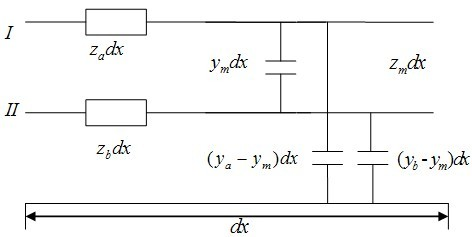
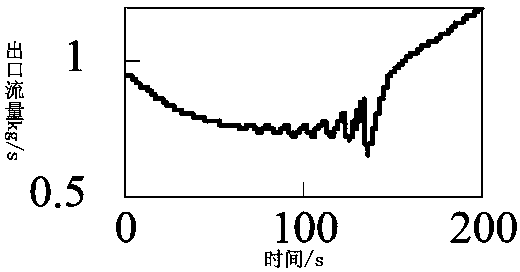
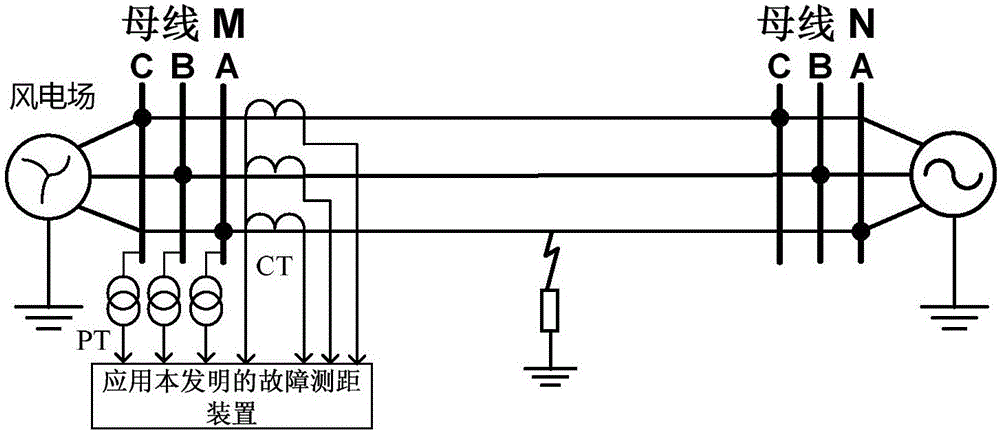
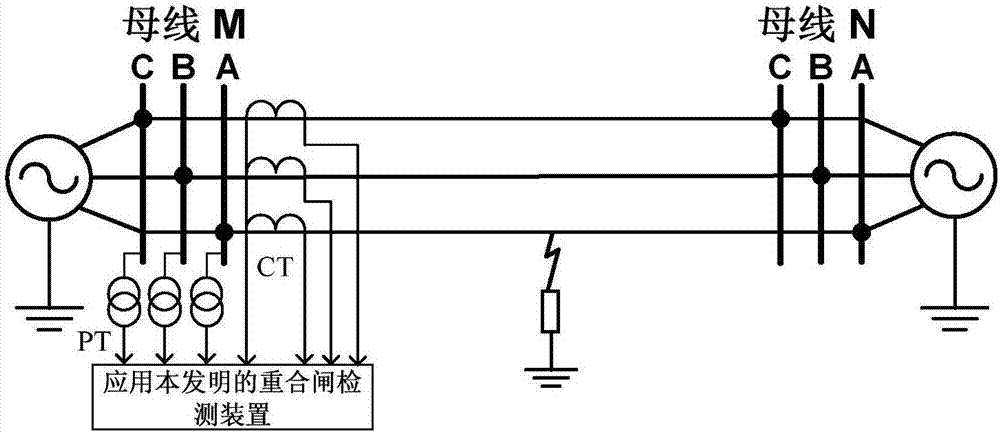
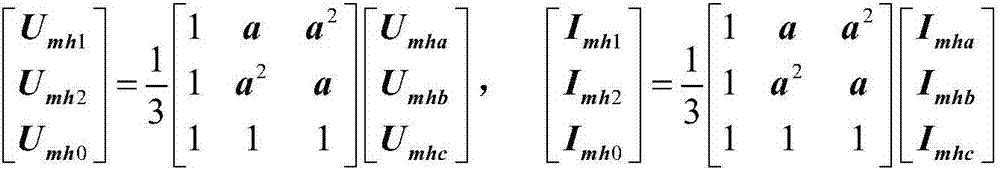
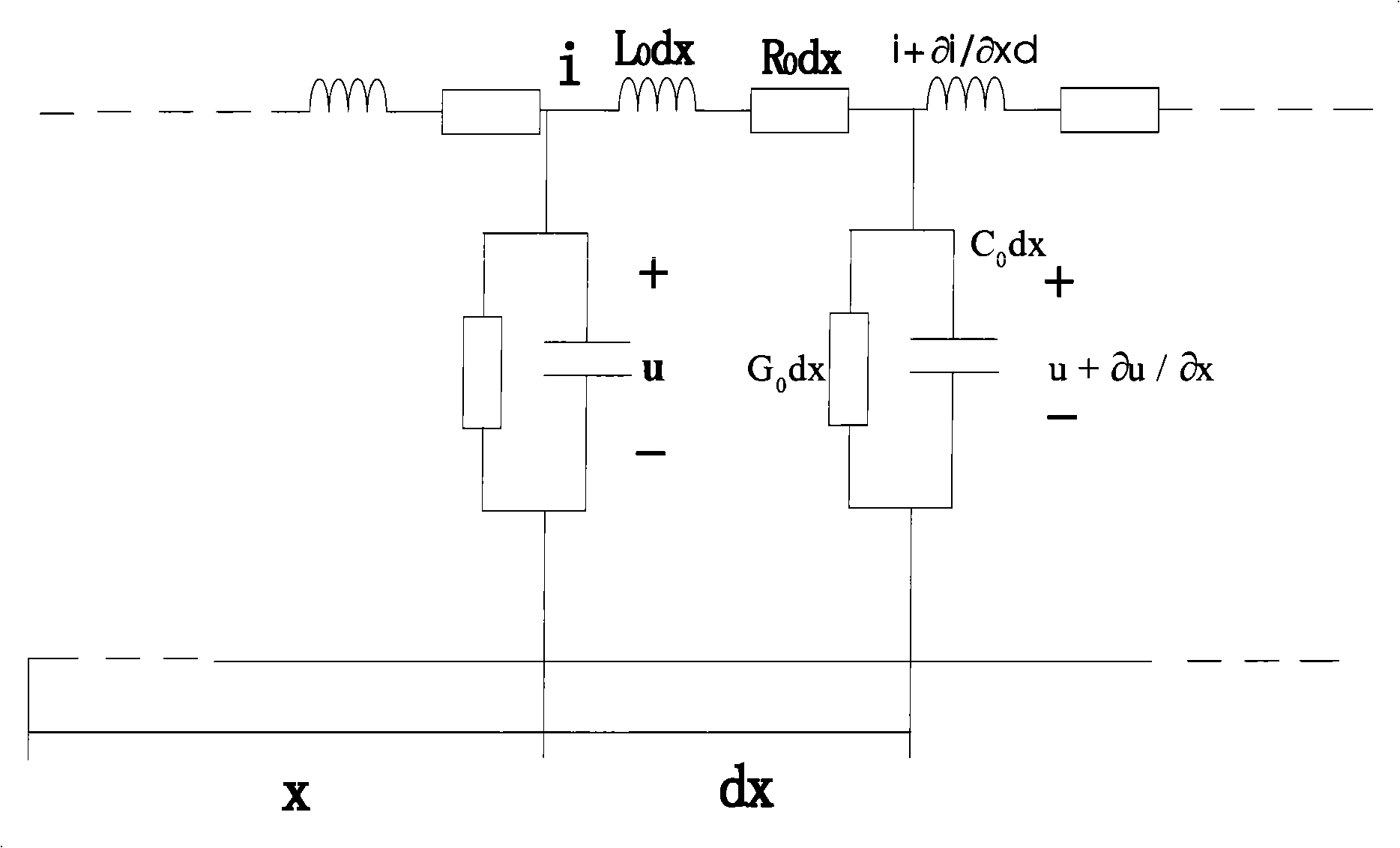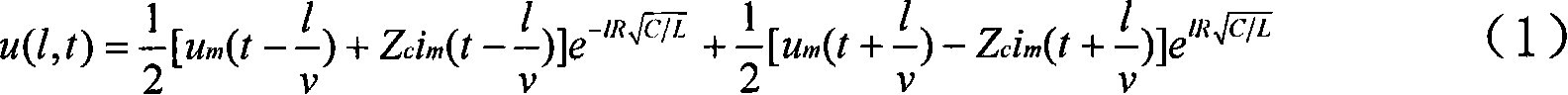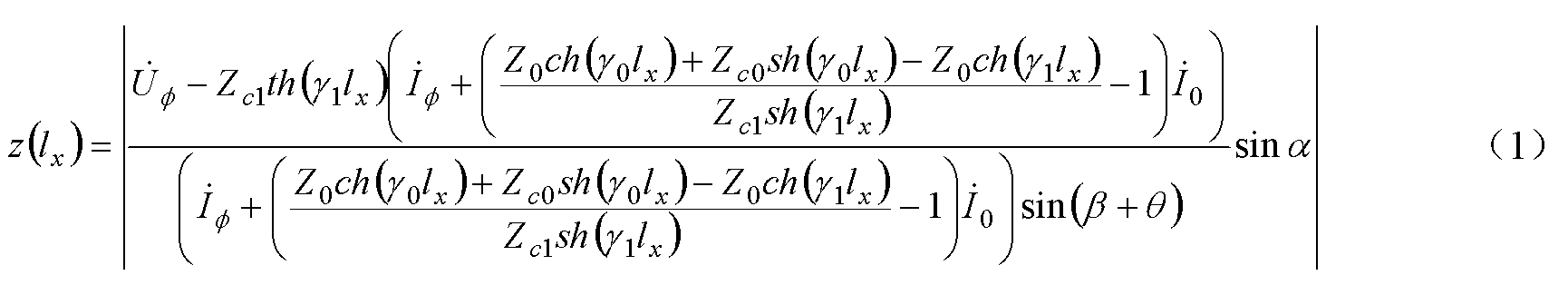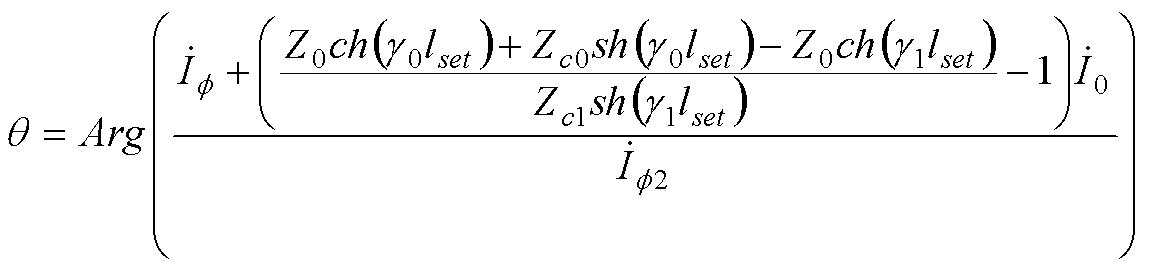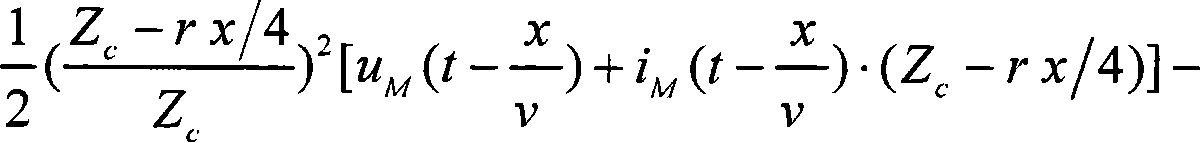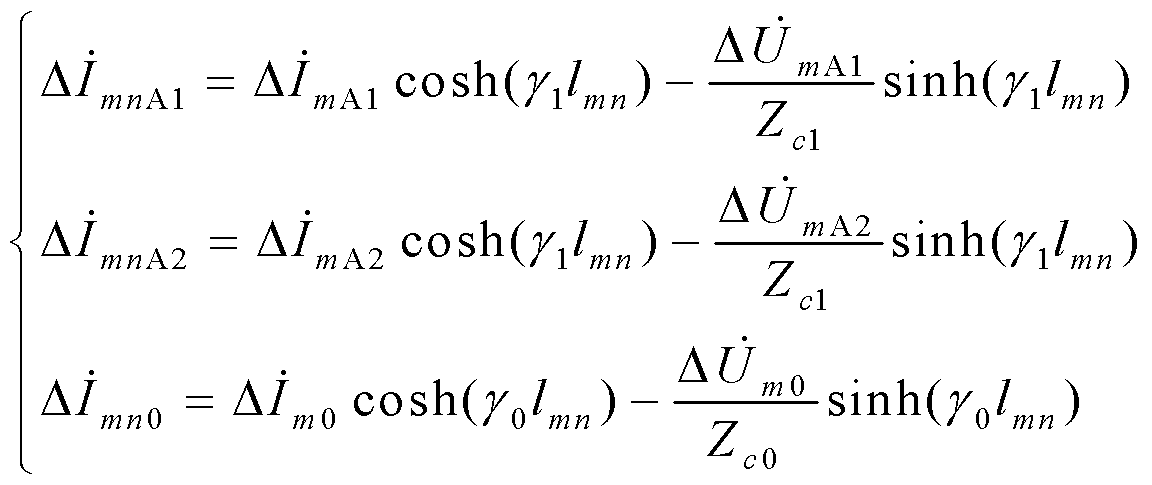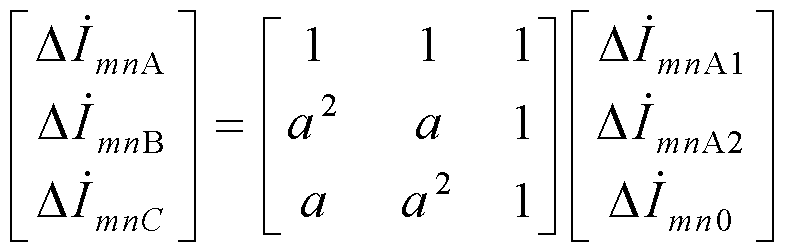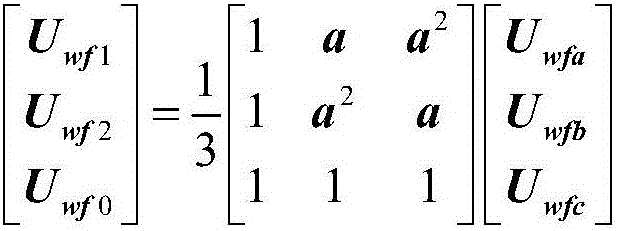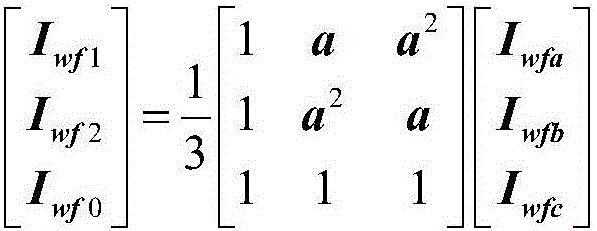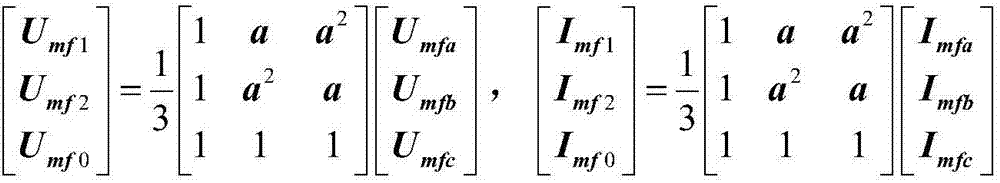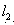Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Distributed parameter model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
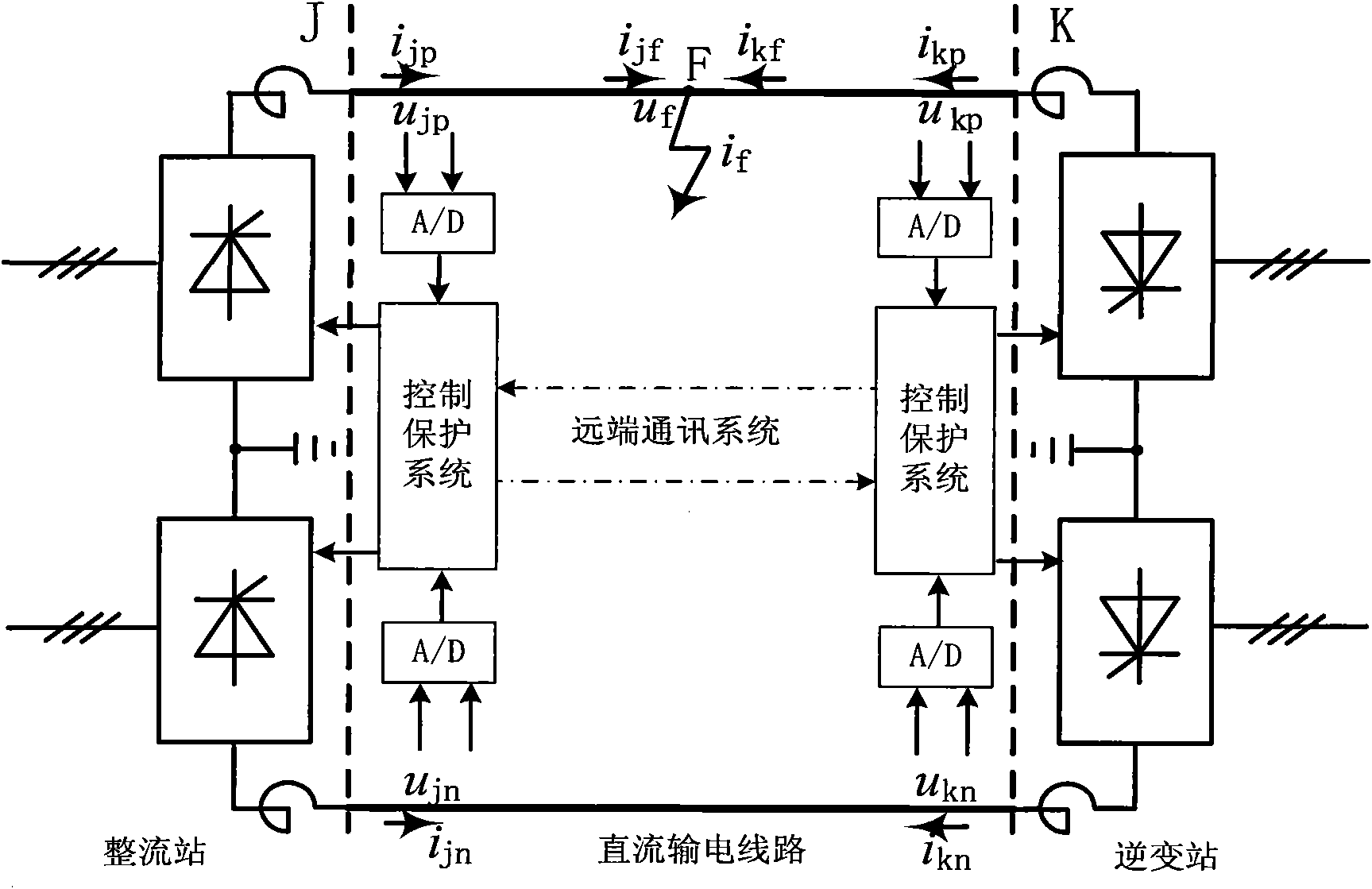
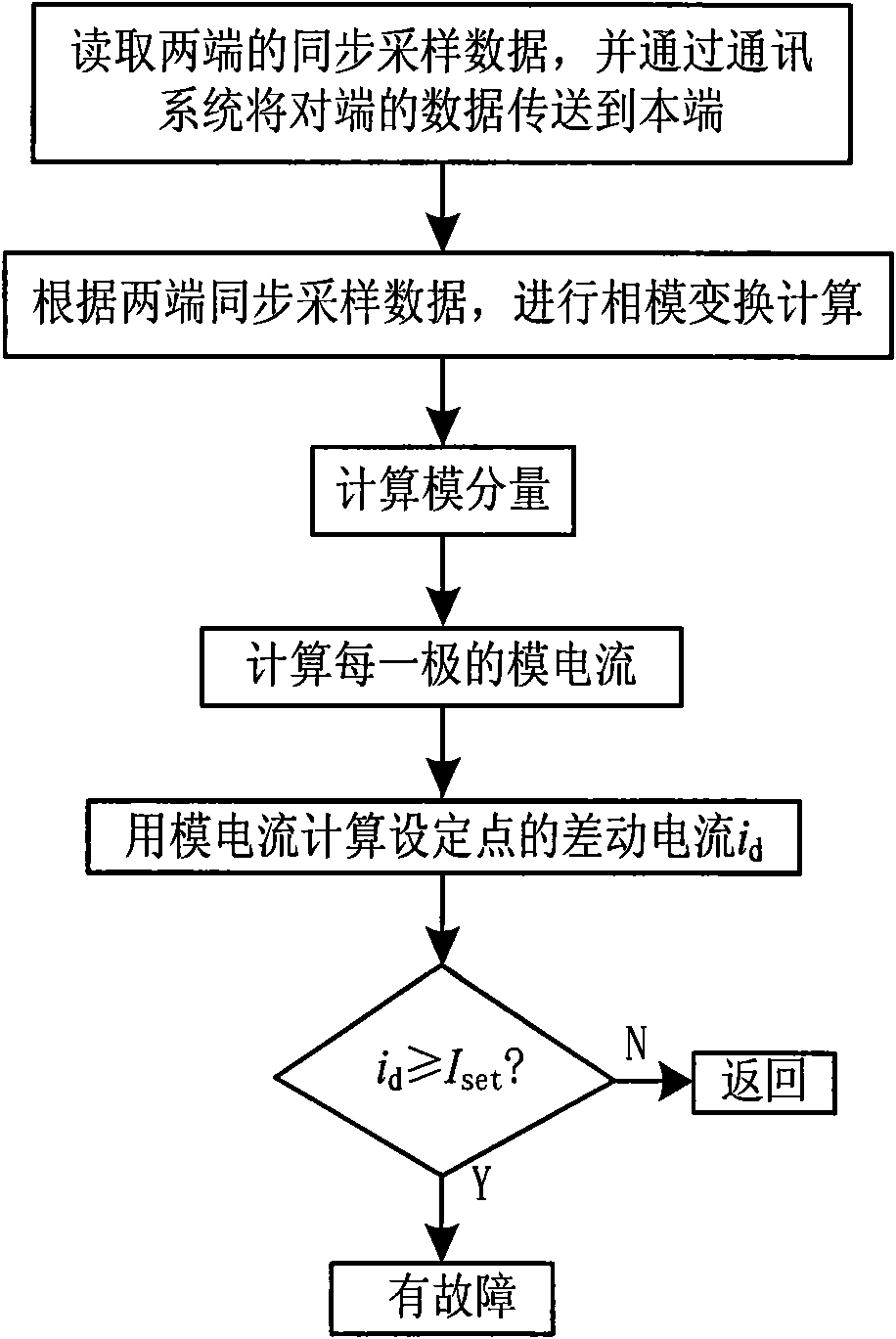
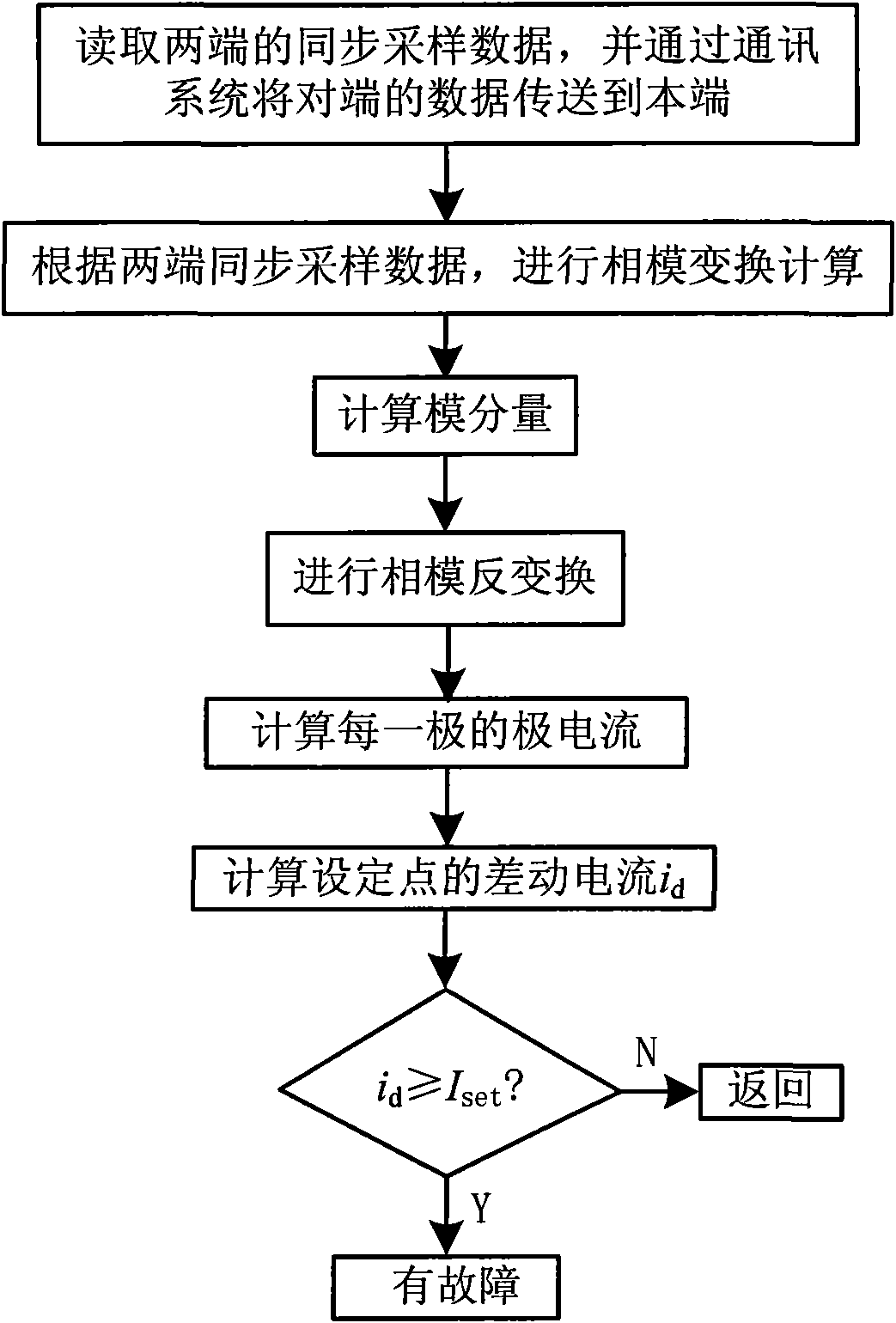
Method for current differential protection of direct current electric transmission line
InactiveCN101577417AImprove reliabilityFast actionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDc currentElectric power system
The invention discloses a method for current differential protection of a direct current electric transmission line, which comprises the following steps: according to a distributed parameter model of the electric transmission line, using mode transformation in a time domain to transform sampling values of direct current and direct current voltage into a modulus; then using the mode voltage and the current of two ends from two ends of a line respectively to calculate mode current of certain point of the line at each moment; and using the mode current to directly construct a current differential protection criterion, or synthesizing electrode current through electrode mode inverse transformation, and then constructing the current differential protection criterion according to the electrode current. The method can improve the sensitivity and the reliability of direct current line protection, has good controllability and high security, has a complete setting theory, overcomes the defects of the conventional traveling-wave protection as the main protection of a high-voltage direct current line, and requires no recognition of a traveling-wave wave head; besides, the calculation is simple. The method is mainly used for the current differential protection of the direct current electric transmission line in an electric power system, in particular for the protection of an ultra / extra high-voltage direct current electric transmission line.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Fault distance-finding method for nonuniform zero sequence mutual inductance same-lever aerial multi-back line
InactiveCN101350521AHigh precisionConvenient online rangingEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault locationElectricityDistributed parameter model
The present invention discloses a failure distance-measuring method of uniform and non-uniform zero-sequence mutual inductance and multi-loop circuit with loops of different voltage levels arranged on the same rod or with the same electricity-transmitting corridor. Based on a distributed parameter model, the method samples the voltage and current synchronously at two ends. As for the parallel multi-loop circuit with the loops arranged on the same rod and with the same electricity-transmitting corridor, the influence of mutual inductance of the positive sequence and negative