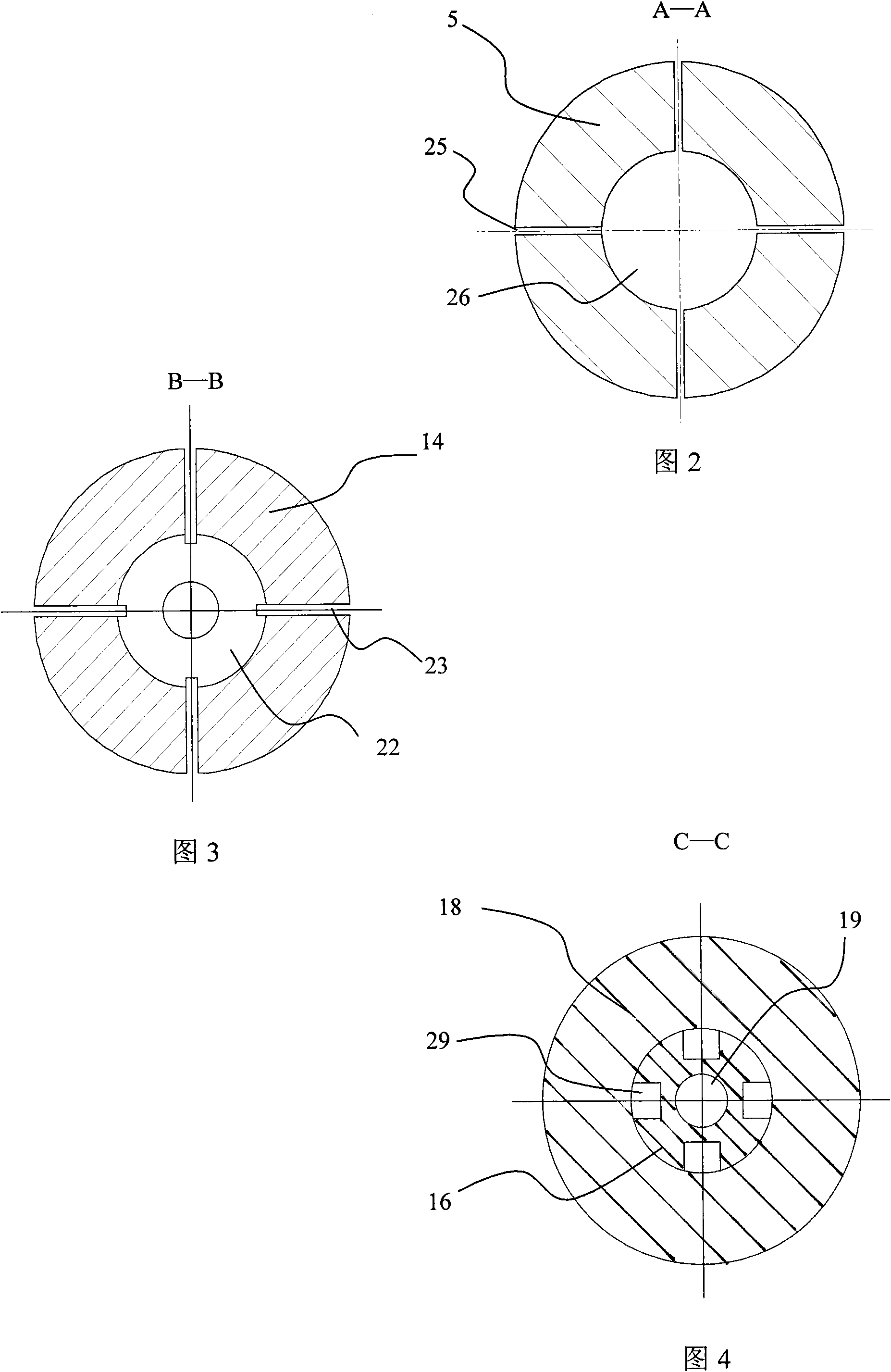
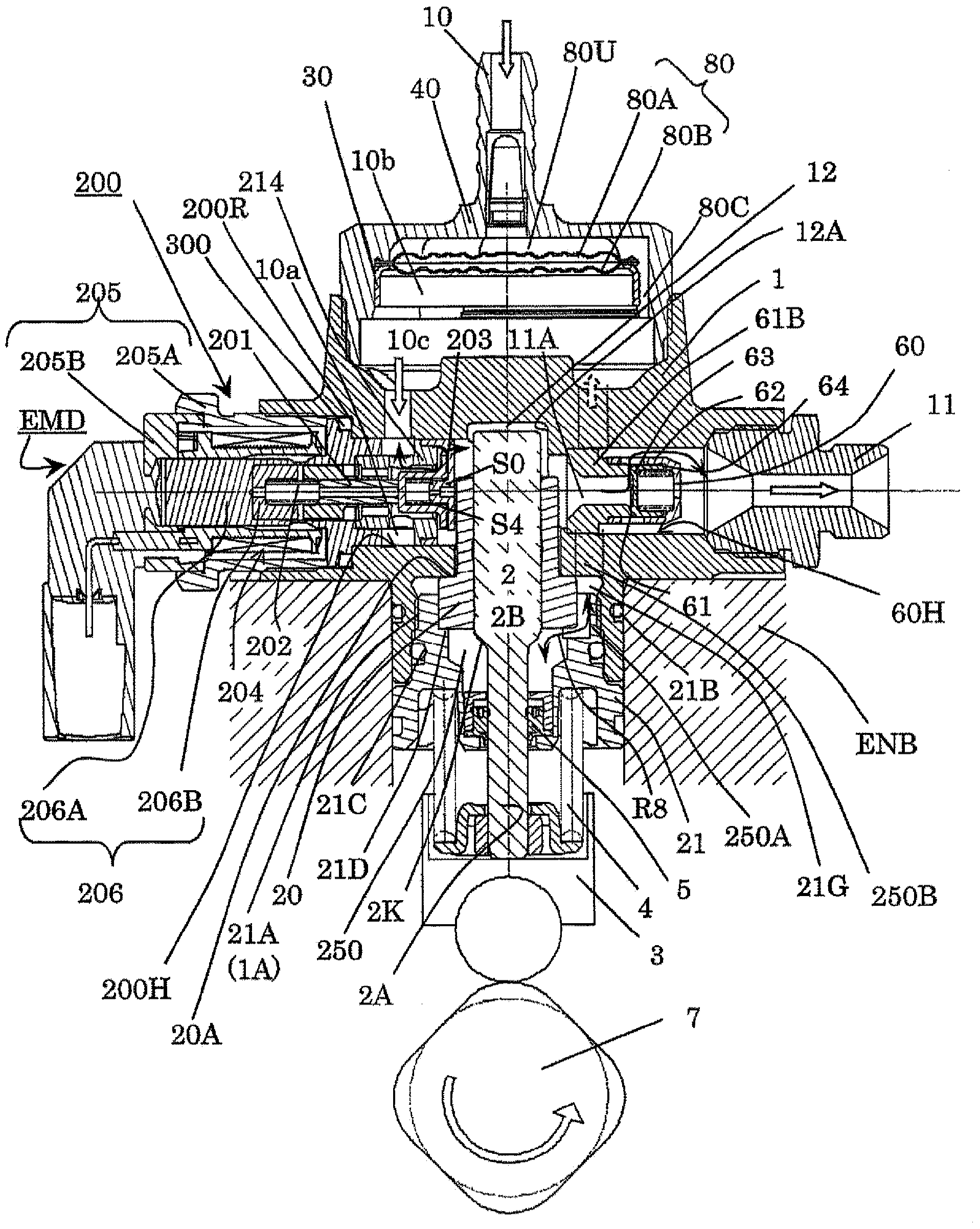
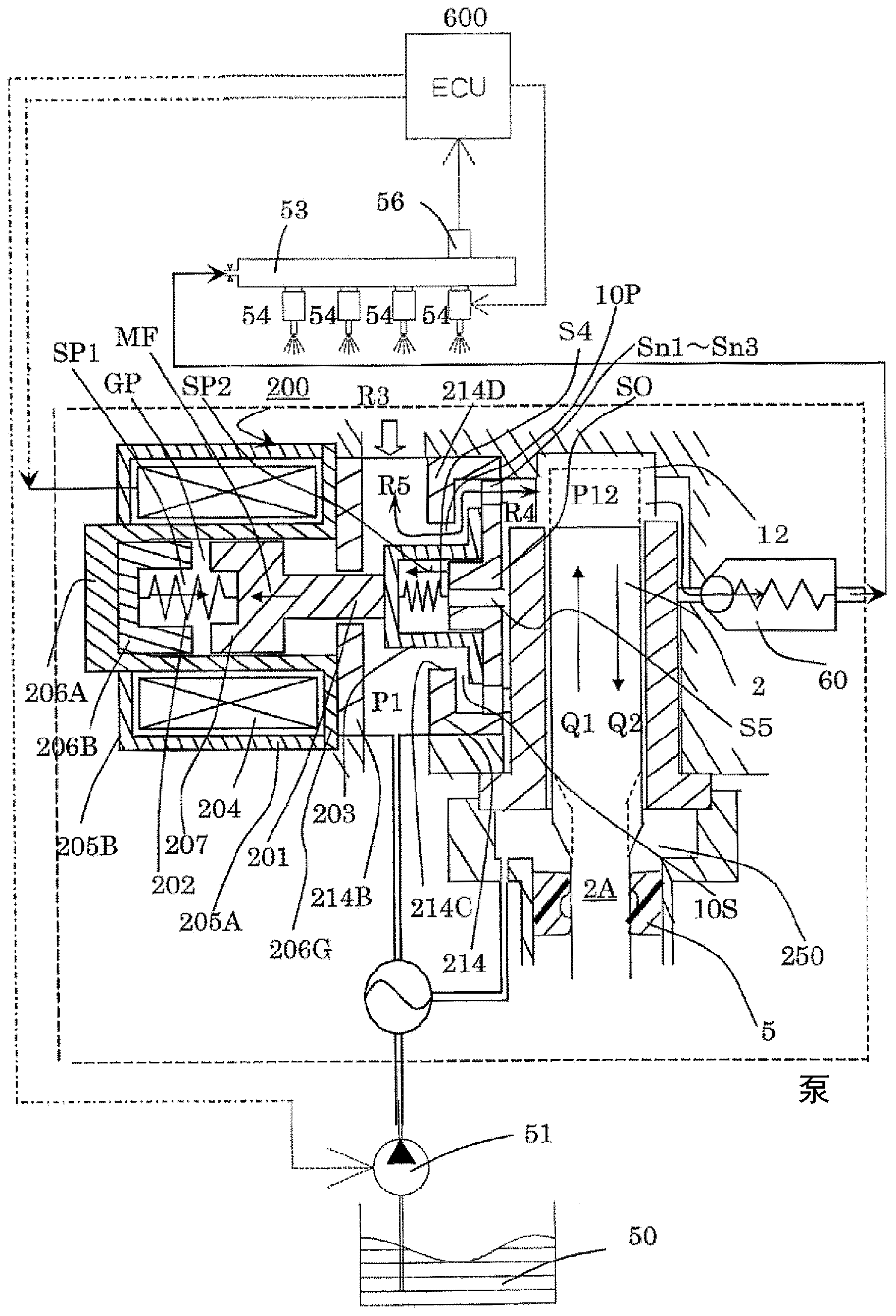
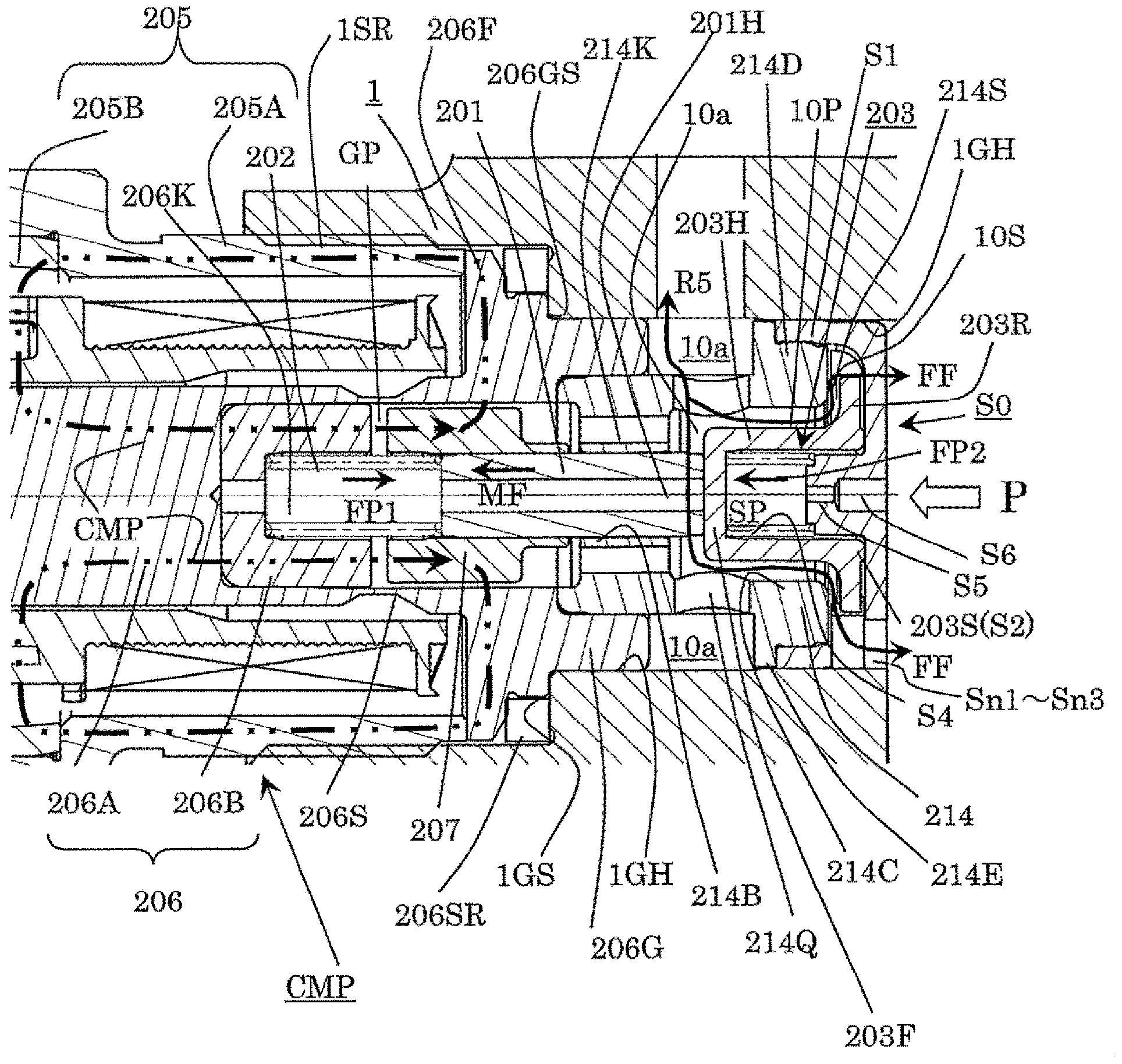
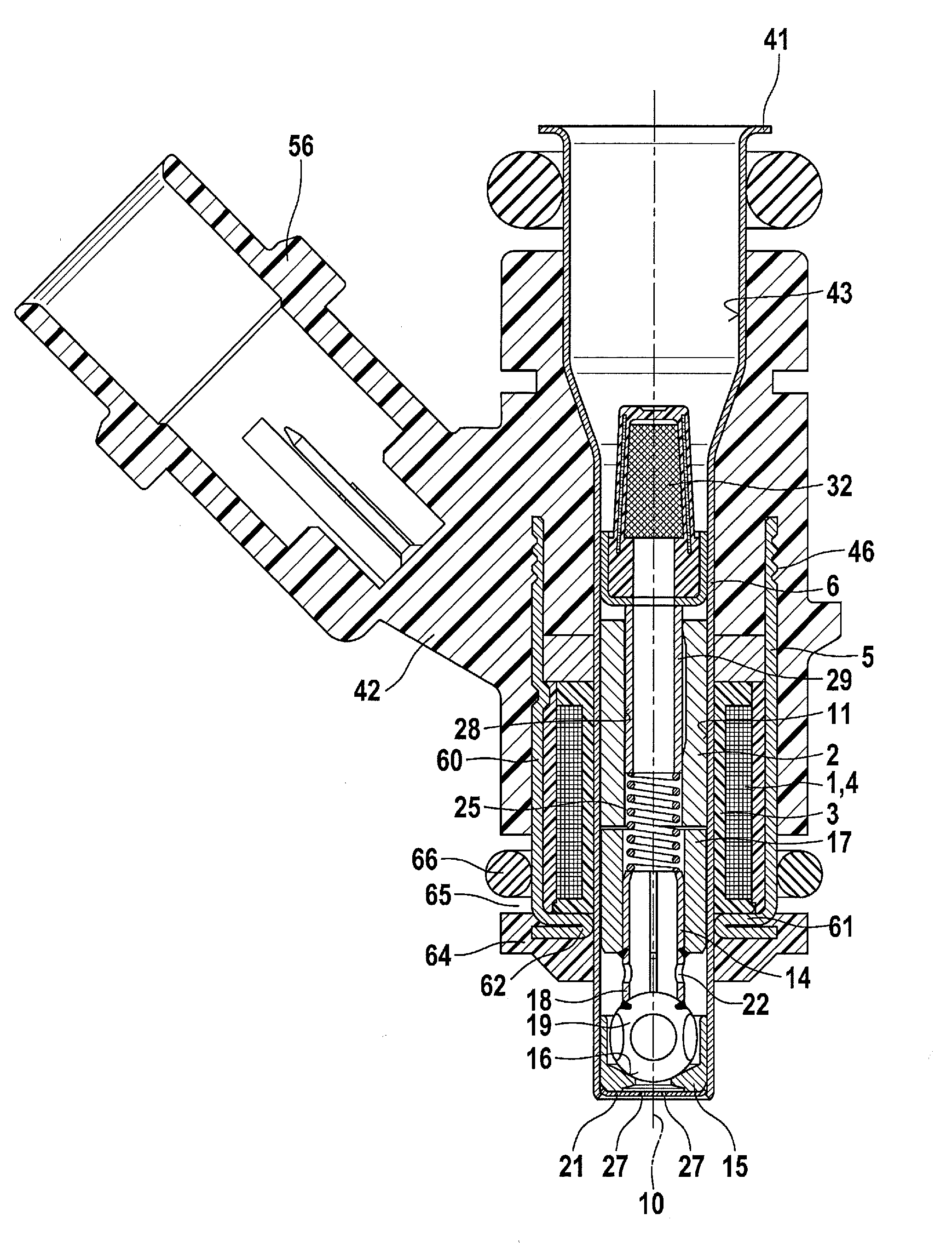
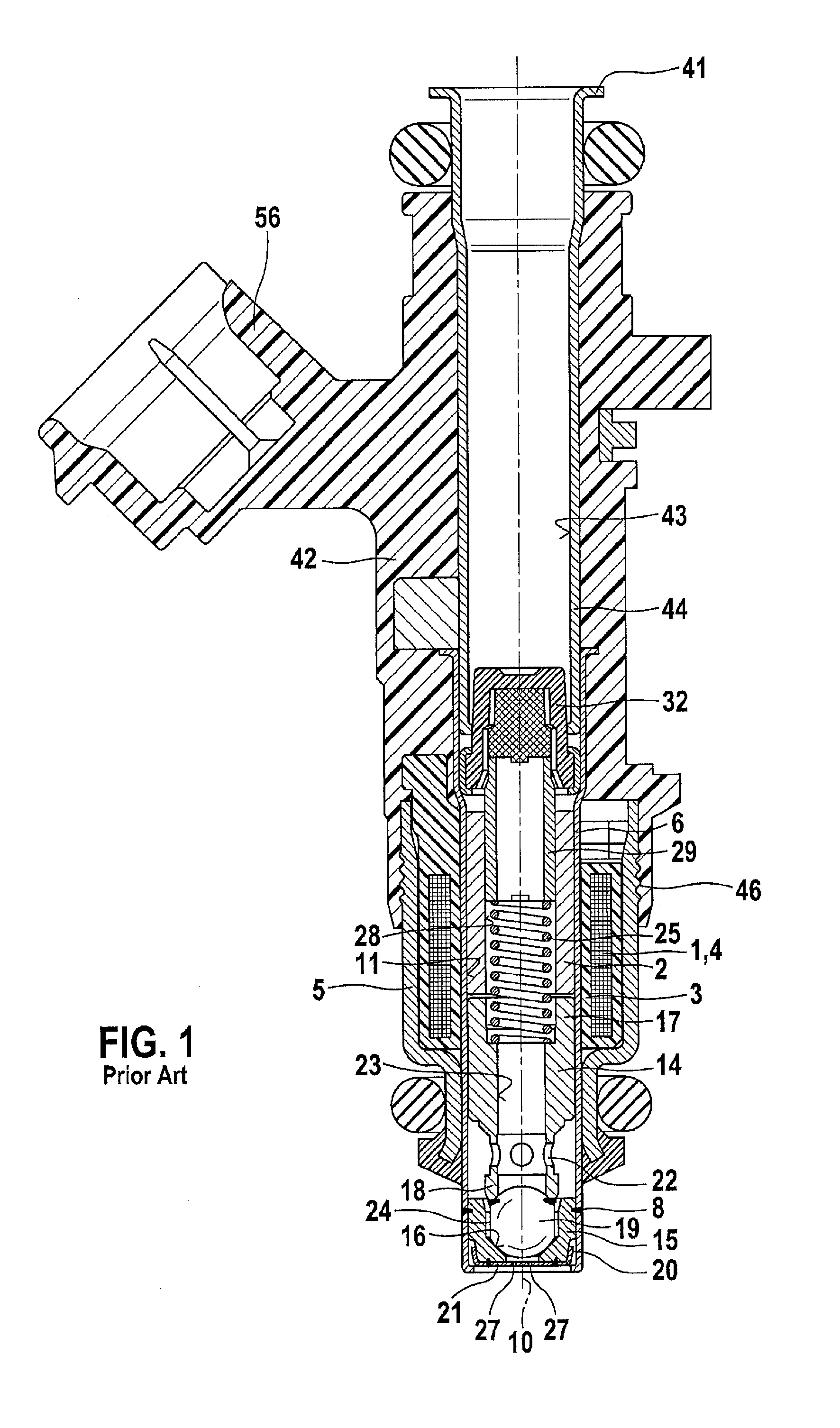
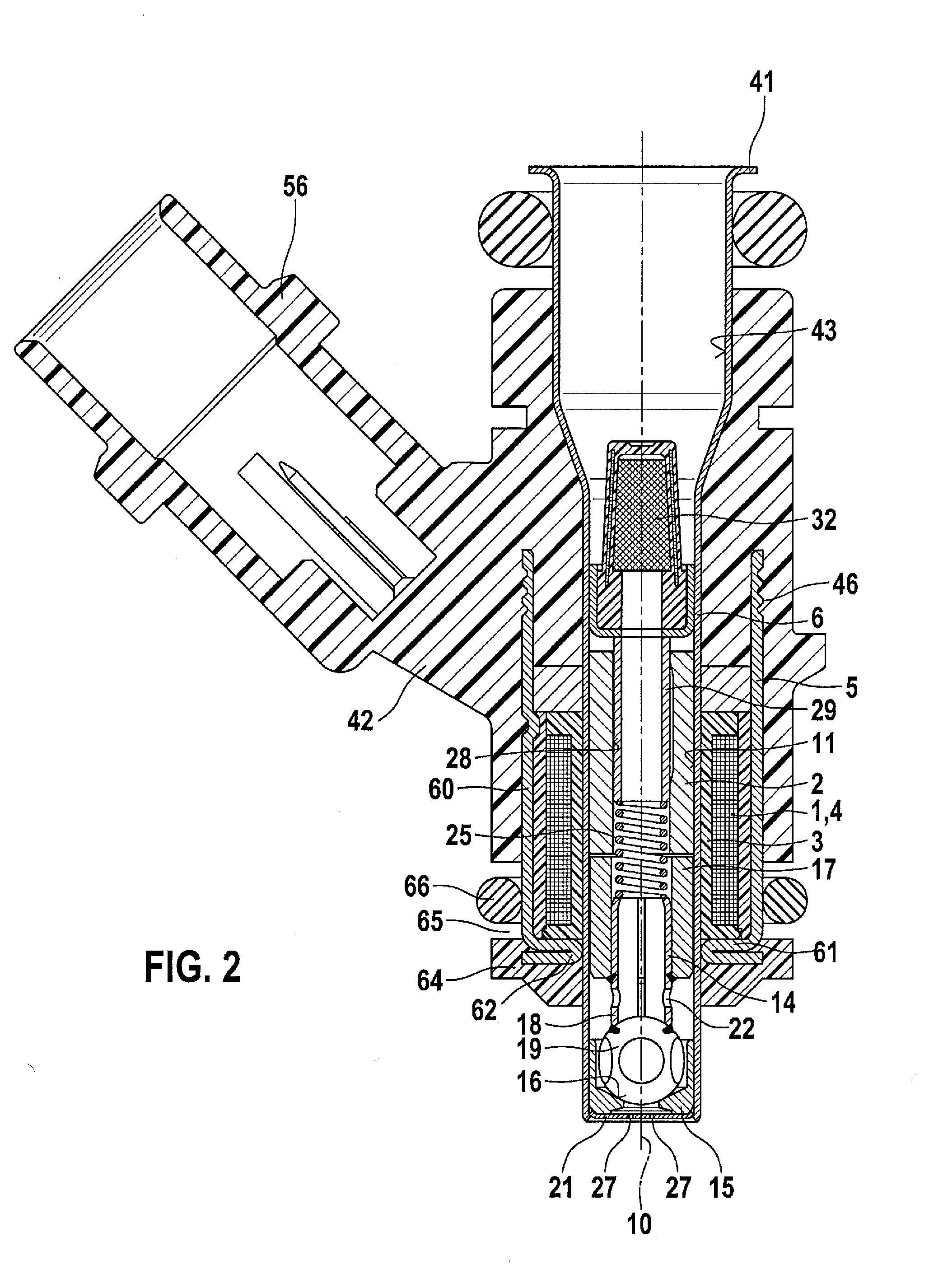
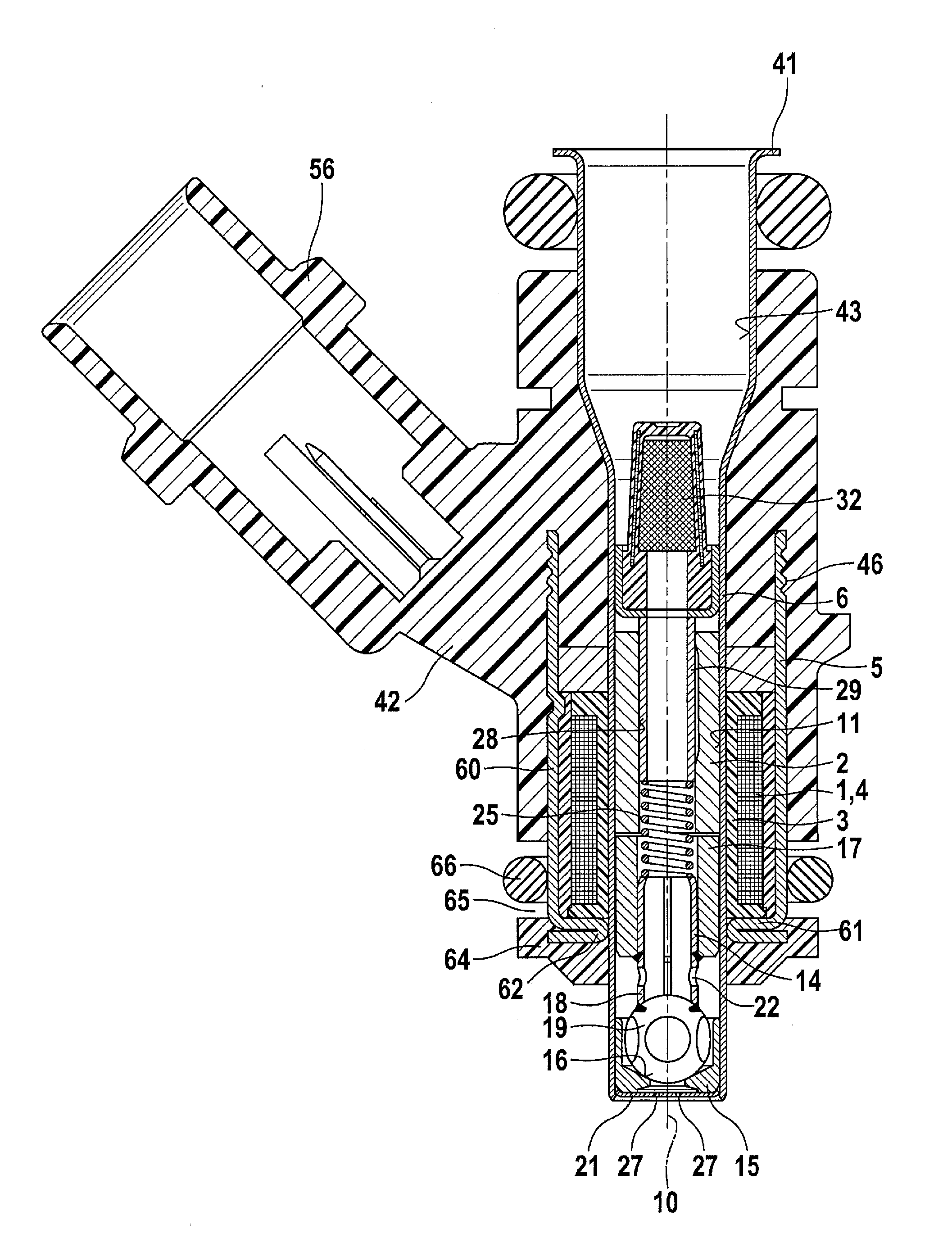
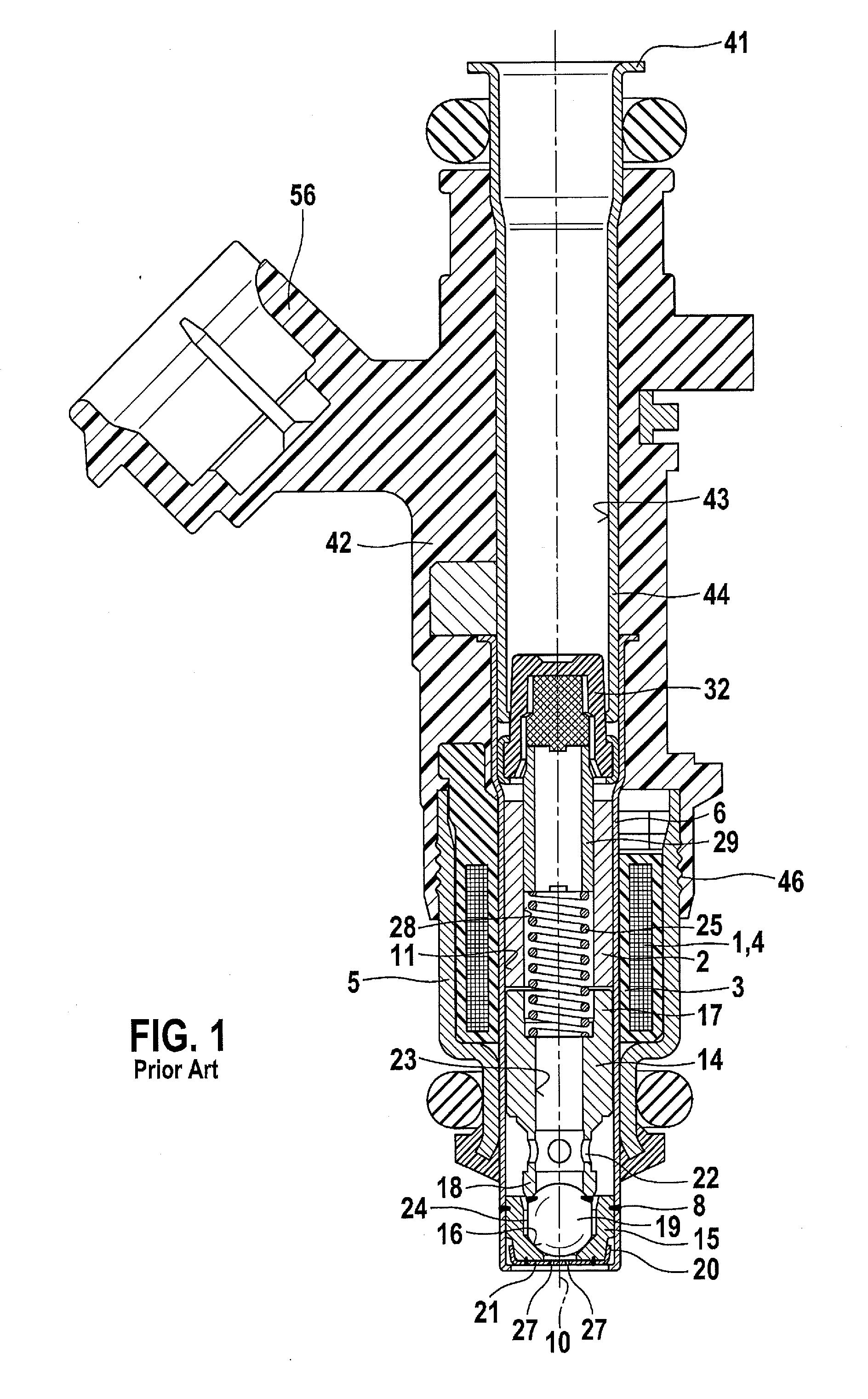
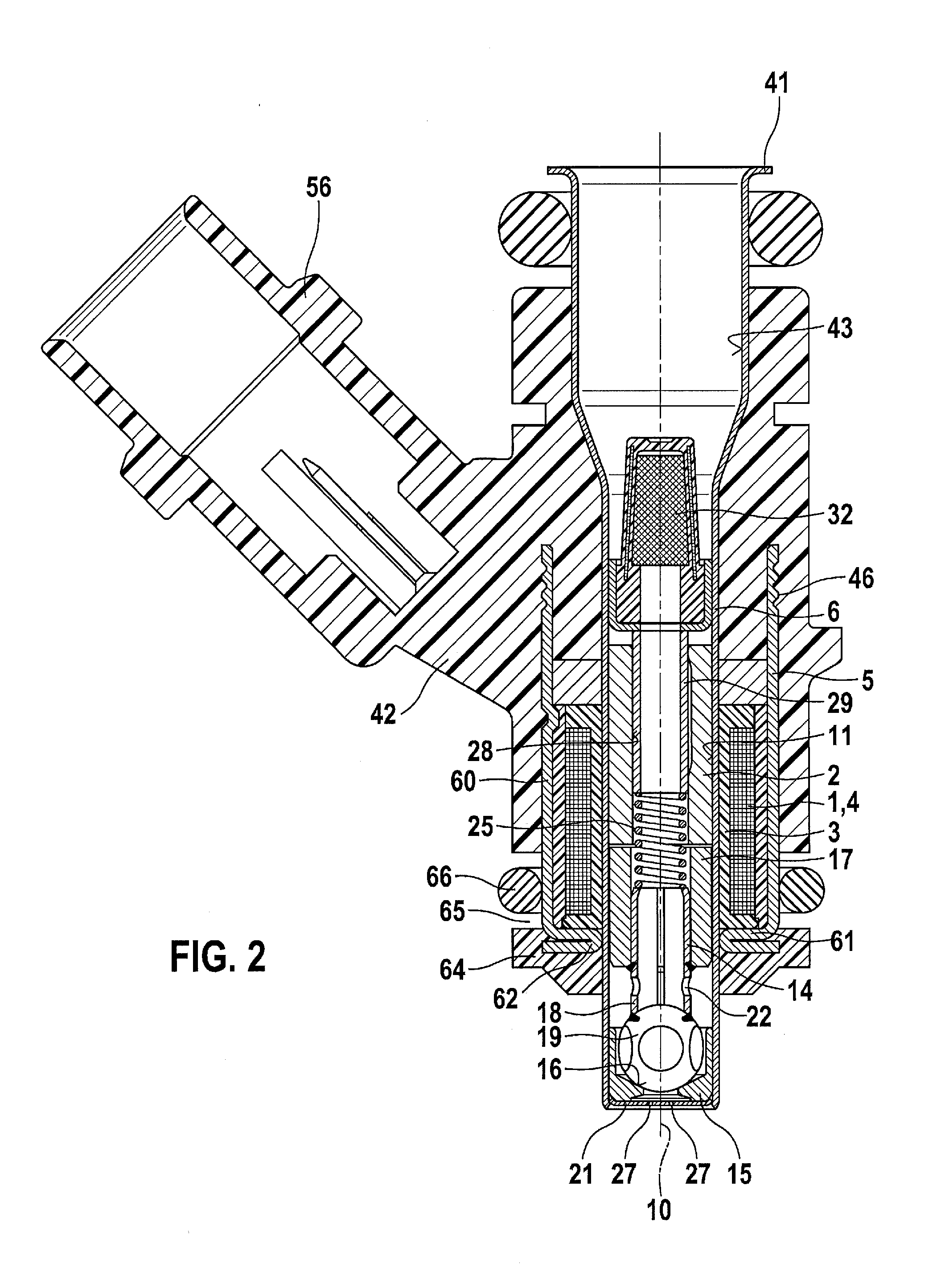
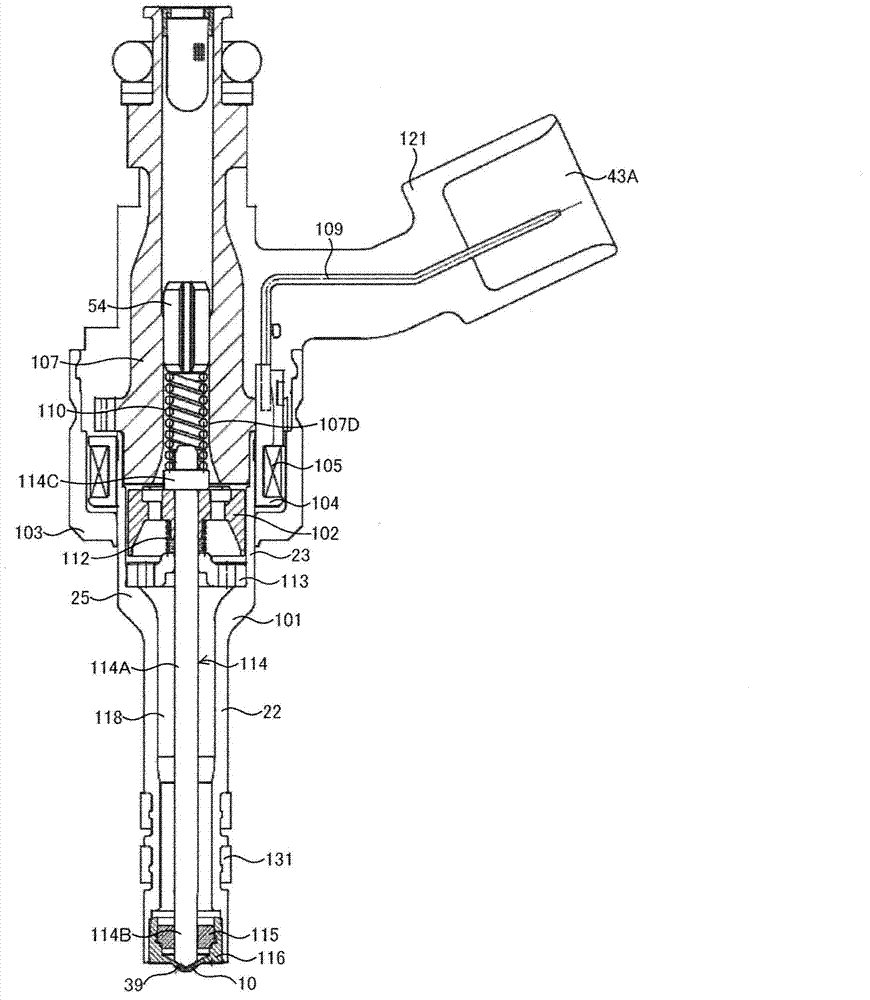
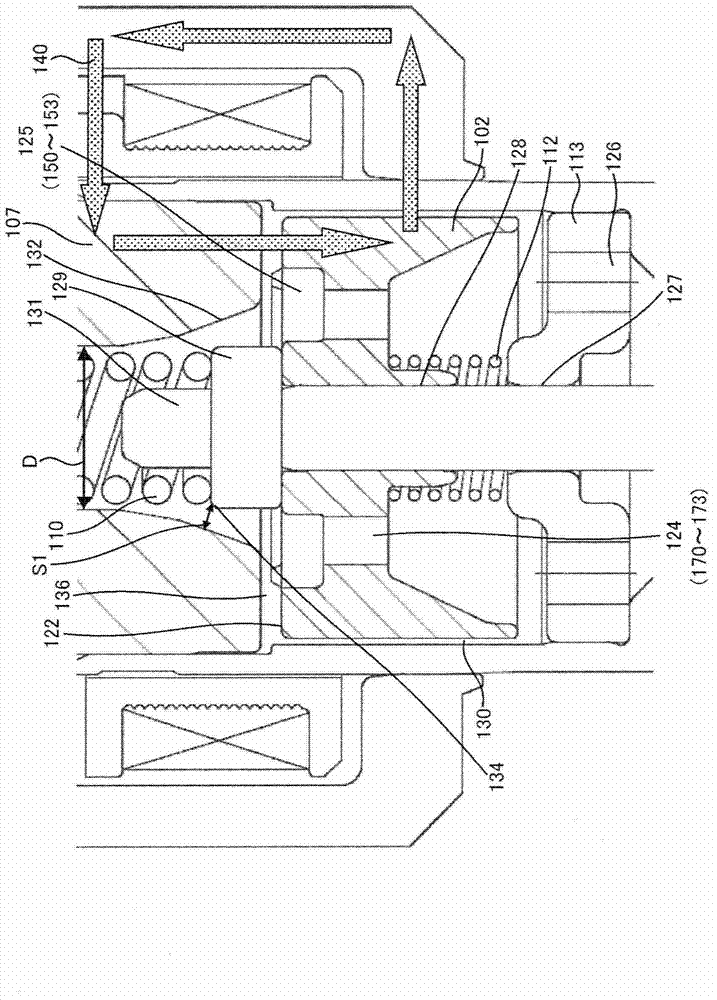
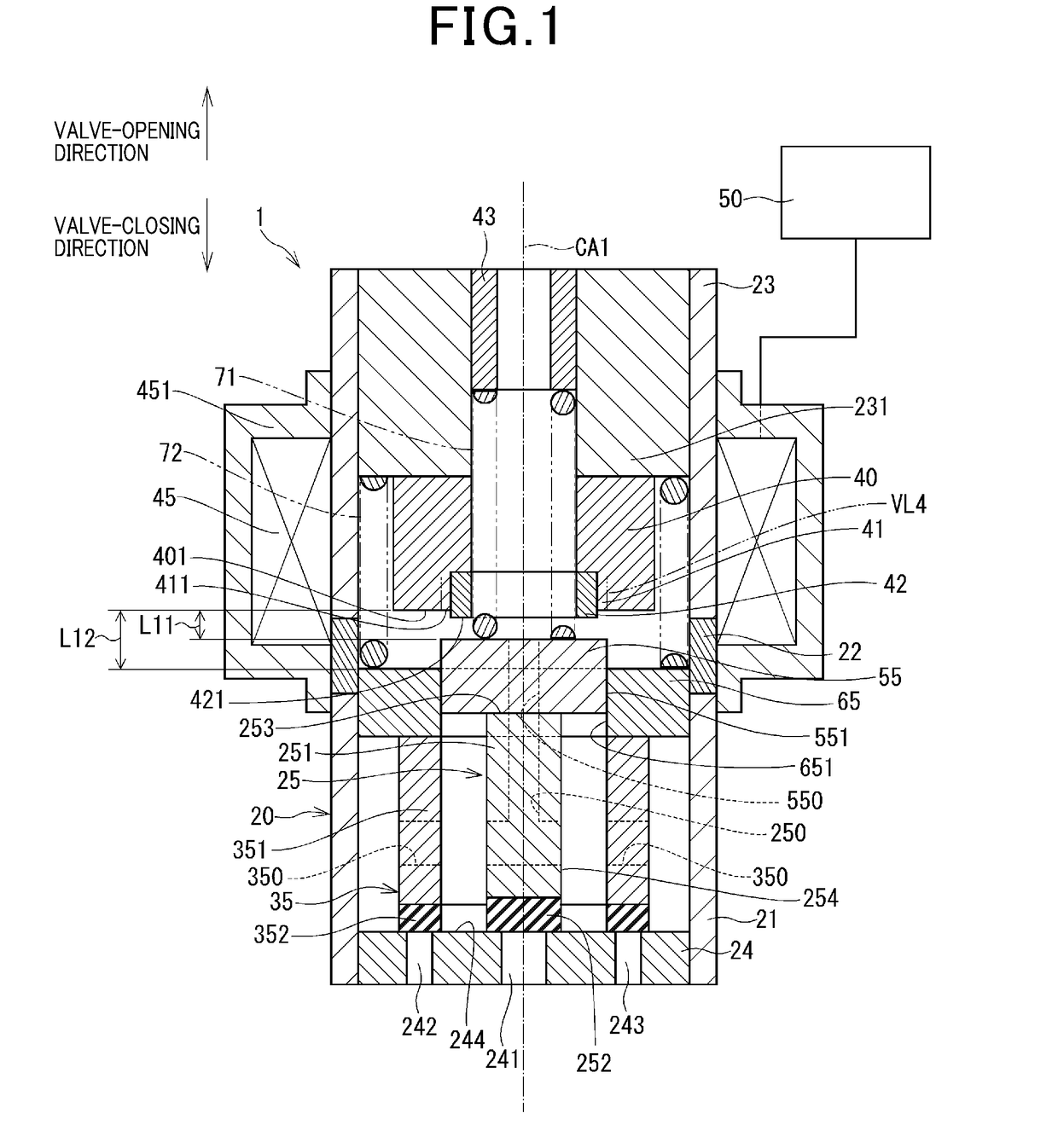
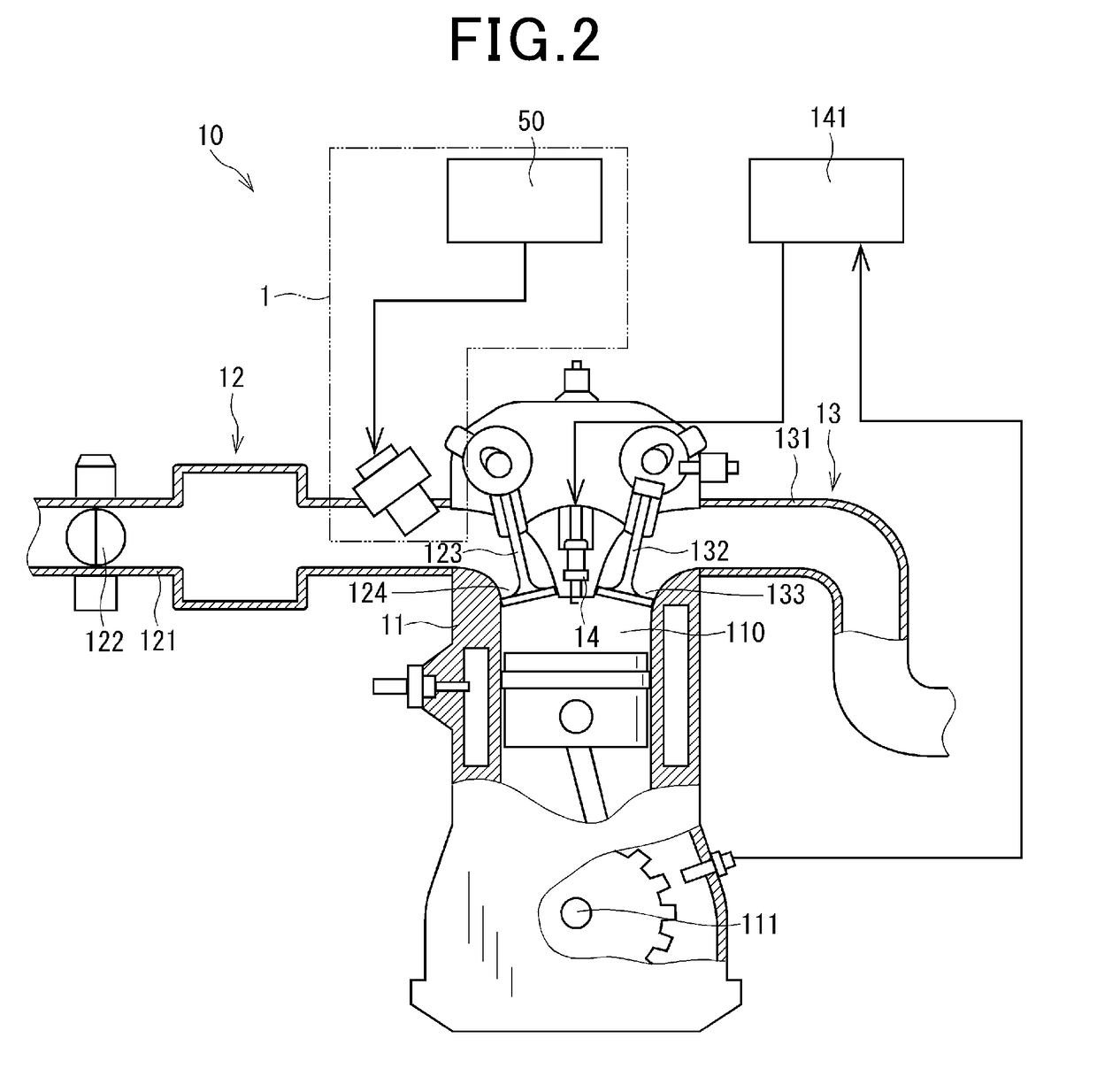
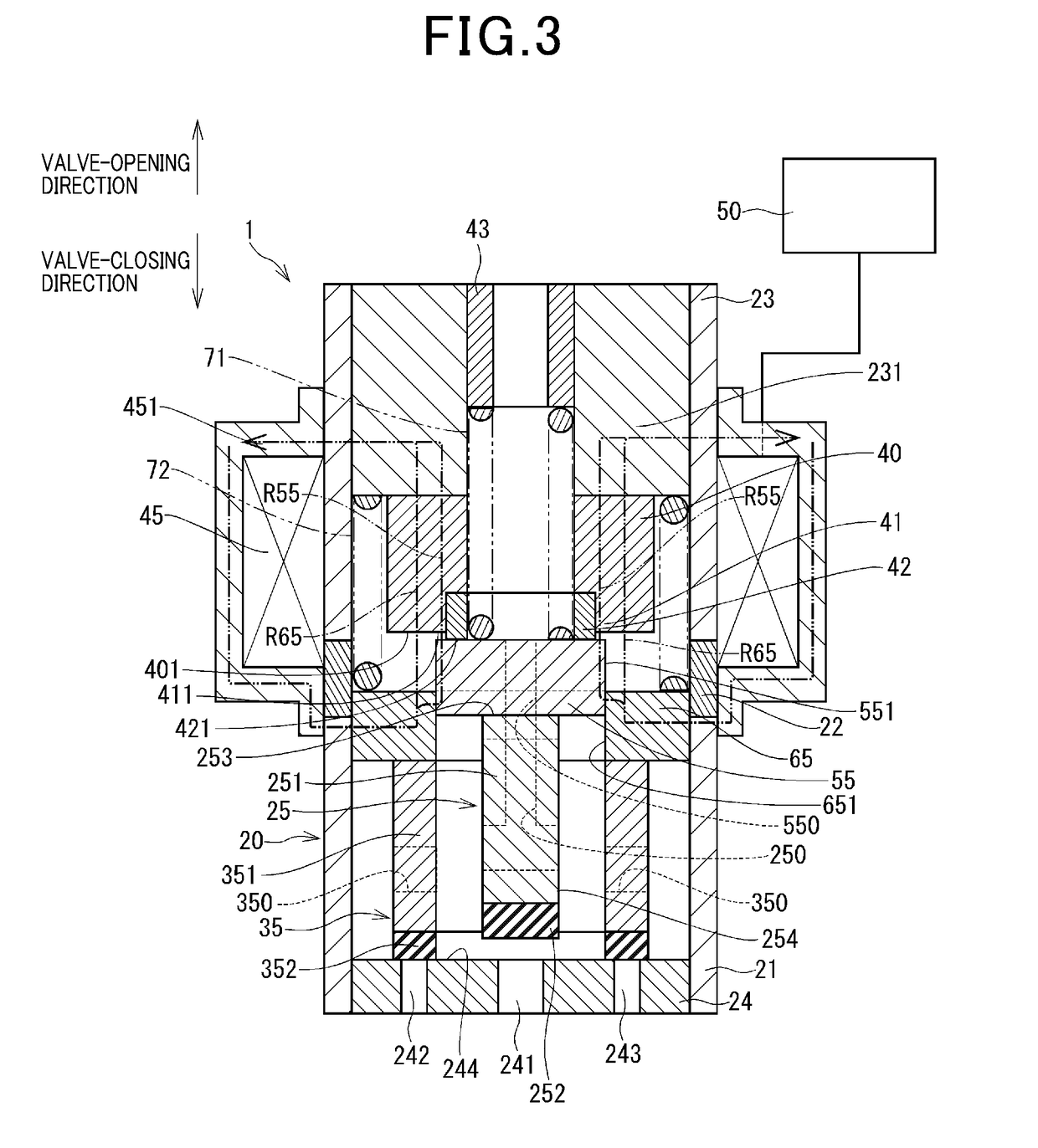
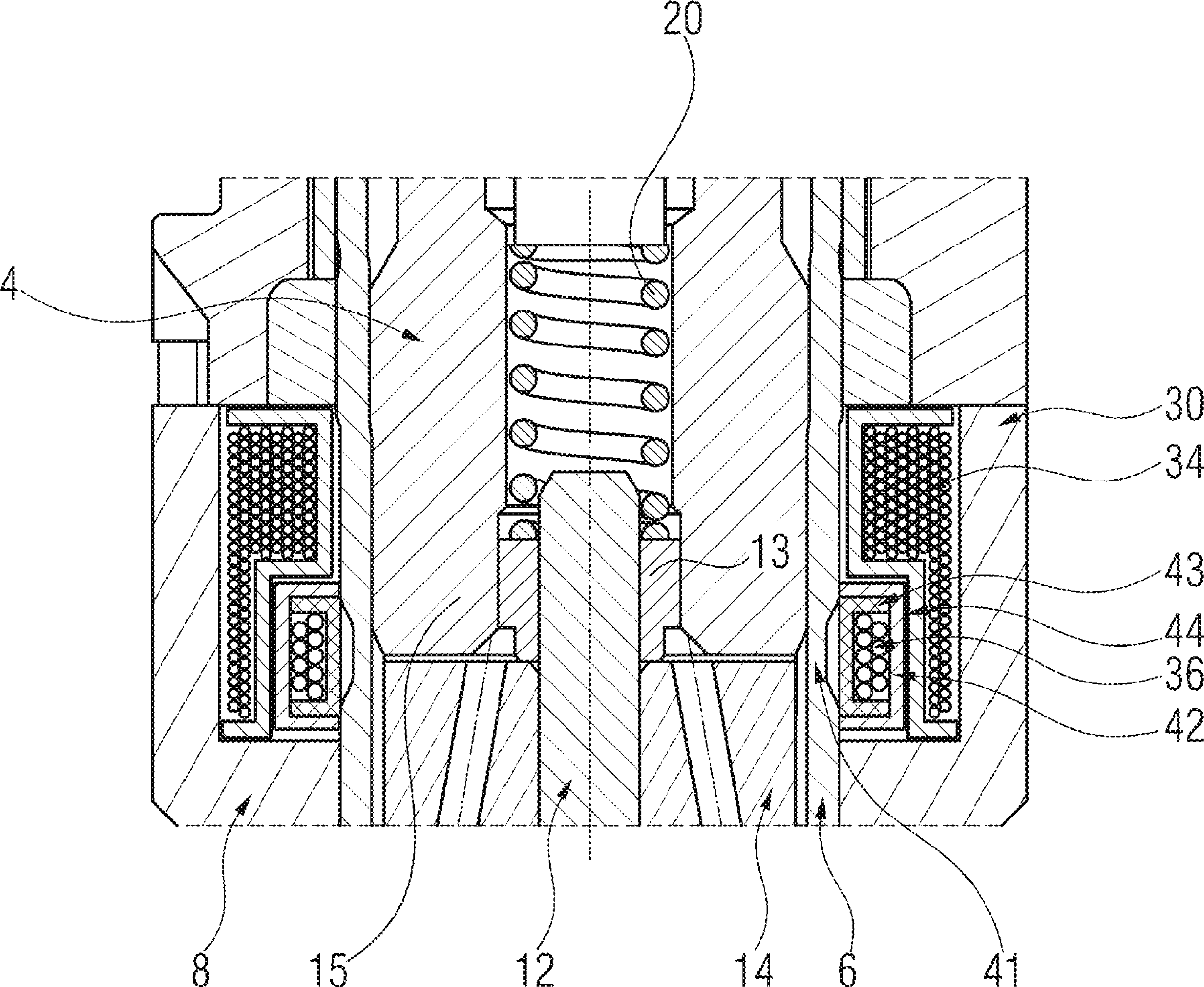
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73results about "Magnetic flux influencing fuel injection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
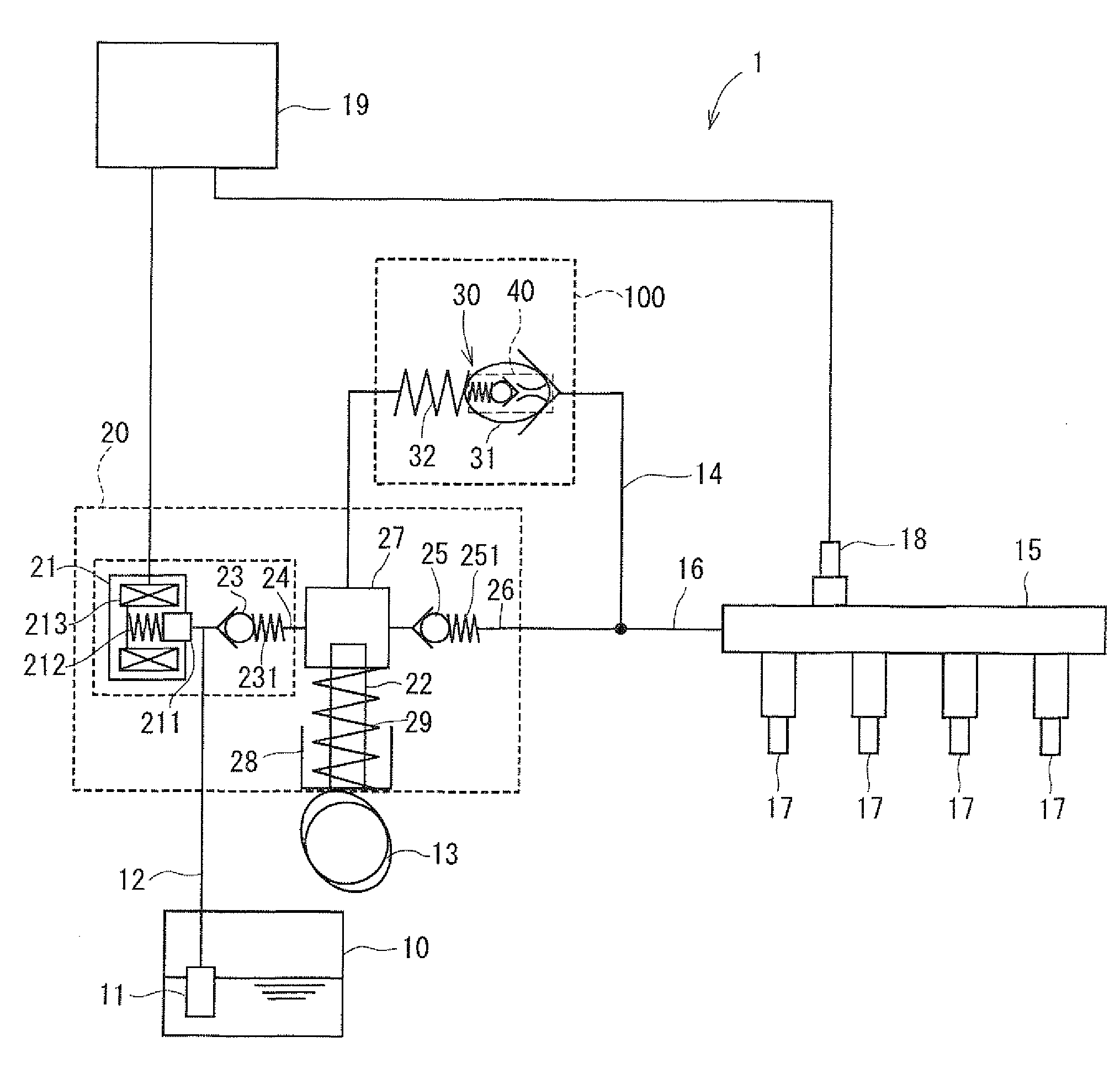
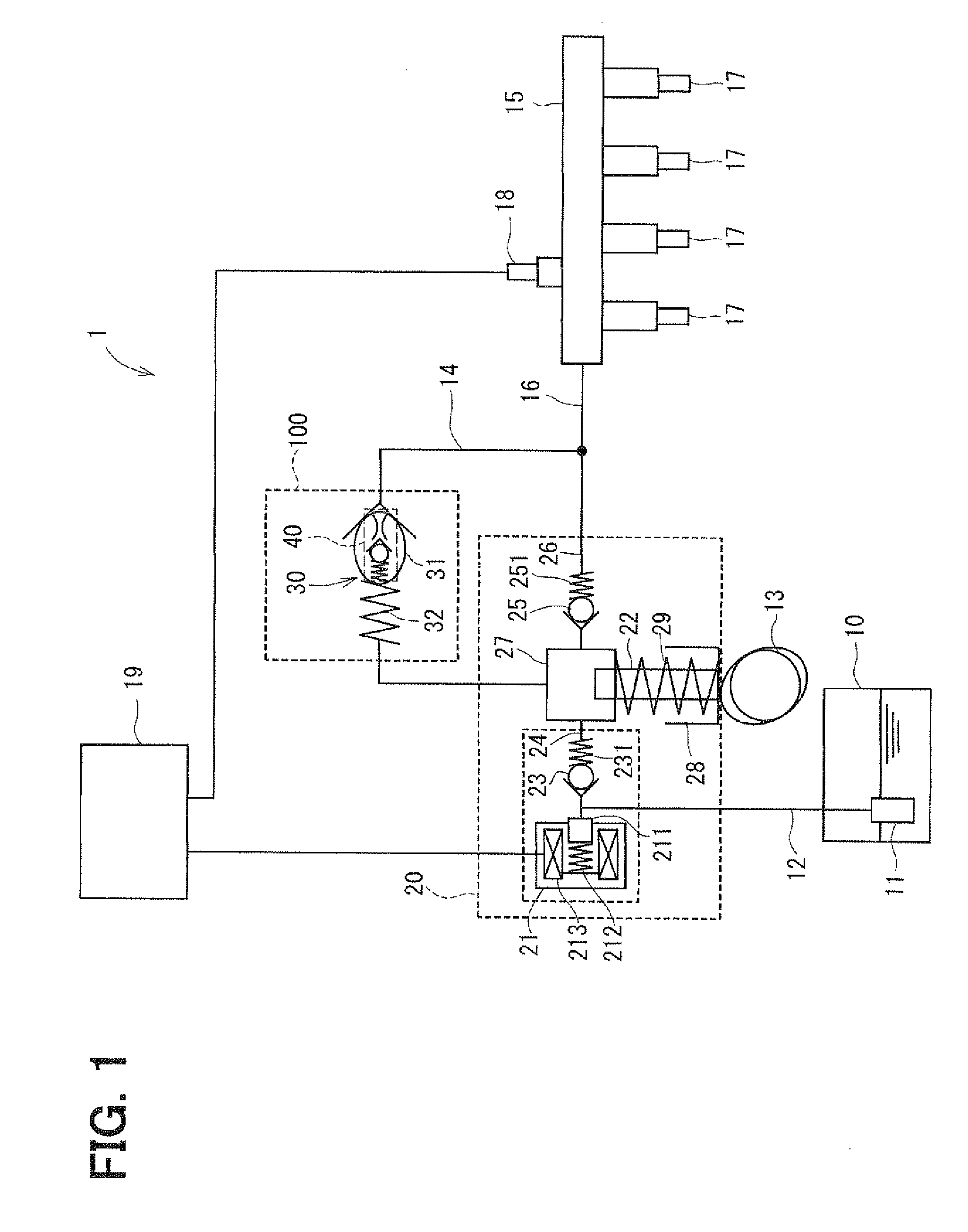
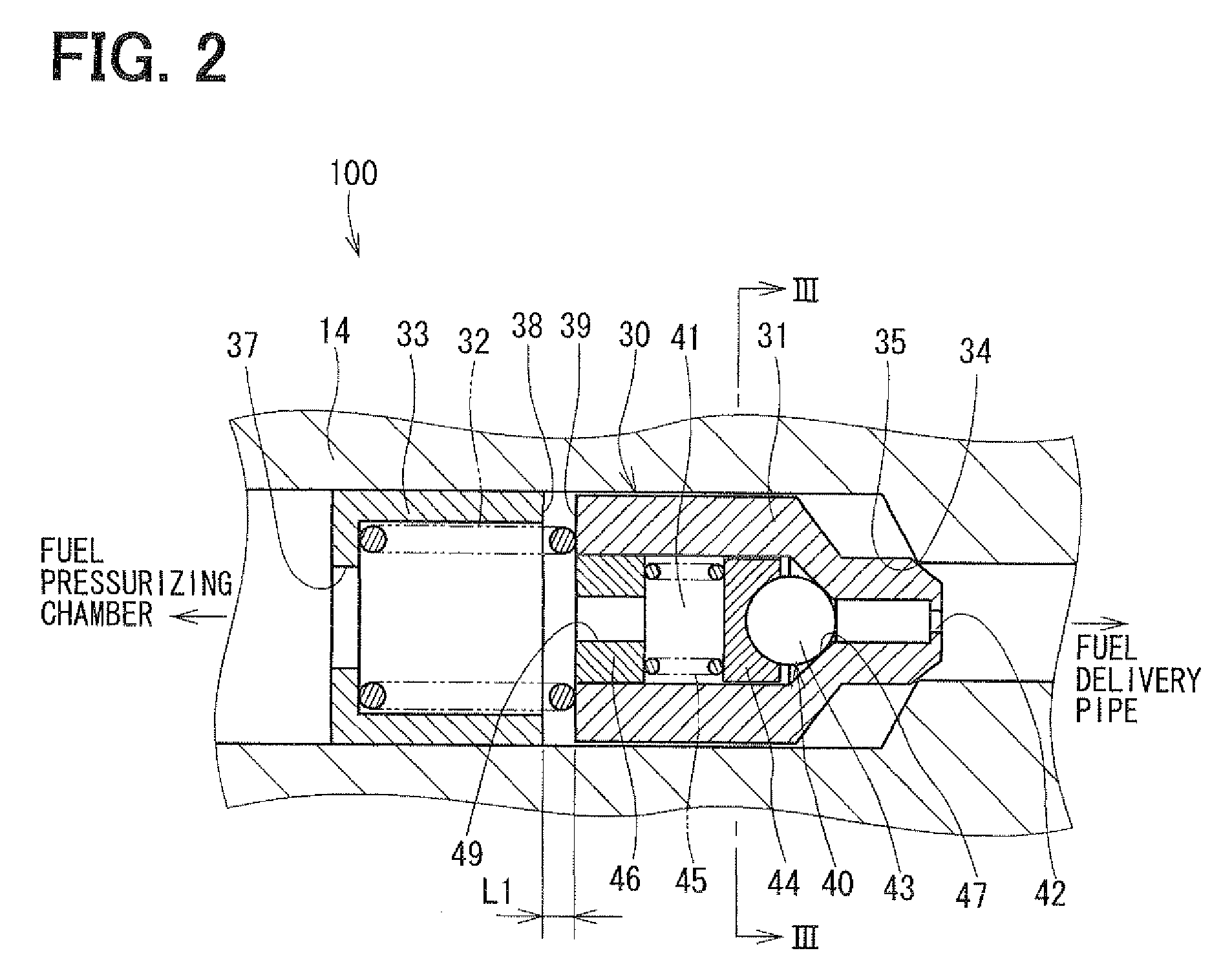
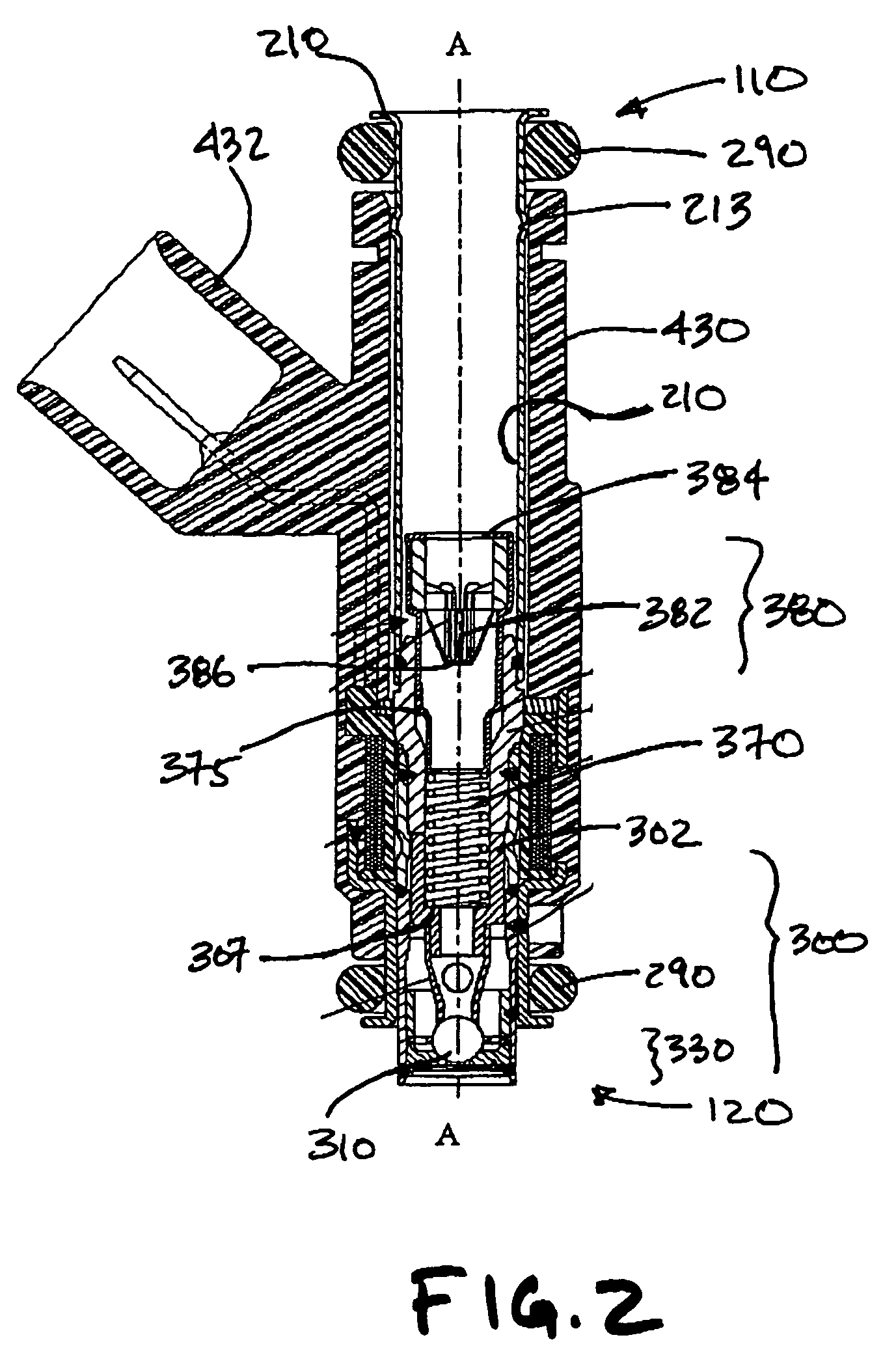
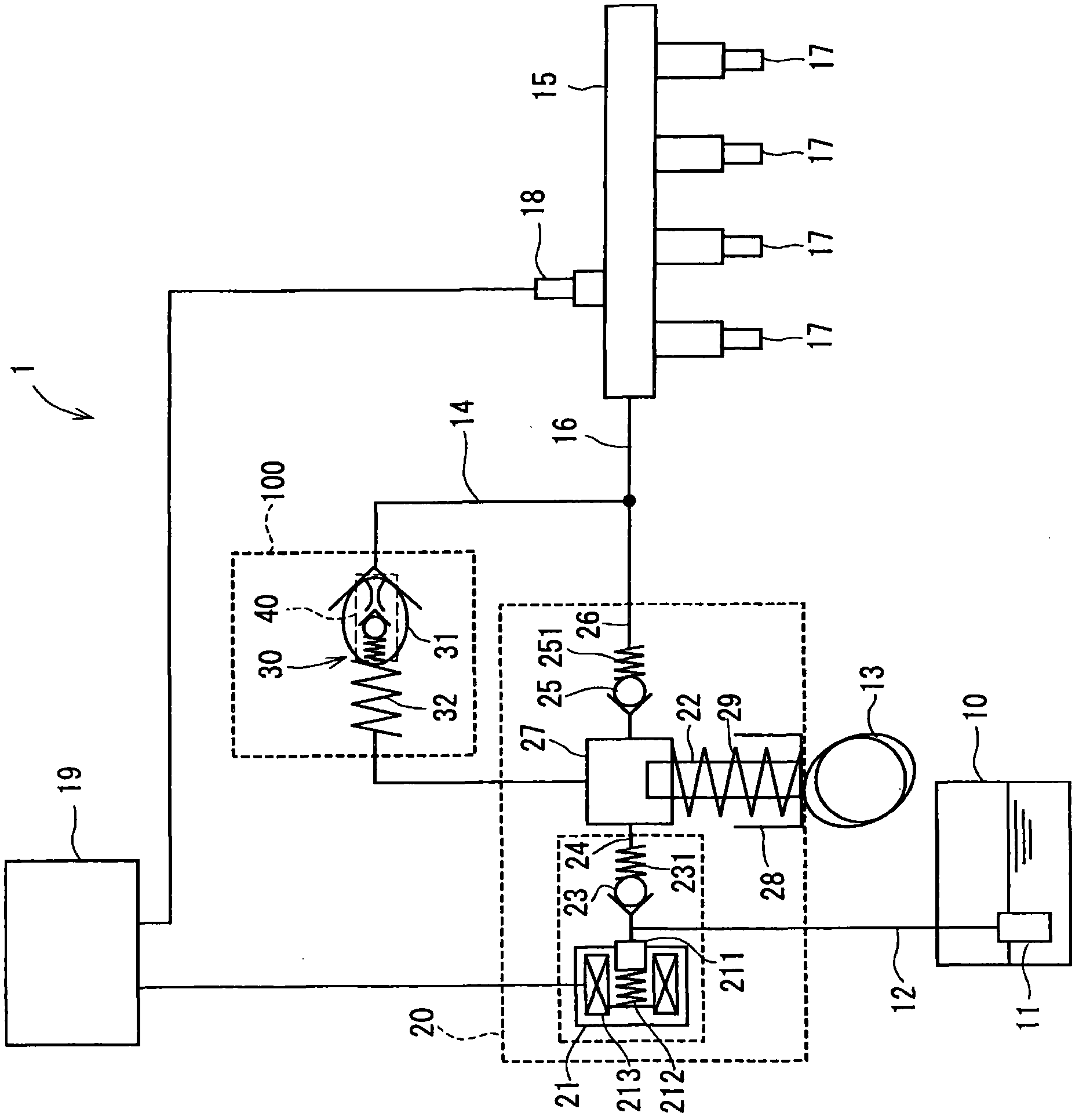
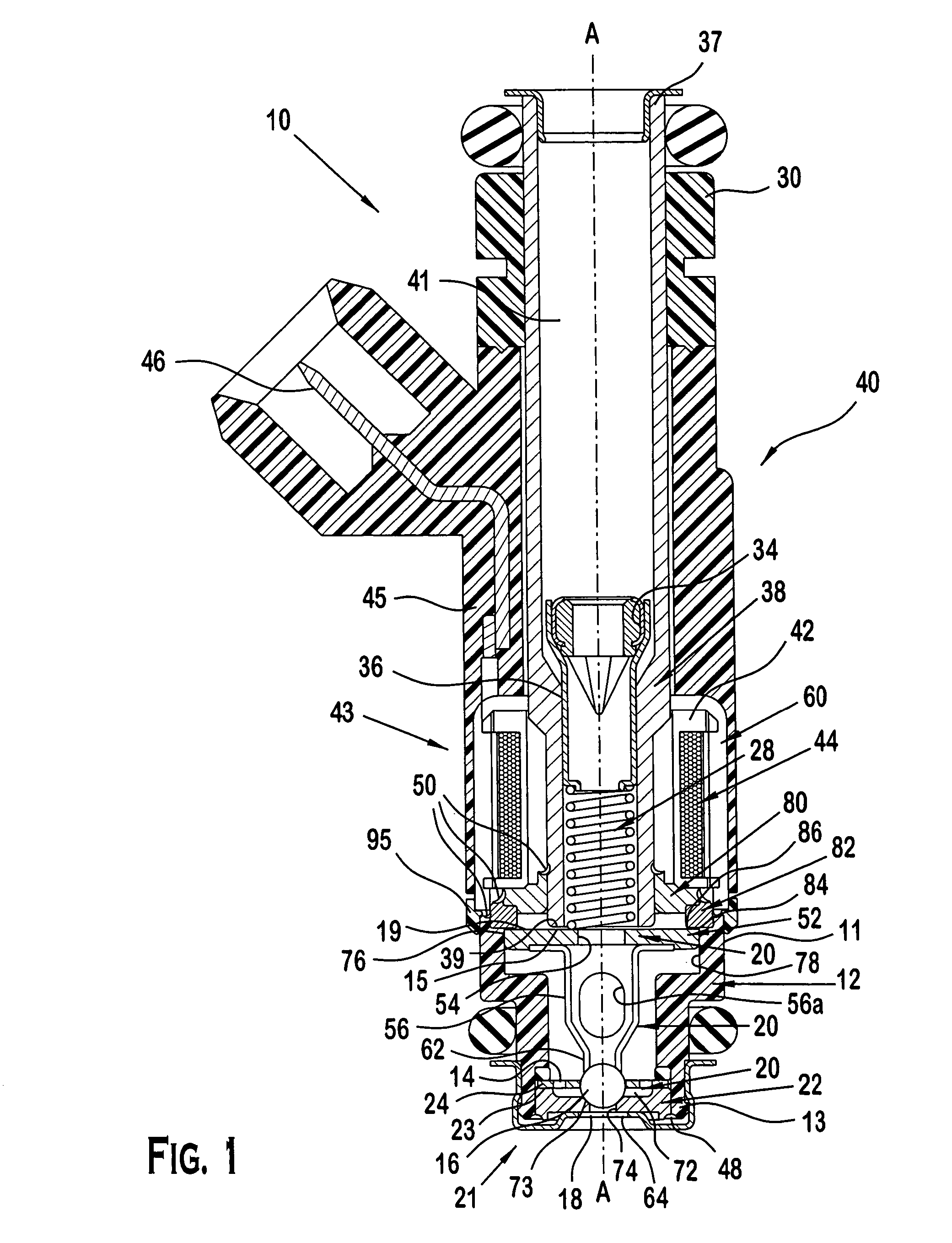
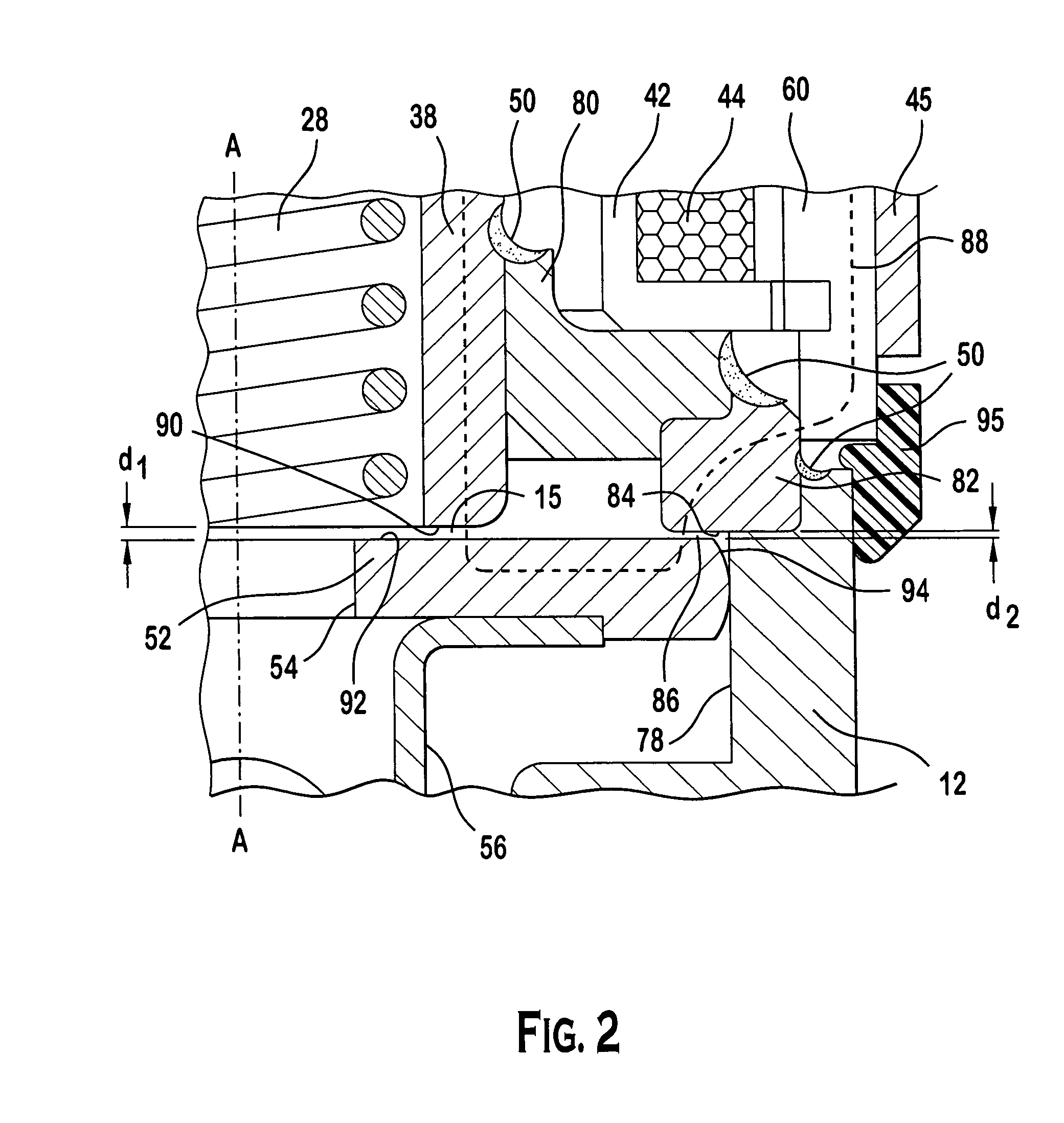
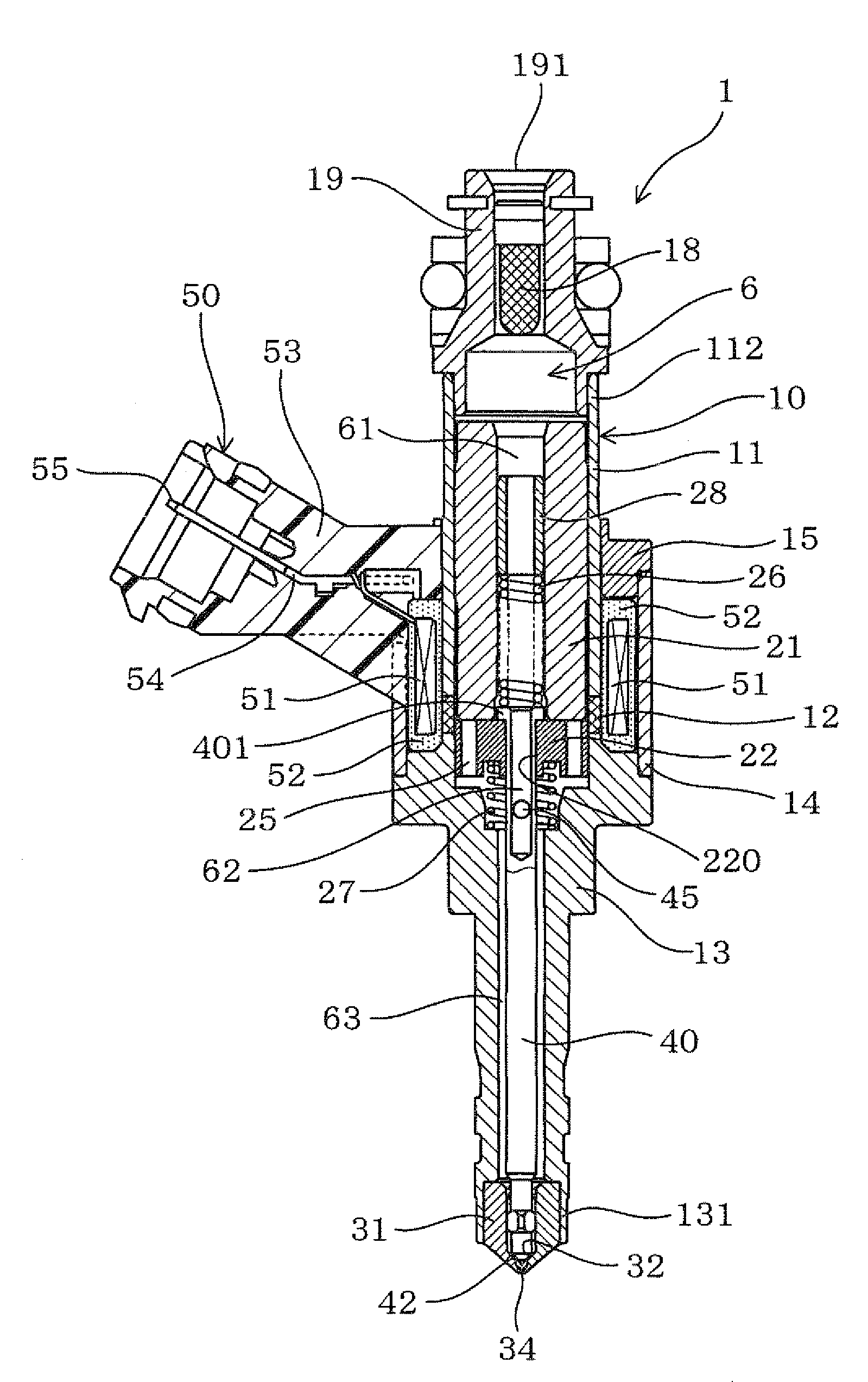
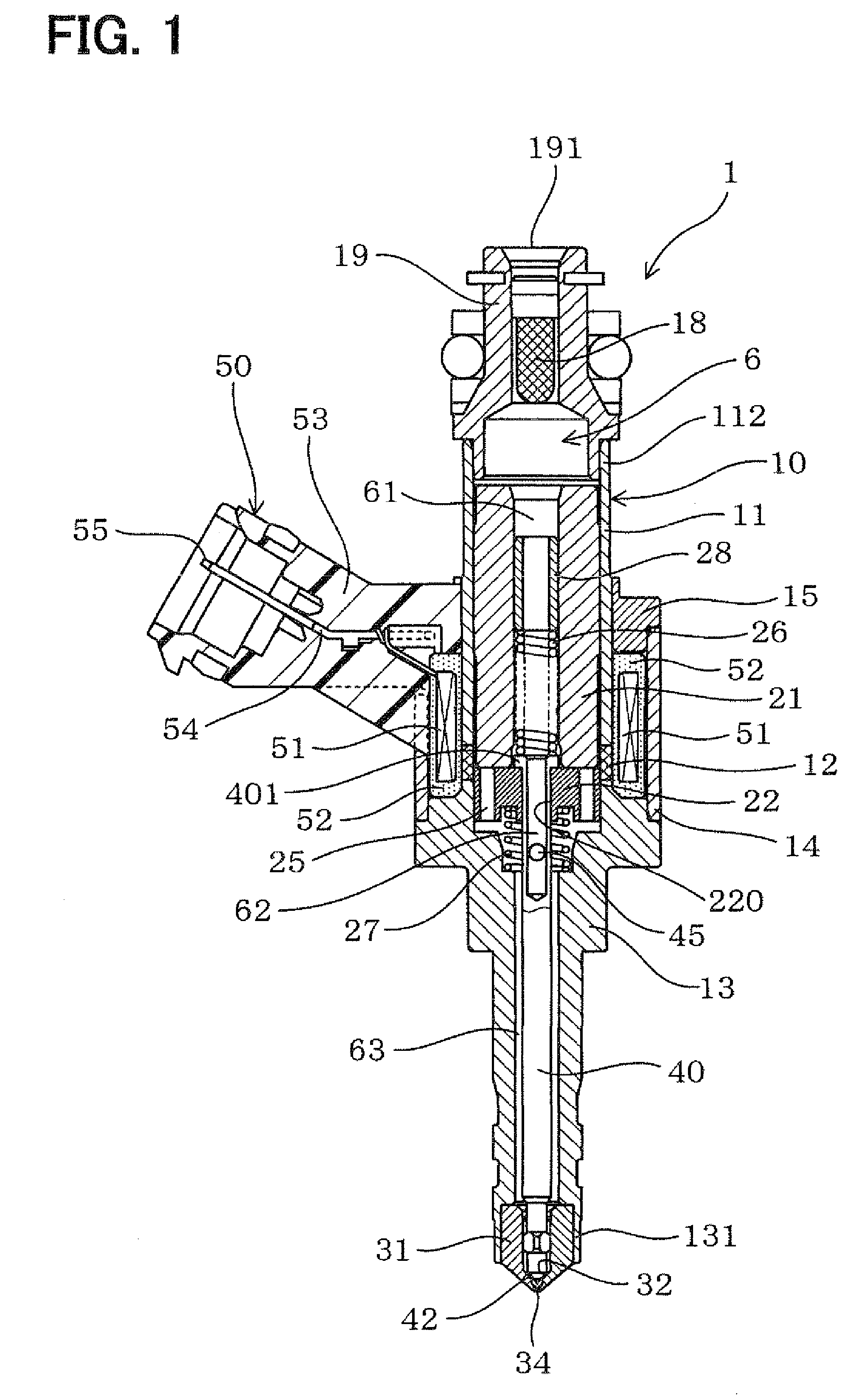
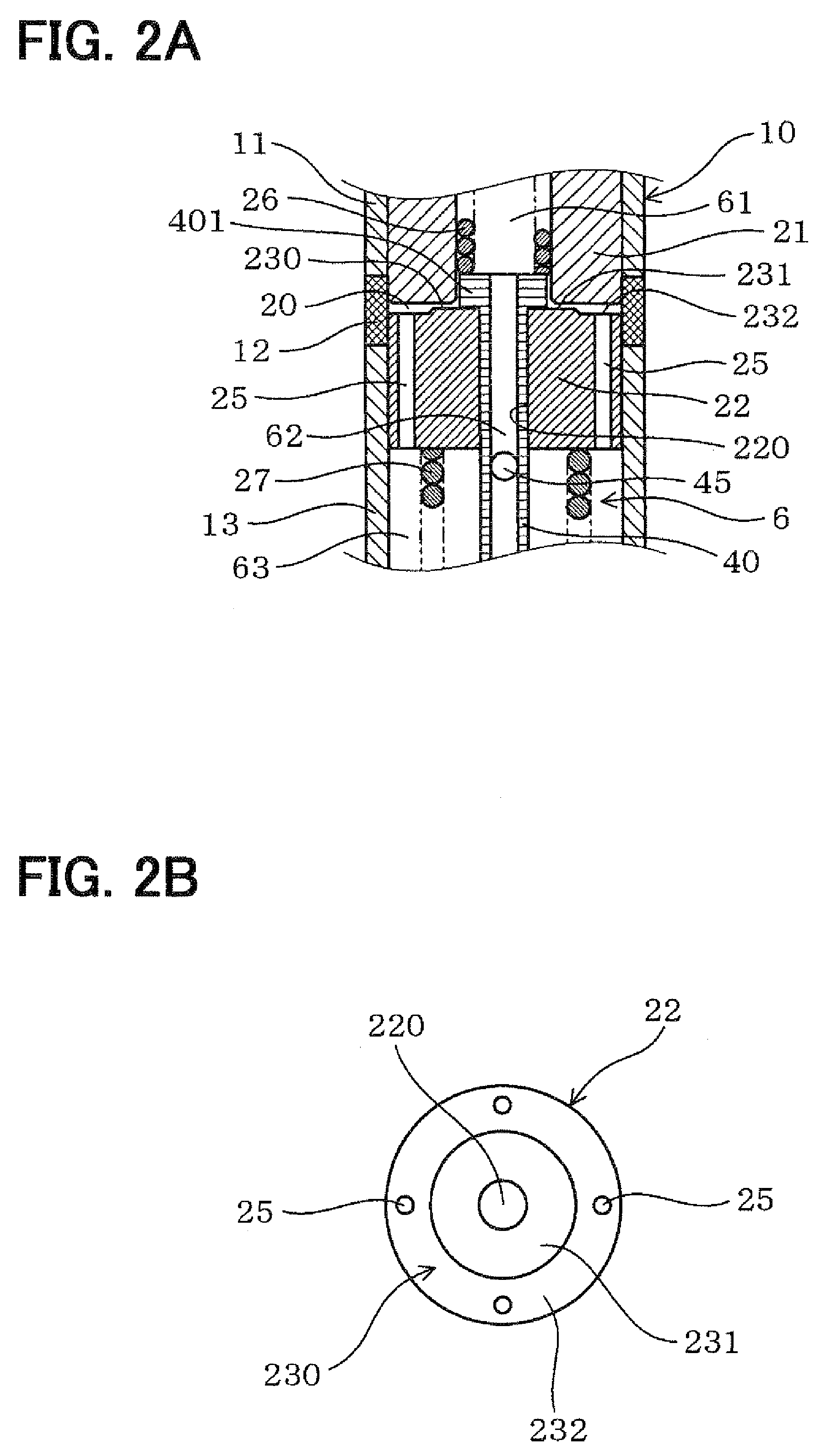
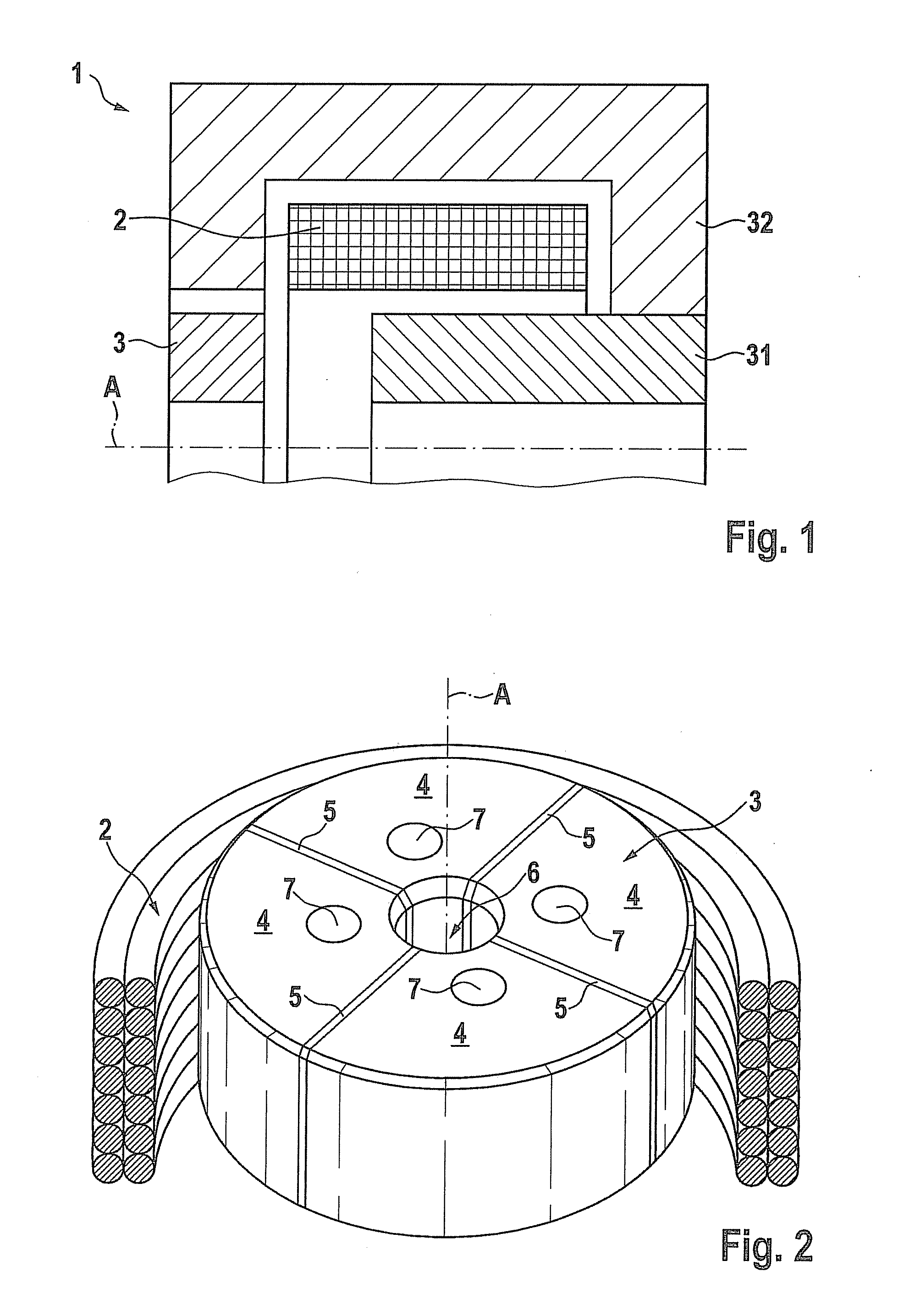
