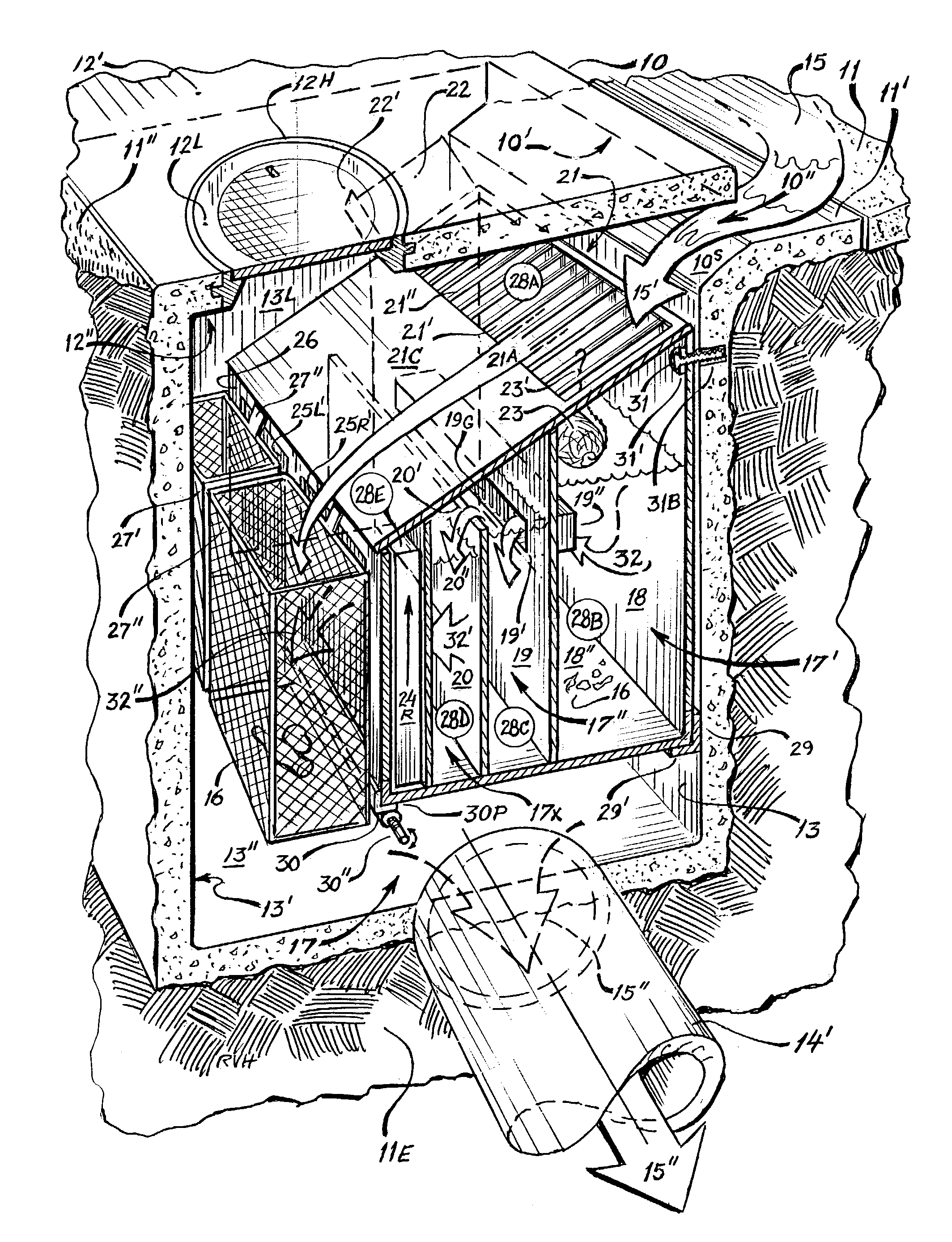
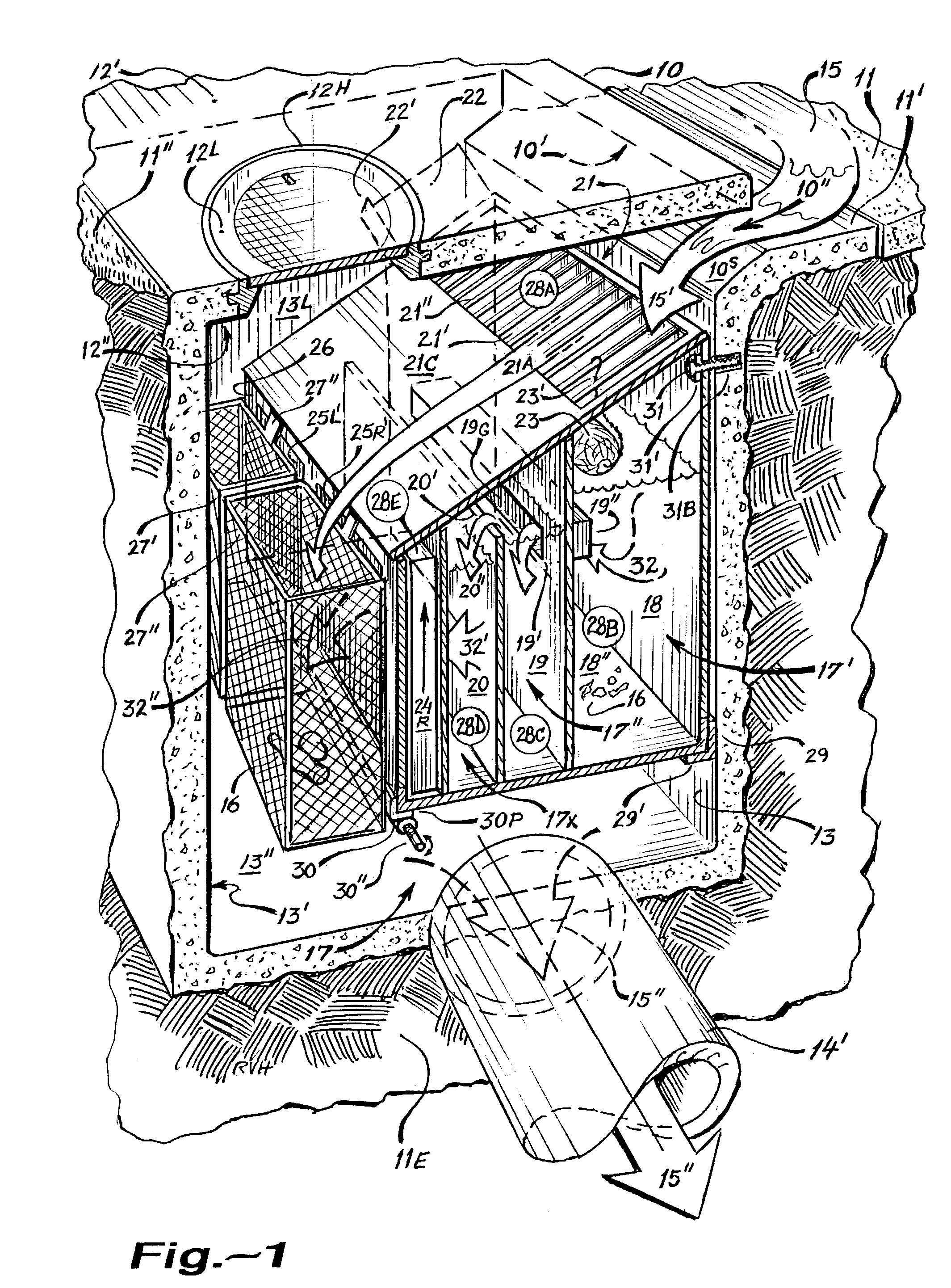
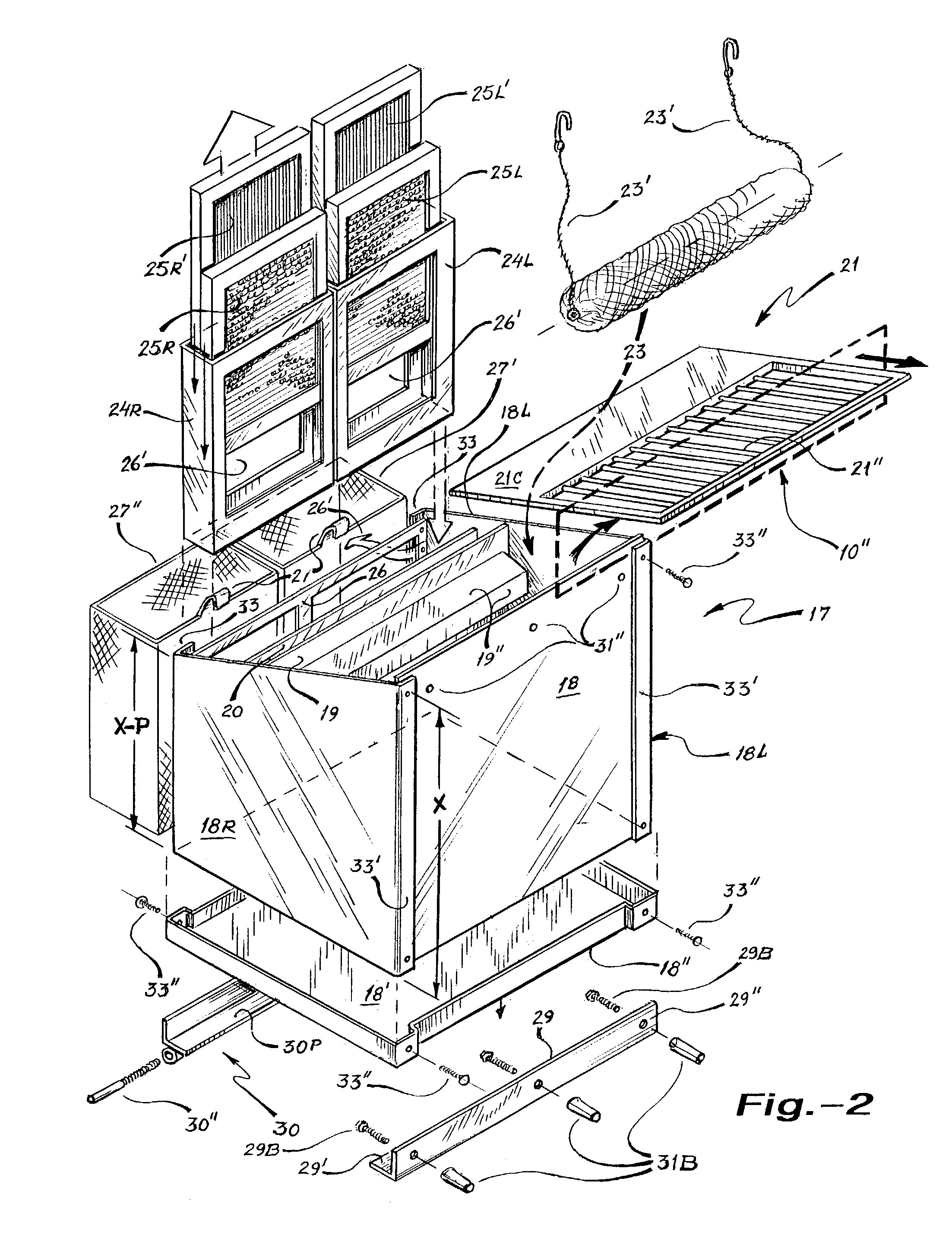
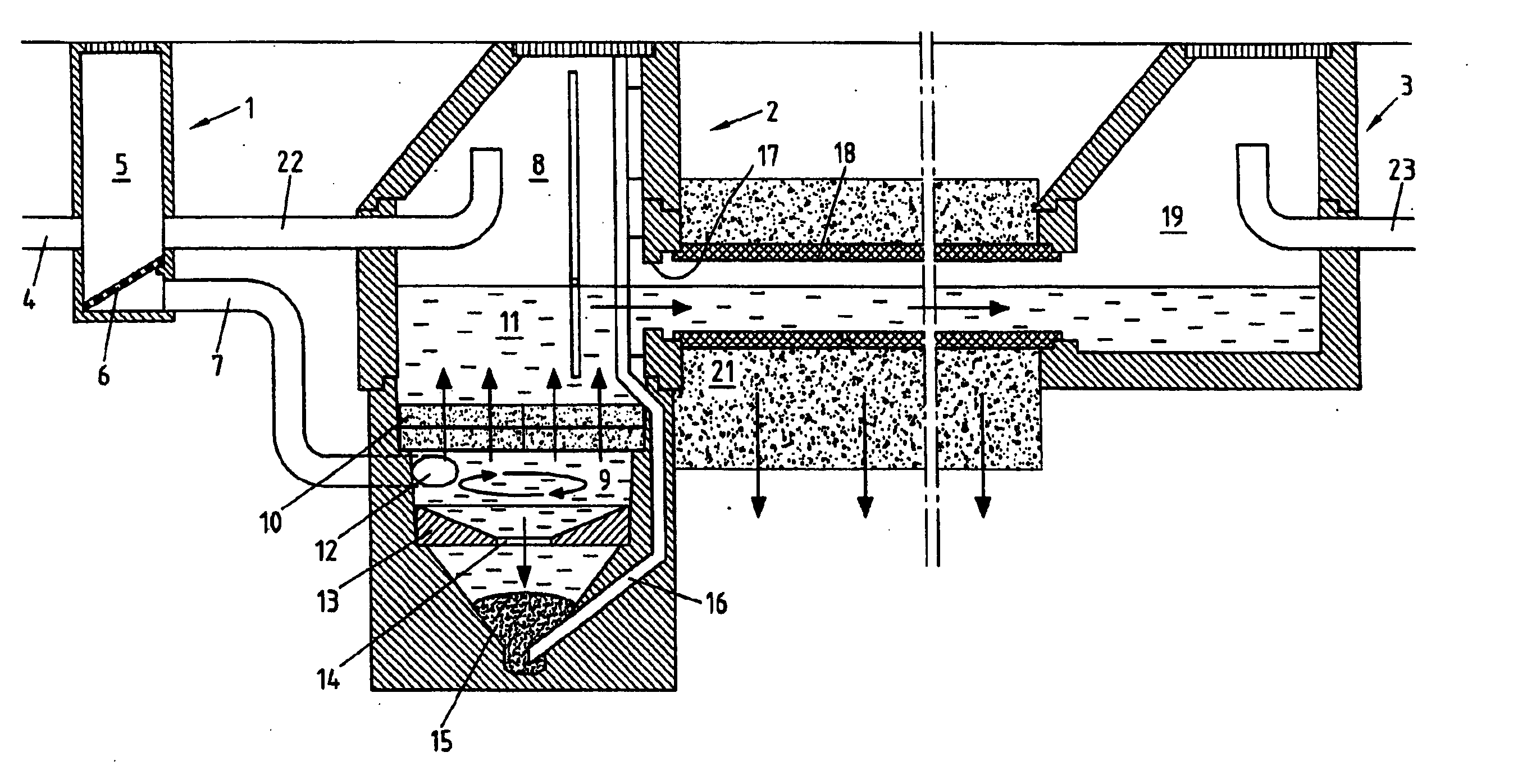
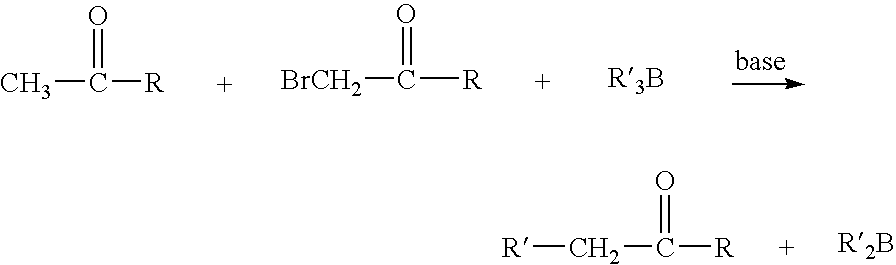
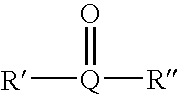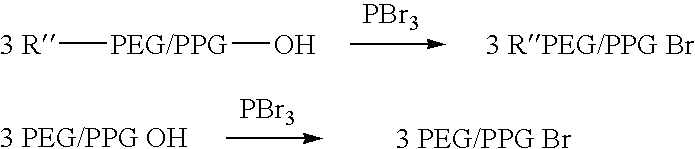Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2623results about "Runoff/storm water treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
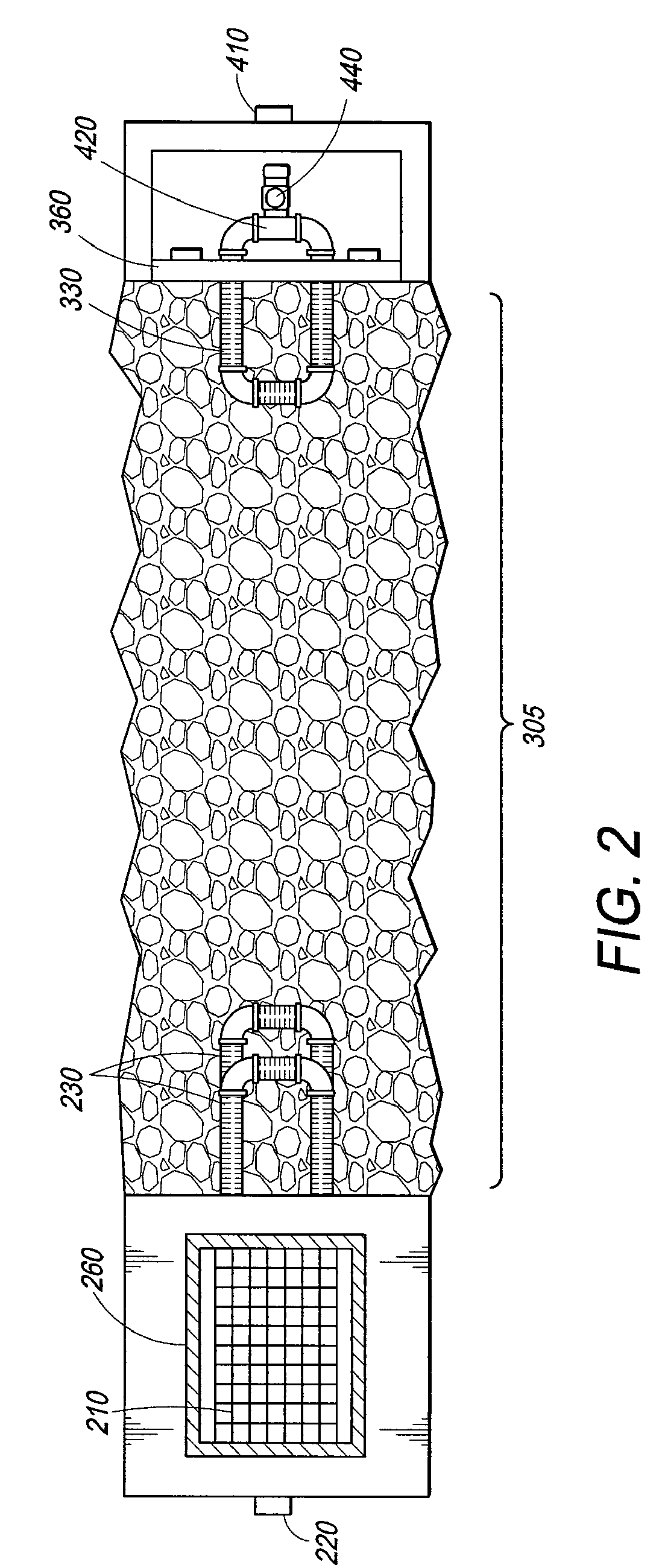
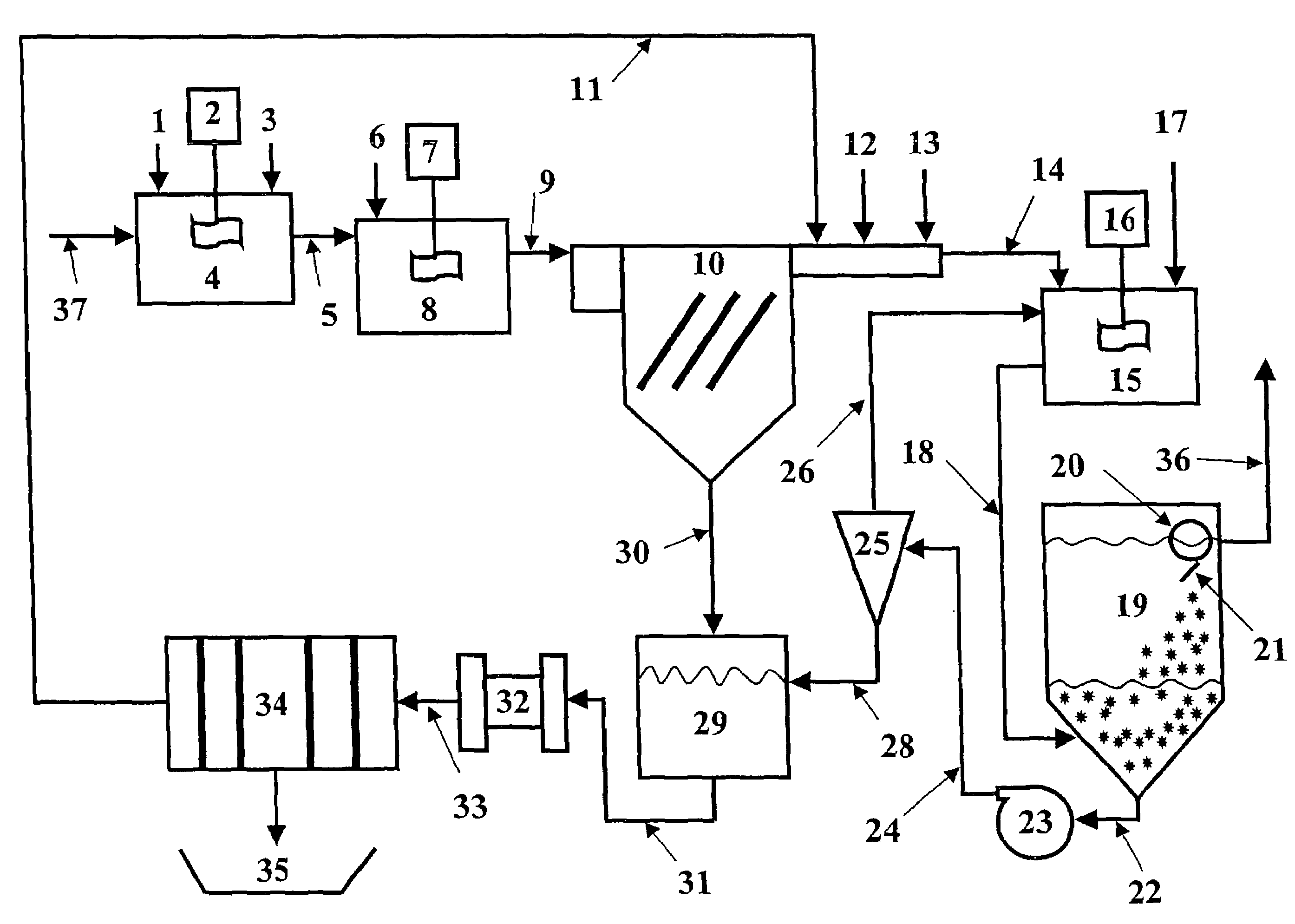
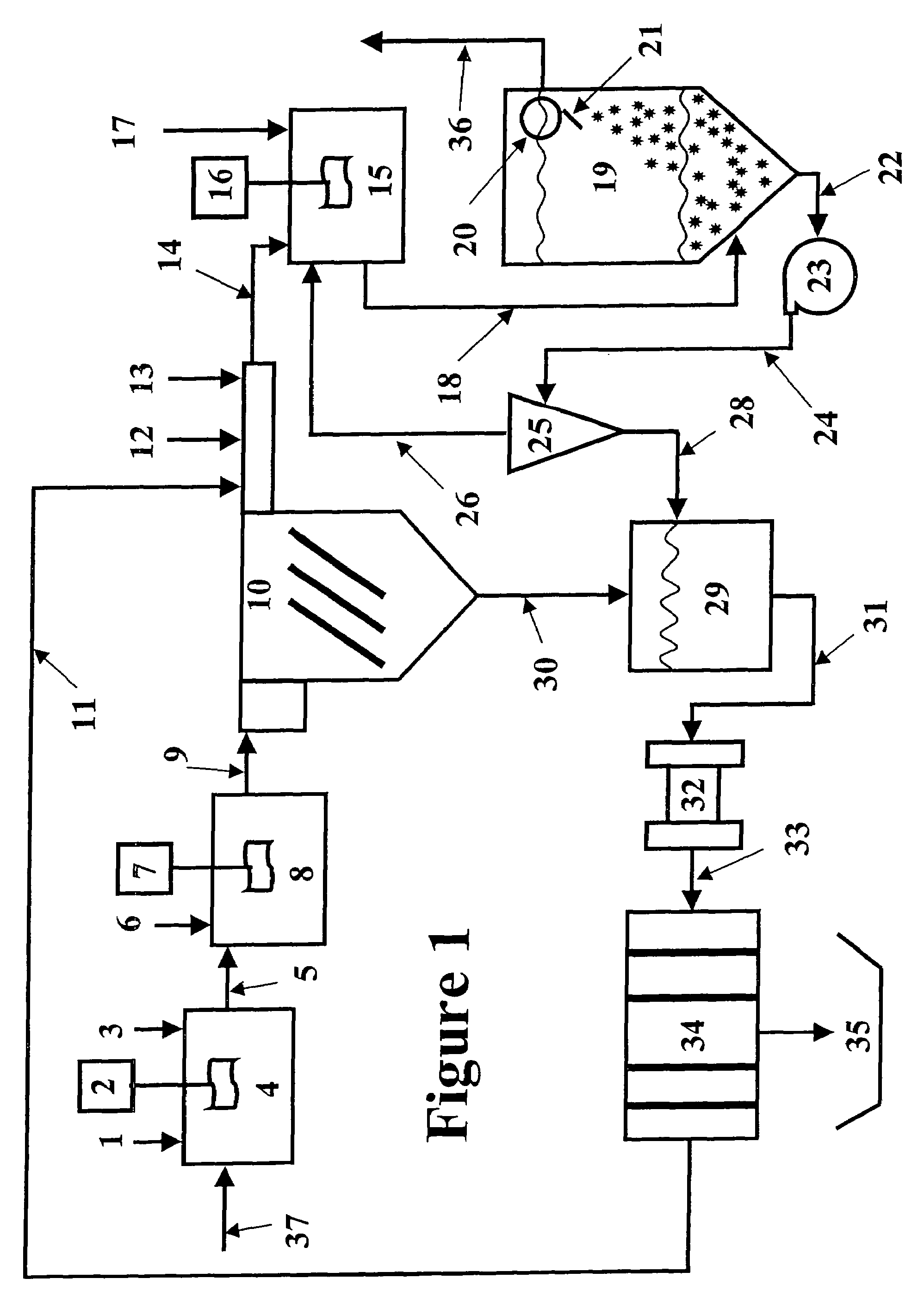
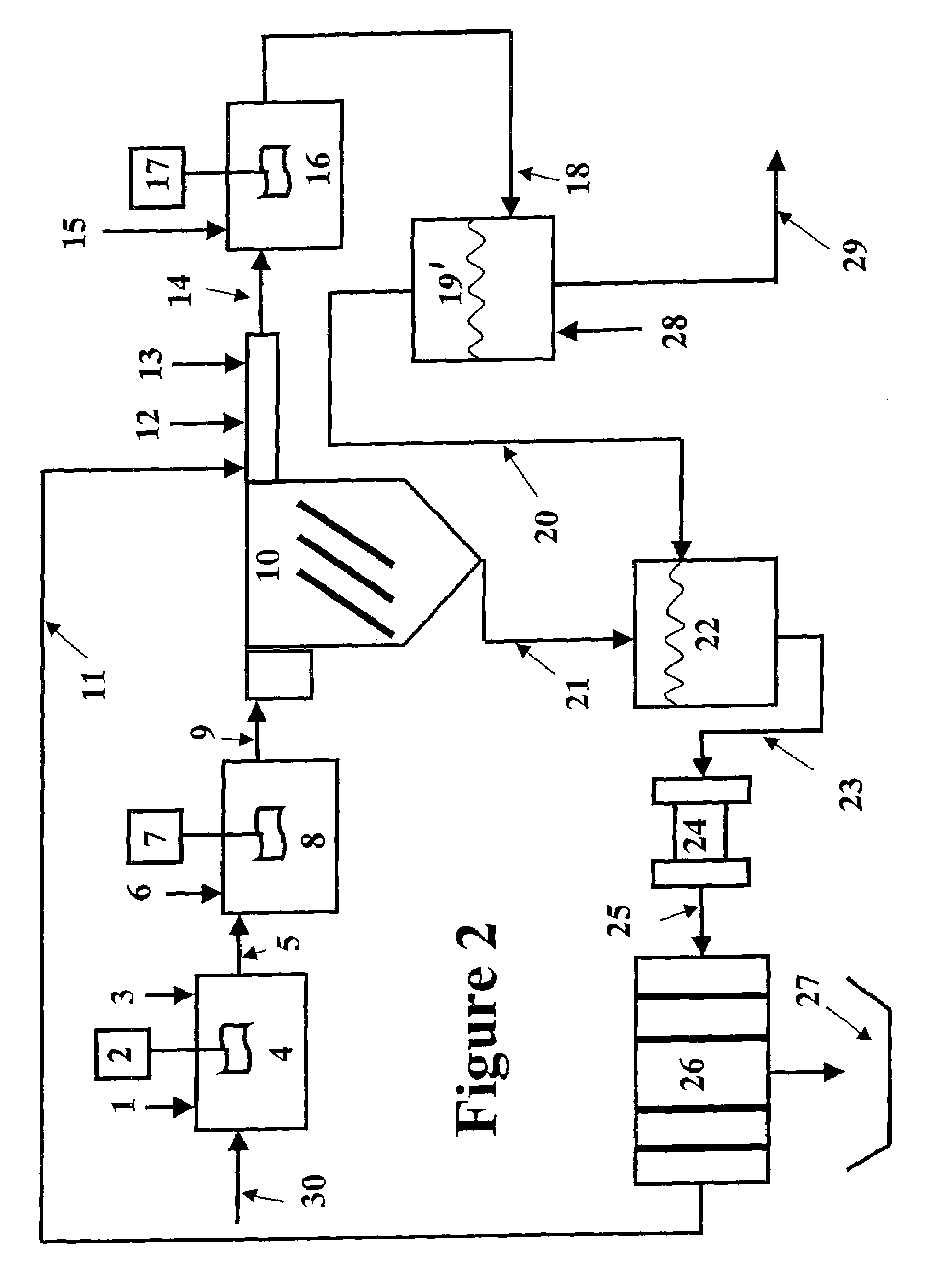
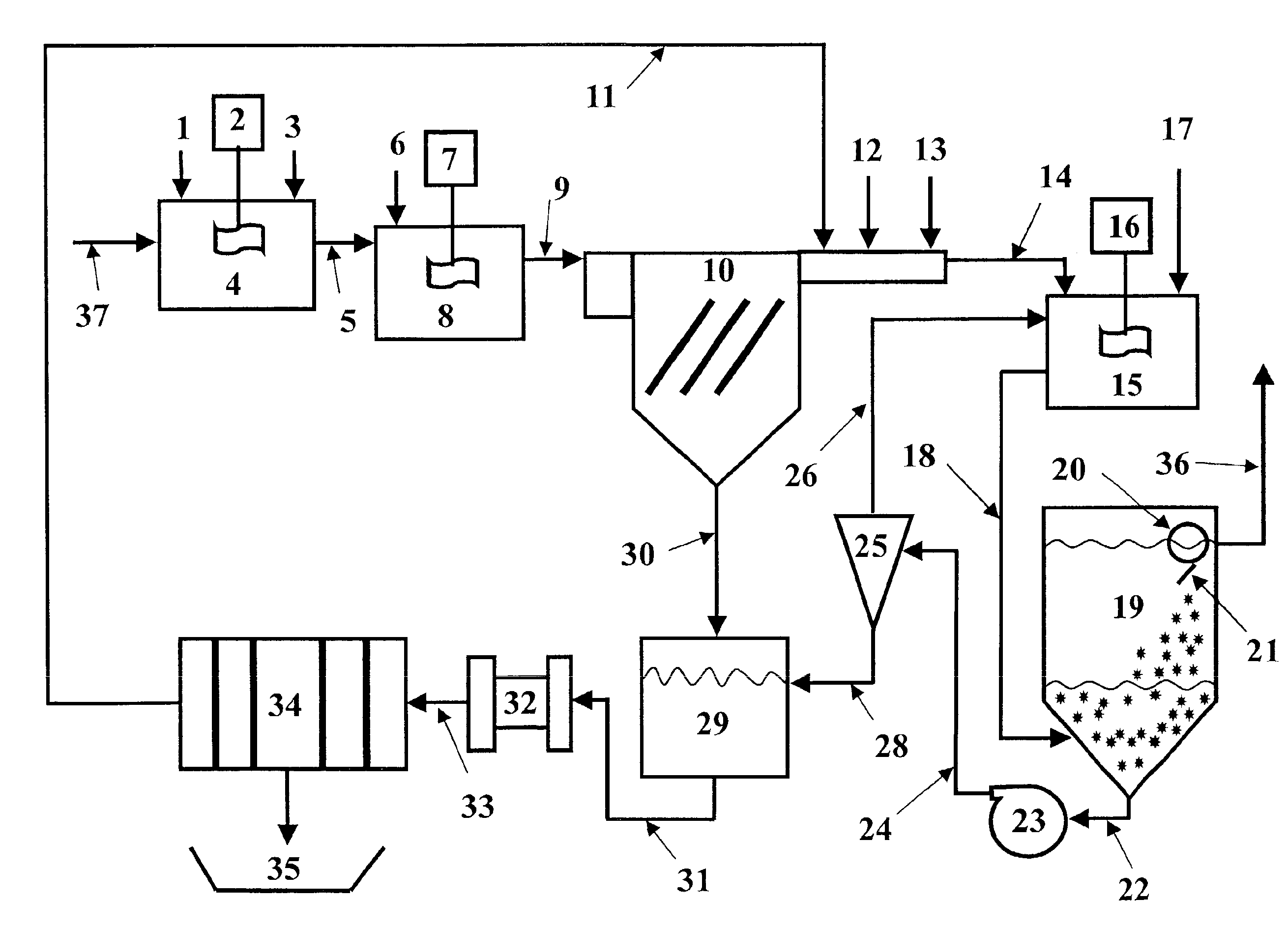
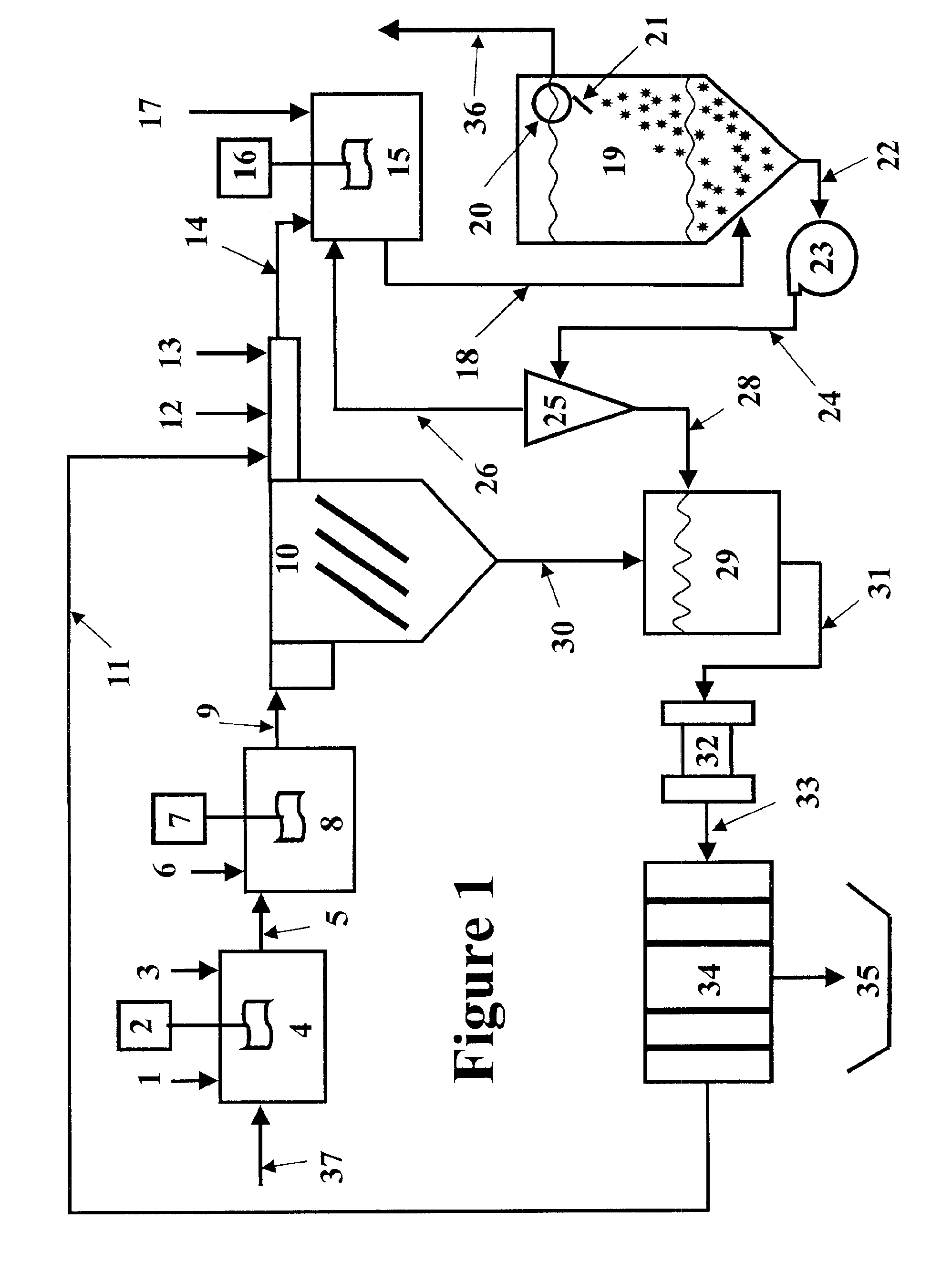
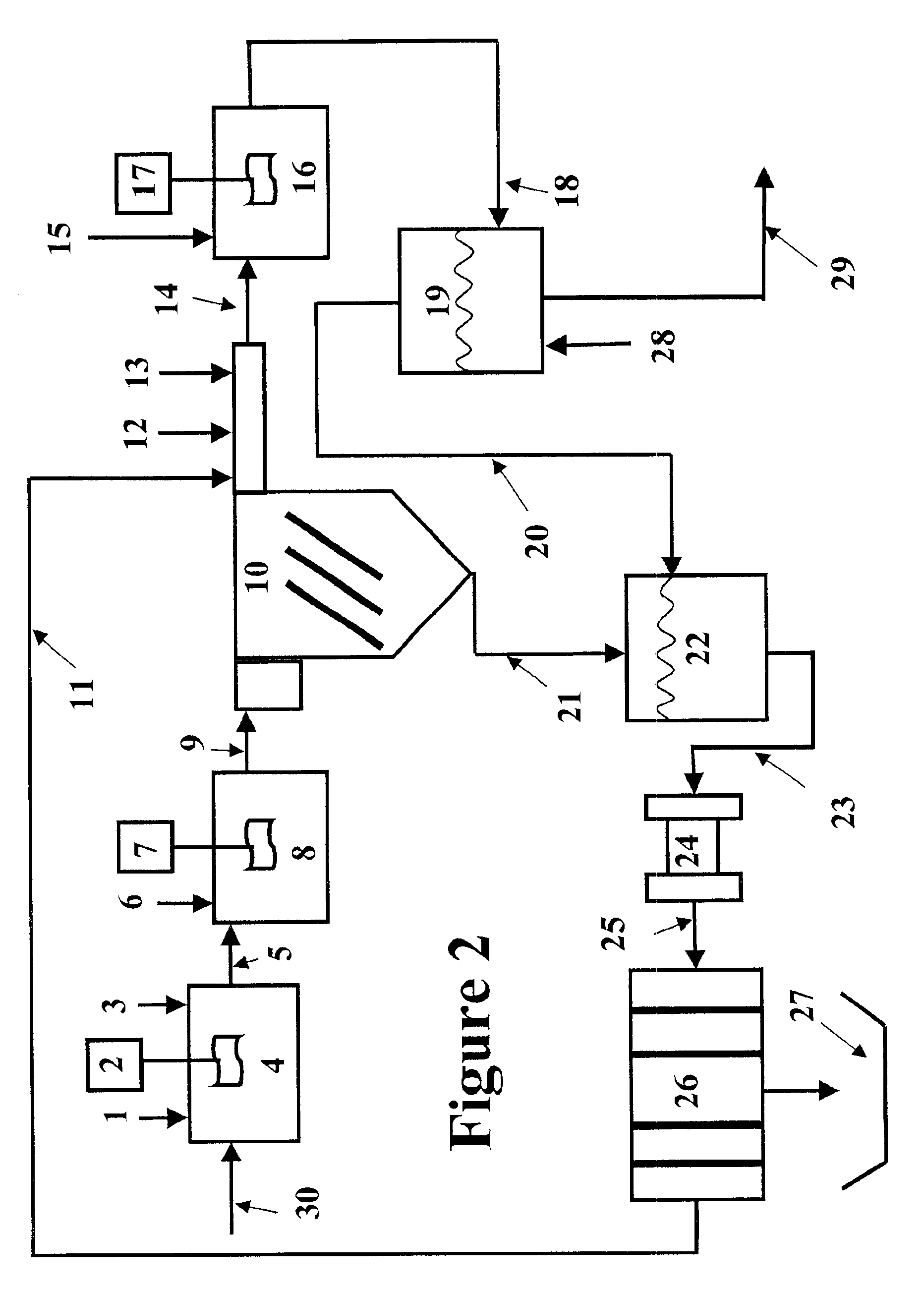
Slurry dewatering and conversion of biosolids to a renewable fuel
ActiveUS20060096163A1Readily removed mechanicallyLow oxygenBio-organic fraction processingBiofuelsEmission standardSlurry
In the processes for treating municipal sewage and storm water containing biosolids to discharge standards, biosolids, even after dewatering, contain typically about 80% water bound in the dead cells of the biosolids, which gives biosolids a negative heating value. It can be incinerated only at the expense of purchased fuel. Biosolids are heated to a temperature at which their cell structure is destroyed and, preferably, at which carbon dioxide is split off to lower the oxygen content of the biosolids. The resulting char is not hydrophilic, and it can be efficiently dewatered and / or dried and is a viable renewable fuel. This renewable fuel can be supplemented by also charging conventional biomass (yard and crop waste, etc.) in the same or in parallel facilities. Similarly, non-renewable hydrophilic fuels can be so processed in conjunction with the processing of biosolids to further augment the energy supply.
Owner:SGC ADVISORS
Methods for adsorption and retention of solvated compounds and ions
InactiveUS6811703B2Avoid leachingImprove water holding capacityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesGolf course turfIon exchange
A solid phase mixed solvent polymer, compositions and methods for removing and retaining solvated organic compounds and inorganic ions from water, wastewater, superficial and ground water, soil and other environmental sources, a soil amendment and method resulting from adhesively coating the polymer onto sand along with at least one ion exchange material, and methods for the containment, reduction, and prevention of organic leaching from soils, agricultural, industrial, and commercial environments, and in particular, sports and athletic turf facilities such as golf courses where pesticides are frequently applied.
