Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68results about How to "Blurred image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
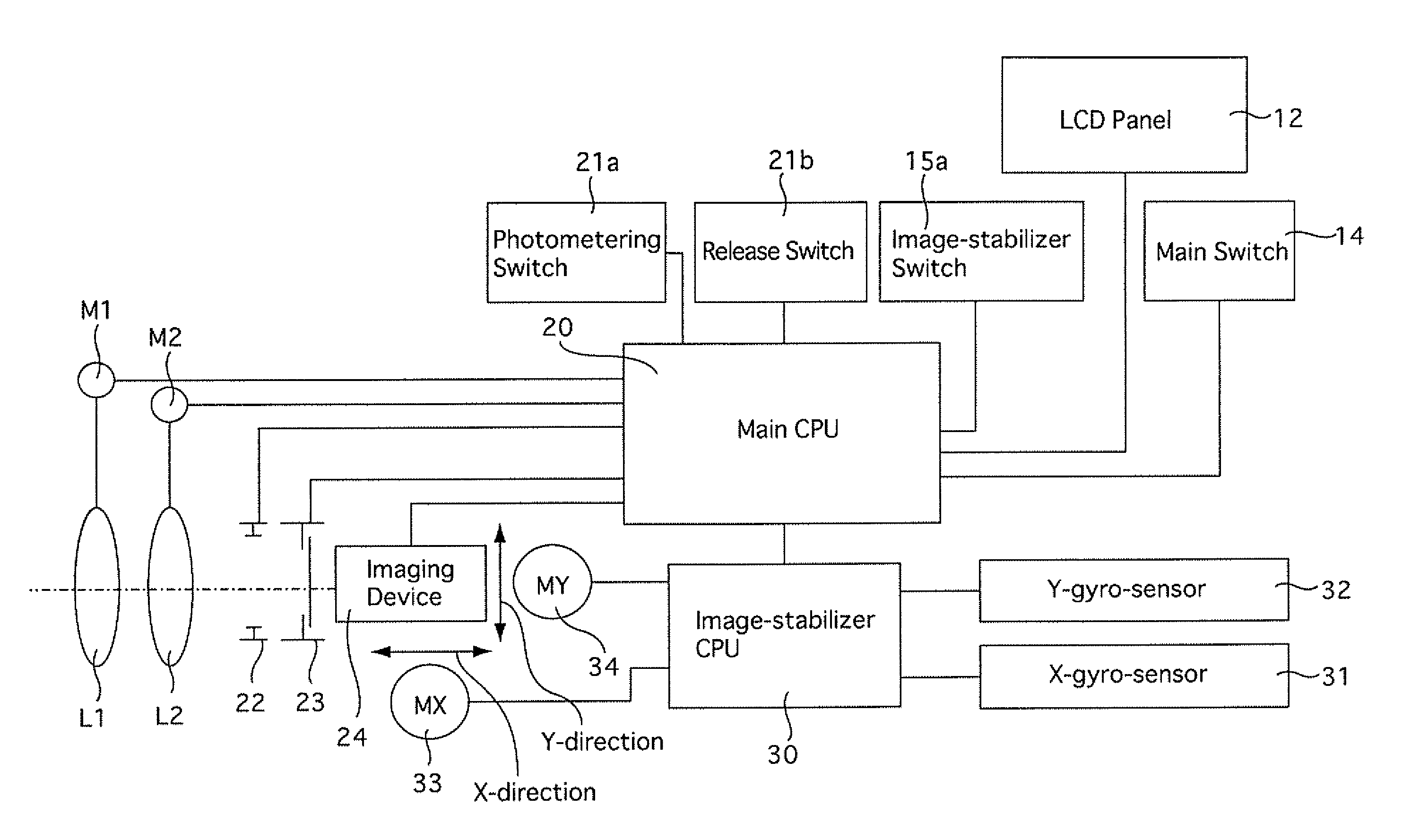
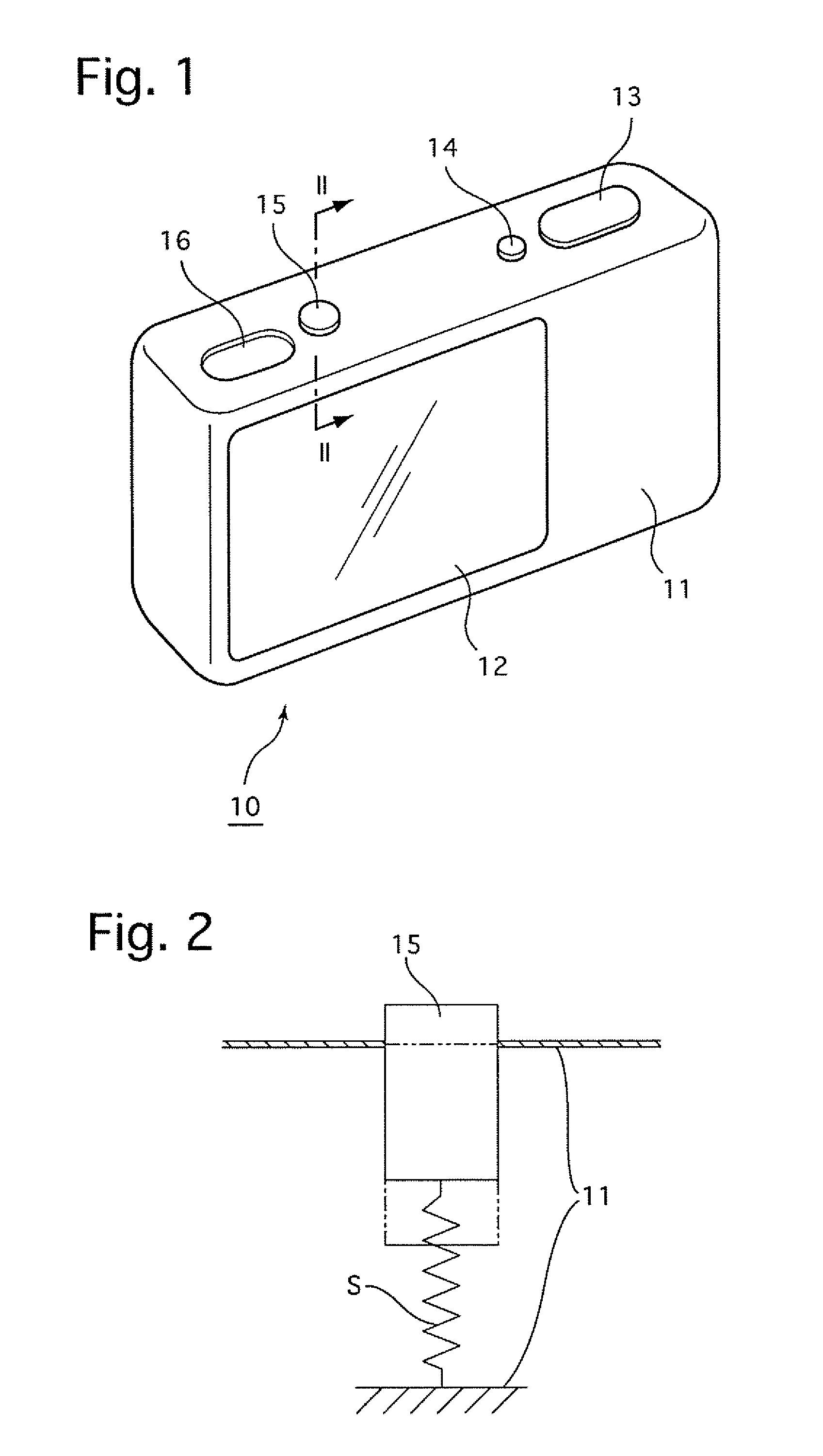
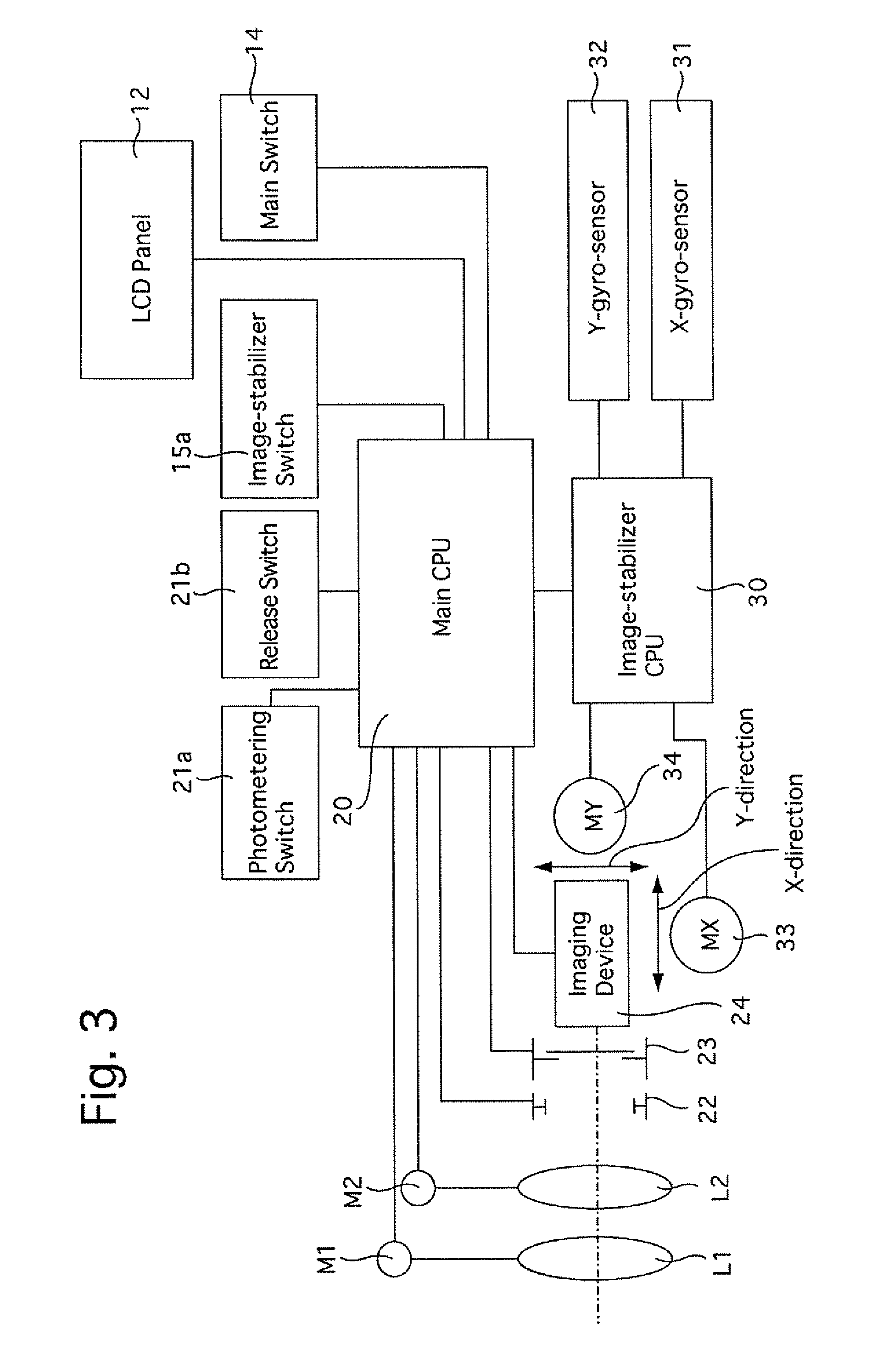
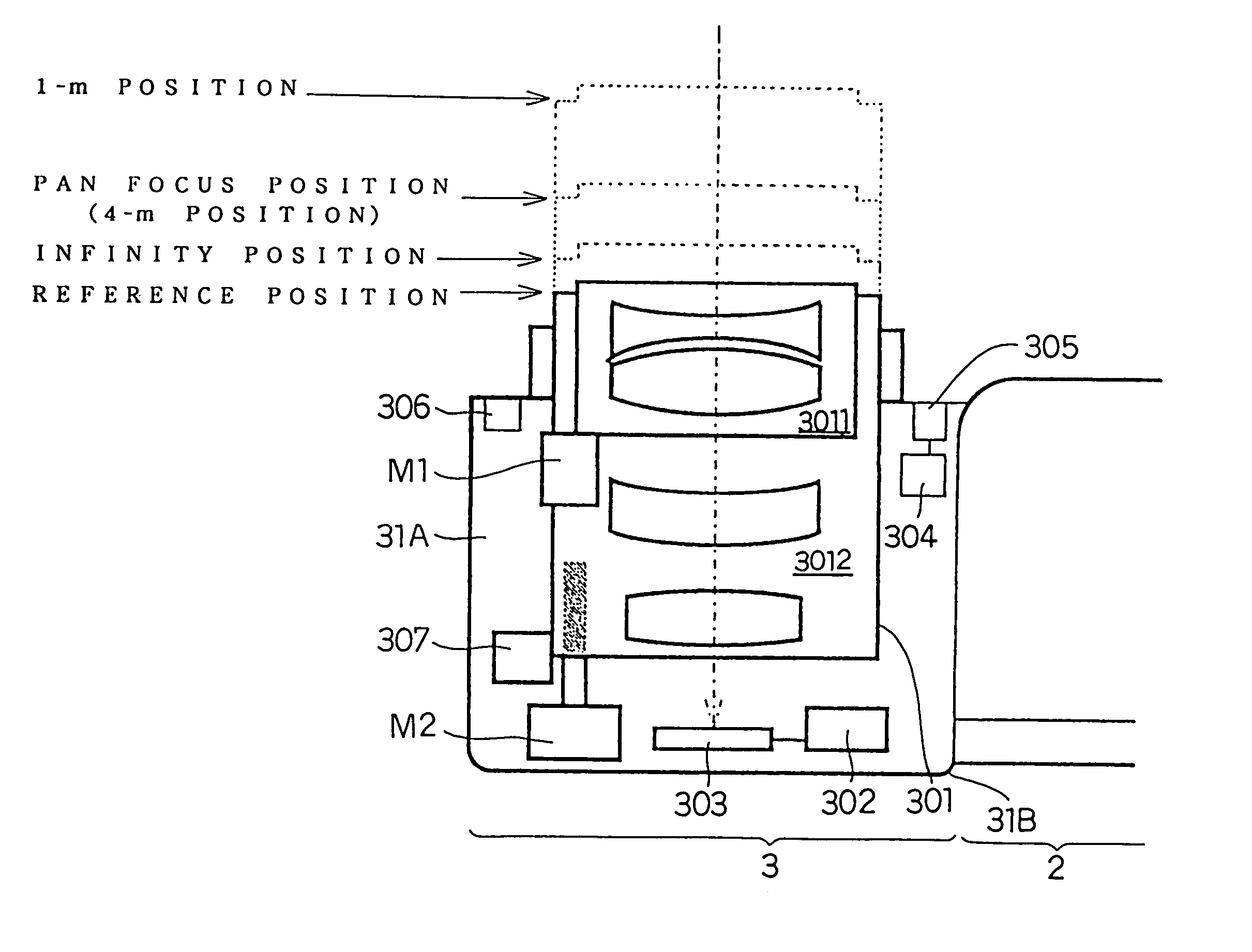
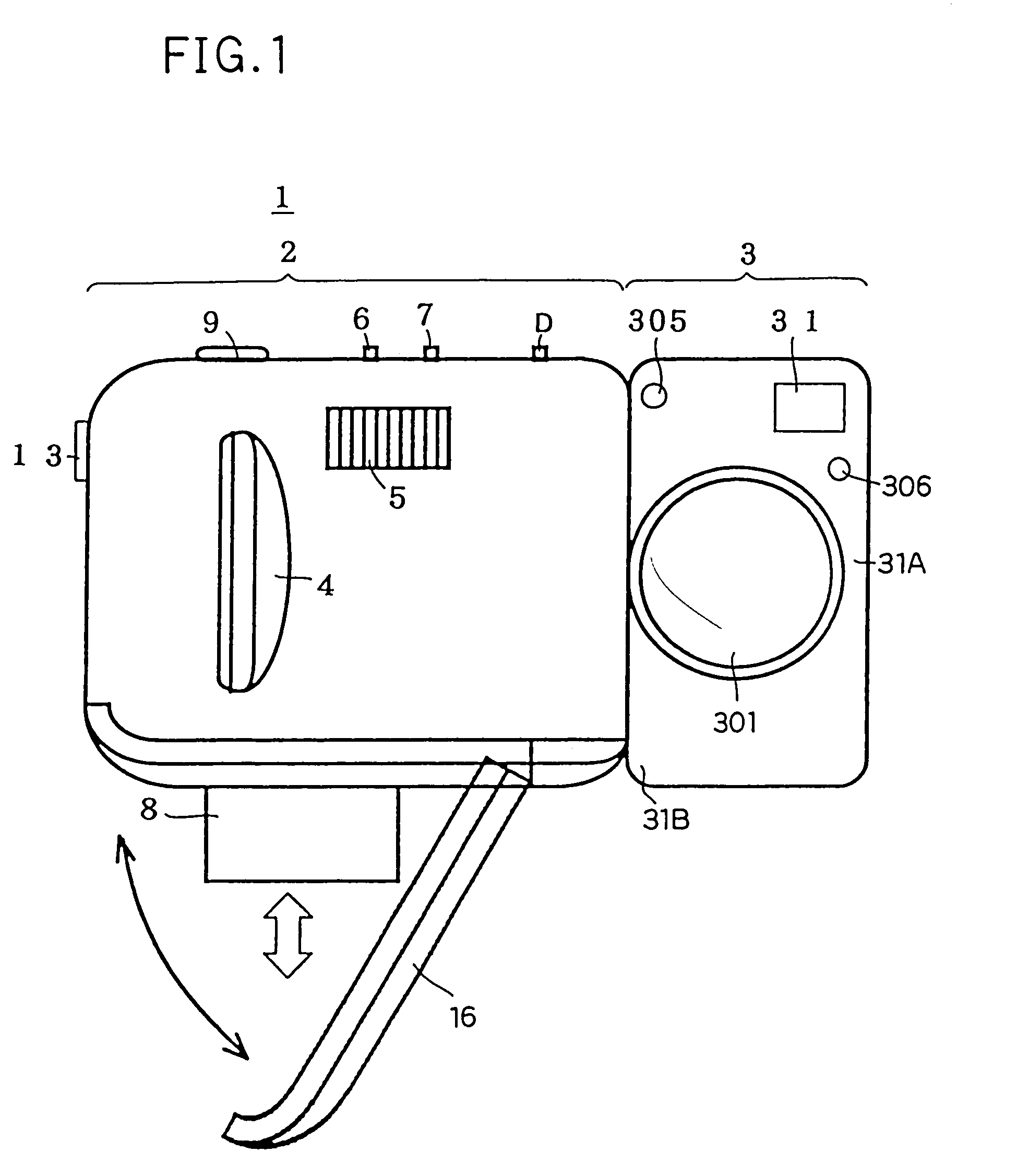
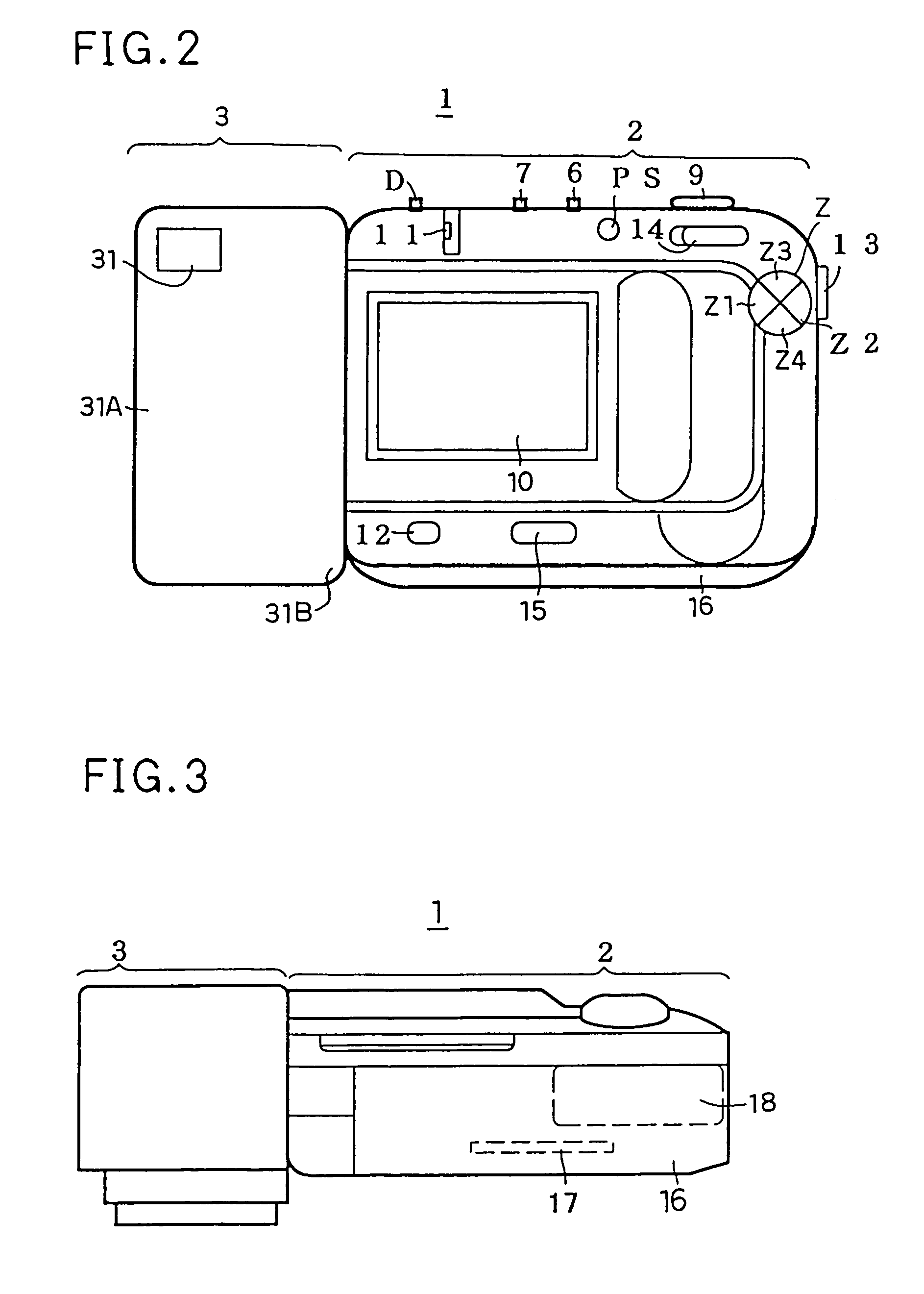
Camera having image-stabilizing function
InactiveUS20070146489A1Blurred imageEfficient workTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHand shakesFree state
A camera having an image-stabilizing function includes an image-stabilizing mechanism which corrects image blur that occurs due to hand shake of the camera; a shutter-release operating member; and an image-stabilizer operating member which is operably movable between an image-stabilizer-activated position and an image-stabilizer-deactivated position, the image-stabilizer operating member being provided separately from the shutter-release operating member on a camera body of the camera. The image-stabilizing mechanism is activated so as to be capable of image stabilization while the image-stabilizer operating member is positioned at the image-stabilizer-activated position. The image-stabilizing mechanism is deactivated so as to be incapable of image stabilization while the image-stabilizer operating member is positioned at the image-stabilizer-deactivated position. The image-stabilizer operating member is biased toward the image-stabilizer-deactivated position so as to be positioned at the image-stabilizer-deactivated position in a free state.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Digital camera having controller for reducing occurrences of blur in displayed images
InactiveUS7167203B1Downsize display deviceReduce the possibilityTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementCamera lensSignal processing circuits
A digital camera comprises a camera body and an image sensing unit. The image sensing unit is provided with a taking lens and an image sensing device for taking images and with an optical viewfinder. The camera body is provided with a controller for controlling the camera, signal processing circuits for processing signals from the image sensing device, a display device for displaying images taken and an interface for recording images taken onto a memory card. The display device serves as a viewfinder. In taking a image, the controller performs an AF control of the taking lens. When power supply to the camera is started, and when the display device is activated, the controller sets the taking lens at a predetermined focus position where in-focus condition is obtained for distant to close-range views, so that blurred images are not displayed on the display device.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
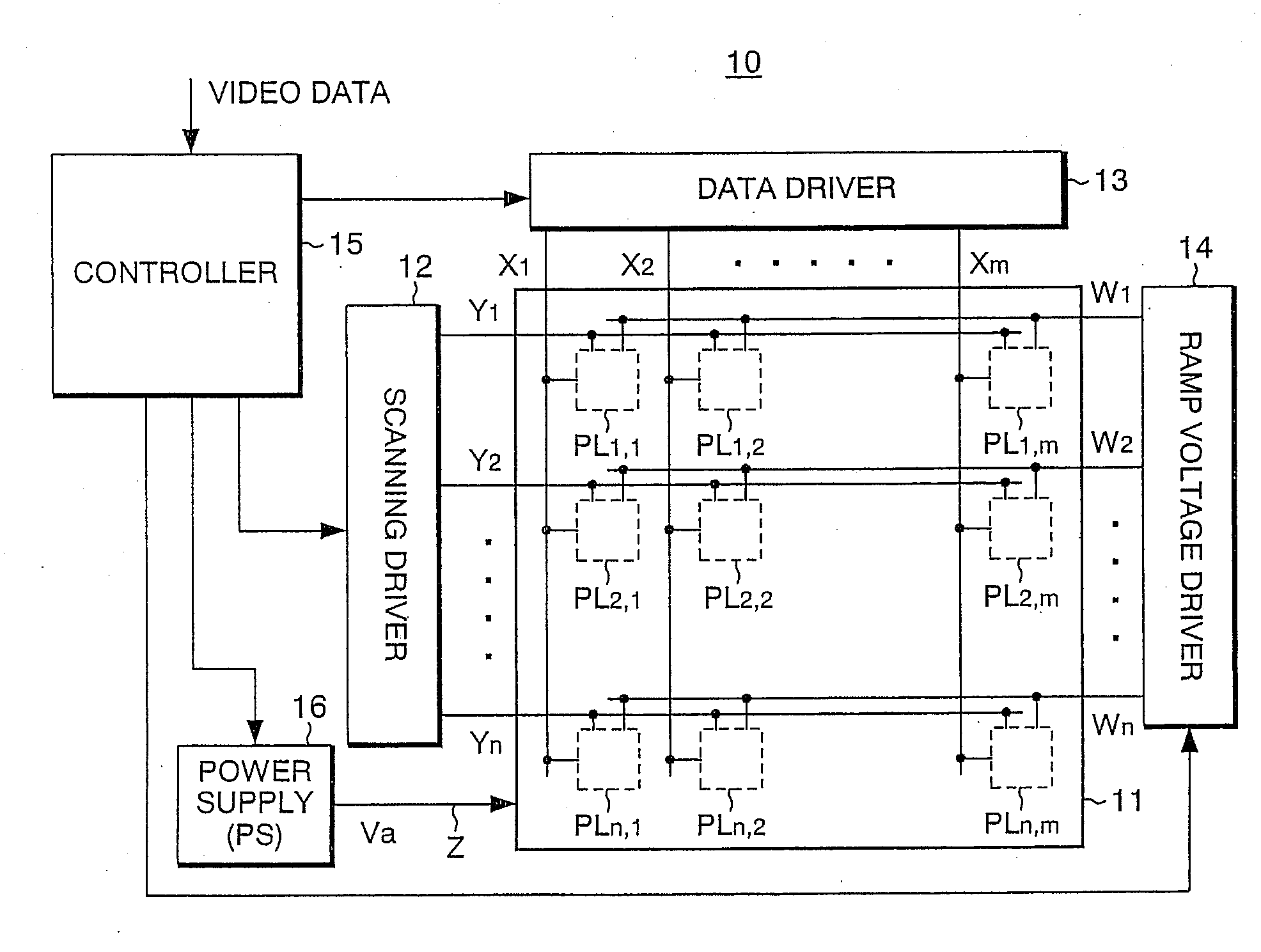
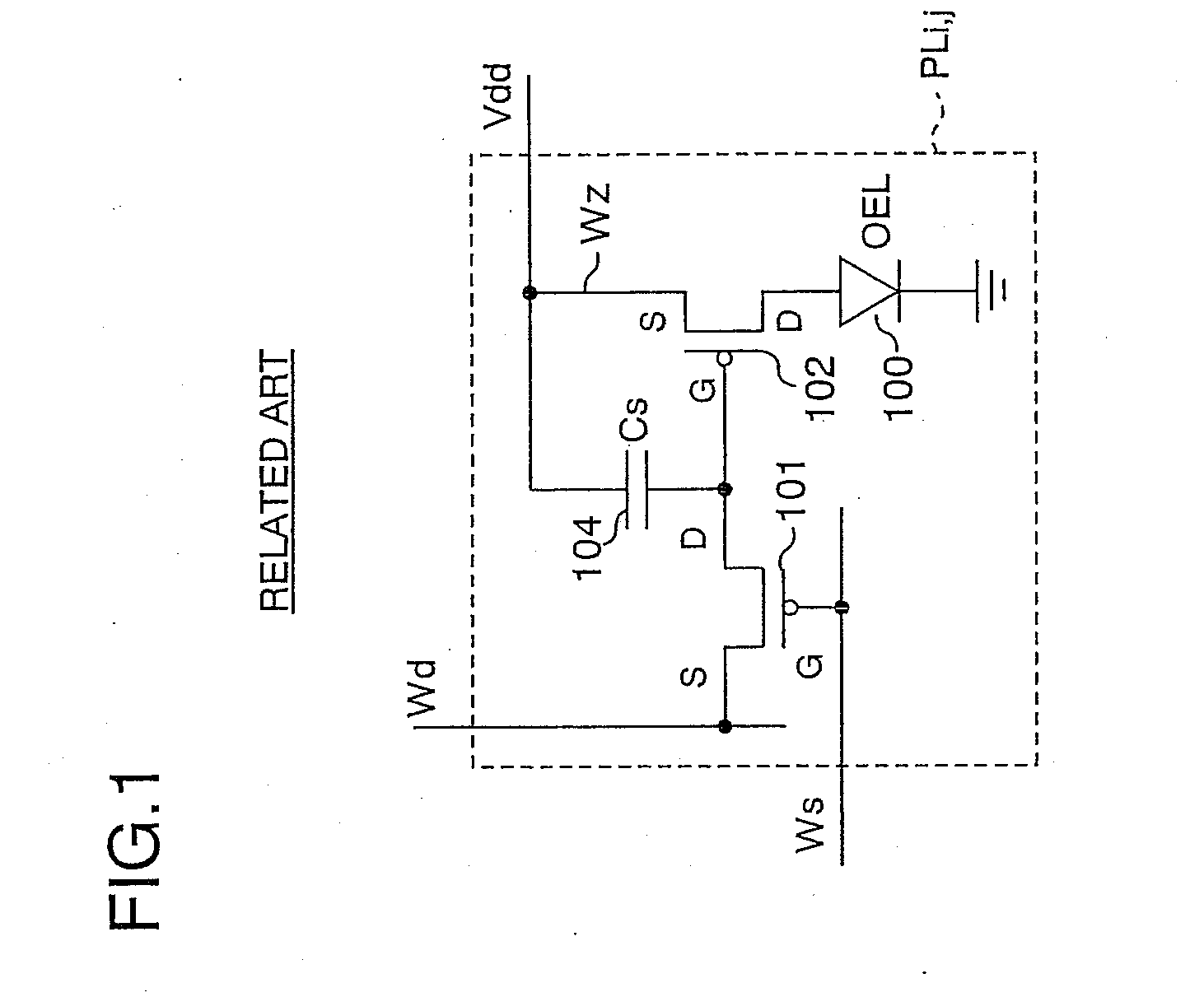
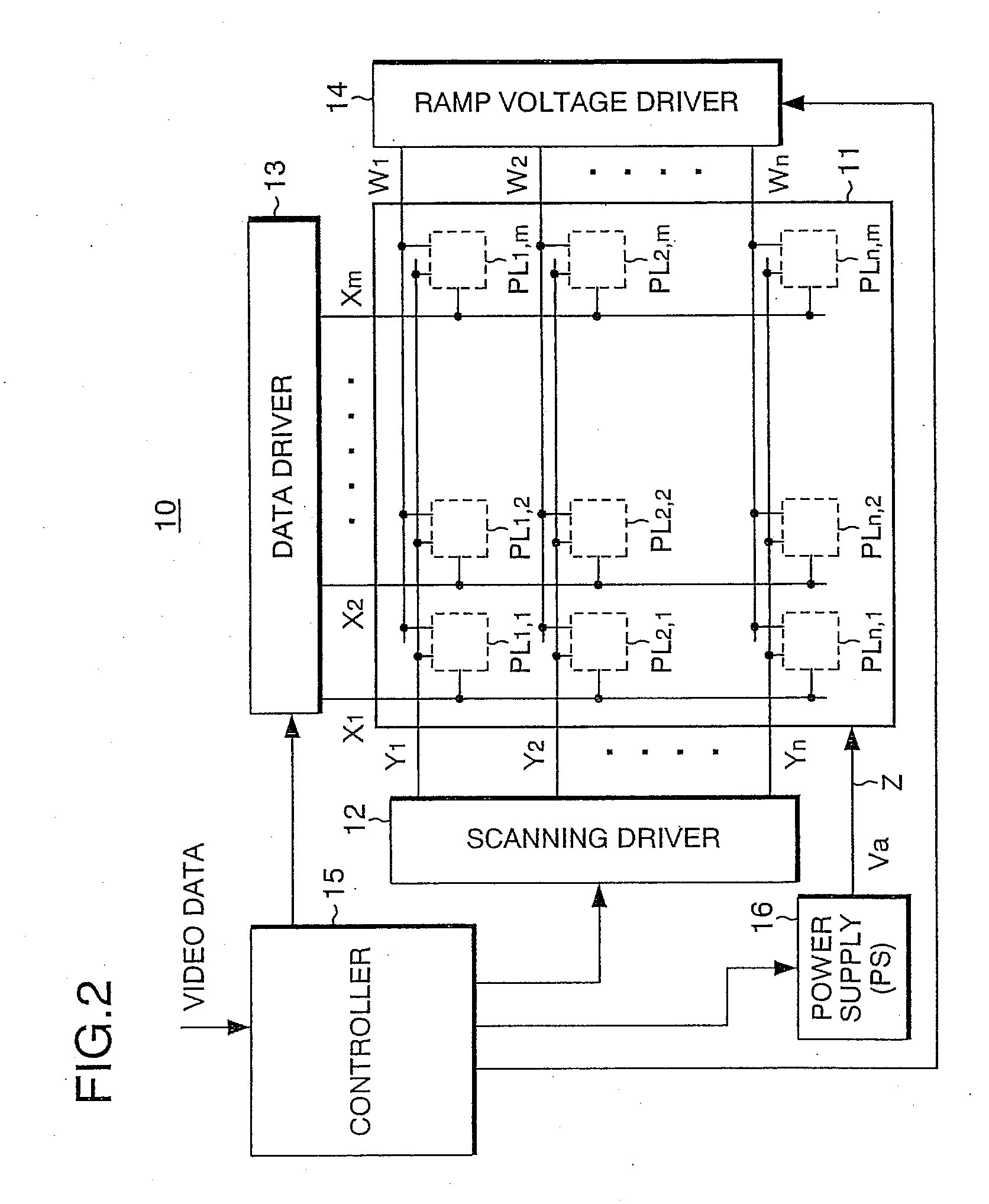
Active matrix display apparatus and driving method therefor
InactiveUS20090167649A1Easy to operateSimple structureCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
A display includes connection lines each of which is provided for the corresponding scanning line of the display and is connected to a light emission element driving circuit, a ramp voltage generating section for generating ramp voltage for varying the control electrode voltage of each of the driver transistors relative to the voltage of the other electrode of the corresponding driver transistor to change the emission state of the corresponding light emission element, and a ramp voltage driver for supplying the ramp voltage to each of the connection lines provided for the corresponding scanning line in response to the scanning.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
