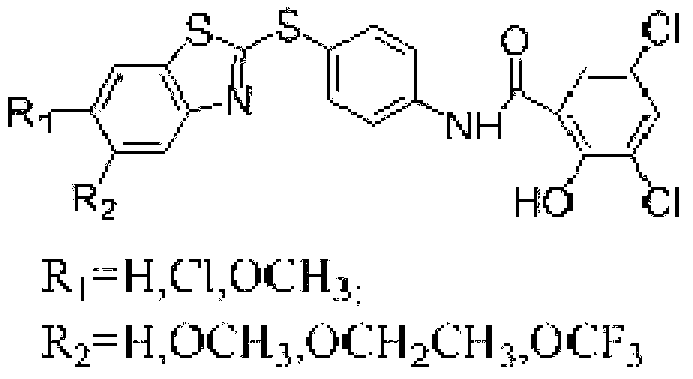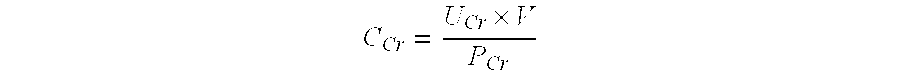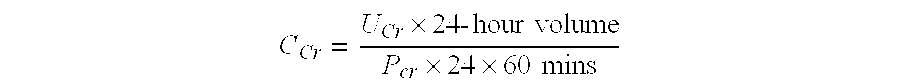Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Cathepsin D" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cathepsin D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTSD gene. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a protein dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. Cathepsin D is an aspartic endo-protease that is ubiquitously distributed in lysosomes. The main function of cathepsin D is to degrade proteins and activate precursors of bioactive proteins in pre-lysosomal compartments. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase A1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of the CTSD gene is initiated from several sites, including one that is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. Homozygous deletion of the CTSD gene leads to early lethality in the postnatal phase. Deficiency of CTSD gene has been reported an underlying cause of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL).
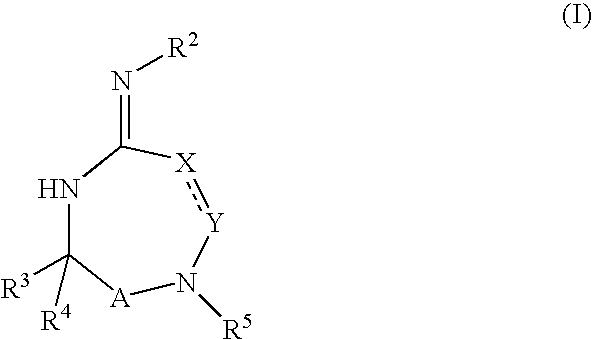
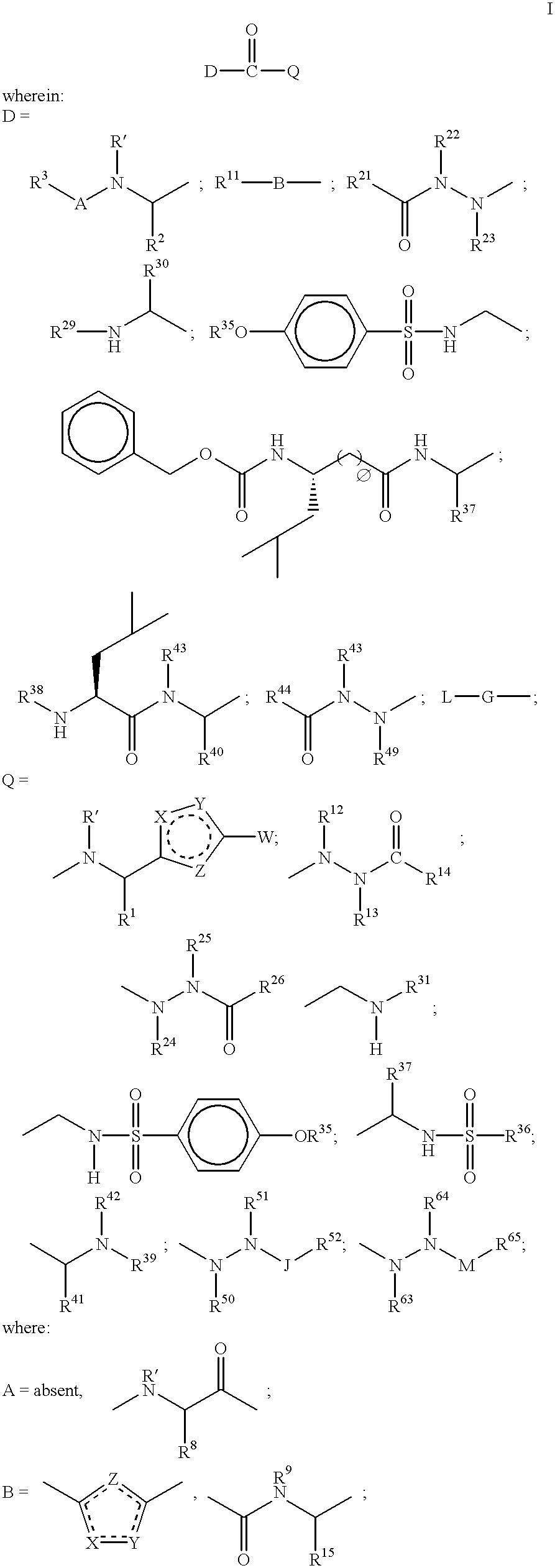
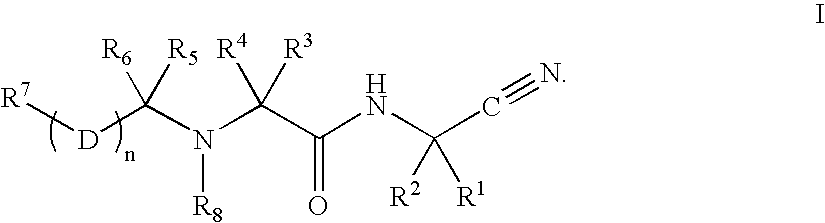
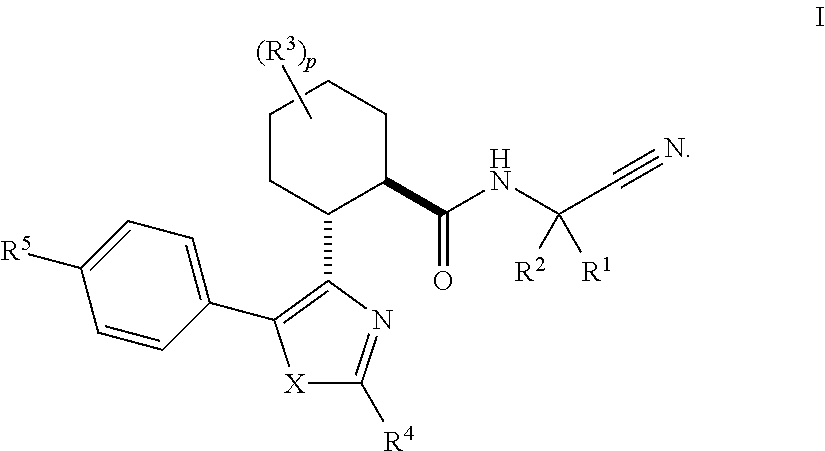
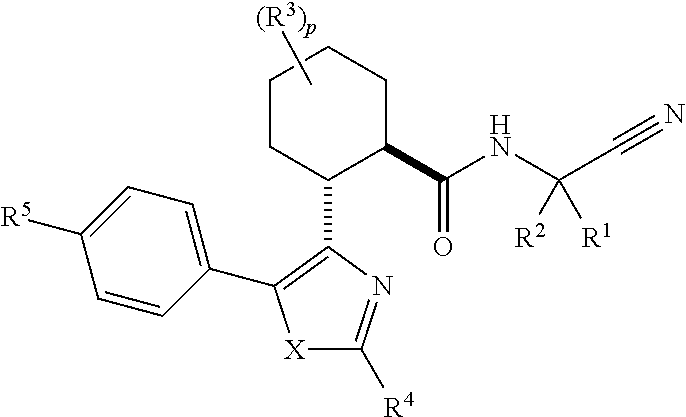
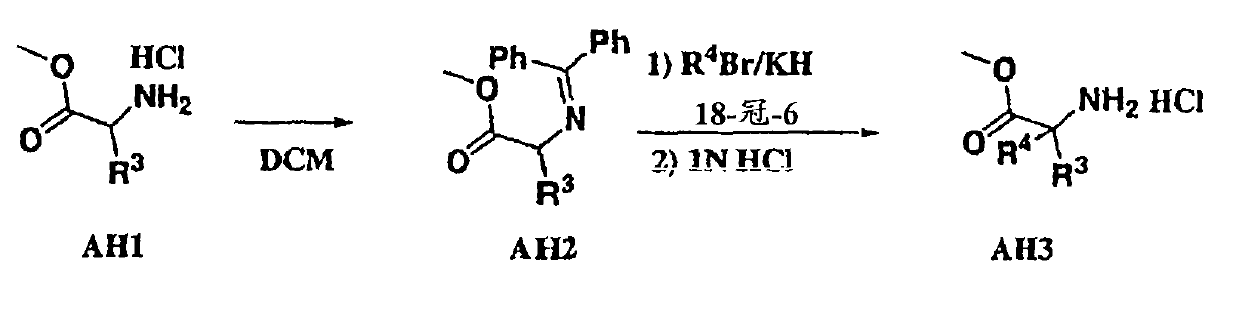
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
