Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57results about How to "Ensure measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
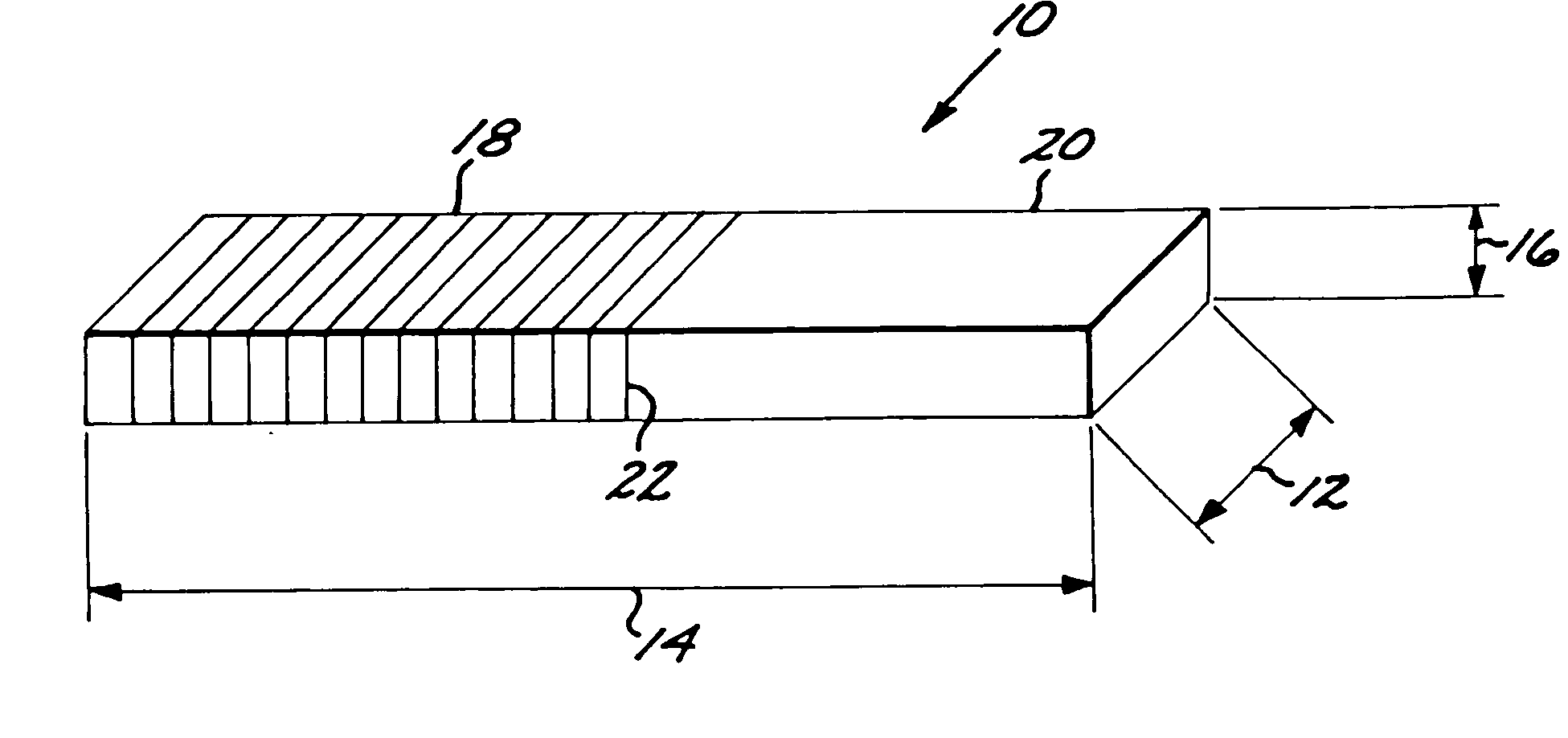
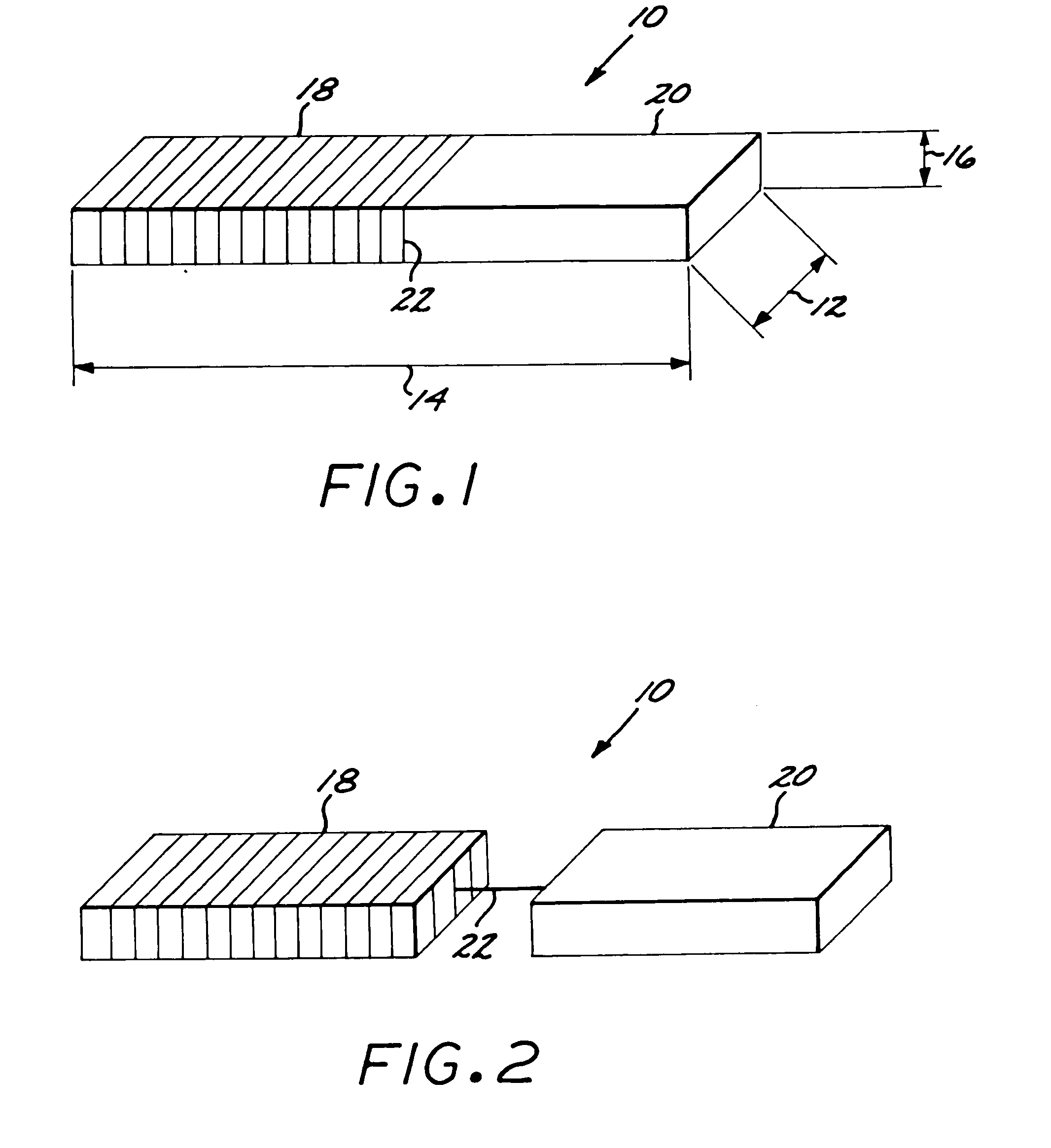
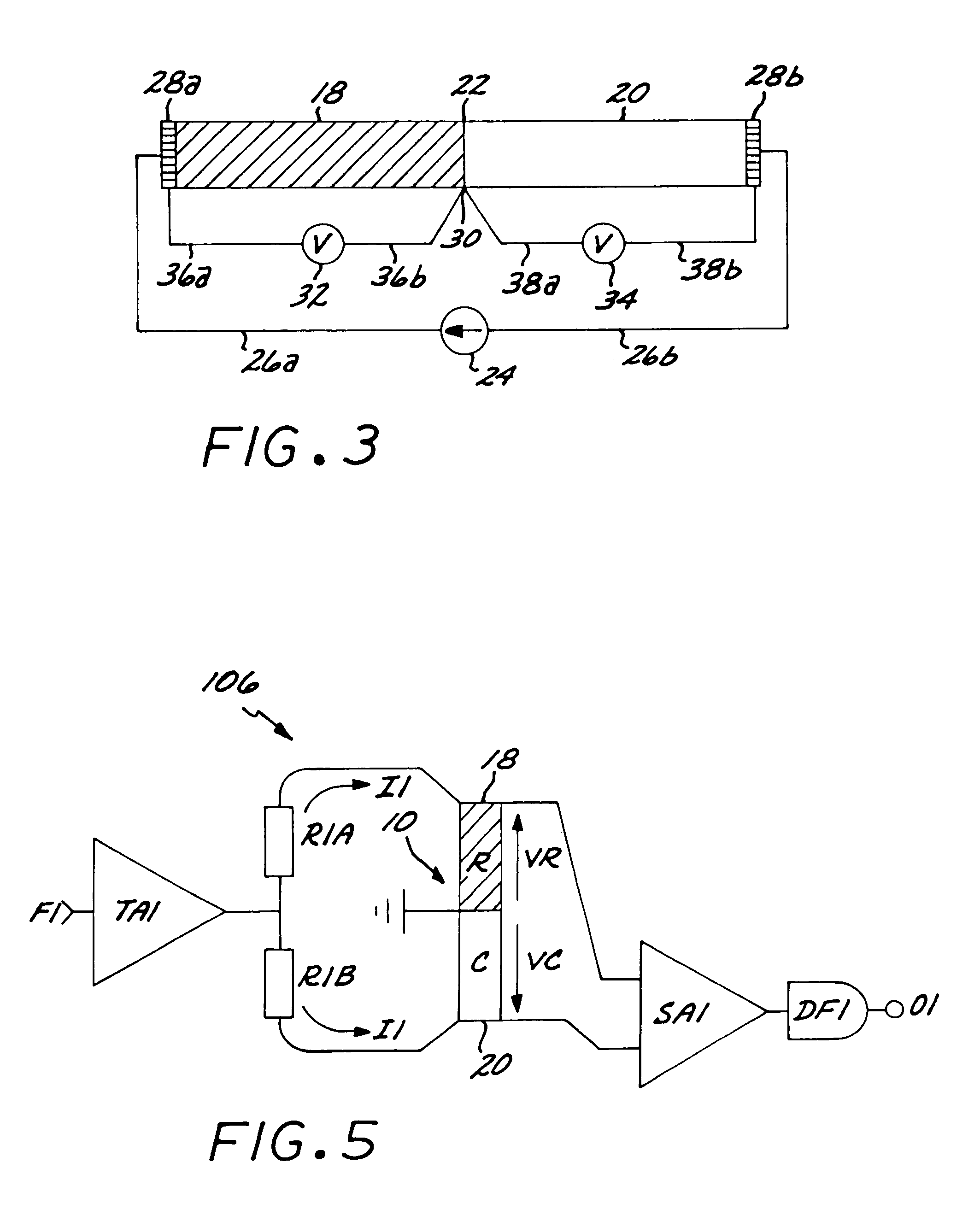
Method and an apparatus for estimating residual noise in a signal and an apparatus utilizing the method
InactiveUS6871066B1Improve performanceReduce equipment production costsTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemDigital radio
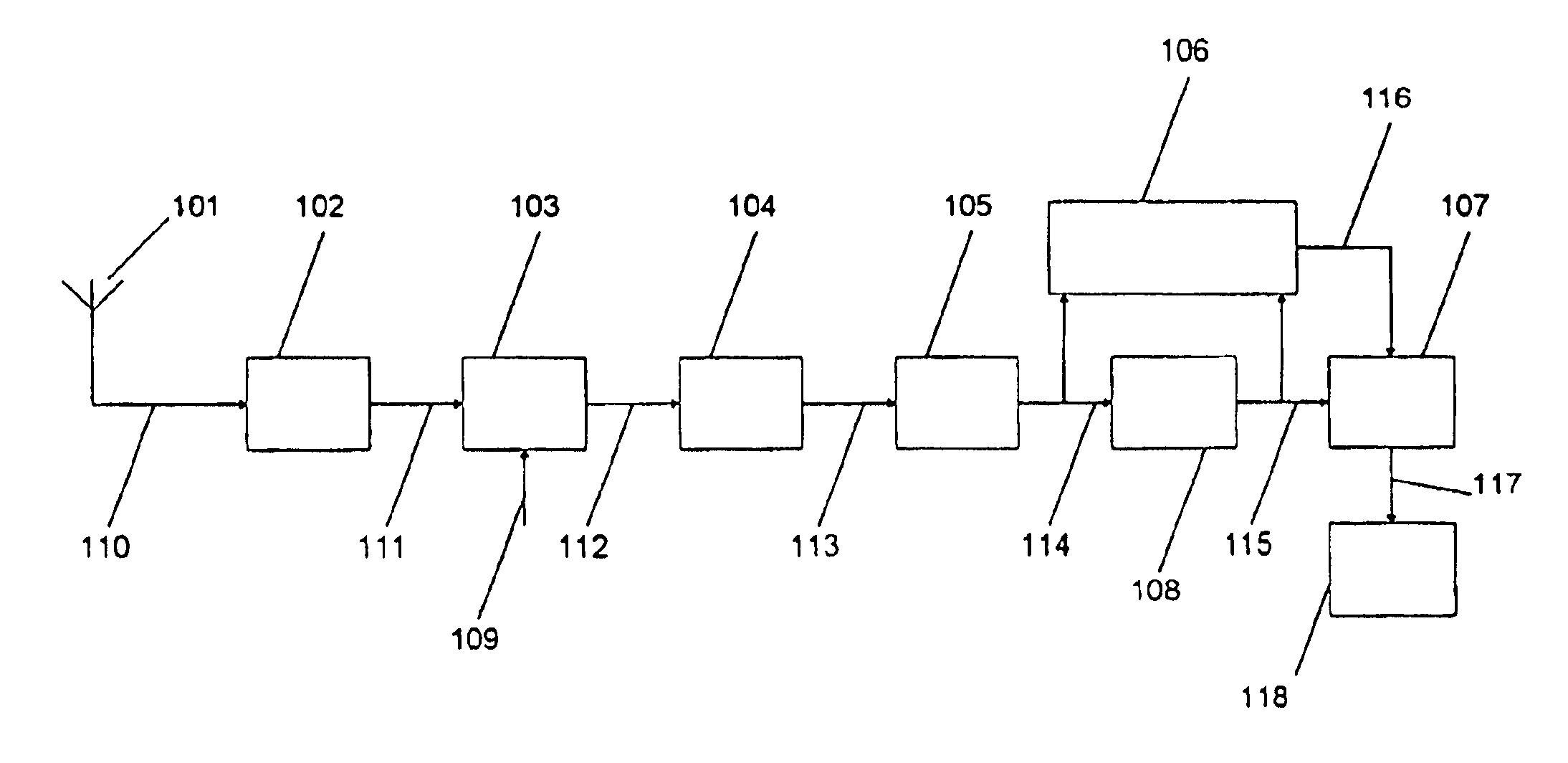
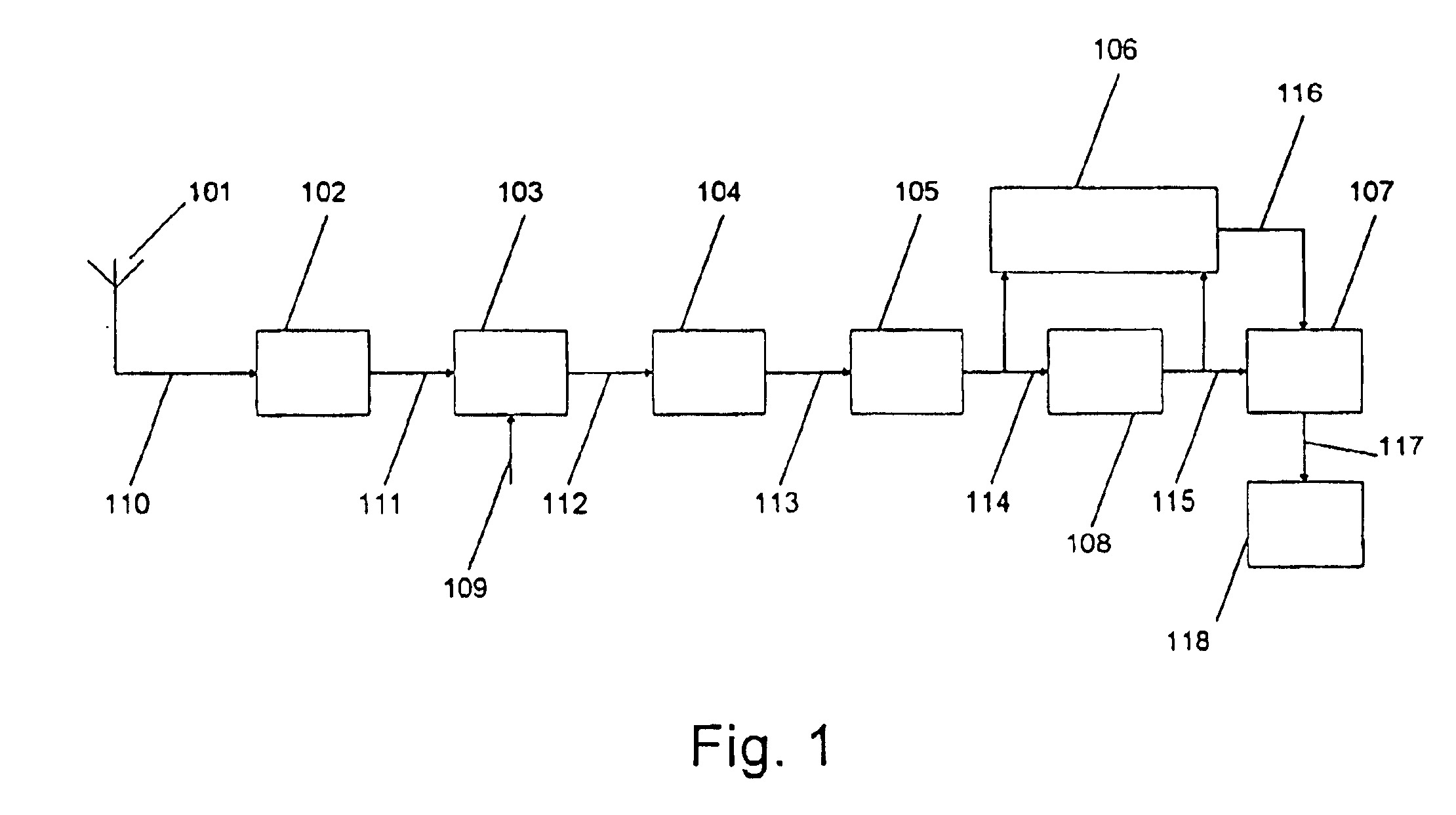
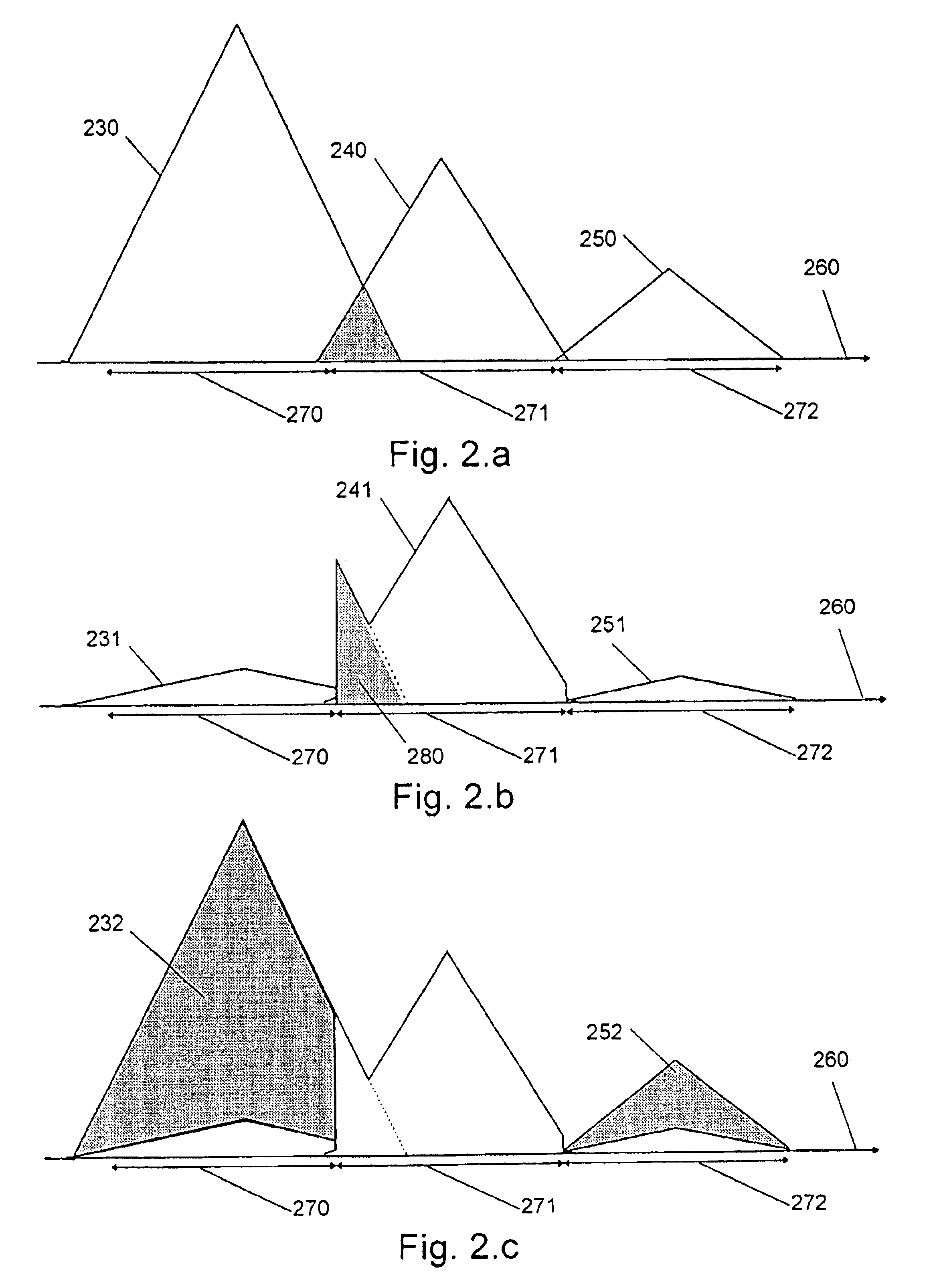
The invention relates to: A method for estimating residual noise in the frequency range (271) of a desired part (240) of a signal to a corresponding apparatus and to a mobile telephone utilizing the method.The object of the present invention is to generate a measure for the residual noise in a signal.The problem is solved in that the amplitude of the signal (114) comprising the noise is modified, and the signal (114) is combined with the modified signal (115) to create a noise estimation measure (116).The invention may e.g. be used in digital radio communications systems to contribute to the monitoring of link quality and therefore to improve payload throughput. One of the advantages of the invention is that an indication of link quality at an early stage in the receiver is provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
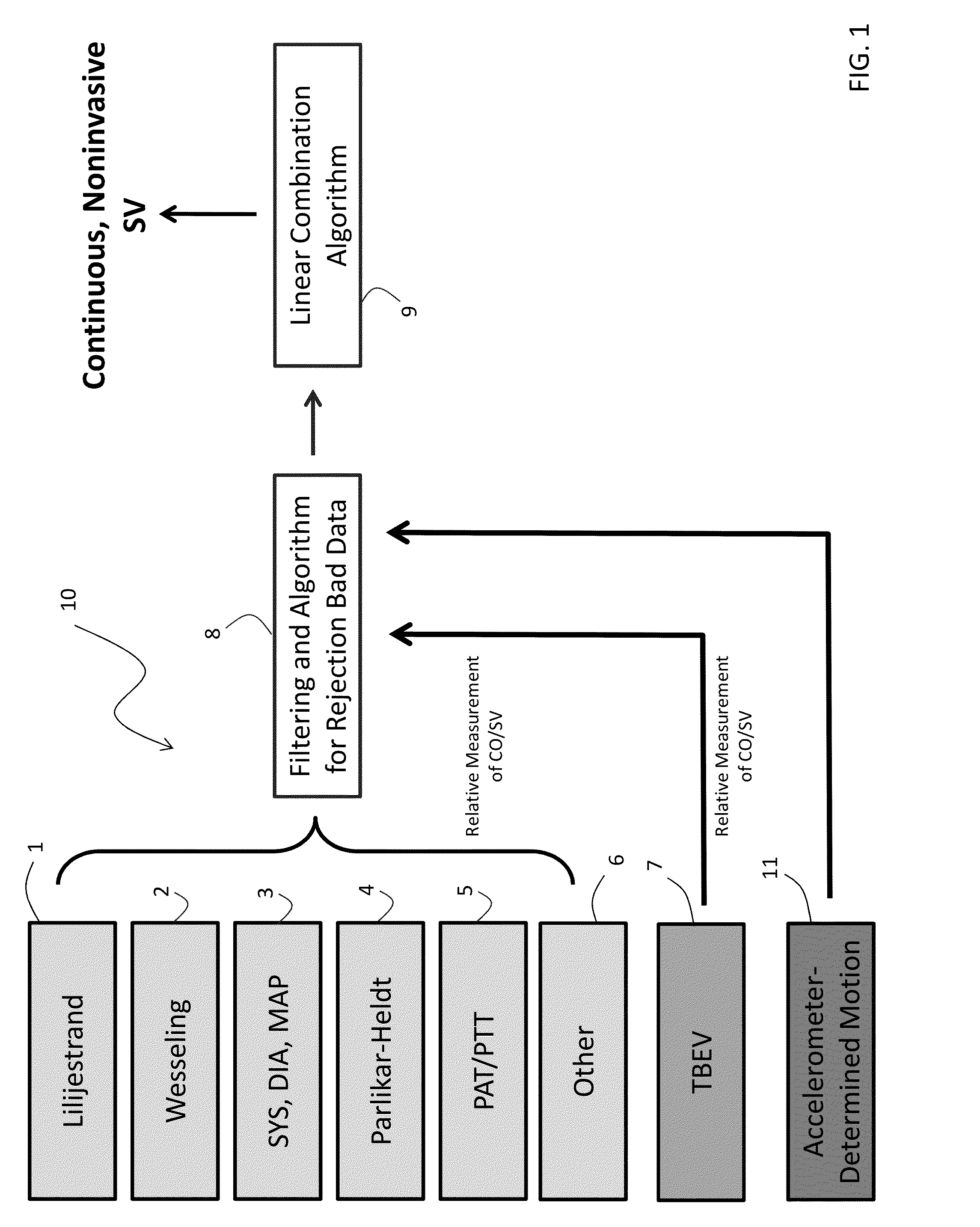
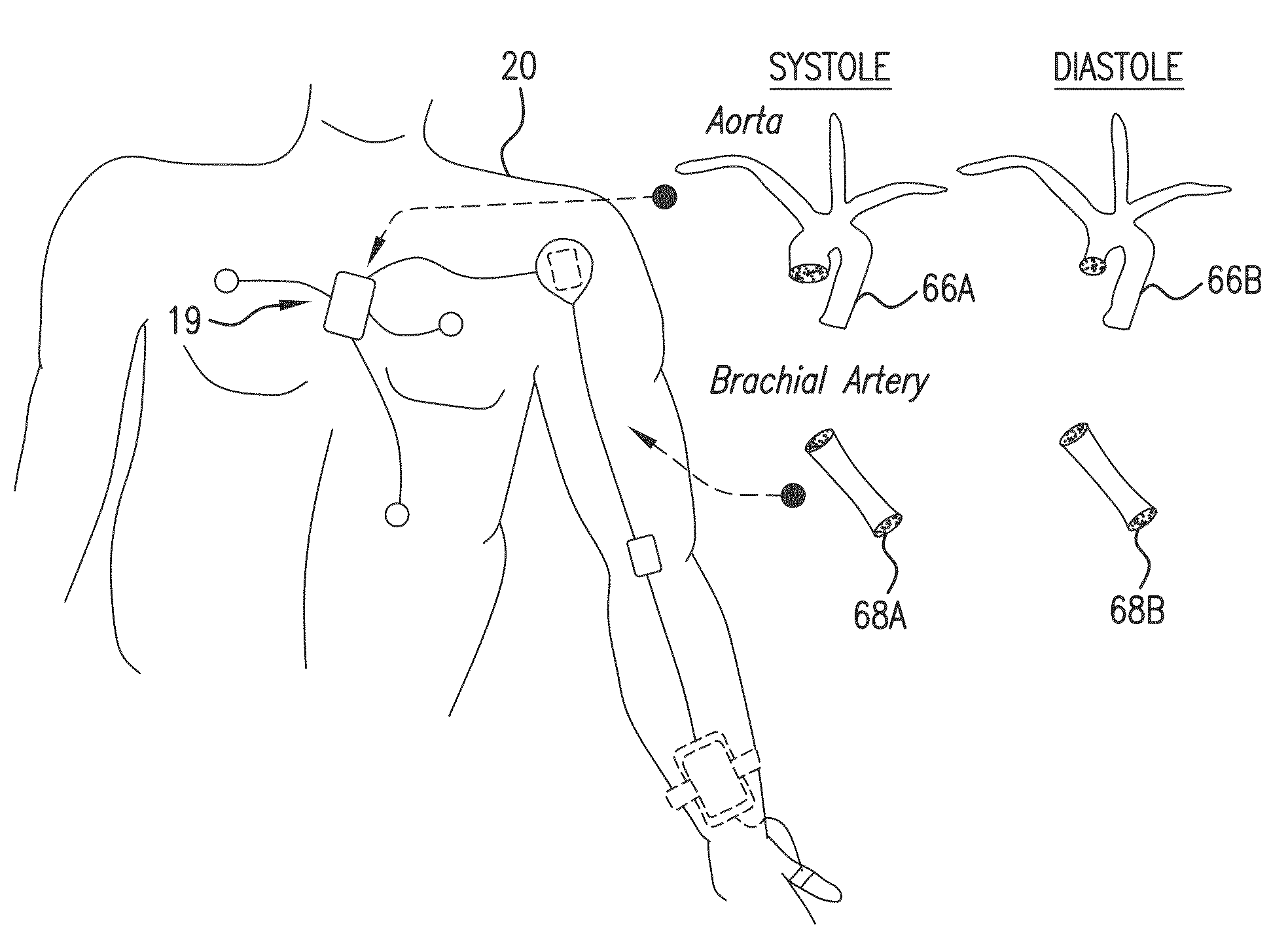
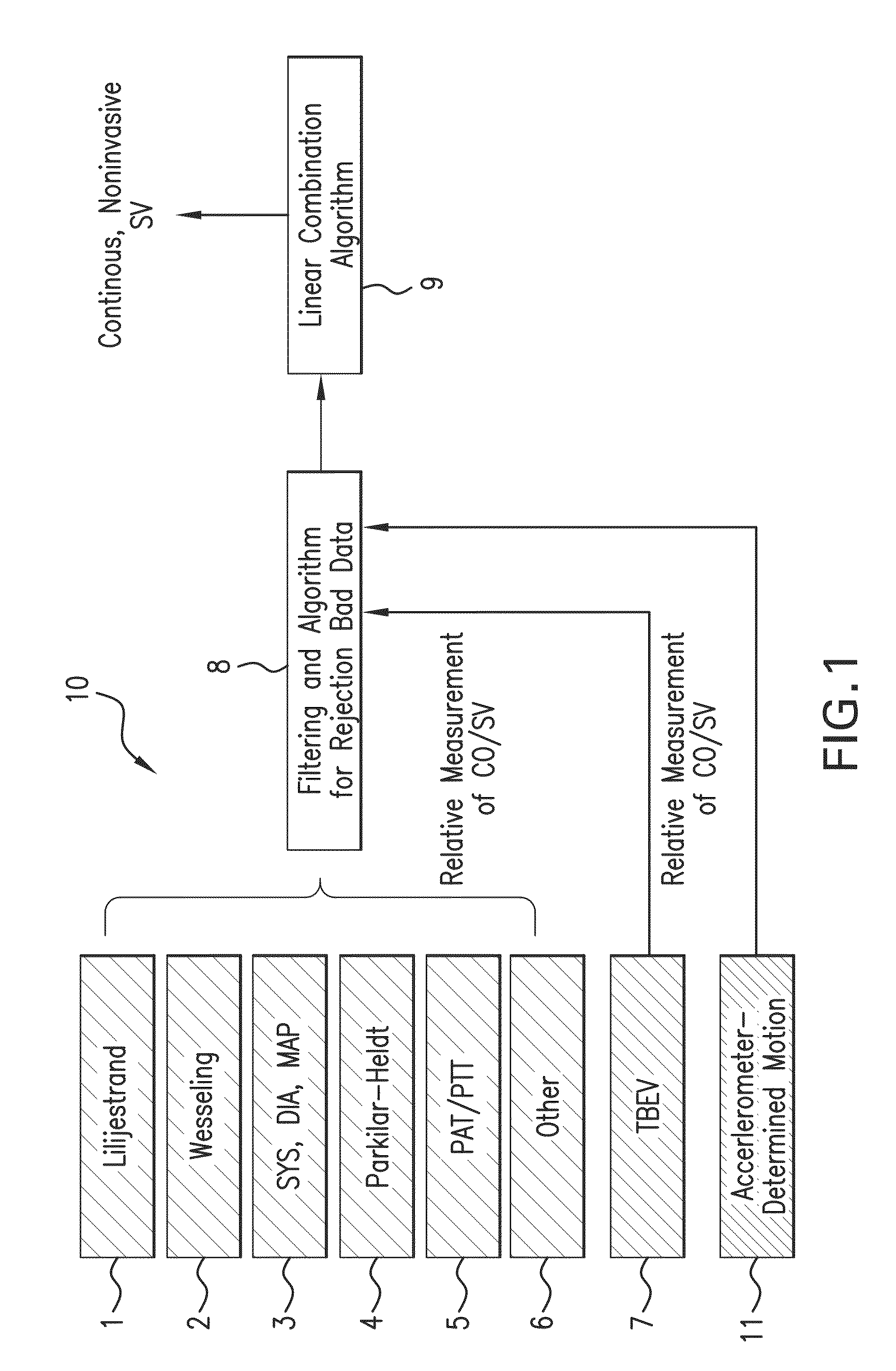
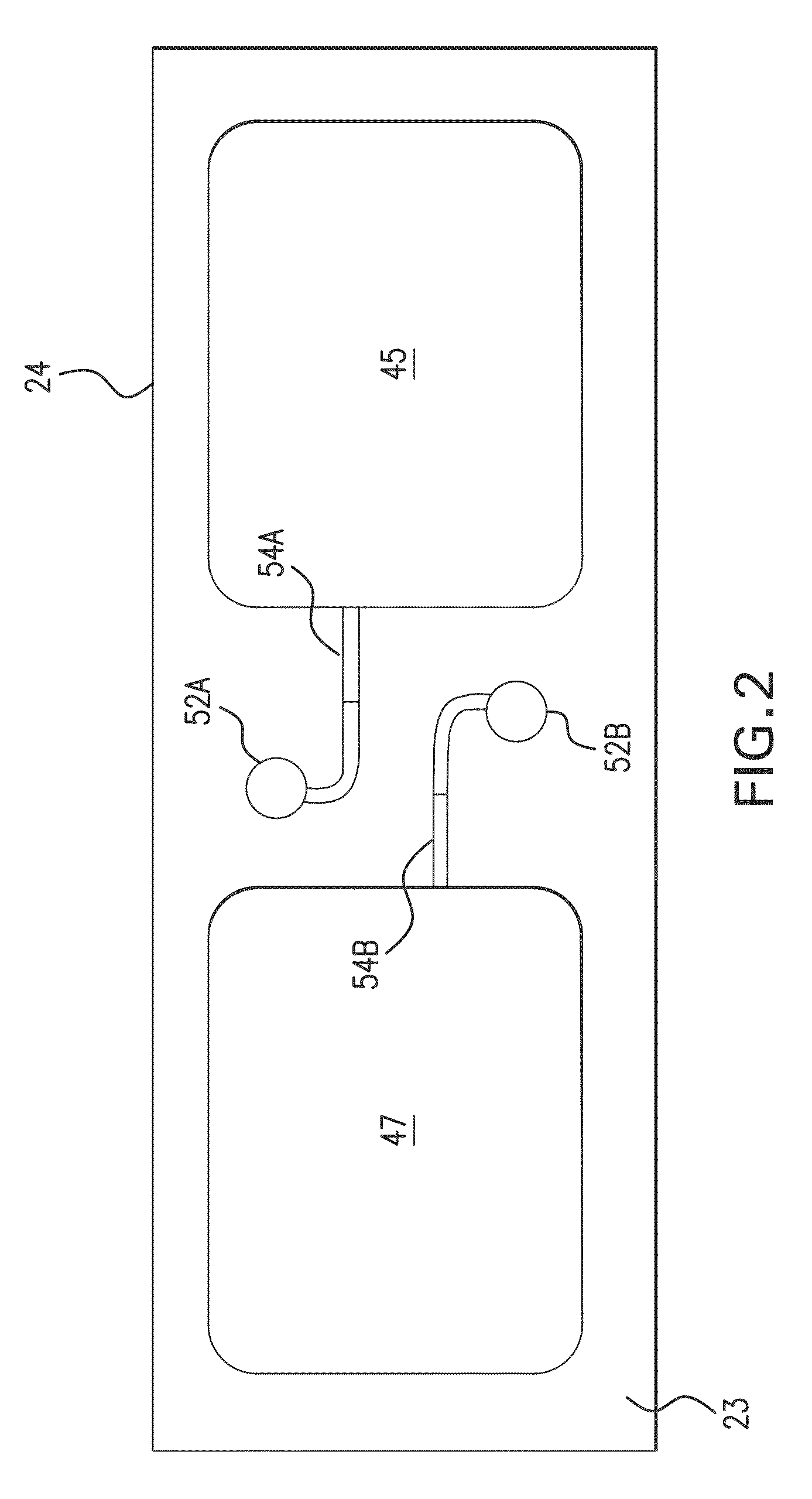
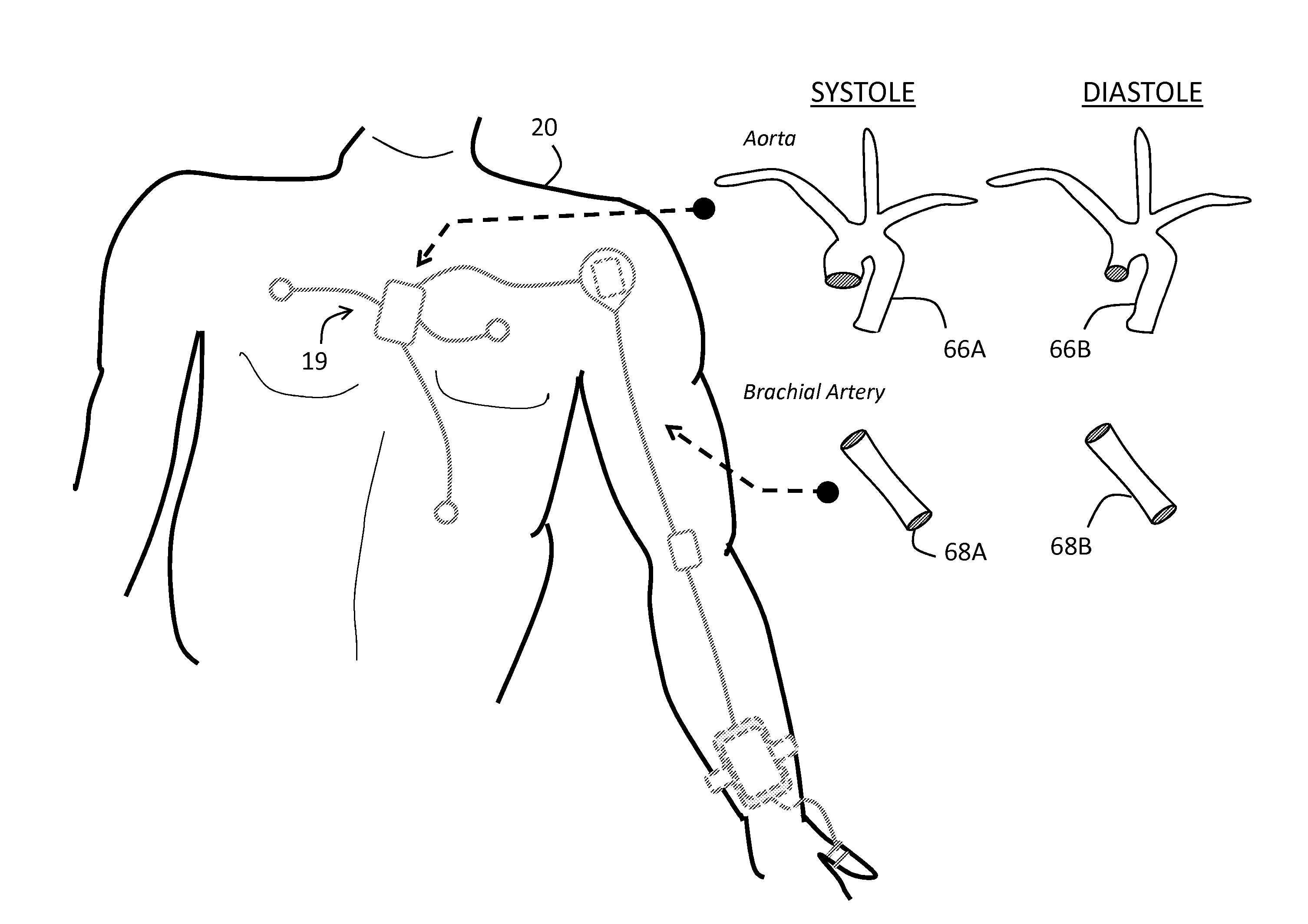
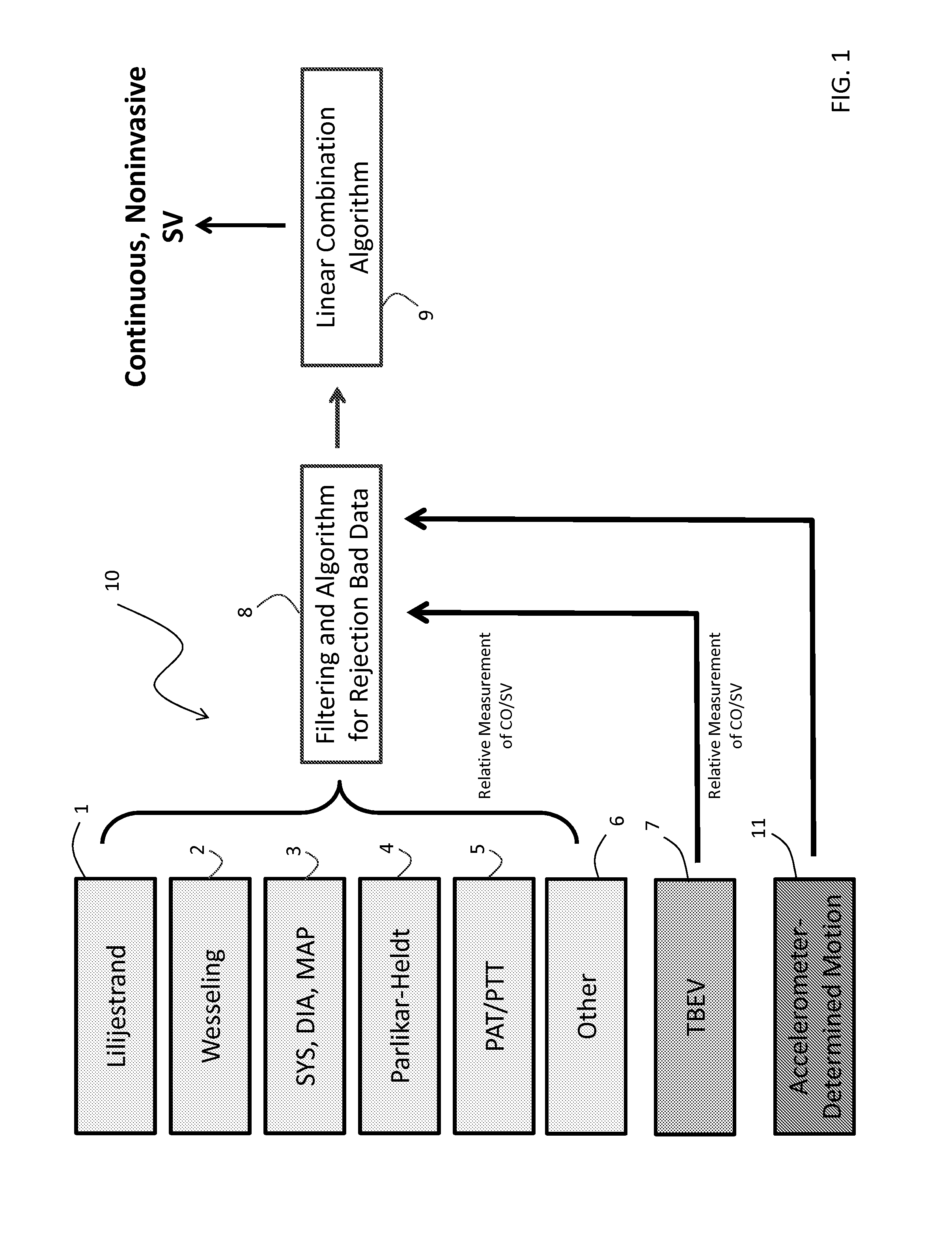
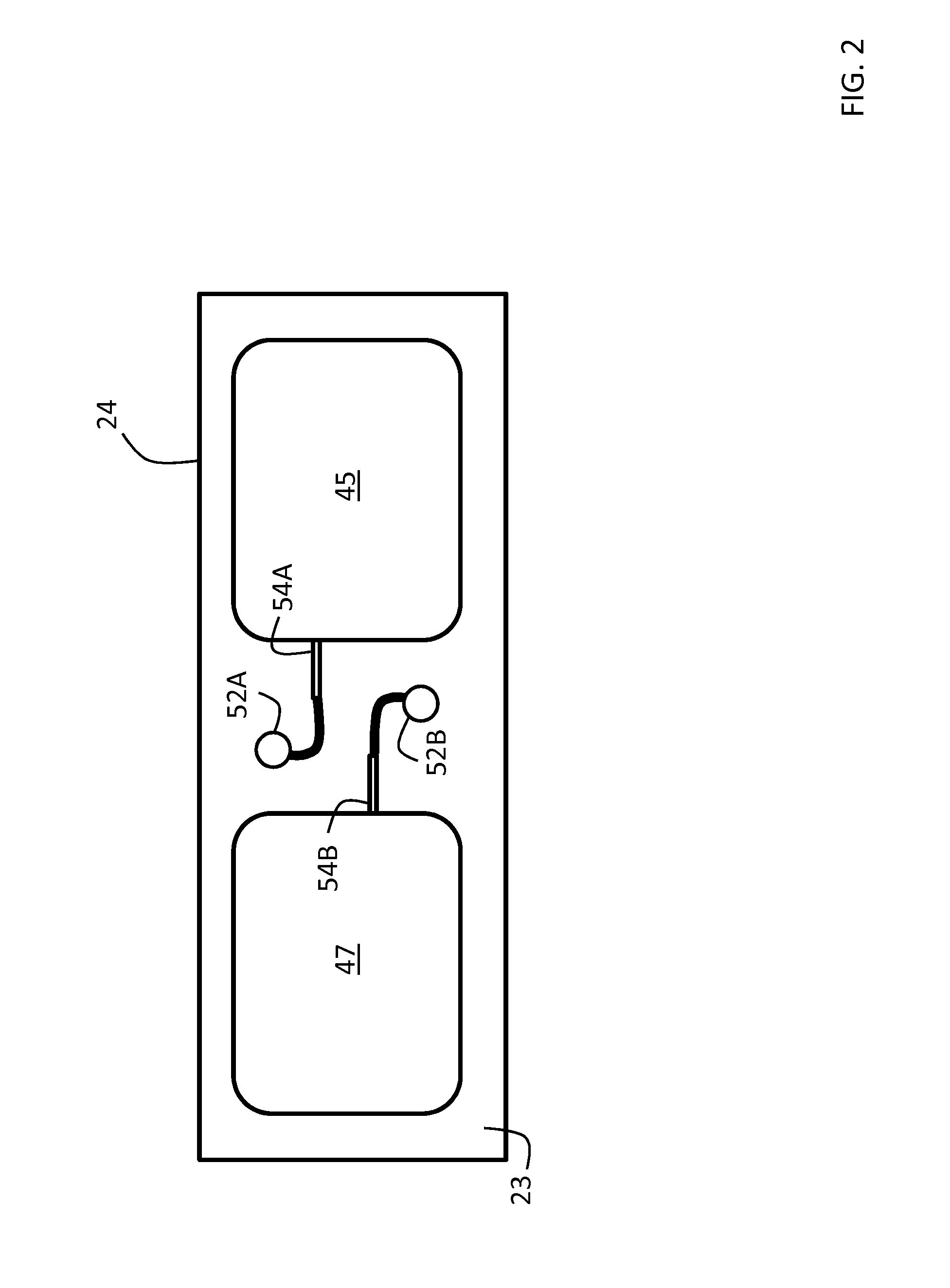
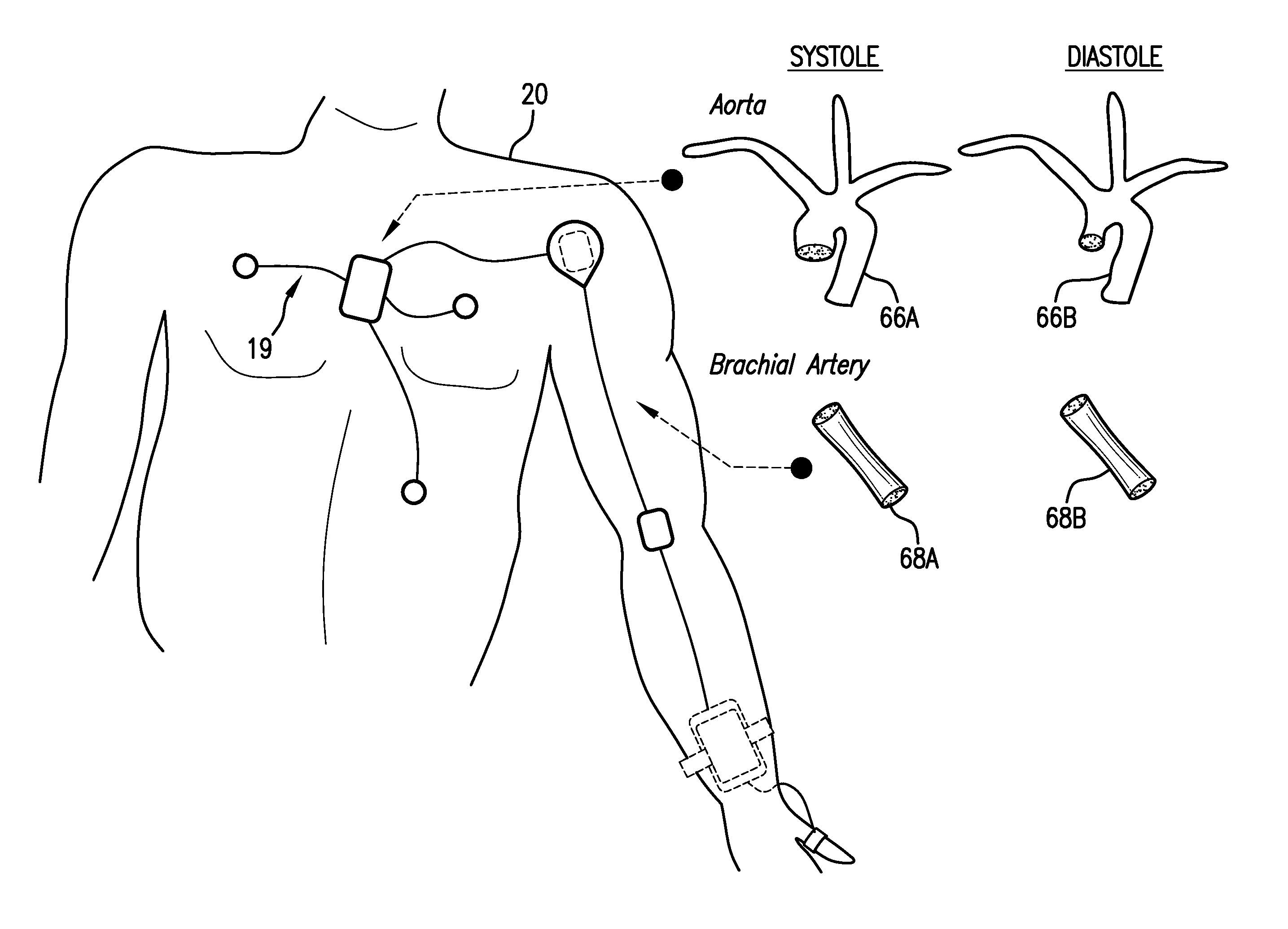
