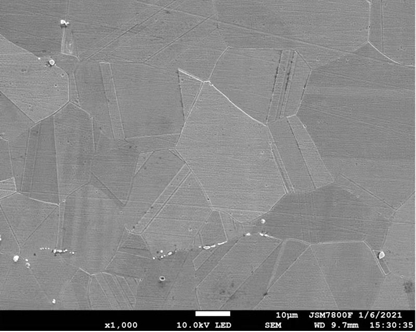
Ultrahigh-strength and ultrahigh-toughness high-density high-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
A high-entropy alloy and high-density technology, applied in the field of alloys, can solve the problems of insufficient performance of high-strength, toughness and high-density alloy materials, refinement of alloy microstructure, and difficulty in thermal deformation, etc., to achieve strong toughness, improve alloy strength, and improve Effects of Stability and Strengthening Capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0048] The application also provides a method for preparing the ultrahigh-strength toughness high-density high-entropy alloy, including:
[0049] The raw material of the ultra-high-strength toughness high-density high-entropy alloy is smelted to obtain an ingot, and then homogenization treatment, forging and heat treatment are sequentially performed.
[0050] Preferably, the melting temperature is 1550-2000°C.
[0051] The smelting process mentioned above means that the master alloy ingot is first smelted by vacuum induction smelting, vacuum induction smelting+vacuum consumable smelting, cold crucible vacuum electromagnetic levitation smelting or other smelting methods that can meet the smelting temperature requirements.
[0052] Optionally, the melting temperature can be 1550°C, 1600°C, 1650°C, 1700°C, 1750°C, 1800°C, 1850°C, 1900°C, 1950°C, 2000°C or any one between 1550-2000°C value.
[0053] Preferably, the homogenization treatment includes: keeping the ingot at 1150° C....
Embodiment 1
[0070] (1) Smelting and casting: using pure metal elements of tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, nickel, and tantalum, and master alloys composed of two or more of the above elements as raw materials, according to the requirements of tungsten, molybdenum, and cobalt , niobium, nickel, and tantalum alloy elements mixed in proportion (the mass fractions of tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, nickel, and tantalum are: 37.13wt%, 19.37wt%, 11.90wt%, 18.76wt%, 11.85wt%, 1.00wt% %), melted in a vacuum induction furnace and cast into ingots at a melting temperature of 1600°C.
[0071] (2) Homogenization treatment: heat the ingot obtained from the above smelting at 1150°C for 20 hours to make the various refractory elements contained in the alloy diffuse evenly.
[0072] (3) Forging: Firstly, the ingot after the above homogenization treatment is billeted into a cuboid forging billet with a square cross section. %. Then, the reverse forging process is used to thicken and elonga...
Embodiment 2
[0077] (1) Smelting and casting: use pure metal elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, nickel, palladium, tantalum, and hafnium, and master alloys composed of two or more of the above elements as raw materials. , molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, nickel, palladium, tantalum, and hafnium alloy elements are mixed in proportion (the mass fractions of tungsten, molybdenum, cobalt, niobium, nickel, palladium, tantalum, and hafnium are: 36.36wt%, 19.92wt%, 11.66wt% %, 17.46wt%, 11.61wt%, 1.00wt%, 1.00wt%, 1.00wt%) were melted and cast into ingots in a vacuum induction furnace at a melting temperature of 1650°C.
[0078] (2) Homogenization treatment: heat the ingot obtained by the above-mentioned smelting at 1150°C for 10 hours to make the various refractory elements contained in the alloy diffuse evenly.
[0079] (3) Forging: Firstly, the ingot after the above homogenization treatment is billeted into a cuboid forging billet with a square cross section. %. Then, the reve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com