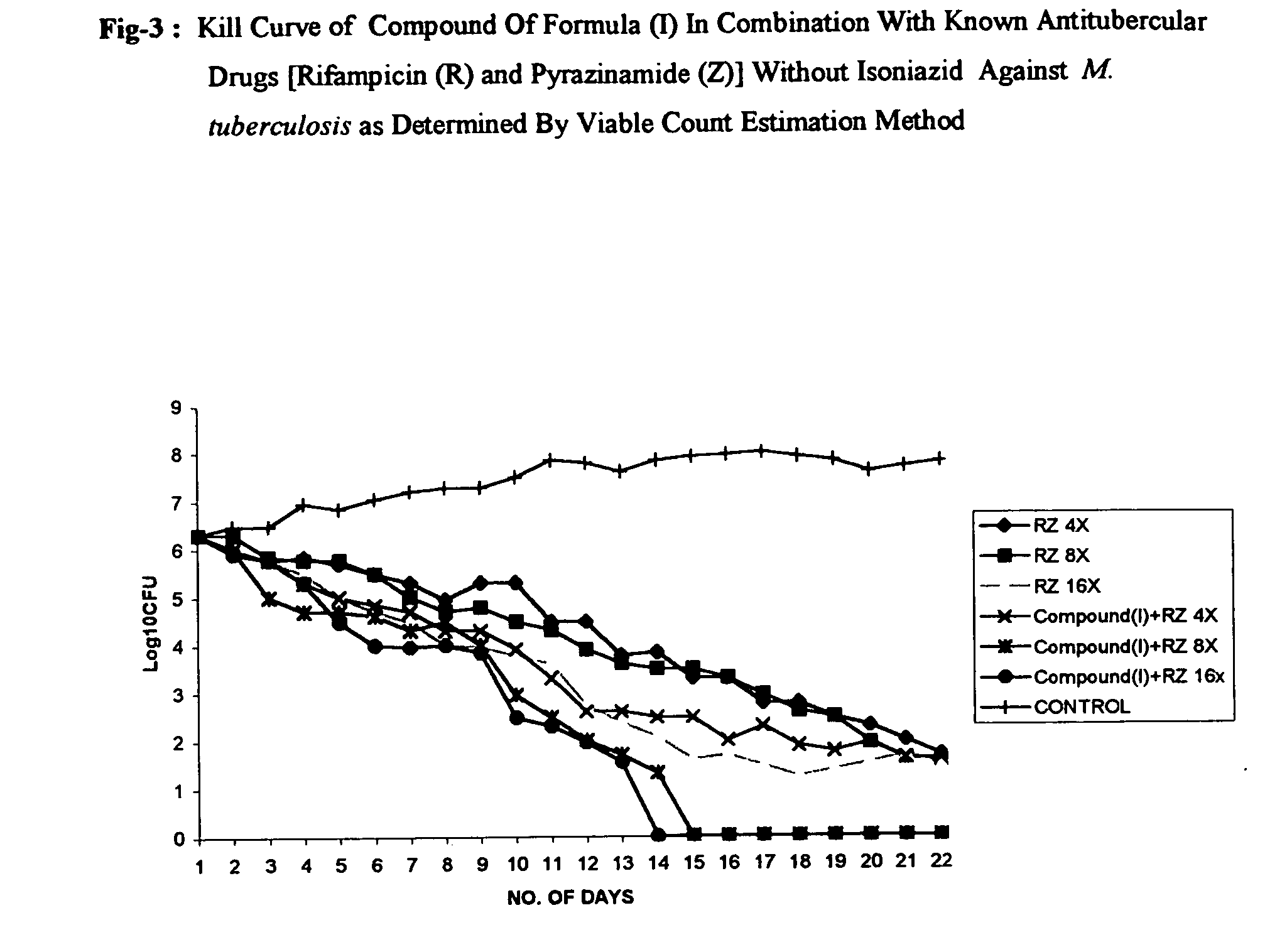
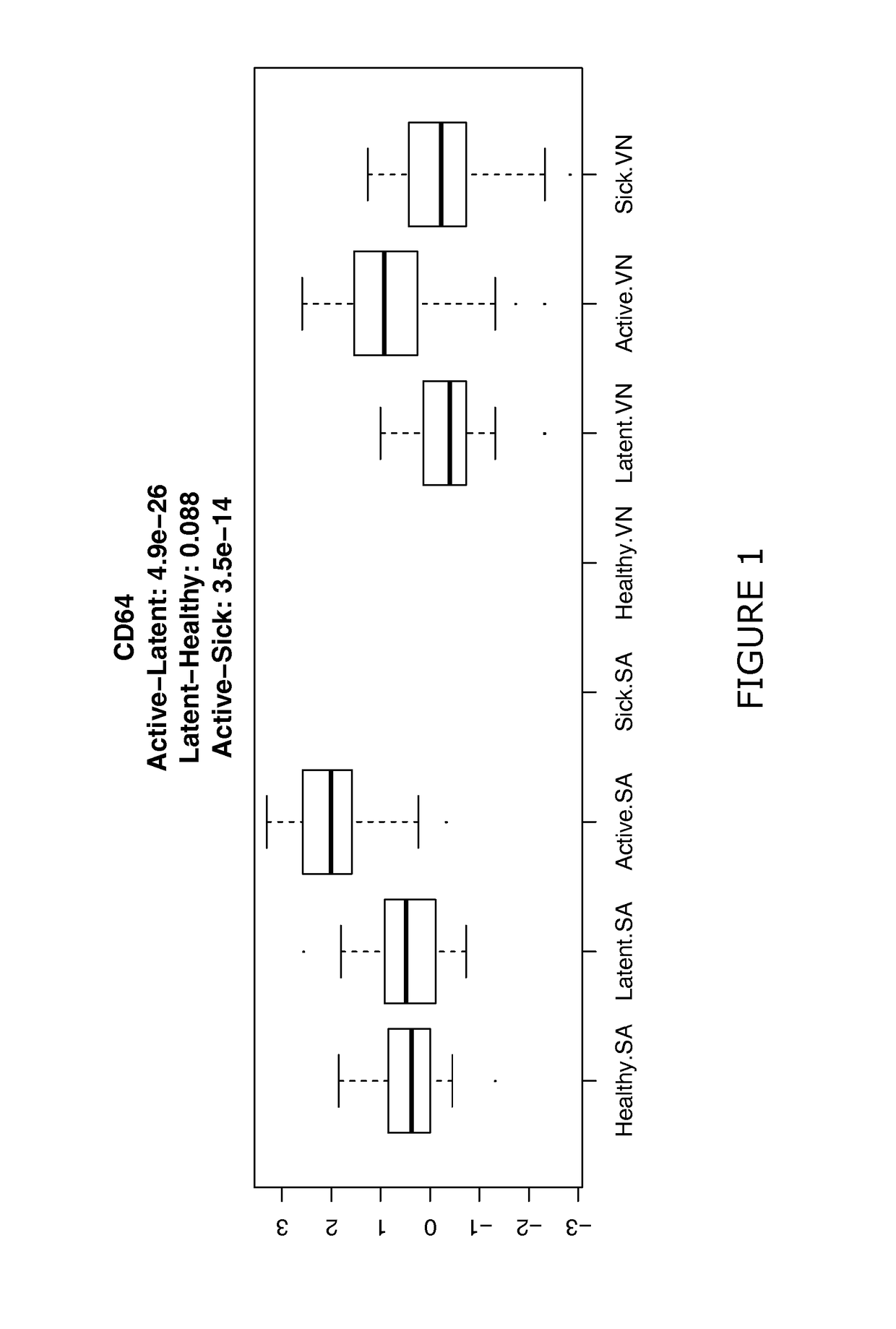
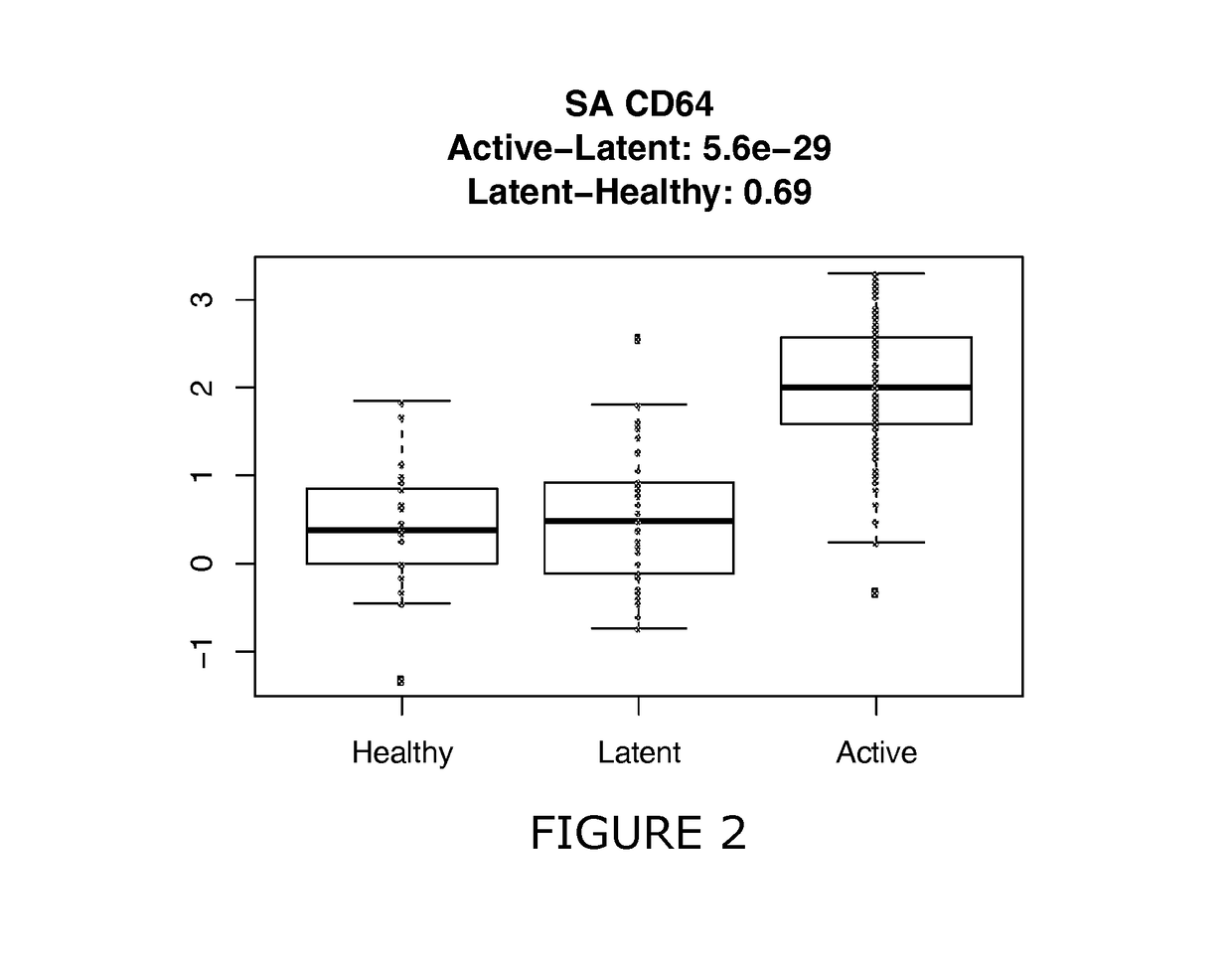
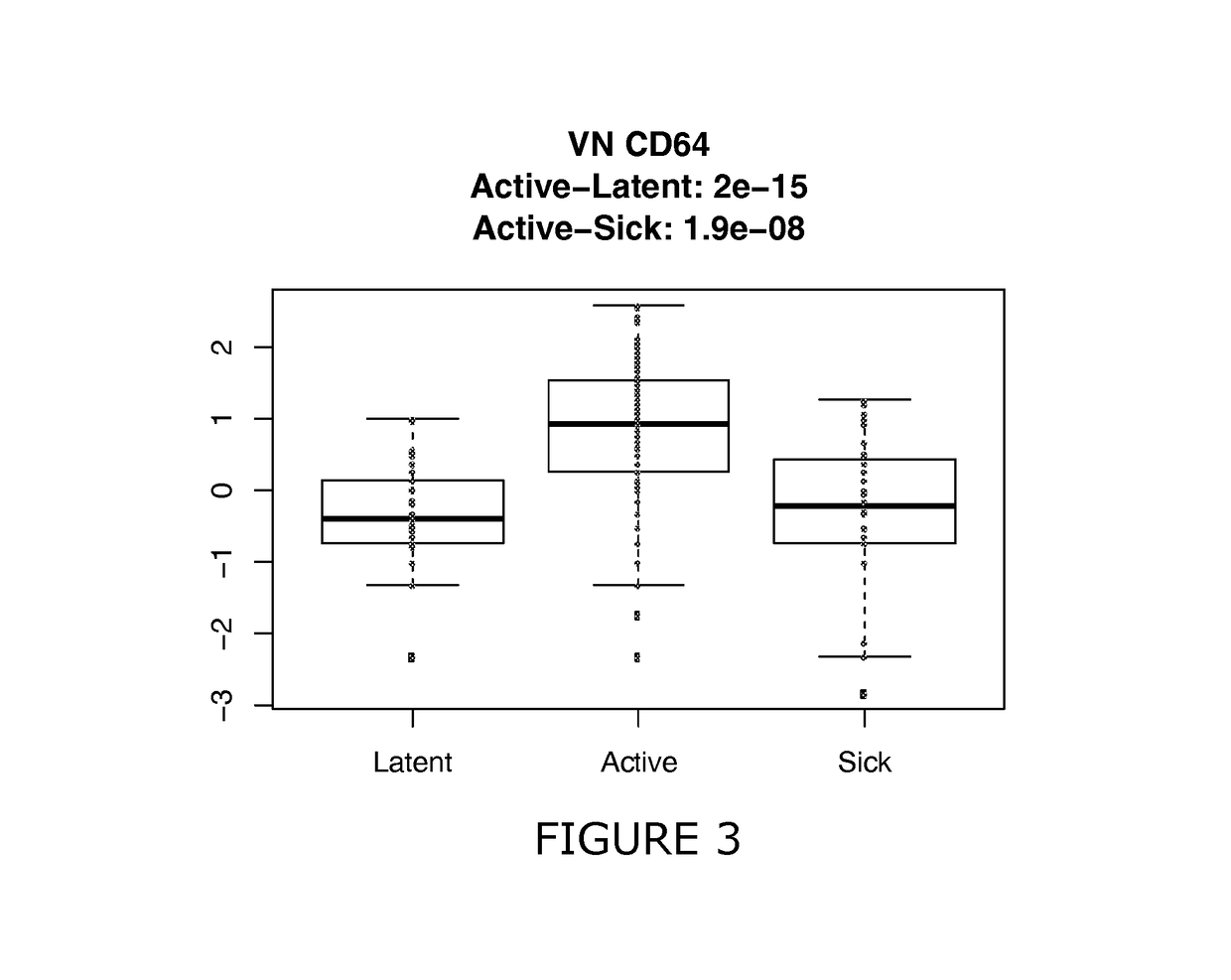
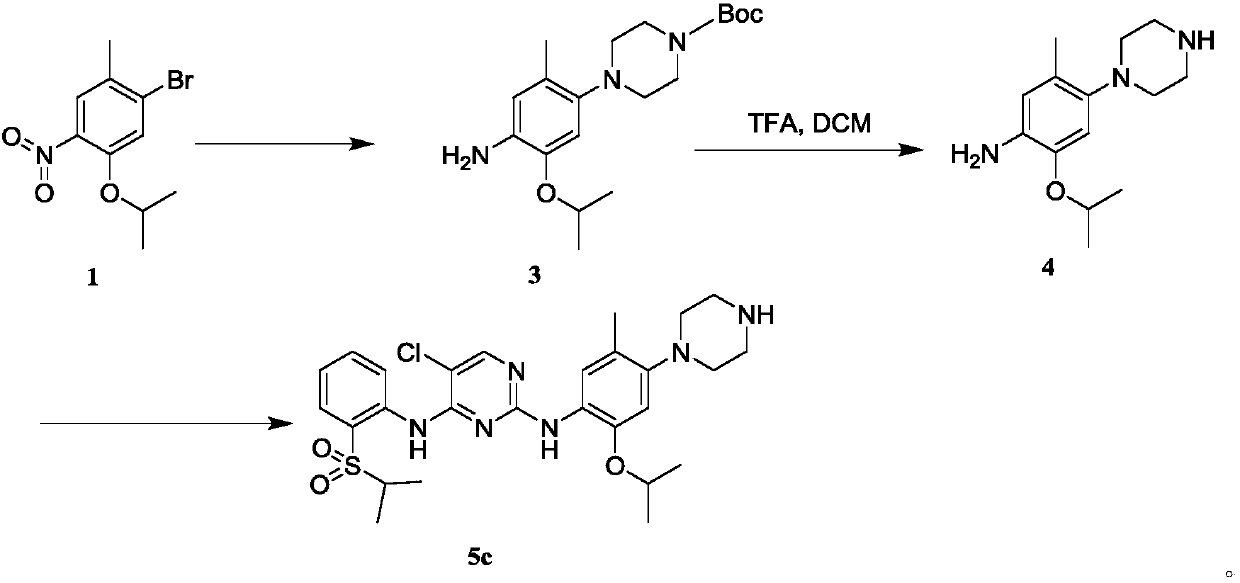
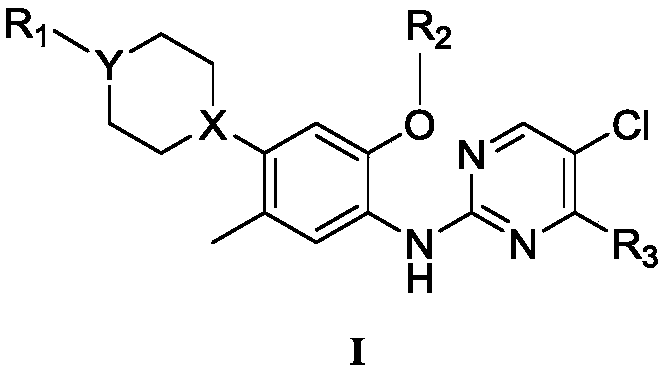
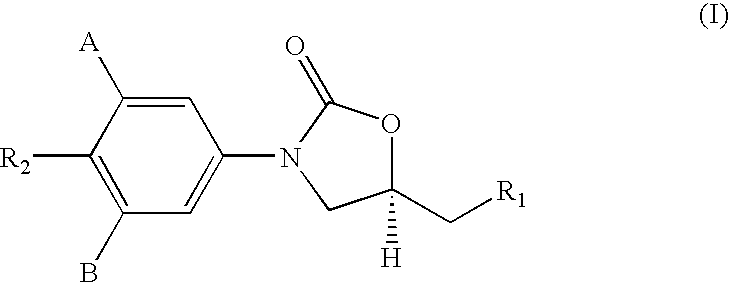
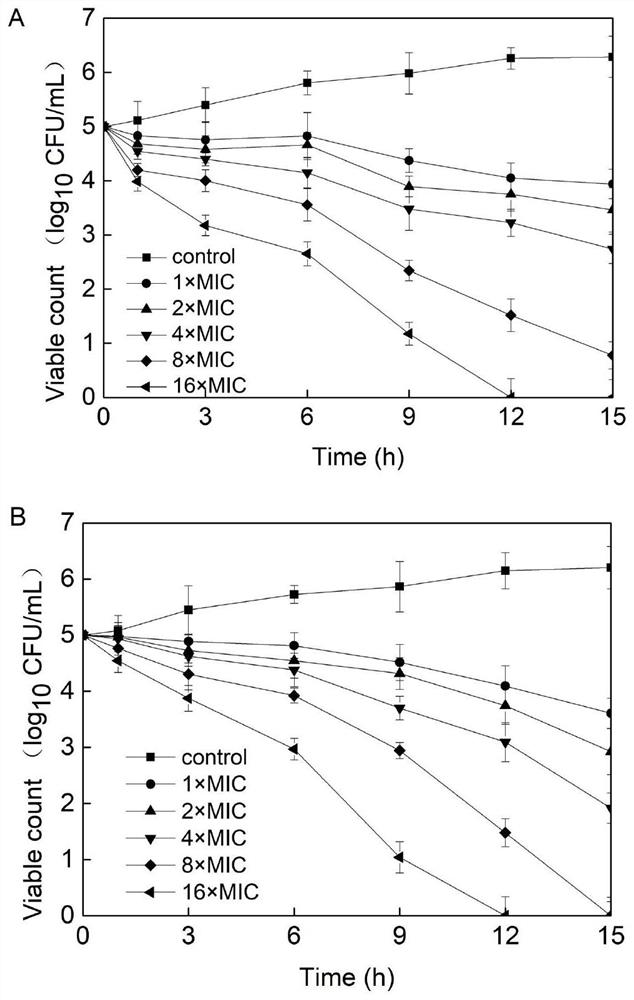
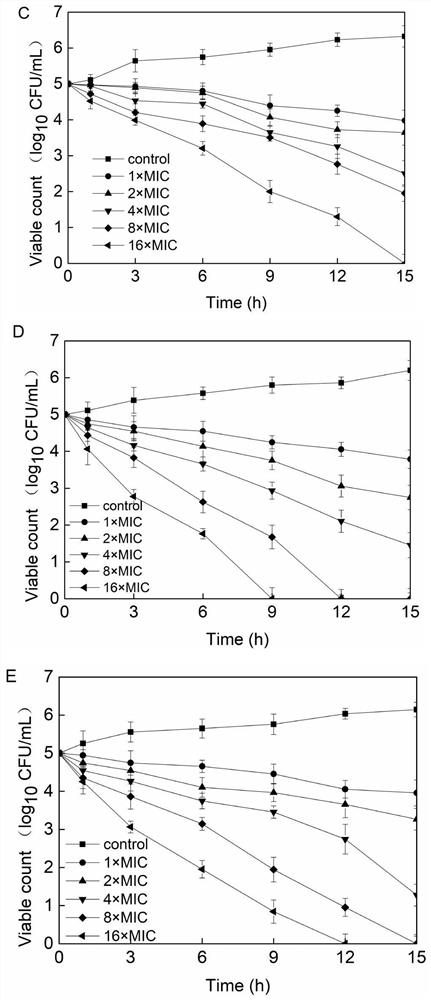
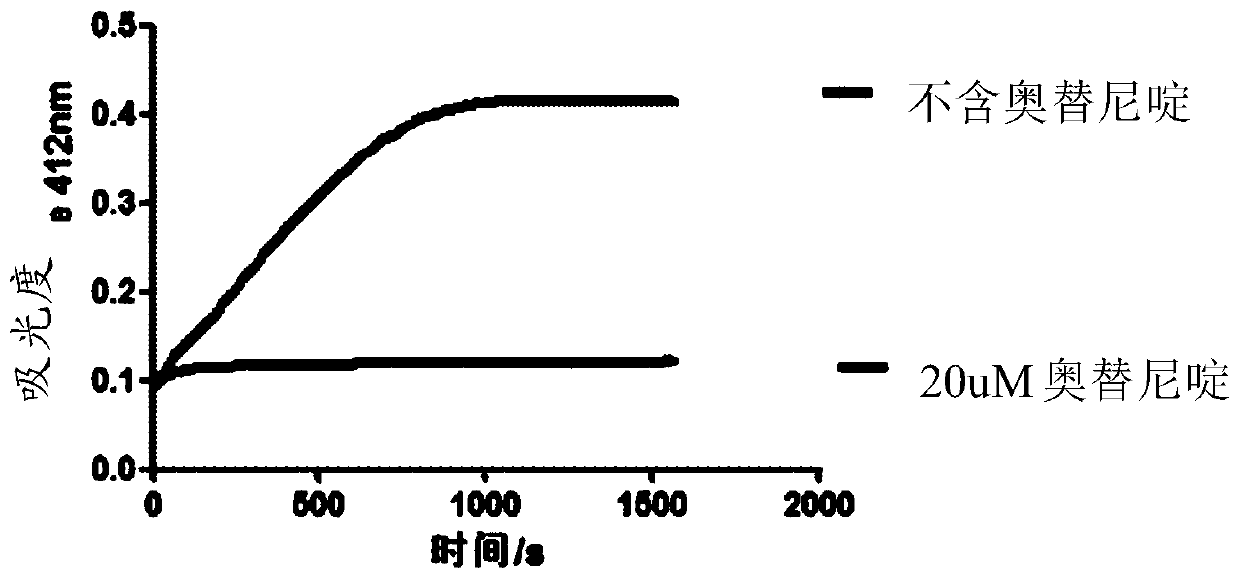
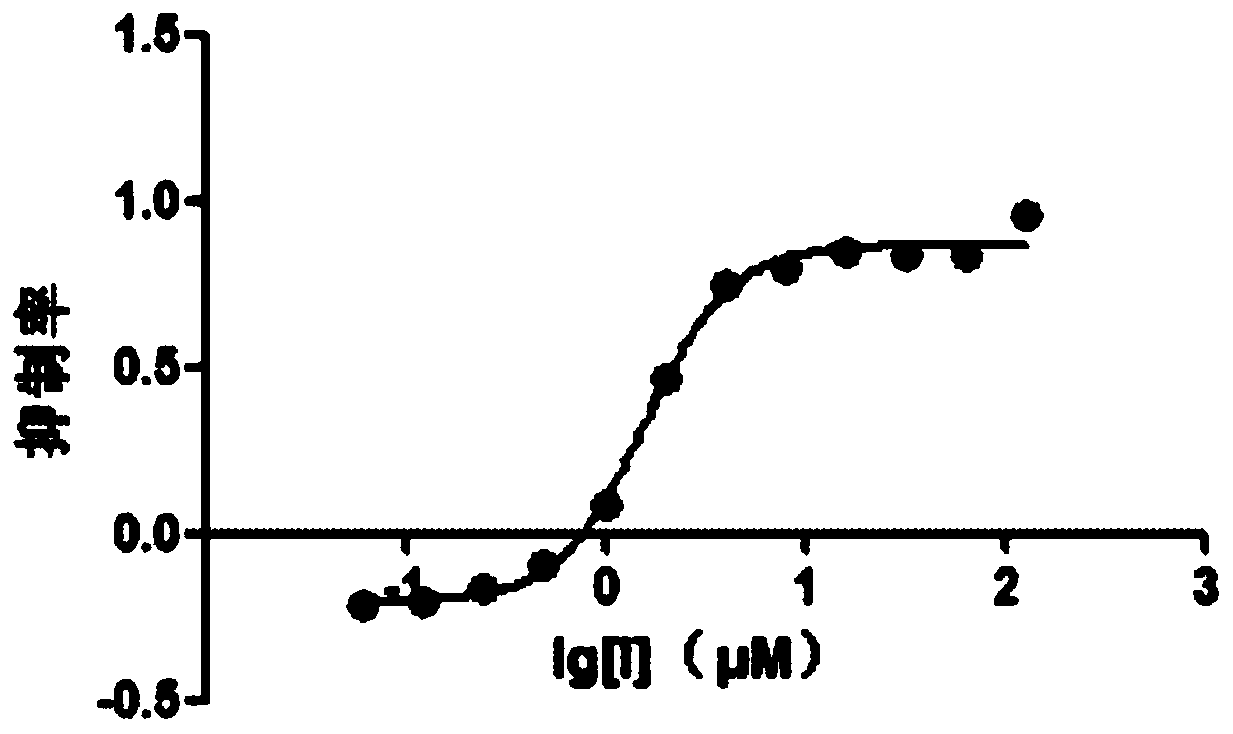
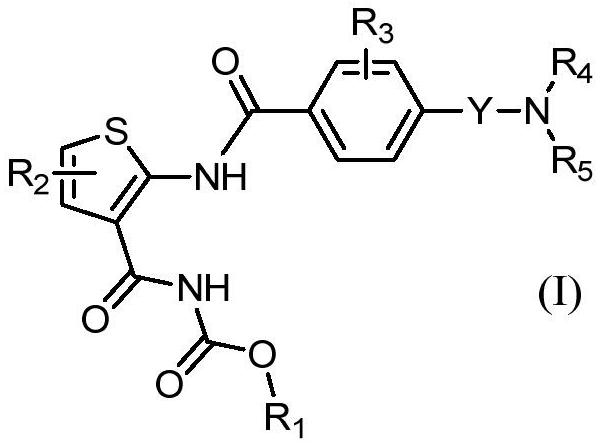
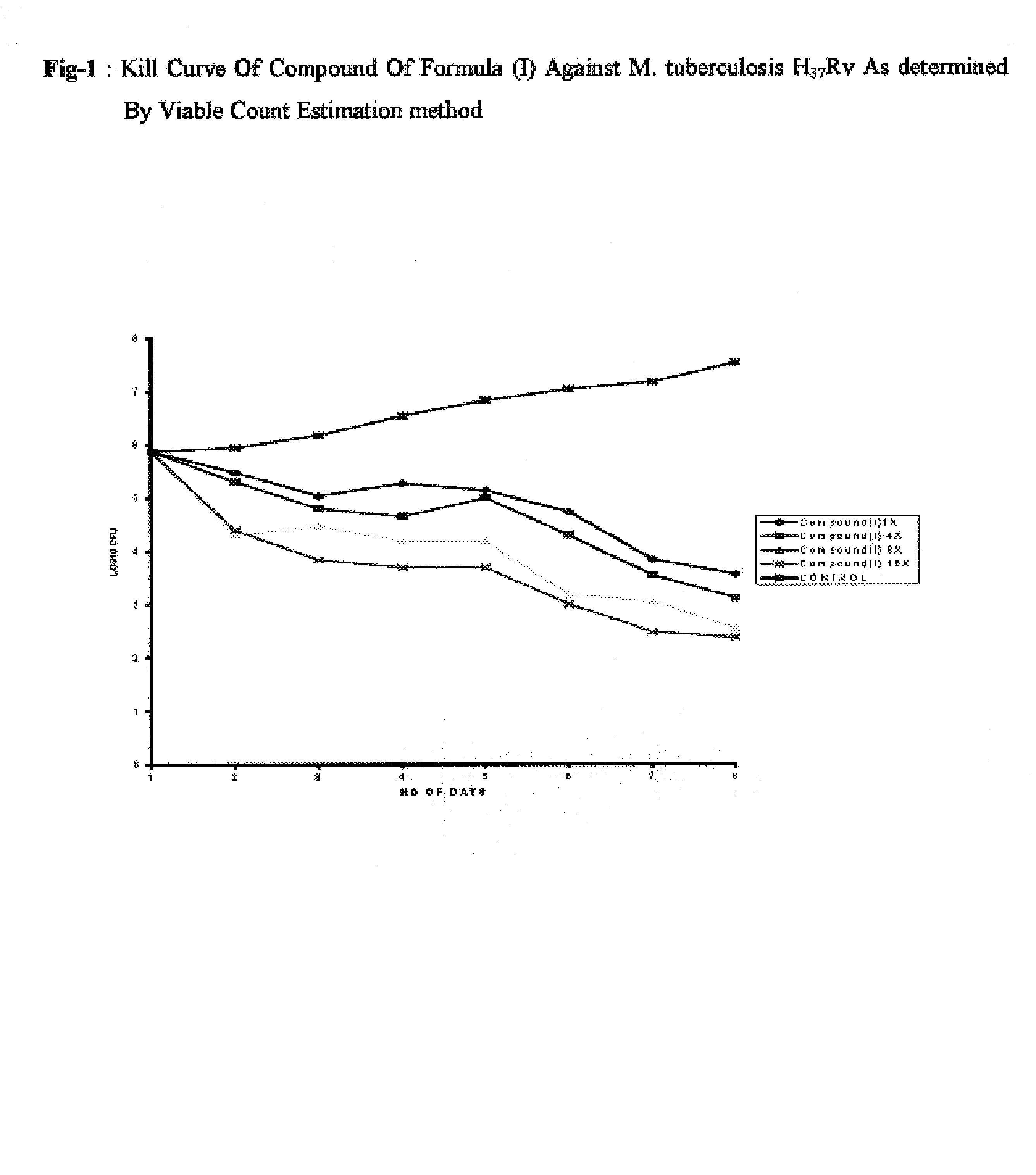
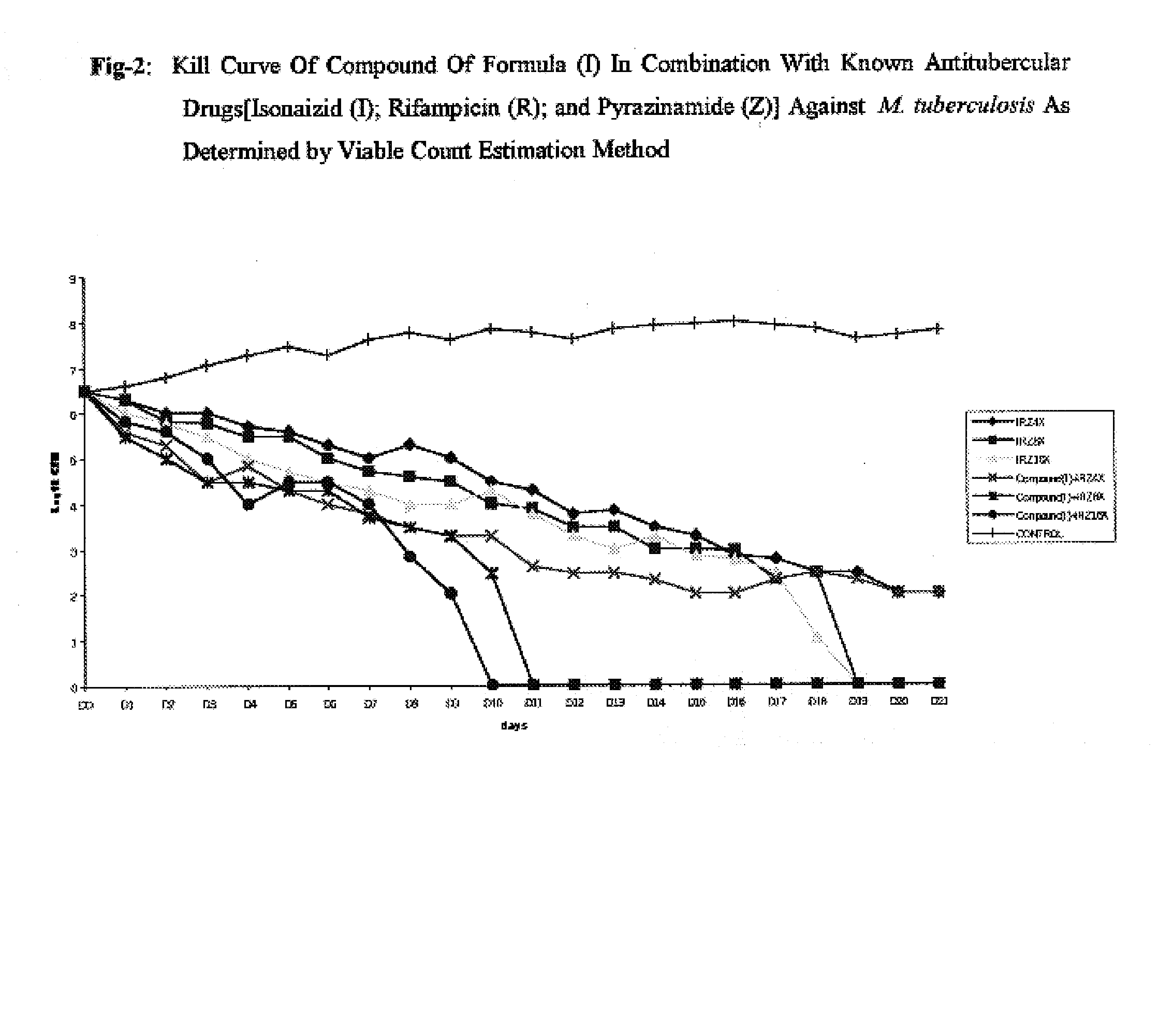
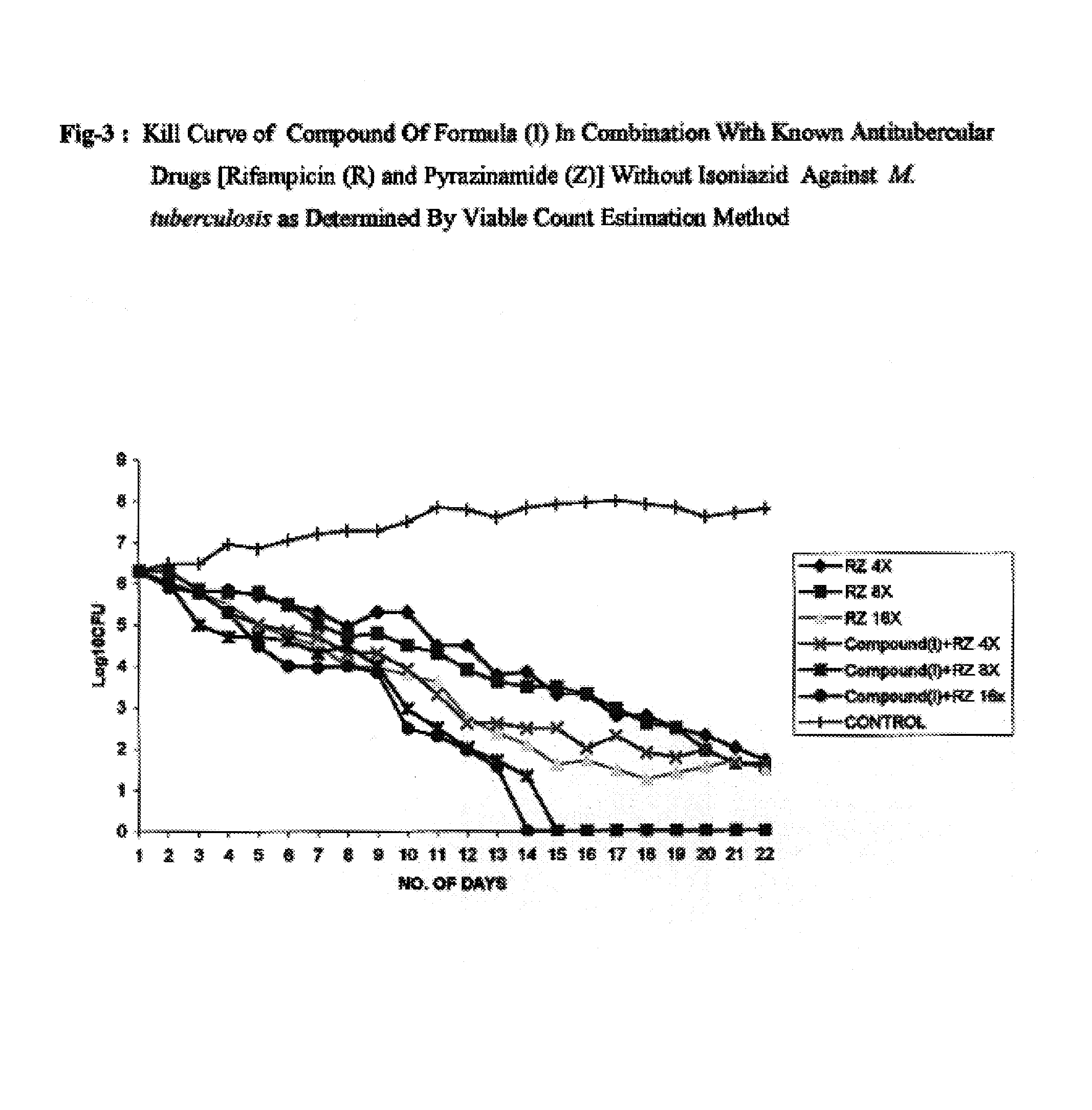
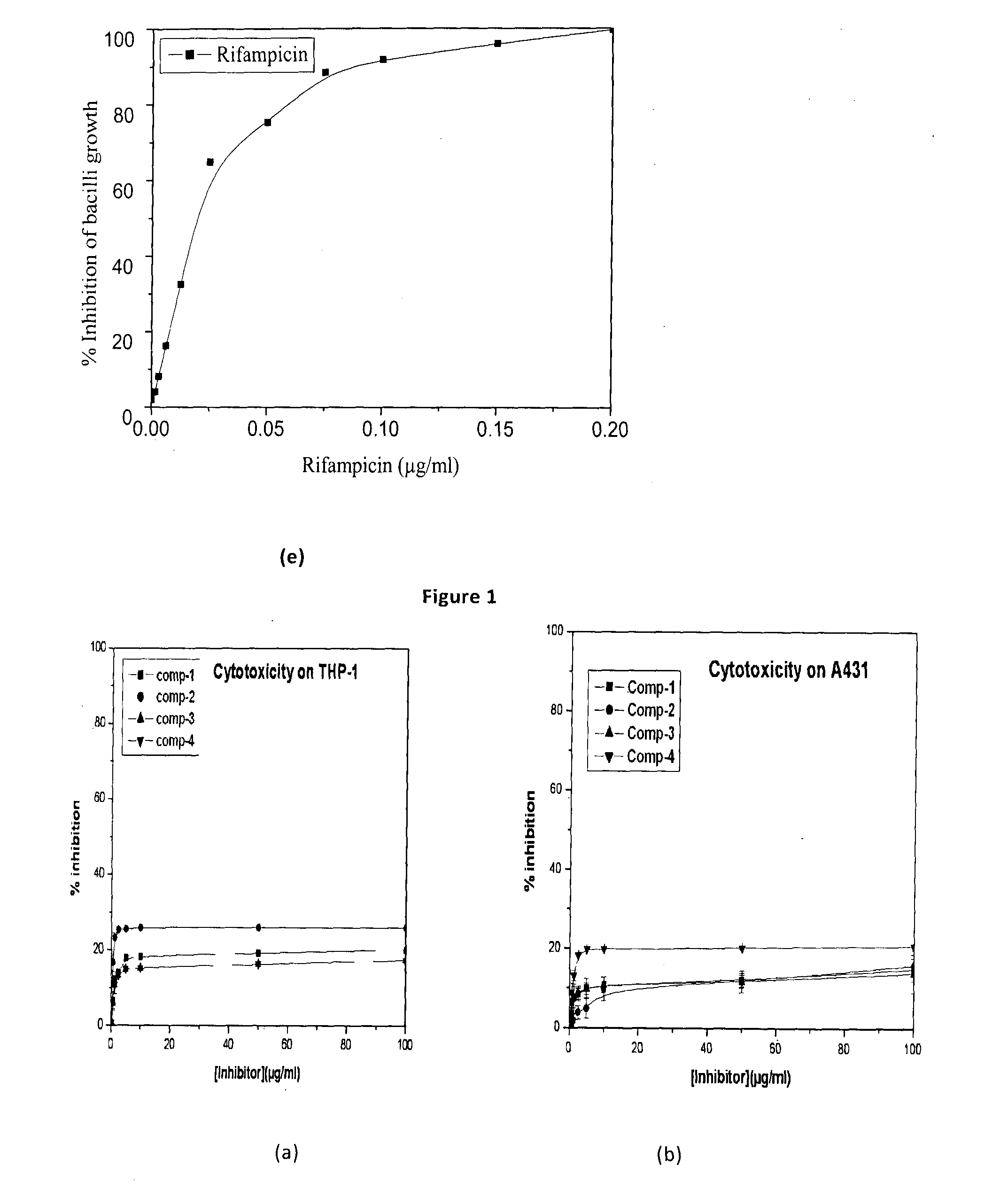
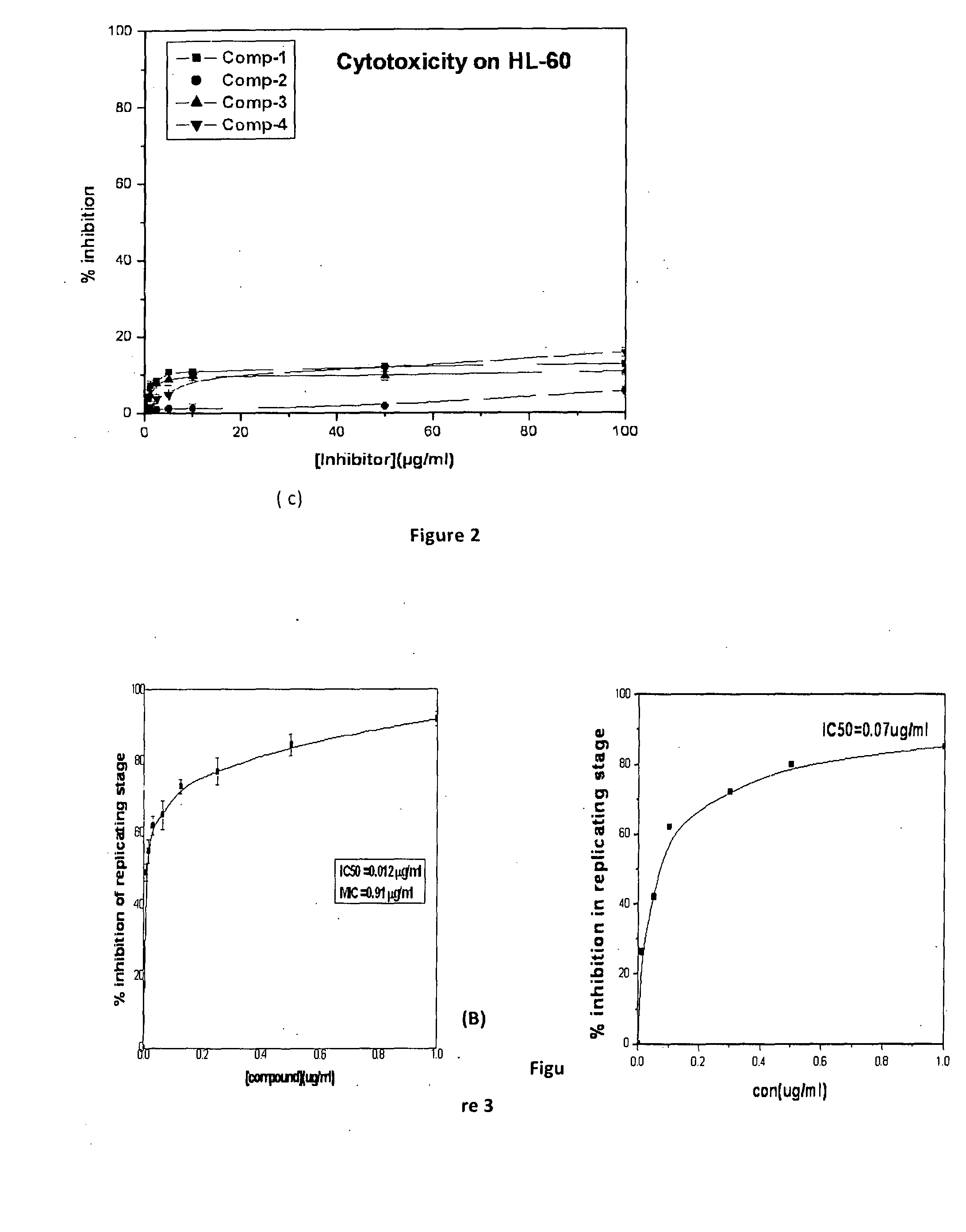
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Antimycobacterial" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An antimycobacterial is a type of medication used to treat Mycobacteria infections.
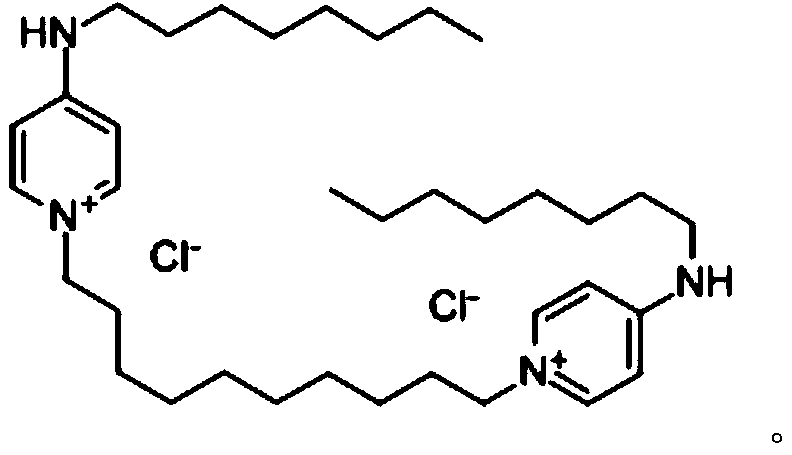
Mid-life vaccine and methods for boosting anti-mycobacterial immunity
InactiveUS7288261B2Boost immune responseIncrease resistanceAntibacterial agentsBacteriaImmunogenicityMycobacterium
Vaccine compositions for boosting immunity to mycobacteria when administered in mid-life in a subject who has been vaccinated neonatally or in early childhood with BCG and in whom protective immunity has waned comprise one or more purified immunogenic proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis from