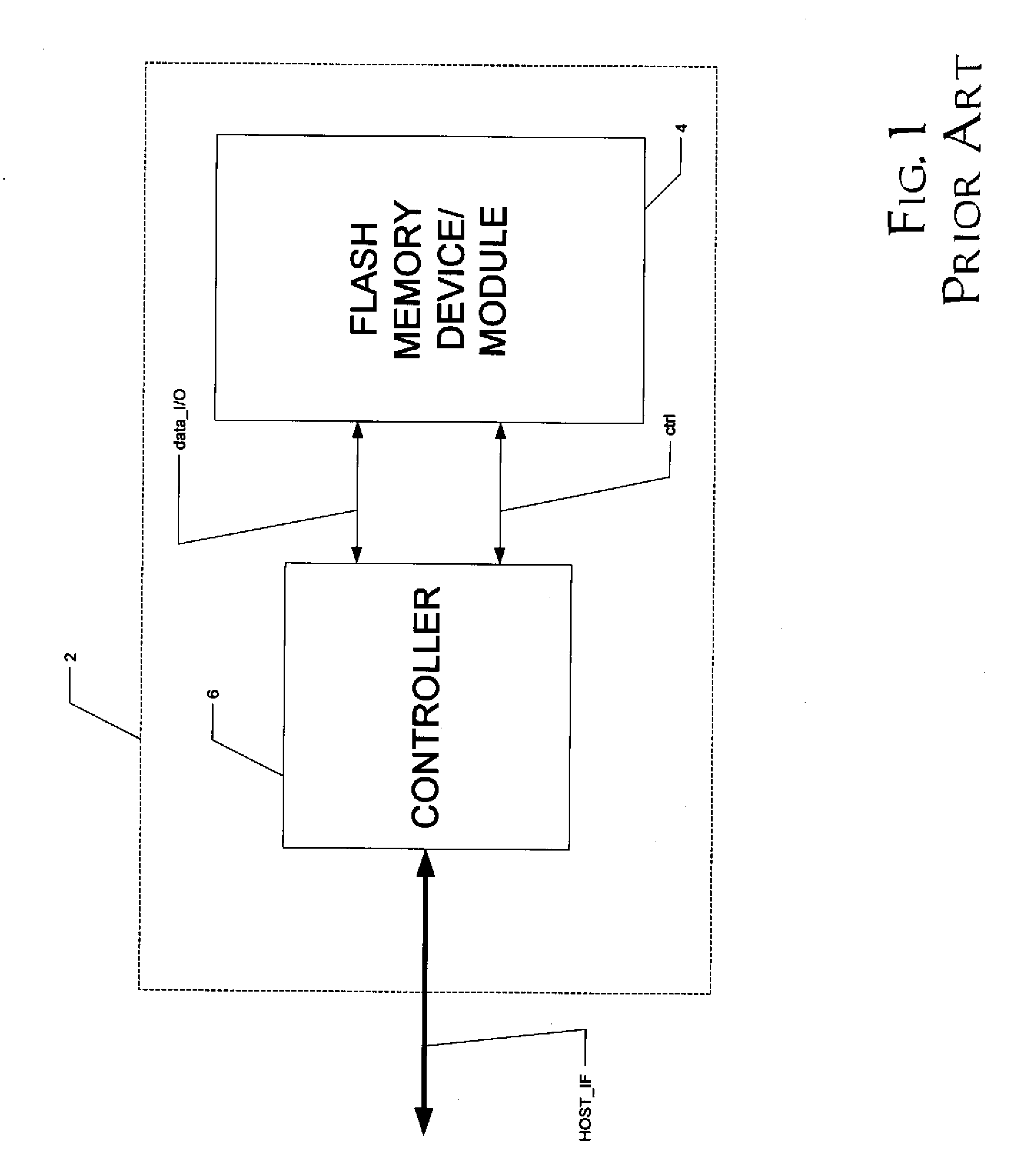
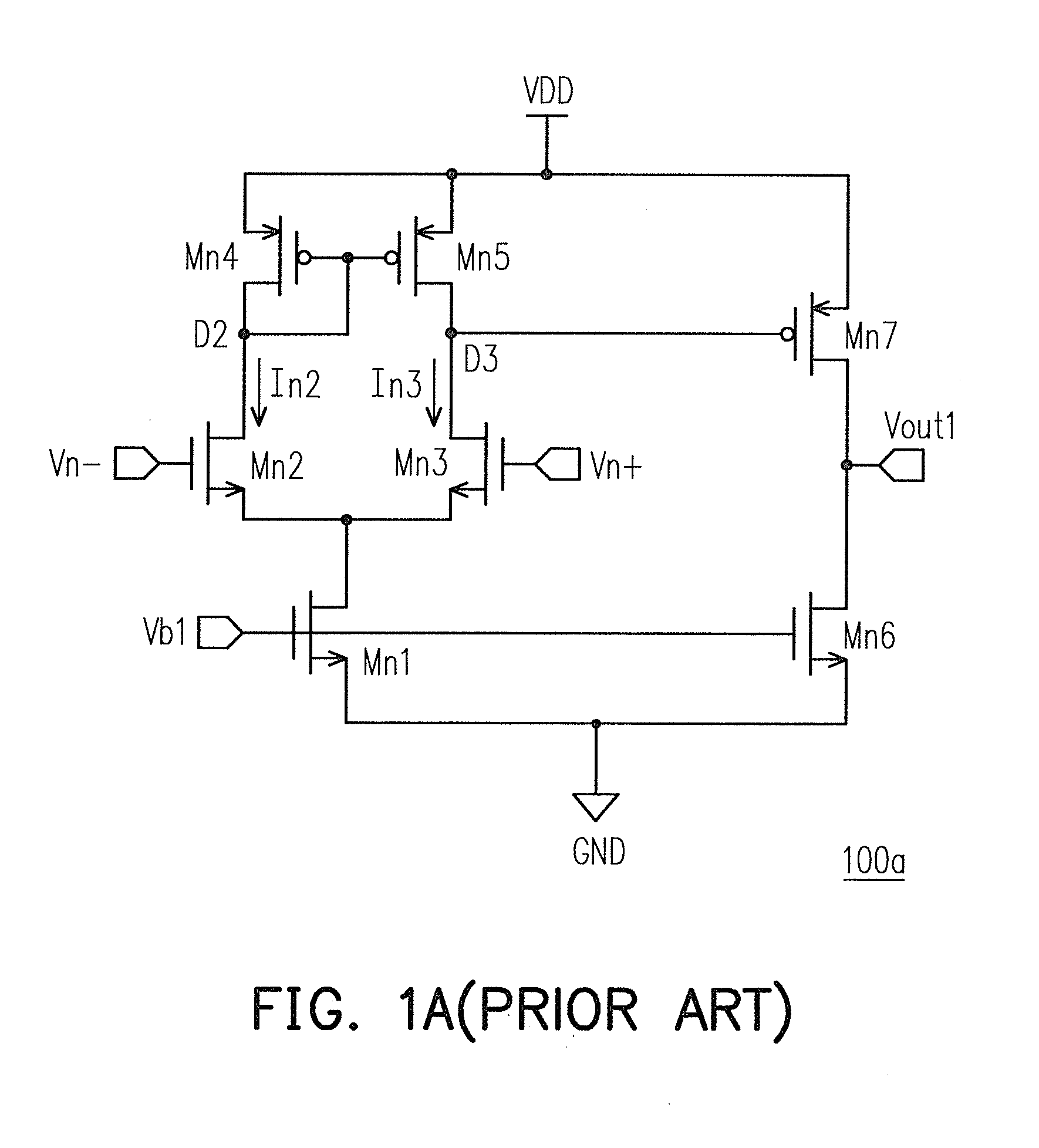
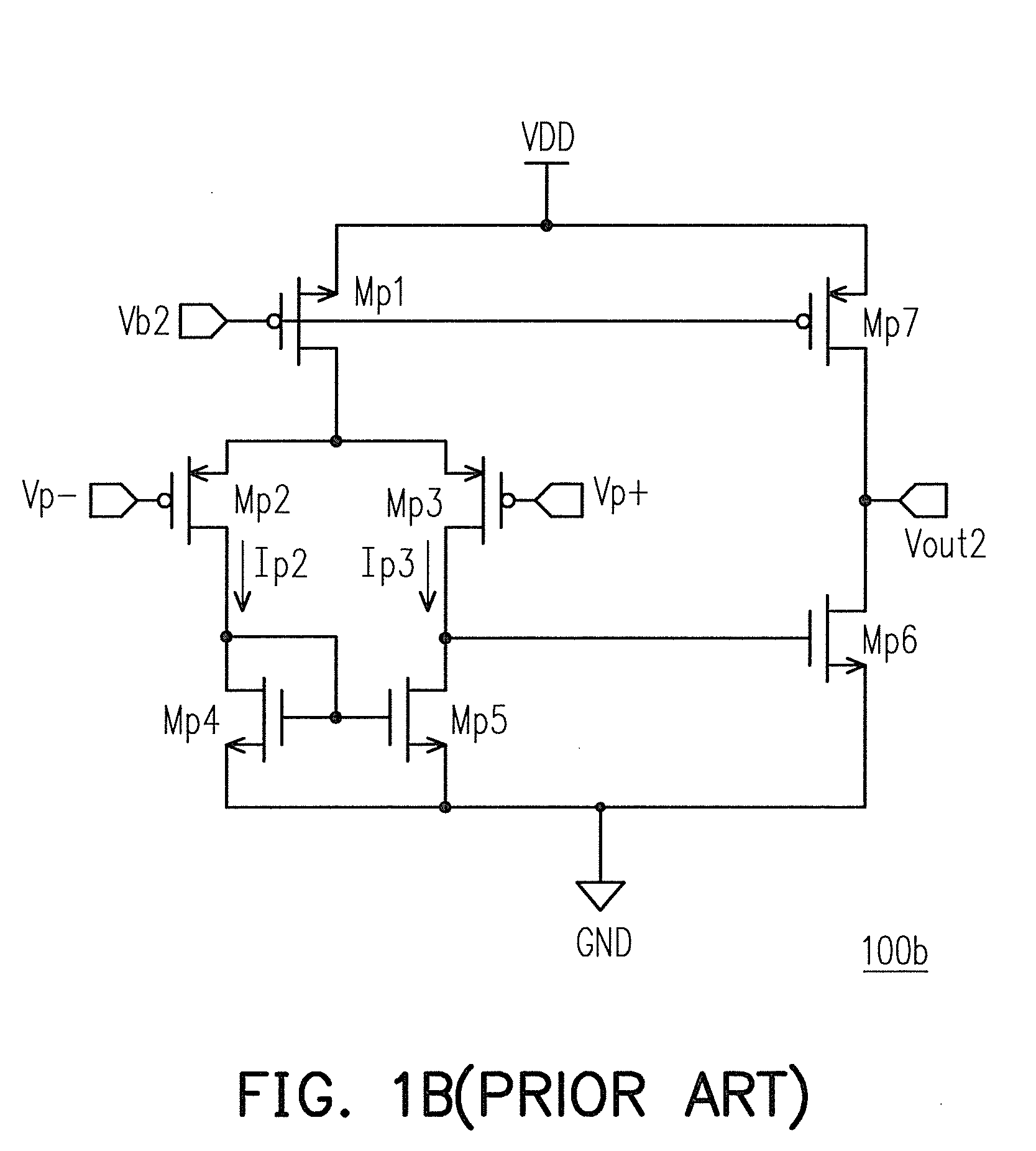
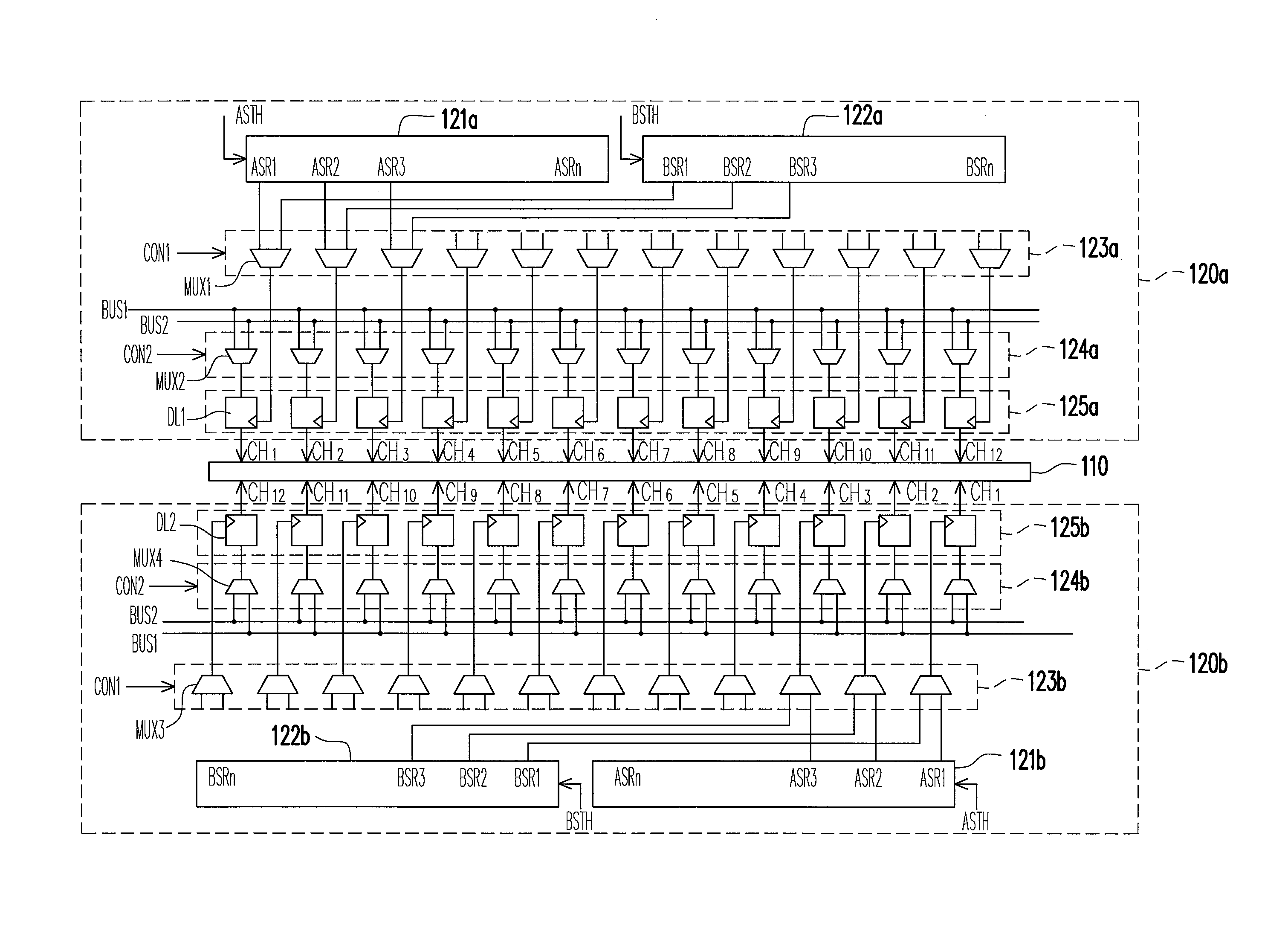
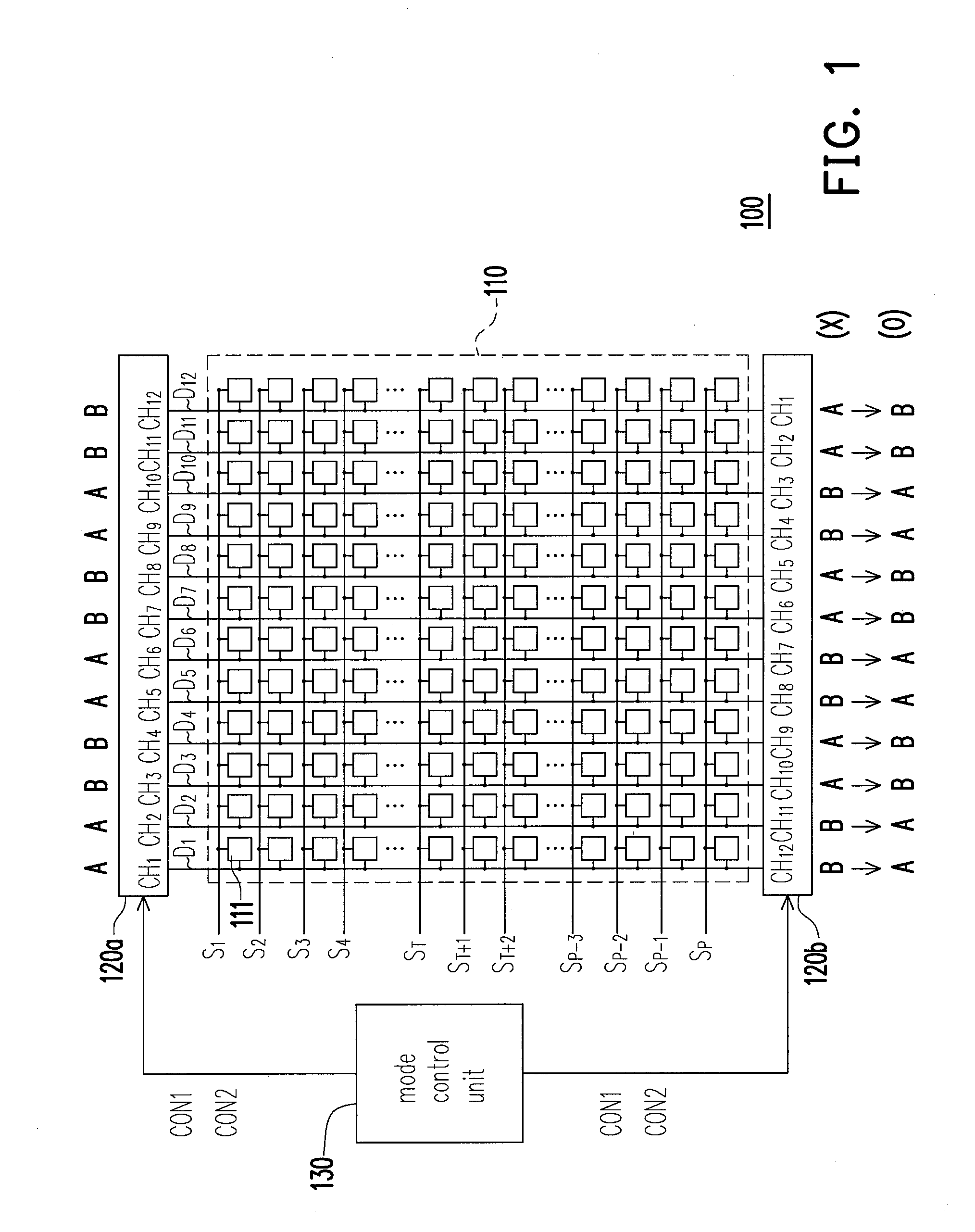
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85results about How to "Reduced voltage swing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
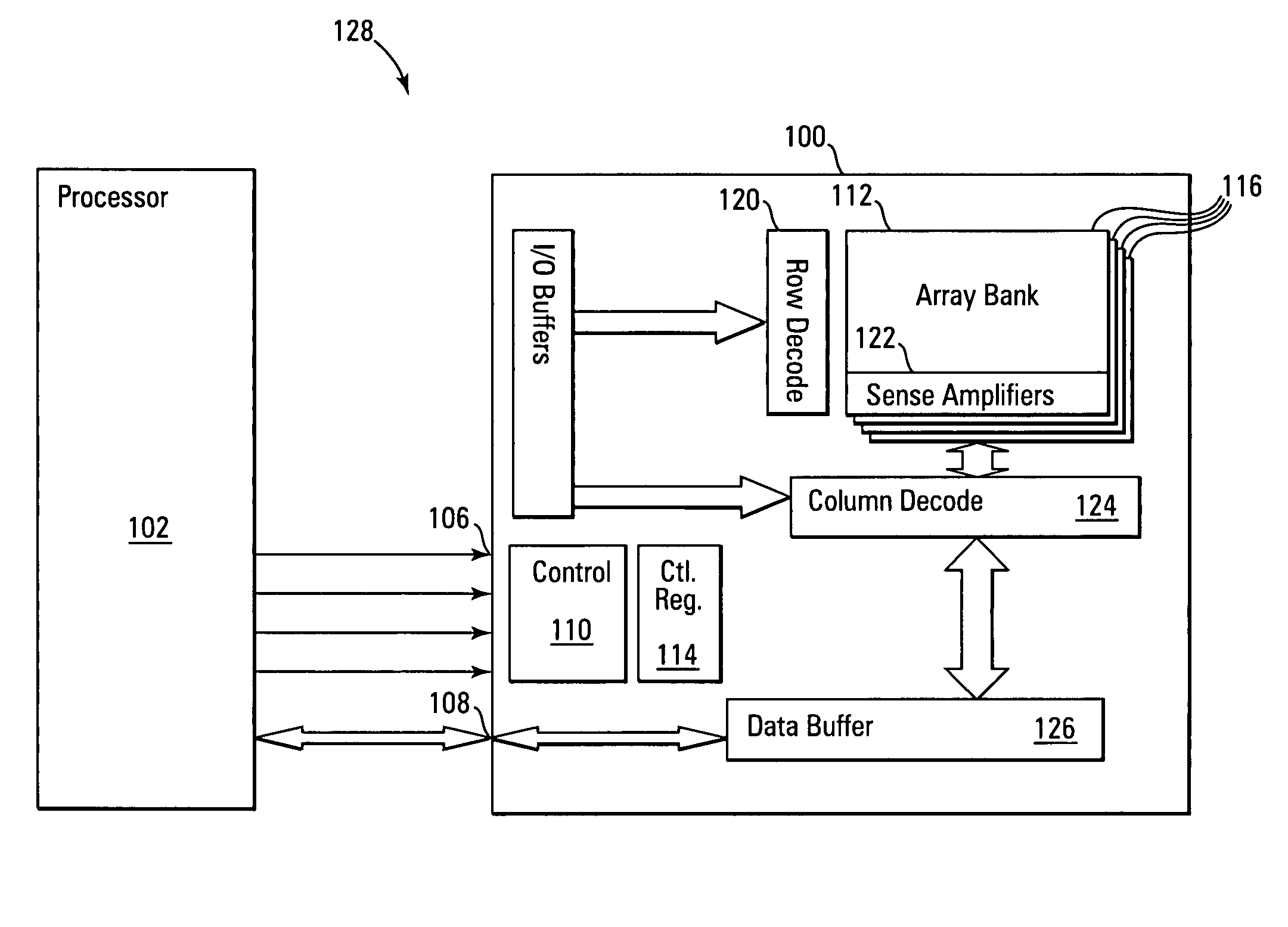
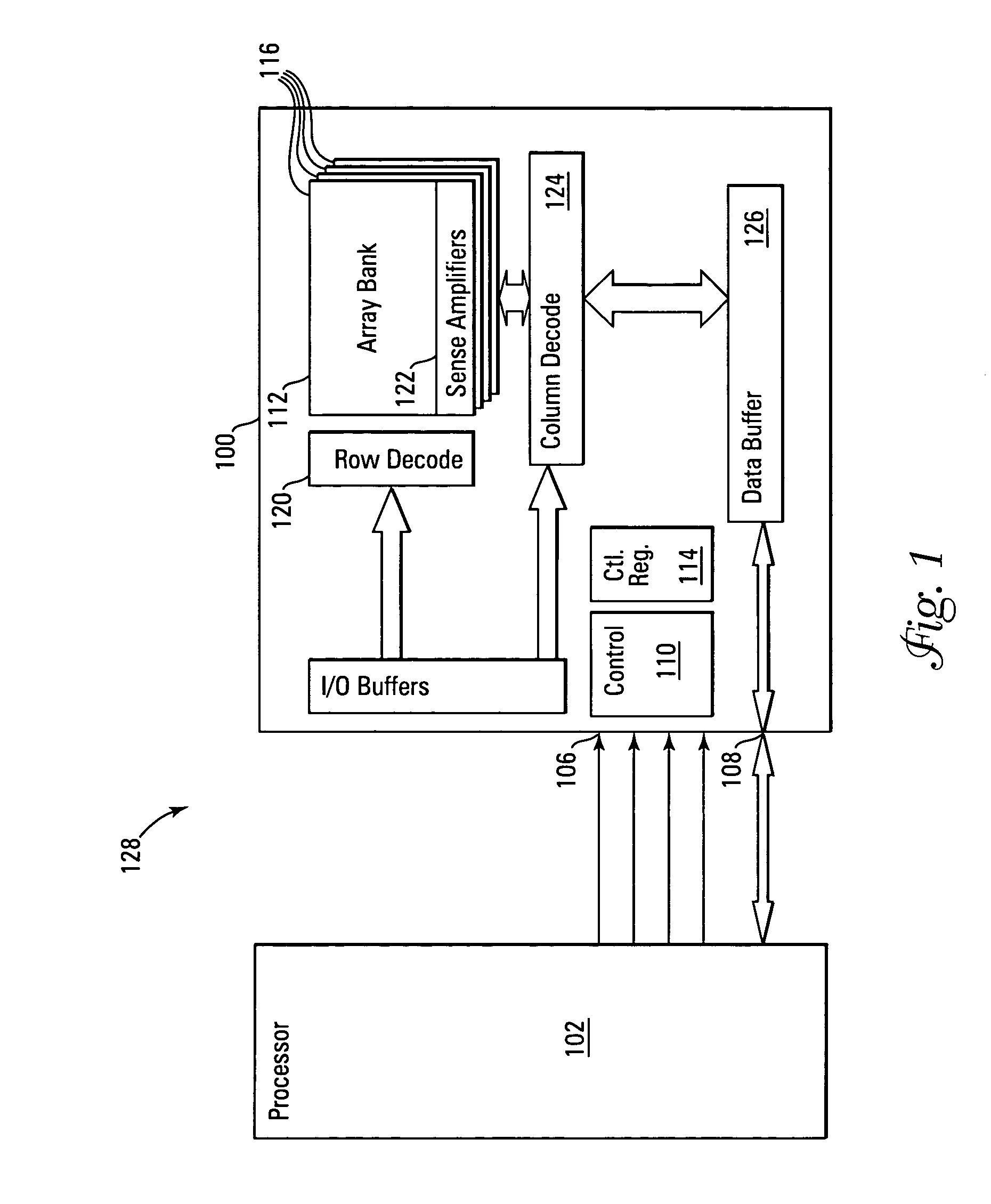
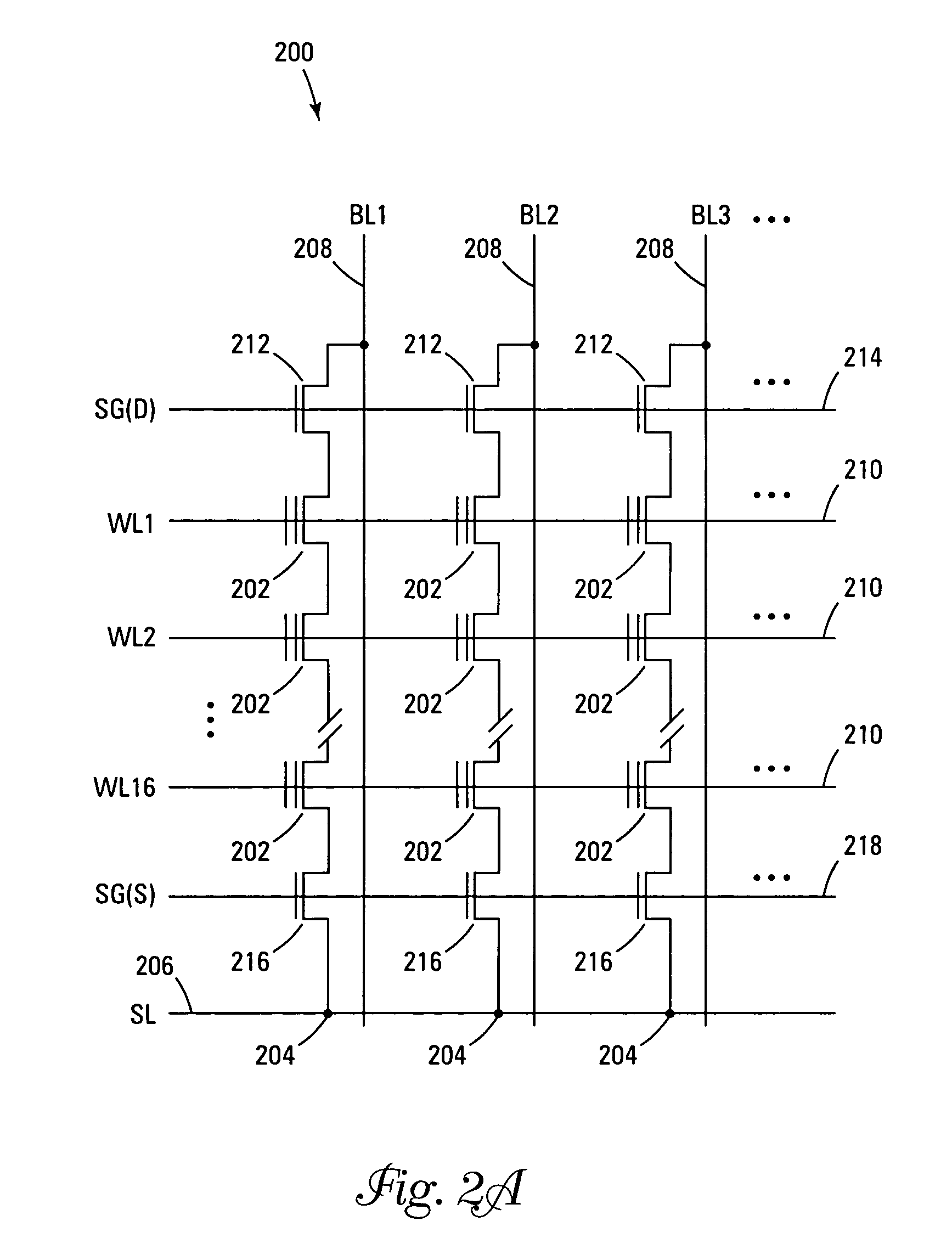
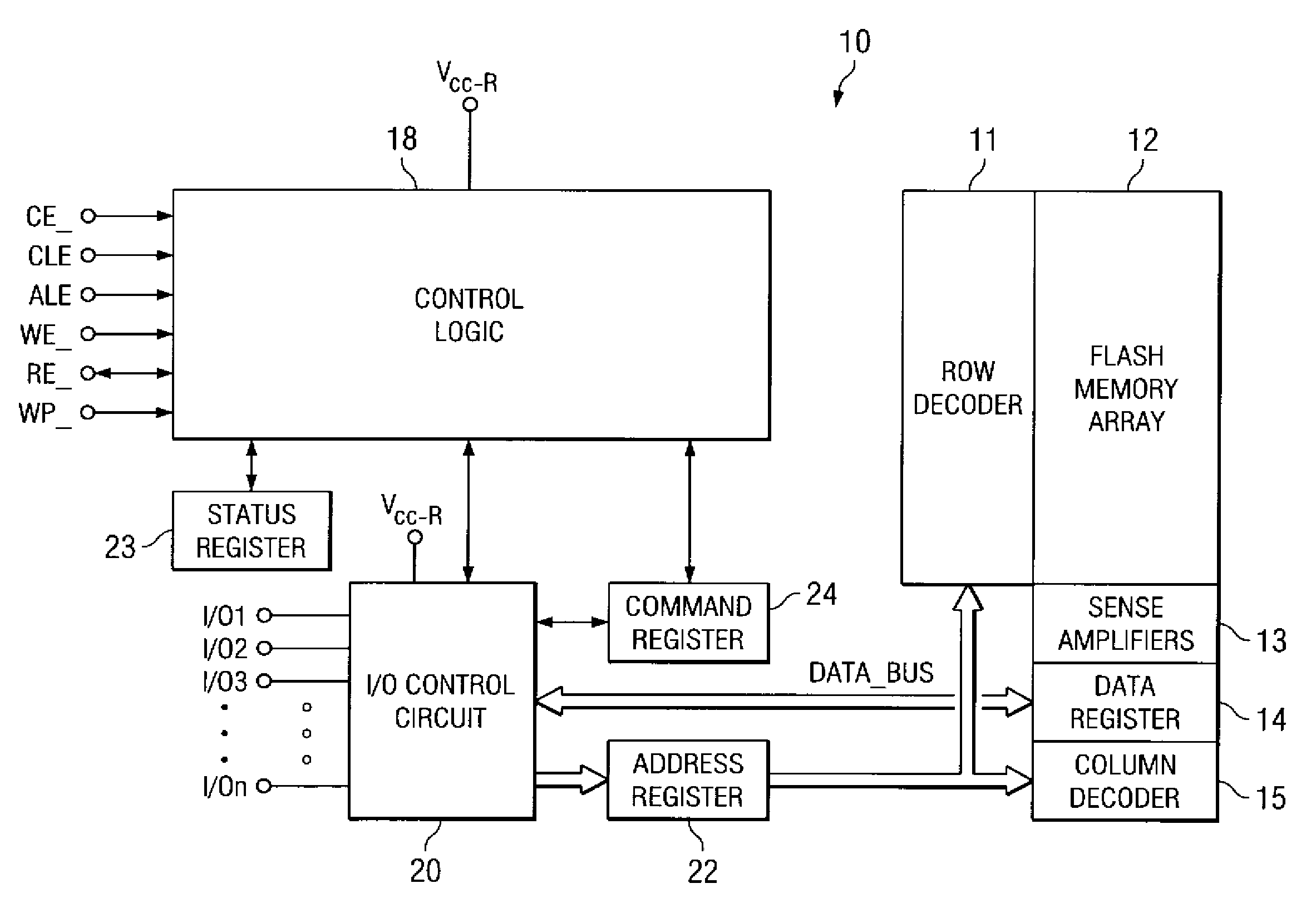
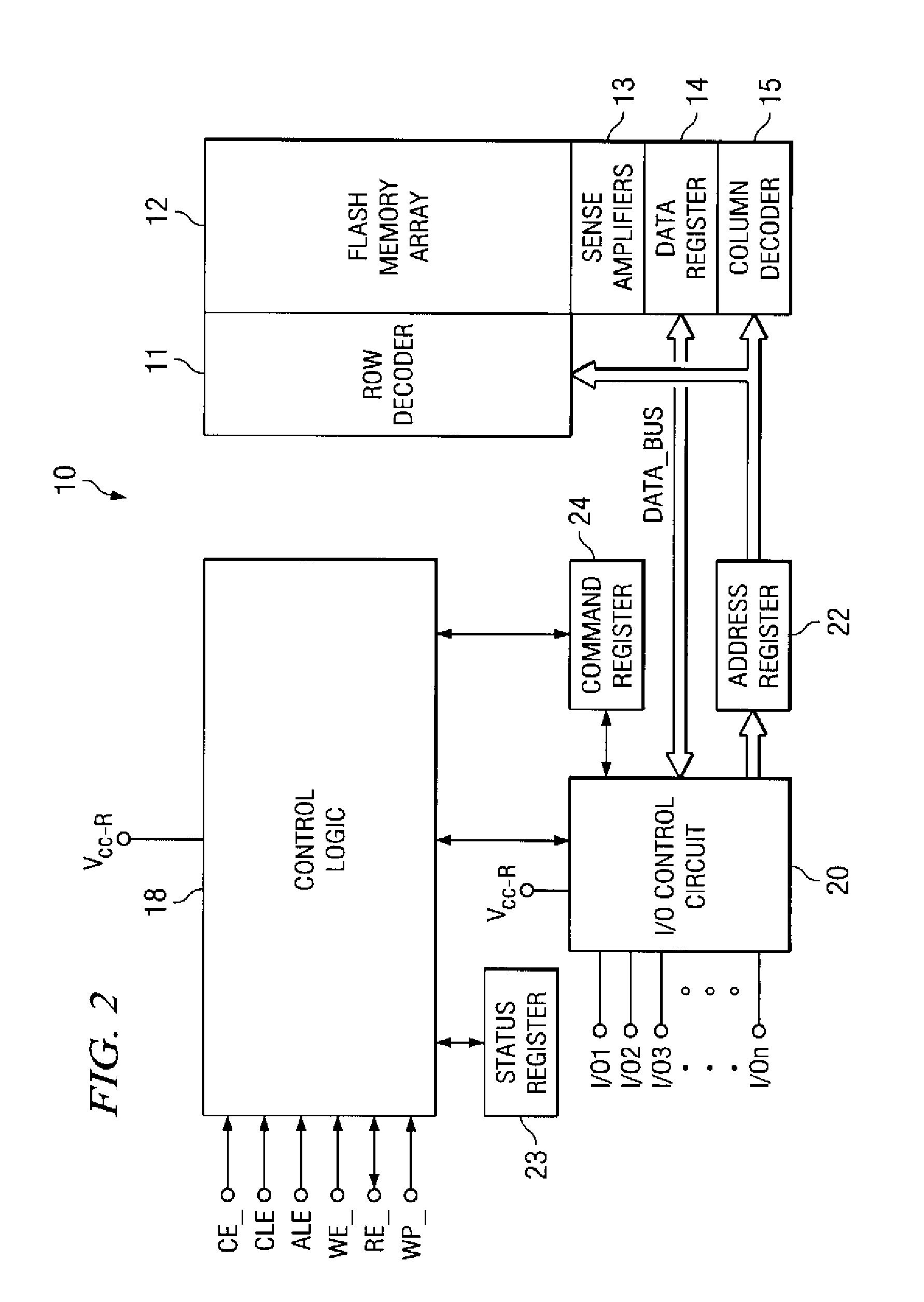
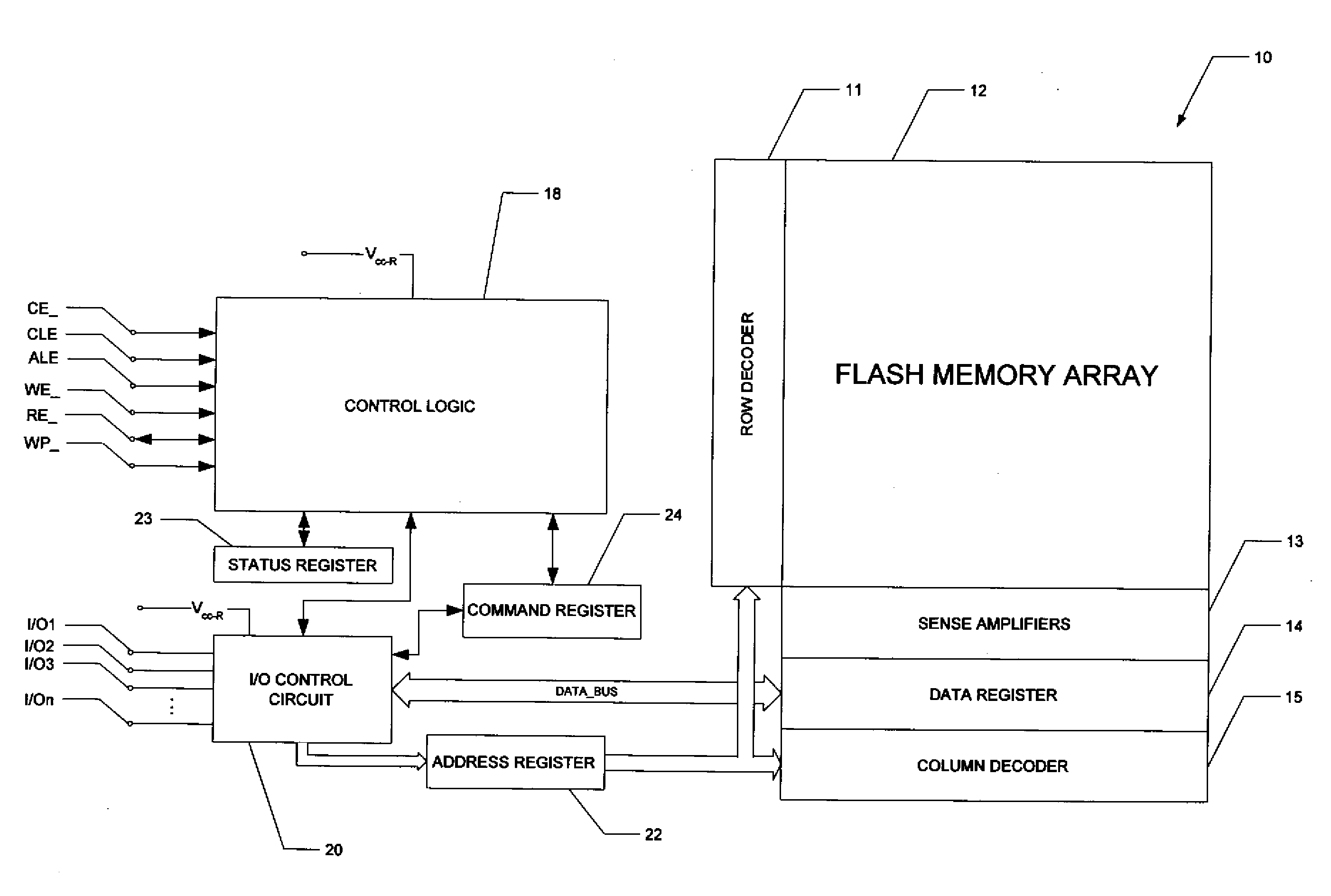
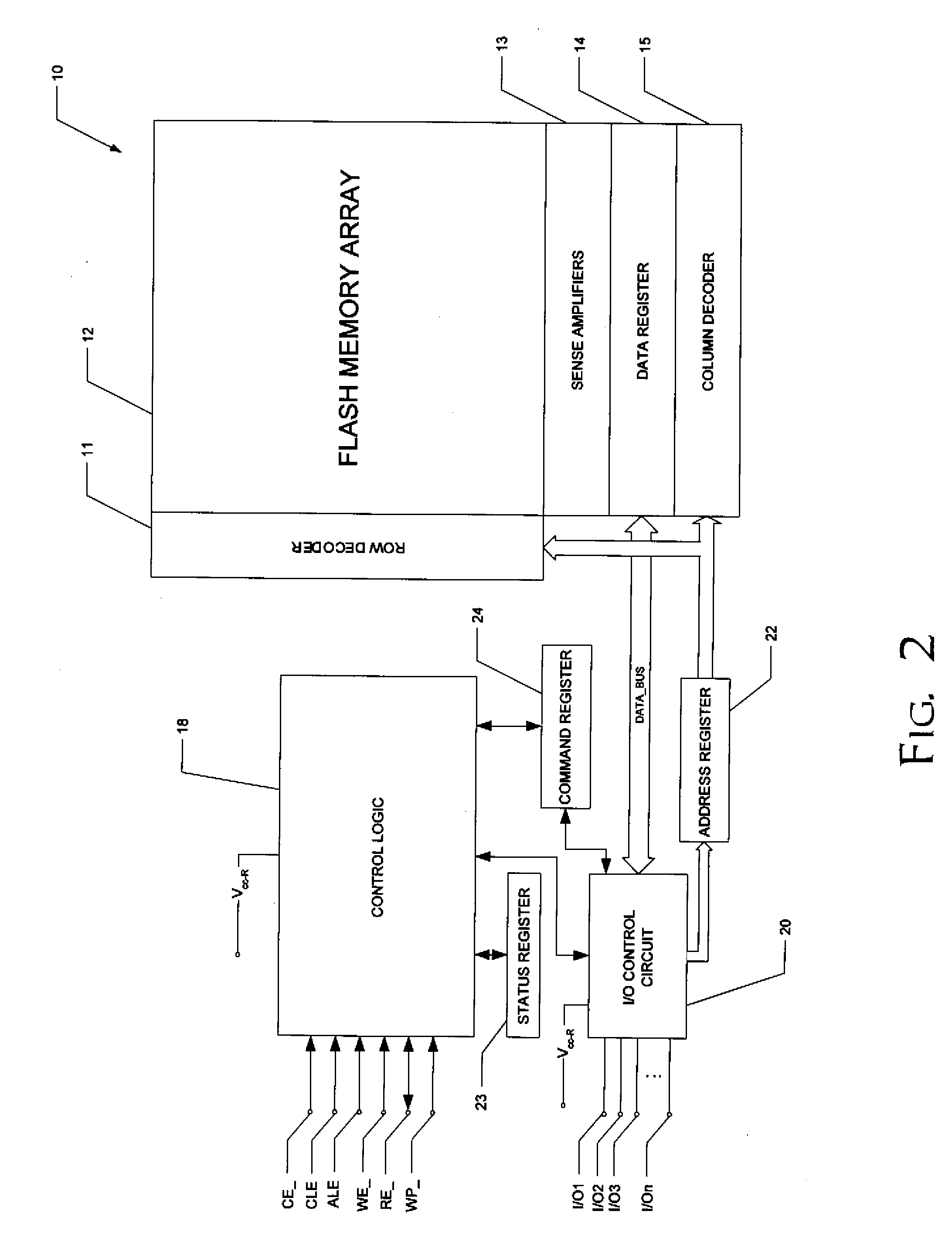
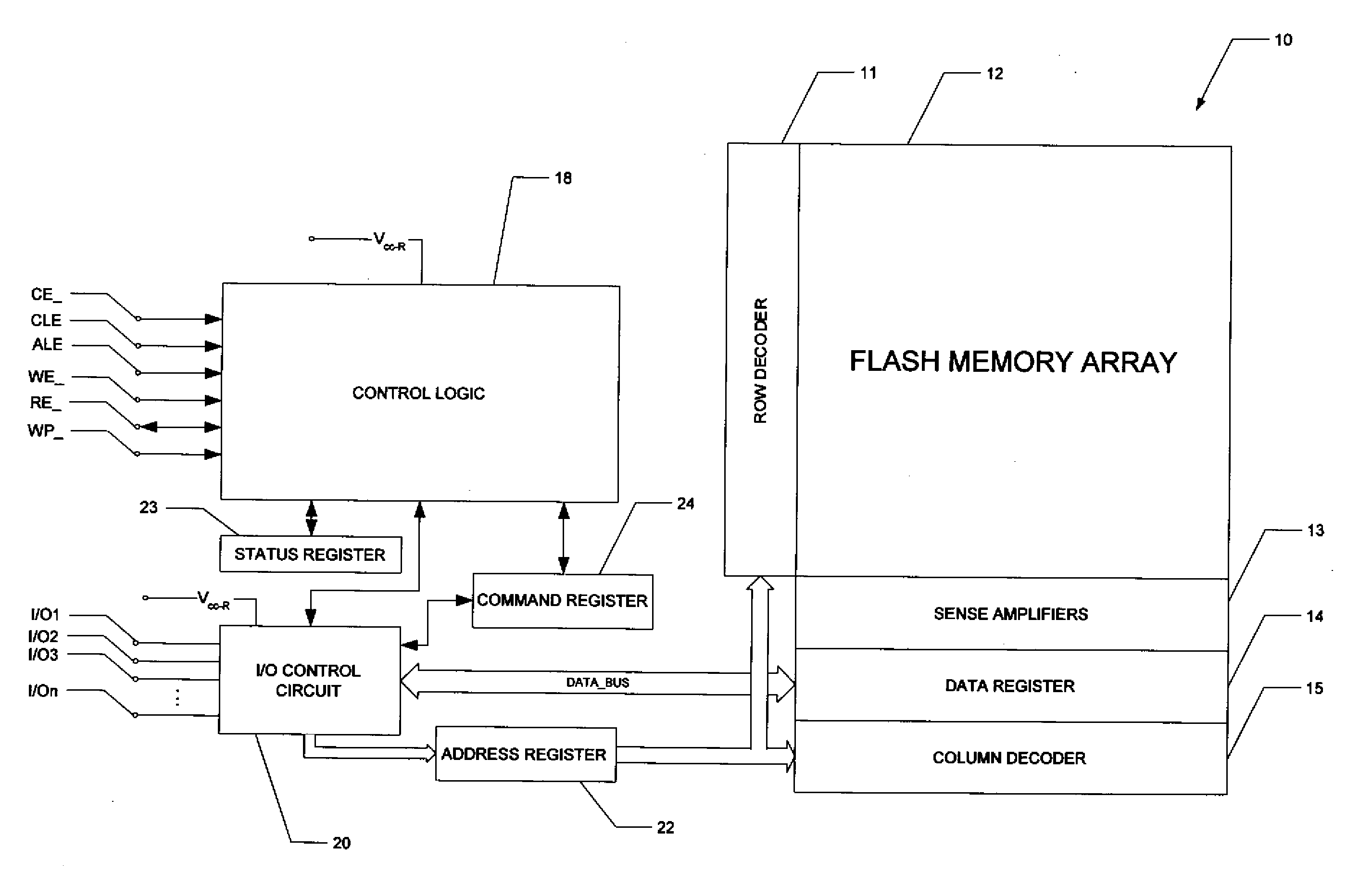
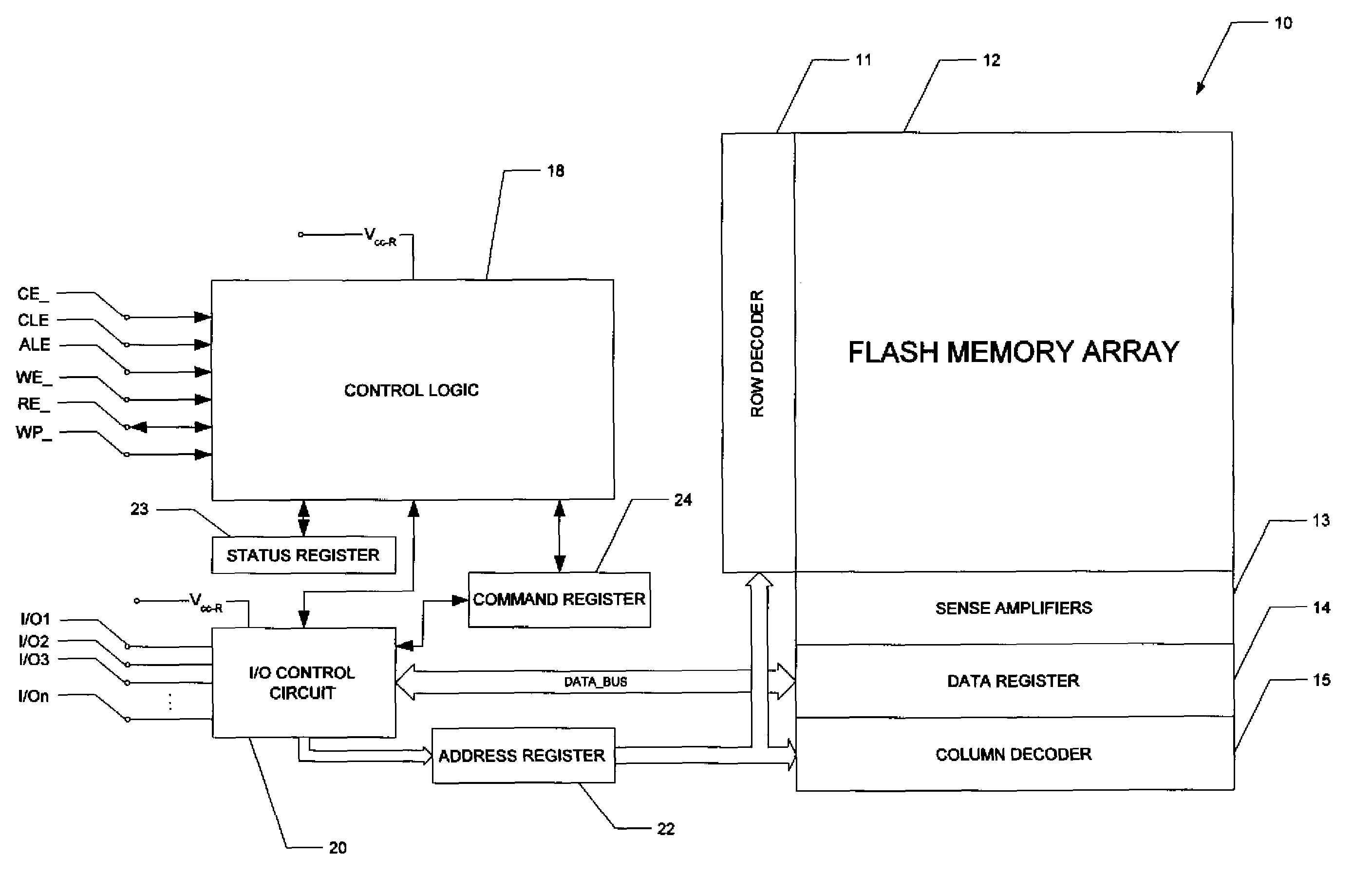
NAND flash depletion cell structure
InactiveUS20060044872A1Scale upIncrease supplyRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceRC time constant
NAND architecture Flash memory strings, memory arrays, and memory devices are described that utilize depletion mode floating gate memory cells. Depletion mode floating gate memory cells allow for increased cell current through lower channel rdS resistance and decreased “narrow width” effect, allowing for increased scaling of NAND memory cell strings. In addition, the required voltages for reading and programming operations are reduced, allowing the use of more efficient, lower voltage charge pumps and a reduction circuit element feature sizes and layouts. Cell inhibit of unselected cells is also increased, reducing the likelihood of cell disturb in the memory array. Operation speed is improved by increasing read current of the selected NAND string and by increasing the ability to overcome the RC time constants of circuit lines and capacitances through lowered voltage swings and increased current supplies.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
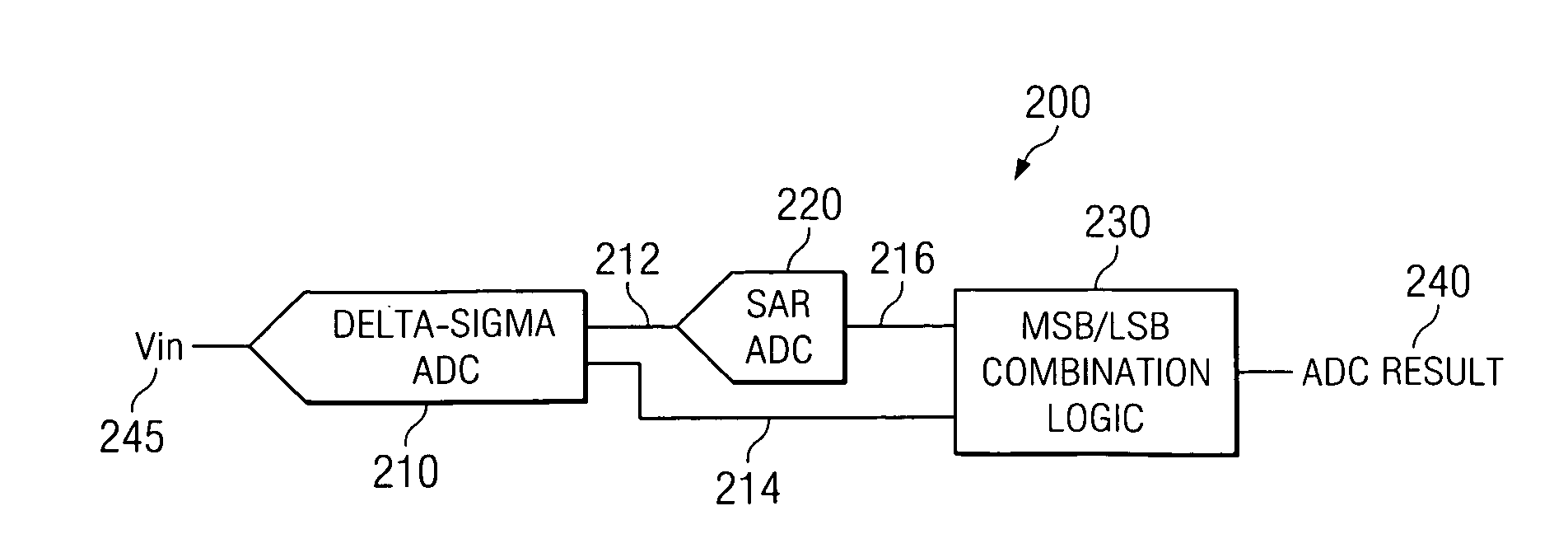
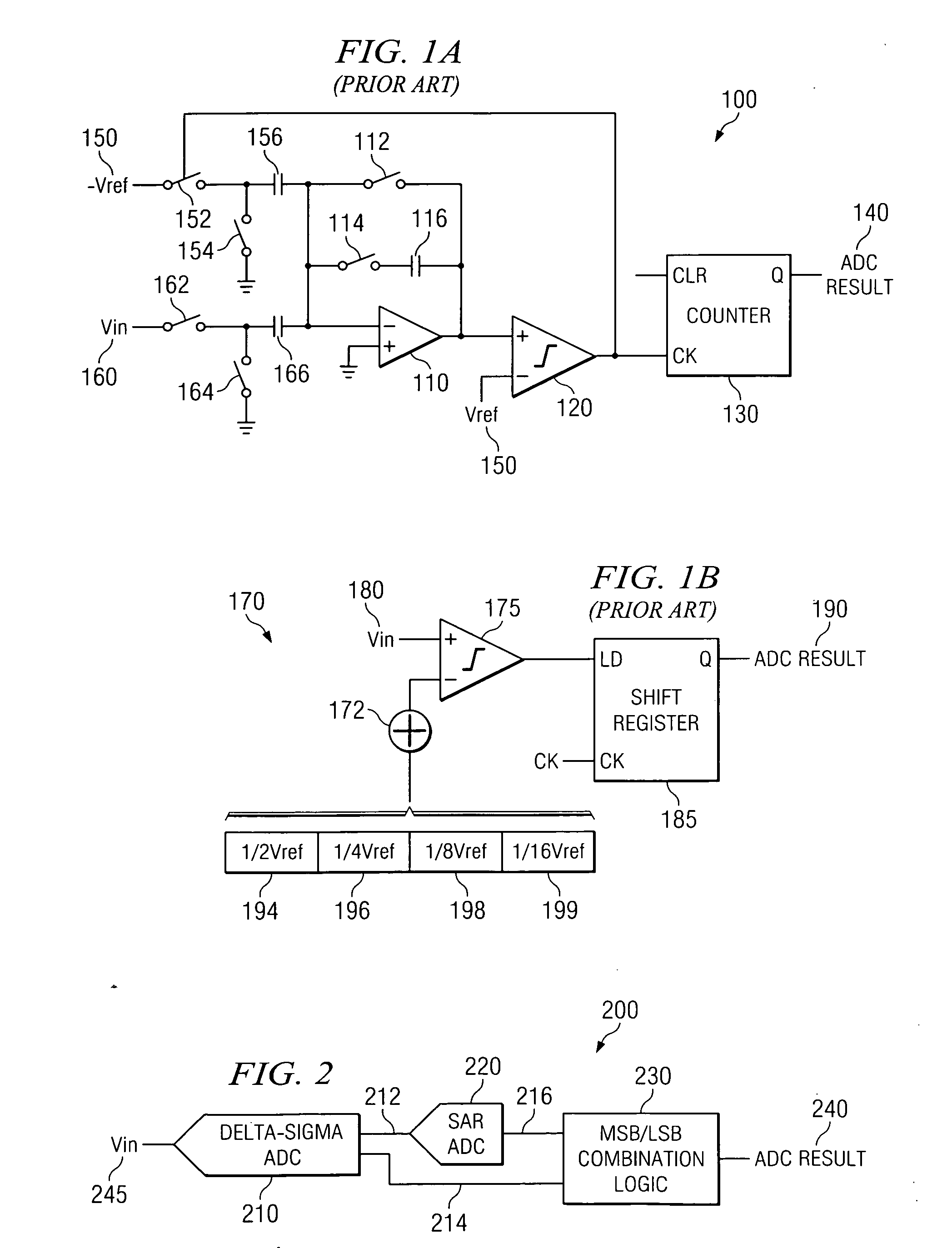
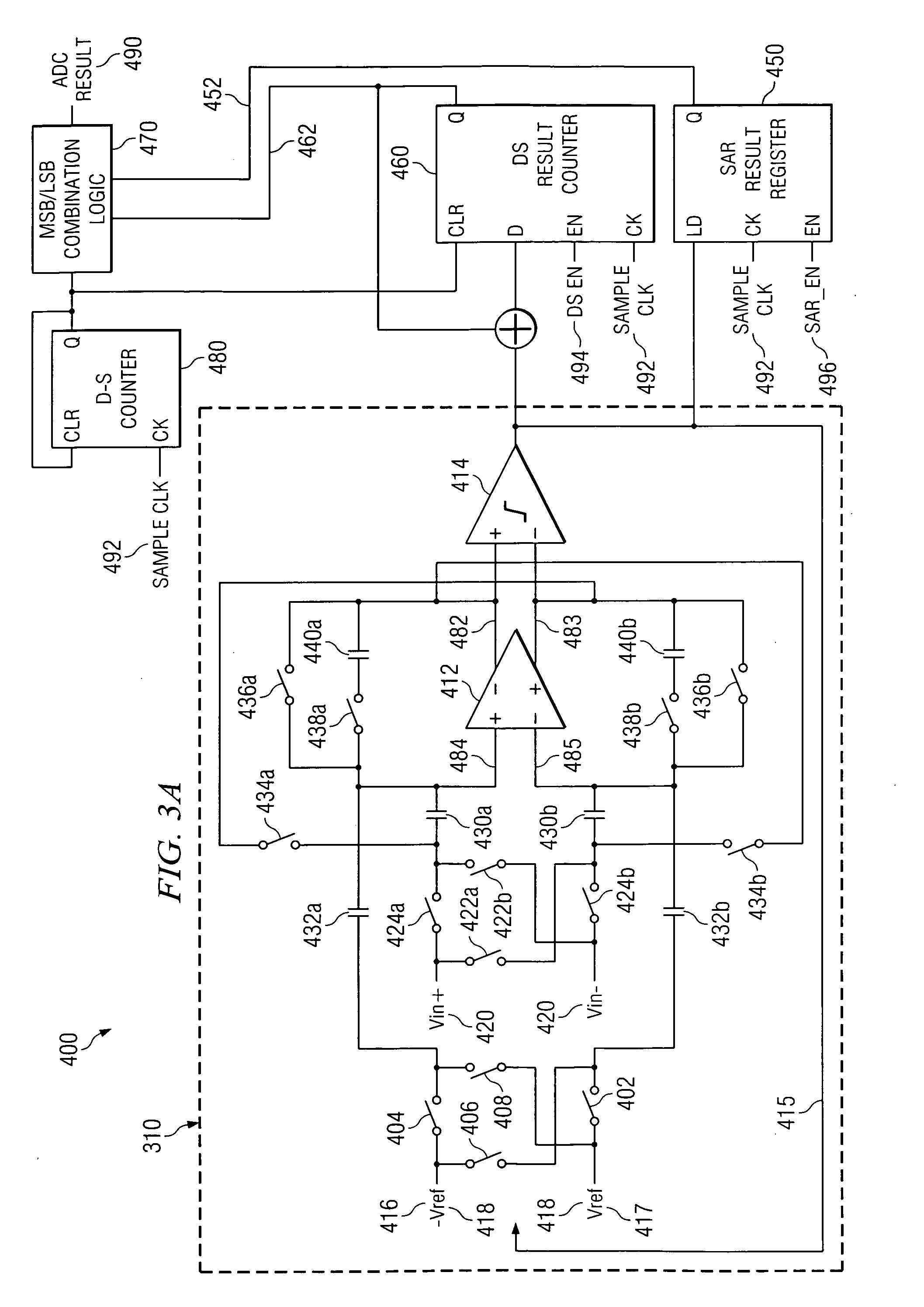
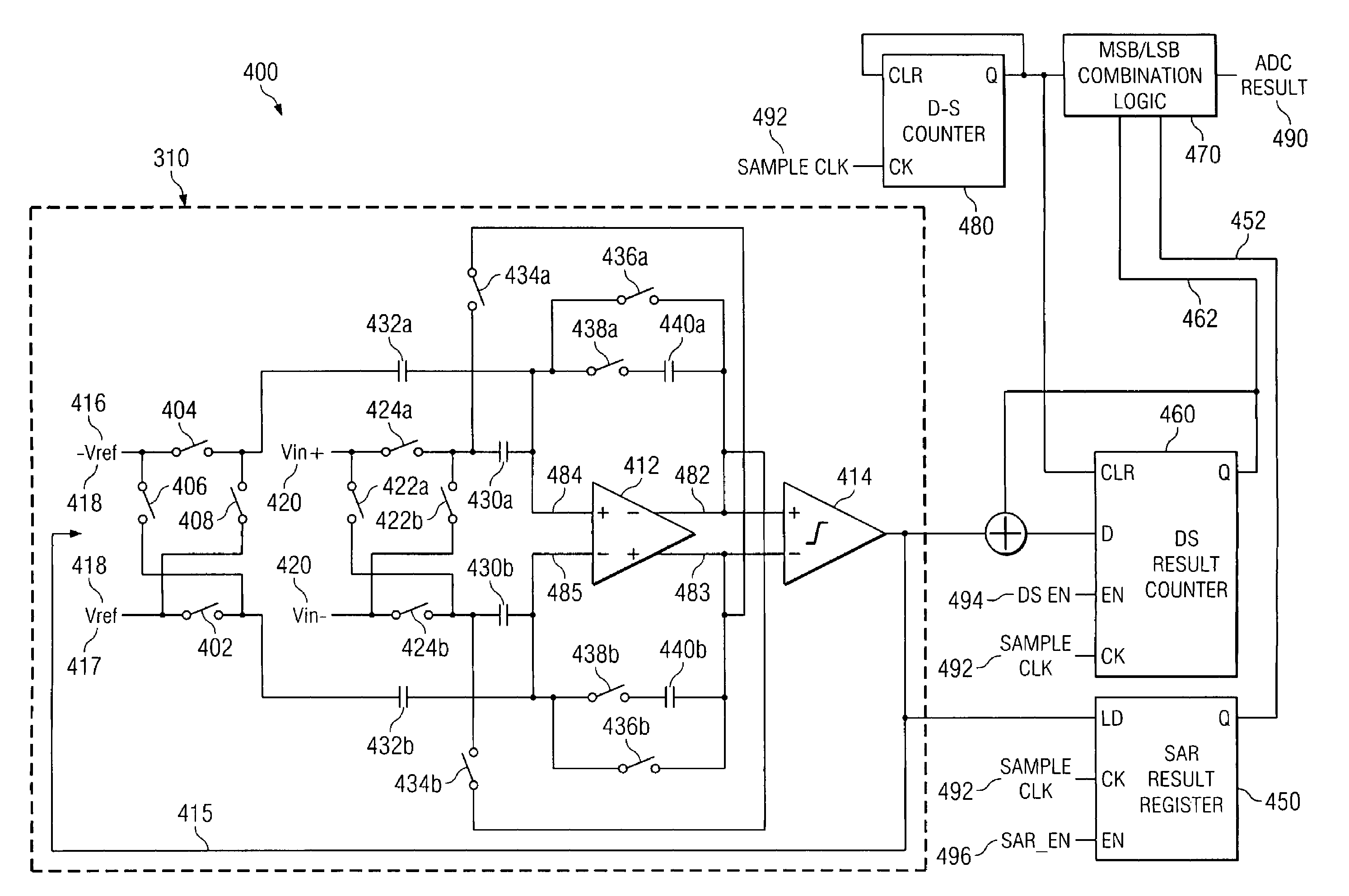
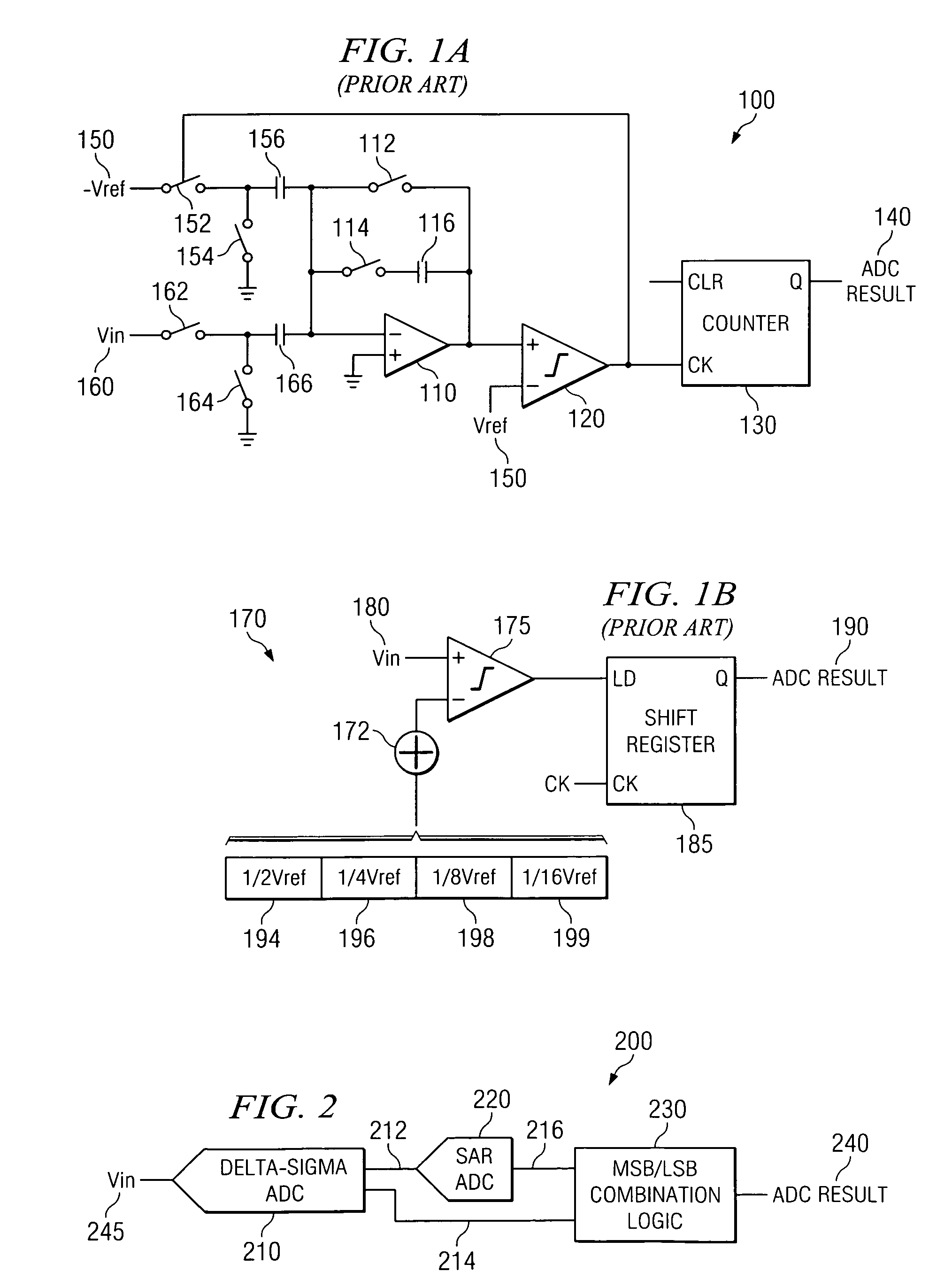
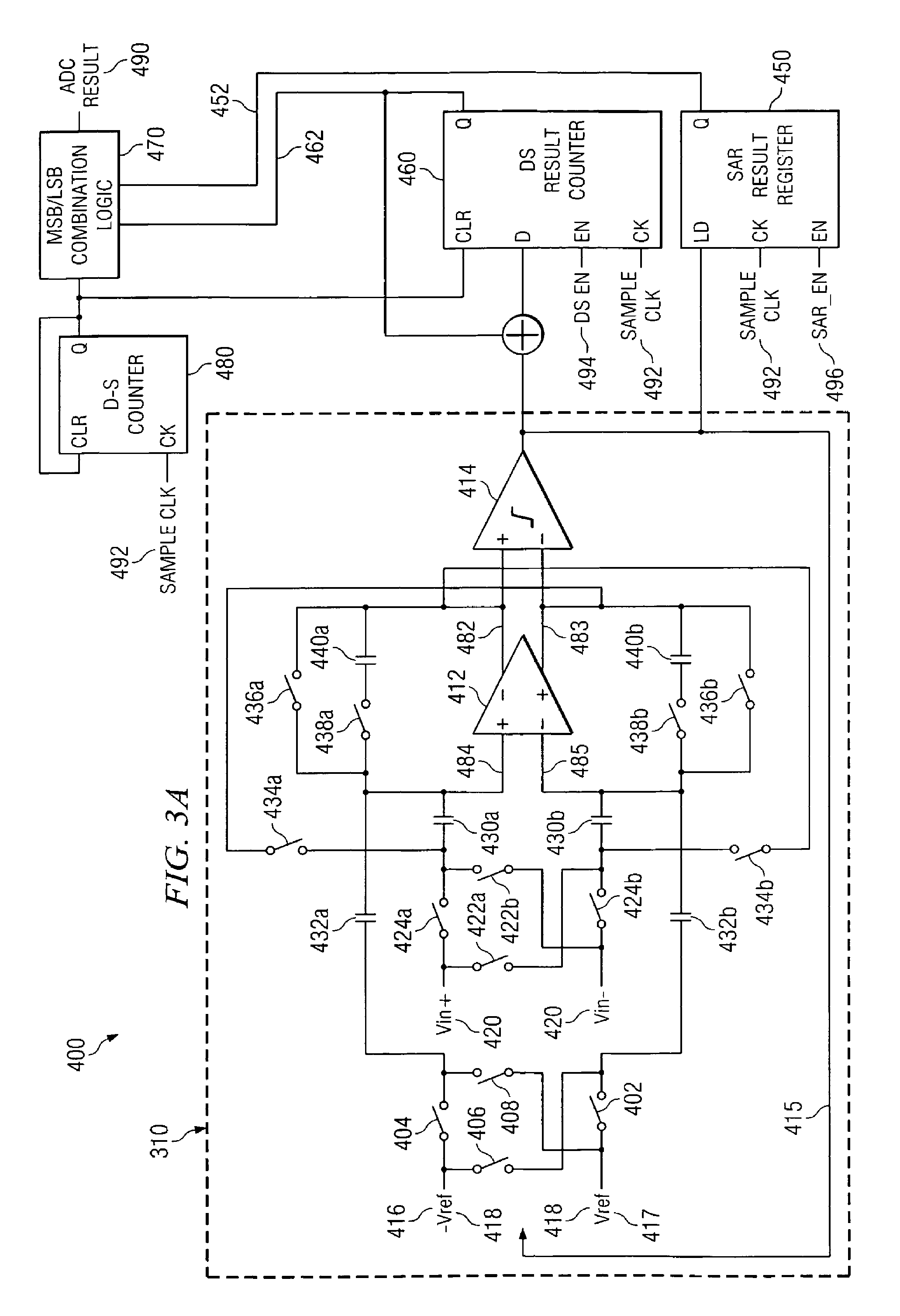
Integrating/SAR ADC and method with low integrator swing and low complexity
ActiveUS20080258959A1Reduce the amount of solutionReduce voltageElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorGreek letter sigma