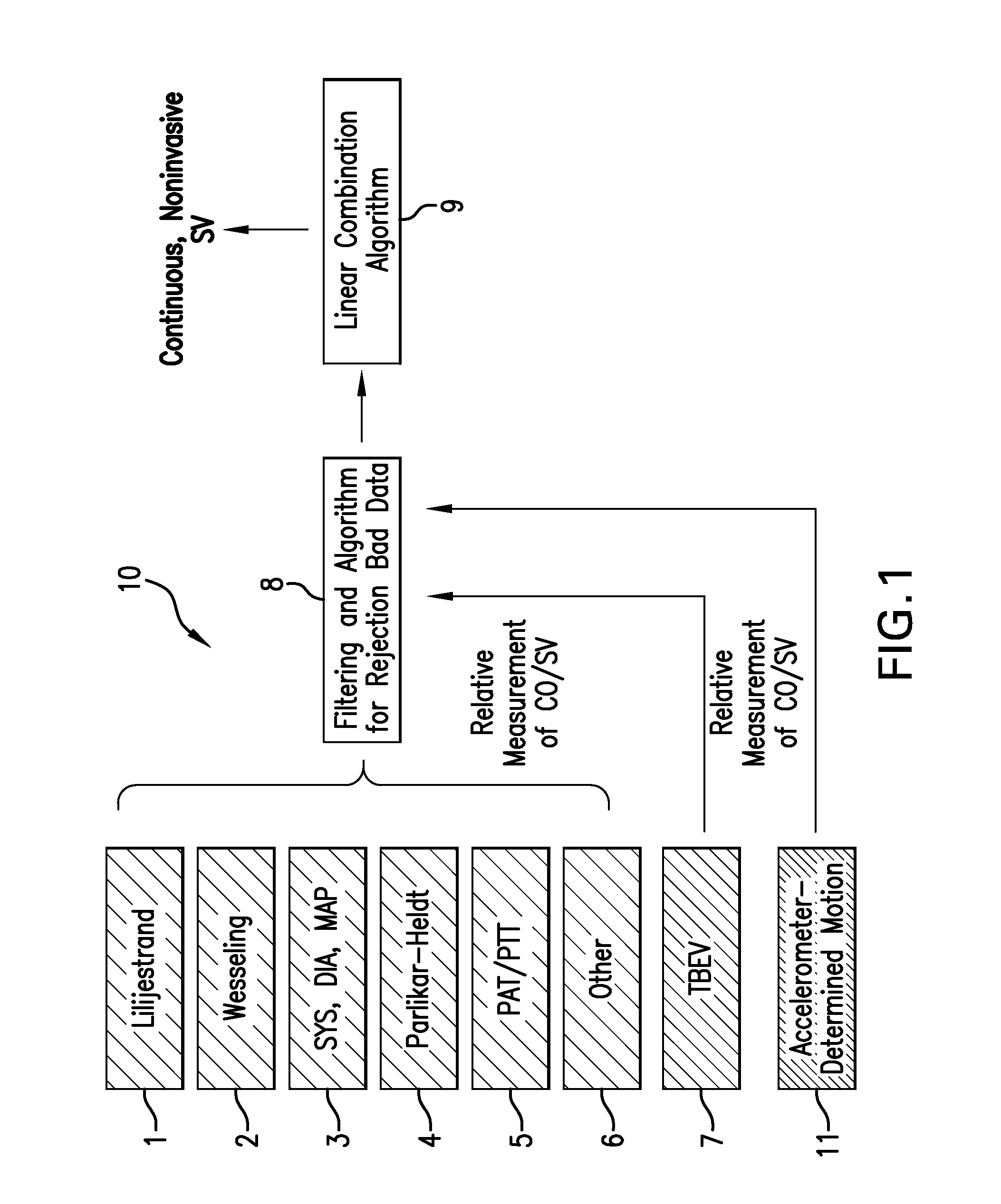
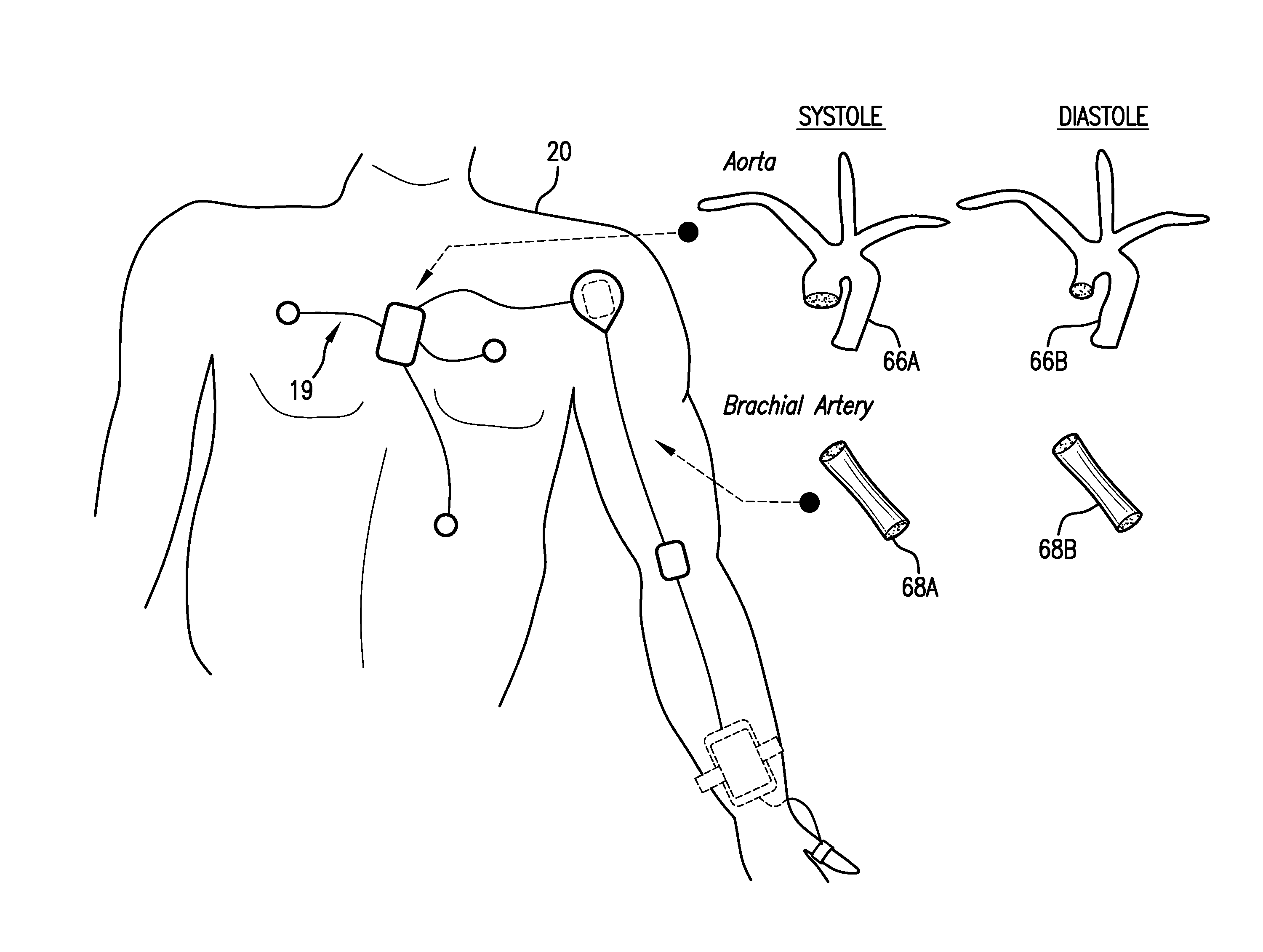
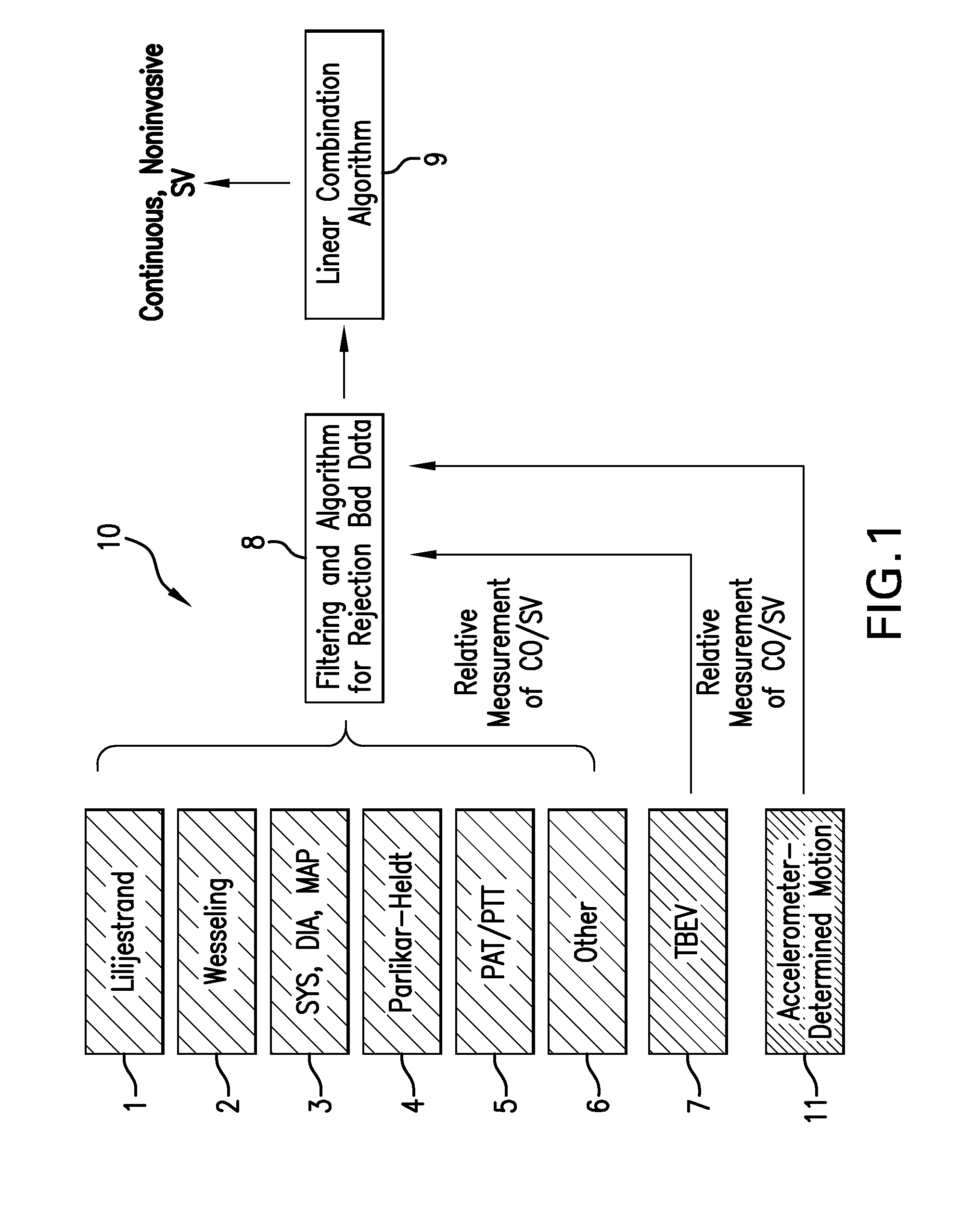
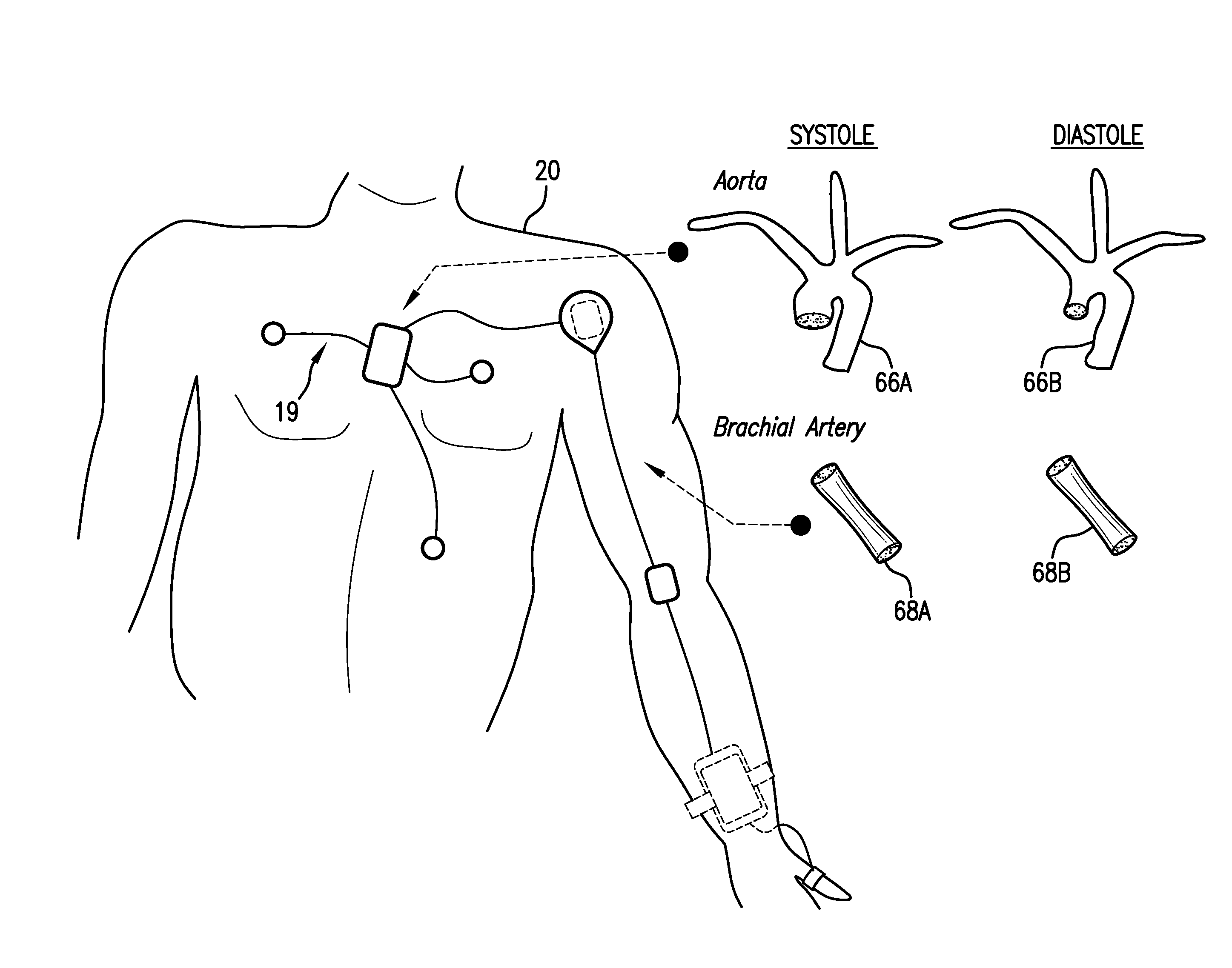
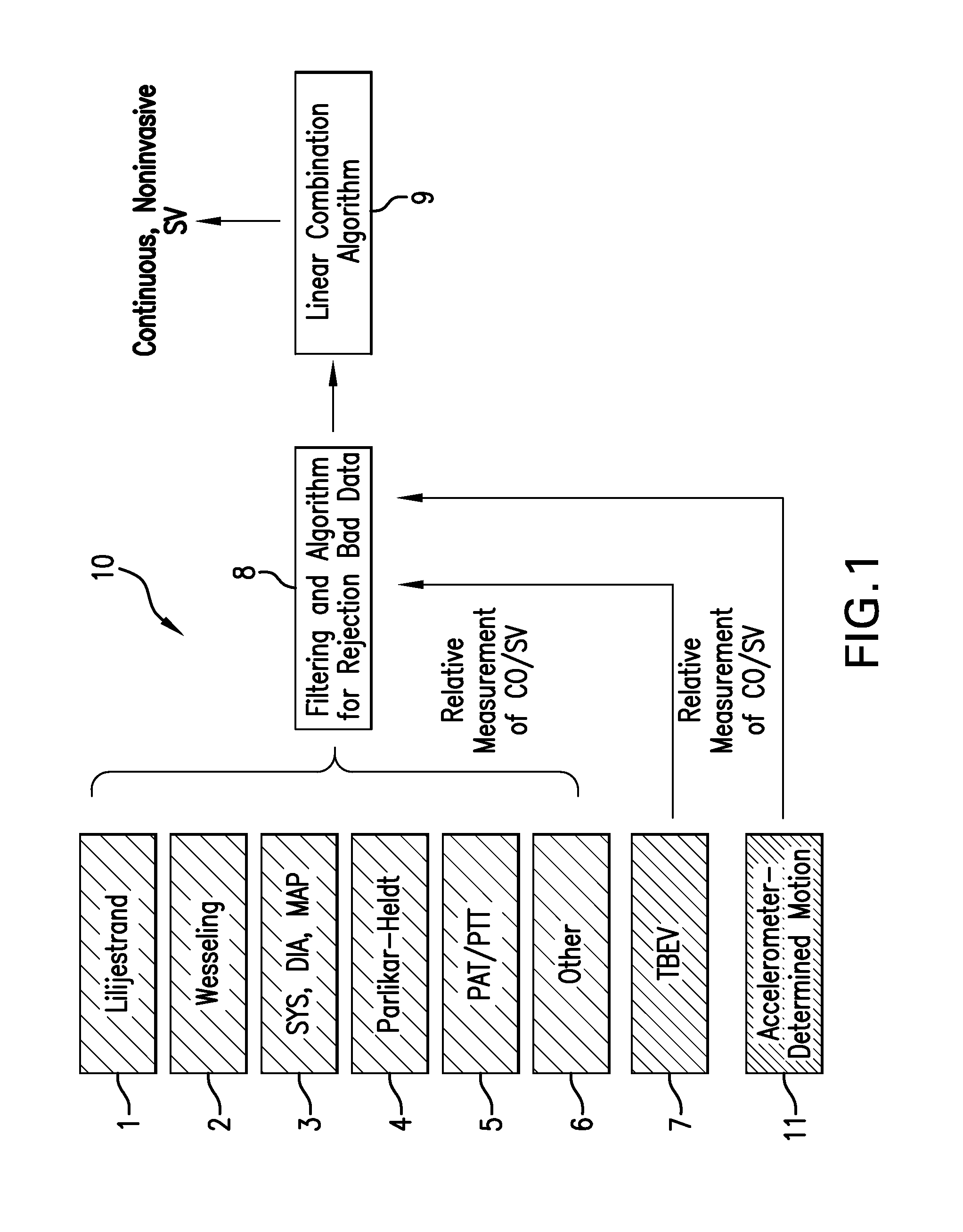
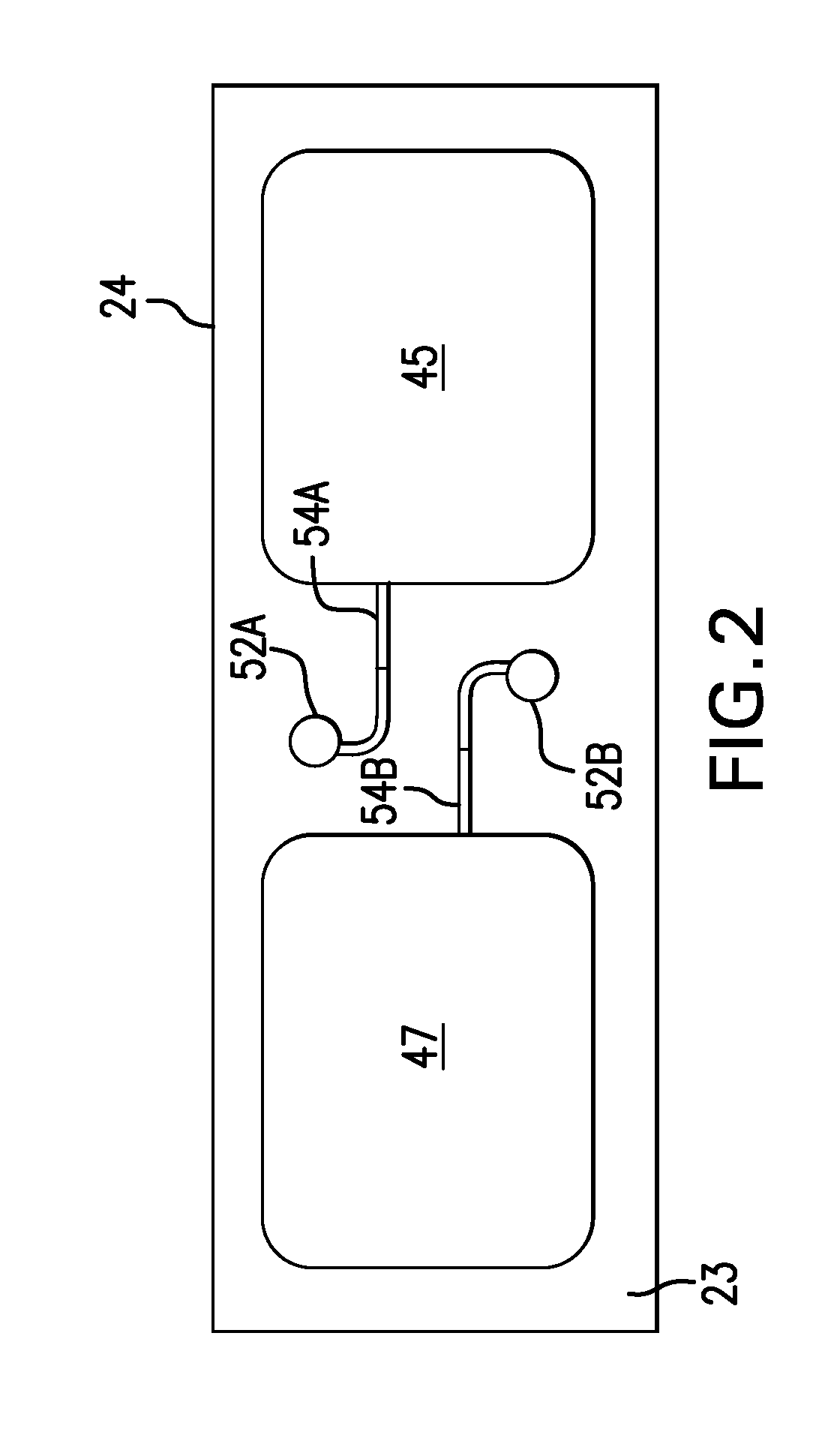
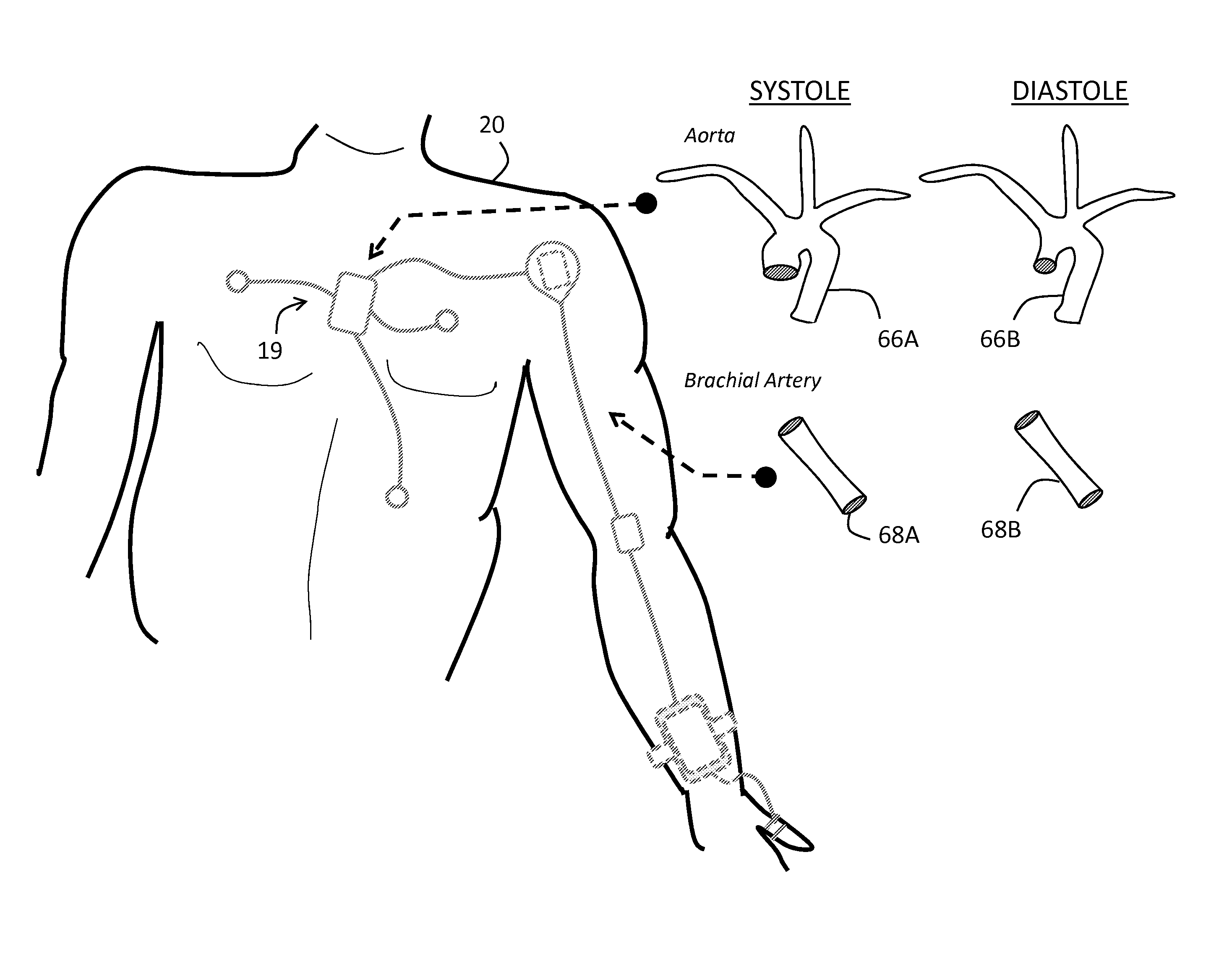
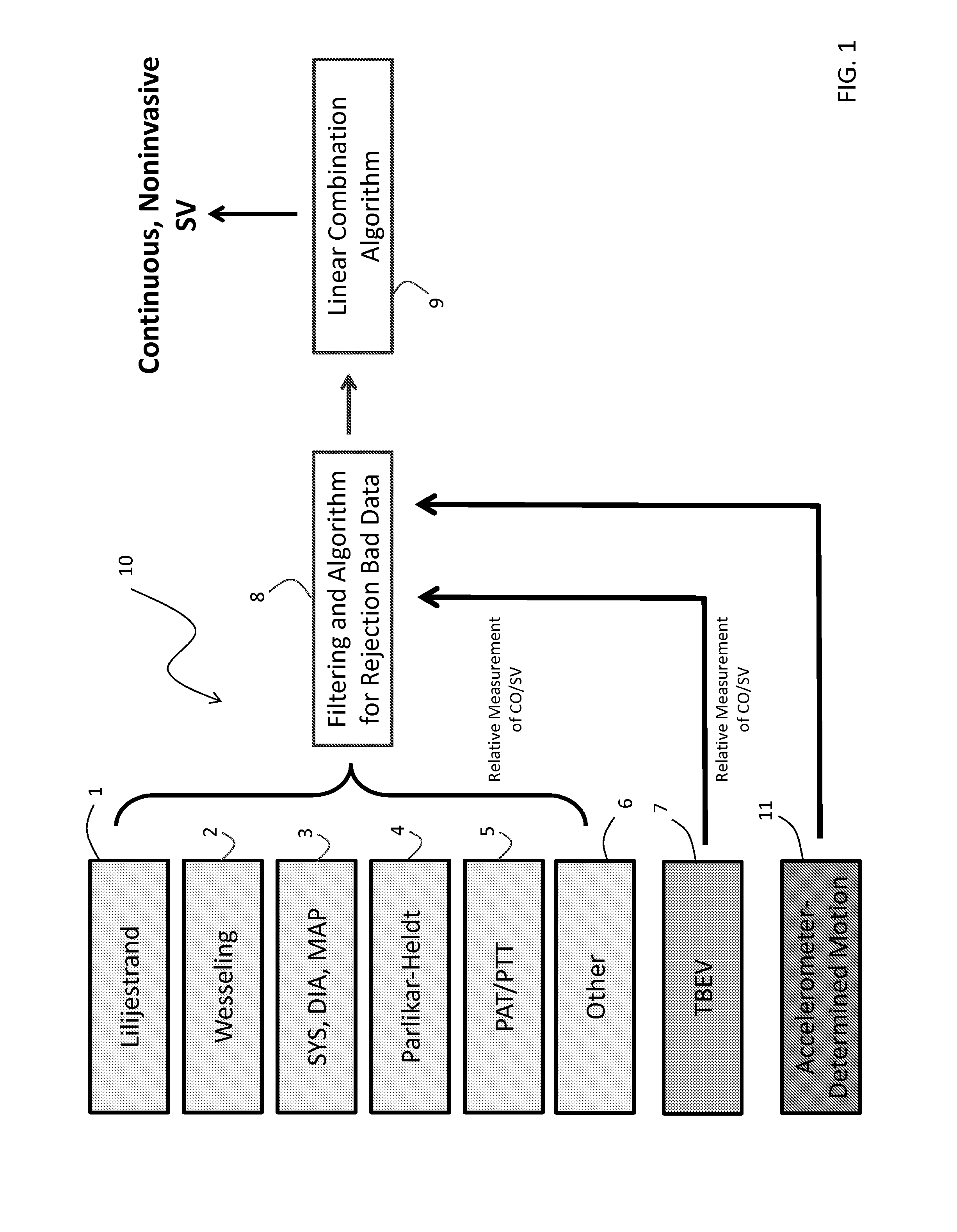
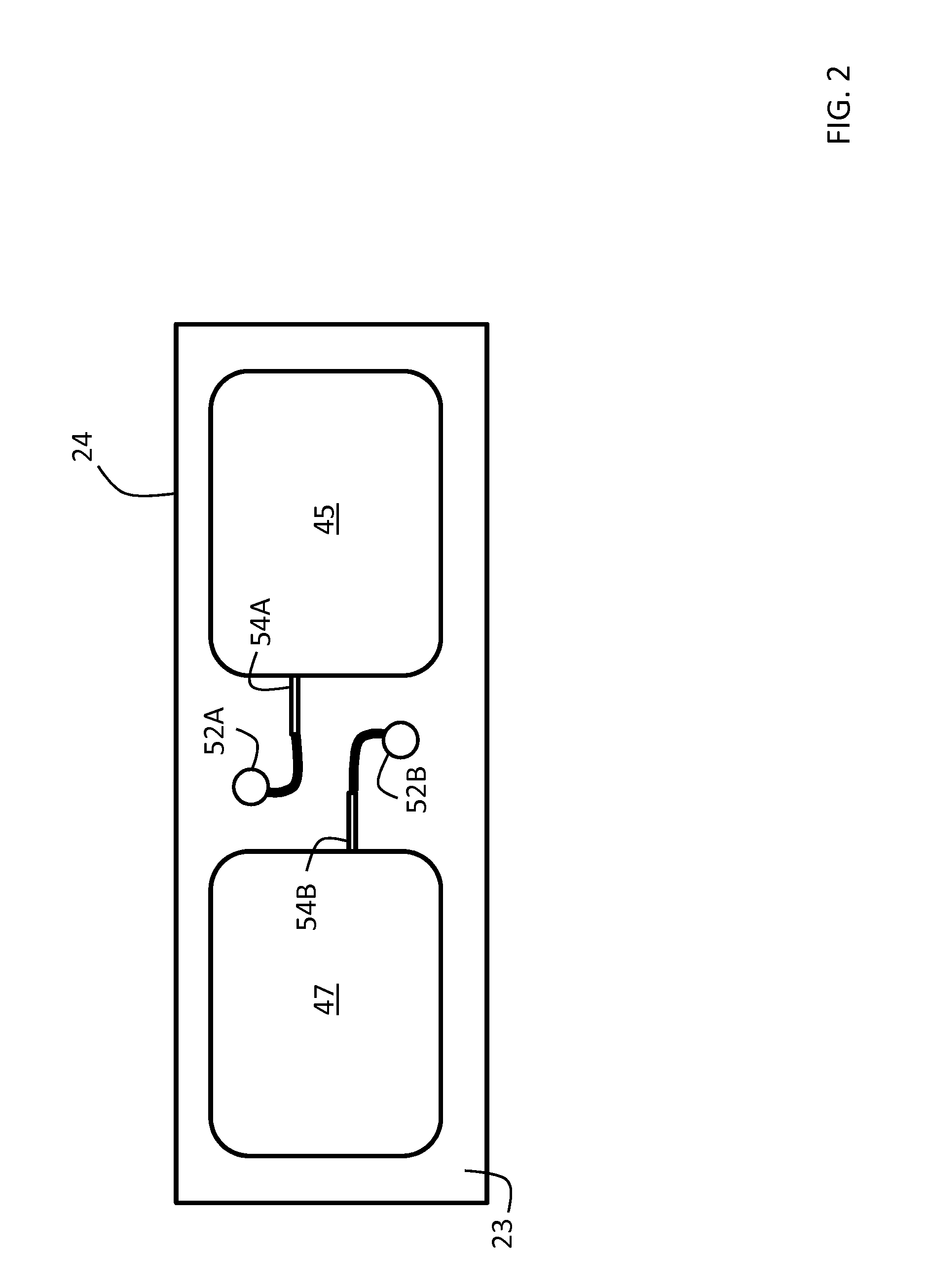
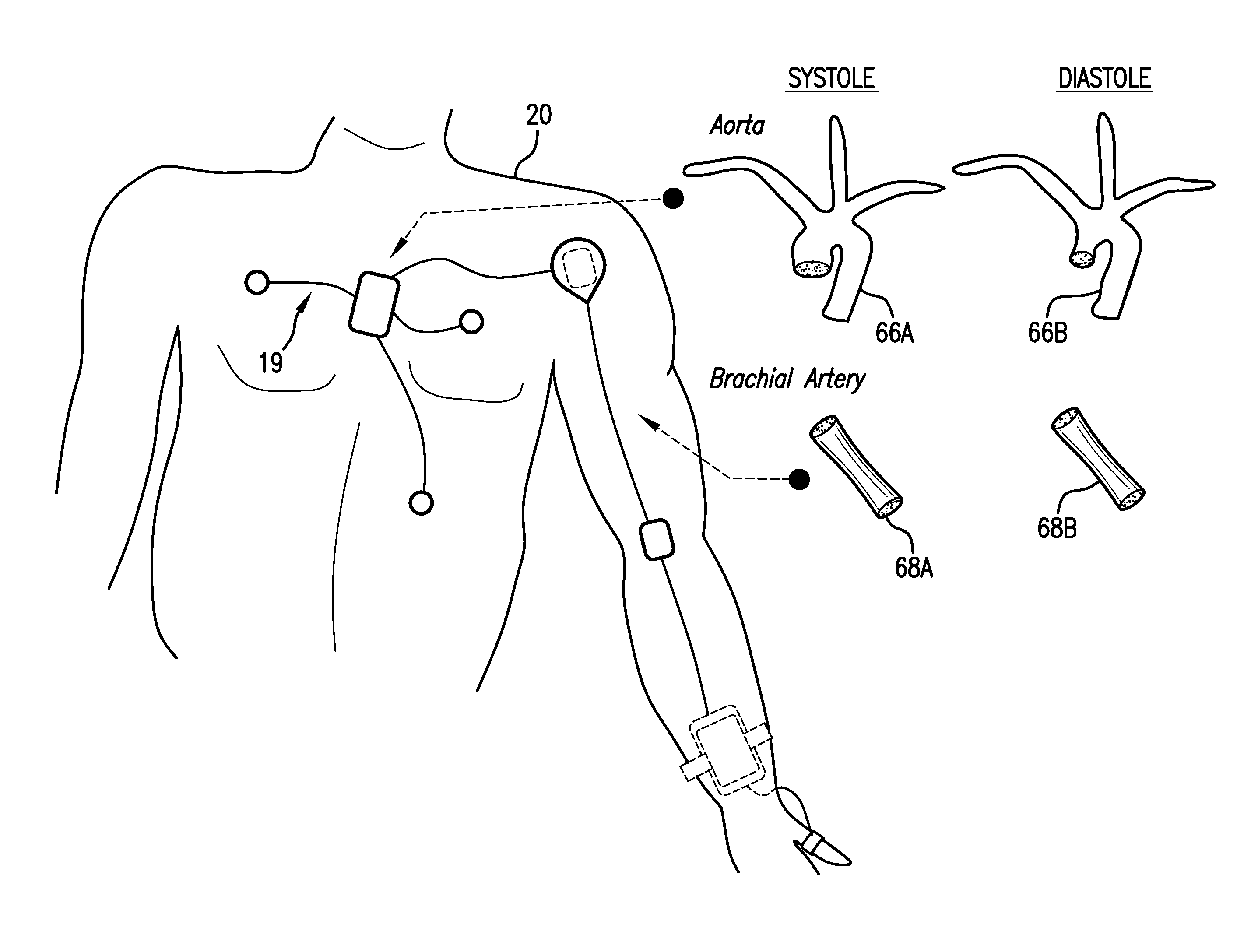
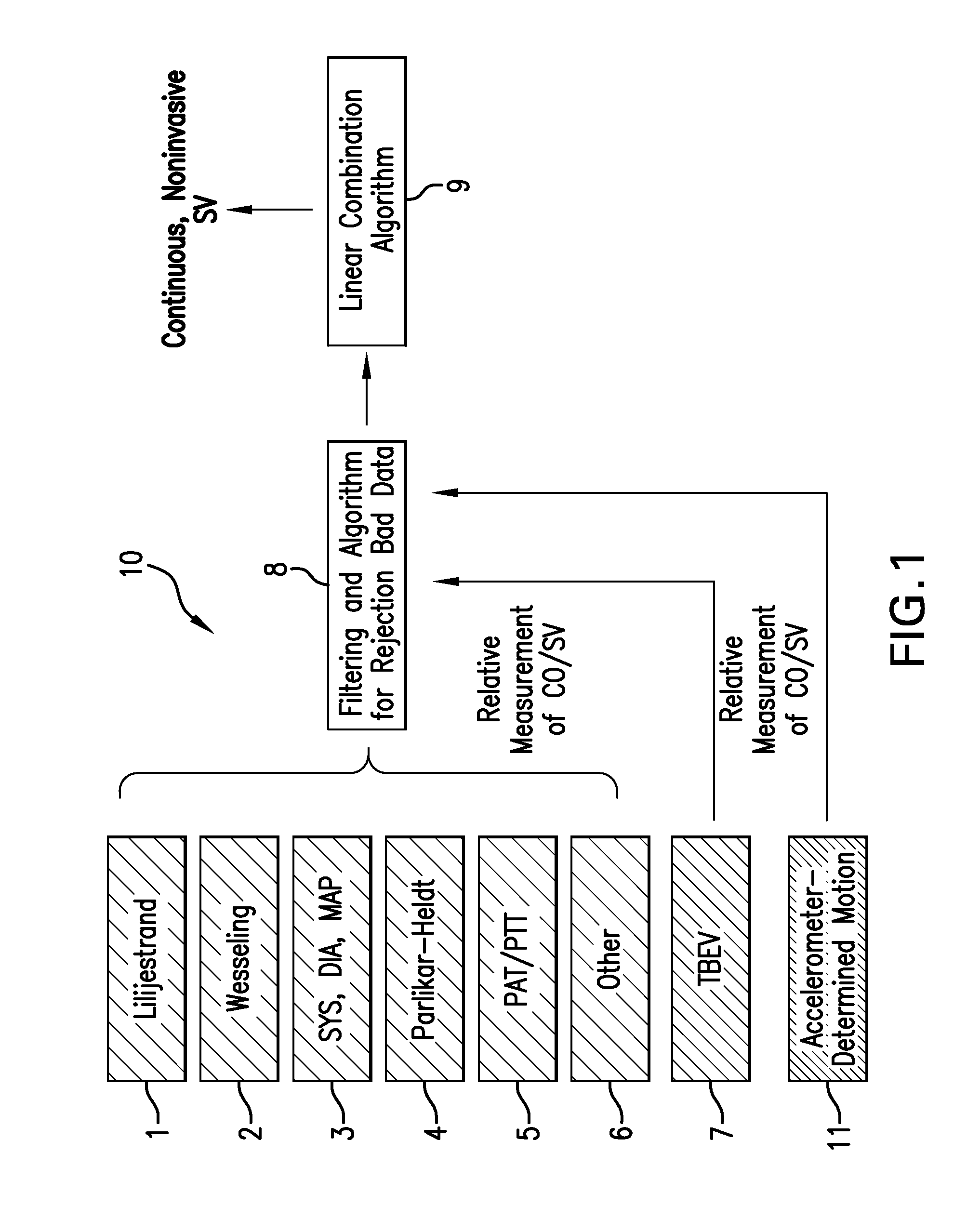
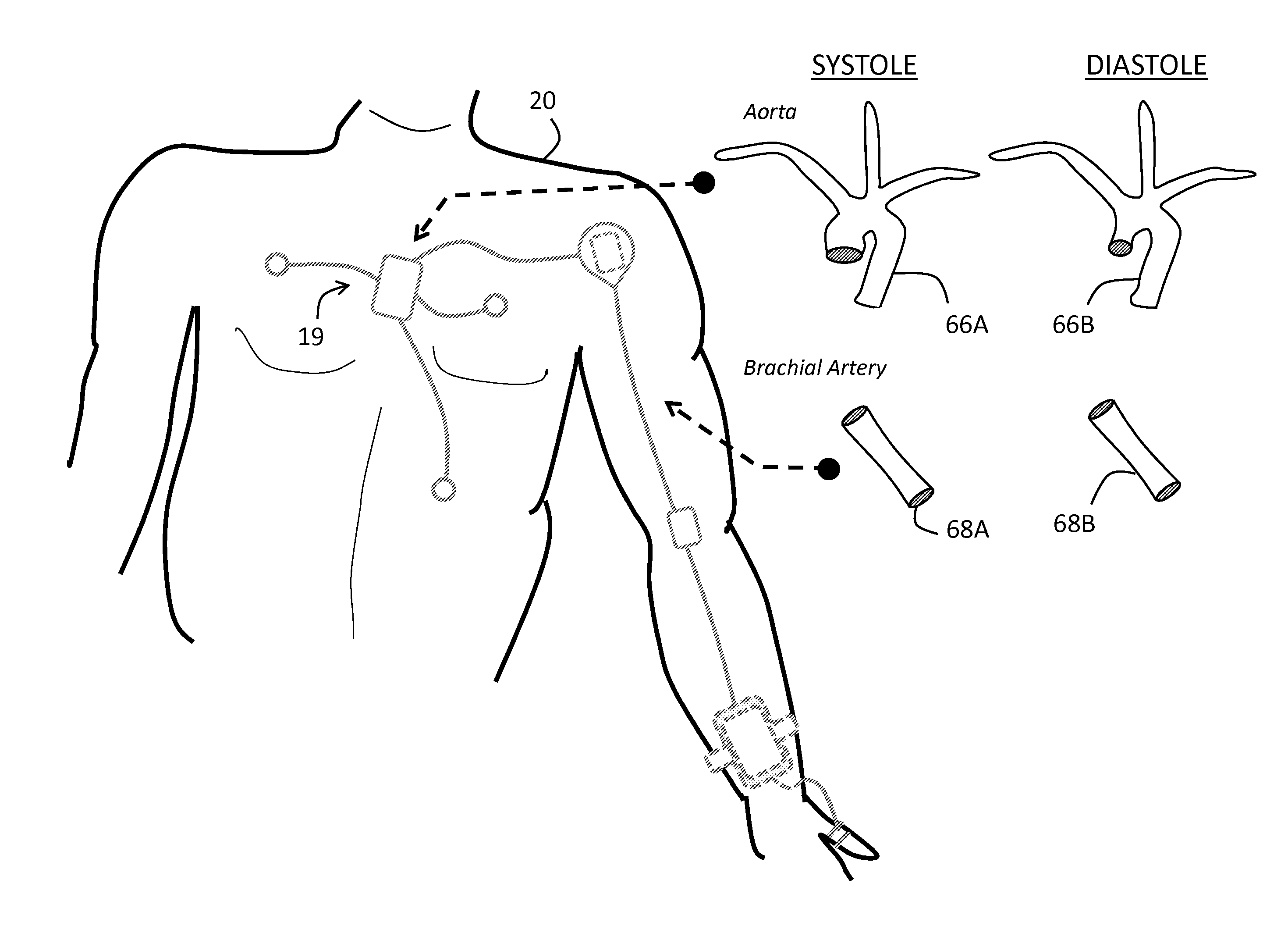
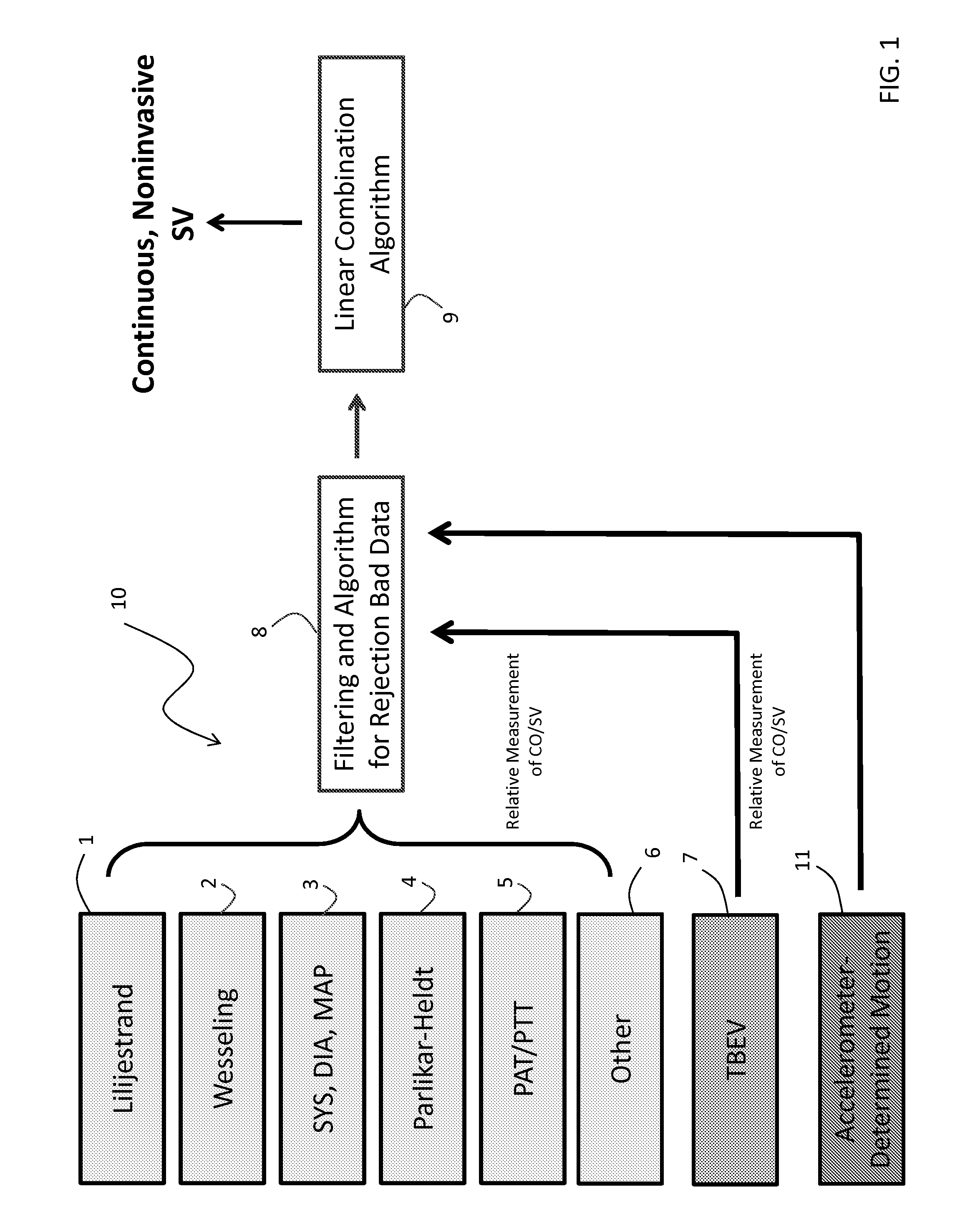
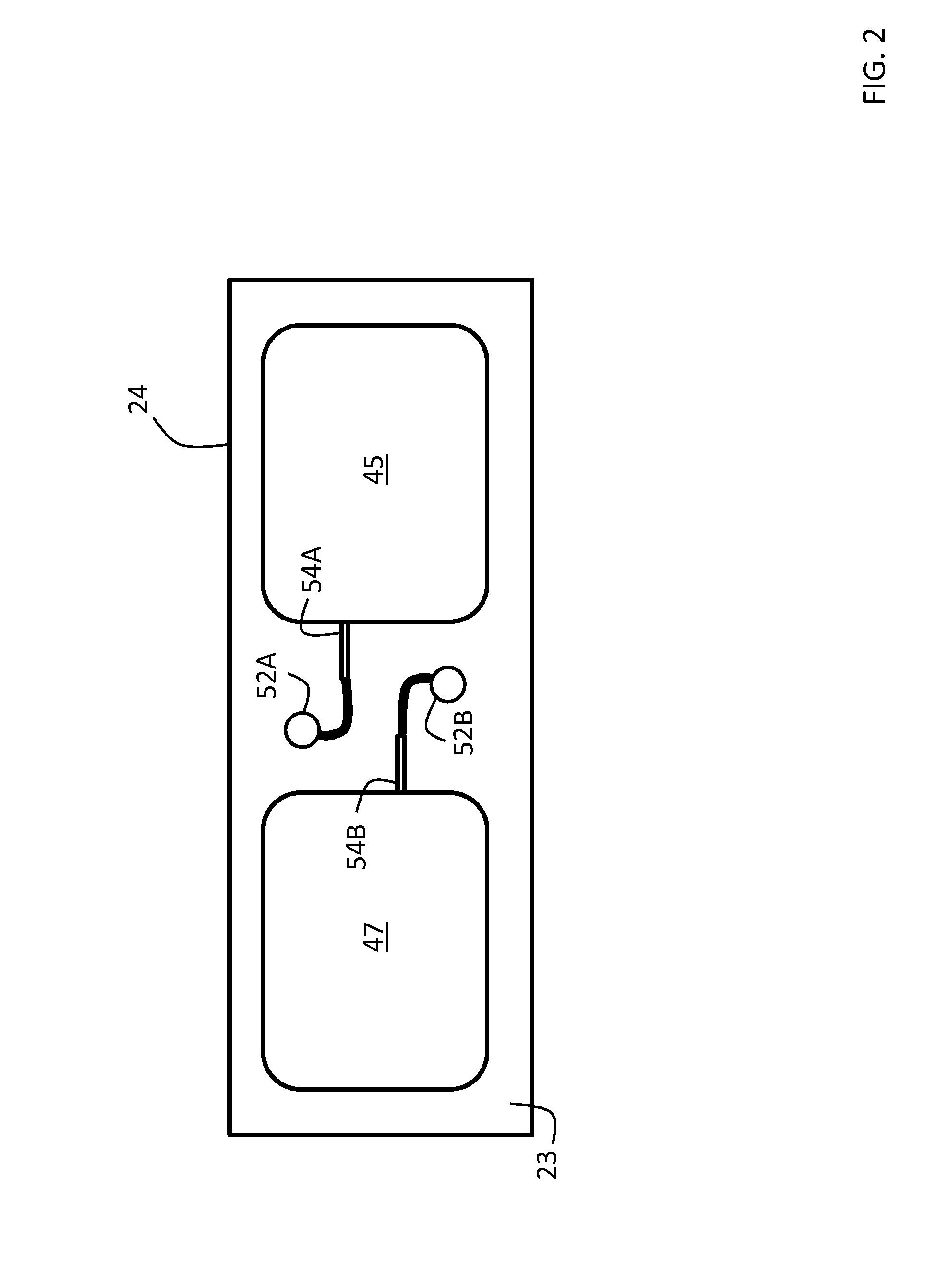
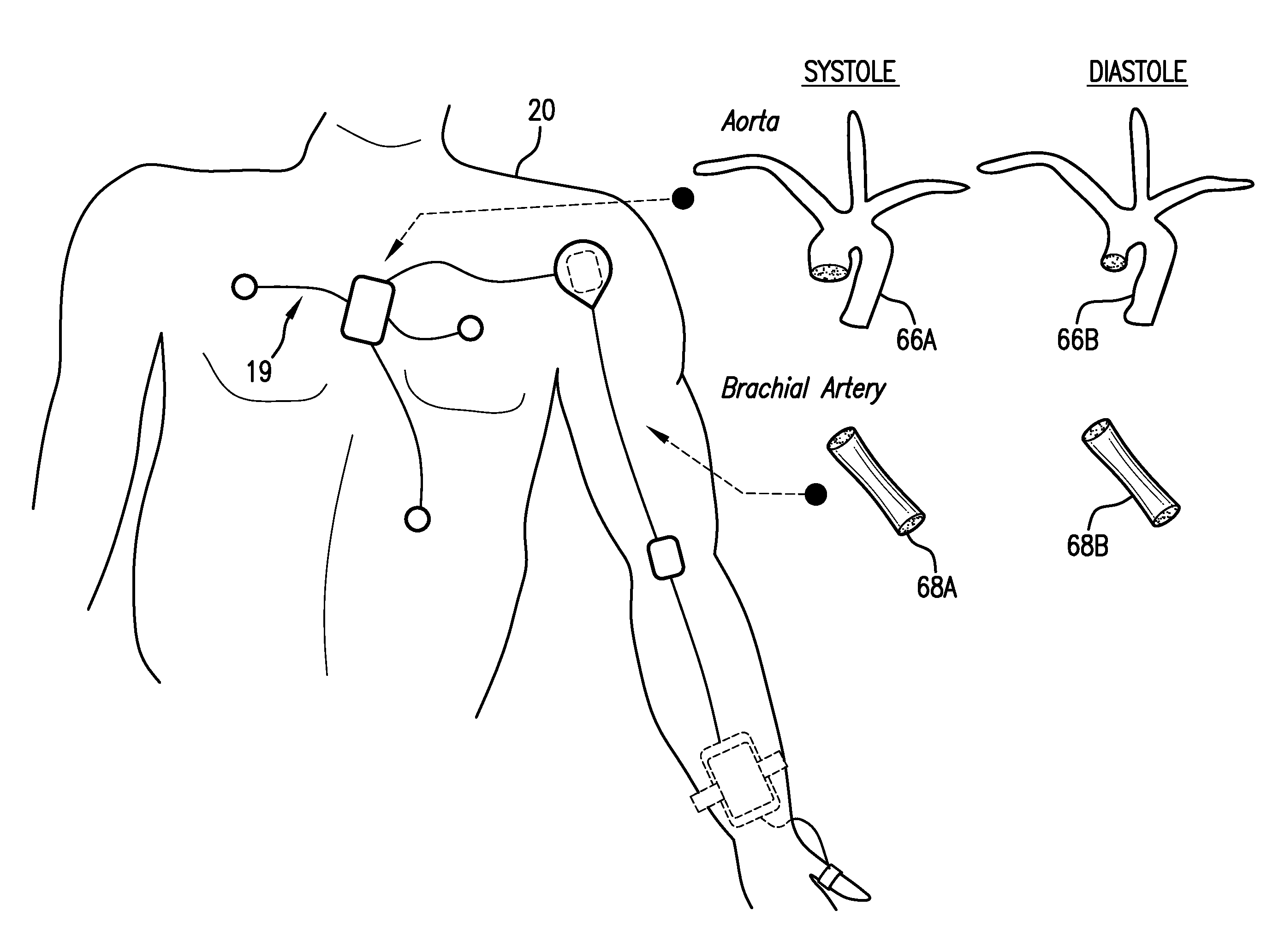
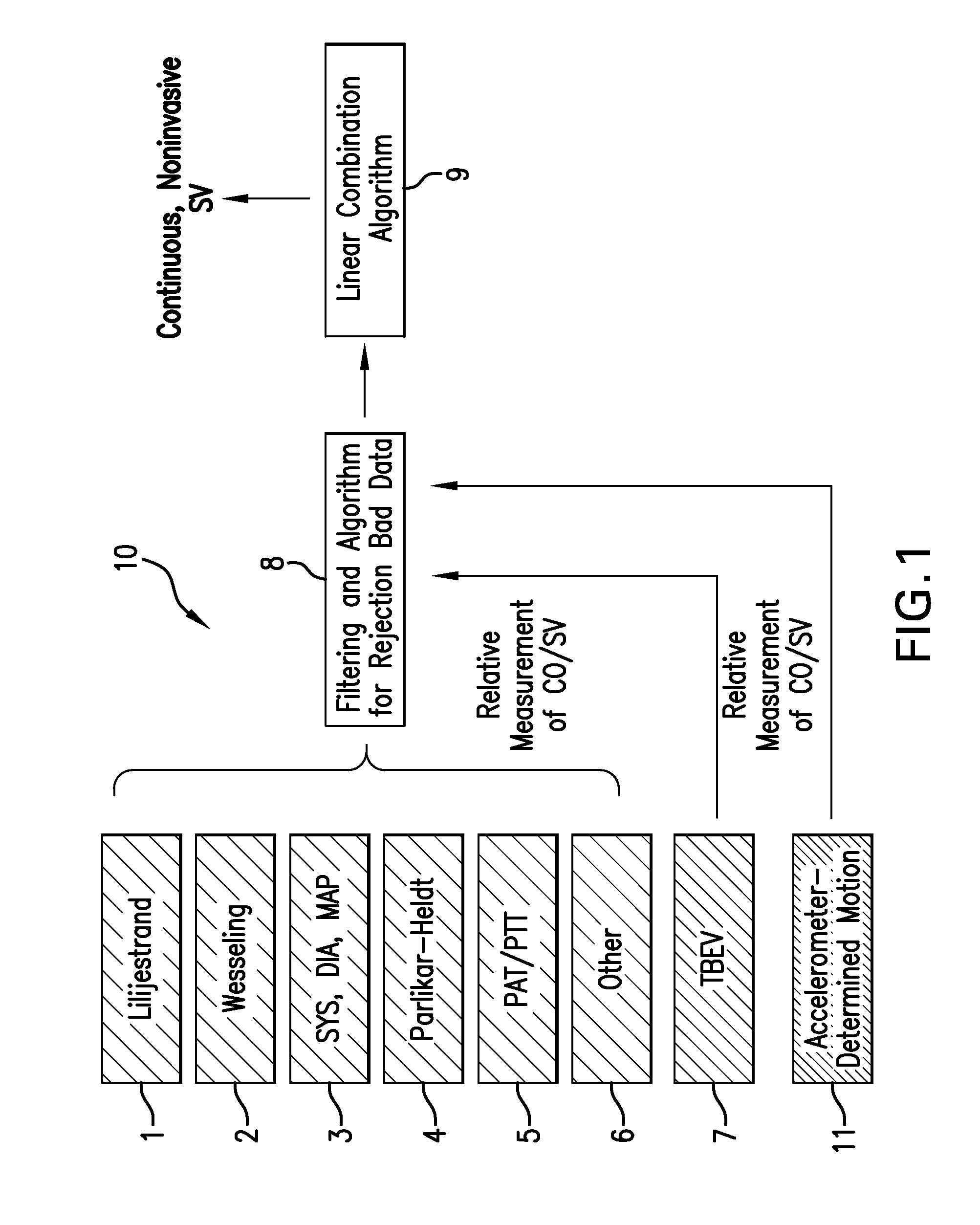
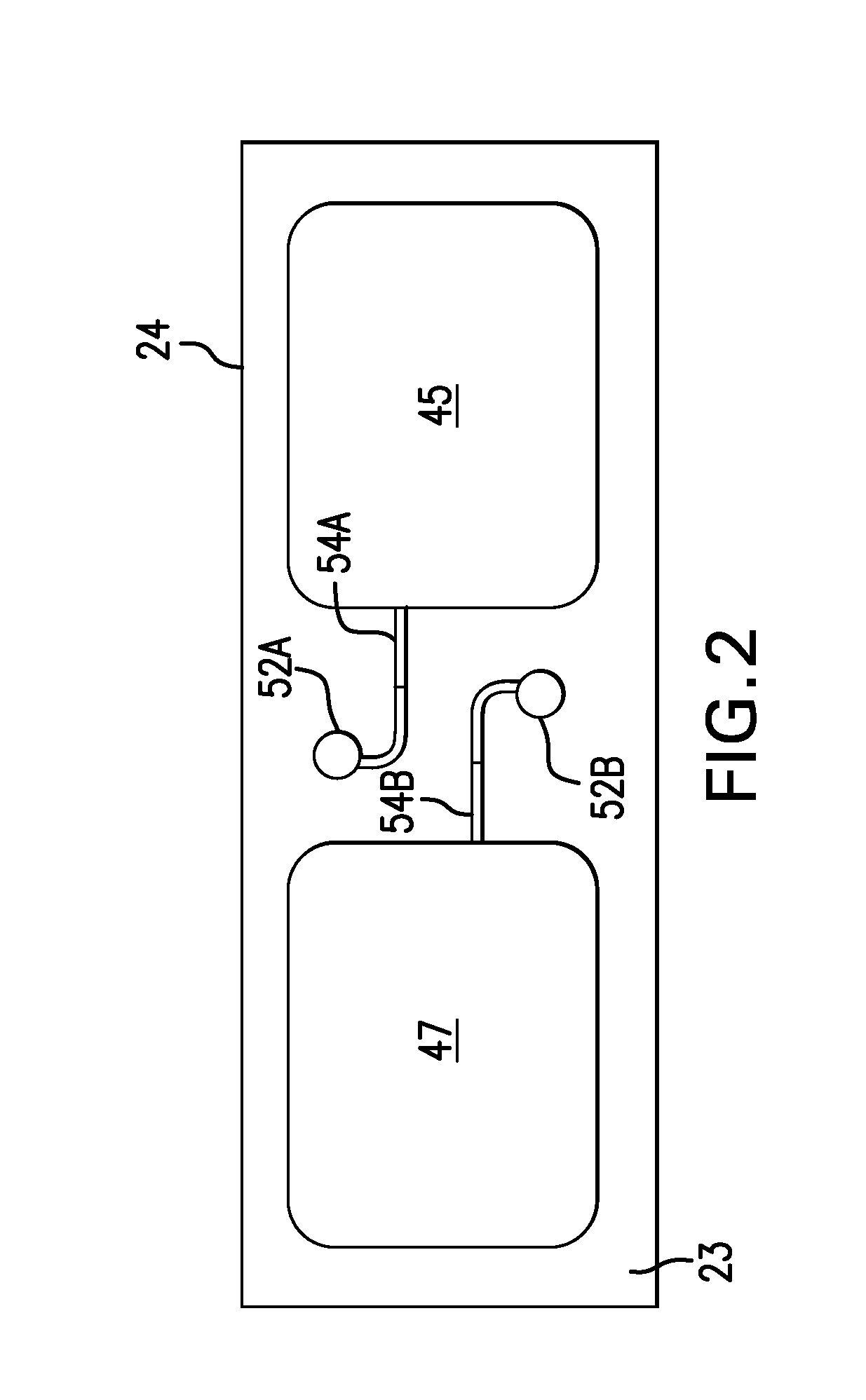
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249431A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure
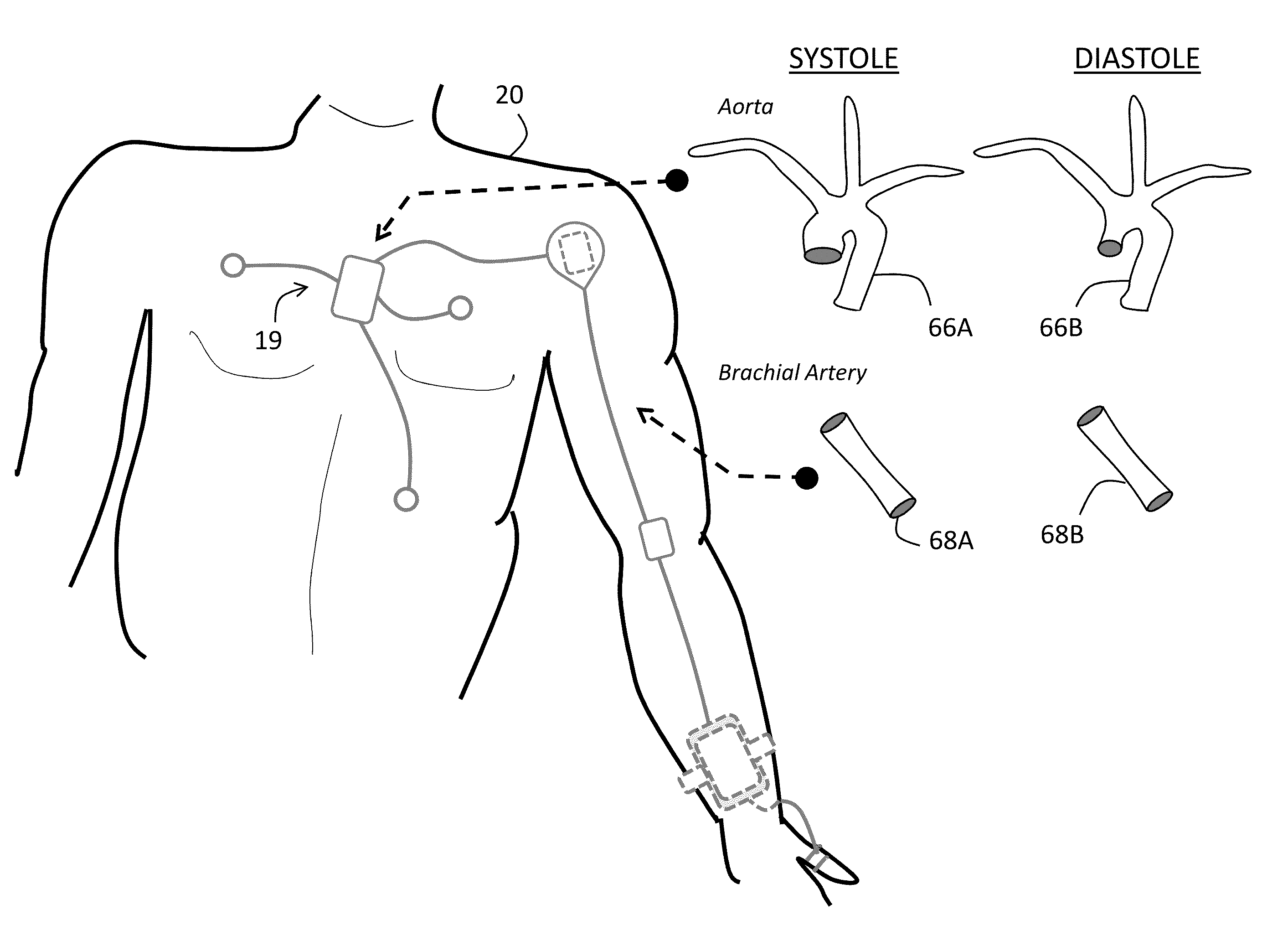
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS9364158B2Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
InactiveUS20140249434A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249440A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249433A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249435A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249441A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
InactiveUS20140249432A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
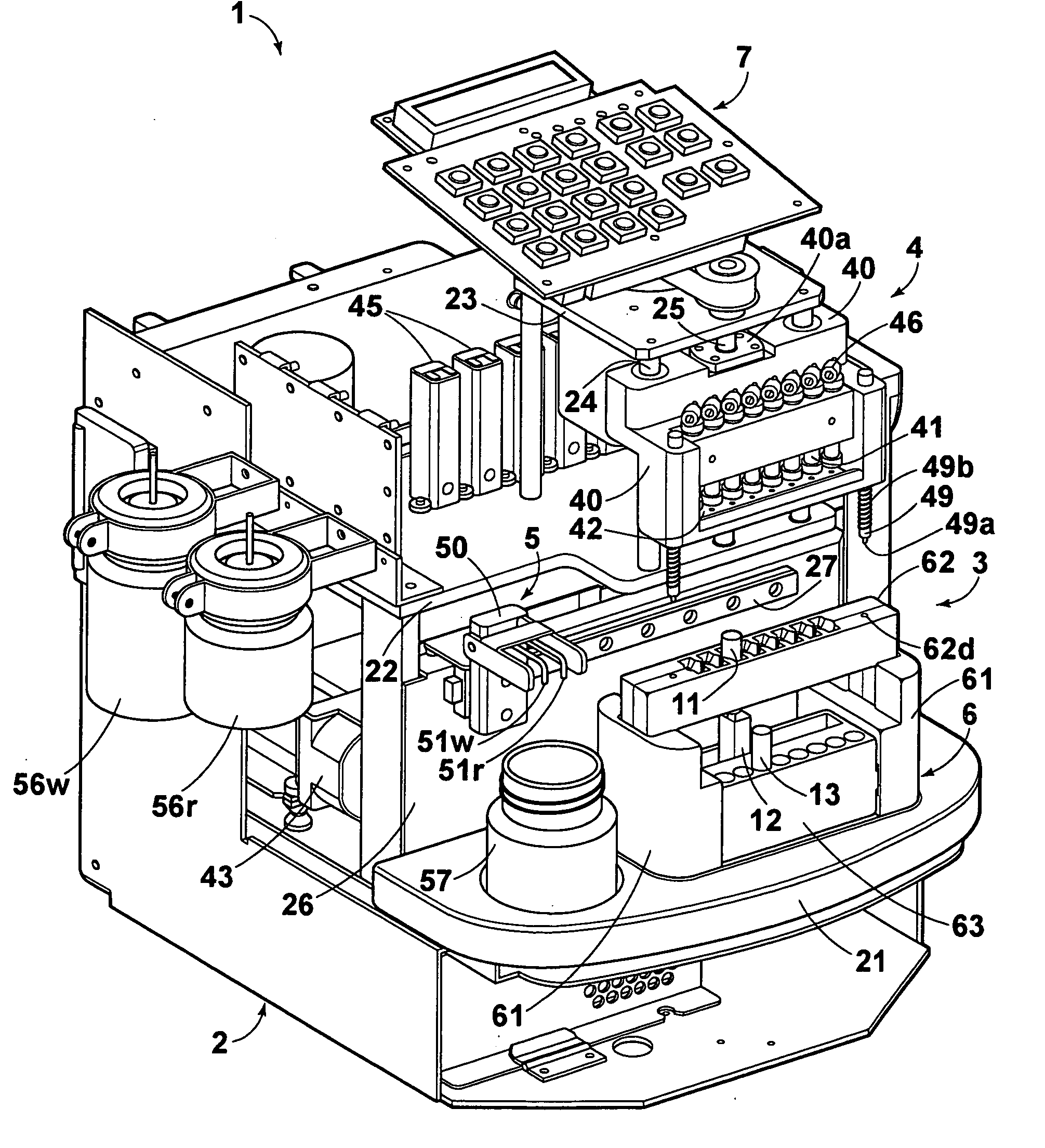
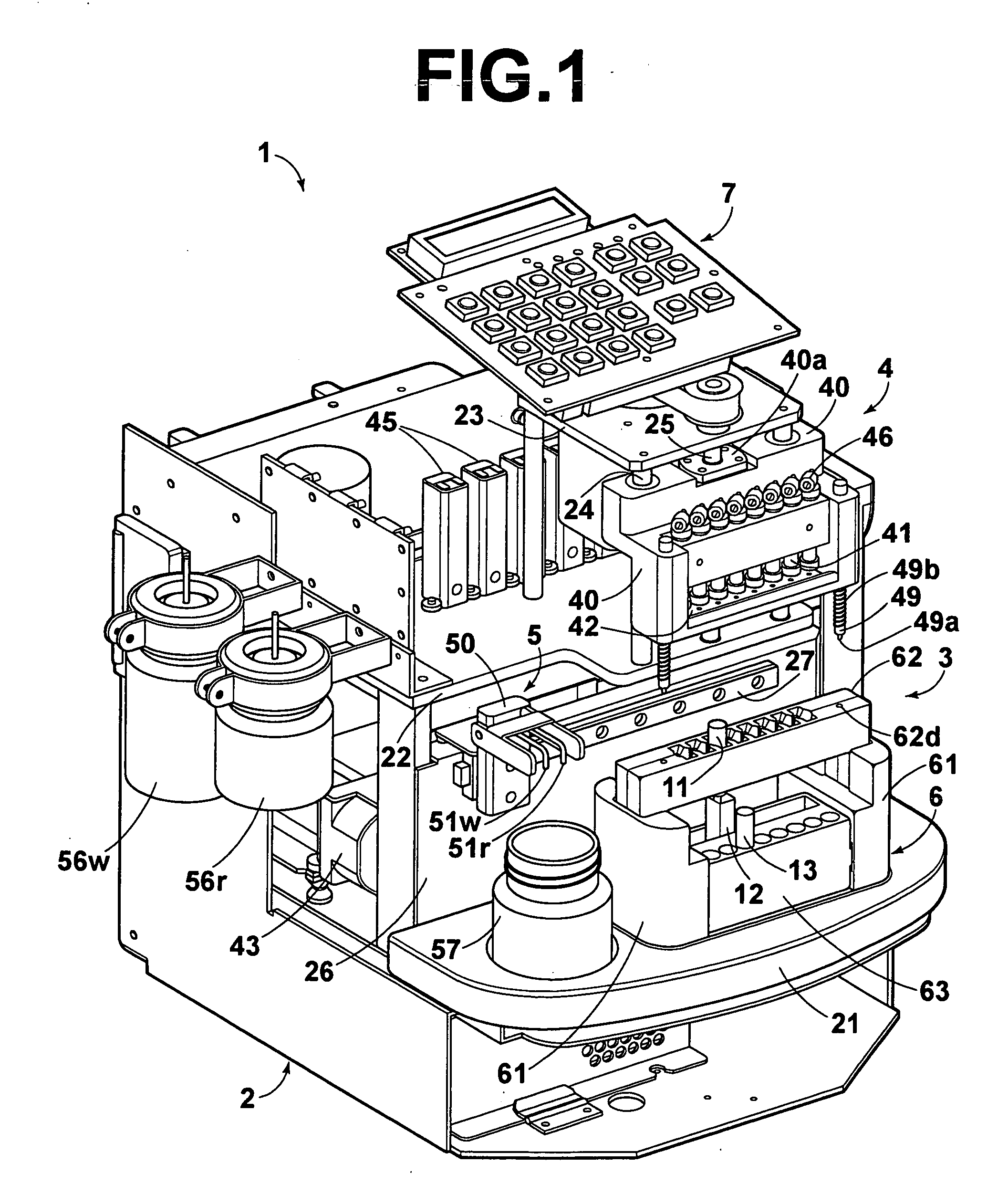
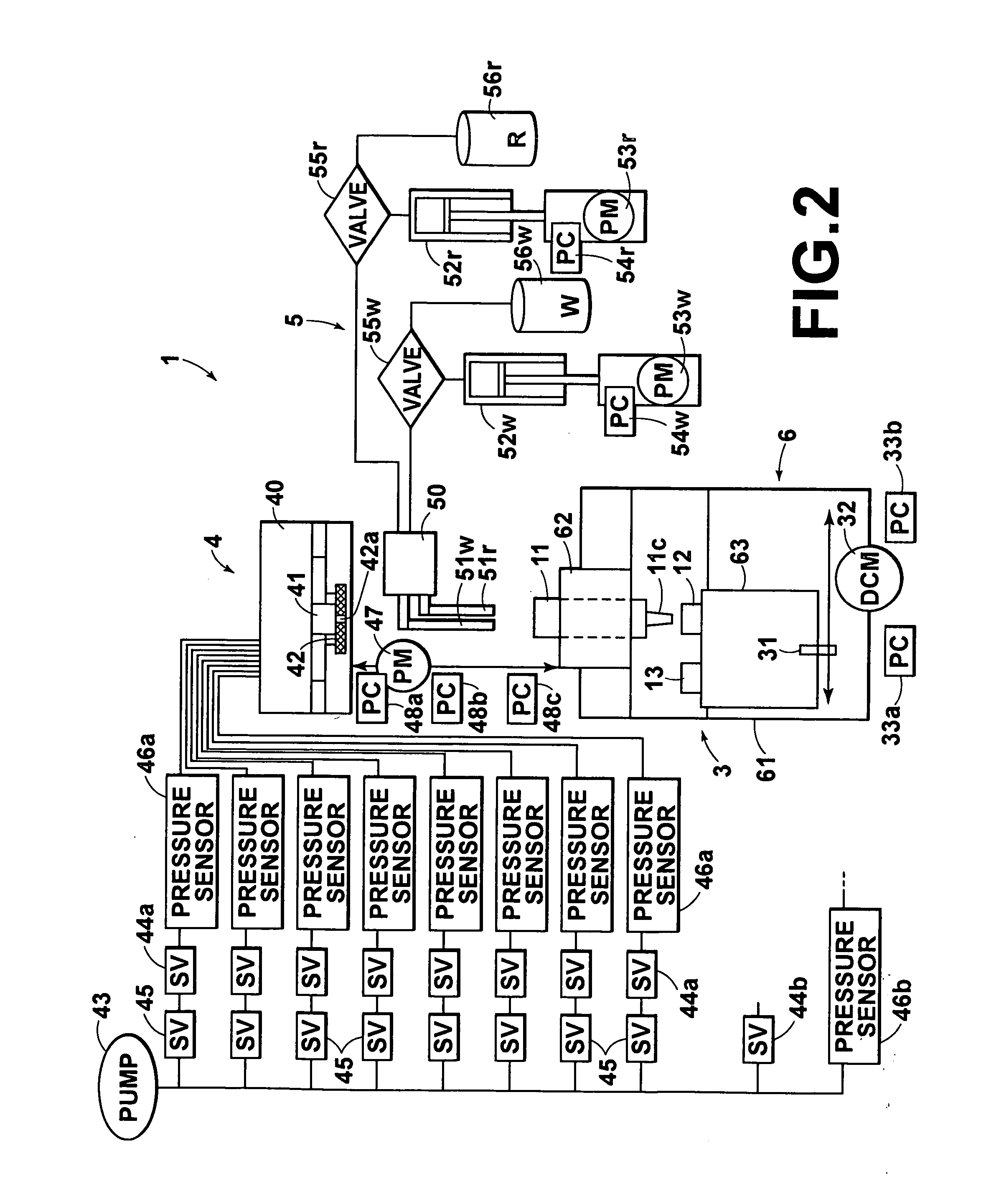
Extraction system
InactiveUS20050161377A1Efficient extractionShort timeSolvent extractionIon-exchanger regenerationAir pumpAtmosphere
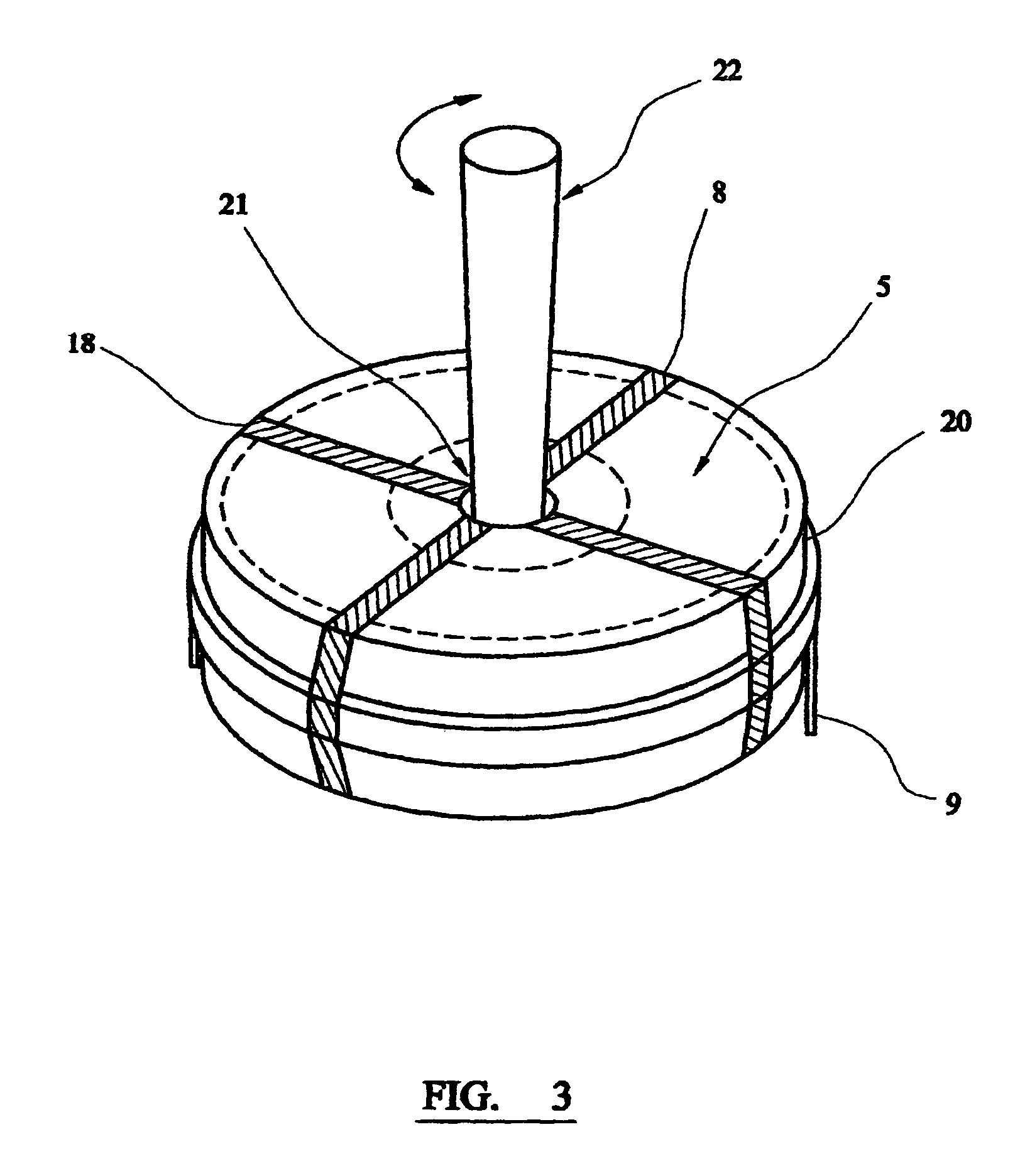
