Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Make up for information loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Telecommunication method
InactiveUS20120039181A1Performs betterImprove system performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer moduleLocation based information
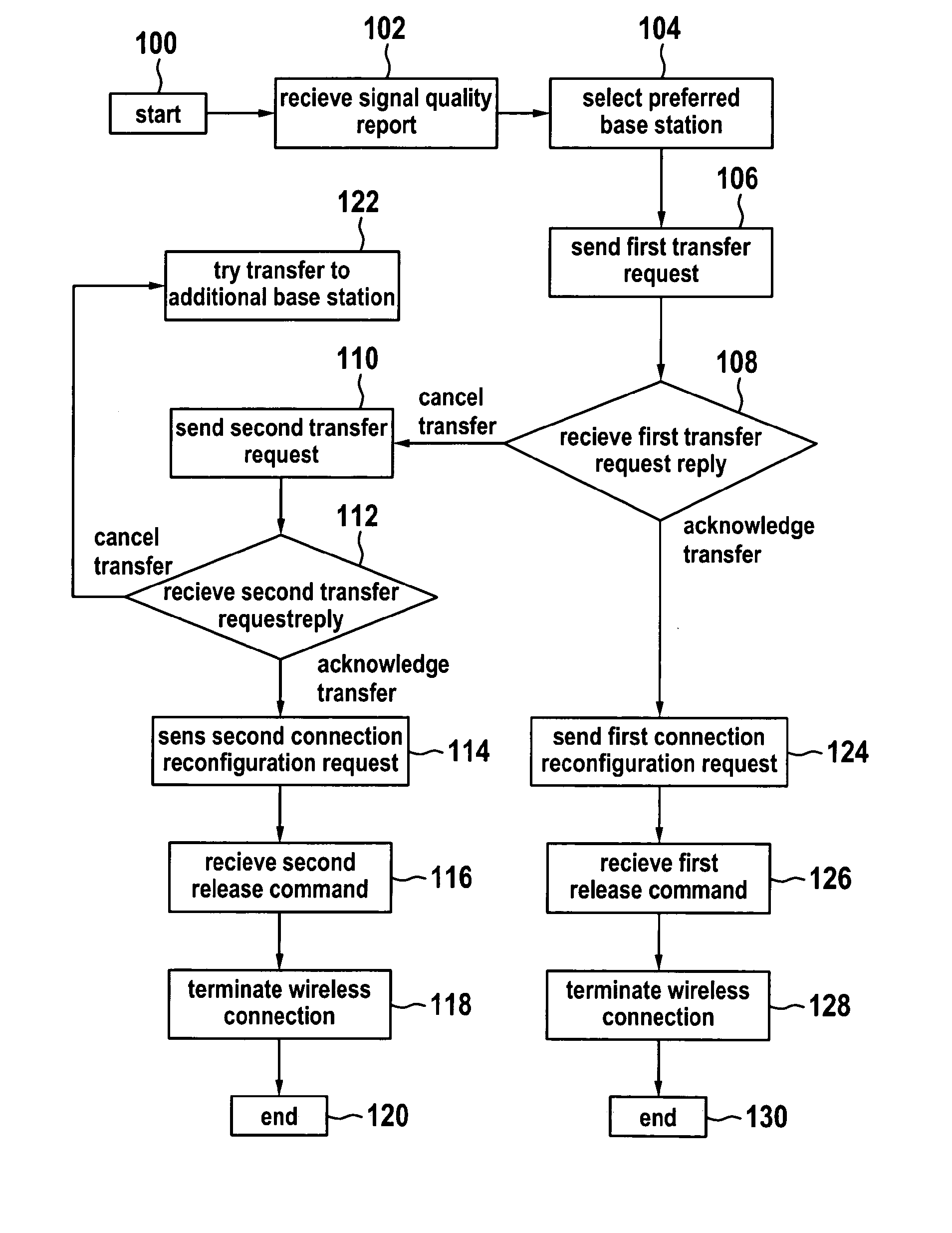
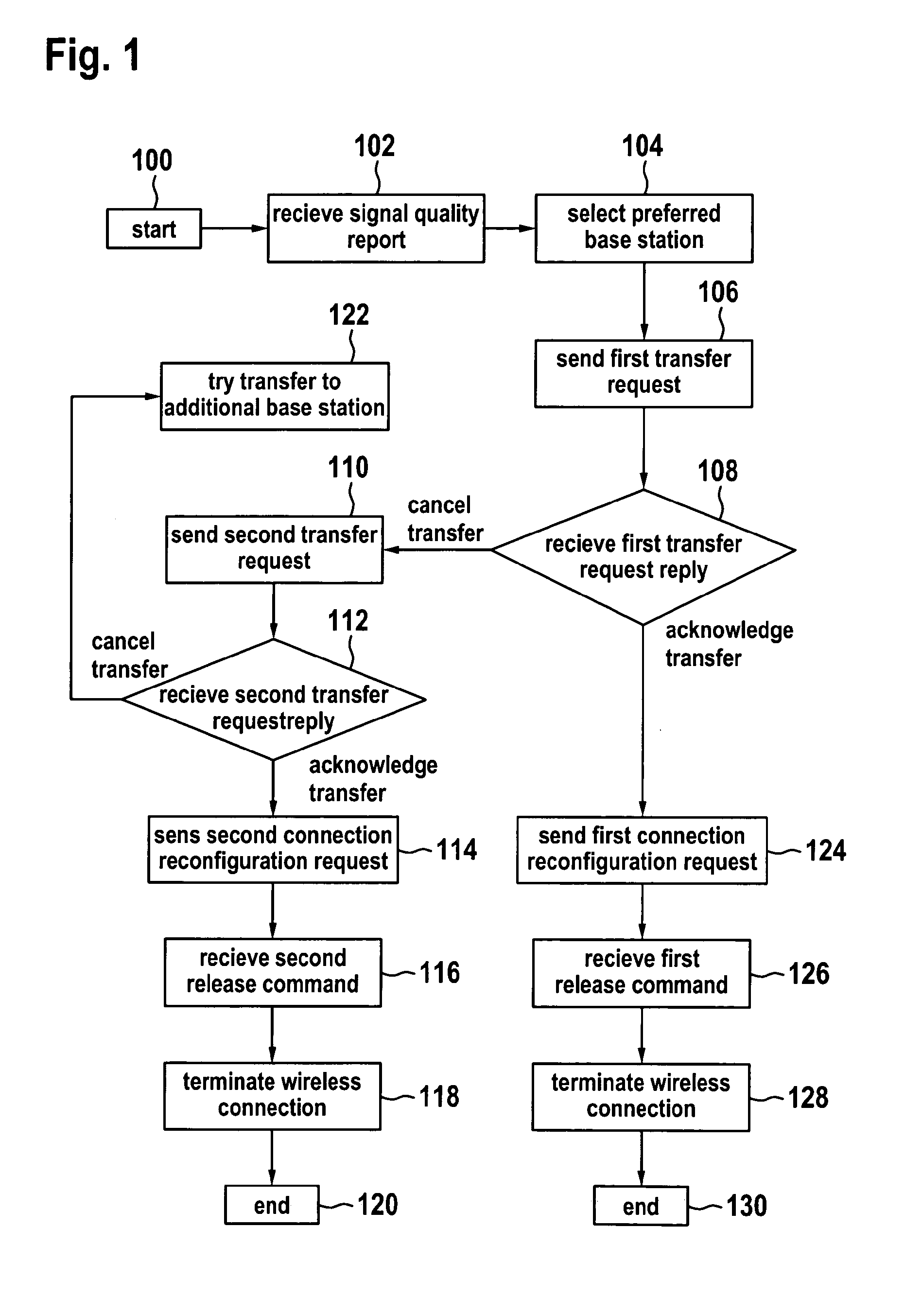
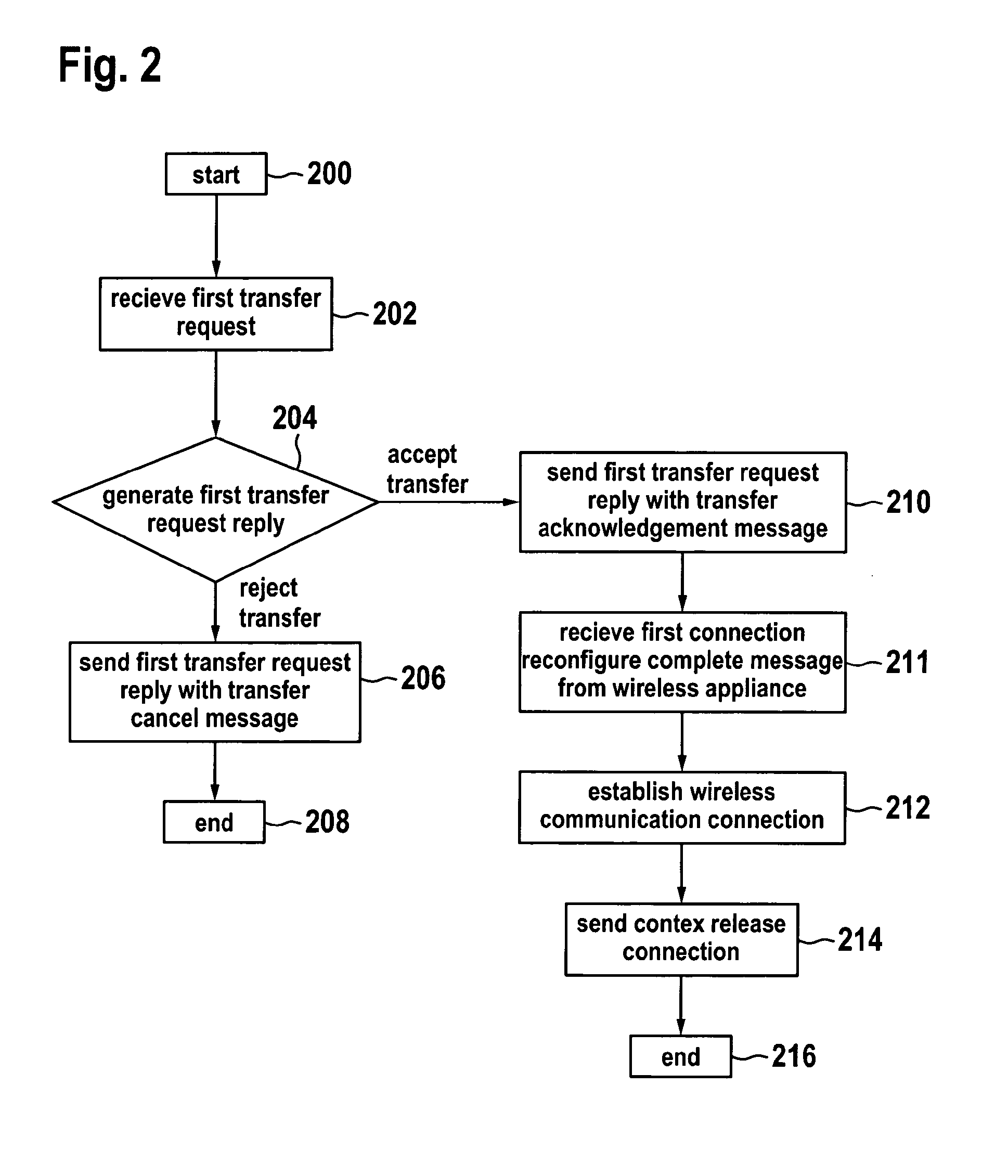
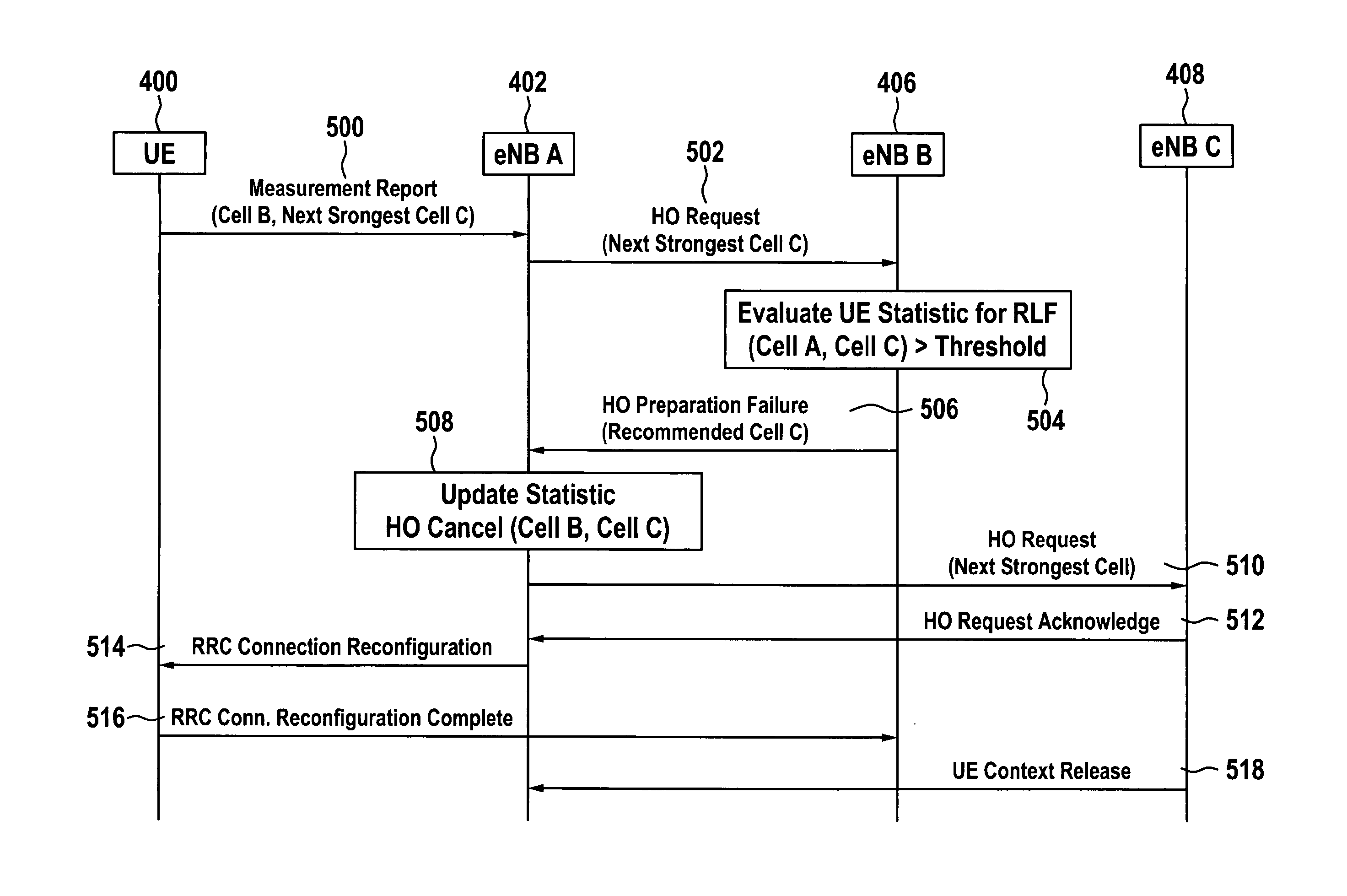
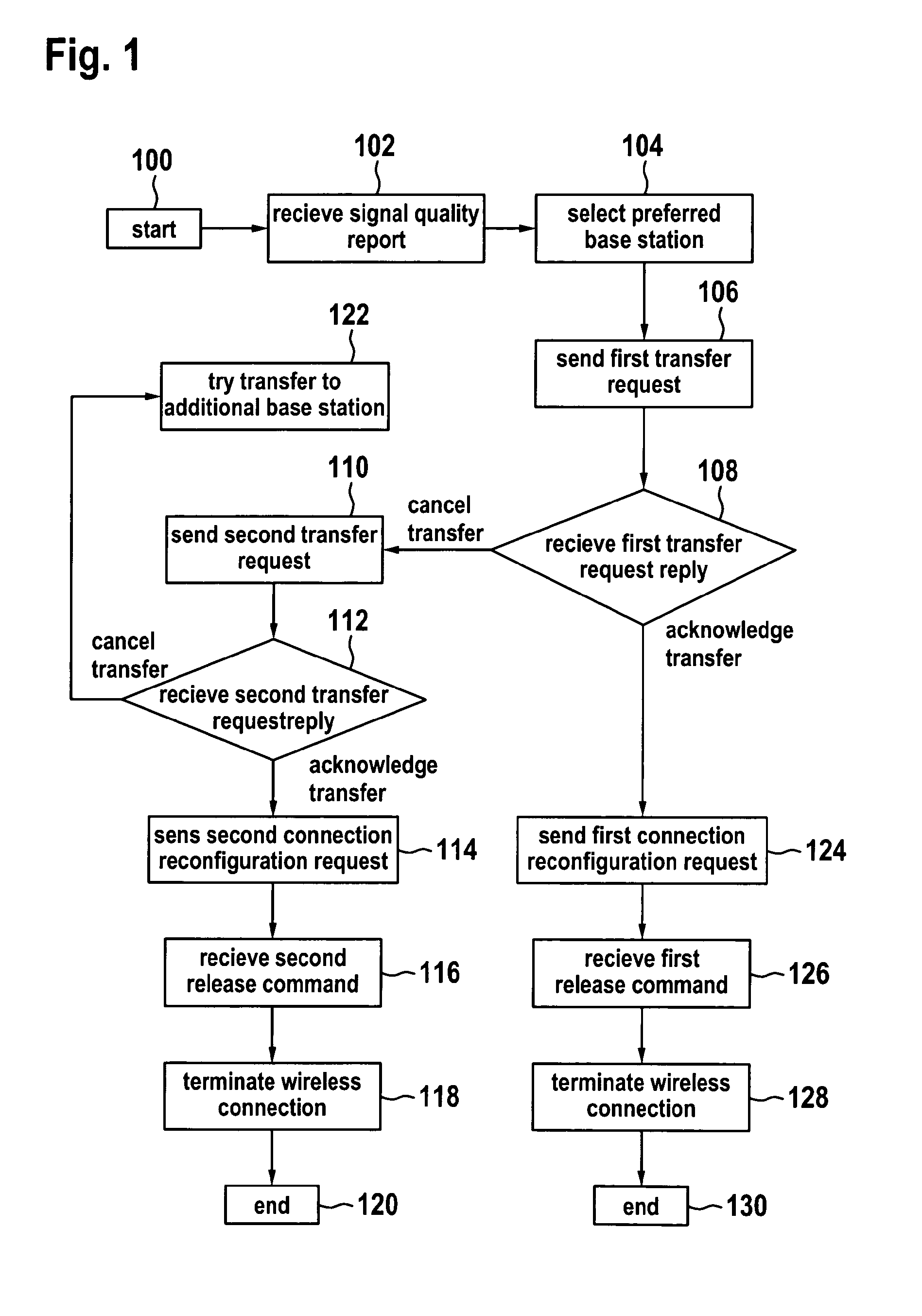
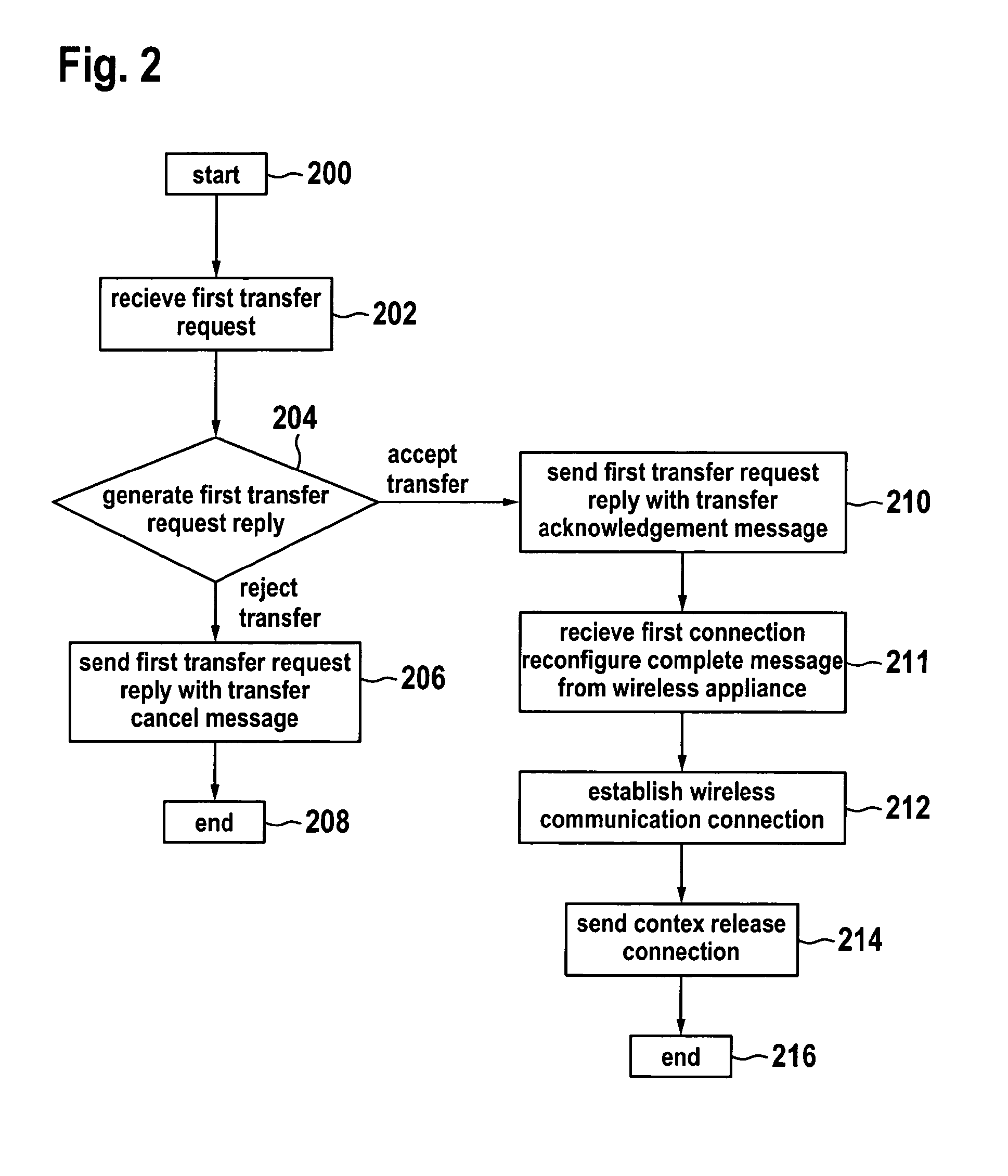
The invention relates to methods of using a trainable software module used in the handover procedure employing the location based information for the self optimization of wireless communication networks, in particular for the self optimization of cellular mobile networks. Embodiments of the invention address the problems of radio link failures and rapid handovers immediately after transferring a wireless appliance from one base station apparatus to the other at certain cell border locations by evaluating which base station apparatus a wireless appliance should have its wireless connection transferred to using either a database or a trainable software module.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Graph with zoom operated clustering functions
InactiveUS20070285426A1More detailed informationLoss of detail informationDrawing from basic elementsGraphicsDisplay device
Software and methods of graphic representation of data are contemplated in which the data points are displayed in a clustered and / or de-clustered format as a function of a user zooming in and out of the display. Most preferably, the zoom is a continuous zoom, and the program further allows for panning within the display.