Owner:ECO VERDE TECH
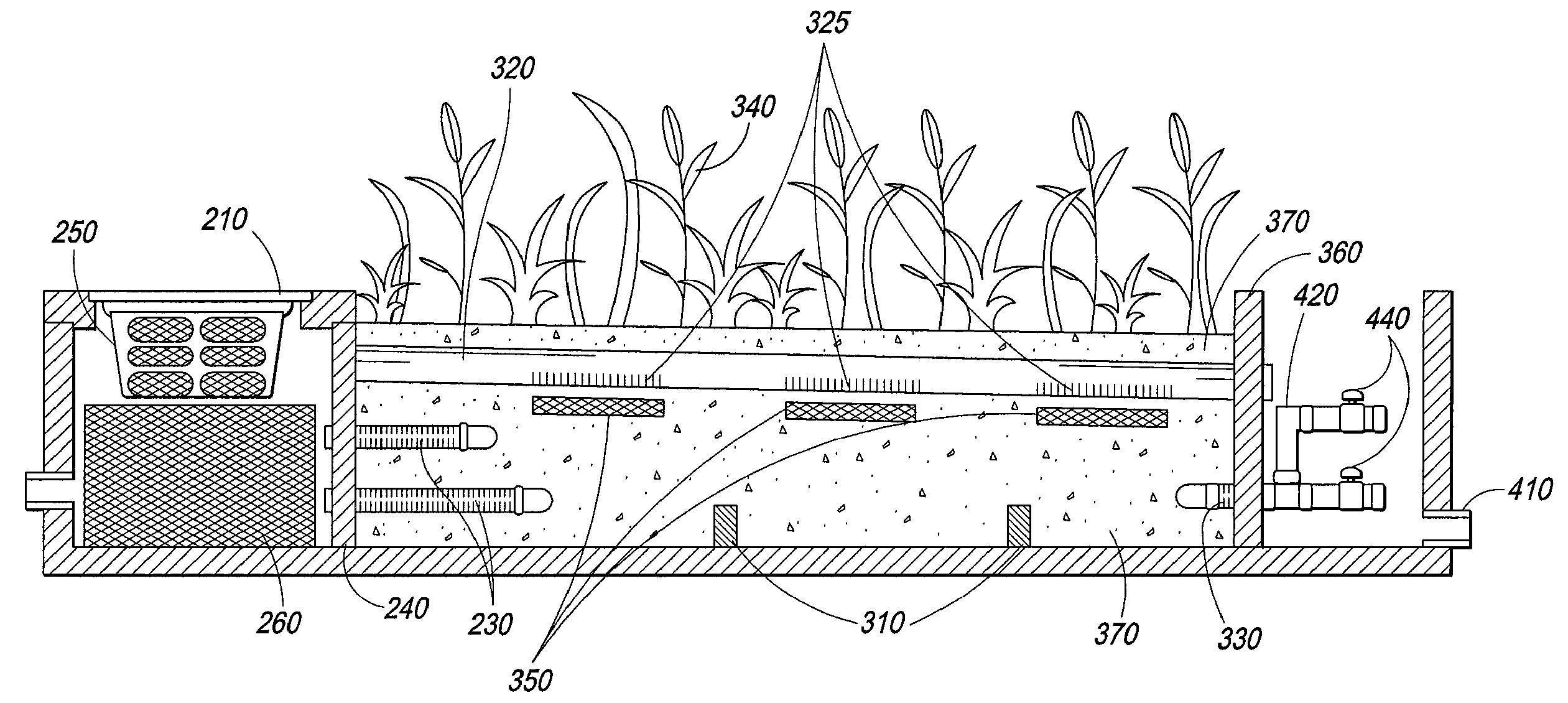
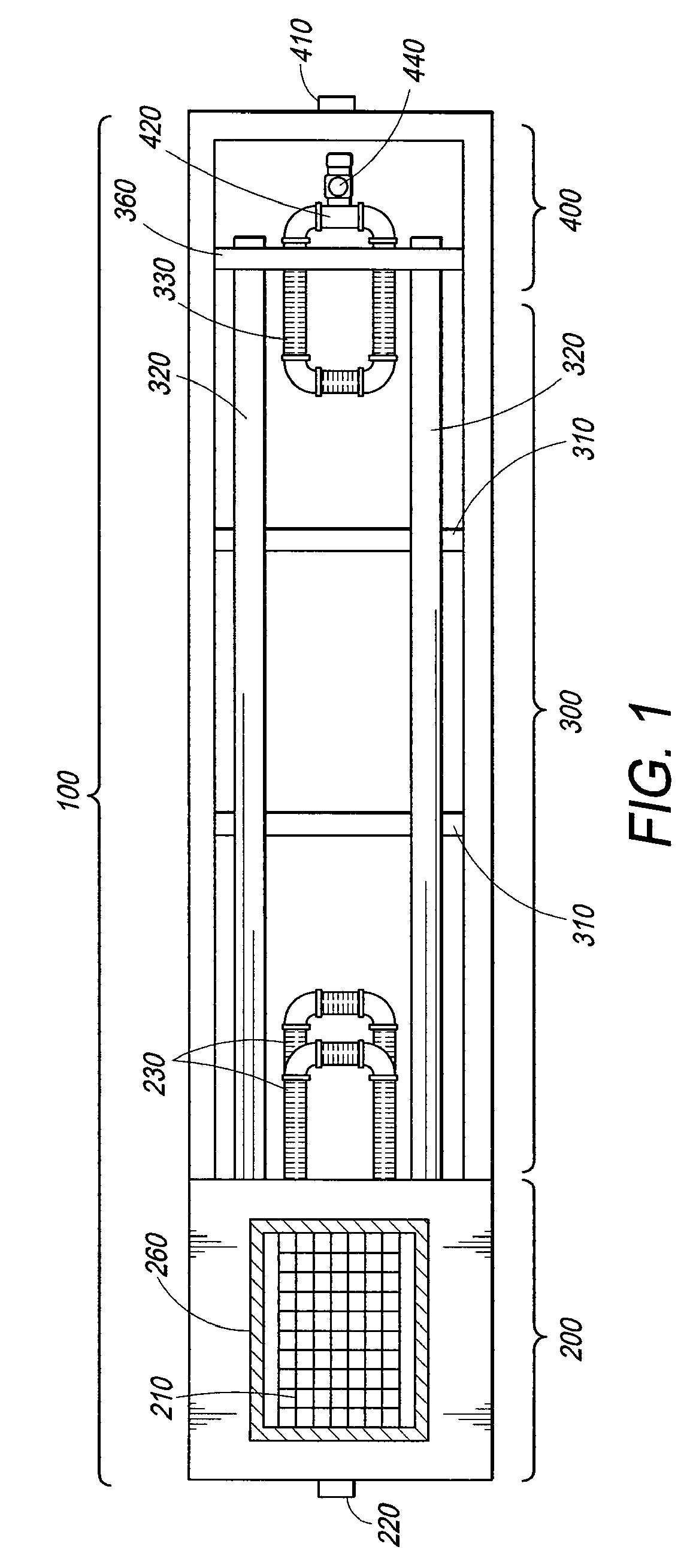
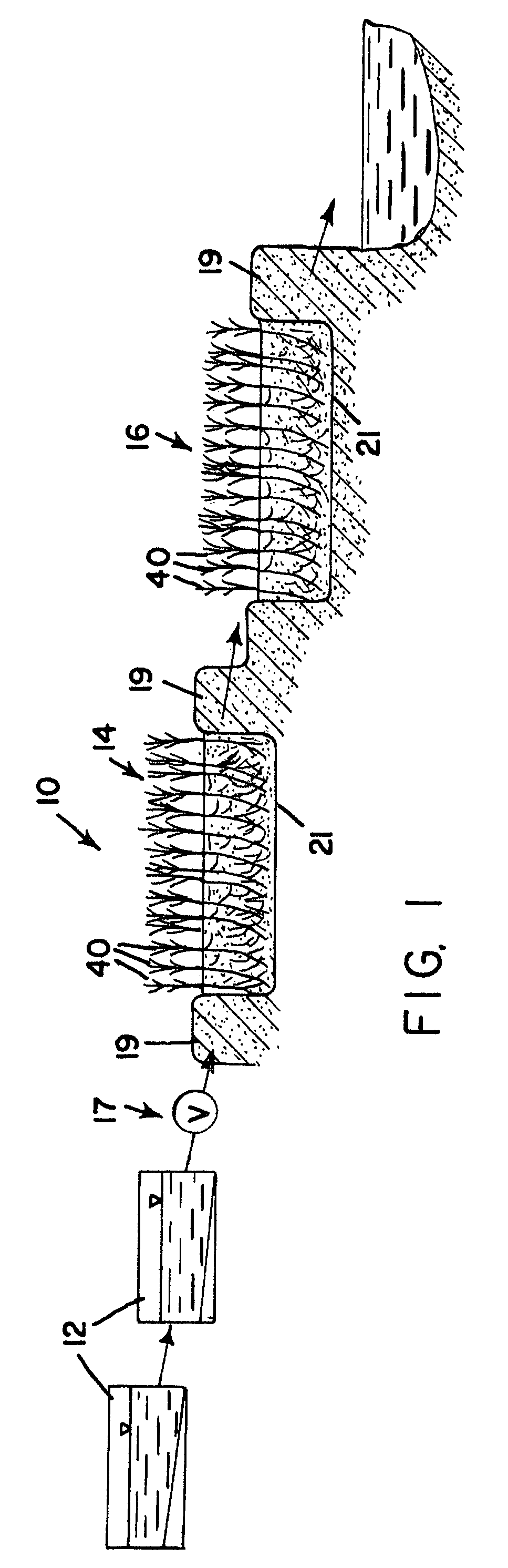
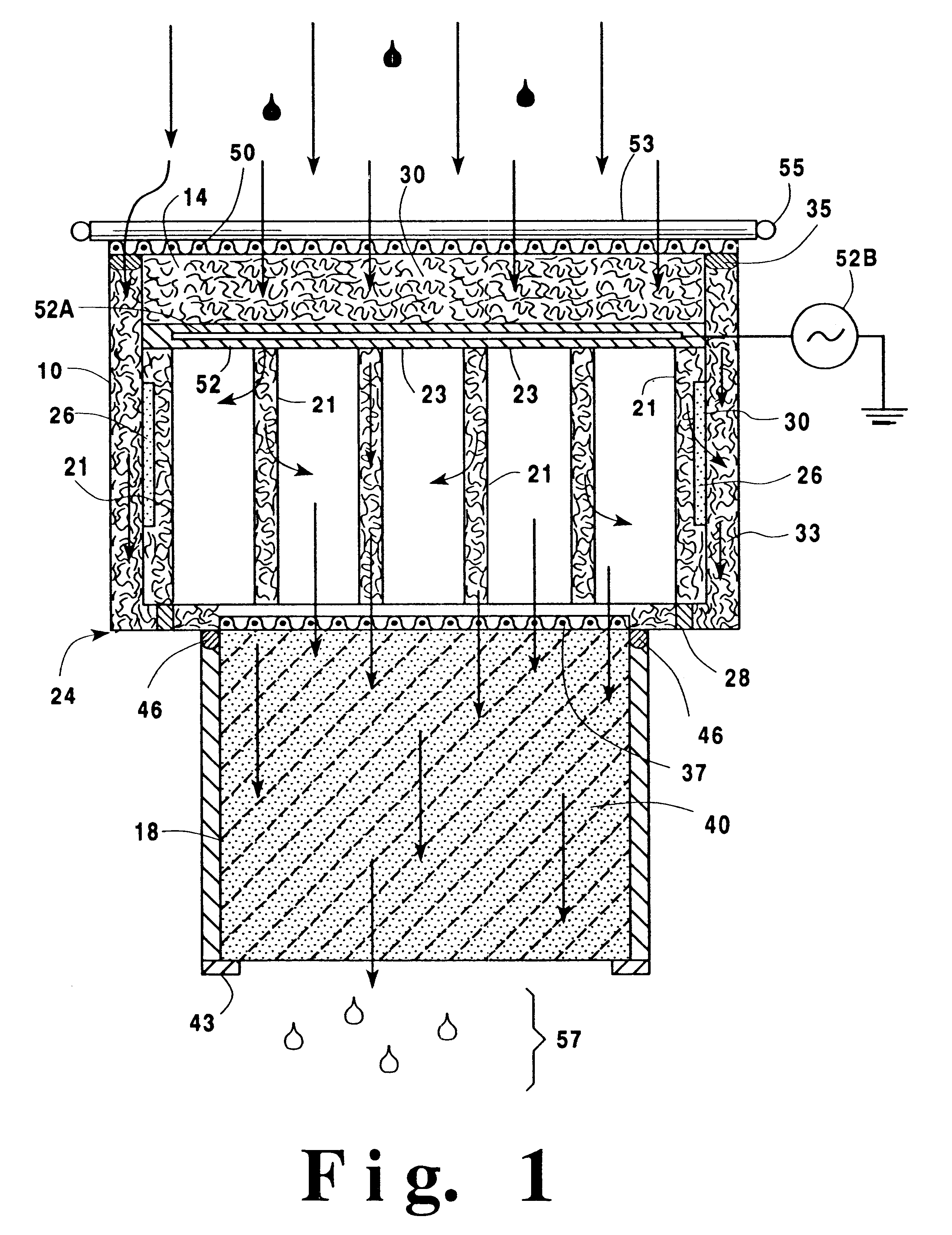
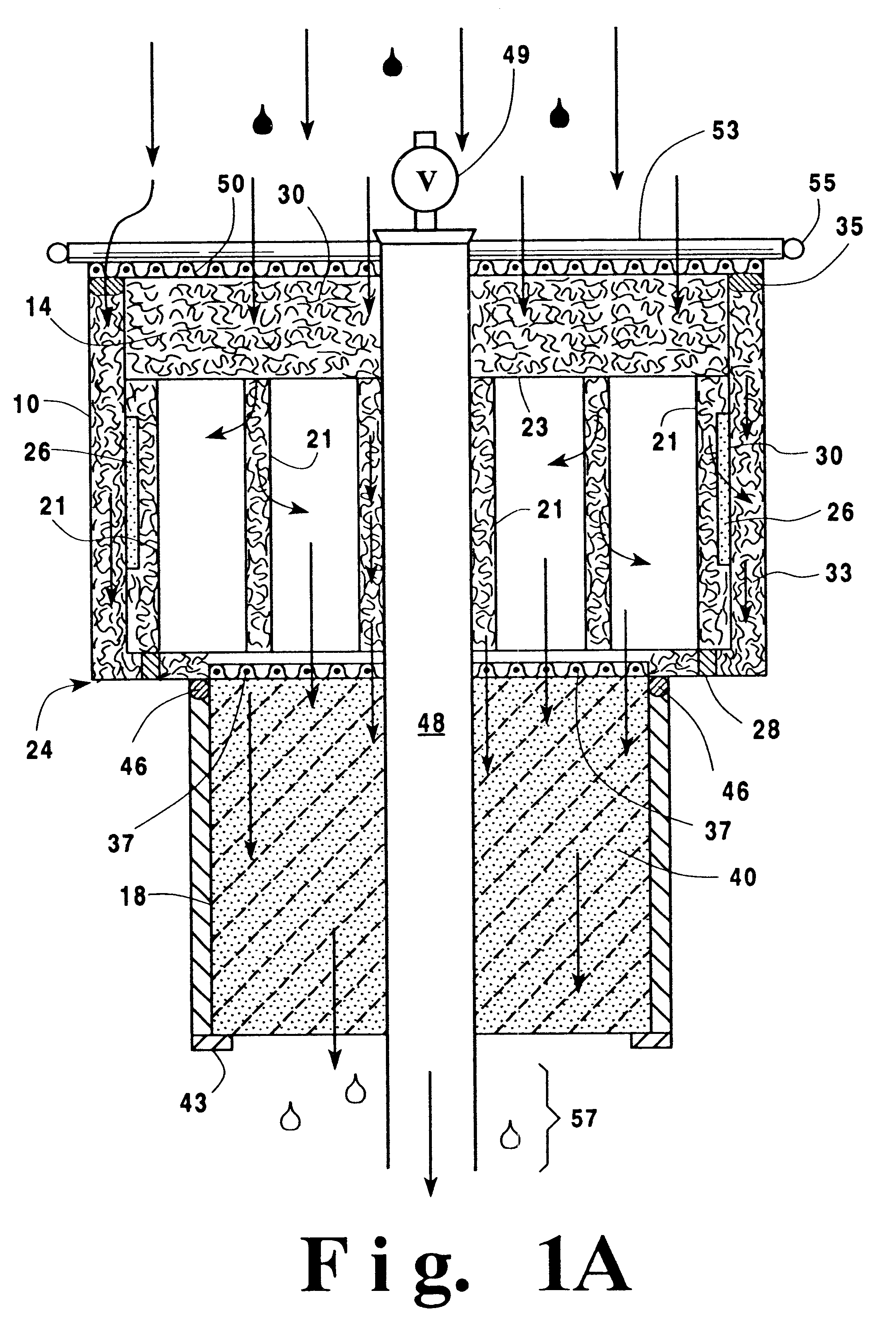
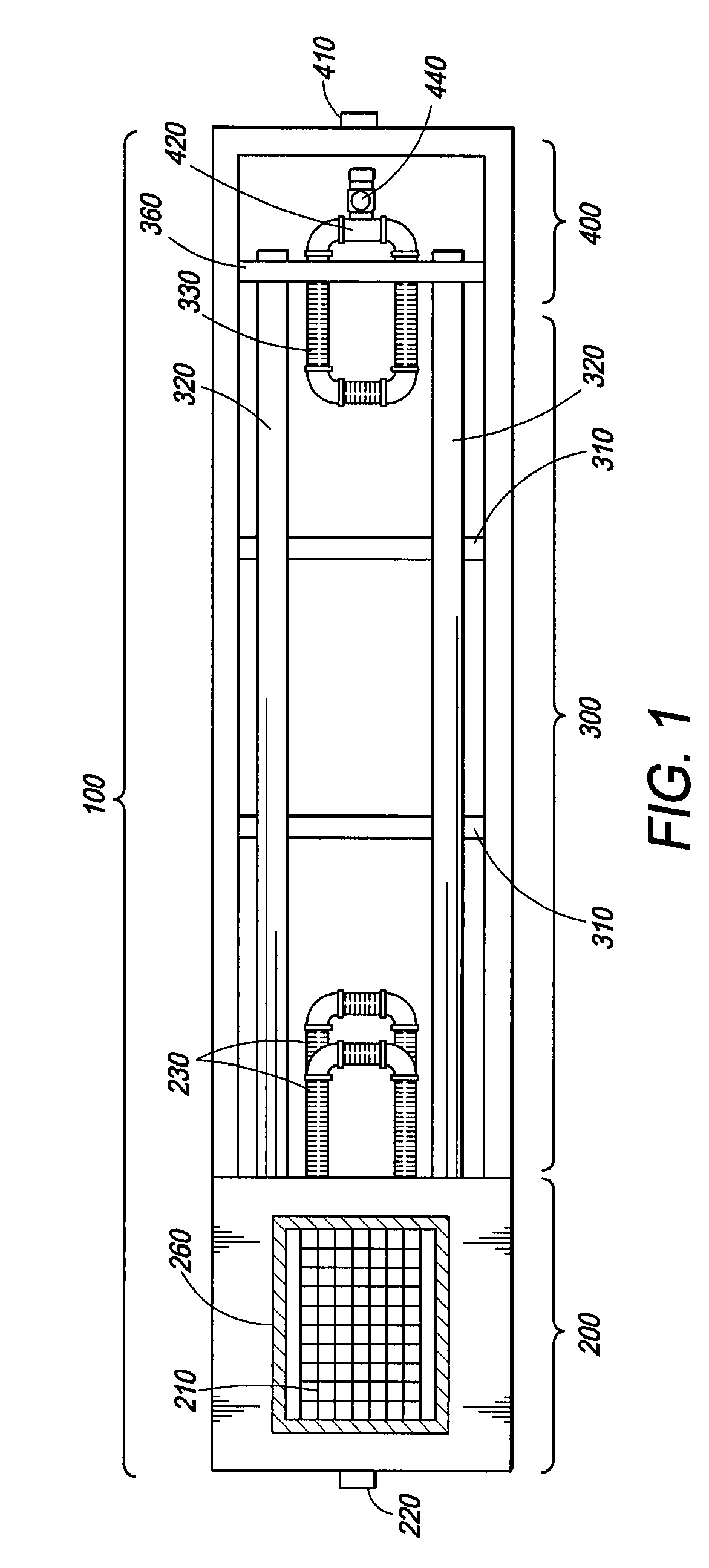
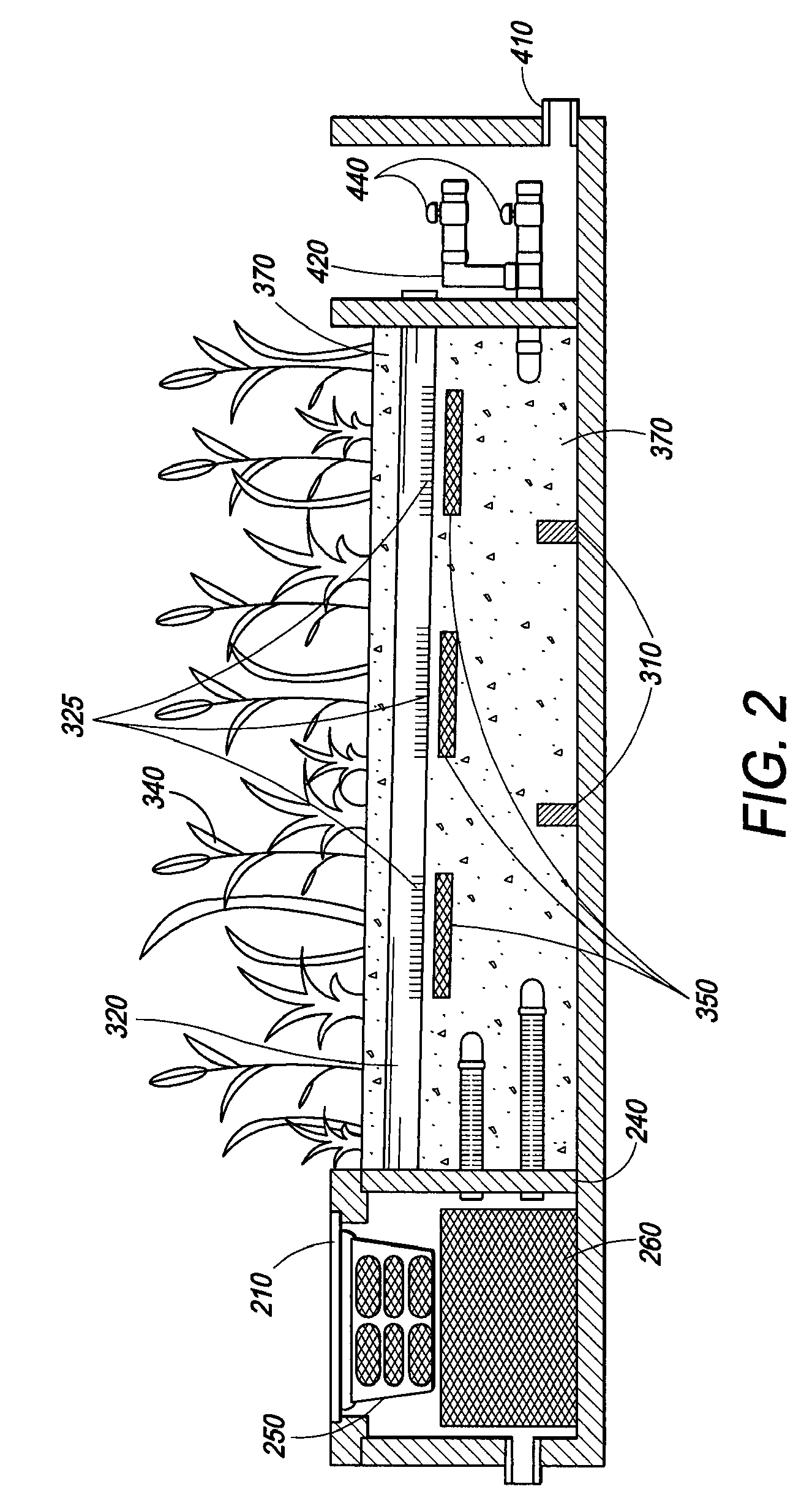
In line wetland water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20080251448A1Easy to useIncrease the lengthFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesWater cleaningWater treatment systemWater flow
A complete storm water management system and process which incorporates a wetlands water treatment system. This system creates an infrastructure, flow control which is multi-level and multi-stage. This is a modular system which includes three or more chambers and / or ditches through which the storm water or other influent passes and is cleaned. The influent which flows into a storm drain, curb inlet, or inflow pipe into the system is directed first into a screening type catch basin inset filter within the first chamber of the system. The influent is treated within the first chamber before it passes out of this chamber into the incorporated wetlands system. The water flows through the wetlands chamber or ditch where it is further filtered and decontaminated through both an aerobic and anaerobic process. In situations of high runoff there is a bypass component.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS20050258103A1Efficient removalEasy to disassembleSedimentation separationDifferential sedimentationParticulatesSulfide
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation ” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation, or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment. Magnetic separation is preferred for the separation of particles precipitated in the second stage. Similar methods can be employed for separation of other particulates from water. Particulates can also be removed by causing them to adhere to particles of expanded plastic, forming a floc lighter than water, so that the floc can be removed by flotation.