sequence between the loops can be ignored. When the power line has a single-line or over-line failure, the positive-sequence voltage and the negative-sequence voltage, which are respectively calculated from two sides of the fault point, should be equal to the sum of the positive-sequence voltage and the negative-sequence voltage, so as to solve the fault distance equation based on the positive-sequence component, negative-sequence component, or the positive-sequence and negative-sequence component. When the protection indicates that the line has an internal failure, the failure distance can be measured according to the fault distance equation. The mutual inductance between the lines which can be even or uneven has no influence on the distance measurement of the loops arranged on the same rod. The method can be used for precise distance measurement of the loops arranged on the same rod, which have various topological structures.
Owner:BEIJING SIFANG JIBAO AUTOMATION +1
Method for measuring zero-sequence parameters of double-circuit transmission lines
ActiveCN102435851AHigh precisionSuitable for measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical testingDistributed parameter modelEngineering
The invention discloses a method for measuring zero-sequence parameters of double-circuit transmission lines. The method comprises the following steps: measuring the zero-sequence parameters of the double-circuit transmission lines in the manner of live line measurement or power cut measurement; by utilizing the global positioning system technology, simultaneously measuring the zero-sequence voltage and the zero-sequence current at the head ends and the tail ends of the double-circuit transmission lines to realize synchronous sampling on the zero-sequence voltage and the zero-sequence current; and then, working out the respective zero-sequence self impedance and zero-sequence self capacitance, and zero-sequence mutual impedance and zero-sequence mutual capacitance between the double-circuit transmission lines. In the method for measuring the zero-sequence parameters of double-circuit transmission lines, the distributed parameter models of the double-circuit transmission lines are established, and the influences of distributed capacitors on measured results are considered, thereby, the accuracy of the measured results of the zero-sequence parameters of the double-circuit transmission lines is greatly improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Simulation method for calculating lightning back-striking performance of UHV transmission lines
InactiveCN103646148ASimulation results are accurateSpecial data processing applicationsTransmission towerDistributed parameter model
The invention discloses a simulation method for calculating the lightning back-striking performance of UHV transmission lines. The simulation method comprises the following steps: dividing wires among long-span transmission towers into a plurality of line segments, establishing a distributed parameter circuit model for each line segment, establishing a multi-wave impedance model for each tower, then selecting the lightning parameters according to lightning activities, integrating all models and calculating the lightning withstand level, and calculating to obtain the back-striking trip rate of the UHV transmission lines according to the lightning withstand level and a series of formulae. The simulation method disclosed by the invention establishes the distributed parameter models of the line segments in consideration of high long-span transmission towers and long line spans, subdivides the wave impedance of different parts of the towers, and establishes the multi-wave impedance models in consideration of the refraction and reflection processes of lightning waves on the tower bodies so as to make the simulation results more precise and practical.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on zero sequence voltage
