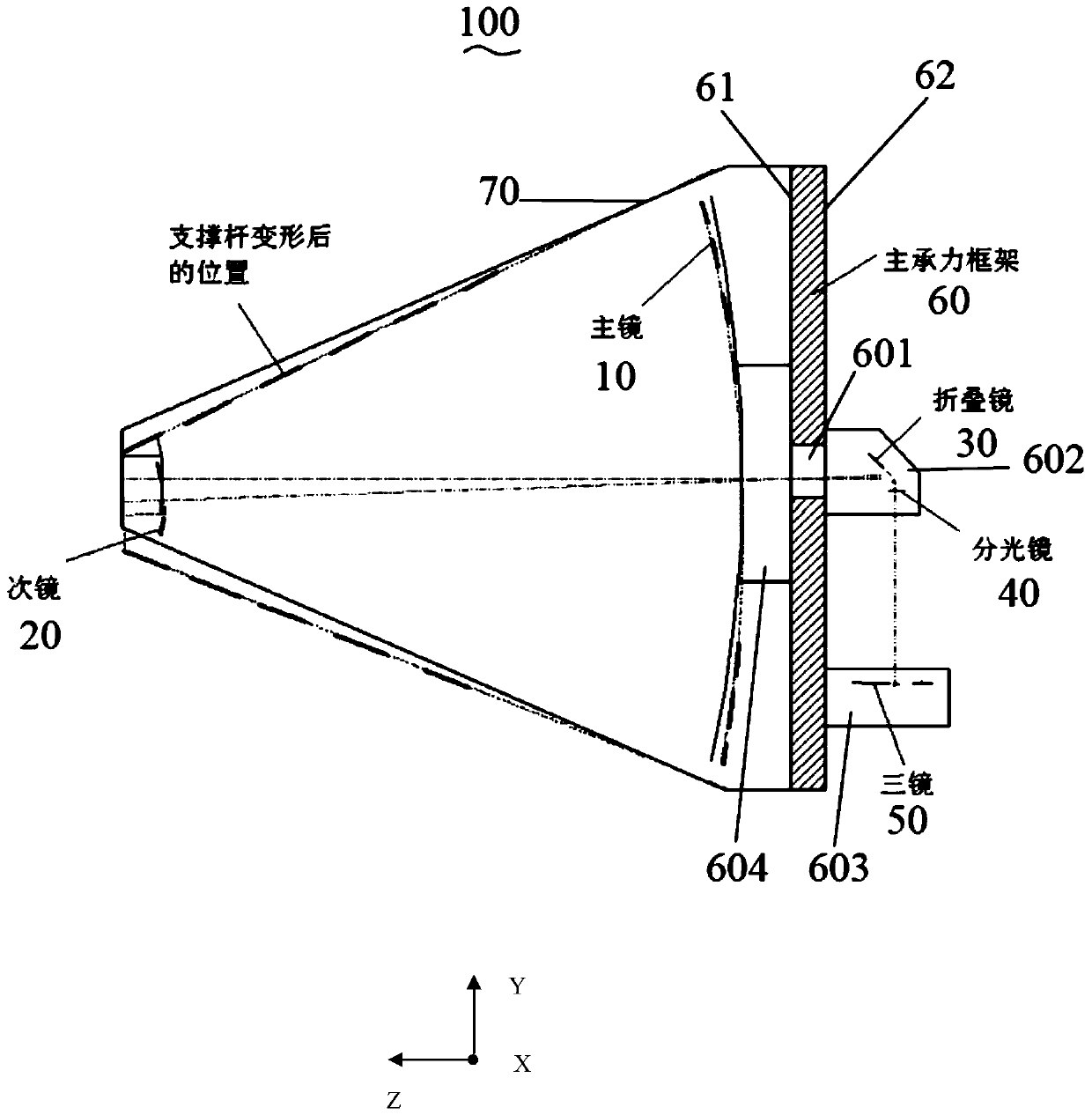
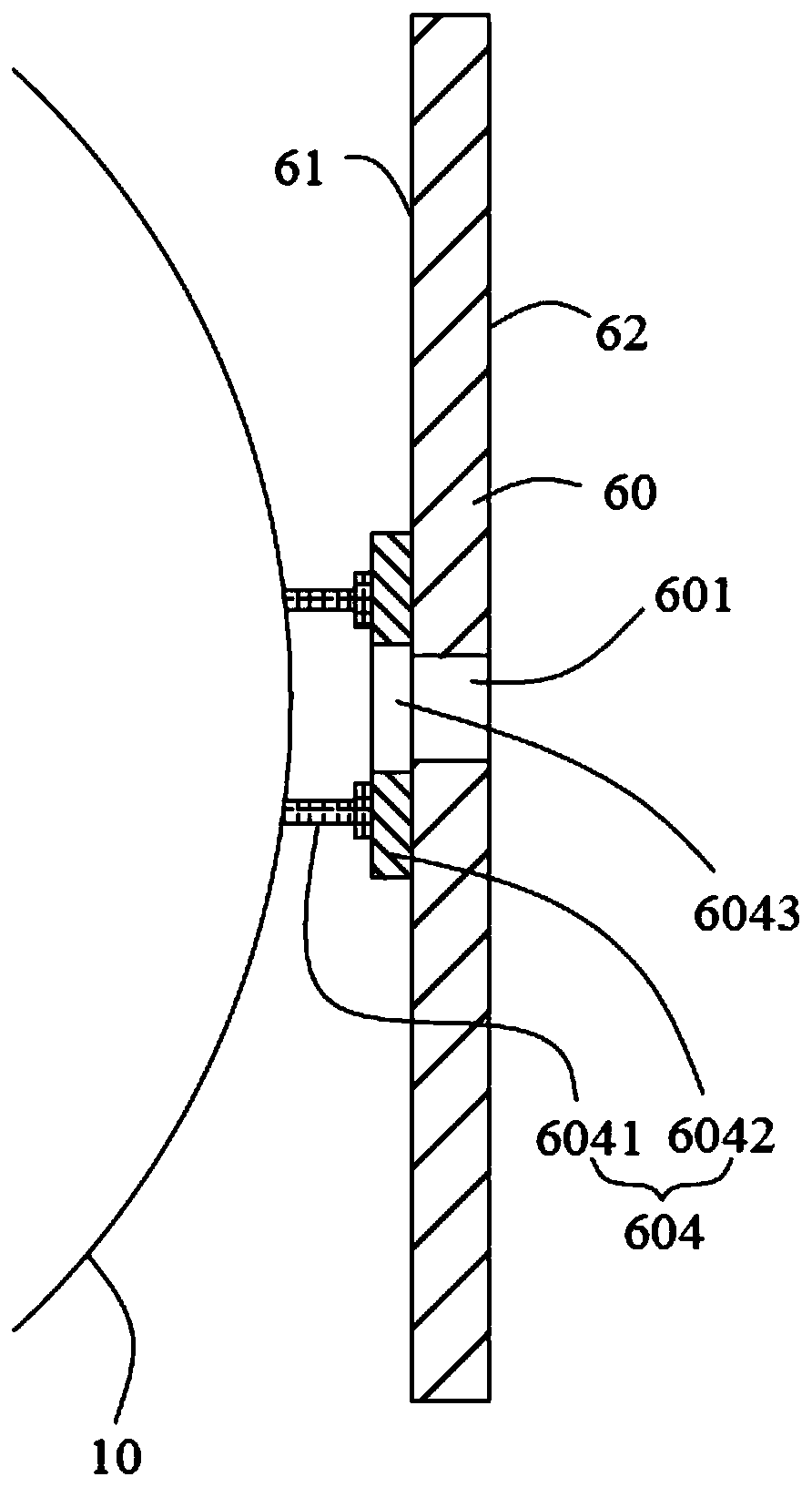
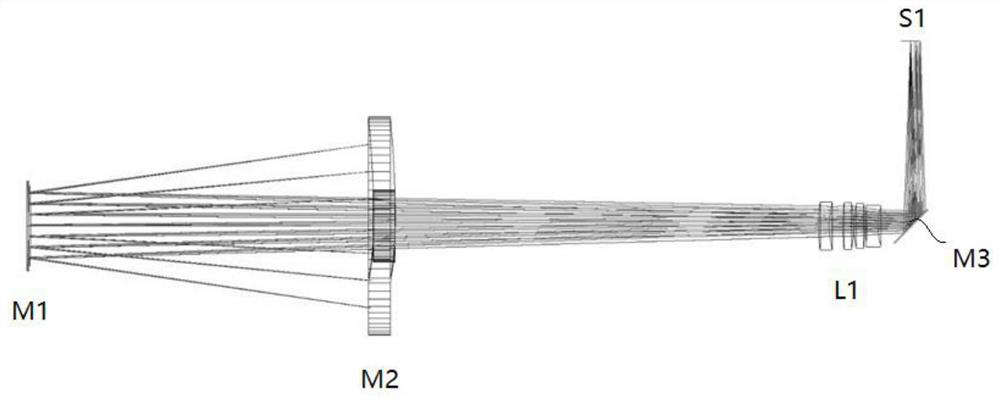
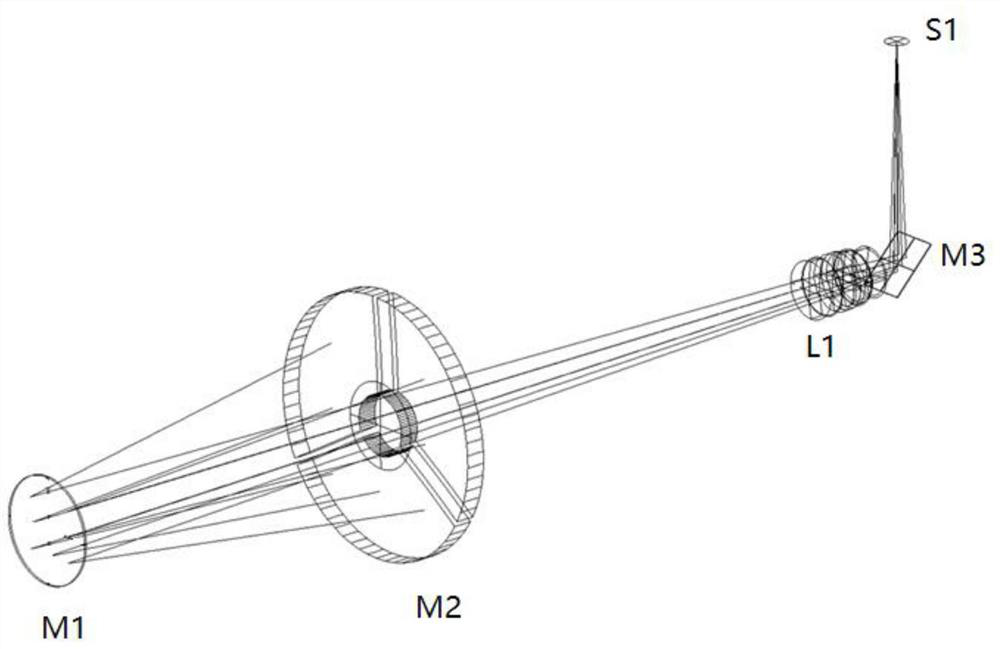
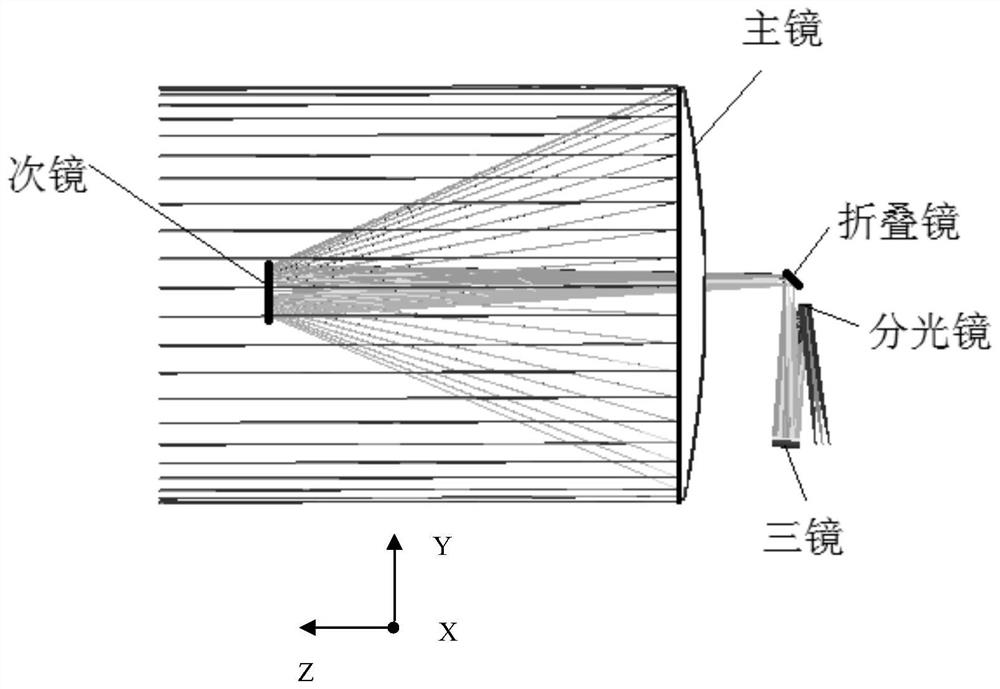
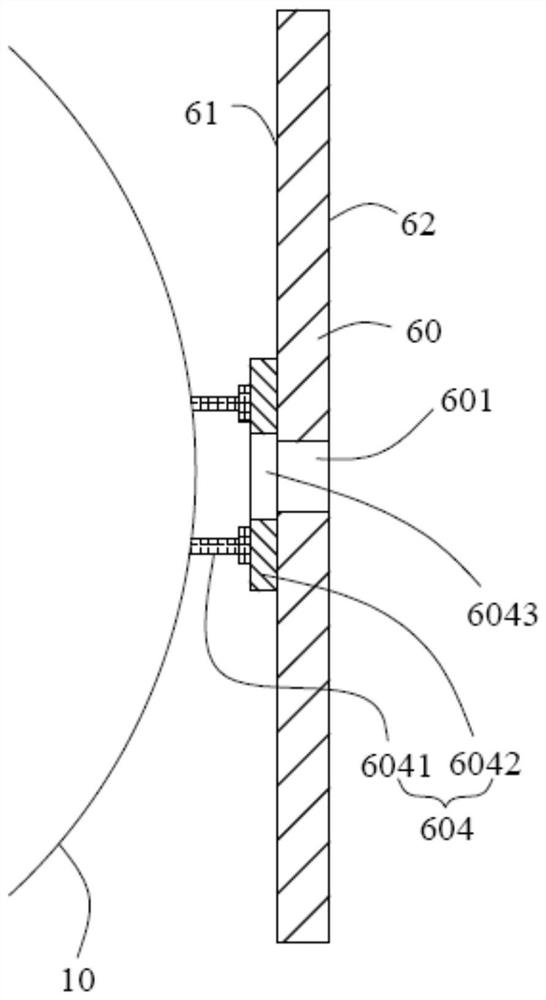
The invention discloses an optical remote sensor using structural deformation amount to compensate the misalignment rate of an optical system. The optical remote sensor using the structural deformation amount to compensate the misalignment rate of the optical system includes a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a folding mirror, a beam splitter, a triple mirror, a main bearing frame and an elastic supporting rod; the main bearing frame includes a front mounting surface and a rear mounting surface back to the front mounting surface; the primary mirror is elastically mounted on the front mounting surface; the secondary mirror is elastically connected to one end of the supporting rod and opposite to the primary mirror in a spaced manner; the end of the supporting rod away from the secondarymirror is connected to the front mounting surface; the folding mirror and the beam splitter are mounted on the rear mounting surface; and the triple mirror is mounted on the rear mounting surface andopposite to the beam splitter in a spaced manner. By means of the optical remote sensor using the structural deformation amount to compensate the misalignment rate of the optical system, the primary mirror and the secondary mirror deviate from the theoretical position by the deformation amount under the action of gravity, so that the best pose of the primary mirror and the secondary mirror is adjusted under the gravity of the ground; after the space remote sensor launches into orbit and gravity deformation rebound release occurs, the position relationship between the primary mirror and the secondary mirror can still maintain the position relationship during adjustment, and the image quality of the space remote sensor is not affected.