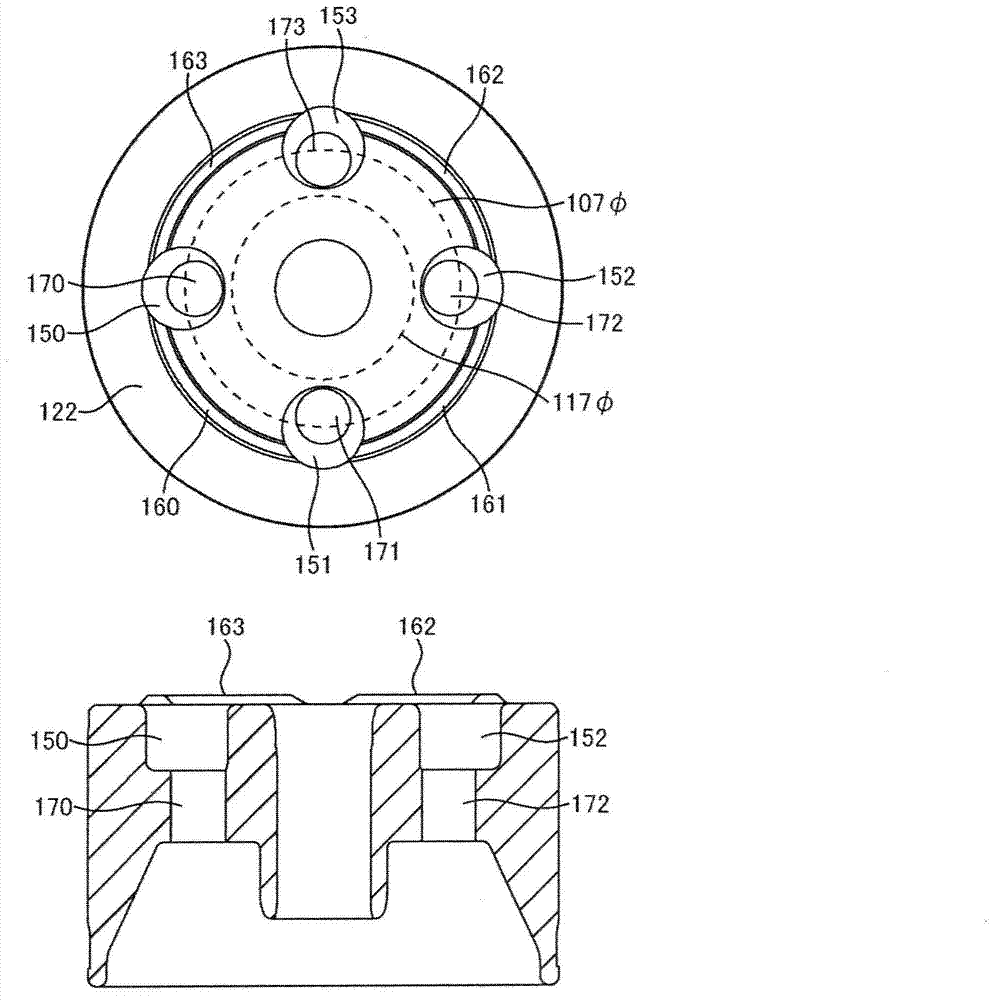
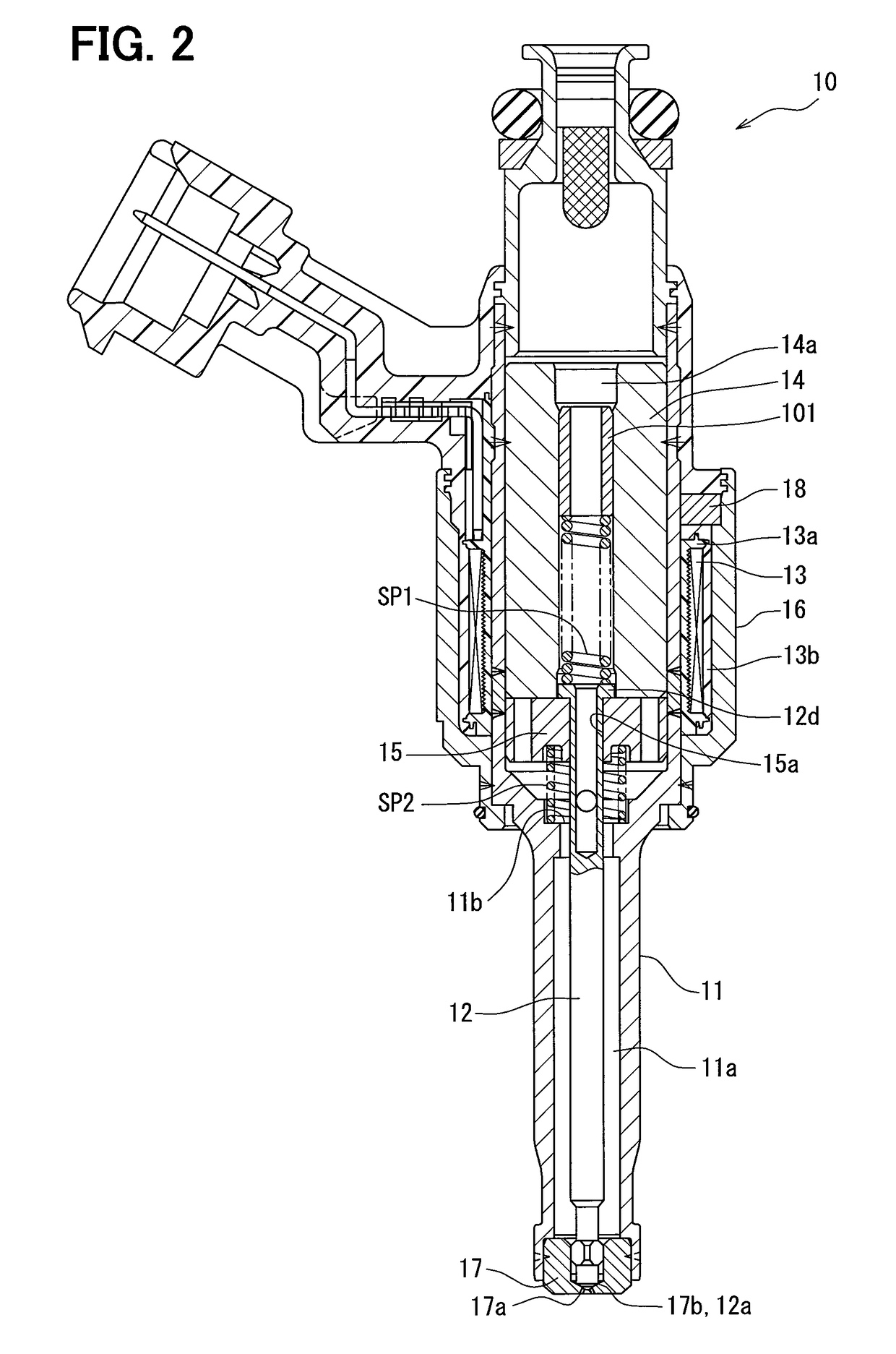
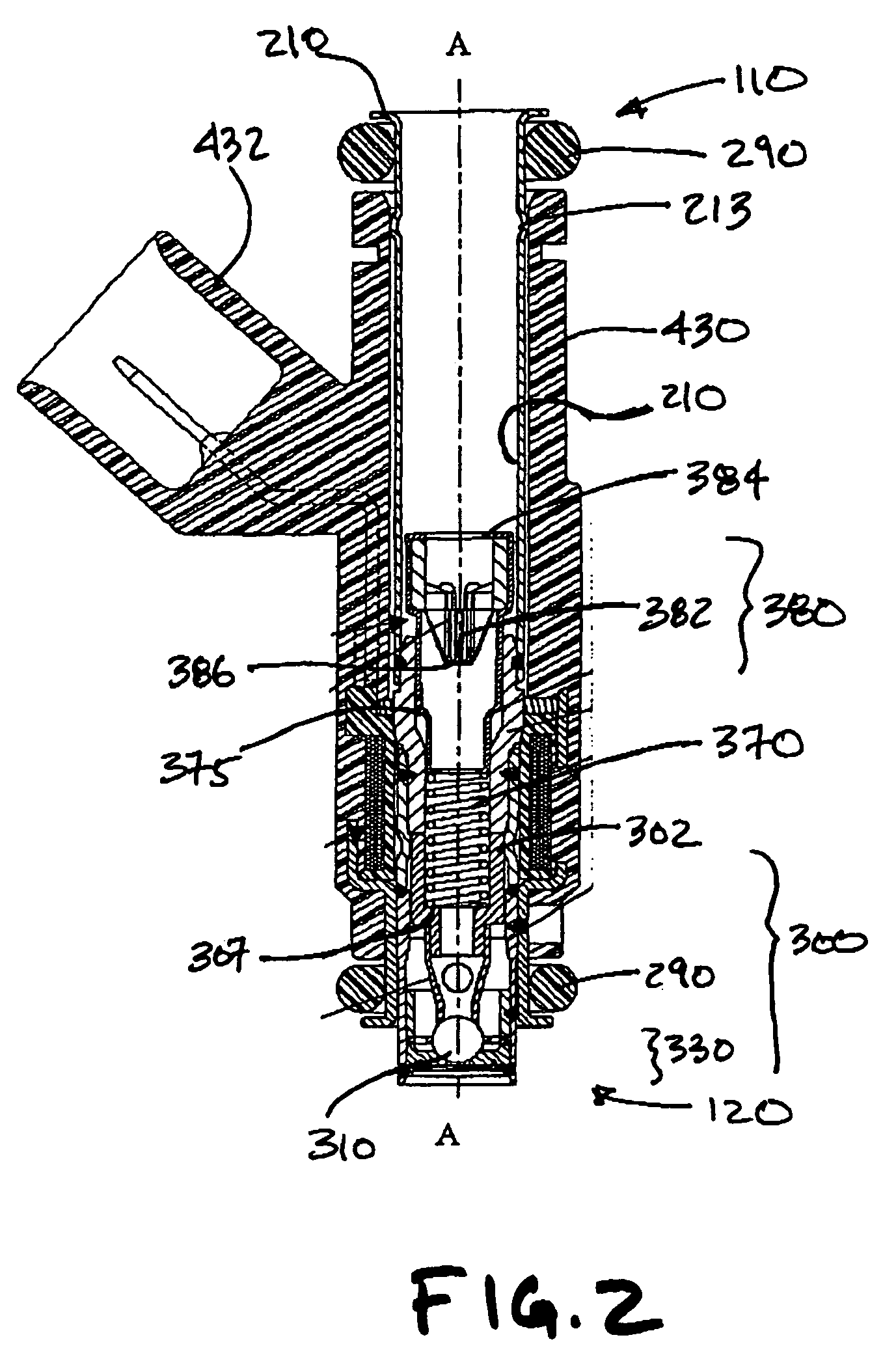
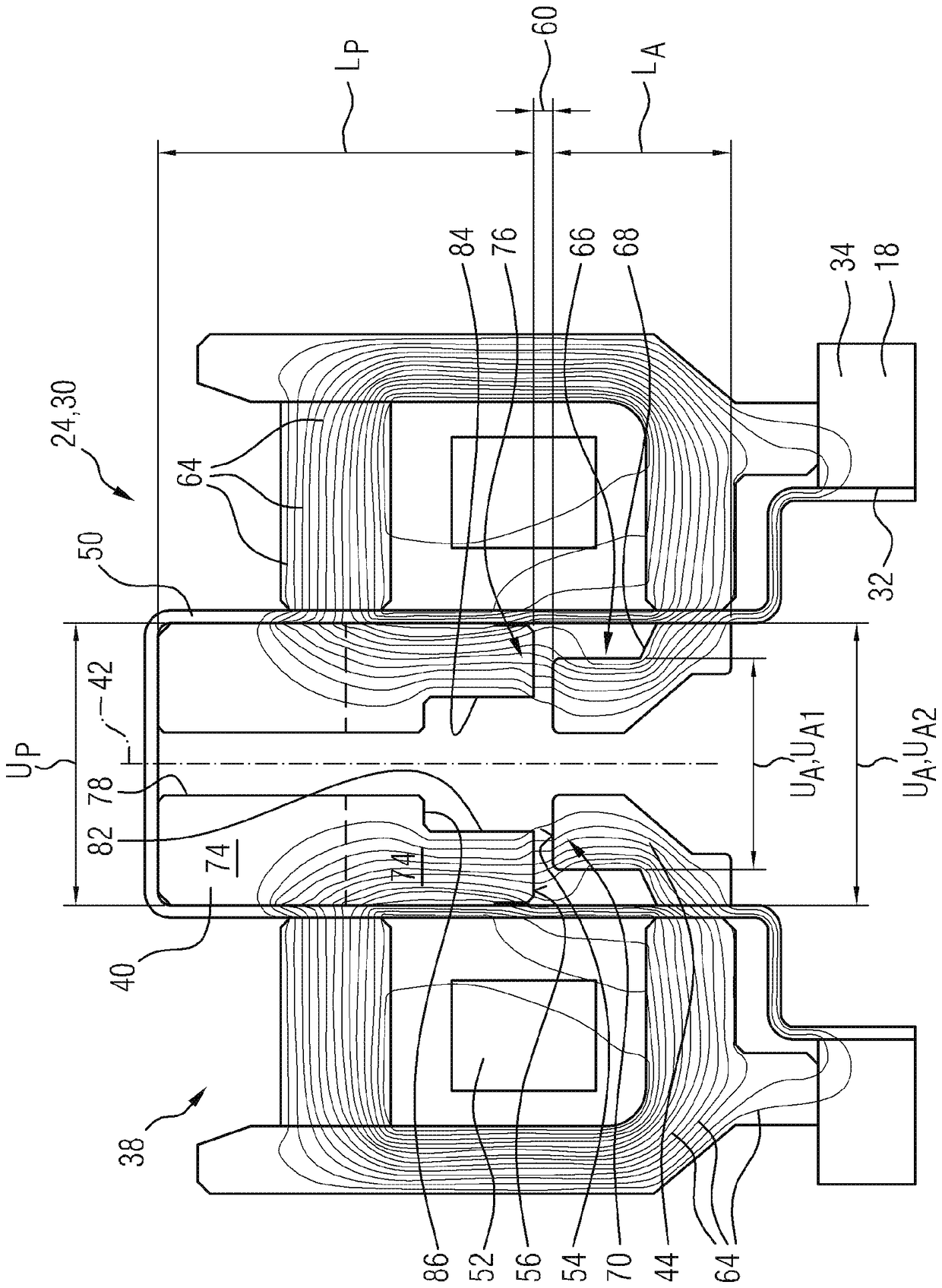
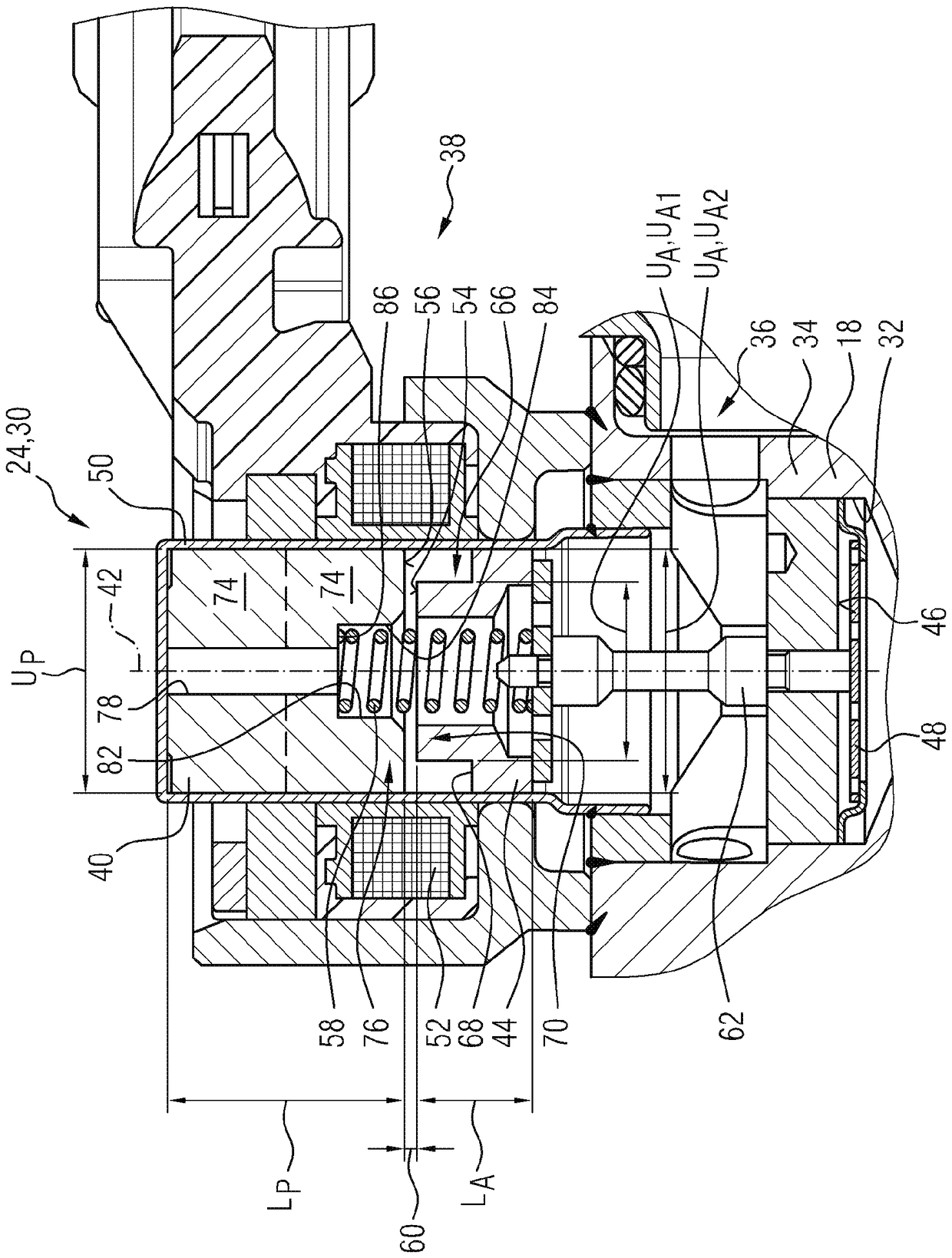
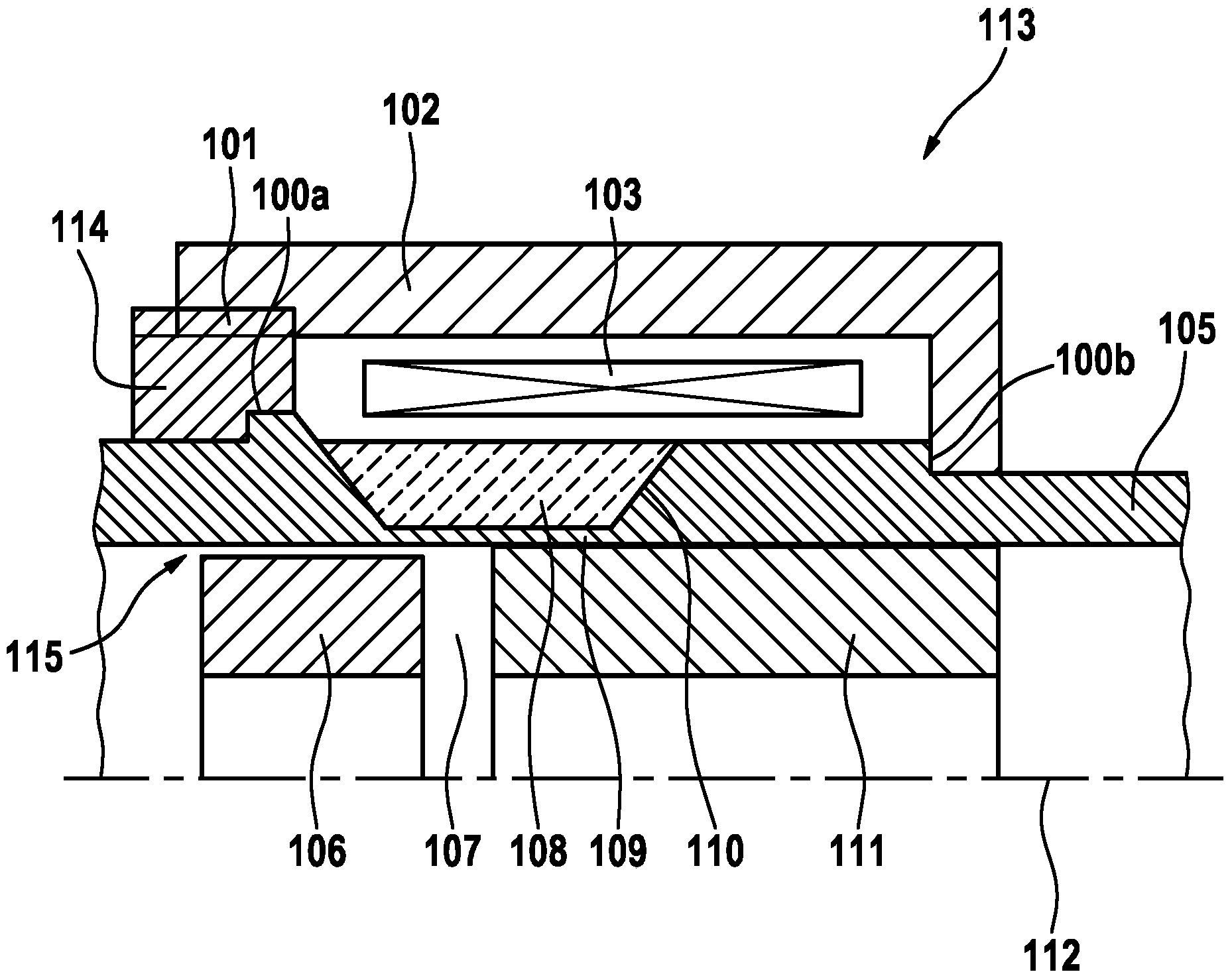
Fuel supply system having pressure control valve
InactiveUS20110125387A1Rapidly increase fuel pressureReduce fuel pressureElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsEngineeringHigh pressure
A pressure control valve is provided in a fuel return pipe connected between a high pressure fuel pipe and a fuel pressurizing chamber of a high pressure pump. A pressure relief valve is opened when fuel pressure in a fuel delivery pipe is higher than a first pressure. A first valve body of the pressure relief valve is brought into contact with a stopper so that a movement of the first valve body is limited. A pressure holding valve, which is provided in an inside of the first valve body, is opened when the fuel pressure in the fuel delivery pipe is larger than a second pressure. When the pressure relief valve is opened and the first valve body crashes into the stopper, a lifting amount of a second valve body of the pressure holding valve is increased by inertia of the second valve body, so that extraneous material attached to the second valve body can be removed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Common rail electronic control jet apparatus
ActiveCN101539084AReduce control linksImprove energy utilizationWear reducing fuel injectionMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionCommon railEngineering
The invention relates to a common rail electronic control jet apparatus, belonging to technology of an electronic control fuel injection system. The controller comprises an oil inlet joint, an oil inlet, an electromagnet device, a nozzle body, a needle valve, a valve seat and a jet orifice; wherein, the electromagnet device includes a static iron core, a moving iron core and a coil, and a working clearance H exists between the static iron core and the moving iron core along the axial direction; the moving iron core is movably connected with the needle valve along the axial direction; the controller also comprises a compression spring acting on the needle valve, a force application mechanism acting on the moving iron core and a blocking mechanism used for providing axial anti-thrust when the moving iron core resets. The common rail electronic control jet apparatus has the advantages of low manufacturing cost, good reliability and low drive energy.
