Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
491results about "Conversion with cinematograph film standard" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
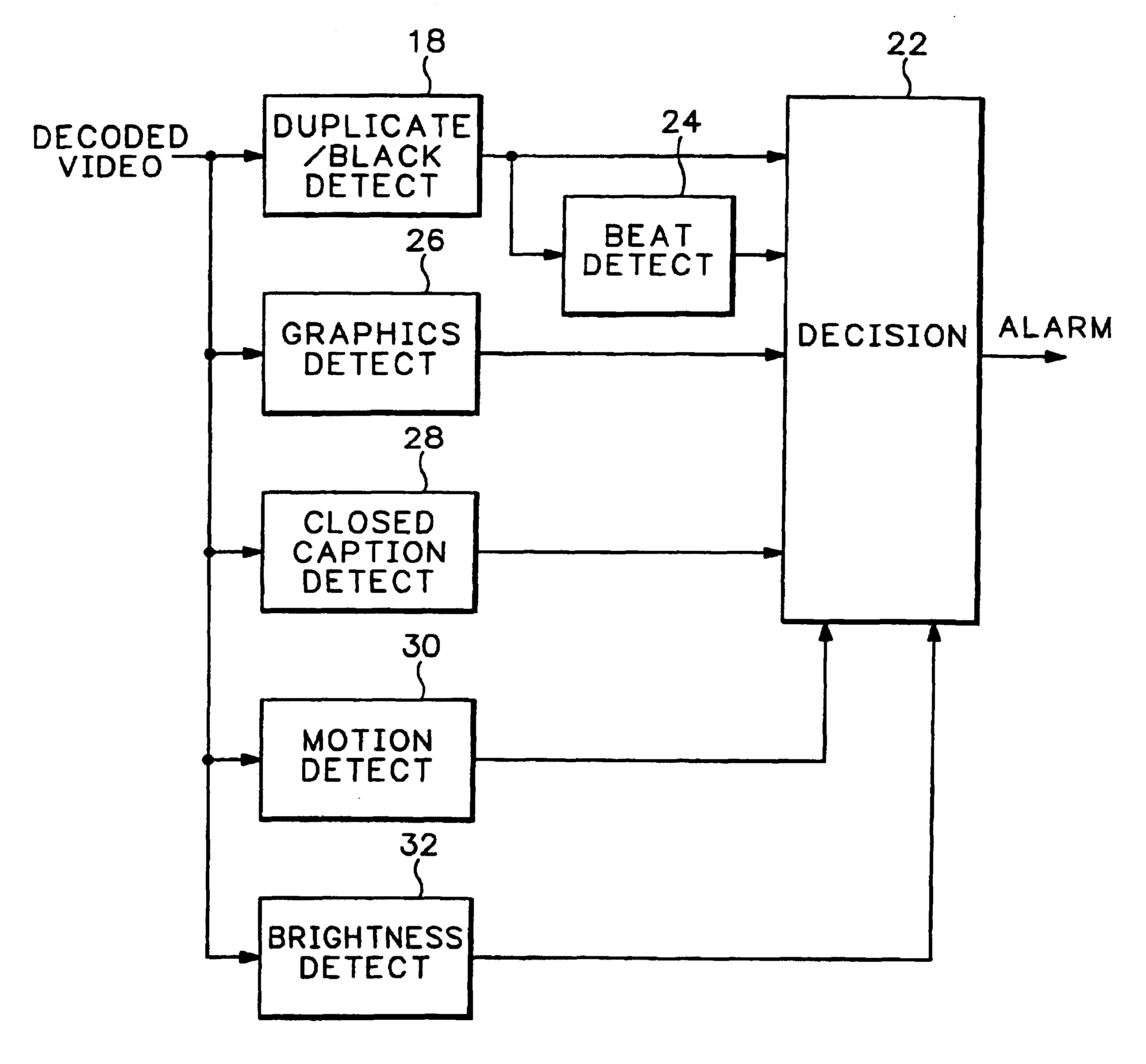
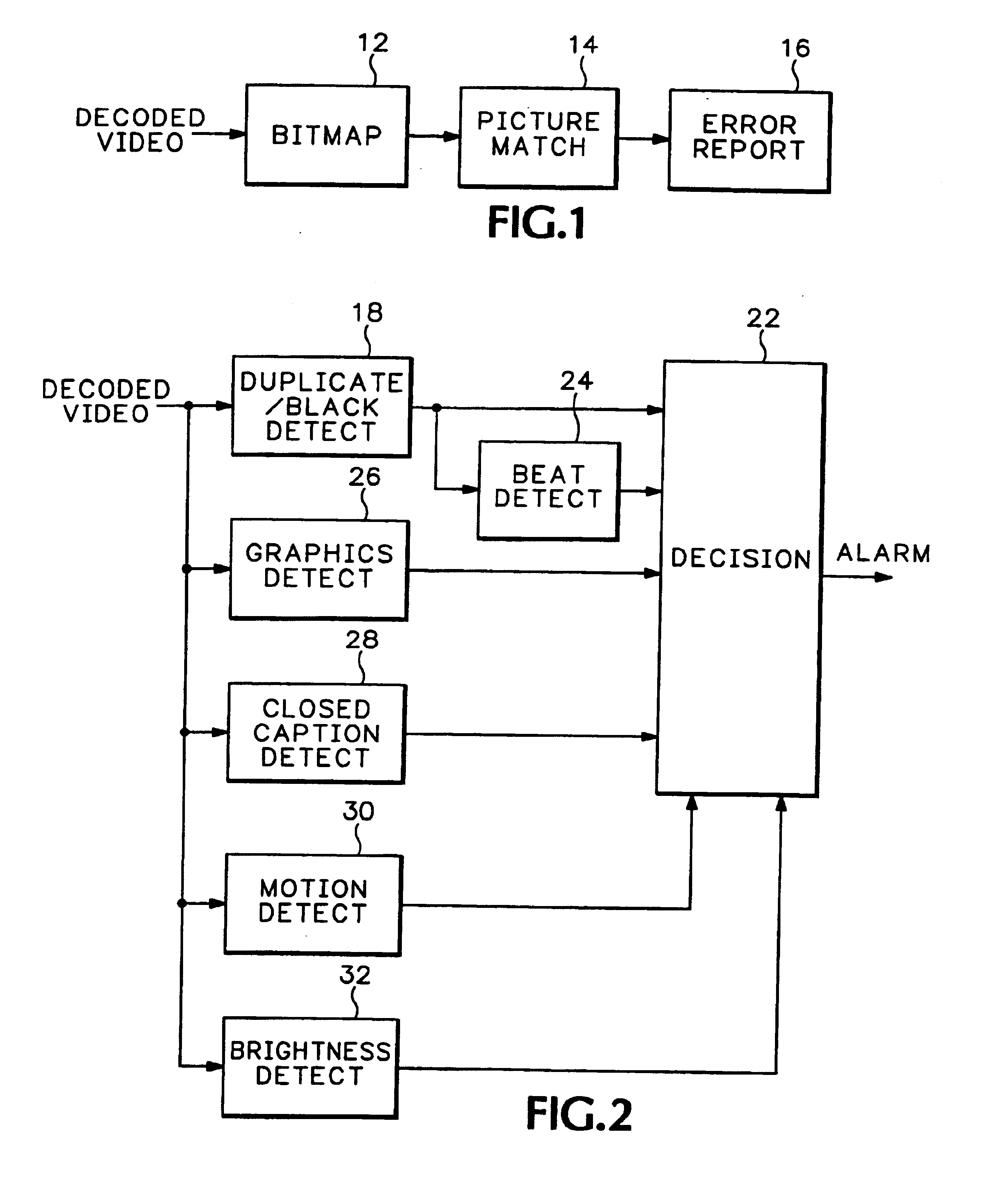
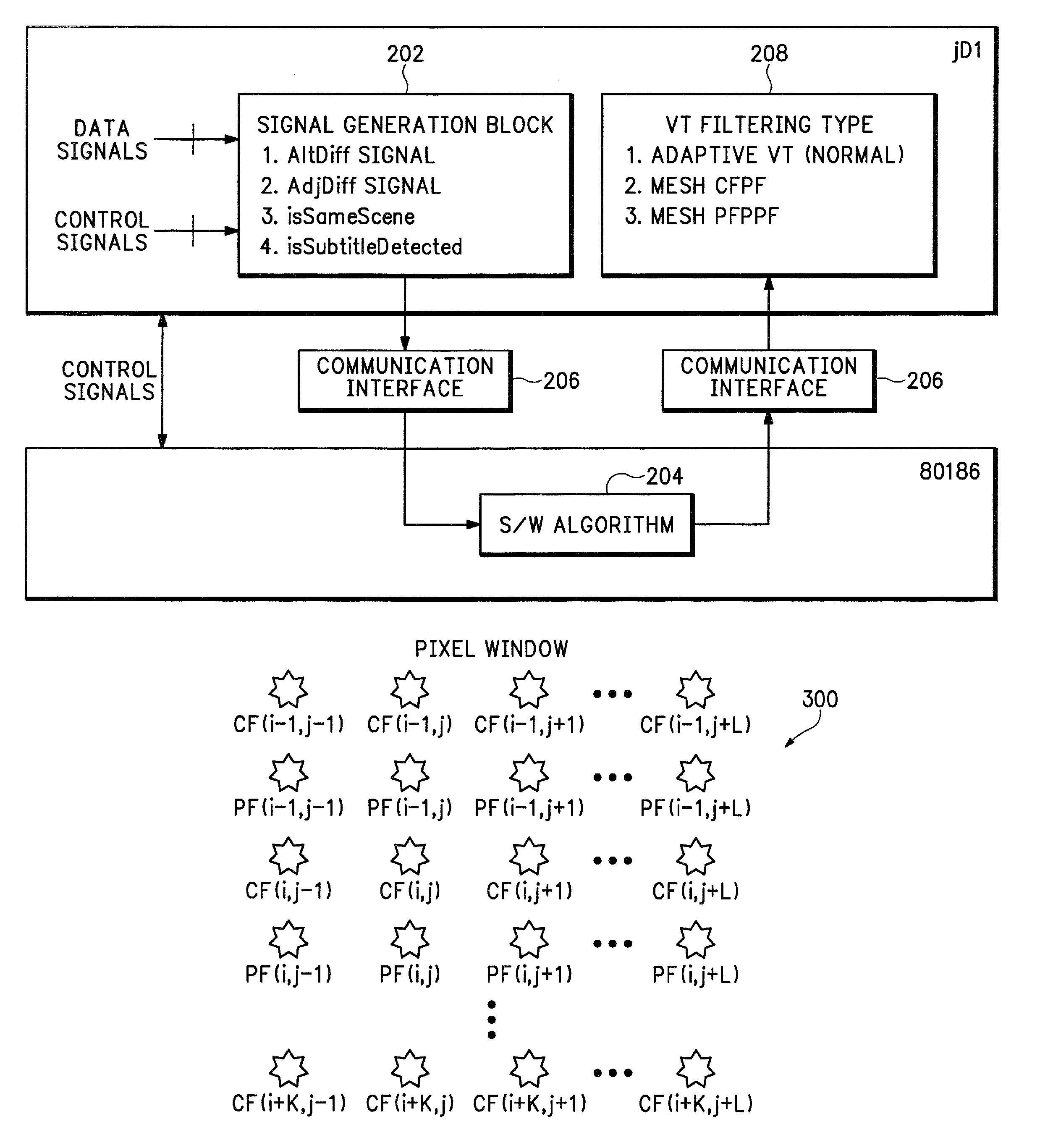
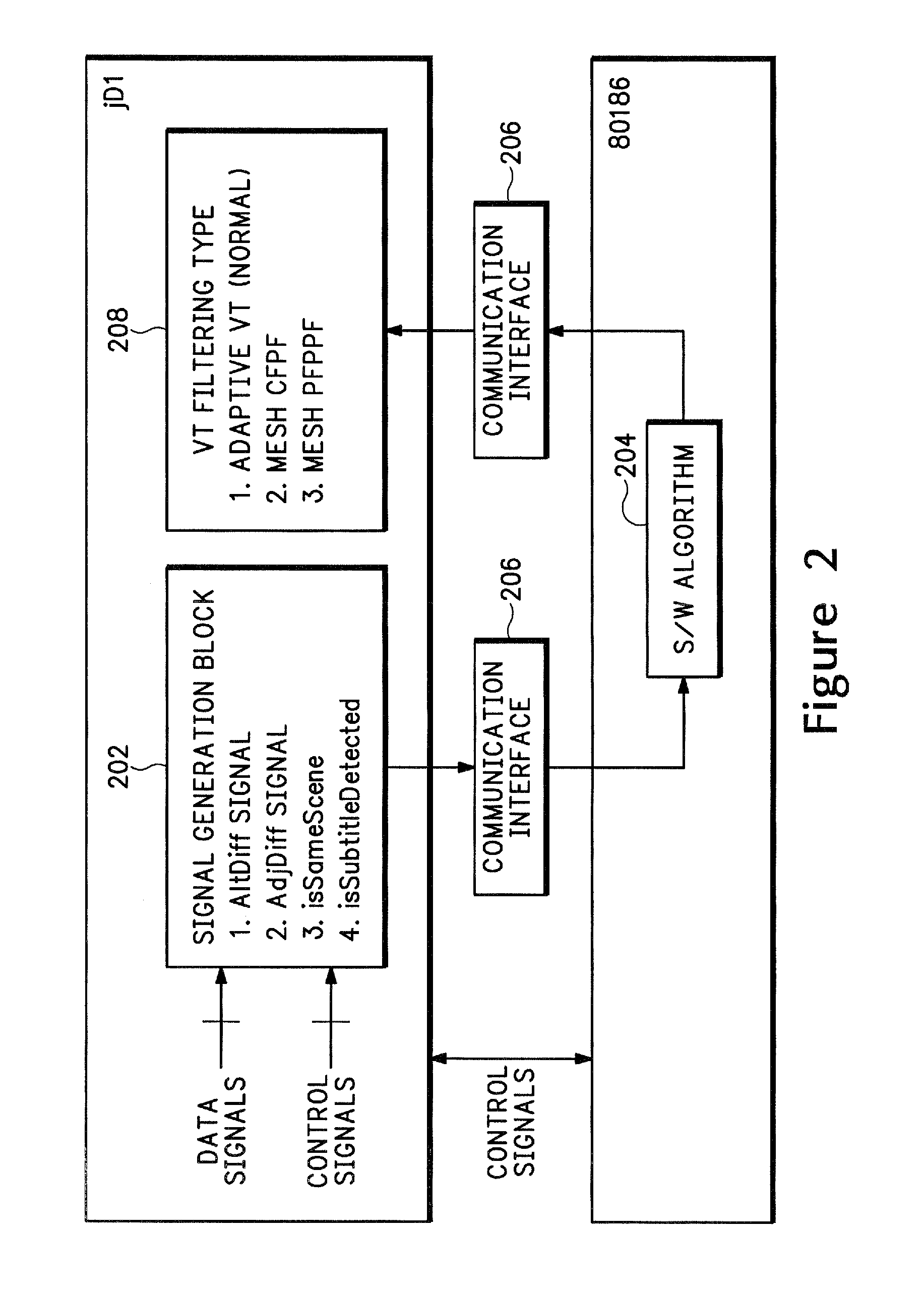
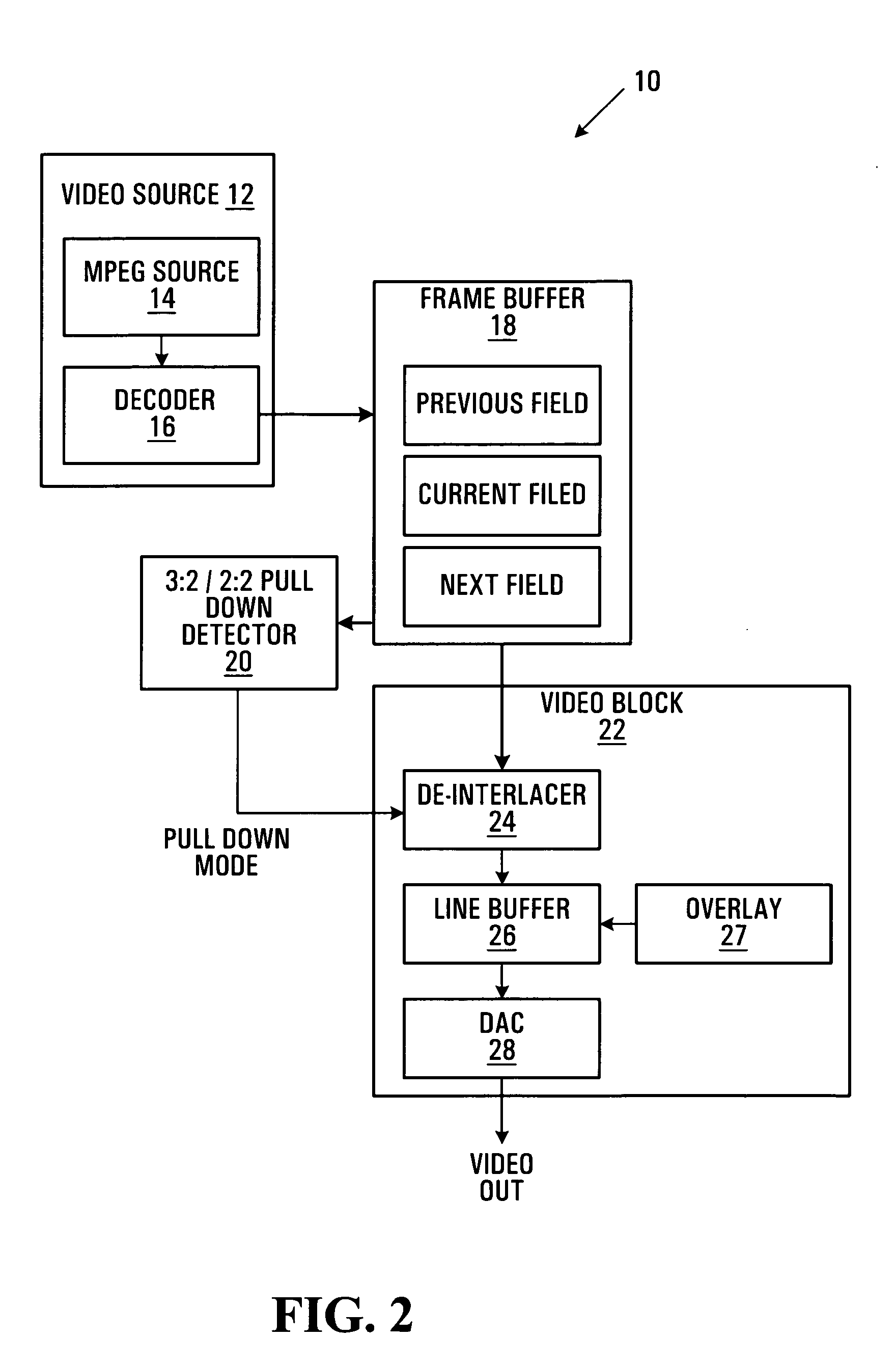
Detecting content based defects in a video stream
InactiveUS6906743B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsGraphicsPattern recognition
A method of detecting content based defects in previously compressed video streams decodes a video channel from the compressed video streams and performs a match on a frame / field basis between each frame / field of the video channel and a black frame / field and / or a previous frame / field to detect missing frames / fields and / or duplicate frames / fields. The number of consecutive missing and / or duplicate frames / fields are counted