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bearing cylinder type main supporting structure of large off-axis three-mirror space remote sensing camera
ActiveCN110529699ASmall envelopeLower launch costsStands/trestlesCamera body detailsWide fieldTitanium alloy
The invention discloses a bearing cylinder type main supporting structure of a large off-axis three-mirror space remote sensing camera. The invention relates to the technical field of space optical remote sensing, and solves the problems of low support rigidity and overlarge size envelope of a camera mirror assembly caused by large length-width ratio and large mass of main, third and folding mirrors of a camera due to the characteristics of long focal length and wide field of view of an optical system in the prior art, and the structure comprises a front frame, a rear frame, a main bearing cylinder, a truss rod assembly and a reinforcing rib assembly, the main bearing cylinder is connected with the front frame and the rear frame through screws. The truss rod assembly comprises two truss rods which are symmetrically arranged, the upper end of each truss rod is in positioning connection with the front frame, and the lower end of each truss rod is in positioning connection with the rear frame; the lower end of the reinforcing rib assembly is connected with the main bearing cylinder and the upper end of the reinforcing rib assembly is connected with the front frame through titanium alloy joints; the front frame, the force bearing cylinder, the rear frame and the truss rod joints are all in a plane assembly form, so that the assembly difficulty is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, theproduction period and the manufacturing cost are greatly reduced.
