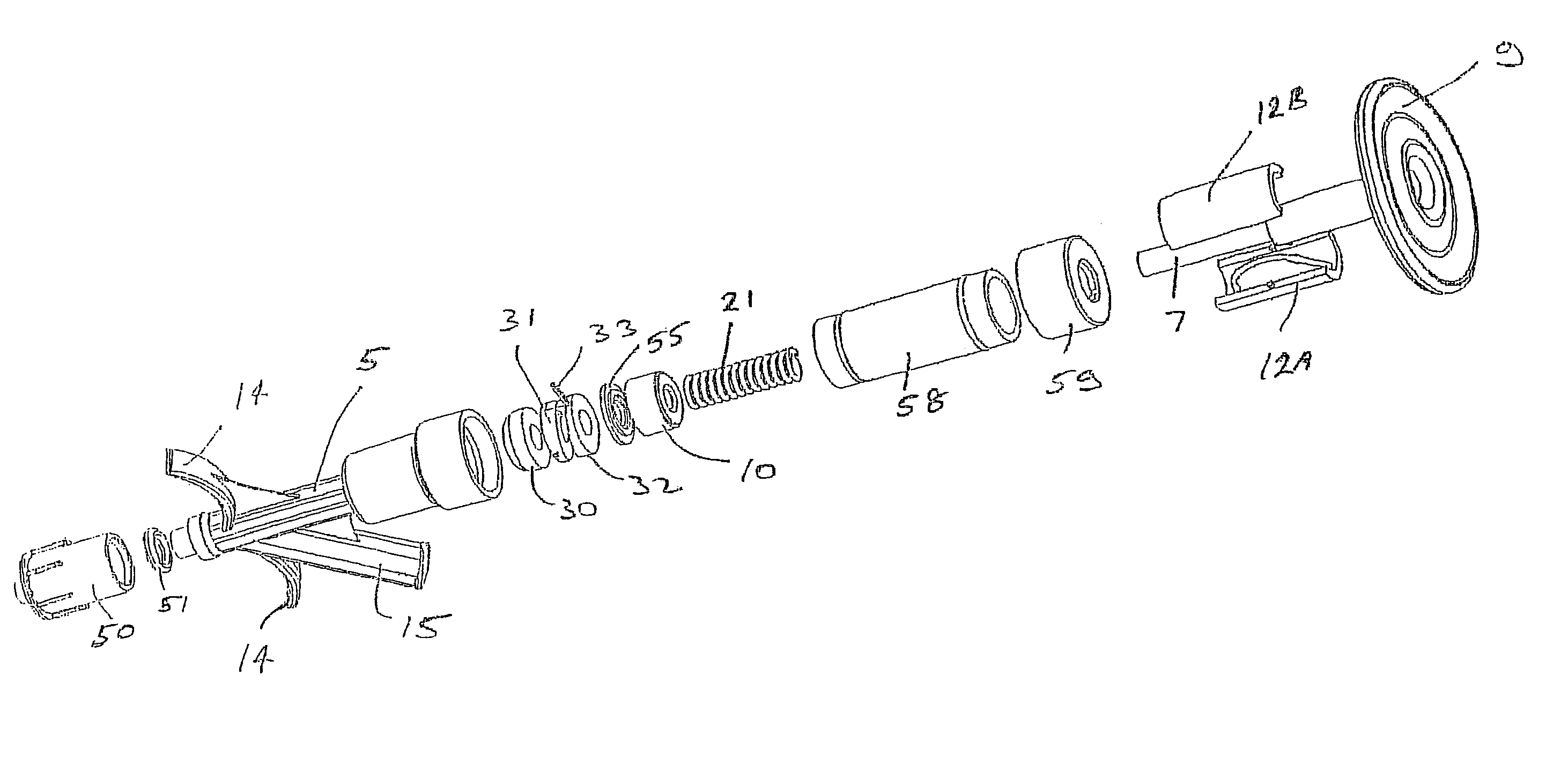Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Avoid blood loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
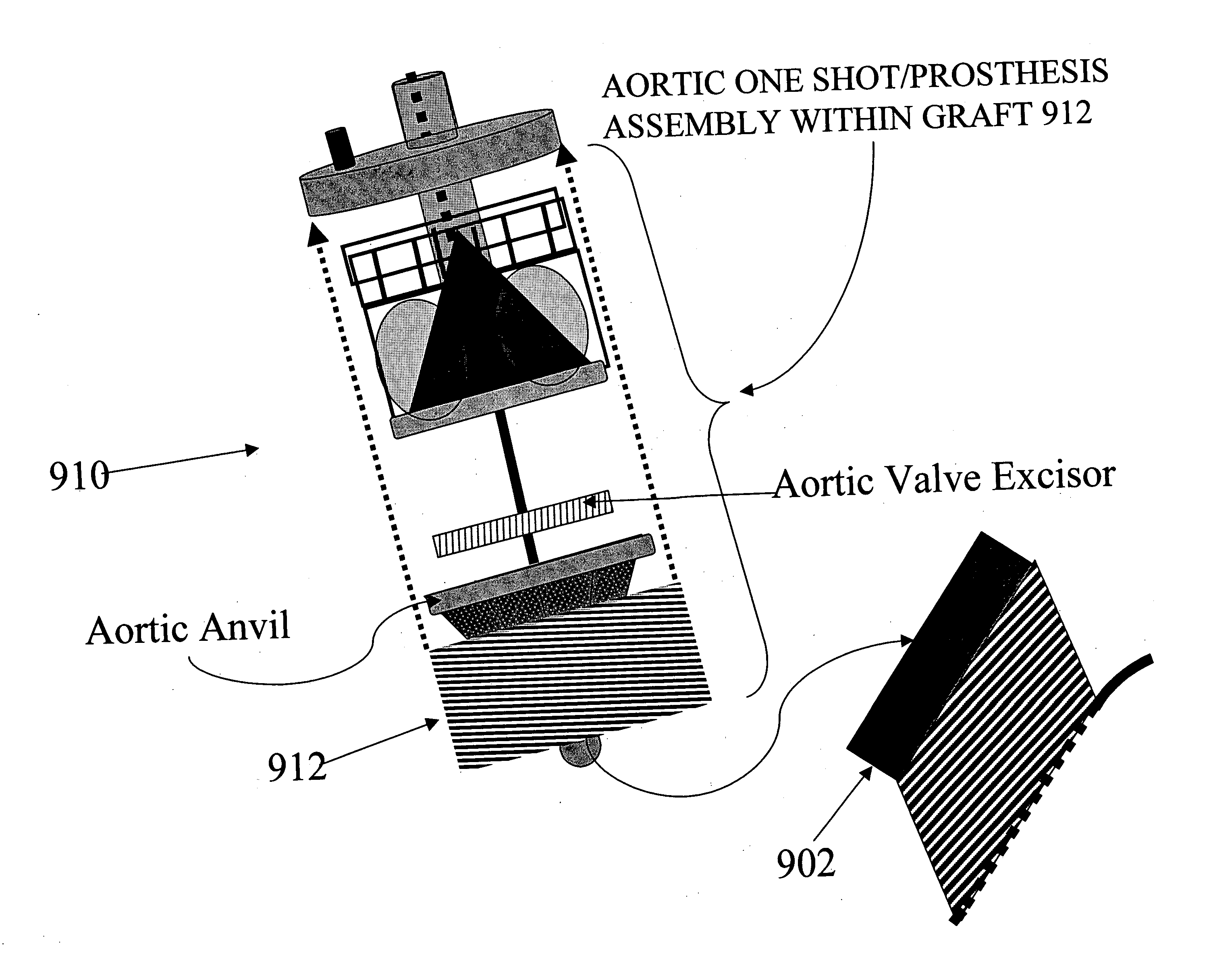
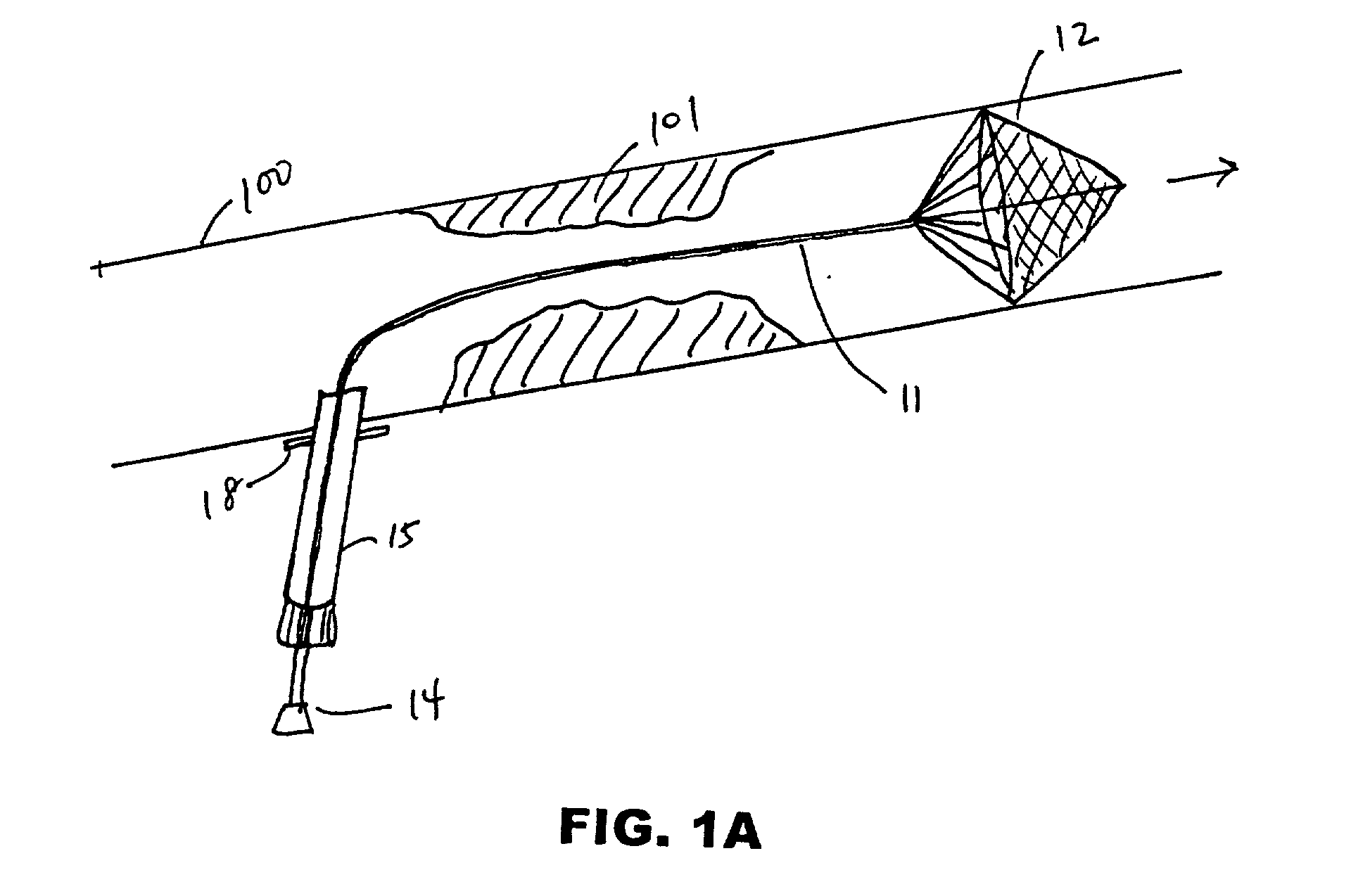
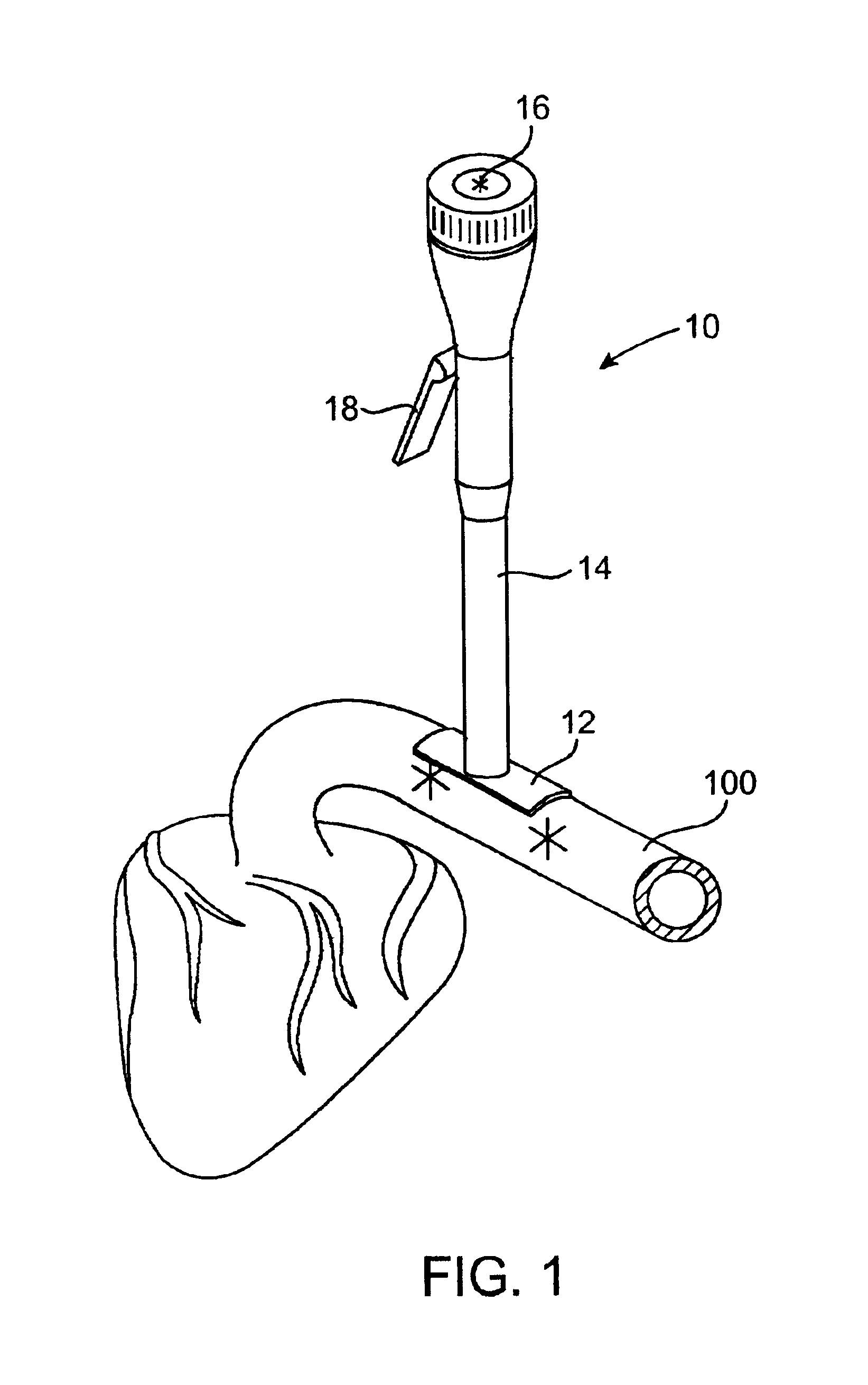
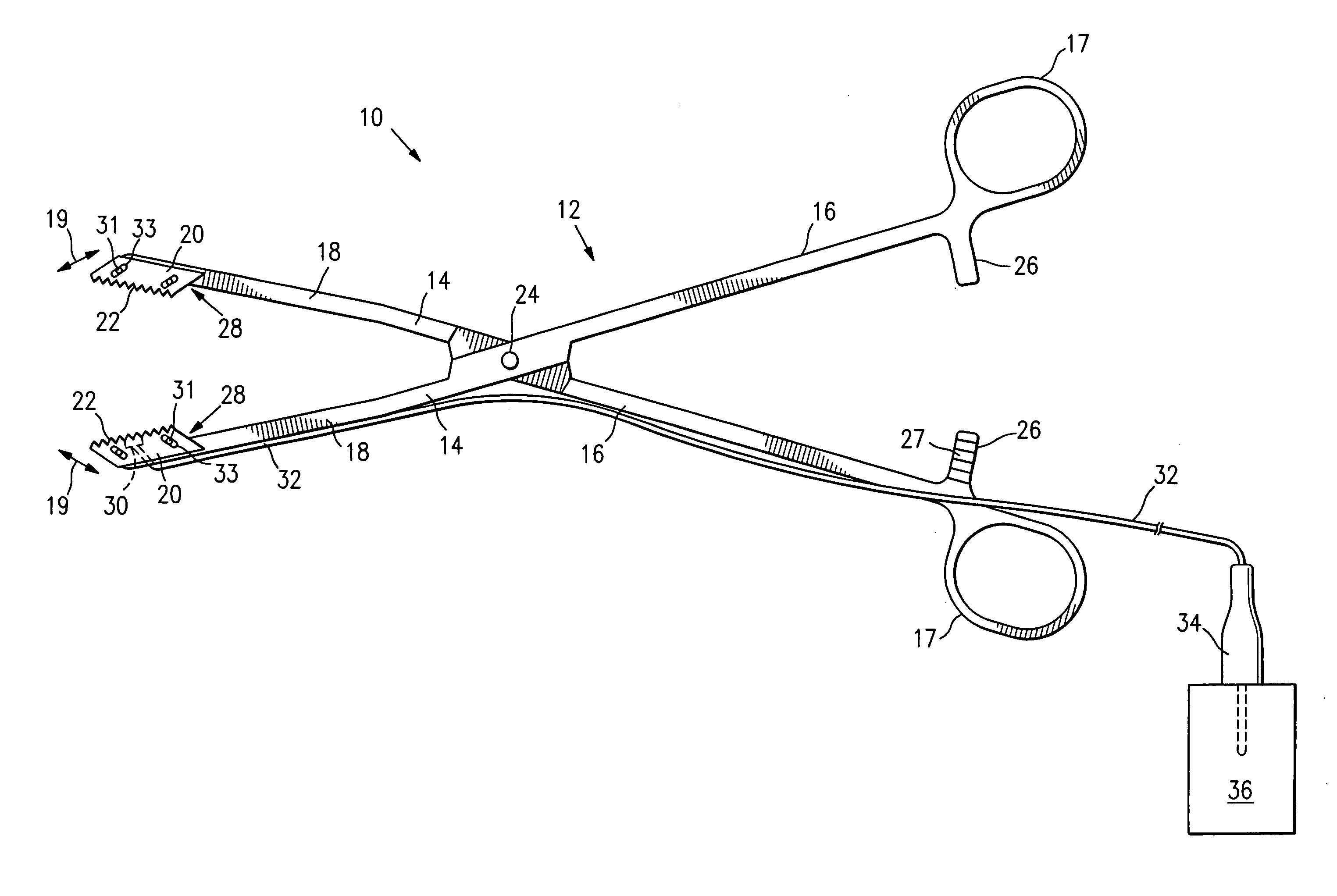
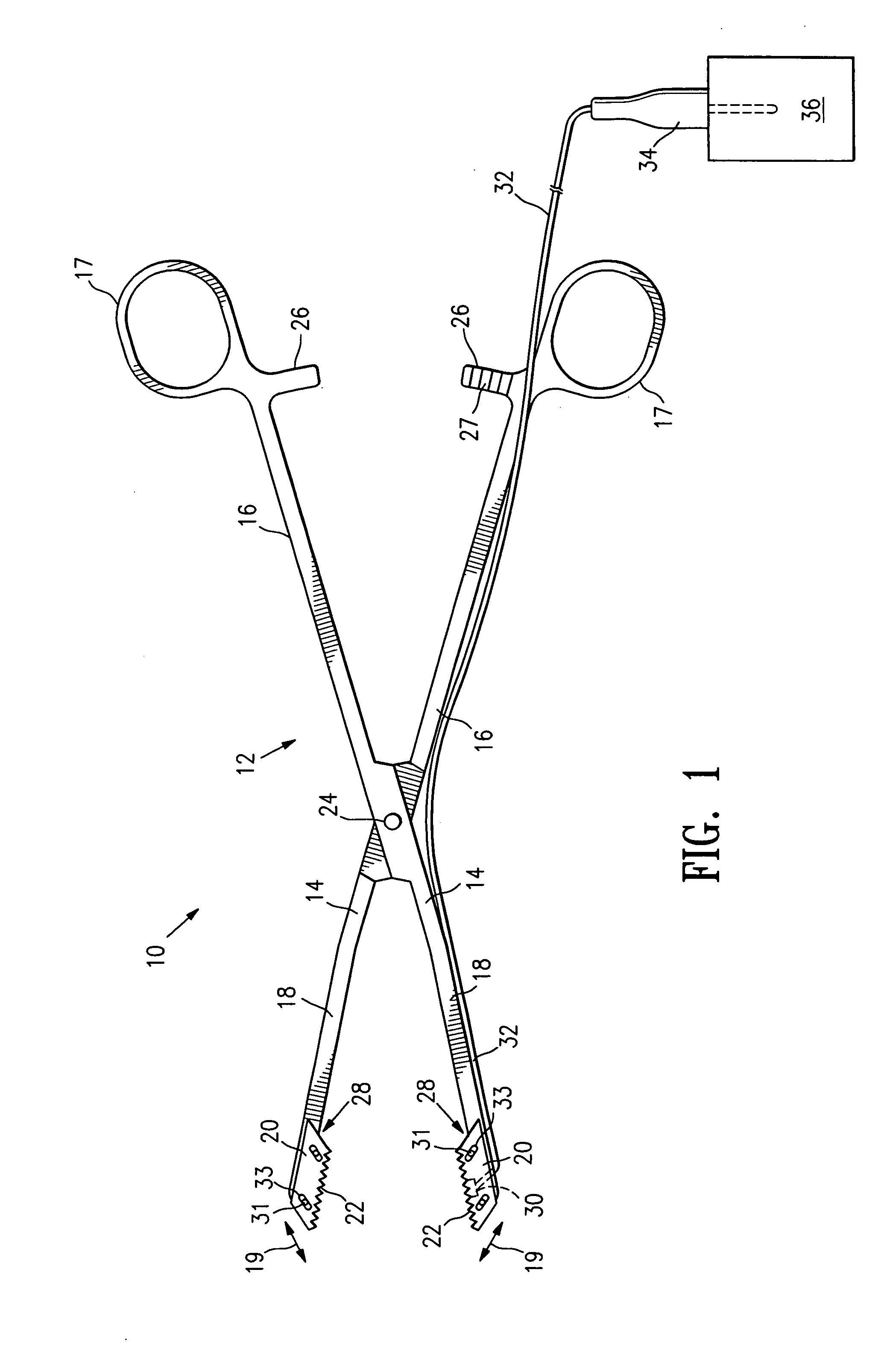
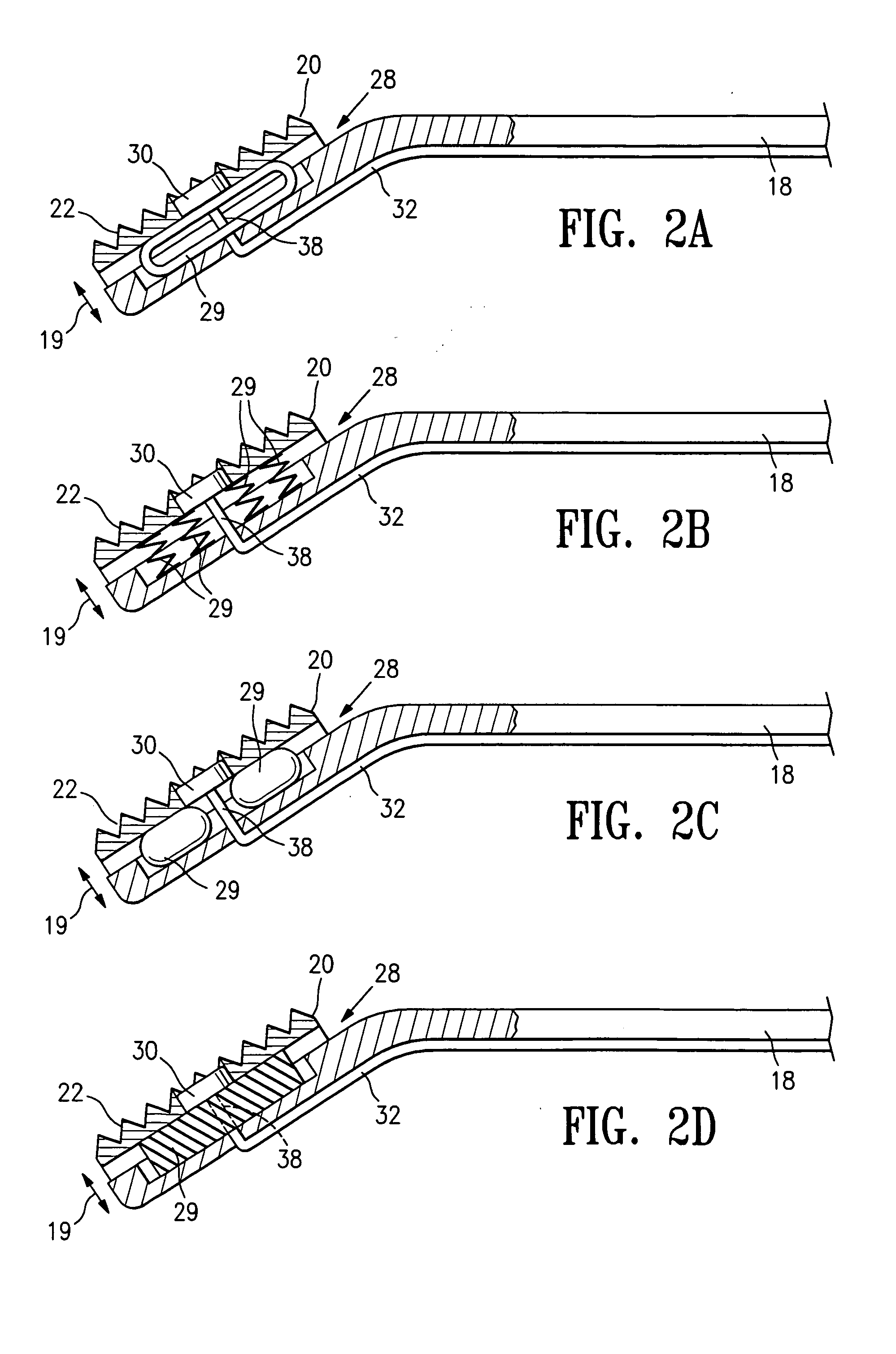
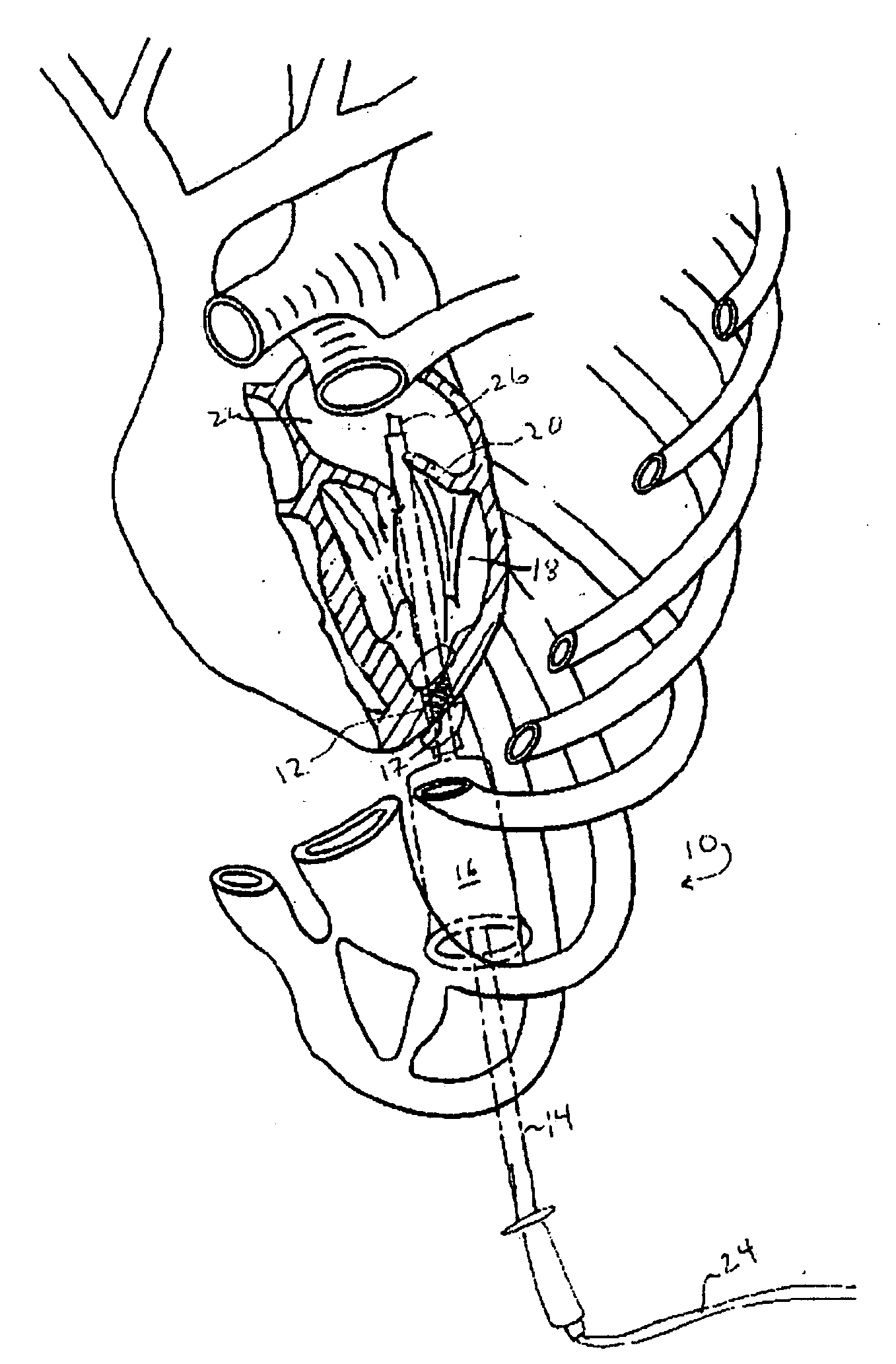
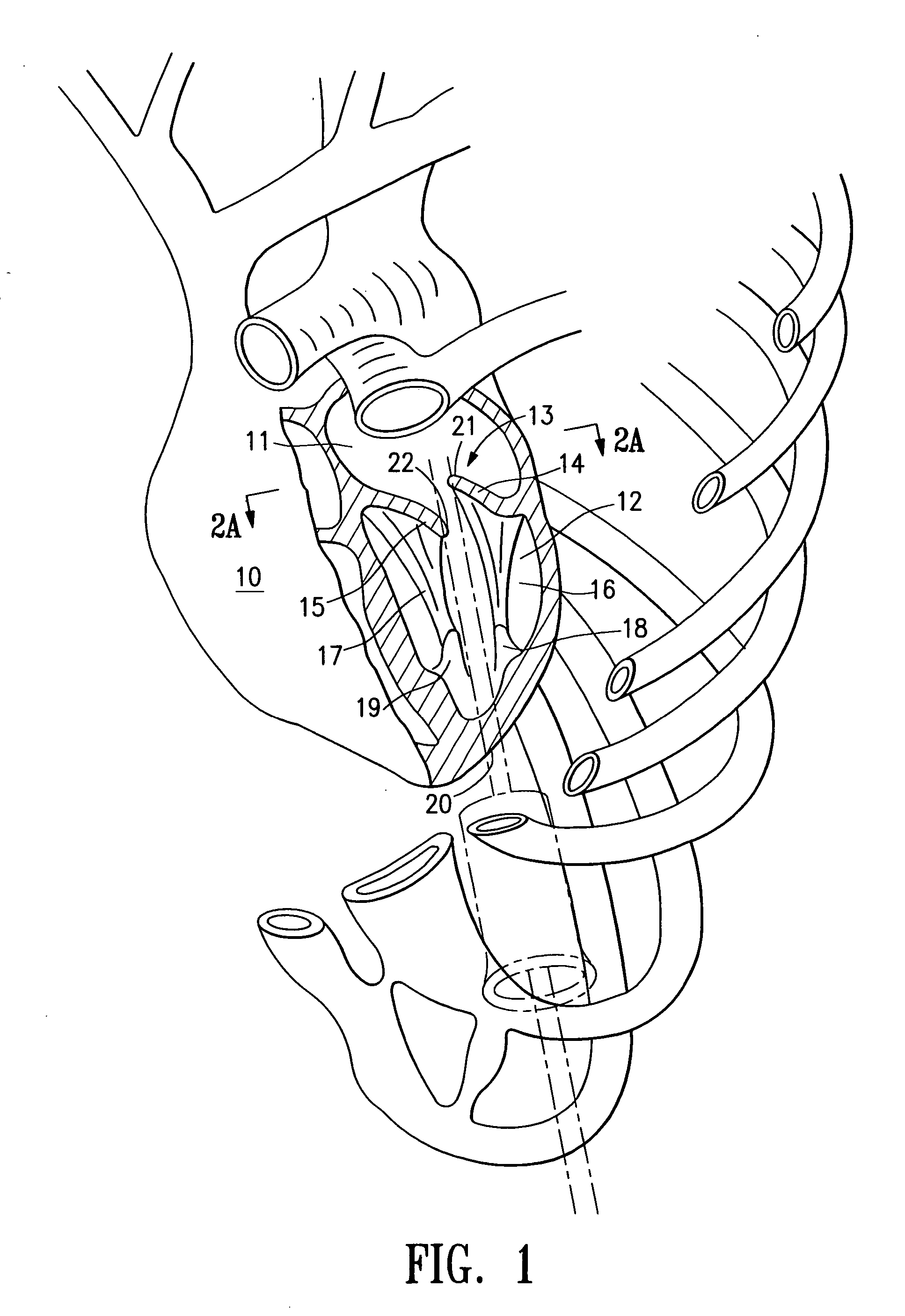
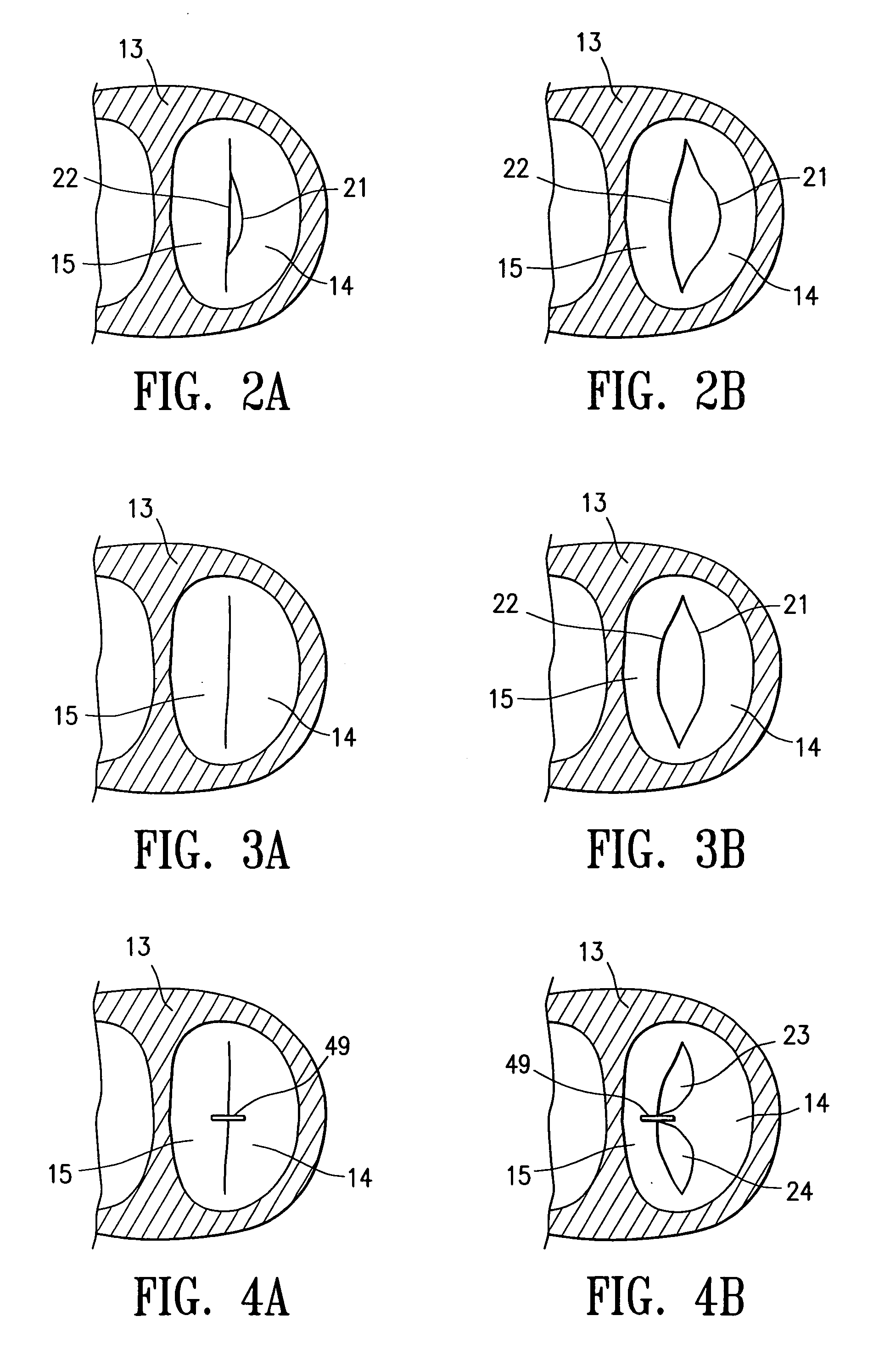
Methods and apparatus for off pump aortic valve replacement with a valve prosthesis
InactiveUS20050203549A1Promote recoveryPromote resultsHeart valvesExcision instrumentsMedicineProsthesis
Methods and apparatus are provided for valve repair or replacement. In one embodiment, the method comprises providing an apparatus having a valve prosthesis, a valve leaflet support and a valve excisor, the apparatus having a first configuration and a second configuration; accessing the aortic root without placing the patient on a heart-lung machine; advancing the apparatus in the first configuration where the valve leaflet support is advanced through a valve, wherein the support is positioned below a valve annulus; expanding the apparatus into a second configuration so that the support will engage the valve; and moving the valve leaflet support and valve excisor together to remove leaflets of the valve. Penetrating members may be advanced into the tissue wherein the penetrating members may act as fasteners to hold the prosthesis in place.
