Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47 results about "Cardiac pressures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
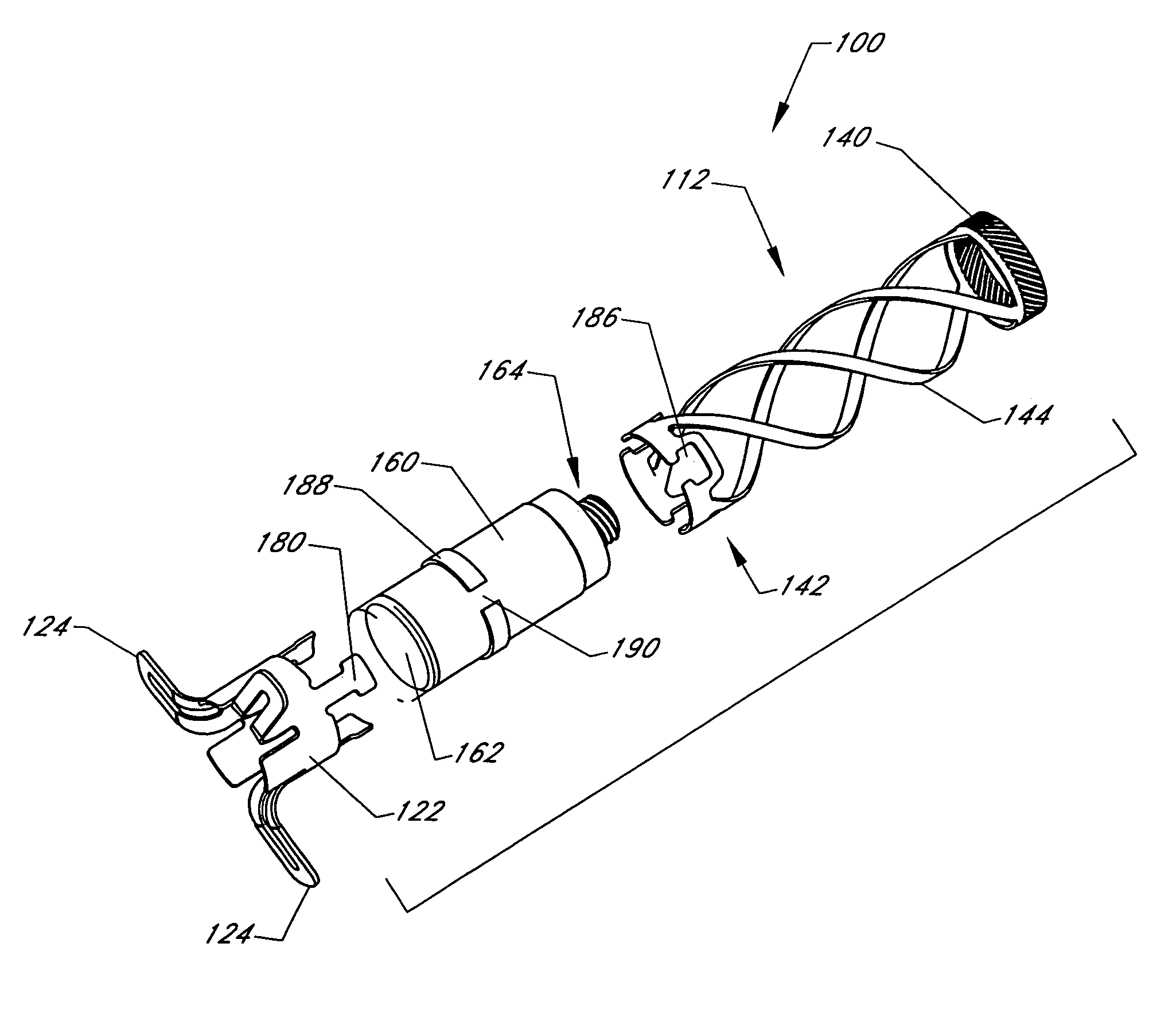
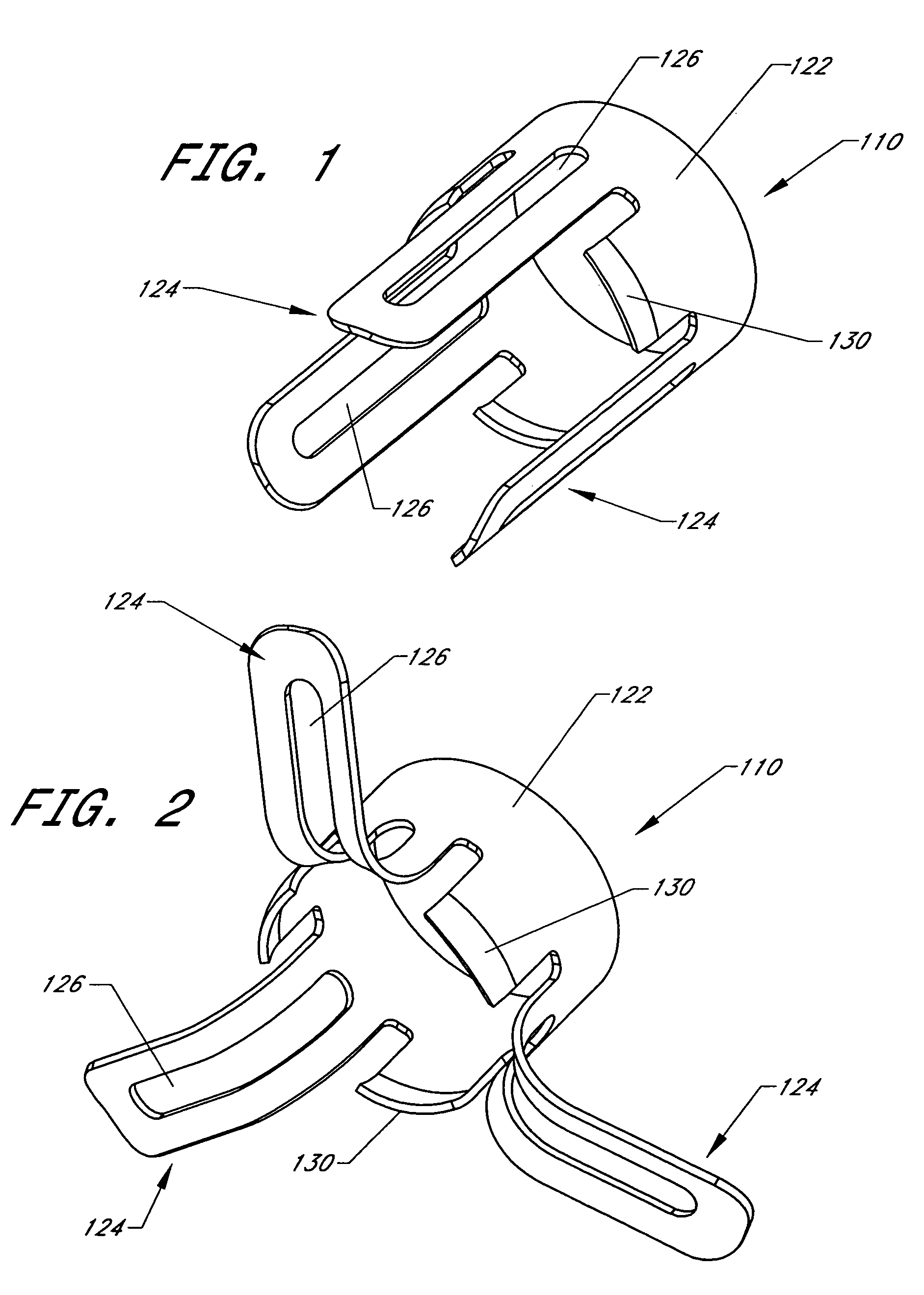
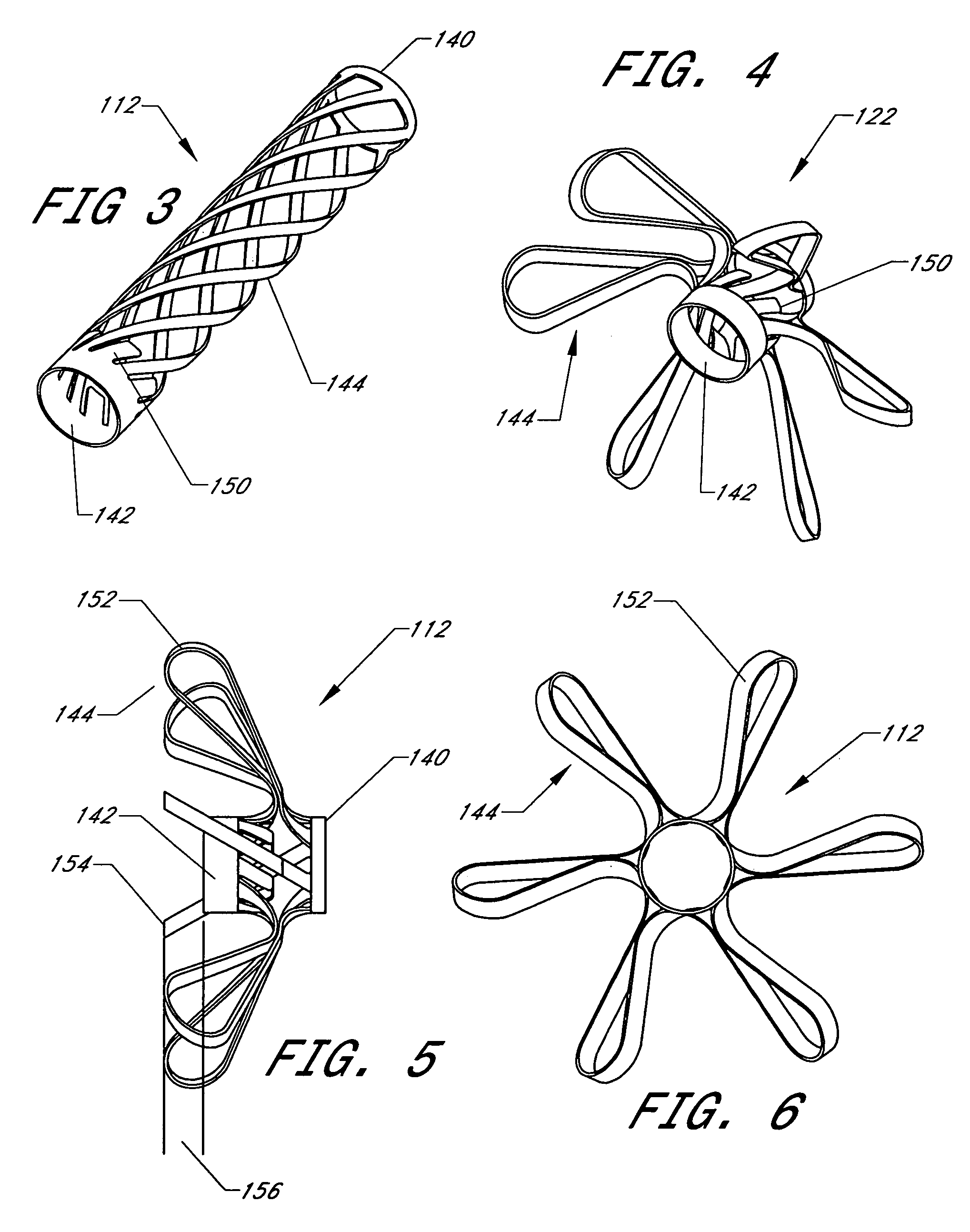
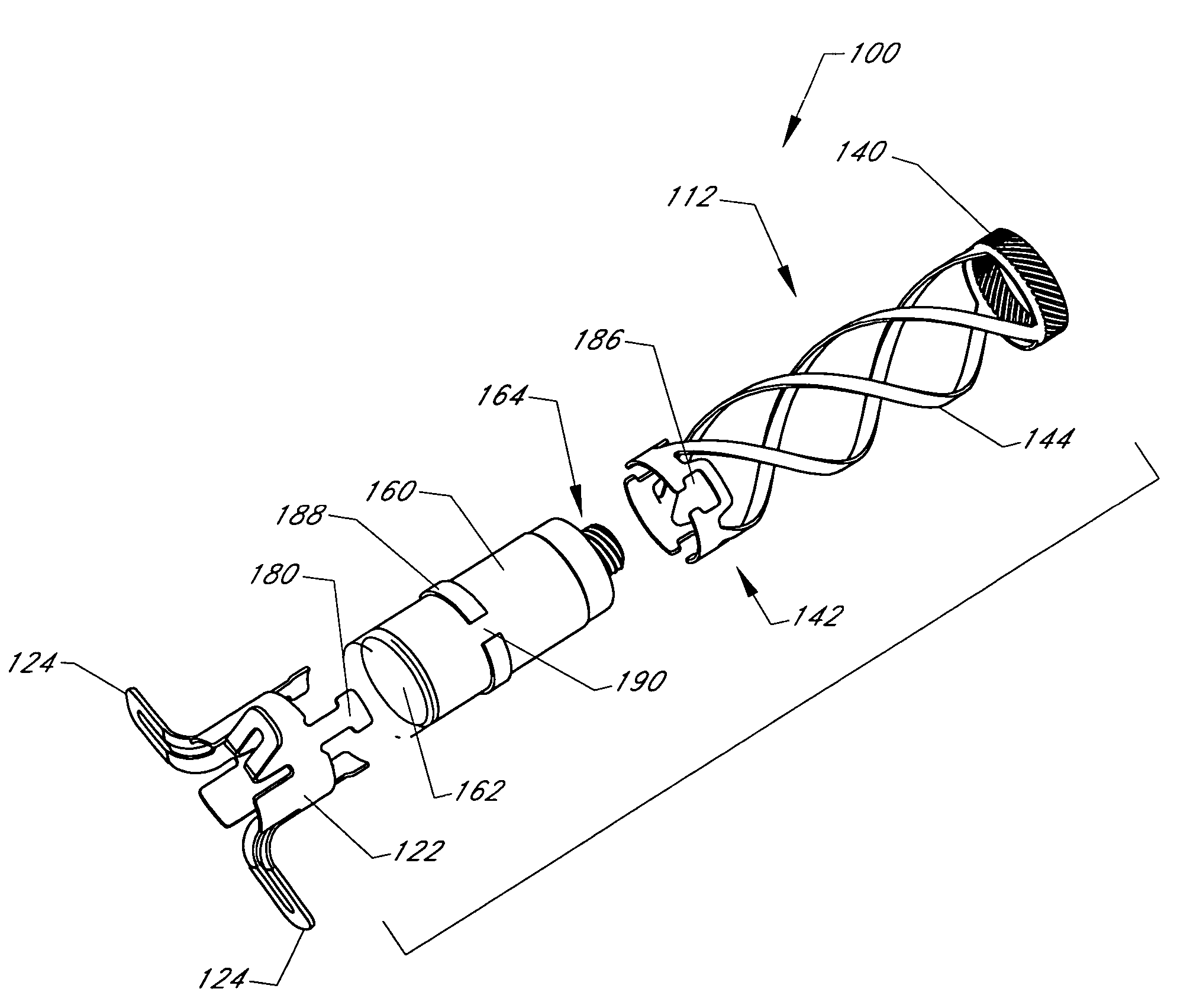
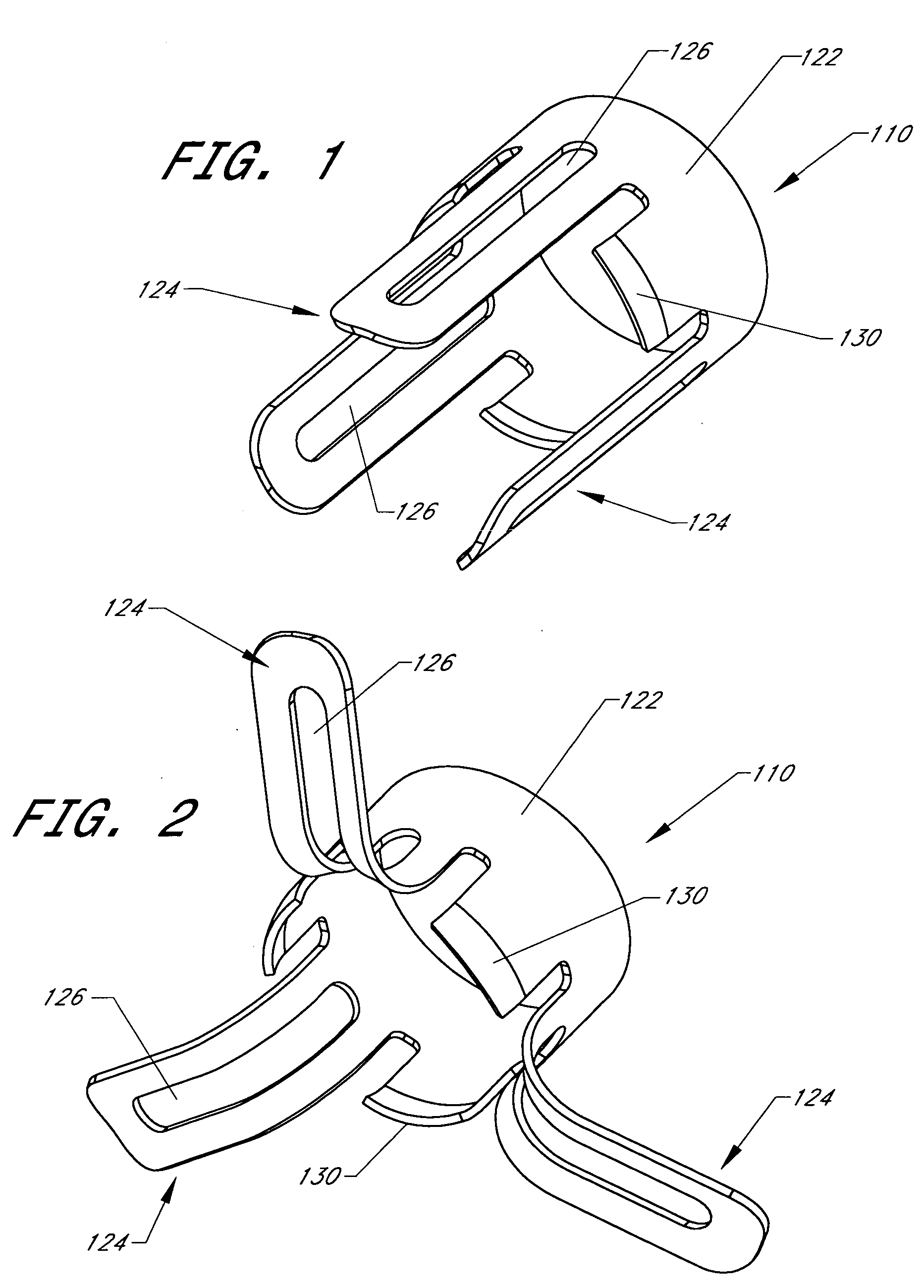
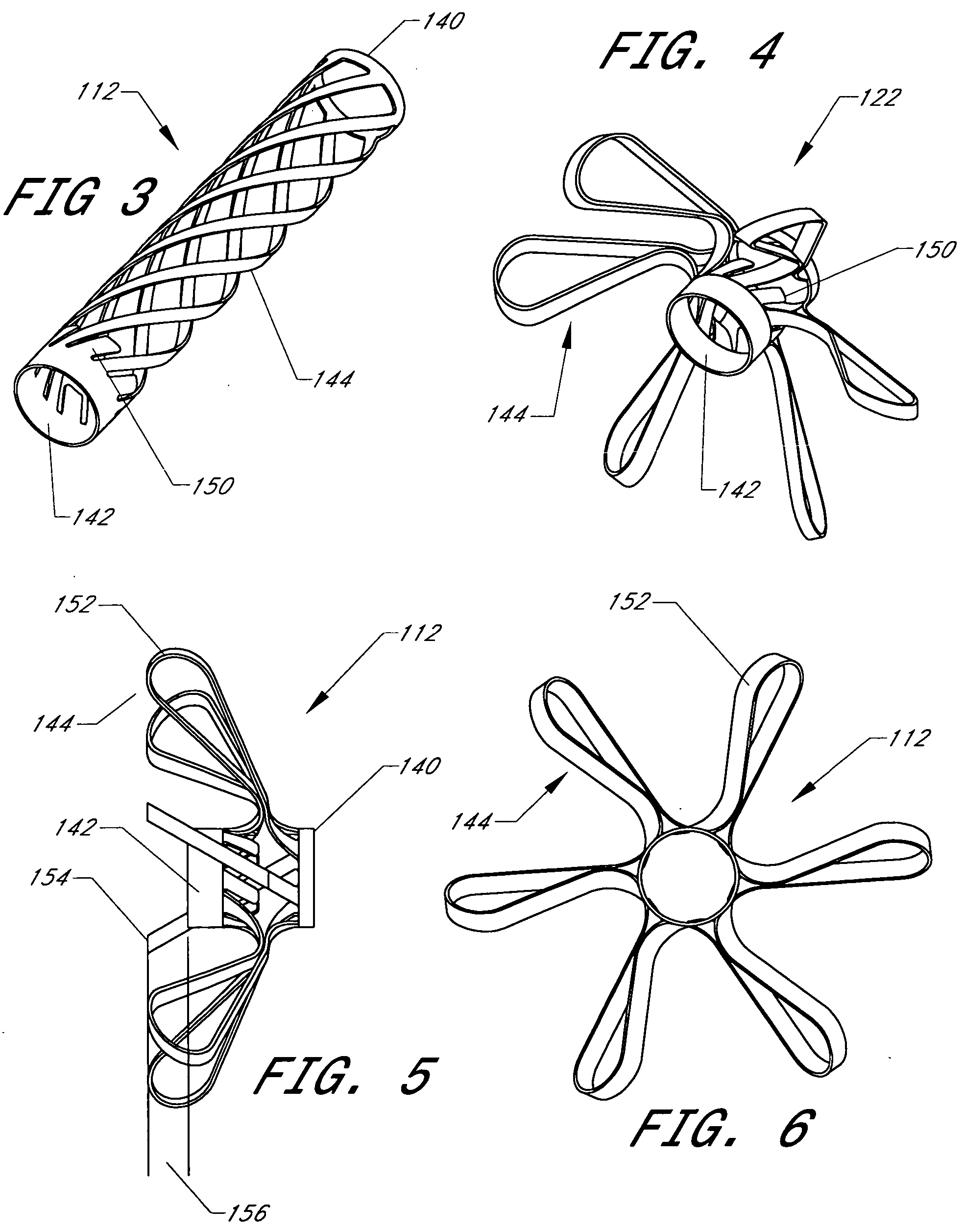
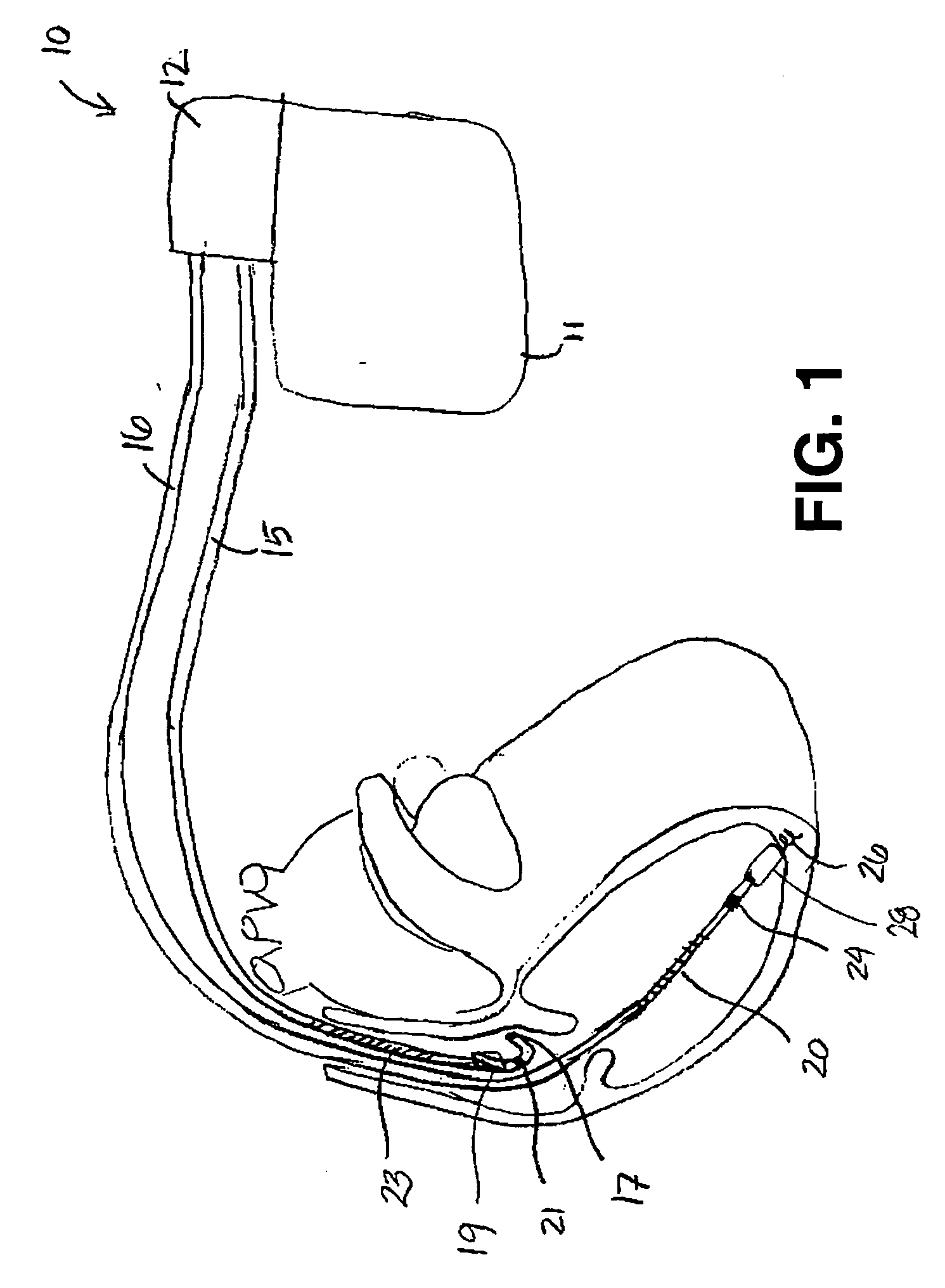
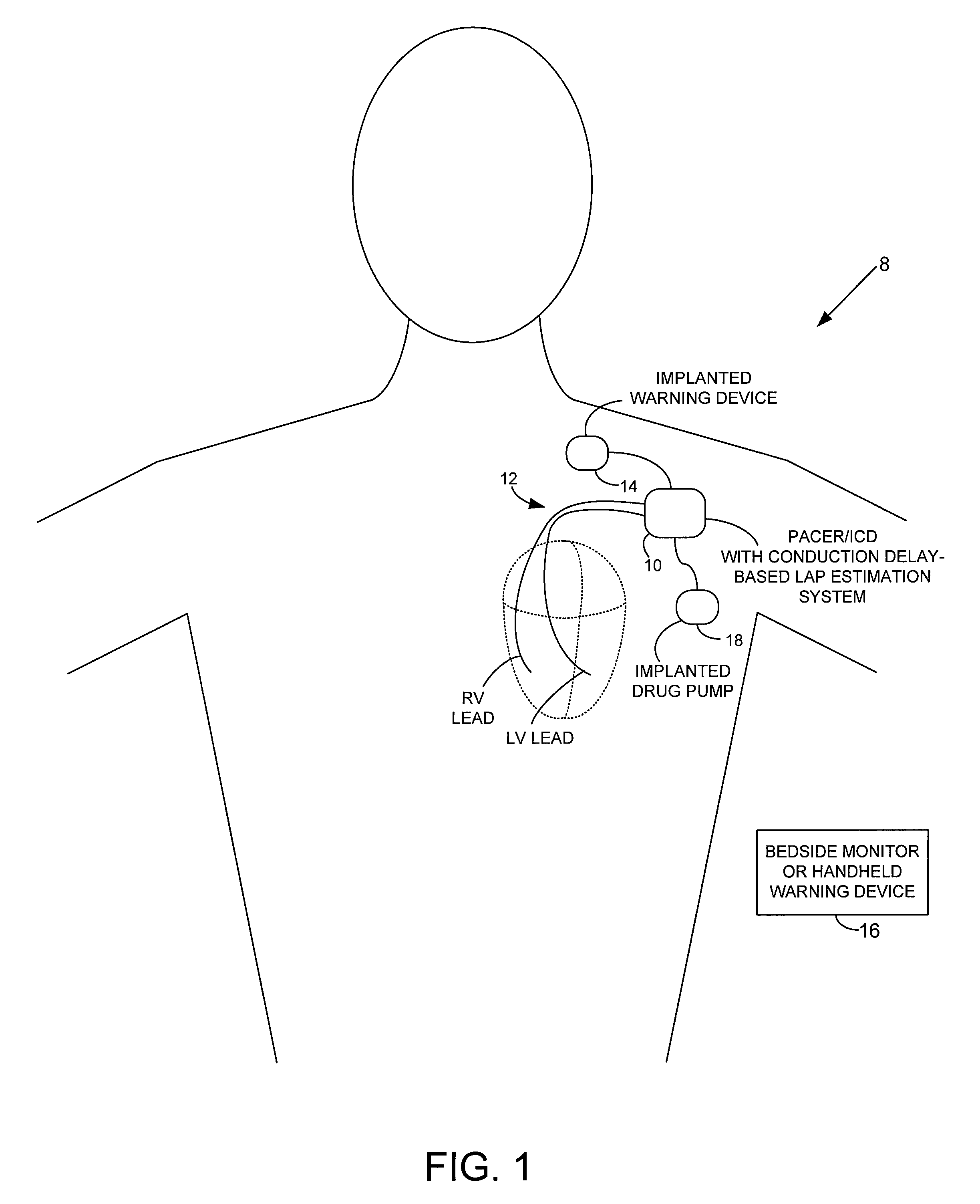
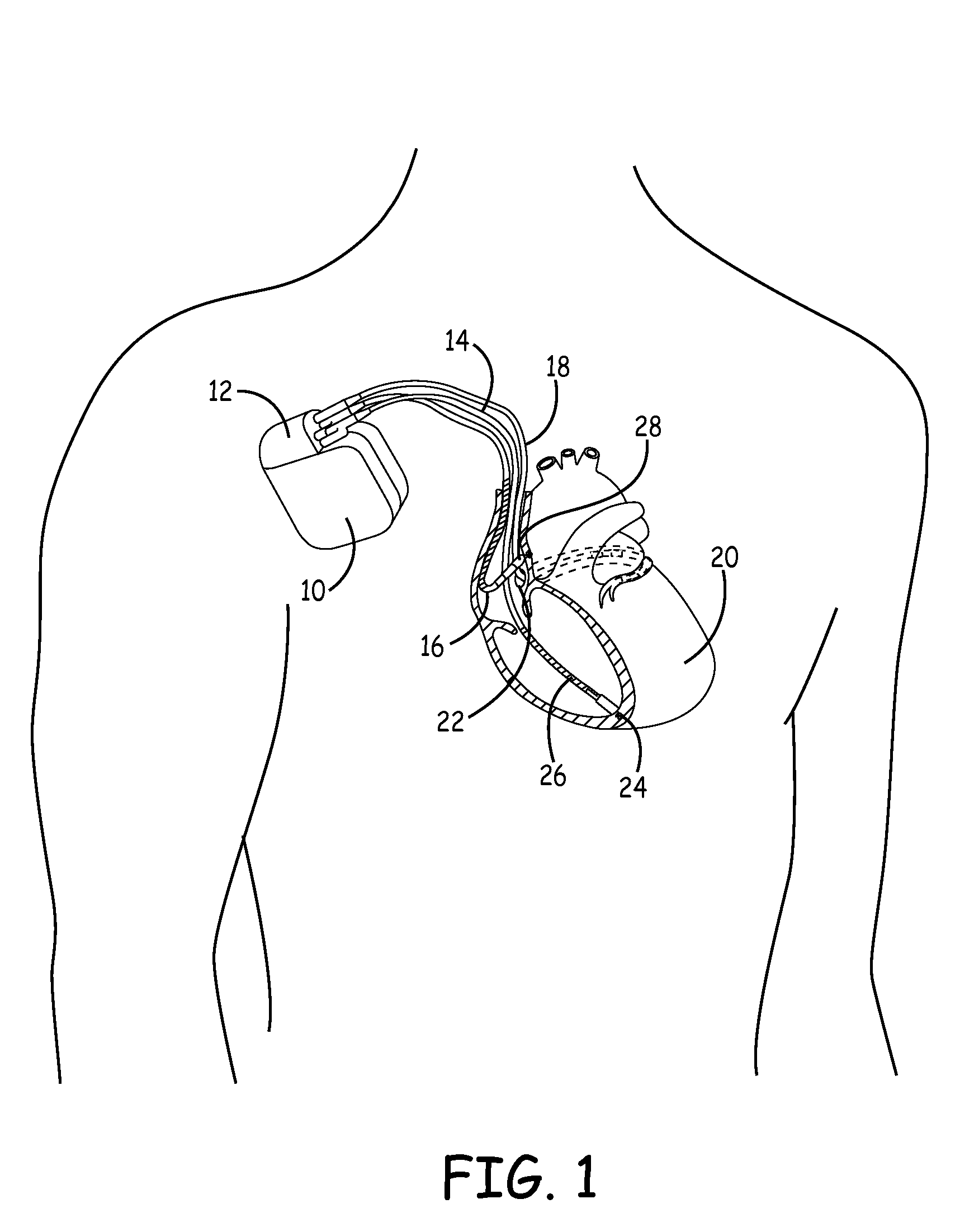
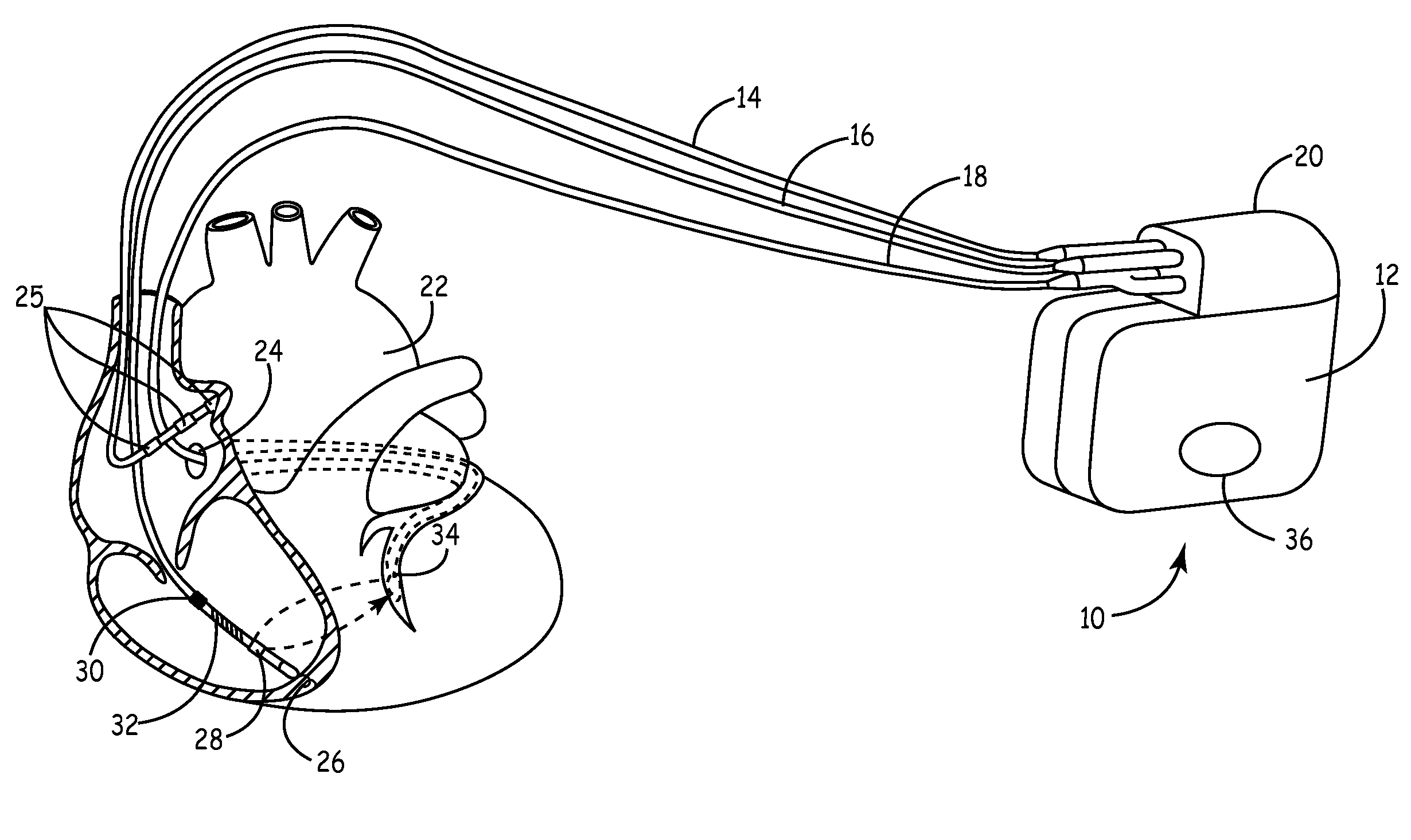
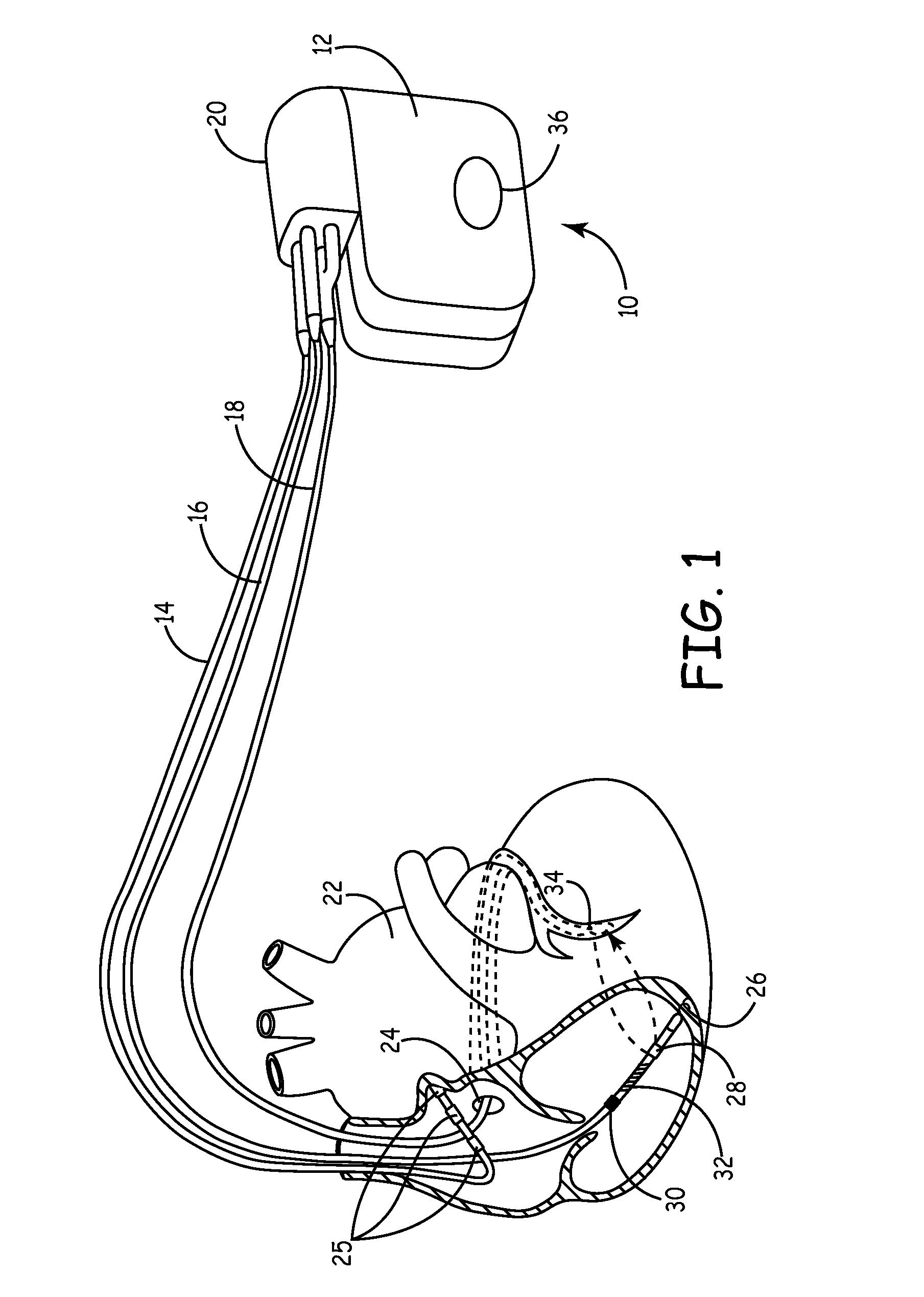
Cardiovascular anchoring device and method of deploying same
InactiveUS7149587B2Efficient deploymentElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesMeasurement deviceOrgan wall
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Retrieval devices for anchored cardiovascular sensors
ActiveUS20070106328A1Efficient deploymentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismStaplesOrgan wallMeasurement device
An anchoring device and a delivery method thereof can effectively provide a means for securing an implant to a wall of an internal organ within a patient in a variety of clinical applications. In one embodiment, an anchoring device used to retain a cardiac pressure measurement device is provided. The device is implanted in the body by deforming it to a small cross section profile, sliding it through a low profile delivery device and ejecting from the delivery device at a targeted site. The anchoring mechanism, when ejected from the delivery device, reverts back to pre-formed configuration and engages opposite sides of an organ wall, thereby anchoring the implant in the organ wall.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for intra-procedural cardiac pressure monitoring
The present disclosure relates to delivery devices and interventional devices configured to enable monitoring of pressure and other hemodynamic properties before, during, and / or after a cardiac procedure. A guide catheter includes a routing lumen or a routing groove for routing a sensor wire to a desired location during a cardiac procedure. A guide catheter includes one or more pressure sensors positioned to provide desired pressure measurements when the guide catheter is deploying an interventional device. An interventional device may also include one or more associated sensors for providing hemodynamic information before, during, and / or after deployment.
Owner:EVALVE
