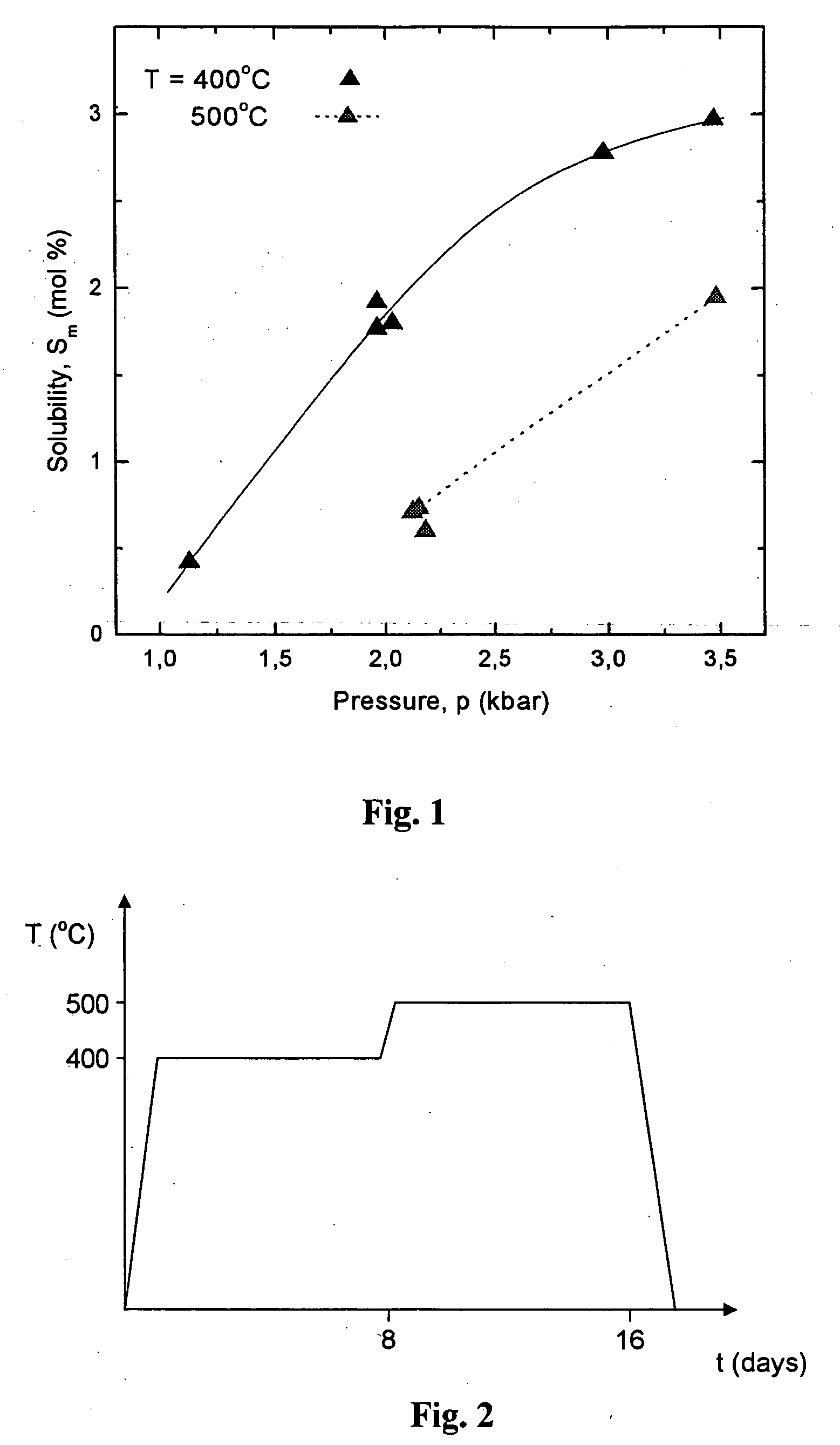
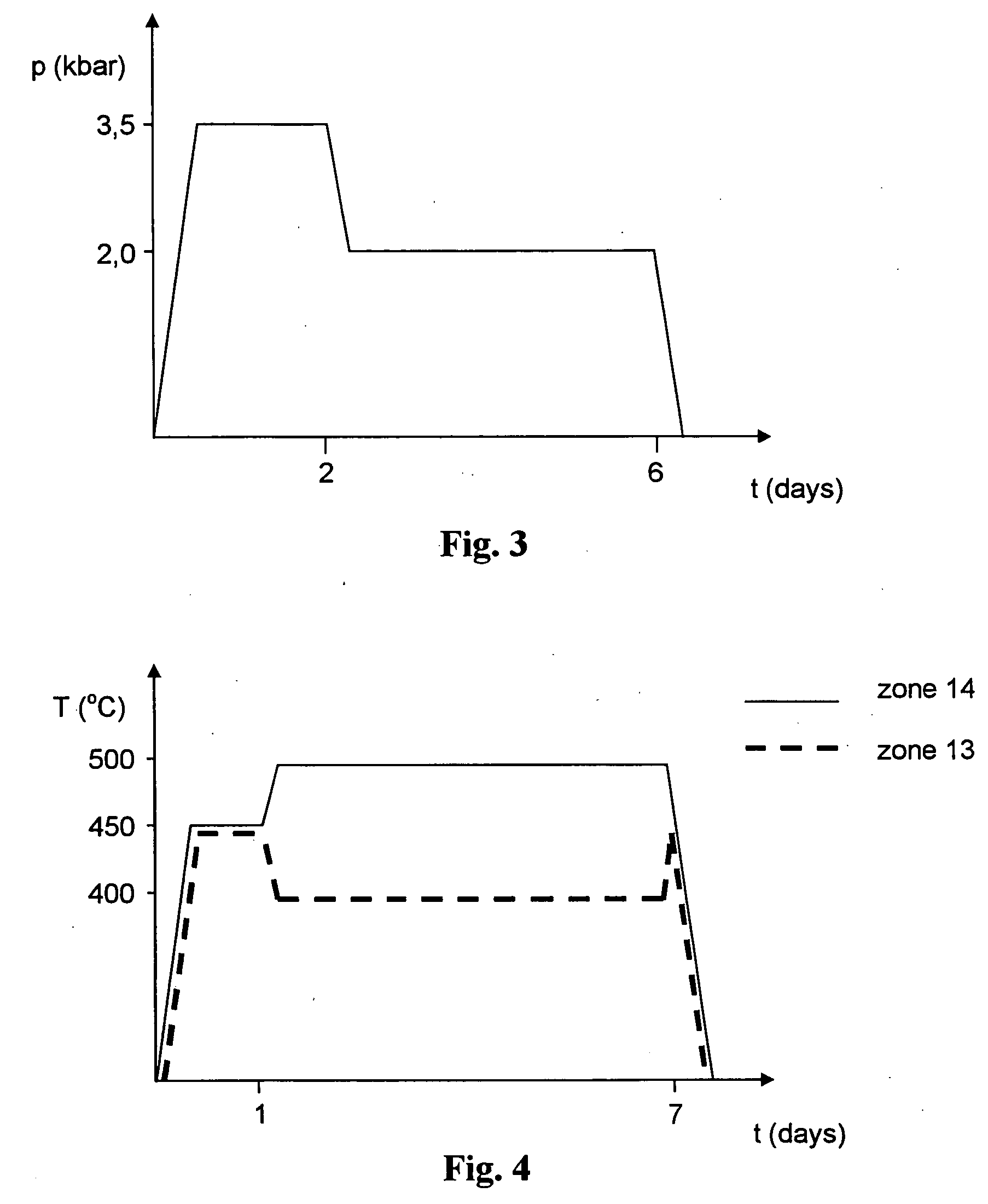
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Lifetime be accurately estimated" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
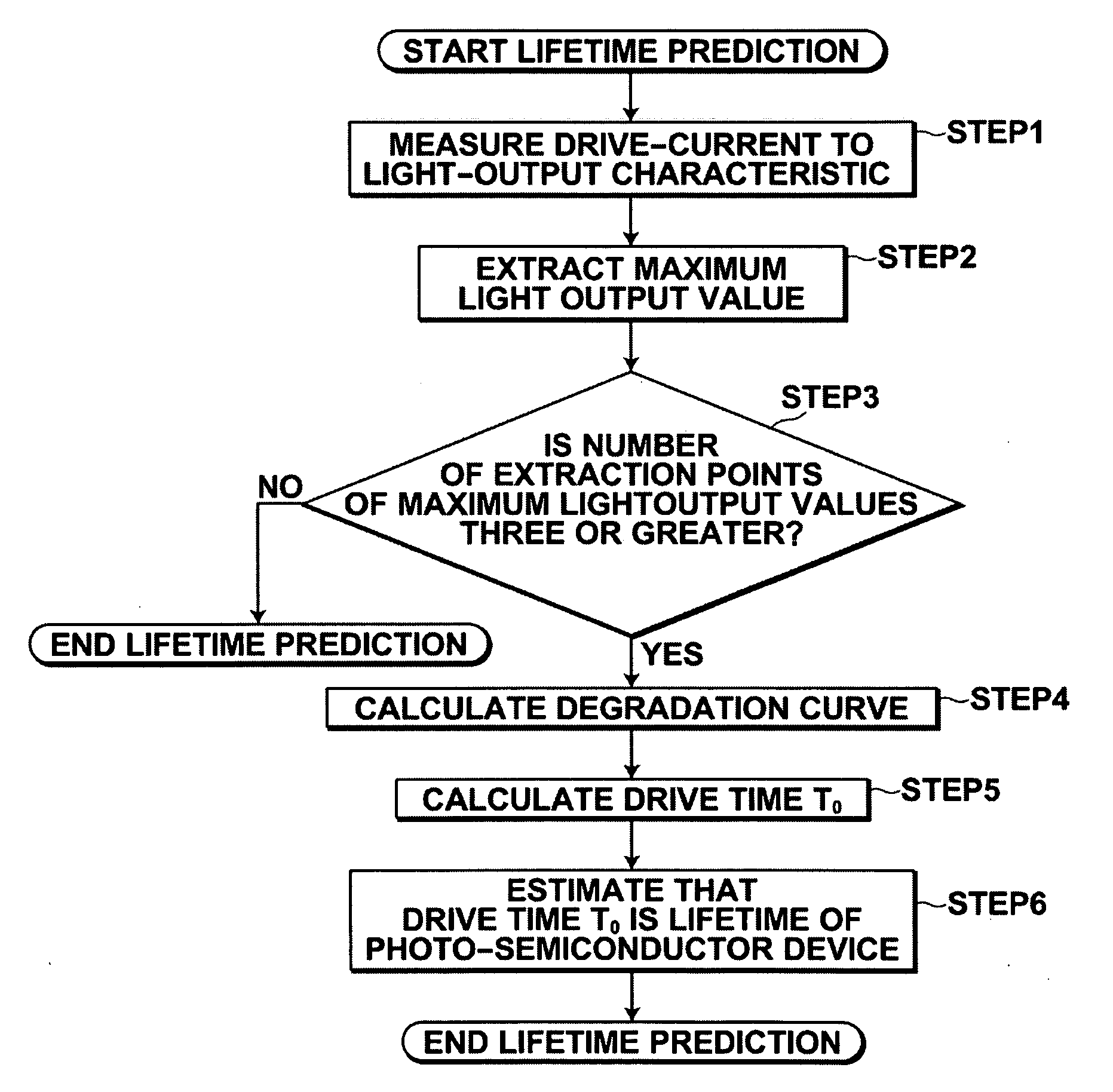
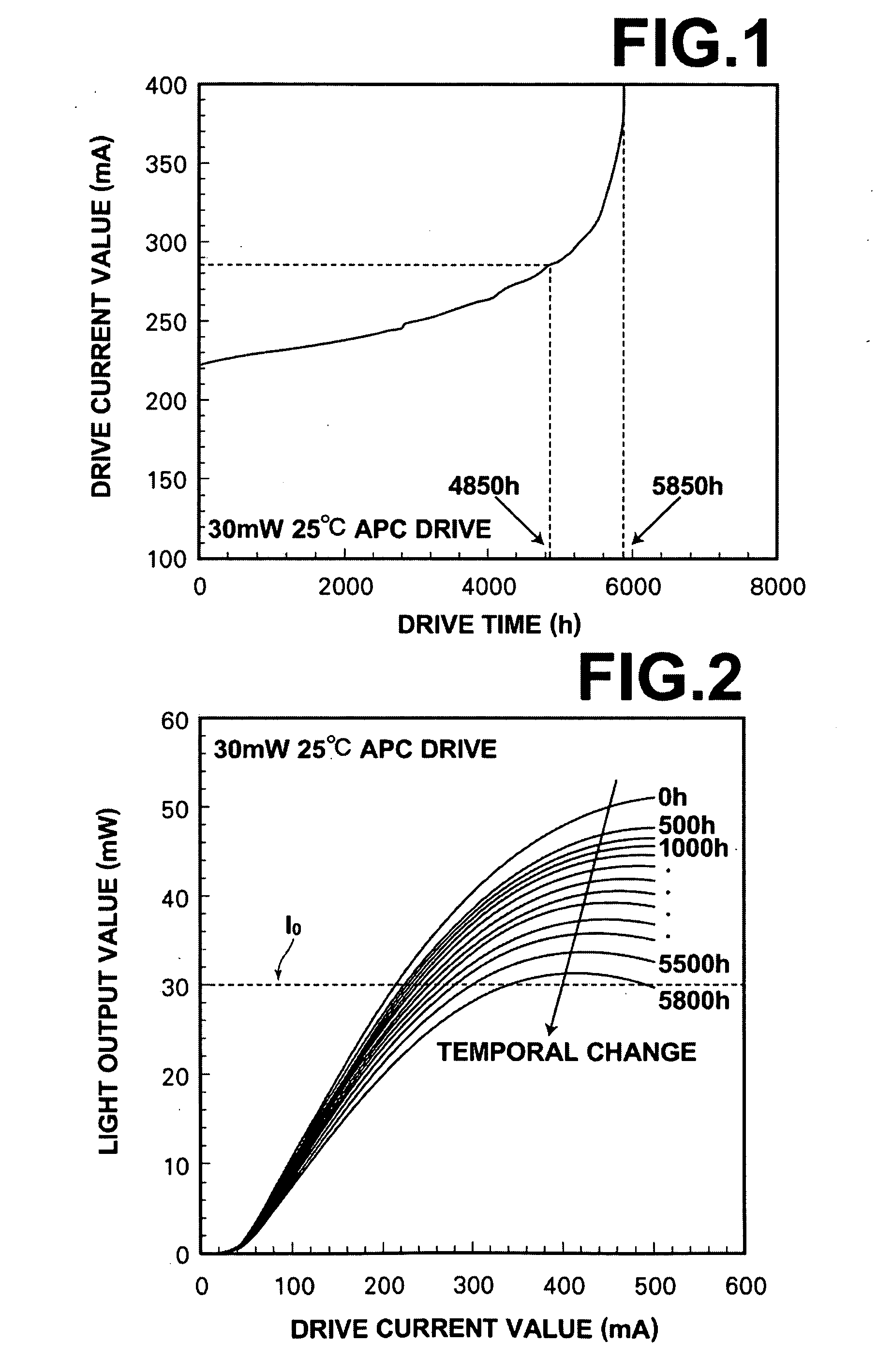
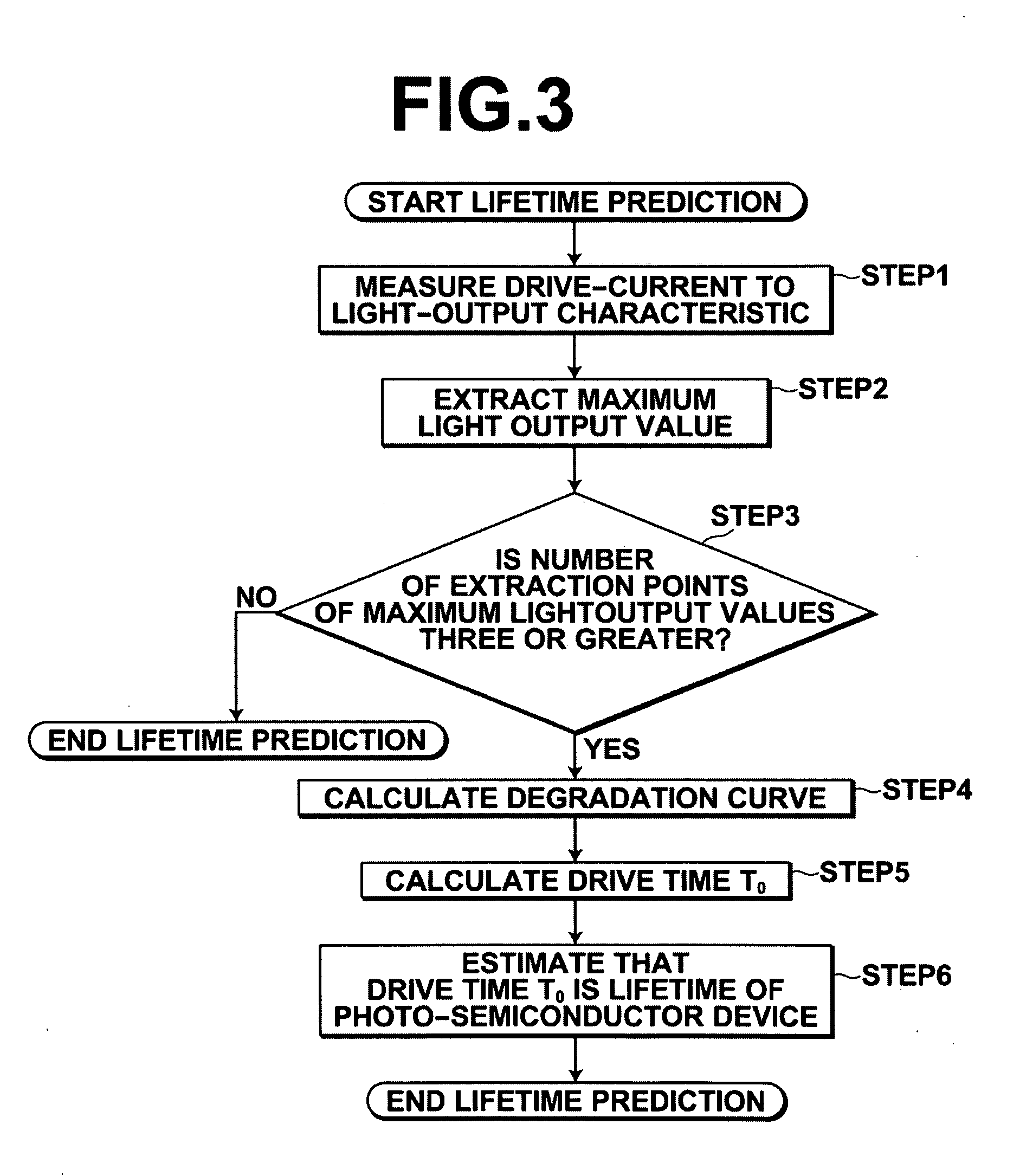
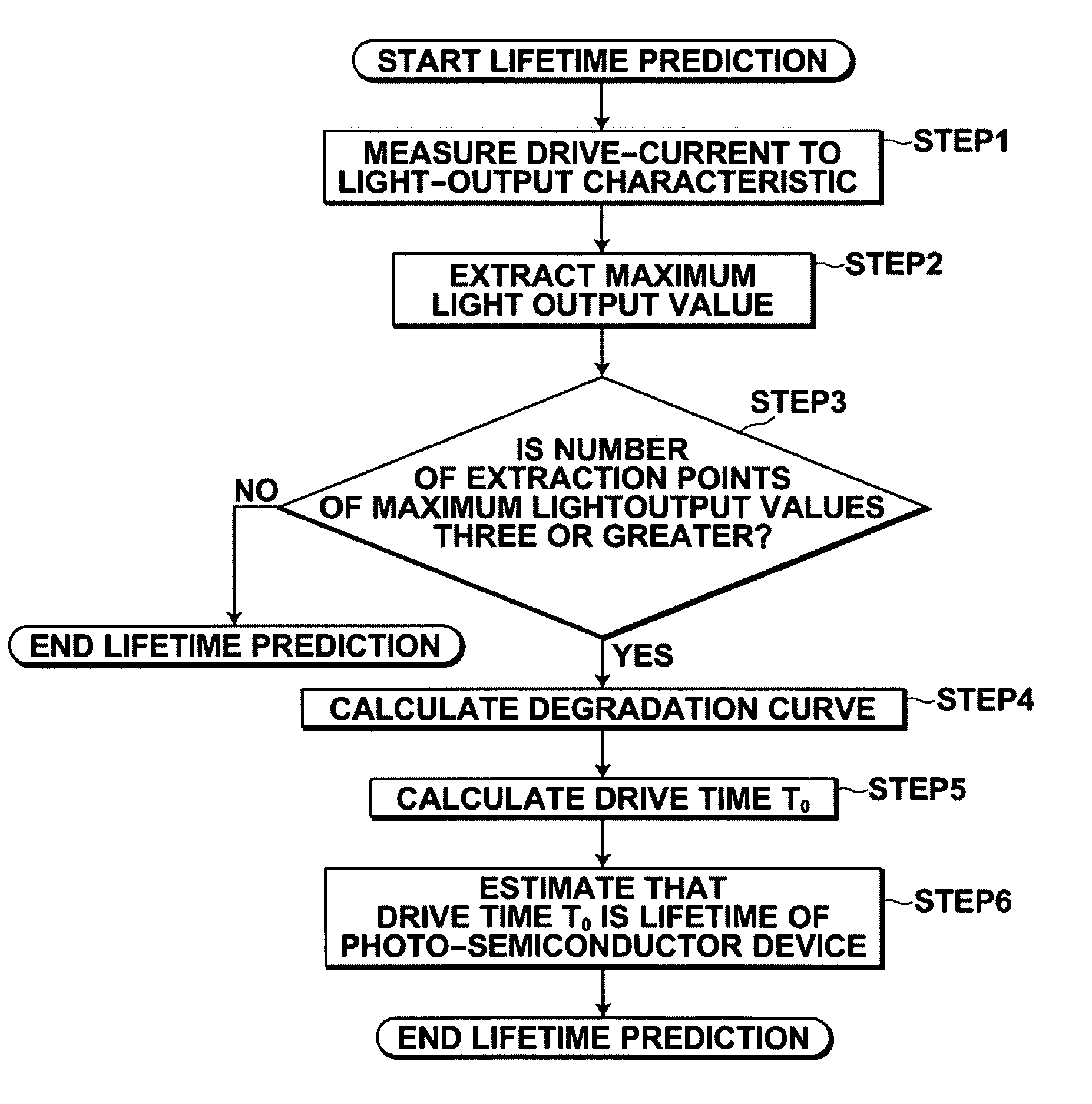
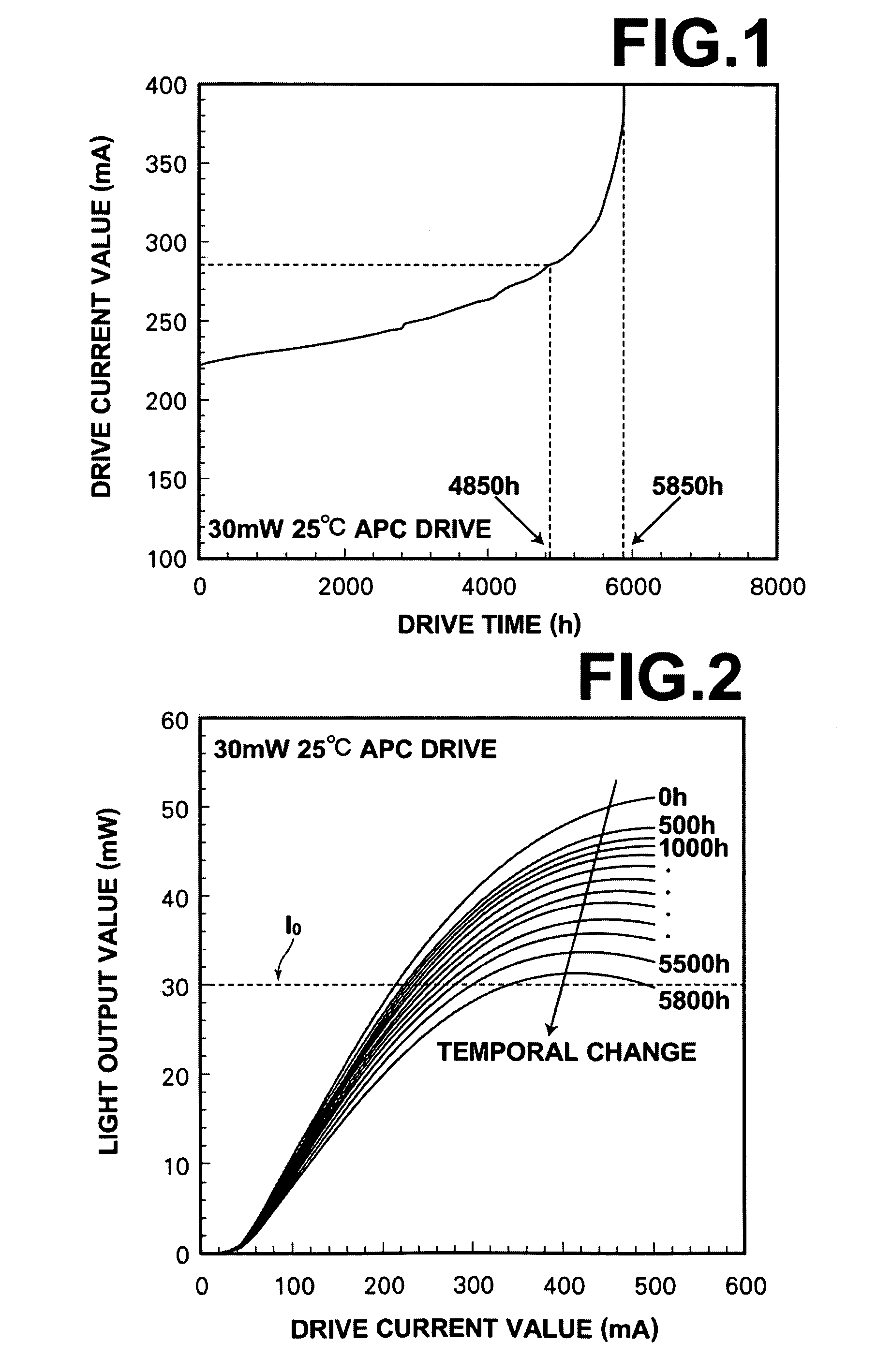
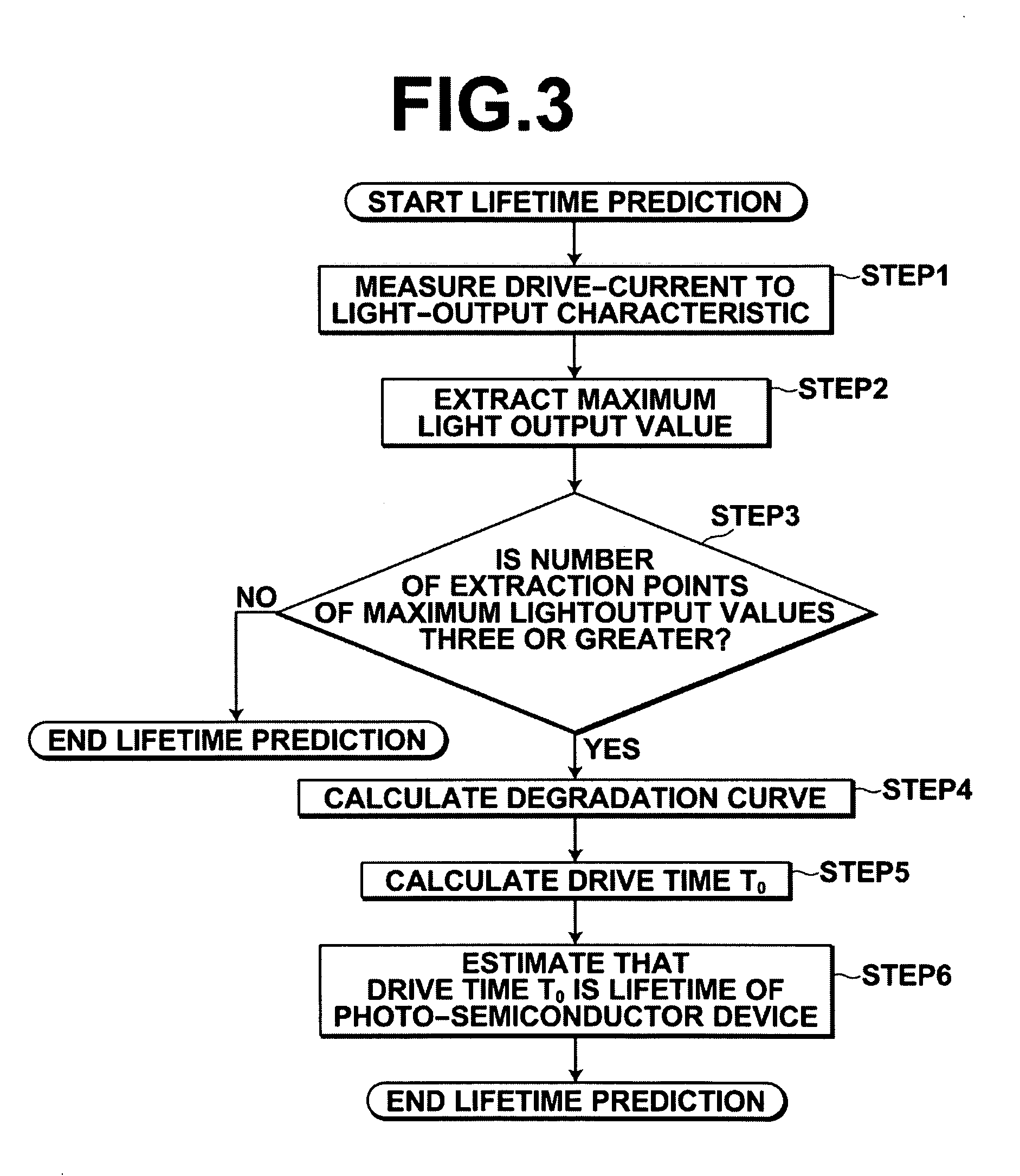
Method for predicting lifetime of photo-semiconductor device and drive apparatus
ActiveUS20090254287A1Wasteful operation can be preventedUsed economicallyPlug gaugesLaser detailsDriving currentDevice material
In a method for predicting the lifetime of a photo-semiconductor device that has a maximum light output value restricted by thermal saturation, the maximum light output value is extracted by measuring the characteristic of light output from the photo-semiconductor device with respect to drive current. The decrease tendency of the maximum output values with respect to drive time is predicted to predict the lifetime of the photo-semiconductor. Further, the predicted lifetime is updated as time passes. Therefore, in this method, even if drive condition changes, or an individual difference of the photo-semiconductor per se is present, it is possible to substantially accurately predict the lifetime of the photo-semiconductor.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Method of manufacturing bulk single crystal of gallium nitride
InactiveUS20040244680A1Quality improvementEasy to controlPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsSolventIon
The present invention provides a process for forming a bulk monocrystalline gallium nitride by using supercritical ammonia. The process comprises the steps of forming a supercritical solvent containing ion or ions of alkali metals in an autoclave; and dissolving a monocrystalline gallium nitride prepared by flux methods as a feedstock in this supercritical solvent to form a supercritical solution, and simultaneously or separately recrystallizing gallium nitride on the face of a seed.