ActiveCN103792465AOvercome the problem of large errorsEasy to implementFault locationLow voltageDistributed parameter model
A power distribution network one-phase grounding fault location method based on a zero sequence voltage belongs to a power distribution network grounding fault location method. The fault location method starts from an overall zero sequence parameter of a single-end radial medium voltage power distribution network, analyzes a one-phase grounding fault while taking a distributed parameter model influence into consideration, measures a steady-state zero sequence voltage value and a zero sequence current of each feeder line at a bus position and at a tail end of each outlet line, and finds zero sequence voltage variation characteristics of a fault feeder line and non-fault feeder line. According to the invention, a large number of existing devices are used, the data sampling requirement is low in terms of being real-time, and the method of the invention is easy to realize; the simulation model analysis is established according to the actual parameters, so that the fault location can be realized in the system in which the neutral point is not grounded or the neutral point is grounded through an arc suppression coil; the precision is quite high; and the location method of the invention can be applied to the medium and low voltage power distribution network.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
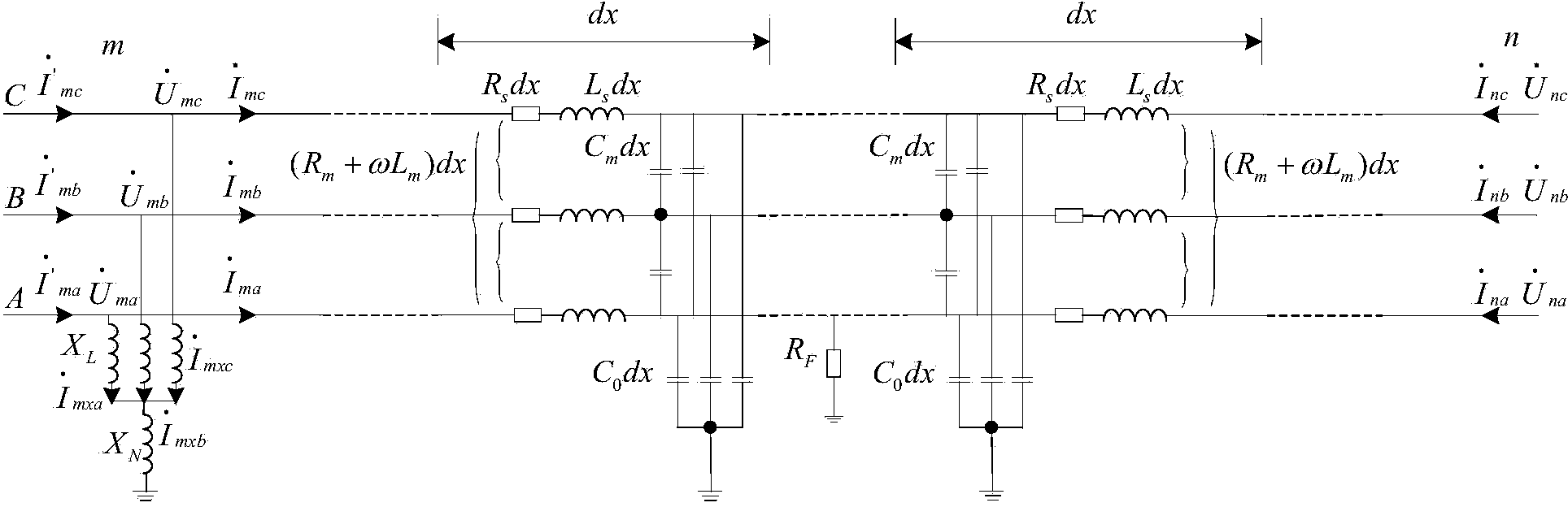
A distance protection method based on distributed parameter model
InactiveCN101242094ALow hardware requirementsImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsState of artCapacitance
The invention relates to the relay protection field of electric transmission line of electric power system, in particular to a distance protection method based on the distributed parameter model. The invention is aimed to solve the problem that the current distance protection is affected by distributed capacitance current and harmonic. The invention uses the voltage and current in the protection mounting place to compensate the end of the section I of the distance according to the distributed parameter model, and simplifies the line between the end of the section I and the fault point into a R-L model. That weather the fault is at inside or outside can be determined by solving differential equation. The invention has the advantages that: comparing to the distance protection based on the R-L model of the electric transmission line, the invention avoids the affect of distributed capacitance current and harmonic; comparing to the distance protection based on the pi model of the electric transmission line, the invention has higher reliability on fault determine; comparing to the distance protection based on the Bergeron model of the electric transmission line, the invention has the advantages of low requirement on sampling rate, low amount of calculation, low requirement on the hardware for the distance protection apparatus.