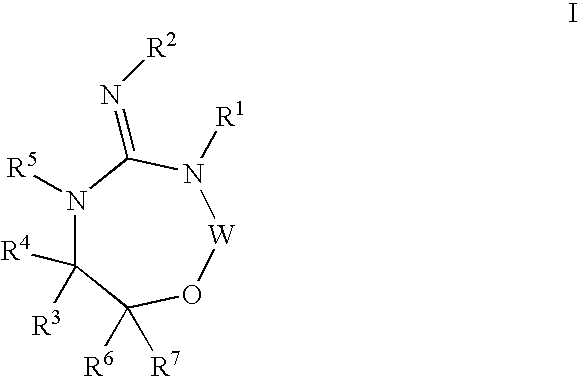
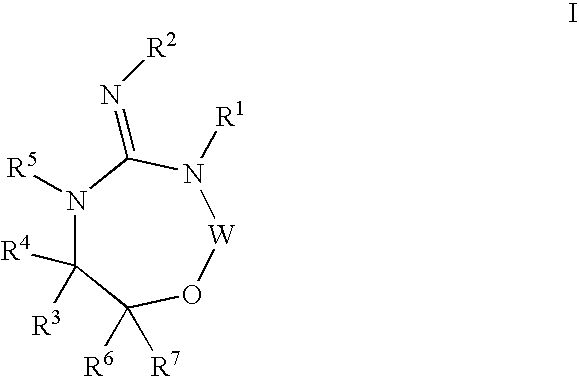
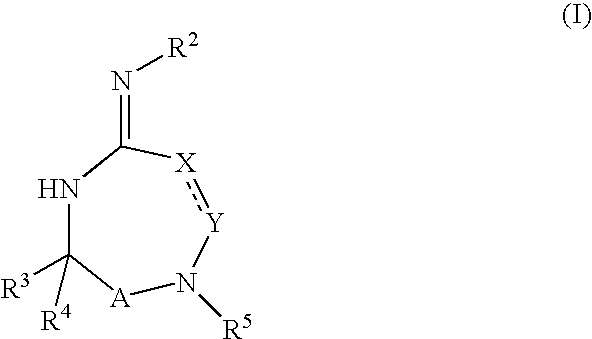
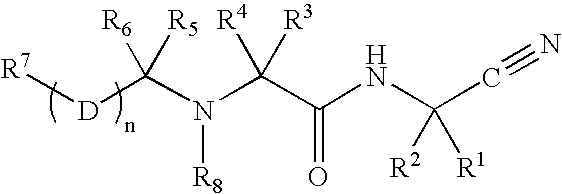
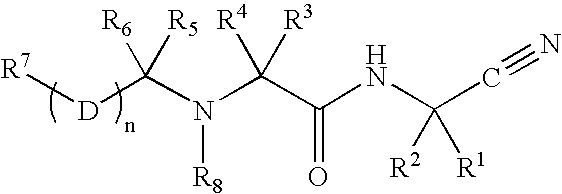
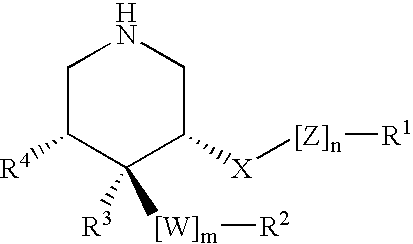
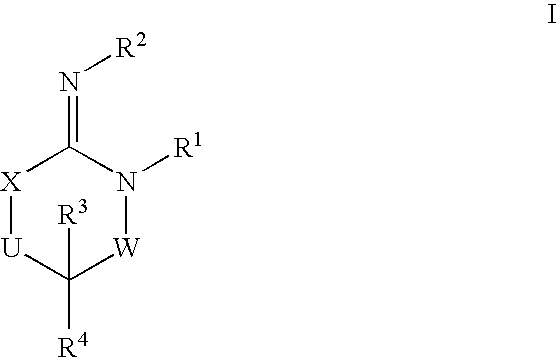
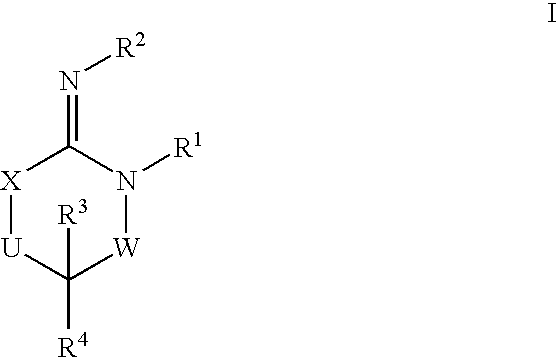
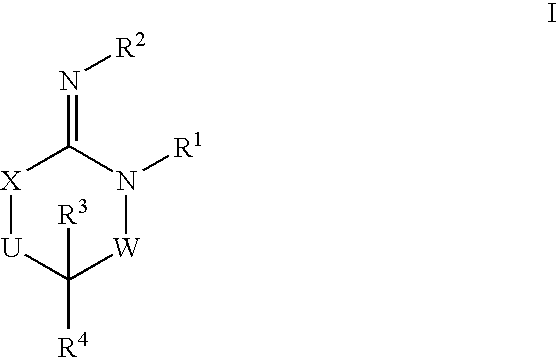
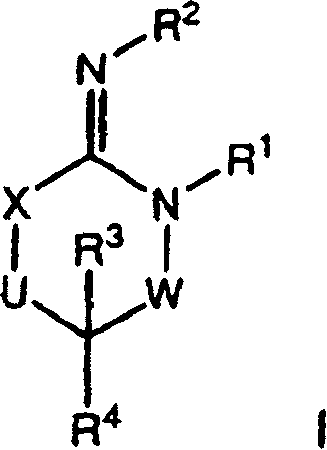
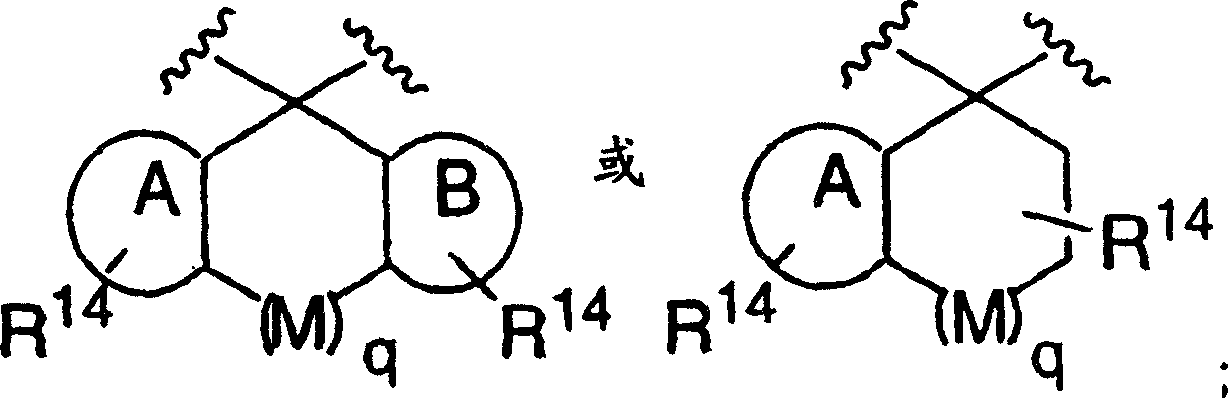
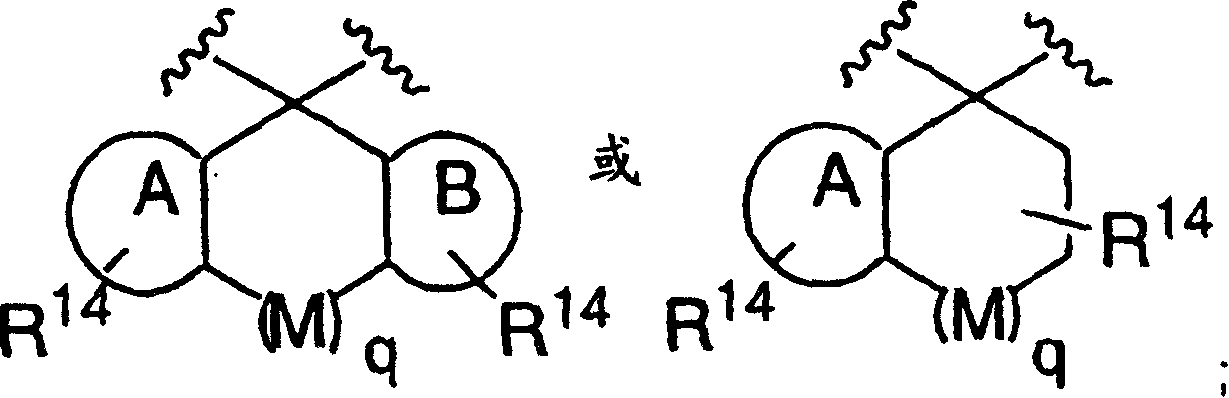
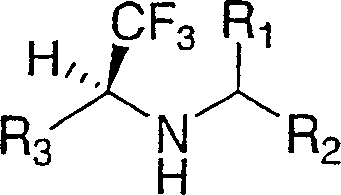
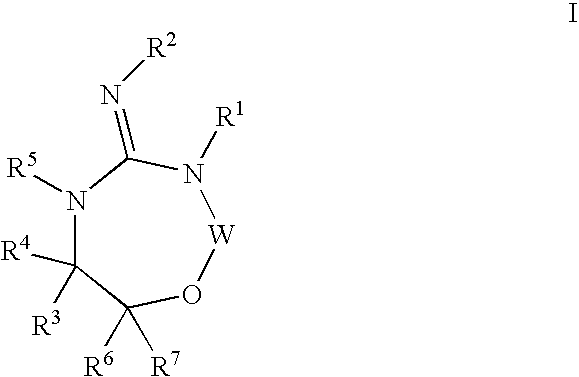
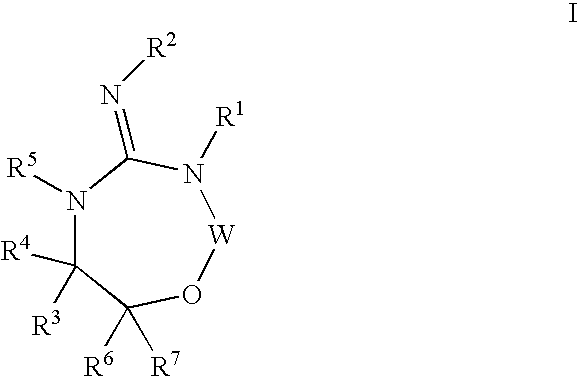
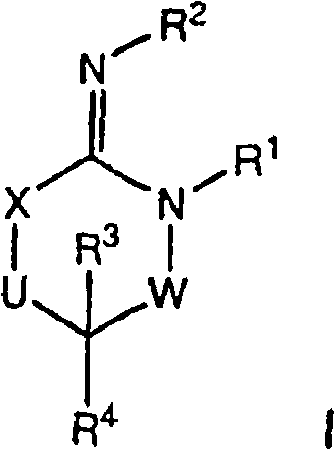
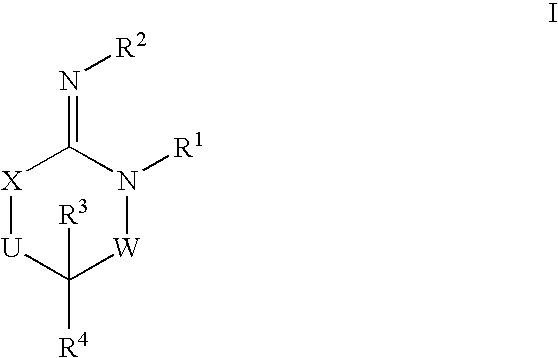
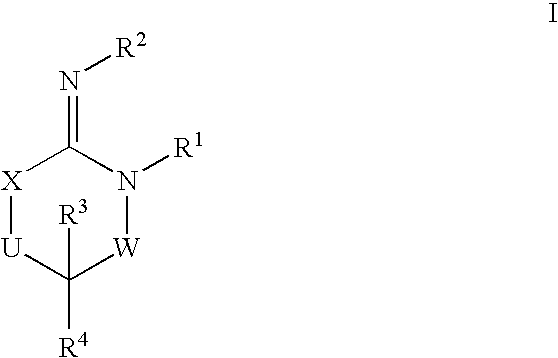
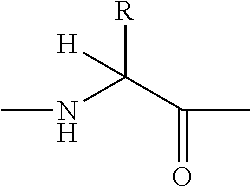
Disclosed are compounds of the formula I or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein W is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—; X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—; U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond; and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic m1 agonist or m2 antagonist.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA DRUG DISCOVERY +1
Aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula I or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein W, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