Owner:CHANGGUANG SATELLITE TECH CO LTD
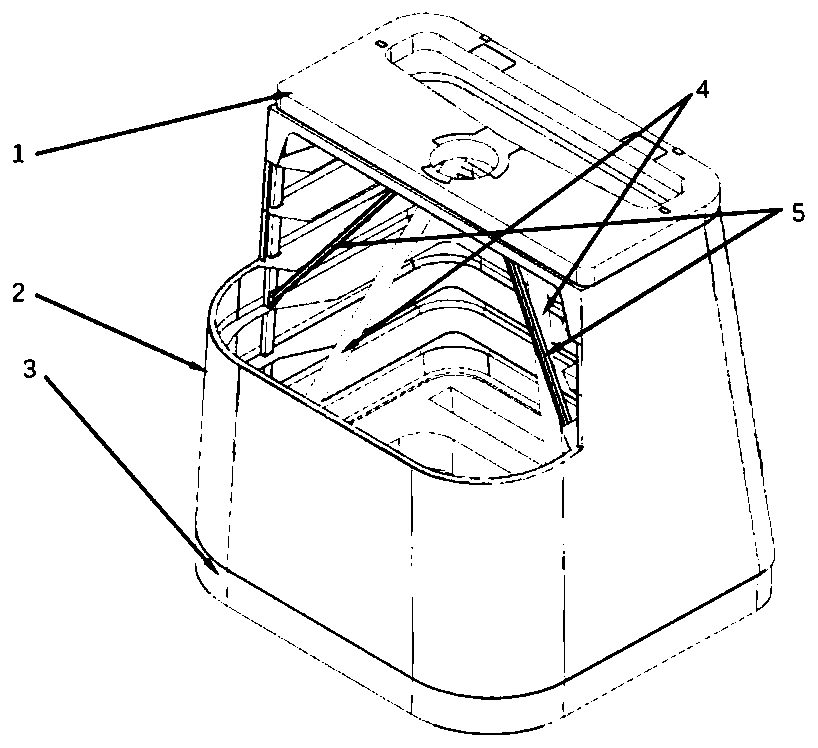
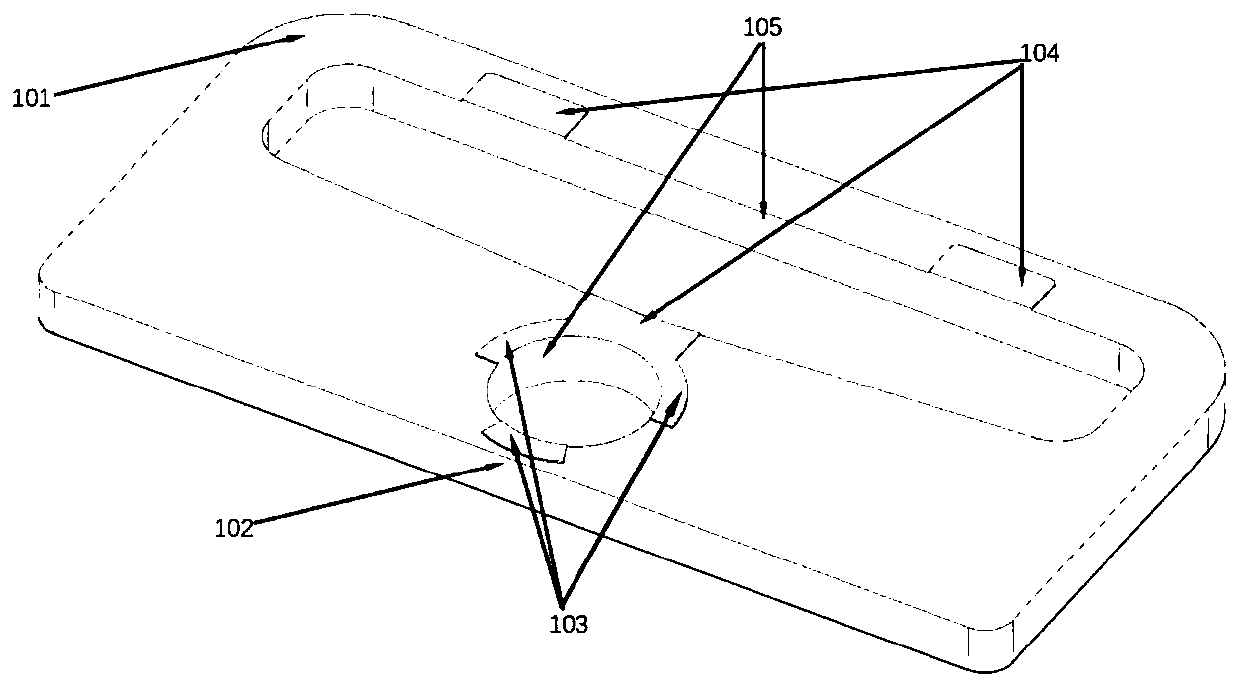
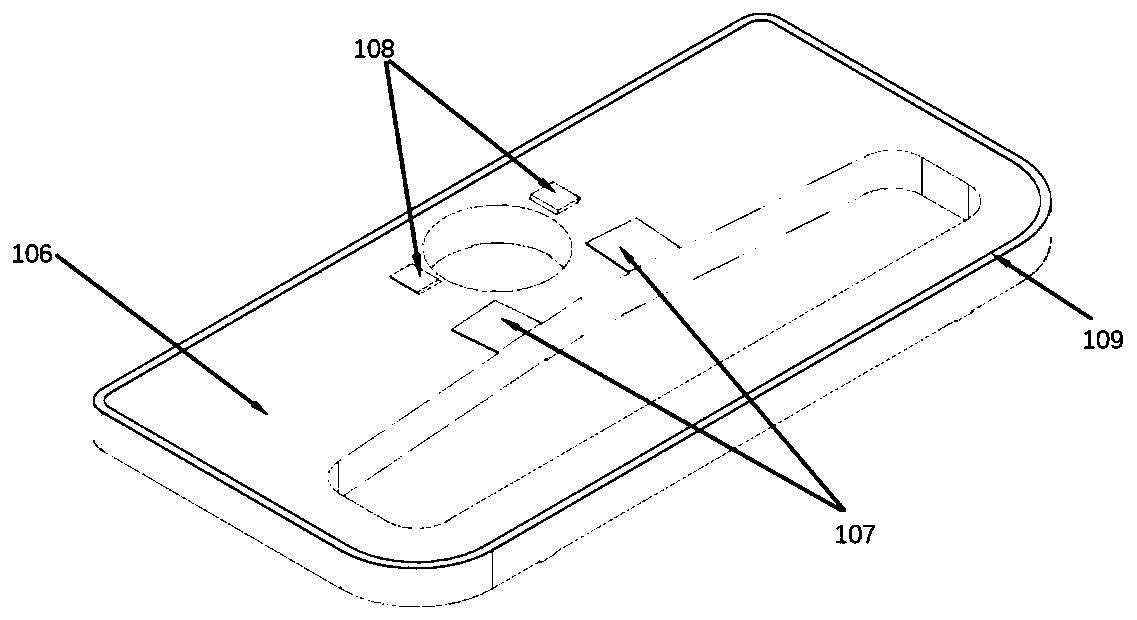
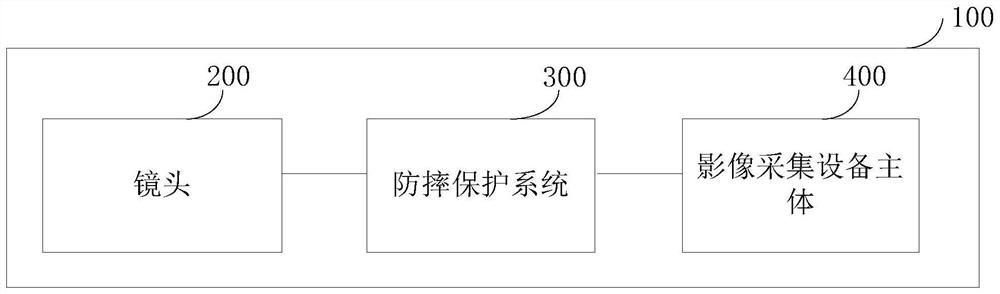
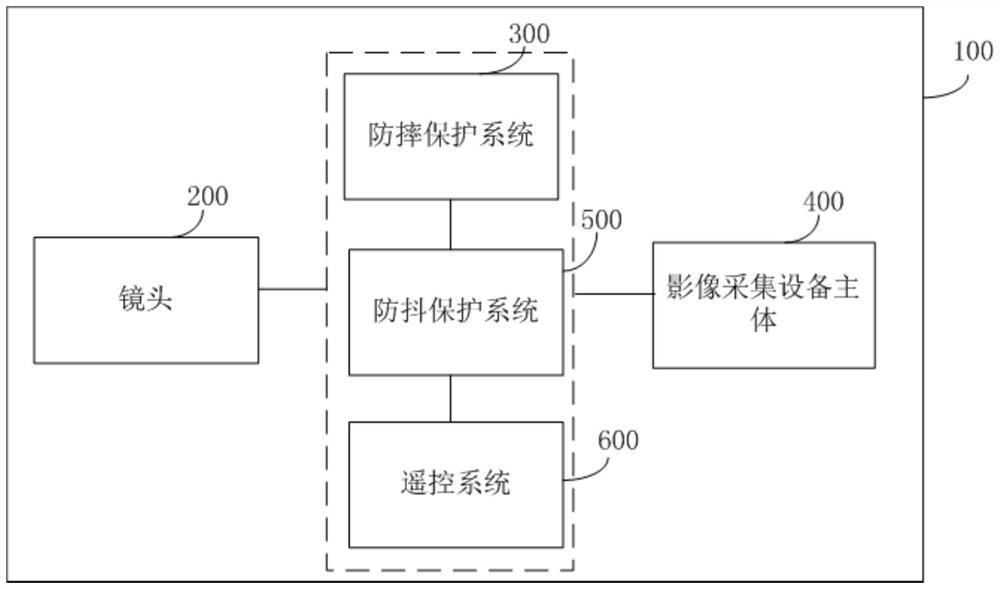
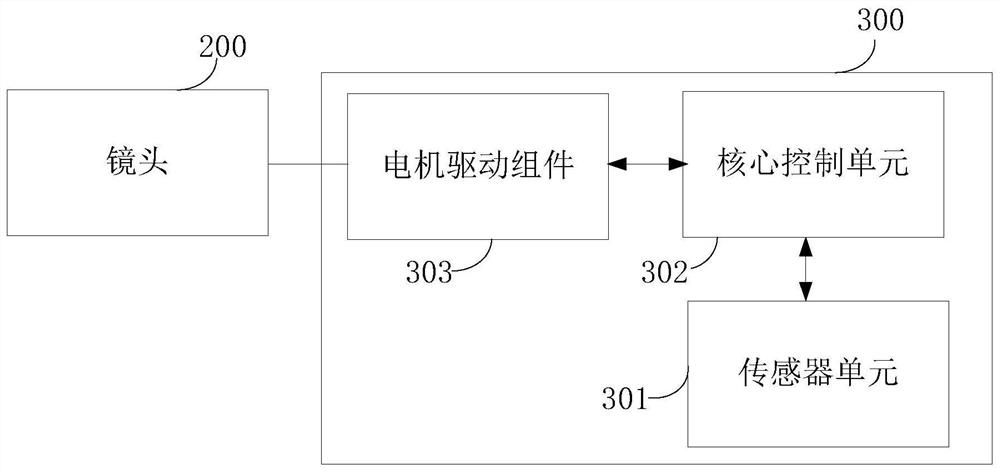
Anti-falling protection system and protection method of lens and image acquisition equipment
ActiveCN111787200AAvoid damageRealize the collectionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMotor driveControl cell
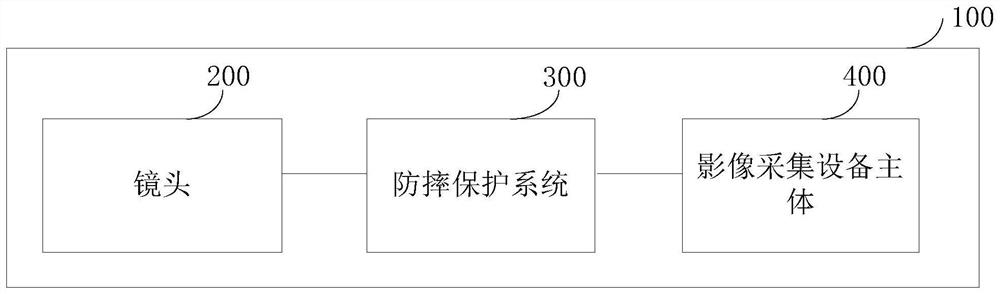
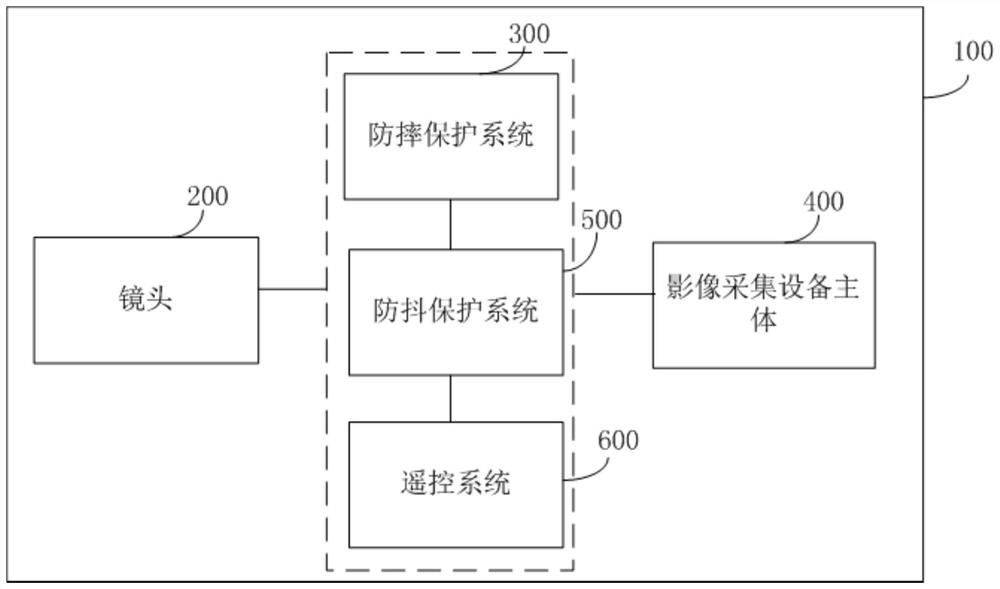
The invention discloses an anti-falling protection system and protection method of a lens and image acquisition equipment. The anti-falling protection system of the lens comprises: a sensor unit, wherein the sensor unit collects acceleration information of the lens, and the acceleration information comprises mutually orthogonal three-axis accelerations in a lens coordinate system; a core control unit which is connected with the sensor unit and is used for calculating the acceleration information so as to calculate the acceleration vector sum of the lens relative to the ground, and outputting motor control information according to a preset acceleration vector and threshold value and the relationship between the acceleration