An extraction cartridge having a filter member extracts a specific material such as a nucleic acid. The specific material is caused to be adsorbed to the filter member by pressurizing a sample liquid containing a specific material. A pressurized-air supply mechanism for introducing pressurized air into a plurality of the extraction cartridges includes an air pump, opening and closing valves for individually starting or stopping supply of the pressurized air to the plurality of extraction cartridges, and pressure relief valves for individually relieving the pressures in the extraction cartridges to the atmosphere. These valves are disposed partway along a feed passage to the extraction cartridges. The extraction cartridges are supplied with pressurized air, and then sealed. Upon completion of the drainage of any one of the extraction cartridges, the pressure relief valve associated with the completely drained extraction cartridge is independently opened to relieve the pressurized air remaining therein.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249442A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249443A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
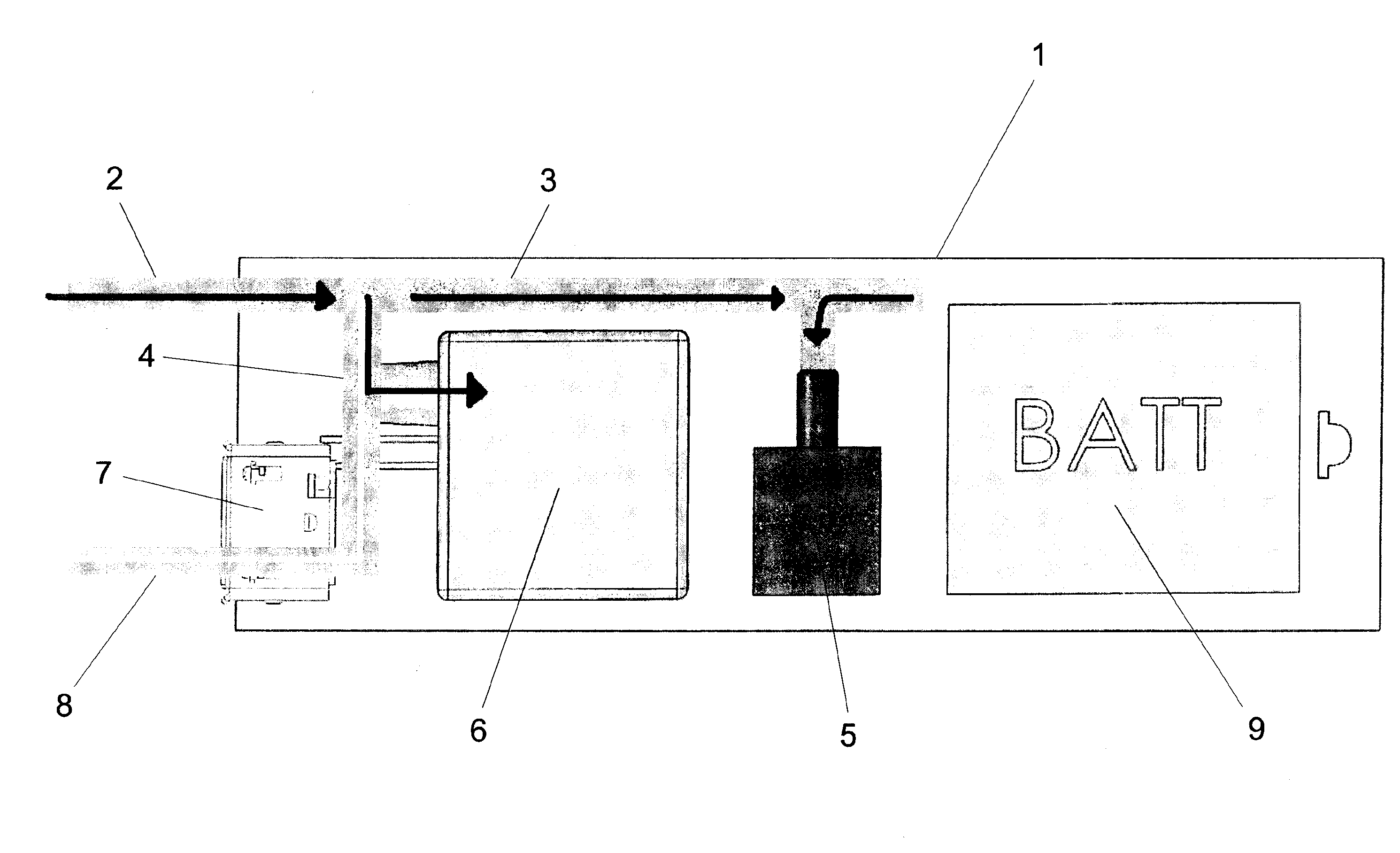
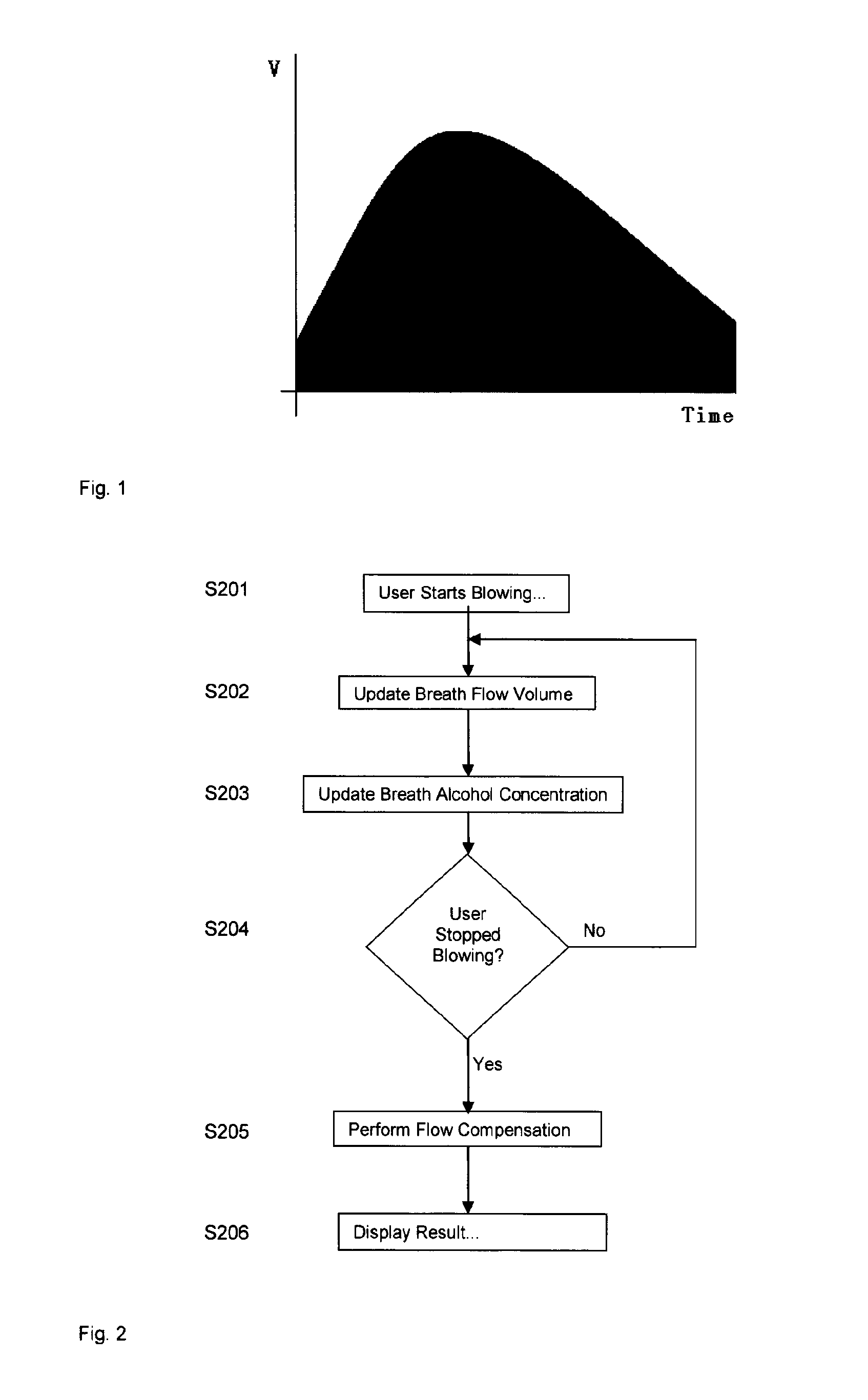
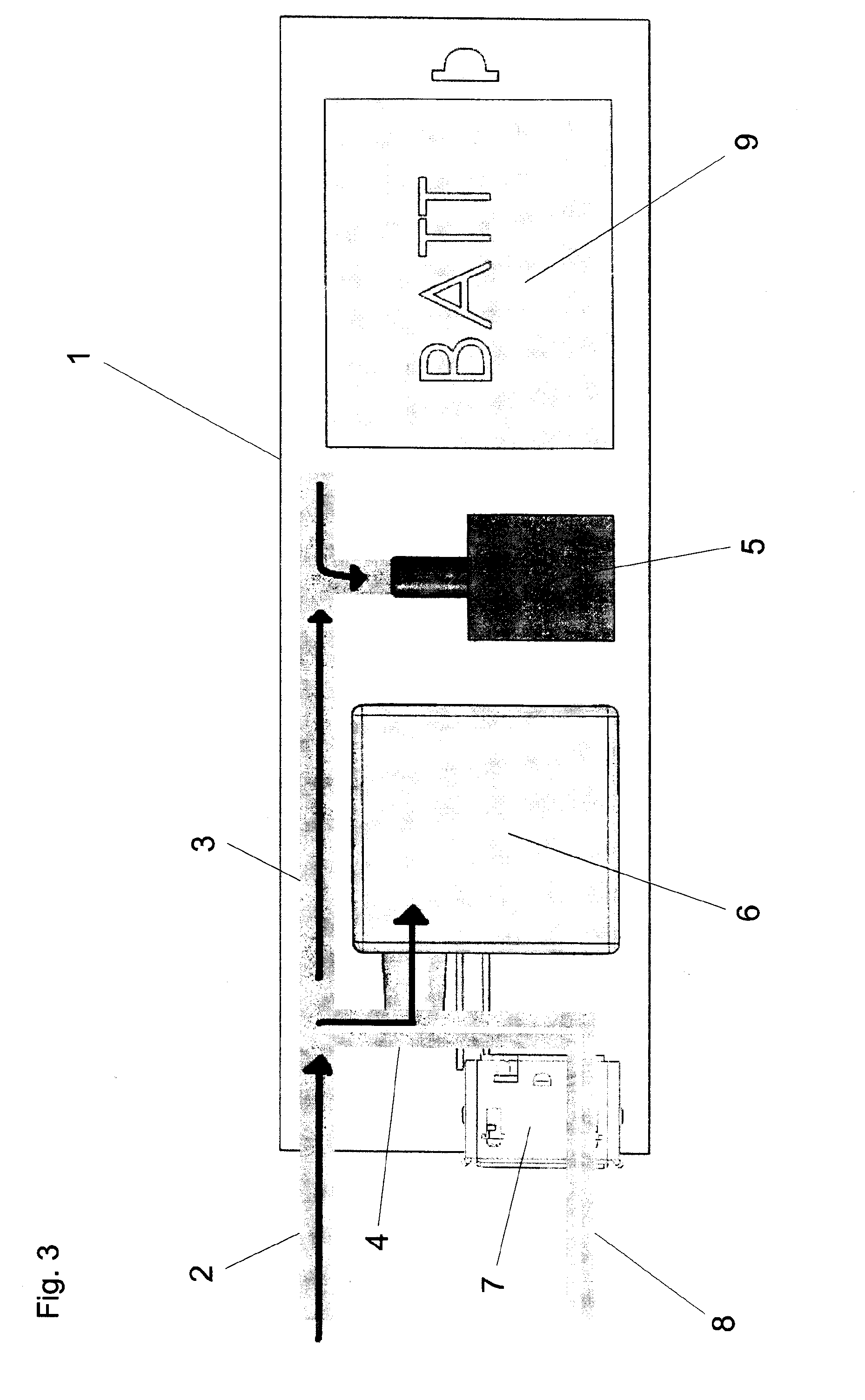
Method for measuring breath alcohol concentration and apparatus therefor
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for measuring breath alcohol concentration of a user. A flow of an expired breath sample is passed through a fuel cell sensor giving an output signal proportional to the amount of alcohol present in the breath sample. By measuring the flow rate, the volume of the breath sample may be calculated, whereas the breath alcohol concentration is calculated based on the fuel cell output signal. Both the sample volume and the breath alcohol concentration values are continually updated by integrating the measured