Owner:浙江朗杰电子有限公司
High-pressure fuel supply pump equipped with electromagnetically driven inlet valve
ActiveCN104066968AEliminate erratic behaviorStable valve closing timingInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusInlet valveInstability
In order to inhibit spring and valve instability due to the introduced pressure when pressure in a pressurization chamber is introduced into a spring accommodating space in which a spring, which energizes the valve in the closing direction and which is provided between a valve stopper and a valve, is inserted, the present invention is configured such that: a pressure equalization hole connecting a peripheral fluid passage and the spring accommodating space provided between the valve and the valve stopper is provided to the valve stopper located between the valve and the pressurization chamber; and the spring-accommodating-space-side opening of the pressure equalization hole opens to a position further inside than the diameter of the spring. As a result, pressure from the pressurization chamber can be introduced to the inside of the spring without traversing the spring, thereby resolving spring and valve instability due to the introduced pressure. Moreover, the force applied to the valve when closing the valve is stabilized, which makes it possible to stabilize valve closing timing.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
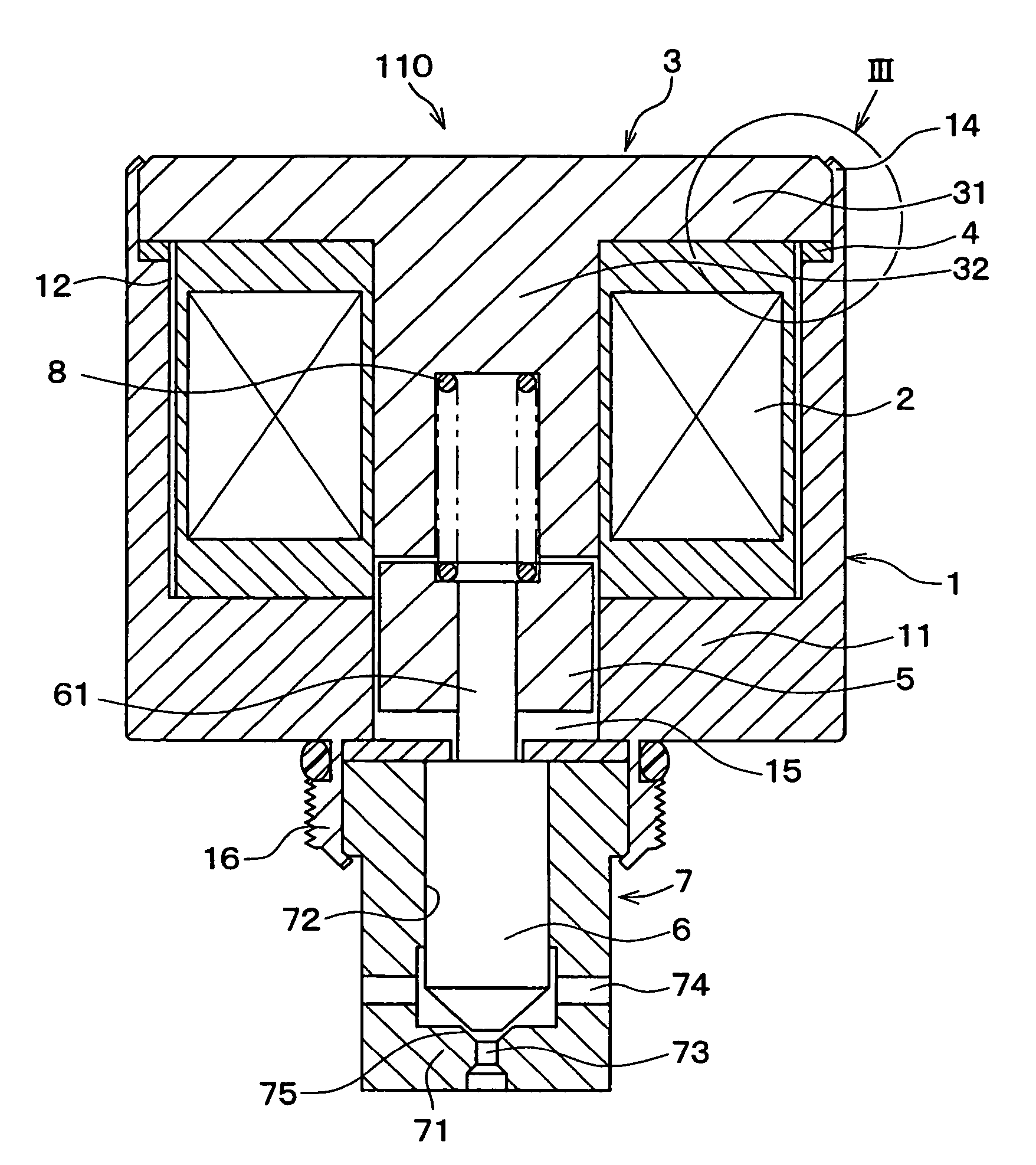
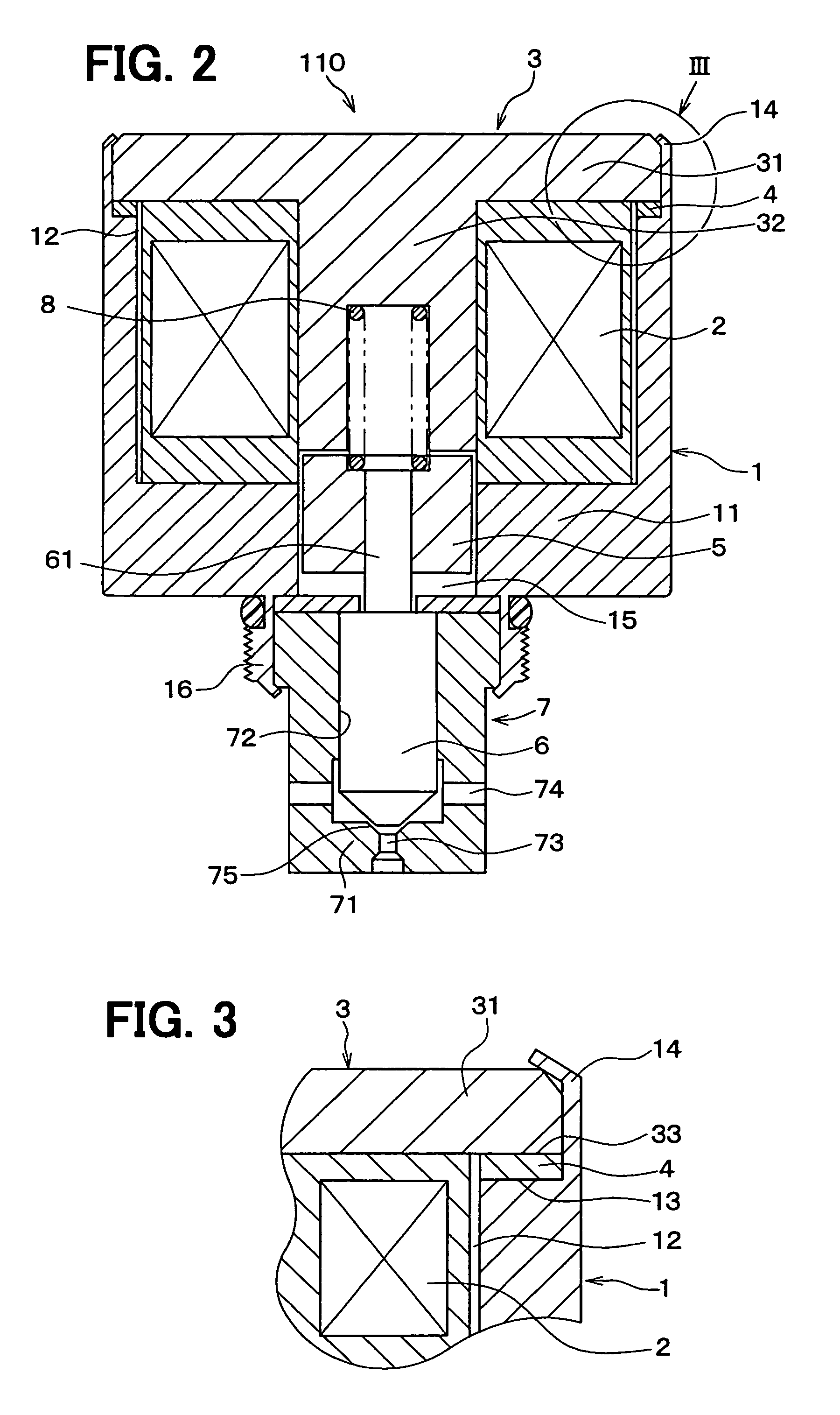
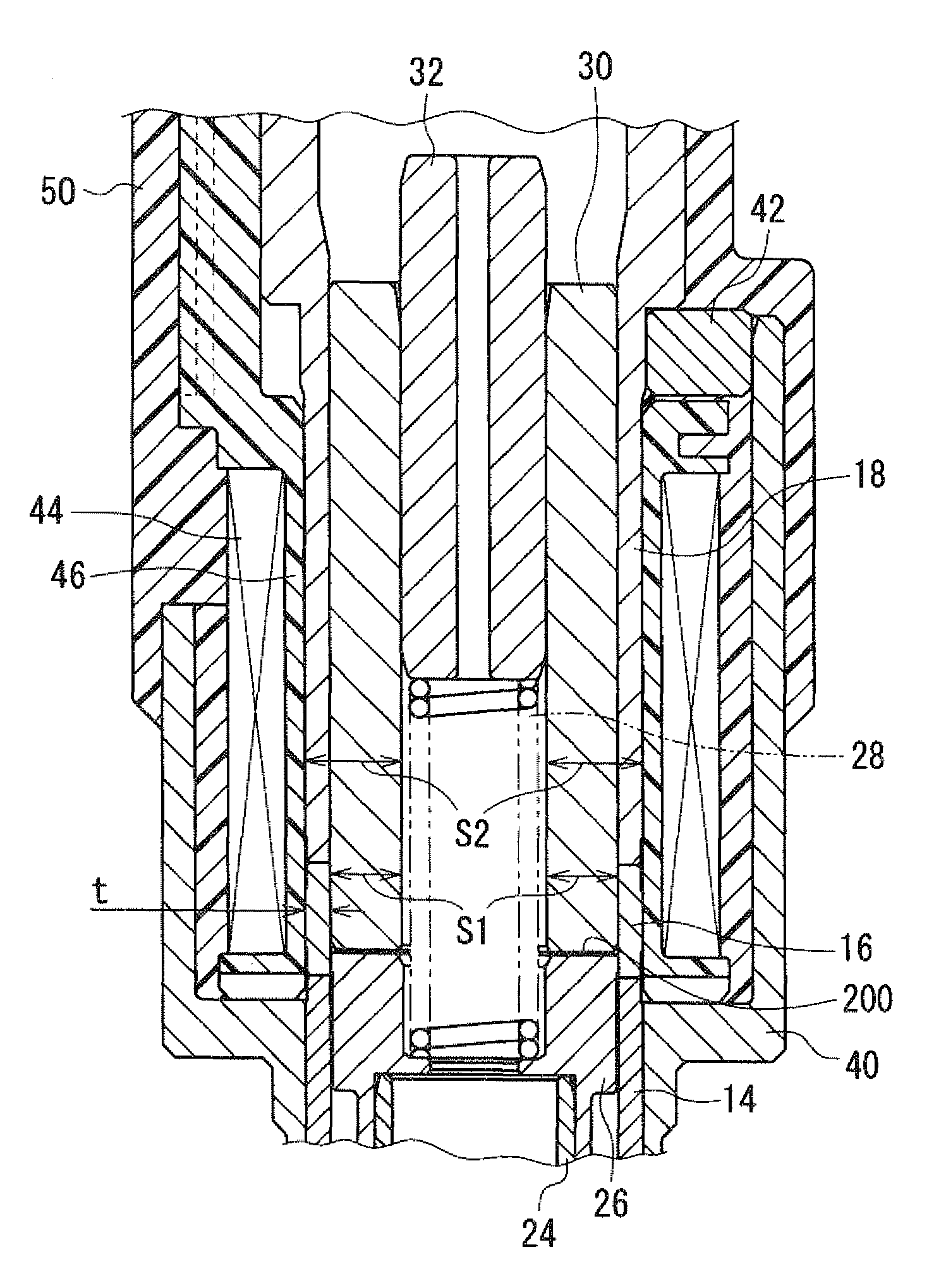
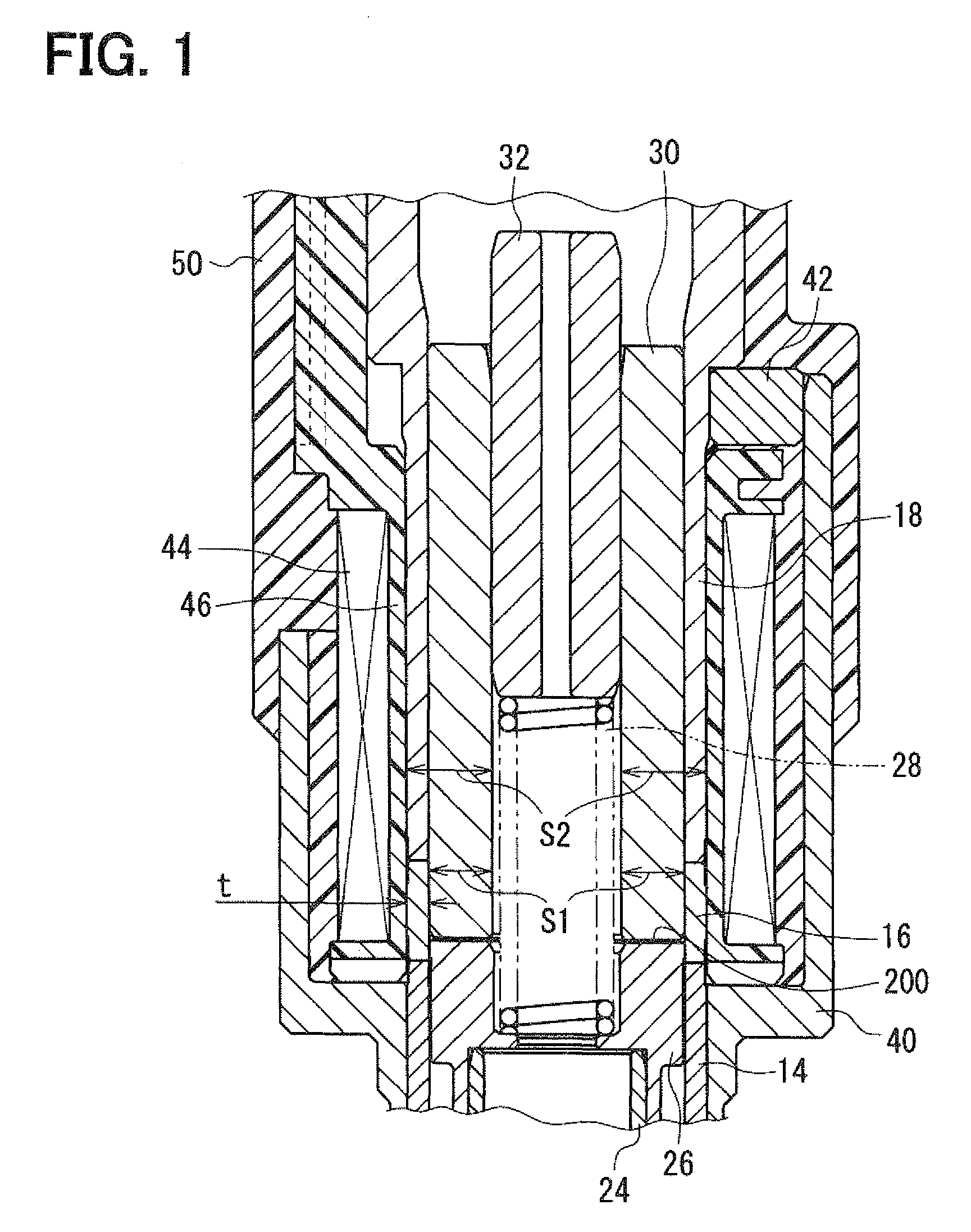
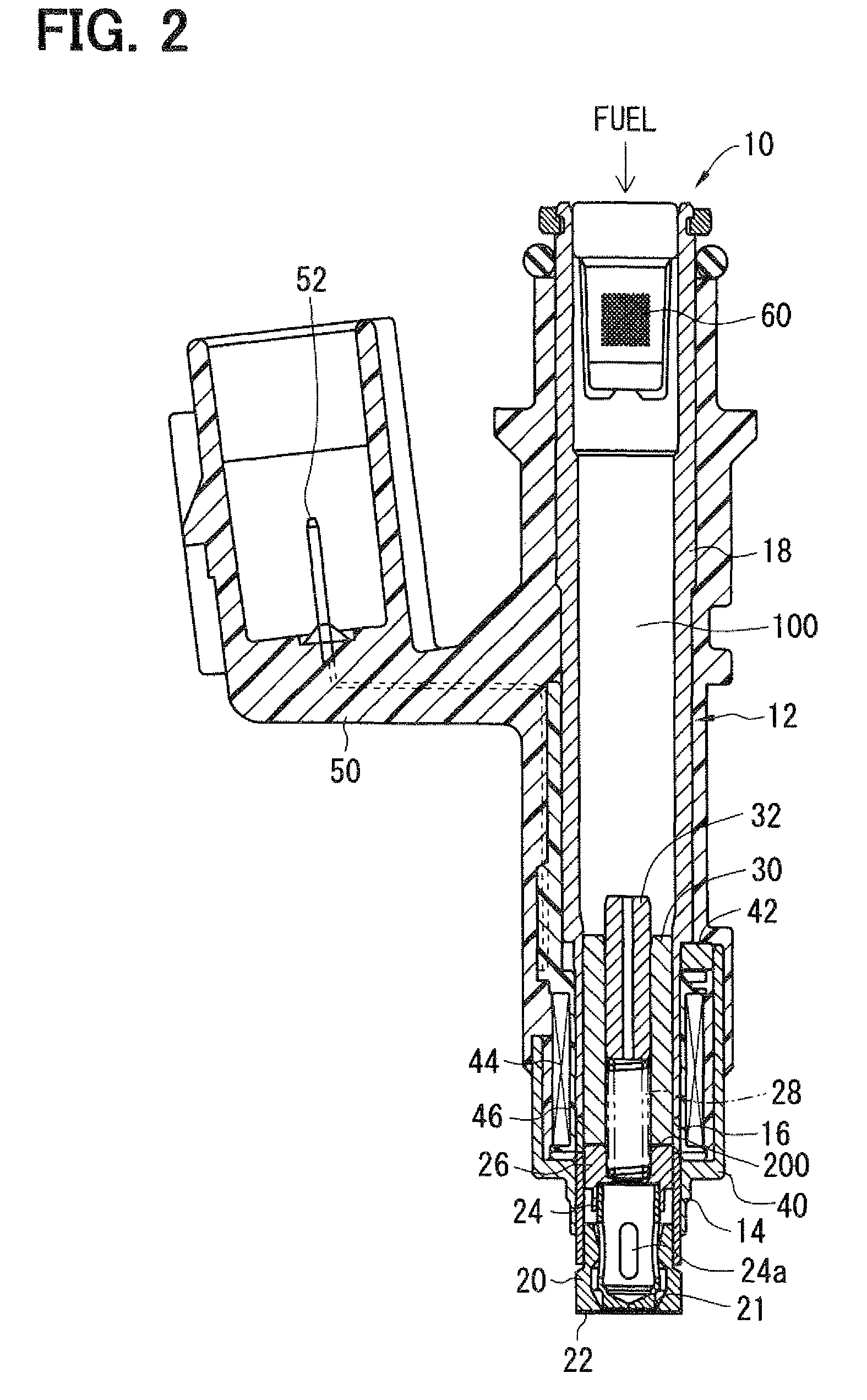
Solenoid valve and fuel injection valve having the same
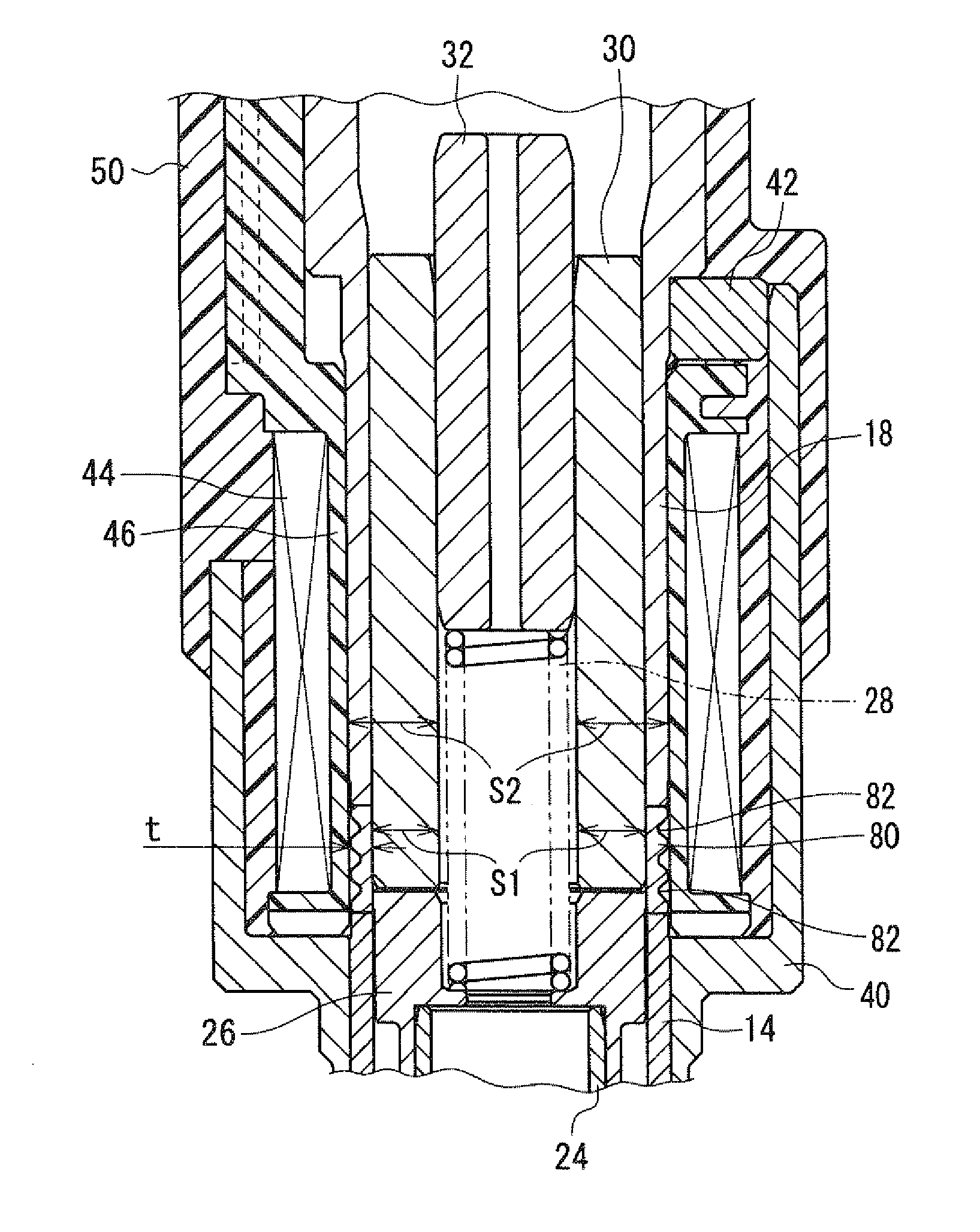
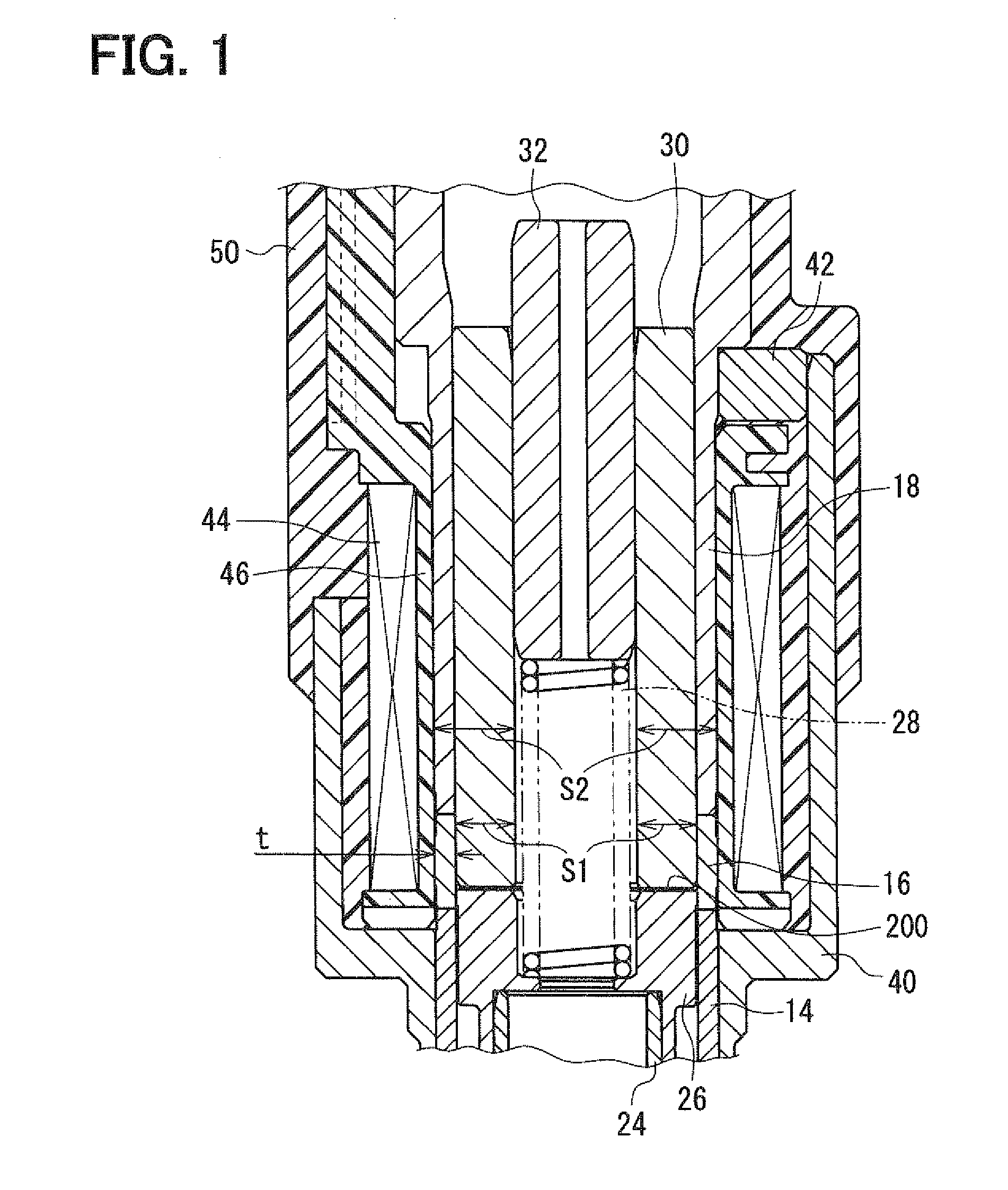
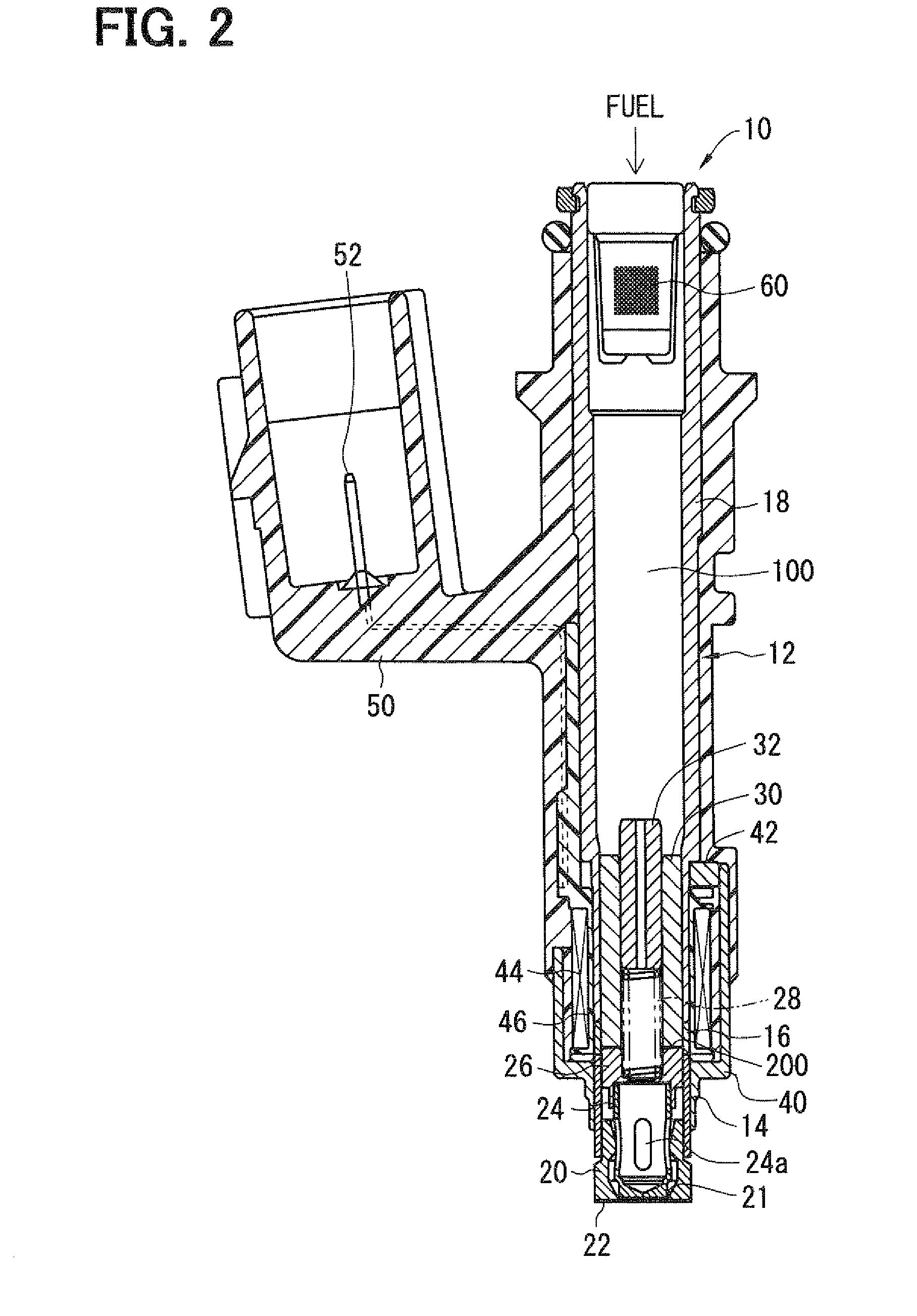
ActiveUS20080237520A1Start fastOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSolenoid valveFuel injection
A solenoid valve includes a movable core, a magnetic opposed portion opposed to the movable core, a nonmagnetic cylindrical portion, a first magnetic cylindrical portion axially close to the movable core, and a second magnetic cylindrical portion located radially outside of the magnetic opposed portion. The nonmagnetic cylindrical portion surrounds radially outside of a gap between the magnetic opposed portion and the movable core. A coil is provided radially outside of the nonmagnetic cylindrical portion. A thickness t of the nonmagnetic cylindrical portion, a cross-sectional area S1 of the magnetic opposed portion, and a total cross-sectional area S2 of both the magnetic opposed portion and the second magnetic cylindrical portion having the thickness t satisfy the relationships of t≦0.6 mm and 0.55≦(S1 / S2).
