Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Electron attachment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron attachment. The combination of an electron with a neutral atom or molecule to form a negative ion.
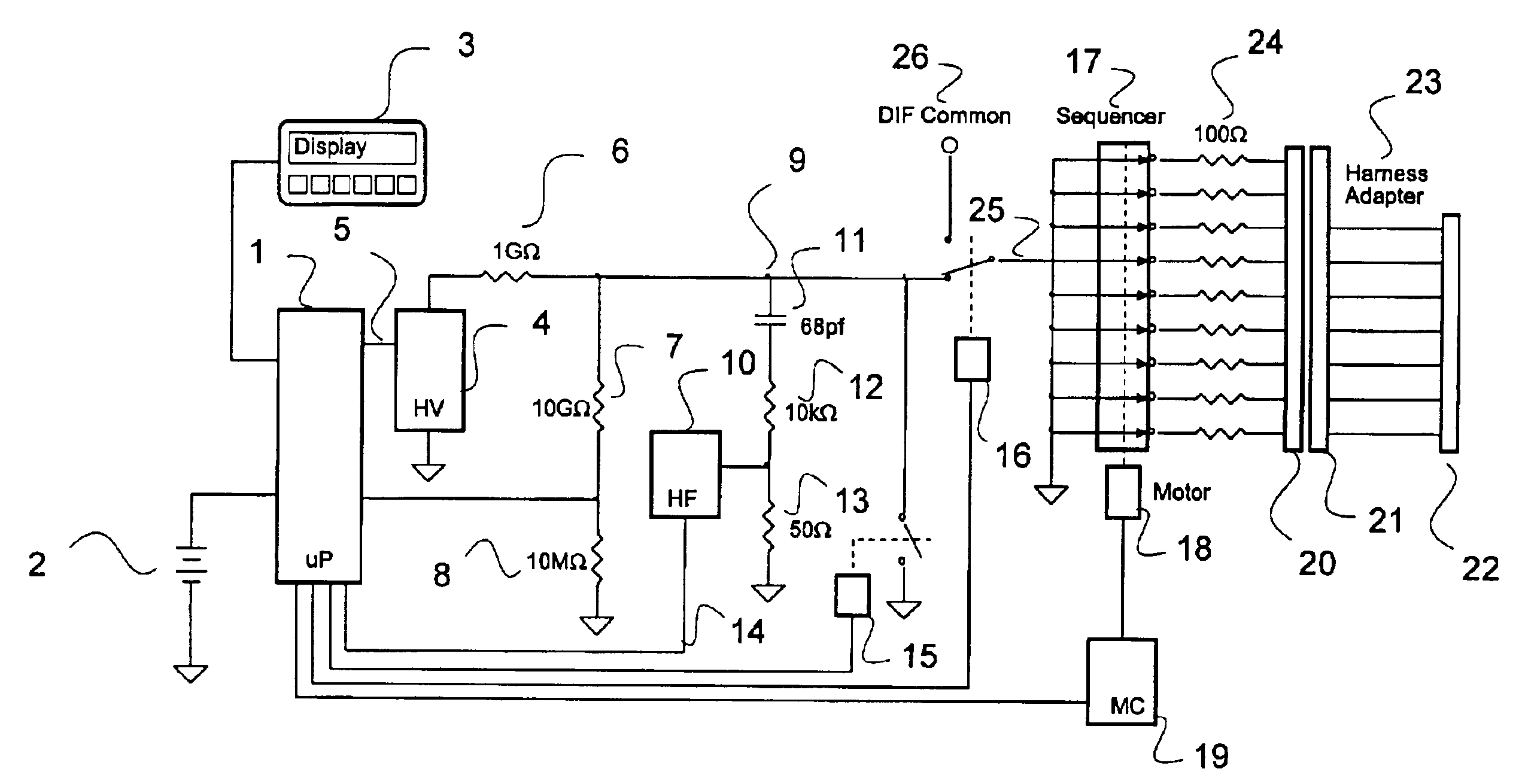
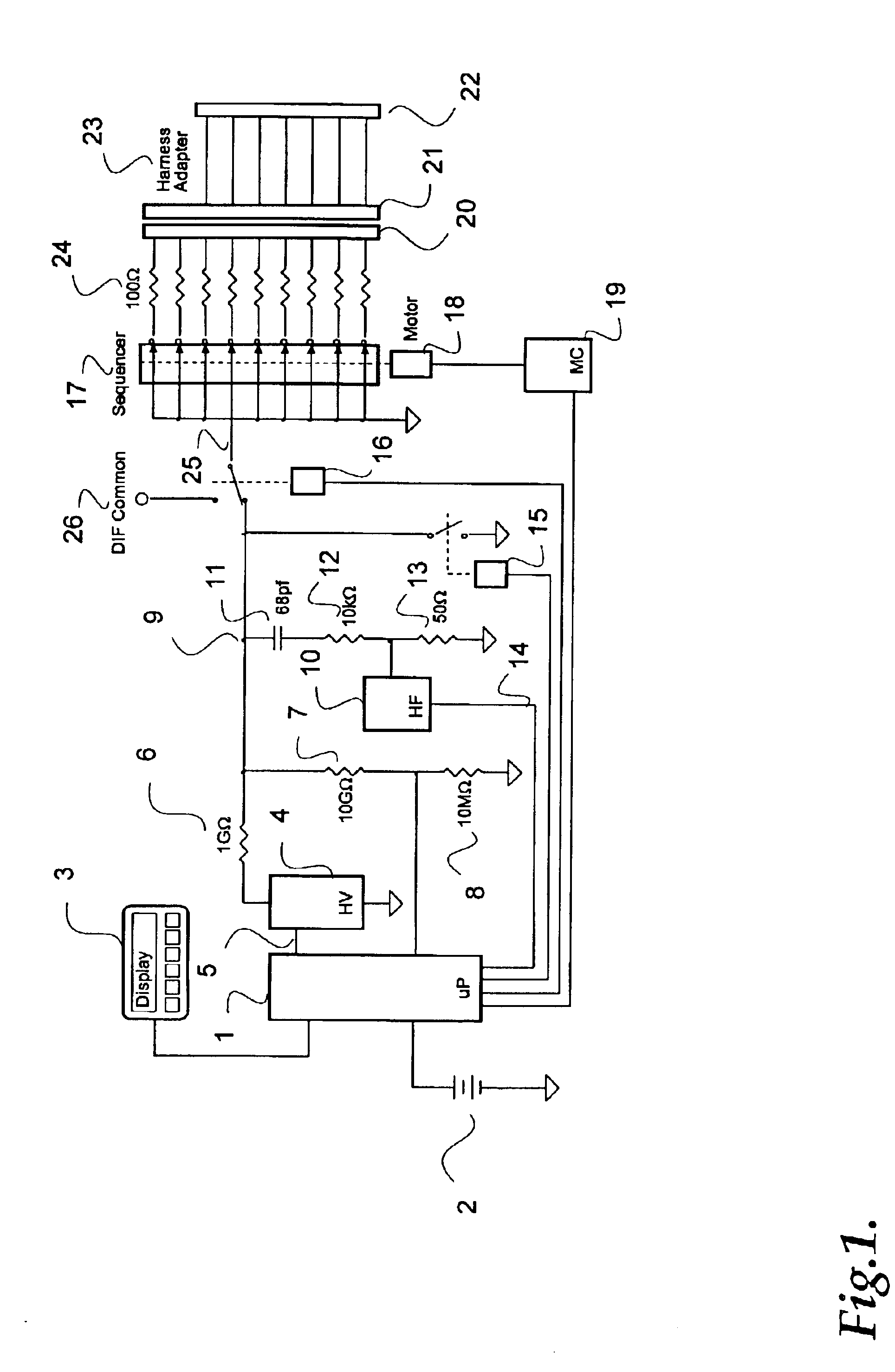
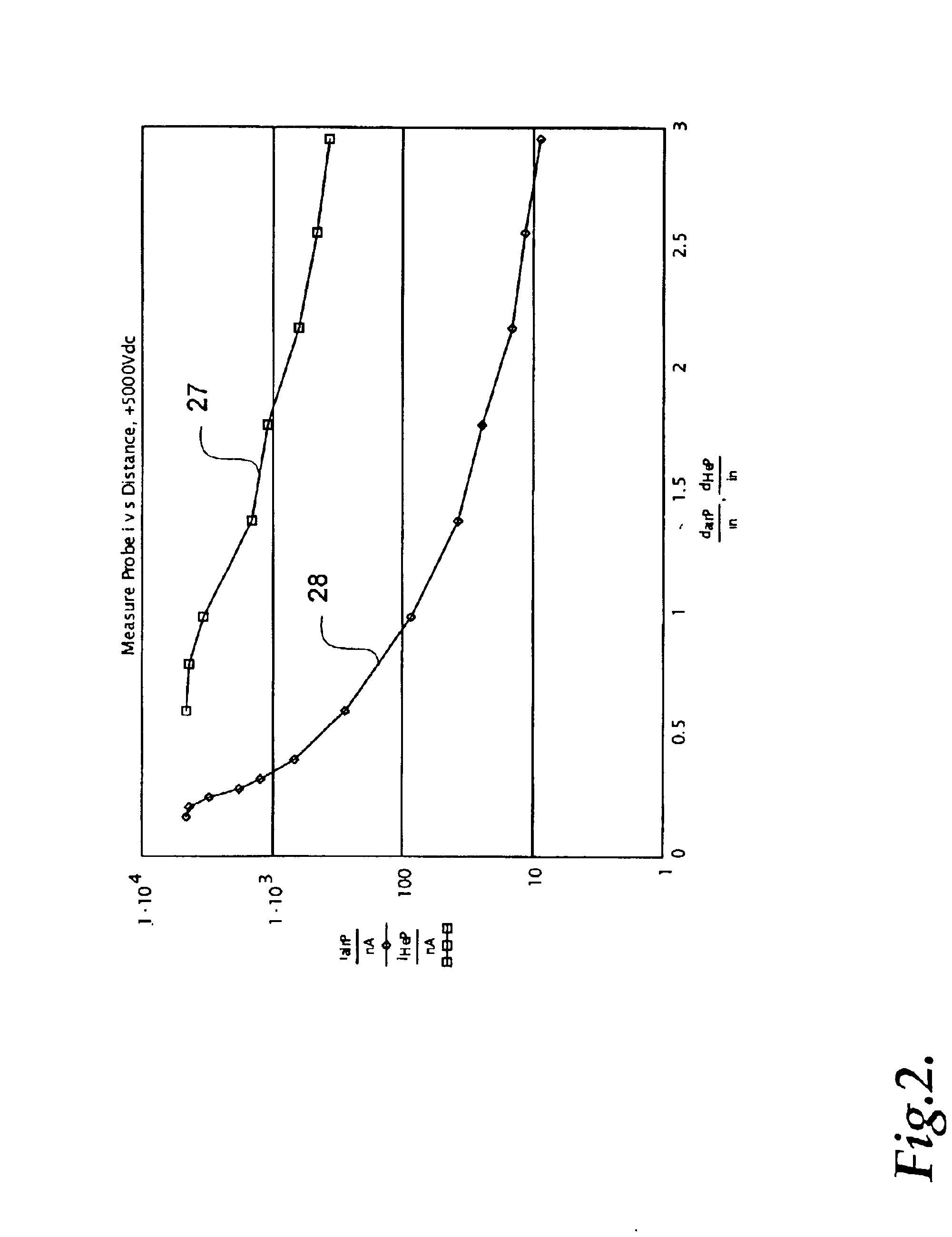
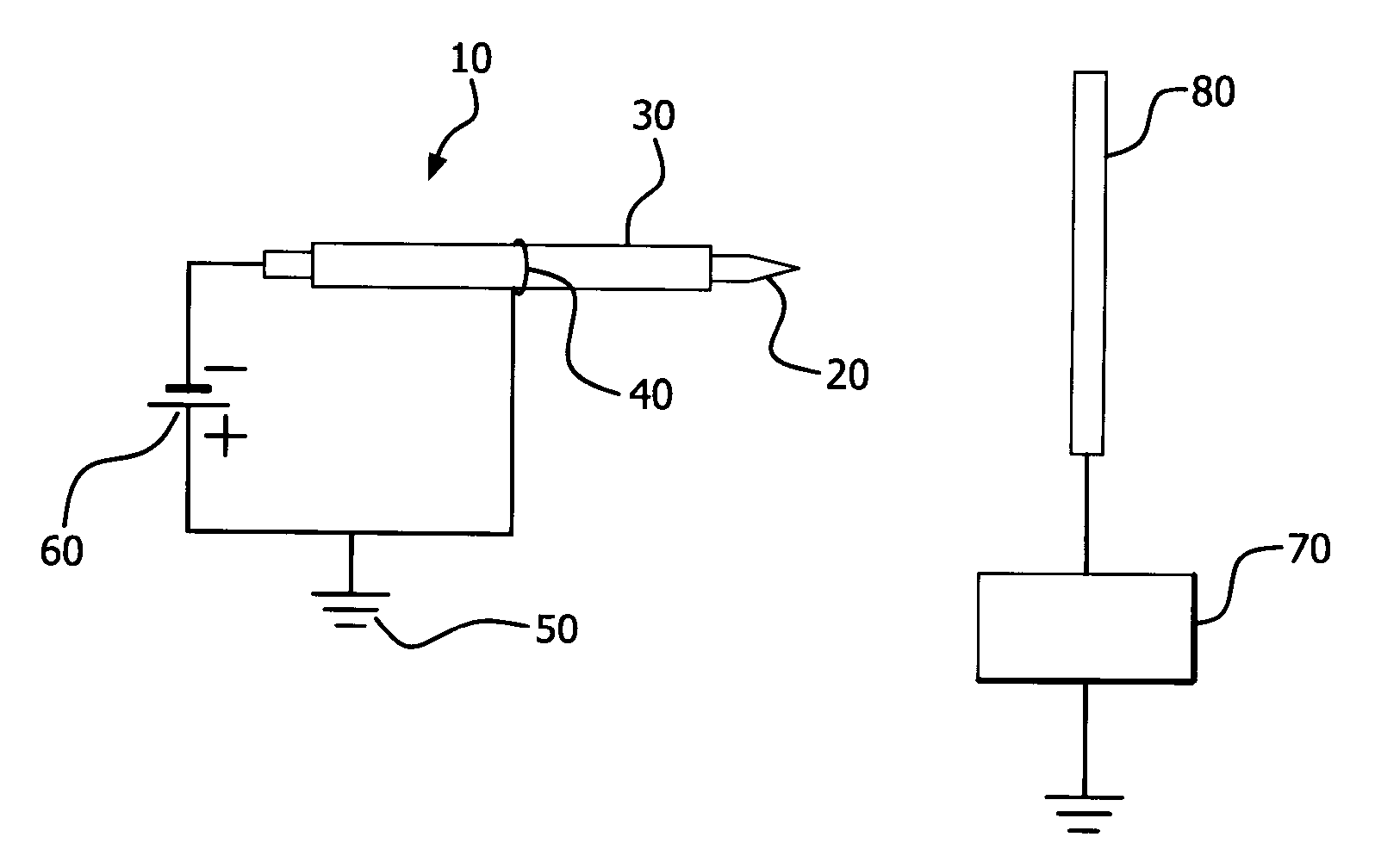
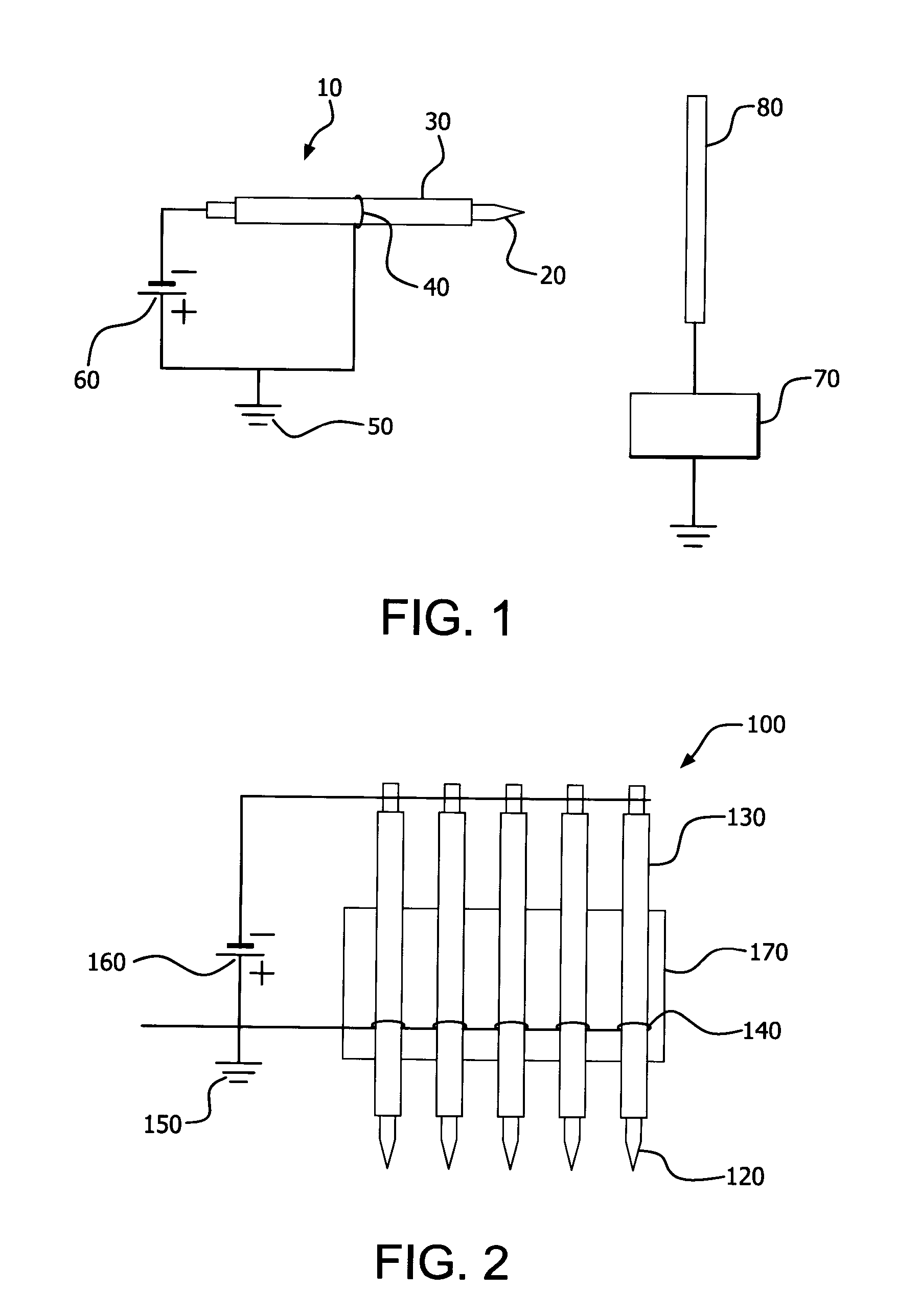
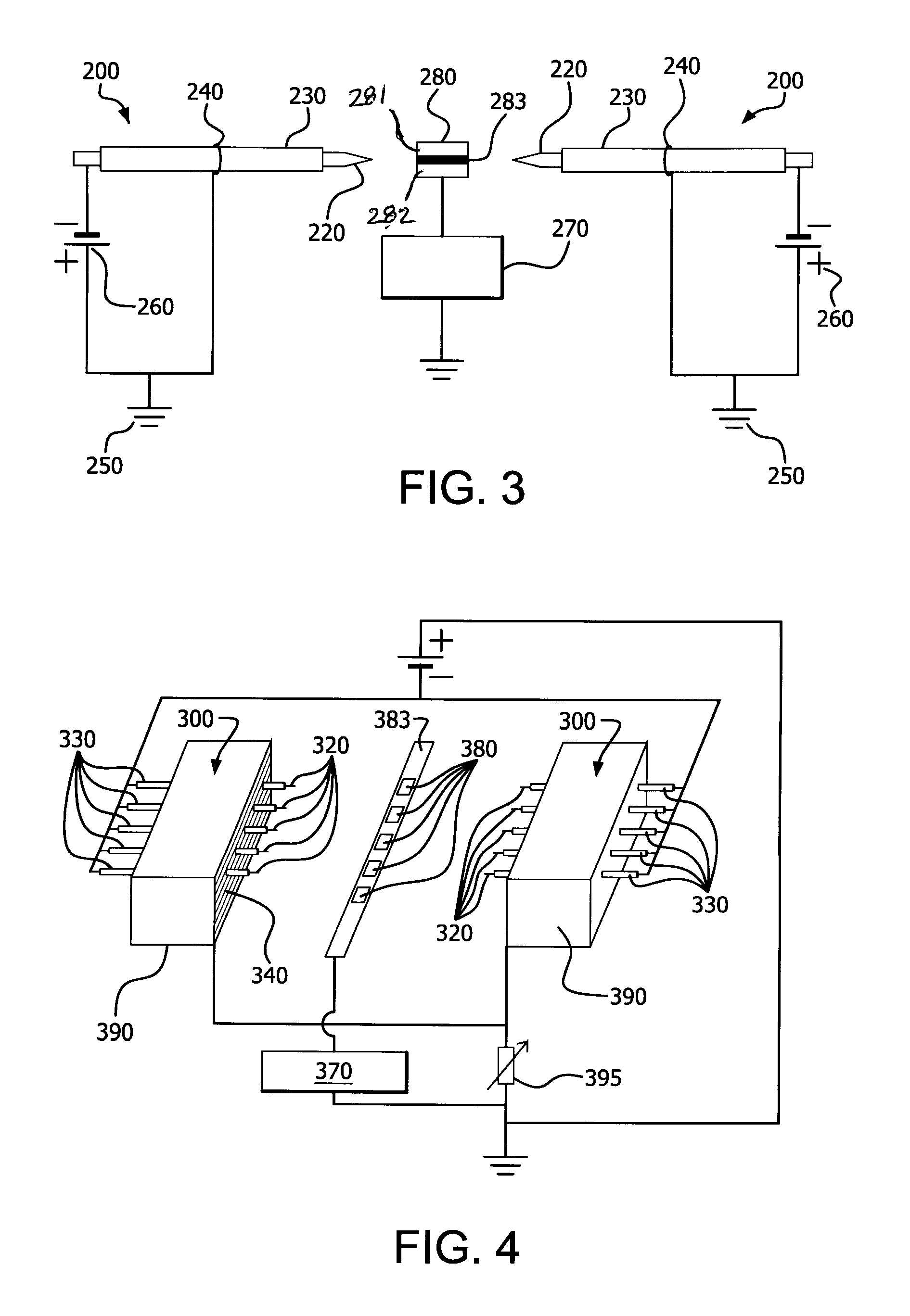
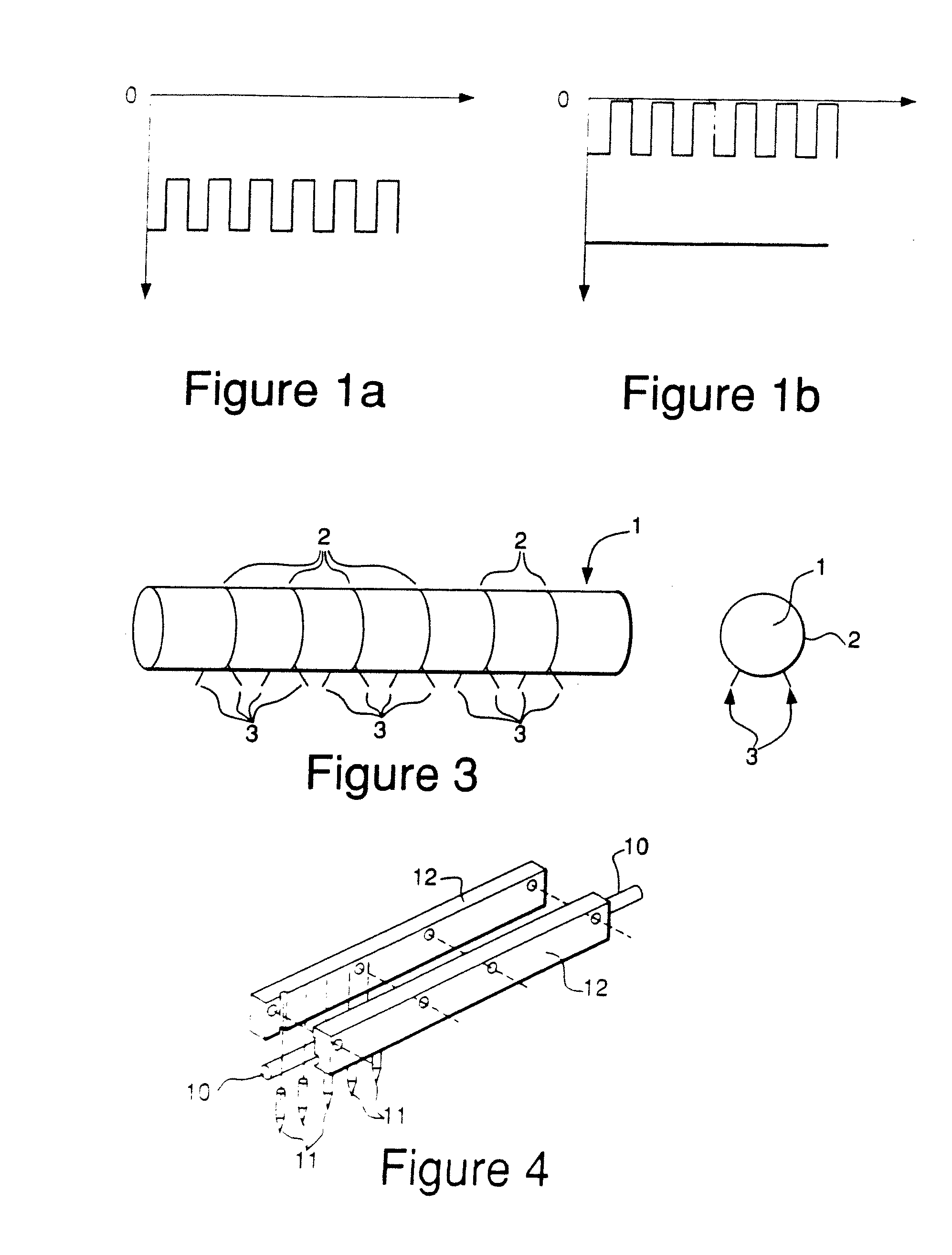
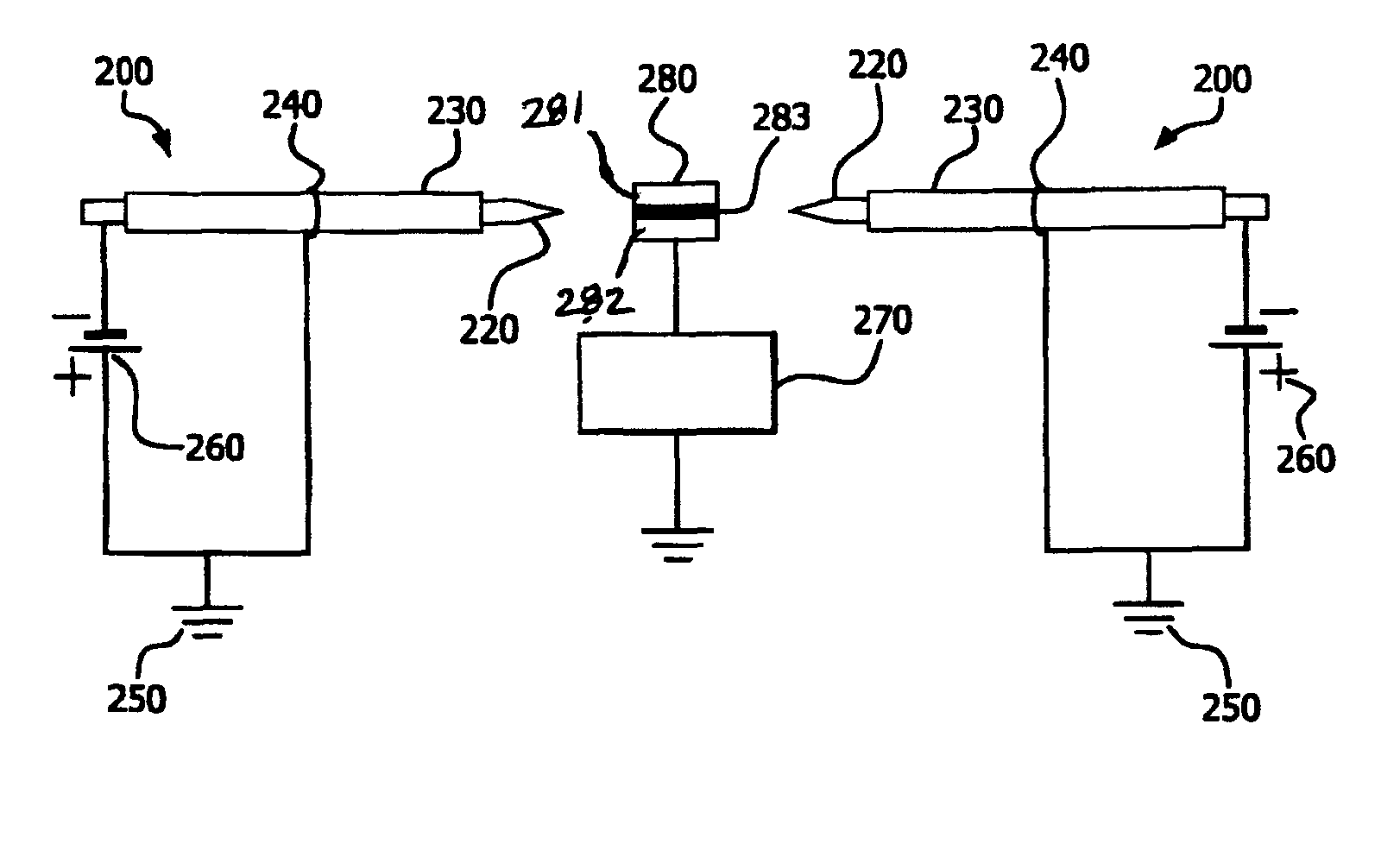
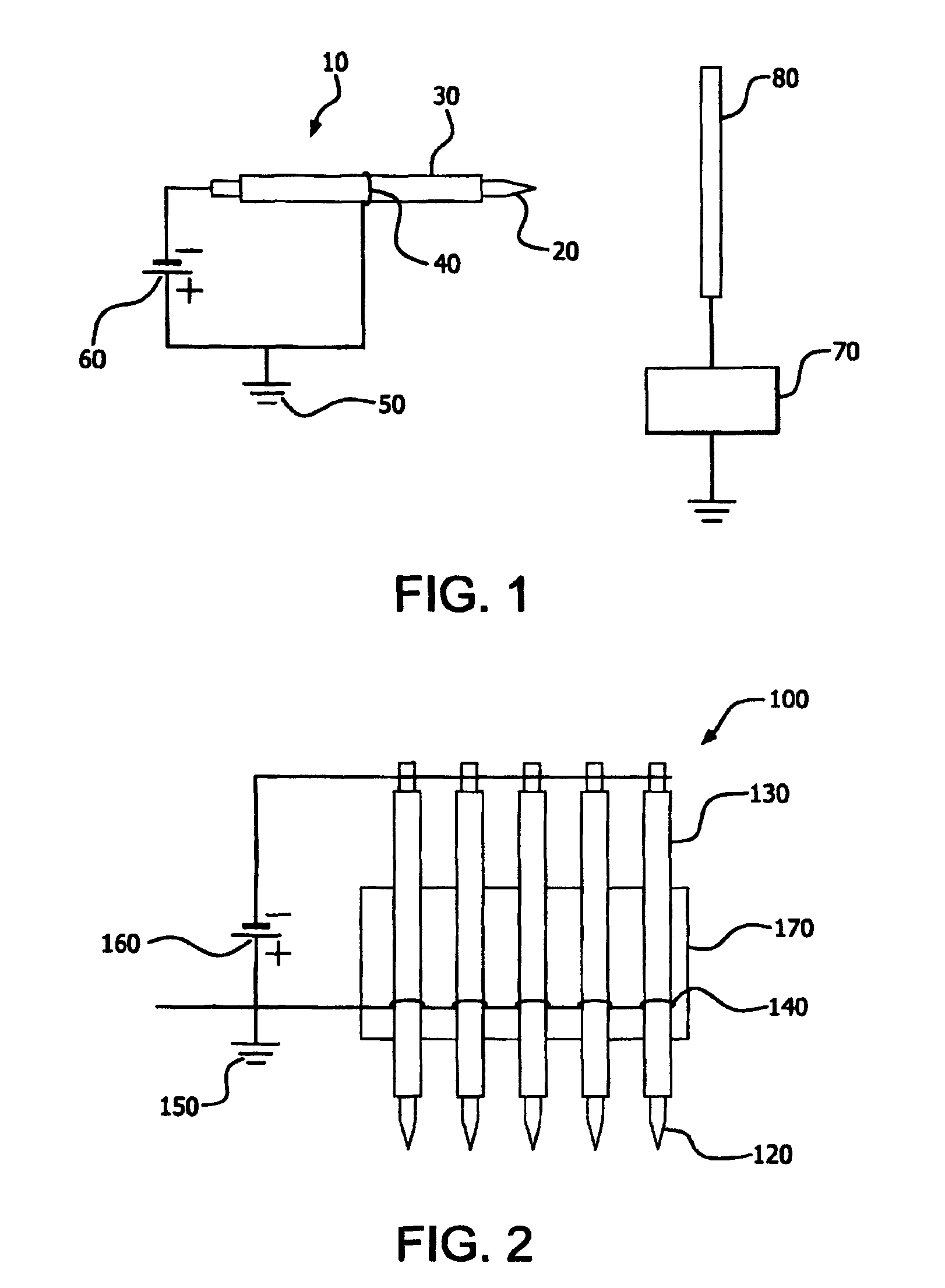
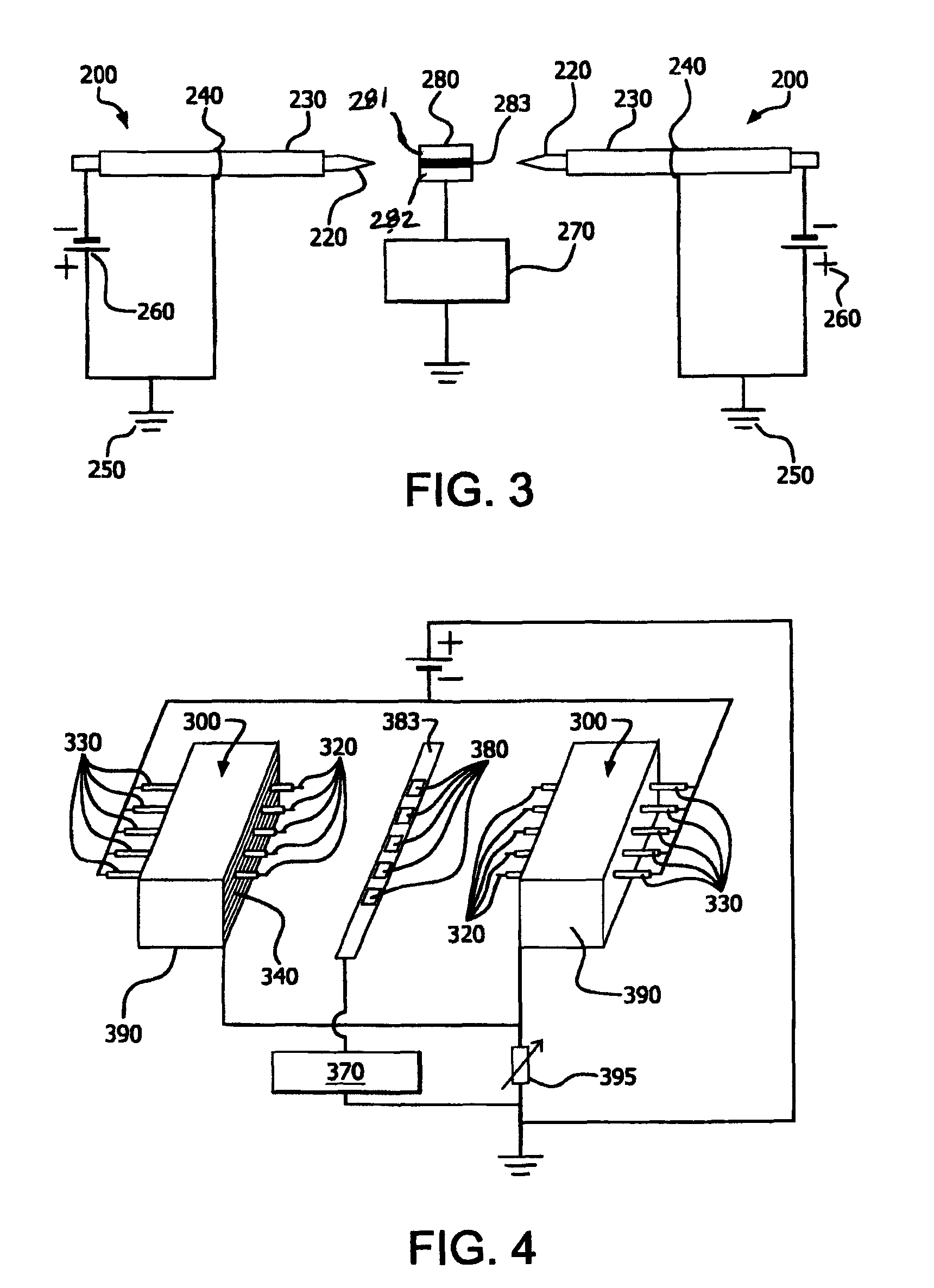
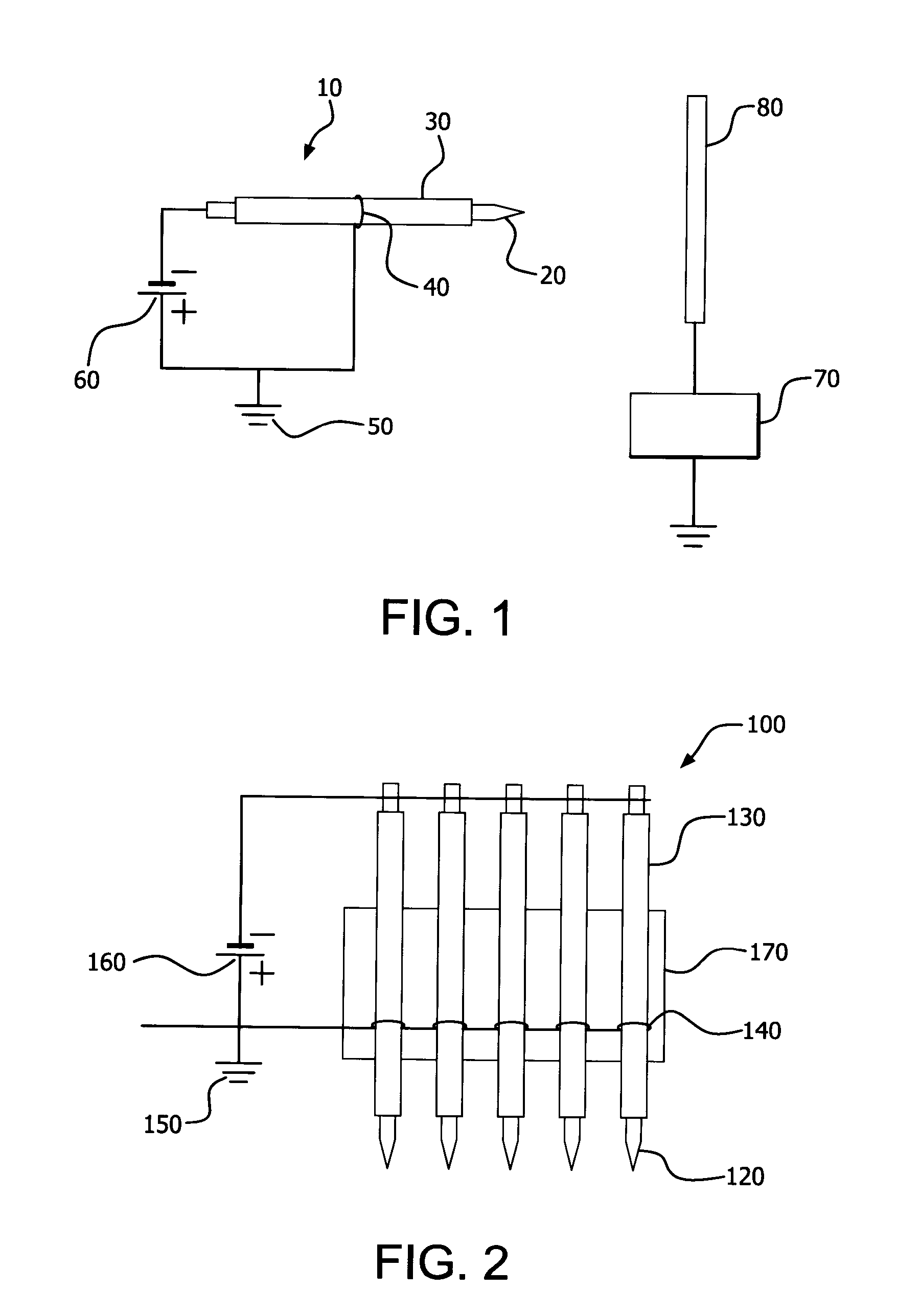
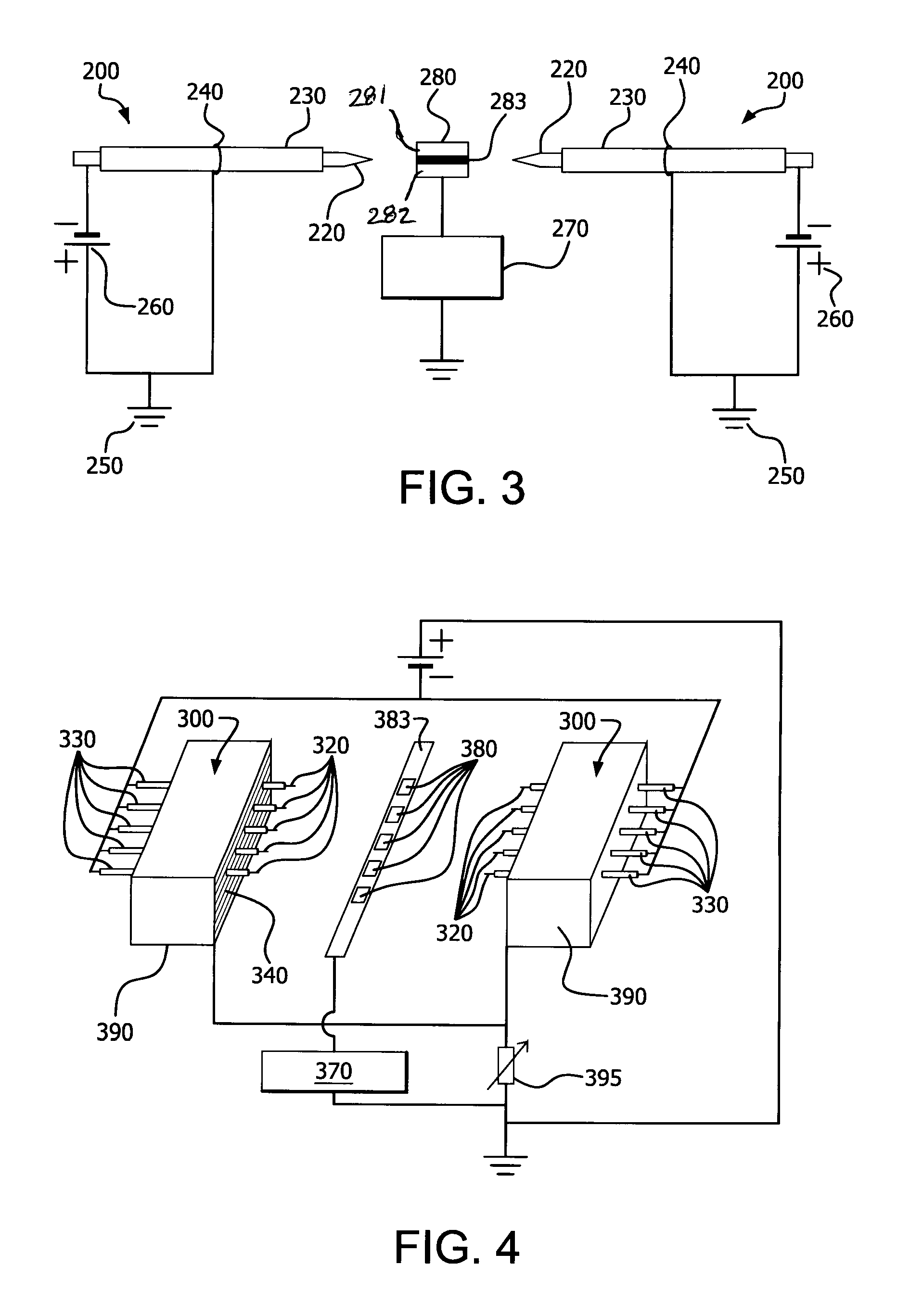
Parallel insulation fault detection system
InactiveUS6876203B2Reduce decreaseEffective insulationTesting dielectric strengthElectric switchesControl signalEngineering