Owner:CORT CHERYL J
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS7255793B2Cost- and chemically-effectiveSedimentation separationWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationParticulatesSulfide
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation ” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation, or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment. Magnetic separation is preferred for the separation of particles precipitated in the second stage. Similar methods can be employed for separation of other particulates from water. Particulates can also be removed by causing them to adhere to particles of expanded plastic, forming a floc lighter than water, so that the floc can be removed by flotation.
Owner:CORT CHERYL J
Methods for removing heavy metals from water using chemical precipitation and field separation methods
InactiveUS6896815B2Small sizeChemical cost reductionSolid sorbent liquid separationGold compoundsWater useSludge
A two-step chemical precipitation process involving hydroxide precipitation and sulfide precipitation combined with “field separation” technology such as magnetic separation, dissolved air flotation, vortex separation or expanded plastics flotation, effectively removes chelated and non-chelated heavy metal precipitates and other fine particles from water. In the first-step, the non-chelated heavy metals are precipitated as hydroxides and removed from the water by a conventional liquid / solids separator such as an inclined plate clarifier to remove a large percentage of the dissolved heavy metals. The cleaned water is then treated in a second precipitation step to remove the residual heavy metals to meet discharge limits. In the second precipitation step, any metal precipitant more effective than hydroxide for metal precipitation can be used. The invention improves metal removal, lowers cost because fewer chemicals are used, produces less sludge, and reduces the discharge of toxic metals and metal precipitants to the environment.
Owner:CORT STEVEN L
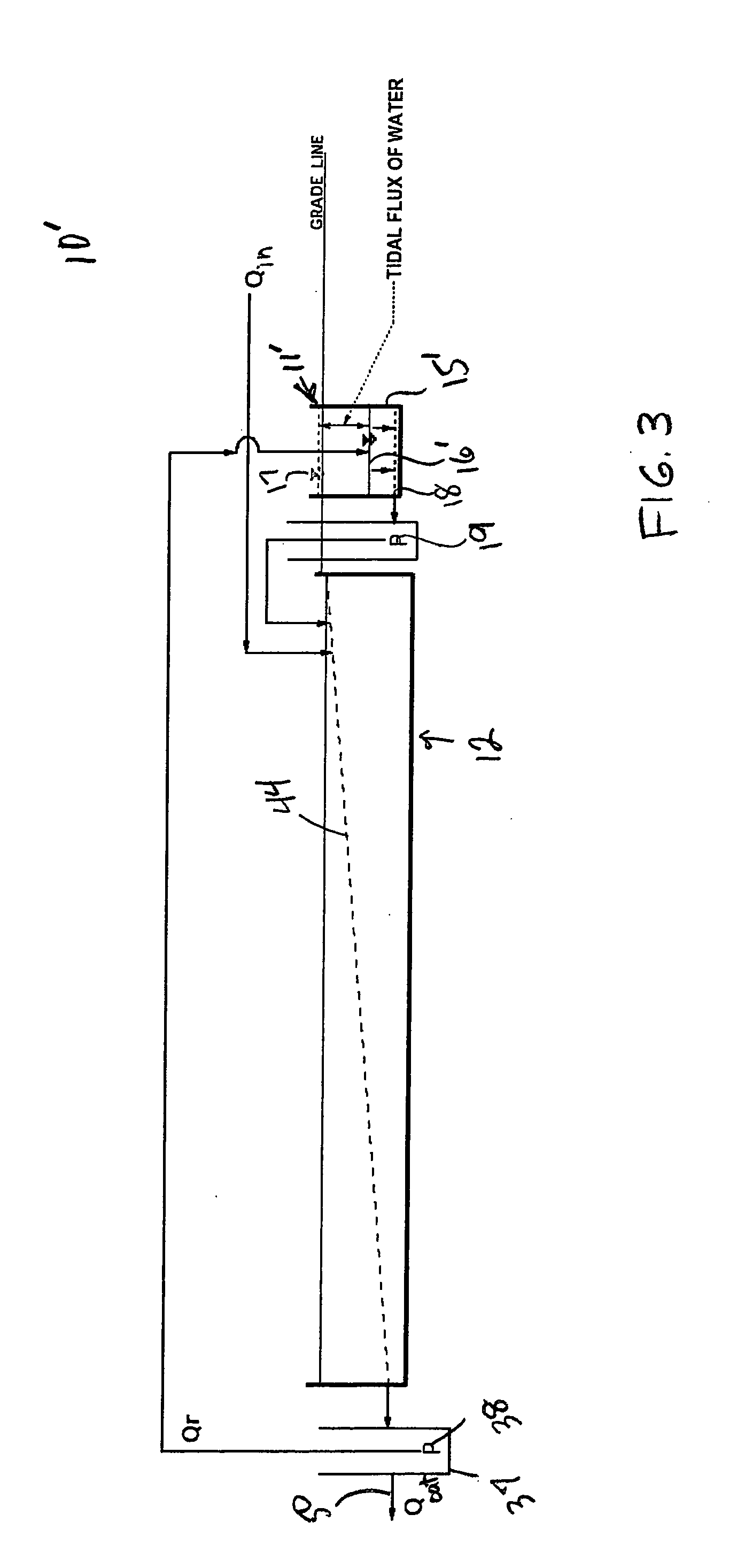
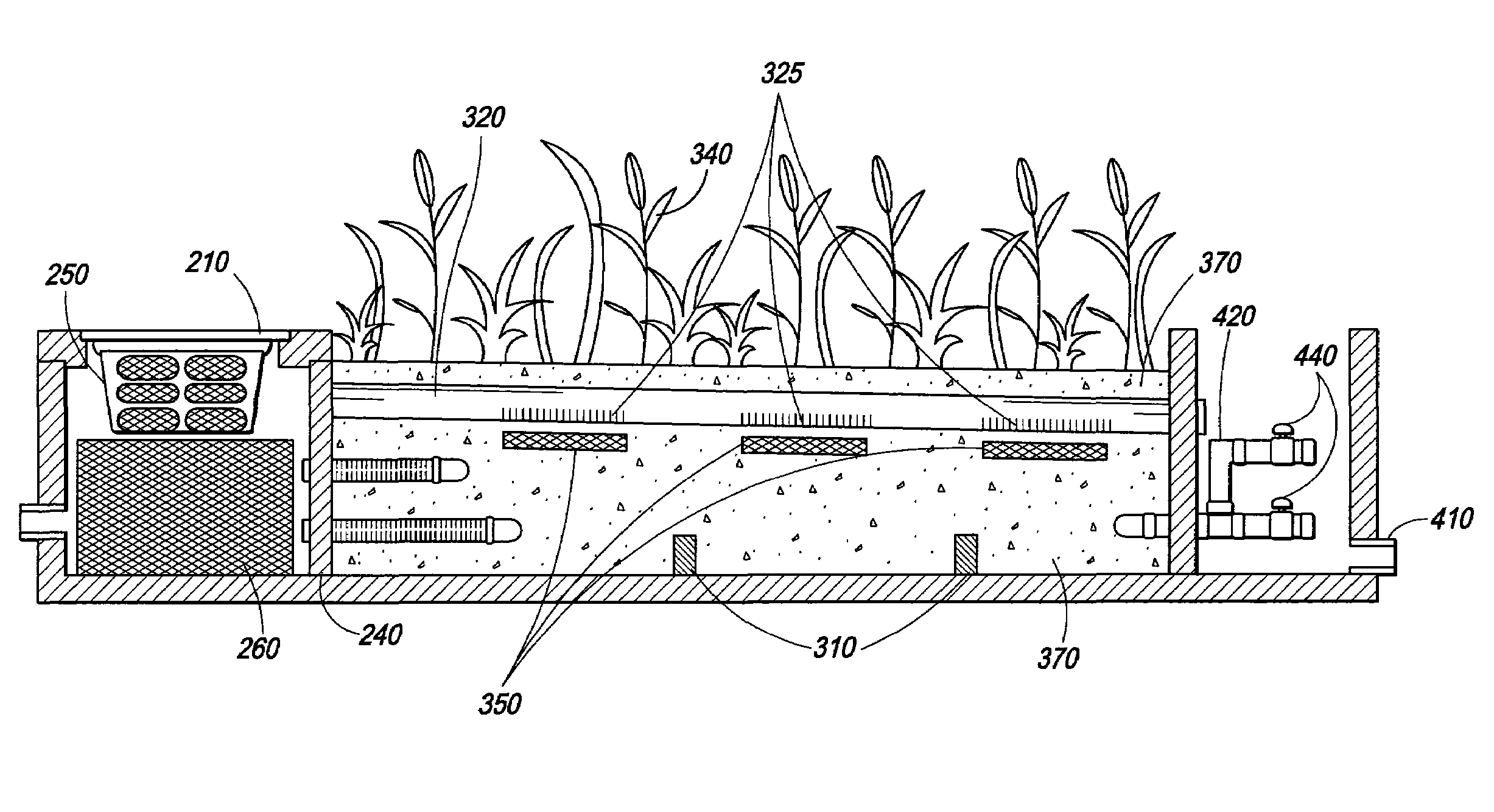
Tidal vertical flow wastewater treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050082222A1Improve performanceIncrease consumptionWater cleaningTreatment using aerobic processesPlant rootsNitrate
A wastewater treatment system includes a vertical flow marsh cell that is adapted to contain media and to support plants having roots extending into the media, the roots and media positioned to contact water flowing downward through the marsh cell during a flooding stage, the media and plant roots providing surfaces to which biofilms can adsorb, the biofilms containing bacteria adapted to adsorb ammonium ions and nitrify ammonium ions to nitrate during an aerated drained phase. The marsh cell is configured to receive water from an outlet of a horizontal wetland that functions essentially anaerobically / anoxically to contain bacteria for transforming nitrate into nitrogen gas. Water to be treated and water exiting the marsh cell outlet are transportable to a wetland inlet, providing dilution of incoming wastewater. Treated water is discharged from the wetland outlet.
Owner:DHARMA IP
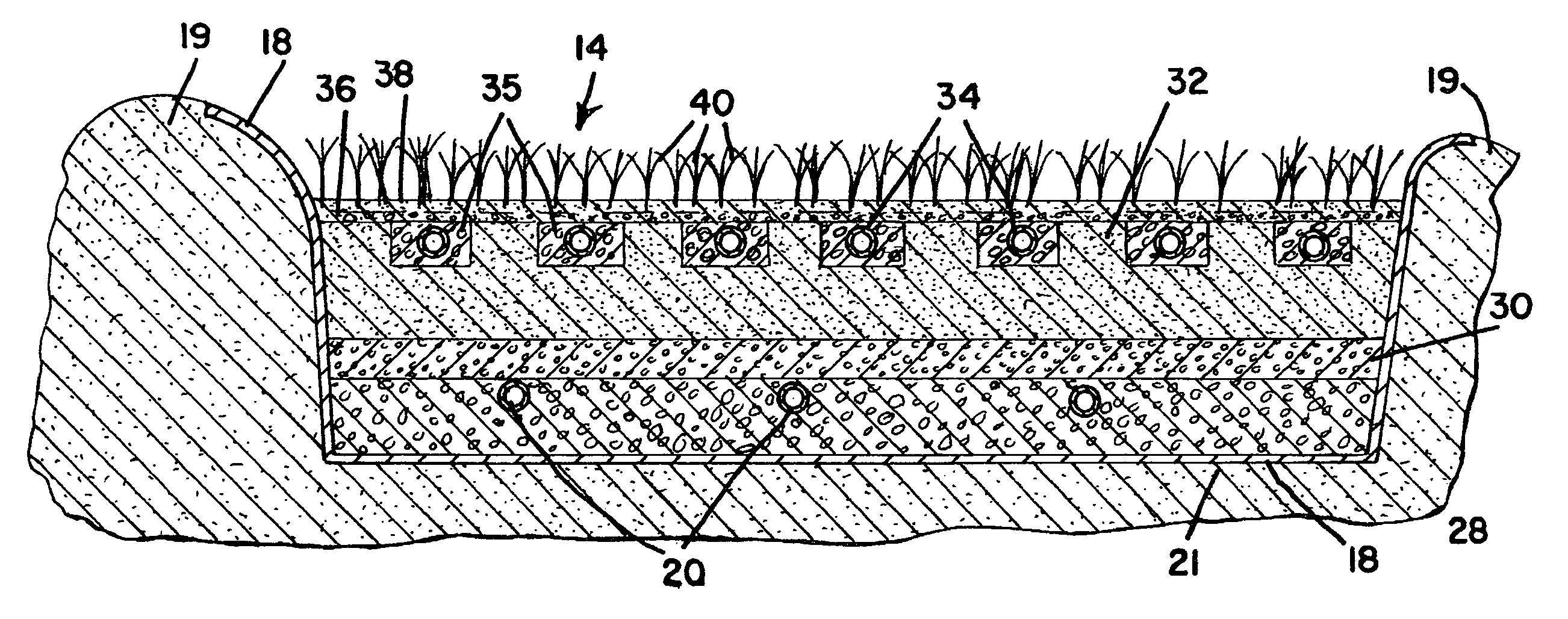
Top loading vertical flow submerged bed wastewater treatment system
InactiveUS7510649B1Efficient reuseEnergy based wastewater treatmentSustainable biological treatmentTreatment systemParticulate material
A system for treating wastewater having a treatment bed of particulate material, inflow distributing plumbing for applying wastewater from a wastewater supply source to upper part of the treatment bed. The wastewater percolates downwardly through the particulate material and is collected by outflow plumbing and conveyed out of the treatment bed. Preferably, the particulate material in the treatment bed is suitable for supporting aquatic plant life.
Owner:LAVIGNE RONALD
Wetland water treatment system
ActiveUS20080142438A1Easy maintenanceEasy constructionWater cleaningCentrifugal force sediment separationParticulatesWater treatment system
A self-contained wetlands treatment system to remove pollutants from water and treat stormwater runoff or other grey water. This is system and method wherein the water is passed through a wetland filtering and treatment system. This invention removes solids, metals (dissolved / particulate), nutrients (dissolved / particulate), oils, and bacterial contaminants from the water. The system and system housing can be fabricated, built, and assembled in a broad range of sizes and materials to accommodate and treat a broad range of influent flow rates.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
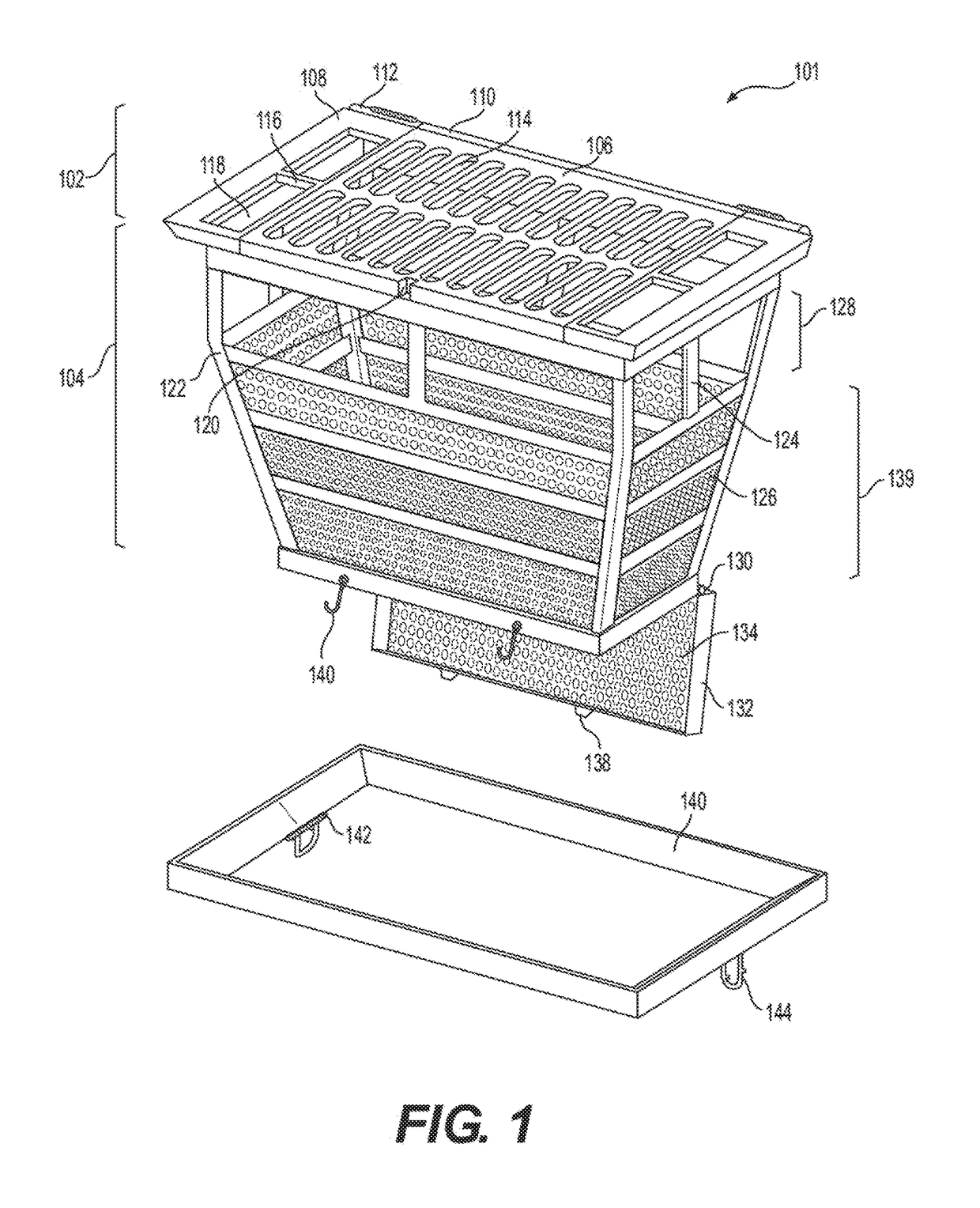
Removable Catch Basin Filter Insert and Lifting Apparatus
ActiveUS20170284077A1Easy to disassembleEfficient designFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesSewerage structuresEnvironmental engineeringStorm drain
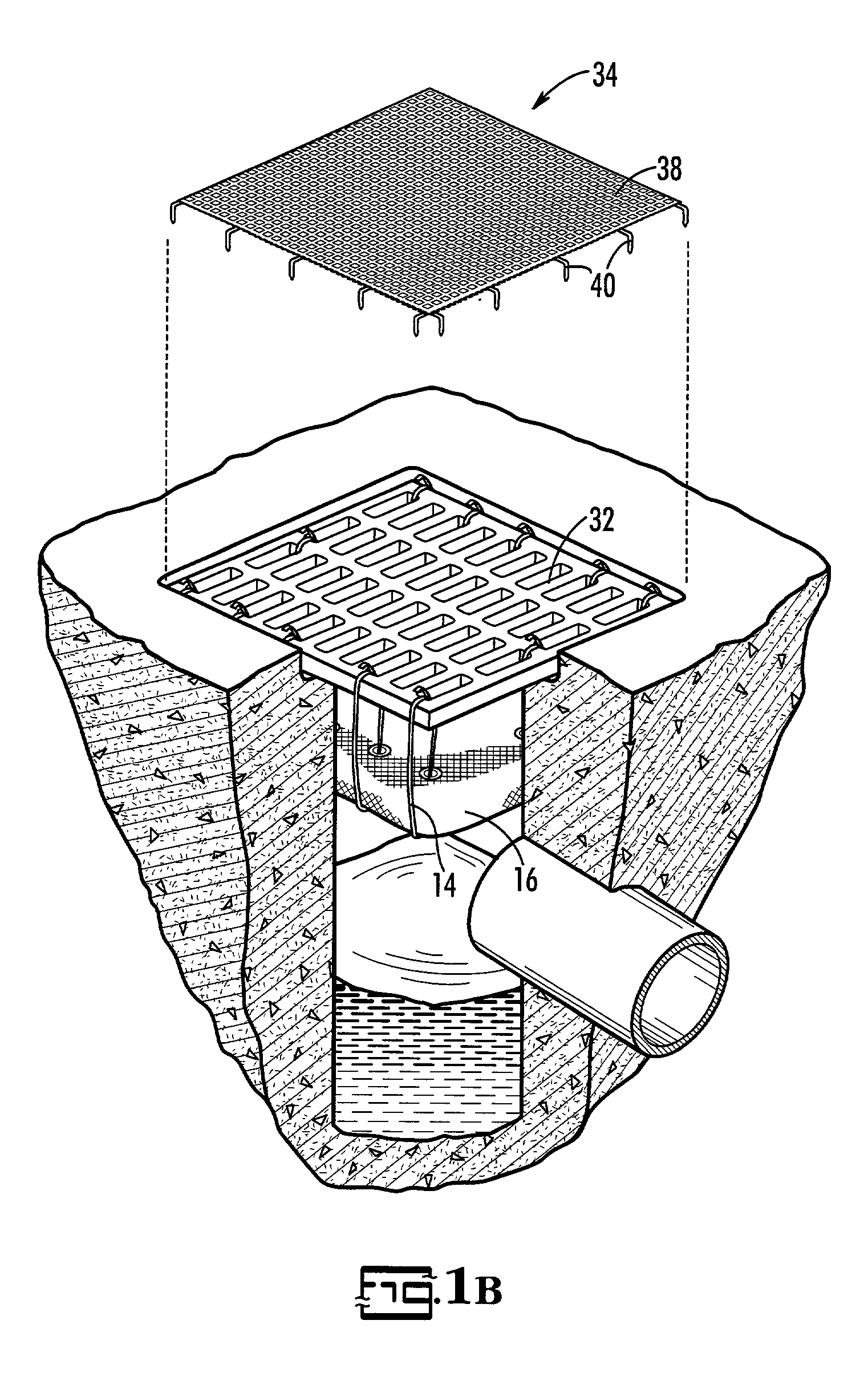
A removable catch basin filter insert includes a filter container is fitted into a catch basin in the ground at the location where the stormwater exits the gutter and enters the stormwater sewer system. The removable catch basin filter provides pollution capture from stormwater while being easily cleaned. A hinged cover is included at the top of the filter insert to allow the captured pollutants to be evacuated through the use of a vehicle or being tipped nearly upside down by a mechanical arm. A hinged trap door is included at the bottom of the filter insert to allow captured pollutants to be evacuated through the bottom of the device and into a container. By capturing the pollutants with the removable catch basin filter insert before the pollutants enter the mainline storm drain system, clean storm drain systems are provided allowing for cleaner waterways.