Owner:REALYVASQUEZ FIDEL
Cerebral protection during carotid endarterectomy and methods of use
A shunt and method of use for maintaining distal blood flow during an arteriotomy procedure is disclosed. The shunt includes first and second tubular members having proximal ports, distal ports, and lumens therebetween. The distal port of the second tubular member is adapted for releasable attachment to the proximal port of the first tubular member. A second lumen merges and communicates at its distal end with the lumen of the first tubular member and includes a hemostatic valve attached to its proximal end. In using the apparatus for performing open endarterectomy, a filter device is inserted into the vessel and deployed downstream the region of interest in the internal carotid artery. The distal end of the shunt is advanced over the filter device and secured onto the artery. The proximal end of the shunt is inserted upstream the region of interest, typically in the common carotid artery.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
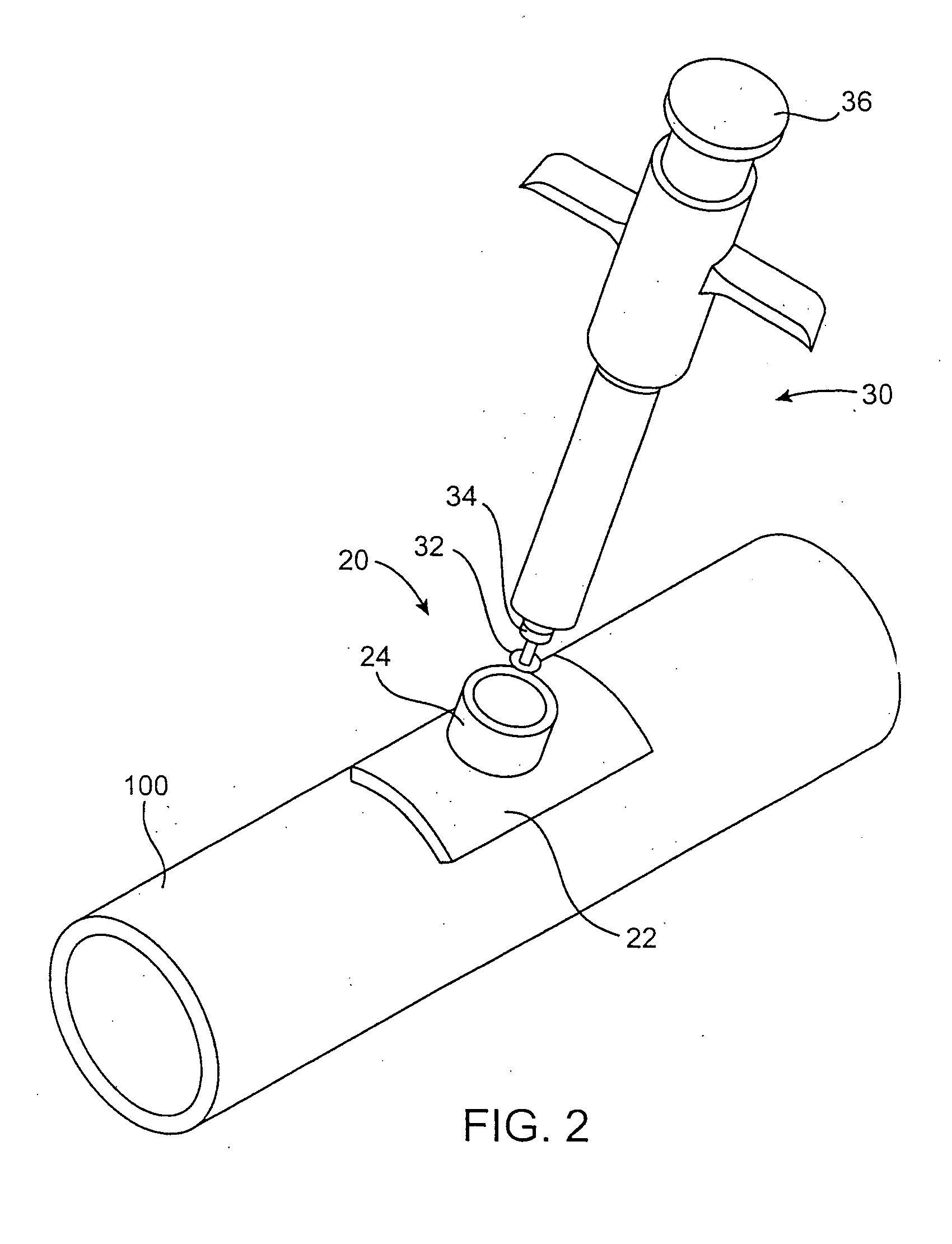
Access port system for anastomosis
A method of performing anastomosis includes securing an access port system to an exterior surface of the target vessel to assist in axial alignment, depth registration, and / or sealing when inserting instruments such as punching instruments and anastomosis instruments into the target vessel.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
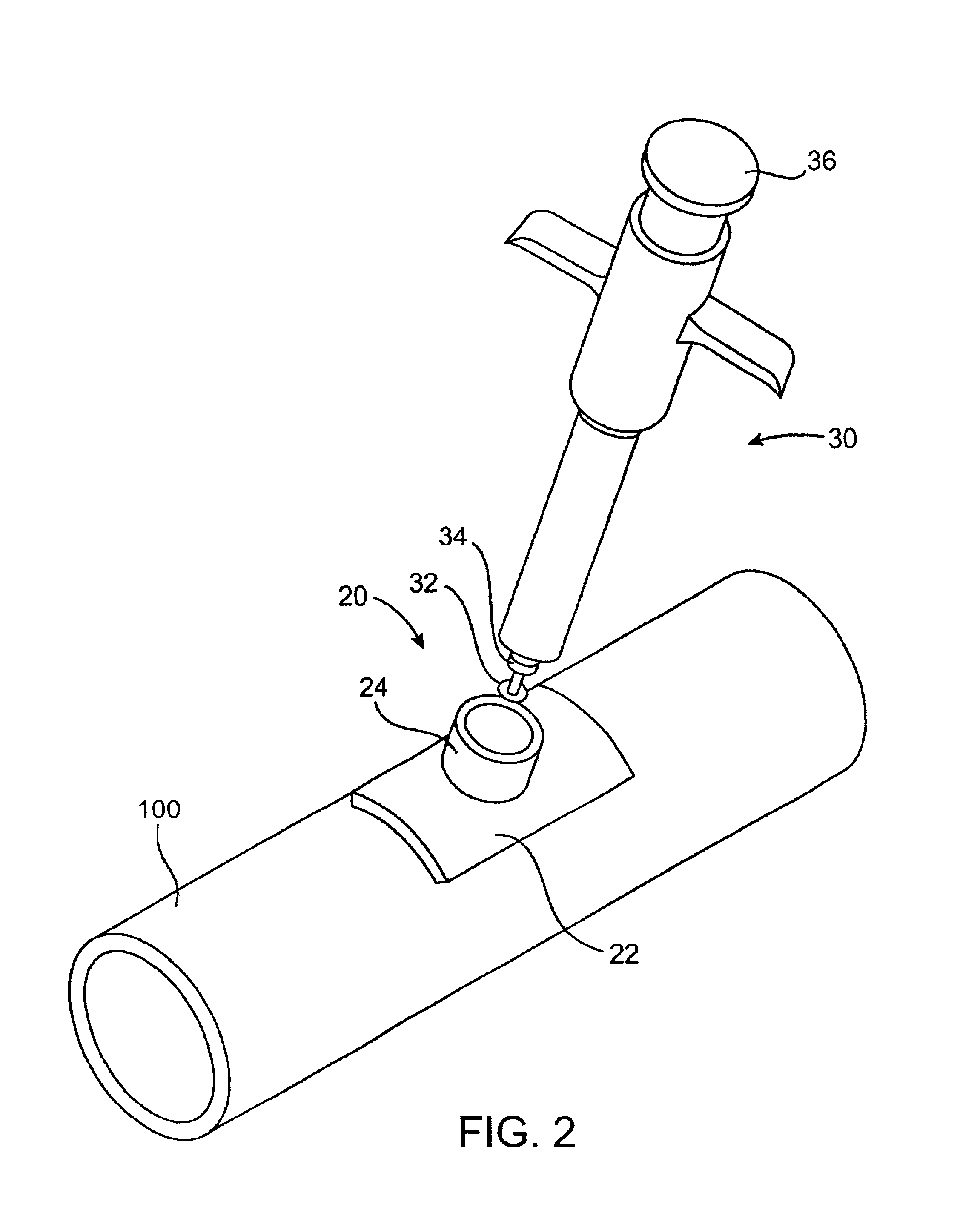
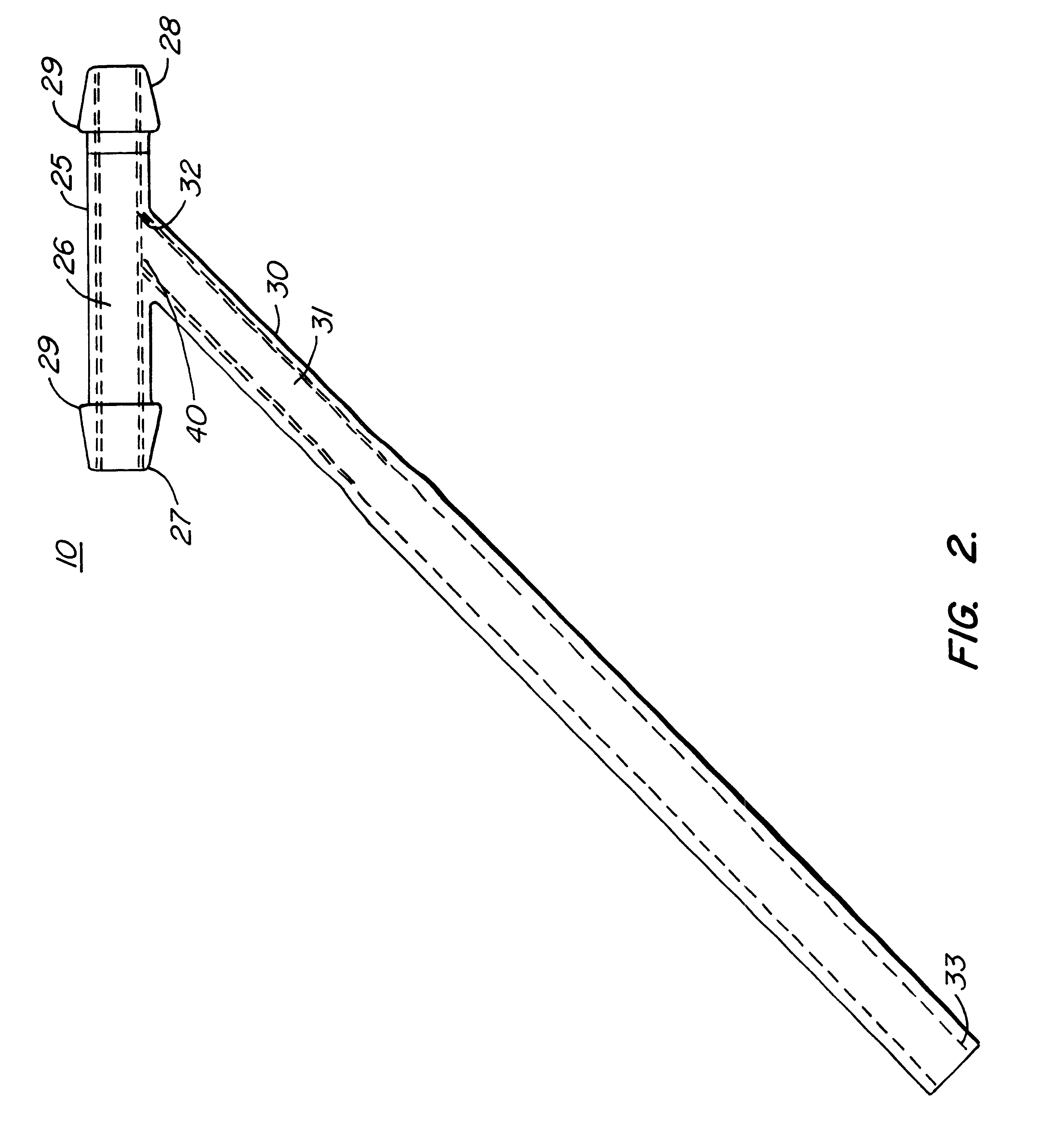
Subcutaneously implanted cannula and method for arterial access
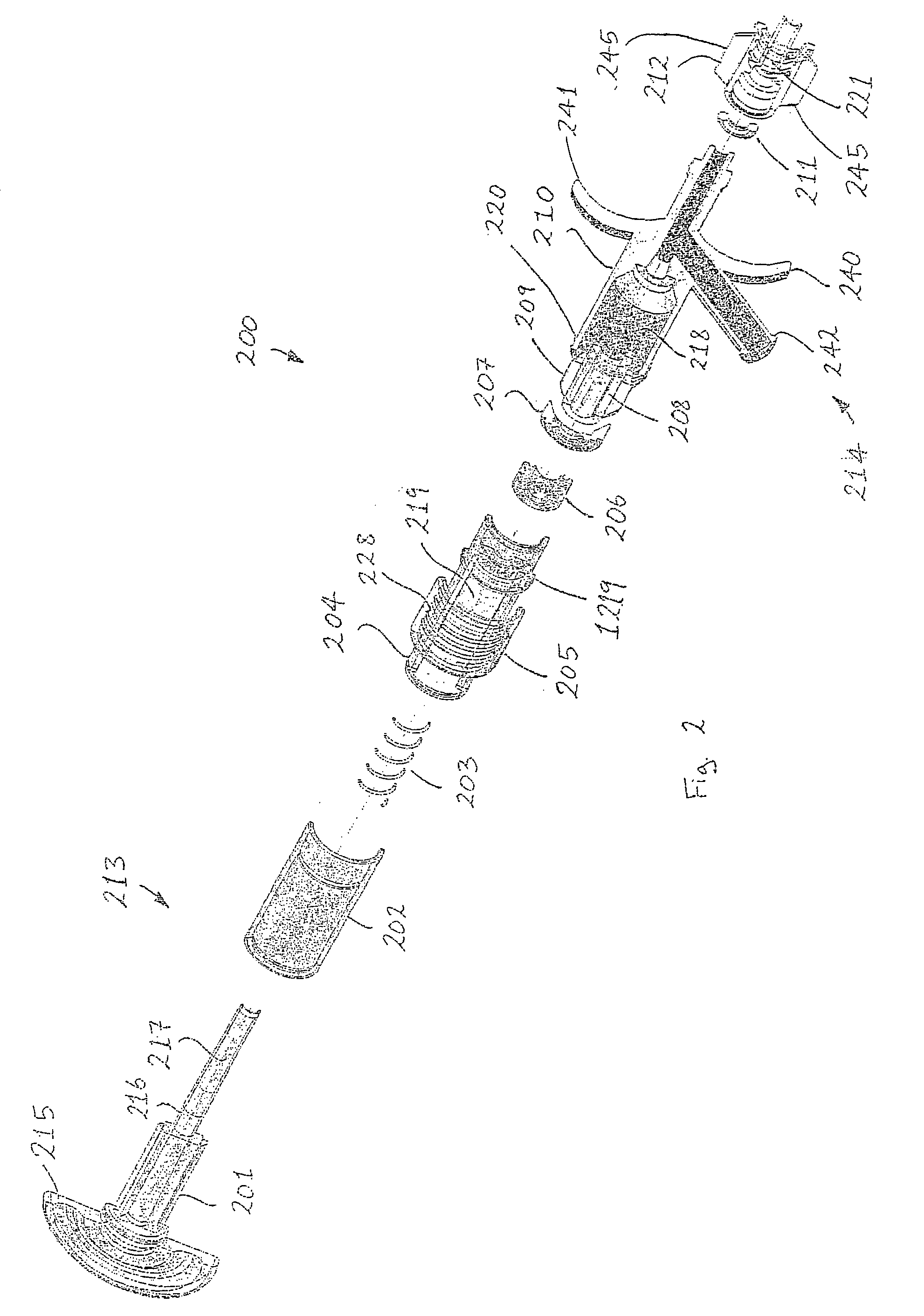
InactiveUS6398764B1Avoid blood lossReduce exerciseMedical devicesCatheterDifferential pressureSubcutaneous implantation
A catheter with valve for implantation in a vascular structure of a living being. The catheter is in the general shape of a "T" with the top of the "T" implanted within the lumen of a vascular structure, and the leg of the "T" extending out of the vascular structure through an incision in the vascular structure. The lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter completely occupies the lumen of the vascular structure, causing all blood flow through the vascular structure to be directed through the implanted portion of the catheter. A valve is placed in the wall of the implanted portion of the catheter which opens into the lumen of the leg of the "T" of the catheter upon application of sufficient differential pressure between the lumens of the two portions of the catheter. The leg of the "T" is connected to the side wall of the implant portion of the catheter at an angle, such that the axis of the lumen of the leg of the "T" intersects the axis of the lumen of the implanted portion of the catheter at approximately a 45 degree angle.