instantaneous flow rate and the fuel cell output signal over time. If the user stops blowing, flow compensation is performed to obtain a compensated fuel cell output signal using a stored calibration volume. Hence, an improved method for accurately measuring the breath alcohol concentration of a test person is achieved, capable of handling varied expired volumes of breath, which obviates the need for a sampling mechanism.
Owner:ALCO SYST SWEDEN
Automobile general pressure sensor
ActiveUS20110290032A1Reduce impactEnsure measurementFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsSignal conditioning circuitsEngineering
A general pressure sensor for an automobile comprising a sensor shell, a silicon piezoresistive sensitive core, a sensor core seat, a signal conditioning circuit, and an automobile electric device interface is disclosed. The silicon piezoresistive sensitive core, the sensor core seat and the signal conditioning circuit are disposed in the inner cavity of the sensor housing. The sensor housing is installed to the automobile electric device interface, and the silicon piezoresistive sensitive core comprises a silicon piezoresistive sensitive element and a glass ring sheet. The silicon piezoresistive sensitive element is welded and fixed to a surface of the glass ring sheet. An insulation oxidation layer is formed on one surface of the glass ring sheet and the silicon piezoresistive sensitive element. The other surface of the glass ring sheet is hermetically fixed to the ring-shape recession surface provided on the sensor core seat. The sensor core seat is hermetically and rotationally fixed to a pressure inlet on the sensor housing, after the inner lead wire on the silicon piezoresistive sensitive core is led to an interposing board provided on one end of the central hole through the other end of the central hole on the ring-shape recession surface of the sensor core seat, and then is led out by the automobile electric device interface via the signal conditioning circuit.