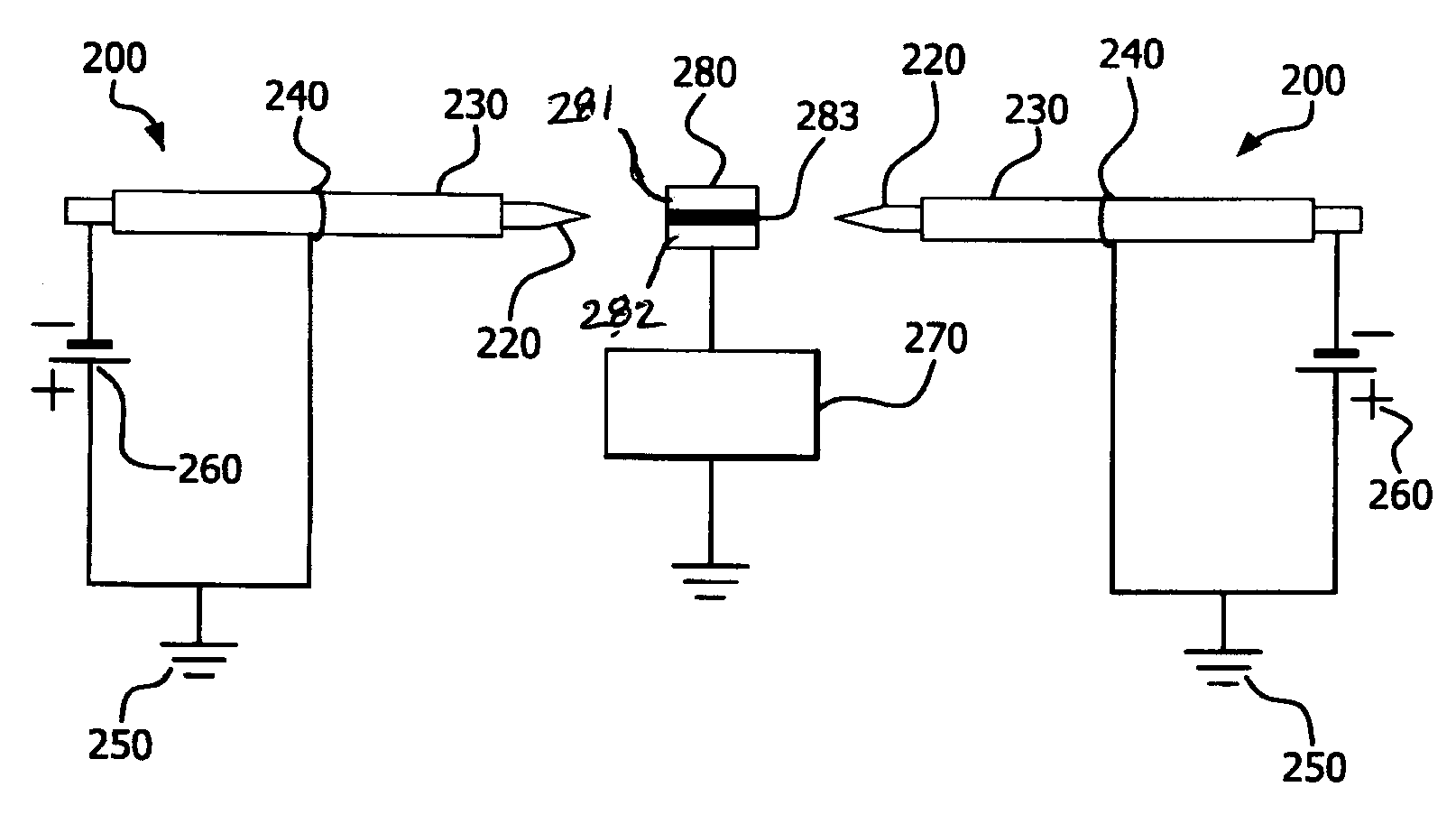
A device for detecting and locating arcs in a set of wires is discussed. The device comprises a probe for discharging controlled current to an exposed portion of a wire in the set of wires. The probe includes a handleable enclosure and an elongated structure which projects from the enclosure for conducting a gas and for enclosing a needle that has a tip. A suitable gas includes gases that have low electron attachment, such as helium. The device further comprises a control unit for communicating control signals as well as the gas to the probe. The control unit includes a controller, a valve being controllable by the controller and being capable of regulating the flow of the gas, and a high-voltage generator being controllable by the controller to generate a high-voltage signal, which can be communicated to the probe by the control unit.