Owner:FROG CREEK PARTNERS LLC
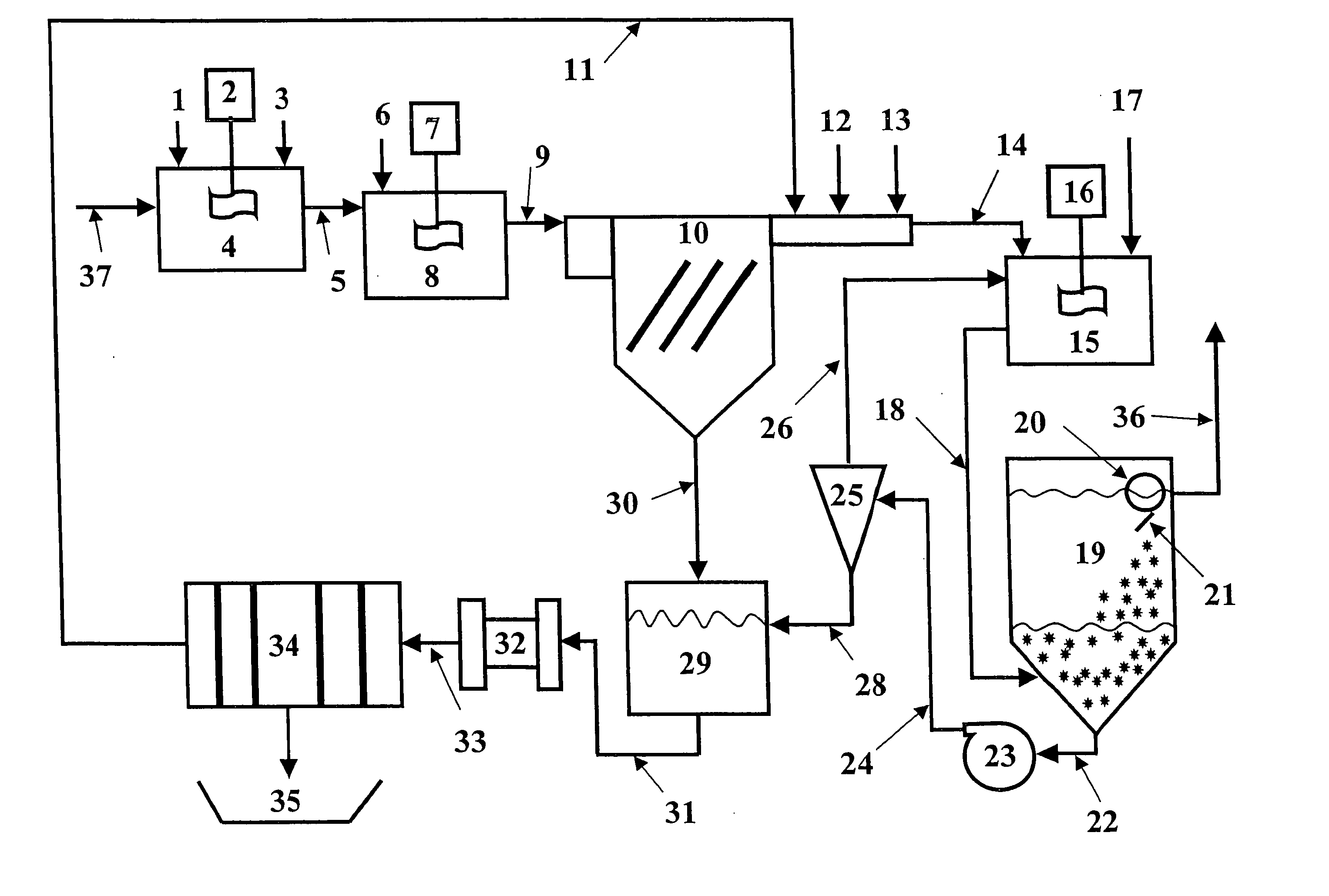
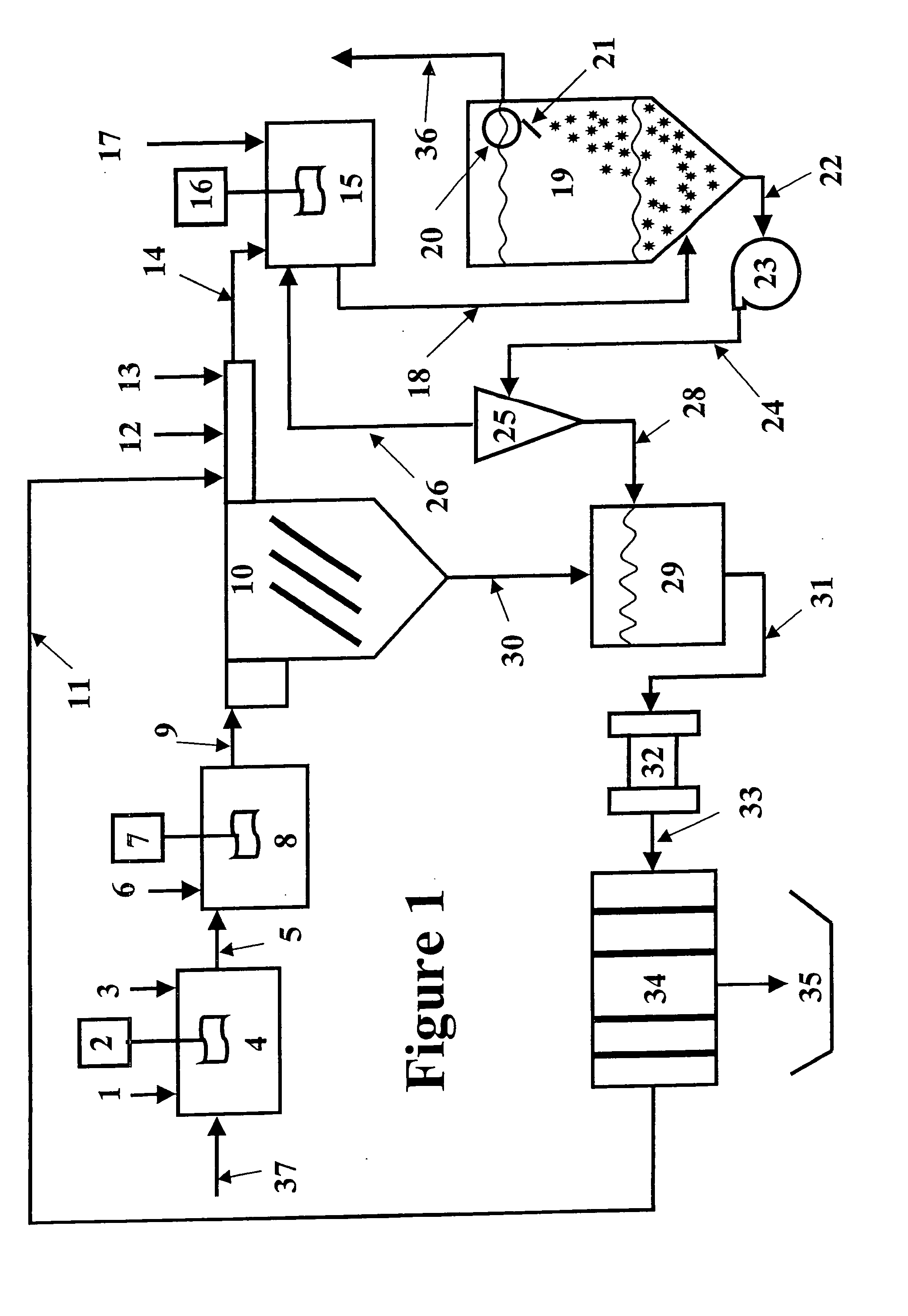
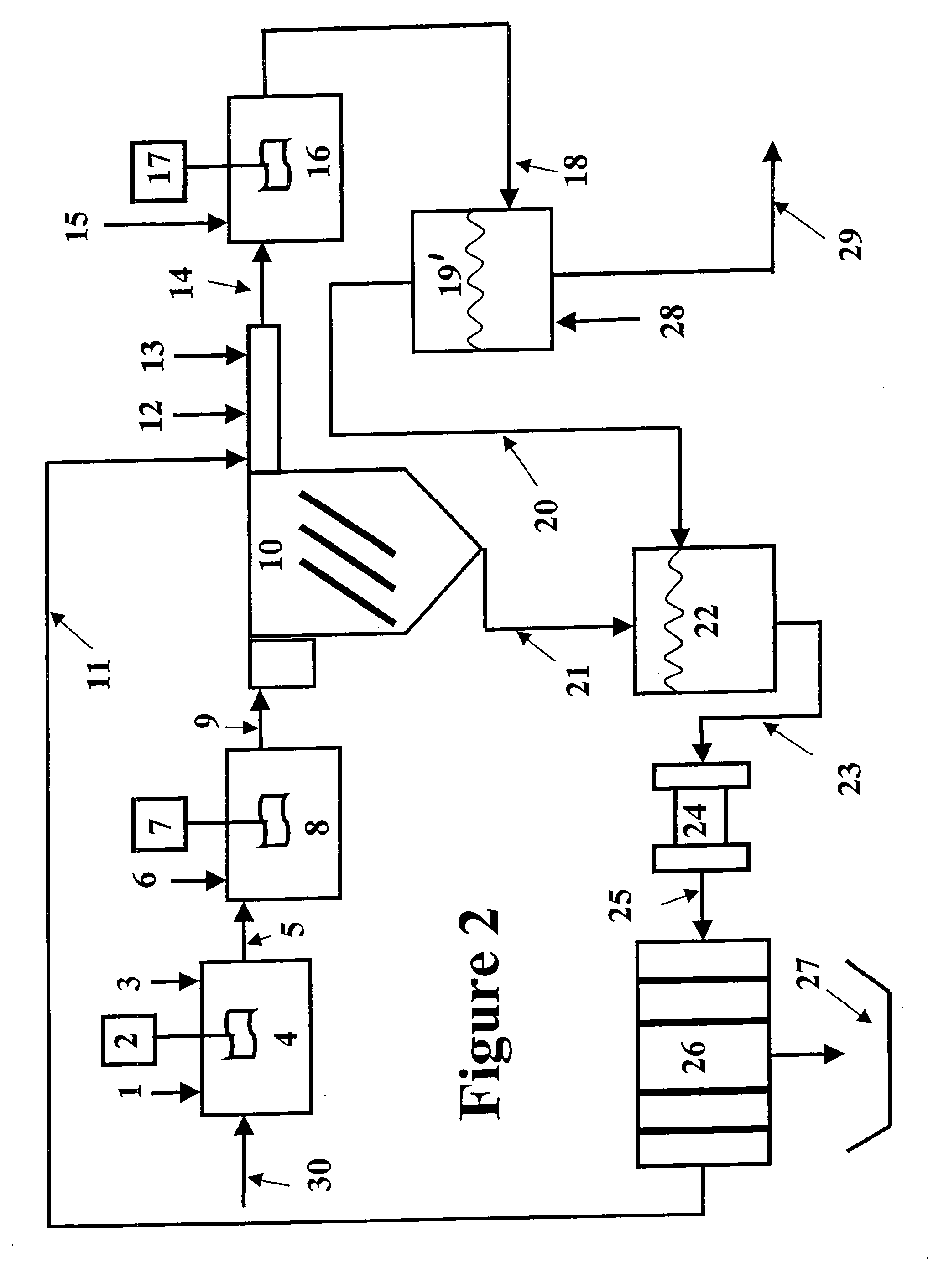
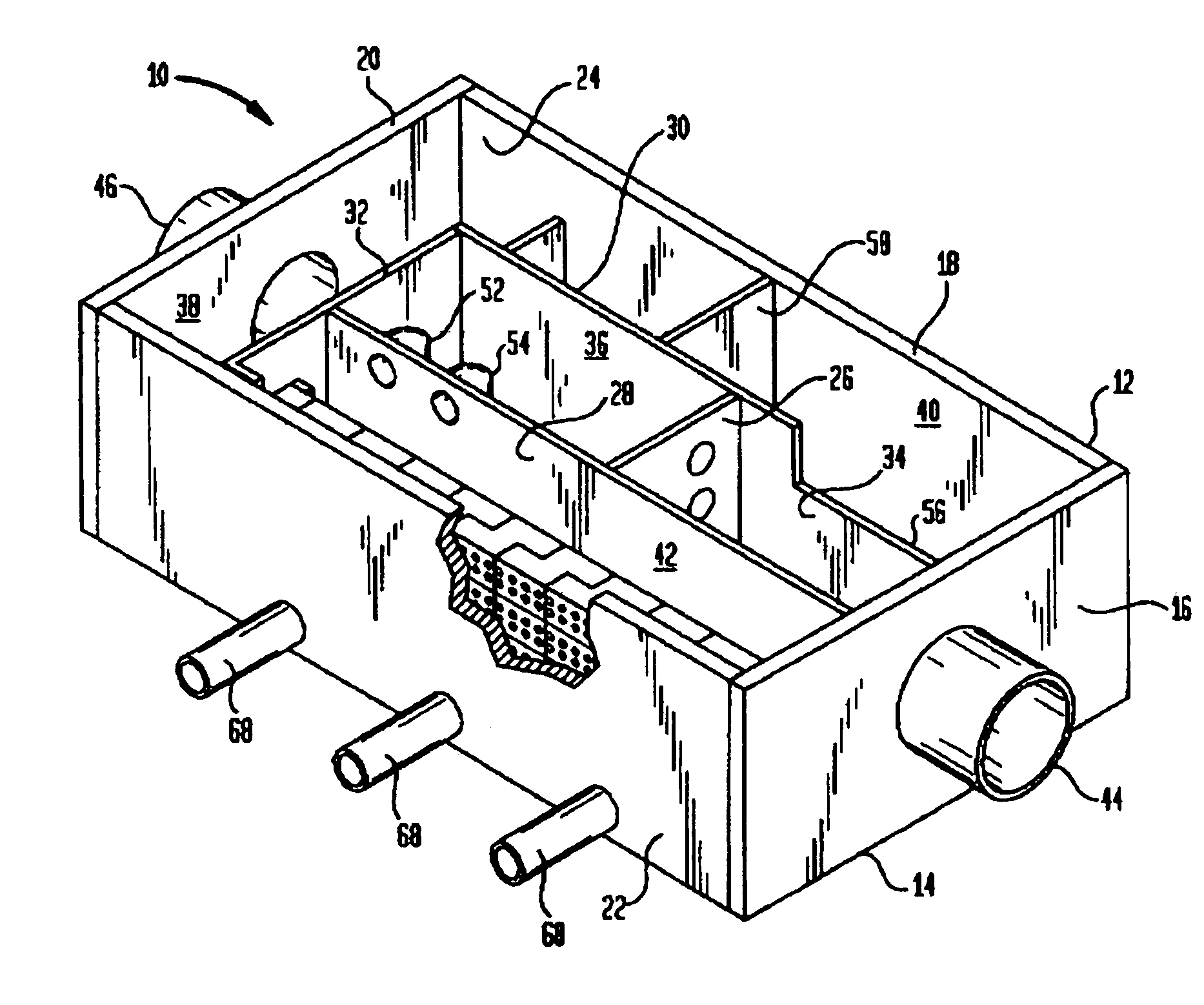
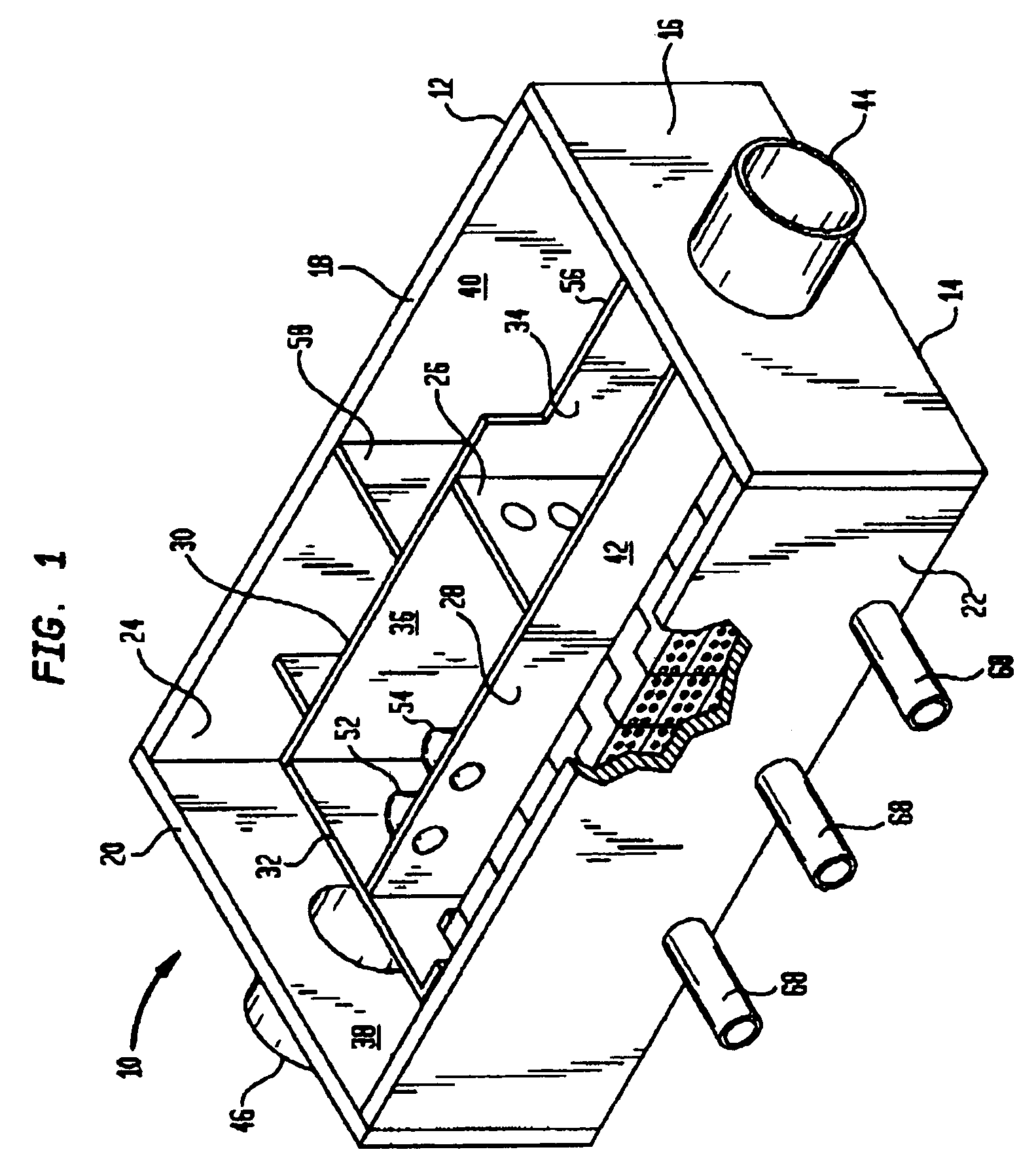
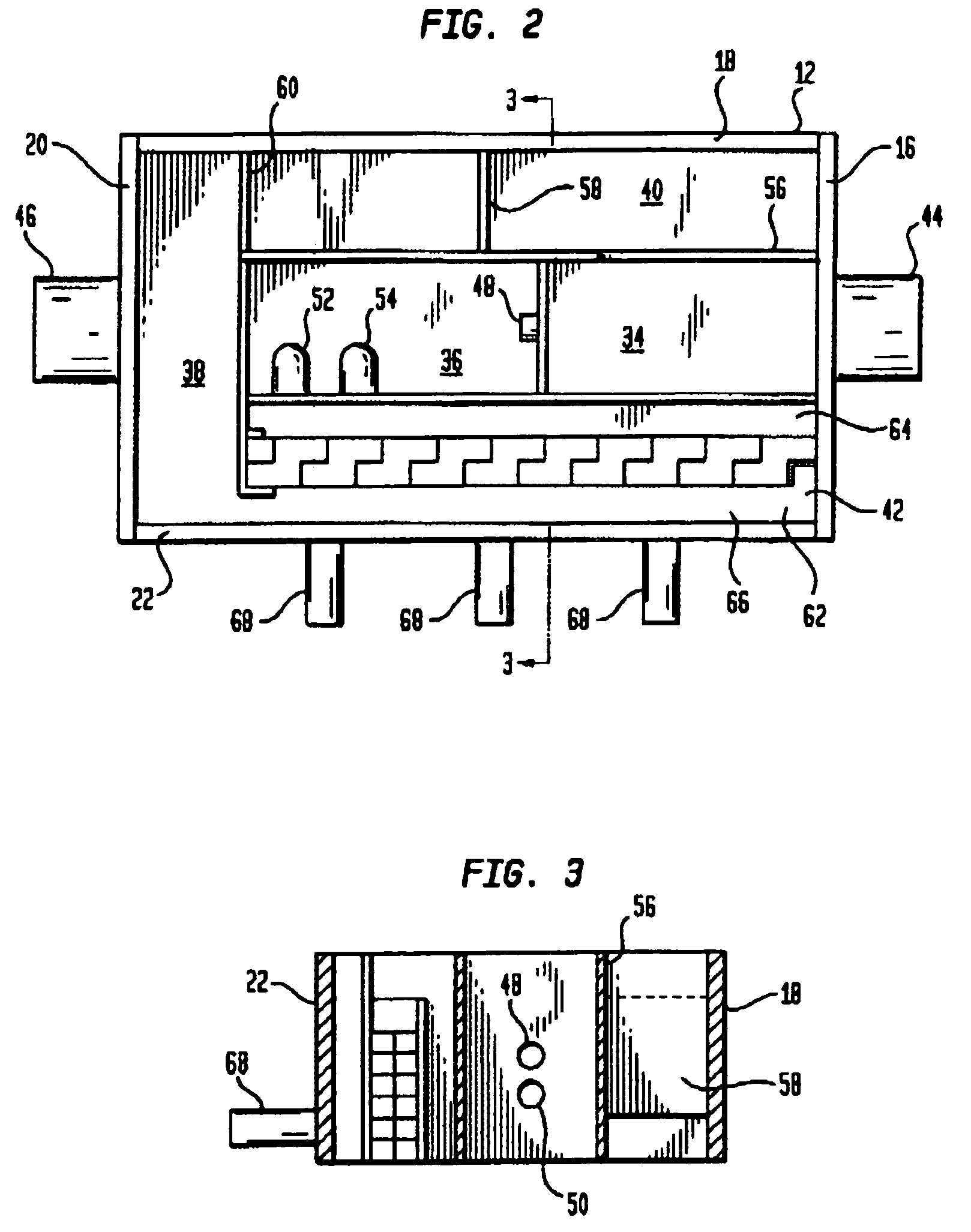
Apparatus for treating storm water
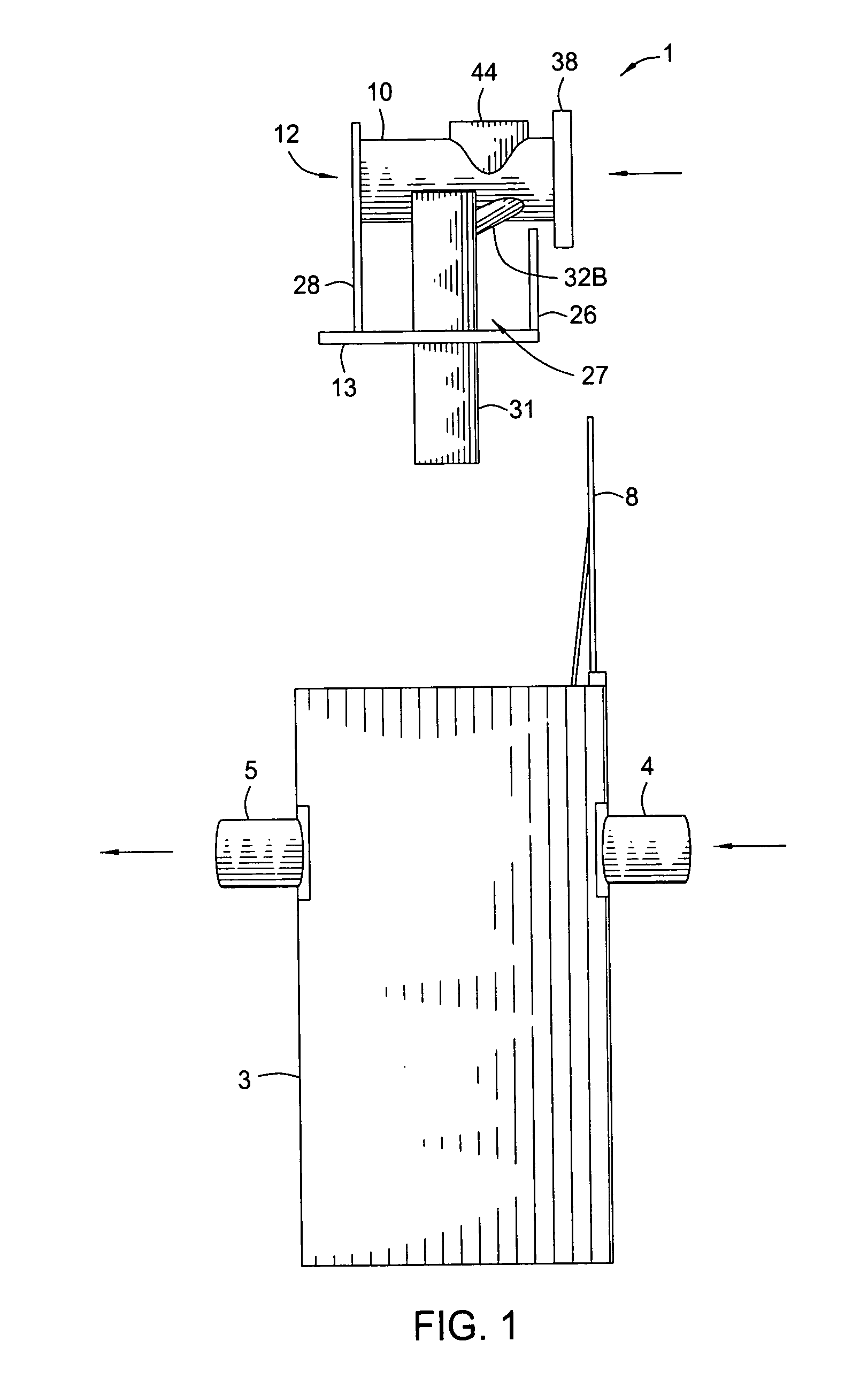
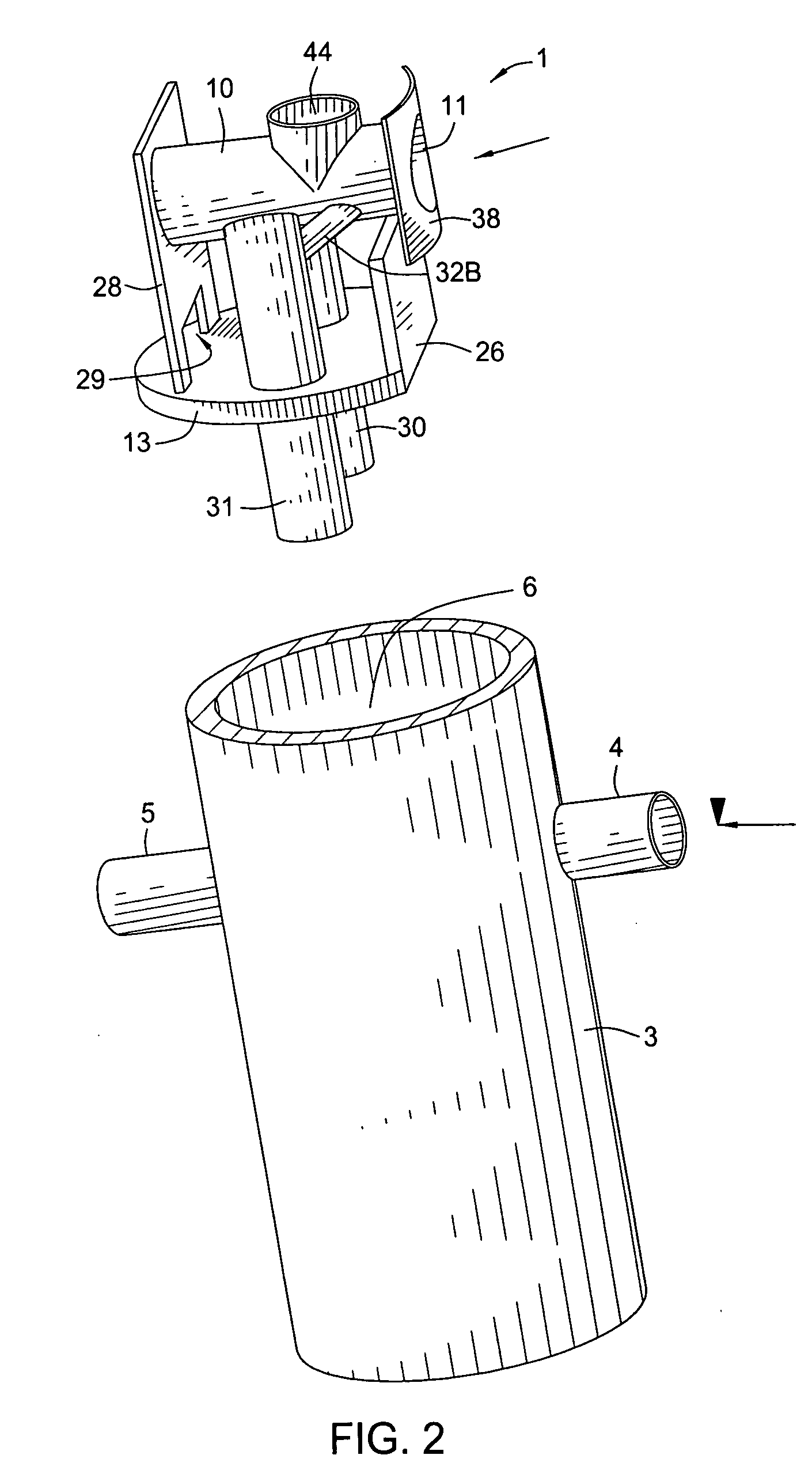
ActiveUS7022243B2Efficient removalLower the volumeLiquid displacementLoose filtering material filtersEnvironmental engineeringStreamflow
A separation tank having an inlet and an outlet and forming a low flow path and a high flow path, both conveying water from the inlet to the outlet. At normal, low flows, the water enters the inlet and passes through the low flow path having treatment chambers to remove, respectively, heavy materials and floatable materials. At high flows such as with heavy storm runoff, water exceeding a predetermined flow rate is conveyed from the low flow path into the high flow path where there are baffles to treat the water to remove both heavy materials and floatable materials. In optional embodiments, there is a filter / recharge chamber that may contain a filter and / or a groundwater conveyance system such that filtered or unfiltered water can be discharged from the low flow path through a groundwater conveyance system to groundwater, to the normal outlet, or both.
Owner:BRYANT GRAHAM
Stormdrain curb-inlet multi-stage filtration-unit
InactiveUS7083721B2Easy to disassembleEasy accessGeneral water supply conservationPaving gutters/kerbsFiltrationPetrochemical
A hydraulic-permeation type environmental water-runoff filtration-system applicable to street curb-inlet type drainage-chambers, which generally cooperatively interconnect with street and parking-lot drains. The BLUEBAY-BMP™ pollution-trap provides advantage of community-tailored filtering stages, the preferred embodiment seting forth a convenient user-friendly prefabricated-kit assembly employing a basic build-in-place containment-housing which can be readily adapted to the studied needs of a given community,—without incuring alteration of existing sewer-stormdrains. The uniquely adaptative capability of the containment-housing enables selectively structuring multi-stages of filtration, which progressions address a variety of ecosystem-contaminants, ranging from basic street-refuse and floatable objects, to coarse sediment, finer silt, and comparatively minute albeit environmentally-hazardous petrochemicals, heavy-metals, phosphates, and nitrates;—all of which are readily retrieved from the apparatus confines via periodic maintenance for transfer to appropriate collection handling facilities.
Owner:STEWART D MCCLURE +3
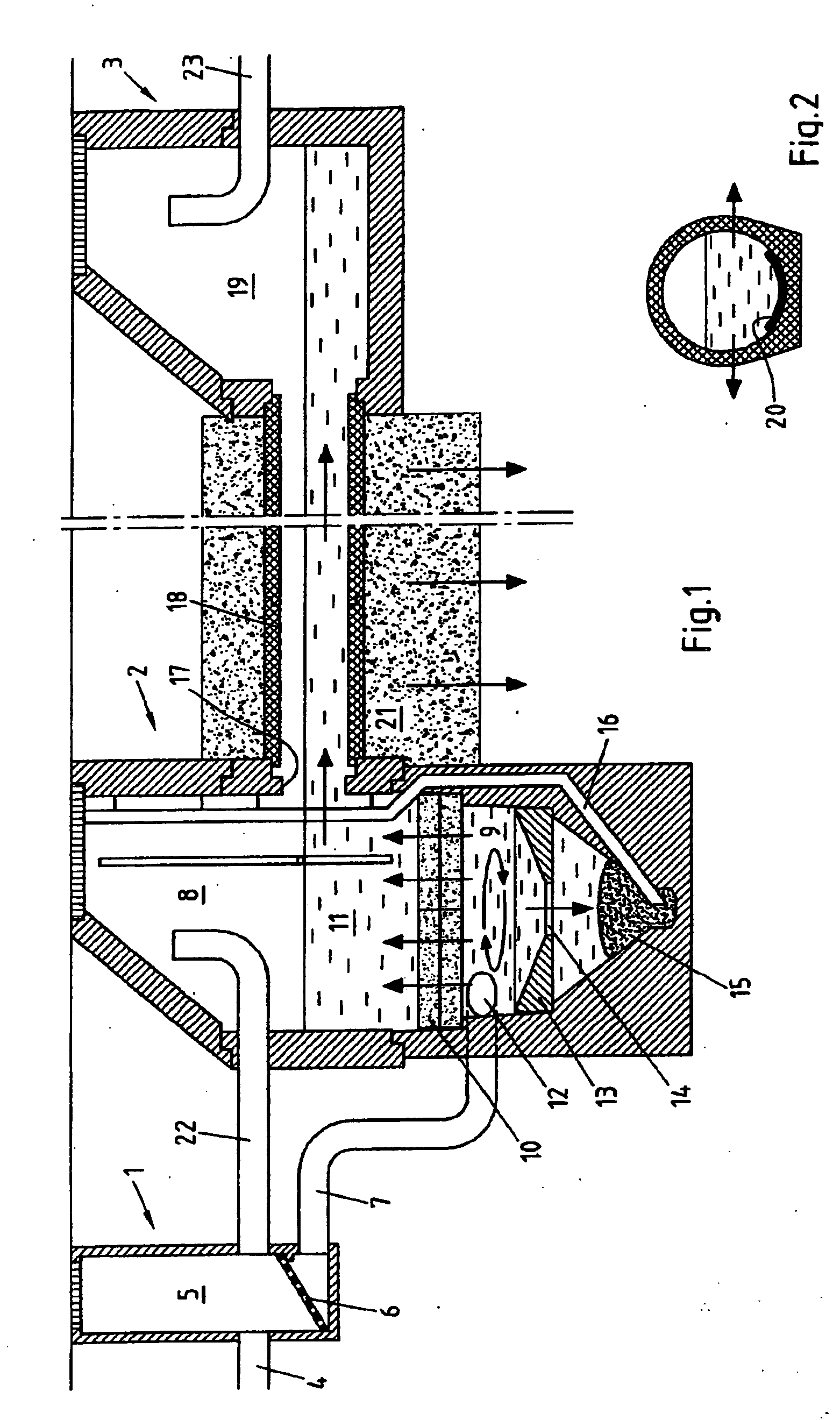
Filter element for water loaded with solid particles and dissolved toxic substances and purification system equipped with said filter element