A reconfigurable circuit (10) includes an integrator (30) having switches (SW1-6) for selectively coupling input capacitors (C0,1,2,3,6,7) and integrating capacitors (C4,5) to terminals of the integrator (30) for operation of a hybrid delta-sigma / SAR ADC (400) so as to create a reference voltage value (Vref) equal to the sum of a first voltage (ΔVbe) and a second voltage (Vbe). A first integration is performed to reduce the integrator output voltage swing. A residue (Vresidue) of the integrator is multiplied by 2. Then the second voltage (Vbe) is integrated in a first direction if a comparator (22) coupled to the integrator changes state or in an opposite direction if the comparator does not change state. The first voltage (ΔVbe) is integrated in a direction that causes the integrator output voltage (Vout) to equal either 2×Vresidue−Vref or 2×Vresidue+Vref.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
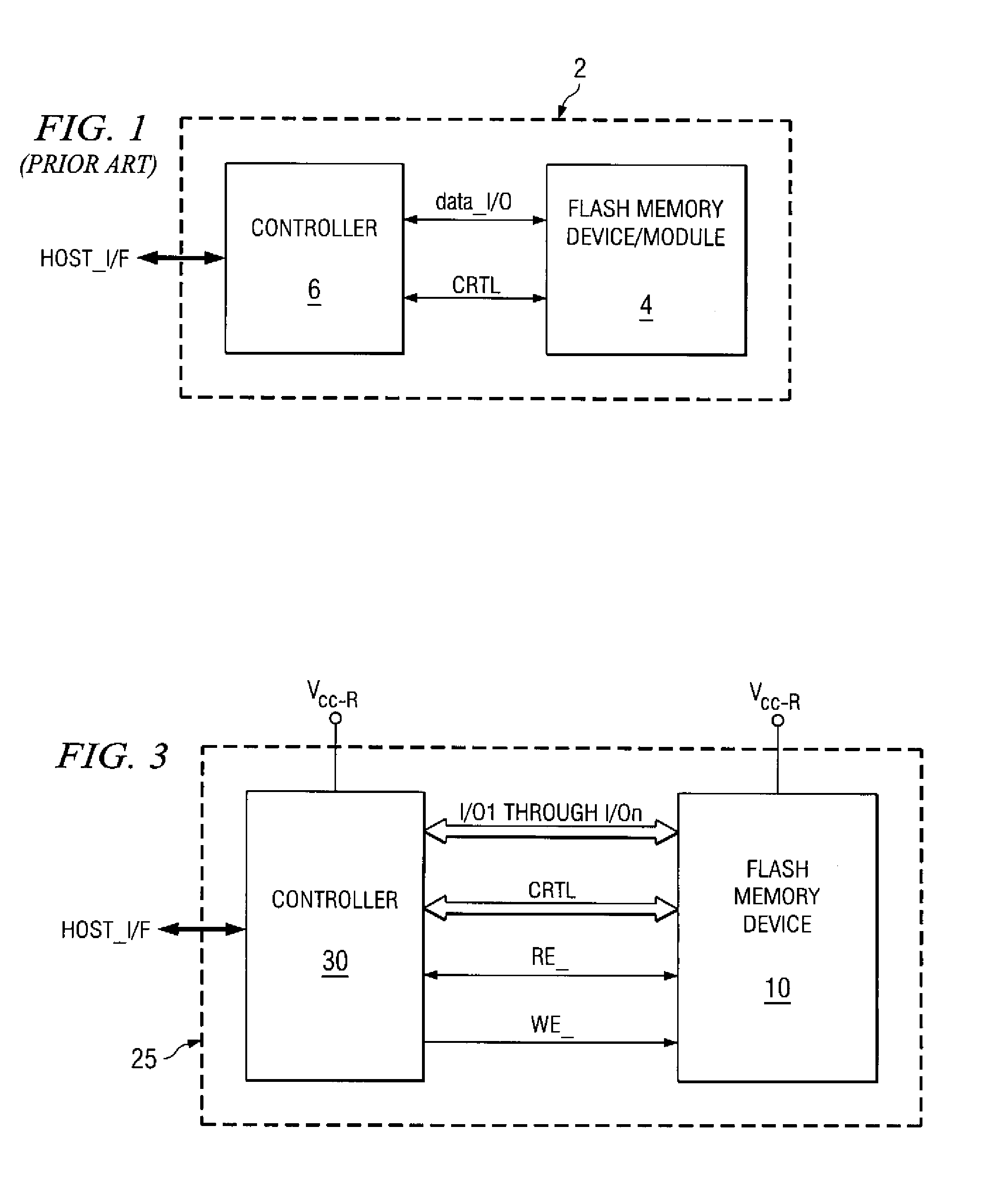
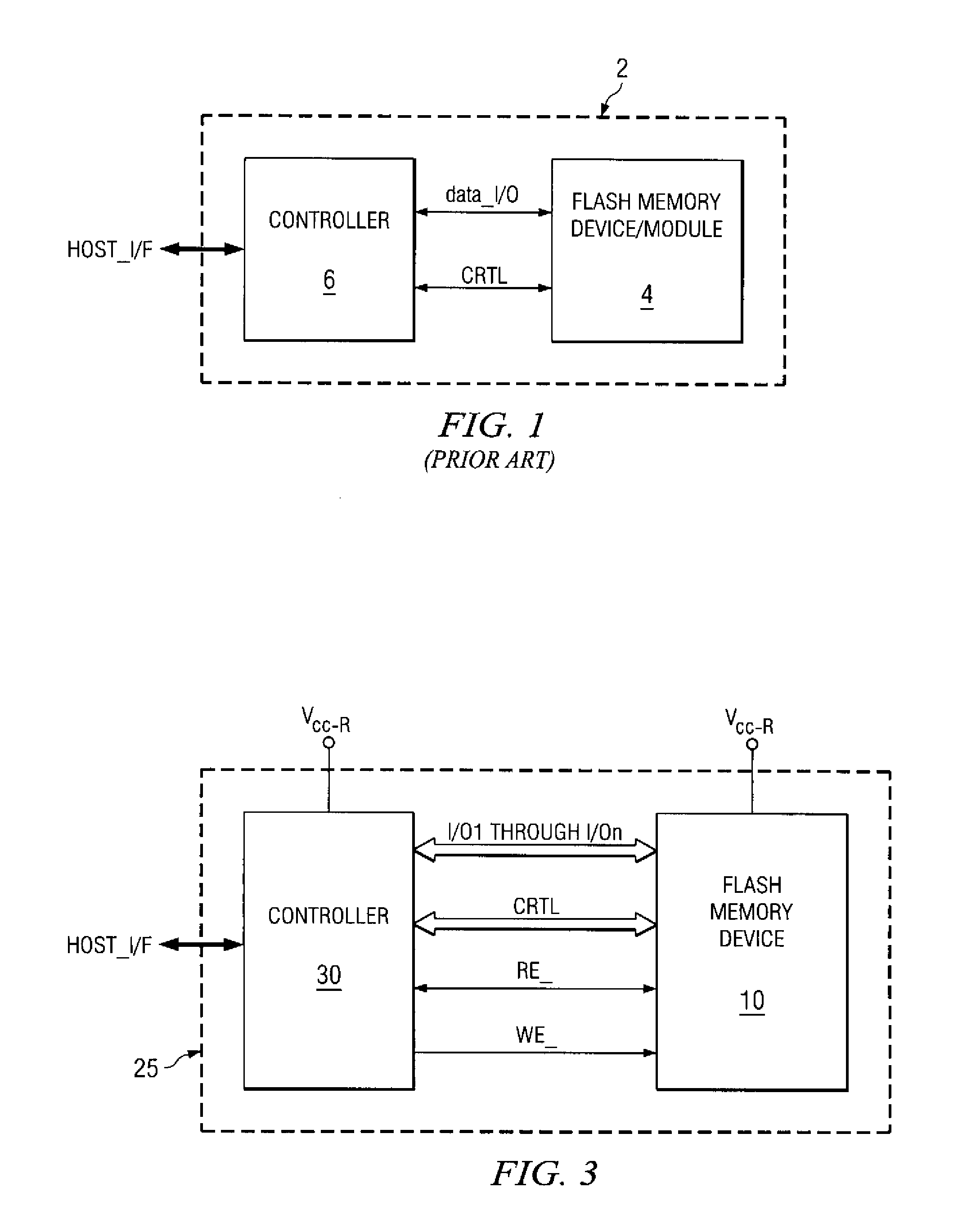
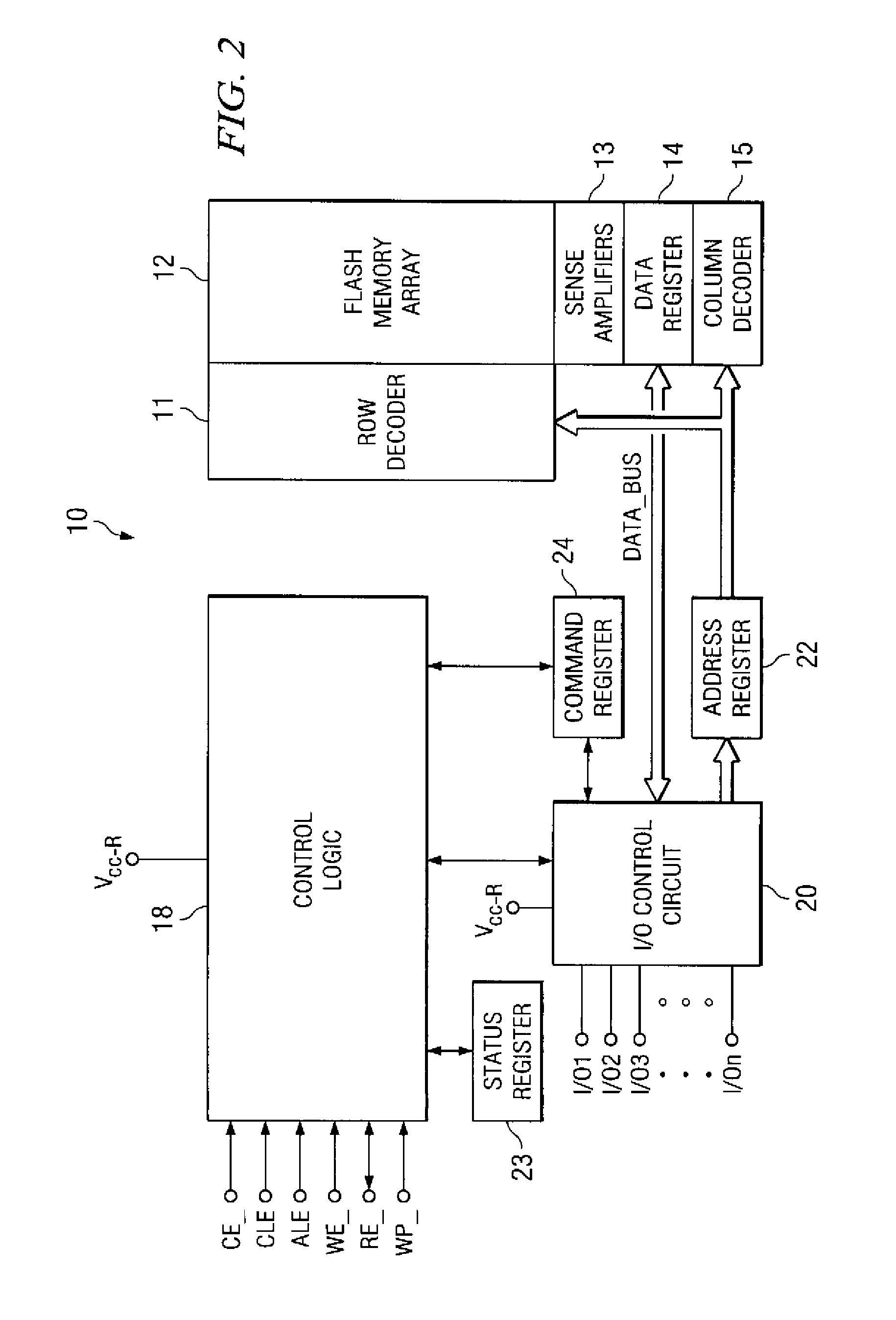
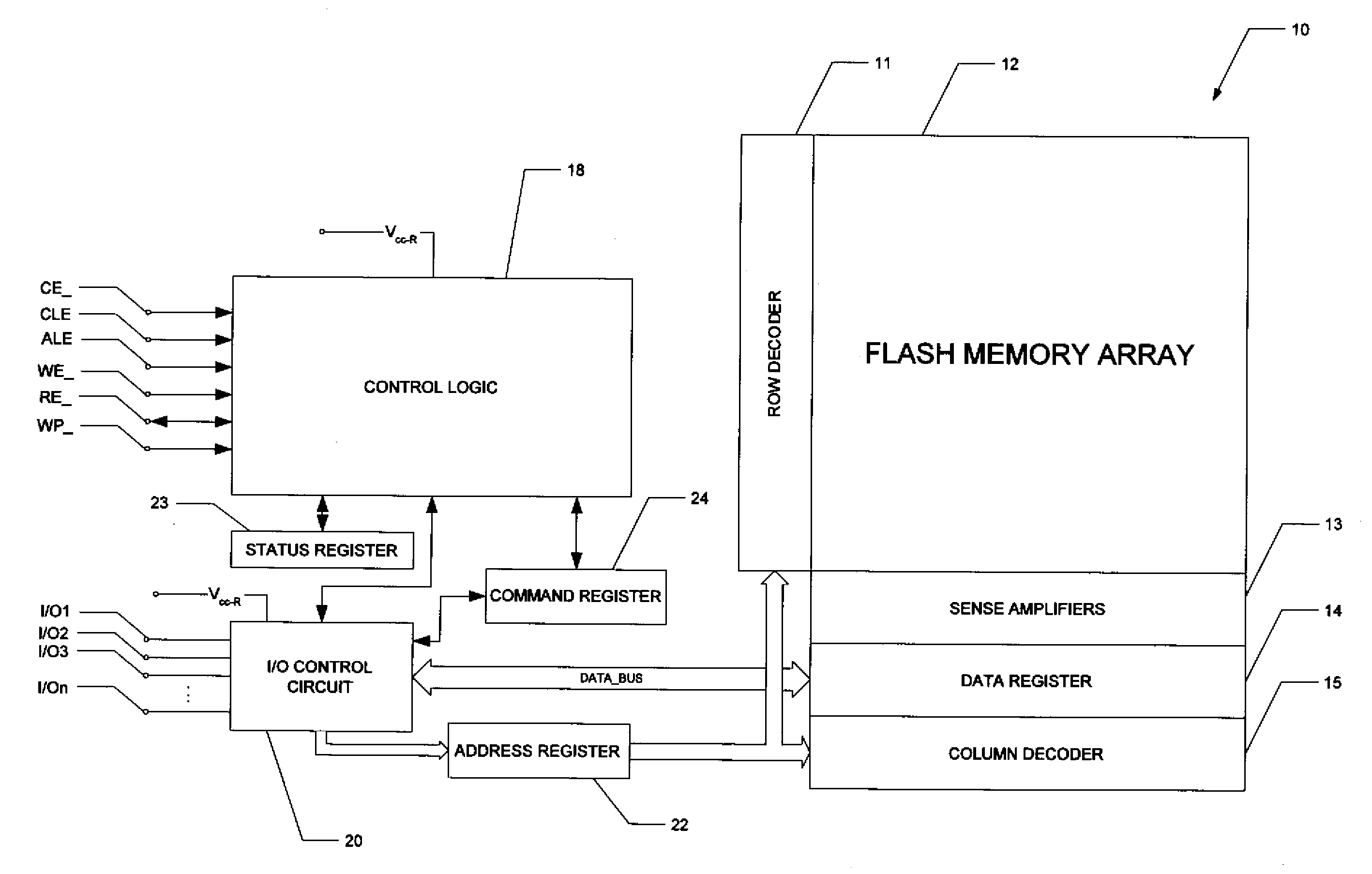
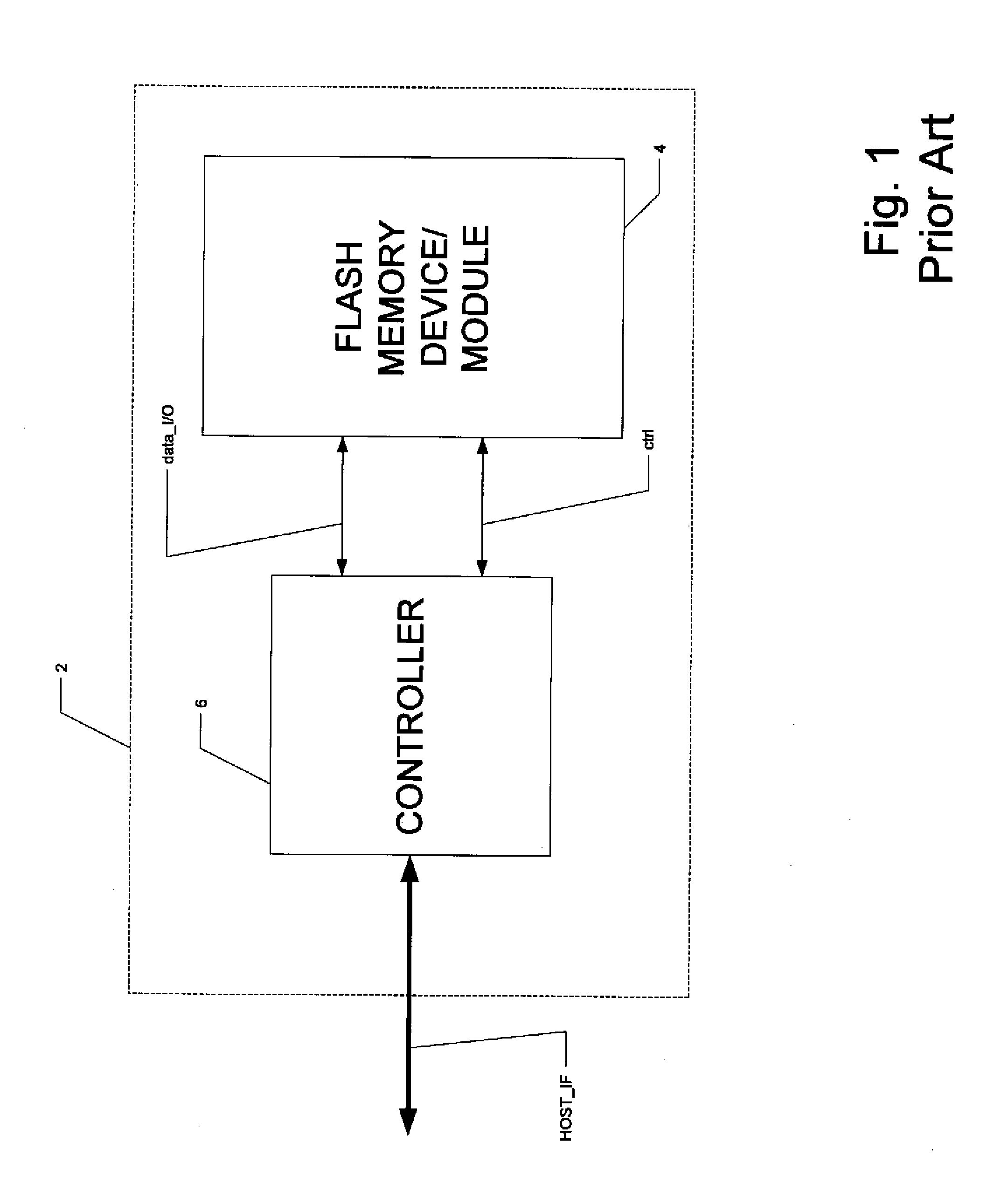
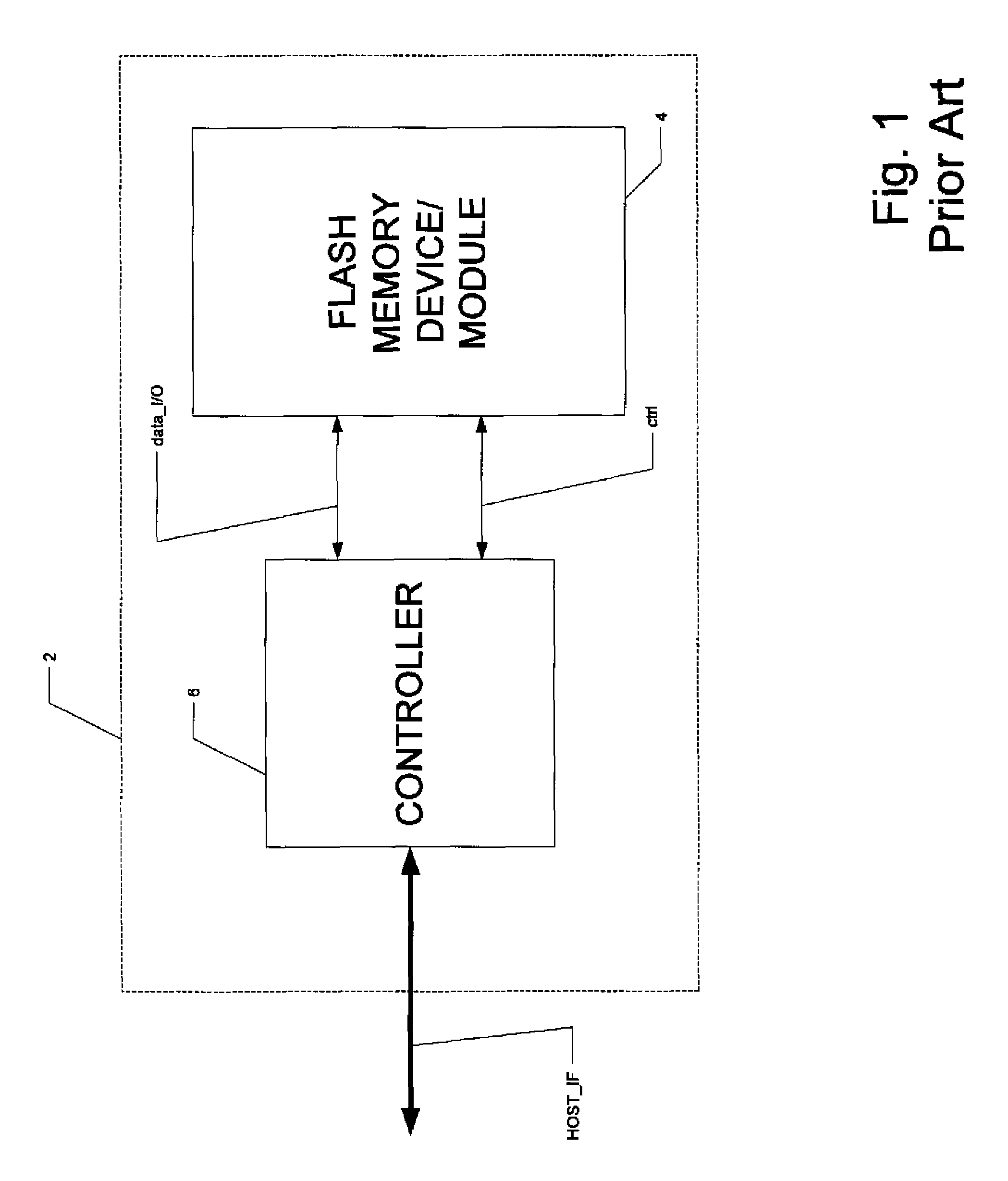
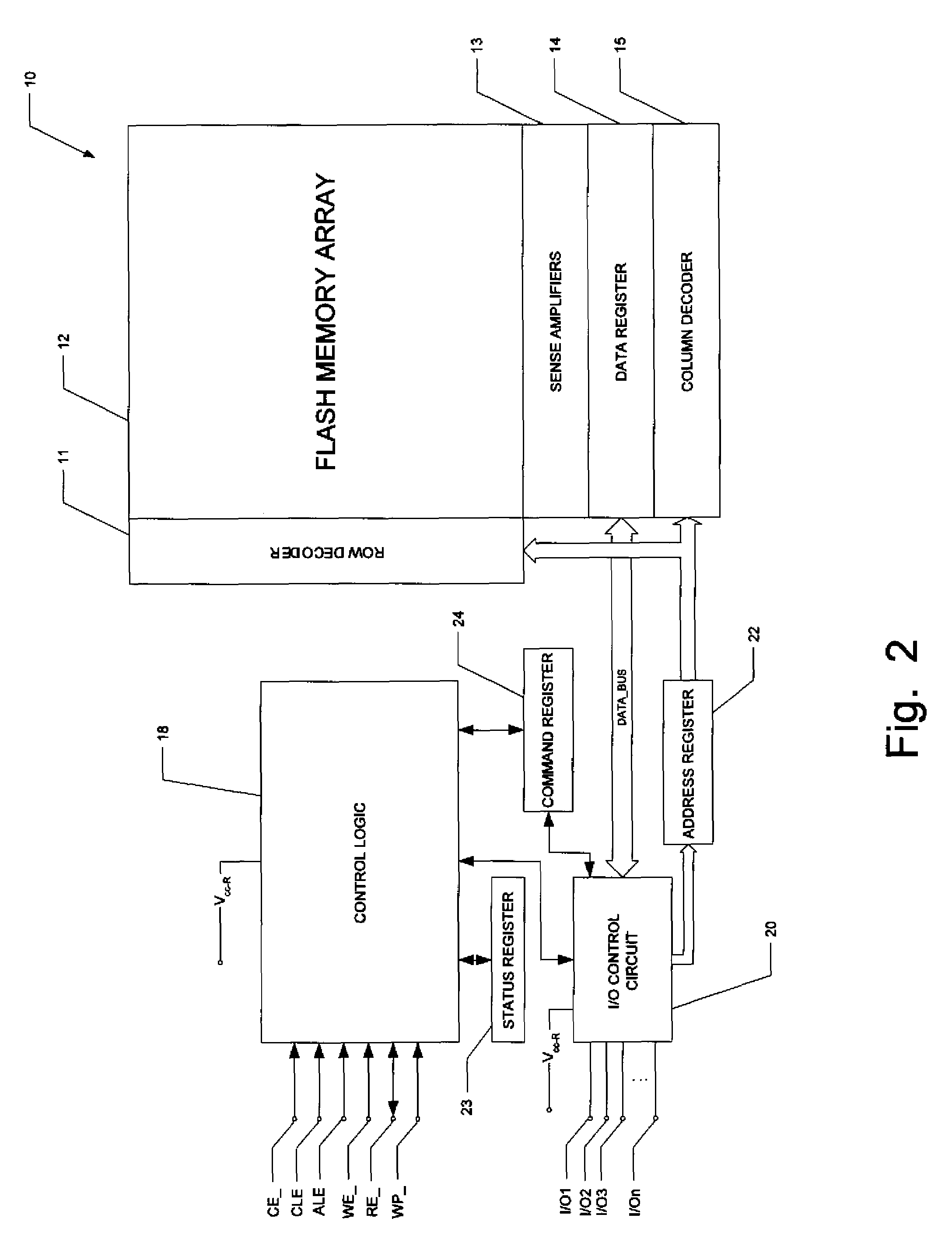
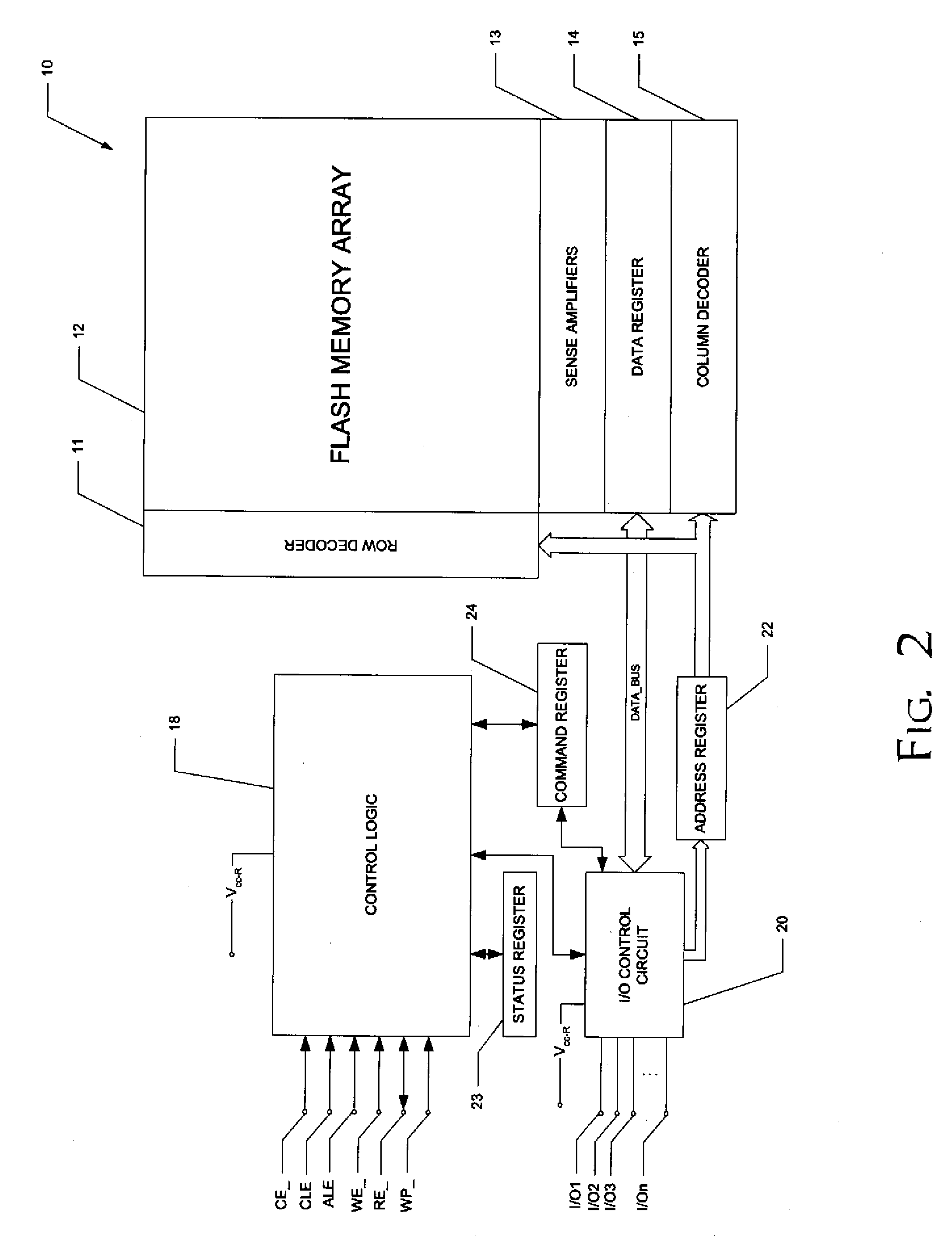
High-performance flash memory data transfer
ActiveUS7366029B2Minimize data transferMinimize data skewRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalNormal mode
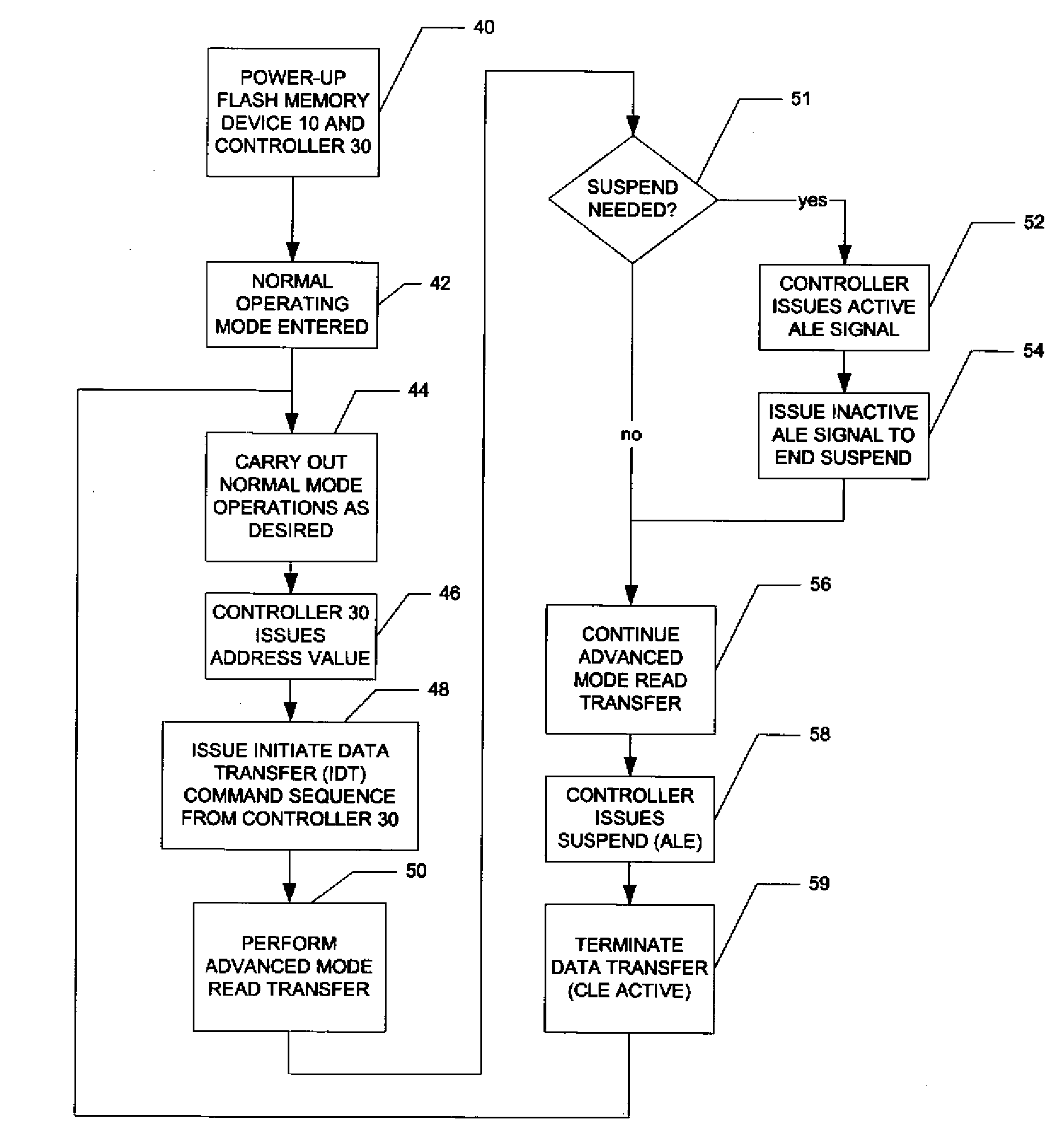
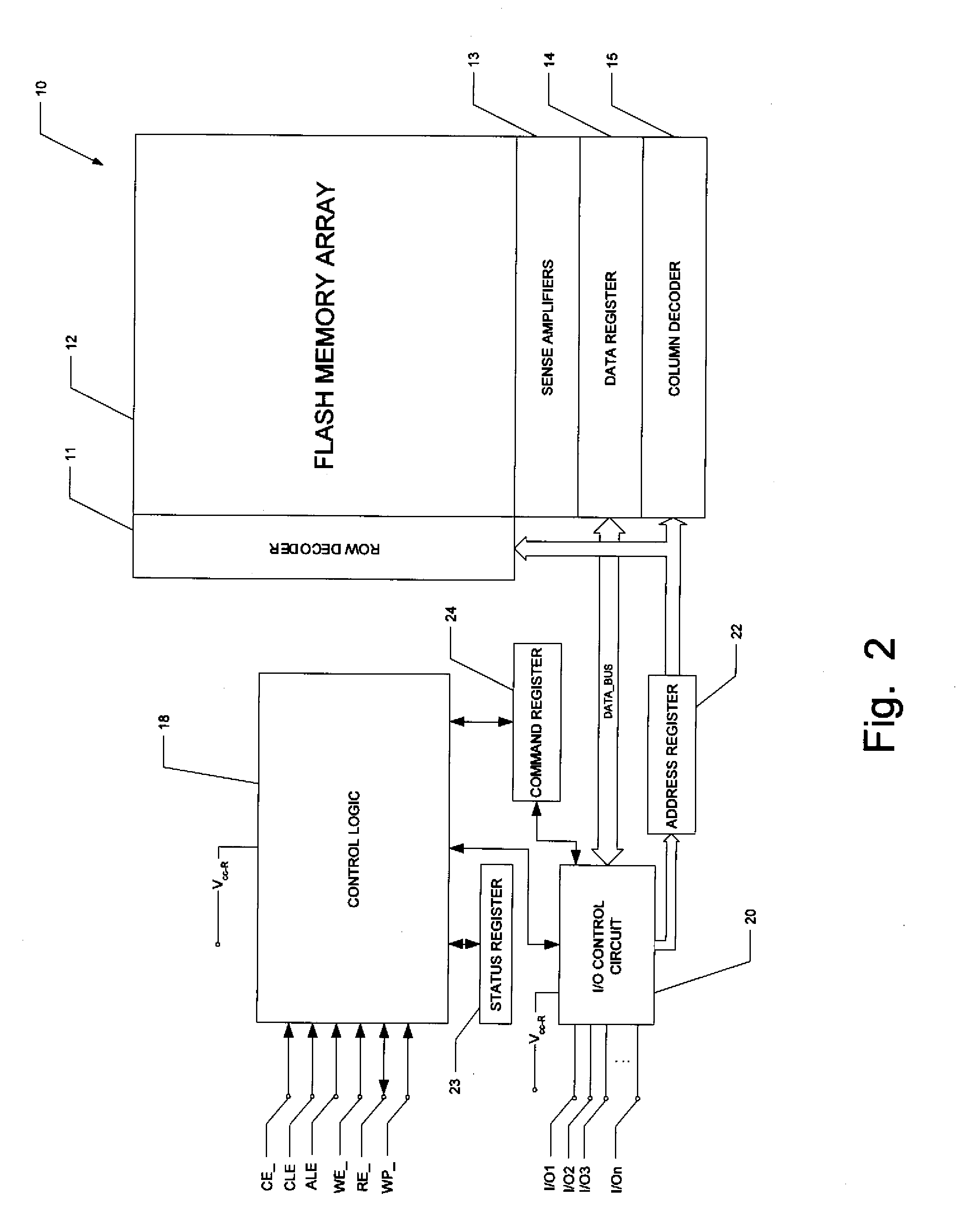
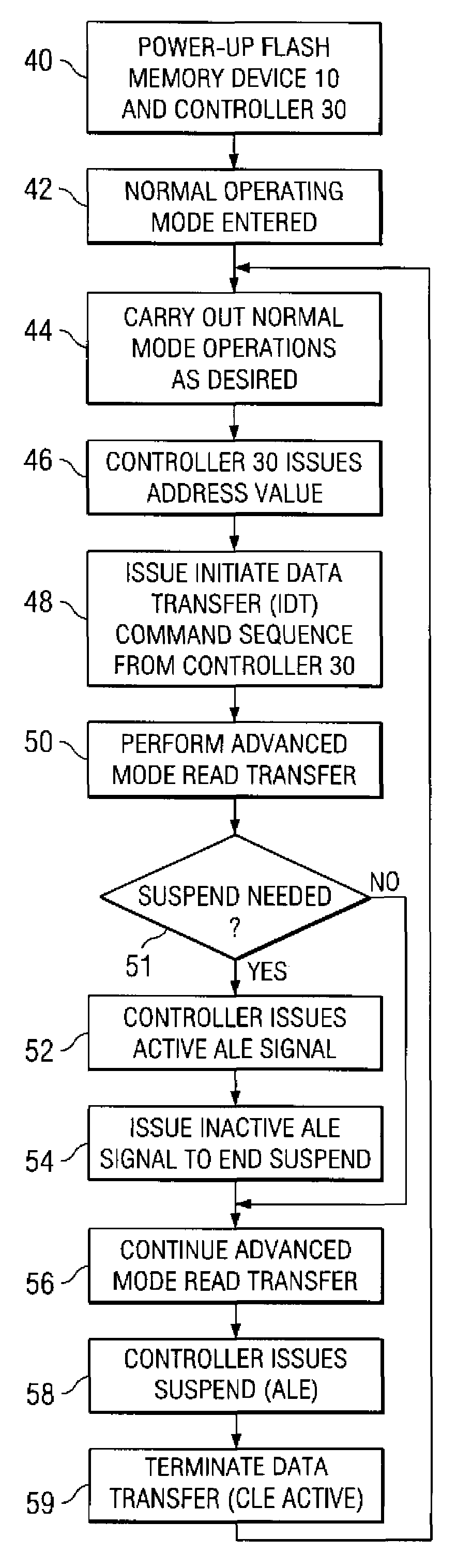
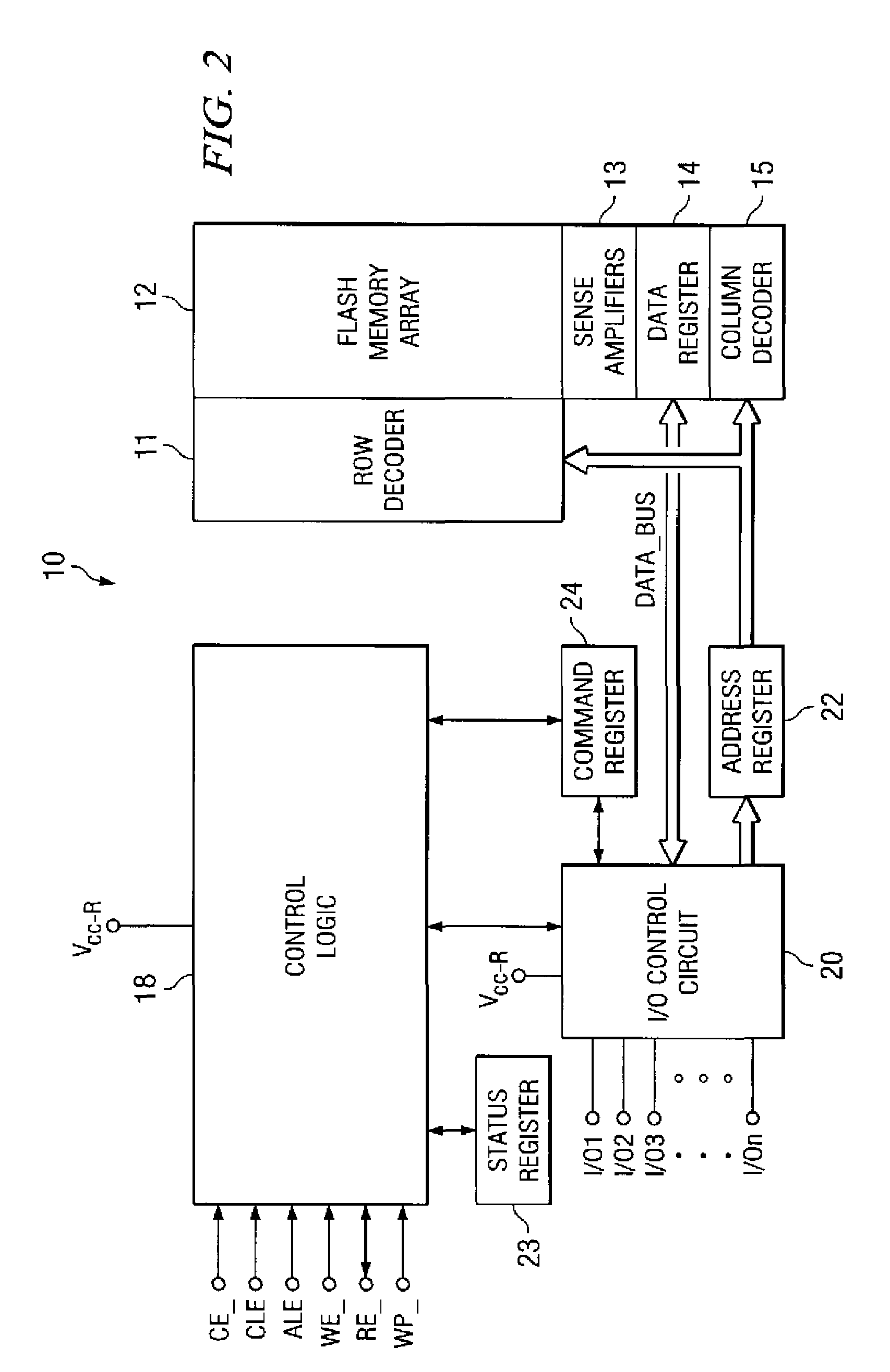
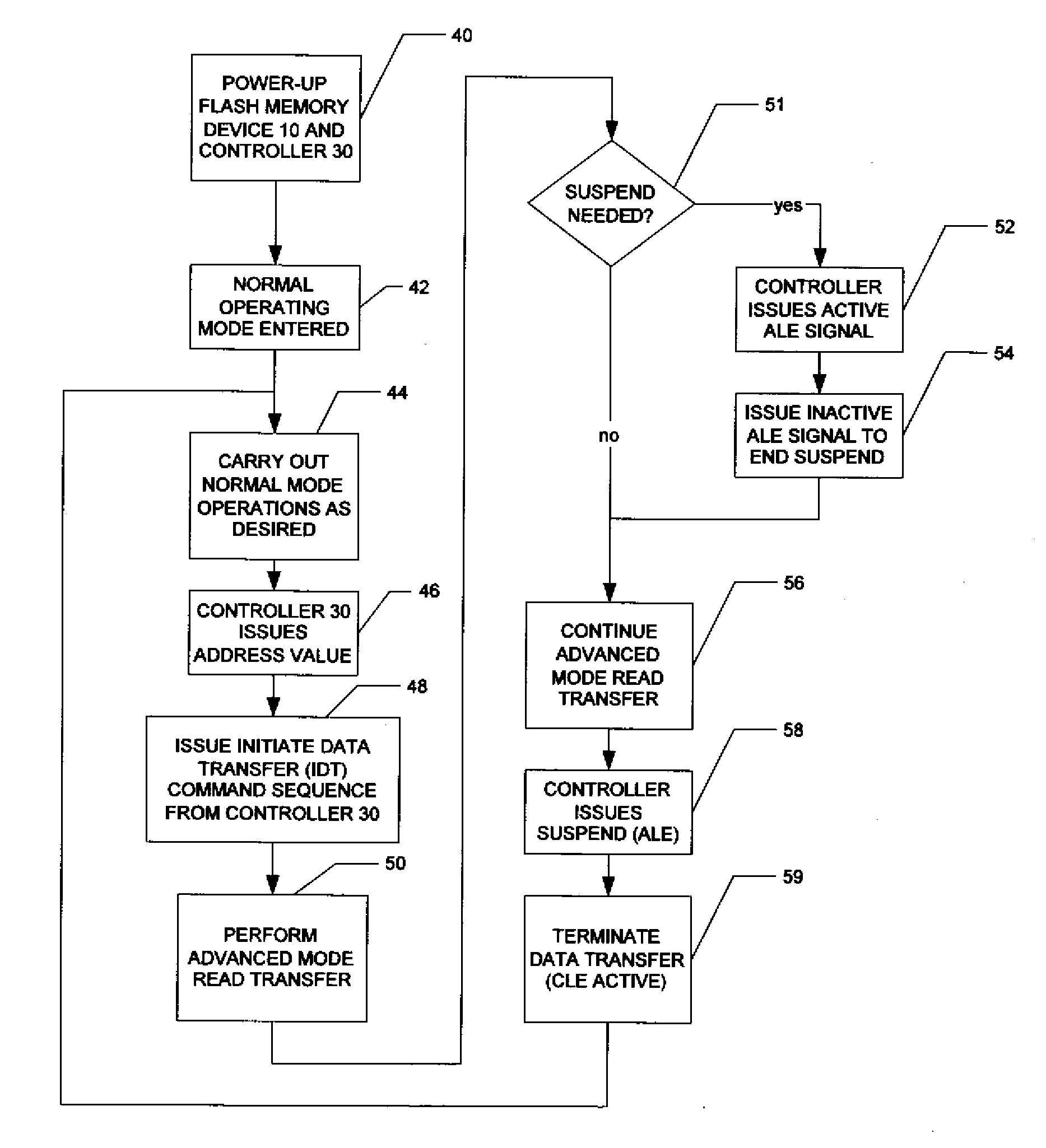
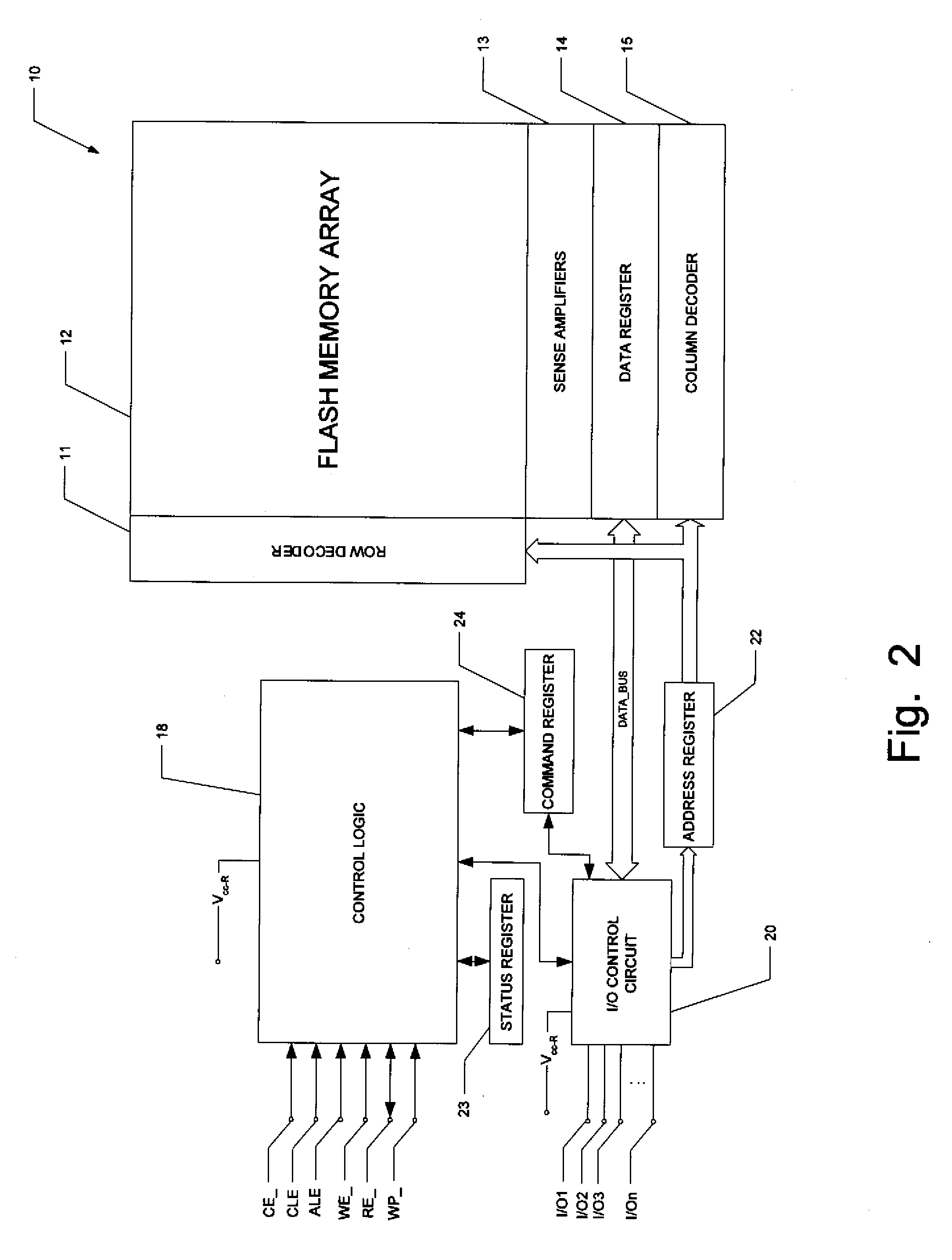
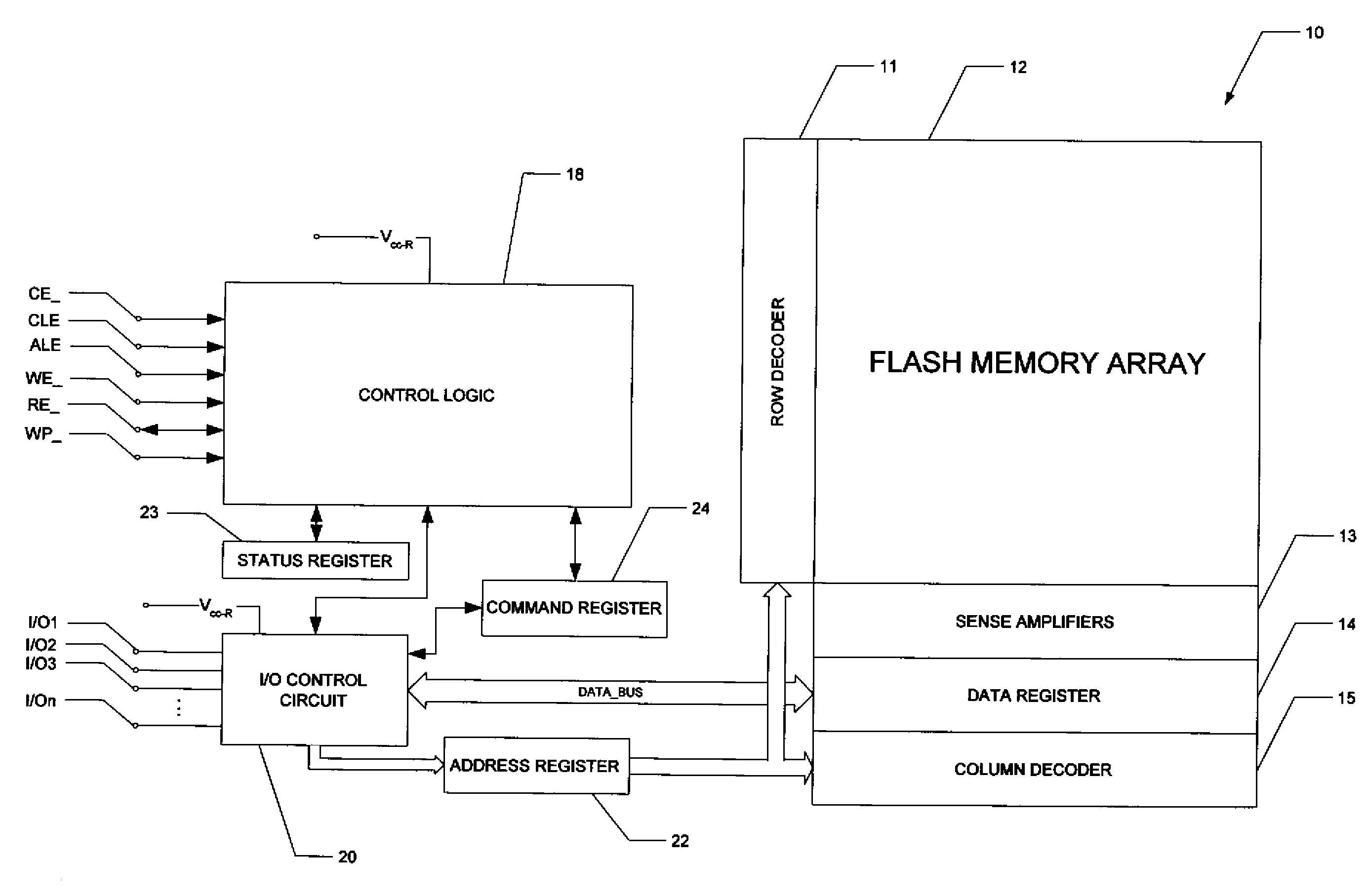
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe at a higher frequency, for example at twice the frequency, of that available in the normal mode. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a higher frequency write data strobe than is available in the normal mode. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Integrating/SAR ADC and method with low integrator swing and low complexity
ActiveUS7511648B2Reduce the amount of solutionReduce voltageElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionIntegratorVoltage reference
A reconfigurable circuit (10) includes an integrator (30) having switches (SW1-6) for selectively coupling input capacitors (C0,1,2,3,6,7) and integrating capacitors (C4,5) to terminals of the integrator (30) for operation of a hybrid delta-sigma / SAR ADC (400) so as to create a reference voltage value (Vref) equal to the sum of a first voltage (ΔVbe) and a second voltage (Vbe). A first integration is performed to reduce the integrator output voltage swing. A residue (Vresidue) of the integrator is multiplied by 2. Then the second voltage (Vbe) is integrated in a first direction if a comparator (22) coupled to the integrator changes state or in an opposite direction if the comparator does not change state. The first voltage (ΔVbe) is integrated in a direction that causes the integrator output voltage (Vout) to equal either 2×Vresidue−Vref or 2×Vresidue+Vref.