Owner:DENSO CORP
Actuator motion control
ActiveUS20150267670A1Electrical controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical equationControl theory
A system for controlling actuation of an electromagnetic actuator includes an actuator having an electrical coil, a magnetic core, and an armature. A controllable drive circuit is responsive to an electric power flow signal for driving current through the electrical coil to actuate the armature. A control module includes an armature motion observer configured to determine an armature motion parameter in the actuator based upon a magnetic flux within the actuator and a predetermined mechanical equation of motion corresponding to the actuator and adapt the electric power flow signal based on the armature motion parameter.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Deep pocket seat assembly in modular fuel injector with fuel filter mounted to spring bias adjusting tube and methods
ActiveUS7309033B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionFuel filterPower group
A fuel injector and various methods relating to the assembly of the fuel injector. The fuel injector includes a power group subassembly and a valve group subassembly having a respectively connected first and second connector portions. The power group subassembly includes an electromagnetic coil, a housing, at least one terminal, and at least one overmold formed over the coil and housing. The valve group subassembly insertable within the overmold includes a tube assembly having an inlet tube and a filter assembly. A pole piece couples the inlet tube to one end of a non-magnetic shell having a valve body coupled to the opposite end. An axially displaceable armature assembly confronts the pole piece and is adjustably biased by a member engaged with an adjusting tube with a filter assembly mounted thereon. The seat assembly includes a flow portion and a securement portion having respective first and second axial lengths at least equal to one another.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
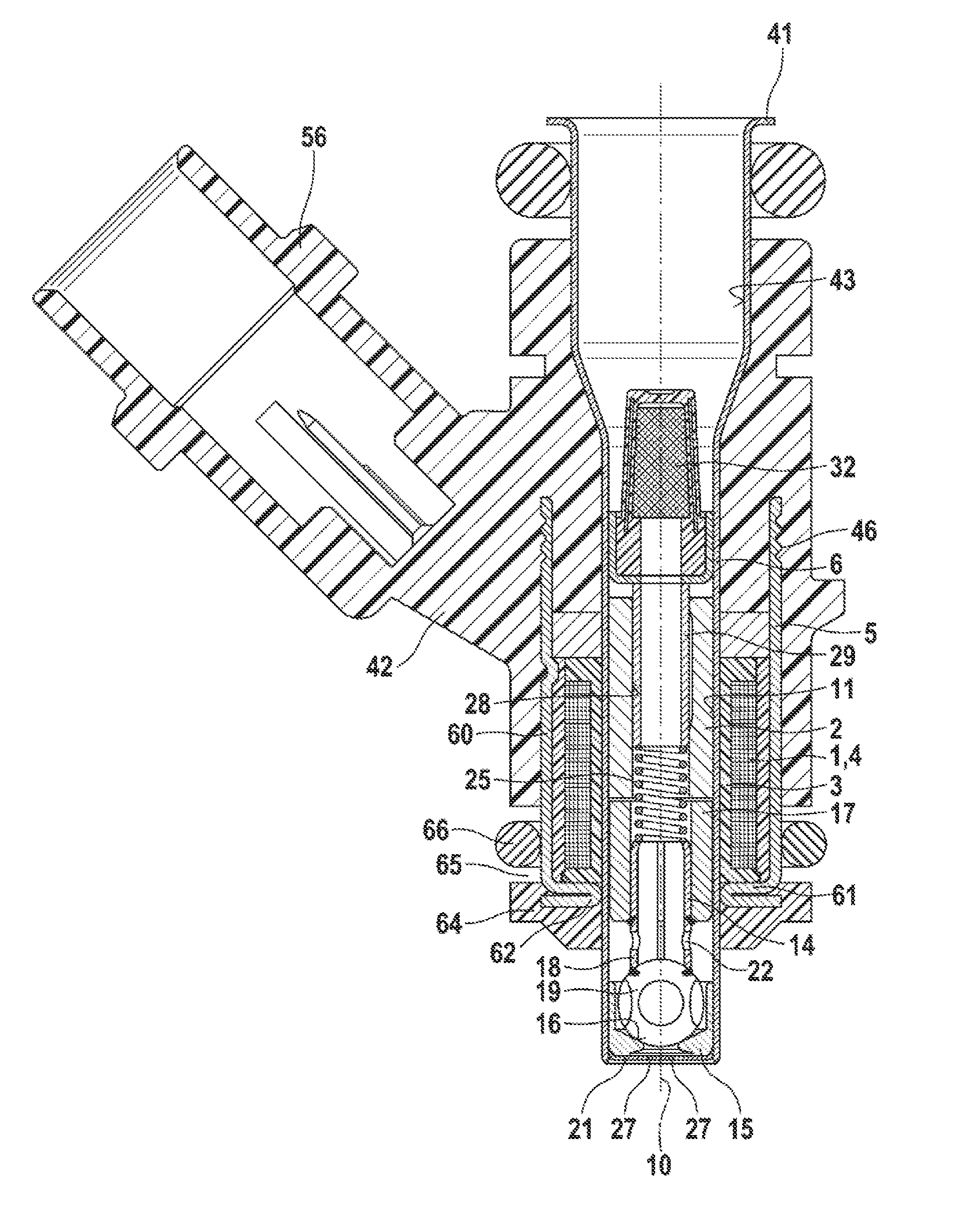
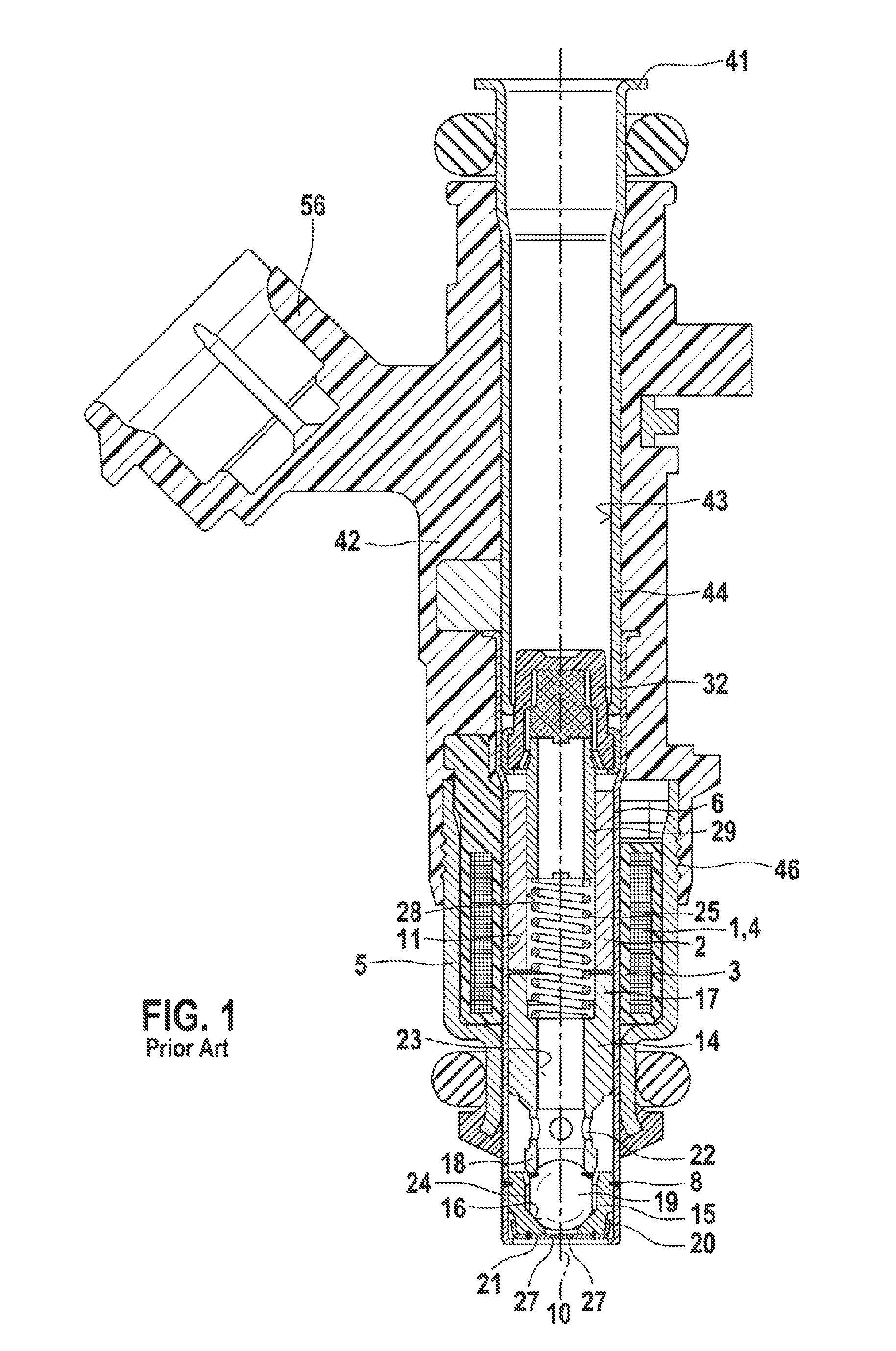
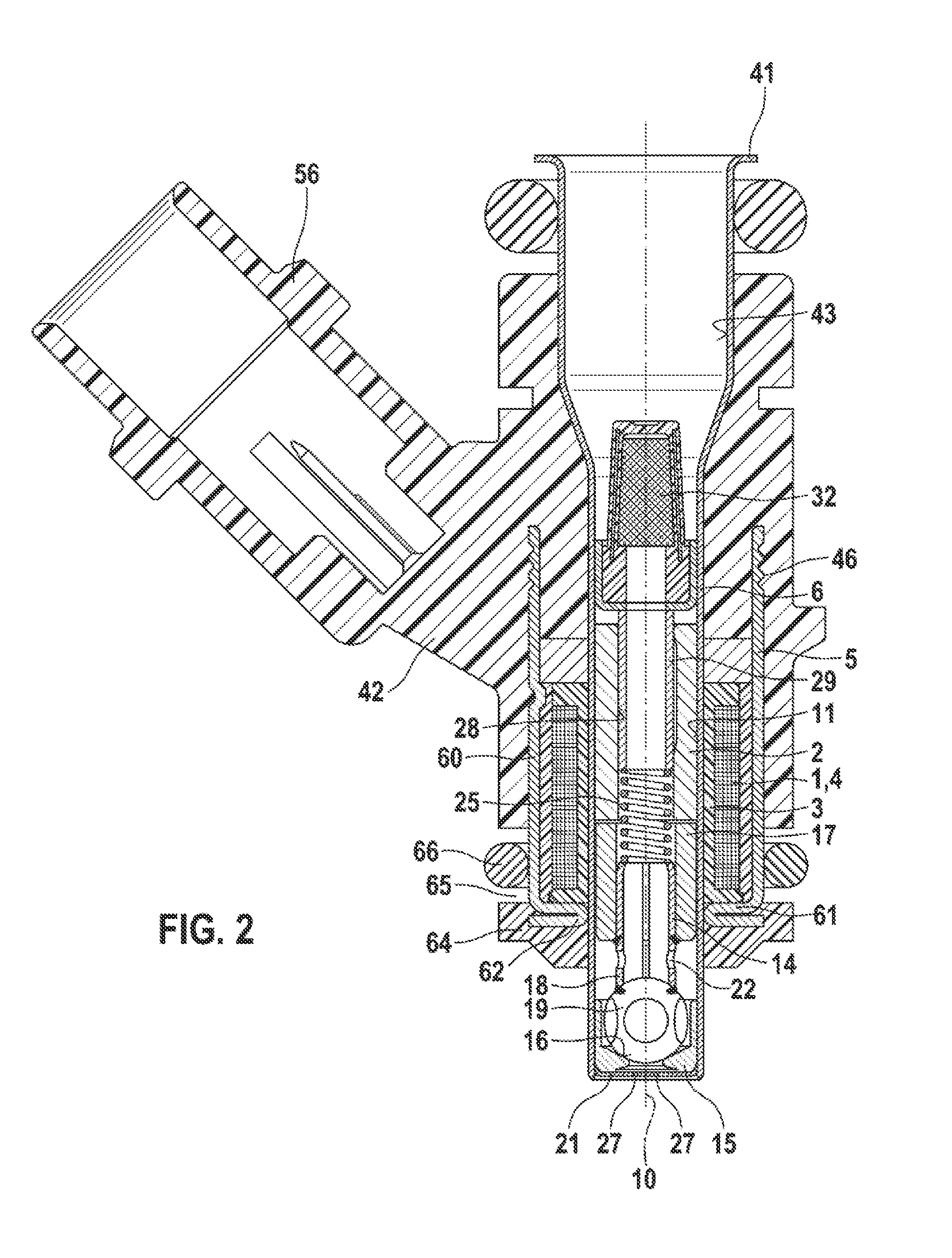
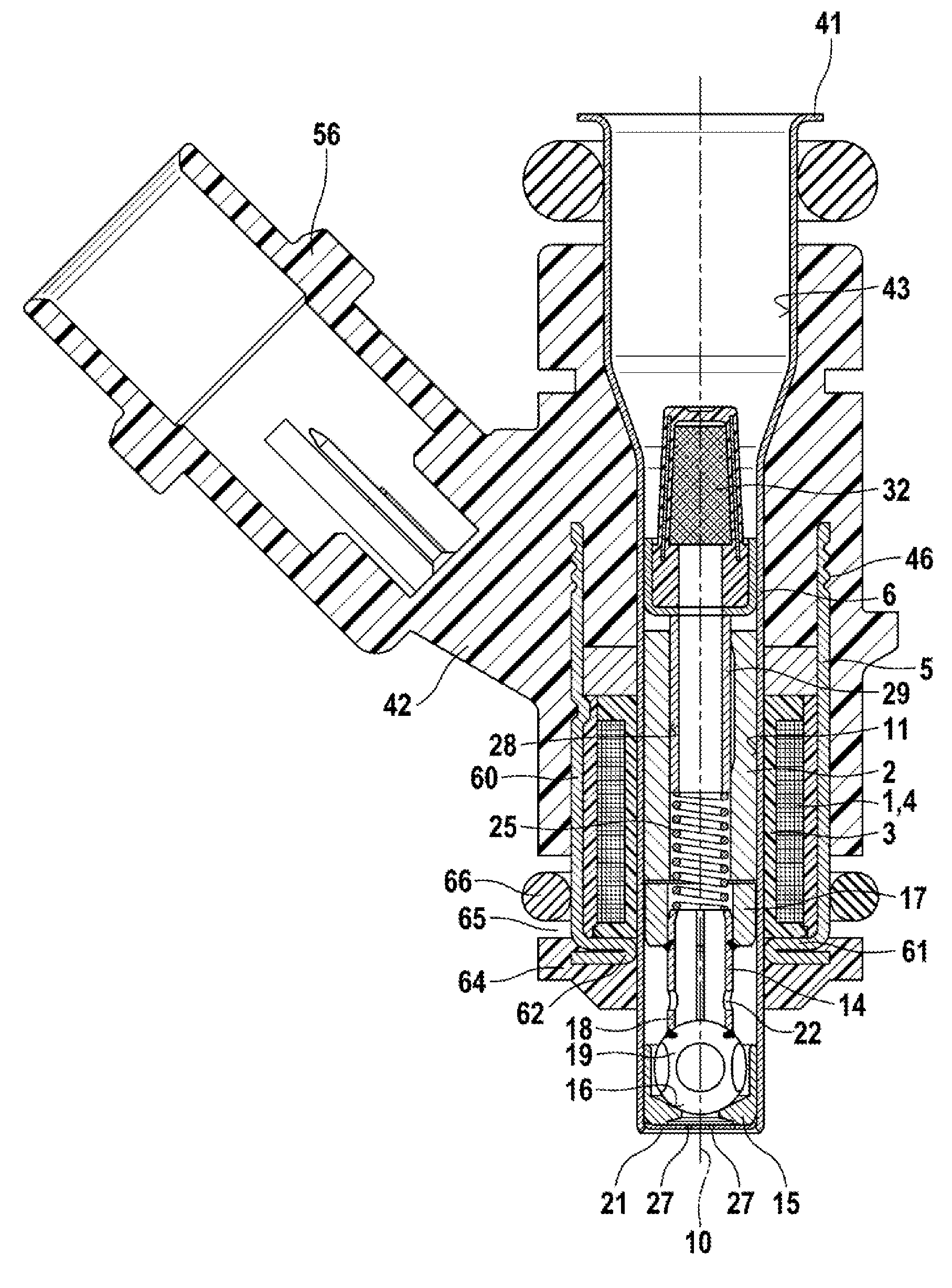
Fuel injector
InactiveUS20130075501A1More responsiveImprove responsivenessWear reducing fuel injectionMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionEngineeringMagnetic flux
Improving the injection fuel mass accuracy of fuel injector, it is necessary to make the fuel injector perform seat valve opening and closing operation quickly. When the shapes of a fixed core and an anchor are optimized to improve the responsiveness of a magnetic flux, it is necessary to ensure a sufficient fuel path area while preventing adhesion by making the adherence phenomenon rarely occur between an end face of the anchor and an end face of the fixed core. A through hole passes through an anchor forming an armature of an electromagnetic fuel injector from a face of the anchor where the anchor faces a fixed core to a back face where the through hole has a large-diameter portion and a small-diameter portion, and the large-diameter portion is located in an upstream part and is offset to the outer periphery with respect to the small-diameter portion.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
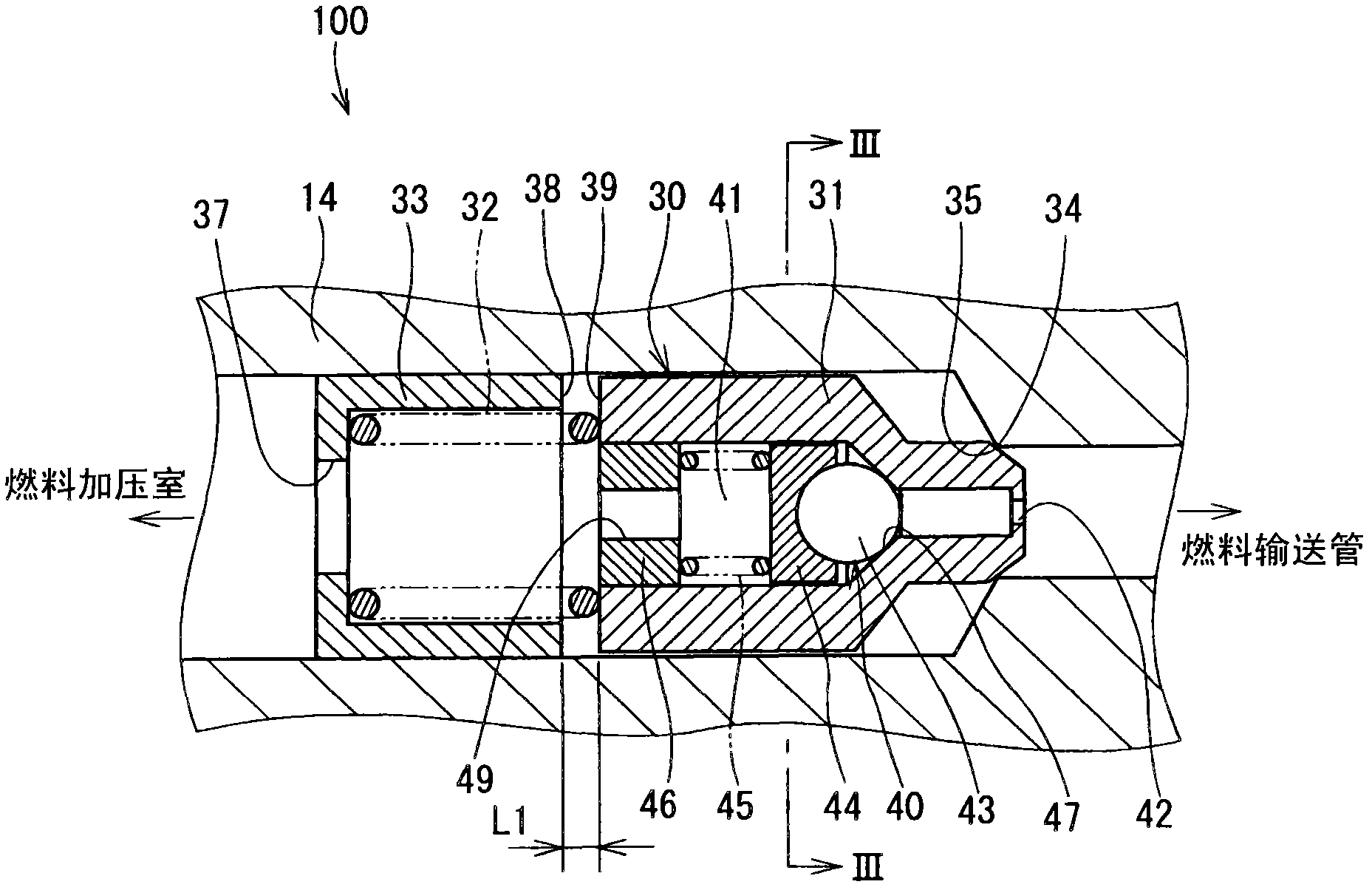
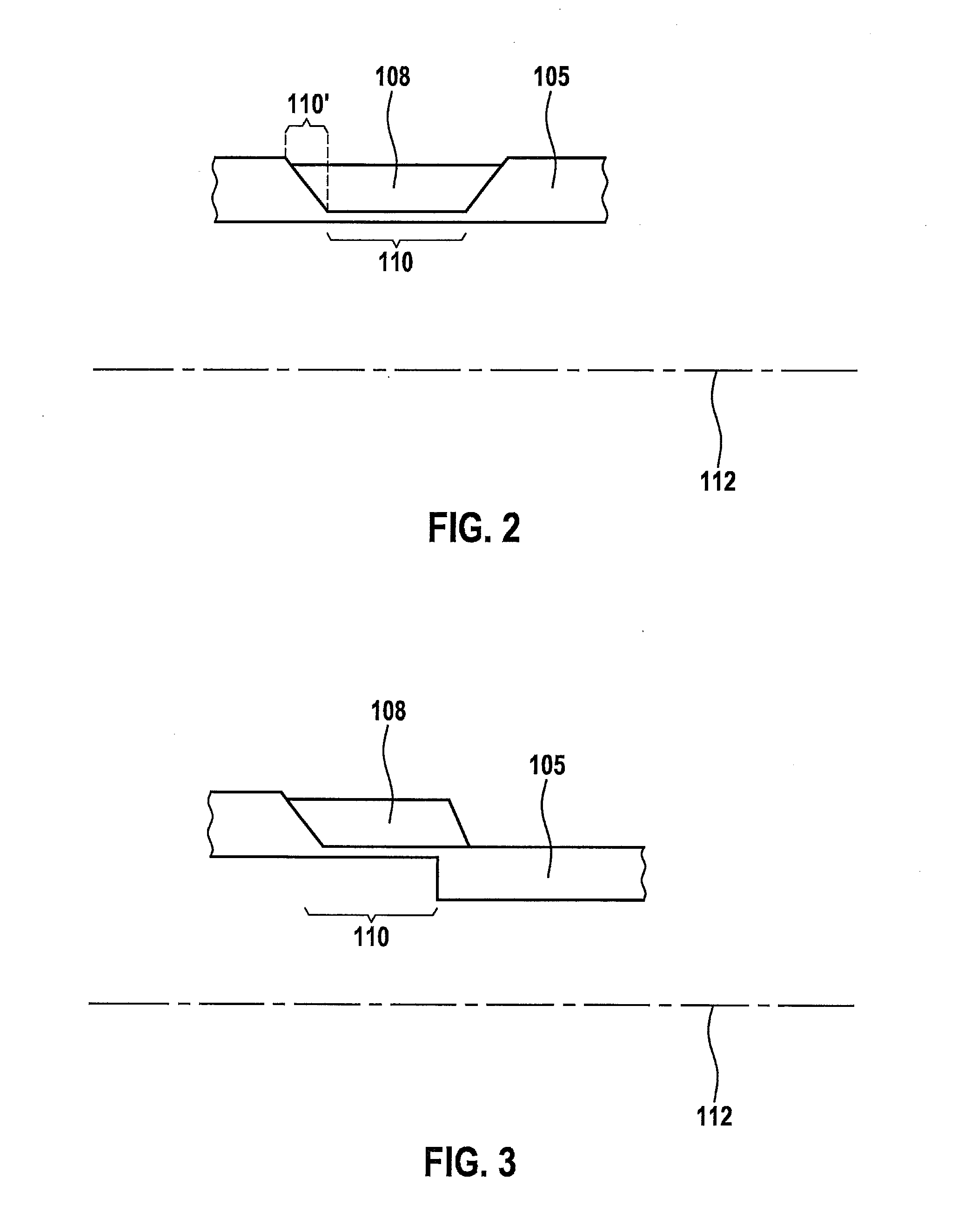
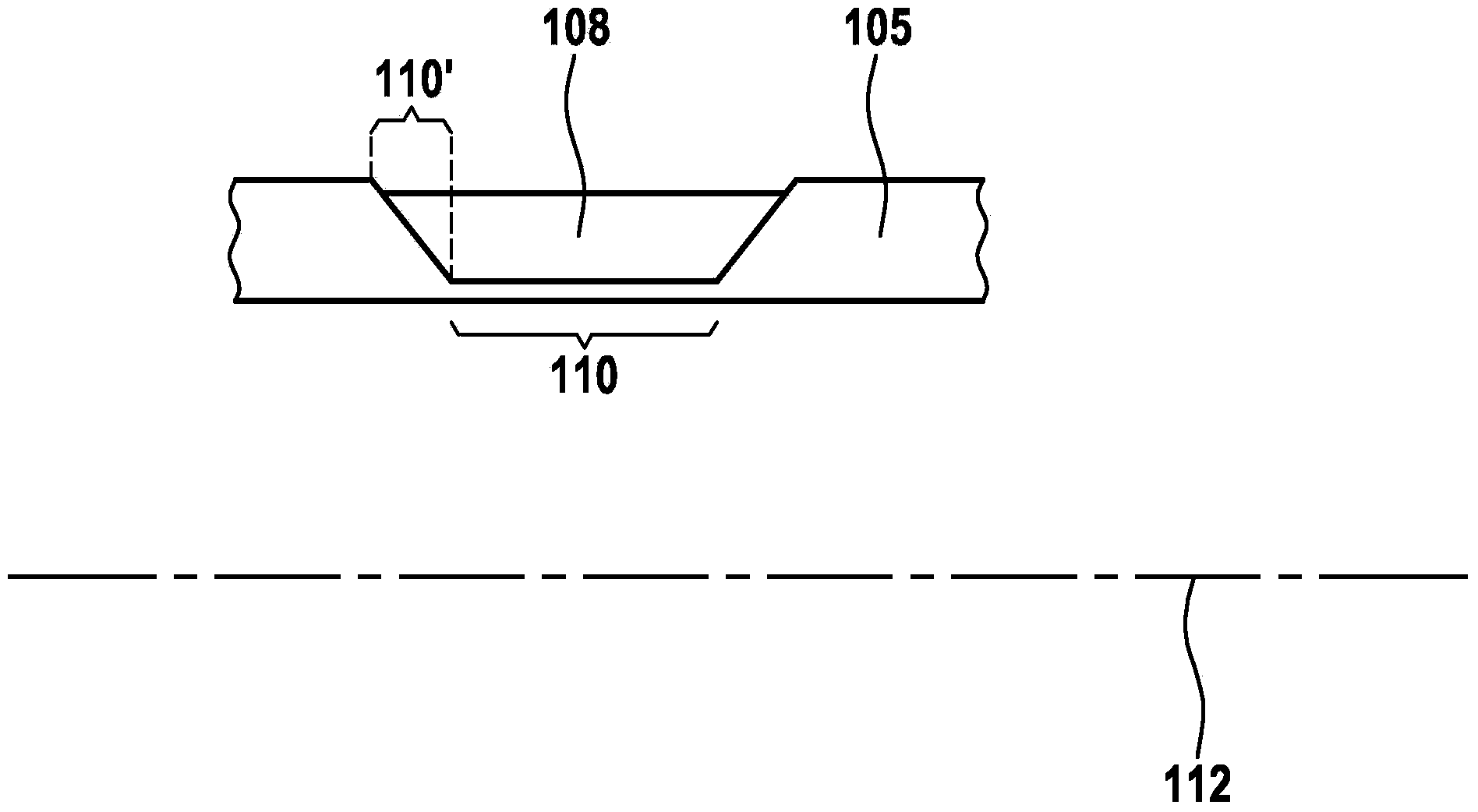
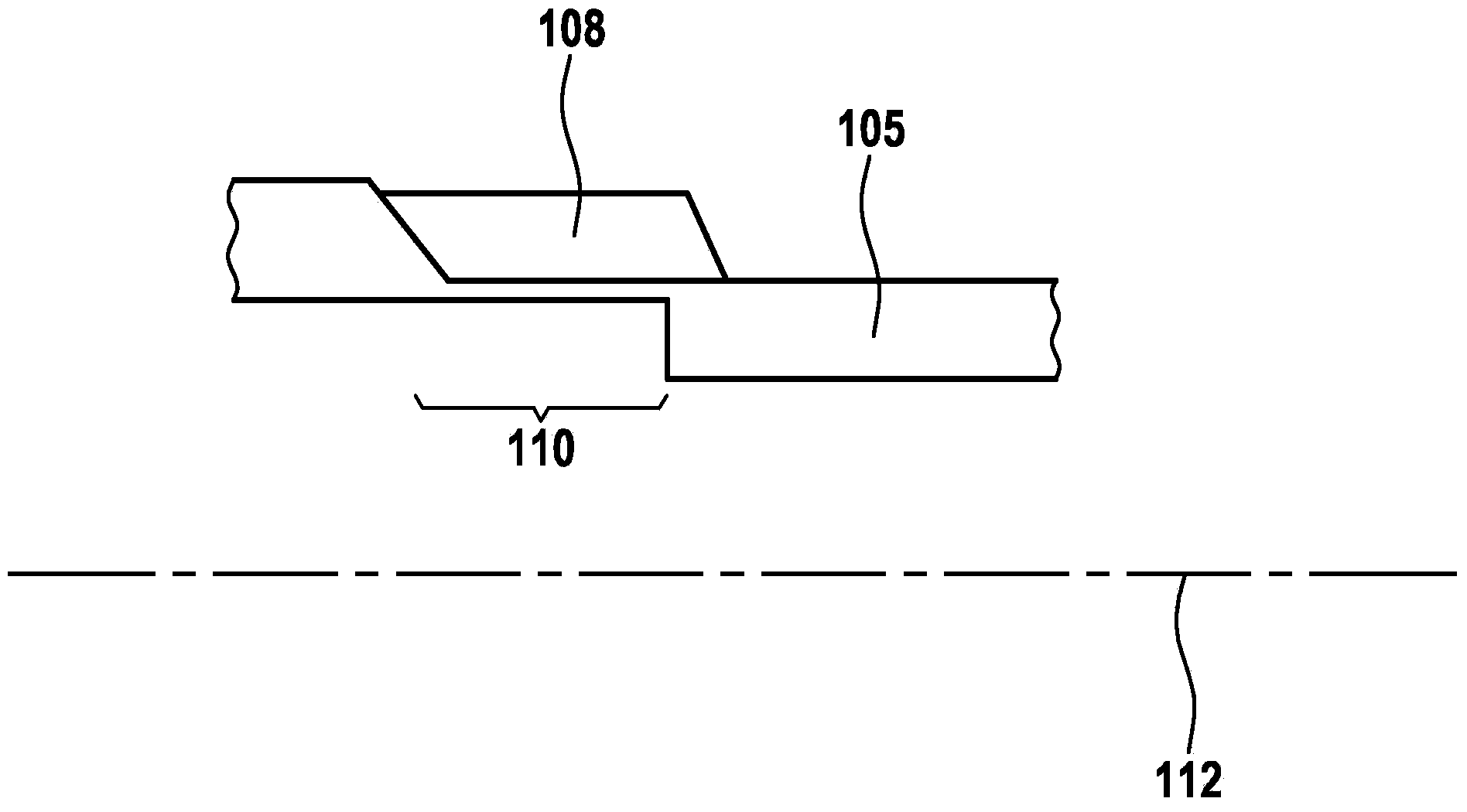
Fuel supply system having pressure control valve
InactiveCN102080616AElectrical controlMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionEngineeringControl valves
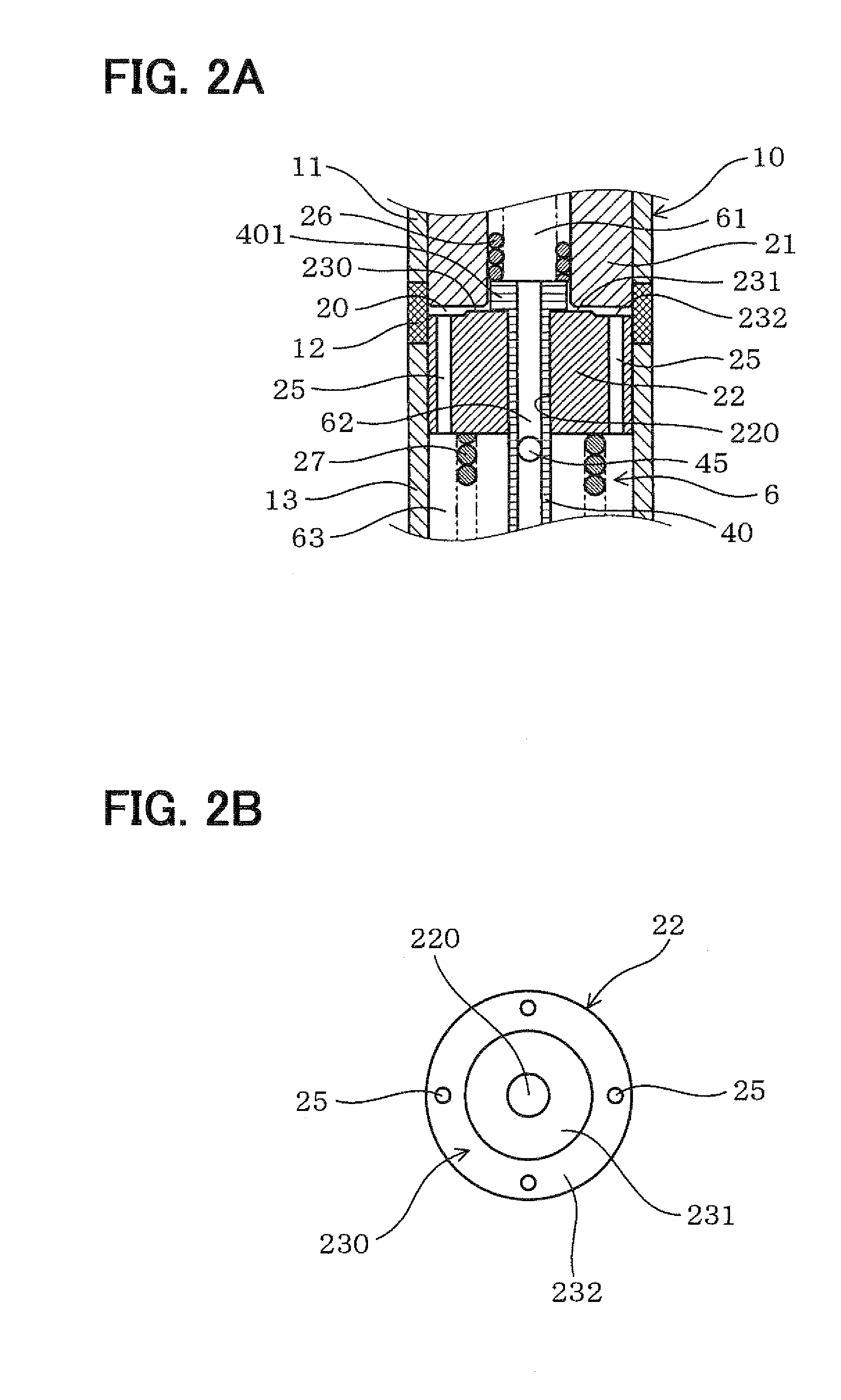
A pressure control valve (100) is provided in a fuel return pipe (14) connected between a high pressure fuel pipe (16) and a fuel pressurizing chamber (27) of a high pressure pump (20). A pressure relief valve (30) is opened when fuel pressure in a fuel delivery pipe (15) is higher than a first pressure. A first valve body (31) of the pressure relief valve (30) is brought into contact with a stopper so that a movement of the first valve body (31) is limited. A pressure holding valve (40), which is provided in an inside of the first valve body (31), is opened when the fuel pressure in the fuel delivery pipe (15) is larger than a second pressure. When the pressure relief valve (30) is opened and the first valve body crashes into the stopper (33), a lifting amount of a second valve body (43) of the pressure holding valve (40) is increased by inertia of the second valve body (43), so that extraneous material attached to the second valve body (43) can be removed.