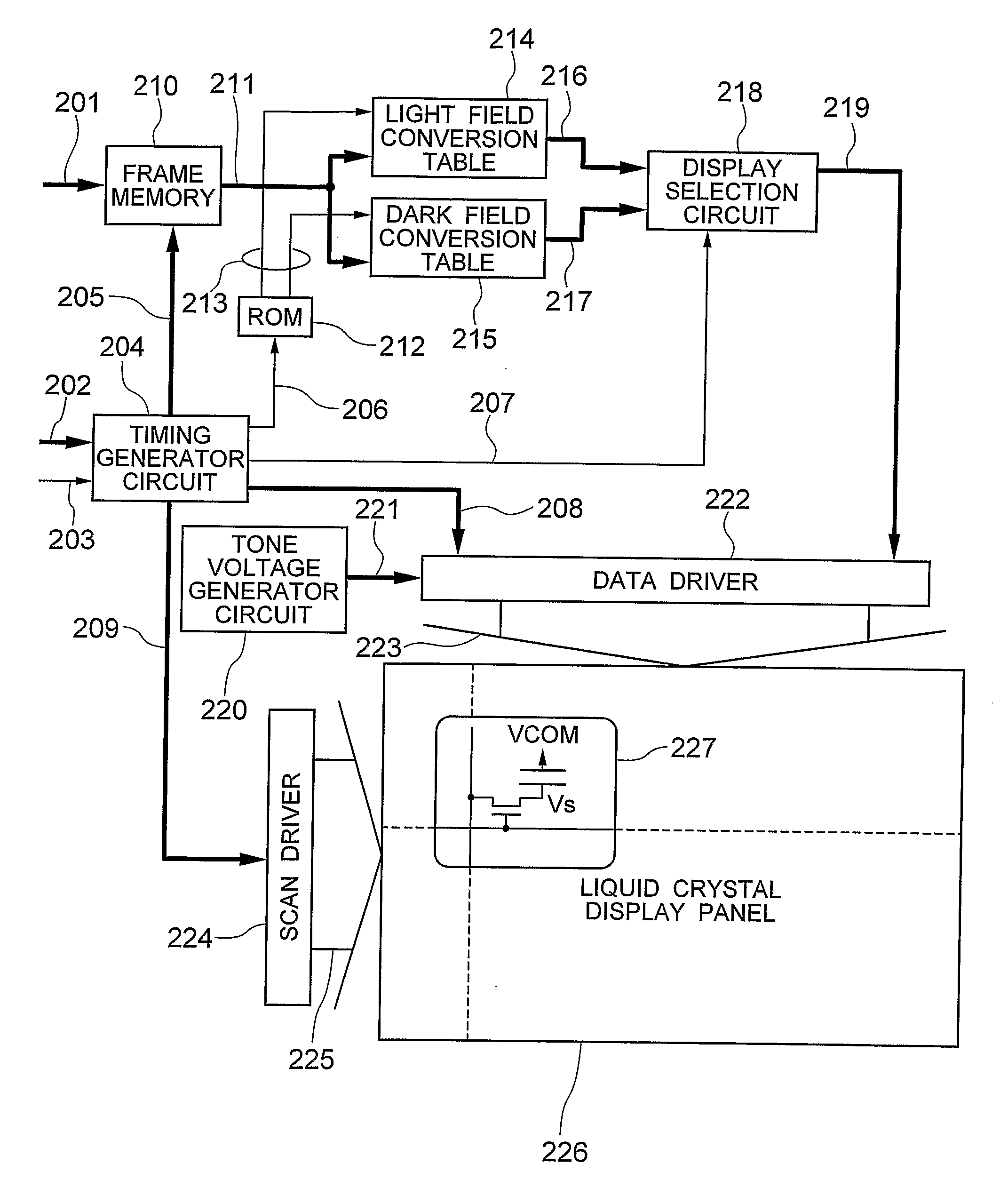
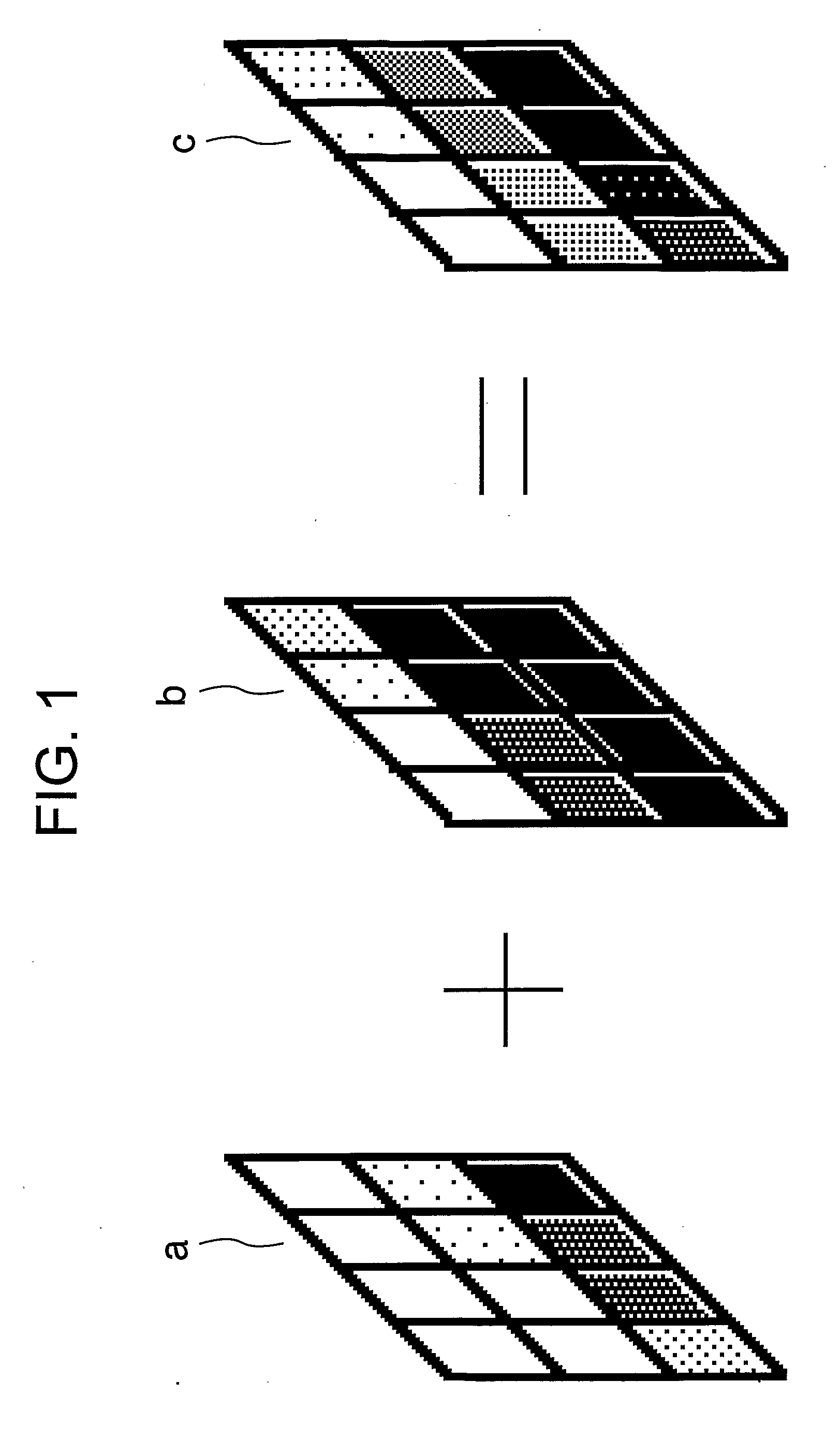
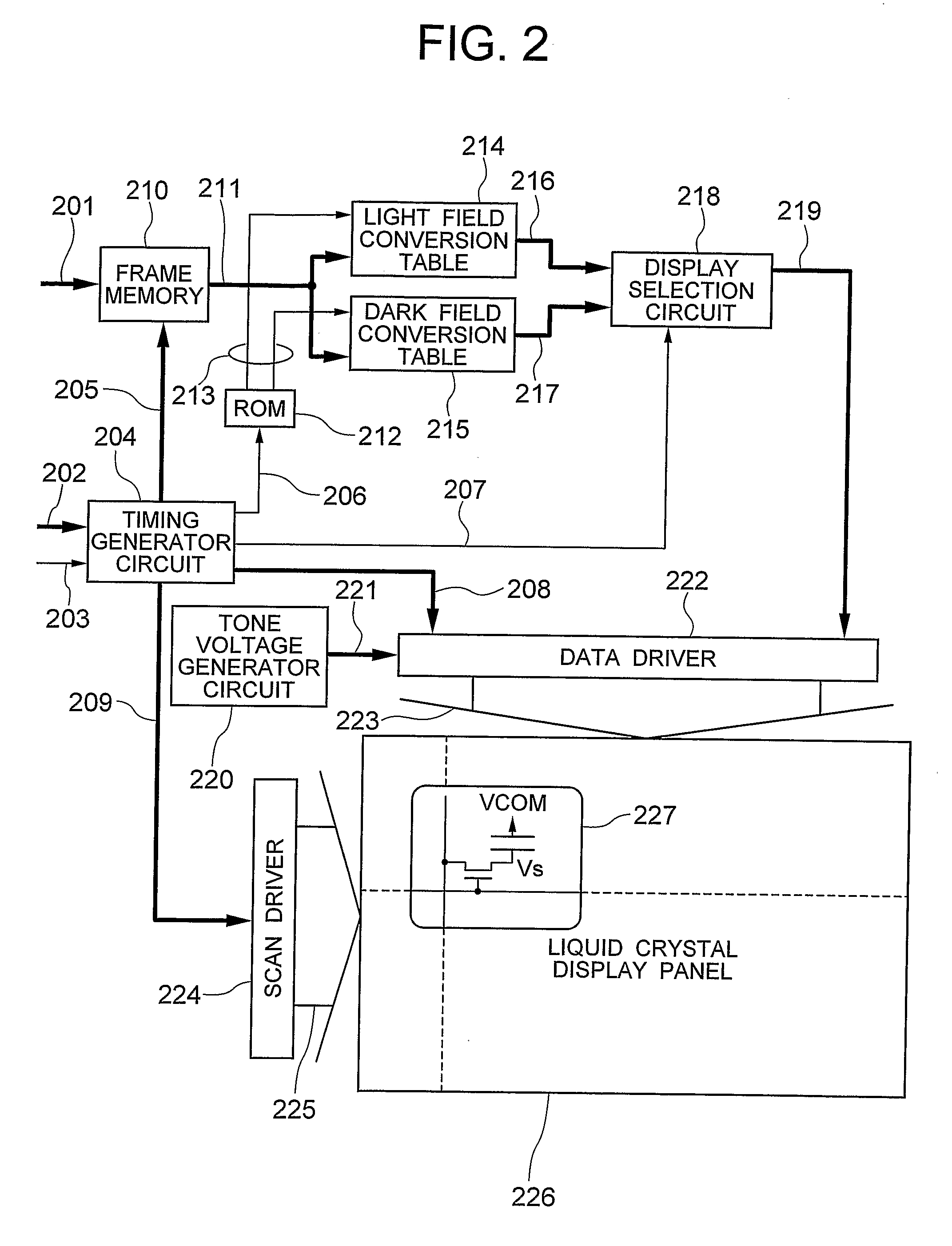
Display Device
InactiveUS20090278869A1Reduce blurImprove luminanceTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceComputer science
A one-frame interval is divided into a light field interval and a dark field interval. In the light field interval, the display data of high tones is displayed, while in the dark field interval, the display data of low tones is displayed. This divisional display makes it possible to pseudoly display the tones of the input display data. Then, in a case that the tones of the input display data is on the lower tone side, the display data of the dark field is set to the corresponding minimum tone with the minimum luminance, while in a case that the tone of the input display data is on the higher tone side, the display data of the light field is set to the corresponding maximum tone with the maximum luminance.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
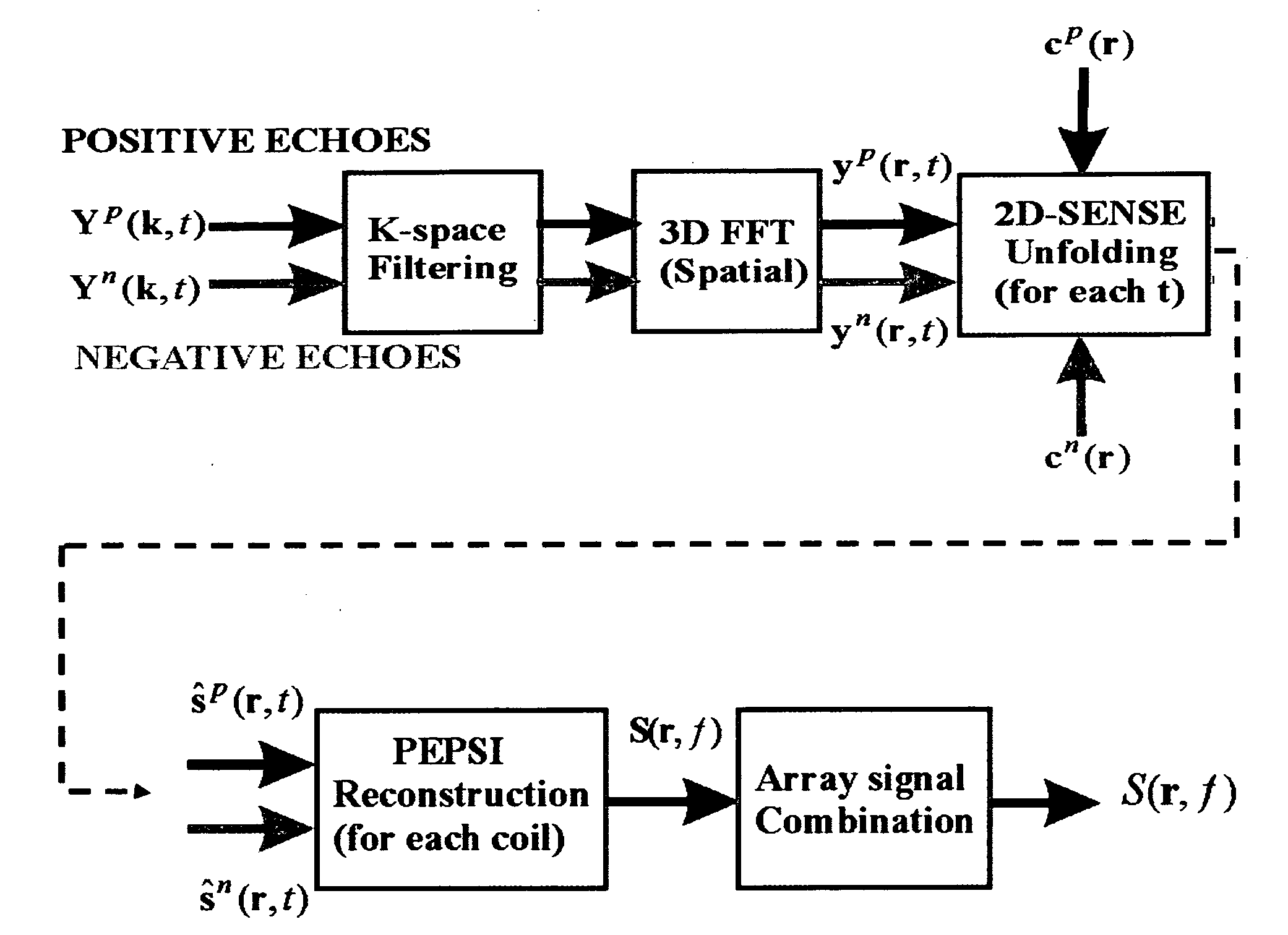
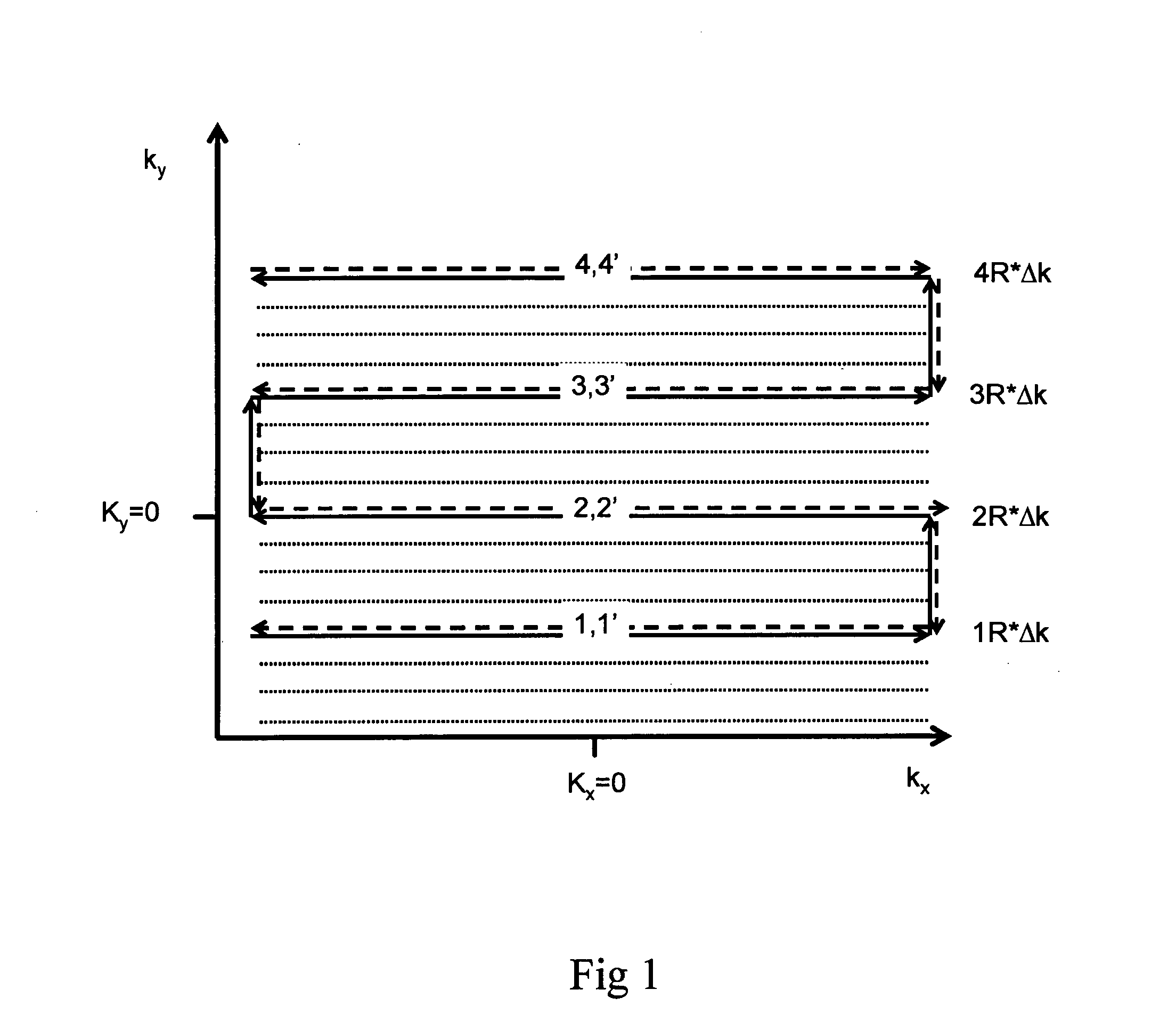
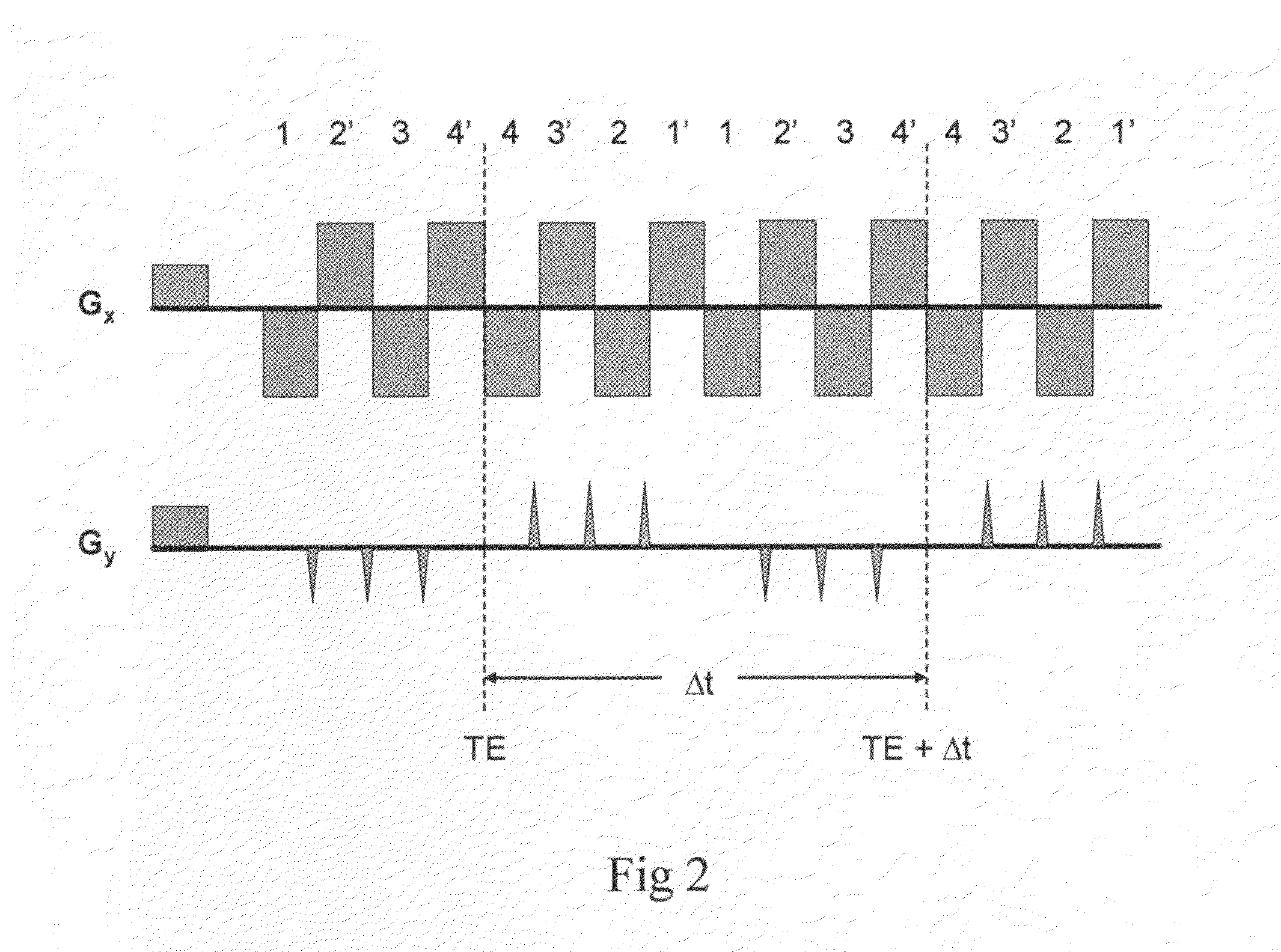
Single-shot magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging with partial parallel imaging
InactiveUS20090091322A1Large spectral width and spatial resolutionMaximize resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonancePhysicsParallel imaging
The present invention has a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method that allows collecting a complete spectroscopic image with one spectral dimension and up to three spatial dimensions in a single signal excitation. The method employs echo-planar spatial-spectral encoding combined with phase encoding interleaved into the echo-planar readout train and partial parallel imaging to reconstruct spatially localized absorption mode spectra. This approach enables flexible tradeoff between gradient and RF encoding to maximize spectral width and spatial resolution. Partial parallel imaging (e.g. SENSE or GRAPPA) is employed with this methodology to accelerate the phase encoding dimension. A preferred implementation is with the recently developed superresolution parallel MRI method, which accelerates along both the readout and phase encoding dimensions and thus enables particularly large spectral width and spatial resolution. The symmetrical k-space trajectory of this methodology is designed to compensate phase errors due to convolution of spatial and spectral encoding. This method is suitable for hyperpolarized MRSI, spatial mapping of the diffusion coefficients of biochemicals and functional MRI using quantitative mapping of water relaxation.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
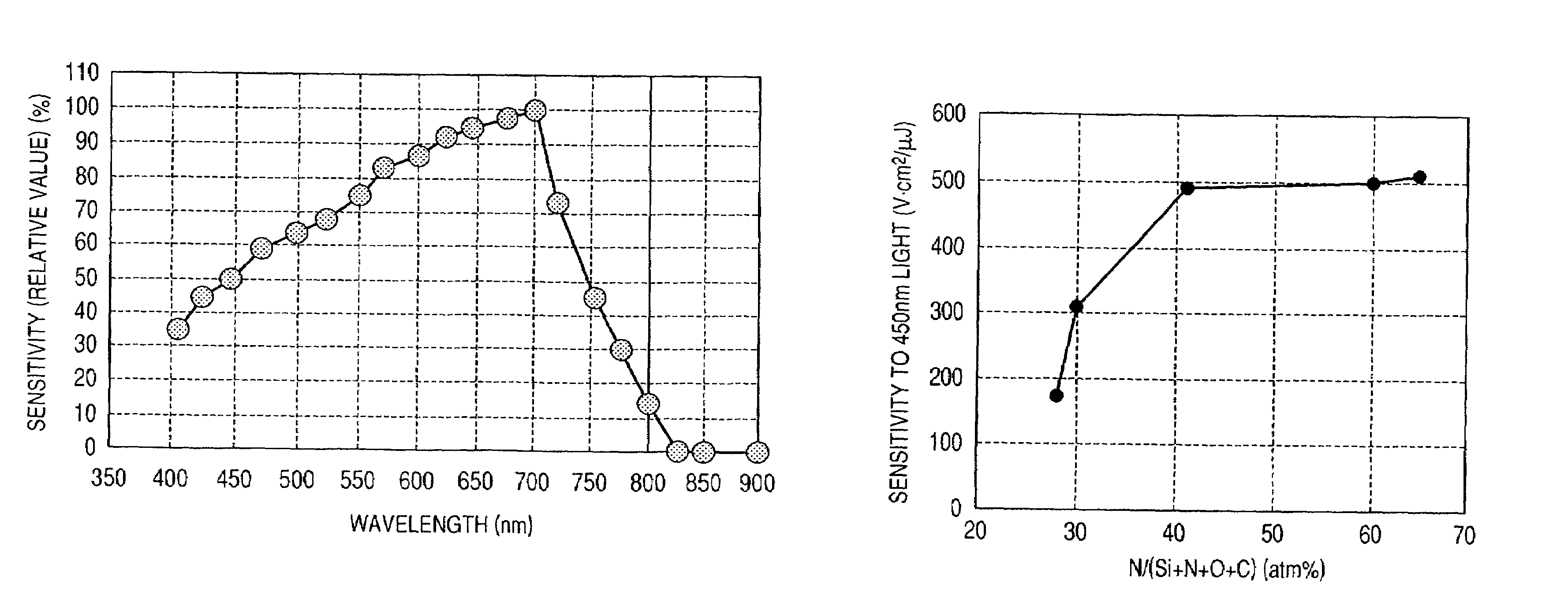
Electrophotographic photosensitive member
InactiveUS7157197B2Maintain hardnessHigh resistivityElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerNitrogen
An electrophotographic photosensitive member is provided which can keep at a minimum the absorption of image exposure light of 380 to 500 nm in wavelength in its surface layer and concurrently can satisfactorily keep electrophotographic properties including resolving power. The electrophotographic photosensitive member has a substrate, and a photoconductive layer and a surface layer in this order provided on the substrate. The surface layer includes an amorphous material composed chiefly of silicon atoms and nitrogen atoms and containing at least oxygen atoms and carbon atoms, and the ratios of the numbers of the respective oxygen atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms to the total number of oxygen atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms contained in the amorphous material are each within a specific range.