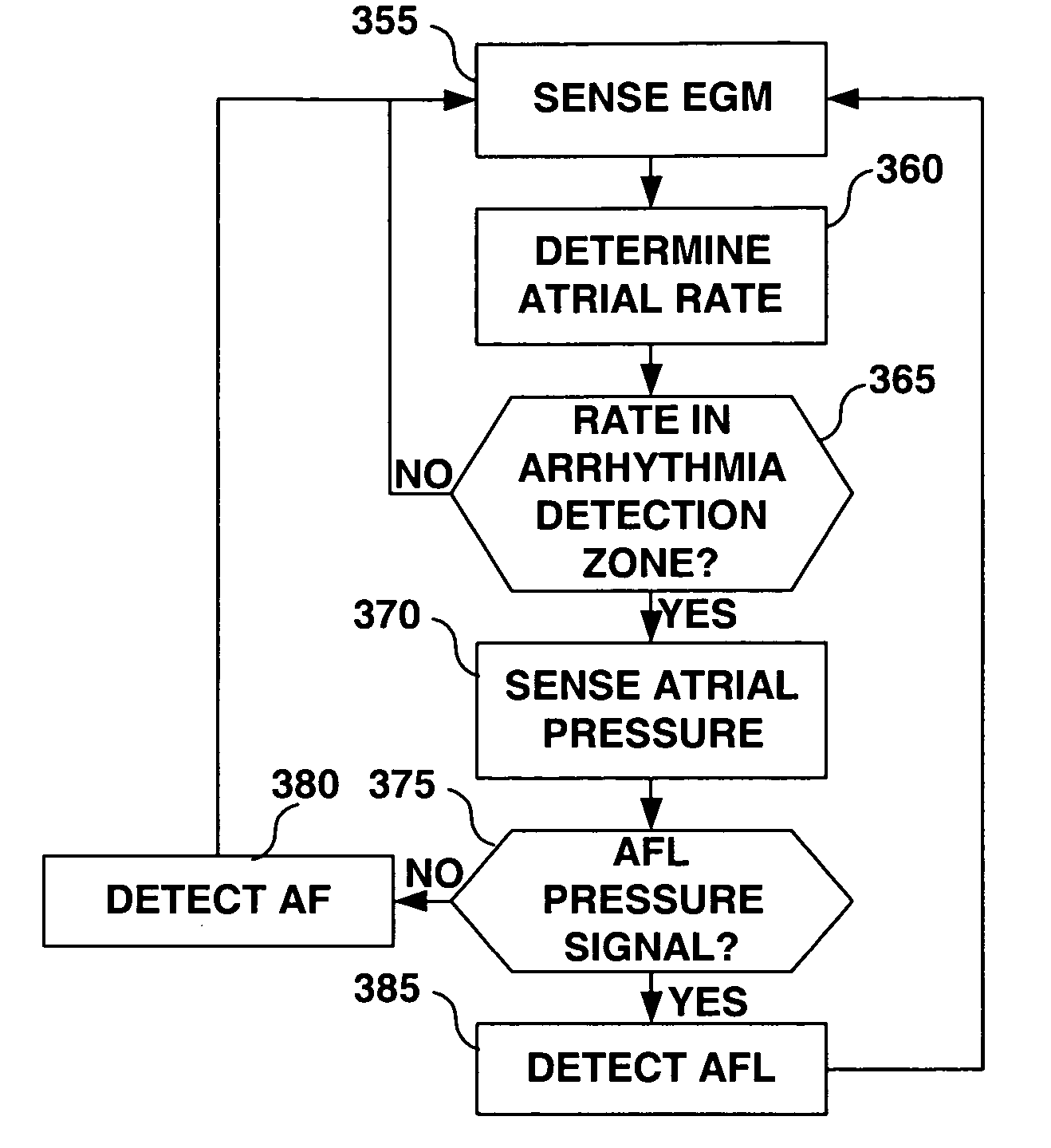
Combination of electrogram and intra-cardiac pressure to discriminate between fibrillation and tachycardia
A system and method for detecting and classifying cardiac arrhythmias based on cardiac pressure signals or the combination of cardiac electrical and cardiac pressure signals. A cardiac electrogram signal is sensed to derive a cardiac rate from which an arrhythmia detection is made when the cardiac rate meets arrhythmia detection criteria. An intracardiac pressure signal is sensed to derive an indicator of tachycardia based on an analysis of the pressure signal in either the time domain or frequency domain. The detected arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia or fibrillation based on the tachycardia indicator wherein the tachycardia indicator is compared to tachycardia detection criteria and the arrhythmia is classified as tachycardia if tachycardia detection criteria are met and the arrhythmia is classified as fibrillation if the tachycardia detection criteria are not met.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Prosthesis for reducing intra-cardiac pressure having an embolic filter
ActiveUS20120053686A1Reducing pressure necrosisImprove radiopacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHeart valvesPatients symptomsProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
Methods and apparatus for reducing localized circulatory system pressure
InactiveUS8091556B2Preventing further deteriorationIncrease pressureDiagnosticsHeart valvesSystoleLeft ventricular size
Methods and apparatus for decreasing cardiac pressure in a patient by implanting a shunt communicating with an area outside a first portion, whereby a volume of blood sufficient to reduce pressure in a first portion is released. Preferably, the end diastolic pressure in the left ventricle is reduced, which is accomplished by having the shunt communicate with the left ventricle so a small volume of blood is released from the left ventricle. Most preferably, the shunt selectively permits flow when a pressure differential between the left ventricle and another chamber of a heart above a threshold pressure, so that shunting is prevented during left ventricular systole, or, alternatively, selectively permits flow when a pressure differential between the left ventricle and another chamber of a heart is between a lower threshold and a higher threshold. In certain embodiments a semi-passive check-valve is controlled and actuated by an external signal.