Owner:AMMONO SP Z O O (PL) +1
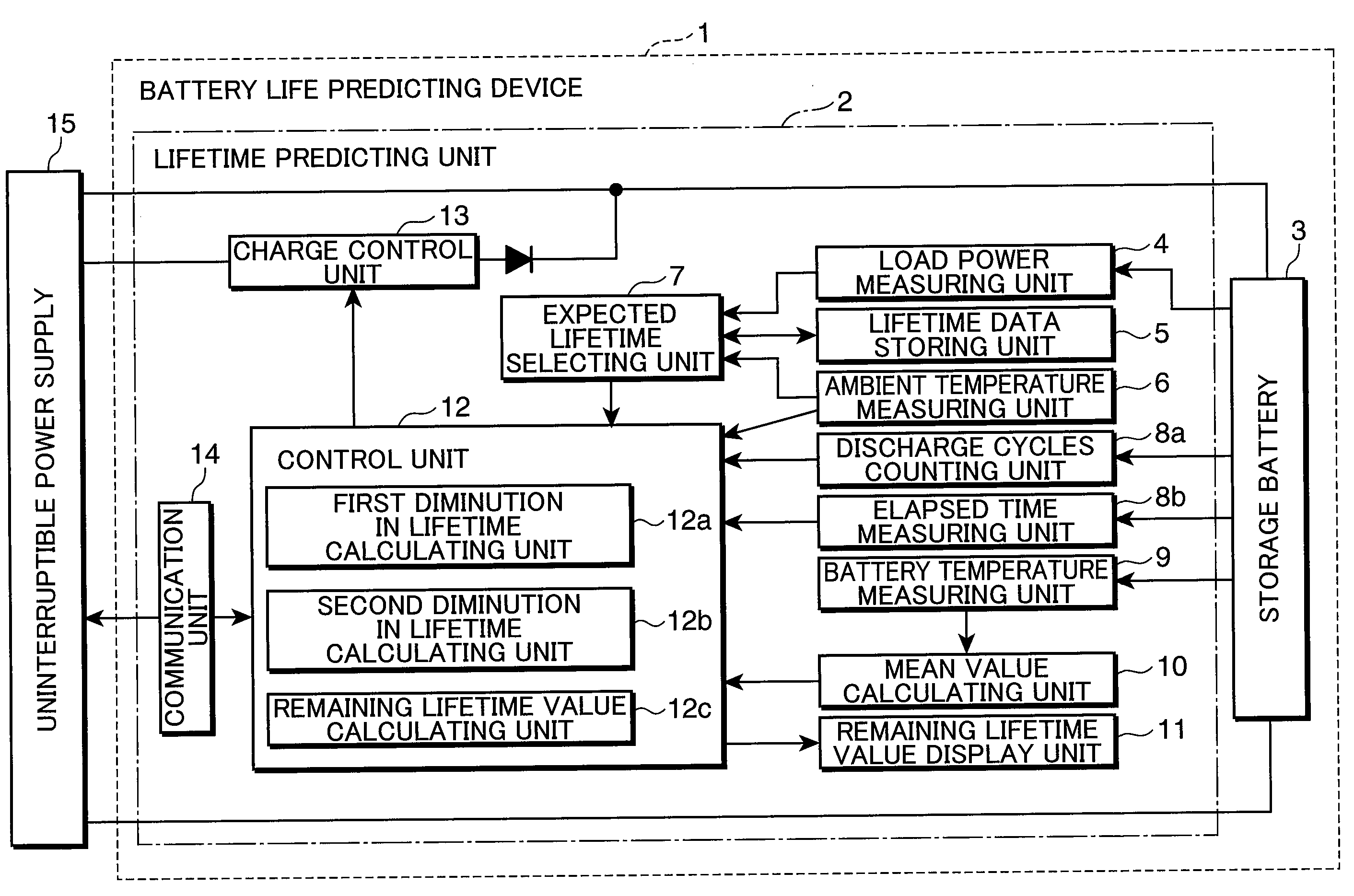
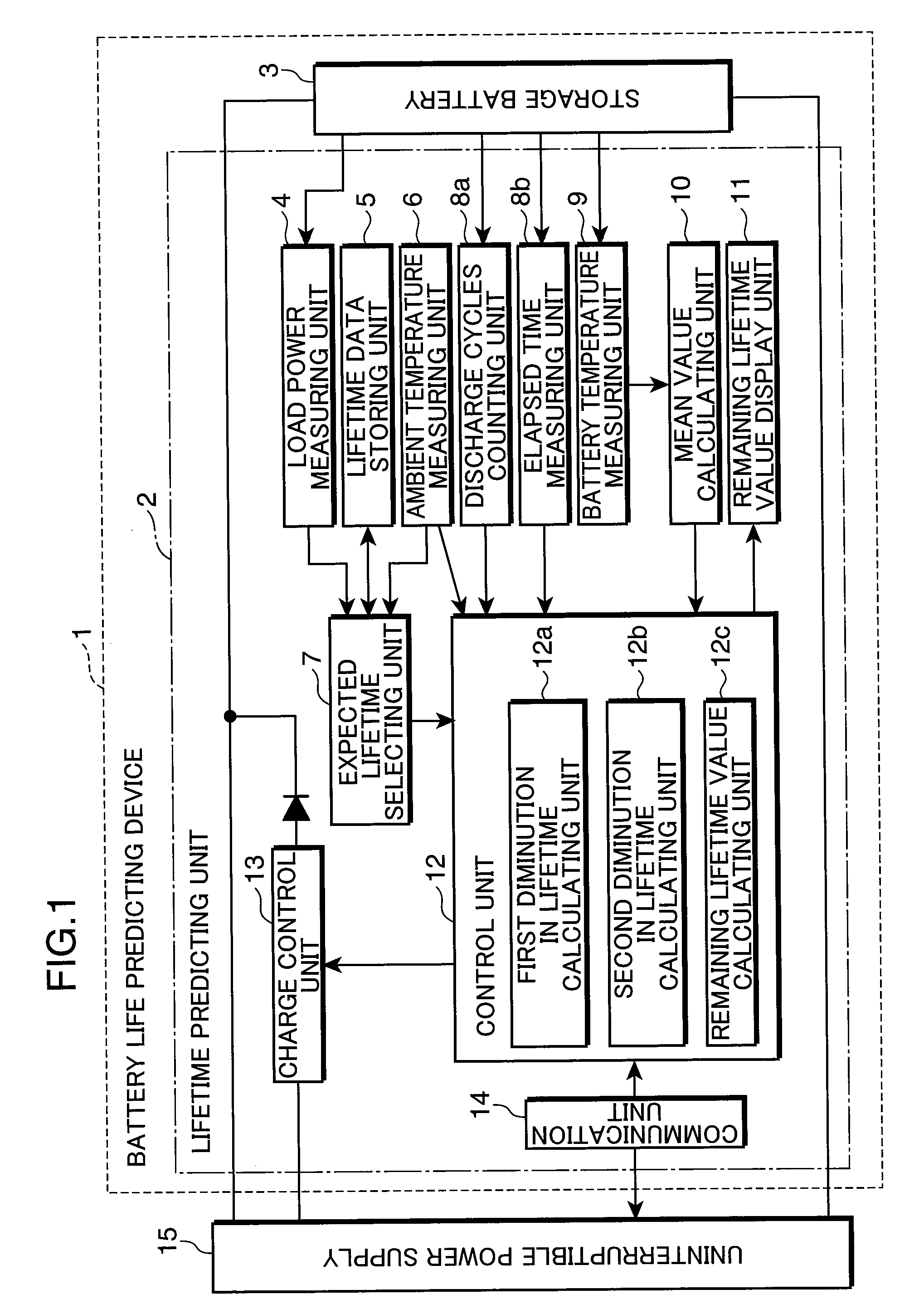
Battery life predicting device and battery life predicting method
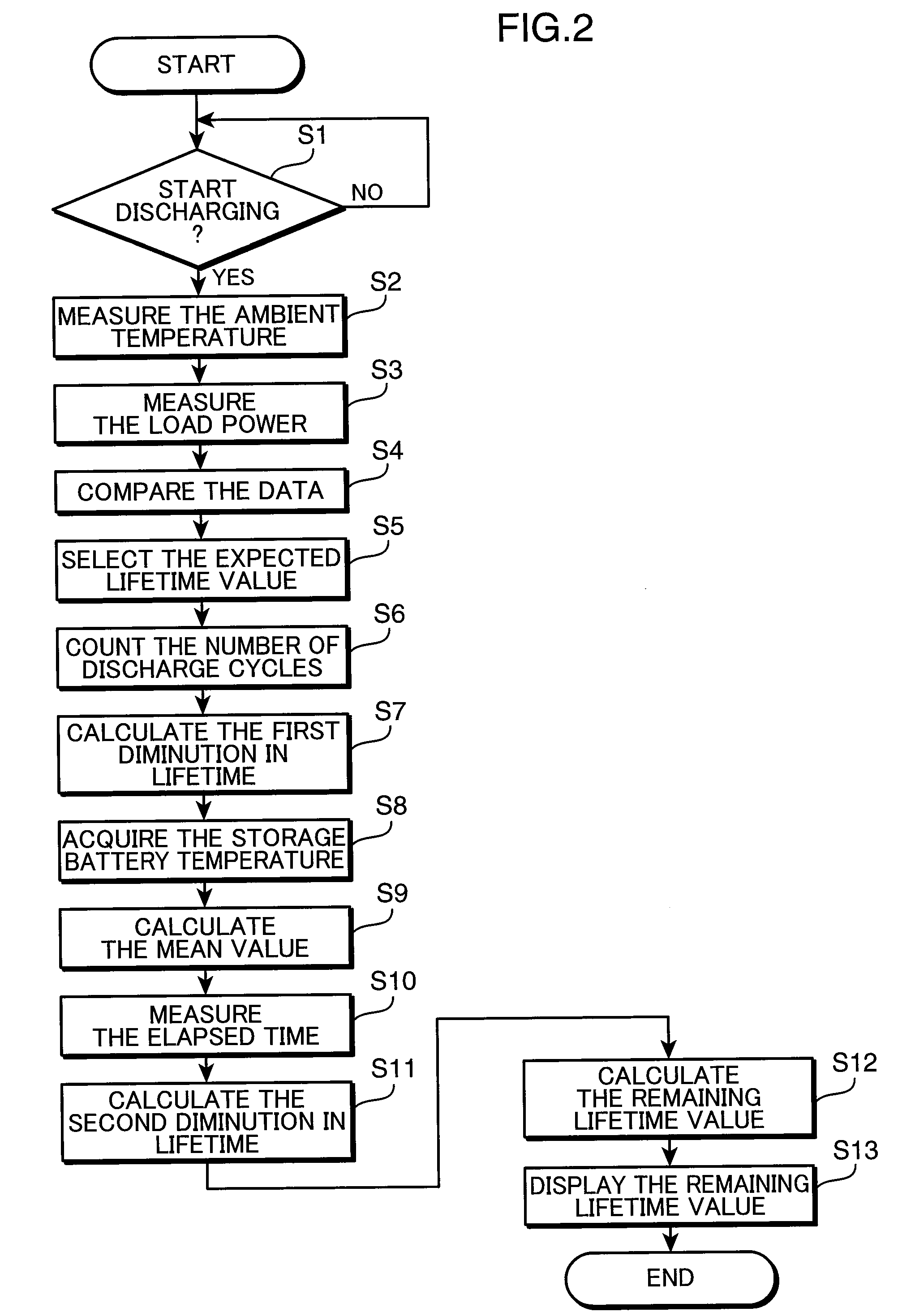
InactiveUS20090037145A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedAccurate predictionBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLife expectancyLongevity
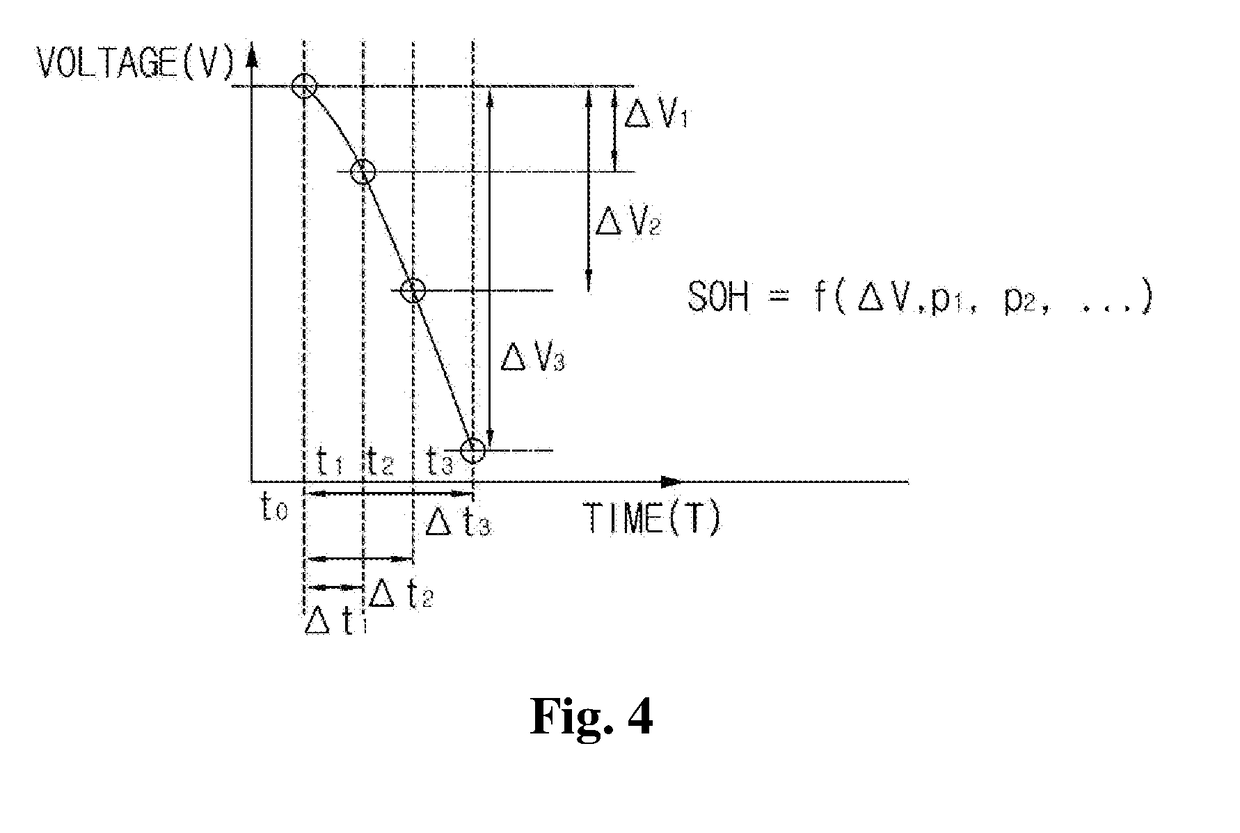
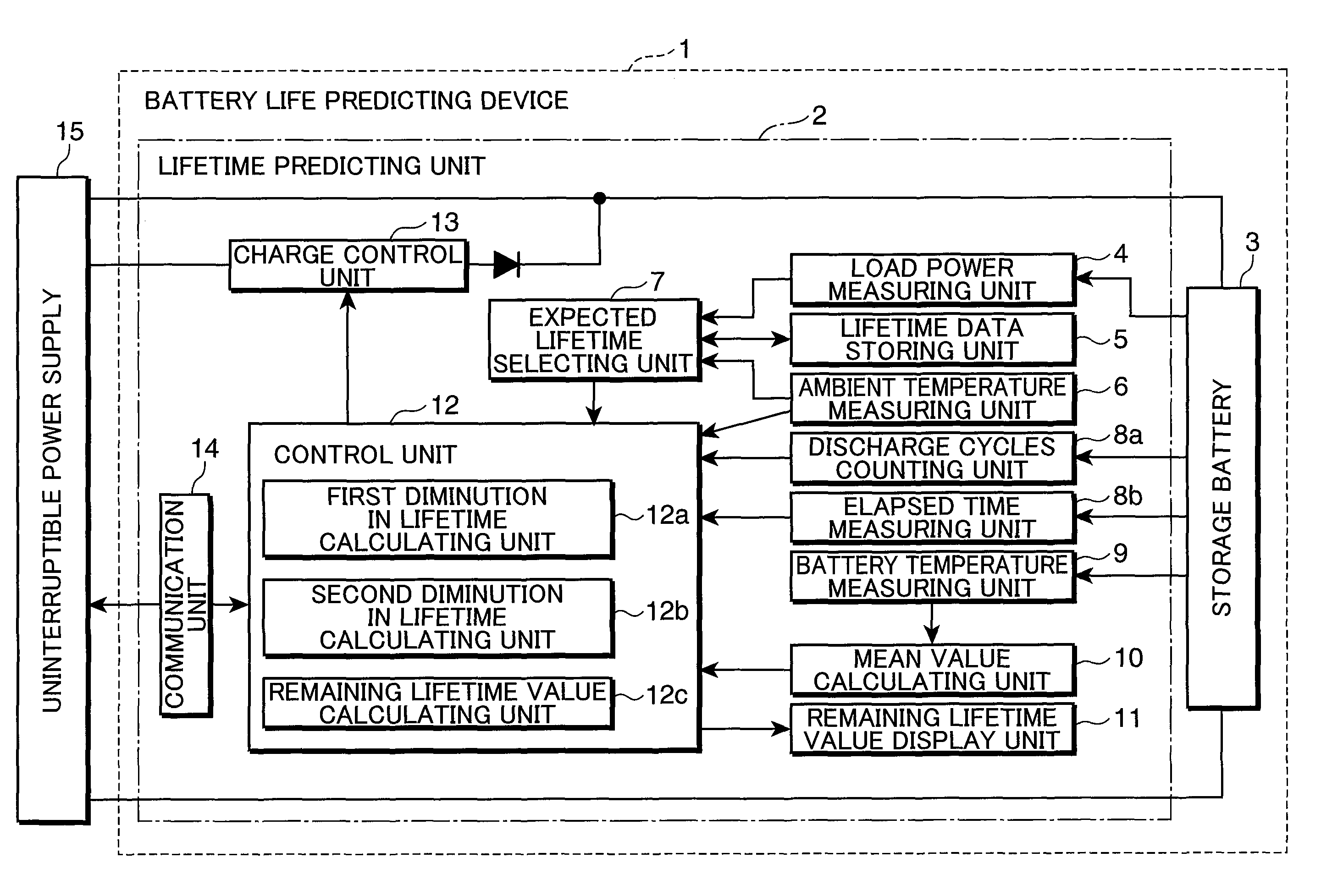
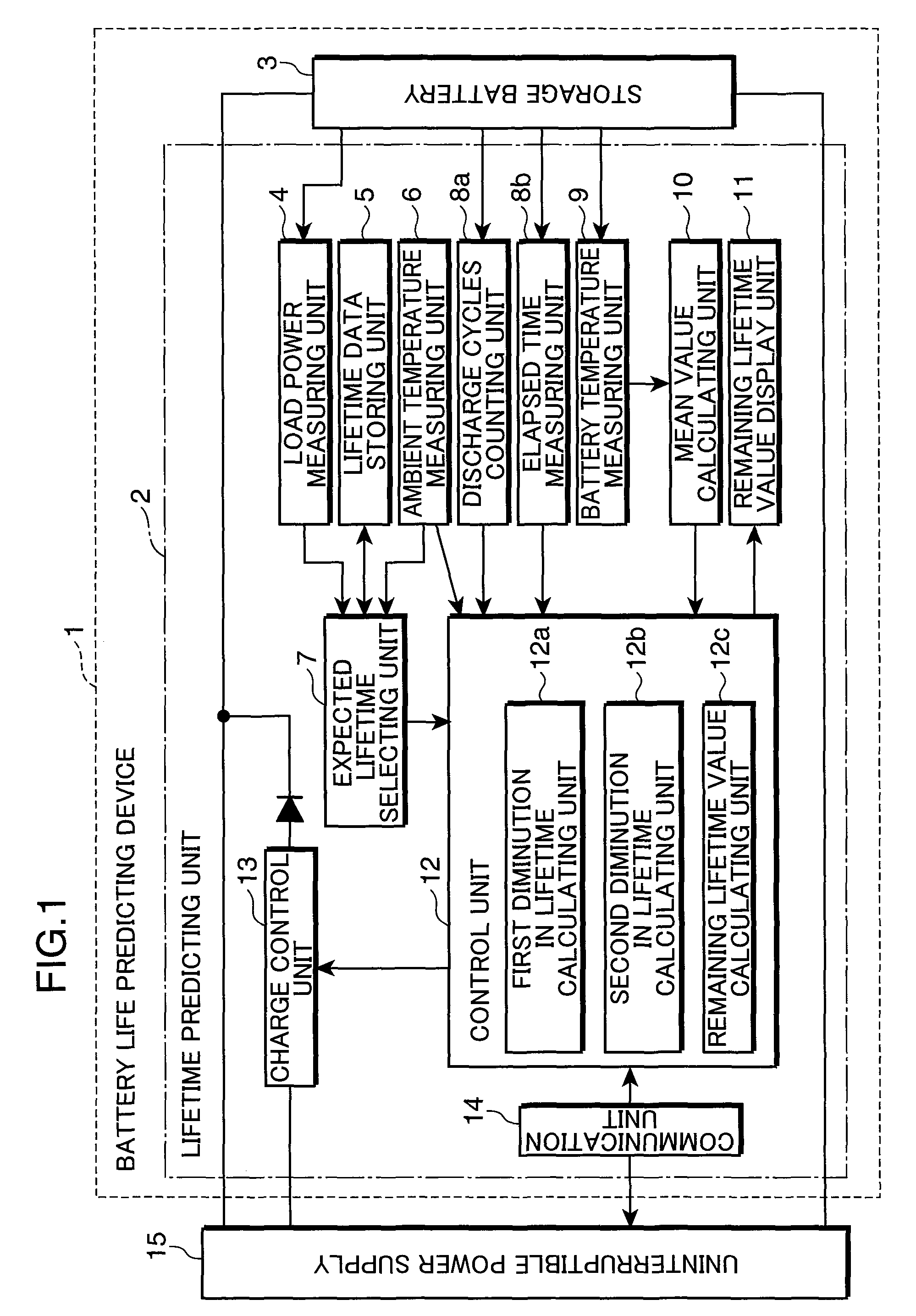
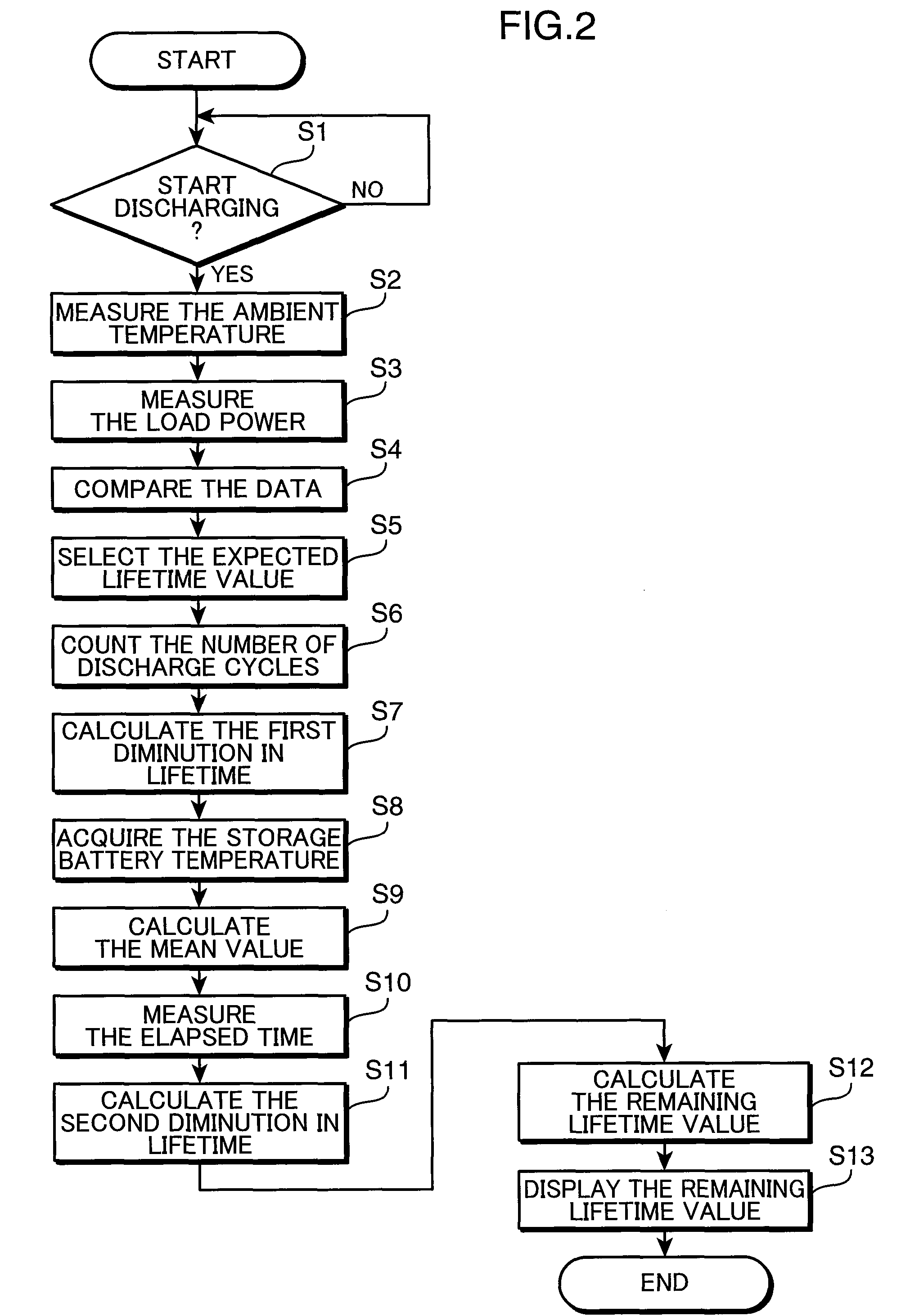
A battery life predicting device and a battery life predicting method capable of accurately predict the lifetime of storage batteries are provided.The expected lifetime value selecting unit 7 selects, as an expected lifetime value, a lifetime value that corresponds to the load power applied by the storage battery during discharge and the ambient temperature of the location where the storage battery 3 is installed while referring to the lifetime data stored in the lifetime data storing unit 5, the first diminution in lifetime calculating unit 12a calculates the first diminution in lifetime based on a natural logarithm function that takes the time obtained by converting the number of discharge cycles of the storage battery 3 as a variable, the second diminution in lifetime calculating unit 12b calculates the second diminution in lifetime from the mean value of the storage battery temperatures during charging, discharging or an idle state, the ambient temperature and the time elapsed after the installation of the storage battery 3, and the remaining lifetime value calculating unit 12c calculates the remaining lifetime value by subtracting the first diminution in lifetime and the second diminution in lifetime from the expected lifetime value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
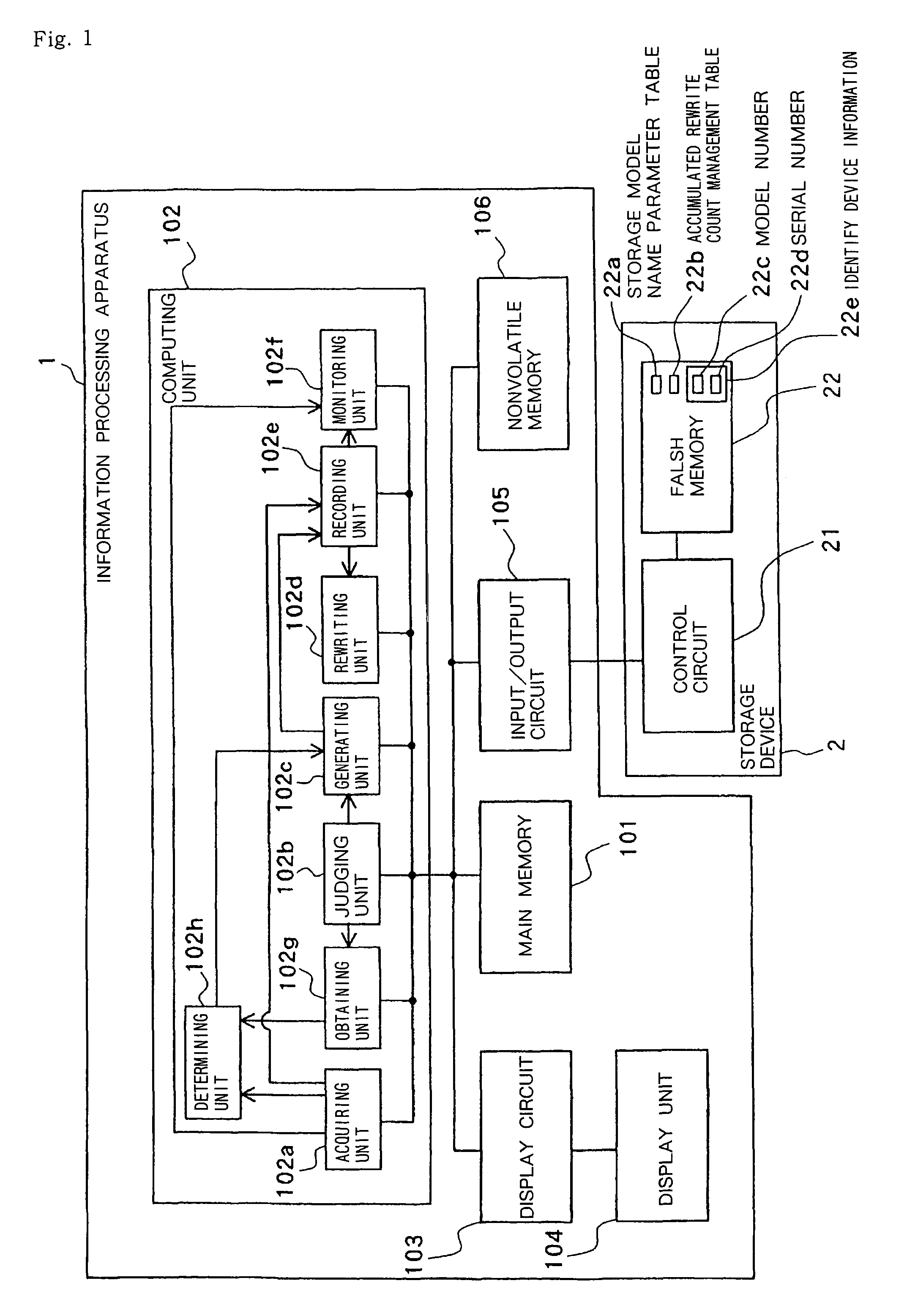
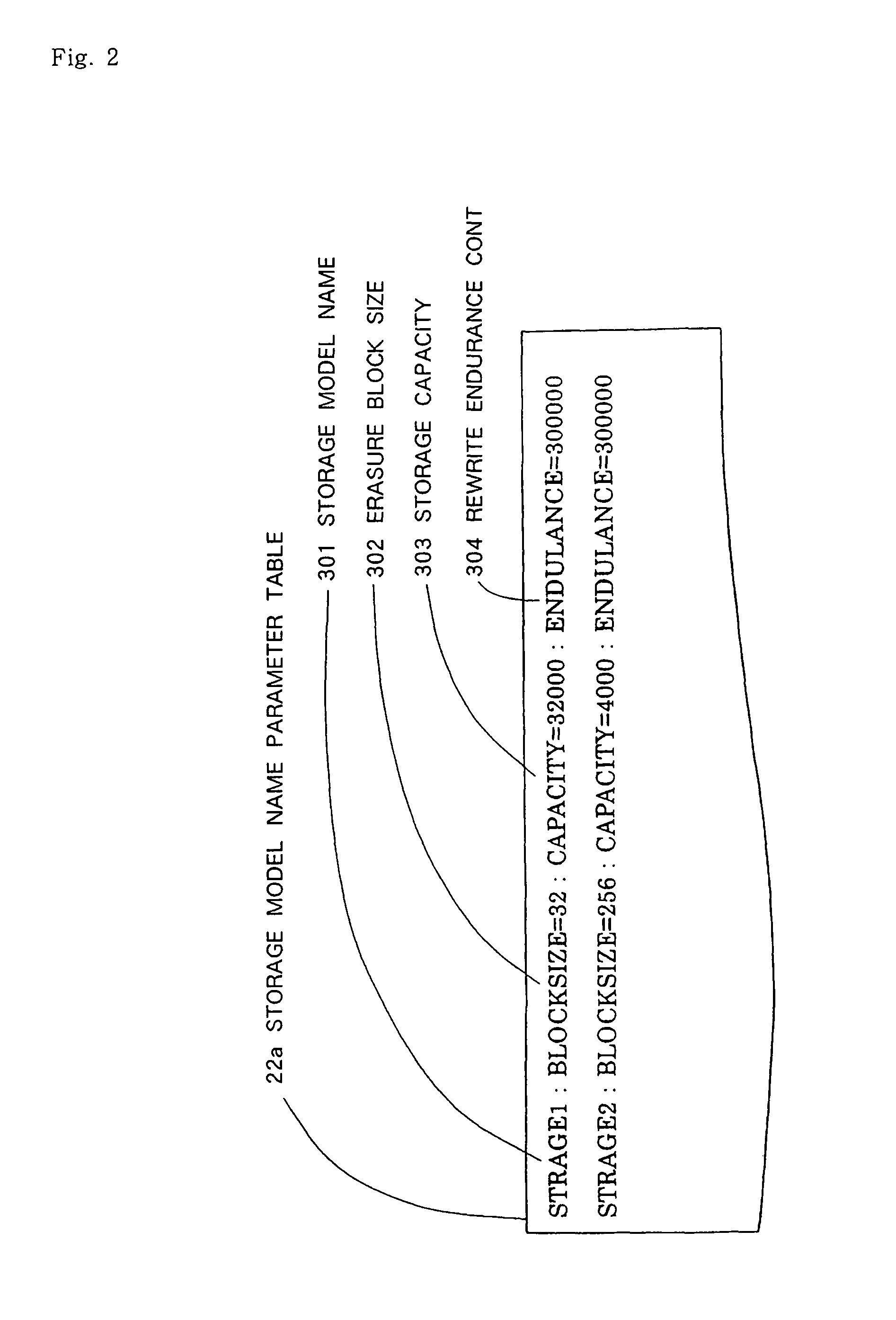
Information processing apparatus, lifetime monitoring method and program for monitoring lifetime of storage device including flash memory
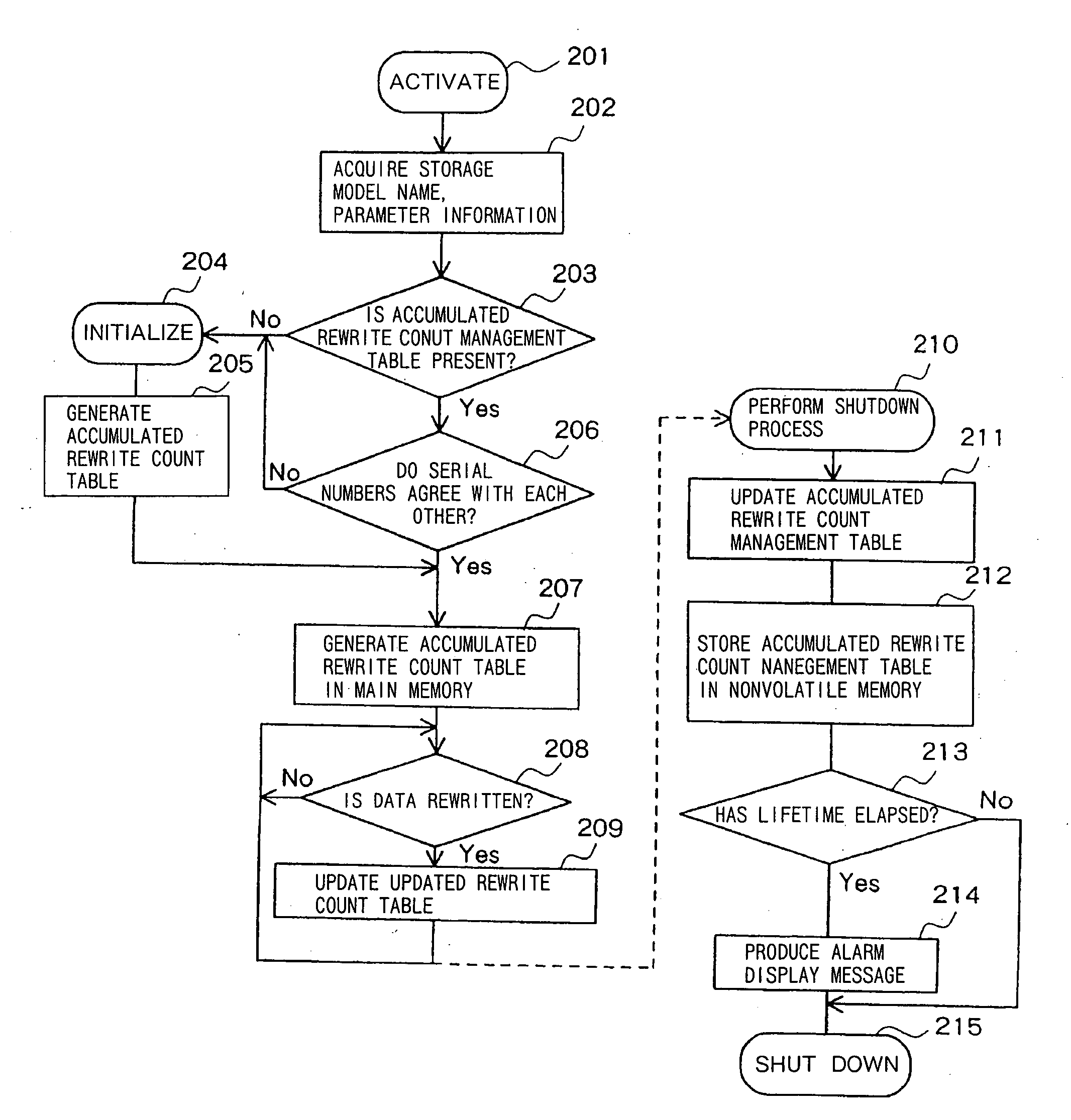
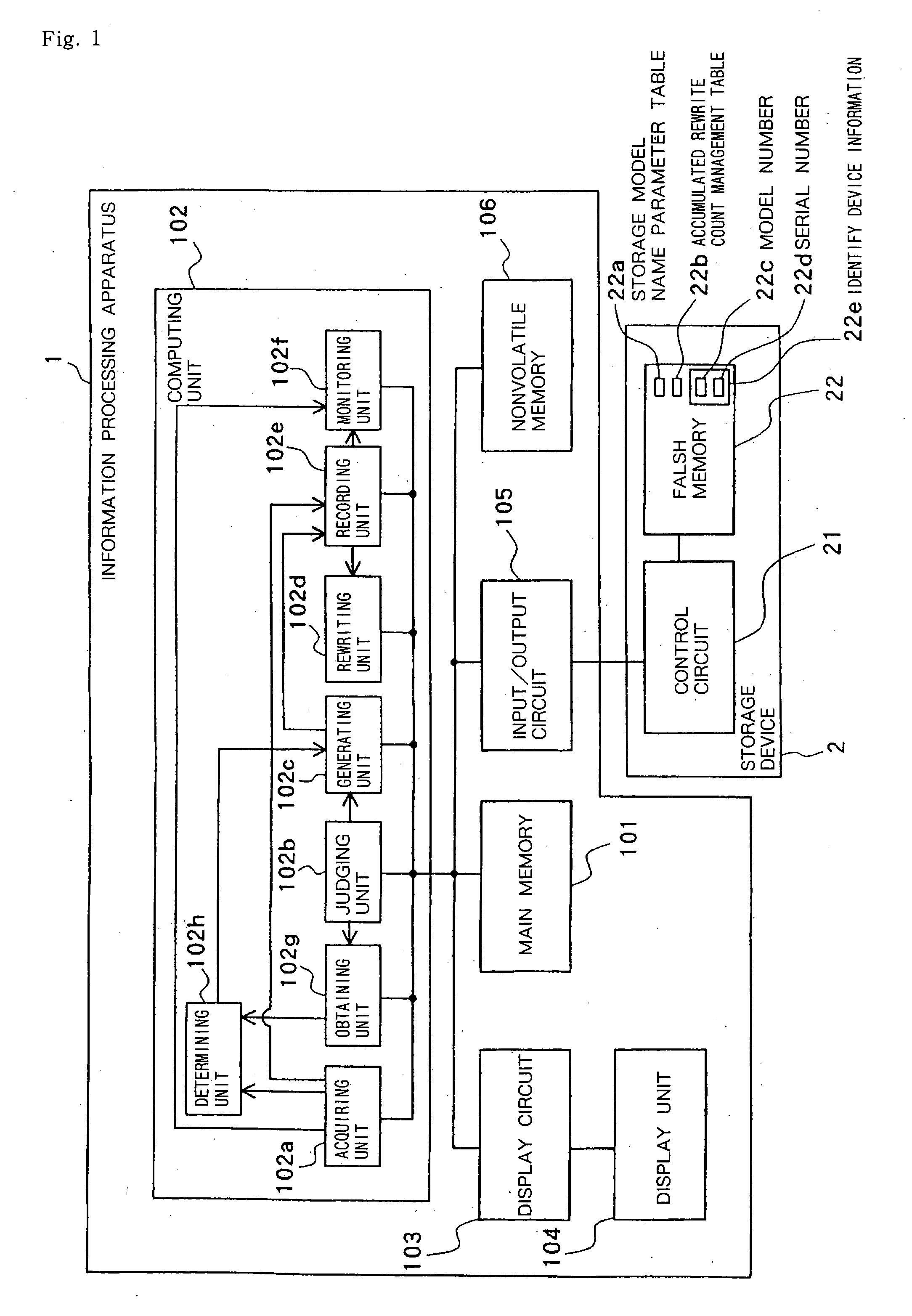
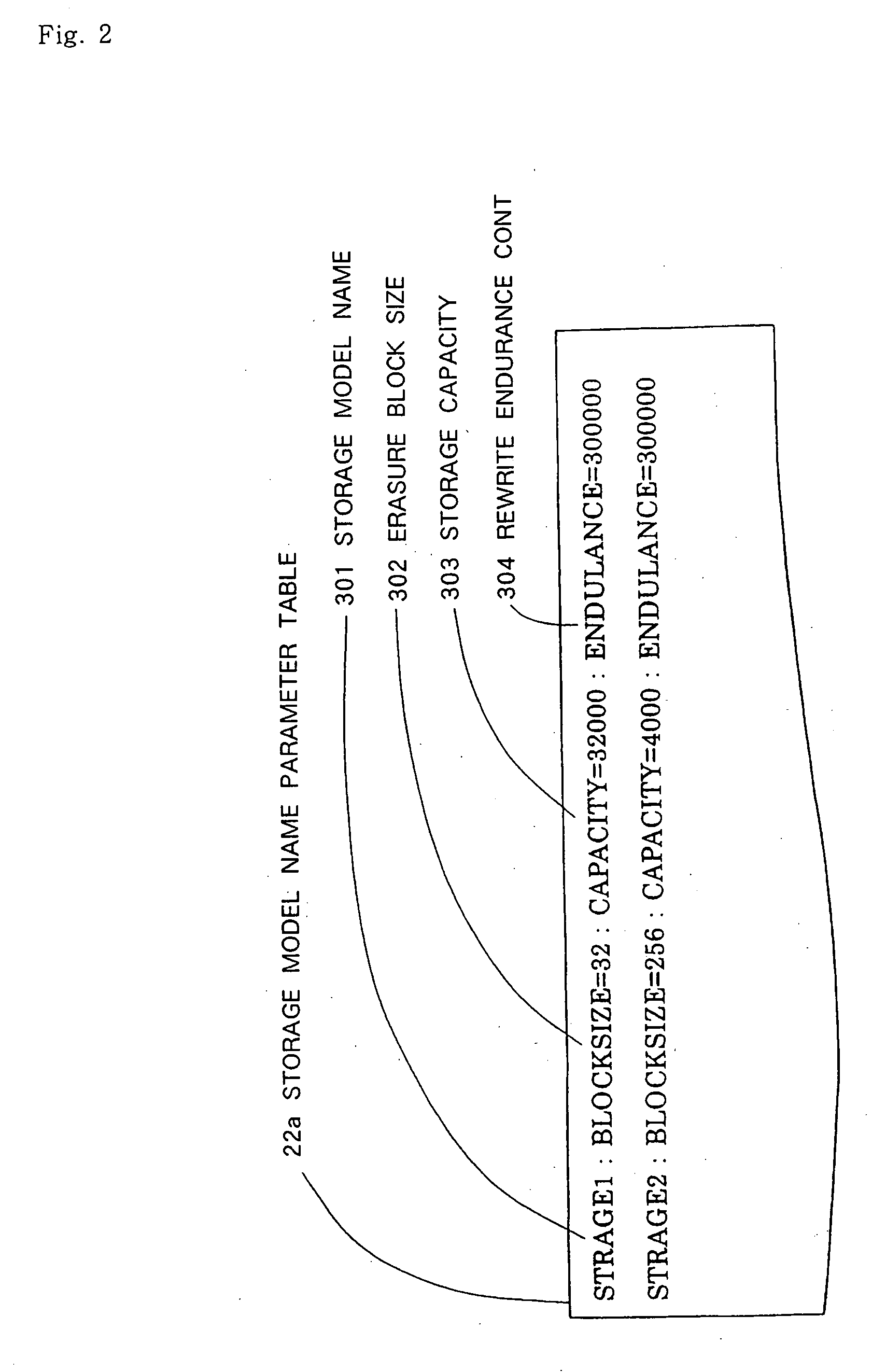
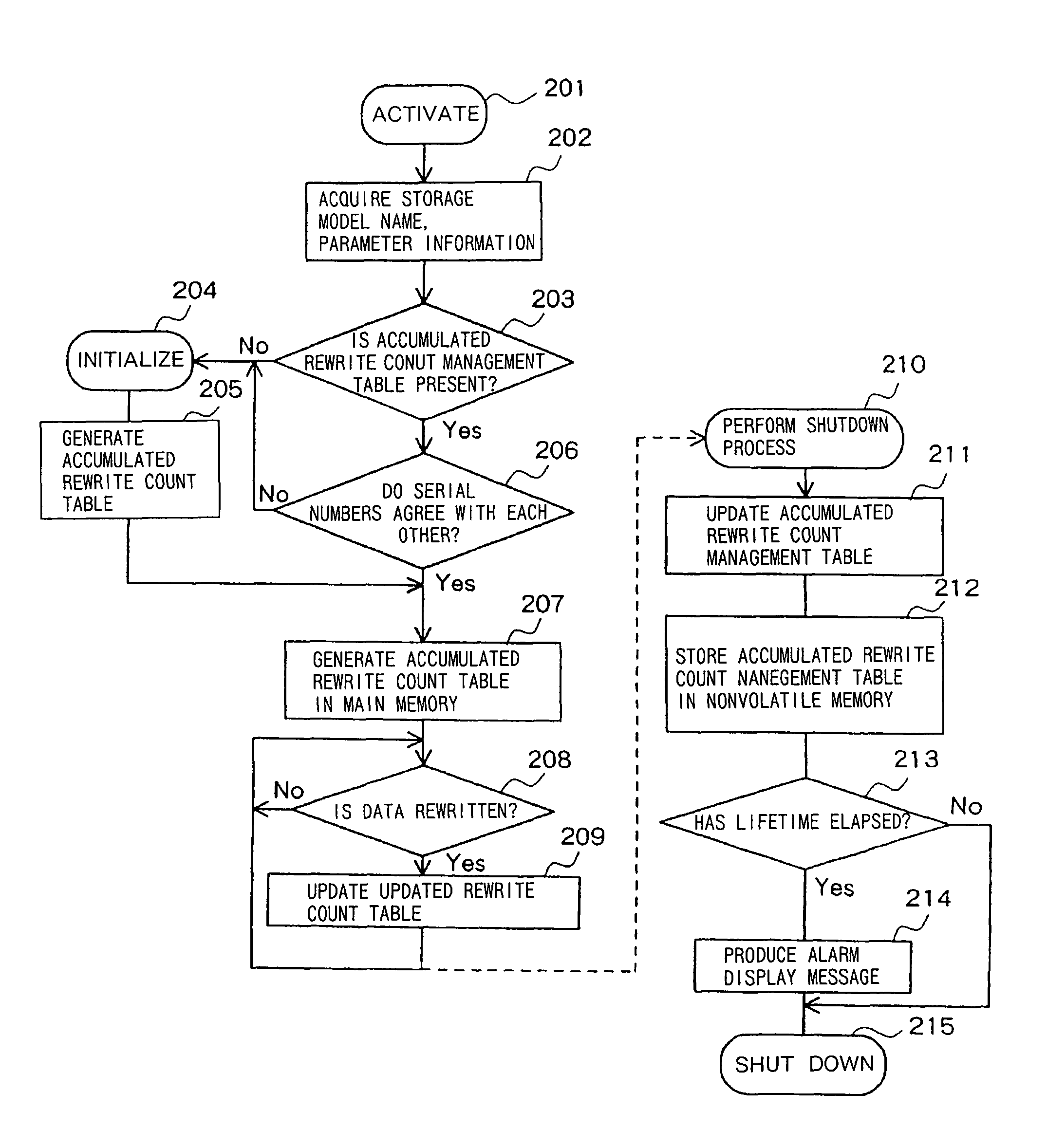
ActiveUS20060265545A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedImprove accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesInformation processingGenerating unit
A judging unit determines whether an accumulated rewrite count management table is in a flash memory. If the accumulated rewrite count management table is not in the flash memory, then a generating unit generates an accumulated rewrite count management table in the flash memory, and a recording unit records an accumulated rewrite count in the accumulated rewrite count management table which is generated. A monitoring unit monitors the lifetime of a storage device based on the accumulated rewrite count recorded in the accumulated rewrite count management table and a rewrite count limitative value recorded in the flash memory.