and an alarm signal is generated when the count exceeds a specified value. A beat pattern detector may be used to differentiate between 3 / 2 pulldown and other duplicate frame / field content errors, and a graphics detector may be used to differentiate between lettering / graphics stills and other duplicate frame / field content errors.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
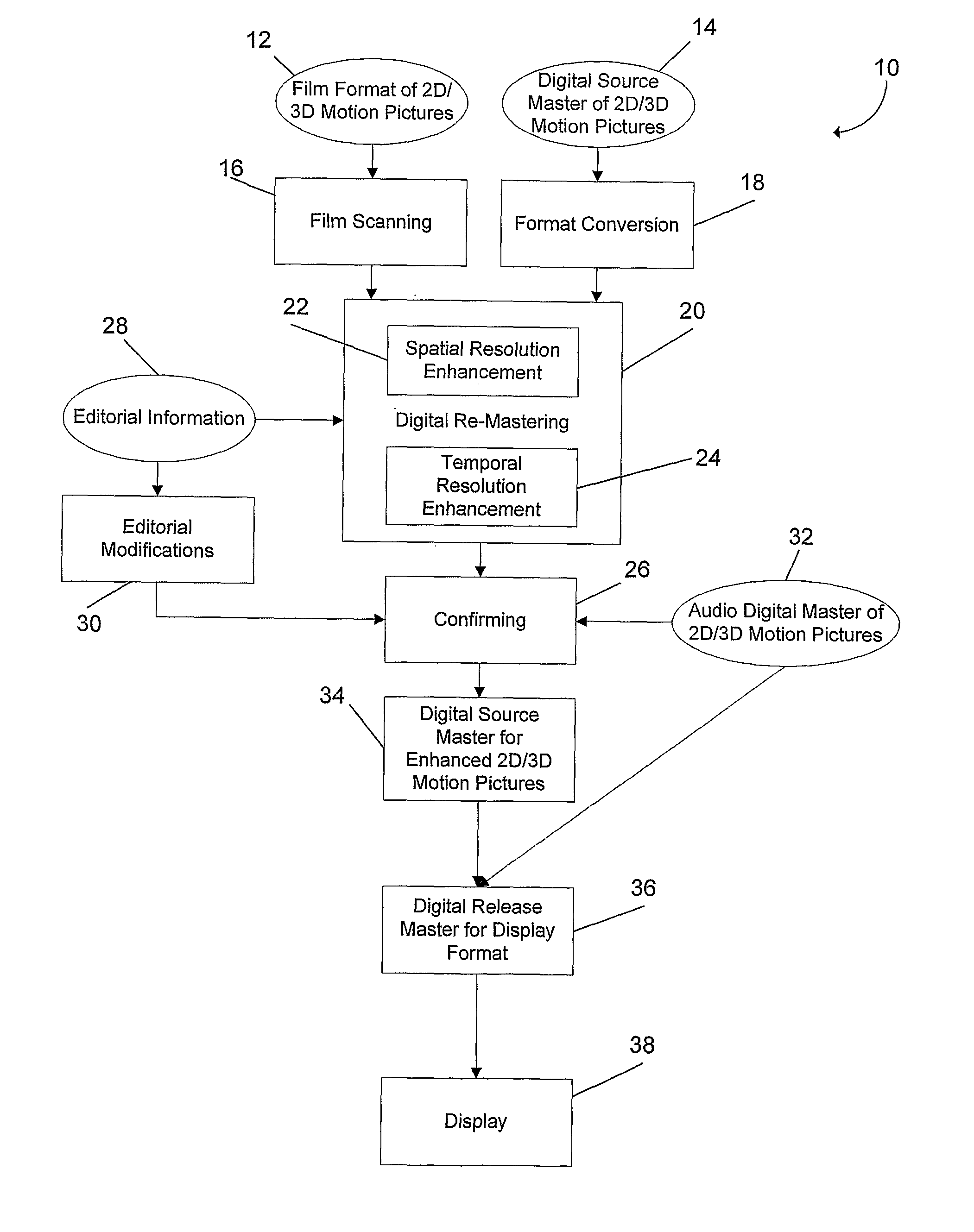
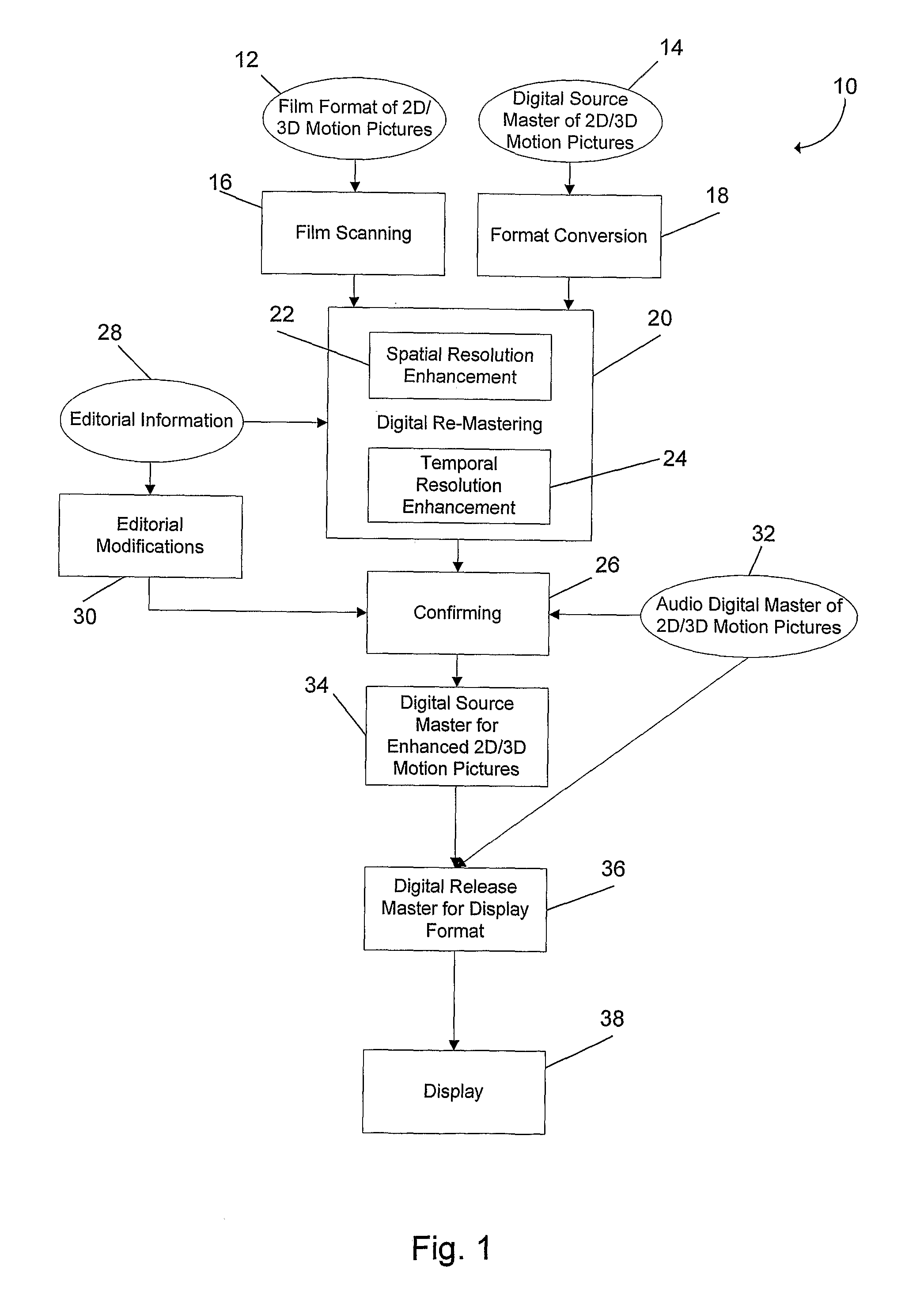
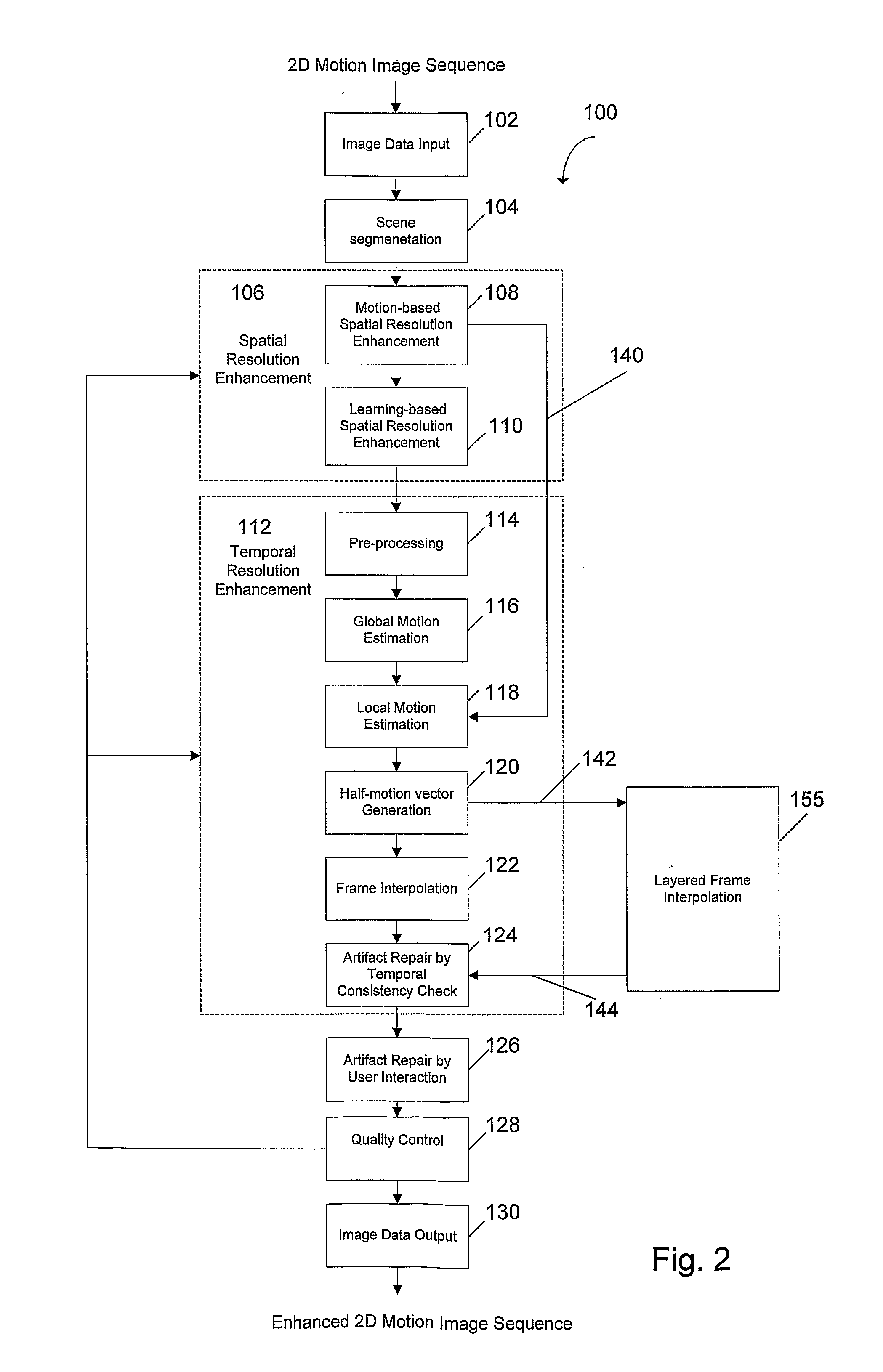
Methods and systems for digitally re-mastering of 2d and 3D motion pictures for exhibition with enhanced visual quality
ActiveUS20100231593A1Enhanced perceived resolutionEnhanced visual image qualityTelevision system detailsImage analysisLearning basedHigh frame rate
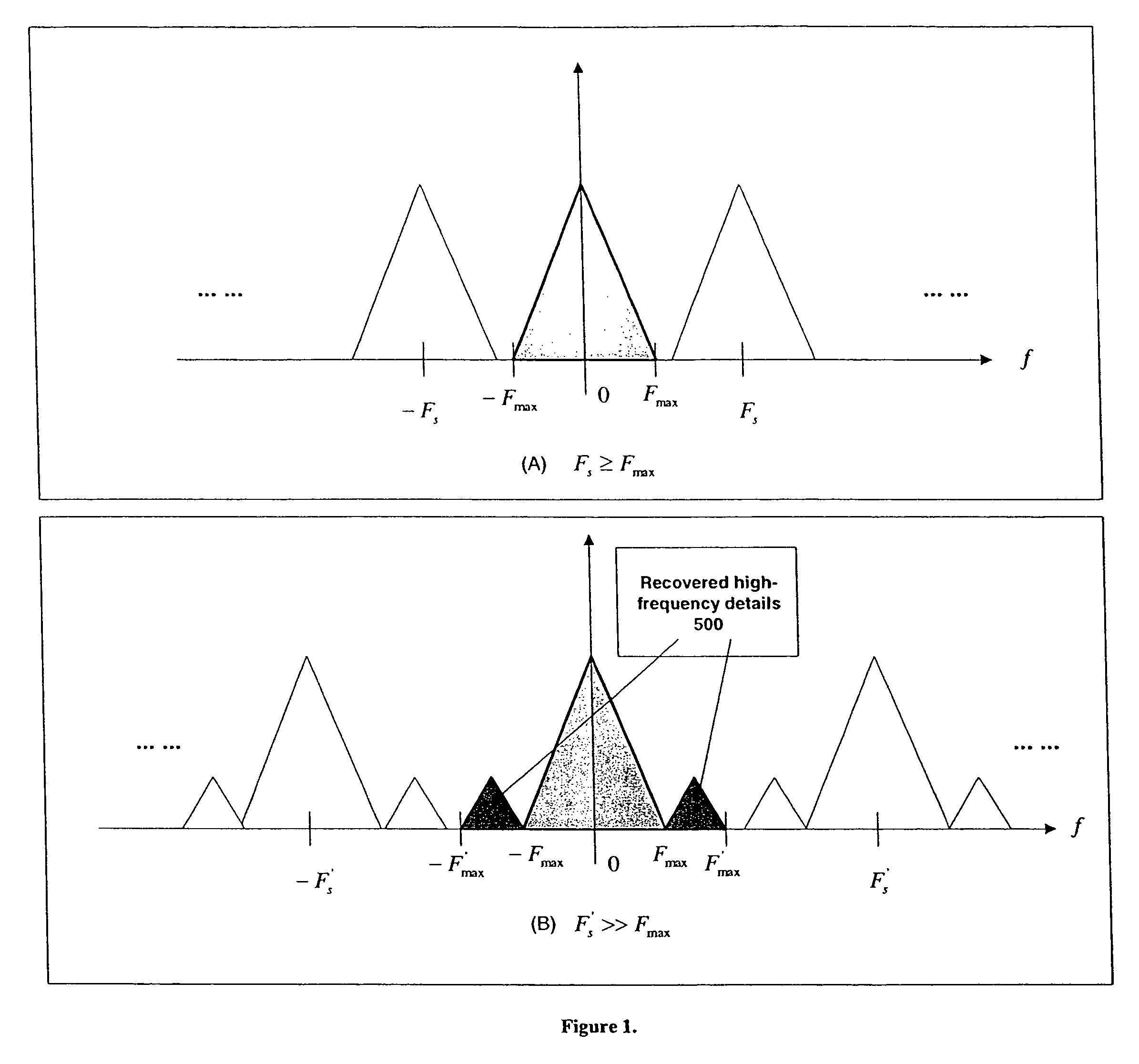
The present invention relates to methods and systems for the exhibition of a motion picture with enhanced perceived resolution and visual quality. The