Owner:XIAN XIRUI CONTROL TECH CO LTD +1
Single-terminal distance measurement method for line single-phase earth faults based on distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude characteristics
ActiveCN103293439AAccurate measurementImprove fault location accuracyFault locationInformation technology support systemElectrical resistance and conductanceDistributed parameter model
The invention discloses a single-terminal distance measurement method for line single-phase earth faults based on distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude characteristics. The method includes adopting a distributed parameter model, selecting an initial value of fault distance as 1x, successively increasing the fault distance by the step length of delta1, sequentially calculating distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude z(1x) until the amplitude z(1x) from every point on the transmission line to a single-phase earth fault point is calculated and selecting the distance between a minimum corresponding point of the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude z(1x) to a protection installation position of the transmission line as the fault distance. The method has the advantages that a principle that the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude corresponding to the single-phase earth fault point reaches the minimum is utilized for achieving single-terminal distance measurement of the single-phase earth faults of the transmission line, influences of transition resistance and load current on accuracy of single-terminal fault distance measurement are eliminated, and particularly when used for distance measurement of single-phase high-impedance earth faults of the transmission lines, the method is capable of accurately measuring fault distance and has quite high fault distance measurement accuracy.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
HVDC transmission line distance protecting method
InactiveCN101232177AThe ranging result is accurateAccurate judgmentEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTime domainElectricity
The invention provides a distance protection method of high-voltage DC transmission circuit. The method is constituted on the basis of a time domain distribution parameter model and comprises following steps: firstly, calculating the voltage and the current at the tail end of a protection range by the distribution parameter model of a power transmission circuit according to the voltage and the current of a protection arrangement position; secondly, calculating the fault distance by a lumped parameter RL model of the transmission circuit according to the voltage and the current of the tail end of the protection range, and determining whether the fault is in or out of a protection region according to the symbol of the fault distance. The calculation of the protection method is carried out in time domain and requires a short data window and a great amount of calculation based on RL model. The method has the advantages of simple calculation and low sampling rate, thus rapidly monitoring the fault.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
UHV DC transmission line protection method utilizing current abrupt change characteristic based on distributed parameter model
ActiveCN106505536AEliminate the effects of protectionThe principle is simpleEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceTransformer
The invention discloses a UHV DC transmission line protection method utilizing current abrupt change characteristics based on a distributed parameter model. The UHV DC transmission line protection method comprises the steps of processing voltage and current signals measured by transformers at both ends of a DC line by means of an intelligent electronic device (IED), and identifying internal and external faults according to polarities of current abrupt variables. The UHV DC transmission line protection method adopts a distributed parameter model for carrying out distributed capacitive current compensation, eliminates the influence of asynchronization of the distributed capacitive current and data. A protection criterion selects components with the frequency band of [0,100] Hz in current information, avoids the electromagnetic coupling between DC side characteristic harmonics and a bipolar DC line and the influence of lightning interference. The polarities of current abrupt variables at both ends of the line are Boolean quantities, and the communication traffic of longitudinal channels is small. The UHV DC transmission line protection method utilizing the current abrupt change characteristics based on the distributed parameter model only utilizes polarities of the current abrupt variables for identifying the internal and external faults, is simple in principle and small in communication traffic, and is stable and reliable.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Ultra-high-voltage transmission line relay protection method based on break variable differential coefficient matrix
ActiveCN103296650ACorrect and reliable identificationRealize relay protection functionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDifferential coefficientCapacitance
The invention discloses an ultra-high-voltage transmission line relay protection method based on a break variable differential coefficient matrix. The method includes by utilizing a distributed parameter model, computing three-phase current break variables of the other end of an ultra-high-voltage transmission line by positive, negative and zero-sequence voltage break variables and current break variables of one end of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line and positive, negative and zero-sequence current break variables of the other end of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line by the aid of a symmetrical component method, further computing the break variable differential coefficient matrix, forming protection criterions according to size relationships of elements of the break variable differential coefficient matrix, and distinguishing fault phases of the ultra-high-voltage transmission line. The distributed parameter model is used as a physical model and unaffected by distributed capacitance current, and the method is applicable to any voltage classes and in particular to ultra-high-voltage transmission lines.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Series-compensation double-circuit line fault locating method based on distributed parameter model
ActiveCN105738769AThe principle of ranging is simpleThere is no false root discrimination problemFault location by conductor typesElectrical resistance and conductanceSeries compensation
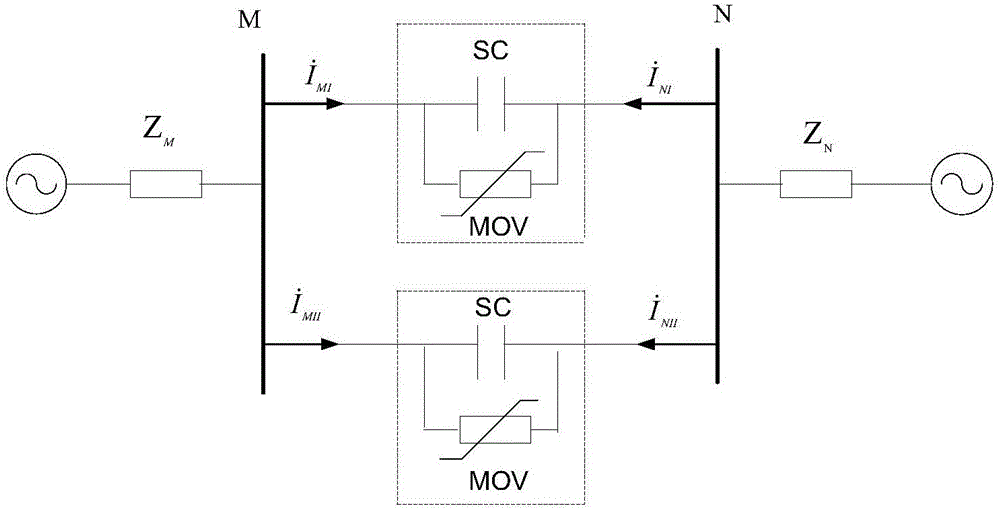
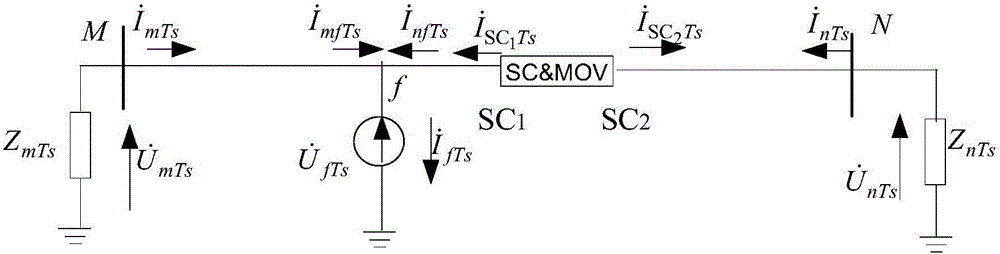
The invention discloses a series-compensation double-circuit line fault locating method based on a distributed parameter model. The method comprises a step I, a six-sequence component method is adopted to perform decoupling, and a reverse voltage cross a bus on two sides is zero when a fault occurs in a circuit after the decoupling is performed; a step II, according to characteristics that voltages at a fault spot are equal and currents at two ends of a series compensation device are reverse and which are respectively reckoned from the two sides, a series compensation voltage and the currents at the two ends in a transmission equation are eliminated; and a step III, by utilizing a pure resistance property of a transition resistor at a position of the fault spot and a fault timing sequence network boundary condition, a fault locating function when double-circuit lines containing series compensation are erected on the same pole is constructed, and a fault distance is solved by utilizing the fault locating function when the fault occurs. The method does not rely on a model of the series compensation device and is not influenced by MOV nonlinearity, a position of the fault spot relative to the series compensation does not need to be known in advance, the ranging principle is simple, one-dimensional searching for the fault distance is needed only, and a pseudo root discrimination problem does not exist.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Zero-sequence parameter measuring method for ultrahigh-voltage transmission line with four-circuit alternating current on one tower and double-circuit double-electrode direct current
ActiveCN103869171ASolve the simultaneity problemResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceUltra high voltage
The invention relates to a zero-sequence parameter measuring method for an ultrahigh-voltage transmission line with a four-circuit alternating current on one tower and a double-circuit double-electrode direct current. By setting up an ultrahigh-voltage transmission line model with the four-circuit alternating current on one tower and the double-circuit double-electrode direct current based on distribution parameters, the zero-sequence voltages and the zero-sequence currents at the head end and the tail end of an ultrahigh-voltage transmission line with the four-circuit alternating current on one tower and the double-circuit double-electrode direct current are simultaneously measured through the GPS, and therefore the zero-sequence voltages and the zero-sequence currents can be synchronously sampled; then, parameters such as zero-sequence resistance, zero-sequence inductance and zero-sequence capacitance of the ultrahigh-voltage transmission line with the four-circuit alternating current on one tower and the double-circuit double-electrode direct current are obtained through the measuring and calculating method. According to the method, by means of the model based on the distribution parameters and a transmission line equation, measuring accuracy is greatly improved, and the method can meet the requirement of actual engineering measurement.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Time-domain fault location method of multibranch direct current line in multiterminal direct current power transmission system
ActiveCN102445638ADistributed parameter characteristics are obviousDownsamplingFault locationTime domainDistributed parameter model
The invention provides a time-domain fault location method of a multibranch direct current line in a multiterminal direct current power transmission system. The method is established on the basis of a distributed parameter model; in a time domain, sampling values of a direct current and a direct current voltage are converted into moduluses by utilizing modular transformation; according to voltages and currents at terminal points of a line, voltages of branch points of the line are calculated; comparison is carried out on voltages that are obtained by calculation of electric quantities at all the terminal points so as to select a fault branch; all good branches are used to calculate a voltage and a current of a branch point, and the electric quantity of the branch point and the electric quantity of the other end of the fault branch form a two-terminal line; and electric quantities of the two terminals are used to respectively calculate voltage distribution along the line, and fault location is realized according to a constant equal situation of voltages calculated at a fault point. According to the invention, a needed sampling rate is low and calculation is simple; and precise fault location with a short data window can be realized. Besides, the fault location method can be applied to a multiterminal direct current system containing branch lines, wherein the multiterminal direct current system can be a parallel system, a tandem type system or a mixing system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
High-voltage direct-current transmission line low-voltage protective method
ActiveCN102170114AFast actionImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsVoltage amplitudeElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a direct-current transmission line low-voltage protective method built on the basis of a time domain distributed parameter model. The voltage value in the end of a protective range is obtained by utilizing a time domain calculating method of a line voltage according to the voltage and current measured values at a protection installation position, and a protection criterion is constructed by utilizing the voltage calculated value of the protective range end. When a line end voltage calculated value and the voltage calculated value at the protection installation position have opposite signs, a metallicity or low-transition resistor fault happens in a power transmission line area is judged, so that quick protection action is carried out; and when the line end calculated voltage amplitude is less than a set value, a high-transition resistor fault or an outside fault happens in the power transmission line area is judged, and selectivity is provided when in related protection coordination, so that at the moment, protection action can be realized after time is delayed. The method is realized in a time domain, so that a needed data window is short and calculating amount is low. The method is mainly used for the relay protection of the direct-current transmission line in an electrical power system.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Range finding method for single-phase earth fault of line based on actual measurement of transition resistance
ActiveCN105891669AImprove ranging accuracyPracticalFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsCapacitance
The invention discloses a range finding method for a single-phase earth fault of a line based on actual measurement of transition resistance. The method includes the steps of measuring fault phase voltage, fault phase current, fault phase negative sequence current and zero sequence current at the protective installation part of a power transmission line, describing the physical characteristics of voltage and current transmission of the power transmission line by using a distributed parameter model, calculating the transition resistance at the single-phase earth fault point of the power transmission line, and sequentially calculating the transition resistance and transition resistance difference function value of each point on the power transmission line by using a one-dimensional searching method. Accurate range finding for the single-phase earth fault of the power transmission line is realized by using the characteristic that the transition resistance difference function value at the fault point of the power transmission line reaches the minimal value, which theoretically eliminating the influence of the factors including distribution capacitance, transition resistor and load current, and ensuring high range finding precision. The method is a searching method which means no false solution problem of equation solving methods and misconvergence problems of iterative methods, and the method is highly practical.
