Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Burst switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
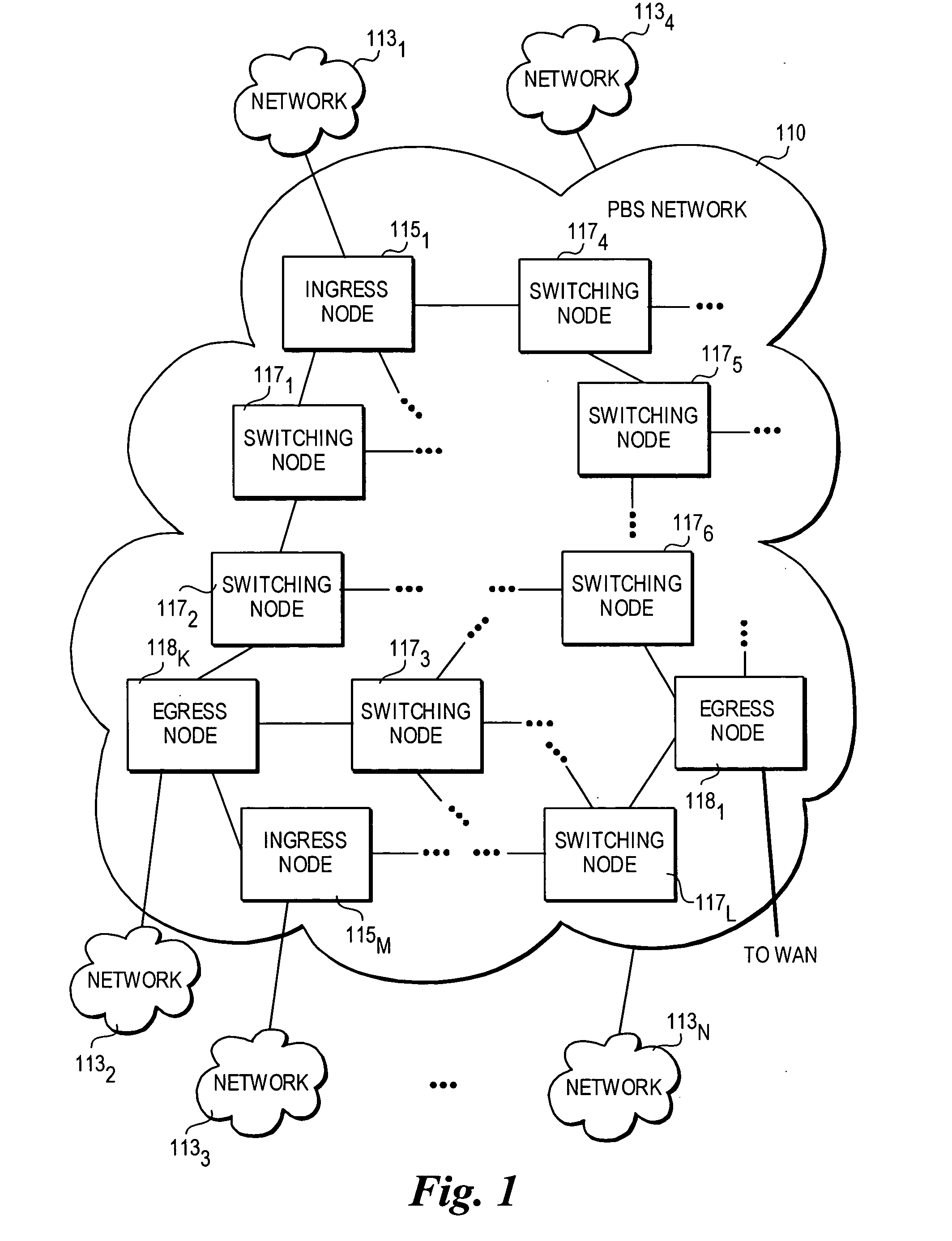
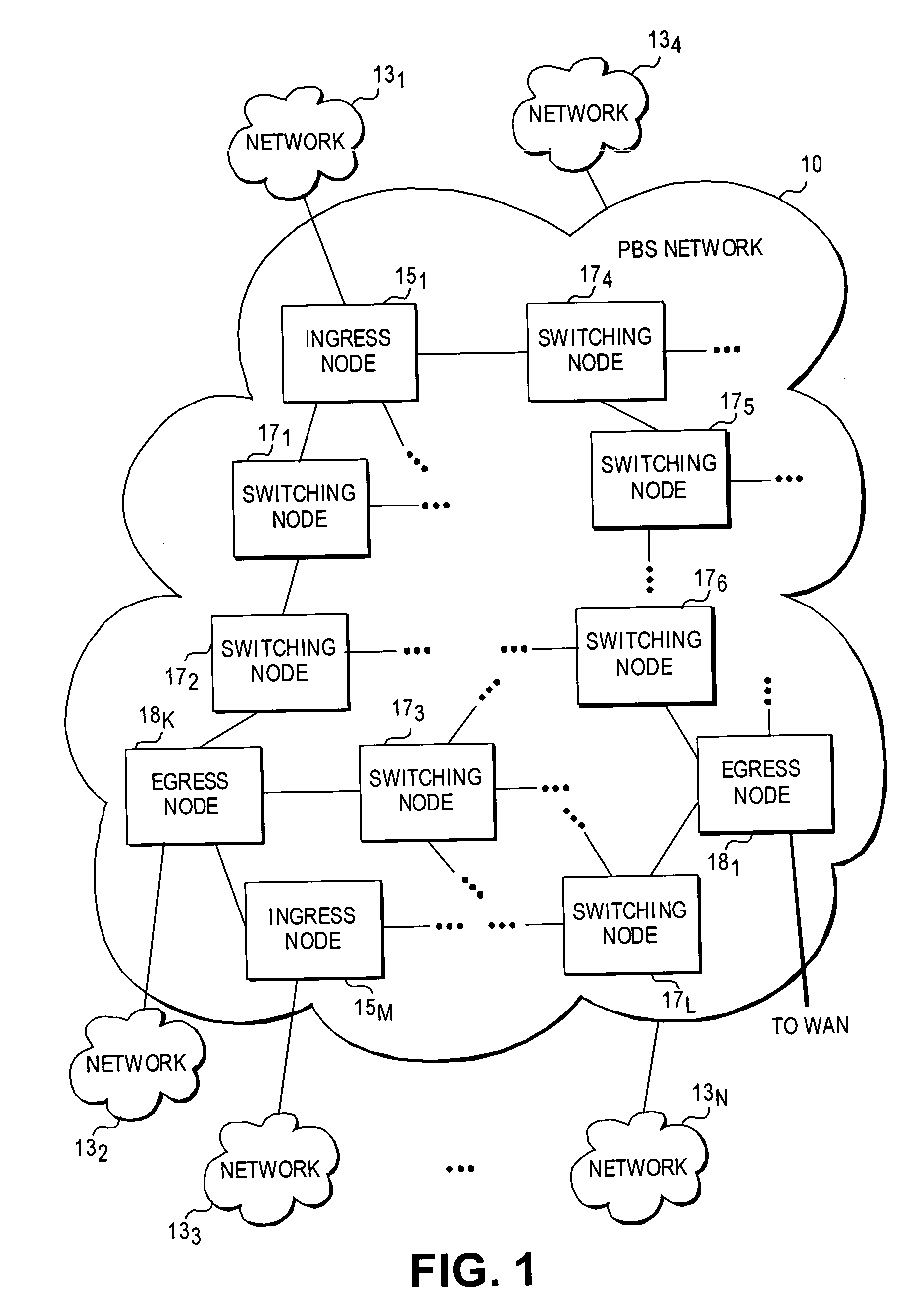
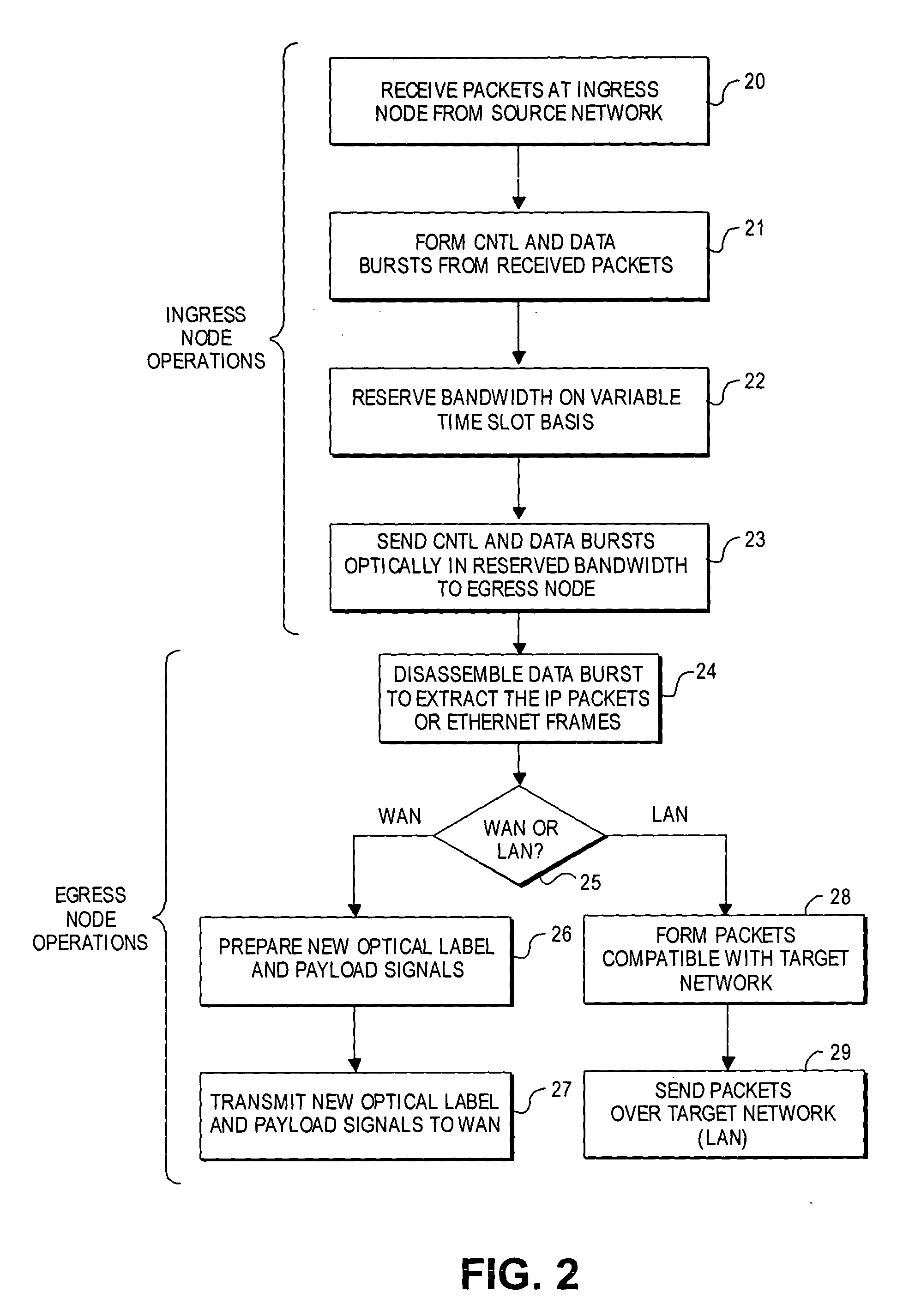
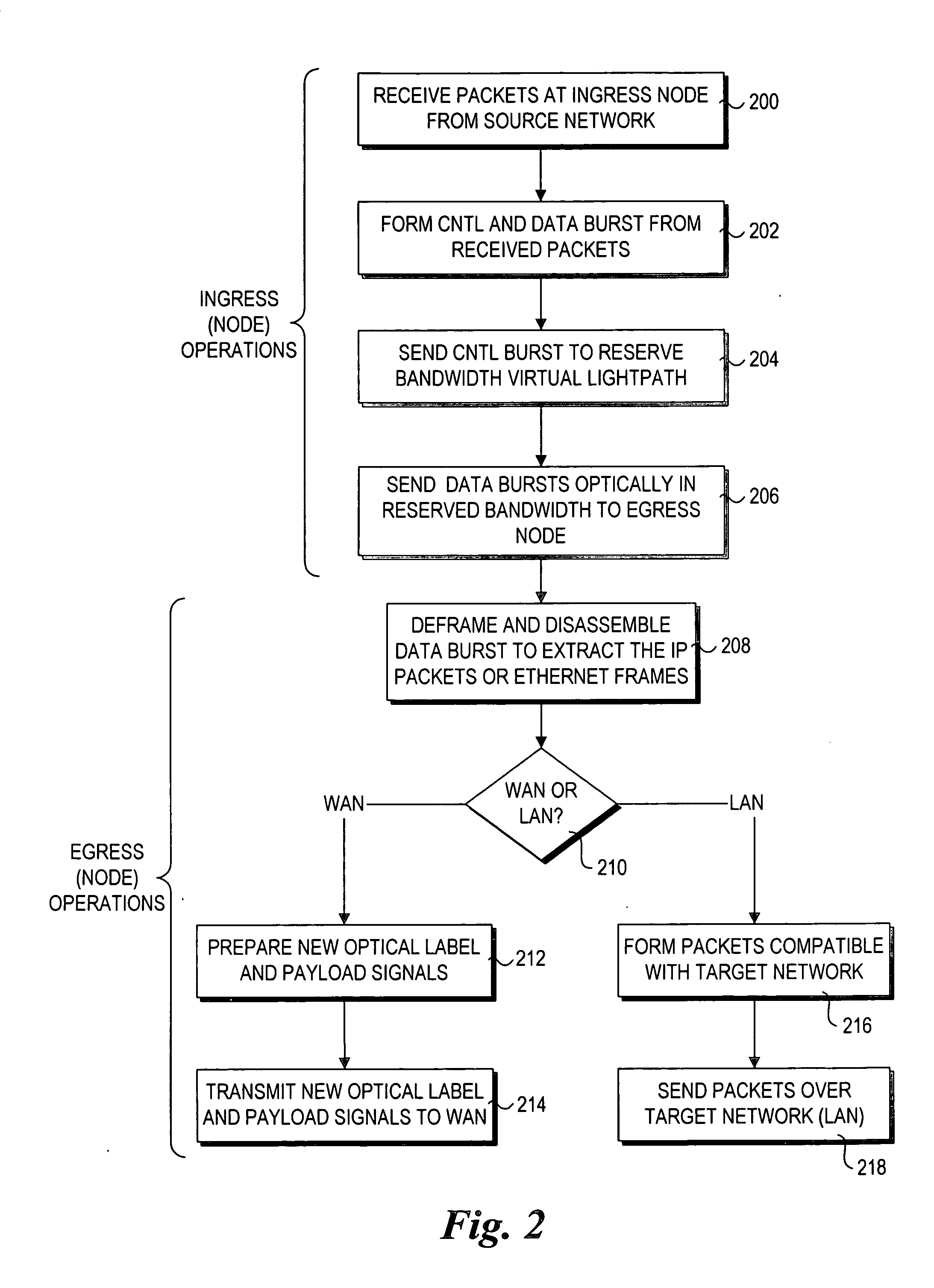
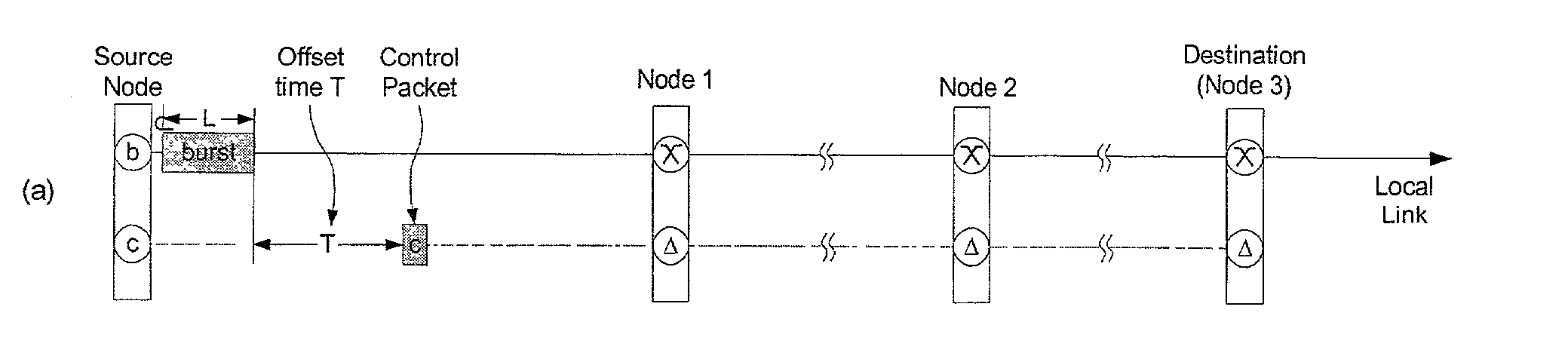
In a packet switched network, burst switching is a capability in which each network switch extracts routing instructions from an incoming packet header to establish and maintain the appropriate switch connection for the duration of the packet, following which the connection is automatically released.