a group of 30 proteins that stimulate T cell immunity and interferon-γ secretion. A preferred protein is Ag85A, the secreted product (SEQ ID NO:31) of the Rv3084c gene. Also disclosed are methods for boosting immunity in such BCG-vaccinated subjects comprising administering an effective amount of the above vaccine composition.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for treating tuberculosis
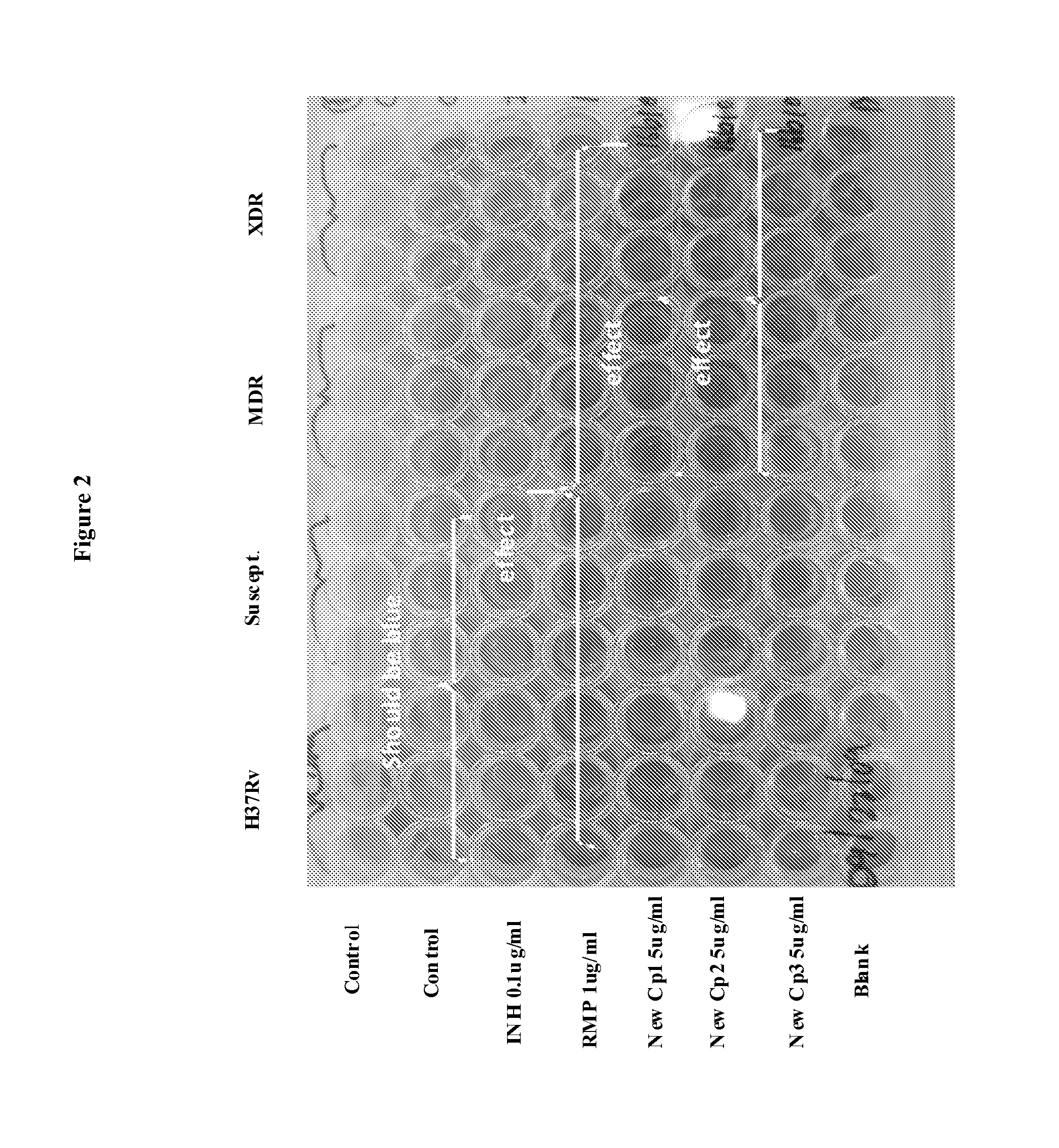
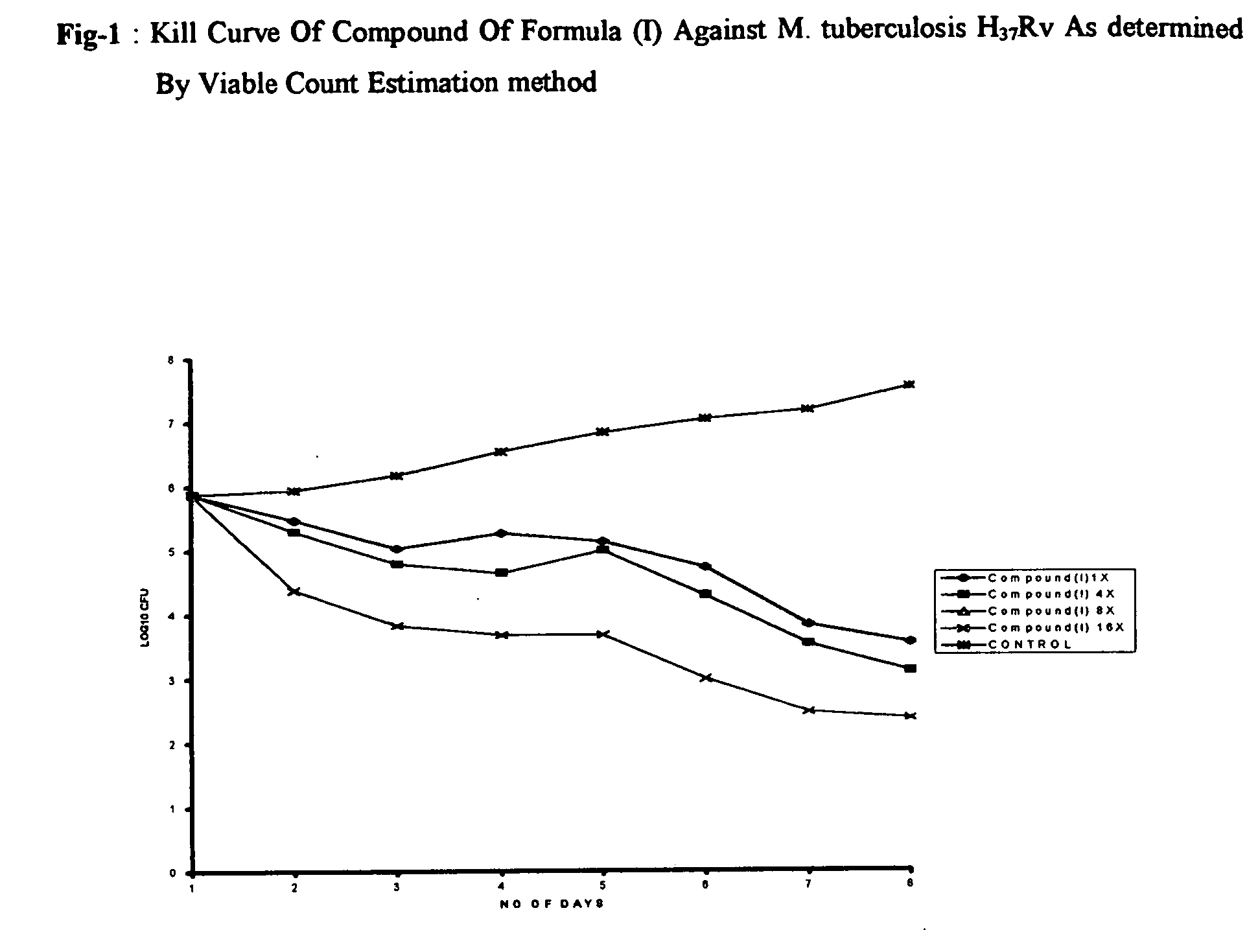
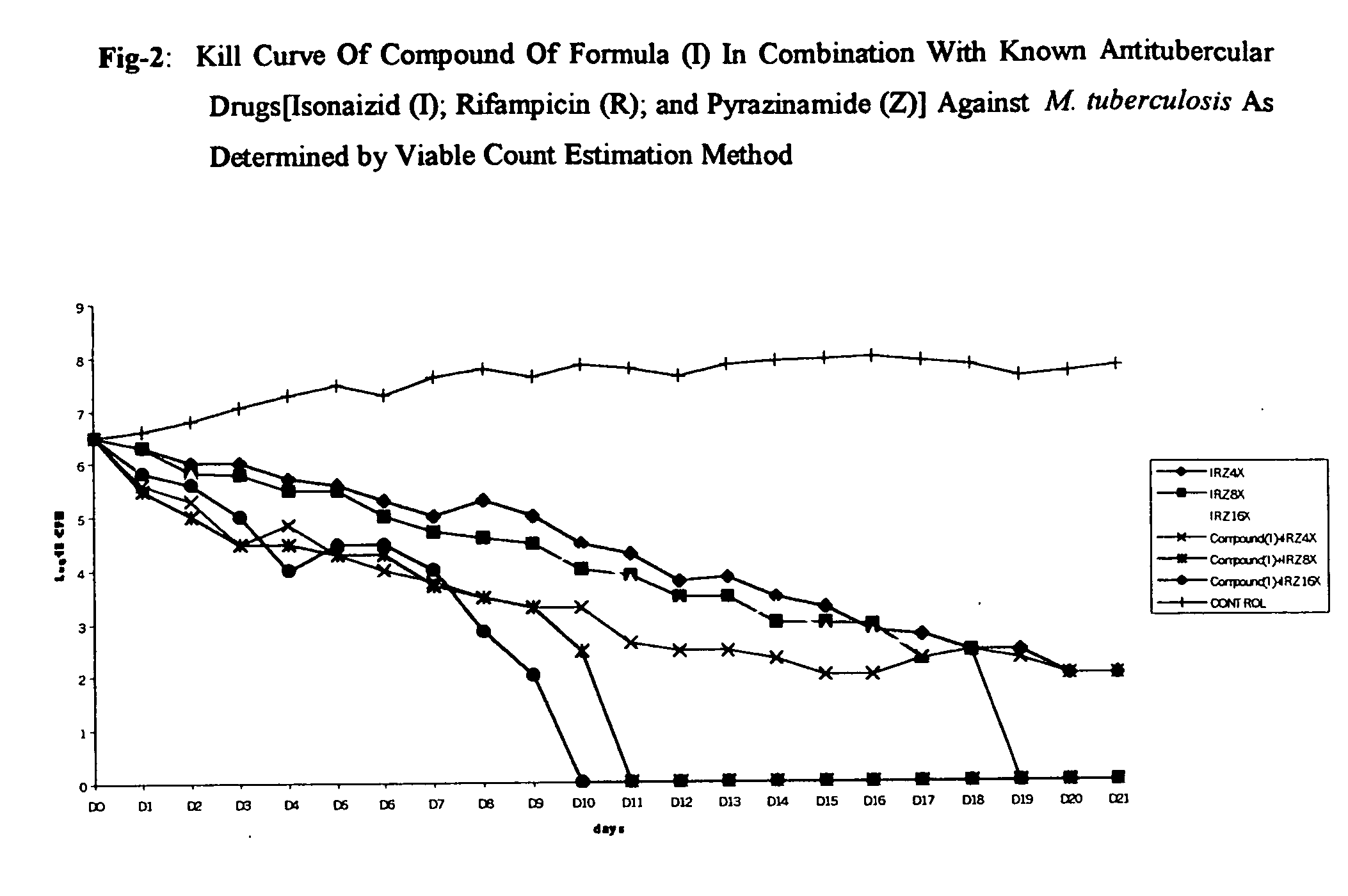
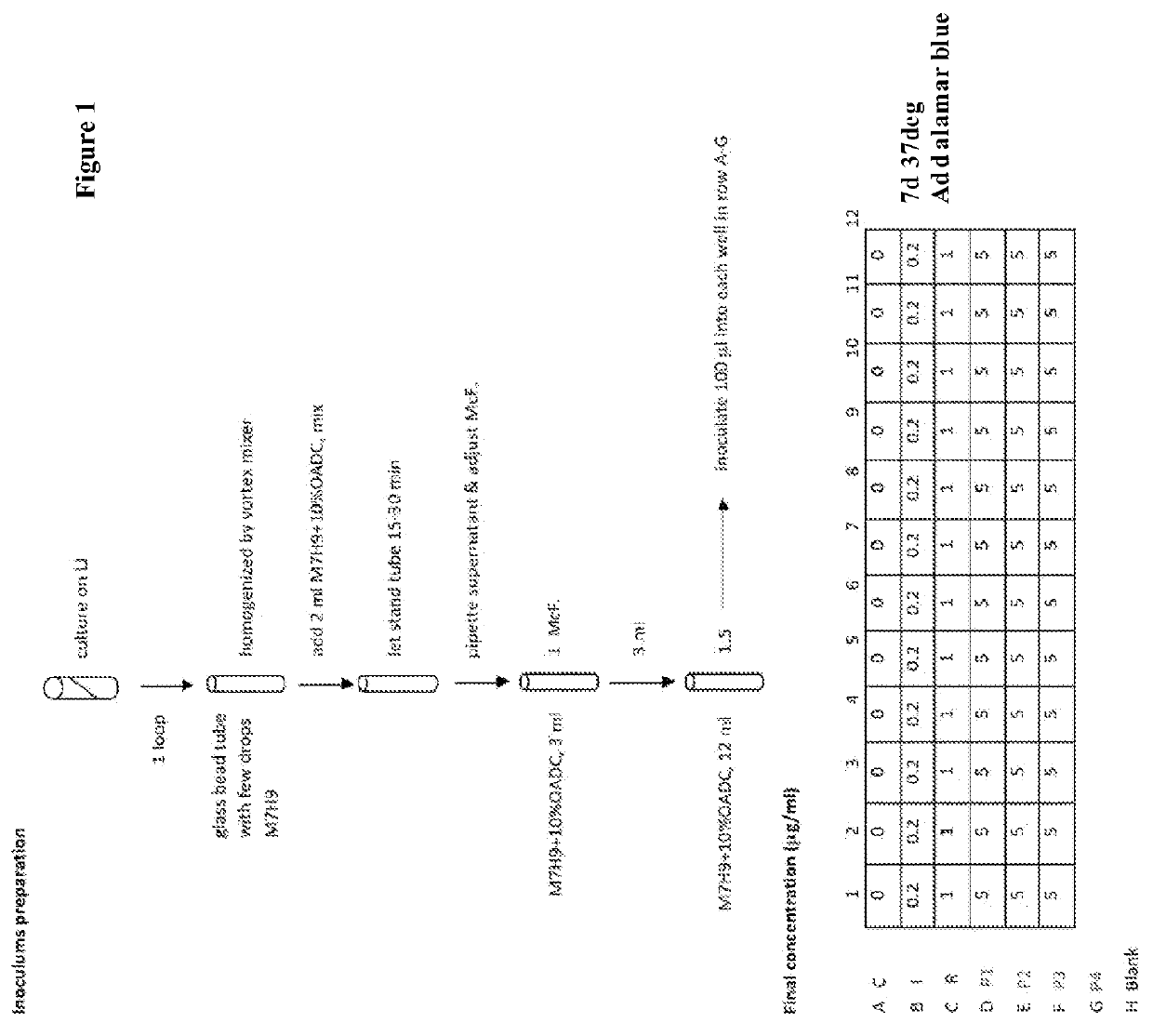
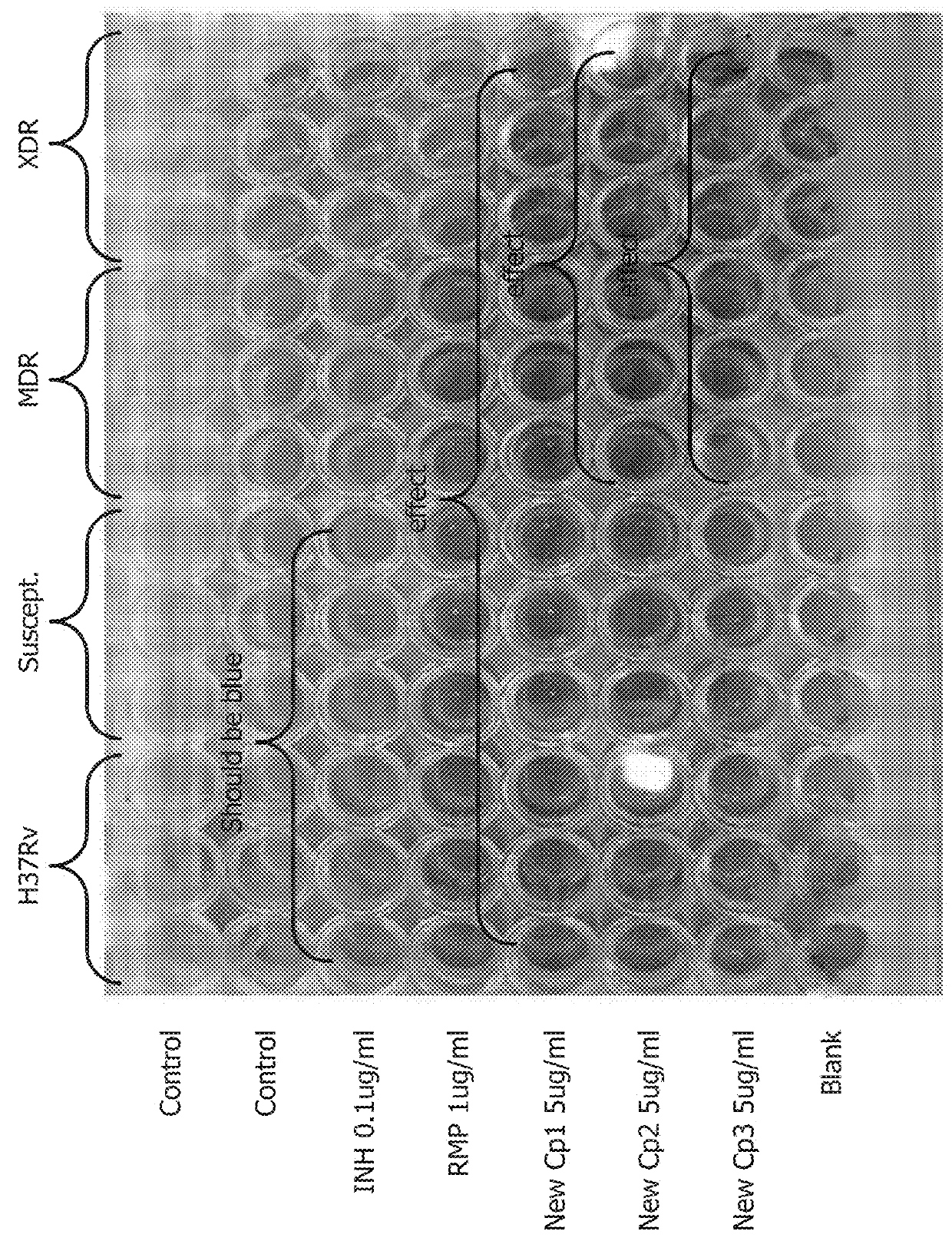
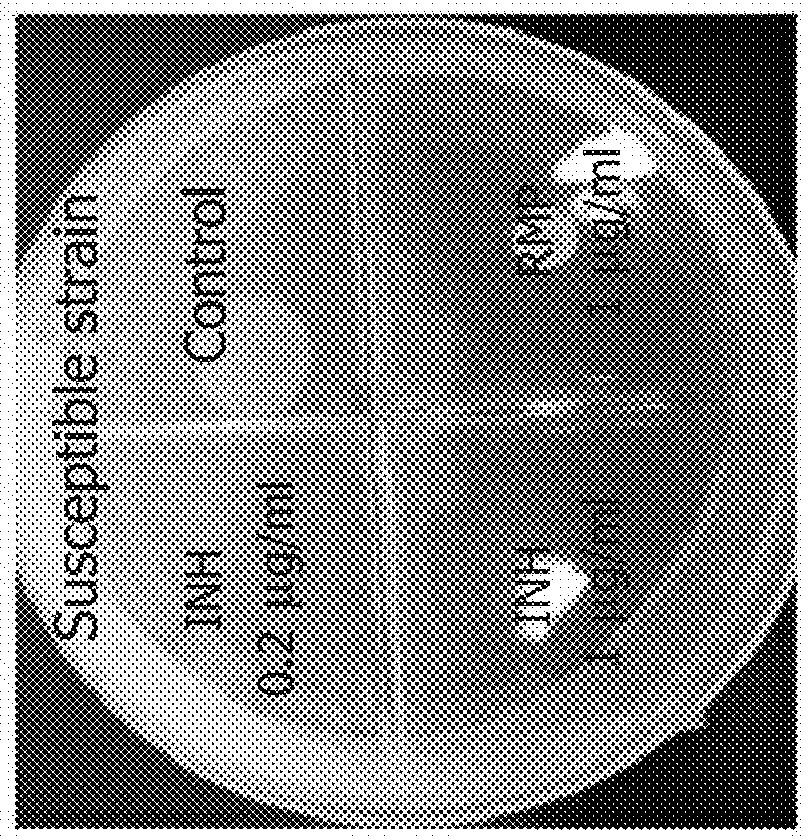
The invention provides for the use of antimicrobial chemical entities based on a nitrothiazolide backbone that exhibit anti-mycobacteria activity, including the mycobacterium causing tuberculosis. Multiple compounds were synthesized and screened for anti-tuberculosis activity. Disclosed herein are a series of compounds with anti-tuberculosis activity, including six leads that completely inhibited bacterial growth at 5 micrograms per ml or less. Three of these compounds were tested to determine MIC and these ranged between 1 and 4 micrograms per ml against both drug susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and strains that are multi-drug resistant (MDR) including XDR strains. The compounds developed are derived from parent compound nitazoxanide, which had no inhibitory