Owner:ASTRONICS ADVANCED ELECTRONICS SYST
Method for removing a substance from a substrate using electron attachment
InactiveUS20050241671A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesHollow article cleaningSemiconductor materialsReactive gas
A method for removing a substance from at least a portion of a substrate which may be for example, a reactor or a semiconductor material, is disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a method comprising: providing a reactor having a surface coated with a substance; providing a first and second electrode in proximal to the reactor wherein the first and second electrode reside within a target area; passing a gas mixture comprising a reactive gas into the target area; supplying energy to the first and / or the second electrodes to generate electrons within the target area wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reactive gas thereby forming a negatively charged cleaning gas; contacting the substance with the negatively charged cleaning gas which reacts with the substance and forms a volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique electron attachment and remote ion generation
ActiveUS7079370B2Printed circuit assemblingDecorative surface effectsElectron attachmentMolecular physics
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the dry fluxing of at least one component and / or solder surface via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a method for removing oxides from the surface of a component comprising: providing a component on a substrate wherein the substrate is grounded or has a positive electrical potential to form a target assembly; passing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas through an ion generator comprising a first and a second electrode; supplying an amount of voltage to at least one of the first and second electrodes sufficient to generate electrons wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas and form a negatively charged reducing gas; and contacting the target assembly with the negatively charged reducing gas to reduce the oxides on the component.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method for cleaning a reactor using electron attachment
A method for cleaning, and / or enhancing the cleaning of, a reactor is disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a method comprising: providing the reactor wherein a surface of the reactor is coated with a substance; providing a first and second electrode in close proximity to the reactor wherein the first and second electrode reside within a target area; passing a gas mixture comprising a reactive gas into the target area; supplying energy to at least one of the first or the second electrodes to generate electrons within the target area wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reactive gas thereby forming a negatively charged cleaning gas; contacting the substance with the negatively charged cleaning gas wherein the negatively charged cleaning gas reacts with the substance and forms a volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reactor.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Device for producing negatively charged nanoparticles and a method for the same
InactiveUS7390384B2High emitter current densityHigh densityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrotherapyHigh current densityNanoparticle
A device and method are provided for producing negatively charged nanoparticles. The device comprises a power supply, an electron supermicroemitter and a controller, the power supply connects with the electron supermicroemitter and the controller respectively. The potential of the electron supermicroemitter to the ground is controlled in the range of −2 kV to −29 kV by the power supply and the controller in accordance with the shape, size and different application of the materials of the emitter, so as to form field electron emitting of tunneling effect. The energy of electrons with high current density produced by the emitter can be adjusted during the electrons' colliding with particles in aerosol such that the electrons are attached to the nanoparticles of different size with wider energy band to form negatively charged nanoparticles.
Owner:FANG MOXI +1
Removal of surface oxides by electron attachment for wafer bumping applications
ActiveUS7387738B2Satisfies needElectrolysis componentsElectric discharge tubesElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
The present invention relates to a method for removing metal oxides from a substrate surface. In one particular embodiment, the method comprises: providing a substrate, a first, and a second electrode that reside within a target area; passing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas through the target area; supplying an amount of energy to the first and / or the second electrode to generate electrons within the target area wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to a portion of the reducing gas and form a negatively charged reducing gas; and contacting the substrate with the negatively charged reducing gas to reduce the metal oxides on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
