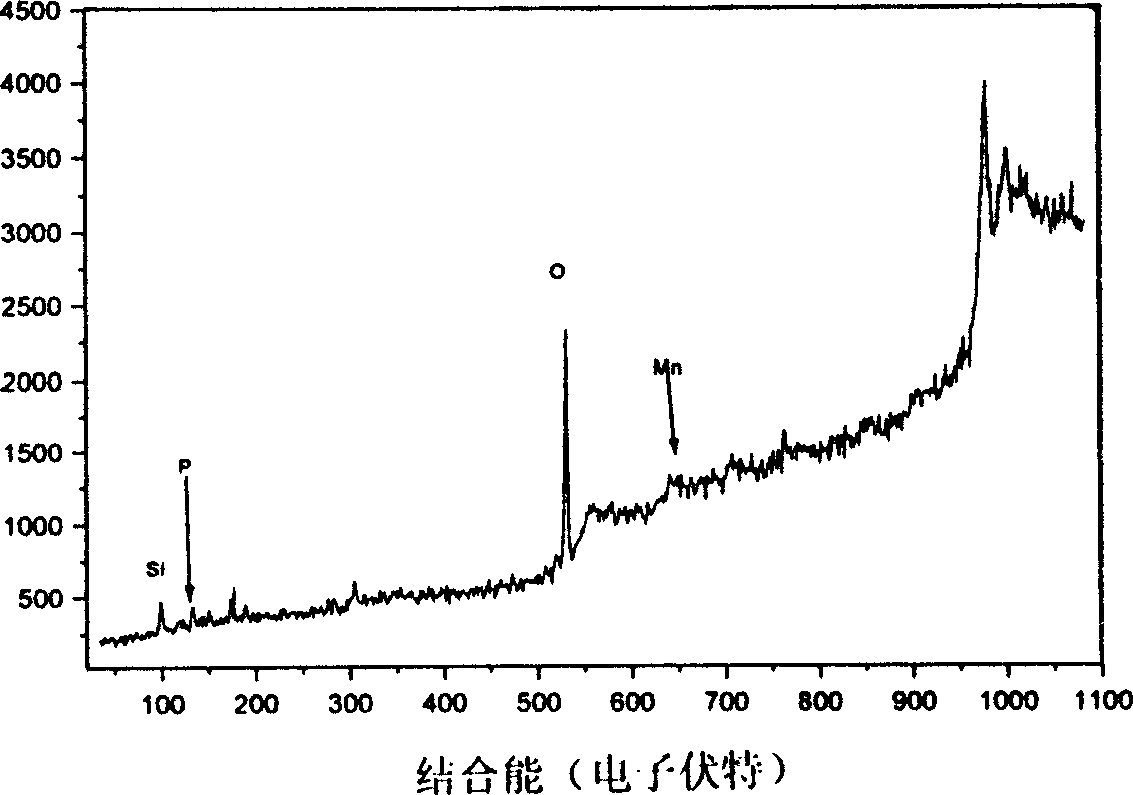
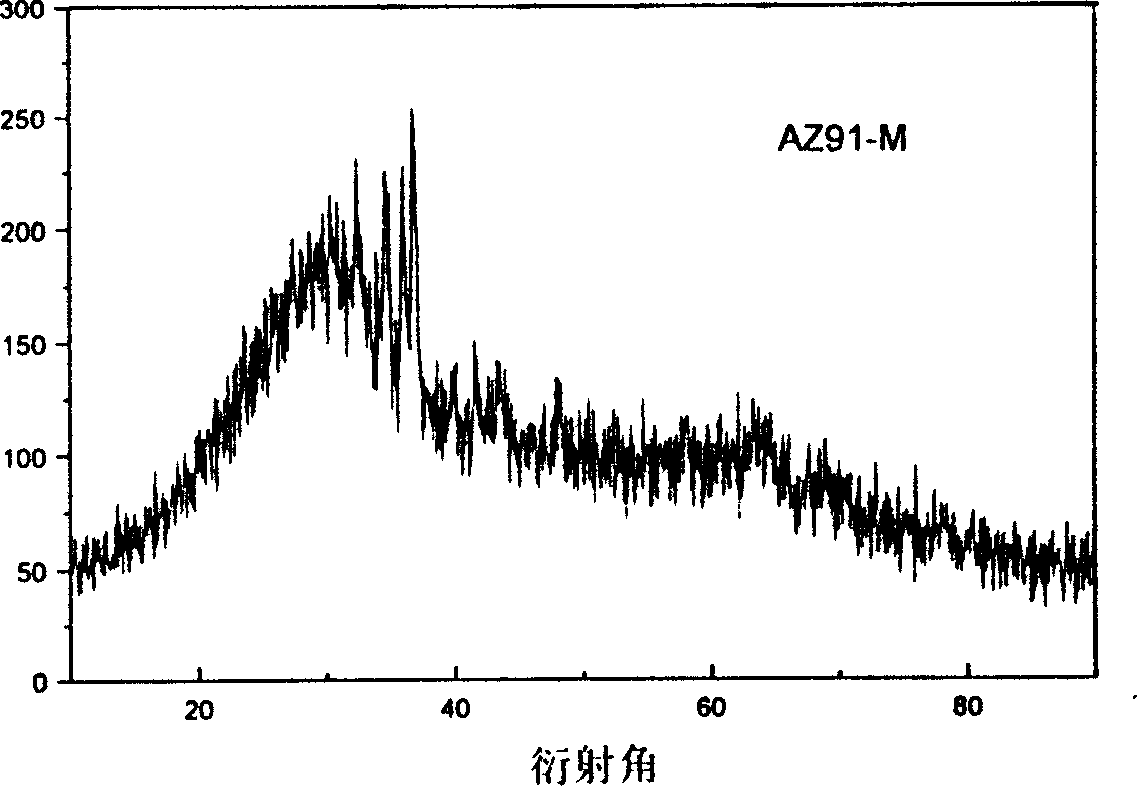
Preparation method of magnesium alloy chromeless chemical conversion film and its used film forming solution
A technology of chemical conversion film and magnesium alloy, which is applied in the coating process of metal materials, etc., can solve problems such as poor adhesion, easy peeling off of the paint film, and serious pollution, and achieve low cost, strong paint film adhesion, and improved durability. erosive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] The composition of the magnesium alloy chromium-free chemical conversion coating solution consists of 20g / l manganese dihydrogen phosphate, 30g / l sodium phosphate and the balance of water;
[0031] The preparation method is as follows: the sample is a die-casting AZ91 D magnesium alloy;
[0032] 1. Mechanical pretreatment: Grinding with sandblasting or sandpaper to remove burrs, firm oxides, lubricants for extrusion, release agents, casting sand, cutting oil and other foreign matter, reduce surface roughness; wash with water;
[0033] 2. Degreasing: wash with a compound solution of 10g / l sodium hydroxide, 15g / l sodium phosphate, and 15g / l sodium carbonate to remove general dirt, lubricants, cutting agents, etc. 5 points; wash with water;
[0034] 3. Pickling: Wash with concentrated hydrofluoric acid and phosphoric acid in a 1:1 compound acid solution to remove scale, corrosion products, sintered lubricants, lubricants, and steel particles that were not removed during d...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The pretreatment method is the same as in Example 1.
[0041] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0042] The sample used is an extruded AZ31D magnesium alloy;