activity in the stringent testing format used herein. The derivatives were synthesized using a di-nitro-thiophene or 4-Chloro-5-Nitro-thiazole scaffold and R groups connected via a peptide bond (NHCO) to cyclic compounds such as benzene, thiophene or furans. Many of these compounds have broad spectrum activity against Gram positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Several of these lead compounds were not toxic for mice at 200 mg / Kg doses administered over a period of three days.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Mycobacterium tuberculosis epitopes and methods of use thereof
The invention provides novel Class I HLA-A2 and Class II HLA-DR4-restricted epitopes and methods for their use in detecting T-cells in peripheral blood specific for infection or latency of mycobacterial infection, including M. tuberculosis and M. leprae as others. For example, methods for diagnosing the presence of infection or exposure by M. tuberculosis utilize multimers of HLA monomers or modified monomers having a bound HLA-binding peptide to perform high throughput screening of patient PBLs. The methods can be used for monitoring the success of anti mycobacterial treatment in patients and to screen vaccines and drugs for effectiveness in treating or preventing exposure, infection and latency of mycobacteria in humans.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Biomarkers for diagnosing and/or monitoring tuberculosis
InactiveCN104823052APromote or inhibit the production ofDisease diagnosisAntimycobacterialCausative organism
The invention relates to biomarkers for diagnosing and / or monitoring tuberculosisin both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, monitoring the responses of individuals to anti-mycobacterial chemotherapy, monitoring the progression of latent tuberculosis to active tuberculosis, differentiating active tuberculosis from latent tuberculosis, and from other clinical conditions that mimic tuberculosis (TB). The invention also relates to methods for diagnosing, treating and monitoring tuberculosis using said biomarkers. The above pertain in all aspects both to pulmonary and extrapulmonary Mycobacterium.tuberculosis infections, with Mycobacterium.tuberculosis being the causative organism in tuberculosis.
Owner:PROTEINLOGIC
Anti-mycobacterial vaccines
Provided herein are genetically modified arenaviruses suitable as vaccines against mycobacterial infections. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for the prevention and treatment of mycobacterial infections. Specifically, provided herein are pharmaceutical compositions, vaccines, and methods of preventing and treating infections in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA
Novel antimycobacterial compounds
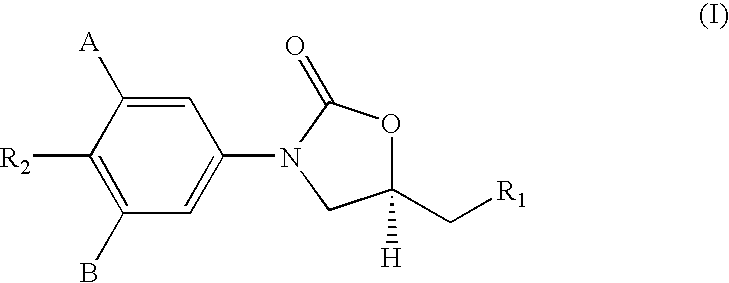