Ultra-low latency multi-protocol optical routers for the next generation internet
InactiveUS6925257B2Control performanceScalability limitationMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical multiplexThe InternetHemt circuits
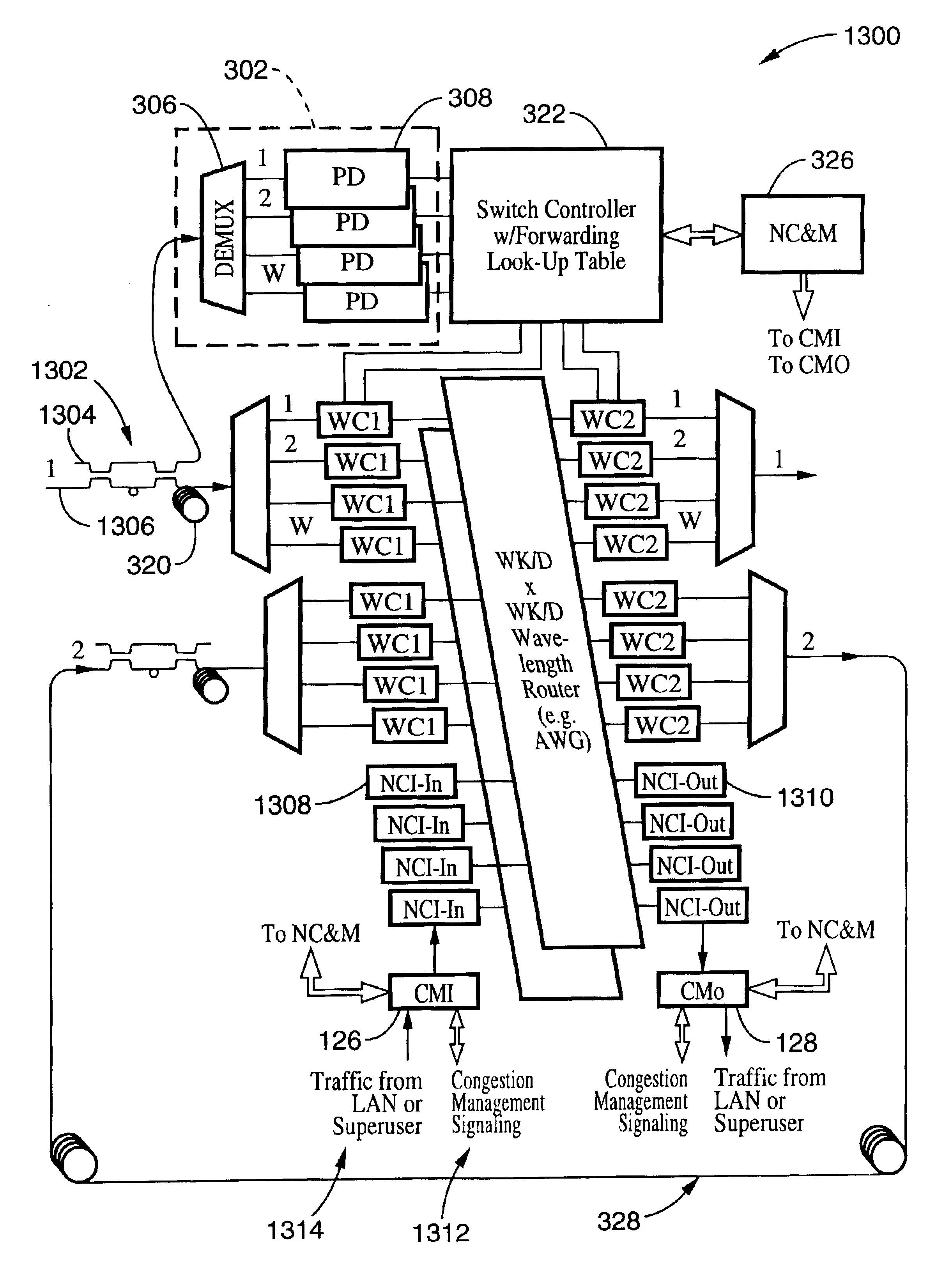
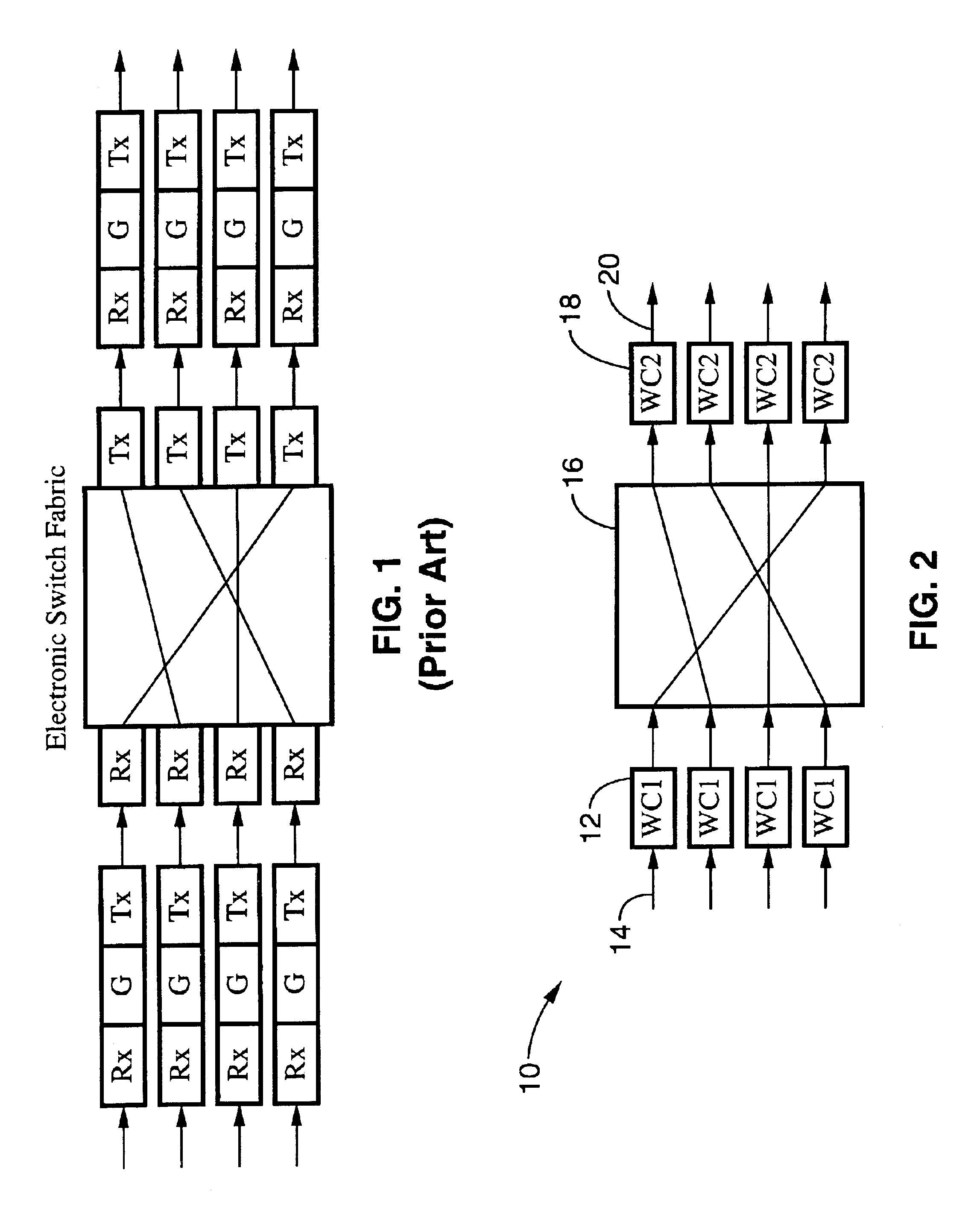
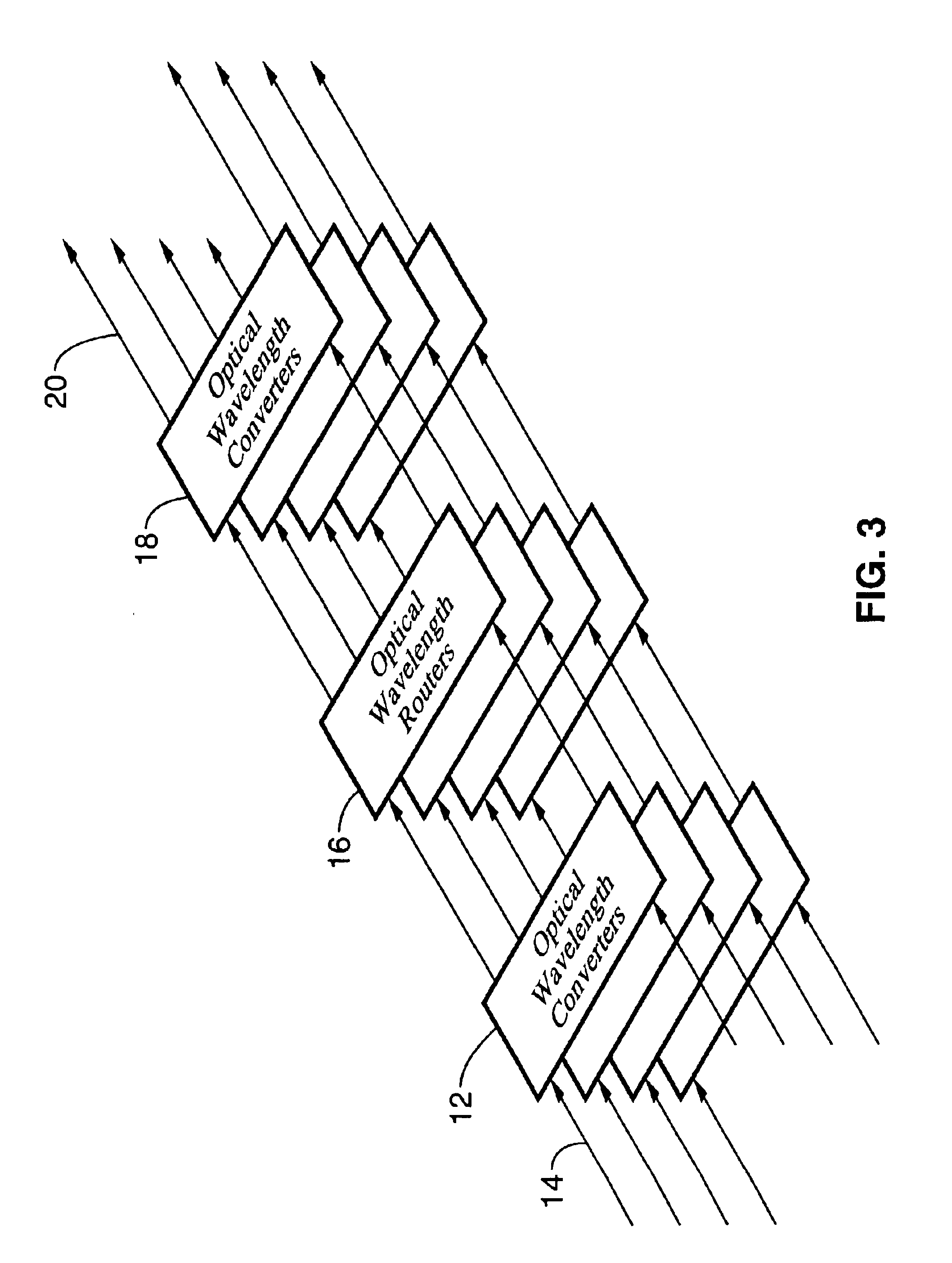
An ultra-low latency optical router with a peta-bit-per-second total aggregate switching bandwidth, that will scale to a total connectivity of 1000 by 1000, and beyond by modular upgrades, that utilizes advanced optical technologies to achieve such high capacity with two to three orders of magnitude less volume and power requirements than the electrical router counter part, that serves as a universal engine to other optical routers being developed by vendors and researchers today, that can function in the context of circuit-switching, flow-switching, burst-switching, and packet-switching, that uses advanced wavelength conversion technology to effectively achieve three methods of contention resolution in the router: deflection in wavelength, deflection in space, and buffering in time, and that interfaces a local network to the Supernet.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method and architecture for security key generation and distribution within optical switched networks
InactiveUS20050177749A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationExchange networkEdge node
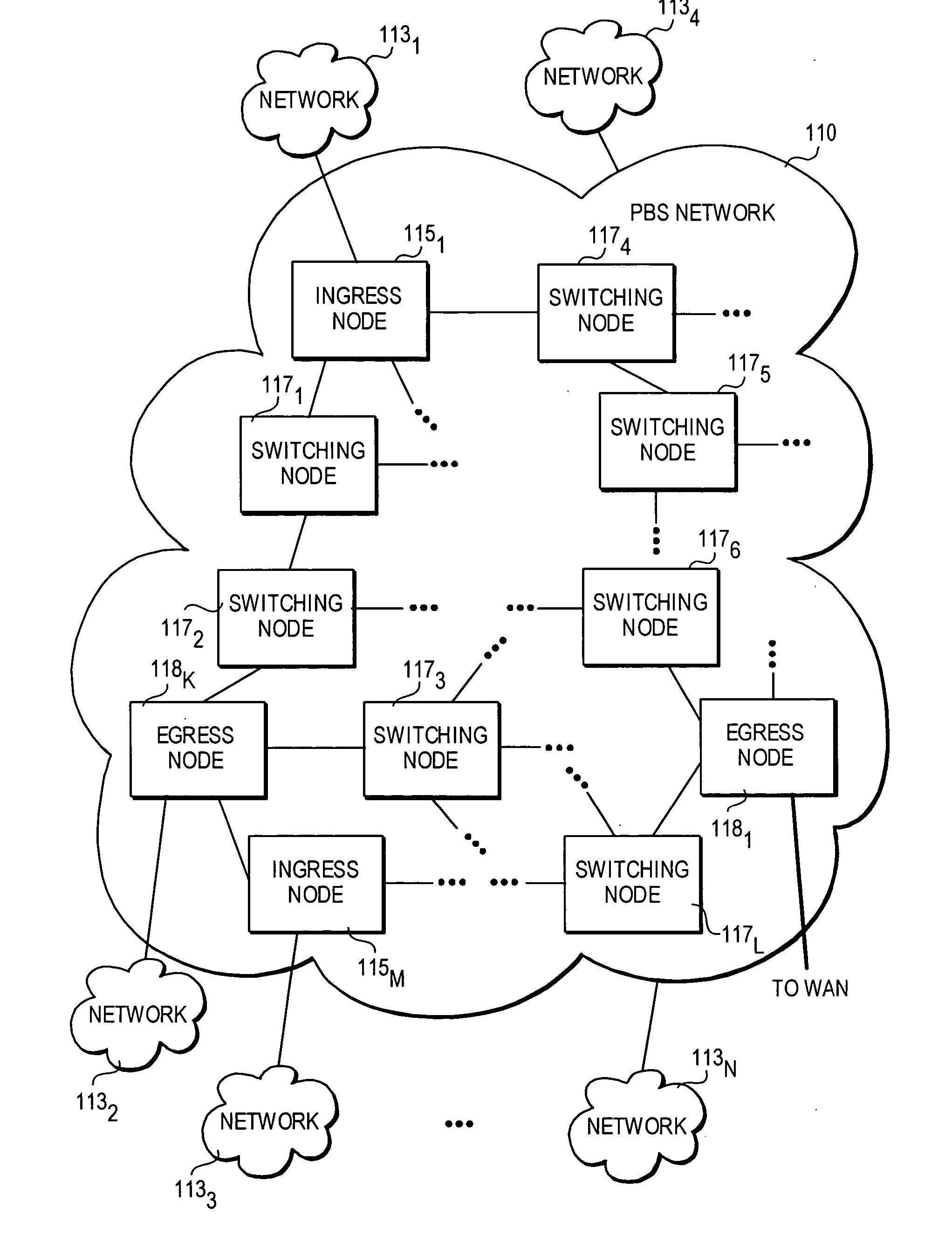
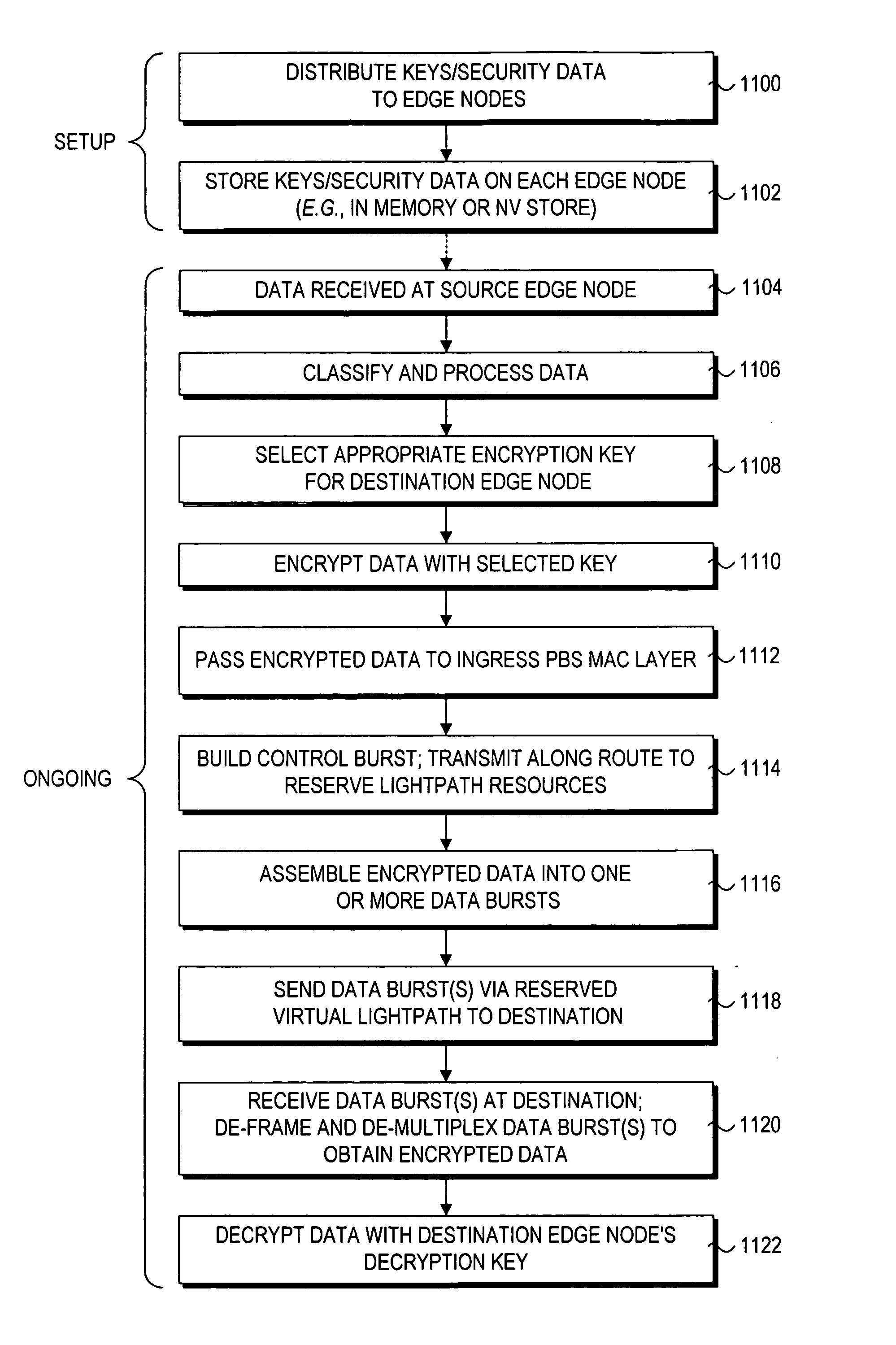
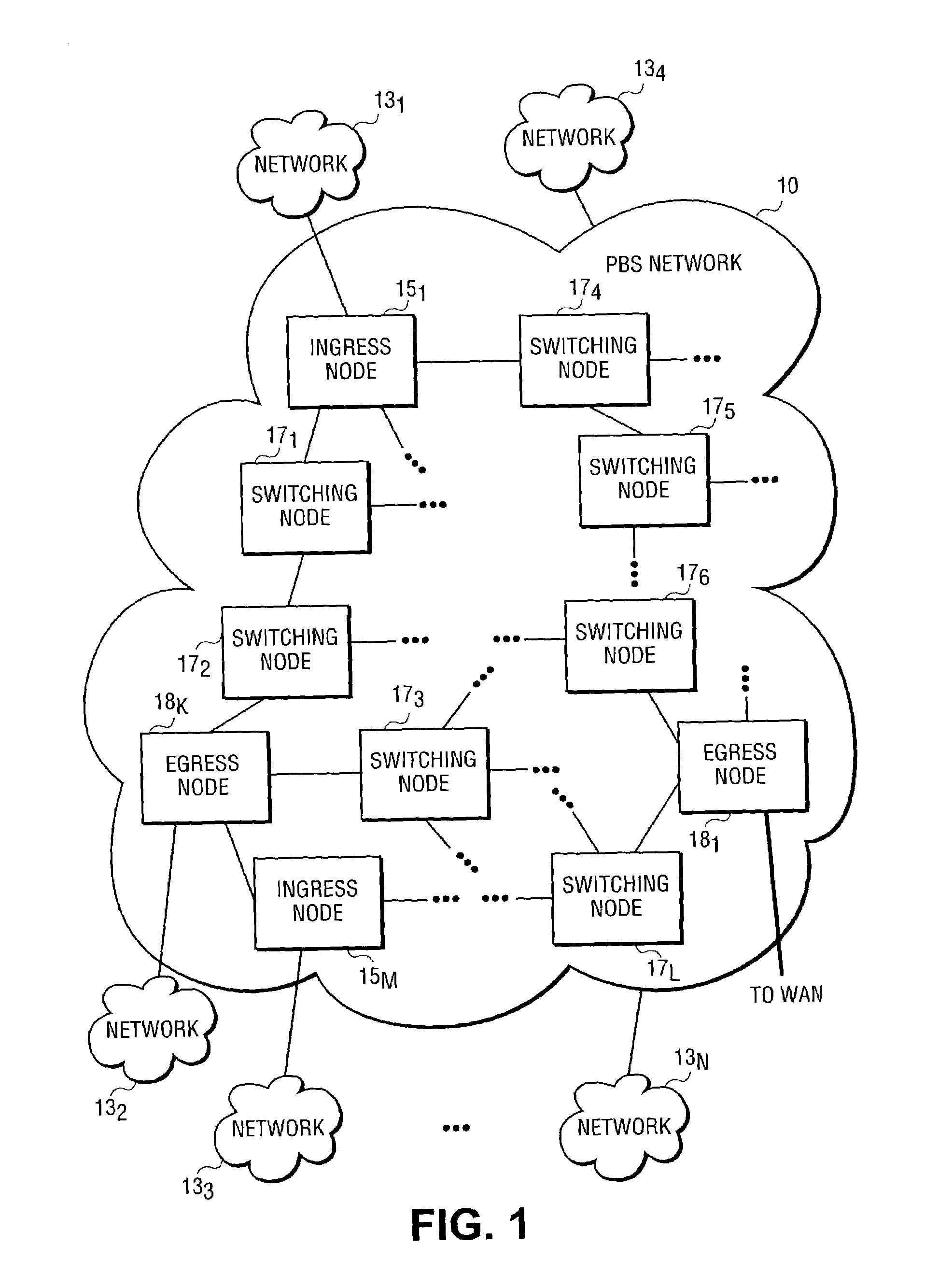
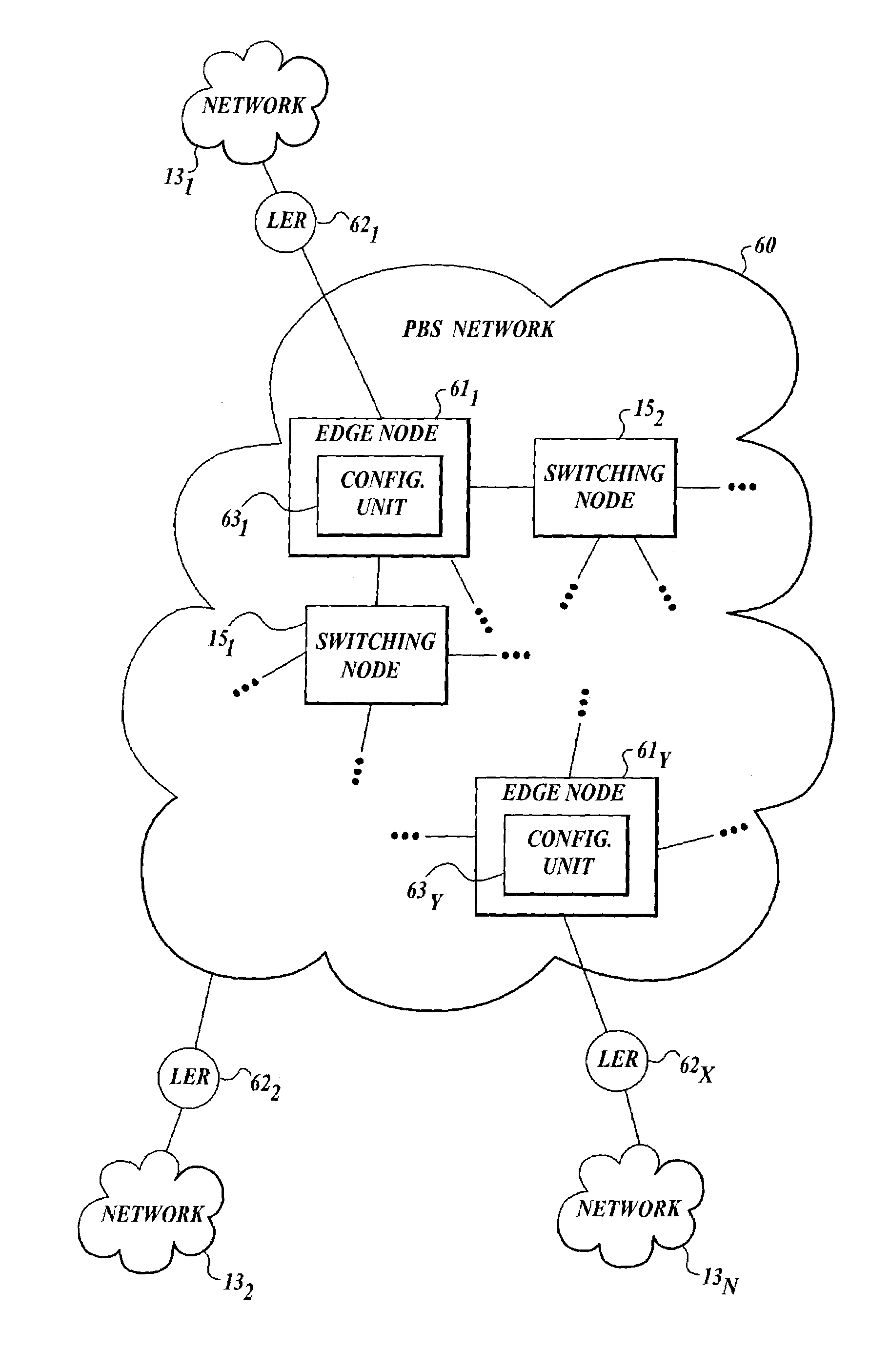
A method and architecture for secure transmission of data within optical-switched networks. In one embodiment, the optical switched network comprises a photonic burst-switched (PBS) network. Under various schemes, security keys including encryption and decryption keys are generated by edge nodes and the decryption keys are distributed to other edge nodes in a PBS network. In one embodiment, the security keys are dynamically generated by a trusted platform module (TPM). A source edge node uses its encryption key to encrypt selected data bursts to be sent to a destination edge node via a virtual lightpath coupling the source and destination edge nodes. Security data are embedded in a control burst header indicates to the destination node whether corresponding data bursts sent via the virtual lightpath are encrypted. The security data also includes the decryption key and may also identify an encryption / decryption algorithm to be used. In some embodiments, public key infrastructure facilities are used in conjunction with employment of private and public keys and digital certificates.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
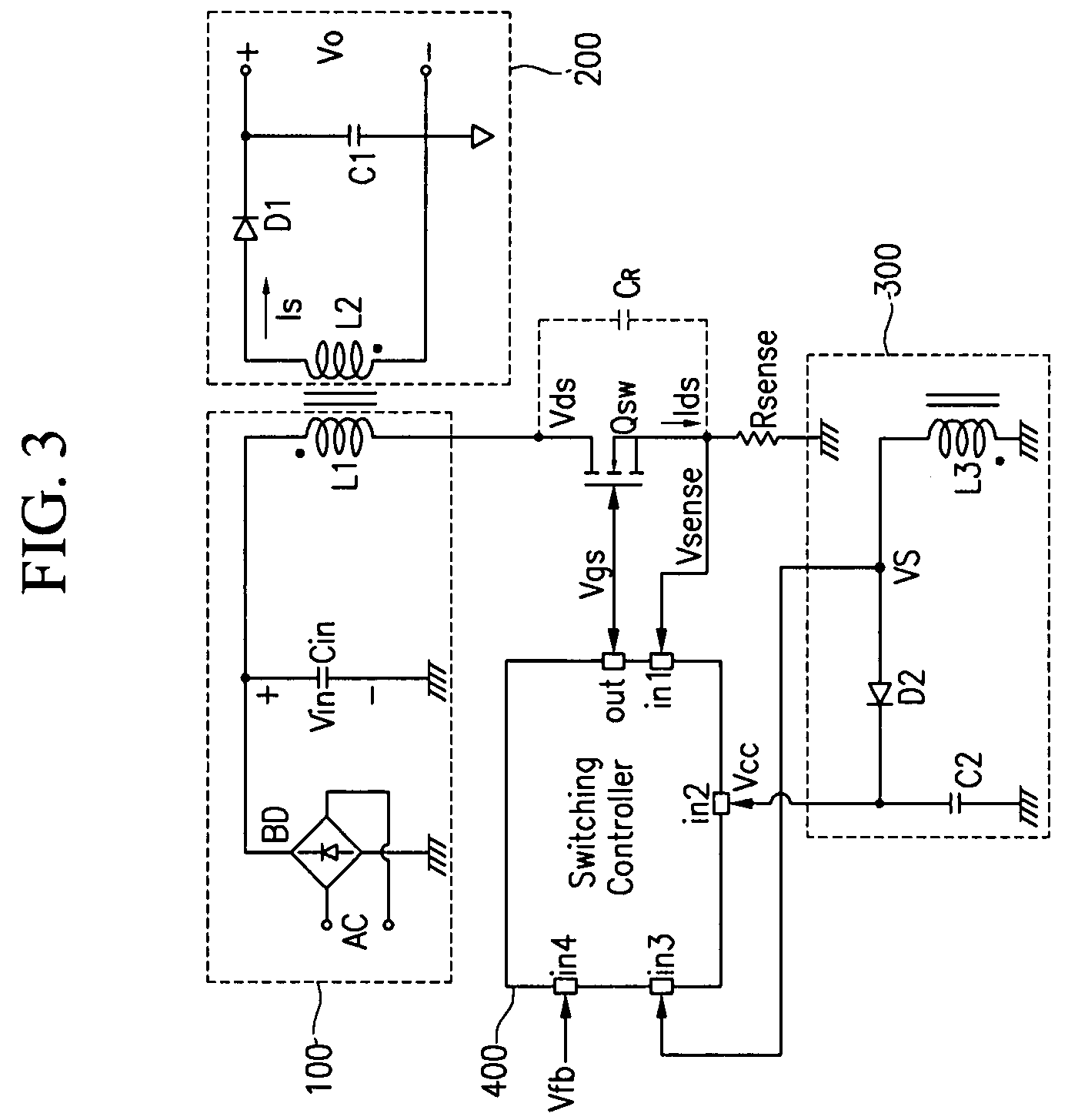
Switch mode power supply and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20080130324A1Reduce switching lossesReduce noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerBurst switching