Owner:CANON KK
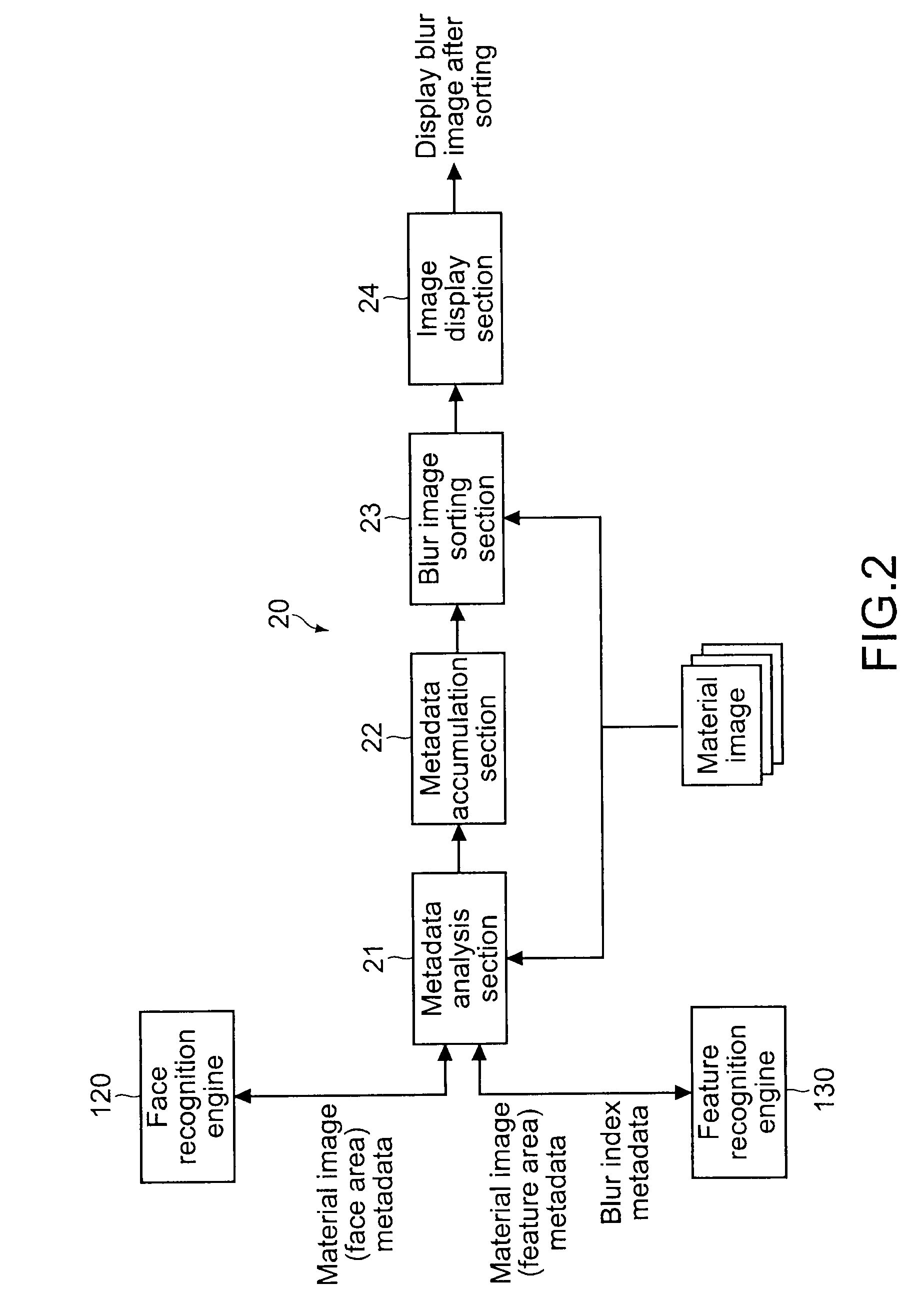
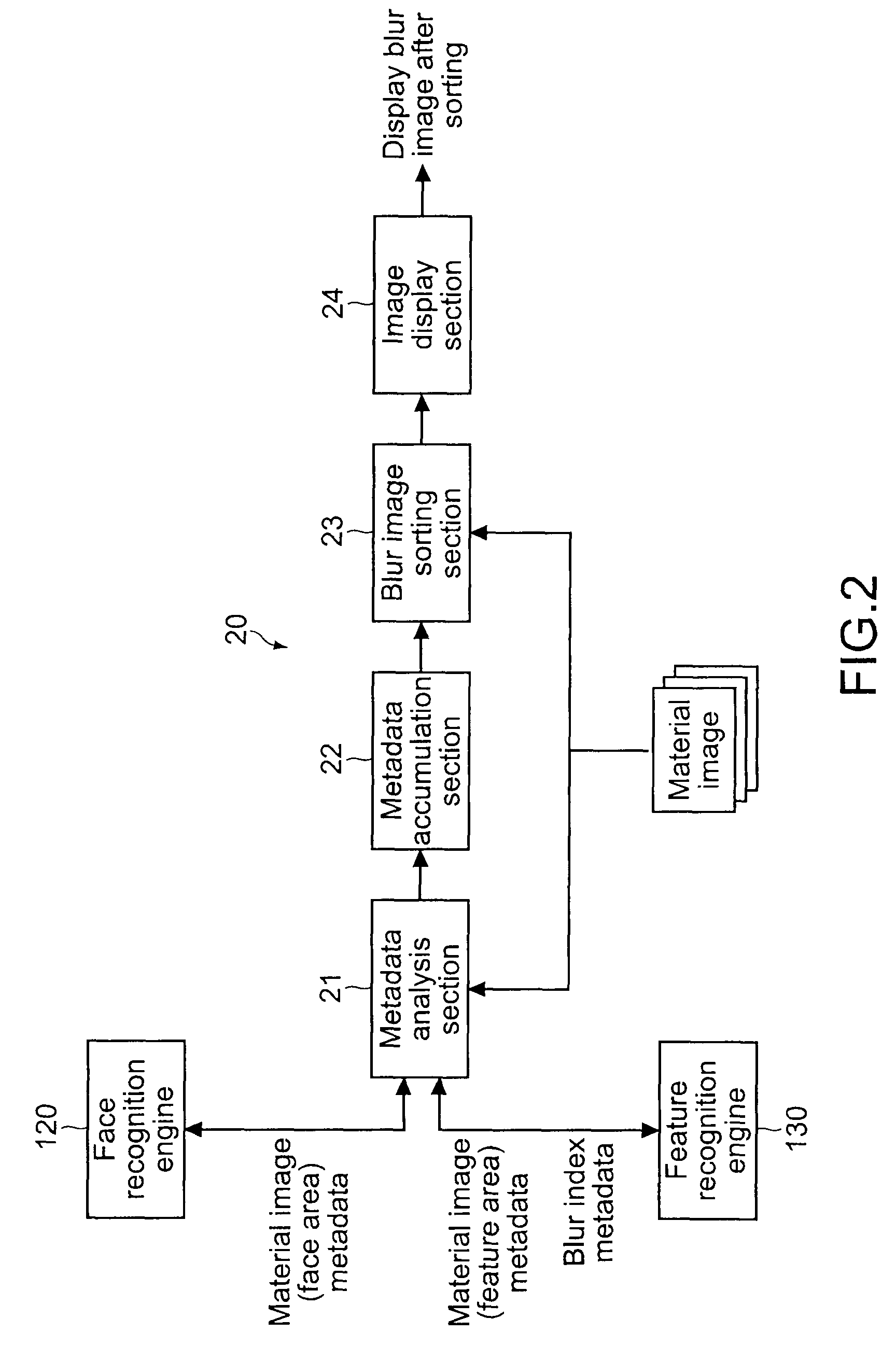
Electronic apparatus, blur image sorting method, and program
InactiveUS20110116726A1Reliable imagingAccurate calculationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
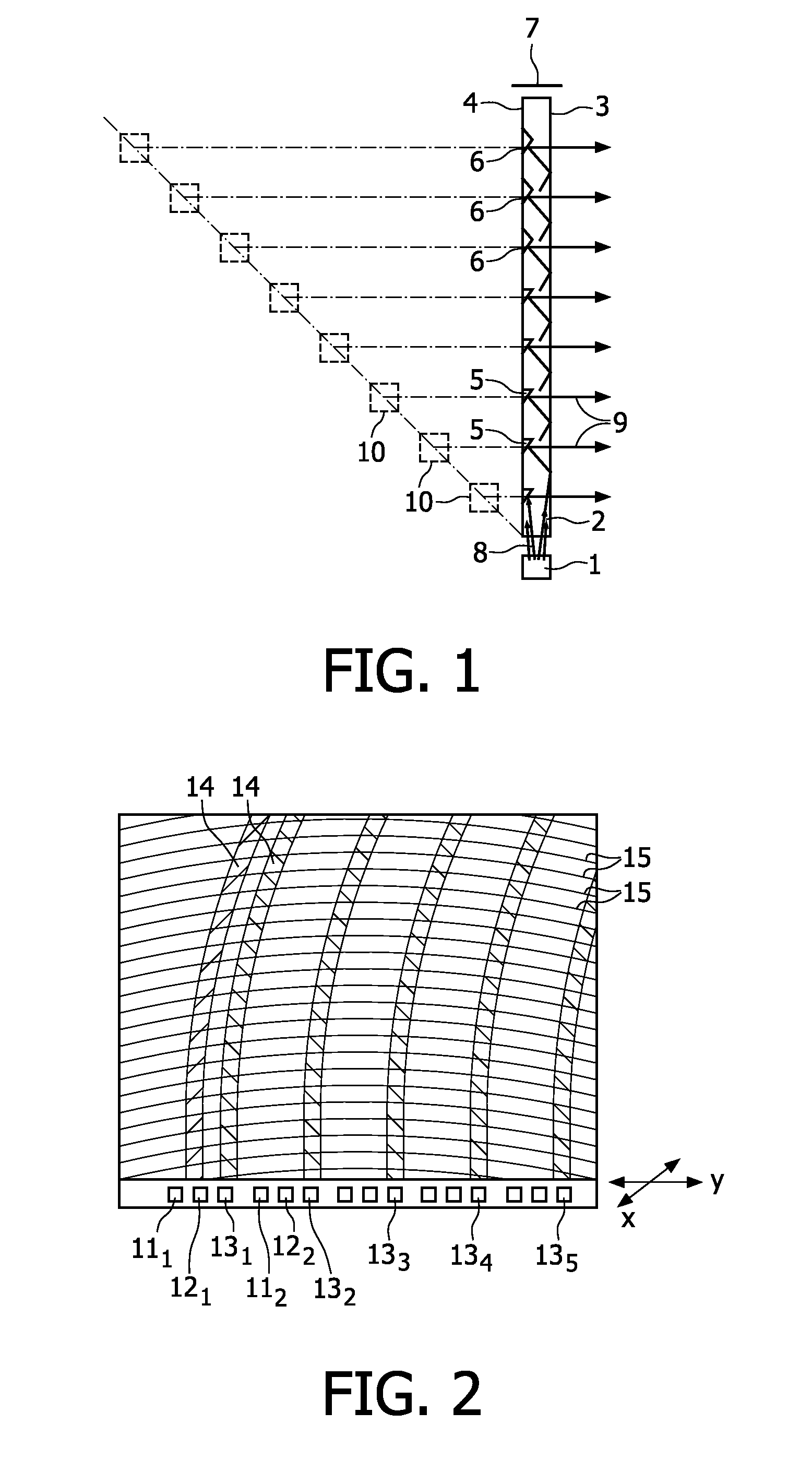
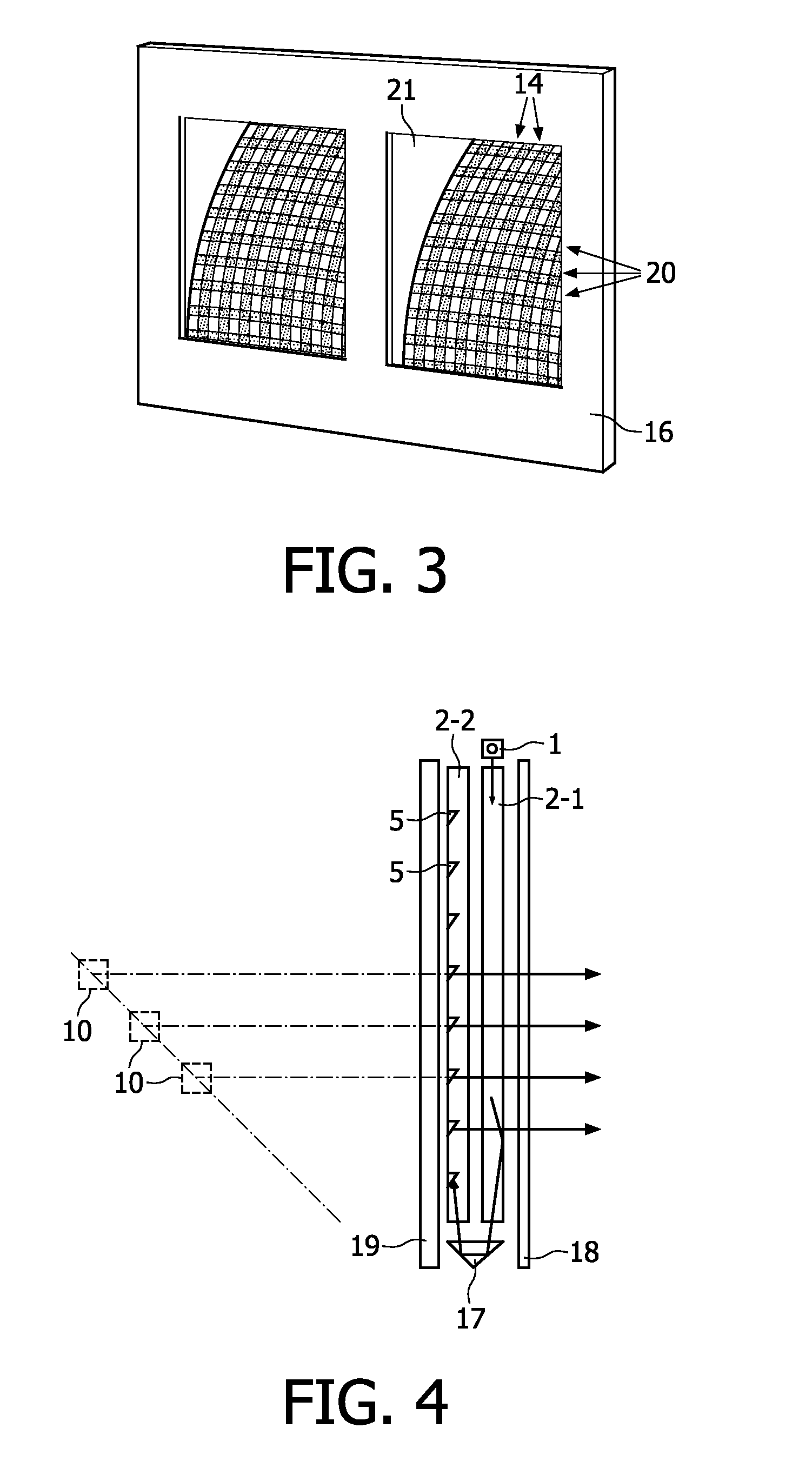
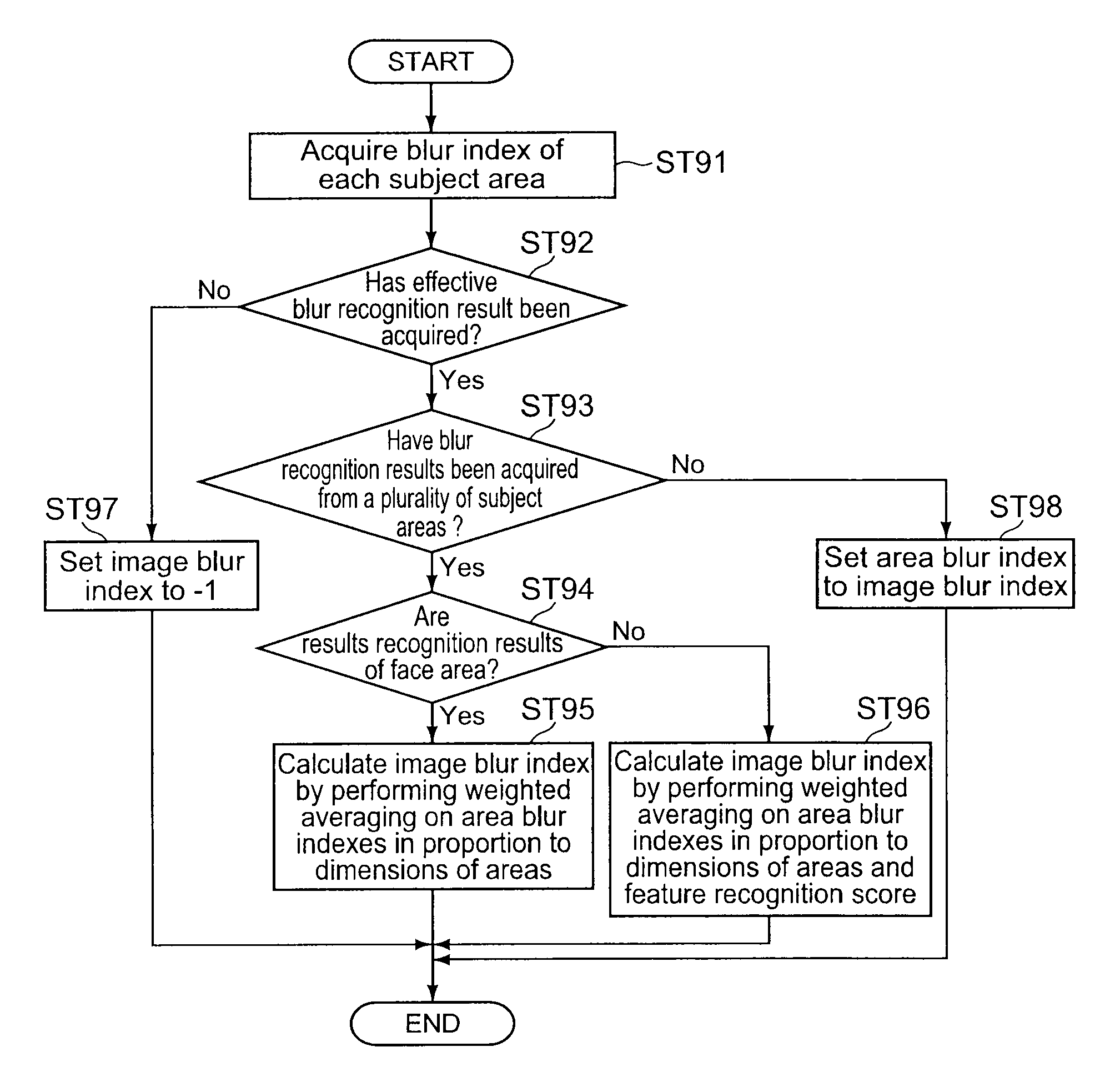
An electronic apparatus includes: an extraction section extracting a subject area having a predetermined feature in an image; a first calculation section calculating a first blur degree indicating a blur degree of the extracted subject area; a second calculation section calculating, when the number of subject areas from which the first blur degree is calculated is one, a second blur degree indicating a blur degree of the entire image based on the first blur degree, and calculating, when the number of subject areas from which the first blur degree is calculated is plural, the second blur degree based on a value obtained by performing weighted averaging on the plural first blur degrees in accordance with dimensions of the plural subject areas; and a sorting section sorting an image having the calculated second blur degree equal to or larger than a predetermined threshold value, as a blur image, from plural images.