Owner:KUNSHAN SHUANGQIAO SENSOR MEASUREMENT CONTROLLING +1
Molded washer assembly
InactiveUS20060182518A1Uniform radial compressionUniform compressionWashersEngineeringRadial compression
A washer formed by two identical C-shaped sections having parallel upper and lower surfaces, two ends, an inside and an outside arcuate edge, the ends having a plurality of tabs and recesses that inter-digitate to form continuous surfaces. The outside arcuate edges have a circumferentially extending groove adapted to receive a circumferentially disposed tension member to apply a substantially uniform radial compression on the washer slot during assembly. The tension member can be molded into the groove to form a single unitary structure with the remainder of the washer.
Owner:UNDERWOOD J LARRY +1
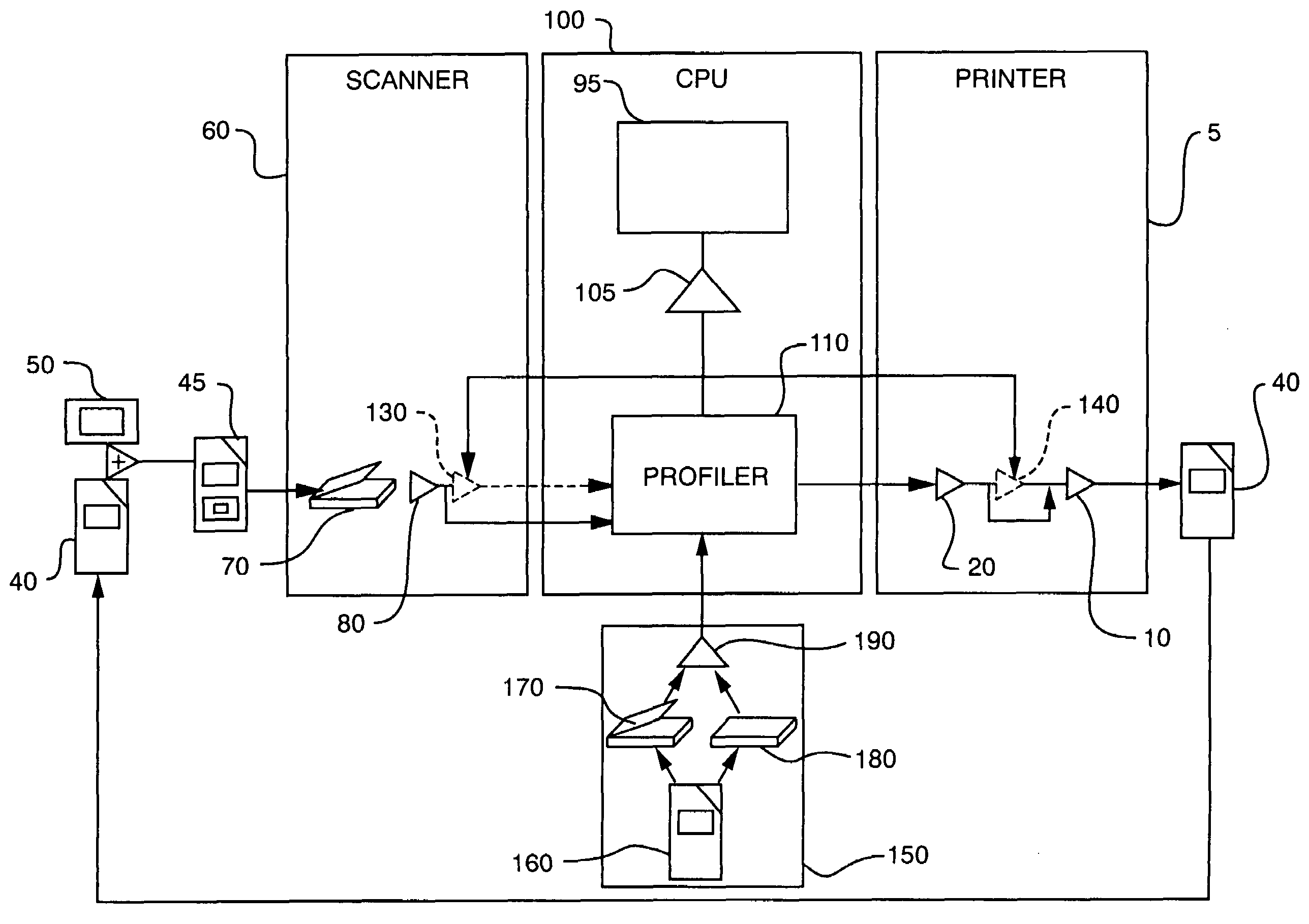
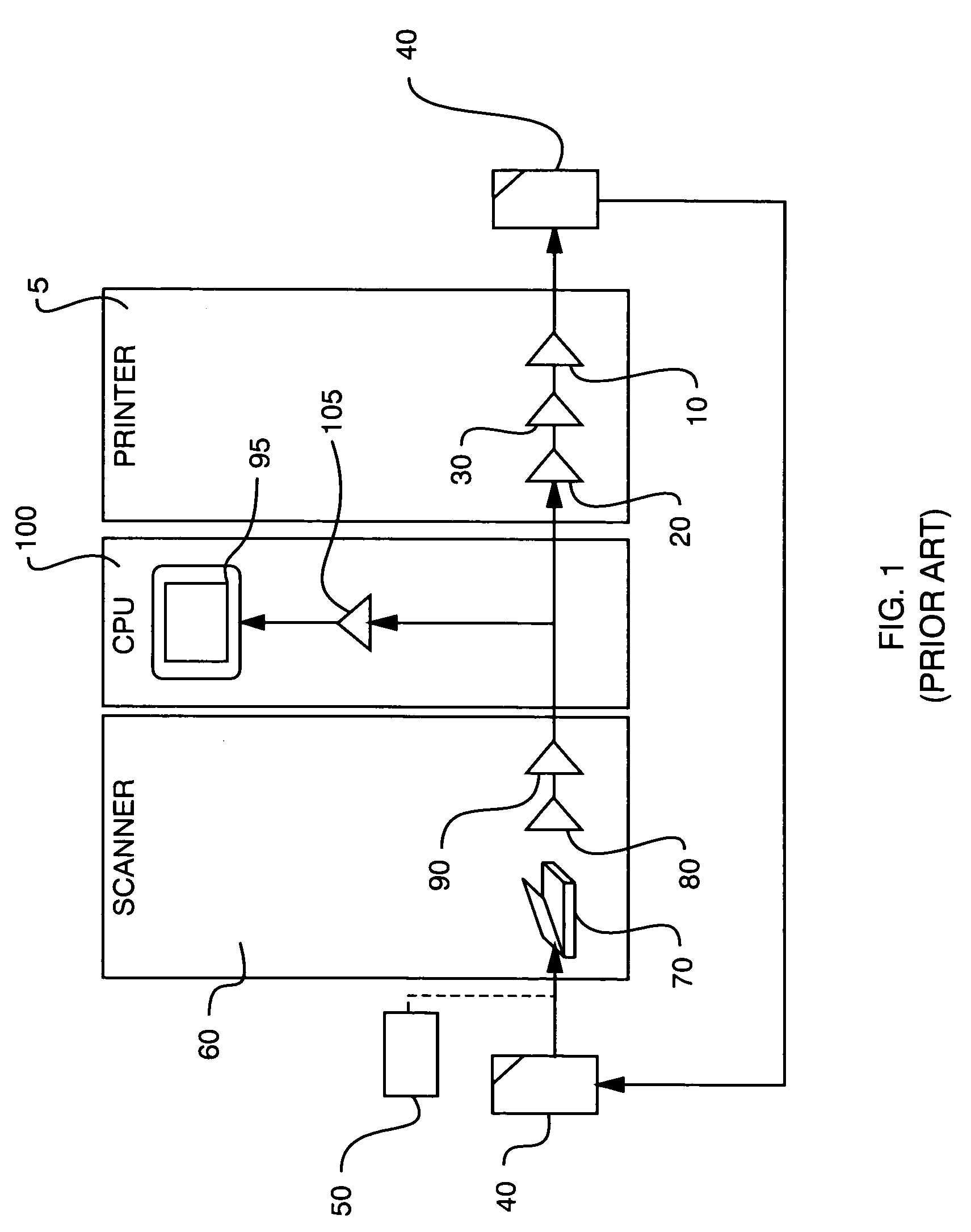
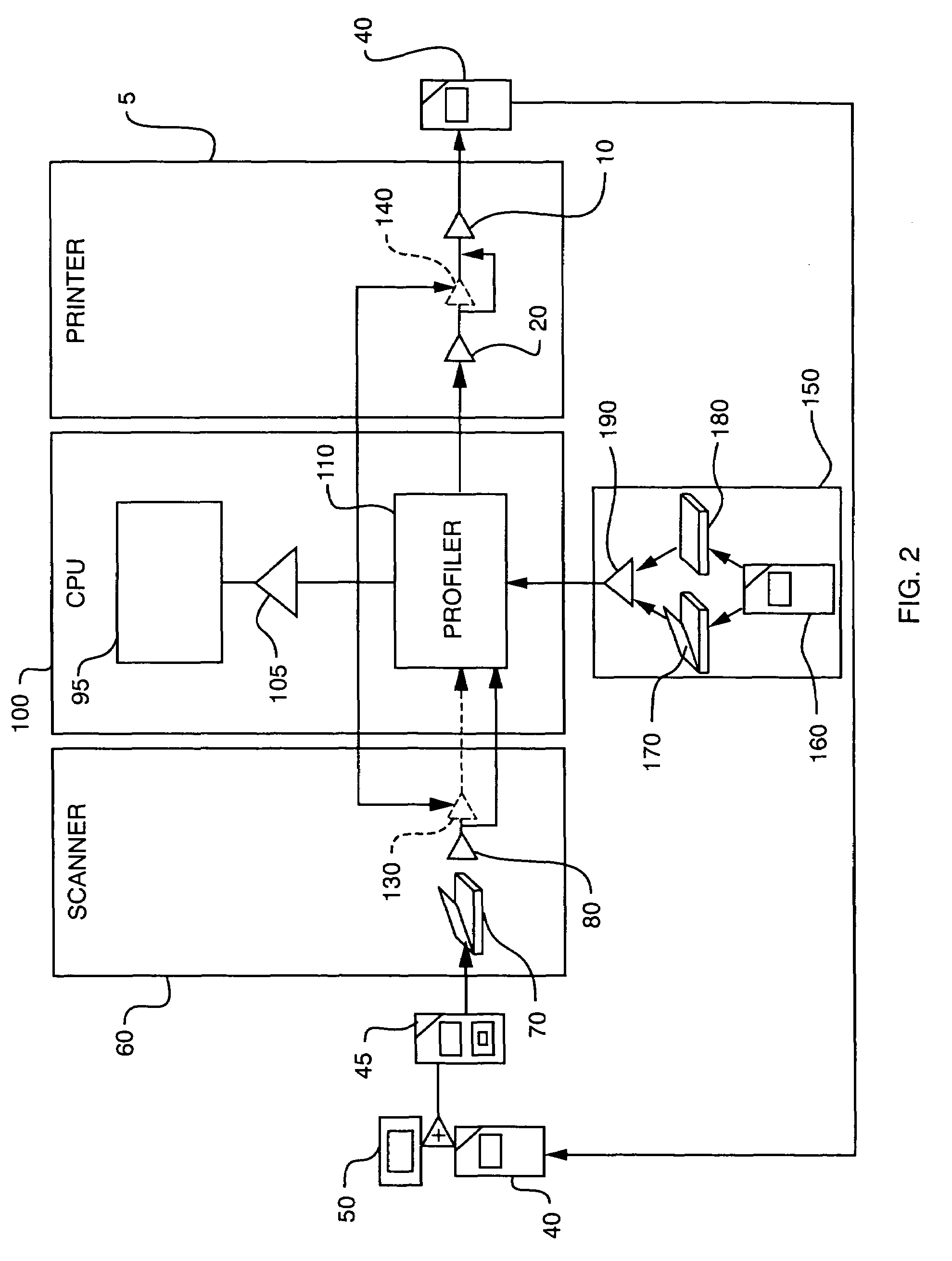
Scanner and printer profiling system
InactiveUS7414752B2Precise processAccurate data collectionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsFile systemColor correction
An improved color correction system and more specifically, a color profiling system for a printer and scanner. Highly accurate device independent printer profiles are generated using a scanner and processing means. The process utilizes the simultaneous scanning of a reference target and a print target to produce a scanner profile. Uncompensated printer profile is developed using the scanner profile and compensation transforms convert the uncompensated printer profile into the printer profile.