Owner:STATE GRID FUJIAN ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD +2
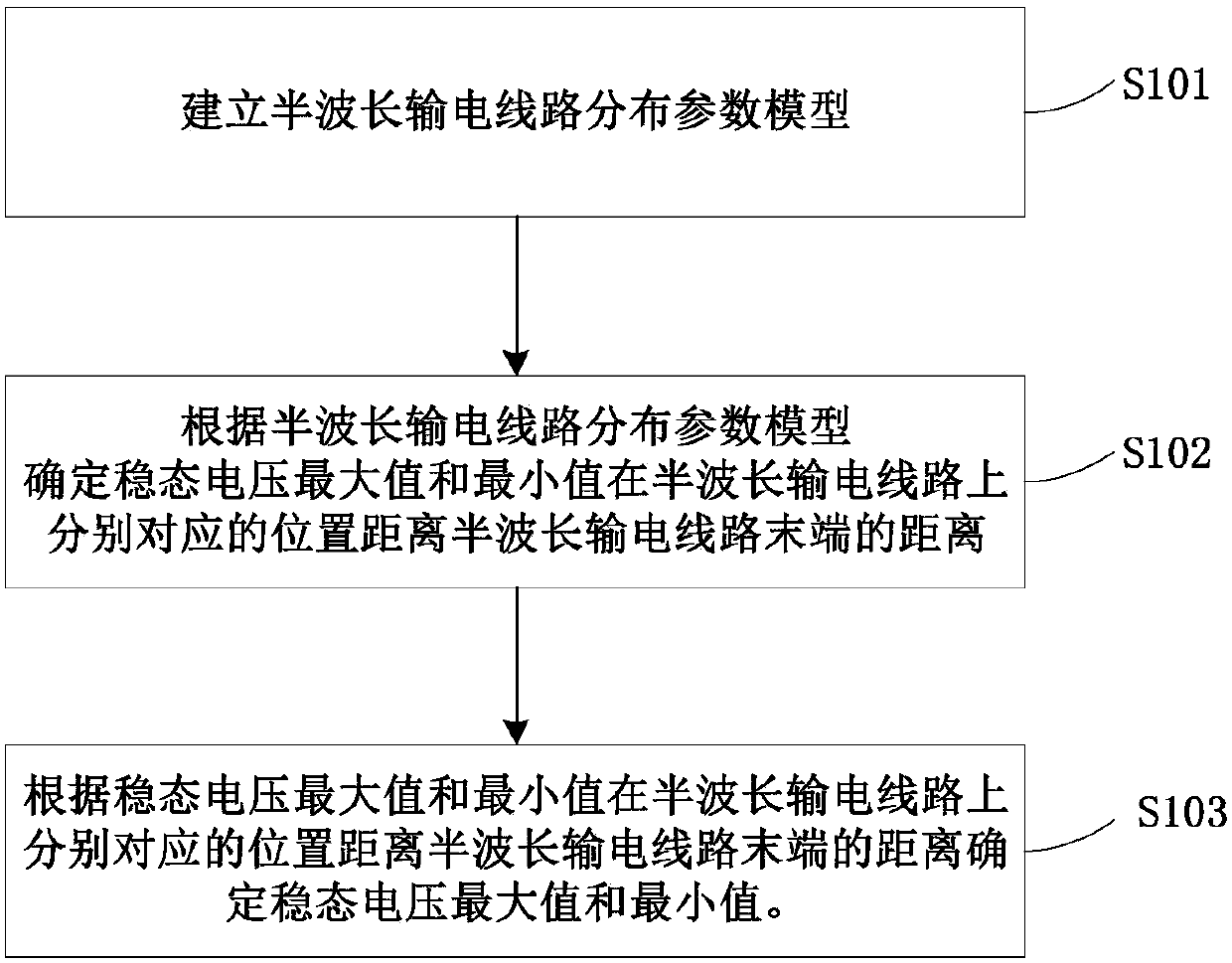
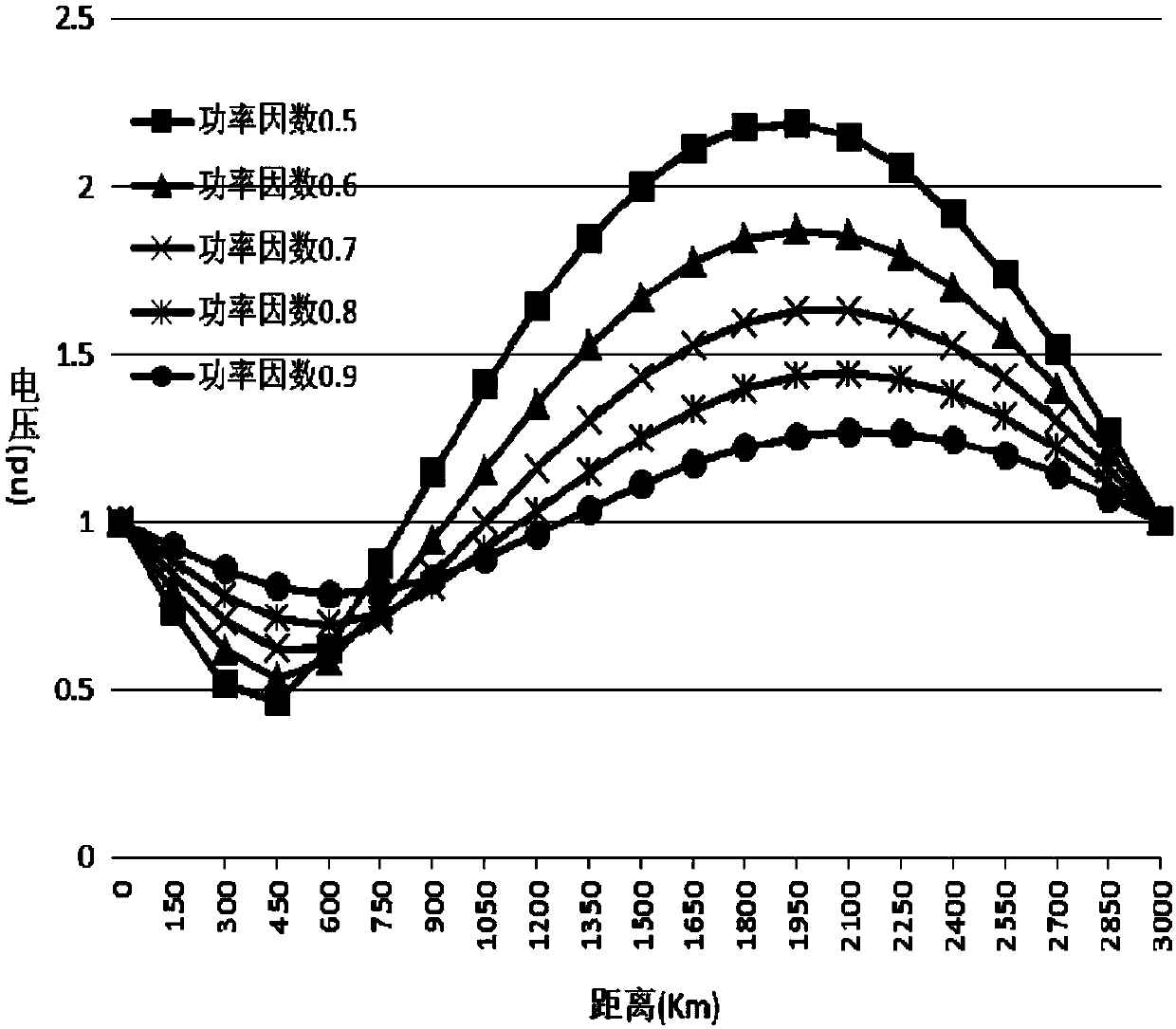
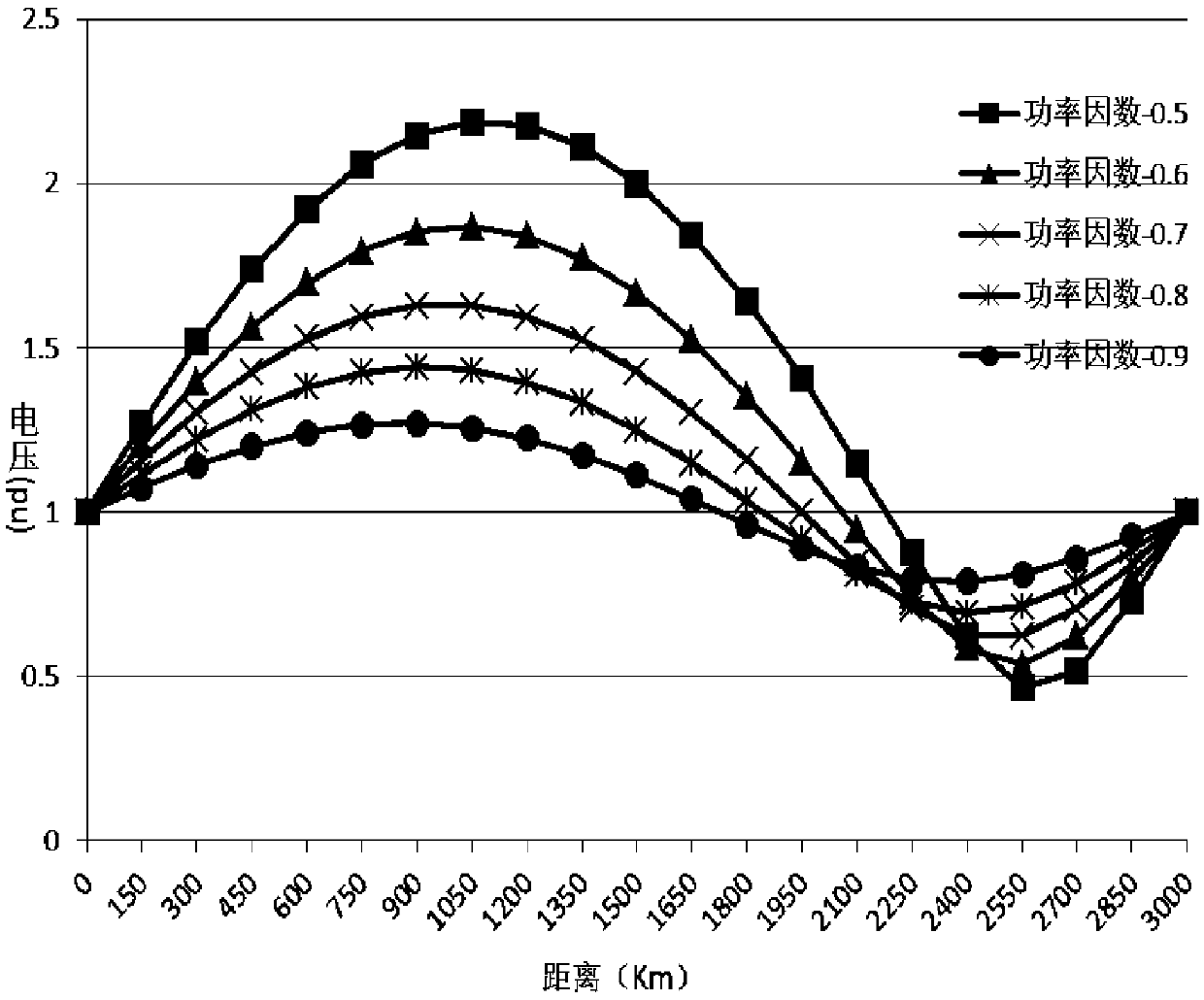
Method and device for determining steady-stage voltage limit of half-wavelength power transmission line
InactiveCN107132409ASimple and reliable processEasy to implementCurrent/voltage measurementElectric power transmissionElectric power system
The invention provides a method and device for determining a steady-stage voltage limit of a half-wavelength power transmission line. The method comprises the steps of building a half-wavelength power transmission line distribution parameter model; determining the distances from the positions respectively corresponding to a maximum value and a minimum value of the steady-state voltage on the half-wavelength power transmission line to the tail end of the half-wavelength power transmission line according to the half-wavelength power transmission line distribution parameter model; and determining the maximum value and the minimum value of the steady-state voltage according to the distance from the positions respectively corresponding to the maximum value and the minimum value of the steady-state voltage on the half-wavelength power transmission line to the tail end of the half-wavelength power transmission line. The method and device provided by the invention for determining the steady-state voltage limit of the half-wavelength power transmission line can be applied to theoretical and simulation analysis of a half-wavelength power transmission system and operation and control for an actual half-wavelength line, facilitate the system operation and analysis personnel to adopt effective control measures and improve the safe and stable operating level of an electric power system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Method for recognizing single-phase permanent fault of single-ended electric transmission line with paralleling reactor
InactiveCN103777114AEasy to determineHigh judgment sensitivityFault locationElectrical resistance and conductancePhase currents
The invention relates to a method for recognizing a single-phase permanent fault of a single-ended electric transmission line with a paralleling reactor. Existing fault property adjustment methods are different in application range and can be influenced by various factors. According to the method for recognizing the single-phase permanent fault of the single-ended electric transmission line with the paralleling reactor, the single-end sound-phase current and the current of the paralleling reactor are sampled firstly after fault-phase tripping, then the quantity of corresponding phases can be extracted with the full-wave Fourier algorithm, and thus the line voltage of the local-end and the current of the line in the flow direction can be represented according to the quantity of the corresponding phases; then, the voltage and current of a fault point relevant to the double-end voltage and current are calculated respectively according to a permanent fault distributed parameter model, it is deduced that the voltage to ground and current to ground of the fault point are only relevant to the single-end sound-phase current and the current of the paralleling reactor according to the boundary conditions which are met by the voltage and current of the fault point and the condition that the phase current of the opposite end is zero after fault tripping, and thus transition resistance can be calculated; the property of the fault can be recognized accurately through continuous calculation of the transition resistance. The method for recognizing the single-phase permanent fault of the single-ended electric transmission line with the paralleling reactor has the advantages that the fault property judgment is influenced by few factors, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for simulating DSG (Direct Steam Generation) trough heat collector by using nonlinear distributed parameter model
InactiveCN103390083AImprove output performanceSpecial data processing applicationsInformation technology support systemDynamic modelsCollector device
The invention discloses a method for simulating a DSG (Direct Steam Generation) trough heat collector by using a nonlinear distributed parameter model and belongs to the technical field of solar energy heat utilization. The method comprises the following steps of establishing and discretizing the nonlinear distributed parameter model of the DSG trough heat collector; solving other physical property parameters of a working medium by using the pressure and the specific enthalphy of the working medium at each time and each position of the DSG trough heat collector; and disturbing the direct solar radiation intensity, the inlet working medium temperature and the inlet working medium quality flow of a DSG trough heat collector control model to test the response of outlet parameters of the DSG trough heat collector. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the established nonlinear distributed parameter dynamic model of the DSG trough solar heat collector considering the space distribution influence of the heat collector embodies a good output performance for outside disturbances such as the solar radiation intensity, the feedwater flow and the temperature.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Wind power farm grid-connected power transmission line instant single-phase grounding fault single-end distance measuring method
ActiveCN106501675ASolving the Ranging Problem of Instantaneous Single-phase Grounding FaultAccurate solutionFault location by conductor typesSimulationCable fault location
The invention discloses a wind power farm grid-connected power transmission line instant single-phase grounding fault single-end distance measuring method. Three-phase voltages and three-phase currents at two specific moments are acquired on a wind farm side, and are used as inputs, and the three-phase voltages and the three-phase currents acquired on the wind farm side at two specific moments are used to calculate corresponding positive, negative, zero sequence voltage, current phasors. Based on a power transmission line distribution parameter model, the calculated wind farm side voltage, current sequence components are used to establish voltage, current relations on two ends of a power transmission line. Power supply potential, equivalent system impedance, fault distances and transition resistors of a system side are adopted as unknown quantities, and an established non-linear electric equation set is solved by using an improved Levenbery-Marquardt method, and an accurate fault distance measuring result is acquired. A problem of wind power farm grid-connected power transmission line fault distance measurement is effectively solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Single-ended fault ranging method of alternating-current line for flexible direct-current feeding
InactiveCN109142974AFix what doesn't applyImprove ranging accuracyFault location by conductor typesElectric power systemSymmetrical components