InactiveUS20060163147A1Enhance adsorption action of filterHigh pH-valueSewerage structuresTreatment involving filtrationWater flowEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a filter element consisting of a molded body of porous concrete, which element is arranged in the water stream of a purification system. In particular, the filter element (10) is a molded pervious concrete layer arranged as a partition between a lower compartment (9) and an upper compartment (11) of a treatment chamber (8), wherein the water inlet (12) opens into the lower compartment (9) and a water outlet (17) issues from the upper compartment (11). The pervious concrete filter layer may contain one or more additives to enhance adsorption of pollutants, such as heavy metal ions, phosphorous, hydrocarbons or other target soluble pollutants.
Owner:ROYAL ENVIRONMENTAL SYST +1
Filtration of hydrocarbon containing liquid
InactiveUS6503390B1Preventing back wash of any liquidLiquid suspension thickening by filtrationPaving gutters/kerbsExtreme weatherFiltration
An apparatus for and method of filtering hydrocarbon contaminated water is disclosed herein. The present invention may be used in drainage openings, particularly in parking lots and containment areas for large sources of hydrocarbons such as oil tanks or electrical transformers, to remove hydrocarbons from hydrocarbon contaminated water. The apparatus has a filtration compartment which filters out debris and sediment which may clog the treatment compartment. A pre-filter attachable to the apparatus may be used to further aid in filtering out sediment. A means for melting snow and ice may be incorporated within the filtration compartment such that liquid flow is not hindered during extreme weather conditions. The treatment compartment contains a hydrocarbon absorption media which absorbs any hydrocarbons present in the water rendering such water substantially hydrocarbon-free for discharge directly into a stream or groundwater. In the event of a hydrocarbon spill, the hydrocarbon absorption media forms a plug which seals off the flow of contaminated water. A hydrocarbon solubilizing material capable of effectively removing sheen in a first pass may be disposed as a top layer over the hydrocarbon absorption media. Preferably, each compartment is manufactured as a cartridge which may be dropped into a housing inserted into a drain opening.
Owner:SPI FILTRATION
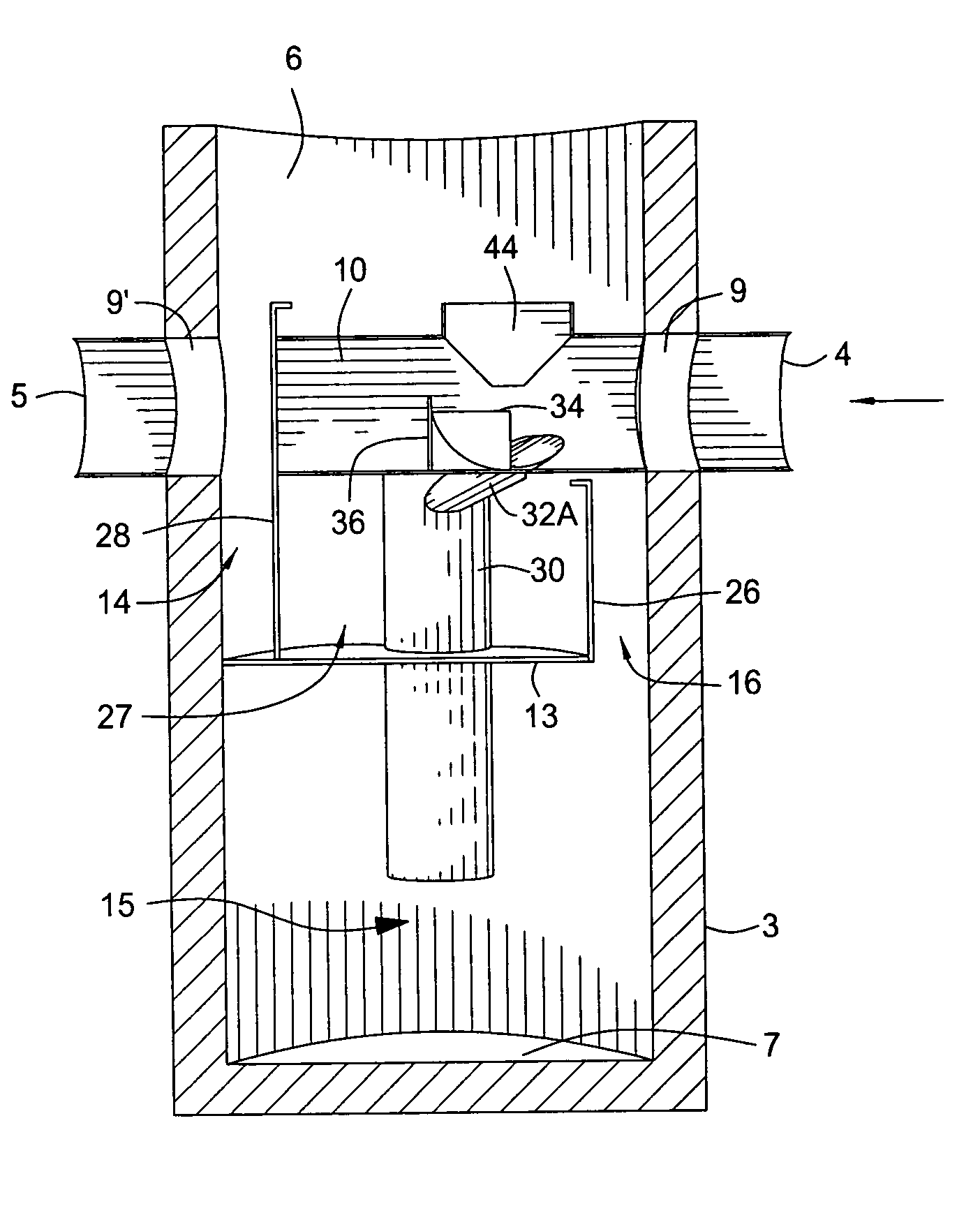
Storm water treatment apparatus employing dual vortex separators
ActiveUS20050184007A1Avoid backupImprove liquidityReversed direction vortexLiquid displacementSuspended particlesEddy current separator
A stormwater treatment device for removing floatables, solids and suspended particles and the like from stormwater run off, whereby a removable assembly is provided for installation into a manhole basin, the assembly including a pass-through member which receives stormwater from an incoming drainage system, and diverts low flows to at least one or more vortex separators, while allowing for high flows to bypass the separators and flow through the assembly untreated to exit the basin without diversion.