enhancement of perceived resolution is achieved both spatially and temporally. Spatial resolution enhancement creates image details using both temporal-based methods and learning-based methods. Temporal resolution enhancement creates synthesized new image frames that enable a motion picture to be displayed at a higher frame rate. The digitally enhanced motion picture is to be exhibited using a projection system or a display device that supports a higher frame rate and / or a higher display resolution than what is required for the original motion picture.
Owner:IMAX CORP
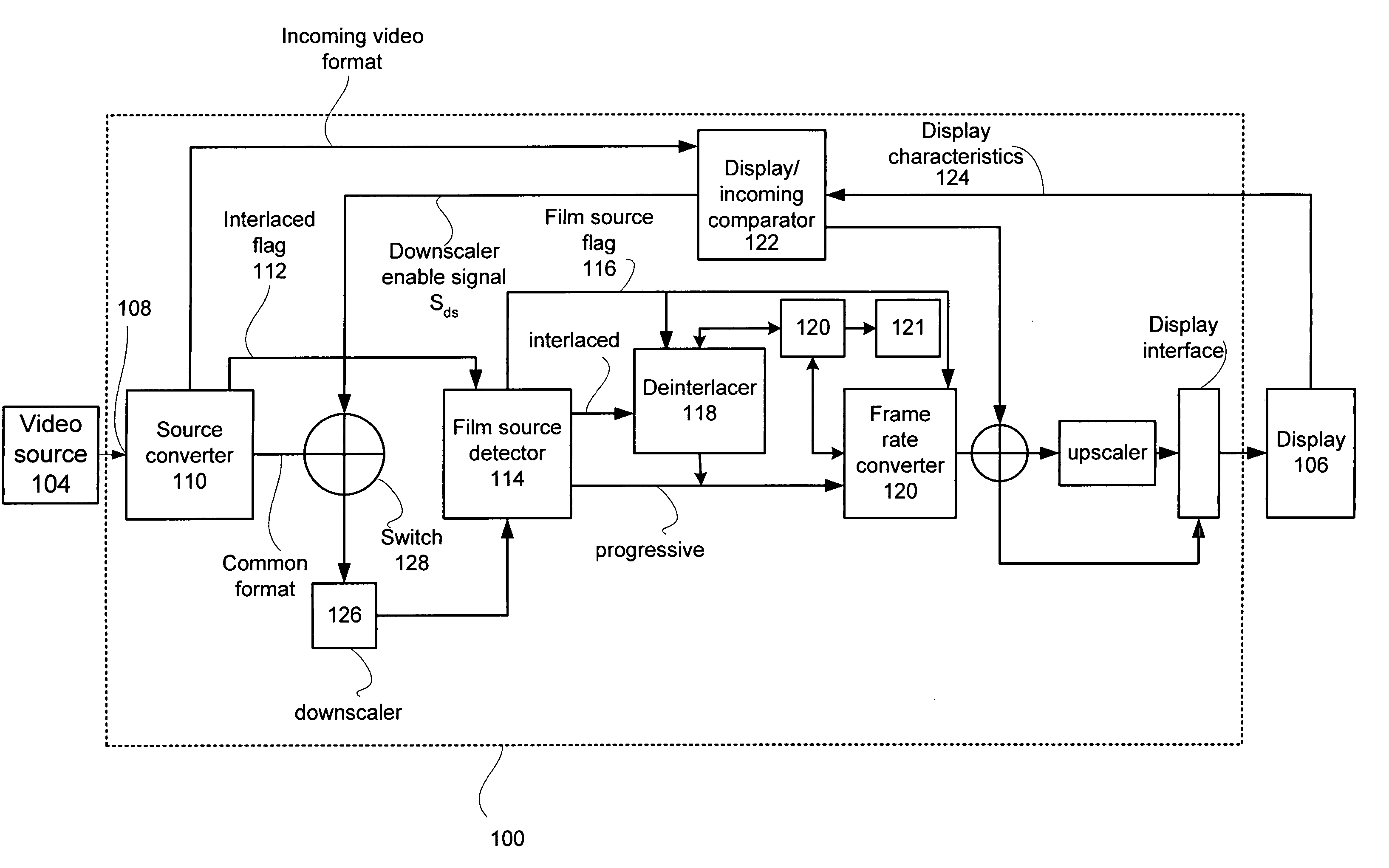
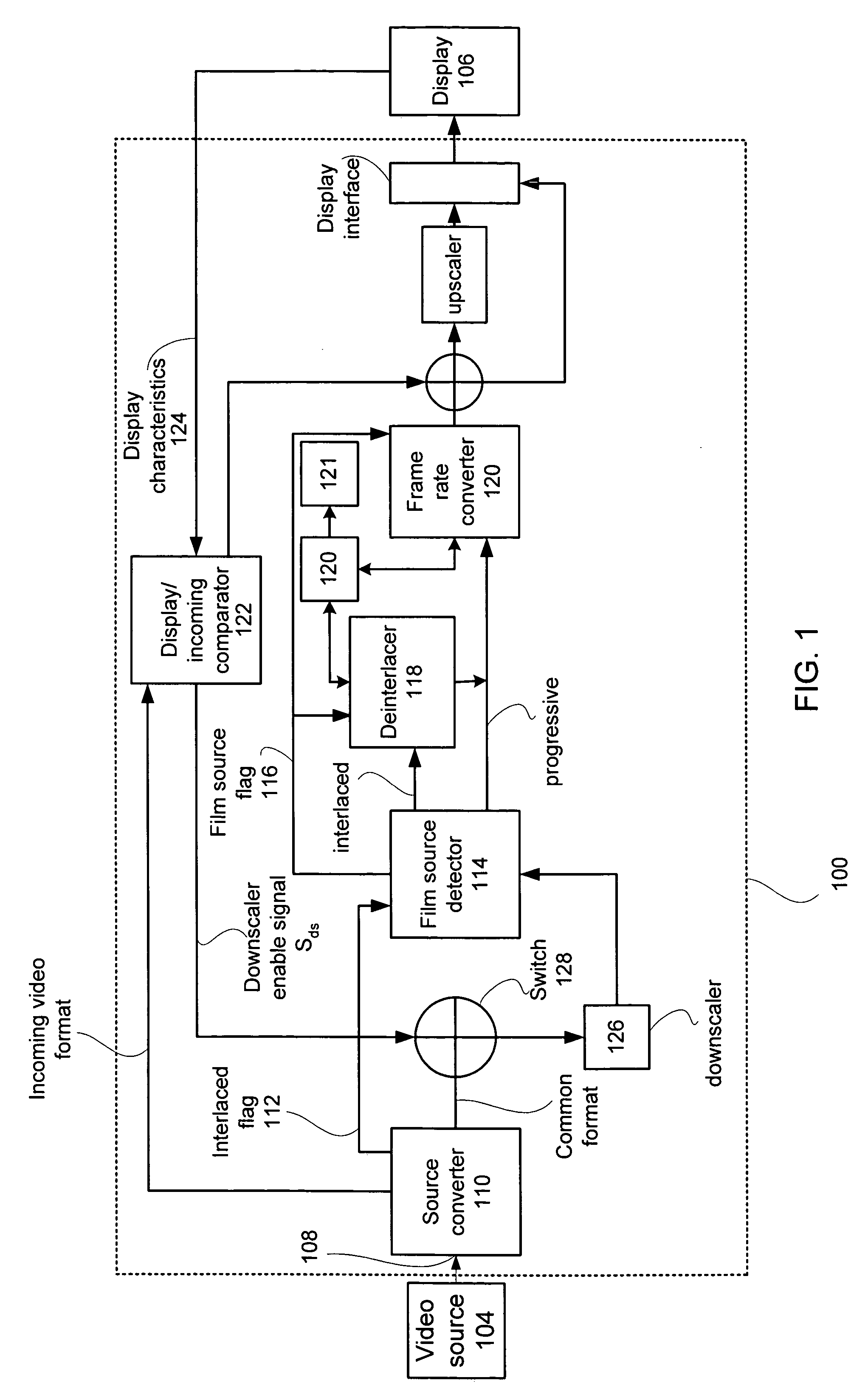
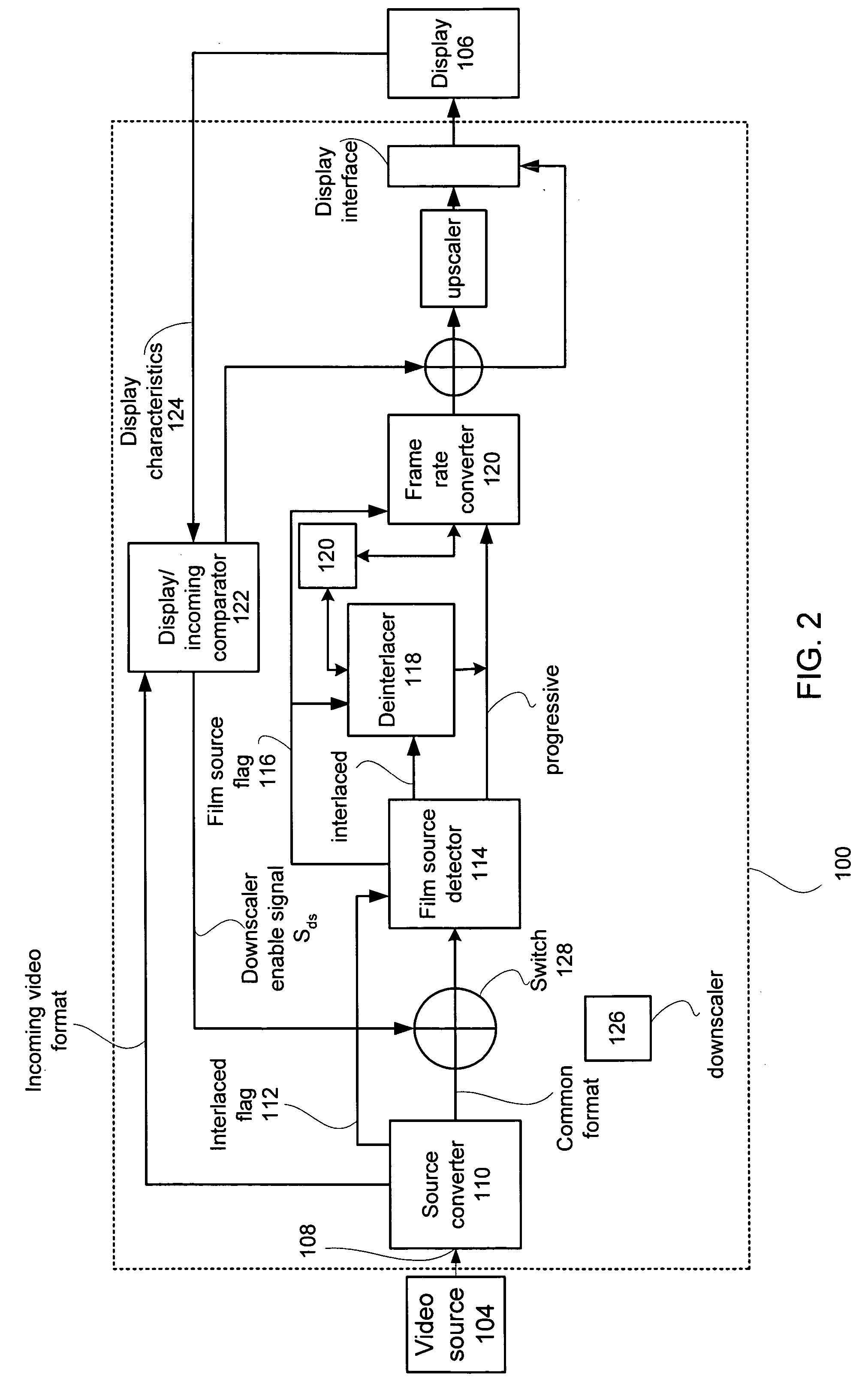
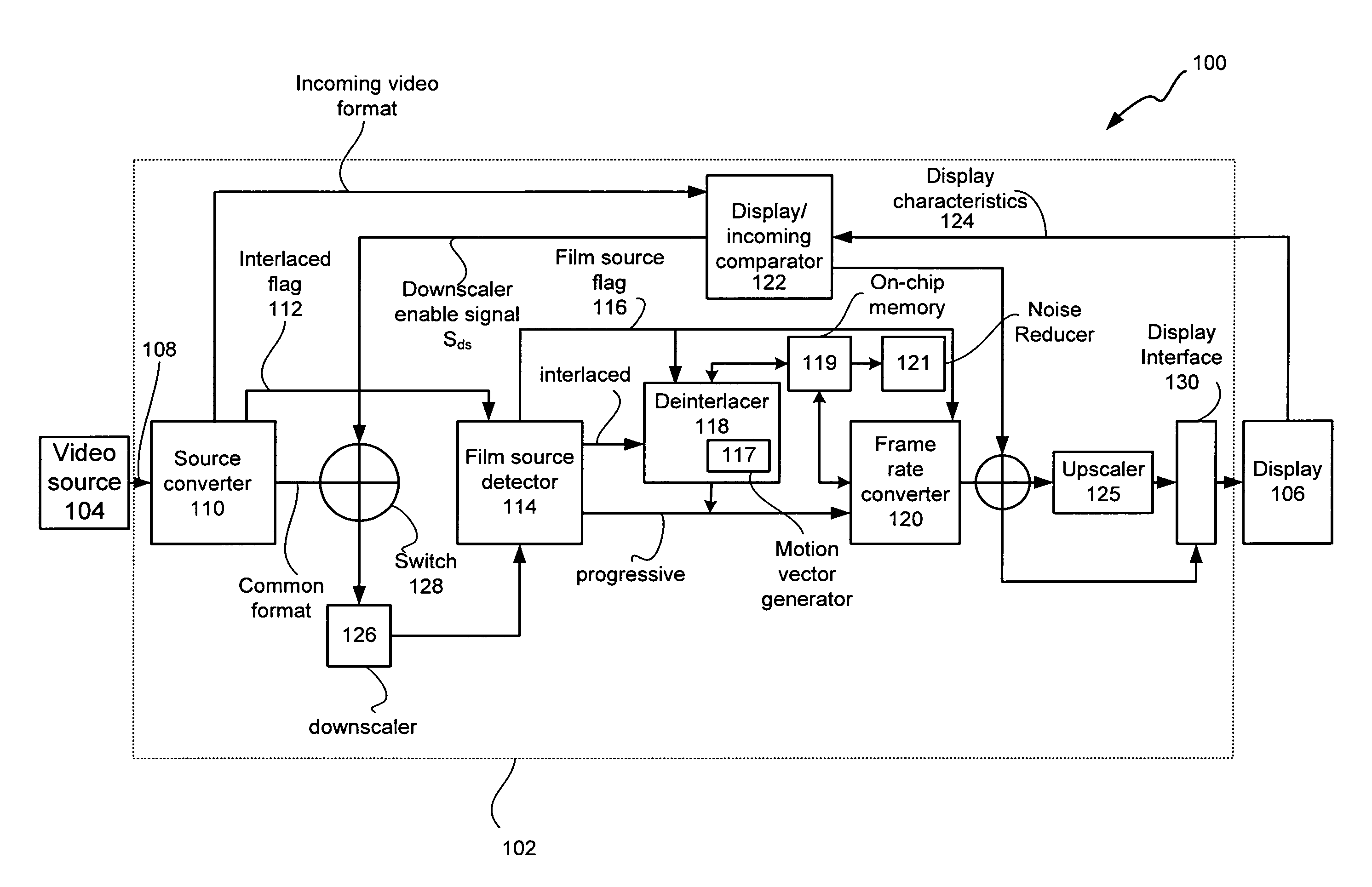
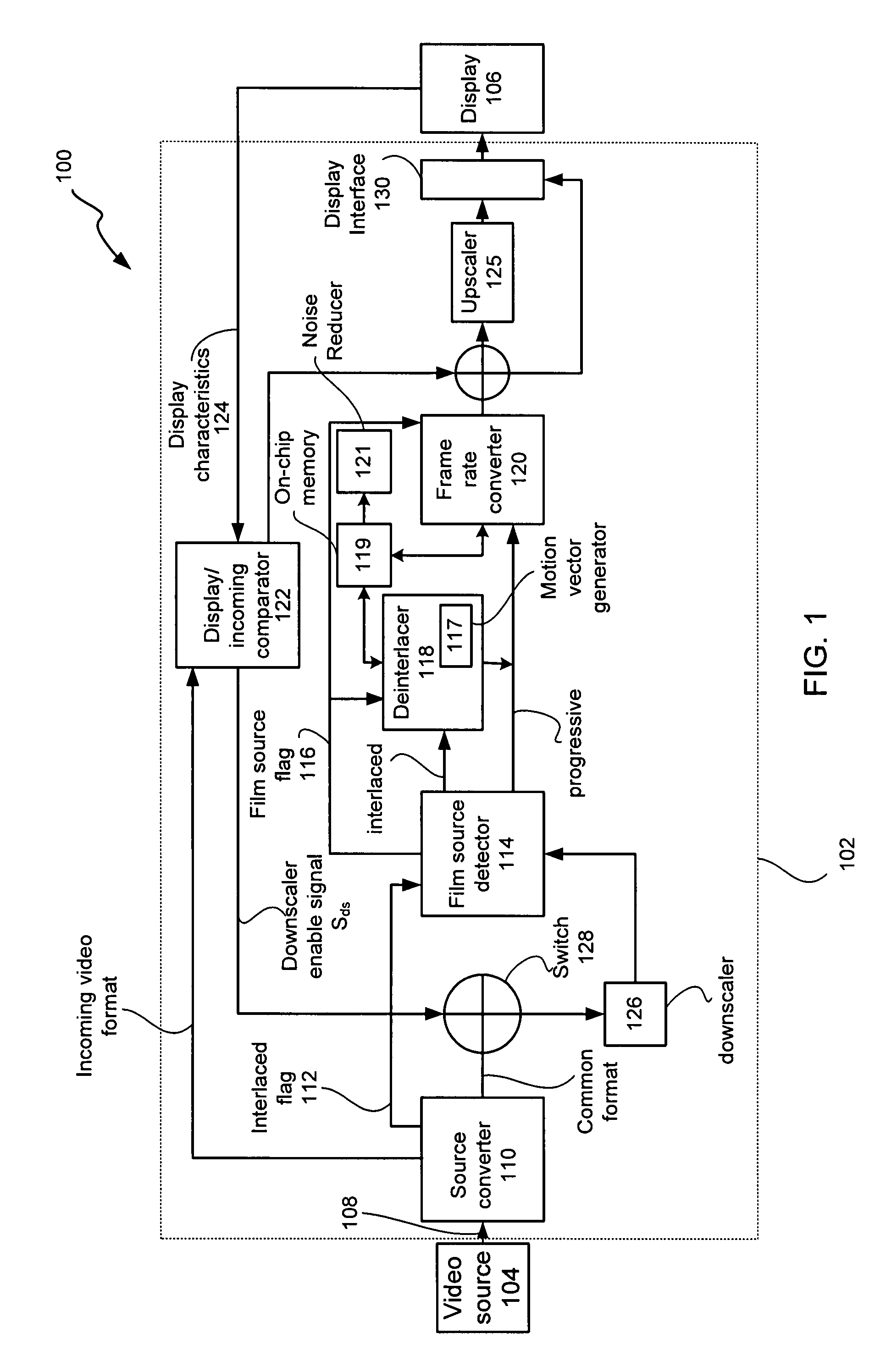
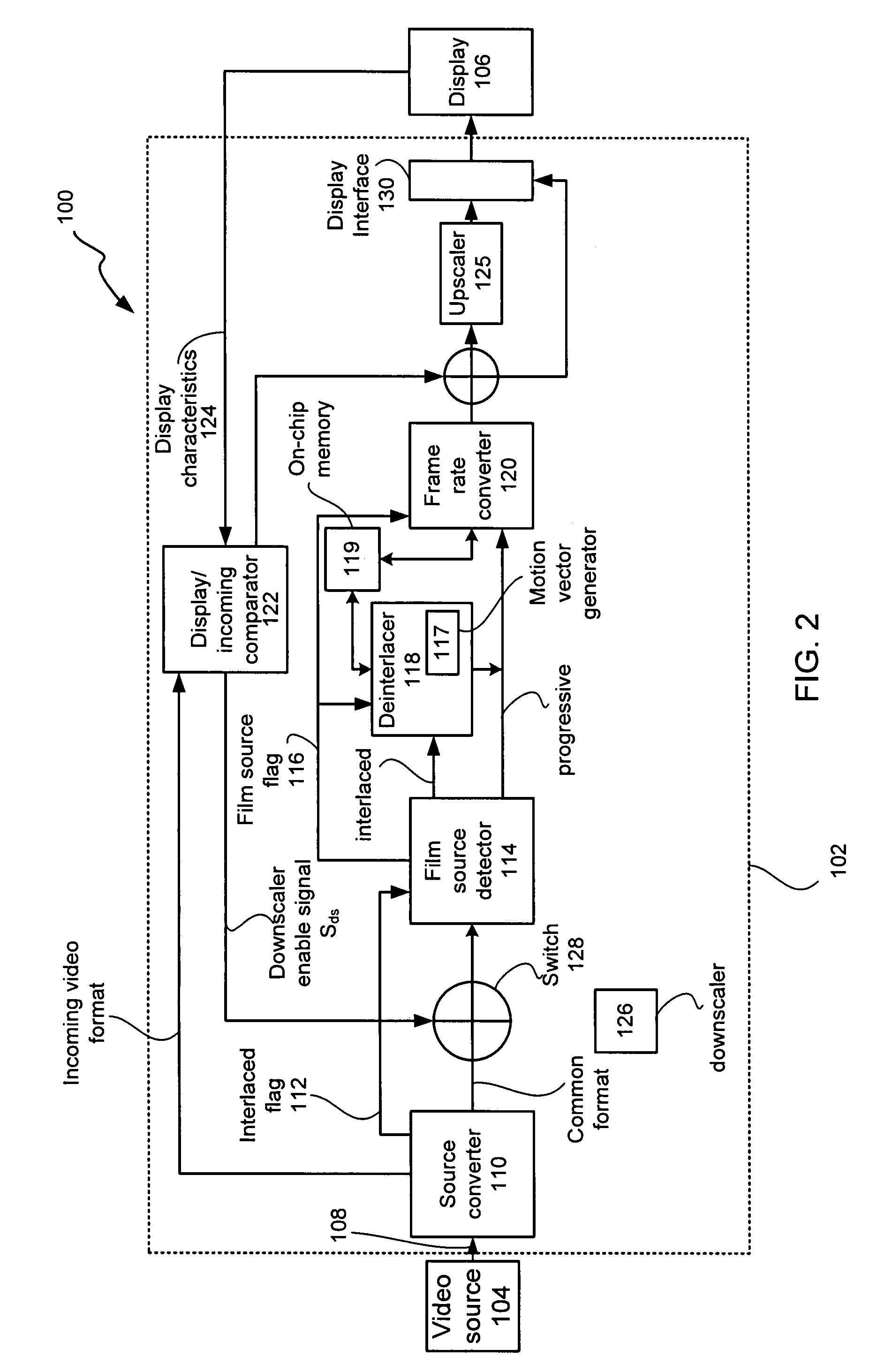
Adaptive display controller
ActiveUS20050134735A1Cancel noiseBandwidthTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti-function displayProgressive scan
A multi-function display controller that includes a source detector unit for determining if the source of an input stream is either film originated source originated or video source originated. A source converter unit for converting the input image stream to a common signal processing format is coupled to the source detector unit. Once converted to the common signal processing format, a determination is made if the input image stream is interlaced or non-interlaced (progressive scan). If the input image stream is interlaced, a de-interlace unit converts the interlaced signal to progressive scan using either motion adaptive or motion compensated de-interlacing techniques. It should be noted that in the described embodiment, motion vectors generated for use by the motion compensated de-interlace can be optionally stored in a memory unit for use in subsequent operations, such as motion compensated frame rate conversion or noise reduction (if any).