Owner:WAVE LTD V
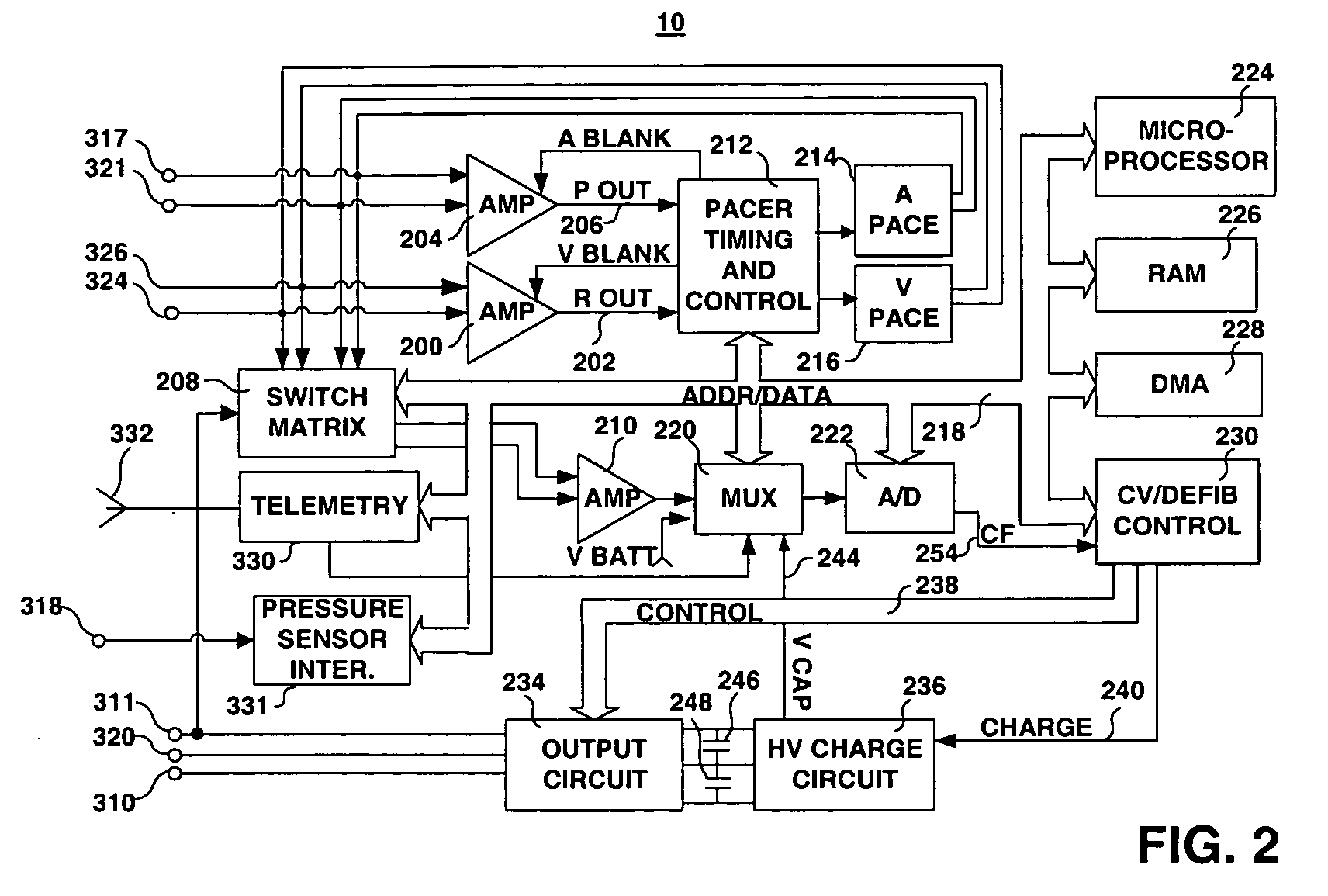
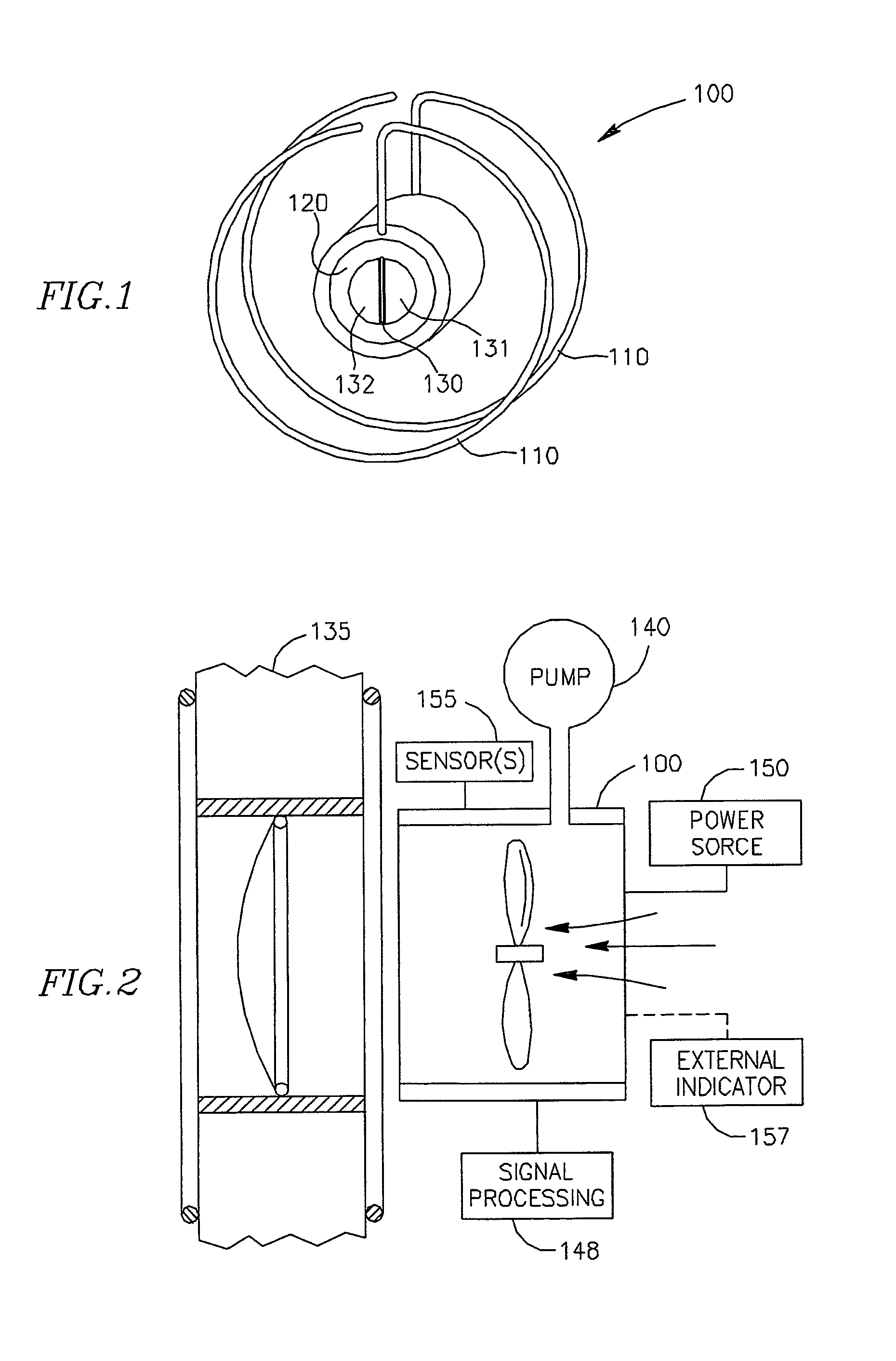
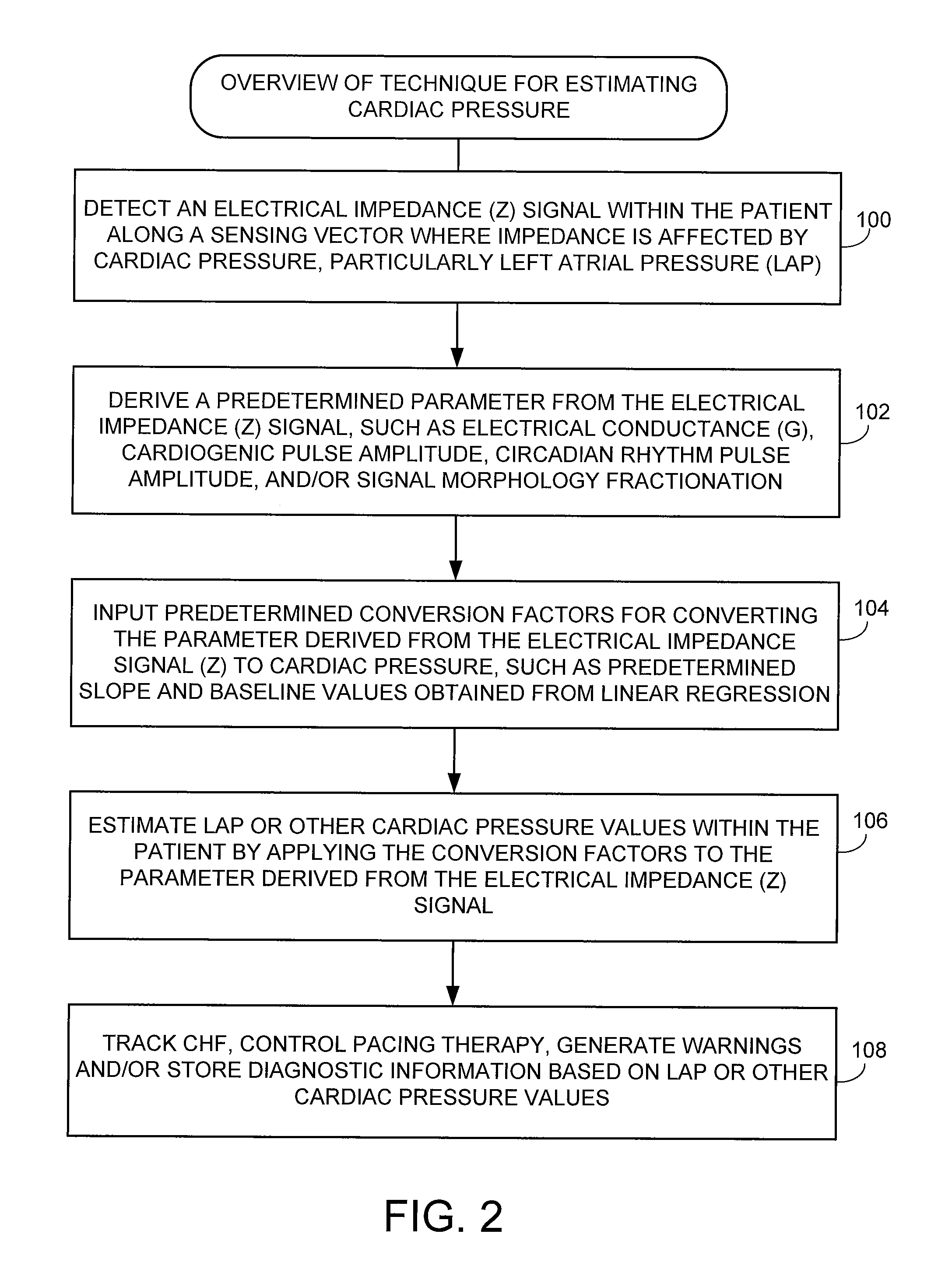
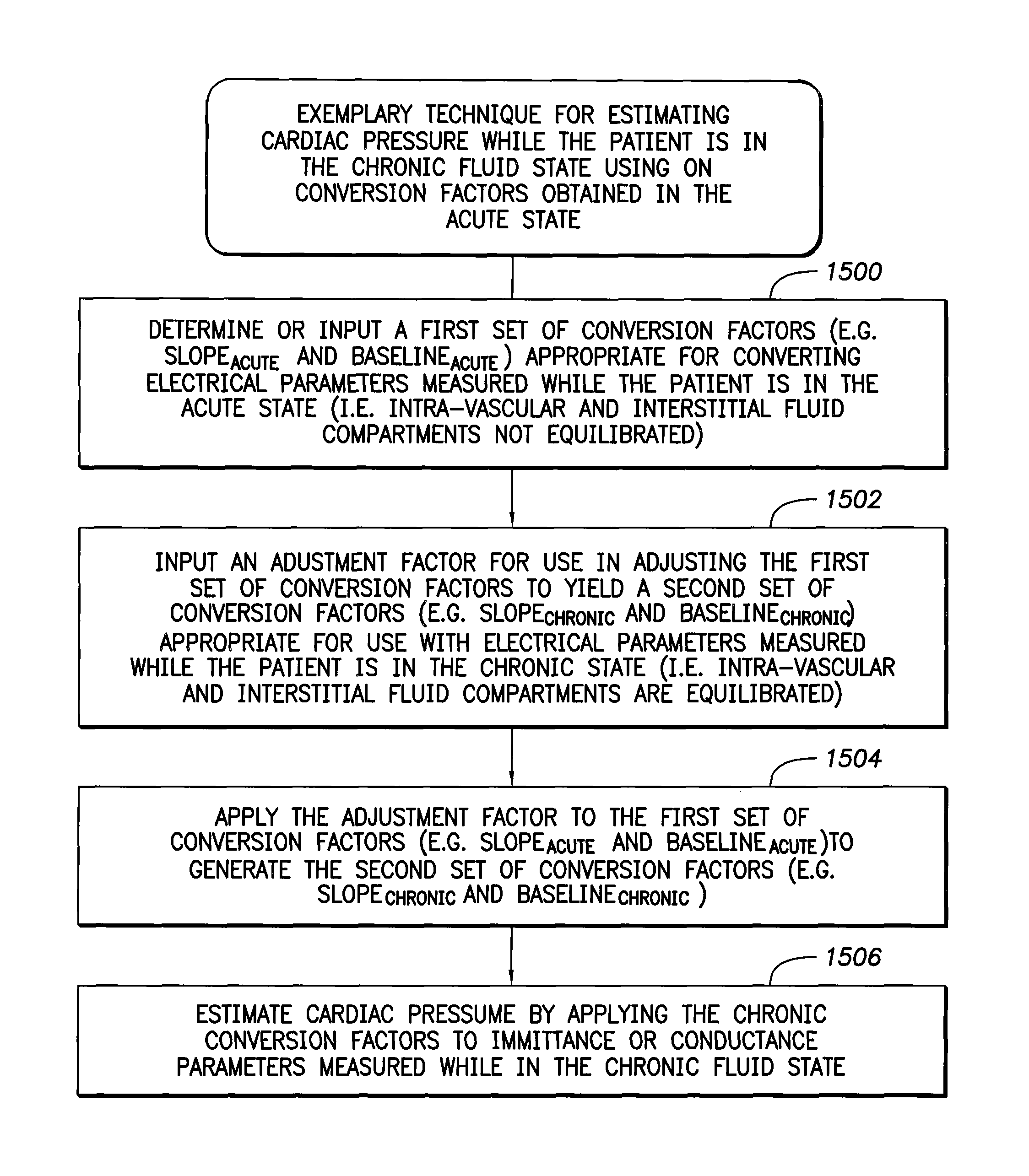
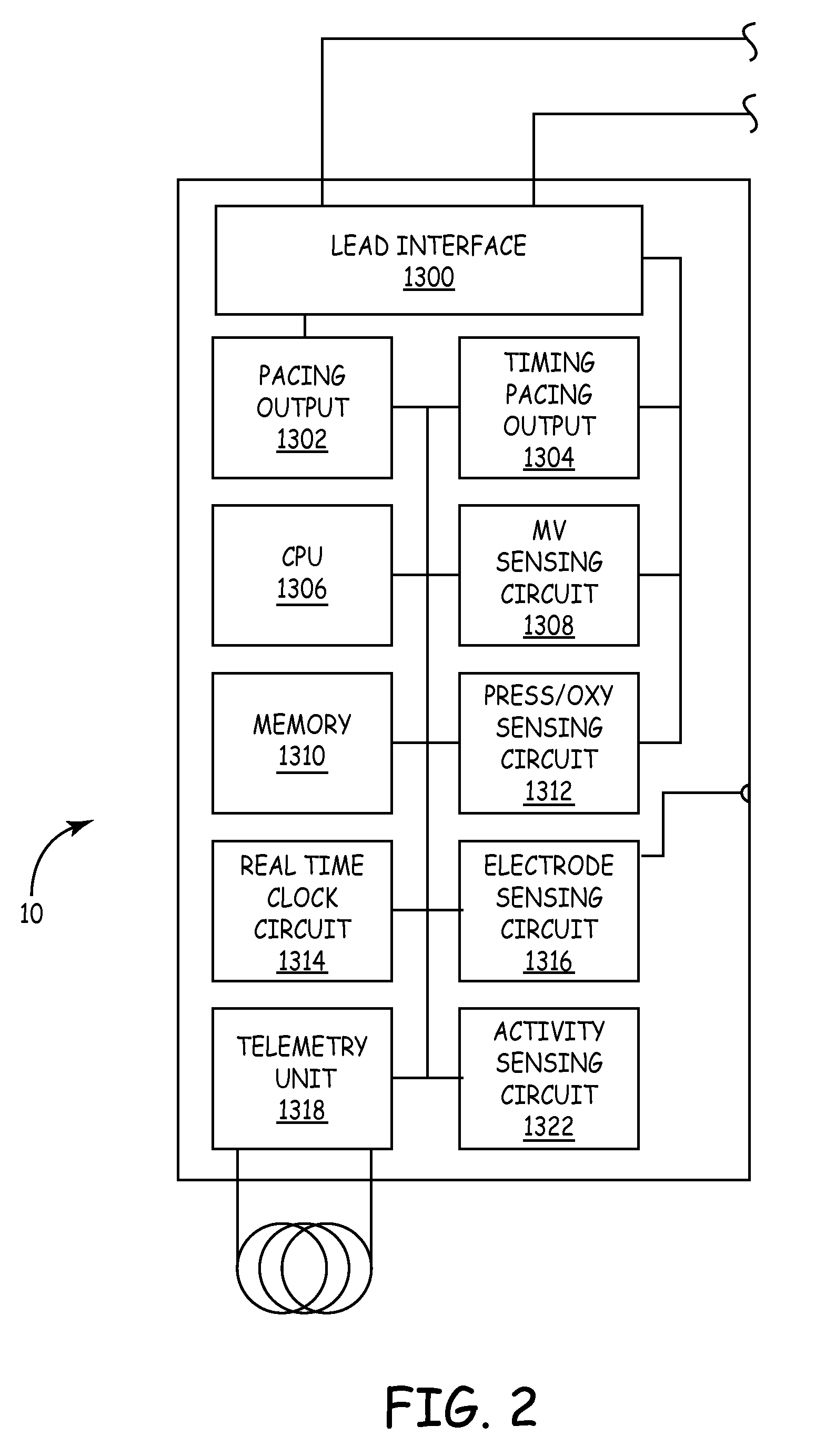
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20080262361A1Accurate CalibrationAccurate slopeElectrotherapyCatheterThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
Various techniques are provided for calibrating and estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) using an implantable medical device, based on impedance, admittance or conductance parameters measured within a patient. In one example, default conversion factors are exploited for converting the measured parameters to estimates of LAP. The default conversion factors are derived from populations of patients. In another example, a correlation between individual conversion factors is exploited to allow for more efficient calibration. In yet another example, differences in thoracic fluid states are exploited during calibration. In still yet another example, a multiple stage calibration procedure is described, wherein both invasive and noninvasive calibration techniques are exploited. In a still further example, a therapy control procedure is provided, which exploits day time and night time impedance / admittance measurements.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
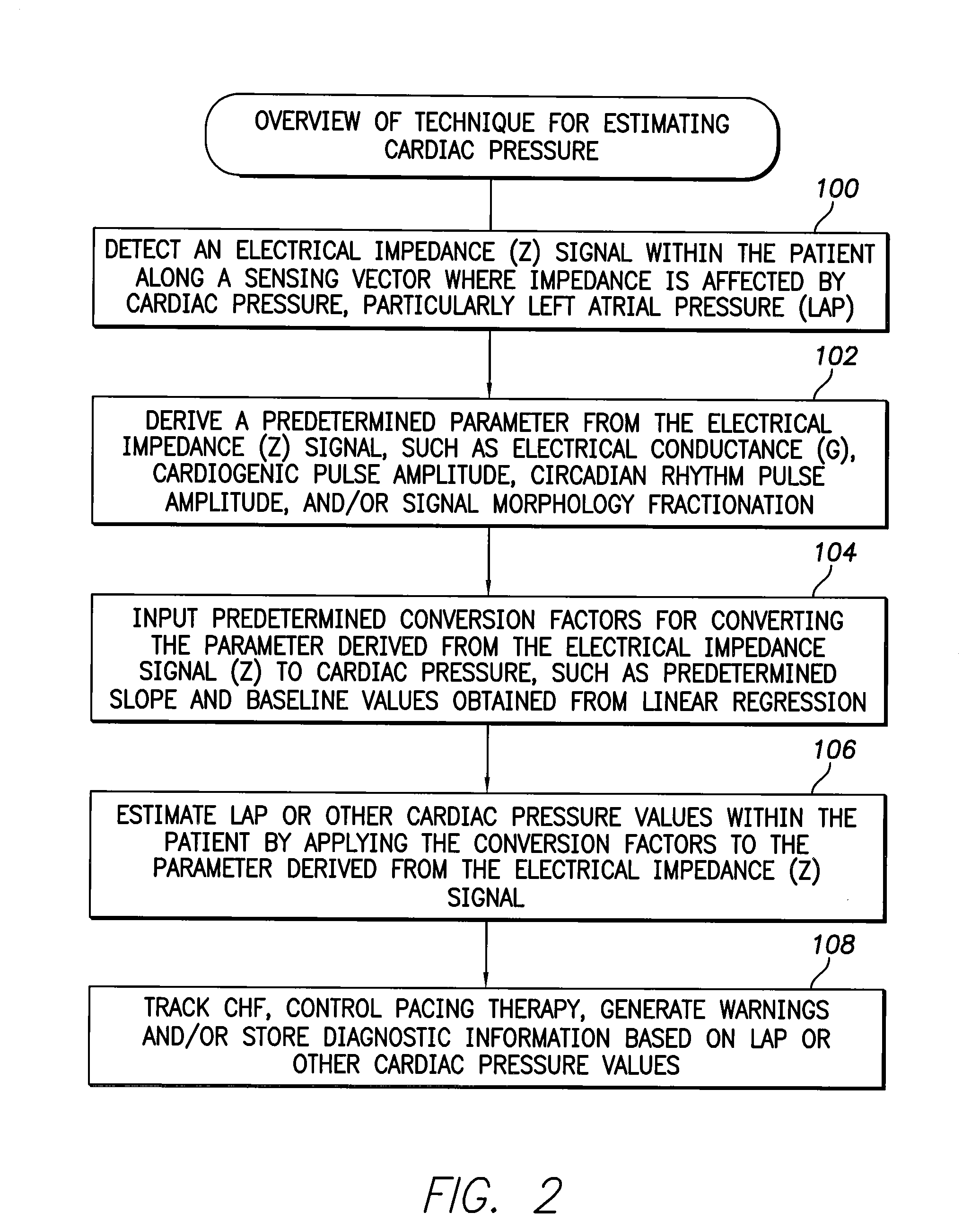
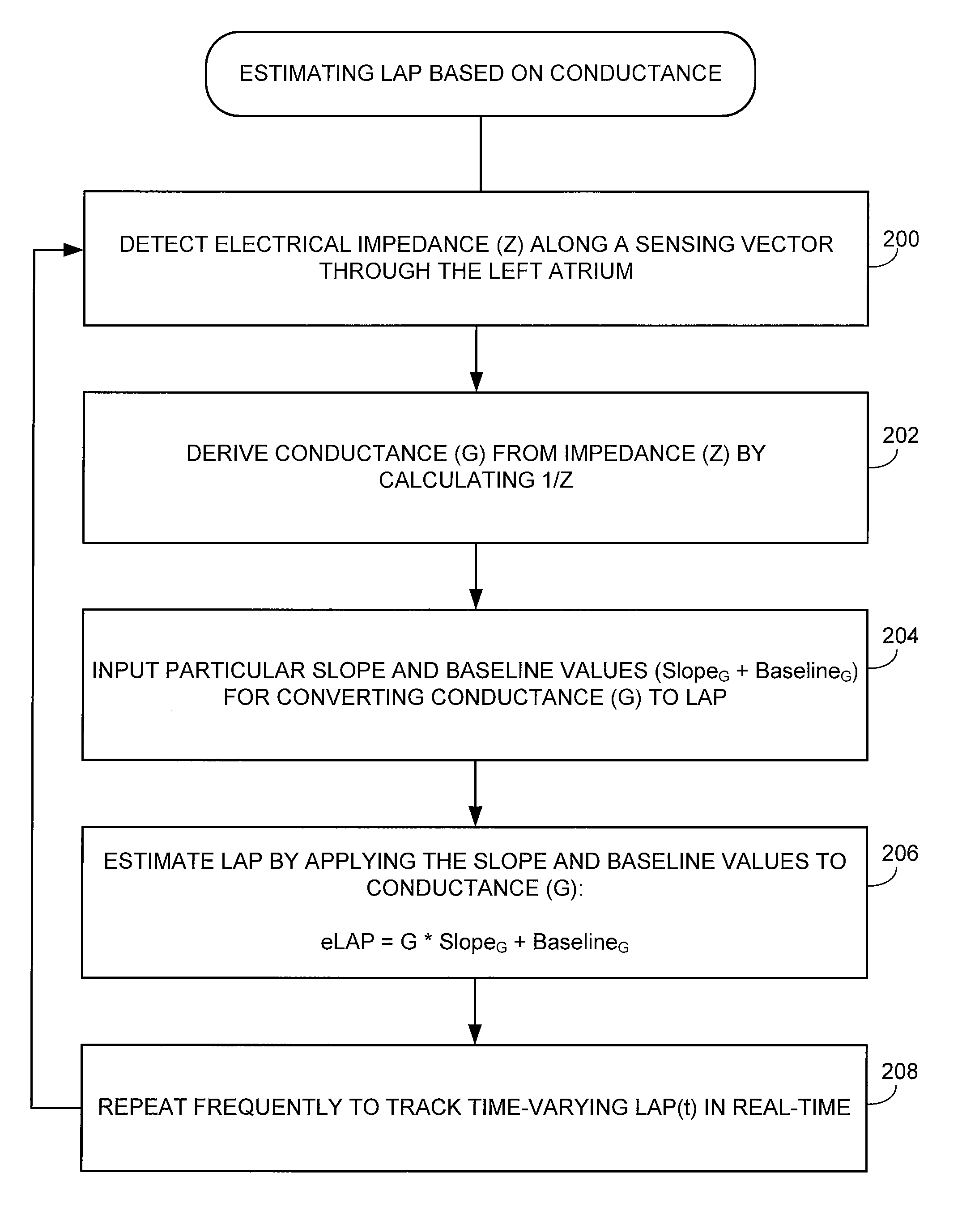
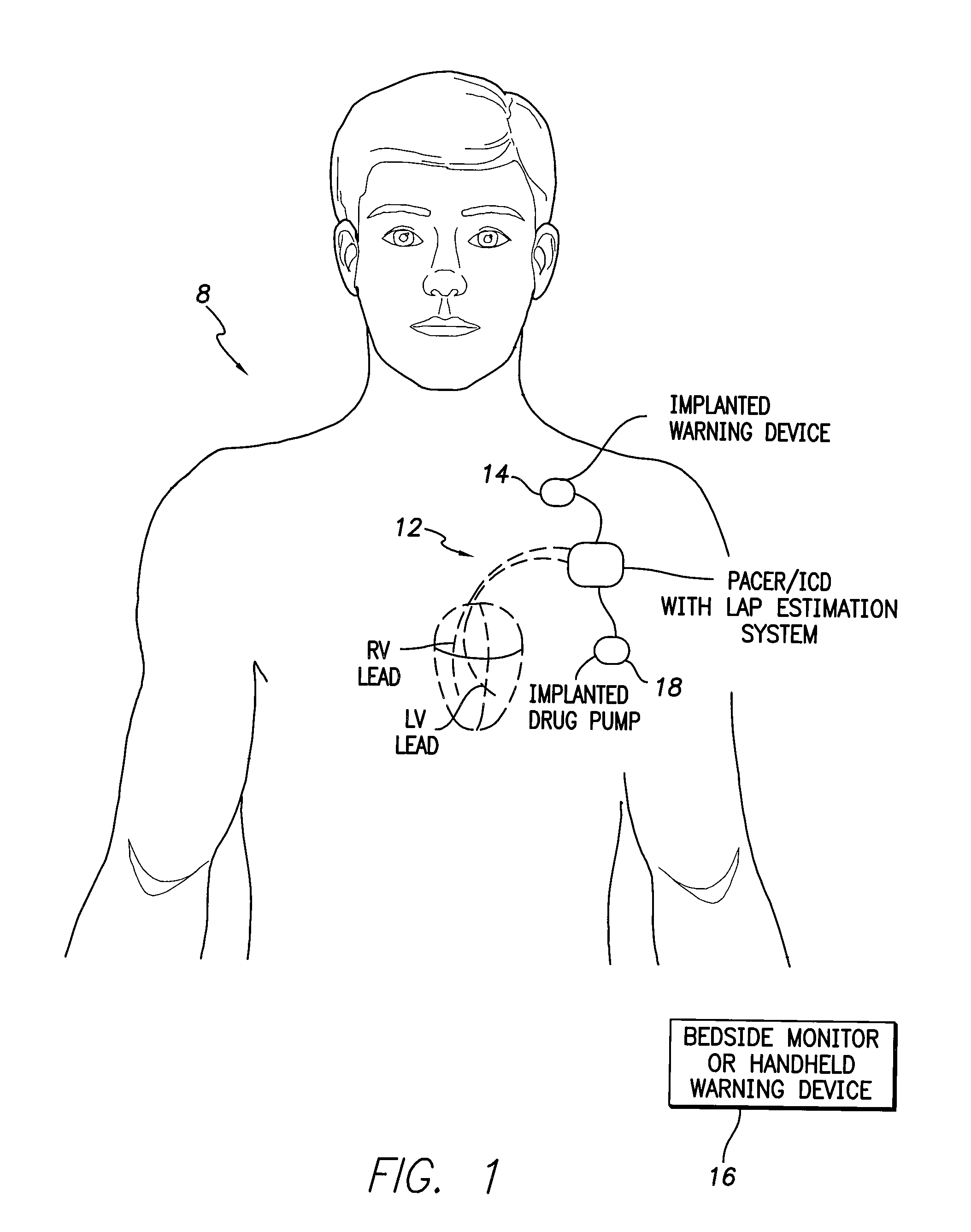
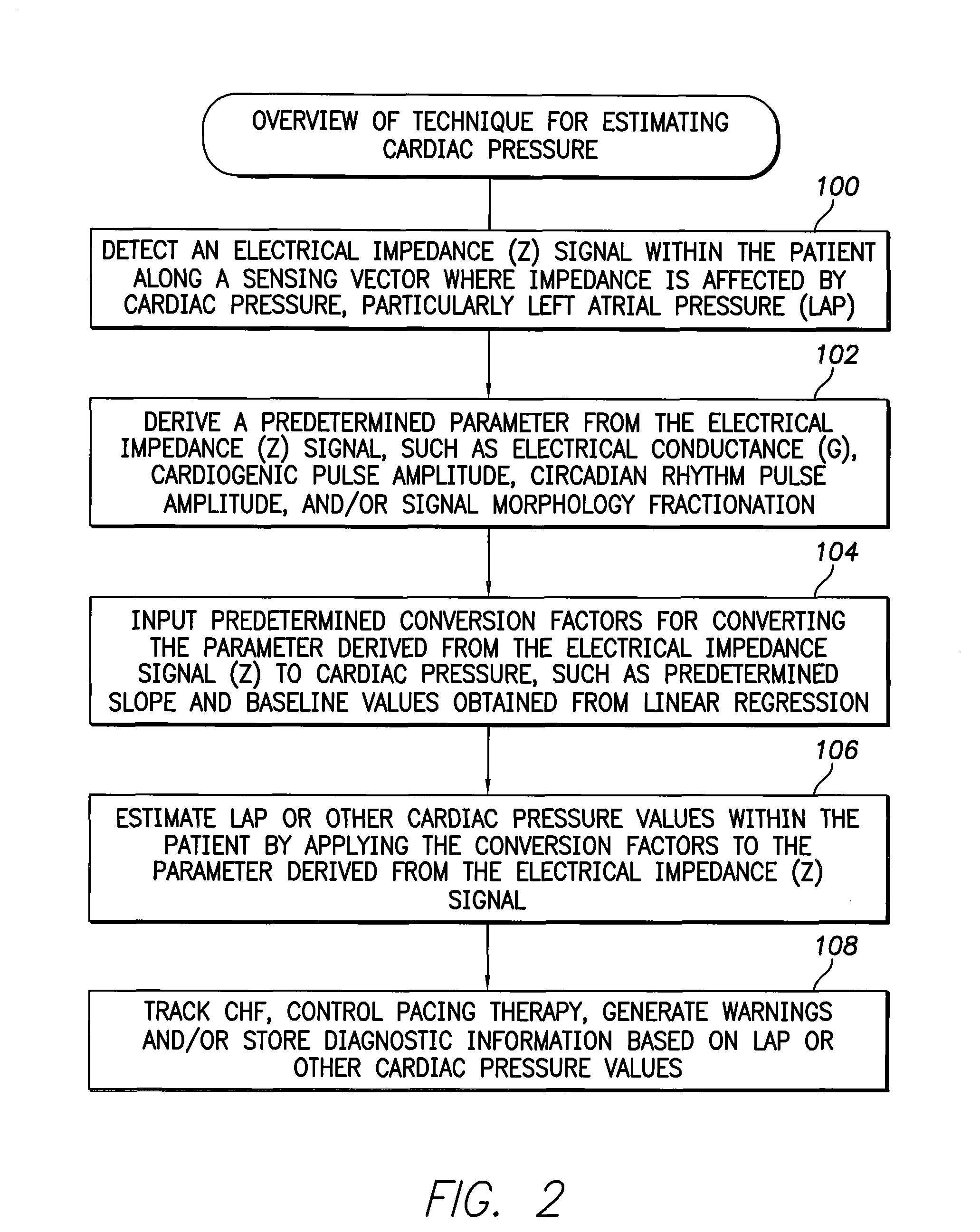
System and method for estimating cardiac pressure using parameters derived from impedance signals detected by an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) or other cardiac pressure parameters based on various parameters derived from impedance signals. In particular, effective LAP is estimated based on one or more of: electrical conductance values, cardiogenic pulse amplitudes, circadian rhythm pulse amplitudes, or signal morphology fractionation values, each derived from the impedance signals detected by the implantable device. Predetermined conversion factors stored within the device are used to convert the various parameters derived from the electrical impedance signal into LAP values or other appropriate cardiac pressure values. The conversion factors may be, for example, slope and baseline values derived during an initial calibration procedure performed by an external system, such as an external programmer. In some examples, the slope and baseline values may be periodically re-calibrated by the implantable device itself.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
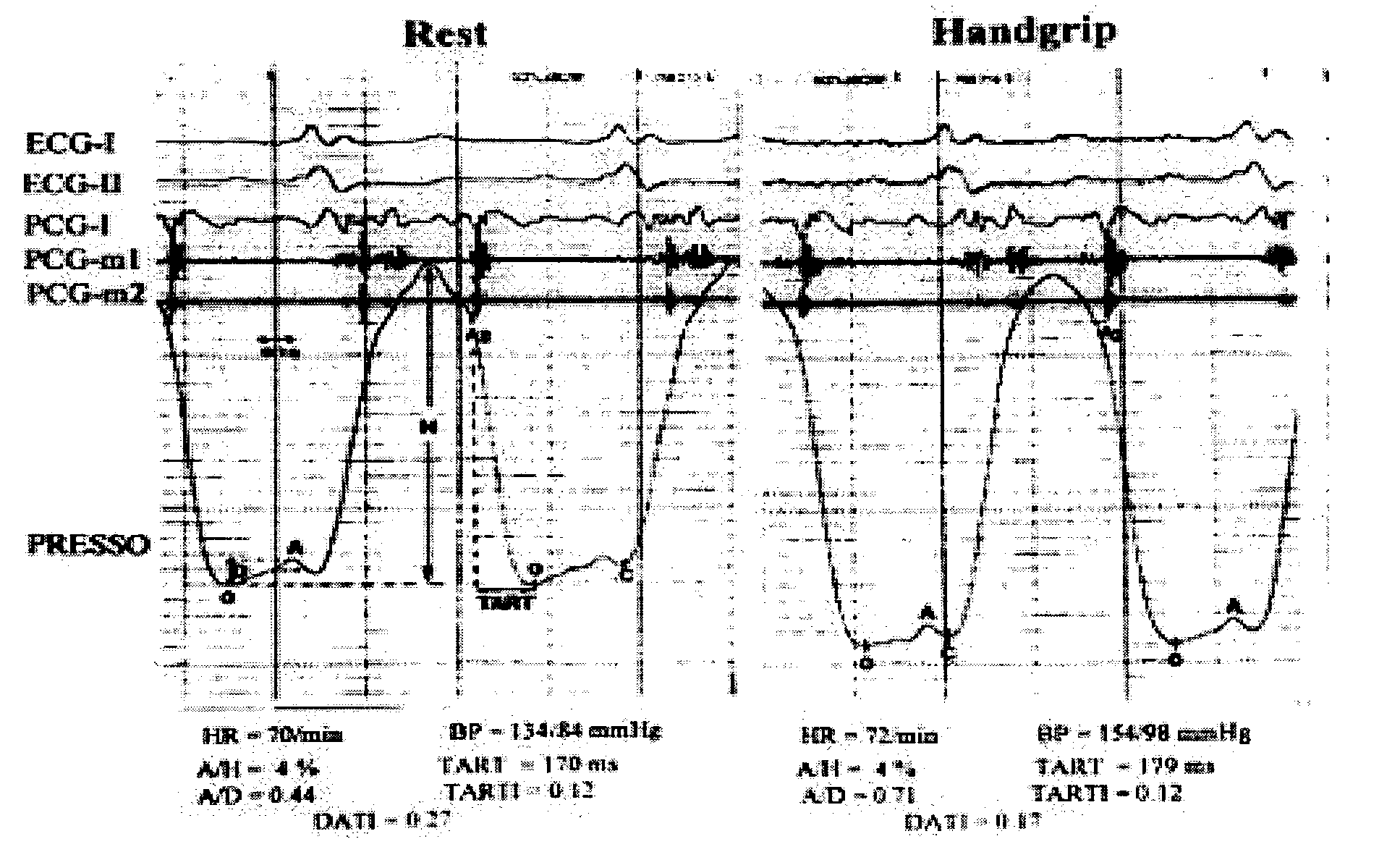
Device for and method of rapid noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile of left ventricular function at rest and with exercise
ActiveUS7107095B2Information can be usedSafe and convenient modalityEvaluation of blood vesselsAuscultation instrumentsLeft ventricular sizeHeart disease
In a method of noninvasive measurement of parameters of diastolic function of left ventricle and automated evaluation of the measured profile at rest and with exercise, a patient performs an isometric exercise. An external pressure sensor and heart sounds microphone are applied in a non-invasive manner on the thoracic wall to obtain a left ventricular pressure mirroring curve (pressocardiogram) and simultaneously the heart sounds (phonocardiogram). An external unit determines and calculates characteristic diastolic parameters derived from the pressocardiographic curve and phonocardiogram at rest, during and after exercise, converts each said pressocardiogram into a digital waveform in the time domain, and automatically categorizes the mentioned characteristic parameters based on exact categorization criteria for defining several differentialforms of diastolic dysfunction of left ventricle in human beings.