Owner:OLDCASTLE PRECAST
Magnetic Metal Oxide Biochar Composite Particles, and Their Use in Recovering Pollutants From Aqueous Solution
InactiveUS20180016162A1Cheap manufacturingEconomical to useBio-organic fraction processingWaste water treatment from animal husbandryPhosphateAgricultural runoff
Composite particles are disclosed comprising magnesium oxide, iron oxide, and biochar; and methods of making and using the composite particles. The composite particles may be used to recover solutes including phosphate, nitrate, ammonium, and organic compounds from aqueous solution, and the resulting solute-loaded particles may be used as a fertilizer to enhance plant growth. The composites be used to remove pollutants from agricultural runoff, wastewater, and surface water. The particles possess magnetic properties that enhance their recovery following solute adsorption.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Stormwater treatment system
InactiveUS6998038B2Treatment involving filtrationLoose filtering material filtersProcess regionStormwater treatment
Owner:CONTECH ENGINEERED SOLUTIONS
Apparatus for trapping floating and non-floating particulate matter
InactiveUS6951619B2Efficient and cost-effectiveReversed direction vortexLiquid displacementParticulatesEngineering
A separation tank with an outer chamber and an inner chamber within the outer chamber. An inlet and outlet are formed in the outer chamber to receive and discharge water, respectively. An inlet opening is located in the inner chamber and is generally aligned with the inlet to receive water from the inlet. An outlet opening is formed in the inner chamber below the inlet opening but above the bottom of the inner chamber. The inner chamber has a cylindrical interior surface such that water from the inlet is directed at a tangent to the interior surface and forms a vortex as the water progresses through the inner chamber. A baffle plate having an opening forming upper and lower weirs is located within the outer chamber just upstream of the outlet to separate both floatable and non-floatable material from the water prior to its discharge.
Owner:BRYANT GRAHAM
Wetland Biofilter Chamber with Peripheral Catch Basin and Method of Use Thereof
ActiveUS20120091057A1Control flowWater cleaningTreatment using aerobic processesParticulatesFiltration
A horizontal flow water treatment method and wetland biofilter apparatus provides a chamber with impermeable outer walls spaced away from permeable interior walls of a media filtration bed such that a catch basin is formed between the outer walls and the interior walls. The catch basin creates an open area around the perimeter of the interior walls for influent water to fill within the open area on all sides before penetrating the filtration media, providing a large surface area for influent water to interact with the media filtration bed. The influent water enters the catch basin in a horizontal flow path to provide for pre-settling of particulates before making contact with the filtration media. The biofilter design increases the available surface area of the media filtration bed by up to four times for a given volume of water, and thereby minimizes the loading or infiltration rate on the media filtration bed.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
Reusable storm water sampler and pollutant filter insert
InactiveUS20020130083A1Easy passEasy to identifyTreatment involving filtrationPaving detailsSurface runoffSolvent
An insert for use in a sewer system to remove oils and solvents carried by surface water runoff. The insert includes a holder and a quantity of water permeable, hydrophobic, oil and solvent absorbing material such as melt blown polypropylene. The holder has two functions. It holds an effective quantity of the absorber and holds it in such a way that the surface water is exposed to the absorber to allow oils and solvents to be absorbed. The insert in preferably placed, cartridge-like, at the inlet or outlet of the sewer system so that it may be quickly checked, replaced and serviced. In one embodiment, the insert also contains a leaf trap.
Owner:WATERPOLLUTIONSOLUTIONS COM
Storm water runoff treatment system
InactiveUS20070012608A1Reduce concentrationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationWater cleaningStorm water runoffSediment
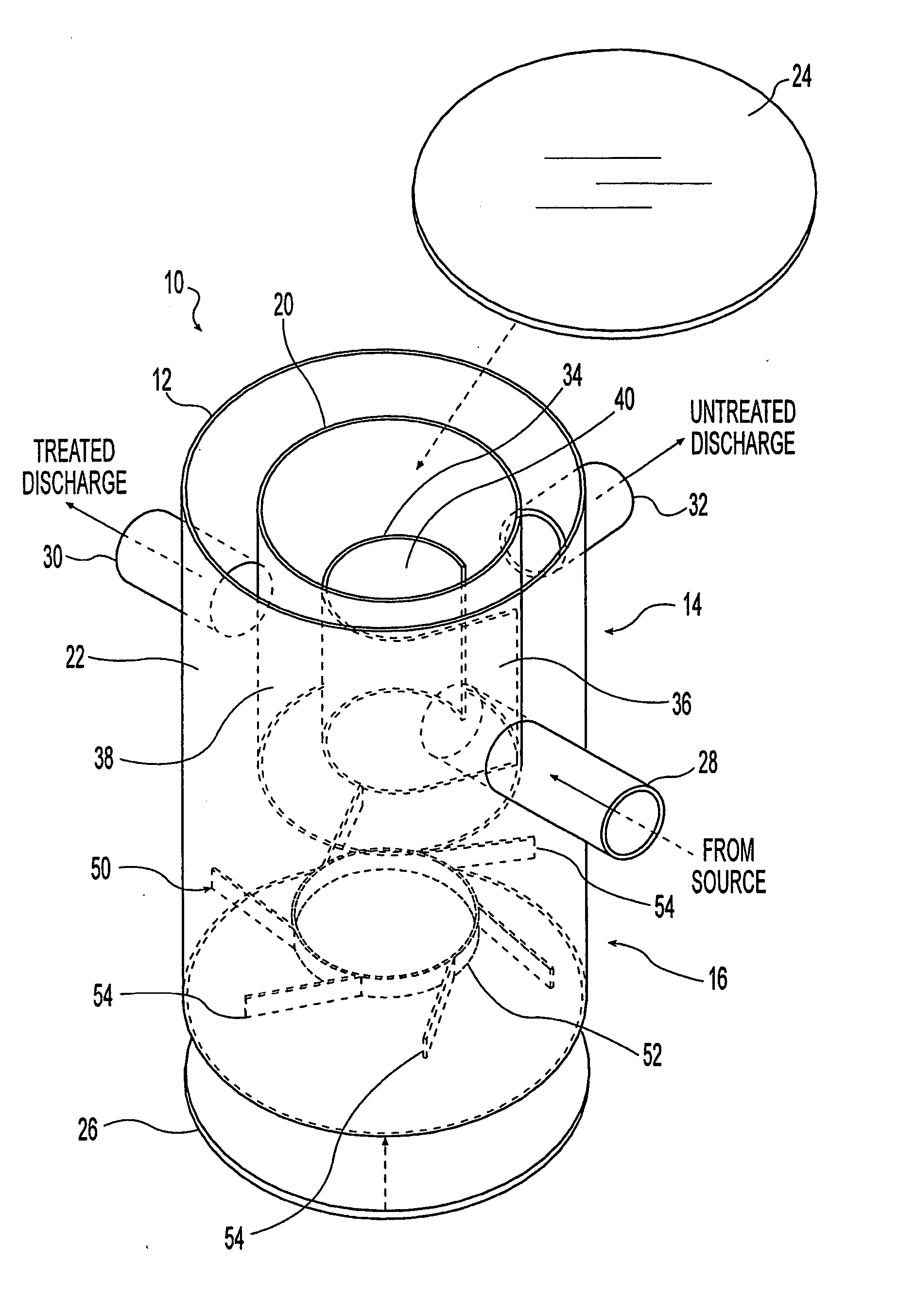
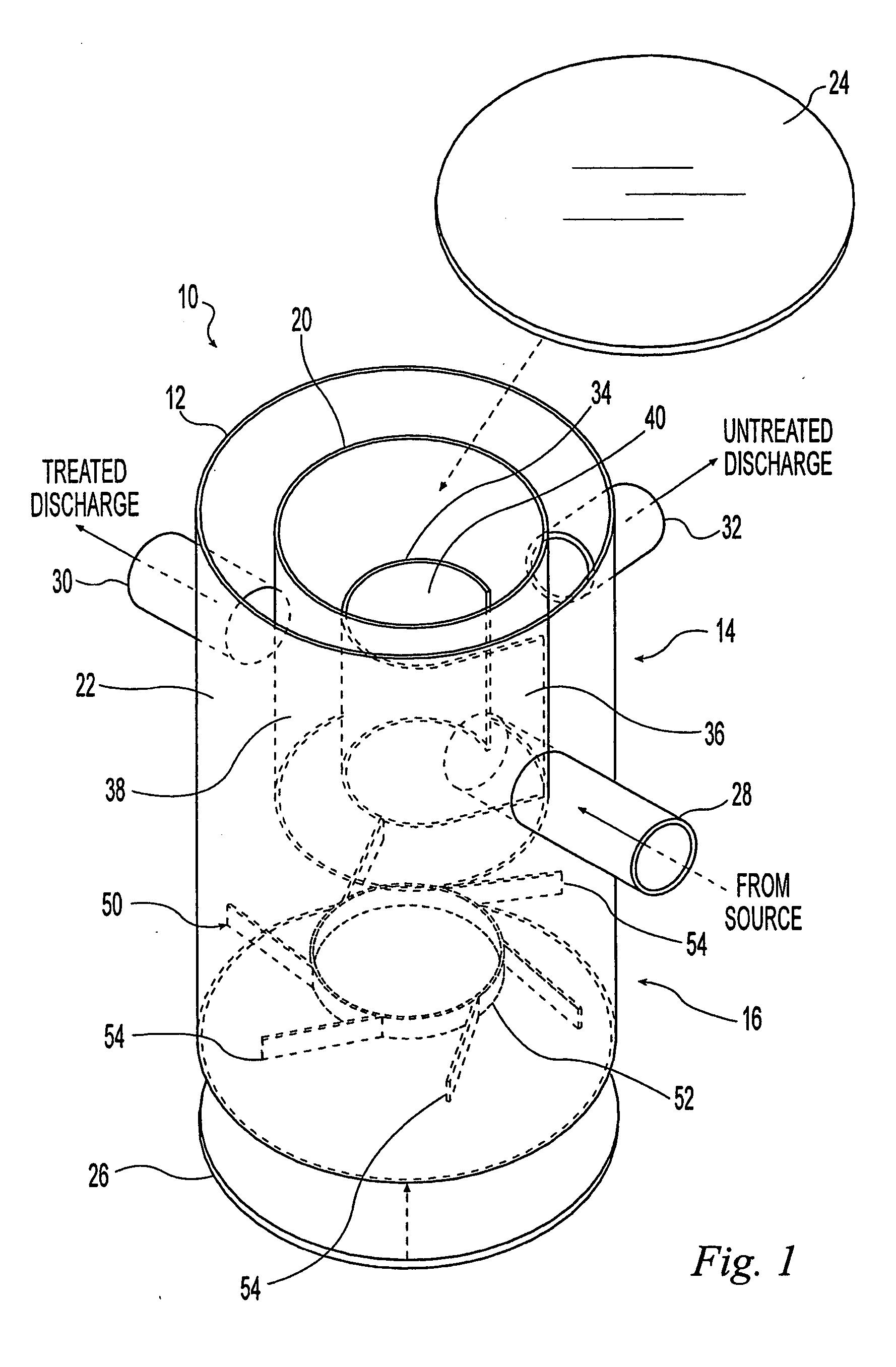
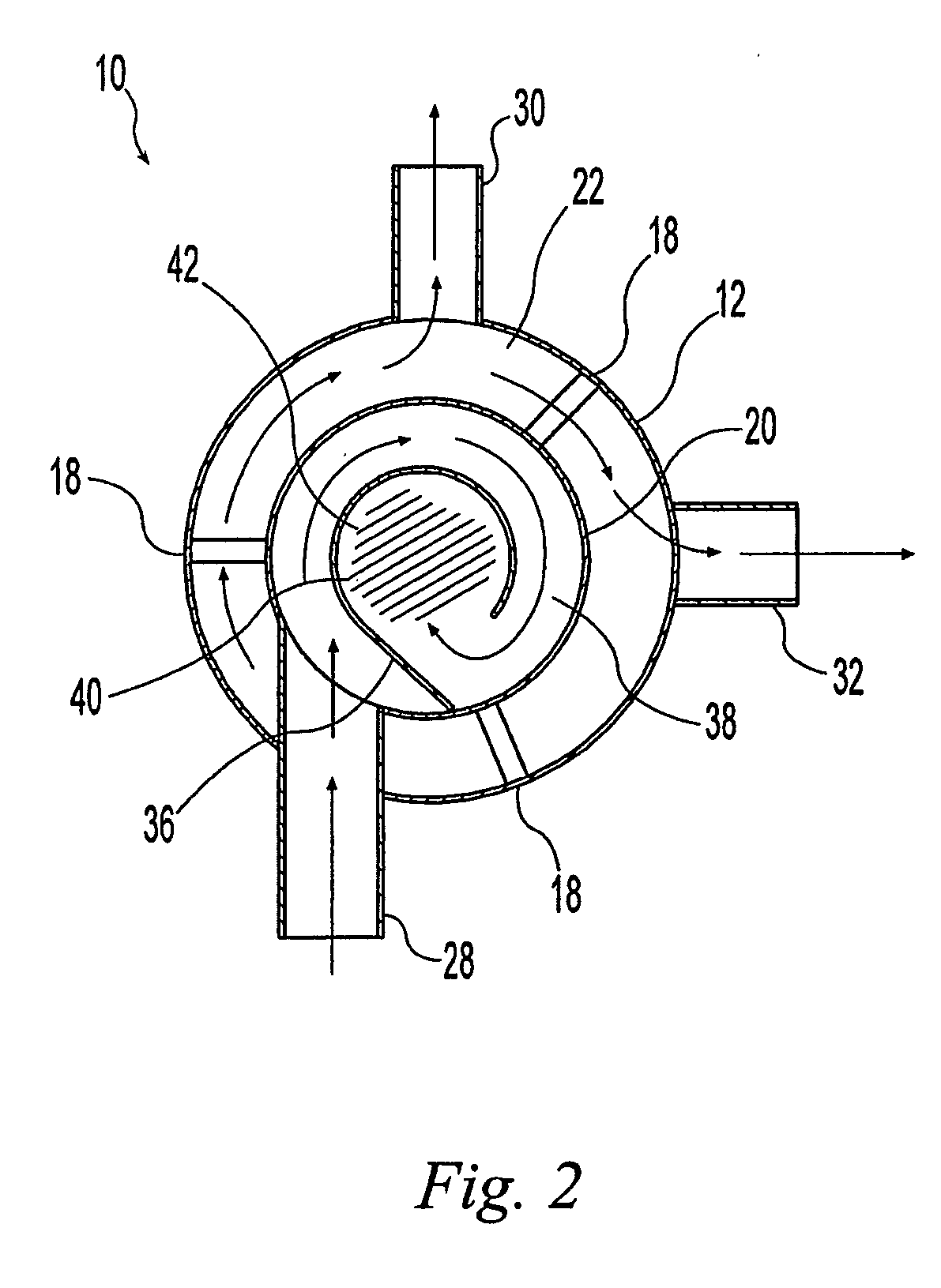
A hydrodynamic device for removing sediment and other materials from storm water runoff is provided. An exemplary embodiment of this device includes: a first substantially cylindrical chamber a second substantially cylindrical chamber concentrically disposed within the upper portion of the first chamber, a first baffle concentrically disposed within the second chamber, and a second baffle disposed within the lower portion of the first chamber. A water inlet is attached to or formed integrally with the second chamber; a water outlet is attached to or formed integrally with the first chamber; and an optional bypass outlet is attached to or formed integrally with the first chamber.
Owner:OHIO UNIV
Materials for removing toxic metals from wastewater
ActiveUS7160465B2Simple designTreatment involving filtrationEnergy based wastewater treatmentWastewaterAbsorbent material
A treatment facility for removing toxic metals from storm water runoff to provide clean water. The treatment facility includes a pretreatment chamber for removing large toxic particles from the storm water runoff and absorbent chamber for removing fine particles of toxic metals from the storm water runoff. The absorption chamber has an absorption bed of three absorptive materials for removing the fine particles of toxic metals from the storm water runoff.
Owner:NAVY UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESTENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Clarification and sorptive-filtration system for the capture of constituents and particulate matter in liquids and gases
A sorptive-filtration system for removing at least one of negatively or positively charged ions, complexes or particulates from an aqueous stream. The system includes a) flow formed substantially from at least one of rainfall-runoff or snowmelt-runoff; b) a filter containment communicating with the runoff stream such that at least part of the stream passes through the filter containment; and c) a granular filter media disposed within the filter containment, the filter media having an amphoteric material applied thereto, wherein the amphoteric material comprises a metal selected from at least one of Fe, Al, Mn, or Si.
Owner:UNIT PROCESS TECH
Storm water treatment apparatus employing dual vortex separators
ActiveUS7182874B2Avoid backupImprove liquidityReversed direction vortexLiquid displacementSuspended particlesEddy current separator
A stormwater treatment device for removing floatables, solids and suspended particles and the like from stormwater run off, whereby a removable assembly is provided for installation into a manhole basin, the assembly including a pass-through member which receives stormwater from an incoming drainage system, and diverts low flows to at least one or more vortex separators, while allowing for high flows to bypass the separators and flow through the assembly untreated to exit the basin without diversion.
Owner:OLDCASTLE PRECAST
River course ecological treatment system
ActiveUS20180320356A1Improve self-cleaning abilityImprove sewage purification efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesStream regulationFluvialEnvironmental engineering
A river course ecological treatment system essentially comprises a plurality of ecological biological water purification systems and a plurality of plastic retaining dams disposed along a river course, and at least one damp land ecological water purification system disposed beside the river course. The plastic retaining dams separate the river course into several retaining regions. The ecological biological water purification systems purify the water in the retaining regions by microorganism purification. Afterward, the water purified by the ecological biological water purification systems is introduced into rainwater channels of the at least one damp land ecological water purification system. After being purified by aquatic plants in the at least one damp land ecological water purification system, the water returns to the retaining regions the downstream portion of the river course. Therefore, a river improvement system capable of performing both step-by-step treatment and joint treatment is effectuated.
Owner:WANG THOMAS
Liquid filtration system
InactiveUS20080121579A1Easy to settleTreatment involving filtrationLoose filtering material filtersFiltrationFilter system
In some embodiments, a filtration system may include one or more of the following features: (a) a housing having a bottom portion, a middle portion coupled to the bottom portion and an upper portion, and a cap coupled to the upper portion, (b) a sediment storage area within the bottom portion, (c) a separator area within the middle portion, (d) a porous filter within the upper portion, (e) an access hatch within the cap, (f) an inlet pipe for allowing storm water within a middle chamber, (g) an outlet pipe for allowing filtered water to be discharged from the filtration system, and (h) a central pipe being a passageway through the porous filter.