Owner:MATINA NICHOLAS A
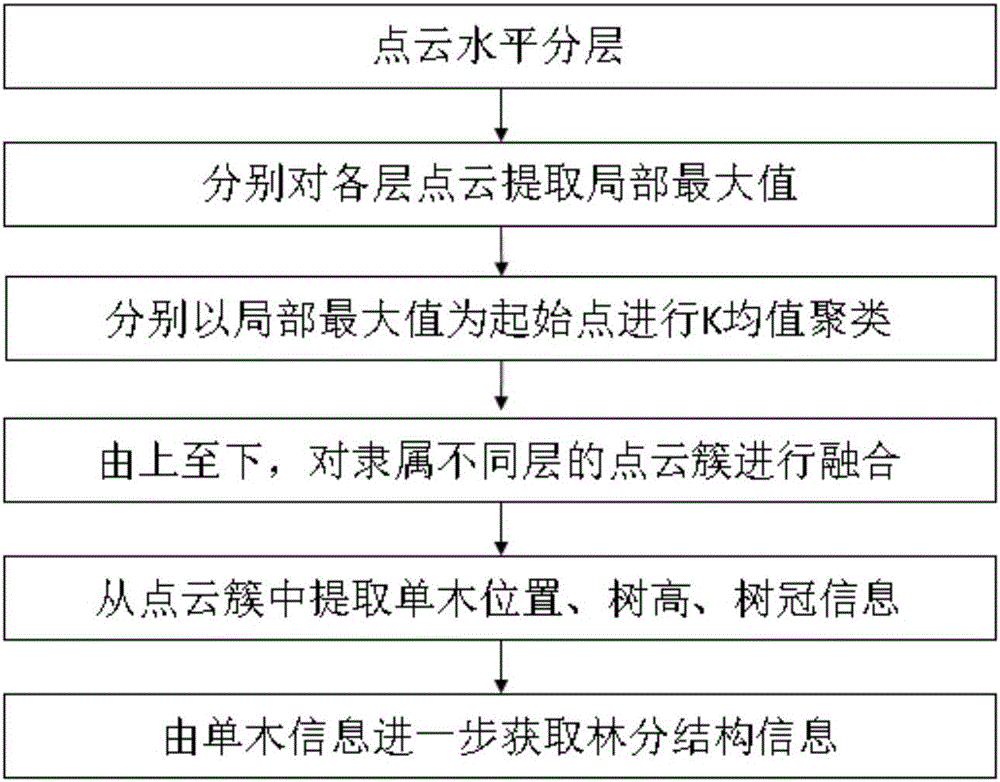
Method for extracting single tree information from LiDAR point cloud in layered clustering mode
ActiveCN106845399APay attention to the extraction effectImprove the extraction effectCharacter and pattern recognitionPoint cloudRelevant information
The invention discloses a method for extracting single tree information from LiDAR in a layered clustering mode and belongs to the scope of LiDAR point cloud data processing and information extraction. According to the key technical point, 1, the point cloud is horizontally layered; 2, all the layers of point cloud are classified in a k mean value clustering mode, and different attribute values are provided for all the layers of point cloud; 3, the point cloud meeting preset conditions is fused; 4, the single tree positions, the tree height, the crown breadth and other information are extracted from the point cloud with the same attribute values, and forest stand structure information is calculated through the single tree information. The method has the key advantages that extraction of floor stratum single trees is achieved, and the number of accurately extracted forest stand forests reaches 80% or above; the function of extracting the single tree information from LiDAR and calculating the forest stand structure is achieved; no excessive requirement on the point cloud density is generated, and it is proved that the point cloud of 2p / m<2> can complete relevant work. The method can be applied to the field of LiDAR inversion information, is especially suitable for the forest stand condition with the complex structure, and can accurately extract the single tree positions, the tree height, the crown breadth, the forest stand structure parameters and other relevant information.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Remote sensing image cloud detection method and device based on full convolutional neural network
ActiveCN111274865AHigh precisionImprove the extraction effectScene recognitionNeural architecturesData setEngineering
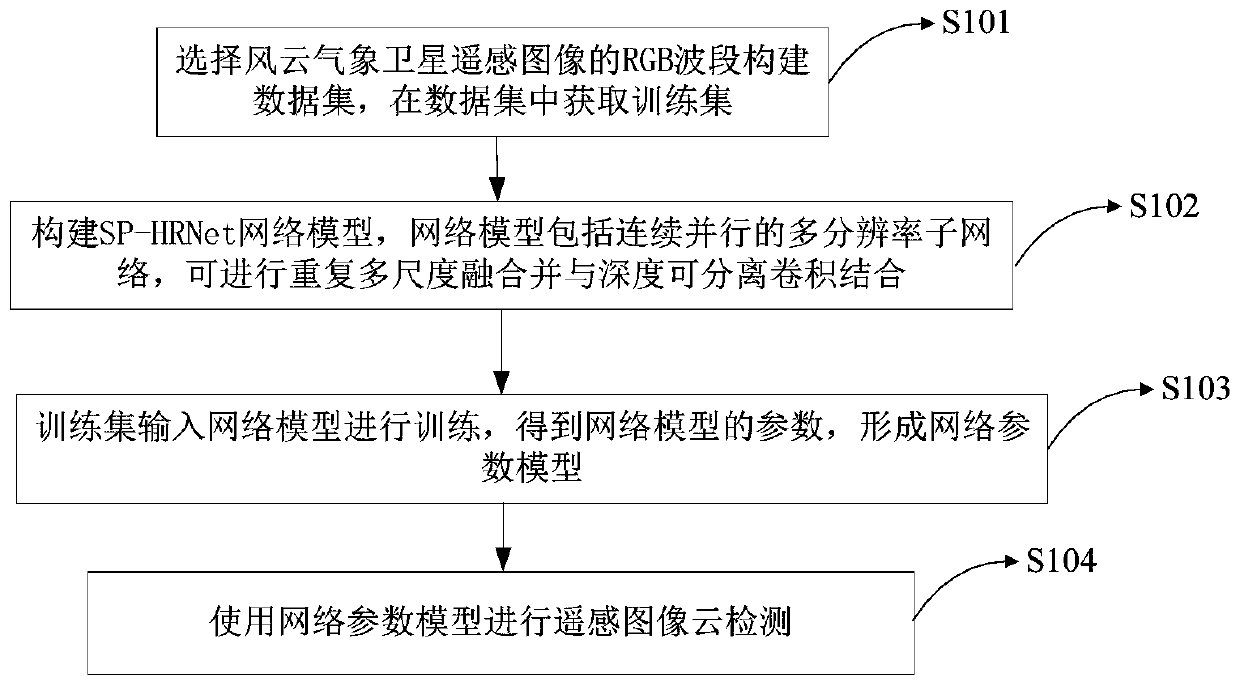
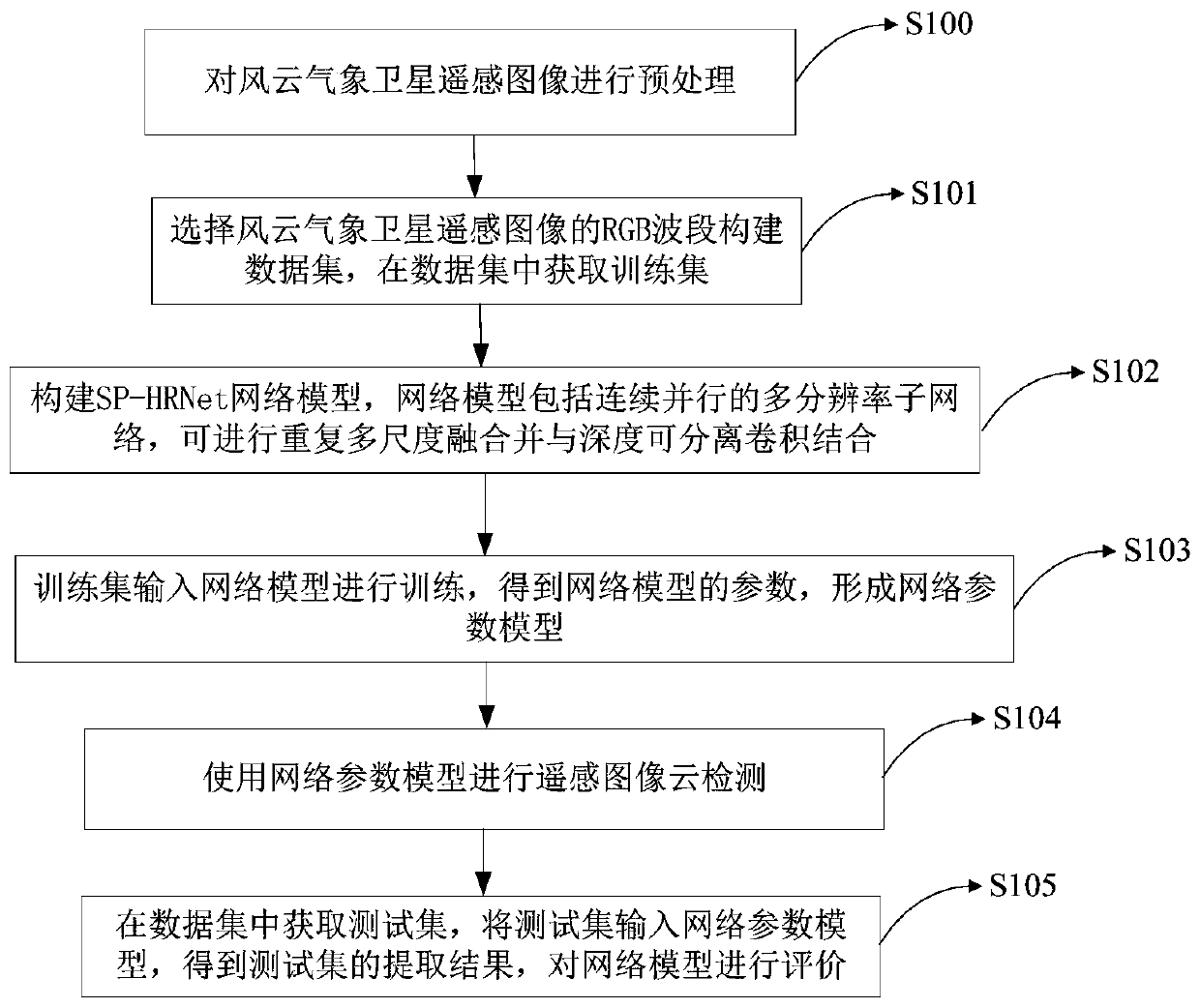
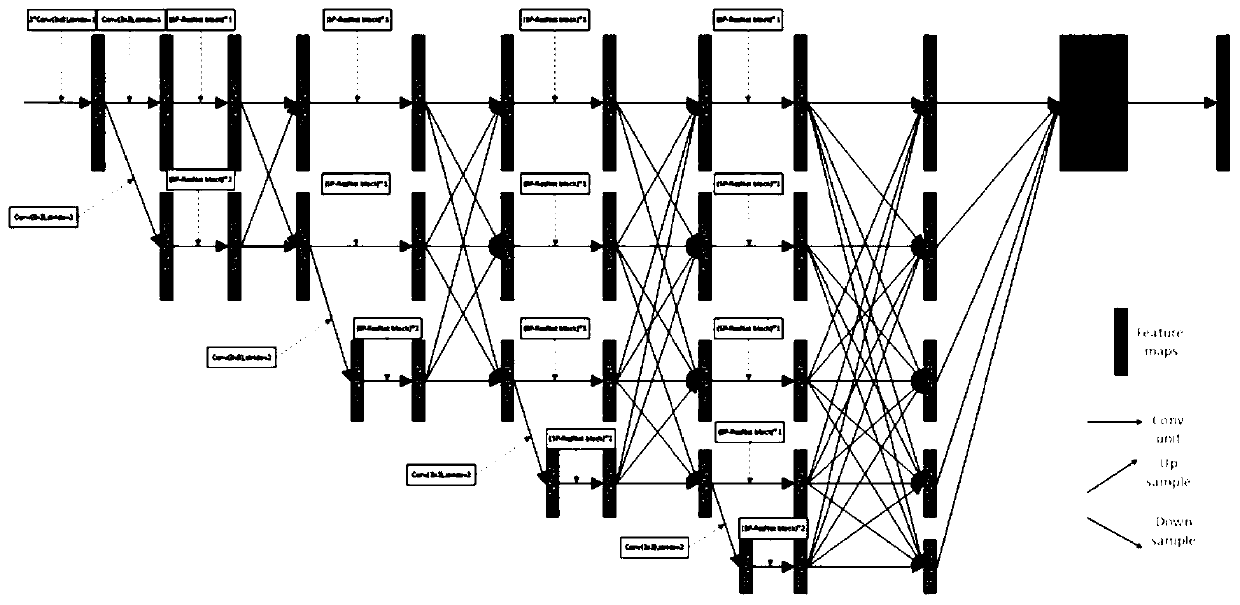
The invention relates to the field of remote sensing detection, in particular to a remote sensing image cloud detection method and device based on a full convolutional neural network. The method comprises the steps of selecting an RGB waveband of a wind cloud meteorological satellite remote sensing image to construct a data set, and obtaining a training set in the data set; constructing an SP-HRNet network model, wherein the network model comprises a continuous and parallel multi-resolution sub-network, a repeated multi-scale fusion module and a depth separable convolution combination module;inputting the training set into a network model for training to obtain parameters of the network model, and forming a network parameter model; and performing remote sensing image cloud detection by using the network parameter model. According to the method and the device, the sub-networks with multiple resolutions can be kept all the time, so that information is not lost in the feature extractionprocess of the image, the network depth is deepened, the depth separable convolution is combined, the feature extraction capability of the network is improved, the detail information of a detection result is enriched, and the cloud detection precision is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method and arrangement for enhancing the handling of TTI identifier
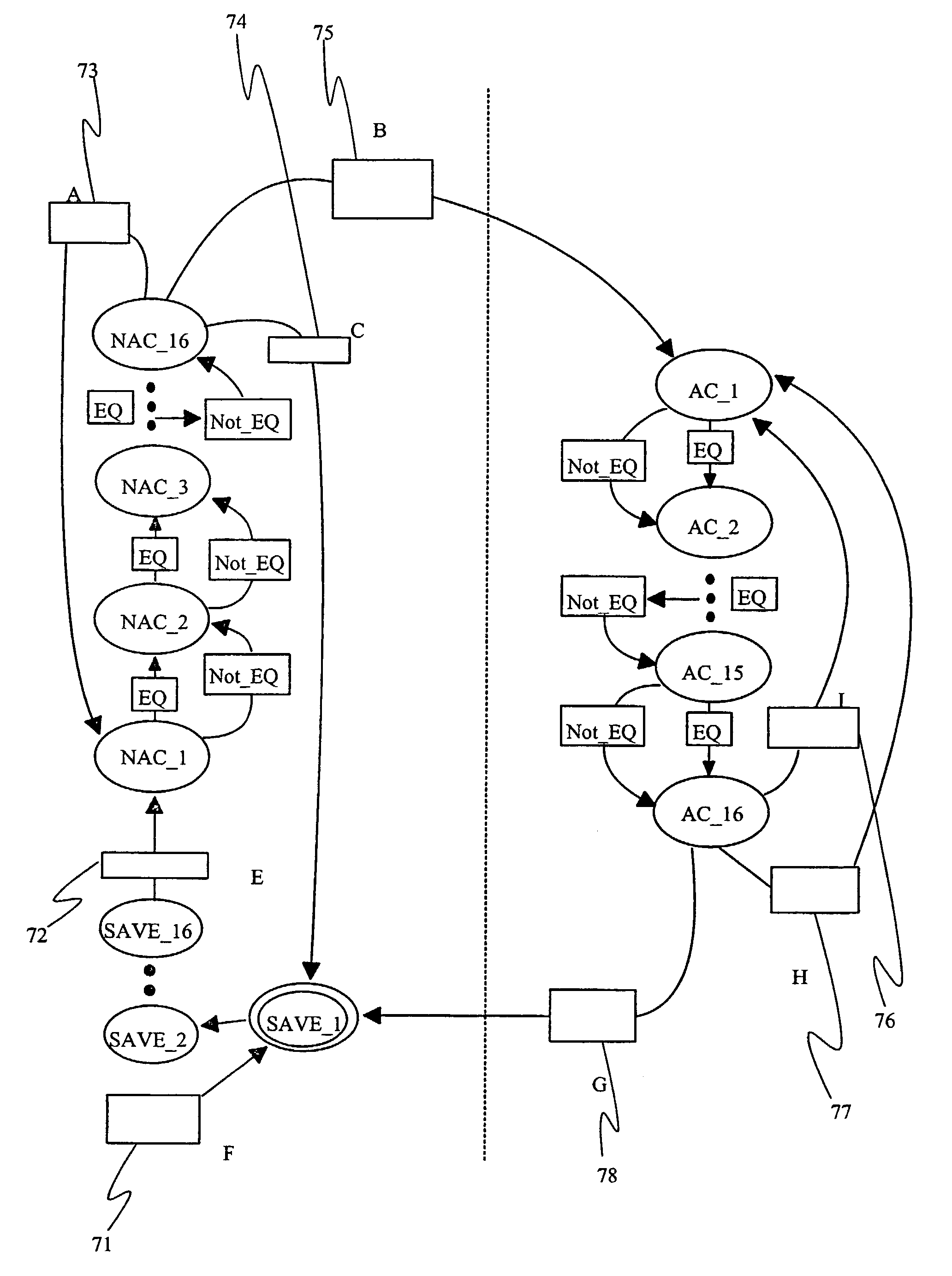
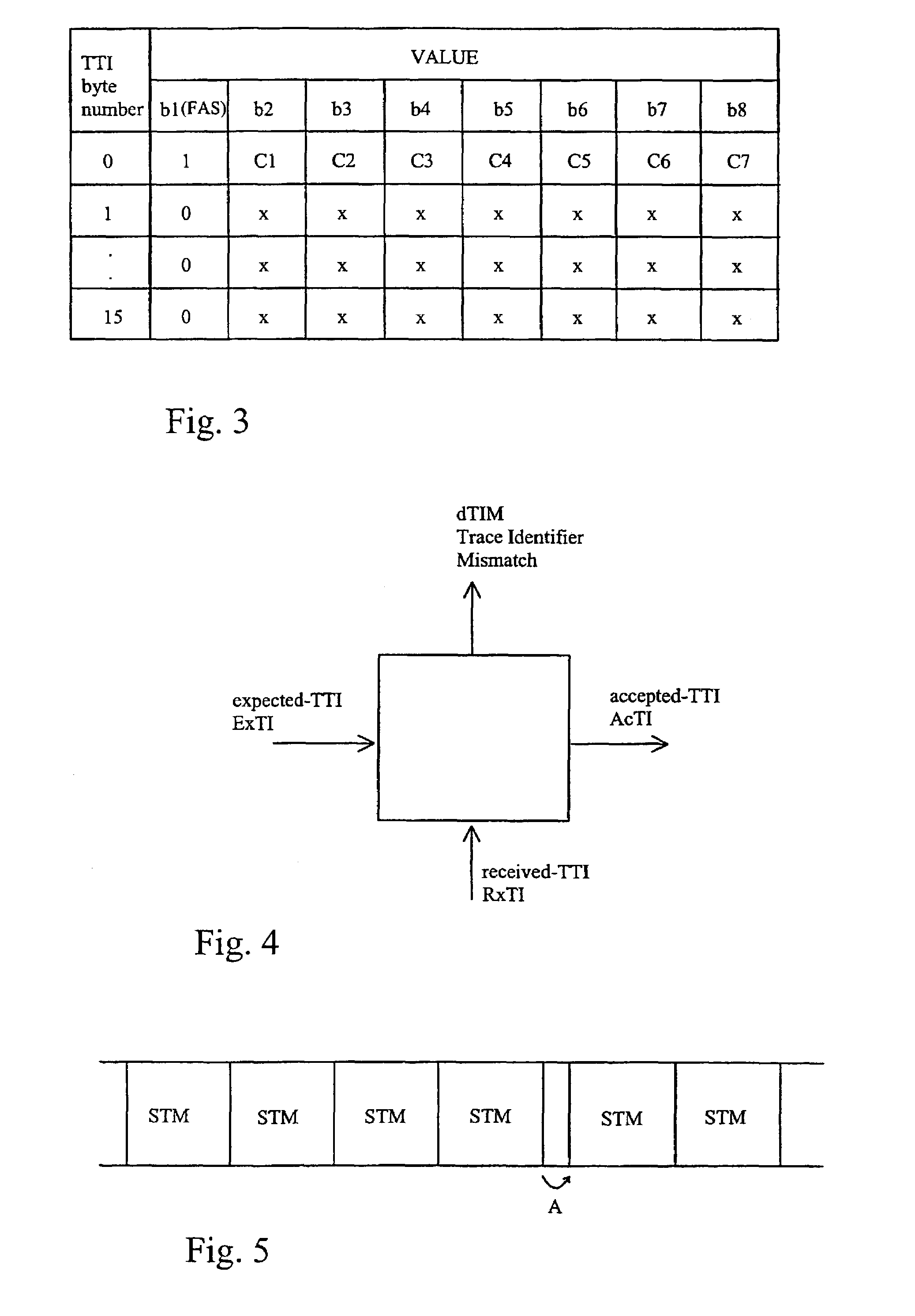
InactiveUS7068685B1Minimizing signal breakMinimize signalingTime-division multiplexTime-division multiplexing selectionComputer science
The invention relates to a method for finding frame alignment and accepting and monitoring TTI identifiers contained in frames in an SDH system. Advantageously the method according to the invention comprises steps in which frame alignment is first sought for by means of a frame alignment signal. When frame alignment has been found, it is monitored that it stays correct and at the same time at least one TTI identifier is read. According to the invention, at least one TTI identifier is saved from a frame after the finding of frame alignment. If a loss of frame alignment is detected, the TTI identifier saved is stored for a predetermined time. The invention further relates to an arrangement comprising means to implement the method described above in an SDH system.