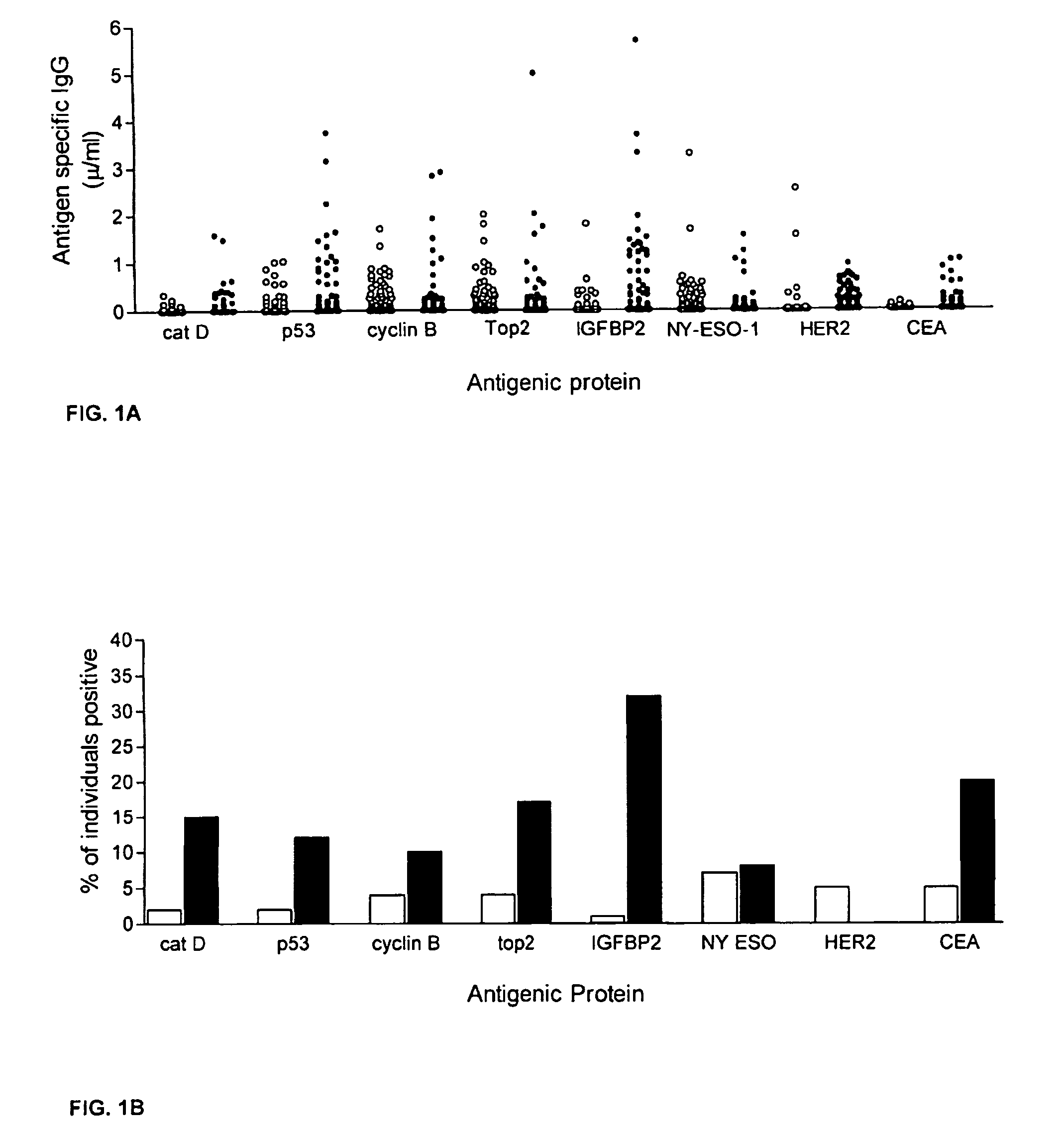
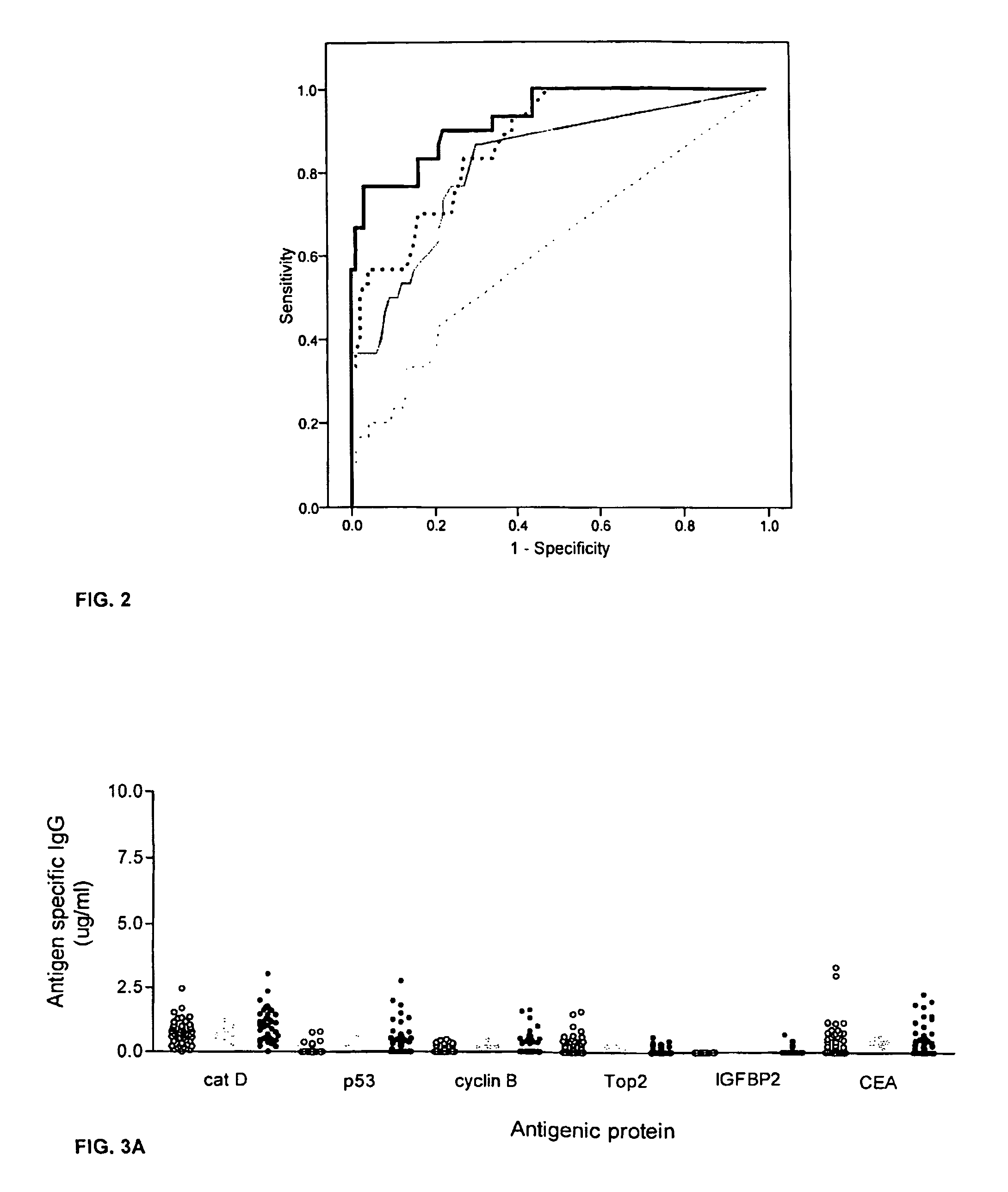
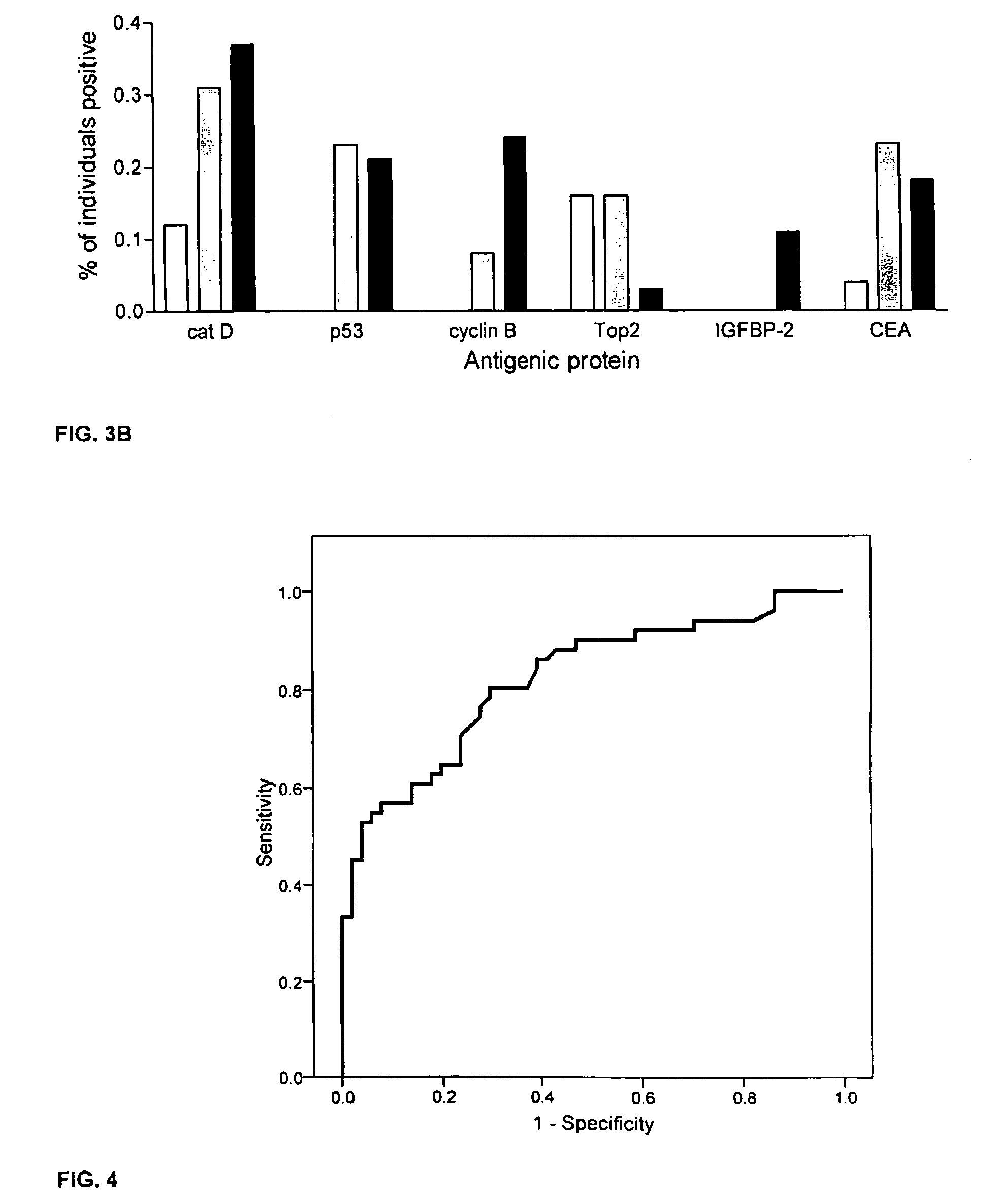
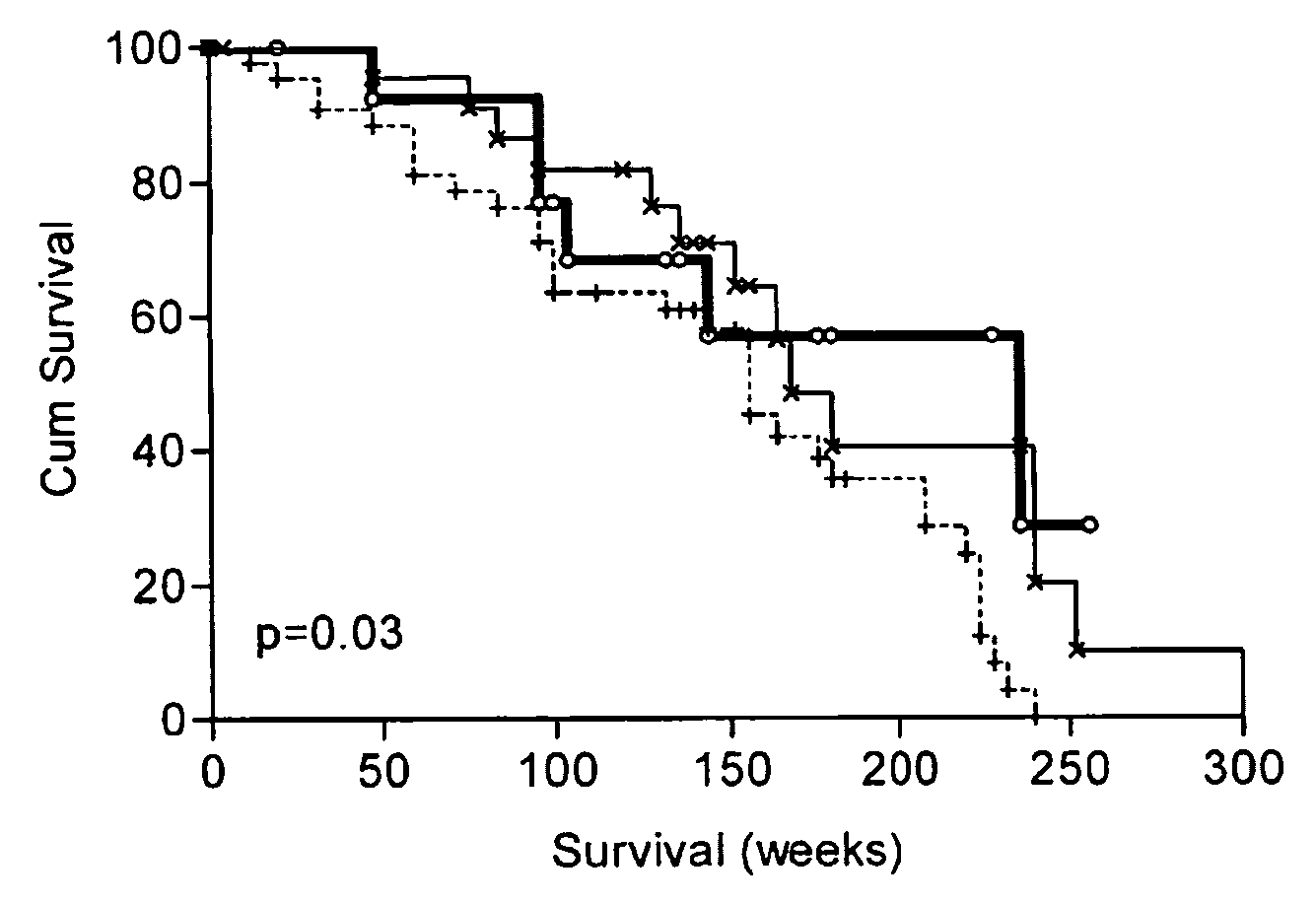
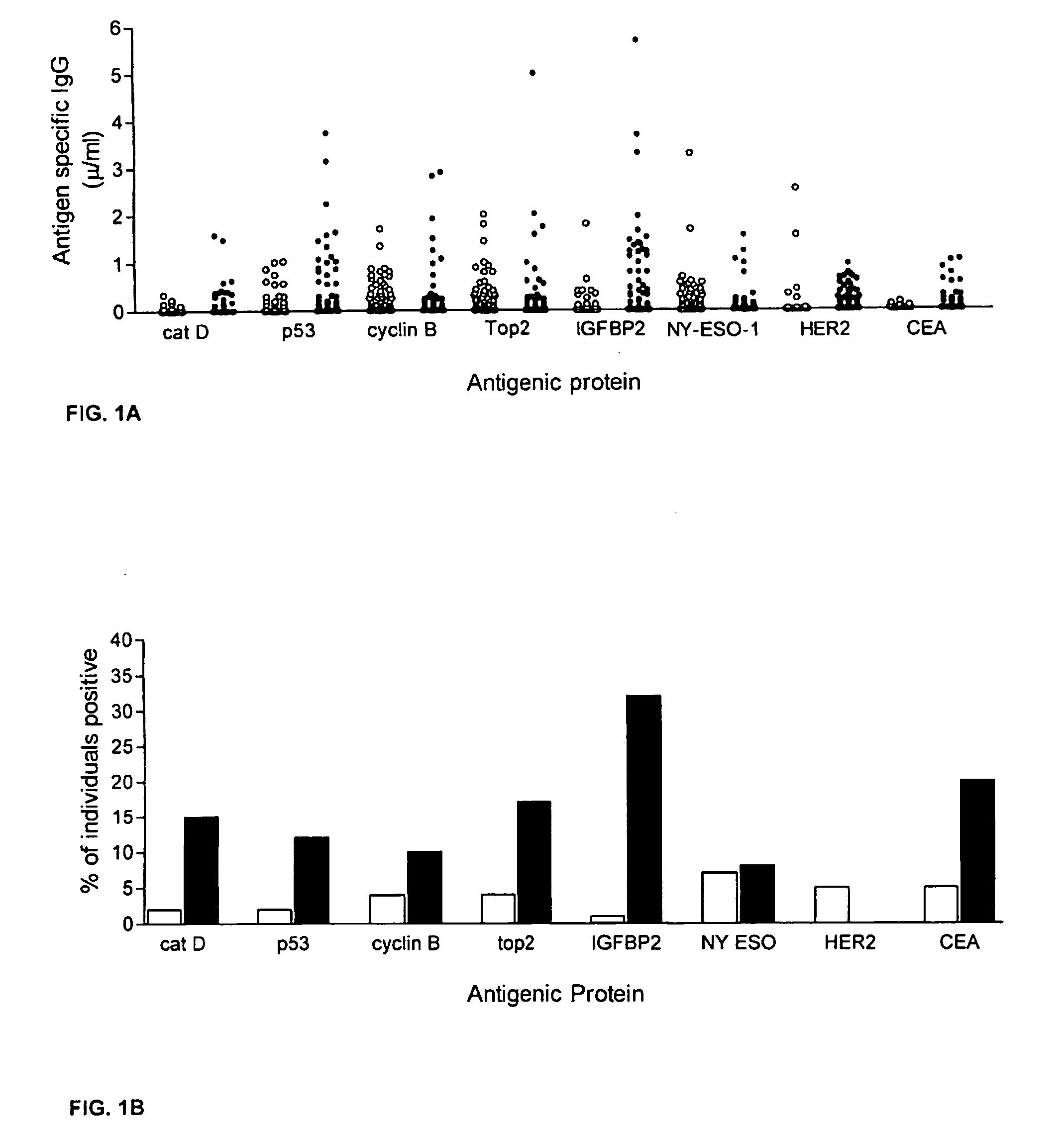
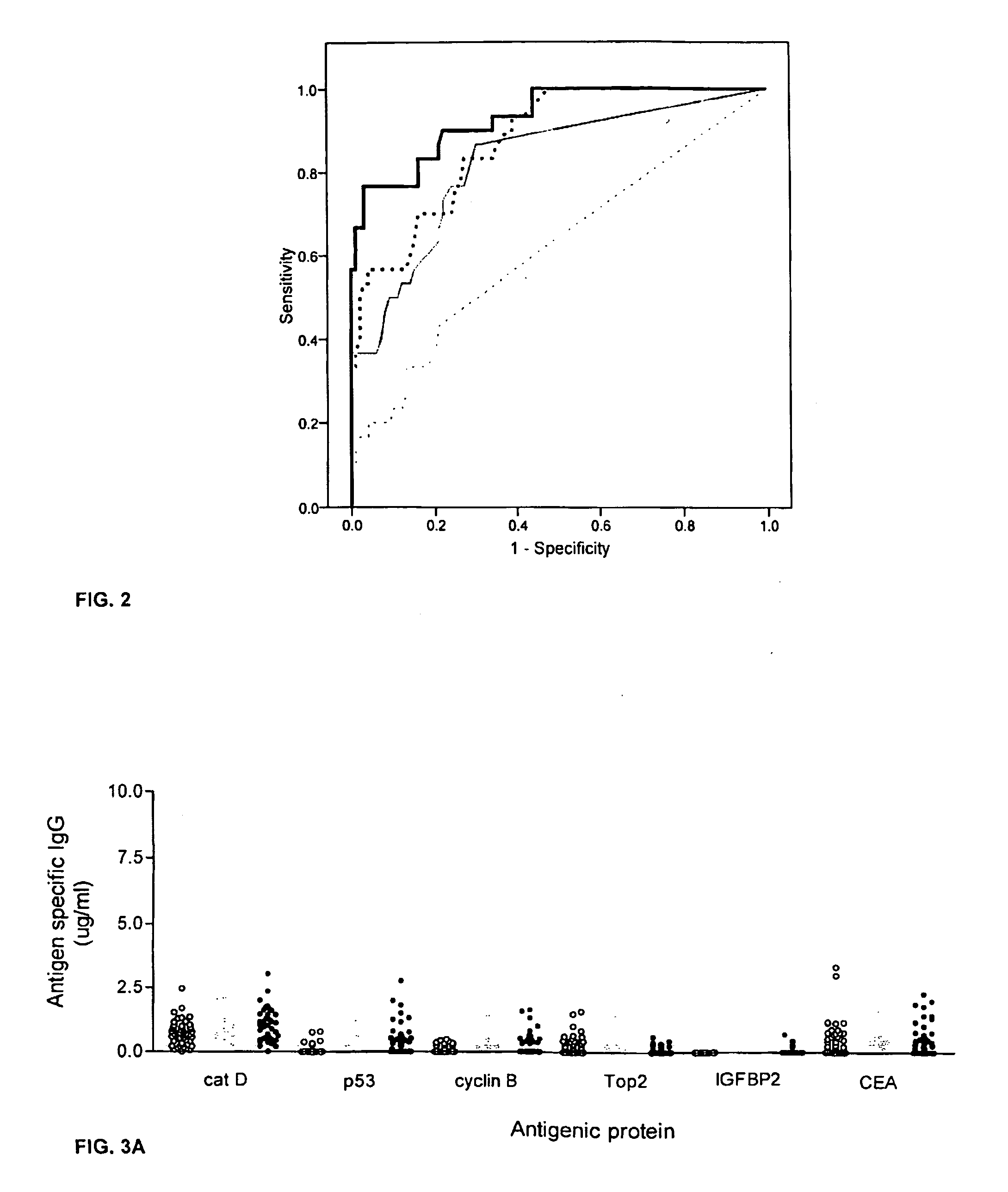
Diagnostic panel of cancer antibodies and methods for use
The invention provides a method for detection of a malignancy in a specimen of bodily fluid. The method comprises contacting the specimen with at least two antigens selected from the group consisting of p53, IGFBP2, Topo2α, cathepsin D, cyclin B, cyclin D1, MUC1, HER-2 / neu and CEA. The method further comprises incubating the specimen and the antigen for a duration and under conditions that are sufficient for the formation of immunocomplexes; and detecting the presence or absence of immunocomplex formation between the antigens and antibodies specific for the antigens in the specimen, thereby determining the presence or absence of the malignancy. Also provided is a method for monitoring the effectiveness of cancer therapy related to a malignancy in a warm-blooded animal, a method for distinguishing between Stage I and Stage II colorectal cancer in a specimen of bodily fluid.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Preparation and use of compounds as aspartyl protease inhibitors
ActiveUS20070010667A1Nervous disorderMetabolism disorderImmunodeficiency virusNeuro-degenerative disease