Owner:DENSO CORP
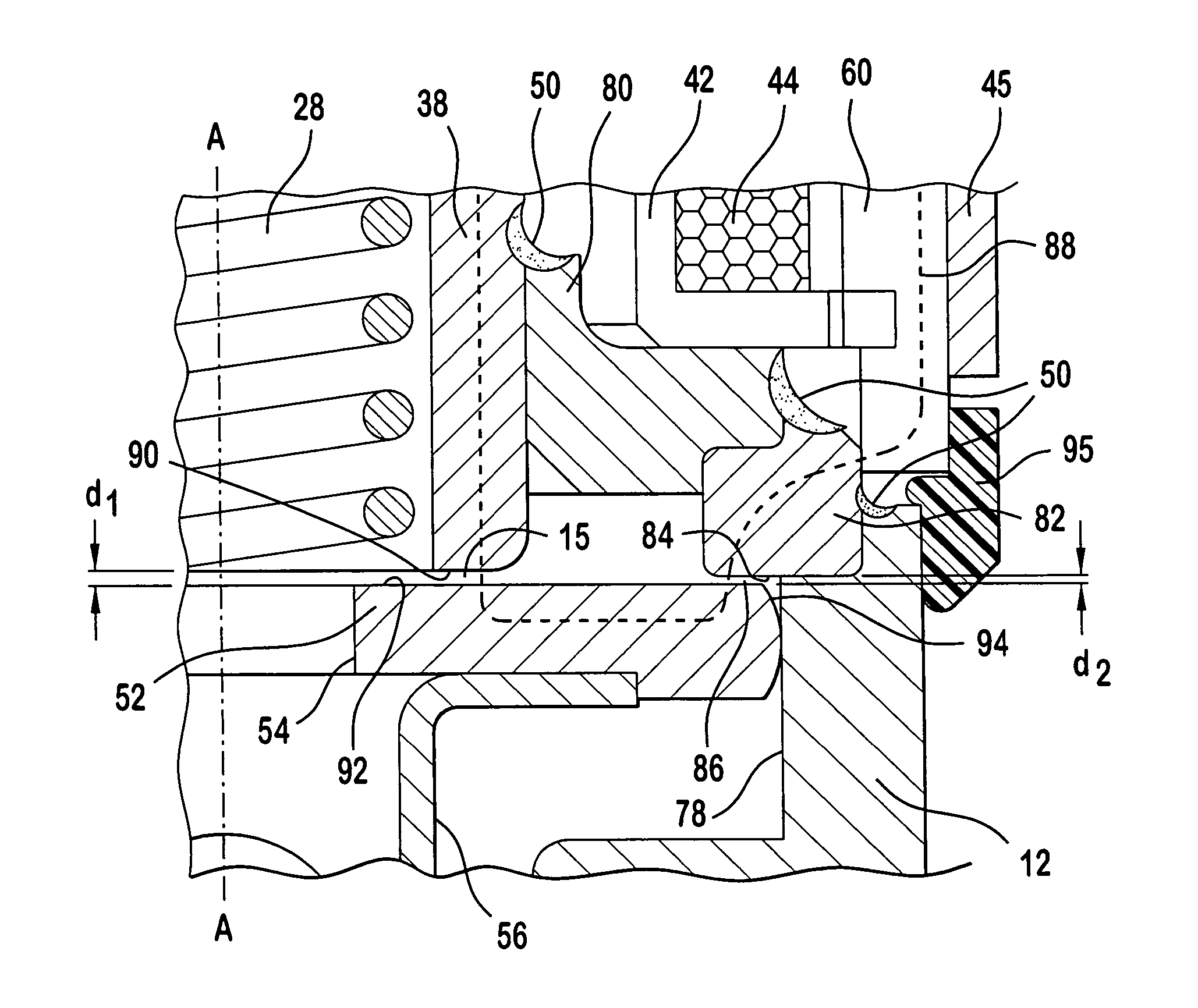
Modular fuel injector with di-pole magnetic circuit
ActiveUS7086606B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesFuel-injection pumpsPower groupEngineering
A modular fuel injector for an internal combustion engine, including a valve group subassembly and a power group subassembly. The valve group subassembly includes a first stator member, a second stator member, a non-magnetic shell disposed between the first and second stator members, a valve body, and an armature member. The armature member defines a first working air gap with the first stator member and a second working air gap with the second stator member. The armature member includes a closure member proximate an outlet end and contiguous to a seat in a first configuration. The power group subassembly includes an electromagnetic coil surrounding the passage, a housing encasing the coil, and an ovemold encapsulating the coil and the housing. The coil is energizable to provide magnetic flux that flows through the first and second working air gaps in the direction of the longitudinal axis.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Fuel injection valve
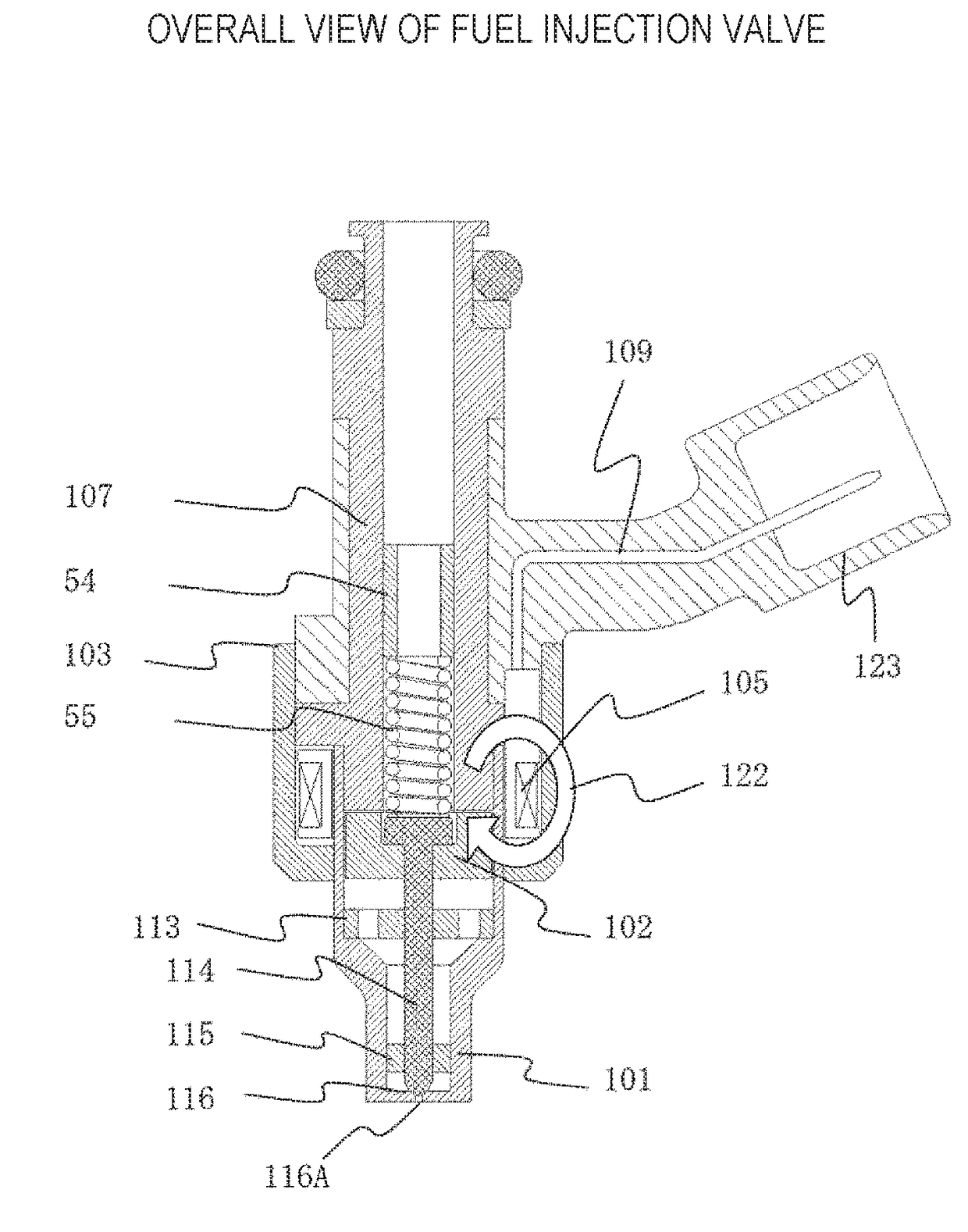
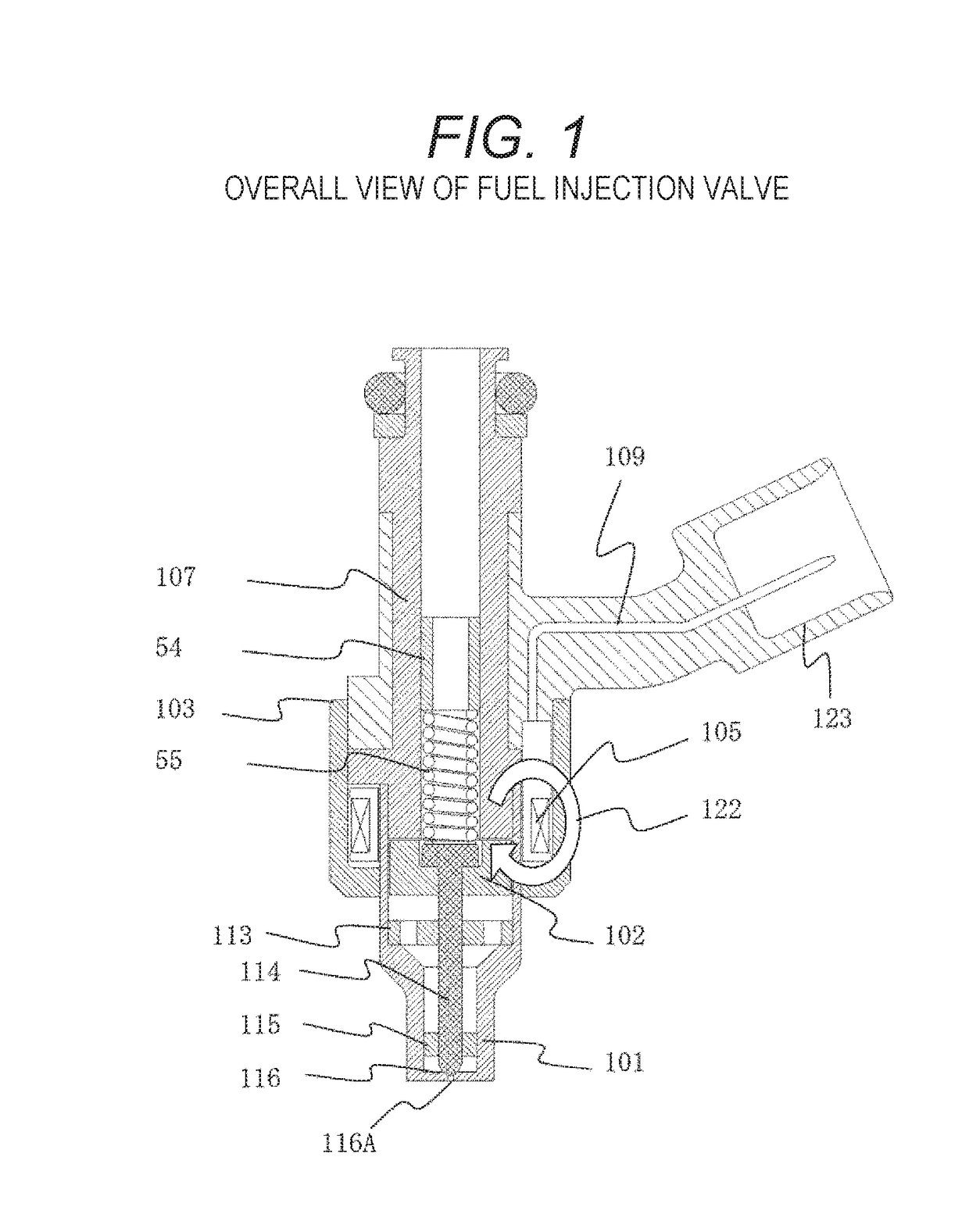
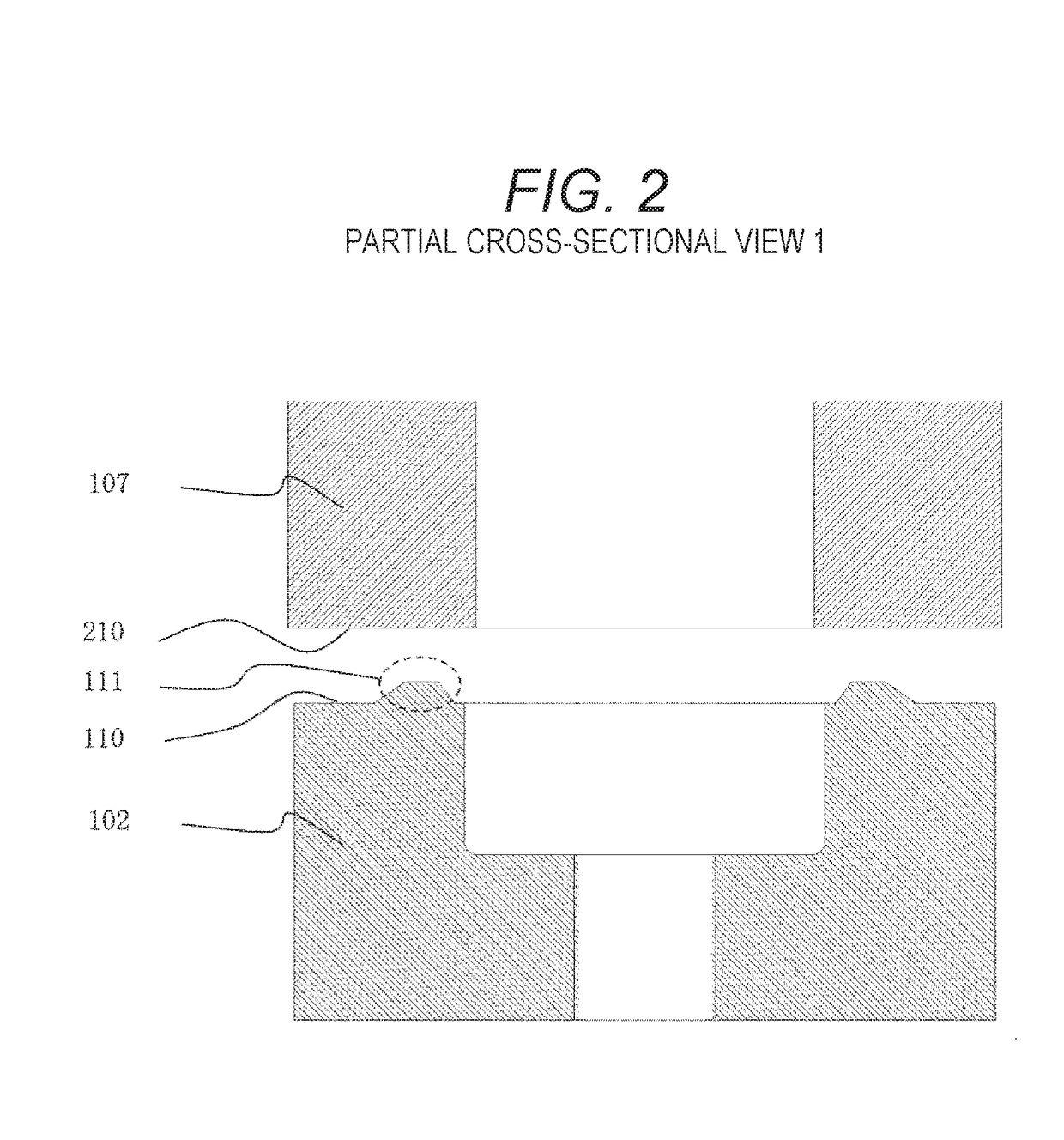
ActiveUS20090159729A1Small bounceExpansion quantityMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSpray nozzlesEngineeringFuel injection
A fuel injection valve includes a housing, a stator, a movable core, a coil, a nozzle hole, a valve member, and at least one communicating passage. The housing receives the stator and movable core. An end face of the movable core has a non-contact surface and a contact surface. The non-contact surface and the stator define a space when the contact surface contacts the stator. The valve member is slidably received in a bore of the movable core. The valve member has a stopper engageable with the movable core such that the valve member is axially movable together with the movable core. The at least one communicating passage connects the space with a corresponding one of a first fuel passage and a second fuel passage of the housing.
Owner:DENSO CORP
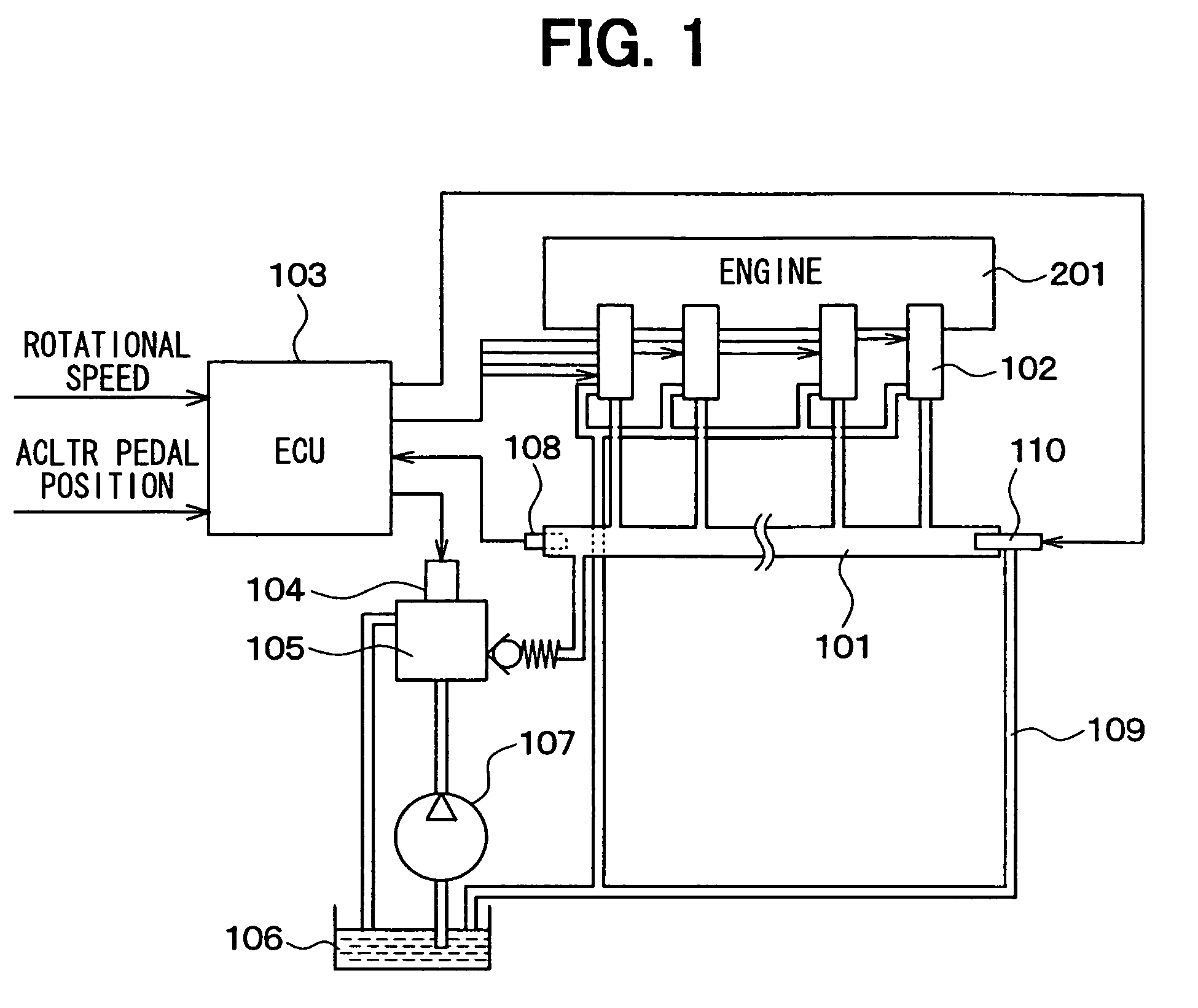
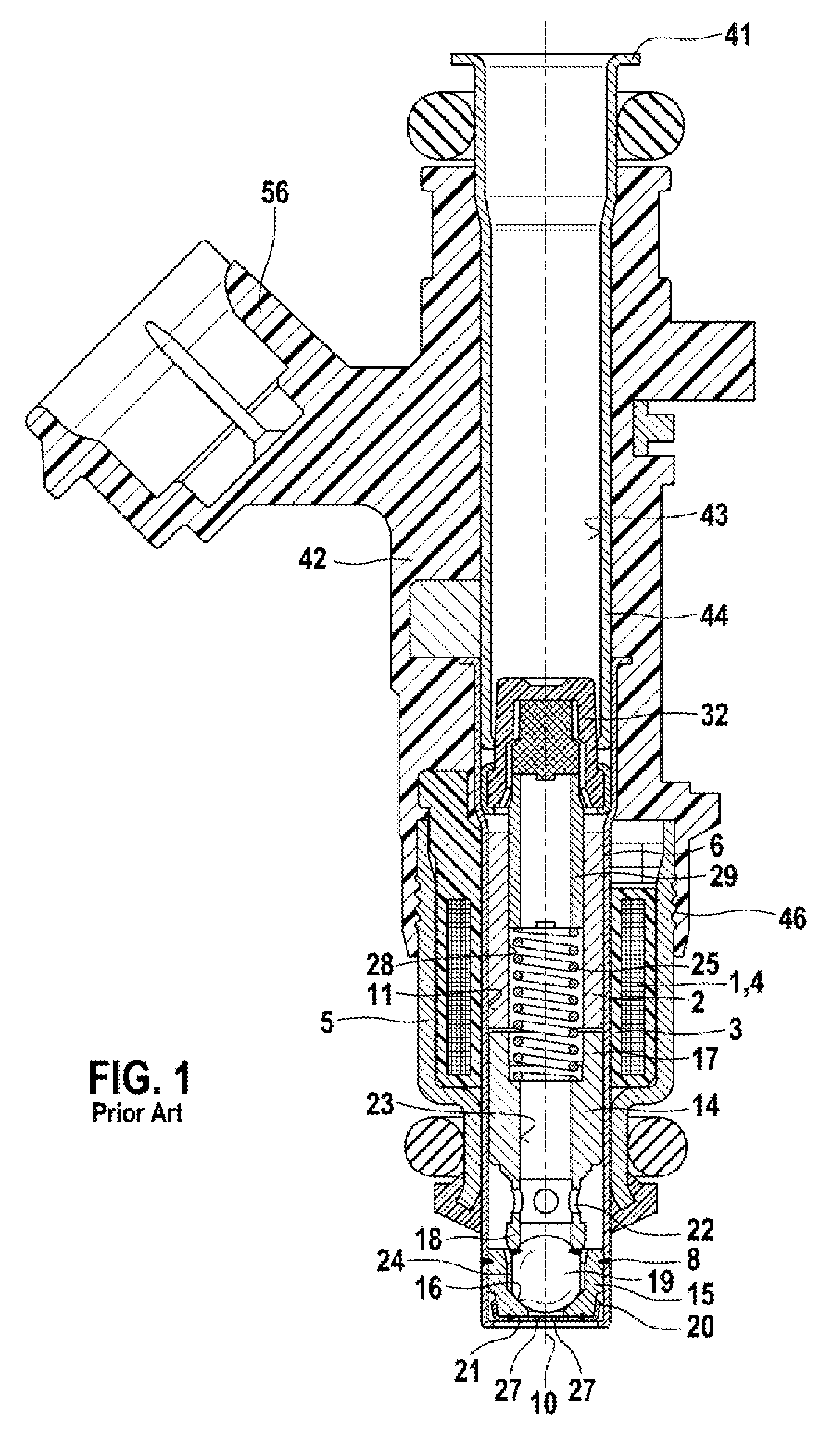
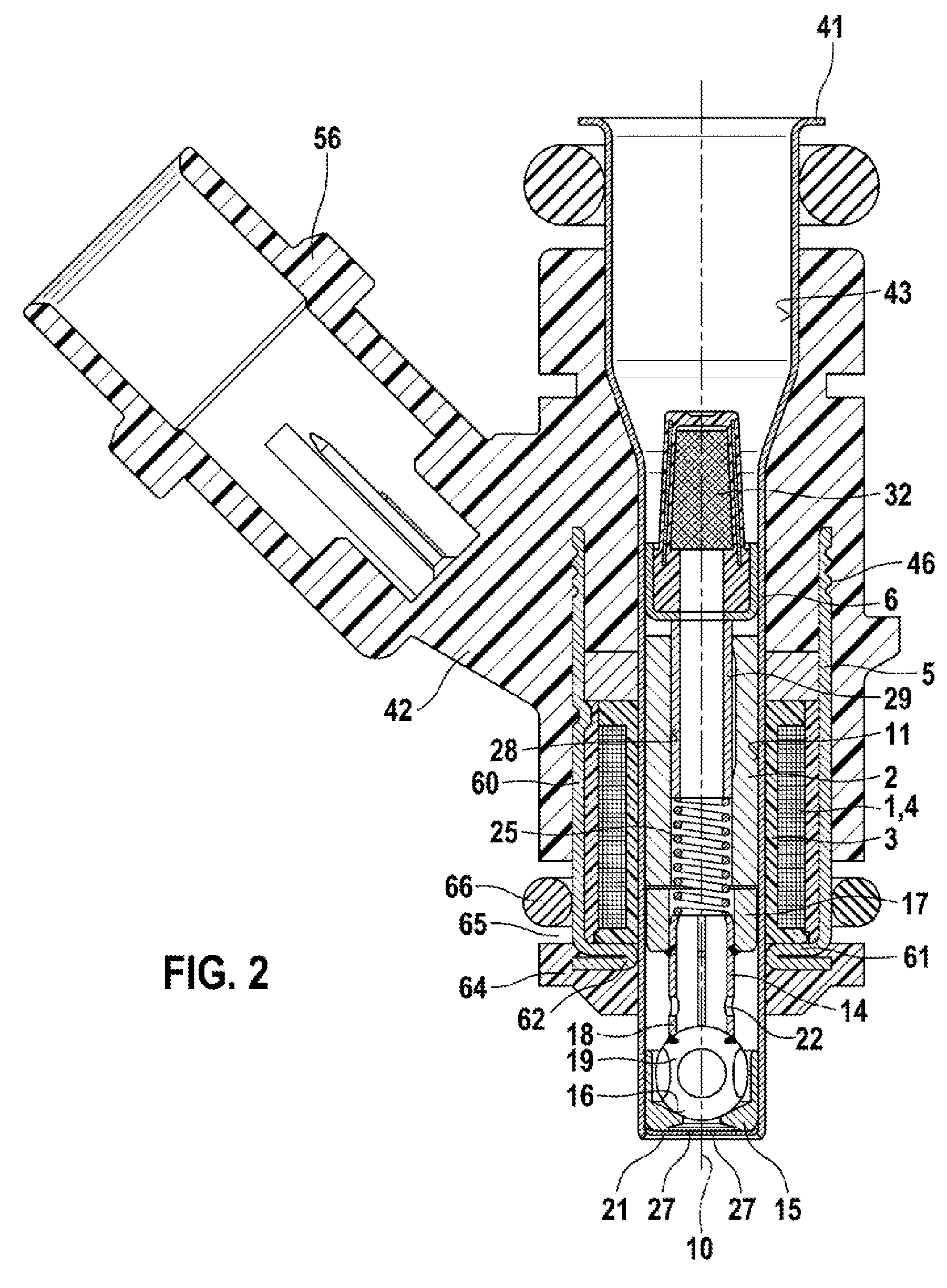
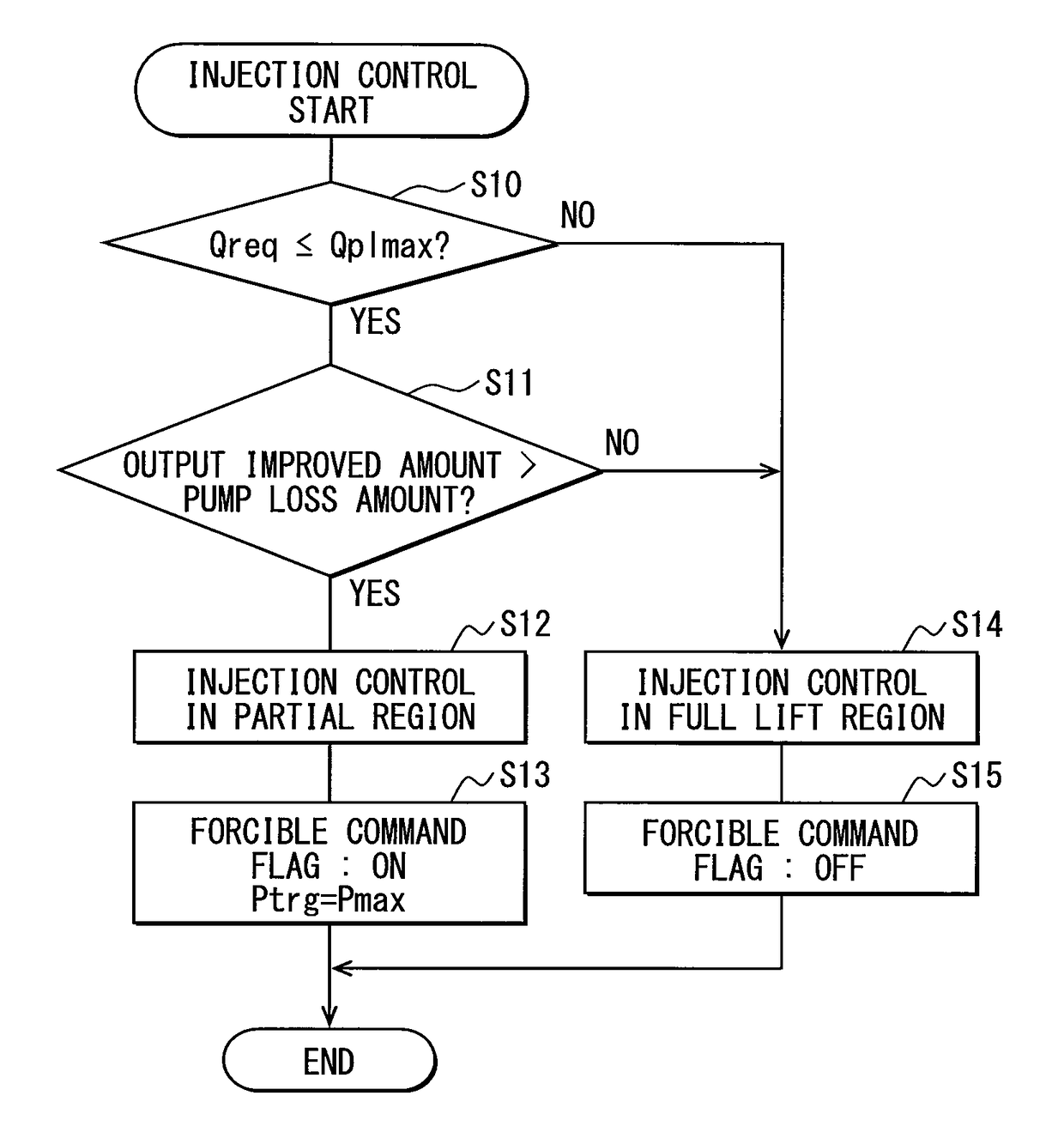
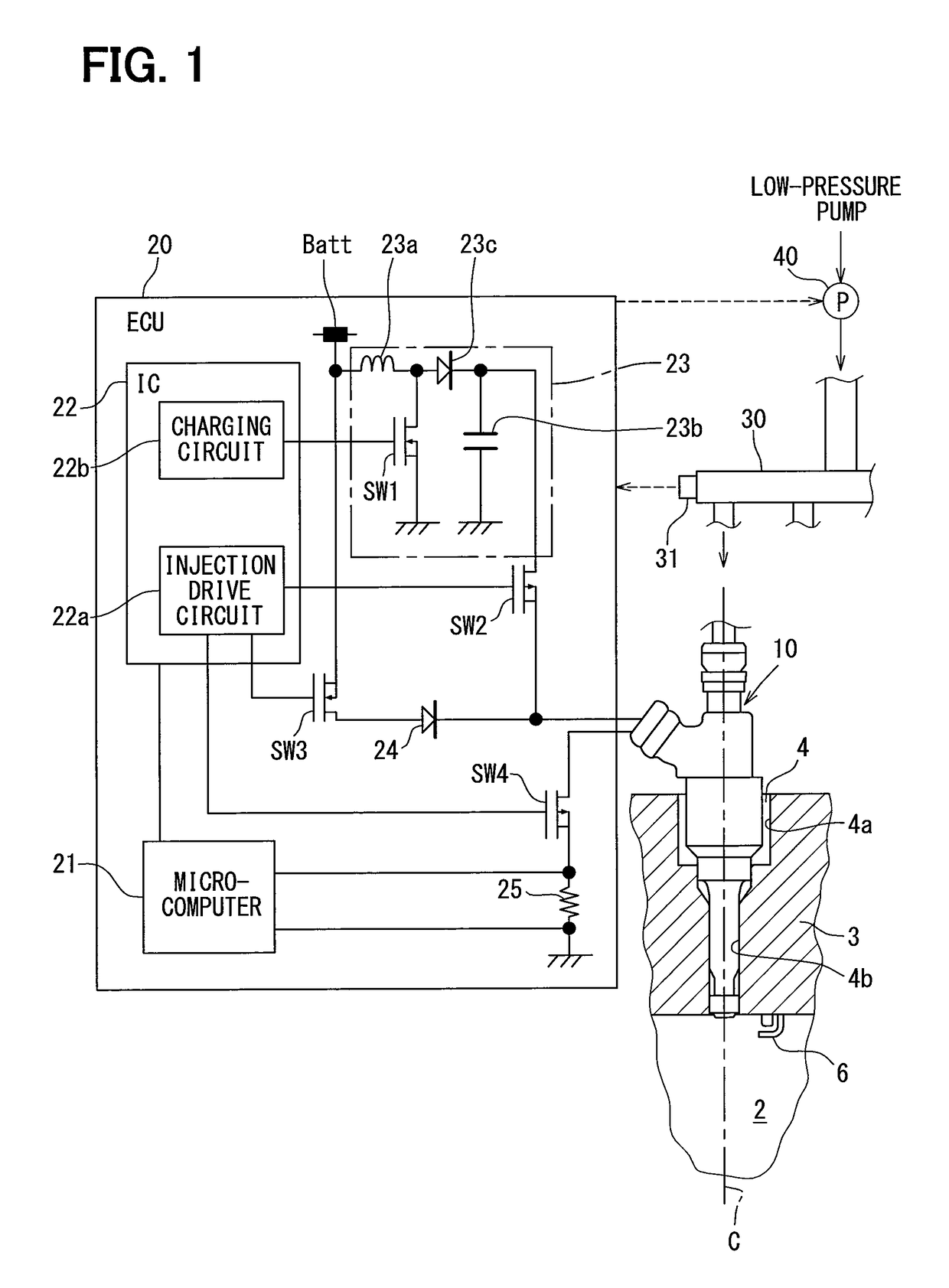
Fuel injection control device and fuel injection system
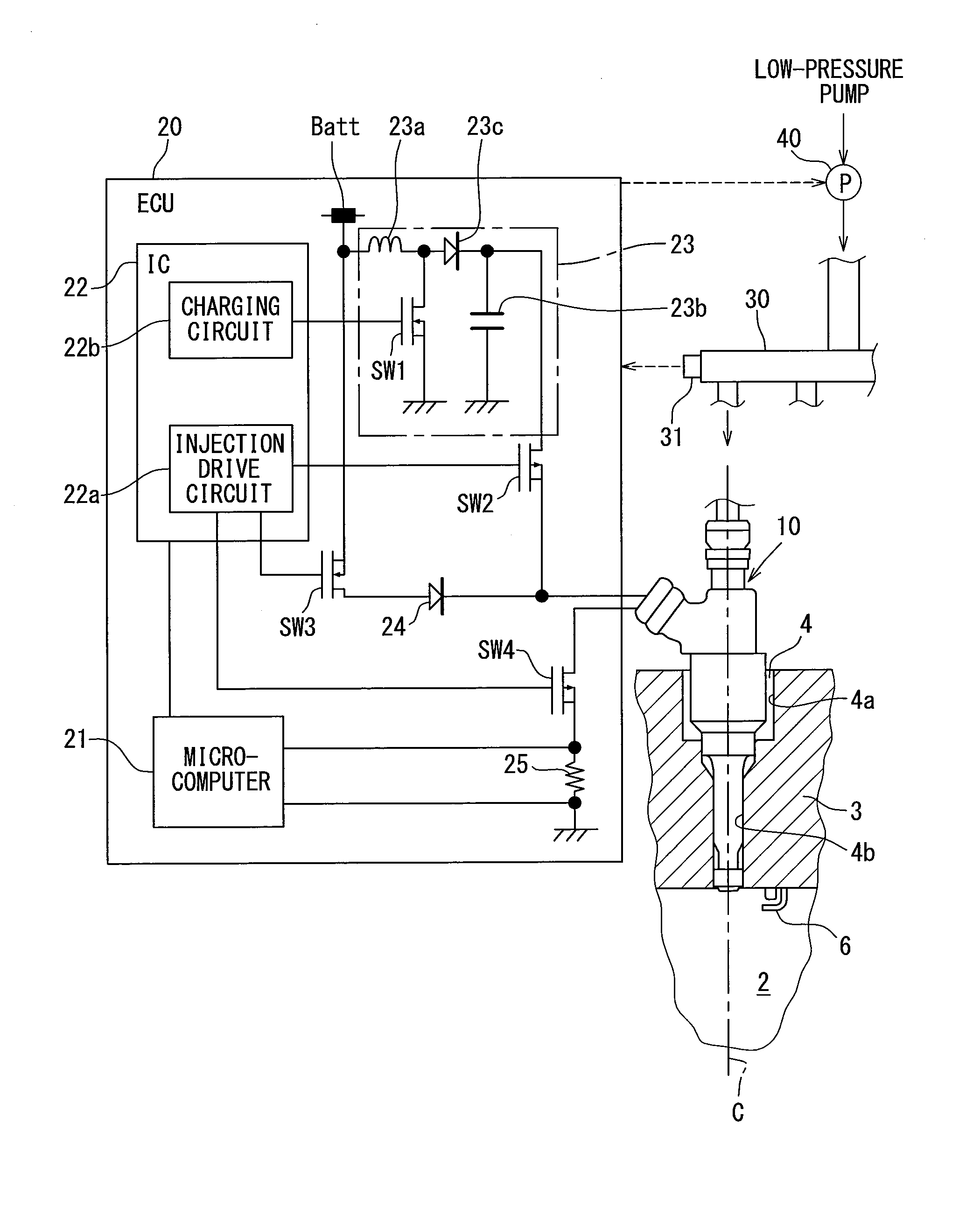
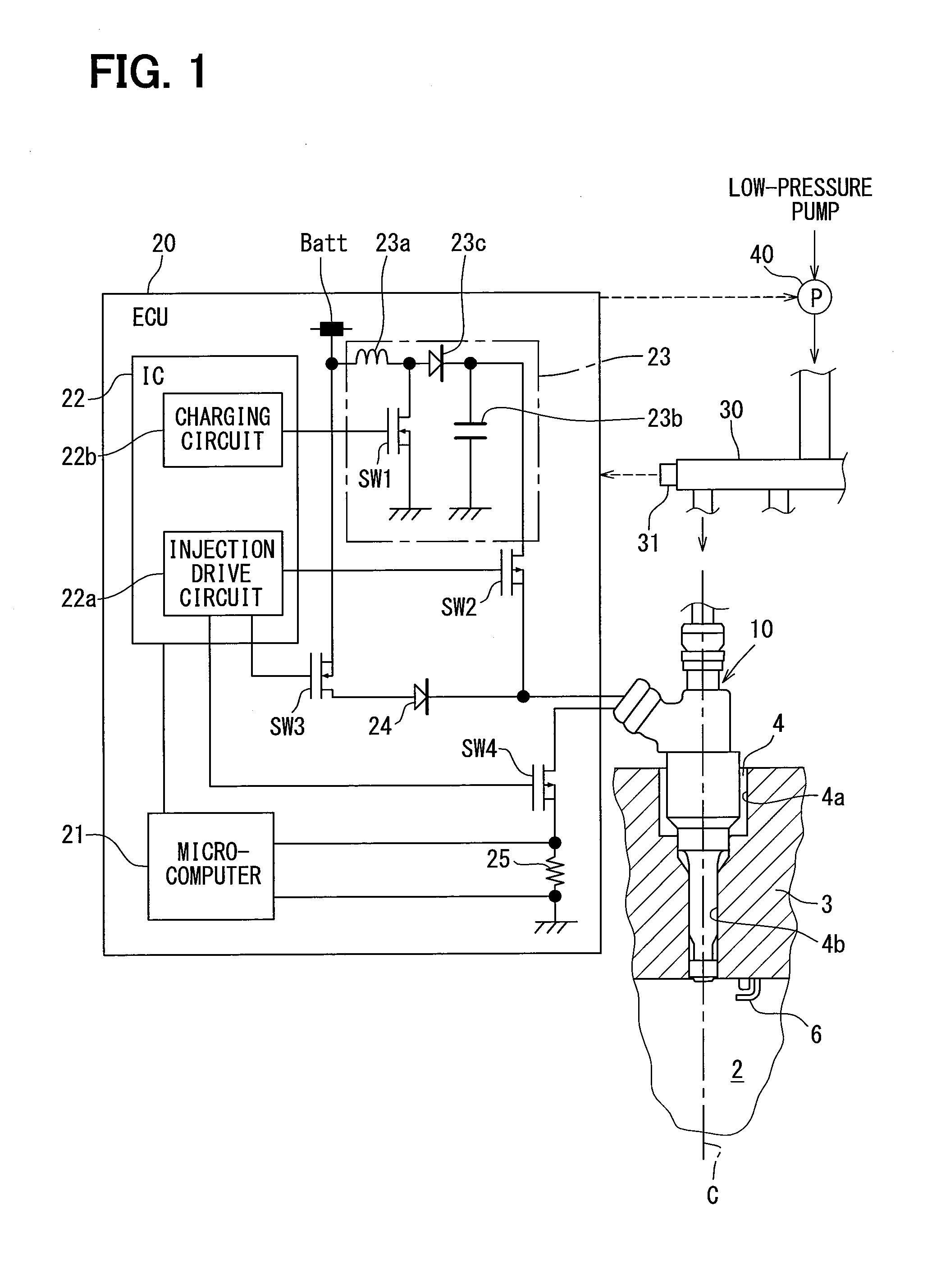
ActiveUS20160061139A1Small spray particle diameterIncrease fuel pressureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHigh pressureFuel supply
A fuel injection control device is adapted for a fuel injection system including an injector and a high-pressure pump that raises pressure of fuel and supplies the fuel to the injector. The fuel injection control device includes a selecting unit for selecting by which one of full lift injection and partial injection to inject fuel, and a pump control unit for controlling operation of the high-pressure pump such that a pressure of fuel supplied to the injector coincides with a target pressure. The selecting unit selects the partial injection when a required injection quantity of fuel is equal to or smaller than a partial maximum injection quantity. A fuel injection system includes the fuel injection control device, the injector, and the high-pressure pump.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injection valve
ActiveUS7866577B2Small bounceExpansion quantityMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSpray nozzlesFuel injectionStator
A fuel injection valve includes a housing, a stator, a movable core, a coil, a nozzle hole, a valve member, and at least one communicating passage. The housing receives the stator and movable core. An end face of the movable core has a non-contact surface and a contact surface. The non-contact surface and the stator define a space when the contact surface contacts the stator. The valve member is slidably received in a bore of the movable core. The valve member has a stopper engageable with the movable core such that the valve member is axially movable together with the movable core. The at least one communicating passage connects the space with a corresponding one of a first fuel passage and a second fuel passage of the housing.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electromagnetically actuatable valve
ActiveUS20120305816A1Total current dropCurrent lossOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionMagnetic actuationActuator
An electrically actuatable valve for injecting fuel includes a magnetic actuator having multiple components, at least one component of the magnetic actuator having multiple sectors made of soft magnetic material and multiple insulating separating webs. A separating web is situated between each two neighboring sectors and entirely separates the neighboring sectors from one another electrically.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Solenoid drive apparatus
ActiveUS7552908B2Engine sealsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectromagnetMagnetic field
A solenoid drive apparatus for driving a driven member by a magnetic attractive force includes a tubular magnetic metallic body, a coil, a magnetic metallic plate, and a magnetic gasket. The tubular magnetic metallic body has an opening portion at one end. The coil is received in the body from the opening portion and provides a magnetic field when the coil is energized. The magnetic metallic plate closes the opening portion of the body. The magnetic gasket is held between the body and the plate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injection valve
InactiveUS20140027545A1Compact structureEasy to moveMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSpray nozzlesCombustionEngineering
A fuel injection valve for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines. The valve includes an electromagnetic actuating element having a solenoid, a solid core, an outer magnetic circuit component, and a movable armature for actuating a valve closing element that works together with a valve seat surface provided on a valve seat element. The valve has extremely small outer dimensions. Due to an optimized dimensioning of the electromagnetic circuit, the outer diameter of the outer magnetic circuit component in the circumferential area of the solenoid DM<=11 mm. This increases flexibility in the installation of fuel injection valves having various valve lengths, which are very easily enabled due to the particular modular construction. The valve is suitable as a fuel injection valve, particularly for use in fuel injection systems of mixture-compressing externally ignited internal combustion engines.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injector
ActiveUS20140008468A1Compact designEasy to moveMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSpray nozzlesCombustionModular design