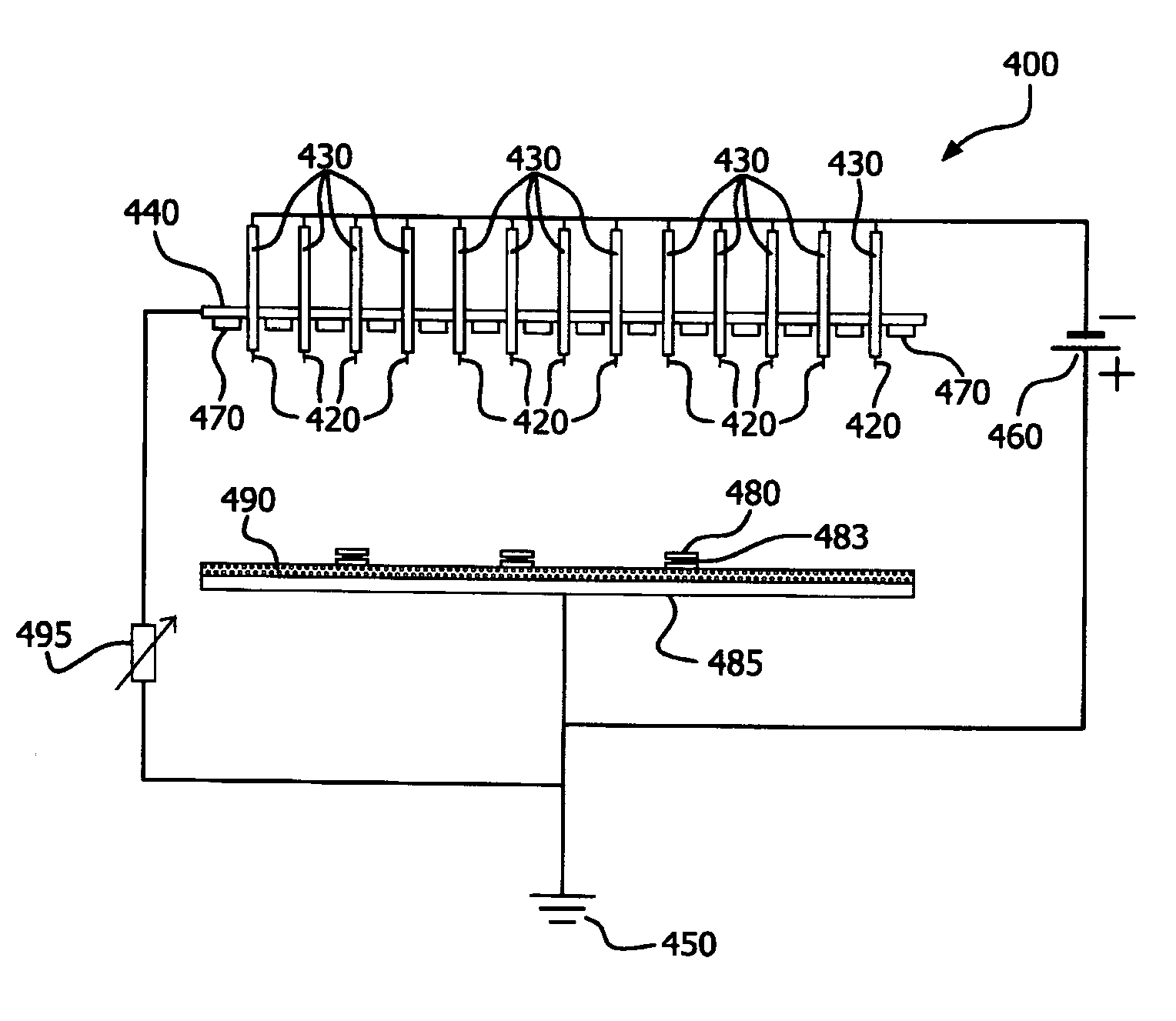
Removal of Surface Oxides by Electron Attachment
ActiveUS20090236236A1From normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityElectron attachmentDc voltage
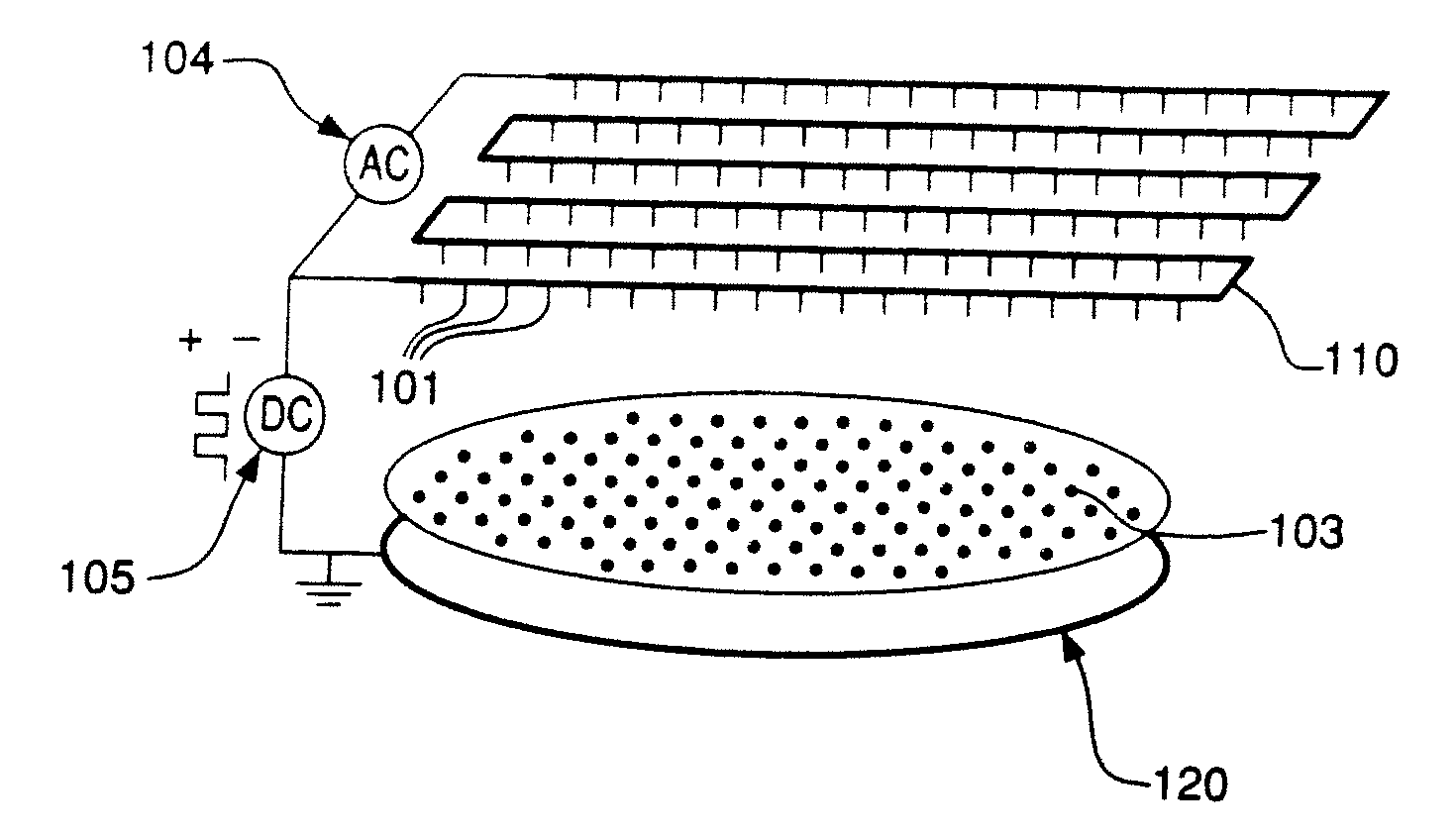
Described herein are a method and an apparatus for removing metal oxides from a substrate surface within a target area. In one particular embodiment, the method and apparatus has an energizing electrode which has an array of protruding conductive tips that are electrically connected by a conductive wire and separated into a first electrically connected group and a second electrically connected group wherein at least a portion of the conductive tips are activated by a DC voltage source that is negatively biased to generate electrons within the target area that attach to at least a portion of a reducing gas that is present in the target area to form a negatively charged reducing gas that contacts the treating surface to reduce the metal oxides on the treating surface of the substrate.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
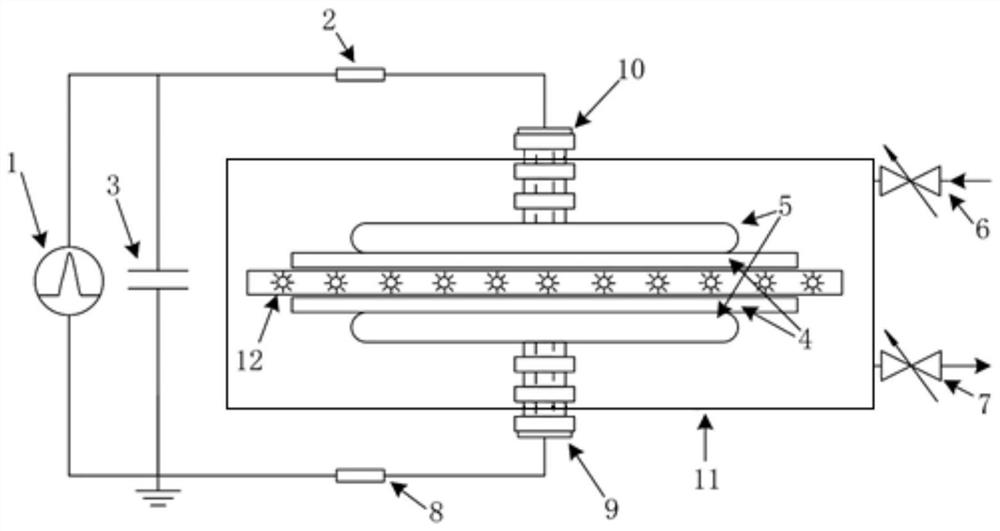
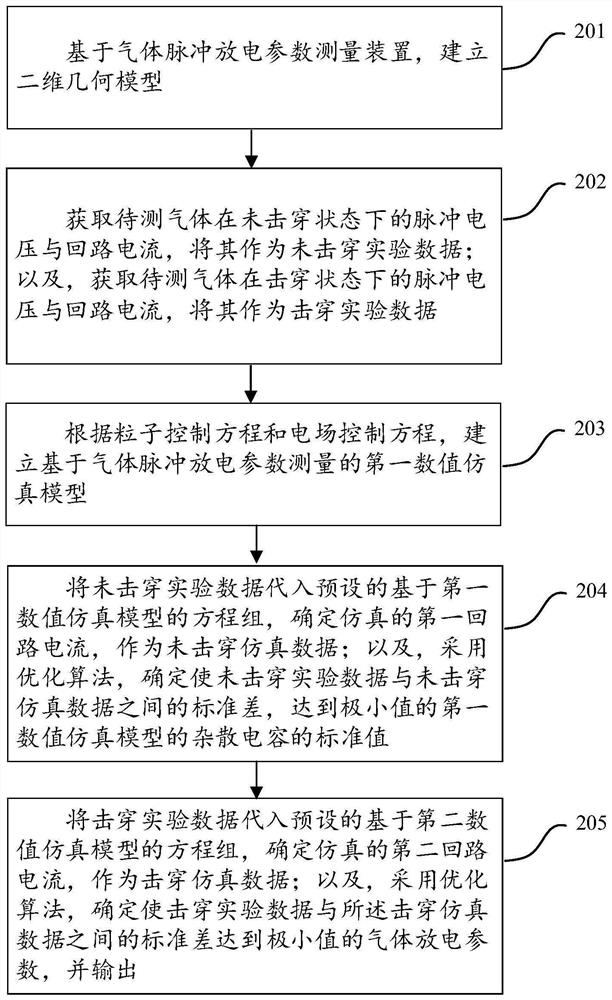
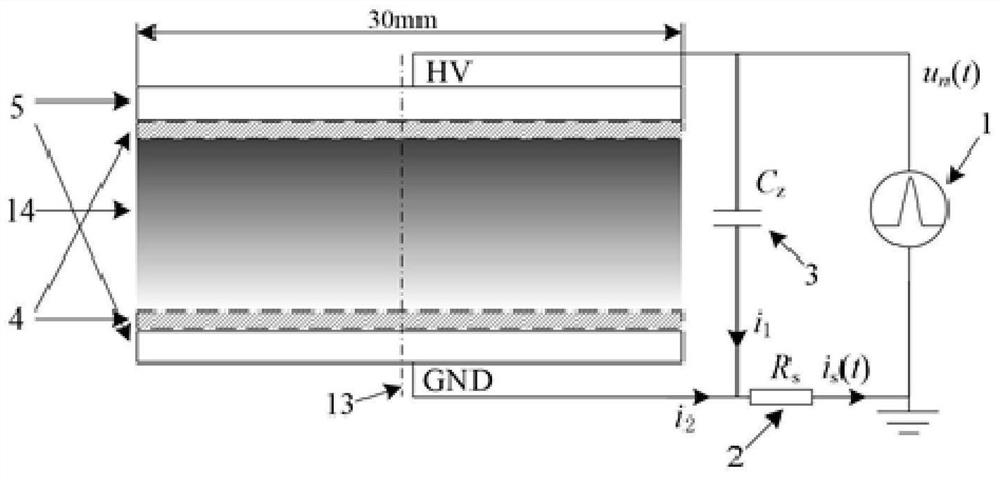
Gas pulse discharge parameter measuring method and device
ActiveCN111880051ARealize measurementFill in the measurement gapsTesting dielectric strengthCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring gas pulse discharge parameters, and the method and device are used for realizing accurate measurement of the gas pulse discharge parametersunder an atmospheric pressure condition. According to the invention, the method comprises the steps: adopting a gas pulse discharge parameter measuring device to respectively obtain a pulse voltage and a loop current of gas to be measured in a non-breakdown state and a breakdown state; establishing a numerical simulation model according to the particle control equation and the electric field control equation; according to the numerical simulation model and a preset equation set, adjusting and optimizing the stray capacitance parameter value of the numerical simulation model through the non-breakdown experiment data; according to the optimized numerical simulation model, obtaining the simulated loop current, and then determining gas discharge parameters such as a soup ionization coefficient, an electron adhesion coefficient, a secondary electron emission coefficient, a photoionization coefficient and the like which enable the breakdown experiment data and the breakdown simulation data to take minimum values by adopting a direction acceleration optimization method, and calculating the standard deviation between the breakdown experiment data and the breakdown simulation data.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique involving electron attachment and remote ion generation
InactiveUS20060164784A1Printed circuit assemblingSoldering apparatusElectron attachmentElectric potential
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for the dry fluxing of at least one component and / or solder surface via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a method for removing oxides from the surface of a component comprising: providing a component on a substrate wherein the substrate is grounded or has a positive electrical potential to form a target assembly; passing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas through an ion generator comprising a first and a second electrode; supplying an amount of voltage to at least one of the first and second electrodes sufficient to generate electrons wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas and form a negatively charged reducing gas; and contacting the target assembly with the negatively charged reducing gas to reduce the oxides on the component.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Removal of Surface Oxides by Electron Attachment for Wafer Bumping Applications
InactiveUS20080149690A1Electric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
The present invention relates to a method for removing metal oxides from a substrate surface. In one particular embodiment, the method comprises: providing a substrate, a first, and a second electrode that reside within a target area; passing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas through the target area; supplying an amount of energy to the first and / or the second electrode to generate electrons within the target area wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to a portion of the reducing gas and form a negatively charged reducing gas; and contacting the substrate with the negatively charged reducing gas to reduce the metal oxides on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
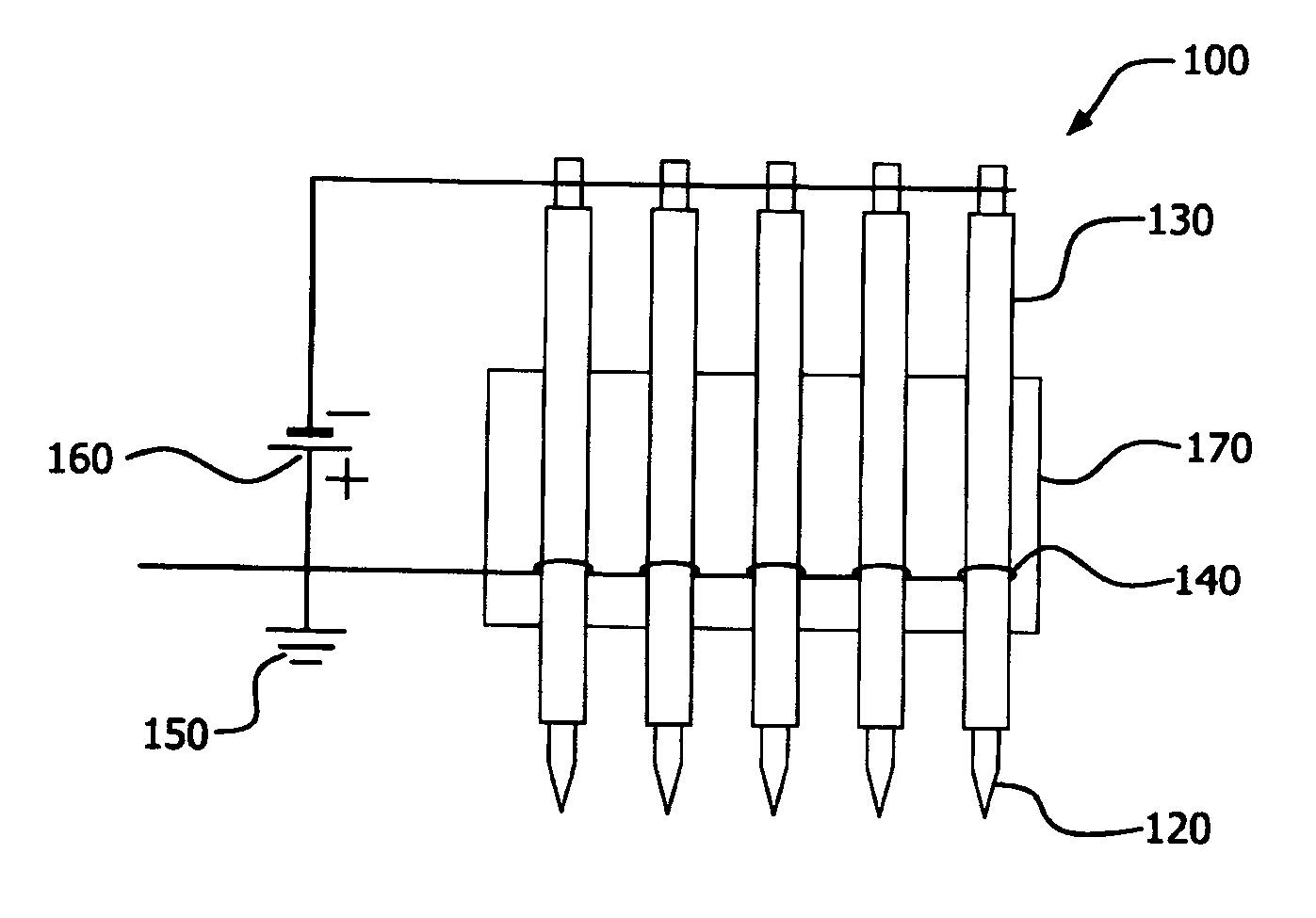
Removal of surface oxides by electron attachment
ActiveUS8361340B2From normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityElectron attachmentDc voltage