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
Low noise encoding and decoding method
InactiveUS6873368B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionLow noiseDecoding methods
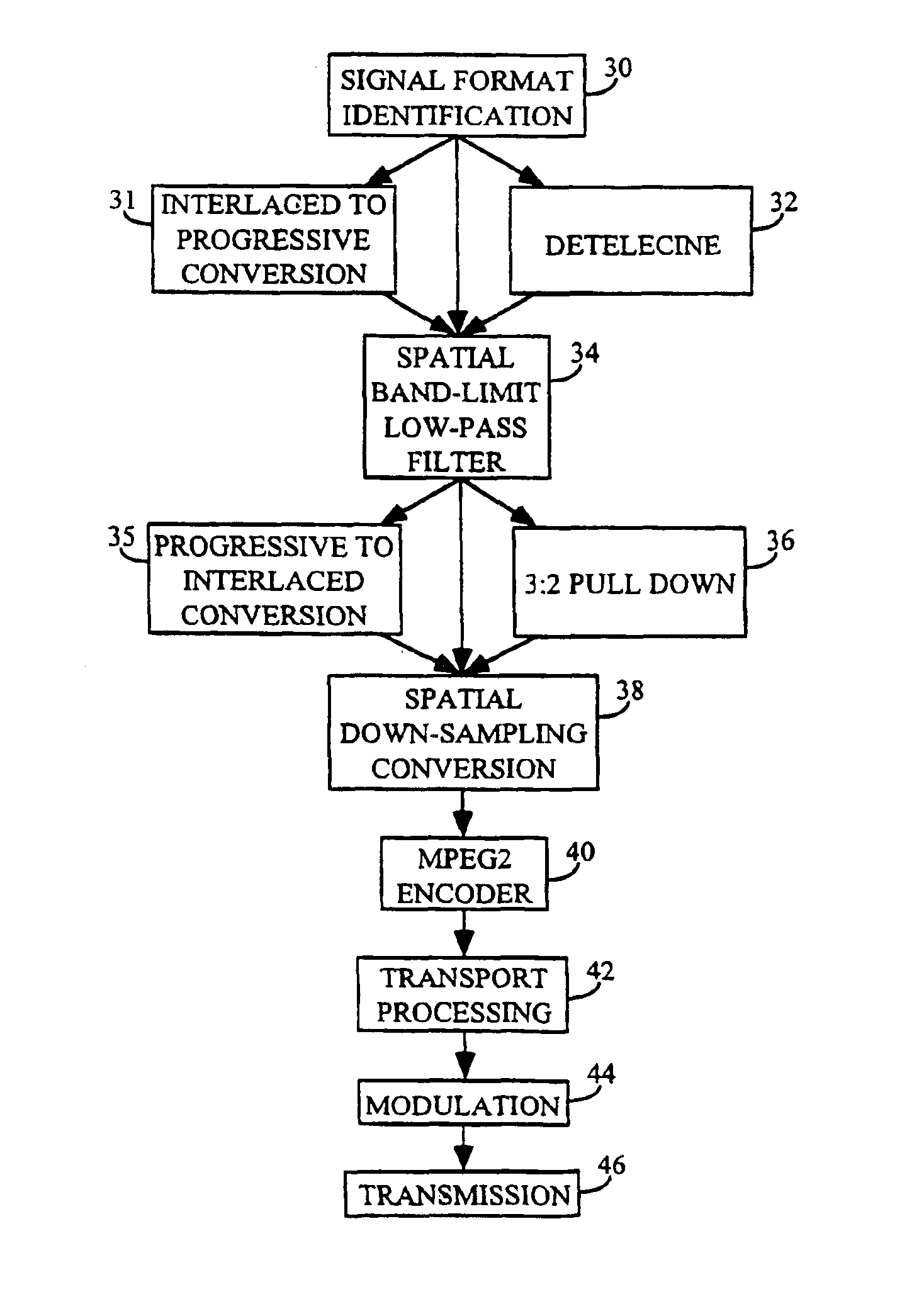
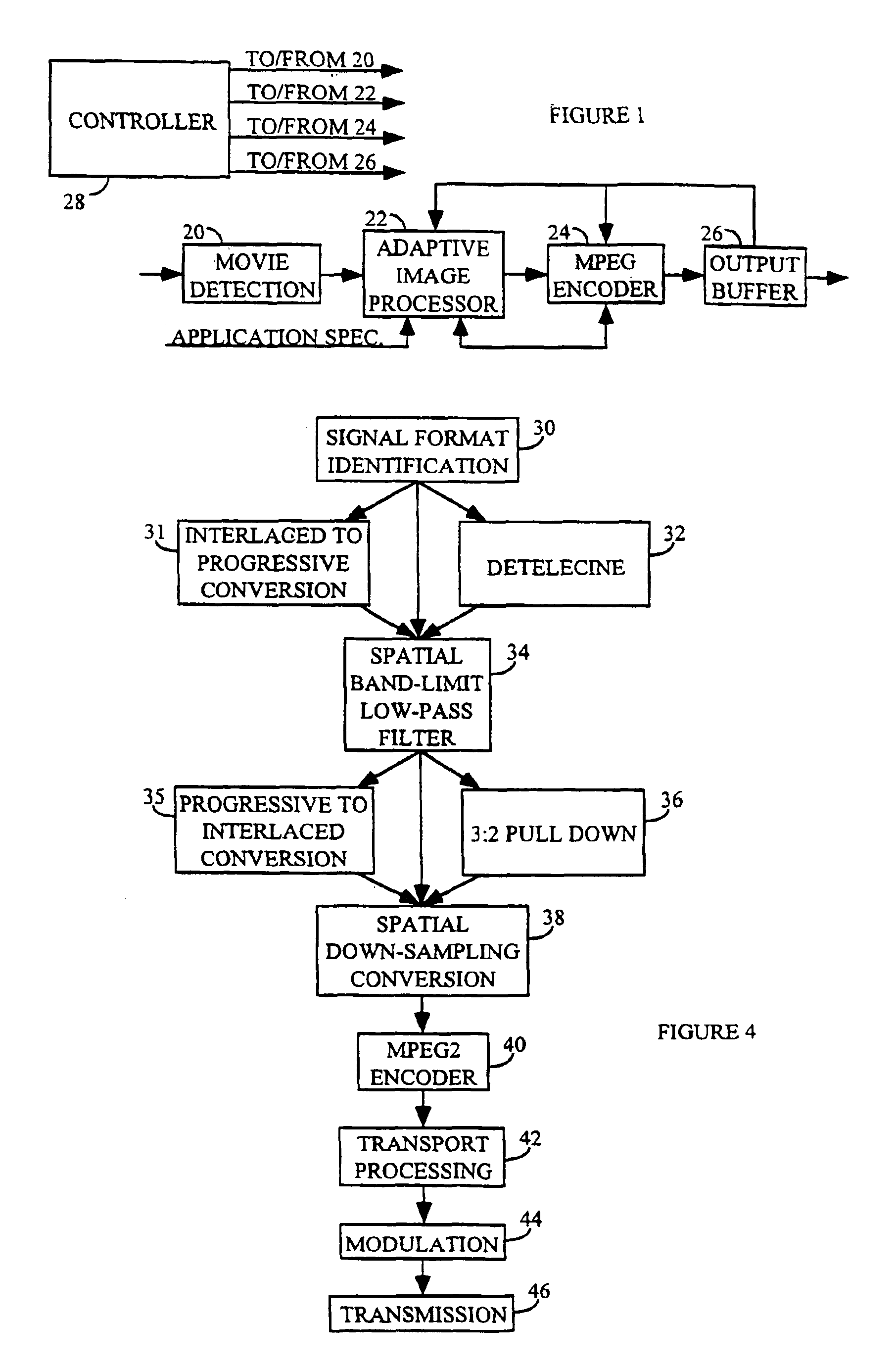
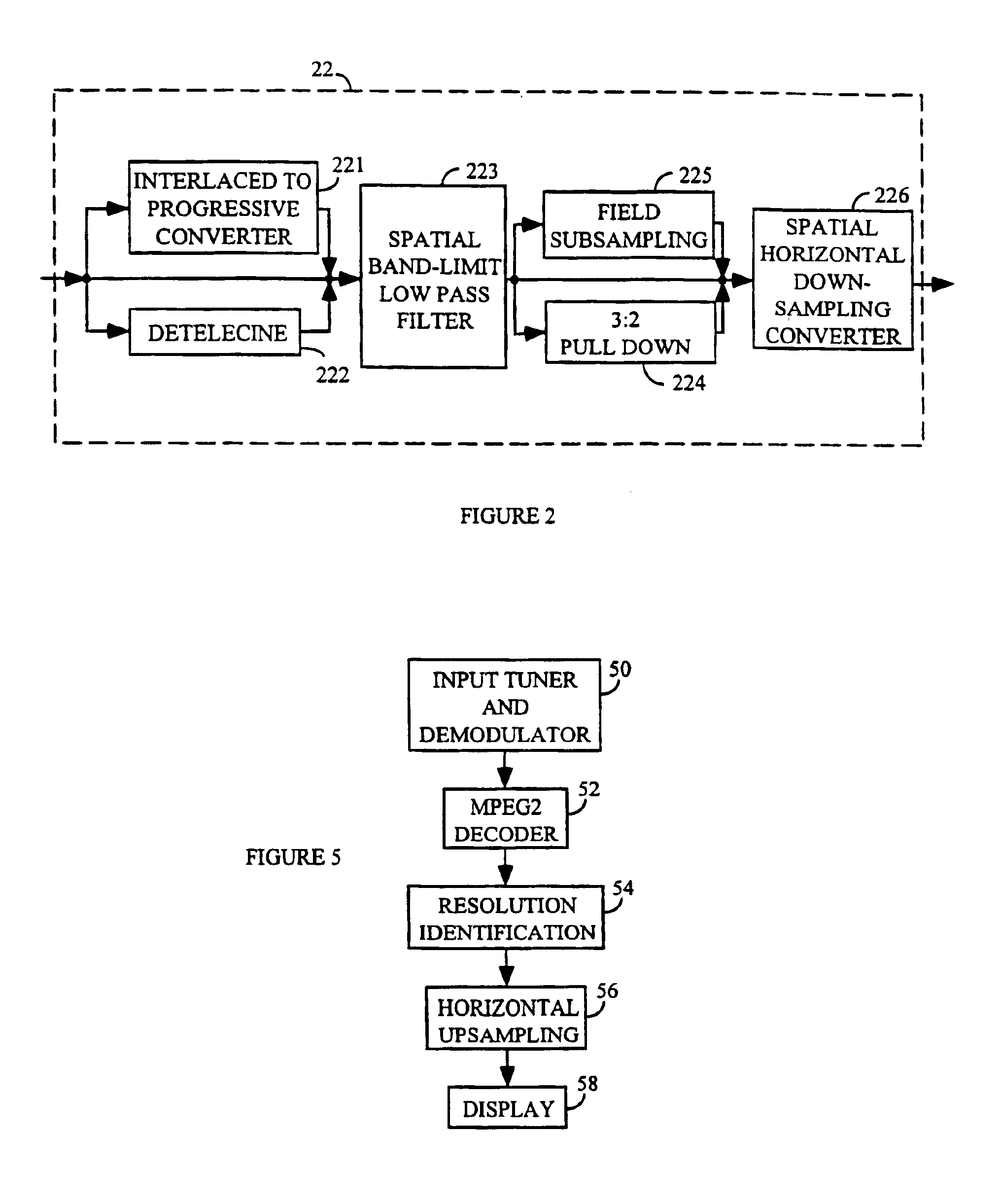
An adaptive digital image processor precedes an MPEG2 encoder. The processor receives a high definition video signal intended for broadcast or storage, and adaptively low-pass filters the signal. The signal is subjected to low-pass two-dimensional filtering to eliminate encoding artifacts and related noise. The video signal is then horizontally down-sampled