A fuel injector for fuel injection systems of internal combustion engines. The valve includes an electromagnetic actuating element which has a solenoid, a solid core, an external magnetic circuit component, and a movable armature for activating a valve closing member which cooperates with a valve seat surface provided on a valve seat member. The valve has extremely small outer dimensions. By optimizing the dimensions of the electromagnetic circuit, the outer diameter of the external magnetic circuit component in the peripheral area of the solenoid is 10.5 mm<DM<13.5 mm. This increases the flexibility in installing fuel injectors having different valve lengths, which are made possible due to the special modular design. The valve is suitable as a fuel injector in particular for use in fuel injection systems of mixture-compressing, spark ignition internal combustion engines.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
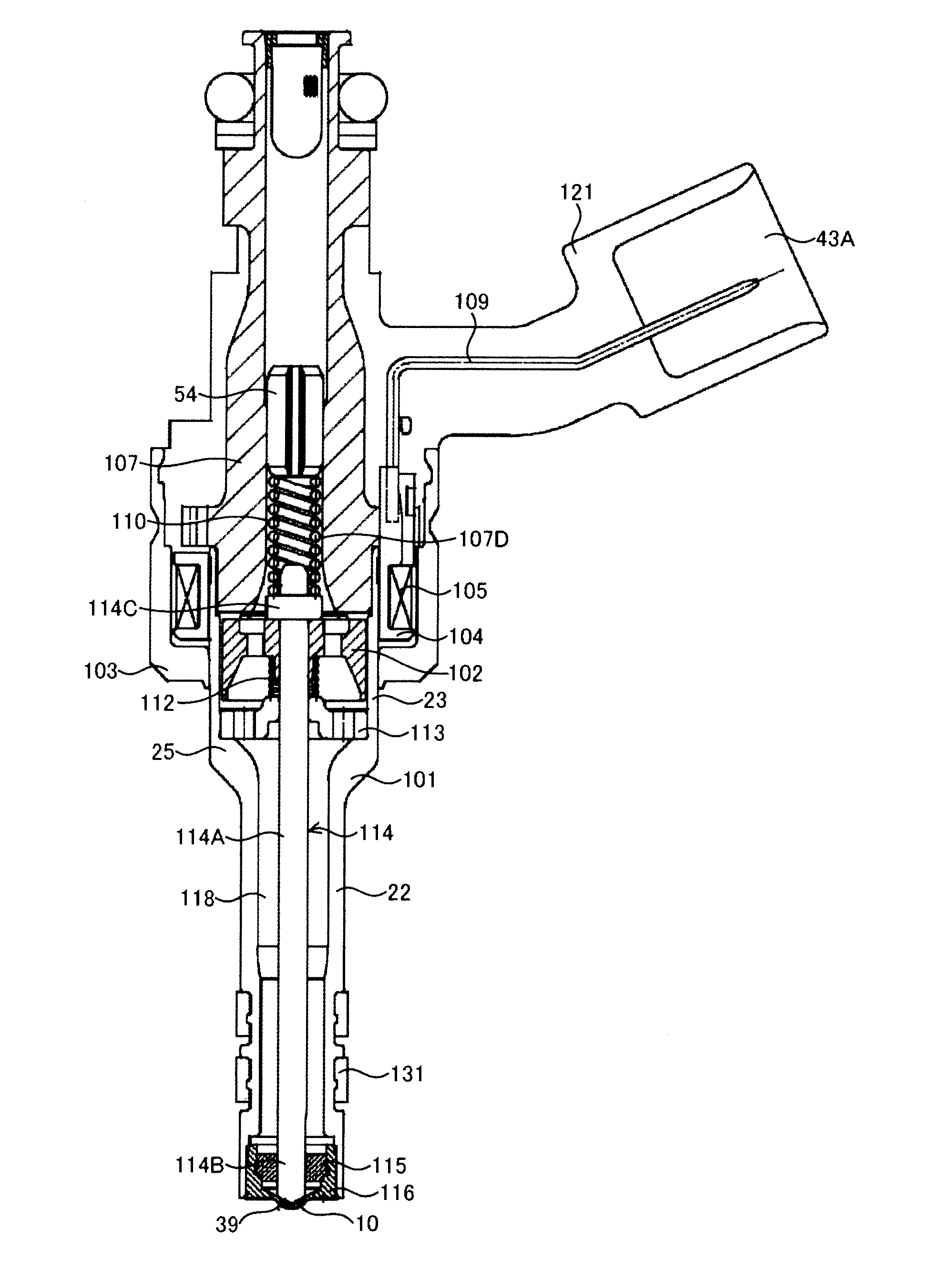
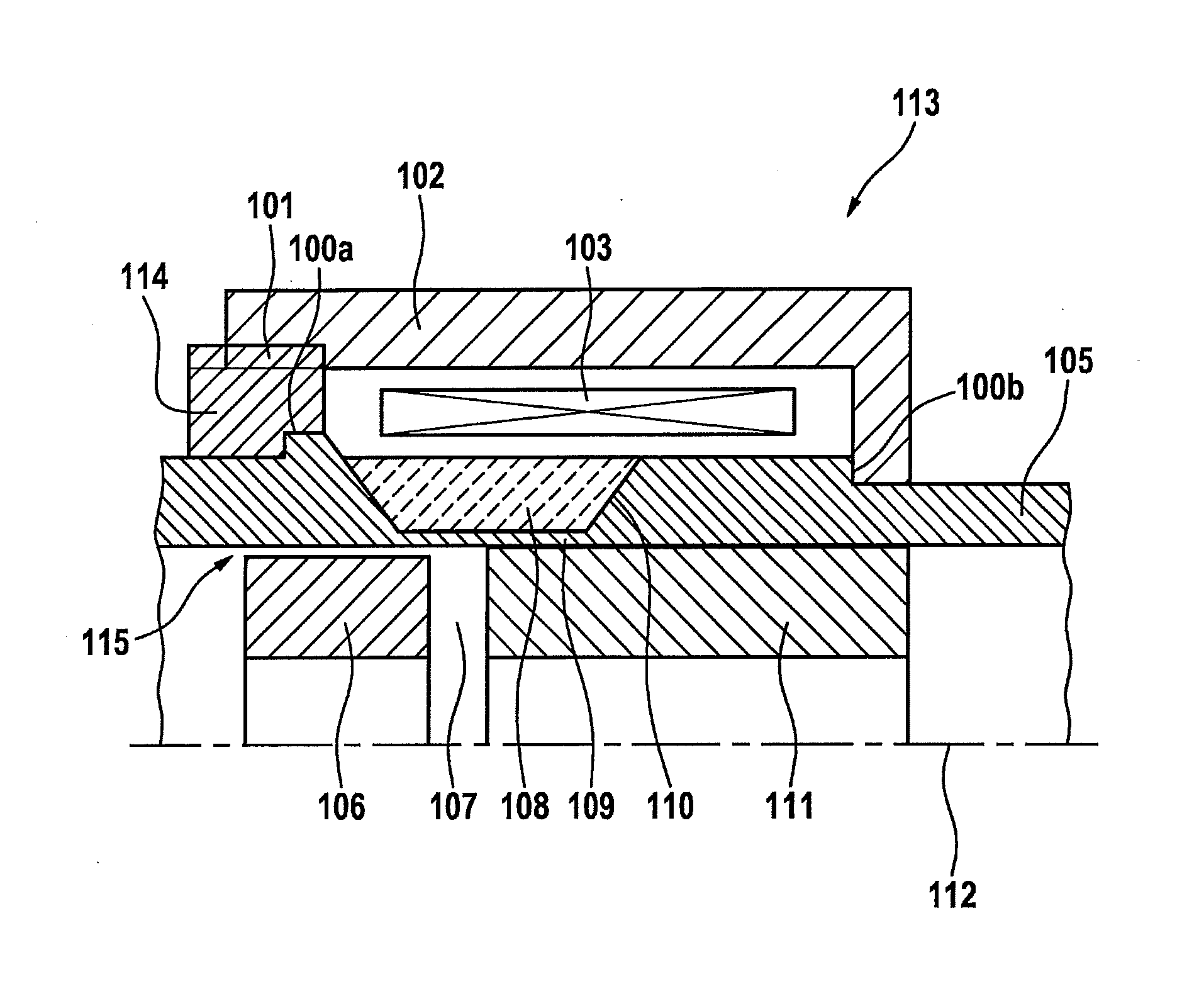
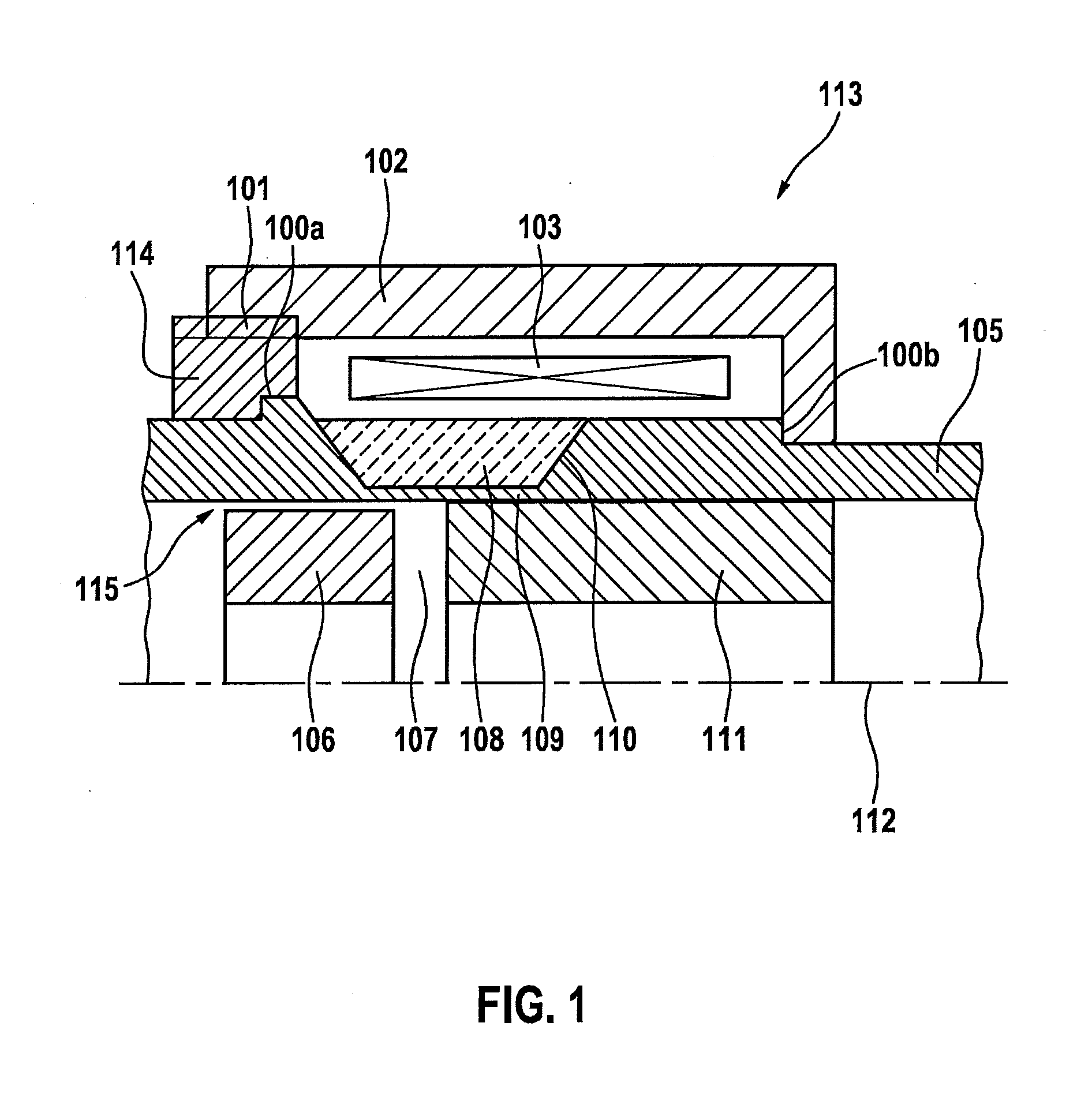
Fuel injector
InactiveCN103016226AImprove injection volume accuracyReduce fitWear reducing fuel injectionMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionEngineeringMagnetic flux
The invention provides a fuel injector. To improve the injection fuel mass accuracy of a fuel injector, it is necessary to make the fuel injector perform seat valve (114B) opening and closing operation quickly. When the shapes of a fixed core (107) and an anchor (102) are optimized to improve the responsiveness of a magnetic flux, it is necessary to ensure a sufficient fuel path area while preventing adhesion by making the adherence phenomenon rarely occur between an end face of the anchor (102) and an end face of the fixed core (107). To achieve the above object, in the invention, a through hole passing through an anchor (102) forming an armature (114) of an electromagnetic fuel injector from a face of the anchor (102) facing a fixed core (107) to a back face is formed so that the through hole has a large-diameter portion (125) and a small-diameter portion (124), wherein the large-diameter portion (125), relative to the small-diameter portion (124), is located at the upstream side and shifts to an outer circumferential side.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD
Solenoid valve and fuel injection valve having the same
ActiveUS7942381B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSolenoid valveEngineering
Owner:DENSO CORP
Fuel injection valve
ActiveUS20130306762A1Compact designEasy to moveMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionMagnetsCombustionModular design
A fuel injector for fuel-injection systems of internal combustion engines includes an electromagnetic actuating element having a solenoid coil, a fixed core, an outer magnetic circuit component, and a movable armature for actuating a valve-closure element, which cooperates with a valve-seat surface provided on a valve-seat element. The injector is characterized by its extremely small outer dimensions. The flexibility in the installation of fuel injectors of varying valve lengths, which is made possible very simply due to the special modular design, is significantly increased in this manner. An optimized dimensioning of the electromagnetic circuit allows for a DFR (dynamic flow range) greater than 17, the DFR being defined as the quotient of qmax / qmin.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injection valve
ActiveUS20130256430A1Compact type of constructionEasy to moveMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSpray nozzlesCombustionEngineering
A fuel injector for fuel-injection systems of internal combustion engines. The valve includes an electromagnetic actuating element having a solenoid coil, a fixed core, an outer magnetic-circuit component and a movable armature to actuate a valve-closure member which cooperates with a valve-seat surface provided on a valve-seat member. The valve is characterized by its extremely small outside dimensions. The entire axially movable valve needle, including armature and valve-closure member, has a mass of only m<=0.8 g. The valve is suitable as a fuel injector, especially for use in fuel-injection systems of mixture-compressing internal combustion engines with externally supplied ignition.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Fuel injection control device and fuel injection system
ActiveUS9765723B2Small diameterIncrease fuel pressureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesHigh pressureFuel supply
A fuel injection control device is adapted for a fuel injection system including an injector and a high-pressure pump that raises pressure of fuel and supplies the fuel to the injector. The fuel injection control device includes a selecting unit for selecting by which one of full lift injection and partial injection to inject fuel, and a pump control unit for controlling operation of the high-pressure pump such that a pressure of fuel supplied to the injector coincides with a target pressure. The selecting unit selects the partial injection when a required injection quantity of fuel is equal to or smaller than a partial maximum injection quantity. A fuel injection system includes the fuel injection control device, the injector, and the high-pressure pump.
Owner:DENSO CORP
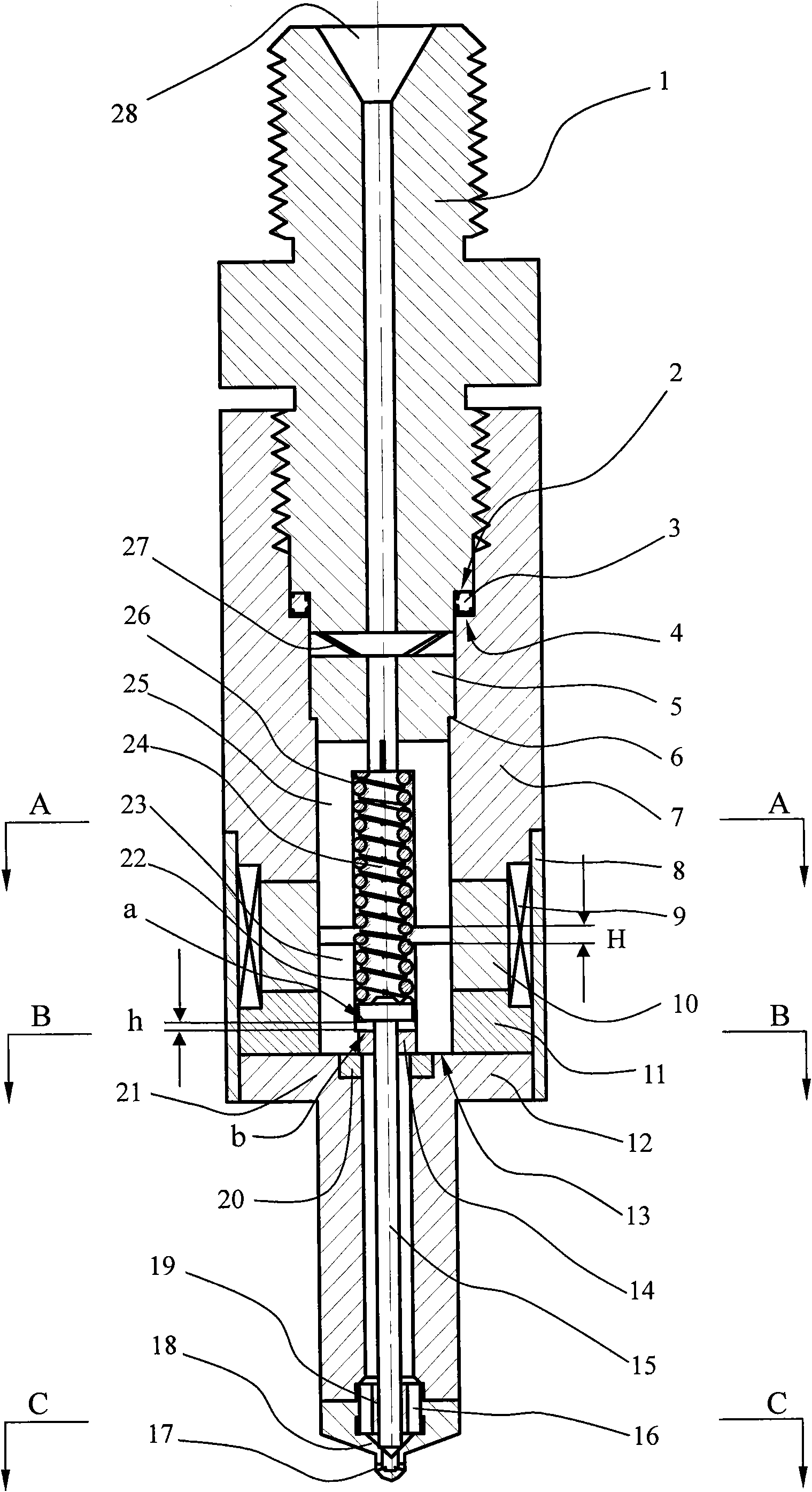
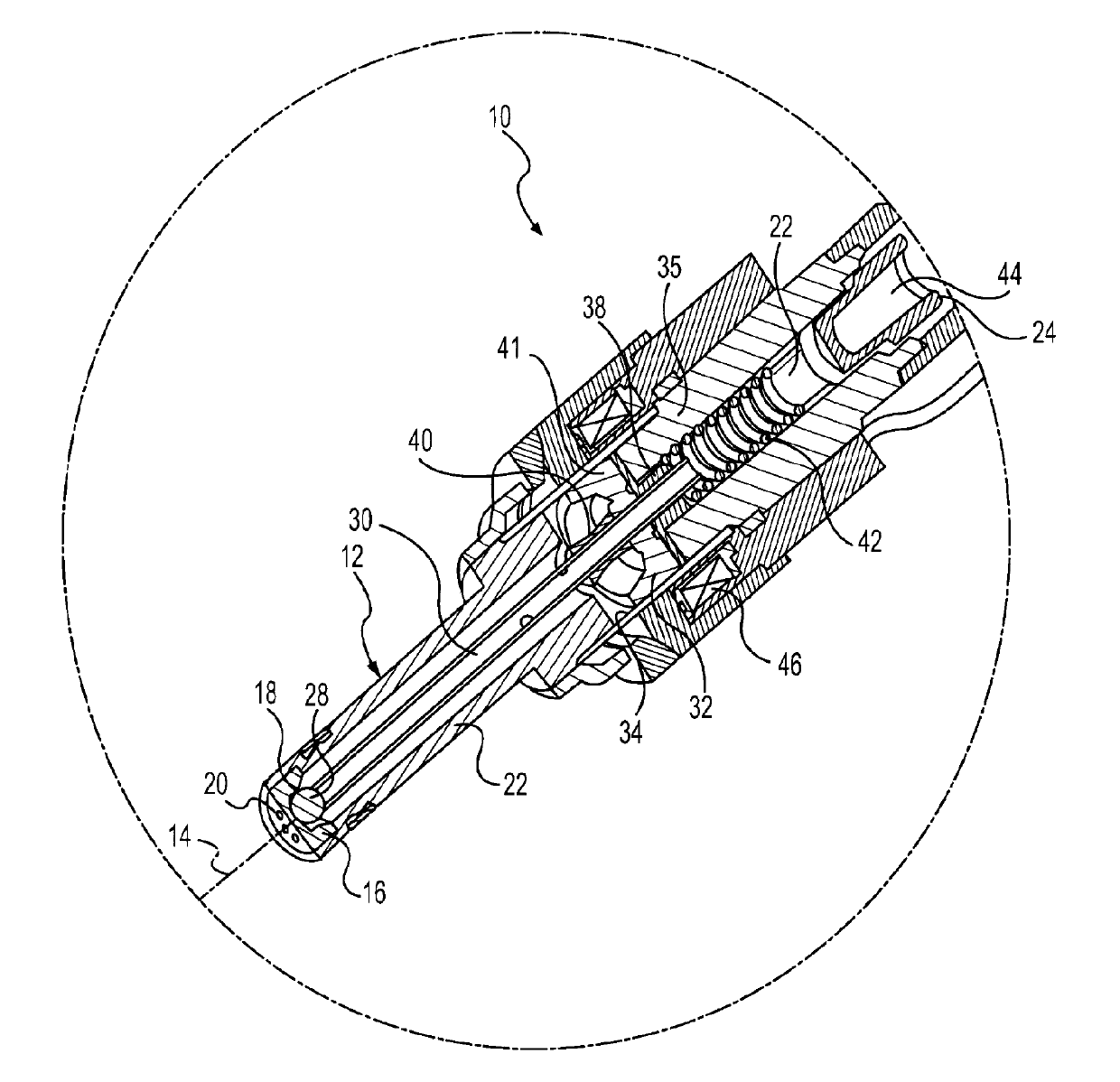
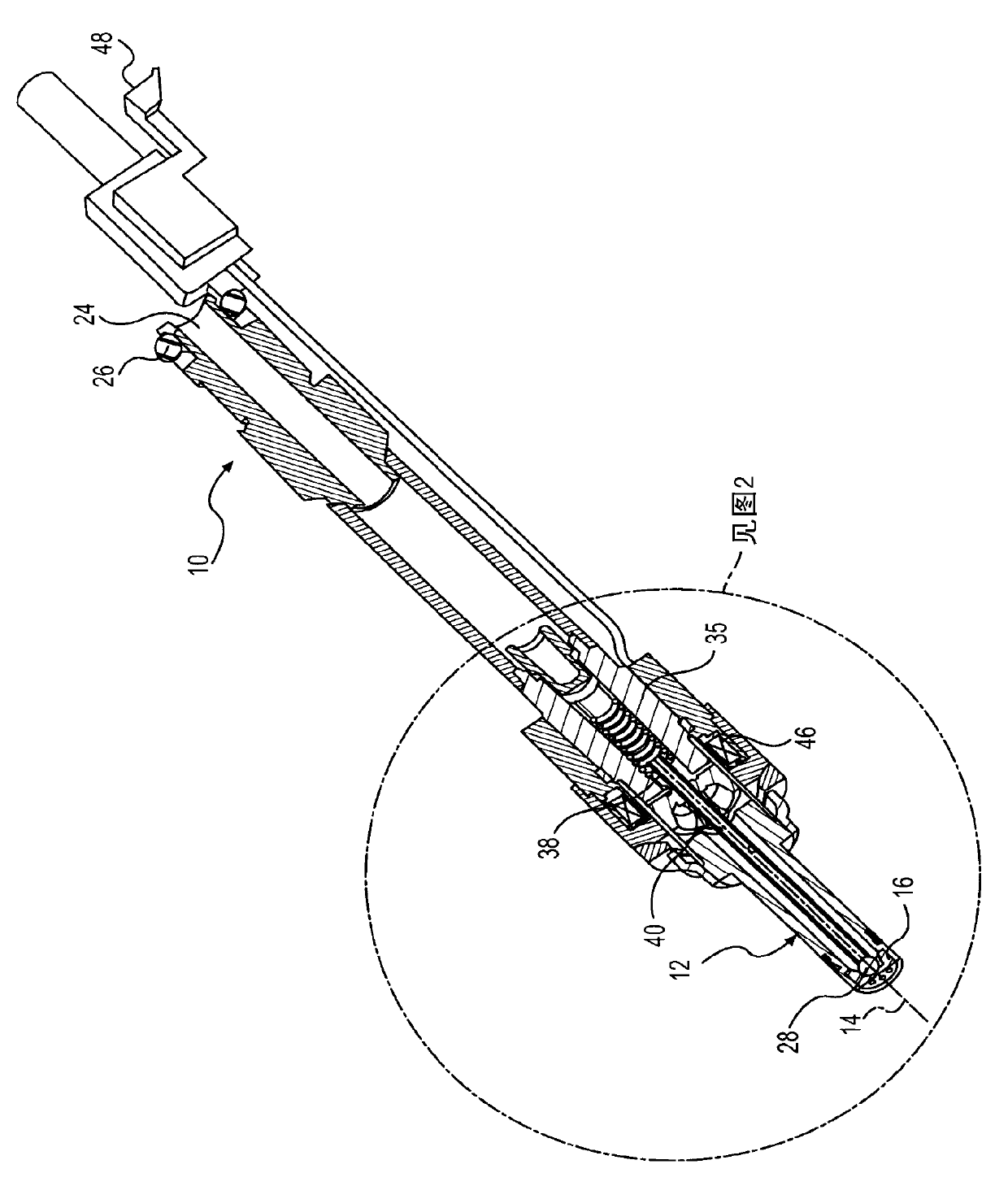
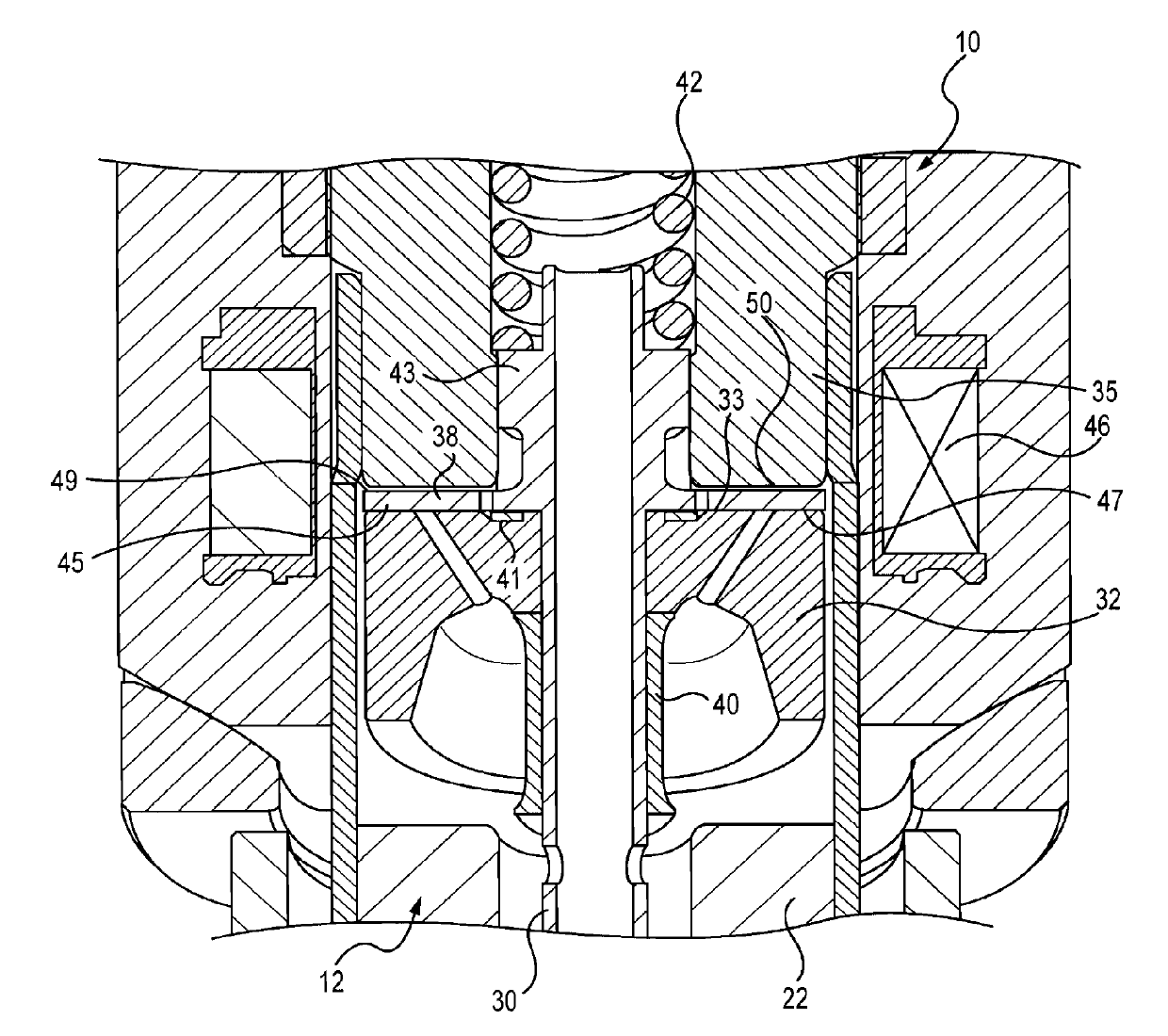
Automotive gasoline solenoid double pole direct injector
ActiveCN102869875ASpraying apparatusMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionAutomotive gasolinePole piece
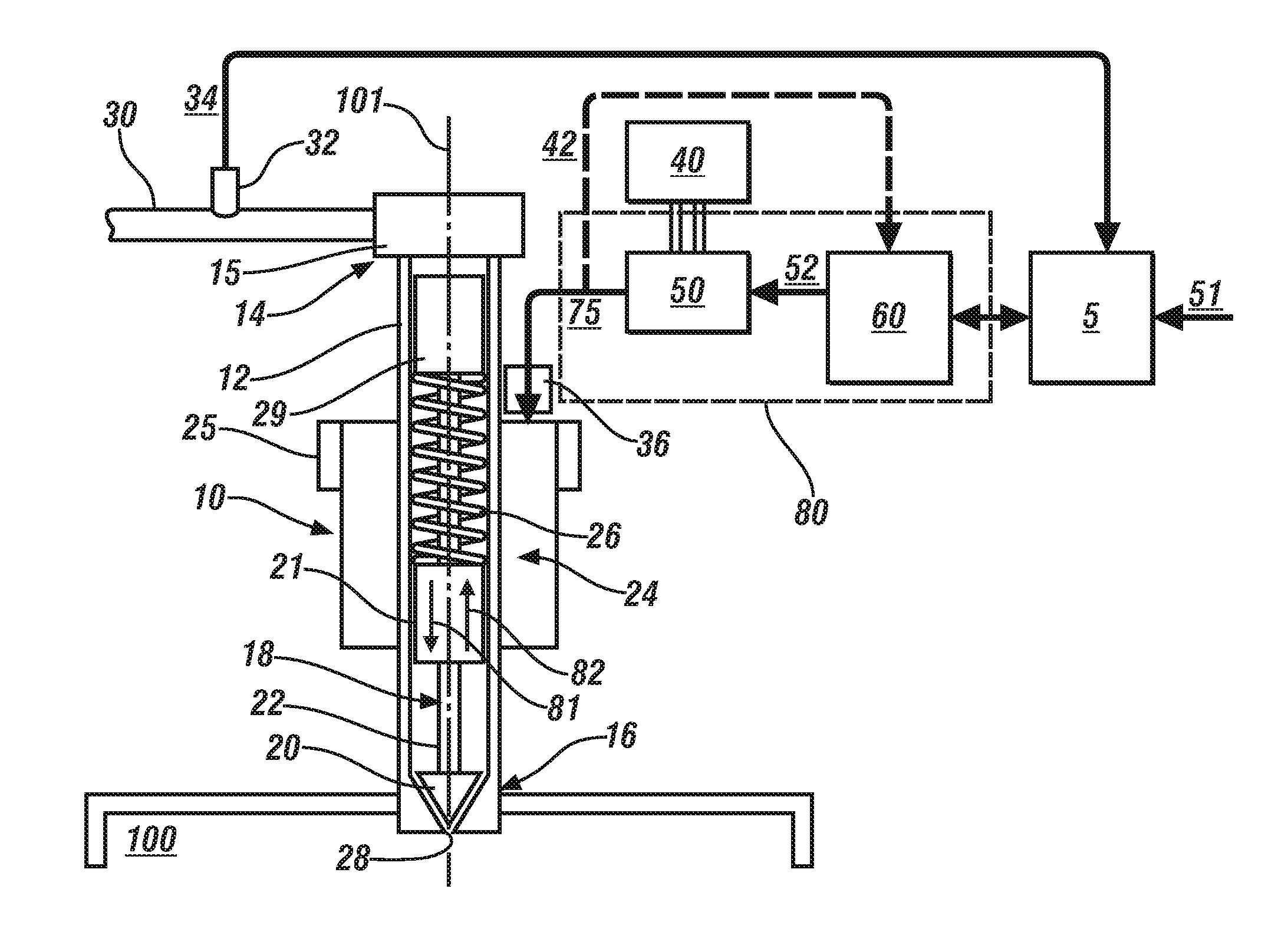
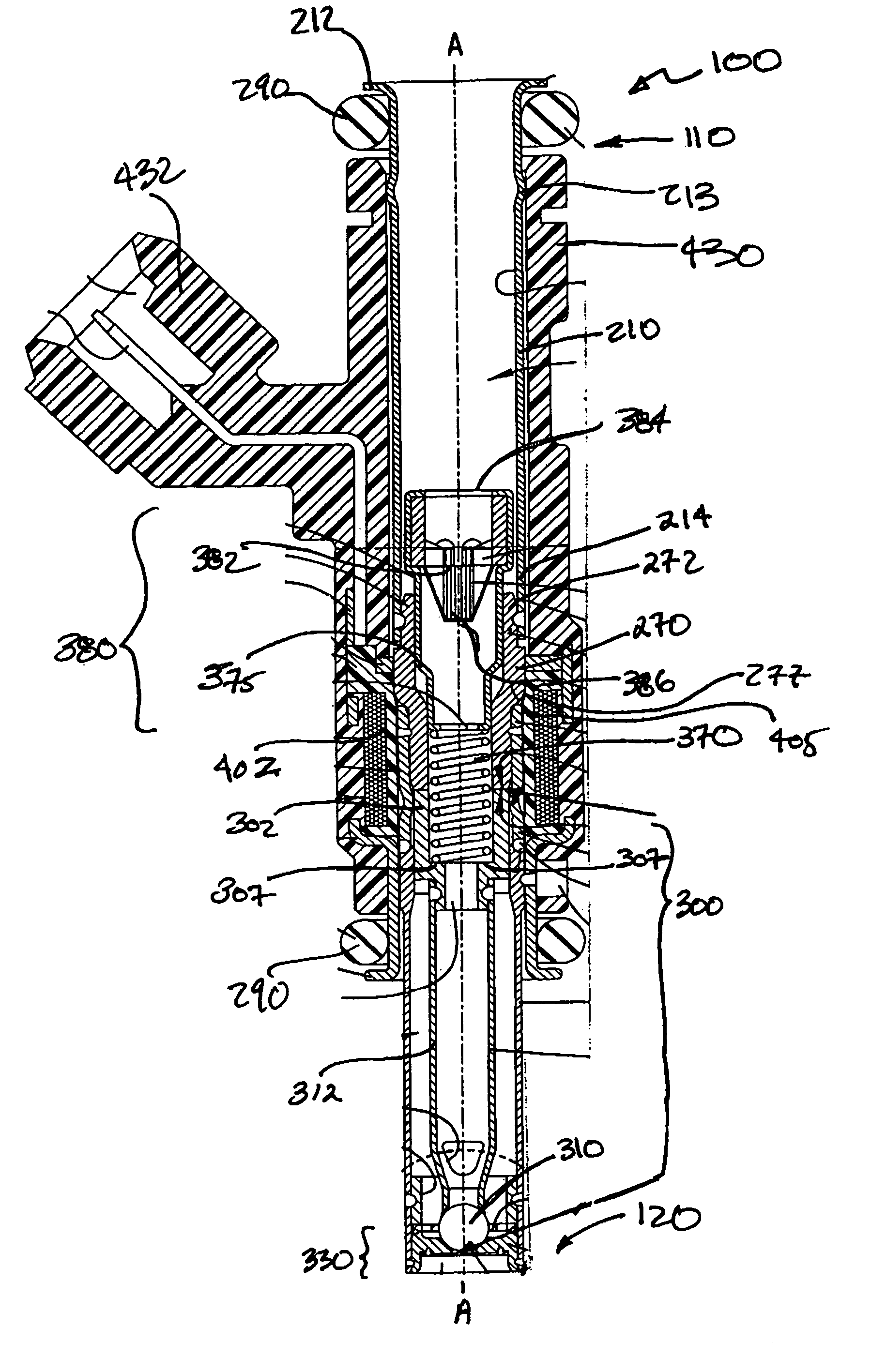
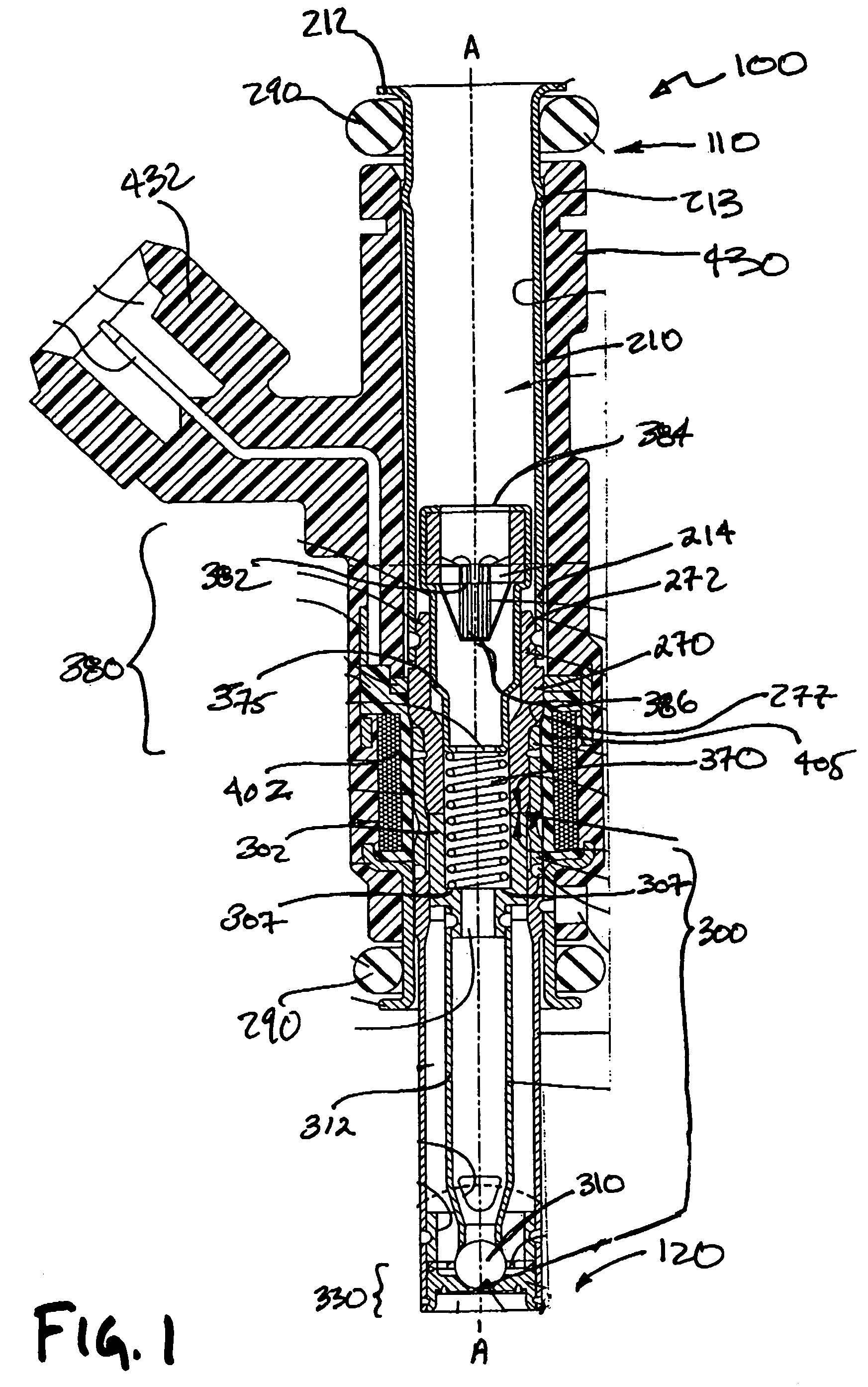
A direct fuel injector (10) includes a body (12) having a passage between inlet and outlet ends. A seat (16) is at the outlet end and a closure member (28) is associated with the seat. A needle member (30) is associated with the closure member and is movable with respect to a pole piece (35) between a first, closed position and a second, open position. A spring (42) biases the needle member to the first position. An armature (32) is free-floating with respect to the needle member. An intermediate pole structure (38) is coupled with the needle member and is disposed between the pole piece and the armature and is decoupled there-from. An armature stop (40) is coupled to the needle member and is spaced from the intermediate pole structure. An electromagnetic coil (46) is associated with the pole piece, intermediate pole structure and armature. The injector reduces bounce of the needle assembly.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA
Valve apparatus
ActiveUS20190032808A1Small volumeIncrease rangeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical controlElectrical and Electronics engineeringMagnetic field
In a valve apparatus, a housing includes a plurality of through holes through which a fluid flows. A first valve member opens and closes a first through hole. A second valve member opens and closes at least one second through hole. A fixed core does not move relative to the housing. A coil forms magnetic field. A first movable core moves integrally with the first valve member. When the coil forms the magnetic field, a magnetic attractive force is generated between the first movable core and the fixed core. A second movable core moves integrally with the second valve member. When the coil forms the magnetic field, a magnetic attractive force is generated between the second movable core and the fixed core. A magnetic constriction portion is provided between the fixed core and the first movable core. The second through hole is opened after the first through hole is opened.
