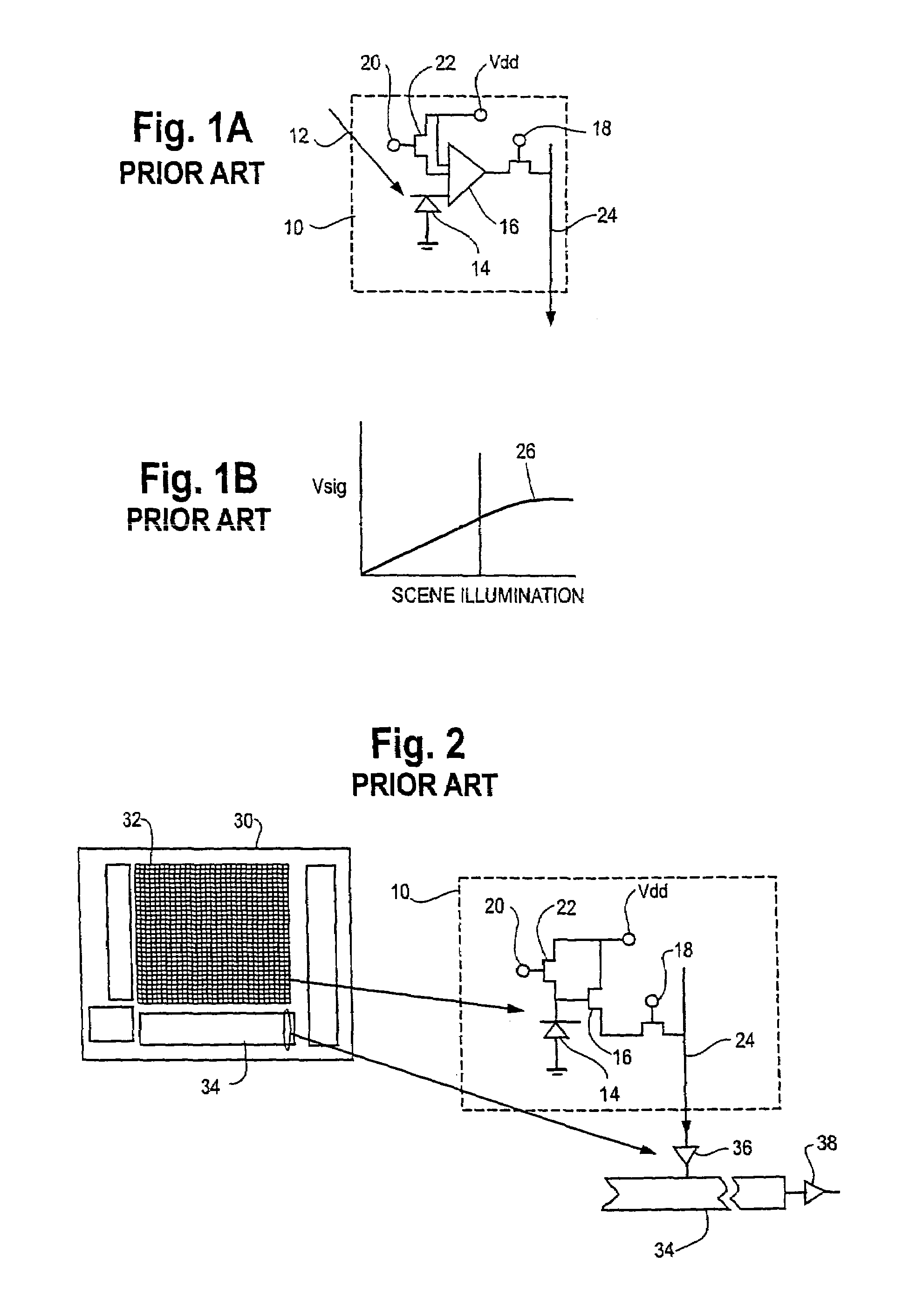
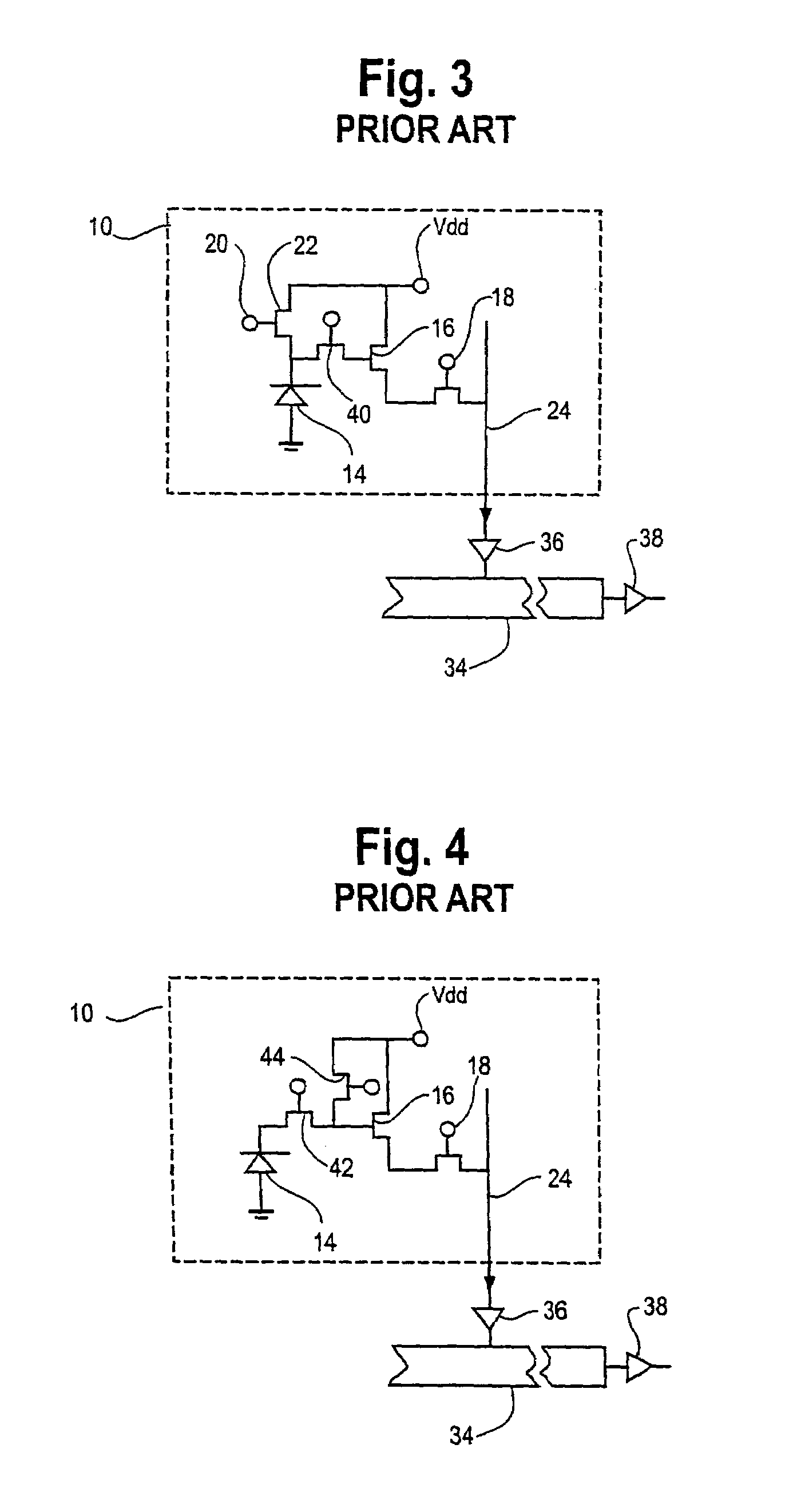
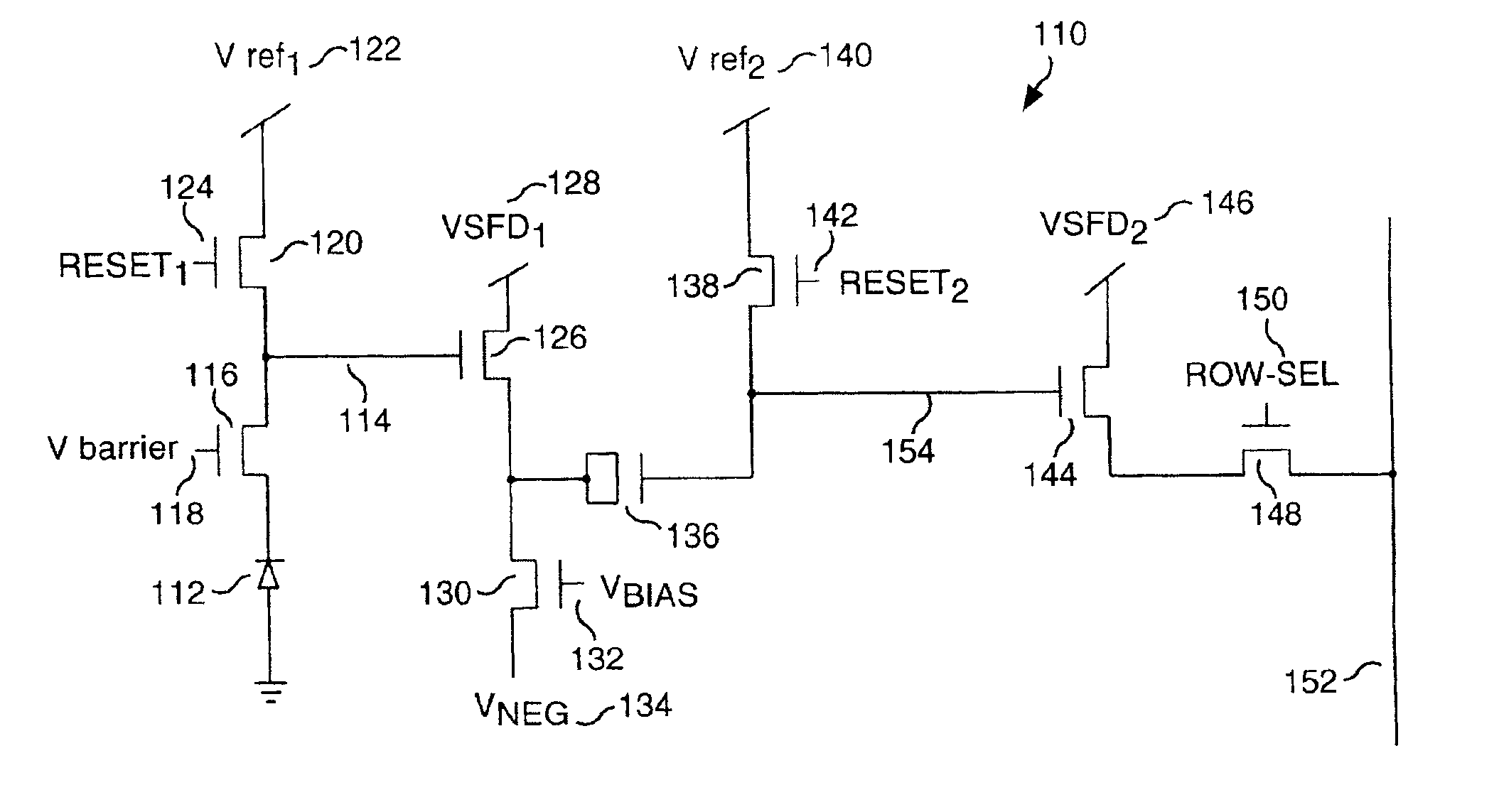
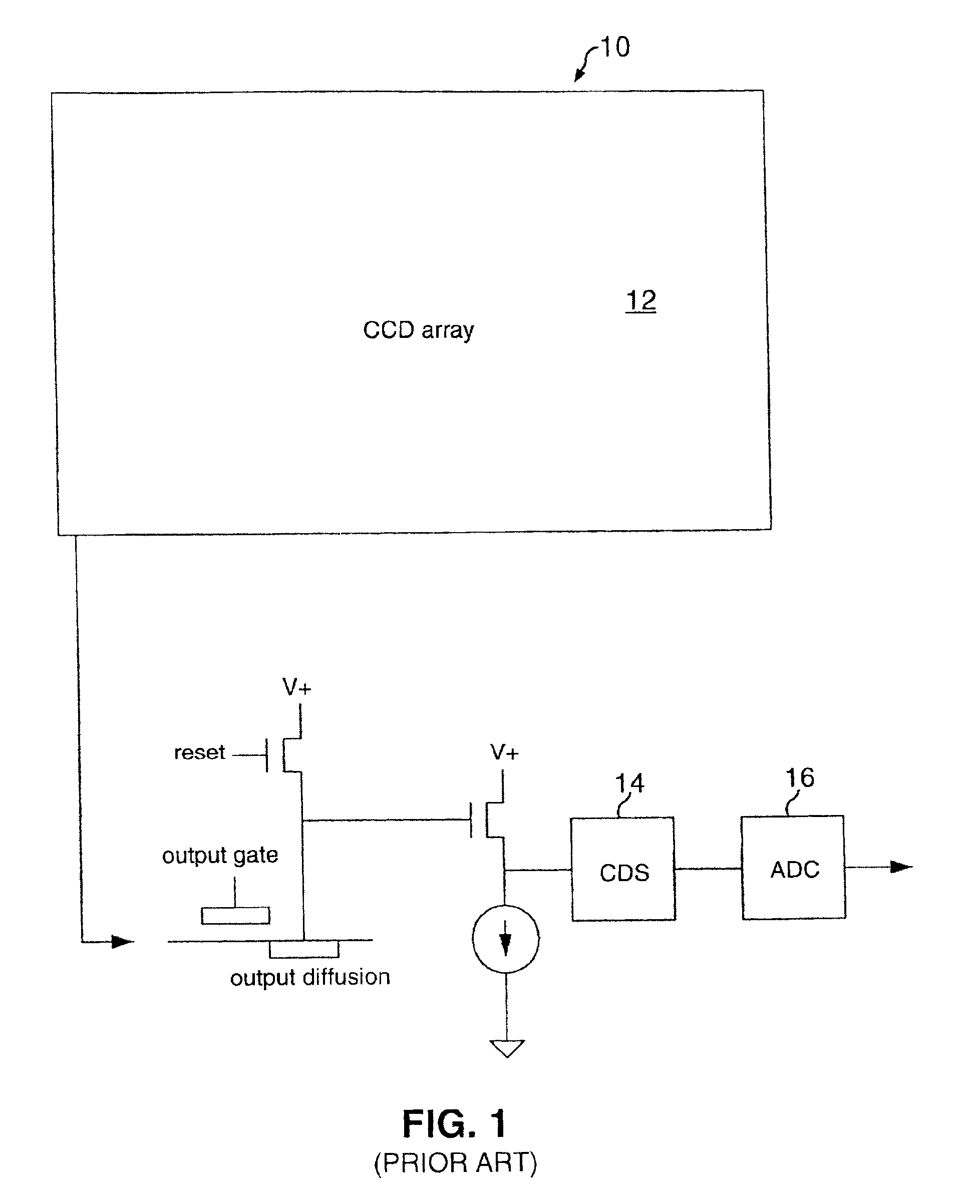
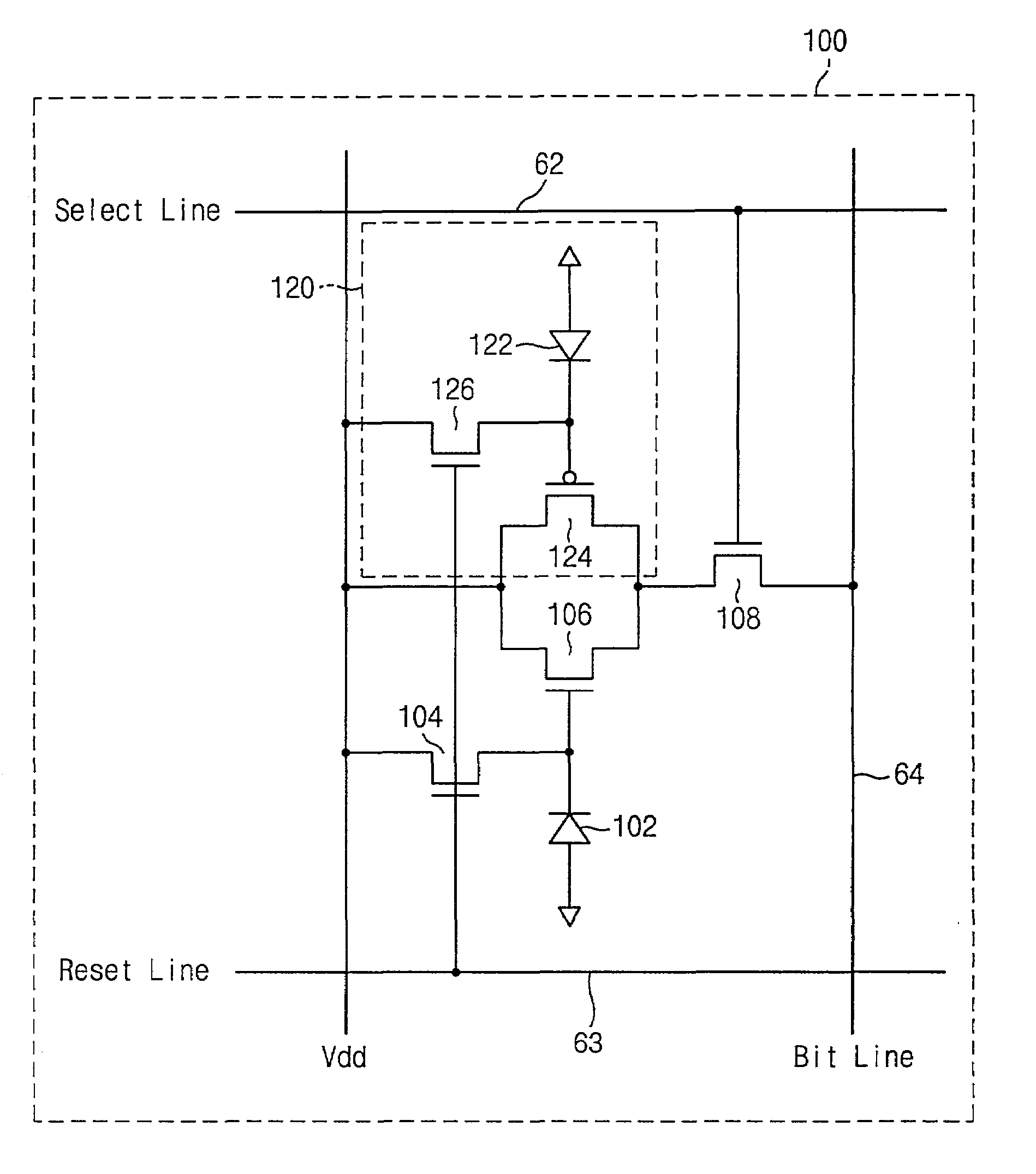
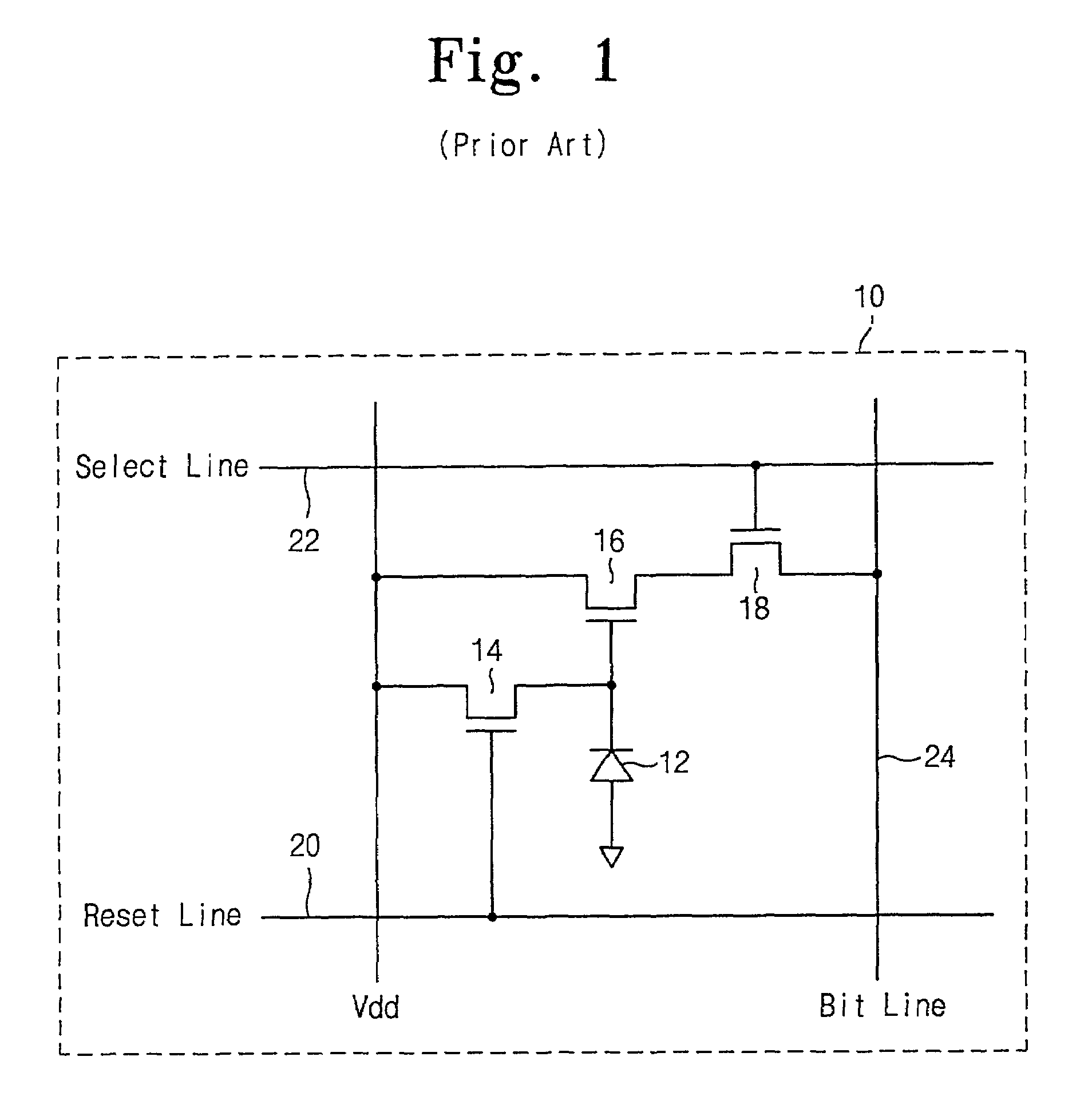
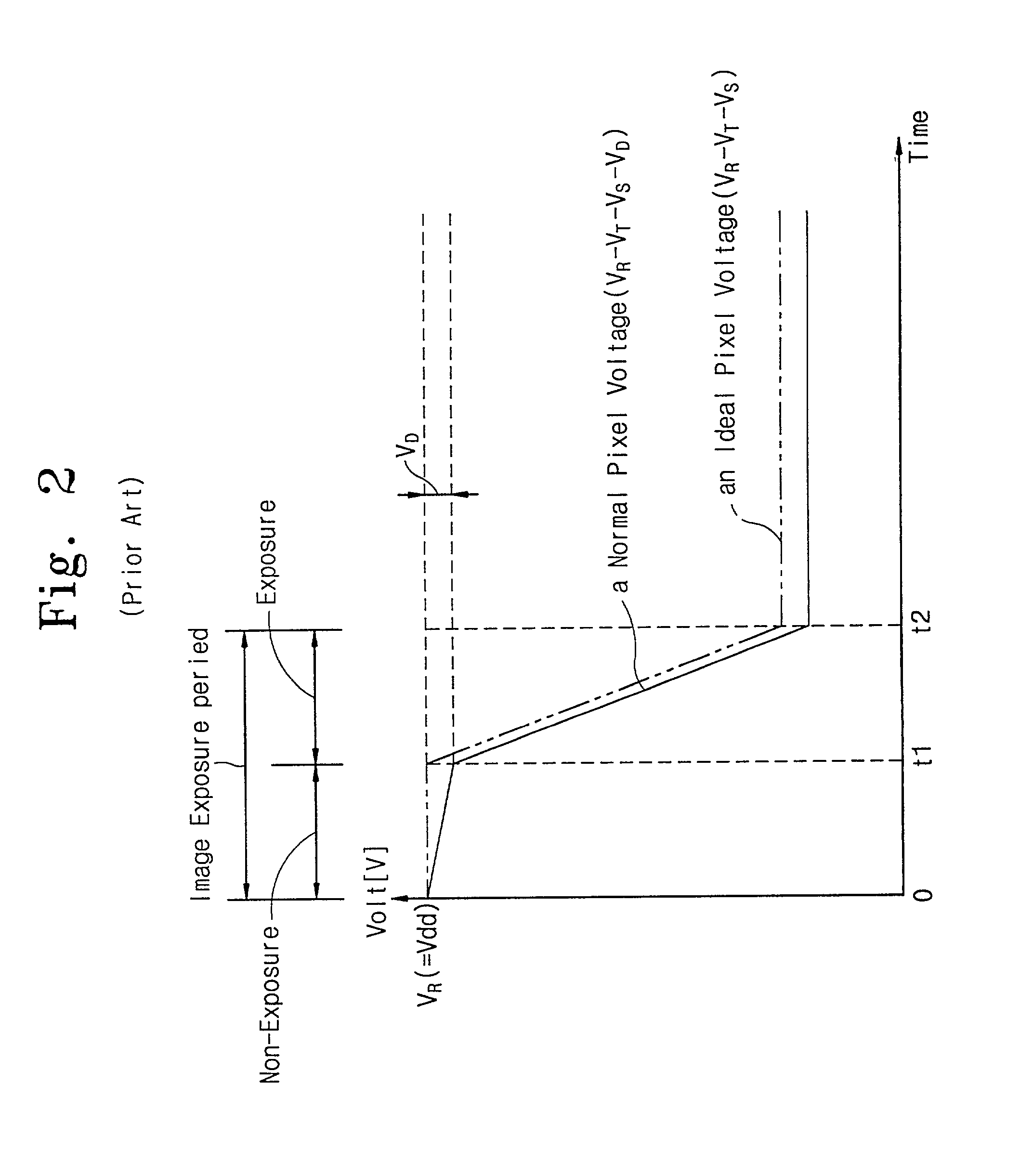
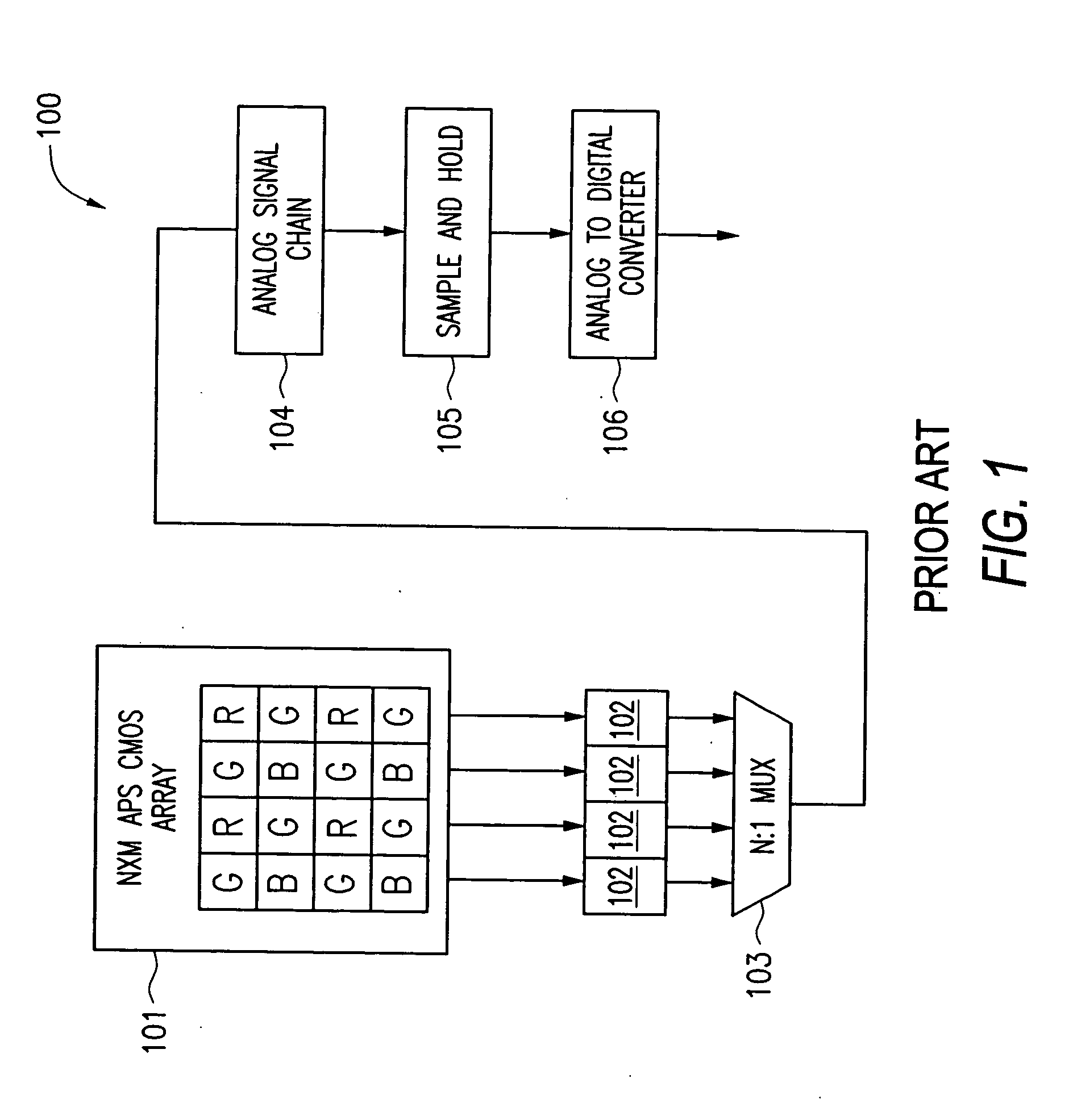
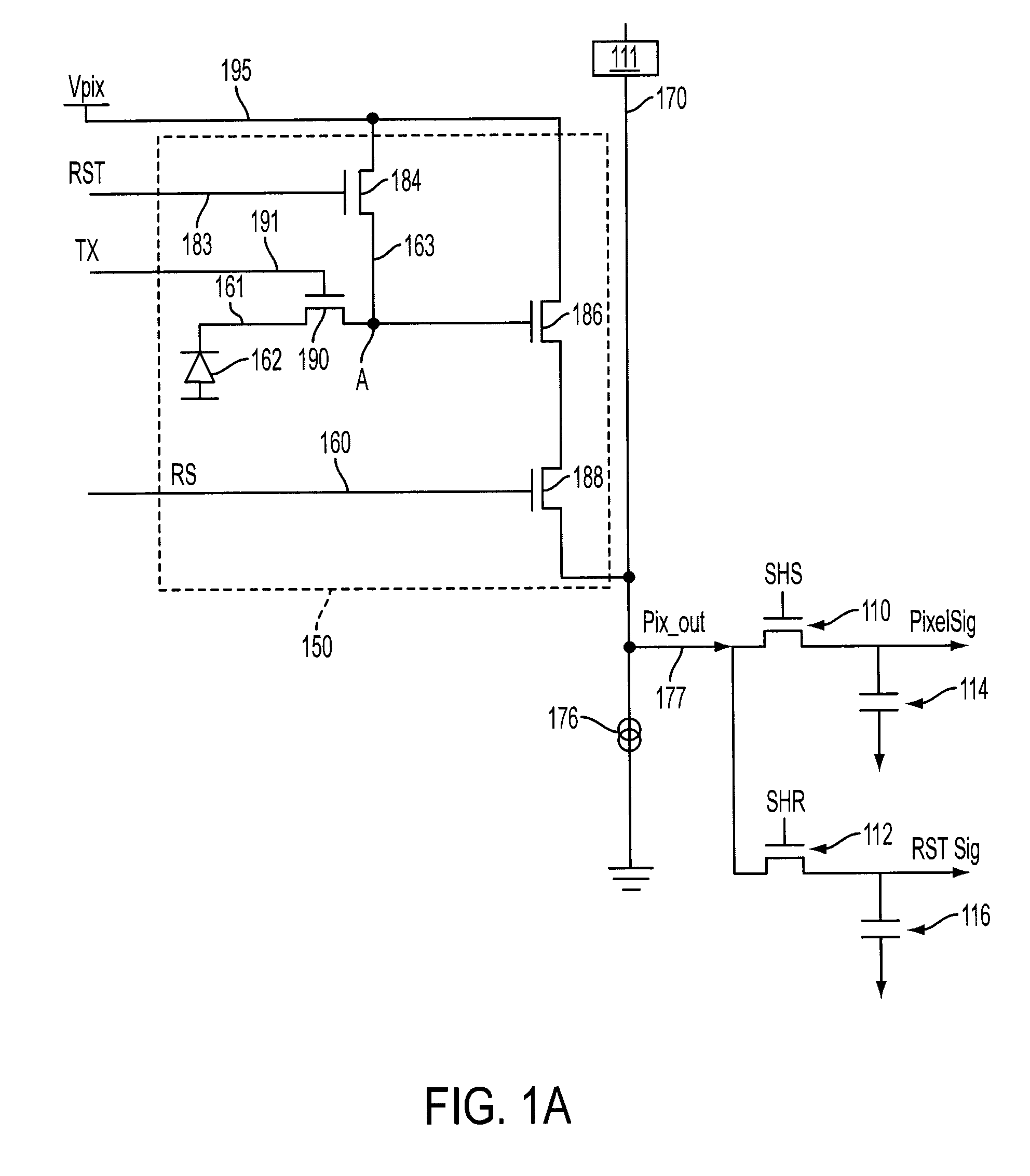
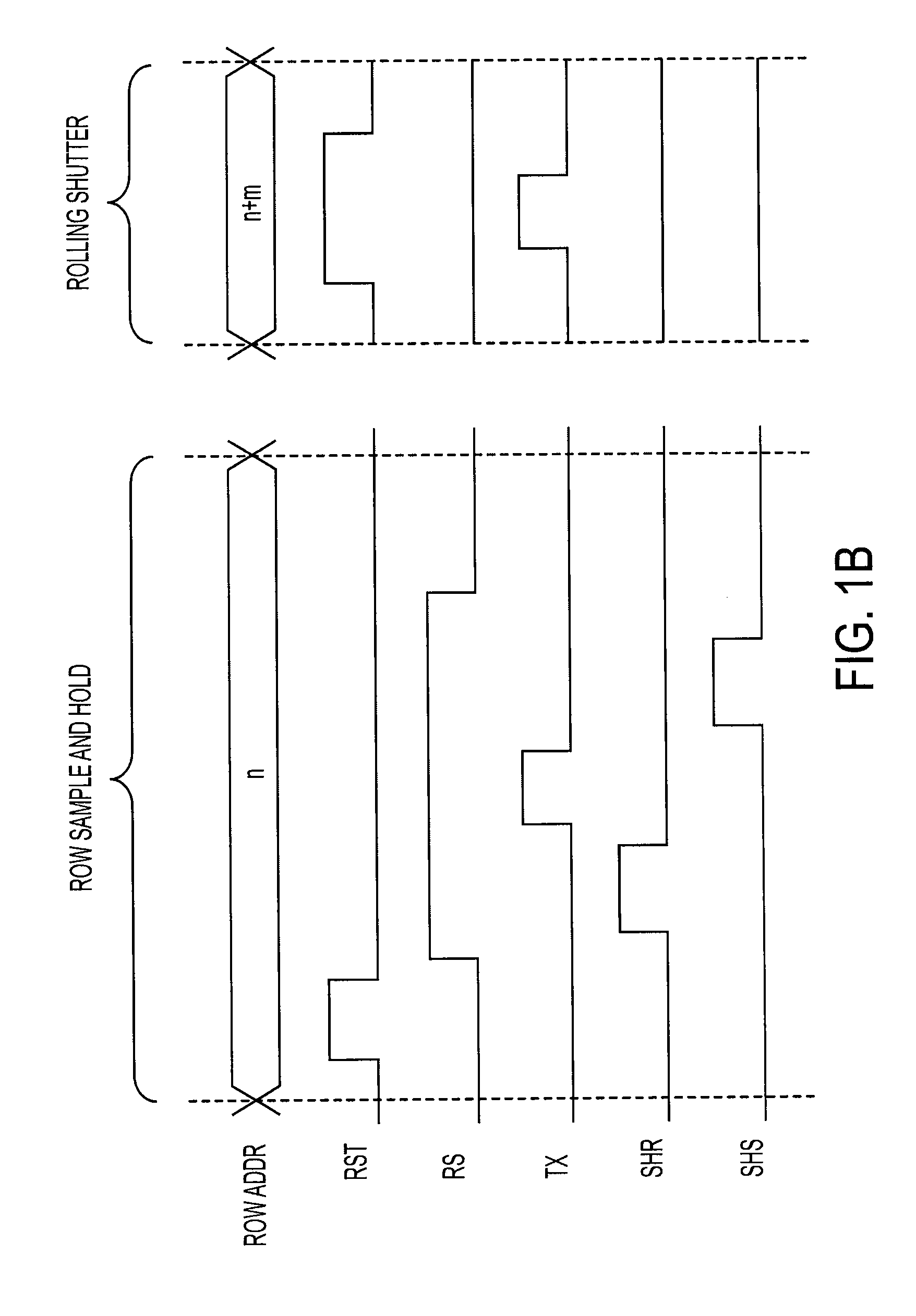
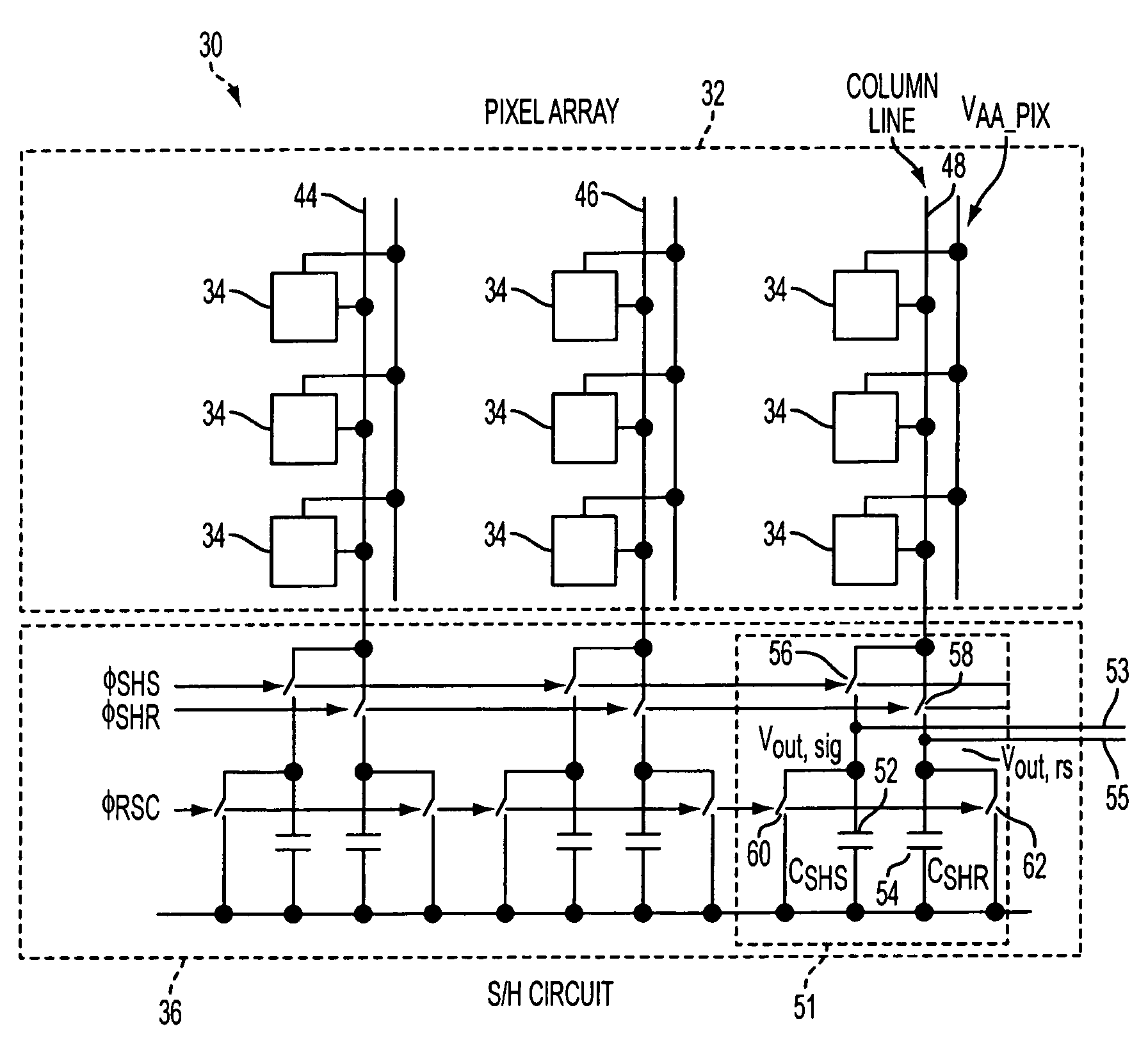
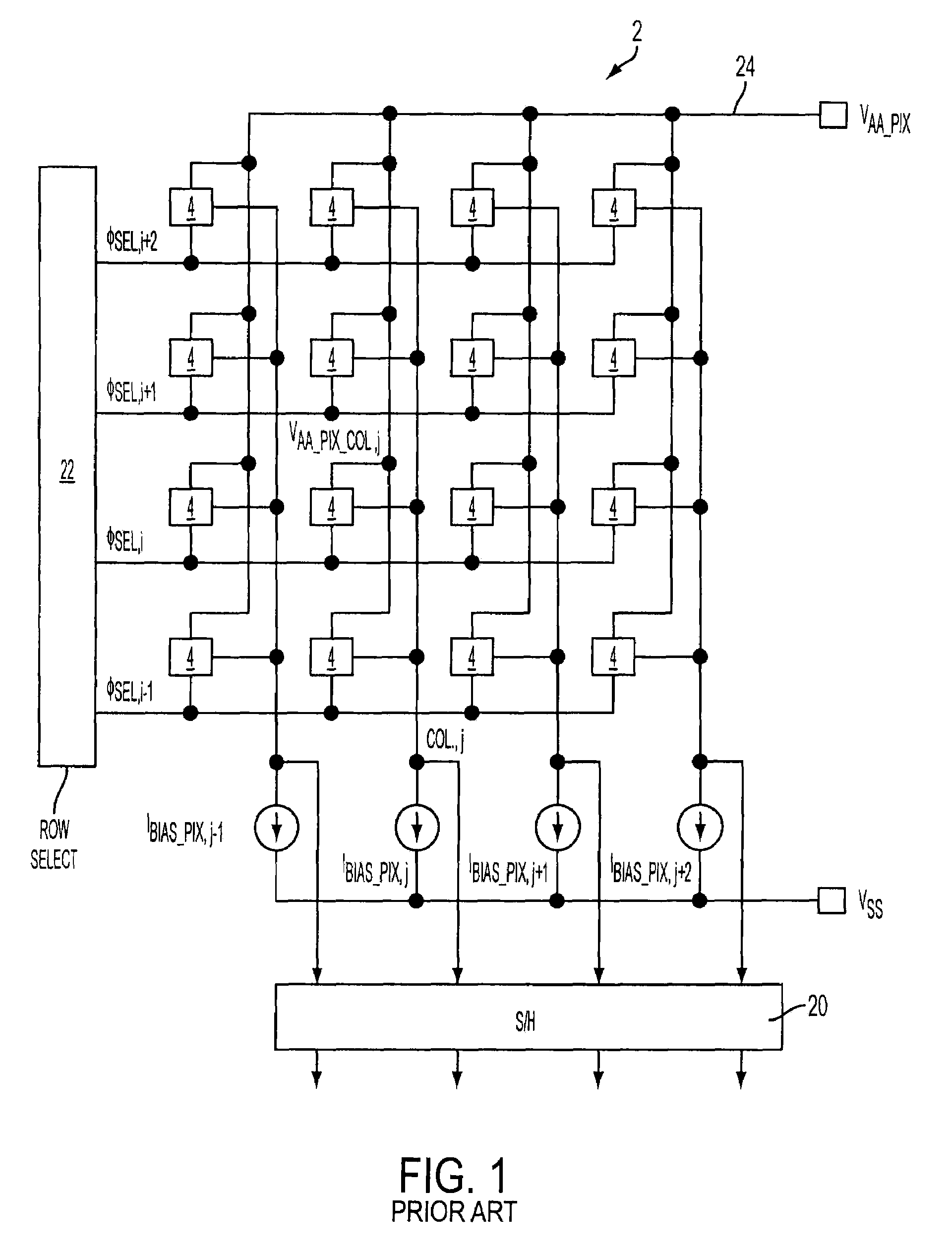
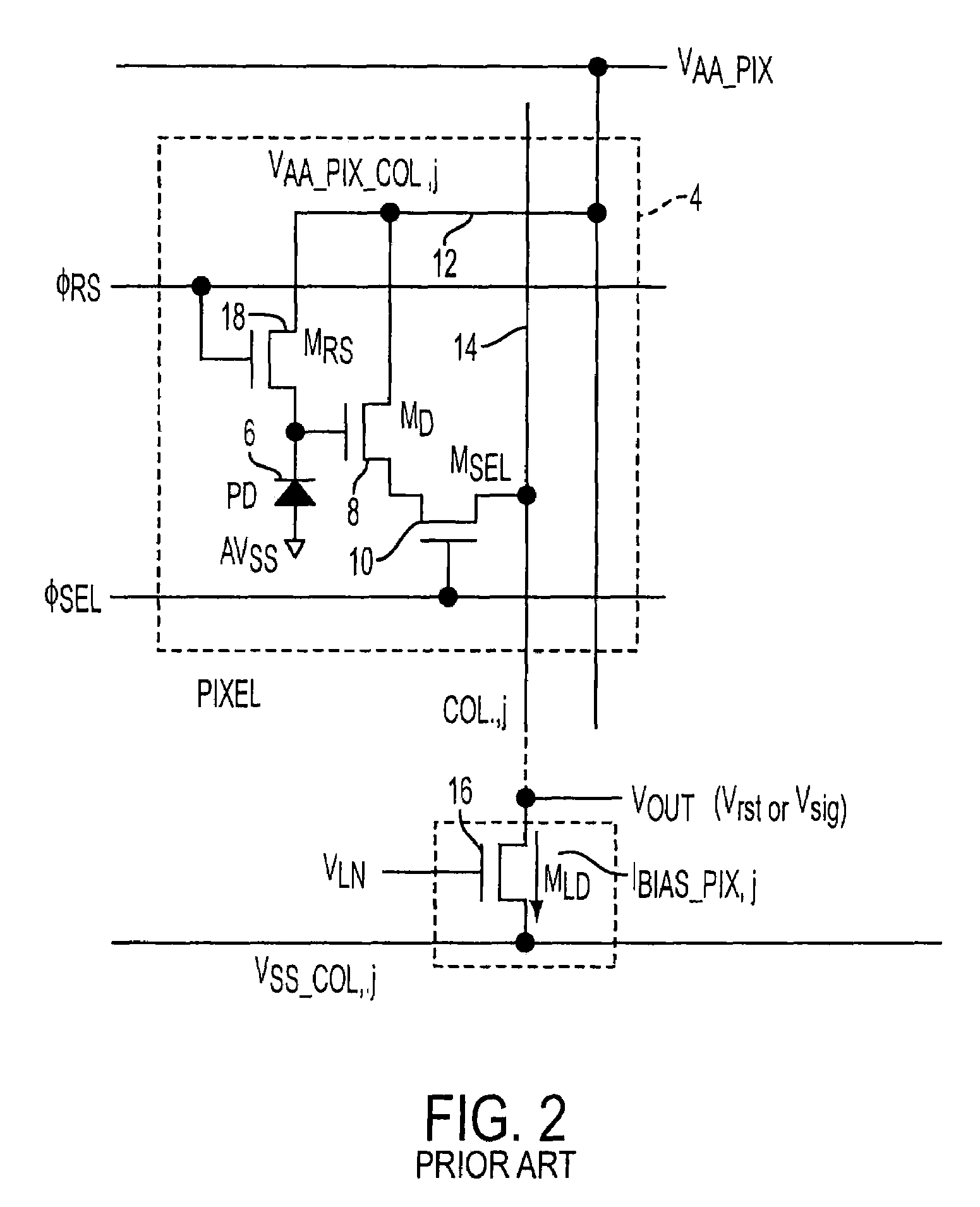
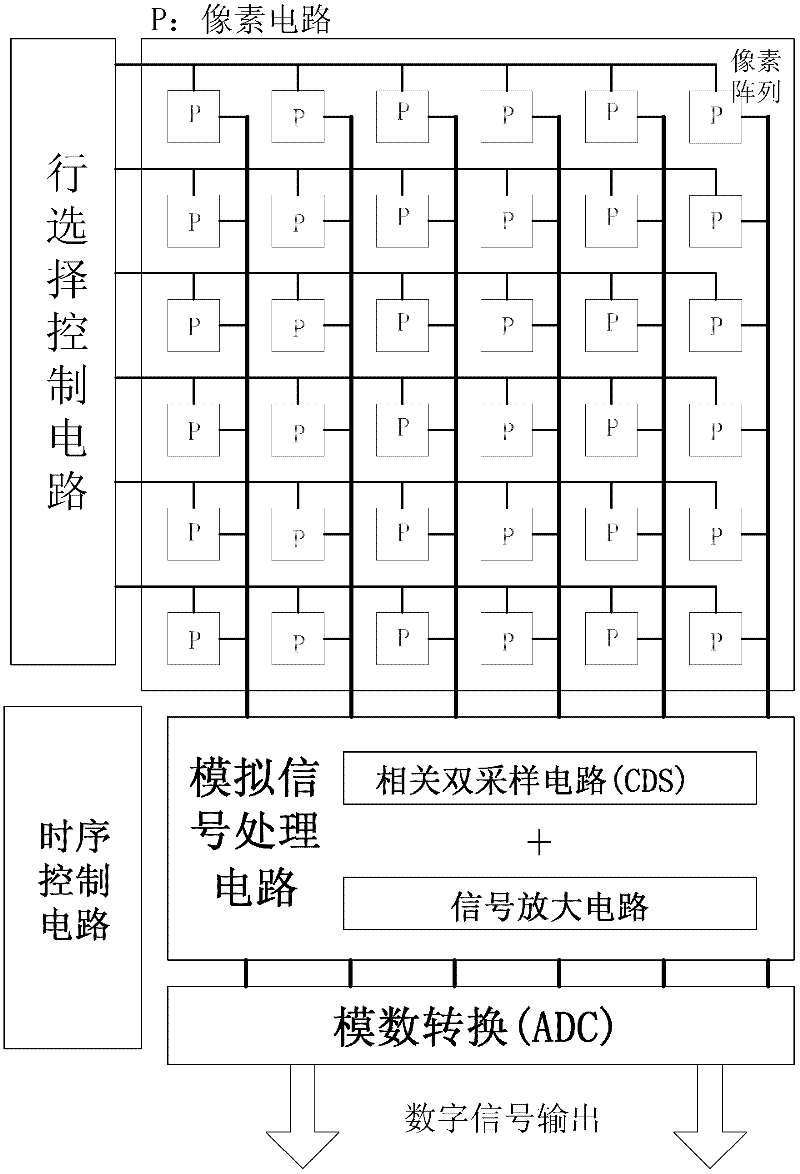
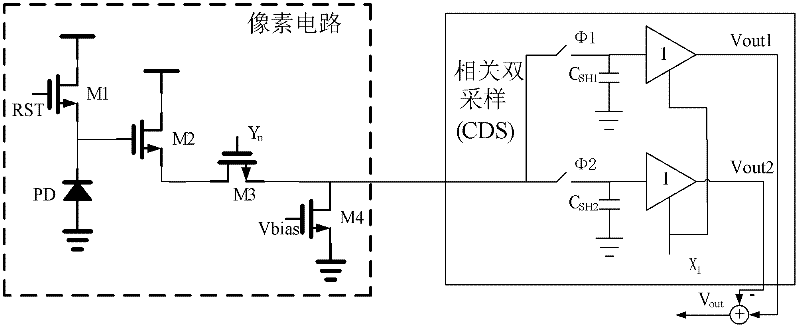
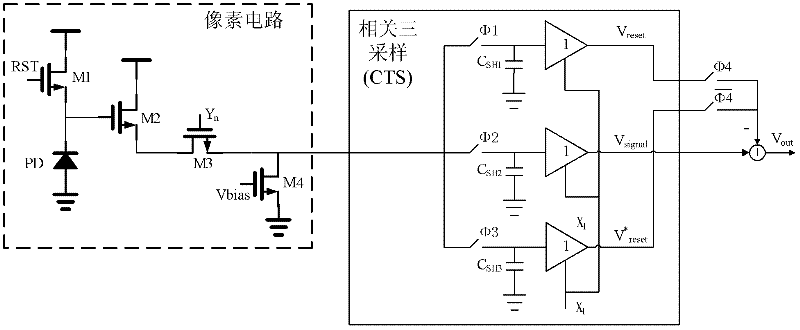
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Cmos active pixel sensor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
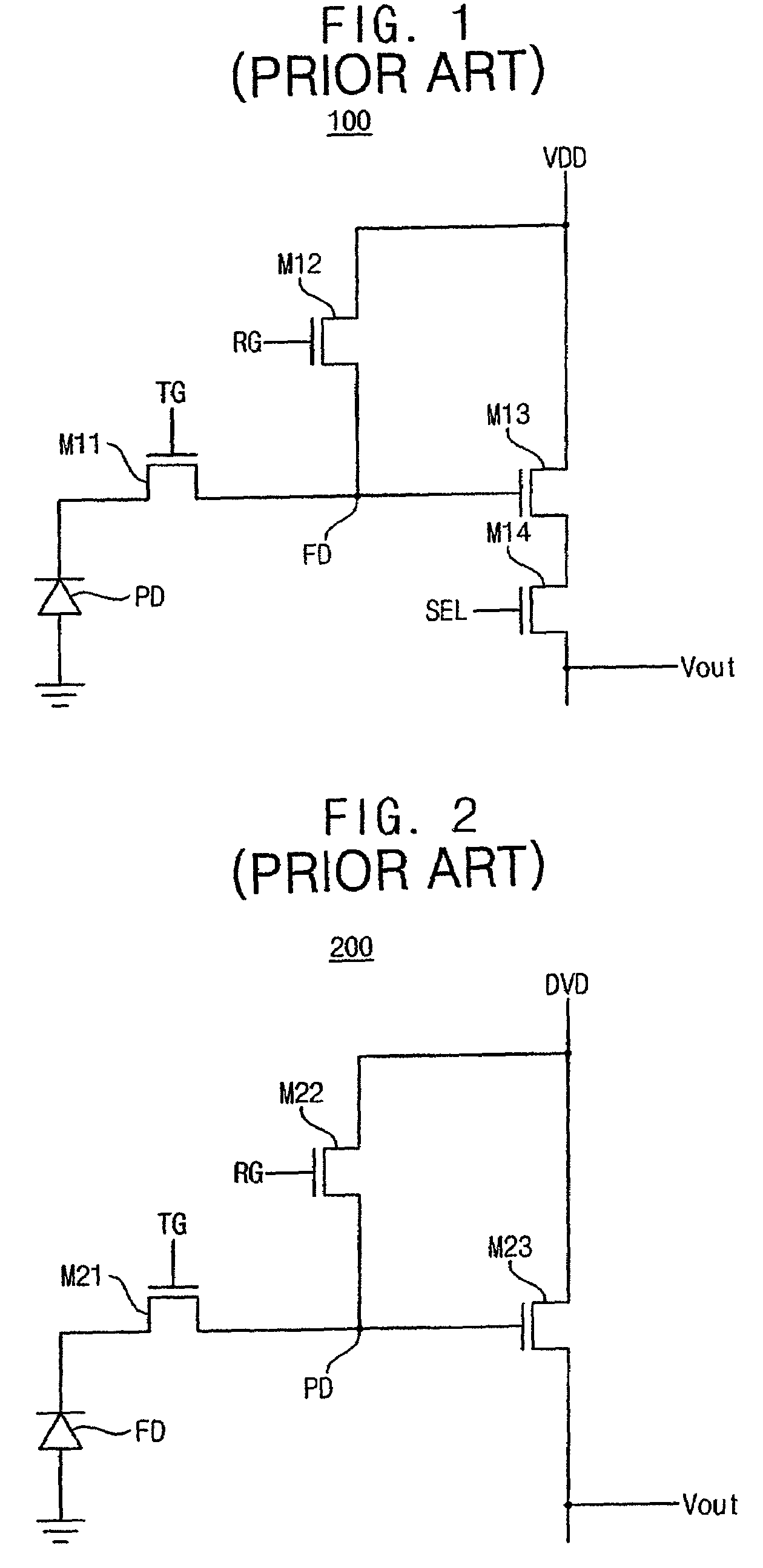
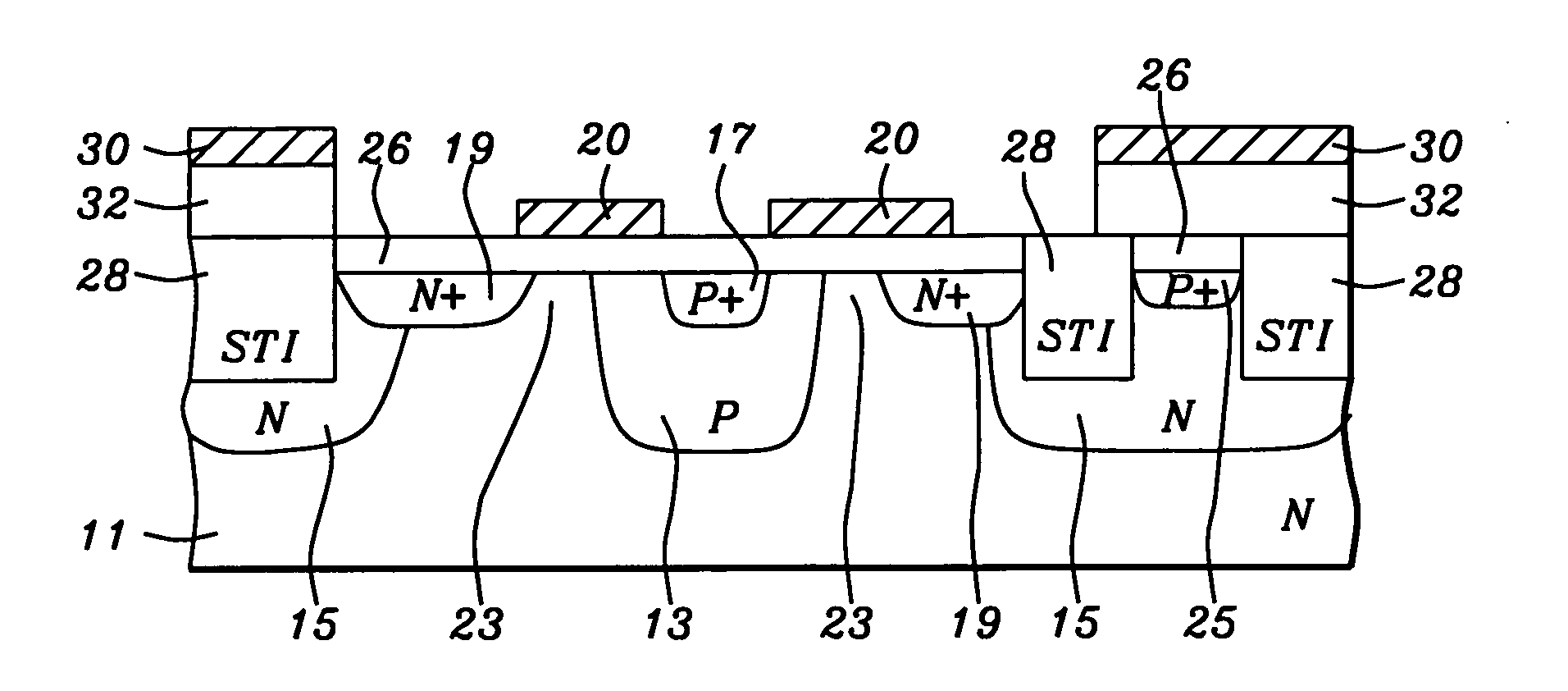
Moisture sensor and windshield fog detector
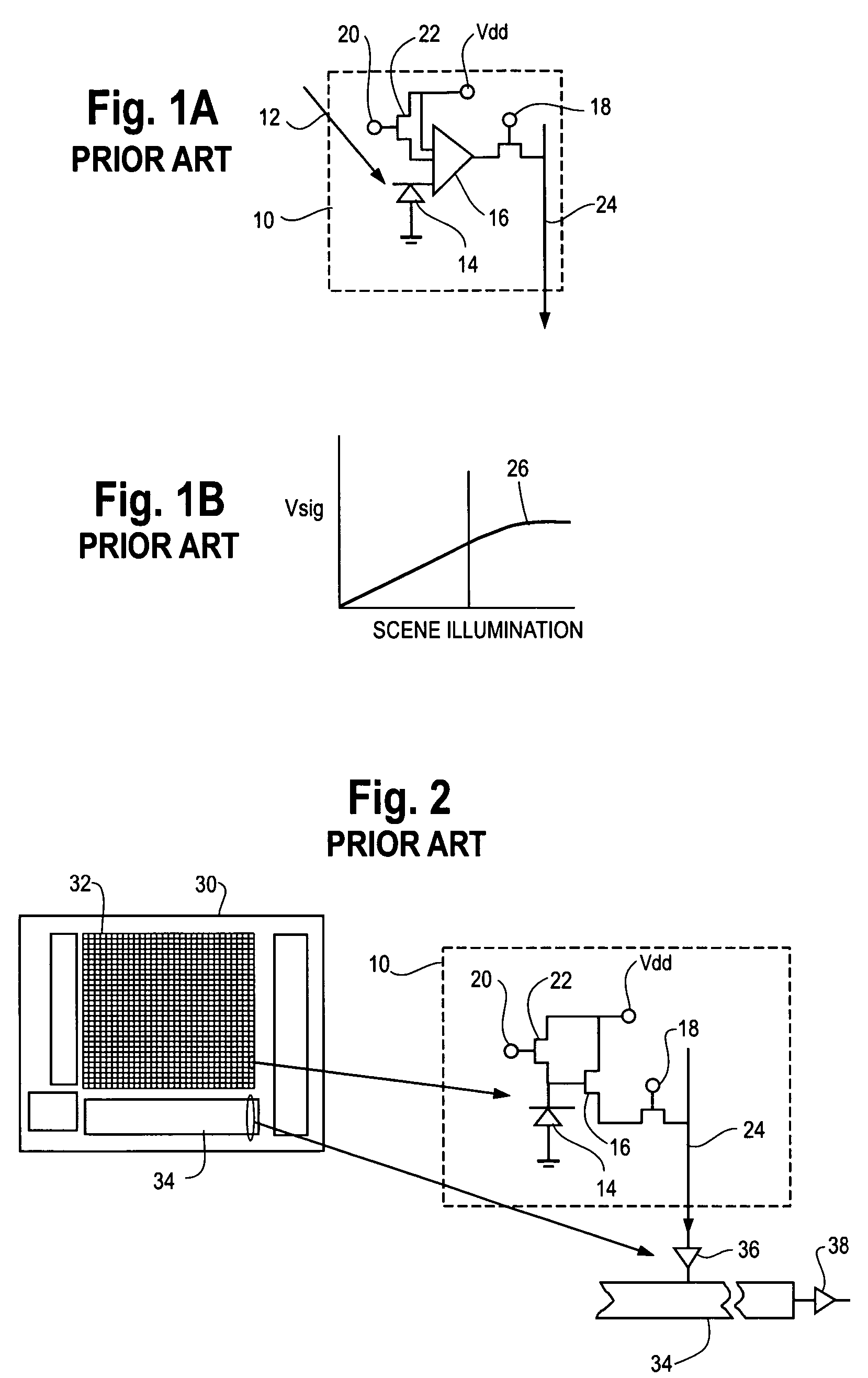