The invention, which belongs to the field of relay protection of a power system, particularly relates to a single-ended fault ranging method of an alternating-current line for flexible direct-currentfeeding. The method comprises the following steps that: after a power transmission system detects a single-phase ground fault, a single-ended electrical quantity of a conventional alternating-currentpower supply side is collected; discrete Fourier transform is carried out on an electrical quantity in a sampled data window and a fundamental frequency component is extracted; with a symmetrical component method, phase-mode transformation is carried out on the fundamental frequency component in a frequency domain to obtain sequence components of a fault voltage and a fault current; on the basis of a distributed parameter model, fault voltage and negative-sequence fault current distribution of a fault phase along a line is calculated; a data group formed by fault voltages and negative-sequencefault currents of fault phases at different distances at different times along the line is obtained in a time domain and fault ranging is carried out by using unary linear regression according to thecharacteristic of meeting a direct proportional linear relationship by the data group only at a fault point. Therefore, a problem that the traditional fault location method has low applicability is solved; and the single-ended fault ranging method has advantages of high ranging accuracy and wide applicability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Low-current grounding fault line selection method based on wide-area zero-sequence voltage distribution characteristics
The invention discloses a low-current grounding fault line selection method based on wide-area zero-sequence voltage distribution characteristics and belongs to low-current grounding fault line selection methods. According to the method, based on a distributed parameter model, a fault line can be selected correctly only under the circumstance of obtaining zero-sequence voltage data in the conditions of different grounding modes, fault distance, transition resistance and small off-tuning degree; difference between a sound line and the fault line in zero-sequence voltage distribution along the lines after a fault occurs is taken as a line selection basis. The method includes: constructing fault measurement factors for each feeder line according to line lengths and zero-sequence voltages measured at tail ends of a bus position and all branches after the fault occurs; then, establishing a relative fault measurement matrix for representing the difference between the sound line and the fault line in zero-sequence voltage distribution along the lines and similarity between the sound line and another sound line in zero-sequence voltage distribution along the lines; selecting the fault line according to a maximum vote principle. The low-current grounding fault line selection method is high in line selection accuracy and insusceptible to the fault distance, the transition resistance and a neutral point grounding mode.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Line inter-phase fault single-terminal location method implemented by aid of measured impedance amplitude characteristics of distributed parameters
ActiveCN103293445AImprove ranging accuracyStrong practical valueFault locationCapacitancePhase currents
The invention discloses a line inter-phase fault single-terminal location method implemented by the aid of measured impedance amplitude characteristics of distributed parameters. The line inter-phase fault single-terminal location method includes measuring fault inter-phase voltages, fault inter-phase currents and fault inter-phase negative-sequence currents at a power transmission line protection mounting position and using the fault inter-phase voltages, the fault inter-phase currents and the fault inter-phase negative-sequence currents as input variables; computing measured impedance of the distributed parameters, selecting an initial value I<x> of the fault distance, sequentially increasing a value of the fault distance by a step delta I on the basis of the initial value I<x>, sequentially computing an absolute value f(I<x>) of the difference between an impedance amplitude value of the distributed parameters of each point on a power transmission line and a measured impedance amplitude value of the distributed parameters until the increased value of the fault distance is equal to the total length of the power transmission line, and selecting the distance from the power distribution line protection mounting position to the point with the minimum value f(I<x>) as the fault distance. The line inter-phase fault single-terminal location method has the advantages that a physical model used in the method is a distributed parameter model, the location precision is unaffected by distributed capacitance currents, and the method is suitable for any voltage grades, and is particularly applicable to ultrahigh-voltage / extra-high-voltage power transmission line inter-phase short-circuit fault single-terminal location.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Line phase-to-phase fault single-end distance measuring method based on distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value characteristics
ActiveCN103323739AImprove ranging accuracyEliminate the impact of single-ended fault location accuracyFault locationCapacitanceDistributed parameter model
The invention discloses a line phase-to-phase fault single-end distance measuring method based on distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value characteristics. According to the line phase-to-phase fault single-end distance measuring method based on the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value characteristics, a distributed parameter model is used as a physical model, a fault distance initial value is selected to be 1x, and the 1x is gradually increased by step length delta1, distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude values z (1x) from each point on a power transmission line to a phase-to-phase fault point are calculated in sequence until the whole length of the power transmission line, the distance, corresponding to the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value z (1x) in a minimum mode, at the point-distance power transmission line protection installing position is selected as the fault distance. According to the line phase-to-phase fault single-end distance measuring method based on the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value characteristics, the distributed parameter model is used as the physical model; the line phase-to-phase fault single-end distance measuring method based on the distributed parameter measurement impedance amplitude value characteristics has a natural capacity for resisting distributed capacitance and current influence, and is suitable for ultra-high / extra-high voltage power transmission line.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Dynamic contrast enhanced imaging using a mamillary distributed parameter model
InactiveUS20050187462A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDynamic contrastDistributed parameter model
