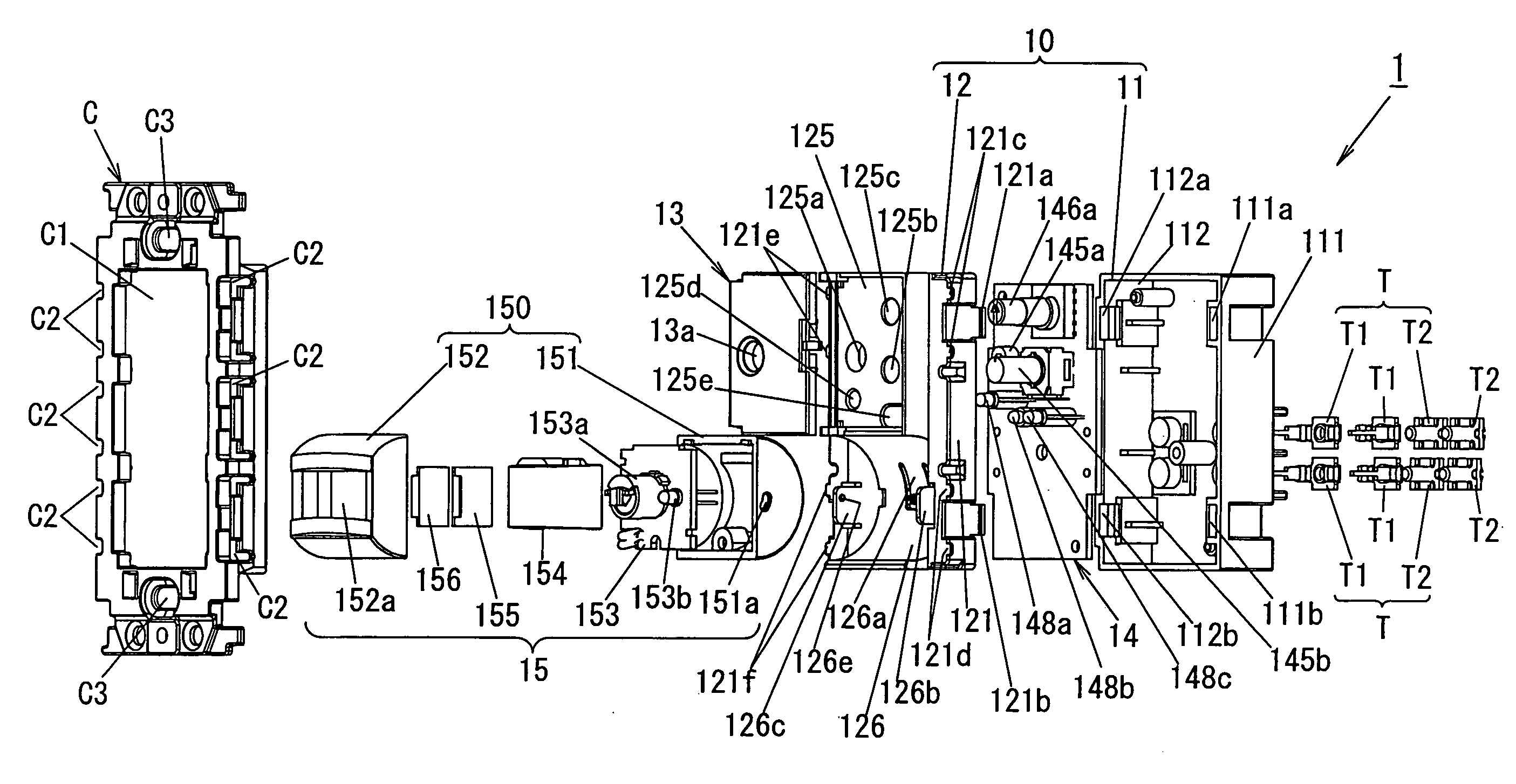
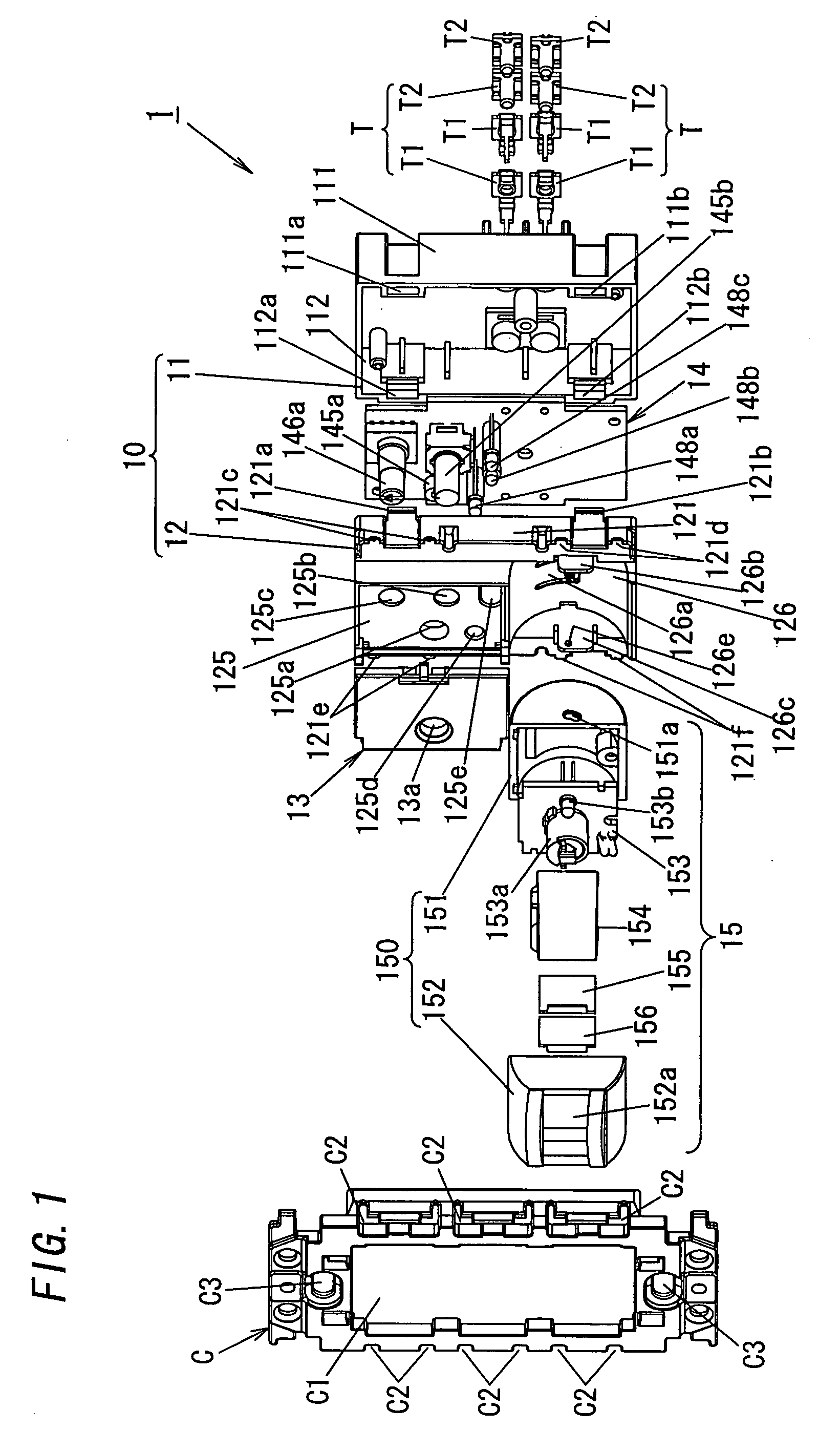
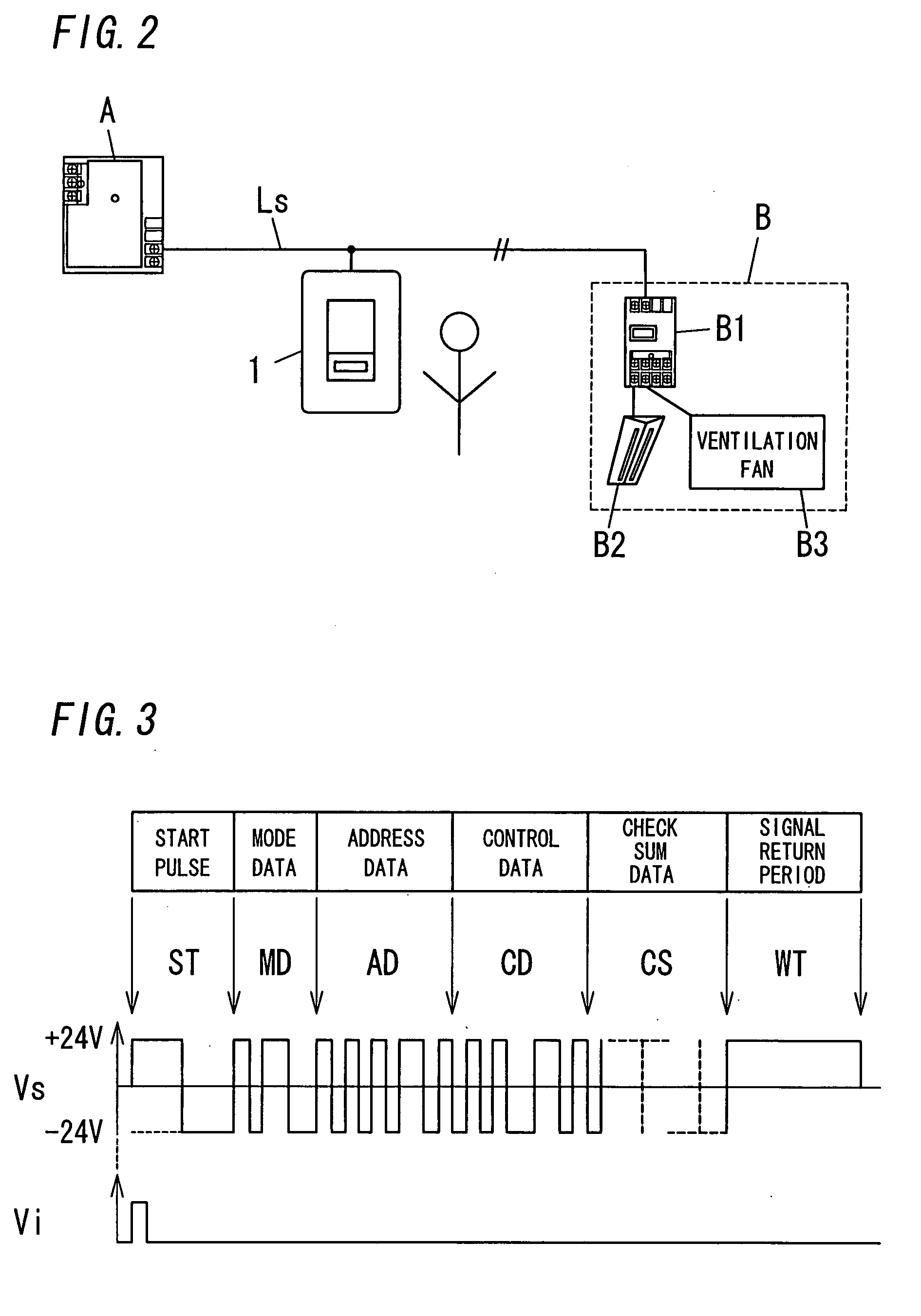
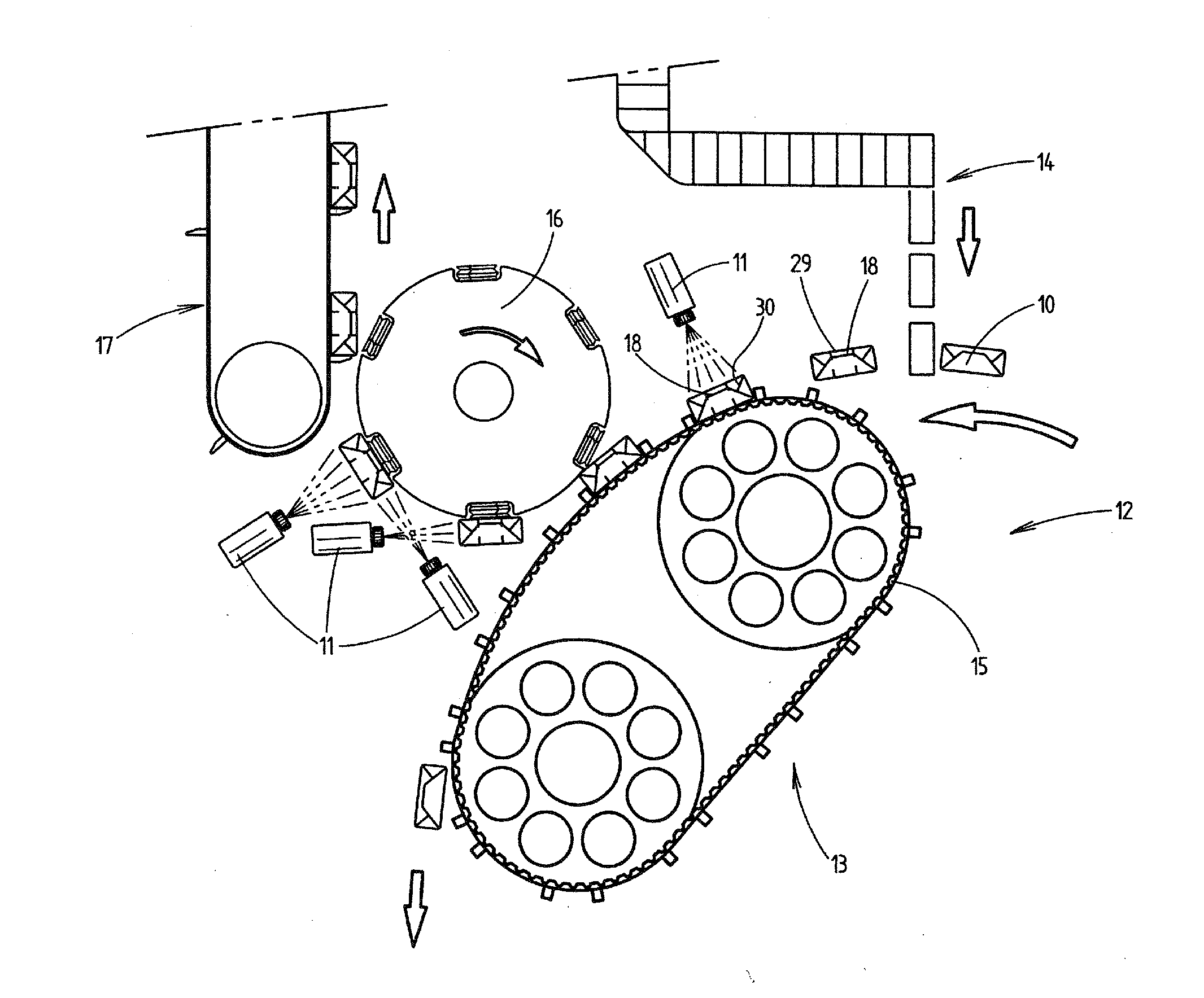
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80results about How to "Easily set" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for handoff to a femtocell in a wireless communication system, and server apparatus for the same
InactiveUS20120129537A1Reduce load and delayEasily setWireless communicationSignal strengthFemto base stations
A method handsoff a terminal to a femtocell in a wireless communication system. The method includes, upon generation of a request for handoff to the femtocell, selecting, by a second server, at least one femtocells located within a predetermined distance from a source base station as candidate femtocells for the handoff, according to a request of a first server which functions as a femtocell gateway, receiving, by the first server, a response message comprising information of the candidate femtocells from the second server, sending, by the first server, a message requesting measurement of a reverse signal strength of a terminal under the handoff to the candidate femtocells, determining, by the first server, a destination femtocell for the handoff among the candidate femtocells based on the measurement result reported from the candidate femtocells, and executing a handoff procedure to the destination femtocell from the source base station.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
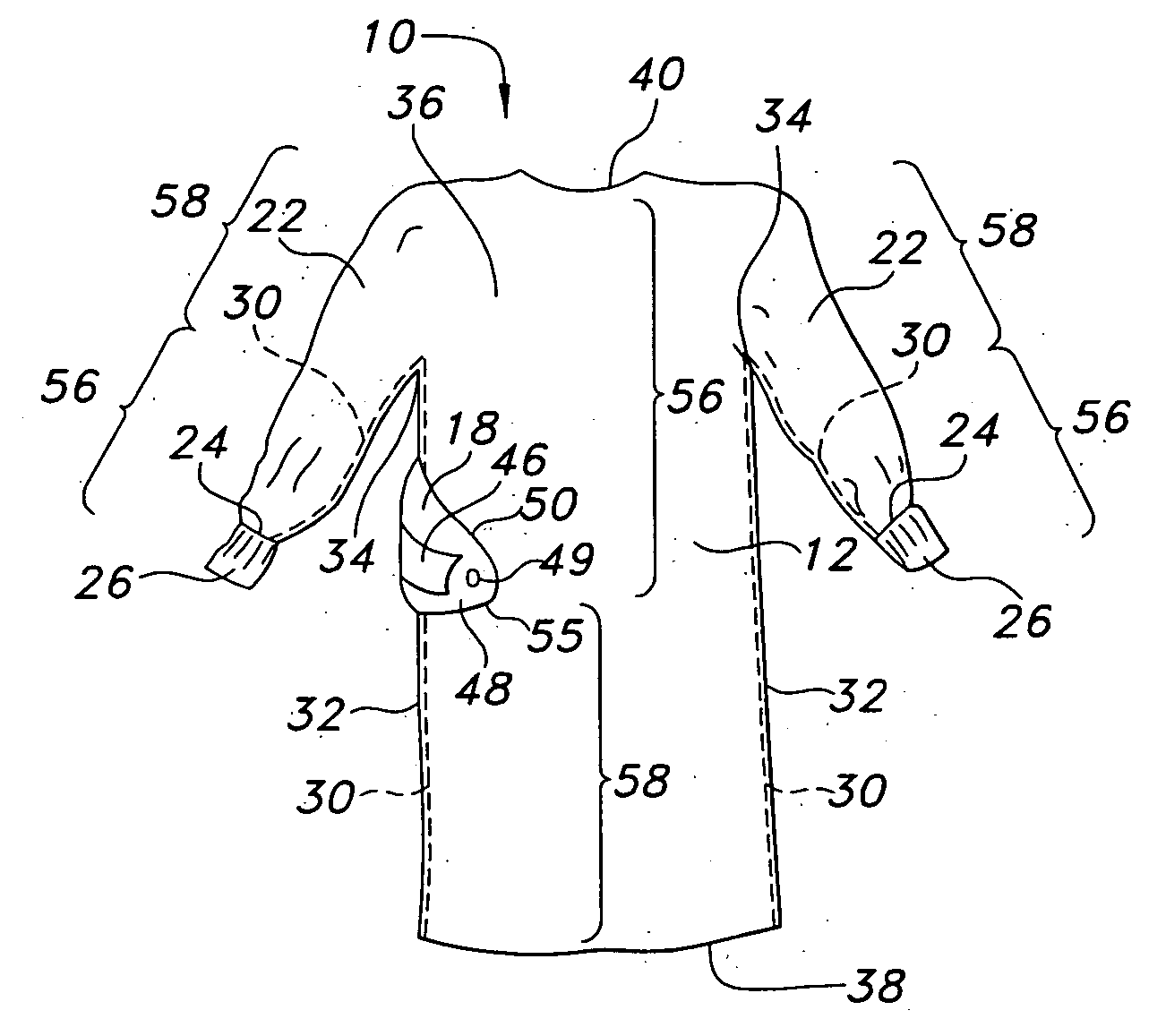
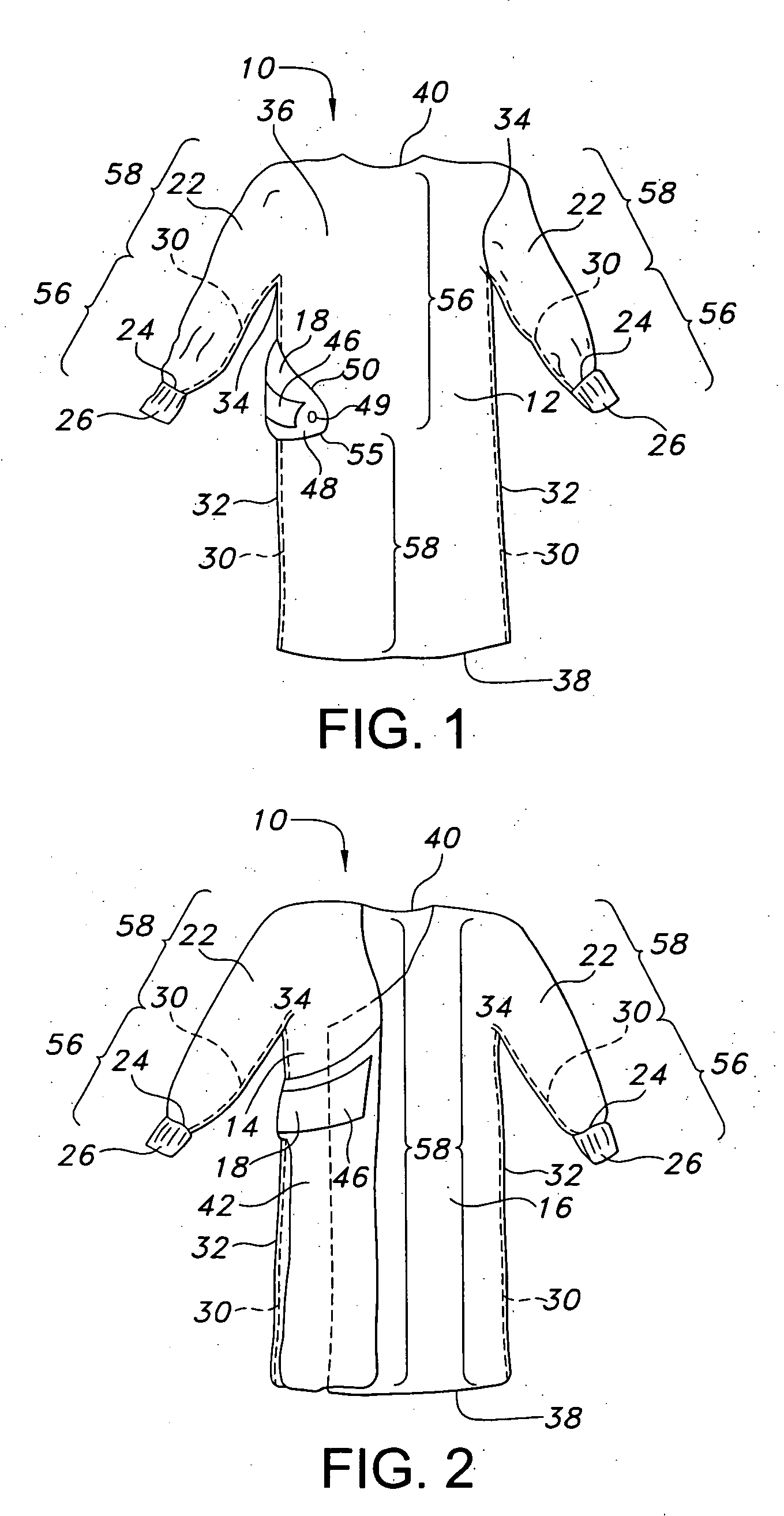
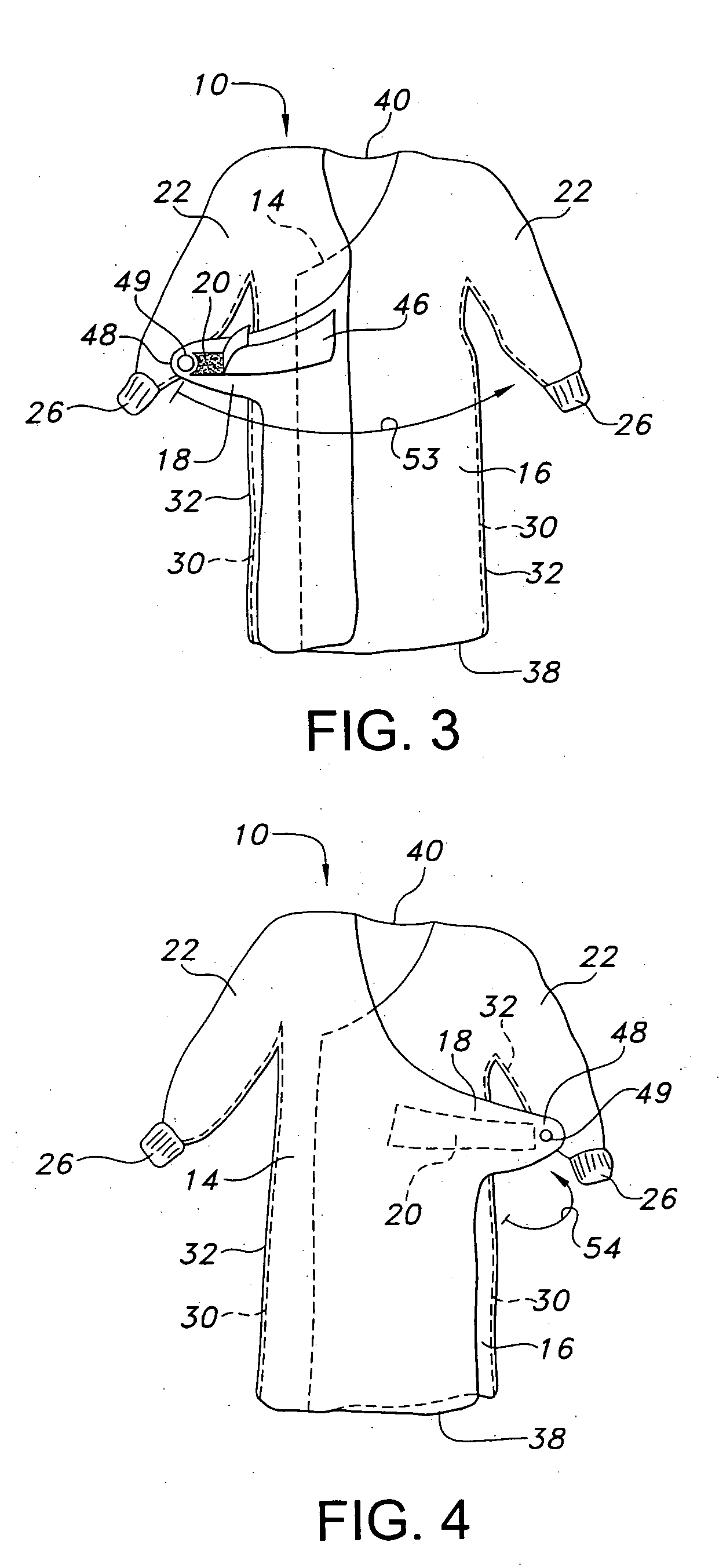
Surgical gown having an adhesive tab and methods of use
InactiveUS20050132465A1Easy to set upFacilitated releasePyjamasUndergarmentsSurgical GownsEngineering