Owner:VASCA
Valved catheters including high flow rate catheters
InactiveUS20050049555A1Reduction of formationHigh flow rateMulti-lumen catheterEqualizing valvesAccidental ingestionCombined use
Owner:NAVILYST MEDICAL
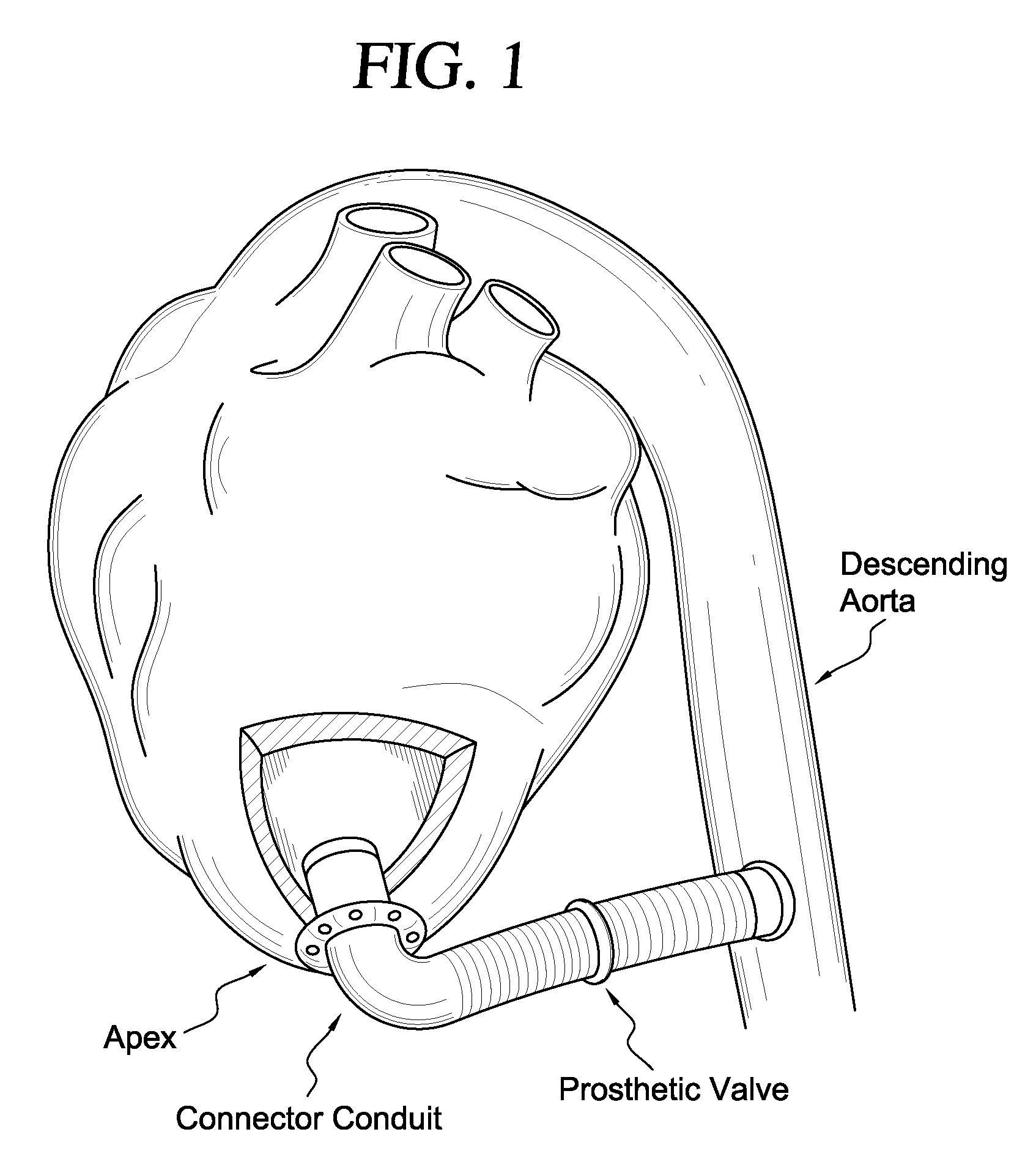
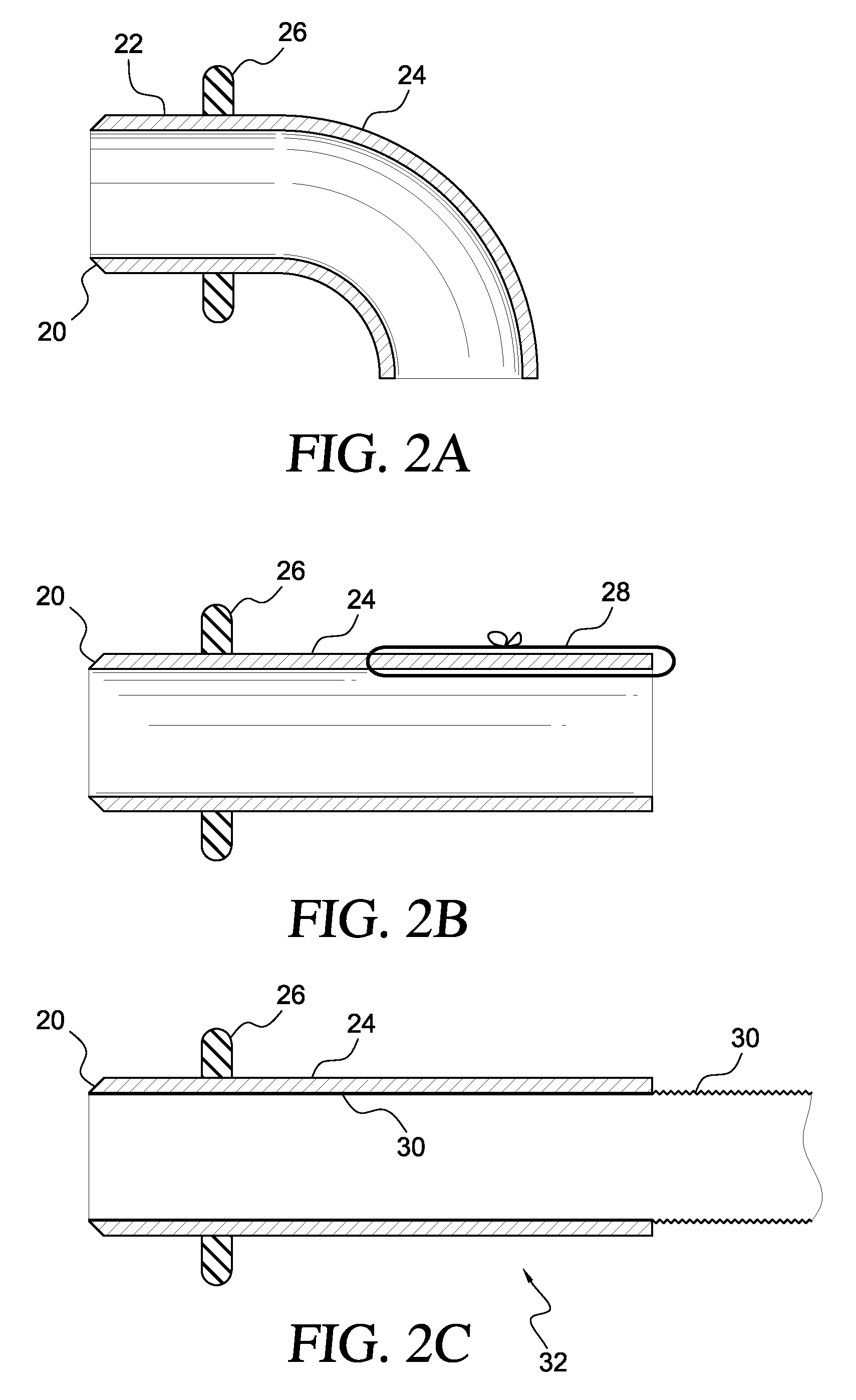
Apparatus and method for suturelessly connecting a conduit to a hollow organ
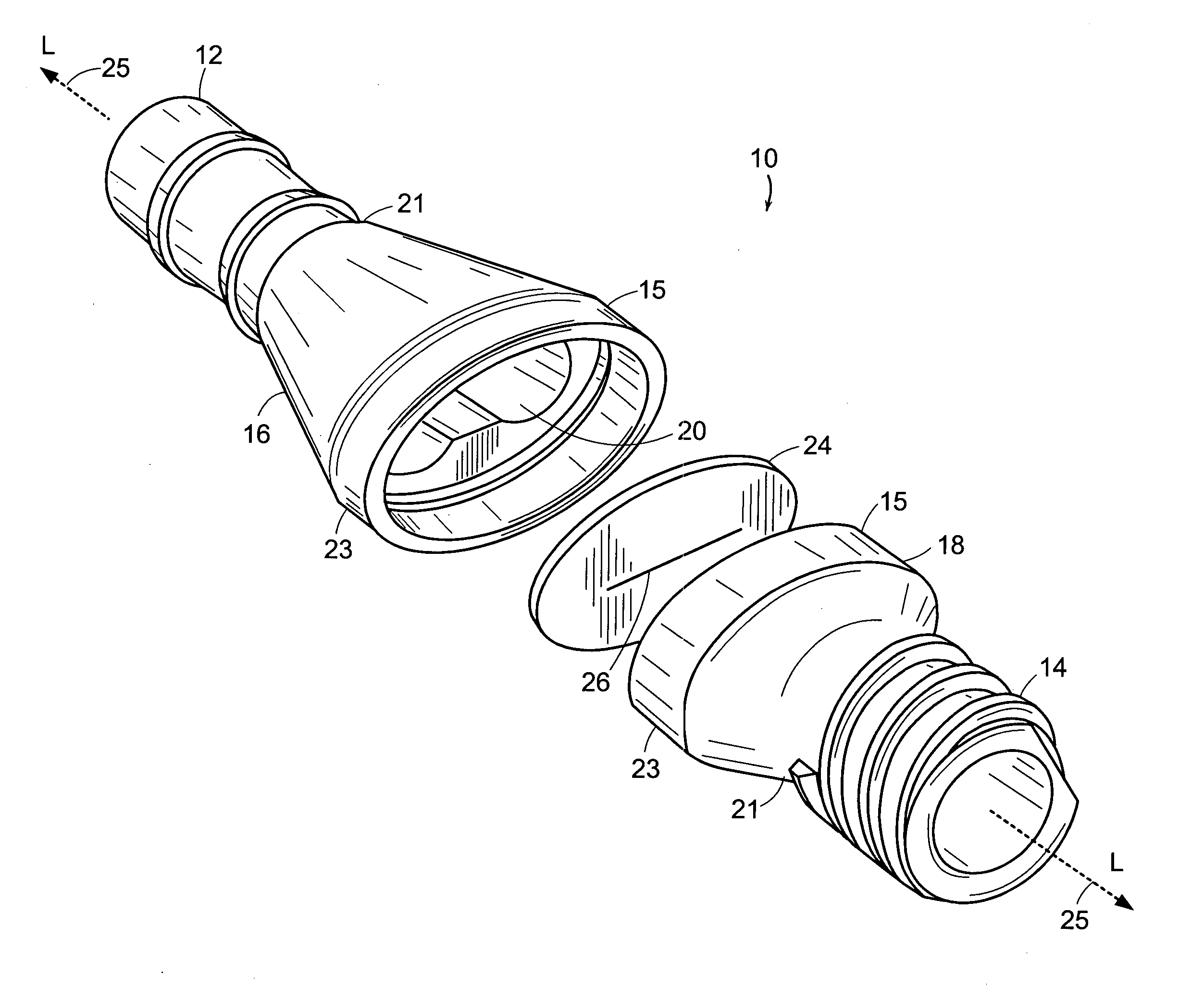
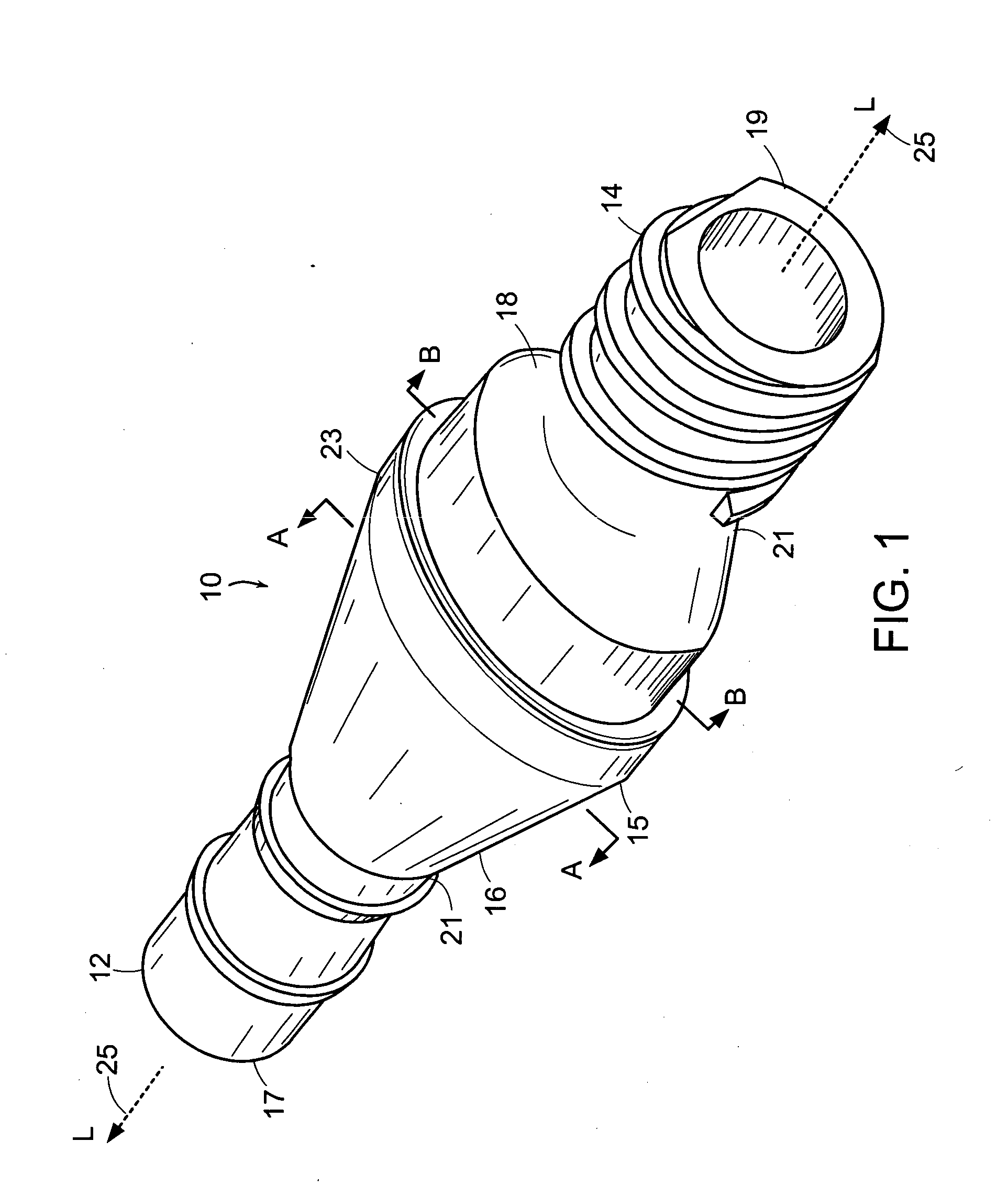
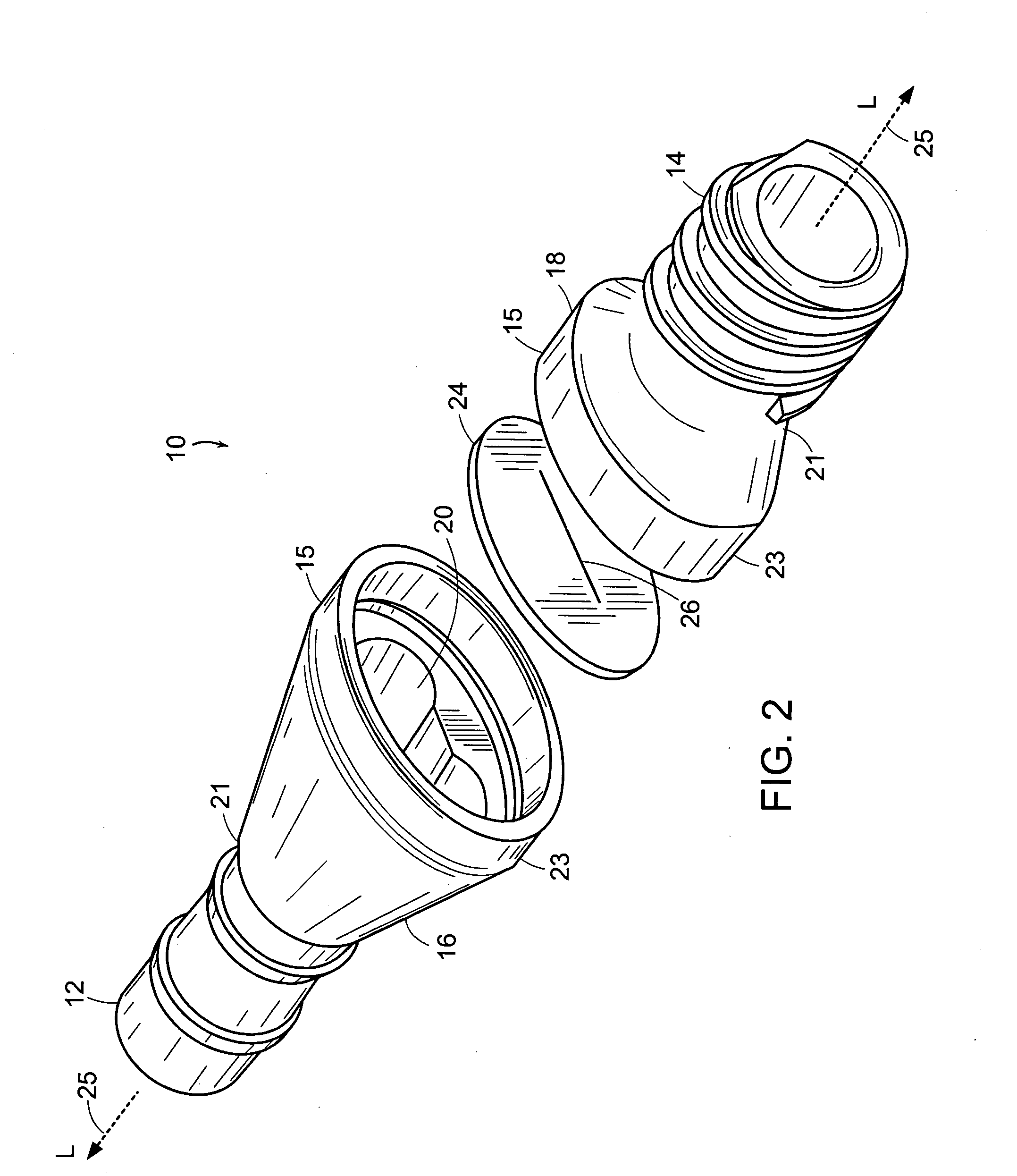
InactiveUS20070265643A1Avoid blood lossPrevent movementBlood vesselsWound clampsOrgan wallCoil spring
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for securing a connector conduit to a hollow organ. The method comprises forming a hole in a wall of the organ; inserting a connector conduit through the hole in the wall of the organ until a flange element comes into contact with the wall of the organ, the flange element being positioned on the connector conduit; and engaging a retention means with the wall of the organ to prevent movement of the connector conduit relative to the wall of the organ, the retention means being positioned on the connector conduit. Exemplary retaining means include a plurality of retaining pins positioned circumferentially around the connector conduit, a plurality of prongs positioned circumferentially around the connector conduit, a balloon positioned on the connector conduit, a torsion spring positioned on the connector conduit, a spiral spring positioned on the connector conduit, or combinations thereof.
Owner:CORREX
Methods and Devices for Removal of Thromboembolic Material
InactiveUS20160166265A1Easy to disassembleMinimize additional blood-lossBalloon catheterExcision instrumentsThrombusRotational energy
Methods and devices to remove thromboembolic material from the human body using rotational energy and aspiration are disclosed. A thromboembolic removal system includes an extraction device and drive unit. The extraction device is introduced to the treatment area and activated by the drive unit to separate, break apart, loosen or soften thromboembolic material and to facilitate its aspiration outside the patient.
Owner:PENUMBRA
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
Methods and Devices for Removal of Thromboembolic Material
ActiveUS20160166266A1Easy to disassembleMinimize additional blood-lossBalloon catheterExcision instrumentsRotational energyEmbolization material
Methods and devices to remove thromboembolic material from the human body using rotational energy and aspiration are disclosed. A thromboembolic removal system includes an extraction device and drive unit. The extraction device is introduced to the treatment area and activated by the drive unit to separate, break apart, loosen or soften thromboembolic material and to facilitate its aspiration outside the patient.