A method of dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) imaging includes: for a region of interest, sampling the concentration of a tracer liquid in a fluid over a time interval to arrive at a plurality of samples; fitting the plurality of samples to a plurality of multi-compartment mamillary pharmacokinetic models, each of the plurality of models modelling fluid flow in a number of interstitial compartments about a central compartment at the region interest, as a result of flow caused by a source of the fluid, so as to determine a plurality of fitting parameters for each of the plurality of models; determining a preferred one of the plurality of models; and presenting indicators indicative of values of the plurality of parameters for the preferred one of the models. Numerous multi-compartment mamillary pharmacokinetic models are disclosed. The models and methods may be used in DCE imaging systems and software.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV
Line single-phase earth fault relay protection method implemented by aid of distributed parameters
ActiveCN103296654ACorrect and reliable actionStrong practical valueEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase currentsCapacitance
The invention discloses a line single-phase earth fault relay protection method implemented by the aid of distributed parameters. The line single-phase earth fault relay protection method includes measuring fault-phase voltages, fault-phase currents, fault-phase negative-sequence currents and a zero-sequence current at a power transmission line protection mounting position and using the fault-phase voltages, the fault-phase currents, the fault-phase negative-sequence currents and the zero-sequence current as input variables; computing voltage drop from a single-phase earth fault point to a power transmission line protection setting range position by the aid of a distributed parameter model, computing voltage drop from the power transmission line protection mounting position to the transmission line protection setting range position by the aid of the distributed parameter model, and then judging whether a leading angle between the voltage drop from the power transmission line protection mounting position to the power transmission line protection setting range position and the voltage drop from the single-phase earth fault point to the power transmission line protection setting range position is within the range between -90 degrees and 90 degrees or not. The line single-phase earth fault relay protection method has the advantages that the action performance is unaffected by distributed capacitance currents or transition resistance or load currents, actions can be correctly and reliably performed by the method when a power transmission line single-phase high-impedance earth fault occurs, and the method has high practical value.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Adaptive reclosing judgment method for single-phase grounding fault of power transmission line
ActiveCN106908692AAccurate discriminationNot affectedFault location by conductor typesMeasurement pointCable fault location
The invention discloses an adaptive reclosing judgment method for a single-phase grounding fault of a power transmission line, and the method comprises the steps: collecting three-phase voltages and three-phase currents of one side of the power transmission line at two moments, and enabling the three-phase voltages and three-phase currents to serve as input; calculating the corresponding positive and negative zero-sequence voltage and current phasors through employing the measured voltages and currents at the two moments; Building equations for two types of possible faults (perpetual single-phase grounding fault and instantaneous single-phase grounding fault) based on a power transmission line distribution parameter model, and describing the relation of voltages and currents of two sides of the power transmission line, and obtaining two systems of nonlinear equations; taking the power potential, equivalent system impedance, fault distance and transition resistance of a measurement point opposite side system as unknown quantities, solving the built systems of nonlinear equations, respectively obtaining fault range finding results of the two systems of nonlinear equations, solving the ratio of the fault range finding results, determining that the perpetual single-phase grounding fault happens if the ratio is less than a threshold value, and locking the reclosing function, or else determining that the instantaneous single-phase grounding fault happens, and carrying out the reclosing.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Frequency domain method of fault location of high-voltage direct current earth electrode line based on distributed parameter model
ActiveCN103744001ANo peer parameter requiredEasy to implementFault locationInformation technology support systemElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric power system
The invention relates to a frequency domain method of fault location of a high-voltage direct current earth electrode line based on a distributed parameter model, and belongs to the field of fault location technologies of power systems. The frequency domain method comprises the following steps of computing voltage distribution along the earth electrode line from a measuring end by utilizing the measured voltage and current of a fault line when the high-voltage direct current earth electrode line has an earth fault; calculating an electrode address point by utilizing the measured voltage and current of a non-fault line, and computing the voltage and the current of the electrode address point; computing the voltage distribution along the earth electrode line from an electrode address end by utilizing the voltage and the current of the electrode address point, writing out a fault location function according to pure resistivity of a transition resistor at the fault point, and computing a fault distance through solving the location function. The frequency domain method is capable of implementing the fault location of a single end of the earth electrode on the basis of the conventional fault measurement data, parameters of an opposite end are not needed, and the frequency domain method has the advantages of simple algorithm and easiness in implementation.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for positioning transmission line fault based on power frequency phasor
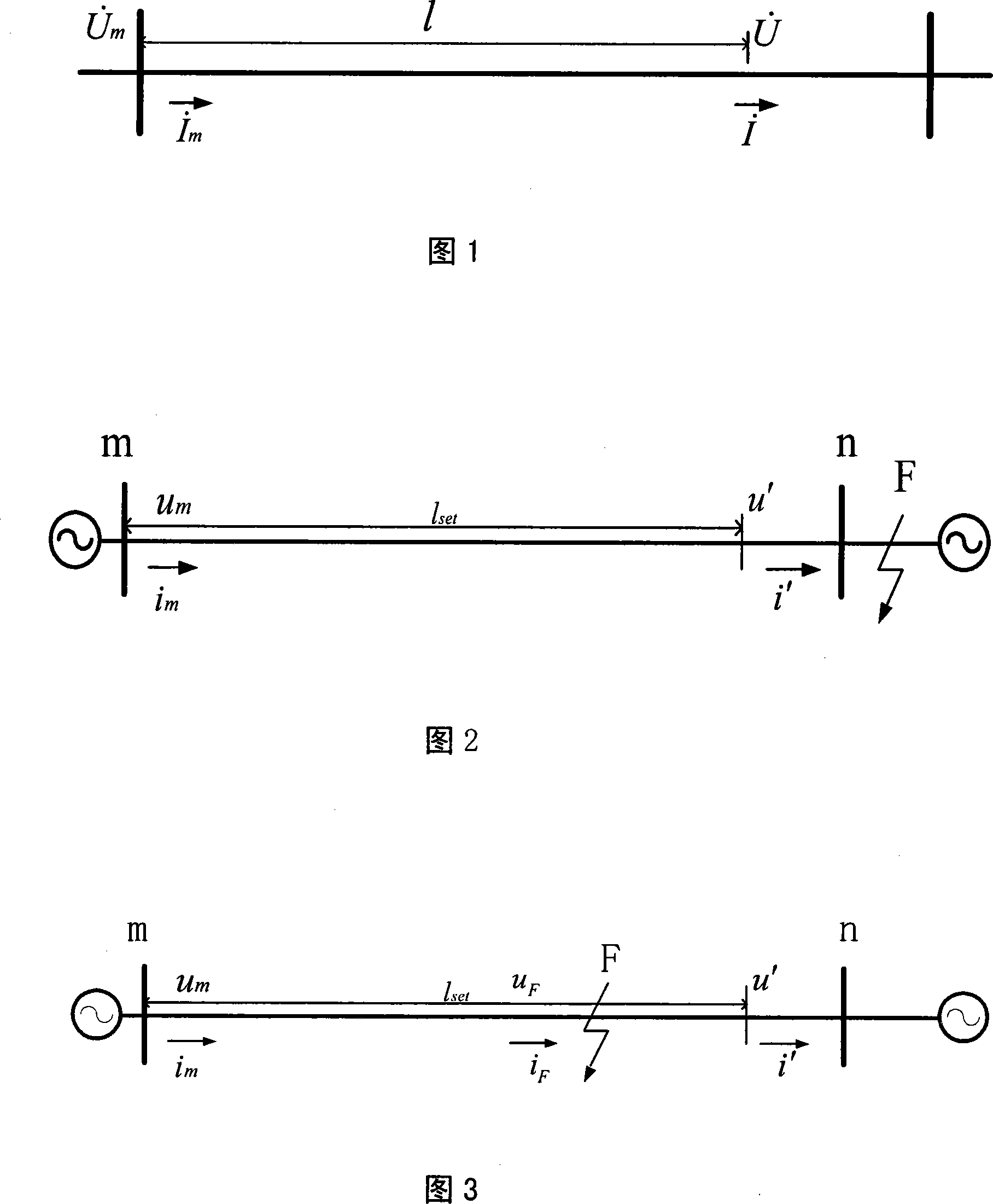
The invention relates to a method for positioning transmission line fault based on power frequency phasor, which comprises the following steps: confirming a characteristic impedance of propagation constant line according to a distribution parameter model of the transmission line; measuring the voltage Un and current In at tail end N of the transmission line by measuring the voltage Um and current Im at the starting end M of the transmission line, wherein DL is the actual length of transmission line; and calculating a distance DMf between the starting end M of the transmission line and the fault point according to the formula: DmF is equal to [th-1(BJ / AJ)] / gammaJ, thereby increasing the precision of positioning the transmission line fault.