Owner:SONY CORP
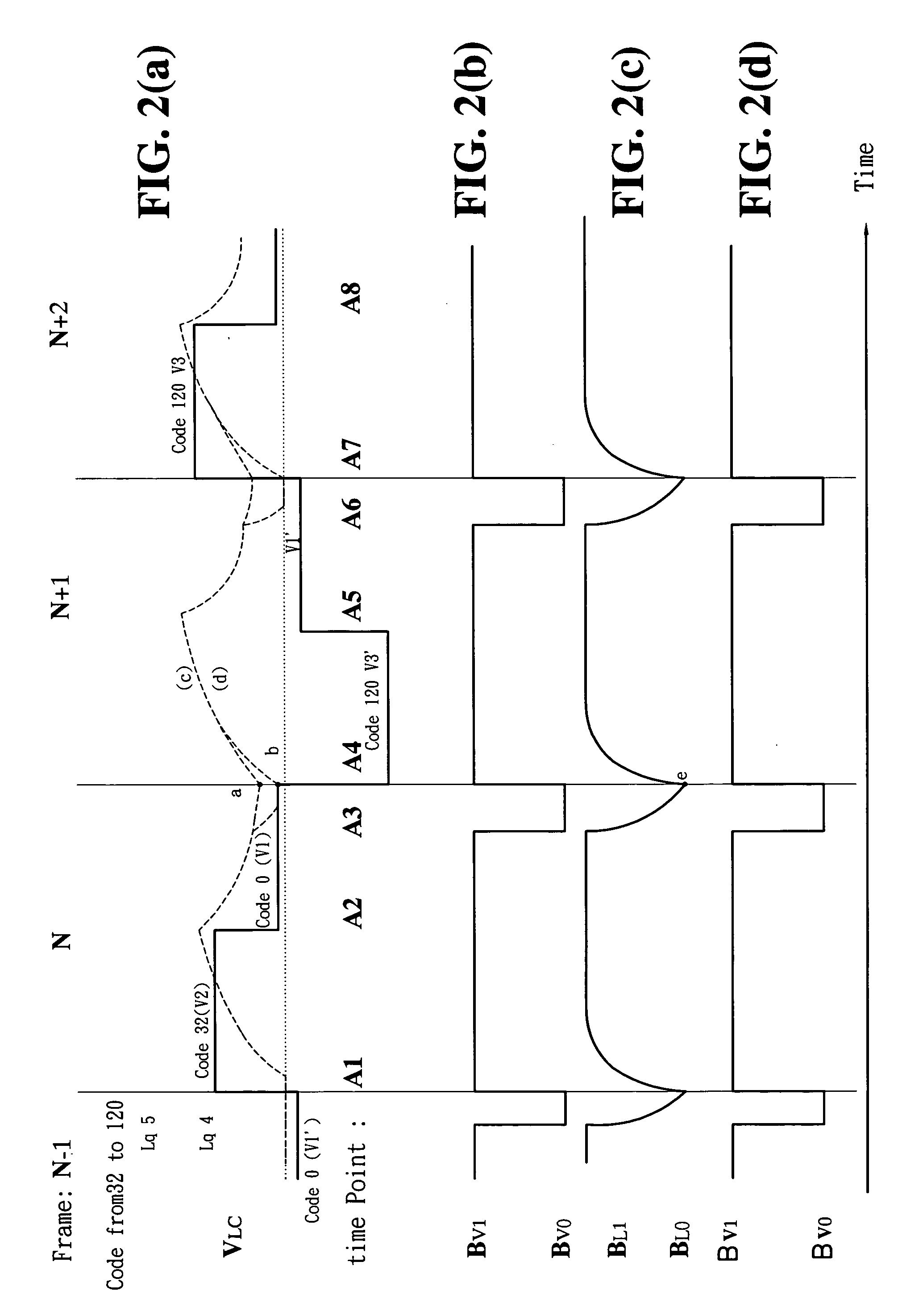
Method and device used for eliminating image overlap blurring phenomenon between frames in process of simulating CRT impulse type image display
InactiveUS20060033698A1Eliminating image overlap blurring phenomenonLuminance of backlight is reducedCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingInput controlControl line
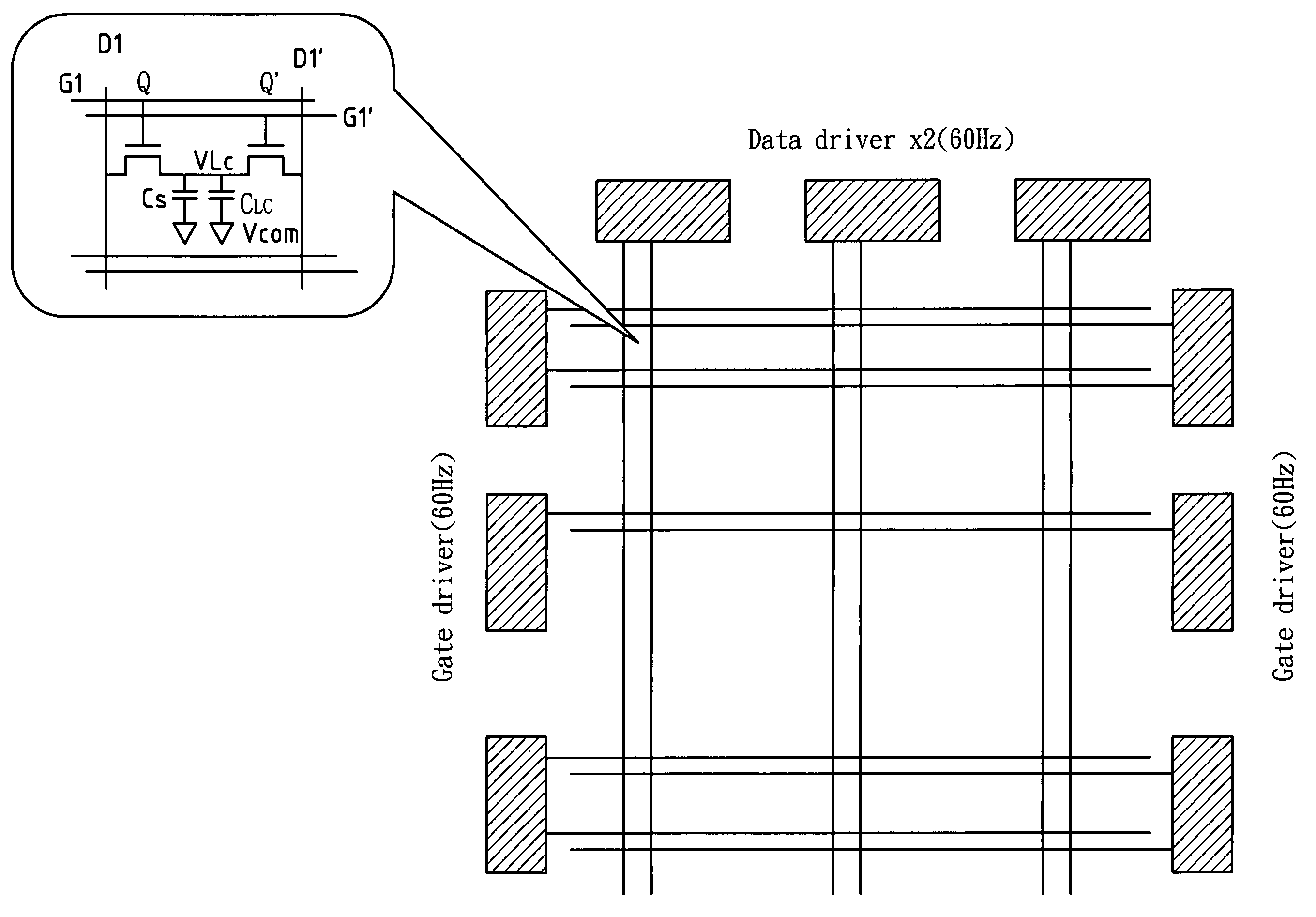
Disclosed is a device for eliminating after image overlap blurring phenomenon between frames in the simulation of CRT impulse type image display with liquid crystal display (LCD), including first and second input control lines; first and second input data lines; first and second capacitors; a driving voltage output line; a first transistor including a first gate connected to a first input control line, a first source connected to a first input data line, and a first drain connected to a driving voltage output line, a first capacitor and the drain of the second transistor; and a second transistor including a second gate connected to a second input control line, a second source connected to a second input data line, and a second drain connected to a driving voltage output line, the drain of the first transistor and the second capacitor. The first and second capacitors are connected to ground respectively. The driving voltage output line supplies a simulation driving voltage to pixels of an LCD panel for displaying images and including a backlight unit with adjustable and controllable luminance and a backlight input voltage control line. The first and second input control lines are connected to a gate driver. The first and second data lines are connected to a data driver respectively. During the interval of black lines scanning, when the luminance of the backlight unit is reduced to the lowest value through its control voltage, the accumulated liquid crystal optical response in that interval is brought to the lowest value.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Defect detecting apparatus and method
InactiveUS20090087079A1Surely detect defectSurely detectedTelevision system detailsImage analysisCover glassCandidate image
A front side surface of a cover glass of a solid state imaging device is focused, and a front side image is captured. Next, a rear side surface of the cover glass is focused, and a rear side image is captured. The front side image and the rear side image are combined with each other to create a composite image. A first threshold value is set for each pixel in the composite image by dynamic thresholding. An image composed of pixels whose gray values exceed the first threshold value is identified as a defect candidate image. The maximum gray value of the defect candidate image is multiplied by a constant rate to set a second threshold value. An image composed of pixels whose gray value is less than the second threshold value is eliminated as a blurred image from the defect candidate image. Thereby, only a spot defect image, an allowable defect image, and a stain defect image remain in the composite image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Determining if an image is blurred
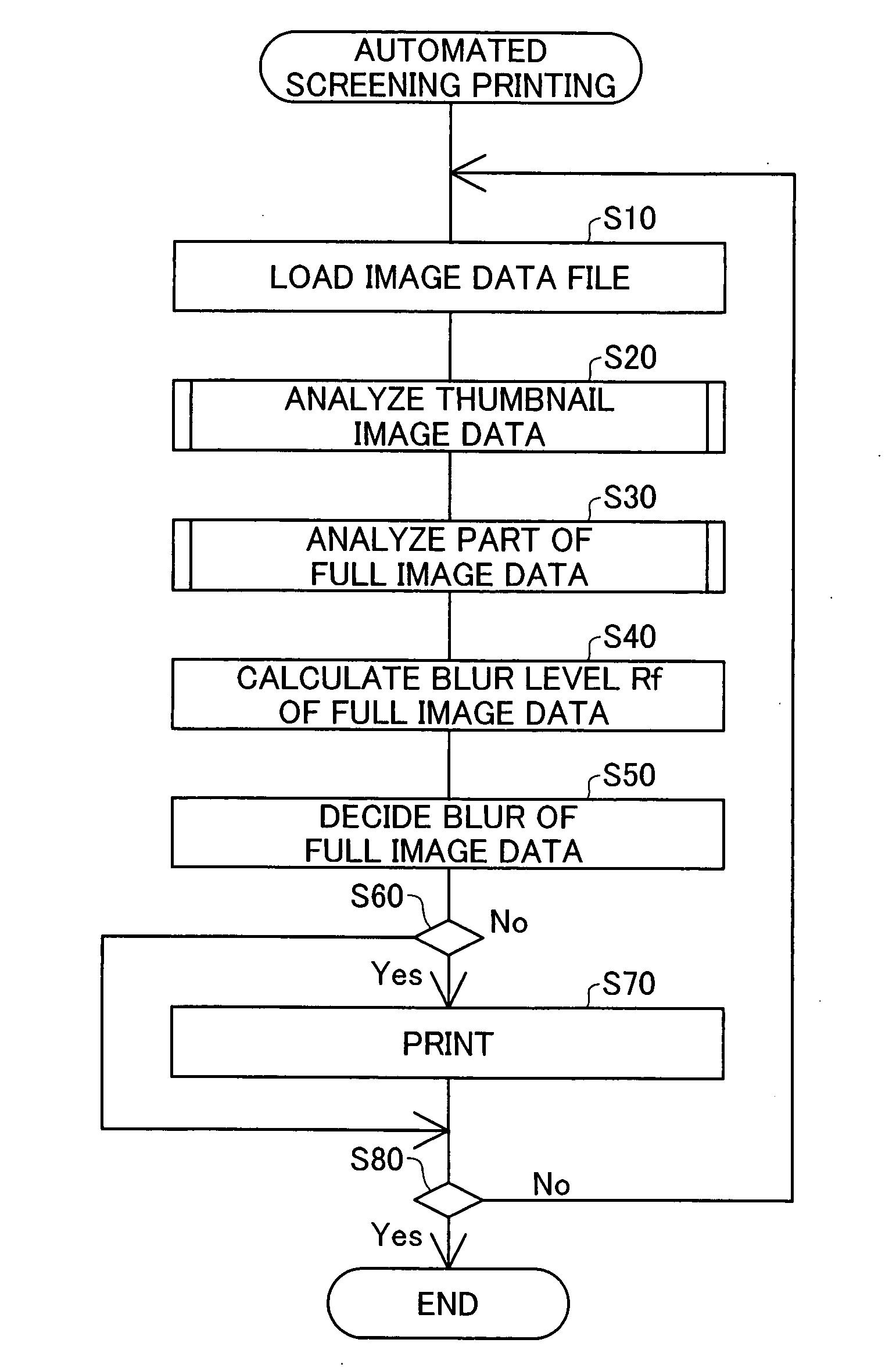
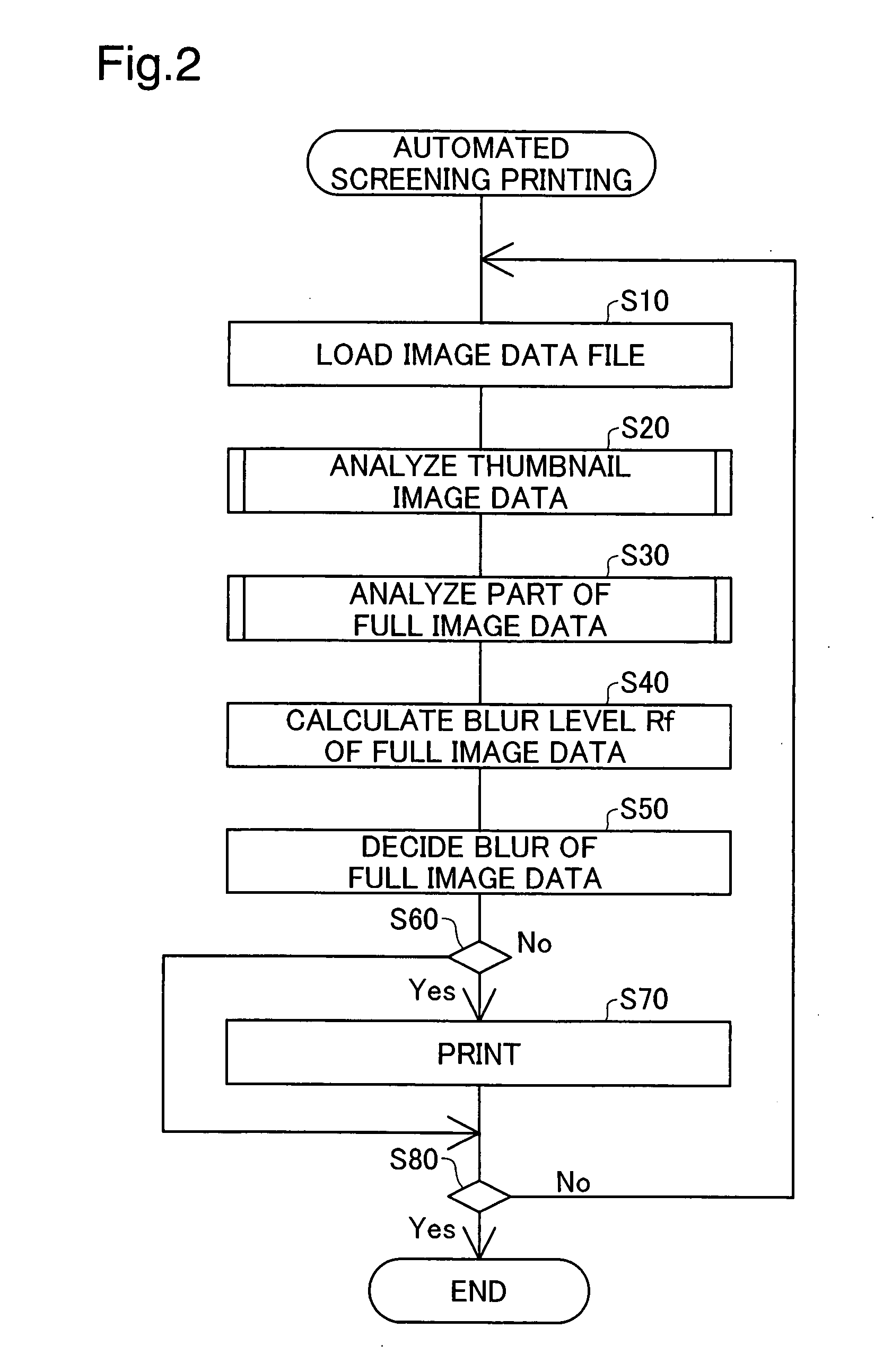
InactiveUS20070279696A1Efficient preparationBlurred imageImage enhancementImage analysisData fileThumbnail Image
A technology for making determinations as to whether the image of an image data file is blurred, with low processing load, is provided. First, photographic image data PID containing pixel color information, as well as thumbnail image data for the photographic image data, are prepared. A specific pixel is then selected from among the pixels of the thumbnail image data. Specifically, on the basis of data of a pixel under examination and data of a pixel neighboring the pixel under examination, it is determined whether the pixel under examination should be designated as the specific pixel. Then, for a specific region Ape which is a region constituting part of the photographic image data PID and which corresponds to the specific pixel of the thumbnail image data, analysis of the photographic image PID is carried out, and a localized blur level that represents indistinctness of the image in the specific region Ape is calculated. Subsequently, in the event that the localized blur level of the specific region Ape contained in the photographic image data PID meets a prescribed condition, it is determined that the image of the photographic image data PID is blurred.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Lamp and use thereof
InactiveUS20100073955A1GamutIncrease brightnessNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceCurve lineLight emission
A lamp for emitting light, comprising a transparent sheet-like lightguide, with at least one light receiving side, a light emission front surface and a back surface opposite the front surface. The lamp further comprises a plurality of light sources, positioned in an array and optically coupled to at least one light receiving side. The back surface of said lamp comprises a plurality of optical extraction structures, for example provided in parallel curved lines. Furthermore, the lamp is substantially free from light scattering structures in a light path of the light to be emitted.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
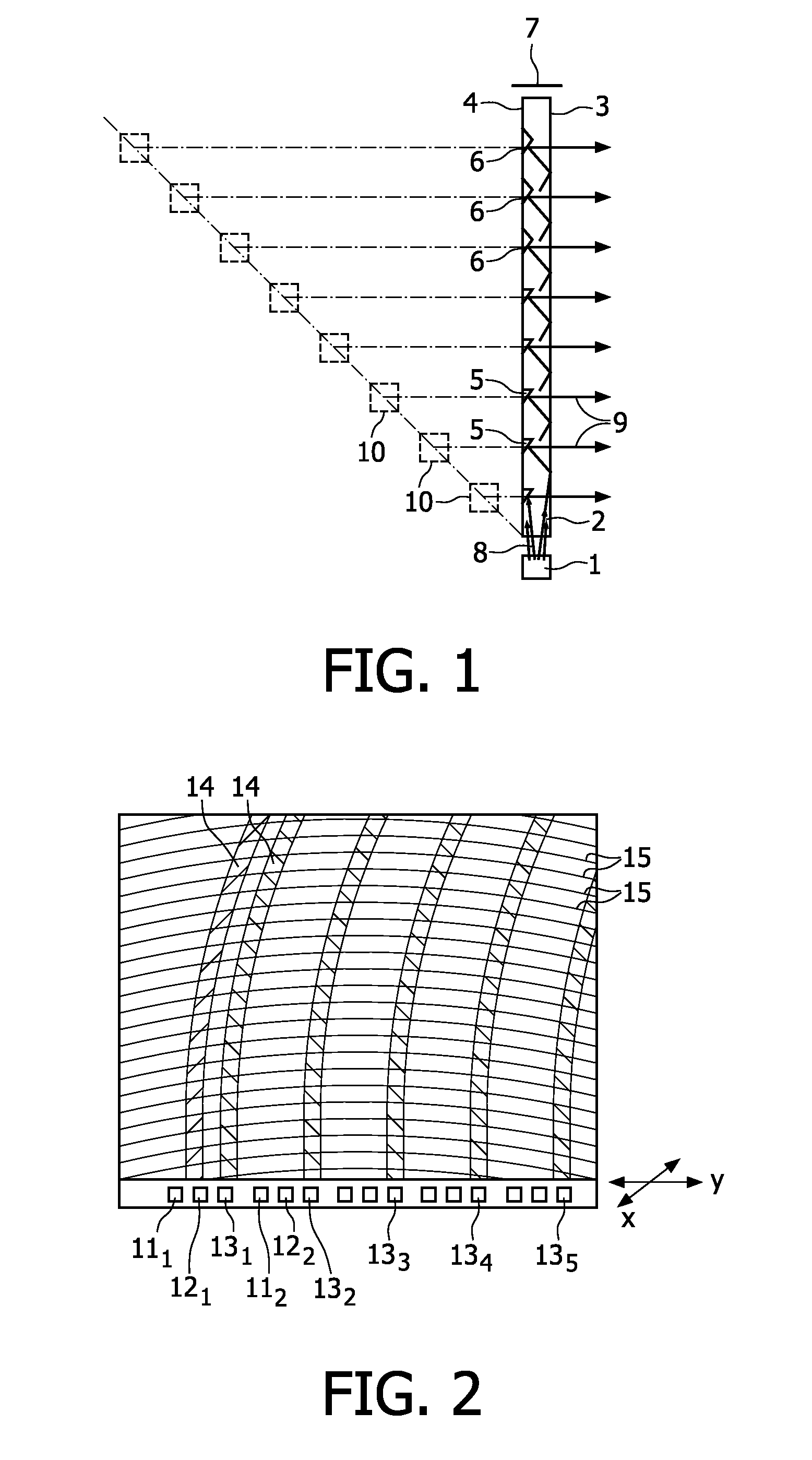
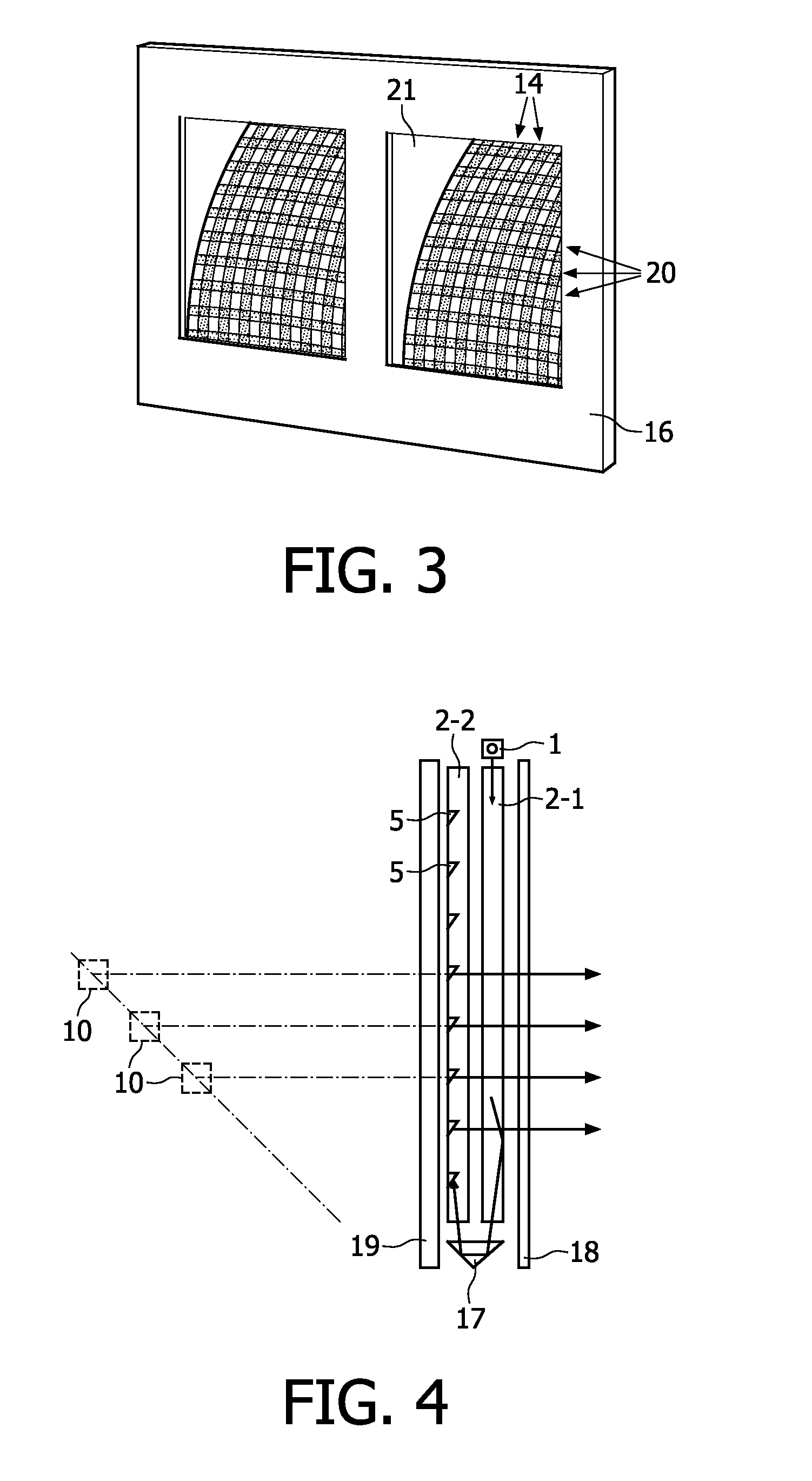
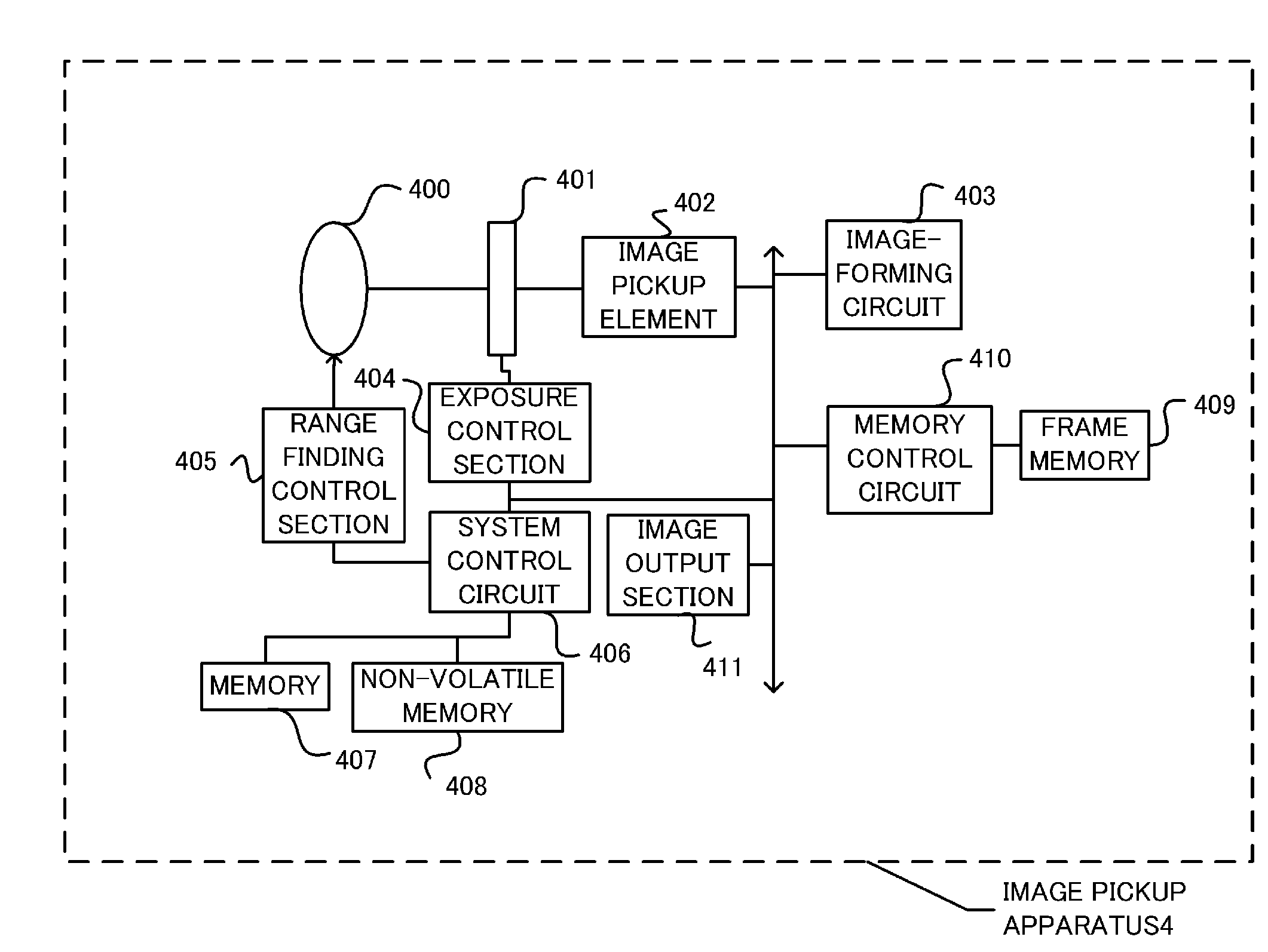
Image processing apparatus, image pickup apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
InactiveUS20130308007A1Quality improvementEliminate degradationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingImage based
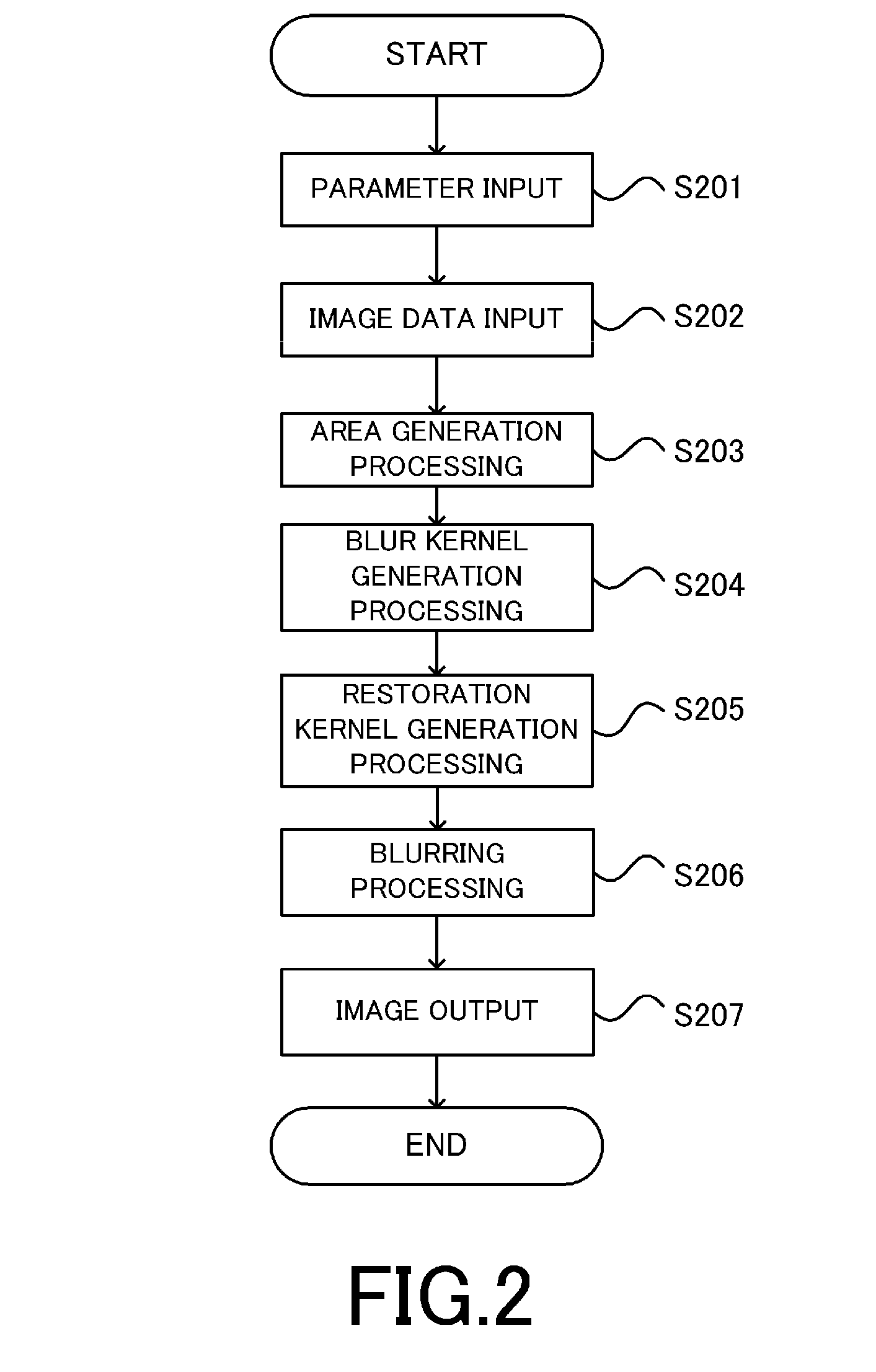
An image processing apparatus that blurs a picked-up image based on distance information on a subject, comprises a restoration kernel acquisition section that acquires a restoration kernel as a kernel for eliminating degradation of an image; a blur kernel acquisition section that acquires a blur kernel as a kernel for blurring the image; a compound kernel acquisition section that acquires a compound kernel obtained by merging the restoration kernel with the blur kernel; and an image processing section that eliminates the degradation of the picked-up image and blurs the picked-up image by using the compound kernel.