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20080019196A1Reduce power consumptionMinimize data transferRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe and also a write data strobe that is out-of-phase relative to the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with one of the edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode for a data write, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a selected edge of both the write data strobe and the read data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
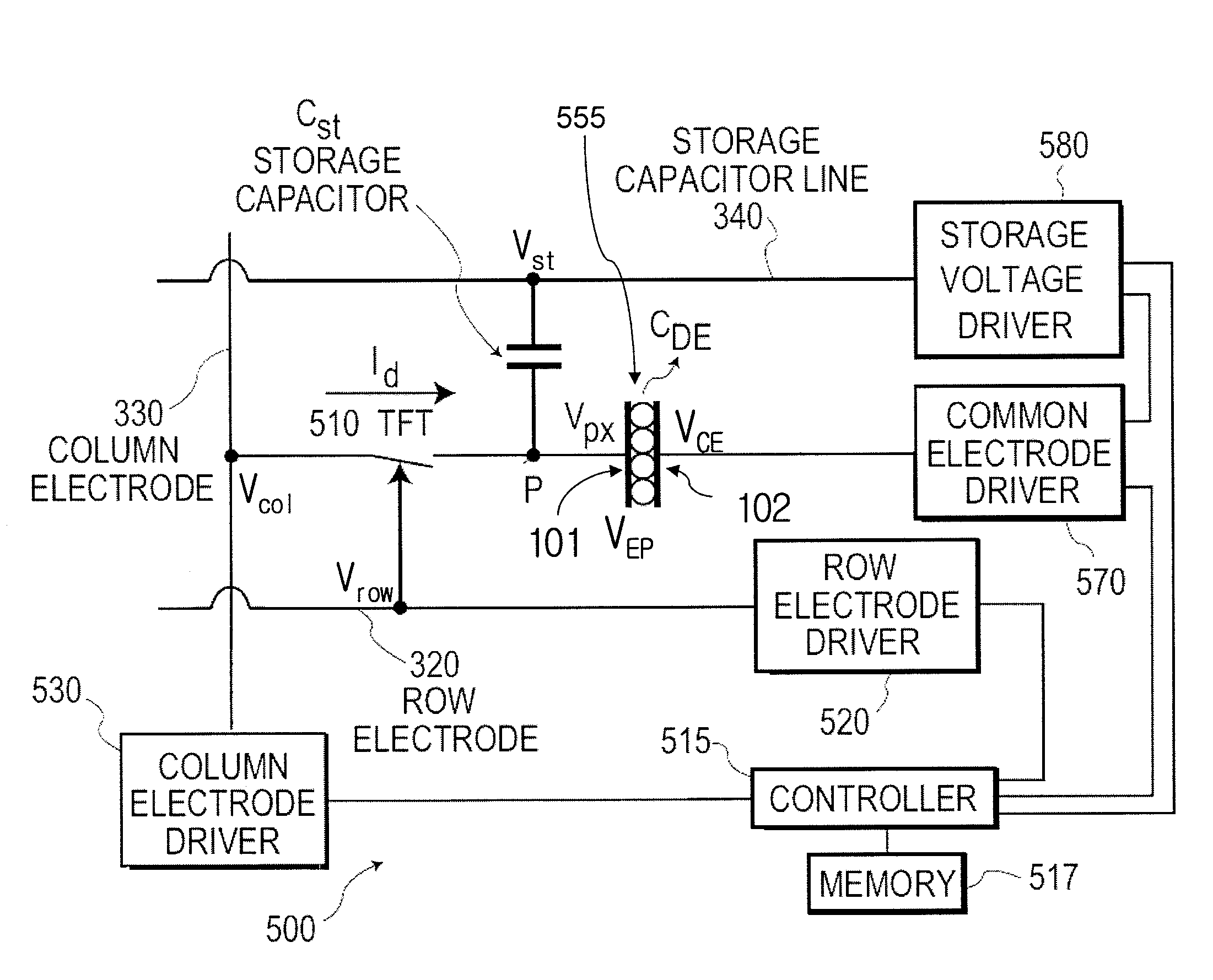
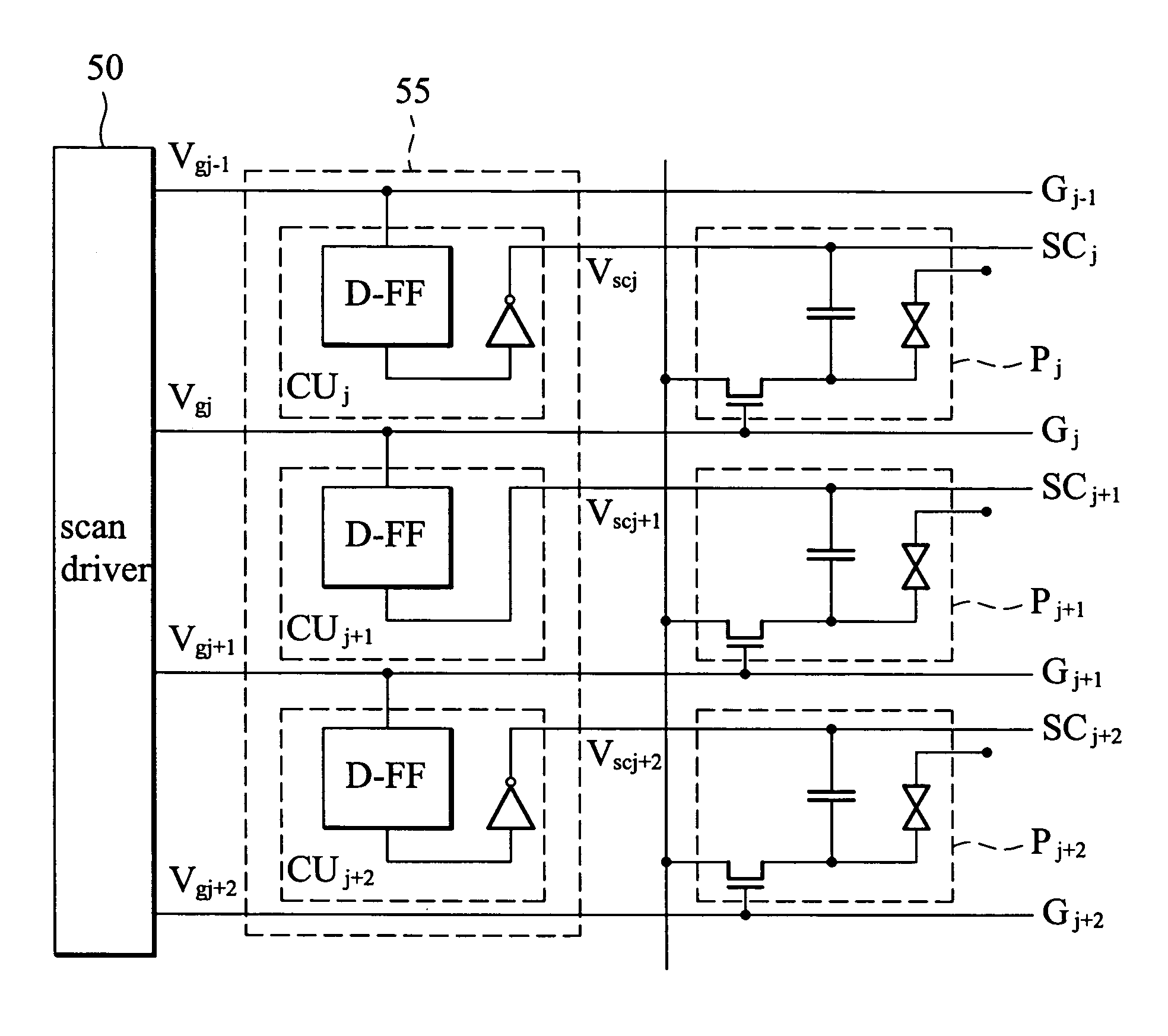
Super Low Voltage Driving Of Displays
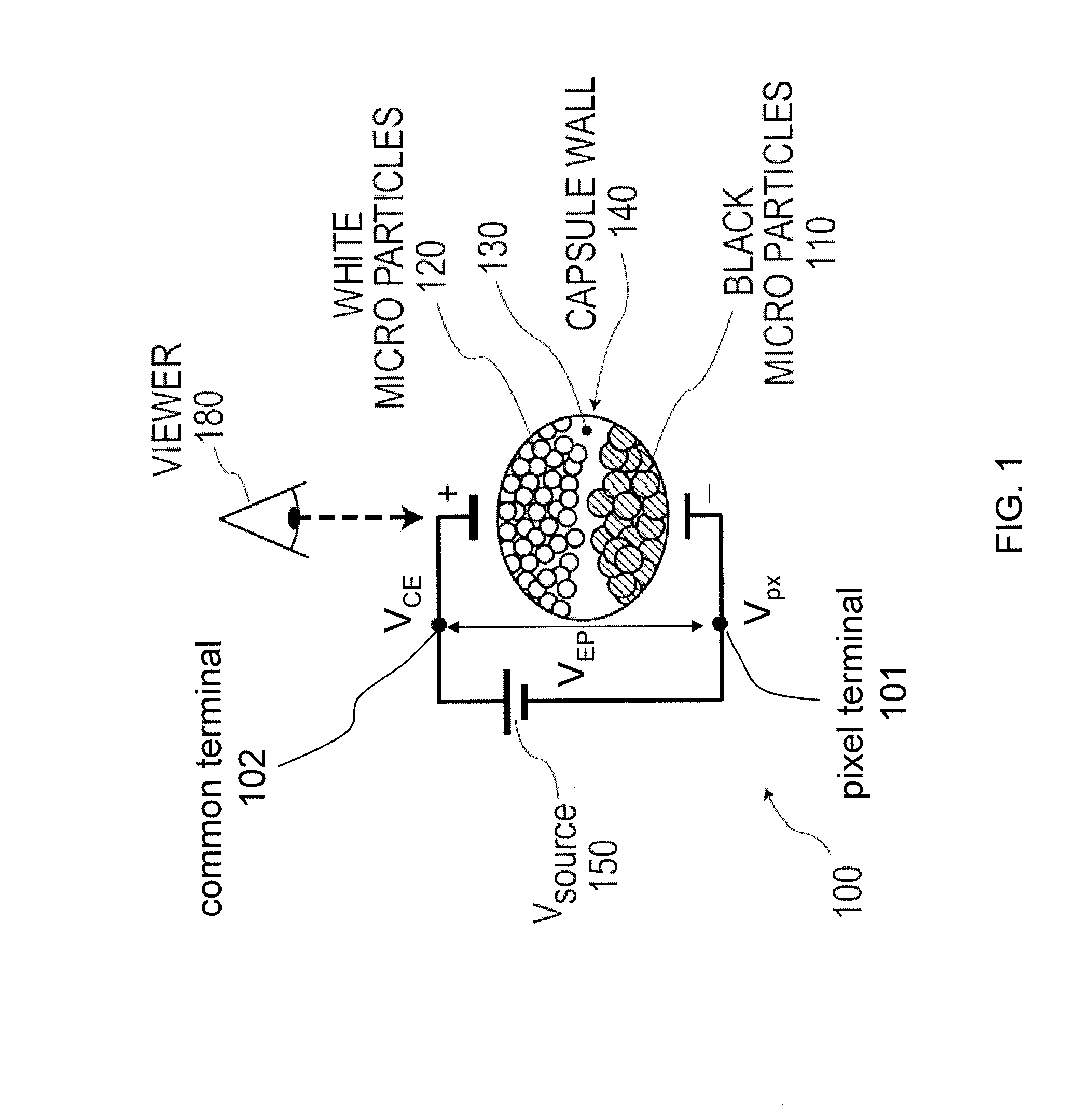
InactiveUS20120182282A1Reduce power consumptionLow costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLow voltageDisplay device
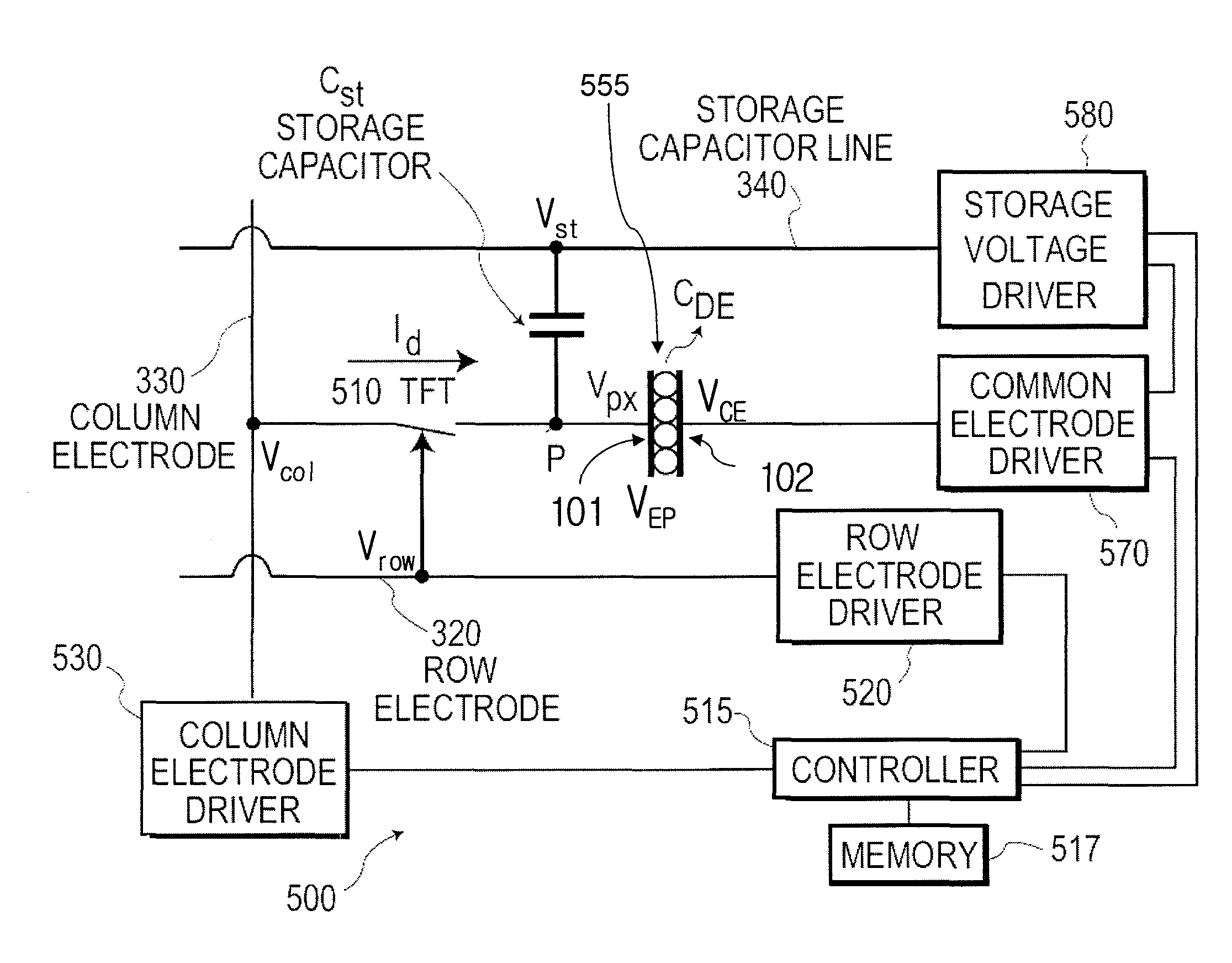
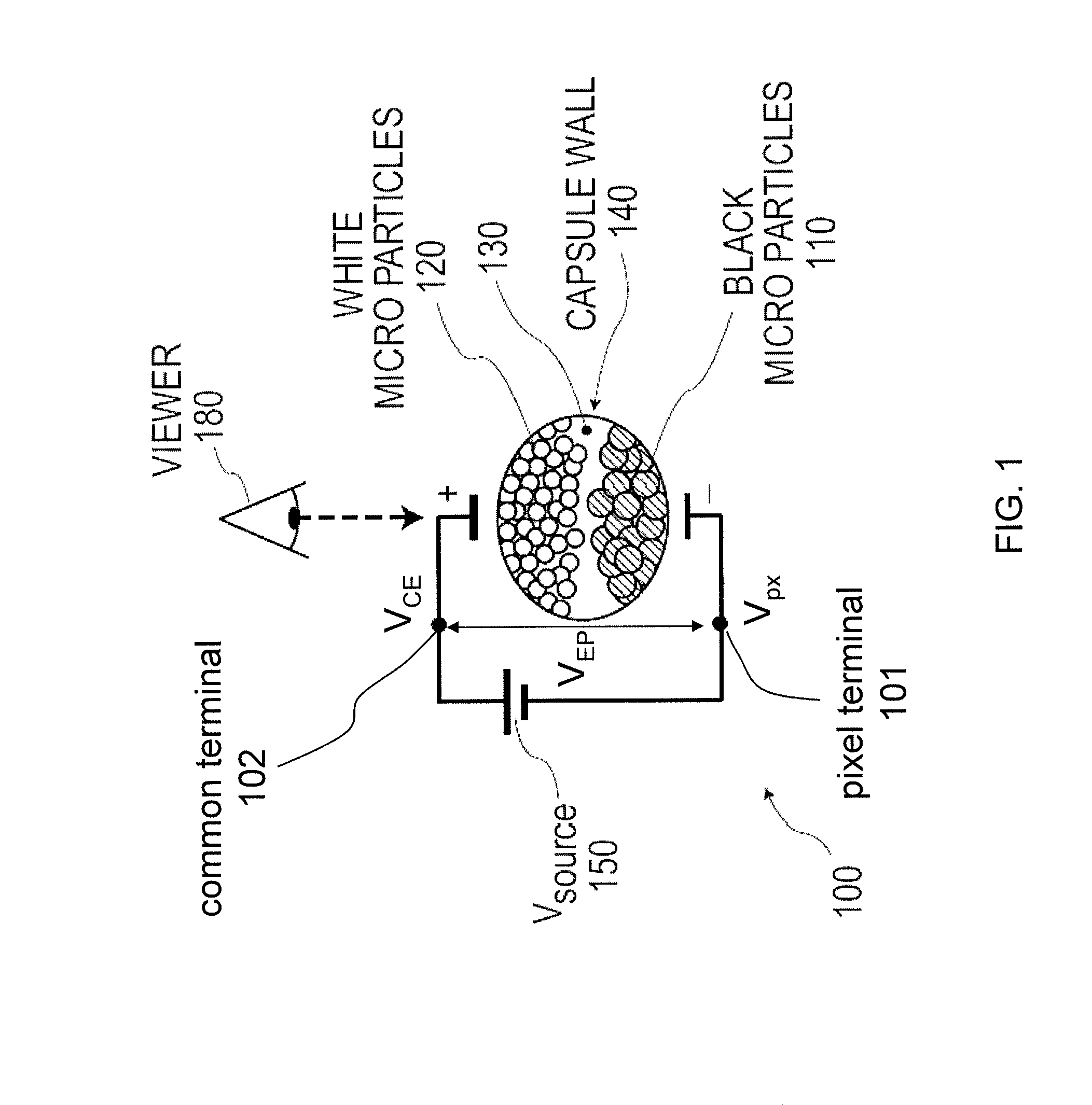
A display device (500) is described with a plurality of pixels (555), each having a pixel state (P) that is driven by a driving voltage differential (VEP) between a pixel voltage (Vpx) applied to a pixel terminal (101) of the pixel and a common voltage (VCE) applied to a common terminal (102) of the pixel. In a first pixel driving state, wherein pixels are driven to a first colour, a common voltage is provided to the common terminals (102) with a first polarity. In a second pixel driving state, wherein pixels are driven to a second colour, a common voltage is provided to the common terminals (102) with a second polarity opposite to the first polarity. An absolute value of the common voltage (VCE) in the first and second pixel driving state is higher than a maximum absolute value of the column voltage (Vcol) in the corresponding pixel driving state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
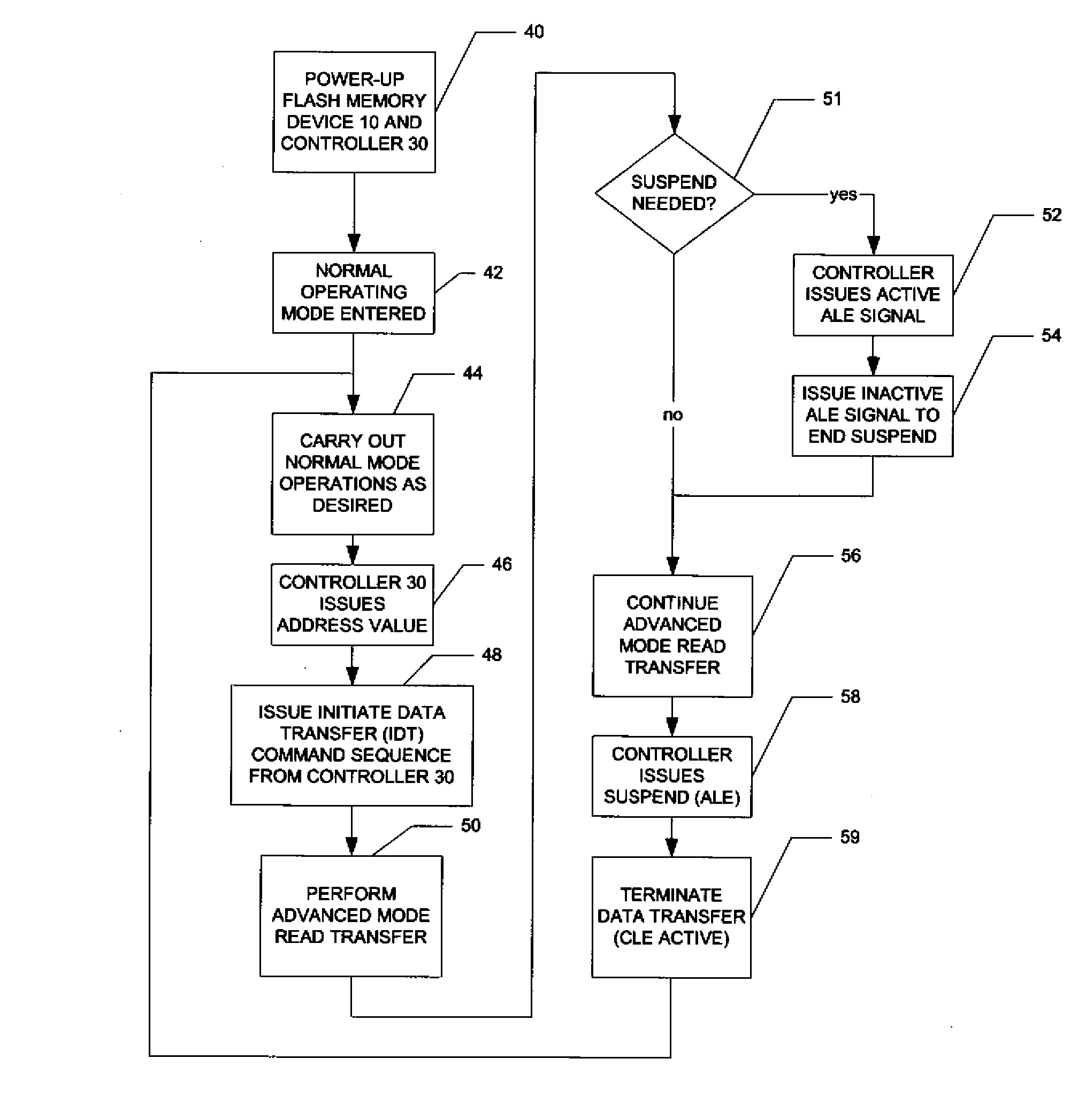
Method of High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20080019189A1Reduce power consumptionData skewRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe and also a write data strobe that is out-of-phase relative to the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with one of the edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode for a data write, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a selected edge of both the write data strobe and the read data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Current switching circuit for high-speed current rudder digital-to-analog converter