to create a lower resolution hybrid signal. A receiver decodes and decompresses the hybrid signal. The hybrid signal is upsampled to its original resolution using existing hardware and software with a software modification.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
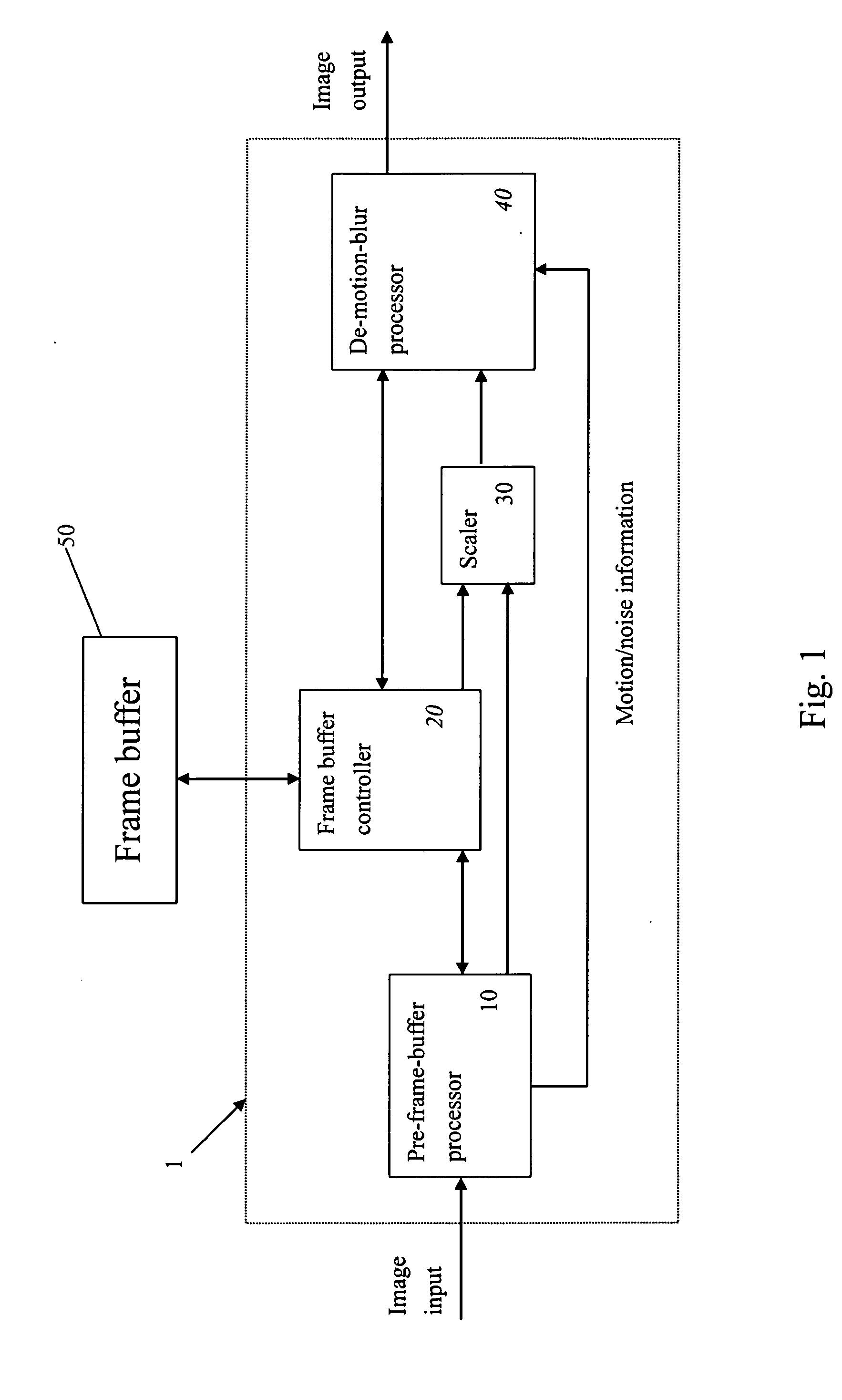
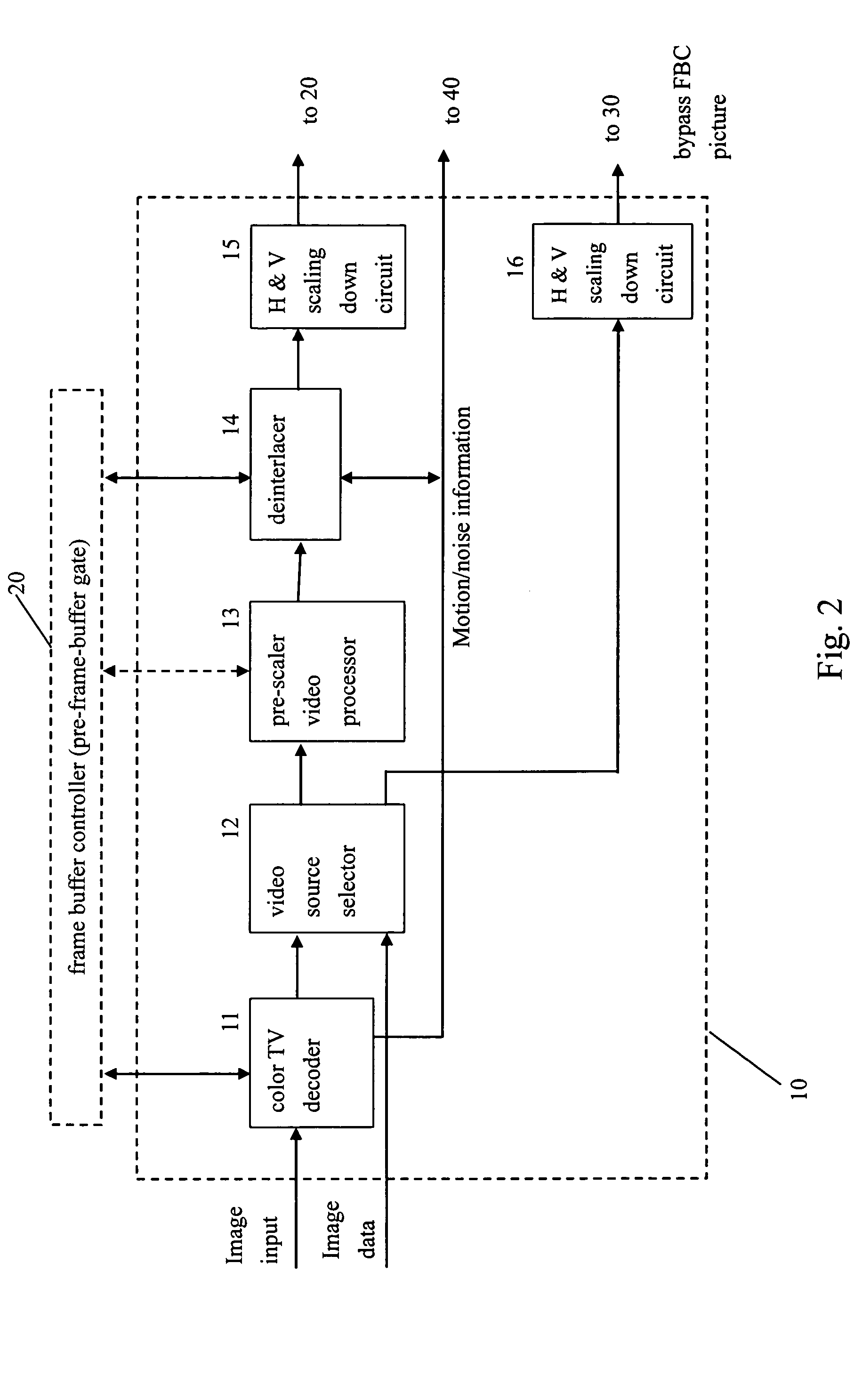
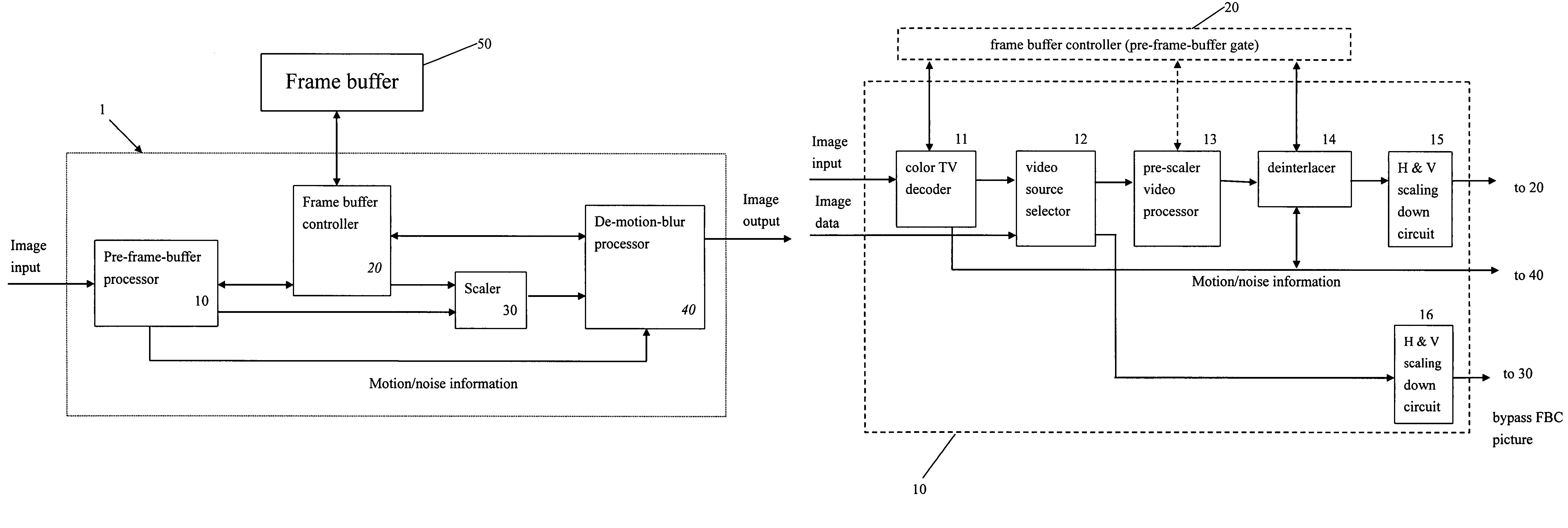
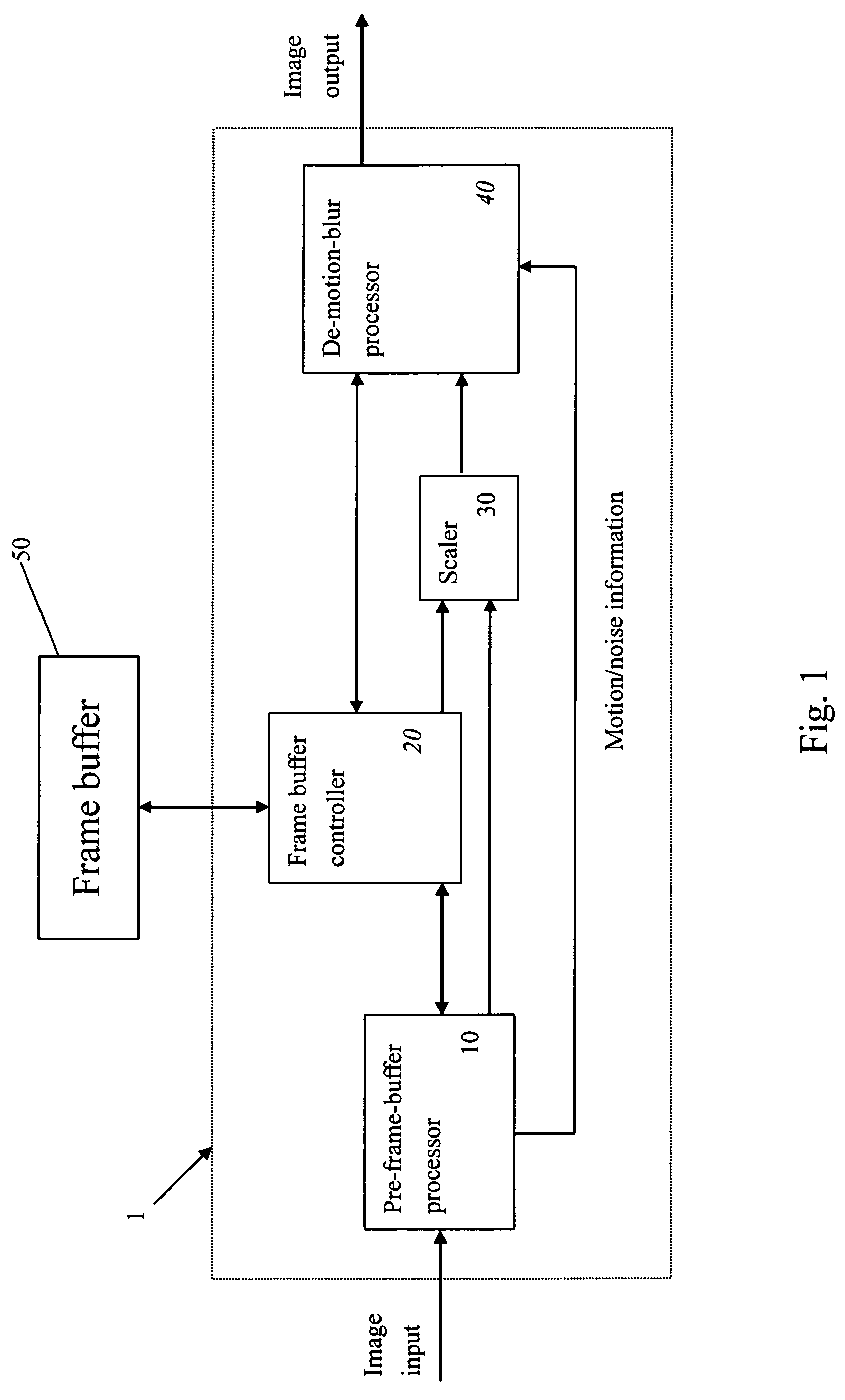
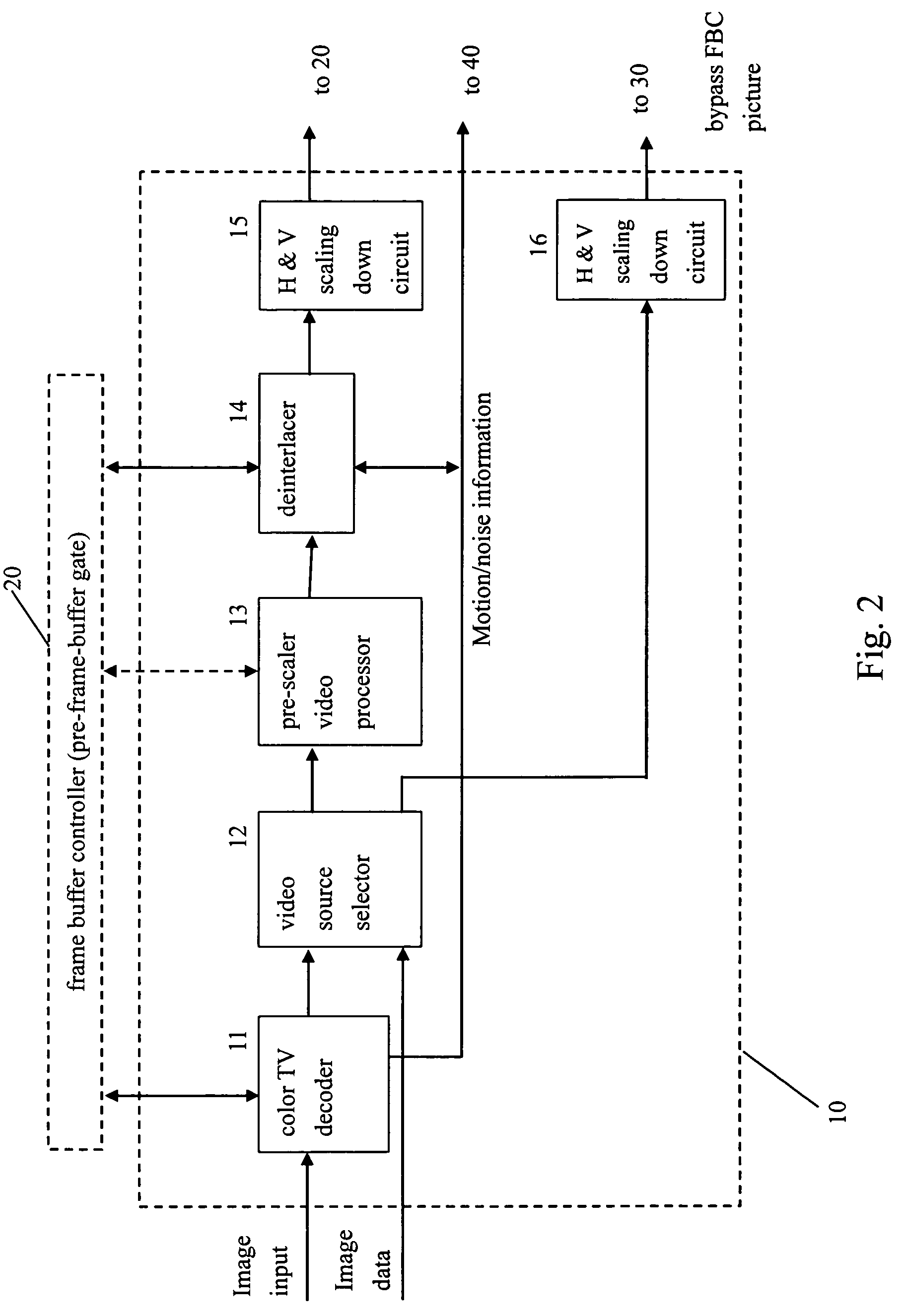
Video system with de-motion-blur processing
ActiveUS20050162566A1Short response timeQuality improvementImage enhancementTelevision system detailsProgressive scanImage resolution