Described herein are a method and an apparatus for removing metal oxides from a substrate surface within a target area. In one particular embodiment, the method and apparatus has an energizing electrode which has an array of protruding conductive tips that are electrically connected by a conductive wire and separated into a first electrically connected group and a second electrically connected group wherein at least a portion of the conductive tips are activated by a DC voltage source that is negatively biased to generate electrons within the target area that attach to at least a portion of a reducing gas that is present in the target area to form a negatively charged reducing gas that contacts the treating surface to reduce the metal oxides on the treating surface of the substrate.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Removal of surface oxides by electron attachment
ActiveUS7897029B2Electrolysis componentsElectric discharge tubesElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method for the Removal of Surface Oxides by Electron Attachment
ActiveUS20110204123A1Decorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
Described herein are a method and an apparatus for removing metal oxides and / or forming solder joints on at least a portion of a substrate surface within a target area. In one particular embodiment, the method and apparatus form a solder joint within a substrate comprising a layer having a plurality of solder bumps by providing one or more energizing electrodes and exposing at least a portion of the layer and solder bumps to the energizing electrode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method of processing a surface of a workpiece
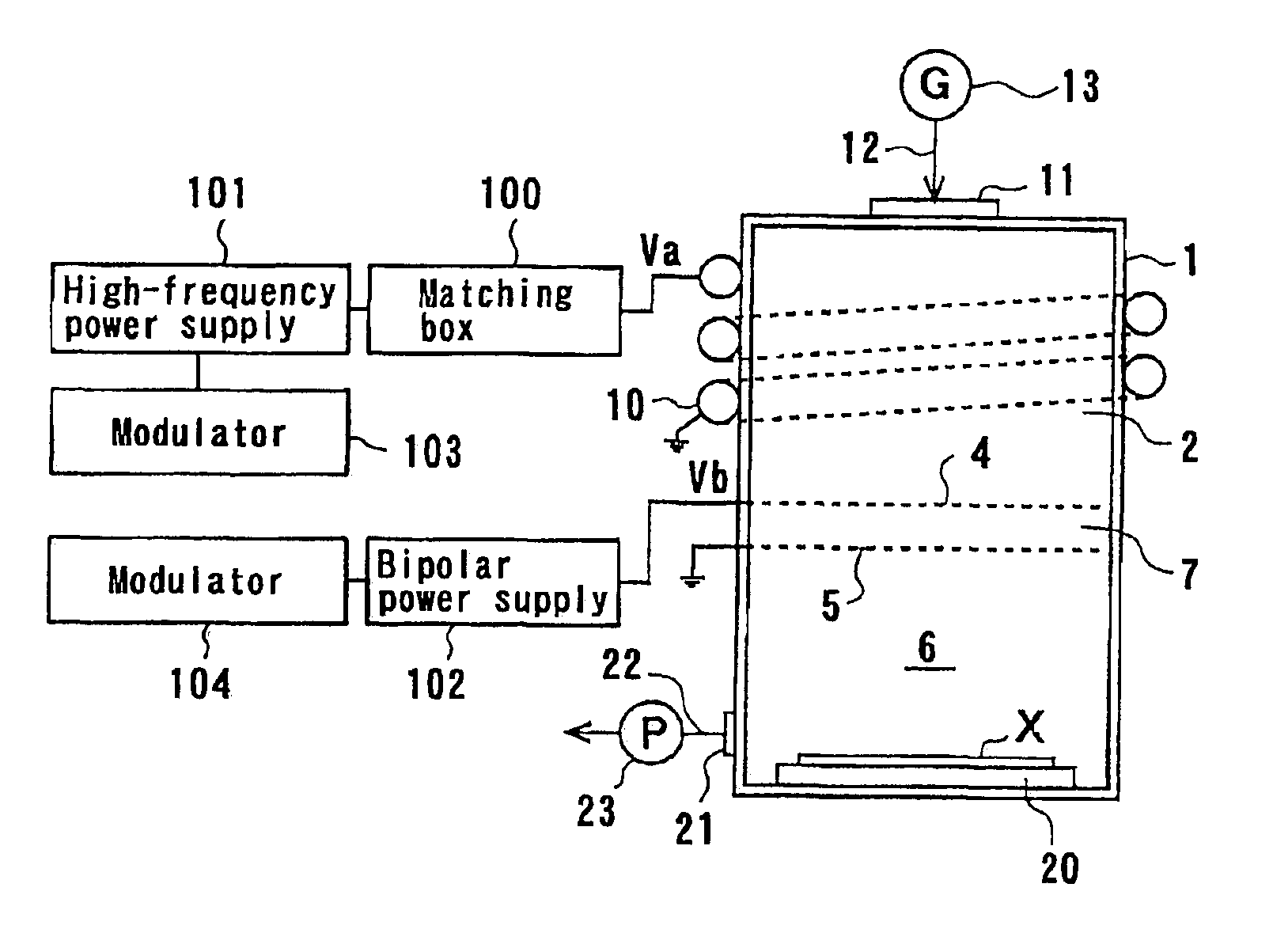
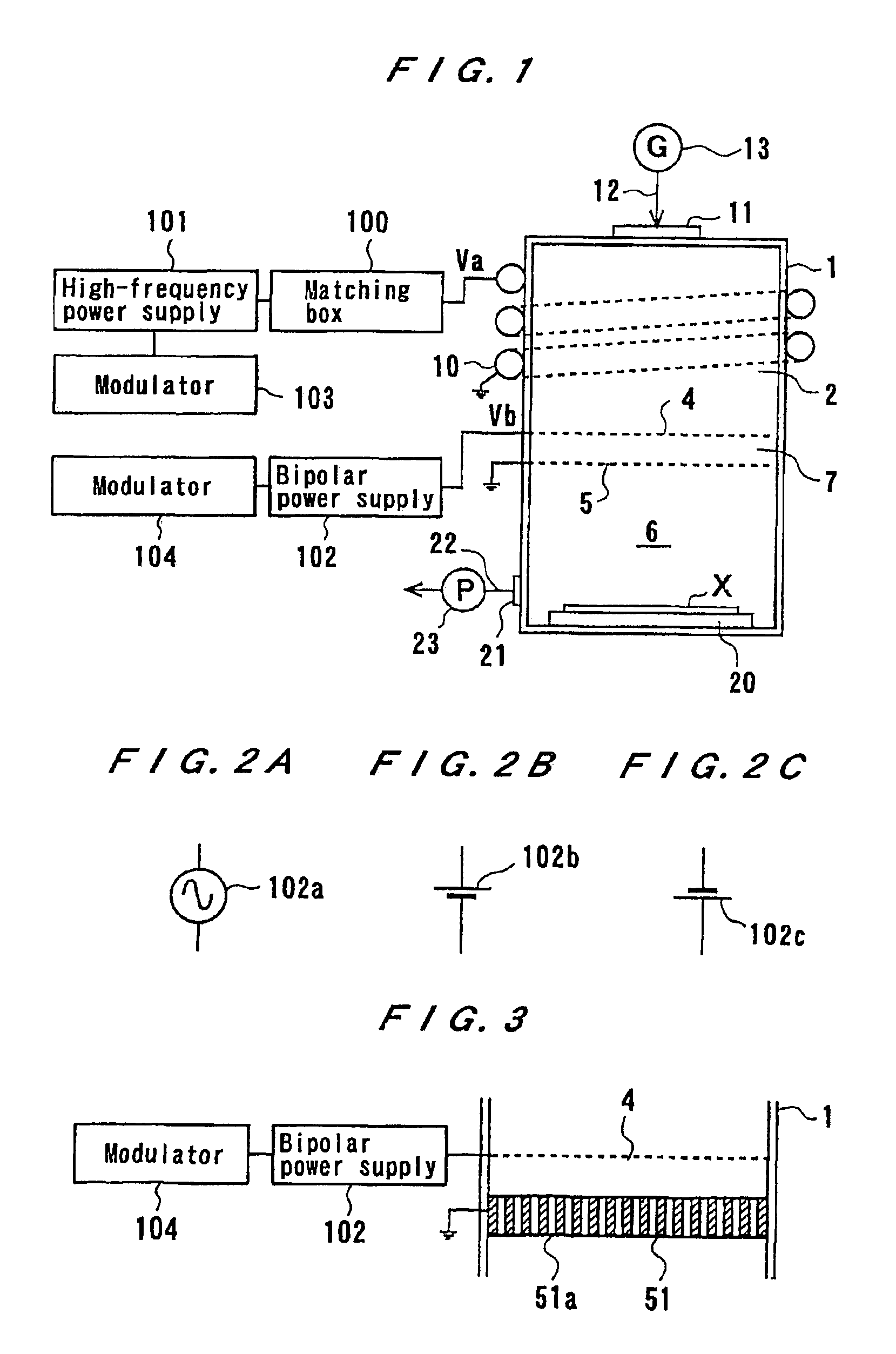
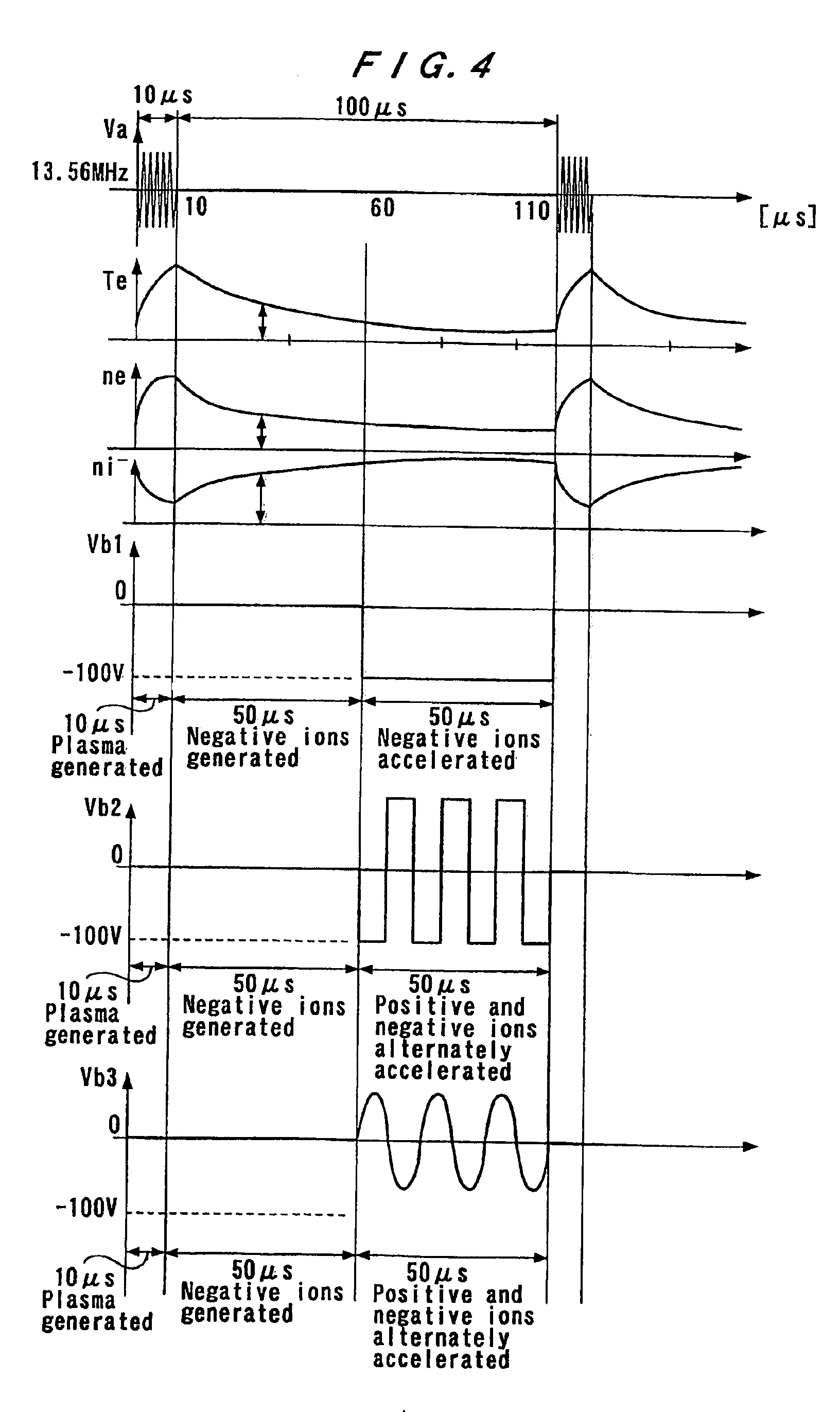
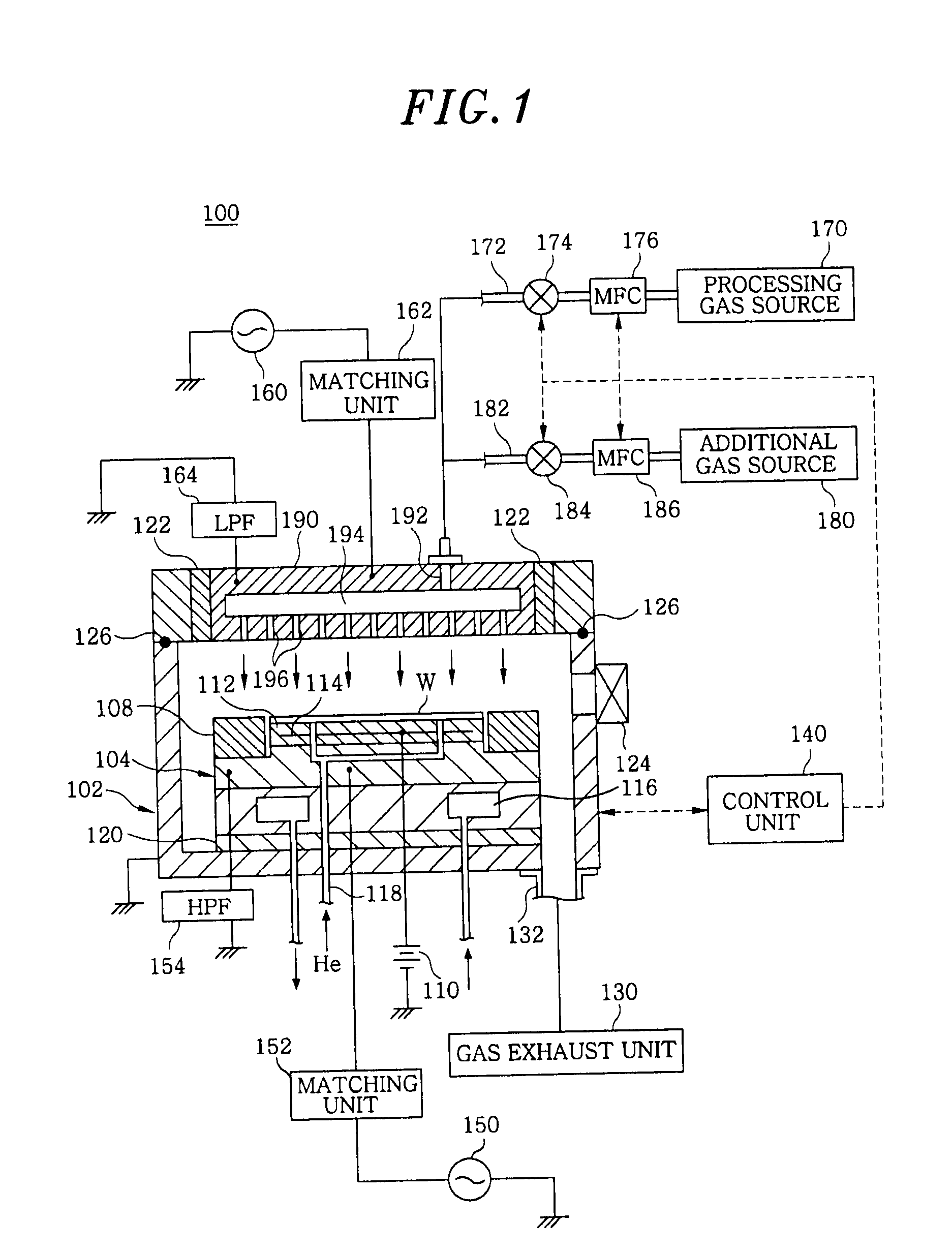
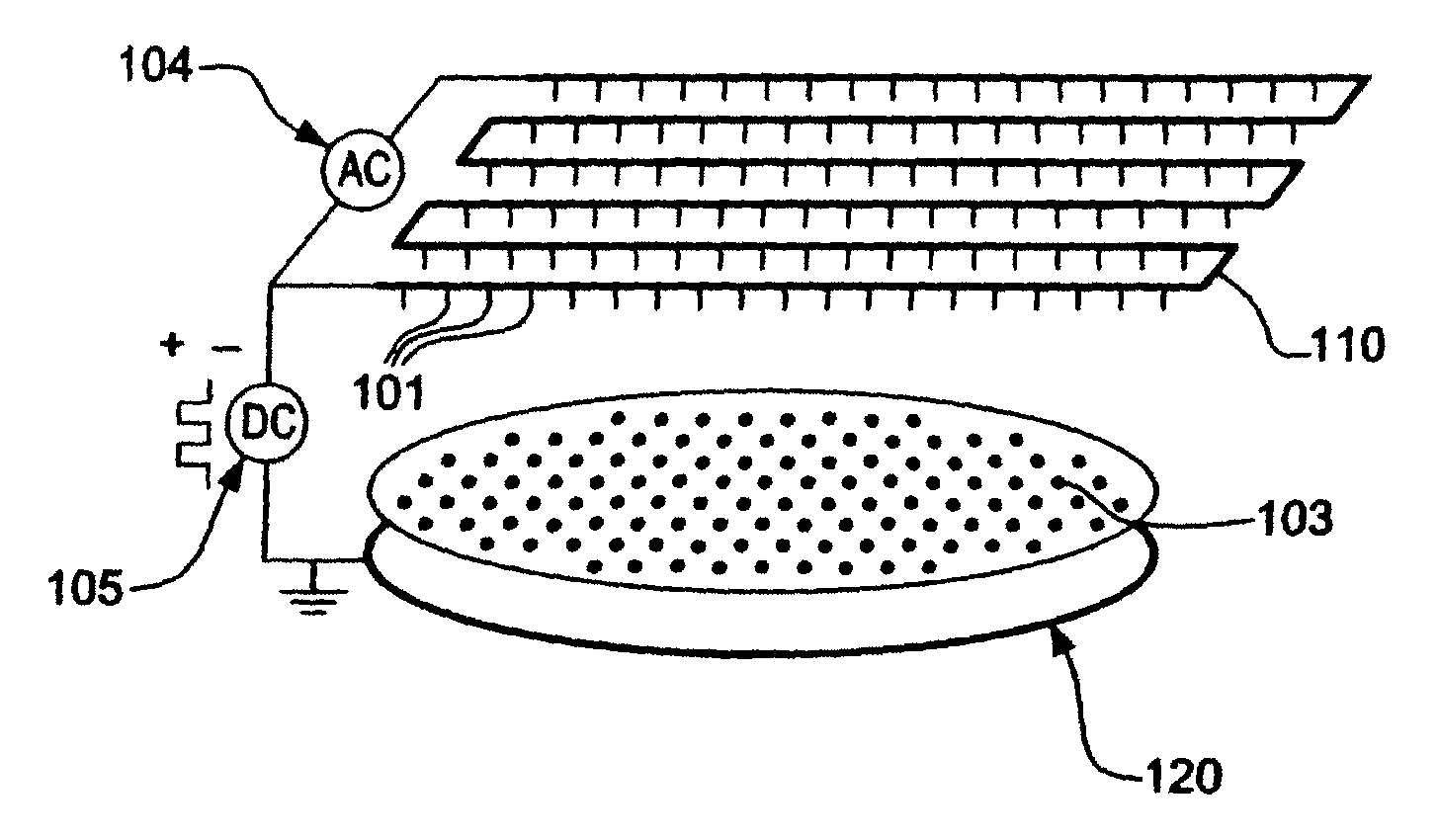
InactiveUS6909087B2Inexpensive and compact structurePrecise processingLaser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPlasma generatorVacuum chamber
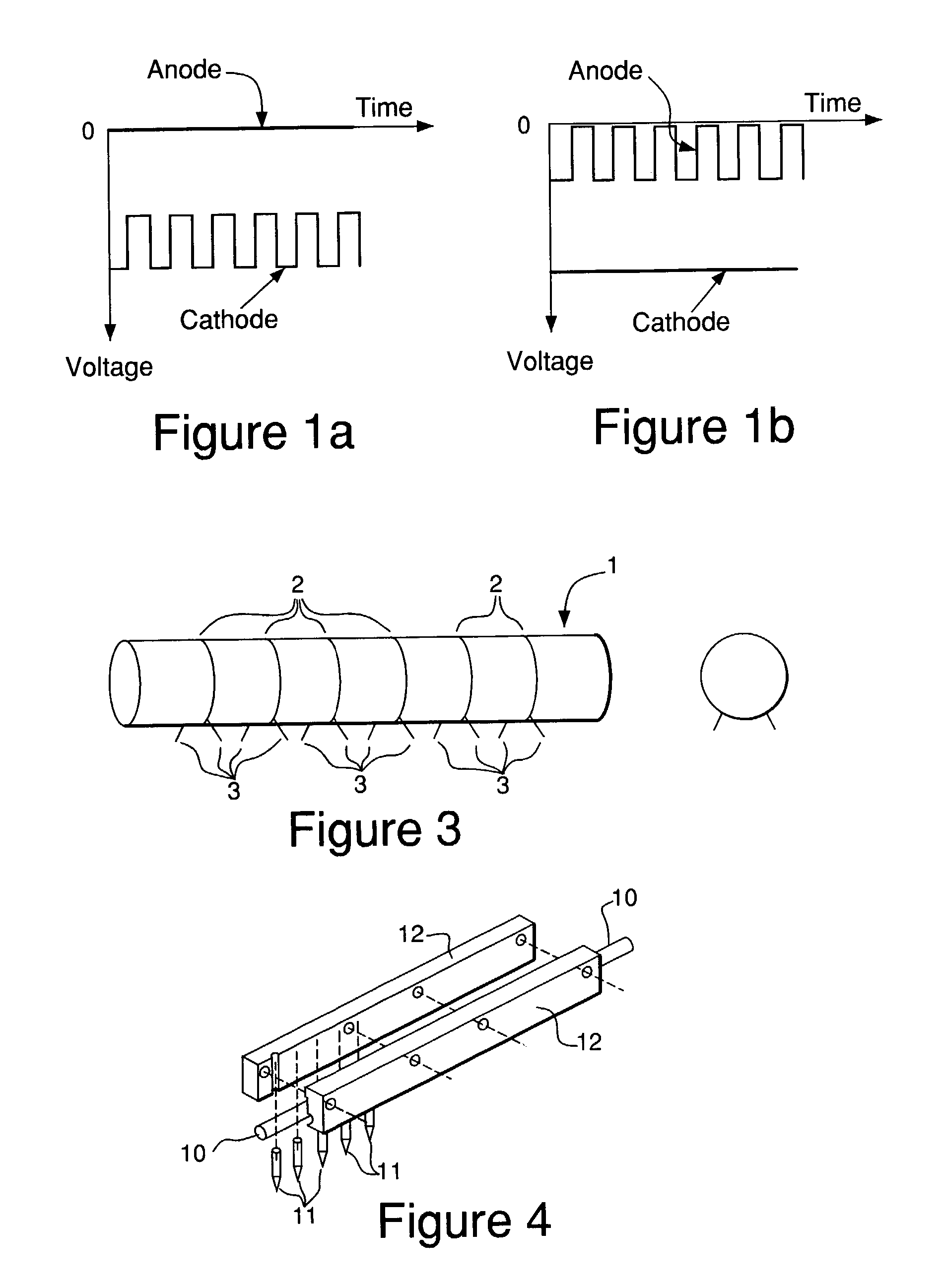
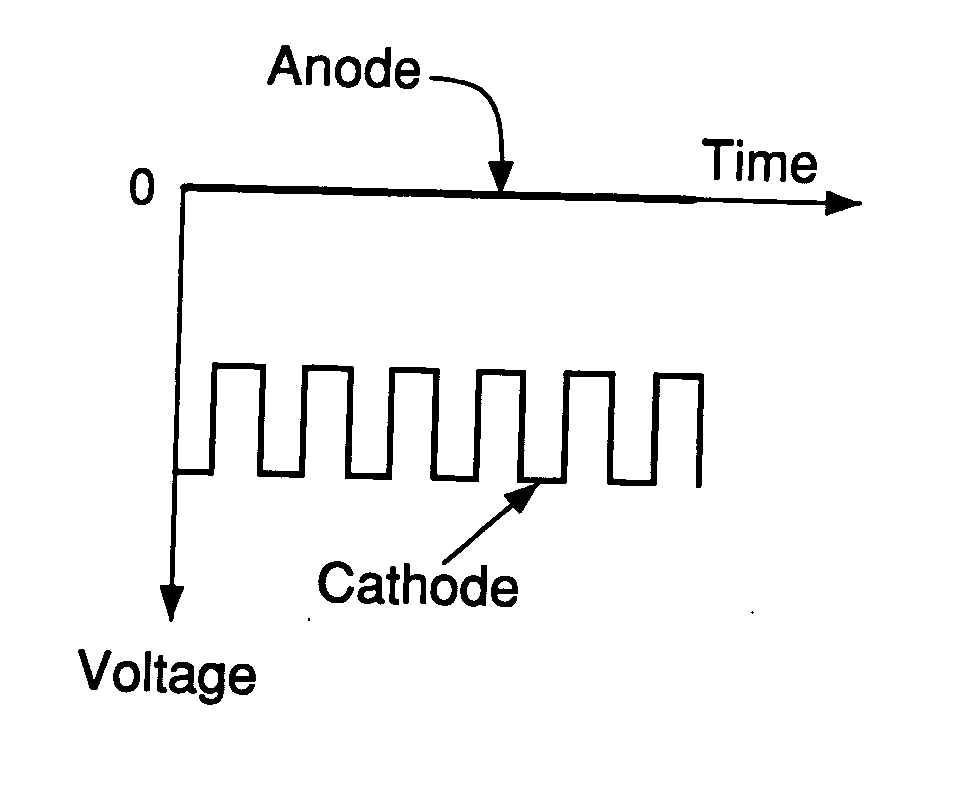
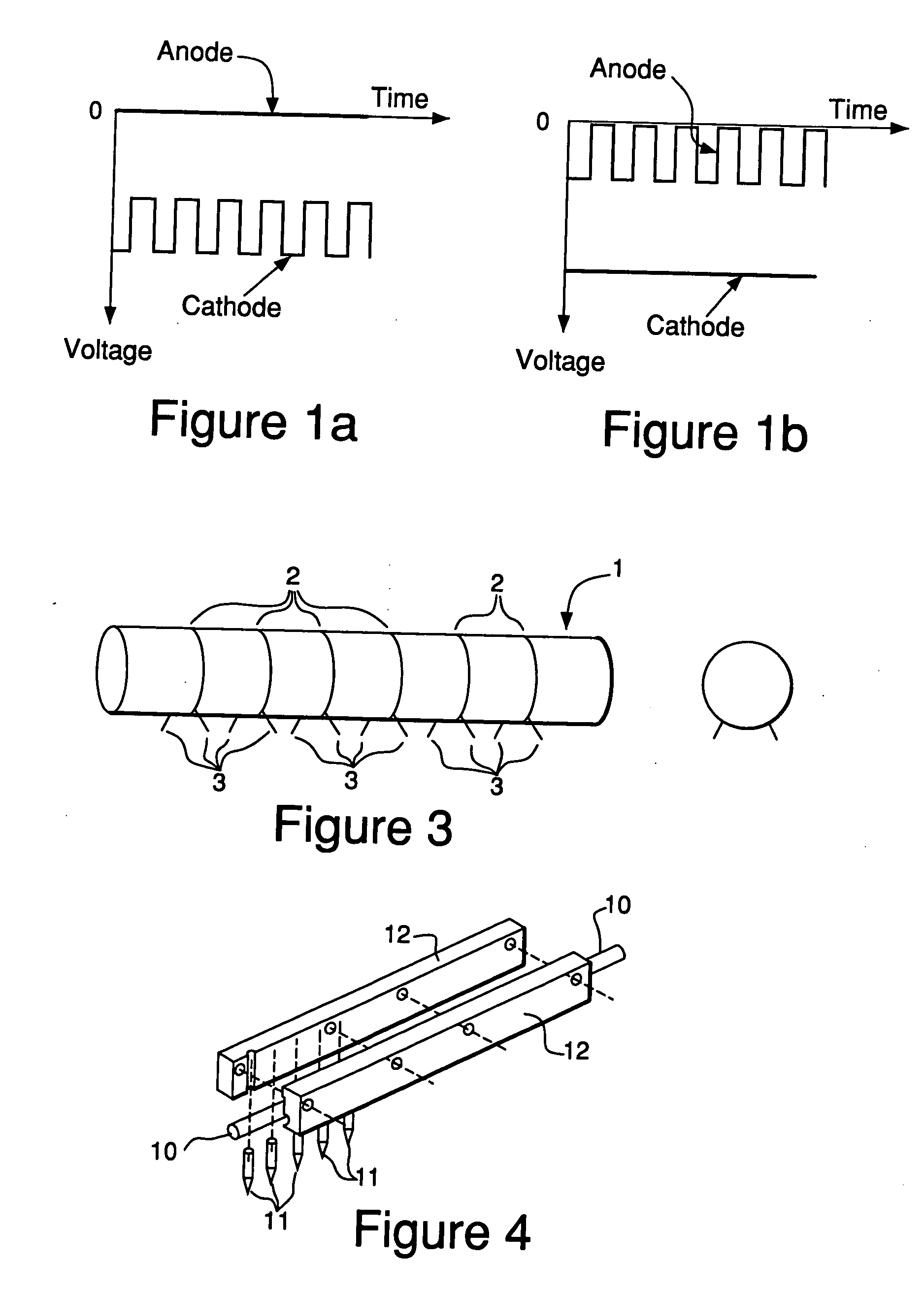
A plasma generator generates positive ions and negative ions in a plasma. An ion extracting portion (4, 5) selectively extracts the generated positive ions and negative ions from the plasma, and accelerates the extracted ions in a predetermined direction. The positive ions and the negative ions are selectively applied to the workpiece (X). The plasma generator applies a high-frequency voltage to a process gas in a vacuum chamber for generating a plasma which is composed of positive ions and electrons from the process gas, and interrupts the high-frequency voltage for attaching the electrons to the residual process gas to generate negative ions. The application of the high-frequency voltage and the interruption of the high-frequency voltage are alternately repeated.
Owner:TOHOKU TECHNO ARCH CO LTD
Method for the removal of surface oxides by electron attachment
InactiveCN102044418ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
Described herein are a method and an apparatus for removing metal oxides and / or forming solder joints on at least a portion of a substrate surface within a target area. In one particular embodiment, the method and apparatus to reduce metal oxides and form a solder joint within a substrate comprising a layer having a plurality of solder bumps by providing one or more energizing electrodes and exposing at least a portion of the layer and solder bumps to the energizing electrode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
System and method for chemical potential energy production
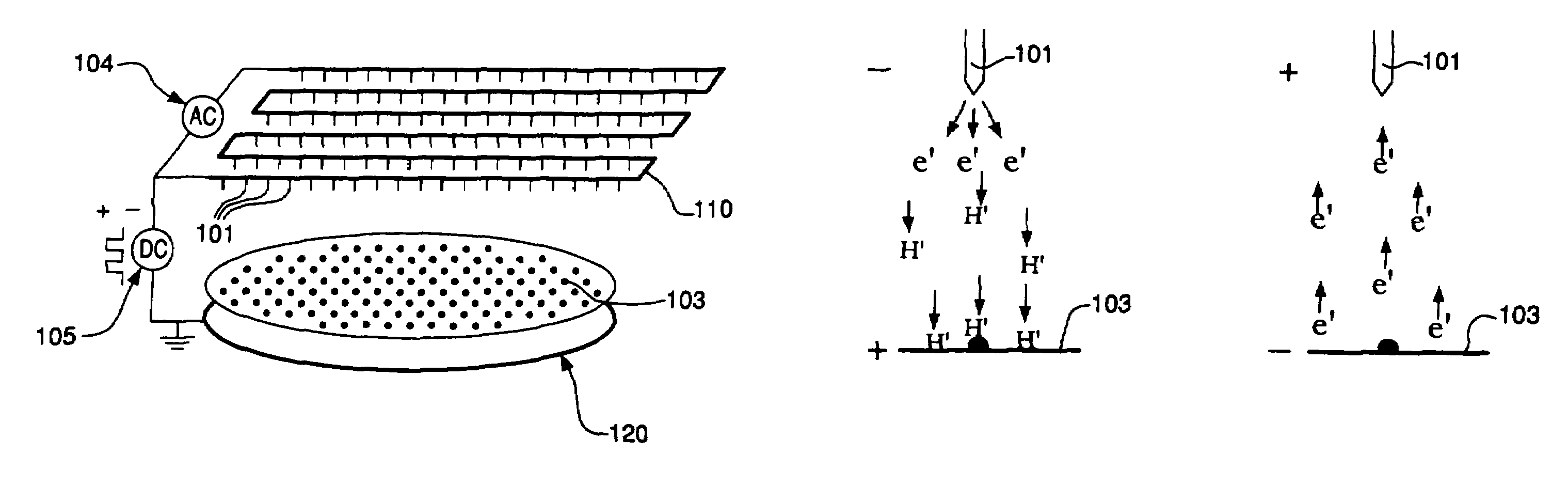
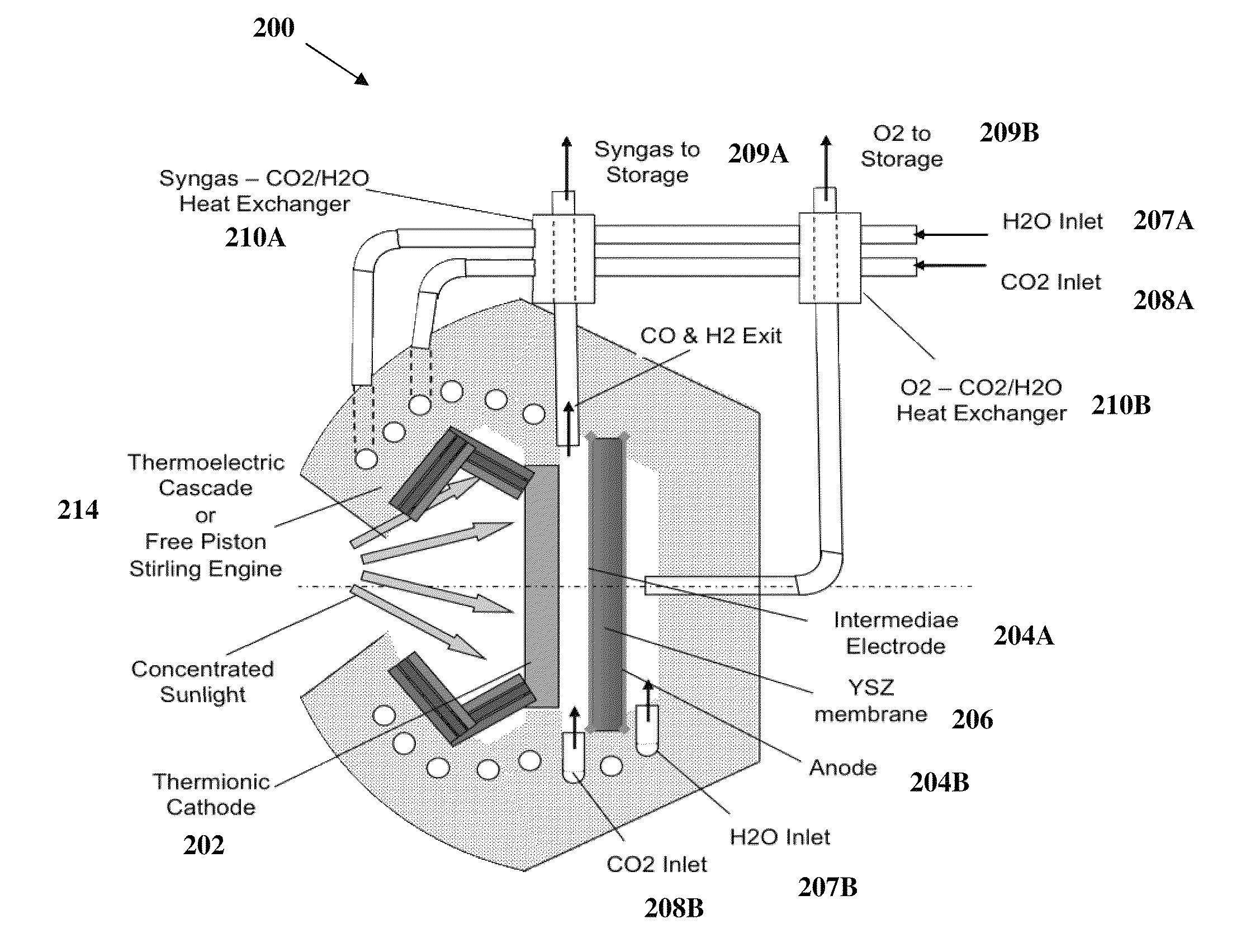
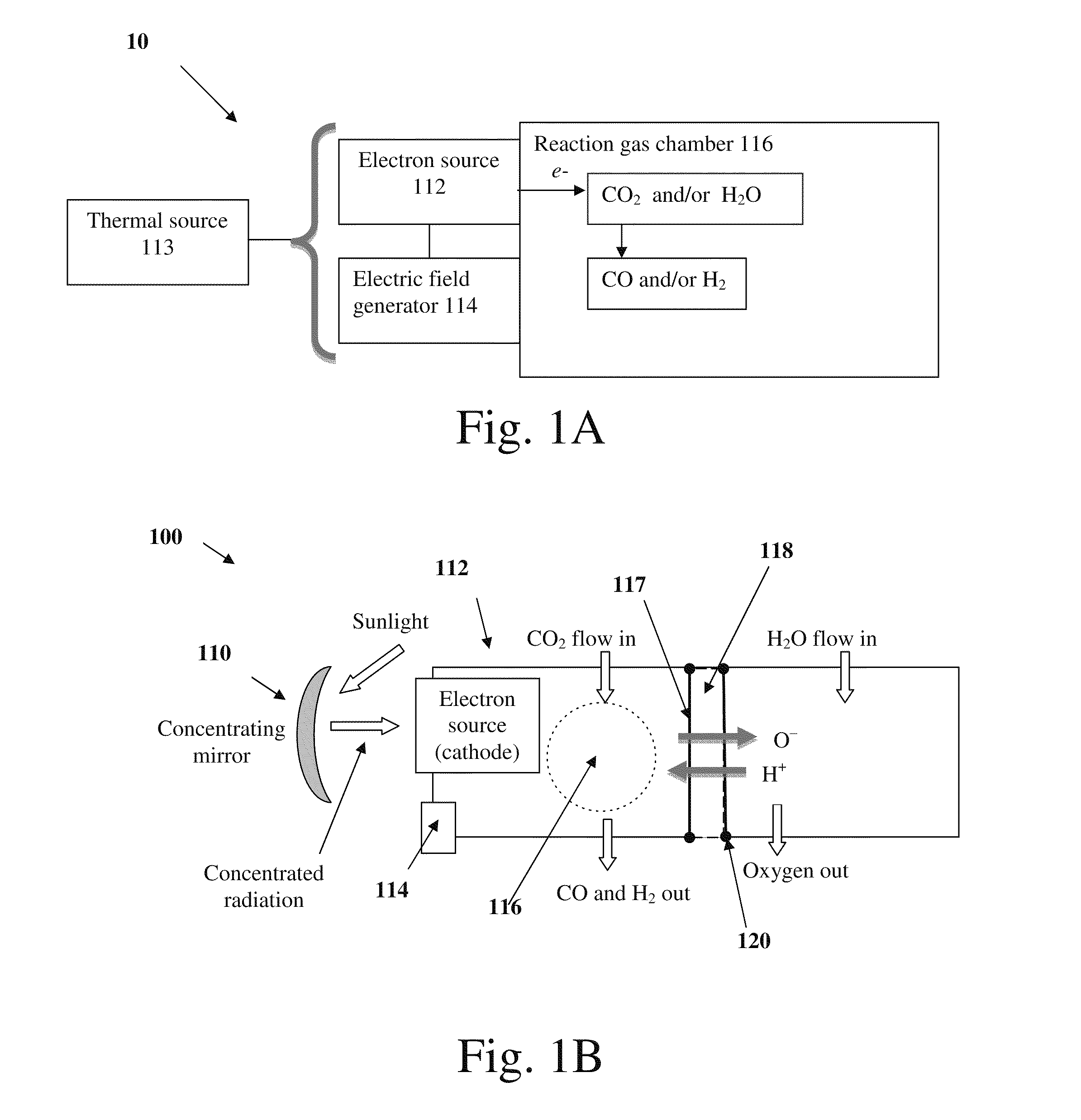
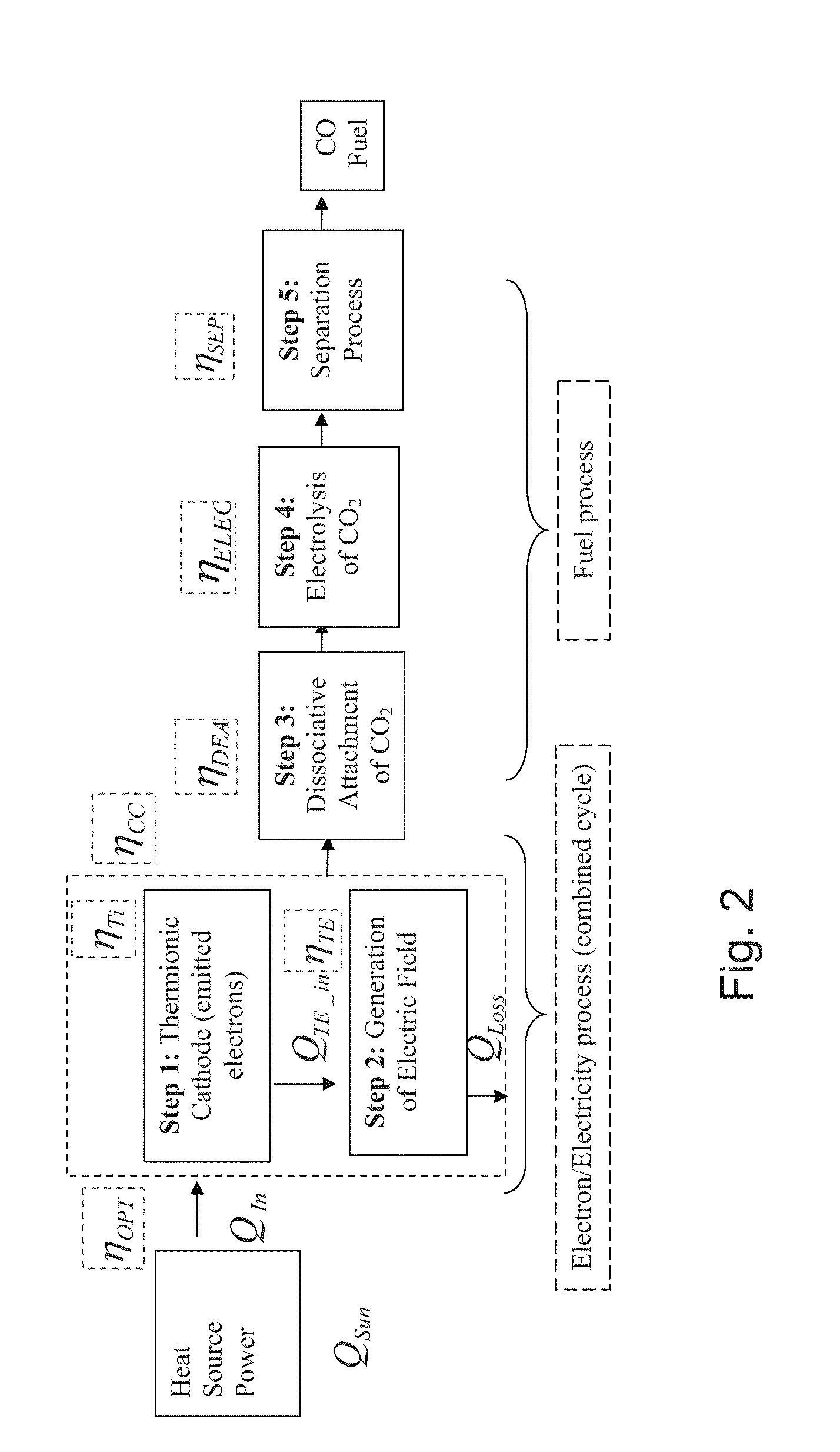
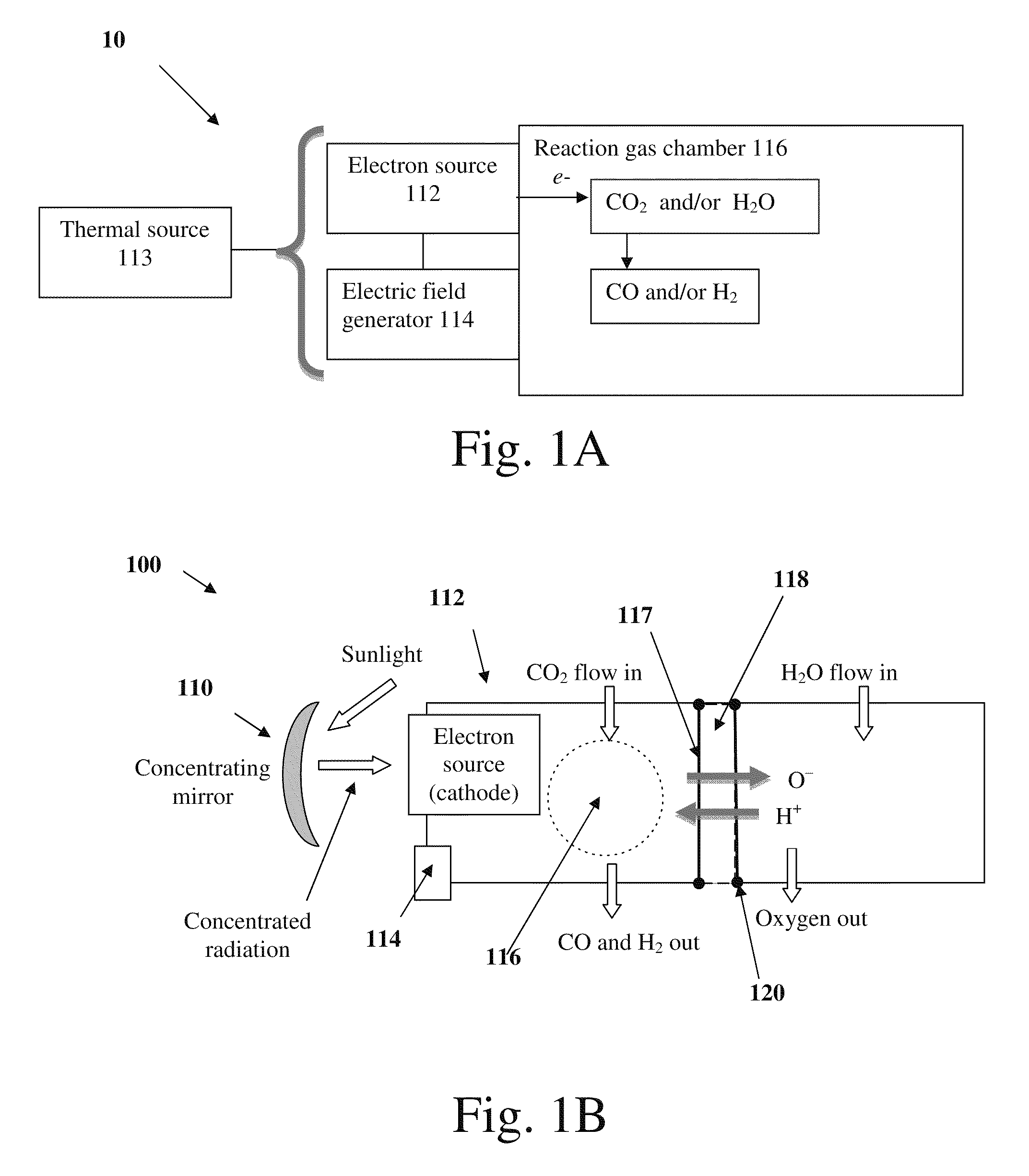
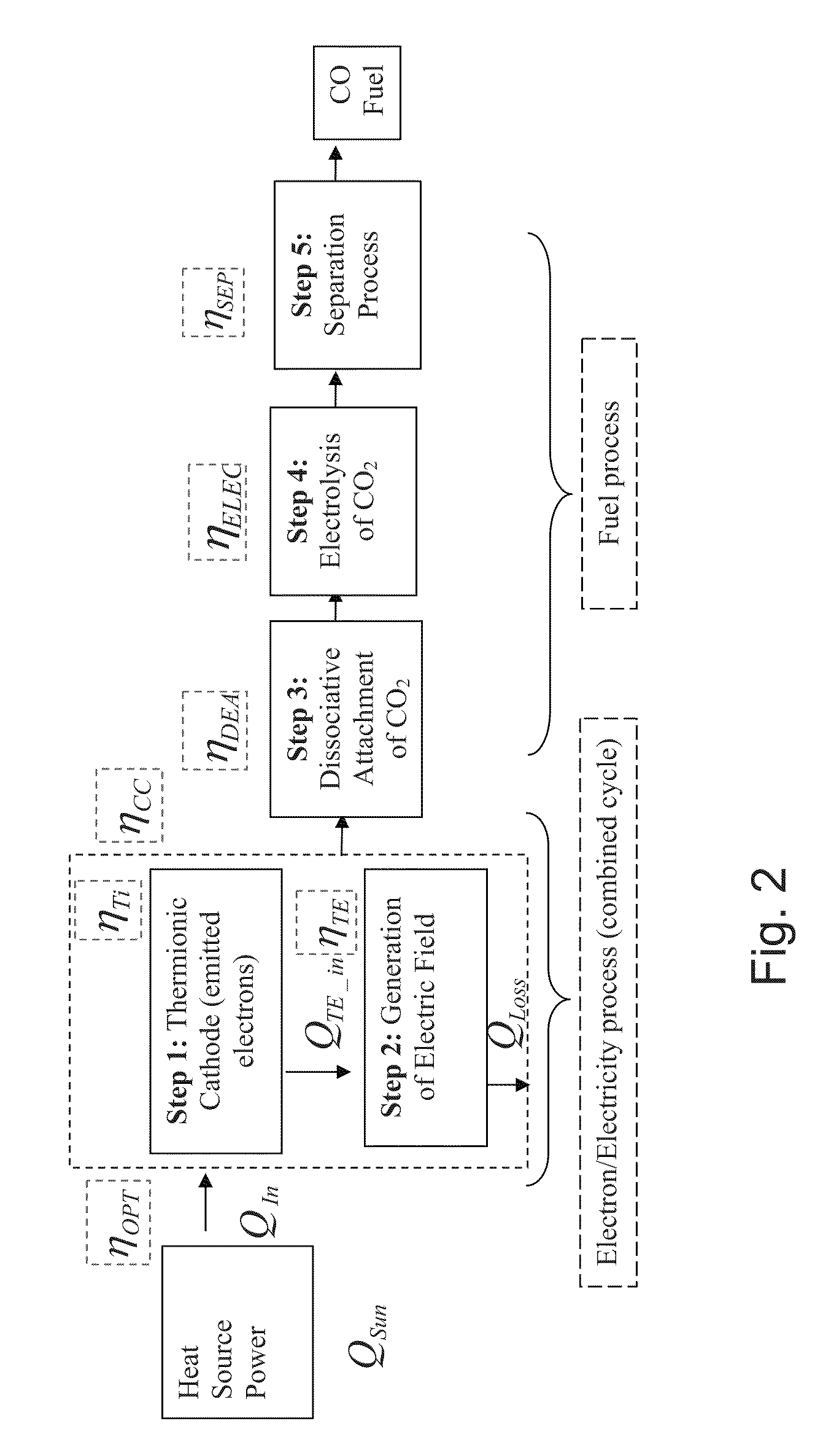
ActiveUS20110108435A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease vibrational energyCellsOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideElectron sourceGas chamber
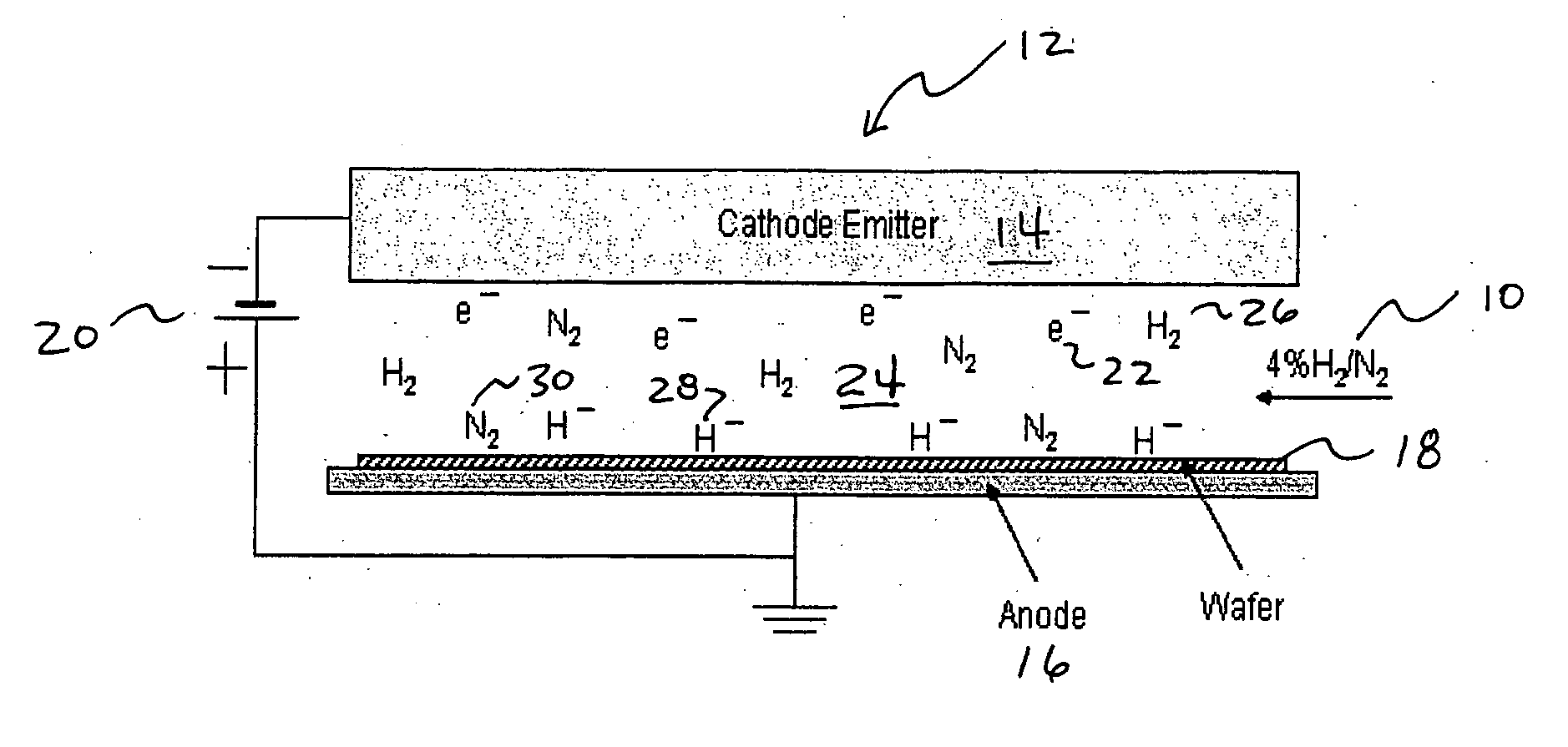
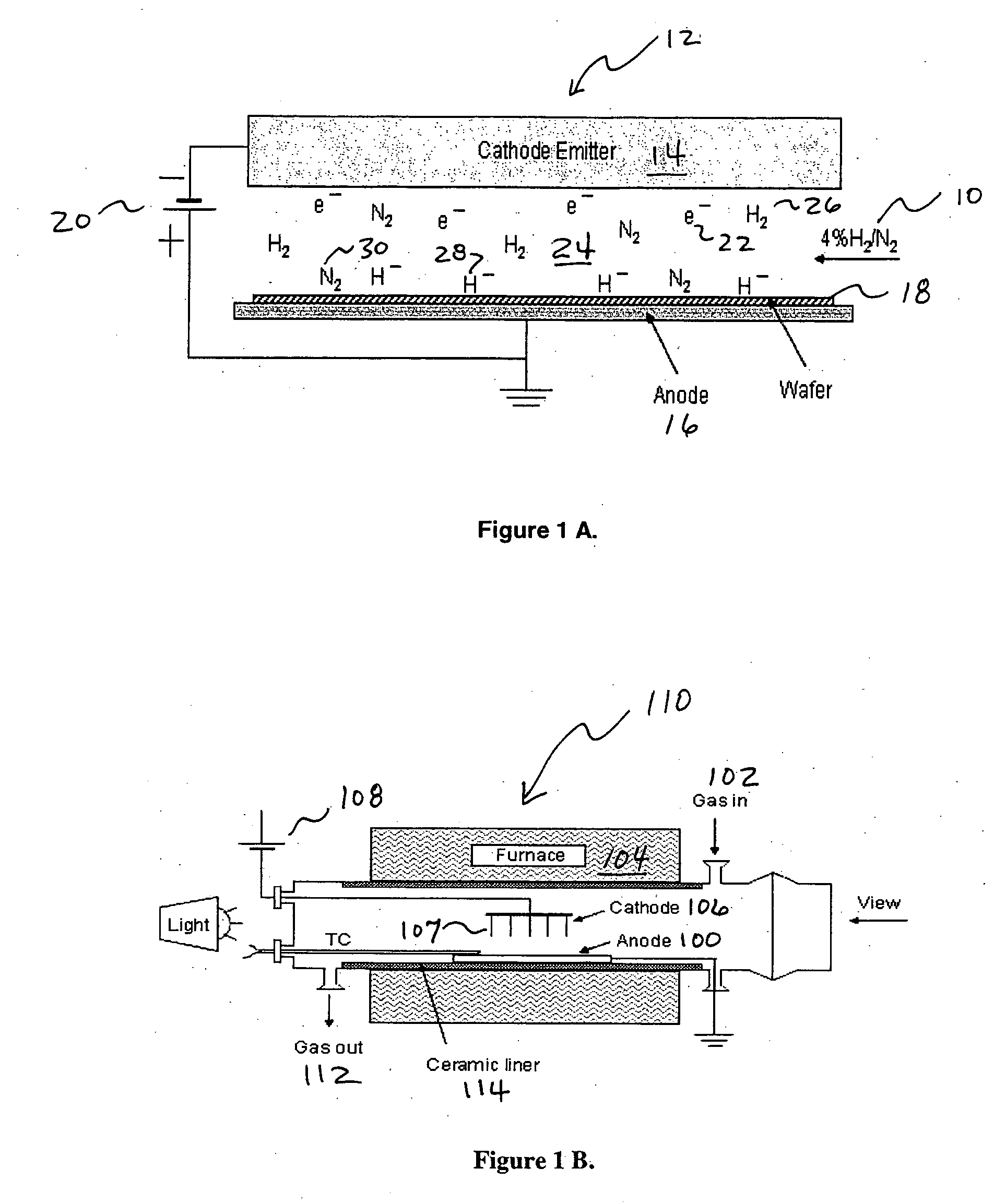
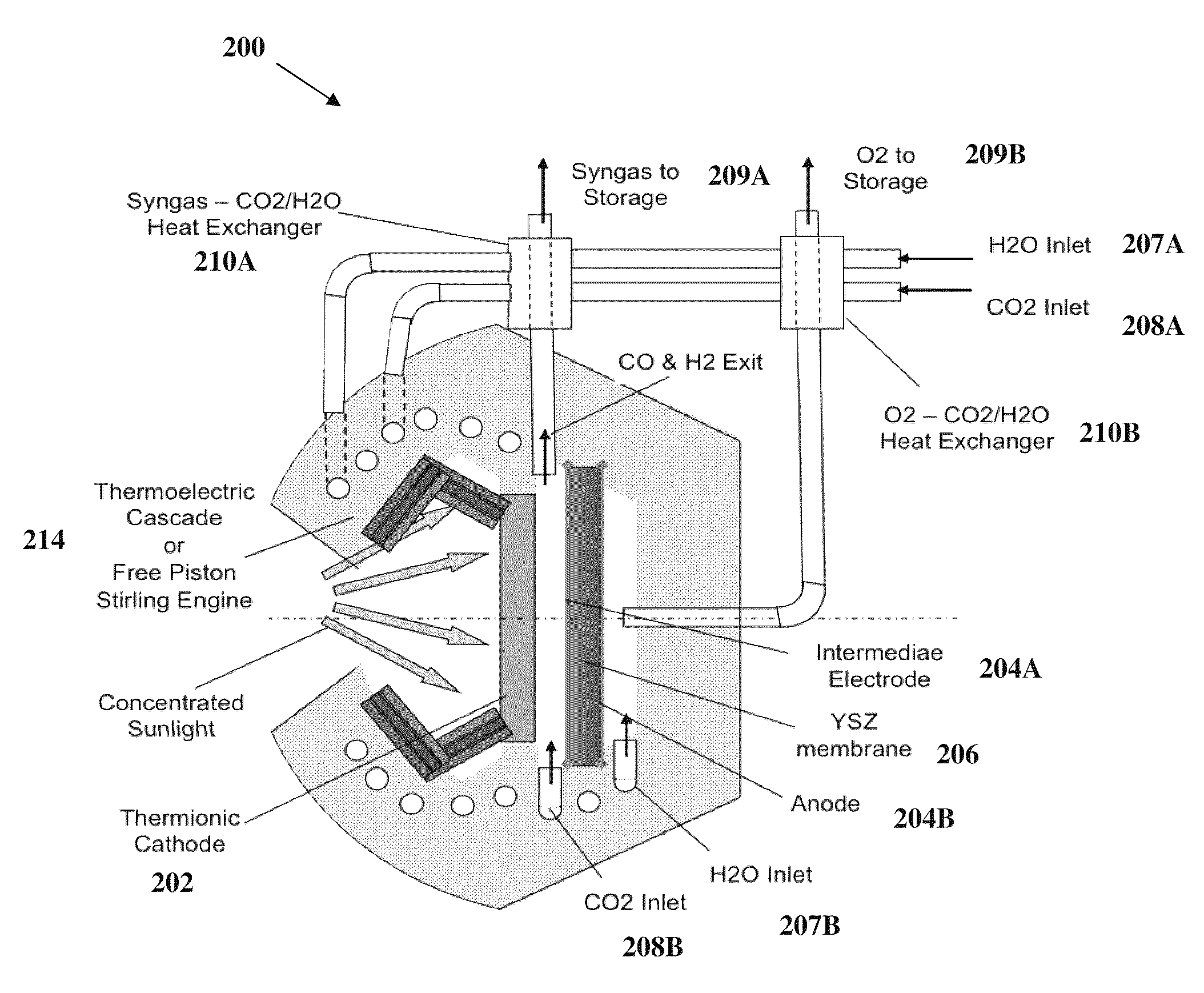
The present invention relates to a system comprising a heat source to provide heat at the desired temperature and energy field (e.g. a solar concentrator); an electron source configured and operable to emit electrons; an electric field generator generating an electric field adapted to supply energy sufficient to dissociate gas molecules; and a reaction gas chamber configured and operable to cause interaction between the electrons with the molecules, such that the electrons dissociate the molecules to product compound and ions via dissociative electrons attachment (DEA) within the chamber.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
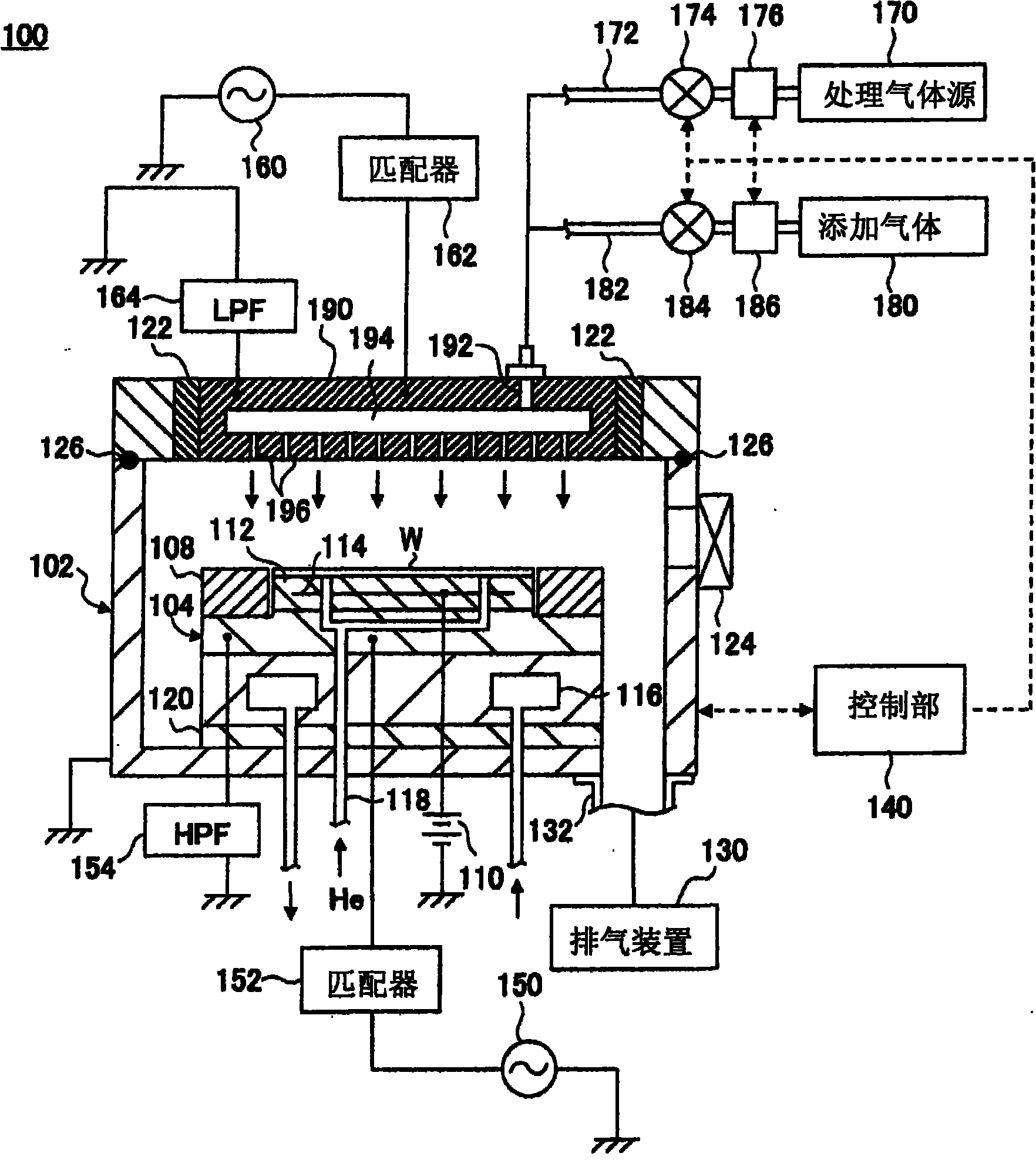
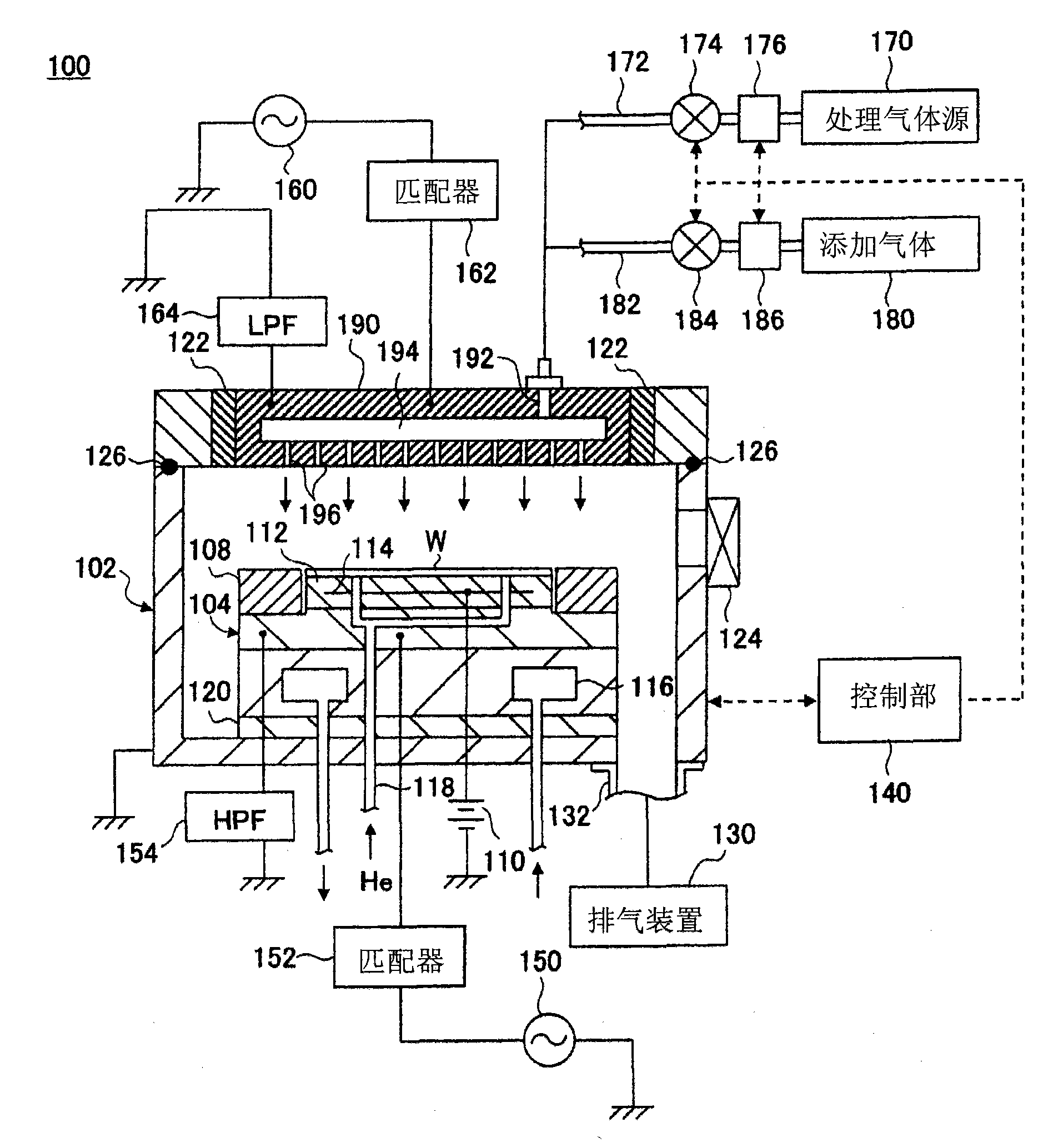