InactiveCN102158211AReduced voltage swingFast switching speedElectronic switchingDriver circuitControl signal
The invention discloses a current switching circuit for a high-speed current rudder digital-to-analog converter, comprising a switch main body circuit, a constant-current circuit which provides a constant flow source for the switch main body switch, a switch drive circuit which provides difference switching signals to the switch main body circuit and a four-phase control signal generating circuit which provides difference control signals for the switch drive circuit. A pre-breakover pull-down MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube is adopted in the switch drive circuit , and a clock feedthrough compensation structure is applied to the switch main body circuit, thus overshooting of the difference switching signals is greatly weakened, falling edges of the difference switching signals at the initial stage of hopping become gentle, symmetry of rising and falling edges of the difference switching signals in case of low swing amplitude is improved and clock feedthrough errors resulting from the difference switching signals are effectively reduced. The current switching circuit is especially applicable to the high-speed and high-precision digital-to-analog converter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20070258295A1Reduce voltage swingReduce consumptionRead-only memoriesDigital storageData transmissionVoltage swing
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with both the falling and rising edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with both edges of the write data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-performance flash memory data transfer
ActiveUS7345926B2Minimize data transferMinimize data skewRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with both the falling and rising edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with both edges of the write data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method of High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20070247933A1Reduce power consumptionData skewRead-only memoriesDigital storageData transmissionVoltage swing
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe at a higher frequency, for example at twice the frequency, of that available in the normal mode. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a higher frequency write data strobe than is available in the normal mode. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Method of high-performance flash memory data transfer