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
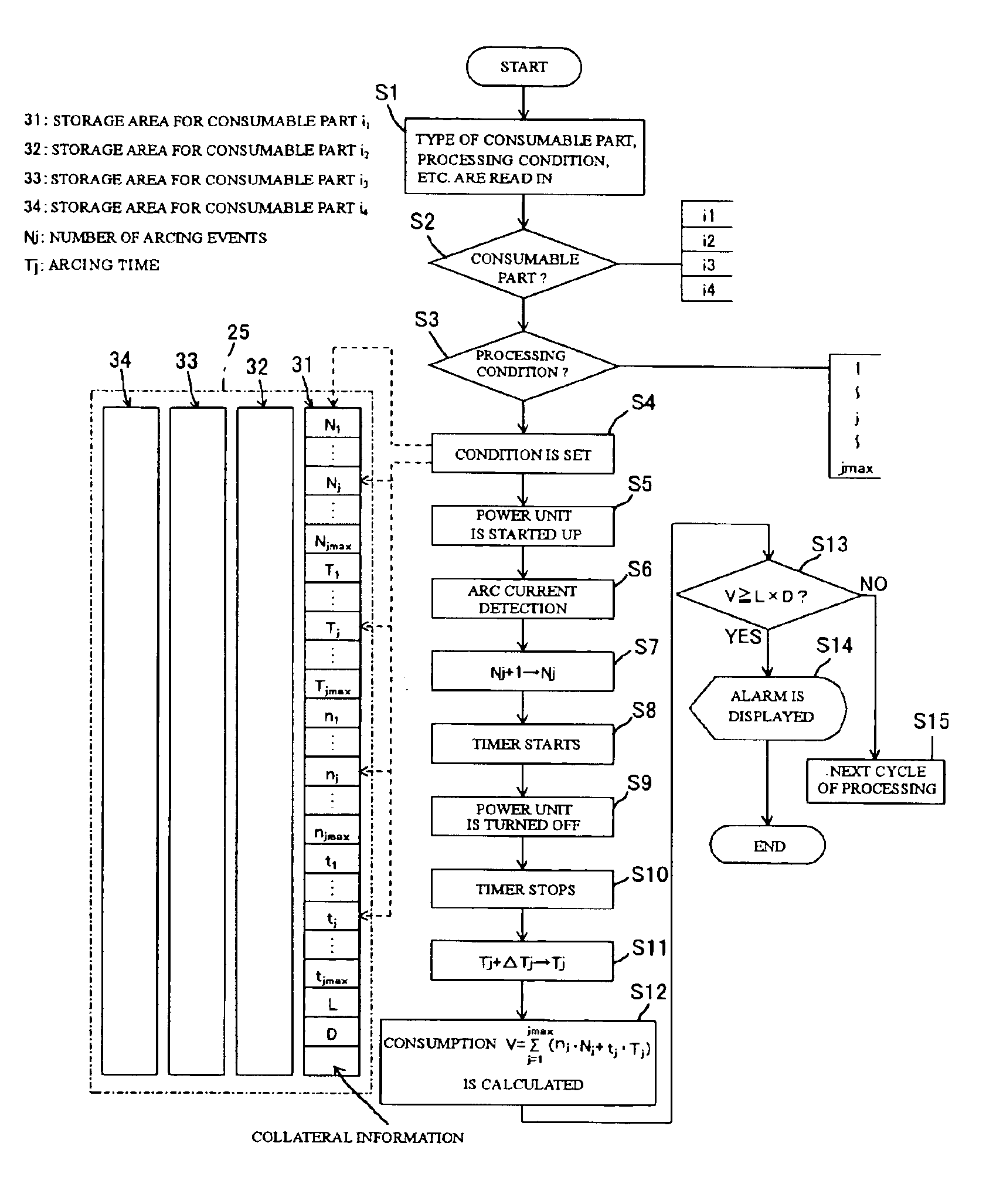
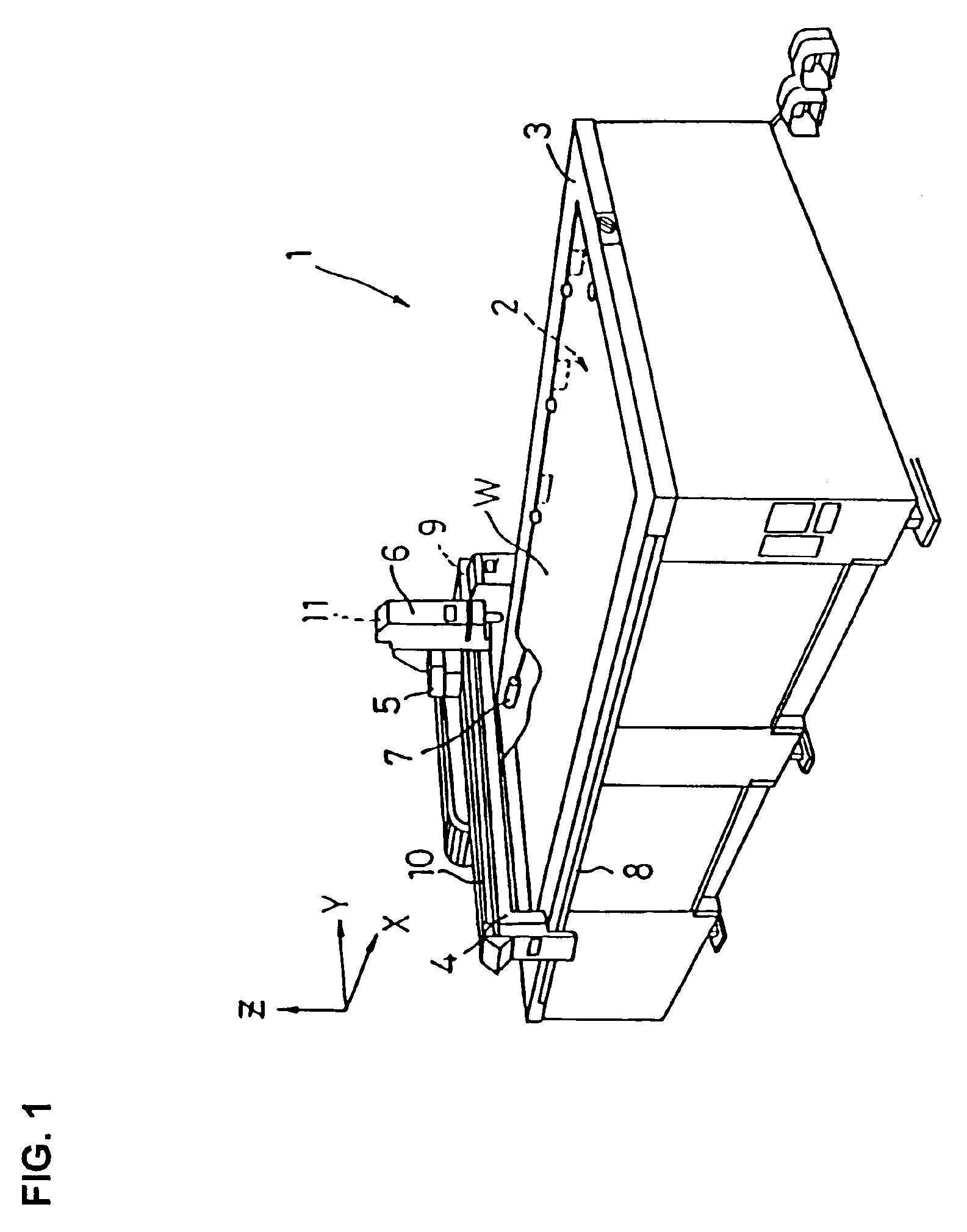
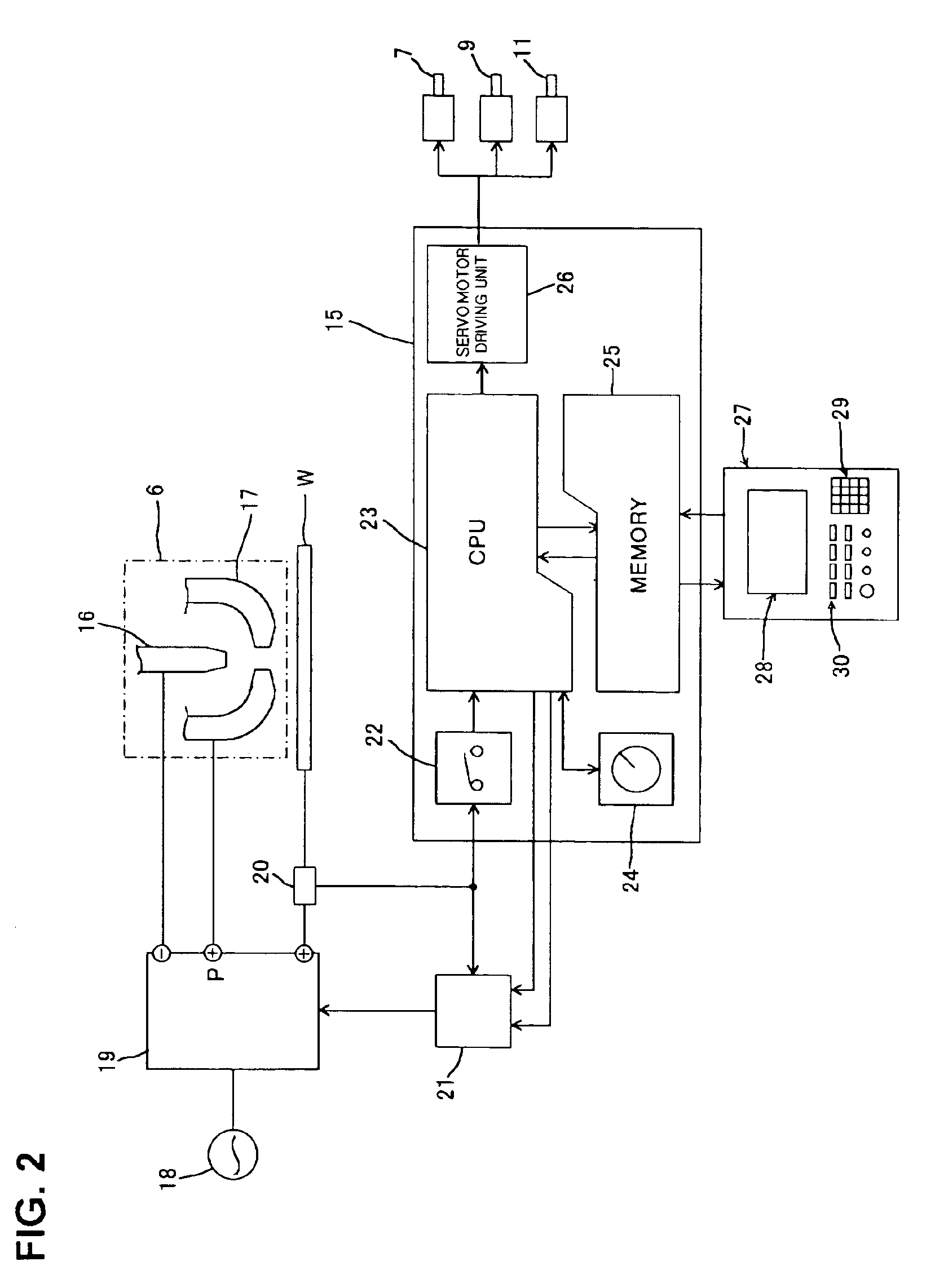
Plasma processing apparatus for monitoring and storing lifetime usage data of a plurality of interchangeable parts
InactiveUS6933462B2SavesImprove automationPlasma welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsEngineeringInterchangeable parts
A plasma processing apparatus capable of making an accurate lifetime assessment for each of plural consumable parts (the definition of “the consumable part” is an electrode and / or a nozzle) so that effective use of the consumable parts becomes possible leading to reduced running cost. In the plasma processing apparatus, a plasma arc is generated from a plasma torch composed of an electrode and a nozzle to perform plasma work on a workpiece. Such a plasma processing apparatus includes a plurality of consumable parts, each consumable part being an electrode and / or a nozzle, and further comprises a memory for storing consumption data on every consumable part, the consumption data being used for calculation of consumption; and a display unit for displaying consumption calculated by a CPU for selecting the consumption data corresponding to a consumable part in use.
Owner:KOMATSU IND CORP
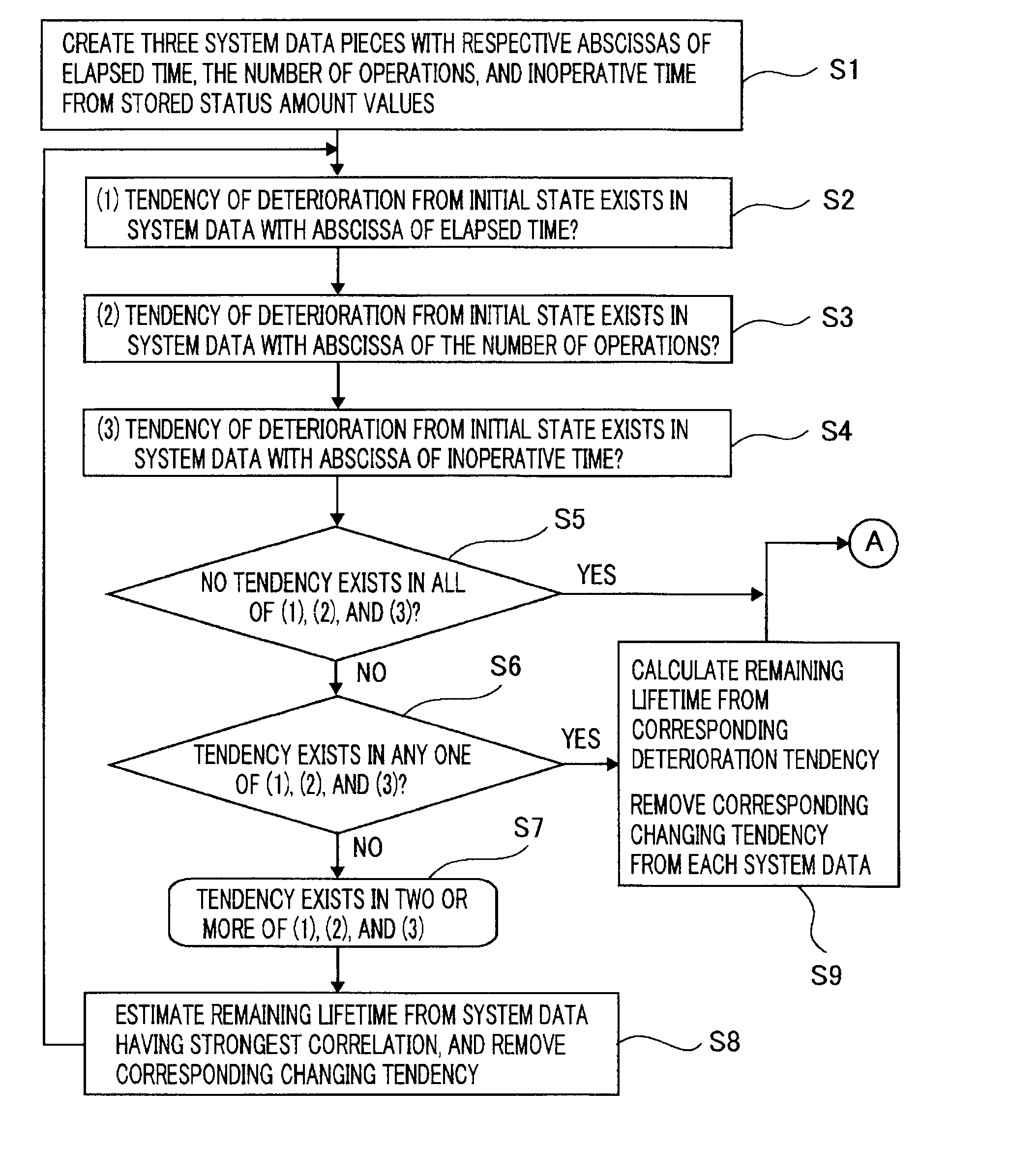
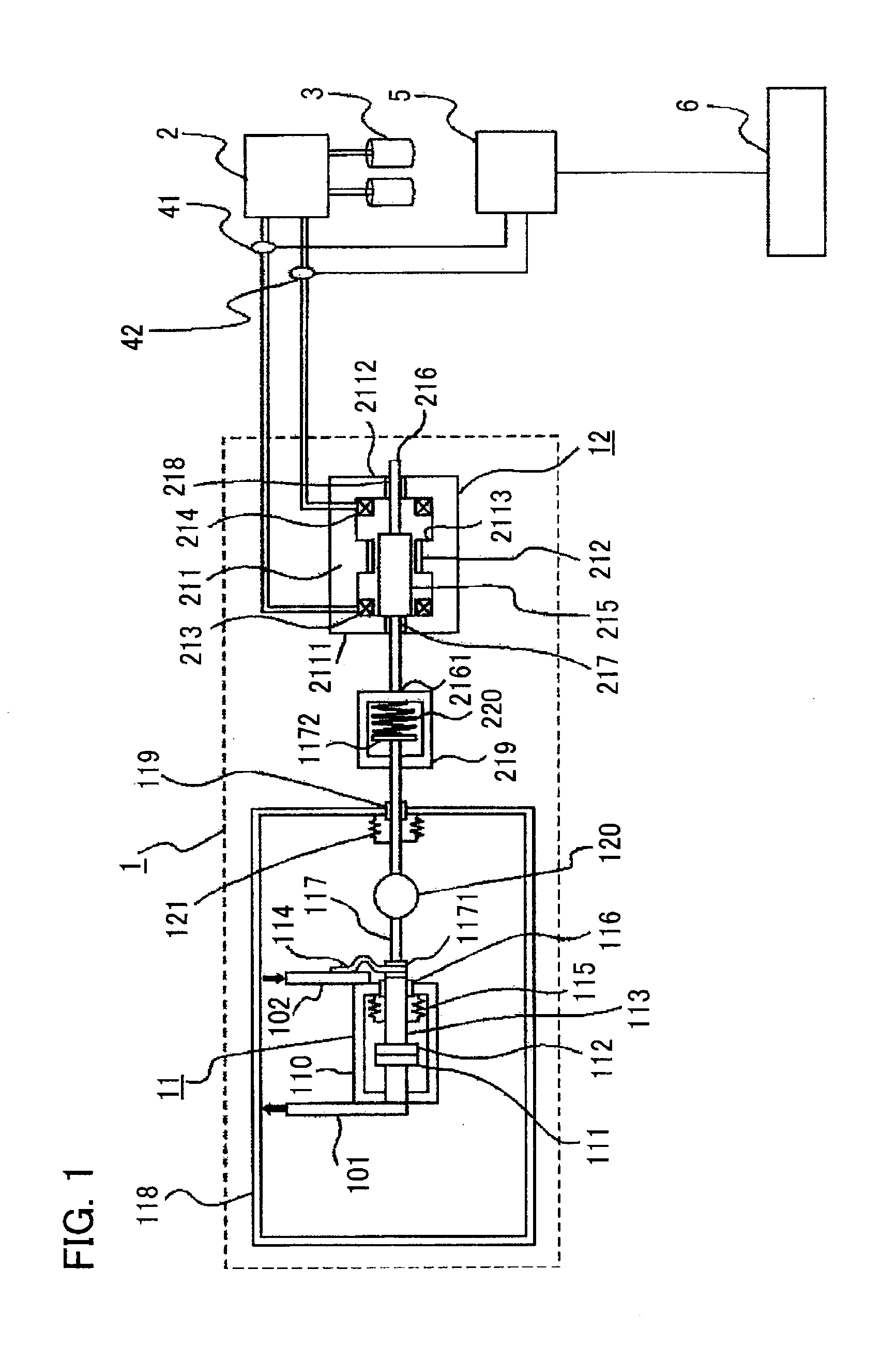
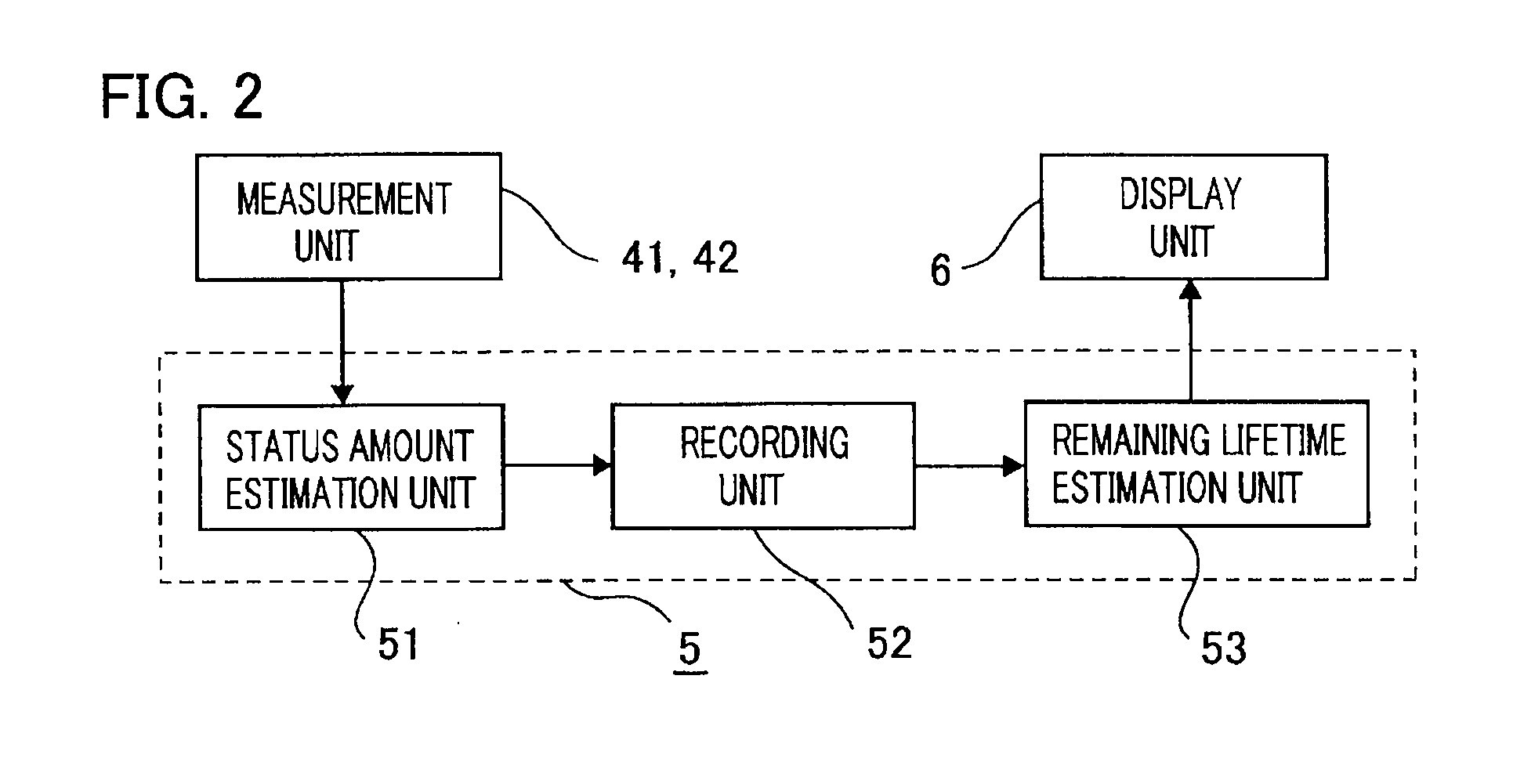
Switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis method and apparatus
ActiveUS20120022797A1Simple configurationLifetime be accurately estimatedProtective switch detailsPlug gaugesState dependentComputer science
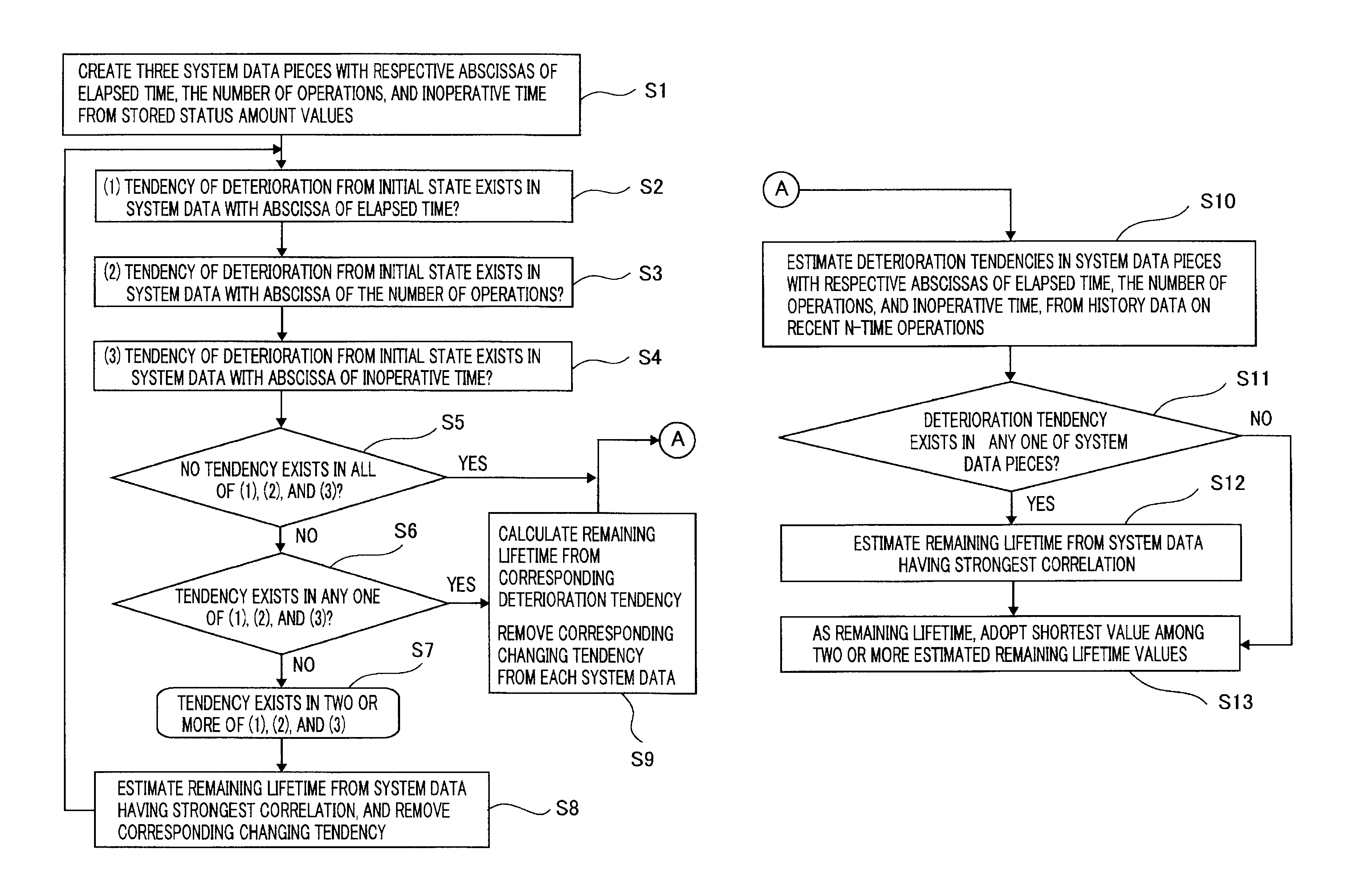
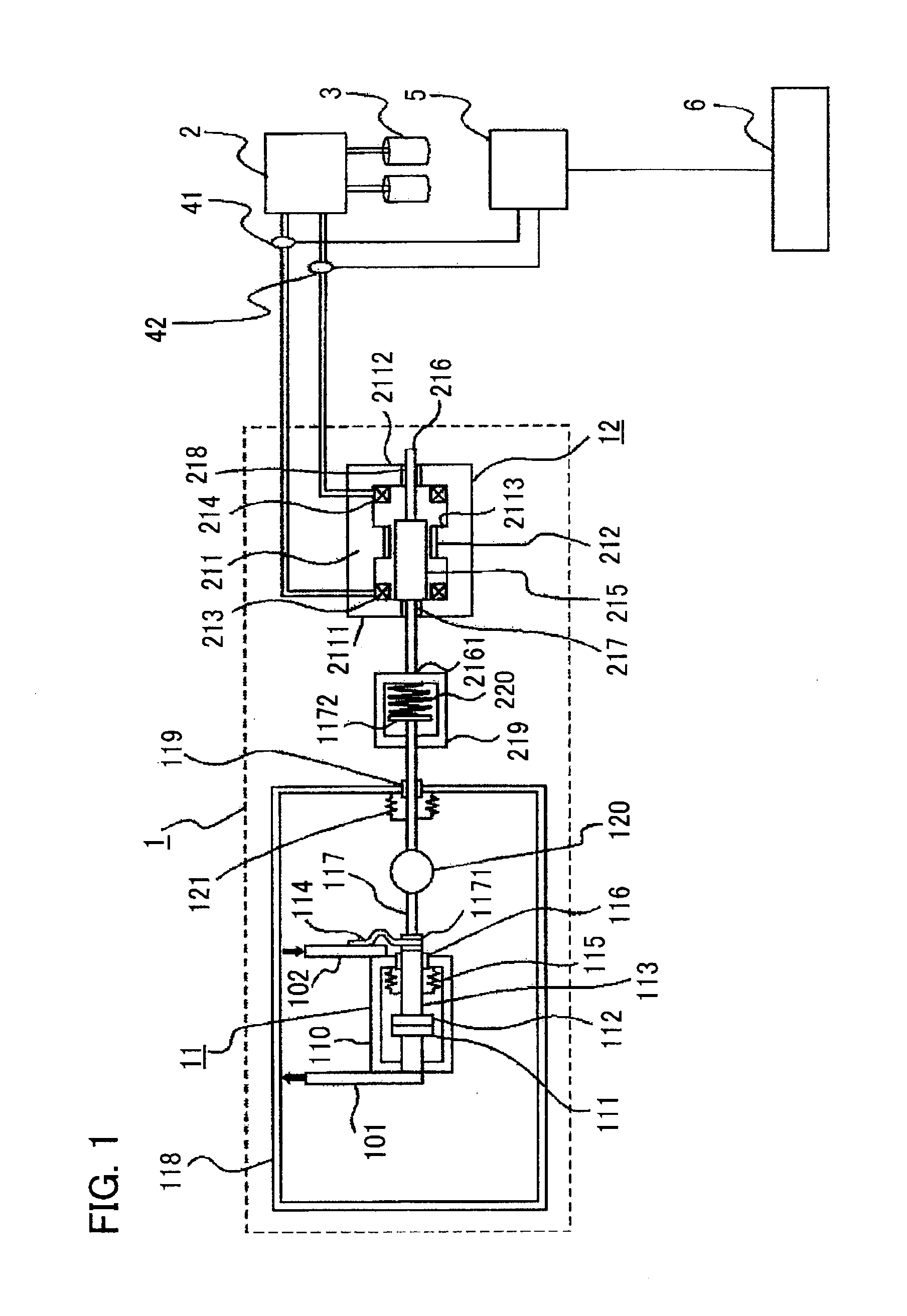
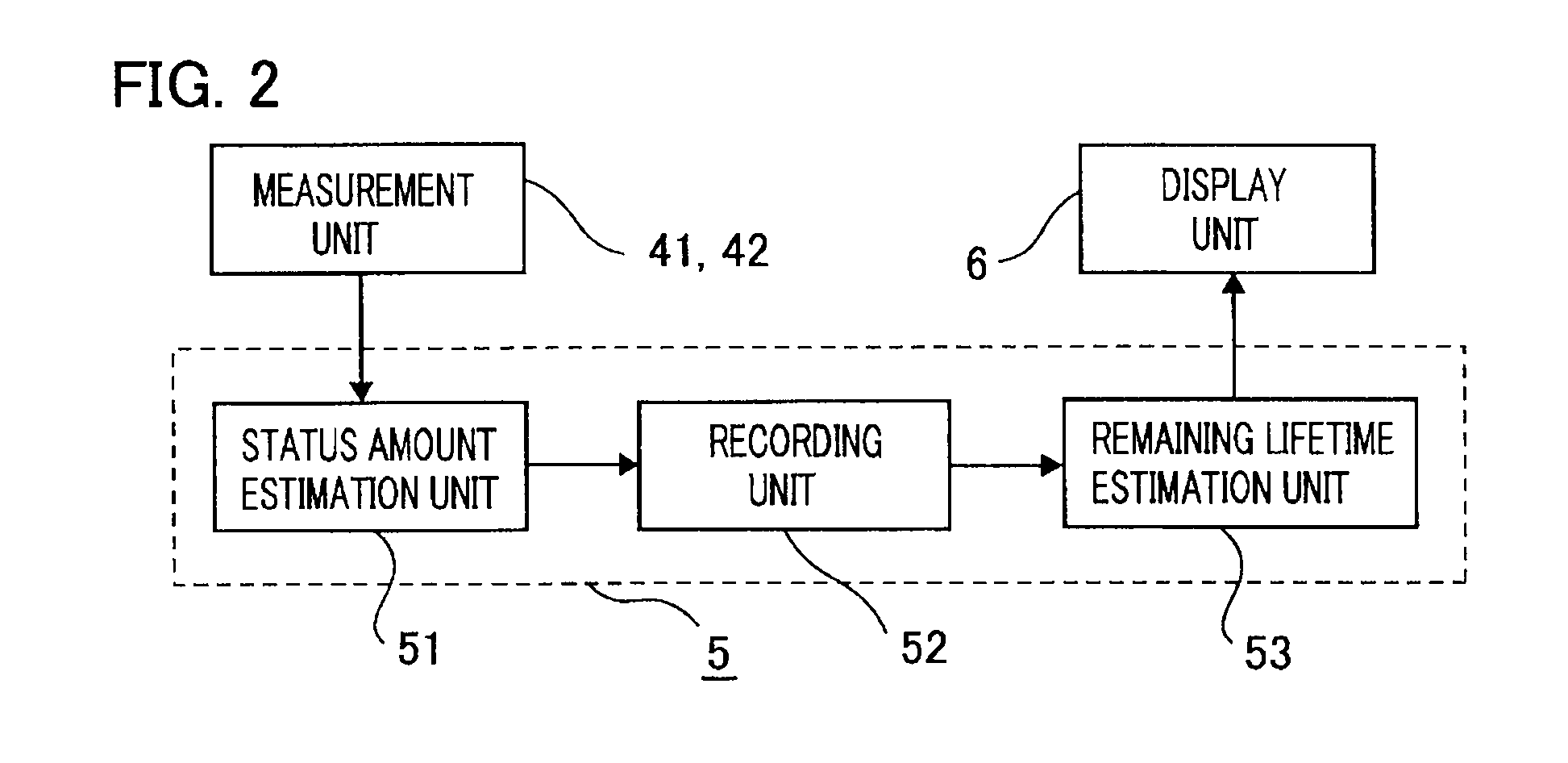
There are provided a switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis method and a switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis apparatus, wherein as status amount history data, there are accumulated status amounts related to a deterioration status of a switching device, estimated based on measurement