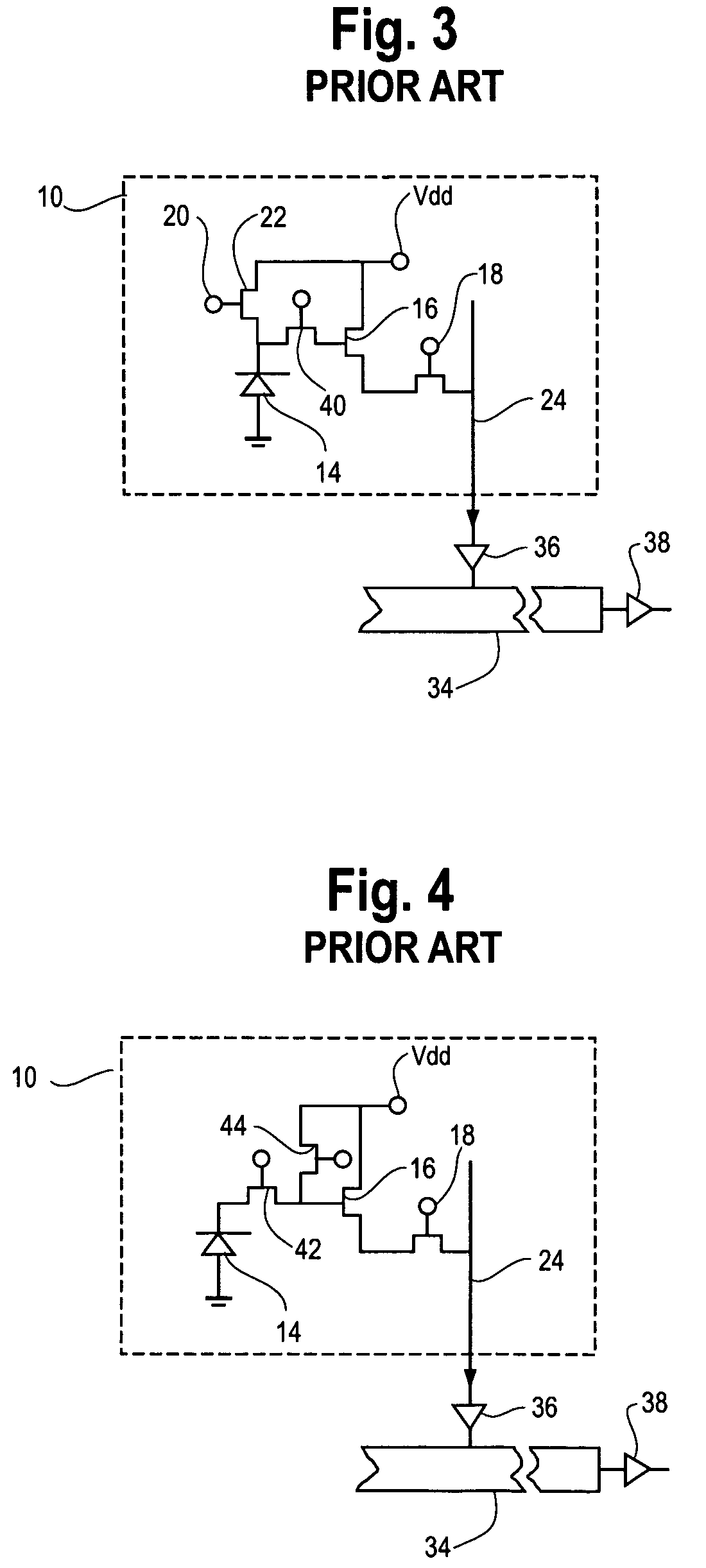
InactiveUS6097024AAutomatic detectionLower performance requirementsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementControl signalEngineering
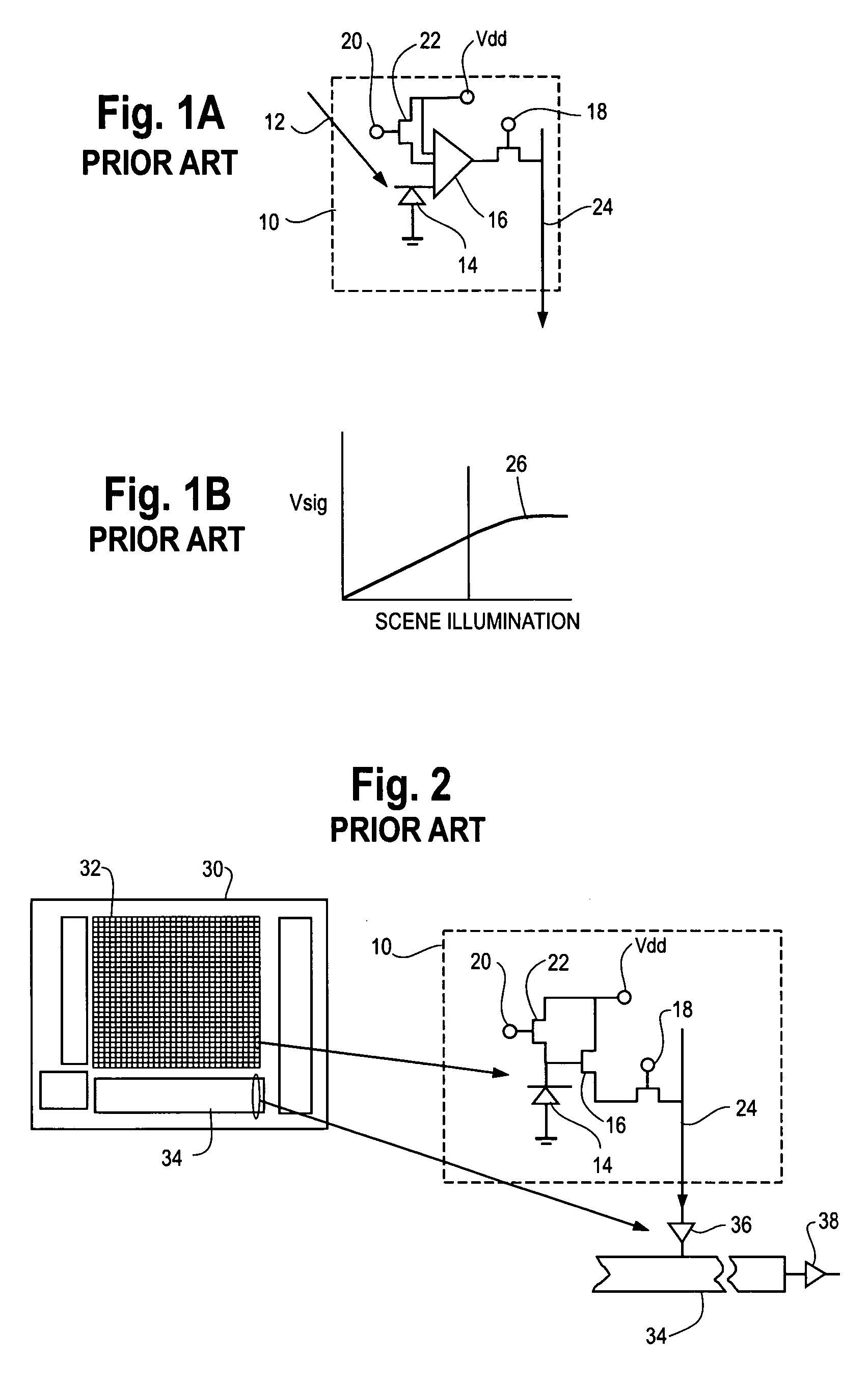
A control system for automatically detecting moisture on the windshield of a vehicle. The automatic moisture detecting system includes an optical system for imaging a portion of the windshield on to an image array sensor, such as a CMOS active pixel sensor. The voltages of each of the pixels which represents the illumination level is converted to a corresponding gray scale value by an analog digital converter. The gray scale values corresponding to the image are stored in memory. The spatial frequency composition of the gray scale values are analyzed to determine the amount of rain present. In order to provide a control signal to control the operation of the windshield wipers of the vehicle as a function of the amount of moisture present. The