Disclosed are compounds of the formula I or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein A is a bond, —C(O)—, or —C(R3′)(R4′)—; X is —N(R1)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; Y is —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —PO(OR9) or —C(R6′R7′)—; is a single or double bond and R, R1, R2, R3, R4, R3′, R4′, R5, R6, R6′, R7 and R7′ are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic m1 agonist or m2 antagonist.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA INC +1
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20120283128A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMatrilysinInterleukin-1beta
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using a plurality of assays, one or more of which is configured to detect a kidney injury marker selected from the group consisting of Hyaluronic acid, Immunoglobulin A, Immunoglobulin G1, Immunoglobulin G2, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7, Alpha-1 antitrypsin, Serum amyloid P component, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2, Hepatocyte growth factor, Intercellular adhesion molecule 1, Beta-2-glycoprotein 1, Interleukin-1 beta, Neutrophil Elastase, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 11B, Interleukin-11, Cathepsin D, C—C motif chemokine 24, C—X—C motif chemokine 6, C—C motif chemokine 13, C—X—C motif chemokines -1, -2, and -3, Matrilysin, Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain, Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3, and Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Method of inhibiting cathepsin K
InactiveUS6274336B1High specificity and stabilityInhibit synthesisHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsProteinase activityCathepsin K
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Cathepsin cysteine protease inhibitors
Owner:AXYX PHARMA INC +1
Dust mite allergen and application thereof
ActiveCN104894089AAvoid treatmentHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementAllergen ingredientsDiseaseToxicology
The invention provides a dust mite allergen and application thereof. The dust mite allergen provided by the invention belongs to a congener of cathepsin D, can be used for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of allergic diseases and especially dust mite allergic diseases, and is especially used for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of allergic diseases caused by the 34th component of the dust mite allergen. The dust mite allergen recombinant protein is prepared by gene cloning and protein expression, and has the advantages of high protein purity, high specificity and high yield. When being used for preparing reagents for diagnosing, preventing or treating allergic diseases caused by the dust mite allergen, the dust mite allergen provided by the invention has the characteristics of high specificity and low cost. Especially, the dust mite allergen can be efficiently used for diagnosing whether the patient is allergic to the 34th component of the dust mite allergen.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in sepsis patients. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more biomarkers selected from the group consisting of Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7, Beta-2-glycoprotein 1, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 2, Alpha-1 Antitrypsin, Leukocyte elastase, Serum Amyloid P Component, C-X-C motif chemokine 6, Immunoglobulin A, Immunoglobulin G subclass I, C-C motif chemokine 24, Neutrophil collagenase, Cathepsin D, C-X-C motif chemokine 13, Involucrin, Interleukin-6 receptor subunit beta, Hepatocyte Growth Factor, CXCL-1, -2, -3, Immunoglobulin G subclass II, Metalloproteinase inhibitor 4, C-C motif chemokine 18, Matrilysin, C-X-C motif chemokine 11, and Antileukoproteinase as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker assays of renal injury in the sepsis patient.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification;and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +1
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic m1 agonist or m2 antagonist.