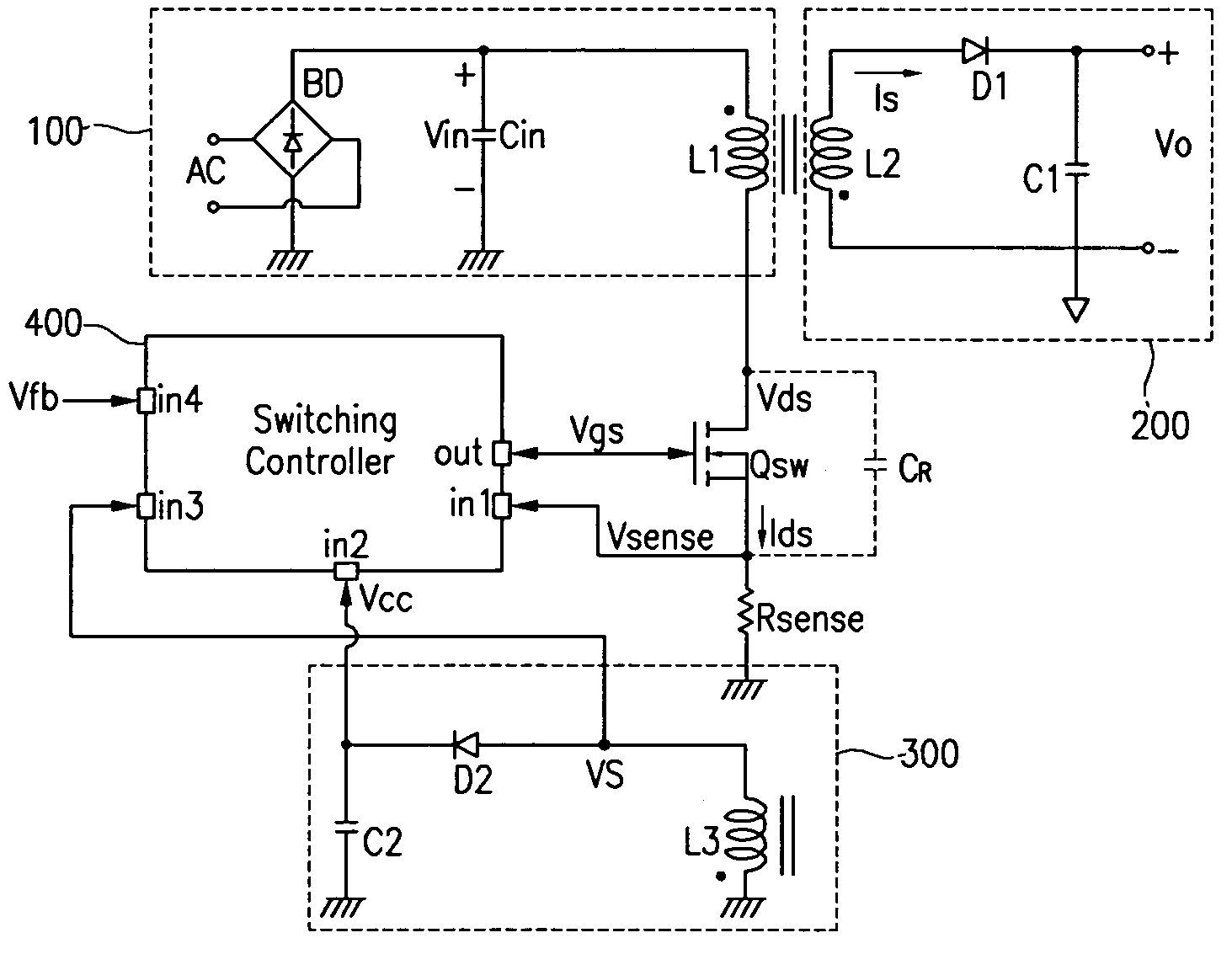
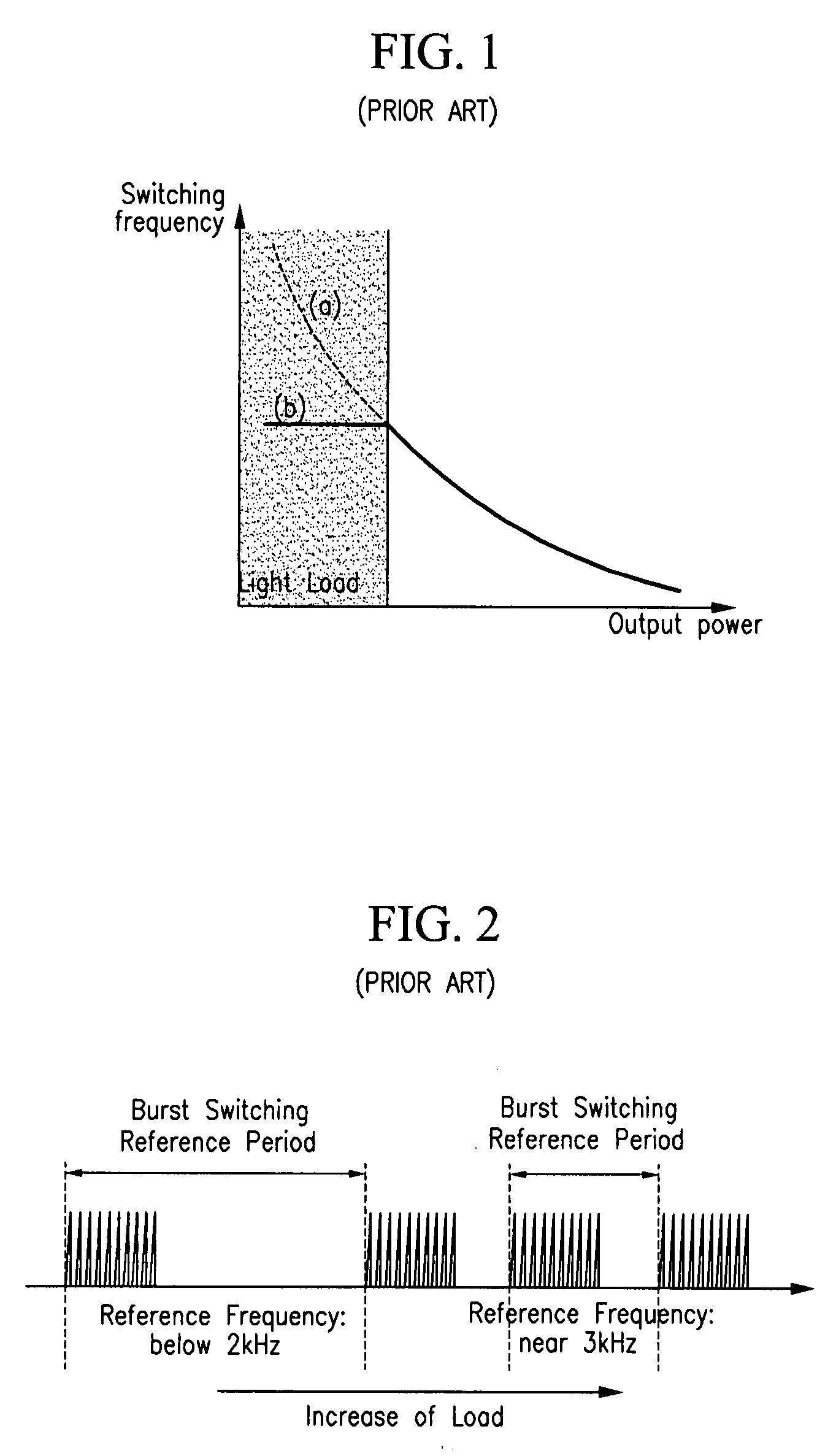
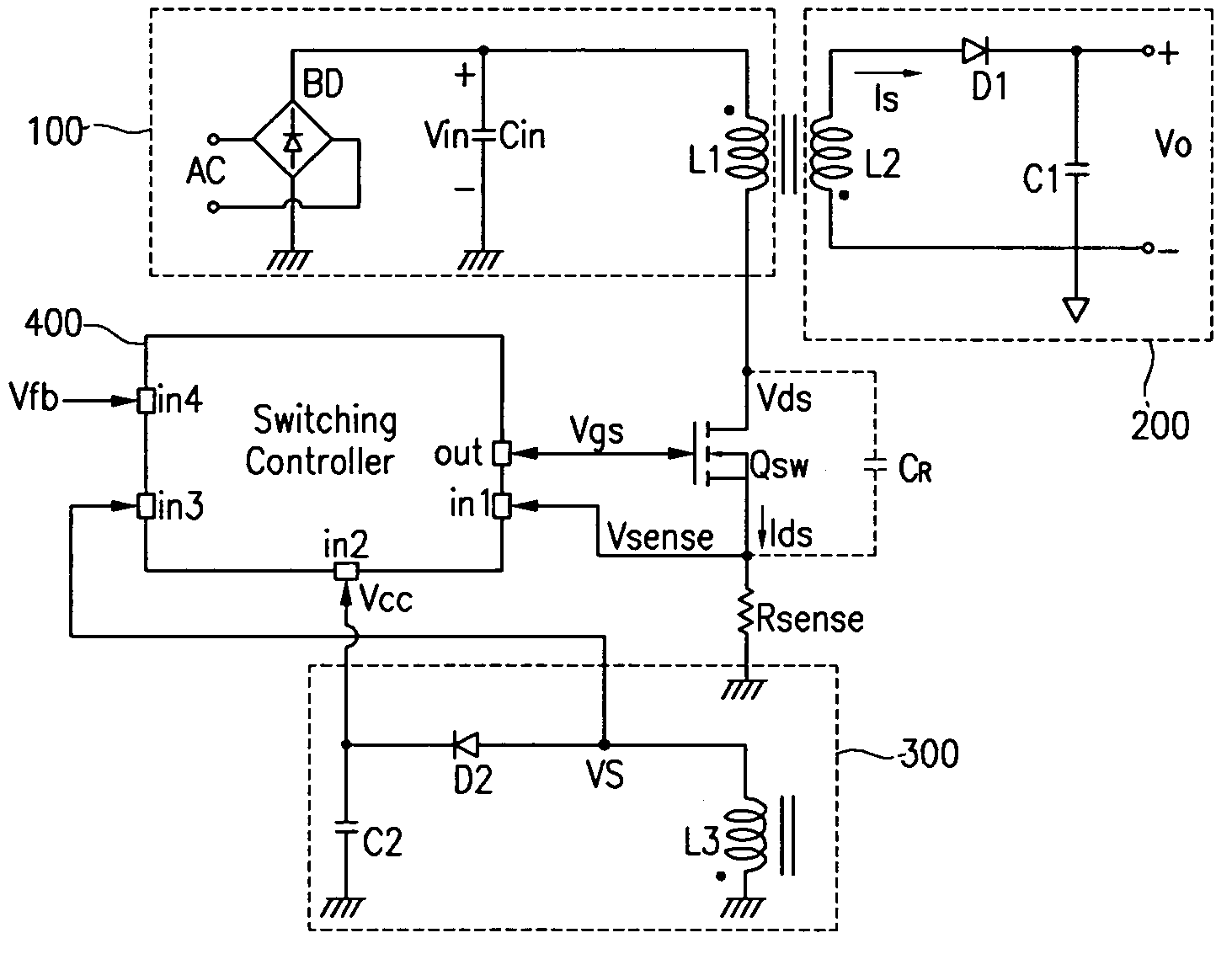
The present invention relates to a switch mode power supply and a driving method for reducing switching loss and audible noise in the burst mode. The switch mode power supply includes a main switch, a power supply, an output unit, and a switch controller. The power supply includes a transformer having a primary coil connected to the main switch, and supplies power to a secondary coil of the transformer according to the operation of the main switch. The output unit is connected to the secondary coil of the transformer and outputs power supplied to the secondary coil of the transformer. The switch controller receives a feedback signal corresponding to the output voltage of the output unit, a sense signal corresponding to the current flowing to the main switch, and a sync signal corresponding to the voltage difference at the main switch, controls the on / off of the main switch, and determines whether to start the burst mode by using the feedback signal, and maintains the switching operation forcibly off period in the burst mode so that the reference frequency of burst switching may be less than a predetermined value.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Reservation protocol signaling extensions for optical switched networks
InactiveUS20050030951A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPhotonicsSignaling protocol
An architecture and method for performing coarse-grain reservation of lightpaths within wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) based photonic burst-switched (PBS) networks with variable time slot provisioning. The method employs extensions to the RSVP-TE signaling protocol, which uses various messages to reserve resources. A resource reservation request is passed between nodes during a downstream traversal of the lightpath route connecting a source node to a destination node via one or more switching nodes, wherein each node is queried to determine whether it has transmission resources (i.e., a lightpath segment) available during a future scheduled time period. Soft reservations are made for each lightpath segment that is available using information contained in a corresponding label. If all lightpath segments for a selected route are available, a reservation response message is sent back upstream along the route from the destination node to the source node. In response to receiving the response, the soft reservations are turned into hard reservations at each node.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and architecture for secure transmission of data within optical switched networks
InactiveUS20050175183A1Key distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsExchange networkSecure transmission