Owner:PENUMBRA
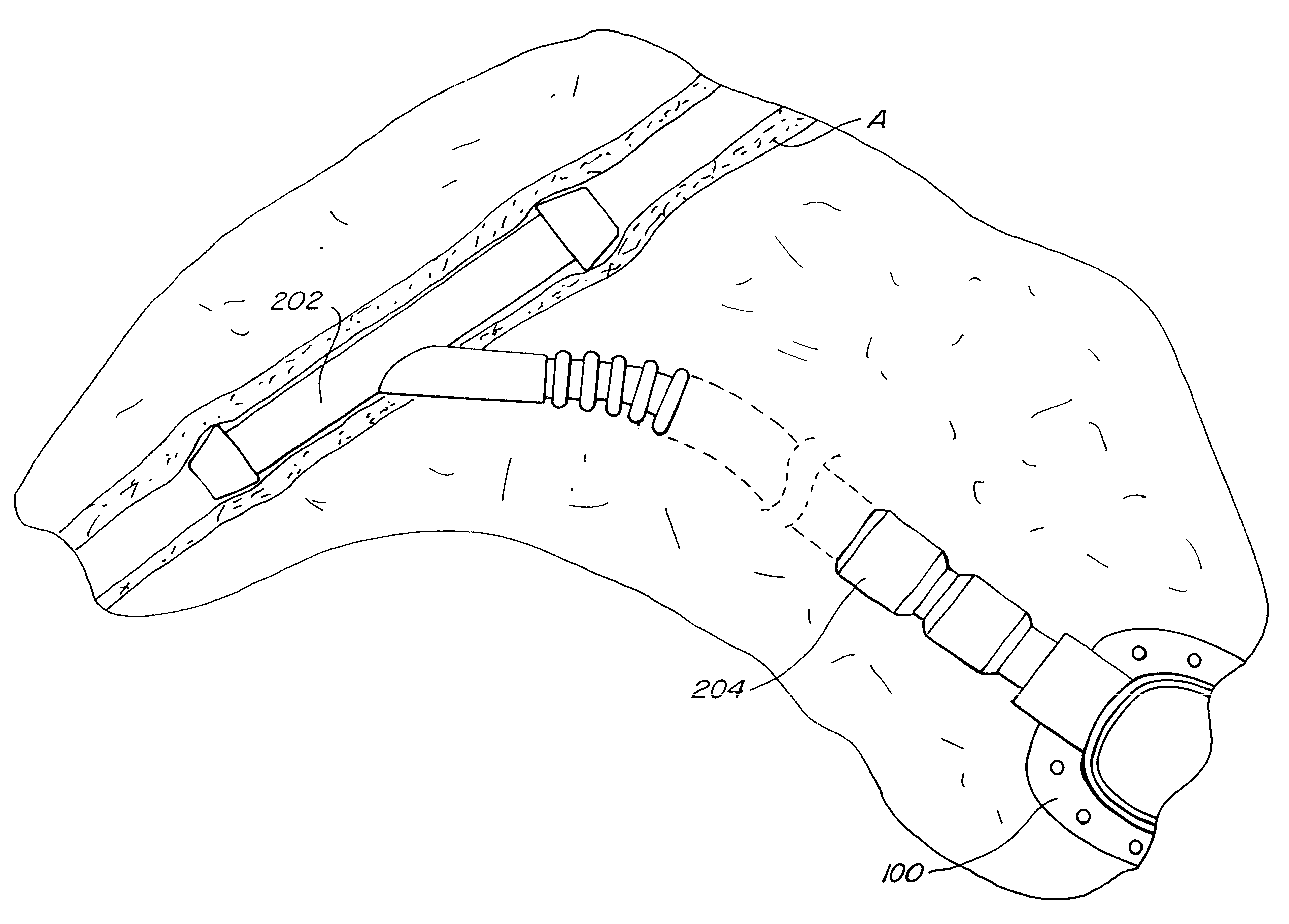
Haemostasis device
ActiveUS20050085789A1Avoid blood lossEasily identifiableInfusion syringesMedical devicesEngineeringOpen type
A haemostasis device (200) comprises a low pressure seal (206) and a high pressure seal (208). A tubular bayonet (201) is movable from a retracted configuration to an inserted configuration to move the low pressure seal (206) between a closed configuration and an open configuration. With the low pressure seal (206) in the open configuration, a guidewire (222) may be inserted through the low pressure seal (206), and with the low pressure seal (206) in the closed configuration, the guidewire (222) may be passed through the low pressure seal (206) while maintaining sealing around the guidewire (222). A collet (209) is movable in a radial direction to move the high pressure seal (208) between an open configuration and a sealing configuration. With the high pressure seal (208) in the sealing configuration, the guidewire (222) is locked in position.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
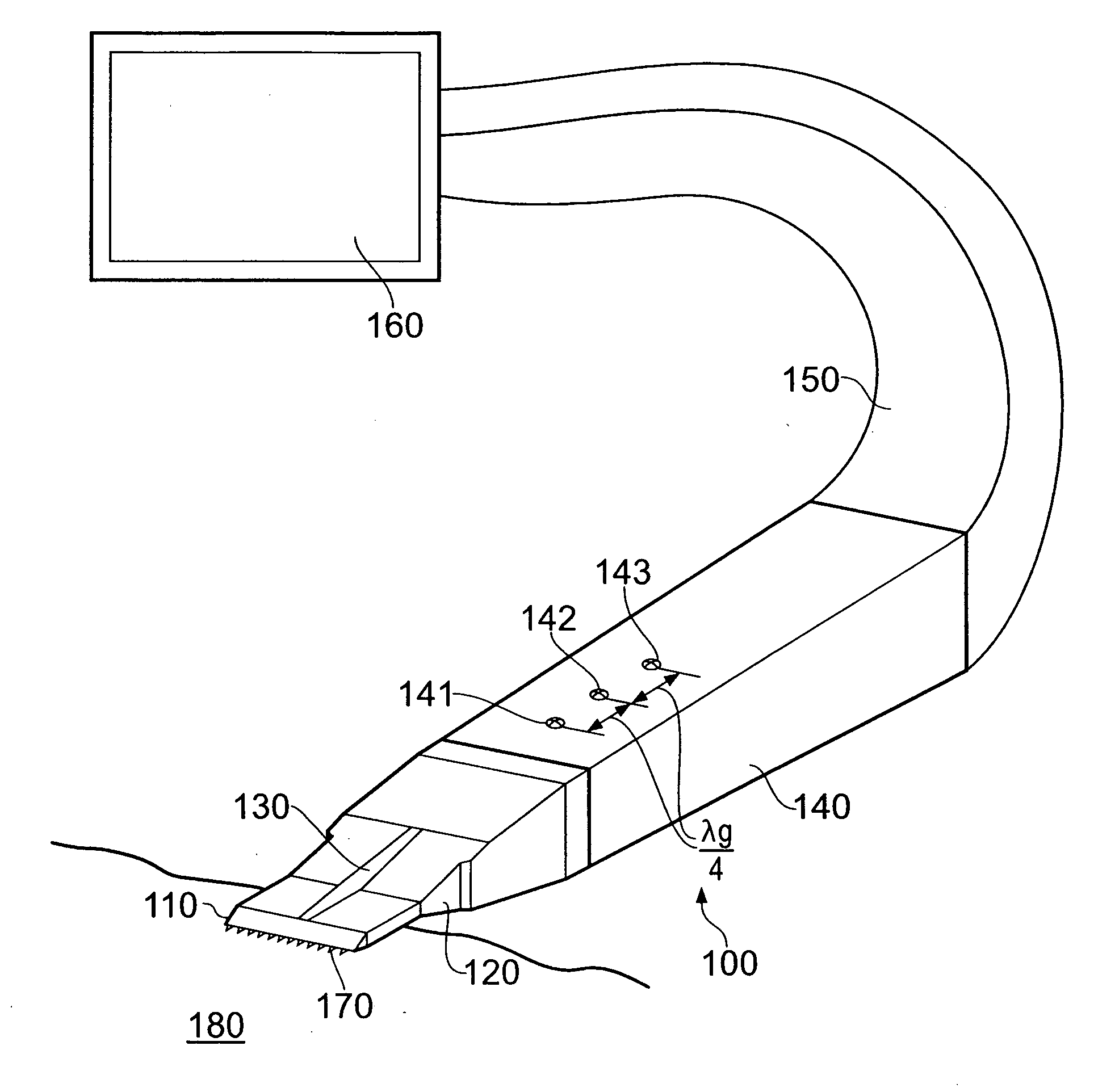
Surgical antenna
ActiveUS20100030207A1Ensure efficient flowPrevents tissue charringIncision instrumentsSurgical instruments for heatingTransformerImpedance matching
A surgical instrument (100) (e.g. scalpel) is disclosed which has an antenna arranged to emit a substantially uniform microwave radiation field (e.g. having a frequency of 5-100 GHz) at an edge of a cutting element (110) (e.g. blade). The emitted radiation can cauterise tissue e.g. broken blood vessels simultaneously with cutting. The antenna may be integral with the cutting element, e.g. a metallised piece of ceramic attachable at an end of a waveguide (120, 150) to receive radiation therefrom. The cutting element (110) can include a quarter wave transformer to couple power efficiently from the waveguide (120). The instrument can be used with impedance matching apparatus to control the energy delivered into the tissue. Also disclosed is an invasive ablation probe (e.g. insertable through a catheter) having a plurality of radiating elements whose emitted field combine to give a uniform effect at an insertion end of the probe.
Owner:CREO MEDICAL LTD
Anastomosis system utilizing an access port
A tool used in the performance of an anastomosis procedure between a graft vessel and a target vessel, where that anastomosis procedure utilizes at least one surgical tool, may include an access system that has a port and a seal connected to the port. The seal may substantially prevent loss of fluid from the target vessel.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Vascular sheath
InactiveUS20050240153A1Large and small diameterIntroduction of large and smallEngine sealsPiston ringsVeinDuring procedure
Disclosed is a vascular sheath for helping to prevent bleeding during procedures in which devices must be inserted into a blood vessel such as an artery or vein. The vascular sheath includes at least one manually compressible primary seal that has a lumen passing therethrough. A device inserted into the blood vessel first passes through the sheath, and thus through the lumen in the primary seal. By manually adjusting the compression of the primary seal the size of at least part of the lumen is made to substantially conform to the outer surface of the device. The primary seal can thus seal against large and small sized devices to prevent bleeding. It is preferred that a secondary seal also be used and one type of secondary seal is a flexible disk or flap with one or more slits through which the device passes.
Owner:JS VASCULAR
Vascular clamp for caesarian section
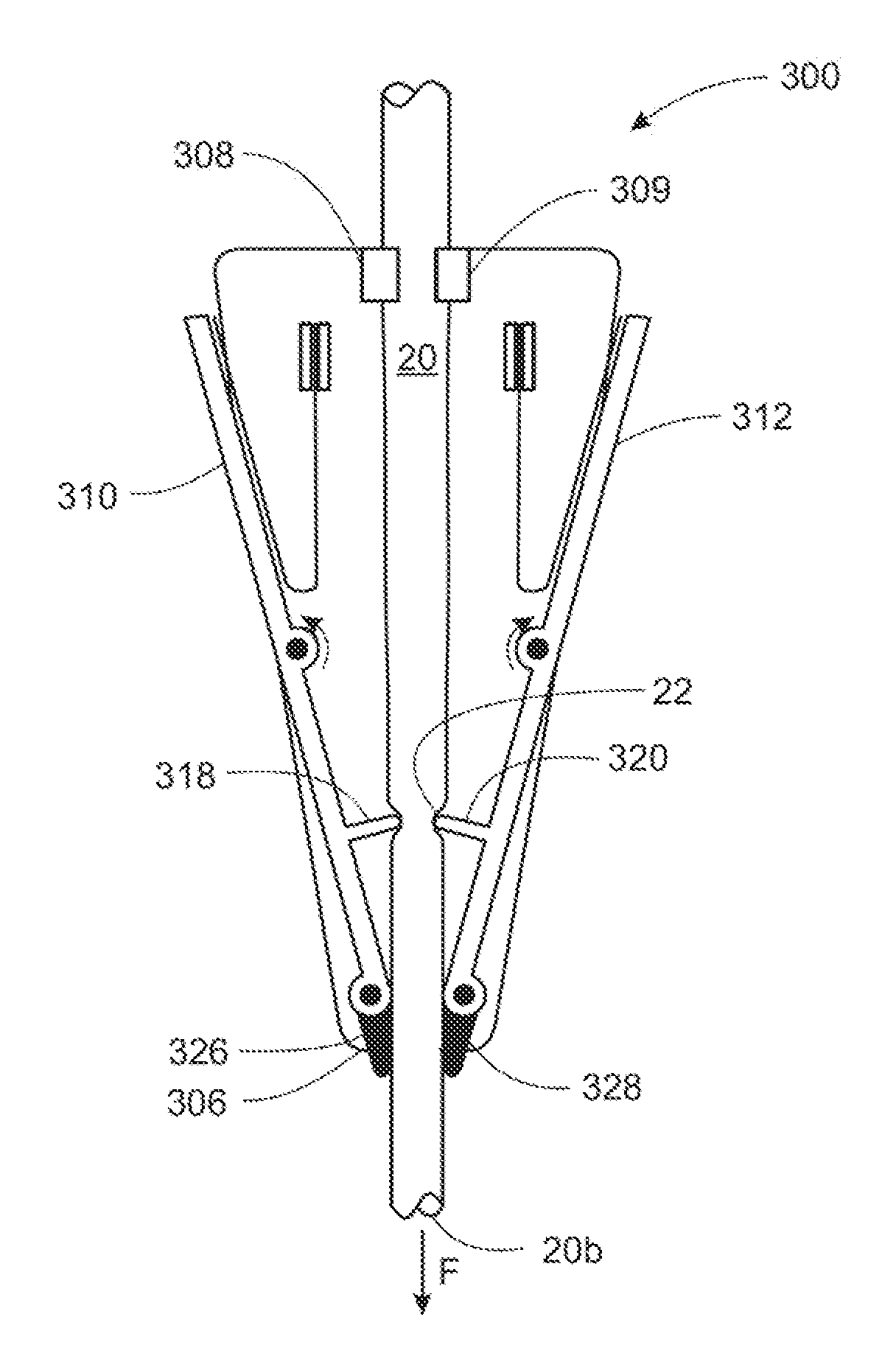
ActiveUS20050101974A1Easy to usePrevent excessive blood lossBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterCaesarian sectionArtery forceps
The invention provides devices, systems and methods for clamping arteries which are useful in reducing or abolishing blood flow in an artery, and may be used to control hemorrhage following a caesarian delivery. A clamping device embodying features of the invention includes a pair of clamping members with opposed pressure-applying members having facing pressure-applying surfaces, at least one of which is a yieldable pressure-applying surface. The yieldable pressure-applying surface is preferably resilient. The clamping members are configured to adjust the distance between pressure-applying surfaces, and a blood flow sensor is disposed on at least one of the pressure-applying members to aid in locating the target artery and also to monitor blood flow through the artery. The clamping device is particularly suitable for occluding uterine arteries by compressing the broad ligament which contains the uterine artery and which is connected to the patient's uterus with the arterial clamp.
Owner:VASCULAR CONTROL SYST
Methods for endocardial ablation
InactiveUS20070270793A1Avoid blood lossCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingTunica intimaCorneal ablation
Methods and devices for performing endocardiac ablation by accessing the interior of the heart through the wall of the heart at its apex.
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
Endovascular catheter air block
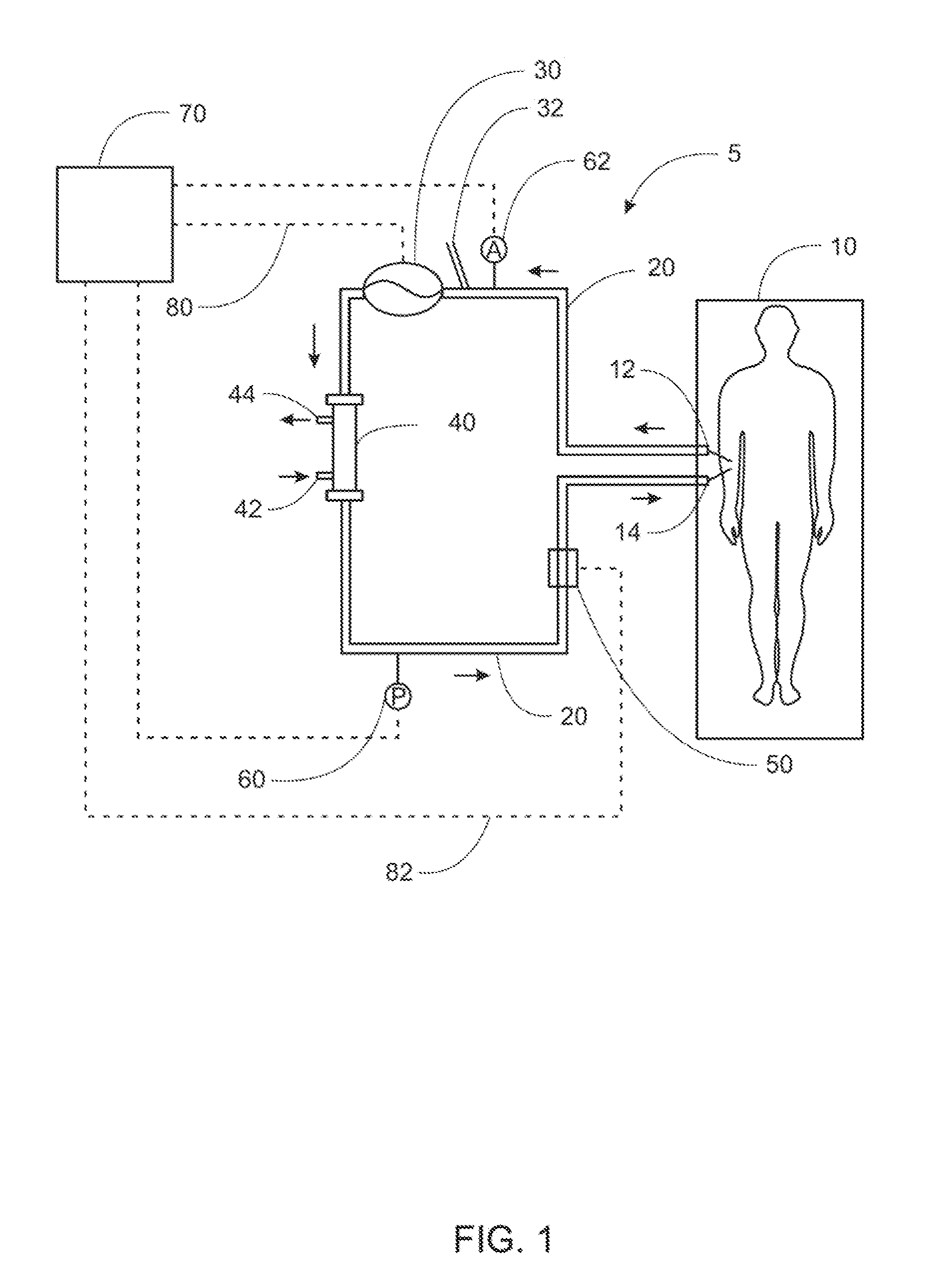
ActiveUS20100010442A1Avoid blood lossAvoid lostMedical devicesHaemostasis valvesCardiac chamberHemostasis valve
This invention is an air block for industrial, medical, and non-medical uses. For example, the air block is connected to the proximal end of a vascular access catheter. The air block is either removably connected to the proximal end of the catheter or it is integral to the proximal end of the catheter. The air block permits introduction of other catheters or instrumentation through its central lumen and on into a lumen of the catheter while minimizing fluid loss or gain into the catheter. The air block further prevents air from entering the catheter and provides for removal of the air or other gas from the central lumen before it can enter the catheter where it could cause harm to the patient. The air block can be attached to various standard proximal catheter terminations including Luer fittings and hemostasis valve outer barrels.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
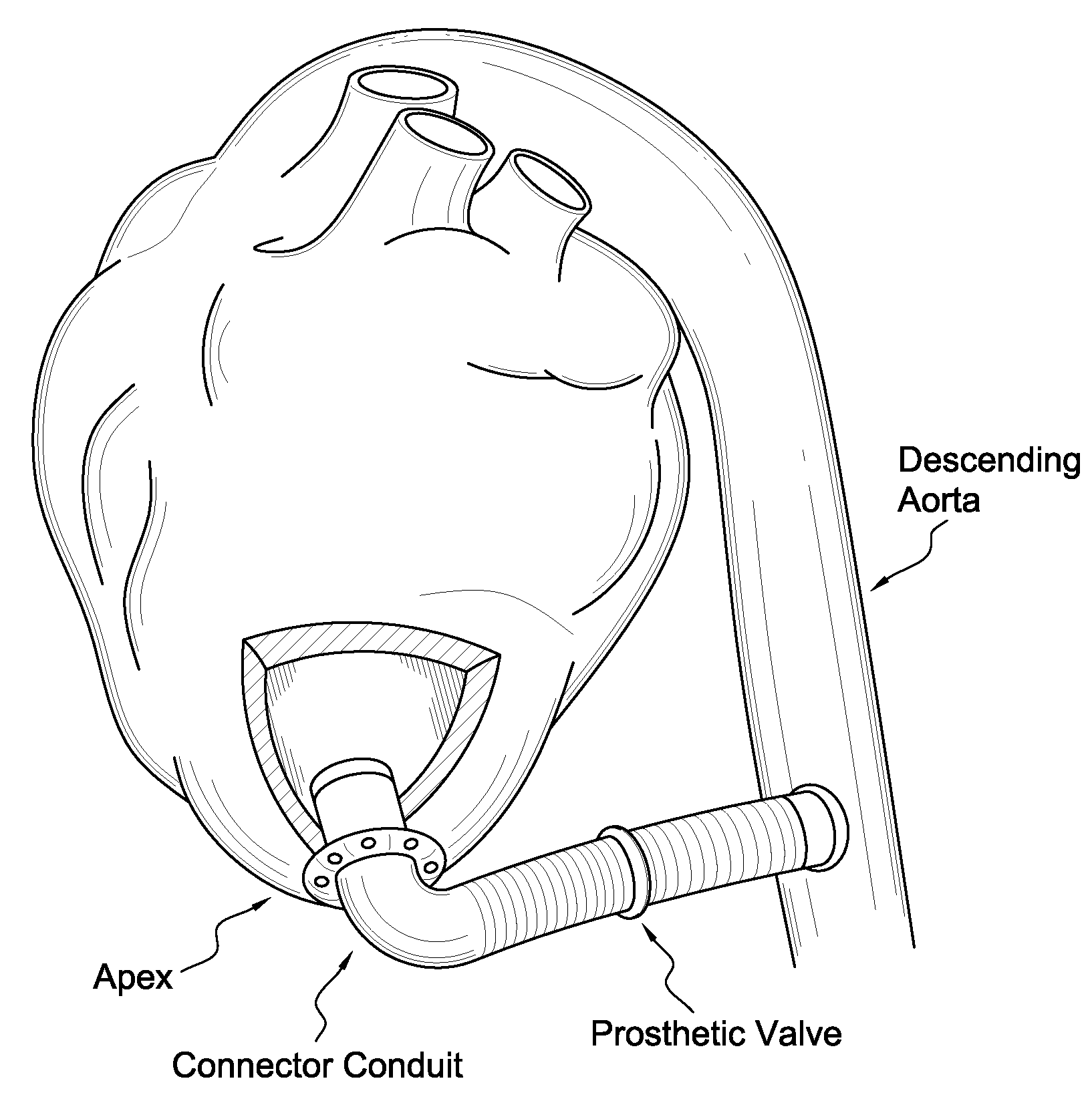
Treatments for a patient with congestive heart failure
InactiveUS20060100698A1Avoid blood lossReduce blood leakageSuture equipmentsCannulasCardiac wallThoracic cavity
The invention is directed to two minimally invasive therapeutic procedures, particularly for patients with congestive heart failure, and devices and systems for such procedures. One procedure involves providing a valved passageway through the patient's left ventricular wall at the apex of the patient's heart and advancing instruments through the valved passageway to connect the valve leaflets of the patient's heart valve, e.g. the mitral valve, in a “Bow-Tie” configuration to prevent or minimize regurgitation through the valve. The second procedure involves advancing a pacing lead and a pacing lead implanting device through a trocar in the patient's chest and implanting the pacing lead on an exposed epicardial region of the patient's heart wall. The pacing lead has a penetrating electrode which is secured within the heart wall. One or both procedures may be performed on a patient with CHF. Improved devices for these procedures include a minimally invasive grasping device having an inner lumen for advancing connecting members and other instruments through the device to the distal end thereof. Other improved devices include a pacing lead implant instrument which is releasably secured by its distal end to the exposed heart wall to facilitate penetration of the pacing lead electrode into the heart wall. Other improved instruments include a leaflet connector with an artificial cordae tendenae strand secured to an end of the leaflet connector.