Novel compounds belonging to the class of oxazolidinones possessing potent antimycobacterial properties especially useful in the treatment of acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai. The compound and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof act as antibacterial agents. Also disclosed is a method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial conditions such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai, comprising administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of the said compound and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. There is also disclosed a process for the manufacture of the said compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Benzothiazinone Derivatives and their Use as Antibacterial Agents
ActiveUS20090239851A1High antibacterial activityHigh selectivityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryLeprosyAntimycobacterial
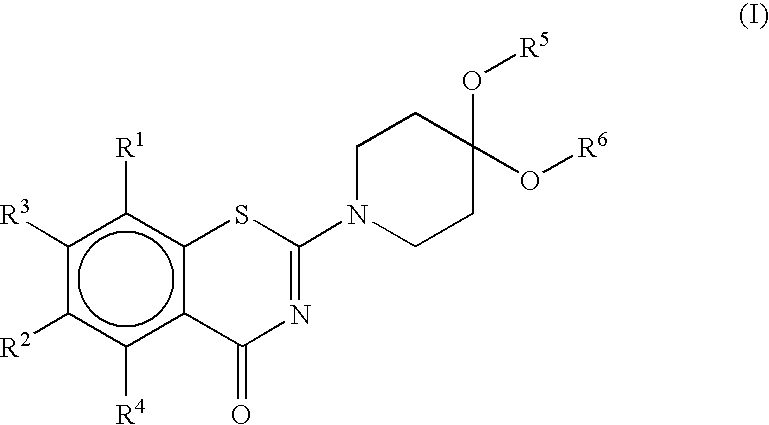
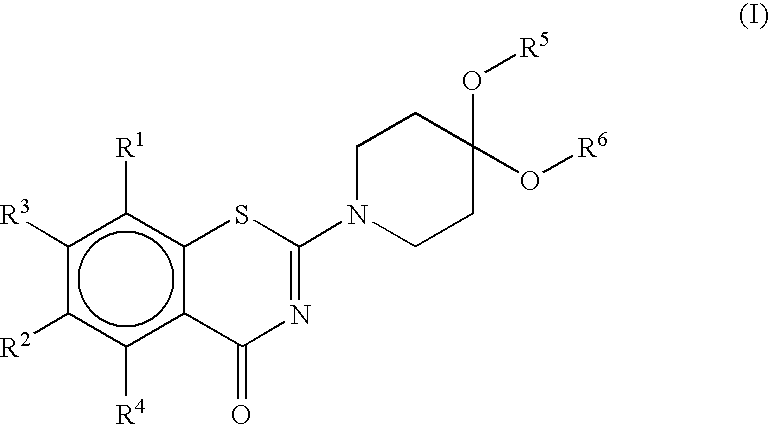
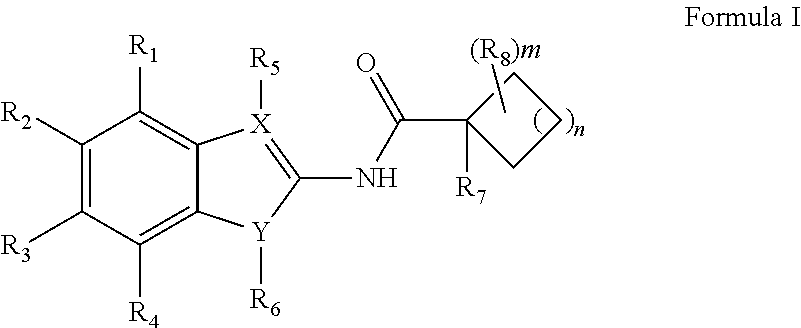
The present invention relates to novel benzothiazin derivatives and their use as antibacterial agents in infectious diseases of mammals (humans and animals) caused by bacteria, especially diseases like tuberculosis (TB) and leprosy caused by mycobacteria.The present invention aims at the generation of new compounds with activity against mycobacteria as potential new tuberculosis drugs to overcome problems concerning resistance and drug intolerance.The solution