A method and architecture for secure transmission of data within optical switched networks. In one embodiment, the optical switched network comprises a photonic burst-switched (PBS) network. Under various schemes, security keys are distributed to each edge node in a PBS network. A source edge node uses an encryption key to encrypt selected data bursts to be sent to a destination edge node via a virtual lightpath coupling the source and destination edge nodes. Security data are embedded in a control burst header indicates to the destination node whether corresponding data bursts sent via the virtual lightpath are encrypted. The security data may also identify an encryption / decryption algorithm and decryption keys to be used. Keys and / or certificates may be generated by or provided to the edge nodes. In some embodiments, public key infrastructure facilities are used in conjunction with employment of private and public keys and certificates.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Method and apparatus for synchronized slotted optical burst switching
InactiveUS6963564B1Efficient and flexibleMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsFiberOptical burst switching
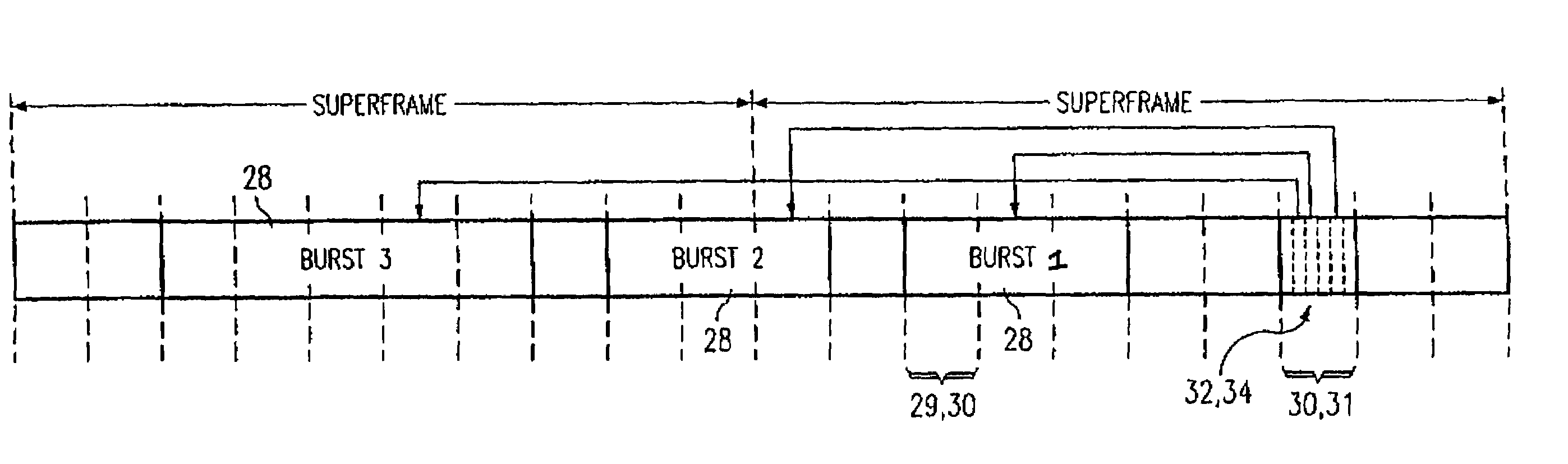
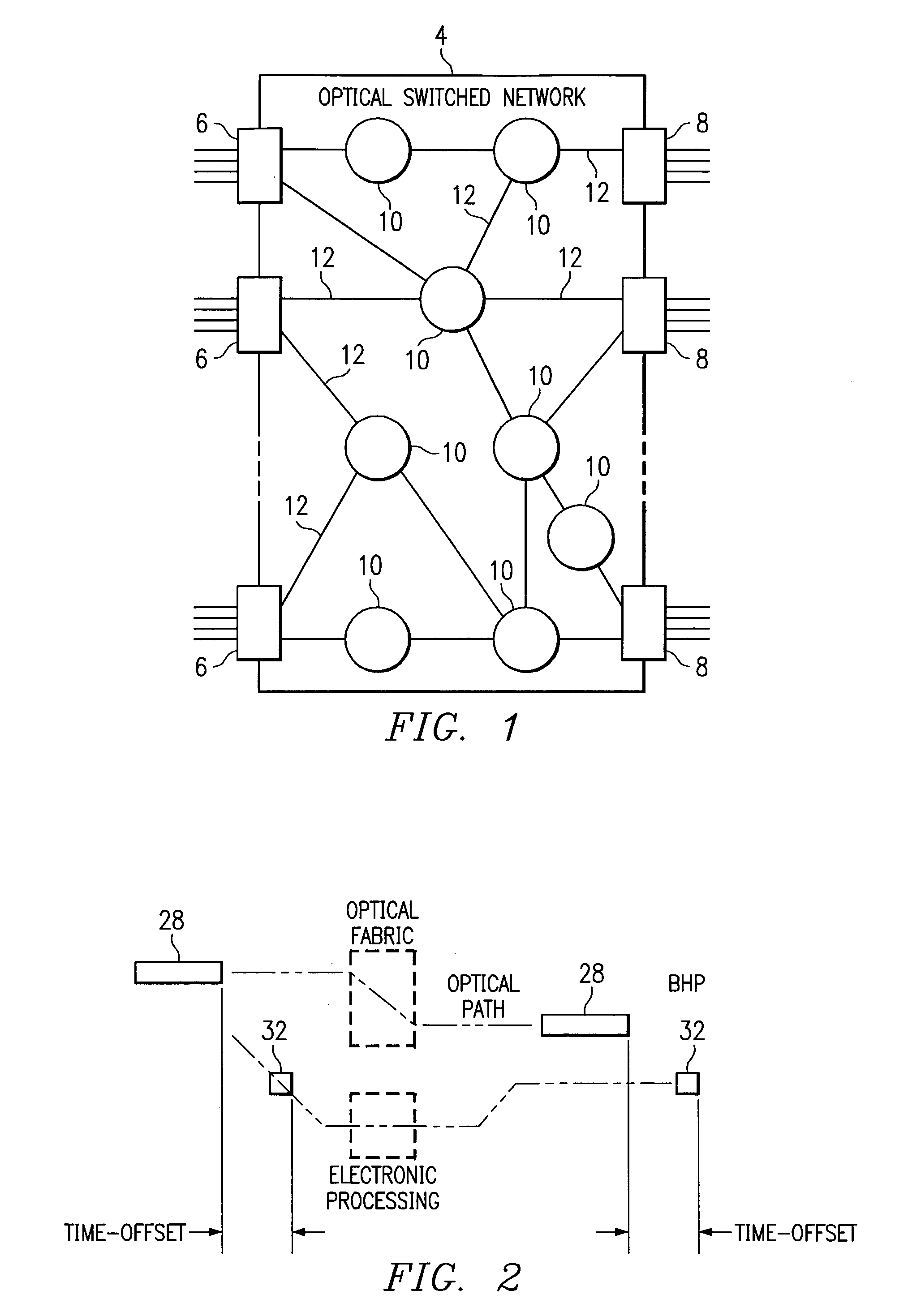
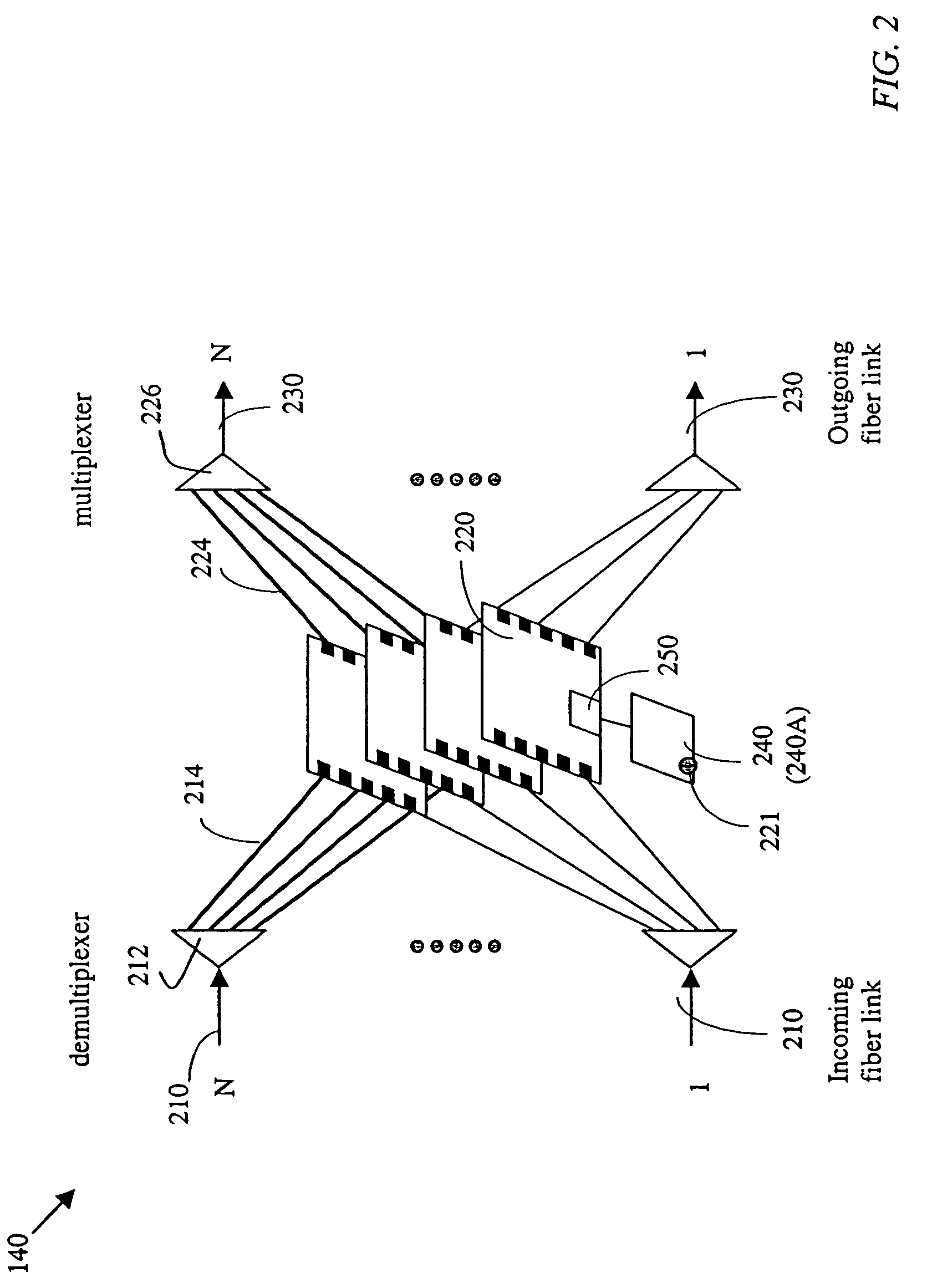
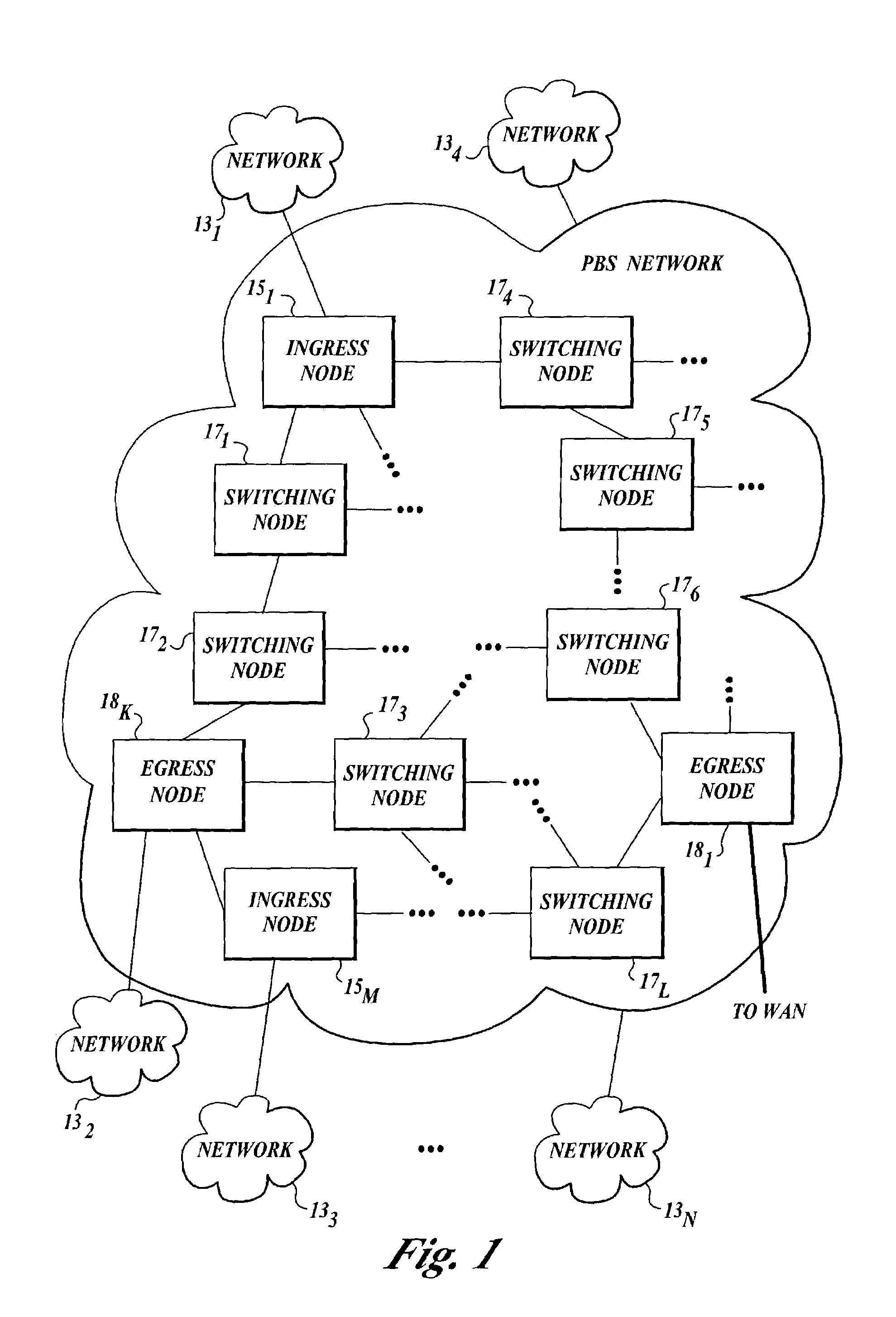
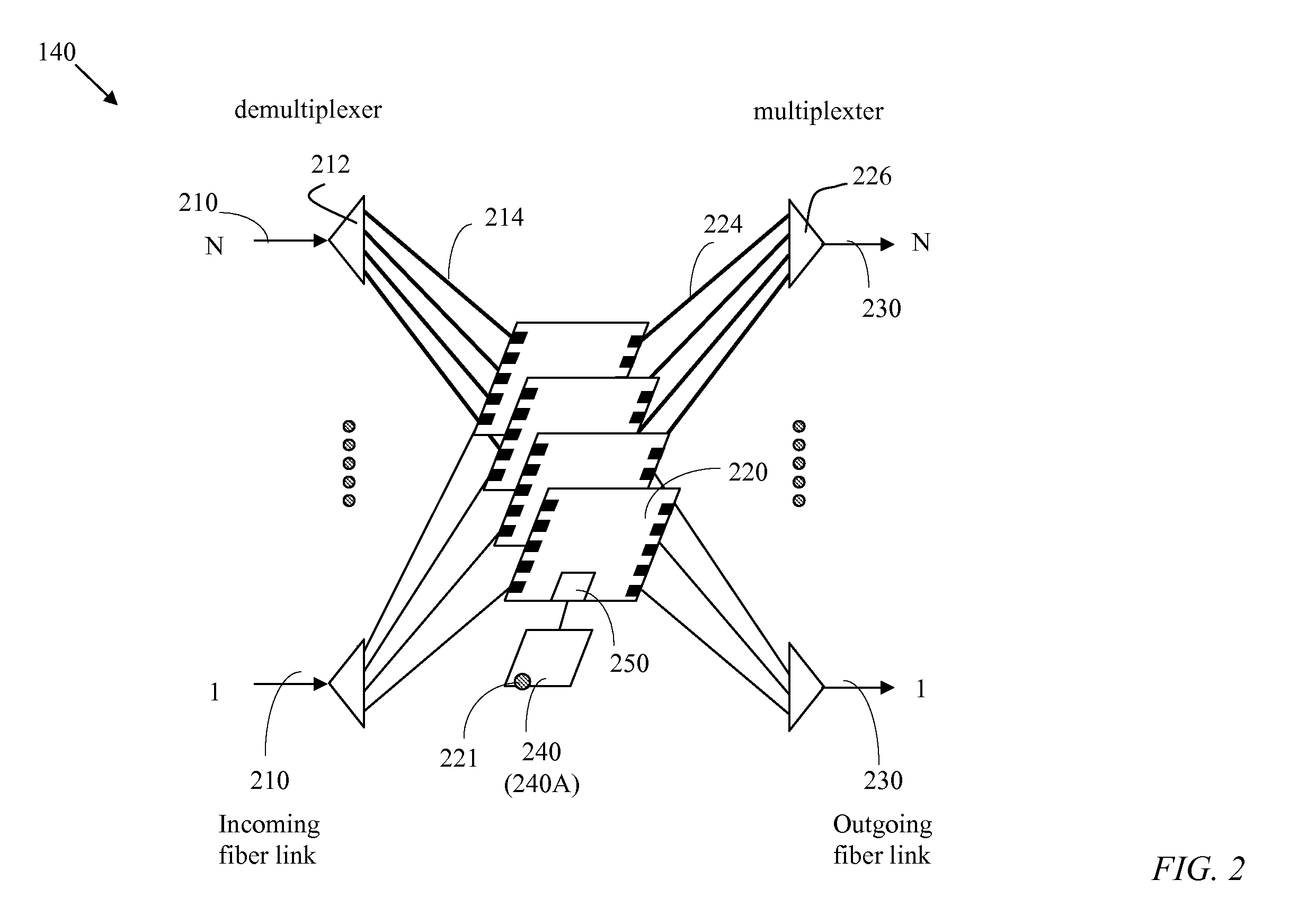
A network (4) includes optical routers (19), which route information in fibers (10). Each fiber carries a plurality of data channels (16), carrying data in data bursts (28) and a control channel, carrying control information in burst header packets (32). A burst header packet includes routing information for an associated data burst (28) and precedes its associated data burst. Information on the data channels and control channel is organized in synchronized slots. Multiple burst header packets occupy portions of a slot, referred to as micro-slots. When the burst header packets are received, an egress processor (52) schedules the routing of their associated bursts. The egress processor (52) determines a time at which a data burst can be scheduled for passing through an optical matrix (40) to the desired output channel group (the burst can be delayed via fiber delay lines (46) if necessary).
Owner:RPX CORP
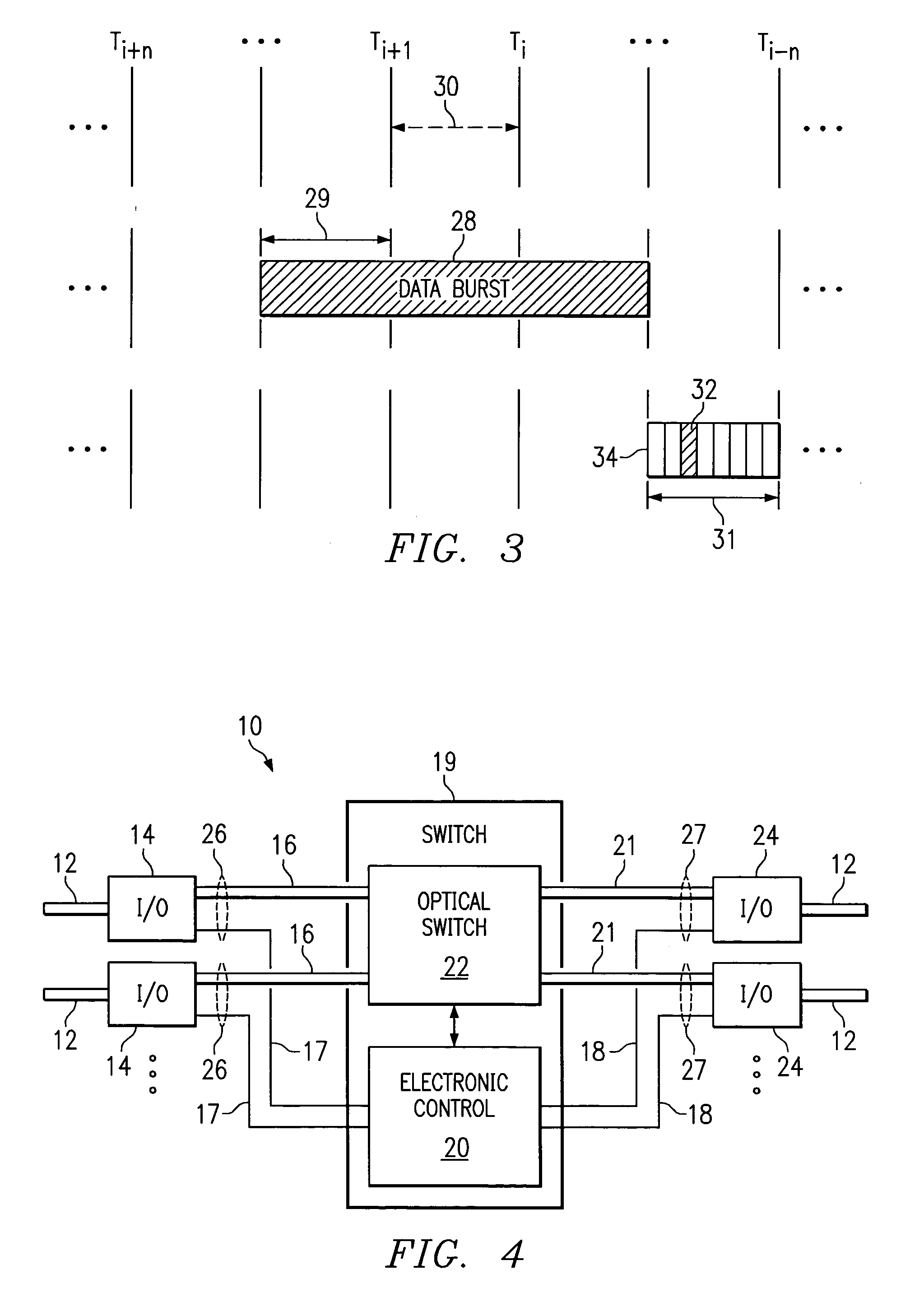
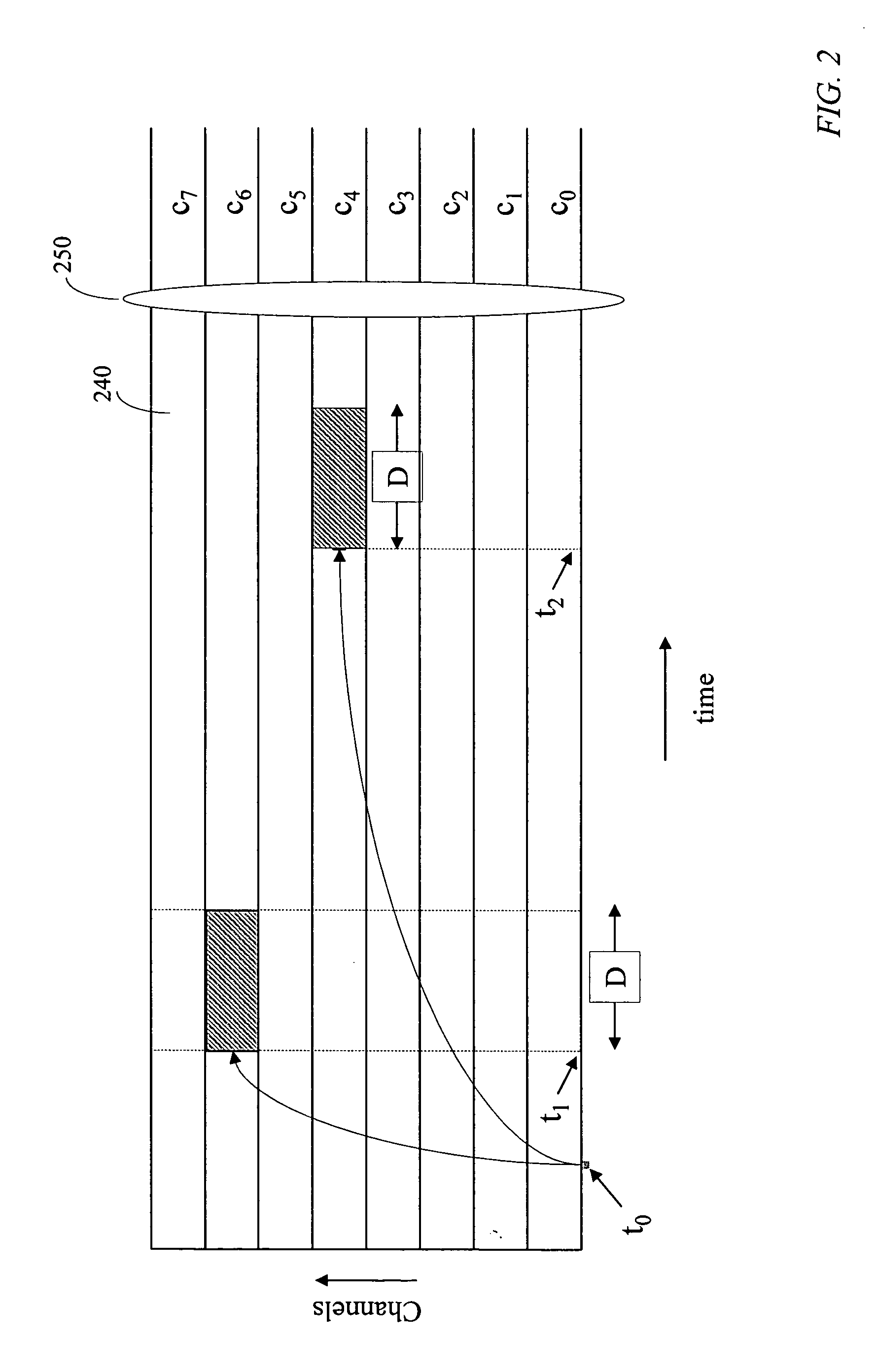
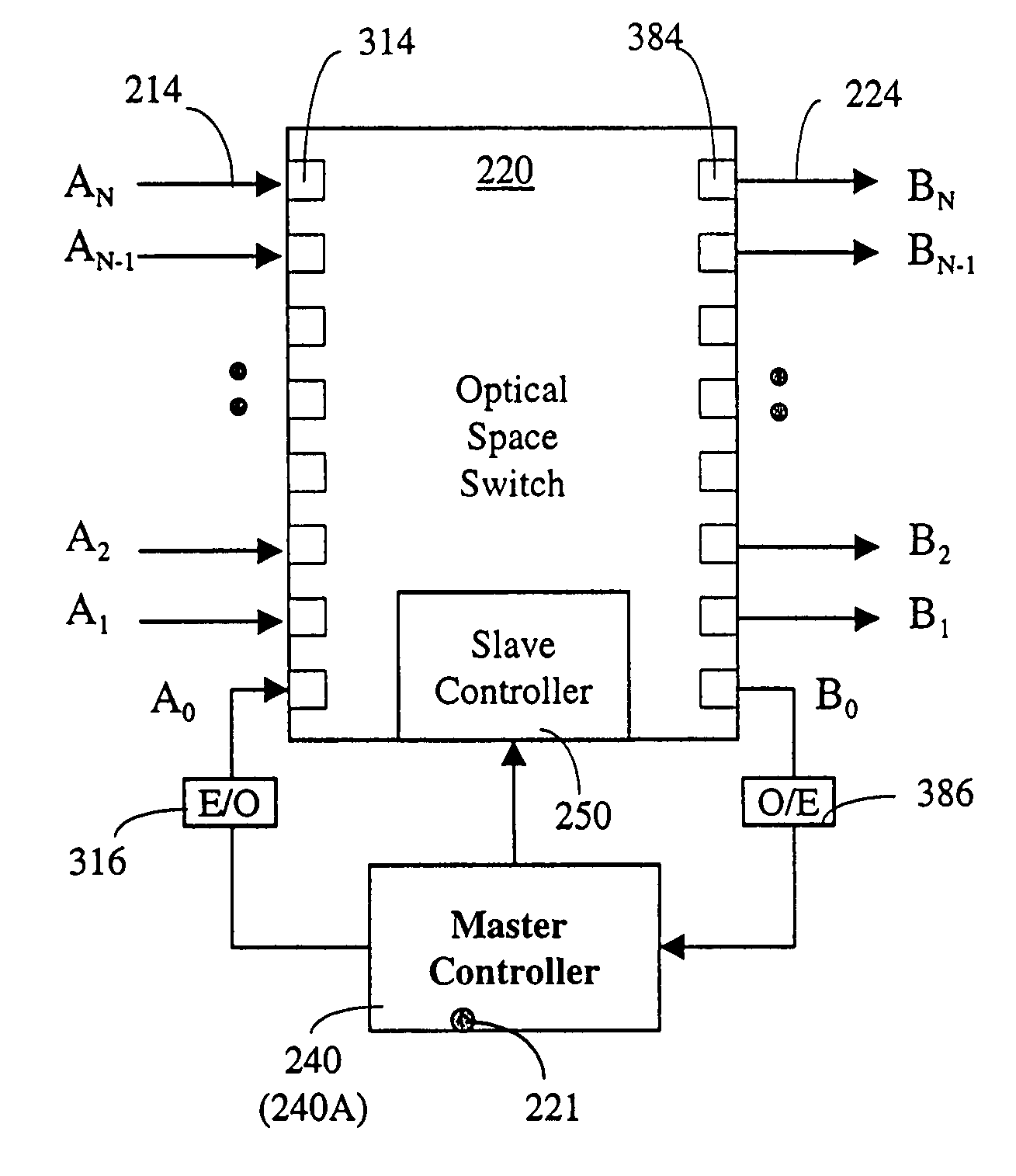
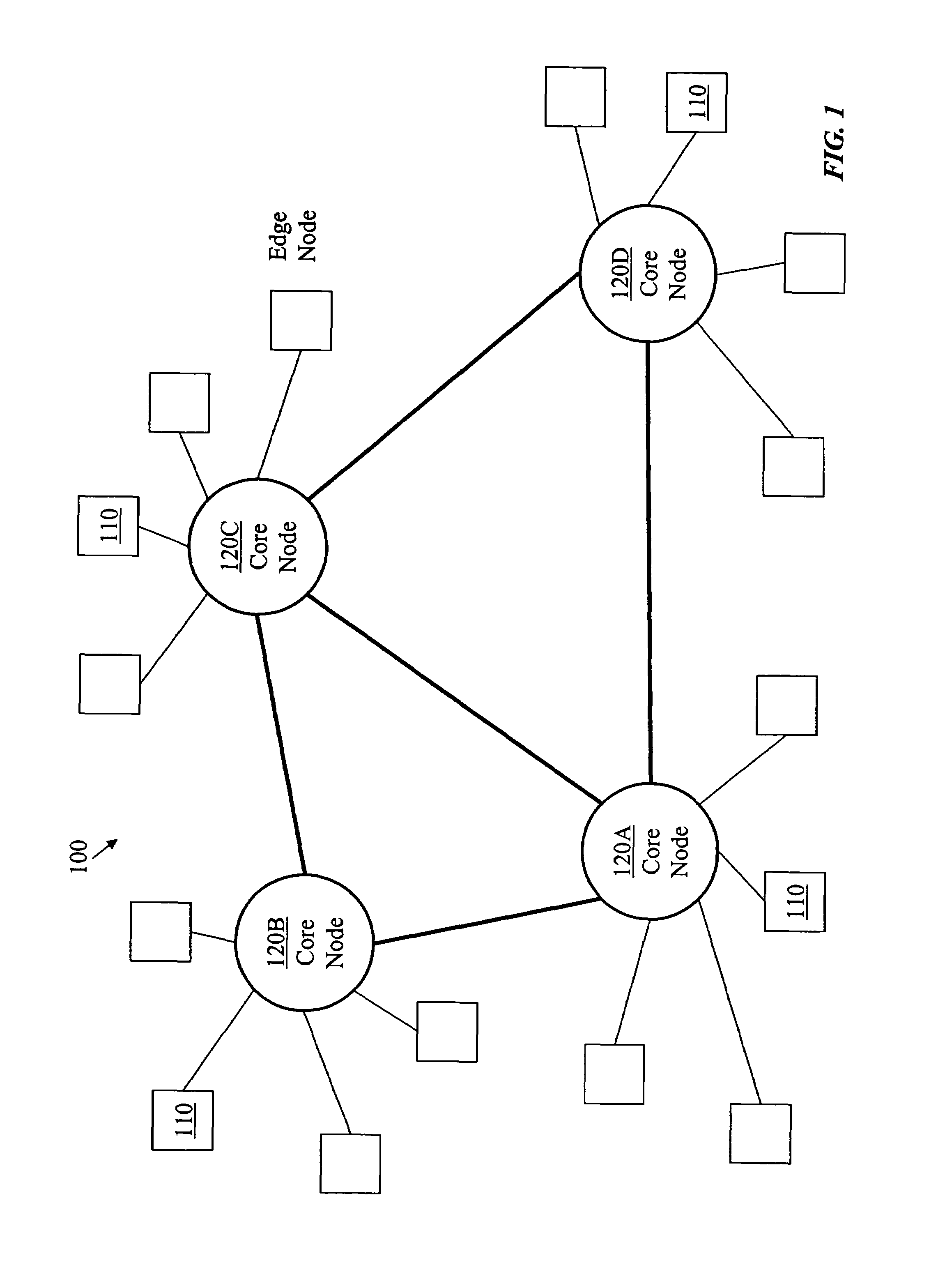
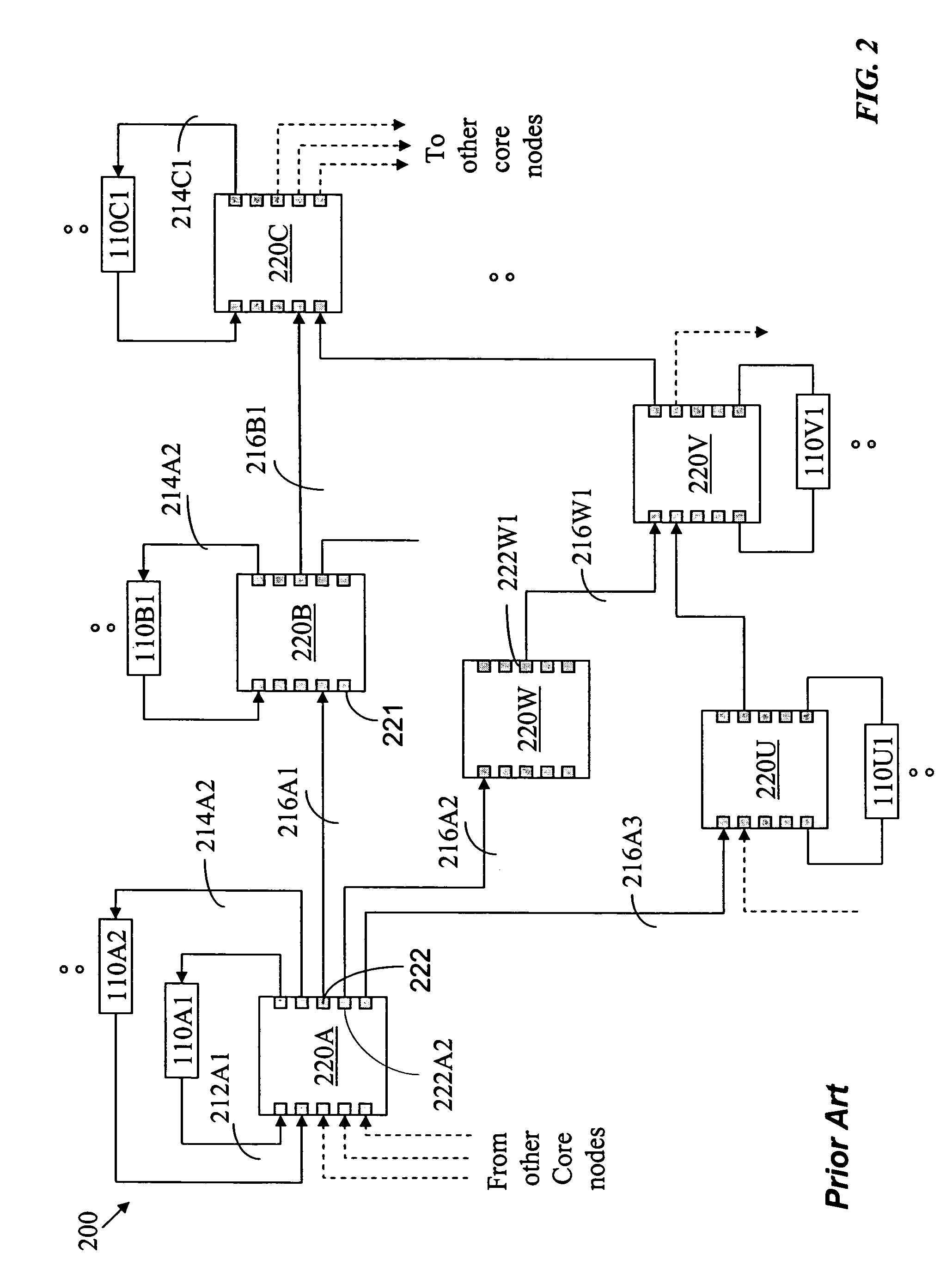
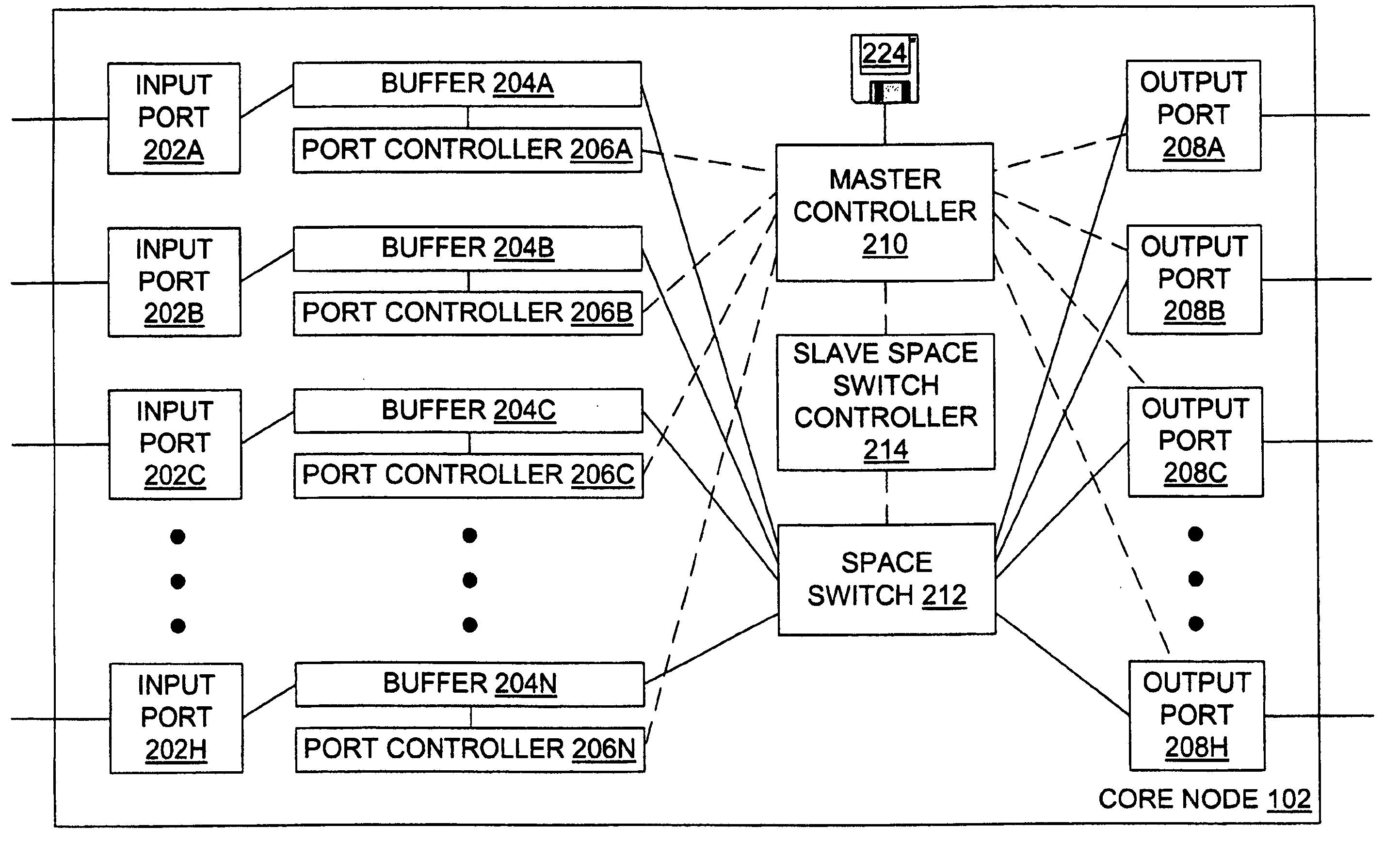
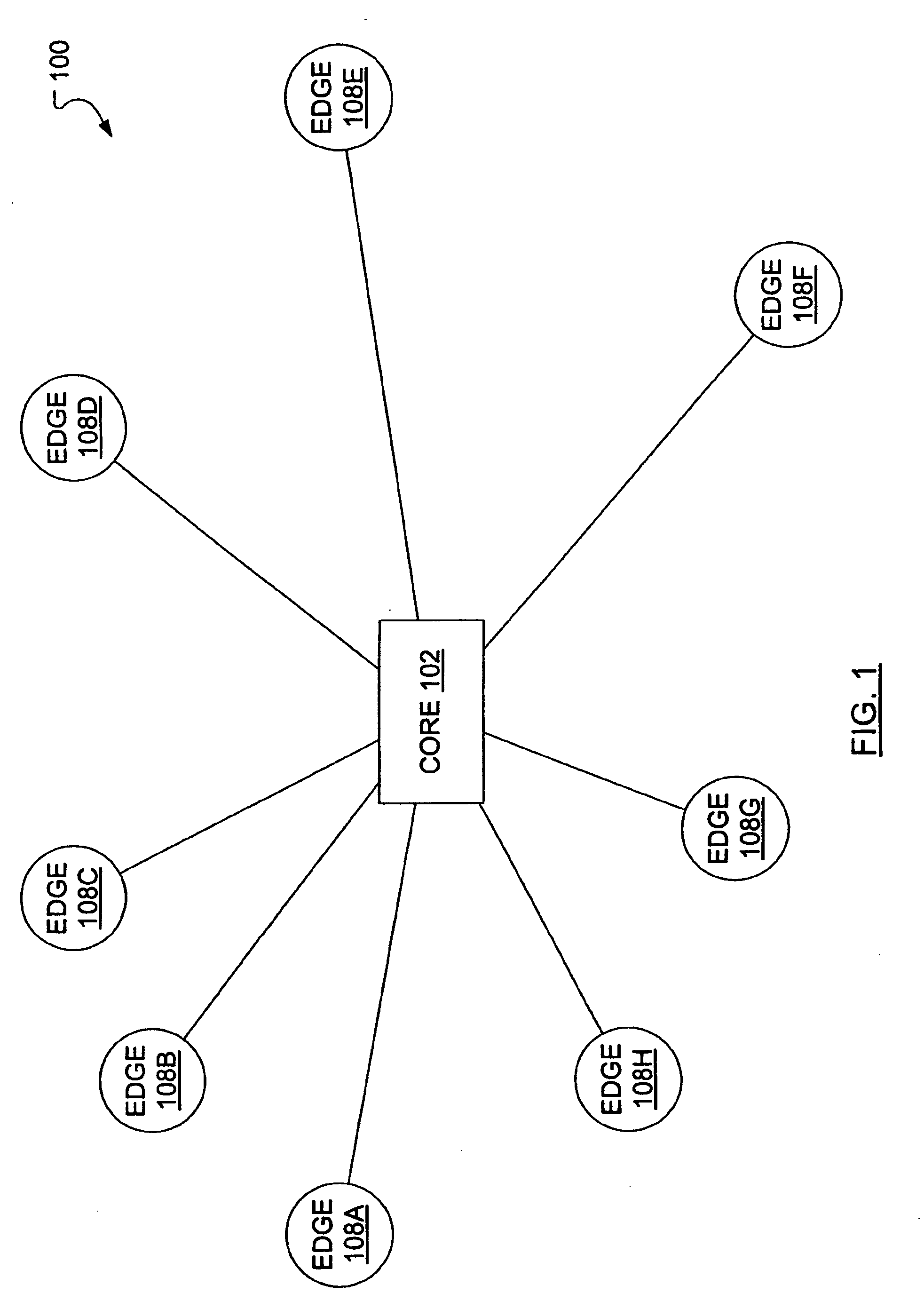
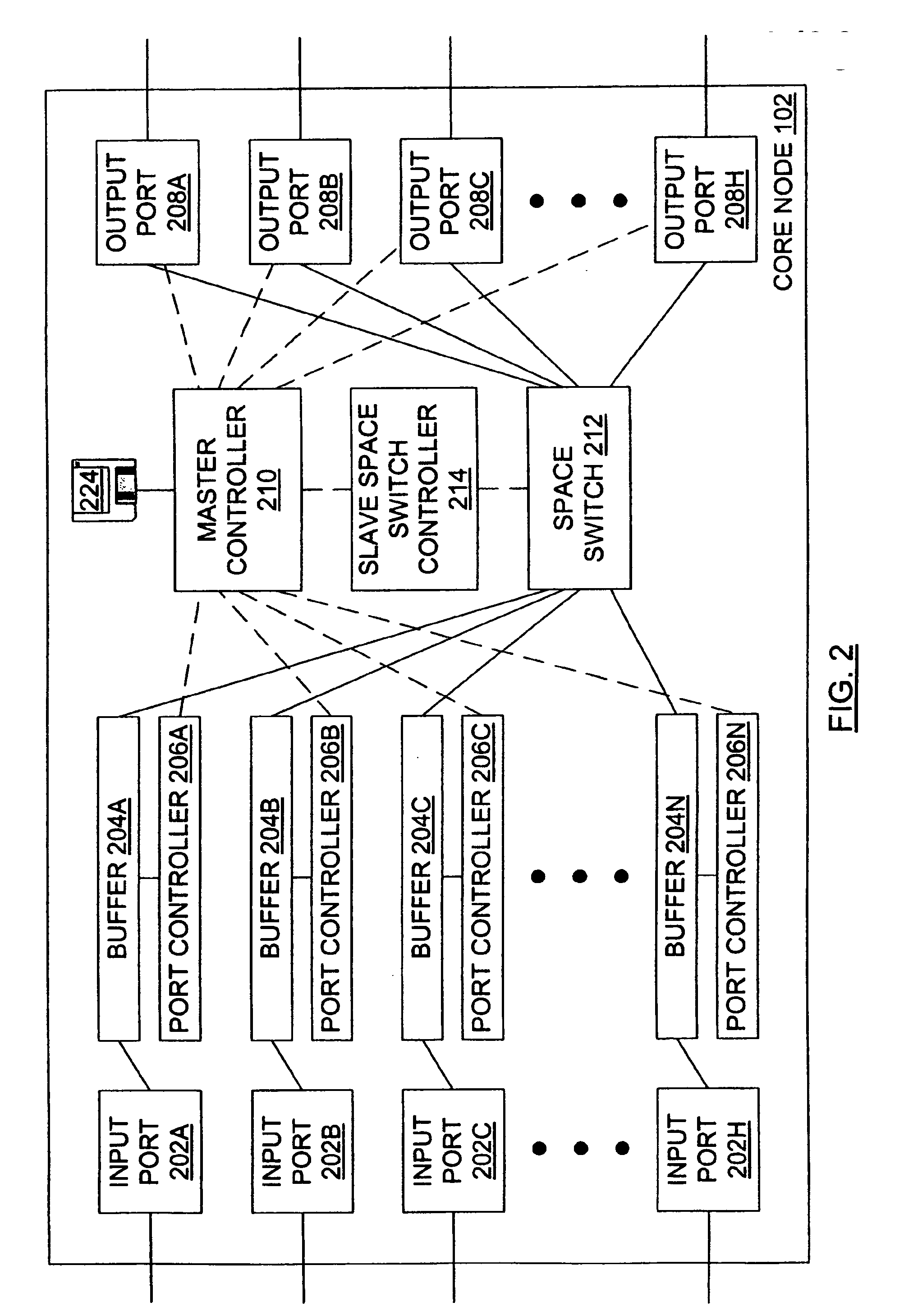
Burst switching in a high capacity network
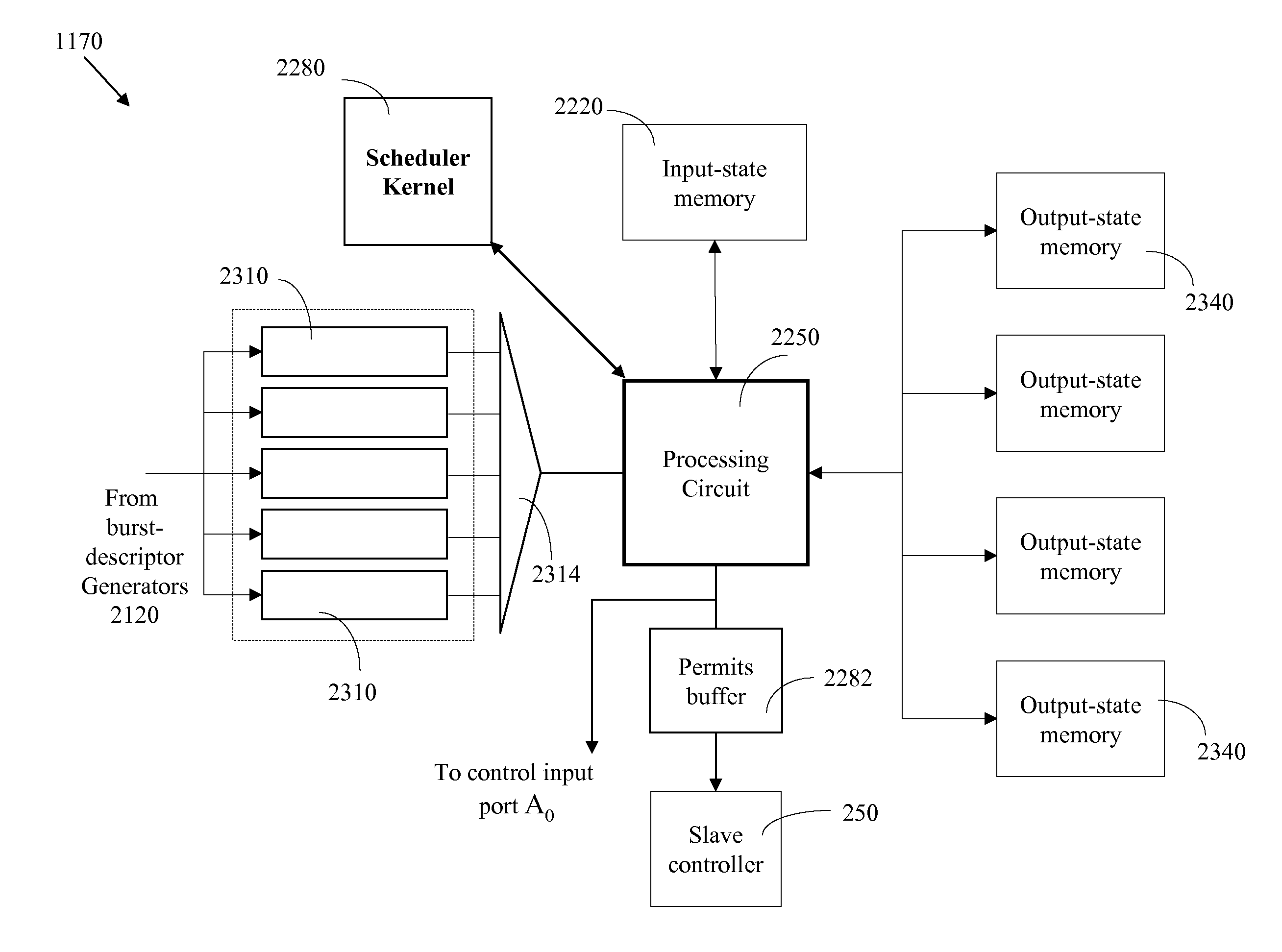
InactiveUS6907002B2Effective utilization of network resourceEfficient comprehensive utilizationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMaster controllerData loss