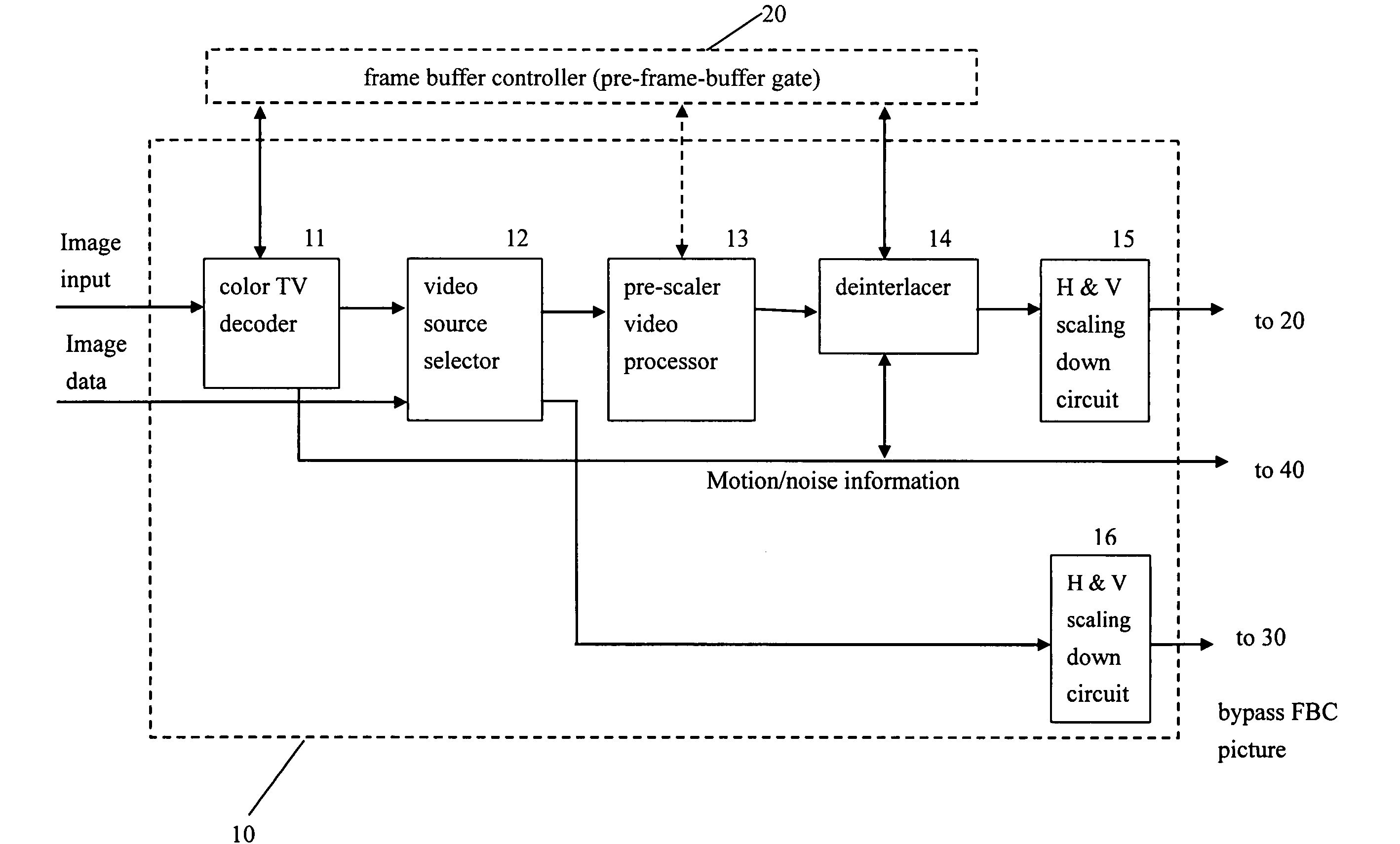
A video system that performs TV signal decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blurring for progressive scan flat panel display is introduced. The system embeds a frame buffer and a scaler for conducting format and resolution conversions for display panels of different sizes. The output of the scaler is sent to a de-motion-blur processor for reducing the blurriness due to the motion of image objects and the slow response time of flat panel display devices. The de-motion-blur processor gets the motion and noise indication signal from scaler or the pre-frame-buffer video processor. Based on the motion and noise information and