of the present invention is a compound of the formula Iwherein R1 and R2 are, independently each from other, NO2, CN, CONR7R8, COOR9, CHO, halogen, NR7R8, SO2NR7R8, SR9, OCF3, mono-, di or trifluoromethyl;R3 and R4 are, independently each from other, H, a saturated or unsaturated, linear or branched aliphatic radical having 1-7 chain members, cycloalkyl having 3-6 carbon atoms, benzyl, SR9, OR9;R5 and R6 are, independently each from other, a saturated or unsaturated, halogenated or unhalogenated, linear or branched aliphatic radical having 1-8 chain members, cycloalkyl having 3-6 carbon atoms, phenyl, or R5 and R6 together represent a bivalent radical —(CR92)m—, or R5 and R6 together represent bivalent radicals:wherein m is 1-4, or represent bivalent radicals a saturated or unsaturated mono or polyheterocycles with heteroatoms N, S, O and substituted by (R10)x, wherein x is 1-4;R7, R8 and R9 are, independently each from other H or a saturated or unsaturated, halogenated or unhalogenated, linear or branched aliphatic radical having 1-7 chain members, mono-, di or trifluoromethyl, halogen, phenyl, or R3 and R4 together represent a bivalent radical —(CH2)n— wherein n is 2-7;R10 is H or a saturated or unsaturated, halogenated or unhalogenated, linear or branched aliphatic radical having 1-7 chain members, NO2, NR7R8, CN, CONR7R8, COOR9, CHO, halogen, SO2NR7R8, SR9, OR9, OCF3, mono-, di or trifluoromethyl, benzyl or phenyl.