data obtained through measurement of performance characteristics of the switching device; based on the accumulated status amount history data, there are created a plurality of system data pieces in which the status amounts are arranged with the respective abscissas of an elapsed time during an operation period of the switching device, the number of operations of the switching device, an inoperative time of the switching device, and an accumulated operation time of the switching device; based on the created system data pieces, the remaining lifetime of the switching device is estimated.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
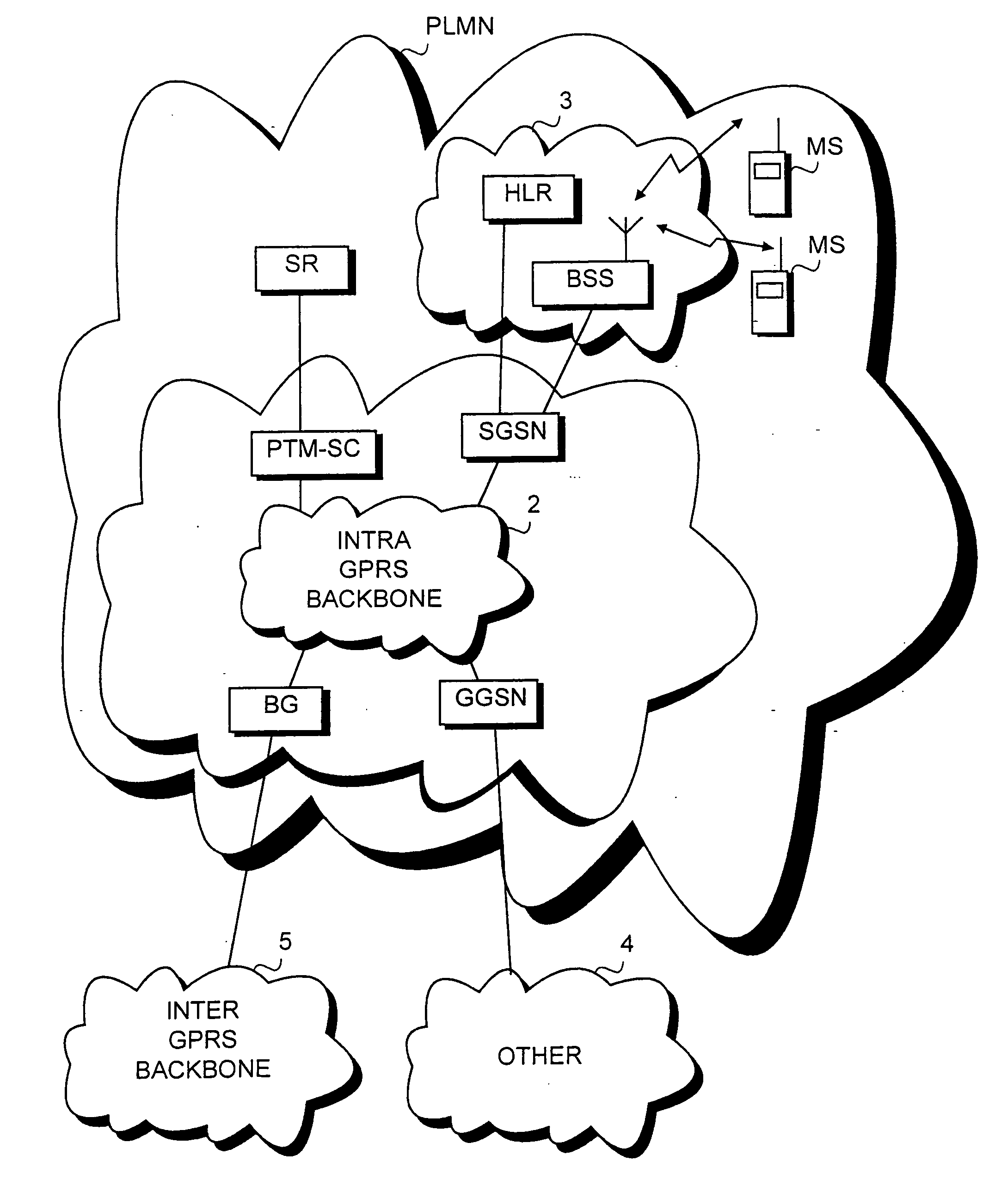
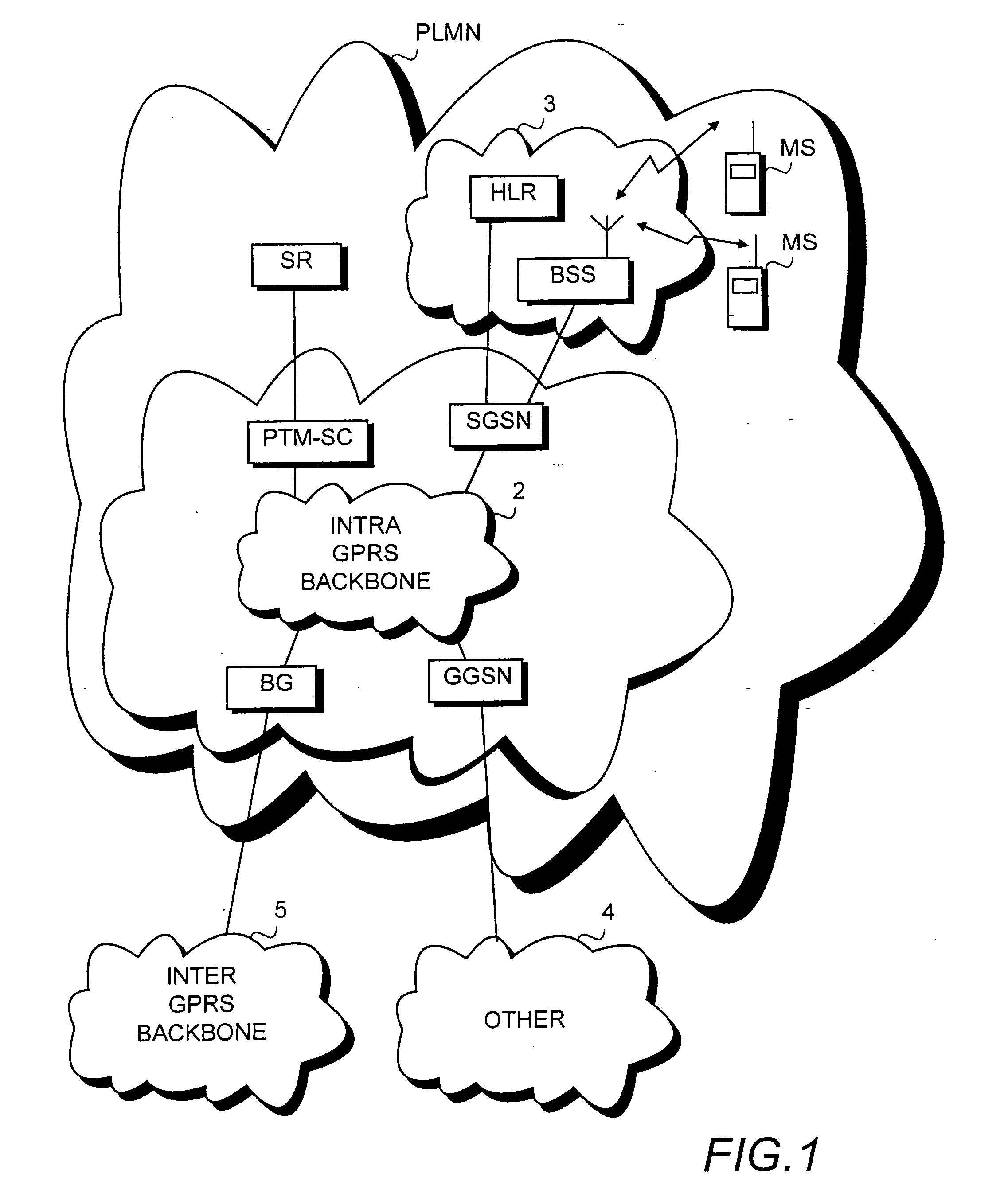
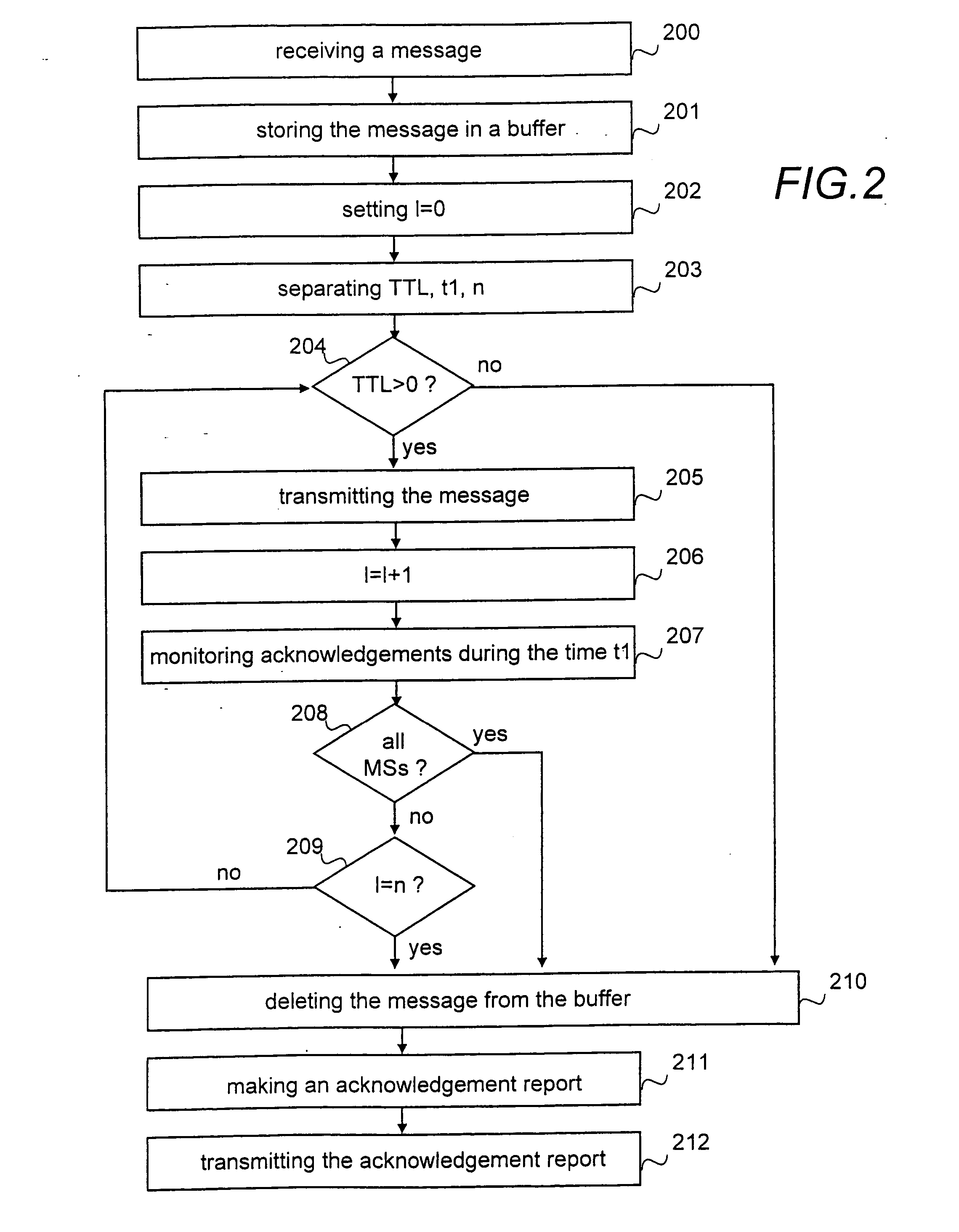
Method, system and a network element for controlling point-to-multipoint transmission in a mobile communication system
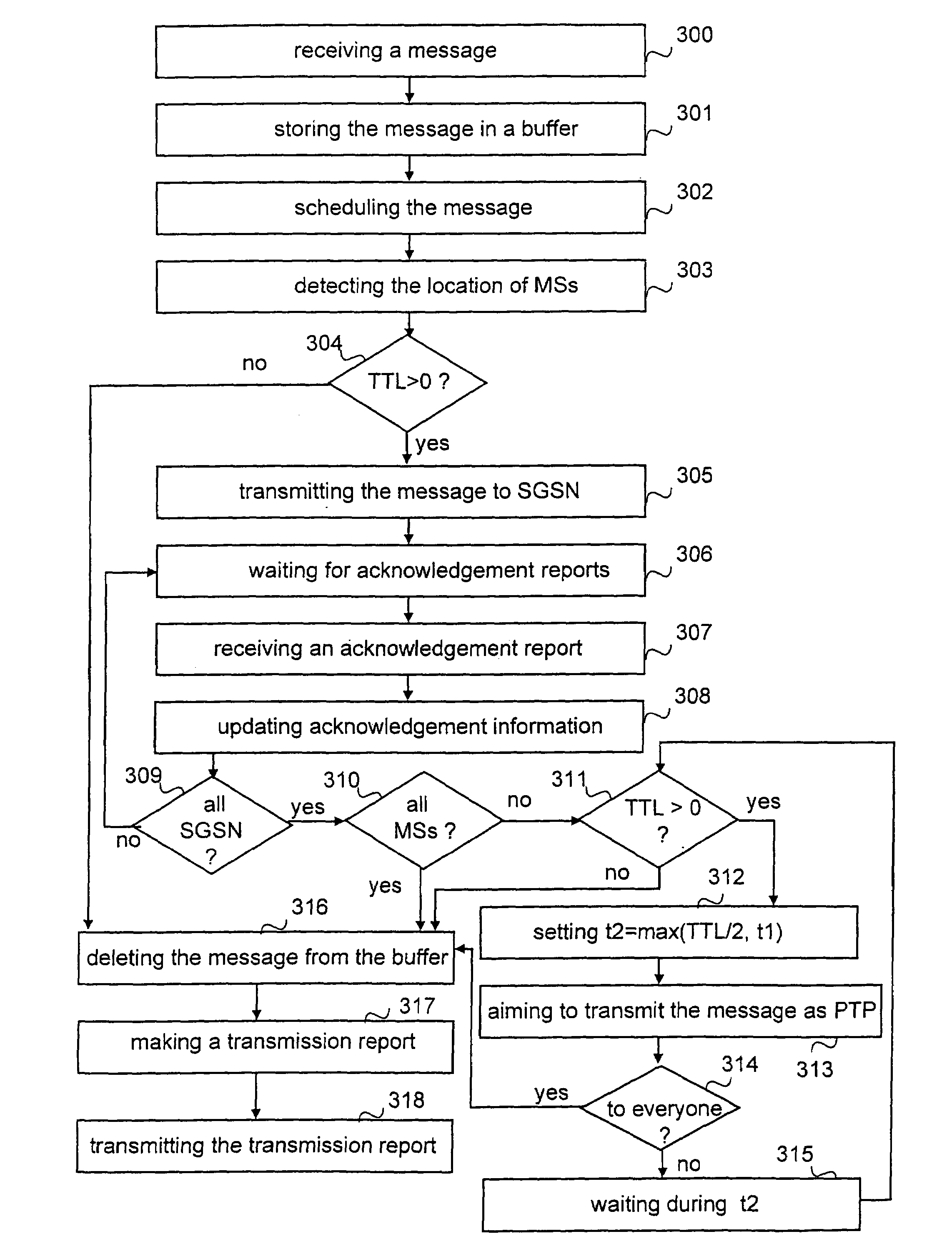
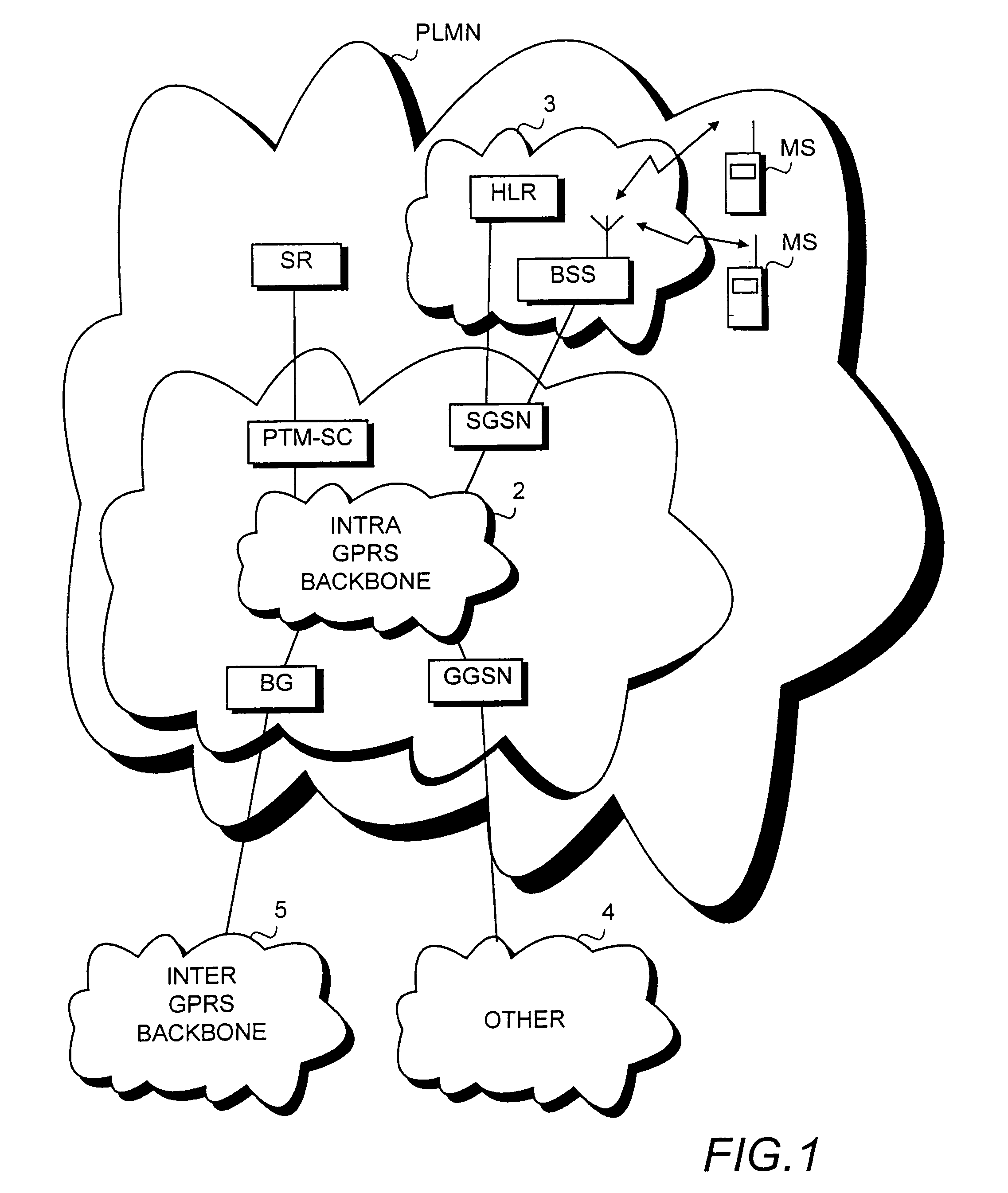
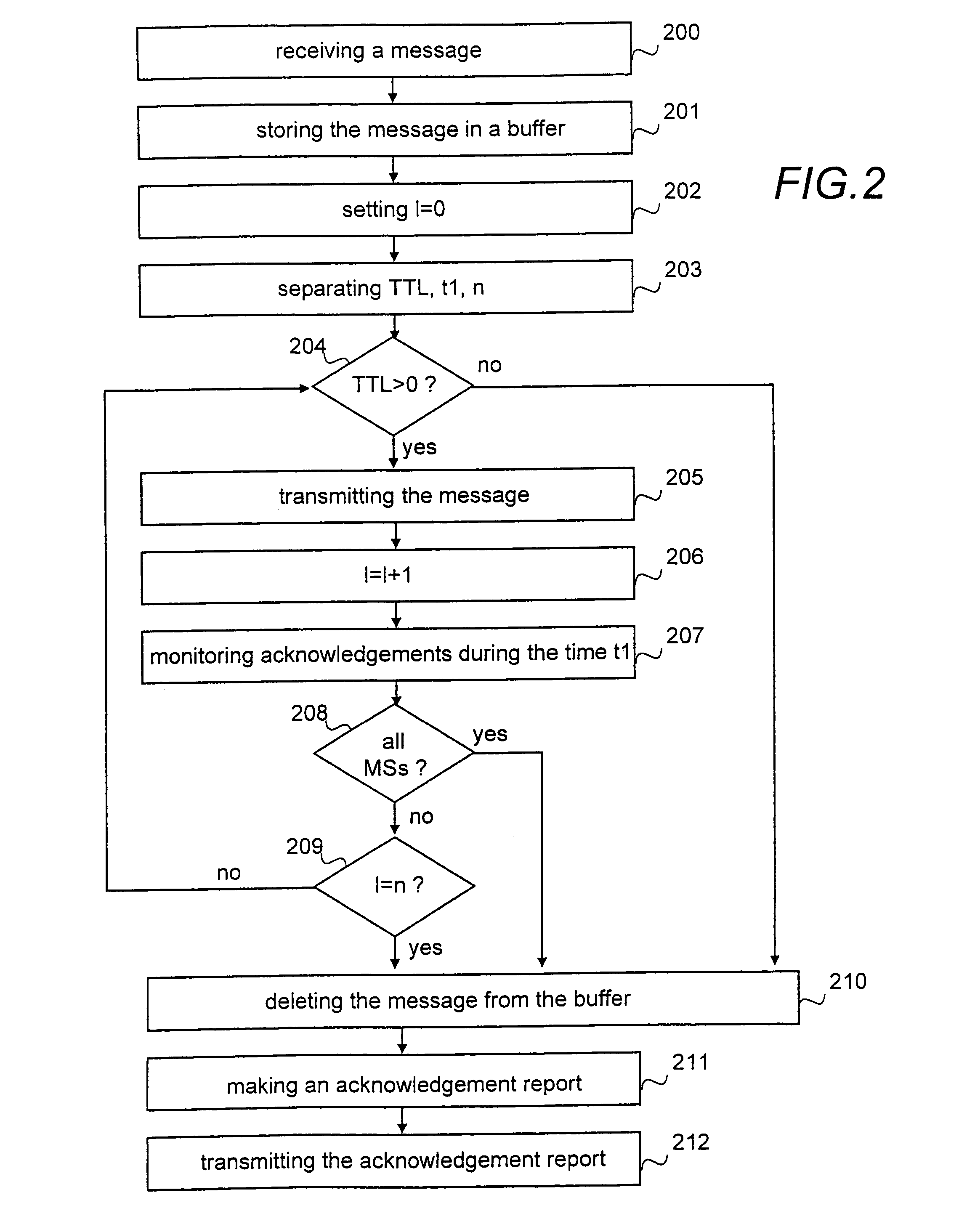
InactiveUS20050169204A1Save network resourcesLifetime be accurately estimatedSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelMobile communication systemsLife time
A method, a system and a network element for controlling the transmission of a message to be transmitted point-to-multipoint in a mobile communication system. In order to take the topicality of the content of the message to be transmitted point-to-multipoint into account, a life time is determined for the message in the method and the message waiting to be transmitted is deleted from the buffer in response to the expiry of the life time.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
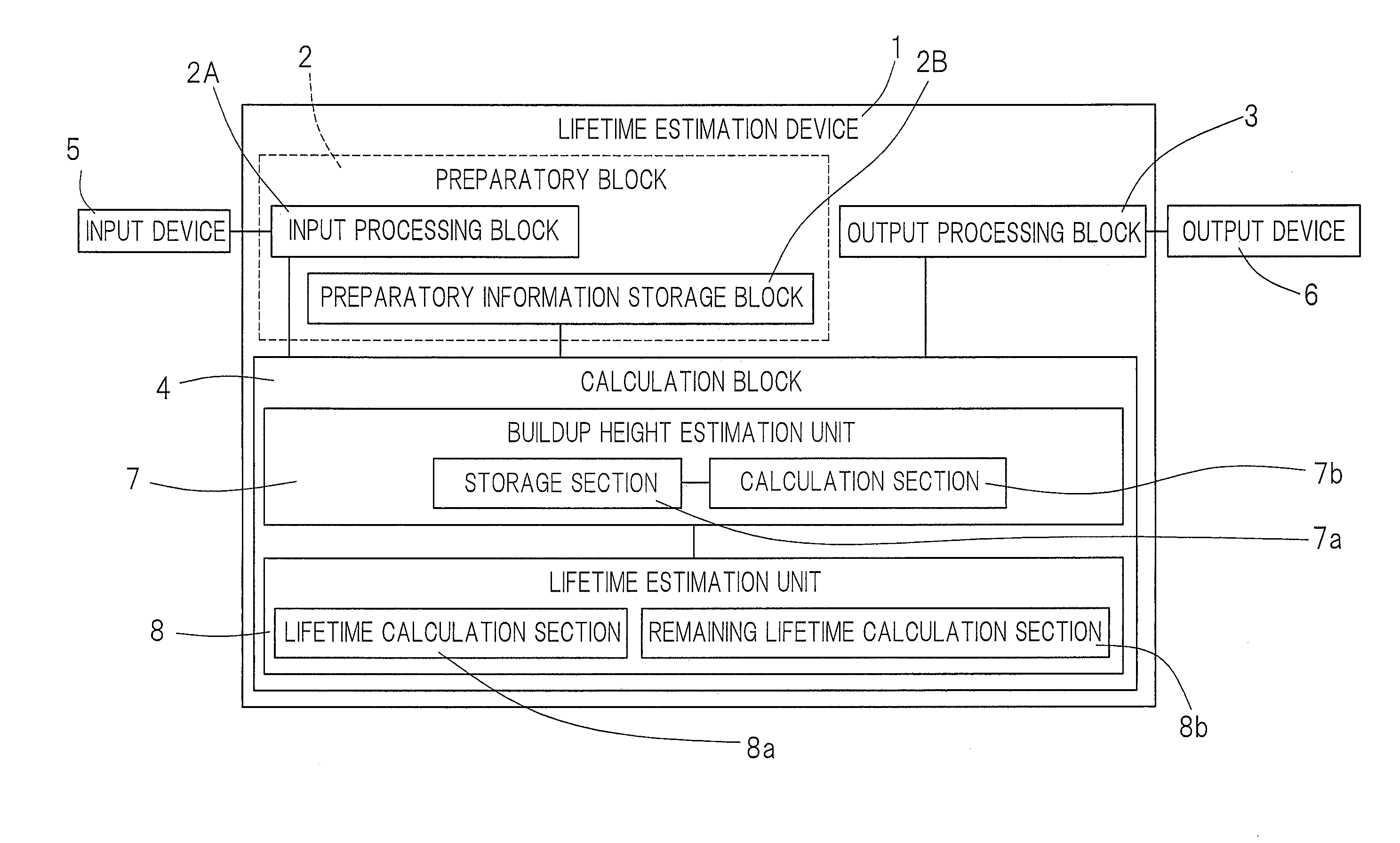
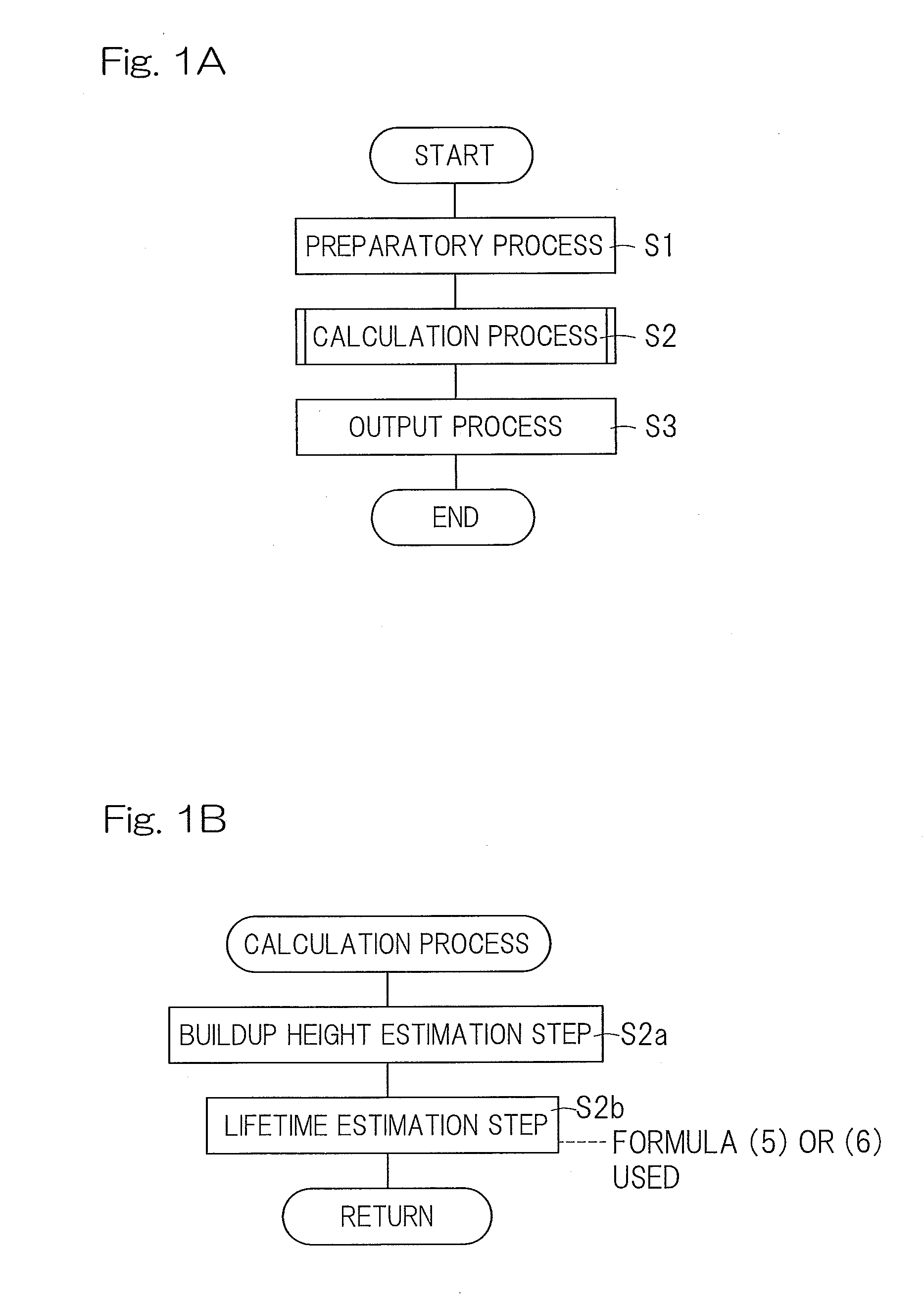
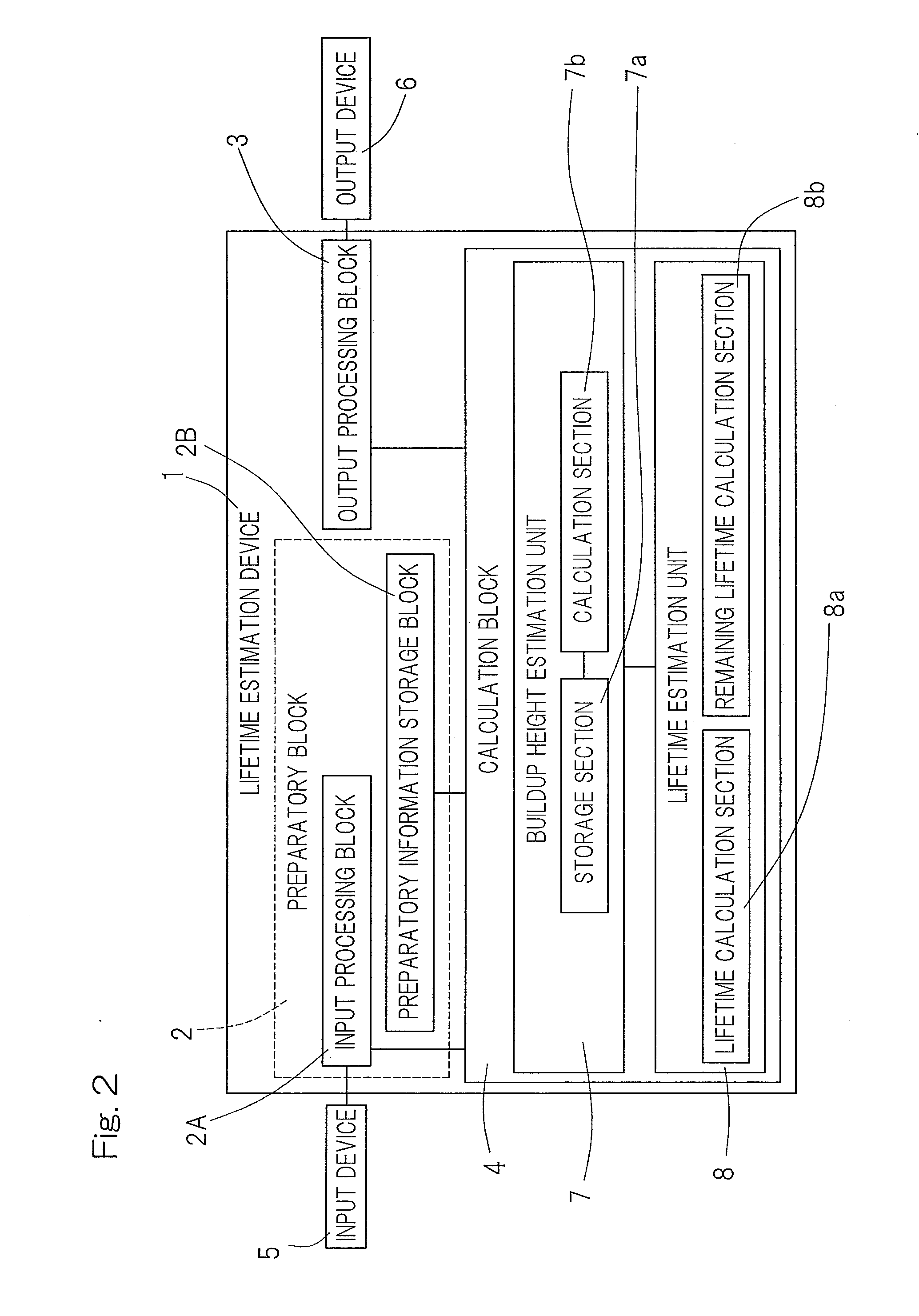
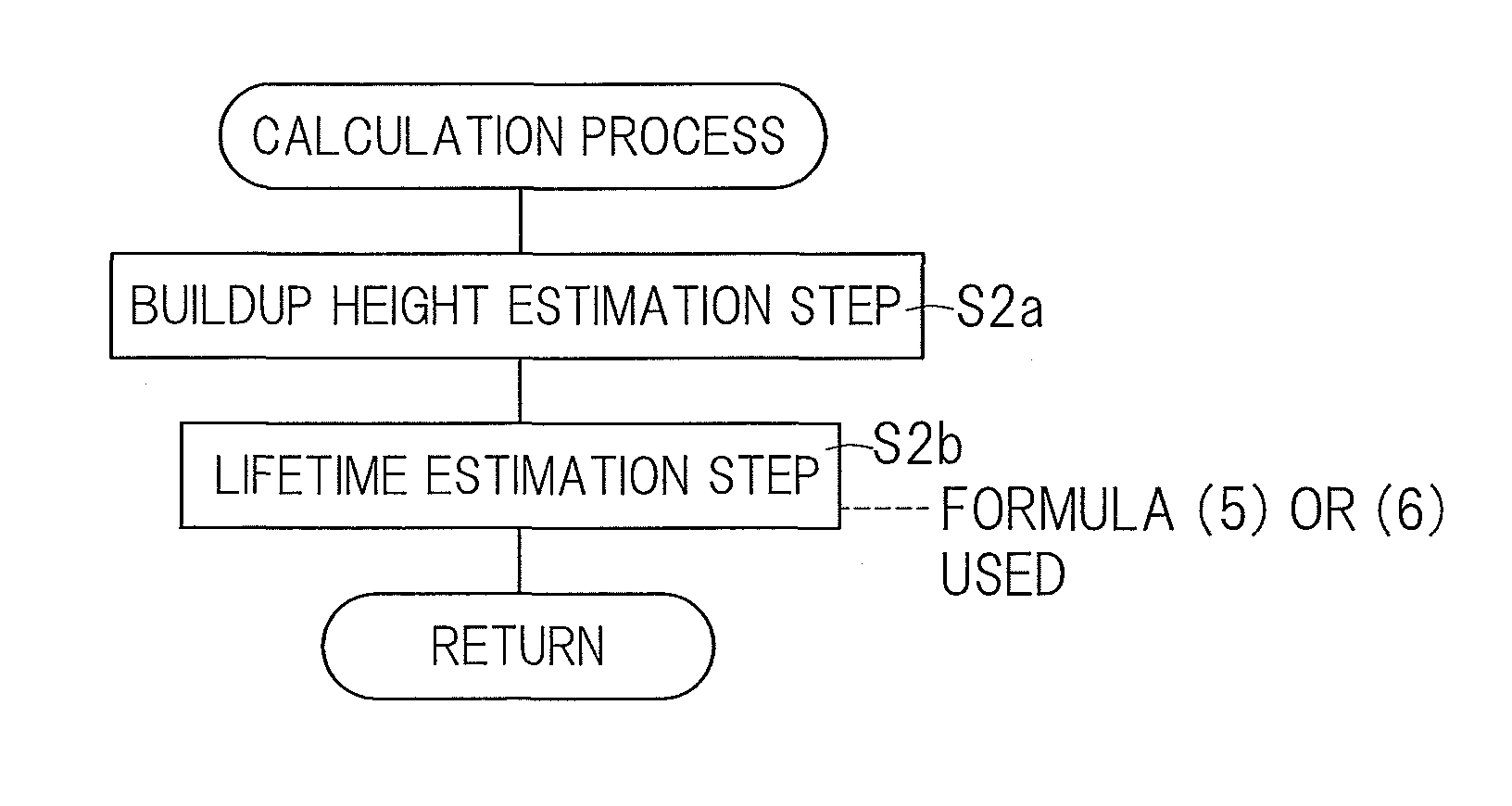
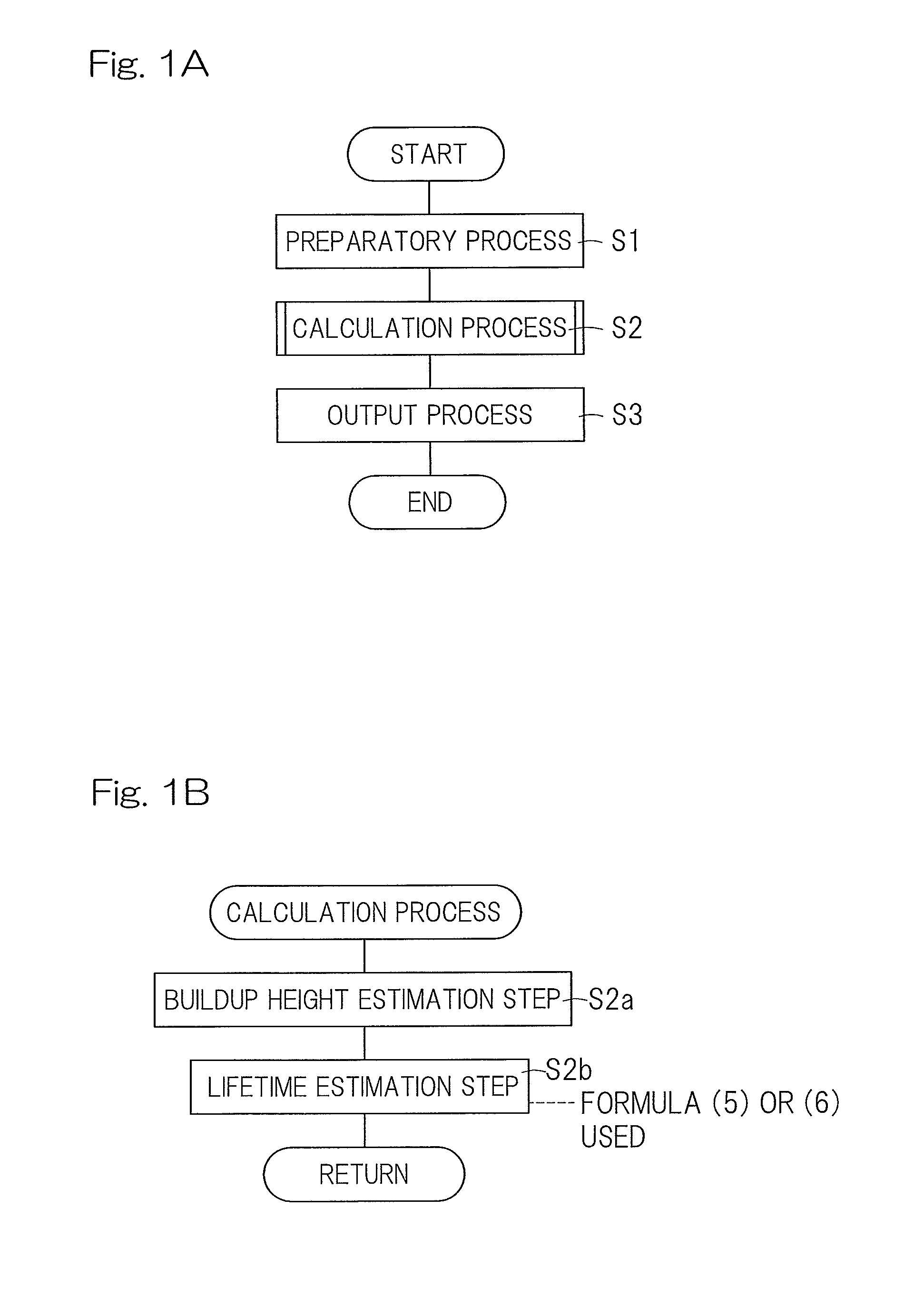
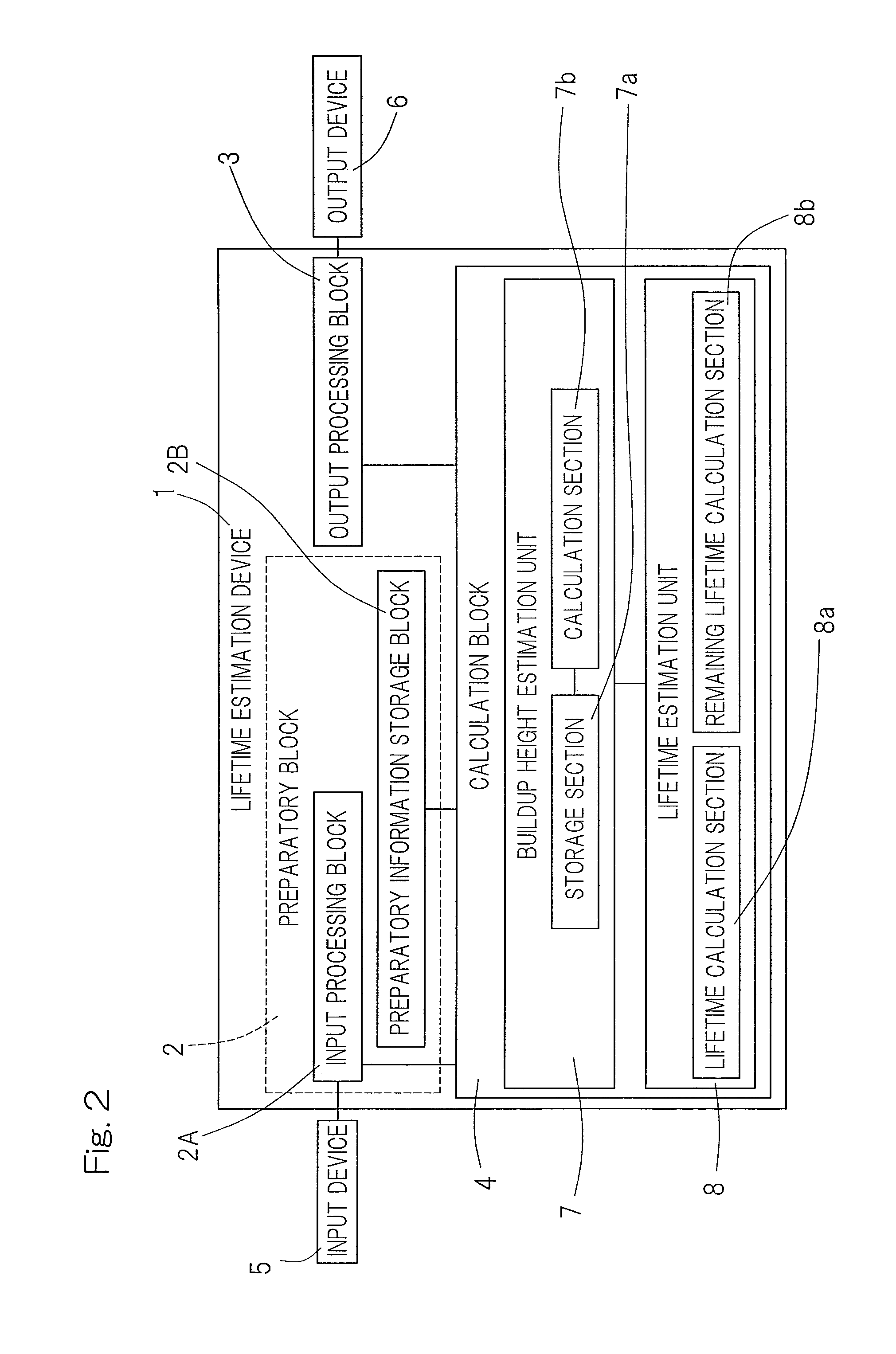
Life estimation device and life estimation method for rolling bearing
ActiveUS20130298704A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedAccurate estimateMachine bearings testingEstimation methodsEngineering