Owner:MANOLAS JAN
Prosthesis for reducing intra-cardiac pressure having an embolic filter
ActiveUS8460372B2Reduce pressureRelieve symptomsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBone implantPatients symptomsProsthesis
The present disclosure relates to devices and methods for implanting a prosthesis into a heart of a mammal, such as a person. The disclosure includes a prosthesis that acts as a pressure vent between the left and right atria of the heart. The intracardiac pressure vents disclosed allow sufficient flow from the left atrium to the right atrium to relieve elevated left atrial pressure and resulting patient symptoms. The devices also limit the amount of flow from the right atrium to the left atrium to minimize the potential for thrombi or other embolic material from entering arterial circulation.
Owner:CORVIA MEDICAL
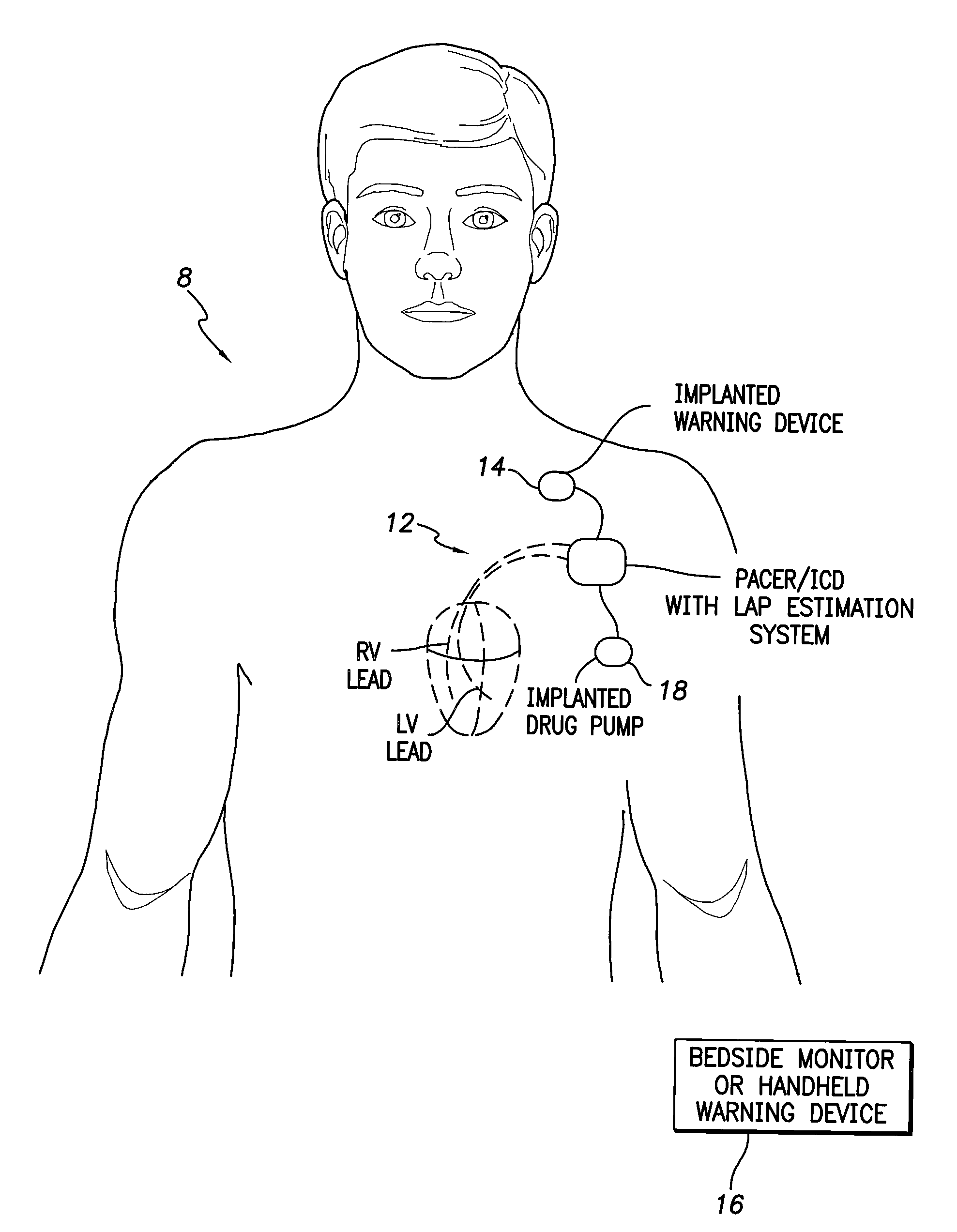
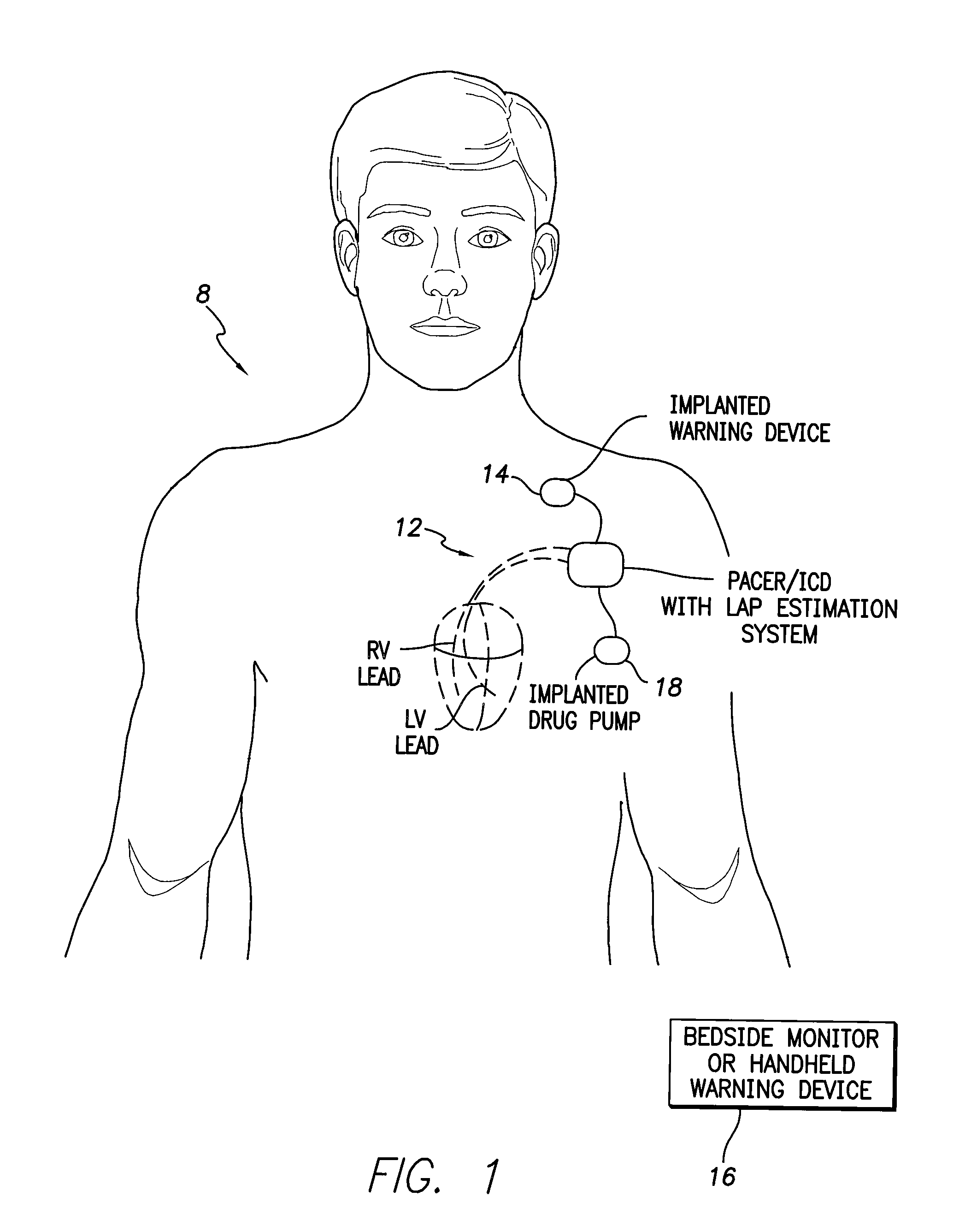
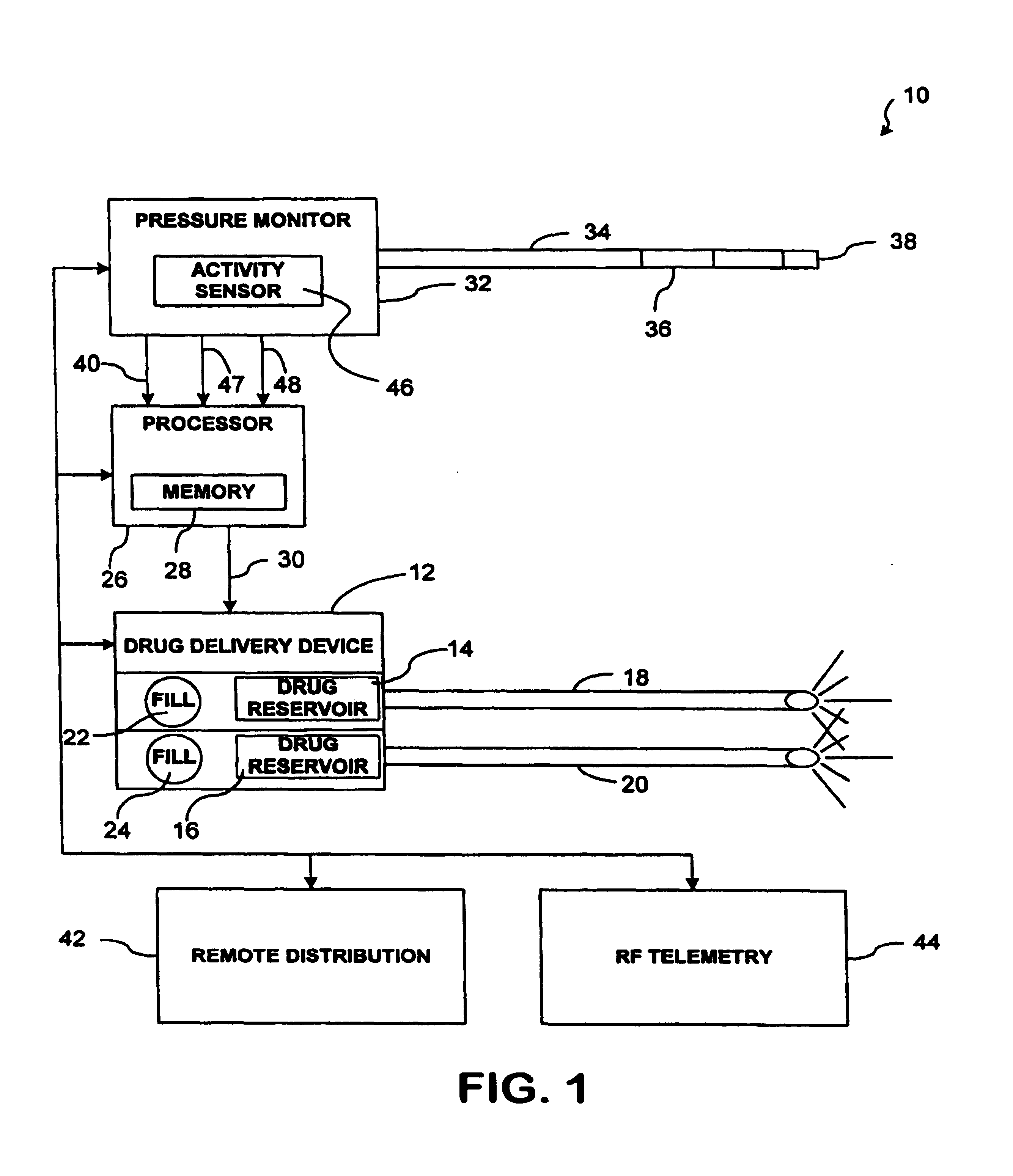
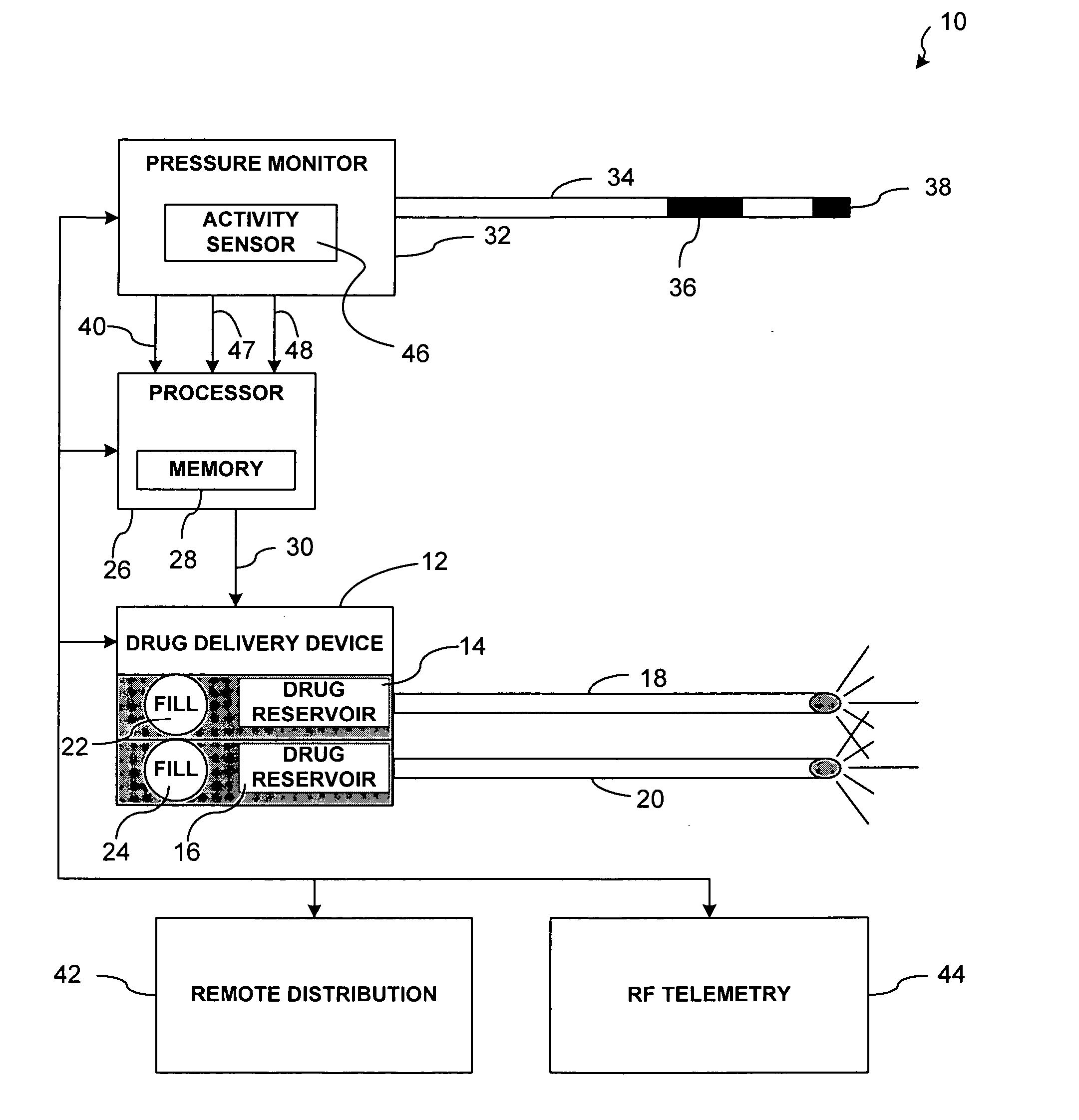
Implantable drug delivery system responsive to intra-cardiac pressure
InactiveUS6969369B2High outputEffective treatmentMedical devicesCatheterPulmonary artery diastolic pressureCongestive heart failure chf
The invention is directed to techniques for monitoring the condition of a patient, such as a patient having congestive heart failure, and appropriately modifying the patient's drug therapy as a function of a pressure in the patient's heart, such as the estimated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure. The drugs may be administered by an implanted drug delivery device. The drug selection, the drug dosage or both may be controlled as a function of the pressure and / or the activity level of the patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
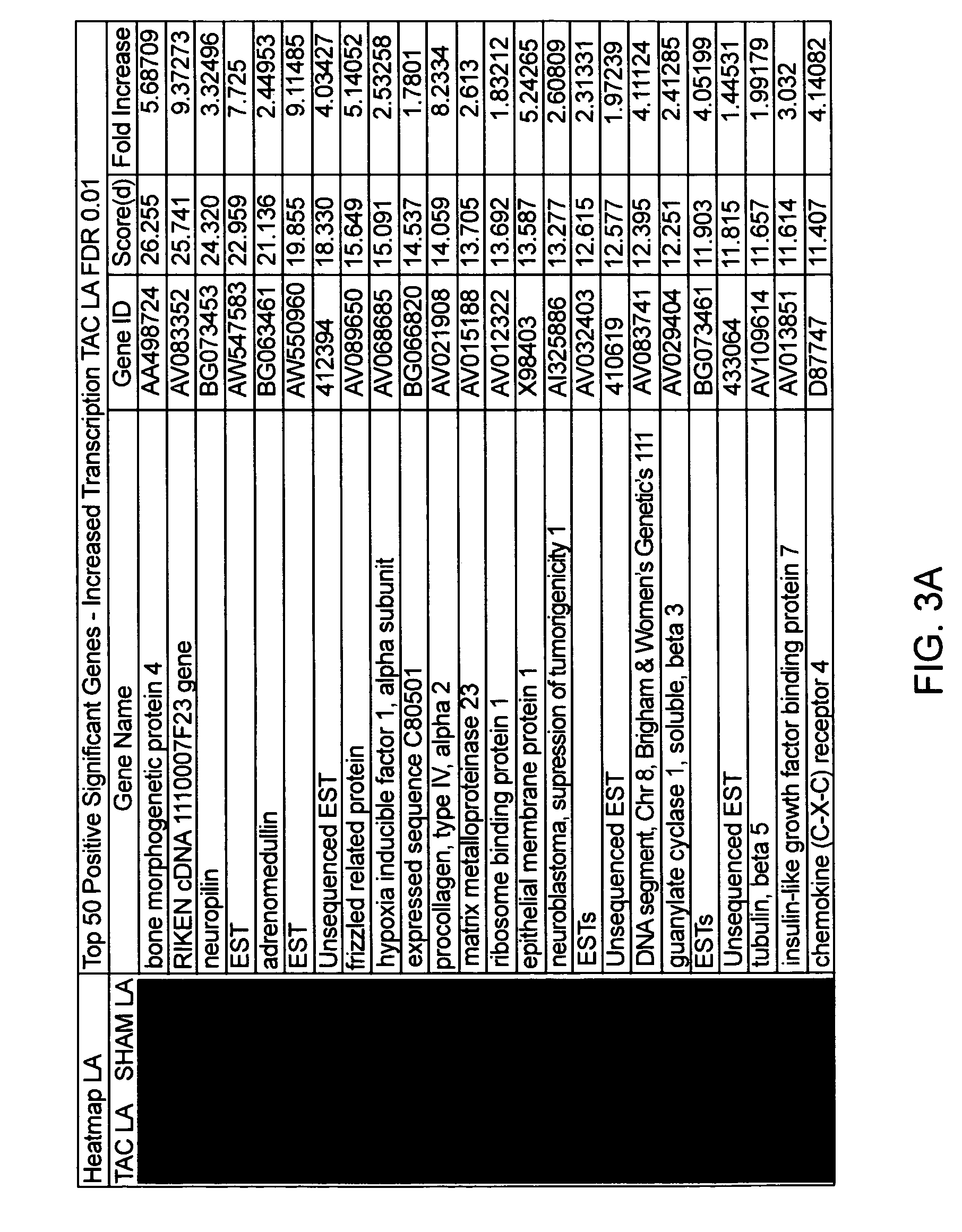
Cardiac pressure overload associated genes
InactiveUS20060094038A1Easy to changeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEtiologyEccentric hypertrophy
The present invention identifies genes whose gene products are differentially expressed pressure overload of the heart. The invention provides methods for diagnosing or assessing an individual's susceptibility to heart failure from many etiologies, as well as the presence and severity of hypertrophy, chamber enlargement, or systolic heat failure. Also provided are therapeutic methods for treating a heart patient or methods for prophylactically treating an individual susceptible to heart failure. Additionally, the invention describes screening methods for identifying agents that can be administered to treat individuals that have suffered a heart attack or are at risk of heart failure.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System and method for calibrating cardiac pressure measurements derived from signals detected by an implantable medical device
ActiveUS8202224B2Easy recalibrationEasy CalibrationElectrotherapyEvaluation of blood vesselsThoracic FluidLeft atrial pressure
Owner:PACESETTER INC
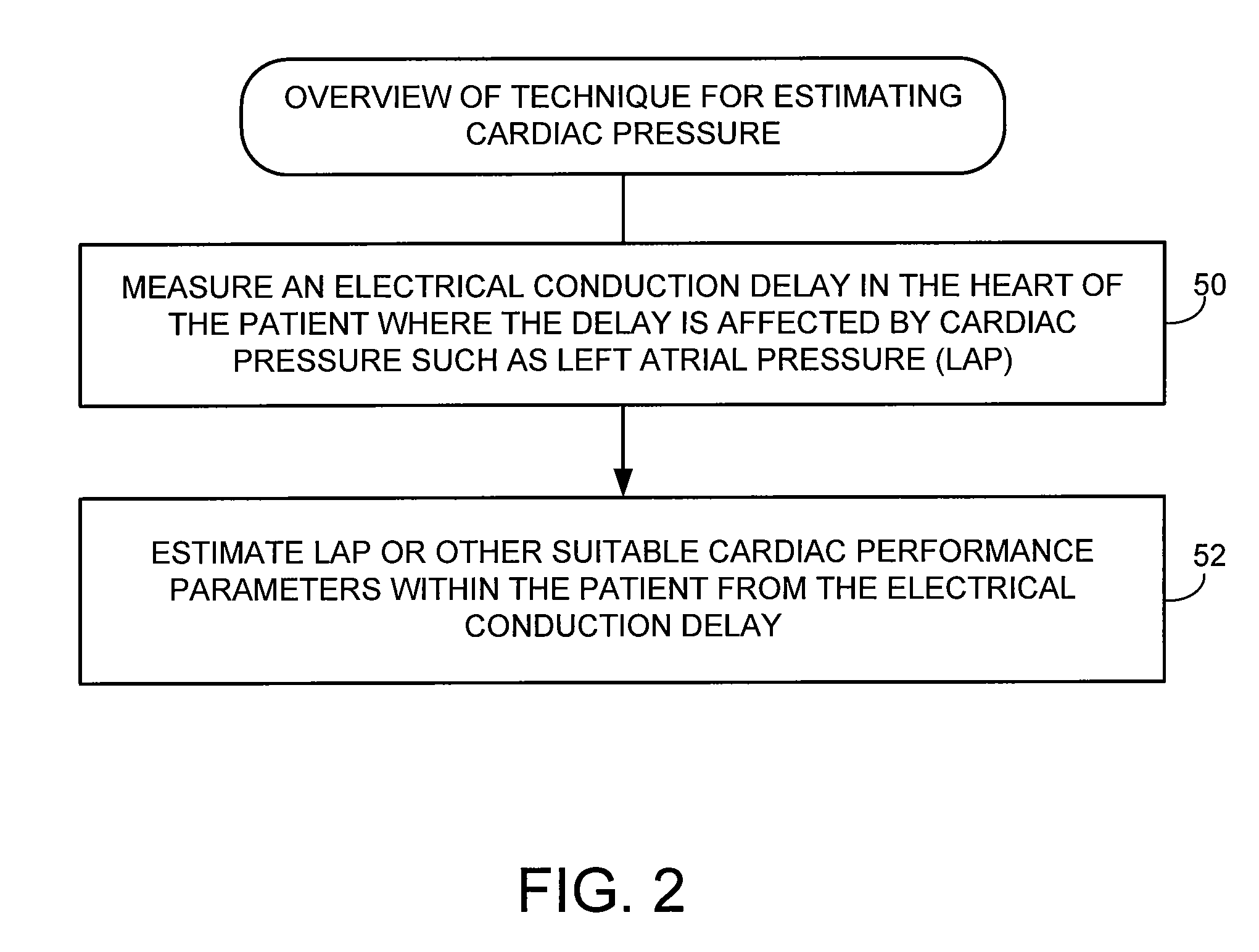
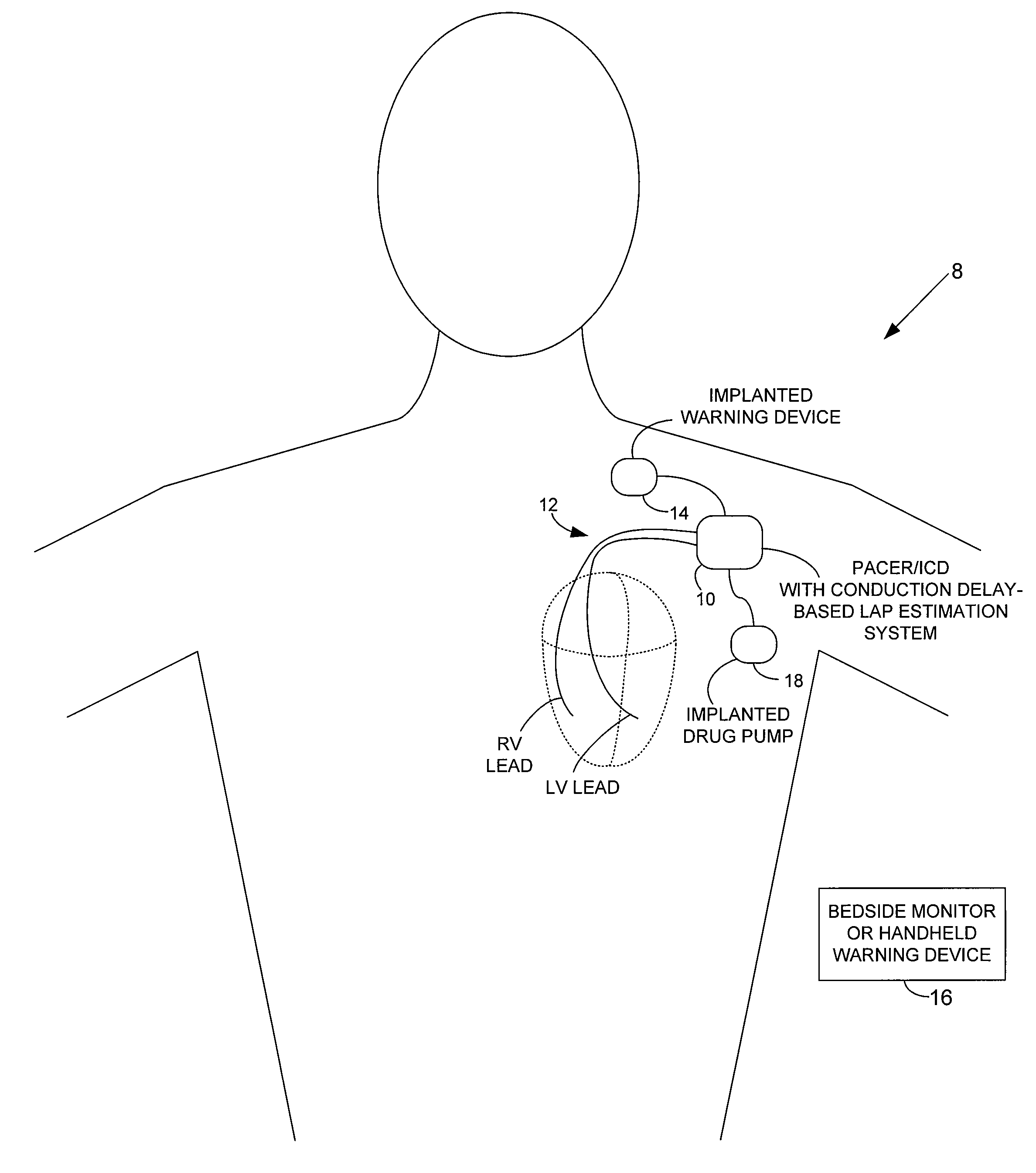
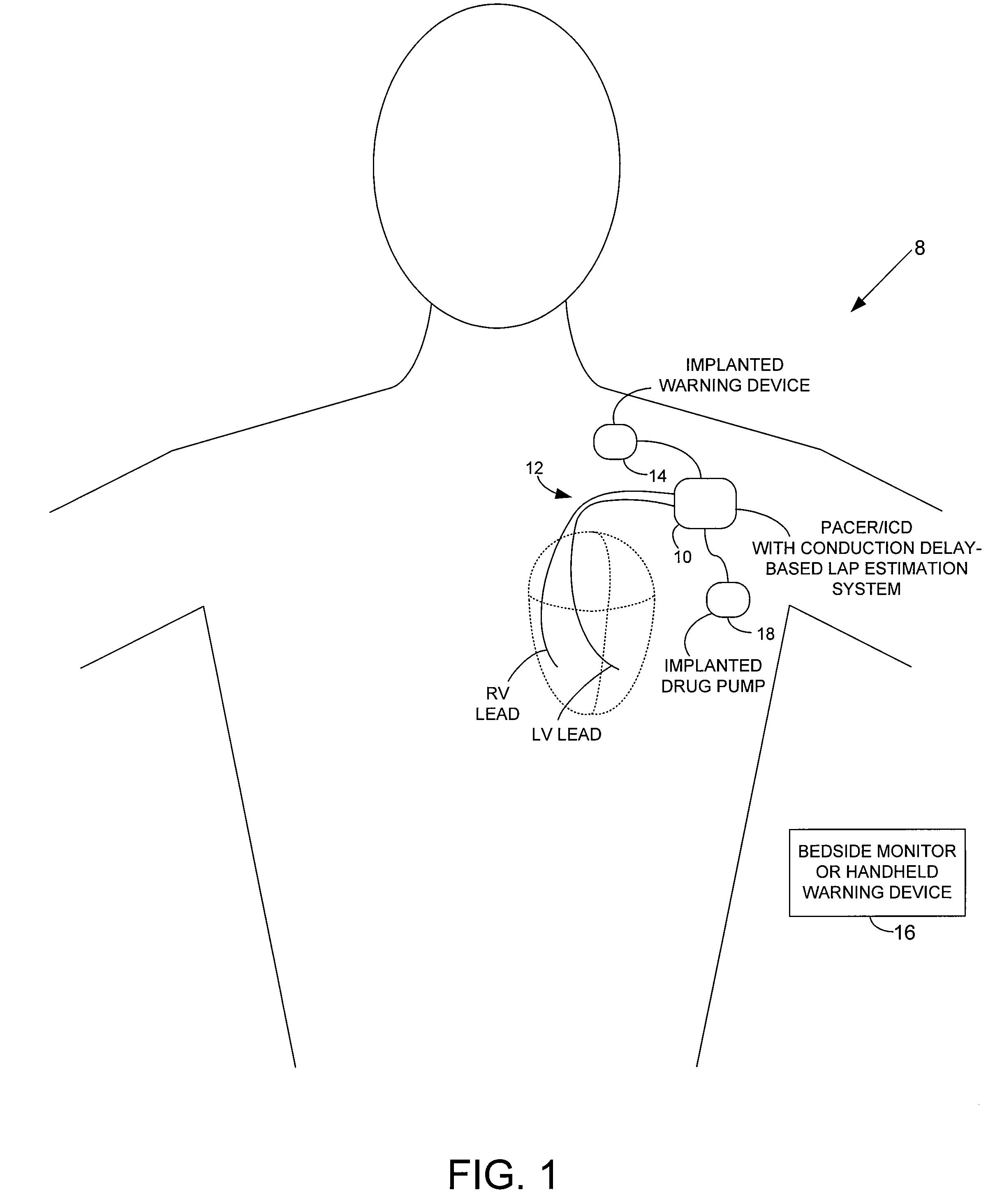
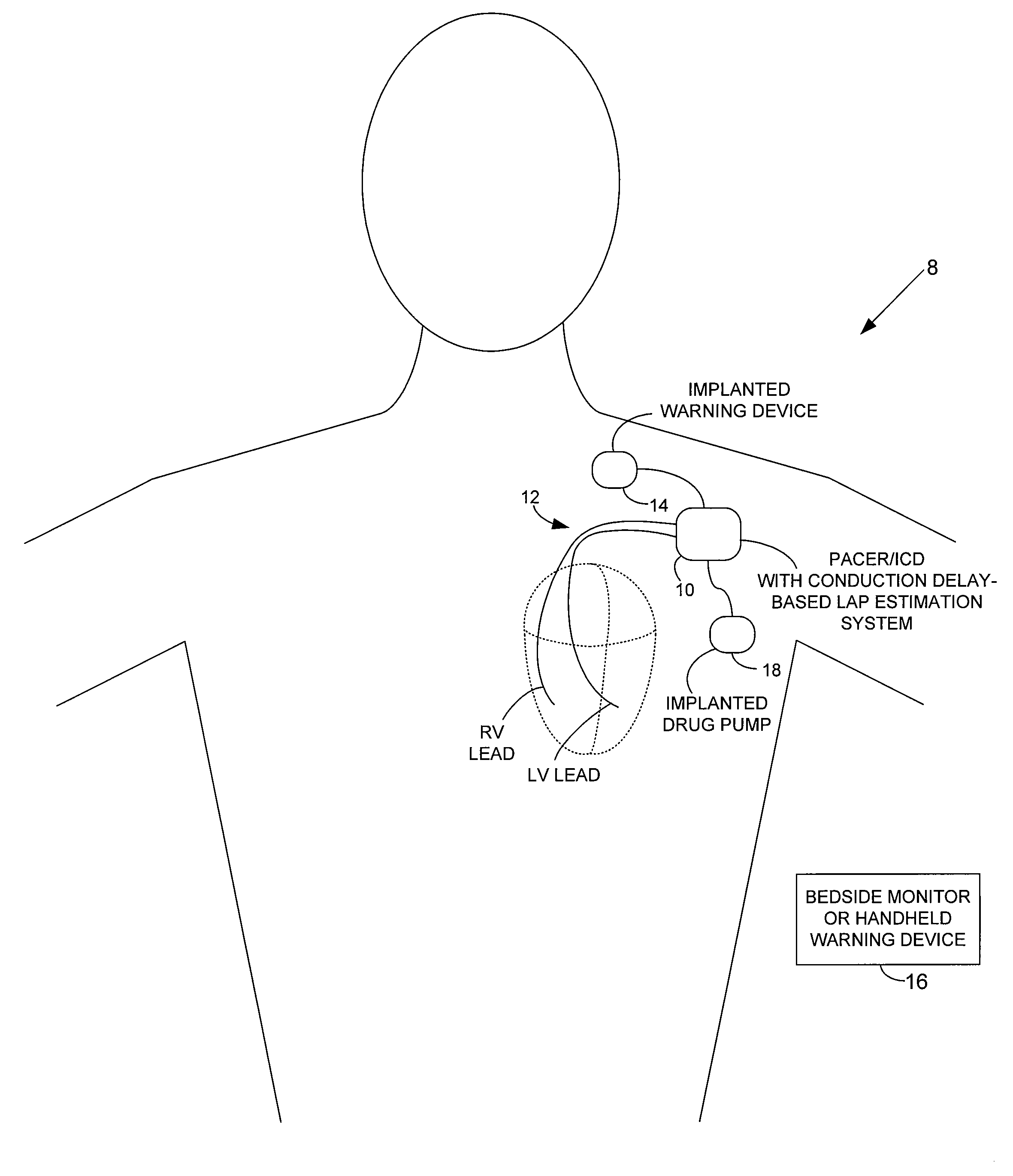
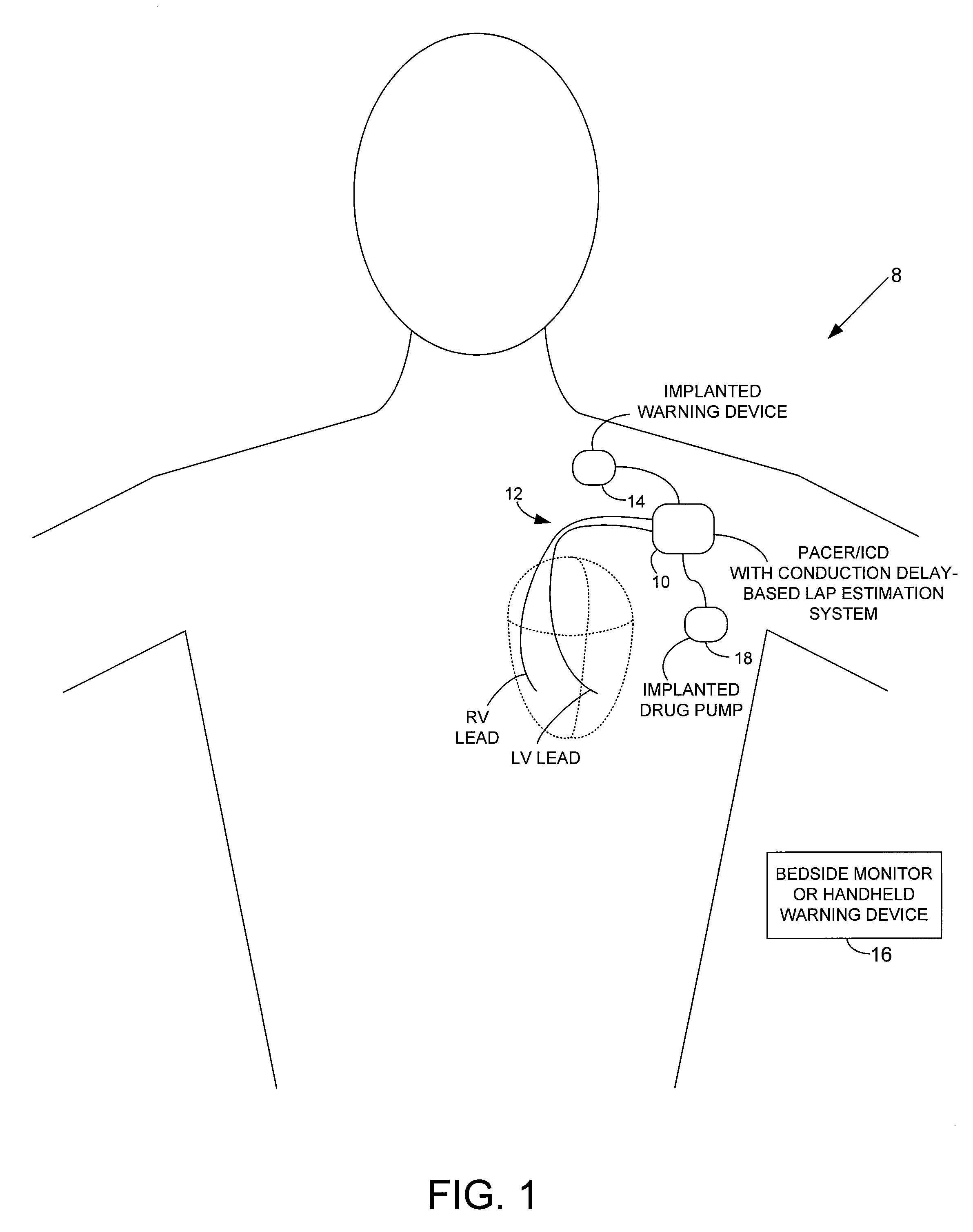
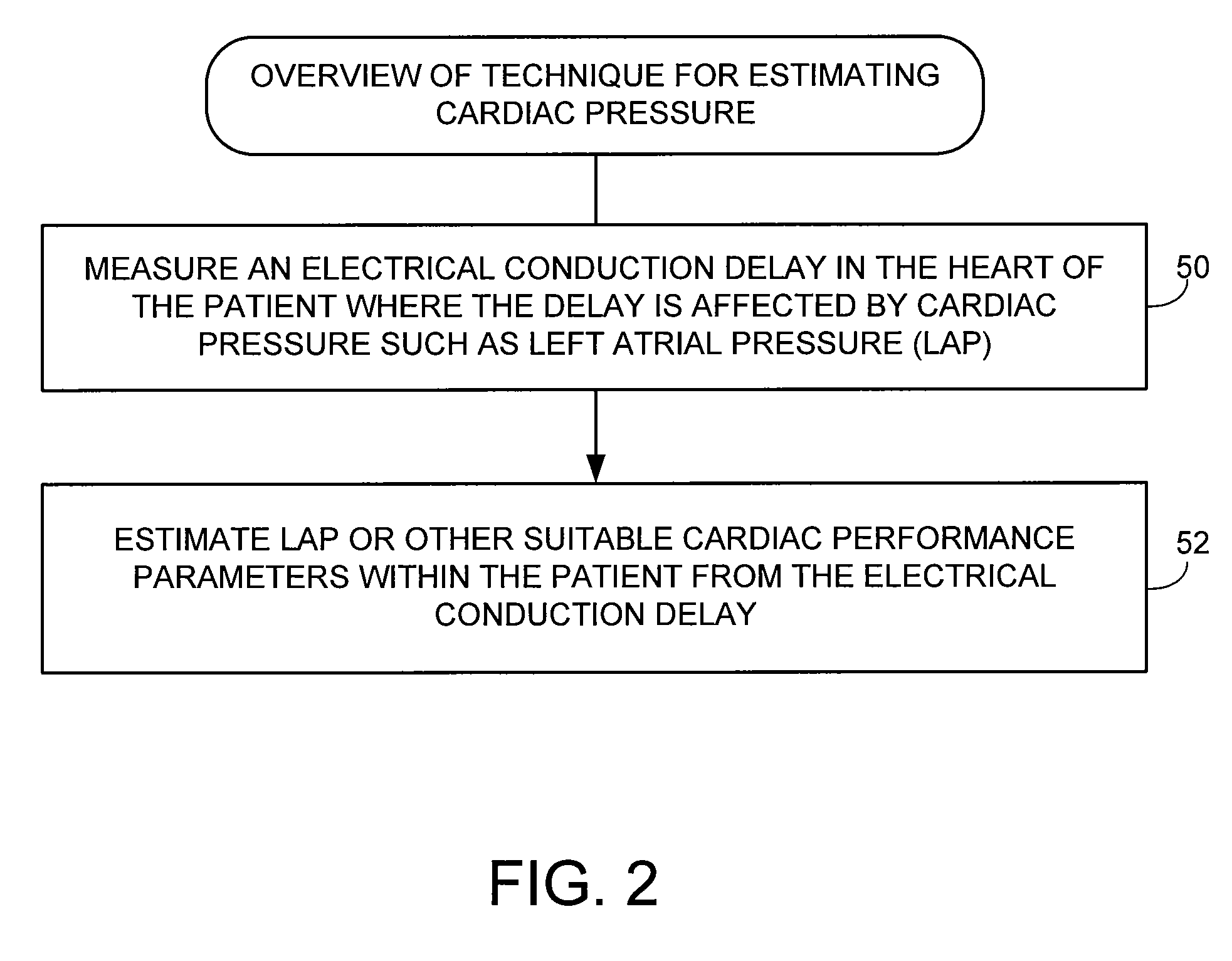
System and method for estimating electrical conduction delays from immittance values measured using an implantable medical device
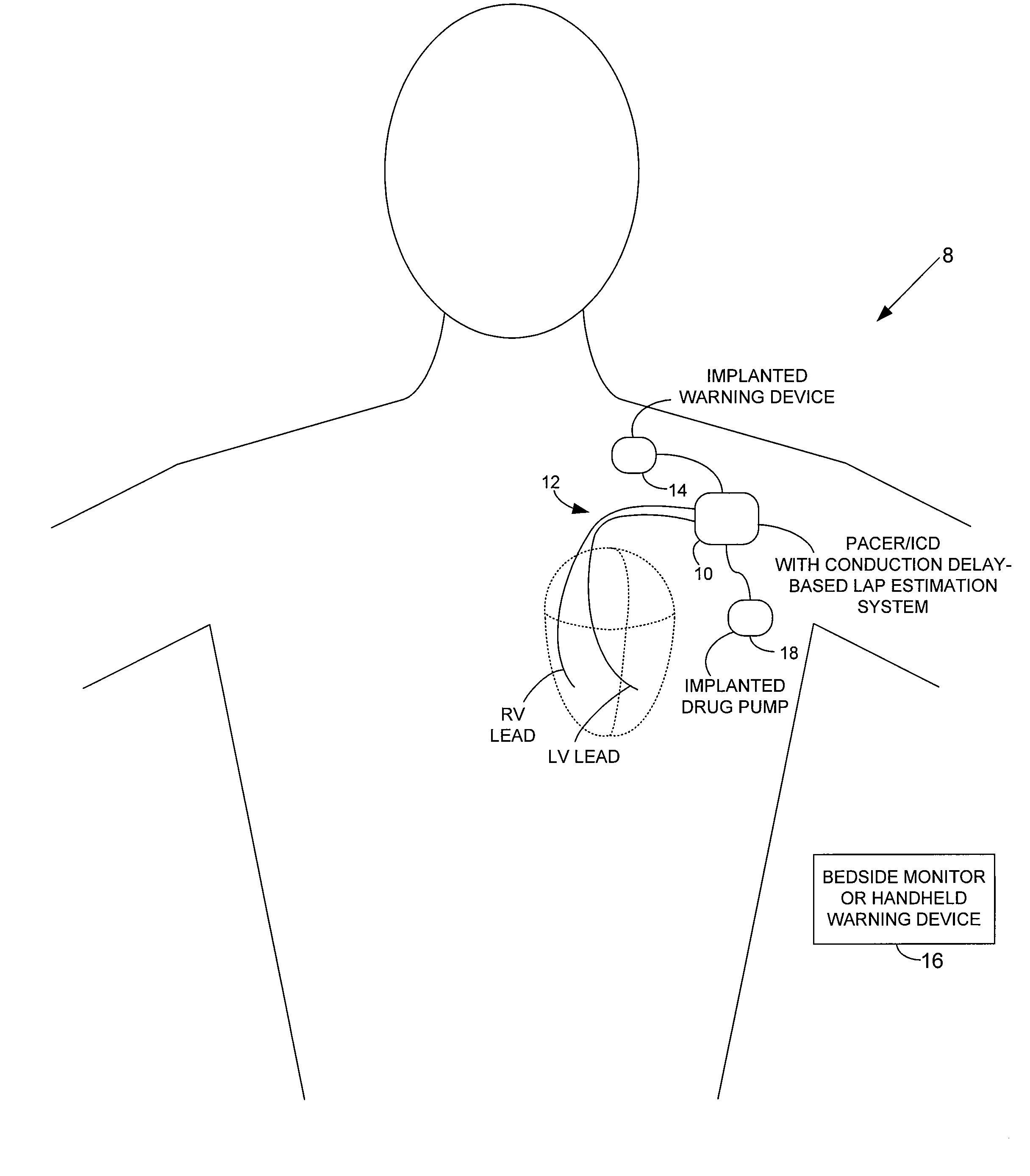
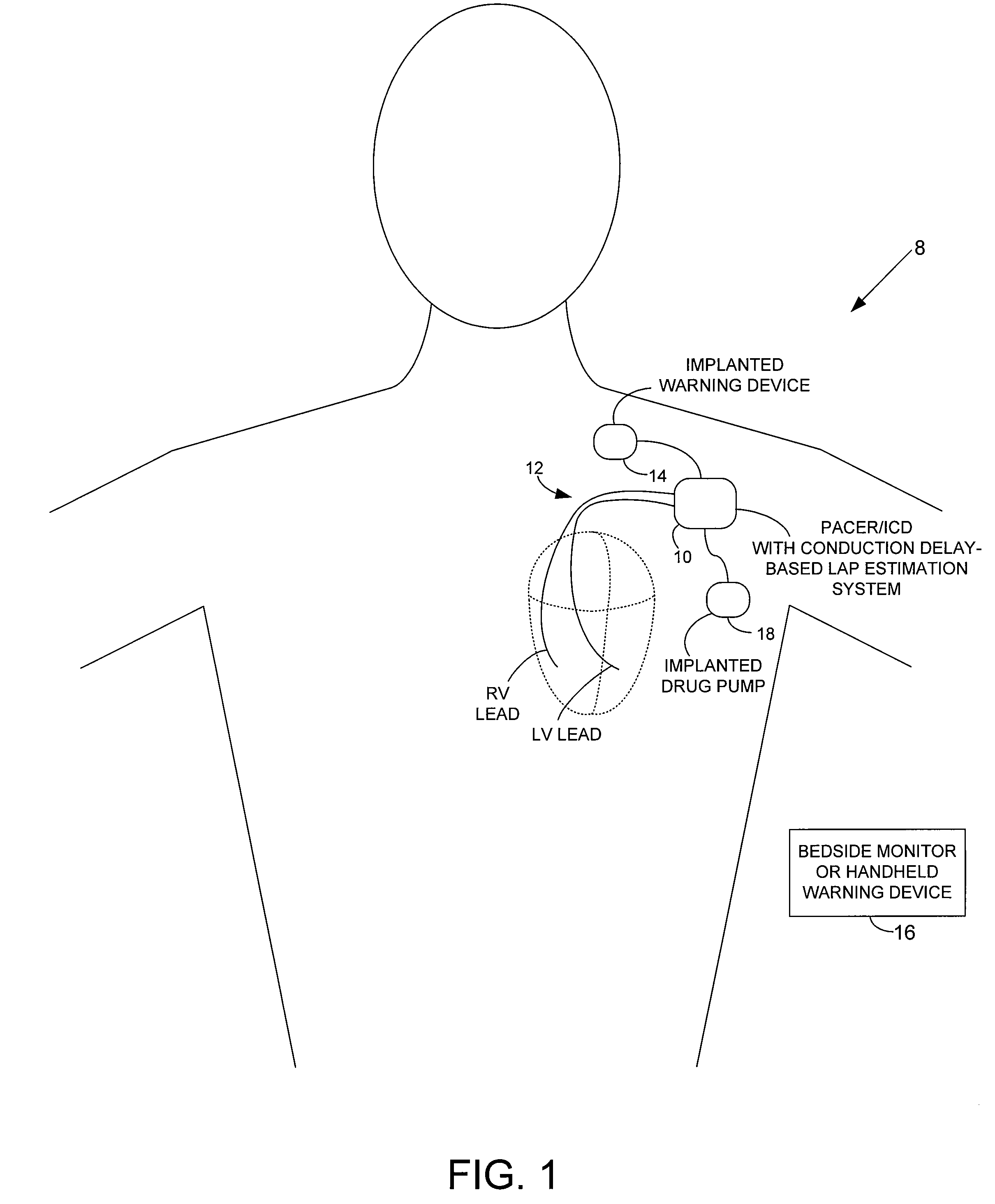
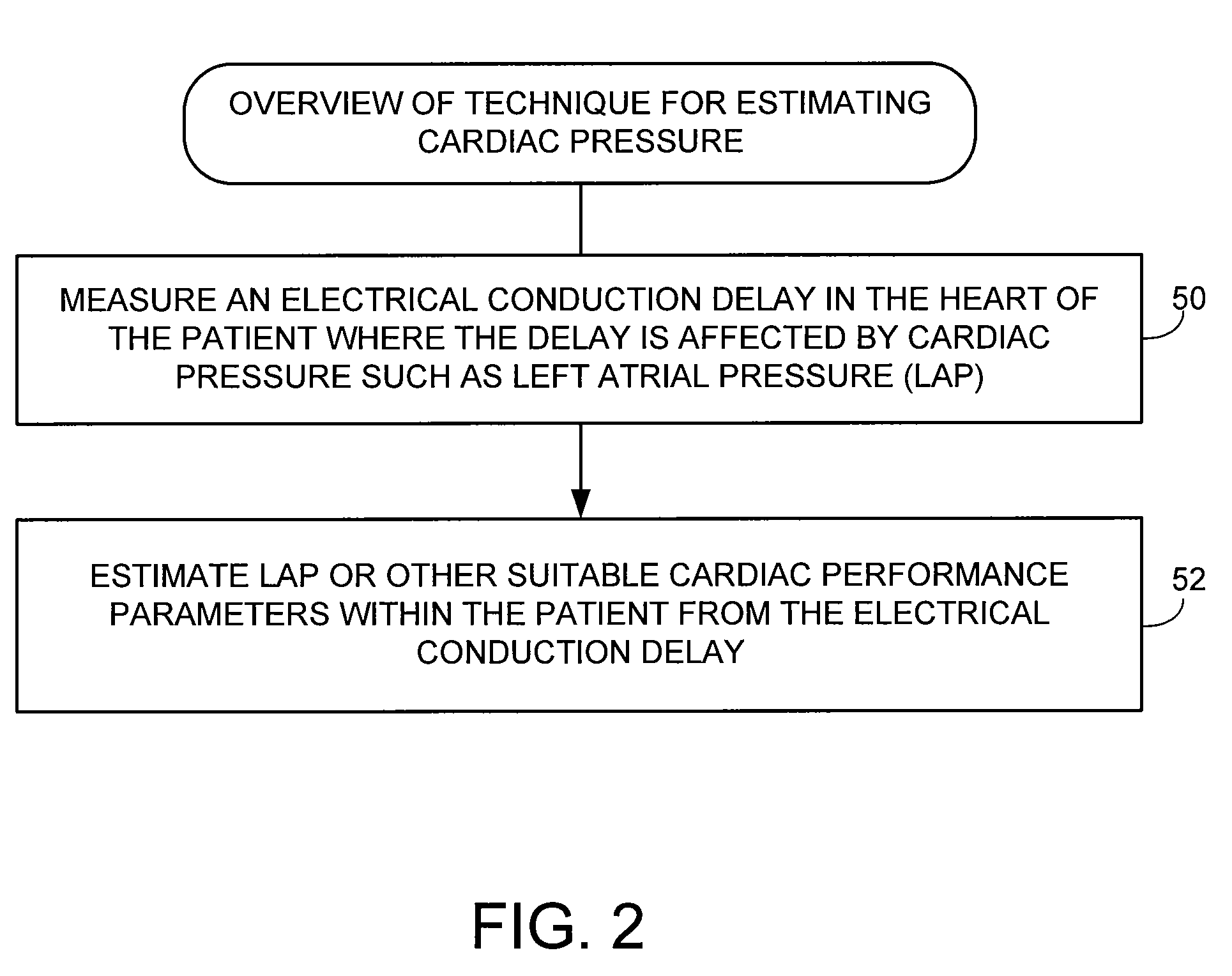