Owner:SCHOFIELD TECH
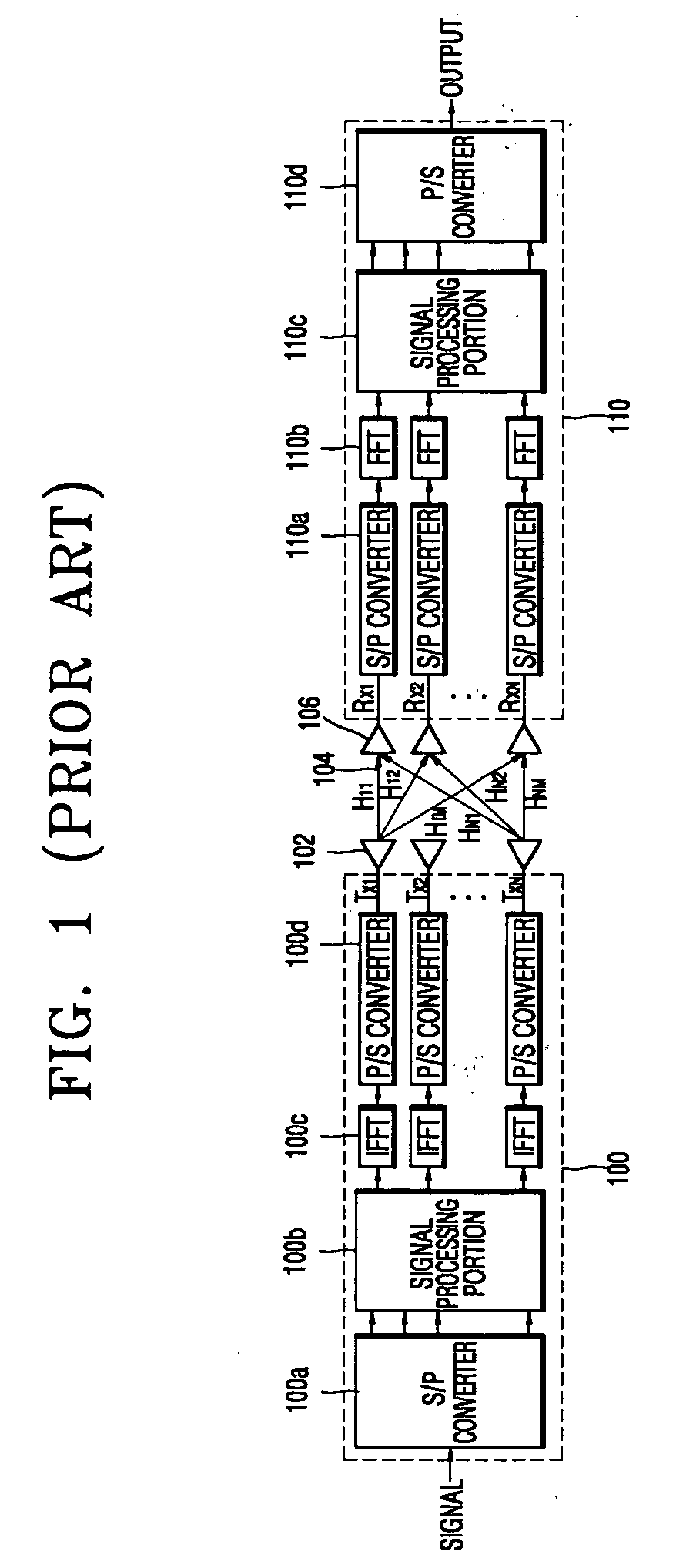
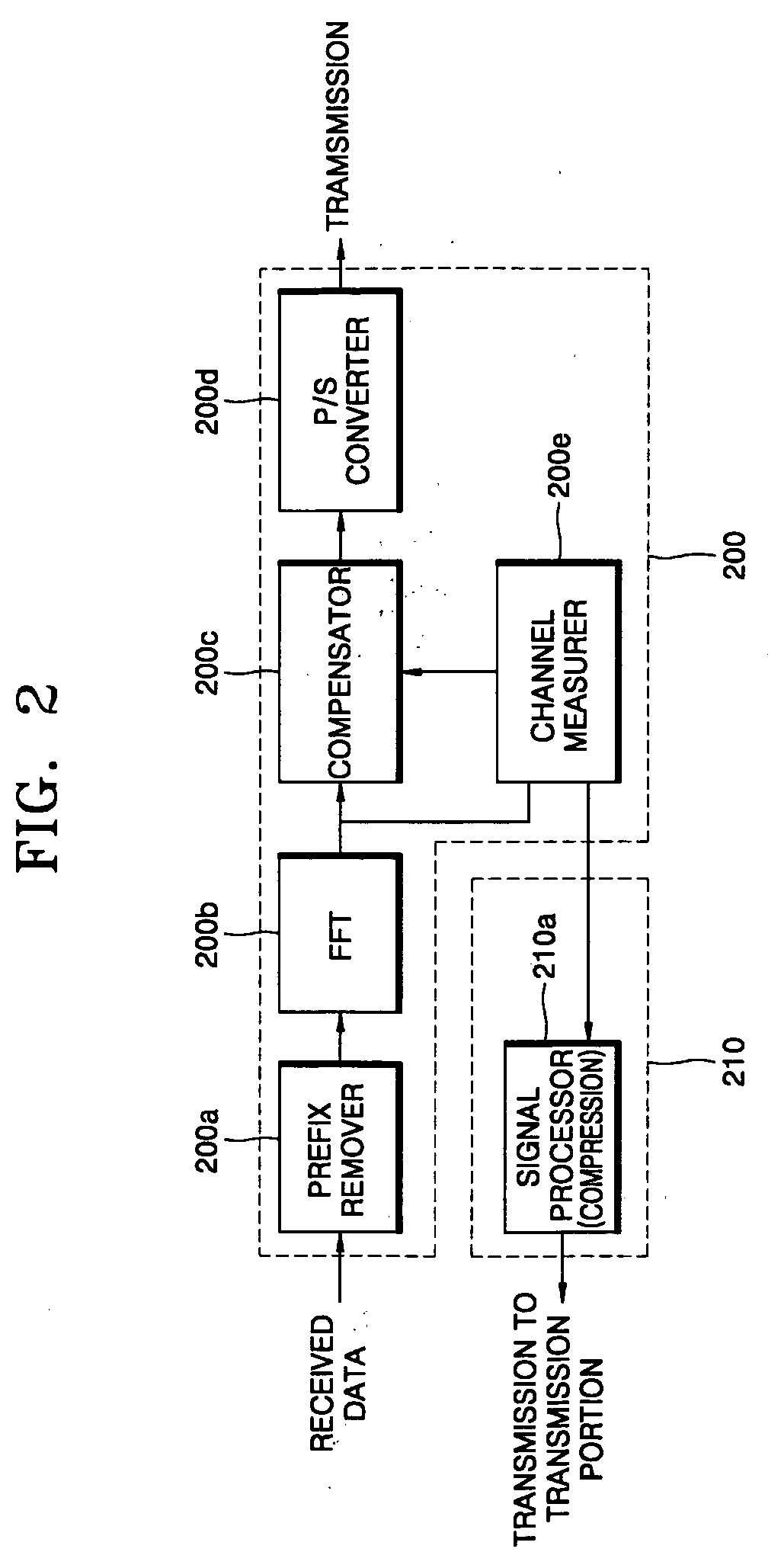
Method and apparatus for transferring channel information in ofdm communications
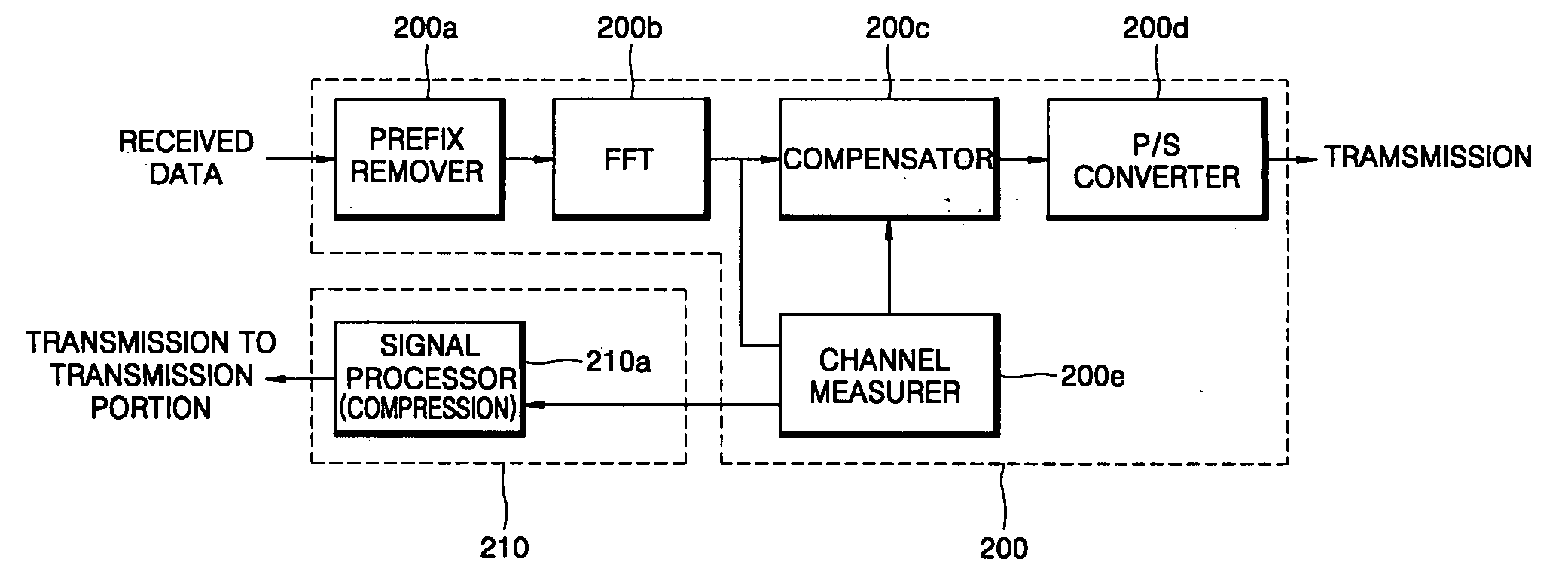
InactiveUS20050259566A1Reduce in quantityEasy to changeReceivers monitoringModulated-carrier systemsTime domainFast Fourier transform
A method and apparatus for transferring channel information in OFDM communications are provided. In the channel information transmission apparatus, a receiving portion includes a prefix remover removing a prefix, attached to the OFDM signal in order to overcome channel fading, from an OFDM signal received from a transmission portion, a fast Fourier transformer transforming a received time domain signal from which the prefix has been removed into a frequency domain signal, a channel measurer extracting a channel value from the frequency region signal obtained by the fast Fourier transformer, a compensator compensating for the output signal of the fast Fourier transformer using the channel value obtained by the channel measurer, a parallel-to-serial converter converting a compensated parallel signal received from the compensator into a serial signal, and a signal processor processing the channel value measured by the channel measurer in order to transmit signal-processed data to the transmission portion.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
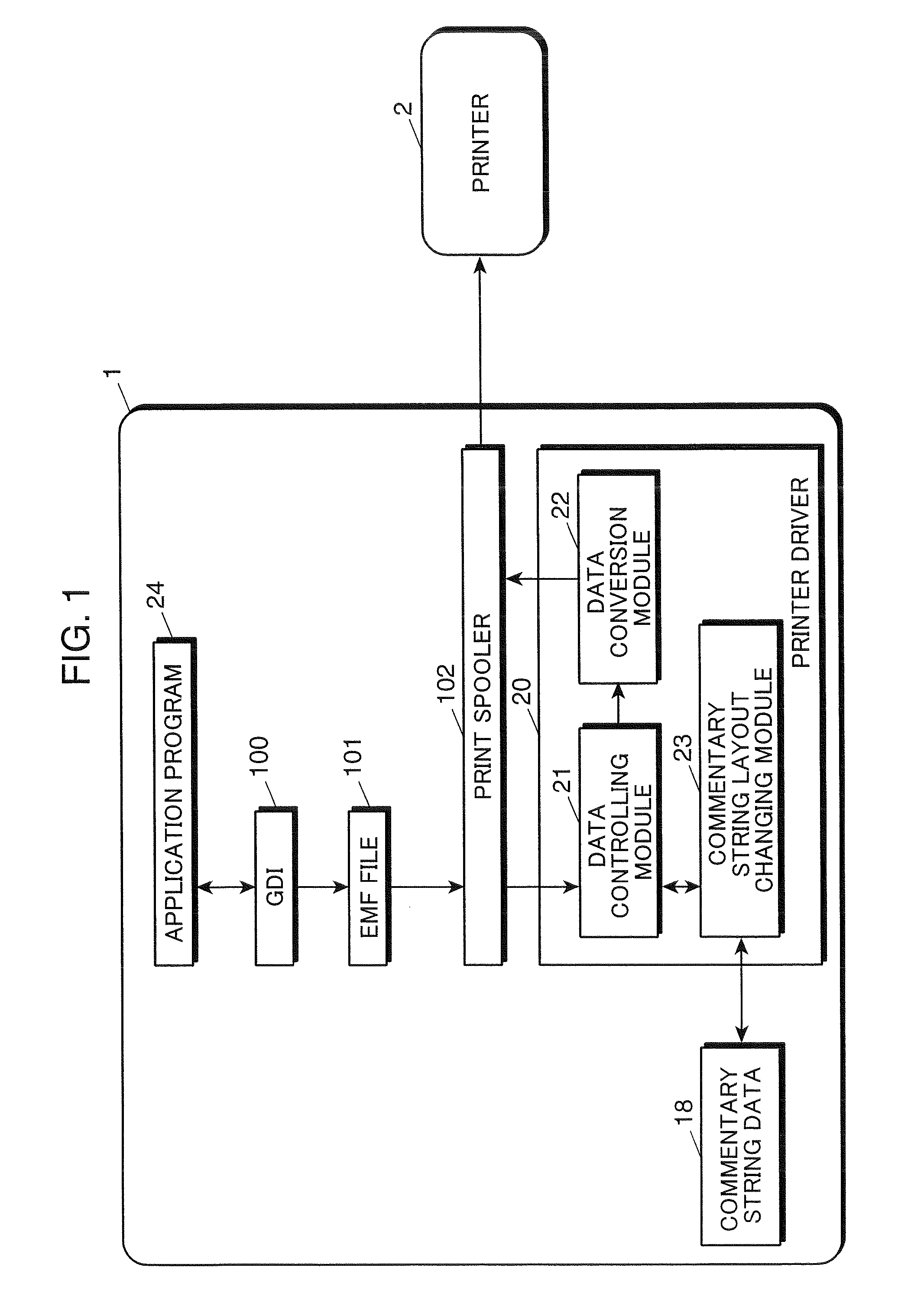
Computer-readable recording medium recorded with printing program
InactiveUS20080170264A1Inhibition lossSmall sizeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData storingData store
A computer-readable recording medium recorded with a printing program causes a processor of a computer to calculate a rendering area of print data stored in a storing section of the computer as a primary area based on the print data, and to calculate a rendering area of commentary string data to be attached to the print data as a sub-area. The program then judges whether the primary area and the sub-area overlap, and whether the sub-area deviates from an effective printing area. The commentary string data can be changed so that the primary area and the sub-area do not overlap, and so that the entire sub-area is within the effective printing area, if at least one of the judgment results in the judging step is affirmative. The changed commentary string data then is attached to the print data.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
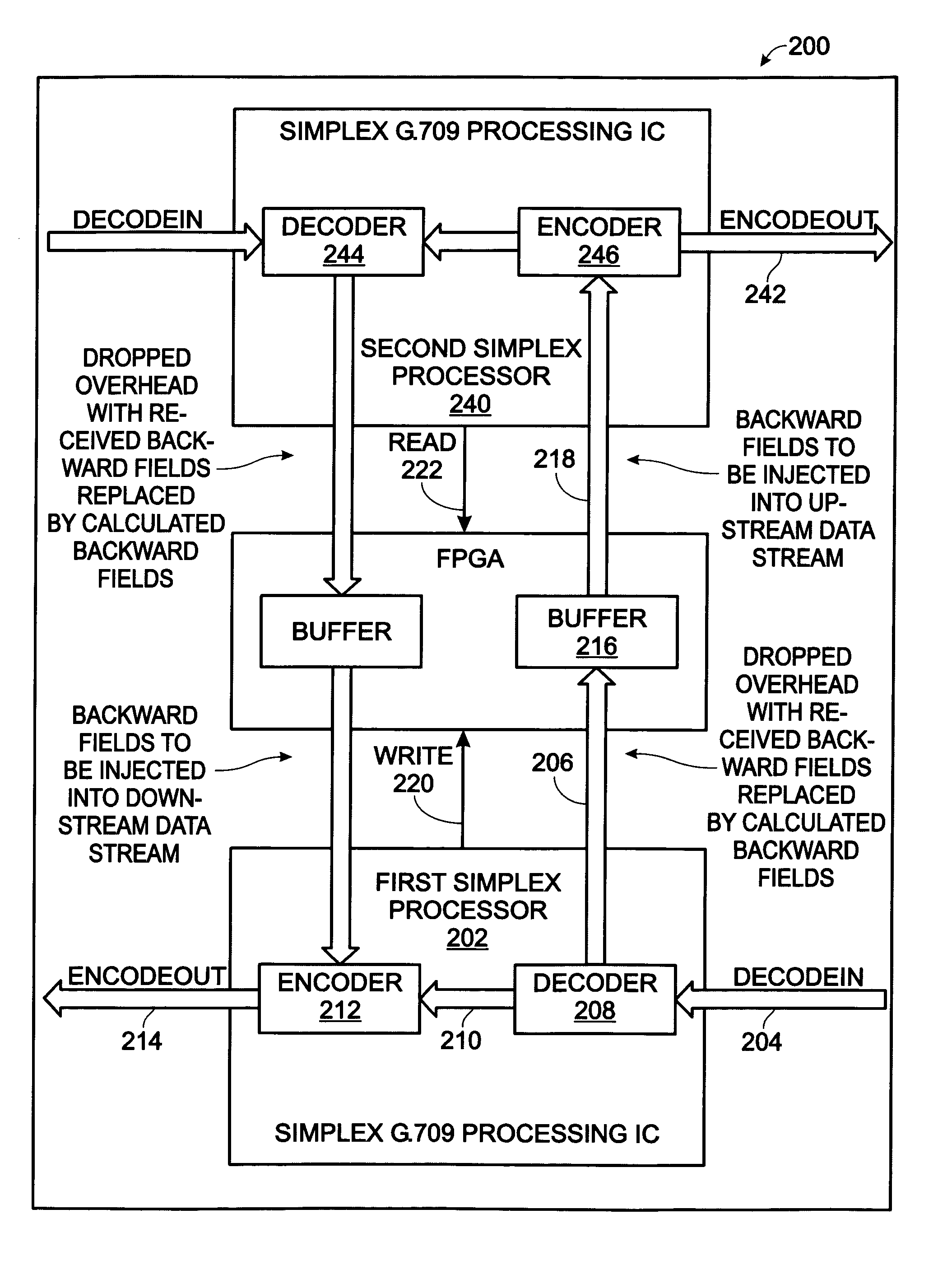
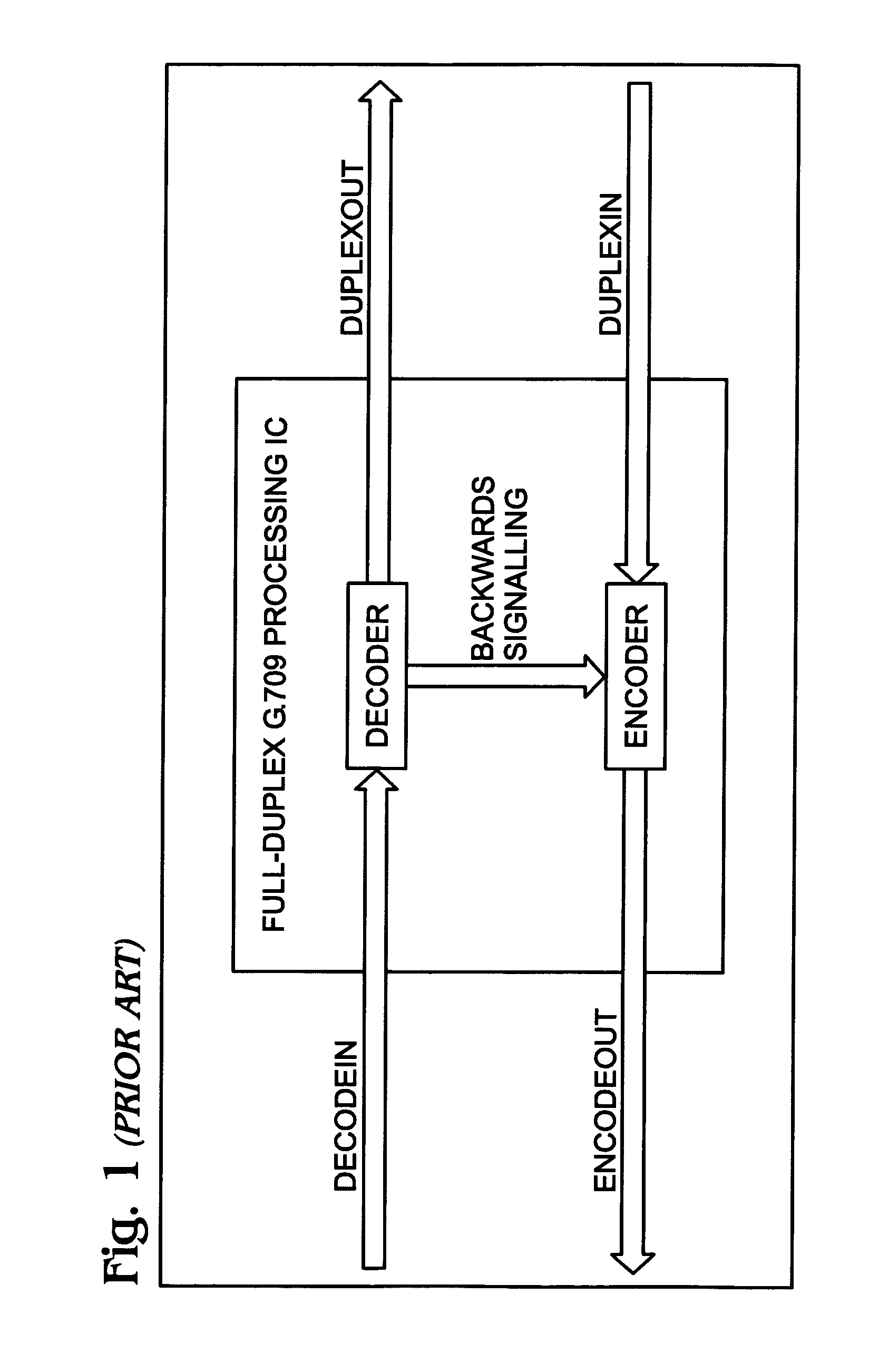
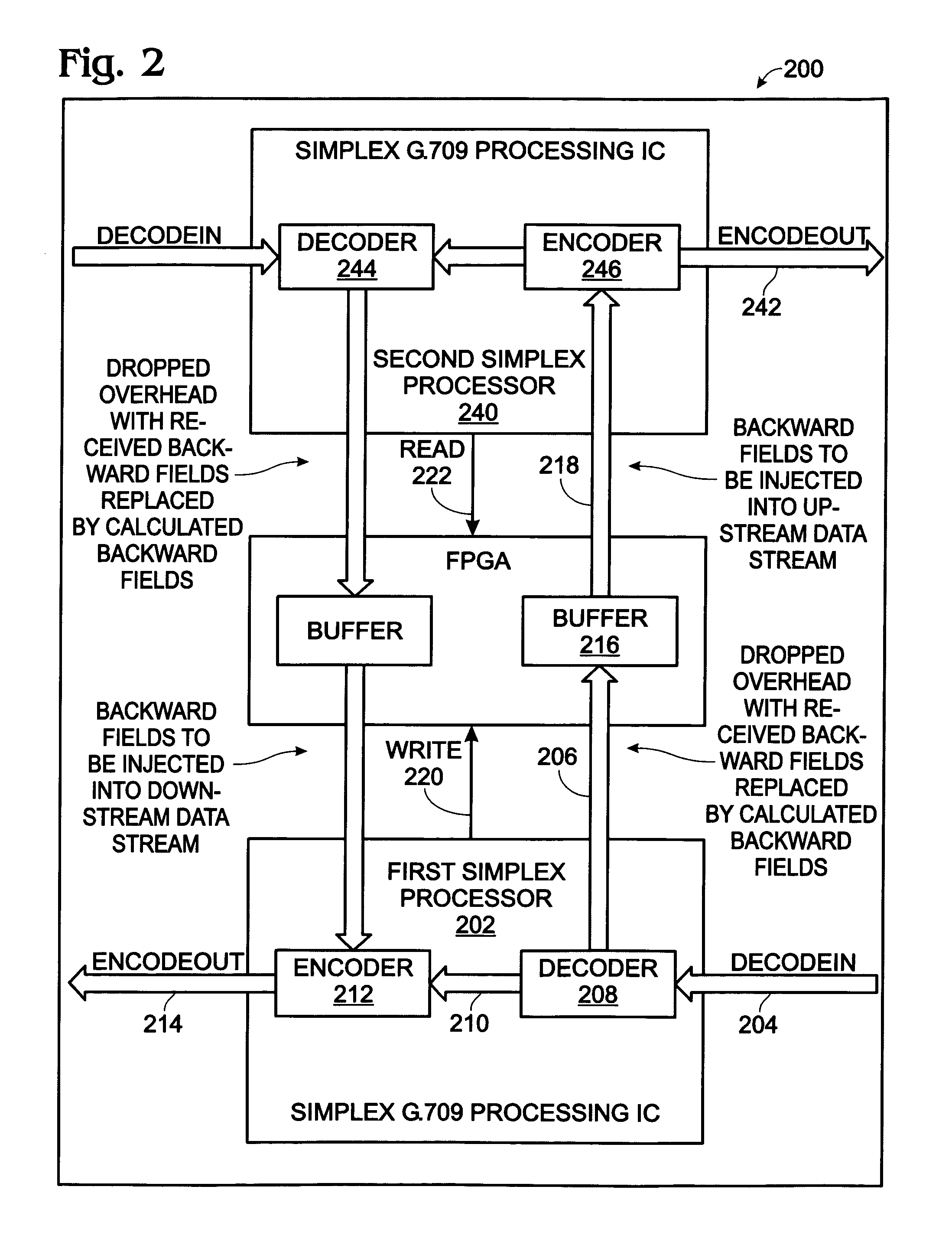
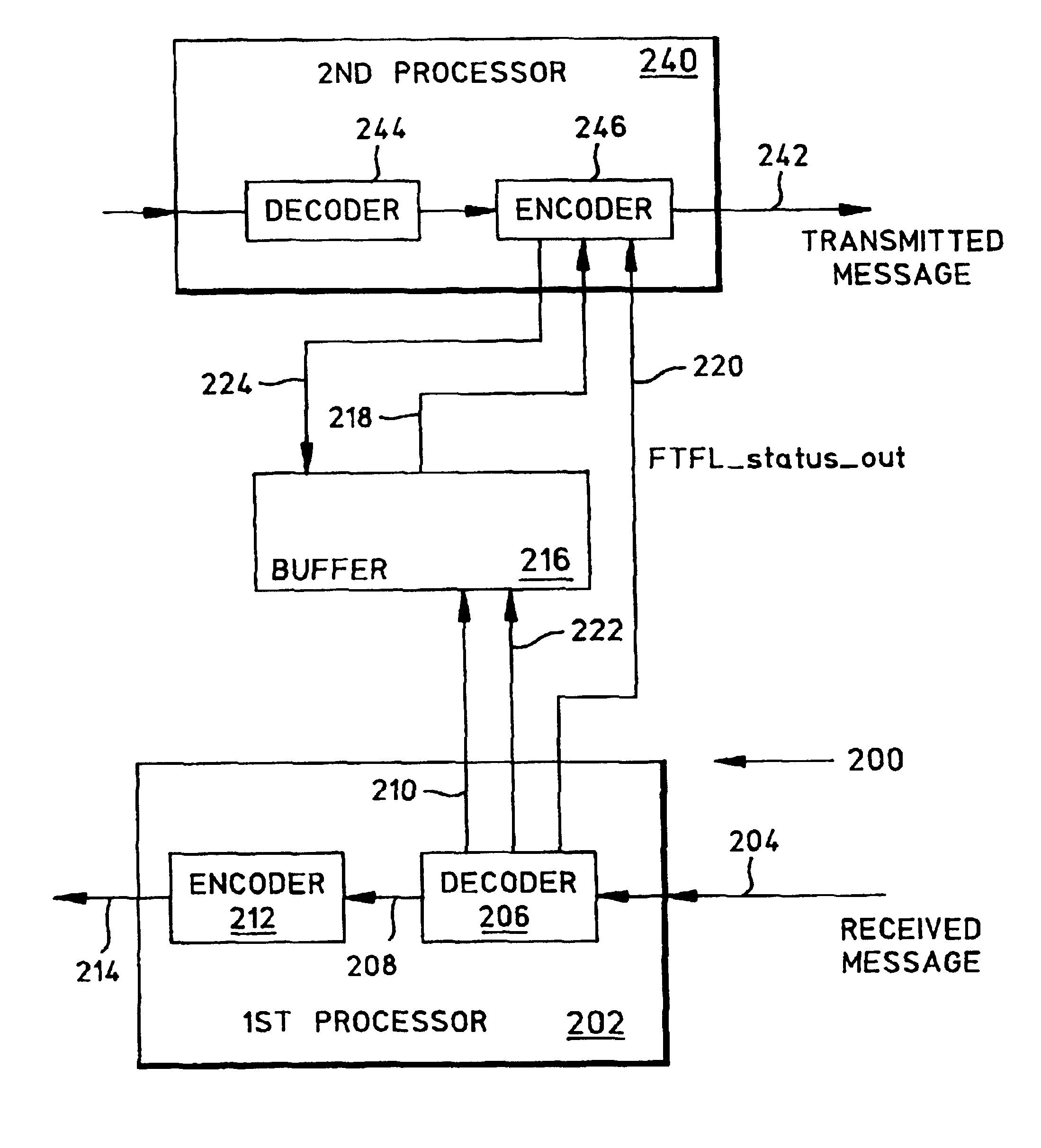
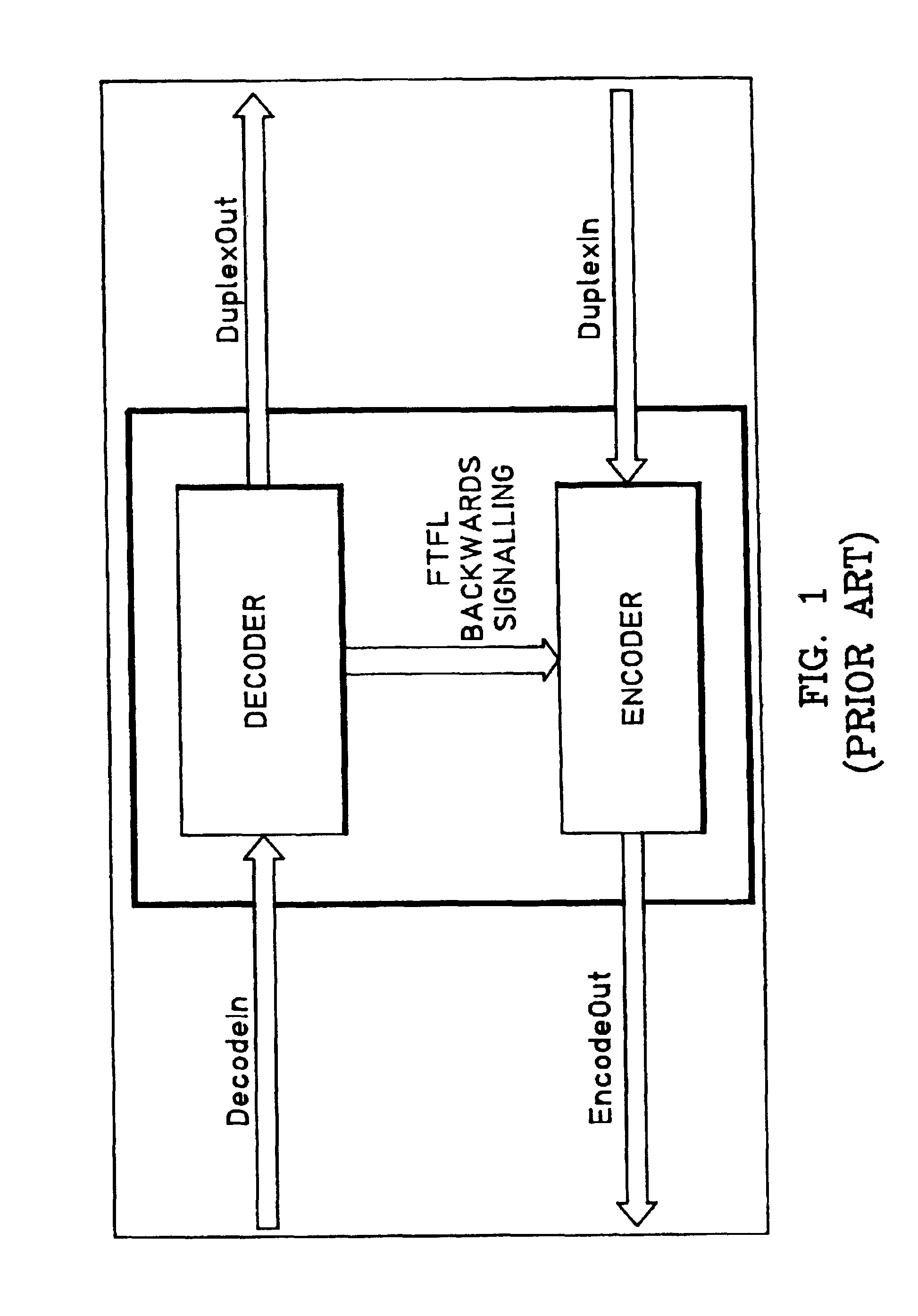
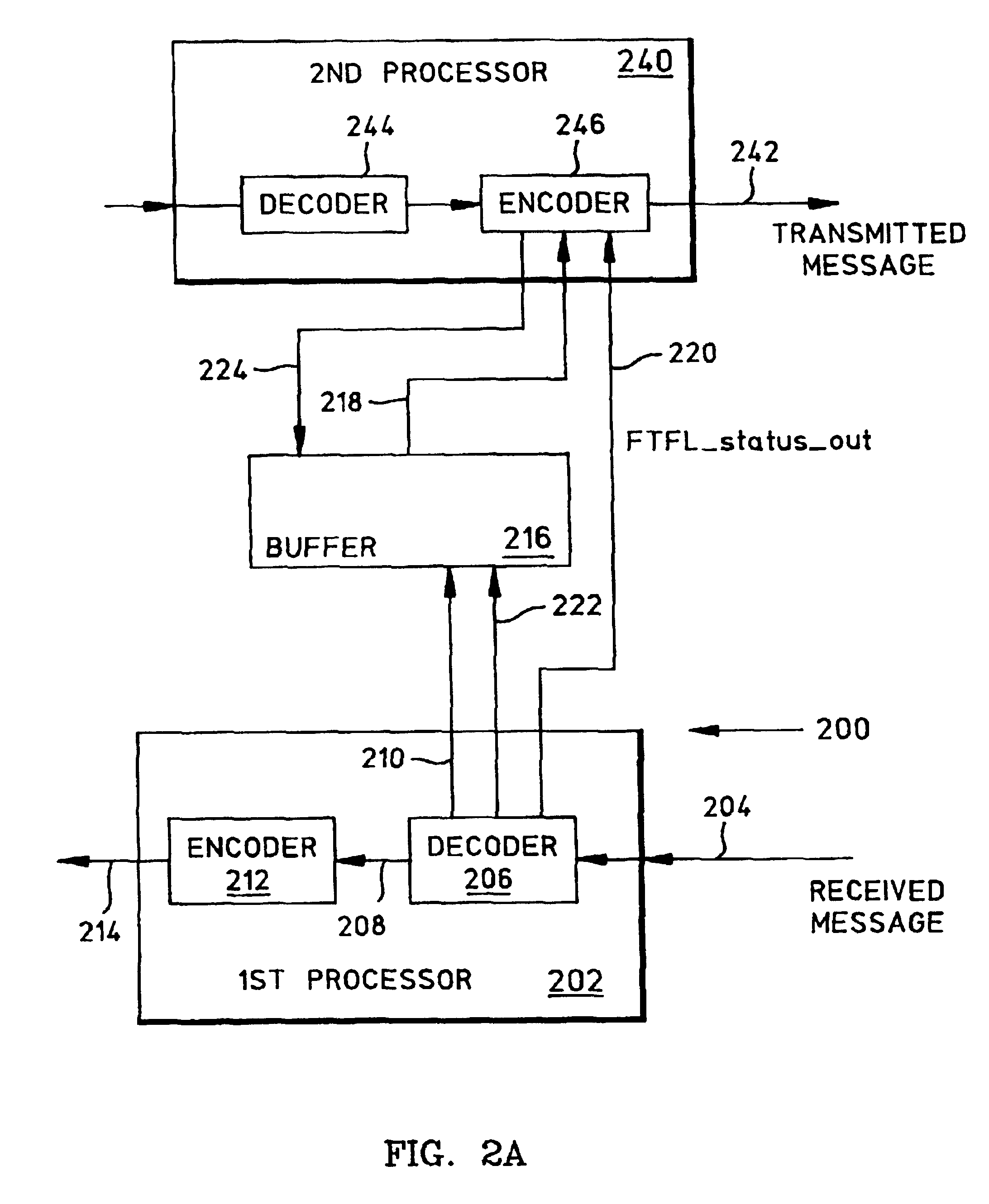
System and method for the transport of backwards information between simplex devices
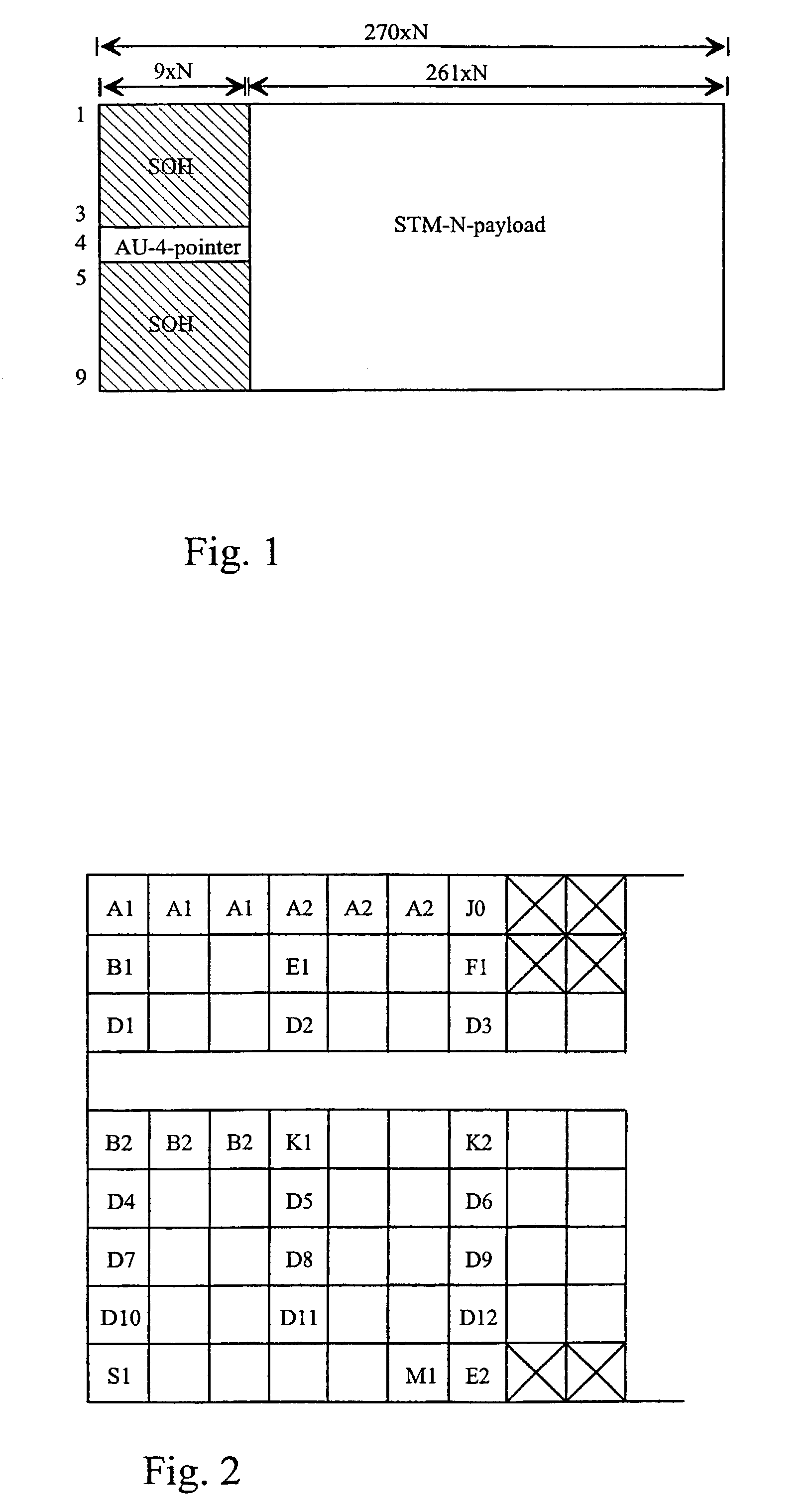
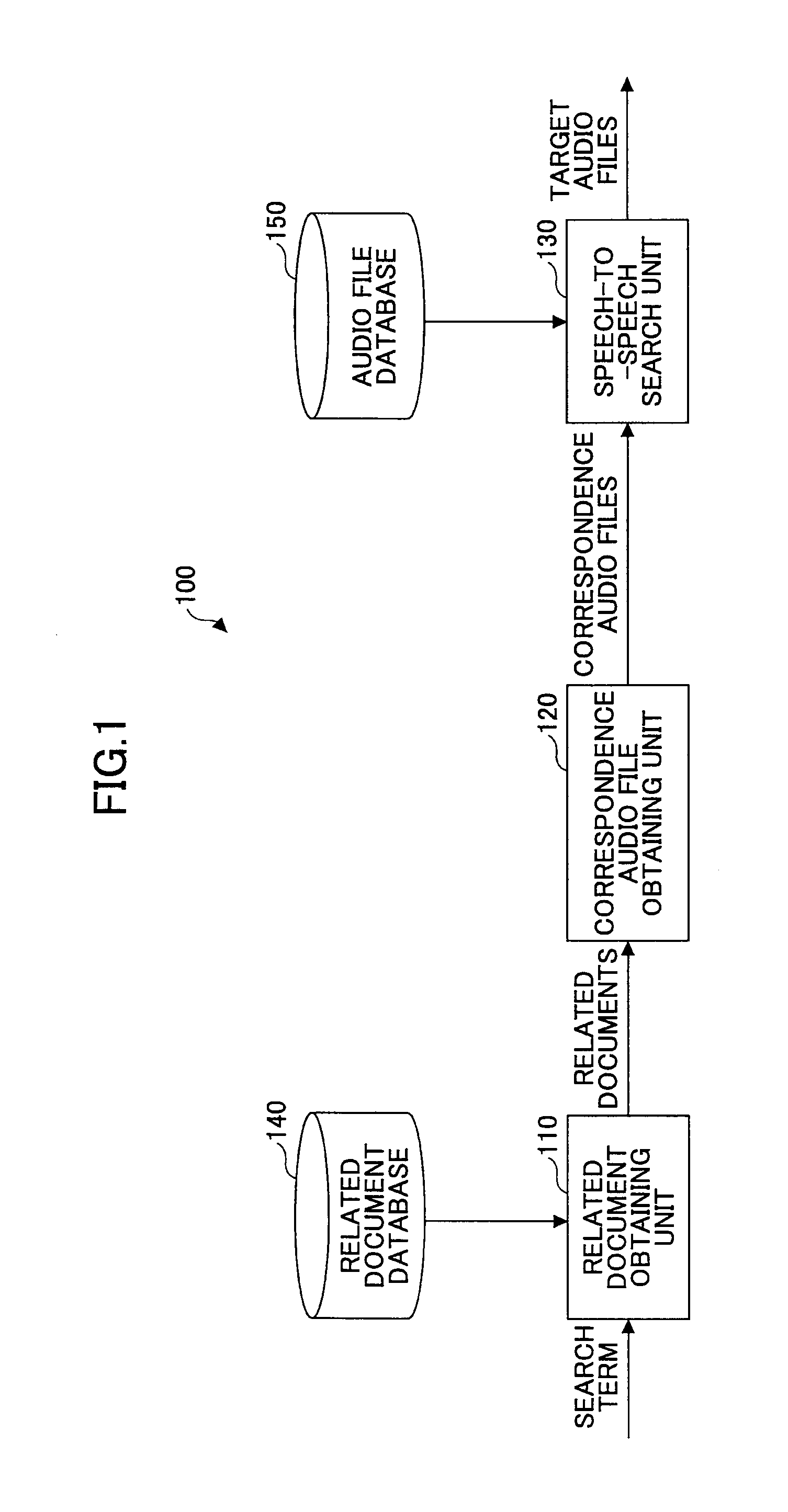
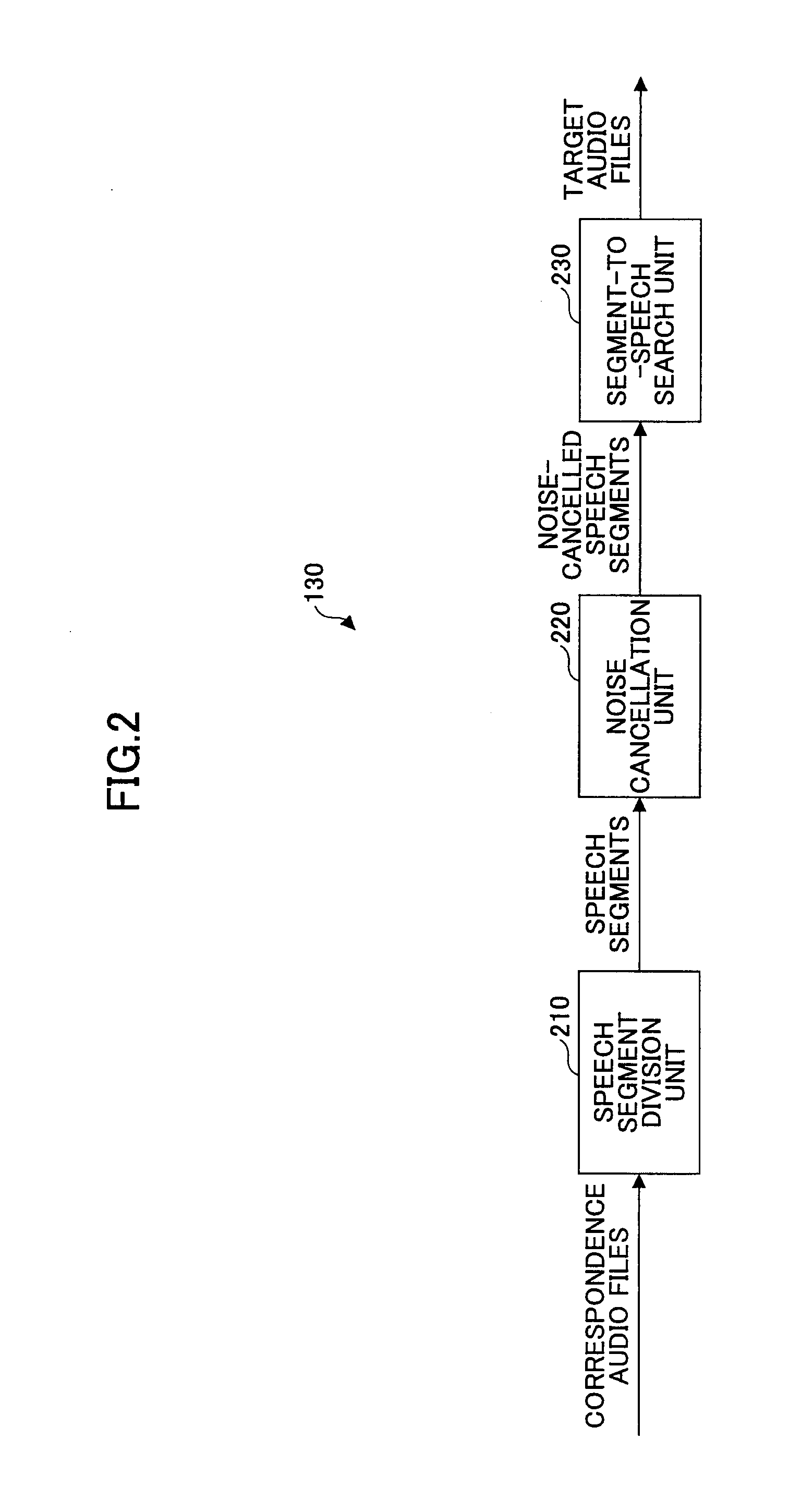
ActiveUS7072361B1Make up for information lossTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationByteComputer science
A system and method are provided for transporting backward information in a digital wrapper format network of connected simplex devices. The system comprises a first simplex processor receiving downstream messages with overhead bytes. The first simplex processor selectively replaces overhead bytes with calculated overhead bytes and supplies the calculated overhead bytes. The system further comprises a buffer receiving the calculated overhead bytes from the first simplex processor and supplying the calculated overhead bytes. A second simplex processor accepts the calculated overhead bytes from the buffer and supplies an upstream message including the calculated overhead bytes. The first simplex processor receives messages in a frame format with an overhead section, drops the overhead section, and selectively reads backward message monitor bytes in the dropped overhead section to determine if upstream communication nodes are receiving transmitted messages.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Handover method between a preferred base station and alternatives base stations
