Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
172 results about "Cochlear prosthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
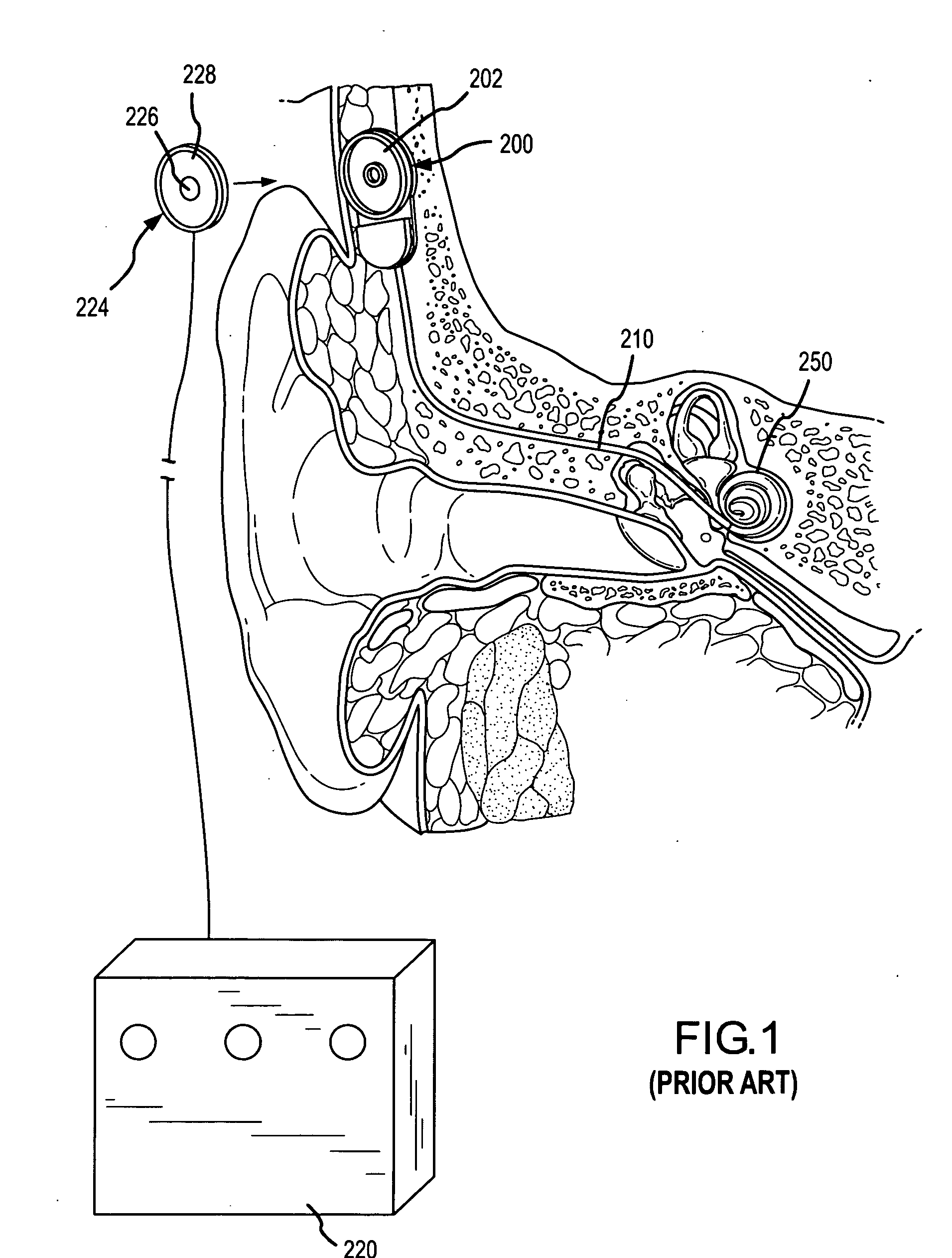
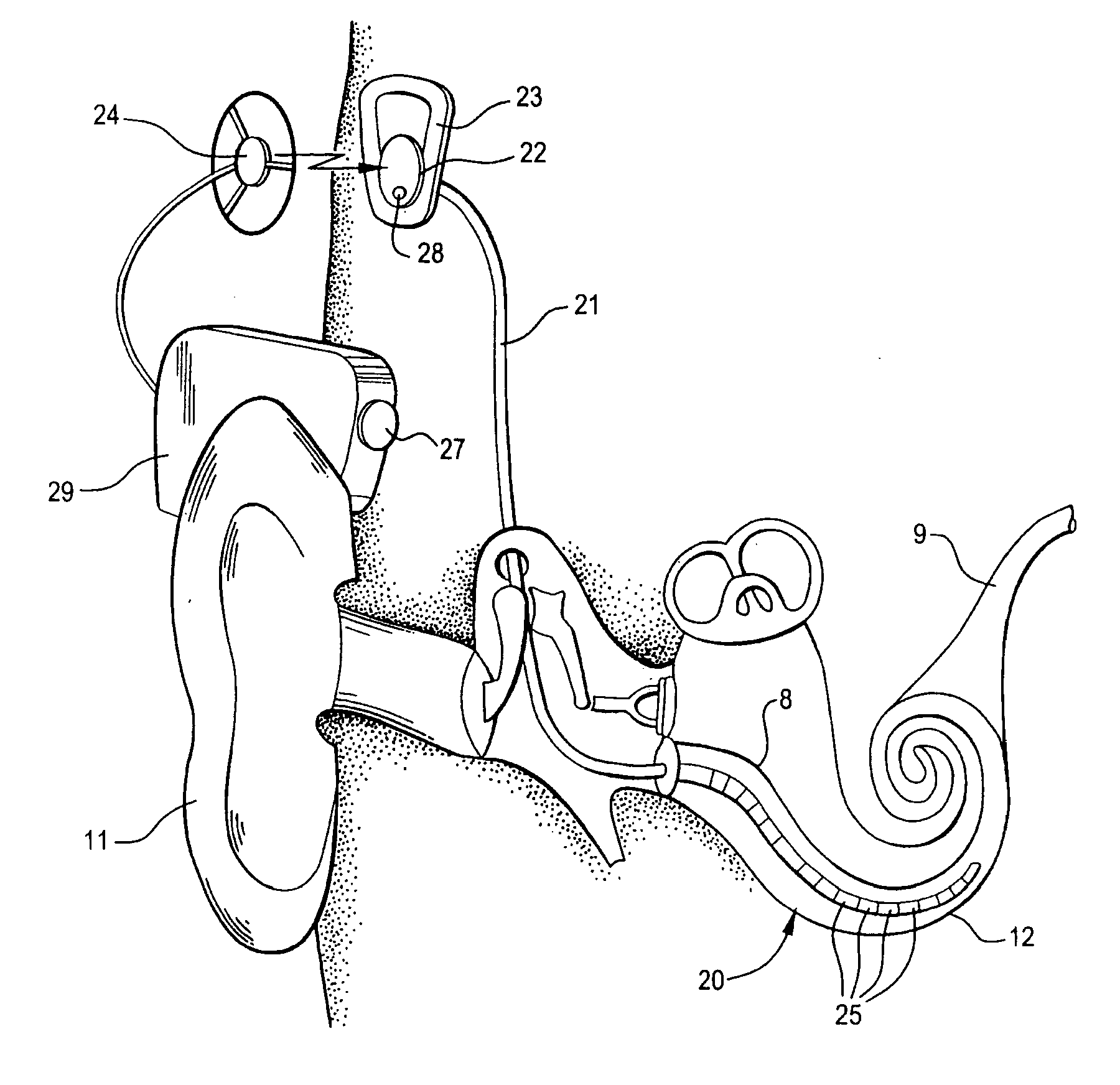
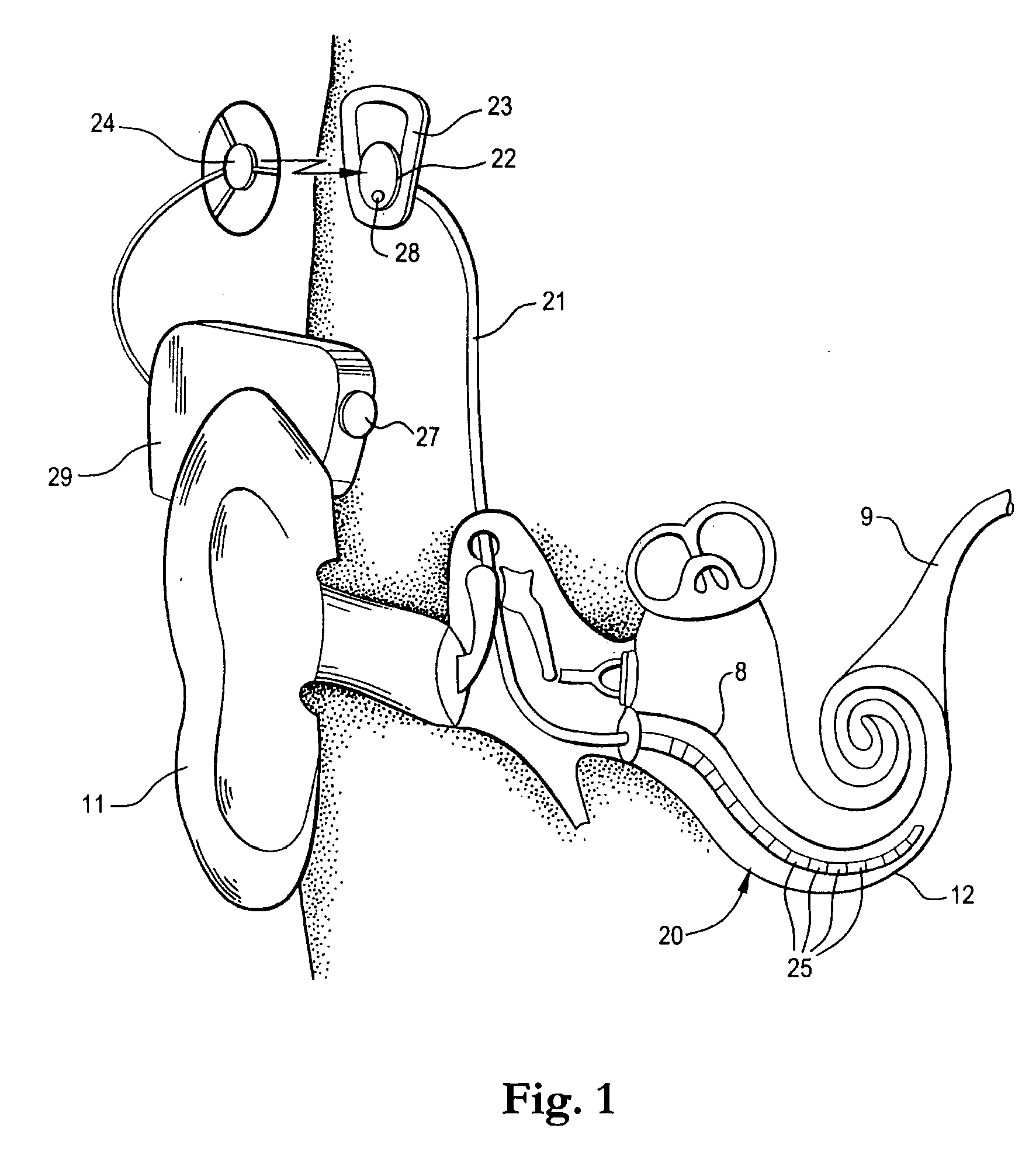
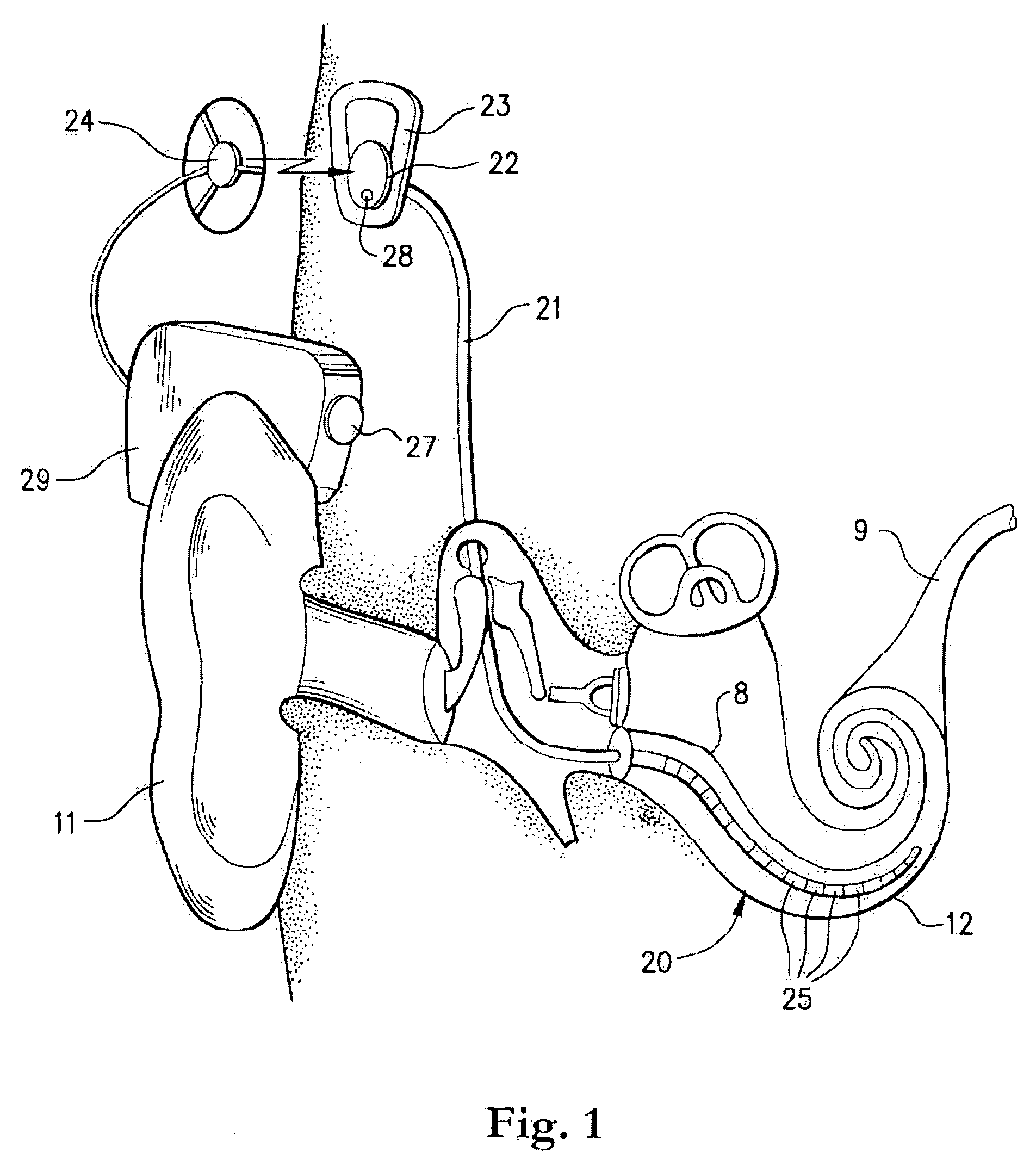
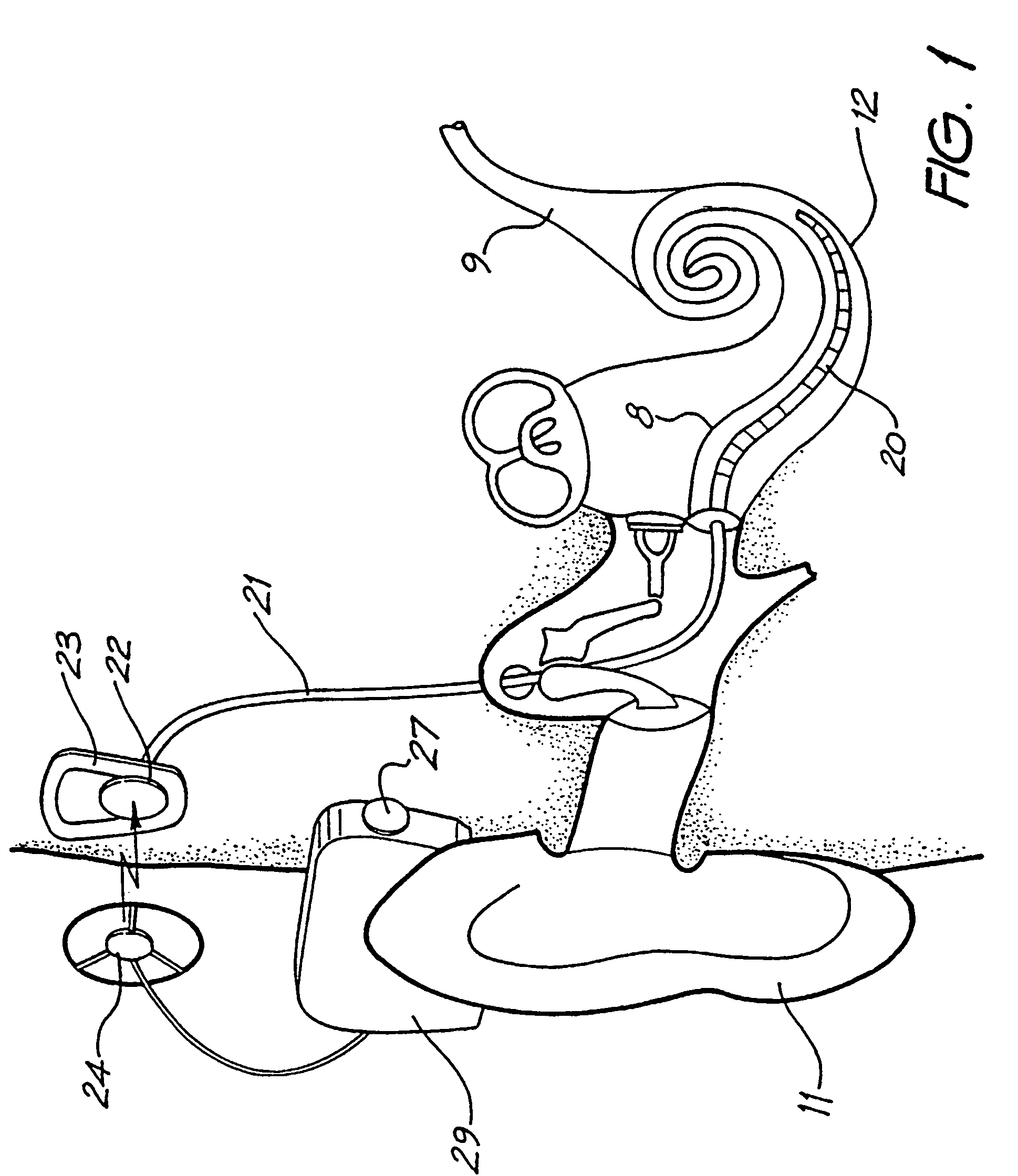
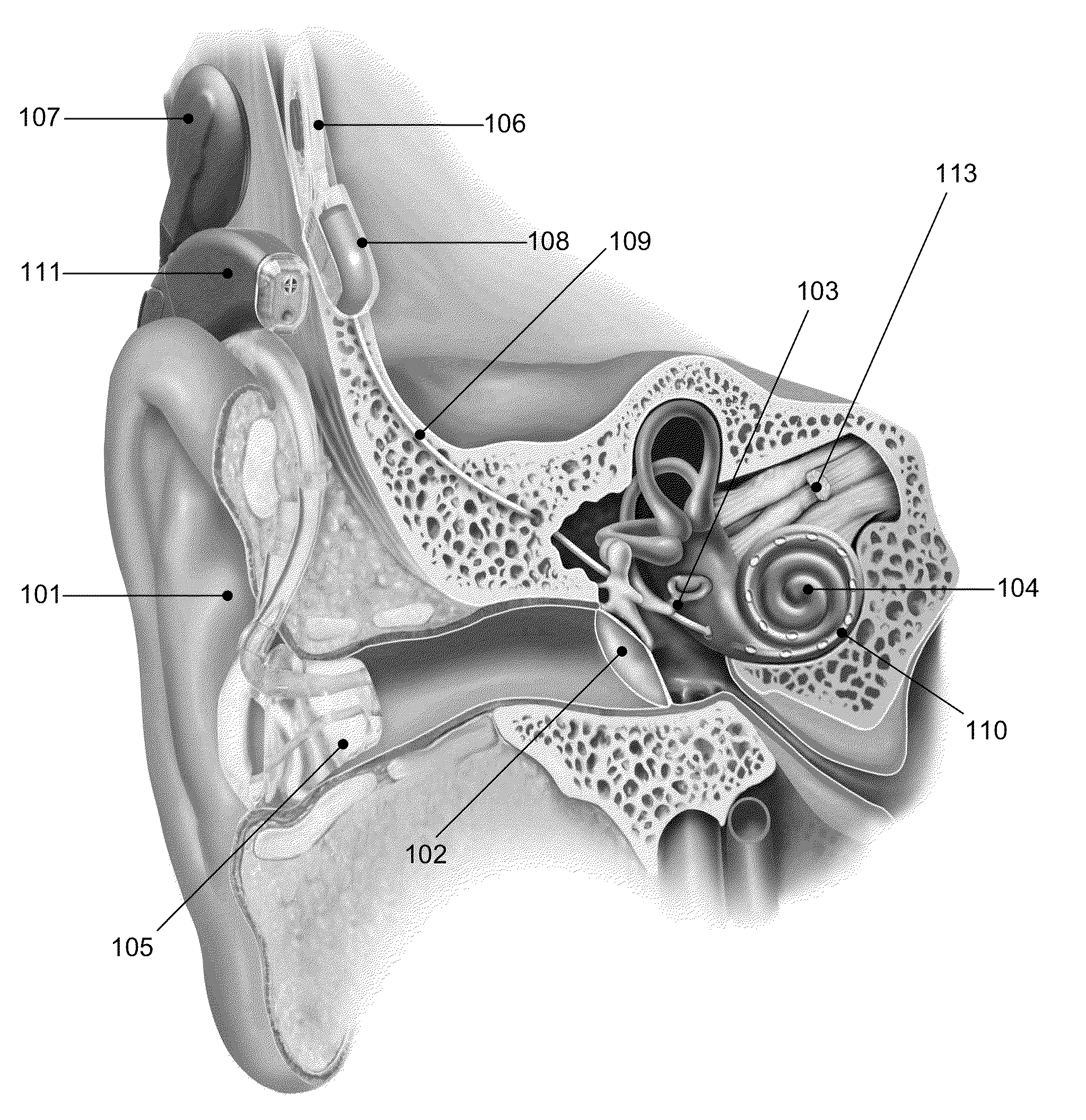
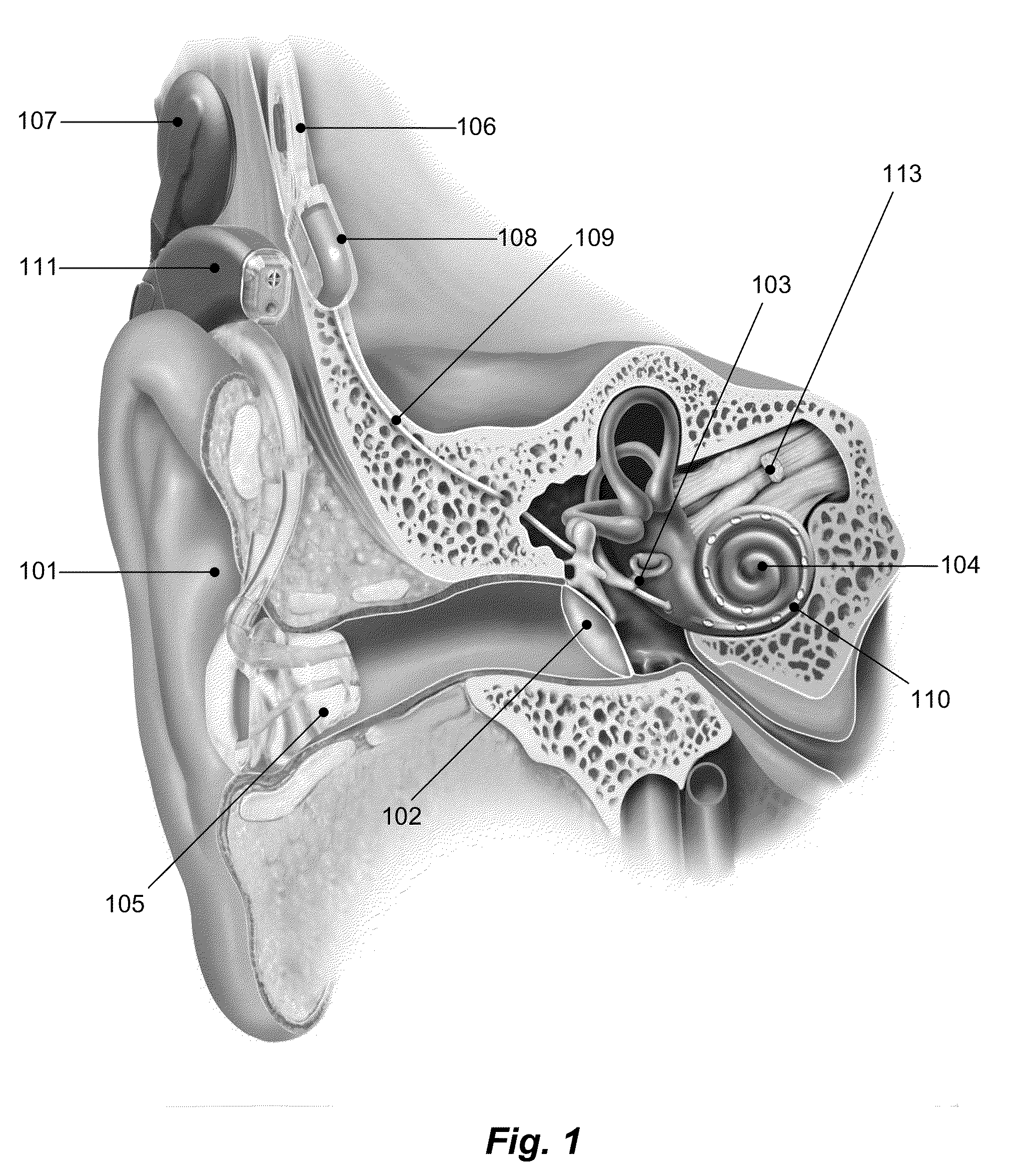
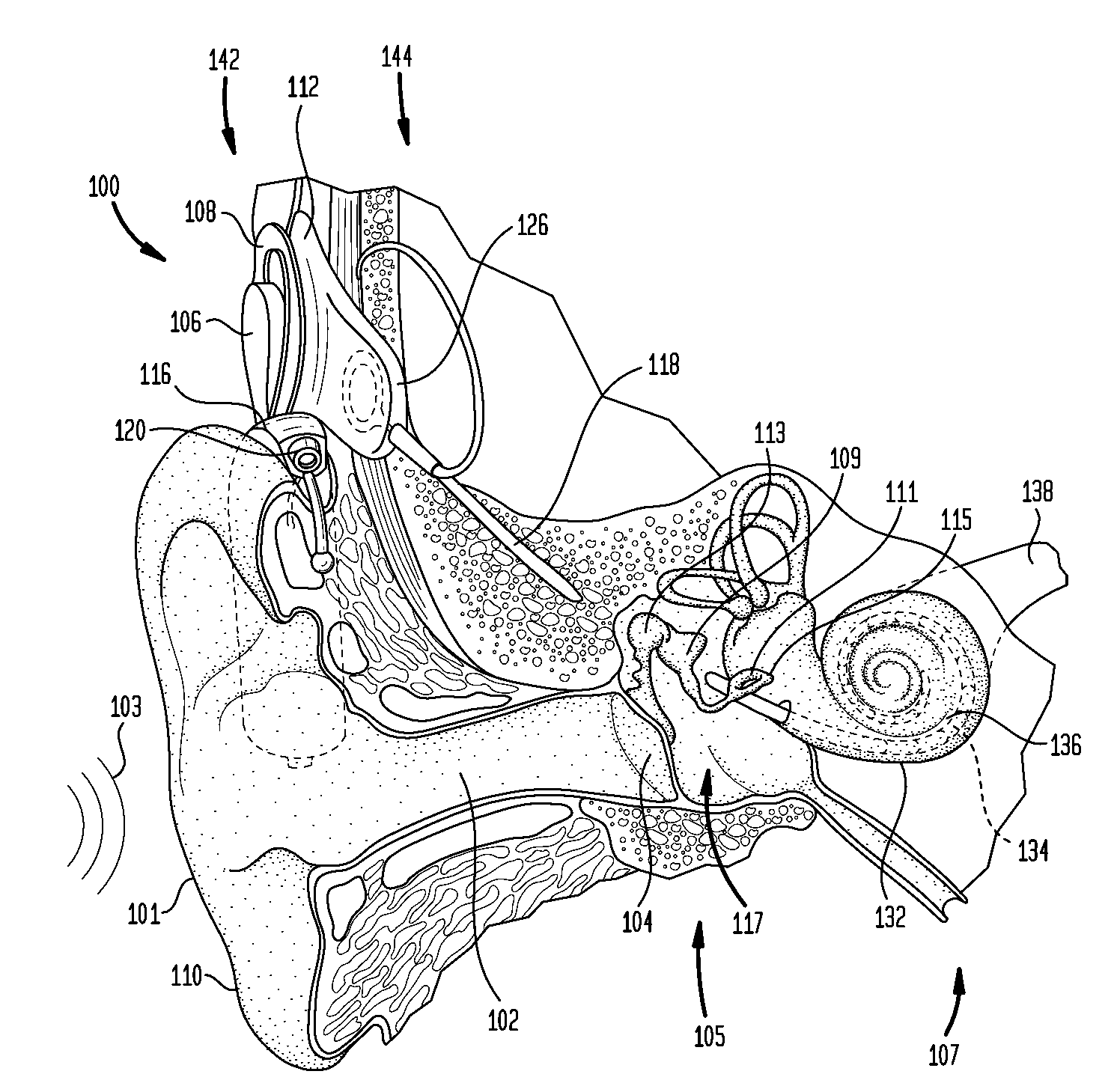
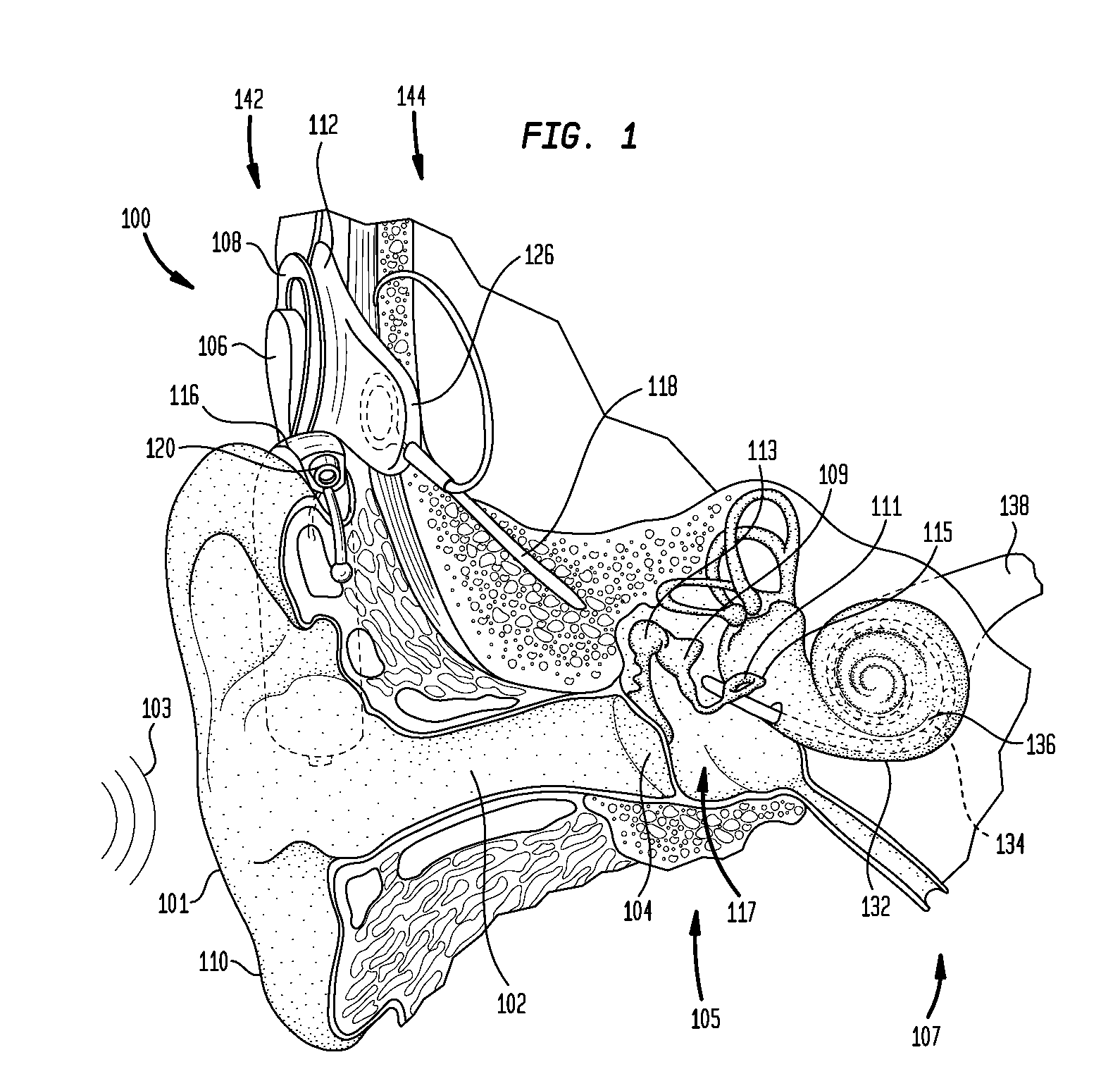
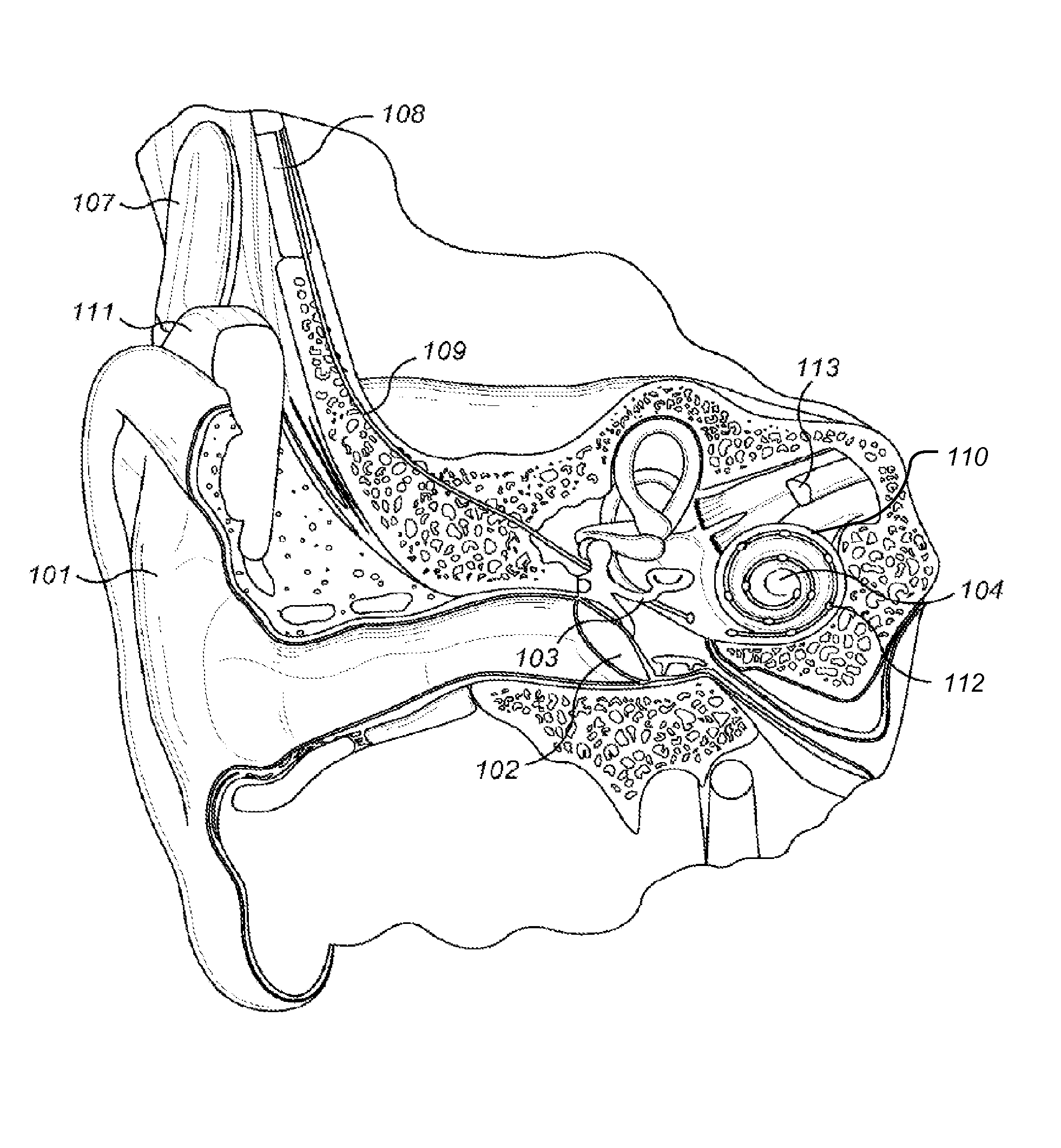