A disposable surgical gown includes a front portion, a pair of sleeves, and first and second back portions. The first back portion includes an adhesive tab which extends from the first back portion to overlap at least a portion of the second back portion when the surgical gown is donned by a wearer. The adhesive tab is configured to overlap to adhere to the gown in a worn position. The adhesive tab includes a pull tab at a free end thereof to permit a wearer to grasp the pull tab to easily set and release the adhesive tab to and from the surgical gown.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
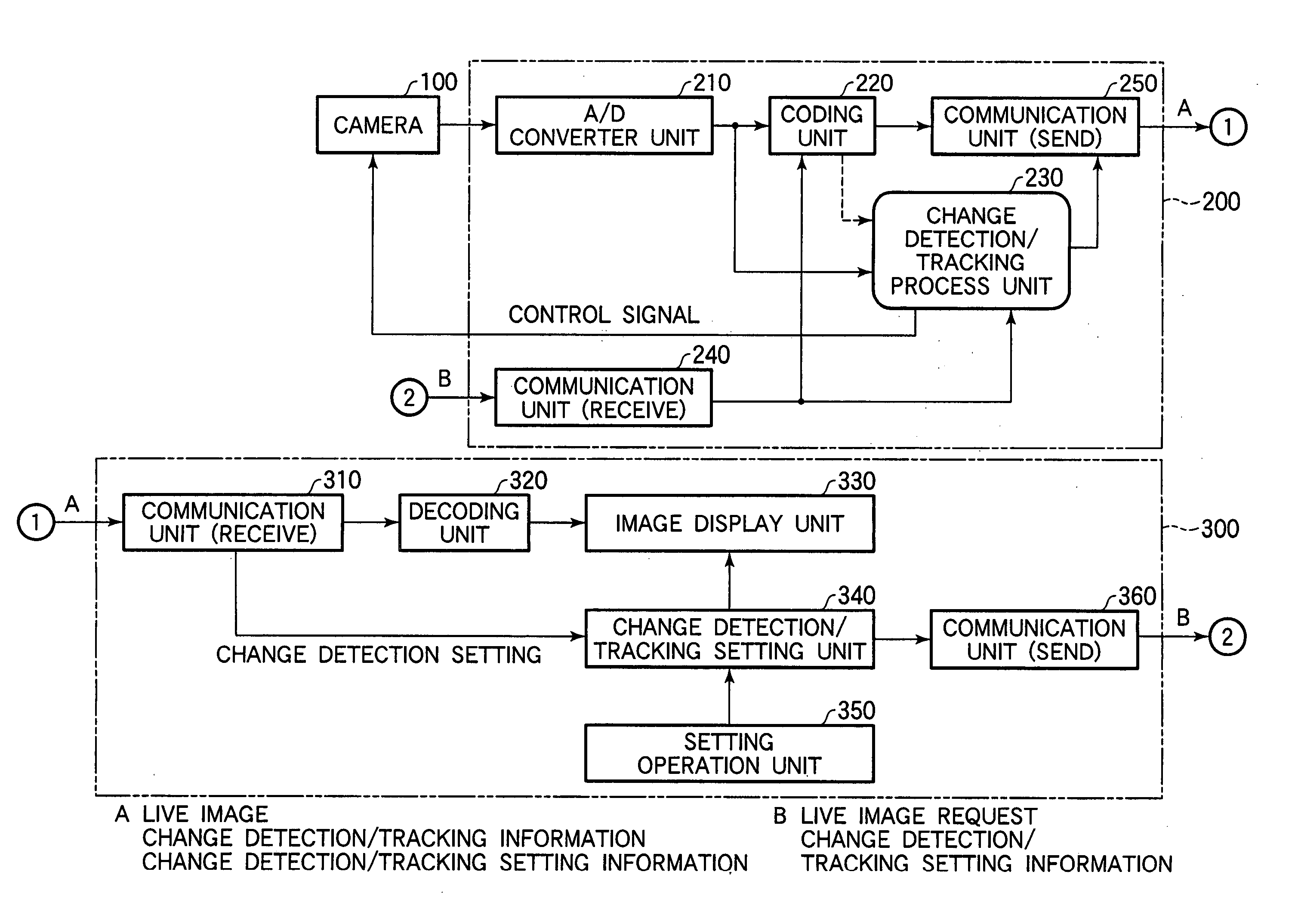
Monitoring system and setting method for the same
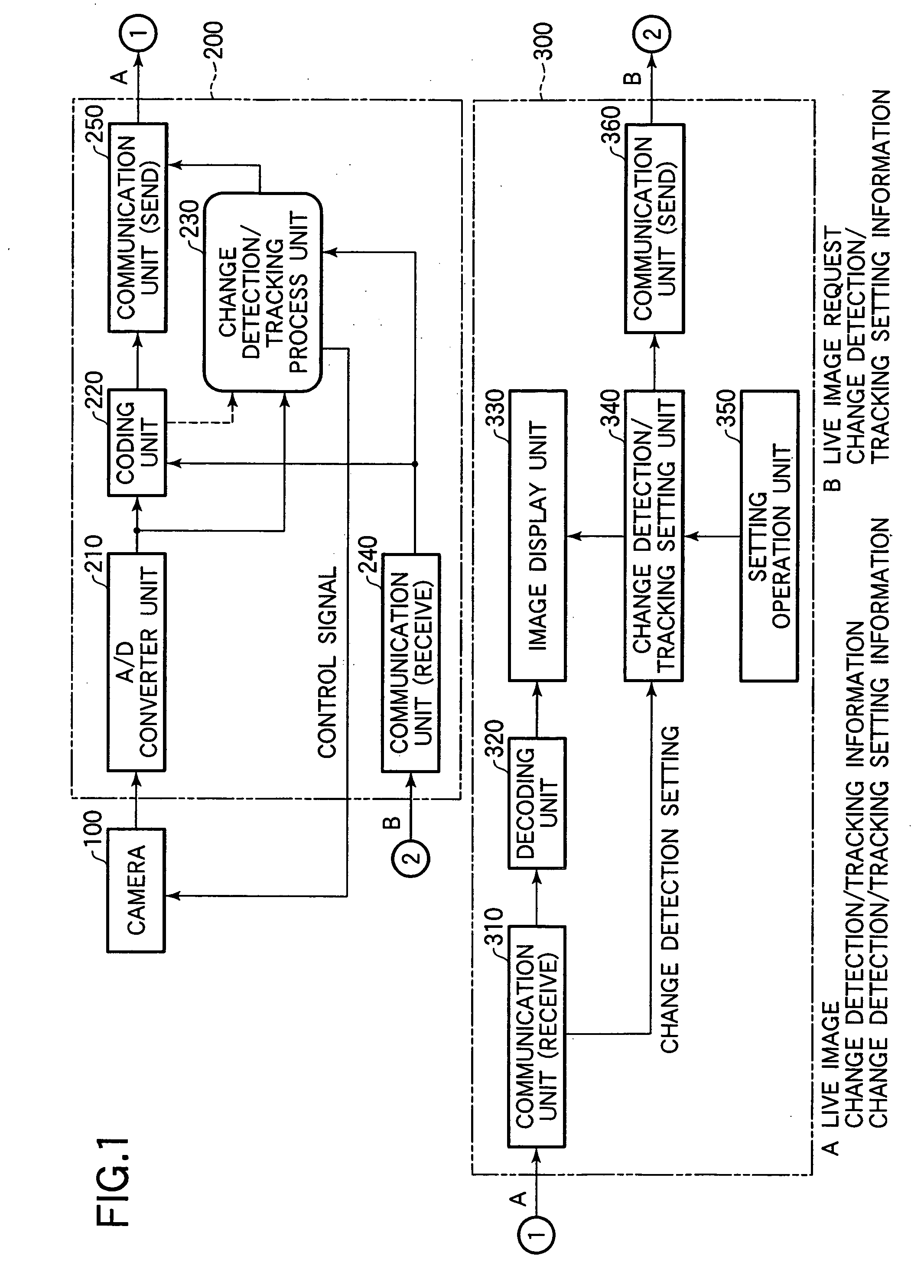
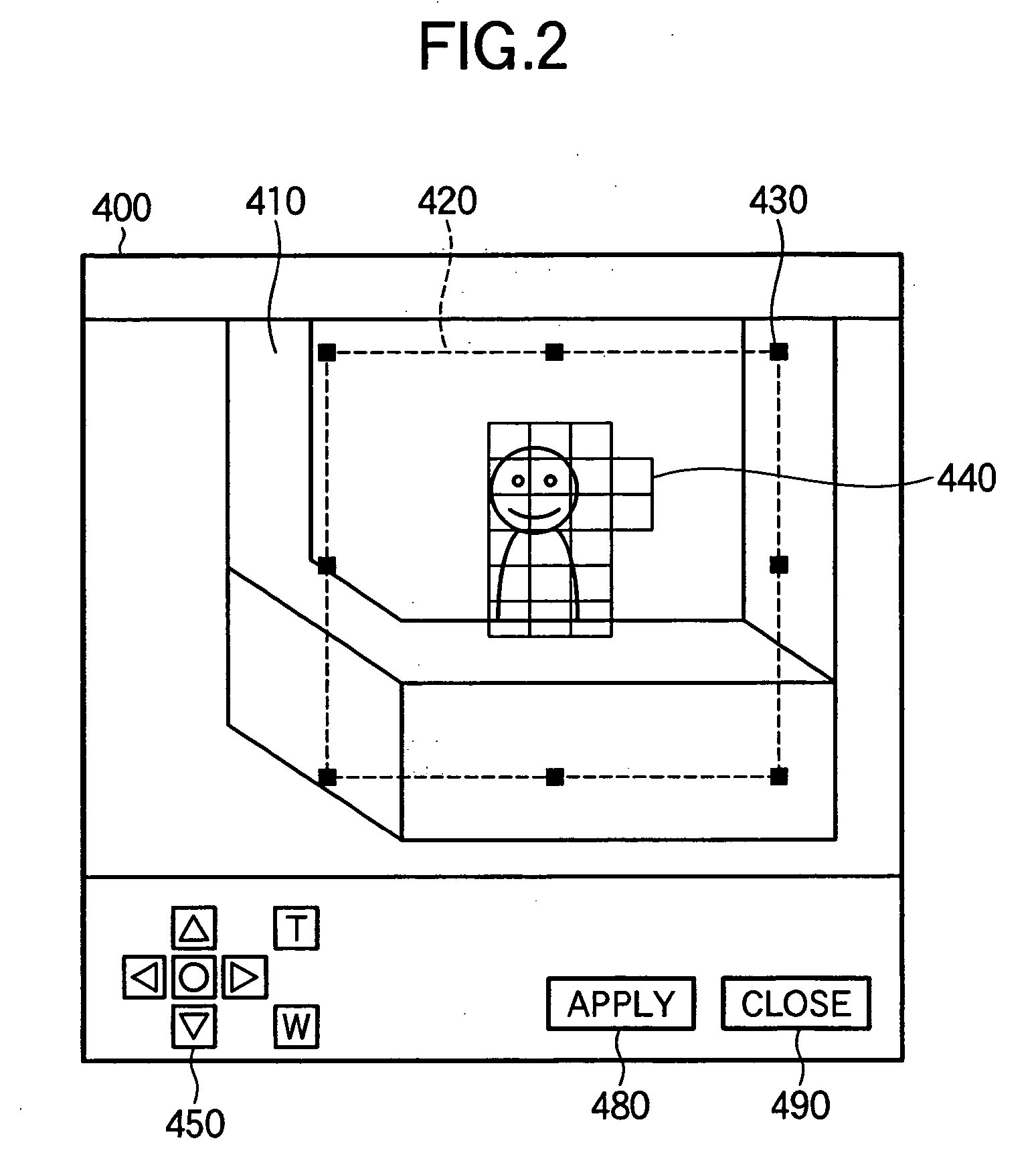
InactiveUS20050213793A1Easily setSimple processCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsComputer graphics (images)Video camera
In order to facilitate a setting of multiple parameters of a tracking function of a camera, in a setting window, an image display window is displayed in which a picked-up image sent from a camera server and an indicator indicating a change detection maximum area as a detection result of an image change detection process by the camera server are superimposingly on the picked-up image. In addition, in the setting window, a window is displayed in which a setting window is displayed which is used to make a setting of a tracking method by referring to an image displayed in the image display window.
Owner:CANON KK
Reinforced cation exchange membrane and production process thereof
InactiveUS20020034904A1Prevent leakageEasily setIon-exchange process apparatusOrganic diaphragmsPlain weaveCationic exchange
A cation exchange membrane wherein a plain weave reinforced cloth is embedded in a fluorinated polymer having a sulfonic acid group and / or a carboxylic acid group, characterized by possessing therein a tubular path which is formed in a direction of a warp and a weft of the plain weave reinforced cloth and has a cross section flat to a direction of thickness of the membrane.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Portable Containment Device and Method
InactiveUS20110056519A1Easily disposeEasily setFouling preventionBagsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CARD TOMMY JACK +1
Image forming method and apparatus, and host
InactiveUS20090006989A1Easy to set upEasily setSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsComputer graphics (images)Image formation
An image forming method and apparatus, and a host in which the image forming method includes setting a processing order of a plurality of operations of a same image data and detailed setup information of the plurality of operations, and executing the plurality of operations using the detailed setup information according to the set processing order.
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Internet radio receiver
InactiveUS20060168097A1Simple controlEasily setMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionStereophonic soundInternet radio
A device used specifically to play internet radio stations using a consistent method for interacting with websites, eliminating the need for a full computer with a keyboard, computer screen and / or mouse. The said device is capable of accessing internet radio websites through a wireless modem and basic internet software, playing and / or streaming from these websites using MP3 player software. The said device, using a simple, standardized format to interact with websites, streams the audio information, allowing it to be played through speakers, or an MP3 capable stereo or other electronic device. The said device can choose a particular internet radio station via a control panel, can preload stations and download software from a computer connection and has a rechargeable power source.