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
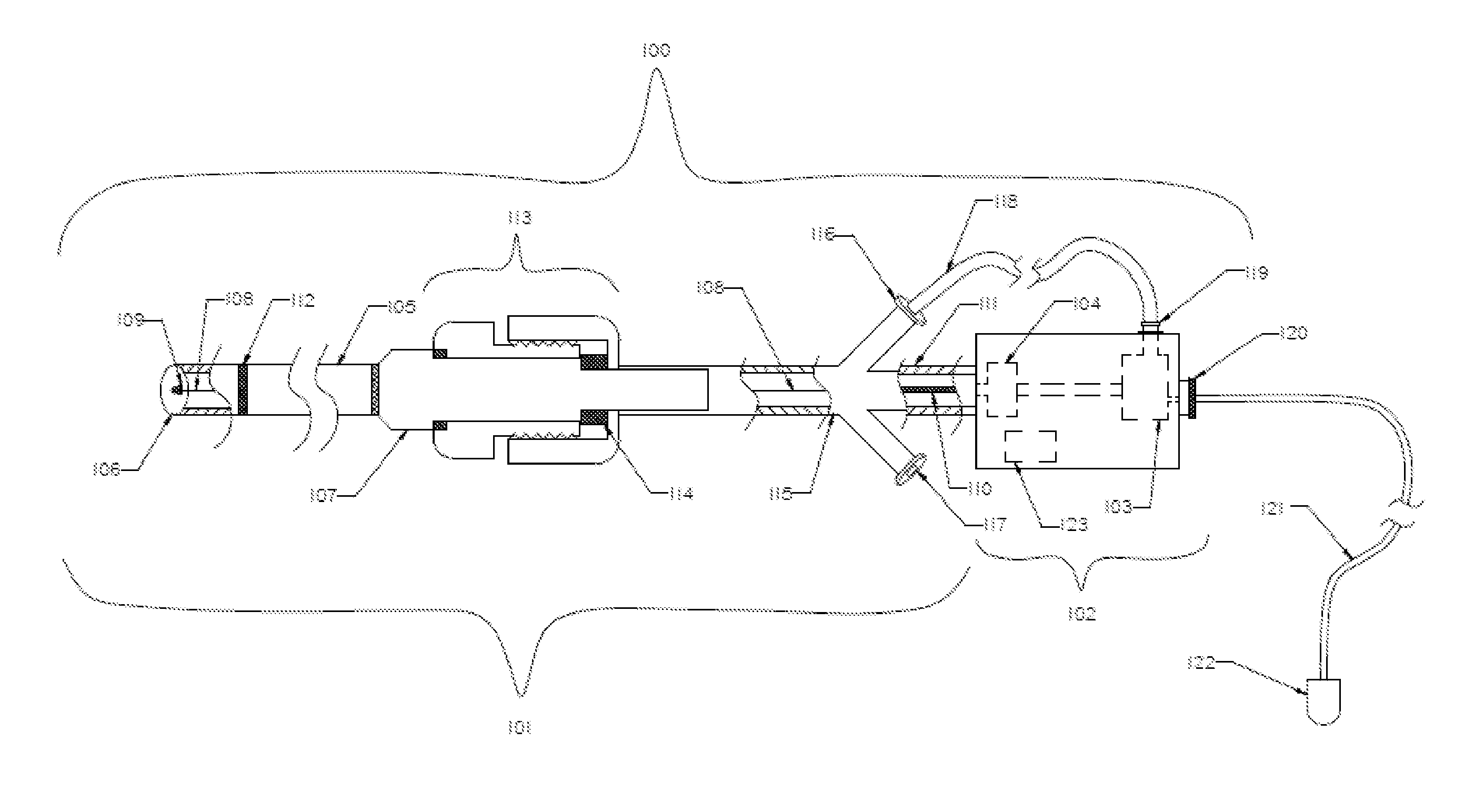
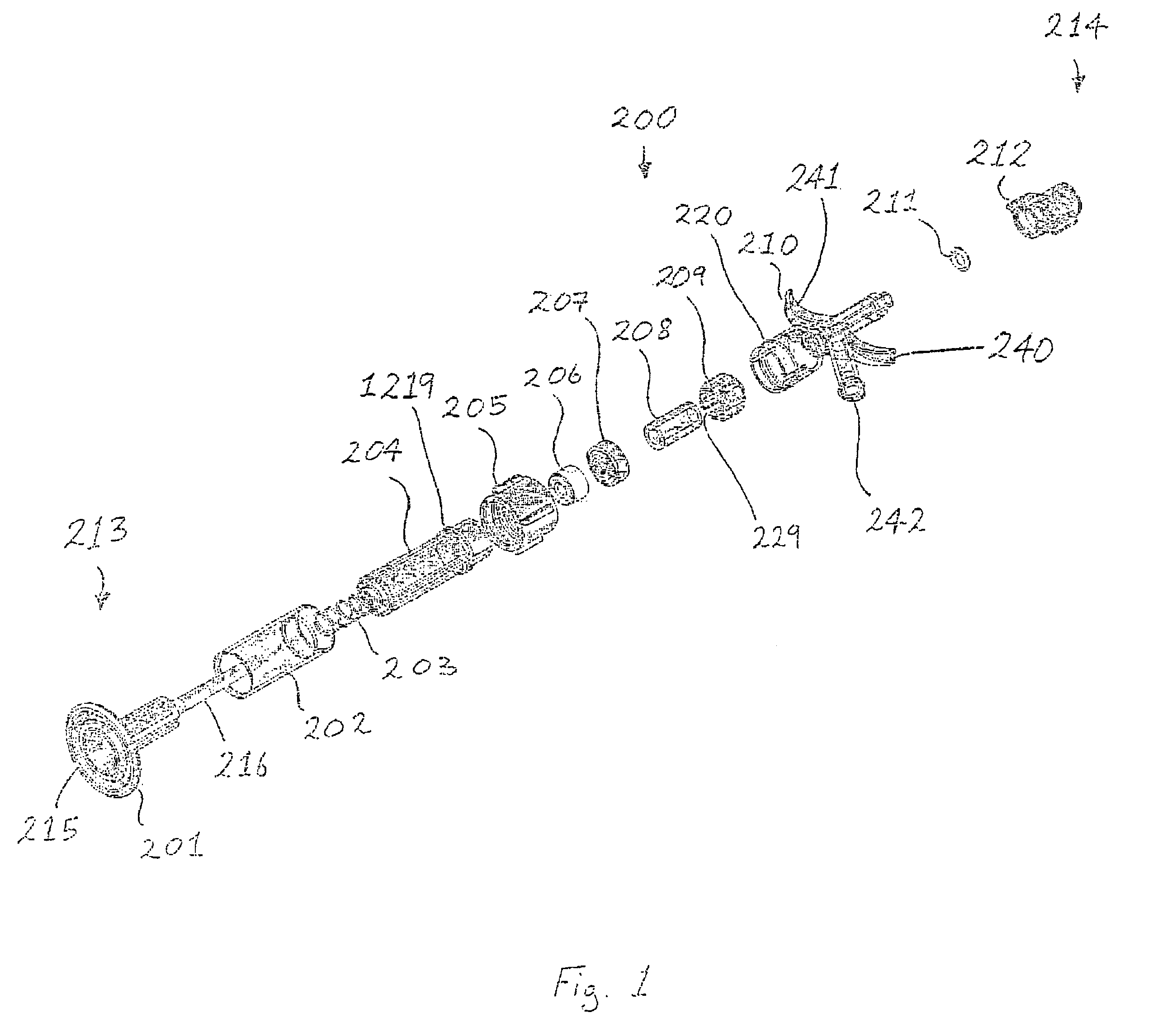
Haemostasis device
ActiveUS7976503B2Avoid blood lossEasily identifiableInfusion syringesHaemostasis valvesEngineeringHigh pressure
A haemostasis device (200) comprises a low pressure seal (206) and a high pressure seal (208). A tubular bayonet (201) is movable from a retracted configuration to an inserted configuration to move the low pressure seal (206) between a closed configuration and an open configuration. With the low pressure seal (206) in the open configuration, a guidewire (222) may be inserted through the low pressure seal (206), and with the low pressure seal (206) in the closed configuration, the guidewire (222) may be passed through the low pressure seal (206) while maintaining sealing around the guidewire (222). A collet (209) is movable in a radial direction to move the high pressure seal (208) between an open configuration and a sealing configuration. With the high pressure seal (208) in the sealing configuration, the guidewire (222) is locked in position.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Devices and Methods For Occluding a Flexible Tube
ActiveUS20100234809A1Prevent accidental blood lossConstricting lumenDiaphragm valvesEngine diaphragmsPull forceSpring force
A device and method to constrict or occlude the lumen of a flexible tube may include an occluder under the influence of an elastic force, such as a spring force, that can compress a portion of the wall of the flexible tube. The occluder can be under the influence of the elastic force, but prevented from occluding the tube by a stop. The stop can be connected to a tube gripping feature, so that a pulling force on the tube near the gripping feature can disengage the stop from the occluder, releasing the occluder to compress the tube. In some embodiments, the pulling force applied to the tube causes movement of the gripping feature by taking up slack in a portion of the tube held in the device. In other embodiments, the pulling force applied to the tube causes the tube to stretch elastically near the gripping feature, causing the gripping feature to move, and disengaging the stop from the occluder.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Special clinical nutrition formula for fracture and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106579460AIncrease bone densityImprove anti-infective ingredientsFood shapingNutrientPeppermints
The invention relates to a special clinical nutrition formula for fracture and a preparation method thereof. The special clinical nutrition formula for fracture is prepared from the following raw materials: protein, fat, carbohydrate, dietary fiber, macroelements, trace elements, fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble vitamins, dietary essences, medicinal and edible components, natural plant compounds and new-resource foods; and the medicinal and edible components are at least one component selected from the following: peppermint, dried citrus reticulata peel, Chinese yams, long-stamen onion bulbs, Chinese wolfberry fruits, Chinese date fruits, longan flesh, and orange peel. The components are prepared into powder in advance, wherein the fat is prepared into fat powder by adopting a micro-capsule embedding technology and the dietary essences are prepared into powder by adopting a freeze-drying technology. The components are accordingly screened and proportioned, so that the special clinical nutrition formula disclosed by the invention is capable of providing complete basic energies and nutrients to the patients with fracture; moreover, components capable of increasing bone density, resisting infection, nourishing the blood and conditioning digestion are added, so that the special clinical nutrition formula is conducive to promoting bone healing, enhancing physical fitness and improving treatment effects on the patients with fracture.
Owner:上海奥医生物医药科技有限公司
Medical clamp
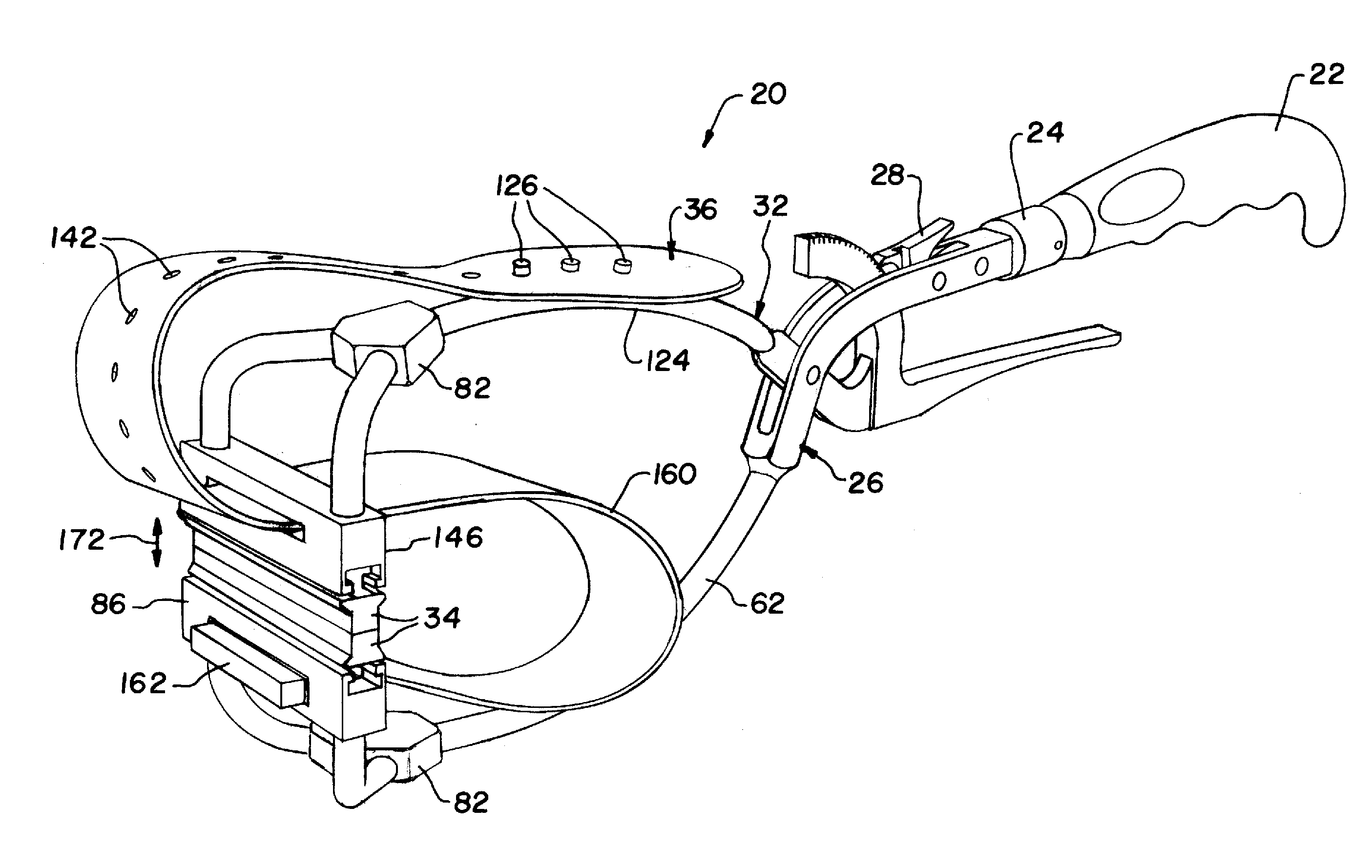
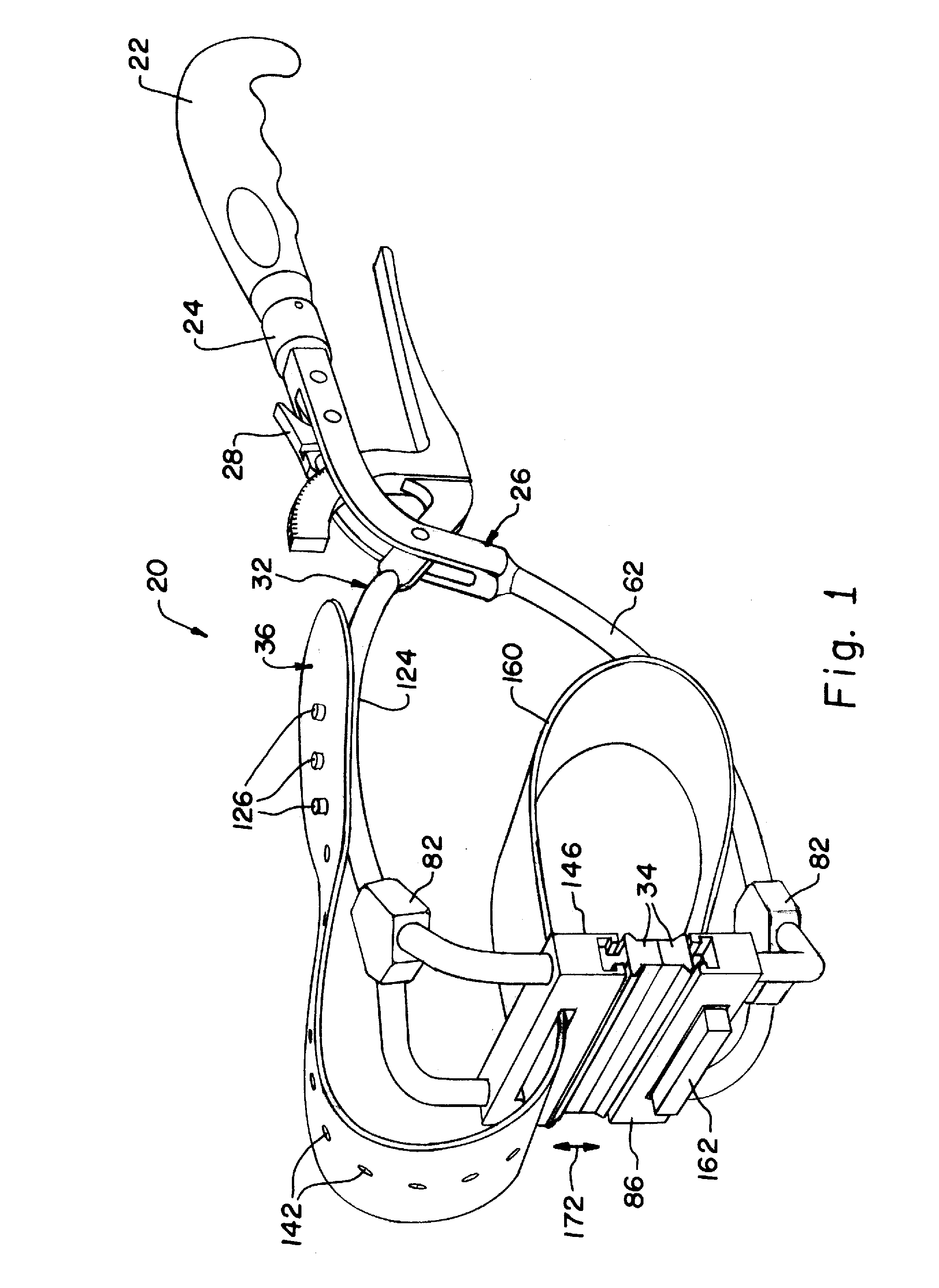
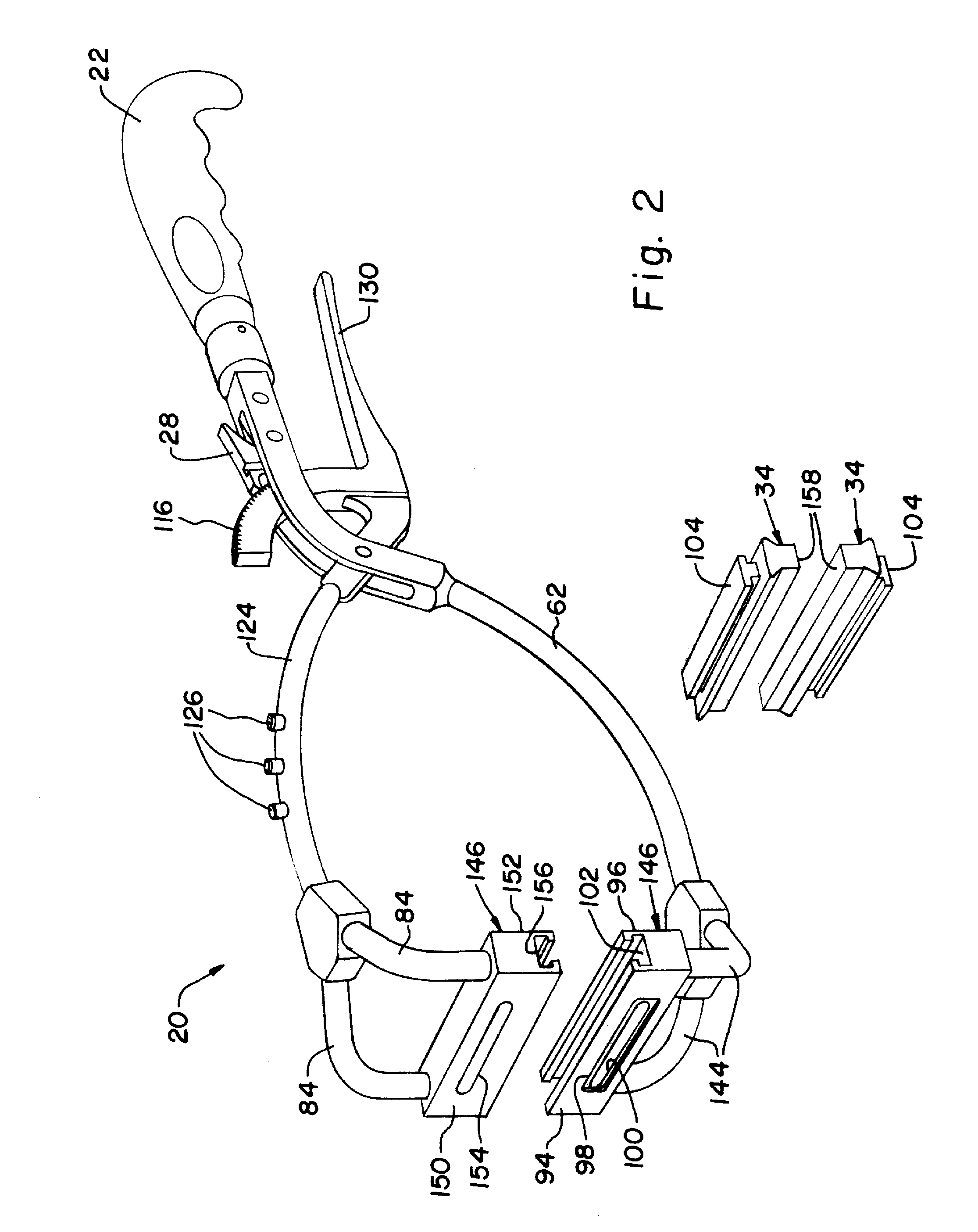
InactiveUS20120010654A1Blood lossQuickly and temporarily controlTourniquetsSurgical veterinaryEngineeringUpper Arms
A medical clamp includes a lower arm assembly, an upper arm assembly, and a belt. The upper arm assembly is pivotally connected to the lower arm assembly. The lower arm assembly and the upper arm assembly are configured for clamping relative to one another. The belt is connected to the lower arm assembly and the upper arm assembly and is configured for forming a loop therebetween.