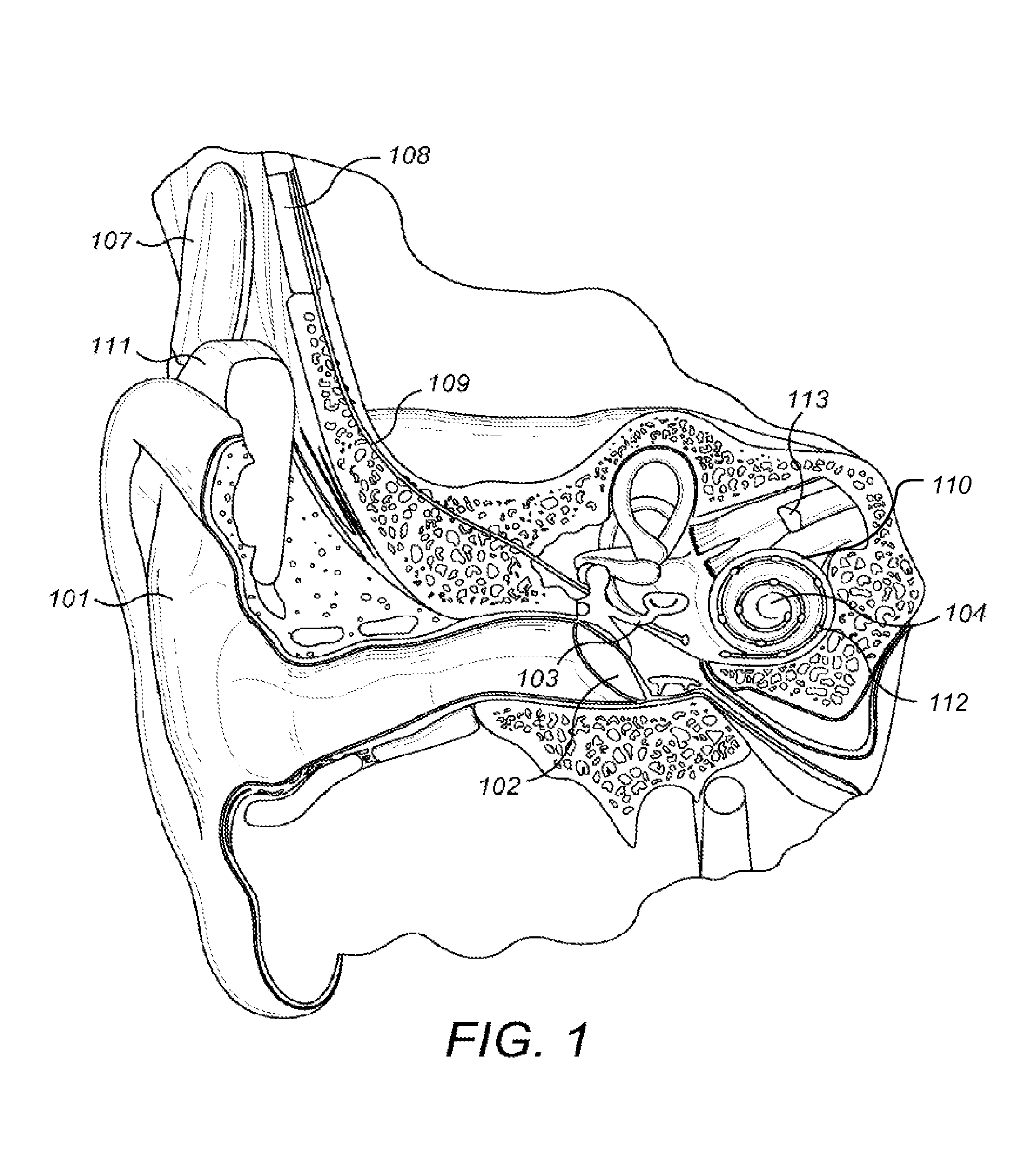
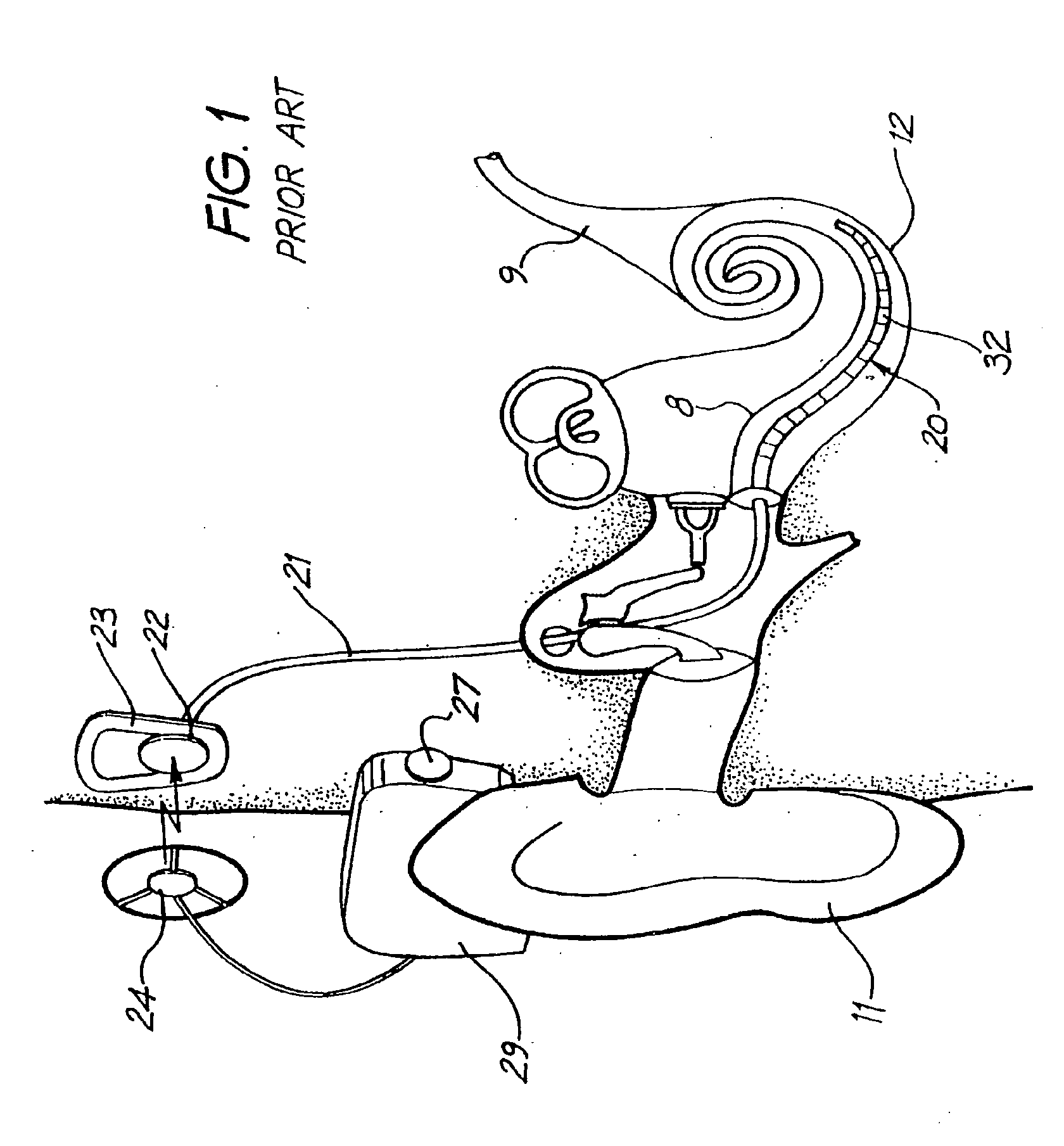
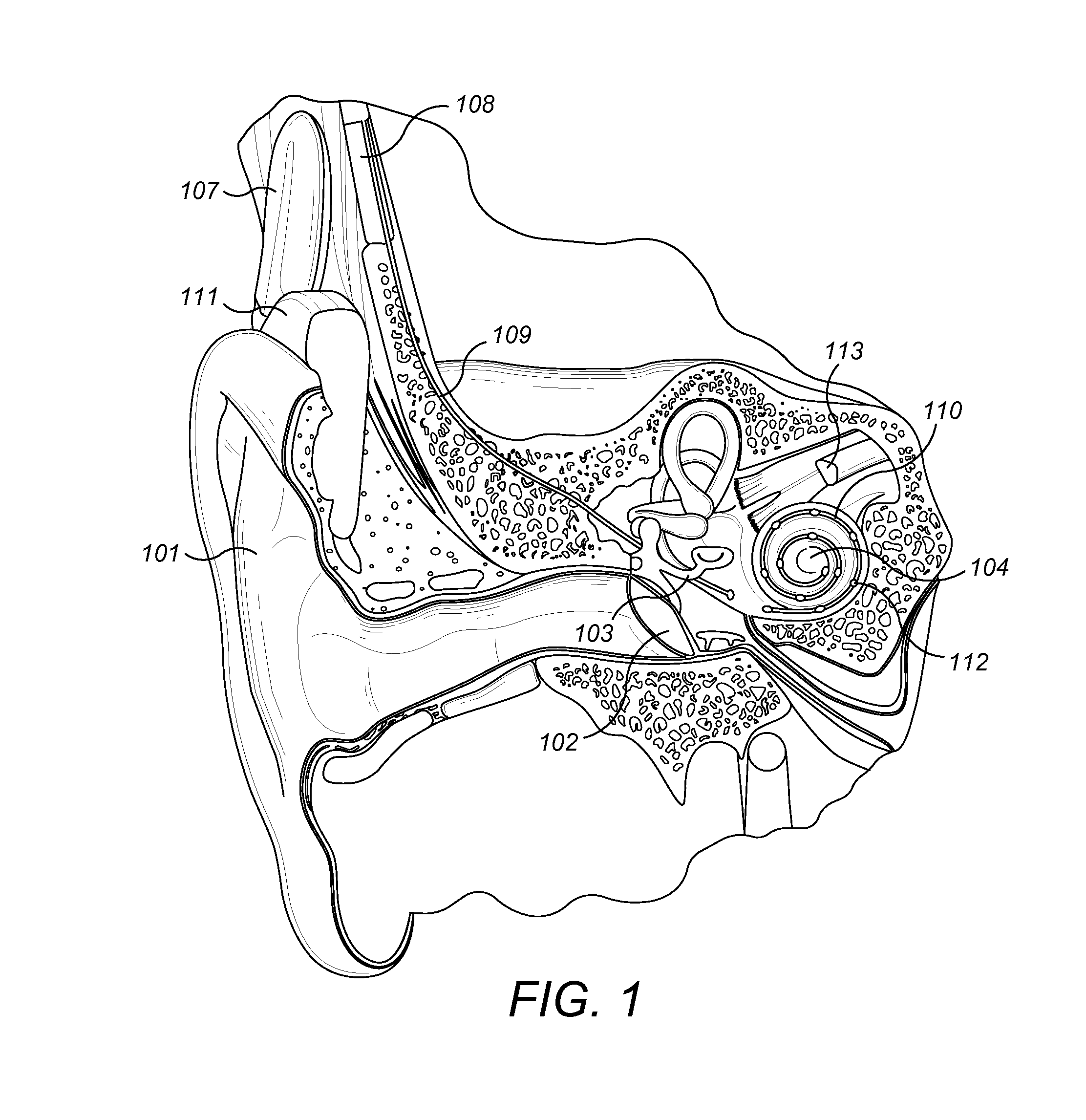
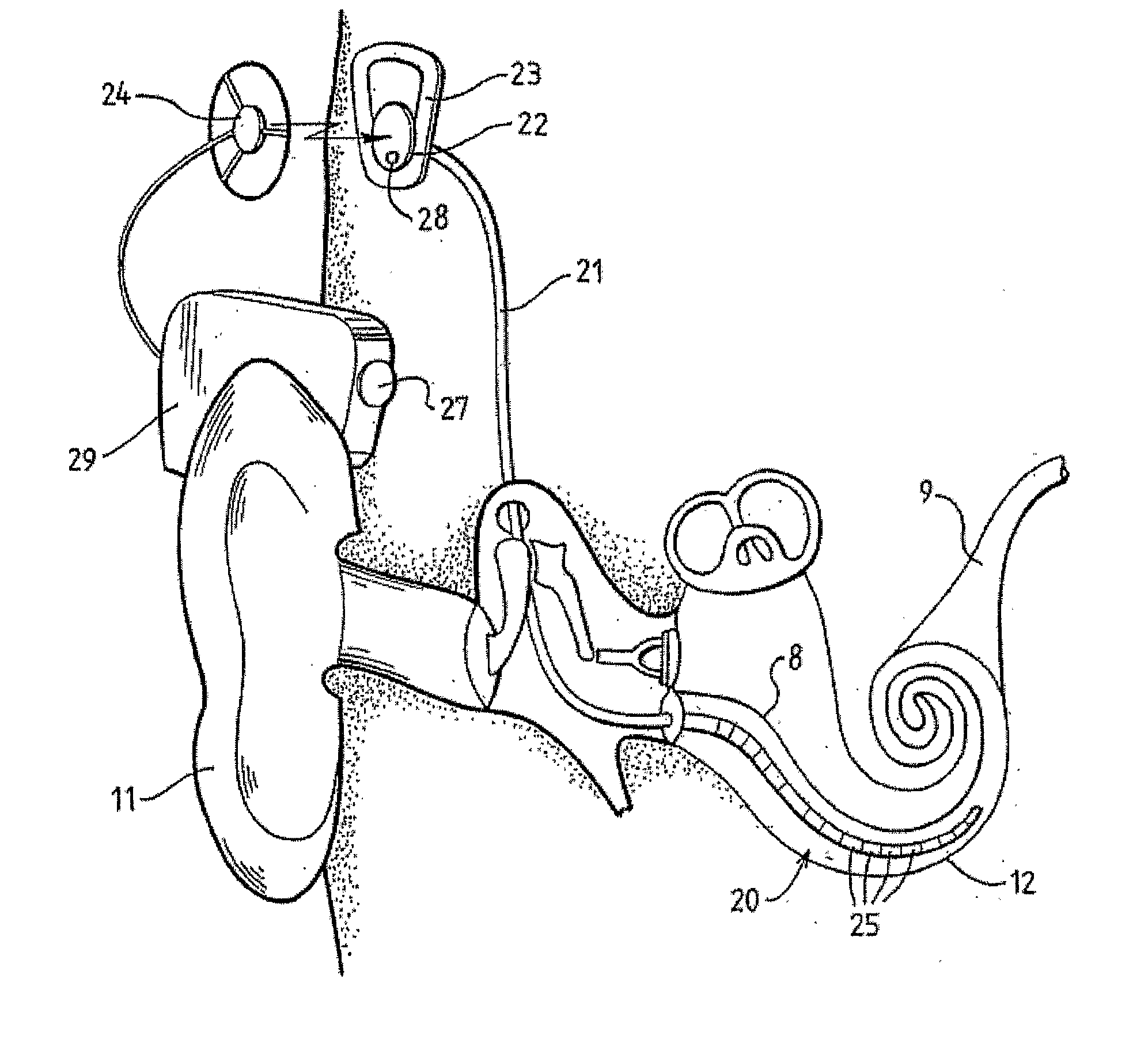
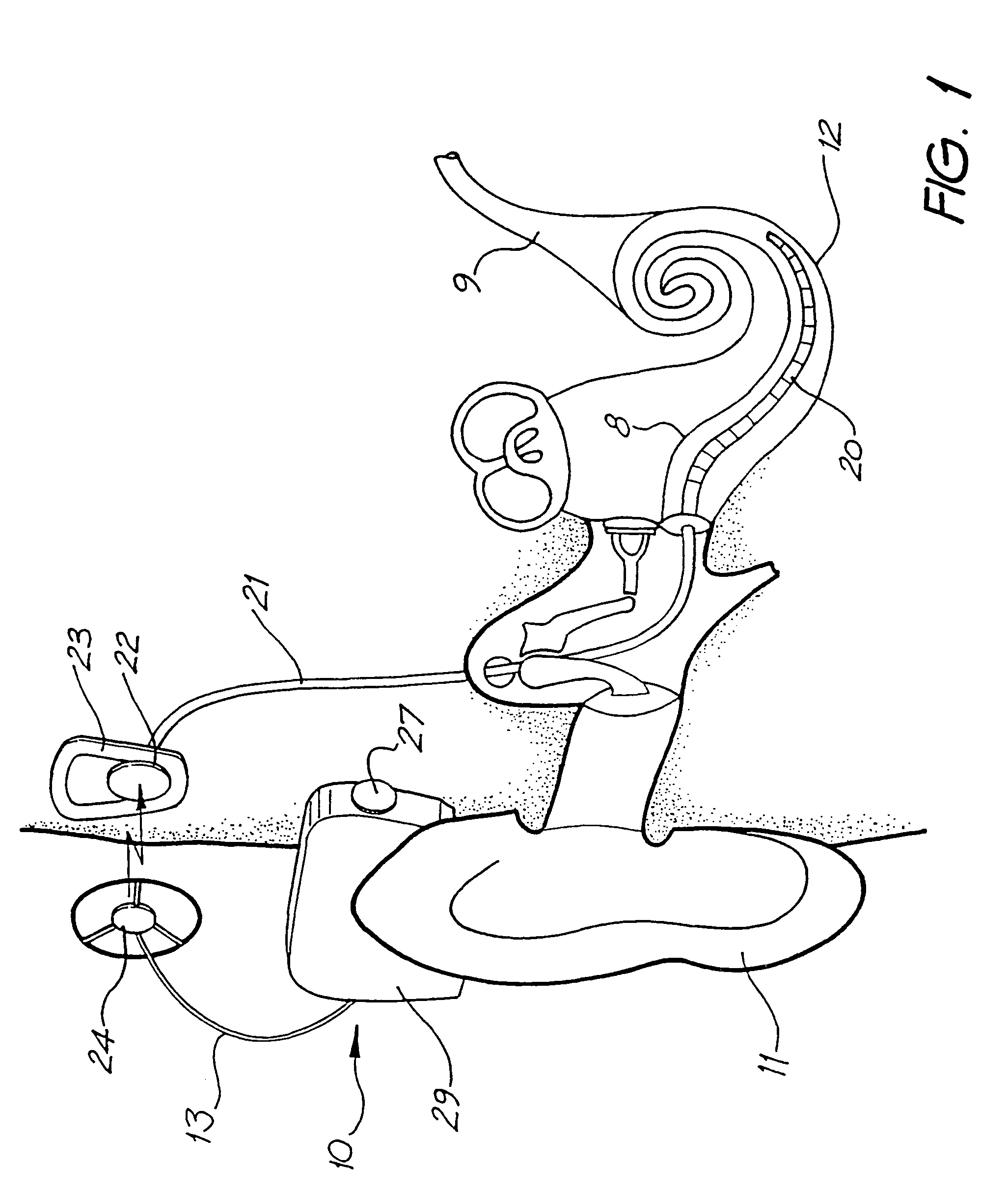
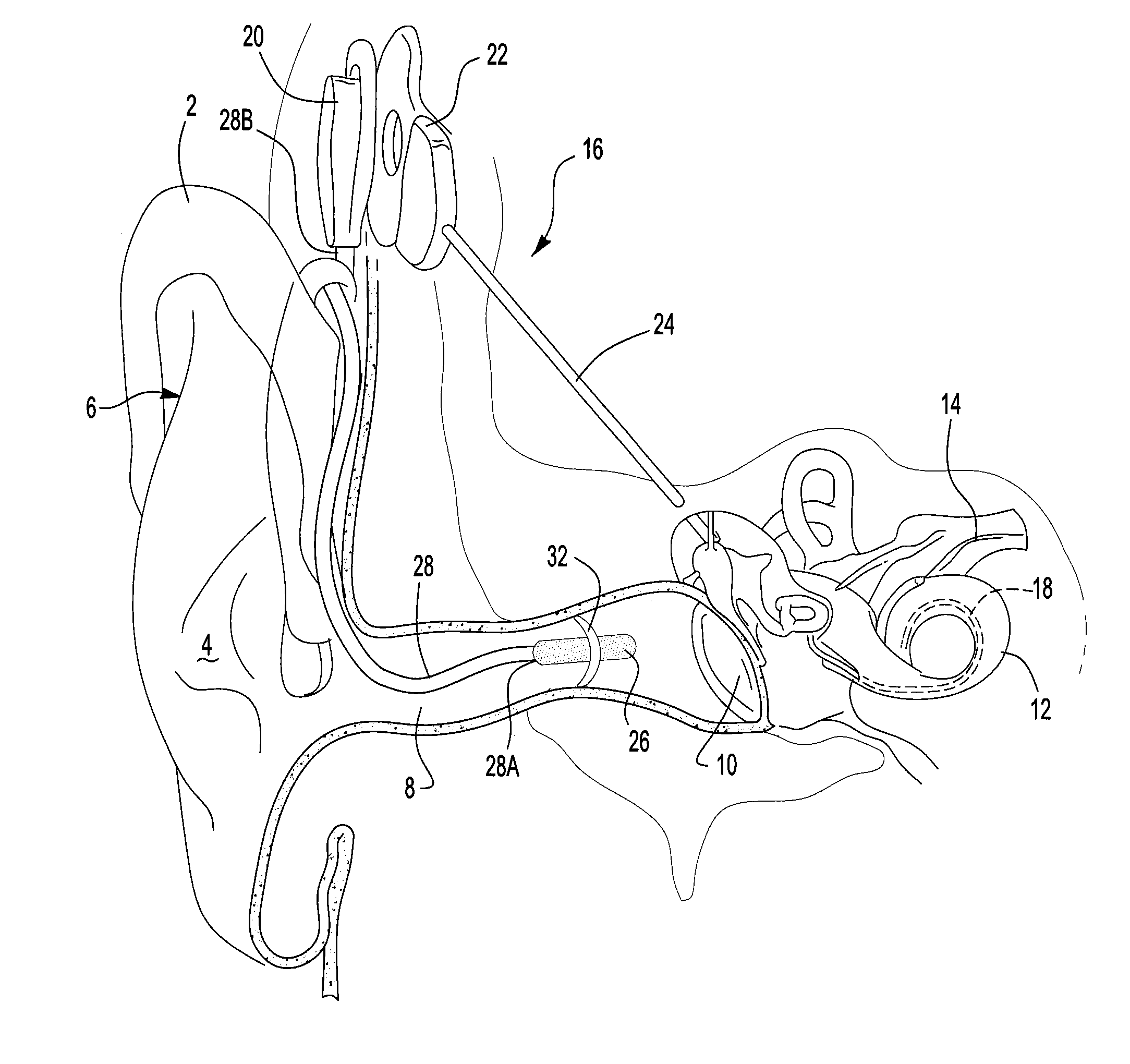
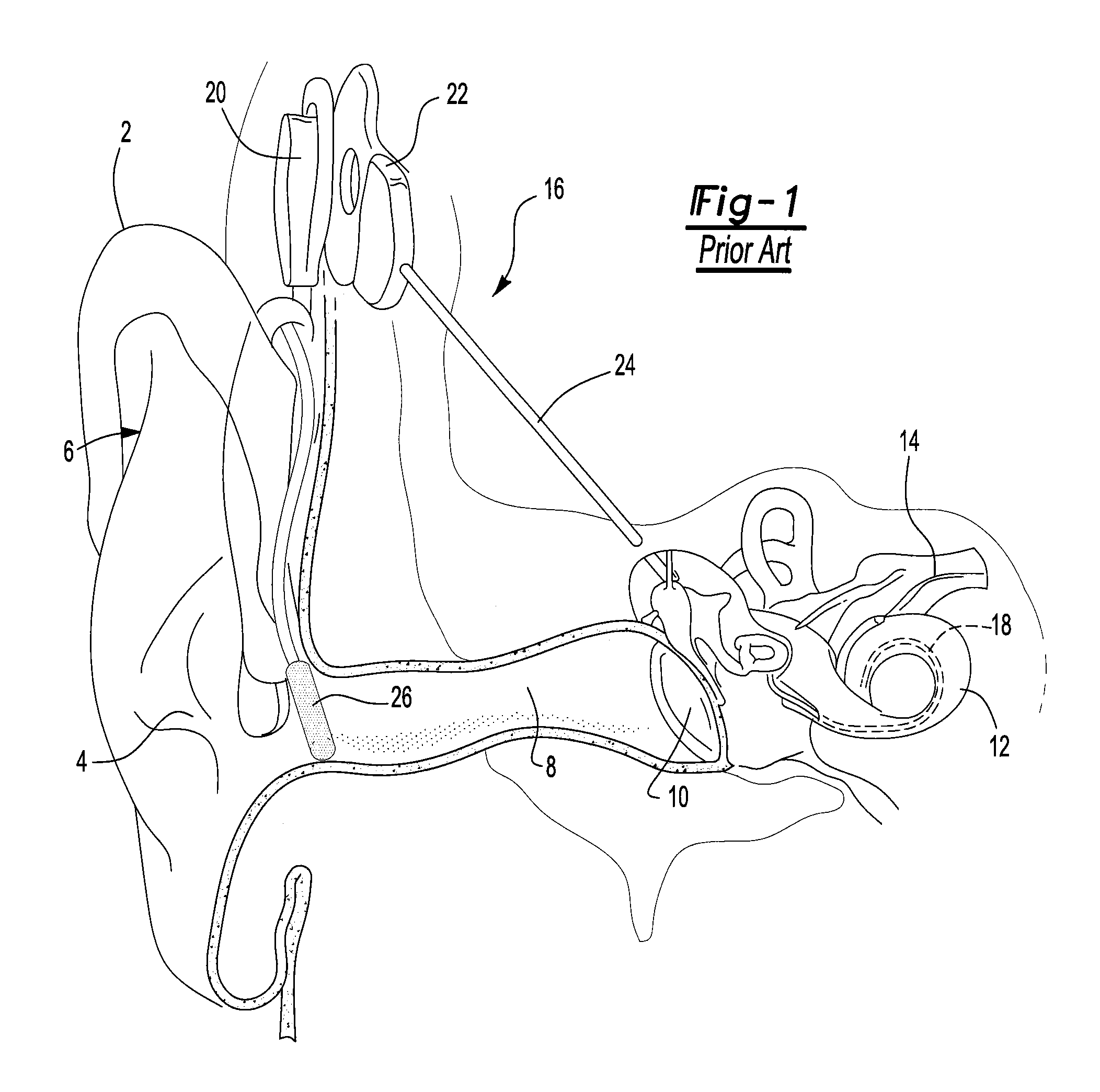
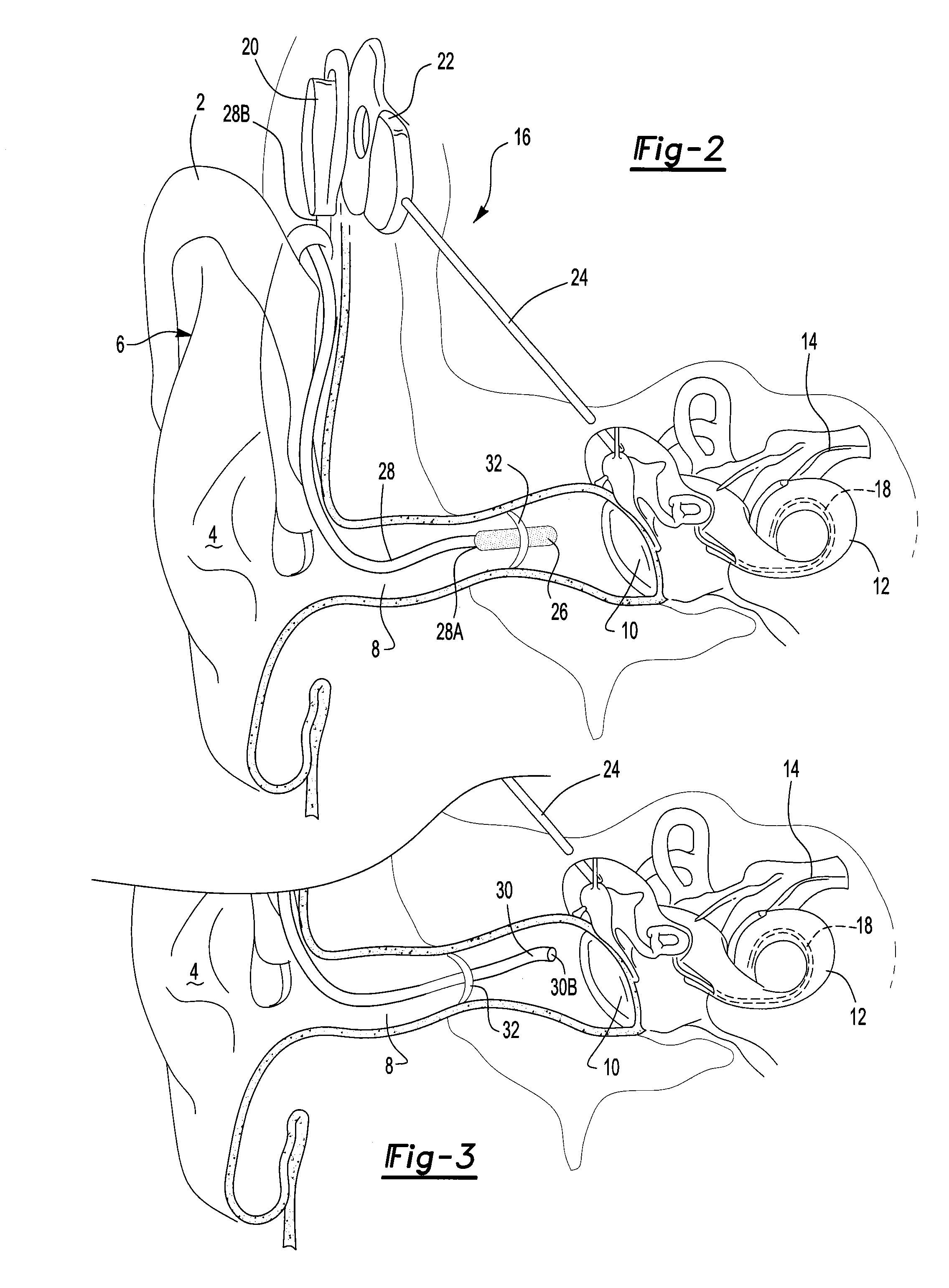
A cochlear implant is an electronic prosthetic device that is surgically placed in the inner ear and under the skin behind the ear for the purpose of providing useful sound perception via electrical stimulation of the auditory nerve.