Techniques are provided for estimating electrical conduction delays with the heart of a patient based on measured immittance values. In one example, impedance or admittance values are measured within the heart of a patient by a pacemaker or other implantable medical device, then used by the device to estimate cardiac electrical conduction delays. A first set of predetermined conversion factors may be used to convert the measured immittance values into conduction delay values. In some examples, the device then uses the estimated conduction delay values to estimate LAP or other cardiac pressure values. A second set of predetermined conversion factors may be used to convert the estimated conduction delays into pressure values. Techniques are also described for adaptively adjusting pacing parameters based on estimated LAP.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
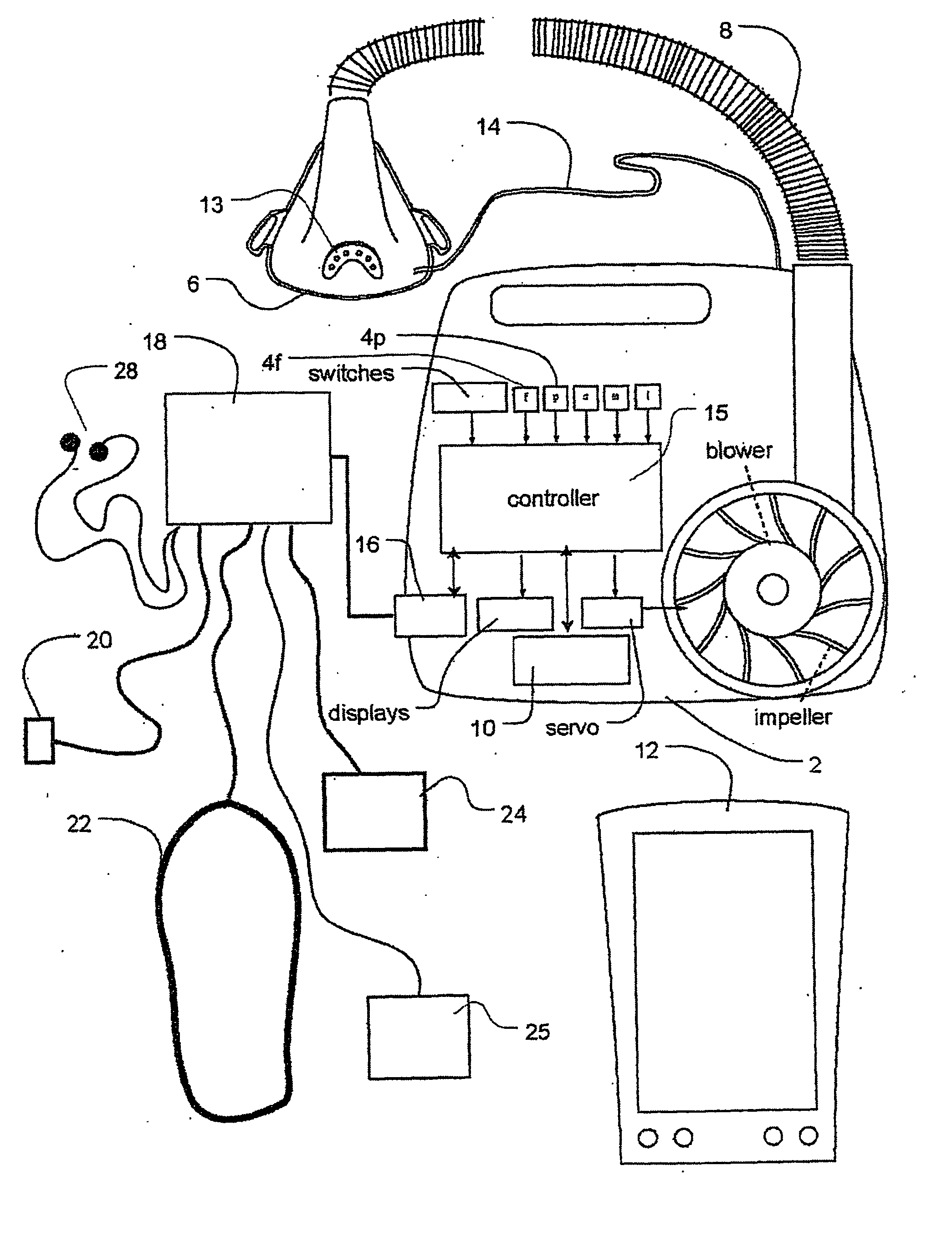
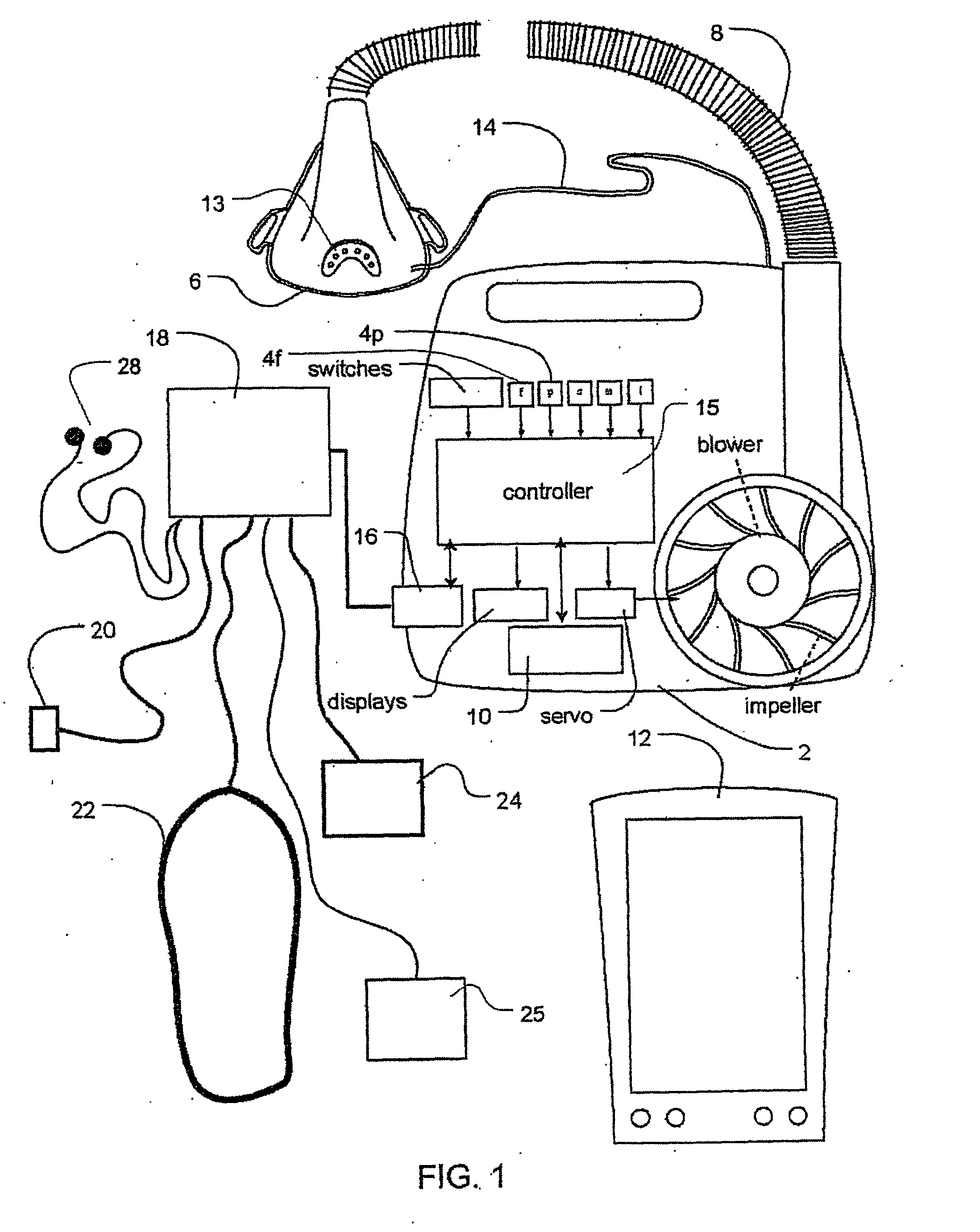
Methods and apparatus for heart failure treatment
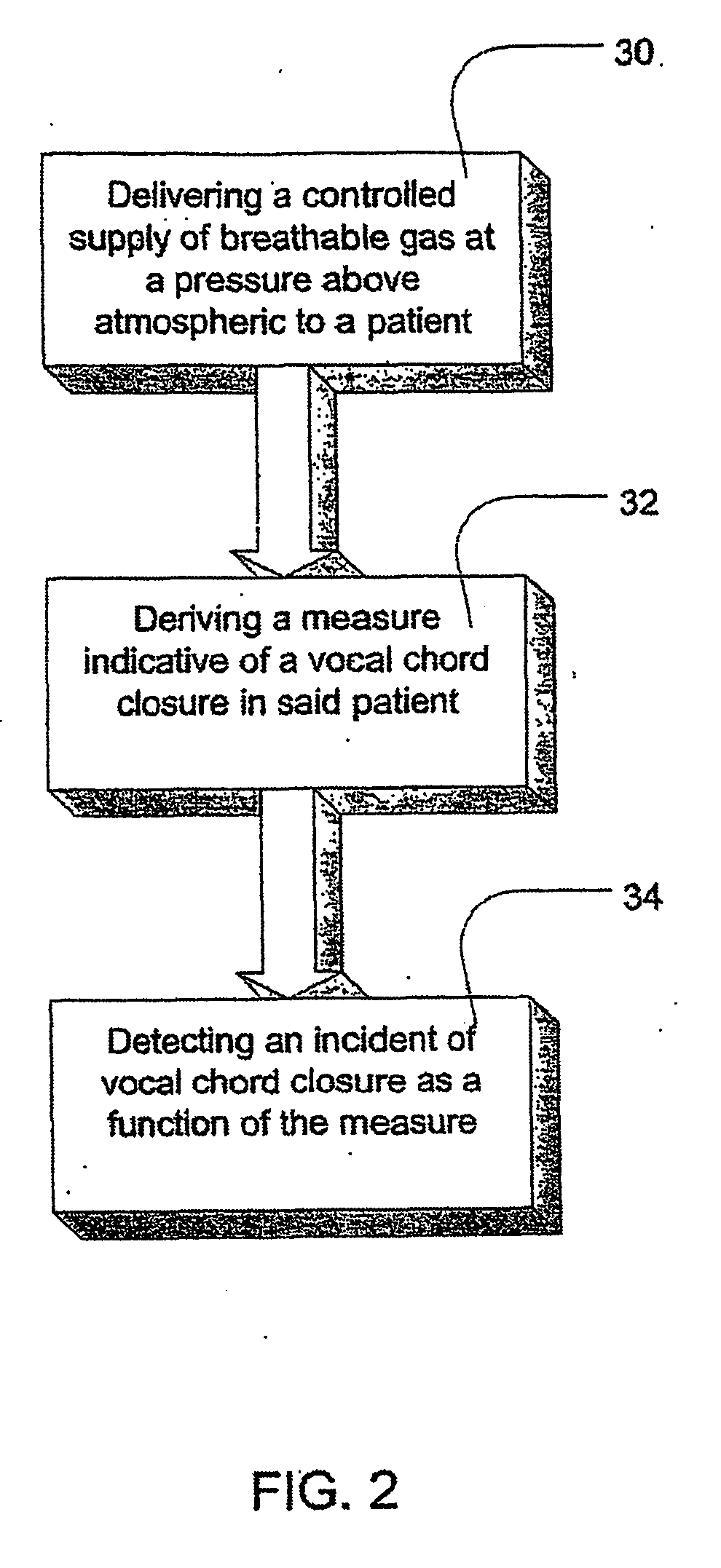
Methods and apparatus for assessing the condition of and treating patients for heart failure by the delivery of continuous positive airway pressure are disclosed. Treatment of obstruction due to reflex vocal cord closure often experienced by heart failure patients is distinguished from treatment of upper airway obstruction typically associated with Obstructive Sleep Disorder. Treatment may also be implemented by delivering synchronized cardiac pressure oscillations superimposed on a respiratory pressure level to provide assistance for the heart. Heart treatment pressure dose indicator may be calculated for prescribing and monitoring the delivery of treatment. The apparatus may also generate data to track heart failure condition that may be indicative of the degree of severity of heart failure based upon breathing patterns to assist in the diagnosis and management of heart failure patients.
Owner:UJHAZY ANTHONY JOHN +4
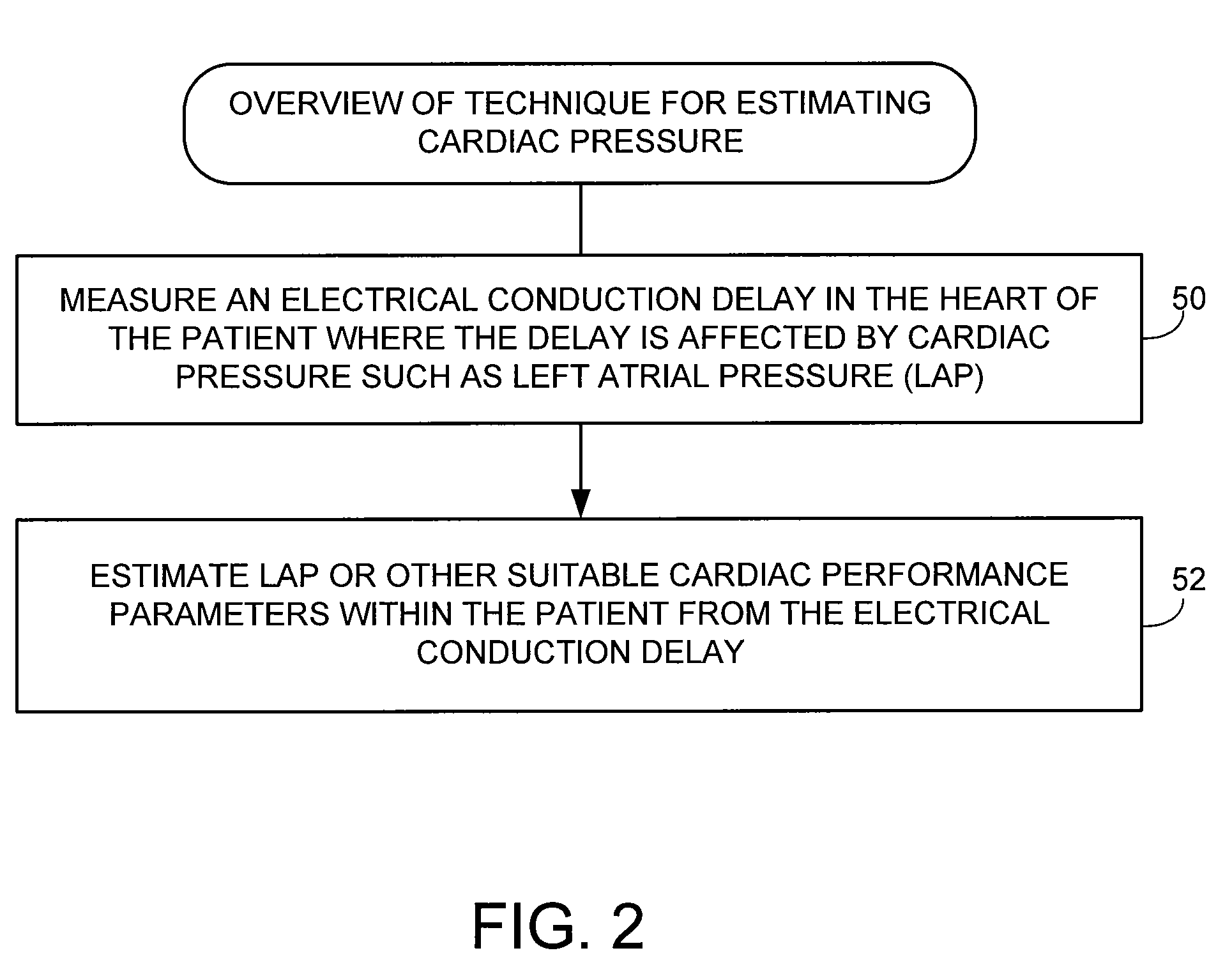
System and method for estimating cardiac pressure based on cardiac electrical conduction delays using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS8504152B2Accurate CalibrationRapid paceDiagnostic signal processingCatheterLeft atrial pressureMedical treatment
Techniques are provided for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) or other cardiac performance parameters based on measured conduction delays. In particular, LAP is estimated based interventricular conduction delays. Predetermined conversion factors stored within the device are used to convert the various the conduction delays into LAP values or other appropriate cardiac performance parameters. The conversion factors may be, for example, slope and baseline values derived during an initial calibration procedure performed by an external system, such as an external programmer. In some examples, the slope and baseline values may be periodically re-calibrated by the implantable device itself. Techniques are also described for adaptively adjusting pacing parameters based on estimated LAP or other cardiac performance parameters. Still further, techniques are described for estimating conduction delays based on impedance or admittance values and for tracking heart failure therefrom.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Implantable drug delivery system responsive to intra-cardiac pressure
InactiveUS20060074404A1High outputEffective treatmentElectrotherapyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPulmonary artery diastolic pressureCongestive heart failure chf
The invention is directed to techniques for monitoring the condition of a patient, such as a patient having congestive heart failure, and appropriately modifying the patient's drug therapy as a function of a pressure in the patient's heart, such as the estimated pulmonary artery diastolic pressure. The drugs may be administered by an implanted drug delivery device. The drug selection, the drug dosage or both may be controlled as a function of the pressure and / or the activity level of the patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for Estimating Cardiac Pressure Based on Cardiac Electrical Conduction Delays Using an Implantable Medical Device