A device for estimating the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly equipped with inner and outer rings and a plurality of rolling elements interposed between respective rolling surfaces of the inner and outer rings is provided. The lifetime estimation device includes a buildup height estimation unit for estimating the buildup height of the indentation, as measured from one of the rolling surface of the inner and outer rings, in which the indentation has been formed, from the depth or the indentation size of the indentation in accordance with a predetermined rule, and a lifetime estimation unit for estimating the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly in accordance with a rule determined by the relationship between the buildup height of the estimated indentation and the rate of reduction in lifetime of the rolling fatigue life and the dynamic equivalent load.
Owner:NTN CORP
Flash memory lifetime evaluation method
InactiveUS20130262942A1Accurate predictionLifetime be accurately estimatedError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesAssessment methodsSpare part
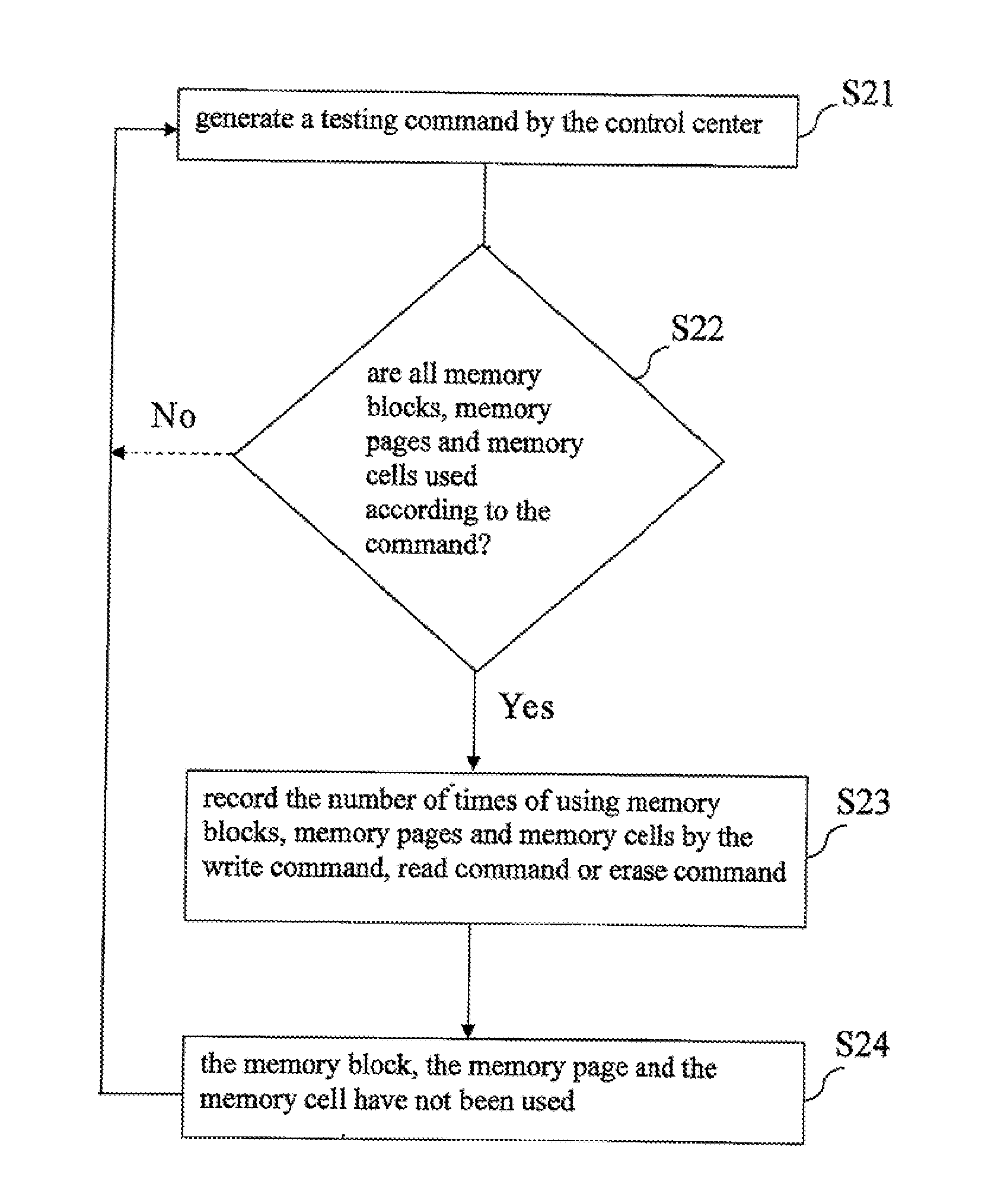
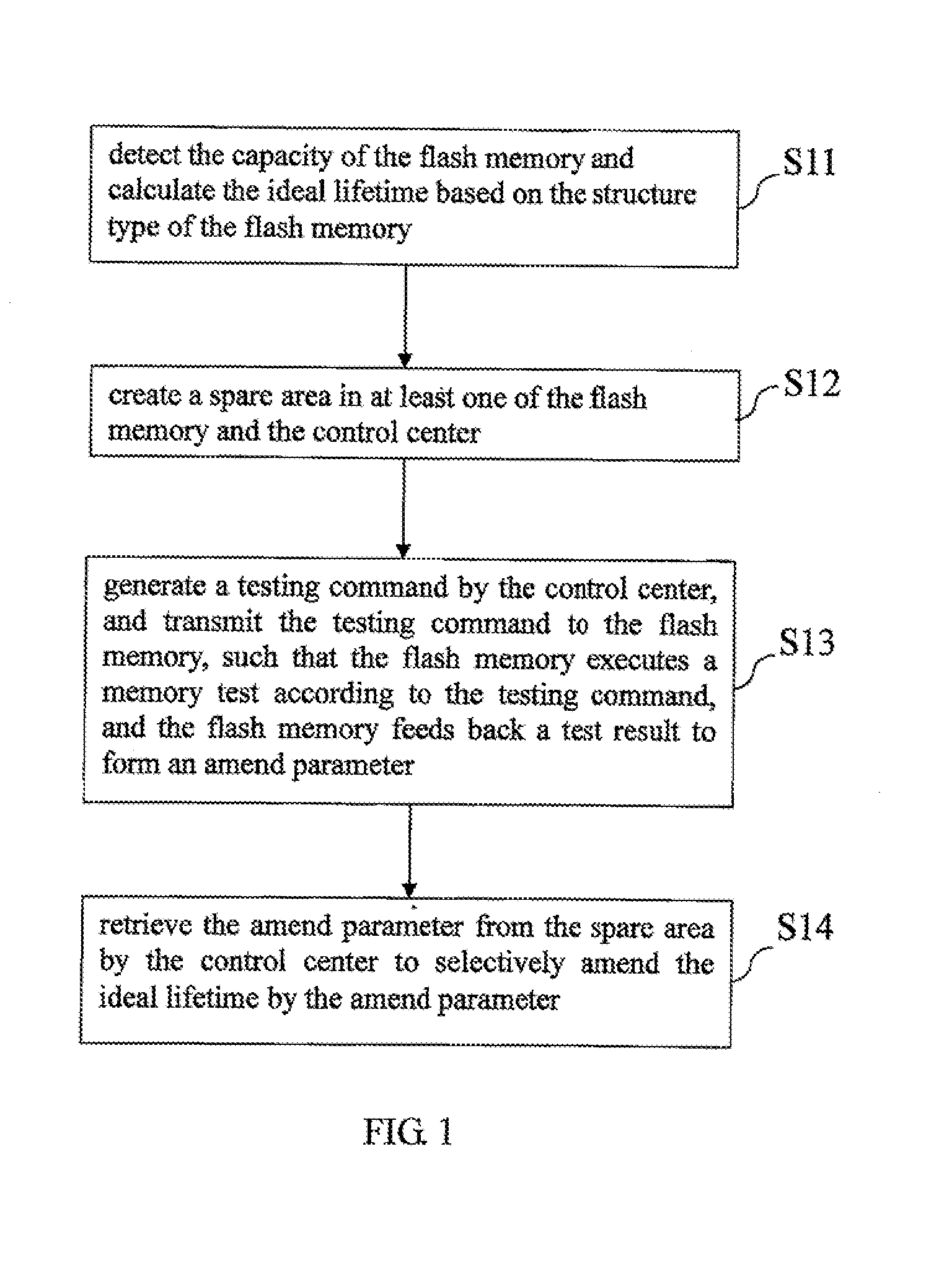
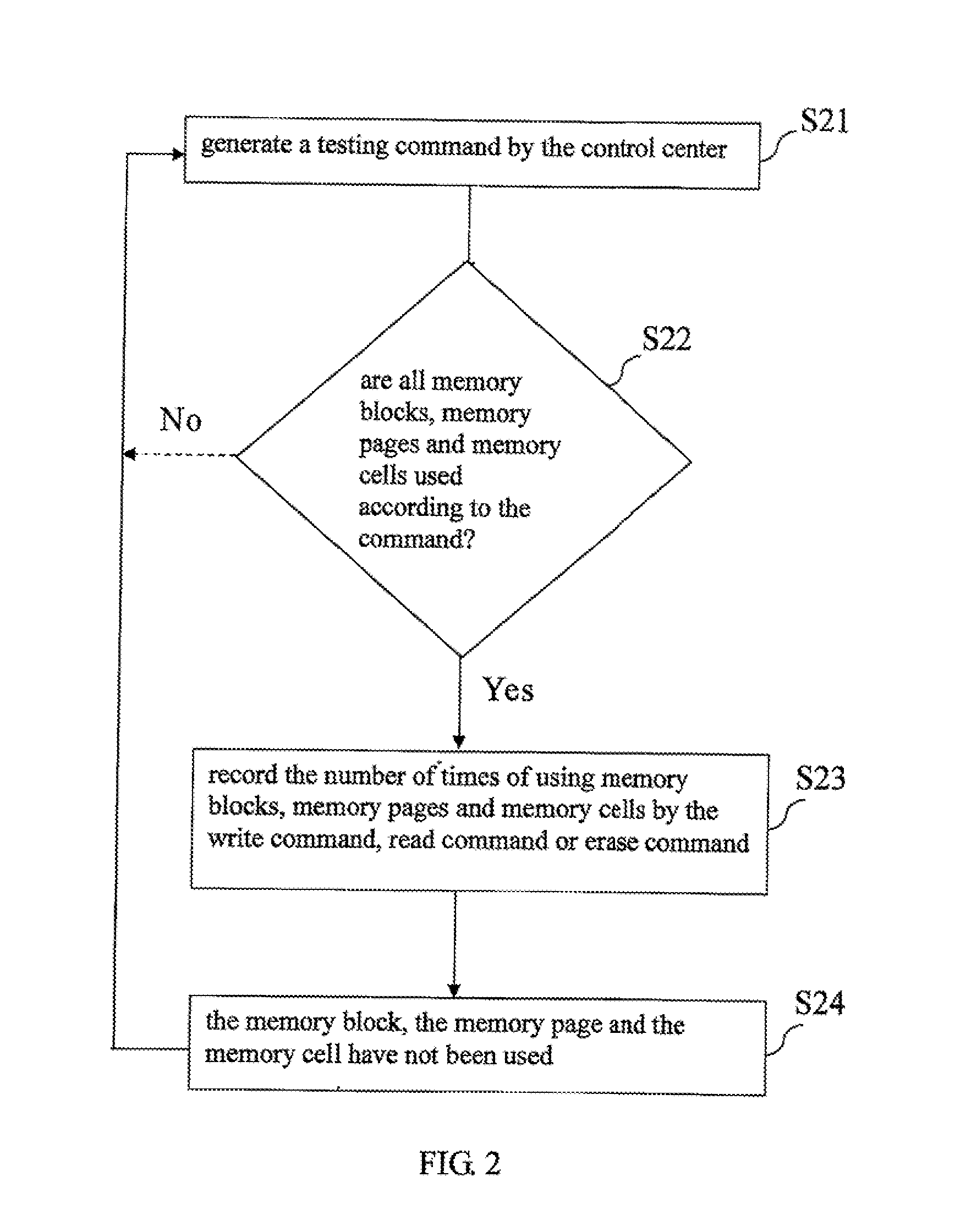
A flash memory lifetime evaluation method is introduced for dynamically amending, detecting and evaluating an ideal lifetime (or standard lifetime) of a built-in or expanded flash memory of an electronic device, and the method comprises the steps of calculating the ideal lifetime according to the capacity of the flash memory, creating a spare area in at least one of the flash memory and the control center, generating a testing command by the control center and transmitting the testing command to the flash memory such that the flash memory executes a memory test according to the testing command, and the flash memory feeds back a test result to the spare area as an amend parameter according to the memory test, and the control center retrieves the amend parameter stored in the spare area to selectively amend the ideal lifetime by the amend parameter.