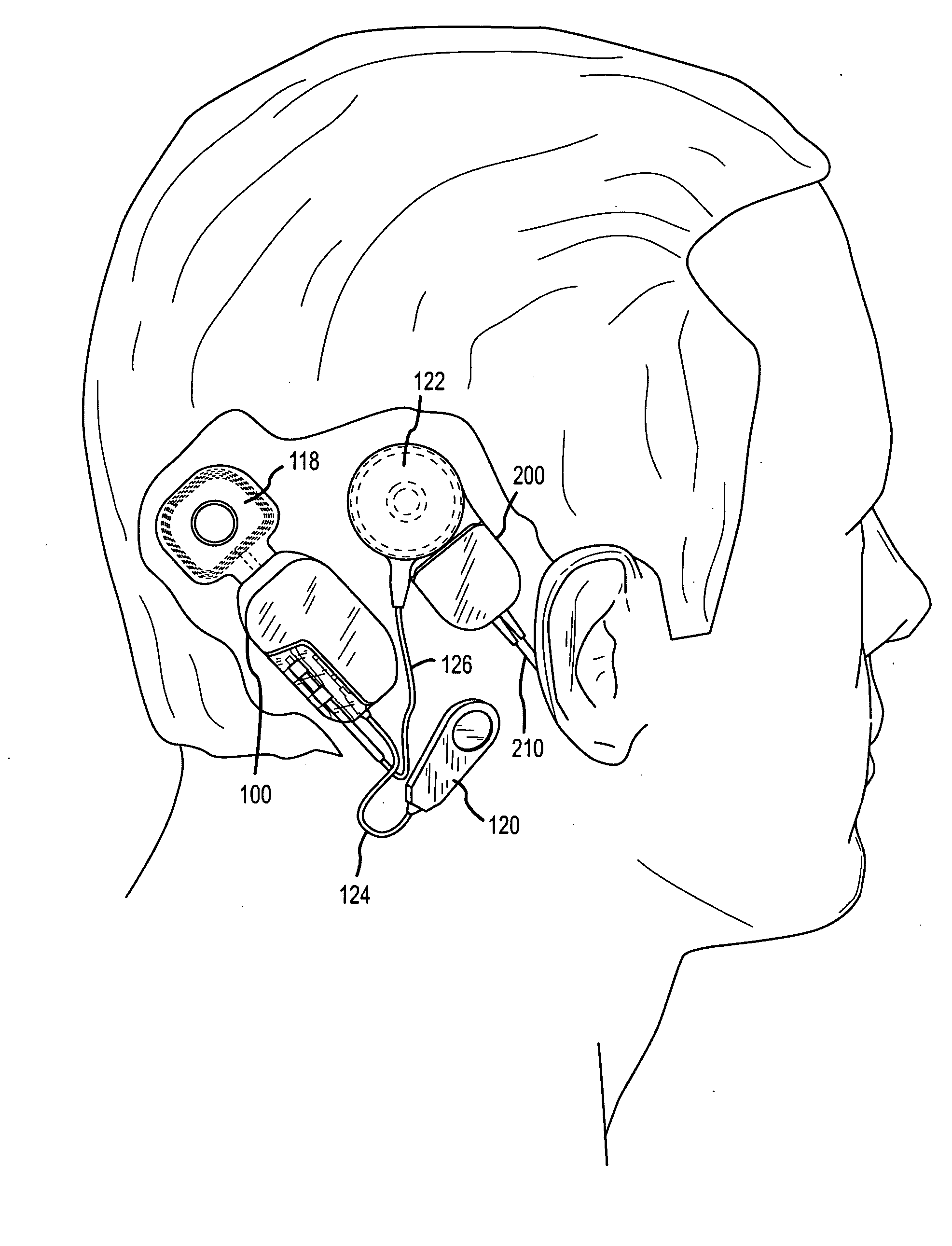
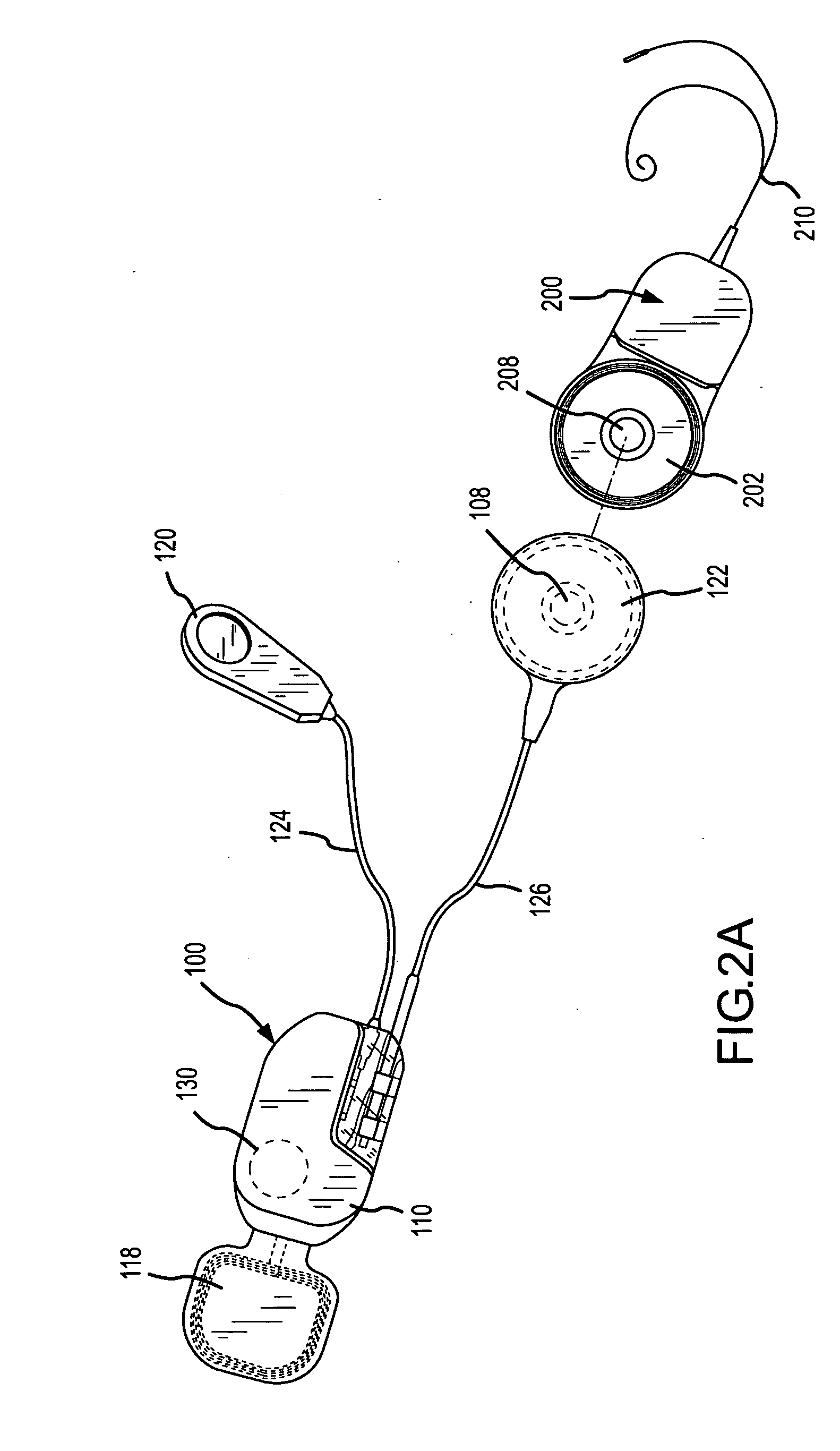
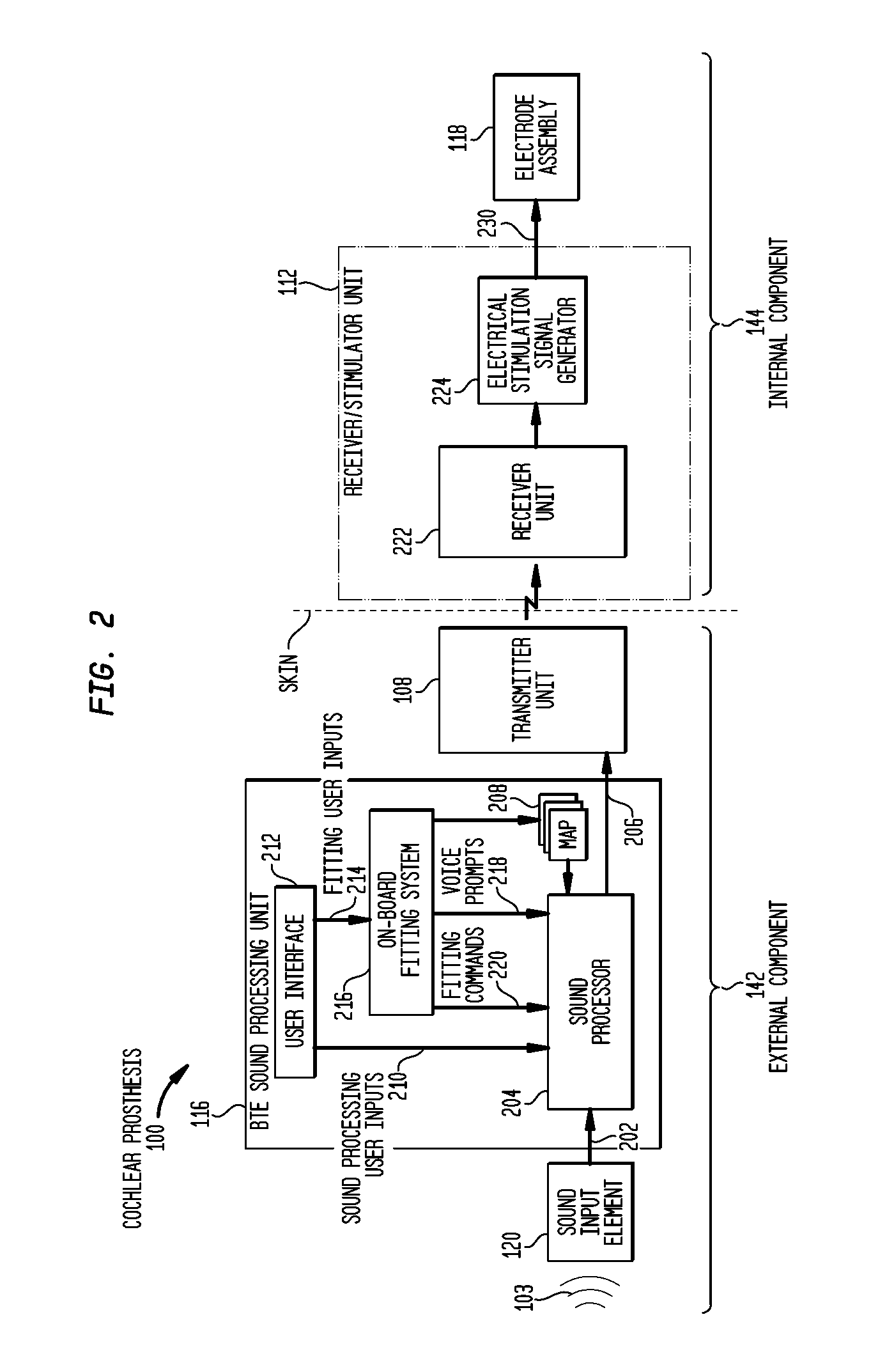
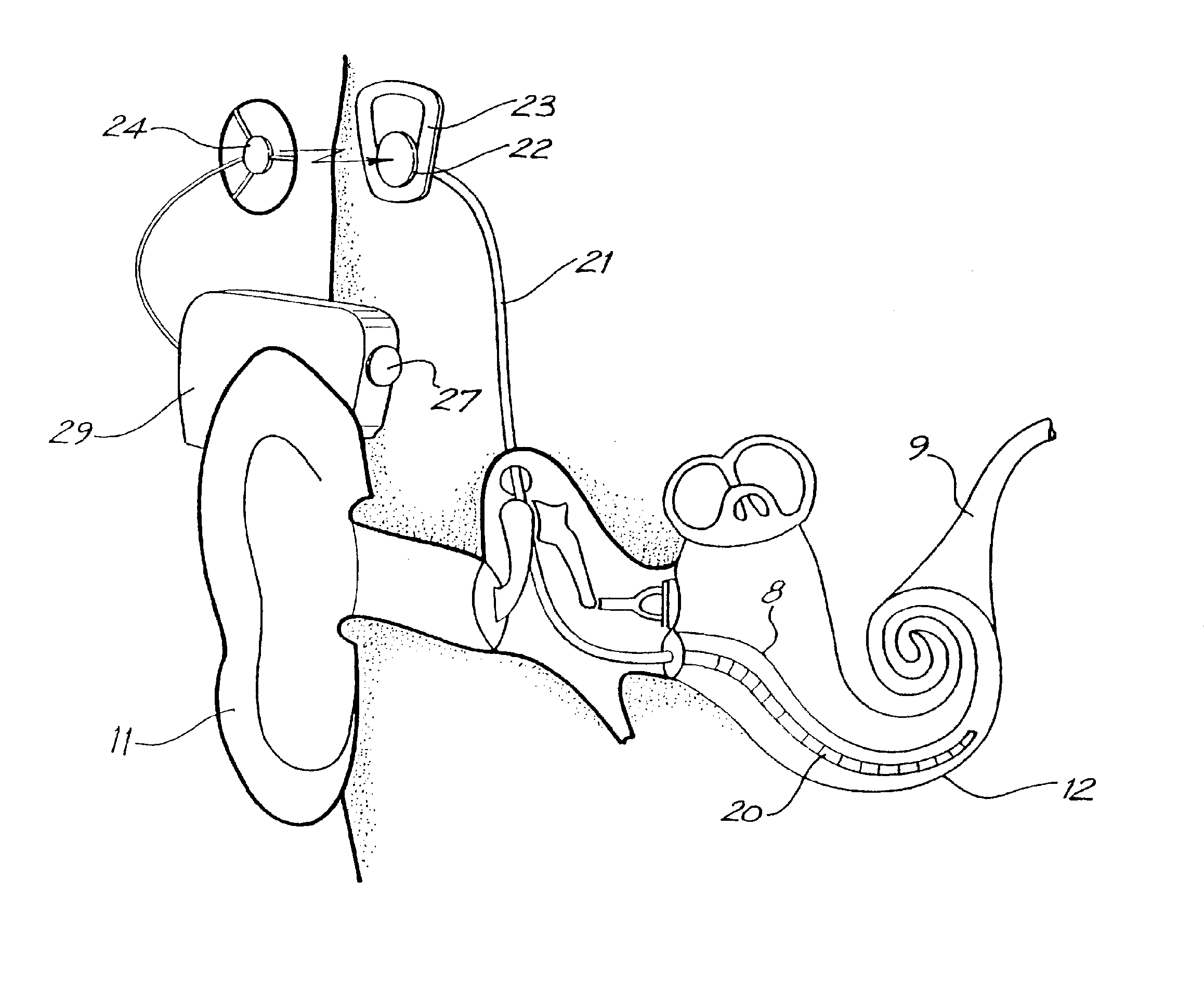
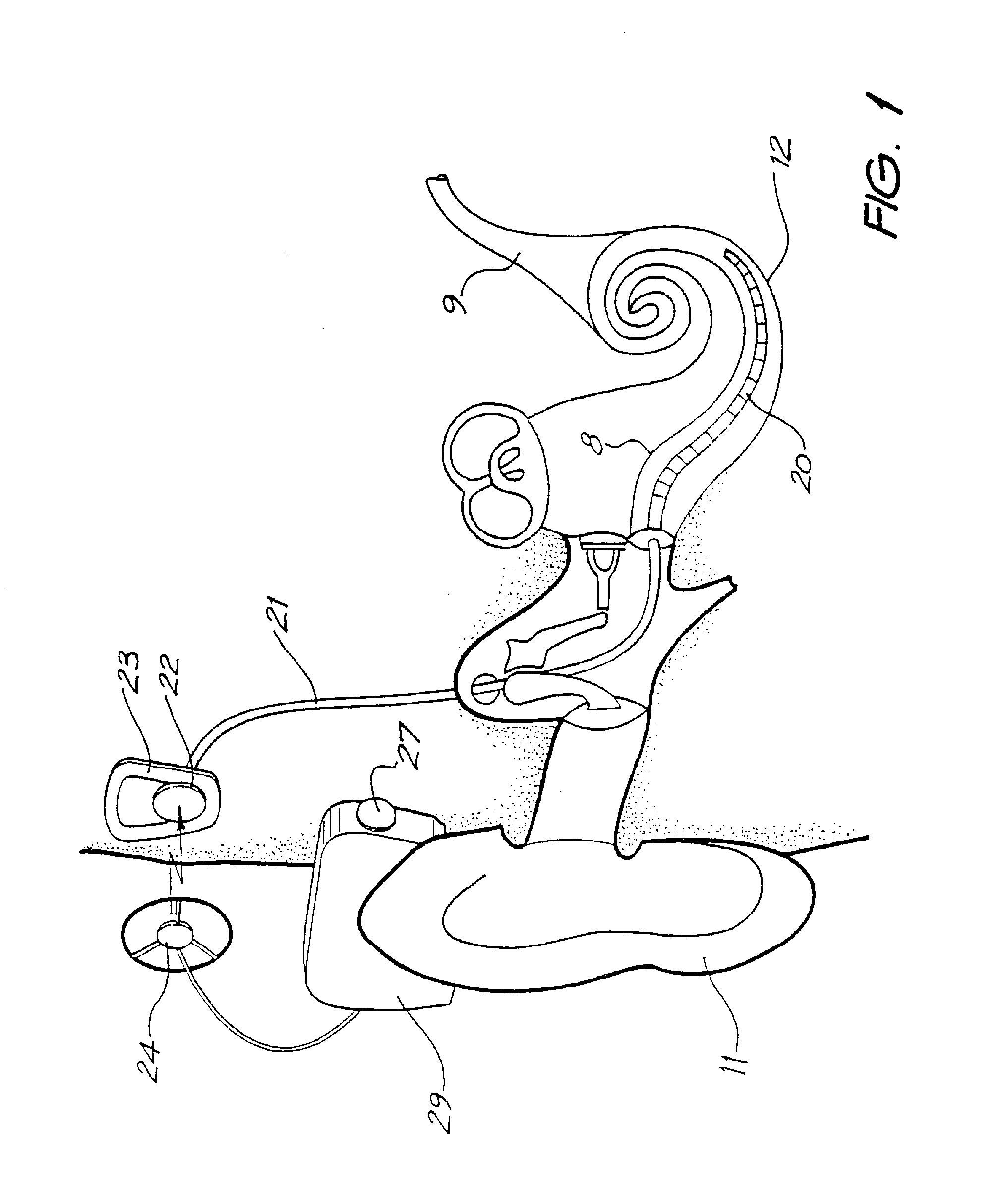
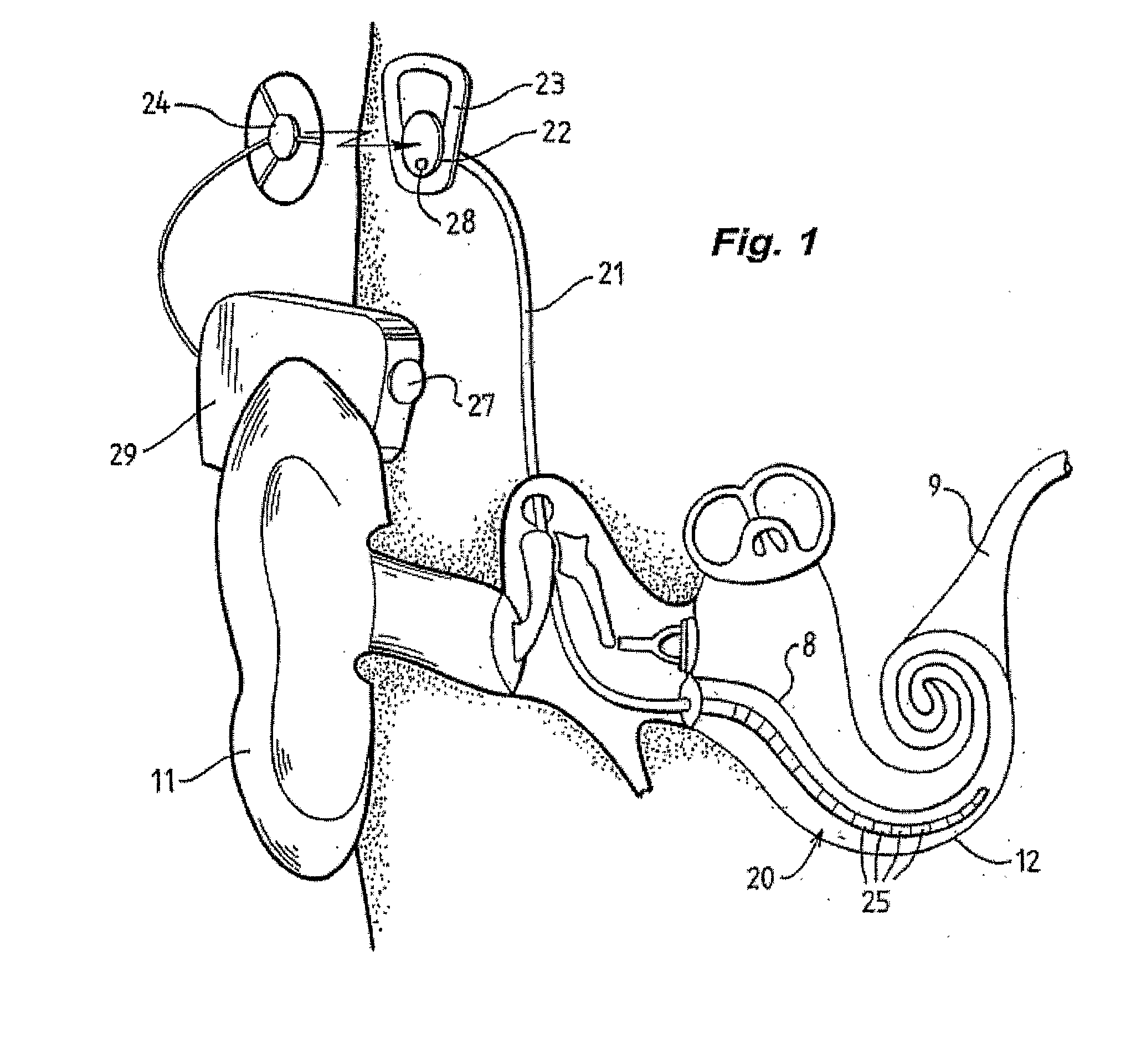
Integrated implantable hearing device, microphone and power unit
InactiveUS20060183965A1Easy accessAvoid difficultyElectrotherapyBehind the ear hearing aidsHearing apparatusElectric power
An implantable hearing unit is provided that includes an implantable microphone, a rechargeable power storage device and a speech signal processor. The hearing unit further includes a signal coupling device that is adapted for electrical interconnection to an implantable auditory stimulation device, which is operative to stimulate an auditory component of a patient. Such a stimulation device may include cochlear implants, brain stem stimulation systems, auditory nerve stimulation systems, and middle or inner ear transducer systems. The signal coupling device is operative to provide processed drive signals from the signal processor to the stimulation device as well provide power from the power storage device to operate the stimulation device. In one arrangement, the signal coupling device is a wireless coupling between first and second coils. In such an arrangement, the hearing unit may be utilized with an existing implanted stimulation device to make that device a fully implanted hearing system.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Surgically implantable hearing aid
InactiveUS20060025648A1Negligible riskAttached with easeEar treatmentDeaf-aid setsDura materAcoustic wave
The invention comprises a surgically implantable hearing aid for hearing impaired persons. The hearing aid includes a vibrational element which is vibrated by sound waves and attached to the skull of the person, and a connector which crosses the mastoid cavity and delivers the sound waves to the dura mater of the human being thereby vibrating the dura mater, the cerebrospinal fluids, and the brain to create a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to act as a tinnitus masker or used in conjunction with a cochlear implant. It can also be used in a modified form to connect directly through the skull of the human being.
Owner:ALAN J LUPIN
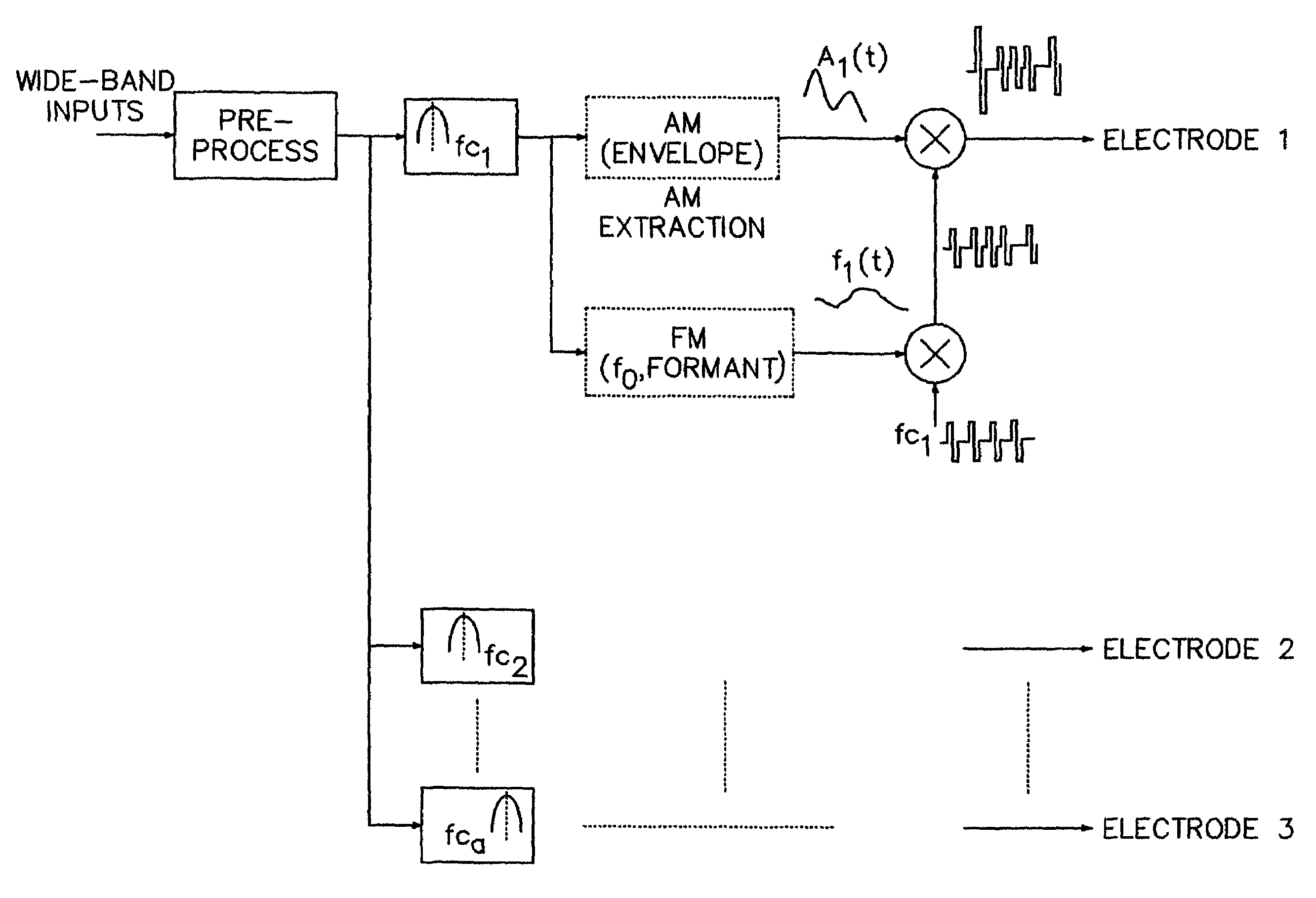
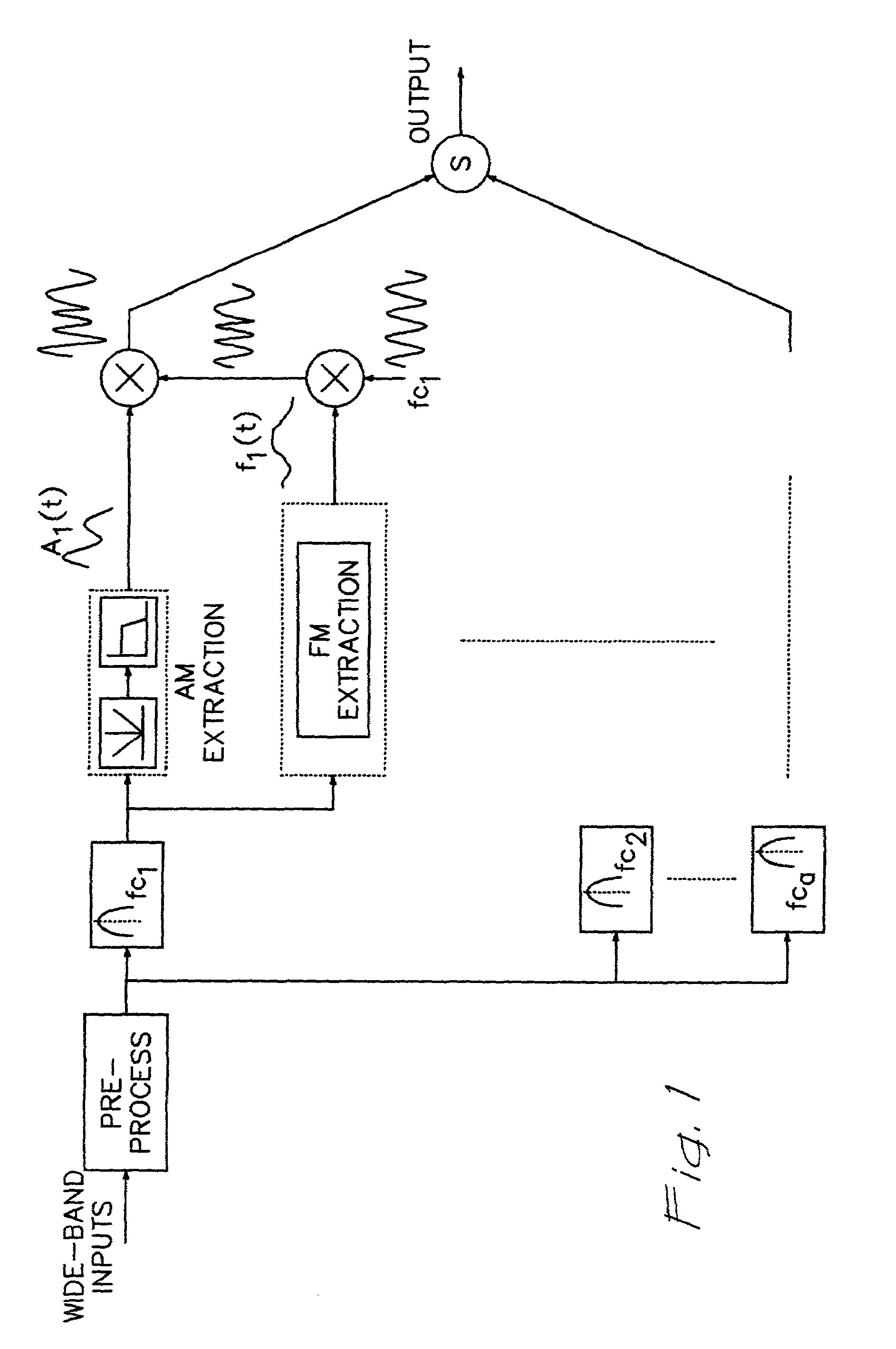
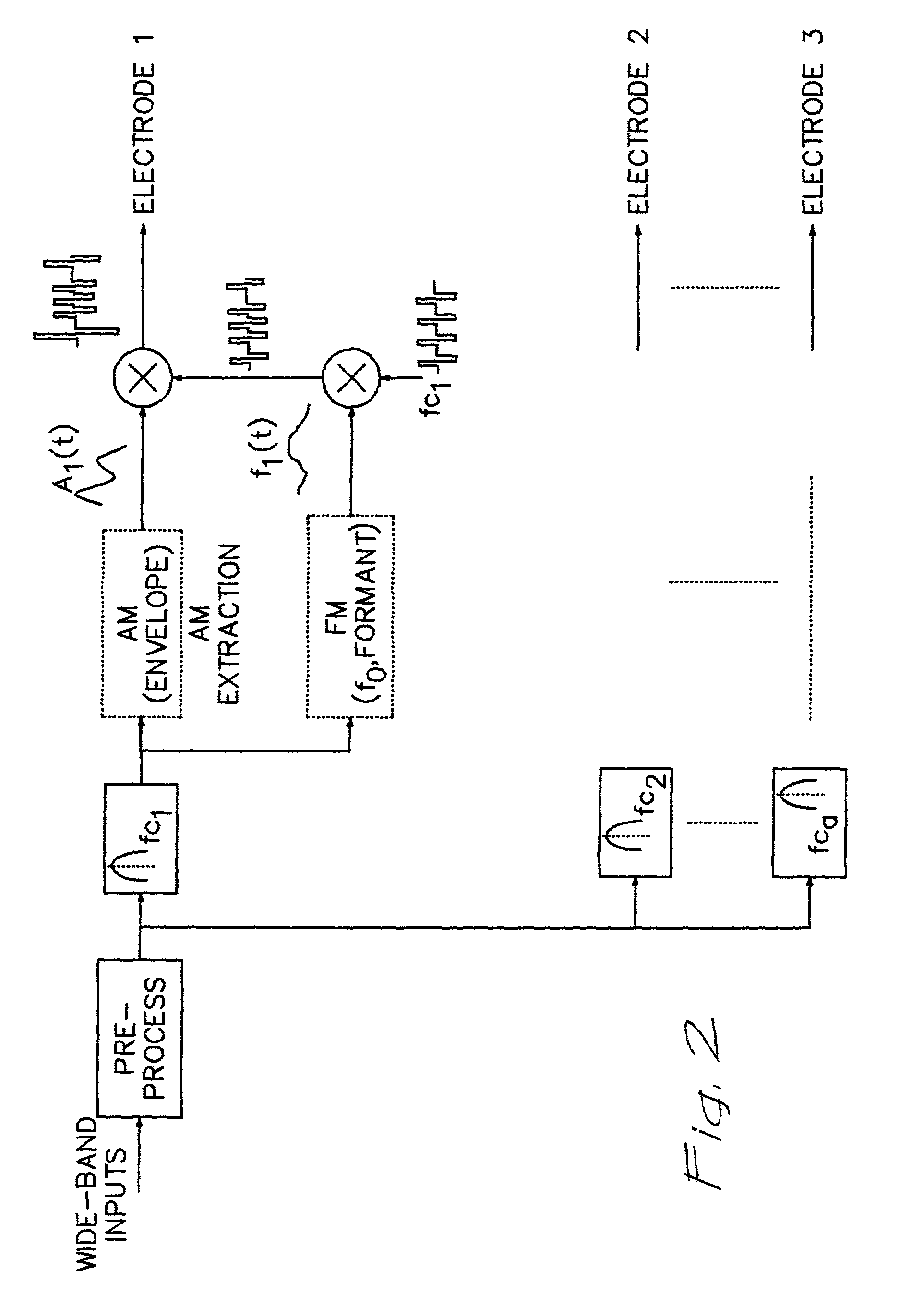
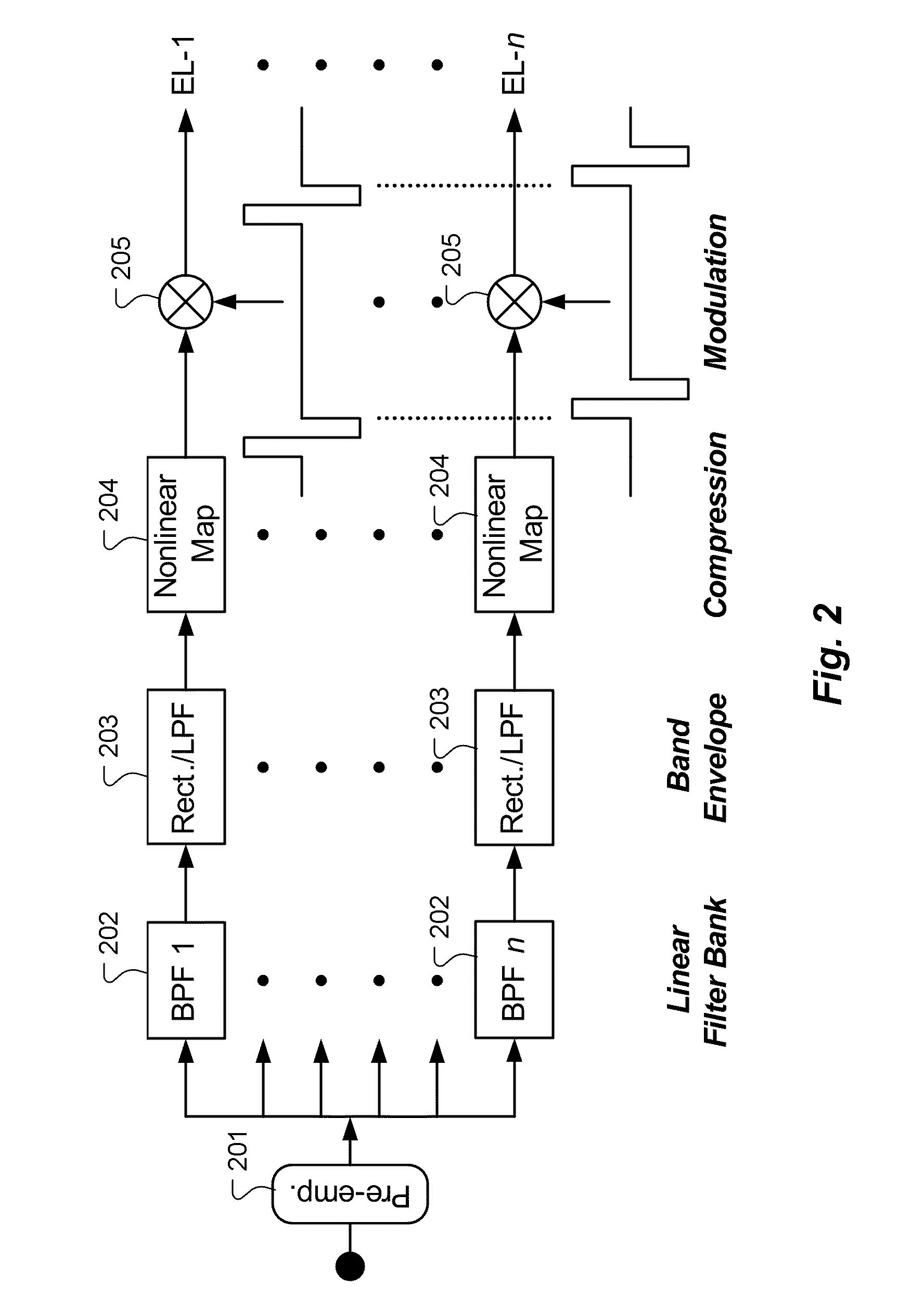
Cochlear implants and apparatus/methods for improving audio signals by use of frequency-amplitude-modulation-encoding (FAME) strategies
ActiveUS7225027B2Quality improvementFacilitate cognitionElectrotherapyBroadcast circuit arrangementsArtificial cochlea implantSound quality
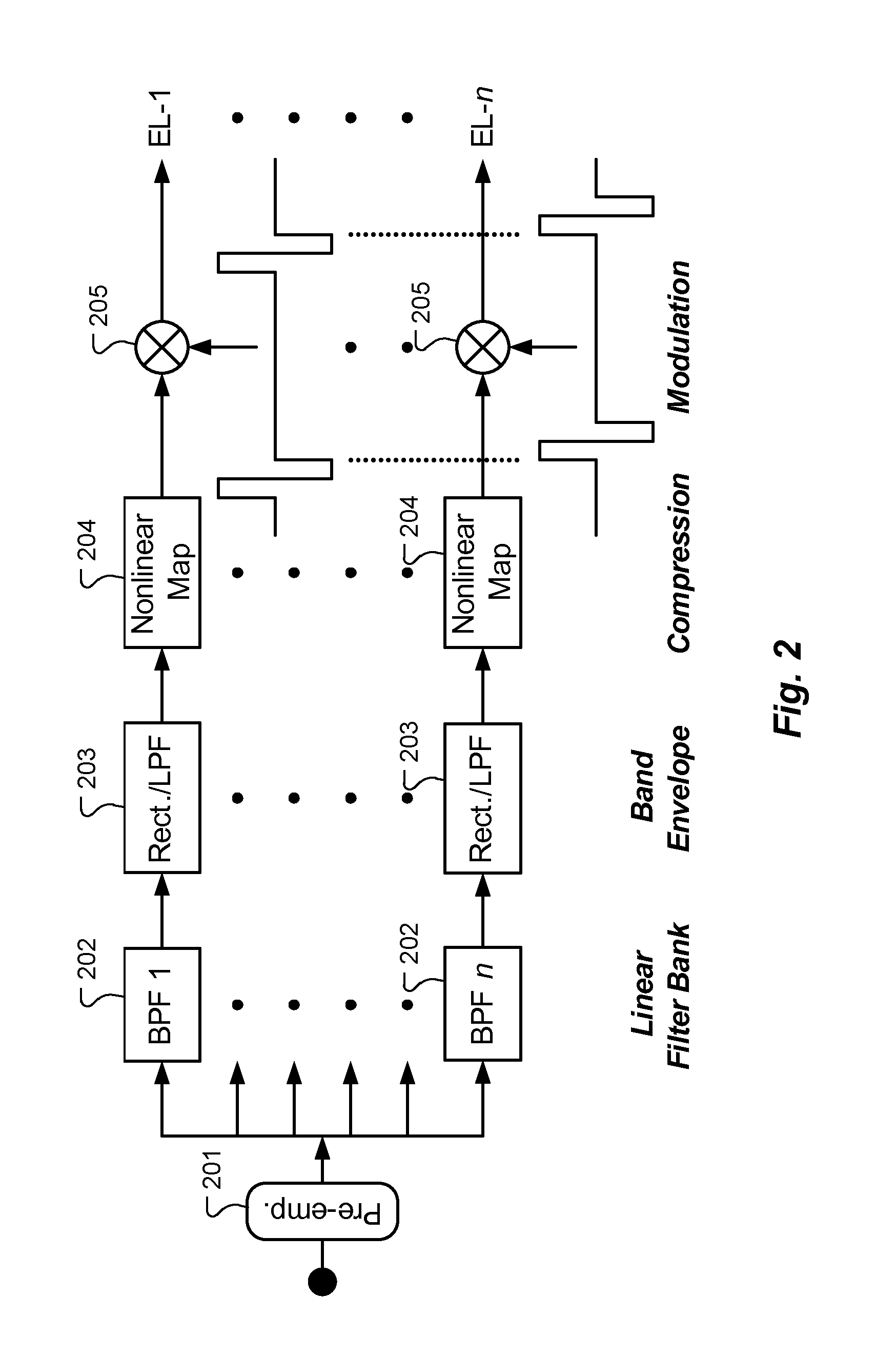
A method of improving sound quality of audio signals that are digitally processed includes steps of extracting amplitude and frequency modulations from one or more narrow bands of the audio signal, and filtering and compressing those modulations to produce amplitude and frequency modulated audio signals that are digitally processed to provide an acoustic signal similar to the original audio signal. The methods may be used in auditory prostheses and telecommunication systems.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hearing implant with MEMS inertial sensor and method of use
An implant device for treating hearing disorders. In one exemplary embodiment, an implant body is dimensioned for attachment to the ossicular chain of a patient. The implant body carries a micro-encapsulated MEMS inertial sensing device that is electrically coupled by a micro-cable to an implantable signal processing system. The MEMS inertial sensor is capable of directly sensing acoustic waves transmitted through the ossicular chain. Signals from the inertial sensor are sent to the signal processing system for filtering, conditioning and amplification to thereafter be carried to a plurality of electrodes carried by a cochlear implant.