vector sums; and a motor driving assembly which is connected with the core control unit, wherein the motor driving assembly rotates and folds the lens according to the motor control information so as to carry out anti-falling protection on the lens. According to theanti-falling protection system of the lens provided by the invention, the folding lens can be rotated in the falling process of the lens, so that the lens is protected from being influenced by the outside.
Owner:迈特考森(江苏)大数据科技有限公司
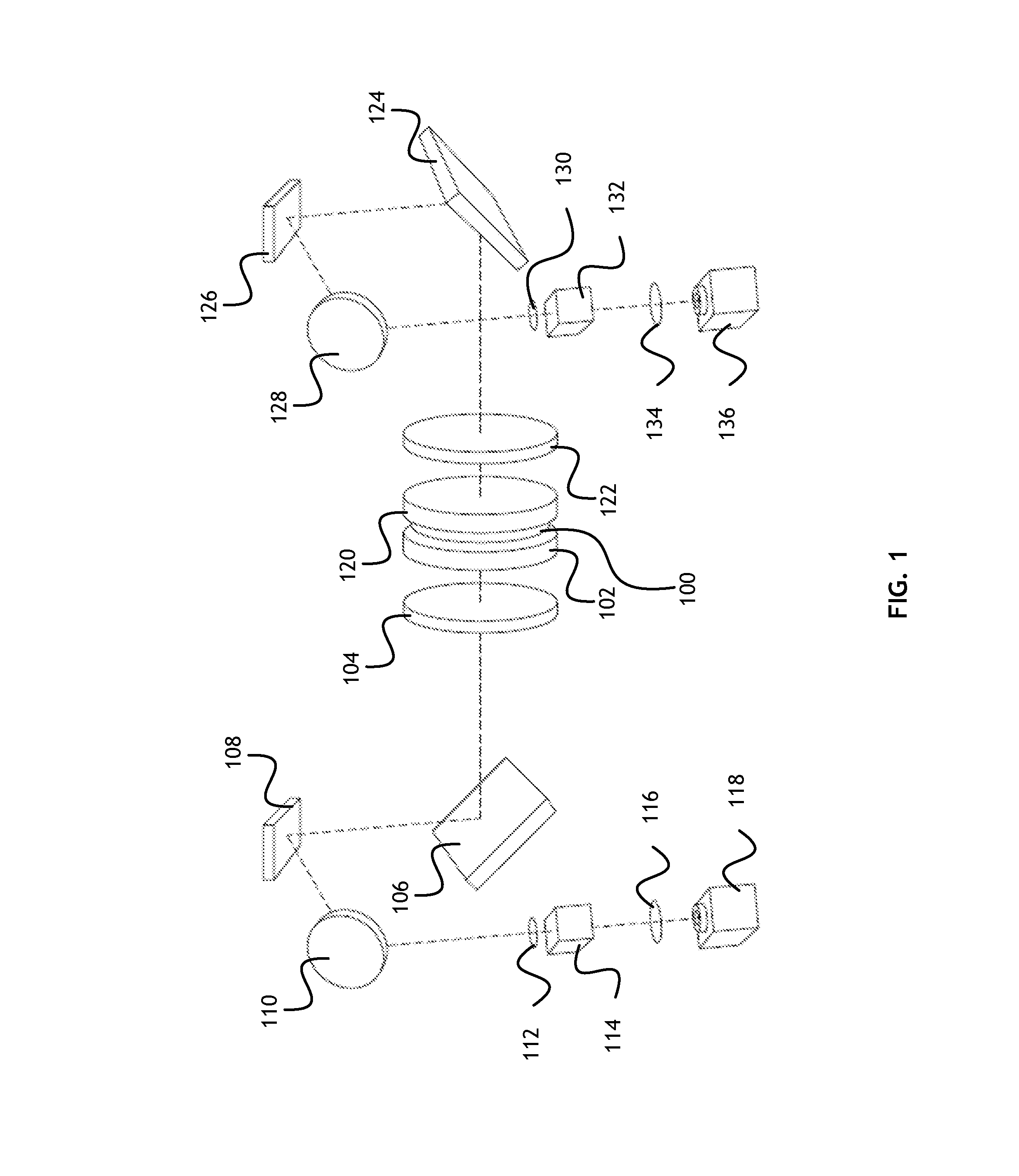
Folded lens system with five refractive lenses
Compact folded lens systems are described that may be used in small form factor cameras. Lens systems are described that may include five lens elements with refractive power, with a light folding element such as a prism, located between a first lens element on the object side of the lens system and a second lens element, that redirects the light refracted from the first lens element from a first axis onto a second axis on which the other lens elements and a photosensor are arranged. The lens systems may include an aperture stop located behind the front vertex of the lens system, for example at the first lens element, and an optional infrared filter, for example located between the last lens element and a photosensor.