ActiveUS7366028B2Data skewMinimize data transferRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with both the falling and rising edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with both edges of the write data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
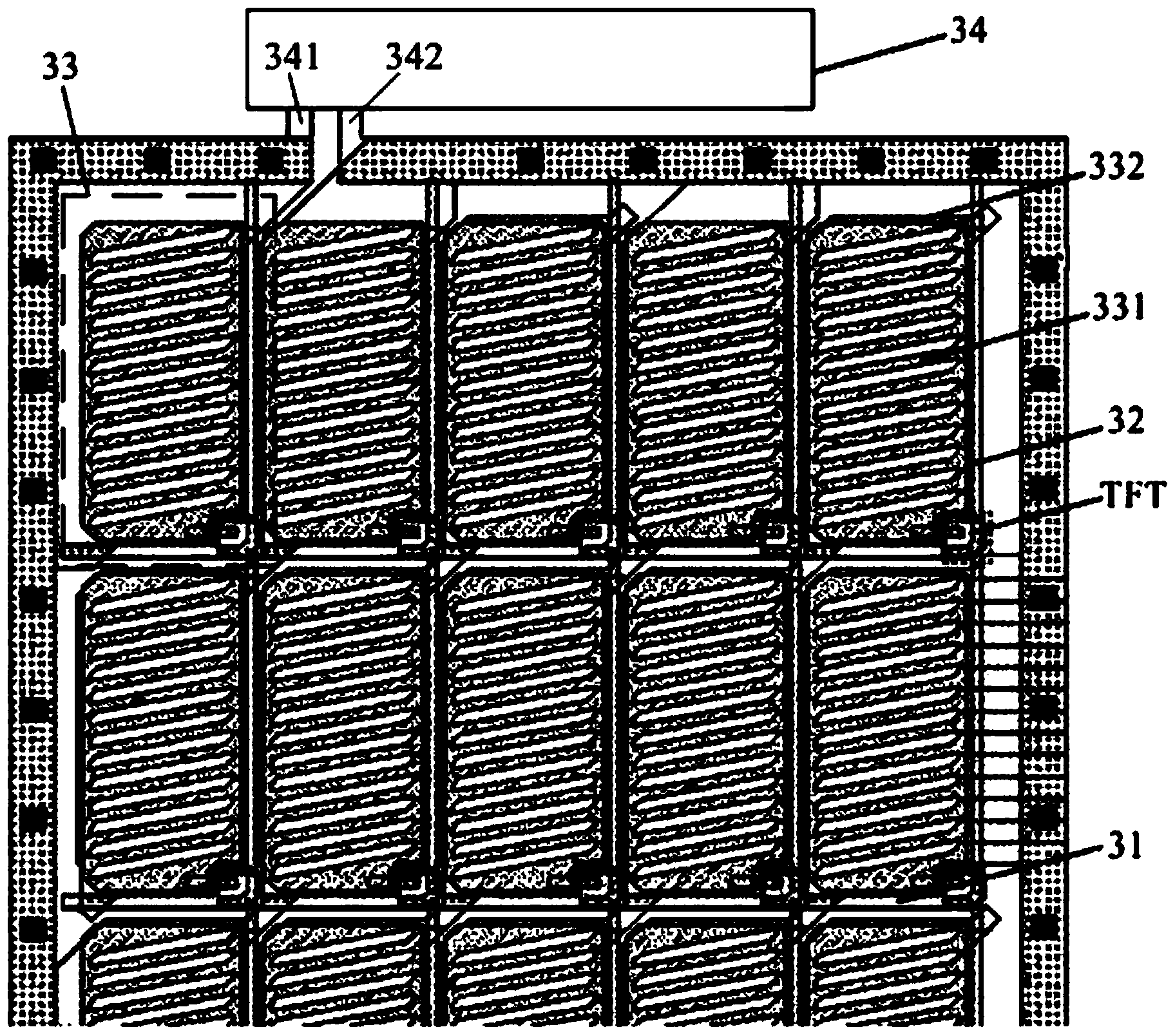
Display and two step driving method thereof
InactiveUS20080303771A1Save power consumptionLower operating temperatureStatic indicating devicesVoltage generatorDisplay device
A display and a two step driving method thereof are provided. The method includes: converting an image signal to a corresponding data driving voltage by using a driver; providing a pre-driving voltage by using a voltage generator; and finally, driving the display panel by using the pre-driving voltage and data driving voltage orderly during a horizontal synchronizing period. A display includes a display panel, a voltage generator, and a driver. The display panel also includes at least one data line. The voltage generator outputs a pre-driving voltage to the data line of the display. The driver outputs a data driving voltage to the data line according to an image signal, in which the data line receives the pre-driving voltage and the data driving voltage orderly during the horizontal synchronizing period.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP +1
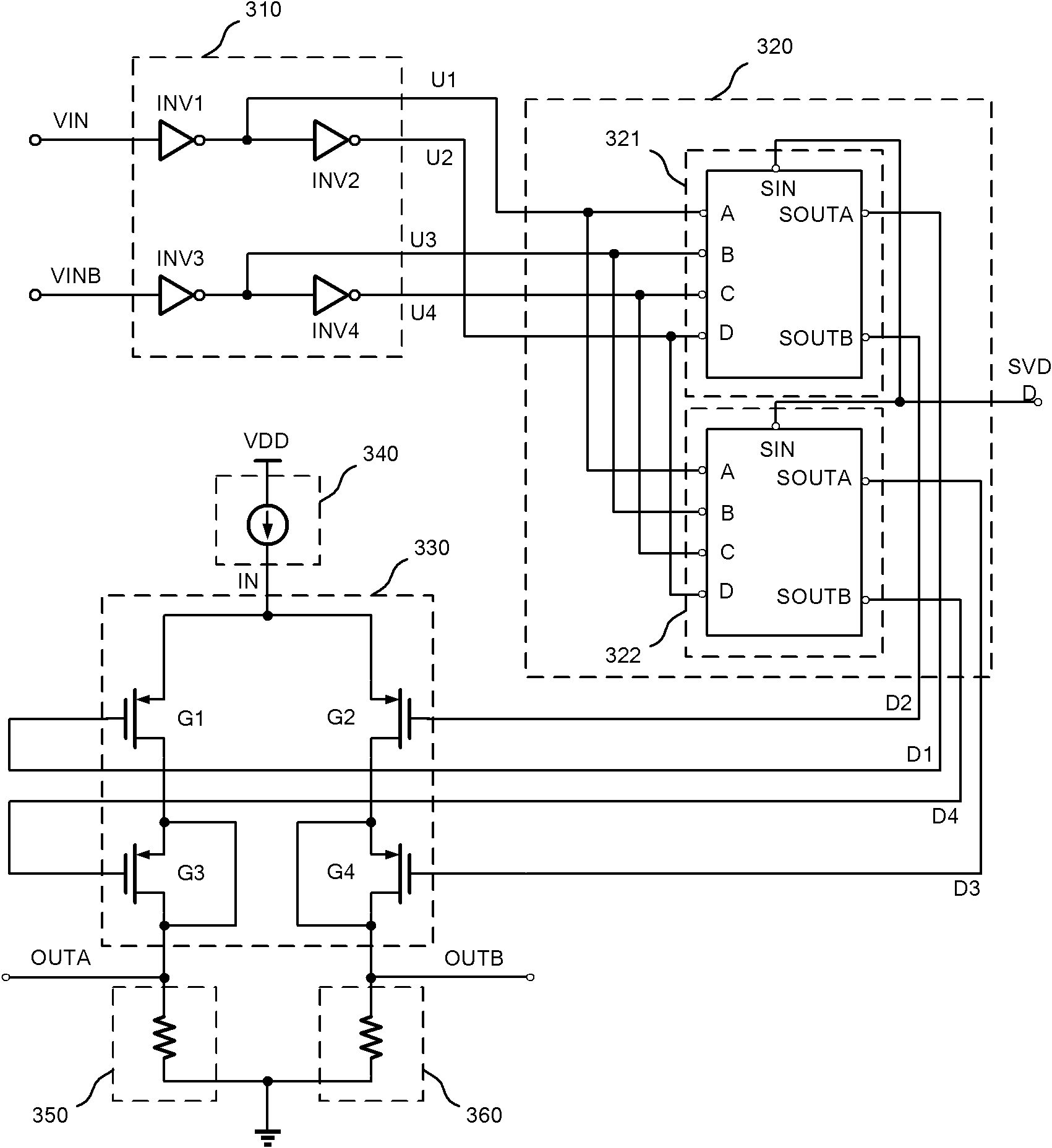
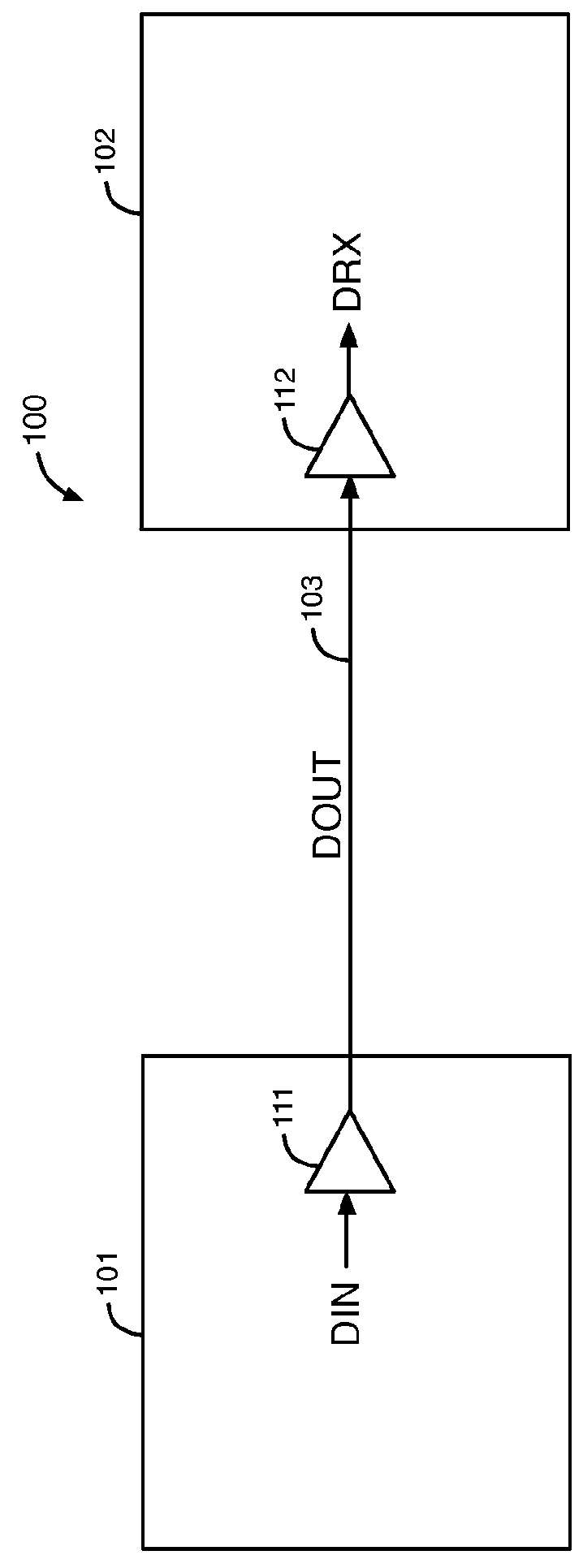
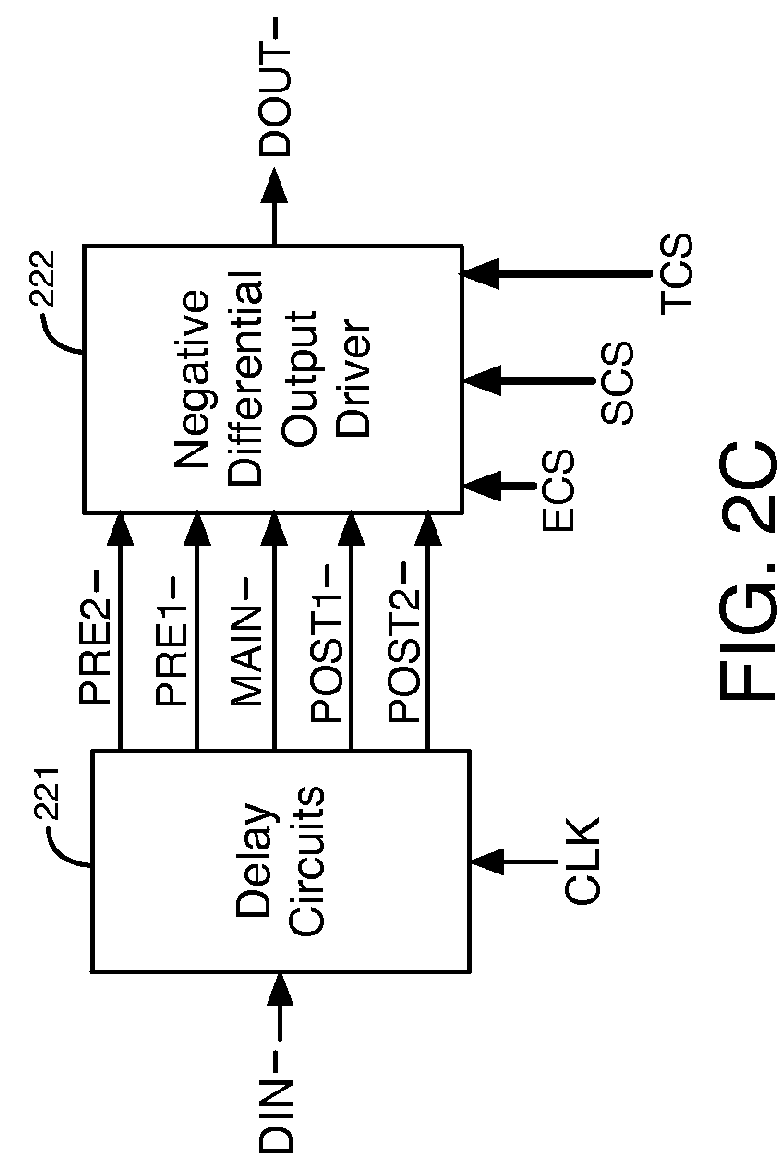
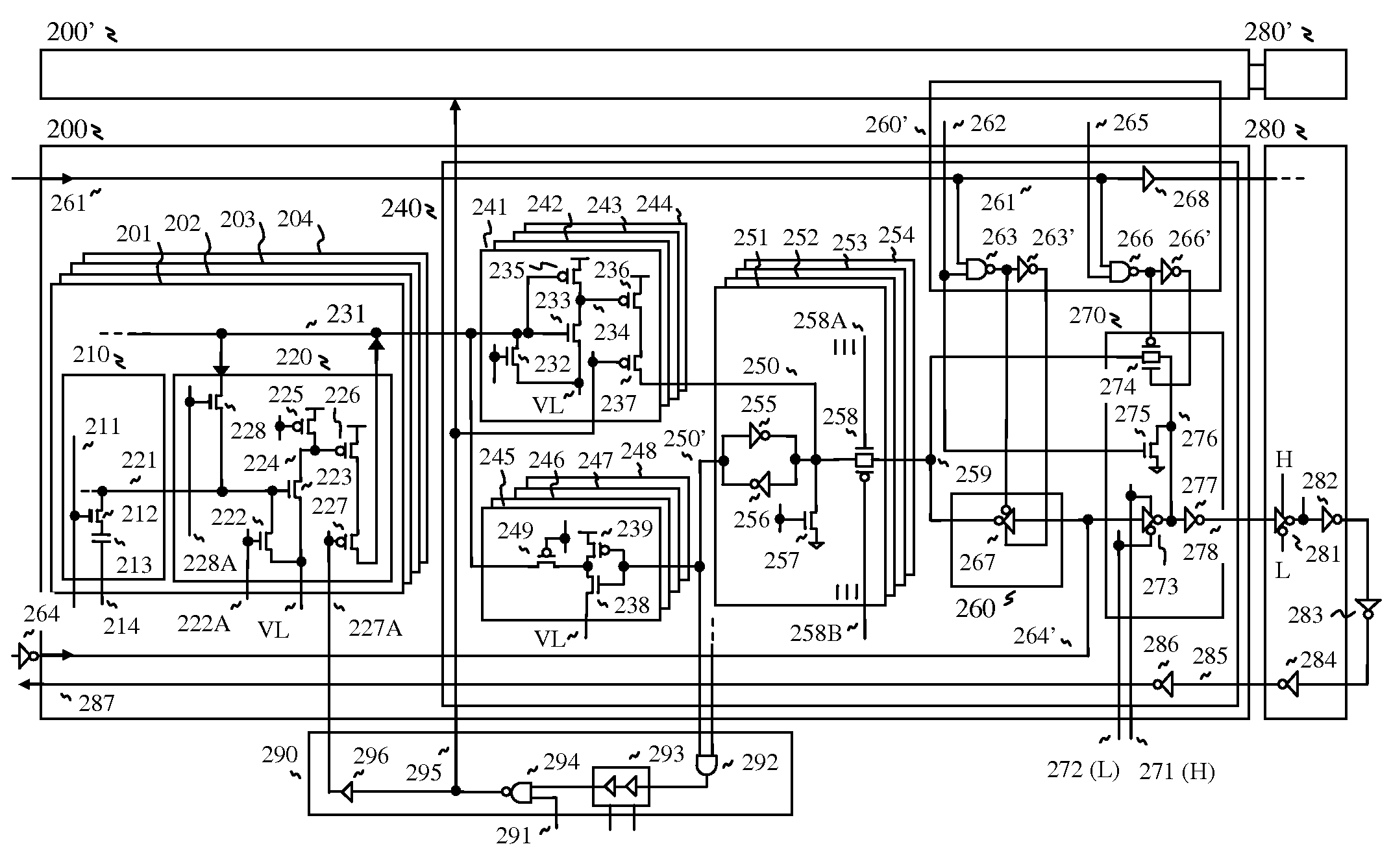
Circuits and methods for adjusting the voltage swing of a signal
ActiveUS9231631B1Reduce voltage swingReduced voltage swingInput/output impedence modificationBaseband system detailsElectrical and Electronics engineeringDriver circuit
A driver circuit includes unit slice circuits that generate an output data signal based on an input data signal. The driver circuit reduces a voltage swing of the output data signal without changing a termination resistance of the driver circuit in response to decreasing a number of the unit slice circuits that generate the output data signal based on the input data signal.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
DRAM including a reduced storage capacitor
InactiveUS20090103352A1Reducing a storage capacitorReduced storage capacitorDigital storageBit lineTime domain