system is also adapted to detect the level of fog both on the interior of the windshield as well as the exterior of the windshield. By providing a system for automatically detecting the presence of fog on the interior and exterior of the windshield, serious performance limitations of known automatic rain sensors are eliminated.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
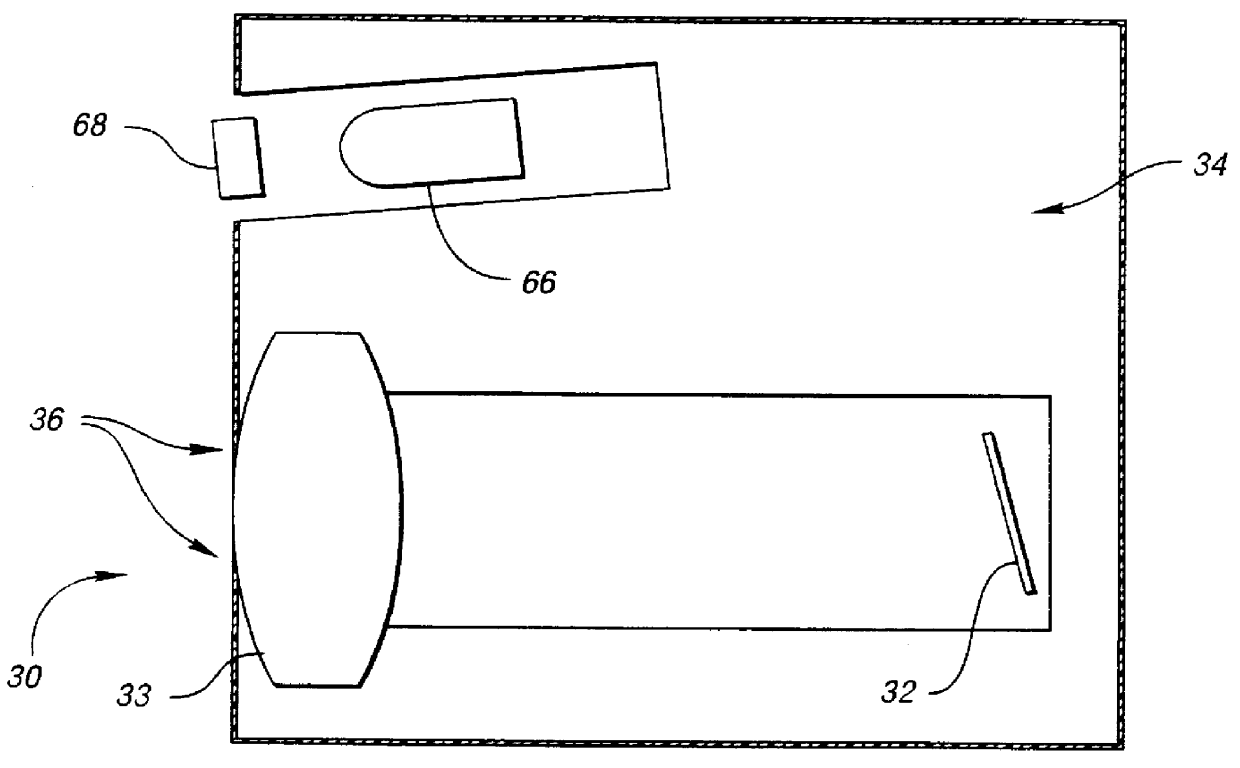
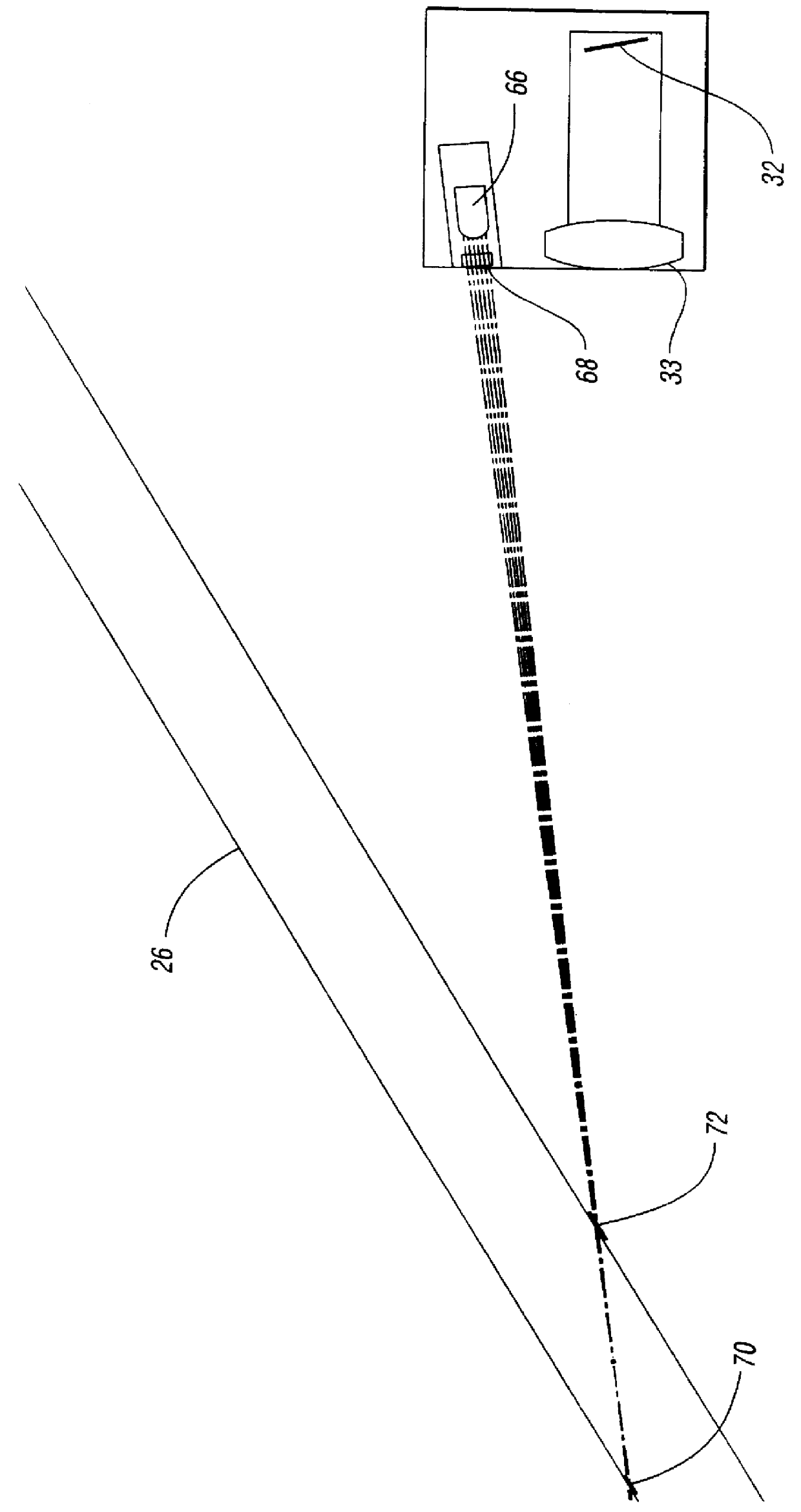
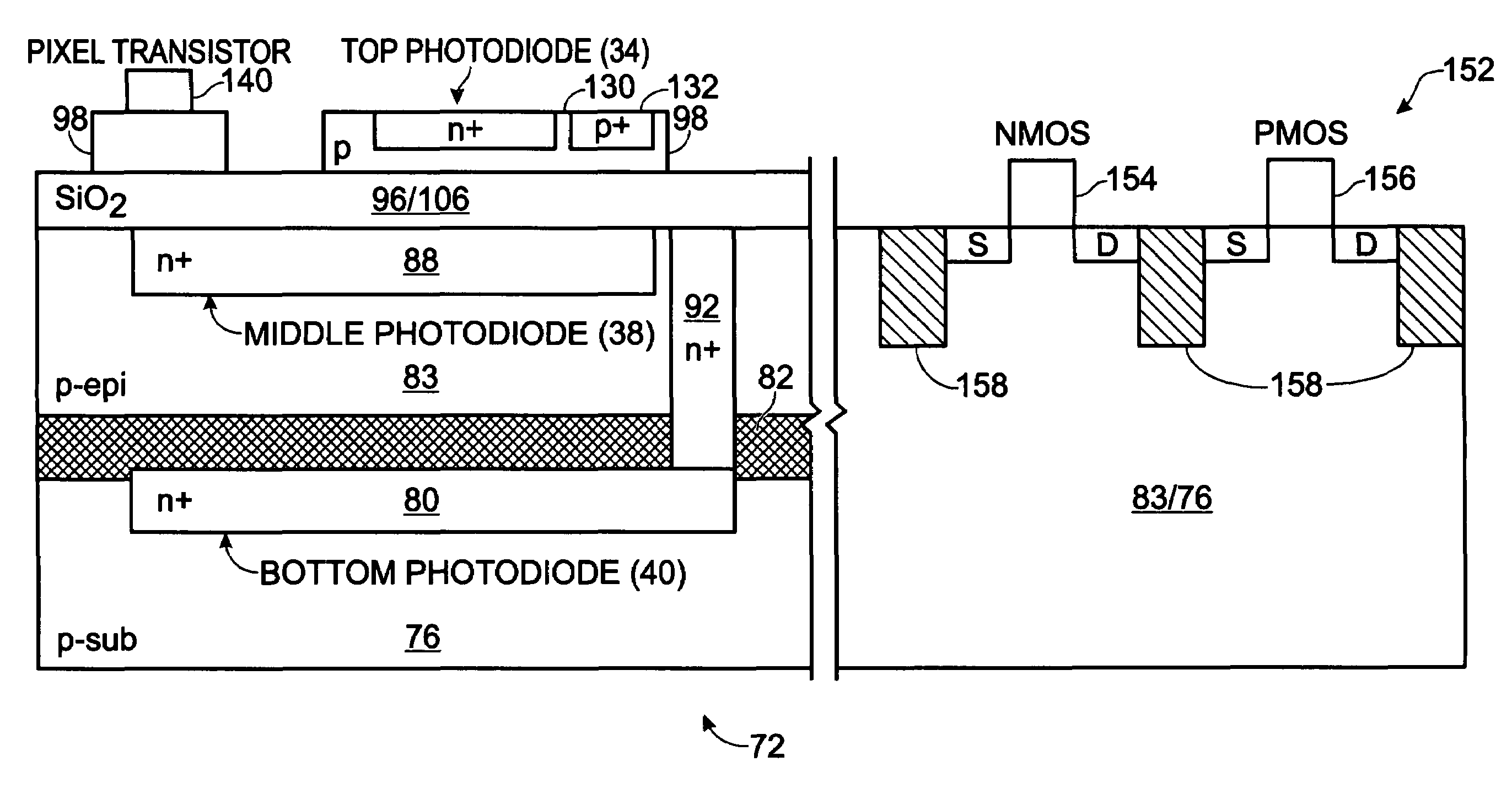
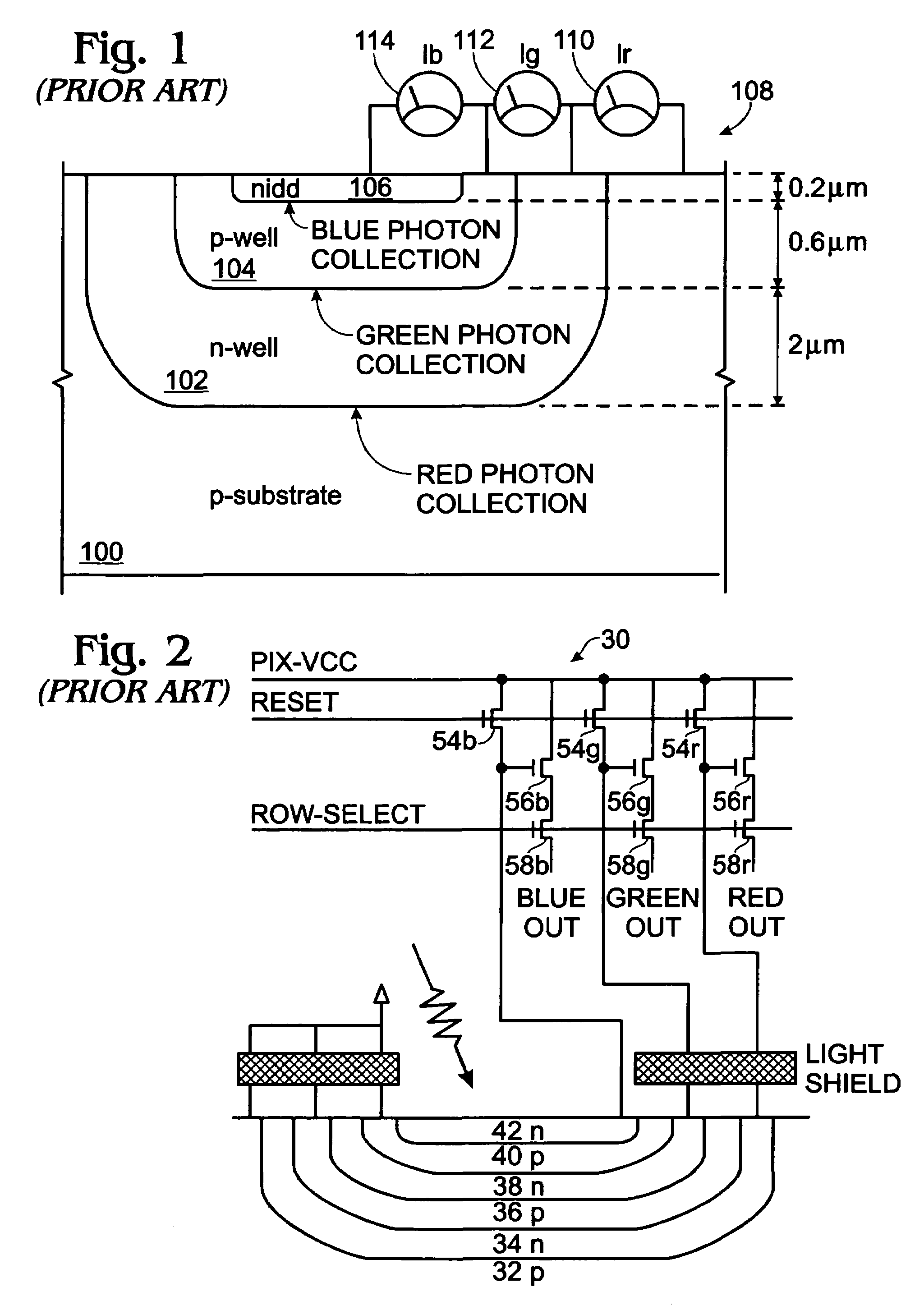
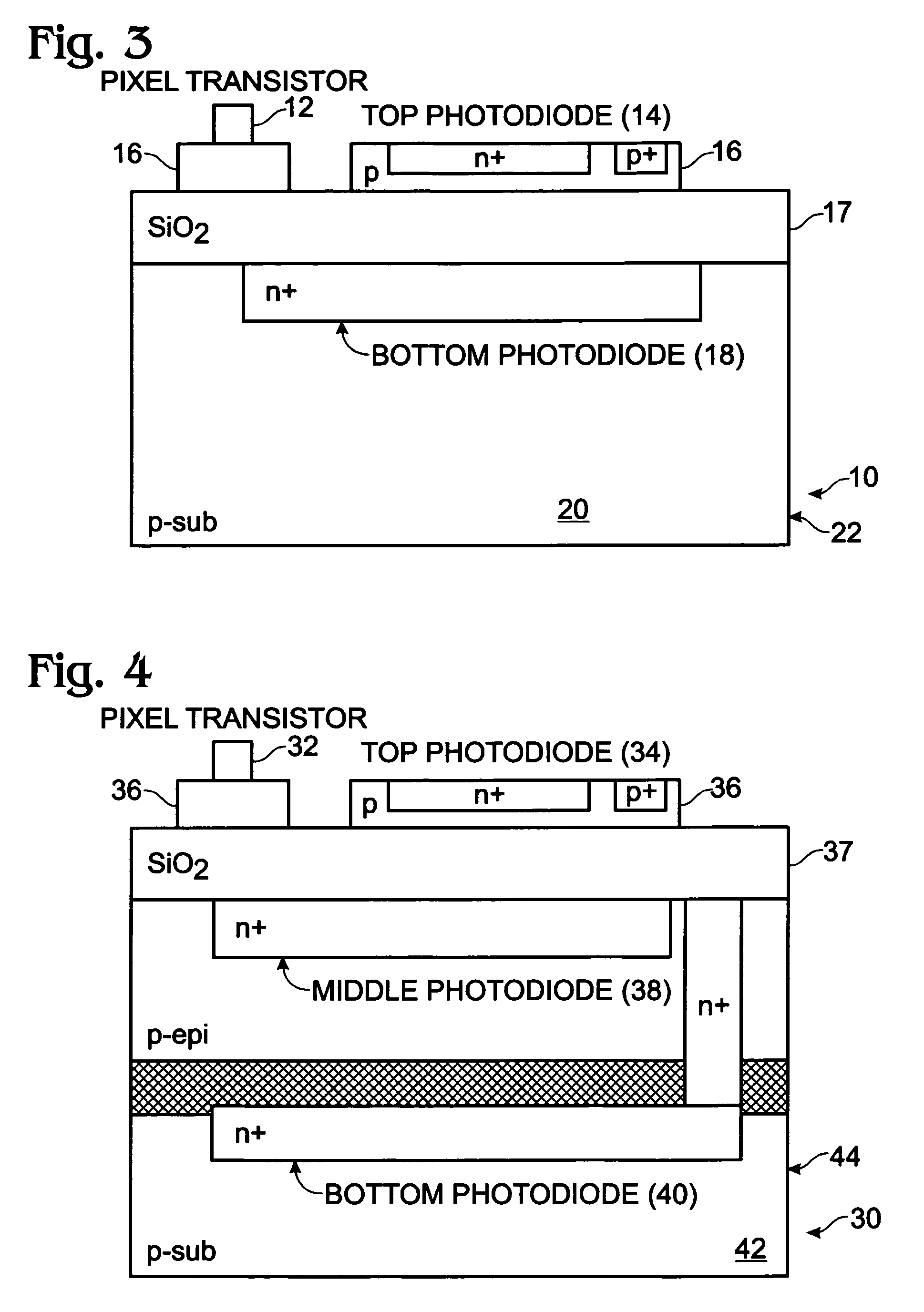
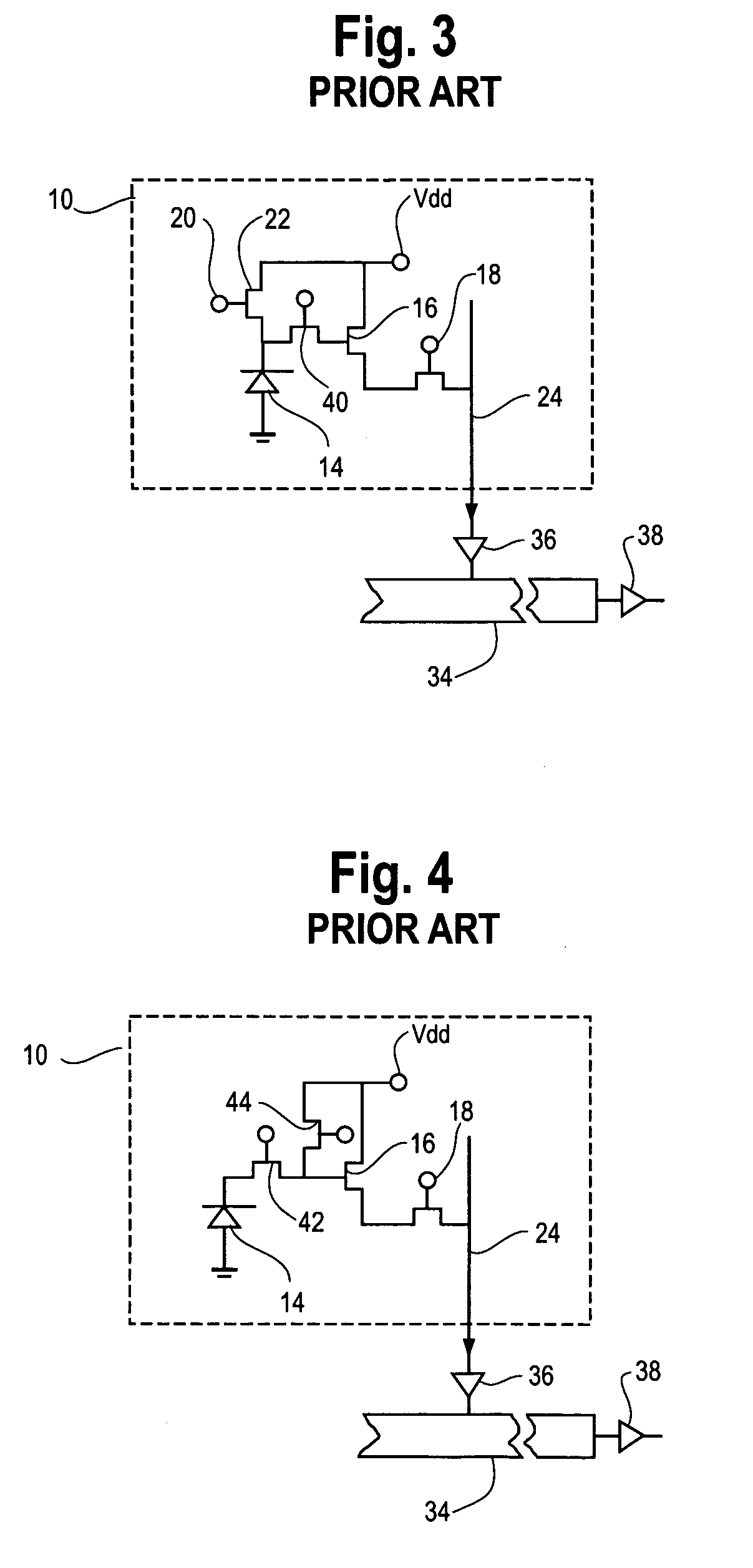
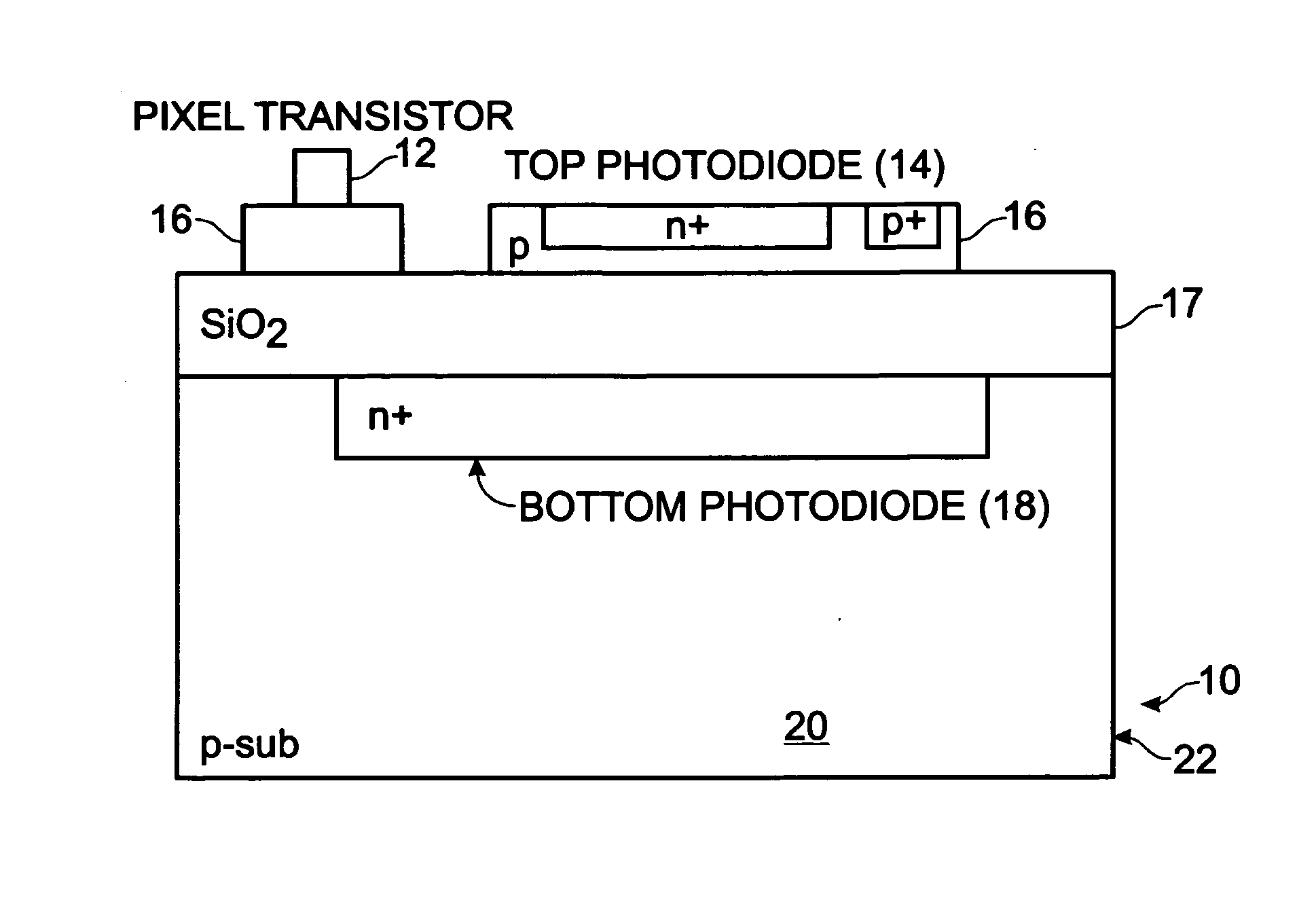
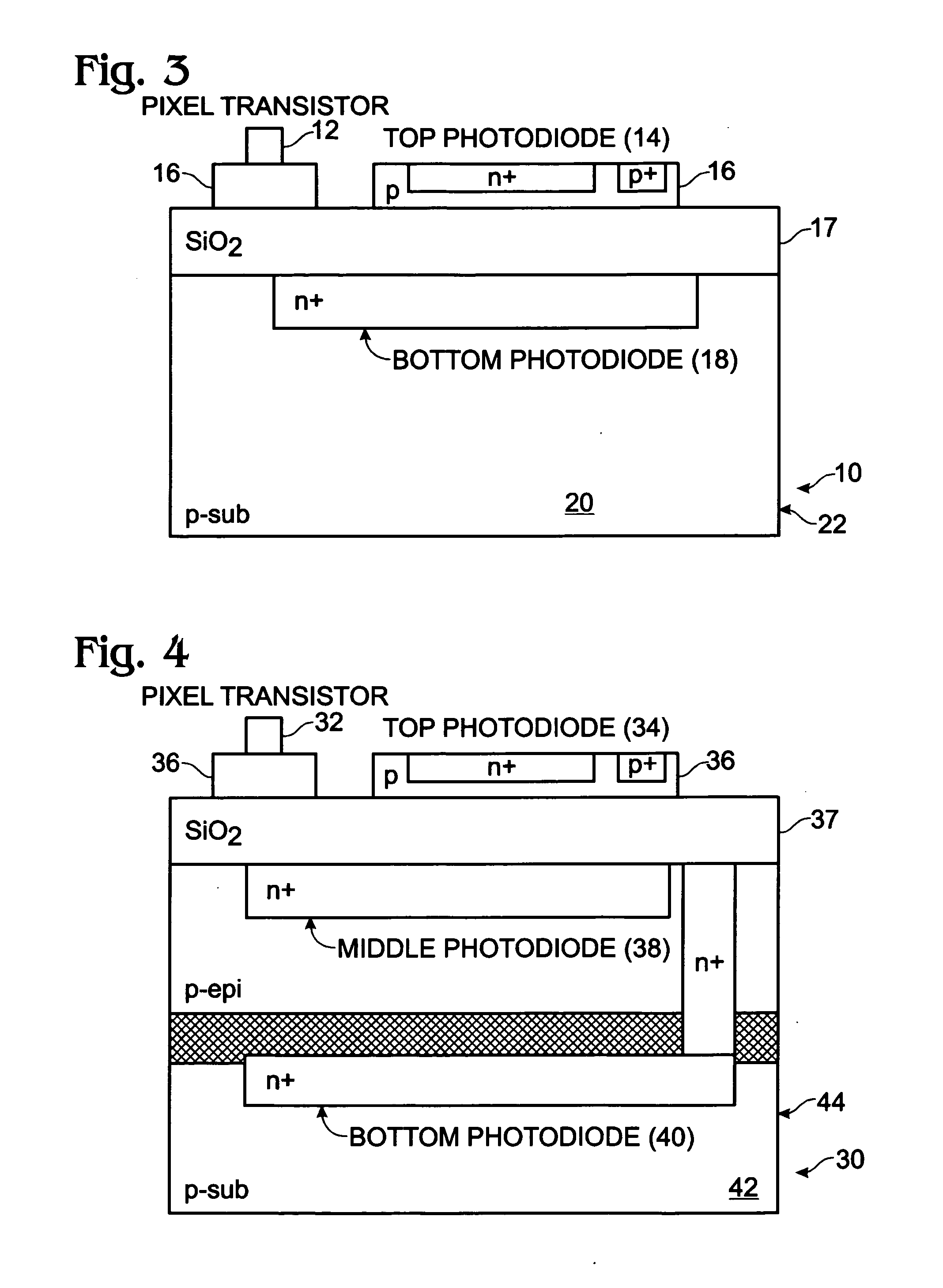
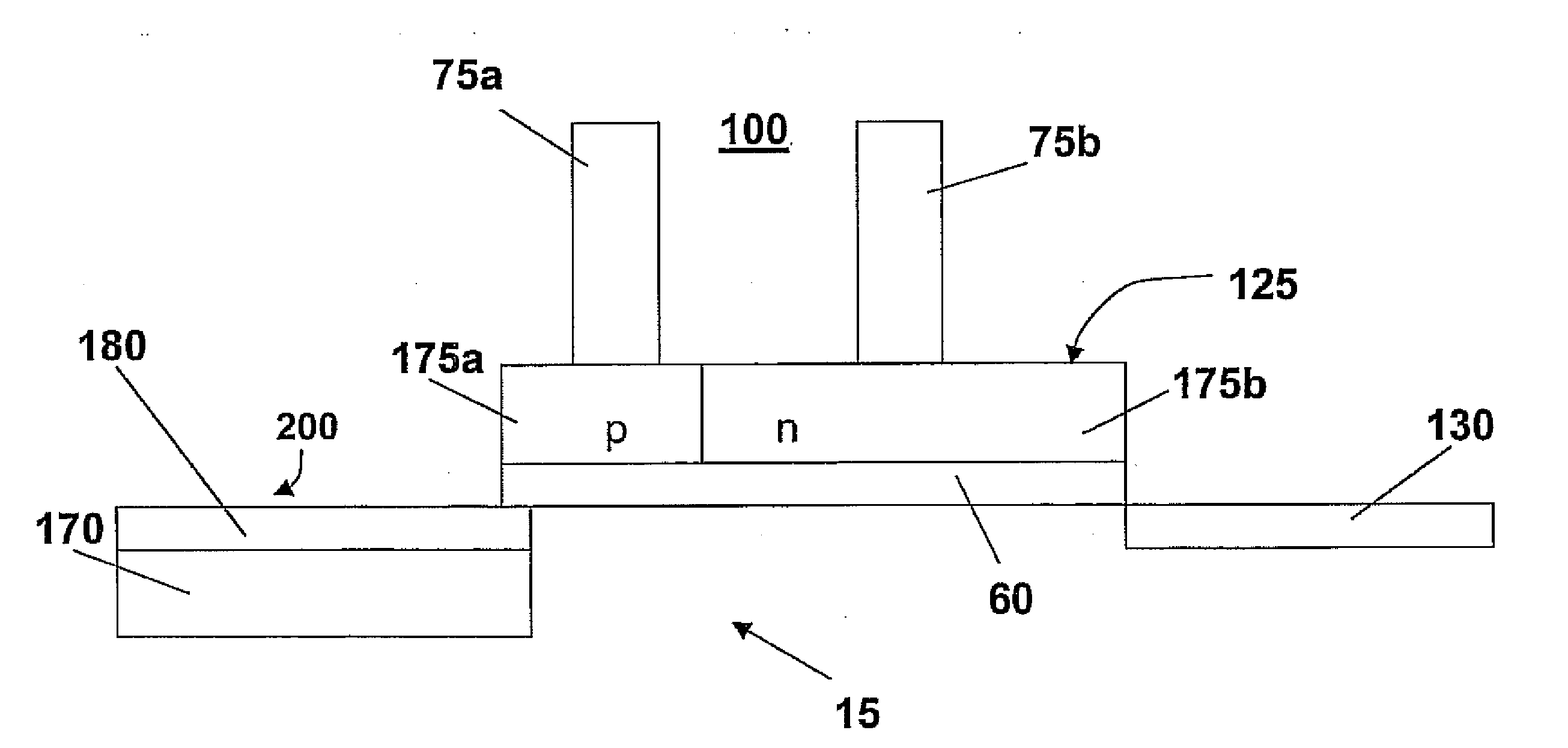
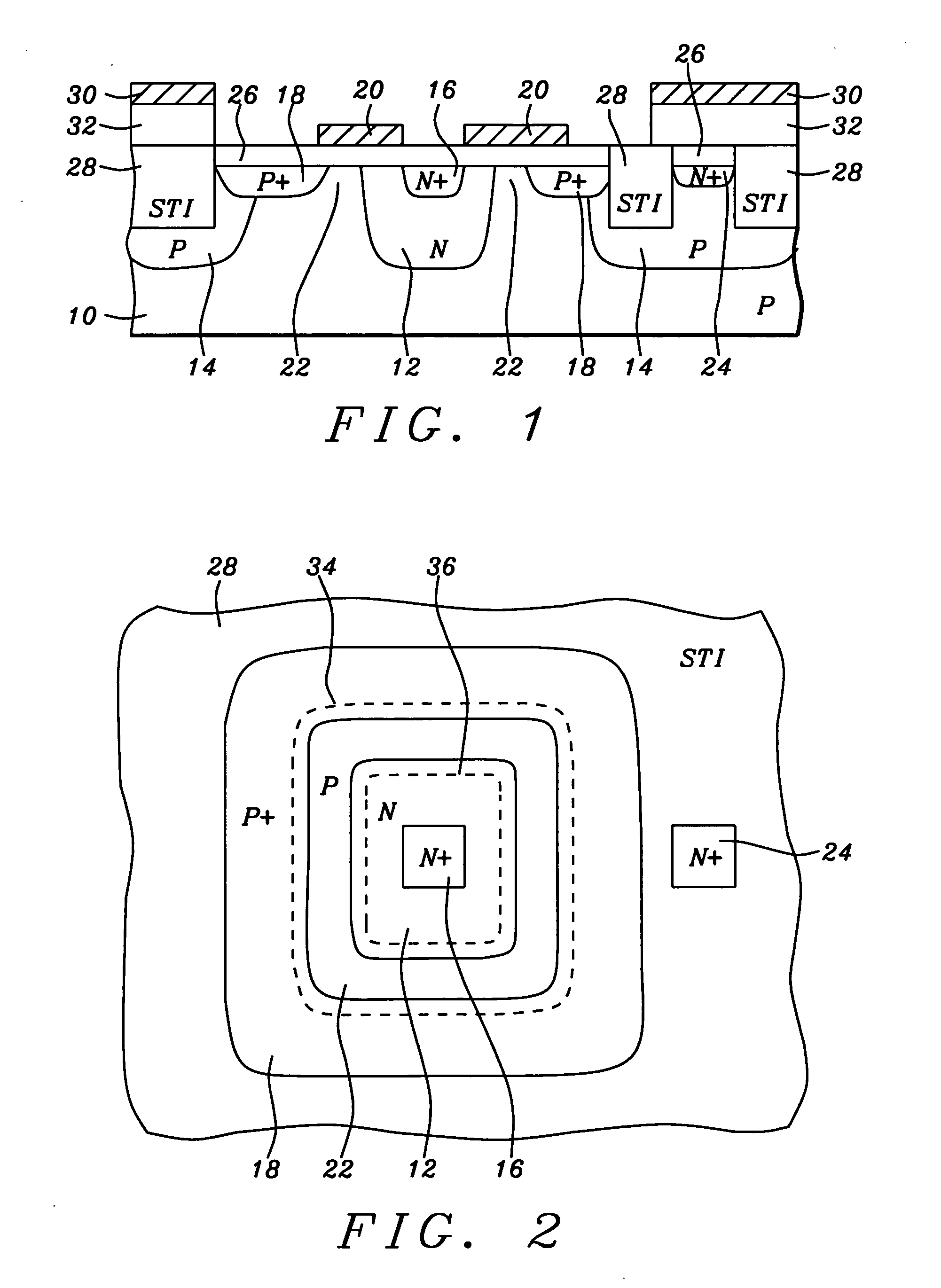
Real-time CMOS imager having stacked photodiodes fabricated on SOI wafer
InactiveUS7419844B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical connectionLength wave
A CMOS active pixel sensor includes a silicon-on-insulator substrate having a silicon substrate with an insulator layer formed thereon and a top silicon layer formed on the insulator layer. A stacked pixel sensor cell includes a bottom photodiode fabricated on the silicon substrate, for sensing light of a longest wavelength; a middle photodiode fabricated on the silicon substrate, for sensing light of a medium wavelength, which is stacked above the bottom photodiode; and a top photodiode fabricated on the top silicon layer, for sensing light of a shorter wavelength, which is stacked above the middle and bottom photodiodes. Pixel transistor sets are fabricated on the top silicon layer and are associated with each pixel sensor cell by electrical connections which extend between each of the photodiodes and respective pixel transistor(s). CMOS control circuitry is fabricated adjacent to an array of active pixel sensor cells and electrically connected thereto.