At a master controller of a space switch in a node in a data network, a request is received from a source node that requests a connection to be established through the space switch. This request is compared to other such requests so that a schedule may be established for access to the space switch. The schedule is then sent to the source nodes as well as to a slave controller of the space switch. The source nodes send data bursts which are received at the space switch during a short guard time between successive reconfigurations of the space switch. Data bursts are received at the space switch at a precisely determined instant of time that ensures that the space switch has already reconfigured to provide requested paths for the individual bursts. The scheduling is pipelined and performed in a manner that attempts to reduce mismatch intervals of the occupancy states of input and output ports of the space switch. The method thus allows efficient utilization of the data network resources while ensuring virtually no data loss.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Bimodal burst switching
InactiveUS7289440B1Lower latencyZero burst lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionTelecommunications networkBurst transmission
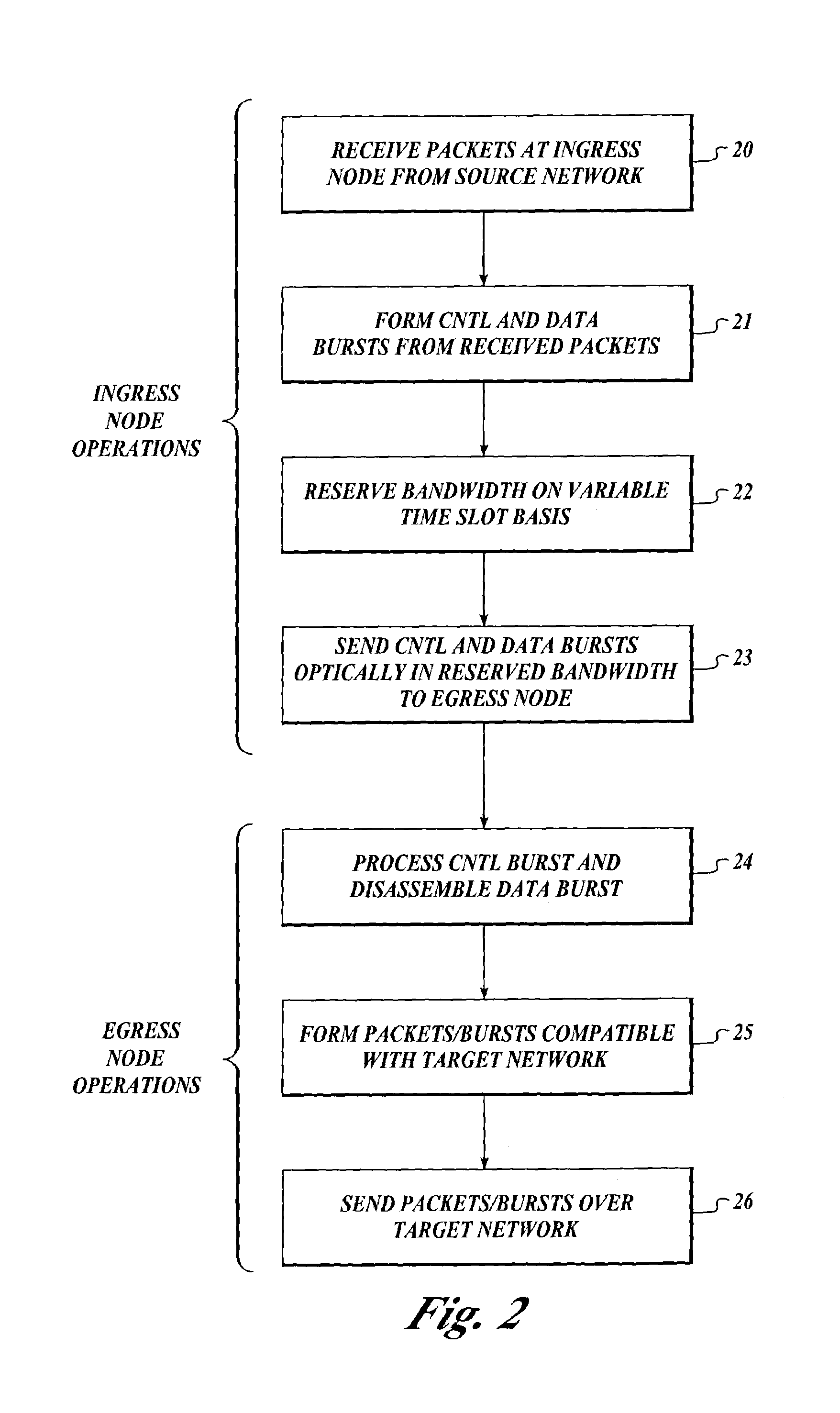
In a first mode of burst communication in a telecommunication network comprising electronic edge nodes interconnected by bufferless core nodes, data bursts are formulated at the edge nodes, respective burst descriptors are communicated to a controller of a core node, and burst-transfer schedules are sent from the core node to respective edge nodes. In a second mode, each burst-stream is allocated a flow rate and a core node determines burst sizes and schedules burst-transfer permits.In a bimodal burst-switching network, an edge node selects to send to a core node burst-transfer requests according to the first mode, or flow-rate-allocation requests according to the second mode, depending on proximity, storage capacity at the edge node, and delay-tolerance specifications.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Switching power supply apparatus
InactiveUS6903945B2Reduce startup timeImprove power usage efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringBurst switching
A switching power supply apparatus operates with less power consumption as a whole as a result of reduced power loss suffered while the switching operation of the main switching device is being stopped in burst switching control. Burst switching control is achieved by a signal level checker circuit 15 repeatedly turning on and off a switch circuit 17 provided in the line by way of which a switching controller circuit 19 is supplied with operating power. In burst switching control, when the switching operation of a main switching device 5 is being stopped, the supply of operating power to the switching controller circuit 19 is also stopped. This helps reduce the power loss suffered while the switching operation is being stopped, and thus helps reduce the power consumption of the apparatus as a whole.