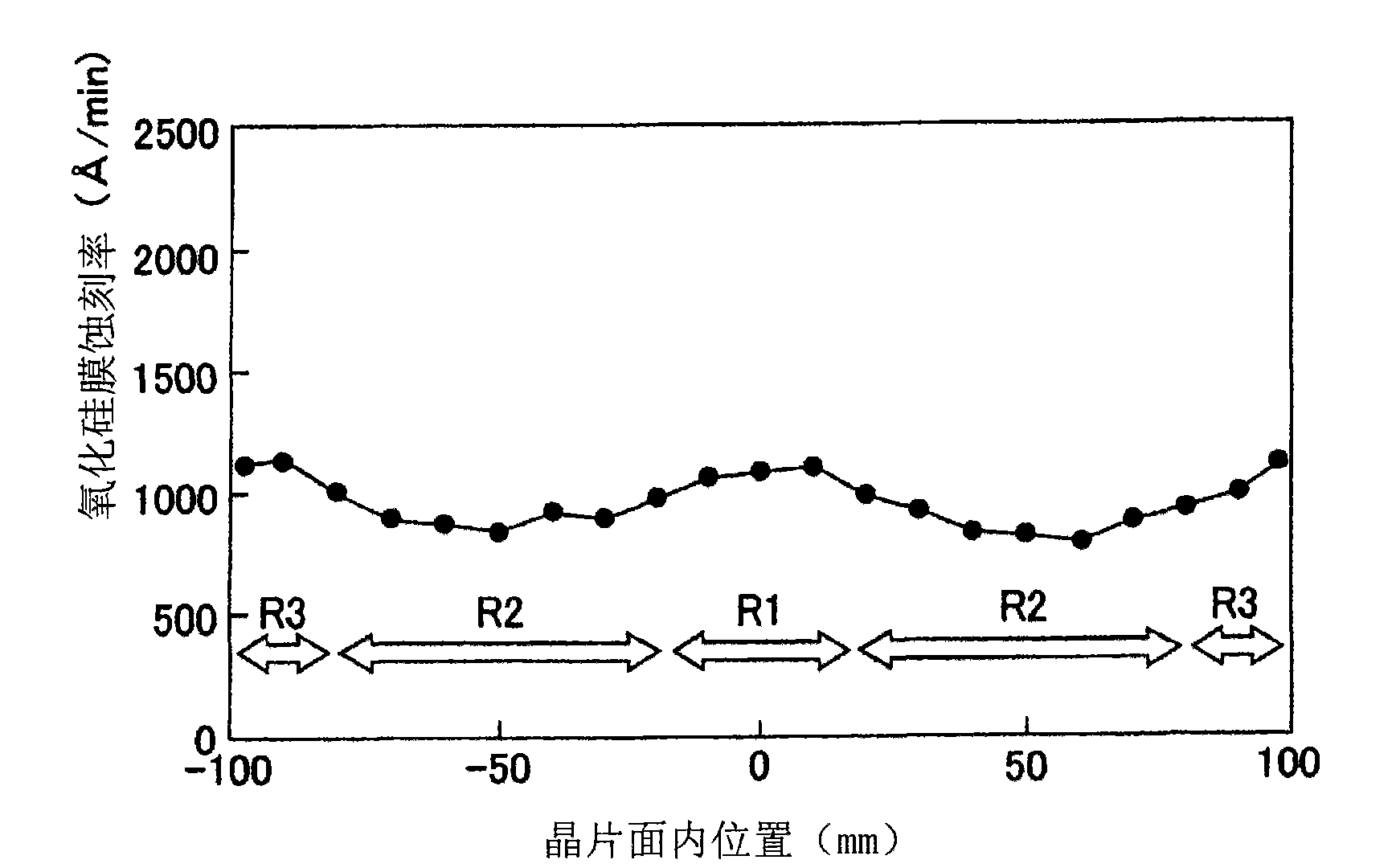
Plasma processing method and apparatus
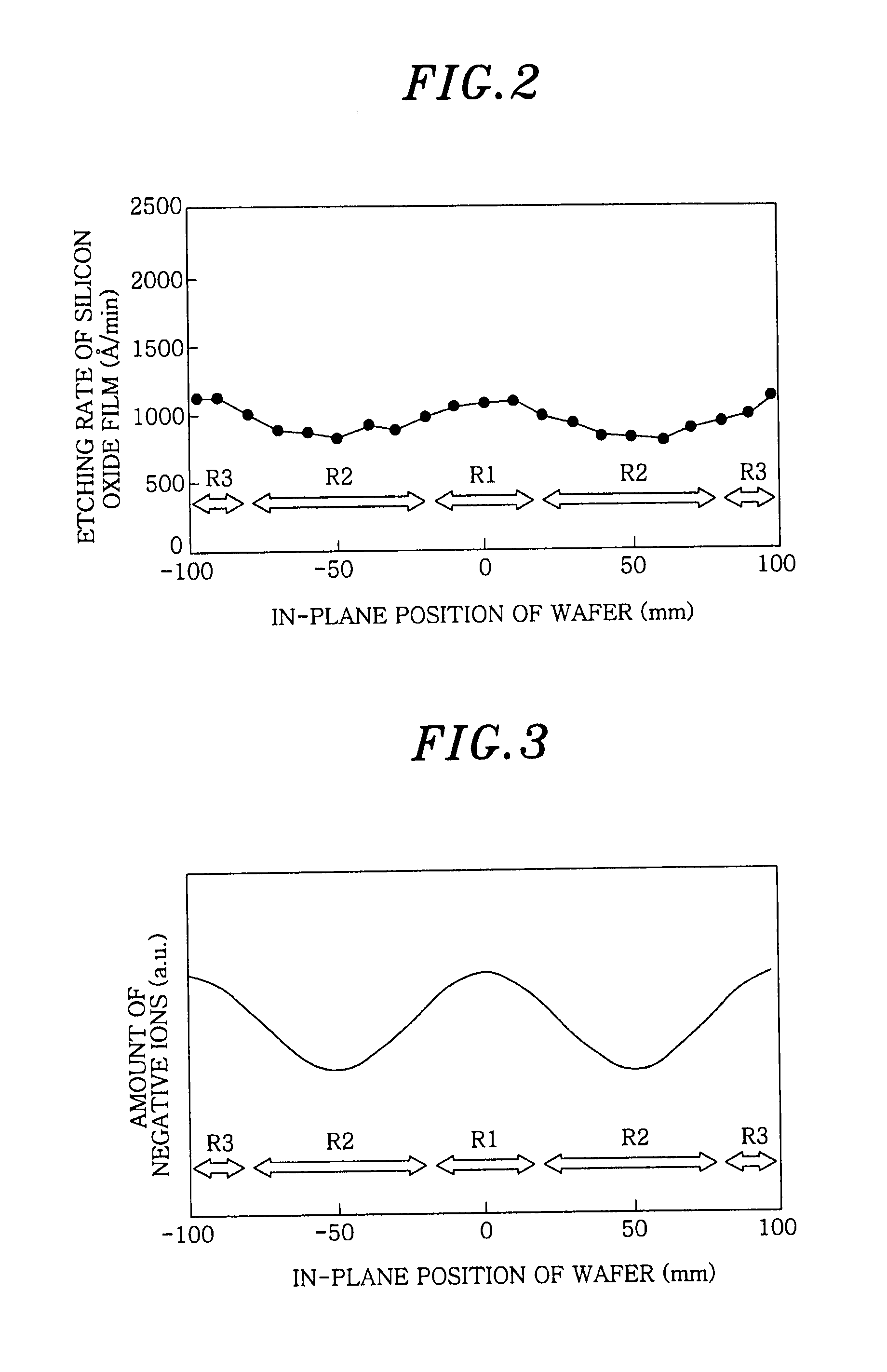
InactiveUS20100267243A1Uniform etch rateImprove in-plane uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeIon density
In the plasma processing by an electrically negative gas, the in-plane uniformity of plasma processing is enhanced compared to the conventional case by controlling the ion density in the plasma. Not only is a processing gas being an electrically negative gas introduced from a processing gas source 170 into a processing chamber 102 but also an electrically negative gas having electron attachment coefficient greater than that of the processing gas is introduced as an additional gas from an additional gas source 180 to thereby form a plasma. In the plasma formation, the ion density in the plasma is controlled by regulating the flow rate of the additional gas relative to that of the processing gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for the removal of surface oxides by electron attachment
Described herein are a method and an apparatus for removing metal oxides and / or forming solder joints on at least a portion of a substrate surface within a target area. In one particular embodiment, the method and apparatus form a solder joint within a substrate comprising a layer having a plurality of solder bumps by providing one or more energizing electrodes and exposing at least a portion of the layer and solder bumps to the energizing electrode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
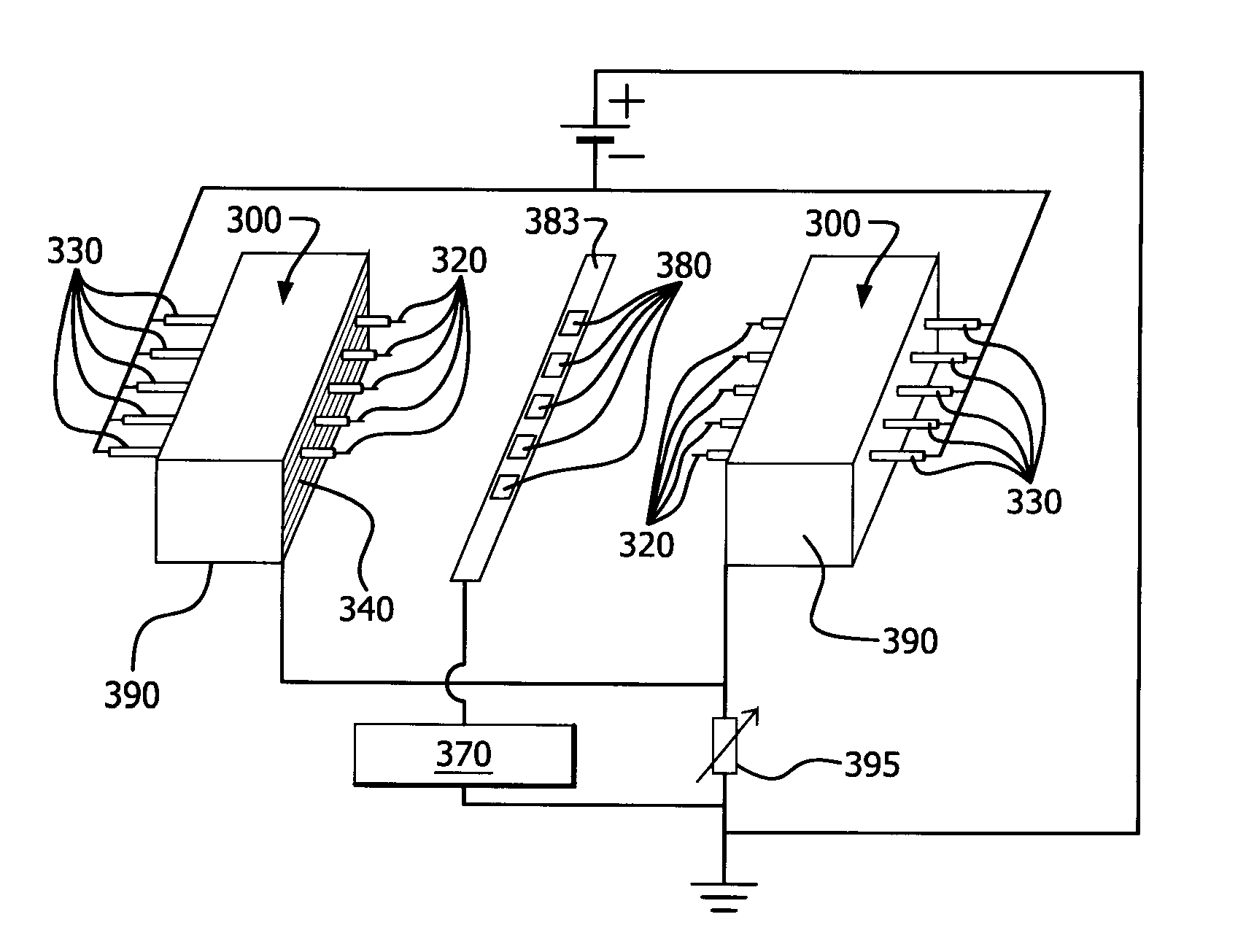
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique involving electron attachment
ActiveUS20130026921A1Increase the electric field strengthElectrode and associated part arrangementsSolid-state devicesField emission deviceHigh surface
Described herein is a method and apparatus for removing metal oxides on a surface of a component via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a field emission apparatus, wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas to form a negatively charged atomic ions which removes metal oxides comprising: a cathode comprising an electrically conductive and comprising at least one or more protrusions having a high surface curvature, wherein the cathode is surrounded by a dielectric material which is then surrounded by an electrically conductive anode wherein the cathode and anode are each connected to an electrical voltage source, and the dielectric material between the cathode and anode is polarized to provide an electric field at one or more protrusions and thereby electrons from the cathode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Removal of Surface Oxides by Electron Attachment
ActiveUS20090223831A1Satisfies needElectrolysis componentsElectric discharge tubesElectron attachmentSubstrate surface
The present invention relates to a method for removing metal oxides from a substrate surface. In one particular embodiment, the method comprises: providing a substrate, a first, and a second electrode that reside within a target area; passing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas through the target area; supplying an amount of energy to the first and / or the second electrode to generate electrons within the target area wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to a portion of the reducing gas and form a negatively charged reducing gas; and contacting the substrate with the negatively charged reducing gas to reduce the metal oxides on the surface of the substrate.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique involving electron attachment
ActiveCN102915903AElectric discharge tubesPrinted circuit manufactureField emission deviceElectrical field strength
Described herein is a method and apparatus for removing metal oxides on a surface of a component via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a field emission apparatus (10, 500), wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas to form a negatively charged atomic ions which removes metal oxides comprising: a cathode (20, 520) comprising an electrically conductive and comprising at least one or more protrusions having an angled edge or high curvature surface, wherein the cathode is surrounded by a dielectric material (30, 530) which is then surrounded by an electrically conductive anode (40, 540) wherein the cathode (20, 520) and anode (40, 540) are each connected to an electrical voltage source (60, 560), and the dielectric material (30, 530) between the cathode (20, 520) and anode (40, 540) is polarized, intensifying the electrical field strength and accumulating electrons at the apex of the cathode to promote field emission of electrons from the cathode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
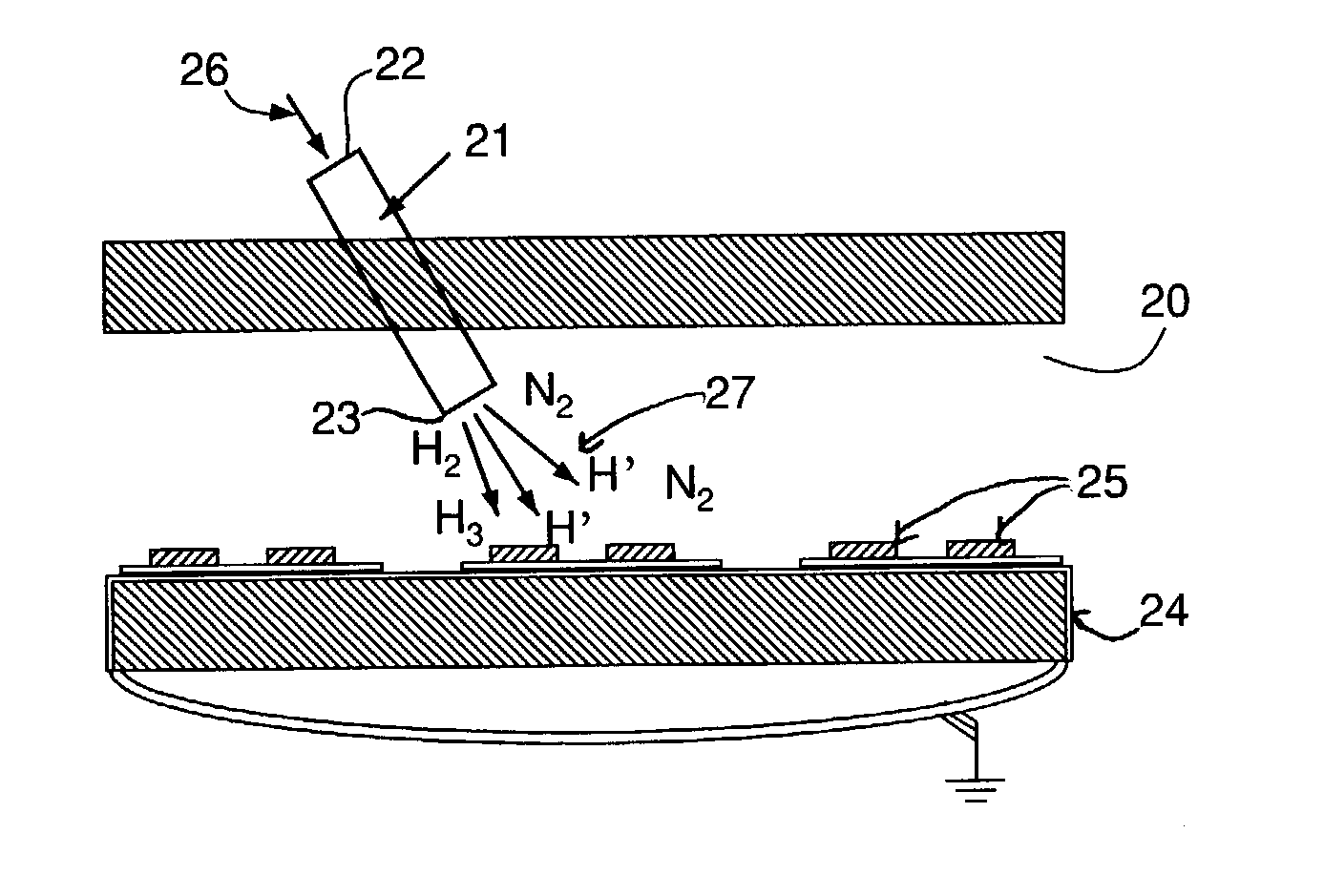
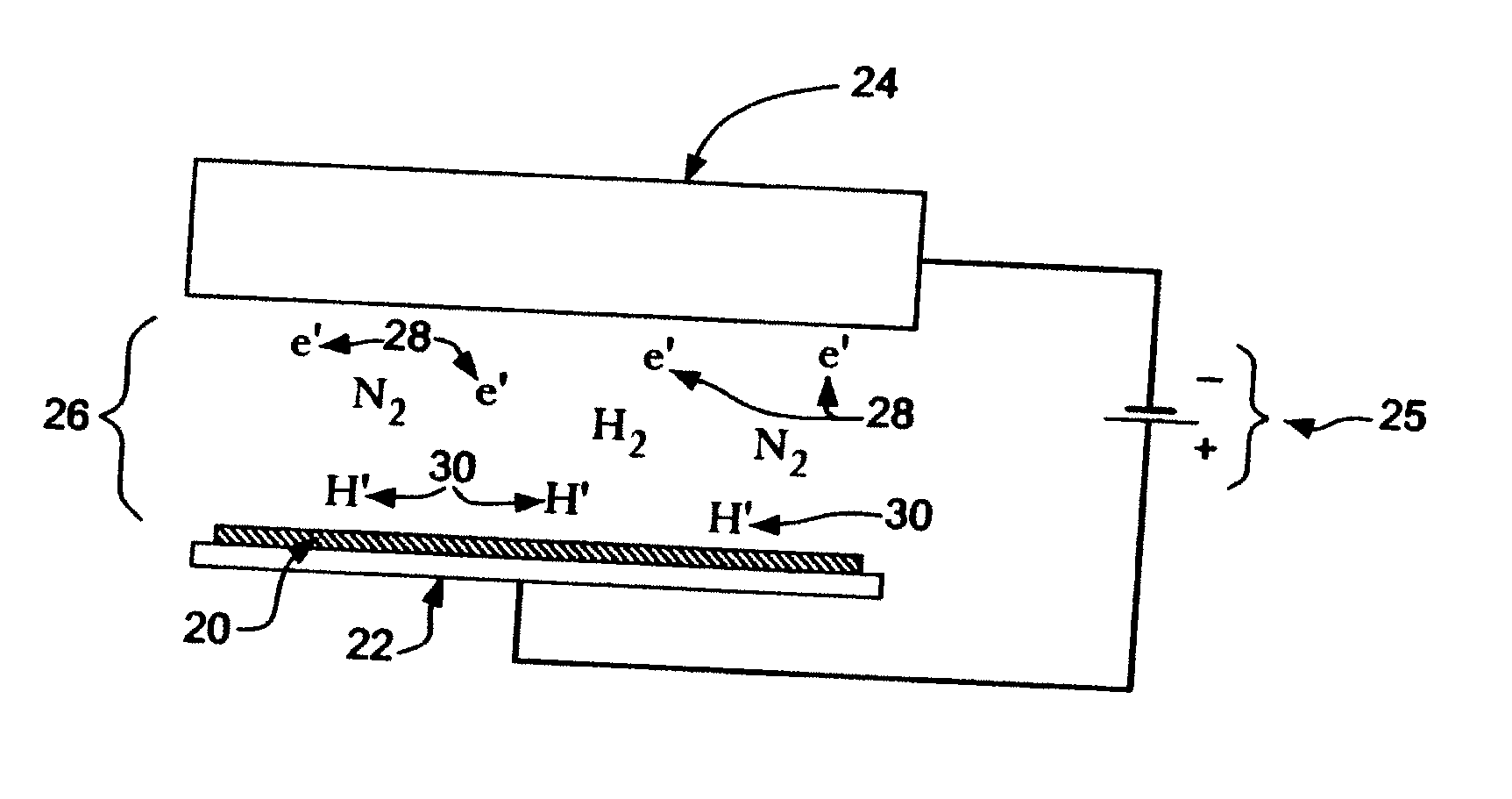
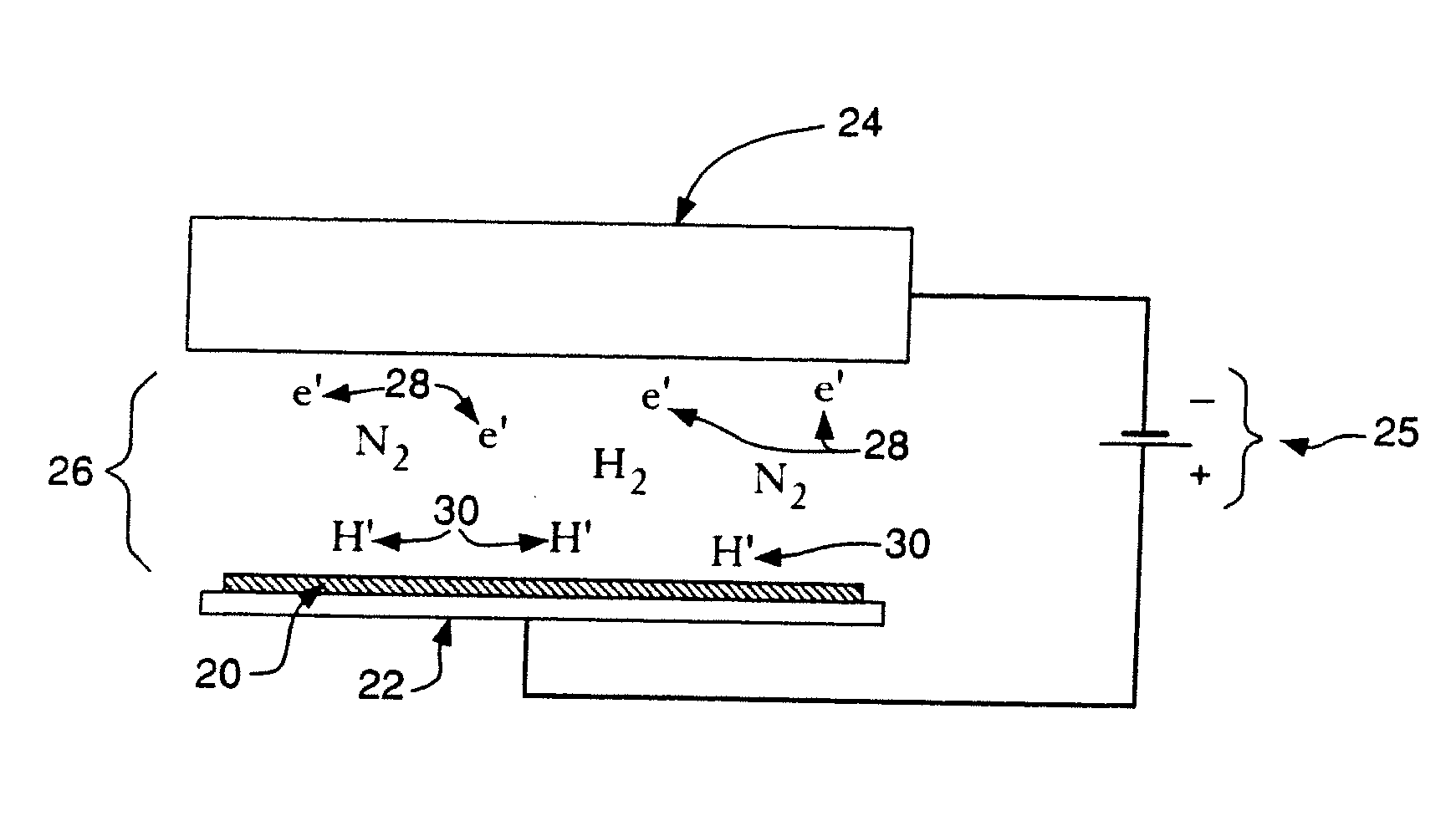
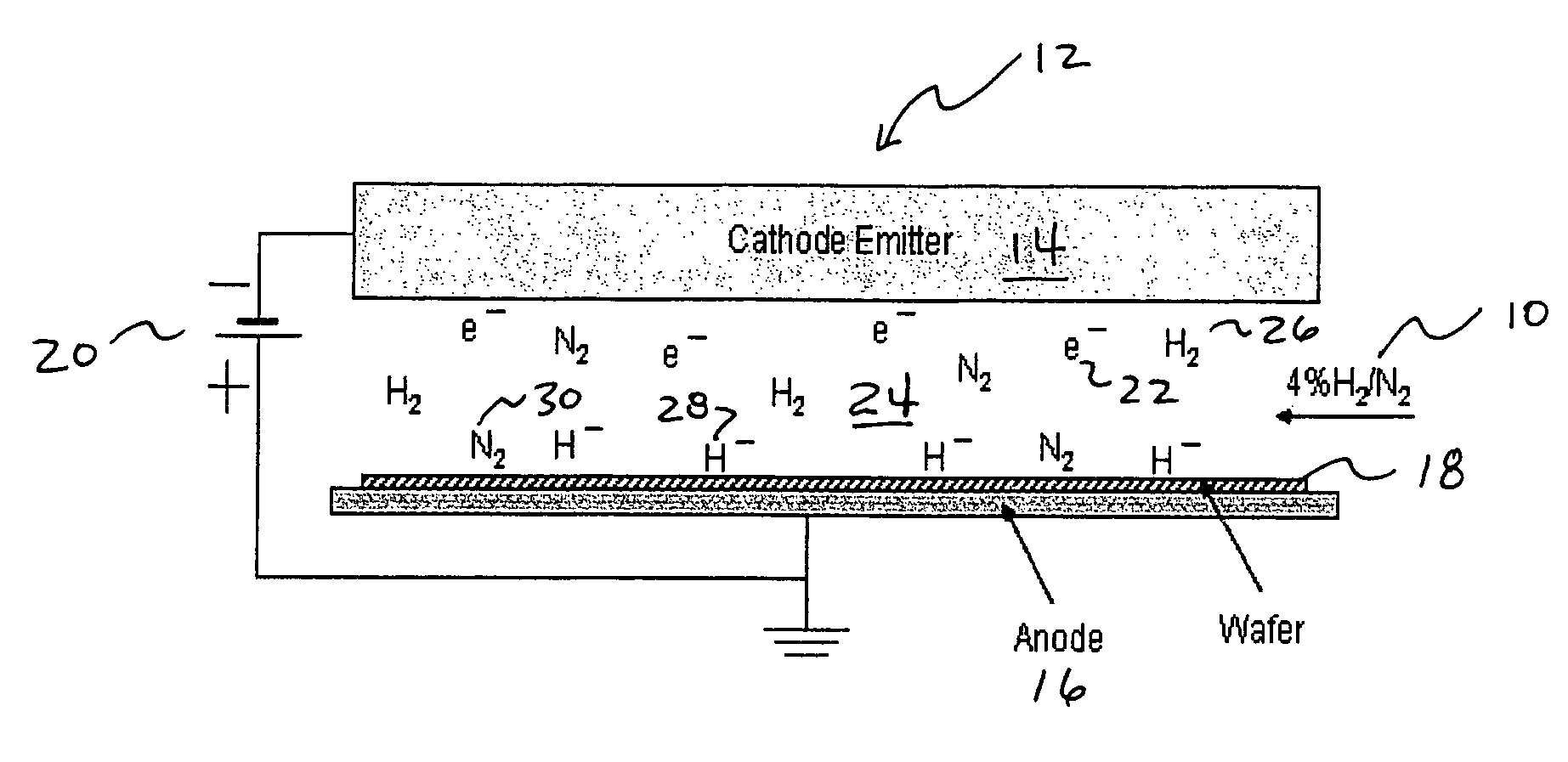
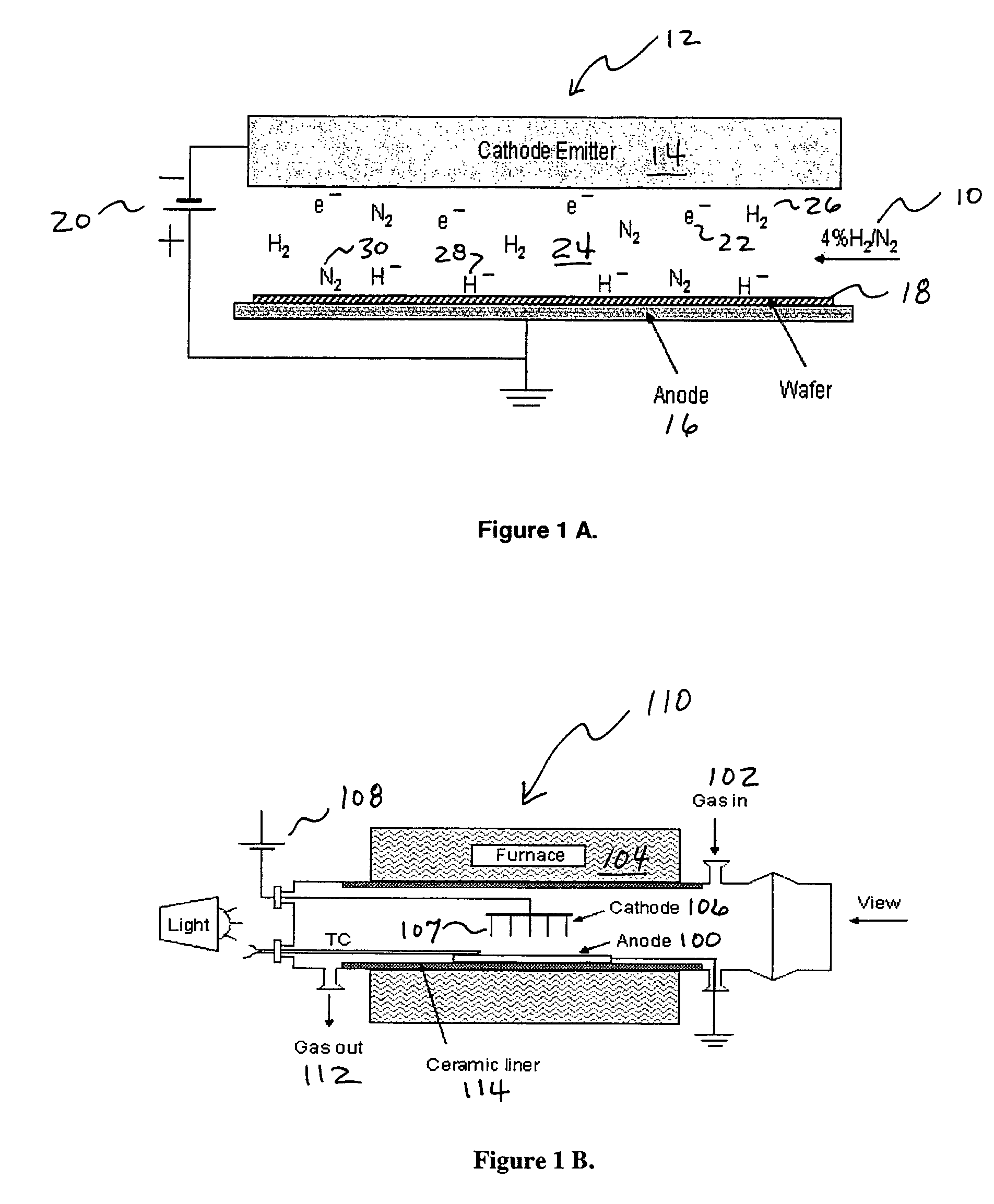
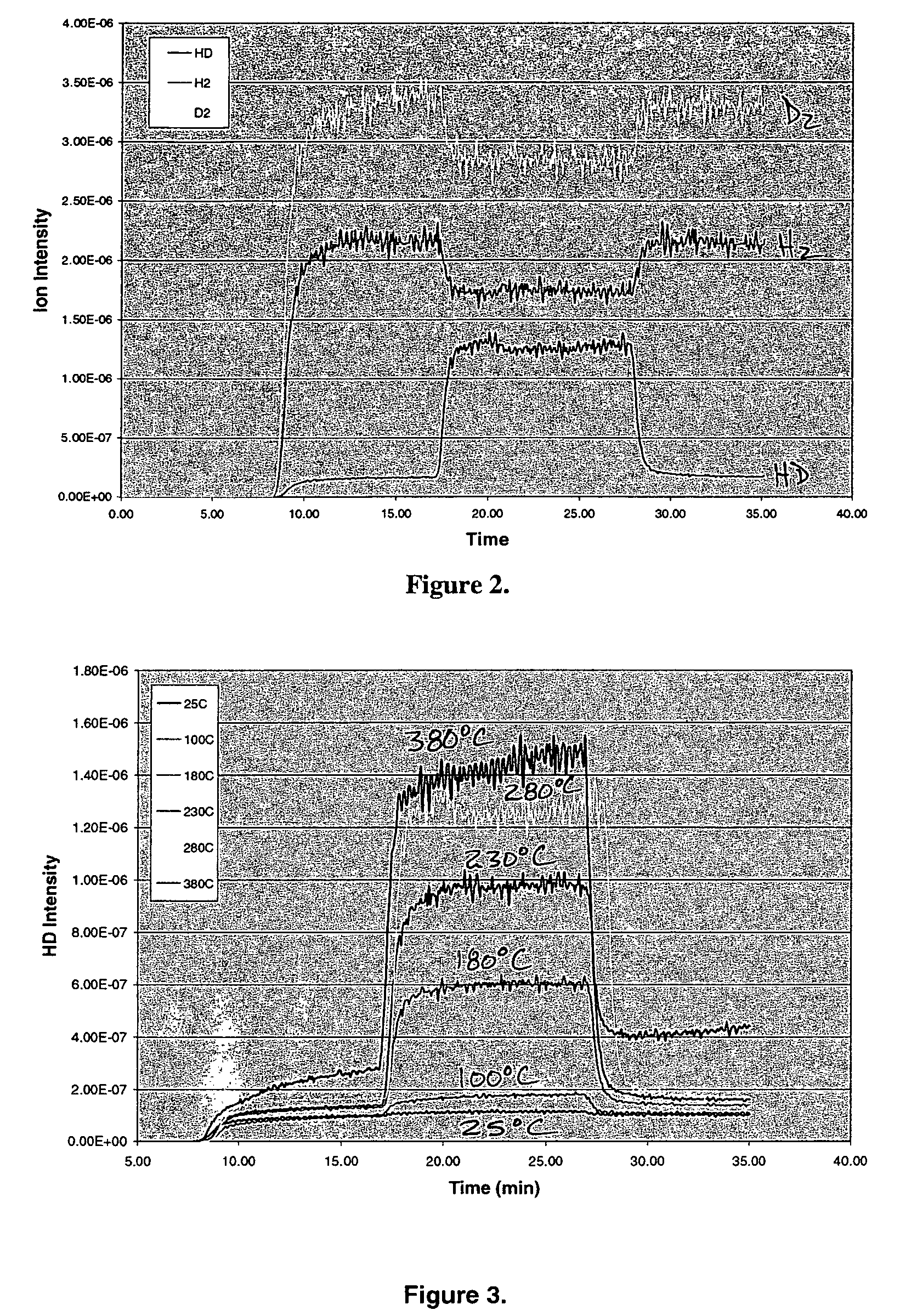