Owner:ROBERSON JOSEPH
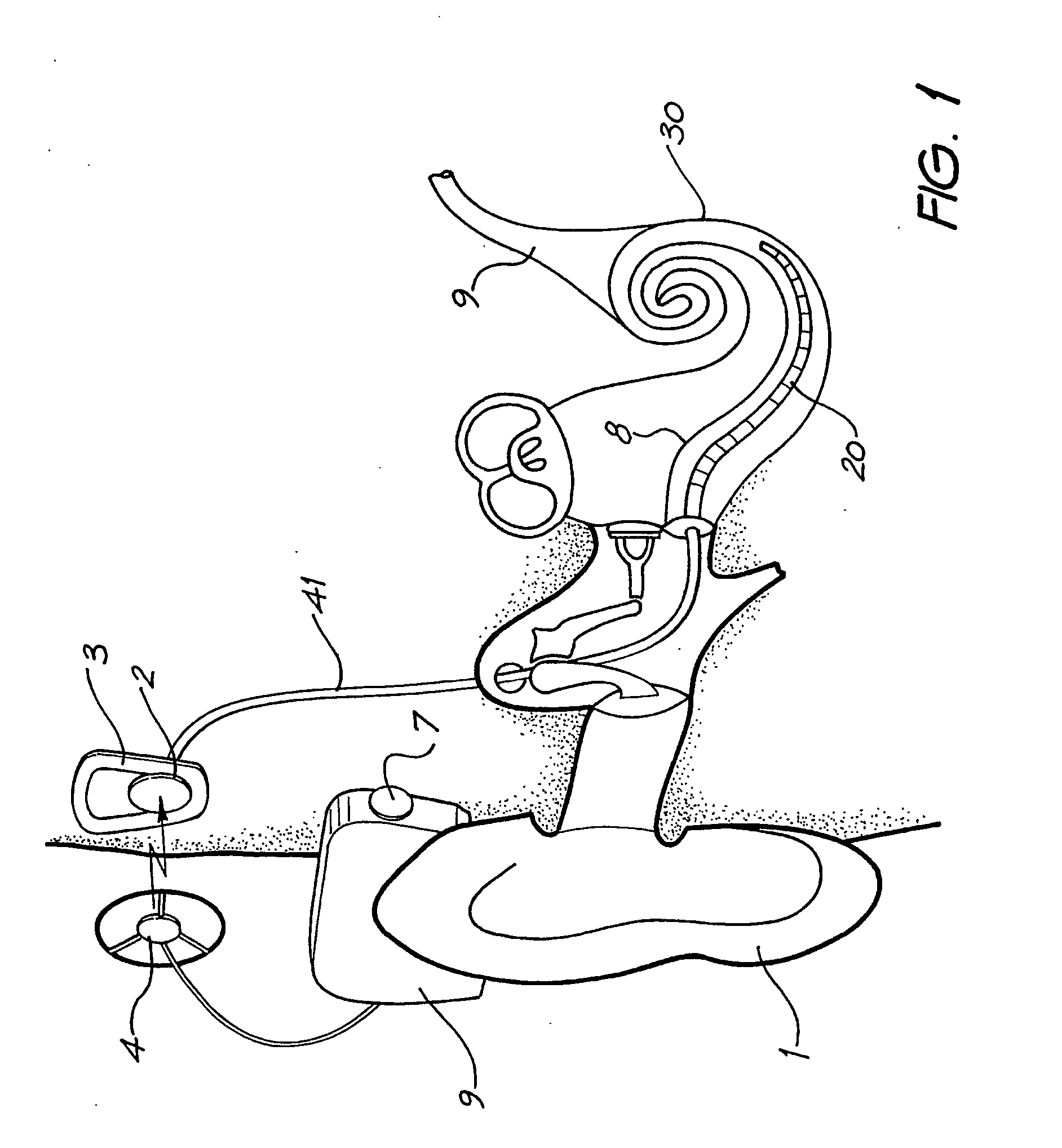
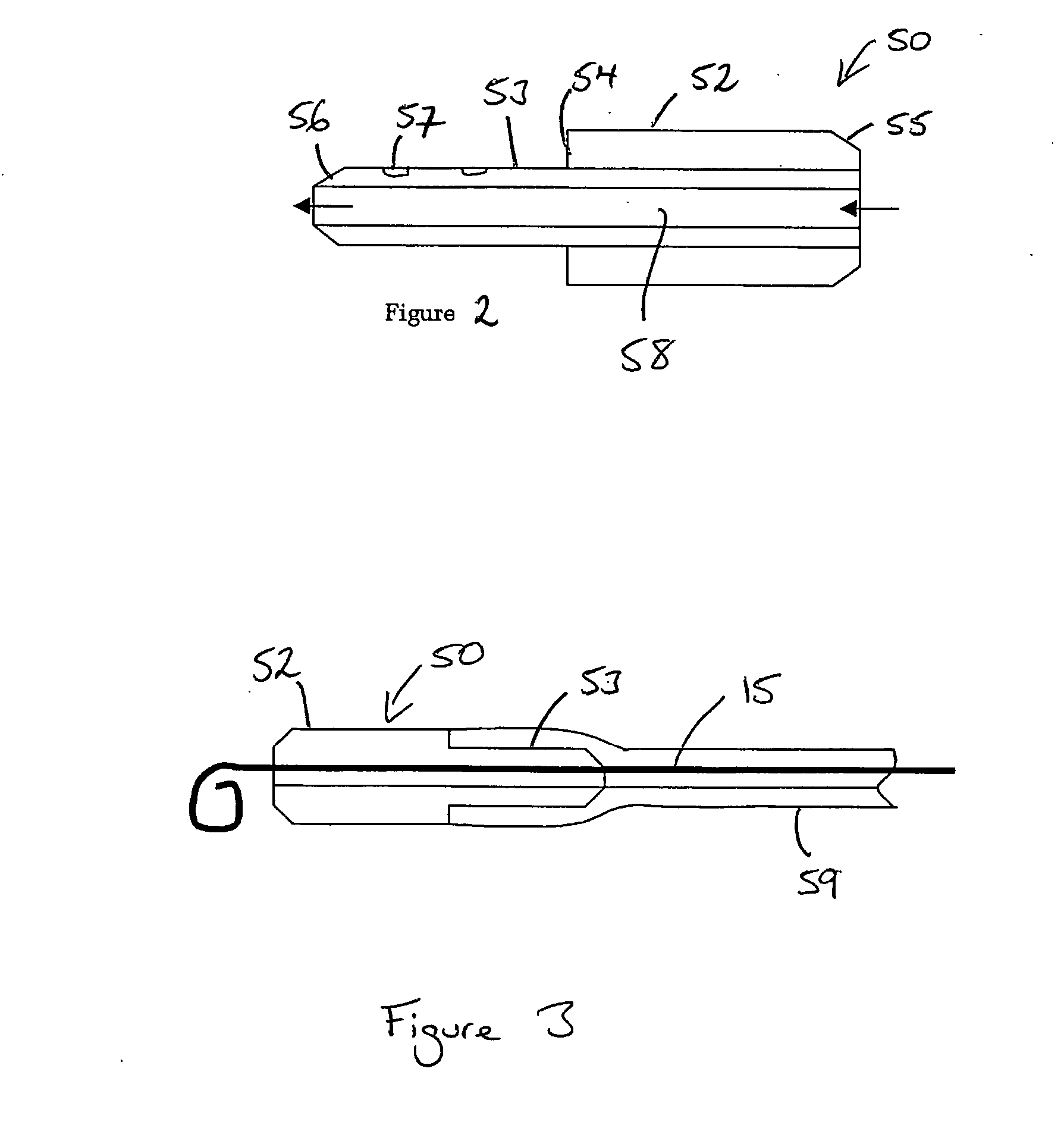
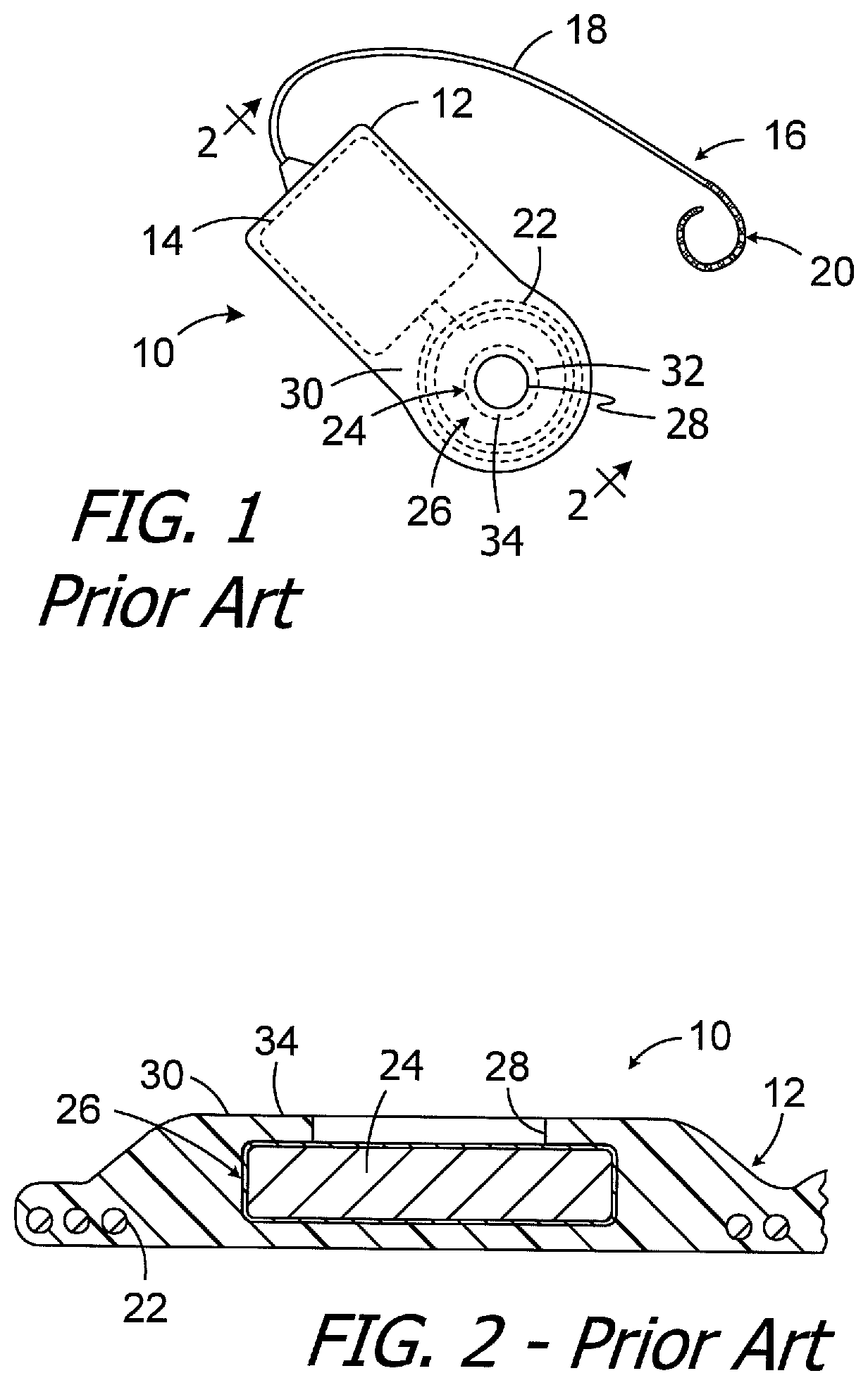
Connector for drug delivery system in cochlear implant
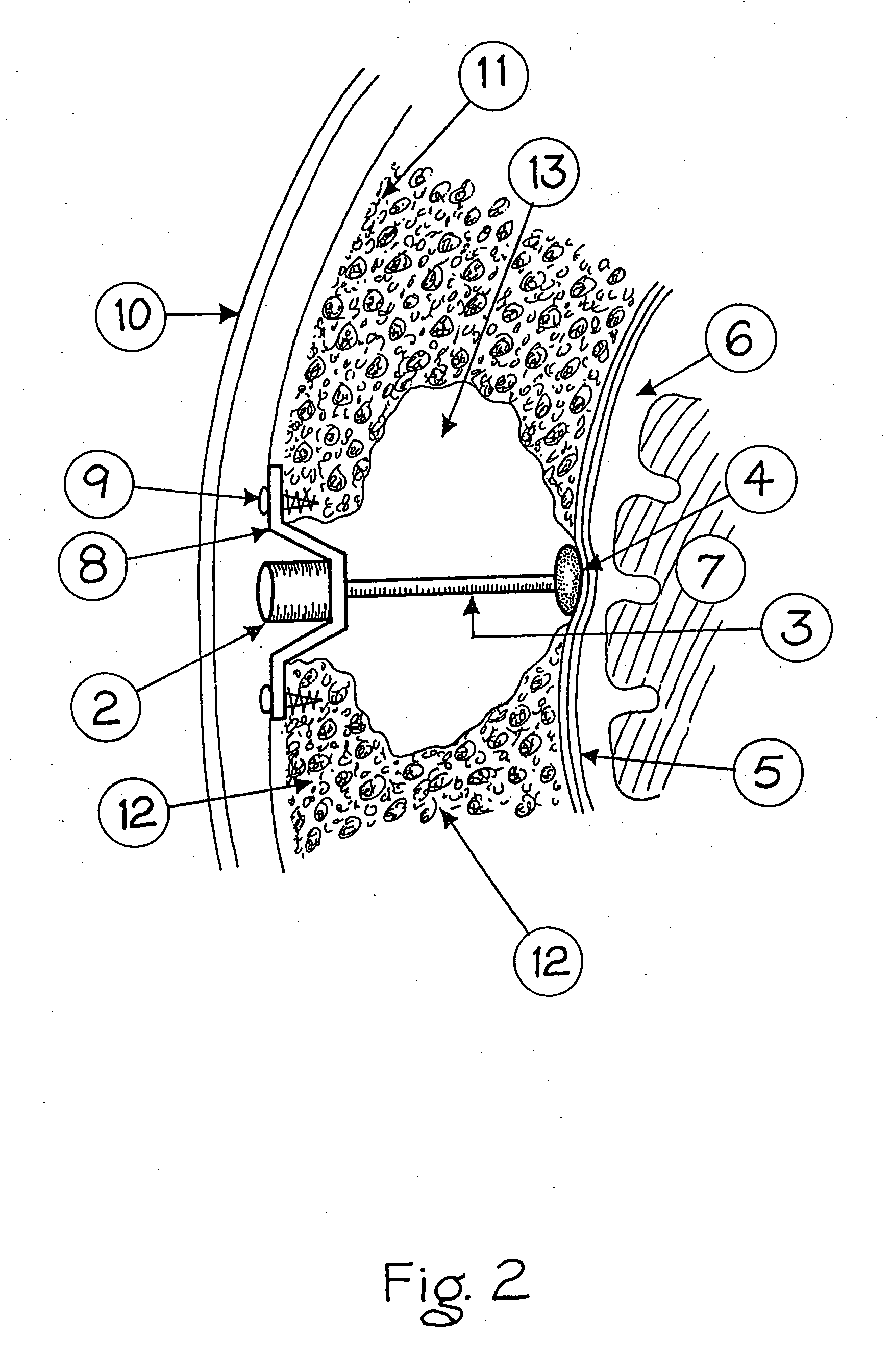
A cochlear implant electrode assembly device comprising an elongate electrode carrier member (10) that has a chamber or lumen (14) for receiving a bioactive fluid that is delivered therein, and a fluid transfer connector (50) that is in fluid communication with the chamber (14) and through which a bioactive fluid can move from a location external the carrier member, such as a reservoir (23), to the chamber (14).
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
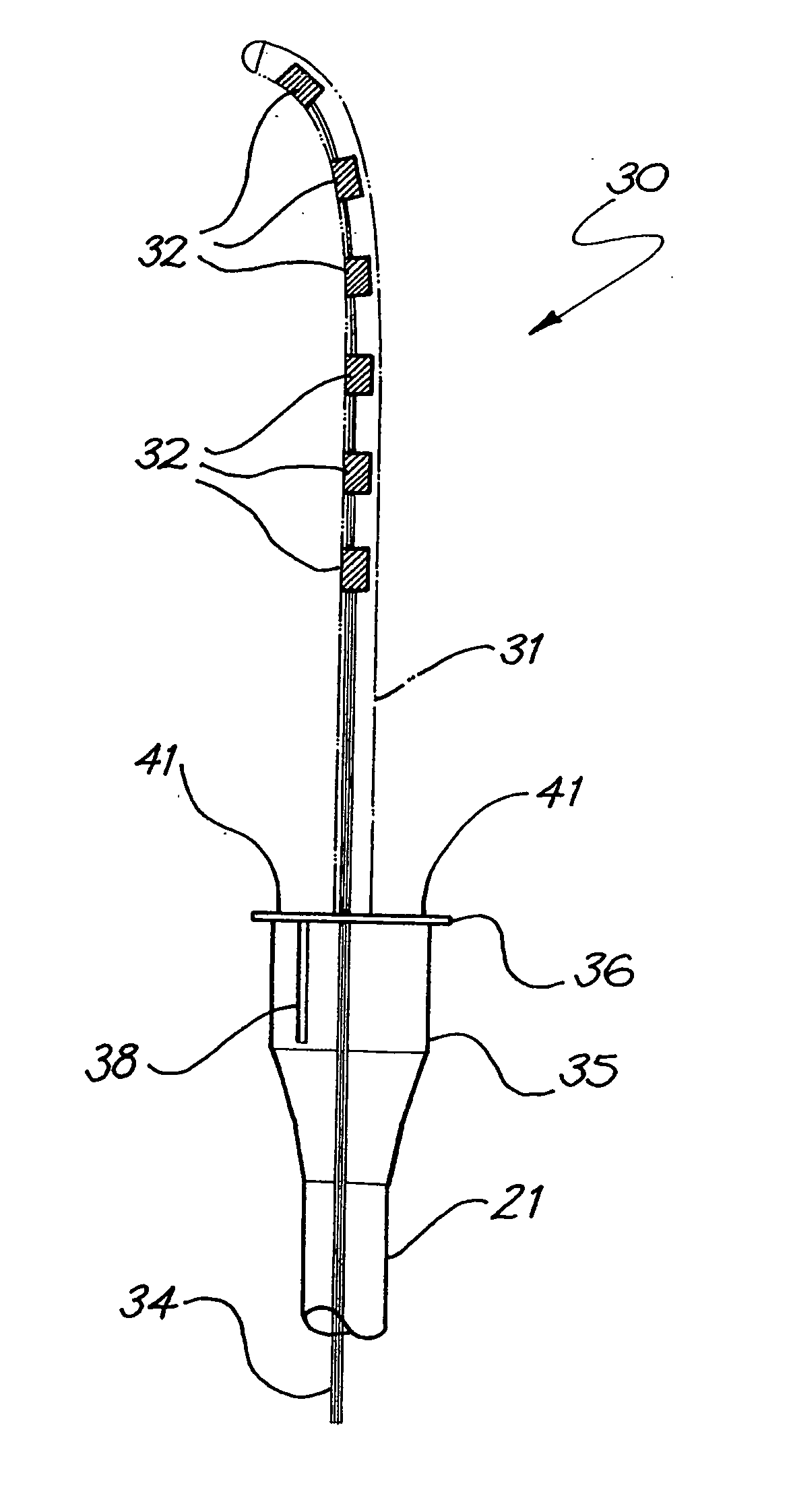
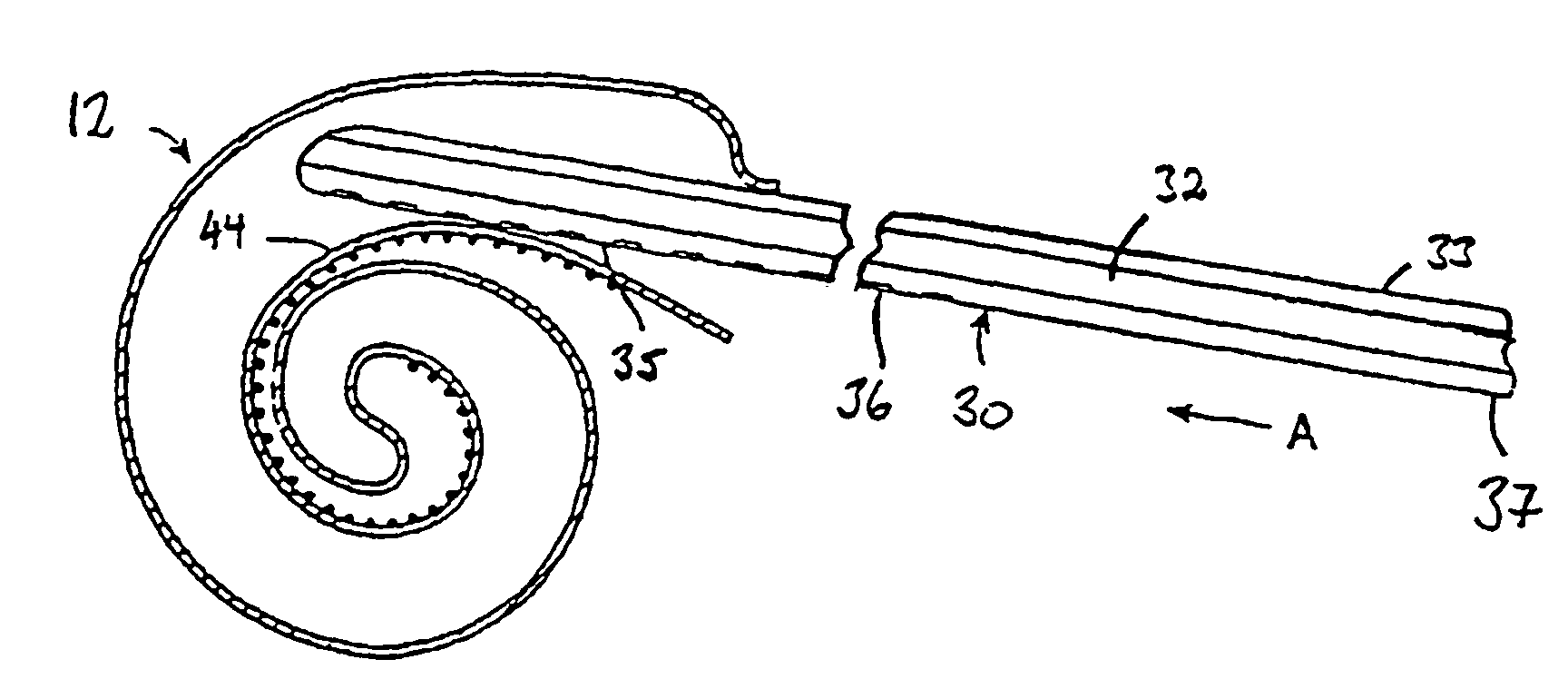
Cochlear implant electrode array
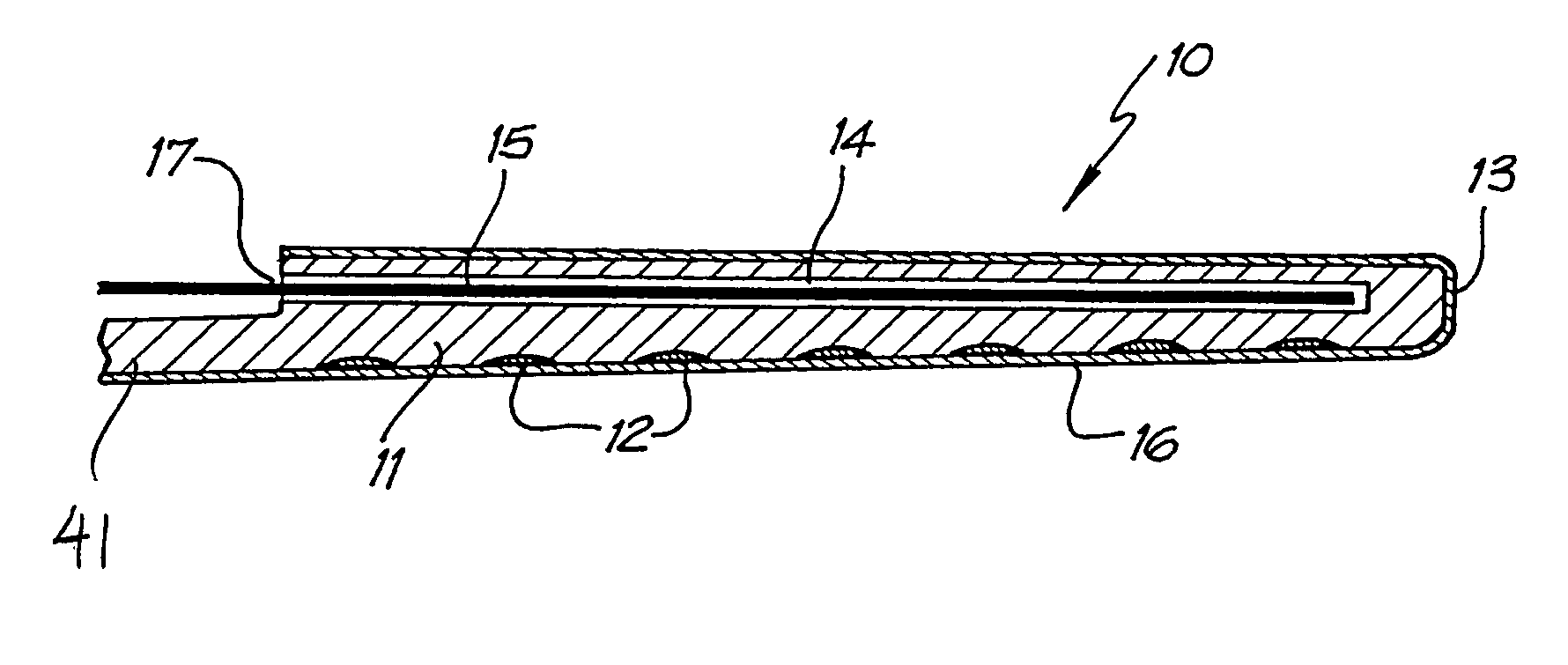
InactiveUS20050256561A1Restore high-frequency sound perceptionProcess safety and stabilityHead electrodesEar treatmentEngineeringElectrode array
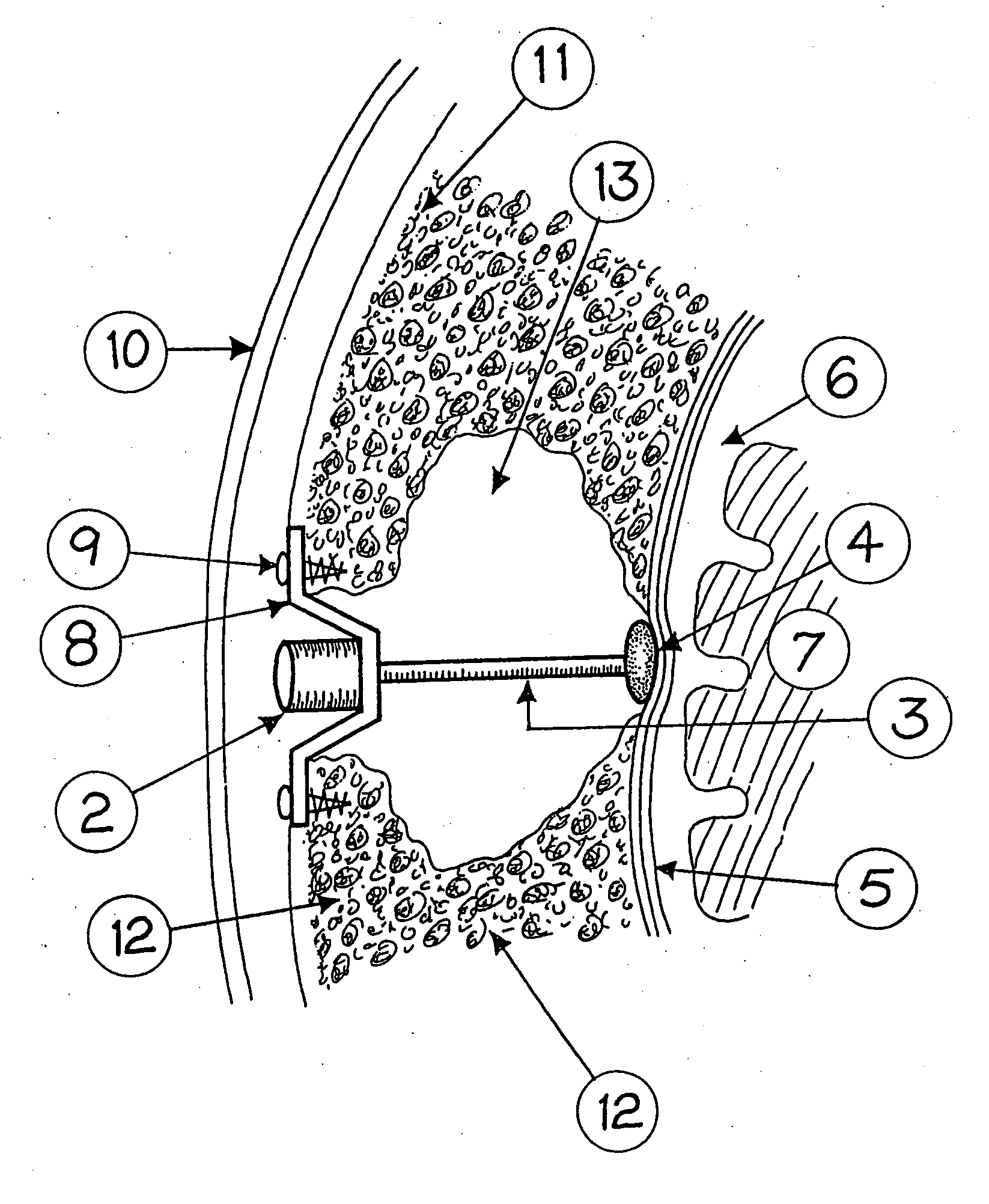
An electrode array (30) which is able to be inserted to a desired depth within the cochlea to provide useful percepts for the recipient which will also preferably not cause damage to the sensitive structures of the cochlea. The electrode array (30) is insertable through an opening in the cochlea and into at least the basal region of the cochlea and comprises an elongate carrier (31) having a proximal end, a distal end, and a plurality of electrodes (32) supported by the carrier at respective spaced locations thereon in a region between the proximal end and the distal end. A stabilising collar (35) extends outwardly from the elongate carrier (31) at or adjacent a proximal end thereof and has an abutment surface adapted to abut a portion of the cochlea surface around the cochleostomy and at least substantially prevent movement of the carrier (31) following completion of insertion of the array (30) into the cochlea.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IOWA +1
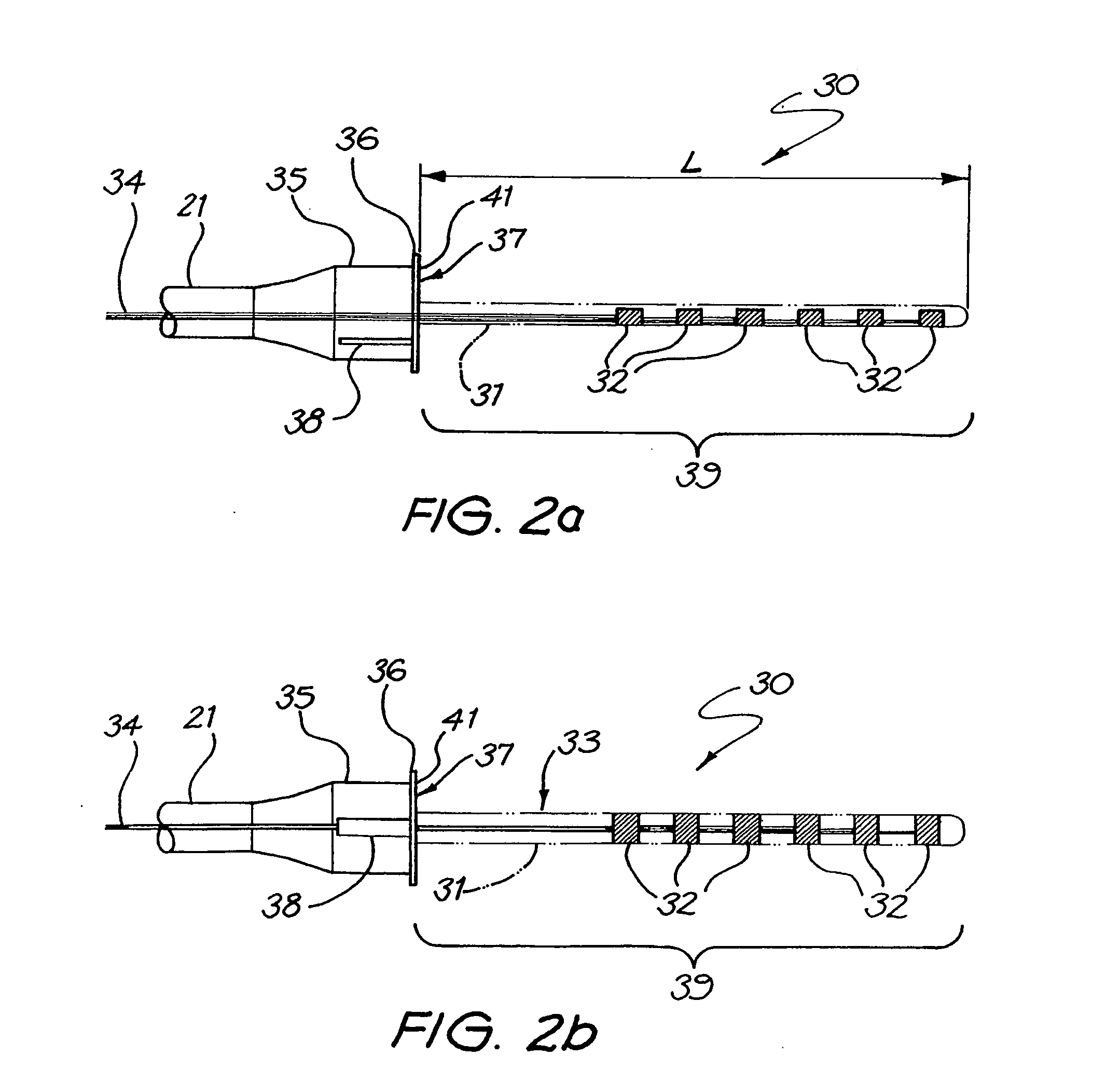
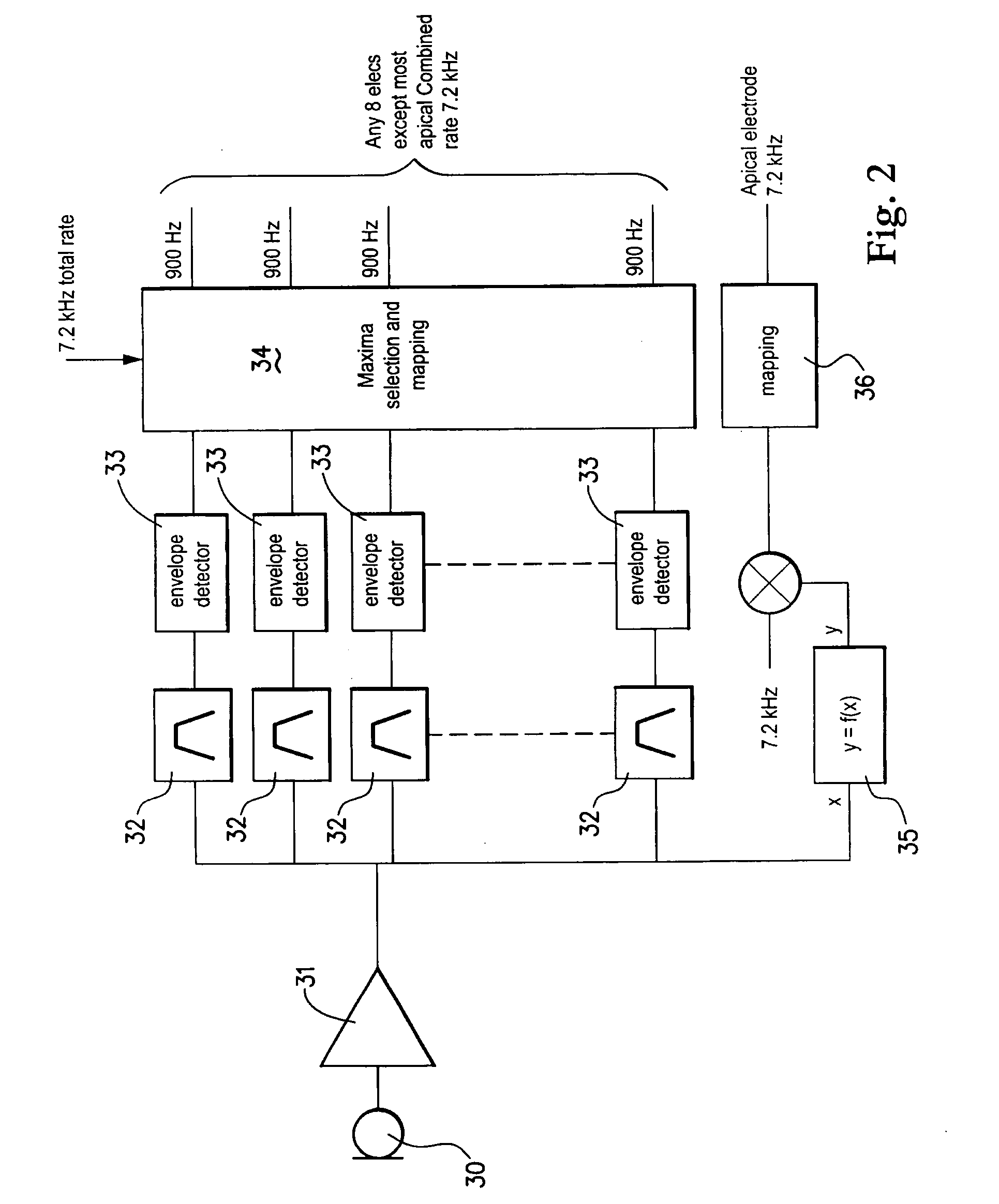
Combined stimulation for auditory prosthesis
InactiveUS20050187592A1Increase chanceBetter speechElectrotherapyArtificial respirationHigh rateProsthesis
A cochlear prosthesis comprises multiple electrodes for stimulating the cochlea. A received sound signal is filtered into frequency channels, and from a subset of the frequency channels pulsatile stimuli are generated to be applied by the electrodes. A modulating signal is also obtained from the received sound signal. High rate stimuli modulated by the modulating signal are generated and applied by at least one of the electrodes.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED +1
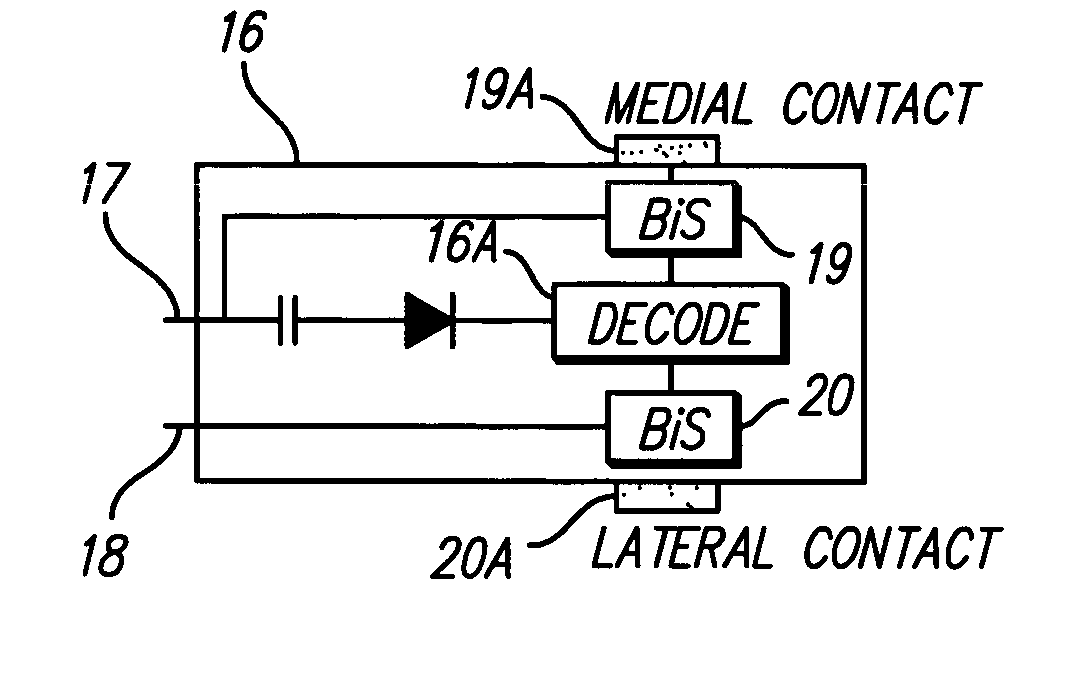
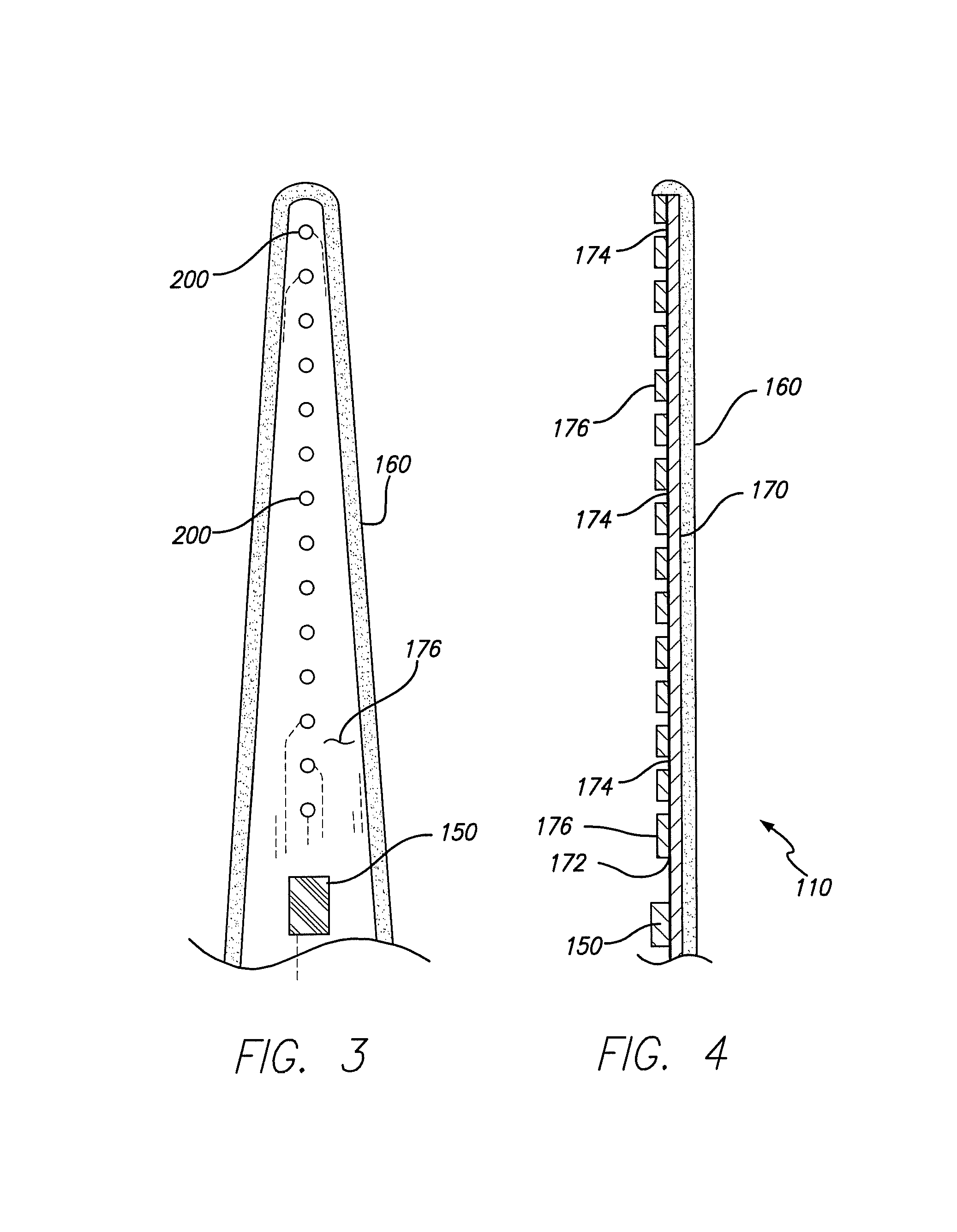
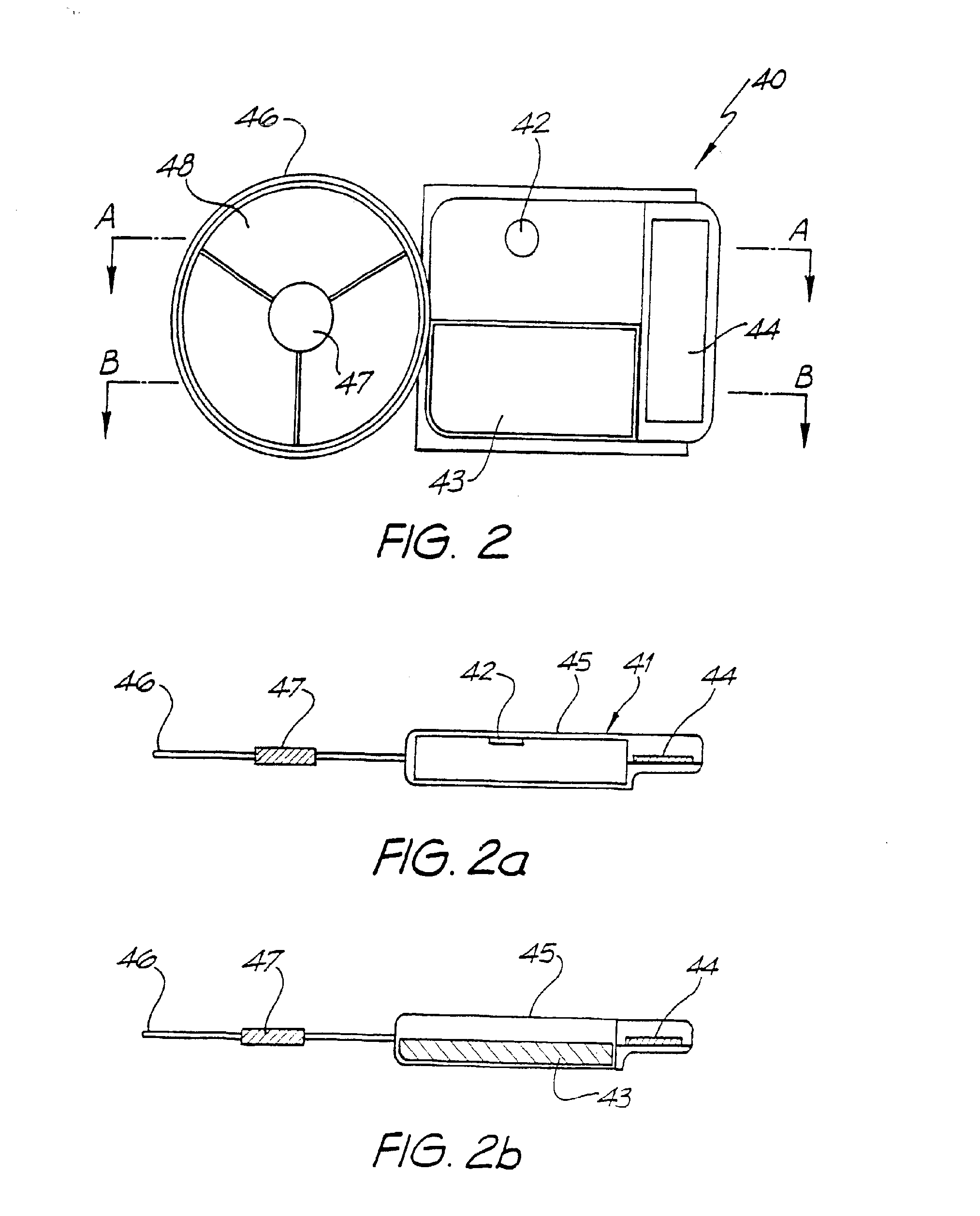
High contact count, sub-miniature, full implantable cochlear prosthesis
InactiveUS6980864B2Reduce power consumptionHigh selectivityElectrotherapyArtificial respirationControl signalElectrical battery
A fully implantable cochlear prosthesis includes (1) an implantable hermetically sealed case wherein electronic circuitry, including a battery and an implantable microphone, are housed, (2) an active electrode array that provides a programmable number of electrode contacts through which stimulation current may be selectively delivered to surrounding tissue, preferably through the use of appropriate stimulation groups, and (3) a connector that allows the active electrode array to be detachably connected with the electronic circuitry within the sealed case. The active electrode array provides a large number of both medial and lateral contacts, any one of which may be selected to apply a stimulus pulse through active switching elements included within the array. The active switching elements included within the array operate at a very low compliance voltage, thereby reducing power consumption. The entire prosthesis is very efficient from a power consumption standpoint, thereby allowing a smaller battery to power the system for longer periods of time before recharging or replacement is required. The hermetically sealed case within which the electronic circuitry, battery, and microphone are housed may be replaced, when needed, through minimally invasive surgery. Further, the electronic circuitry housed within the hermetically sealed case may be programmed, as needed, using acoustic and / or RF control signals. In one embodiment, such control signals may be realized using phase-shift keyed (PSK) modulation of an acoustic signal within a very narrow frequency band centered at about 6 KHz.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
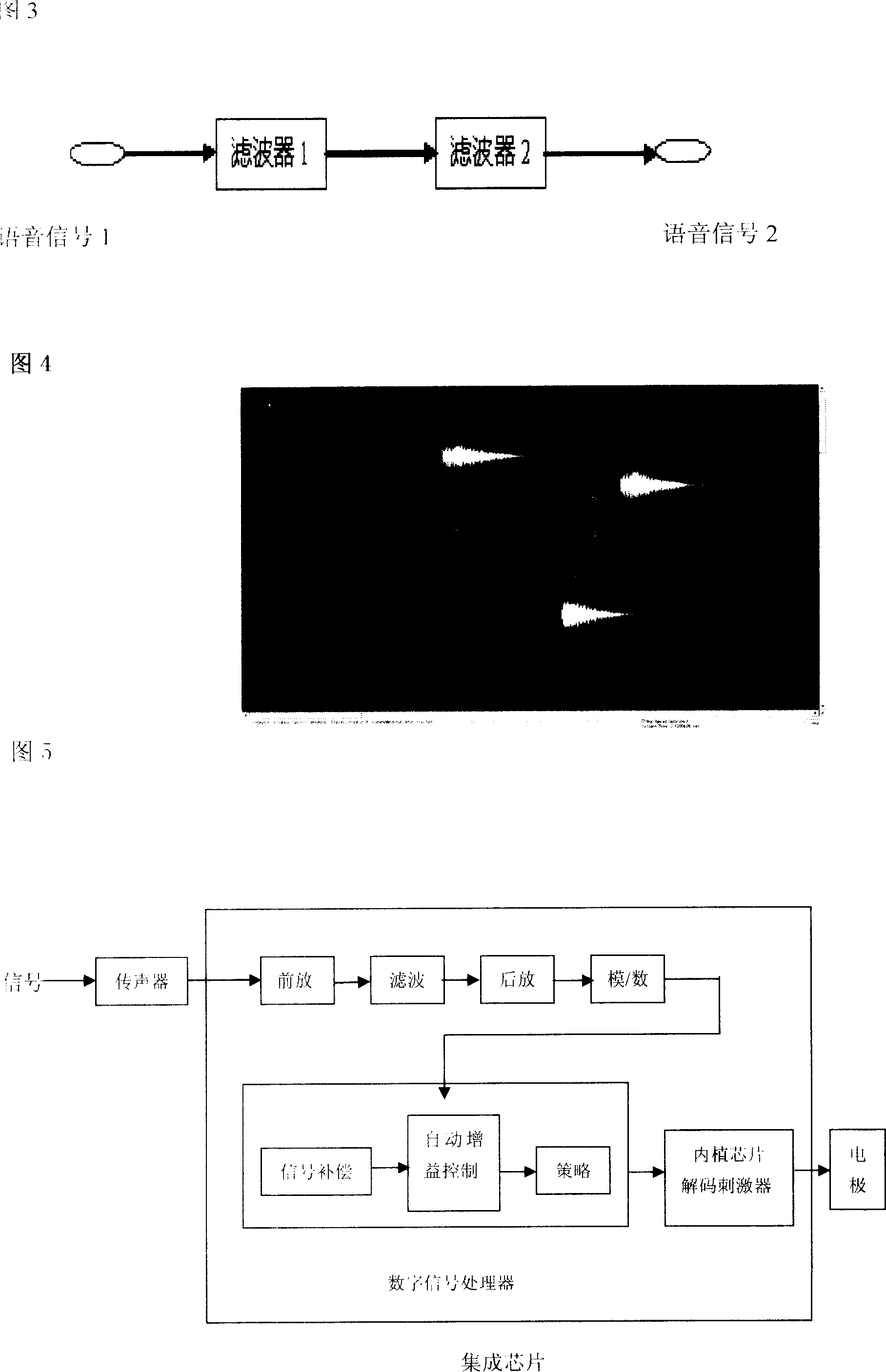
Full-implanting type artificial cochlea and method for making same