Owner:SPECIALTY SURGICAL INSTR INC
Exsanguination preventing device
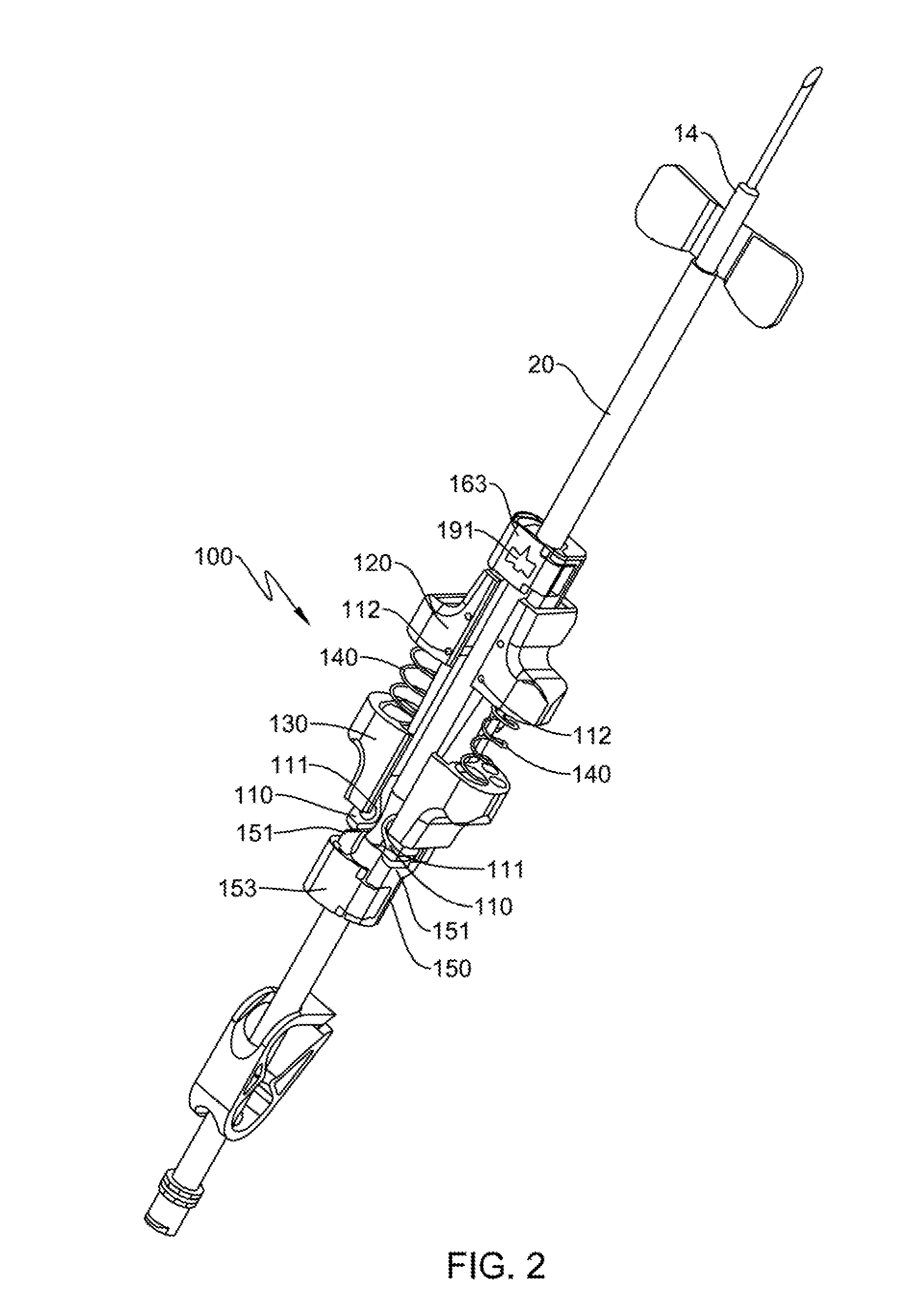
ActiveUS20140234166A1Easy to useAvoid blood lossOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsInjury mouthCatheter
In one embodiment, an exsanguination preventing device includes a collection container having an inlet configured to receive blood from a patient and an outlet configured to discharge the blood; a pump operatively coupled to the collection container; a conduit fluidly coupled to the collection container, which receives the blood from the collection container, the blood being moved by the pump; and an insertion device, which delivers the blood from the conduit to a bodily part of the patient. The collection container is configured to be sealingly coupled to a wound on the patient and air entrapped within the exsanguination preventing device is removed by an air removal system, such to prevent unwanted discharge of air into the bodily part of the patient. All the components of the exsanguination preventing device are sized such to make it portable in a pocket of a garment or backpack of a soldier.
Owner:ERICKSON DIRK JEROME
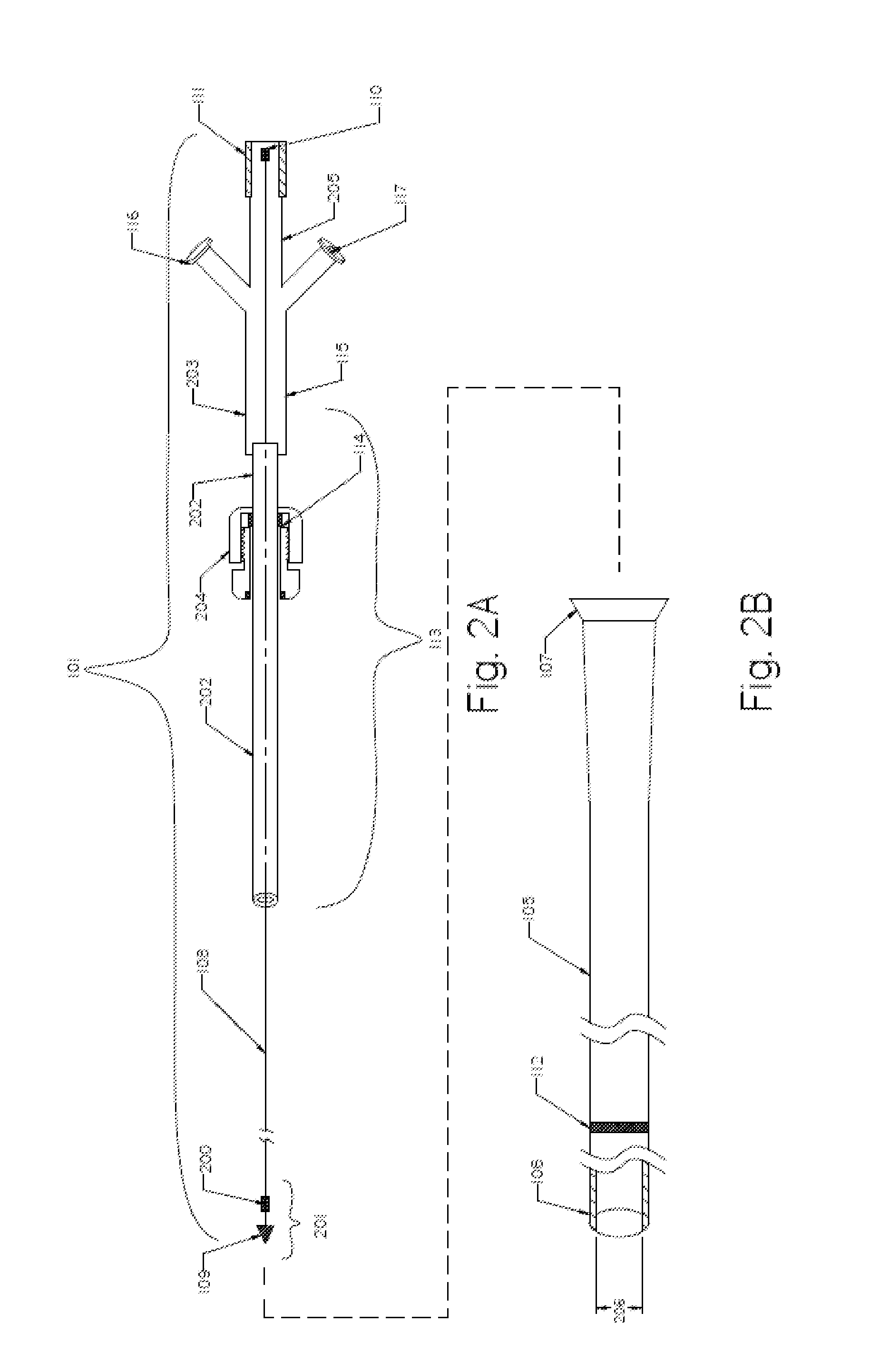
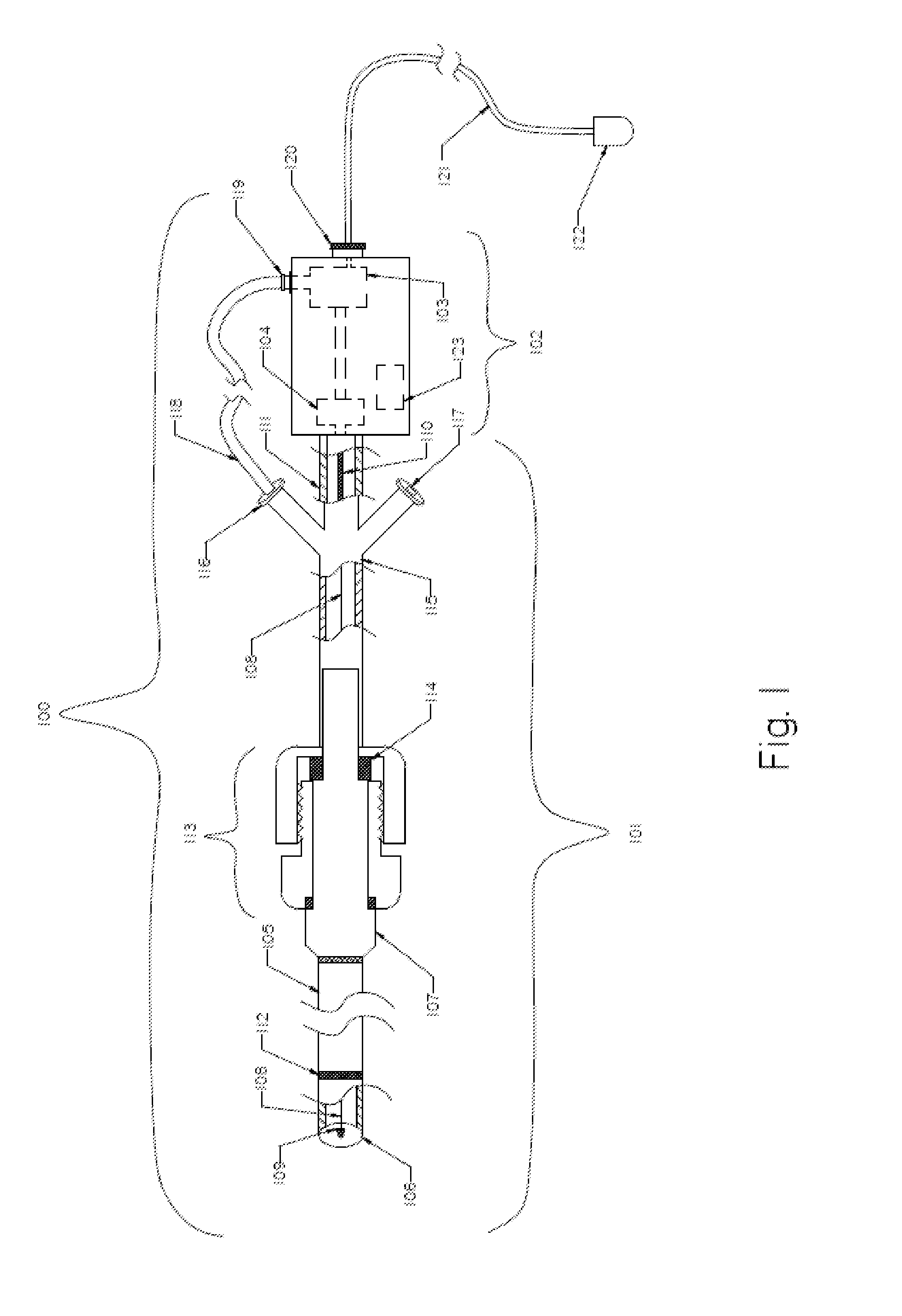
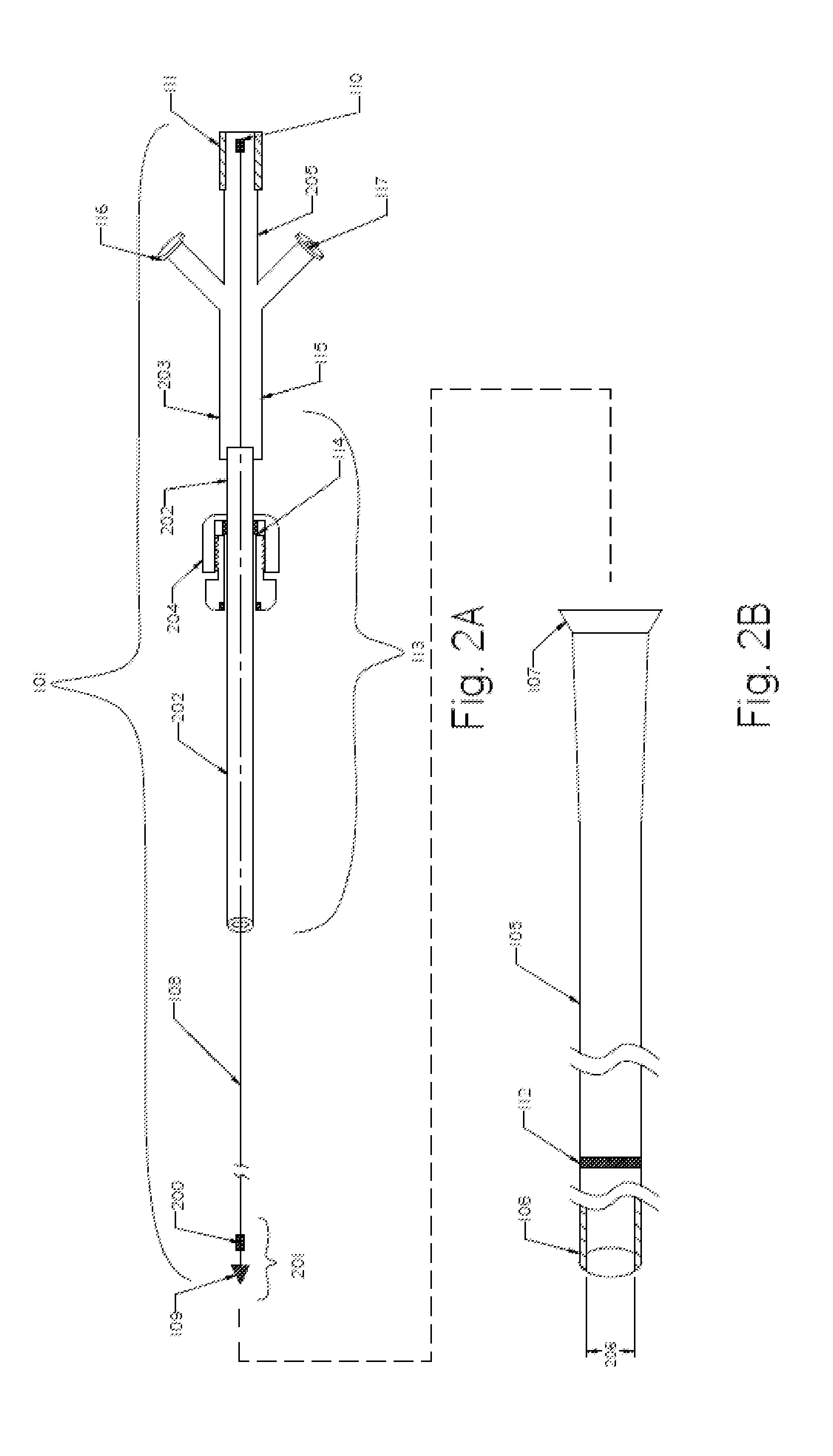
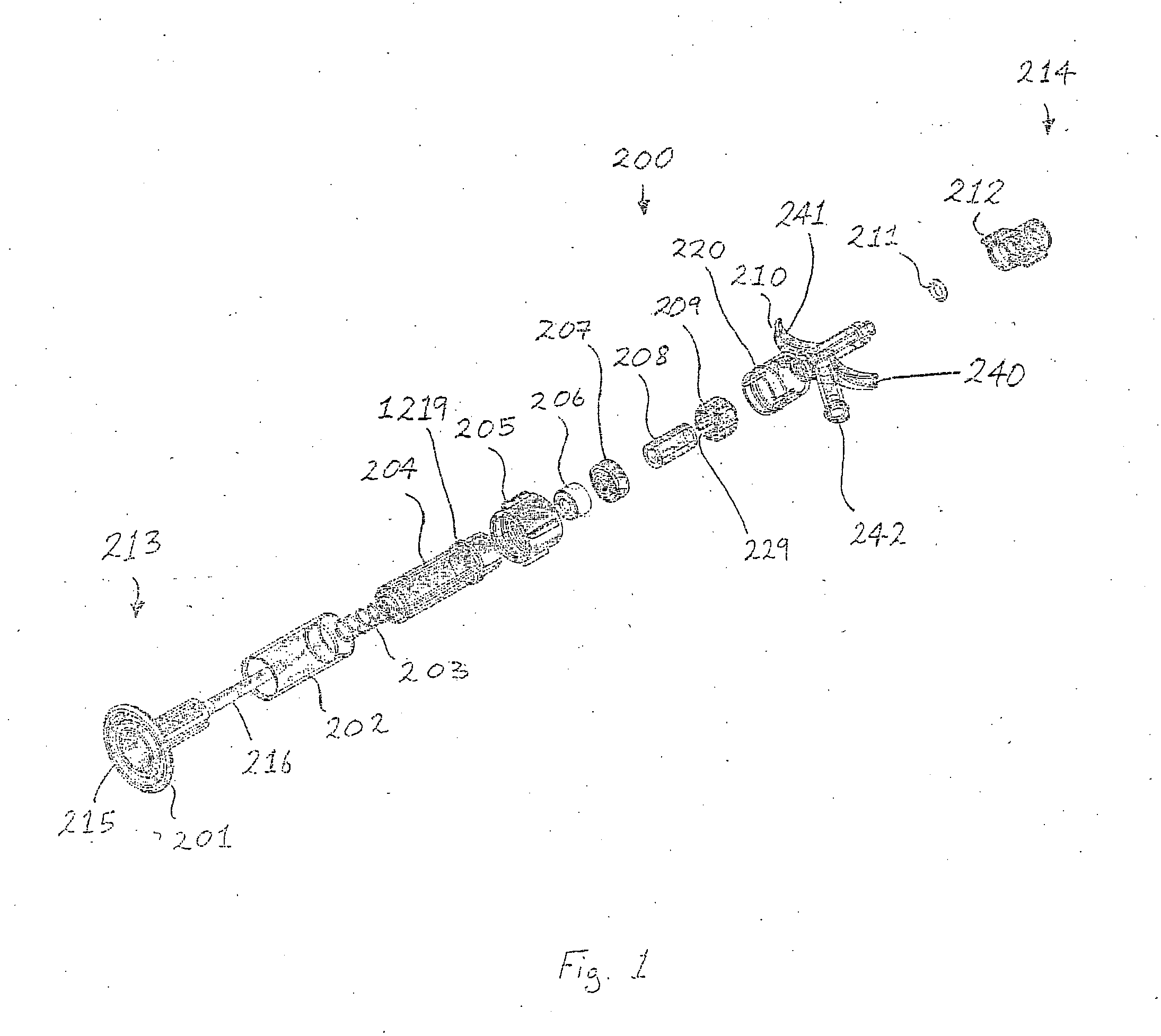
Variable Hemostasis valve and Method of Use
ActiveUS20110251565A1Avoid blood lossPermit introductionHaemostasis valvesIntravenous devicesEngineeringHemostasis valve
A variable hemostasis valve is disclosed that may be used during medical procedures to prevent blood loss while permitting the percutaneous introduction, operation, and removal of medical instruments. A flexible tubular seal element is disclosed that is disposed within the variable hemostasis valve to provide a fluid-tight, adjustable seal. After insertion of a medical instrument into the valve through at least a portion of the flexible tubular seal element, a proximal portion of the valve housing may be rotated to cause the tension of the flexible tubular seal element to increase over the inserted medical instrument and engage the valve in a closed position. The proximal portion of the valve housing may then be rotated in an opposite direction to release the seal and return the tubular seal element to a relaxed lumen open position.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Joining and/or Sealing Tissues Through Photo-Activated Cross-Linking of Matrix Proteins
ActiveUS20090306707A1Demonstrate efficacyCreate quicklyBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsCross-linkMetal
A method of joining and / or scaling tissues in a surgical procedure or medical treatment, comprising the steps of: (1) applying a matrix protein, a photoactivatable metal-ligand complex and an electron acceptor to a tissue portion; (2) irradiating said tissue portion to photactivate the photoactivatable metal-ligand complex: thereby initiating a cross-linking reaction of the matrix protein to seal said tissue portion or join said tissue portion to an adjacent tissue portion.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Cryoablation system with multiple safety detection and prevention device