Owner:CANON KK
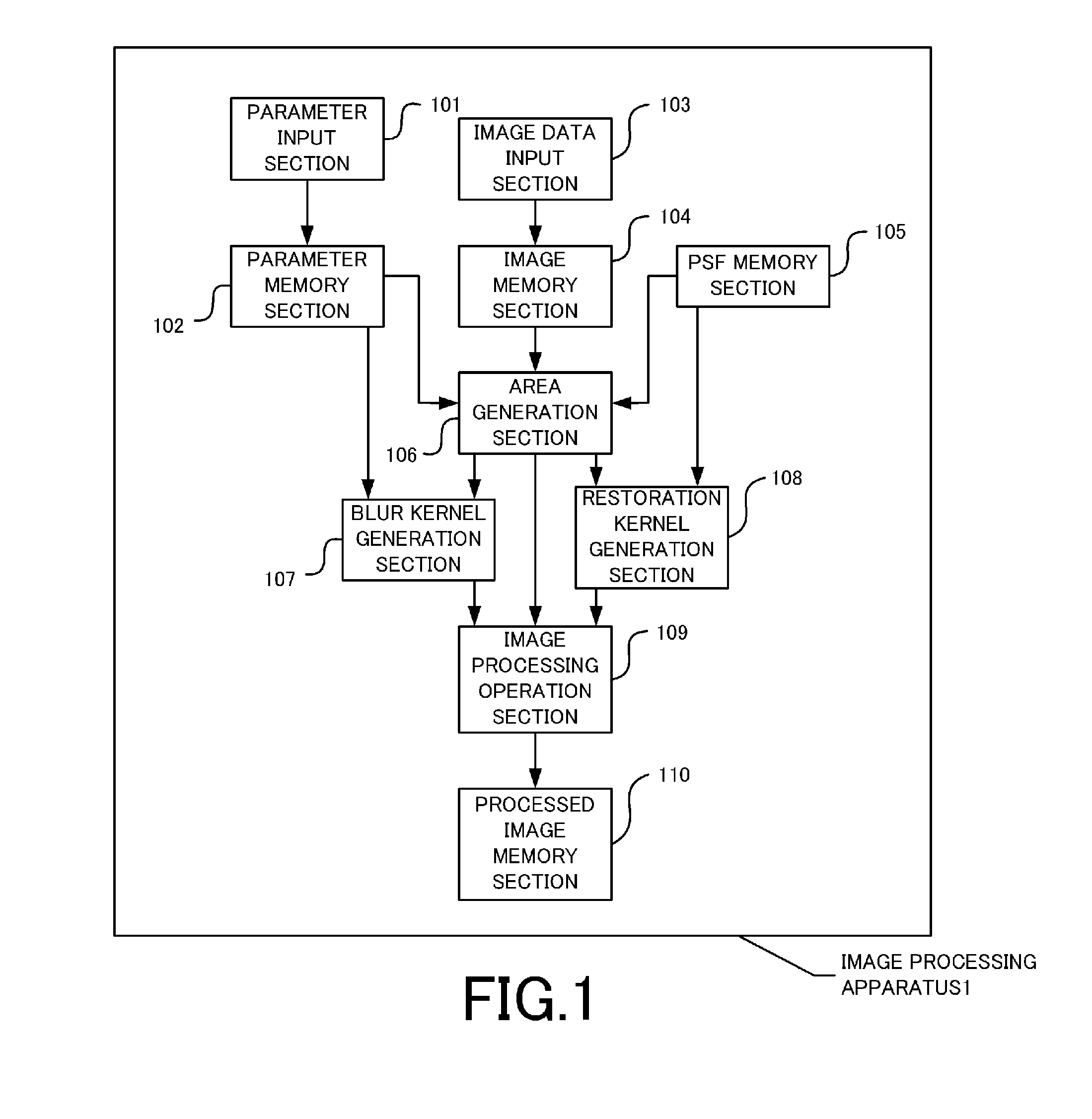
Image processing apparatus, imaging apparatus, and computer readable medium
ActiveUS20110249151A1Reduce noiseBlurred imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingRadiology
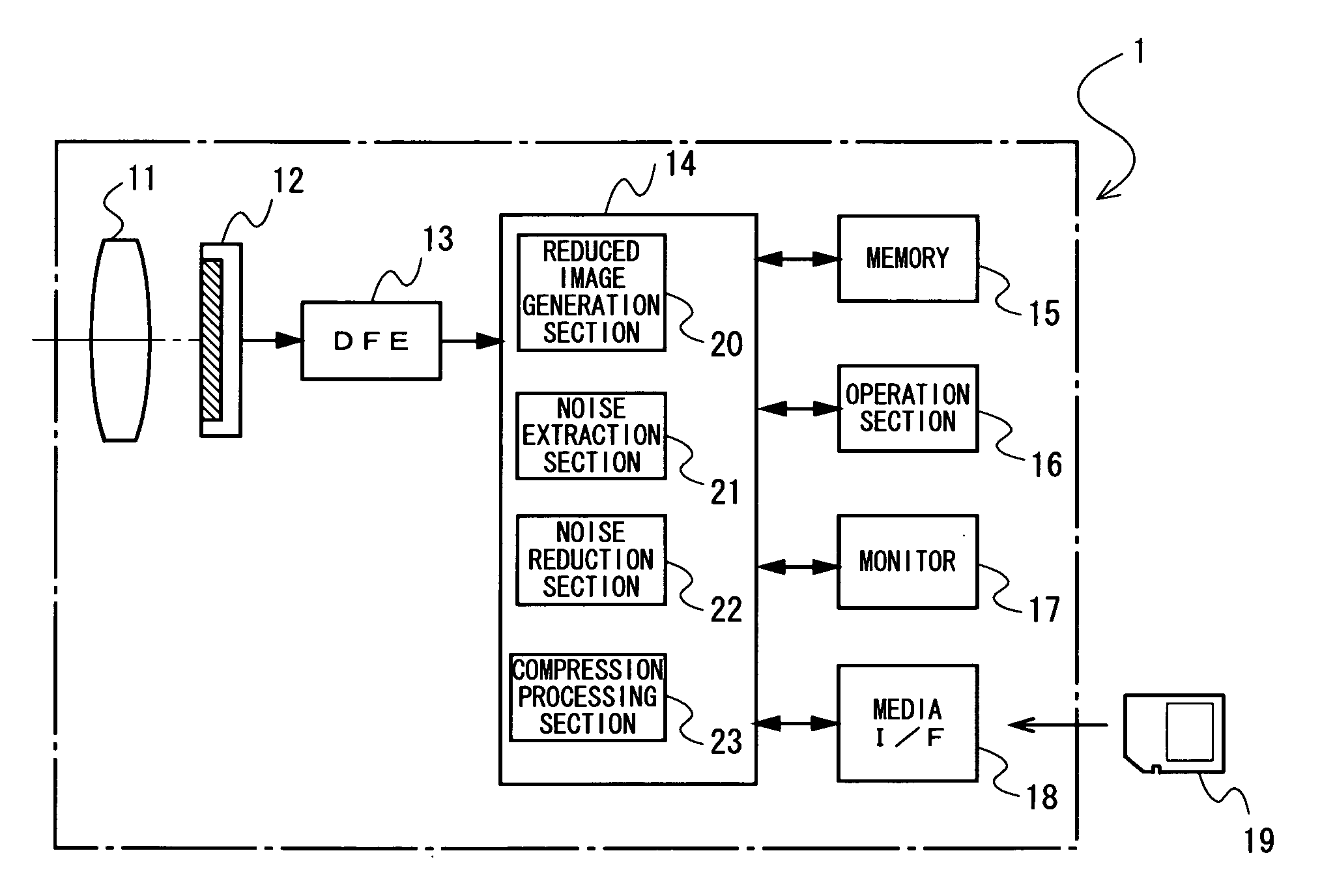
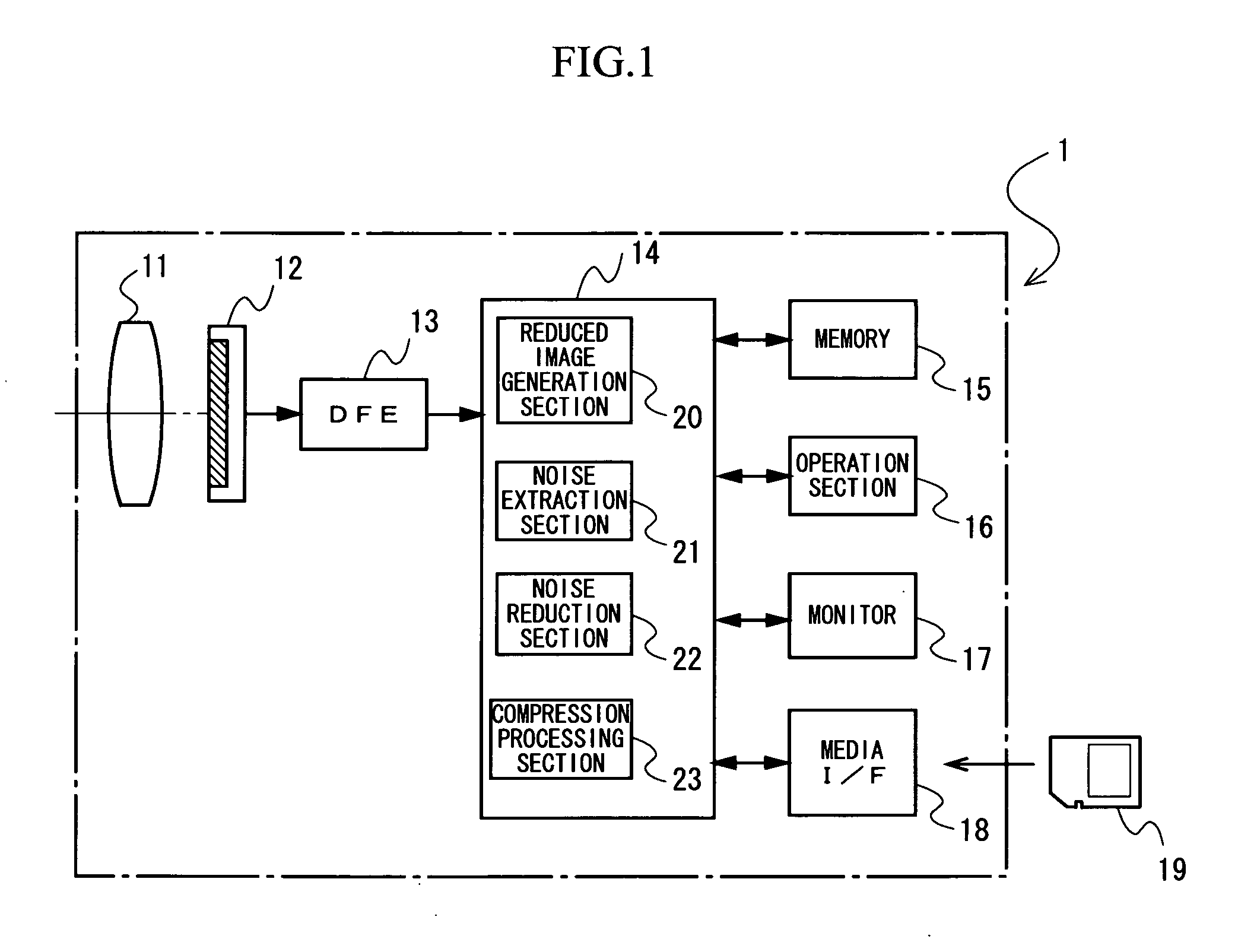
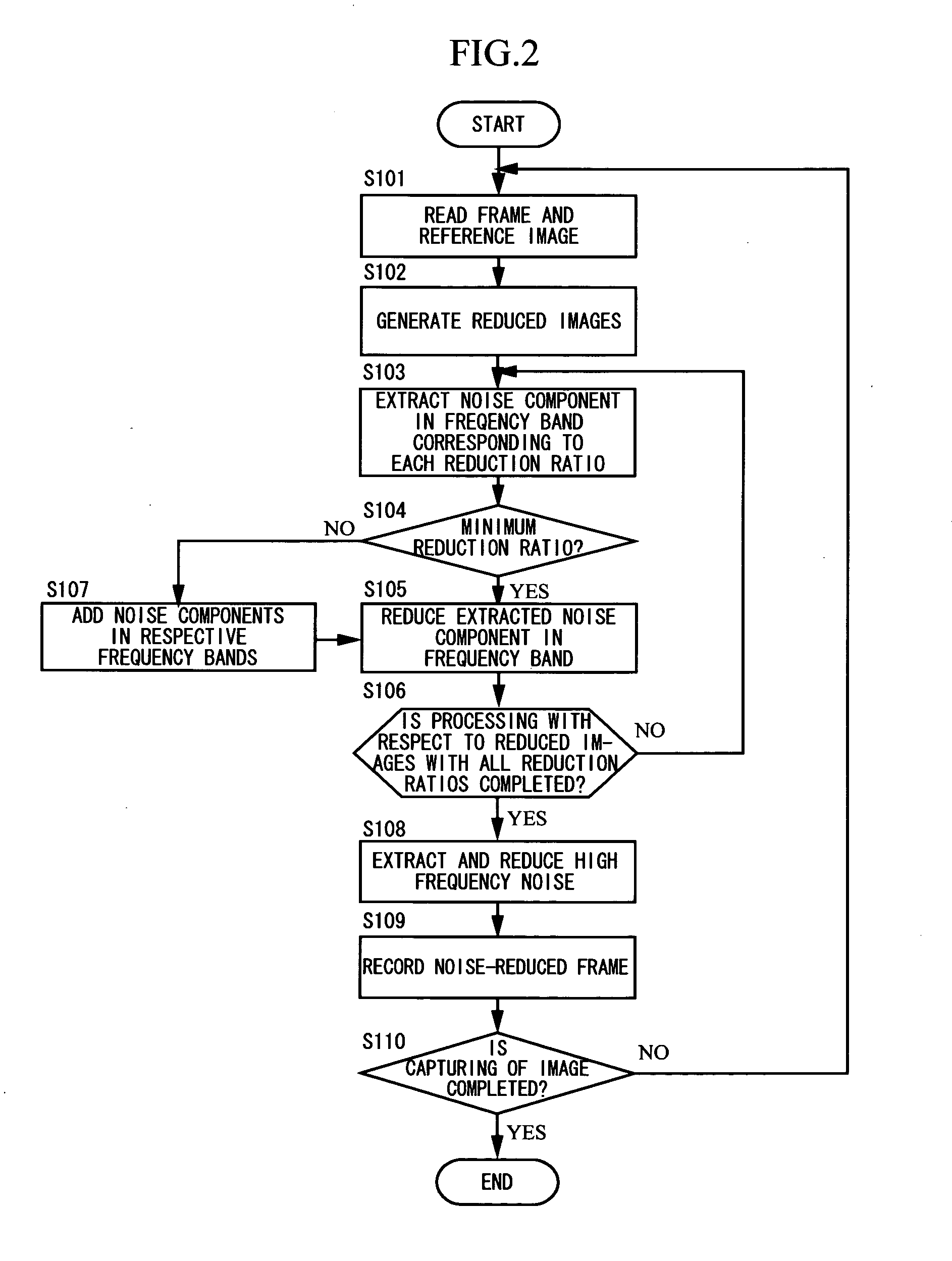
An image processing apparatus of the present application includes a reduced image generation section generating a first reduced image obtained by reducing at least a target image being a noise reduction target, out of the target image and a reference image to be a reference of a noise reduction processing, a noise extraction section extracting a noise component in a frequency band corresponding to a reduction ratio of the first reduced image by using at least the first reduced image, and a noise reduction section reducing the noise component in the frequency band from a pixel value of each pixel of the target image based on the noise component in the frequency band being extracted.
Owner:NIKON CORP
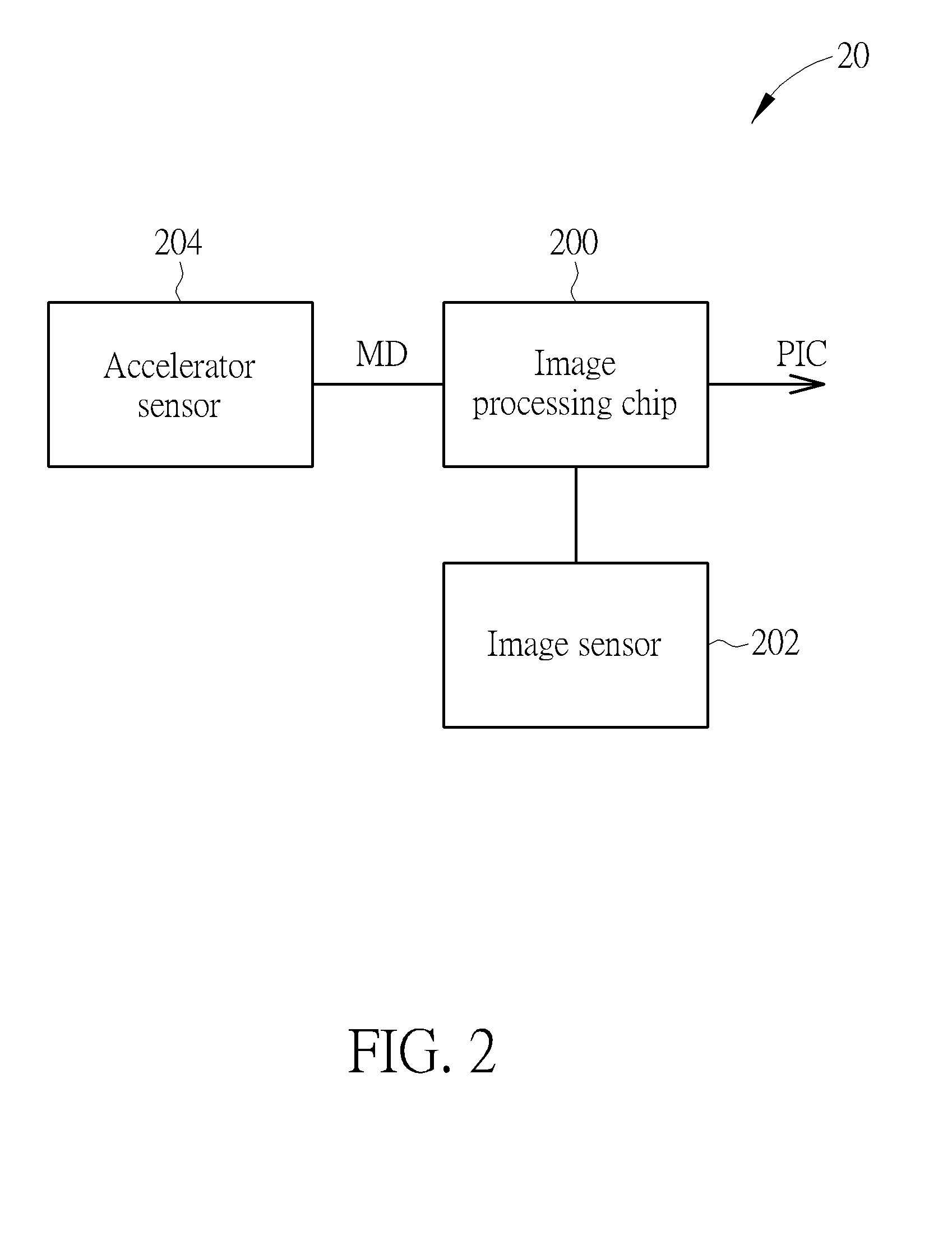
Image Blurring Avoiding Method and Image Processing Chip Thereof
InactiveUS20140294370A1Blurred imageAvoid image blurCamera body detailsOptical elementsImage processing
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Organic Light Emitting Display Device and Method for Manufacturing the Same
ActiveUS20200083484A1Improve luminanceSimple manufacturing processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceHigh luminance
An organic light-emitting display device capable of improving luminance and light extraction efficiency thereof while preventing image blur, and a method for manufacturing the same is disclosed. In accordance with the device and the method, image blur is suppressed and luminance and light-emitting efficiency are improved by forming micro-lenses on an encapsulating layer for protecting organic light-emitting elements at precise positions corresponding to the elements in a self-aligned and self-assembled manner.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Method and Apparatus Converting moving Image, Method and Apparatus for Reproducing Moving Image, and Computer Program
InactiveUS20090015710A1Reduce in quantityBlurred imageTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationLow-pass filterHarmonic
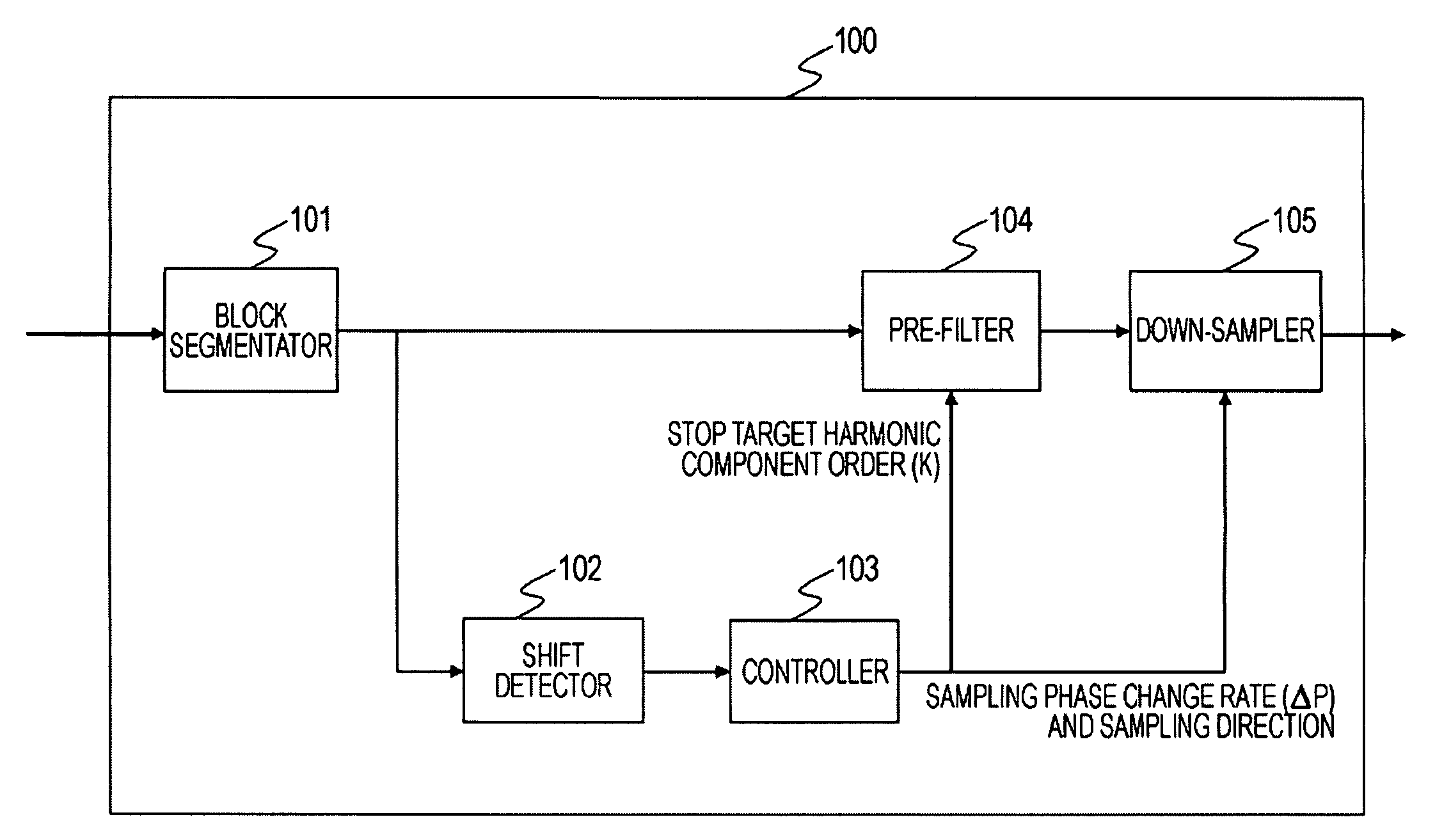
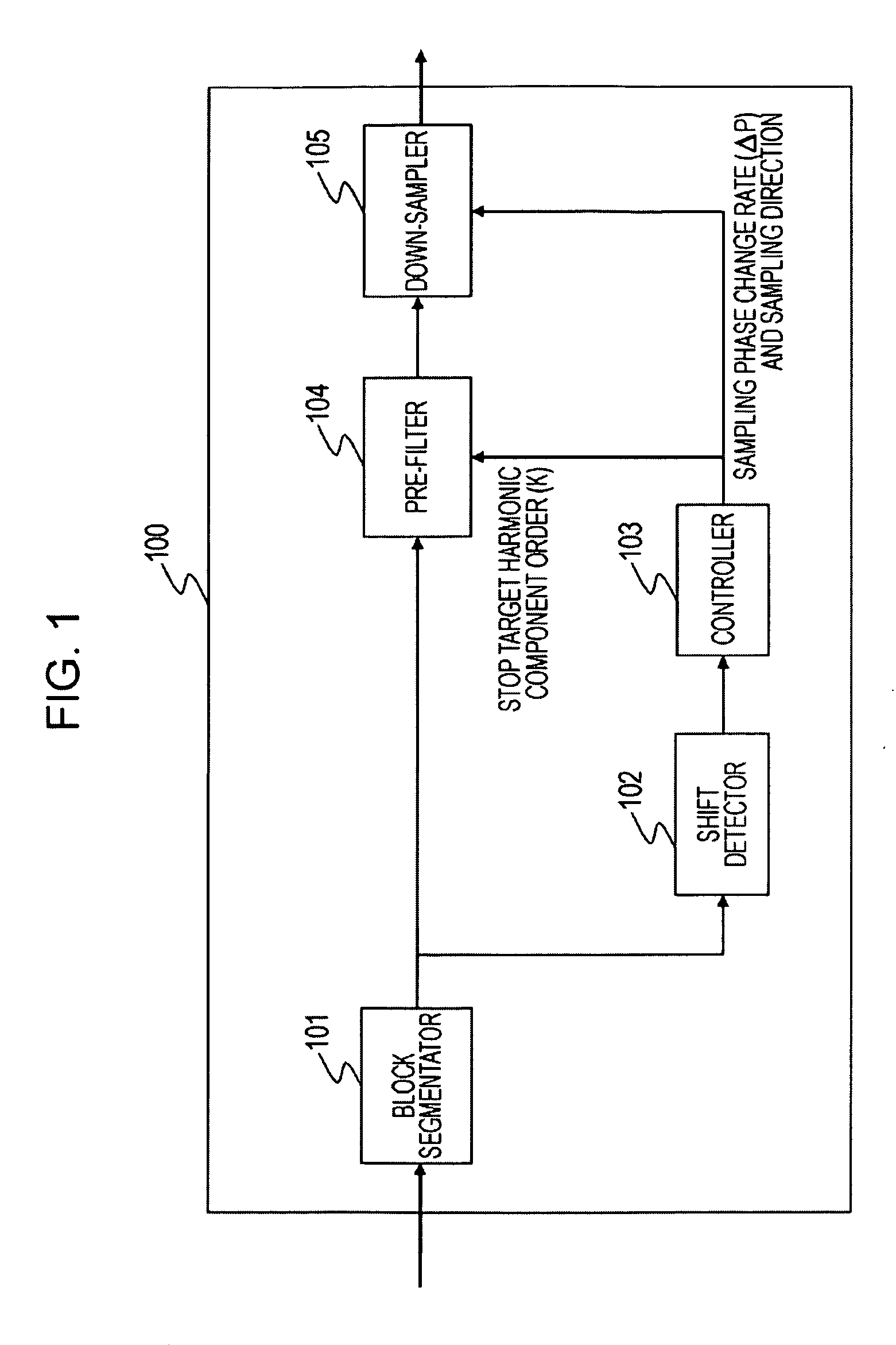
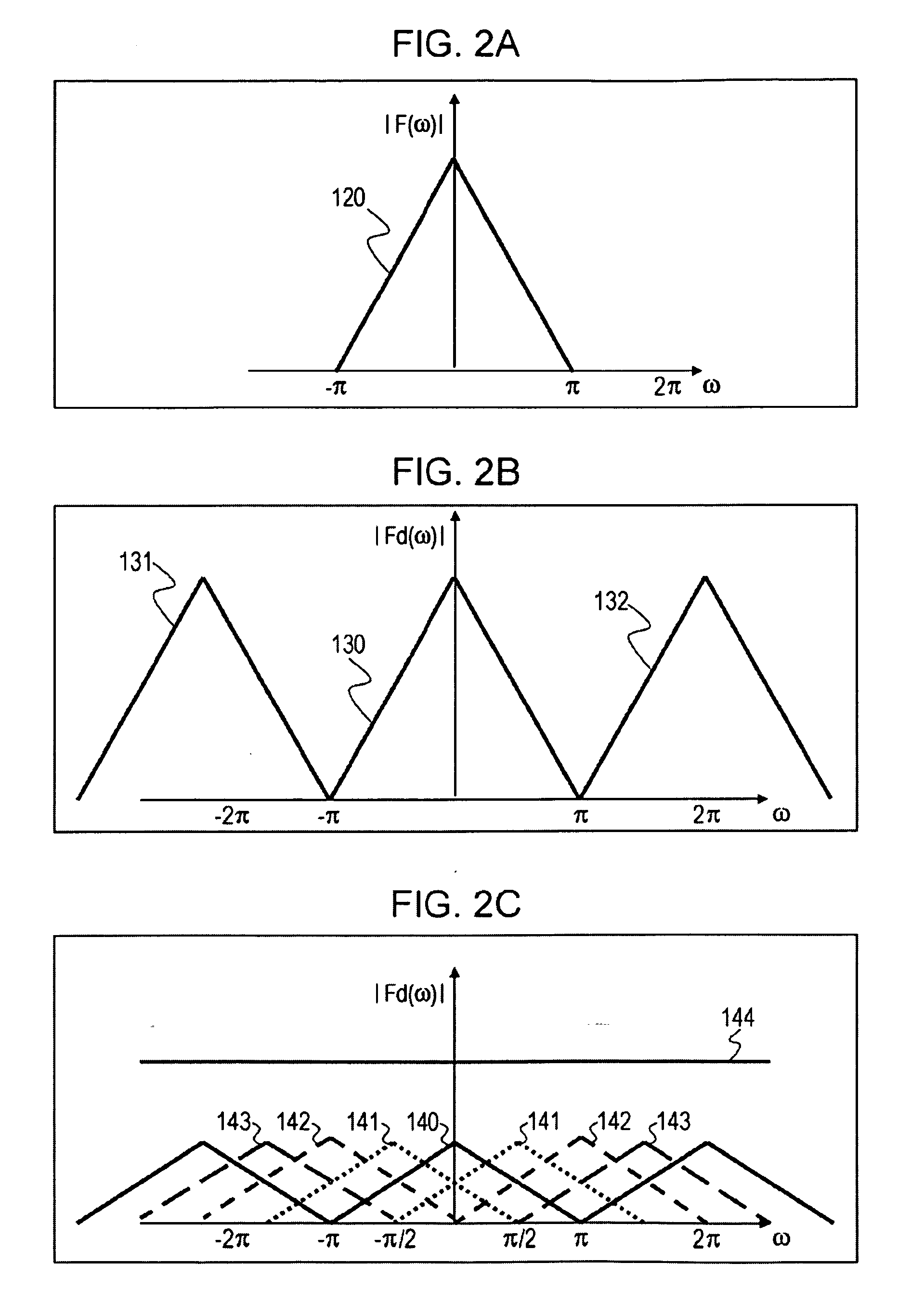
A down-sampling operation is performed on moving image data to reduce a sample count of the data to 1 / M times the original sample count. In the down-sampling operation, a band-limitation operation is performed on the moving image data using a low-pass filter. The low-pass filter has a stop band frequency that prevents a harmonic component having a K-th order or higher, of harmonic components generated in the down-sampling operation, from overlapping an original signal component. The down-sampling operation is then performed on the band-limited moving image data, thereby compressing the moving image data. Aliasing distortion caused by a harmonic component of a high order is controlled. The resulting compressed image is free from a substantial loss of a high-frequency component of the original signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