A reduced storage capacitor is used for shrinking a memory cell in DRAM, and local bit line is divided into short line for reducing parasitic capacitance. For reading, a first reduced swing amplifier as a local sense amp reads the memory cell through the local bit line, and a second reduced swing amplifier as a global sense amp reads the local sense amp through a global bit line. With the multi-stage sense amps, time domain sensing scheme is realized such that a voltage difference in the local bit line is converted to a time difference, for differentiating high data and low data, and also fast read operation is realized. And write operation is executed by a reduced swing write driver. With reduced voltage swing, pseudo negative word line scheme is realized for retaining data, and power consumption is reduced. In addition, various alternative circuits and memory cell structures are implemented.
Owner:KIM JUHAN
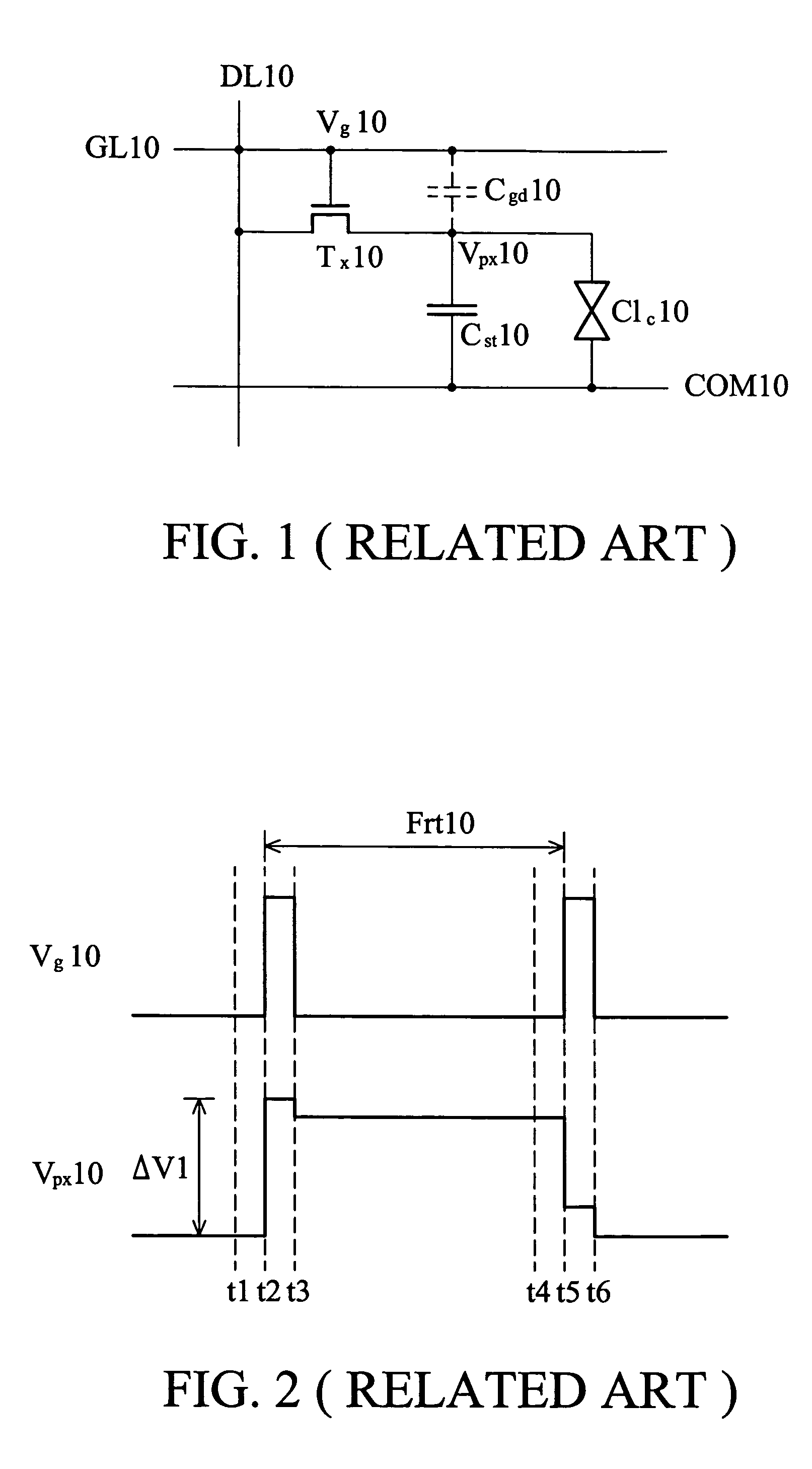
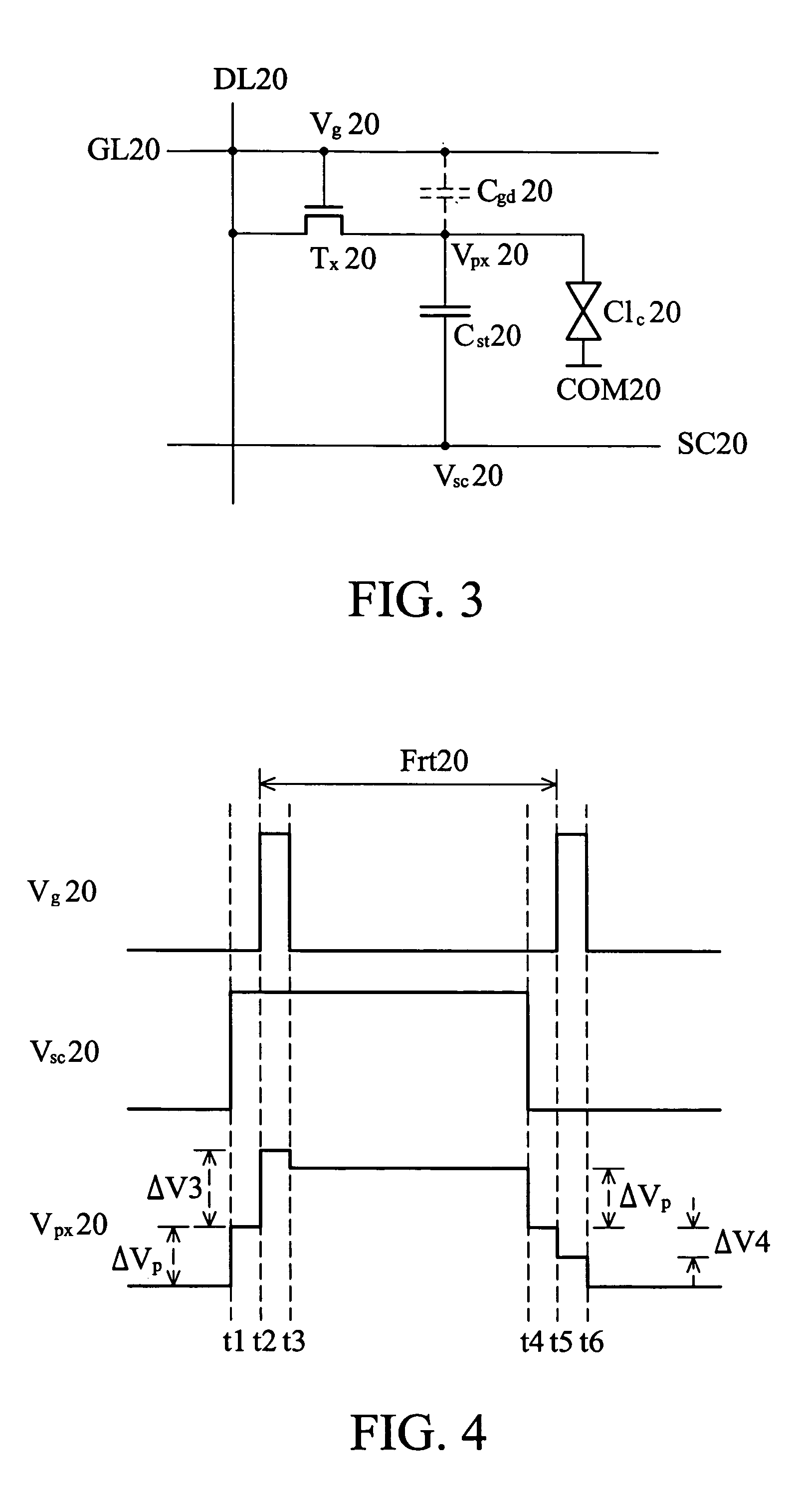
Liquid crystal display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20050057465A1Fast chargingReduced voltage swingStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayScan line
A driving method of liquid crystal display. Voltage levels of pre-charging signals applied to storage electrodes vary before scan signals are applied to scan lines. Partial response voltage of the variations in voltage levels of pre-charging signals are respectively coupled to storage capacitors within pixels by capacitors. When the scan signals are applied to the scan lines, voltage swings of the pixel capacitors charged by image data on data lines decrease, rapidly charging the pixels.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
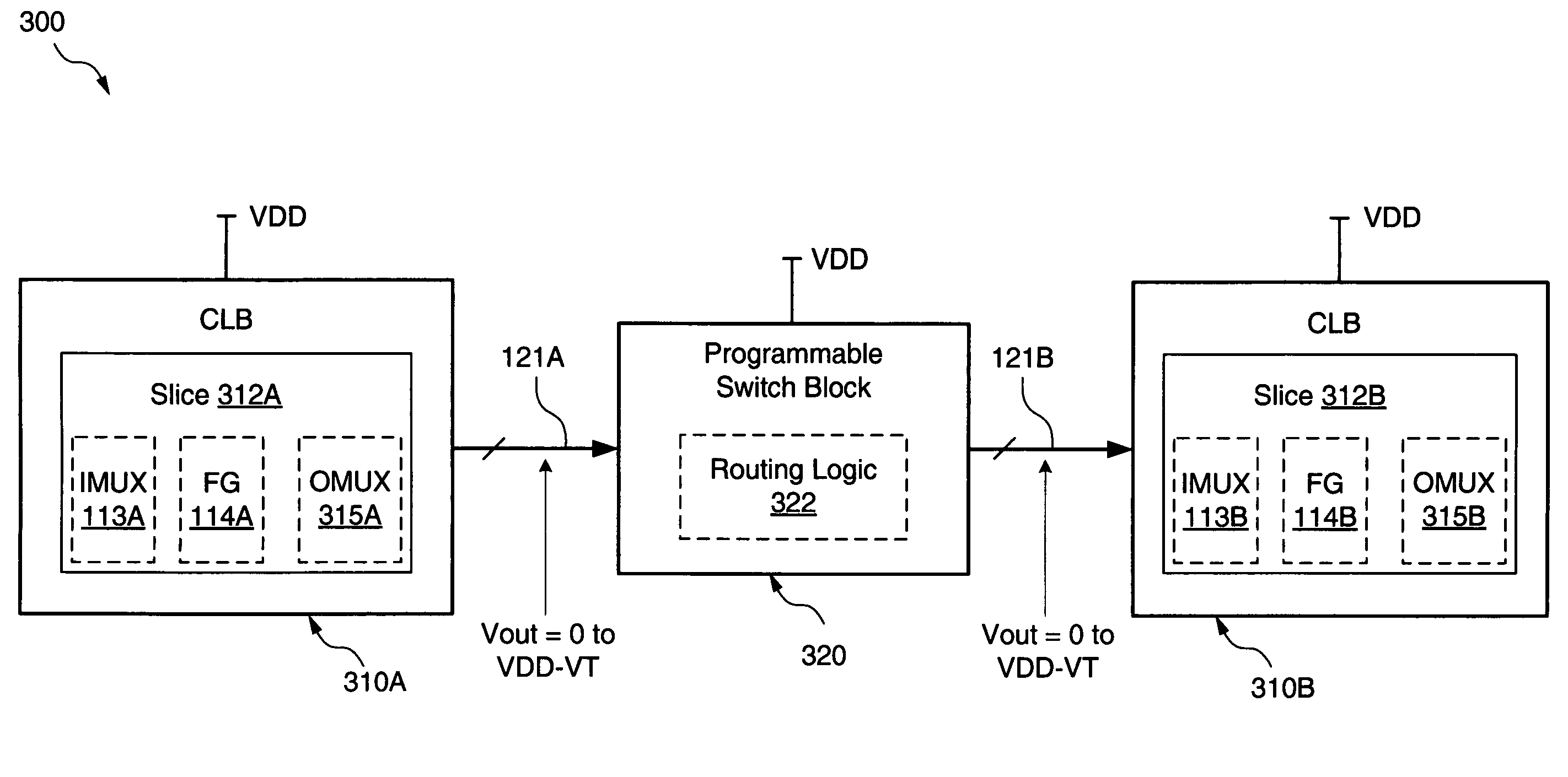
Low-swing interconnections for field programmable gate arrays
ActiveUS7417454B1Reduce dynamic power consumptionPerformance maximizationLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSolid-state devicesMultiplexingPeak value
An apparatus is disclosed that may reduce the dynamic power dissipation of a configurable IC device such as an FPGA by reducing the peak-to-peak voltage swing of signals transmitted over the device's interconnect signal lines without including additional level shifter circuits. For some embodiments, existing multiplexing circuit architectures provided within logic resources of various logic blocks of the configurable IC device may be used as level shifter circuits to increase the voltage swing of signals received into the blocks from the interconnect signal lines, and modified multiplexing circuit architectures provided within the logic resources may be used to reduce the voltage swing of signals output from the logic blocks onto the interconnect signal lines.