Owner:APPLE INC
Free-form surface optical system for folding projection
PendingCN113093464AQuality improvementSave packing spaceProjectorsOptical elementsDisplay deviceMirror image
The invention discloses a free-form surface optical system for folding projection, the free-form surface optical system comprises a display device, a lens group, a folding mirror and an output mirror, the lens group focuses light emitted by the display device onto the folding mirror, and the folding mirror folds and transmits the received light onto the output mirror. The output mirror projects the received light onto a screen, and the output mirror is of a free-form surface structure. According to the system, the folded mirror image is inserted between the virtual image and the output mirror image, so that the packaging space is saved, and the main light path is shortened. And moreover, the output mirror is arranged in a curved surface shape, so that the quality of an output image is improved.
Owner:四川省靓固智能科技有限公司
A lens anti-drop protection system, protection method and image acquisition device
ActiveCN111787200BAvoid damageRealize the collectionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMotor driveControl cell
Owner:迈特考森(江苏)大数据科技有限公司
Load-bearing cylinder main support structure of large off-axis three-mirror space remote sensing camera
ActiveCN110529699BSmall envelopeLower launch costsStands/trestlesCamera body detailsWide fieldStructural engineering
The main bearing structure of the large-scale off-axis three-mirror space remote sensing camera involves the field of space optical remote sensing technology. It solves the problem of large aspect ratios of the main, third and folding mirrors of the camera due to the characteristics of the long focal length and wide field of view of the existing optical system. Due to the large mass, the supporting rigidity of the camera mirror assembly is low and the size envelope is too large, including the front frame, the rear frame, the main load-bearing cylinder, the truss rod assembly and the rib assembly; the main load-bearing cylinder and the front frame and the rear frame All are connected by screws; the truss rod assembly includes two symmetrically arranged truss rods, the upper end of each truss rod is positioned and connected with the front frame, and the lower end of each truss rod is positioned and connected with the rear frame; And the upper end of the rib assembly is connected with the front frame by a titanium alloy joint; the joints of the front frame, the load-bearing tube, the rear frame and the truss rod of the present invention are all in the form of plane assembly, which greatly reduces the difficulty of assembly, and at the same time greatly reduces the production cycle and manufacturing cost.
Owner:CHANGGUANG SATELLITE TECH CO LTD
Optical system and virtual reality device having same
The invention discloses an optical system and a virtual reality device having the same. The optical system sequentially includes a first lens, a folding mirror group, and a display unit along the optical axis; the first lens includes a first surface away from the display unit and a surface close to the display unit. The second surface; the effective aperture of the first lens is smaller than the effective aperture of the folding mirror group, and the first lens is used to reduce the effective aperture of the optical system; the folding mirror group includes a third surface and a fourth surface; the incident light emitted by the display unit is from The fourth surface enters the folding mirror group and is reflected between the third surface and the fourth surface. When the incident light passes through the third surface for the second time, it exits the third surface and enters the first lens from the second surface. The first surface exits the first lens and transmits to the pupil. The present invention provides an optical system and a virtual reality device with the same, aiming at solving the problem of large size and small viewing angle of the virtual reality device in the prior art.
Owner:GOERTEK OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Physical experiment table device for optical teaching
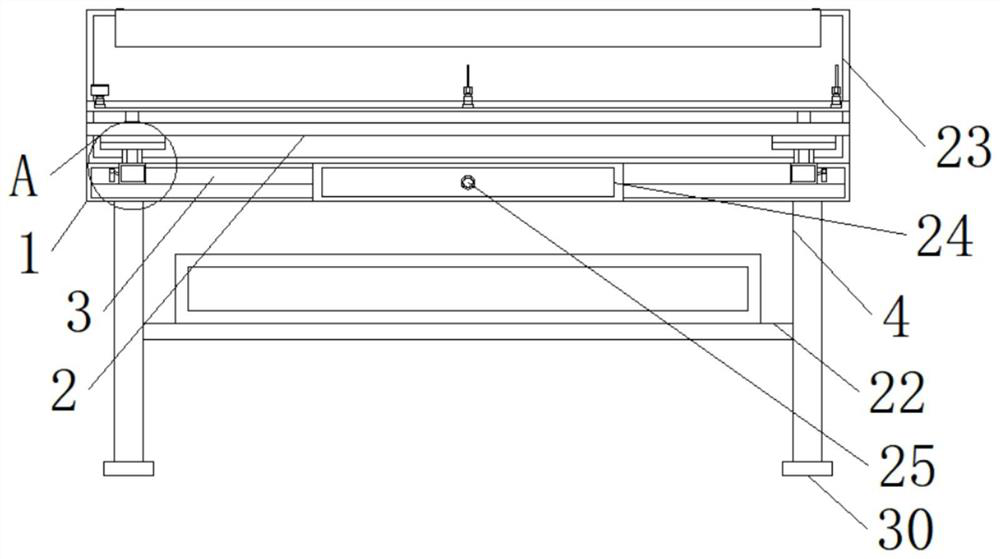
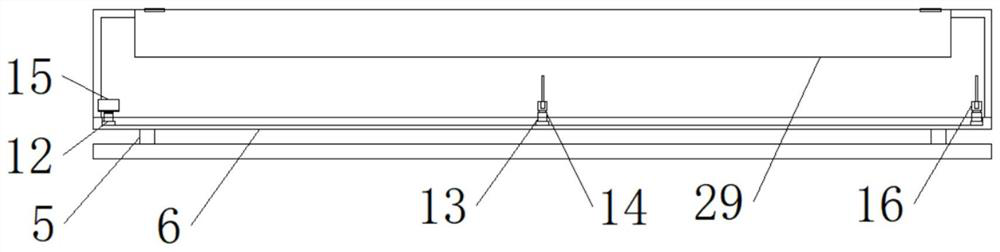
PendingCN113304794APrevent inversionGood tutorialEducational modelsLaboratory benches/tablesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a physical experiment table device for optical teaching, which comprises a device main body, a supporting plate and an internal groove, the supporting plate is fixedly connected above the device main body, the internal groove is fixedly connected inside the lower part of the supporting plate, device table legs are fixedly connected to two sides of the bottom of the device main body, and supporting rods are fixedly connected to two sides of the top of the supporting plate. The top of the supporting rod is fixedly connected with an experiment plate, the two sides of the experiment plate are fixedly connected with adjusting plates, the middle of one side of each adjusting plate is fixedly connected with an experiment transverse plate, the top of each experiment transverse plate is fixedly connected with an experiment vertical plate, the interior of each experiment vertical plate is fixedly connected with an adjusting groove, and the front face of the lower portion of each adjusting groove is fixedly connected with an anti-skid layer. The anti-skid layer can well prevent devices from being collided to cause falling of articles, a folding mirror surface can be unfolded, then a light source is reflected through the mirror surface, teaching is better carried out, a bottom pad is soft in texture, friction force between device table legs and the ground can be increased, the physical experiment table device is better stabilized, and the physical experiment table device is prevented from moving easily.