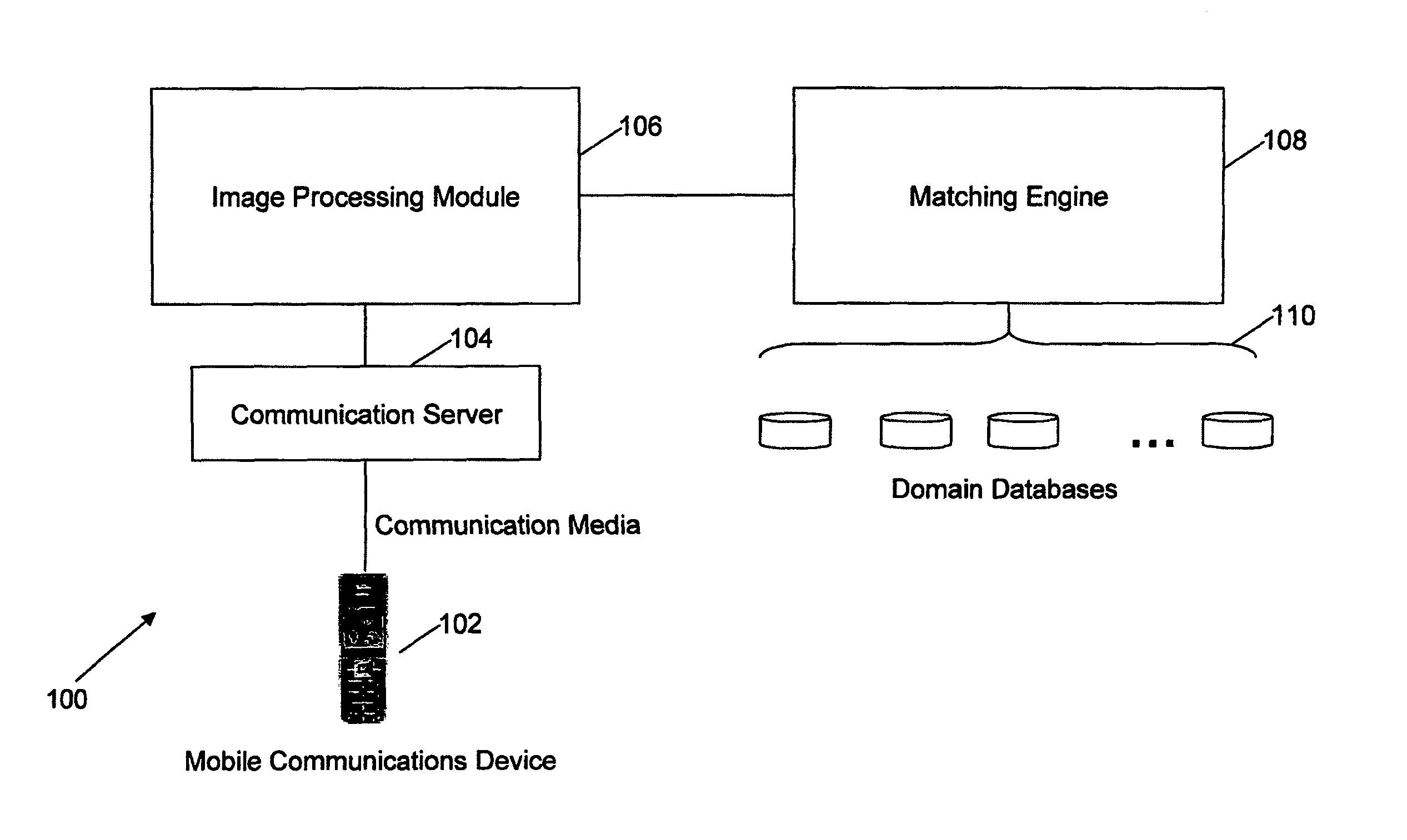
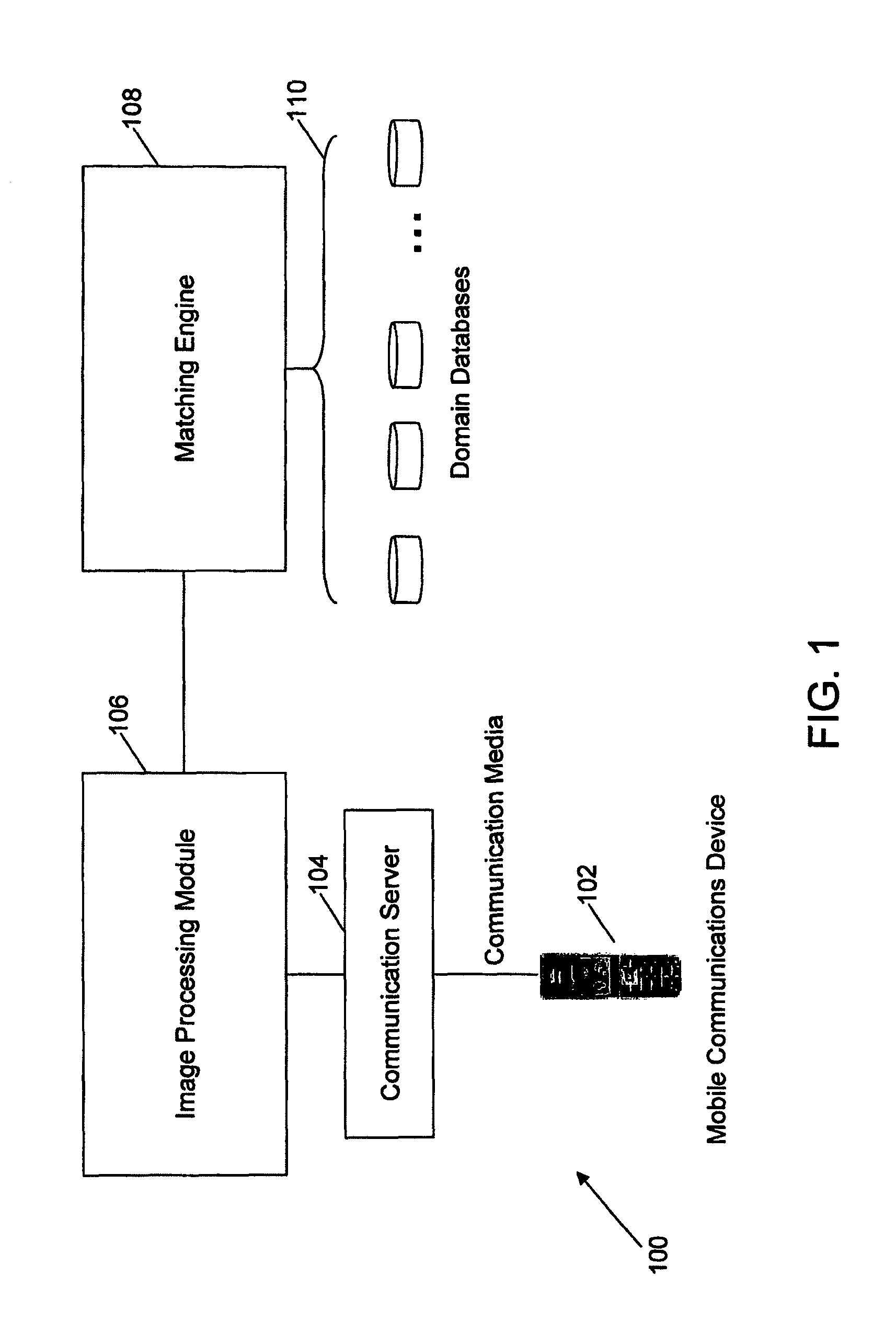
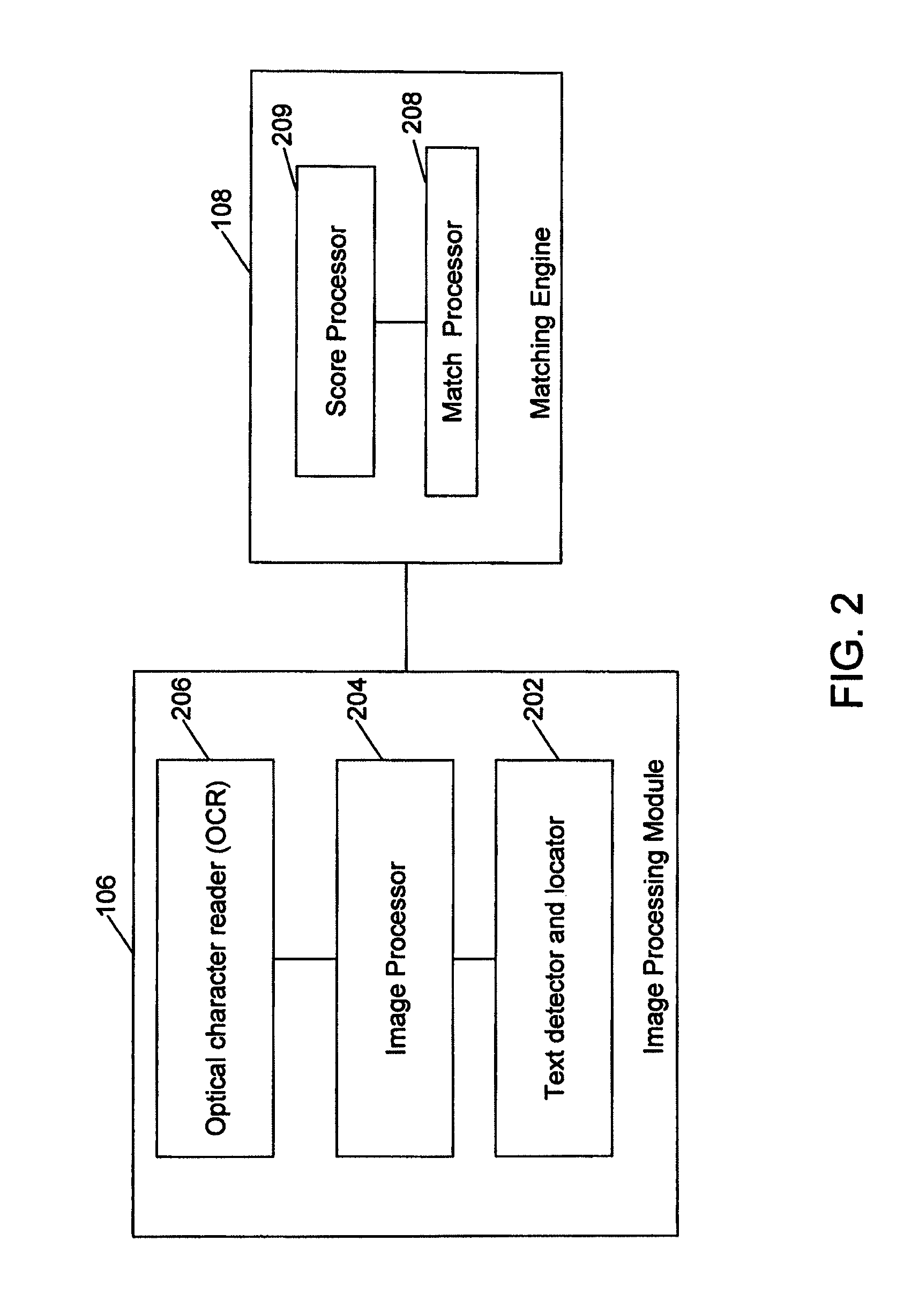
Method and system for searching for information on a network in response to an image query sent by a user from a mobile communications device
ActiveUS8249347B1Quality improvementBlurred imageSpecial data processing applicationsCharacter recognitionImage queryNetwork on
Owner:A9 COM INC
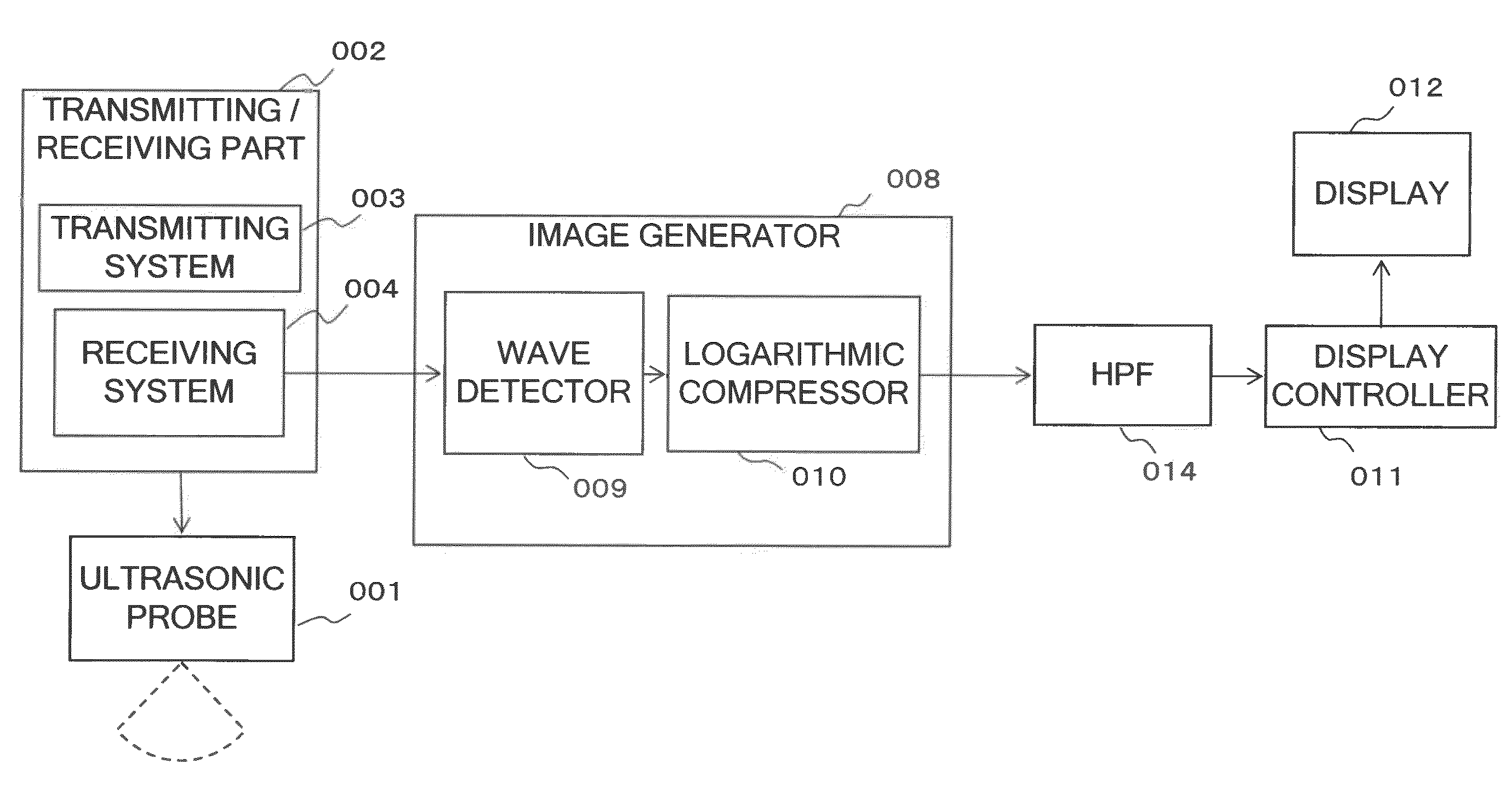
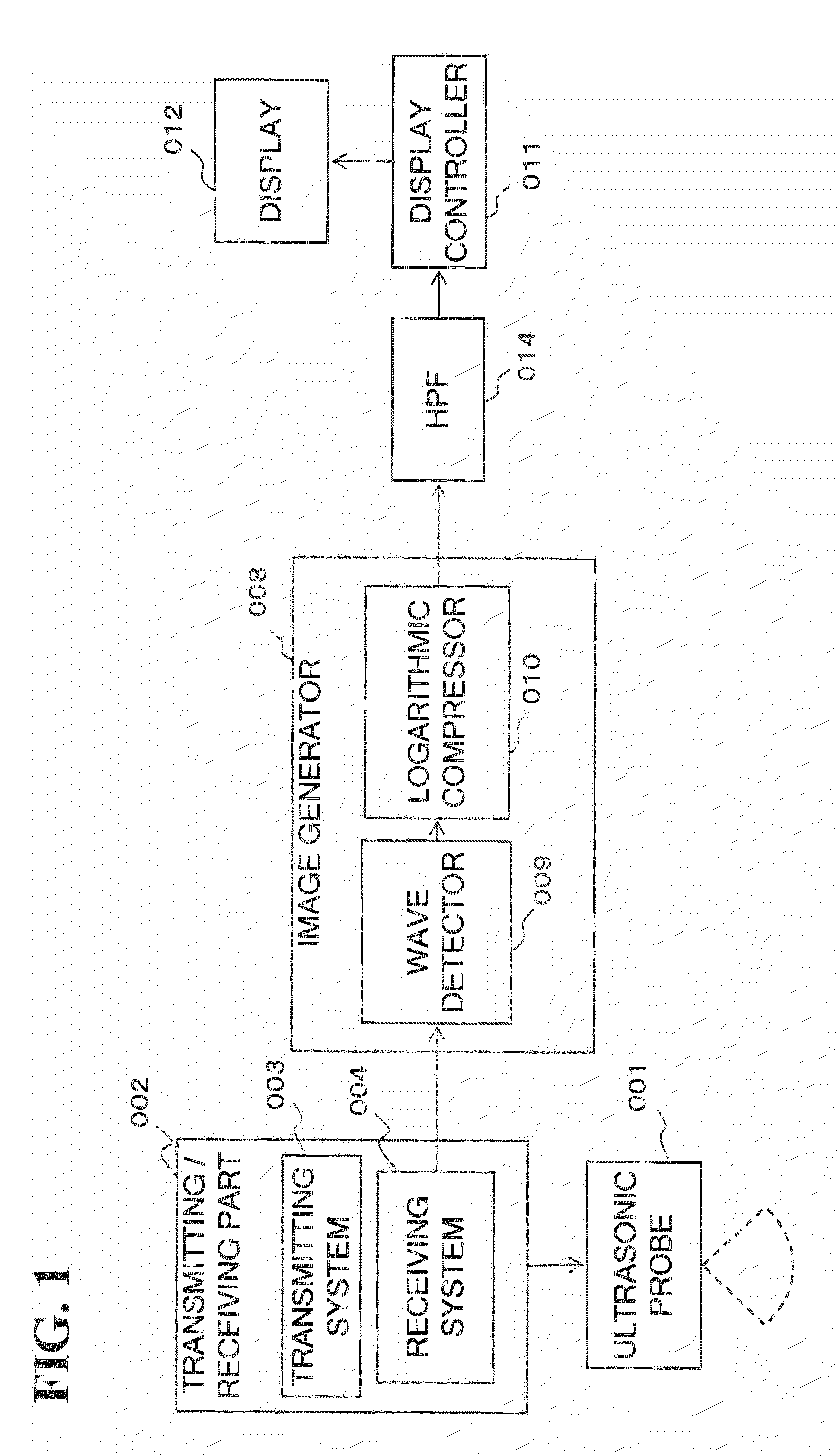
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus and control method for ultrasonic imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20100137715A1Promote generationLarge amplitudeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsSmall amplitudeSonification
A scanning part ultrasonically scans a cross section of a subject corresponding to a frame period. The filter processor uses time-series received signals that are obtained from the scanning part corresponding to a plurality of frames to attenuate low-frequency components from the received signals of a plurality of locations within the cross section. The amplitude-comparator compares the amplitudes of the received signals with the amplitudes of the signals for which the low-frequency components have been attenuated, and the signals with smaller amplitudes are output. The image-generator generates morphological images of the subject based on the output signals from the amplitude-comparator.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
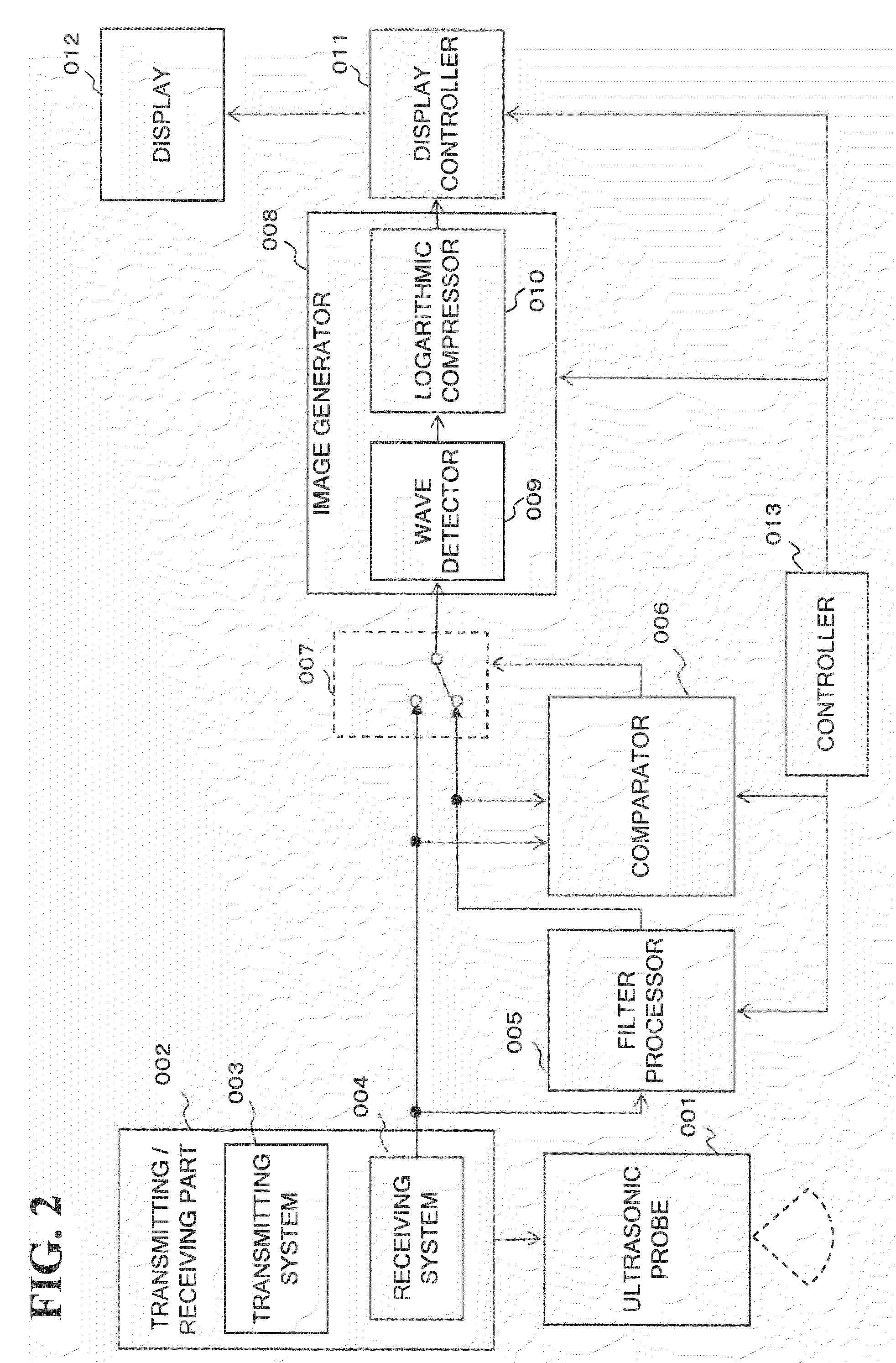
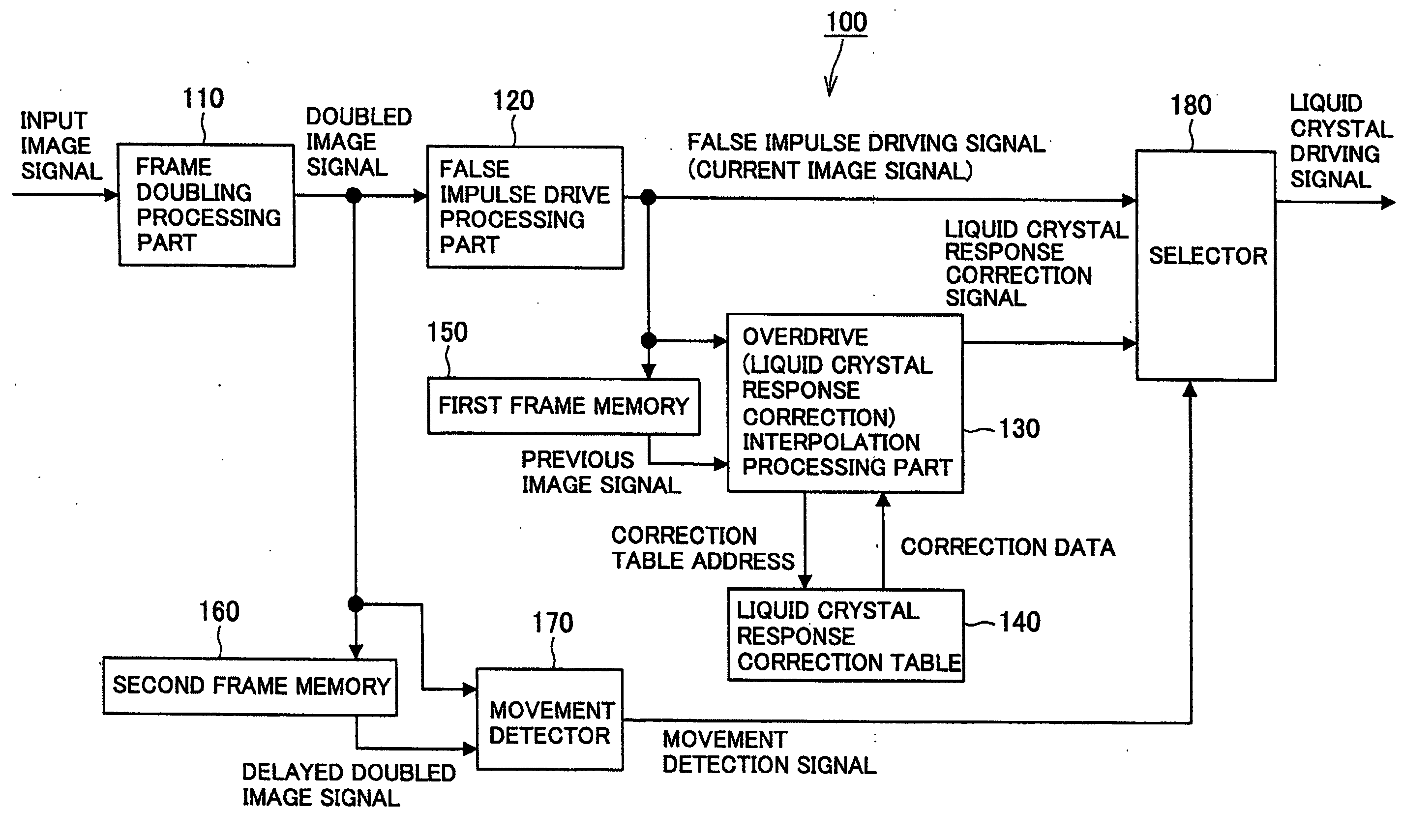
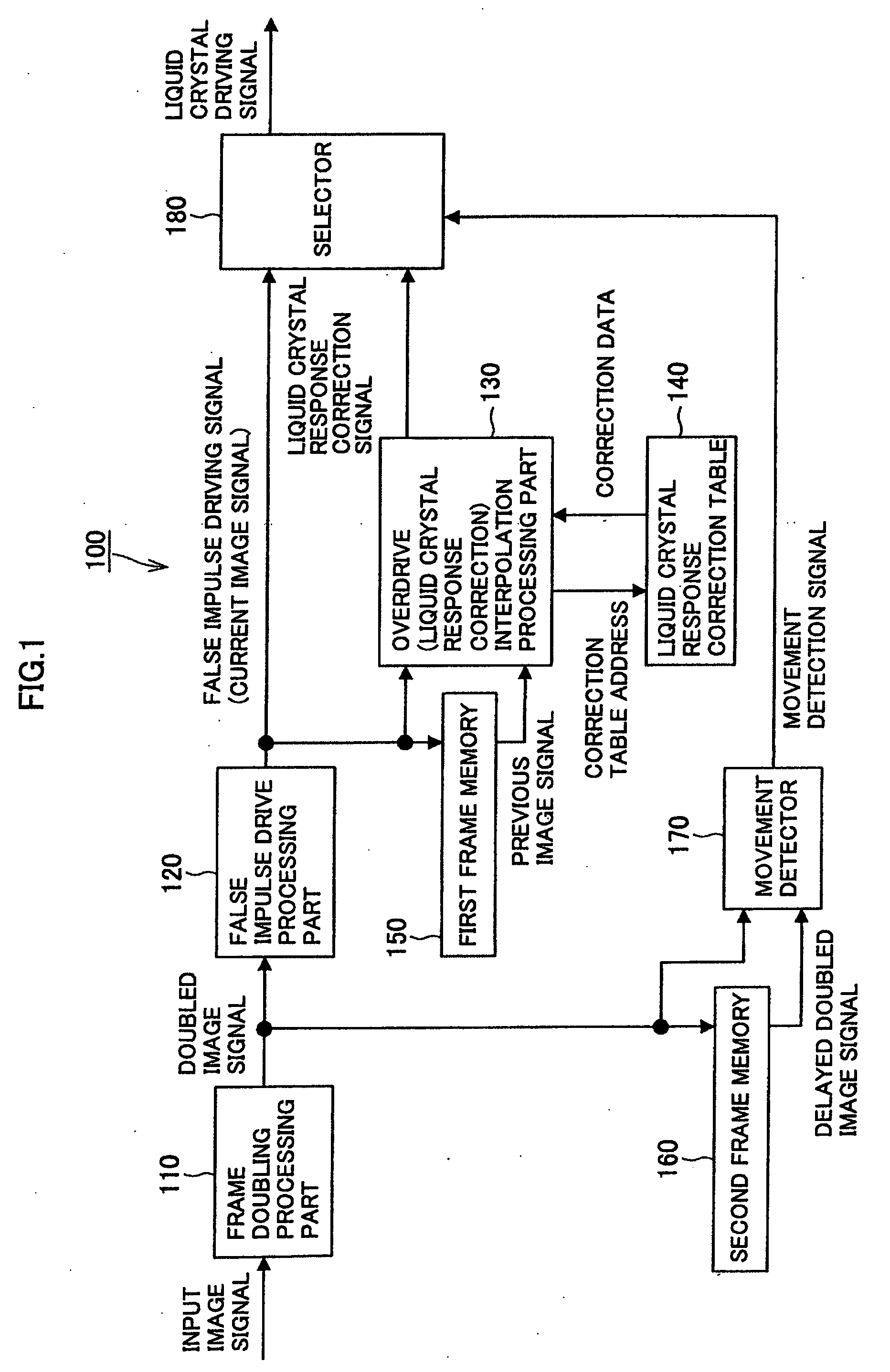
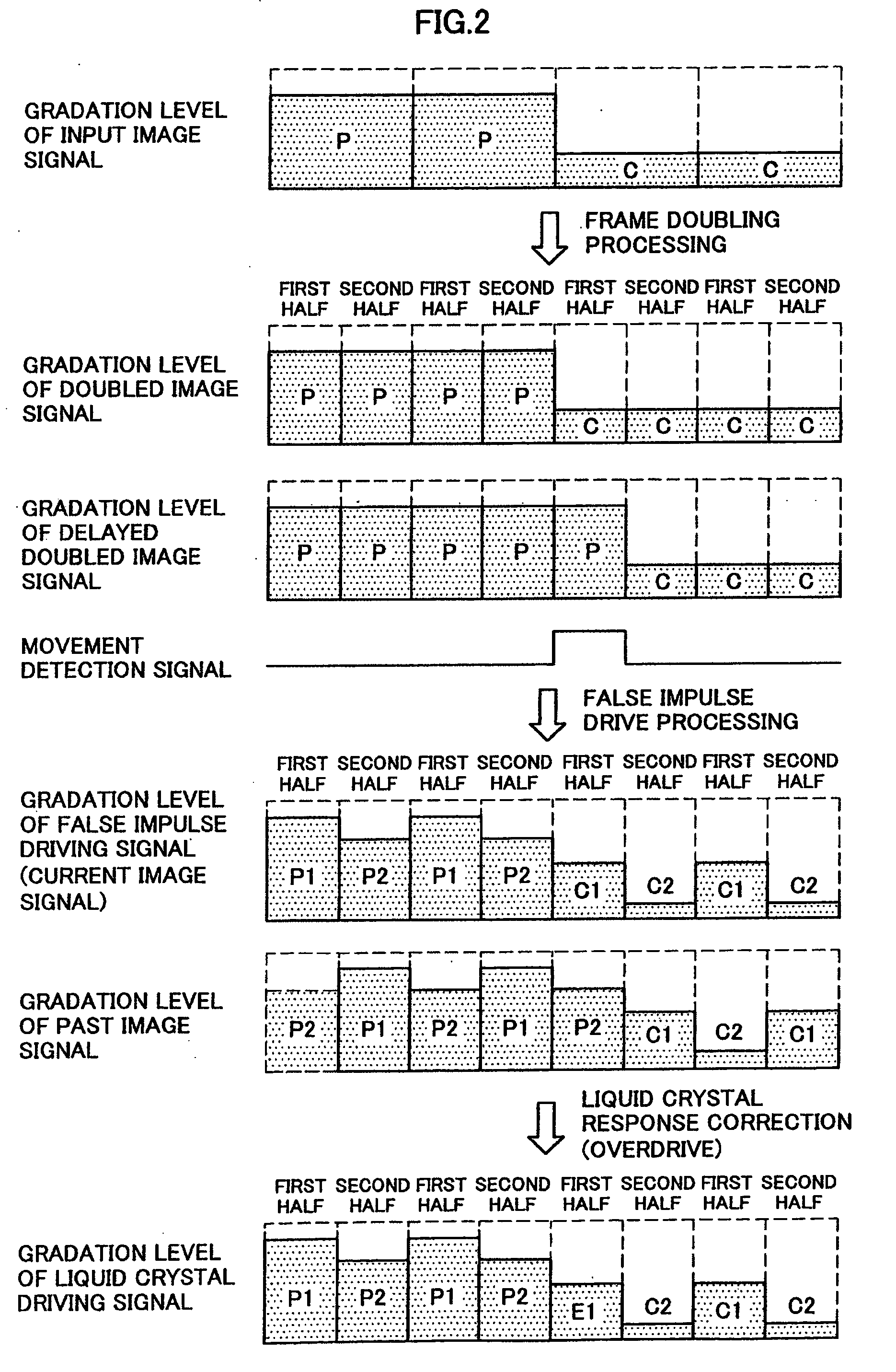
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and computer program
InactiveUS20090009509A1Avoid image blurImprove image blurCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingImaging SignalImage signal
An image processing apparatus including a frame doubling processing part for generating a doubled image signal, a false impulse drive processing part for outputting a current image signal after dividing the doubled image signal, a first frame memory for outputting the current image signal as a previous image signal delayed by one sub-frame, a correction processing part for correcting a gradation level of the current image signal after the previous image signal and the current image signal being input thereto, a second frame memory for outputting a delayed doubled image signal from the doubled image signal, and a movement detector for outputting a movement detection signal after the delayed doubled image signal and the doubled image signal being input thereto is provided, wherein the correction processing part corrects the gradation level of the current image signal when the movement detection signal is a signal indicating a dynamic image.
Owner:SONY CORP
Ultraviolet-curable liquid developer