Owner:SHARP KK
Switch mode power supply and driving method thereof
ActiveUS7957162B2Reducing switching loss and noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
The present invention relates to a switch mode power supply and a driving method for reducing switching loss and audible noise in the burst mode. The switch mode power supply includes a main switch, a power supply, an output unit, and a switch controller. The power supply includes a transformer having a primary coil connected to the main switch, and supplies power to a secondary coil of the transformer according to the operation of the main switch. The output unit is connected to the secondary coil of the transformer and outputs power supplied to the secondary coil of the transformer. The switch controller receives a feedback signal corresponding to the output voltage of the output unit, a sense signal corresponding to the current flowing to the main switch, and a sync signal corresponding to the voltage difference at the main switch, controls the on / off of the main switch, and determines whether to start the burst mode by using the feedback signal, and maintains the switching operation forcibly off period in the burst mode so that the reference frequency of burst switching may be less than a predetermined value.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
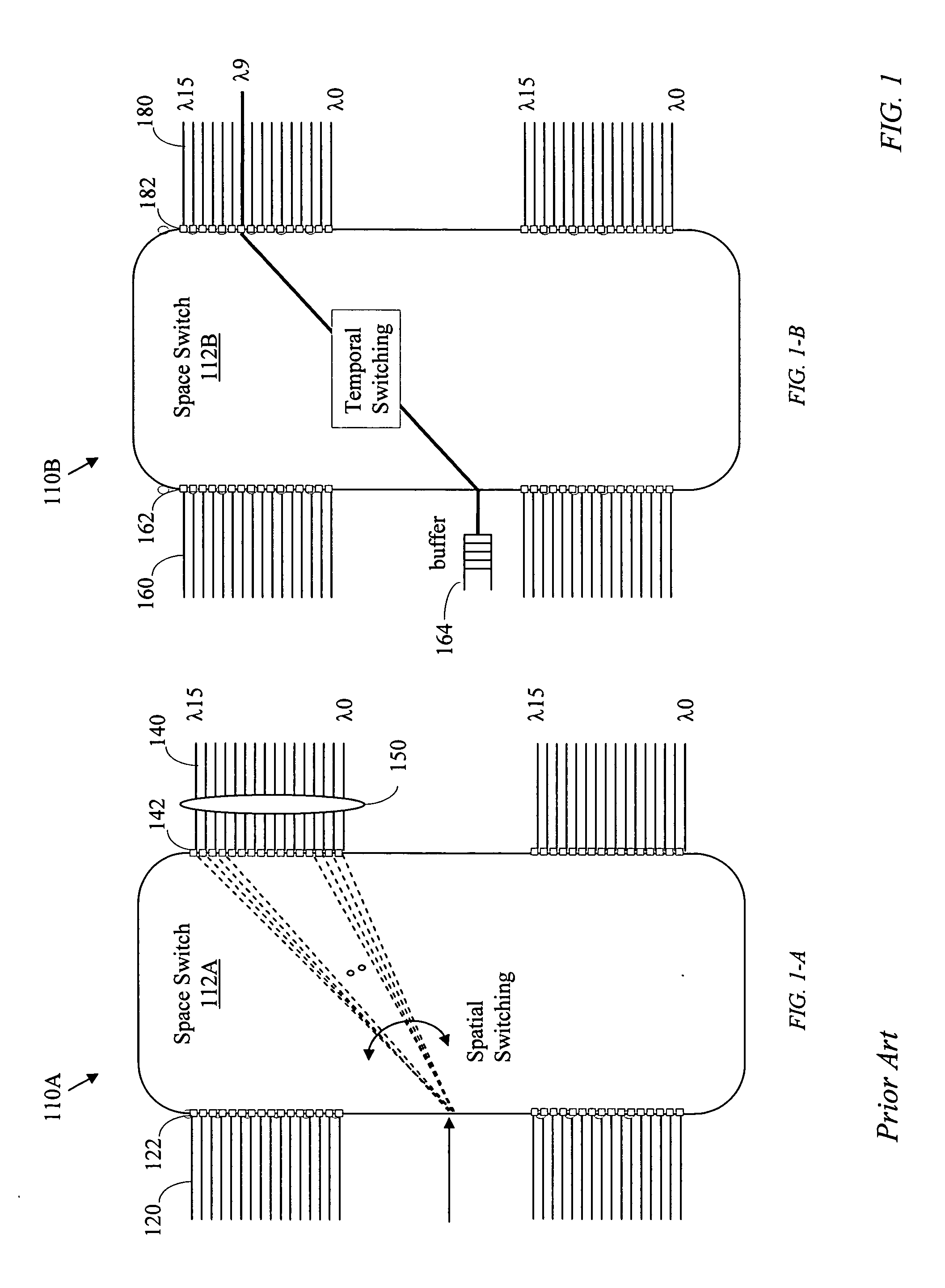
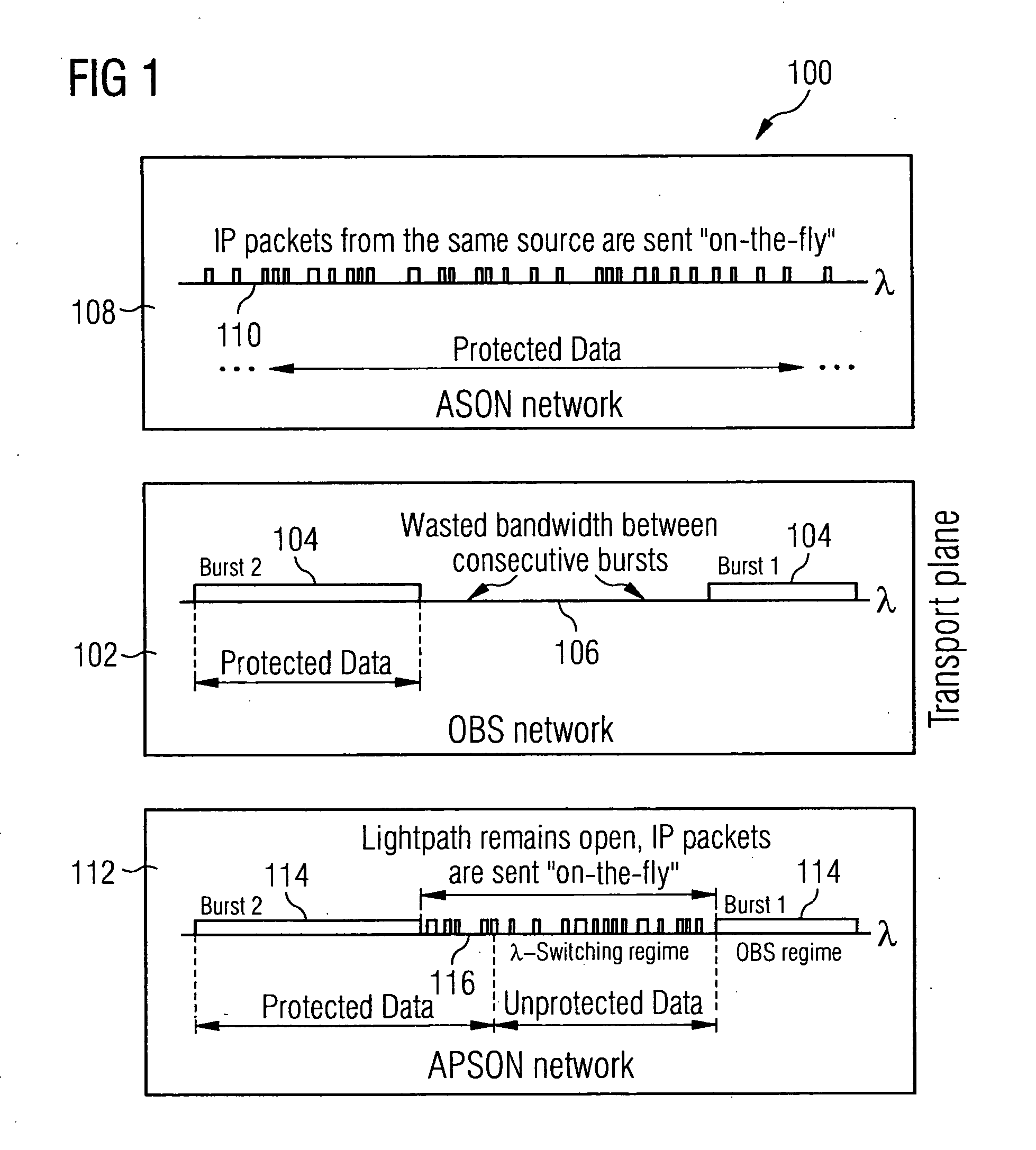
Temporal-spatial burst switching
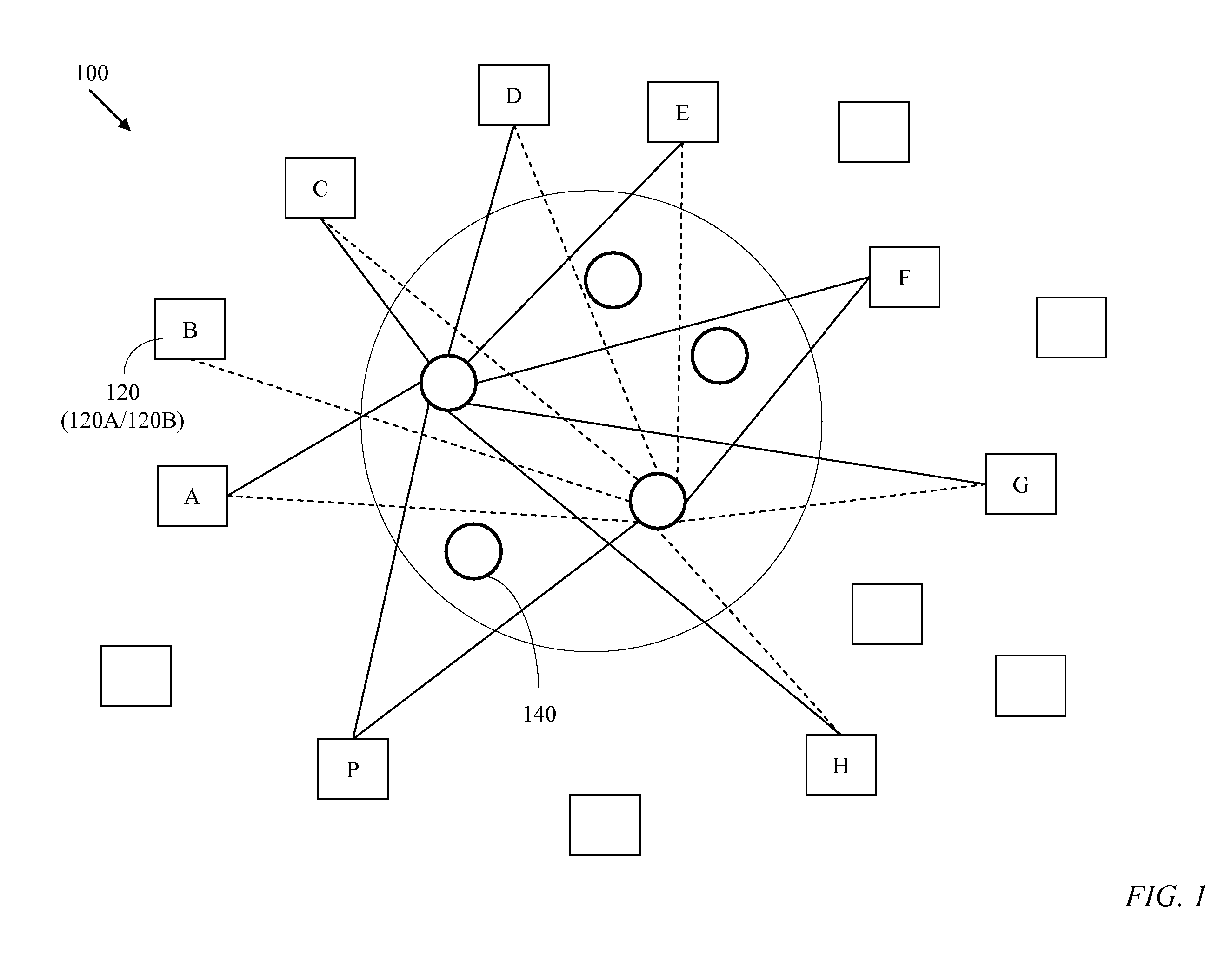
InactiveUS20050078666A1Expand coverageDecreasing mean numberMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionEdge nodeLength wave
Expanding the coverage of a time-shared network comprising electronic edge nodes interconnected by bufferless fast-switching optical nodes is enabled by combining spatial switching with temporal switching. The output side of each edge node preferably connects to a large number of core switches through individual time-locked channels and the input side preferably connects to each of a small number of core switches through a channel band having a sufficiently large number of channels. Wavelength routers may be used to aggregate individually-routed channels into WDM links.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Modular reconfigurable multi-server system and method for high-speed networking within photonic burst-switched network
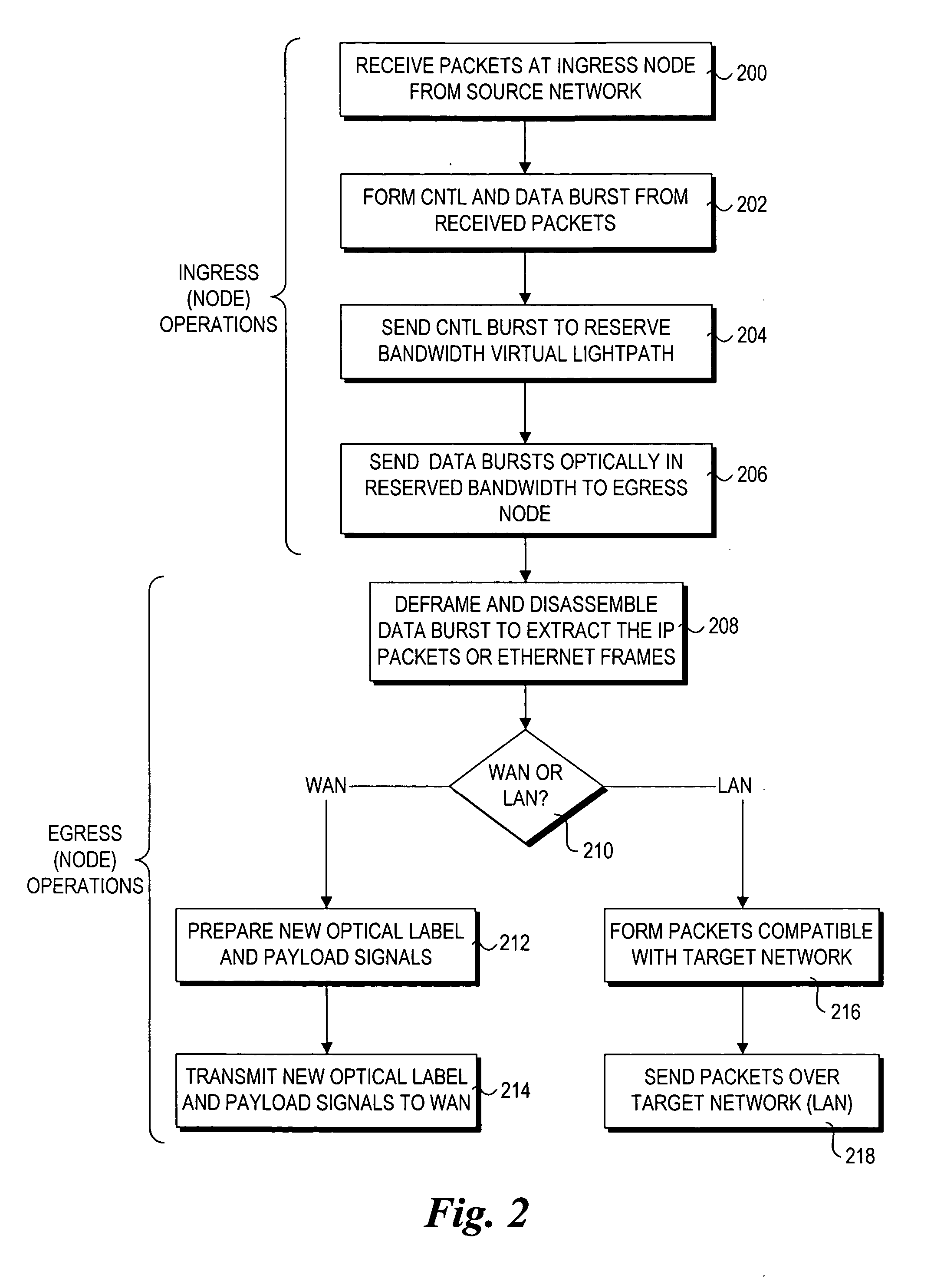
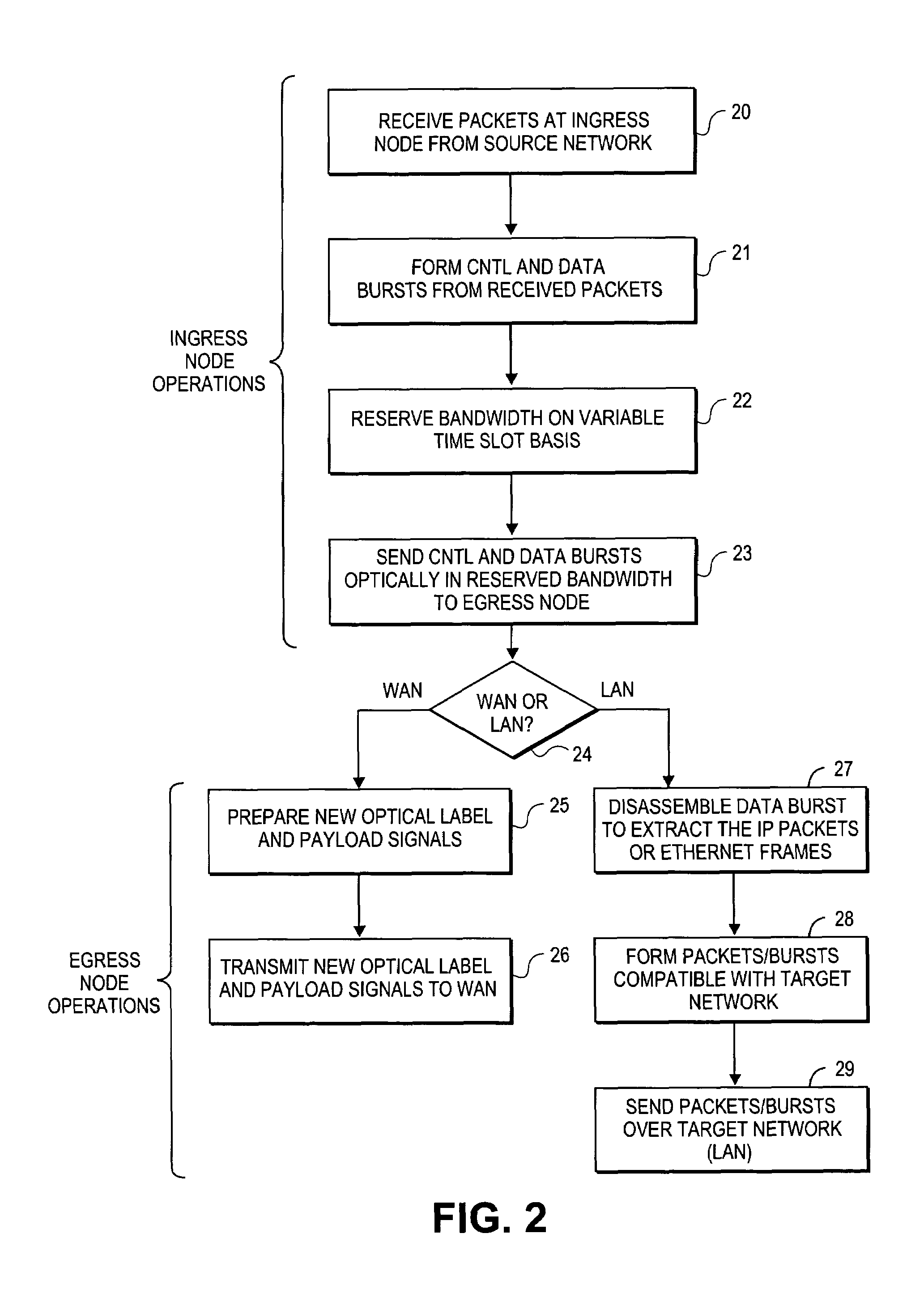
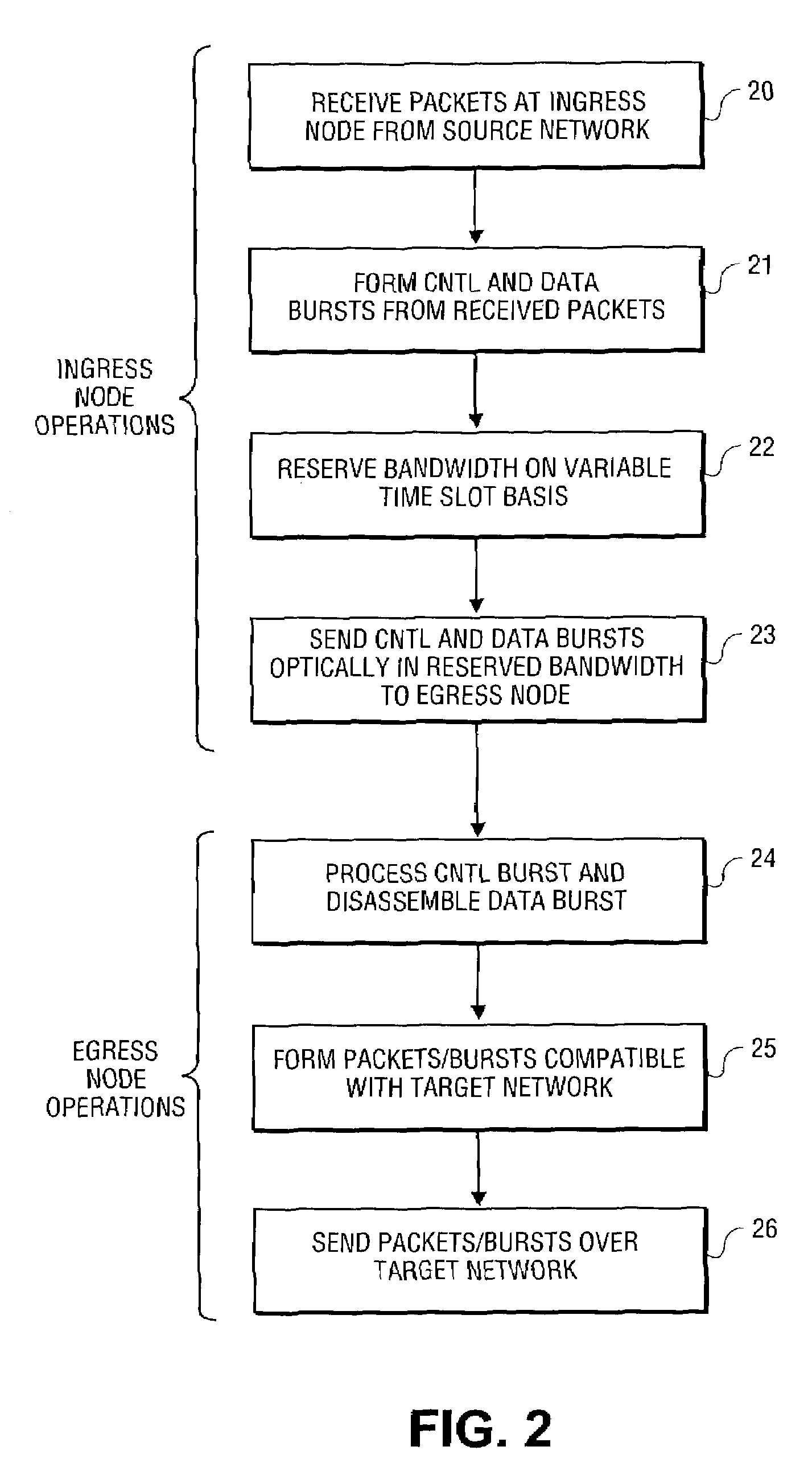
A modular reconfigurable multi-server system with hybrid optical and electrical switching fabrics for high-speed networking within a wavelength-division-multiplexed based photonic burst-switched (PBS) network with variable time slot provisioning. An optical high-speed I / O module within the multi-server system includes an optical switch with the control interface unit. A server module of the multi-server system statistically multiplexes IP packets and / or Ethernet frames to be transmitted over the PBS network, generate control and data bursts and schedule their transmission. Then, the server E-O converts the bursts, and then transmits the optical bursts to the optical I / O module. The optical I / O module then optically transmits the bursts to the next hop in the optical path after processing the optical control burst to configure the optical switch, which then optically switches the optical data burst without performing an O-E-O conversion.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Time-coordination in a burst-switching network
InactiveUS7212551B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexEdge nodeMaster controller
In a wide-coverage network comprising electronic edge nodes interconnected by bufferless core nodes, where each edge node comprises a source node and a sink node, both sharing an edge-node controller and having means for data storage and managing data buffers, the transfer of bursts from source nodes to sink nodes via the core nodes requires precise time coordination to prevent contention at the bufferless core nodes. A core node preferably comprises a plurality of optical switches each of which may switch entire channels or individual bursts.Each source node has a time counter and each core node has at least one time counter. All time counters have the same period and time-coordination can be realized through an exchange of time-counter readings between each source node and its adjacent core nodes. The time-counter readings are carried in-band, alongside payload data bursts destined to sink nodes, and each must be timed to arrive at a corresponding core node during a designated time interval. The difficulty of securing time-coordination arises from two interdependent requirements:communicating a time-counter reading from a controller of a source node to a controller of a core node requires that the source node be time-locked to the core node, andtime-locking a source node to a core node necessitates that a controller of the core node be able to receive a time-counter reading from the source-node controller during a designated interval of time.To initiate or restore time locking, a secondary mechanism is required for directing upstream signals received from source nodes toward said master controller. The present disclosure provides such mechanisms.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Flow-Rate-Regulated Burst Switches
InactiveUS20090207859A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityData segment