Owner:EASTERN GANSU UNIVERSITY
Systems, devices, and methods for increasing resolution in wearable heads-up displays
Systems, devices, and methods for increasing resolution in wearable heads-up displays (WHUD) are described. A WHUD includes a support structure, a scanning laser projector (SLP), a fold mirror, a split mirror, an optical splitter, and an optical combiner. When the WHUD is worn on the head of a user, the optical combiner is positioned in a field of view of the user. The SLP scans light signals onto the fold mirror which reflects light onto one of at least two reflective surfaces of the split mirror, based on a state of the fold mirror. The split mirror redirects the light signals onto the optical splitter, which, in turn, redirects the light signals towards the optical combiner. The optical combiner redirects the light signals to the eye at exit pupils containing the full usable resolution of the SLP.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
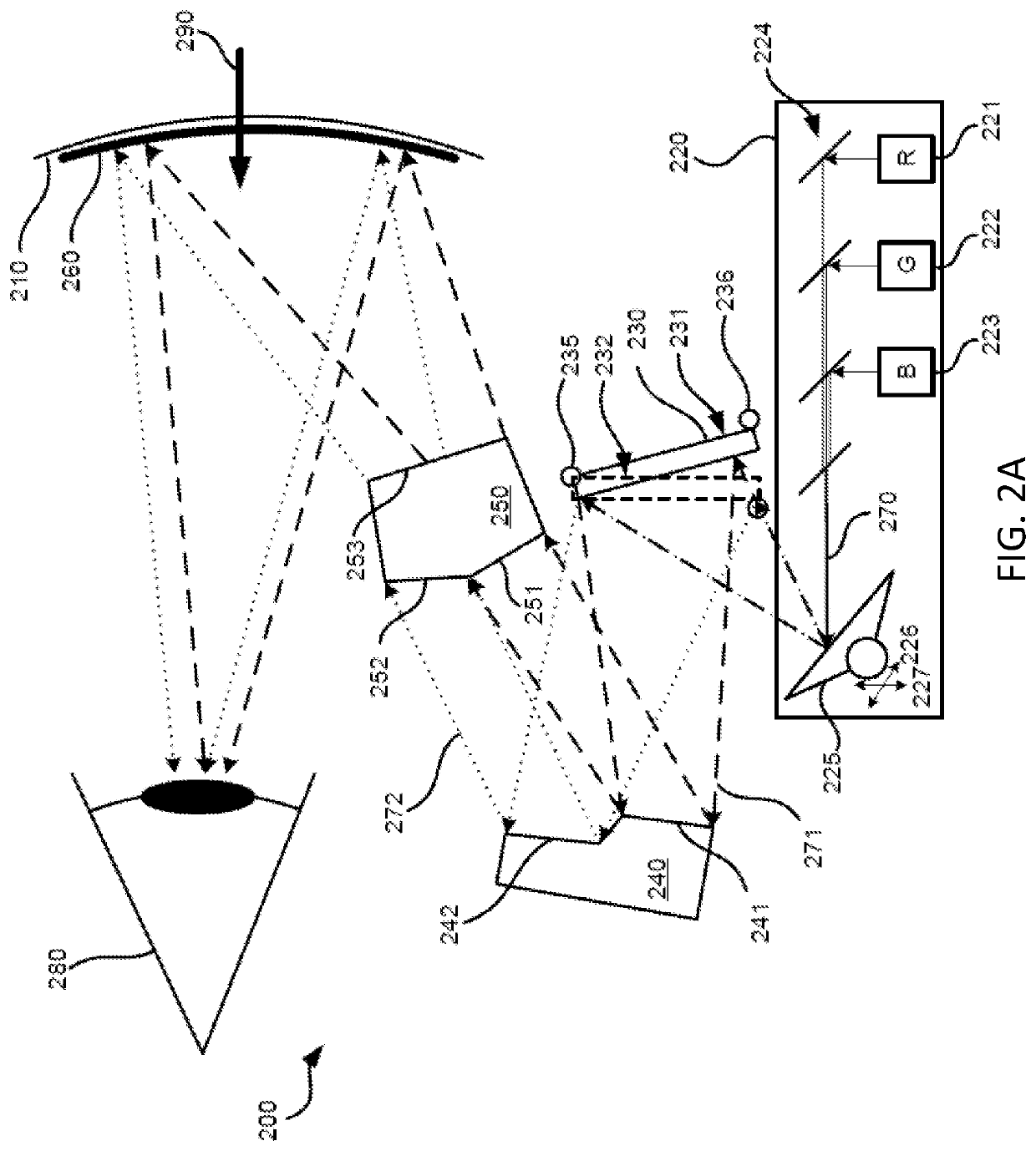
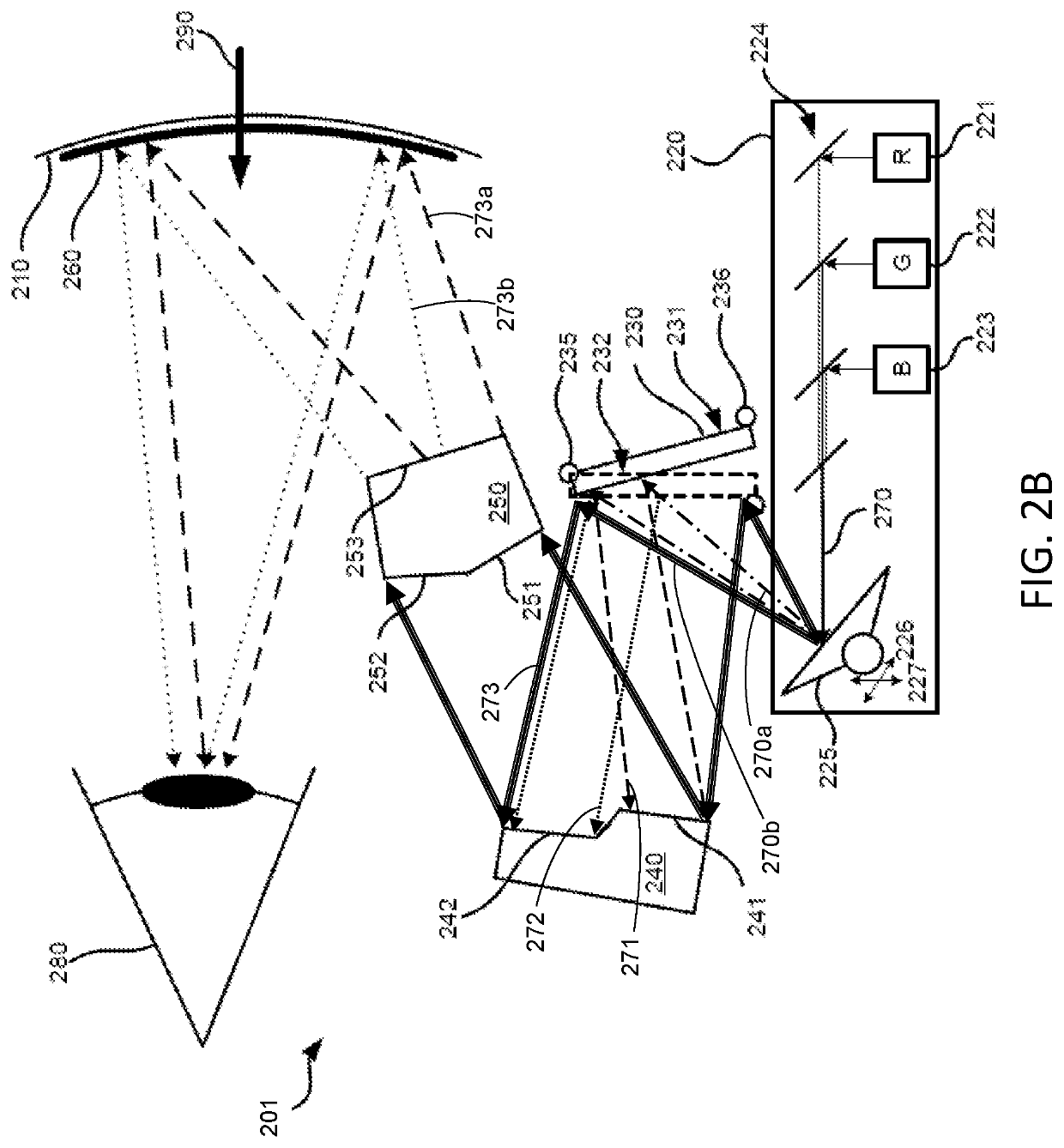
Aperture-fold imaging system
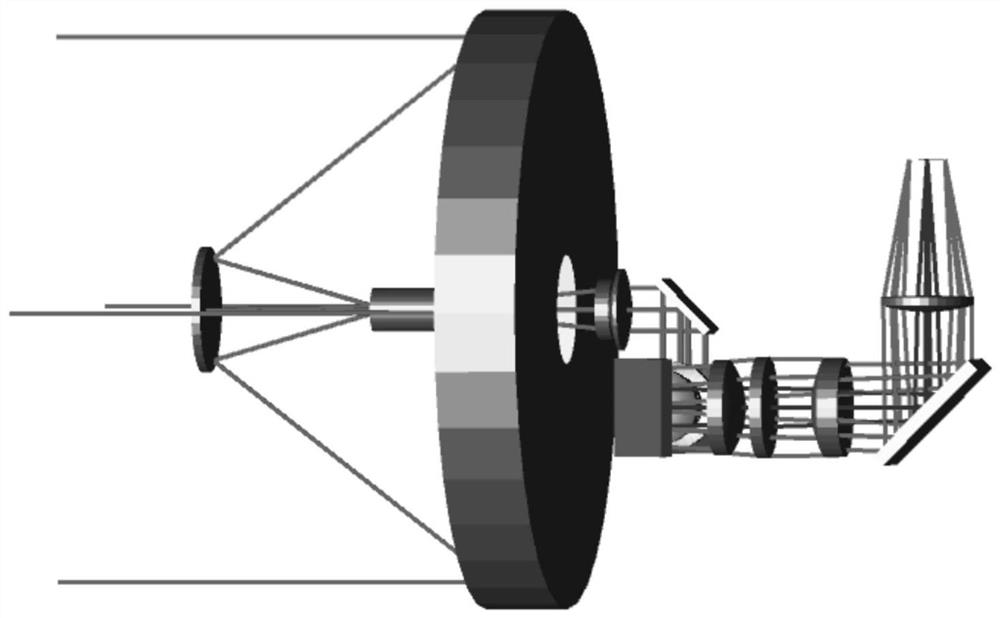
A folded optical system includes a powered optical element, at least one folding mirror and an aperture and defines an optical path through the optical system. The powered optical element, the at least one folding mirror and the aperture are configured to fold the optical path at the aperture, thereby providing a compact optical system. The optical system may include an optical block that totally internally reflects the optical signal at the aperture. Optionally or alternatively, discrete optical components may be used, such as an aperture made of a conventional material or a metamaterial, an off-axis parabolic mirror or lens and one or more folding mirrors. Some embodiments include a wavelength dispersive element, so as to implement a spectrometer.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Contact lens inspection in a plastic shell
ActiveUS10885621B2Easily integrated into automated inspection systemImage enhancementImage analysisHigh resolution imagingOptical Module
An inspection system and method to detect the presence or absence of ophthalmic lenses in a plastic shell just before the seal is applied comprising a high resolution imaging device suitably integrated with an optical module; a UV illumination module suitably mounted below the ophthalmic lens holder; a Visible LED based Top lighting module suitably mounted on Top of the Ophthalmic lens holder; the inspection system which captures images of the lens immersed in a saline solution in a the plastic shell; analyzing the image and determining the characteristics of the lens perimeter and the optical center; making a decision to reject the inspected item if the analyzed image indicates the presence of a flipped, multiple and folded lens or the absence of the lens; making a decision to accept the inspected item, if the analyzed image indicates the presence of a single lens positioned in the correct orientation.