InactiveUS20160349651A1Low resistivityImage deteriorationElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersVinyl etherUltraviolet
An ultraviolet-curable liquid developer containing a cationically polymerizable liquid monomer, a photoinitiator, and a toner particle, wherein the cationically polymerizable liquid monomer contains a vinyl ether compound, the molar average SP value of the cationically polymerizable liquid monomer is not more than 9.0, the molar average number of functional groups for the cationically polymerizable liquid monomer is at least 1.8, the photoinitiator contains a specified compound, and the content of the specified compound is at least 0.01 mass parts and not more than 5.00 mass parts per 100 mass parts of the cationically polymerizable liquid monomer.
Owner:CANON KK
Imaging device
ActiveUS20070070225A1Reduce outputBlurred imageTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryLow-pass filterFalse color
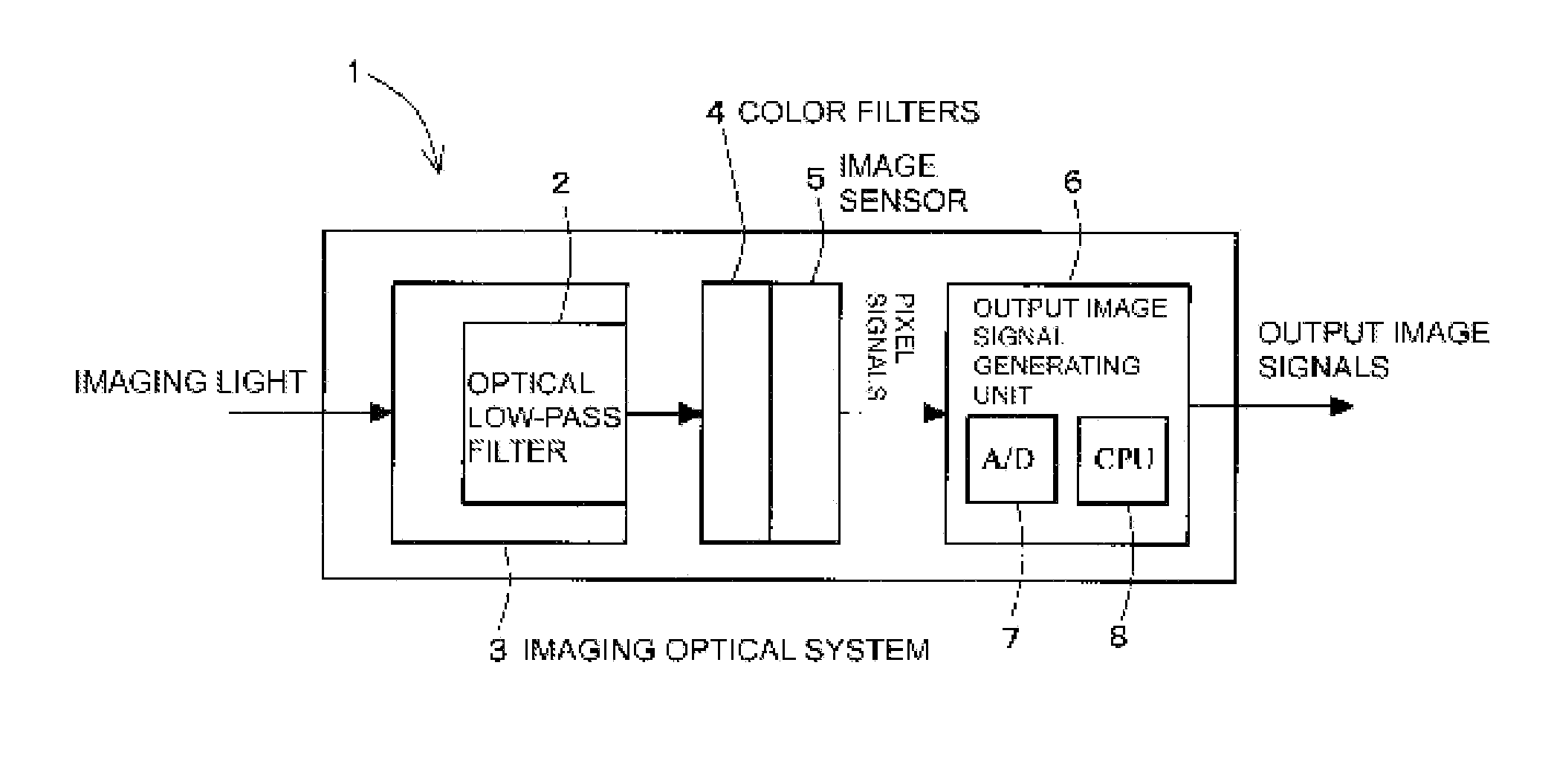
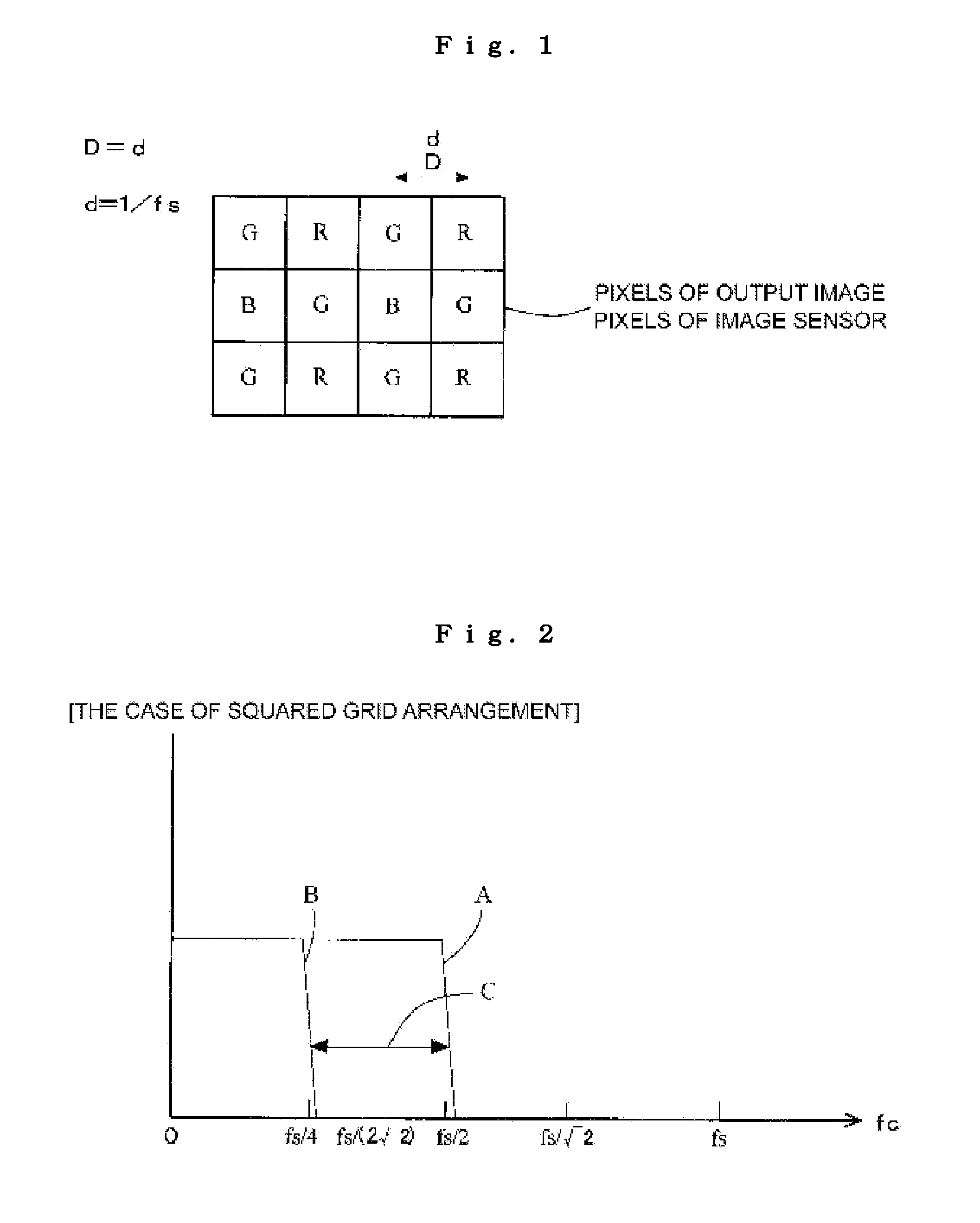
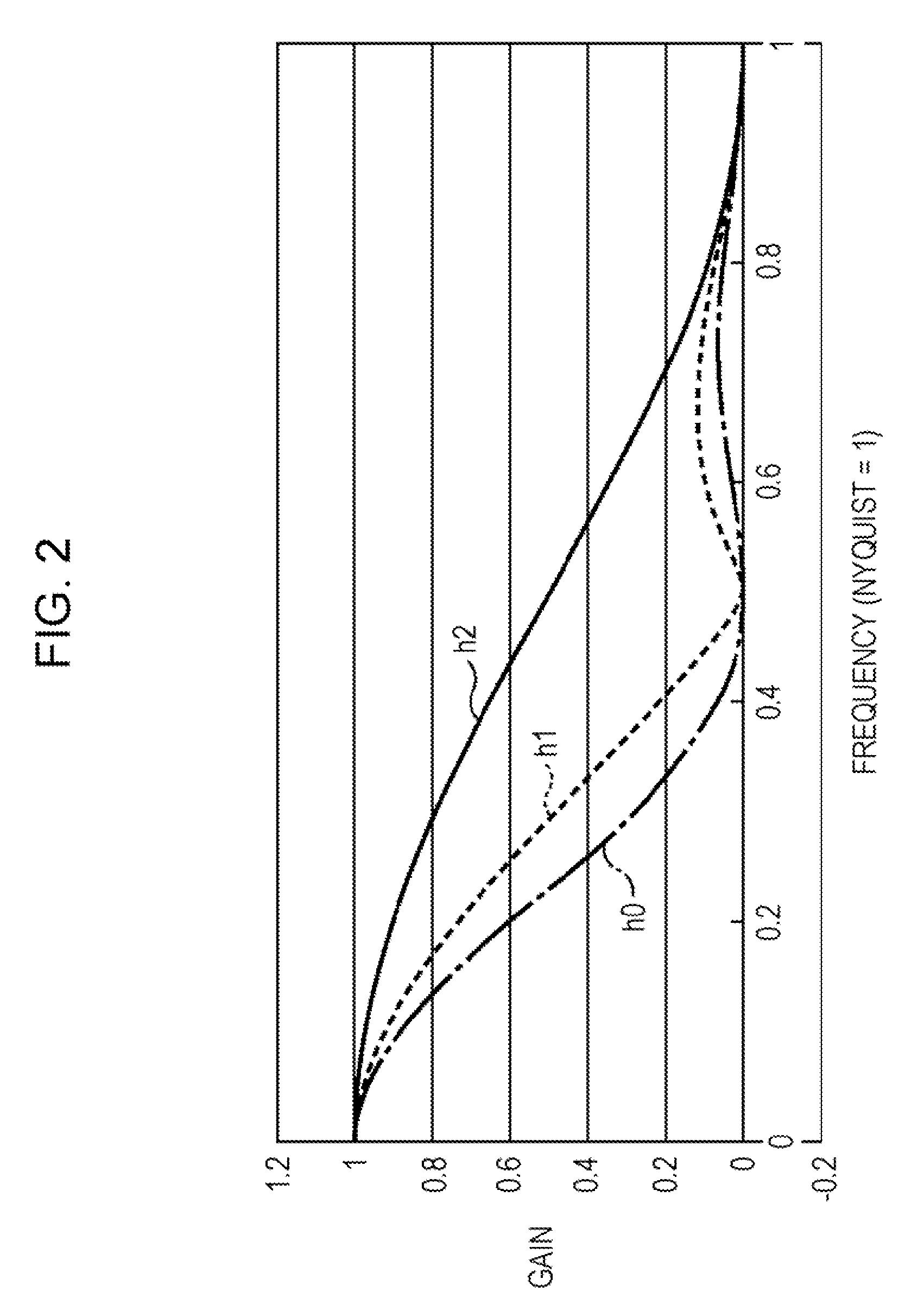
Frequency characteristics of an optical low-pass filter (2) are set in such a way that a first false color passing rate indicative of the rate of frequency components passing through a frequency component region not lower than the Nyquist frequency fa for the lowest sampling frequency fs among the sampling frequencies in the longitudinal, the lateral, and the oblique directions for each color in an image sensor (5), i.e. a frequency component region lower than one half of the Nyquist frequency fs of the sampling frequency fs of the image sensor (5), is not higher than a specified value. An output image signal is created from a pixel signal created by the image sensor (5) so that N pixel signals (N is real number of 2 or above) created by the image sensor (5) correspond to one output image signal.
Owner:RDA TECH
Image processing device and method and program
InactiveUS20090097773A1Suppressing image failureSuppressing image deteriorationTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImaging processingLow-pass filter
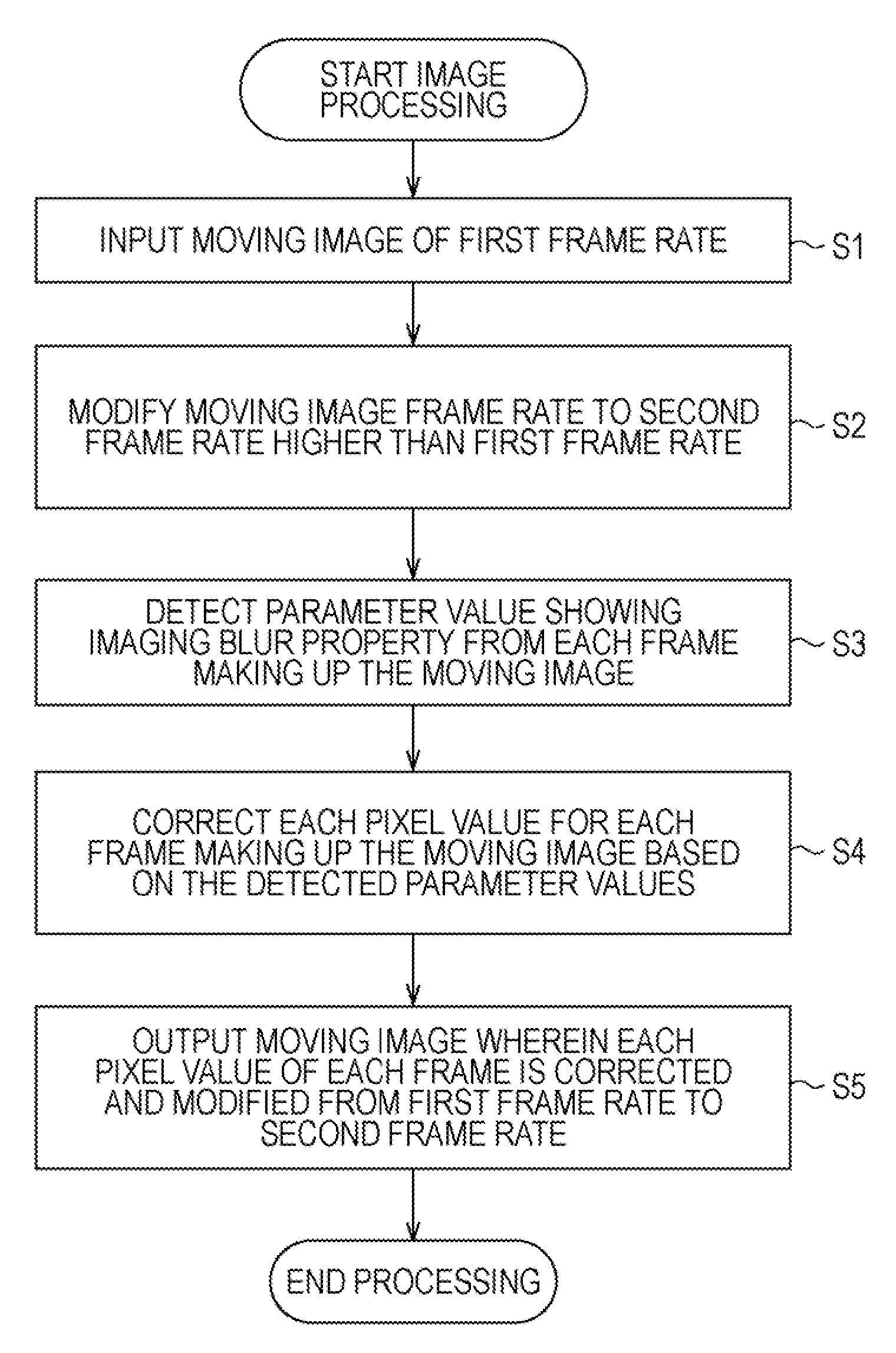
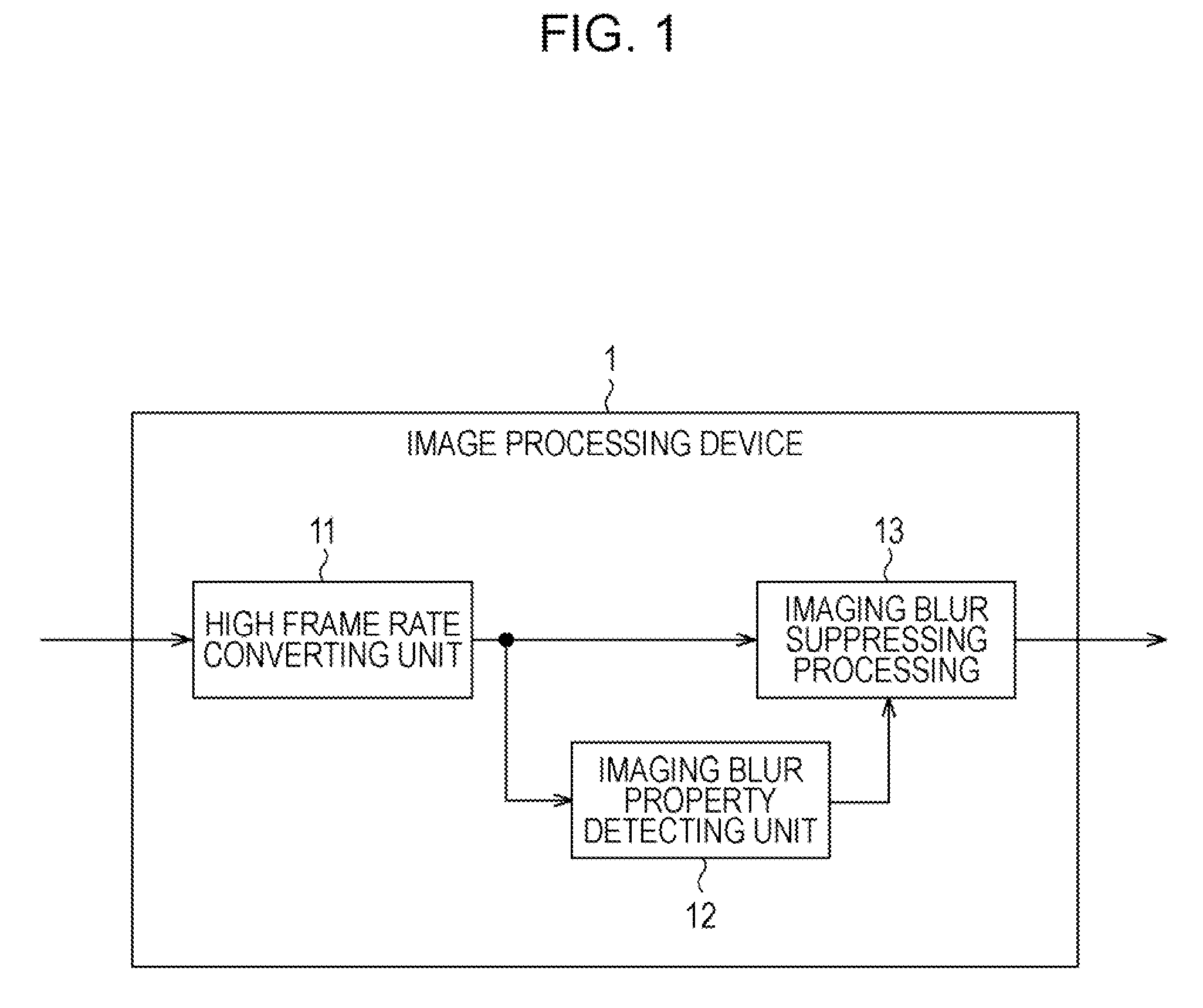
An image processing device to process a moving image, which is shot by a video shooting device, in increments of access units, includes: a correcting unit to correct the access unit to be processed by changing the properties of a low-pass filter which indicates imaging blur according to parameter values showing the properties of imaging blur which occurs at the time that the moving image is shot with the video shooting device, generating an inverse filter having inverse properties as to the low-pass filter, and performing processing to apply the inverse filters as to the access unit to be processed; wherein, with a frequency of which the frequency property of the low-pass filter indicating the imaging blur is zero being zero points, performing processing to apply the inverse filter is forbidden for predetermined frequency components of the frequency components of the access unit to be processed including the zero points.