Owner:SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER SCHOOL
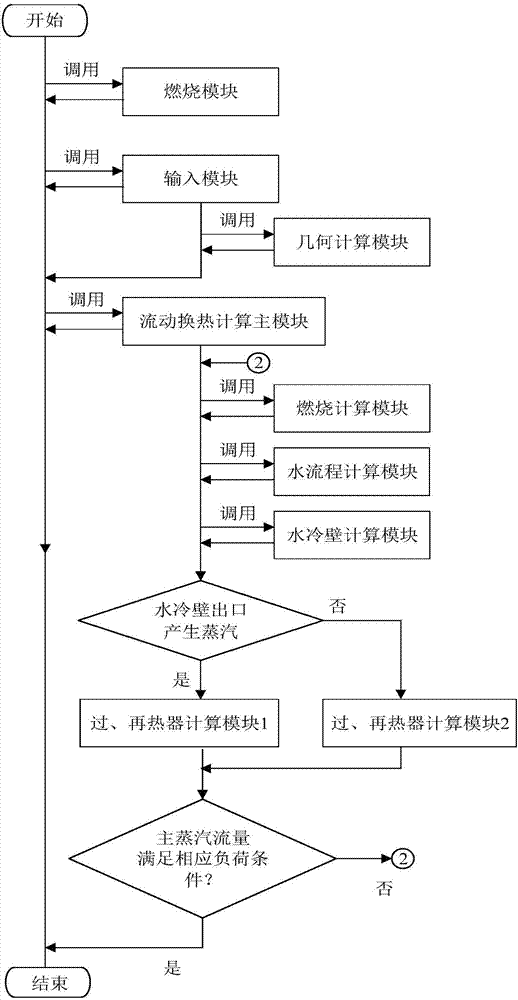
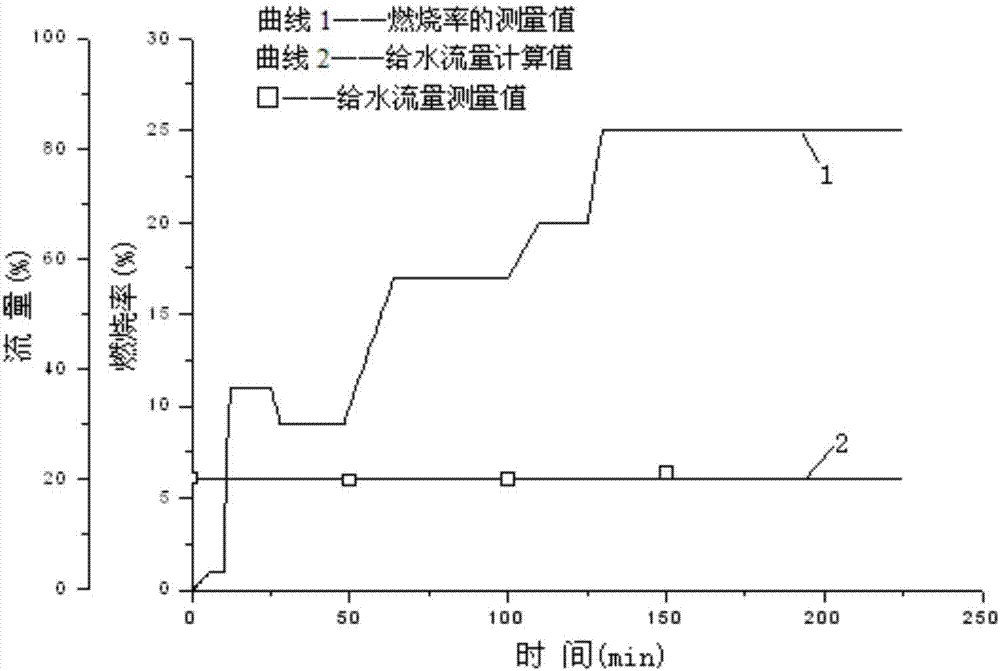
Start calculation method and system for supercritical boiler
ActiveCN107292006AOptimal Start CurveBest BoostDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelEngineering
The invention discloses a start calculation method and system for a supercritical boiler. According to the method, first, furnace combustion calculation is performed, wherein a furnace is divided into two parts, namely a radiation heat exchange area and a radiation convection area, and calculation is performed on the two parts respectively to obtain furnace outlet smoke temperature, furnace heat absorption percentage and smoke specific heat under different combustion rates; and second, boiler heating surface heat exchange calculation is performed, wherein on the basis of analyzing and simplifying flowing heat transfer characteristics of an in-pipe working medium side and an out-pipe smoke side in a heating surface in the boiler starting process, a distributed parameter model considering changes of thermal parameters along with position coordinate changes is adopted, mathematic models of change laws of working medium temperature, pressure, enthalpy values, heating surface metal temperature and smoke temperature in the starting process are established according to a mass conservation equation, a momentum conservation equation, an energy conservation equation, a metal heat reservation equation and a complementary equation, and solving is performed. Through the start calculation method and system, arrangement forms of different boiler starting systems can be calculated and compared, and an optimal boiler starting system can be provided for a user.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +2
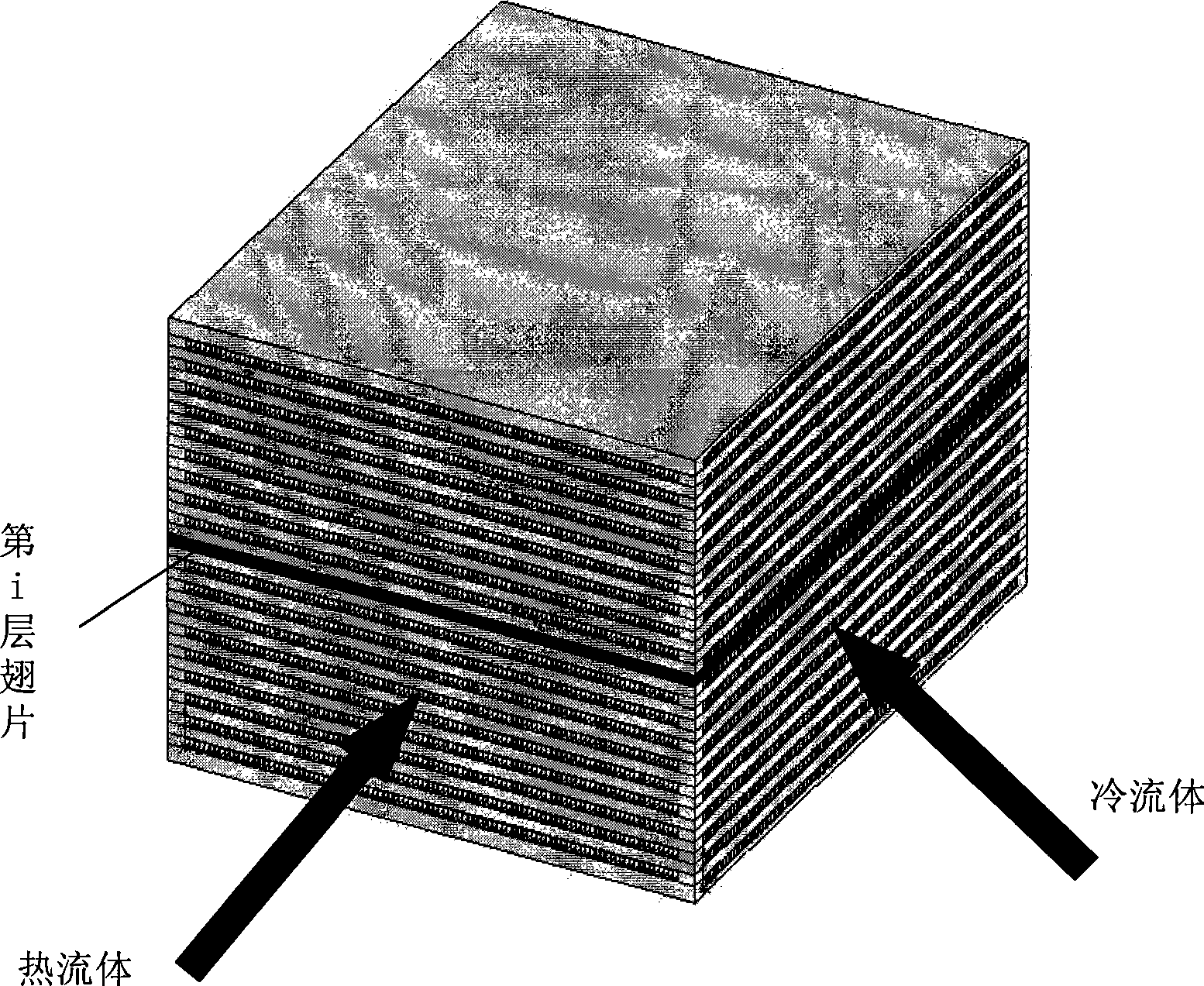
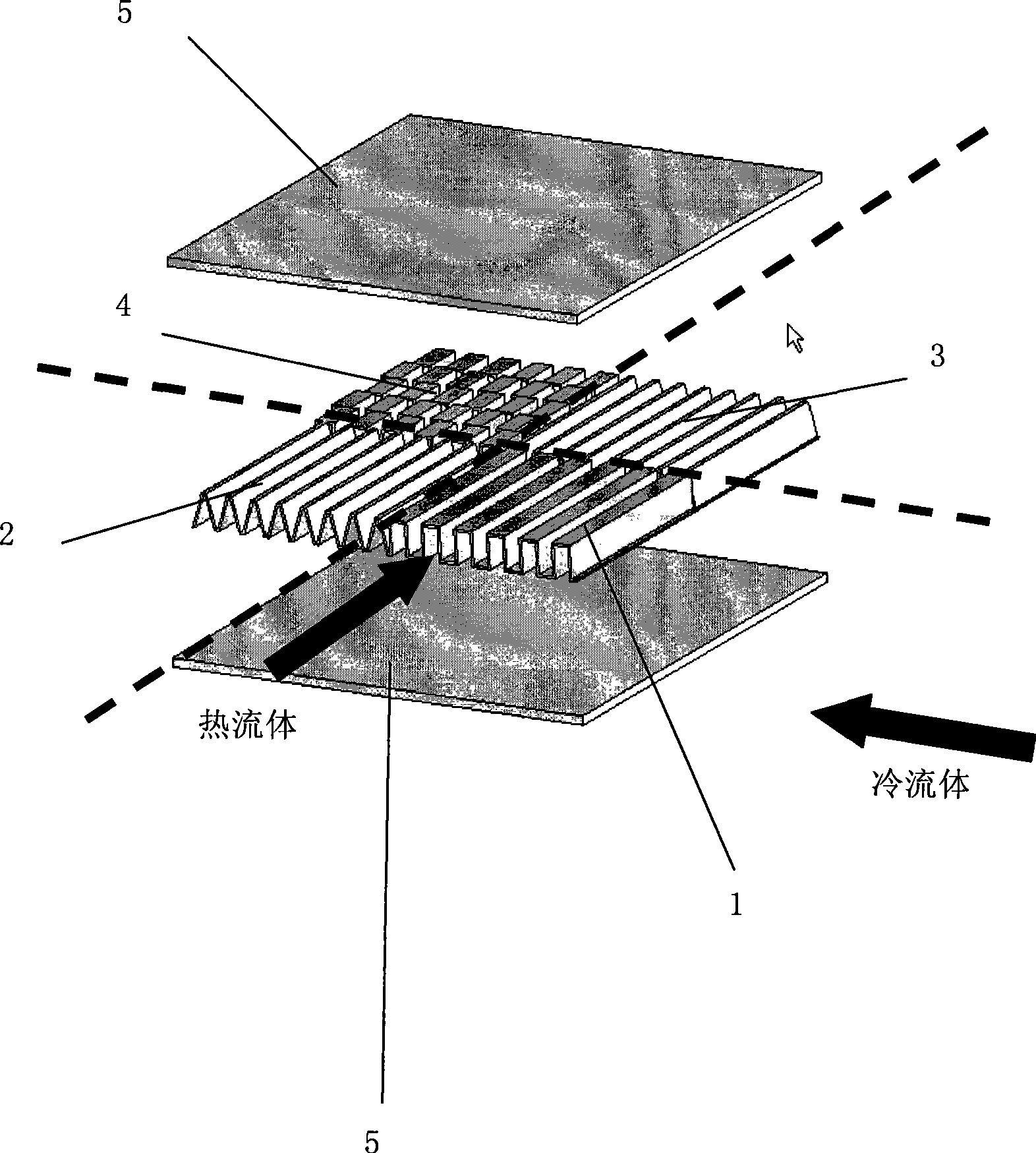
Distributed finned heat exchanger
The invention provides a novel distribution type fin compact heat exchanger designed by the combination with a distributed parameter model, which comprises a baffle plate, a hot fluid side fin, a cold fluid side fin, an end cover and the like. The heat exchanger is characterized in that the idea of the distributed parameter model is applied to the design of the heat exchanger, and the fin types, the number of fins and the fin sizes at different positions in the heat exchanger can be particularly designed according to the heat exchanging conditions at the positions, and the heat exchanging capability in the limited space can be maximized, and the resistance is minimized, thereby lowering energy consumption and saving materials; moreover, the hot side fin and the cold side fin can both be the combination of the fins with various structural sizes.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com