InactiveUS20090018597A1Reduced venous returnAccurate CalibrationDiagnostic signal processingCatheterLeft atrial pressureMedical treatment
Techniques are provided for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) or other cardiac performance parameters based on measured conduction delays. In particular, LAP is estimated based interventricular conduction delays. Predetermined conversion factors stored within the device are used to convert the various the conduction delays into LAP values or other appropriate cardiac performance parameters. The conversion factors may be, for example, slope and baseline values derived during an initial calibration procedure performed by an external system, such as an external programmer. In some examples, the slope and baseline values may be periodically re-calibrated by the implantable device itself. Techniques are also described for adaptively adjusting pacing parameters based on estimated LAP or other cardiac performance parameters. Still further, techniques are described for estimating conduction delays based on impedance or admittance values and for tracking heart failure therefrom.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for discriminating hypervolemia, hypovolemia and euvolemia using an implantable medical device
Techniques are provided for use by an implantable medical device or diagnostic sensor for detecting and discriminating euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia. In one example, the device detects a pressure signal within the patient representative of changes in cardiac pressure overall several cardiac cycles. The device generates separate time-domain and frequency-domain representations of the pressure signal and then discriminates among euvolemia, hypervolemia and hypovolemia within the patient based on an analysis of the time-domain and the frequency-domain representations of the signal. Depending upon the capabilities of the device, suitable warnings may be generated to alert the patient or caregiver. Diuretics or other medications can be titrated to address abnormal fluid conditions such as a fluid overload during hypervolemia. Techniques for detecting a pressure alternans pattern indicative of imminent decompensation are also described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
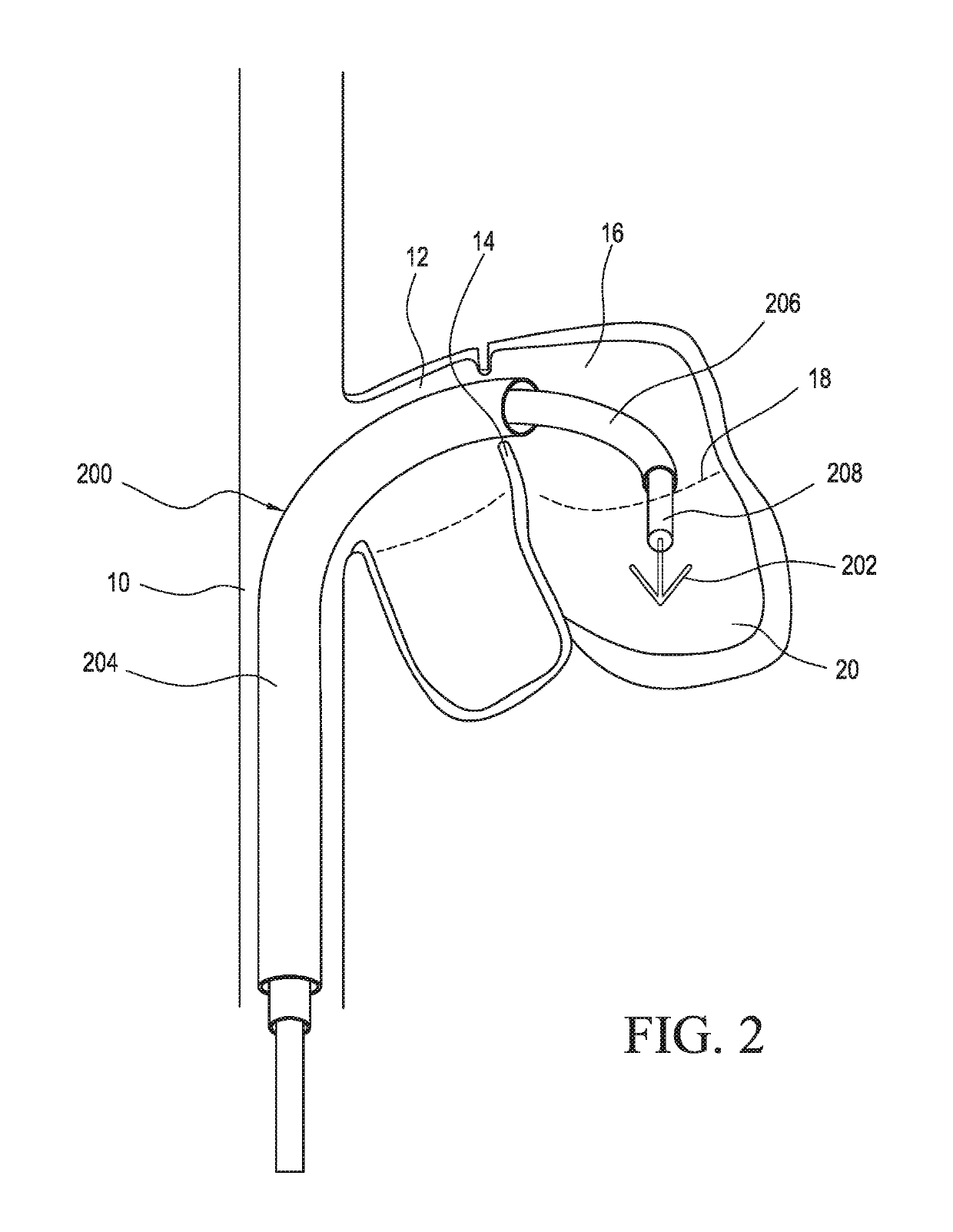
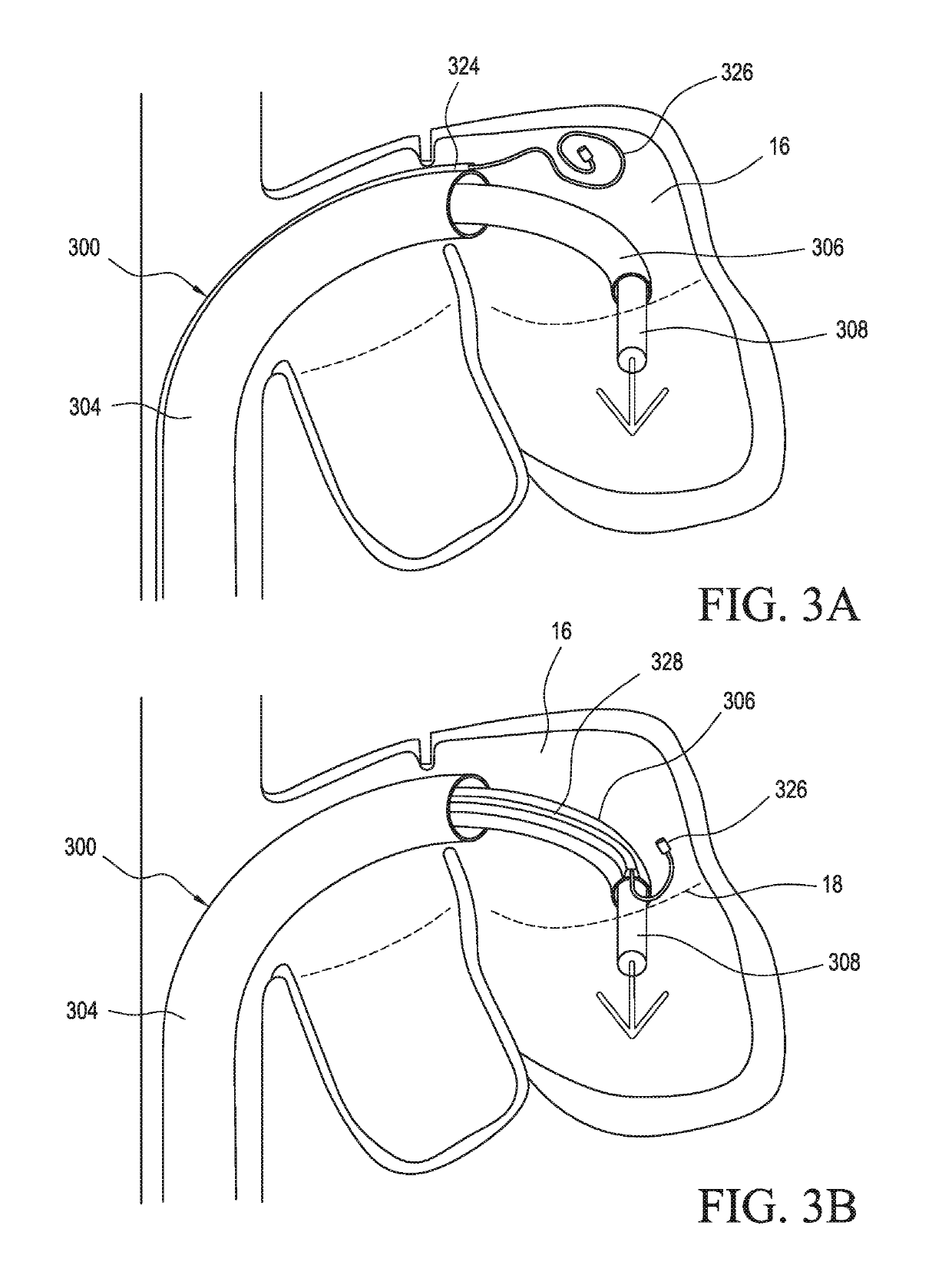
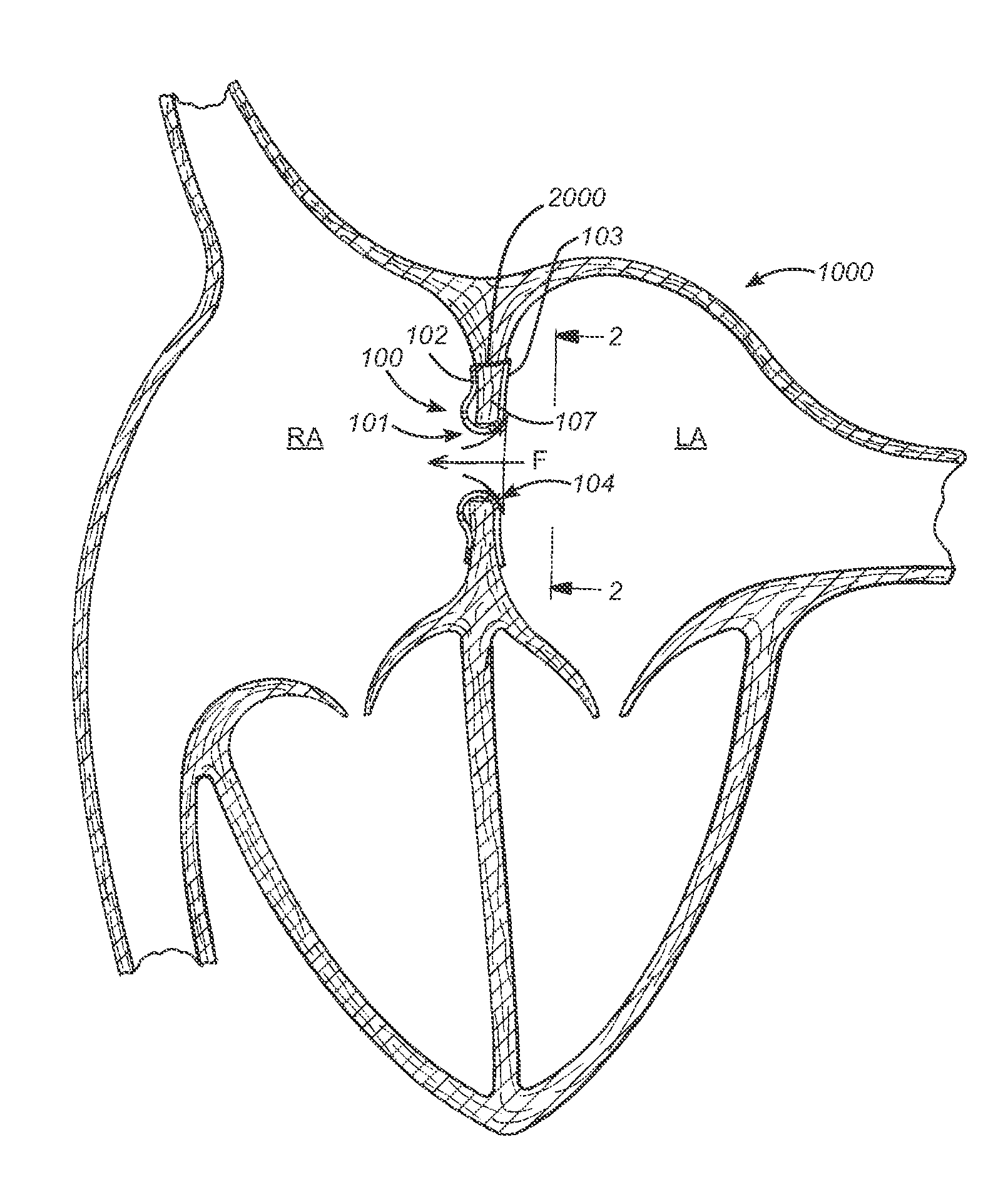
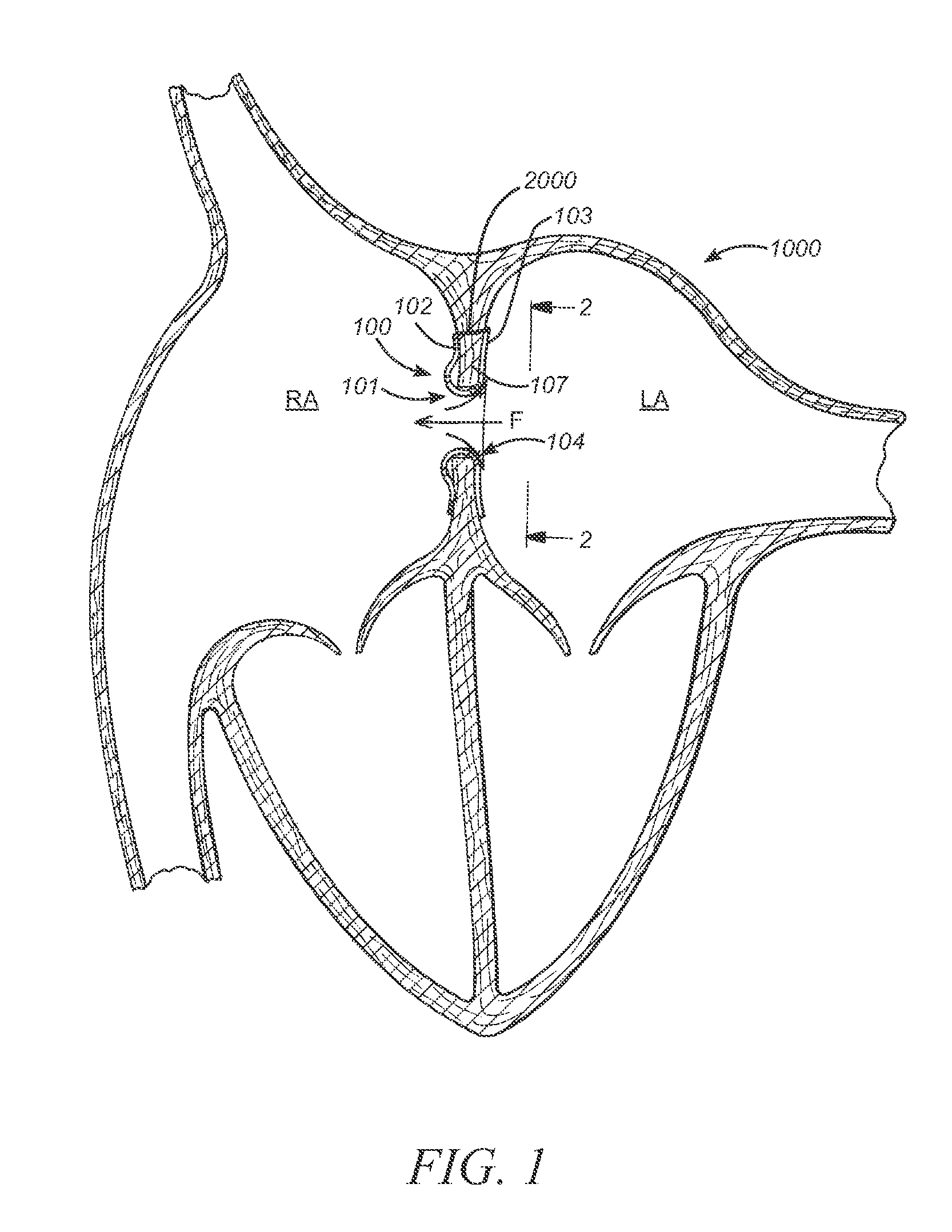
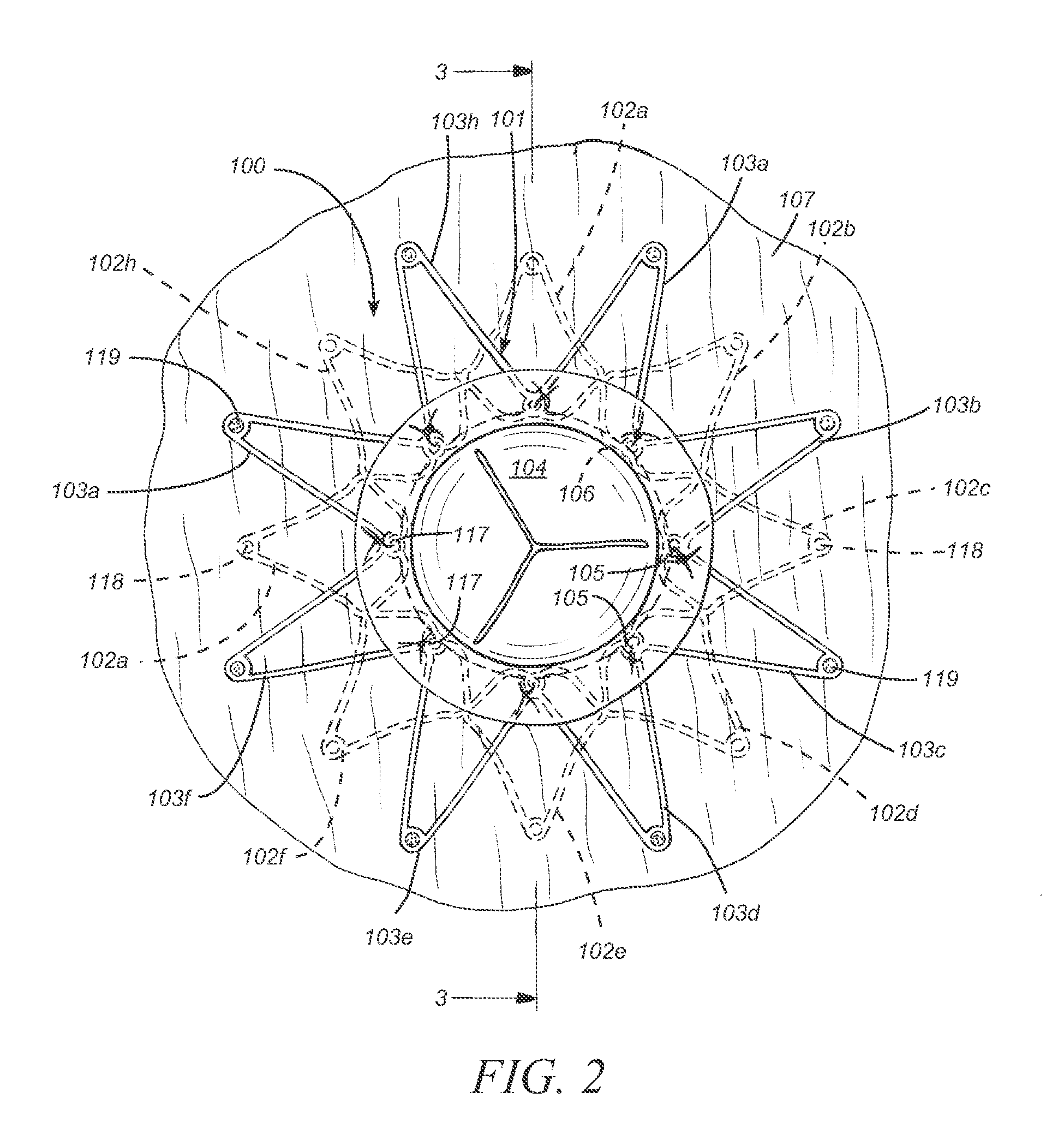
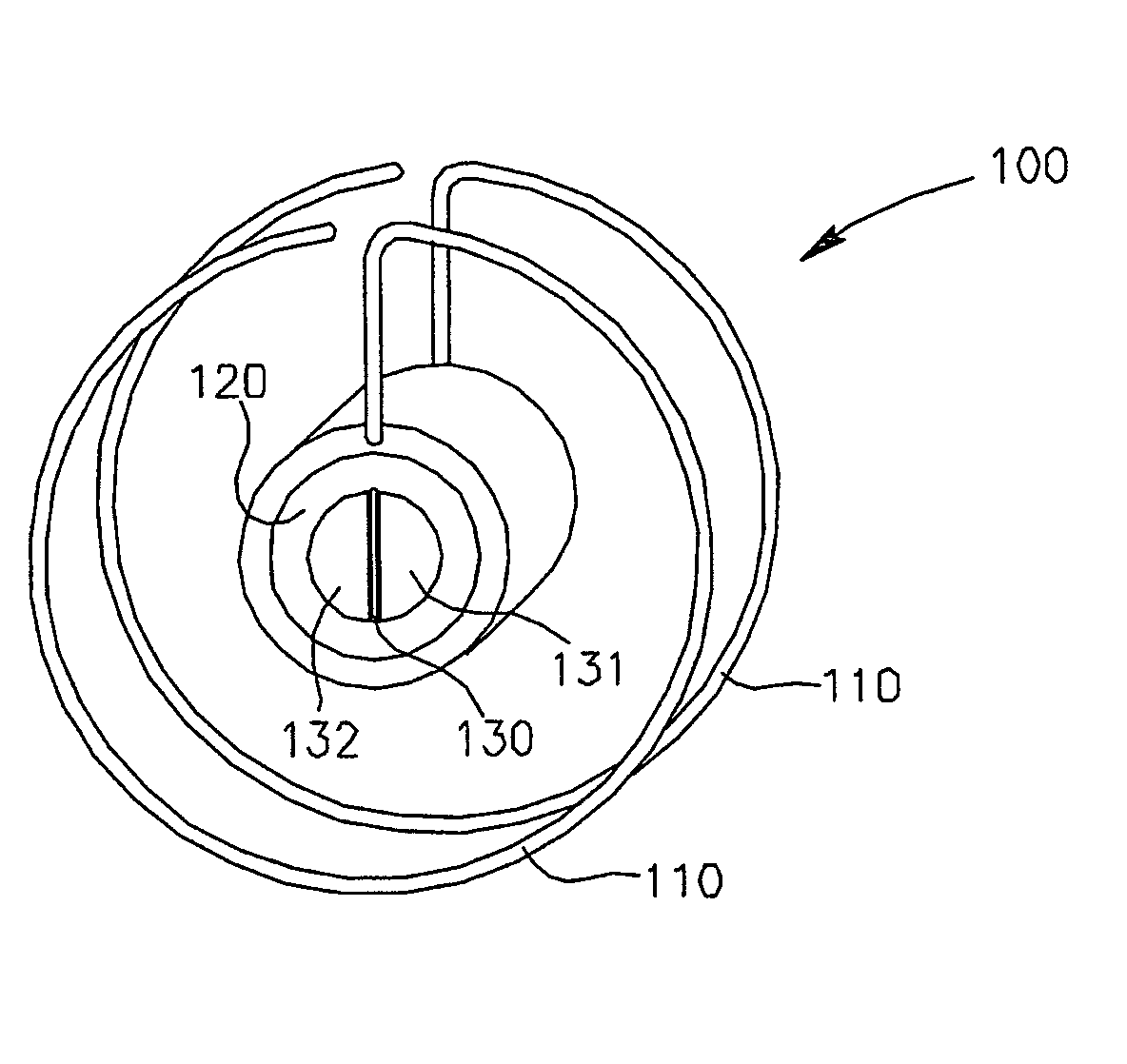
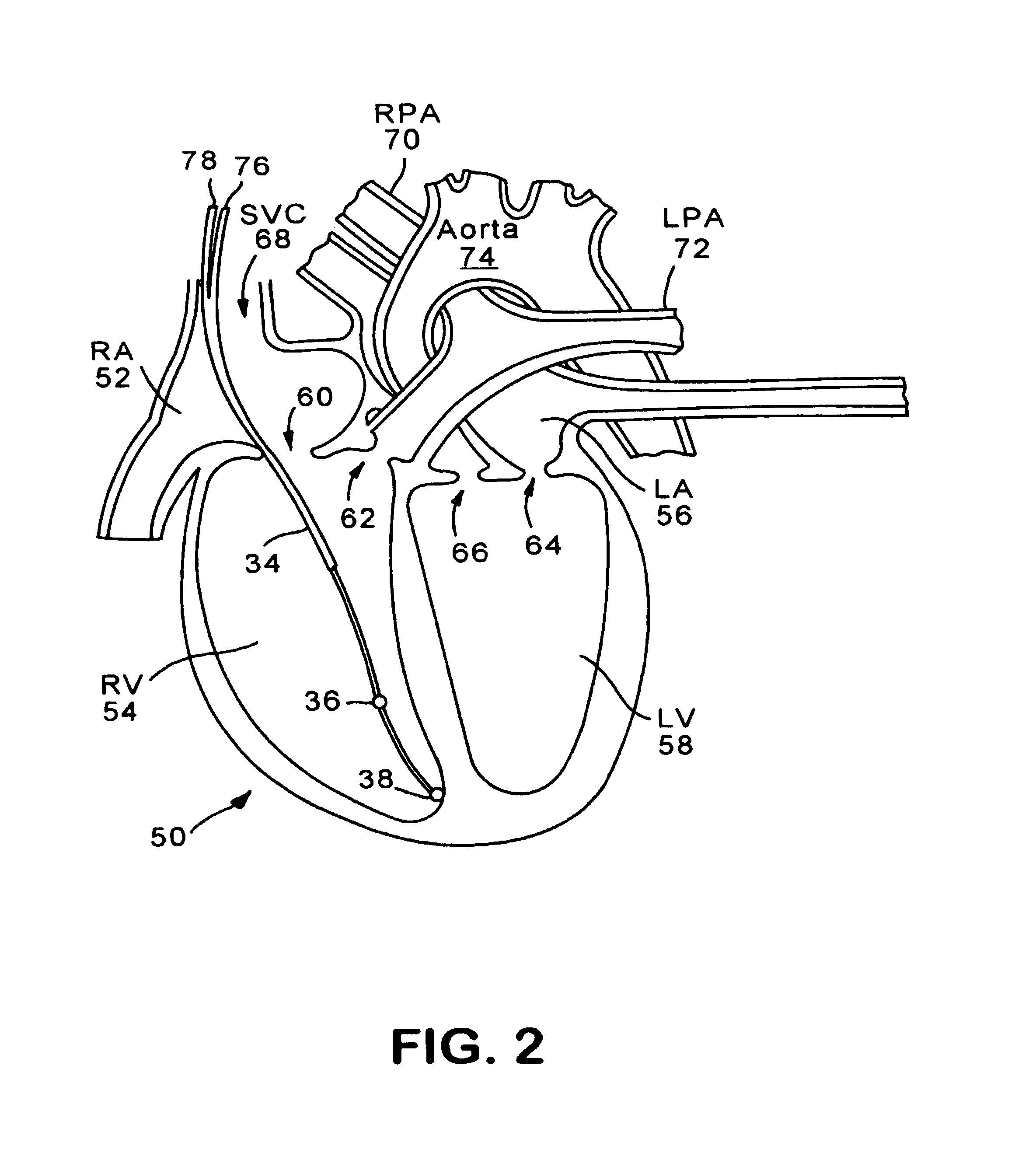
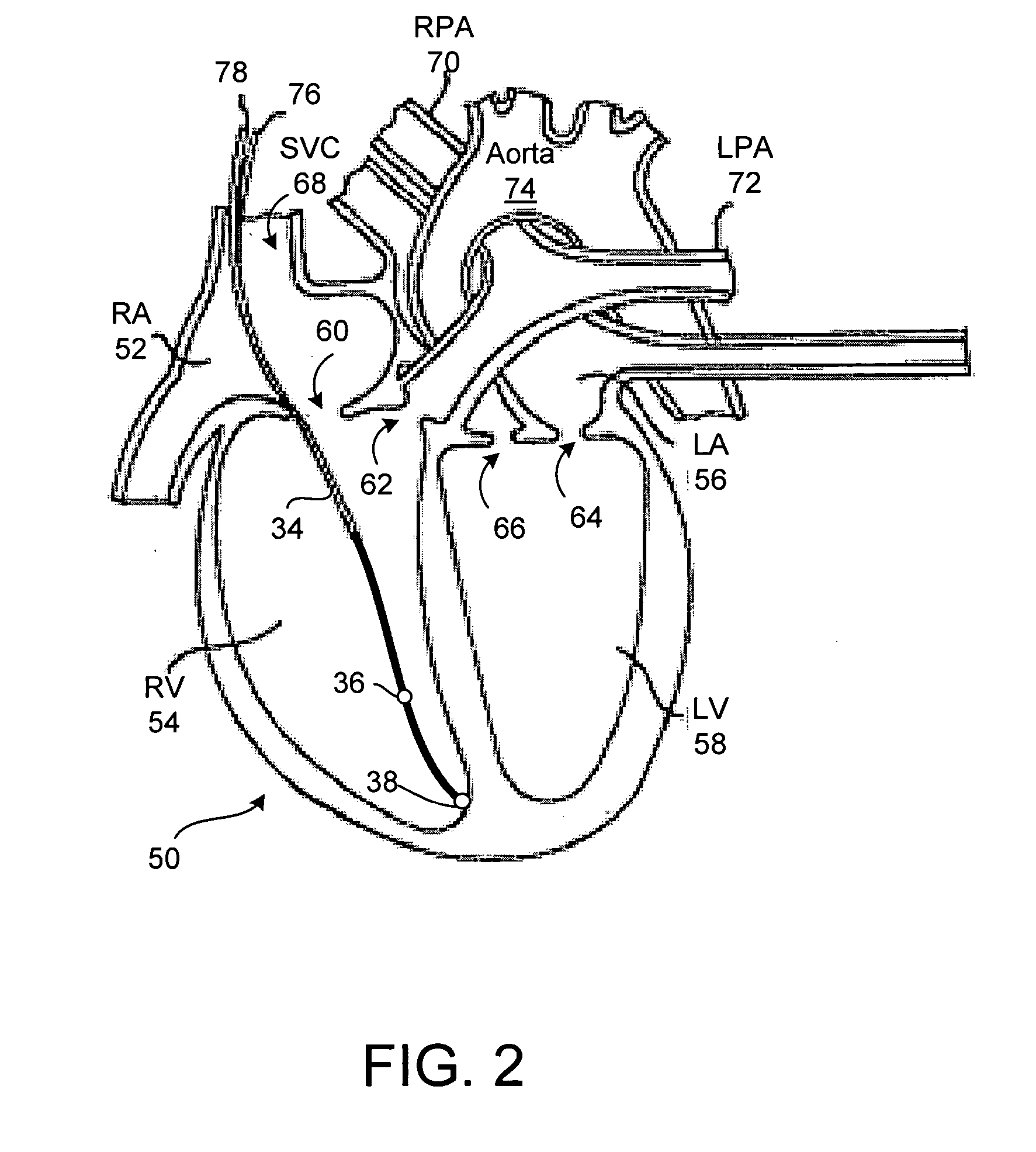
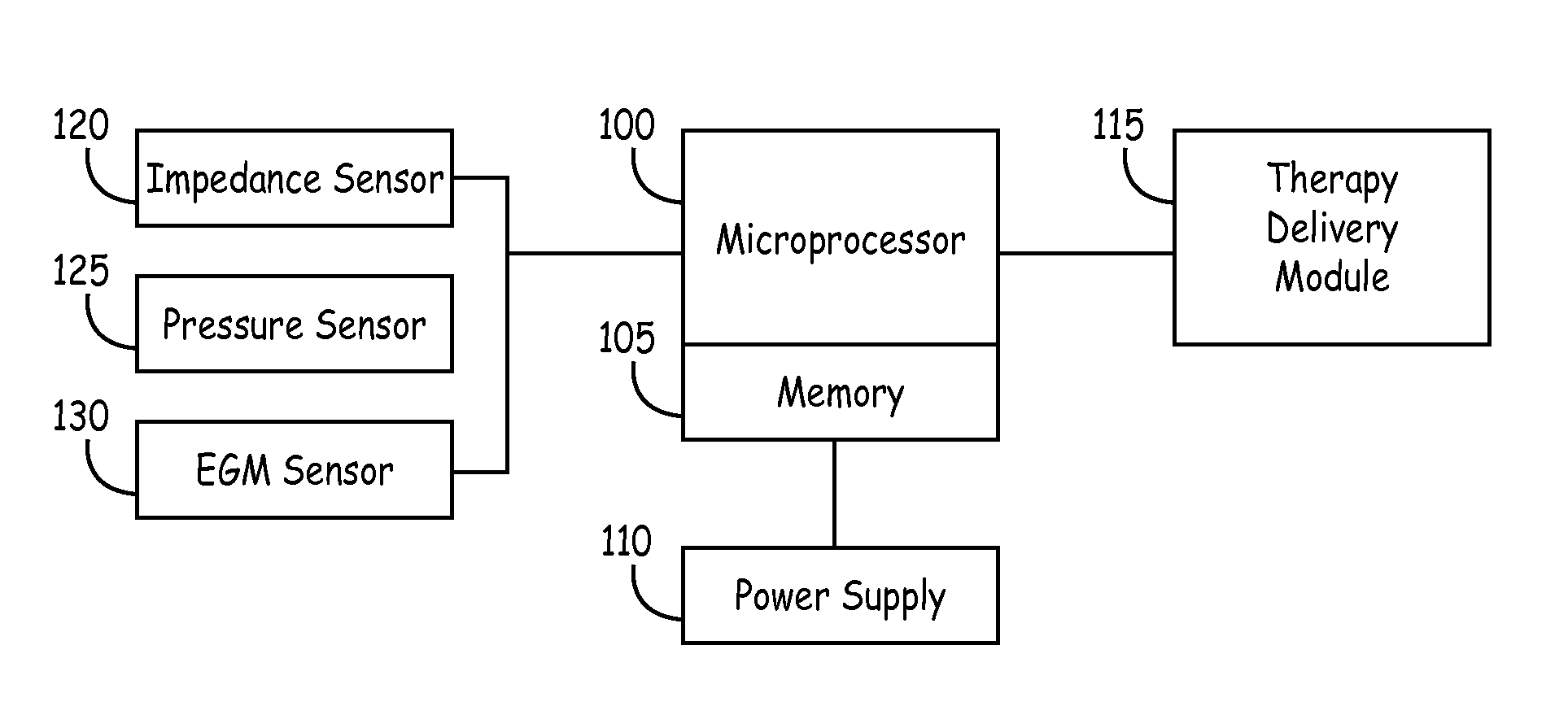
System and method of determining cardiac pressure
A pressure sensor is deployed in the right atrium and is in contact with the tissue of the fossa ovalis. The fossa ovalis acts as a membrane and the pressure sensor determines the relative and / or absolute pressure within the left atrium while remaining within the right atrium. A variety of embodiment are provided to deploy and anchor the sensor into the proper position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and Method for Estimating Cardiac Pressure Based on Cardiac Electrical Conduction Delays Using an Implantable Medical Device
ActiveUS20090287267A1Accurate CalibrationRapid paceDiagnostic signal processingCatheterLeft atrial pressureAv conduction