InactiveUS8570981B2Improve system performanceMinimize handover failureWireless commuication servicesLocation based informationHandover procedure
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Image converting apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS7068285B2Accurately representing color informationValid conversionColor signal processing circuitsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionColor image
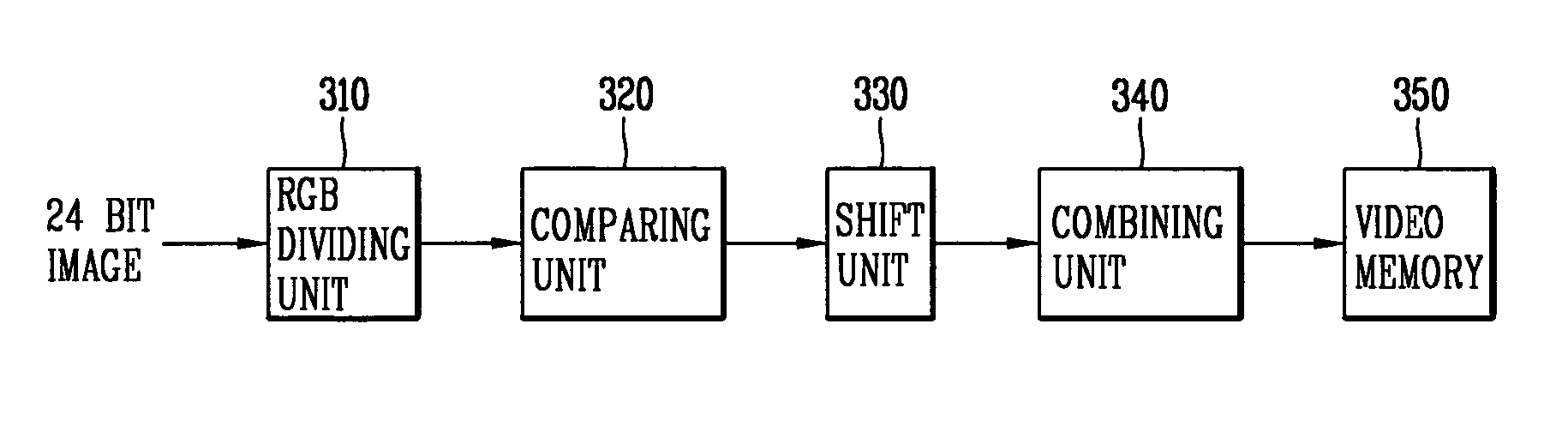
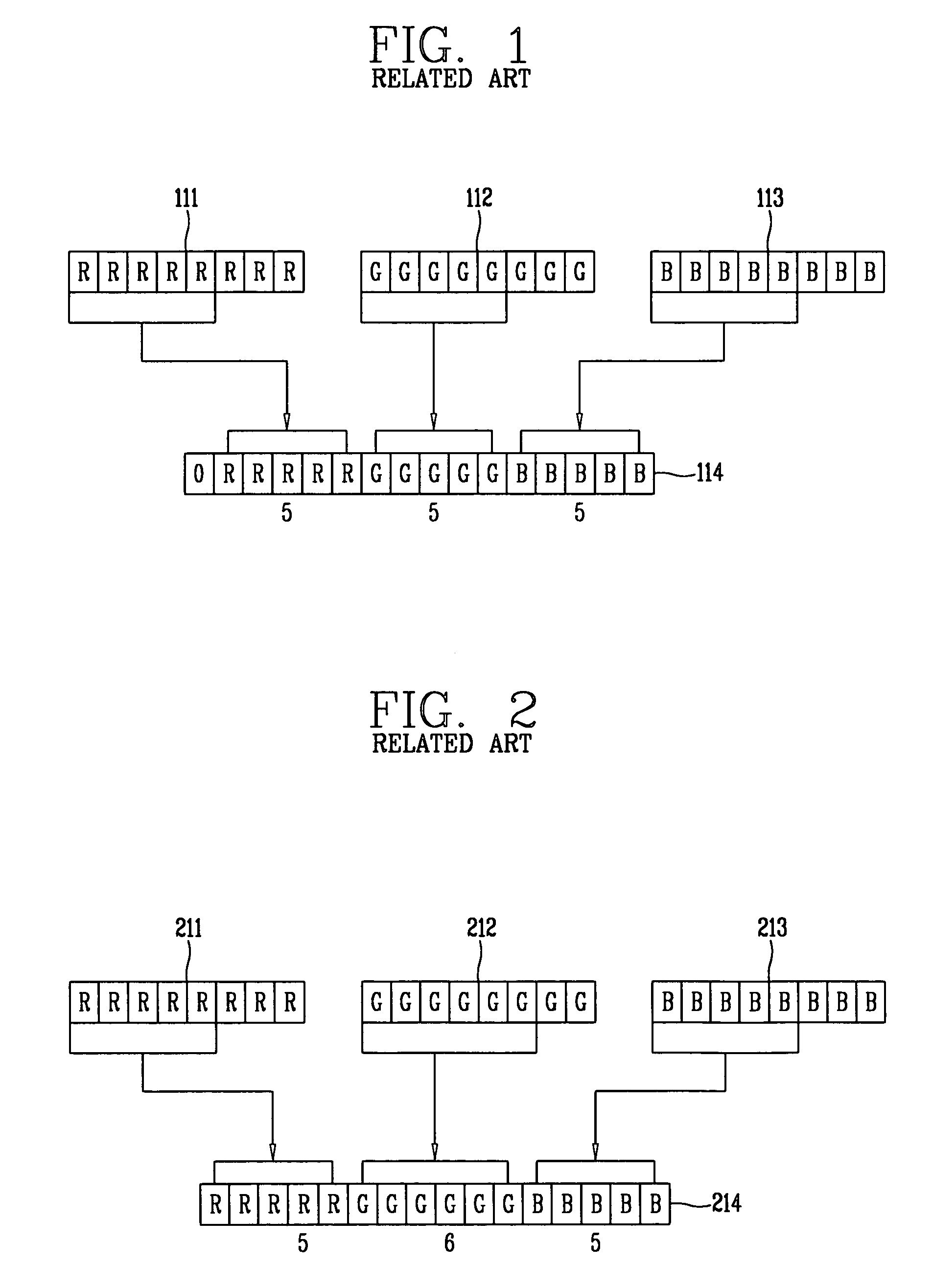
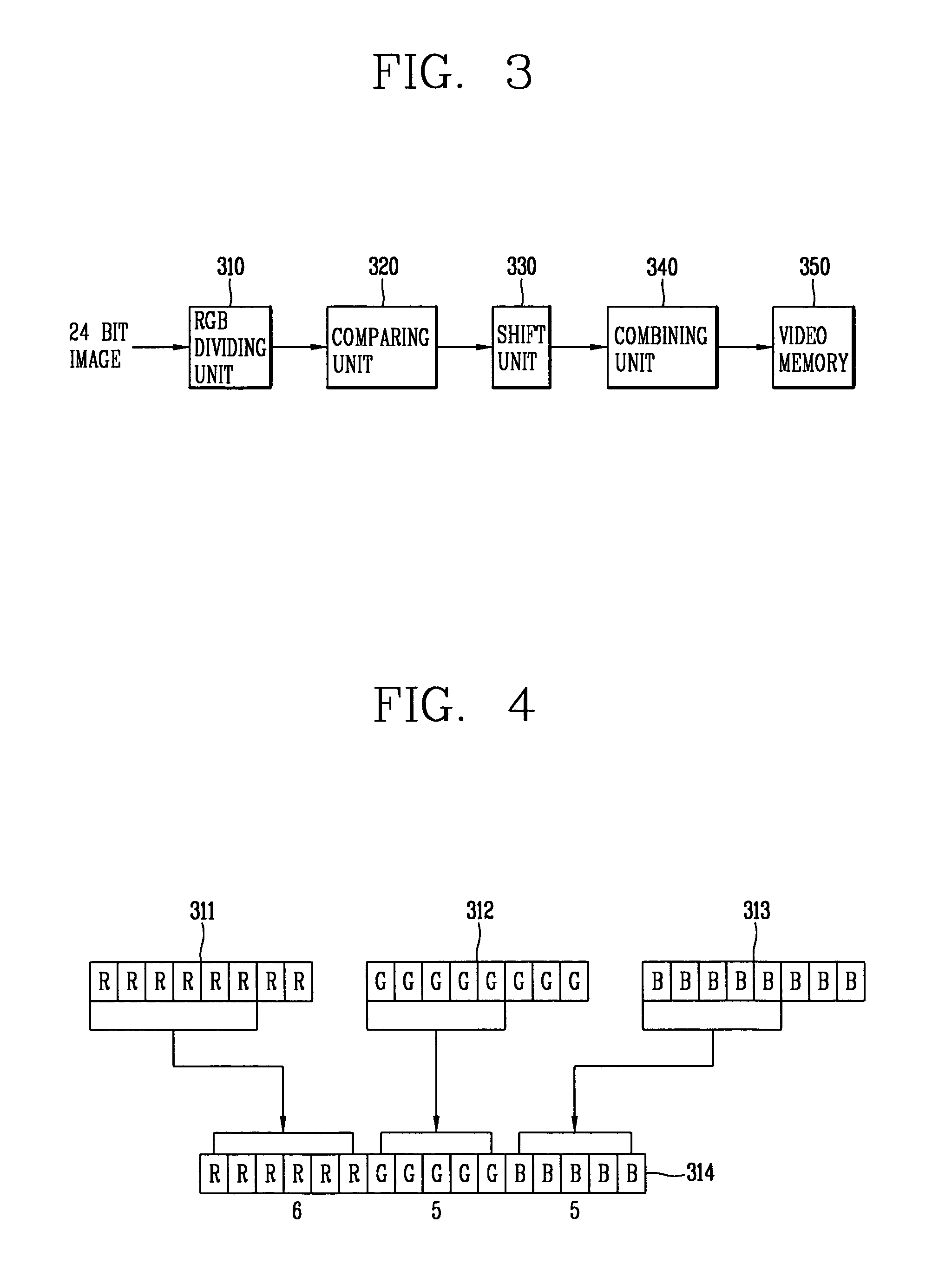
A system and method for converting color images divides a first image into first RGB values per pixel, determines which of the RGB colors in the first image has a greater specific gravity, converts the first RGB values into second RGB color values based on the color with the greater specific gravity, and forms a second image based on the second RGB values. The color value conversion involves allocating a first number of bits to represent the second RGB value corresponding to the color having the predetermined specific gravity and a second number of bits to represent the RGB values corresponding to remaining ones of the colors. The first and second numbers of bits are different and preferably the first number is greater than the second number. Through this system and method, an M-bit color image may be converted into an N-bit color image with greater color accuracy than other methods which have been proposed.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
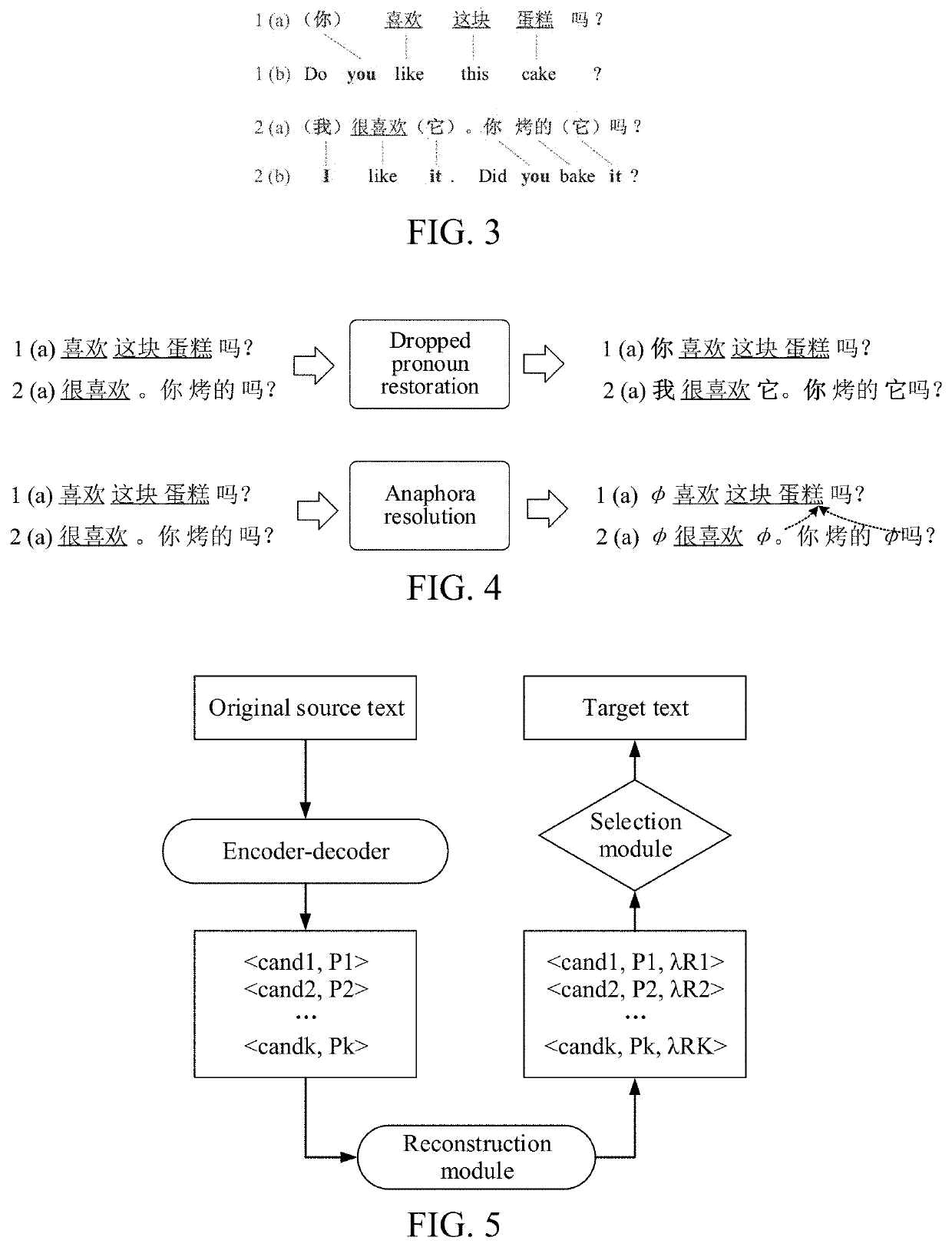
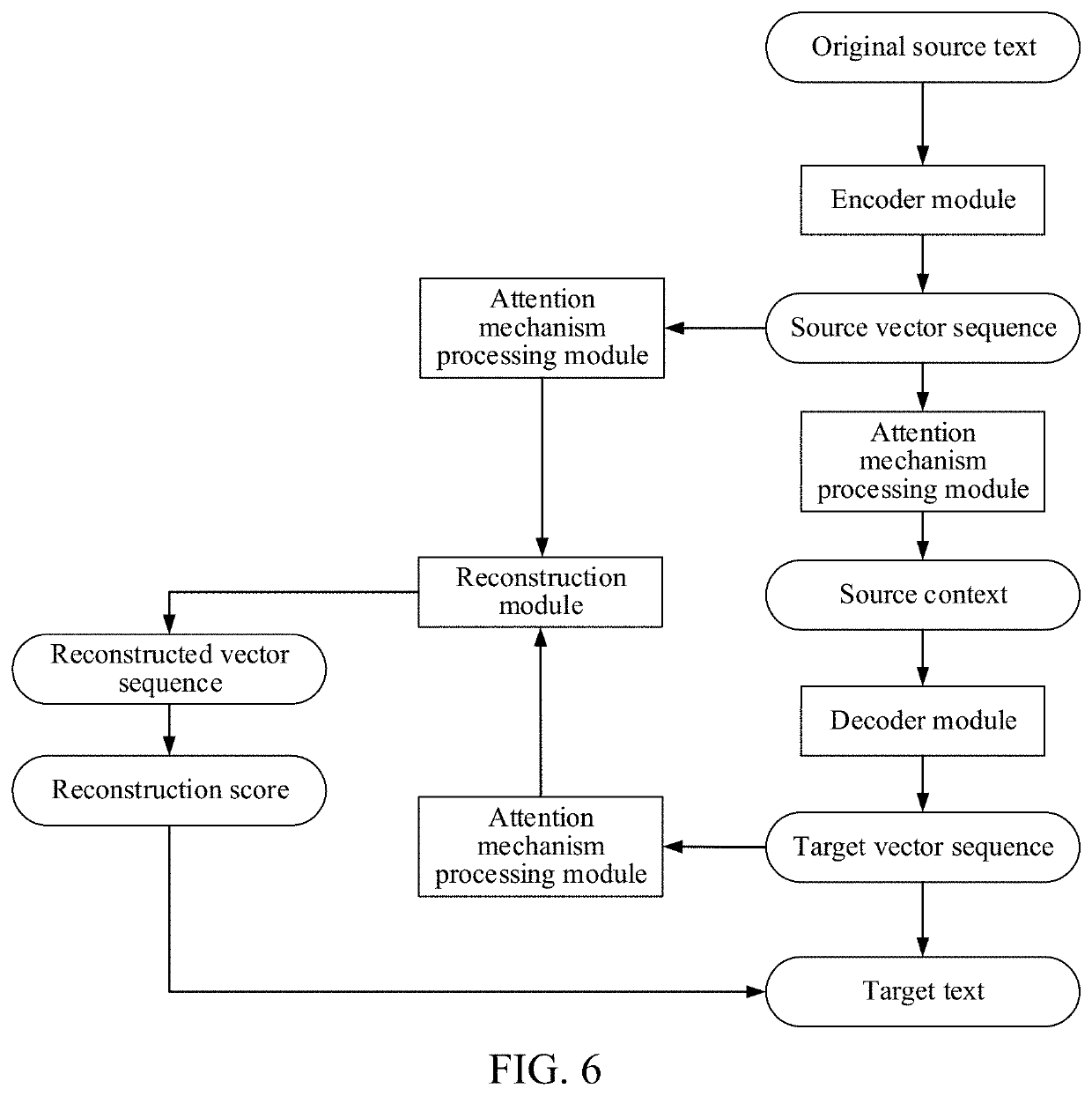
Text translation method and apparatus, storage medium, and computer device
PendingUS20210019479A1The result is accurateRedundant informationNatural language translationSemantic analysisAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
This application relates to a machine translation method performed at a computer device. The method includes: obtaining an original source text and a reconstructed source text; performing semantic encoding on the original source text, to obtain a source vector sequence; sequentially decoding the source vector sequence to obtain target vectors by performing decoding on the source vector sequence at a current time according to a word vector of a candidate target word determined at a previous time, determining a candidate target word at the current time according to a target vector at the current time, and forming a target vector sequence accordingly; performing reconstruction assessment on the source vector sequence and the target vector sequence using the reconstructed source text, to obtain reconstruction scores corresponding to the candidate target words; and generating a target text according to the reconstruction scores and the candidate target words.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
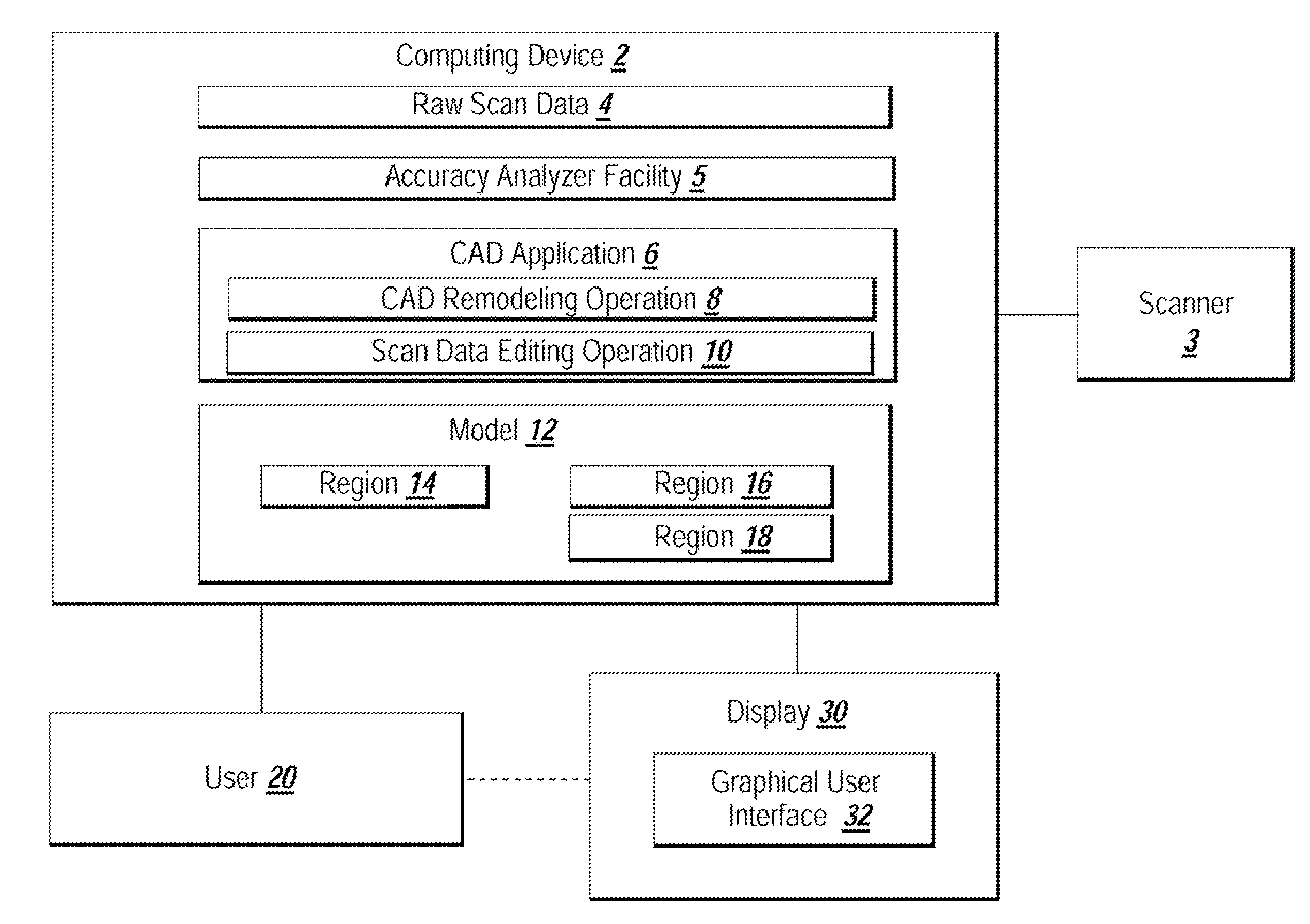
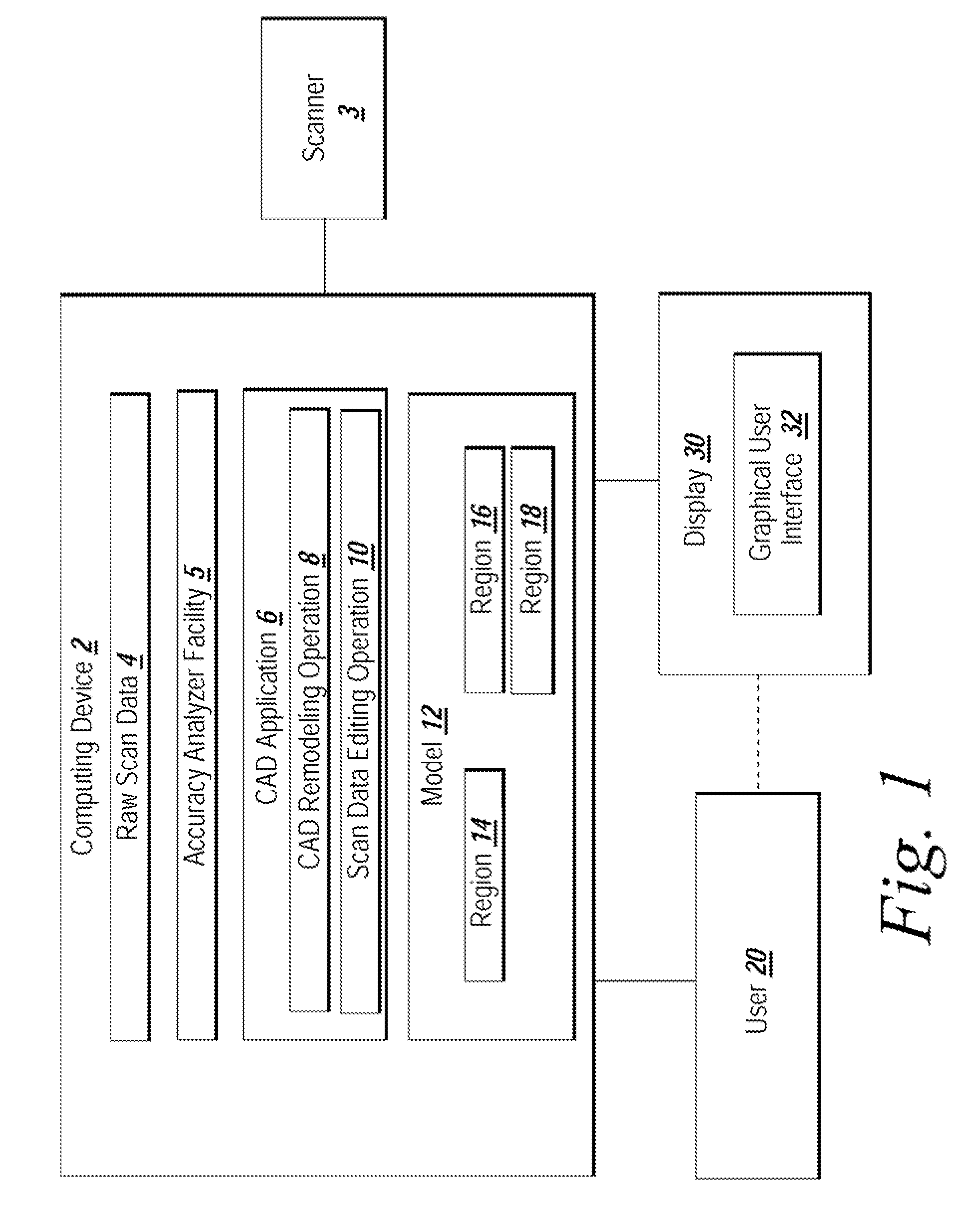
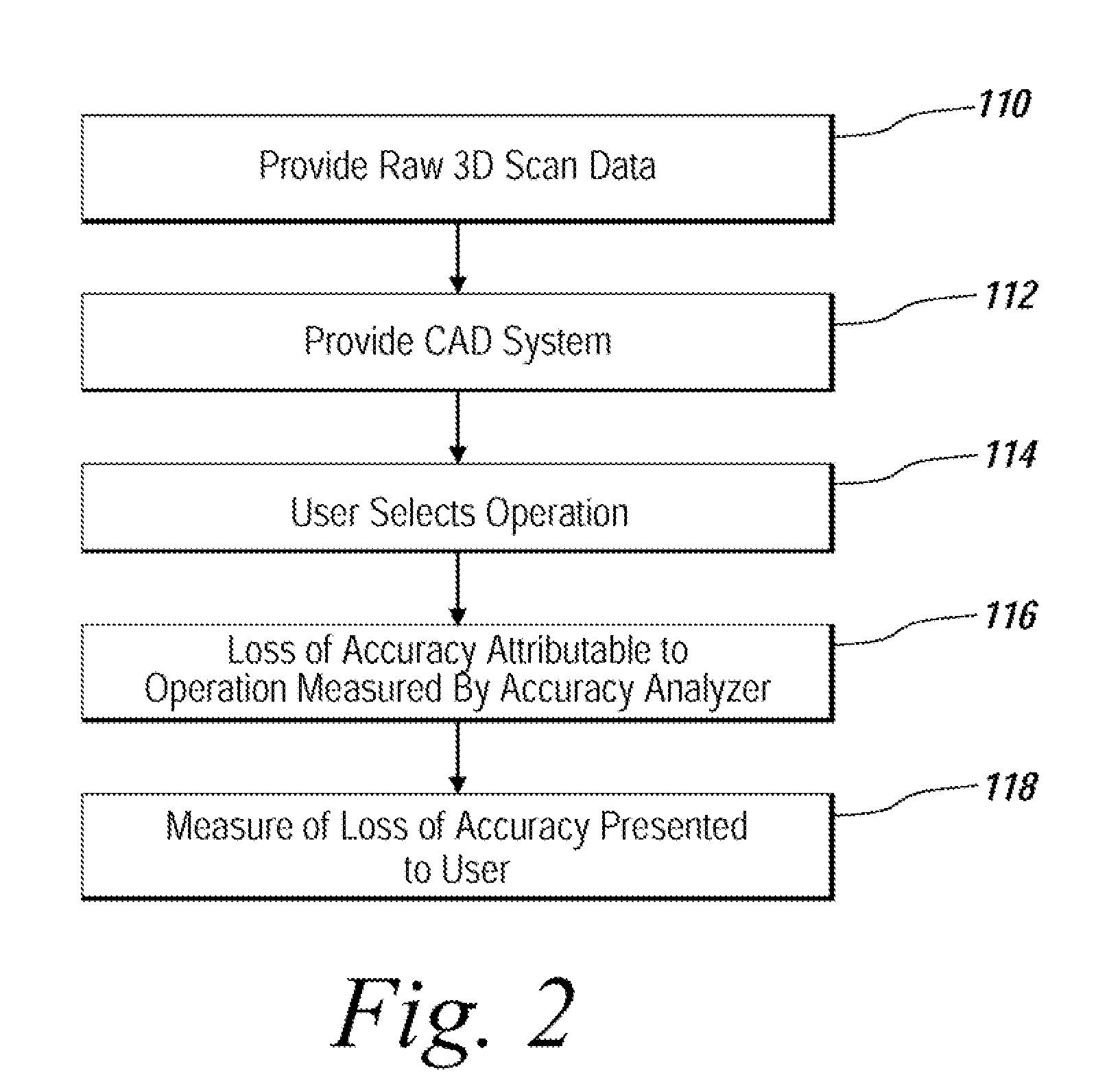
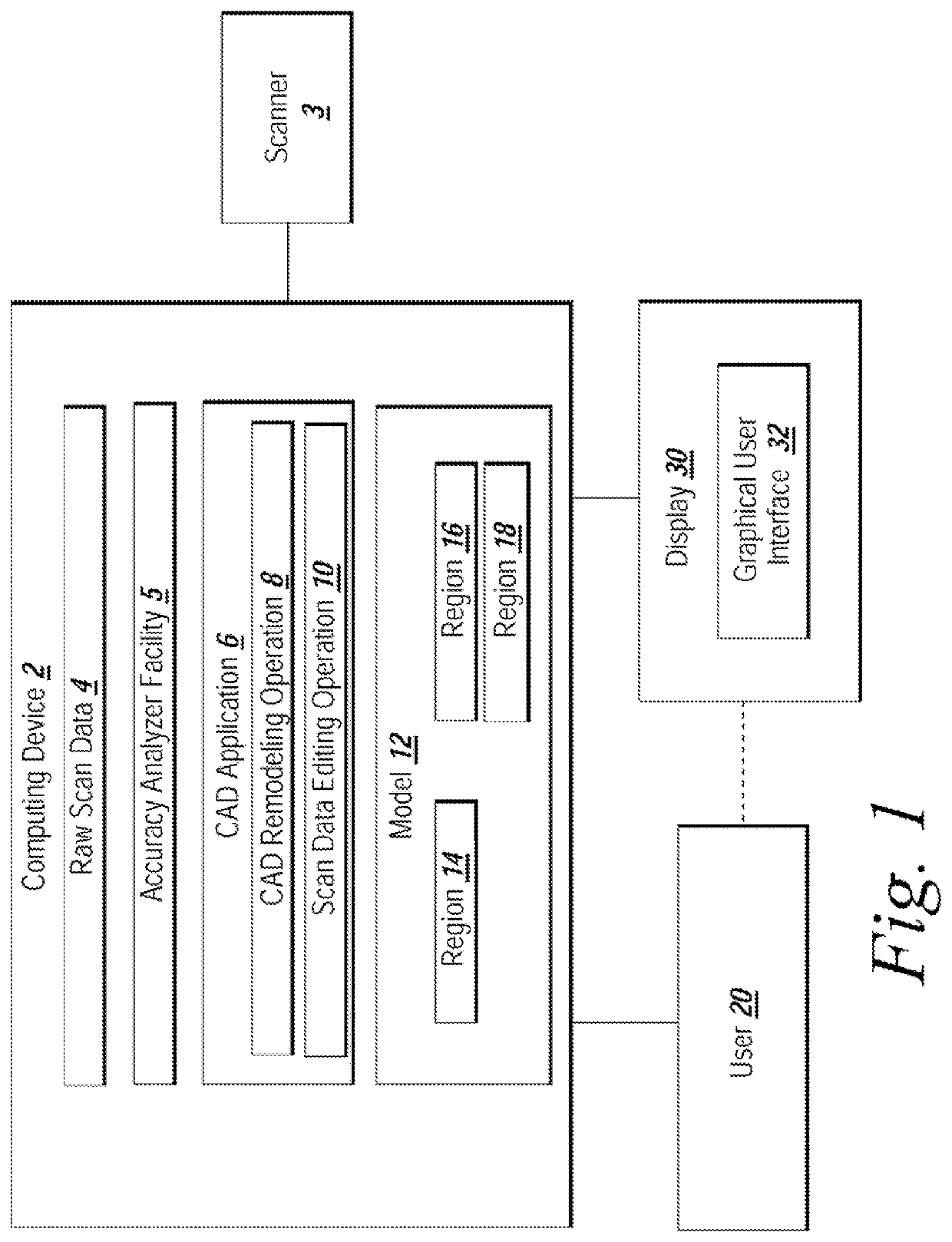
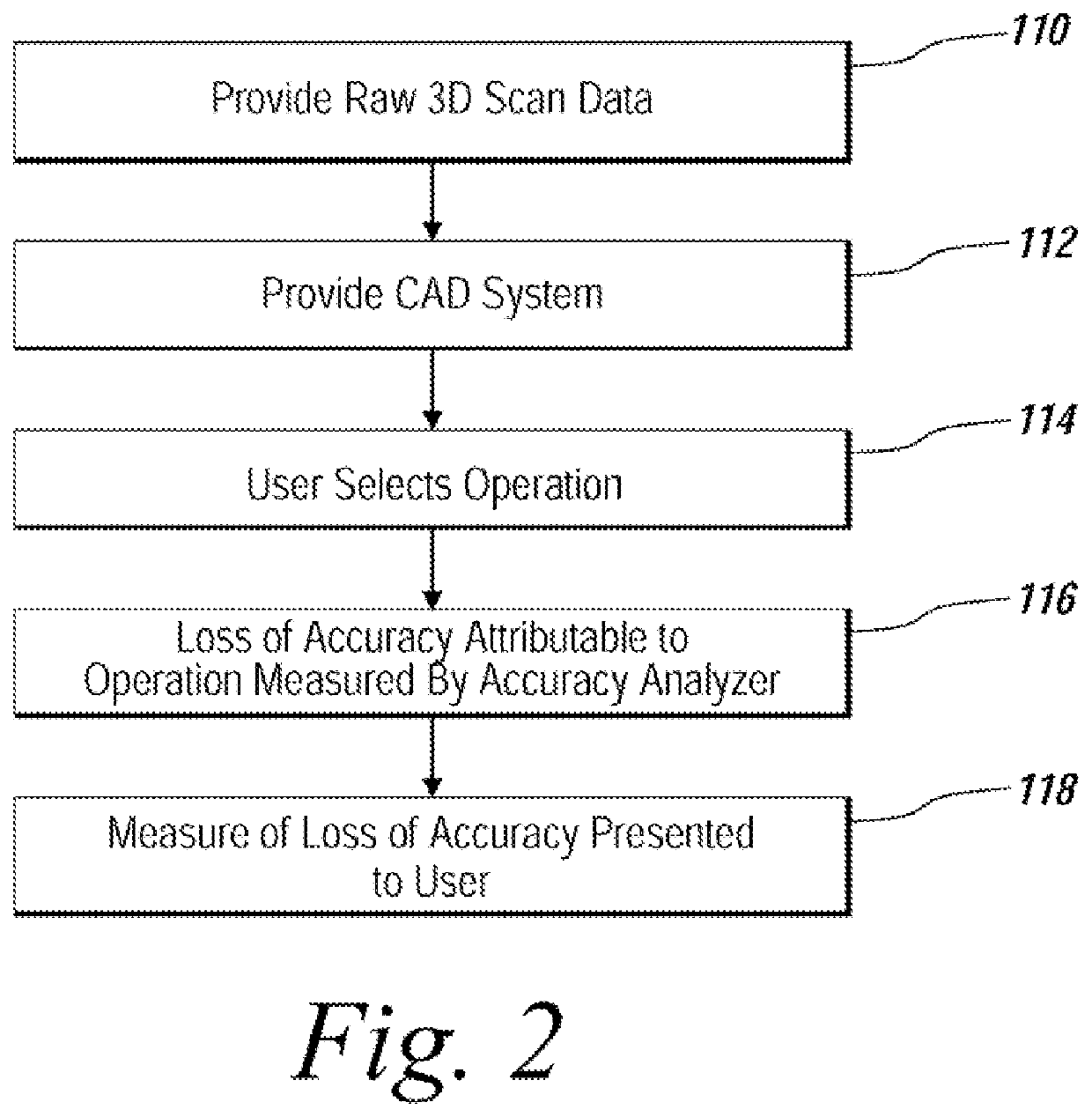
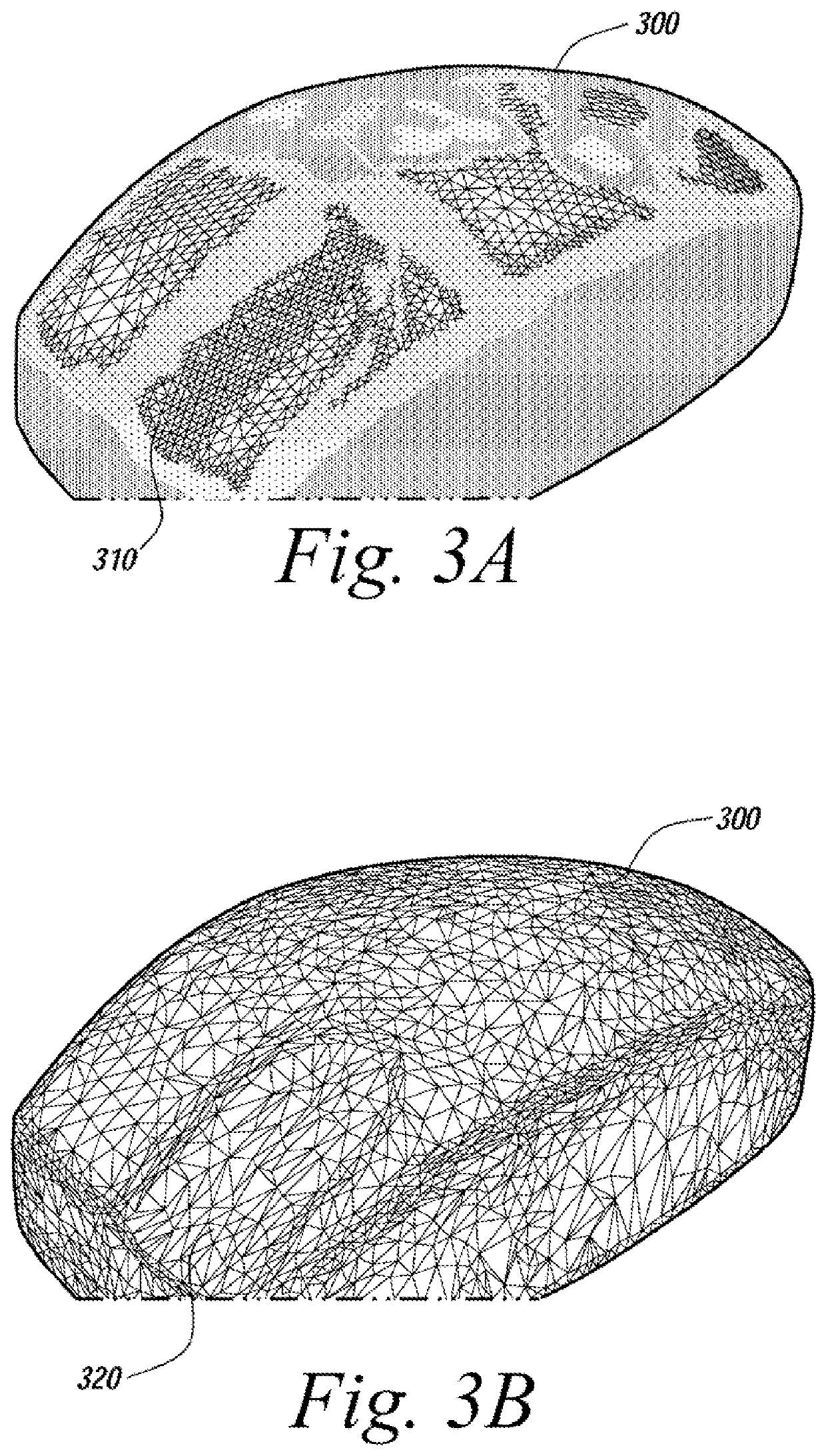
System and method for analyzing modeling accuracy while performing reverse engineering with 3D scan data
ActiveUS7821513B2Make up for information lossMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsColor mapping
An automated mechanism for measuring the amount of accuracy loss attributable to reverse engineering processes that use 3D scan data is discussed. The embodiments provide a mechanism that displays to a user the effect scan data editing and CAD remodeling operations have on scan data accuracy. Additionally, the user can choose the way the graphical display illustrates the error distribution on the model such as by color mapping and whisker mapping. The accuracy loss may be displayed to the user after finishing an editing / modeling command or during the previewing of the command thereby allowing a user to take appropriate action. Parameters may also be adjusted programmatically based on the amount of accuracy loss determined to be attributable to scan data editing or CAD remodeling operations.