Owner:FLUIDITECH IP
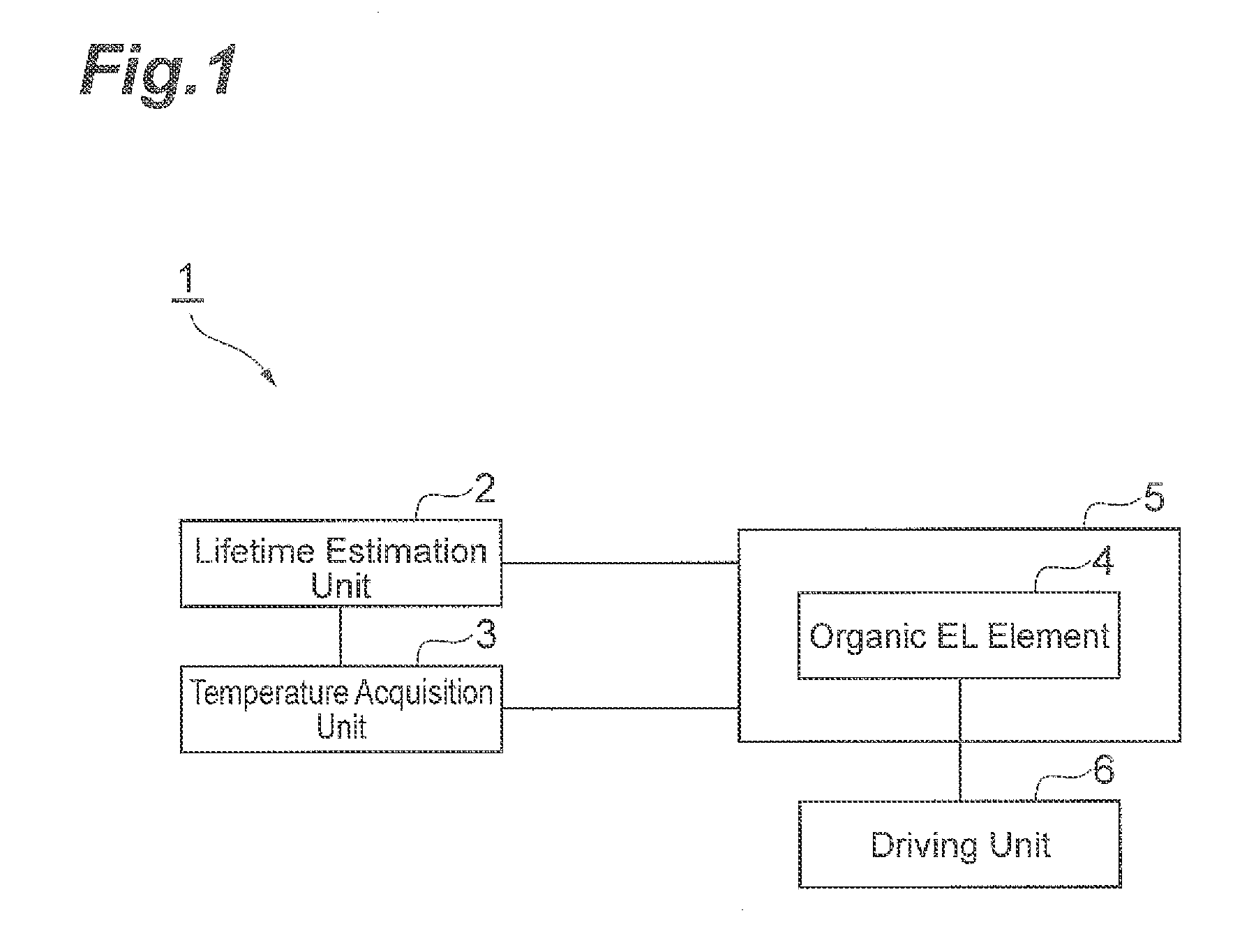
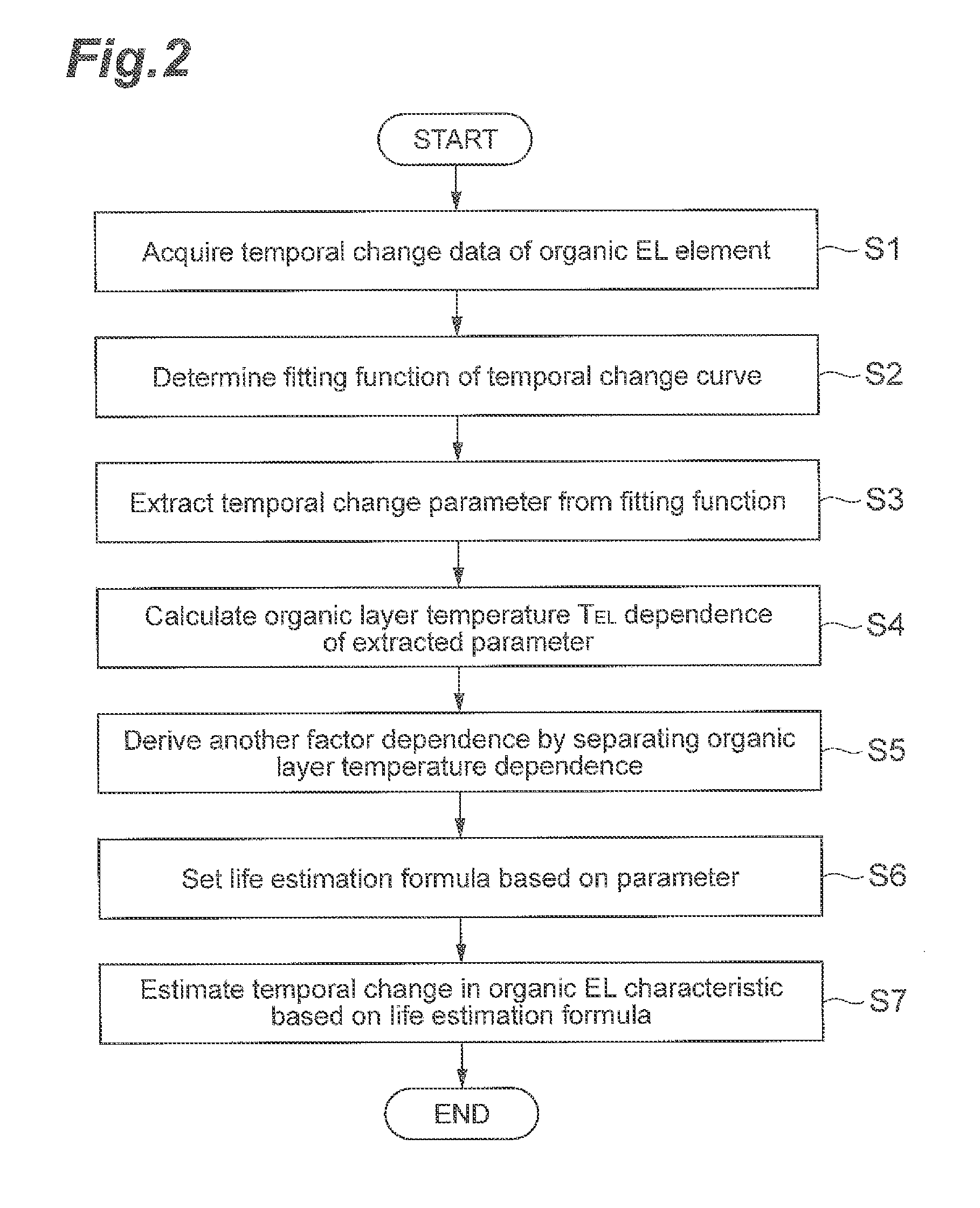
Method for Estimating Life of Organic EL Element, Method for Producing Life Estimation Device, and Light-Emitting Device
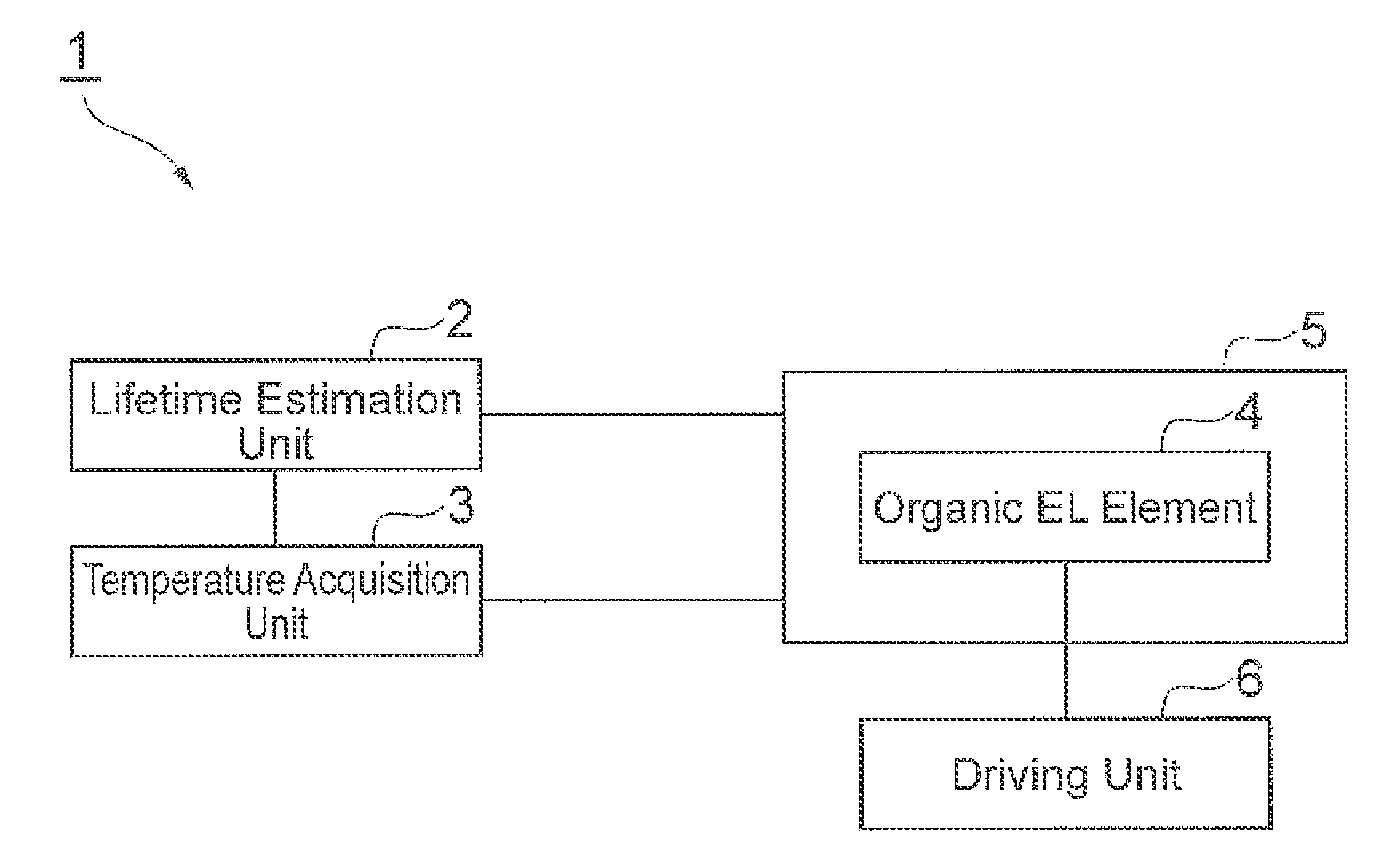
InactiveUS20160103171A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedAccurate estimateThermometer detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhysical chemistryOrganic layer
A method for estimating a lifetime of an organic EL element comprising a pair of electrodes and an organic layer, comprises: a step of acquiring degradation data of characteristics of the element when a current density applied to the element and / or an atmosphere temperature of the element are / is changed; a step of calculating a fitting function of the degradation data and extracting a degradation parameter characterizing a degradation in the characteristics at the applied current density and / or the atmosphere temperature from the fitting function; a step of calculating a temperature dependence of the degradation parameter based on a temperature rise value of the organic layer upon light emission at the applied current density and / or the atmosphere temperature and setting a lifetime estimation formula of the element; and a step of estimating the lifetime of the organic EL element based on the lifetime estimation formula.
Owner:CHEM MATERIALS EVALUATION & RES BASE
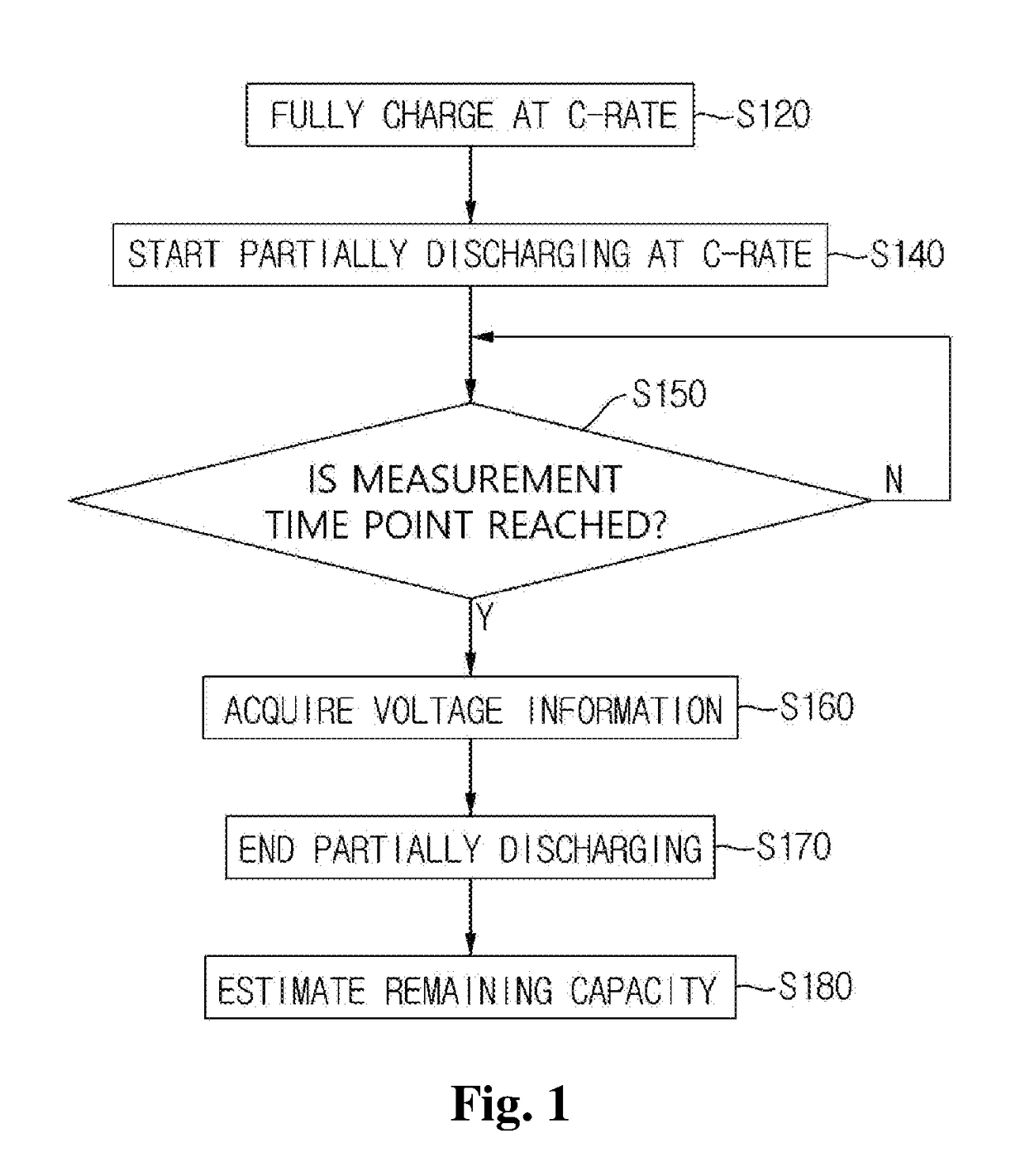
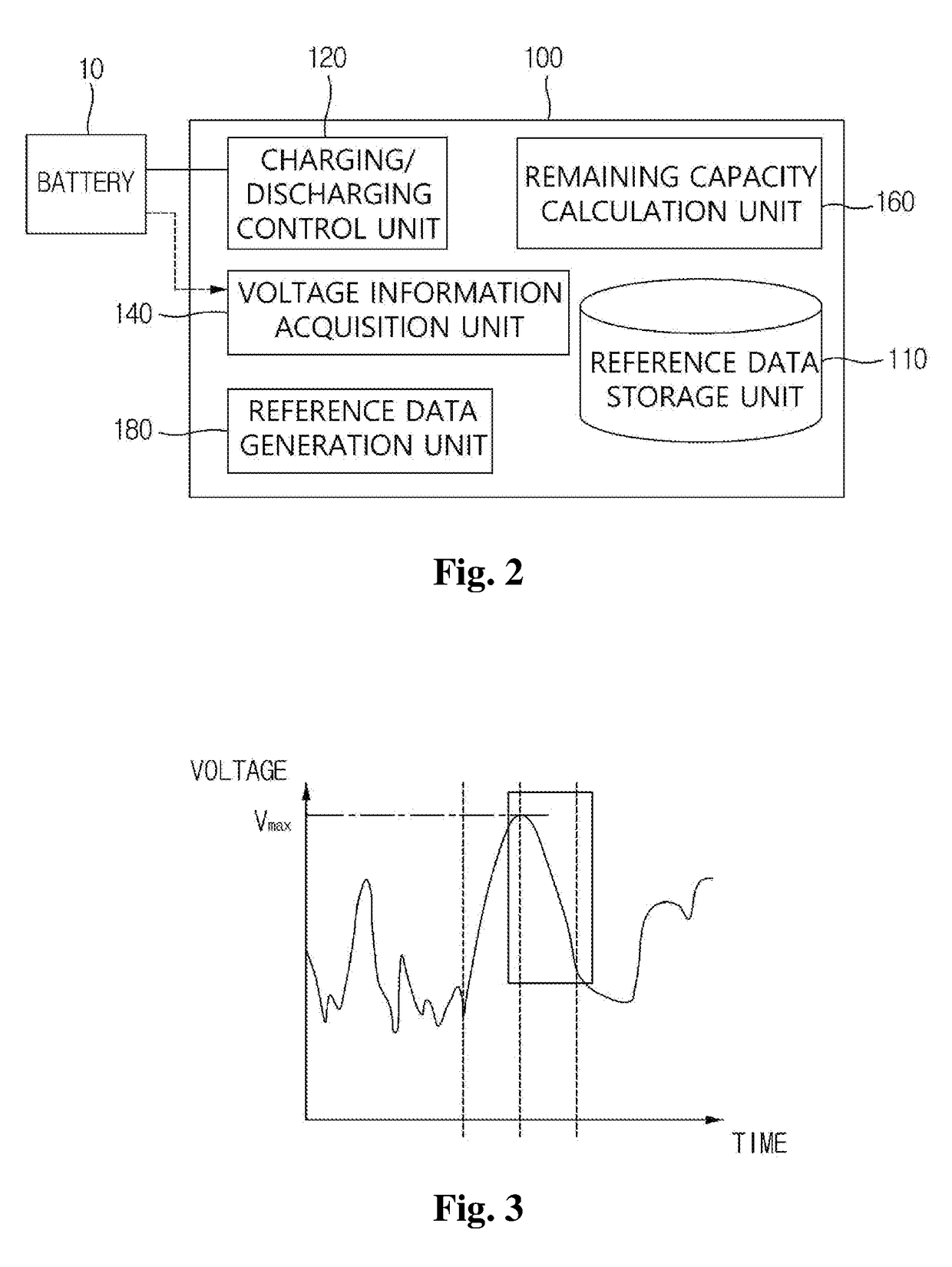
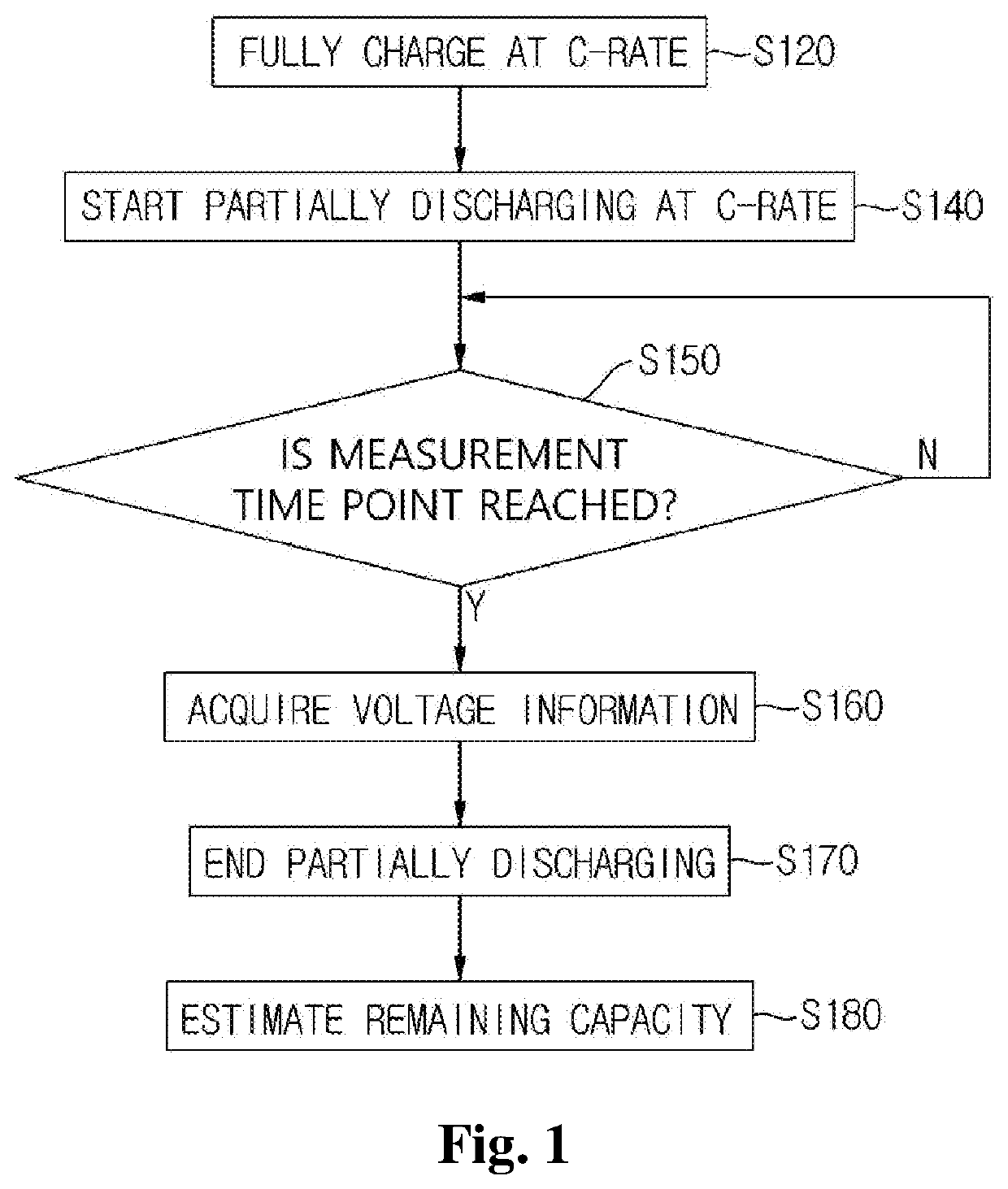
Method and device for estimating battery life
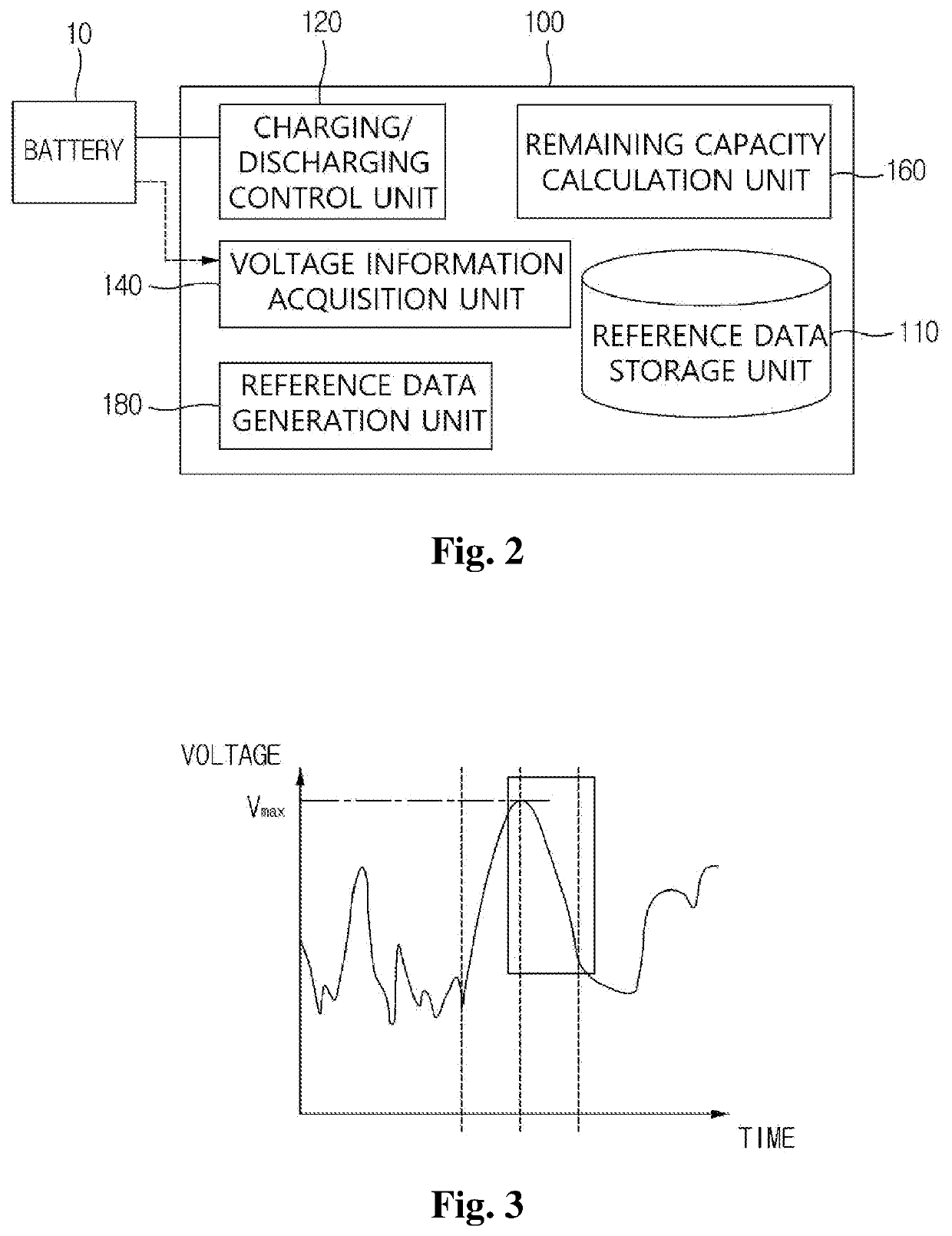
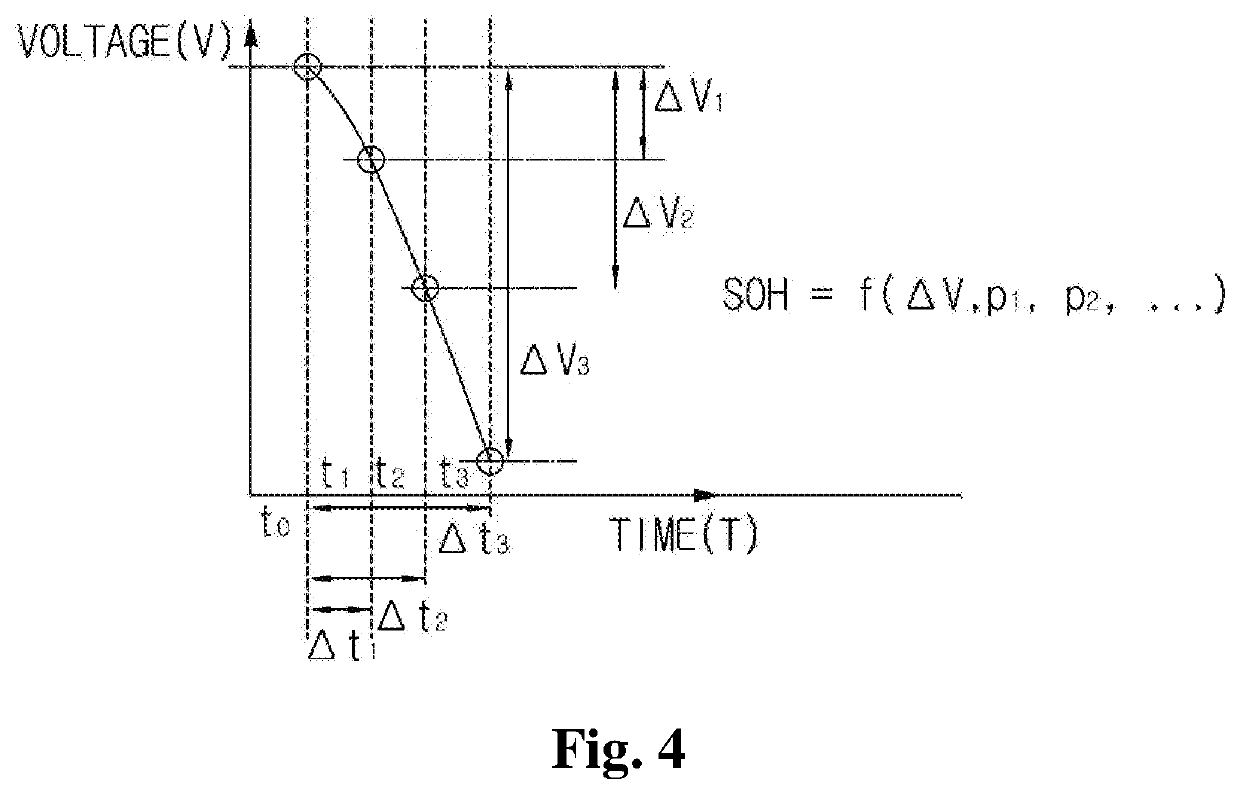
ActiveUS20190011505A1Emphasize product reliabilityAccurately estimate the remaining lifetime of a battery in useElectrical testingSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectrical batteryVoltage drop
Provided is a battery lifetime estimating method including steps of: fully charging a battery according to a predetermined charging condition; partially discharging the fully charged battery according to a predetermined discharging condition; acquiring voltage information at a plurality of predetermined measurement time points while performing the partially discharging; and estimating a remaining capacity of the battery by using the acquired voltage information. Herein, the step of estimating the remaining capacity of the battery includes steps of: calculating the capacity of the battery in one cycle of fully charging / discharging in which the measurement is performed from the measured voltage drop amounts; and estimating the remaining lifetime of the battery by applying a statistical technique to the capacity of the battery calculated with respect to a plurality of cycles of fully charging / discharging.