Burst-switching nodes using a common-memory or a time shared space switch and employing flow-rate control are disclosed. Within a switching node, data bursts are segmented into data segments of a fixed size with some segments containing information bits as well as null bits. A switching node handles data streams allocated different flow rates and, for any data stream, the internal flow rate through the switching node can be higher than the external flow rate due to null padding of segmented data. The switching node is provided with a sufficient internal capacity expansion in order to offset the effect of null padding. A controller of the switching node is provided with a flow-rate-regulation apparatus to enable scheduling the transfer of data segments across the switching node in a manner that guarantees adherence to the allocated information flow rates.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Virtual Burst-Switching Networks
InactiveUS20080232809A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division optical multiplex systemsTraffic capacityEdge node
A time-shared network comprising edge nodes and optical core nodes may be dynamically divided into several embedded networks, each of which covering selected edge nodes. At least one of the edge nodes may host an embedded-network controller operable to form multiple-source flow-rate allocation requests each of the requests specifying flow-rate allocations to a plurality of paths from several source nodes to several sink nodes. A core node may also host an embedded-network controller or several embedded-network controllers. The time-shared network may use both time-division multiplexing and burst switching.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
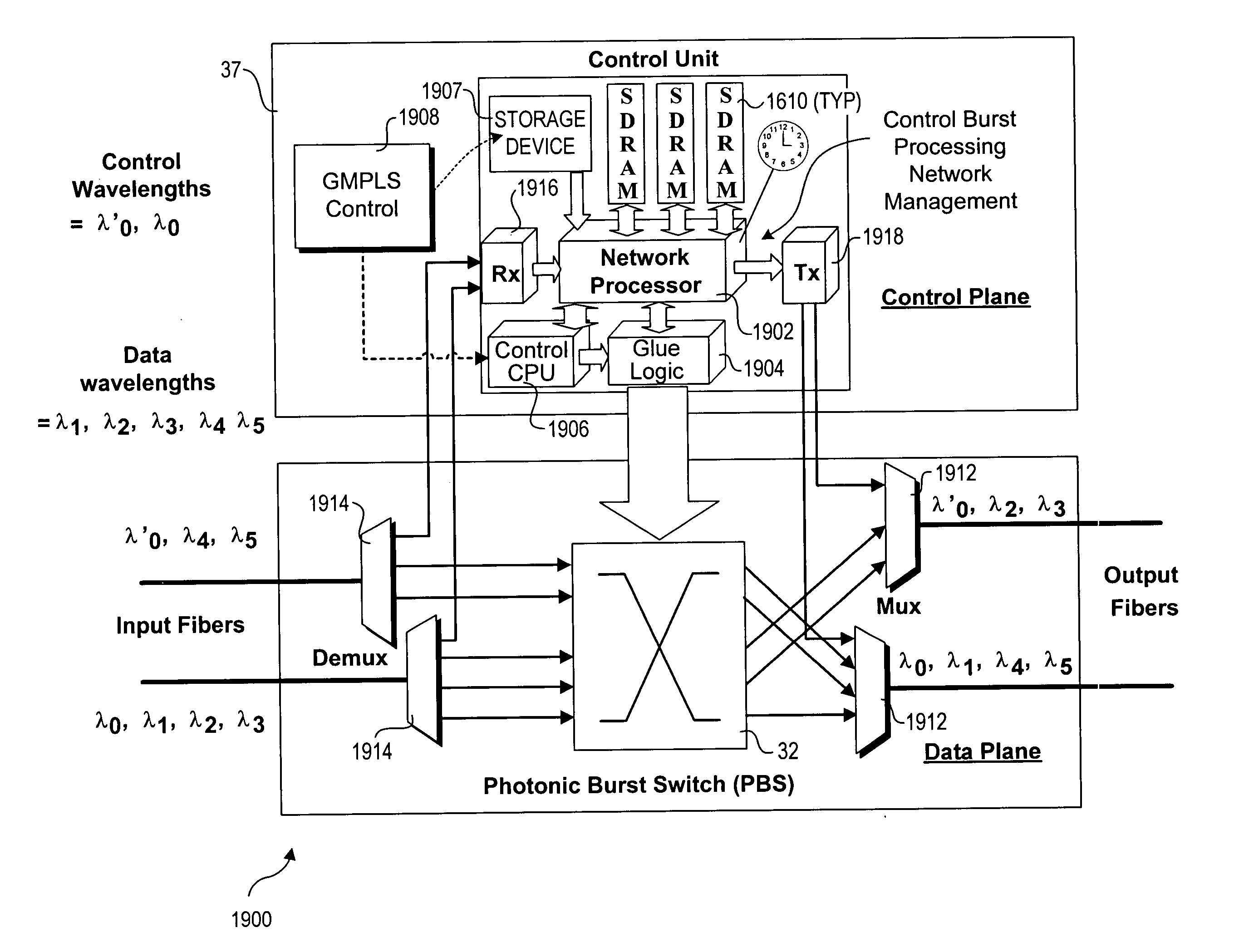
Generic multi-protocol label switching (GMPLS)-based label space architecture for optical switched networks
ActiveUS7272310B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationExchange networkPhotonics
An architecture and method for performing coarse-grain reservation of lightpaths within wavelength-division-multiplexed (WDM) based photonic burst switched (PBS) networks with variable time slot provisioning. The method employs a generalized multi-protocol label switched (GMPLS)-based PBS label that includes information identifying each lightpath segment in a selected lightpath route. A resource reservation request is passed between nodes during a forward traversal of the route, wherein each node is queried to determine whether it has transmission resources (i.e., a route lightpath segment) available during a future timeframe. Soft reservations are made for each lightpath segment that is available using information contained in a corresponding label. If all lightpath segments for a selected route are available, the soft reservations turn into hard reservations. The stored reservations enable quick routing of control burst that are employed for routing data during scheduled use of the lightpaths.
Owner:INTEL CORP
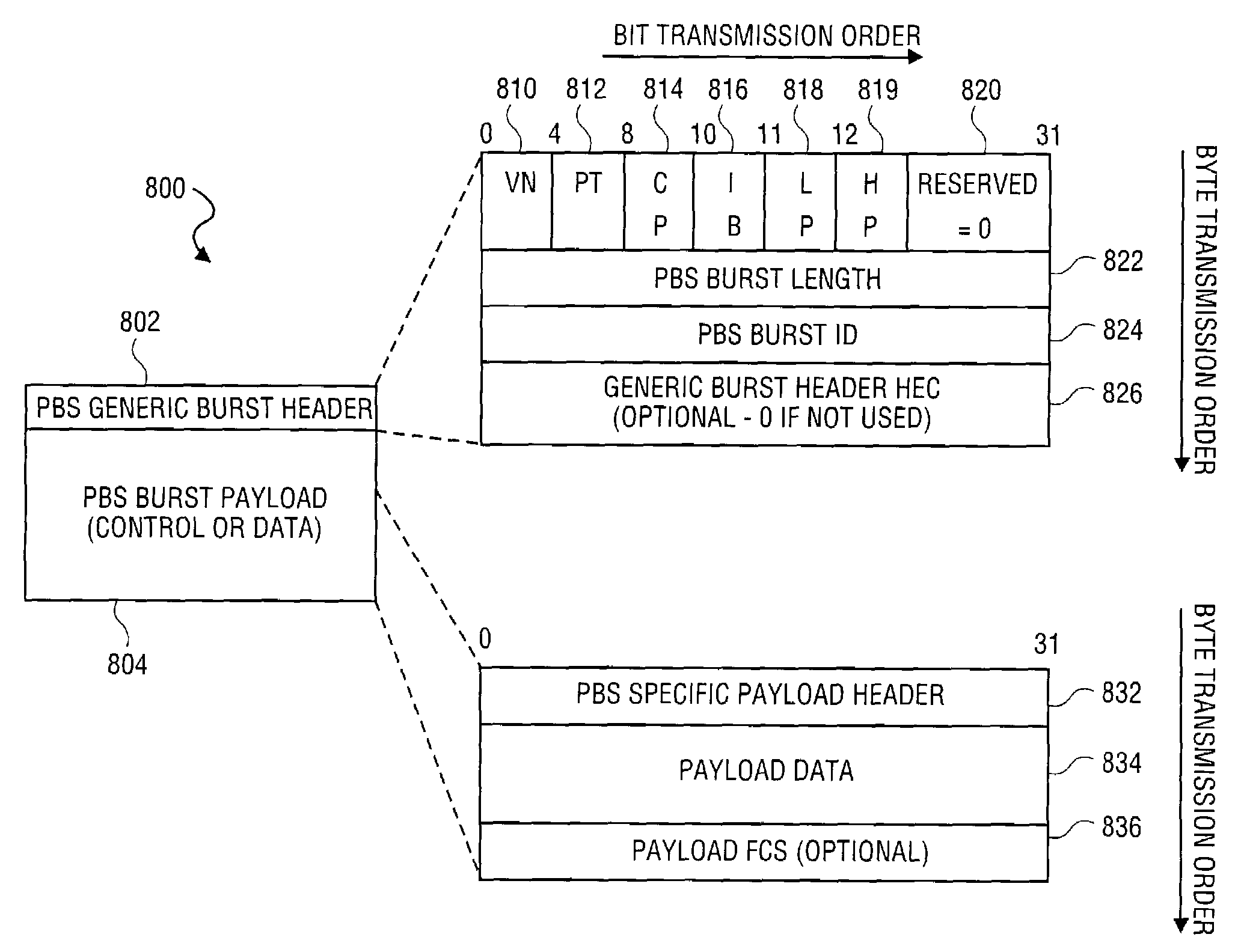
Architecture and method for framing optical control and data bursts within optical transport unit structures in photonic burst-switched networks
InactiveUS7526202B2Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationPhotonic crystalExchange network
An optical network, which includes edge and switching nodes, optically communicate information formatted into bursts that are included in one or more optical channel transport unit (OTU) frames that are based on ITU-T recommendation G.709. The overhead portion of the OTU frame can include all of the fields defined in the G.709 standard, except that the two reserved bits are used to define an OTU frame type. When the FEC function is not used, the OTU frame can be arbitrarily partitioned to carry optical burst information. The information can be either control and / or data bursts or metadata related to the optical network and / or optical burst flow. When the FEC function is used, the OTU frame is used to include optical control or data bursts or optical metadata in the payload portion of the G.709 OTU frame.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hybrid Processor With Switching Control Based on Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation for Multi-Beam Satellite Systems
ActiveUS20190028185A1Effective supportControl impactRadio transmissionSelection arrangementsOn boardStructure of Management Information
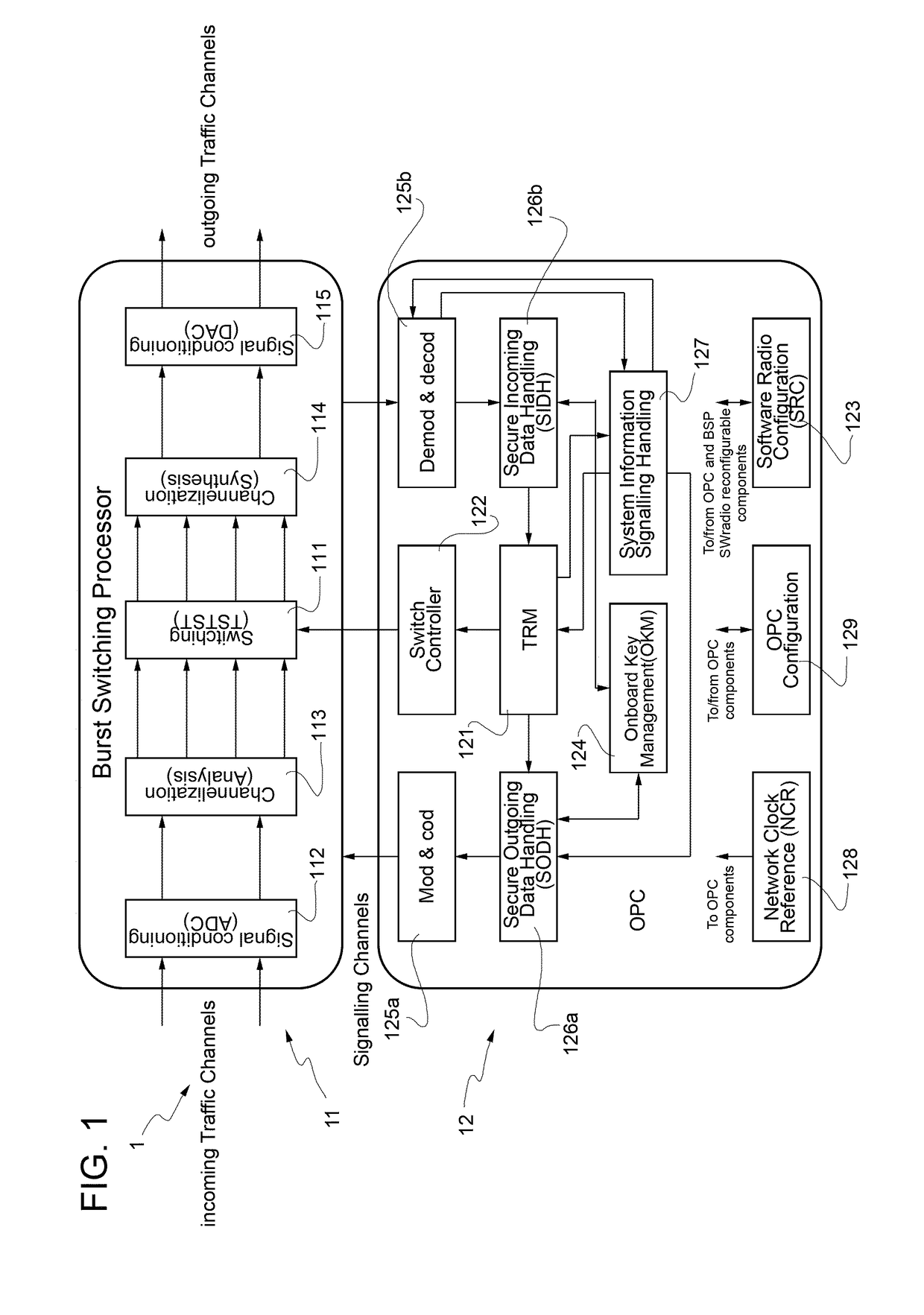
A hybrid processor system for use on board a telecommunications multi-beam satellite is provided that is controllable by a network control centre via one or more control channels. The system links to ground terminals by: providing uplink and downlink traffic channels on several satellite beams; routing atomic switched information blocks from the uplink traffic channels to the downlink traffic channels; and exchanging signaling data with the ground terminals on one or more uplink signaling channels and one or more downlink signaling channels. The atomic switched information blocks have the same given time duration and the same given baseband bandwidth. The hybrid processor system includes a burst switching processor and an on-board processor controller which is configured to store service information items indicative of: the given time duration and the given baseband bandwidth of the atomic switched information blocks; the respective uplink bandwidth, the respective uplink frequencies, a respective time length of the respective uplink time slots, and respective structure features of the respective uplink time frames and superframes of each uplink channel; the respective downlink bandwidth, the respective downlink frequencies, a respective time length of the respective downlink time slots, and respective structure features of the respective downlink time frames and superframes of each downlink channel; and quality of service and priority rules for serving the ground terminals. The on-board processor controller is further configured to extract, from incoming signaling data capacity requests sent by the ground terminals by demodulating and decoding the incoming signaling data.