Owner:SONY CORP
Printing control device, image forming apparatus, and image forming method
ActiveUS20120062957A1Increase contrastBlurred image2D-image generationVisual presentationCommunication interfaceImage formation
A printing control device is disclosed. The printing control device includes a user interface unit to receive an print command for a print job, an extraction unit to extract a bitmap image from the print job, a sketch image generating unit to generate a sketch image by using the extracted bitmap image, a print data generating unit to replace the bitmap image by the generated sketch image in the print job to generate print data, and a communication interface unit to transmit the generated print data to an image forming apparatus.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Electrophotographic photosensitive member
InactiveUS20060160004A1Maintain hardnessHigh resistivityElectrographic process apparatusSurface layerImage resolution
An electrophotographic photosensitive member is provided which can keep at a minimum the absorption of image exposure light of 380 to 500 nm in wavelength in its surface layer and concurrently can satisfactorily keep electrophotographic properties including resolving power. The electrophotographic photosensitive member has a substrate, and a photoconductive layer and a surface layer in this order provided on the substrate. The surface layer includes an amorphous material composed chiefly of silicon atoms and nitrogen atoms and containing at least oxygen atoms and carbon atoms, and the ratios of the numbers of the respective oxygen atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms to the total number of oxygen atoms, carbon atoms and nitrogen atoms contained in the amorphous material are each within a specific range.
Owner:CANON KK
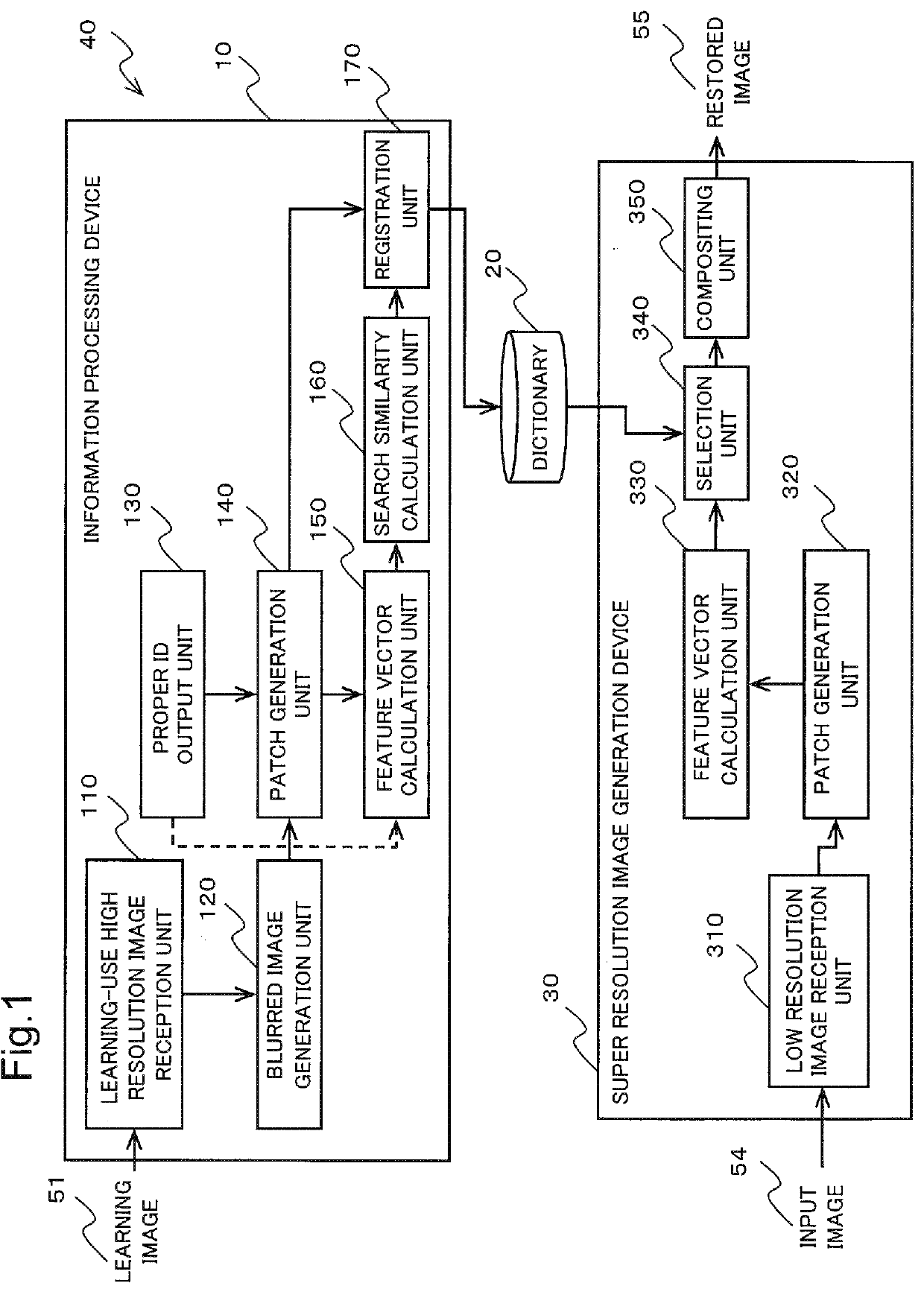
Information processing device, image processing method and medium
ActiveUS20160055627A1Blurred imageImage enhancementImage analysisInformation processingFeature vector
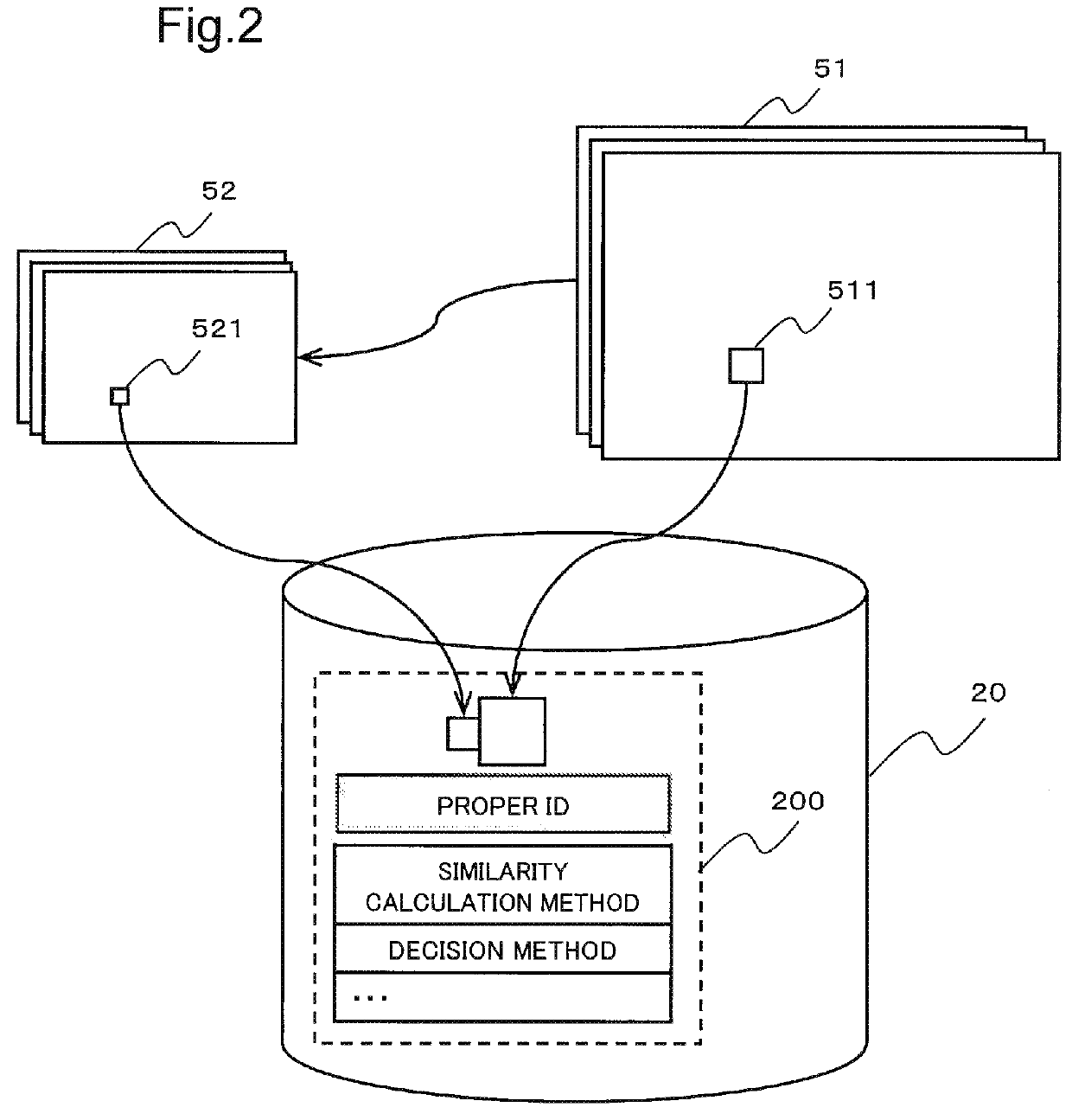
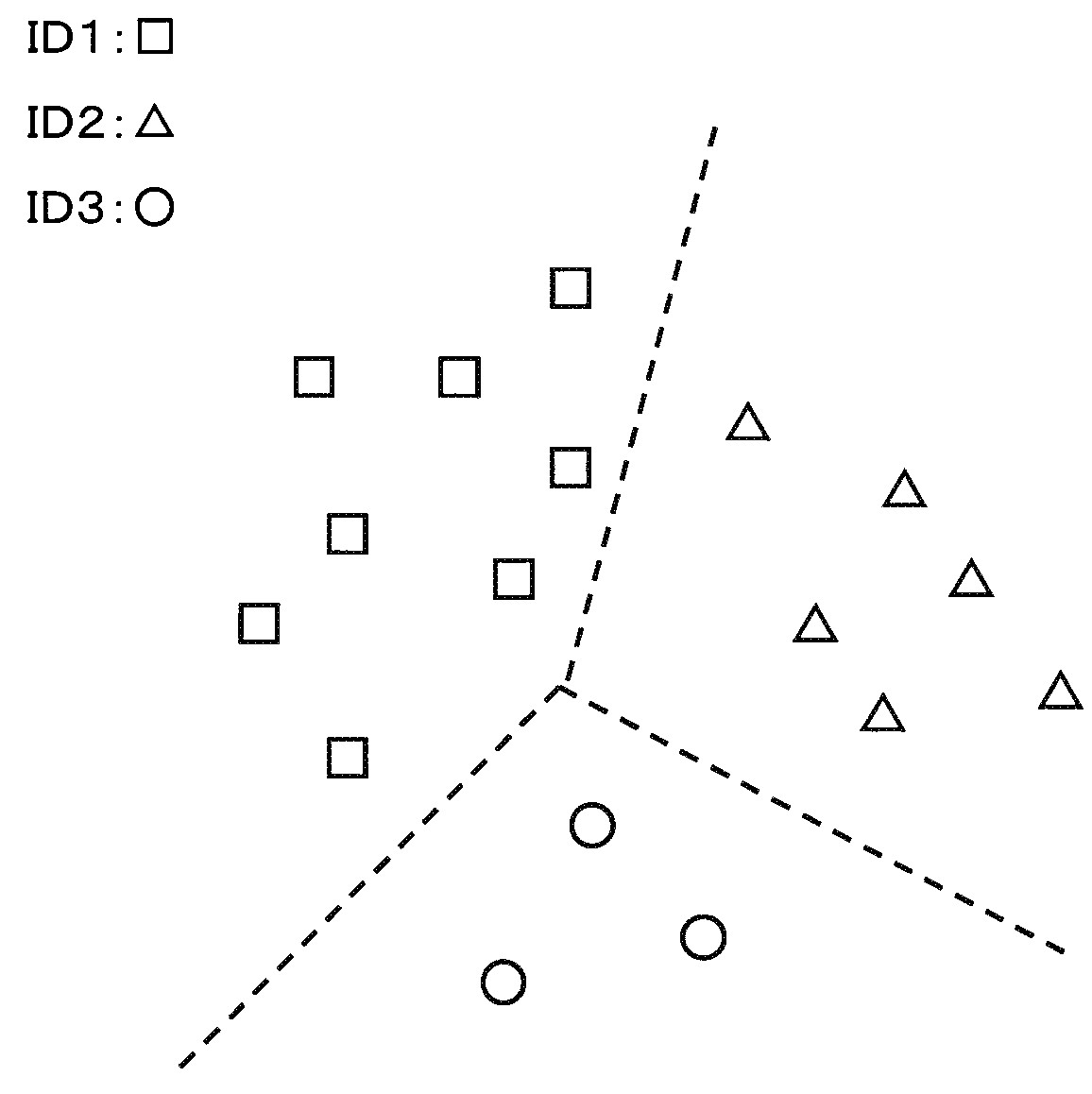
An information processing device according to the present invention includes: a proper identifier output unit which outputs proper identifiers for identifying learning images; a feature vector calculation unit which calculates feature vectors of at least a part of patches included in registered patches that are registered in a dictionary for compositing a restored image; and a search similarity calculation unit which calculates a similarity calculation method that classifies the proper identifiers to be given to the registered patches based on the feature vectors.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and device used for eliminating image overlap blurring phenomenon between frames in process of simulating CRT impulse type image display
InactiveUS7224342B2Eliminating image overlap blurring phenomenonImprove image display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingDisplay deviceInput control
Disclosed is a device for eliminating after image overlap blurring phenomenon between frames in the simulation of CRT impulse type image display with liquid crystal display (LCD), including first and second input control lines; first and second input data lines; first and second capacitors; a driving voltage output line; a first transistor including a first gate connected to a first input control line, a first source connected to a first input data line, and a first drain connected to a driving voltage output line, a first capacitor and the drain of the second transistor; and a second transistor including a second gate connected to a second input control line, a second source connected to a second input data line, and a second drain connected to a driving voltage output line, the drain of the first transistor and the second capacitor. The first and second capacitors are connected to ground respectively. The driving voltage output line supplies a simulation driving voltage to pixels of an LCD panel for displaying images and including a backlight unit with adjustable and controllable luminance and a backlight input voltage control line. The first and second input control lines are connected to a gate driver. The first and second data lines are connected to a data driver respectively. During the interval of black lines scanning, when the luminance of the backlight unit is reduced to the lowest value through its control voltage, the accumulated liquid crystal optical response in that interval is brought to the lowest value.
Owner:VASTVIEW TECH
Defect detecting apparatus and method
InactiveUS8107716B2Surely detectedBlurred imageTelevision system detailsImage analysisCover glassCandidate image
A front side surface of a cover glass of a solid state imaging device is focused, and a front side image is captured. Next, a rear side surface of the cover glass is focused, and a rear side image is captured. The front side image and the rear side image are combined with each other to create a composite image. A first threshold value is set for each pixel in the composite image by dynamic thresholding. An image composed of pixels whose gray values exceed the first threshold value is identified as a defect candidate image. The maximum gray value of the defect candidate image is multiplied by a constant rate to set a second threshold value. An image composed of pixels whose gray value is less than the second threshold value is eliminated as a blurred image from the defect candidate image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Directional interpolation method and device for increasing resolution of an image
InactiveUS7532773B2Improve imaging resolutionBlurred imageTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationPattern recognitionImage resolution
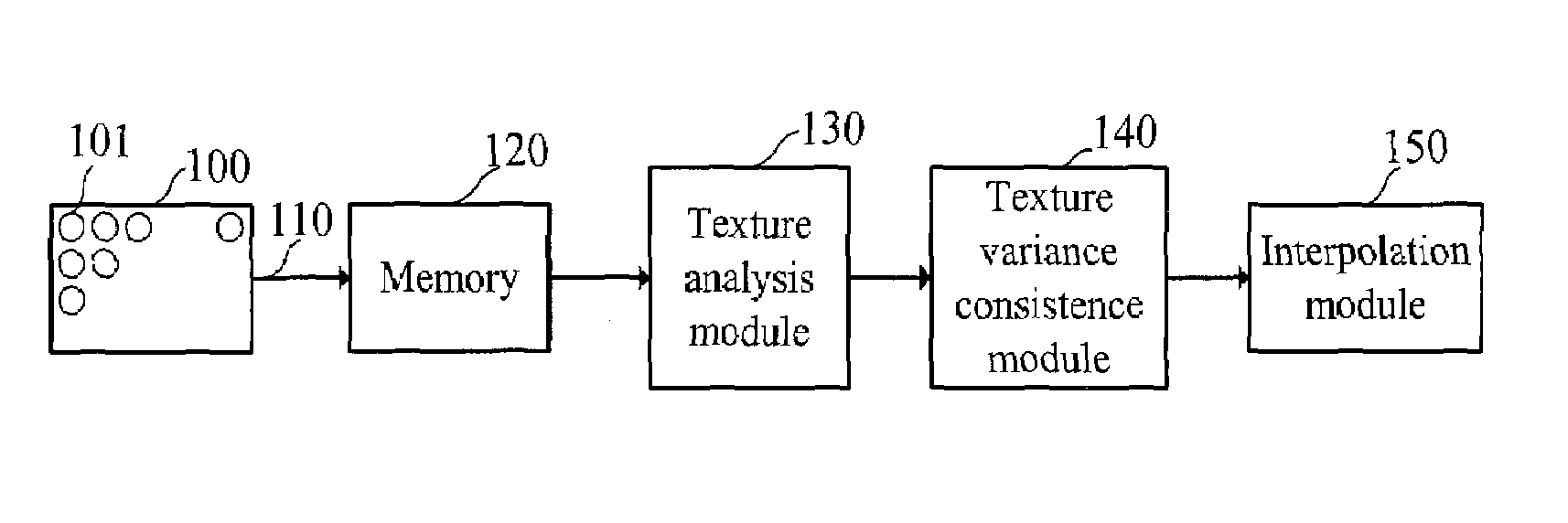
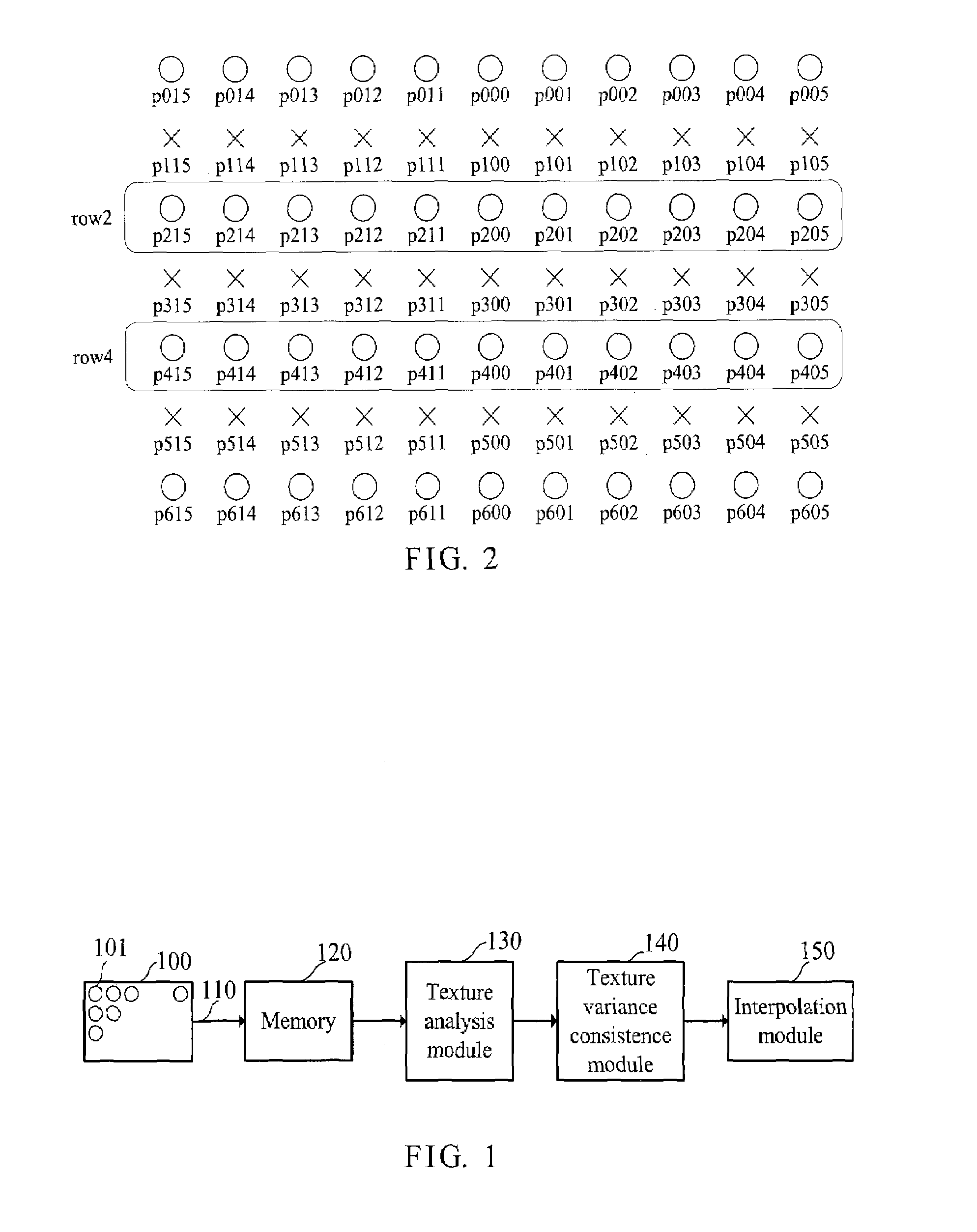
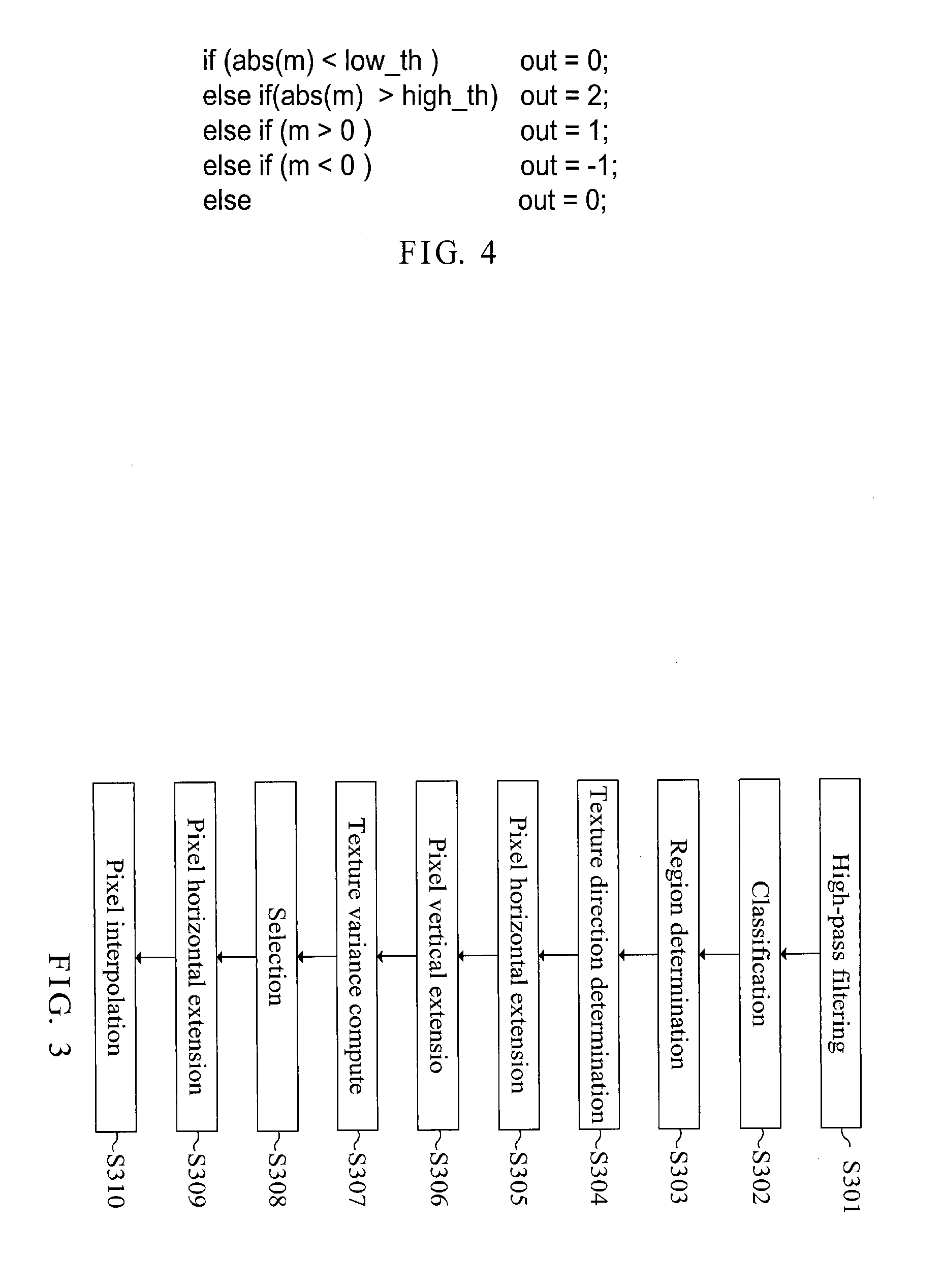
A directional interpolation method and device for increasing resolution of an image is disclosed. The device includes an input terminal, a memory, a texture analysis module, a texture variance consistence module and an interpolation module. The input terminal receives signals representing the pixels of the image. The memory stores the pixels in row direction. The texture analysis module obtains a monotone variation area by taking the position as a center. The texture variance consistence module computes all directional texture variances in a closest upper and a closest lower rows of pixels within the monotone variation area in the case of taking the position as a center and accordingly finds two pixels having texture variance consistence. The interpolation module finds a value of pixel to be interpolated to the position through a median filter in accordance with the two pixels and their neighbor pixels.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
Lamp having plurality of optical extraction structures
InactiveUS7997782B2Blurred imageNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceOptical couplingLight emission
A lamp for emitting light, comprising a transparent sheet-like lightguide, with at least one light receiving side, a light emission front surface and a back surface opposite the front surface. The lamp further comprises a plurality of light sources, positioned in an array and optically coupled to at least one light receiving side. The back surface of said lamp comprises a plurality of optical extraction structures, for example provided in parallel curved lines. Furthermore, the lamp is substantially free from light scattering structures in a light path of the light to be emitted.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Electronic apparatus, blur image sorting method, and program
InactiveUS8300972B2Accurate calculationImprove convenienceImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
An electronic apparatus includes: an extraction section extracting a subject area having a predetermined feature in an image; a first calculation section calculating a first blur degree indicating a blur degree of the extracted subject area; a second calculation section calculating, when the number of subject areas from which the first blur degree is calculated is one, a second blur degree indicating a blur degree of the entire image based on the first blur degree, and calculating, when the number of subject areas from which the first blur degree is calculated is plural, the second blur degree based on a value obtained by performing weighted averaging on the plural first blur degrees in accordance with dimensions of the plural subject areas; and a sorting section sorting an image having the calculated second blur degree equal to or larger than a predetermined threshold value, as a blur image, from plural images.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com