Owner:PITTELLI STEPHEN JOSEPH
Lighting device and lighting system
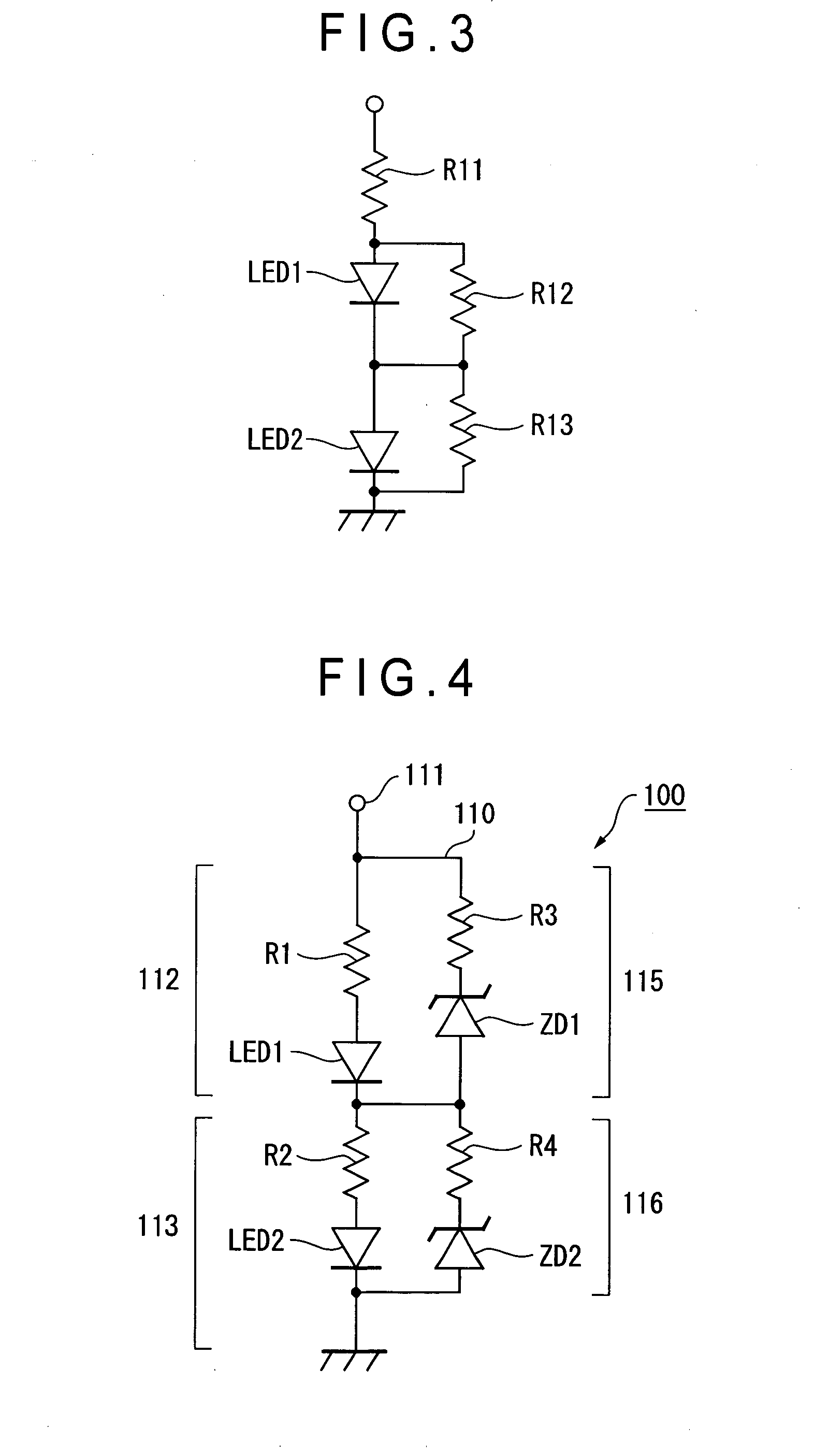
InactiveUS20050168162A1Easily setSimple configurationElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementLighting systemZener diode
First resistors (R1, R2) for setting a forward current value are connected in series to light-emitting diodes (LED 1, LED 2) respectively to constitute first serial circuits (112, 113), which are connected to an input terminal (111). Second serial circuits (115, 116) are connected in parallel to the first serial circuits (112, 113) respectively. The second serial circuits (115, 116) are constituted by a combination of a Zener diode (ZD1) and a second resistor (R3), and another combination of a Zener diode (ZD2) and a second resistor (R4). When a higher voltage than rated voltages of the light-emitting diodes (LED 1, LED 2) is applied, the Zener diodes (ZD1, ZD2) shunt current into the second serial circuit (115, 116) to allow the light-emitting diodes (LED 1, LED 2) to light up at desirable luminance levels different from each other. When a supplied power voltage decreases, current is not shunted, so that the same forward current flows through the light-emitting diodes (LED 1, LED 2), allowing the light-emitting diodes (LED 1, LED 2) to go off at the same timing.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Content use control device, reording device, reproduction device, recording medium, and content use control method
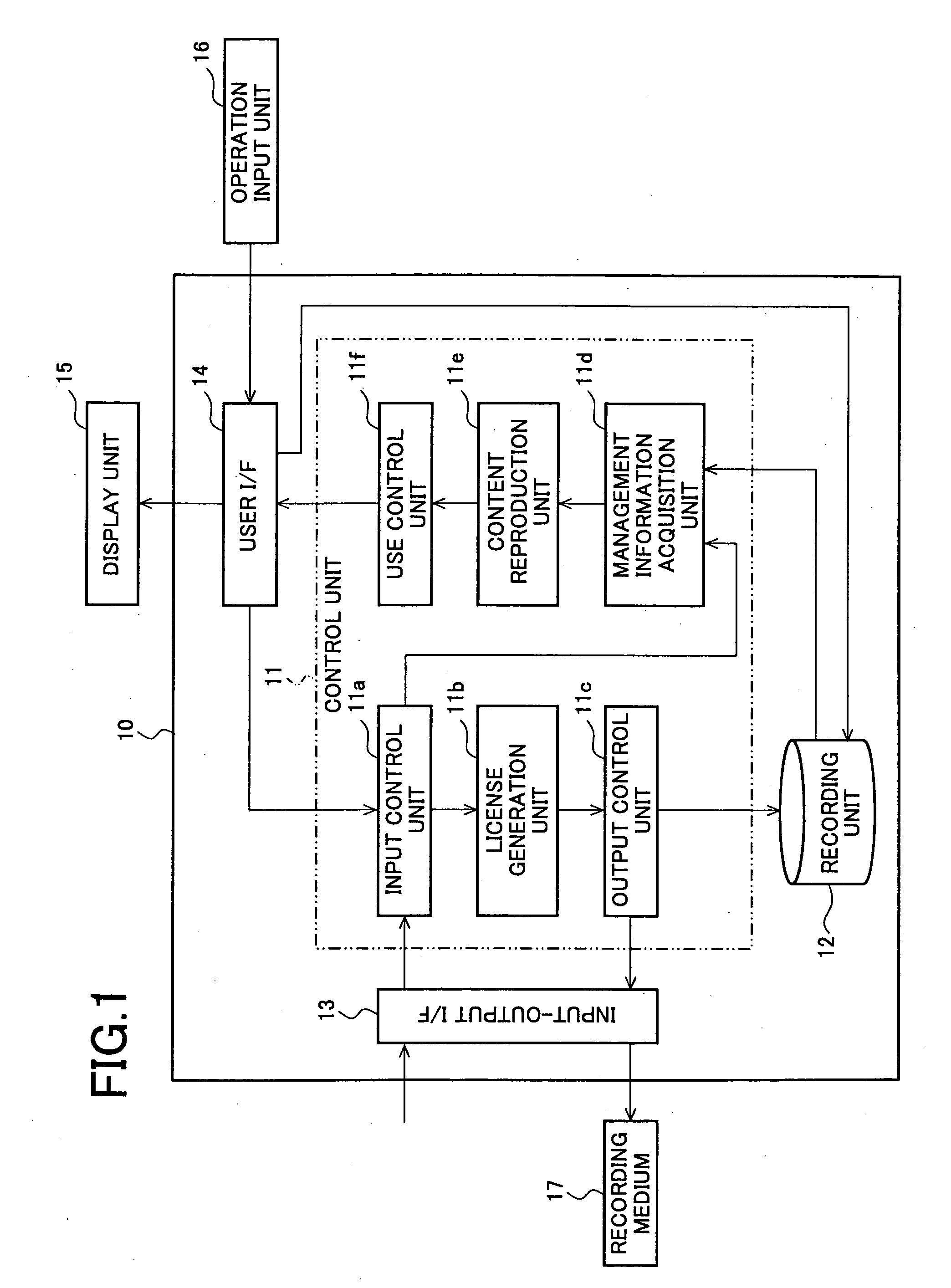
InactiveUS20070124251A1Prevent their useEasily setInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsInput/outputControl equipment
A collective content consisting of a plurality of partial contents holding license information including a use condition can be appropriately used according to the use condition contained in the license information in each of the partial contents. A content use control device includes an input / output I / F, license generation unit, output control unit, content reproduction unit, and use control unit. The partial content holding the license information including the use condition is inputted via the input / output I / F. License information is assigned to each of the partial contents inputted and constituting a collective content. Single license information collecting the assigned license information and its collective content are outputted to a recording medium. The content use control device reproduces a partial content contained in the collective content recorded on the recording medium and controls the use of the reproduced partial content according to its use condition.
Owner:SHARP KK
Lubricating system for a vehicle power unit
InactiveUS20070272196A1Accurately restrictEasily setLubrication of auxillariesGearboxesPower unitEngineering
A lubricating system for a vehicle transmission is provided by which the transmission is effectively lubricated, without increasing the number of component parts. The transmission includes an input shaft, an intermediate shaft and an output shaft, each of which are contained in the inside of a power unit case. The intermediate shaft has with an axially extending oil passage that establishes communication between both opposed ends of the intermediate shaft such that one end of the intermediate shaft permits communication between the axial oil passage and a first oil passage formed in a first case half, and a second end of the intermediate shaft permits communication between the axial oil passage and a second oil passage formed in a second case half. The intermediate shaft also includes radial oil passages extending radially outward from the axial oil passage and opening in an outer peripheral surface thereof.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
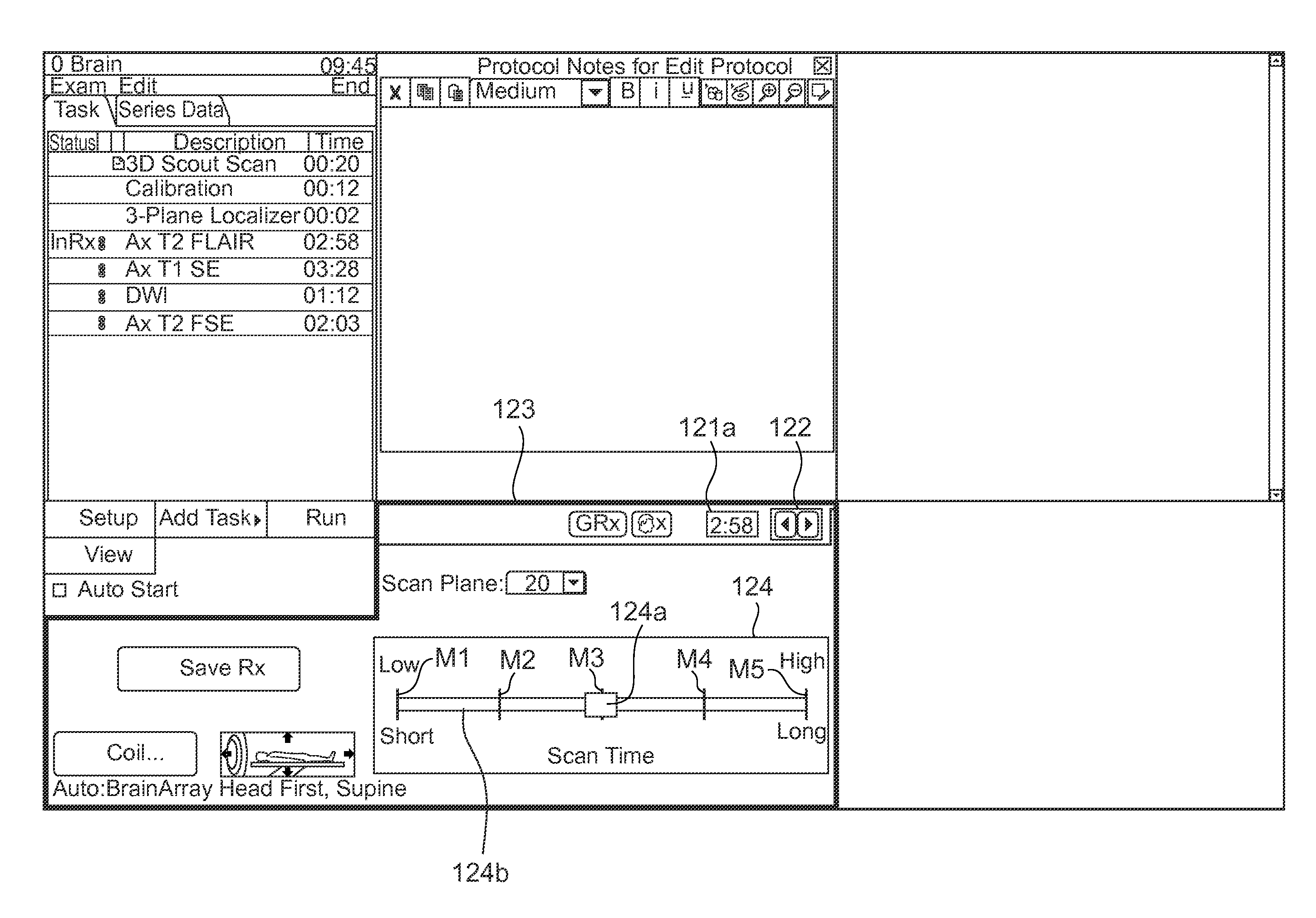
Scan conditioning setting apparatus, medical apparatus and method of setting scan condition
InactiveUS20110113376A1Easily setEasy to set upMagnetic measurementsInput/output processes for data processingScan timeImaging quality
A scan condition setting apparatus sets a scan condition used upon scanning a subject. The apparatus includes a selection device having a plurality of combinations of scan times and image quality and selecting one from within the combinations according to a manipulation of an operator, and a scan condition storage device for storing scan conditions corresponding to the combinations of the scan times and image quality therein. The scan condition corresponding to the combination of the scan times and image quality selected by the selection device is set as the scan condition used when the subject is scanned.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Information display device
ActiveUS20090040357A1Quickly and easily setEasily setTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMedical physicsImaging Signal
The present invention provides an information display device including an imaging unit that executes an imaging process to image a subject to output an imaging signal; a monitor capable of displaying an image of the subject based on the imaging signal; a switching part located near the monitor; a first display controller for displaying, in a menu on the monitor, each of a first group of items consisting of a plurality of items associated with the imaging process, whereby first setting data can be set; and a second display controller for displaying, in a menu on the monitor, each of a second group of items associated with a plurality of particular items in the first group and having fewer items than the first group, whereby second setting data can be set, wherein switching between the first and second display controllers is performed by operating the switching part.
Owner:XACTI CORP
Material handling assembly
InactiveUS20070289173A1Easy constructionEasy to installMechanical machines/dredgersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A material handling assembly is described herein. The material handling assembly provides an assembly mountable on the articulated arm of the machine consisting generally of a bucket pivotally connectable to the articulated arm of the machine and the means for pivoting the bucket about the pivotal connection of the bucket to the articulated arm, an arm member pivotally connectable to the articulated arm and cooperable with the bucket when mounted on the articulated arm for clamping material being handled therebetween, a bracket mountable on the articulated arm, a strut having a first end thereof pivotally connected to the arm member and second end thereof received within and displaceable along the bracket, and means for detachably securing the second end of the strut to the bracket at selected points along the length of the bracket in a safe and efficient manner.