Owner:PHARMACOPEIA INC +1
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof,whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Compounds of the formula I or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC +1
Cathepsin inhibitors
InactiveCN1842515AReduce chargeInhibition is effectiveOrganic compound preparationAntipyreticDiseaseCathepsin K
This invention relates to a novel class of compounds, represented by the formula (I) below, wherein the meanings of R1, R2, R3 and R4 are indicated therein, which are cysteine protease inhibitors, including but not limited to, inhibitors of cathepsins K, L, S and B. These compounds are useful for treating diseases in which inhibition of bone resorption is indicated, such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Owner:MERCK FROSST CANADA INC
Reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis
InactiveCN102445543AIncrease credibilityPracticalBiological testingStainingPolymeric immunoglobulin receptor
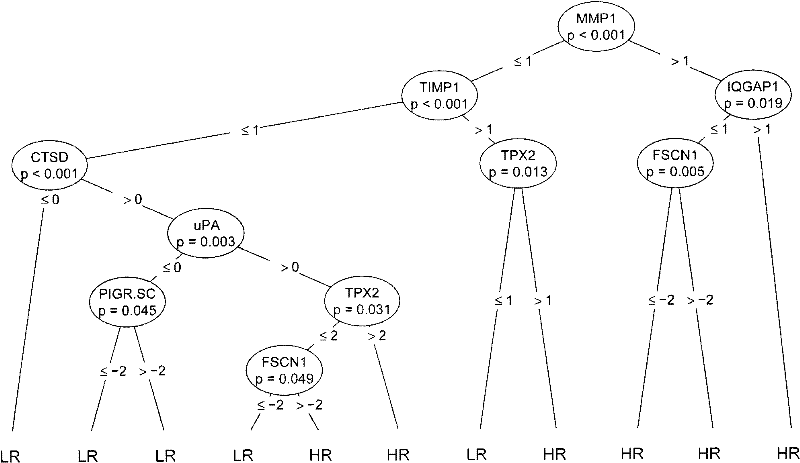
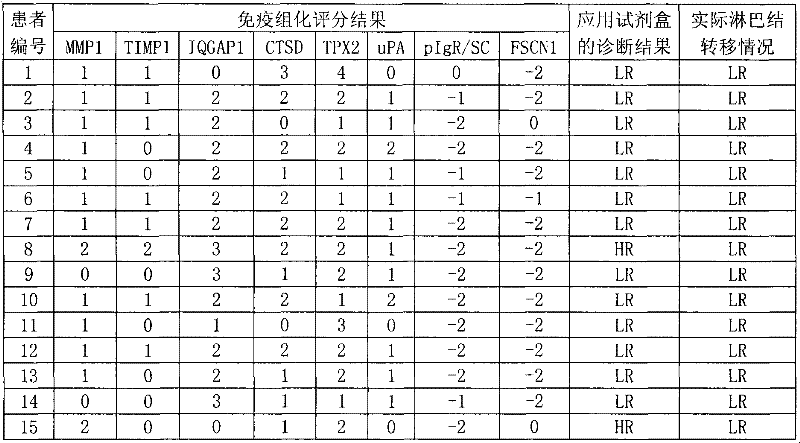
The invention discloses a reagent for auxiliarily diagnosing lung cancer lymph node metastasis, comprising 8 antibodies which are used for detecting 8 protein markers which are MMP1 (matrix metalloproteinase-1), TIMP1 (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases metallopeptidase inhibitor 1), IQGAP1 (IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1), TPX2 (targeting protein for Xklp2), uPA (Urokinase-type plasminogen activator), Cathepsin-D, Fascin and pIgR / SC (polymeric immunoglobulin receptor / secretory component). By adopting the 8 antibodies and an immunohistochemical staining result, lung cancer lymph node metastasis can be auxiliarily diagnosed, and the reagent is expected to be used for the risk estimation of lung squamous cell cancer lymph node metastasis and the prognostic prediction. The reagent has high creditability, strong practicability and clinical use value based on the clinical routine immunohistochemical staining technology when the reagent is used for auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Cathepsin D antigen polypeptide and application thereof as well as detecting kit containing polypeptide
InactiveCN101735317AStrong specificityImprove detection efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsDrug targetFhit gene
The invention provides a tumor marker Cathepsin D antigen polypeptide which has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ IDNo.1 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses a method for cloning and expressing the protein by a gene, preparing a specific antibody of the protein and judging gastric cancer biological behavior. The Cathepsin D antigen polypeptide and the antibody thereof prepared by the method can be used for preparing the tumor detecting kit and the research and development of a drug target.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein W, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification; and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Cathepsin cysteine protease inhibitors
ActiveUS20160244417A1Treating and preventing cathepsin dependent conditionTreating and preventing and disease stateOrganic chemistrySkeletal disorderDiseaseCathepsin K
This invention relates to a novel class of compounds which are cysteine protease inhibitors, including but not limited to, inhibitors of cathepsins K, L, S and B. These compounds are useful for treating diseases in which inhibition of bone resorption is indicated, such as osteoporosis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Preparation and use of compounds as protease inhibitors
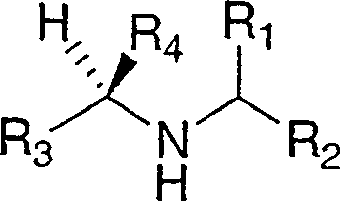
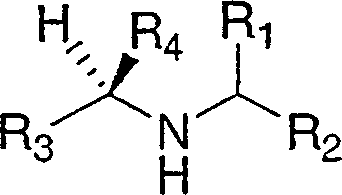
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein,X is —C(R3R4)—;Y is —N(R5)—;Z is (—C(═N—R5′)—;and R1, R2, R3, and R4 are as defined in the specification;and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Diagnostic panel of cancer antibodies and methods for use
InactiveUS20090215091A1Determine effectivenessBiological material analysisBiological testingImmune complex formationCyclin D1
The invention provides a method for detection of a malignancy in a specimen of bodily fluid. The method comprises contacting the specimen with at least two antigens selected from the group consisting of p53, IGFBP2, Topo2α, cathepsin D, cyclin B, cyclin D1, MUC1, HER-2 / neu and CEA. The method further comprises incubating the specimen and the antigen for a duration and under conditions that are sufficient for the formation of immunocomplexes; and detecting the presence or absence of immunocomplex formation between the antigens and antibodies specific for the antigens in the specimen, thereby determining the presence or absence of the malignancy. Also provided is a method for monitoring the effectiveness of cancer therapy related to a malignancy in a warm-blooded animal, a method for distinguishing between Stage I and Stage II colorectal cancer in a specimen of bodily fluid.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula (I) or a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof. Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes. Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula (I) in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic antagonist. The formula (I) is shown in the description.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC +1
Acylguanidines for treating osteoarthritis
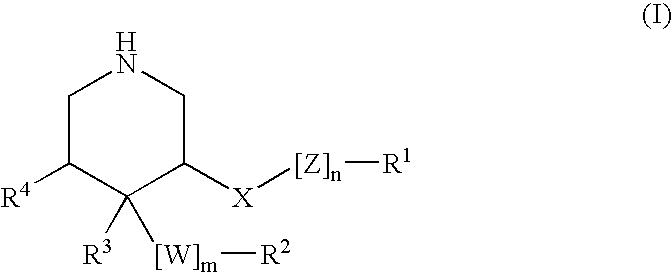
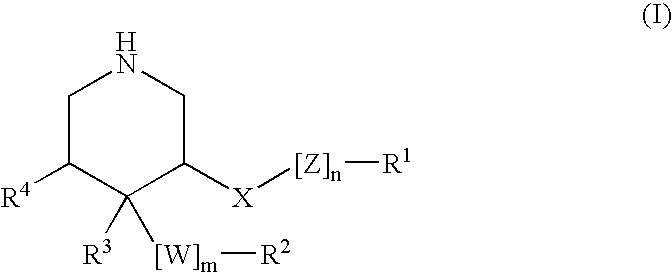
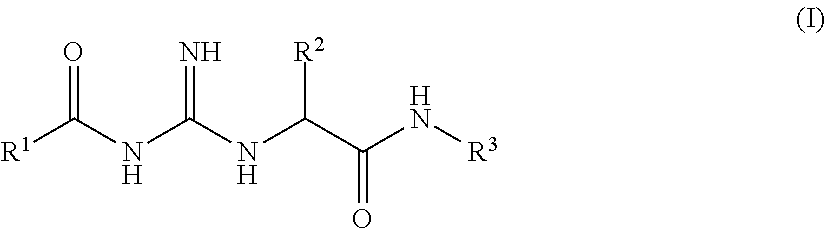
ActiveUS20150361037A1Less side effectsImprove stabilityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryCartilage lesionAcyl group
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula (I) and in particular to medicaments comprising at least one compound of the formula I for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathophysiological conditions in the triggering of which cathepsin D is involved, in particular for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of osteoarthritis, traumatic cartilage injuries, arthritis, pain, allodynia or hyperalgesia.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