Owner:3D SYST KOREA INC
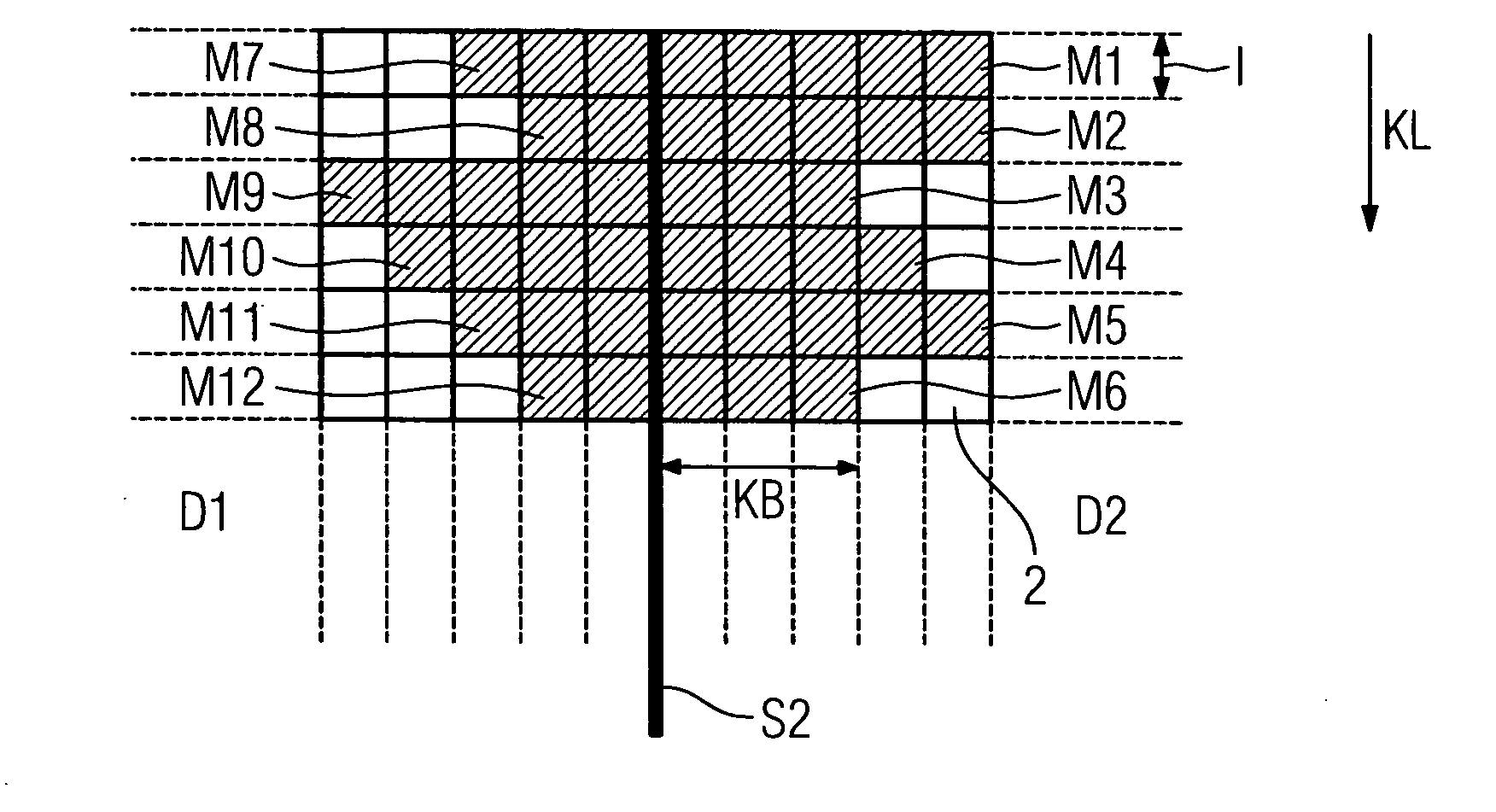
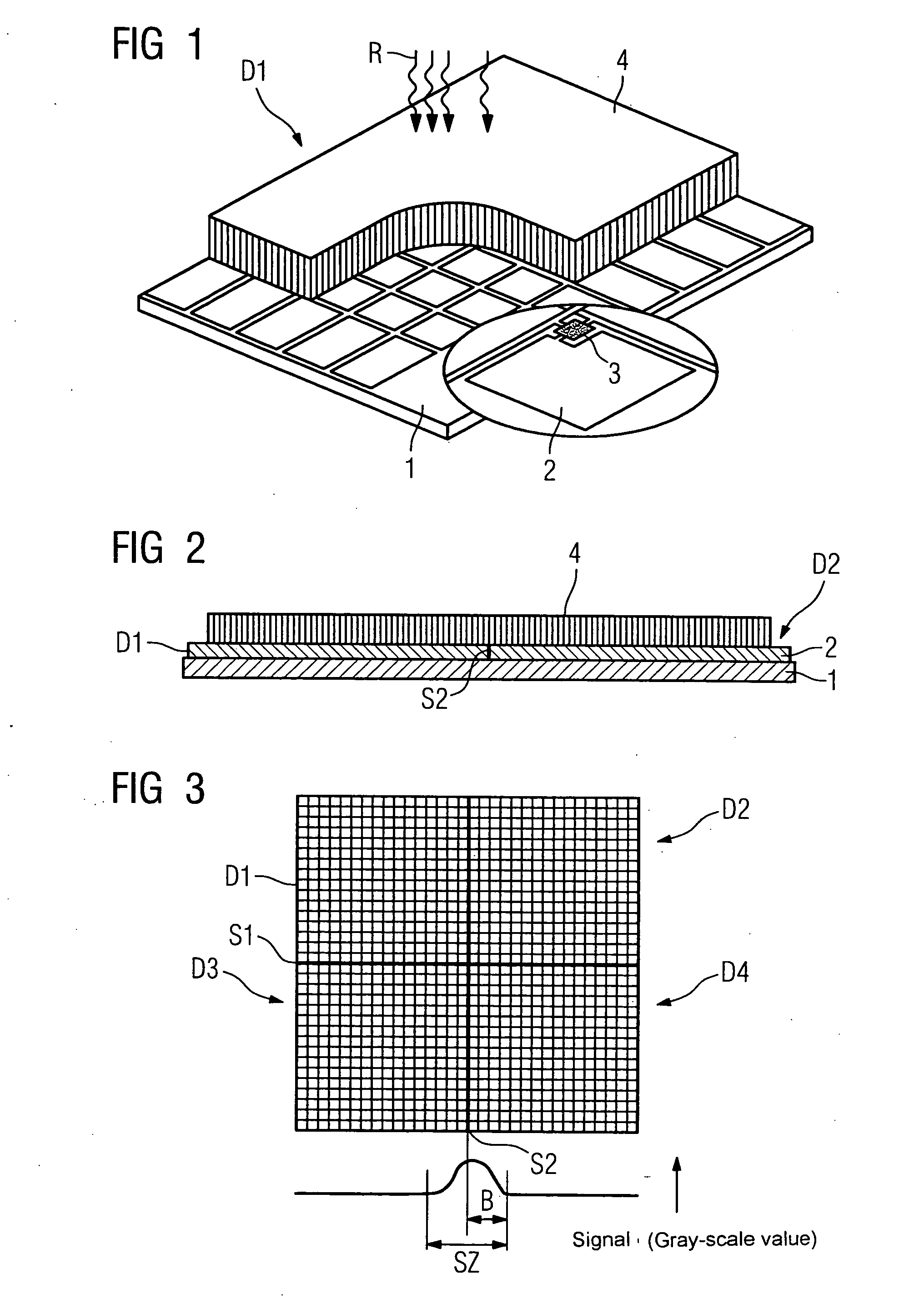
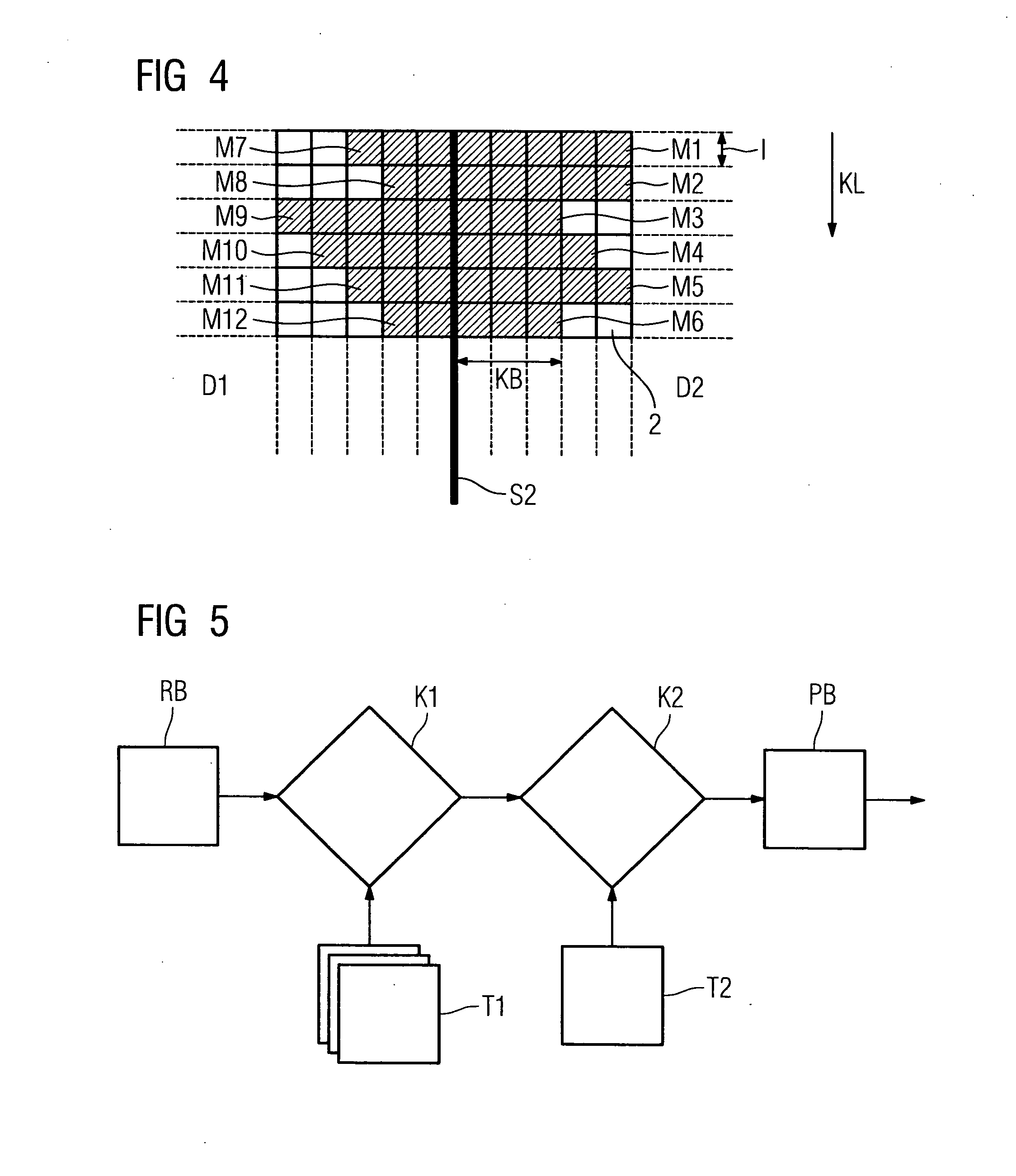
Method for correcting butting zone artifacts with an x-ray detector and an x-ray detector
InactiveUS20070007447A1Easy to replaceMake up for information lossTelevision system detailsCalibration apparatusPhysicsX-ray detector
The invention relates to a method for correcting butting zone artifacts with an x-ray detector, which comprises a number of laminar detector modules arranged next to one another by forming a butting zone. To improve a known algorithm, it is proposed to determine a necessary correction width for measuring fields on the basis of a correction image.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
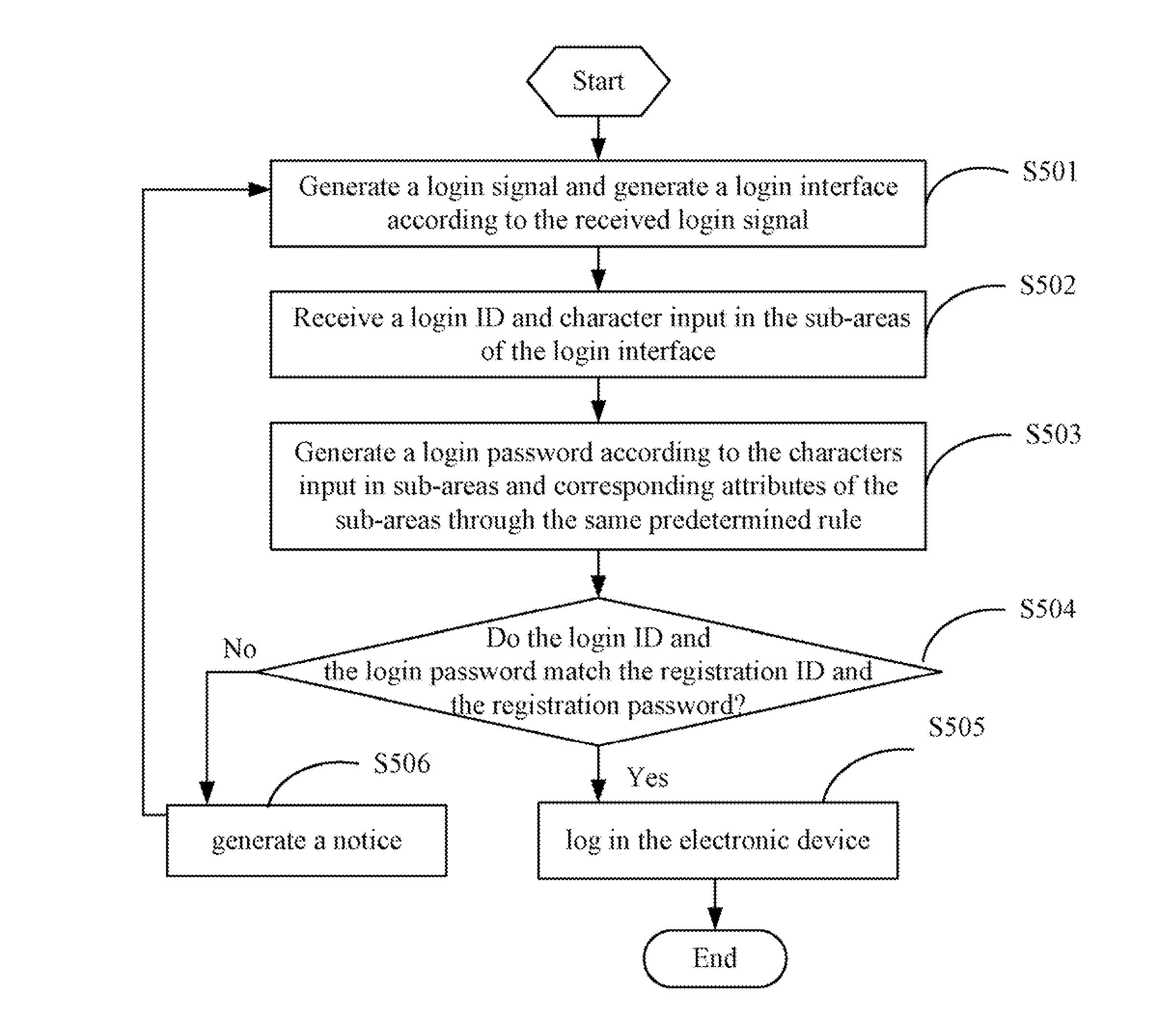
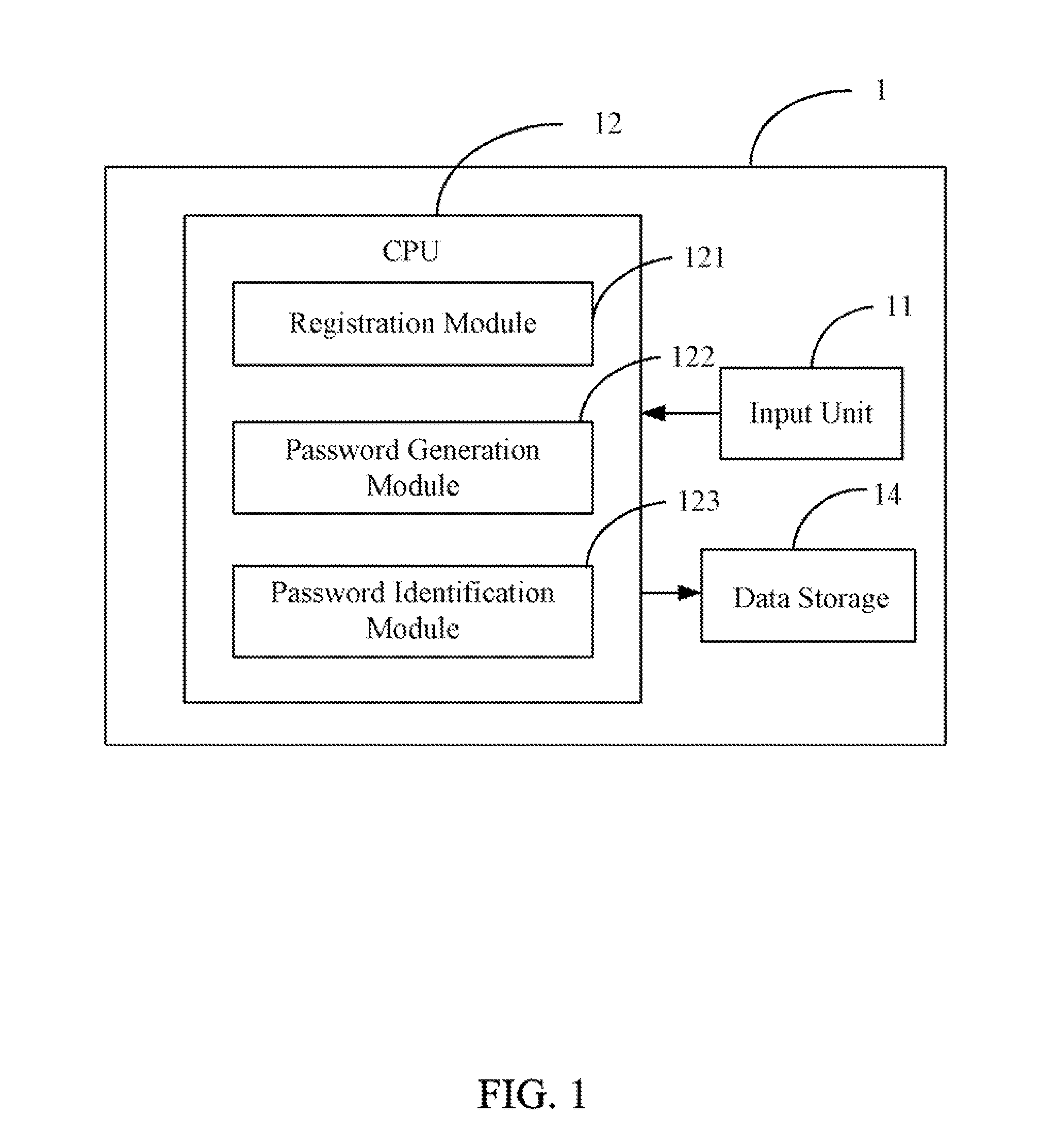
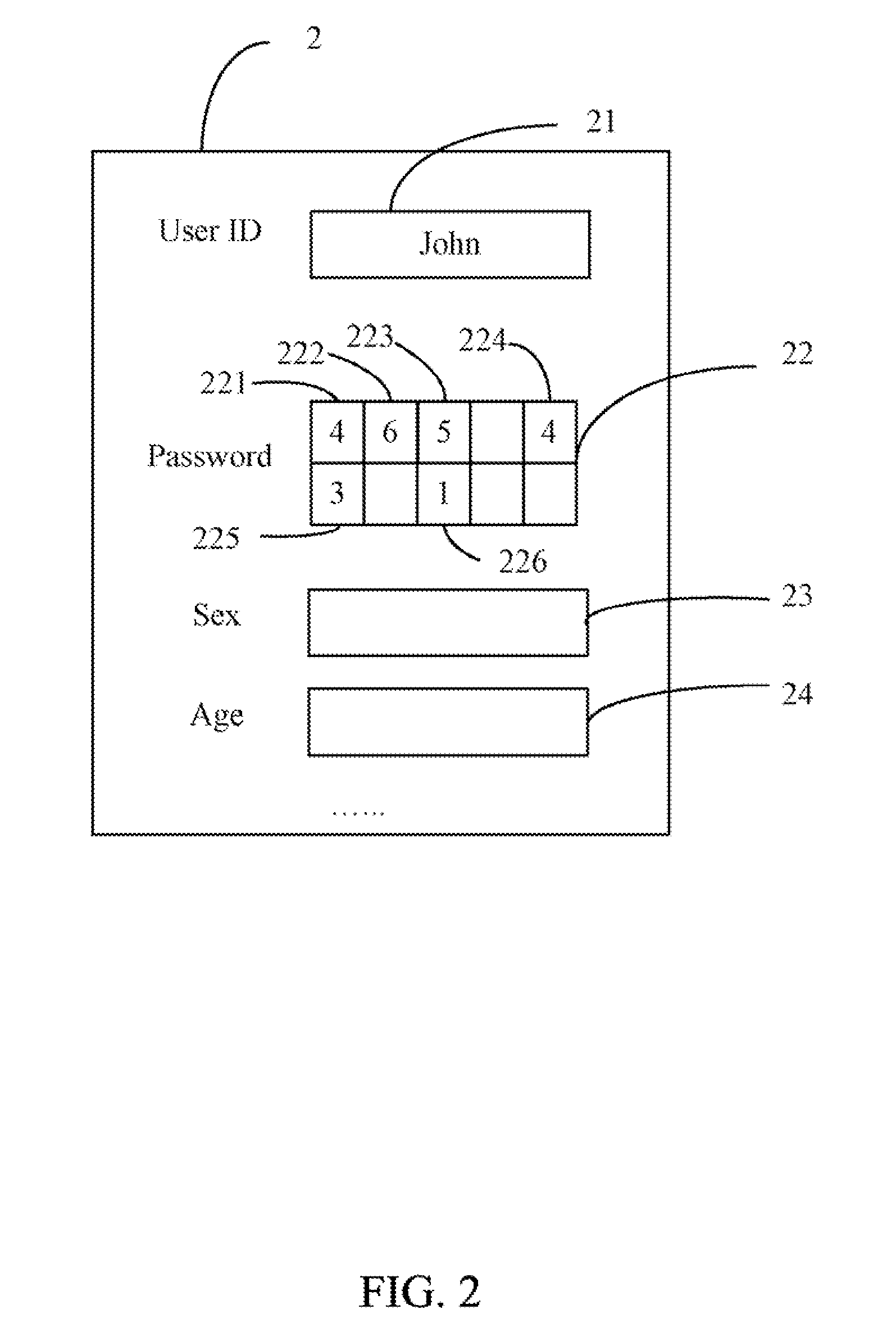
Electronic device with password protection function and method thereof
InactiveUS20110154483A1Easy to be stolenMake up for information lossDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordElectronic equipment
An electronic device with a password protection function is provided. The electronic device provides a password input area, which includes a number of sub-areas. Each of the sub-areas is designated a distinctive attribute, and is provided for inputting a single character. The characters and the attributes of the sub-areas are used to generate a login password according to a predetermined rule, thus the security of the login password is strengthened.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
Image processor and imaging device
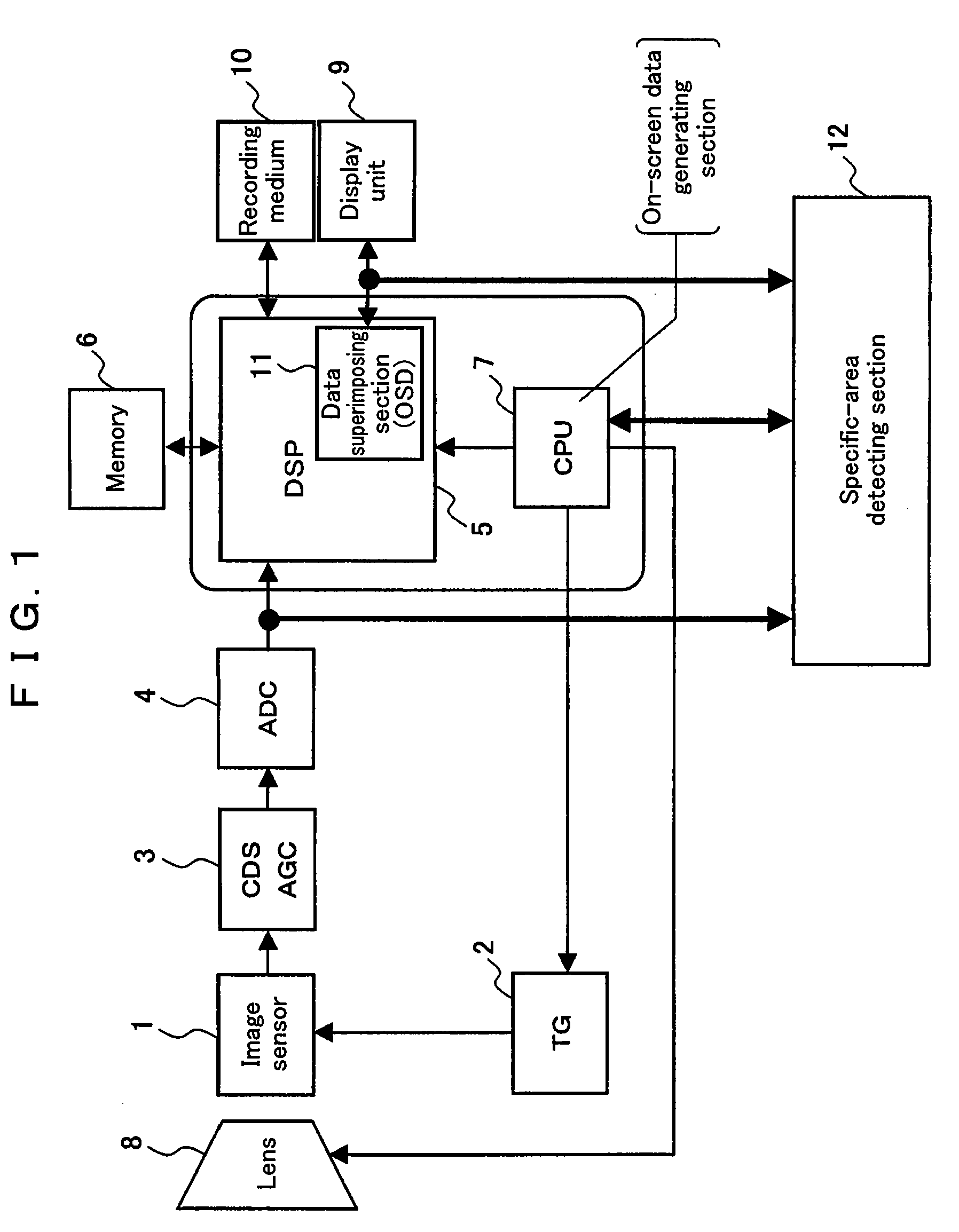
InactiveUS20080151077A1Improve detection accuracyMake up for information lossTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareImaging equipment
An on-screen data generating section generates on-screen data that becomes a superimposed image that is superimposed on an image displayed based upon a standard digital signal. A data superimposing section superimposes the on-screen data on the standard digital signal. A specific-area detecting section detects a specific area in an image displayed based upon the standard digital signal with the on-screen data superimposed thereon. In such a configuration, the on-screen data generating section generates the on-screen data only from color signal data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Thermal head printer and process for printing substantially light-insensitive recording materials
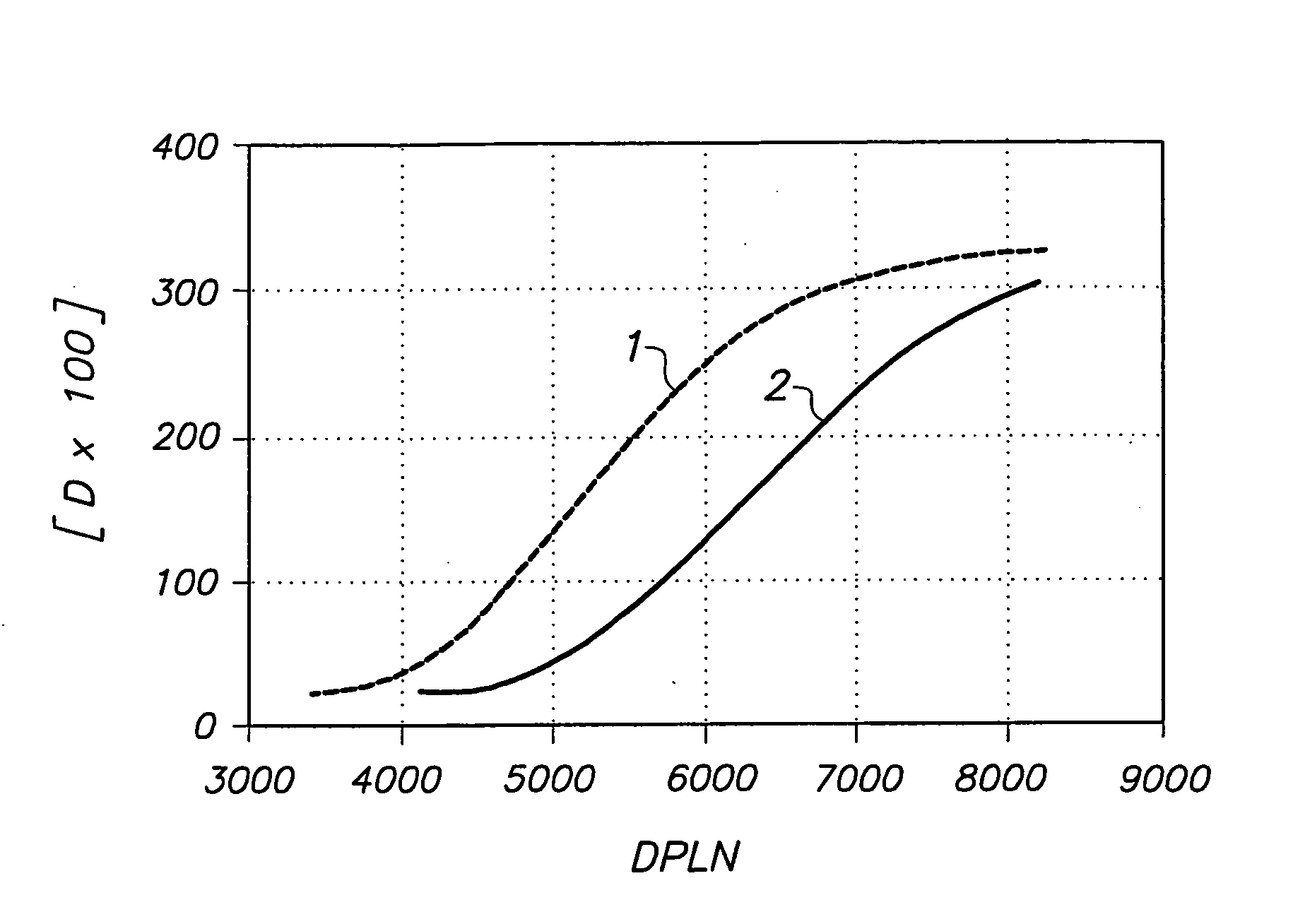
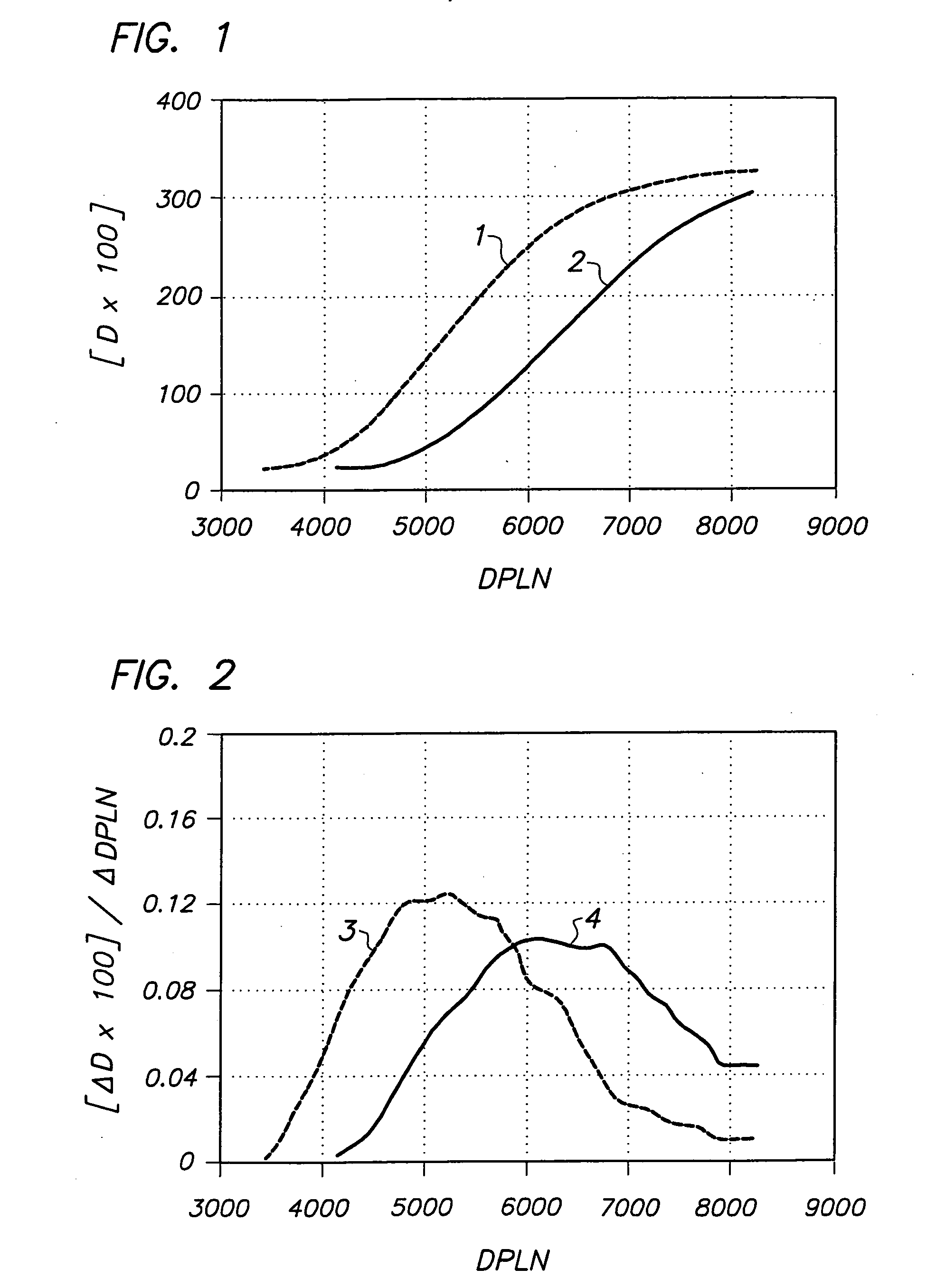
ActiveUS20040183887A1Decrease printing speedAvoid failure of heating elementRecording apparatusDiffusion transfer processesDensitometerPower level
A thermal head printer with image-invariant printing speeds for printing a substantially light-insensitive thermographic material having a print density-driving power level characteristic, the thermal head printer comprising a transport means, one or more thermal heads each having an array of heating elements, a thermal print head drive system capable of supplying power to each of the printing elements, and a calibration means based on the print density-driving power level characteristic of the thermographic material; a process for calibrating a thermal head printer with image-invariant printing speeds, the thermal head printer comprising one or more thermal heads each having an array of heating elements connected to a power supply capable of supplying a given number of heating element driving power levels from 0 to a maximum driving power level number, corresponding to Pmax, to each heating element for printing a substantially light-insensitive thermographic material by image-wise heating the thermographic material with the heating elements, the process comprising the steps of: (i) putting the printer into a calibration mode; (ii) printing one or more step-wedges of print densities by heating the thermographic material with the heating elements at different DPLN'S; (iii) determining the optical density of each step of the step-wedge(s) of print densities with a densitometer thereby obtaining the dependence of the print density upon DPLN; (iv) deriving from the dependence, or all the dependences of the print density upon DPLN, a single smoothed dependence of the rate of change of print density, D, with DPLN, DeltaD / DeltaDPLN, as a function of DPLN for the thermographic material; (v) establishing a threshold rate of print density change per DPLN for the specific thermographic material being printed; and (vi) setting up the thermal head printer so that the threshold rate of print density increase