Owner:SHARP KK
CMOS image sensors having pixel arrays with uniform light sensitivity
ActiveUS20060132633A1Improved response uniformityImprove uniformityTransistorTelevision system detailsPixel arraySolid-state
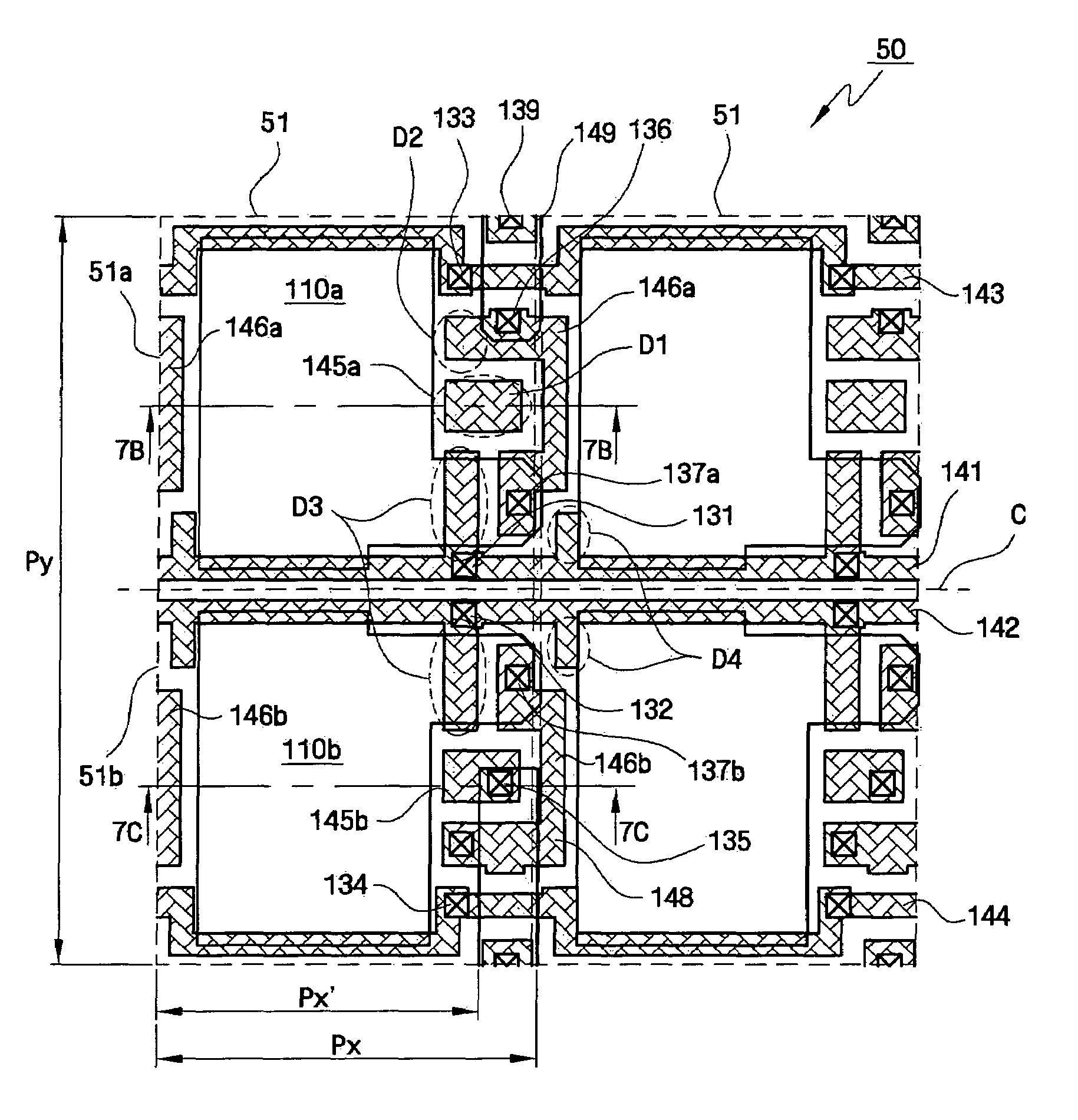
Solid state CMOS active pixel sensor devices having unit pixels that are structured to provide improved uniformity of pixel-to-pixel sensitivity across a pixel array without the need for an additional light shielding layer. For example, unit pixels with symmetrical layout patterns are formed whereby one or more lower-level BEOL metallization layers are designed operate as light shielding layers which are symmetrically patterned and arranged to balance the amount of incident light reaching the photosensitive regions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for biasing a CMOS active pixel sensor above the nominal voltage maximums for an IC process
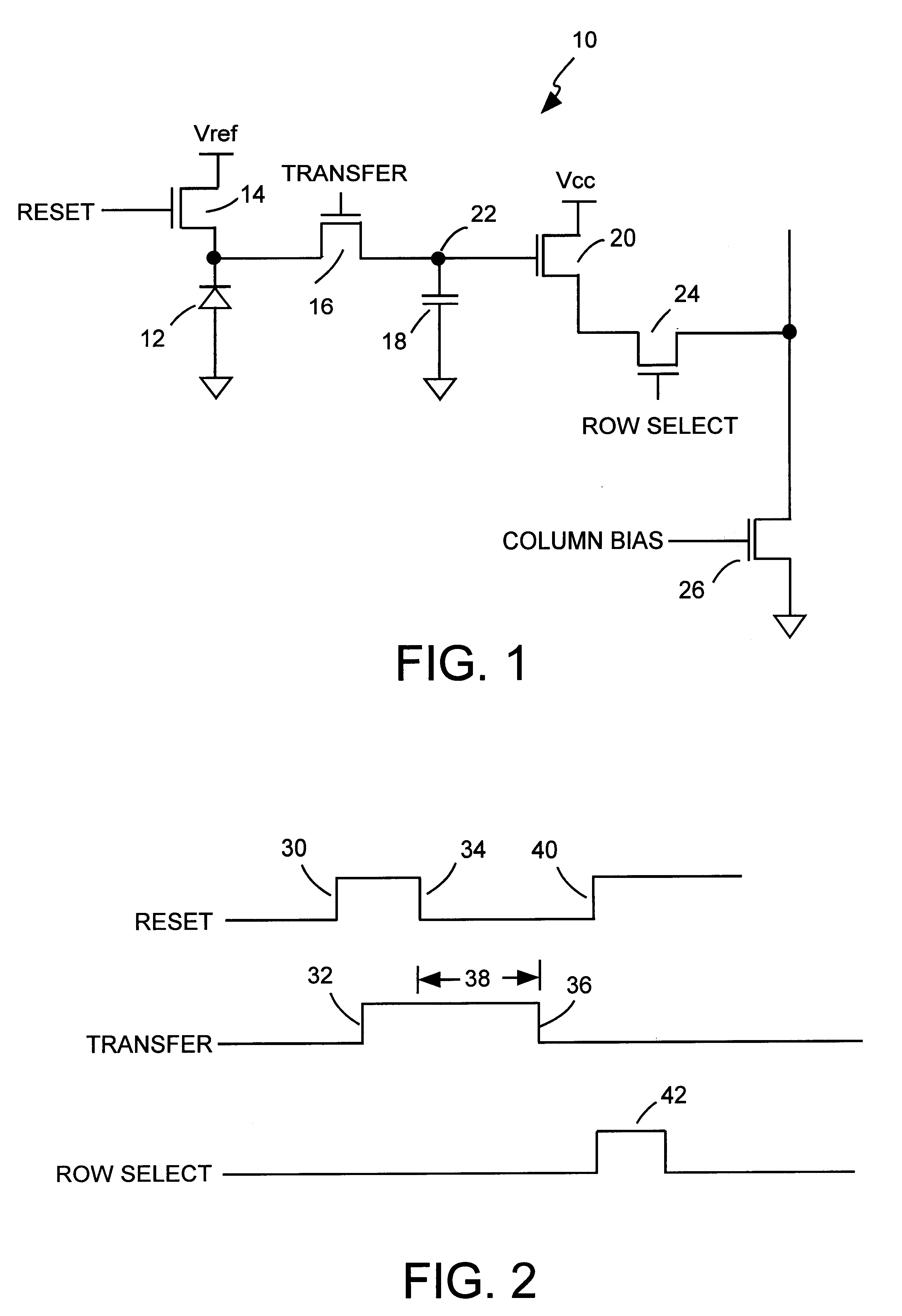
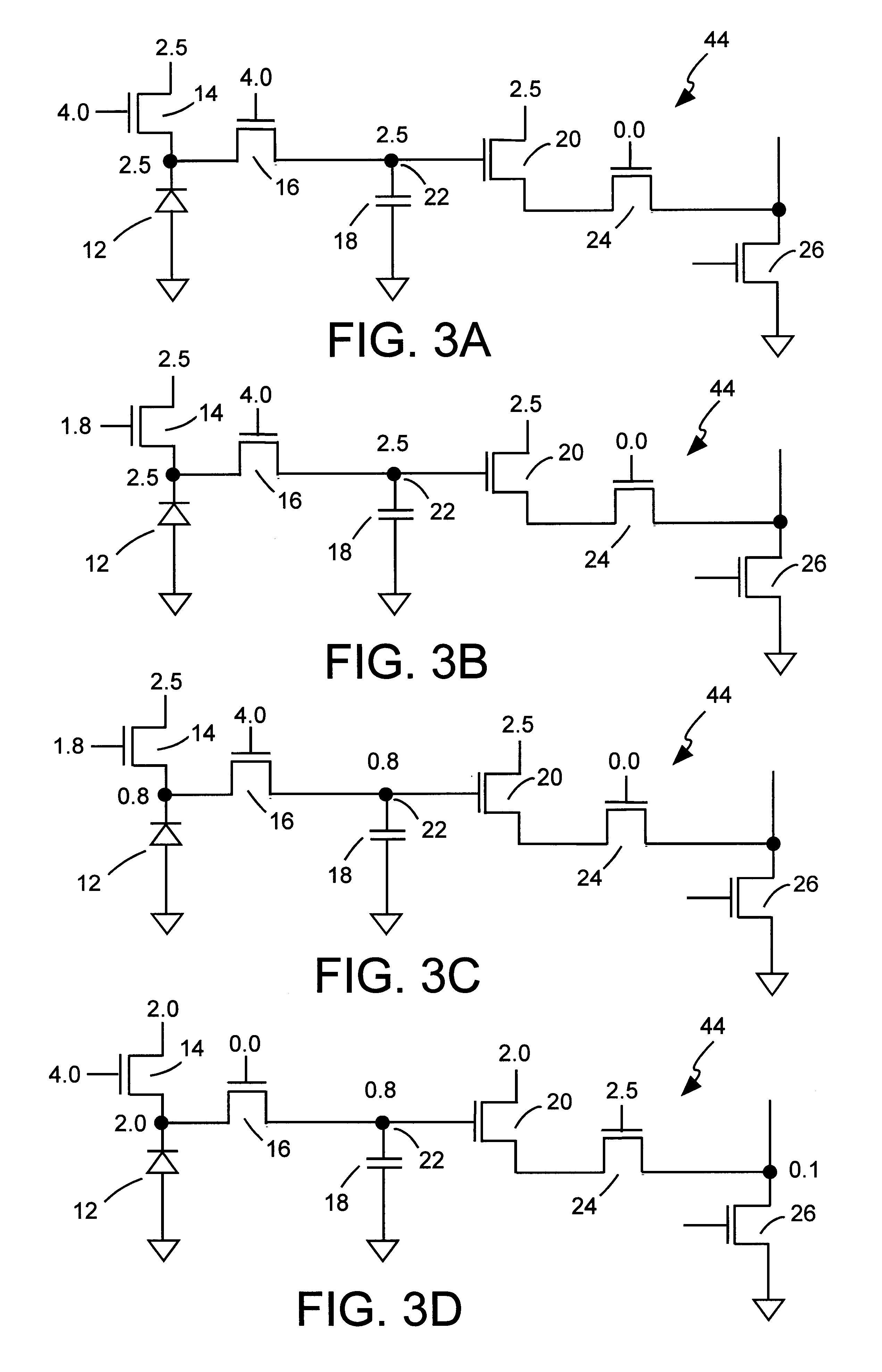
An active pixel sensor is operated with voltages that exceed the nominal operating voltages for a particular integrated circuit process. Voltages that exceed the nominal operating voltages are employed during the reset, integration and readout periods in the operating cycle of the active pixel sensor. The lower limit of the voltage representing the capture of photocharge in the active pixel sensor is fixed by setting the voltage applied to the gate of a reset transistor in the active pixel sensor to a level during integration which prevents the voltage across the dielectric of a transfer transistor from exceeding a preselected value. Read disturb caused by impact ionization current from a readout transistor to a storage node is reduced by lowering the voltage applied to the drain of a readout transistor to reduce the Vds of the readout transistor at the start of a readout period.
Owner:FOVEON
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
ActiveUS20060146159A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorLinearity
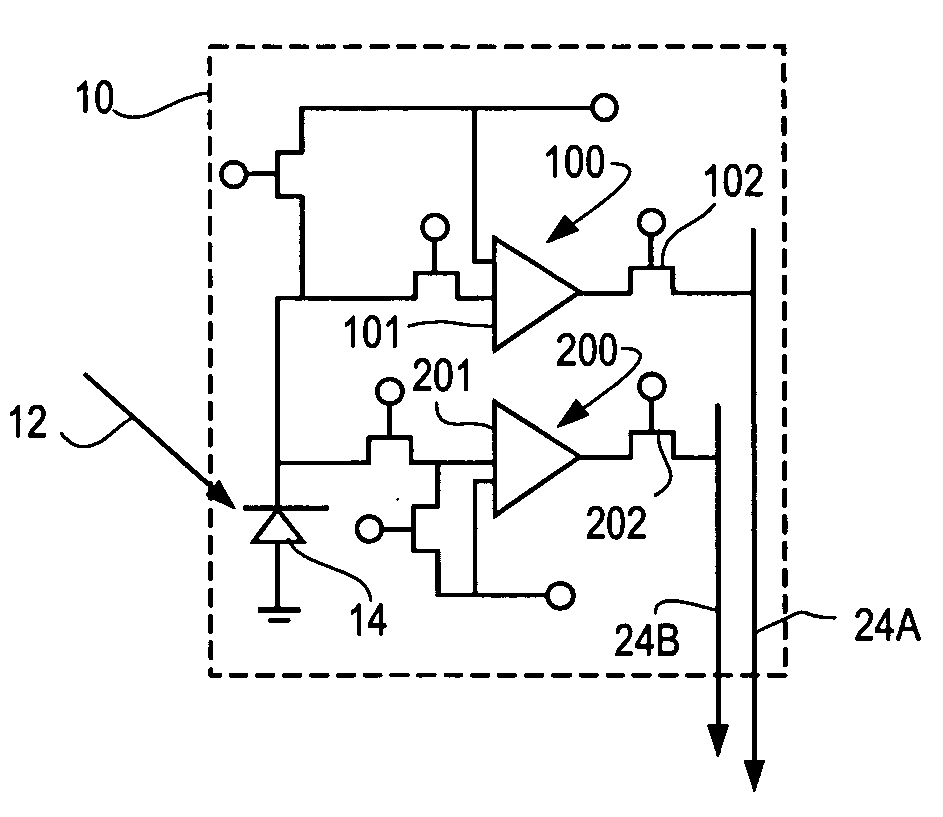
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
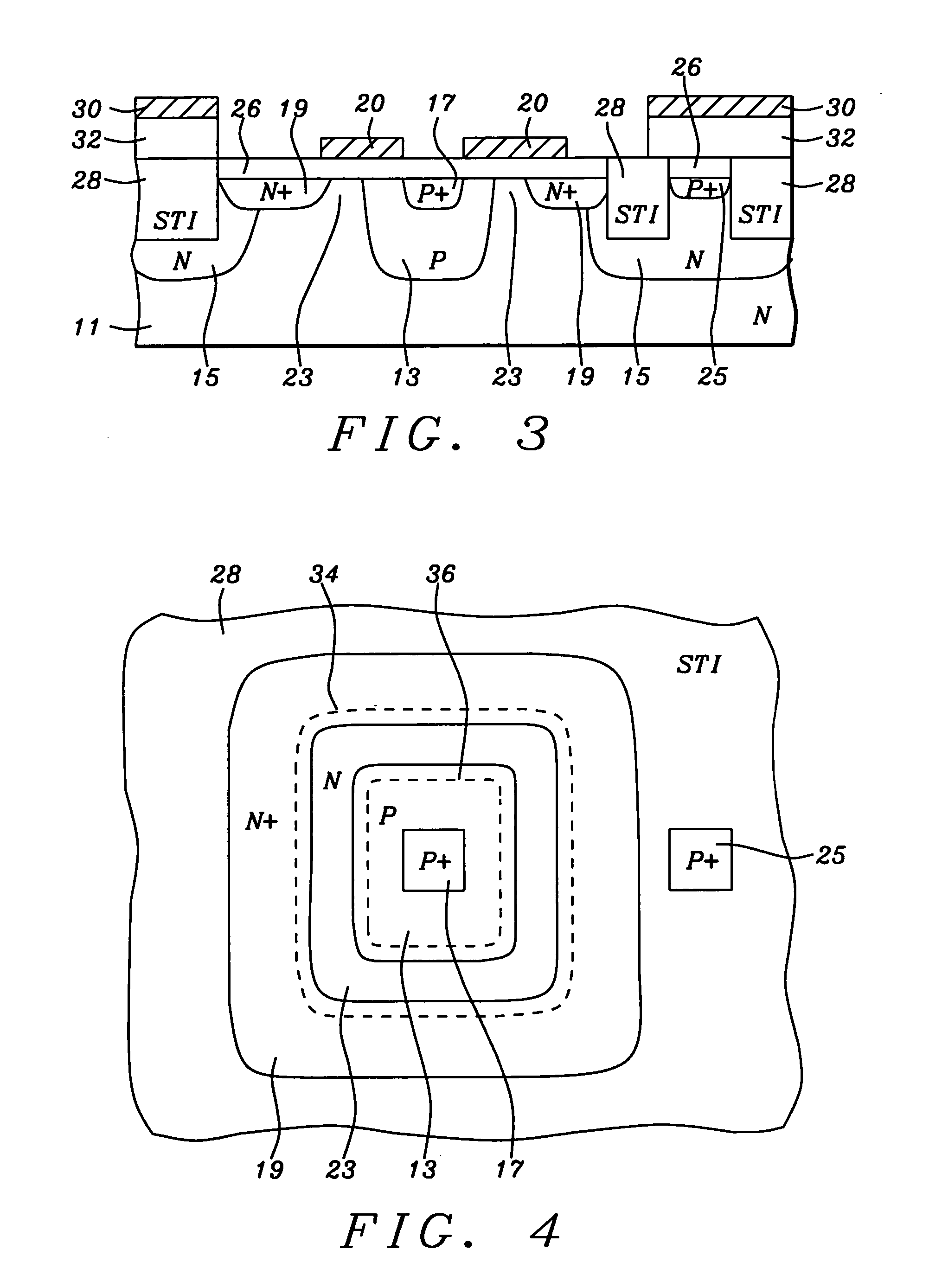
Real-time CMOS imager having stacked photodiodes fabricated on SOI wafer
InactiveUS20070218578A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical connectionLength wave
A CMOS active pixel sensor includes a silicon-on-insulator substrate having a silicon substrate with an insulator layer formed thereon and a top silicon layer formed on the insulator layer. A stacked pixel sensor cell includes a bottom photodiode fabricated on the silicon substrate, for sensing light of a longest wavelength; a middle photodiode fabricated on the silicon substrate, for sensing light of a medium wavelength, which is stacked above the bottom photodiode; and a top photodiode fabricated on the top silicon layer, for sensing light of a shorter wavelength, which is stacked above the middle and bottom photodiodes. Pixel transistor sets are fabricated on the top silicon layer and are associated with each pixel sensor cell by electrical connections which extend between each of the photodiodes and respective pixel transistor(s). CMOS control circuitry is fabricated adjacent to an array of active pixel sensor cells and electrically connected thereto.
Owner:SHARP KK
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation
ActiveUS7518645B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotodetectorEngineering
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. A first output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the first circuit to a first output multiplexer. A second output select circuit is provided for directing the output of the second circuit to a second output multiplexer. Thus, separate outputs of the first and second circuits are provided for each of the individual pixel sensors of the CMOS imaging array. Alternative embodiments incorporate two ore more photodetectors and two or more amplifier circuits and output select circuits. Three photodetectors and three amplifier circuits are useful for an embodiment where the sensor includes a three-color filter matrix.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
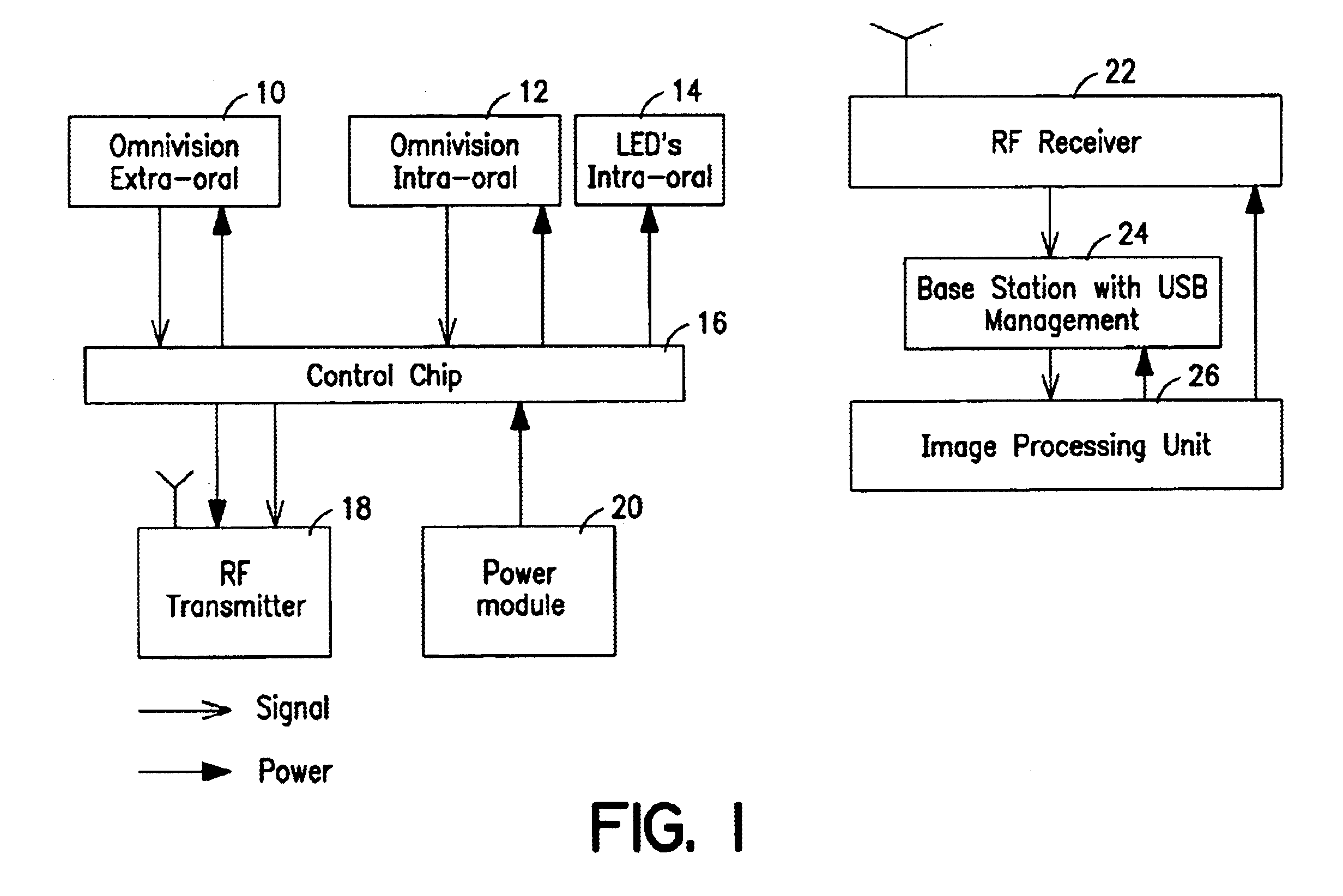
Dental camera utilizing multiple lenses
A dental camera is provided having multiple lenses. The dental camera has at least a first lens for use in an intra-oral mode, and at least a second lens for use in an extra-oral mode. The dental camera is switchable between the intra-oral mode and the extra-oral mode. Each lens is associated with an image sensor, for example, a CMOS active pixel sensor or a charge-coupled device.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL
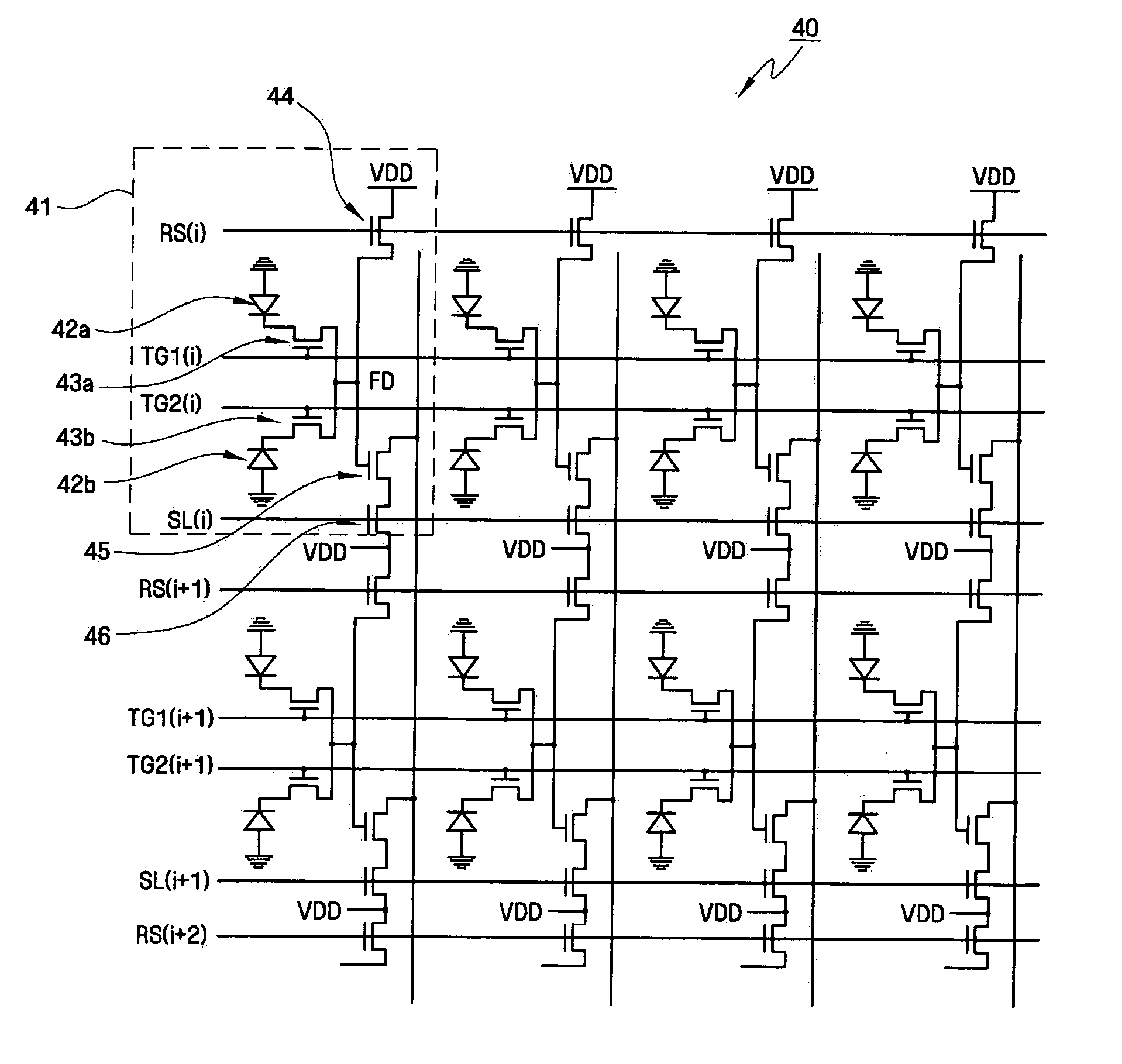
Low lag transfer gate device
ActiveUS20090179232A1Prevent overflowTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorCharge carrier
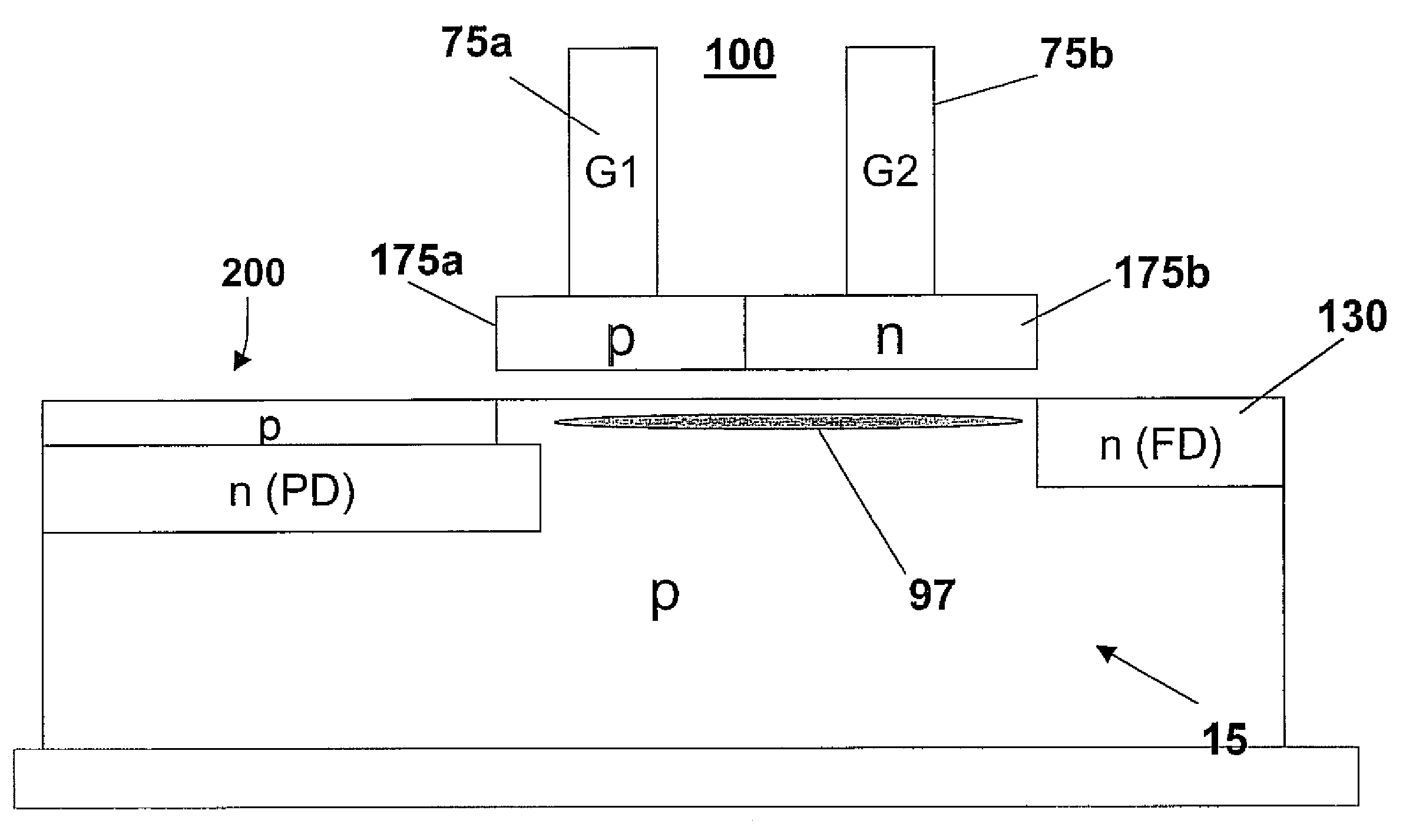
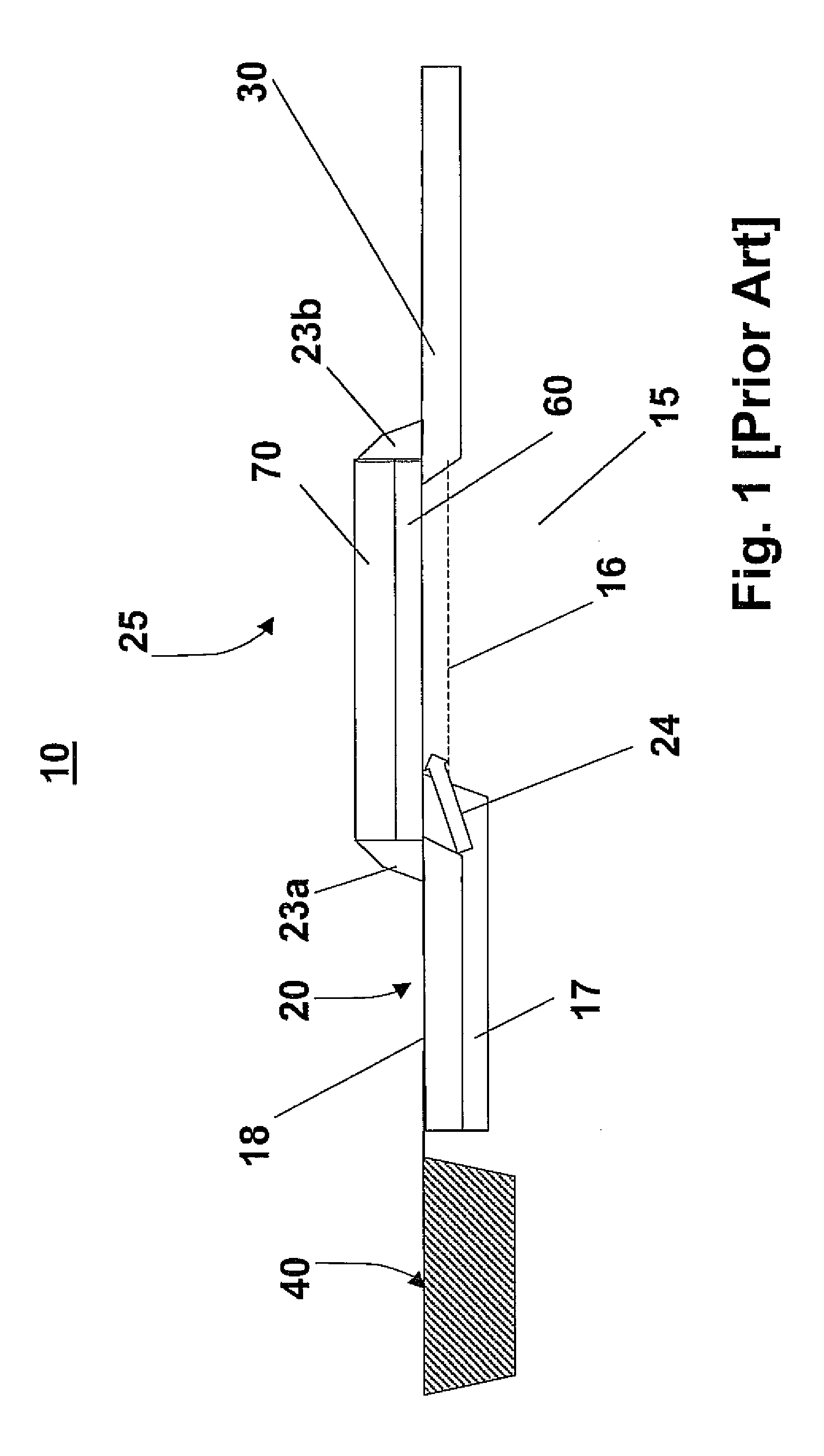
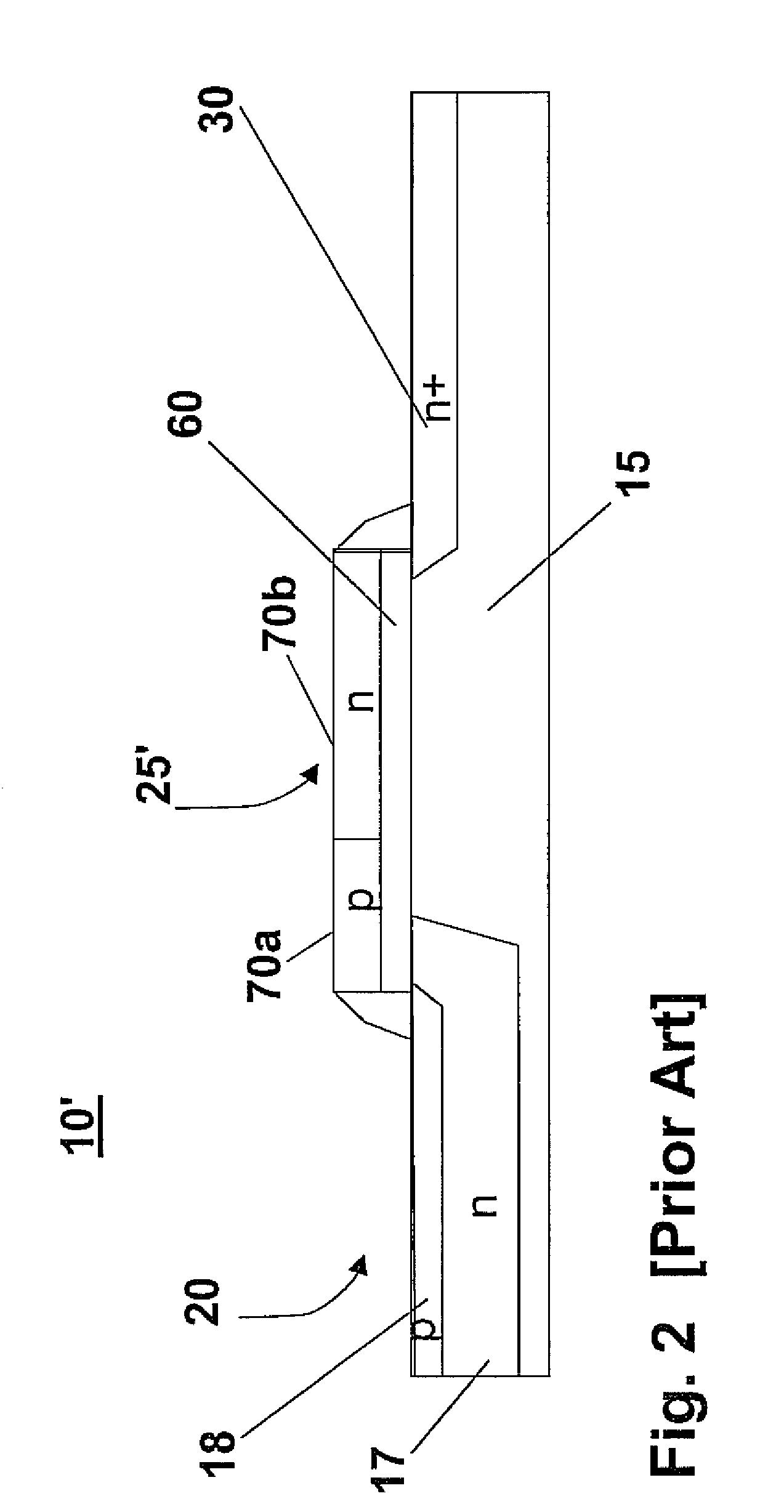
A CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure includes at least one transfer gate device and method of operation. A first transfer gate device comprises a diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure having a first doped region of first conductivity type material and a second doped region of a second conductivity type material. A photosensing device is formed adjacent the first doped region for collecting charge carriers in response to light incident thereto, and, a diffusion region of a second conductivity type material is formed at or below the substrate surface adjacent the second doped region of the transfer gate device for receiving charges transferred from the photosensing device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device upon timed voltage bias to the diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure. Alternately, an intermediate charge storage device and second transfer gate device may be provided which may first temporarily receive charge carriers from the photosensing device, and, upon activating the second transfer gate device in a further timed fashion, read out the charge stored at the intermediate charge storage device for transfer to the second transfer gate device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device. The APS cell structure is further adapted for a global shutter mode of operation, and further comprises a light shield element is further provided to ensure no light reaches the photosensing and charge storage devices during charge transfer operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
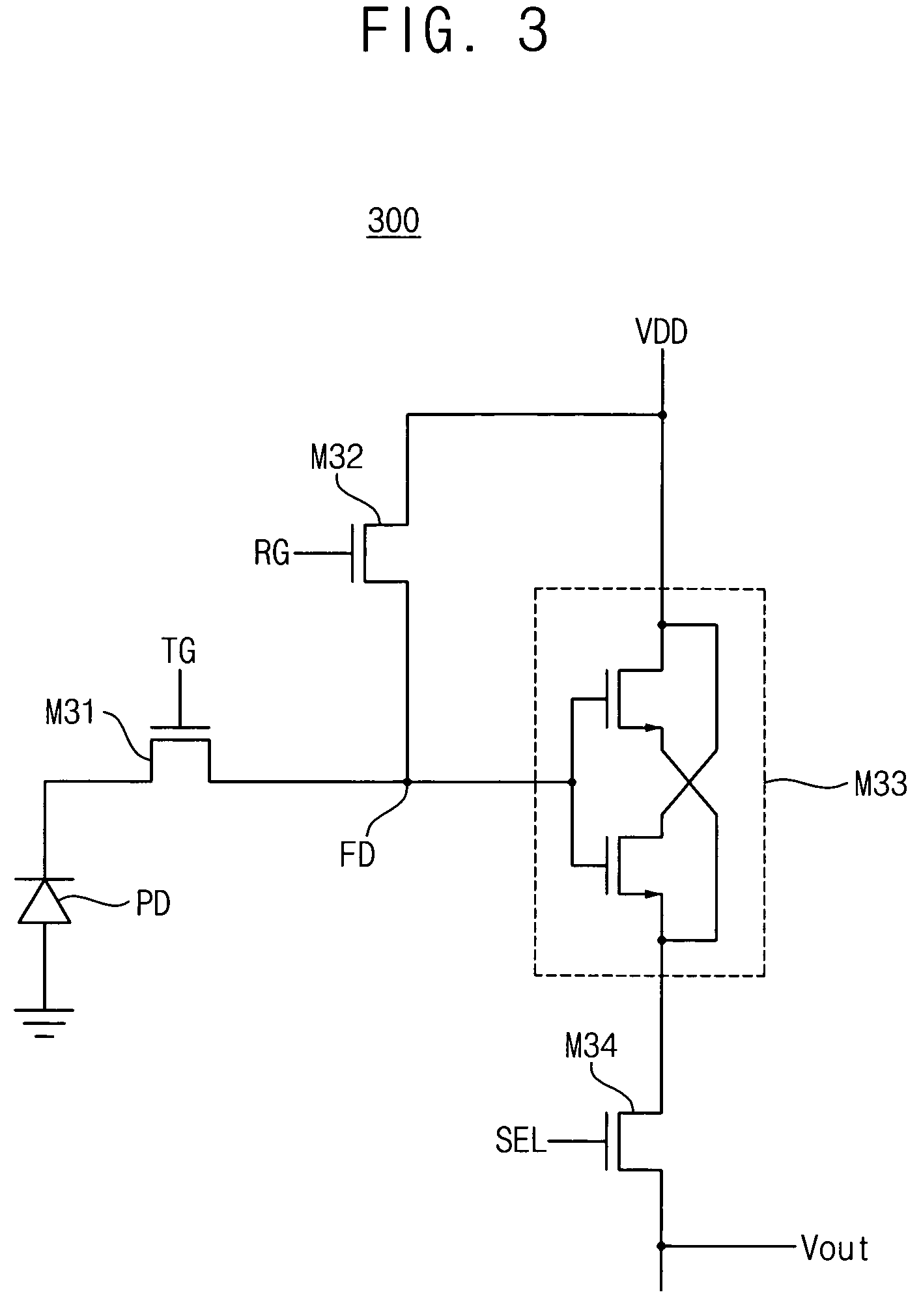
Active pixel sensor with coupled gate transfer transistor