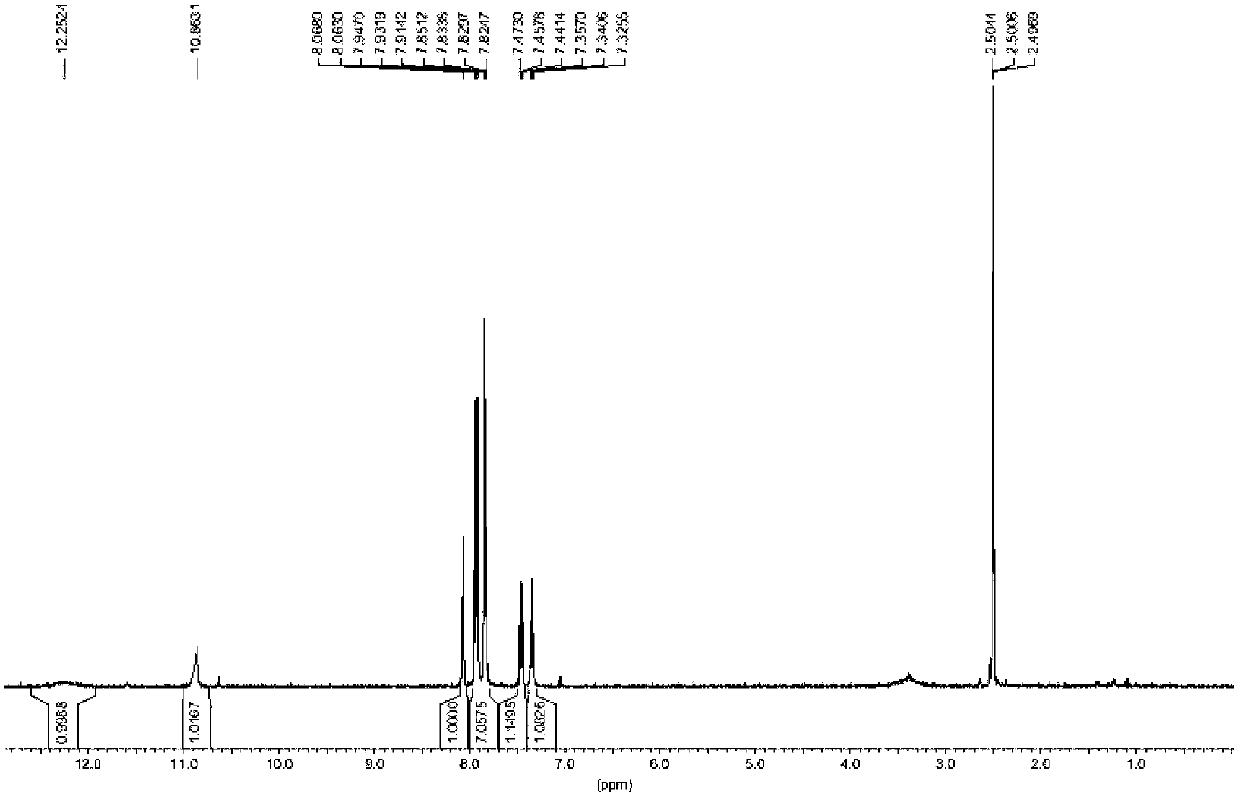
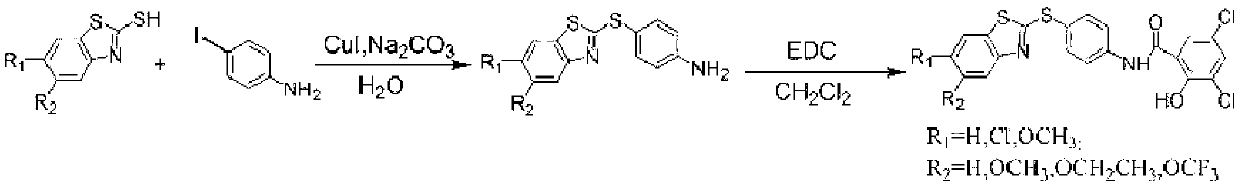
Preparation method of micromolecule cathepsin D inhibitor
ActiveCN103275034ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getSimple reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryAnilinePollution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a micromolecule cathepsin D inhibitor. The preparation method comprises the following steps that 2-mercaptobenzothiazole or its derivatives and 4-iodoaniline as starting materials undergo a reaction in a water phase by catalytic C-S coupling to produce 4-(2-benzothiazolylthio)aniline or its corresponding derivatives (A); and the 4-(2-benzothiazolylthio)aniline or its corresponding derivatives (A), and 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid undergo an amidation reaction to produce the micromolecule cathepsin D inhibitor (B). The preparation method has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simple reaction conditions, simple and convenient operation, low toxicity and pollution, simple post-treatment processes, high yield and high purity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
InactiveUS20130165344A1Eliminate needLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisInsulin-like growth factor bindingCancer antigen
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Heterocyclic aspartyl protease inhibitors
Disclosed are compounds of the formula Ior a stereoisomer, tautomer, or pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, whereinW is a bond, —C(═S)—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)—, —O—, —C(R6)(R7)—, —N(R5)— or —C(═N(R5))—;X is —O—, —N(R5)— or —C(R6)(R7)—; provided that when X is —O—, U is not —O—, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(═O)— or —C(═NR5)—;U is a bond, —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —C(O)—, —O—, —P(O)(OR15)—, —C(═NR5)—, —(C(R6)(R7))b— or —N(R5)—; wherein b is 1 or 2; provided that when W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, U is not —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—; provided that when X is —N(R5)— and W is —S(O)—, —S(O)2—, —O—, or —N(R5)—, then U is not a bond;and R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, and R7 are as defined in the specification;and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of formula I.Also disclosed is the method of inhibiting aspartyl protease, and in particular, the methods of treating cardiovascular diseases, cognitive and neurodegenerative diseases, and the methods of inhibiting of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, plasmepins, cathepsin D and protozoal enzymes.Also disclosed are methods of treating cognitive or neurodegenerative diseases using the compounds of formula I in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor or a muscarinic m1 agonist or m2 antagonist.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Cathepsin inhibitor, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108250107AUnique anti-tumor mechanismIncreased drug resistanceSulfonic acid amide preparationAmide active ingredientsCathepsinPeptoid
The invention relates to the field of medicinal chemistry, particularly to a cathepsin inhibitor, a preparation method and applications thereof, more particularly to a tumor-associated cathepsin L inhibitor and a tumor-associated cathepsin D inhibitor, and a preparation method of the tumor-associated cathepsin L inhibitor and the tumor-associated cathepsin D inhibitor. Specifically the present invention further relates to a novel peptoid compound or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, a solvate, a pharmaceutical composition and a pharmaceutical preparation, a preparation method of thecompound, and applications of the peptoid compound or the pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, the solvate, the pharmaceutical composition and the pharmaceutical preparation in preparation of antitumor drugs, wherein the structure formula of the compound is defined in the specification, and R1, R2 are defined in the claims and the specification. The formula (I) is defined in the specification.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Hydroxy-ethylene derivatives for the treatment of arthrosis
InactiveUS20160145297A1Lowering of ground state energyReduction in rate in rate-limiting bond breakageNervous disorderCarbamic acid derivatives preparationCartilage injuryMedicine
The present invention relates to compounds of the formula I and in particular medicaments comprising at least one compound of the formula I for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of physiological and / or pathophysiological conditions in the triggering of which cathepsin D is involved, in particular for use in the treatment and / or prophylaxis of arthrosis, traumatic cartilage injuries, arthritis, pain, allodynia or hyperalgesia.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Model for neurodegenerative diseases involving amyloid accumulation
The present invention provides brain cells, such as normal brain cells, apolipoprotein E deficient brain cells, or apoE4 containing brain cells, that are treated with a compound which can modulate integrins and / or integrin receptors to produce increased sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The present invention also provides methods for producing such cells and methods for using the cells for screening an agent or substance that modulates the sequestration of and / or accumulation of and / or uptake of Aβ, and / or lysosomal dysfunction, and / or changes in cathepsin D content and / or microglia activation in the brain cells. The method further provides a new therapeutic target, antagonism of glutamate receptors, for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases which are characterized by inter alia, abnormal amyloid uptake and / or accumulation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com