per DPLN cannot be undercut; and a process for printing a substantially light-insensitive thermographic material with a thermal head printer comprising one or more thermal heads each having an array of heating elements connected to a power supply capable of supplying a given number of heating element driving power levels from 0 to a maximum driving power level number, corresponding to Pmax, the process comprising the steps of: calibrating the thermal head printer according to the above-described calibration process, transporting the substantially light-insensitive thermographic material past the thermal head, and image-wise heating of the substantially light-insensitive thermographic material by means of the heating elements.
Owner:AGFA NV
Method for storing plant process signals
InactiveUS20070162213A1Reduce storage space requirementsLoss of important informationAnalogue computers for vehiclesSampled-variable control systemsProcess engineeringEngineering
Disclosed is a method for storing process signals of a plant or technical installation. A compression method is adapted for a current operating state of the plant is applied to the set of process signals in accordance with the current operating state of the plant and a compressed process signal set which is determined during the application of the compression method is stored.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
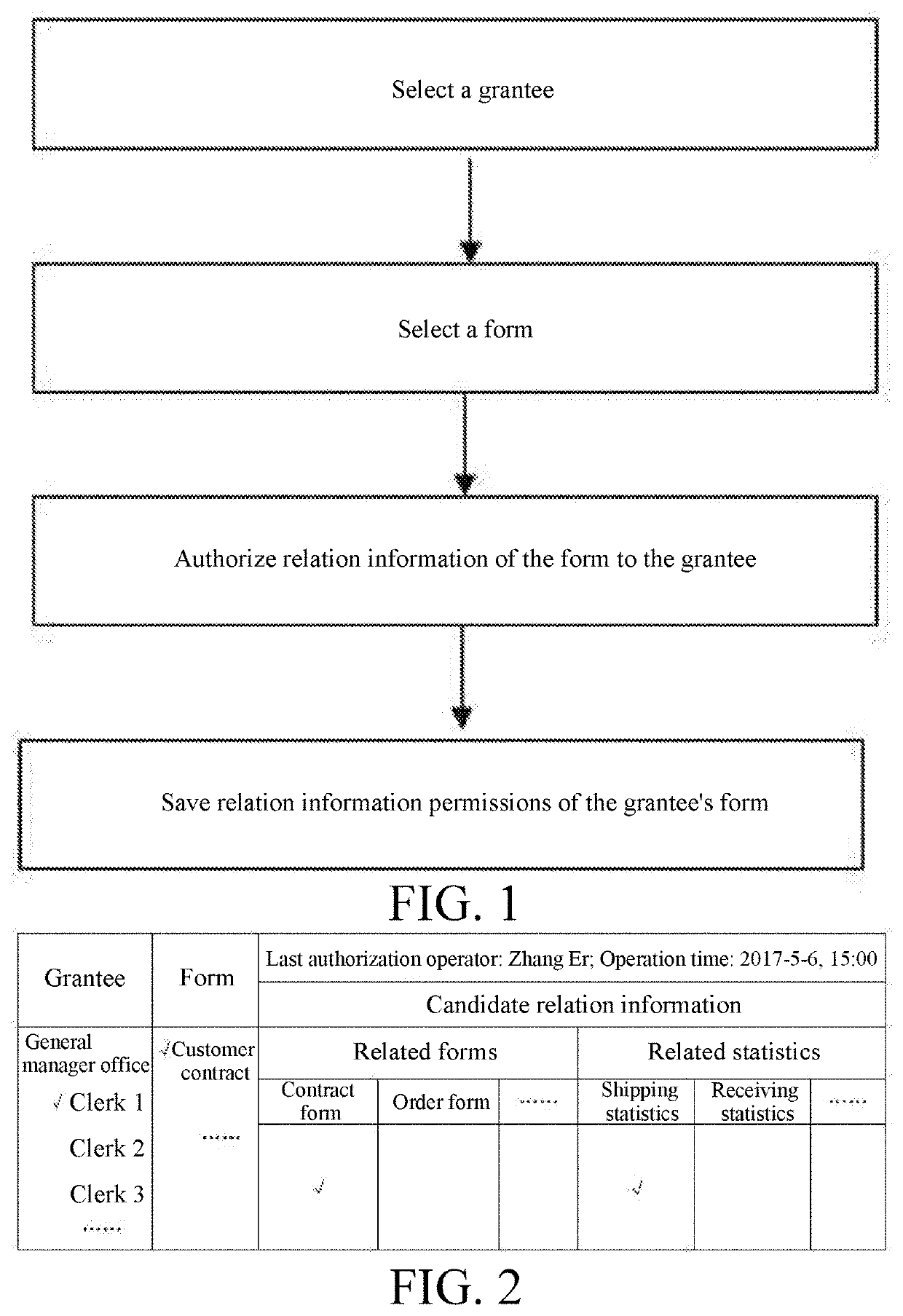
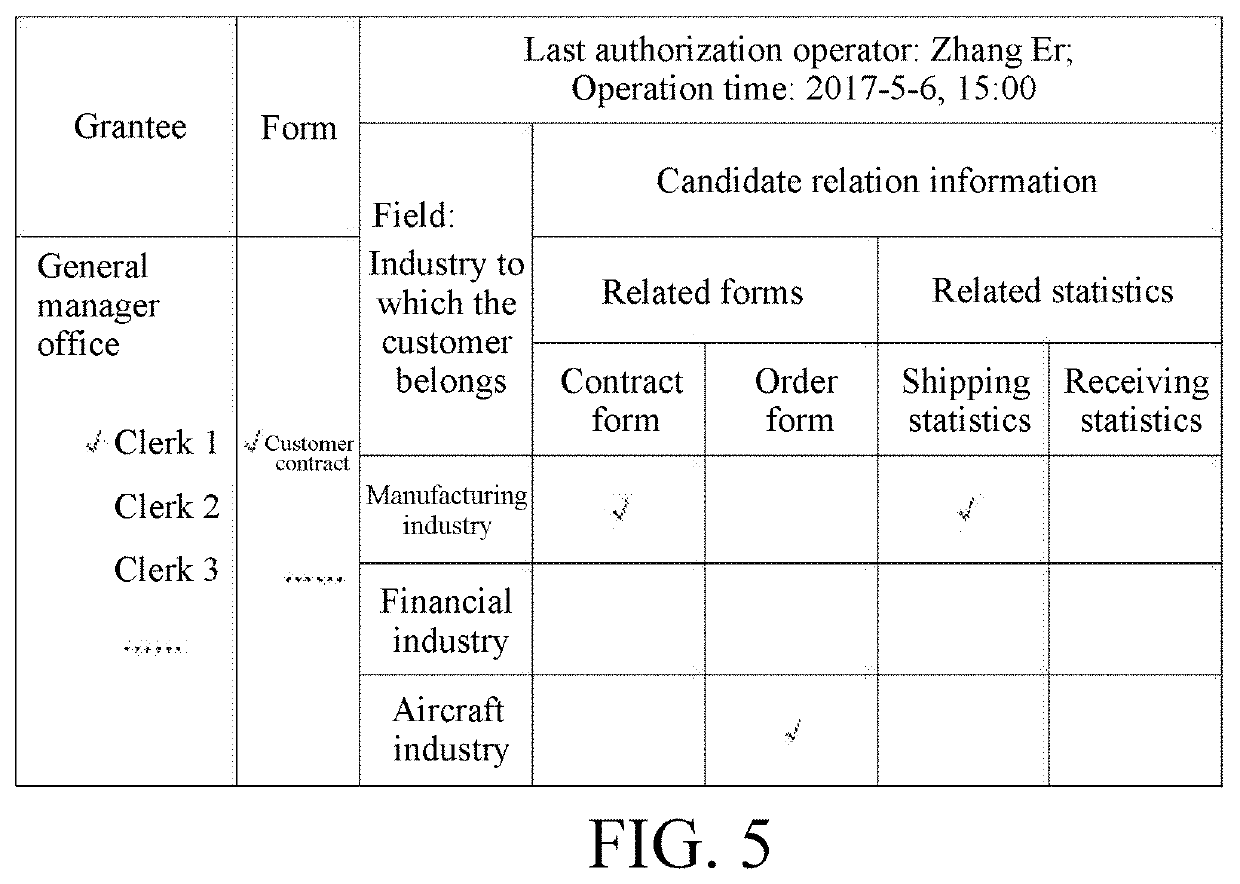
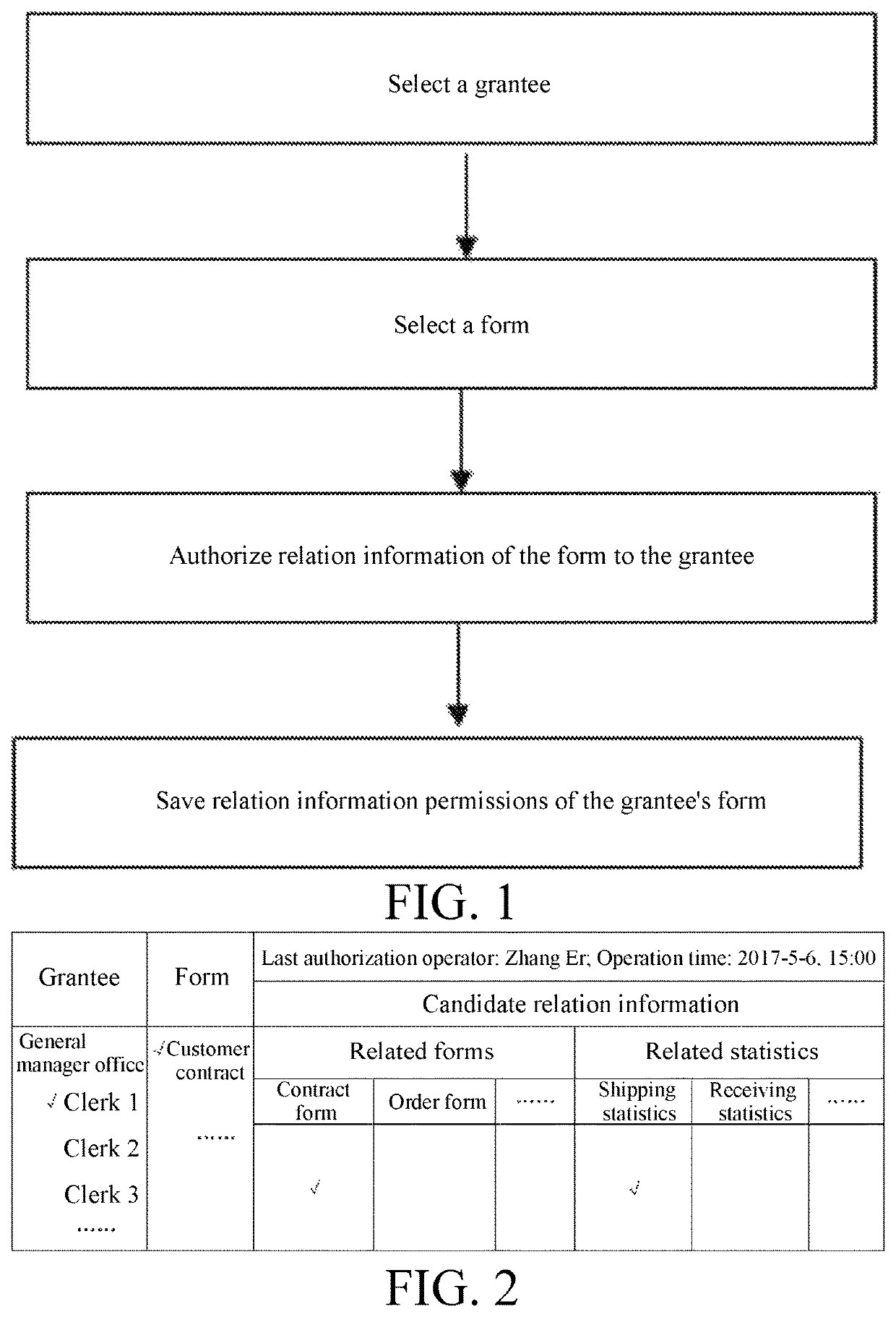
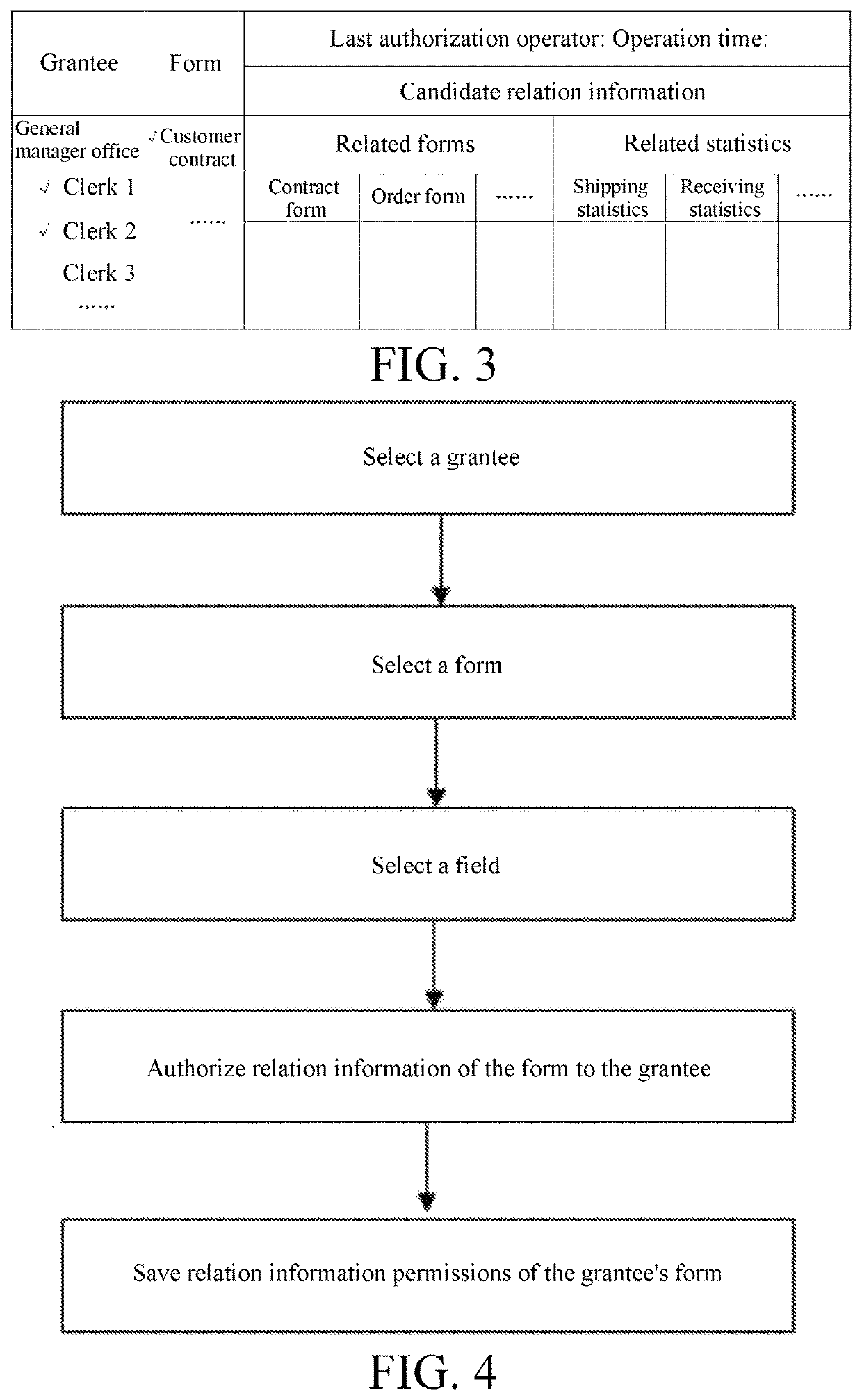
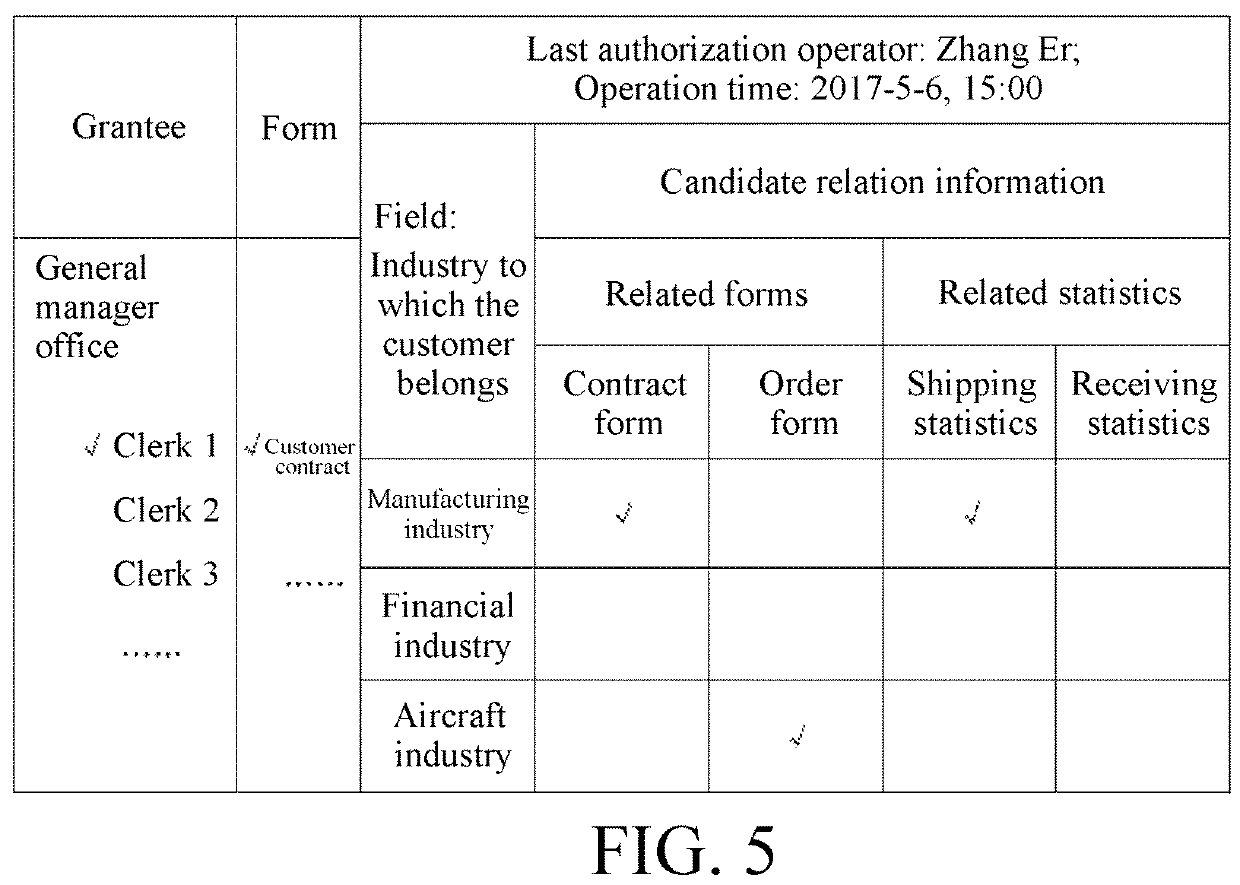
Association information authorization method for form
ActiveUS20200218818A1Avoid lossImprove efficiencyDigital data protectionDigital data authenticationEngineeringData mining
Owner:CHENGDU QIANNIUCAO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
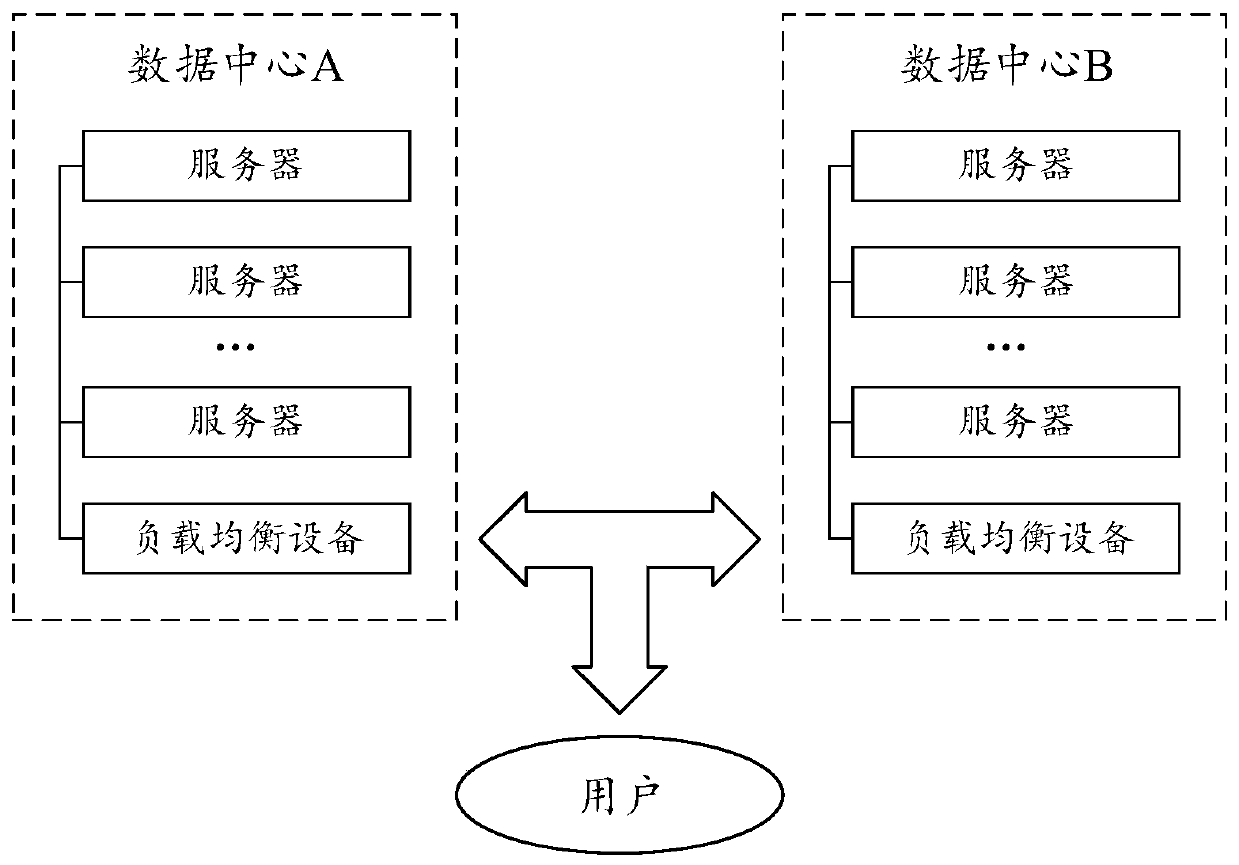
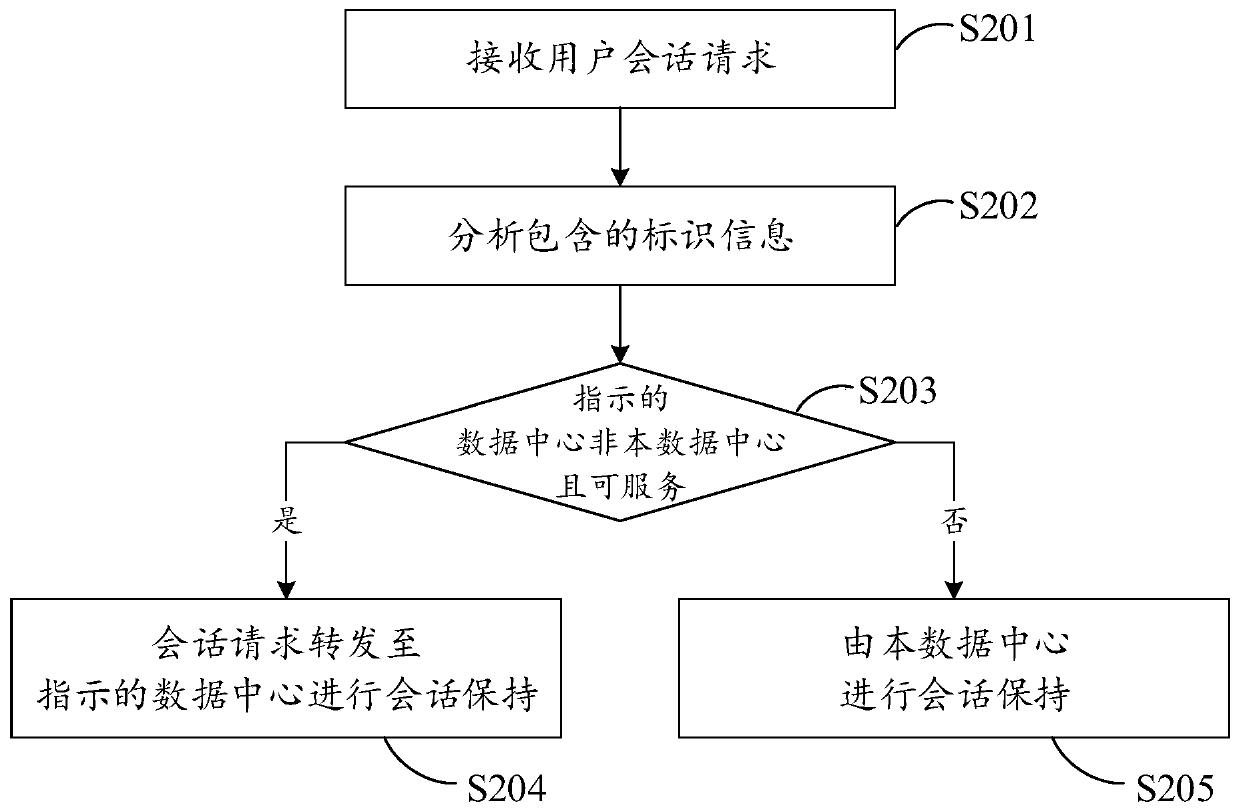
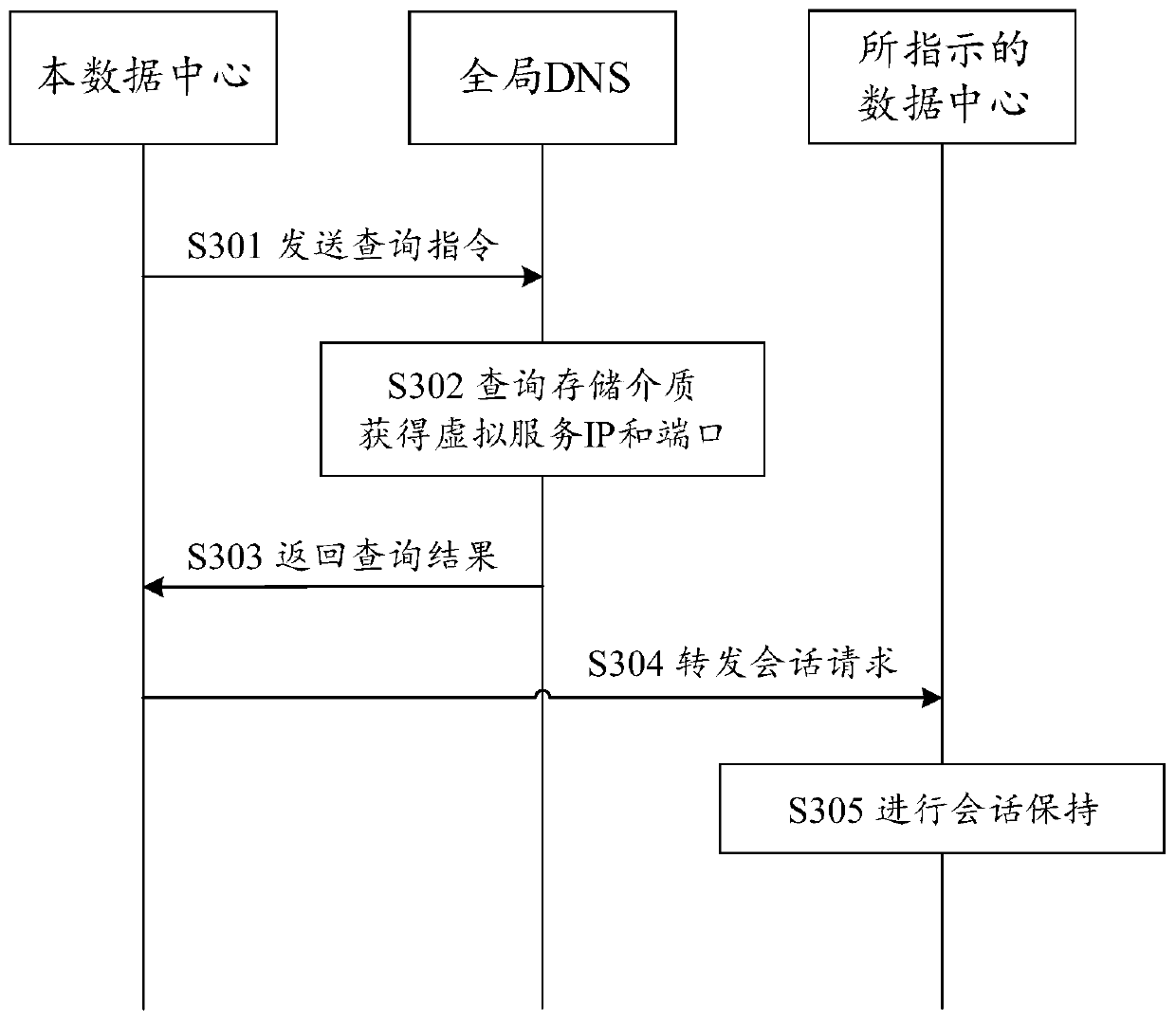
Session keeping method and device
The invention discloses a session keeping method, which relates to the field of computer networks, the session keeping method is applied to a multi-data center network, and is characterized in that any data center in the multi-data center network executes the following operations: receiving a user session request which carries identification information for session keeping; the identification information is analyzed, and a data center indicated by the identification information; under the condition that the indicated center is not the data center and is in a serviceable state, forwarding the session request is determined to the indicated data center, so that the indicated data center performs session keeping on the session request; otherwise, the data center is made to carry out session keeping on the session request. By applying the method and the corresponding device, cross-data-center session keeping can be completed, data loss caused by a traditional method is avoided, and servicecontinuity is guaranteed.
Owner:HANGZHOU DPTECH TECH
Optical transmission system
InactiveUS20030090770A1Improve signal qualityBroaden spectrumDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersFrequency spectrumOptical correction
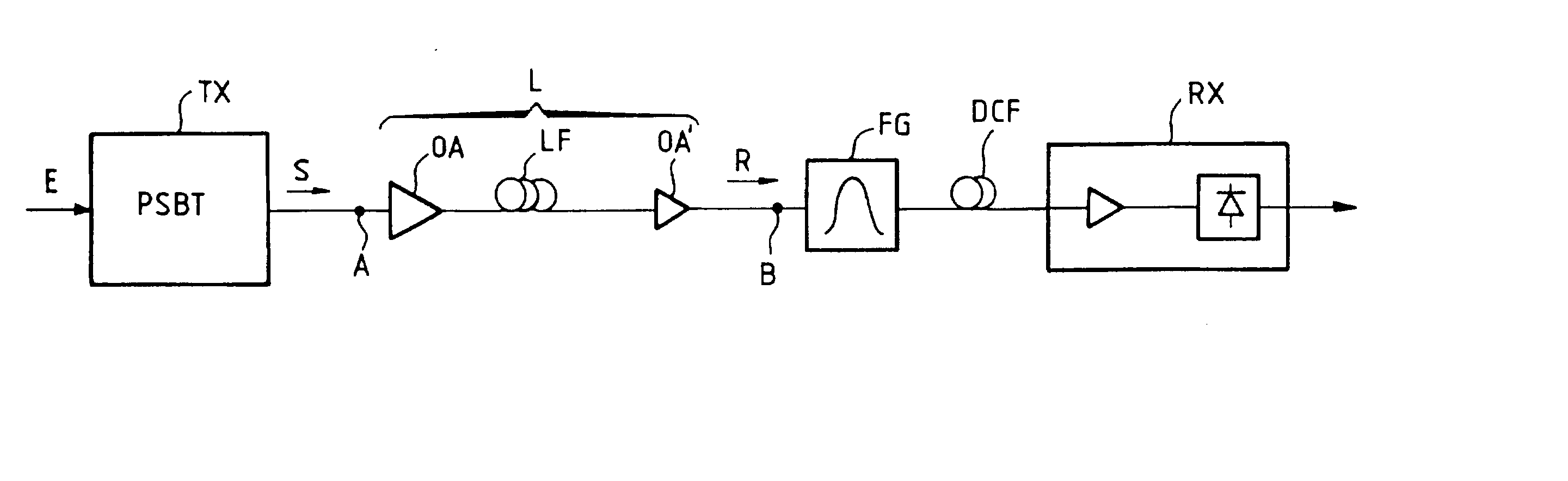
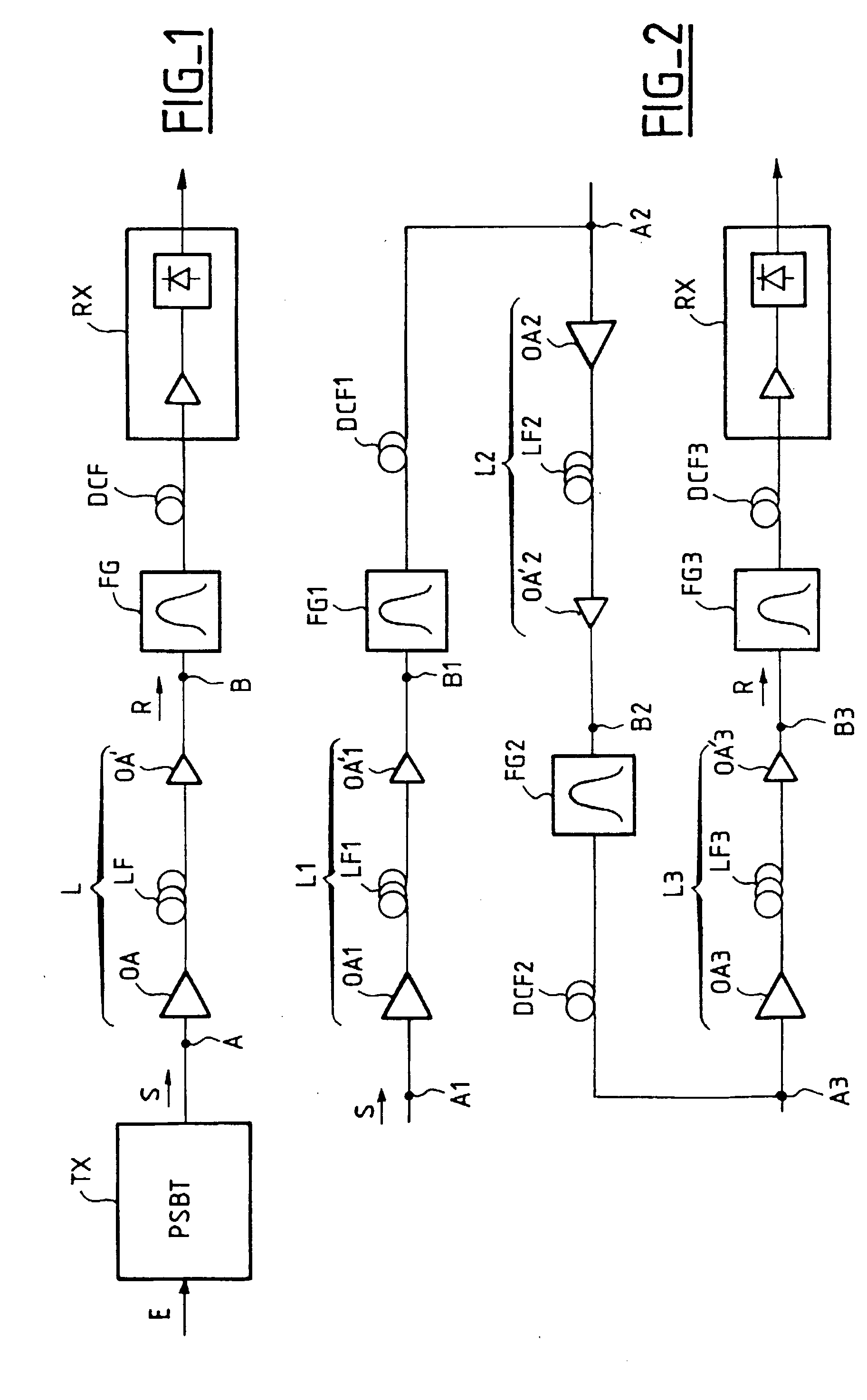
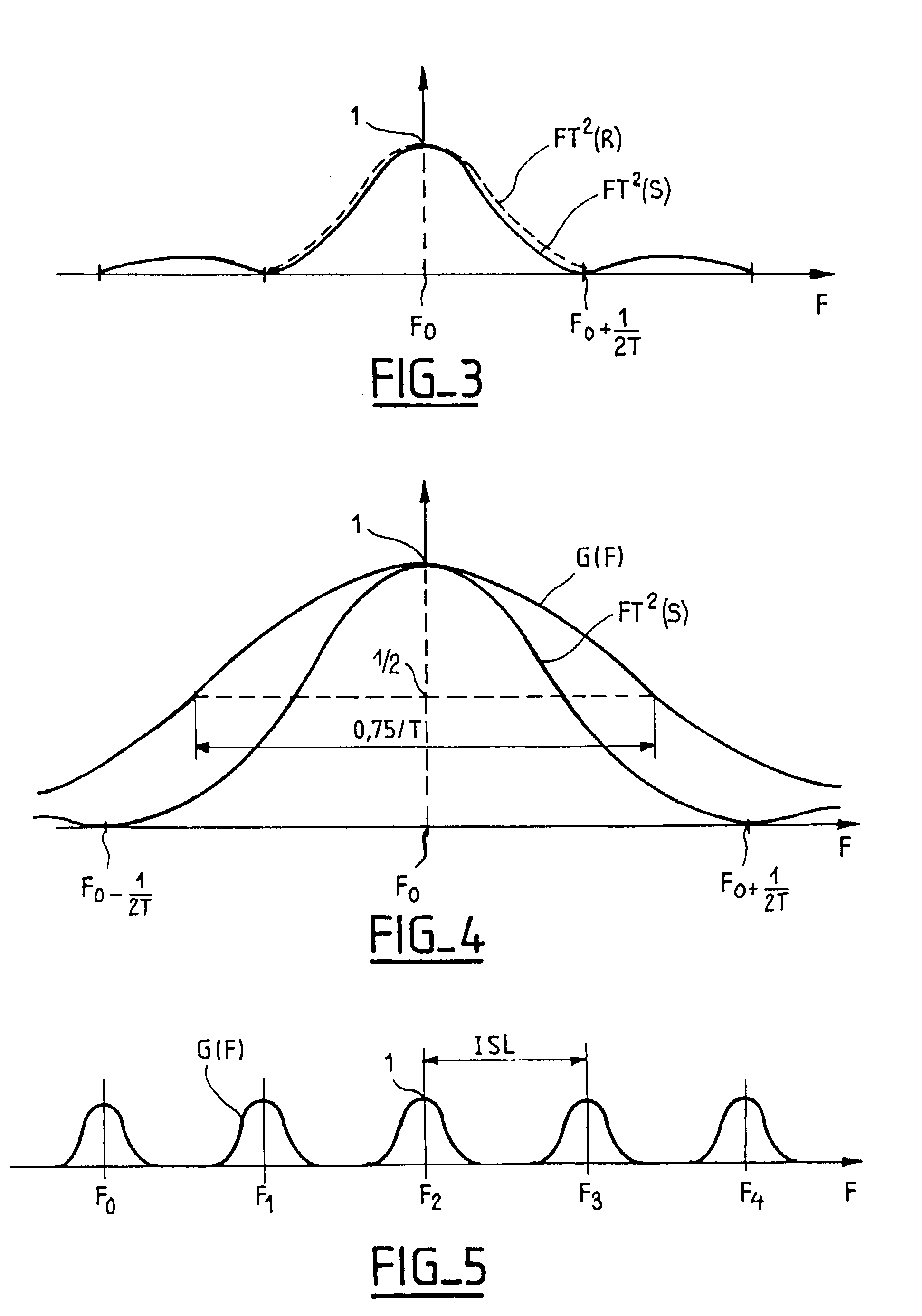
The transmission system is suitable for amplitude modulated controlled phase optical signals (S) having an optical phase in each low level pulse that precedes or follows a high level pulse. The system includes an optical link (L) and, to allow a high transmitting power, optical corrector means (FG) are provided for applying optical filtering to the signal R at the exit (B) of the link and / or at one point or a plurality of points of the link (L), to compensate widening of its spectrum that the controlled phase signal (S) may suffer because of phase self-modulation during its transmission. Application to long-haul optical transmission.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for correcting butting zone artifacts with an x-ray detector and an x-ray detector
InactiveUS7427749B2Make up for information lossEasy to replaceTelevision system detailsCalibration apparatusComputer modulePhysics
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and computer system for carrying out a simulation
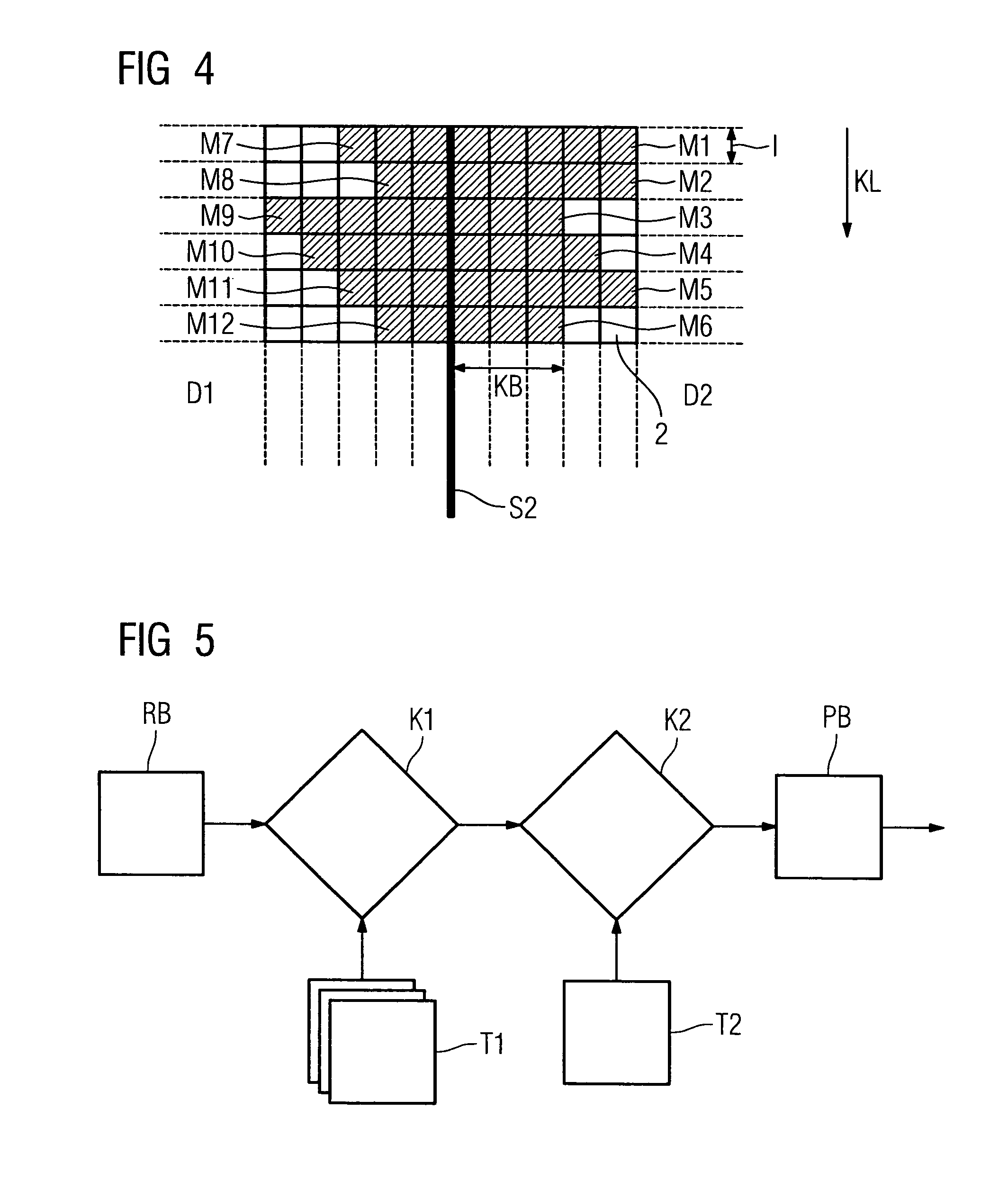
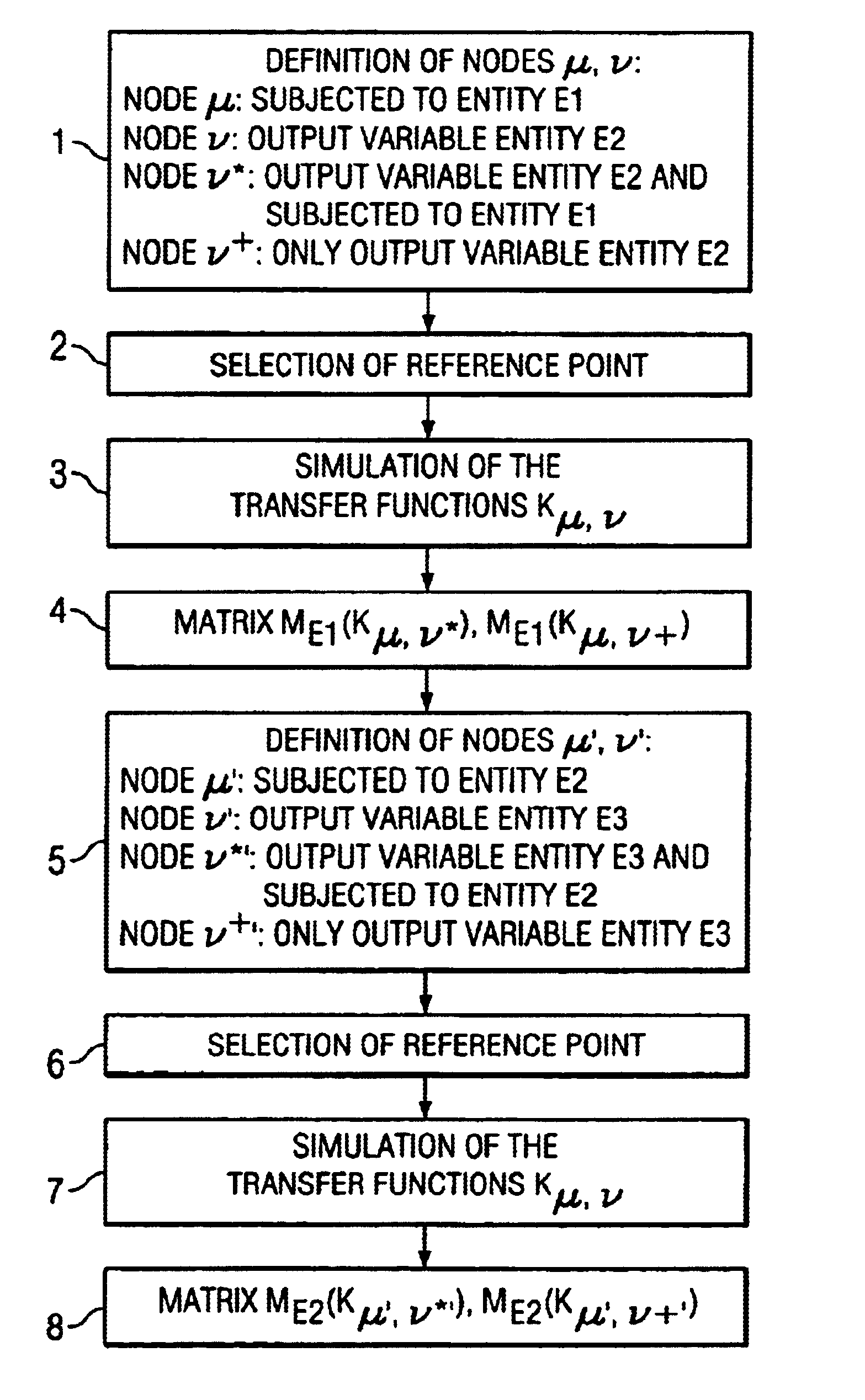
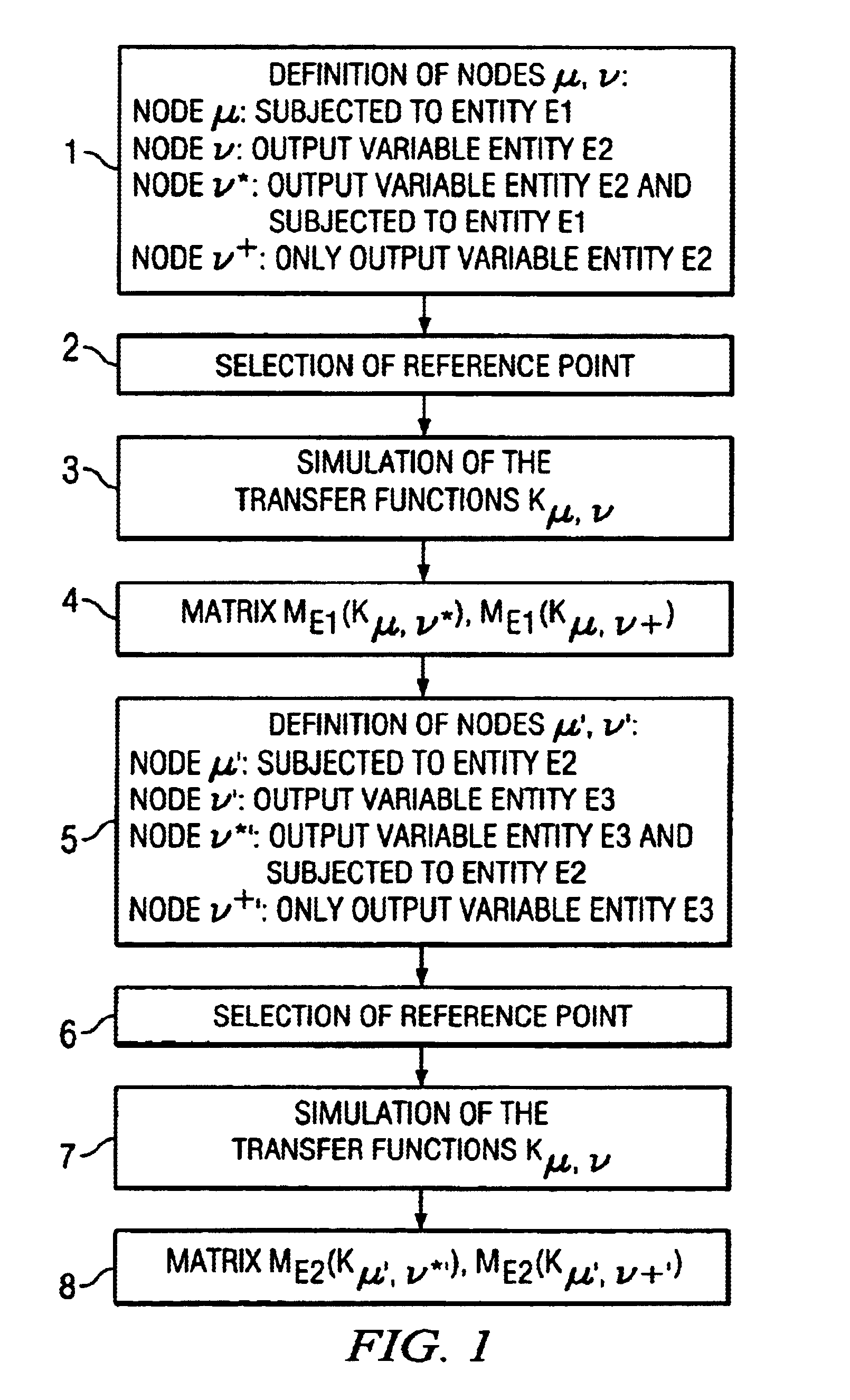
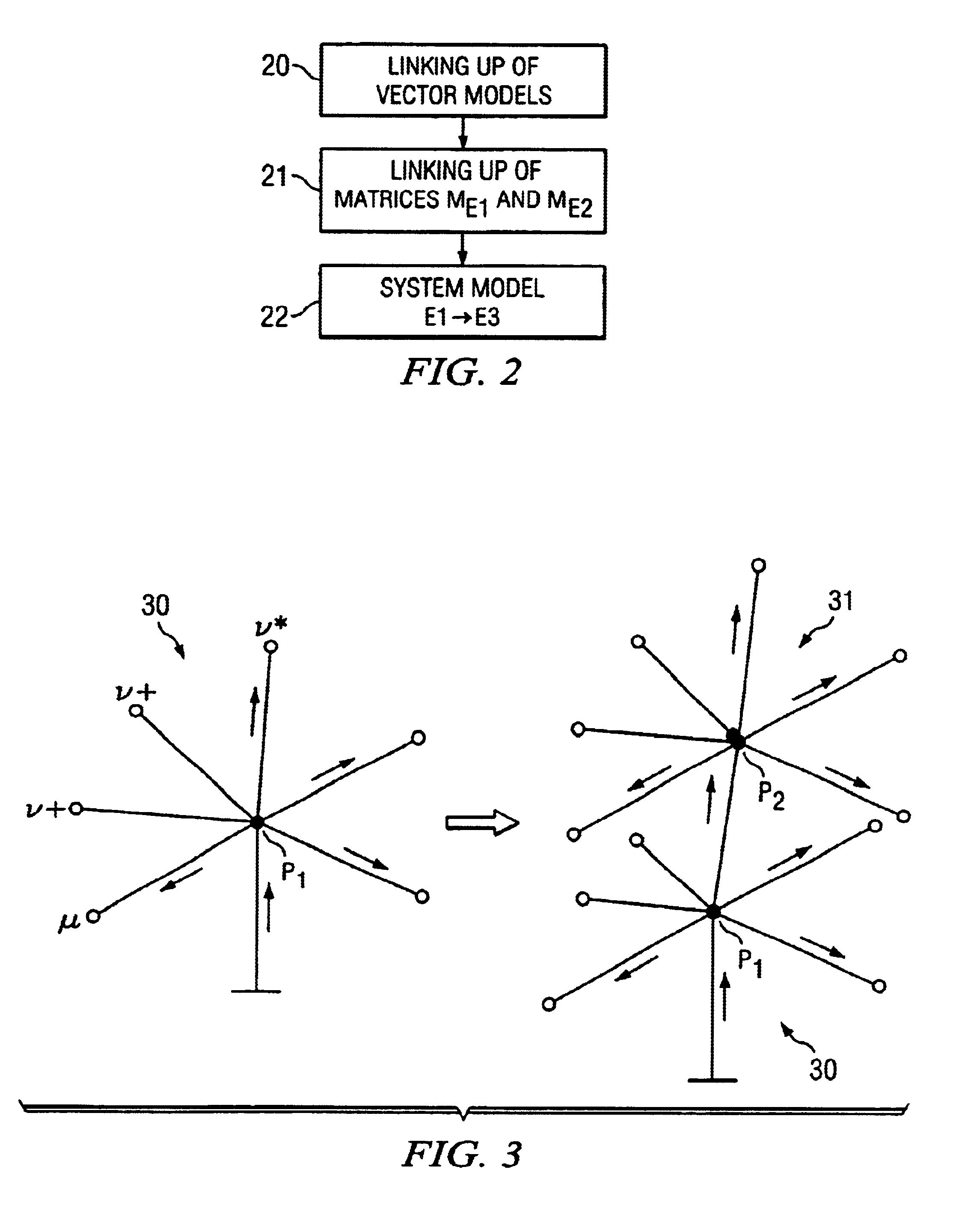
InactiveUS6917906B2Simple calculationMake up for information lossObject oriented databasesForecastingAlgorithmSimulation methods