Addition of D2 to H2 to detect and calibrate atomic hydrogen formed by dissociative electron attachment
InactiveUS20070131736A1High trafficElectrolysis componentsDecorative surface effectsHydrogenProduct gas
A method of detecting and calibrating dry fluxing metal surfaces of one or more components to be soldered by electron attachment using a gas mixture of reducing gas comprising hydrogen and deuterium, comprising the steps of: a) providing one or more components to be soldered which are connected to a first electrode as a target assembly; b) providing a second electrode adjacent the target assembly; c) providing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas comprising hydrogen and deuterium between the first and second electrodes; d) providing a direct current (DC) voltage to the first and second electrodes to form an emission current between the electrodes and donating electrons to the reducing gas to form negatively charged ionic reducing gas and molecules of hydrogen bonded to deuterium; e) contacting the target assembly with the negatively charged ionic reducing gas and reducing oxides on the target assembly. Related apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
System and method for chemical potential energy production
ActiveUS8268138B2Increase vibrational energyCellsOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideElectron sourceGas chamber
The present invention relates to a system comprising a heat source to provide heat at the desired temperature and energy field (e.g. a solar concentrator); an electron source configured and operable to emit electrons; an electric field generator generating an electric field adapted to supply energy sufficient to dissociate gas molecules; and a reaction gas chamber configured and operable to cause interaction between the electrons with the molecules, such that the electrons dissociate the molecules to product compound and ions via dissociative electrons attachment (DEA) within the chamber.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for removing substance from substrate using electron attachment
InactiveCN1770390ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingSemiconductor materialsReactive gas
A method of removing species from at least a portion of a substrate, such as a reaction chamber or a semiconductor material, is disclosed herein. In one aspect, there is provided a method comprising: providing a reaction chamber having a surface coated with a substance; providing first and second electrodes proximate to the reaction chamber, wherein the first and second electrodes are located within a target region; delivering a gas mixture comprising a reactive gas; energizing the first and / or second electrodes to generate electrons in the target region, wherein at least a portion of the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reactive gas, thereby forming a negatively charged purge gas; contacting the substance with a negatively charged purge gas, the negatively charged purge gas reacts with the substance and forms a volatile product; and removing the volatile product from the reaction chamber.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Superconducting material for negative ion, reaction film and negative ion generating device
PendingCN109494010ATypical Semiconductor CharacteristicsStrong far-infrared reflection abilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesFar infraredOxygen
The invention discloses a superconducting material for a negative ion, a reaction film and a negative ion generating device. The superconducting material comprises the following raw materials, by weight: 5 to 10 parts of conductive powder, 10 to 20 parts of electric powder, 10 to 20 parts of negative ion powder, 37 to 70 parts of nano materials, and 10 to 20 parts of carbon crystal powder. According to the invention, the superconducting-material-based reaction film has constant far-infrared absorption and reflection functions and the typical semiconductor characteristic and the absorption bandis mainly located in the far infrared region; the dipole moment changes due to the thermoelectric and piezoelectric effects, so that the powerful reflection capability is realized and the occurrenceof negative ions is also caused. When the external conditions like the temperature, humidity, far-infrared radiation, friction and the like change, an electric field is induced to ionize the air and the knocked electrons are attached to adjacent oxygen molecules, so that the electrons are transformed into small-size negative ions.
Owner:张桂林
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique involving electron attachment