Owner:DENSO CORP
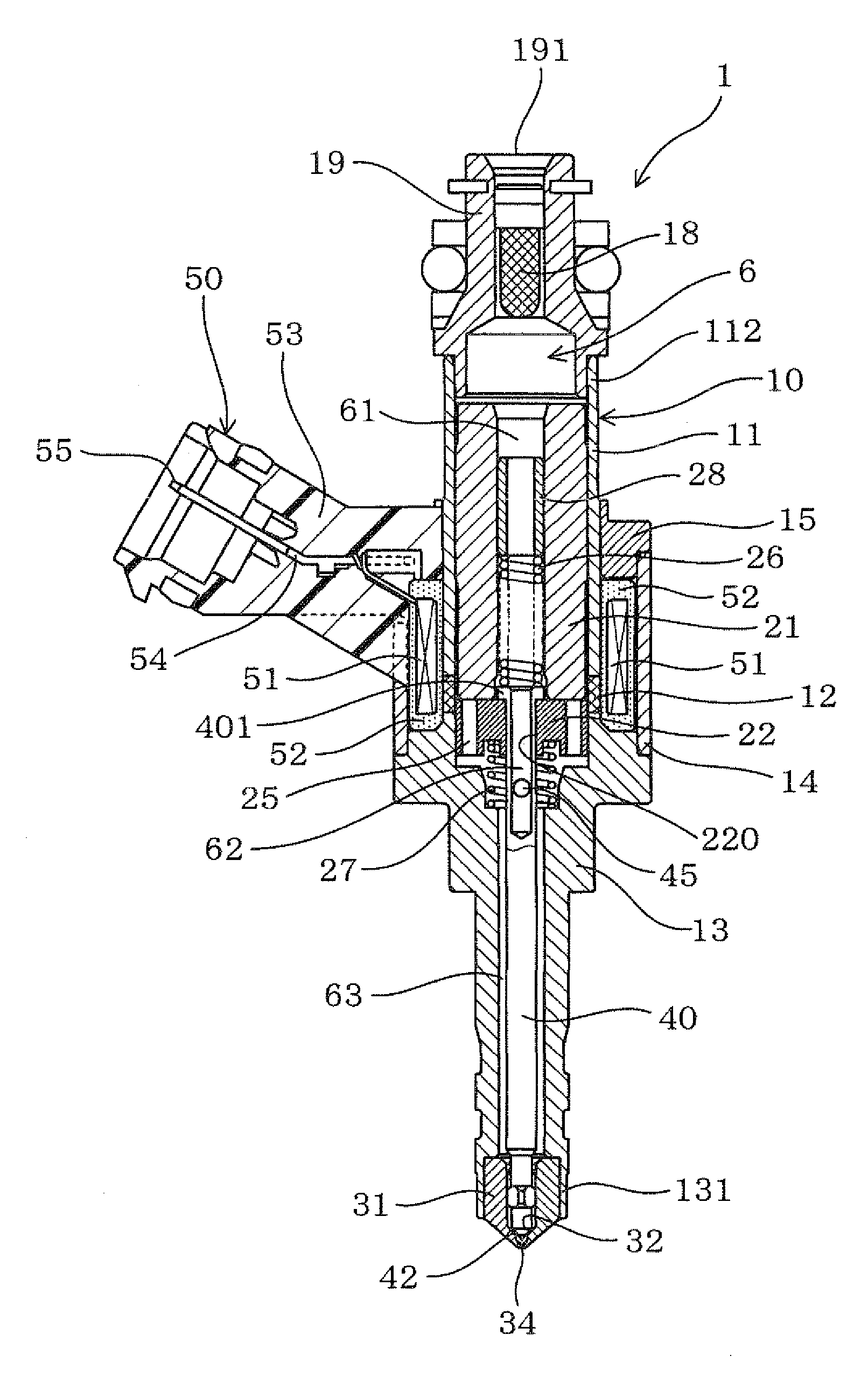
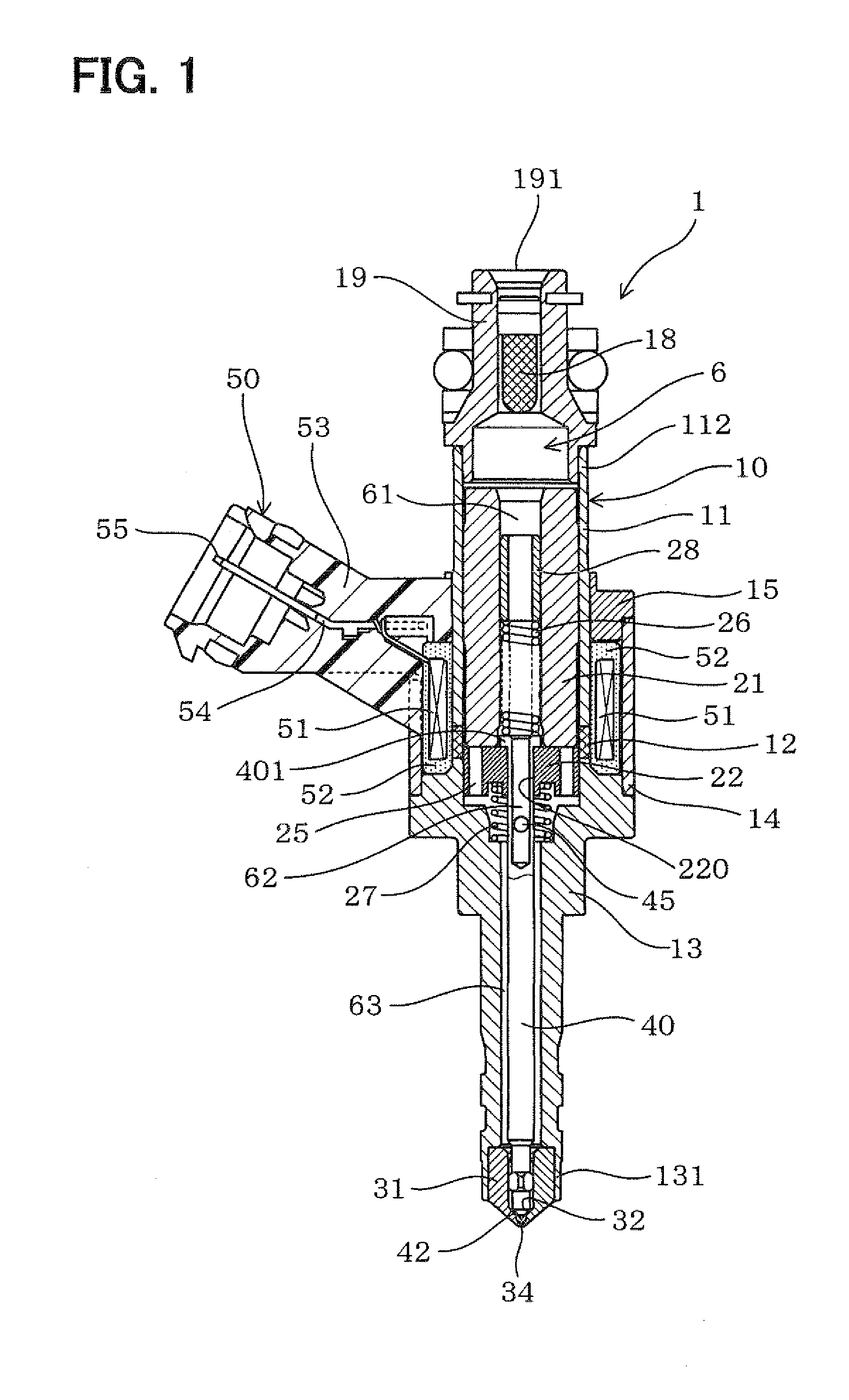
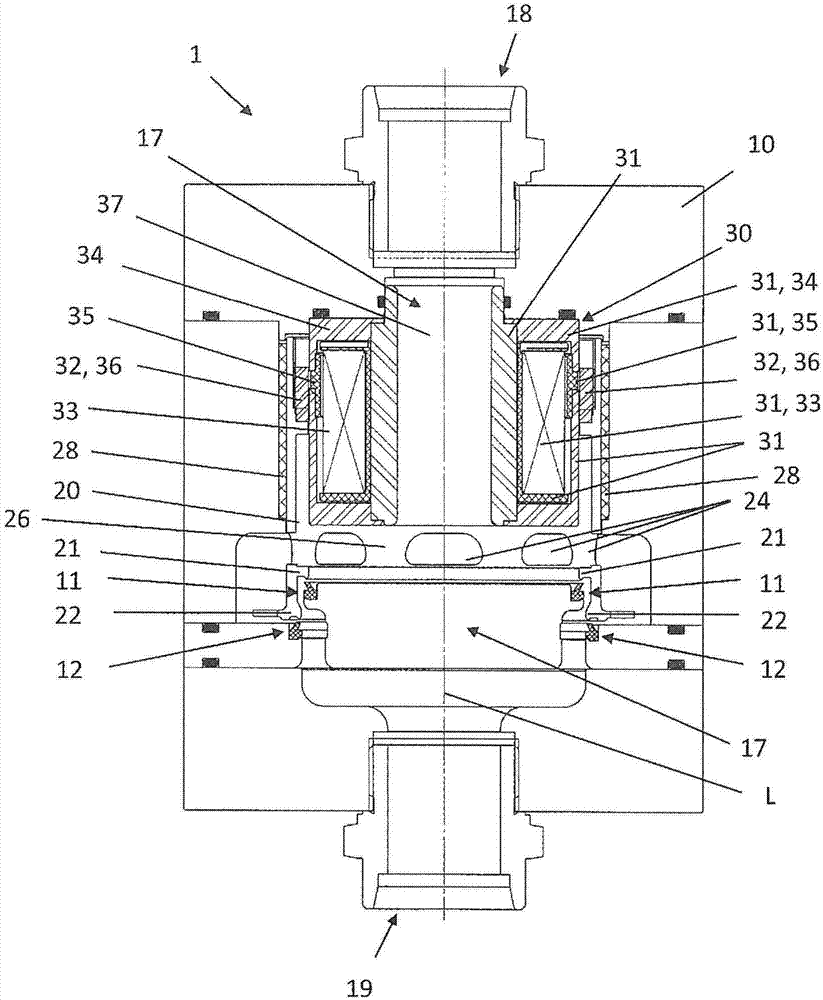
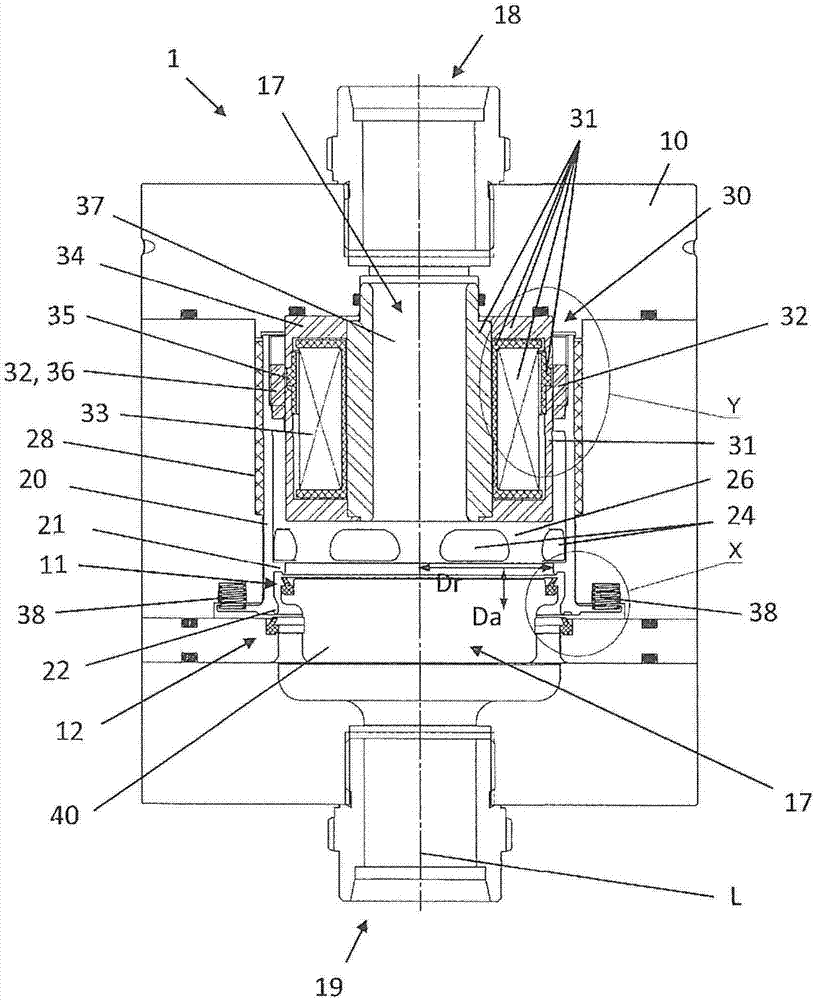
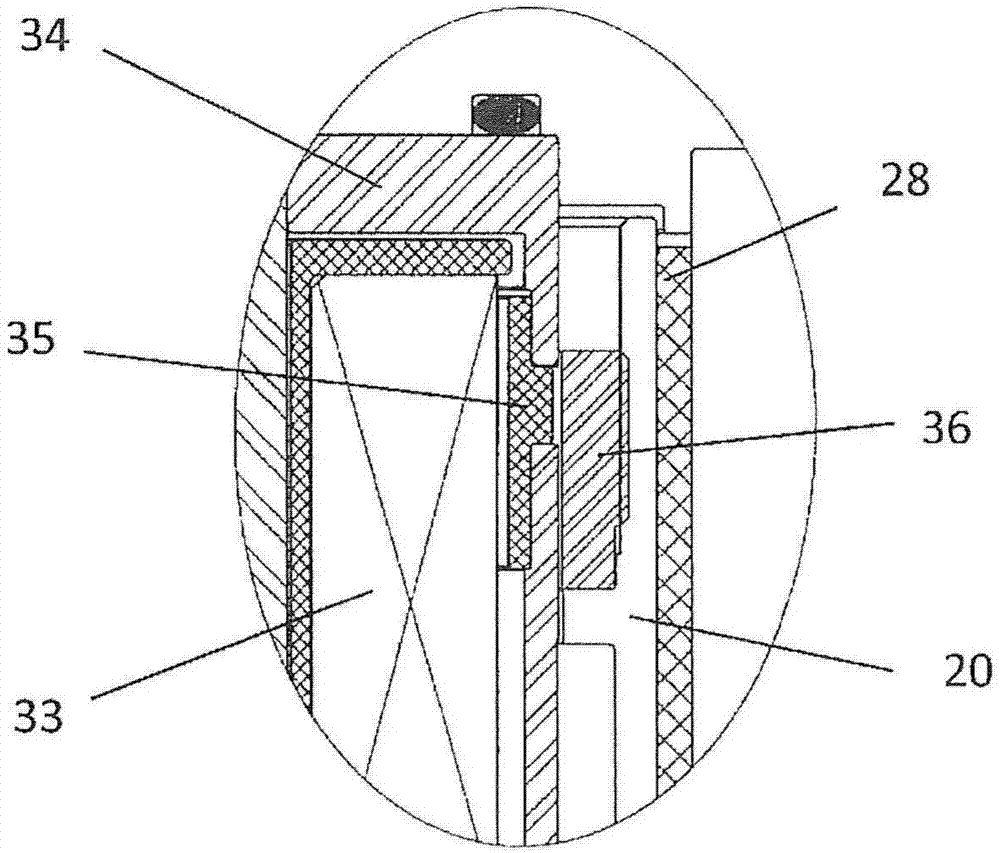
Fluid Injector And Method For Operating Fluid Injector
ActiveCN104343603AIncrease power consumptionQuality improvementElectrical controlMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionBiomedical engineeringFluid injection
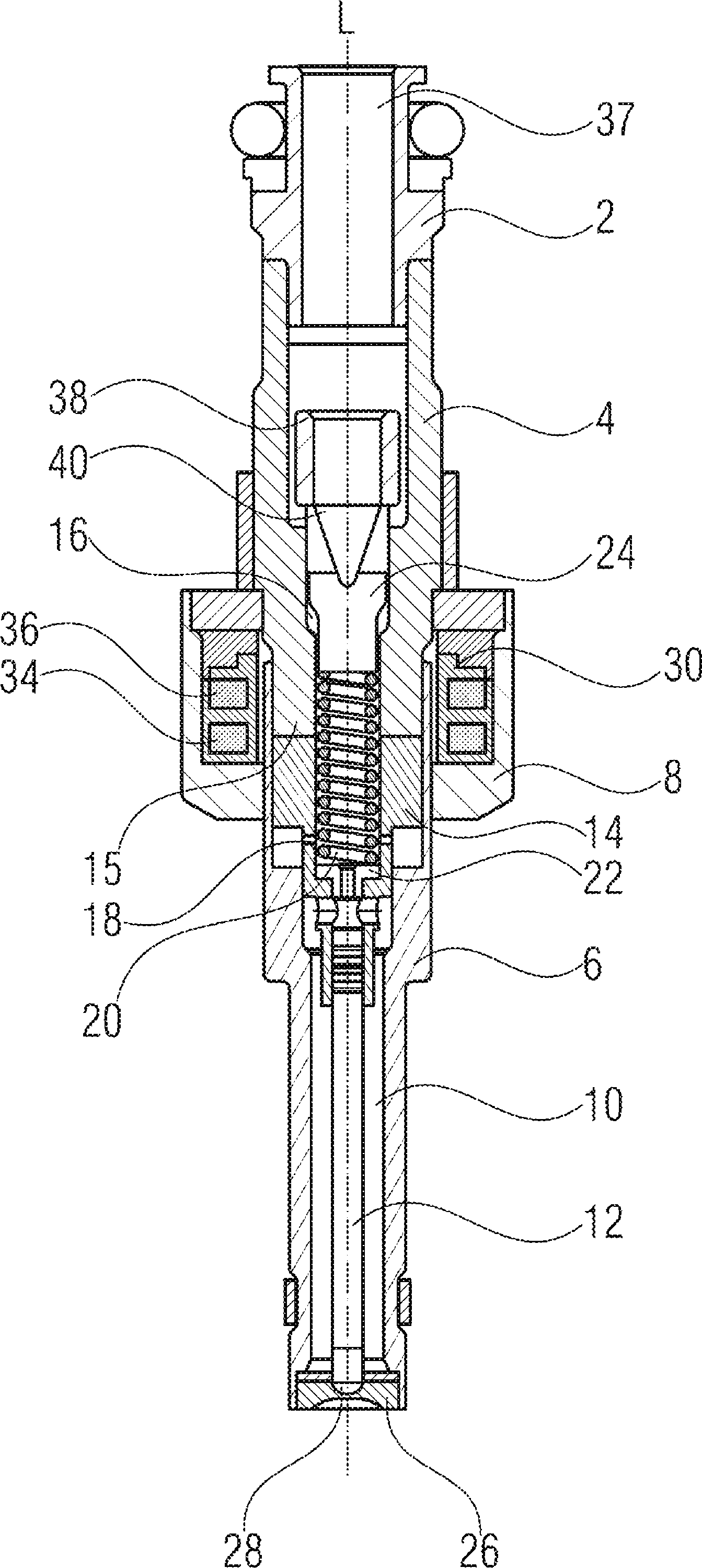
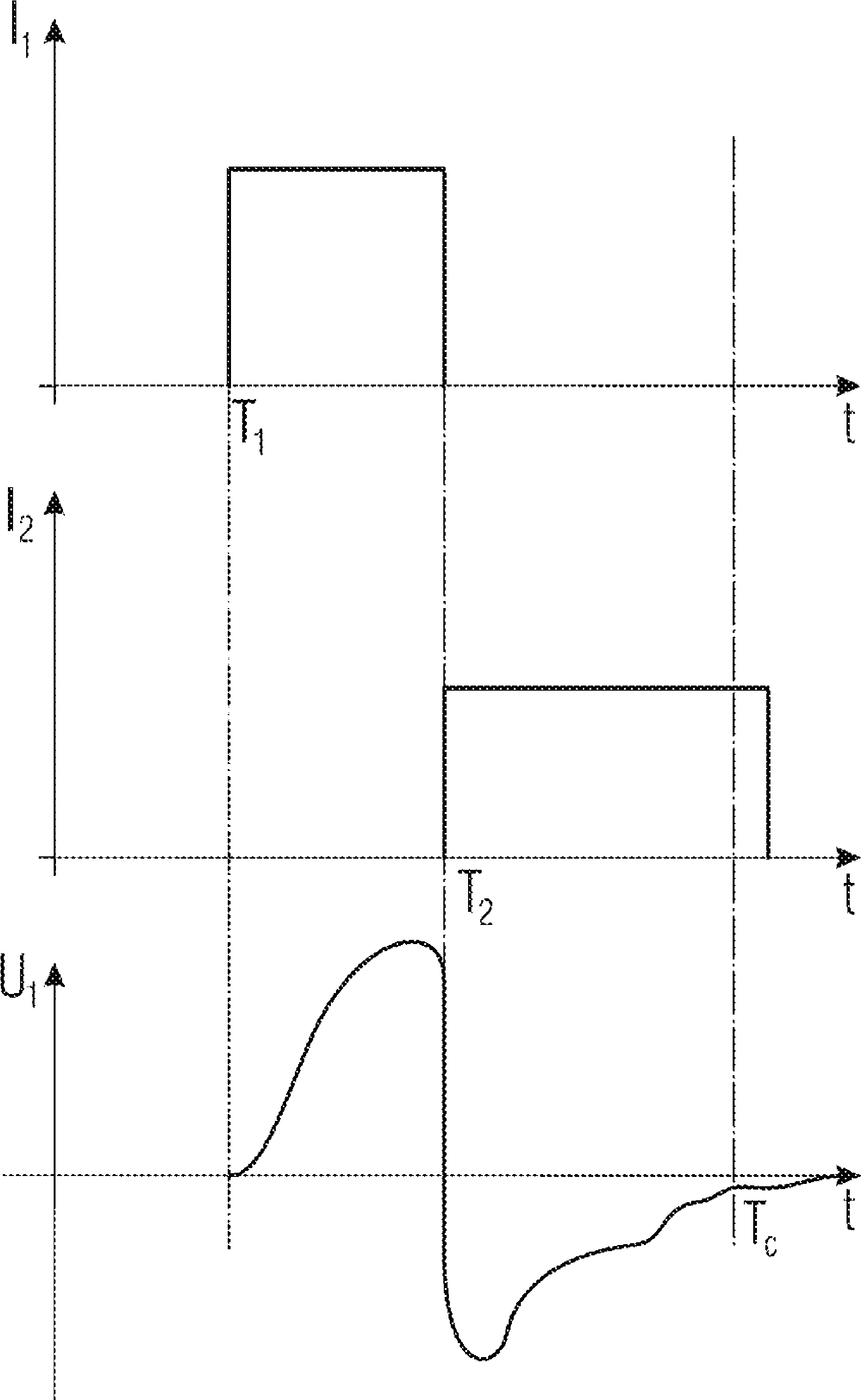
A fluid injector is specified. The fluid injector has a longitudinal axis (L) and comprises a valve body (6), a valve needle (12), being received in the valve body (6), being axially moveable and being operable to prevent a fluid injection in a closing position and to permit the fluid injection in further positions, an armature (14) being mechanically coupled to the valve needle (12) so that it is operable to displace the valve needle (12) away from the closing position, and a solenoid assembly (30) comprising at least a first and second coil (34, 36) and being operable to magnetically actuate the armature (14) via an electrical signal (I 1 ). A method for operating the fluid injector comprises applying the electrical signal (I 1 ) to the first coil (34) to generate a primary magnetic field to move the armature (14) for displacing the valve needle (12) away from the closing position, evaluating a voltage (U 1 ) across terminals of the first coil (34), and controlling the second coil (36) with a further electrical signal (I 2 ) to saturate a magnetic field in a portion of the valve body (6) which is located between the armature (14) and the solenoid assembly (30) during evaluating the voltage (U 1 ).
Owner:VTESCO TECH GMBH
Deep pocket seat assembly in modular fuel injector with fuel filter mounted to spring bias adjusting tube and methods
ActiveUS20060071101A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionEngineeringFuel filter
A fuel injector and various methods relating to the assembly of the fuel injector. The fuel injector includes a power group subassembly and a valve group subassembly having a respectively connected first and second connector portions. The power group subassembly includes an electromagnetic coil, a housing, at least one terminal, and at least one overmold formed over the coil and housing. The valve group subassembly insertable within the overmold includes a tube assembly having an inlet tube and a filter assembly. A pole piece couples the inlet tube to one end of a non-magnetic shell having a valve body coupled to the opposite end. An axially displaceable armature assembly confronts the pole piece and is adjustably biased by a member engaged with an adjusting tube with a filter assembly mounted thereon. The seat assembly includes a flow portion and a securement portion having respective first and second axial lengths at least equal to one another.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
Valve for controlling a fluid flow
ActiveCN107429635AReduce usageFast and precise switchingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesStructural engineeringActuator
The invention relates to a valve (1) having a valve housing (10) in which, for the purpose of opening and closing a fluid connection between a fluid inlet (18) and a fluid outlet (19) of the valve housing (10), a closure element (20) having at least one sleeve section (23) can be moved along its sleeve longitudinal axis (L) by means of an actuator (30), wherein the actuator (30) has parts (31, 32) that are respectively stationary and movable with respect to the valve housing (10) and at least the movable parts (32) of the actuator (30) and the closure element (20) are arranged entirely within a fluid space (17), enclosed by the valve housing (10), between the fluid inlet (18) and the fluid outlet (19), and wherein the valve (1) has at least one double-seal seat which has on the sleeve section (23) a first and a second seal device (21, 22), spaced apart therefrom along the sleeve longitudinal axis (L), and on the valve housing (10) a first and a second counter-seal device (11, 12), accordingly spaced apart equally, wherein in order to close the fluid connection the first seal device (21) is in sealing contact with the first counter-seal device (11) along a first closed seating line and the second seal device (22) is in sealing contact with the second counter-seal device (12) along a second closed seating line, and wherein, with regard to the at least one double-seal seat, the ratio between a first area enclosed by the first sealing line in projection along the sleeve longitudinal axis (L) and a second area enclosed by the second sealing line in projection along the sleeve longitudinal axis (L) is between 6 / 10 and 10 / 6.
Owner:오이겐자이츠아게
Electromagnetic Valve
ActiveUS20170074222A1Relieve pressureSuppression of deformationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesWear reducing fuel injectionProduction rateSolenoid valve
It is important not to form the partial bump in the collision structural part, however the fixed core and the movable core are relatively inclined due to an accumulation of tolerances and therefore even if each collision structural part of the fixed core and the movable core in formed in a flat shape, the fixed core and the movable core are contacted with not the whole of the collision structural parts but a part of the collision structural parts at the moment of the collision. In a case in which the collision structural part is formed in a ring shape or an intermittent ring shape, the fixed core and the movable core are contacted with each other at outer peripheral parts. Thus, when the fixed core and the movable core are collided with each other, a high stress is applied to the outer peripheral parts contacted first. Accordingly, the shape of the outer peripheral parts of the collision structural parts is important, however since such a part, which is a tiny protruding shape, requires high processing accuracy, to reduce stress occurred during collision while keeping productivity is difficult. In the present invention, an R-shaped part and a flat part are provided in order from an outer peripheral side of a collision structural part. Further, the R-shaped part and the flat part are connected in a tangent manner.
Owner:HITACHI ASTEMO LTD
Electromagnetic switching valve and high-pressure fuel pump
ActiveCN108425775ALight in massReduced conversion timeElectrical controlNoise reducing fuel injectionEngineeringPole piece
The invention relates to an electromagnetic switching valve (30) for a fuel injection system (10) of an internal combustion engine having an actuator region (38) for moving a closing element (48) witha pole piece (40) and an armature (44) and a solenoid (52) Generating a magnetic flux in the armature (44) and pole piece (40), wherein the armature (44) has a magnetic flux concentration region (66).
Owner:VTESCO TECH GMBH
Method for manufacturing a magnetic separation for a solenoid valve
InactiveUS20140346383A1Inexpensively producibleImprove pressure resistanceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSolenoid valveMolten bath
A method for manufacturing a solenoid valve or a fuel injector, including a sleeve, a valve needle situated inside the sleeve in a radial direction and guided so as to slide, a solenoid coil situated outside of the sleeve in a radial direction, a magnetic core situated inside the sleeve in a radial direction, and a magnet armature situated inside the sleeve in a radial direction, axially opposite to the magnetic core; the magnet armature being situated on the valve needle, the sleeve having a low wall thickness in a thin-walled region situated between the magnet armature and the solenoid coil, the thin-walled region strengthened by a reinforcing element for absorbing radial forces; and a method step, during which, the reinforcing element is deposited onto the sleeve, in the thin-walled region, in a radial direction, outside of the sleeve, using a molten bath or cold gas spraying method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for producing a magnetic separation for a solenoid valve
InactiveCN103890871AHigh tensile strengthImprove rigidityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMagnetic flux influencing fuel injectionSolenoid valveMagnet coil
The invention relates to a method for producing a solenoid valve, in particular a fuel injection valve, wherein the solenoid valve has a sleeve, a valve needle, which is arranged inside the sleeve in a radial direction and guided in a displaceable manner, a magnetic coil, which is arranged outside the sleeve in a radial direction, a magnetic core, which is arranged inside the sleeve in a radial direction, and a magnetic armature, which is arranged inside the sleeve in a radial direction, axially opposite the magnetic core, wherein the magnetic armature is arranged on the valve needle, wherein the sleeve has a smaller wall thickness in a thin-walled region arranged between the magnetic armature and the magnetic coil, wherein the thin-walled region is reinforced by means of a reinforcement element to absorb radial forces, wherein the method has a method step in which the reinforcement element is applied to the sleeve in the radial direction outside the sleeve in the thin-walled region by means of a melt bath spraying method or by means of a cold gas spraying method during the method step.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com