Owner:LEIBNIZ INST FOR NATURAL PROD RES & INFECTION BIOLOGY
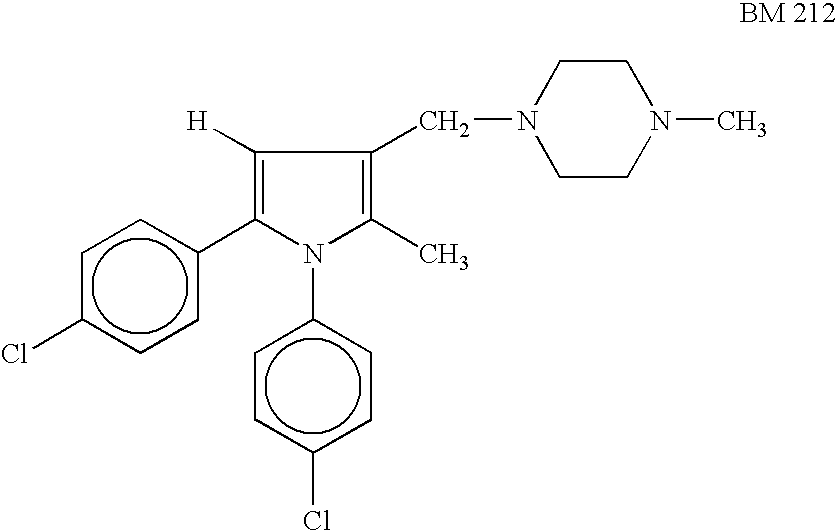
Antimycobacterial pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20050256128A1Prevent relapseShorten treatment timeAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntifungalAntimycobacterial
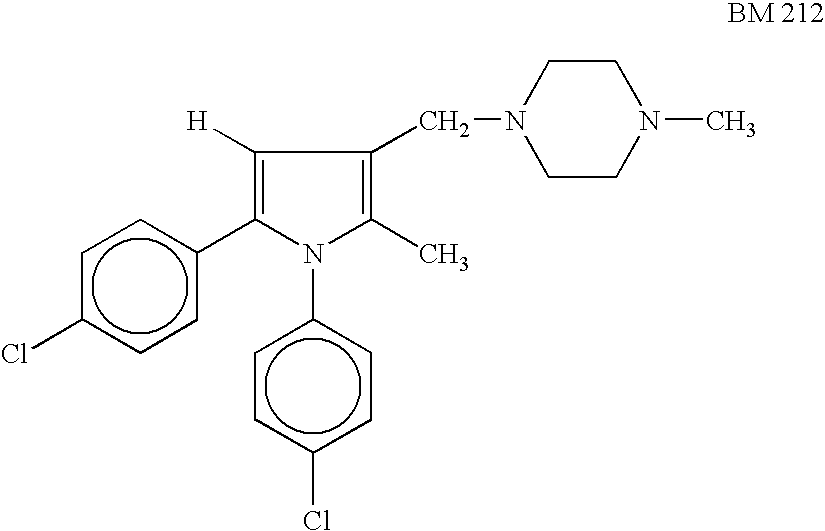
An antimycobacterial combination and composition for treating tuberculosis are described. The compounds used are N-(3-[[4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazinyl]methyl]-2-methyl-5-phenyl-pyrrolyl)-4-pyridylcarboxamide of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic salt thereof and an amount of one or more first line antitubercular drugs.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Methods of diagnosing and treating active tuberculosis in an individual
ActiveUS10191052B2Raise the potentialImprove diagnostic capabilitiesDisease diagnosisImmune compromisedAnti mycobacterial
The invention relates to biomarkers for diagnosing, monitoring and / or treating tuberculosis in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals with or without co-infection with HIV, monitoring the responses of individuals to anti-mycobacterial chemotherapy, monitoring the progression of latent tuberculosis to active tuberculosis, differentiating active tuberculosis from latent tuberculosis, and from other clinical conditions that mimic tuberculosis (TB). The invention also relates to methods for diagnosing, monitoring and / or treating tuberculosis using said biomarkers. The above pertain in all aspects both to pulmonary and extrapulmonary Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections, with Mycobacterium tuberculosis being the causative organism in tuberculosis. The invention therefore finds great utility in assisting with future drug discovery efforts for tuberculosis and also provides proxy clinical end points as well as being an effective predictor of a response to treatment.
Owner:PROTEINLOGIC
Pyrrole derivatives as antimycobacterial compounds
InactiveUS20080242676A1Low toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisAntimycobacterial
Novel pyrrole derivatives of formula (I)and their pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts having superior antimycobacterial activity against clinically sensitive as well as resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as well as having lesser toxicity compared to known compounds. The use of the novel compounds of formula (I) for treatment of latent tuberculosis including Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB). The methods for preparation of the novel compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing the novel compounds and method of treating MDR TB by administration of compounds of formula (I).
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Application of antimicrobial peptides in anti-mycobacteria infection drugs
ActiveCN110615830AEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesAntimycobacterial
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, in particular to application of antimicrobial peptides in anti-mycobacteria infection drugs. According to the application, starting with antimicrobial peptides, a series of antimicrobial peptides aiming at mycobacteria with special structures and unusual action modes are researched and developed, the antimicrobial peptides kill bacteria through a membrane destruction mechanism, and the bacteria do not generate drug resistance. The antimicrobial peptides, as main potential medicament for treating tuberculosis, fill the gap of no new anti-tuberculosis drugs in China for a long time. Therefore, the antimicrobial peptides provided by the application can be used for preparing effective drugs aiming at the mycobacteria, are expected to be the anti-mycobacteria infection potential drugs, and are the main potential medicament for treating the tuberculosis.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of pyrimidine small-molecule compounds in preparation of drugs with mycobacterium resistance
PendingCN110563656AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsChemical structureAntituberculous drugs
The invention provides pyrimidine compounds. The pyrimidine compounds have a chemical structure as shown in a formula I, wherein definitions of X, Y, R1, R2 and R3 are shown in the description and claim. At the same time, the invention also provides application of the compounds in mycobacterium resistance. The compounds have good activity of mycobacterium tuberculosis resistance, and can be applied to preparation of tuberculosis resistant drugs.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
Antimycobacterial compounds
Novel compounds belonging to the class of oxazolidinones possessing potent antimycobacterial properties especially useful in the treatment of acid fast organisms such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai. The compound and its pharmaceutically acceptable salts act as antibacterial agents. Also mentioned is a method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial conditions such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, drug resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium avium-intracellular complex, M. fortuitum and M. kansai., including administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of the compound and / or pharmaceutically acceptable salts. There is also mentioned a process for the manufacture of the compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
Novel antimycobacterial heterocyclic amides
The present invention provides novel heterocylic amide compounds having useful antimycobacterial activity. Use of these compounds as pharmaceutical compositions and method of their production are alsoprovided.
Owner:REPLIDYNE
Nargenicin compounds and uses thereof as antibacterial agents
ActiveUS20180186808A1Antibacterial agentsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsTuberculosis mycobacteriumNargenicin
The present invention relates to novel nargenicin related compounds which can inhibit DnaE and have antibacterial, particularly antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis by administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of nargenicin or a nargenicin-related compound and / or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Application of Antimicrobial Peptides in Drugs Against Mycobacterial Infection
ActiveCN110615830BEnhanced inhibitory effectHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesAntimycobacterial
The invention relates to the field of pharmacy, in particular to the application of antimicrobial peptides in anti-mycobacterium infection drugs. The present invention starts with antimicrobial peptides and develops a series of antimicrobial peptides targeting mycobacteria with special structures and unusual modes of action. The antimicrobial peptides kill bacteria through a membrane destruction mechanism, and bacteria will not develop drug resistance. Antimicrobial peptides, which are the main potential agents for the treatment of tuberculosis, have filled the gap in the absence of new anti-tuberculosis drugs in China for a long time. Therefore, the antimicrobial peptide provided by the present invention can be used to prepare effective drugs against mycobacteria, and is expected to become a potential drug against mycobacterial infection and a main potential drug for treating tuberculosis.
Owner:LIAONING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of octenidine in inhibiting acetyltransferase and resisting mycobacterium infection
InactiveCN110787164AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsTuberculosis mycobacteriumMycobacterium Infections
The embodiment of the invention provides application of octenidine in inhibiting acetyltransferase and resisting mycobacterium infection. The structure formula of the octenidine is as shown. Experiments show that the octenidine can well inhibit acetyltransferase and has a remarkable inhibition effect on mycobacterium tuberculosis and clinical mycobacterium tuberculosis wide drug-resistant strains499 and 421.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE +1
Pyrrole derivatives as antimycobacterial compounds
InactiveUS20050107370A1Low toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisAntimycobacterial
Novel pyrrole derivatives of formula (I) and their pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts having superior antimycobacterial activity against clinically sensitive as well as resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as well as having lesser toxicity compared to known compounds. The use of the novel compounds of formula (I) for treatment of latent tuberculosis including Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis (MDR TB). The methods for preparation of the novel compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing the novel compounds and method of treating MDR TB by administration of compounds of formula (I).