Owner:HYOSUNG HEAVY IND CORP
Battery life predicting device and battery life predicting method
InactiveUS8035395B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedAccurate predictionBatteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringData storing
A battery life predicting device and a battery life predicting method capable of accurately predict the lifetime of storage batteries are provided. The expected lifetime value selecting unit 7 selects, as an expected lifetime value, a lifetime value that corresponds to the load power applied by the storage battery during discharge and the ambient temperature of the location where the storage battery 3 is installed while referring to the lifetime data stored in the lifetime data storing unit 5, the first diminution in lifetime calculating unit 12a calculates the first diminution in lifetime based on a natural logarithm function that takes the time obtained by converting the number of discharge cycles of the storage battery 3 as a variable, the second diminution in lifetime calculating unit 12b calculates the second diminution in lifetime from the mean value of the storage battery temperatures during charging, discharging or an idle state, the ambient temperature and the time elapsed after the installation of the storage battery 3, and the remaining lifetime value calculating unit 12c calculates the remaining lifetime value by subtracting the first diminution in lifetime and the second diminution in lifetime from the expected lifetime value.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
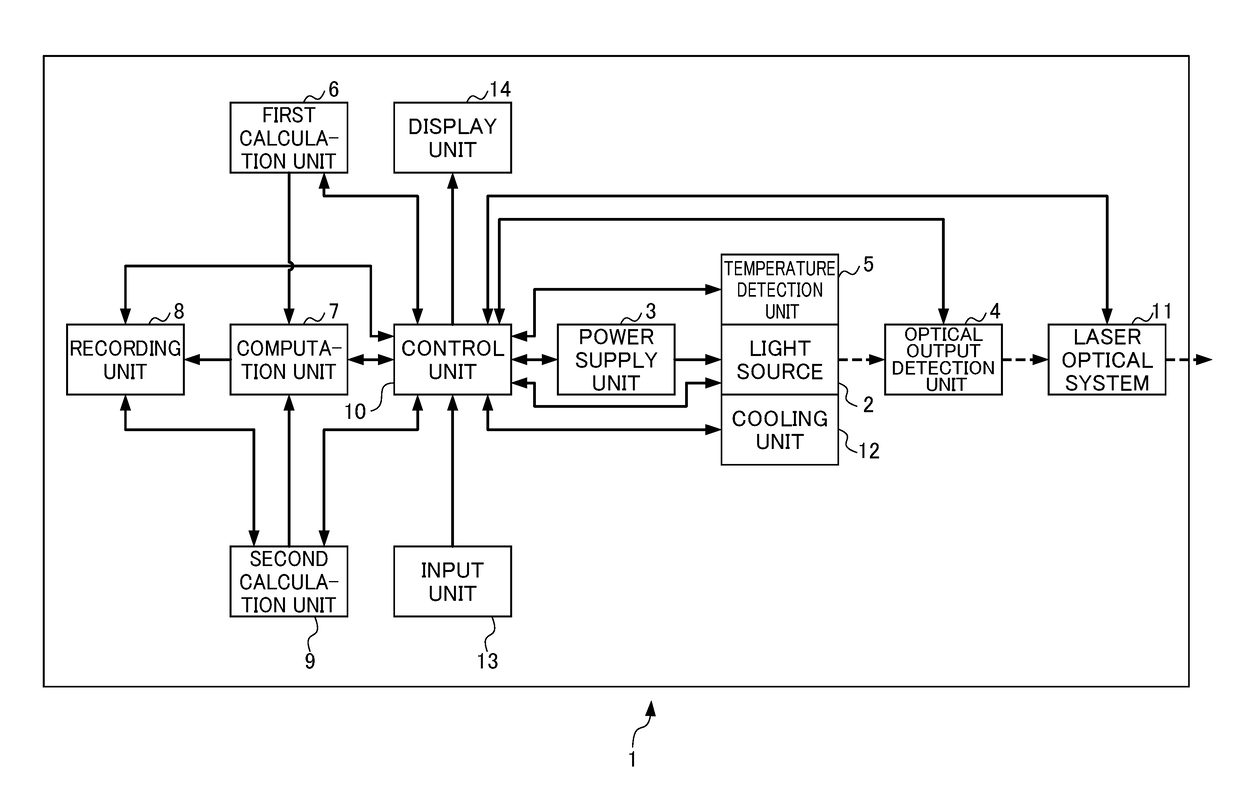
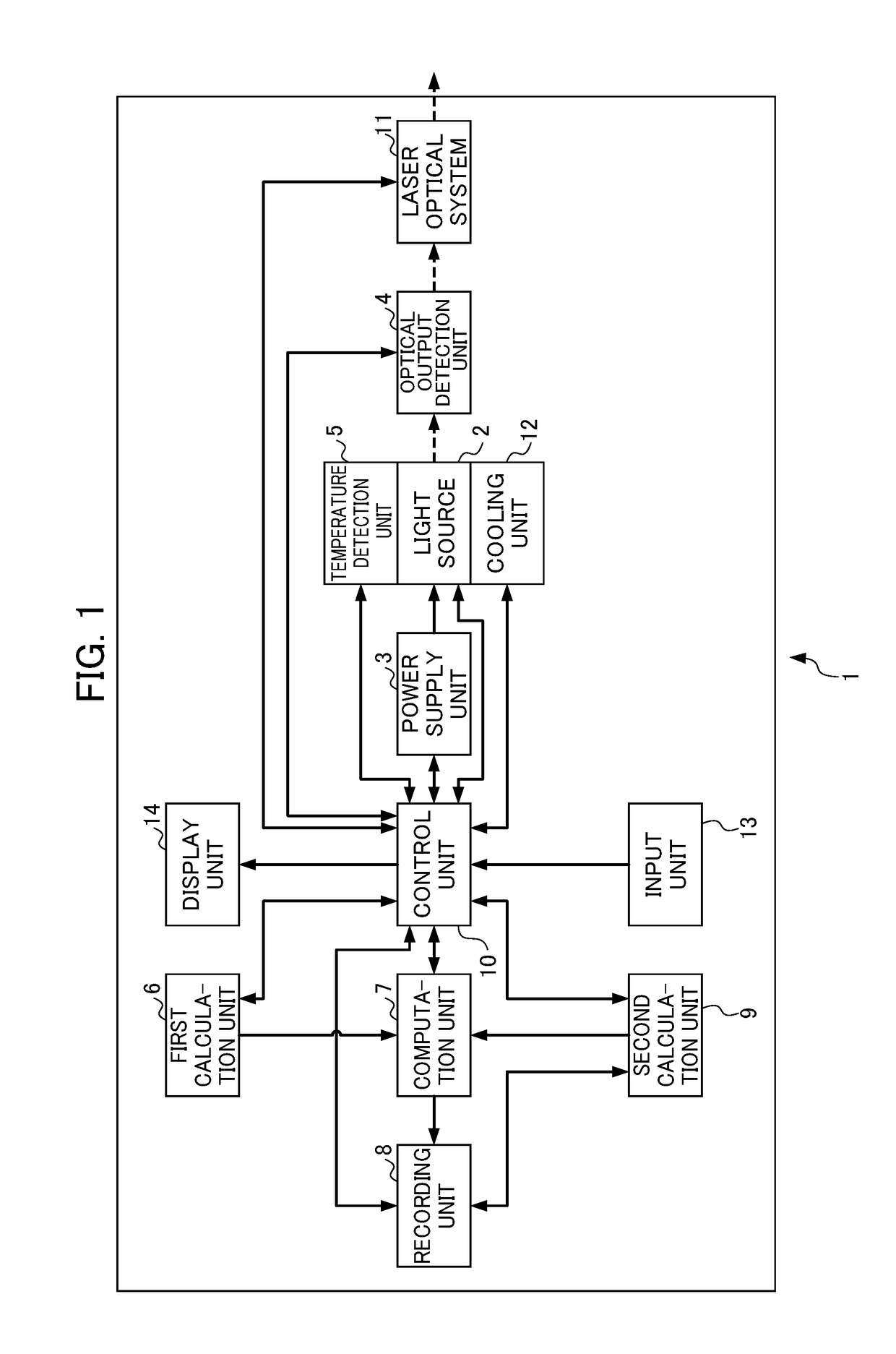
Laser apparatus enabling calculation of effective driving time and remaining lifetime taking account of drive conditions including temperature
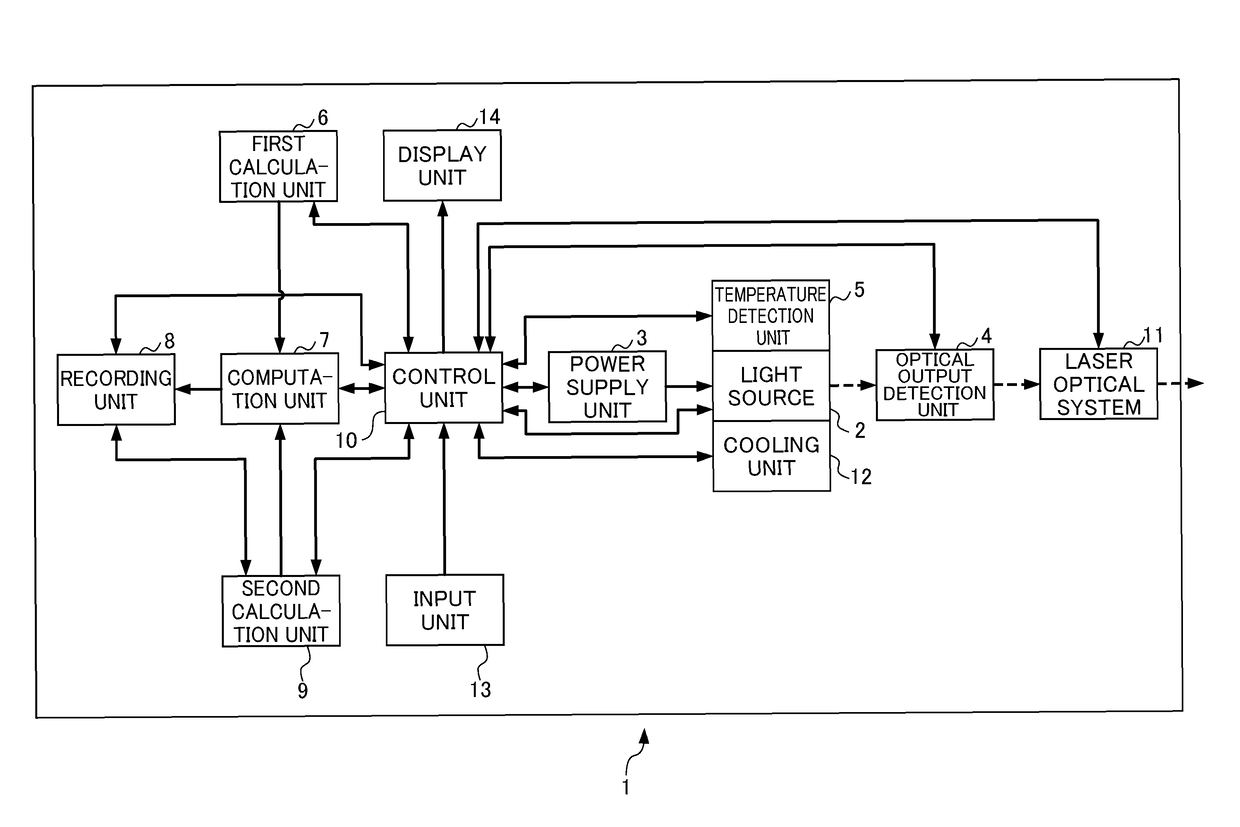
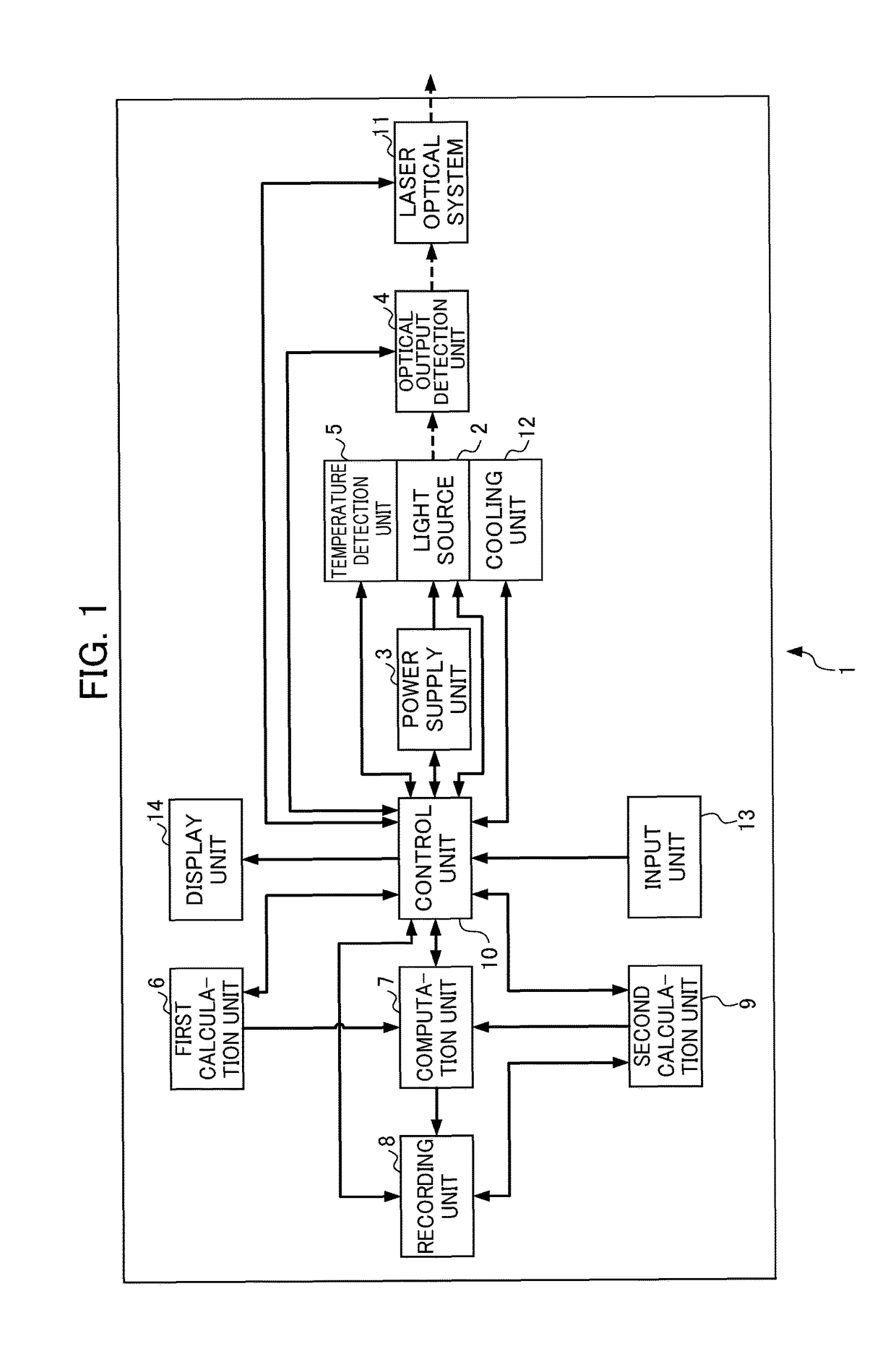
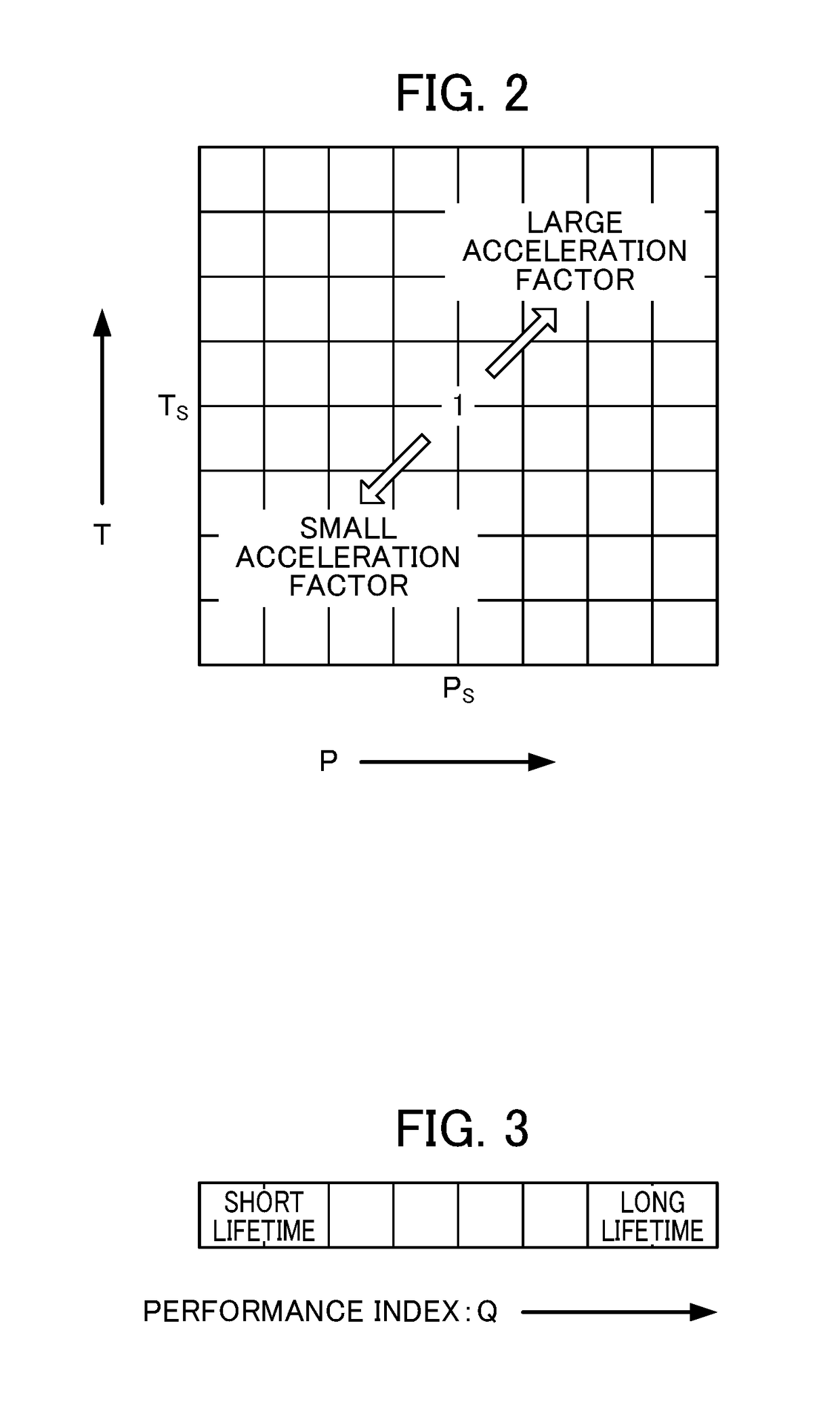
ActiveUS20180013259A1Reduced referenceReduce dataLaser detailsAnalysis by electrical excitationAcceleration factorPerformance index
A first calculation unit calculates an acceleration factor of lifetime consumption of the light source with as case of a standard temperature and standard drive condition as a reference, a second calculation unit calculates a whole lifetime or remaining lifetime of individual light sources relative to a performance index of the individual light sources or a change rate of the performance index, a computation unit obtains an effective cumulative driving time at which the magnitude of influence imparted on the lifetime is equivalent with a case of driving at the standard temperature and standard drive condition, by calculating a time integral of the acceleration factor, and a recording unit records the effective cumulative driving time and the whole lifetime or remaining lifetime together with an optical output characteristic of the light source.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Lifetime estimating method and deterioration suppressing method for rechargeable lithium battery, lifetime estimating apparatus, deterioration suppressor, and battery pack and charger using the same
InactiveUS8373419B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedCapacity reduction can be suppressedBatteries circuit arrangementsCell electrodesSuppressorLife time
In a lifetime estimating method for a rechargeable lithium battery, the open circuit voltages of the rechargeable lithium battery after discharging for at least two different charge / discharge cycle numbers are detected while charge / discharge cycles go on. Next, at least the two of the voltage values are plotted for respective cycle numbers, and a circular arc passing the plotted points is drawn. Furthermore, the lifetime of the rechargeable lithium battery is estimated based on a size of the circular arc. The progression of deterioration can be suppressed by controlling the charge and discharge of the rechargeable lithium battery based on the lifetime estimation.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser oscillator and method of estimating the lifetime of a pump light source
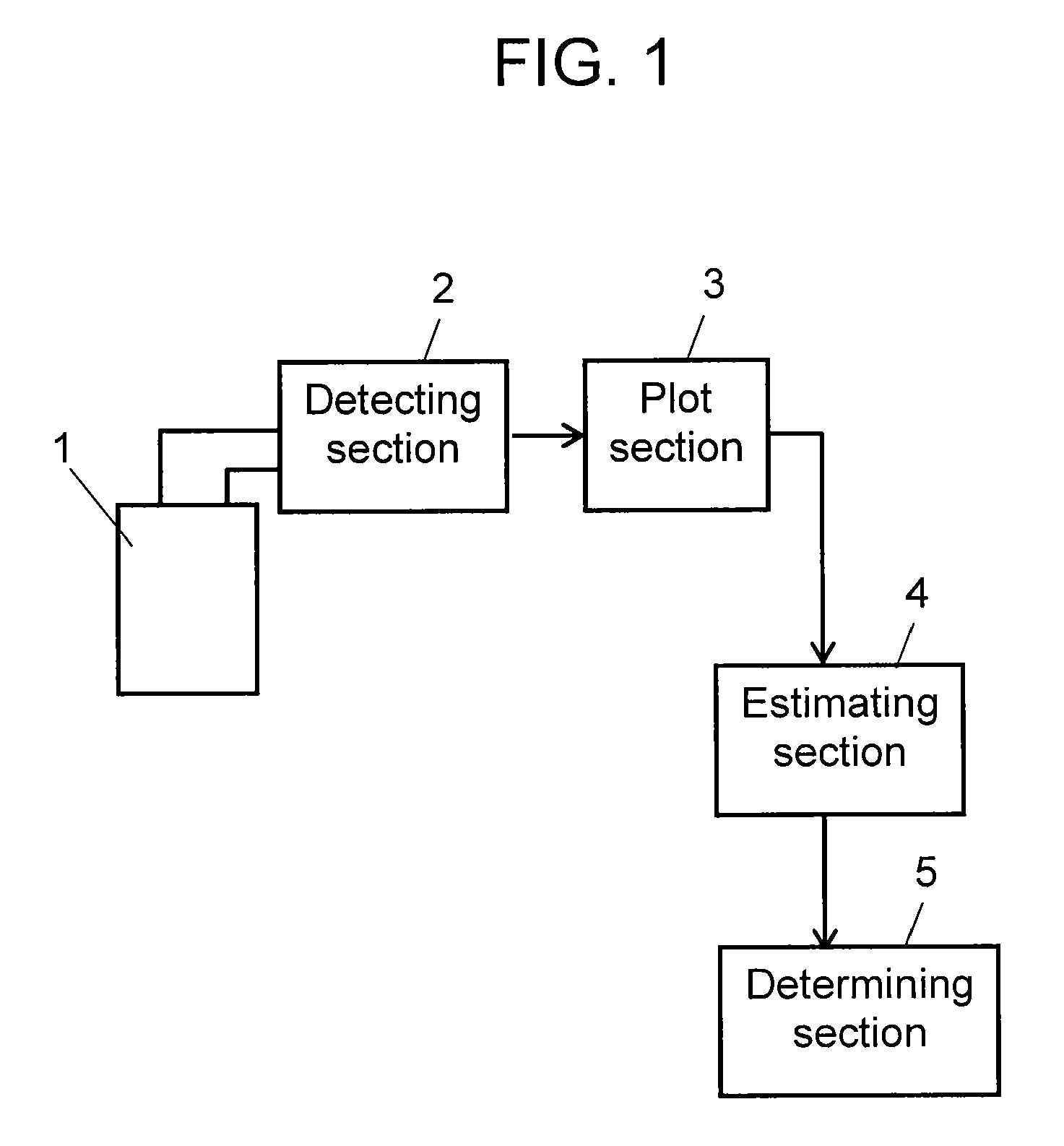
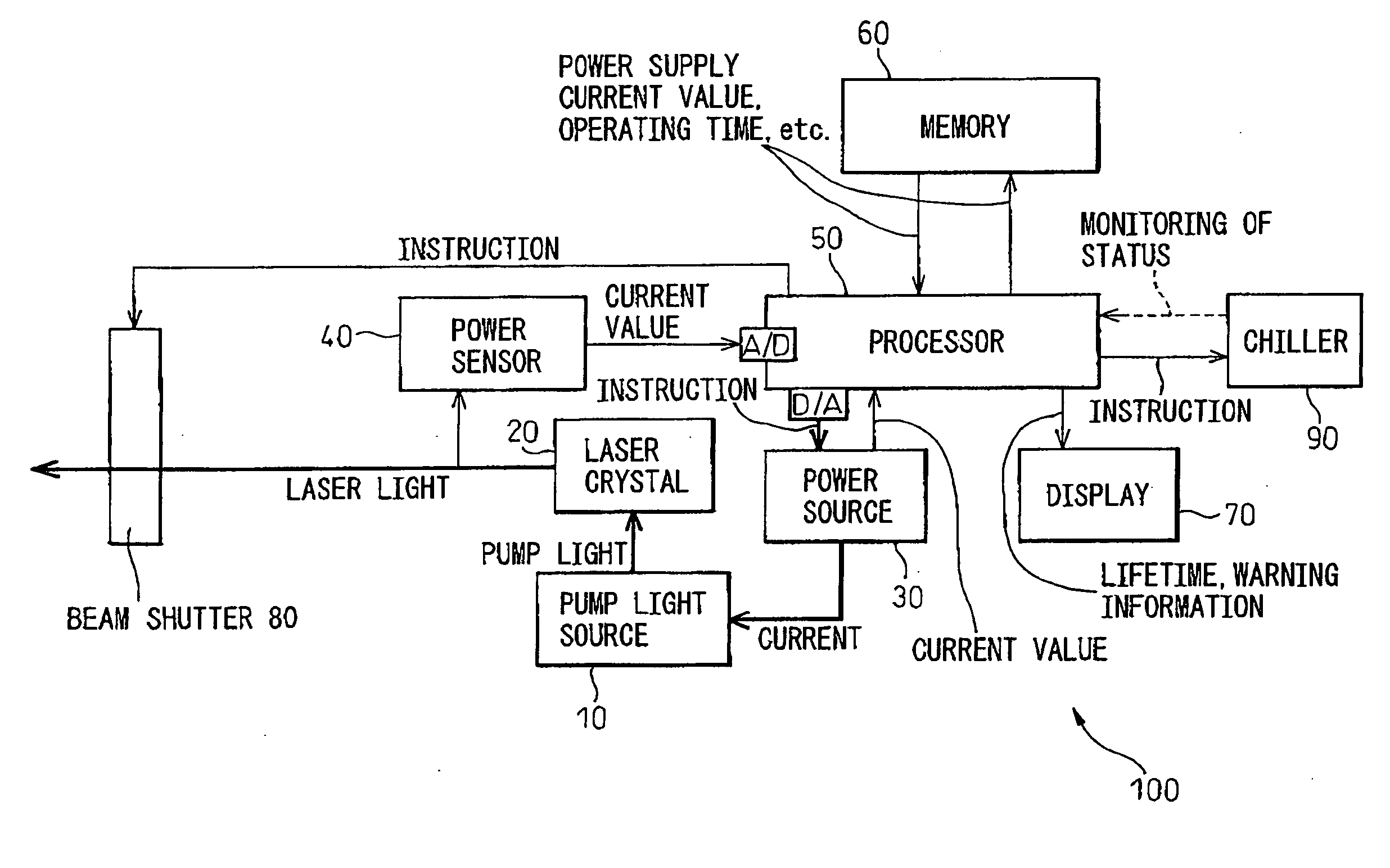
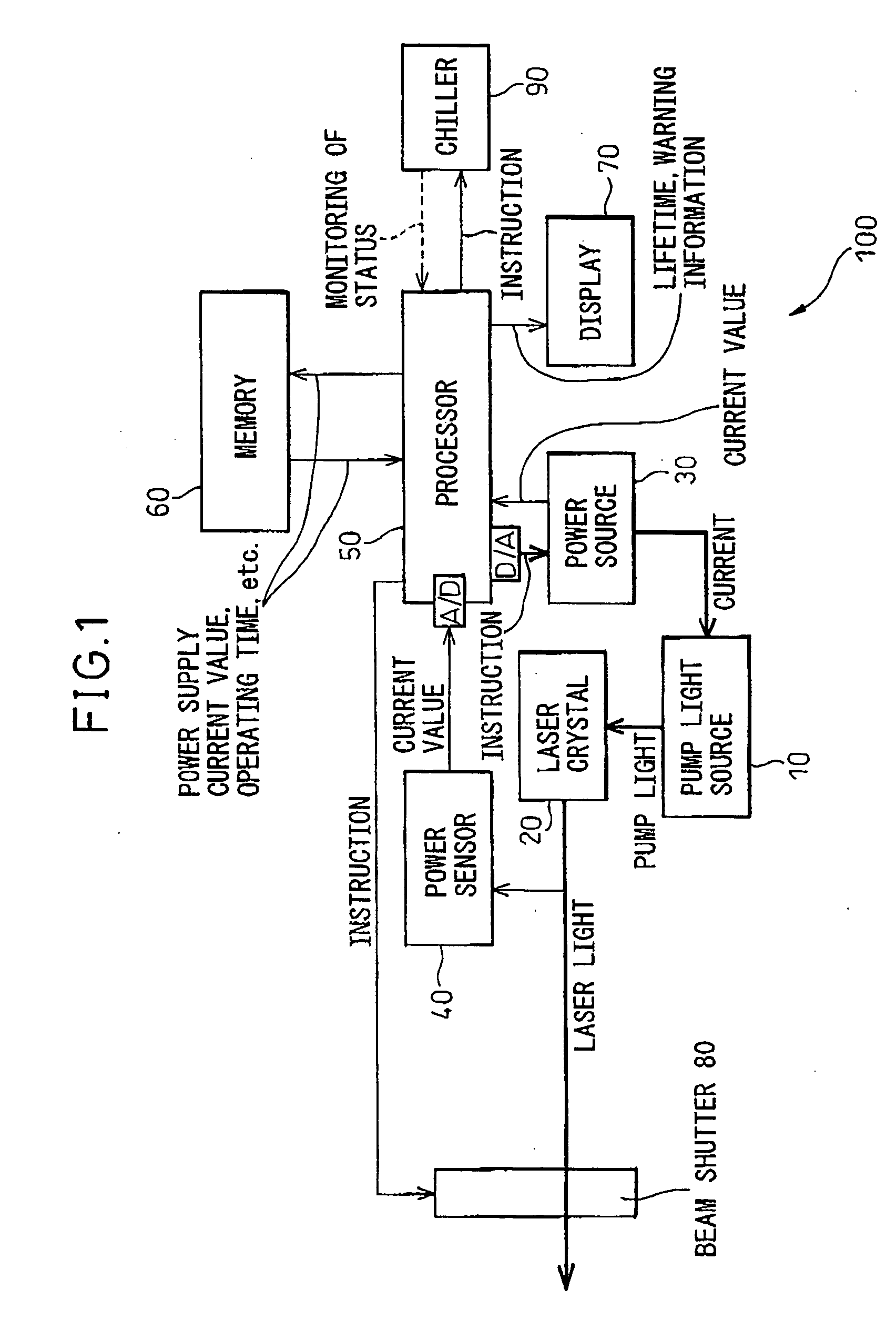
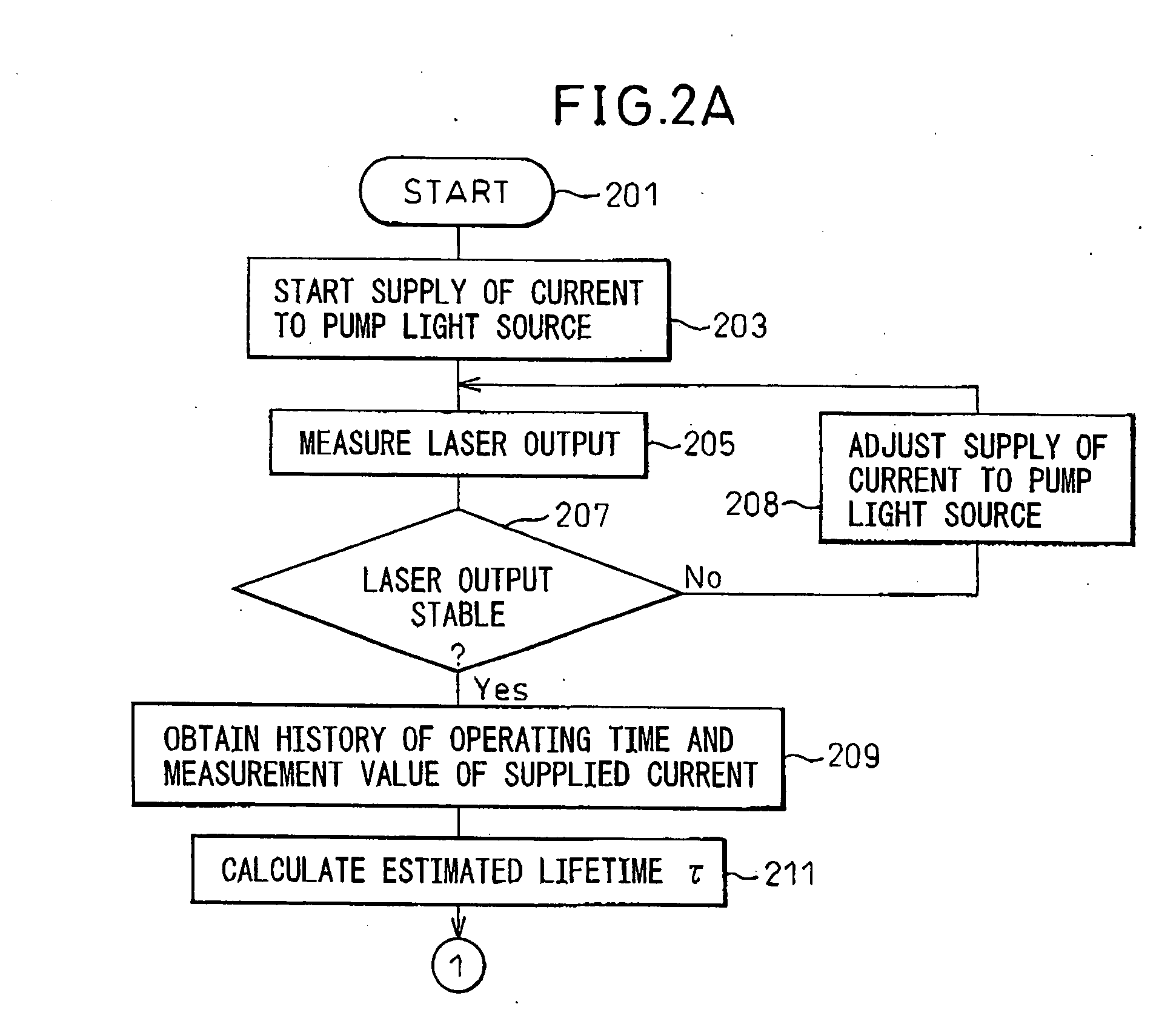
InactiveUS20060159140A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedSimple configurationSemiconductor lasersLaser monitoring arrangementsPower sensorLaser light
A laser oscillator enabling estimation of the lifetime of the pump light source by a simple configuration, provided with a pump light source, a power source supplying current to the pump light source, a laser crystal outputting laser light by the pump light emitted from the pump light source, a power sensor receiving laser light generated from the laser crystal and outputting a signal corresponding to the intensity of the laser light, a memory storing the operating time of the laser oscillator, and a processor judging if the signal output by the power sensor satisfies a predetermined condition and, if satisfying the predetermined condition, uses the value of the current supplied by the power source to the pump light source and the operating time stored in the memory to estimate the lifetime of the pump light source.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method, system and a network element for controlling point-to-multipoint transmission in a mobile communication system
InactiveUS7295854B2Save network resourcesLifetime be accurately estimatedSpecial service provision for substationError prevention/detection by using return channelMobile communication systemsLife time
A method, a system and a network element for controlling the transmission of a message to be transmitted point-to-multipoint in a mobile communication system. In order to take the topicality of the content of the message to be transmitted point-to-multipoint into account, a life time is determined for the message in the method and the message waiting to be transmitted is deleted from the buffer in response to the expiry of the life time.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis method and apparatus
ActiveUS8958993B2Accurate estimateLifetime be accurately estimatedPlug gaugesSwitchgear arrangementsWork periodState dependent
There are provided a switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis method and a switching-device remaining lifetime diagnosis apparatus, wherein as status amount history data, there are accumulated status amounts related to a deterioration status of a switching device, estimated based on measurement data obtained through measurement of performance characteristics of the switching device; based on the accumulated status amount history data, there are created a plurality of system data pieces in which the status amounts are arranged with the respective abscissas of an elapsed time during an operation period of the switching device, the number of operations of the switching device, an inoperative time of the switching device, and an accumulated operation time of the switching device; based on the created system data pieces, the remaining lifetime of the switching device is estimated.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Information processing apparatus, lifetime monitoring method and program for monitoring lifetime of storage device including flash memory
ActiveUS7904637B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedImprove accuracyMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesInformation processingGenerating unit
Owner:NEC PLATFORMS LTD
Life estimation device and life estimation method for rolling bearing
ActiveUS9329100B2Accurate estimateNo substantial correction efficient addedMachine bearings testingReduction rateEstimation methods
A lifetime estimation device to estimate a lifetime of a rolling bearing assembly comprising inner and outer rings includes a buildup height estimation unit to estimate in accordance with a predetermined rule a buildup height of the indentation based on the inputted depth of the indentation or the inputted indentation size; and a lifetime estimation unit to estimate the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly, the lifetime estimation unit being configured to determine a preliminary estimate of the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly based on a dynamic equivalent load, determine a rate of reduction in a rolling fatigue life based on the buildup height of the indentation, and apply the determined rate of reduction in a rolling fatigue life to the preliminary estimate of the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly to determine an estimate of the lifetime of the rolling bearing assembly.