Techniques are provided for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) or other cardiac performance parameters based on measured conduction delays. In particular, LAP is estimated based interventricular conduction delays. Predetermined conversion factors stored within the device are used to convert the various the conduction delays into LAP values or other appropriate cardiac performance parameters. The conversion factors may be, for example, slope and baseline values derived during an initial calibration procedure performed by an external system, such as an external programmer. In some examples, the slope and baseline values may be periodically re-calibrated by the implantable device itself. Techniques are also described for adaptively adjusting pacing parameters based on estimated LAP or other cardiac performance parameters. Still further, techniques are described for estimating conduction delays based on impedance or admittance values and for tracking heart failure therefrom.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
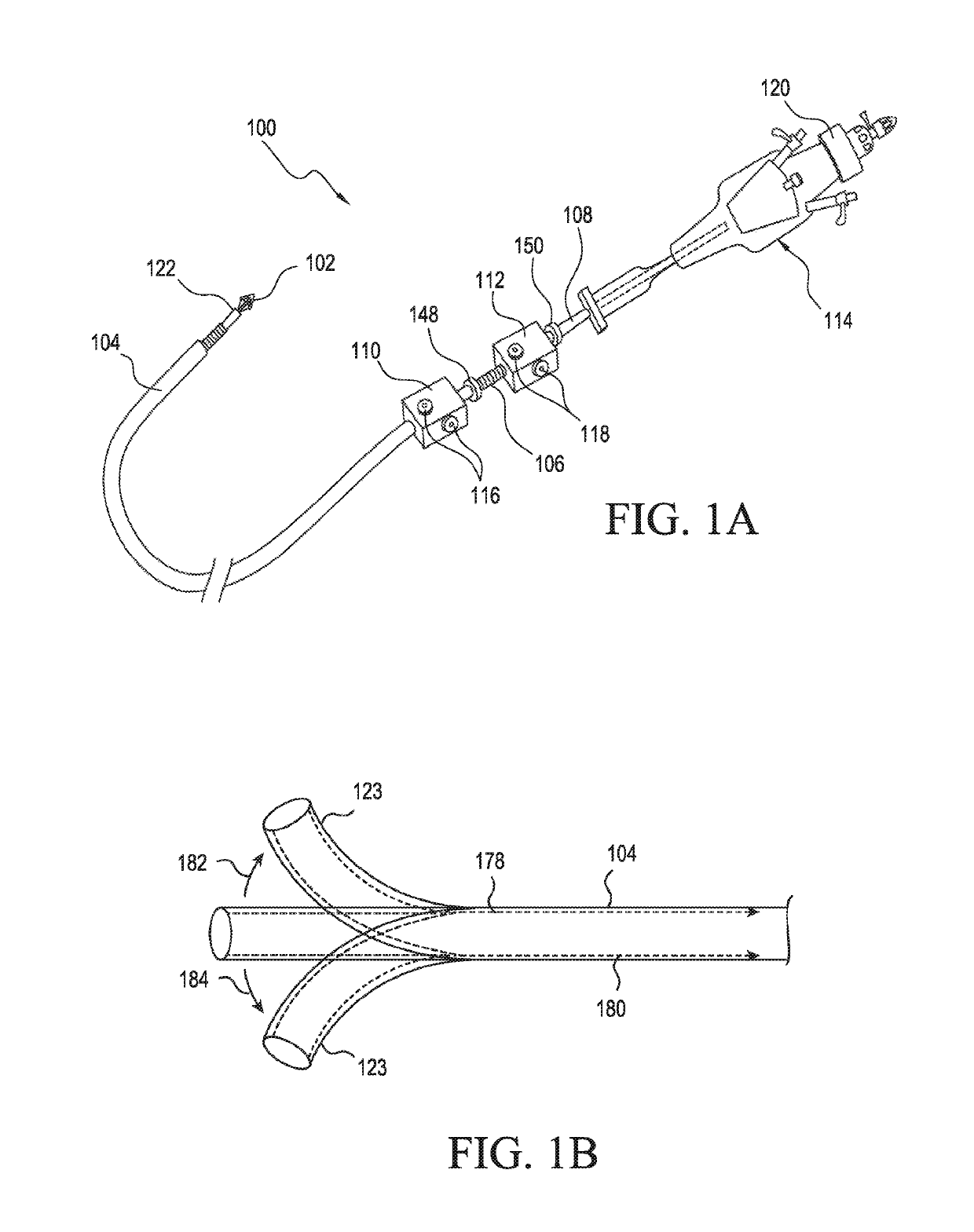
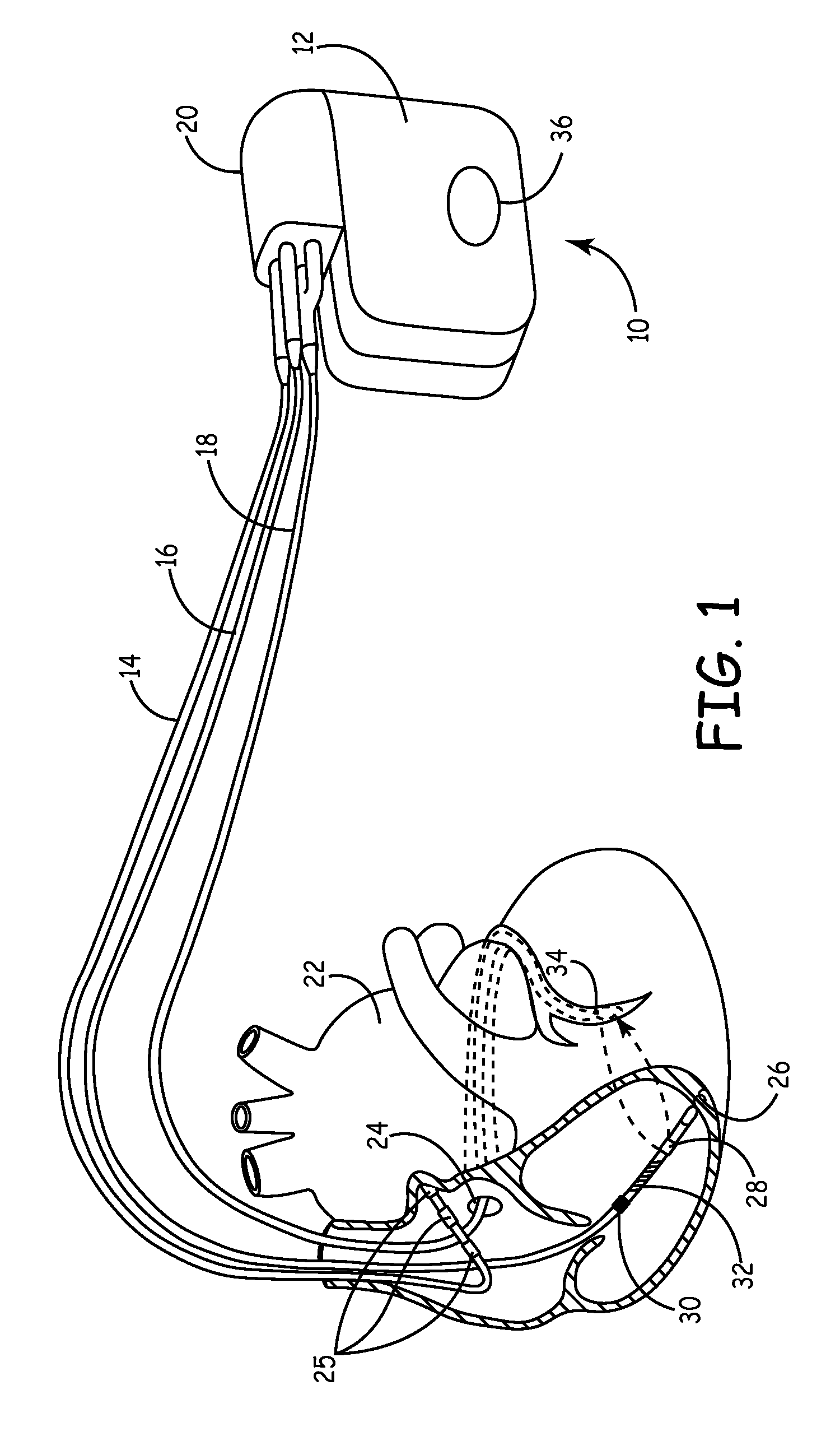
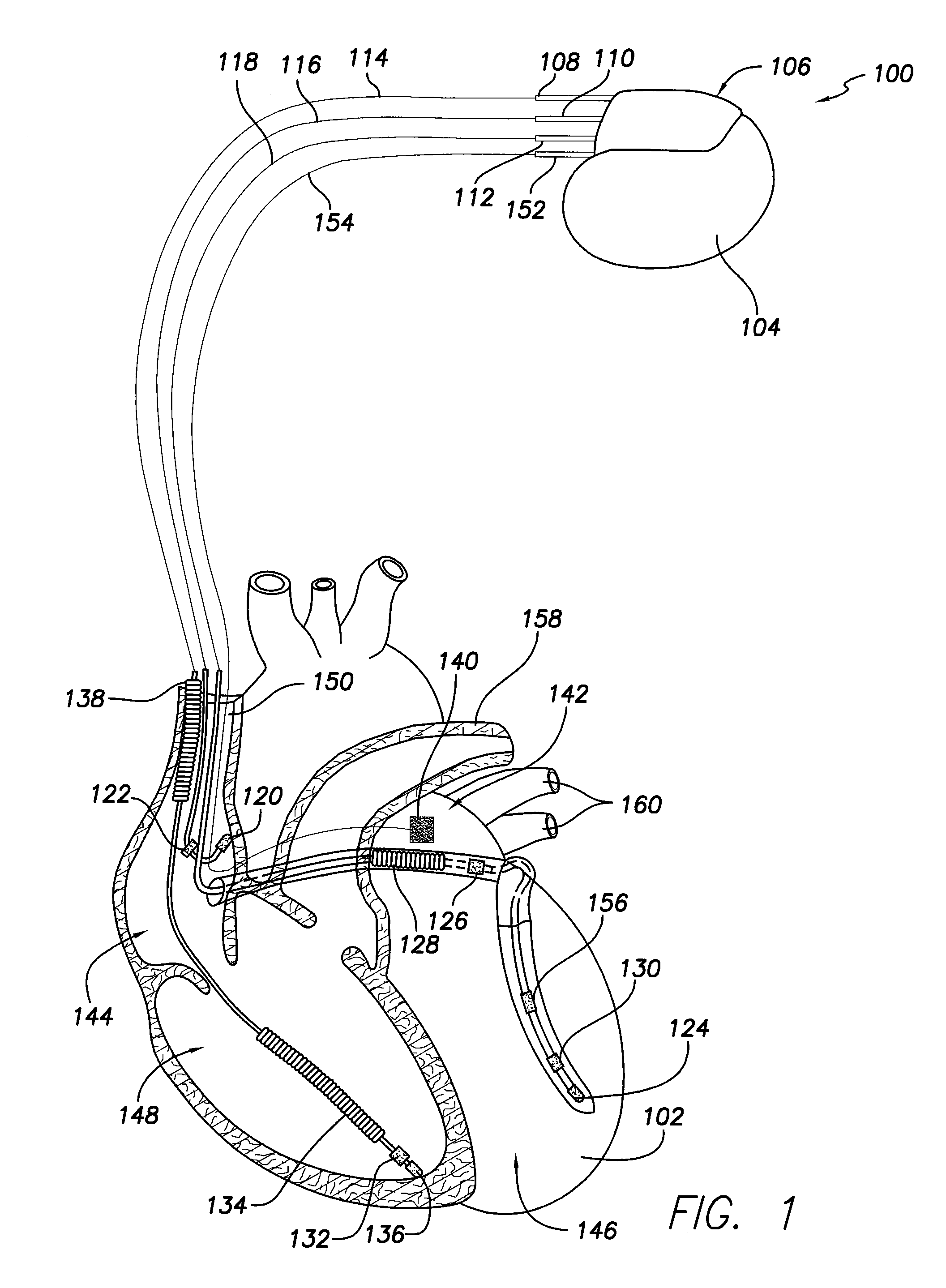
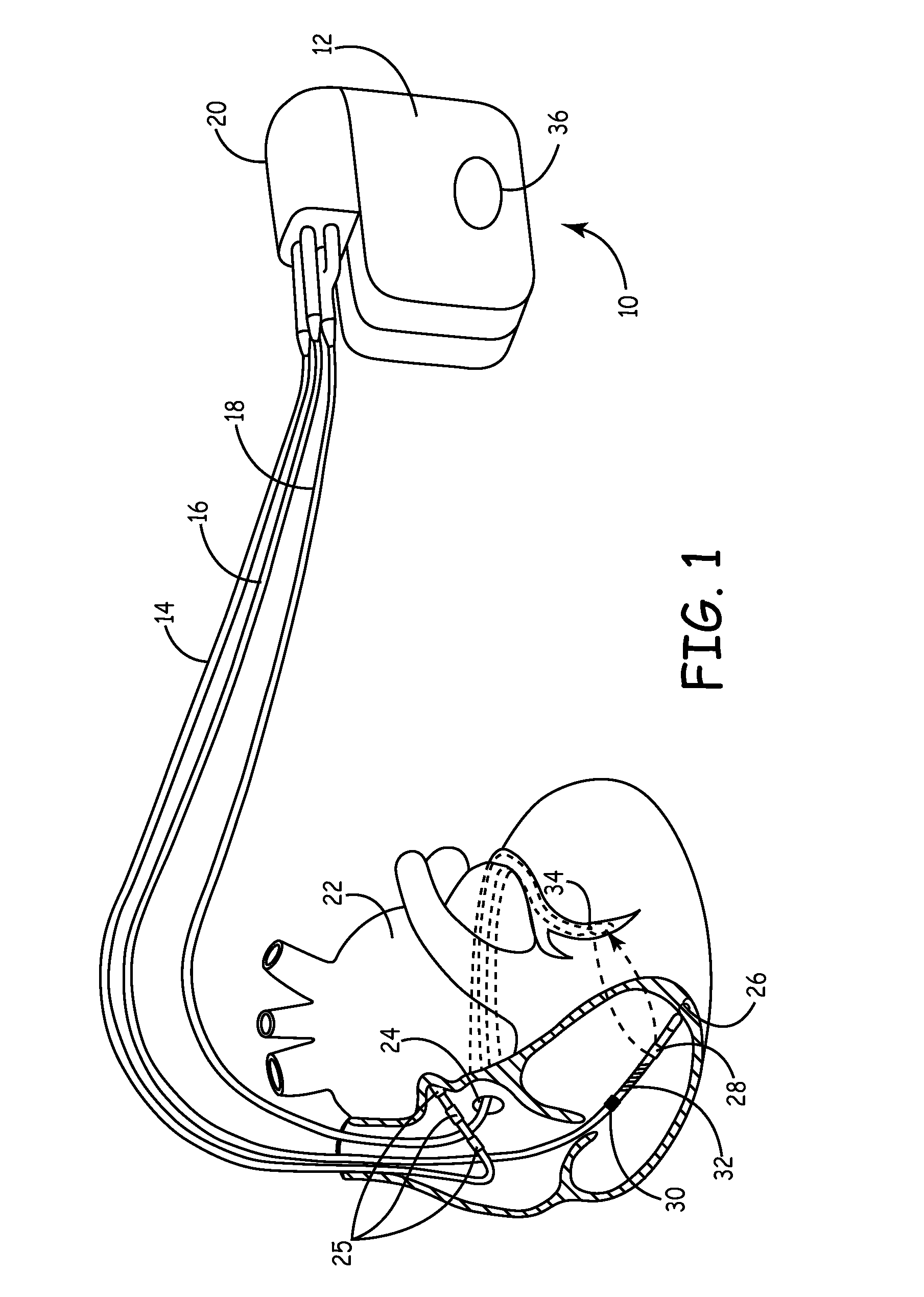
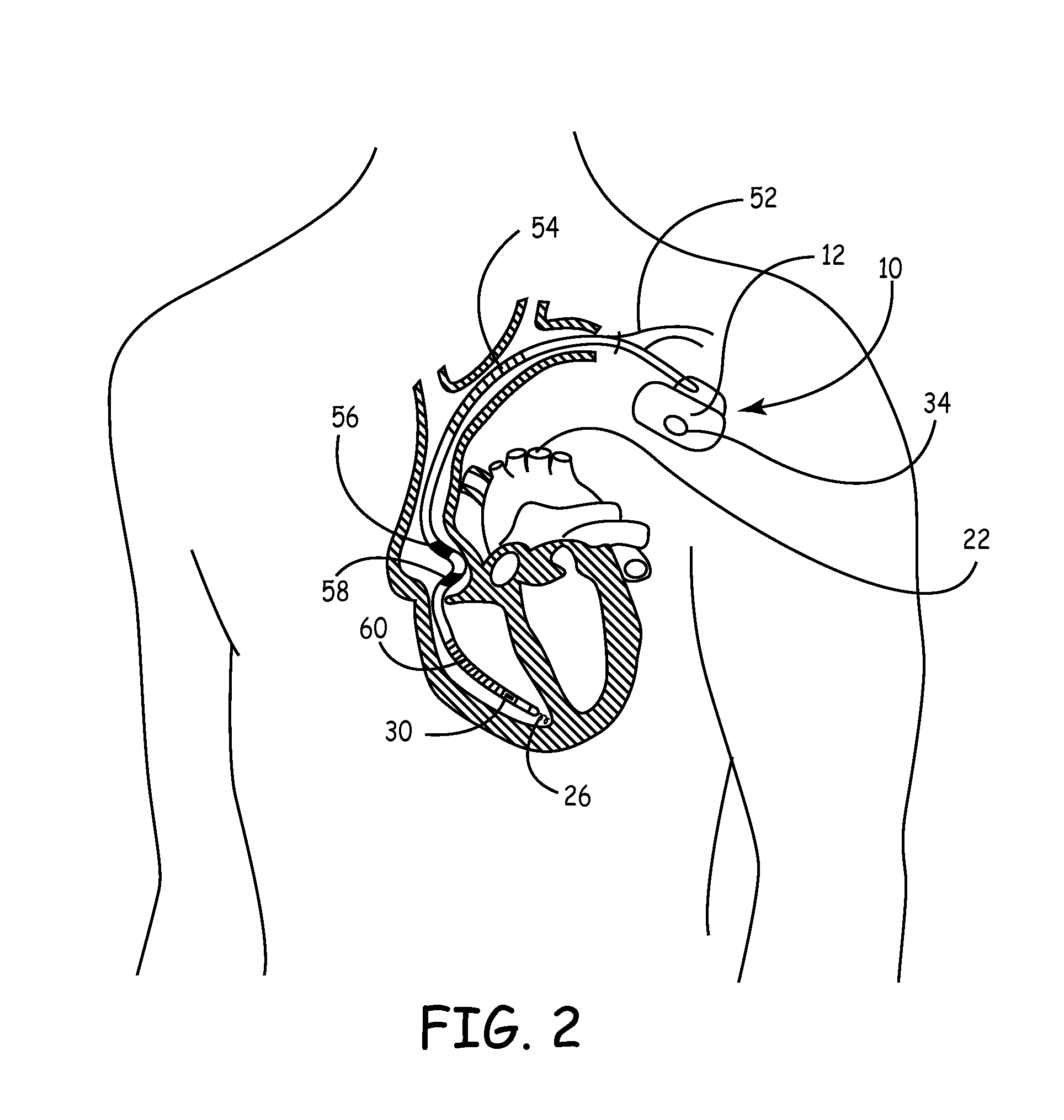
Left chamber pressure sensor lead delivery system
An apparatus for and method of measuring pressure through a septum in a patient's heart. A lead inserted into the right side of a heart is routed through the septum to gain access to the left side of the heart. The lead includes a mounting mechanism that secures the lead to one or both sides of the septal walls. The lead also includes one or more sensors for measuring cardiac pressure on the left side of the heart and, as necessary, the right side of the heart.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Pressure and Impedance Based Discrimination of Hemodynamic Stability
ActiveUS20090270933A1Heart defibrillatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringHemodynamically stableImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator evaluates the hemodynamic stability of an arrhythmia to determine whether or not to defibrillate. The device obtains cardiac pressure and cardiac impedance data and evaluates a phase relationship between these parameters. Hemodynamically stable rhythms will result in an out of phase relationship.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for estimating left atrial pressure (LAP) in patients with acute mitral valve regurgitation for use by an implantable medical device
Various techniques are provided for use with an implantable medical device for estimating cardiac pressure within a patient based on admittance (or related electrical values such as impedance or conductance) that takes into account the presence of acute MR within the patient. Briefly, the device detects an indication of acute MR, if occurring within the patient. The device also applies electrical fields to tissues of the patient and measures electrical parameters influenced by the electrical field, such as admittance, impedance or conductance. The device then estimates cardiac pressure within the patient based on the measured electrical parameter and the indication of acute MR. In one example, different linear correlation functions are used to convert admittance values to left atrial pressure (LAP) values depending upon the presence or absence of acute MR within the patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and Methods for Adjusting a Pacing Rate Based on Cardiac Pressure
An implantable medical device includes a pressure input, an excitation source, a detector module, and a processor. The pressure input is configured to be joined to a pressure sensor located proximate to a cardiac chamber of the heart. The pressure input receives pressure measurements representative of a pressure in the cardiac chamber. The excitation source is configured to deliver stimulation pulses to the heart. The detector module communicates with the pressure sensor to receive and compare the pressure measurements to a pressure threshold. The processor instructs the excitation source to deliver the stimulation pulses at a pressure-based rate based on the comparison of the pressure measurements to the pressure threshold.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Pressure and impedance based discrimination of hemodynamic stability