Owner:XILINX INC
Low voltage logic circuit with set and/or reset functionality
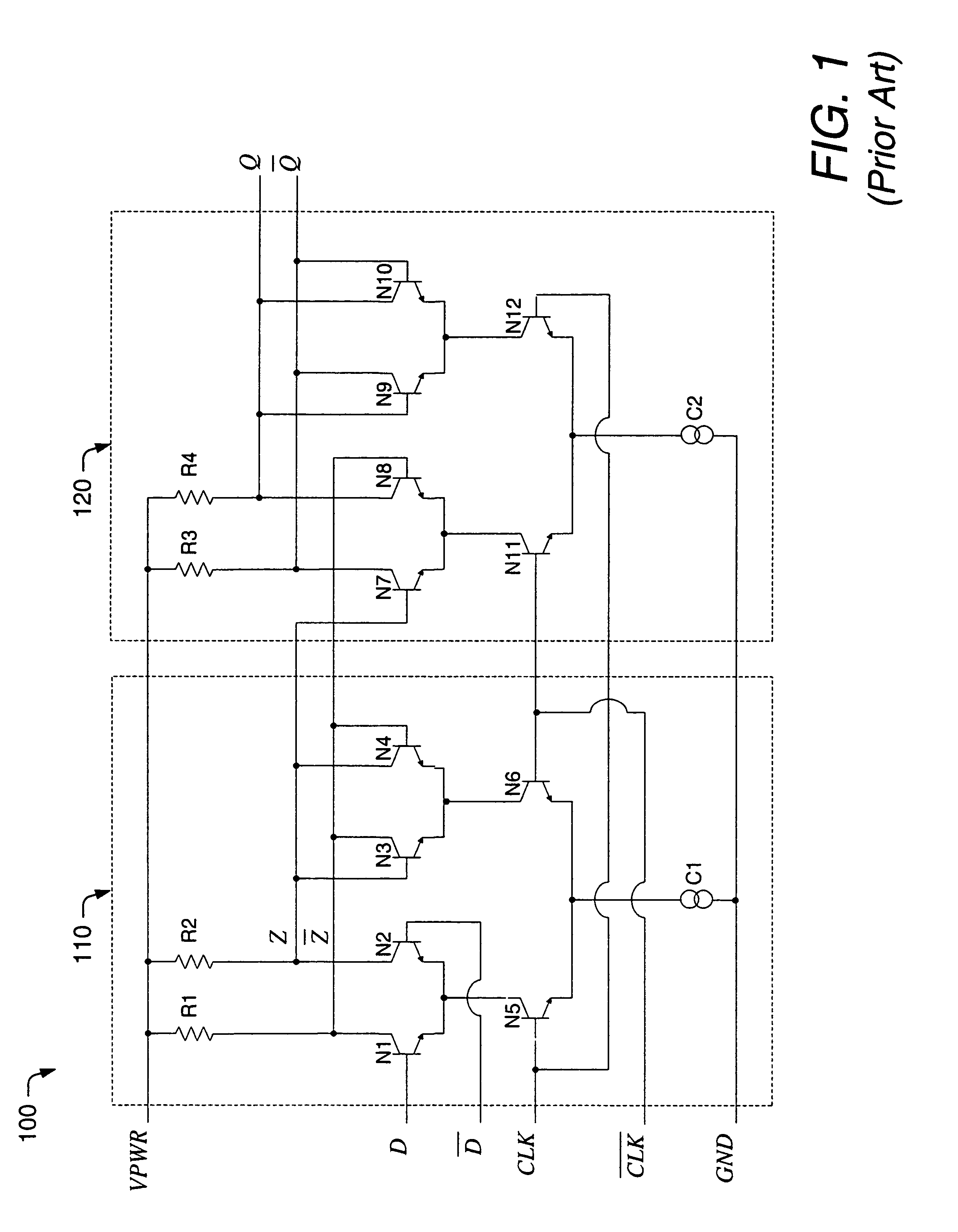
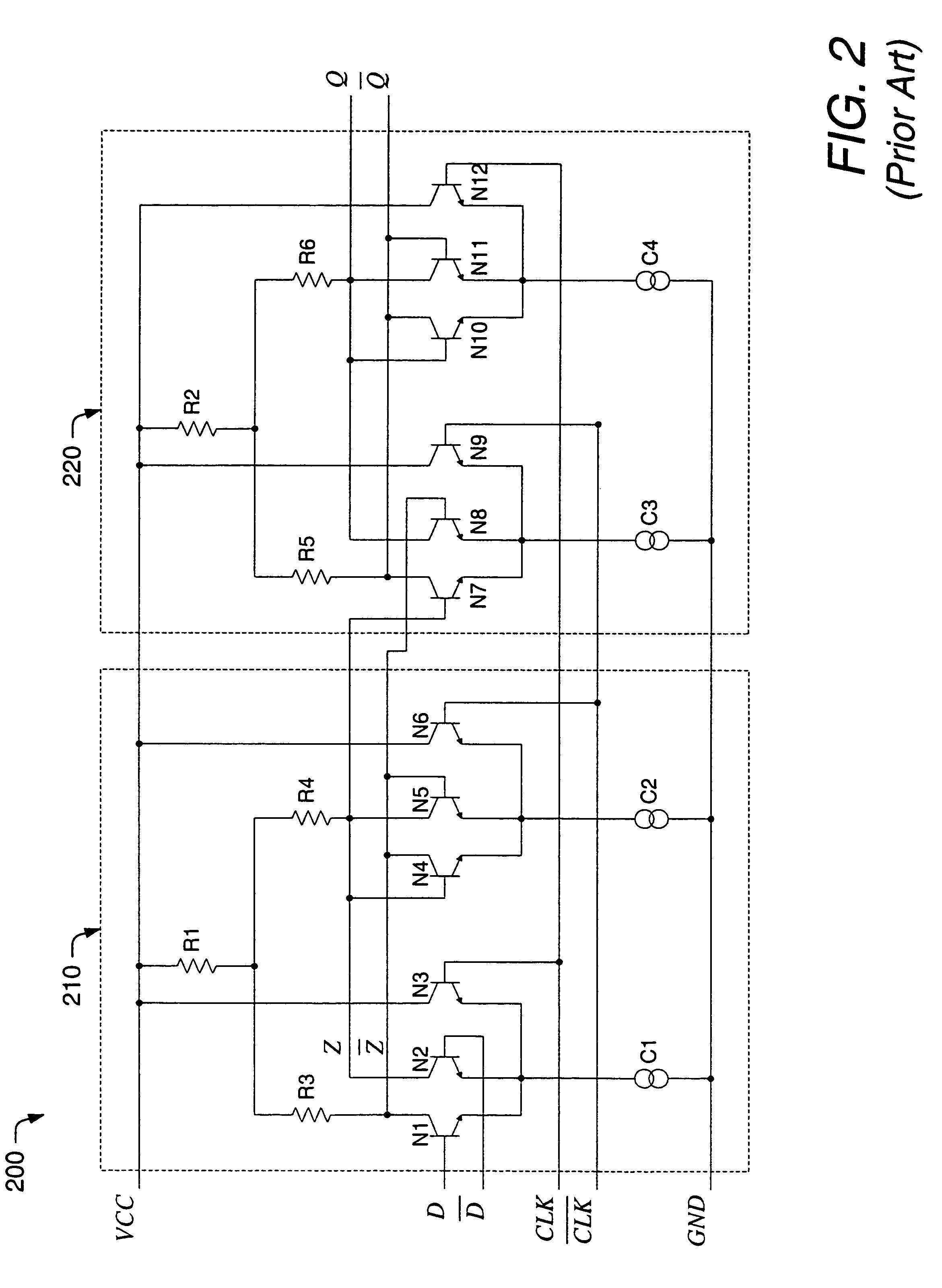
ActiveUS7215170B1Reduced voltage swingMore signalsElectric pulse generatorLow voltage circuitsMultiplexer
A low voltage logic circuit with asynchronous SET and / or RESET functions is described herein. The low voltage logic circuit may be primarily used in forming low voltage flip-flop circuits, but may also be used to form multiplexers and other logic configurations. The flip-flop circuit described herein improves upon existing low voltage architectures by providing a flip-flop circuit, which can operate at relatively low supply voltages (e.g., less than about 1.8V), with SET and / or RESET capability. In doing so, the improved flip-flop circuit may be used within a phase frequency detector, programmable counter, or frequency divider of a phase locked loop (PLL) or delay locked loop (DLL) device. However, the improved flip-flop circuit may be used with any low voltage circuit or device that may require, use or benefit from a SET or RESET function. In some embodiments, one or more level shift circuits may be included so that the low voltage flip-flop circuit may receive CML, TTL and / or CMOS logic levels (among others).
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Method of high-performance flash memory data transfer
ActiveUS7525855B2Data skewMinimize data transferRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system includes a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe at a higher frequency, for example at twice the frequency, of that available in the normal mode. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a higher frequency write data strobe than is available in the normal mode. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20070245065A1Reduce power consumptionMinimize data transferRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with both the falling and rising edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with both edges of the write data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-Performance Flash Memory Data Transfer
ActiveUS20070247934A1Reduce power consumptionMinimize data transferRead-only memoriesDigital storageData transmissionVoltage swing
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe at a higher frequency, for example at twice the frequency, of that available in the normal mode. In the advanced mode, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a higher frequency write data strobe than is available in the normal mode. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High-performance flash memory data transfer
ActiveUS7499339B2Minimize data transferMinimize data skewRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl signalTransfer mode
A flash memory system including a flash memory device and a controller, operable according to an advanced data transfer mode is disclosed. The flash memory device is operable both in a “legacy” mode, in which read data is presented by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a read data strobe from the controller, and in which input data is latched by the memory synchronously with each cycle of a write data strobe from the controller. In the advanced mode, which can be initiated by the controller forwarding an initiation command to the memory, the flash memory itself sources the read data strobe and also a write data strobe that is out-of-phase relative to the read data strobe, and presents data synchronously with one of the edges of that read data strobe. In the advanced mode for a data write, the input data is presented by the controller synchronously with a selected edge of both the write data strobe and the read data strobe. The voltage swing of the data and control signals is reduced from conventional standards, to reduce power consumption.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
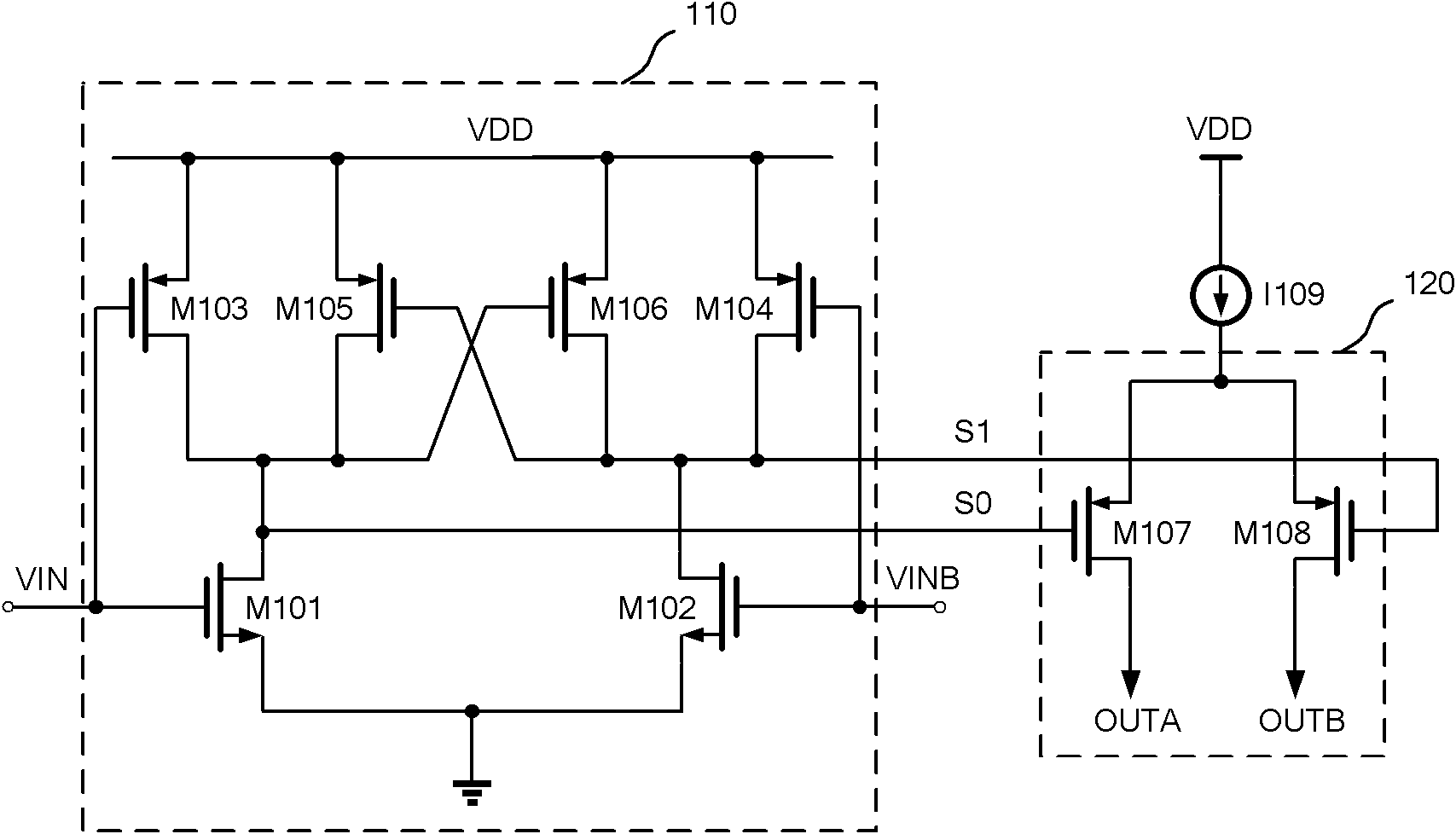
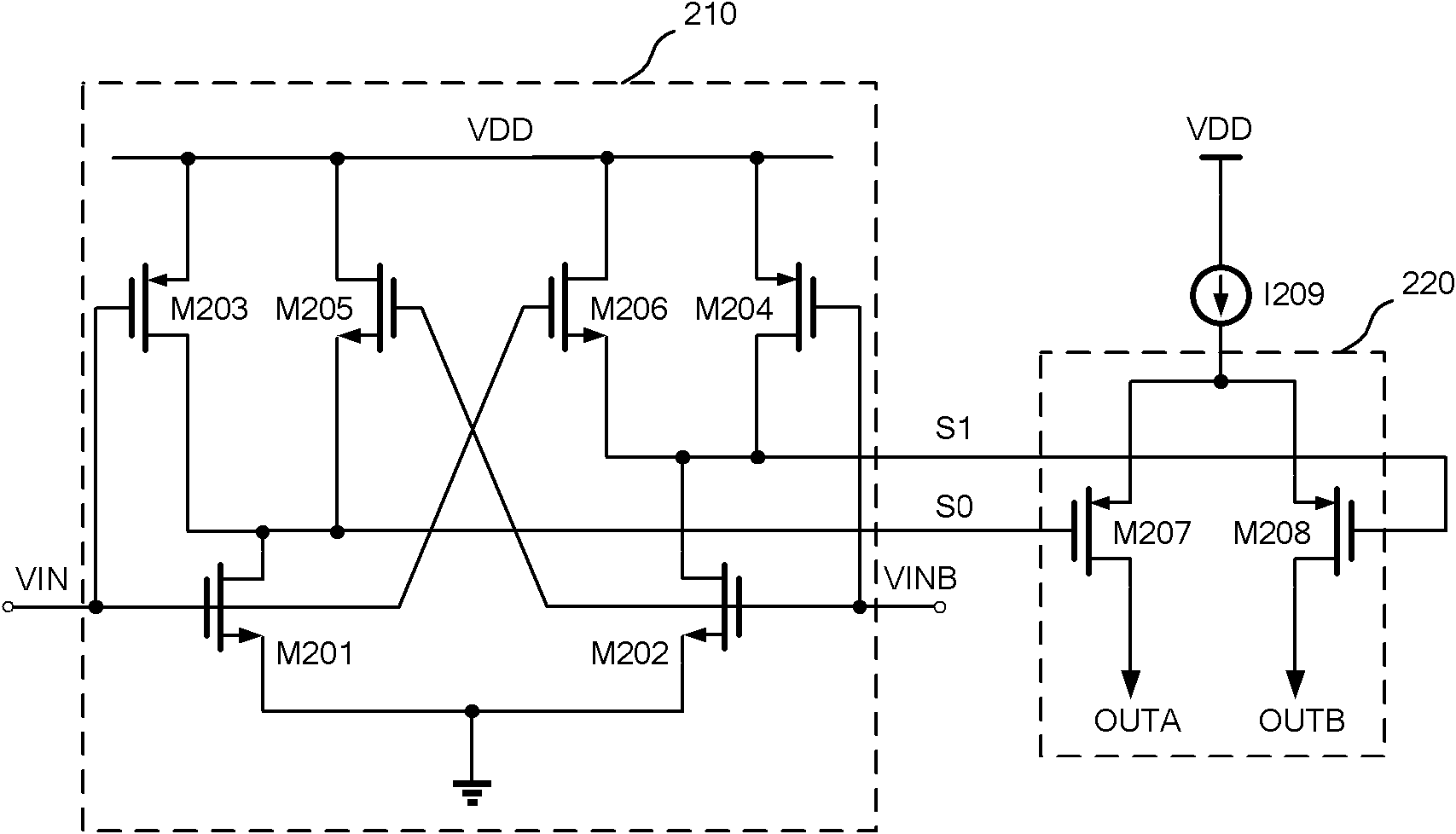
Reduced swing differential pre-drive circuit
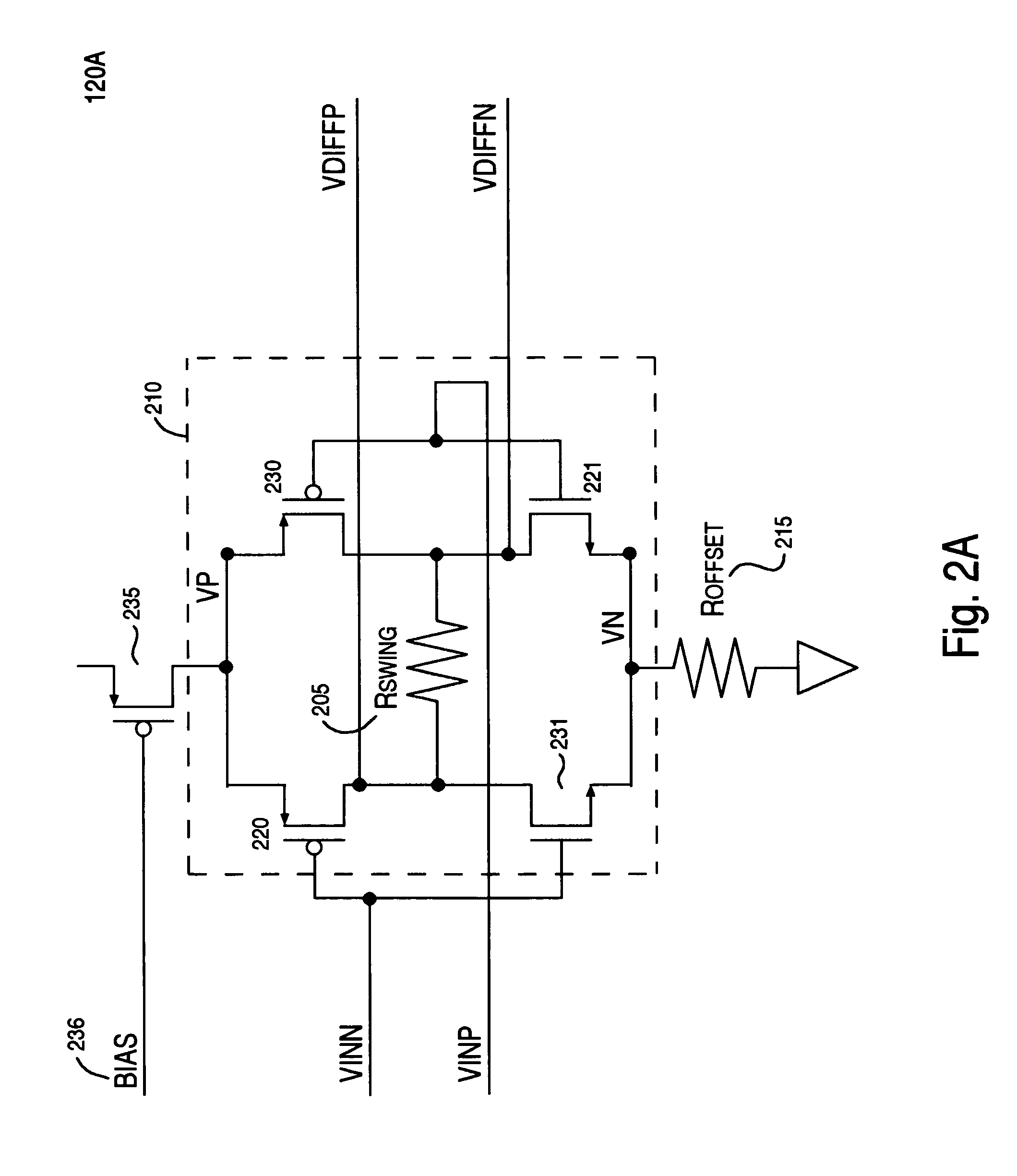
ActiveUS8289257B1Reduced voltage swingReduce offsetStatic indicating devicesDifferential amplifiersElectrical resistance and conductanceOptical transistor
A circuit for reducing and offsetting the voltage swing of a differential pre-drive circuit. The circuit includes a first H-bridge of transistors receiving a differential pair of input signals. A swing resister is coupled to the H-bridge for reducing a voltage swing of the differential pair of input signals. The reduced swing is generated as a differential pair of output signals. Also, the differential pre-drive circuit includes an offset resistor that is coupled to the H-bridge. The offset resistor acts to offset the differential pair of output signals. As such, the differential pair of output signals having reduced swing and offset as applied to gates of output transistors in an output stage allow the output transistors to remain in the saturation operating state.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Super low voltage driving of displays
InactiveUS8780103B2Low costReduce voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLow voltageElectrical polarity
A display device is described with a plurality of pixels, each having a pixel state that is driven by a driving voltage differential between a pixel voltage applied to a pixel terminal of the pixel and a common voltage applied to a common terminal of the pixel. In a first pixel driving state, wherein pixels are driven to a first color, a common voltage is provided to the common terminals with a first polarity. In a second pixel driving state, wherein pixels are driven to a second color, a common voltage is provided to the common terminals with a second polarity opposite to the first polarity. An absolute value of the common voltage in the first and second pixel driving state is higher than a maximum absolute value of the column voltage in the corresponding pixel driving state.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Liquid crystal display and driving method thereof
ActiveUS7190341B2Reduced voltage swingFast chargingStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayScan line
A driving method of liquid crystal display. Voltage levels of pre-charging signals applied to storage electrodes vary before scan signals are applied to scan lines. Partial response voltage of the variations in voltage levels of pre-charging signals are respectively coupled to storage capacitors within pixels by capacitors. When the scan signals are applied to the scan lines, voltage swings of the pixel capacitors charged by image data on data lines decrease, rapidly charging the pixels.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
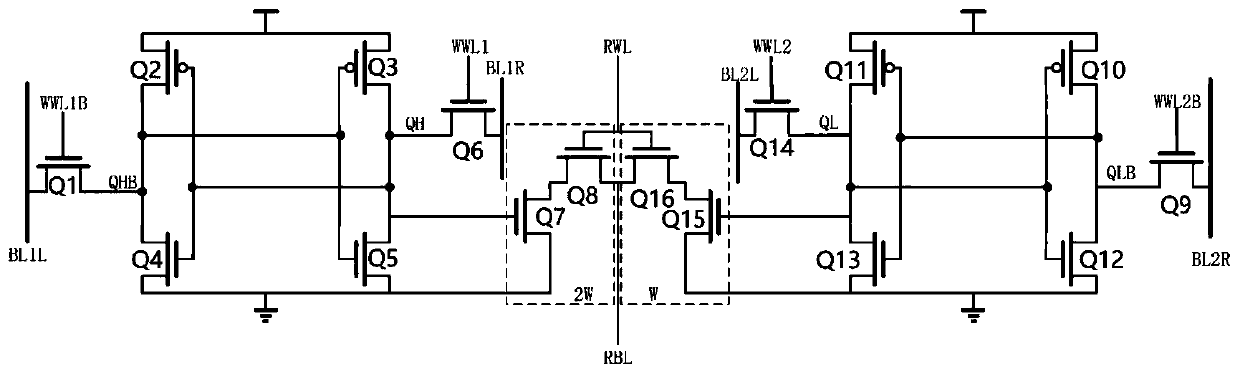
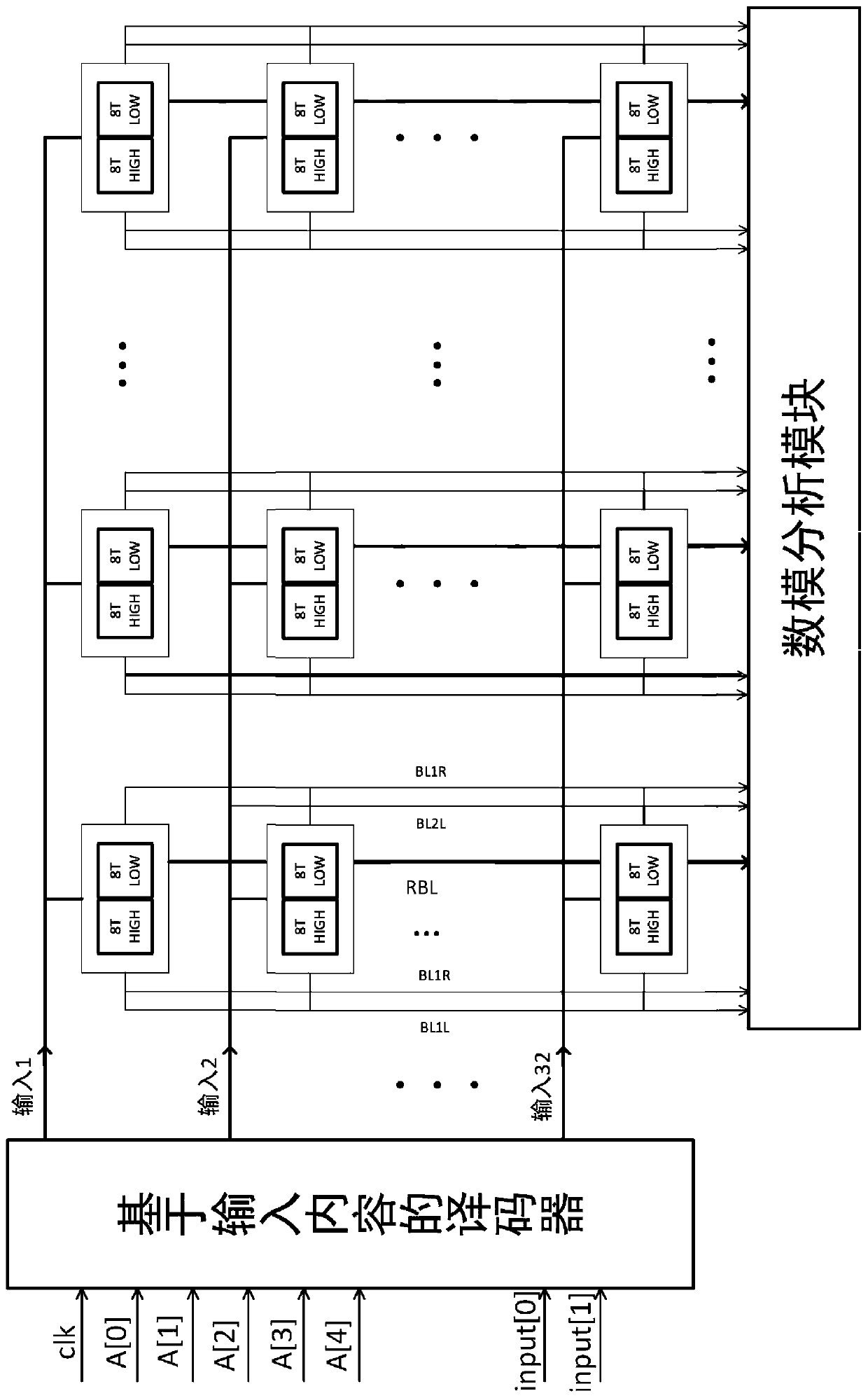
Storage unit of novel low-power-consumption static random access memory and application thereof
The invention provides a storage unit of a novel low-power-consumption static random access memory, which is characterized by comprising five word lines and four bit lines, the five word lines are respectively a word line I, a word line II, a word line III, a word line IV and a word line 5, and the four bit lines are respectively a bit line I, a bit line II, a bit line III and a bit line IV. Compared with the most advanced technology, energy consumption is reduced to 24.5% of original energy consumption, and the method has the advantages that the characteristic that cmos channel current and grid voltage are positively correlated is utilized, and a set of analog voltage values serve as the result of driving a SRAM through the grid voltage, so that in the same starting time, the voltage analog value on the bit line represents the multiplication result.