Owner:MILLONZI INT PRODS GROUP
Communication system having management apparatus and user apparatus, management apparatus, user apparatus, and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS20110040862A1Easily setEasy to set upDigital computer detailsData switching networksStorage cellServer appliance
To facilitate account information setting, in a communication system including a management apparatus which manages account information to be used to use a service provided by a server apparatus, and a user apparatus which uses the service, the management apparatus selects, based on device classification information acquired from the user apparatus, account information to be provided to the user apparatus from one or more pieces of account information stored in a storage unit, and provides the account information to the user apparatus. The user apparatus sends the device classification information of the user apparatus to the management apparatus, receives, from the management apparatus, the account information selected based on the device classification information, and uses the service provided by the server apparatus.
Owner:CANON KK
Electric shaver
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Function setting method for a control panel of an exercise equipment
InactiveUS20130015945A1Easily setEasy to set upComputer controlStatic indicating devicesExercise equipmentEngineering
A function setting method for a control panel of an exercise equipment combines buttons of the control panel with a light source, which makes it easy for the user to tell which button needs to be pressed when the user is setting functions since the button that needs to be pressed has a turned-on backlight, namely, it turns on the button that needs to be pressed to guide the user to press, so as to reduce the possibility of pressing the wrong button and enable the user to use the control panel in a dim environment.
Owner:P & F BROTHER INDAL
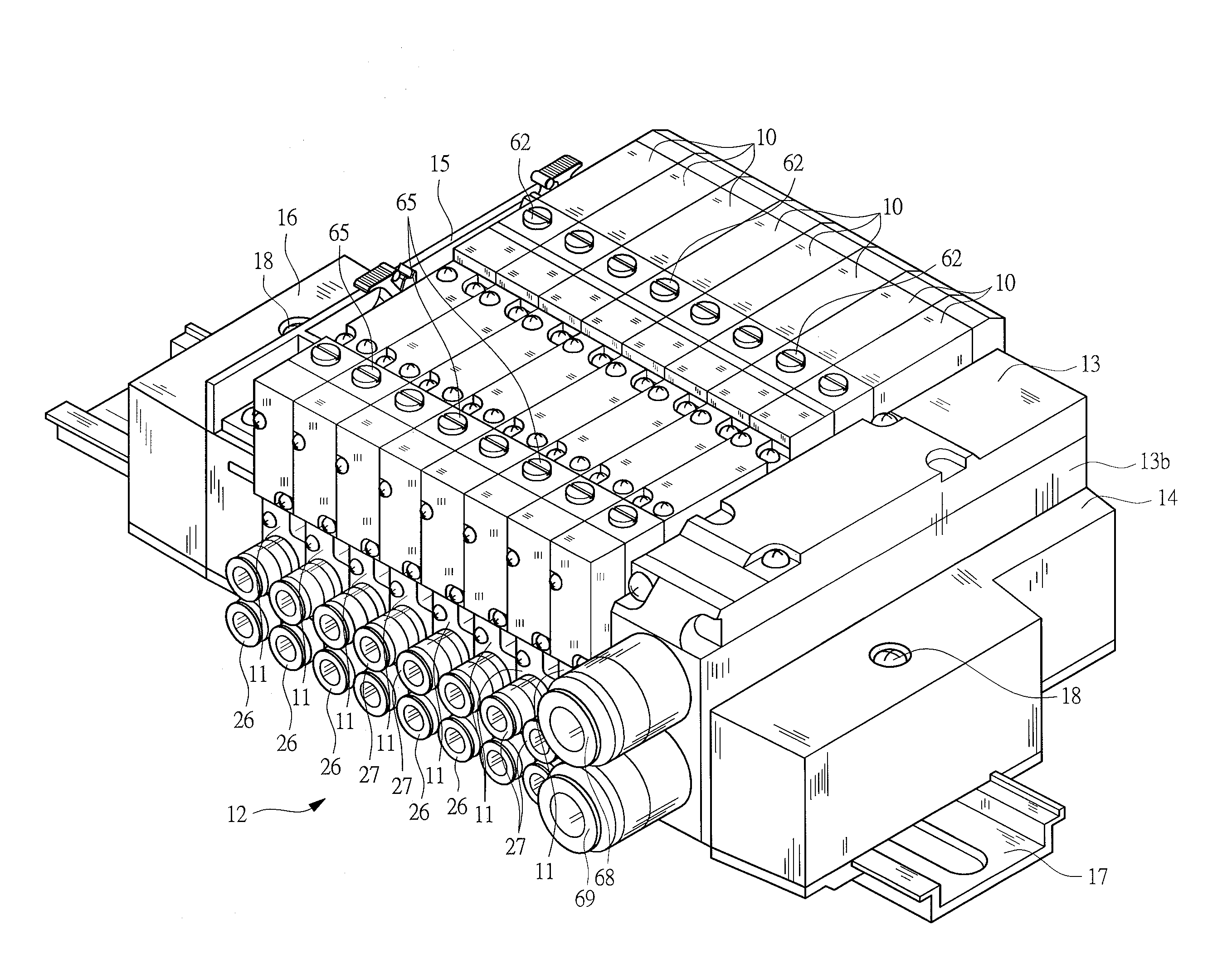
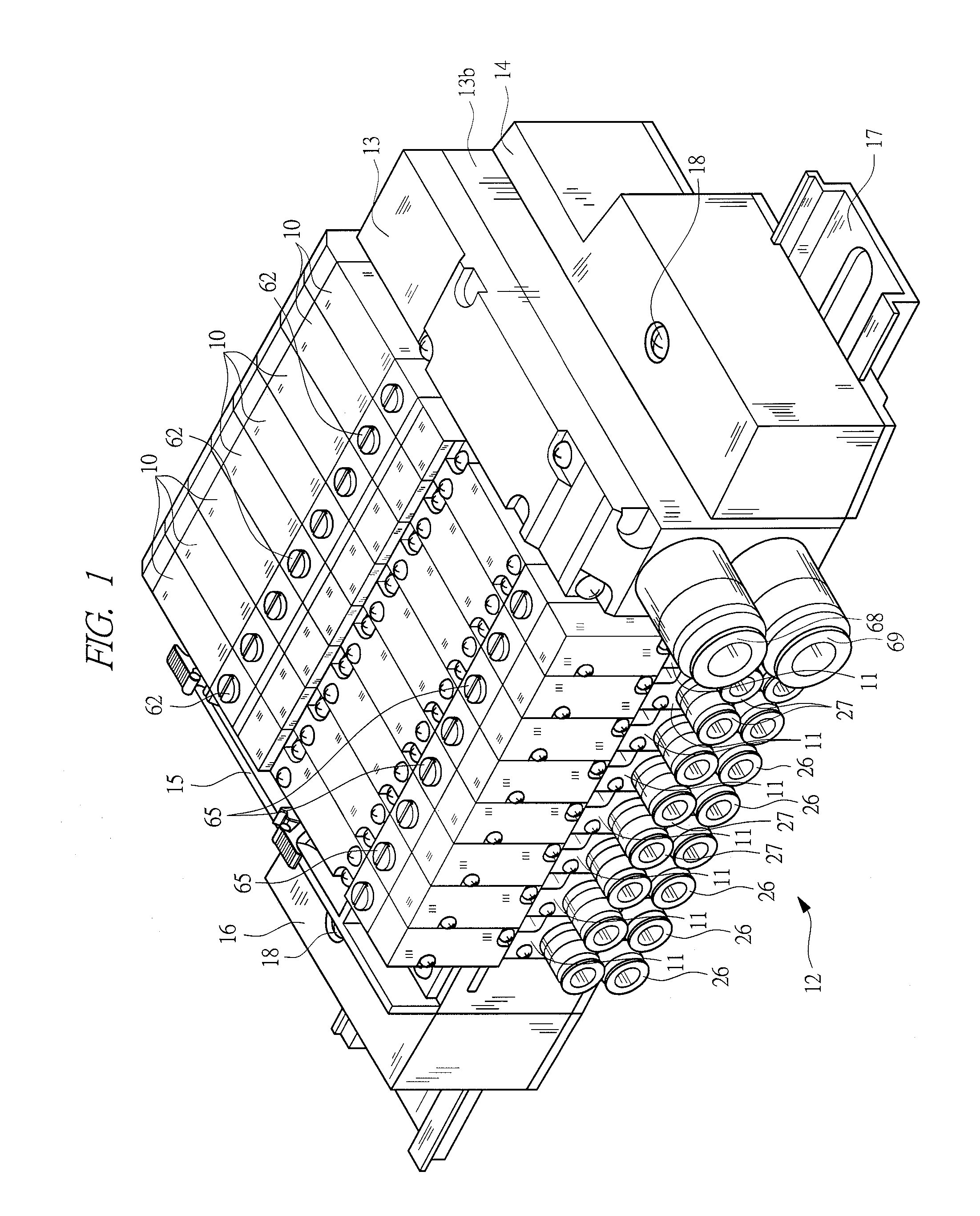
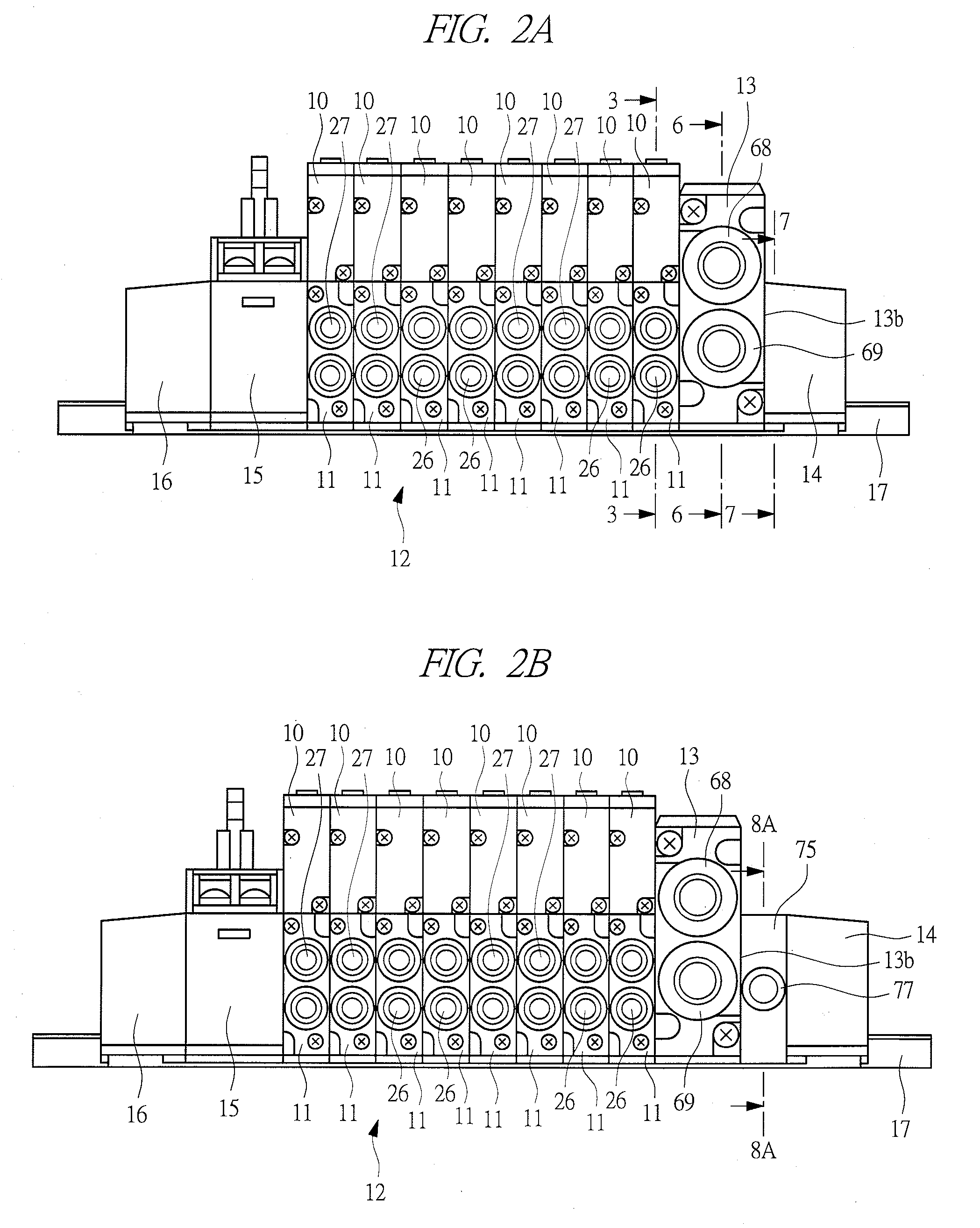
Manifold solenoid valve
InactiveUS20090212247A1Easily setEasy to set upOperating means/releasing devices for valvesServomotor componentsAerospace engineeringVALVE PORT
A plurality of valve assemblies are provided to a base, and an air-supply flow path for supplying compressed air to each valve assembly is formed in the base. A main flow path communicating with the air-supply flow path and communicating with a pilot air-supply flow path is formed in an air supply block. When the compressed air is supplied to the air-supply flow path and the pilot air-supply flow path from the main flow path, a manifold solenoid valve becomes an internal pilot type. An external pilot flow path communicating with the pilot air-supply flow path is formed in an external pilot block, and when the external pilot block is provided, communication between the main flow path and the pilot air-supply flow path is shut off, and the manifold solenoid valve becomes an external pilot type in which the pilot pressure is supplied from the external pilot flow path.