In an integrated simulation method and system, first points, which are subjected to a first entity, and second points, with a second entity as the output variable, are defined. The second points are subdivided into a first subset and a second subset, and the second points of the first subset are subjected to a similar operation. The calculation of the transfer functions between pairs of points takes place with a simulation program, so that corresponding matrices of transfer functions result. Corresponding matrices are also generated with regard to further entities. The corresponding vector models and matrices can be linked up with one another to generate flexible system models.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
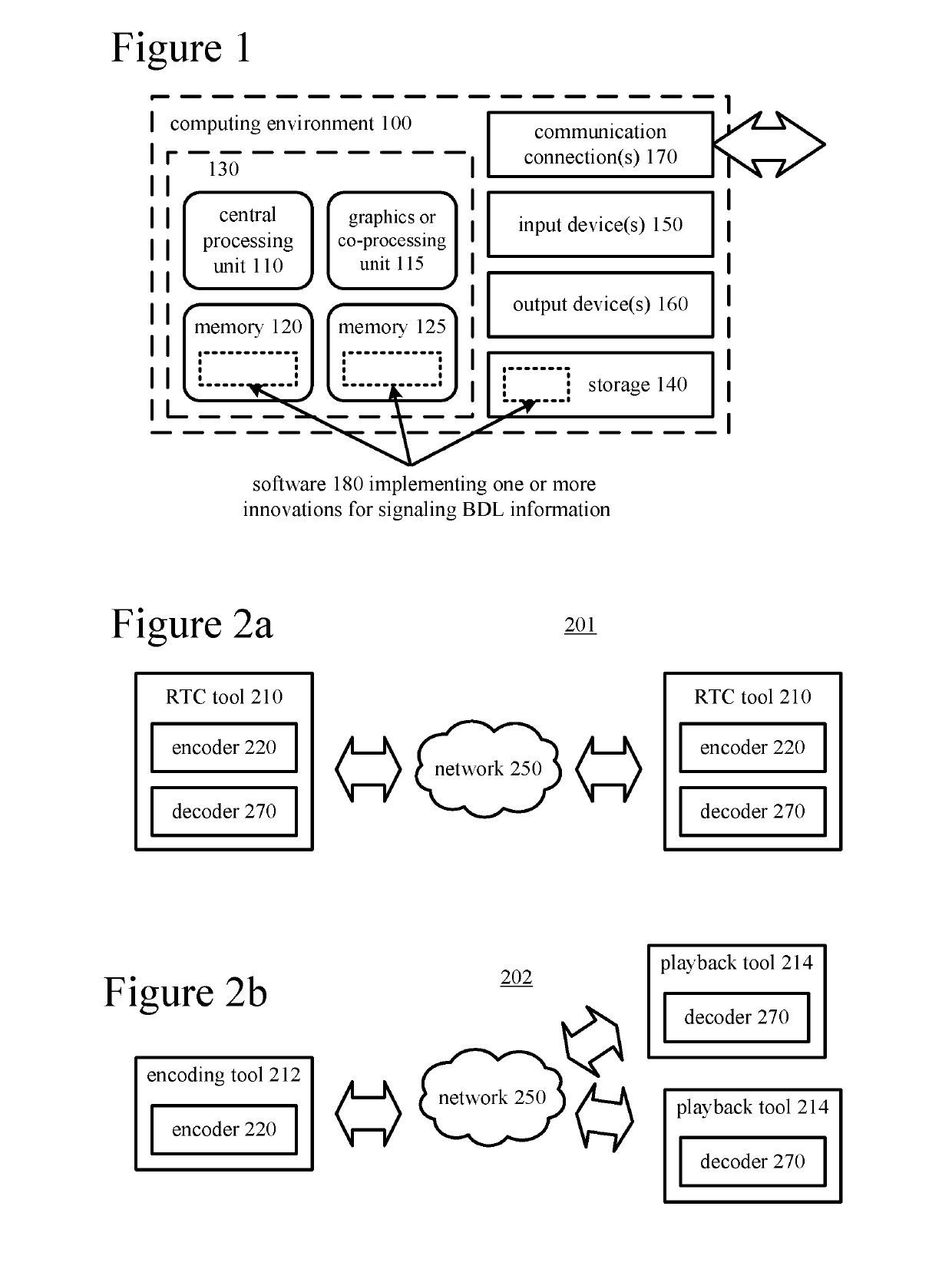
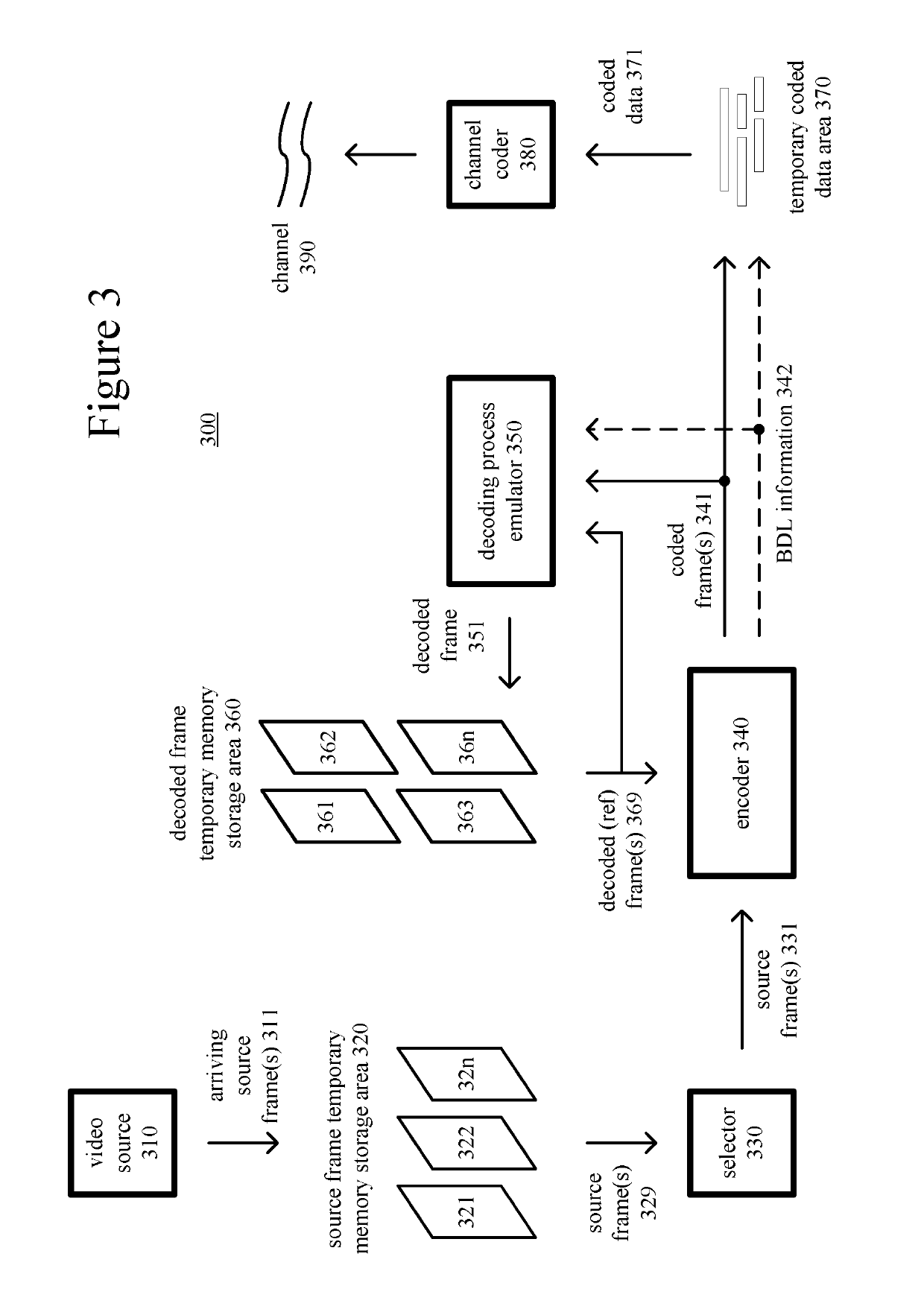
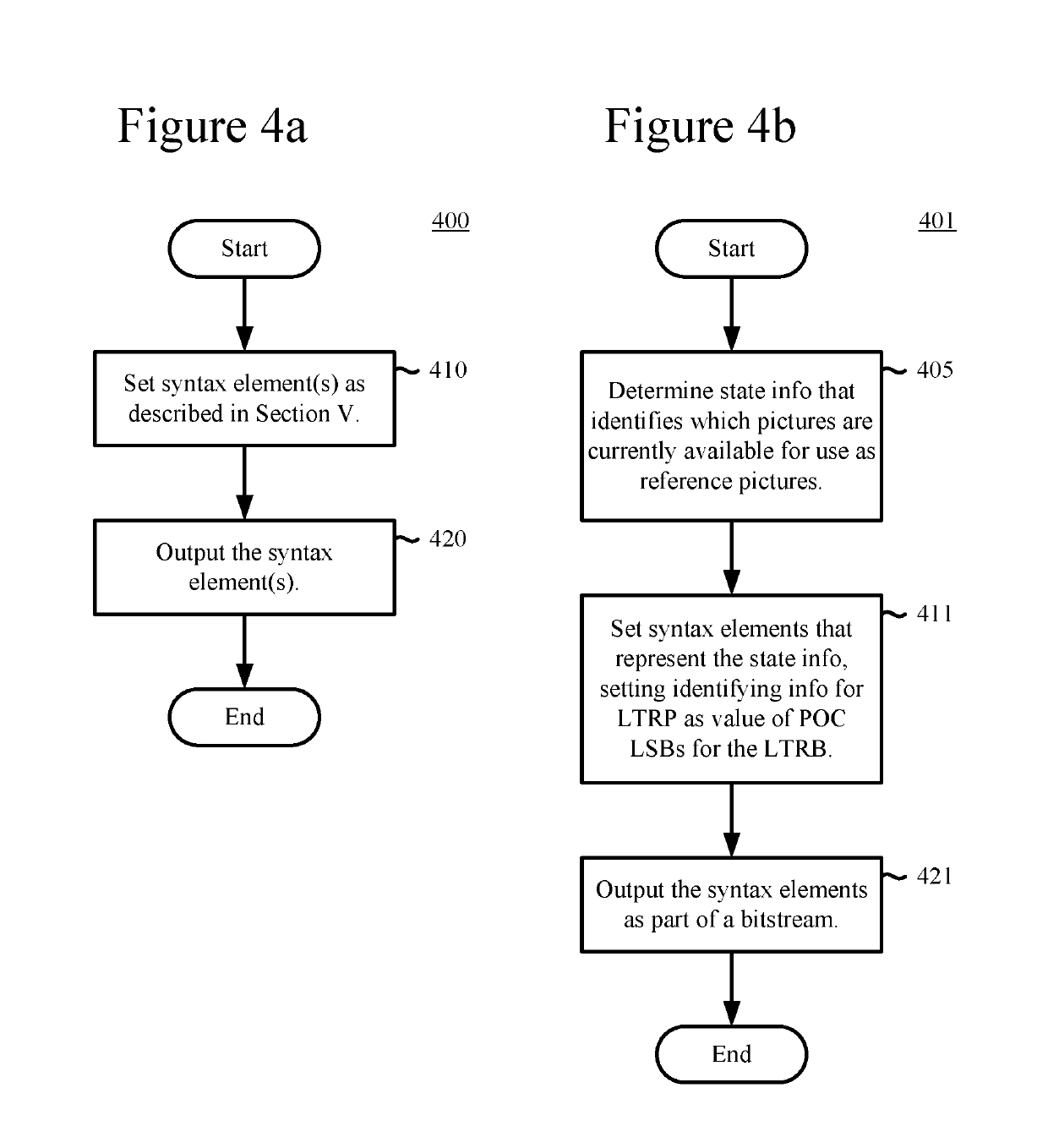
Signaling of state information for a decoded picture buffer and reference picture lists
ActiveUS10432964B2Reduce bitrateMake up for information lossDigital video signal modificationReference mapAlgorithm
Innovations for signaling state of a decoded picture buffer (“DPB”) and reference picture lists (“RPLs”). In example implementations, rather than rely on internal state of a decoder to manage and update DPB and RPLs, state information about the DPB and RPLs is explicitly signaled. This permits a decoder to determine which pictures are expected to be available for reference from the signaled state information. For example, an encoder determines state information that identifies which pictures are available for use as reference pictures (optionally considering feedback information from a decoder about which pictures are available). The encoder sets syntax elements that represent the state information. In doing so, the encoder sets identifying information for a long-term reference picture (“LTRP”), where the identifying information is a value of picture order count least significant bits for the LTRB. The encoder then outputs the syntax elements as part of a bitstream.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Printing program that adjusts annotation location and size
InactiveUS7973964B2Inhibition lossSmall sizeCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual presentationData storingComputer science
A computer-readable recording medium recorded with a printing program causes a processor of a computer to calculate a rendering area of print data stored in a storing section of the computer as a primary area based on the print data, and to calculate a rendering area of commentary string data to be attached to the print data as a sub-area. The program then judges whether the primary area and the sub-area overlap, and whether the sub-area deviates from an effective printing area. The commentary string data can be changed so that the primary area and the sub-area do not overlap, and so that the entire sub-area is within the effective printing area, if at least one of the judgment results in the judging step is affirmative. The changed commentary string data then is attached to the print data.
Owner:KYOCERA DOCUMENT SOLUTIONS INC
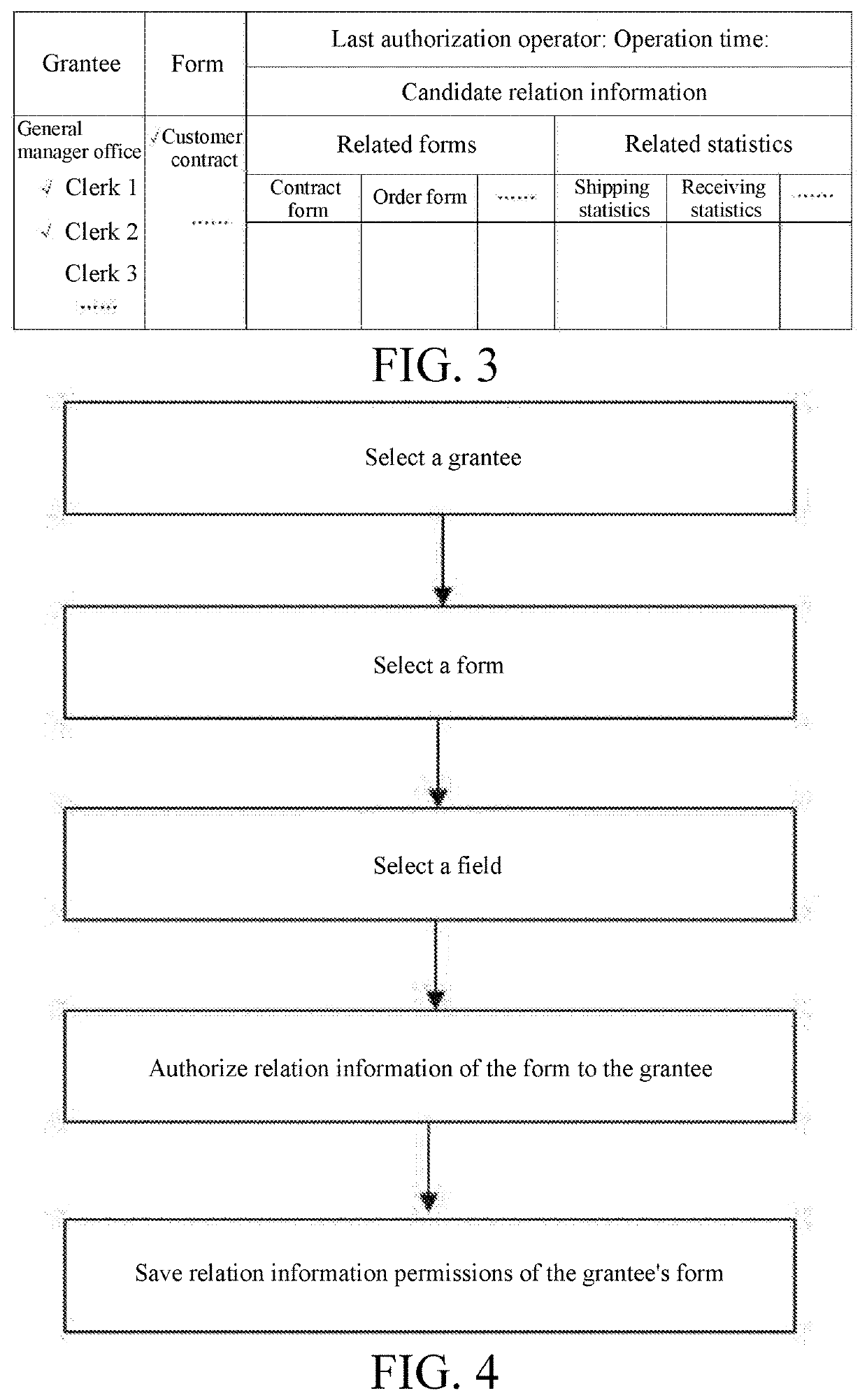
Authorization method for form related information
ActiveUS11507679B2Make up for information lossImprove efficiencyDigital data protectionDigital data authenticationEngineeringData mining
Owner:CHENGDU QIANNIUCAO INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
A control method of a drone, the drone (100), and a machine readable storage medium
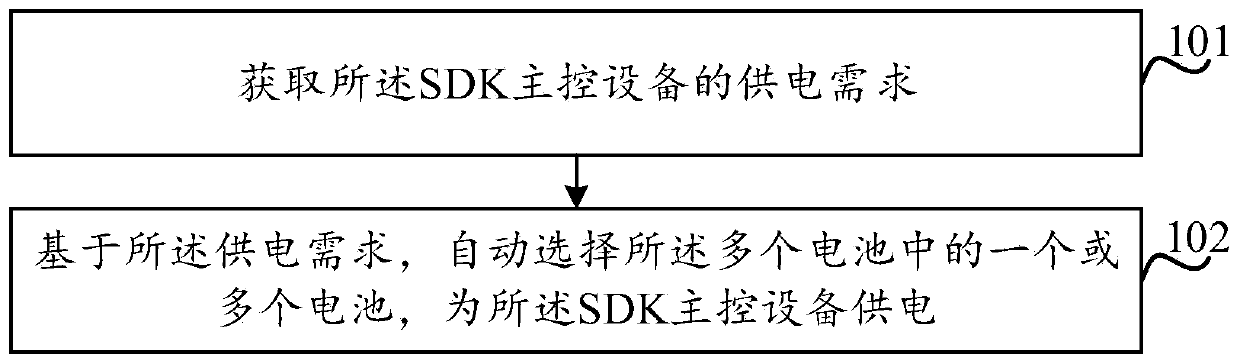
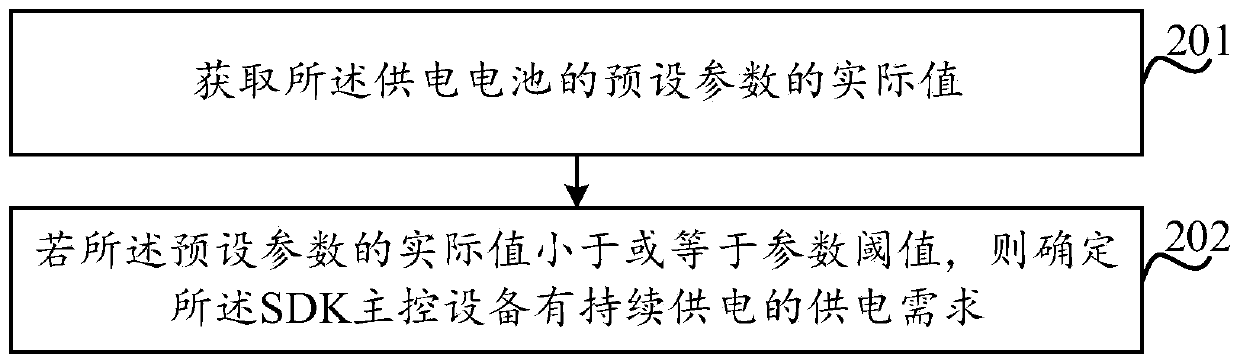
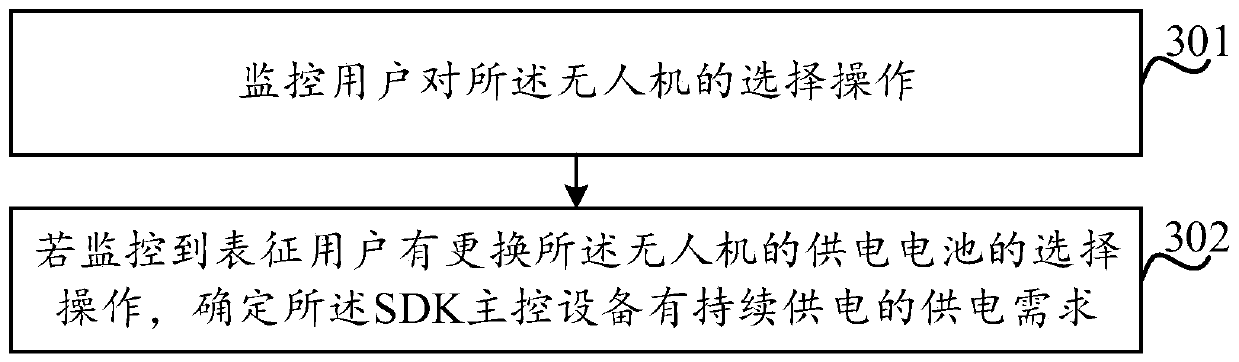
ActiveCN110959241AGuaranteed power supplyMake up for information lossElectric powerPropulsion by batteries/cellsMachineBattery cell
A control method of a drone (100), the drone (100), and a machine readable storage medium storing the control method are provided. The drone (100) at least comprises a machine body (110), a power supply battery (120) arranged on the machine body (110), SDK main control equipment and a power system (130); the power supply battery (120) comprises a plurality of cells, and the power supply battery (120) can supply power to the power system (130) and the SDK main control equipment at the same time. The power system (130) provides flight power for the drone (100), obtains the power supply demand ofthe SDK master control equipment, and then selects one or more cells from the power supply battery according to the power supply demand to supply power to the SDK master control equipment, thereby ensuring continuous power supply to the SDK master control equipment. Therefore, the information of the SDK main control equipment cannot be lost, and the use experience of a user can be improved.