Owner:LUPIN LTD
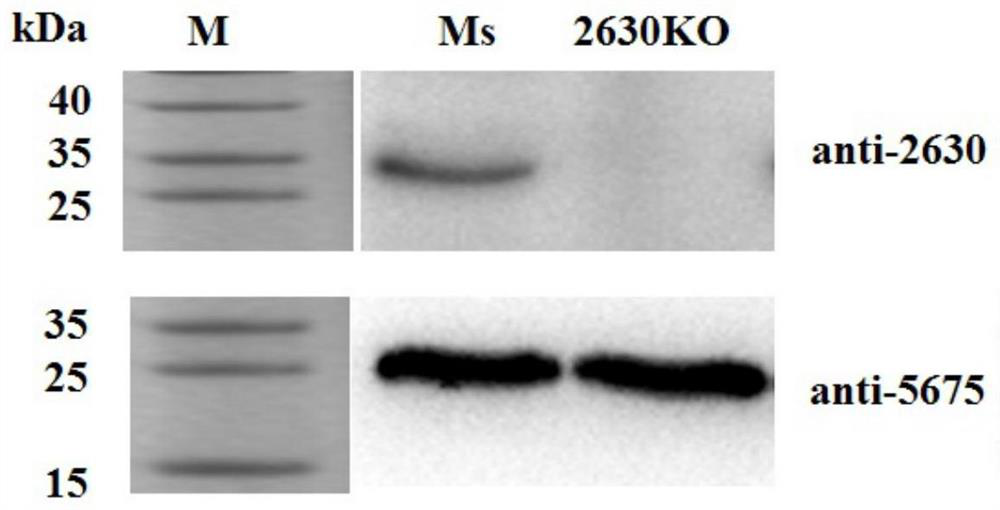
A kind of recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain of knocking out c-di-amp decomposing enzyme and its application
The invention relates to a recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain with a knockout c-di-AMP clastic enzyme. Upstream and downstream homologous arms of a mycobacterium smegmatis c-di-AMP degrading enzyme gene MSMEG-2630 are connected to a pMSG360 carrier separately; recombinant plasmids are transformed into a mycobacterium smegmatis competent cell containing recombinase gp60 and gp61pJV53 plasmid, and the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain (rMS-deltaCnpB) with the knockout c-di-AMP clastic enzyme is screened and obtained, wherein the preservation number is CCTCC M 2016336. Mice are immunized by the strain rMS-deltaCnpB, mice humoral and cell immune responses, especially a mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected Th1 cell immune response can be adjusted, and the protective ability of the organism resistant to mycobacterium infection is improved, so that the recombinant mycobacterium smegmatis strain can be applied to development of vaccines and preparations for preventing and / or treating tuberculosis and has a relatively good application prospect.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Dormancy induced mycobacterium proteins
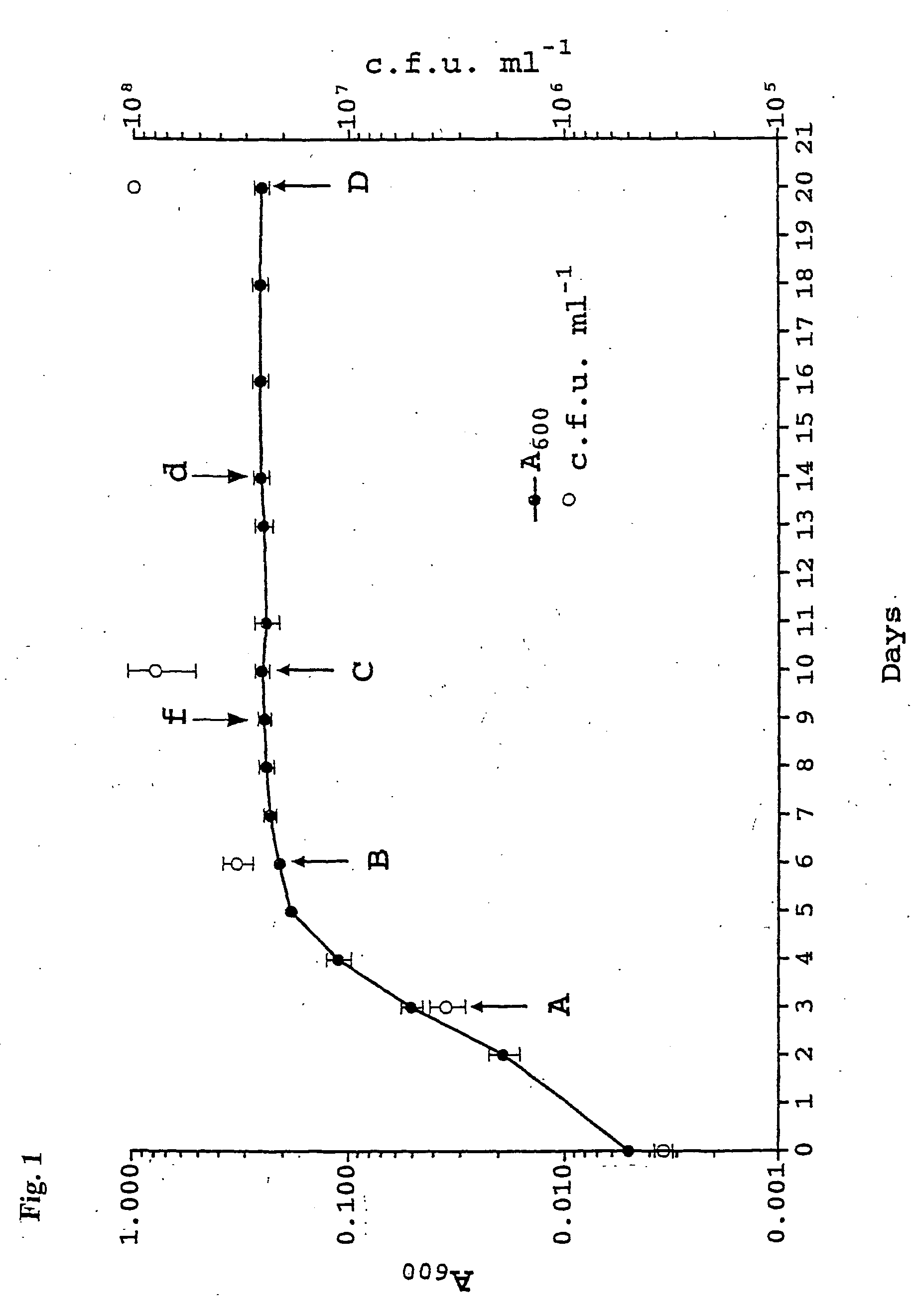
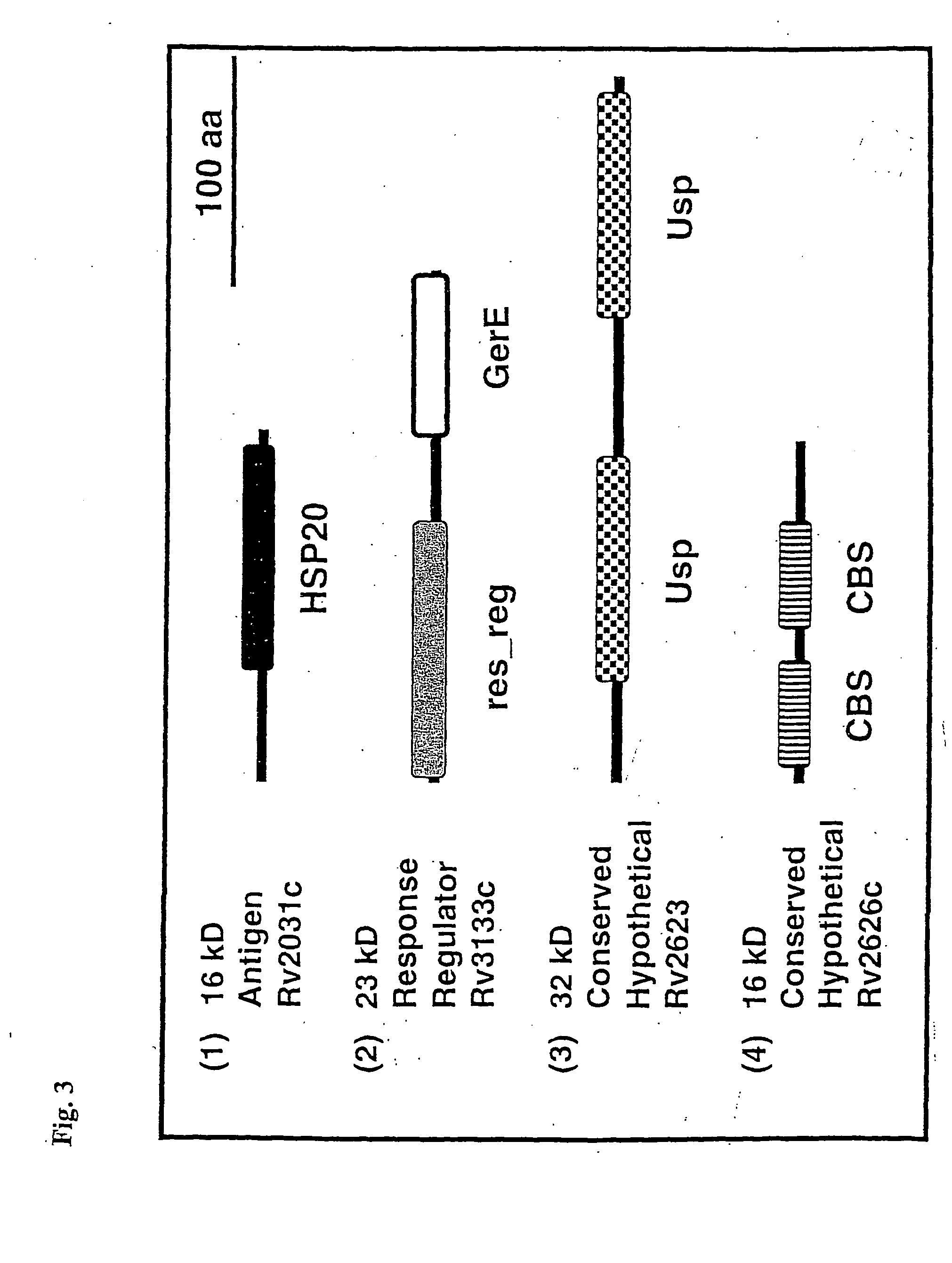
A method for the identification of an anti-mycobacterial agent that modulates the activity and / or expression of a protein expressed by a Mycobacterium in non-oxygen limiting stationary phase, hypoxic stationary phase or hypoxic growth phase, which method comprises: (i) contacting a test agent and a protein selected from RV3133c, Rv2623, Rv2626c, a variant of Rv3133c, Rv2623 or Rv2626 and a fragment of Rv3133c, RV2623, Rv2626c or said variant, or a polynucleotide or expression vector encoding said protein; (ii) monitoring the effect of the test agent on the activity and / or expression of said protein, thereby determining whether the test agent modulates the activity and / or expression of a protein expressed by a Mycobacterium in non-oxygen limiting stationary phase, hypoxic stationary phase or hypoxic growth phase.
Owner:INST OF MOLECULAR & CELL BIOLOGY
2-arylamide substituted thiophene imide ester compound and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN110759889BAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntimycobacterialProphylactic treatment
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Antimycobacterial pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS7491721B2Shorten treatment timeEffective treatmentAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntifungalMedicine
An antimycobacterial combination and composition for treating tuberculosis are described. The compounds used are N-(3-[[4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazinyl]methyl]-2-methyl-5-phenyl-pyrrolyl)-4-pyridylcarboxamide of formula (I) or a pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic salt thereofand an amount of one or more first line antitubercular drugs.
Owner:LUPIN LTD
4-substituted benzoxaborole compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS10774096B2Good effectAvoid selectivityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticMycobacterium InfectionsChemical compound
Owner:ANACOR PHARMA INC +1
Nargenicin compounds and uses thereof as antibacterial agents
ActiveUS9944654B2Antibacterial agentsGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsMedicineMycobacterium Infections
The present invention relates to novel nargenicin related compounds which can inhibit DnaE and have antibacterial, particularly antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis by administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of nargenicin or a nargenicin-related compound and / or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Potential application of zinc bacitracin in resisting mycobacterium infection
InactiveCN111166866AEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsCyclic peptide ingredientsTuberculosis mycobacteriumMycobacterium Infections
The invention provides an application of zinc bacitracin in resisting mycobacterium infection. A compound can reduce the activity of mycobacterium tuberculosis glycogen branching enzyme, and has a strong inhibition effect on mycobacterium tuberculosis Ra strain at a bacterial level. Therefore, the compound provided by the invention is expected to become an effective inhibitor of mycobacteria.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Method for detecting the presence of mycobacterial material in a sample using at least two antigens
ActiveUS11243204B2Fast and reliableImprove sensitivity and reliabilityEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesAntigen testingAntimycobacterial
Disclosed is a method of detecting the presence of antibodies against mycobacterial material in a sample by detecting binding of antibodies in said sample to at least two types of immobilised antigen, which antigens are capable of binding to an antibody which is indicative for the presence of mycobacterial material in a human or animal. Also disclosed is a solid substrate including a combination of said at least two antigens immobilised to said substrate, and to a biosensor having at least two types of immobilised antigen, which antigens are capable of binding to an antibody which is indicative for the presence of mycobacterial material in a human or animal.
Owner:KEI INT LTD +1
Nargenicin compounds and uses thereof as antibacterial agents
The present invention relates to novel nargenicin related compounds which can inhibit DnaE and have antibacterial, particularly antimycobacterial activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The present invention also relates to method for inhibiting growth of mycobacterial cells as well as a method of treating mycobacterial infections by Mycobacterium tuberculosis by administering an antimycobacterially effective amount of nargenicin or a nargenicin-related compound and / or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Compositions and methods for treating tuberculosis
The invention provides for the use of antimicrobial chemical entities based on a nitrothiazolide backbone that exhibit anti-mycobacteria activity, including the mycobacterium causing tuberculosis. Multiple compounds were synthesized and screened for anti-tuberculosis activity. Disclosed herein are a series of compounds with anti-tuberculosis activity, including six leads that completely inhibited bacterial growth at 5 micrograms per ml or less. Three of these compounds were tested to determine MIC and these ranged between 1 and 4 micrograms per ml against both drug susceptible Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains and strains that are multi-drug resistant (MDR) including XDR strains. The compounds developed are derived from parent compound nitazoxanide, which had no inhibitory activity in the stringent testing format used herein. The derivatives were synthesized using a di-nitro-thiophene or 4-Chloro-5-Nitro-thiazole scaffold and R groups connected via a peptide bond (NHCO) to cyclic compounds such as benzene, thiophene or furans. Many of these compounds have broad spectrum activity against Gram positive bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Several of these lead compounds were not toxic for mice at 200 mg / Kg doses administered over a period of three days.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Novel Antimycobacterial Heterocyclic Amides
ActiveUS20210002239A1Useful in treatmentEasy to adaptAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryAntimycobacterialPharmaceutical Substances
The present invention provides novel heterocylic amide compounds having useful antimycobacterial activity. Use of these compounds as pharmaceutical compositions and method of their production are also provided.
Owner:REPLIDYNE
10-a/BETA-D-ARABINOFURANOSYL-UNDECENES AS POTENTIAL ANTI-MYCOBACTERIAL AGENTS AND PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION THEREOF
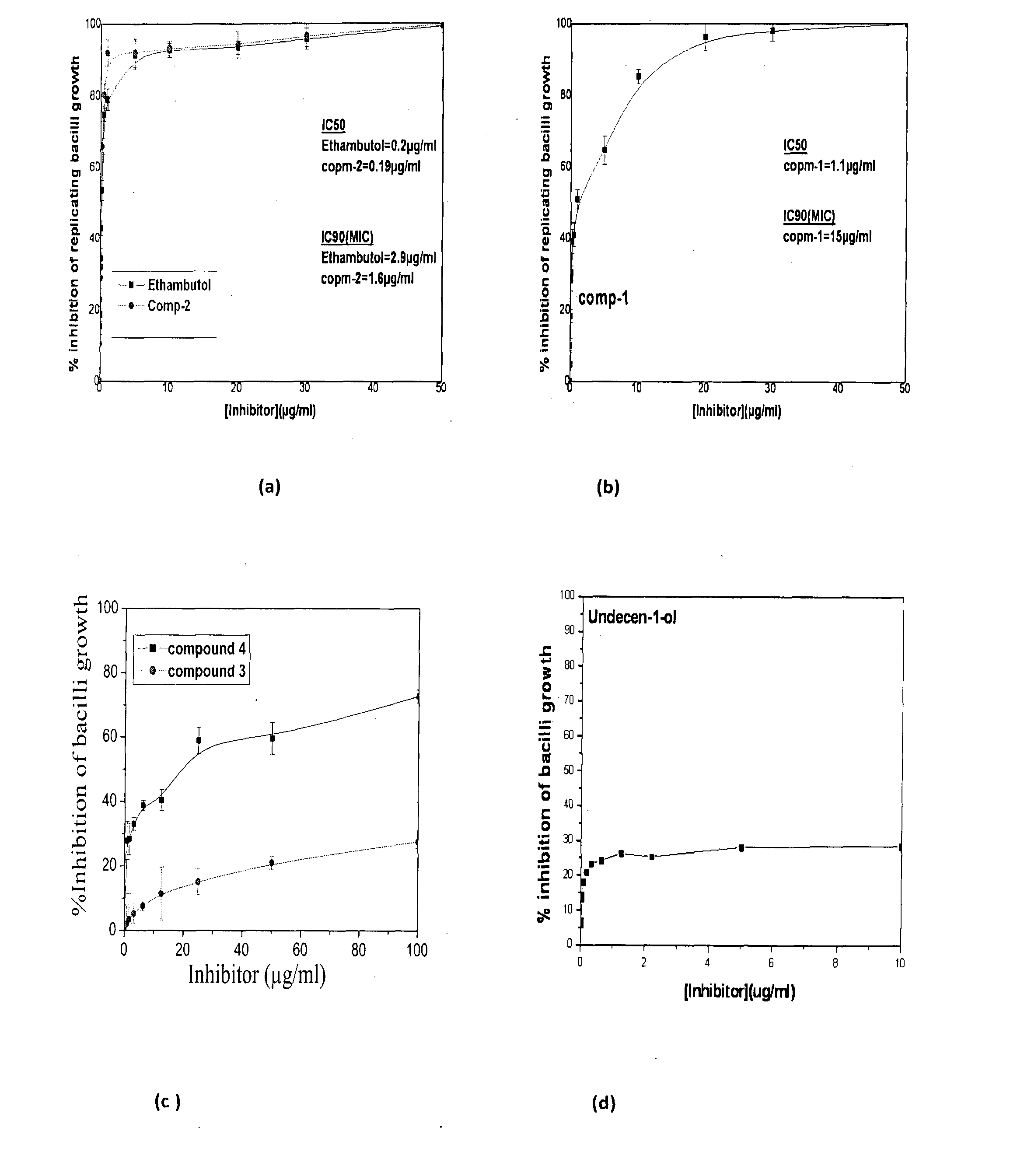
Disclosed herein is 10-α / β-D-Arabinofuranosylundecenes of general Formula (II) or pharmaceutically acceptableN salts thereof as anti-mycobacterial agents in vitro; (II) wherein R, R1 and R″ are as defined herein in the specification. The present invention also discloses a simple stereoselective synthesis 10-α / β-D-Arabinofuranosylundecenes of Formula (II) to target enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of cell wall of Mycobacterium and thus useful as inhibitors in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug development.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com