The present invention relates to biomedicine engineering and bionics, and is especially one new type of implanted artificial cochlea and its making process. The implanted artificial cochlea consists of one implanted piezoelectric or fiber type microphone, one signal amplifier, one phonetic processor and one decoding stimulator. It has optimized MSPR mixed coding mode and multiple stimulating modes. Experiment shows that the implanted artificial cochlea has high sensitivity and good frequency characteristic, and is suitable for sufferer, especially children sufferer, of deafness.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
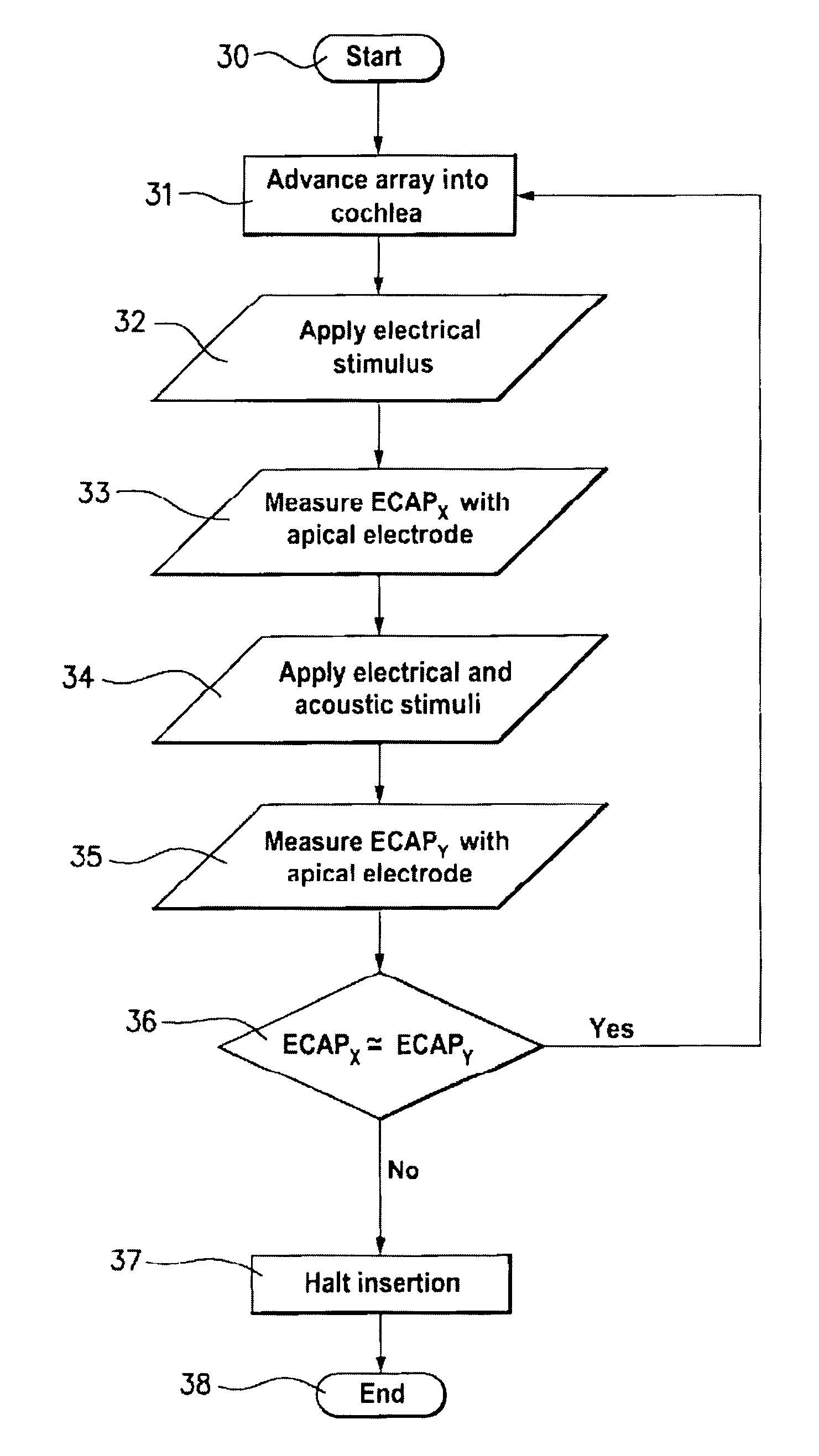
Cochlear implant fitting
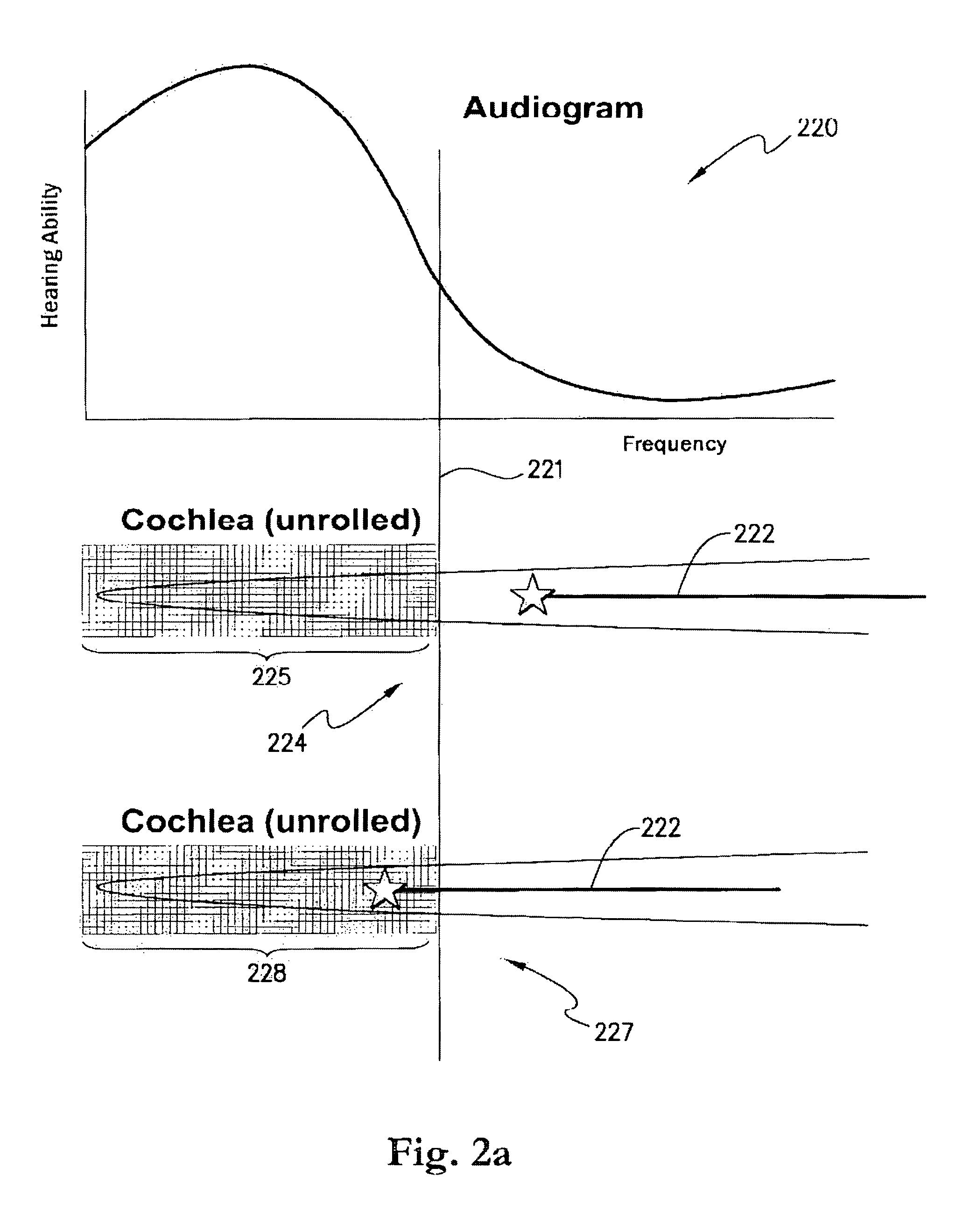
A method for fitting a cochlear prosthesis to a cochlea having residual acoustic hearing capability, in order to exploit the residual acoustic hearing capability to the extent possible. A portion of the cochlea having residual acoustic hearing capability is determined by measuring the neural response to acoustic and / or electrical stimulations. Electrical stimulations are applied only to the portions of the cochlea lacking acoustic hearing capability, or possessing only partial acoustic hearing capability. Surgical implantation depth may be optimised by the method, and / or a patient map may be suitably defined to implement the method.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Functionalized implantable flexible electrode and application thereof
PendingCN109350847AGuaranteed biocompatibilityReduce surgical riskHead electrodesEpicardial electrodesImplantable ElectrodesPower flow
The invention relates to a functionalized implantable flexible electrode and an application thereof. The functionalized implantable flexible electrode at least comprises a function layer capable of generating a current or voltage. In the invention, through adopting the function layer which can generate the current or the voltage via triggering, the flexible electrode does not need complex line connection and device packaging and the function of a nerve stimulation device can be realized so that an operation risk and the safety risk of long-term implantation are greatly reduced, and the application field of the nerve stimulation device is expanded. The invention also provides the applications of the above functionalized wide-width implantable electrode in manufacturing an implantable artificial retina, an implantable artificial cochlea, an implantable cardiac pacemaker, and an implantable deep brain stimulator.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
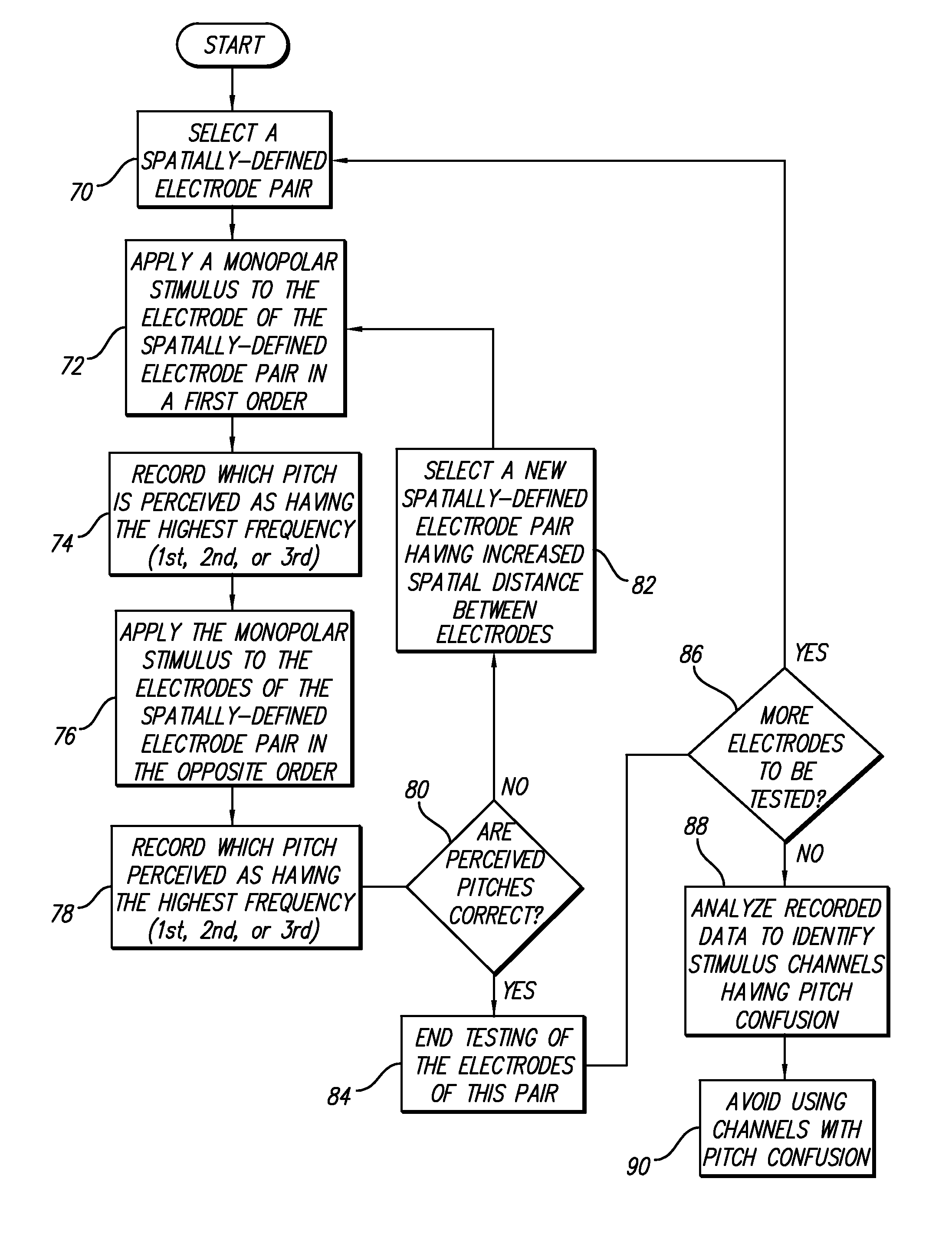
Adaptive place-pitch ranking procedure for optimizing performance of a multi-channel neural stimulator
An adaptive place-pitch ranking procedure for use with a cochlear implant or other neural stimulation system provides a systematic method for quantifying the magnitude and direction of errors along the place-pitch continuum. The method may be conducted and completed in a relatively short period of time. In use, the implant user or listener is asked to rank the percepts obtained after a sequential presentation of monopolar stimulation pulses are applied to a selected spatially-defined electrode pair. Should the patient's judgment of pitch order be correct for all applied interrogations, then no further testing involving the tested electrode pair (two electrode contacts) is undertaken. However, should there be errors in the place-pitch ranking, which errors evidence perceptual place-confusions, then a search is undertaken for the spread of the perceptual confusion by separating the target channel and competing channel by one electrode contact at a time. This search for the spread of confusion continues until no errors are made in all directions. Identified channels wherein pitch confusion exists may be deselected (not used) during normal operation of the cochlear implant.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
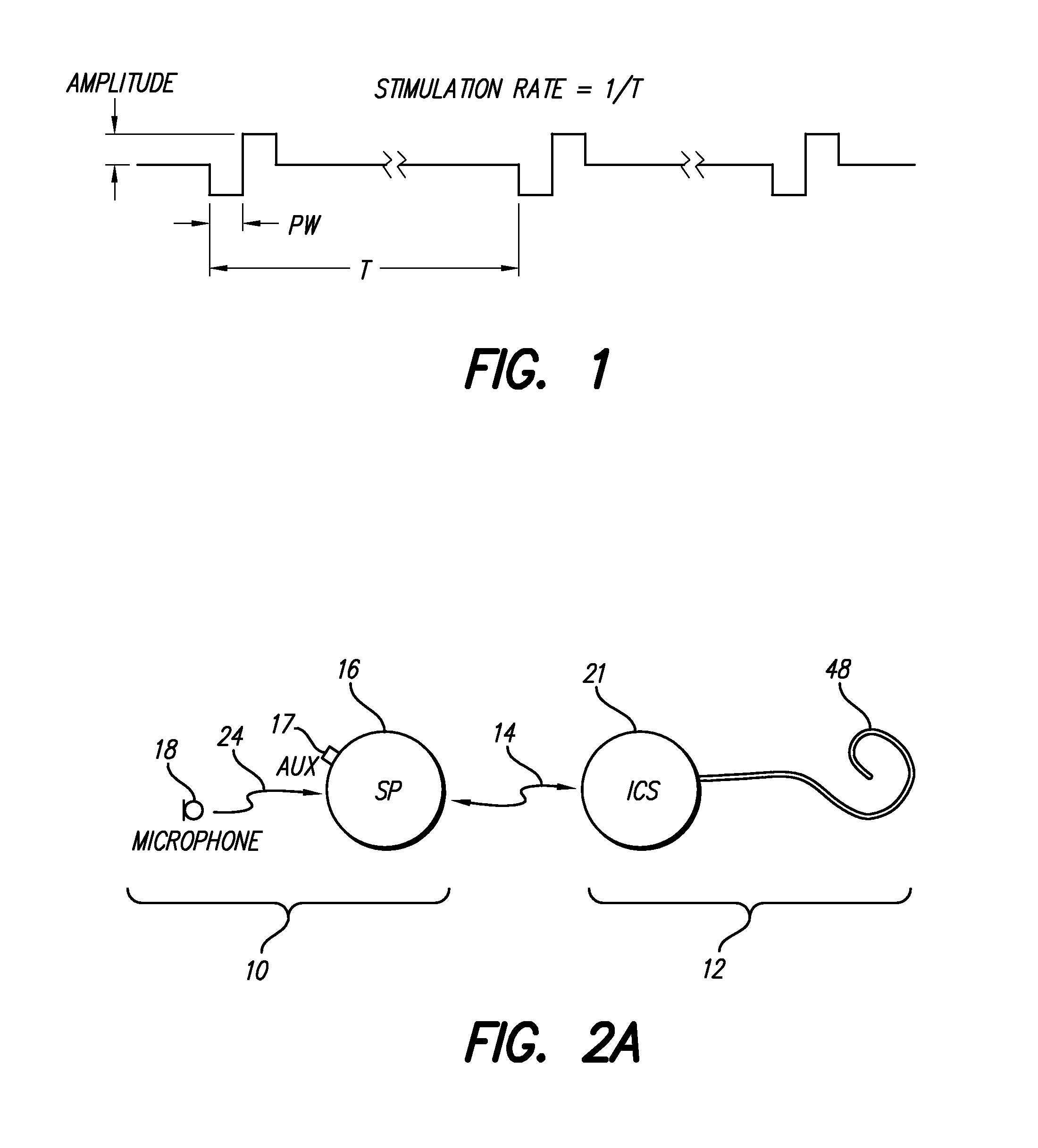
Cochlear implant apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20120130449A1Place pitch perceptIncreasing temporal pitch perceptHead electrodesEar treatmentCouplingCochlear implantation
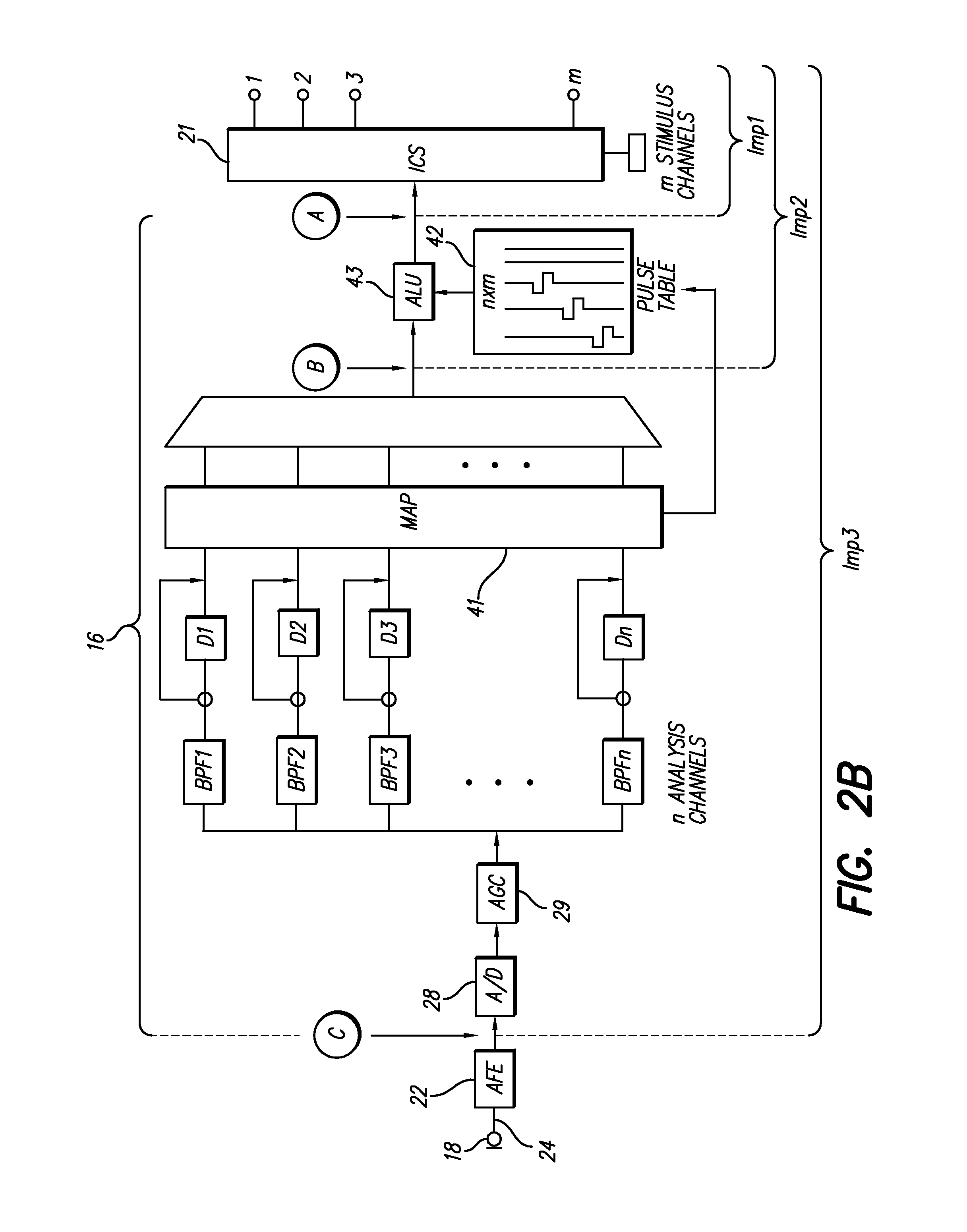
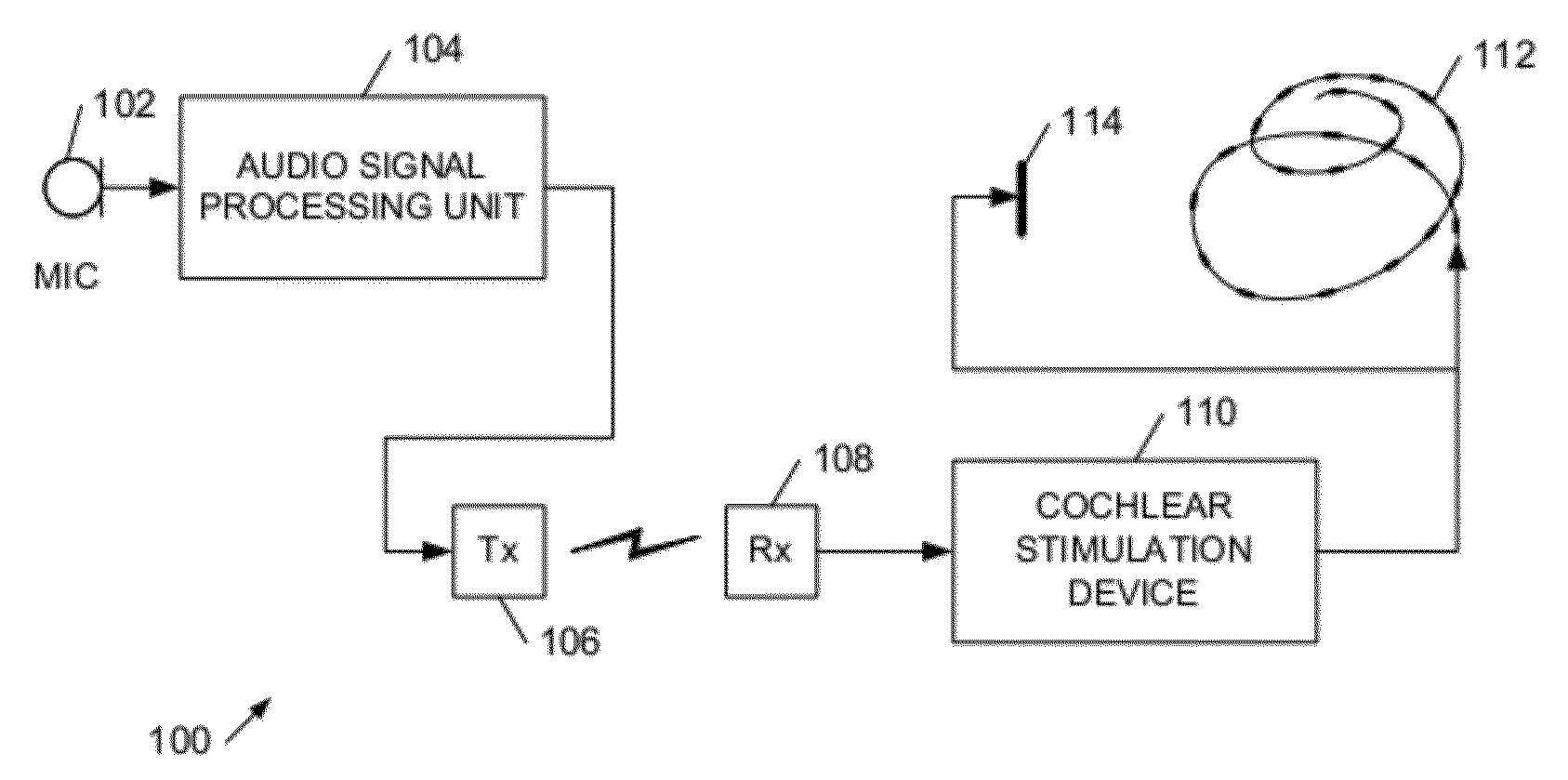
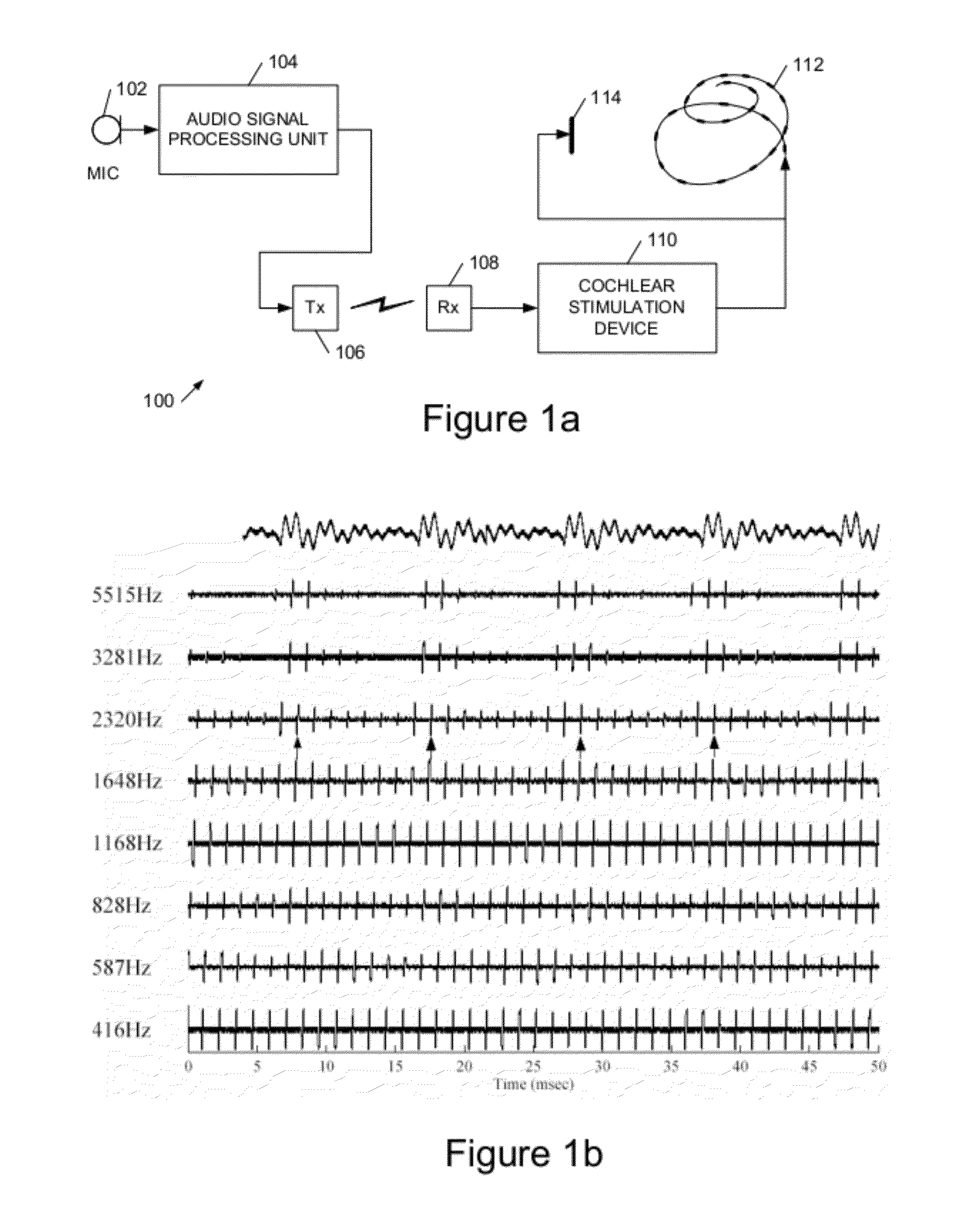