Owner:KOGANEI
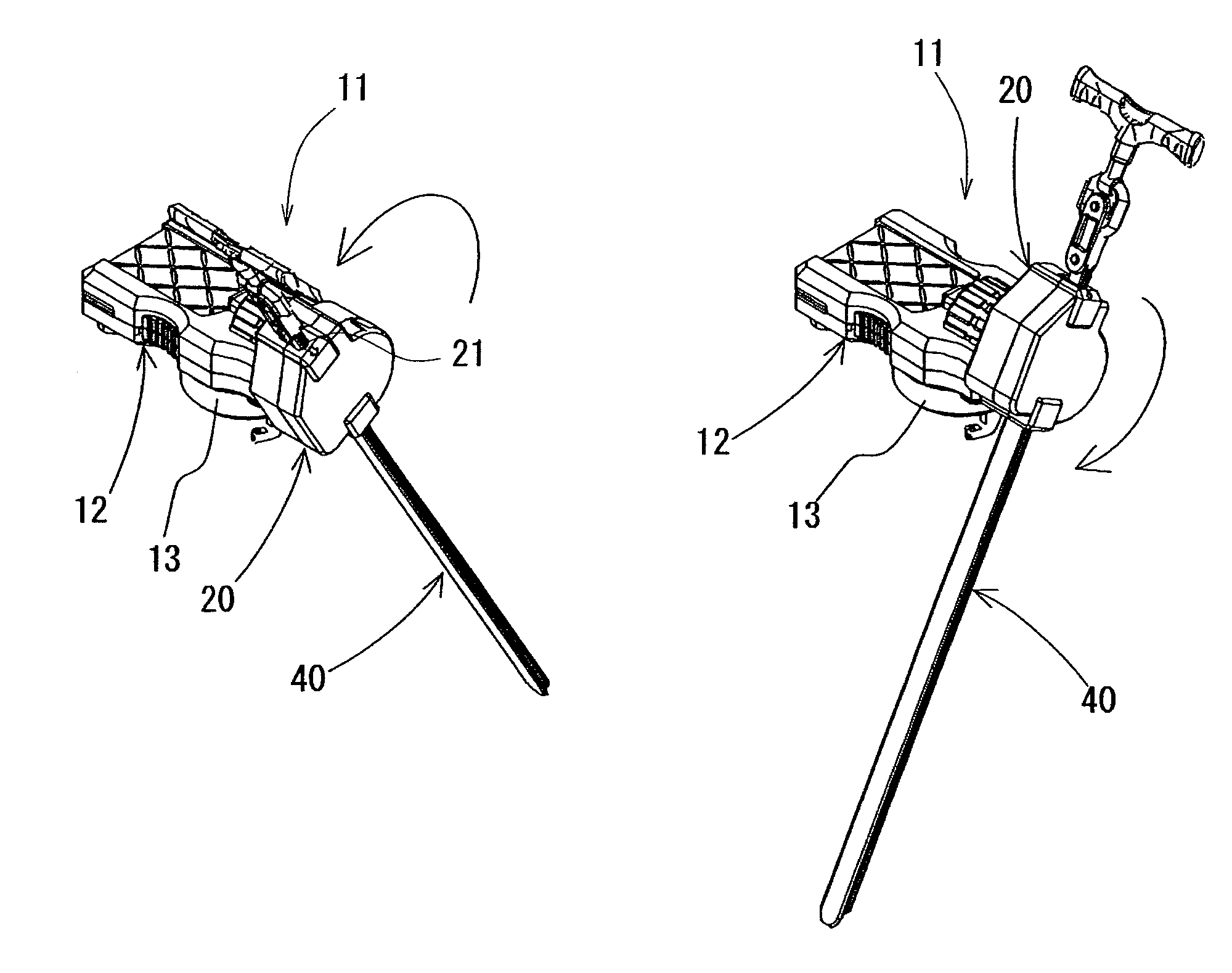
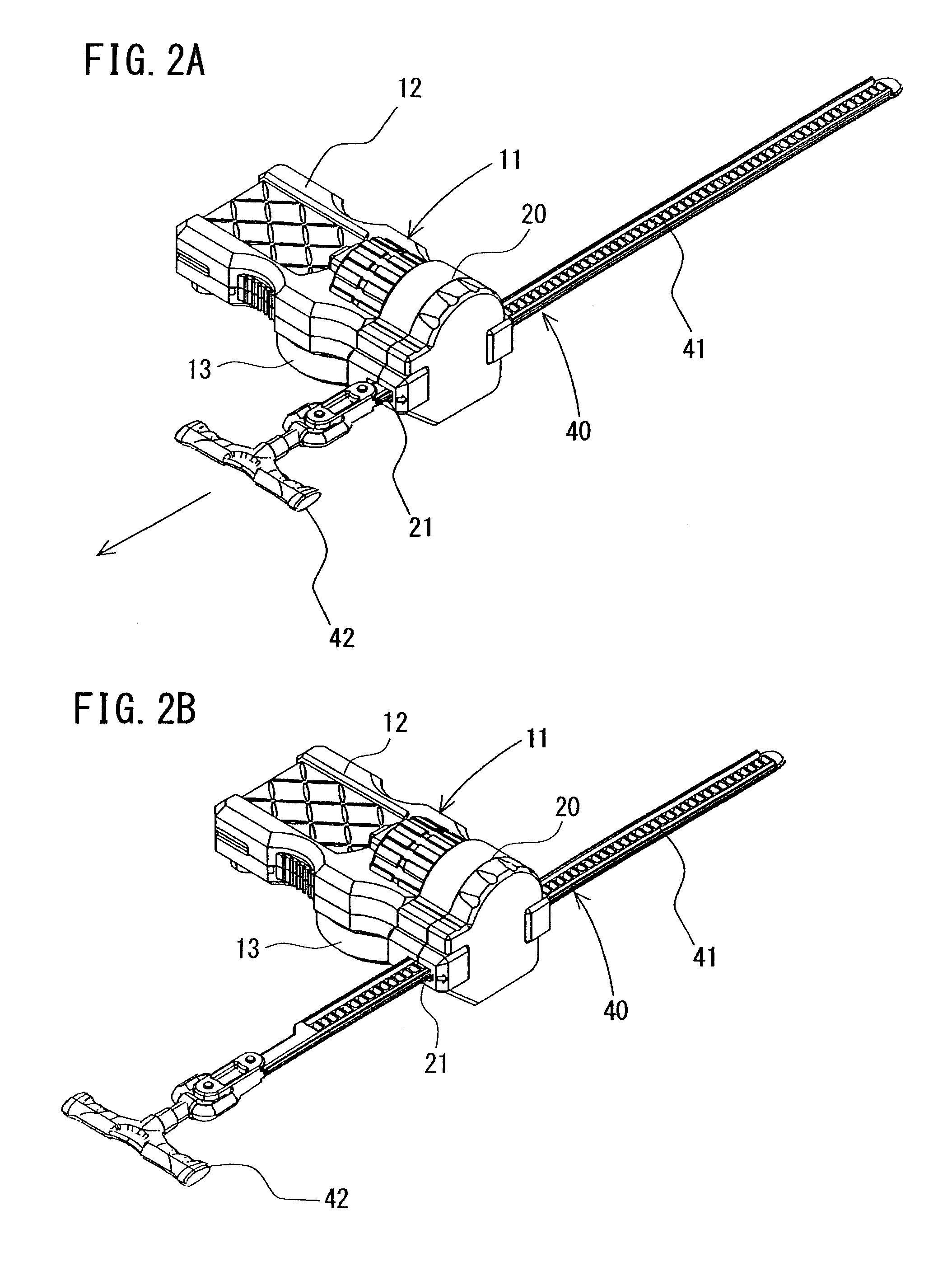
Spinner for toy top
A spinner for a toy top enables a launching position of a toy top to be easily set and held in place even when a rack belt is vigorously pulled out. The spinner includes an elongated rack belt having a rack gear, and a spinner main body formed with an insertion hole through which the rack belt is inserted. The spinner main body includes a toy top mounting part rotatably provided on one surface thereof. Inside the spinner main body, a rotating mechanism that is actuated by pulling out the rack belt to impart a rotational force to the toy top mounting part is provided. The rack belt can be inserted into and pulled out from the insertion hole in a same direction an axis of rotation of the toy top mounting part.
Owner:TOMY CO LTD
Spinner for toy top
A spinner for a toy top enables a launching position of a toy top to be easily set and held in place even when a rack belt is vigorously pulled out. The spinner includes an elongated rack belt having a rack gear, and a spinner main body formed with an insertion hole through which the rack belt is inserted. The spinner main body includes a toy top mounting part rotatably provided on one surface thereof. Inside the spinner main body, a rotating mechanism that is actuated by pulling out the rack belt to impart a rotational force to the toy top mounting part is provided. The rack belt can be inserted into and pulled out from the insertion hole in a same direction as an axis of rotation of the toy top mounting part.
Owner:TOMY CO LTD
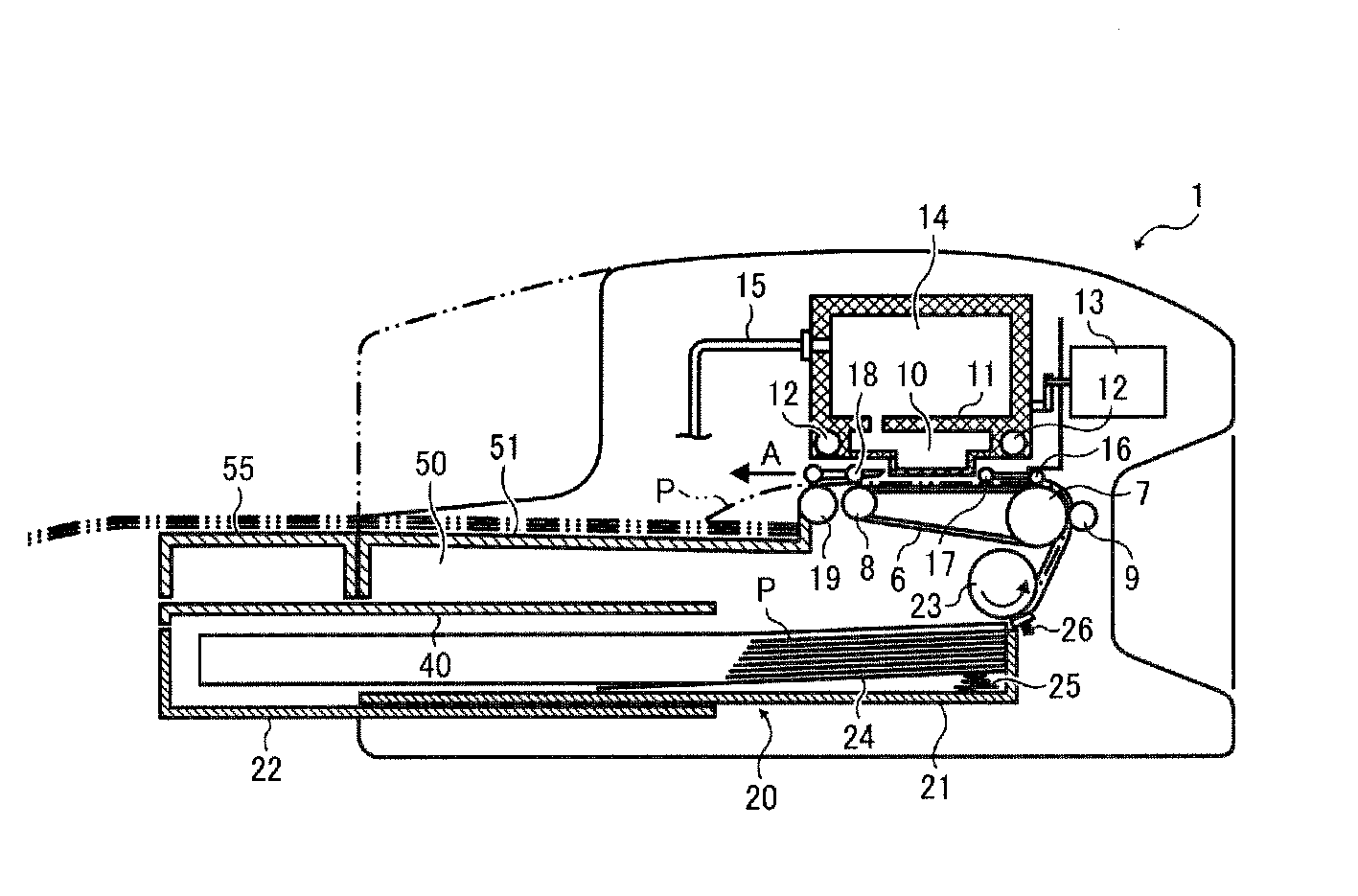
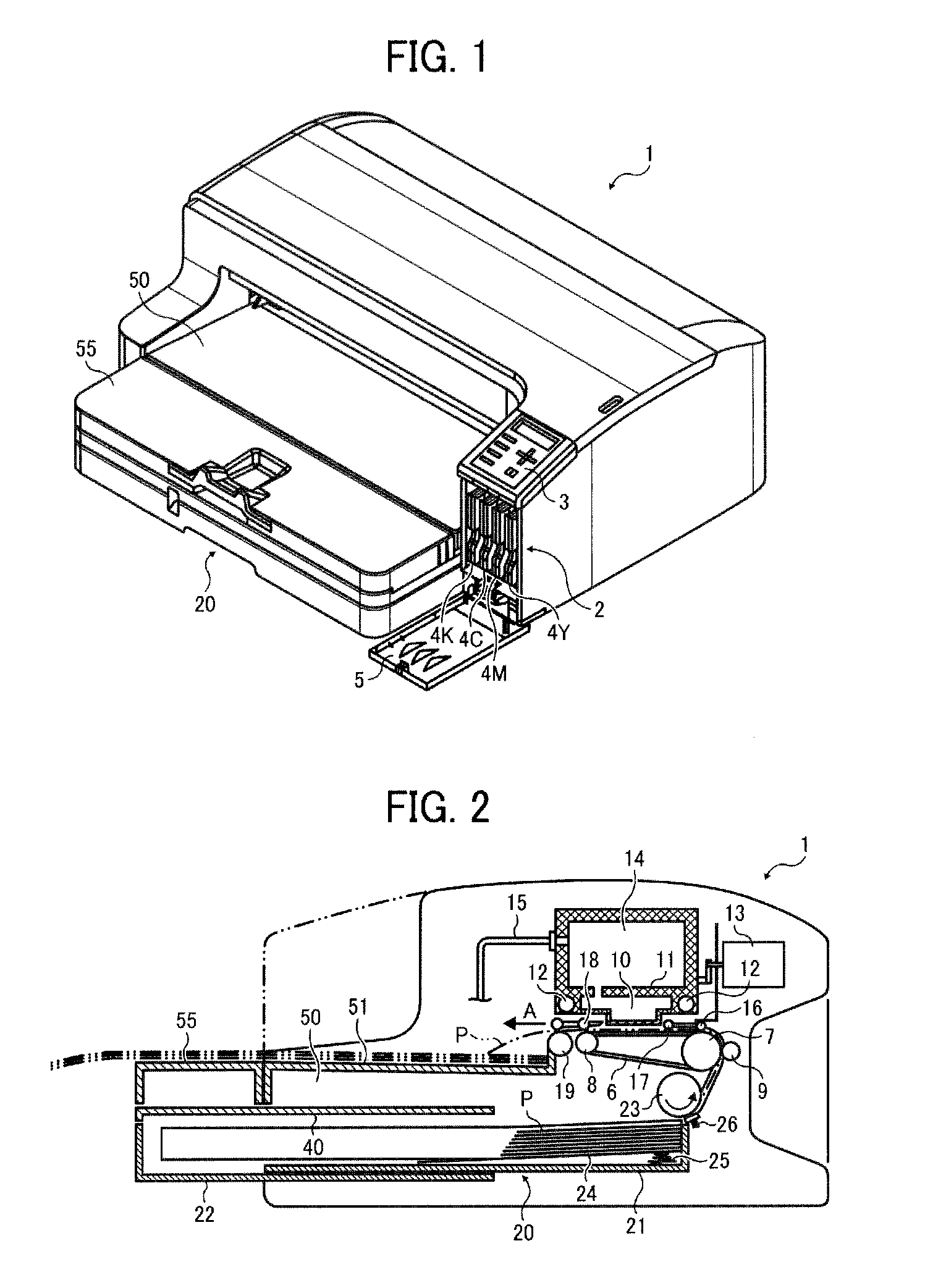
Image forming apparatus
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Audio output control device and audio output control method
InactiveUS20090136060A1Easily setEasy to set upTelevision system detailsGain controlExecution controlLoudspeaker
Owner:SONY CORP
Universal adjusting mechanism for tripods
Owner:KU HENG CHUN
Method for adjusting image-quality and display unit enabling the same
ActiveUS20110069081A1Easily setEasy to set upCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Imaging quality
A method of displaying images, which includes displaying a first image in a first display portion, receiving a first image-quality condition for setting a first image quality of the first image displayed in the first display portion, generating, via a first display controller of the first display portion, a first image-quality setting image by applying the first image-quality condition to the first image displayed in the first display portion, transmitting the generated first image-quality setting image from the first display controller to a second display controller of a second display portion, and displaying the transmitted first image-quality setting image on the second display portion.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Image processing apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20070146752A1Easily setEasy to set upDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor processingHue
This invention provides a sample print which allows the user to easily set color adjustment parameters. To this end, upon outputting images which undergo color processing using a plurality of different parameter sets, a sample print mode of parallelly outputting a reference image and images which have different parameter sets of the image processing from the reference image, and are arranged around the reference image, and a sample print mode of parallelly outputting the reference image which is arranged at a corner of an image group including images in a specific hue direction, and images which have different parameter sets of the color processing from the reference image and are arranged between the corner and other corners, are prepared.