ActiveUS20060138489A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce image lagTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFloating diffusion
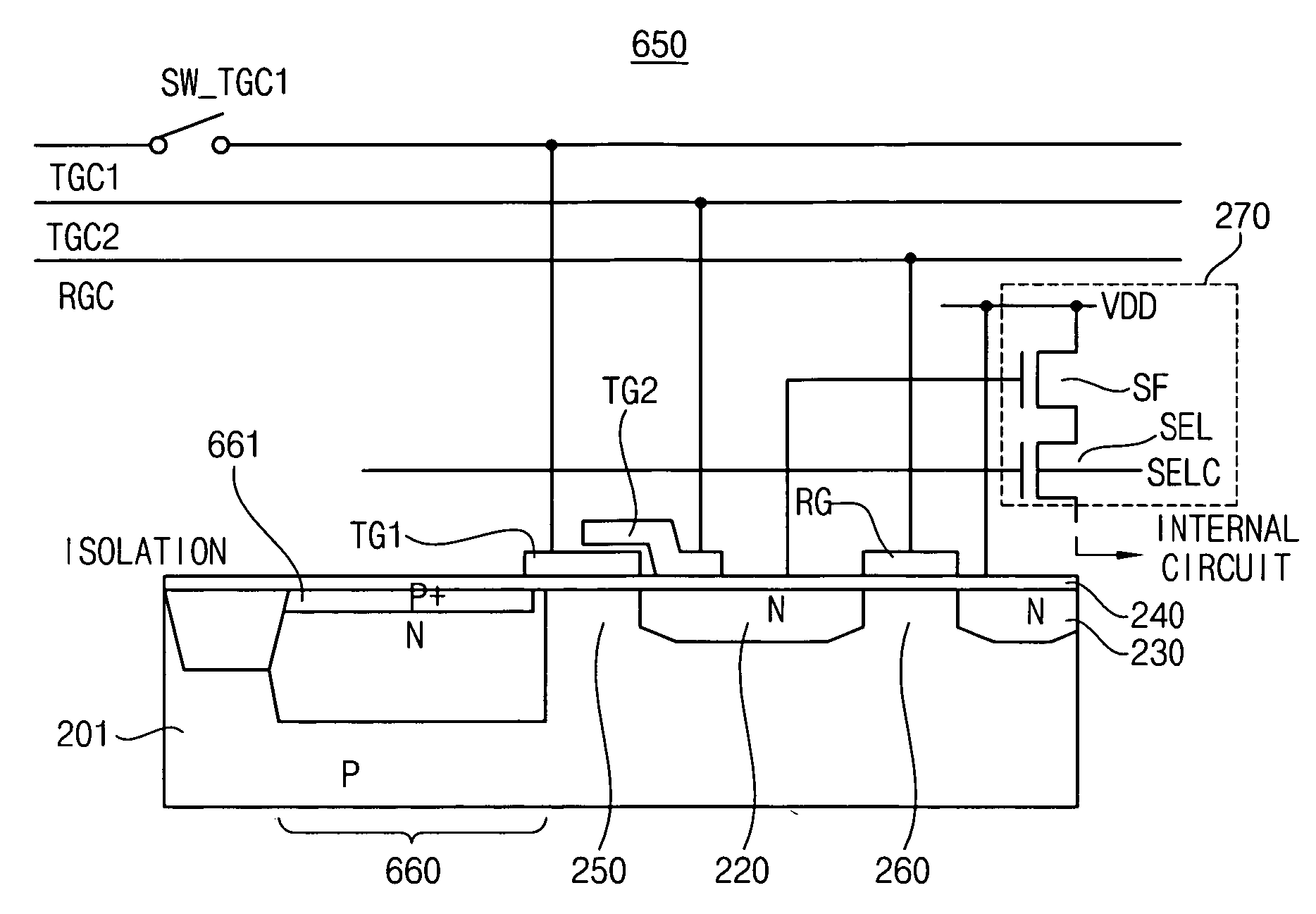
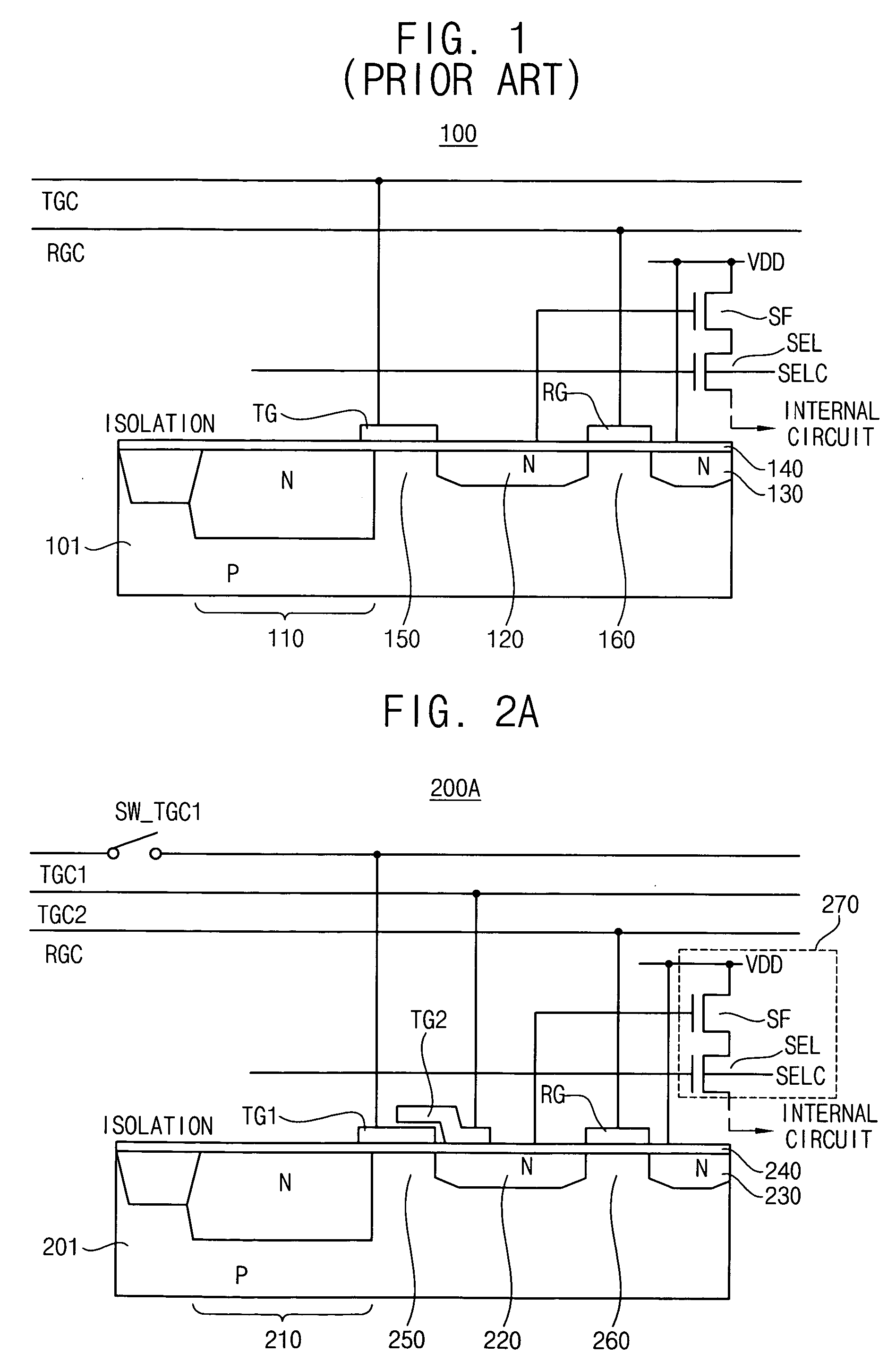
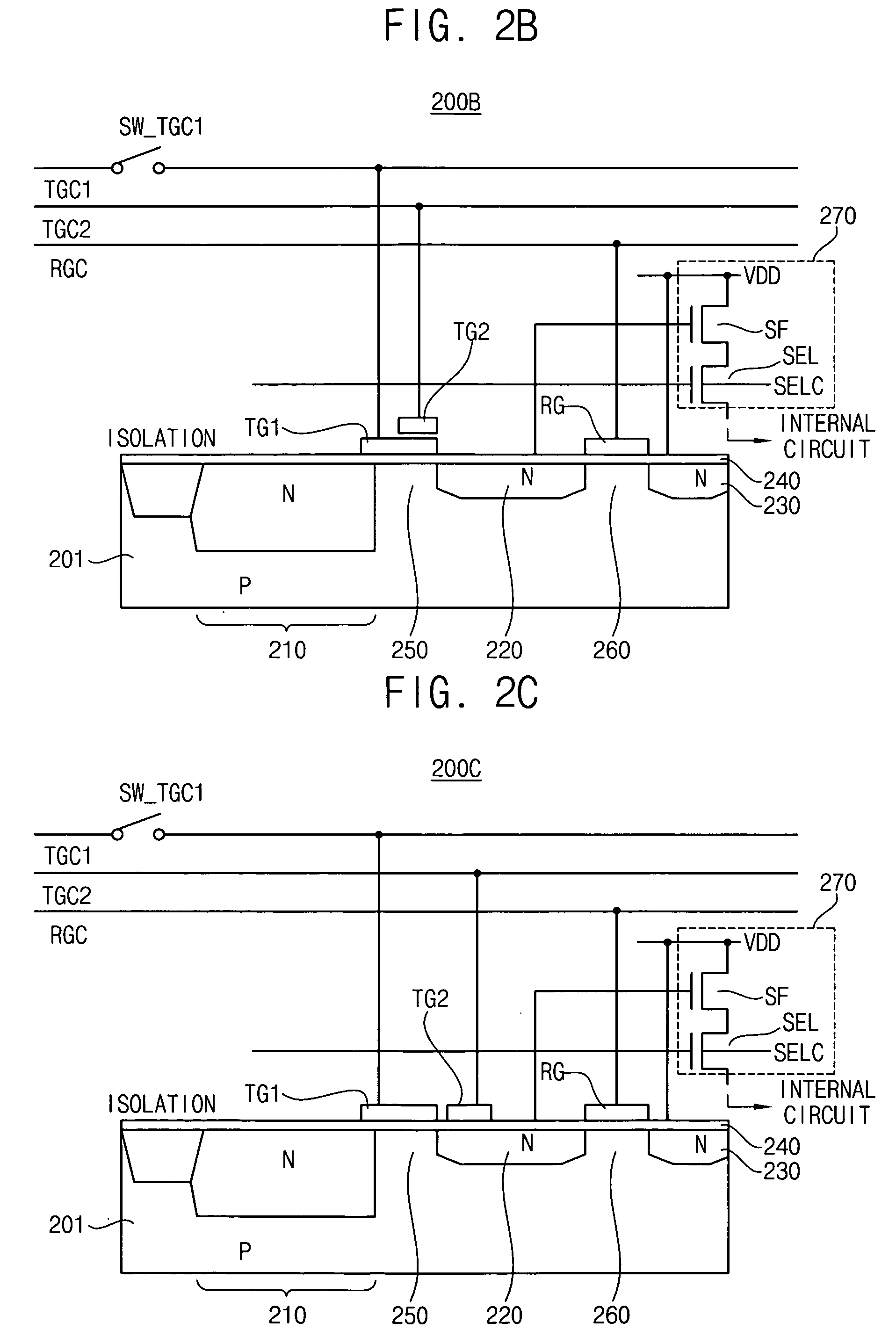
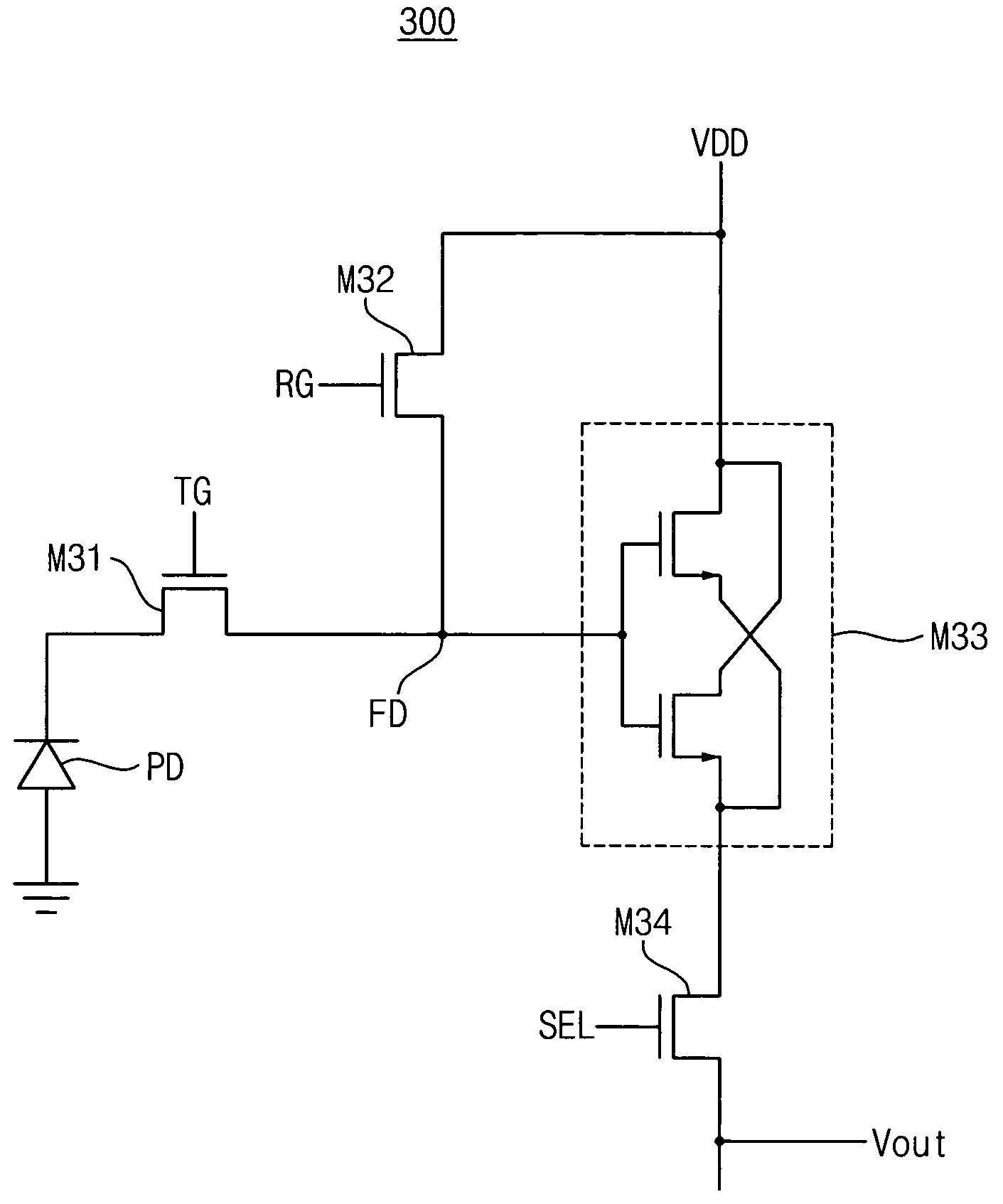
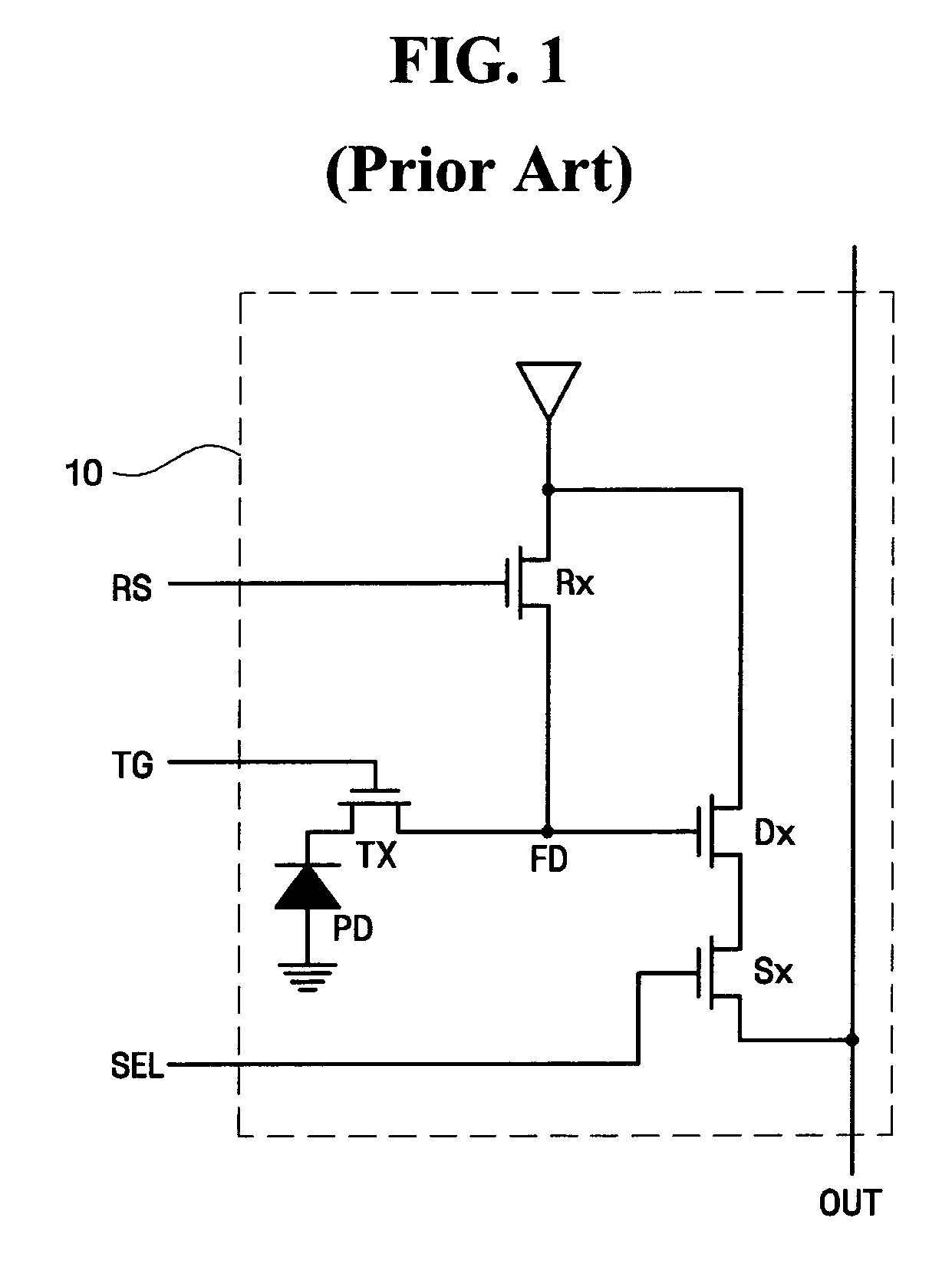
A complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) active pixel sensor includes a photodiode, a transfer transistor with a coupled gate, a reset transistor and a signal transfer circuit, where the photodiode generates electric charges in response to incident light, the transfer transistor transfers the electric charges integrated in the photodiode to a floating diffusion node, wherein the transfer transistor has a first transfer gate and a second transfer gate, and the first and second transfer gates have a coupled gate structure, the reset transistor resets a potential level of the floating diffusion node by a given voltage level, the signal transfer circuit transfers the potential level of the floating diffusion node to an internal circuit in response to a selection signal, and the CMOS active pixel sensor with the coupled gate may increase a capacity of the photodiode and reduce an image lag by using a voltage coupling effect of the coupled gate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
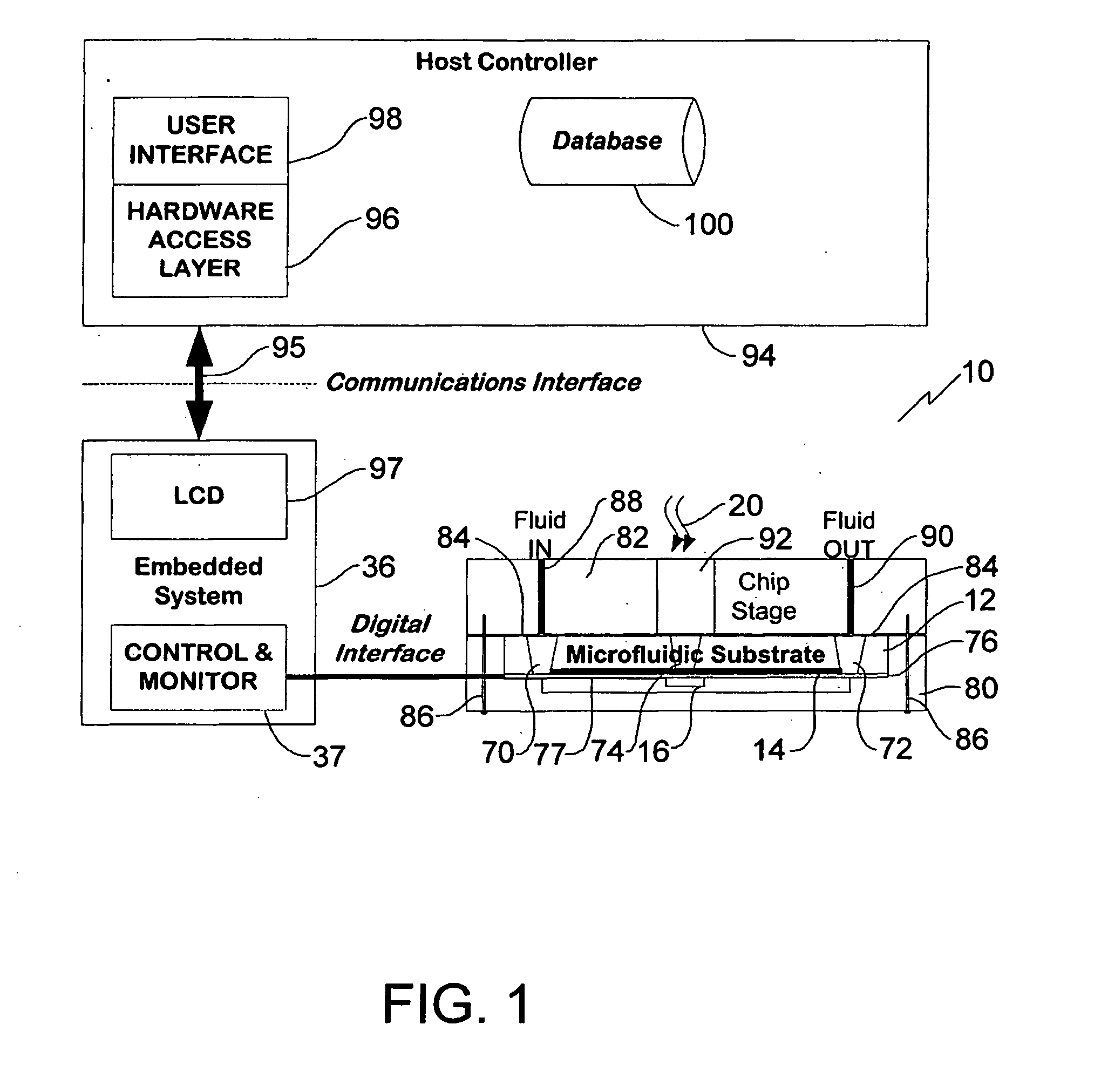
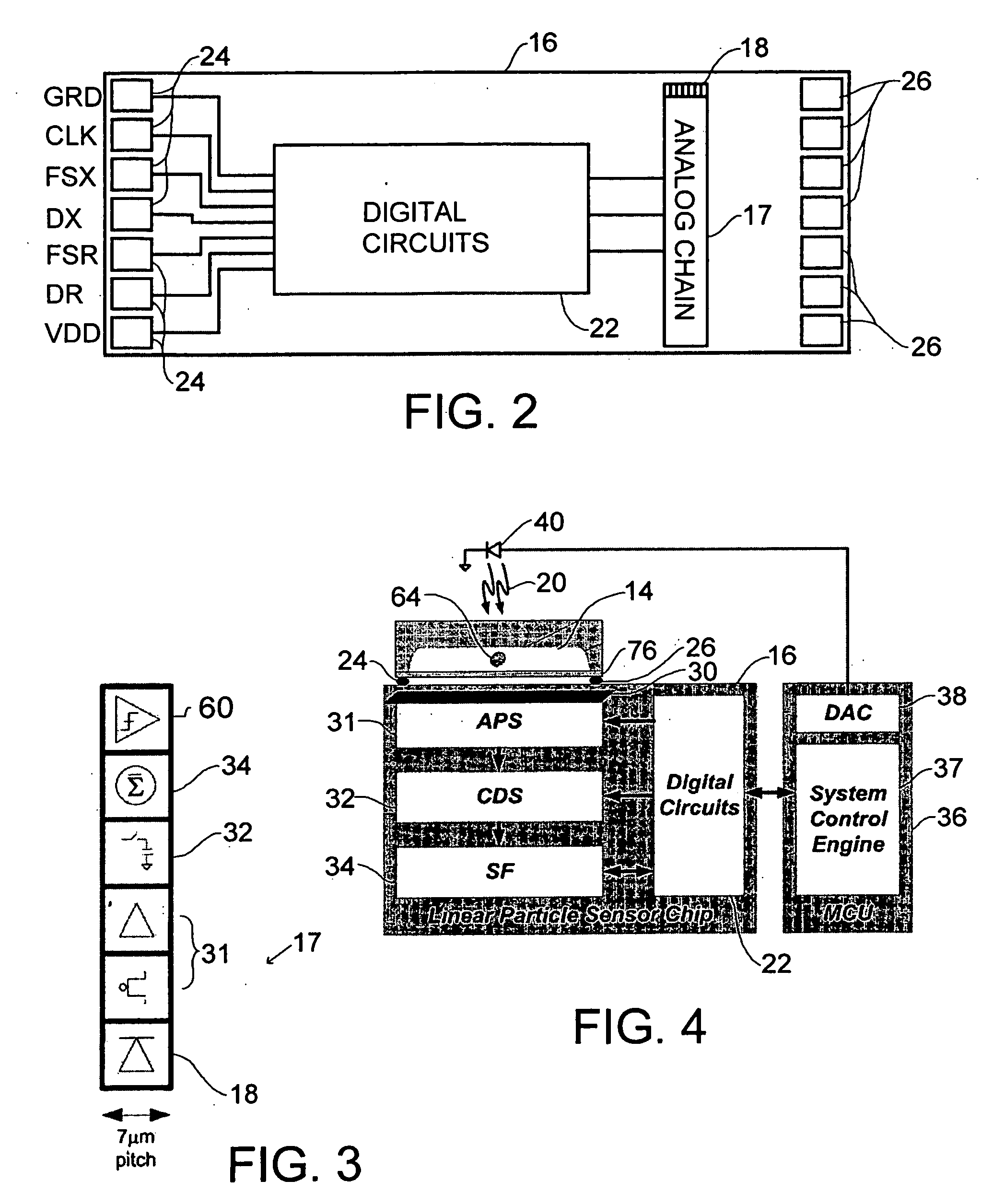
Cytometer
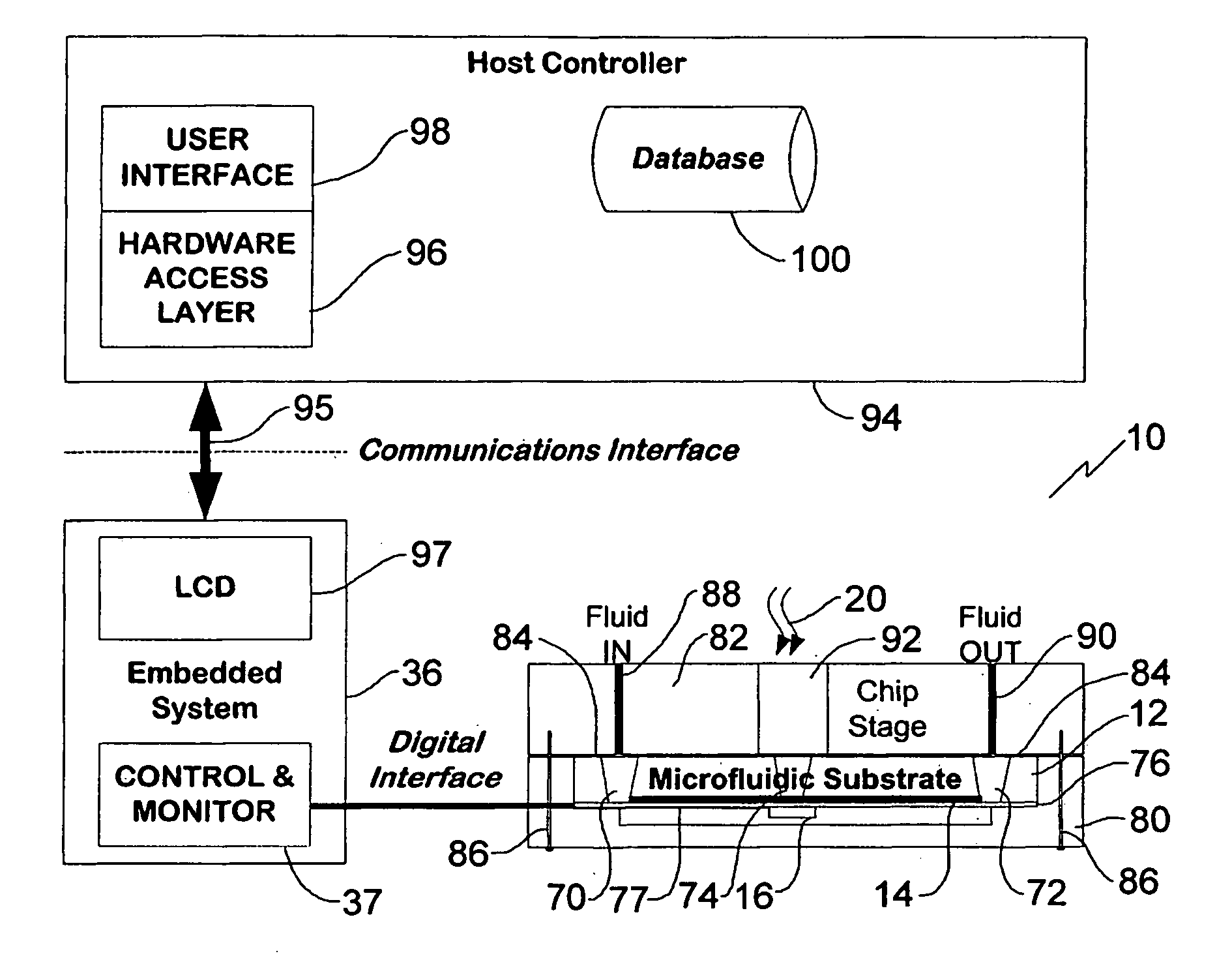
A real-time digital cytometer on a chip system utilizing a custom near field CMOS active pixel intelligent sensor that is flip-chip attached to a fluidic microchannel etched in a thin glass substrate. The CMOS active pixel sensor, fabricated using a 0.18 micron process, is a mixed signal chip comprising a sixteen pixel linear adaptive spatial filter coupled to a digital serial interface. This near field hybrid digital sensor topology obviates the need for both high resolution analog to digital conversion as well as conventional microscopy for the realization of real time optical cytometry. The custom sensor based design approach affords efficient scaling into a tiled multi-channel sensing configuration. The complete system, supported by a handheld graphical user interface and control module, demonstrates a viable micro total analysis sub-system for sample preparation and analysis which can support a wide range of applications ranging from cytometry to cell growth kinetics and analysis and various forms of fluid and droplet metering on an integrated and compact microfluidic platform.
Owner:UTI LLP
Silicide strapping in imager transfer gate device
ActiveUS20080128767A1Improve barrier propertiesReduce performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideElectrical conductor
A CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure having dual workfunction transfer gate device and method of fabrication. The transfer gate device comprises a dielectric layer formed on a substrate and a dual workfunction gate conductor layer formed on the dielectric layer comprising a first conductivity type doped region and an abutting second conductivity type doped region. The transfer gate device defines a channel region where charge accumulated by a photosensing device is transferred to a diffusion region. A silicide structure is formed atop the dual workfunction gate conductor layer for electrically coupling the first and second conductivity type doped regions. In one embodiment, the silicide contact is smaller in area dimension than an area dimension of said dual workfunction gate conductor layer. Presence of the silicide strap prevents the diodic behavior from allowing one or the other side of the gate to float to an indeterminate voltage.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC +1
Low lag transfer gate device
A CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure includes at least one transfer gate device and method of operation. A first transfer gate device comprises a diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure having a first doped region of first conductivity type material and a second doped region of a second conductivity type material. A photosensing device is formed adjacent the first doped region for collecting charge carriers in response to light incident thereto, and, a diffusion region of a second conductivity type material is formed at or below the substrate surface adjacent the second doped region of the transfer gate device for receiving charges transferred from the photosensing device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device upon timed voltage bias to the diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
CMOS active pixel sensor and active pixel sensor array using fingered type source follower transistor
A CMOS active pixel sensor includes a photodiode, a transmitting transistor, a reset transistor, a fingered type source follower transistor and a selecting transistor, where the photodiode generates charge in response to incident light, the transmitting transistor transmits the charge stored in the photodiode to a sensing node, the reset transistor, coupled to a power supply voltage, resets a voltage of the sensing node so that the sensing node has substantially a level of the power supply voltage, the fingered type source follower transistor amplifies the voltage of the sensing node, the selecting transistor transmits a voltage of a source electrode of the fingered type source follower transistor into an internal circuit in response to a selection signal, thus, the channel width of the source follower transistor may be increased, and the MOS device noise due to the source follower transistor may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low lag transfer gate device
ActiveUS20090180010A1Prevent overflowTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectrical conductorEngineering