The invention relates to cochlear implants and to improved methods of operating such implants. We describe cochlear implant apparatus comprising an audio signal processing unit with a wired or wireless coupling to an implantable cochlear stimulation device, wherein said audio signal processing unit has an audio input to receive an audio signal representing a sound, wherein said implantable cochlear stimulation device includes an electrical pulse generator coupled to an electrode array for intracochlear stimulation, wherein the apparatus is configured to apply stimulation to said electrode array to represent said sound, wherein said stimulation comprises application of an electrical pulse across two intracochlear electrodes of said electrode array, and wherein said electrical pulse has a pulse waveshape which is asymmetric under an operation comprising inverting the waveshape about a zero level and then time reversing the waveshape.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +1
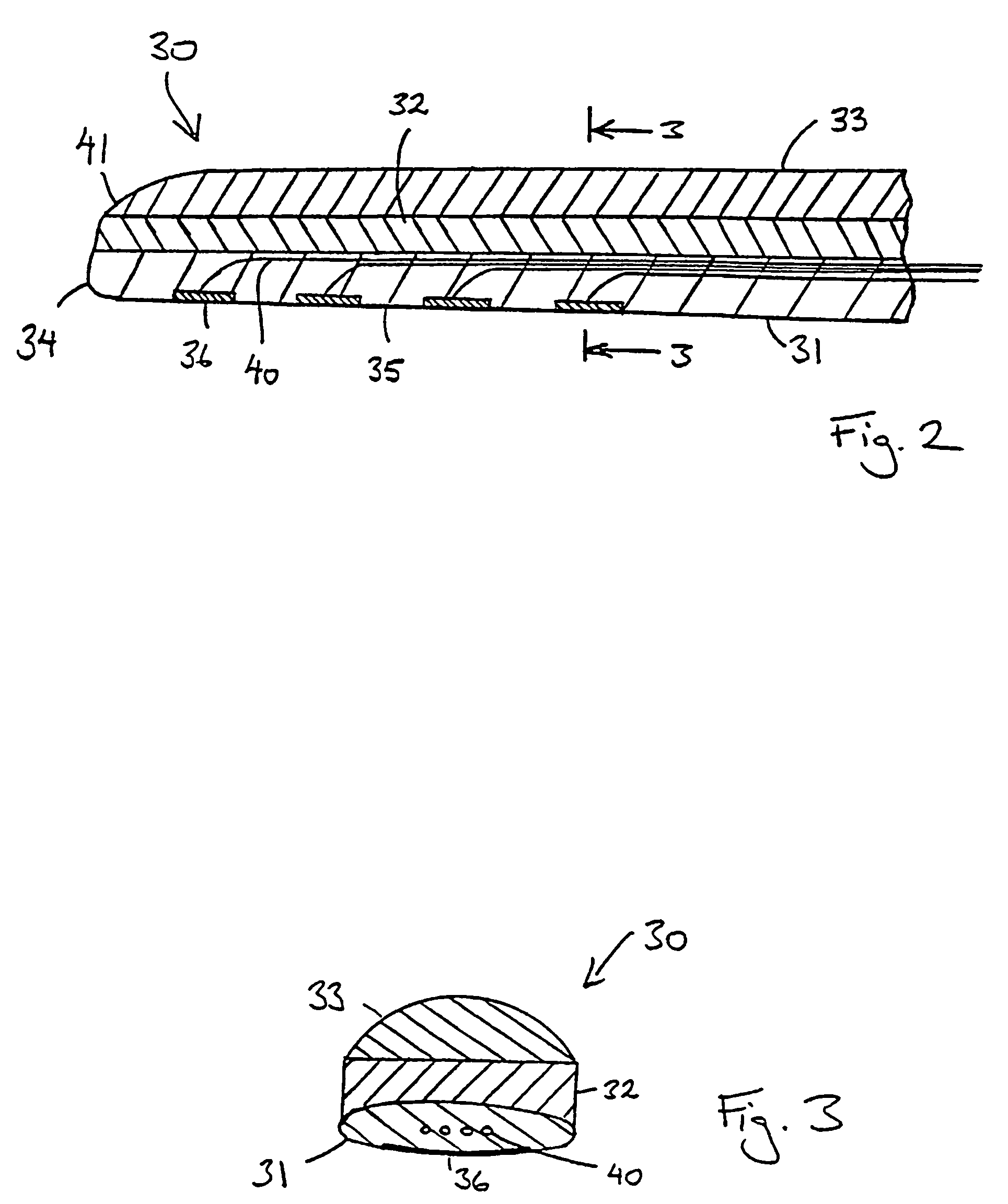
Laminated electrode for a cochlear implant
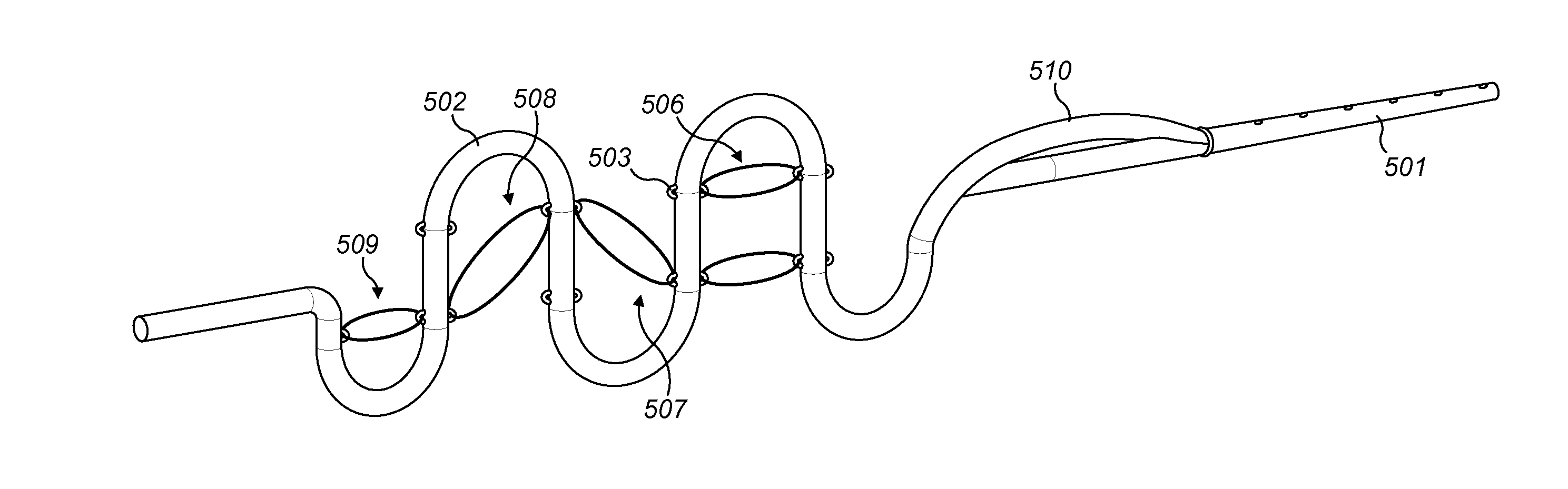
InactiveUS7406352B2Prevent fluid flowAvoid flowHead electrodesExternal electrodesCochlear implantationElectrode array
An implantable cochlear implant electrode array (30) that can adopt a first, preferably straight, configuration selected to allow the array to be inserted into the cochlea and at least a second, preferably, spirally curved, configuration wherein the electrode array (30) is adapted to apply tissue stimulation. The electrode array (30) comprises an elongate carrier (31) having a proximal end (37), a distal end (34), and a plurality of electrodes supported by the carrier (31) at respective spaced locations thereon, the carrier (31) is formed, preferably moulded, to preferentially adopt the second configuration or another configuration different to said first configuration. The outer layer (33) is releasably connected to the elongate carrier (31) by an adhesive layer (32) and is formed so as to bias the carrier (31) into the first configuration when connected thereto. A method of forming the electrode array (30) is also disclosed.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
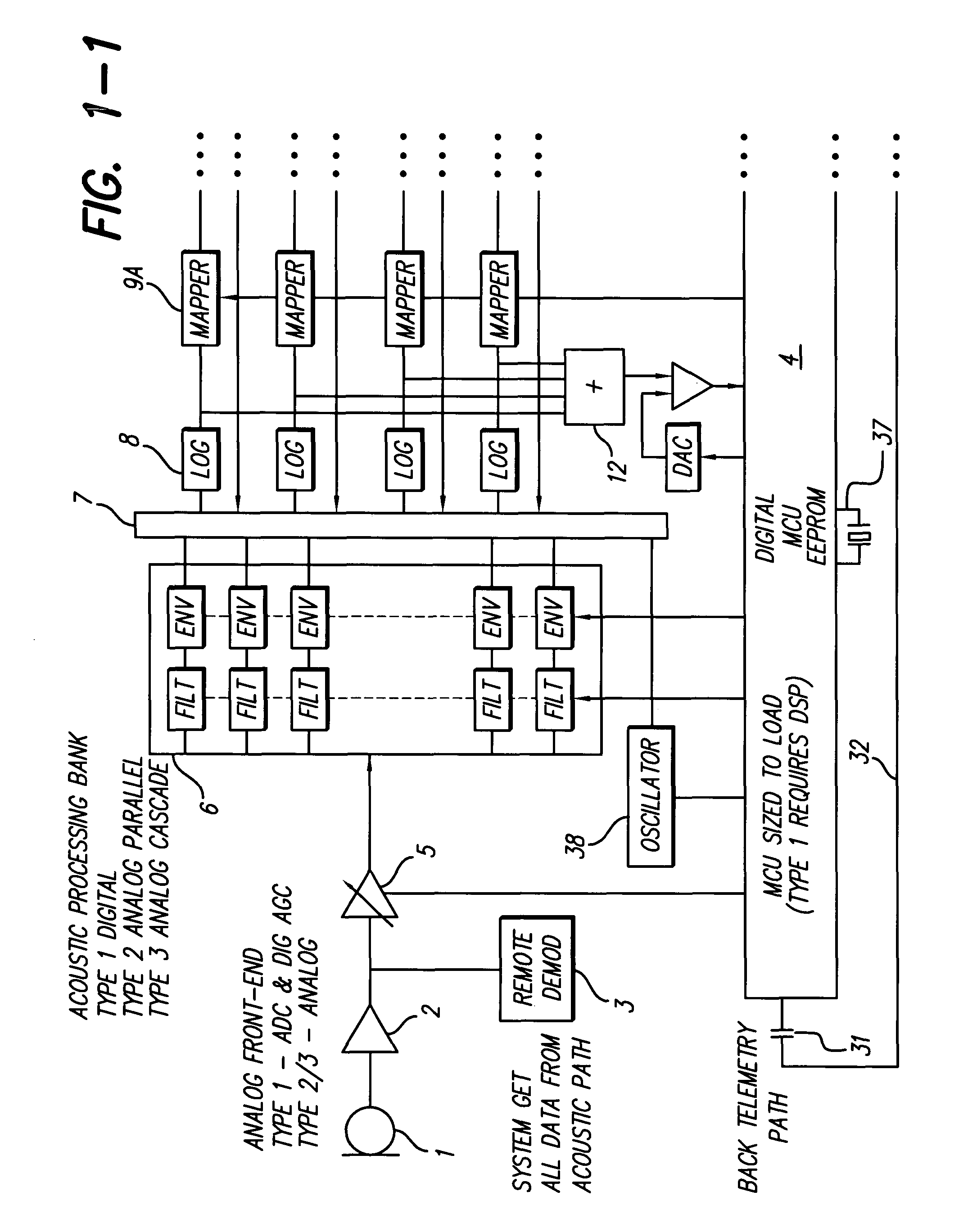
Low Pulse Rate Cochlear Implant Stimulation In Conjunction With A Separate Representation Of Fundamental Frequencies And Voiced/Unvoiced Distinctions
ActiveUS20110066210A1High frequencyResidual hearingHead electrodesEar treatmentAuditory systemFundamental frequency
A method is described for generating stimulus signals for an auditory prosthesis system. A high frequency signal conveys higher frequency audio information including exceptionally low rate band-pass envelope characteristics. This high frequency signal represents at least the upper part if not all of the range of frequencies for speech, music, and other sounds that are audible to listeners with normal hearing. A separate low frequency signal is also provided representing lower audio frequency information including periodicity characteristics (voiced / unvoiced or periodic / aperiodic distinctions) and for periodic sounds, fundamental frequency characteristics. The high frequency signal is applied to the auditory system of a patient by an associated high frequency stimulator, and the low frequency signal is applied to the auditory system of the patient by an associated low frequency signal.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Recipient-controlled fitting of a hearing prosthesis
A method for fitting to a recipient a cochlear prosthesis having a sound processor that processes received sound in accordance with a MAP, the method comprises providing, by the hearing prosthesis, combinations of voice prompts and test stimuli for testing values of an element of the MAP; receiving from the recipient an indication of which of said values are desirable; and revising the MAP with the desired value for the tested element. A neural-stimulating device for stimulating nerve cells of a recipient is provided.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
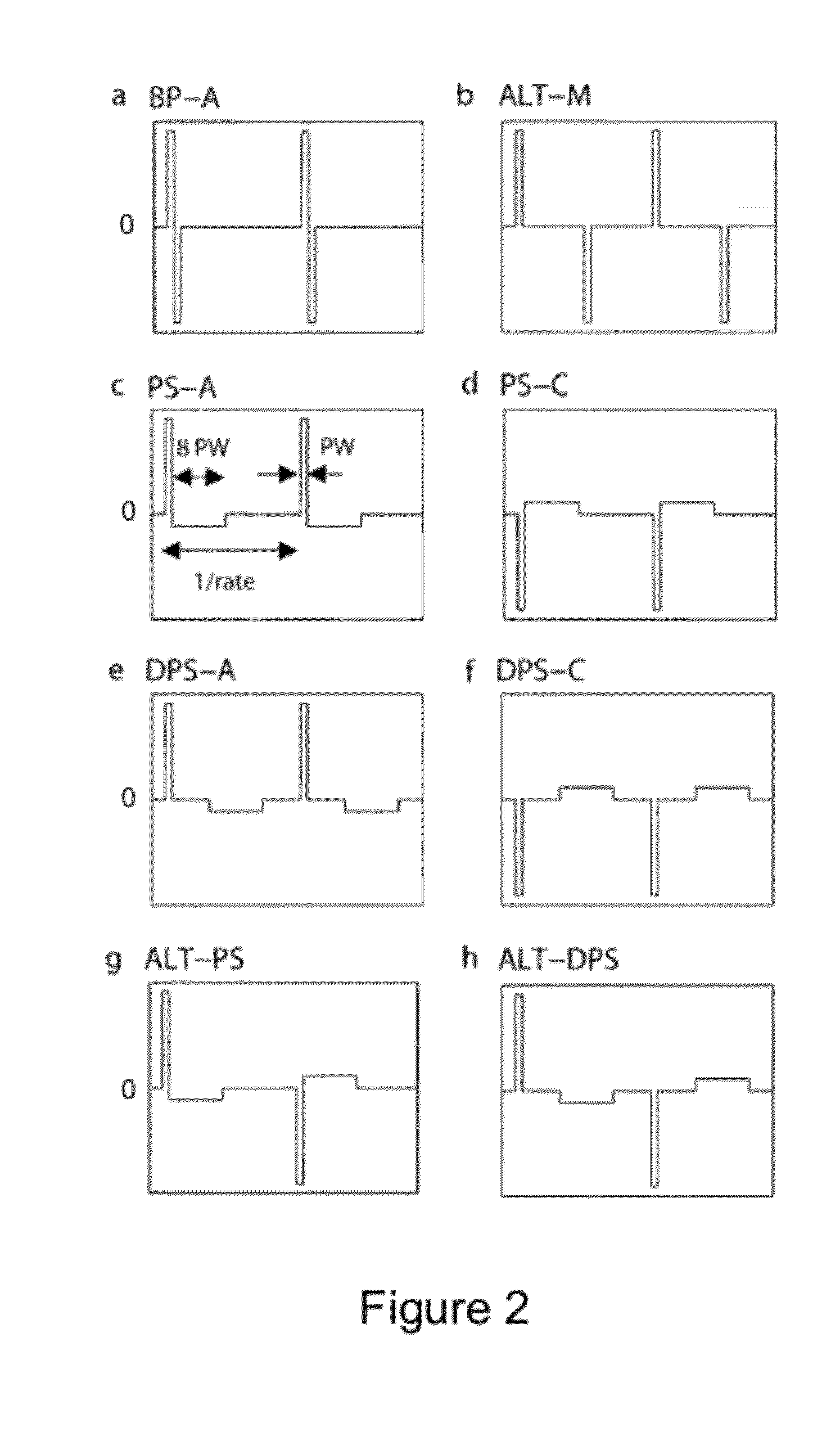
Using Alternative Stimulus Waveforms To Improve Pitch Percepts Elicited With Cochlear Implant Systems
InactiveUS20130245717A1Easy to distinguishGreat spatial specificityHead electrodesArtificial respirationNervous tissueCochlear implantation
A cochlear implant system is described which includes an electrode array for implantation in the scala tympani of a cochlea. Electrodes on the outer surface of the electrode array apply electrode stimulation signals to nearby neural tissue. An implantable stimulator module develops the electrode stimulation signals. The electrode stimulation signals have different waveforms. A basal waveform for one or more electrodes at the basal end of the electrode array has the form of a sequence of conventional high-amplitude short-duration electrode stimulation signals. An apical waveform for one or more electrodes at the apical end of the electrode array has the form of a sequence of lower-amplitude longer-duration electrode stimulation signals. The apical waveform is adapted to selectively stimulate peripheral neural processes towards the apical end of the electrode array so as to provide a tonotopic place-pitch response to the electrode stimulation signals.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