Owner:FORTERRA CONCRETE PROD INC +1
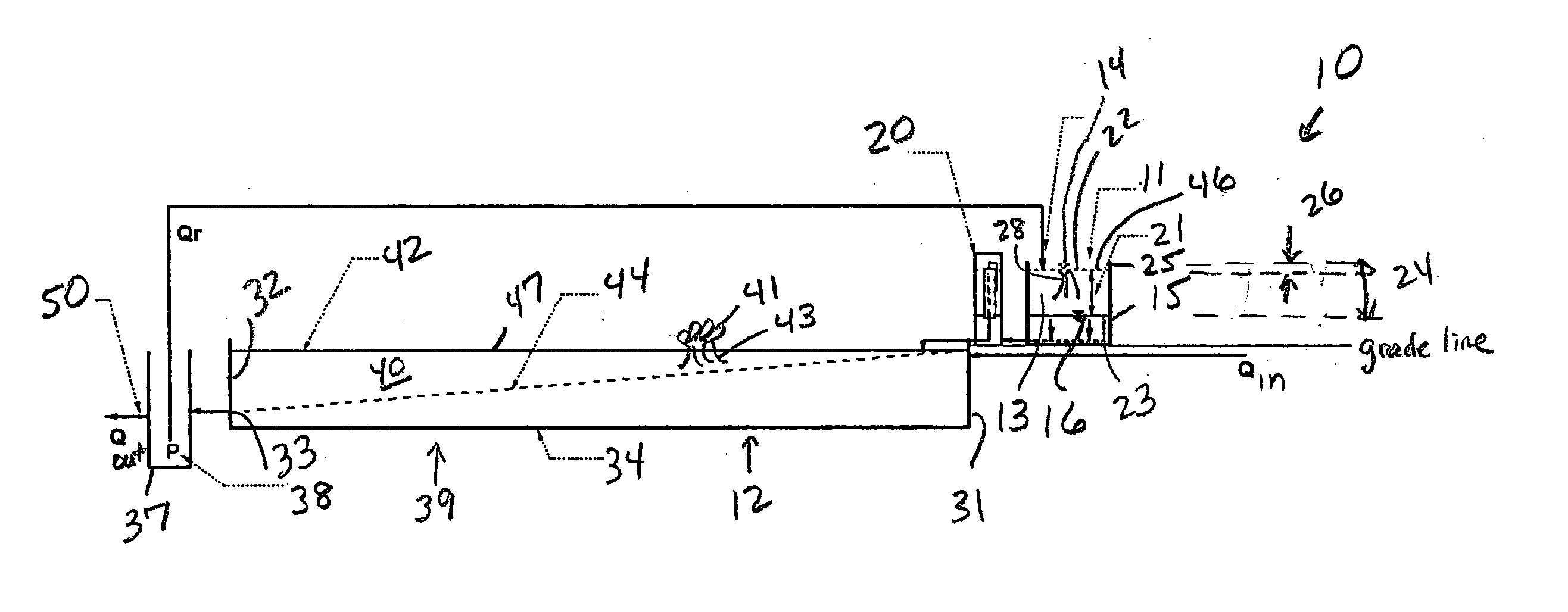
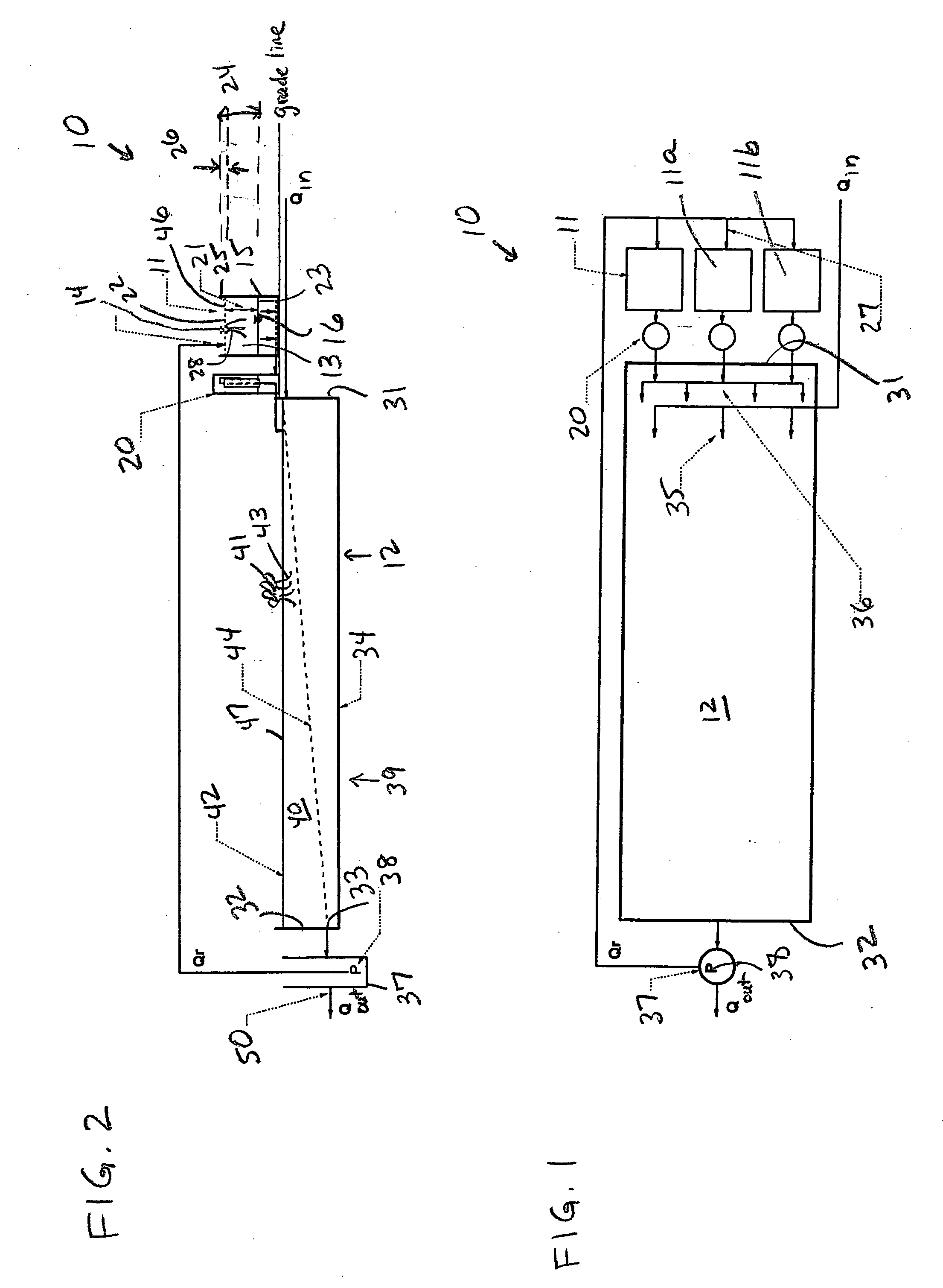
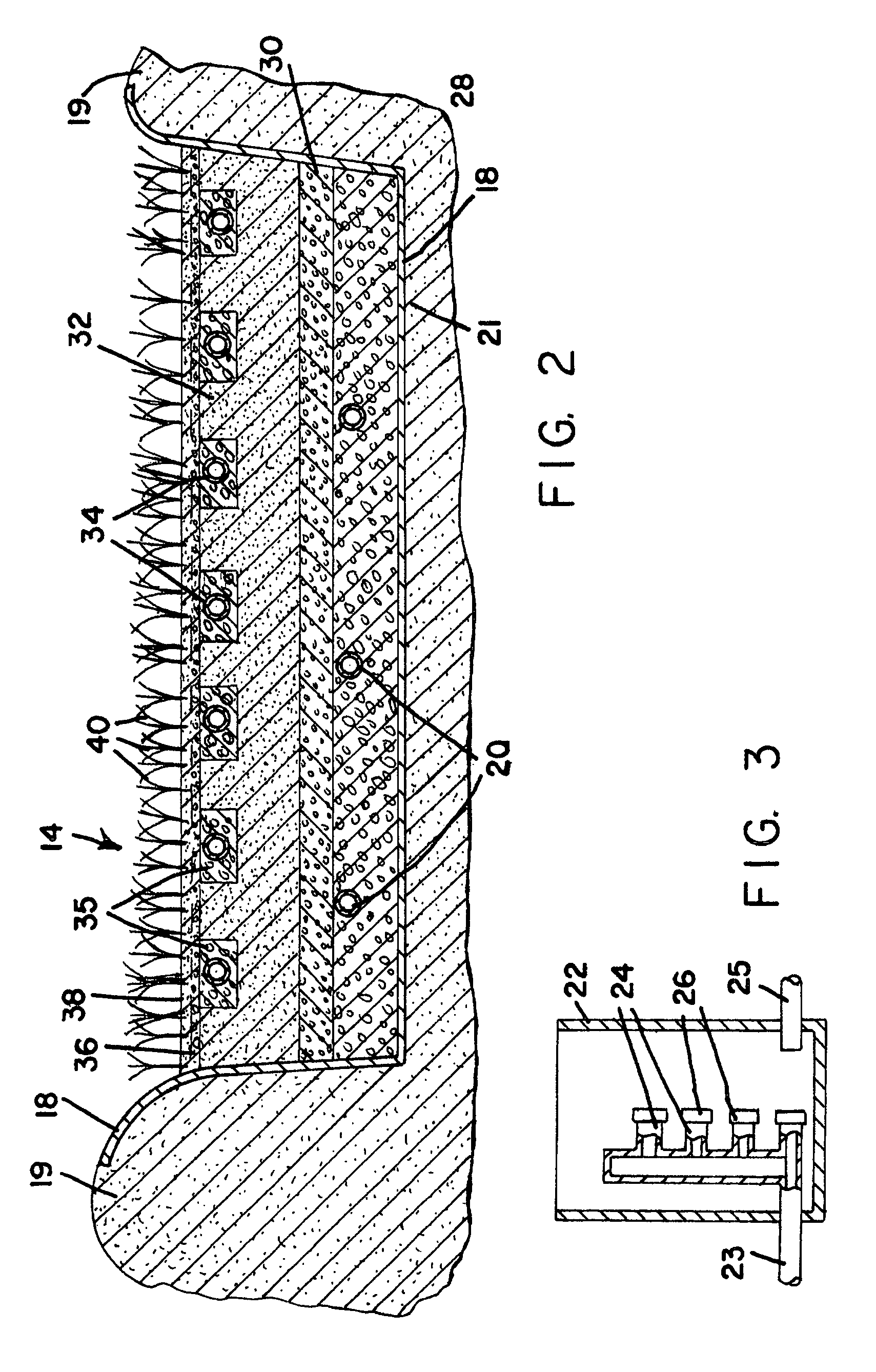
In line wetland water treatment system
ActiveUS7425262B1Reduce maintenanceEasy to useTreatment using aerobic processesGeneral water supply conservationWater treatment systemWater flow
A complete storm water management system and process which performs both drainage and treatment tasks and incorporates a wetlands water treatment system. This system creates an infrastructure, flow control which is multi-level and multi-stage. This system incorporates a self-contained wetlands treatment system. This is a modular system which includes three or more linear chambers through which the storm water or other influent passes and is cleaned. The influent which flows into a storm drain, curb inlet, or inflow pipe into the system is directed first into a screening type catch basin inset filter within the first chamber of the system. The wetlands chamber is composed of one or more modular segments which may be made in various depths, lengths and widths. The influent is treated within the first chamber before it passes out of this chamber into the incorporated wetlands system. The water flows through the wetlands chamber where it is further filtered and decontaminated through both an aerobic and anaerobic process. In situations of high runoff there is a bypass component which runs directly from the first chamber and bypasses the wetlands chamber dumping the pretreated water into the discharge final chamber. This system is fitted with a variable level treatment component designed in such a way to offer variable discharge rates and thus vary the level of treatments over a wide range of flow rates. The system can be placed underground, and below concrete, such as in parking lots or park areas.
Owner:MODULAR WETLAND SYST
Porous pavement for water quantity and quality management
A pavement material for the capture of waterborne constituents. The pavement material comprises a porous pavement substrate and an amphoteric compound bonded to the substrate. The porous pavement material may have a hydraulic conductivity ranging from about 0.001 to about 1.0 cm / sec and may act as a storm water storage basin.
Owner:UNIT PROCESS TECH
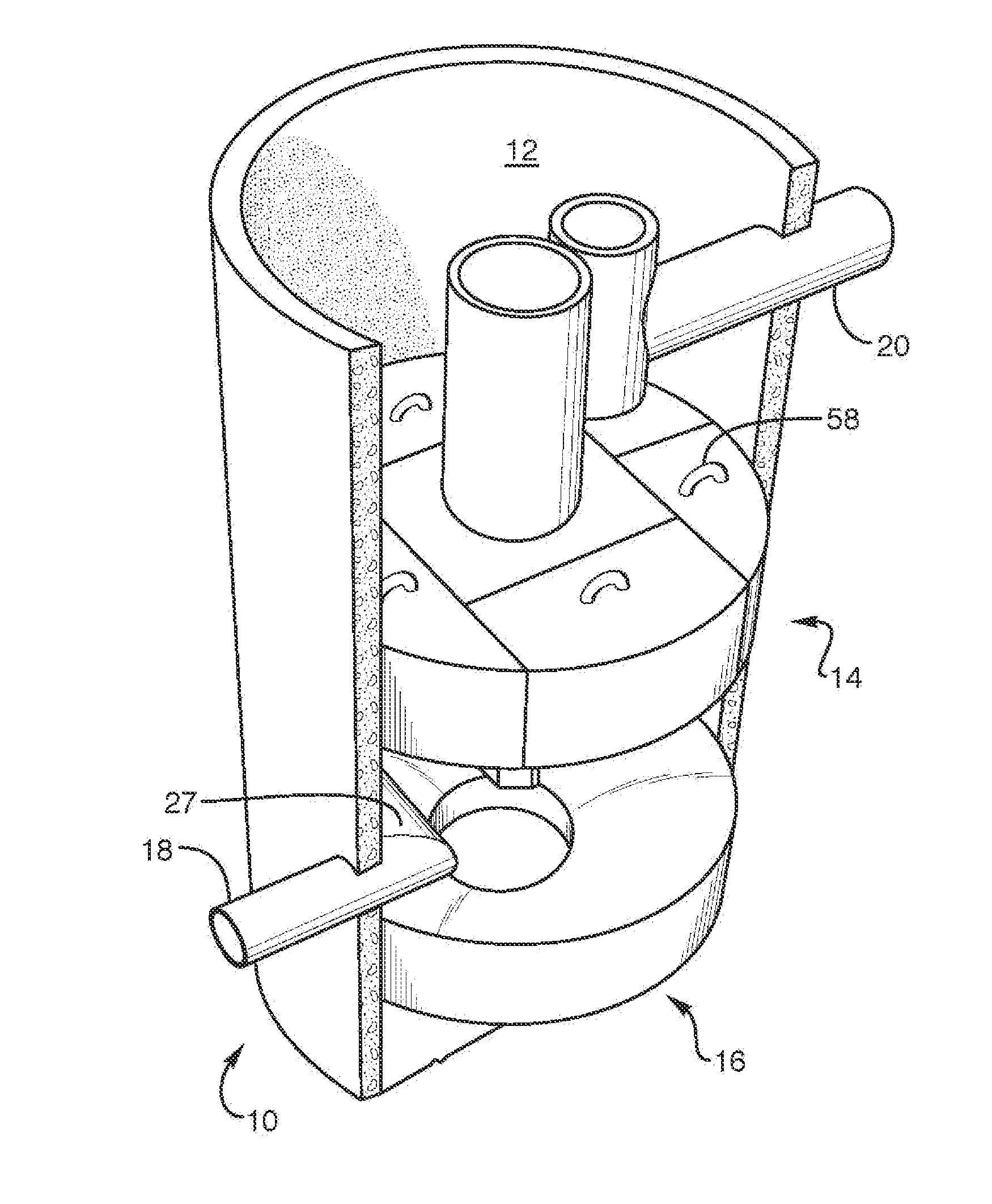
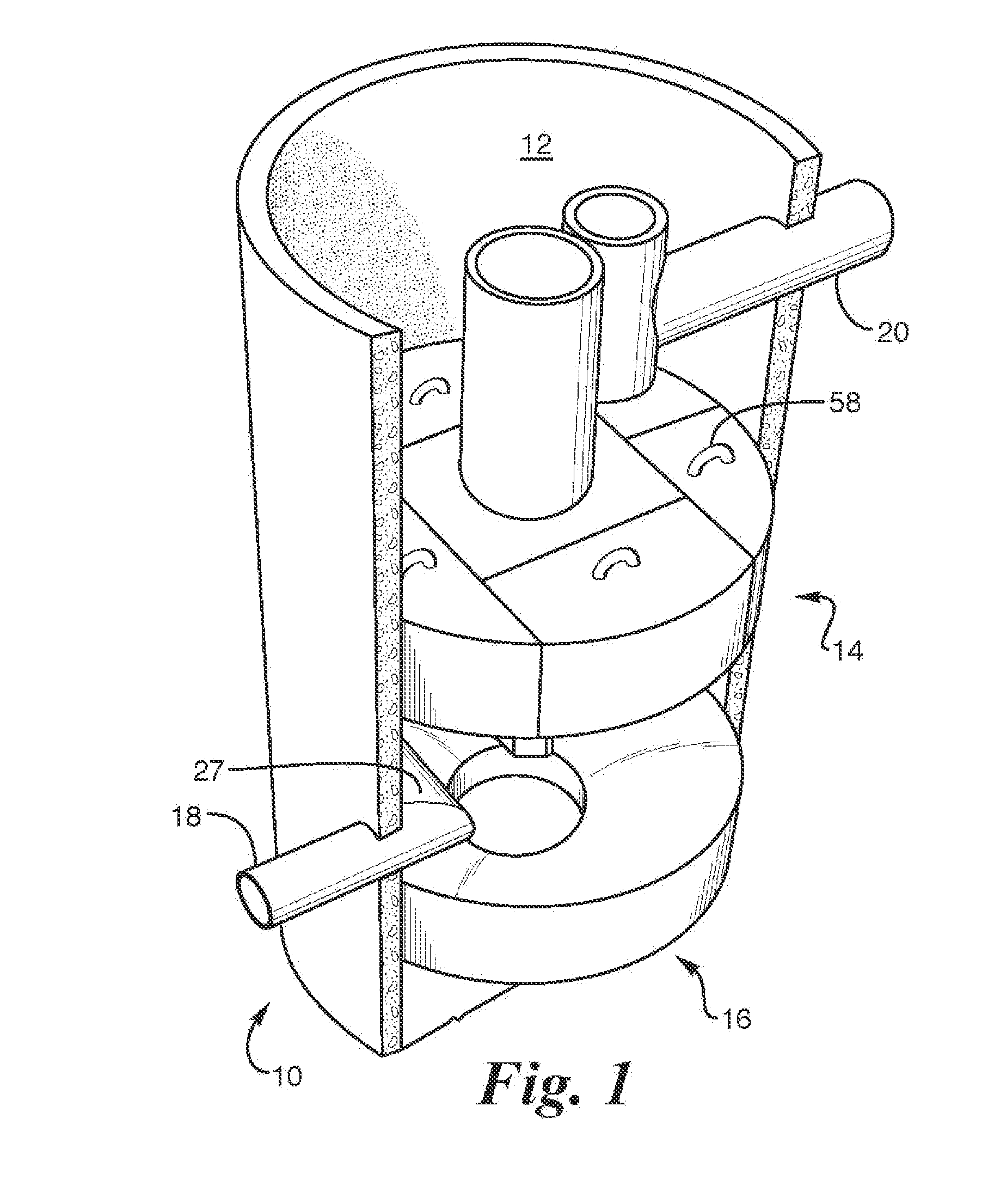
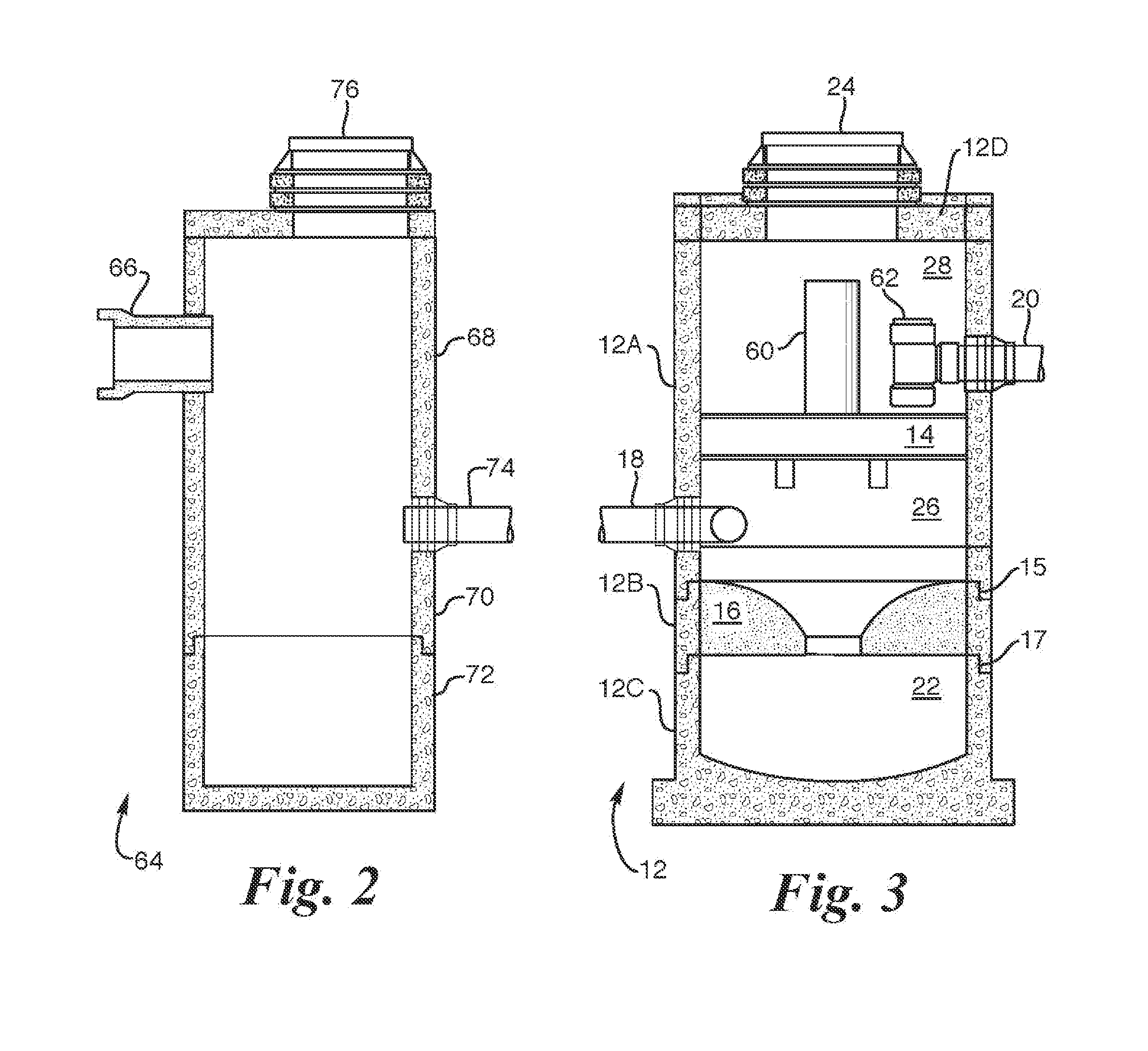
Device for Removing Magnetic Floc from a Magnetic Collector in a Water Treatment System
InactiveUS20080073280A1Water treatment compoundsHigh gradient magnetic separatorsMagnetic tension forceWater treatment system
A water treatment system that utilizes magnetic seeding and magnetic separation to treat water. A magnetic collector is provided for collecting magnetic floc from the water being treated. A floc removal device in the form of a scraper is magnetically held adjacent to or in contact with the magnetic collector for scraping magnetic floc from the magnetic collector. Also disclosed is a disk type magnetic collector that includes a plurality of spaced apart magnetic disks supported on a shaft. A plurality of hook shaped floc removal devices are supported on the shaft with each hook shaped floc removal device being disposed between two magnetic disks or at least adjacent one magnetic disk. The hook type removal devices are spaced so as to engage an adjacent surface of a rotating magnetic disk. As the disk type magnetic collector is rotated, the hook type removal devices engage magnetic floc collected on the surfaces of the magnetic disks and scrape the magnetic floc from the disks.
Owner:CORT STEVEN L
Compositions and methods for adsorption and retention of solvated compounds and ions
InactiveUS20040195182A1Avoid leachingImprove water holding capacityIon-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesGolf course turfIon exchange
A solid phase mixed solvent polymer, compositions and methods for removing and retaining solvated organic compounds and inorganic ions from water, wastewater, superficial and ground water, soil and other environmental sources, a soil amendment and method resulting from adhesively coating the polymer onto sand along with at least one ion exchange material, and methods for the containment, reduction, and prevention of organic leaching from soils, agricultural, industrial, and commercial environments, and in particular, sports and athletic turf facilities such as golf courses where pesticides are frequently applied.
Owner:ECO VERDE TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com