Owner:CANON KK
Infrared sensor switch
ActiveUS20070241896A1Easy to adjustEasy to checkElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesHorizontal axisEngineering
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and device for visually inspecting objects to be tested during the production and/or packaging of cigarettes
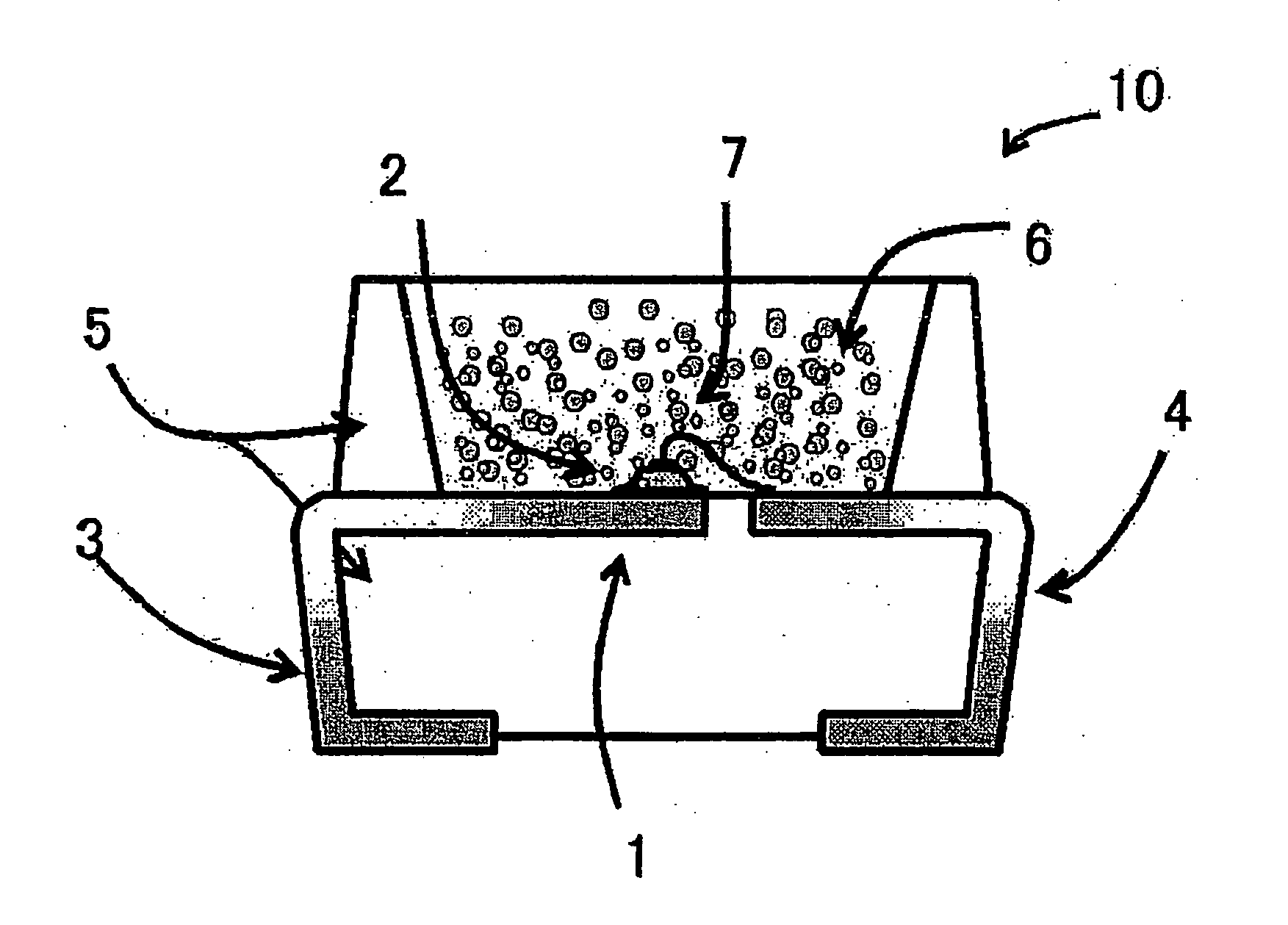
ActiveUS20140226892A1Simplify settingEasily setImage enhancementImage analysisCigarette packTest object
A method and a device for the optical testing of objects during the production and / or packaging of cigarettes, in particular of cigarette packs and / or blanks for cigarette packs and / or overprints and / or print substrates on or for cigarette packs, with the aid of a suitable testing device. For at least one feature characterizing the test object, in particular in a visual respect, a set of feature-value alternatives for the corresponding feature that are stored in a memory is displayed on a display means. By means of an input device, one of the displayed feature values of the set of feature-value alternatives is selected. The testing device is automatically set up or preset for the subsequent testing operations, in particular an evaluating device and / or an illuminating device and / or a suitable light detector of the testing device, the selection of the feature value influencing the setting up of the testing device.
Owner:FOCKE & CO (GMBH & CO KG)
Image forming apparatus
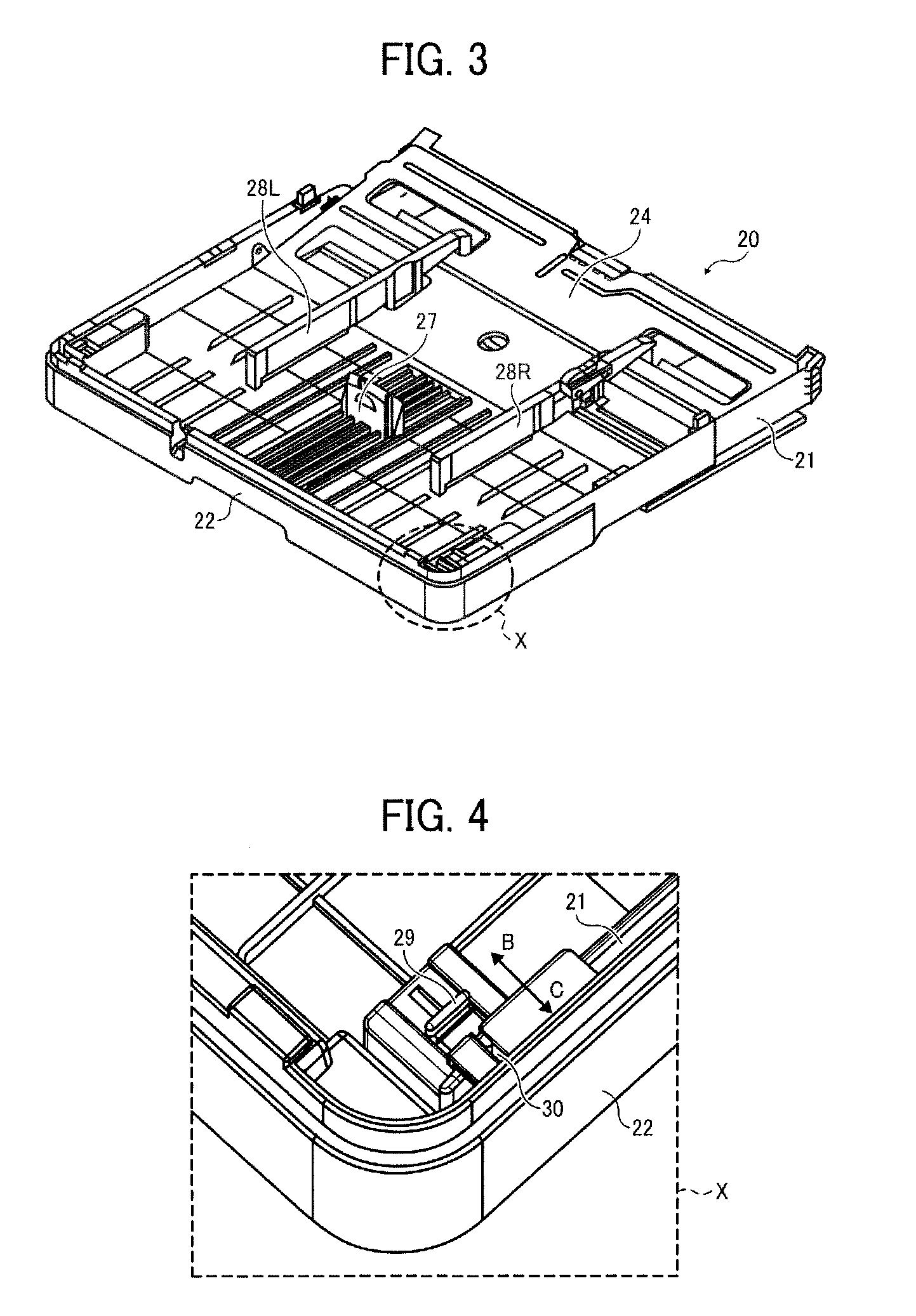
An image forming apparatus including a sheet feed cassette to hold a stack of recording media, a cover detachably attachable to the sheet feed cassette to cover an opening of the sheet feed cassette through which the recording media are supplied, an image forming part to form images on the recording media, and a discharge tray having a top surface on which the recording media discharged from the image forming apparatus after image formation are stacked. The sheet feed cassette is disposed below the discharge tray and is contractibly extendable, protruding outwardly from the image forming apparatus to accommodate large-sized recording media in its extended state. The cover includes a displaceable discharge auxiliary member slidable against the cover so as to be flush with the top surface of the discharge tray and detachably attachable to the sheet feed cassette together with the cover.