Owner:EMAGE VISION
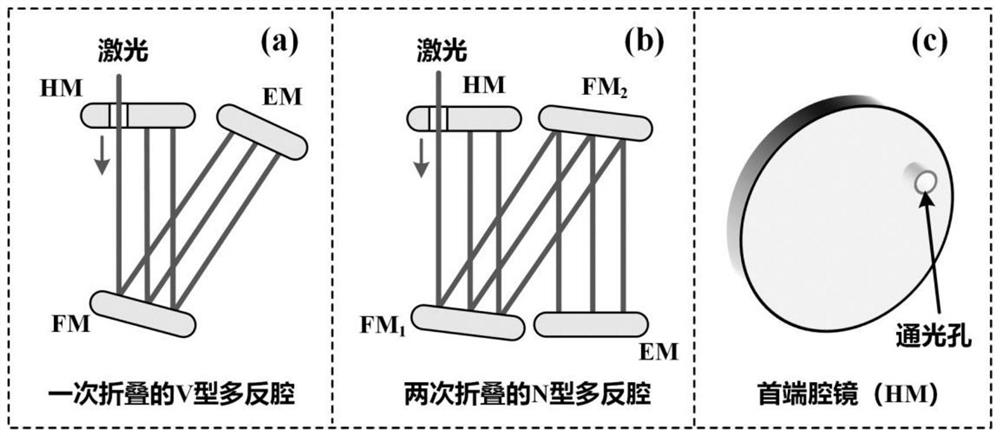
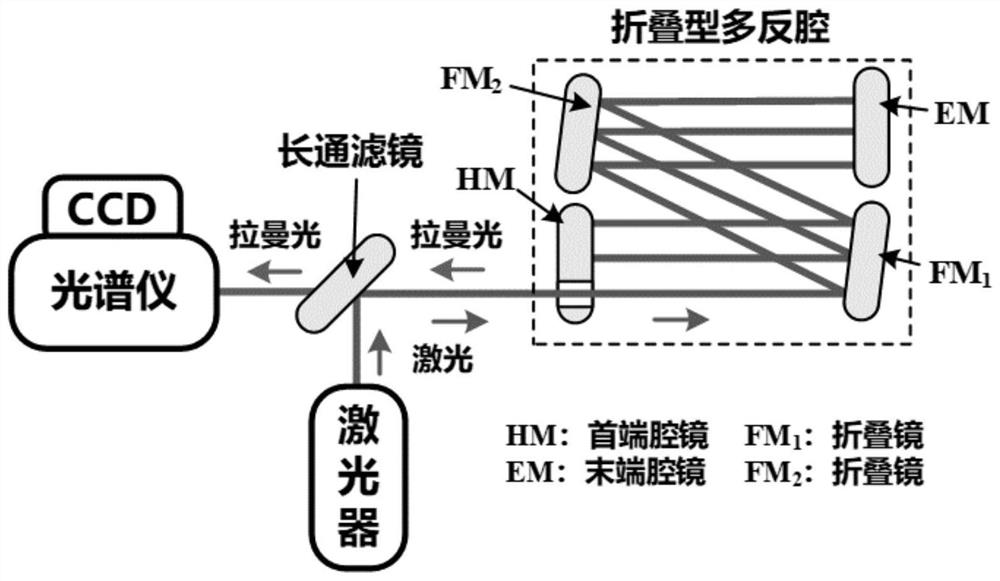
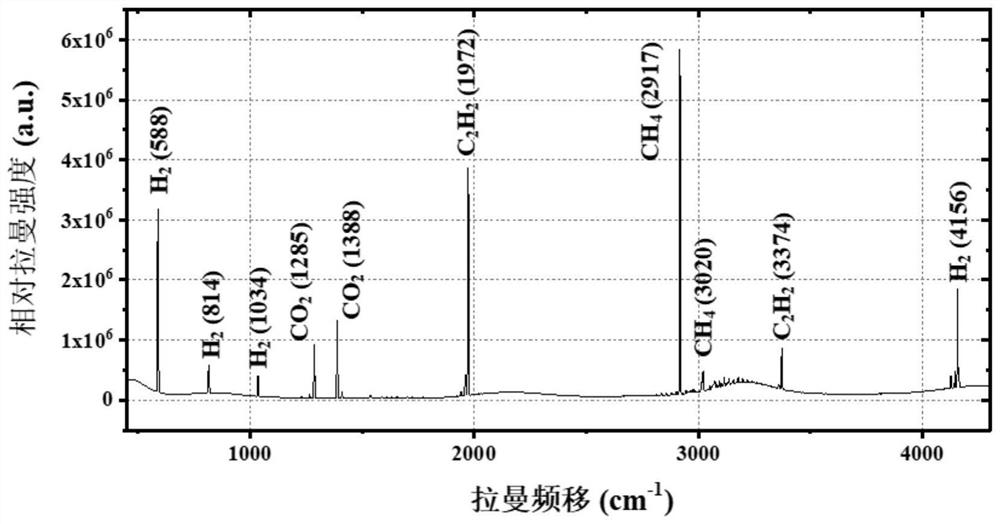
Folding type multi-reflection cavity for enhancing gas Raman signal
The invention discloses a folding type multi-mirror cavity for enhancing a gas Raman signal. The folding type multi-endoscope comprises a head-end endoscope, a tail-end endoscope and a plurality of folding mirrors, the head-end endoscope, the tail-end endoscope and the folding mirrors form an enhancement cavity for reflecting light path folding; the head-end endoscope is provided with a light through hole, laser passes through the head-end endoscope through the light through hole to enter the enhancement cavity, and the incident direction of the laser is not perpendicular to the angle between the folding mirror which the laser reaches first after the laser enters the enhancement cavity; after entering the enhancement cavity, the laser is reflected by the folding mirror to reach the tail-end endoscope and then is reflected; and the reflected laser is reflected for multiple times in the enhancement cavity along different paths until the laser reaches the head-end endoscope, just passes through the light through hole again and is emitted out of the enhancement cavity. According to the folding type multi-reflection cavity provided by the invention, laser can be reflected for hundreds of times in the cavity, and the detection limit of multi-component gas Raman spectrum detection can reach sub-ppm magnitude.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Compact star tracker with photonic crystal pointing
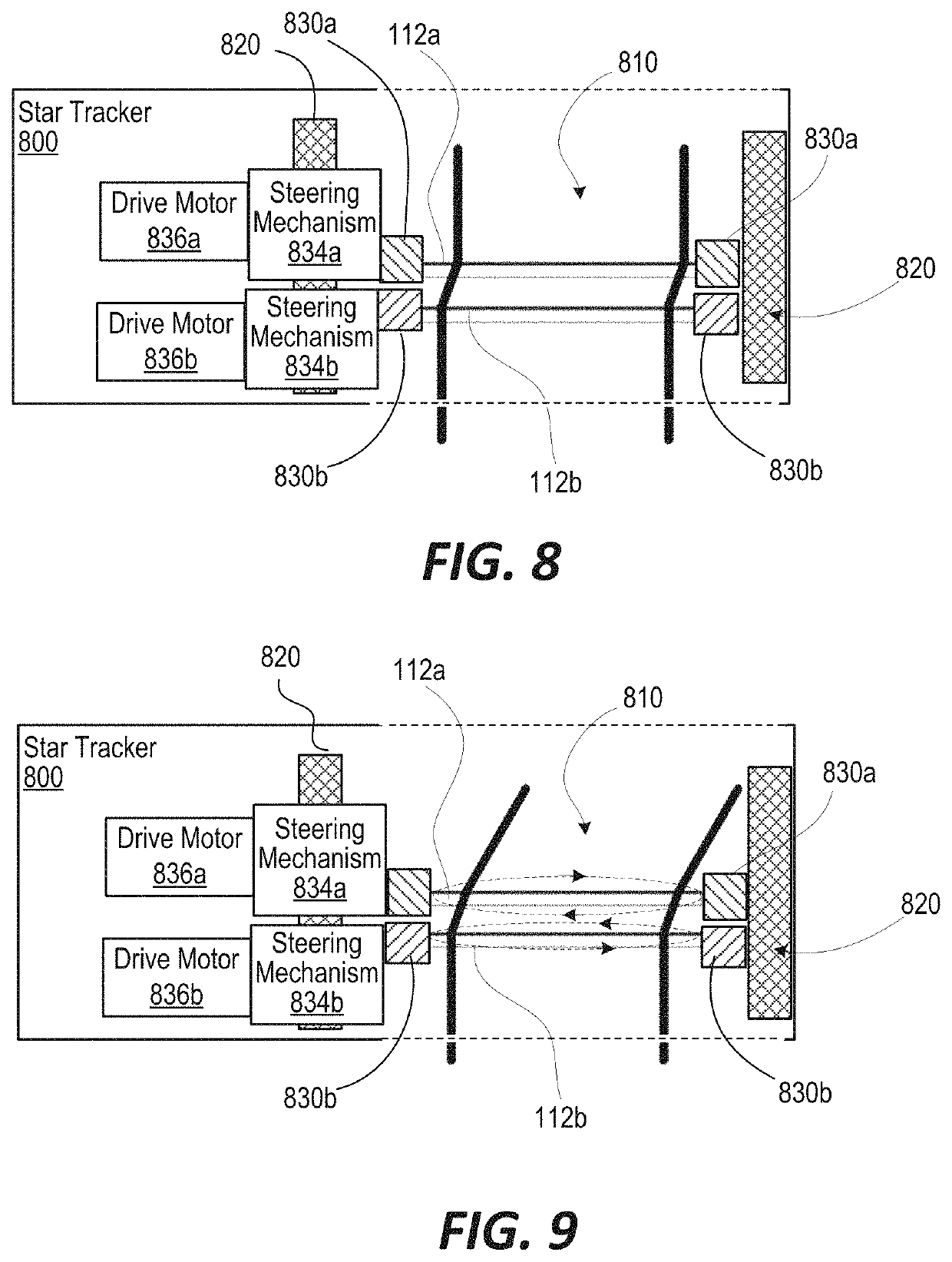
ActiveUS11353627B2Direction/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsTelescopesPhotonic crystalStar tracker
A star tracker includes imaging optics comprising a folding mirror, a lens, and a detector. The folding mirror bends light received from an optical axis through the lens that focuses the bent light onto the detector. The star tracker includes a steering mechanism that steers light from an adjustable field of view (FOV) to the optical axis of the imaging optics. The steering mechanism includes: (i) a first photonic crystal element comprising beam pointing spatially variant photonic crystals (SVPCs); (ii) a second photonic crystal element comprising beam pointing SVPCs that is positioned adjacent and axially aligned with the first photonic crystal element; and (iii) a housing that receives the first and second photonic crystal elements for independent rotation.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Method and apparatus to fold optics in tools for measuring shape and/or thickness of a large and thin substrate
A semiconductor measuring tool has a folding mirror configuration that directs a light beam to pass the same space multiple times to reduce the size and footprint. Furthermore, the folding mirrors may reflect the light beam at less than forty-five degrees; thereby allowing for smaller folding mirrors as compared to the prior art.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Catadioptric imaging telescopic optical system