A method of forming a CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure having at least one transfer gate device and method of operation. A first transfer gate device comprises a diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure having a first doped region of first conductivity type material and a second doped region of a second conductivity type material. A photosensing device is formed adjacent the first doped region for collecting charge carriers in response to light incident thereto, and, a diffusion region of a second conductivity type material is formed at or below the substrate surface adjacent the second doped region of the transfer gate device for receiving charges transferred from the photosensing device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device upon timed voltage bias to the diodic or split transfer gate conductor structure. Alternately, an intermediate charge storage device and second transfer gate device may be provided which may first temporarily receive charge carriers from the photosensing device, and, upon activating the second transfer gate device in a further timed fashion, read out the charge stored at the intermediate charge storage device for transfer to the second transfer gate device while preventing spillback of charges to the photosensing device. The APS cell structure is further adapted for a global shutter mode of operation, and further comprises a light shield element is further provided to ensure no light reaches the photosensing and charge storage devices during charge transfer operation.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
CMOS active pixel sensor and active pixel sensor array using fingered type source follower transistor
A CMOS active pixel sensor includes a photodiode, a transmitting transistor, a reset transistor, a fingered type source follower transistor and a selecting transistor, where the photodiode generates charge in response to incident light, the transmitting transistor transmits the charge stored in the photodiode to a sensing node, the reset transistor, coupled to a power supply voltage, resets a voltage of the sensing node so that the sensing node has substantially a level of the power supply voltage, the fingered type source follower transistor amplifies the voltage of the sensing node, the selecting transistor transmits a voltage of a source electrode of the fingered type source follower transistor into an internal circuit in response to a selection signal, thus, the channel width of the source follower transistor may be increased, and the MOS device noise due to the source follower transistor may be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS image sensors having pixel arrays with uniform light sensitivity
ActiveUS7710477B2Improve uniformityImprove responseTransistorTelevision system detailsPixel arraySolid-state
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS active pixel sensor with a sample and hold circuit having multiple injection capacitors and a fully differential charge mode linear synthesizer with skew control
InactiveUS6861634B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMultiple injectionCapacitance
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Silicide strapping in imager transfer gate device
ActiveUS7675097B2Improve barrier propertiesReduce performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideElectrical conductor
A CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) cell structure having dual workfunction transfer gate device and method of fabrication. The transfer gate device comprises a dielectric layer formed on a substrate and a dual workfunction gate conductor layer formed on the dielectric layer comprising a first conductivity type doped region and an abutting second conductivity type doped region. The transfer gate device defines a channel region where charge accumulated by a photosensing device is transferred to a diffusion region. A silicide structure is formed atop the dual workfunction gate conductor layer for electrically coupling the first and second conductivity type doped regions. In one embodiment, the silicide contact is smaller in area dimension than an area dimension of said dual workfunction gate conductor layer. Presence of the silicide strap prevents the diodic behavior from allowing one or the other side of the gate to float to an indeterminate voltage.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC +1
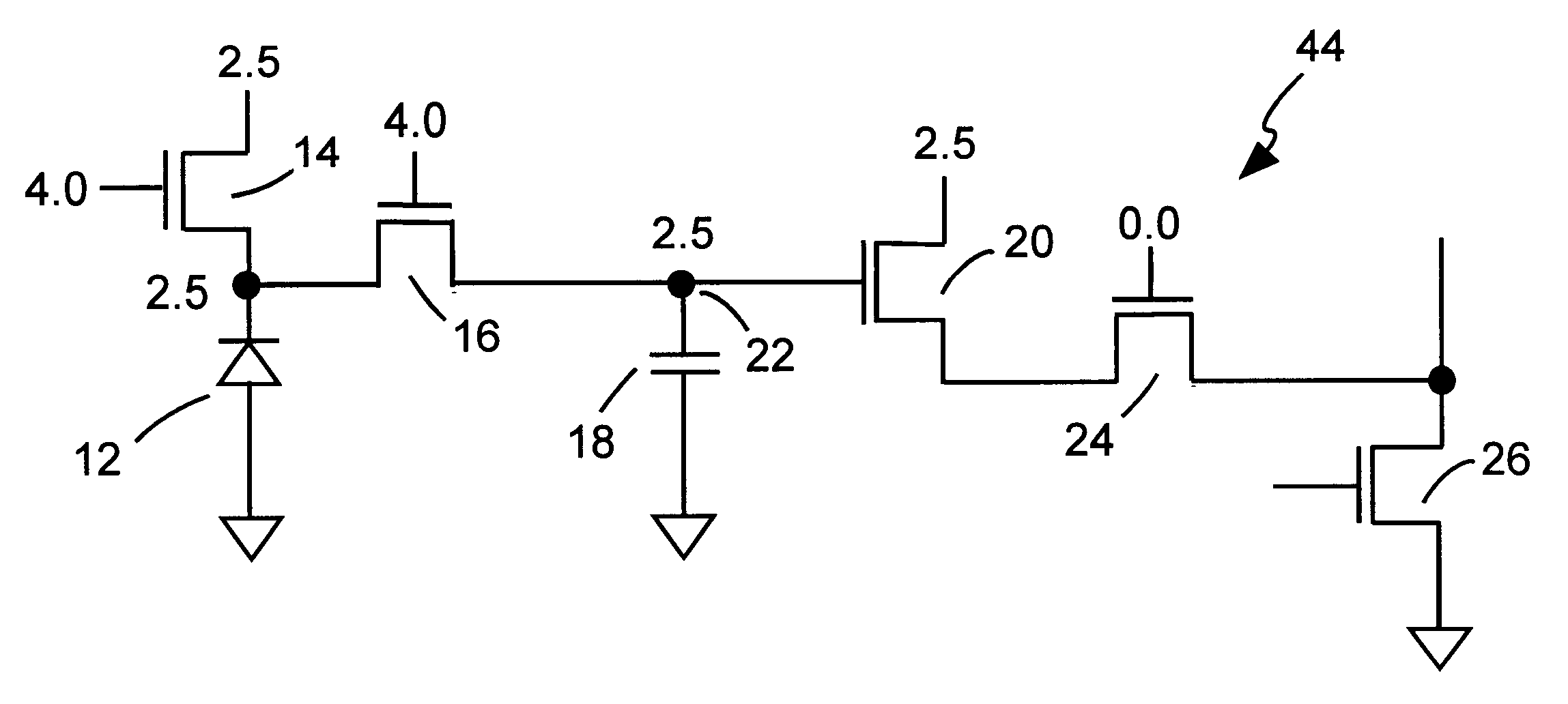
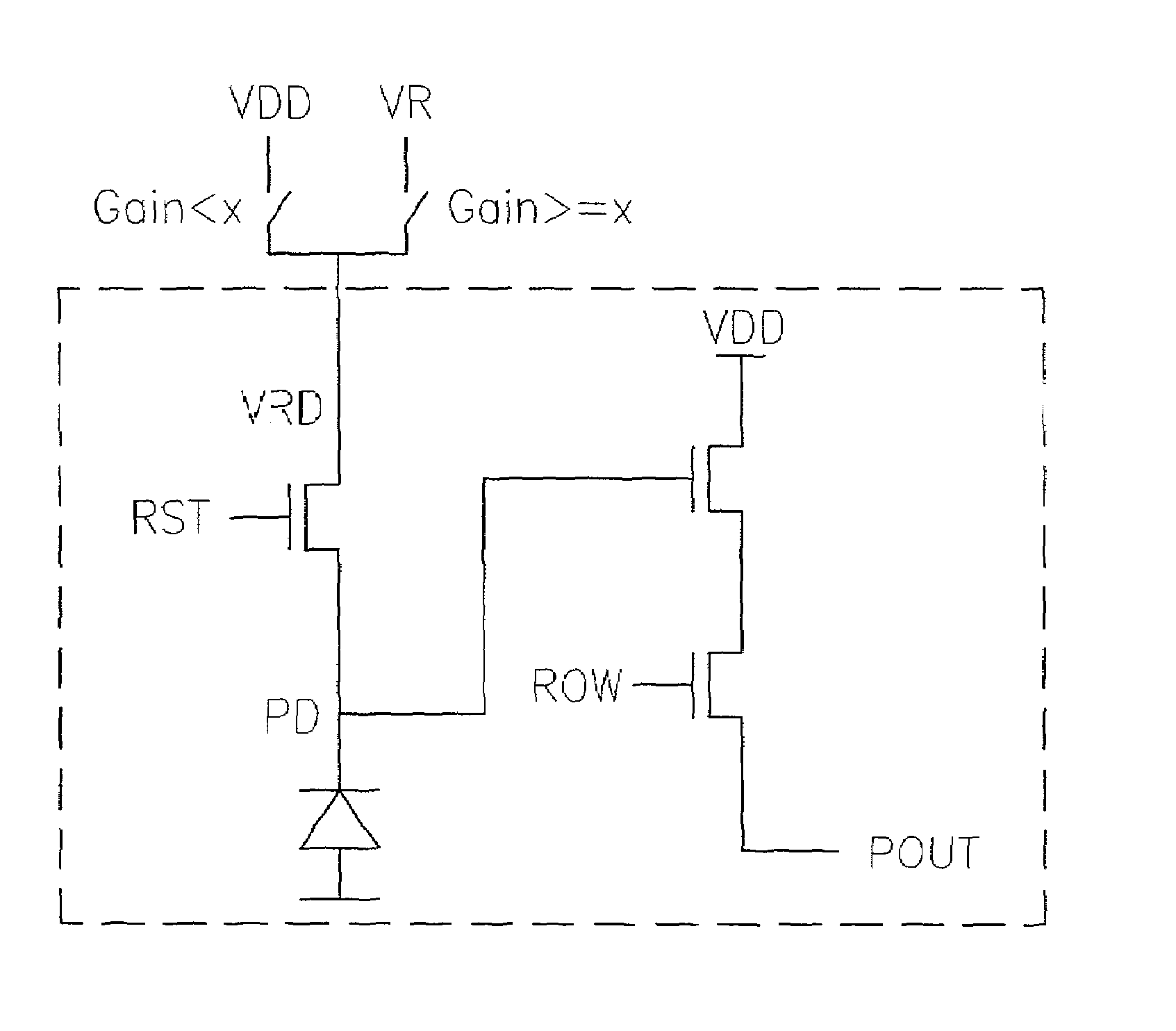
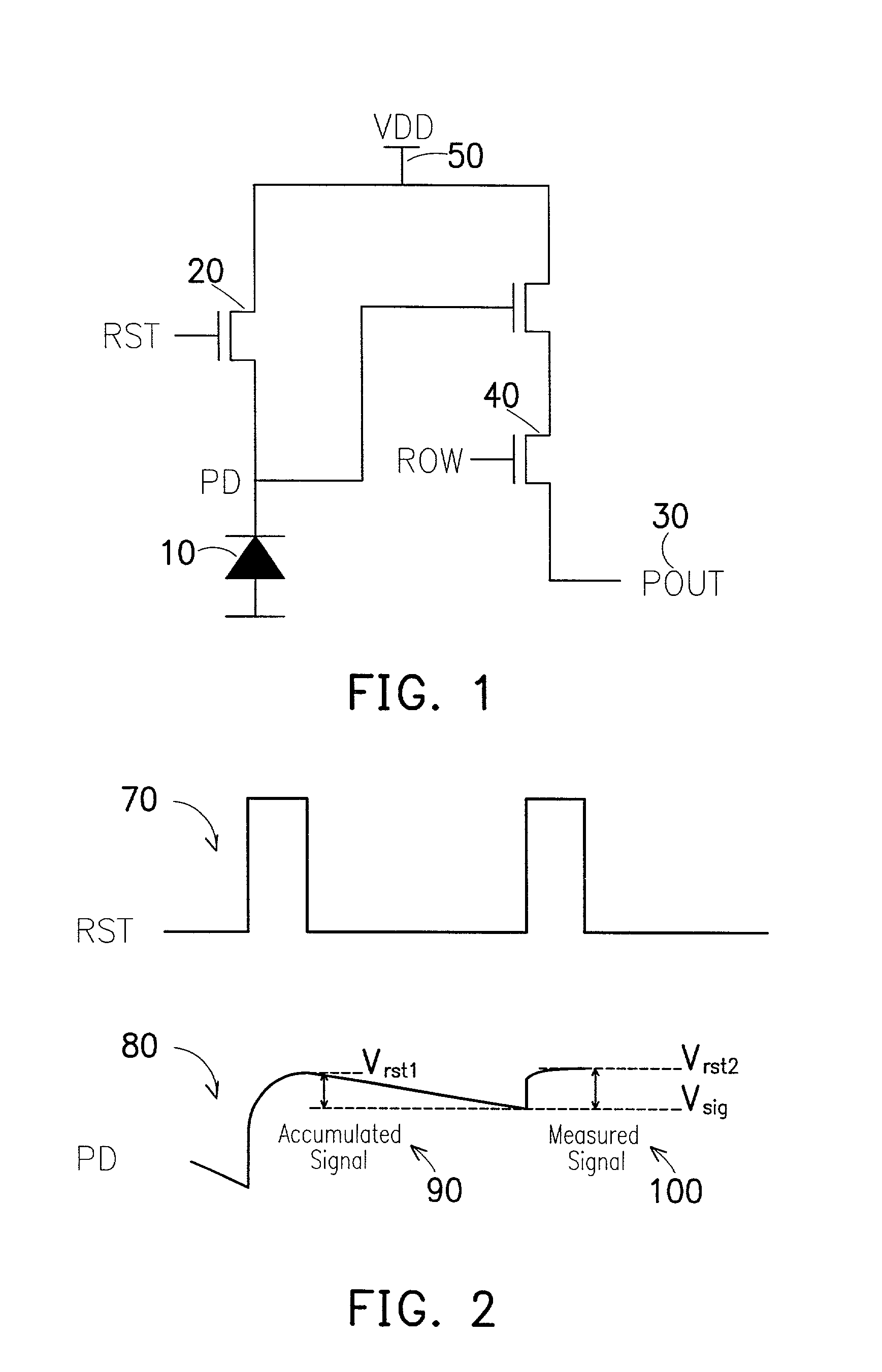
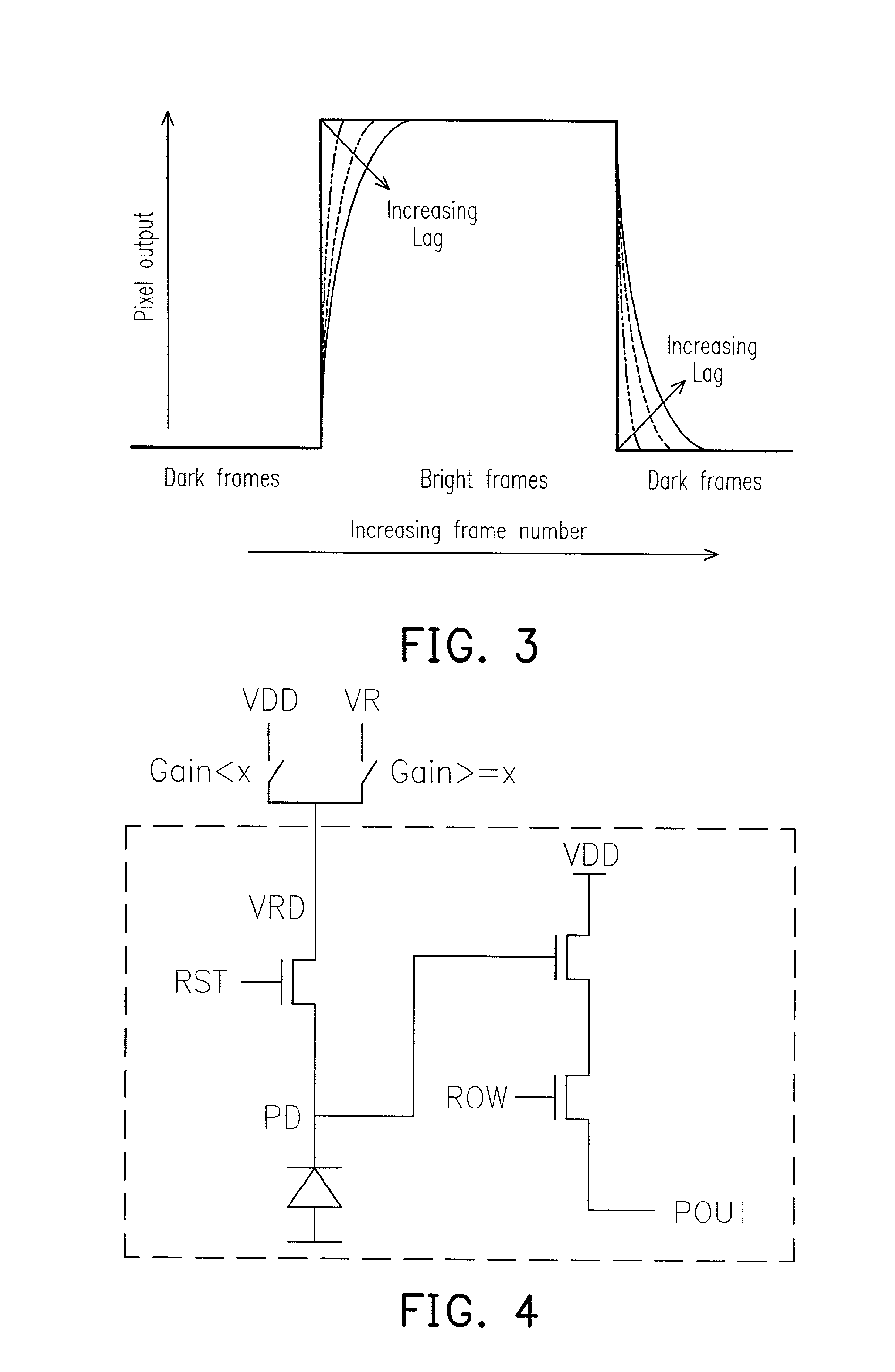
Method and apparatus of controlling a pixel reset level for reducing an image lag in a CMOS sensor
ActiveUS6958776B2Reduce image lagPerformance is not affectedTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsAudio power amplifierIlluminance
The invention provides a method and apparatus for reducing image lag in CMOS active pixel sensors at low light levels by controlling the reset level. By ensuring that the reset level is independent of the preceding signal level, the problem of image lag can be avoided. Always resetting a photodiode to a fixed voltage is a hard reset. The maximum signal swing is limited by the reset level and the column readout amplifier. If the column circuits are not modified, using hard reset can reduce the maximum signal swing. However in dark images only a portion of the full scale is used. Therefore the amplifier gain setting can be used to determine whether to use a hard reset or soft reset. This method and apparatus for using hard or soft reset dependent on signal level improves image quality at low light levels without compromising performance at high illumination.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dynamic range and method of operation for object motion detection
ActiveUS7616231B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsObject motionPhotodetector
A CMOS imaging array includes a plurality of individual pixels arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel is constructed the same and includes a photodetector (e.g., photodiode) receiving incident light and generating an output. A first, relatively lower gain, wide dynamic range amplifier circuit is provided responsive to the output of the photodetector. The first circuit is optimized for a linear response to high light level input signals. A second, relatively higher gain, lower dynamic range amplifier circuit is also provided which is responsive to the output of the photodetector. The second circuit is optimized to provide a high signal to noise ratio for low light level input signals. Subtraction of output signals from the amplifier circuits, preferably after gain compensation, can be used to detect moving objects in the scene where the integration times for the two circuits are not the same, e.g., are staggered in time or have a different period.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Active pixel sensor with noise cancellation
InactiveUS6940551B2Reduce pixel areaSame level of resolutionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A CMOS active pixel sensor with noise reduction employs a photodetector. A reset switch is coupled between a reset potential line and the photodetector and is controlled by a reset line. An amplifier is coupled to the photodetector. A kTC noise reducing circuit is disposed within the pixel sensor. A readout circuit is coupled to the kTC noise reducing circuit and is controlled by a row-select line.