Owner:X-RITE
Automatic cutting machine
ActiveCN106735531AReduce impactEnsure measurementShearing machinesShearing machine accessoriesEngineeringMachine tool
The invention discloses an automatic cutting machine. The automatic cutting machine comprises a bottom frame, a feeding mechanism and cutting units. A platform is arranged on the bottom frame. The two sides of the platform are provided with guide rails correspondingly. The feeding mechanism is located on the rear portion of the platform. A large bottom plate at the lower end of the feeding mechanism is in sliding connection with the guide rails. The feeding mechanism comprises a feeding bracket, an upper press roll and a lower press roll. The bottom of the feeding bracket is fixedly connected with the large bottom plate. The upper press roll and the lower press roll are vertically arranged on the feeding bracket. The lower press roll is driven by a first servo motor installed on one side of the feeding bracket. The front side and the rear side of the feeding mechanism are provided with material clamping mechanisms correspondingly. The three cutting units comprise the first cutting unit, the second cutting unit and the third cutting unit and are arranged on the guide rails from back to front in sequence. Through the cutting units of the cutting machine, impact force to a machine tool is decreased, equipment noise is lowered, the cutting precision is high, and the cutting machine is suitable for cutting sheets of various models; and the amount of cutting waste is small, the automation degree is high, and the production efficiency and safety are greatly improved.
Owner:青岛瑞宜利特变压器设备有限公司
Mobile communication terminal and mobile communication method
InactiveUS20080146218A1Improve communication qualityMeasurement accuracyReceivers monitoringRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsComputer scienceSignal processing
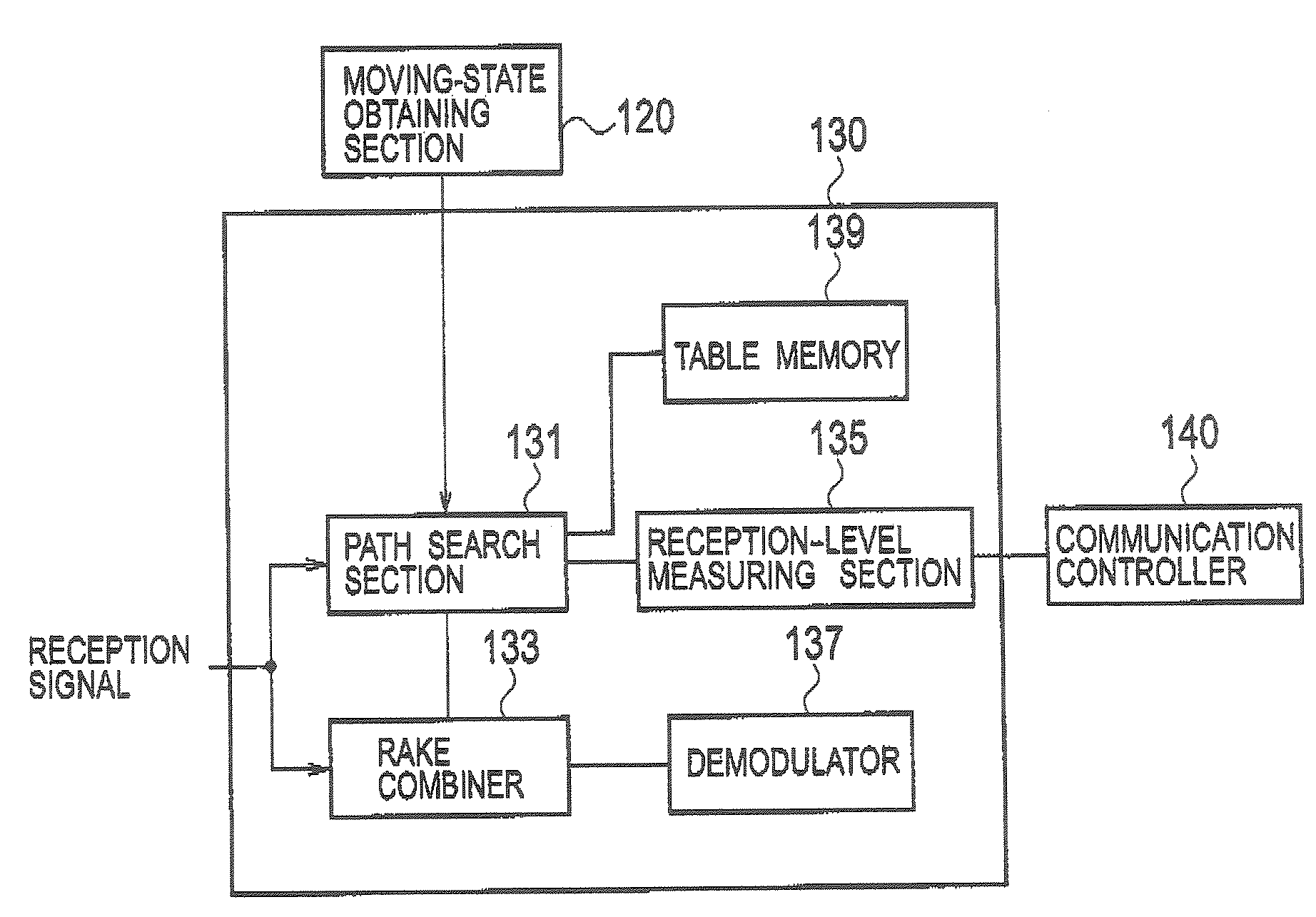
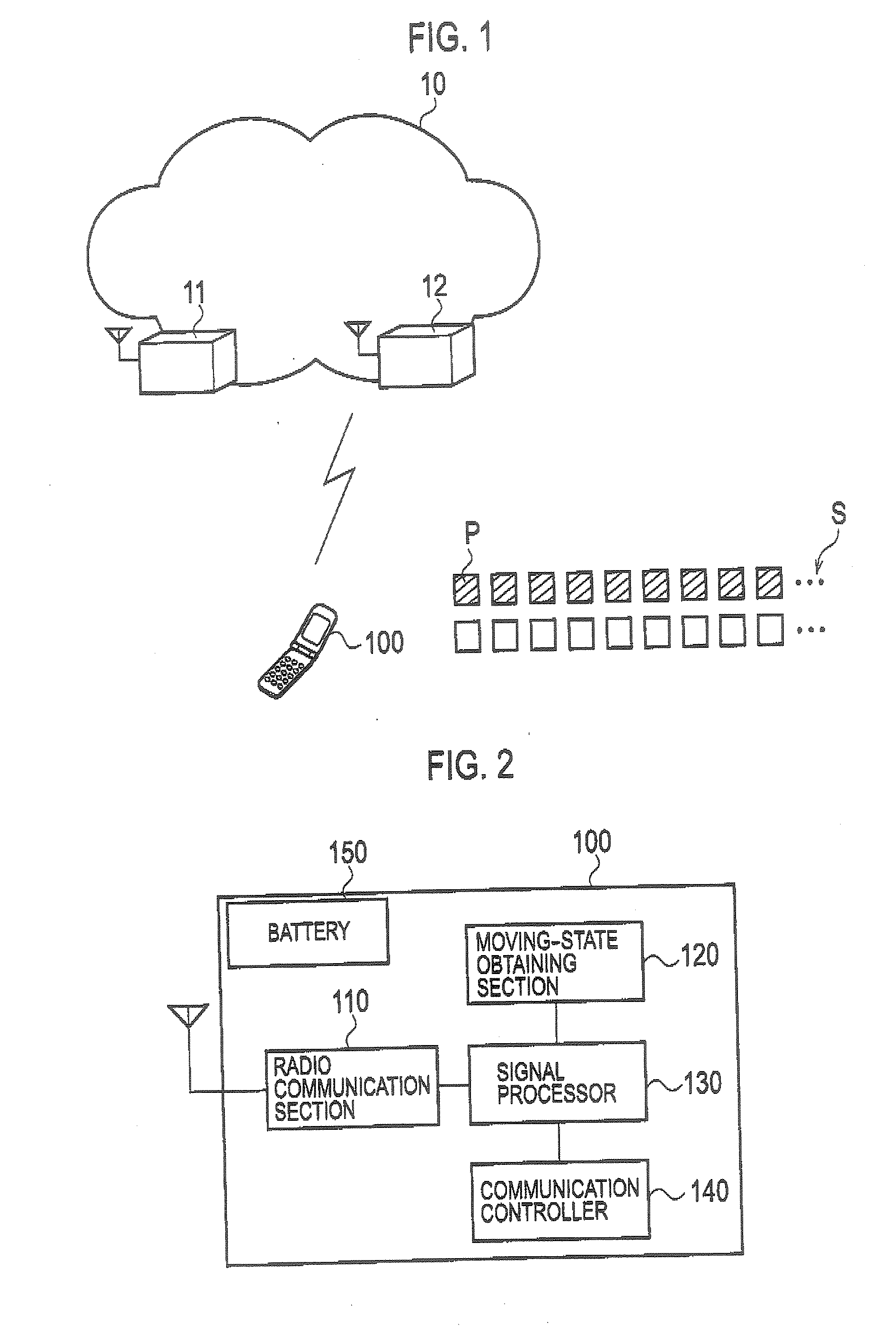
Provided is a mobile communication terminal including: a moving-state obtaining section for obtaining a moving state of the mobile communication terminal; a path search section for determining a measurement condition including any one of the number of known signals and an interval for measuring the radio signal according to the moving state obtained by the moving-state obtaining section; and a reception-level measuring section and a demodulator for performing signal processing by use of the radio signal under the measurement condition determined by the path search section. The known signal is used for estimating the influence of propagation path of the received radio signal, and has setting values that are known by both the transmitting side and receiving side.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and system for developing and administering subject-appropriate implicit tests of association
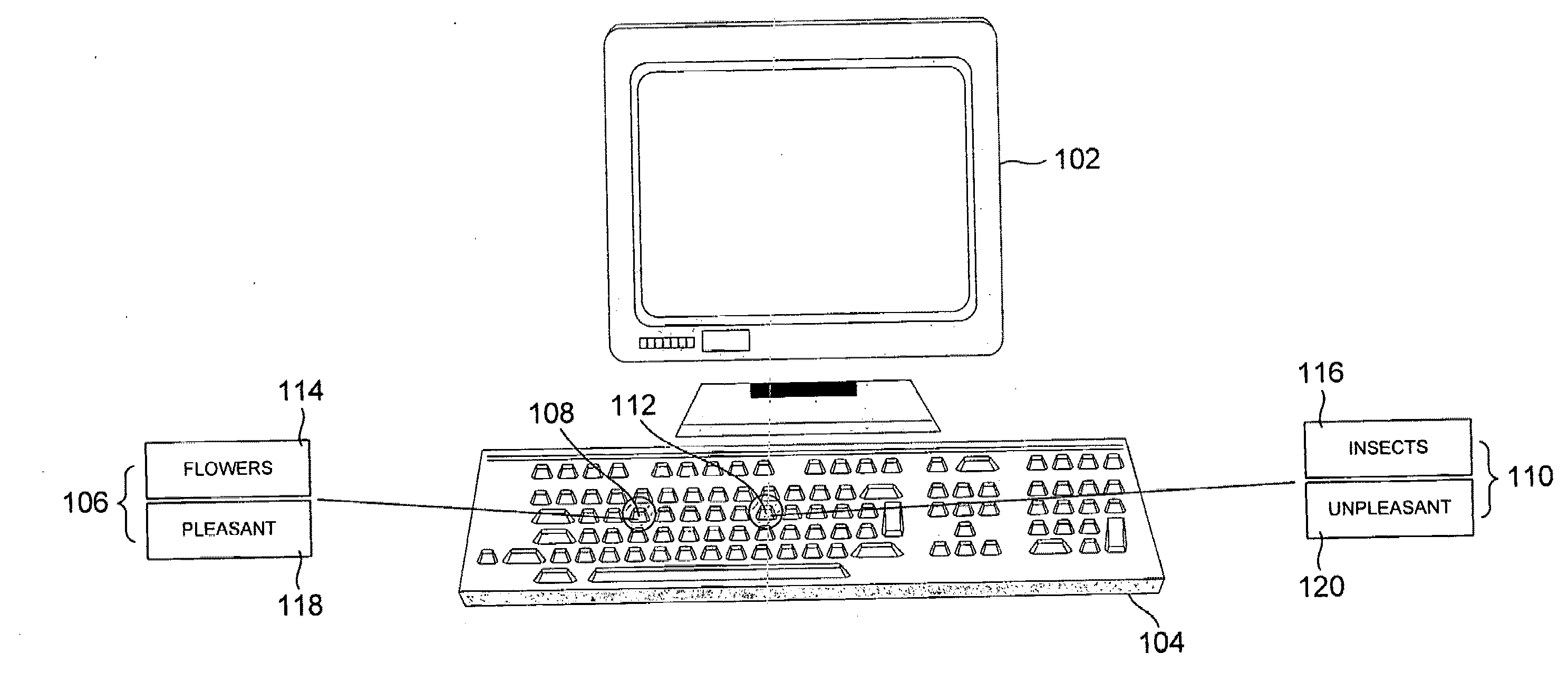
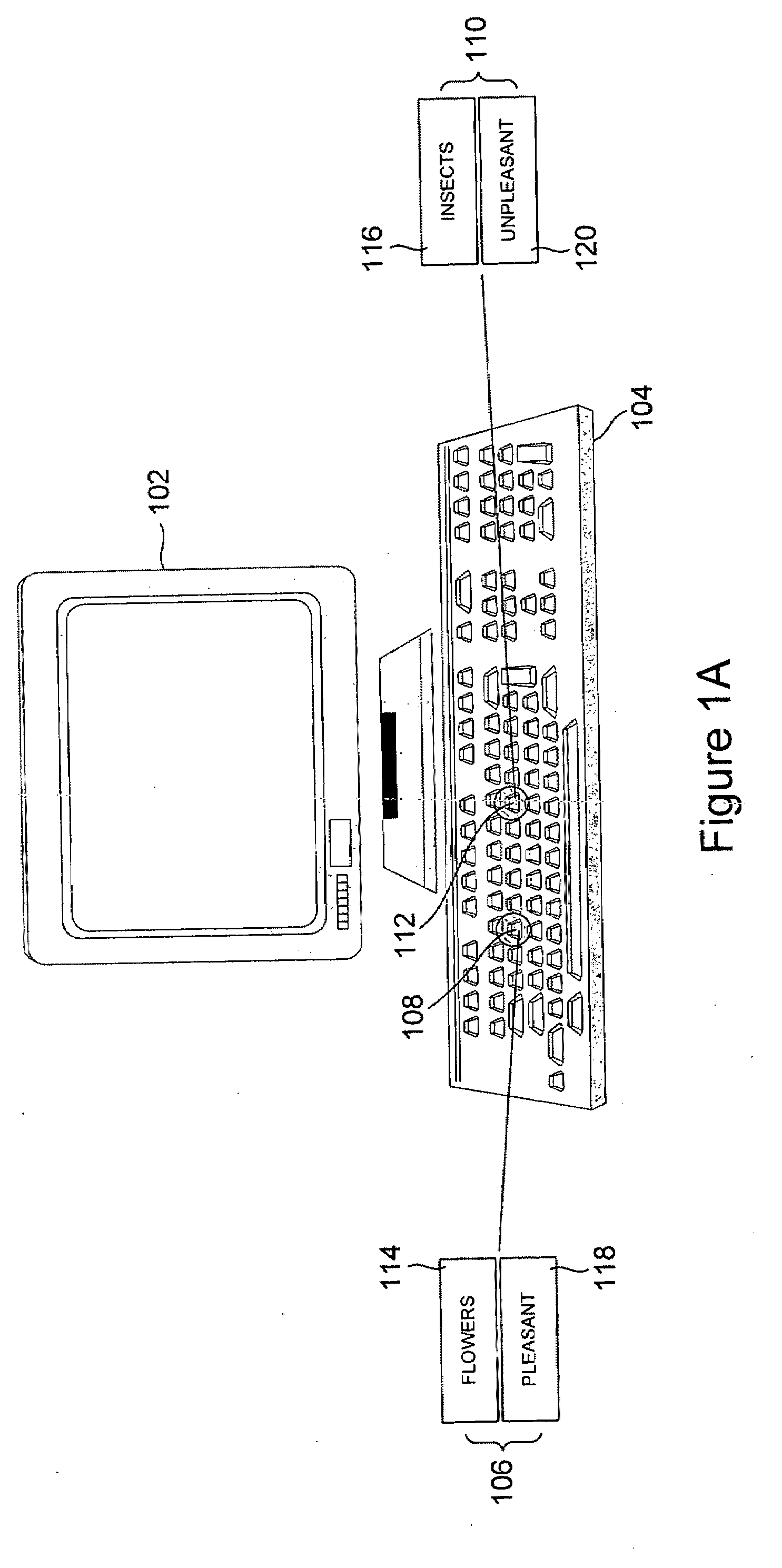
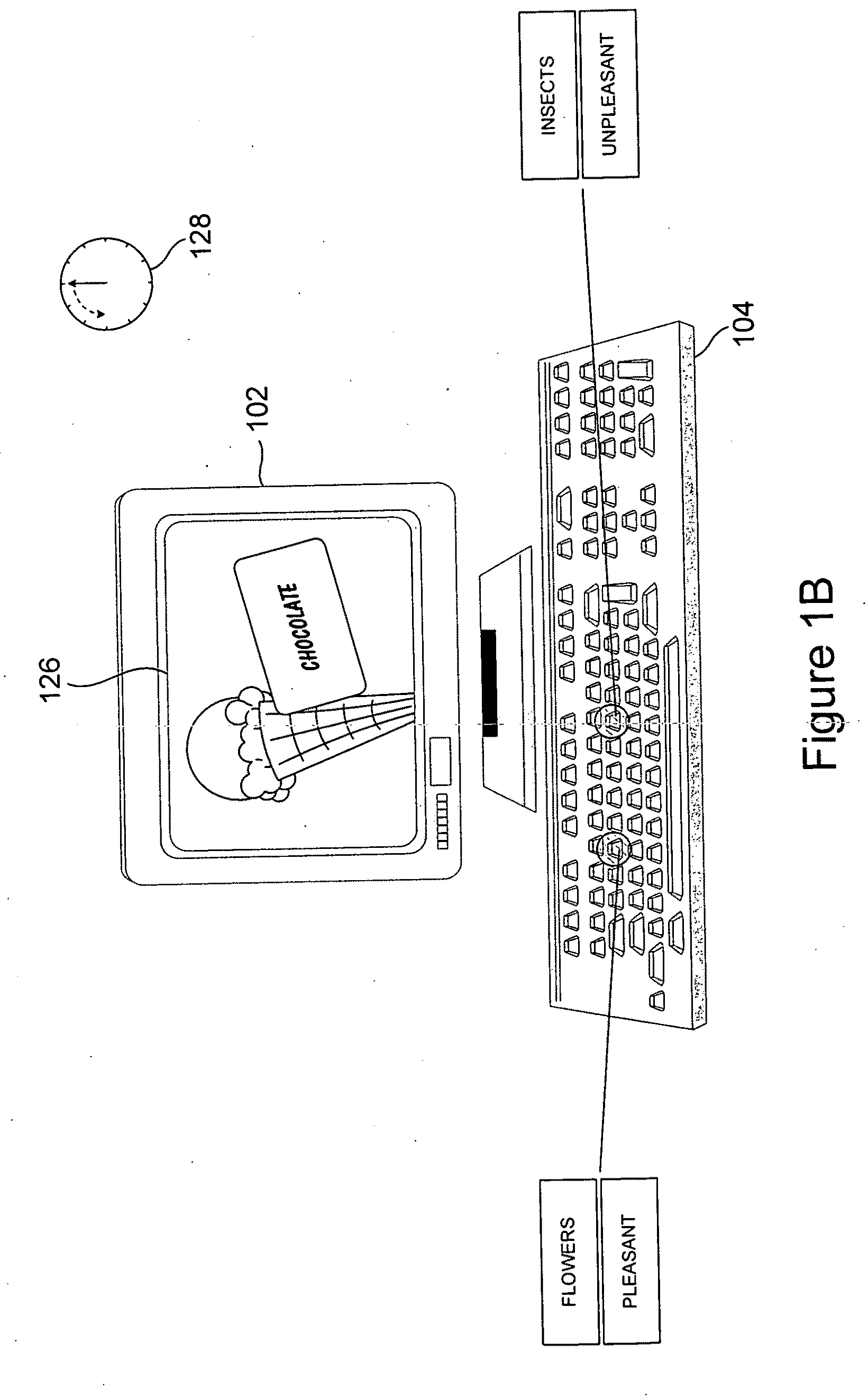
InactiveUS20090275006A1Ensure measurementElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusSystems approachesComputer science
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Flexible multi-layered probe for measuring a signal from an object
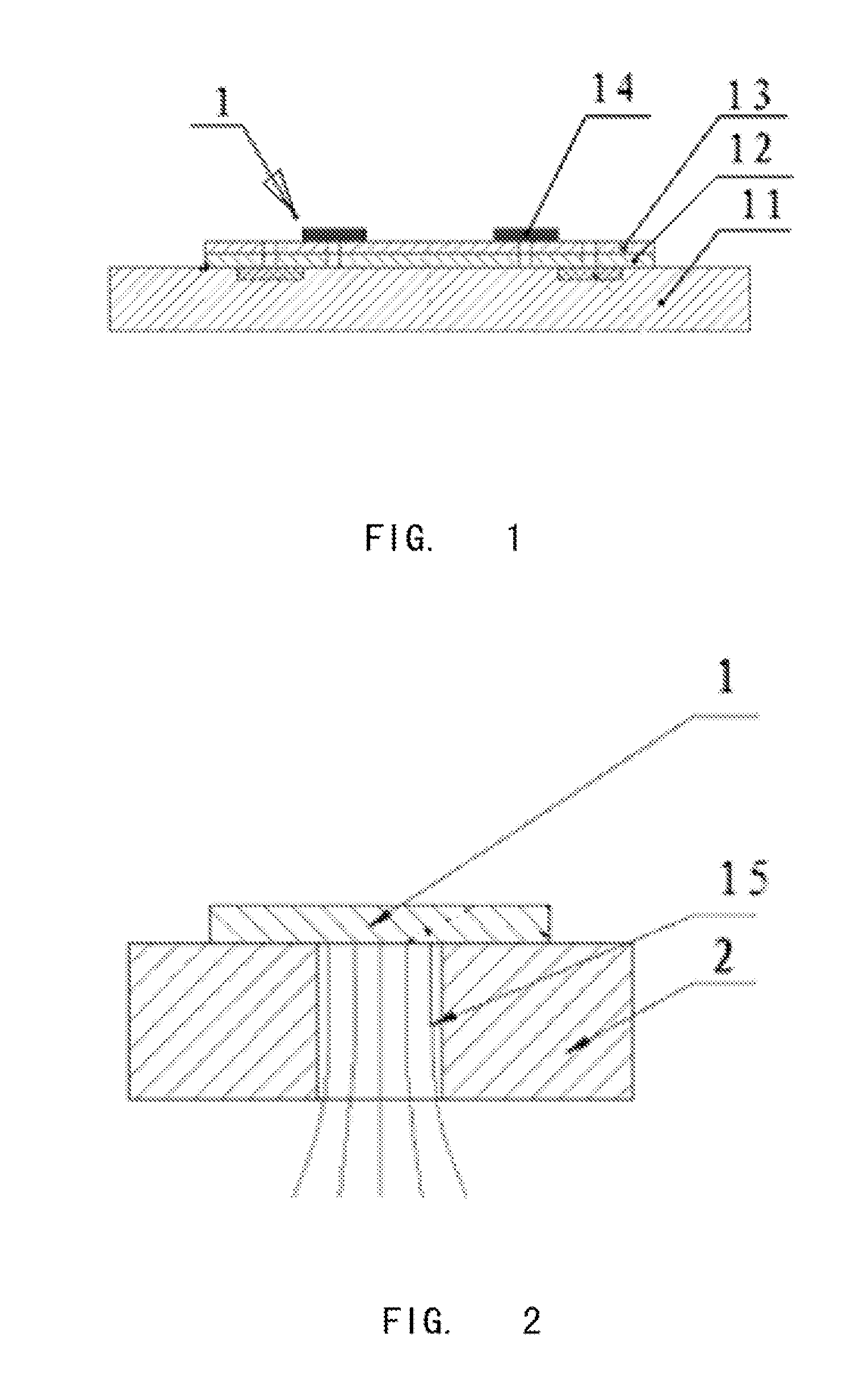
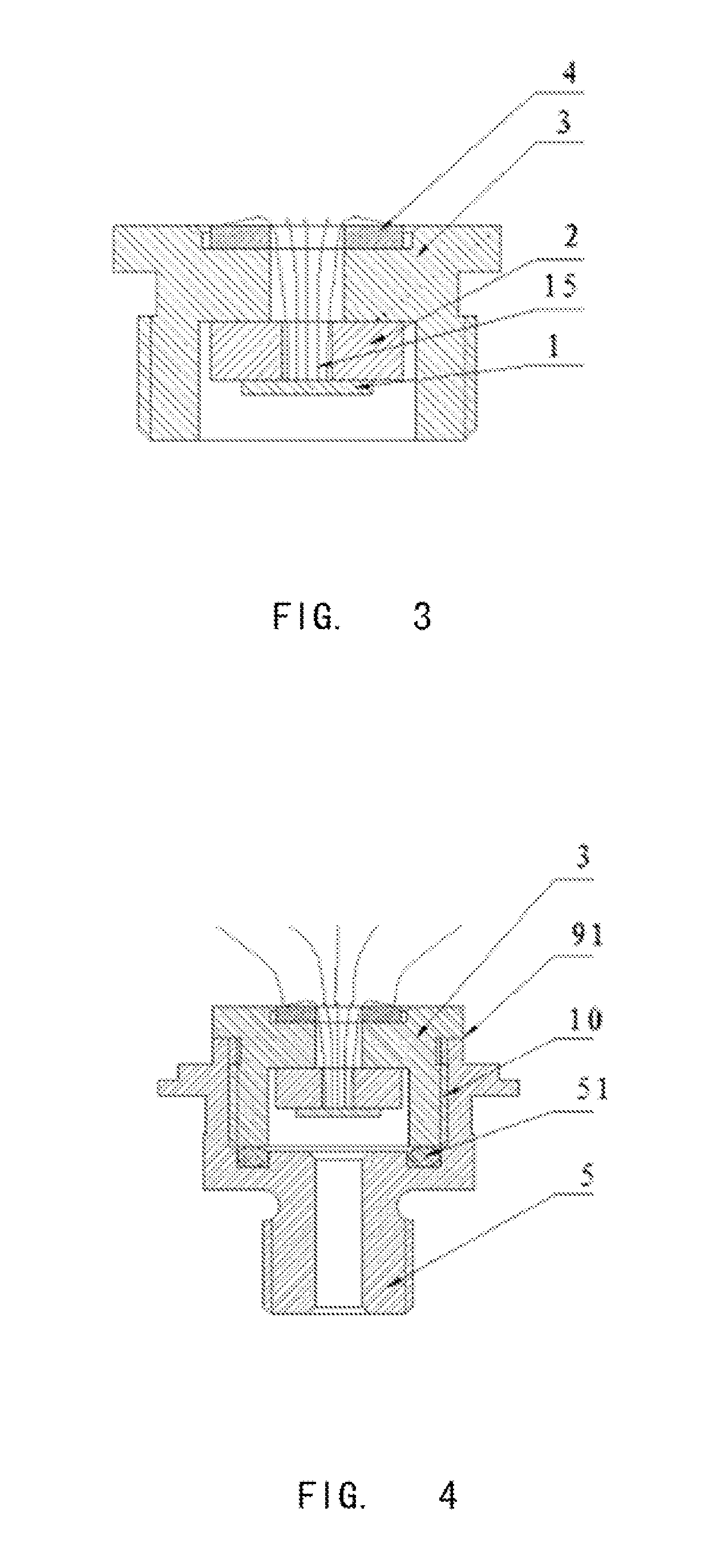
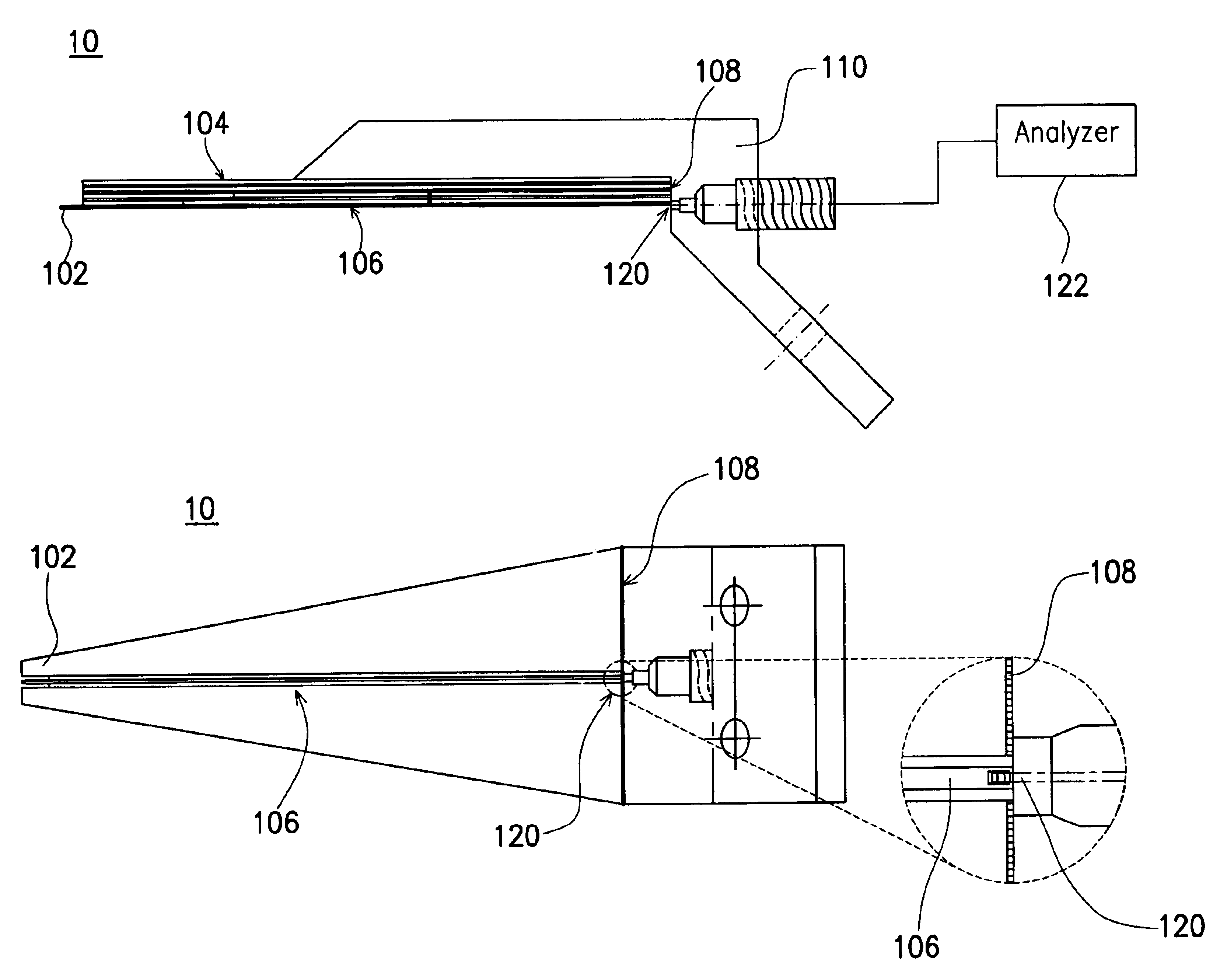
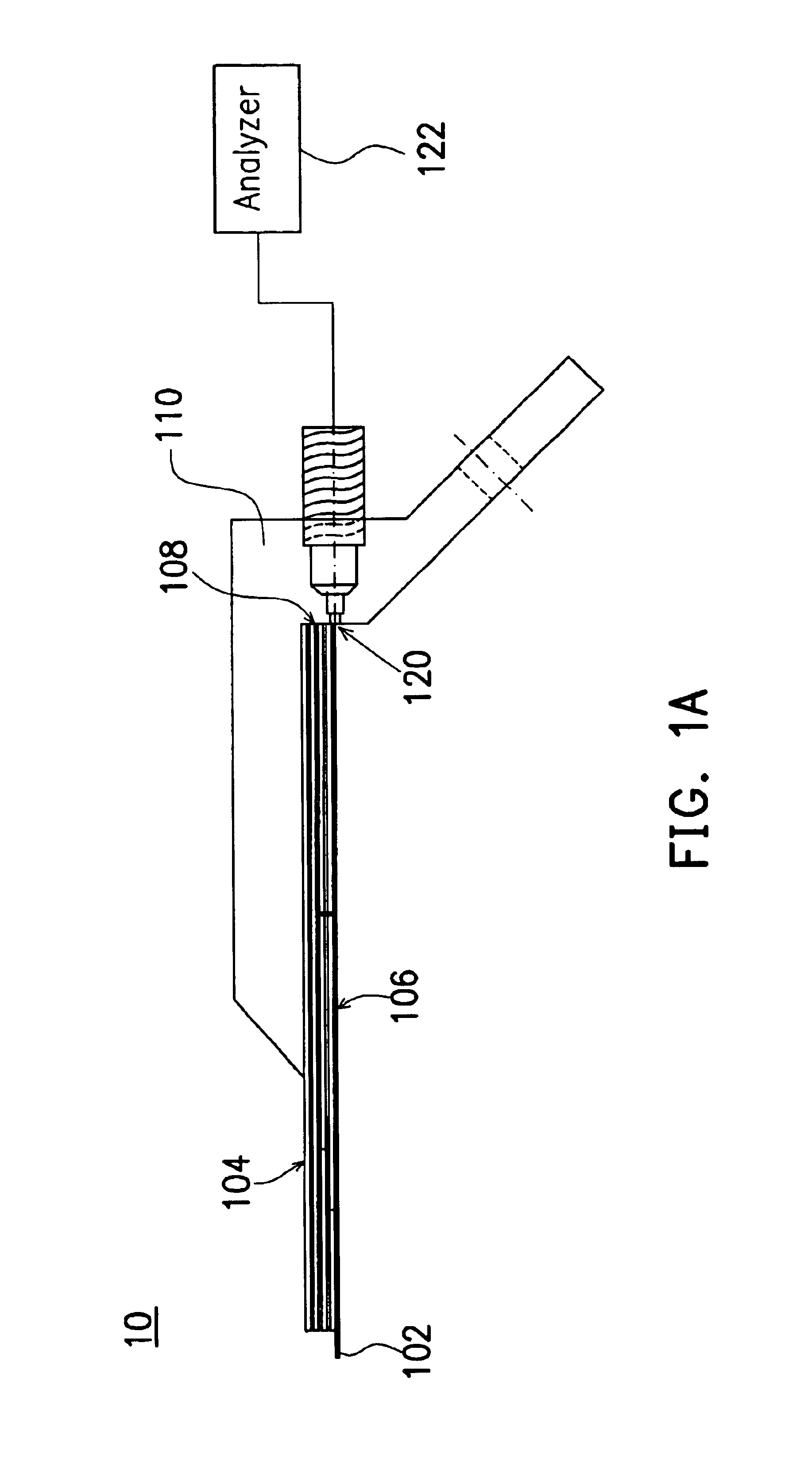
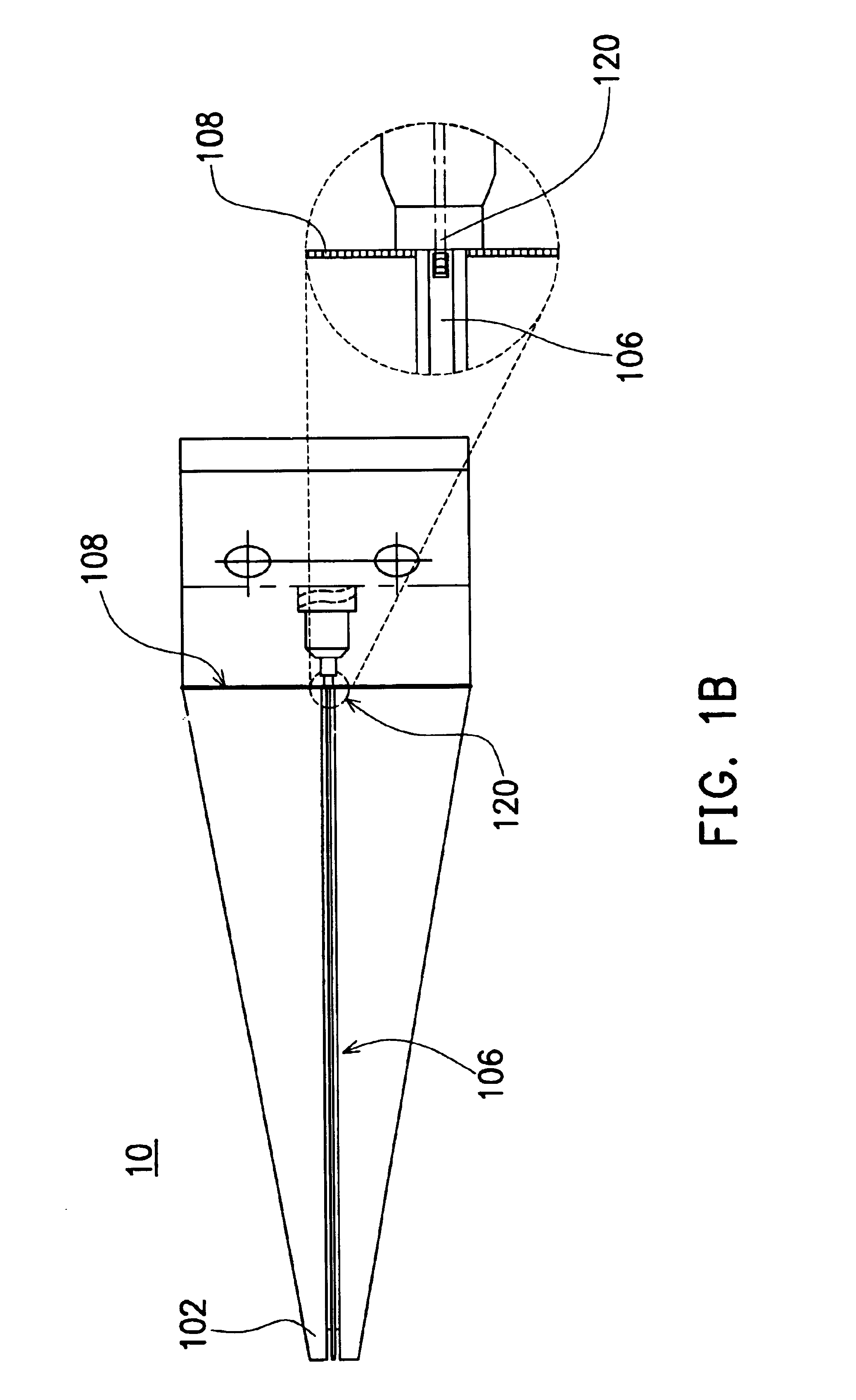
InactiveUS6930497B2Guaranteed accuracyEnsure measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingDielectric substrateElectrical and Electronics engineering
A flexible probe, applicable for measuring signals from the object with an uneven surface, includes at least a probe tip, a flexible multi-layered dielectric substrate, a planar transmission structure and a coaxial transmission structure. The probe tip is connected to the planar transmission structure and extends beyond the flexible dielectric substrate. The planar transmission structure is attached to and supported by the flexible dielectric substrate and then connected to the coaxial transmission structure.
Owner:NAT CHUNG SHAN INST SCI & TECH
A method for automatically tidying and selecting papers