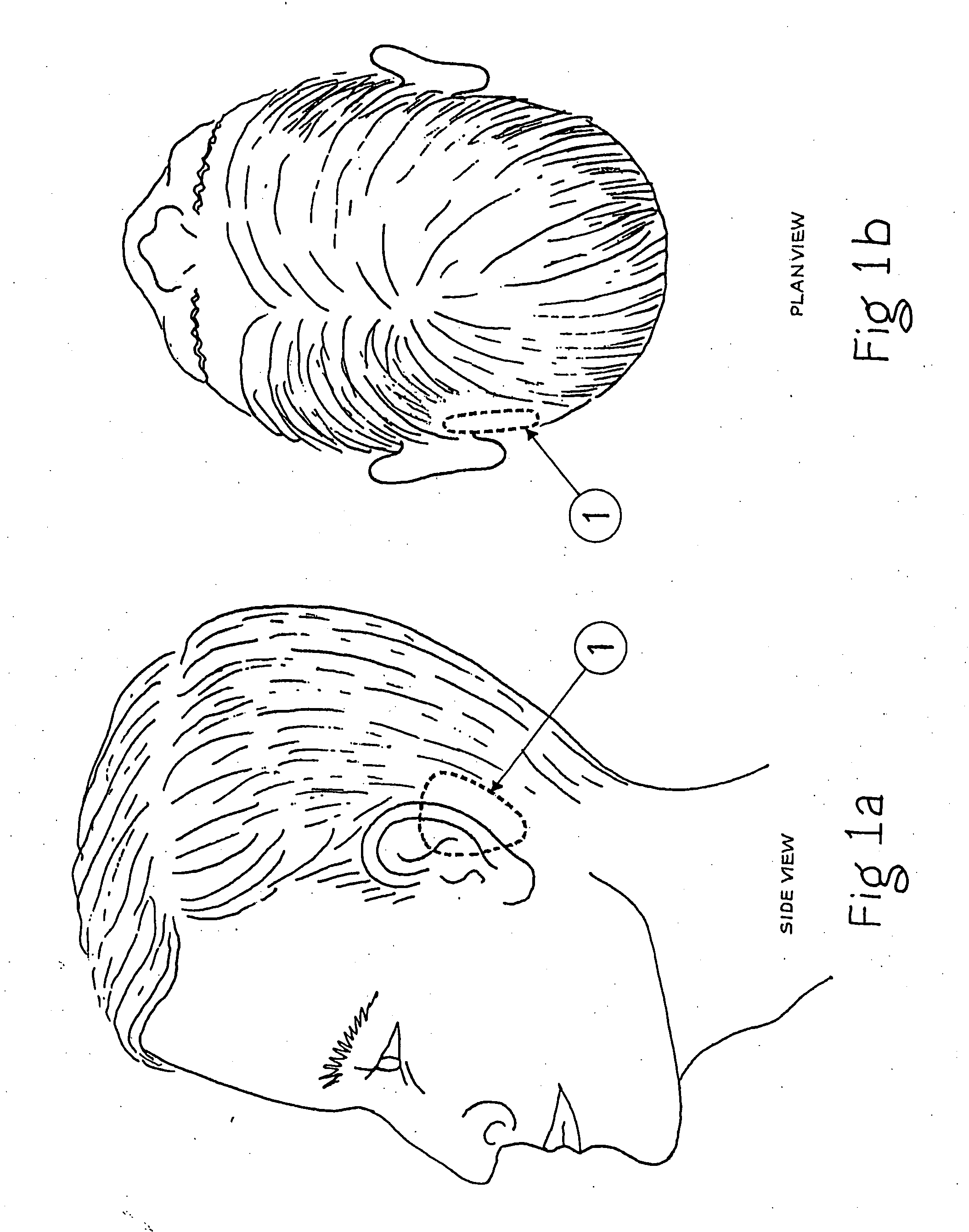
Apparatus and methods for percutaneous cochlear implantation
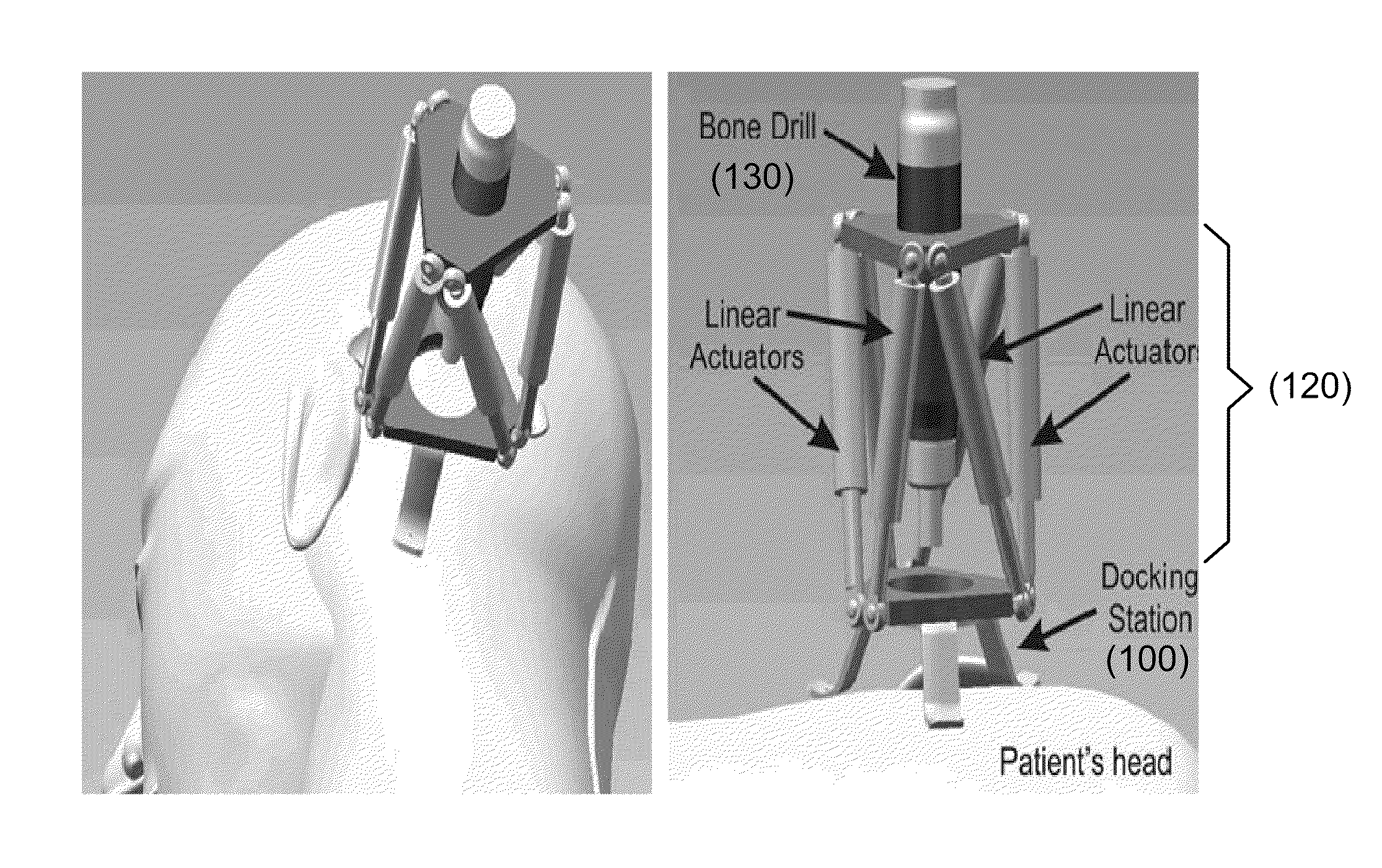
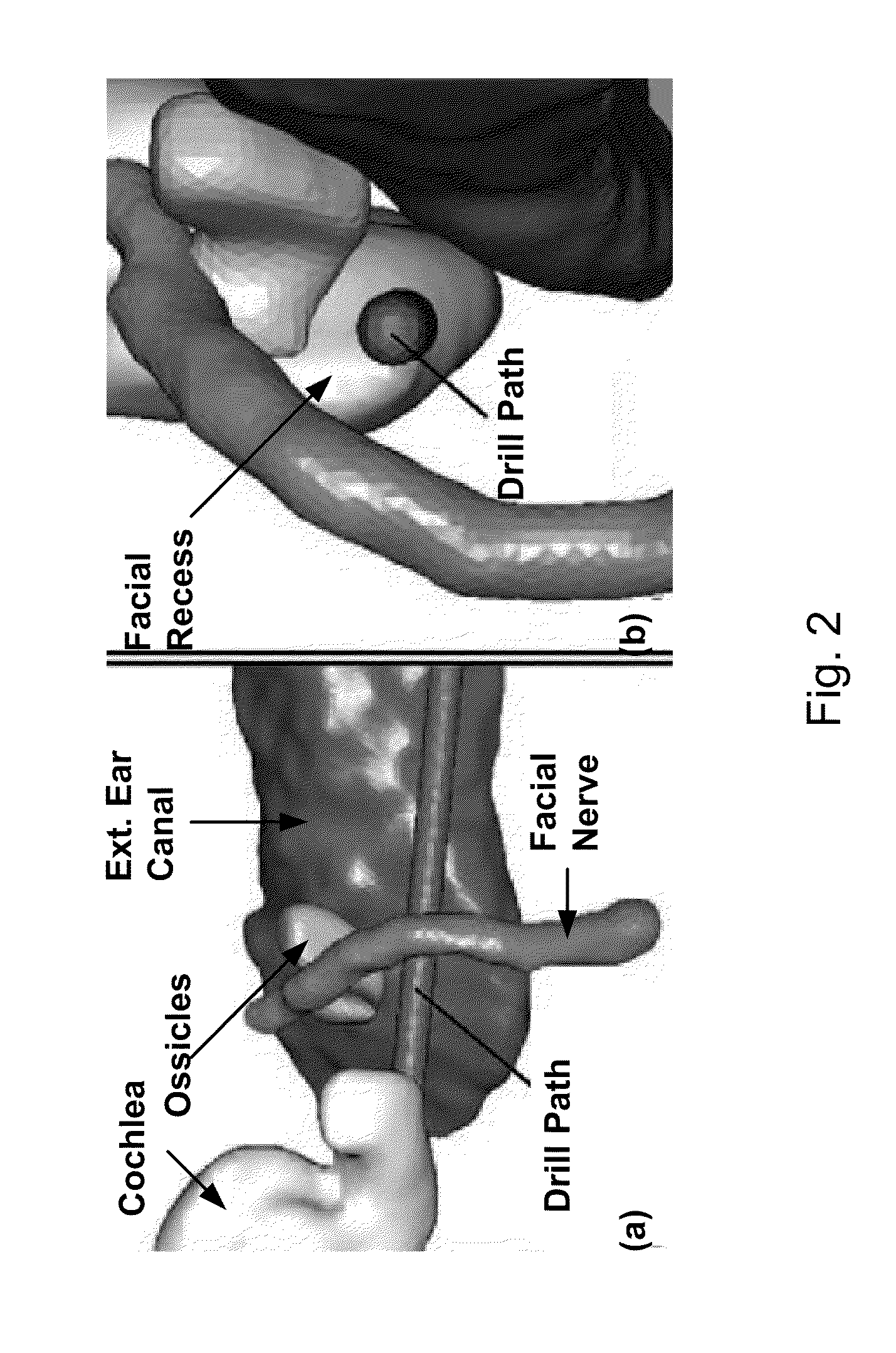
A method and apparatus of percutaneous cochlear implantation (PCI). In one embodiment, the method includes the steps of (a) implanting a plurality of anchor members in a skull of a patient surrounding an ear of the patient, (b) attaching a docking frame to the plurality of anchor members, wherein the docking frame has a docking platform and a plurality of fiducial members, (c) acquiring a computed-tomography (CT) image of an area of the patient's head including the ear and the plurality of fiducial members, (d) determining a centroid of each of the plurality of fiducial members and a trajectory for a PCI according to the CT image, (e) configuring a parallel robot by a computer processor according to the CT image such that a top platform of the parallel robot is aligned with the trajectory with respect to the centroids of the plurality of fiducial members, (f) attaching the configured parallel robot to the docking frame, and (g) performing the PCI using one or more surgical tools received by the top platform of the parallel robot.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
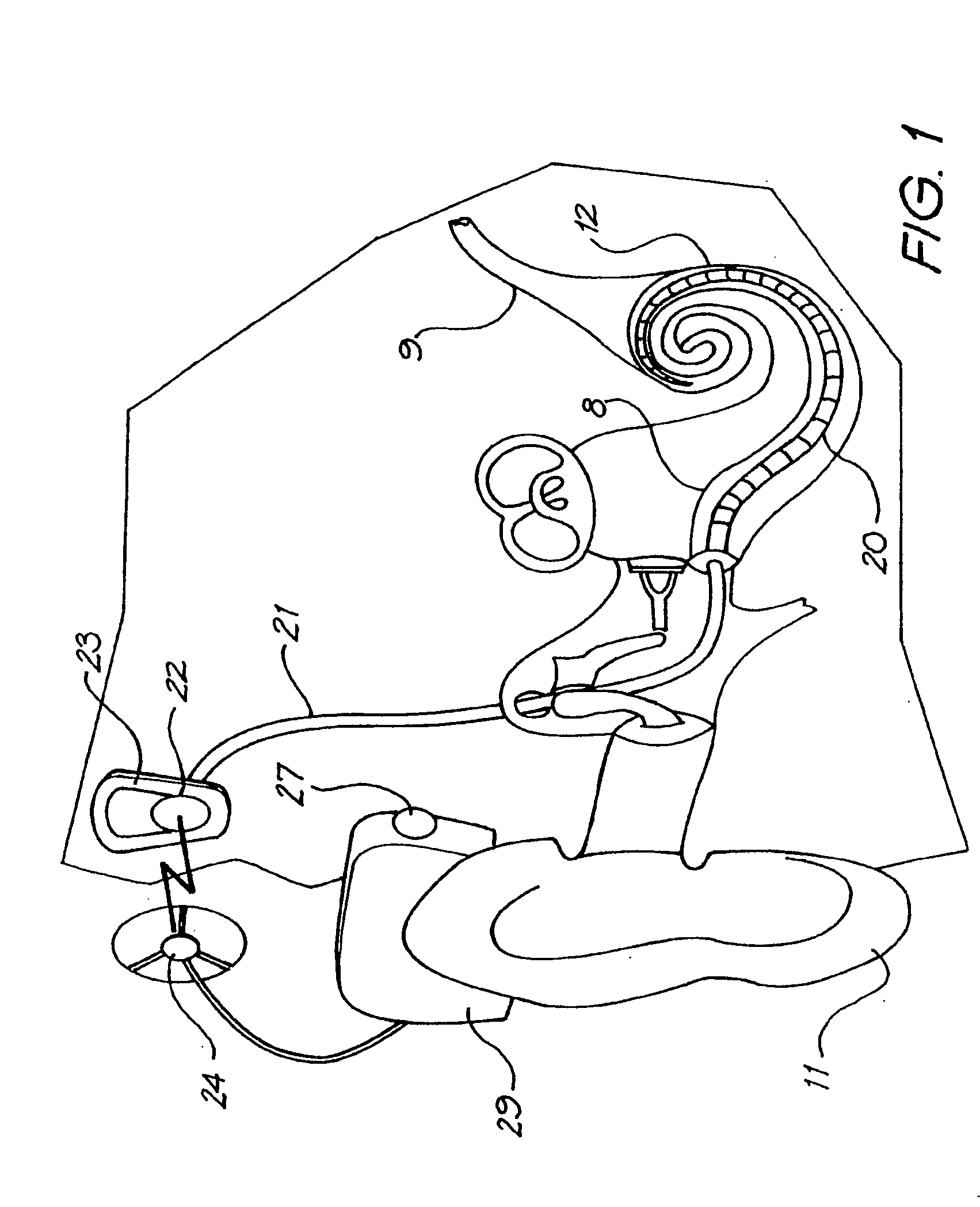
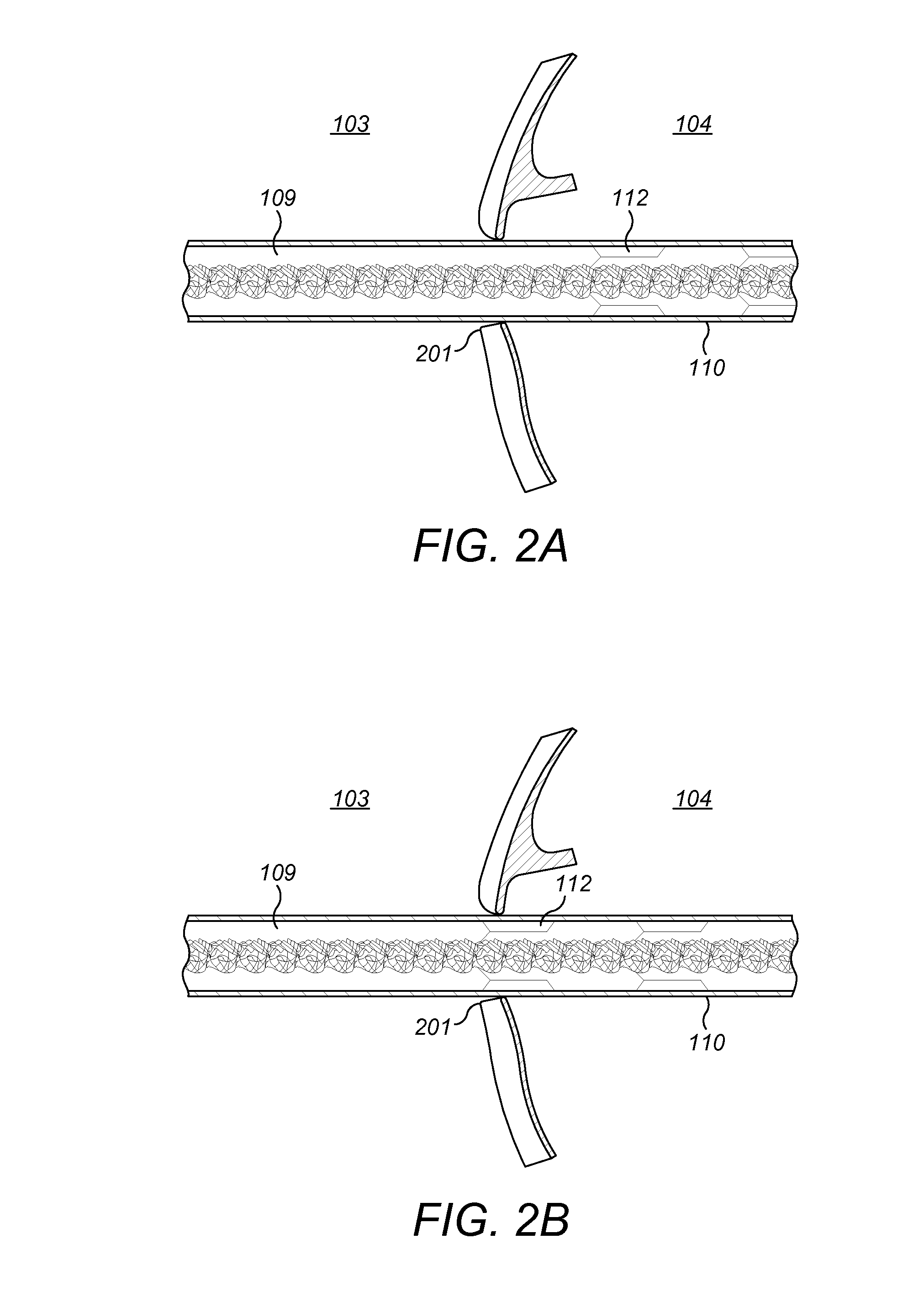
Cochlear stimulation device
ActiveUS8874239B2Reduce widthHigh charge transfer capabilityHead electrodesExternal electrodesCapacitanceElectrode array
A cochlear stimulation device comprising an electrode array designed to provide enhanced charge injection capacity necessary for neural stimulation. The electrode array comprises electrodes with high surface area or a fractal geometry and correspondingly high electrode capacitance and low electrical impedance. The resultant electrodes have a robust surface and sufficient mechanical strength to withstand physical stress vital for long term stability. The device further comprises wire traces having a multilayer structure which provides a reduced width for the conducting part of the electrode array. The cochlear prosthesis is attached by a grommet to the cochleostomy that is made from a single piece of biocompatible polymer. The device, designed to achieve optimum neural stimulation by appropriate electrode design, is a significant improvement over commercially available hand-built devices.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
Cochlear implant
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
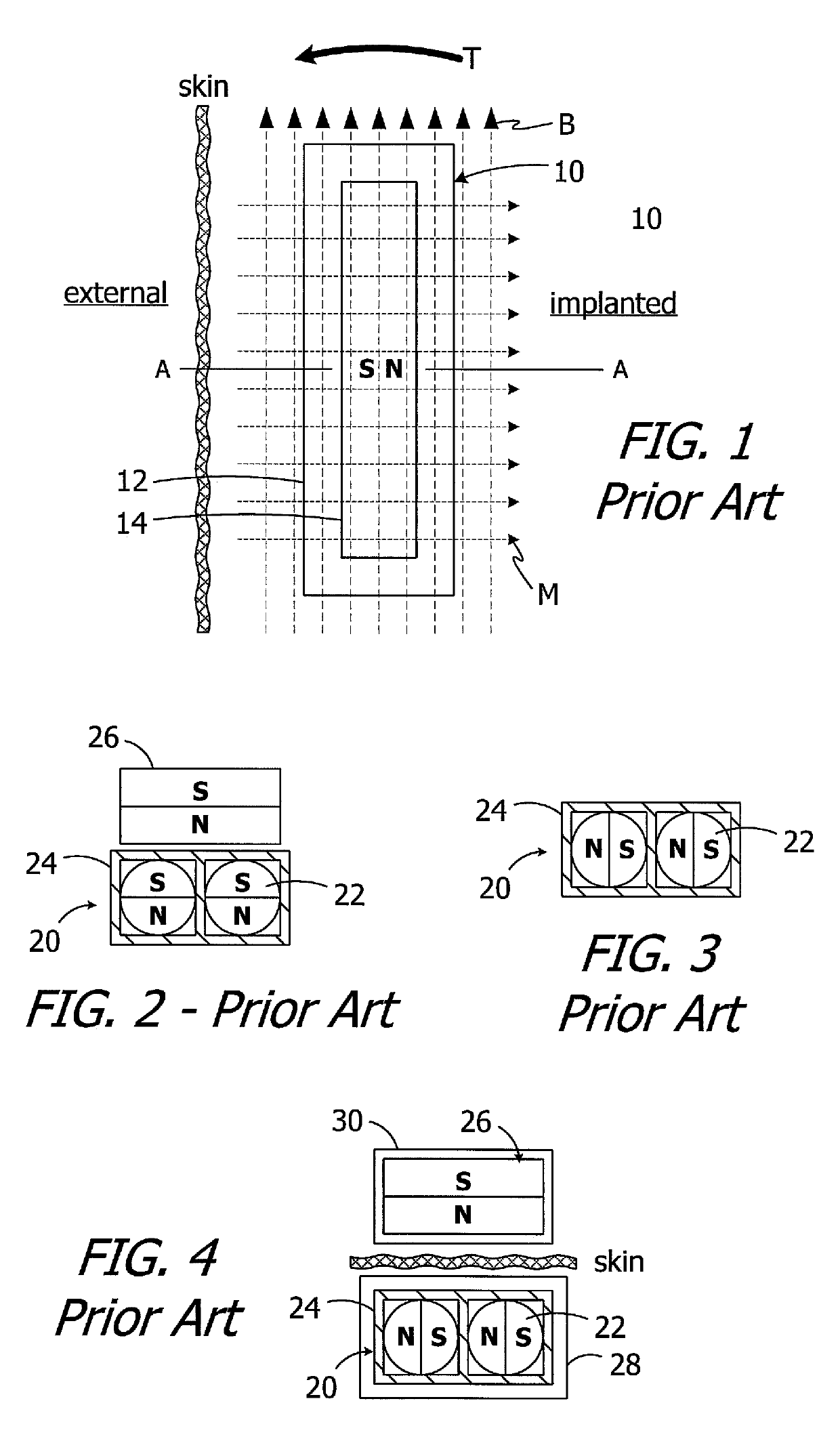
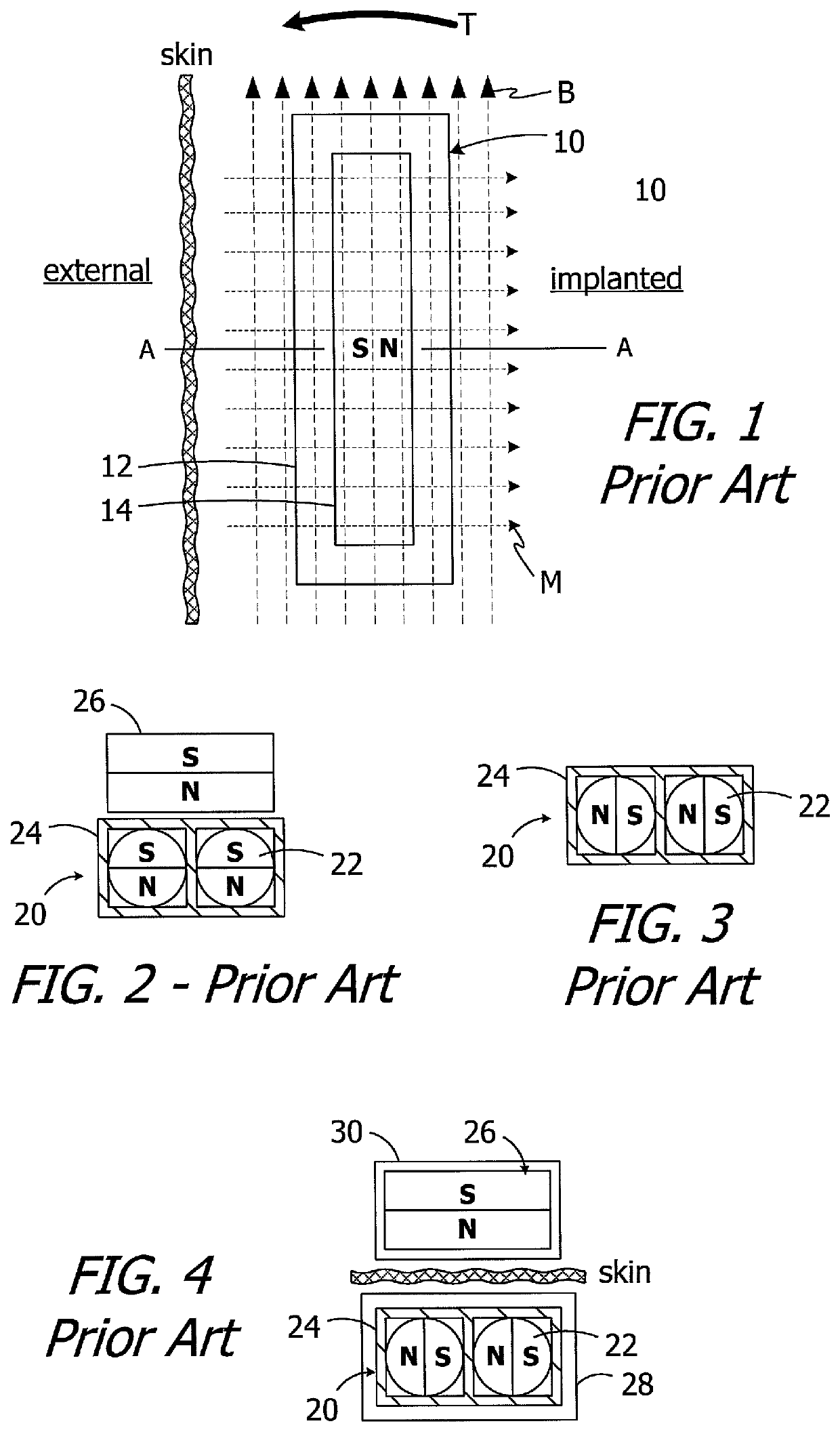
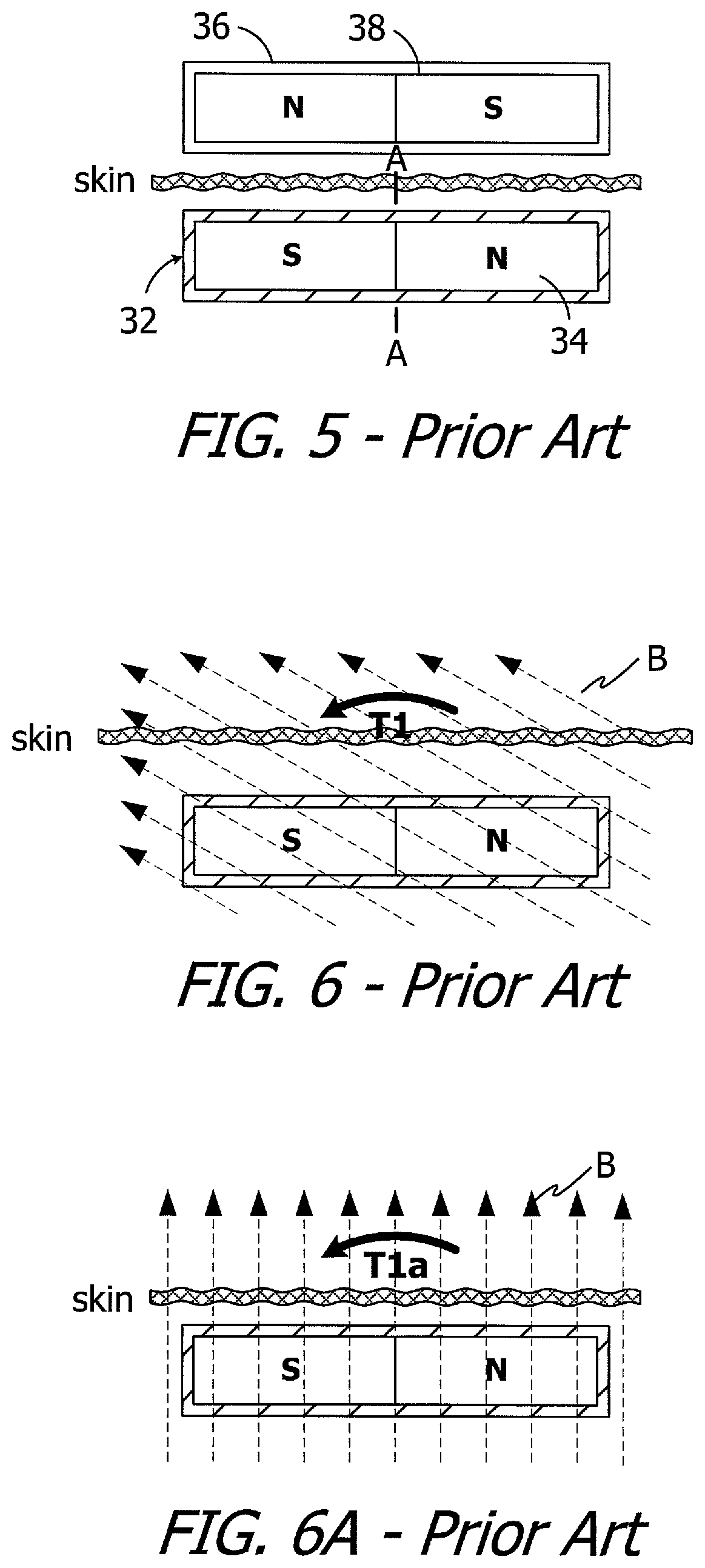
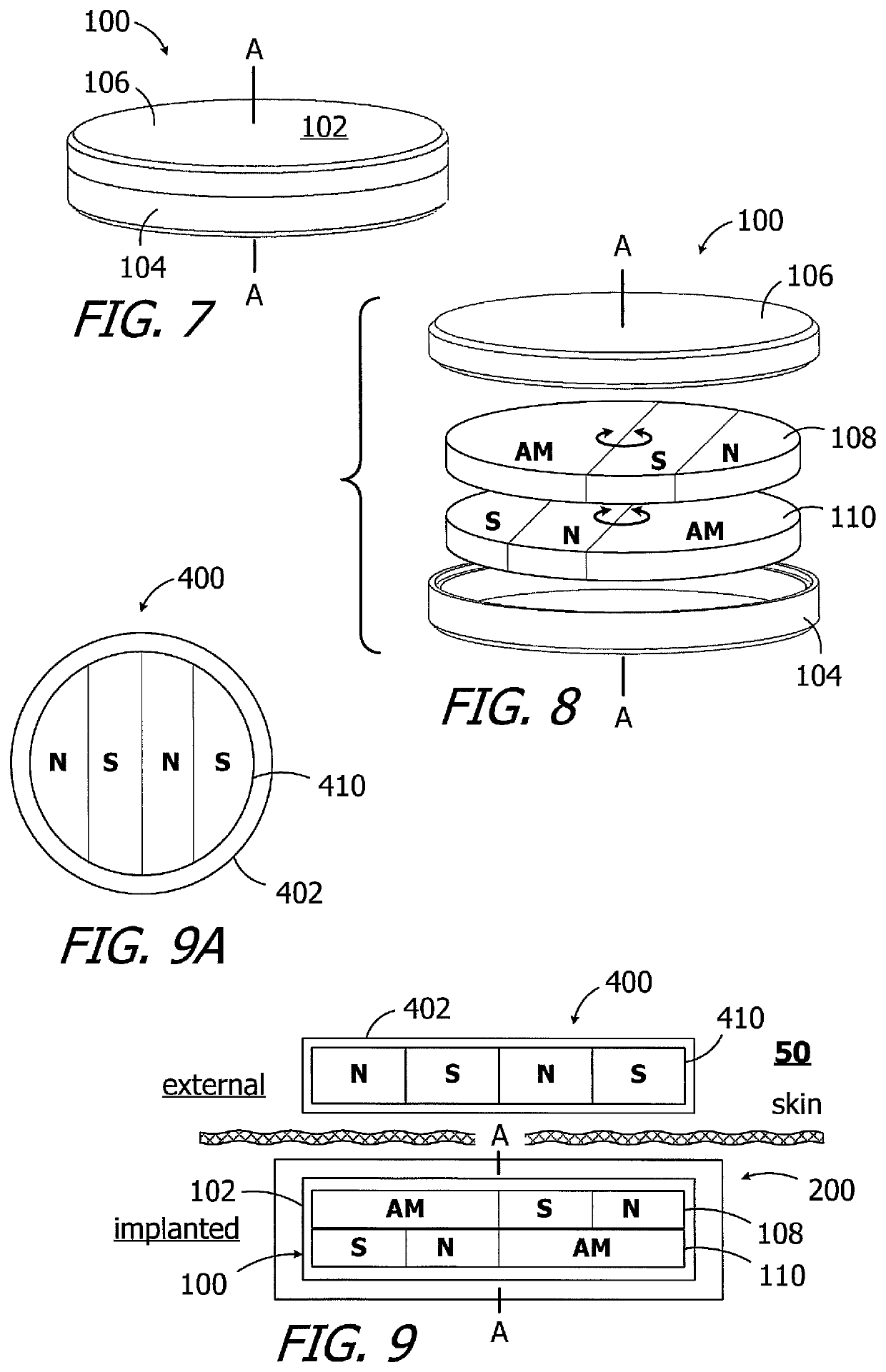
Cochlear implants having MRI-compatible magnet apparatus and associated methods
A cochlear implant including a cochlear lead, an antenna, a stimulation processor, and a magnet apparatus, associated with the antenna, including a case defining a central axis, a magnet frame within the case and rotatable about the central axis of the case, and a plurality of diametrically magnetized magnets that are located in the magnet frame, the magnets defining a longitudinal axis and a N-S direction and being rotatable about the longitudinal axis relative to the magnet frame and biased by the magnet frame to a predetermined N-S rotational orientation.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
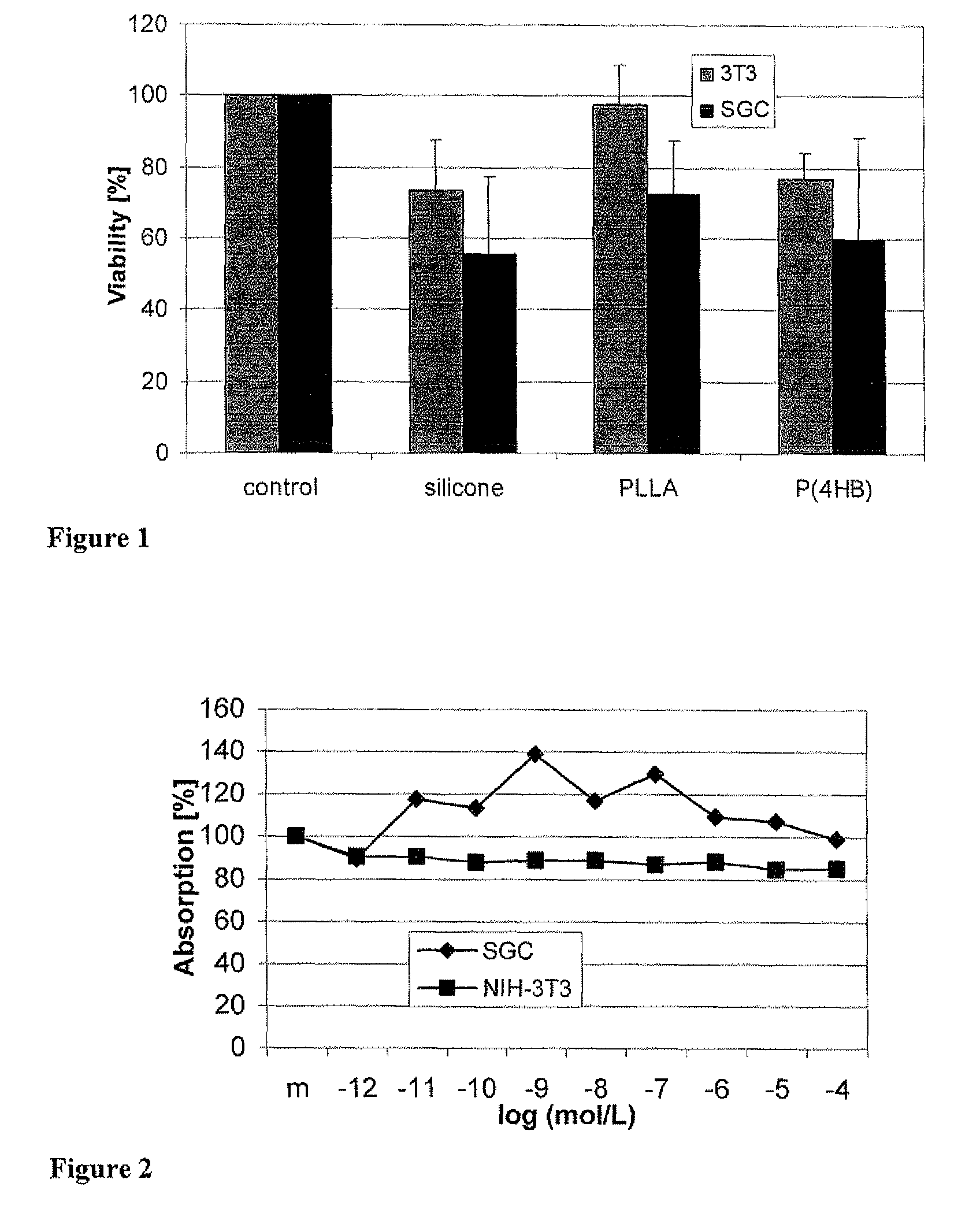
Drug eluting cochlear implants
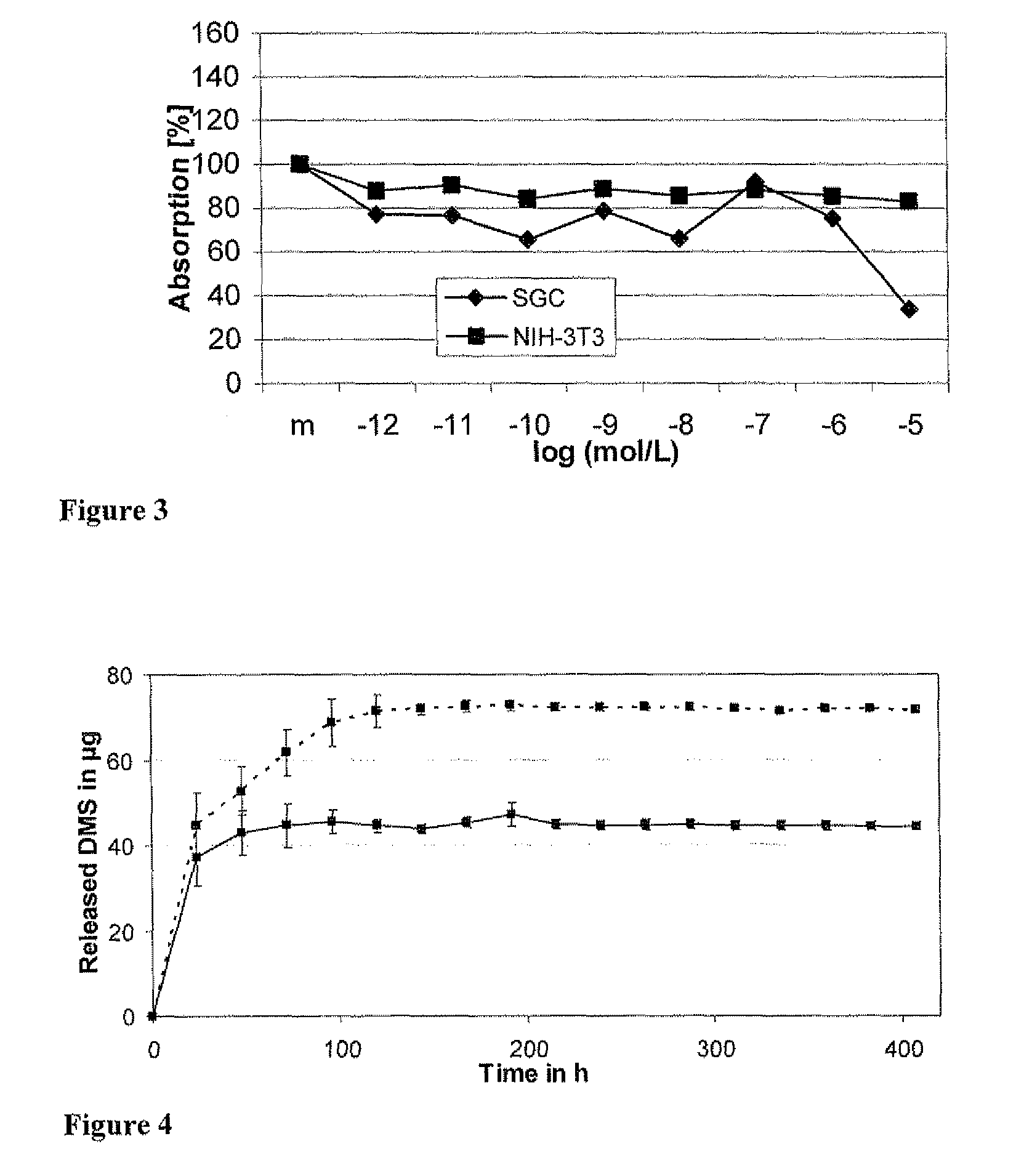
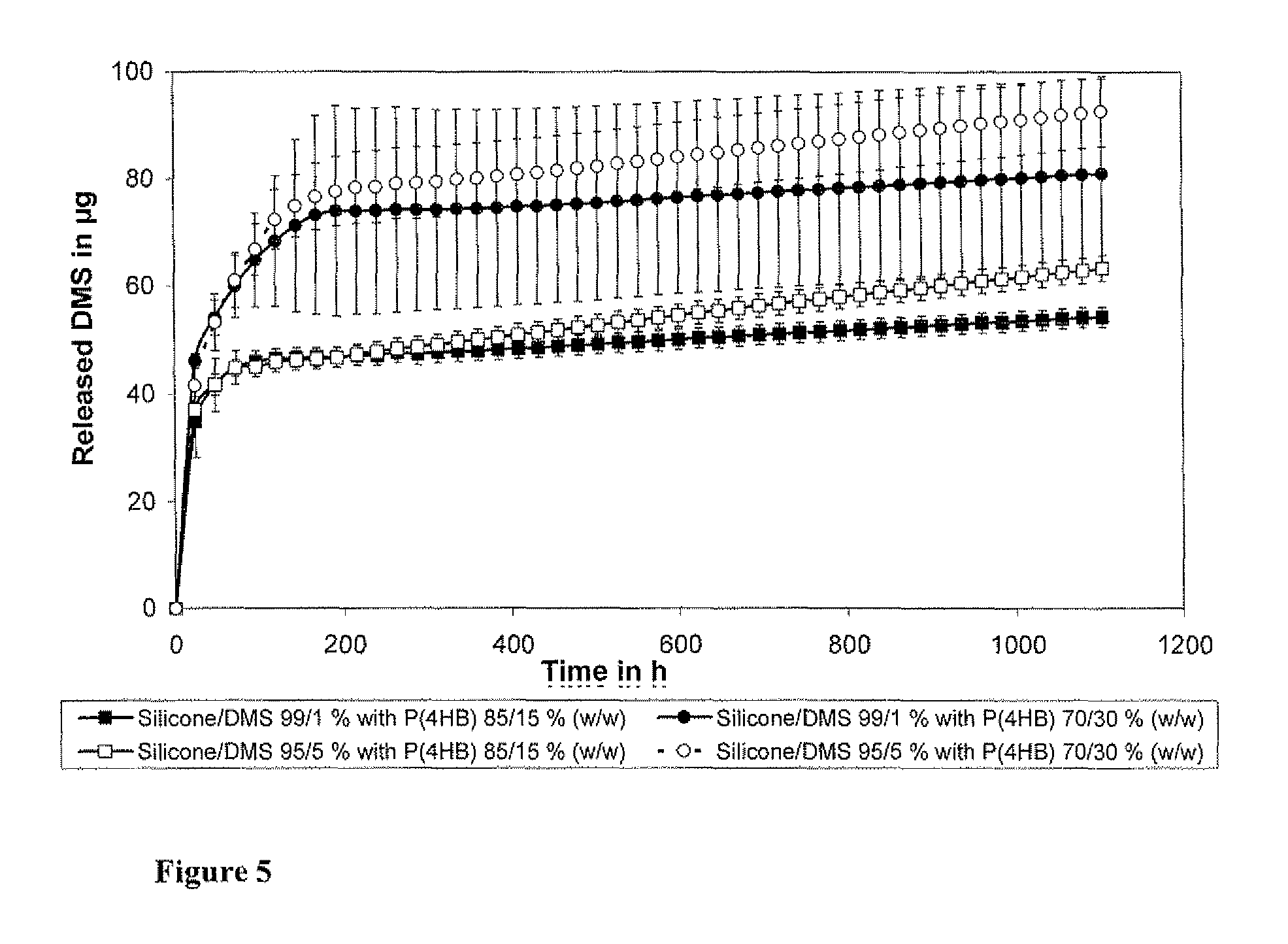
ActiveUS9162010B2Improve the lubrication effectEasy to insertElectrotherapyMedical devicesBiocompatible coatingCopolymer
Drug delivery systems and biocompatible coatings for use with implantable stimulation devices such as cochlear implants have been developed. These drug delivery systems and coatings comprise polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) polymers and copolymers. The drug delivery systems may be used to deliver pharmacologically active substances, for example, directly from a cochlear implant to the inner ear. The coatings can impart lubricity to cochlear devices for ease of insertion of the electrodes. In the preferred embodiment, the drug delivery system comprises a polyhydroxyalkanoate polymer, and in the most preferred embodiment, the PHA polymer comprises poly(4-hydroxybutyrate) (P(4HB)) or copolymer thereof. A particularly preferred embodiment is where the silicone sheath of the cochlear implant electrodes has been surface modified, and coated with P(4HB), and the P(4HB) either contains a pharmacologically active substance or has been coated with such a substance.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Cochlear implant drug delivery device