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical lenses and optical design, and provides a catadioptric imaging telescopic optical system, which comprises a secondary mirror and a primary mirror of a concave reflector assembly adopting a splicing structure which are sequentially arranged along an optical axis, and further comprises a lens assembly used for correcting the spherical aberration of an edge view field generated by the primary mirror and the secondary mirror together, and a folding mirror used for turning a light path. Most optical surfaces in the catadioptric imaging telescopic optical system are spherical surfaces, so that the catadioptric imaging telescopic optical system is good in imaging quality, low in manufacturing cost and good in verification effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical Remote Sensor Using Structural Deformation to Compensate Optical System Misalignment
An optical remote sensor that uses structural deformation to compensate for the misalignment of an optical system, including a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a folding mirror, a beam splitter, three mirrors, a main load-bearing frame and an elastic support rod; the main load-bearing frame includes a front mounting surface and the rear mounting surface opposite to the front mounting surface; the primary mirror is elastically installed on the front mounting surface, the secondary mirror is elastically connected to one end of the support rod and is opposite to the primary mirror, and the end of the support rod away from the secondary mirror is connected to the front mounting surface connection; the folding mirror and the beam splitter are installed on the rear installation surface; the three mirrors are installed on the rear installation surface and are opposite to the beam splitter at intervals. The invention makes the primary mirror and the secondary mirror deviate from the theoretical position through the deformation amount under the action of gravity, so that the optimal pose of the primary mirror and the secondary mirror installed under the action of gravity on the ground will be deformed by gravity after the space remote sensor is launched into orbit When the rebound is released, the positional relationship between the primary mirror and the secondary mirror can still maintain the positional relationship during assembly and adjustment, and the imaging quality of the space remote sensor will not be affected.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
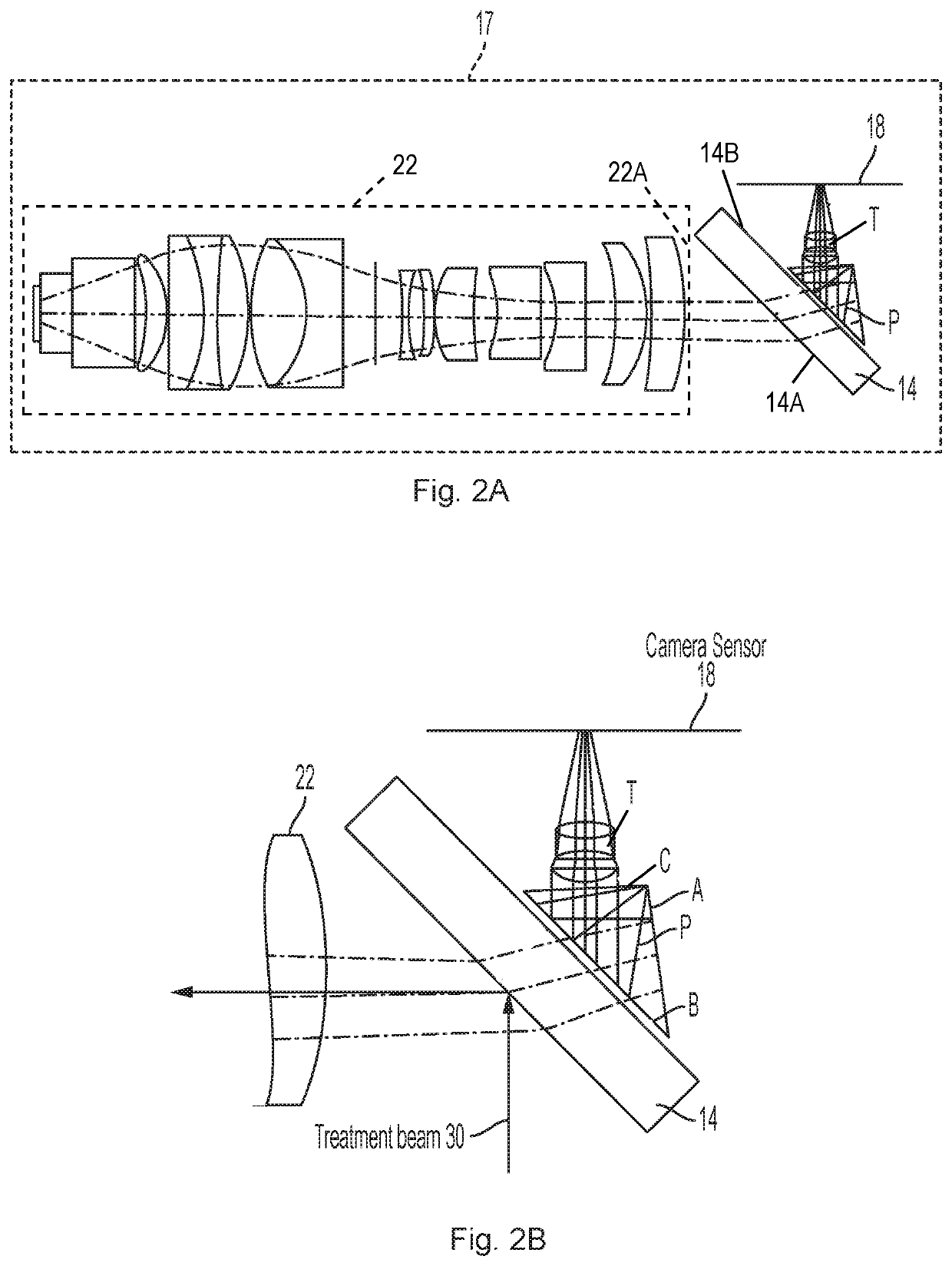
Miniature imaging system for ophthalmic laser beam delivery system
An optical imaging system for an ophthalmic laser beam delivery system, which includes a focusing objective including a plurality of lenses, a semi-transparent folding mirror disposed near an entrance of the focusing objective for reflecting a treatment laser beam into the focusing objective, a prism disposed adjacent a back surface of the folding mirror, the prism having a first, a second and a third surface, the second surface being disposed adjacent the back surface of the folding mirror, the prism being configured to reflect a light that has entered the second surface sequentially by the first surface and by the second surface toward the third surface to be output, a focusing lens module disposed adjacent the third surface of the prism to focus light output from the third surface of the prism, and an image sensor disposed to receive the light focused by the focusing lens module to form an image.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com