The invention discloses a method for automatically sorting and classifying paper, and belongs to a quality detection and sorting method of a paper making process. The purpose is to provide the method that paper is decomposed into a single piece of paper to detect the appearance quality, and the single piece of detected paper is classified and respectively counted by adopting a linking automatic equipment, and then sorted the ream output or the quire output. The method mainly comprises the following steps: quires of flat paper are outputted by utilizing a paper conveying machine in the form of a single piece of flat paper; at the outlet end of the paper conveying machine, the appearance quality of the paper is detected by utilizing a computer visual processing system; the appearance quality of the paper is detected by utilizing a computer visual processing system; the paper is counted and selected; the ream and the quire are sorted to qualified paper; reams or quires of paper are outputted. The invention can be suitable for the quality detection and the sorting and the classifying of various pieces of paper in the paper making production.
Owner:CHINA BANKNOTE PRINTING & MINTING
Method and apparatus for measuring accumulated and instant rate of material loss or material gain
InactiveUS20050263395A1Ensure measurementWeather/light/corrosion resistanceElectrical/magnetic thickness measurementsCorrosion resistantMicroprocessor
Owner:METRICORR
Automobile general pressure sensor
ActiveUS8459124B2Reduce impactEnsure measurementFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsSignal conditioning circuitsEngineering
A general pressure sensor for an automobile comprising a sensor shell, a silicon piezoresistive sensitive core, a sensor core seat, a signal conditioning circuit, and an automobile electric device interface is disclosed. The silicon piezoresistive sensitive core, the sensor core seat and the signal conditioning circuit are disposed in the inner cavity of the sensor housing. The sensor housing is installed to the automobile electric device interface, and the silicon piezoresistive sensitive core comprises a silicon piezoresistive sensitive element and a glass ring sheet. The silicon piezoresistive sensitive element is welded and fixed to a surface of the glass ring sheet. An insulation oxidation layer is formed on one surface of the glass ring sheet and the silicon piezoresistive sensitive element. The other surface of the glass ring sheet is hermetically fixed to the ring-shape recession surface provided on the sensor core seat. The sensor core seat is hermetically and rotationally fixed to a pressure inlet on the sensor housing, after the inner lead wire on the silicon piezoresistive sensitive core is led to an interposing board provided on one end of the central hole through the other end of the central hole on the ring-shape recession surface of the sensor core seat, and then is led out by the automobile electric device interface via the signal conditioning circuit.
Owner:KUNSHAN SHUANGQIAO SENSOR MEASUREMENT CONTROLLING +1
Differential pressure gauge
InactiveUS8146435B1Eliminate effectiveEliminate differencesFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsPressure difference measurement between multiple valvesDifferential pressureEngineering
A differential pressure gauge includes a housing, a leaf spring having a magnetic steel, a measuring diaphragm, a helix, a dial, a range adjusting device and a diaphragm cover. The measuring diaphragm is connected with the leaf spring by connectors. The range adjusting device includes an adjusting spring provided at a lower end of the measuring diaphragm, a balance spring provided at an upper end of the measuring diaphragm, an adjusting screw and a slider which are provided at a lower end of the adjusting spring. The adjusting end of the adjusting screw is provided outside of the housing. The adjusting spring can be compressed by the upper and lower displacement of the slider driven by the adjusting screw, thus affecting the rigidity of the system to change the range of the differential pressure gauge. The differential pressure gauge facilitates adjusting the range and has the accurate measurement.
Owner:SAILSORS INSTR BEIJING
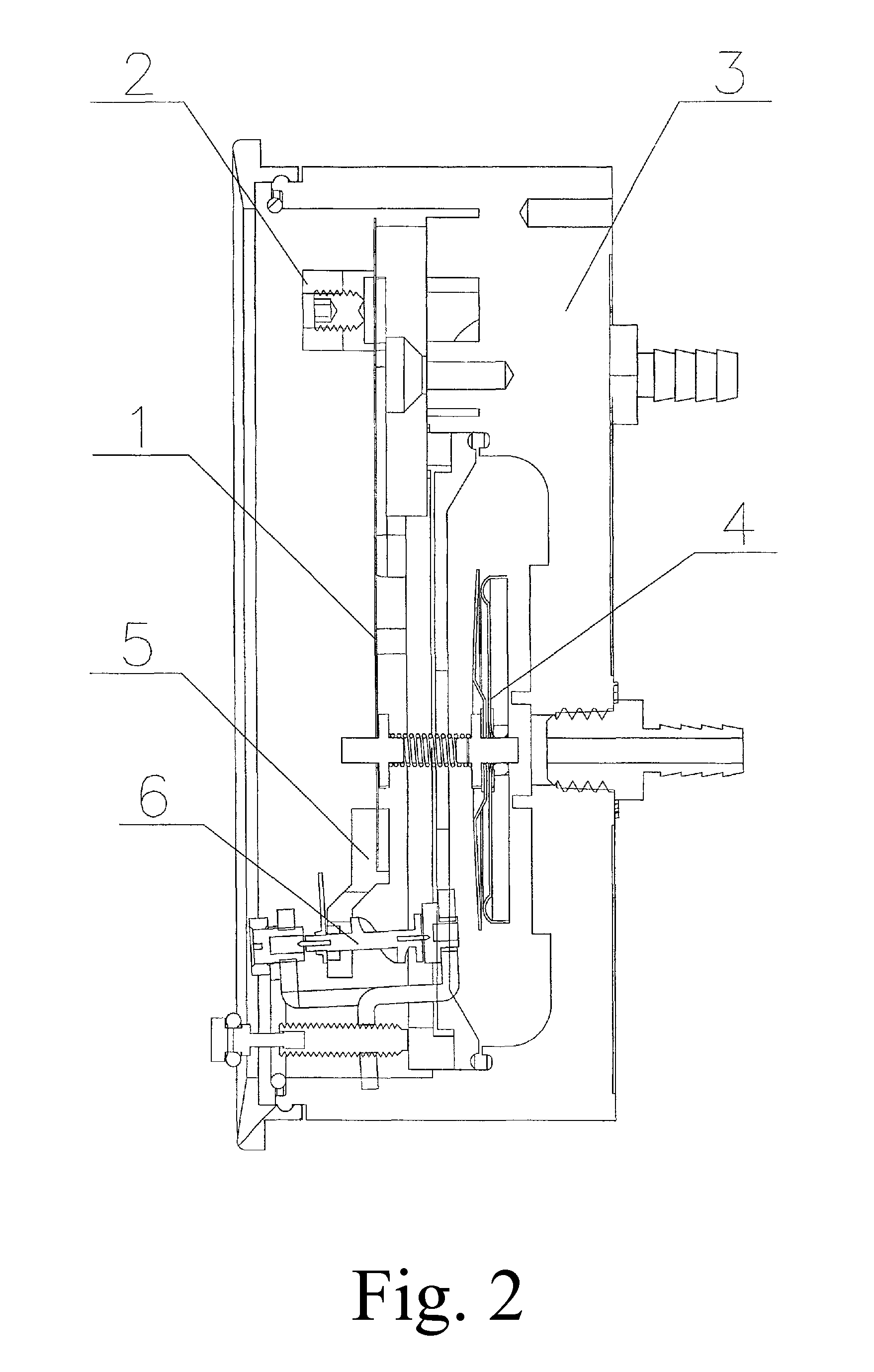
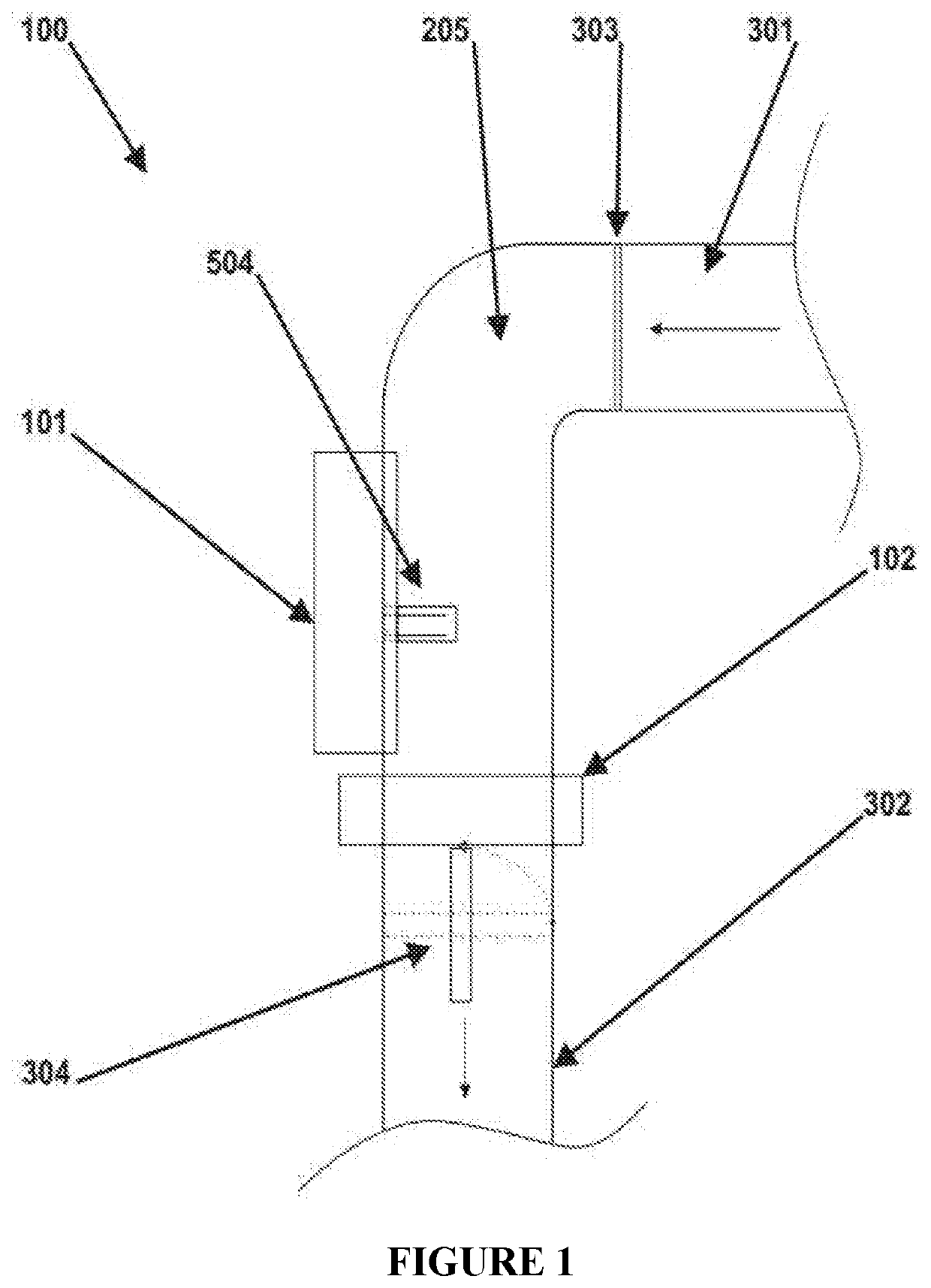
Smart fueling elbow
InactiveUS20200207606A1Energy need is guaranteedPreventing situationFlow propertiesLiquid transferring devicesFuel qualityEngineering
The invention includes a device (205) which prevents situations of fueling incorrect or poor-quality fuels to the tanks during fueling to the storage tanks (210) at fueling stations (200), by analyzing fuel quality and fuel type considering many physical parameters with the help of a sensor (504) that is consist of mechanical resonators, and a smart fueling elbow which has mobile characteristics making possible for the user to carry the elbow to the usage field.