InactiveUS20120158114A1Small dimensionReduce frictionHead electrodesSurgical drugsBiologyBiomedical engineering
Owner:DEBRUYNE KRISTINE +5
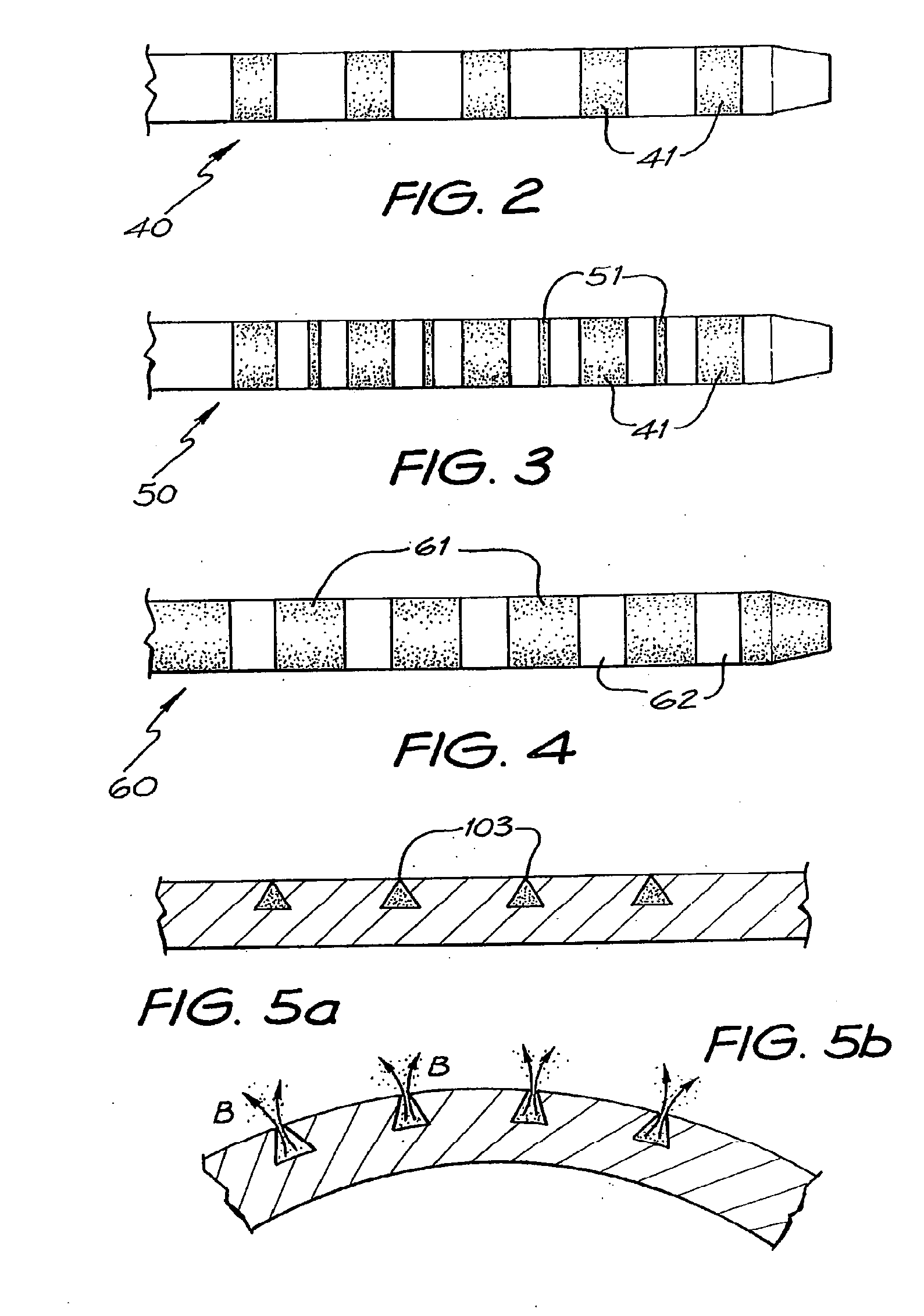
Optical fibre bending sensor for monitoring artificial cochlea electrode bending implantation and use thereof
InactiveCN1613437ASimple structureEasy to useEar treatmentCochlear implantationSingle-mode optical fiber
An optical-fibre curvature sensor for monitoring the curve implantation of artificial cochlear electrode is composed of light source, circulator, optical fibre, photoelectric detector, signal processing and displaying unit, and sensing probe with a planar front end with reflecting film and protecting film. Its application includes such steps as putting the sensing probe and a fine metal wire in said electrode, and implanting the electrode into cochlea while detecting the power of reflected light to obtain the curvature.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
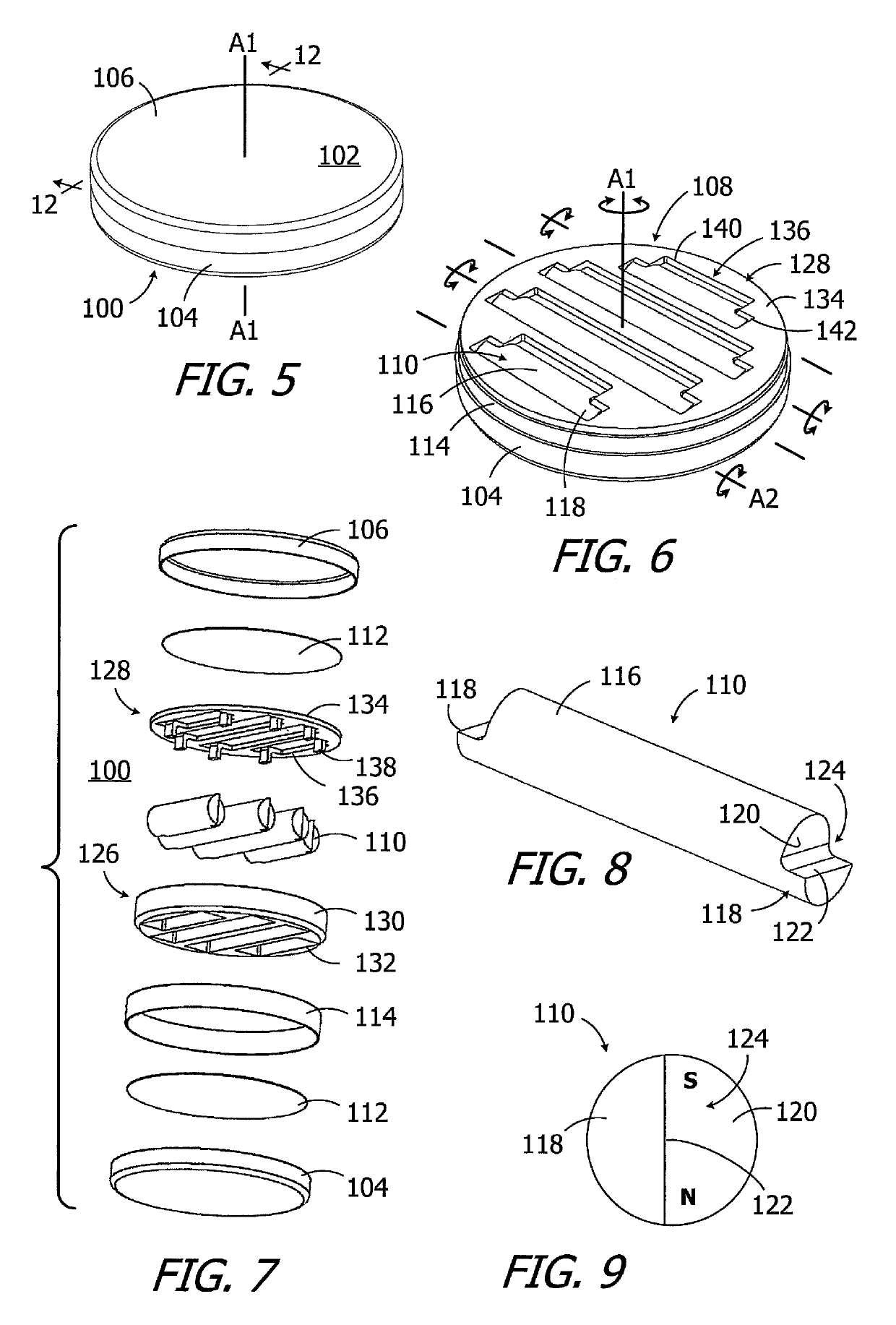
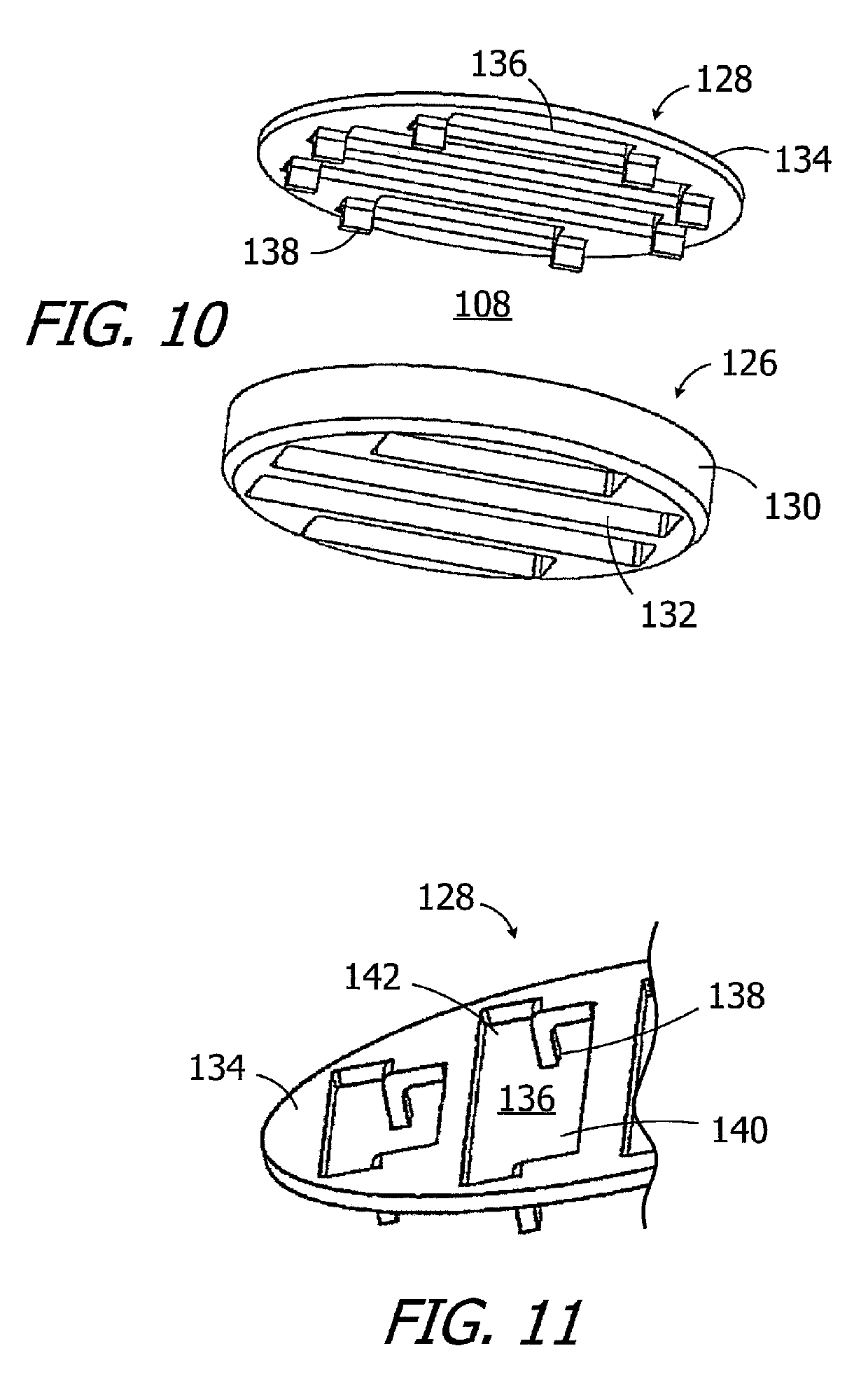
Modified Electrode Lead for Cochlear Implants
ActiveUS20160096012A1Mechanical strainHead electrodesExternal electrodesImplantable ElectrodesMedicine
An implantable electrode arrangement for a cochlear implant system is described. The arrangement includes a flexible intracochlear electrode array having an outer surface with electrode contacts for applying cochlear stimulation signals to target neural tissue within the implanted cochlea. A flexible extracochlear electrode lead is coupled at a lead proximal end to an implanted signal processor that provides the cochlear stimulation signals, and connected at a lead distal end to a proximal end of the electrode array. A lead holder is connected to the lead distal end and has an initial shape. The lead holder is malleable and adapted to be intra-surgically deformed into and retain a new desired shape so as to secure the lead distal end at the electrode opening into the implanted cochlea and decouple post-surgical mechanical strain at the lead distal end from the electrode array.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Cochlear implants having MRI-compatible magnet apparatus
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
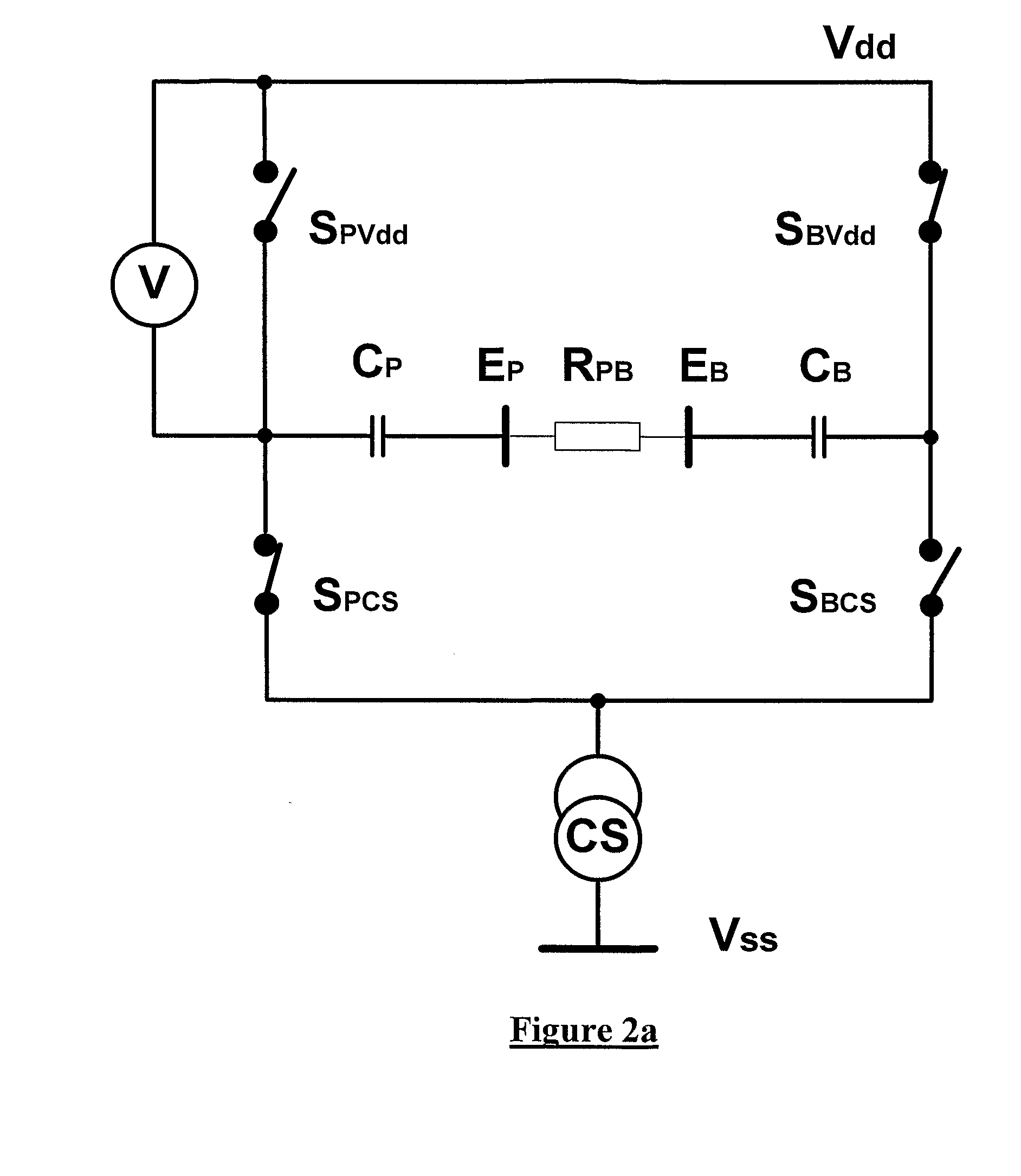
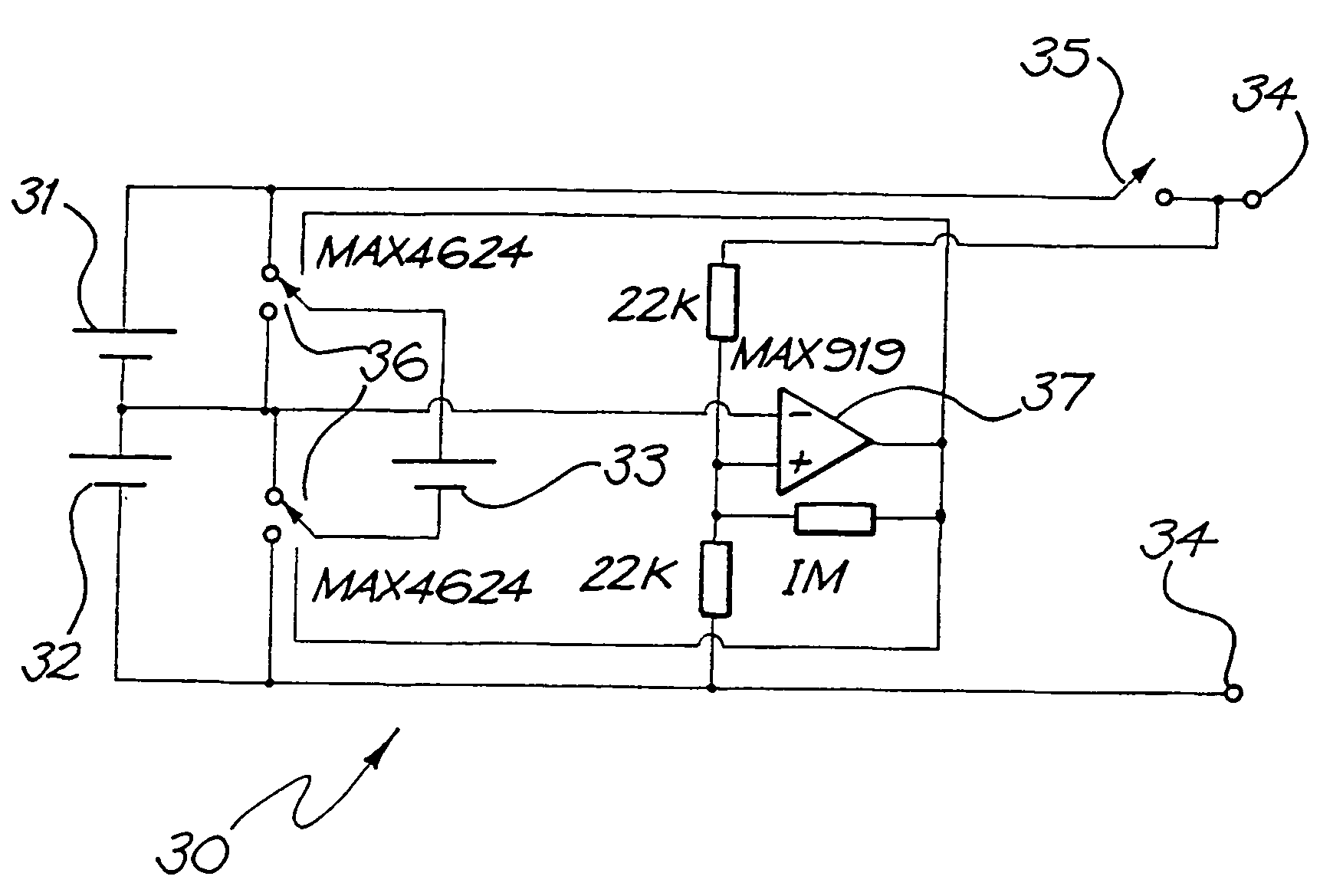
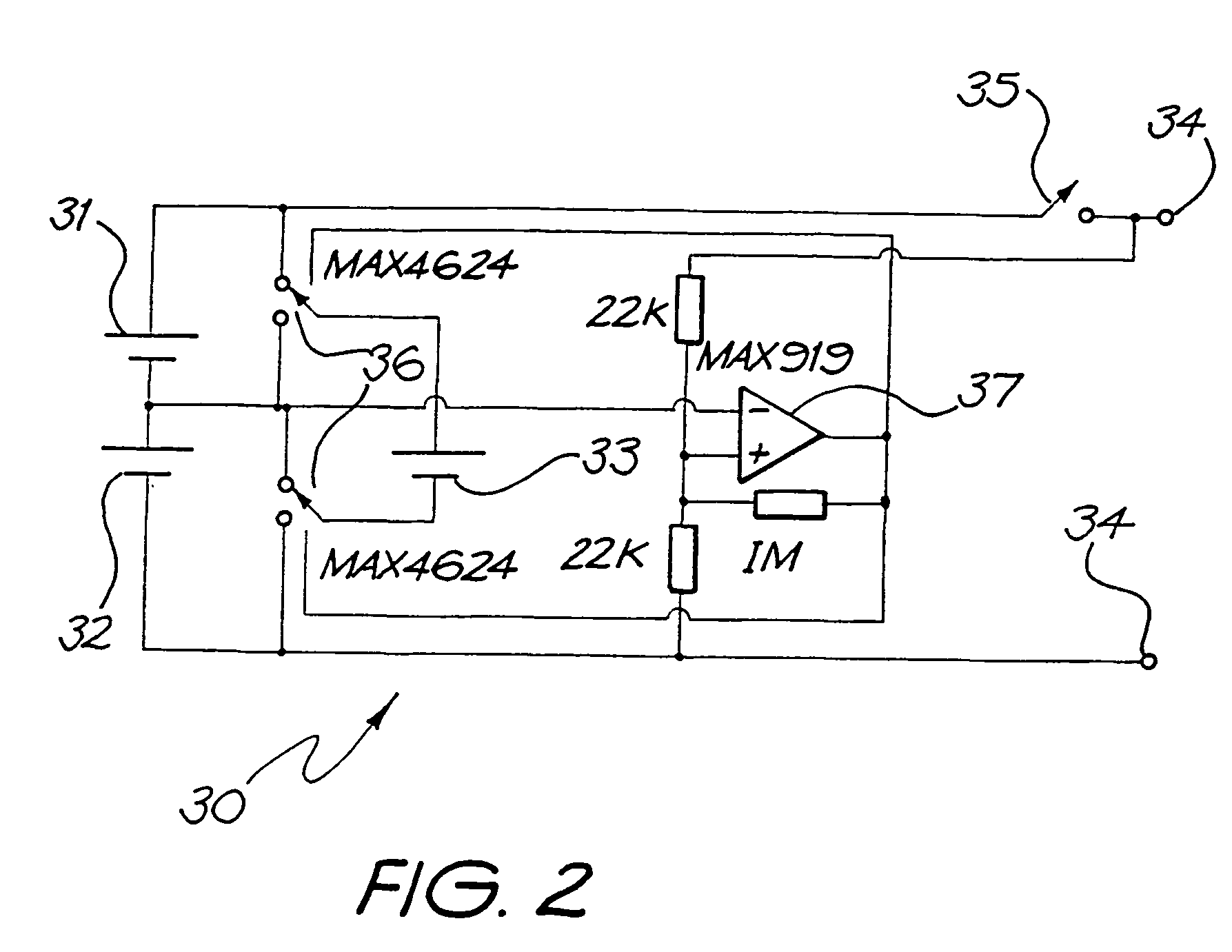
Power supply for a cochlear implant
InactiveUS7157808B2Maximize device performanceLower performance requirementsElectrotherapyEar treatmentElectricityLow voltage
A power supply control system for use with a tissue stimulating prosthesis, such as a cochlear implant. The power supply control system comprises a first battery (31), a second battery (32), at least a third battery (33), and a switching system (36). The first and second batteries (31, 32) are electrically connected in series to provide power to the prosthesis, while the third battery (33) is electrically connectable through the switching means (36) in parallel with either the first battery (32). The third battery (33) is electrically connected by the control system in parallel with whichever one of said first battery (31) or said second battery (32) has lowest voltage.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Cochlear implant
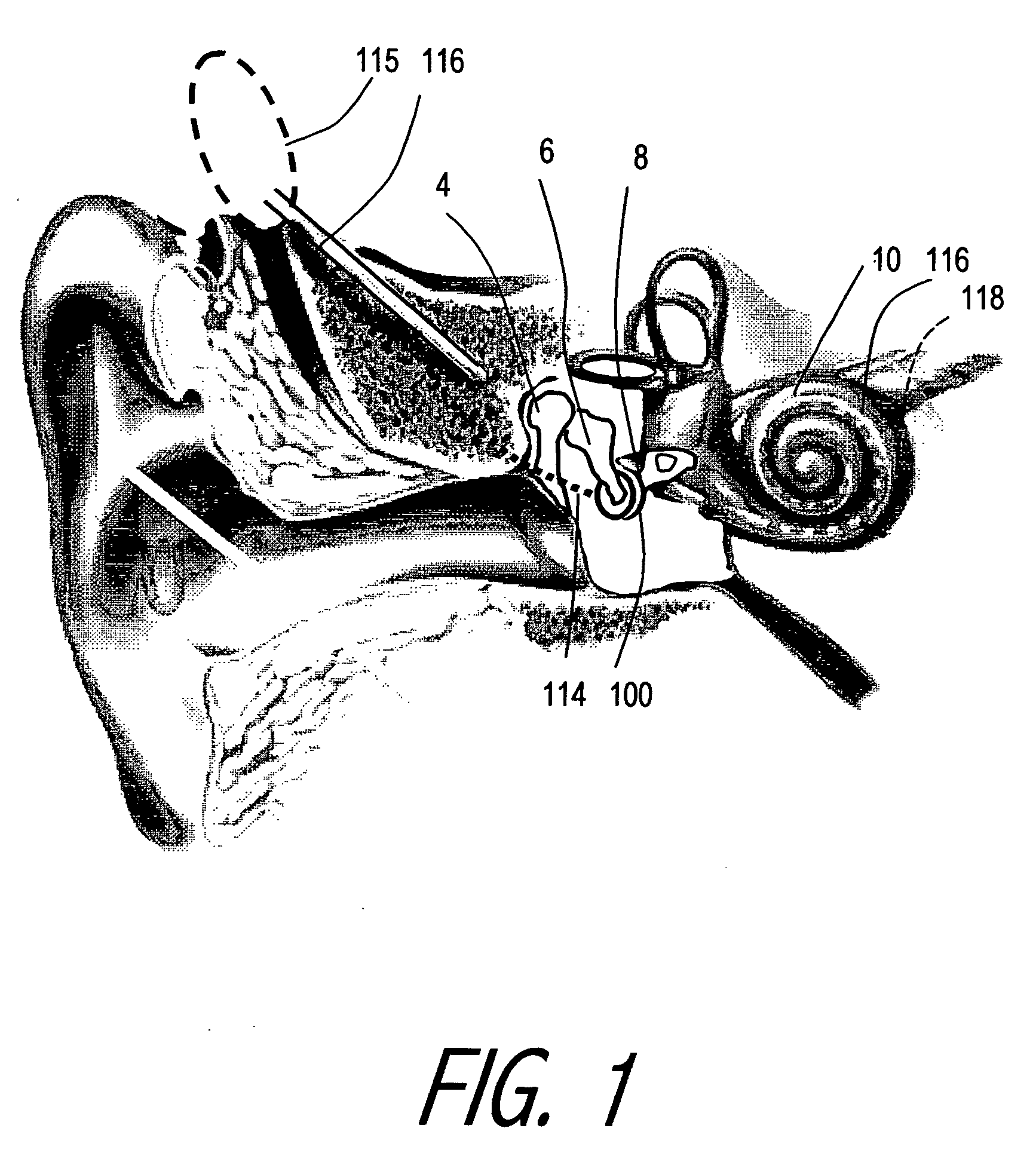
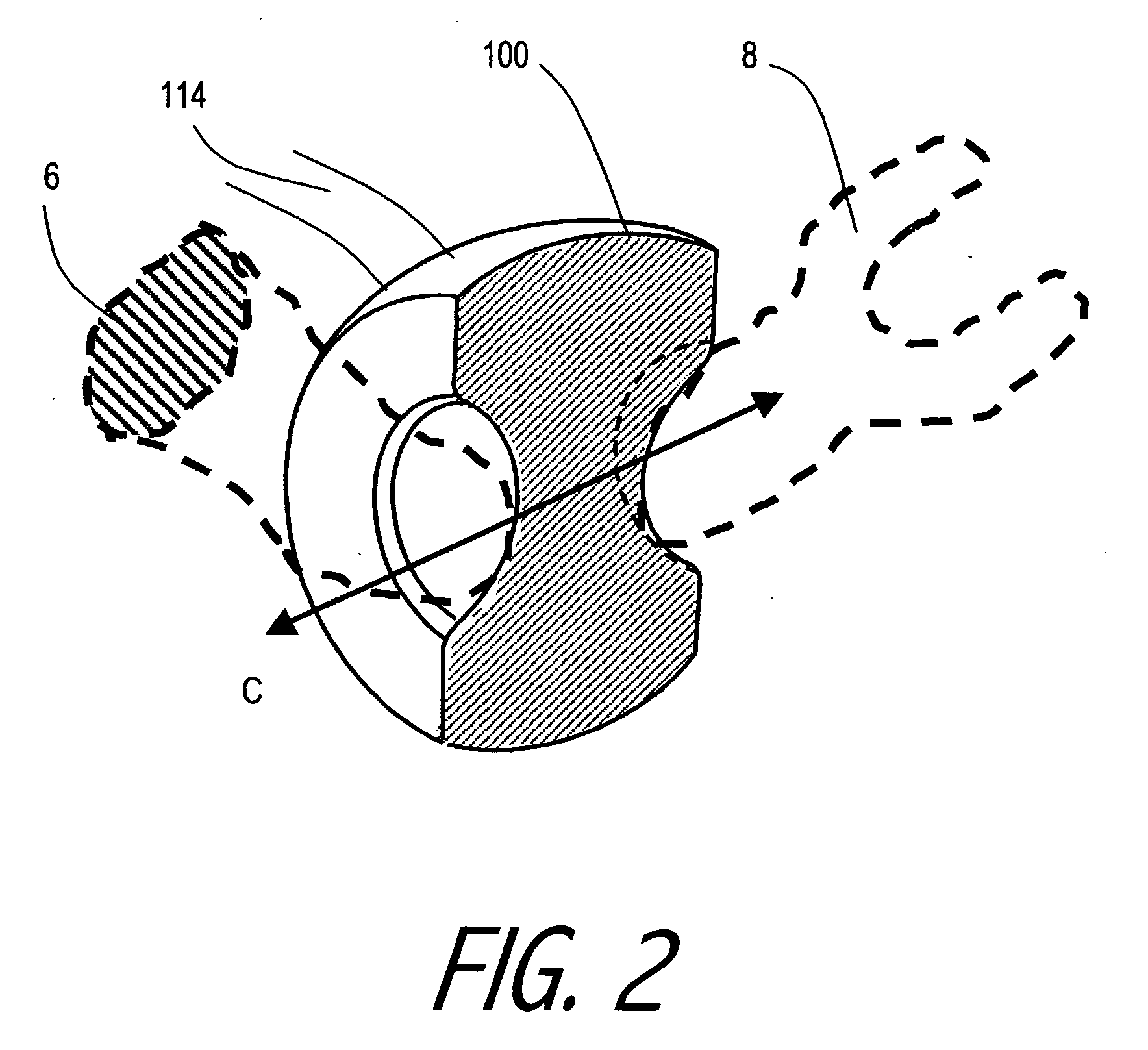
InactiveUS20110098787A1Improve hearingImprove abilitiesMicrophonesElectrotherapyCochlear implantationHearing perception
An improved cochlear implant and method are disclosed. The present invention relates particularly to an external processing unit of a cochlear implant which processes sounds from within the ear canal of the patient. The implant comprises a microphone placed within the ear canal of the patient. The implant can alternatively comprise a hollow tube placed within the ear canal of the patient which is used to carry sound to a microphone located elsewhere. The method may comprise the steps of: providing a microphone in the ear canal, thereby improving the hearing of said hearing-impaired subject. The method may comprise the steps of: providing in the ear canal a tube that delivers sound to a microphone, thereby improving the hearing of said hearing-impaired subject.
Owner:SPEARMAN MICHAEL R +1
Cochlear implants and magnets for use with same
ActiveUS10646718B2Increase distanceHead electrodesExternal electrodesPhysical therapyMechanical engineering
A cochlear implant including a cochlear lead, a housing, a magnet apparatus located within the flexible housing and including a first partial disk shaped magnet member and a second partial disk shaped magnet member spaced apart from the first partial disk shaped magnet member, an antenna within the housing, and a stimulation processor.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com