Thermal-resistant anti-cutting ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber and preparation method thereof
An ultra-high molecular weight, polyethylene fiber technology, applied in the field of fiber production, can solve problems such as no comfort, difficult and uniform spinning, and cumbersome and complicated implementation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
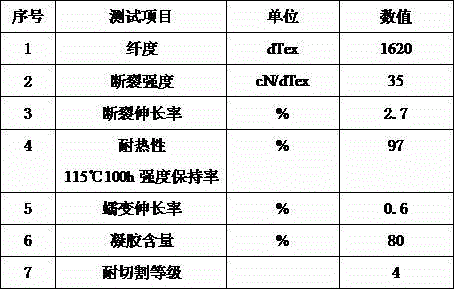
[0039] 7 parts by weight of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder (Gur 4022 of Ticona Company, the molecular weight range is 5 million), 0.07 parts by weight of antioxidant 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol and 80 parts by weight of volatile solvent decahydronaphthalene , swell at 90°C for 4 hours to form a fully swollen ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension A; then take 10 parts by weight of the volatile solvent decahydronaphthalene, and use a high-speed stirrer to stir at a speed of 1000 rpm, while Stir to add the crosslinking agent 2-ethyl methacrylate of 0.35 weight part, the initiator azobisisobutyronitrile of 0.21 weight part, the nanometer titanium dioxide of 0.14 weight part and the curing agent maleic anhydride of 0.35 weight part, stir 10 After mixing evenly for 1 minute, solution B was obtained. Add solution B to solution A. After mixing evenly, extrude and spin through the screw, and then evaporate or volatilize the solvent in the fiber under the prote...
Embodiment 2
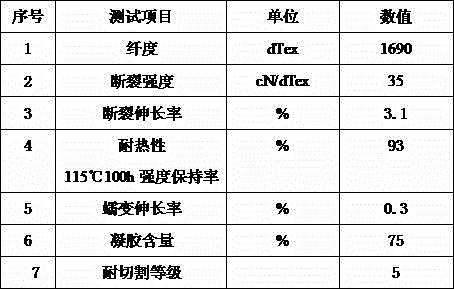
[0043] 7 parts by weight of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder (Gur 4022 from Ticona, with a molecular weight range of 5 million), antioxidant 2, 4, 6-tri-tert-butylphenol and 0.37 parts by weight of dilauryl thiodipropionate ( 2:1 ratio) and 83 parts by weight of the volatile solvent tetralin, swelled at 90°C for 5 hours to form a fully swollen ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension A; then take 10 parts by weight of the volatile solvent tetralin, Use a high-speed stirrer, stir at a speed of 1200 rpm, and add 0.38 parts by weight of crosslinking agent p-toluenesulfonyl isocyanate, 0.65 parts by weight of initiator dibenzoyl peroxide, and 0.24 parts by weight of nanometer dibenzoyl peroxide while stirring. Silica and 0.35 parts by weight of curing agent phthalic anhydride, stirred for 30 minutes and mixed uniformly to obtain solution B, added solution B to solution A, mixed uniformly, passed through screw extrusion spinning, and then under nitrogen pro...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 7 parts by weight of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene powder (Gur 4022 from Ticona, with a molecular weight range of 5 million), 0.3 parts by weight of antioxidant 4, 4'-thiobis(6-tert-butyl-3-methylphenol) and 83 parts by weight of volatile solvent xylene and n-hexane (2:1 ratio), swell at 90°C for 4 hours to form a fully swollen ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene suspension A; then take 10 parts by weight of volatile solvent II Toluene, using a high-speed stirrer, stirred at a speed of 1500 rpm, while stirring, added 0.95 parts by weight of crosslinking agent ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate, 0.28 parts by weight of initiator benzophenone, 0.14 parts by weight The nano-zinc oxide of weight part and the curing agent p-phenylenediamine of 1.35 weight part, stir 30 minutes and mix uniformly to obtain solution B, solution B is added in the solution A, after mixing uniformly, through screw extruding spinning, then in Evaporate or volatilize the solv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com