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator evaluates the hemodynamic stability of an arrhythmia to determine whether or not to defibrillate. The device obtains cardiac pressure and cardiac impedance data and evaluates a phase relationship between these parameters. Hemodynamically stable rhythms will result in an out of phase relationship.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
System and method of determining cardiac pressure
A pressure sensor is deployed in the right atrium and is in contact with the tissue of the fossa ovalis. The fossa ovalis acts as a membrane and the pressure sensor determines the relative and / or absolute pressure within the left atrium while remaining within the right atrium. A variety of embodiment are provided to deploy and anchor the sensor into the proper position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Pressure and impedance based discrimination of hemodynamic stability
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator evaluates the hemodynamic stability of an arrhythmia to determine whether or not to defibrillate. The device obtains cardiac pressure and cardiac impedance data and evaluates a phase relationship between these parameters. Hemodynamically stable rhythms will result in an out of phase relationship.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Pressure and Impedance Based Discrimination of Hemodynamic Stability
ActiveUS20090270934A1ElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsHemodynamically stableImplantable cardioverter-defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator evaluates the hemodynamic stability of an arrhythmia to determine whether or not to defibrillate. The device obtains cardiac pressure and cardiac impedance data and evaluates a phase relationship between these parameters. Hemodynamically stable rhythms will result in an out of phase relationship.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
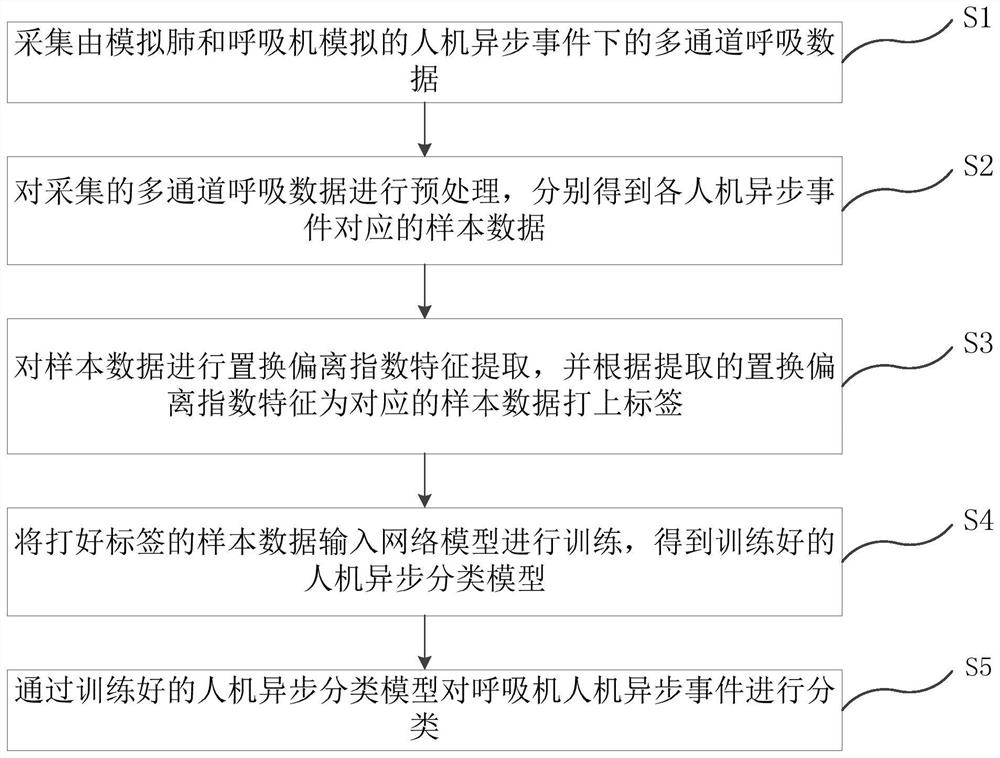
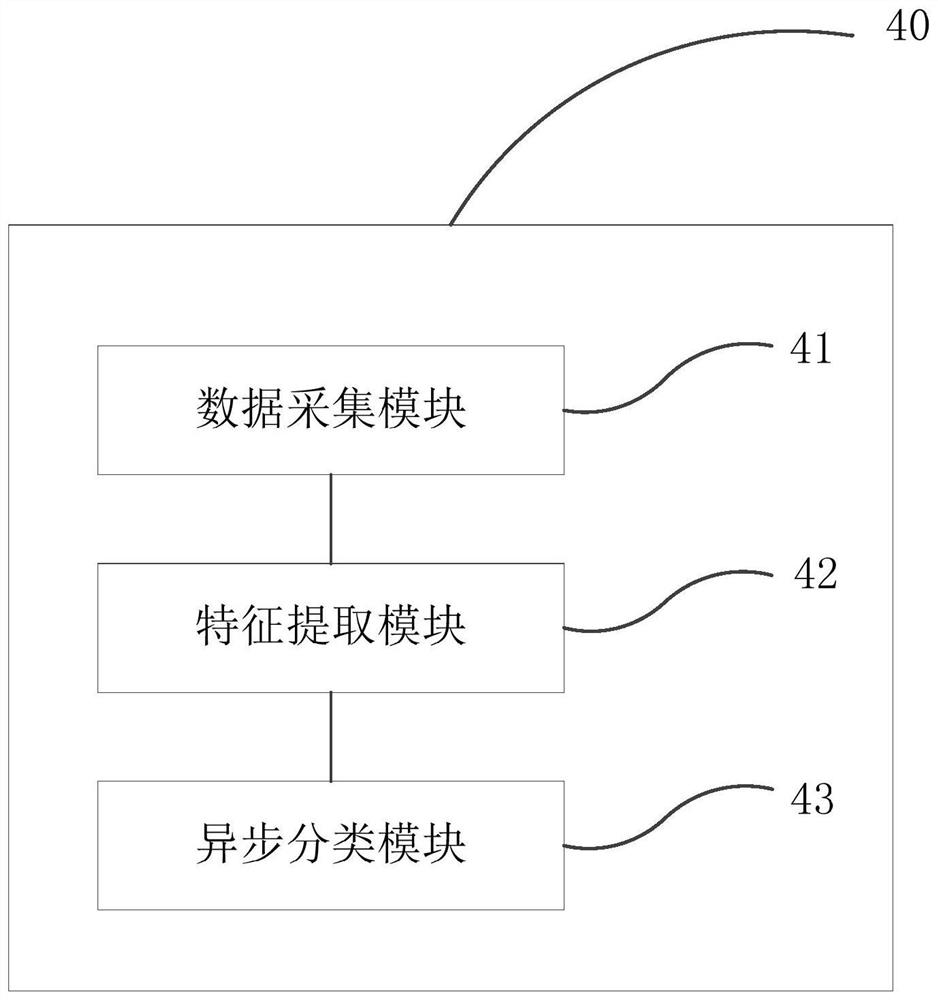
Breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method, terminal and storage medium
PendingCN113539501AEasy to collectReduce distractionsMedical simulationMedical data miningLung alveolusTidal volume
The invention relates to a breathing machine man-machine asynchronous classification method and system, a terminal and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: collecting the multi-channel breathing data of a simulated flow channel, a tidal volume channel, airway pressure, alveolar pressure, pleural cavity internal pressure, cardiac pressure, a corrugated pipe position channel and the like under a man-machine asynchronous event simulated by a simulated lung and a breathing machine; carrying out replacement deviation index (PDI) feature extraction on the respiration data, and labeling the respiration data according to the extracted PDI features; inputting the labeled respiration data into a network model for training to obtain a trained man-machine asynchronous classification model; and classifying the breathing machine man-machine asynchronous events through the trained man-machine asynchronous classification model. According to the embodiment of the invention, the acquired respiration data is small in interference and convenient to acquire, difference analysis of the respiration data of the adjacent channels is carried out by using the PDI features, and the accuracy of man-machine asynchronous classification is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com