Owner:NTN CORP
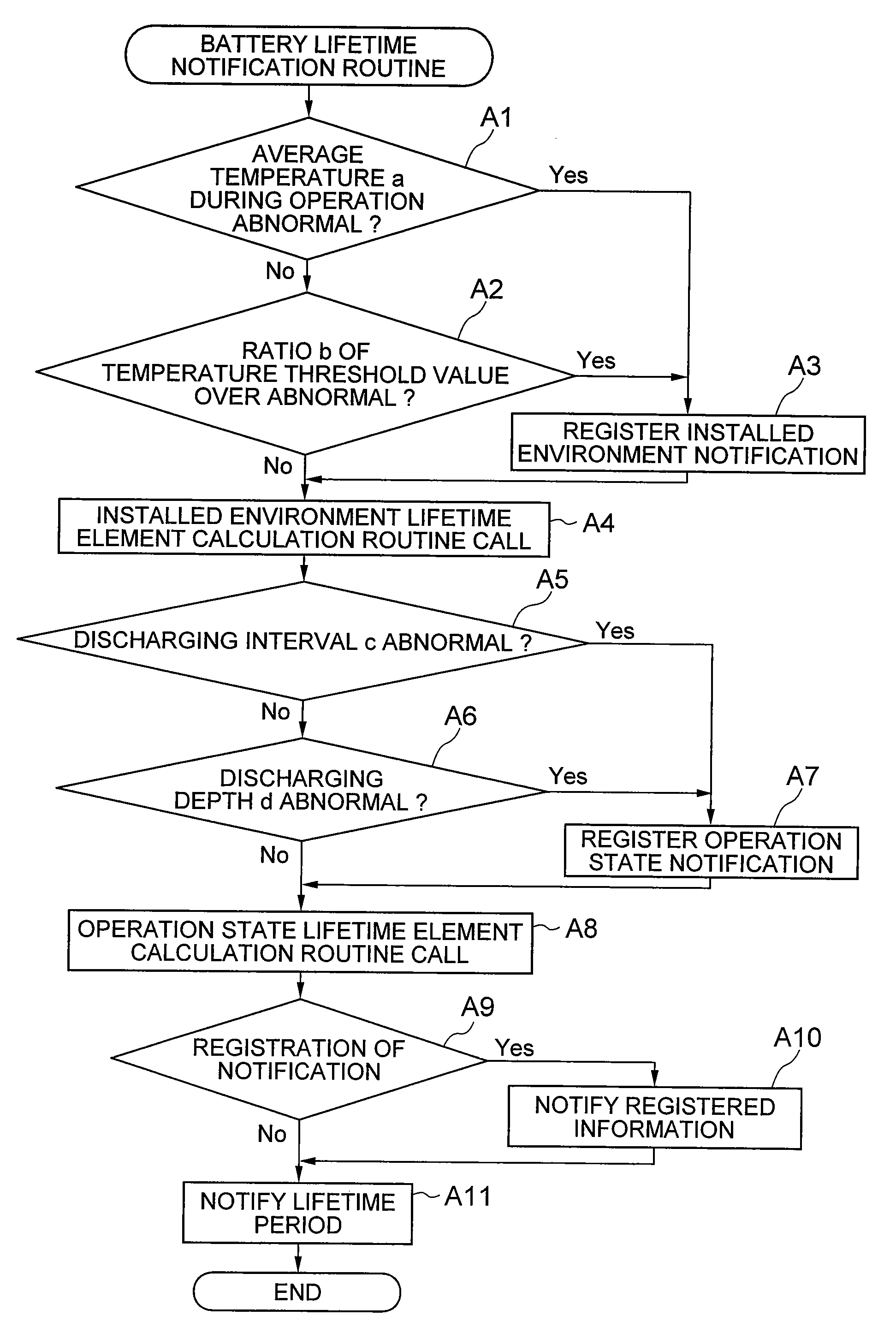
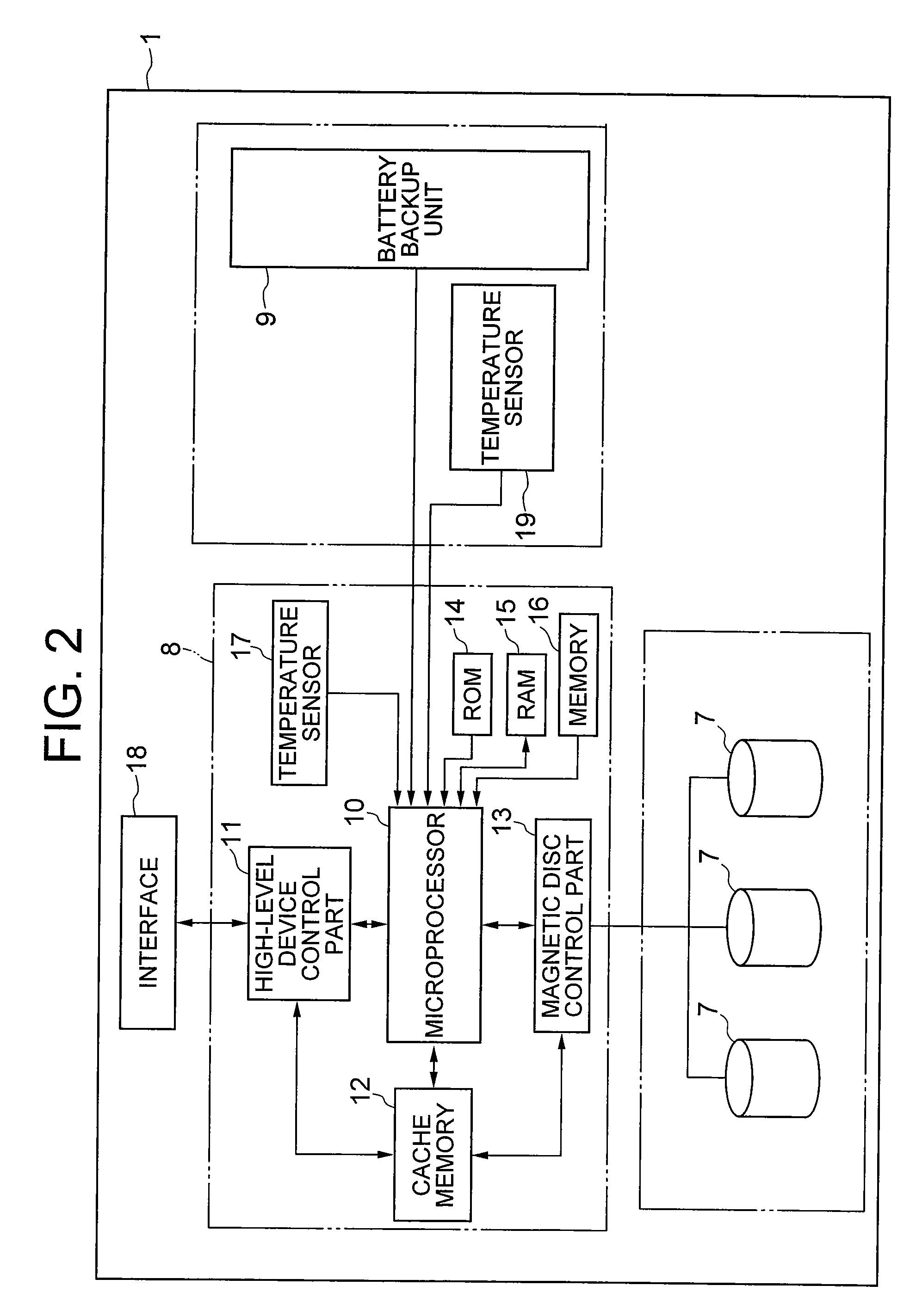
Disc array device
InactiveUS20080208535A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedLow reliabilityElectrical testingSecondary cellsEngineeringLife time
The present invention aims to provide a disc array device capable of efficiently managing the replacement time of a battery backup unit of the disc array device. Installed environment information and operation state information of a battery backup unit of a disc array device are acquired in the disc array device. If the installed environment is determined as not appropriate from such information, the inappropriateness of the installed environment is notified to the user. If the operation state is not appropriate, the inappropriateness of the operation state is notified to the user. Furthermore, the lifetime of the battery backup unit is predicted and the replacement period is notified to the user.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for predicting lifetime of photo-semiconductor device and drive apparatus
ActiveUS8301399B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedInhibition lifetimePlug gaugesLaser detailsPower semiconductor deviceDriving current
In a method for predicting the lifetime of a photo-semiconductor device that has a maximum light output value restricted by thermal saturation, the maximum light output value is extracted by measuring the characteristic of light output from the photo-semiconductor device with respect to drive current. The decrease tendency of the maximum output values with respect to drive time is predicted to predict the lifetime of the photo-semiconductor. Further, the predicted lifetime is updated as time passes. Therefore, in this method, even if drive condition changes, or an individual difference of the photo-semiconductor per se is present, it is possible to substantially accurately predict the lifetime of the photo-semiconductor.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
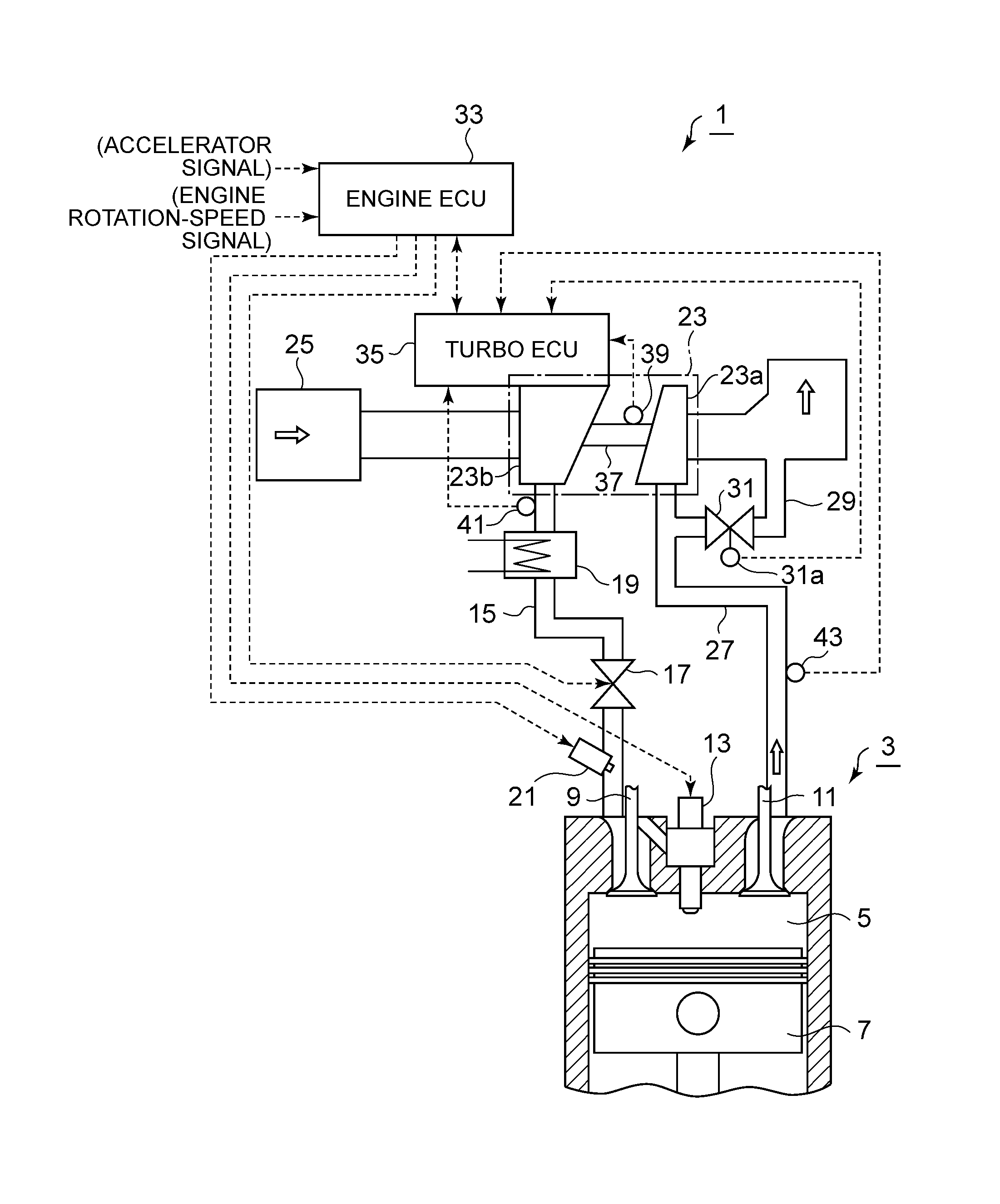
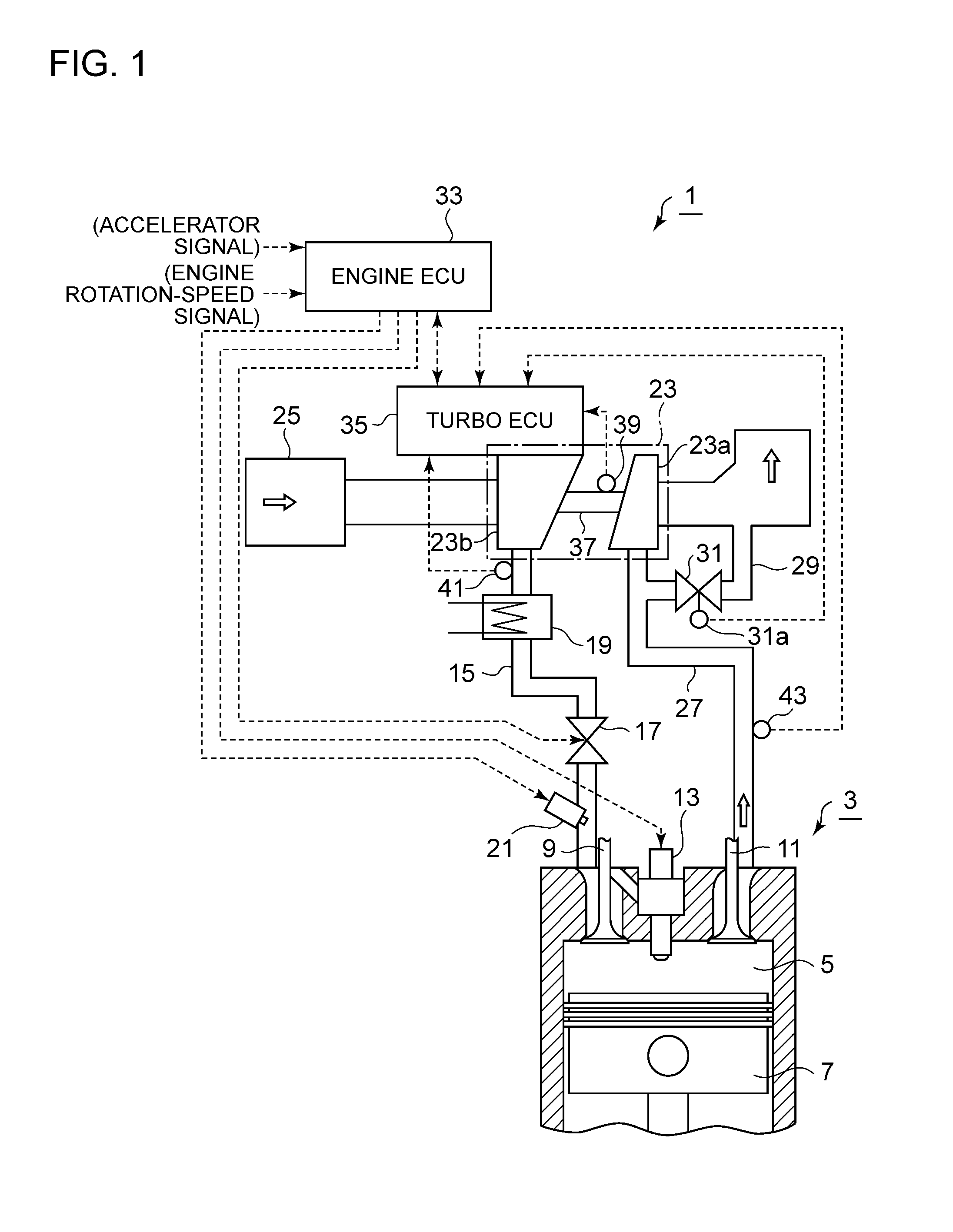
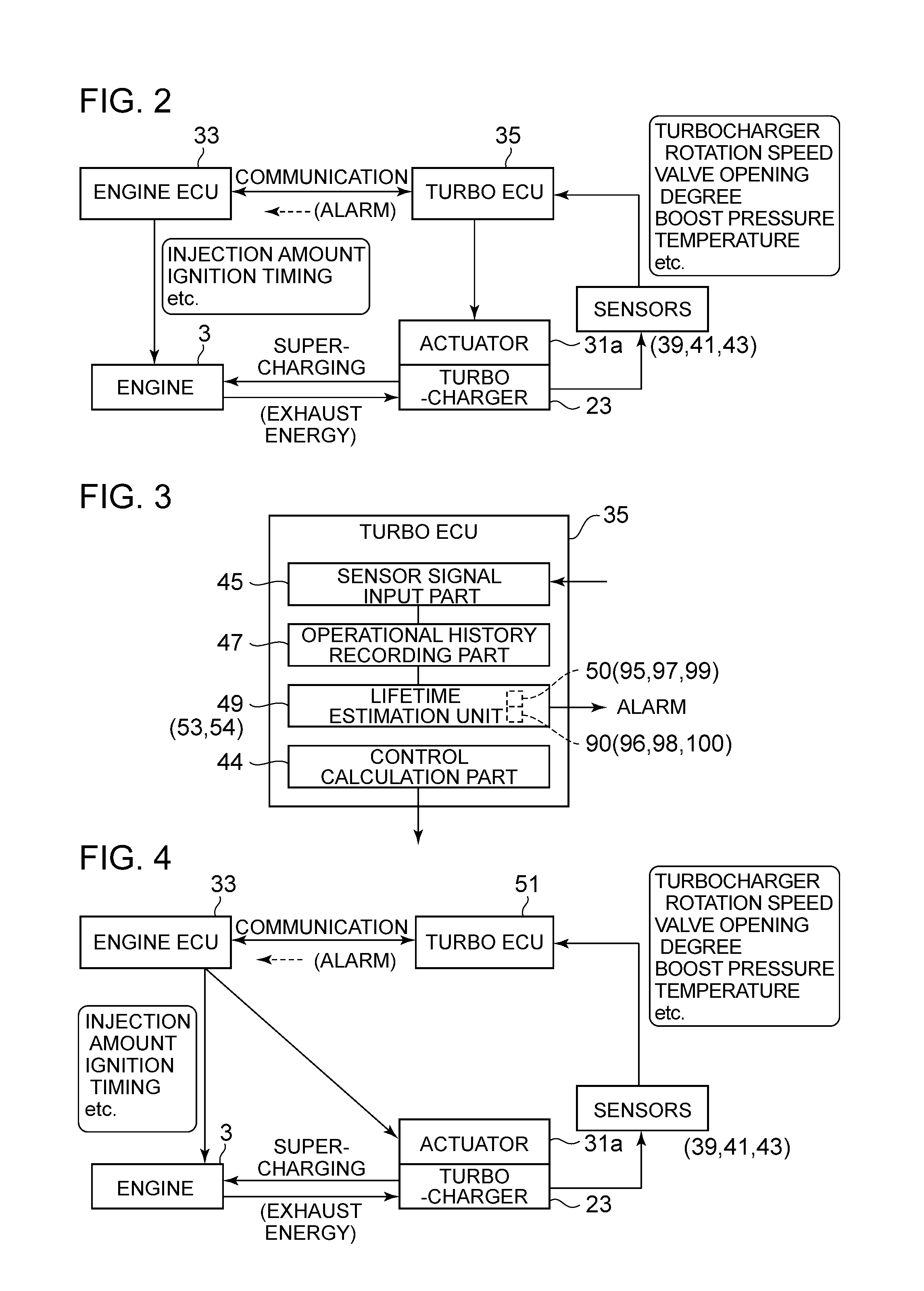
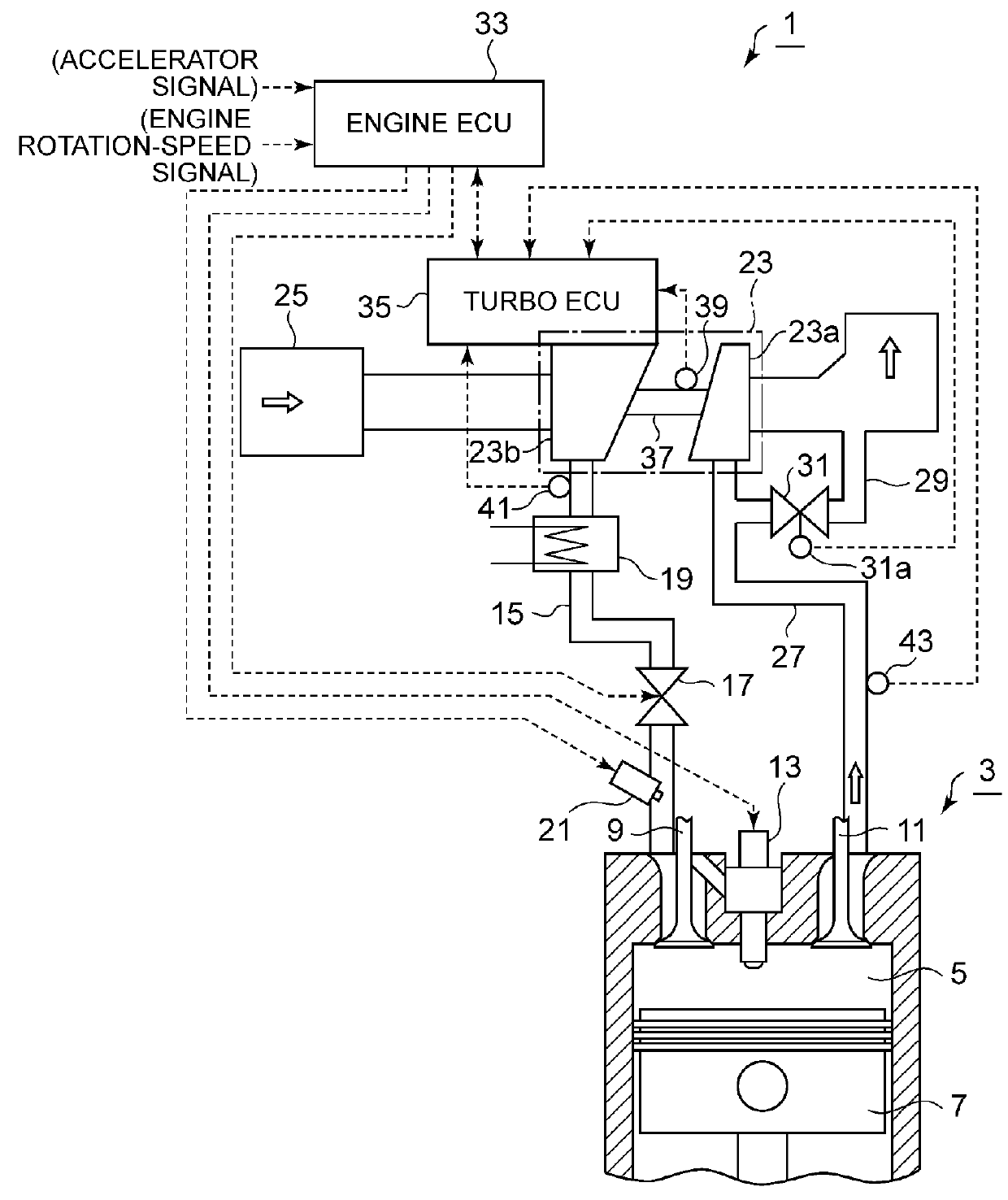
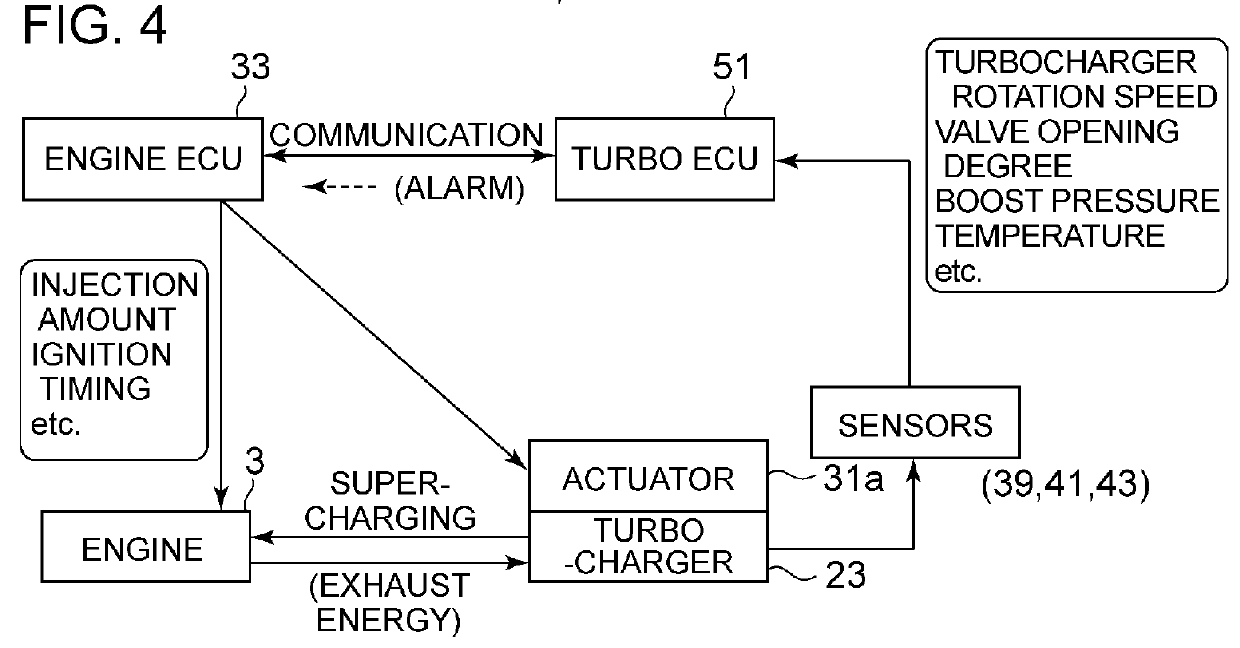
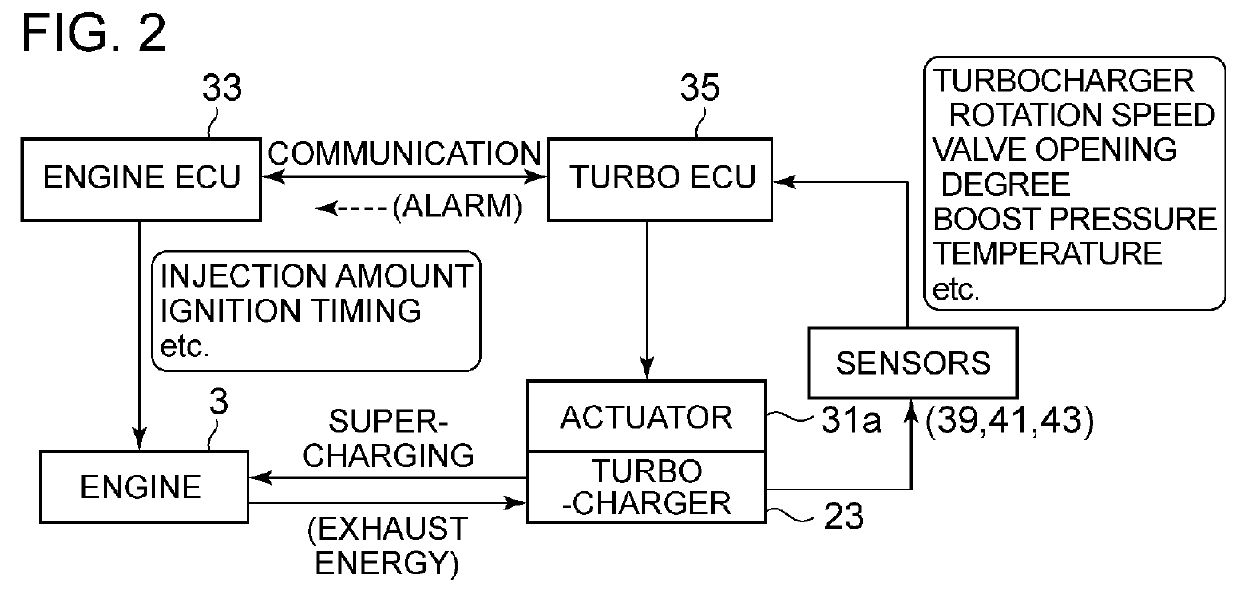
Turbocharger device
ActiveUS20160312688A1Facilitate acquisitionLower initial costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerControl theory
A turbocharger device includes: a turbocharger (3); and a turbo controller (35) configured to control a waste-gate valve (31) or a variable-displacement mechanism of an exhaust-gas amount supplied to the turbine to control a boost pressure of the turbocharger, the turbo controller (35) including a control calculation part (44) and a sensor signal input part (15) provided separately and independently from an engine controller (33) and being mounted to a compressor housing at a side of the compressor (23b) of the turbocharger (3).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
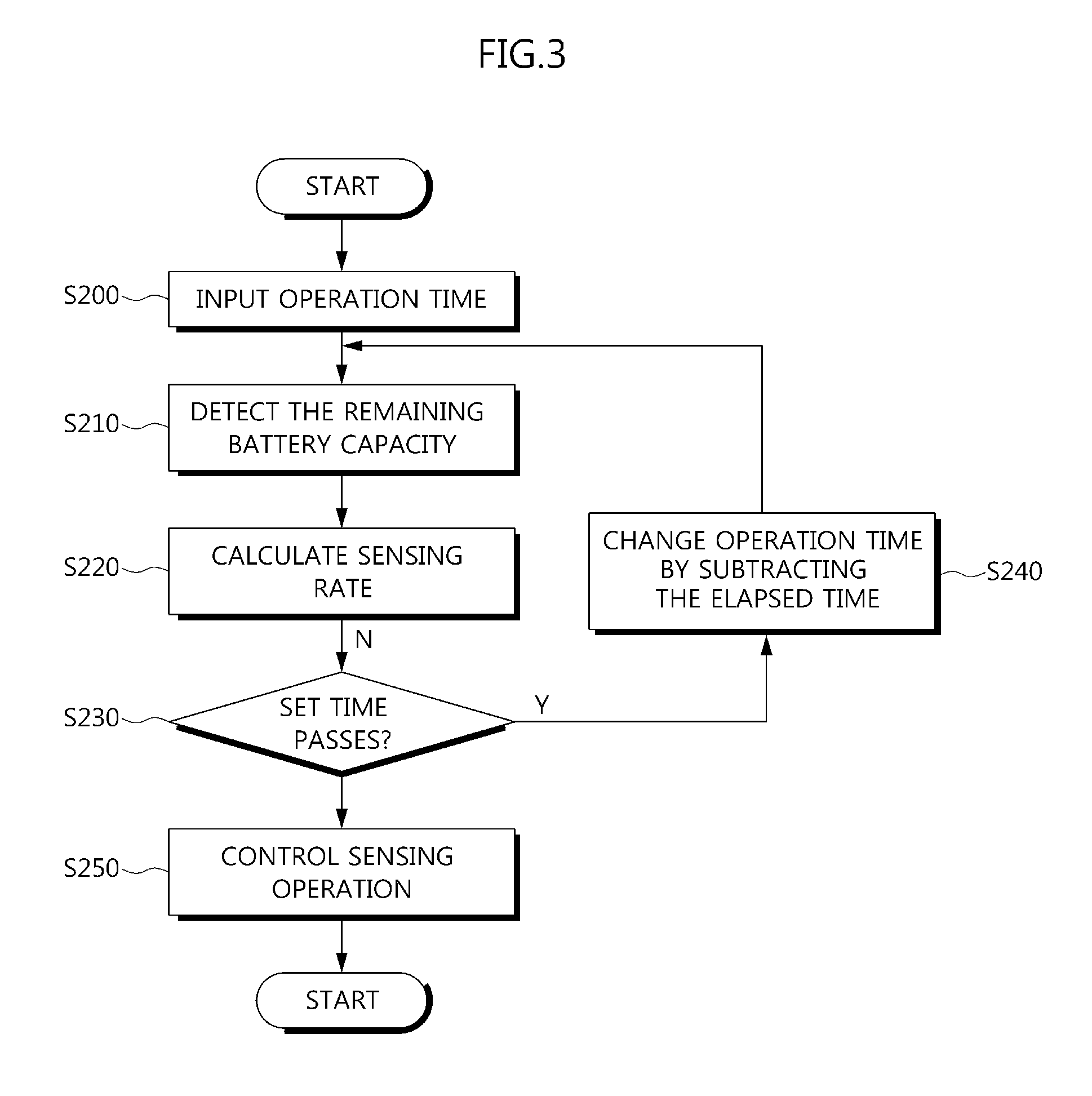
Sensor node and control method thereof
ActiveUS20120173186A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedPower managementMeasurement devicesSensor nodeReal-time computing
A sensor node for accurately guaranteeing a lifetime of a USN sensor node, and a control method thereof are provided. The sensor node control method includes receiving an operation time of a sensor node from a user; based on the input operation time, calculating a sensing rate which is the number of sensings of the sensor node per unit time; and according to the calculated sensing rate, controlling a sensing operation of the sensing node.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRONICS TECH INST
Method of installing elastomer ring in semiconductor processing equipment and guiding sheet and jig used in installing elastomer ring
ActiveUS20160163518A1Lifetime be accurately estimatedPrevent leakageElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElastomerEngineering
Provided are a method, a guiding sheet, a partial filling jig, and a full filling jig for installing an elastomer ring in the semiconductor processing equipment. The guiding sheet, the partial filling jig, and the full filling jig dispose the elastomer ring in the groove of the semiconductor processing equipment smoothly and evenly. Furthermore, the surface of the elastomer ring may be divided to multiple arcs portions. Each one of the arc portions may be pressed by the partial filling jig or the full filling jig in a particular sequence. When the groove is filled by the elastomer ring accurately and completely, the elastomer ring may block the fluid and the etching gas effectively. The elastomer ring may help the semiconductor processing equipment to work continuously and maintain qualities of the etching wafers.
Owner:MFC SEALING TECH
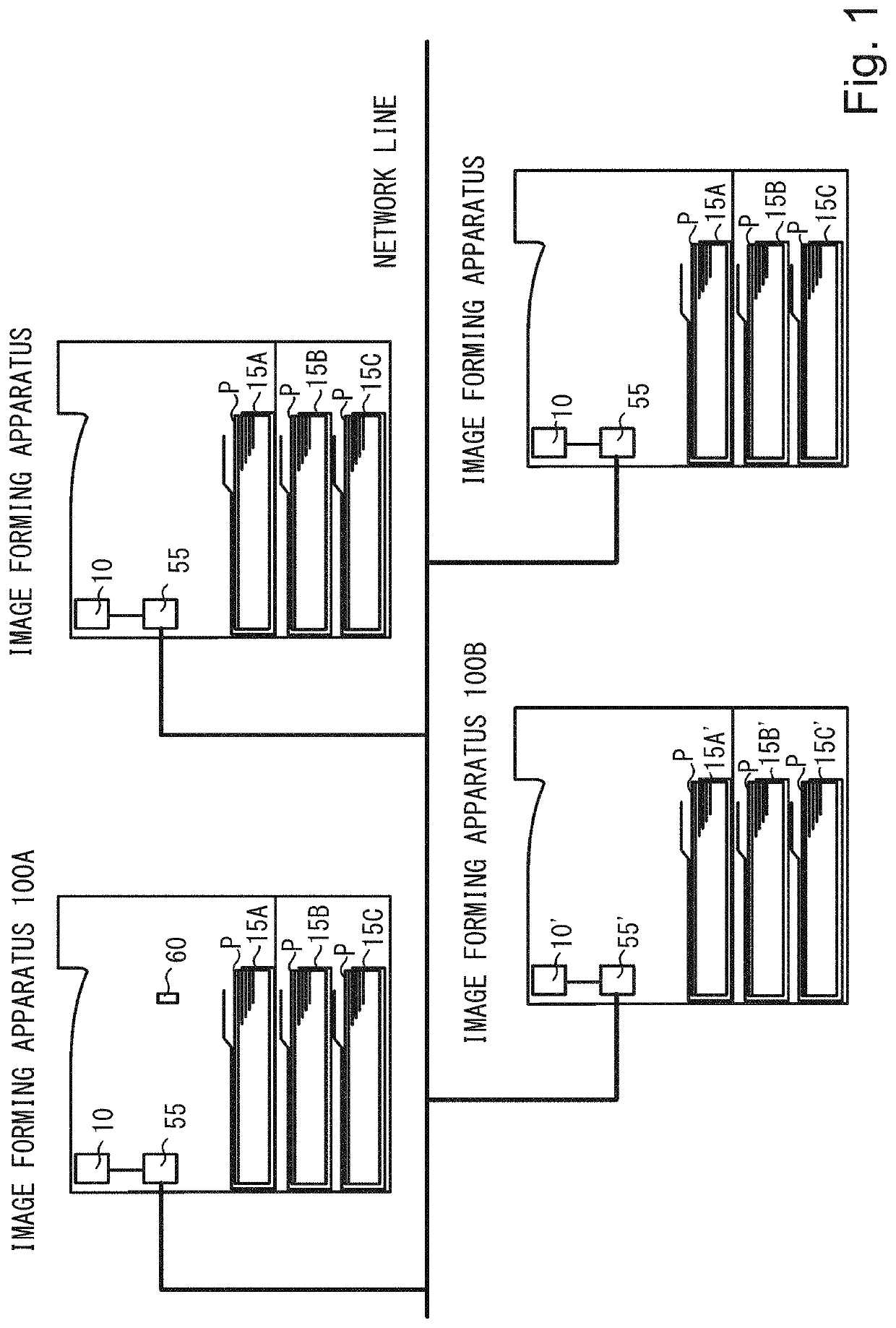
Image forming apparatus and image forming system
ActiveUS11454913B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedElectrographic process apparatusComputer graphics (images)Radiology
An image forming system includes a first image forming apparatus and a second image forming apparatus connected with the first image forming apparatus by a network line. When a second stacking portion of the second image forming apparatus is associated with a first stacking portion of the first image forming apparatus by a setting portion, an arithmetic portion acquires information related to the characteristic of a second recording medium stacked by the second stacking portion via the network line and obtains a degree of deterioration of a feeding rotatable member of the first image forming apparatus based on the acquired information related to the characteristic of the second recording medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and device for estimating battery life
ActiveUS10908222B2Accurately estimate the remaining lifetime of a battery in useLifetime be accurately estimatedBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingElectrical batteryVoltage drop
Provided is a battery lifetime estimating method including steps of: fully charging a battery according to a predetermined charging condition; partially discharging the fully charged battery according to a predetermined discharging condition; acquiring voltage information at a plurality of predetermined measurement time points while performing the partially discharging; and estimating a remaining capacity of the battery by using the acquired voltage information. Herein, the step of estimating the remaining capacity of the battery includes steps of: calculating the capacity of the battery in one cycle of fully charging / discharging in which the measurement is performed from the measured voltage drop amounts; and estimating the remaining lifetime of the battery by applying a statistical technique to the capacity of the battery calculated with respect to a plurality of cycles of fully charging / discharging.
Owner:HYOSUNG HEAVY IND CORP
Laser apparatus enabling calculation of effective driving time and remaining lifetime taking account of drive conditions including temperature
ActiveUS9887514B2Improve accuracyImprove calculation accuracyLaser detailsRadiation pyrometryAcceleration factorPerformance index
A first calculation unit calculates an acceleration factor of lifetime consumption of the light source with as case of a standard temperature and standard drive condition as a reference, a second calculation unit calculates a whole lifetime or remaining lifetime of individual light sources relative to a performance index of the individual light sources or a change rate of the performance index, a computation unit obtains an effective cumulative driving time at which the magnitude of influence imparted on the lifetime is equivalent with a case of driving at the standard temperature and standard drive condition, by calculating a time integral of the acceleration factor, and a recording unit records the effective cumulative driving time and the whole lifetime or remaining lifetime together with an optical output characteristic of the light source.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Method of installing elastomer ring in semiconductor processing equipment and guiding sheet and jig used in installing elastomer ring
ActiveUS10153140B2Lifetime be accurately estimatedPrevent leakageElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElastomerEngineering
Provided are a method, a guiding sheet, a partial filling jig, and a full filling jig for installing an elastomer ring in the semiconductor processing equipment. The guiding sheet, the partial filling jig, and the full filling jig dispose the elastomer ring in the groove of the semiconductor processing equipment smoothly and evenly. Furthermore, the surface of the elastomer ring may be divided to multiple arcs portions. Each one of the arc portions may be pressed by the partial filling jig or the full filling jig in a particular sequence. When the groove is filled by the elastomer ring accurately and completely, the elastomer ring may block the fluid and the etching gas effectively. The elastomer ring may help the semiconductor processing equipment to work continuously and maintain qualities of the etching wafers.
Owner:MFC SEALING TECH
Turbocharger device
ActiveUS10006348B2Facilitate acquisitionLower initial costElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerControl theory
A turbocharger device includes: a turbocharger (3); and a turbo controller (35) configured to control a waste-gate valve (31) or a variable-displacement mechanism of an exhaust-gas amount supplied to the turbine to control a boost pressure of the turbocharger, the turbo controller (35) including a control calculation part (44) and a sensor signal input part (45) provided separately and independently from an engine controller (33) and being mounted to a compressor housing at a side of the compressor (23b) of the turbocharger (3).
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Conveyor belt for marginal life prediction
ActiveUS10894669B2Function increaseEasy to wearConveyorsControl devices for conveyorsLife timeConveyor belt
There is provided a conveyor belt for marginal life prediction, in which wear of the degree of the conveyor belt can be well and visually recognized without stopping of the conveyor belt on operation, and the replacement time of the conveyor belt can be easily predicted in advance, thereby to predict and efficiently manage the life time of the conveyor belt. It was difficult to check abrasion extents step by step and exactly predict the life time in the conventional conveyor belts. Further, the accidents of carrying articles released out of the conveyor belt were frequently occurred since troughs of the conveyor belt are not formed enough, and the angle of the trough is so small. As the way of solving the problems as above, while the wear of the conveyor belt is progressed, and when the abrasion check colored rubbers, which are embedded inside the conveyor belt, are exposed outwardly and checked visually by eyes, the extent of the abrasion of the conveyor belt can be estimated and the exchange time of the conveyor belt can be well predicted. The number of the exposed abrasion check colored rubbers is well detected by installing the abrasion check colored rubbers in multi-layers with installation number reduced downwardly, thereby to enable anybody to predict the life time of the conveyor belt step by step precisely.
Owner:KIM WOOJEONG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com