Owner:SHANGHAI TECH UNIV
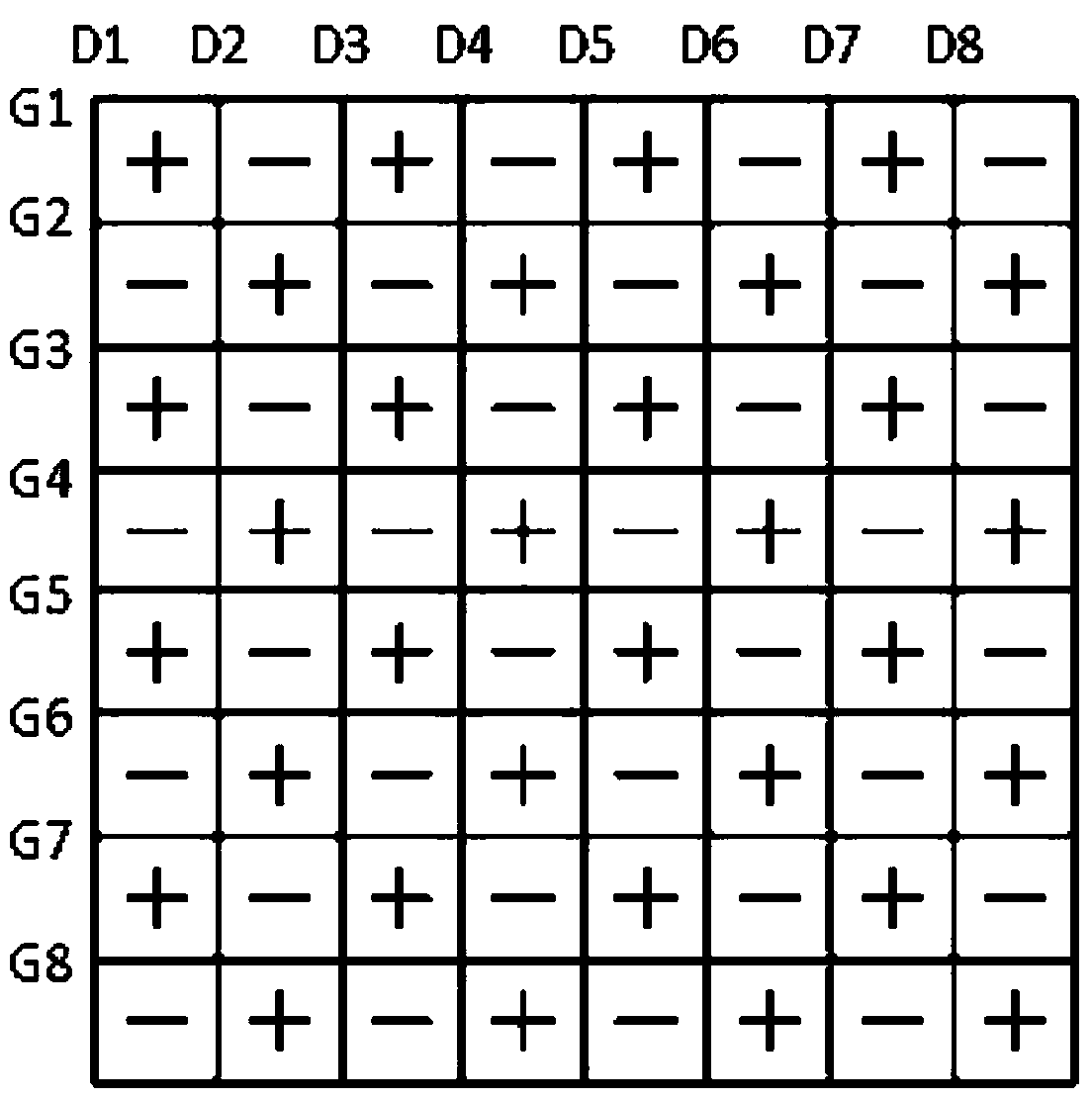
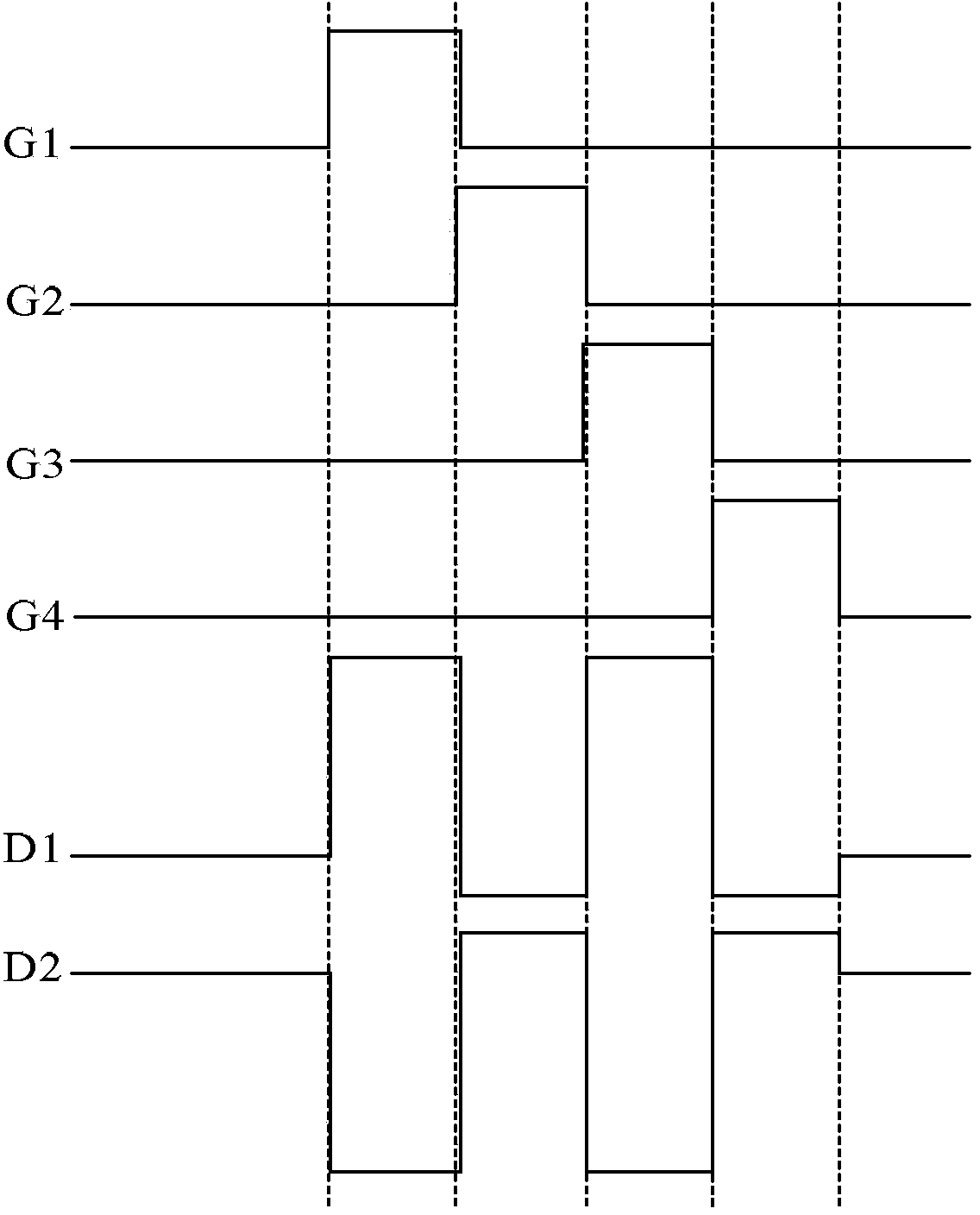
Array substrate, driving method thereof and display device
InactiveCN103472605AReduce power consumptionReduced voltage swingStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsGray levelVoltage polarity
An embodiment of the invention discloses an array substrate, a driving method thereof and a display device, and relates to the technical field of display. The array substrate comprises a plurality of pixel units in matrix arrangement, a plurality of horizontally and vertically cross grid lines and data lines are divided into the pixel units, and each pixel unit comprises pixel electrodes and common electrodes. In the pixel unit matrix, the common electrodes corresponding to the pixel units with the same sum of line number and row number are the same in voltage polarity, and the common electrodes of the adjacent pixel units are opposite in voltage polarity. By the aid of the array substrate with the structure, dot inversion is driven, and the voltage swing of data line driving voltage between a positive polarity gray level and a negative polarity gray level is greatly reduced, so that power consumption of the array substrate in a dot inversion driving mode is effectively reduced.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
Driver circuit of display device
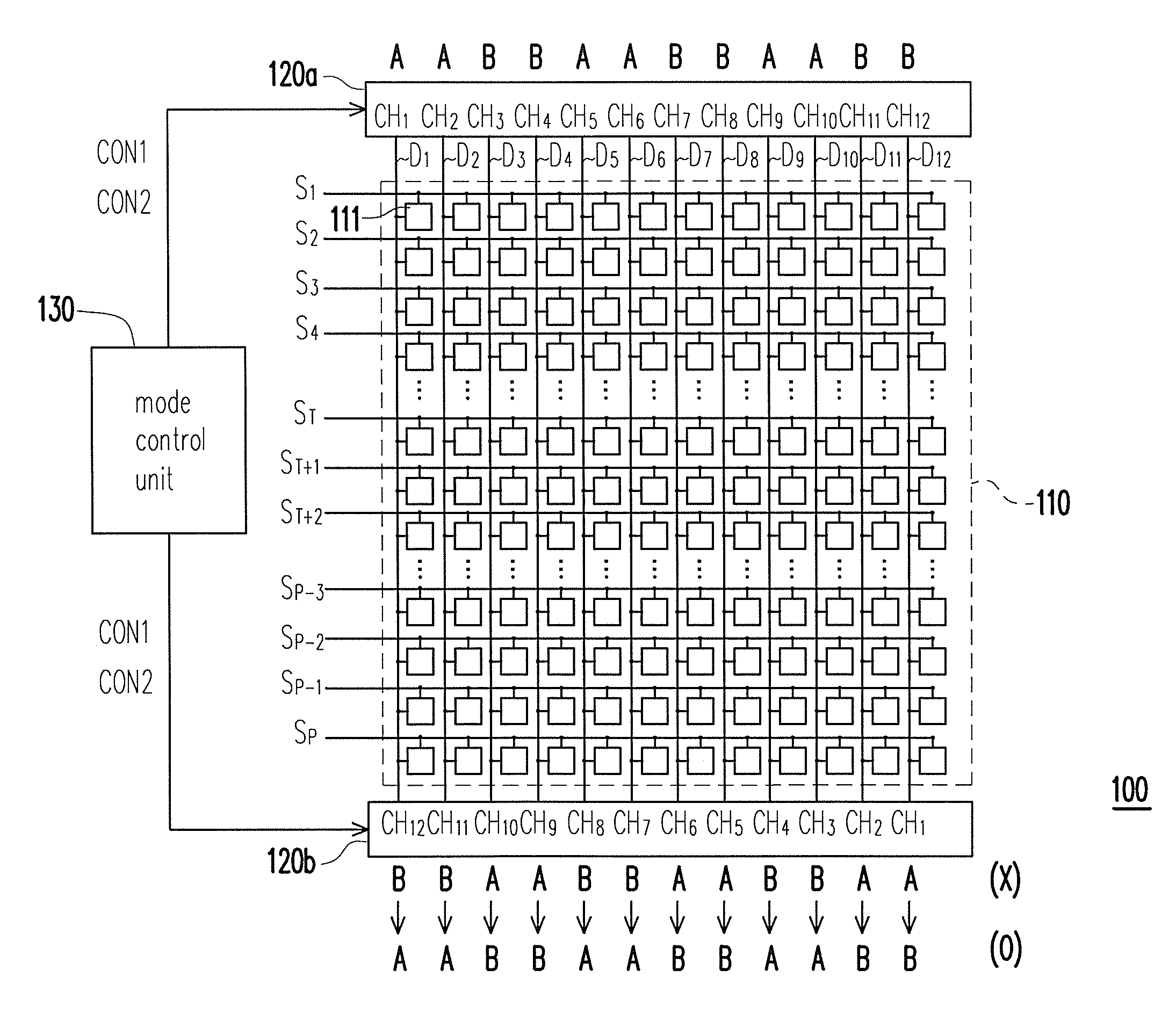
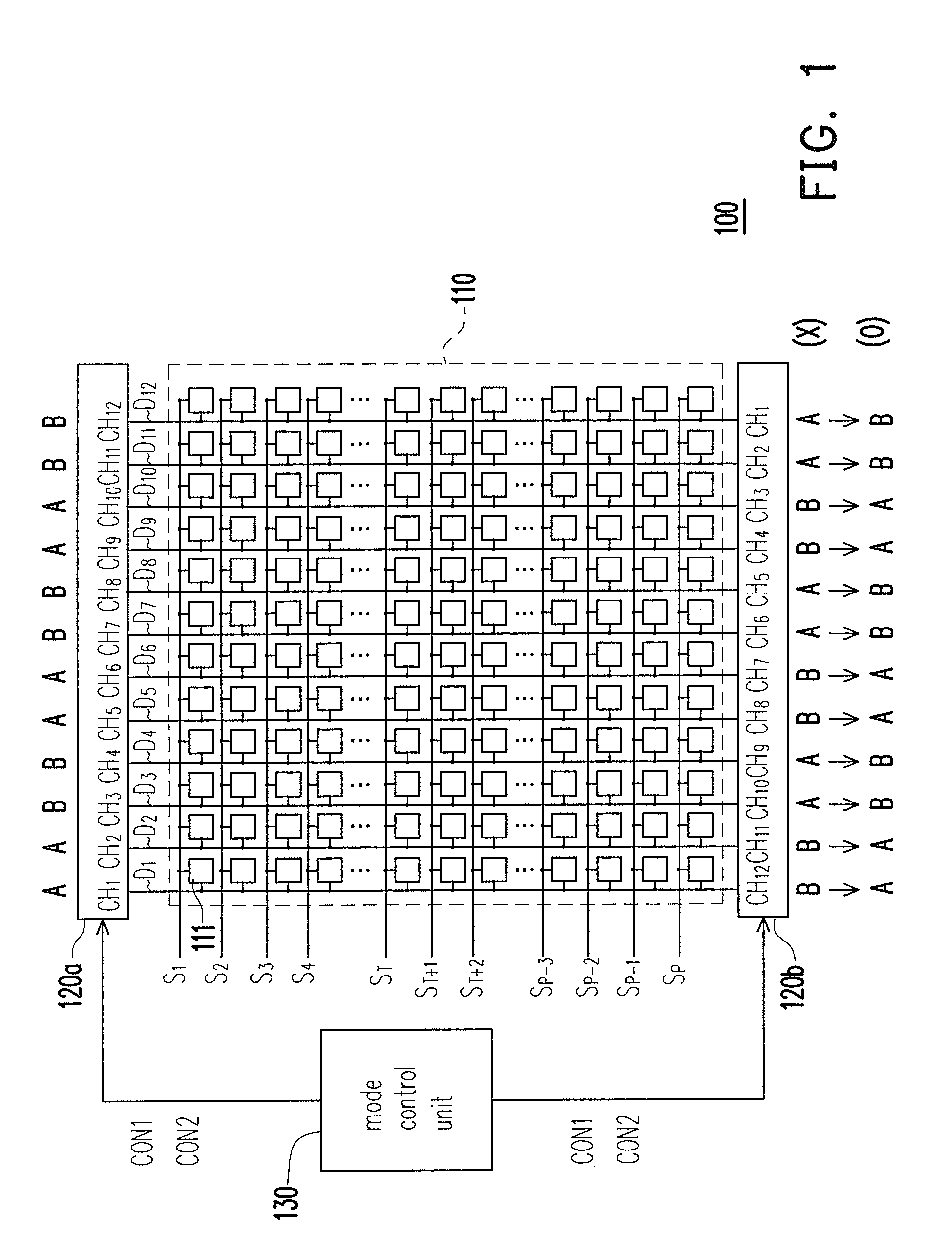
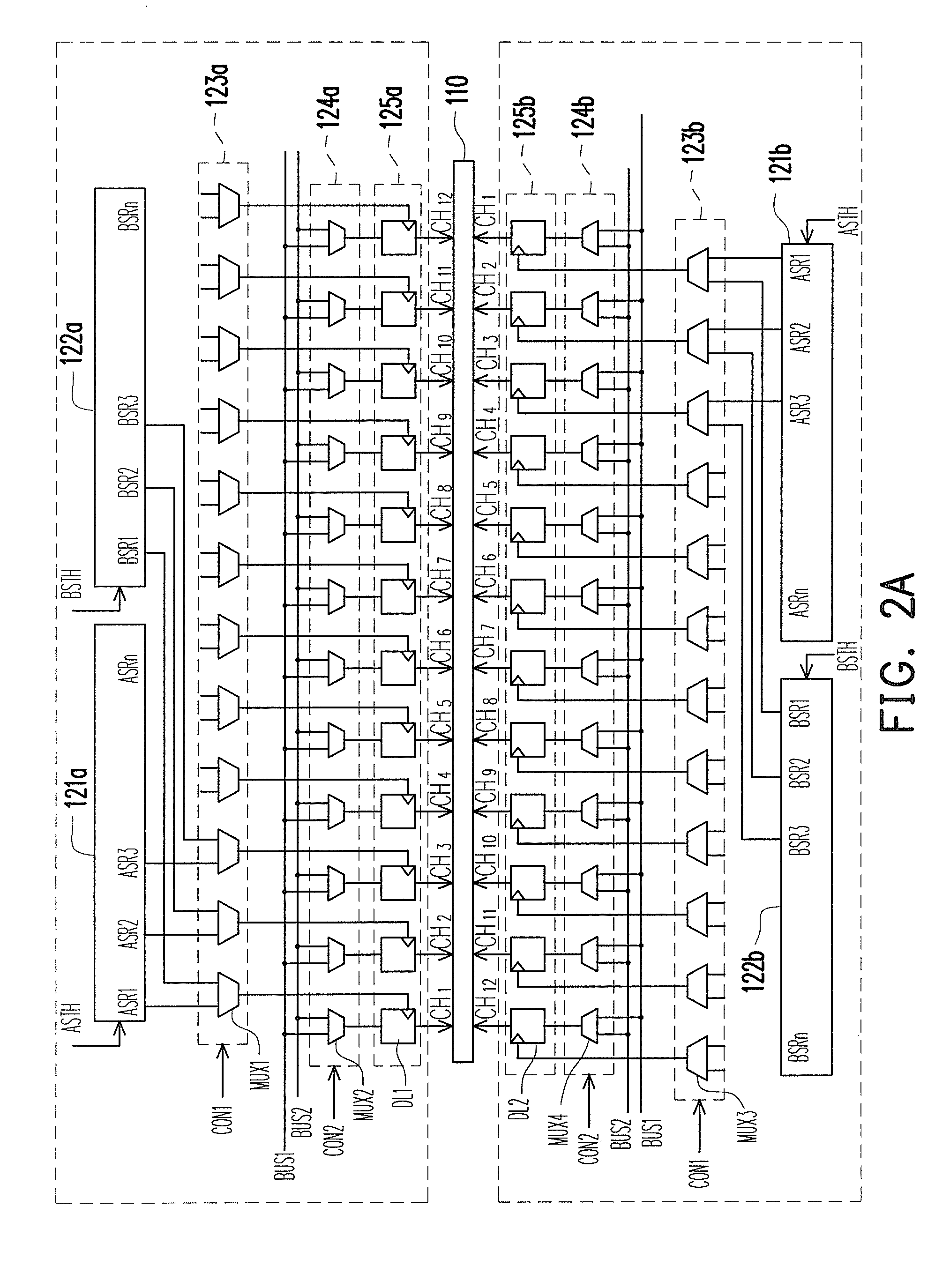
ActiveUS20100259522A1Save power consumptionReduced voltage swingCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitMode control
A driver circuit includes a mode control unit and a plurality of source drivers to drive a display panel including N pixel cells on each scan line. Each source driver has M driving channels, and a first subset of the driving channels and a second subset of the driving channels are respectively in a first mode and a second mode according to a preset mode sequence, wherein M≧N. The 1st through Nth driving channels of a first source driver and the Mth through (M−N+1)th driving channels of a second source driver respectively drive the 1st through Nth pixel cells during a first scan period and a second scan period. The modes of the Mth through 1st driving channels of the second source driver are respectively altered to match the modes of the 1st through Mth driving channels of the first source driver by the mode control unit.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Output buffer and source driver using the same
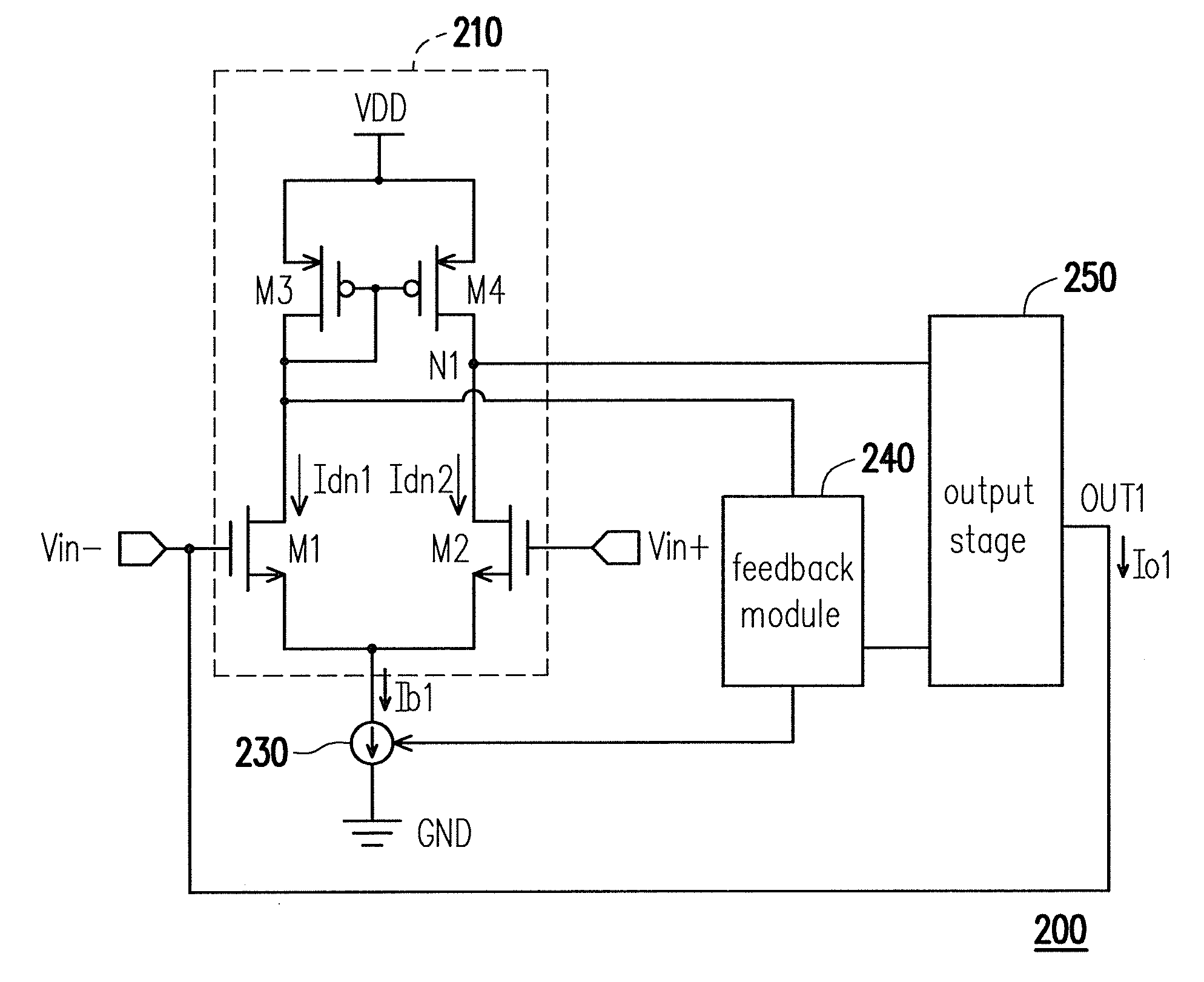
ActiveUS20100079431A1Enhance signal for drivingSave power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsDifferential amplifiersElectrical currentCurrent source
An output buffer and a source driver for a display panel are provided. The output buffer includes a differential input stage, a bias current source, a feedback module, and an output stage. The differential input stage has a first input terminal and a second input terminal receiving a first input signal and a second input signal respectively, and a first output terminal. The bias module provides a bias current to the differential input stage. The output stage has a second output terminal coupled to the first input terminal for providing an output current to the second output terminal based on a signal of the first output terminal. The feedback module adjusts the bias current and the output current based on the first input signal and the second input signal. The output buffer has ability of switching the output voltage to be low level and high level in high-speed.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD +1
Driver circuit of display device
ActiveUS20110234262A1Save power consumptionIncrease qualityStatic indicating devicesElectric pulse generatorMode controlEngineering
A driver circuit includes a mode control unit and a plurality of source drivers to drive a display panel including pixel cells on each scan line. Each source driver has M driving channels, and two subsets of the driving channels are respectively in a first mode and a second mode according to a preset mode sequence. The 1st through Nth driving channels of each of first source drivers and the Mth through (M−N+1)th driving channels of each of second source drivers respectively drive the pixel cells during a first scan period and a second scan period, wherein M≧N. The modes of the Mth through 1st driving channels of the second source drivers are respectively altered to match the modes of the 1st through Mth driving channels of the first source drivers by the mode control unit.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com