Owner:FOVEON
Dark current reduction circuitry for CMOS active pixel sensors
InactiveUS7015448B2Reduce GIDLMinimizing gate induced drain leakageTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDriver circuitLow voltage
A row driver circuit is disclosed for supplying a reset voltage to a plurality of reset transistors of an active pixel sensor array while minimizing gate induced drain leakage (GIDL). The row driver circuit is configured to supply a high voltage level (e.g., Vdd or higher) to the reset transistors of the array during a reset operation. The row driver circuit is further configured to supply a low voltage level (e.g., a voltage level higher than ground) to the reset transistors of the array when the pixels are not being reset (e.g., during integration). The reduced potential difference realized between the respective gates of the reset transistors and the respective photodiodes of the pixels, when the pixels are not being reset, results in reduced GIDL.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Methods for improving sensitivity of CMOS active pixel sensors
InactiveUS7053947B2Loss of performanceTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsBit lineCMOS
The present invention relates to a CMOS active pixel sensor which includes a compensation circuit capable of compensating a lowered pixel voltage output due to leakage current of a photodiode. The CMOS active pixel sensor having a light sensing unit for generating an output voltage when light is incident thereupon, the sensing unit having an amount of leakage current before the incidence of light. A reset unit resets the output voltage of the light sensing unit to an initial reset voltage in response to a reset signal. A sense transistor has a source, a drain coupled to a power source voltage, and a gate coupled to the output of the light sensing unit. A select transistor has a drain connected to a source of the sense transistor, and provides the voltage of the sense transistor to a bit line, in response to a select signal. A compensation unit supplies a voltage corresponding to the output voltage of the light sensing unit lowered by the leakage current.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
CMOS active pixel sensor with a sample and hold circuit having multiple injection capacitors and a fully differential charge mode linear synthesizer with skew control
InactiveUS20050001919A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceMultiple injection
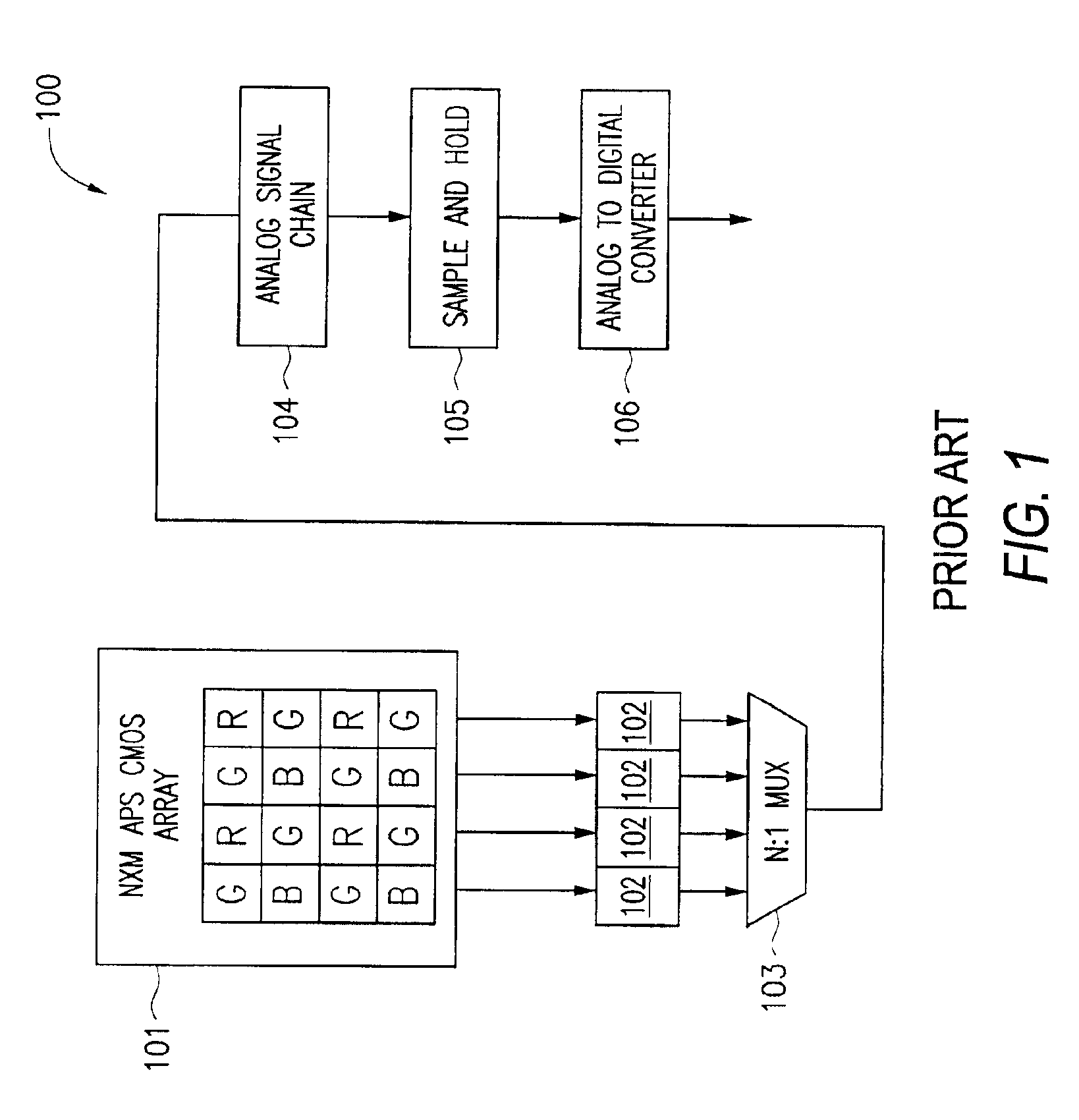
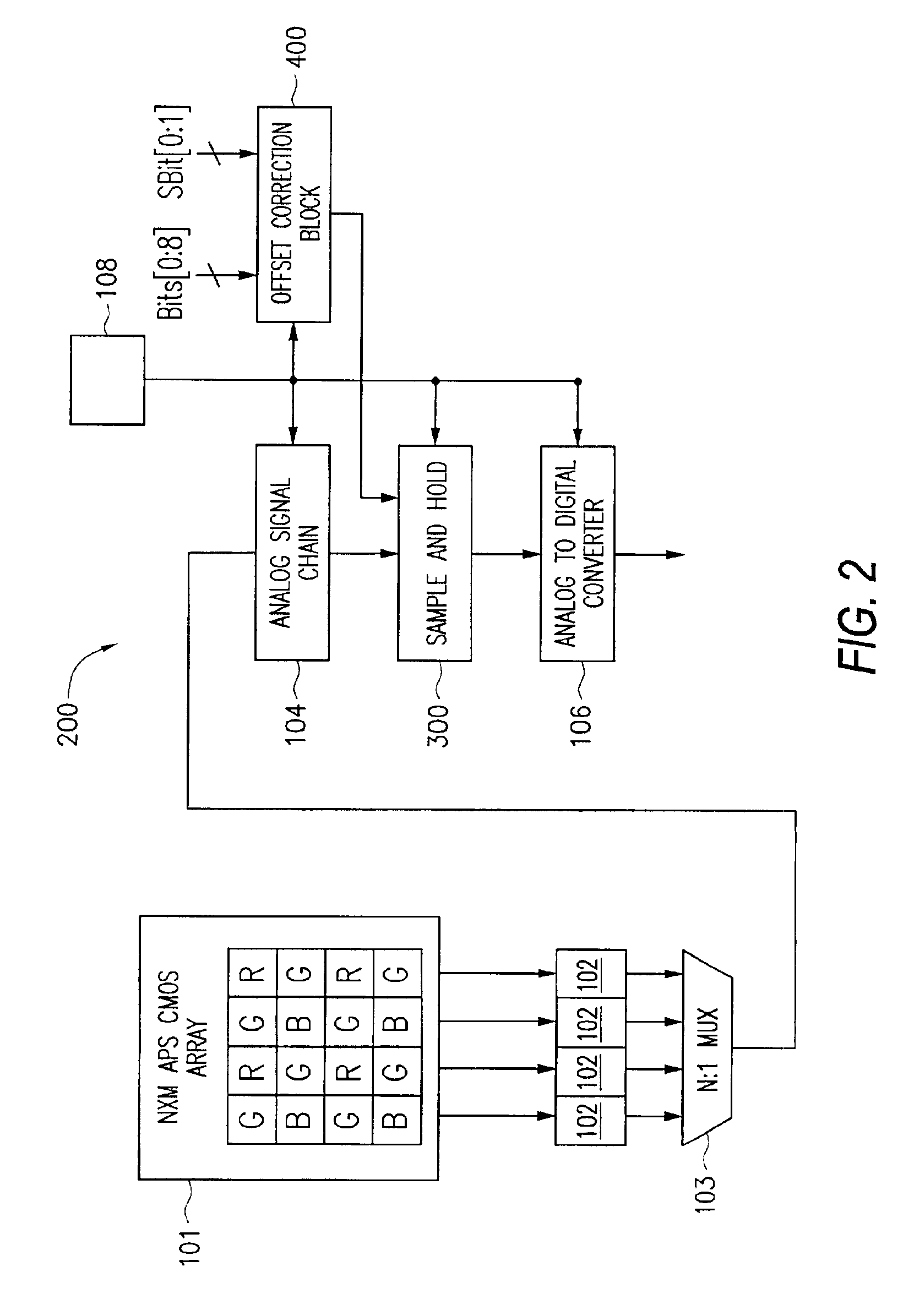
An CMOS active pixel sensor (APS) imaging system include circuitry to compensate for different analog offset levels from the CMOS pixel array. More specifically, the compensation is performed in the analog (charge) domain. A digital correction value, which may be measured as part of the operation or testing of the CMOS APS system, is provided to a offset correction block circuit, to generate an analog electrical signal. The analog electrical signal is supplied to a sample-and-hold circuit including a charge amplifier. The signal read from the pixel array, after conditioning through an analog signal chain, is also supplied to the charge amplifier, which has a linear transfer function and outputs the compensated signal.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
CMOS active pixel sensor with improved dark current and sensitivity
ActiveUS20060017072A1Reduce dark currentHigh sensitivityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricElectron
An active pixel sensor which provides reduced dark current, improved sensitivity, and improved modulation transfer function. An N well, surrounded by a P well is formed in a P type epitaxial substrate. A P+ region is formed extending from within the P well into the substrate leaving a gap between the P+ region and the N well. A gate dielectric is formed covering at least the gap, part of the P+ region, and part of the N well. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric over the gap, part of the P+ region, and part of the N well. The gate electrode is biased so that the region of the substrate under the gate electrode is accumulated with holes and the region of the N well under the gate electrode is depleted of electrons. This will reduce the dark current and improve the sensitivity of the active pixel sensor. In a second embodiment the P type epitaxial substrate is replaced by an N type epitaxial substrate, the N well is replaced by a P well, N+ regions are replaced by P+ regions, and P+ regions are replaced by N+ regions. In this second embodiment the gate electrode is biased so that the region of the substrate under the gate electrode is depleted of electrons and the region of the P well under the gate electrode is accumulated with holes.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
System for reducing sensor area in a back side illuminated CMOS active pixel sensor
ActiveUS20120187514A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention relates to a backside illuminated (BSI) imager having a plurality of layers. A plurality of pixel sensors are positioned on a first layer of a substrate. Pixel select conductors are positioned on the substrate in front of the first layer. Pixel readout conductors including a plurality of output lines, pixel power conductors, and a ground conductor are positioned on the substrate in front of the pixel select conductors. A plurality of sample and hold capacitors coupled to the pixel output lines are positioned vertically and / or horizontally on the substrate in front of the ground conductor.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Biasing scheme for large format CMOS active pixel sensors
ActiveUS7408577B2Reliable hard and soft reset operationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsVoltage dropPixel array
An image sensor includes circuitry compensating for voltage drops in a VSS line. The image sensor includes a plurality of photoreceptors arranged in a pixel array having a number of column lines, and read-out circuitry on the column lines. The read-out circuitry provides substantially equal currents on each column line so as to compensate for voltage drops in the VSS line and provide more accurate pixel signals. The image sensor also includes circuitry for filtering noise from a voltage supply line, and for providing hard and / or soft reset operations.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
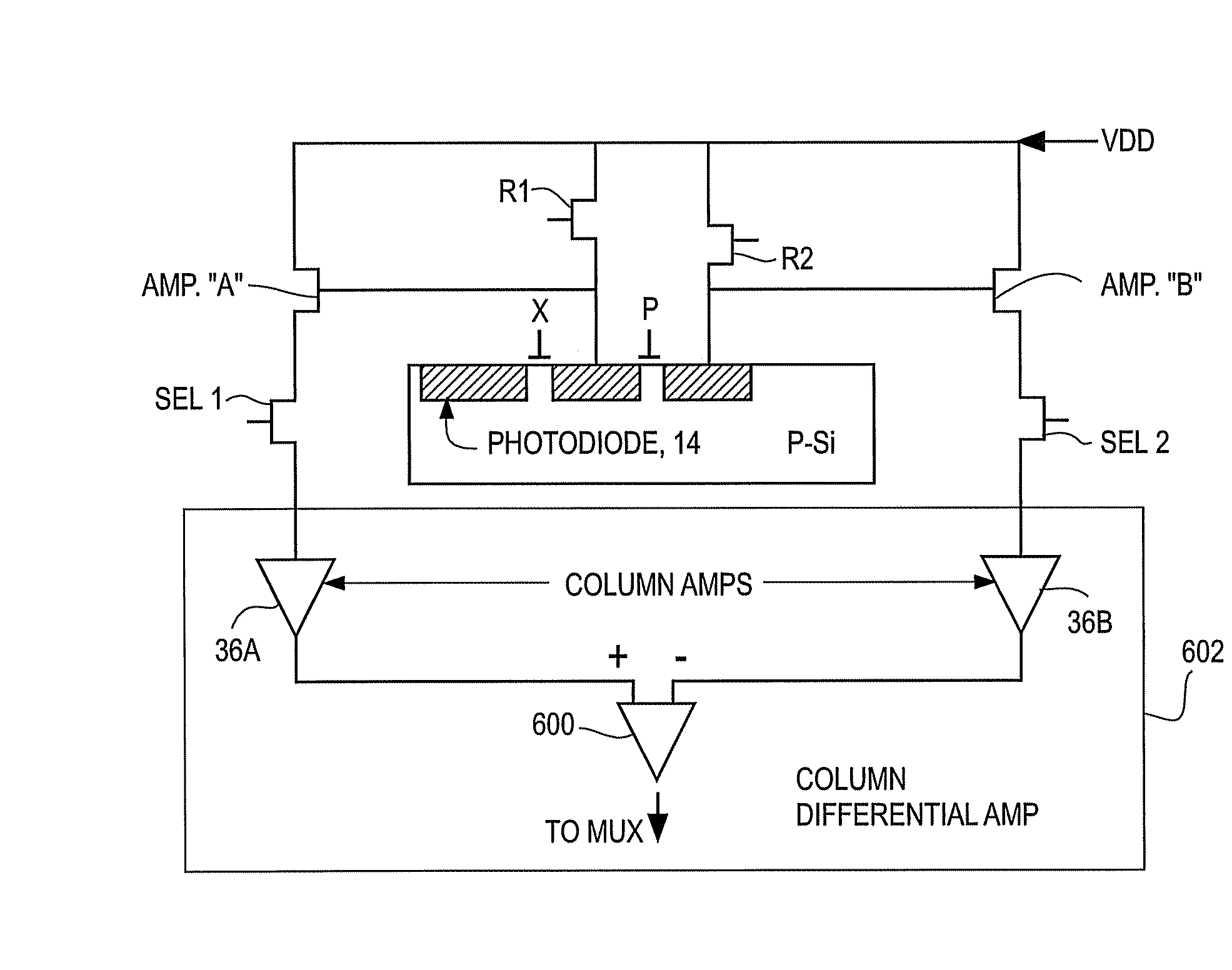
Correlated three sampling circuits for CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) active pixel sensor
InactiveCN102510452ASimple designImproved noise suppressionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRandom noiseCircuit design
The invention discloses correlated three sampling circuits for a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) active pixel sensor, which relates to CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) active pixel sensor (APS) signal noise processing circuit design. Line degrees of the sensor adopt the correlated three sampling circuits, i.e. three line degree sampling hold circuits are sued for sampling and holding an output signal of a CMOS active pixel, so that two options for effectively inhibiting random noise in the pixel output signal under different working conditions, where one option is characterized in that: 'signal voltage' and 'reset voltage' of the pixel in the same frame are differentiated after being sampled and held, so that FPN (Fixed Pattern Noise) is eliminated and low frequency noise is inhibited; and the other option is characterized in that: 'signal voltage' of the pixel and 'reset voltage' of the next frame are differentiated after being sampled and held, so that FPN (Fixed Pattern Noise) is eliminated and low frequency noise is inhibited. The correlated three sampling circuits can provide different noise elimination schemes for different working conditions such as variation of integration time, and the noise can be better inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
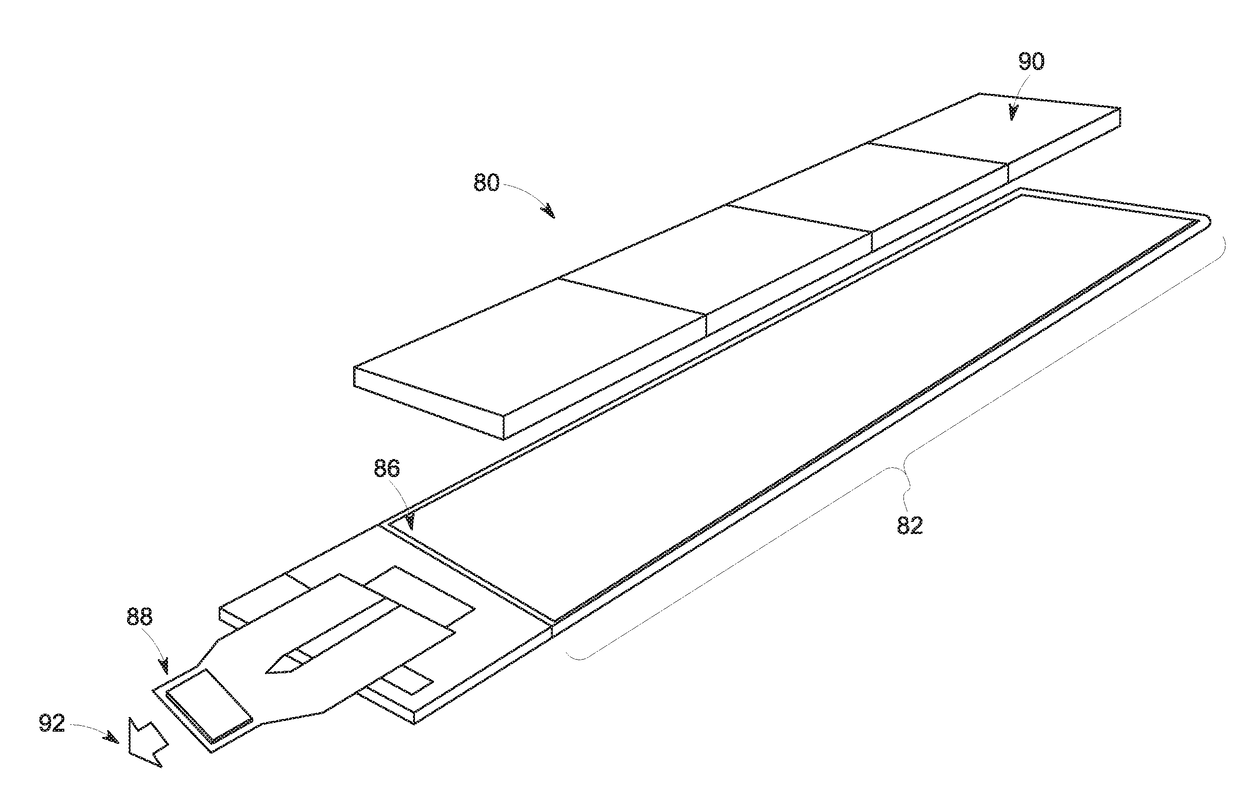
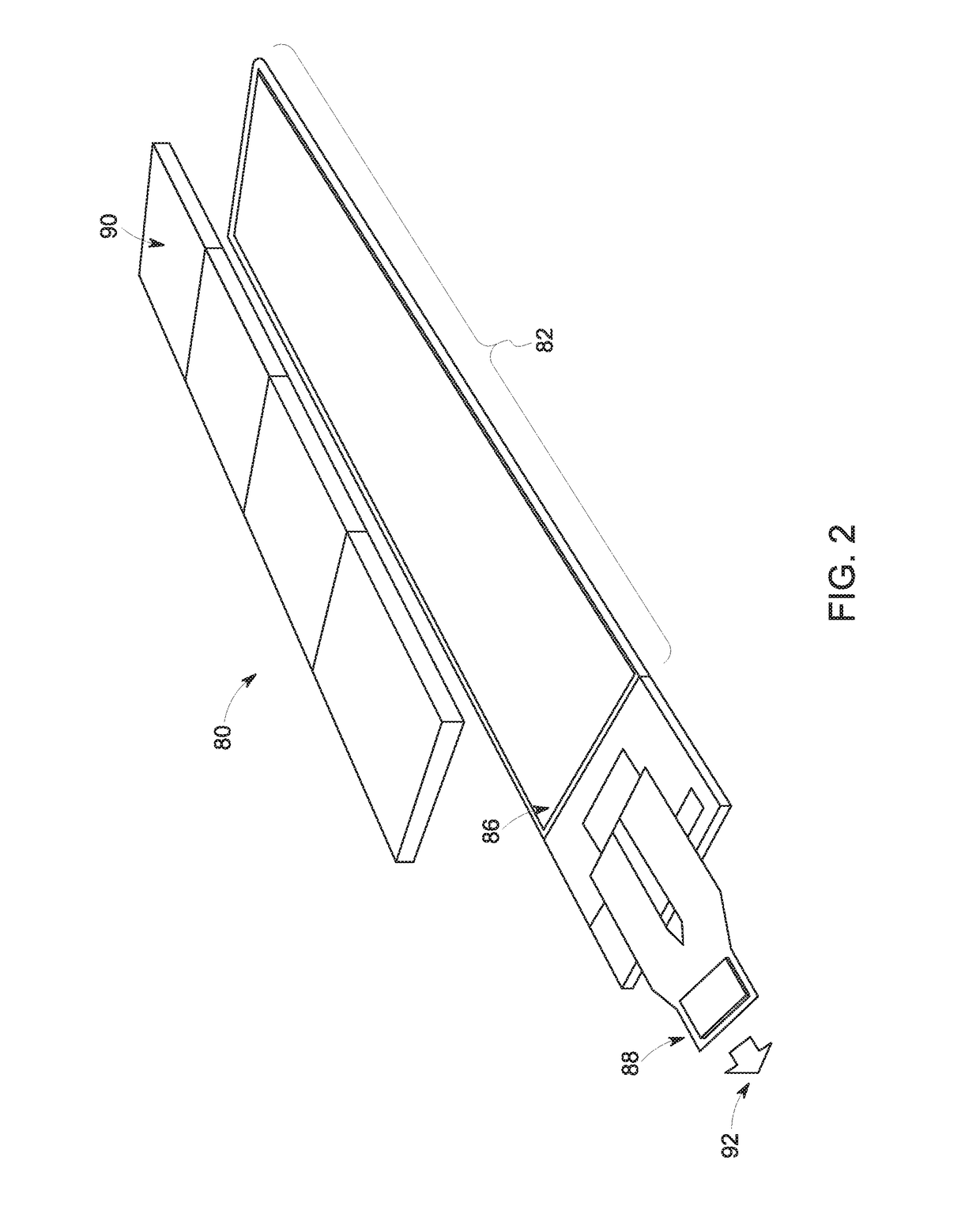
Active pixel sensor computed tomography (CT) detector and method of readout
ActiveUS20180331137A1Facilitate the multiplexed read out of a detector panelsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesComputing tomographyTomography
The present approach relates to implementations of a CT detector integrating CT scintillator packs on a fast, low electronic noise and scalable CMOS active pixel sensor substrate. In one embodiment, a large 3-side buttable CMOS active pixel array with built-in column analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) circuitry (e.g., ASICs) integrated onto the same wafer is used.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com