Described herein is a method and apparatus for removing metal oxides on a surface of a component via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a field emission apparatus, wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas to form a negatively charged atomic ions which removes metal oxides comprising: a cathode comprising an electrically conductive and comprising at least one or more protrusions having an angled edge or high curvature surface, wherein the cathode is surrounded by a dielectric material which is then surrounded by an electrically conductive anode wherein the cathode and anode are each connected to an electrical voltage source, and the dielectric material between the cathode and anode is polarized, intensifying the electrical field strength and accumulating electrons at the apex of the cathode to promote field emission of electrons from the cathode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
High-pressure type accelerator
InactiveCN103108484AHigh energyImprove insulation performanceAcceleratorsNuclear engineeringHigh energy
The invention discloses a high-pressure type accelerator which comprises an accelerator body. An air inlet and an air outlet are formed in the two sides of the lower end of the accelerator body. Insulating gas which is sulfur hexafluoride is filled in the interior of the accelerator body. The high-pressure type accelerator solves the problem that in the prior art, the accelerator fails to obtain higher energy due to the fact that the insulating gas in the accelerator is not good in the insulating property. Due to the fact that the sulfur hexafluoride is filled in the accelerator, the good electronegativity of the sulfur hexafluoride is utilized to have the functions of absorbing electron energy and causing electron attachment to extinguish electrons, the accelerator is enabled to have higher insulating capability and excellent arc extinguishing performance, the whole performance of the accelerator is improved, the accelerator is enabled to be capable of obtaining the higher energy, and therefore a design objective is achieved, the cost is low, and the sulfur hexafluoride can be reused.
Owner:CGN DASHENG ELECTRON ACCELERATOR TECH
Method of plasma treatment and plasma treatment apparatus
InactiveCN101809720AUniform density distributionImprove uniformityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeState of art
In the plasma treatment by an electrically negative gas, the in-plane uniformity of plasma treatment is enhanced over the prior art by controlling the ion density in the plasma. Not only is a treating gas being an electrically negative gas introduced from a treating gas source (170) into a treatment chamber (102) but also an electrically negative gas greater in electron attachment coefficient than the treating gas is introduced as an addition gas from an addition gas source (180) to thereby form a plasma. In the plasma formation, the ion density in the plasma is controlled by regulating the flow rate of the addition gas relative to the treating gas.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Addition of D2 to H2 to detect and calibrate atomic hydrogen formed by dissociative electron attachment
InactiveUS7434719B2High trafficElectrolysis componentsDecorative surface effectsHydrogenElectron attachment
A method of detecting and calibrating dry fluxing metal surfaces of one or more components to be soldered by electron attachment using a gas mixture of reducing gas comprising hydrogen and deuterium, comprising the steps of: a) providing one or more components to be soldered which are connected to a first electrode as a target assembly; b) providing a second electrode adjacent the target assembly; c) providing a gas mixture comprising a reducing gas comprising hydrogen and deuterium between the first and second electrodes; d) providing a direct current (DC) voltage to the first and second electrodes to form an emission current between the electrodes and donating electrons to the reducing gas to form negatively charged ionic reducing gas and molecules of hydrogen bonded to deuterium; e) contacting the target assembly with the negatively charged ionic reducing gas and reducing oxides on the target assembly. Related apparatus is also disclosed.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Apparatus and method for removal of surface oxides via fluxless technique involving electron attachment
ActiveUS9006975B2Increase the electric field strengthElectric discharge tubesSolid-state devicesElectricityHigh surface
Described herein is a method and apparatus for removing metal oxides on a surface of a component via electron attachment. In one embodiment, there is provided a field emission apparatus, wherein the electrons attach to at least a portion of the reducing gas to form a negatively charged atomic ions which removes metal oxides comprising: a cathode comprising an electrically conductive and comprising at least one or more protrusions having a high surface curvature, wherein the cathode is surrounded by a dielectric material which is then surrounded by an electrically conductive anode wherein the cathode and anode are each connected to an electrical voltage source, and the dielectric material between the cathode and anode is polarized to provide an electric field at one or more protrusions and thereby electrons from the cathode.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com