Owner:BULGURCU BILGEN GOZDE +1
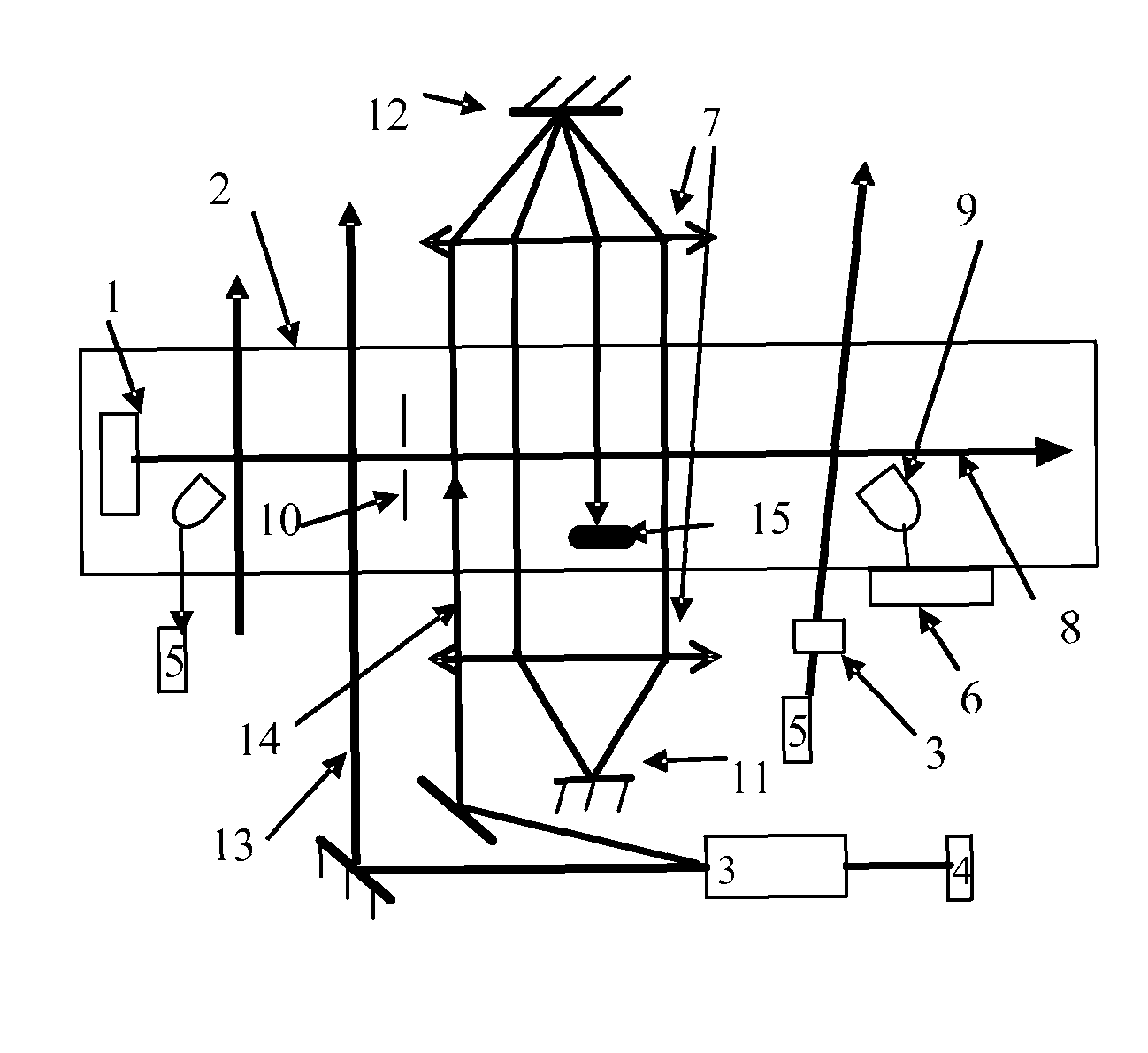
Atomic beam optical frequency atomic clock and a producing method thereof
ActiveUS8143956B2Improve detection efficiencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioLaser detailsApparatus using atomic clocksFrequency spectrumExcited state
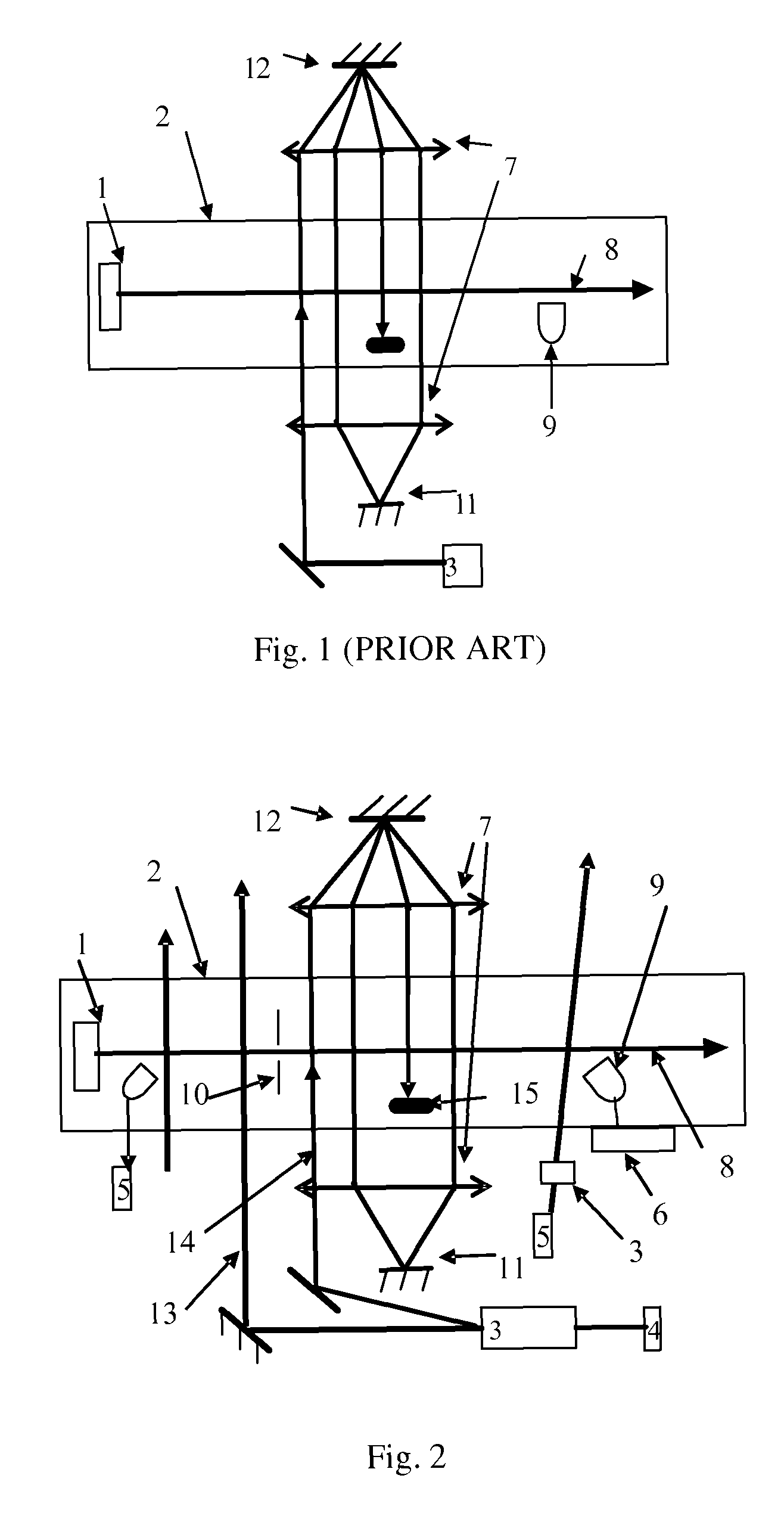
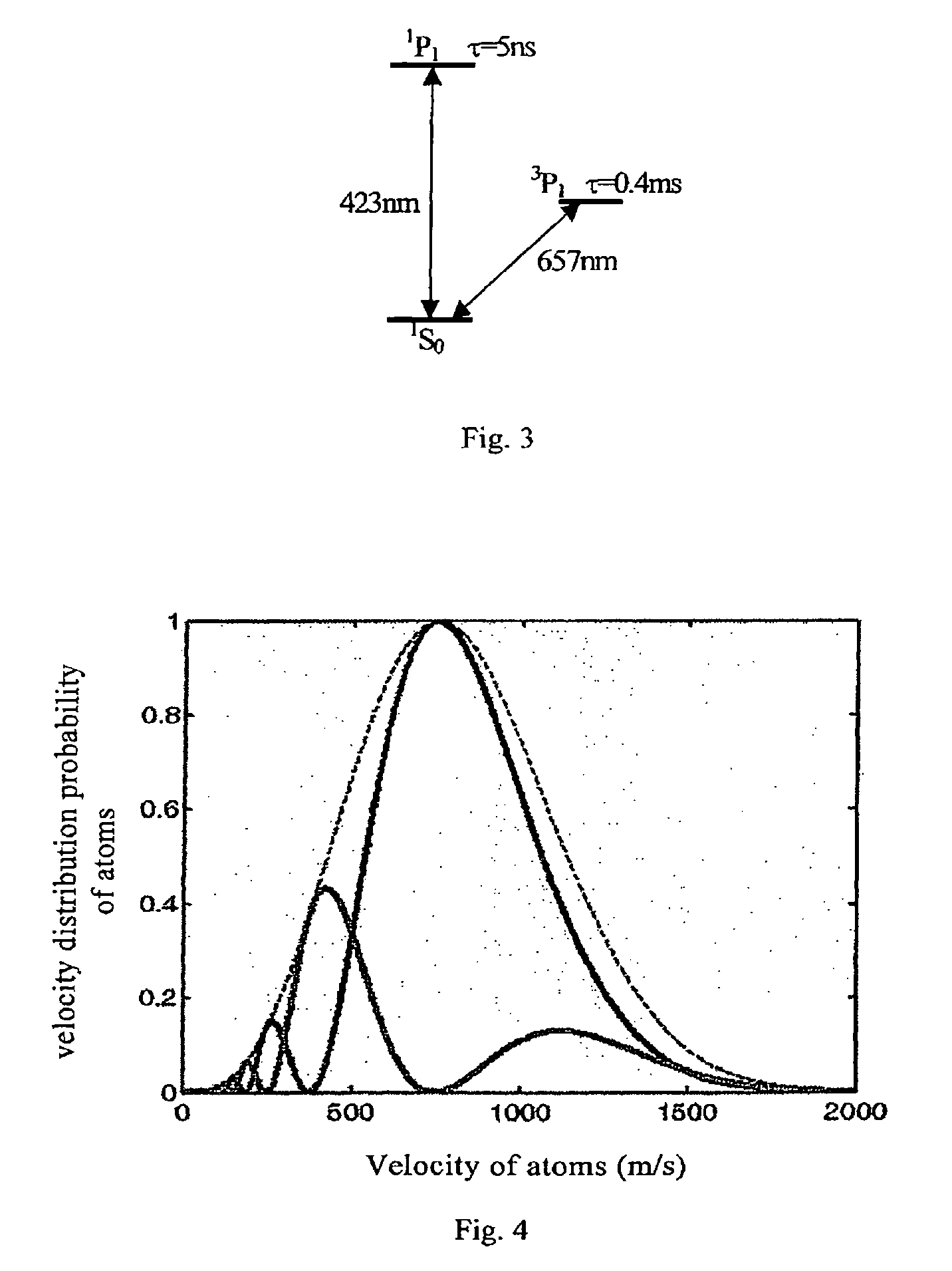
An atomic clock at optical frequency based on atomic beam and a method for generating the atomic clock comprises: The atomic beam (8) is ejected from a pile mouth after heating an atomic pile (1) in a vacuum chamber (2); A laser (4) corresponding to frequency of a clock transition transfers the atomic beam (8) from a ground state of the clock transition to an excited state of the clock transition in a adiabatic passing mode; After interaction with the laser corresponding to the frequency of a clock transition, the atomic beam (8) passes a signal detection region with a detection laser (5), and after the interaction with the detection laser (5), each of the atoms gives off a photon of spontaneous emission; An emitted fluorescence photon signal from atoms which is excited by the detection laser (5) is explored; A clock laser (4) for exploring transition frequency of an atomic clock is modulated. The signal which is detected performs frequency locking for the frequency of the clock laser which is locked on the clock transition spectrum of the atoms so as to implement the atomic clock.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Electromagnetic inclinometer
InactiveUS7222433B2Avoid problemsSimple and ruggedPlumb lines for surveyingIncline measurementConductor CoilVertical axis
Owner:AUTONNIC RES
Method and apparatus for automatically measuring the concentration of TOC in a fluid used in a semiconductor manufacturing process
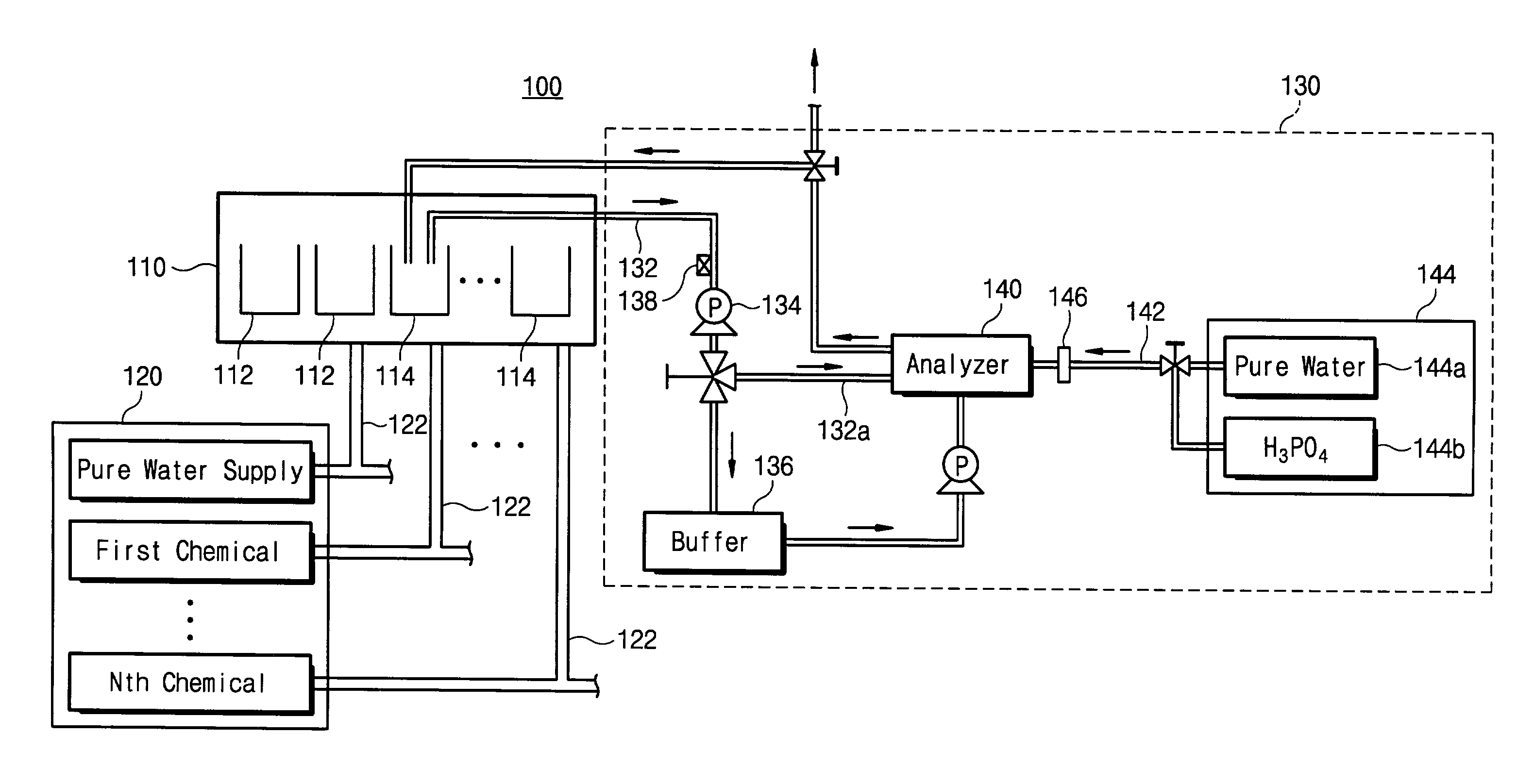
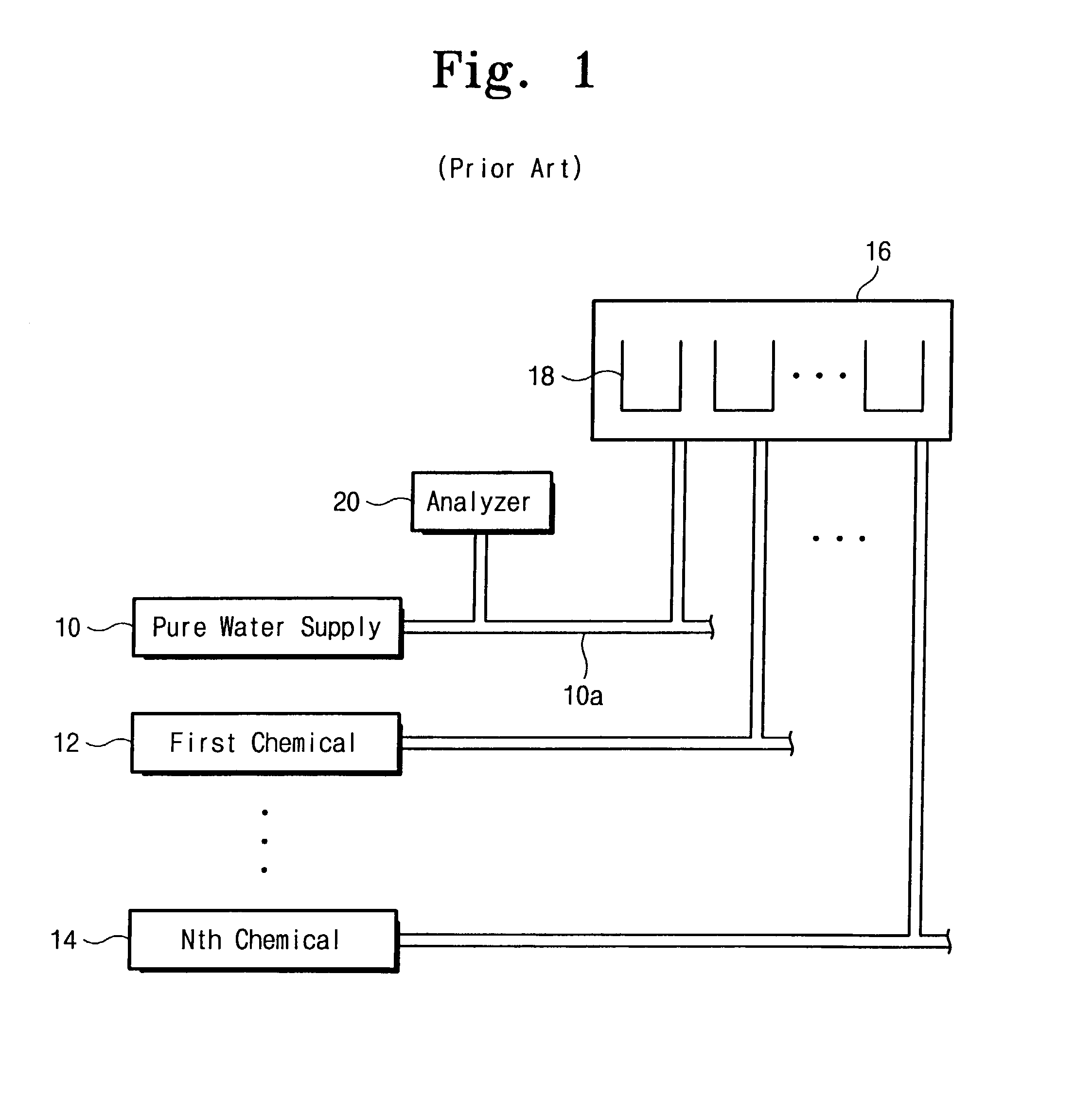
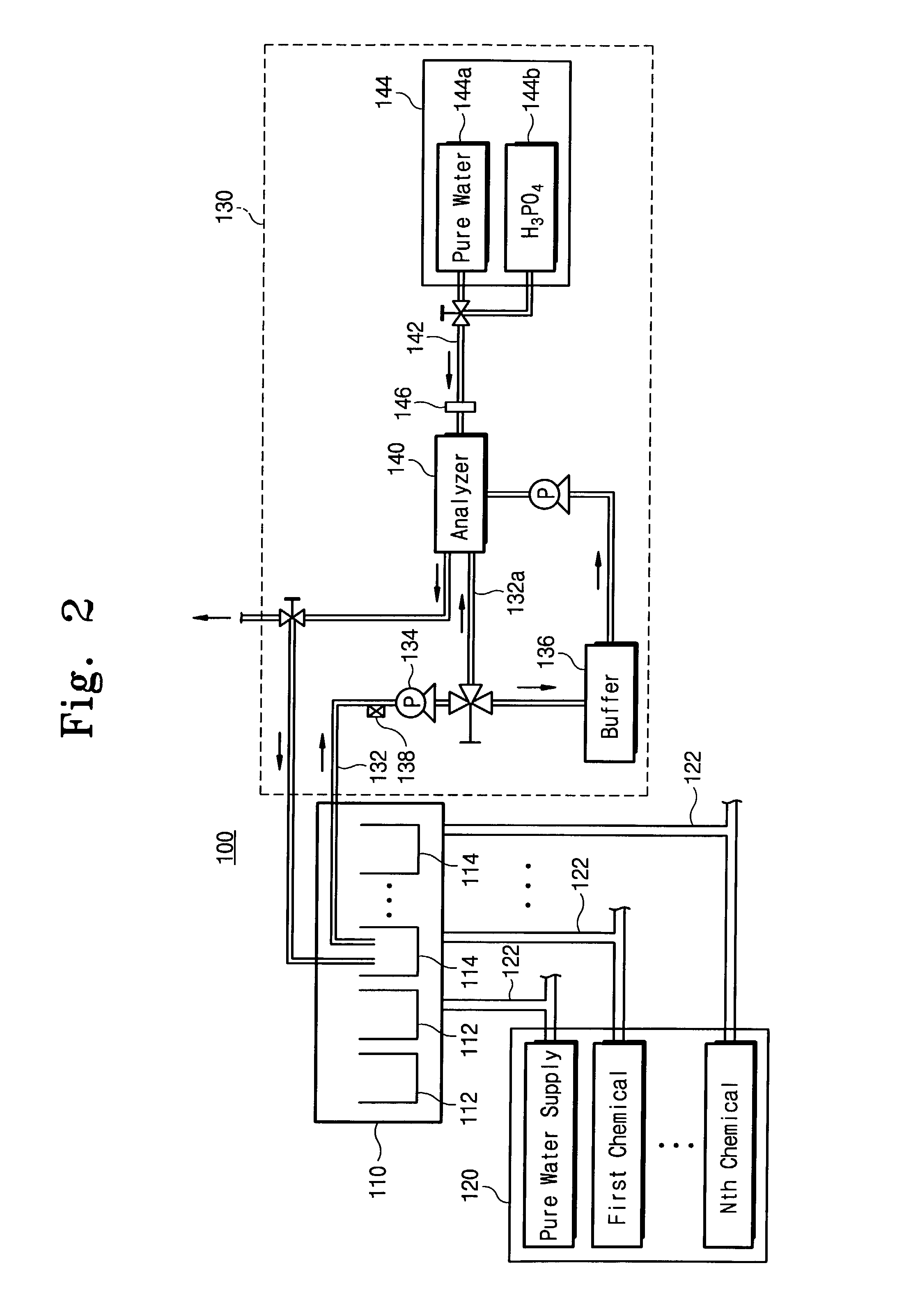
InactiveUS7081182B2Measuring reliability is ensuredEnsure measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingForeign matterCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to a method and apparatus for automatically measuring the concentration of total organic carbon (TOC) in chemicals and ultra-pure water that are used in a wet etch process. The apparatus includes a sampling line extending from a processing bath, and a pump, for extracting a fluid sample from the processing bath, a buffer for filtering foreign material or air bubbles from the fluid, and an analyzer for analyzing the concentration of TOC in the fluid.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for performing an intake manifold injection
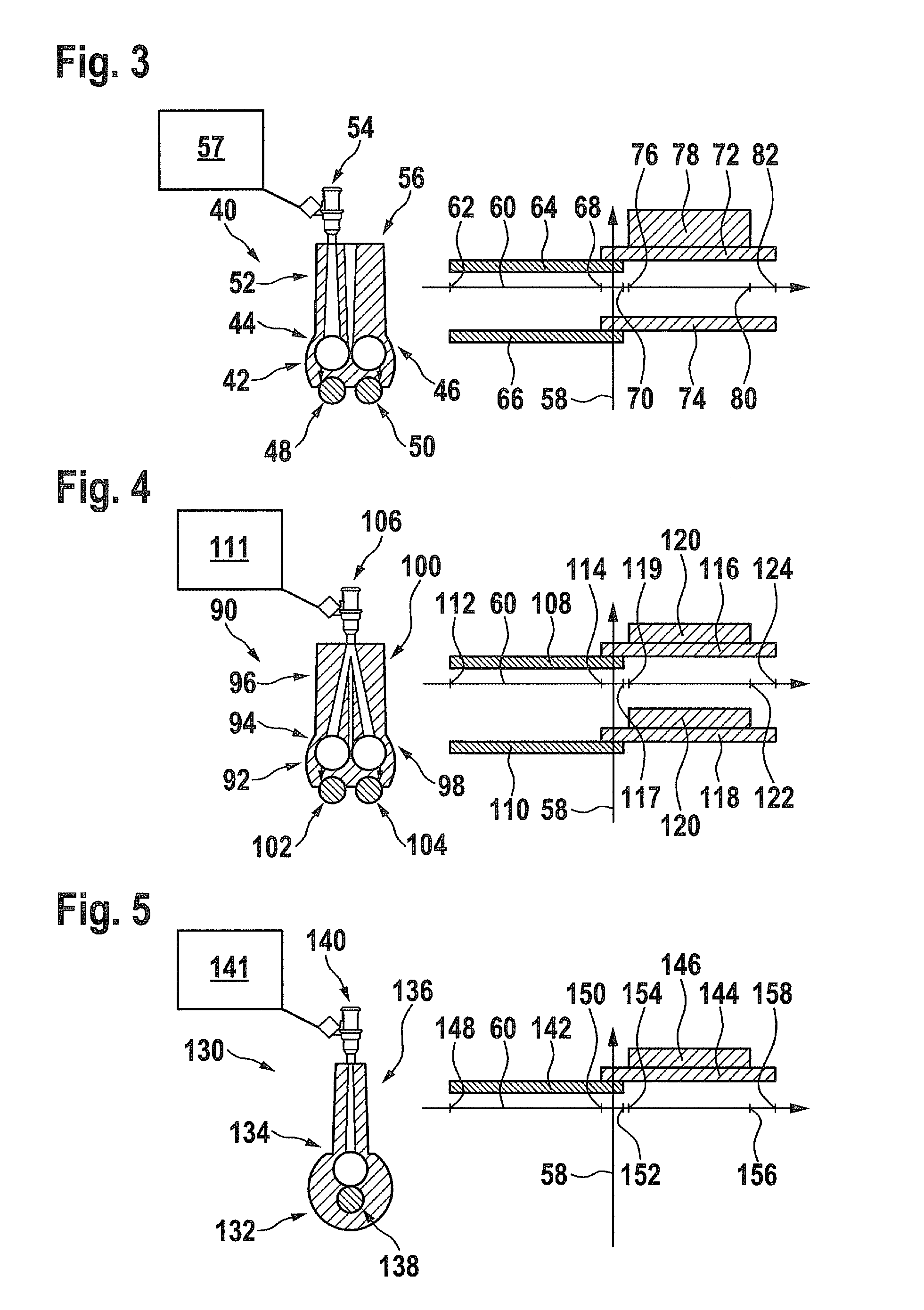
InactiveUS20110041806A1Increase torqueAvoid heavy burdenElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion chamberExhaust valve
A method for performing an intake manifold injection for at least one combustion chamber of an internal combustion engine, at least one intake valve being connected to an intake port, at least one exhaust valve and at least one injector being assigned to at least one combustion chamber, fuel being injected into the at least one intake port by the at least one injector during an injection time, the injection time being started after the closing of the at least one exhaust valve and terminated before the closing of the at least one intake valve for performing the method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
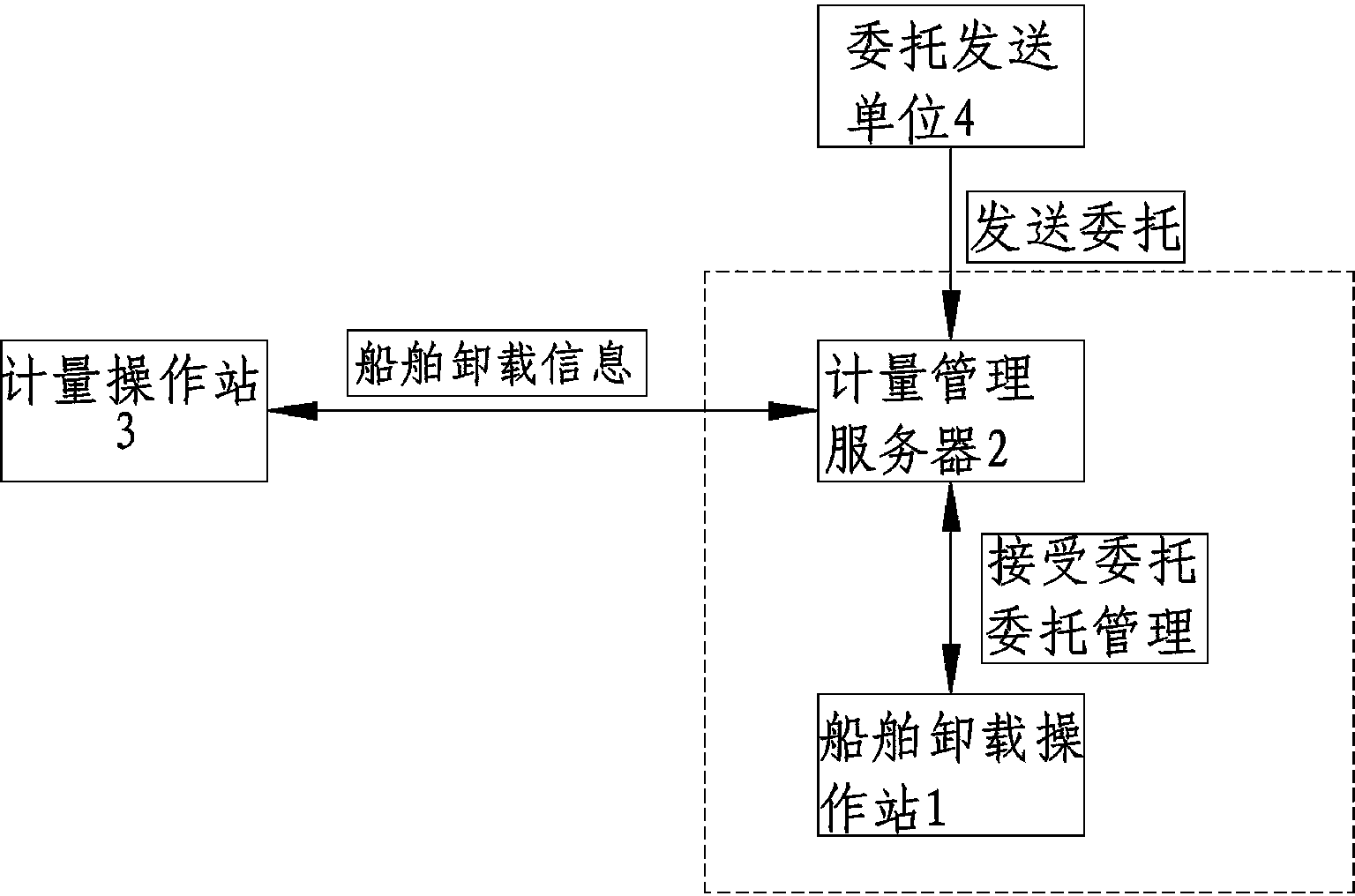
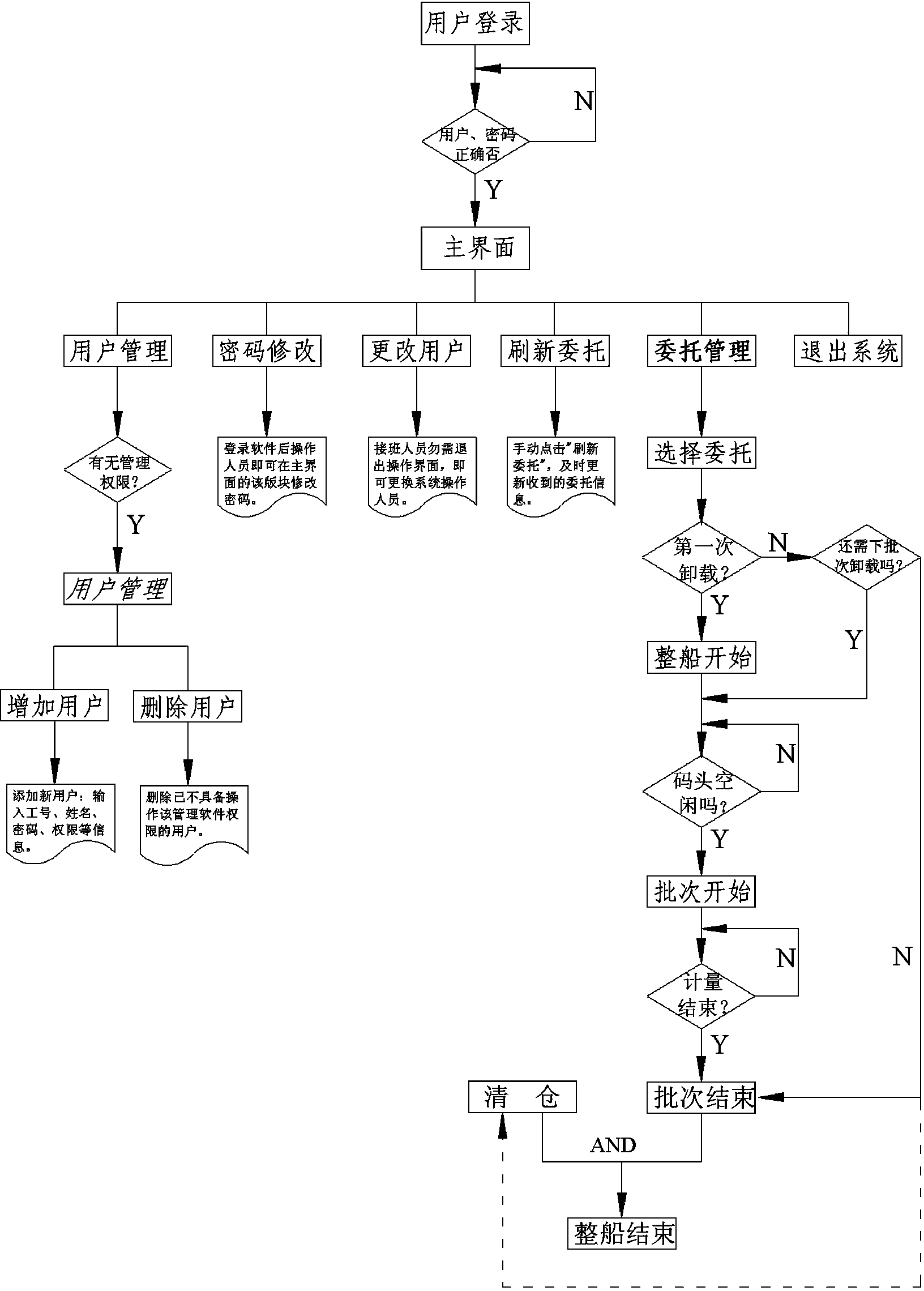
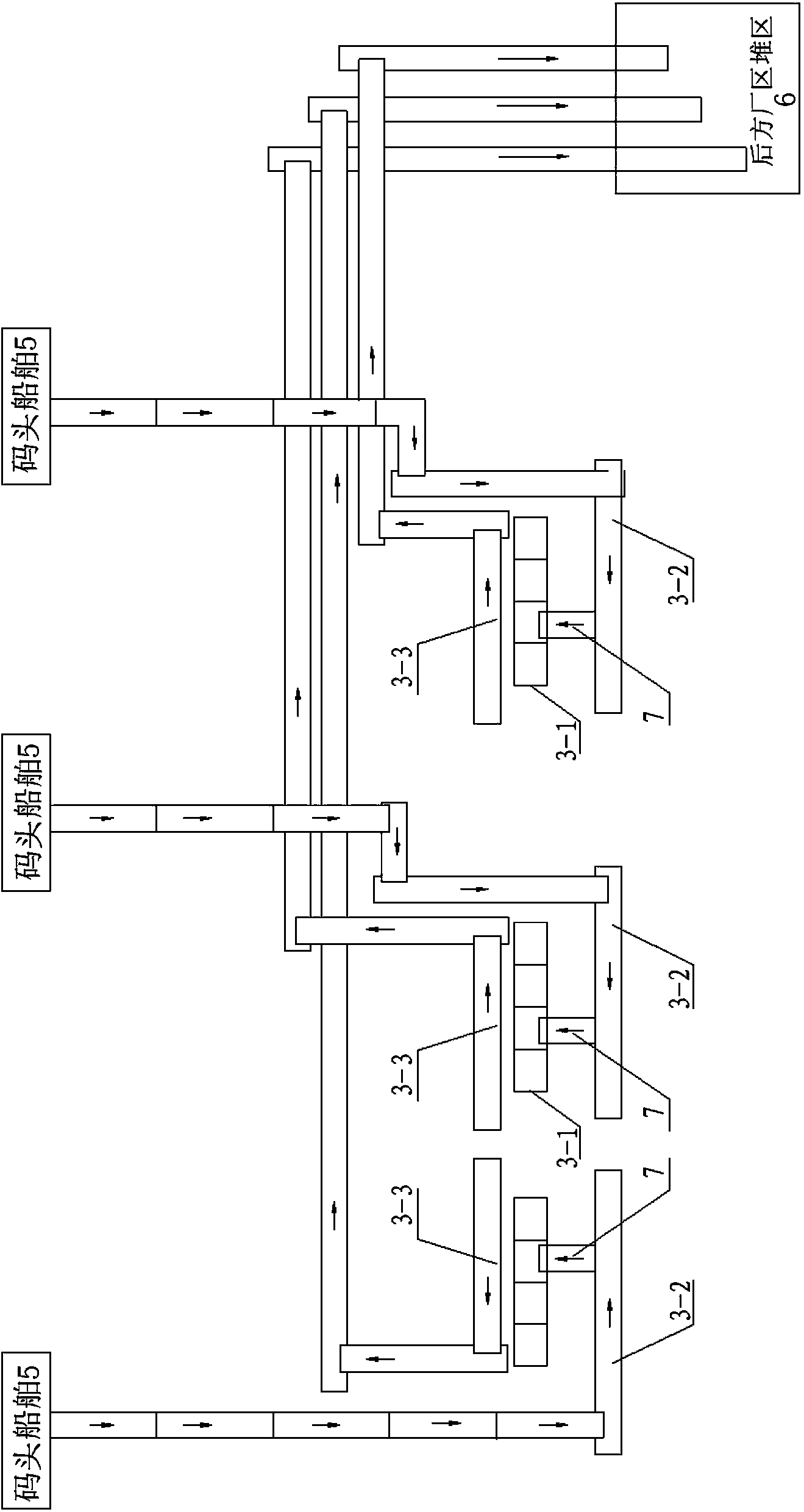
Measurement commission management system and method for wharf material unloading
ActiveCN104299122AReduce in quantityAvoid errorsWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowLogisticsStop timeStart time
The invention discloses a measurement commission management system and method for wharf material unloading. A measurement operation station and a ship unloading operation station are connected with a measurement management server through a network. The measurement management server is used for storing measurement commission information, sent by a commission sending unit, of a ship to be unloaded, ship material unloading control information sent by the ship unloading operation station and ship material weighing data and measurement status information which are sent by the measurement operation station. The ship unloading operation station is provided with a commission management module which is used for dispatching ship unloading wharves, controlling start time and stop time of ship material unloading and sending dispatching information and control information to the measurement management server. The measurement operation station is used for weighing received materials of the ship to be unloaded and sending weighing data and weighing state information to the measurement management server in real time. The measurement commission management system and method for wharf material unloading realize informatization management of wharf material measurement, reduce the number of wharf operators, improve work efficiency and reduce losses of material procurement.
Owner:CHONGQING IRON & STEEL GRP ELECTRONIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com