Owner:RICOH KK
Light emitting apparatus, liquid crystal display apparatus and lighting apparatus
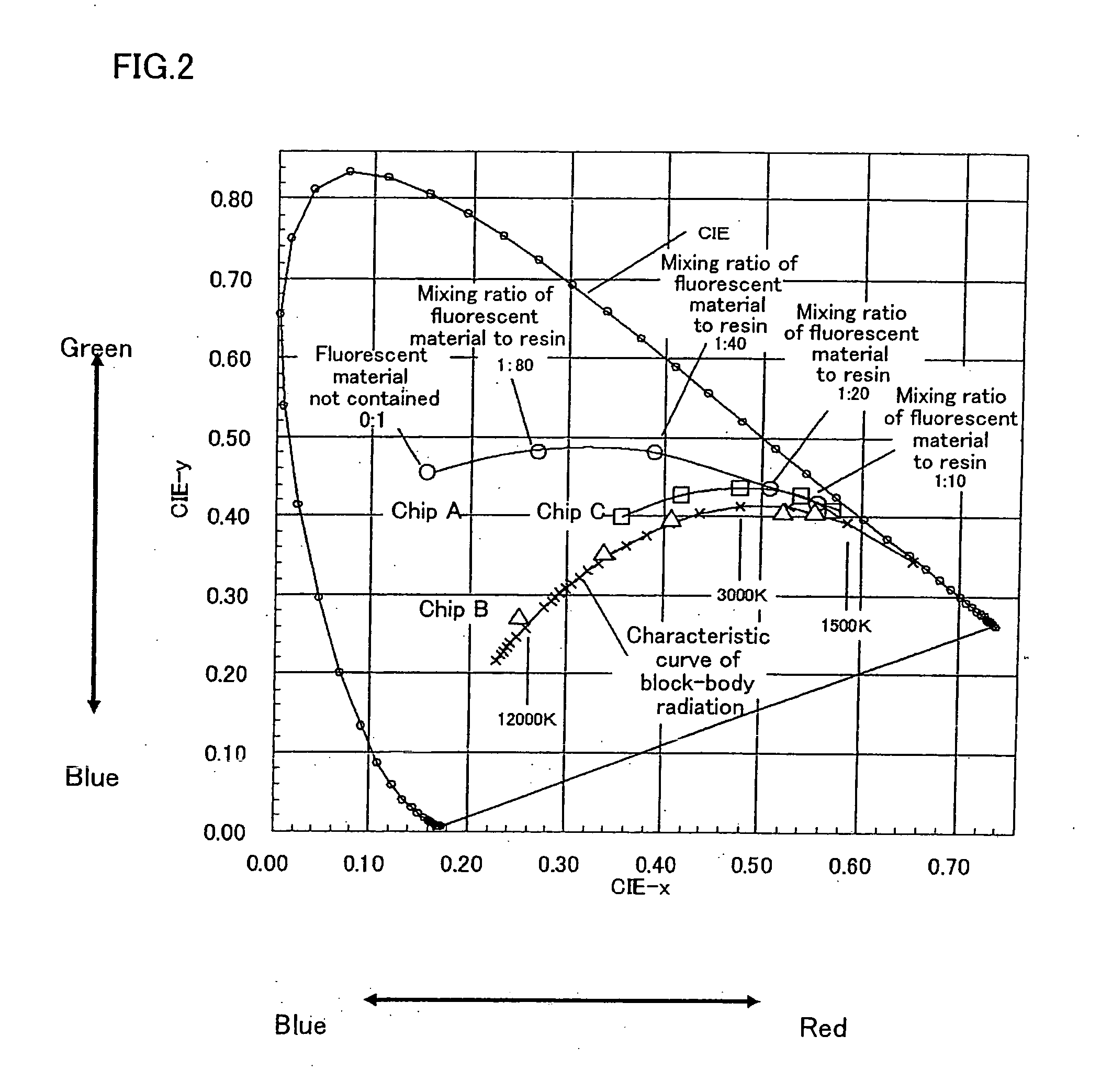
InactiveUS20060255712A1Easy to controlEfficiency advantageDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesBlack-body radiationLiquid-crystal display
A light emitting apparatus includes: a semiconductor light emitting element capable of emitting light of two wavelength components; and a fluorescent material section, having a fluorescent material contained therein, capable of emitting light, the light being radiated as a result of fluorescence from the fluorescent material when the fluorescent material is excited by the two wavelength components, wherein the two wavelength components and the wavelength component resulting from the fluorescence are adjusted so as to be set at an arbitrary color temperature on a characteristic curve of black-body radiation.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid droplet ejection control apparatus and liquid droplet ejecting apparatus
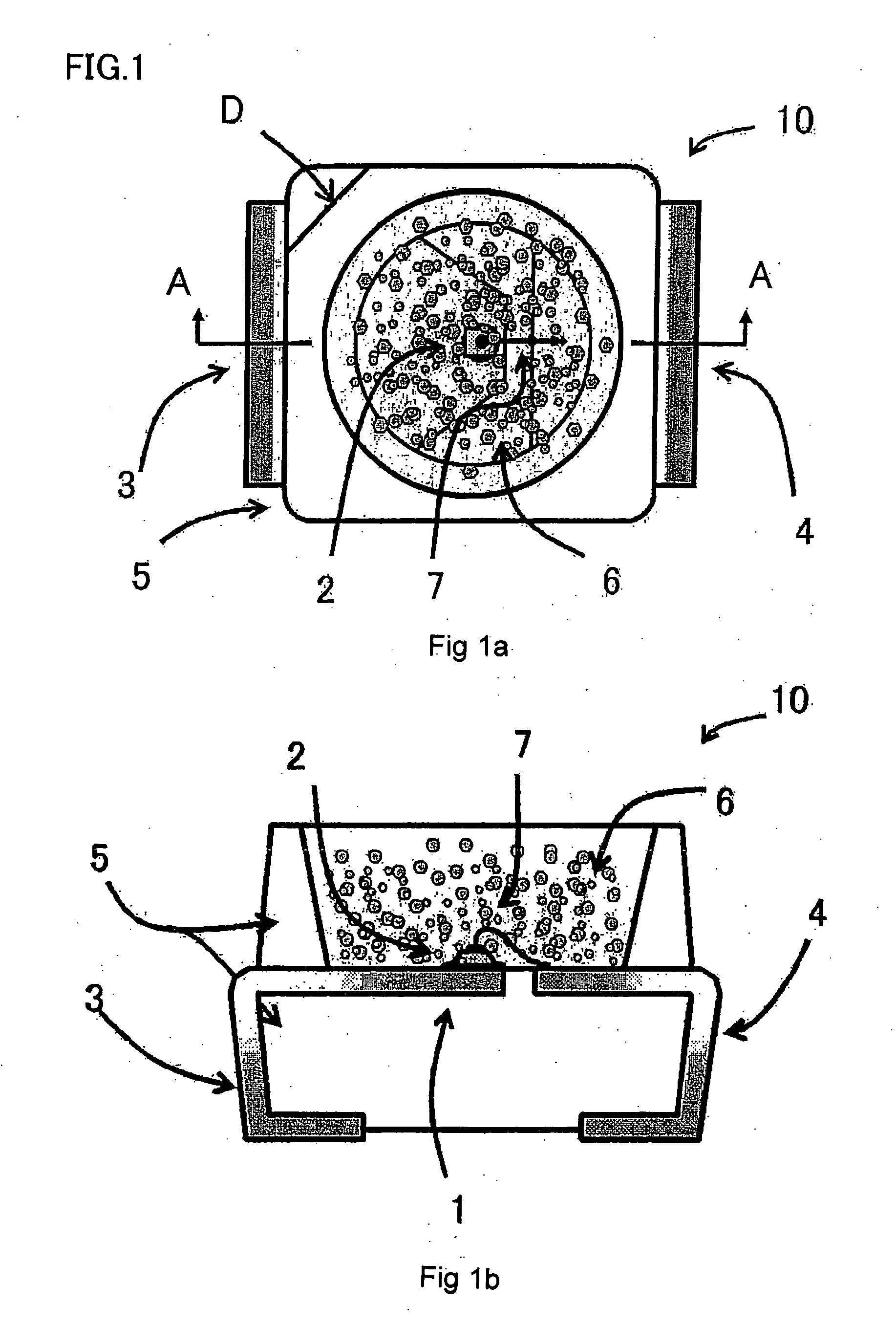
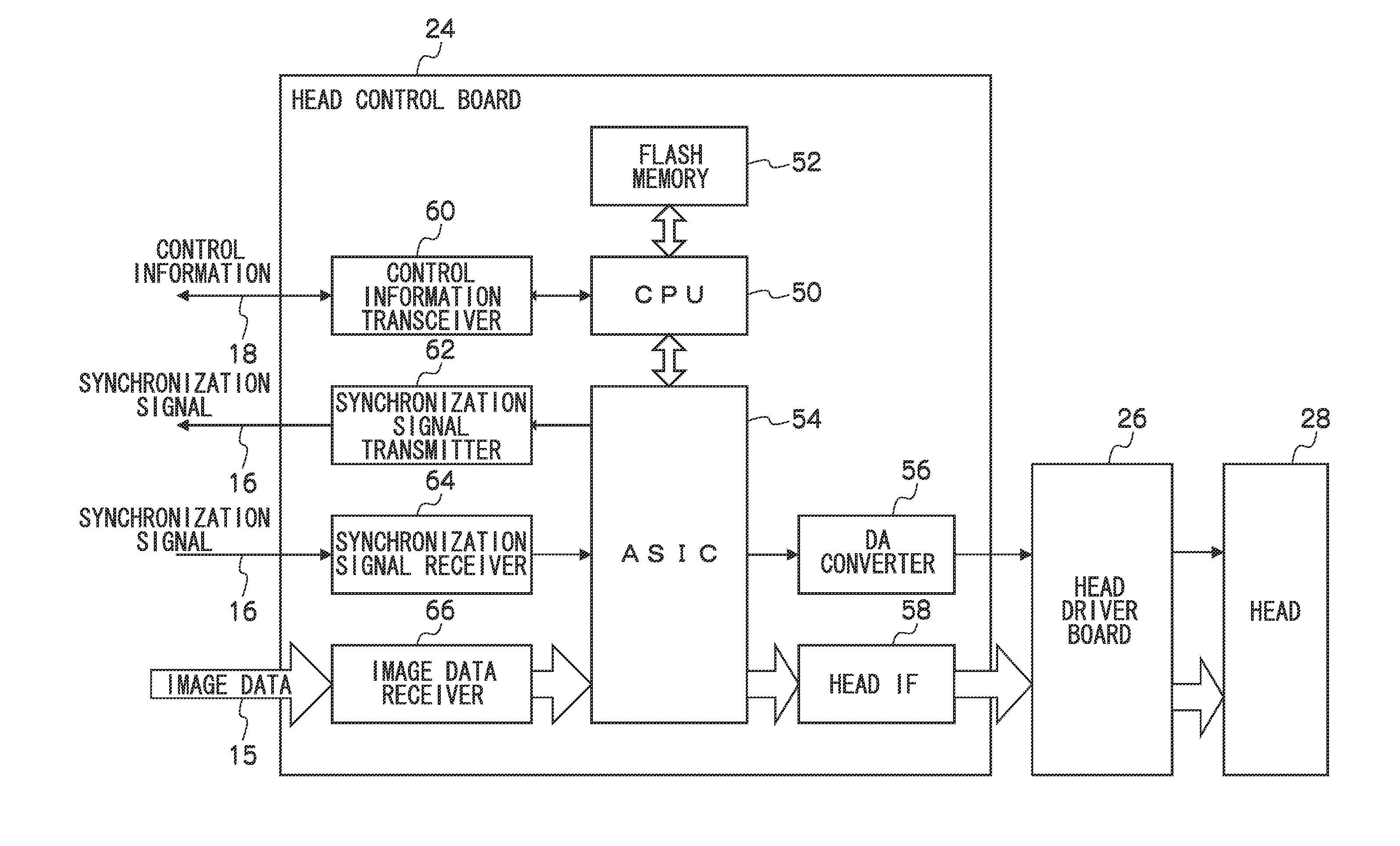
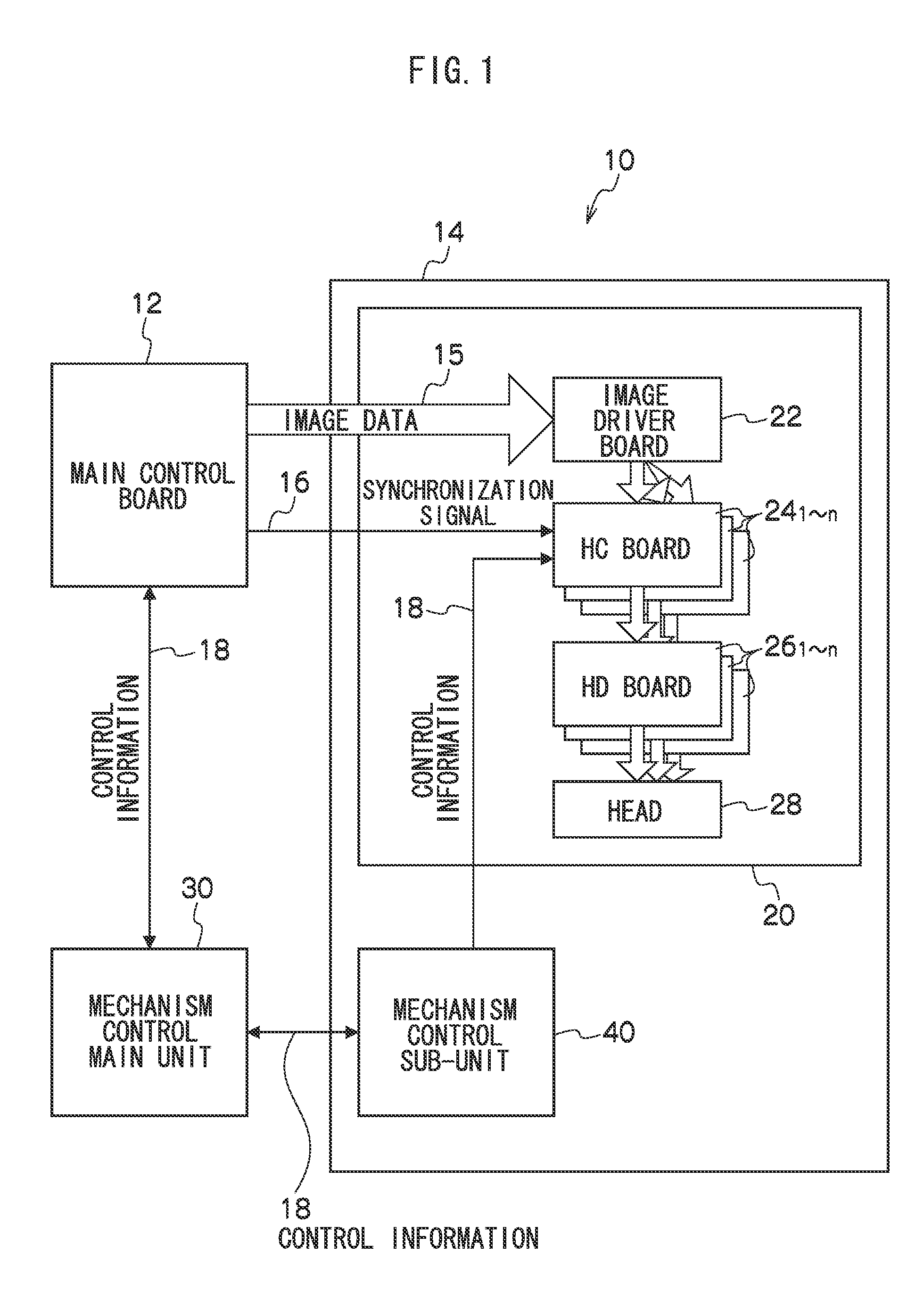
InactiveUS20100073416A1Simple configurationEasily setOther printing apparatusInjectorControl equipment
In a liquid droplet ejection control apparatus, a plurality of head control (HC) boards are disposed in correspondence to ejectors that eject liquid droplets and are plurally arrayed in a liquid droplet ejecting head, and the HC boards are connected to each other in a daisy chain by a synchronization signal line. Each of the HC boards is equipped with a memory for storing identification information. When an identification signal representing the identification information is superimposed on a synchronization signal received via the synchronization signal line from a prior stage, the identification information that the identification signal represents is stored in the memory, the identification signal superimposed on the received synchronization signal is changed so as to represent identification information different from the identification information that the identification signal represents, and the synchronization signal on which the changed identification signal has been superimposed is transmitted to a later stage.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Host apparatus for image forming apparatus and printing account management method thereof
InactiveUS20090147301A1Easily setReduce usageDigital computer detailsDigital output to print unitsComputer graphics (images)Image formation
Owner:S PRINTING SOLUTION CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com