PendingCN110882050AAvoid enteringAvoid blood lossCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingCatheterBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a cryoablation system with a multiple safety detection and prevention device. The system consists of cryoablation equipment and a cryoablation catheter, the cryoablation equipment comprises a human-computer interaction module, a control module and a gas circuit module, the man-machine interaction module is electrically connected with the control module; the control moduleis electrically connected with the gas circuit module; the gas circuit module is connected with the cryoablation catheter; the cryoablation catheter comprises a catheter slender shaft, wherein a catheter handle is arranged at the near end of the catheter slender shaft, a freezing unit is arranged at the far end of the catheter slender shaft, and an air inlet pipe and an air return pipe are arranged in a cavity of the catheter slender shaft. The air inlet pipe and the air return pipe are in fluid communication with an inner cavity of the freezing unit, a liquid plugging mechanism is arranged inthe far end of the catheter slender shaft, and the liquid plugging mechanism is provided with a hydrophobic micropore structure.
Owner:CRYOFOCUS MEDTECH (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Hemostatic bio-material composition and method
InactiveUS20100092573A1Easy to spreadStop the bleedingBiocideSurgical adhesivesChemical compositionProximate
The present invention relates to a haemostatic bio-material composition and method for achieving hemostasis. The method for providing hemostasis generally comprises: supplying a dry potassium phosphate based hemostat mixture comprising: monobasic potassium phosphate, a metal oxide, and a tertiary calcium phosphate, wherein the weight percent ratio of monobasic potassium phosphate to metal oxide is between about 3:1 and 1:1; mixing the dry potassium phosphate based hemostat mixture with an aqueous solution forming an activated hemostat slurry; applying an hemostasis-promoting amount of the activated potassium phosphate based hemostat slurry to a site of bleeding; wherein the site of bleeding is in, on, or proximate to bone.
Owner:LALLY THOMAS +1
Hemostatic bio-material composition and method
InactiveUS20120308552A1Improve adhesionWell mixedBiocideSurgical adhesivesMonopotassium phosphateSlurry
The present invention relates to a haemostatic bio-material composition and method for achieving hemostasis. The method for providing hemostasis generally comprises: supplying a dry potassium phosphate based hemostat mixture comprising: monobasic potassium phosphate, a metal oxide, and a tertiary calcium phosphate, wherein the weight percent ratio of monobasic potassium phosphate to metal oxide is between about 3:1 and 1:1; mixing the dry potassium phosphate based hemostat mixture with an aqueous solution forming an activated hemostat slurry; applying an hemostasis-promoting amount of the activated potassium phosphate based hemostat slurry to a site of bleeding; wherein the site of bleeding is in, on, or proximate to bone.
Owner:LALLY THOMAS +1
Preparation for treating angiocardiopathy and its preparation method
InactiveCN100998835AIncrease surface areaHas a wetting effectPharmaceutical product form changePill deliveryDiseaseVascular disease
Owner:SHANDONG TAITIAN NEW MEDICINE DEV
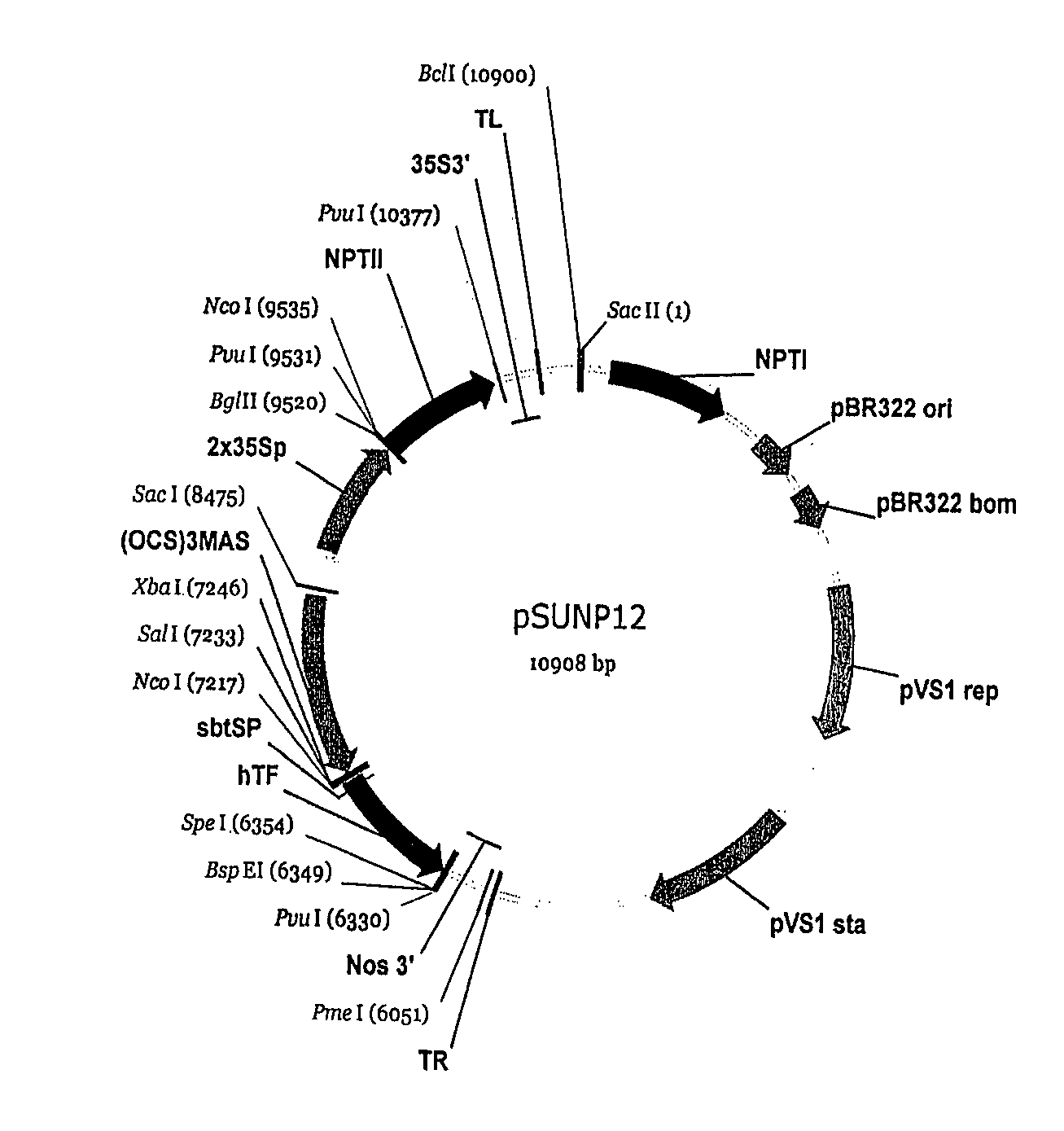
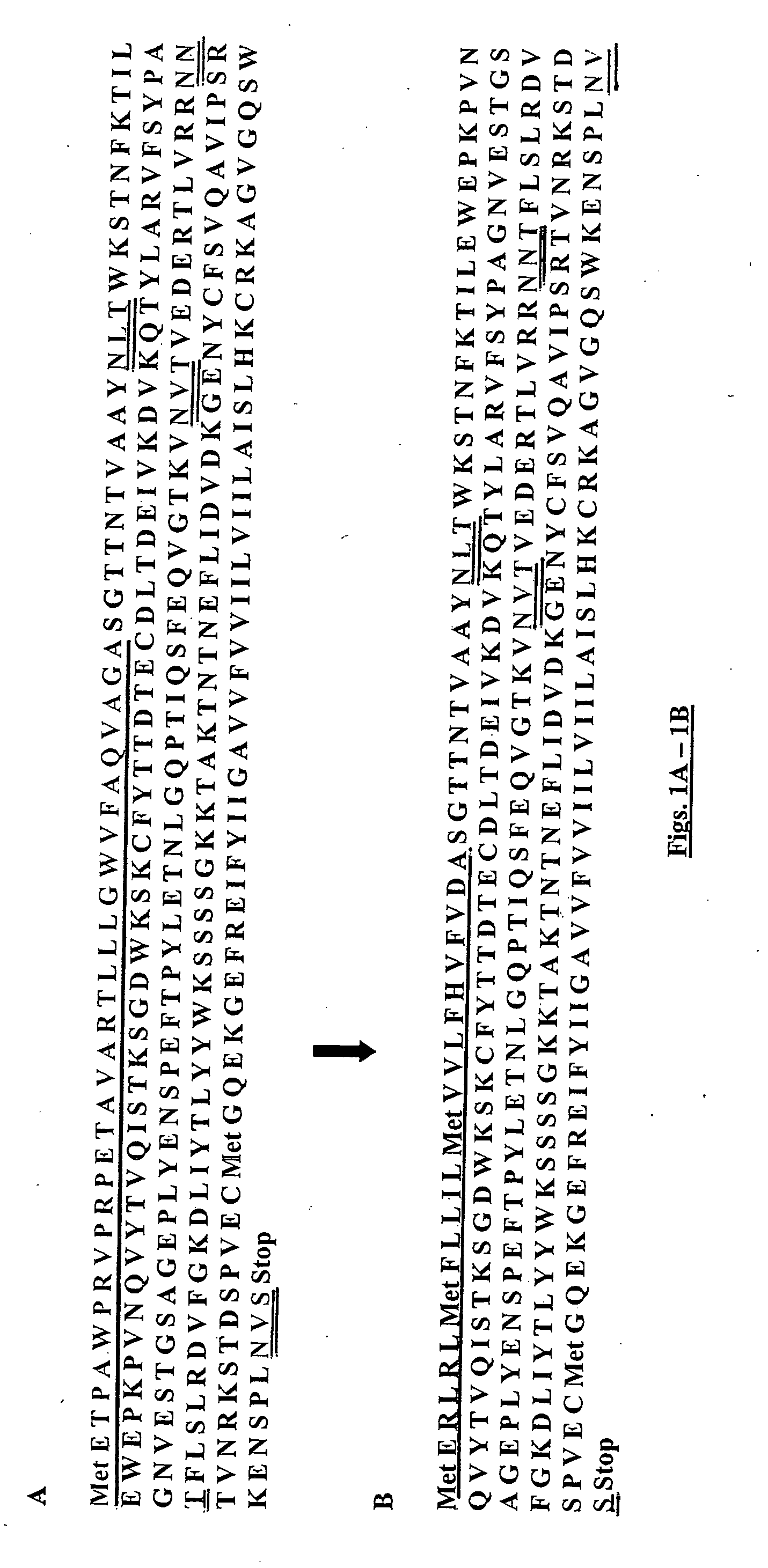
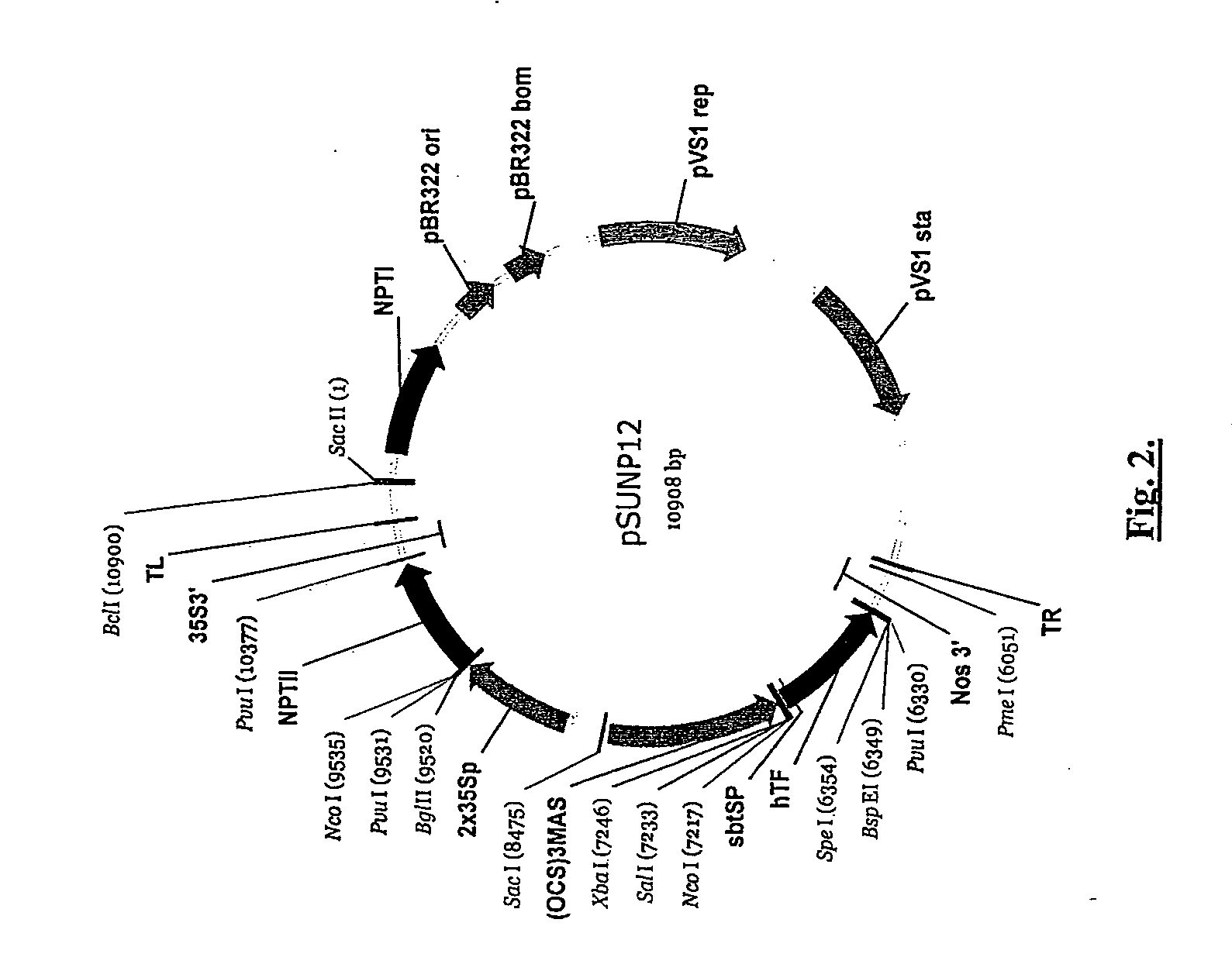
Production of tissue factor in plants
InactiveUS20070292490A1High activitySubstantial lipidationPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsTissue factorGenetics
The instant invention provides transgenic plants that express mammalian, e.g., human, recombinant tissue factor (rhTF) as well as methods for making rhTF. The invention further provides rhTF or functional fragment thereof that are obtained from a transgenic plant. The invention also provides methods of treating a subject using the rhTF or a fragment thereof.
Owner:ALTOR BIOSCIENCE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com