Owner:SZ DJI TECH CO LTD
System and method for communicating fault type and fault location messages
A system and method are provided for transporting FTFL messages in a G.709 network-connected simplex device. The method comprises: receiving messages from a first source in a digital wrapper frame format with overhead bytes in every frame; recovering FTFL information from the received message overhead bytes; and, selectively supplying modified FTFL information for transmit message overhead bytes to the first source. Recovering FTFL information from the received message overhead bytes includes recovering a 256 byte FTFL message, including a 128-byte forward message and a 128-byte backward message. Selectively supplying modified FTFL information for transmit message overhead bytes to the first source includes the substeps of: examining the received messages to determine errors; generating a backward message to report the determined errors; overwriting the received backward message with the generated backward message to create the modified FTFL information; and, in response to overwriting the received backward message with the generated backward message, sending a FTFL_status_out signal. Then, the method further comprises: transmitting messages to the first source with the modified FTFL information in response to the FTFL_status_out signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
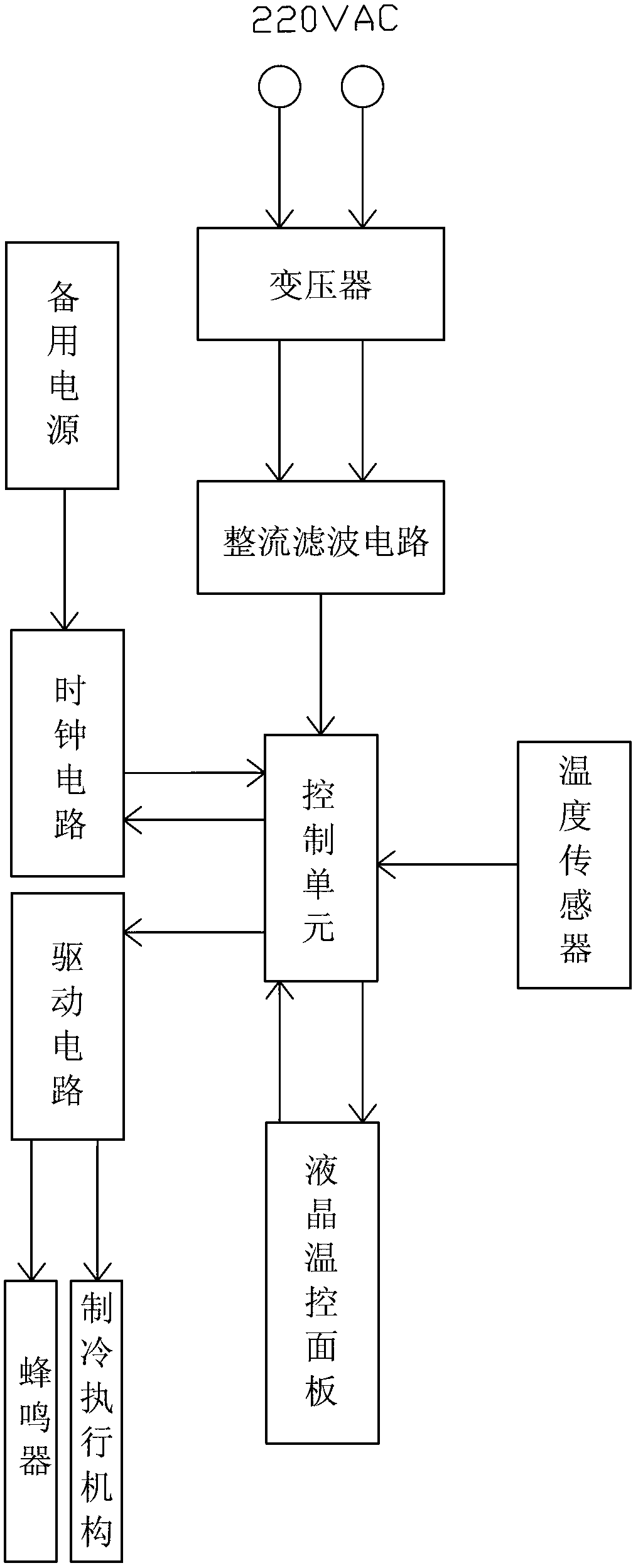
Glass door refrigerator with liquid crystal temperature control panel
InactiveCN103344087APrecise temperature controlMake up for information lossDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusTime informationTemperature control
The invention discloses a glass door refrigerator with a liquid crystal temperature control panel. The glass door refrigerator with the liquid crystal temperature control panel comprises a transformer, a rectification filter circuit, a temperature sensor, the liquid crystal temperature control panel, a drive circuit, a refrigeration executing mechanism, a clock circuit, a backup power source, a buzzer and a control unit, wherein the temperature sensor is used for monitoring temperature in real time, the liquid crystal temperature control panel is used for displaying and setting current temperature of a refrigerating chamber, the drive circuit is used for providing control signals to the refrigeration executing mechanism which is used for receiving the signals of the drive circuit and carrying out refrigerating operations, the clock circuit is used for storing temperature information, the backup power source is used for supplying power for the clock circuit in power failure, the buzzer provides confirming signals for operations, and the control unit is respectively connected with the rectification filter circuit, the temperature sensor, the liquid crystal temperature control panel, the drive circuit and the clock circuit, receives information and sends out corresponding control signals. According to the glass door refrigerator with the liquid crystal temperature control panel, the liquid crystal temperature control panel is arranged on the glass door refrigerator, and precision of temperature control is improved. Meanwhile, the glass door refrigerator with the liquid crystal temperature control panel achieves the functions of setting and storing temperature information, time information and timing startup and shutdown information, has operation tips and is extremely convenient to use.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TENGYUN REFRIGENRATION TECH
System and method for analyzing modeling accuracy while performing reverse engineering with 3D scan data
ActiveUSRE48498E1Make up for information lossComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsColor mapping
An automated mechanism for measuring the amount of accuracy loss attributable to reverse engineering processes that use 3D scan data is discussed. The embodiments provide a mechanism that displays to a user the effect scan data editing and CAD remodeling operations have on scan data accuracy. Additionally, the user can choose the way the graphical display illustrates the error distribution on the model such as by color mapping and whisker mapping. The accuracy loss may be displayed to the user after finishing an editing / modeling command or during the previewing of the command thereby allowing a user to take appropriate action. Parameters may also be adjusted programmatically based on the amount of accuracy loss determined to be attributable to scan data editing or CAD remodeling operations.
Owner:3D SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com