[0043] The degreasing temperature is controlled at 90°C, and the time is 10 minutes; the pickling temperature is 20°C, and the time is 5 minutes; the activation or finishing temperature is 60°C, and the time is 0.5 minutes;
[0044] Film formation: immerse the pretreated magnesium alloy sample in an aqueous solution whose main components are manganese salt, phosphate and fluoride (that is, 20g / l manganese nitrate, 50g / l sodium dihydrogen phosphate and 2g / l potassium fluoride, and the remaining The amount is water), the temperature is controlled at 60°C, the soaking time is 60 minutes, and the pH value of the solution is kept at 5, a dark gray phosphate chemical conversion coating can be obtained;
[0045] The post-treatment immersion time was 50 minutes.
[0046] The obtained magnesium alloy chemical conversi...
Embodiment 3
[0048] The pretreatment method is the same as in Example 1.
[0049] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0050] The sample used is extruded AM60 magnesium alloy;
[0051] The degreasing temperature is controlled at 40°C, and the time is 8 minutes; the pickling temperature is 60°C, and the time is 0.5 minutes; the activation or finishing temperature is 20°C, and the time is 10 minutes;
[0052] Film formation: immerse the pretreated magnesium alloy sample in an aqueous solution of manganese salt and phosphate (ie 30g / l manganese nitrate, 40g / l sodium dihydrogen phosphate, and the balance is water), and control the temperature at 85°C. The immersion time is 40 minutes, and the pH value of the solution is kept at 2.0 to obtain a silver-gray phosphate chemical conversion coating;
[0053] Post-treatment: Immerse in an aqueous solution containing 15g / l cerium nitrate at a temperature of 40°C for 30 minutes to form a golden yellow surface film on the surface of the phosphate chemi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com