Owner:THALES ALENIA SPACE ITAL SPA
Architecture, method and system of multiple high-speed servers to network in WDM based photonic burst-switched networks
ActiveUS7298973B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexExchange networkPhotonics
A modular reconfigurable multi-server system for use in a wavelength-division-multiplexed based photonic burst switched (PBS) network with variable time slot provisioning. An optical high-speed I / O module within the multi-server system enables it to serve as an edge node in the PBS network. The optical I / O module statistically multiplexes the incoming packets (e.g., IP packets or Ethernet frames) received from a legacy network, generates control and data bursts, which are then scheduled for transmission over the PBS network. The optical I / O module then optically transmits and receives the scheduled optical bursts according to traffic priority and available network resources.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Rate-Controlled Optical Burst Switching
InactiveUS20070115956A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsNetwork traffic/resource managementOptical burst switchingEdge node
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Virtual burst-switching networks
InactiveUS7397792B1Lower latencyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityEdge node
A time-shared network comprising edge nodes and optical core nodes may be dynamically divided into several embedded networks, each of which covering selected edge nodes. At least one of the edge nodes may host an embedded-network controller operable to form multiple-source flow-rate allocation requests each of the requests specifying flow-rate allocations to a plurality of paths from several source nodes to several sink nodes. A core node may also host an embedded-network controller or several embedded-network controllers. The time-shared network may use both time-division multiplexing and burst switching.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Ring network for a burst switching network with distributed management
InactiveUS20060104296A1Reduce in quantityImpacting costMultiplex system selection arrangementsLoop networksNetwork packetRing network
Transmitting data in a ring network that transmits bursts and data packets. A path setup message is sent to request a data transmission between a source node and a destination node j through intermediate nodes connecting the source node and the destination node j. Each intermediate node determines that a connection to a next node along the path is available when the connection to the next node, that normally transmits bursts and data packets, transmits data packets. A current data transmission of data packets on the path is stopped when the entire path is determined to be available.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG
Burst switching in a high capacity network
InactiveUS20050207339A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationEfficient use ofError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMaster controllerData loss
Owner:BESHAI MAGED E +1
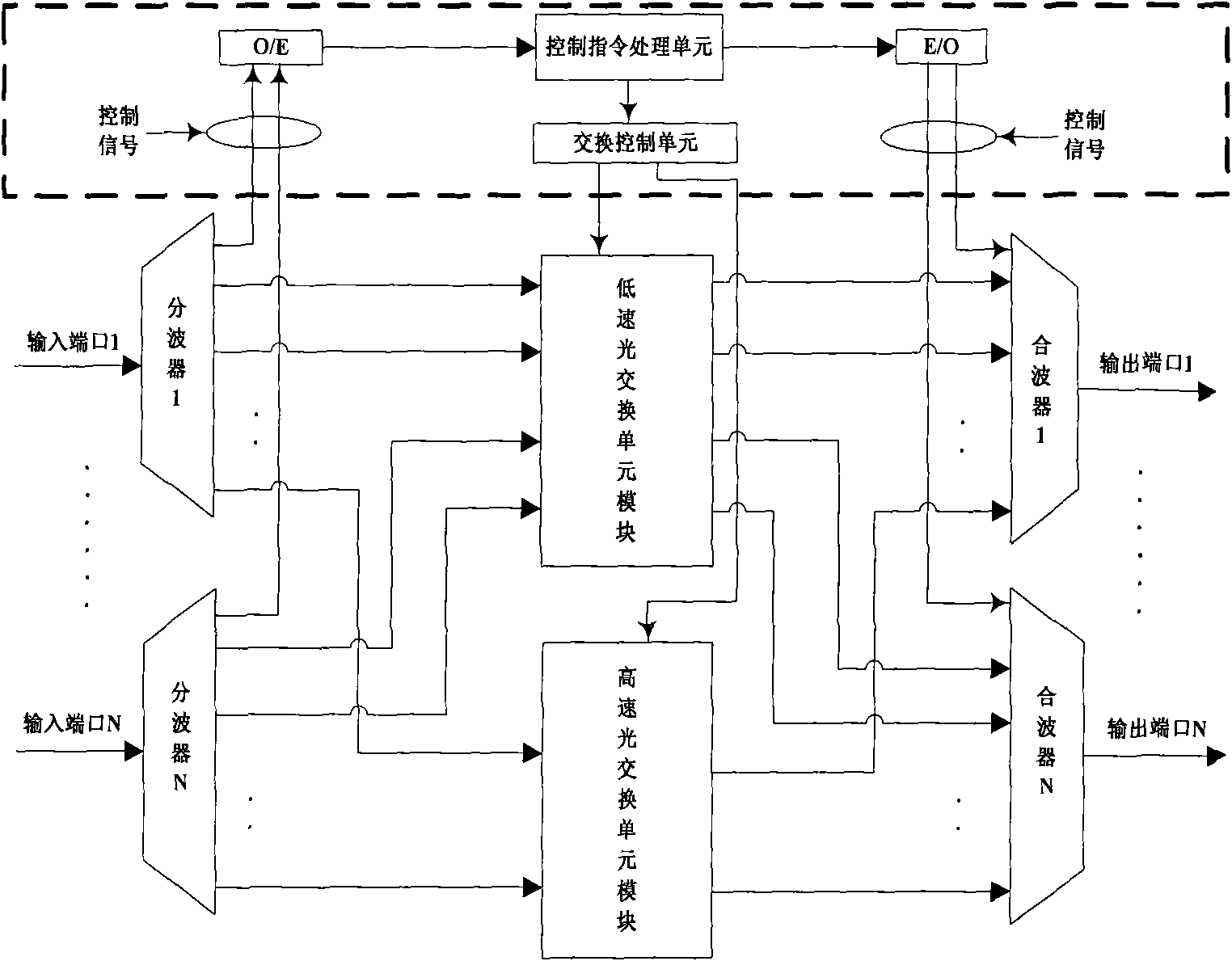
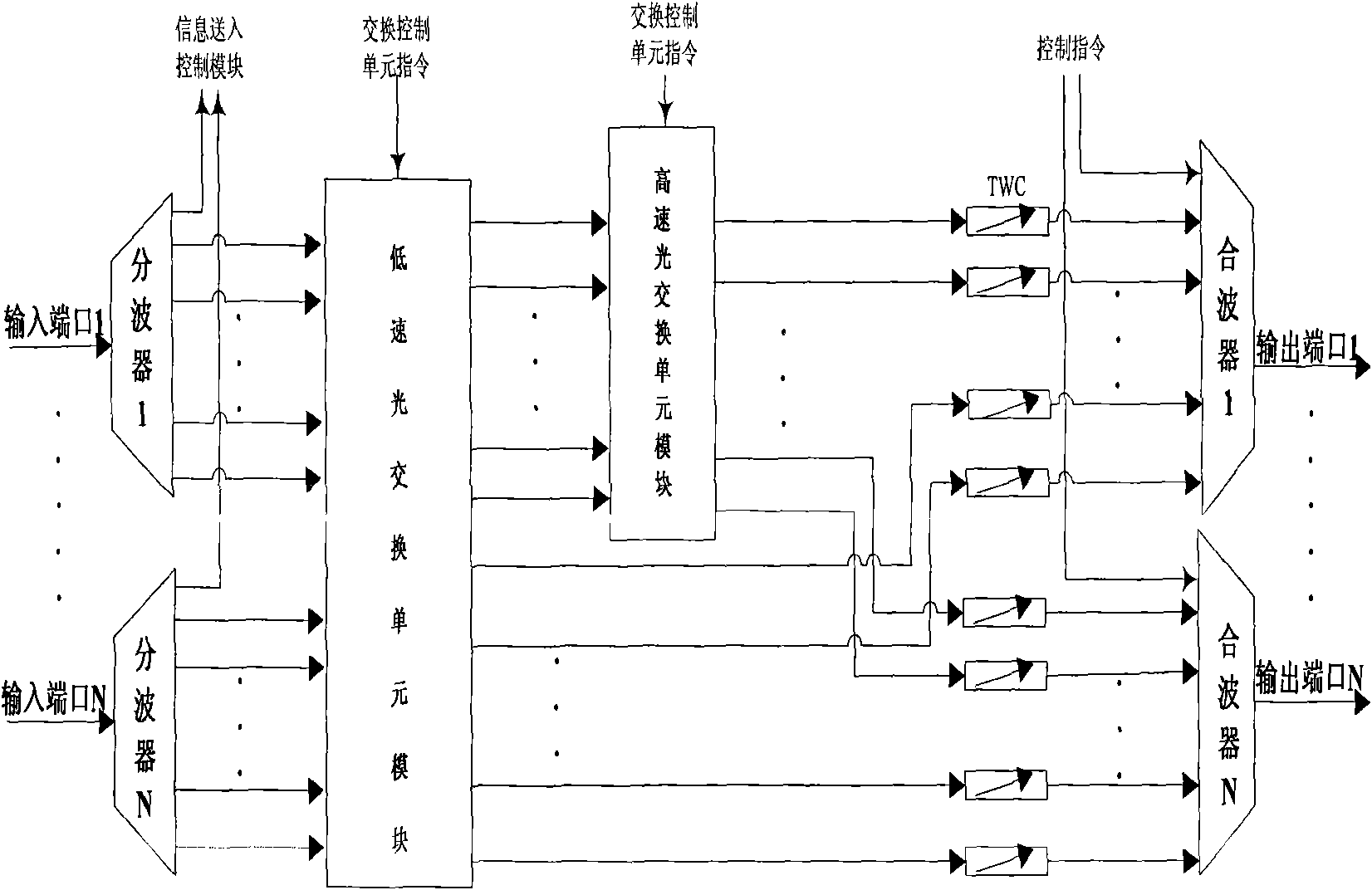
Switch processor matched with core node of hybrid optical switching network
InactiveCN101621719AFlexible automatic deploymentConvenient automatic provisioningMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic network arrangementsLow speedExchange network
The invention relates to a switch processor matched with a core node of a hybrid optical switching network in an optical network communication technology. The switch processor comprises a wave separator set, a wave combiner set, a low-speed optical switch unit module, a high-speed optical switch unit module and tunable wavelength converters, wherein the wave separator set and the wave combiner set are provided with an input port and an output port; the low-speed optical switch unit module and the high-speed optical switch unit module are sequentially arranged between the wave separator set and the wave combiner set in series and respectively provided with an interface connected with a switching control unit in a node; and the tunable wavelength converters are arranged between a high-speed optical switch unit module output port and wave combiners and a low-speed optical switch unit module output port and the wave combiners. The low-speed optical switch unit module in the switch processor is used for supporting optical circuit switching, and the high-speed optical switch unit module simultaneously supports optical burst switching and the optical circuit switching; therefore the switch processor has the characteristics of flexibly, conveniently, reliably and automatically deploying hybrid optical switching modes, improving the flexibility of the optical burst switching / the optical circuit switching, the utilization rate of wavelength resources, the bearing capacity of the optical circuit switching in a network, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
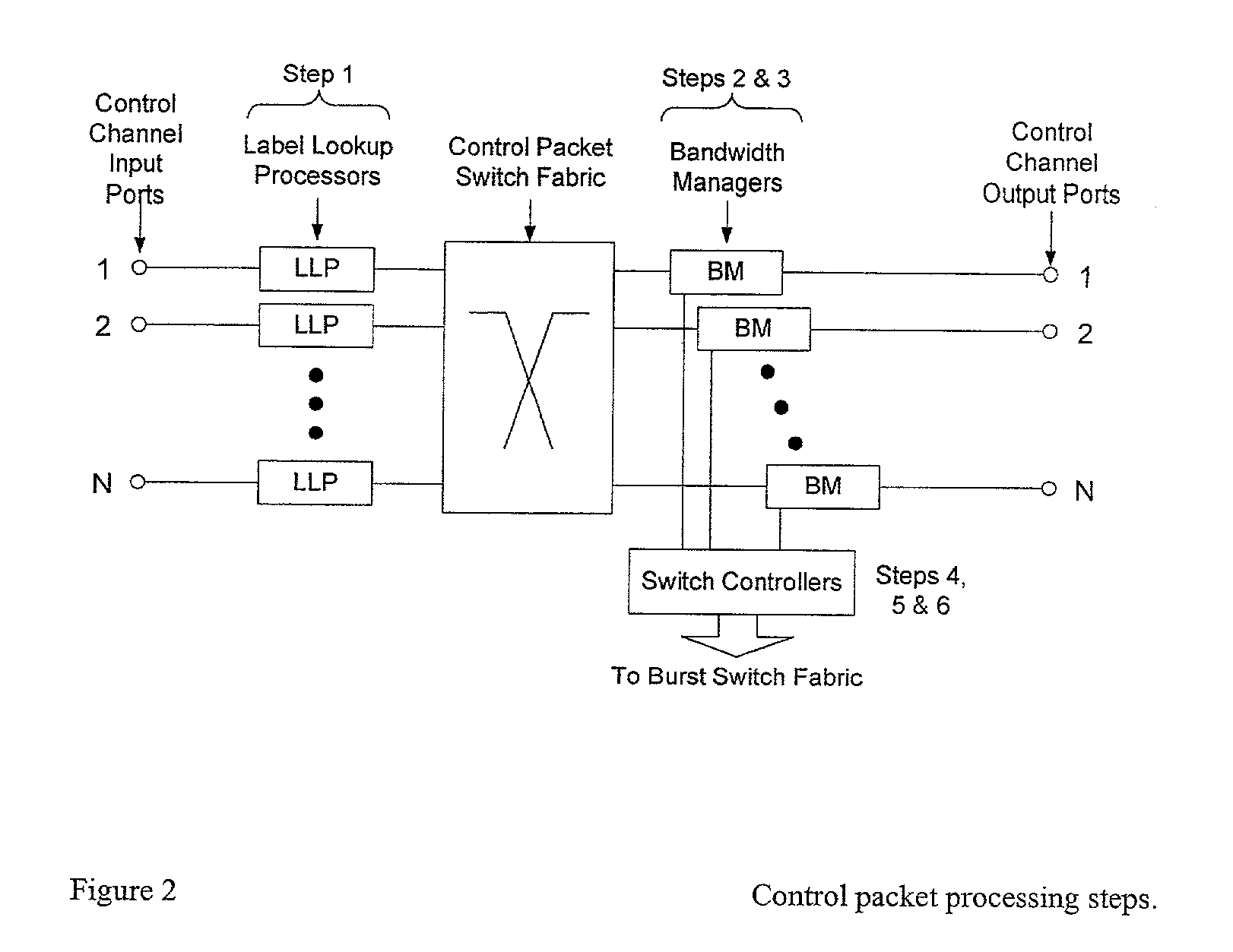
Method and apparatus for burst scheduling
InactiveUS7257127B1Quantity minimizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsLoop networksControl channelTime difference
Control information associated with data bursts to be switched on a burst-switched router is transmitted using payload envelopes (100) on one or more control channels (16). A control channel scheduling module (86) defines sets of contiguous payload envelopes, referred to as “frontiers” (110). A frontier contains a predetermined number of payload envelopes that could be transmitted over a maximum time difference from the time of arrival of a control packet to a latest time of departure for the control packet. After selecting a control packet, a current frontier is determined from a current time and a frontier index. Scheduling information for the current and next frontiers is stored in memory (116). The memory is searched for an available gap to accommodate the control packet (144) in one of either the current set or a next frontier based on the scheduling information.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Optical path structure of bust ring network node based on fixed transmission tunable reception
InactiveCN101013990AEasy to upgradeSupport fault monitoringMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexerRing network
The invention discloses one light burst ring network point path structure based on fix attuning light, which comprises the following parts: de-multiplexer, first light split, light plug multiple device, multiplexer, light amplifier, second light split device, attuning receiver set and wave converter, wherein, the de-multiplexer, first light split device, light plug multiplexer device and multiplexer are connected and first split device divides out other path and light amplifier device and second light split are connected and the second light split device and attuning receiver parts.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Packing and unpacking method of ultra high-speed optical burst-switched network and system thereof
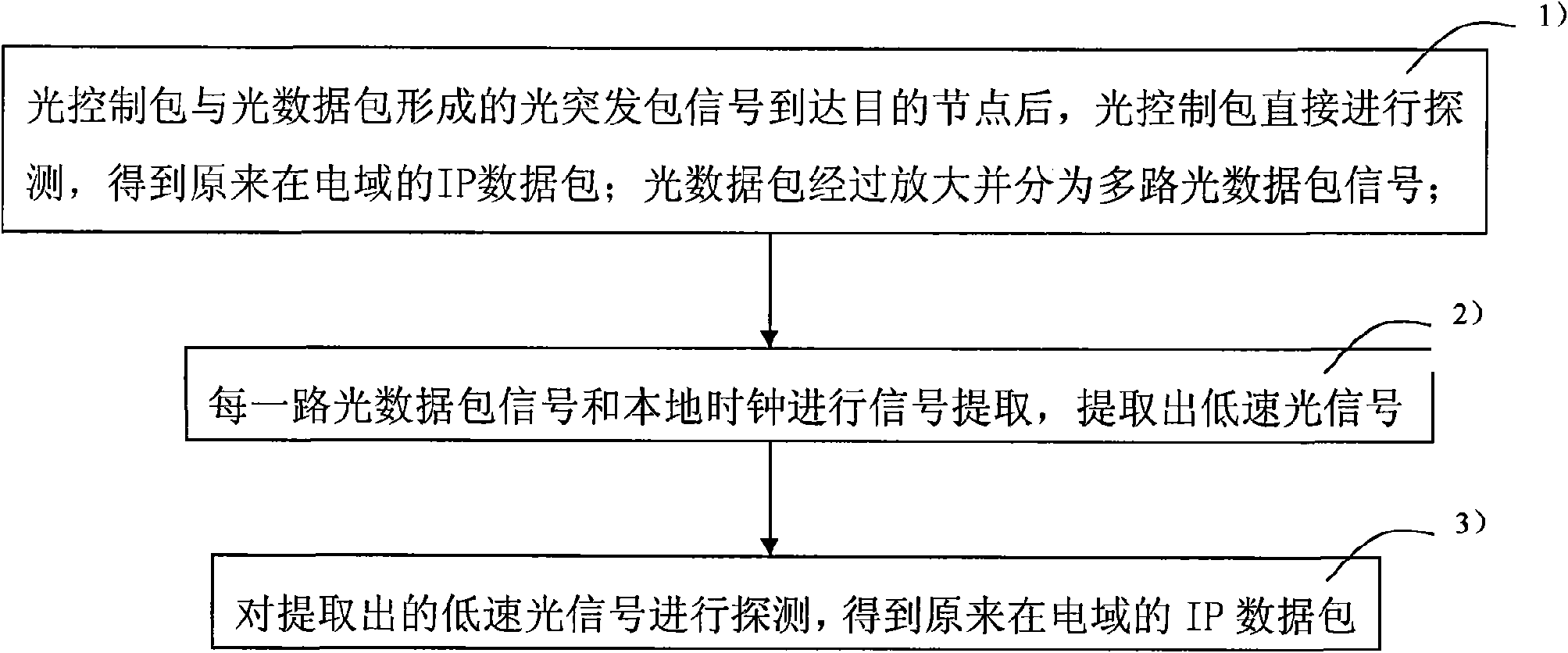
InactiveCN101677416AIncrease transfer rateLarge amount of informationMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionUltra high speedNetwork packet
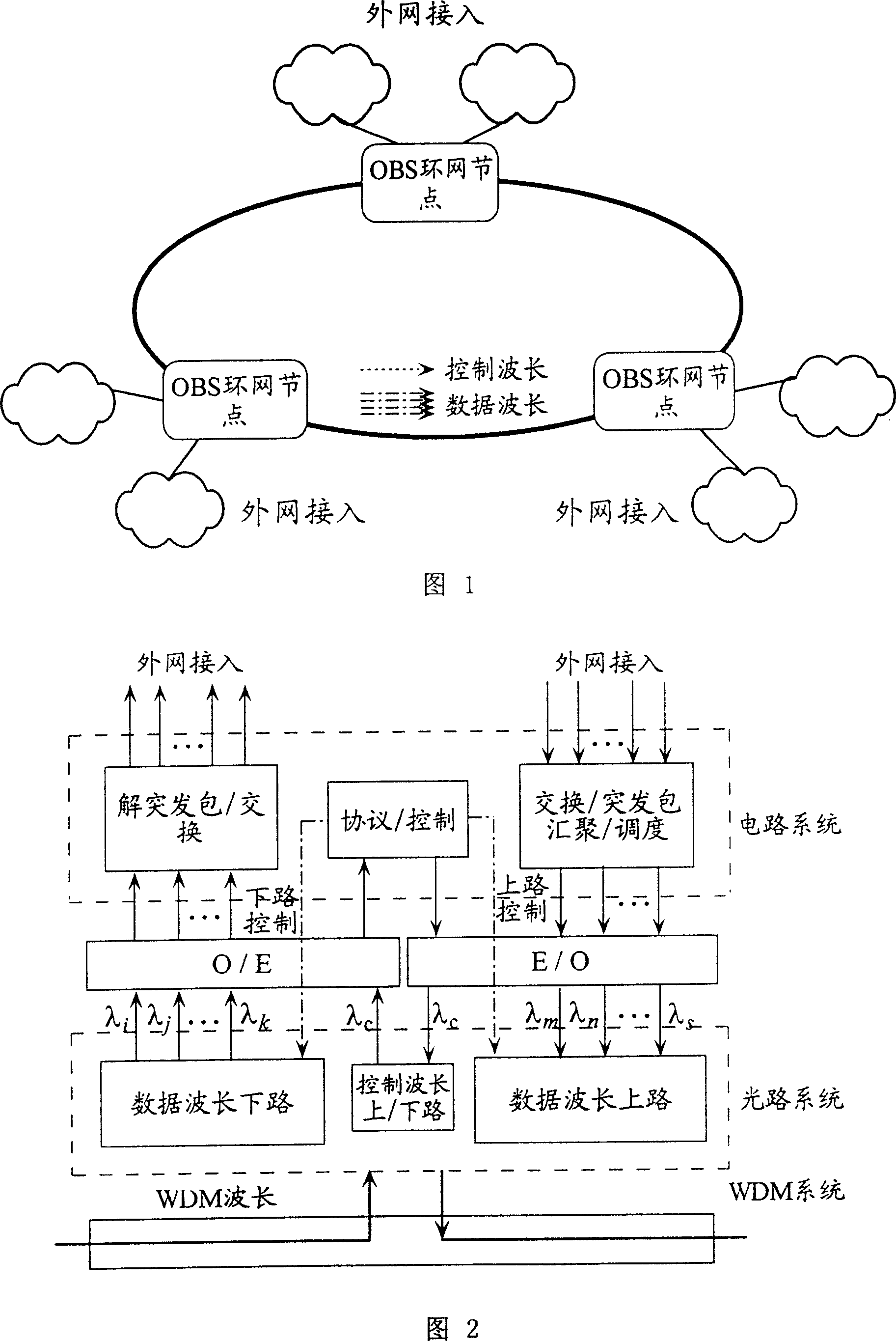
The invention relates to a packing and unpacking method of an ultra high-speed optical burst-switched network and a system thereof. The packing method comprises the following steps: 1) gathering an electric field IP data packet; 2) generating offset time after the gathered IP data packet is subject to route analysis, and forming an optical control packet; 3) modulating the IP data packet into an optical signal, and performing rate multiplication to the modulated optical signal to form an optical data packet; 4) forming a packet optical bursting packet by the optical control packet and the optical data packet, and transmitting the packet optical bursting packet. The invention provides the packing and unpacking method of ultra high-speed optical burst-switched network and the system thereof, which ensures that OBS network has high transmission rate, simple structure and low cost.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for supporting real-time service in optical burst exchange
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Methods to process and forward control packets in OBS/LOBS and other burst switched networks
InactiveUS20020141398A1Improve business performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsData packOptical burst switching
The invention provides a novel method to reduce the minimum offset time and pre-transmission delay for each data burst in Optical Burst Switching or Labeled Optical Burst Switching or other packet or burst switched systems. Under this method, the control packet is relayed as soon as it is determined if bandwidth for the data burst at the data burst output port(s) can be reserved successfully, greatly speeding up the setup and configuration of the Switching Element.
Owner:BRILLIANT OPTICAL NETWORKS
Laser power grid
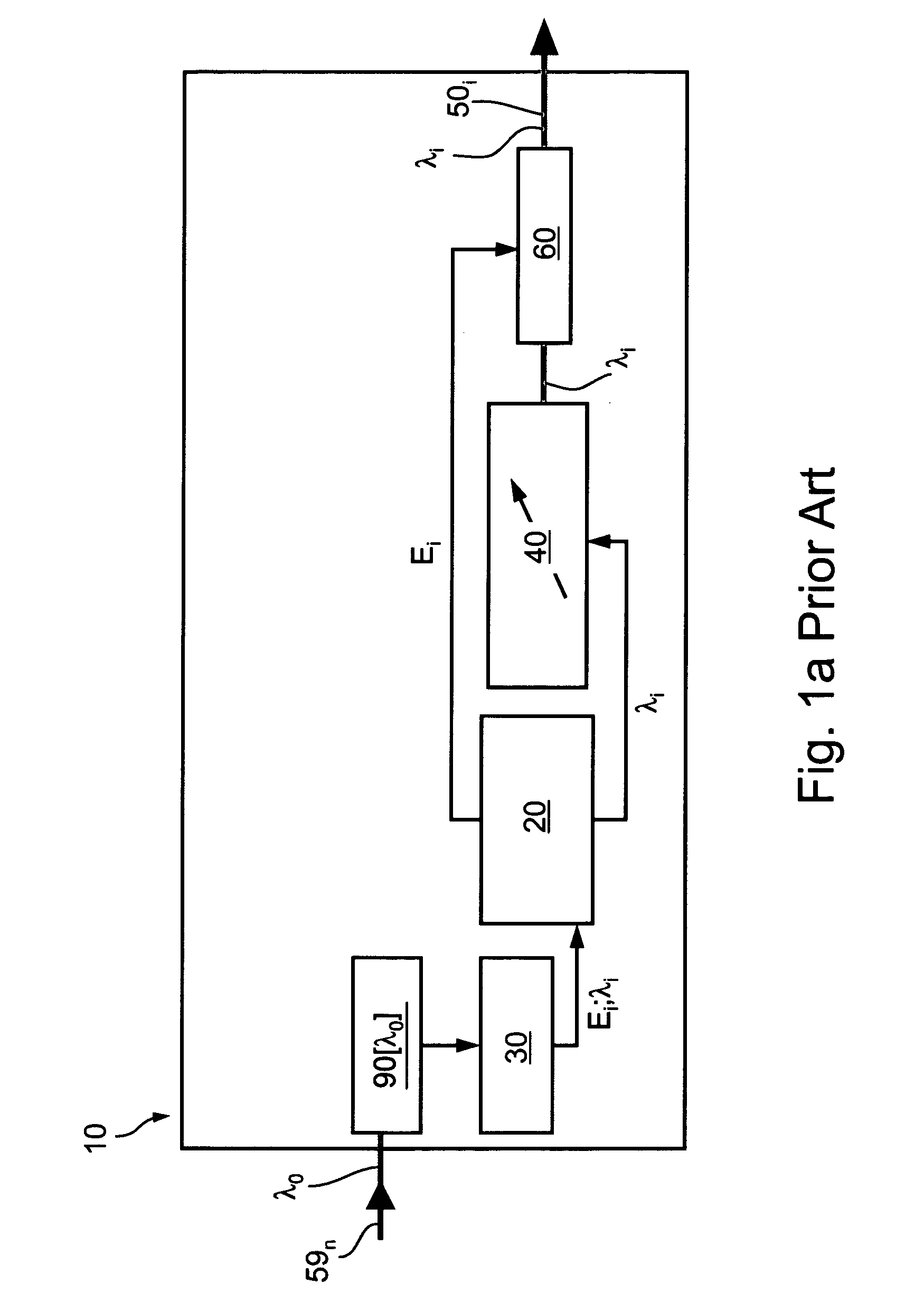
InactiveUS20060062514A1Produce heatFaster and cheapWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesExchange networkPower grid
A laser power grid for operation with data networks employs WDM and incorporates wavelength addressing. The laser power grid (100) includes a laser power supply station (110) comprising a plurality of continuous-work laser sources (112, 114, 115, 116, 118), a laser distribution grid (130) for distributing light propagations of different wavelengths throughout a data network and an optical switching network (142, 144, 145, 146, 148) coupled to the laser distribution grid for locally turning the laser power on when it is needed. The laser power grid replaces systems of tunable lasers. It is considerably faster and cheaper than systems of tunable lasers and produces less waste heat within the data network surroundings. The laser power grid incorporates parallel fast optical communication in complex multi-node communication and computer networks and enables the implementation of burst switching and packet switching by wavelength addressing.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com