the information of temporal difference, the de-motion-blur processor performs over driving for the display panel interface and improves the rising and falling response time of the flat panel display. The decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blur processing share the same frame buffer controller so the entire system can be optimized in cost and performance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
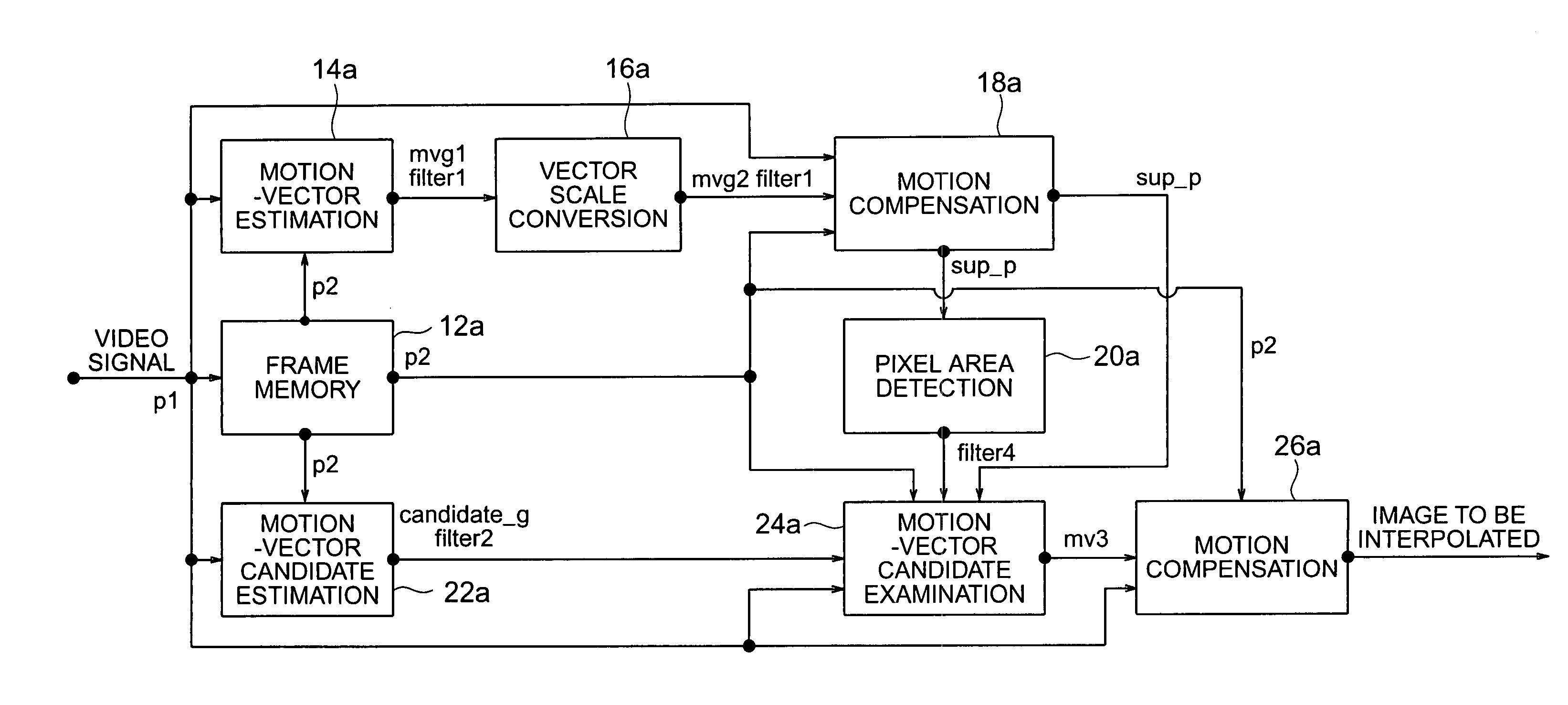
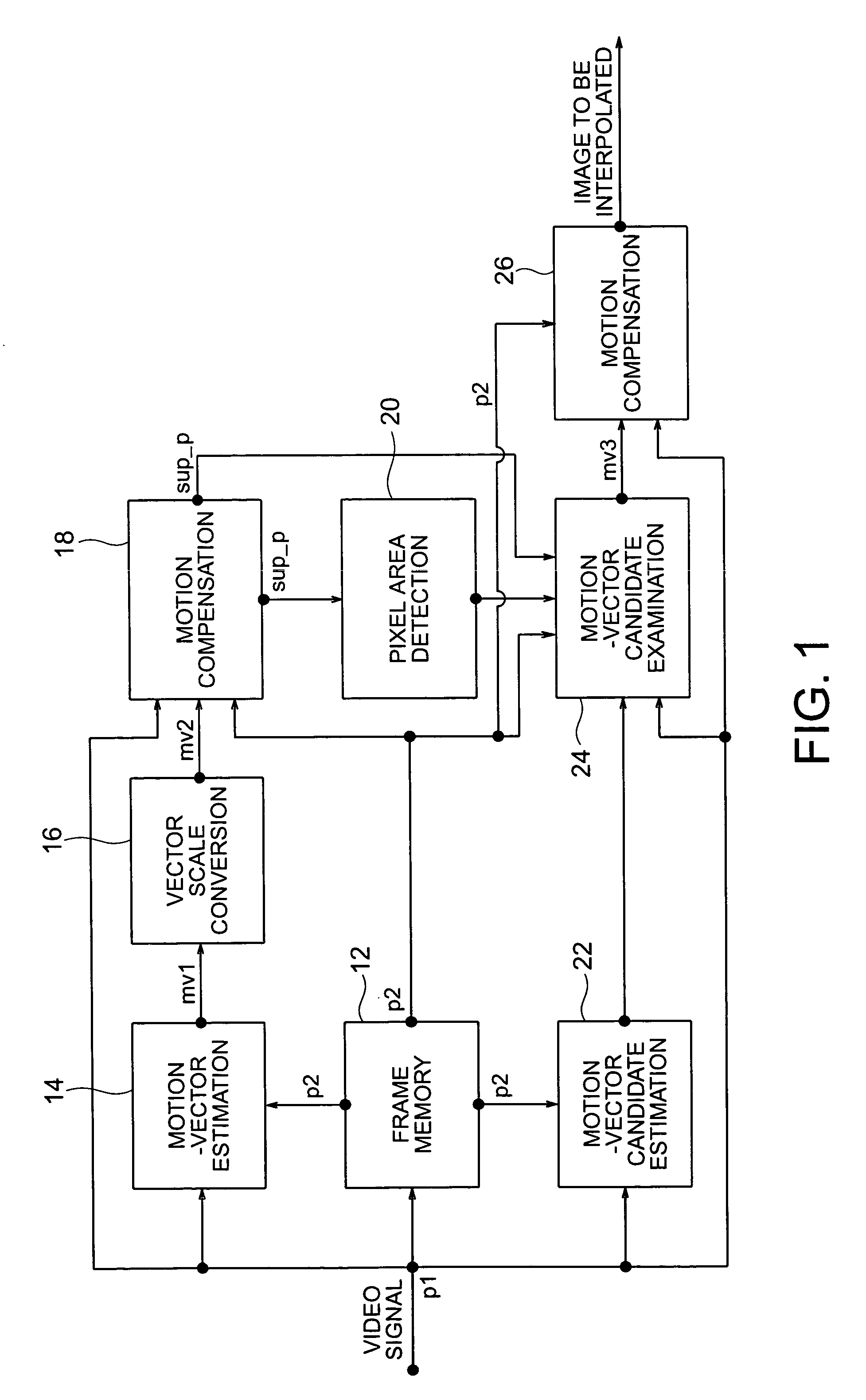
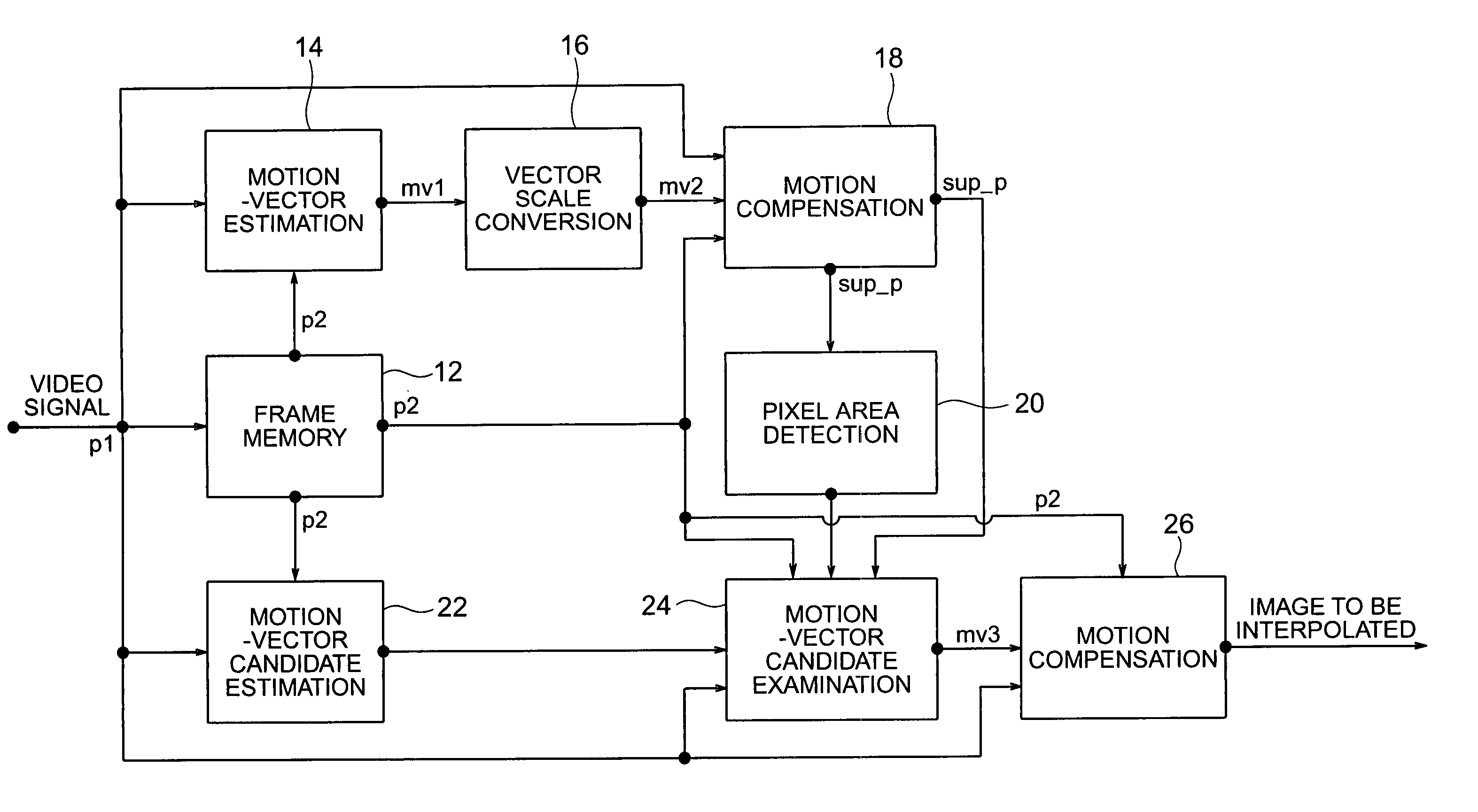
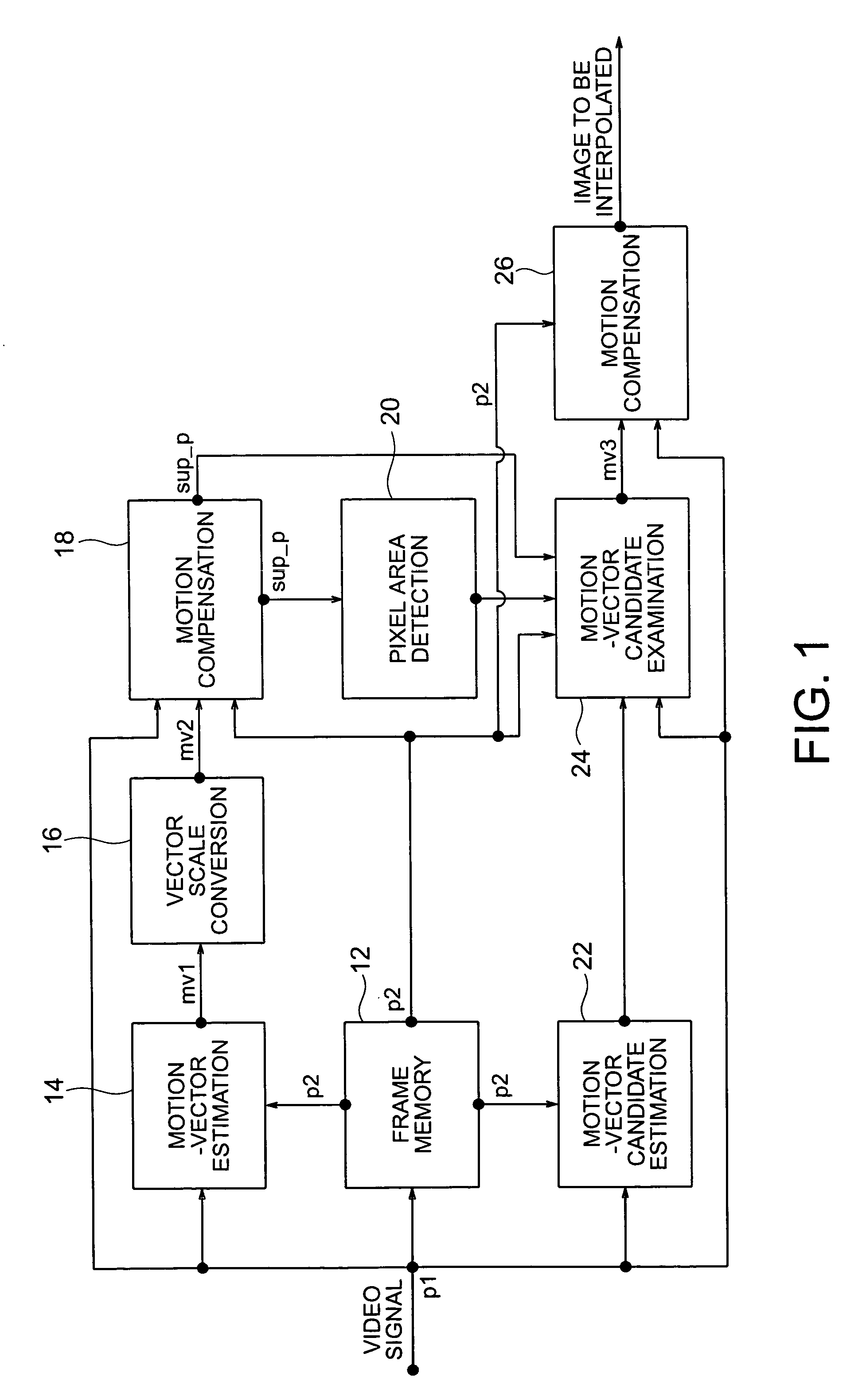
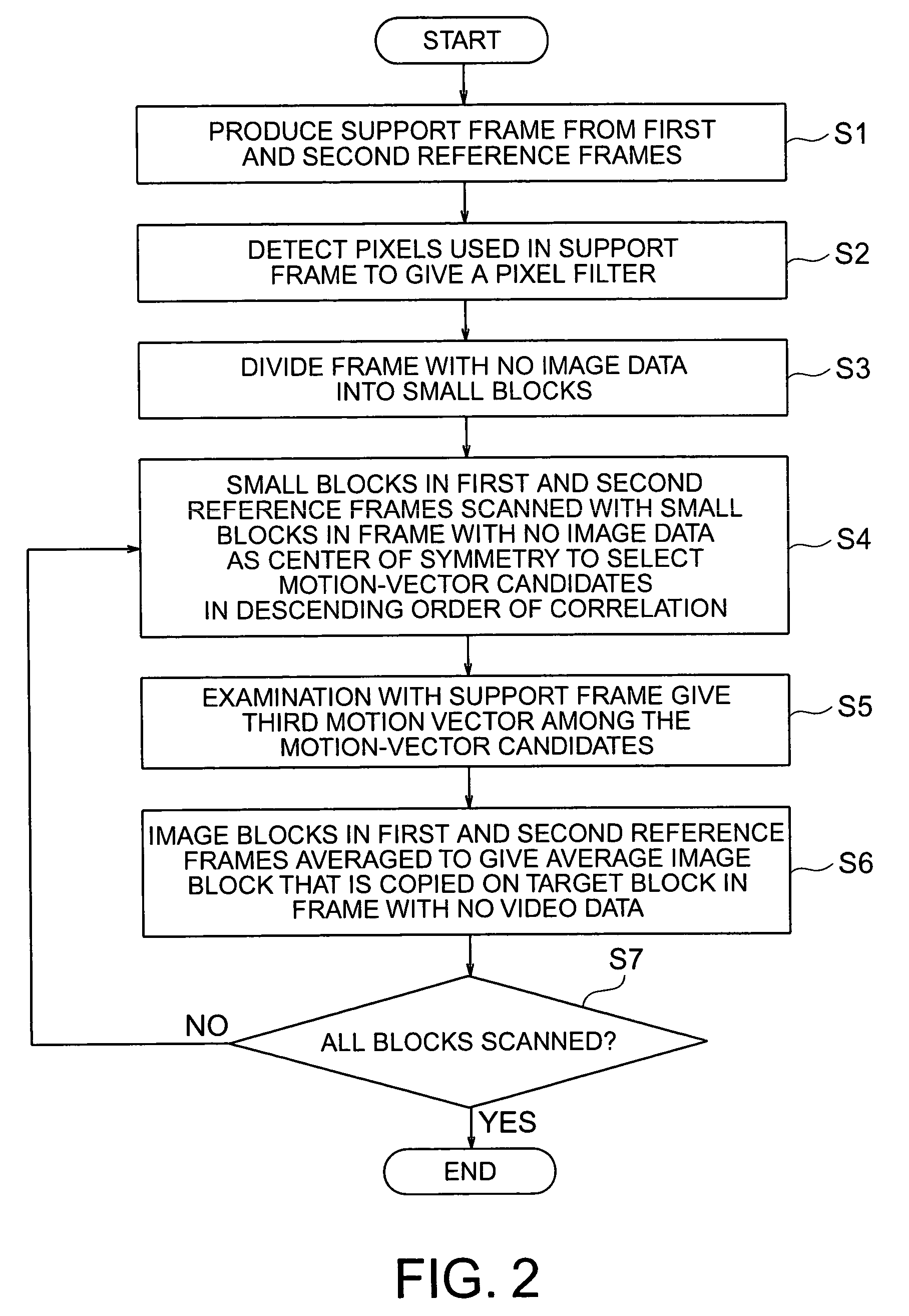
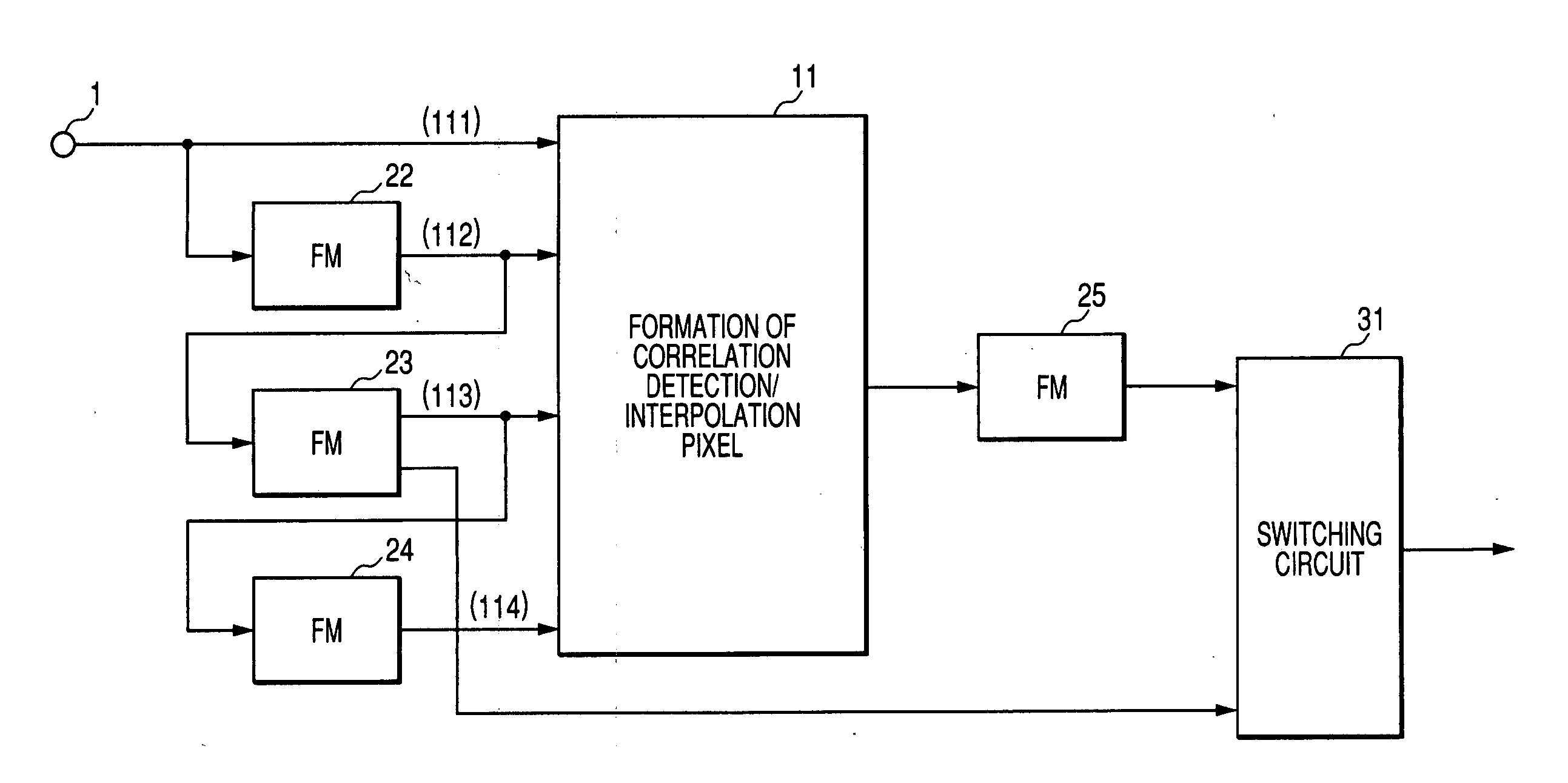
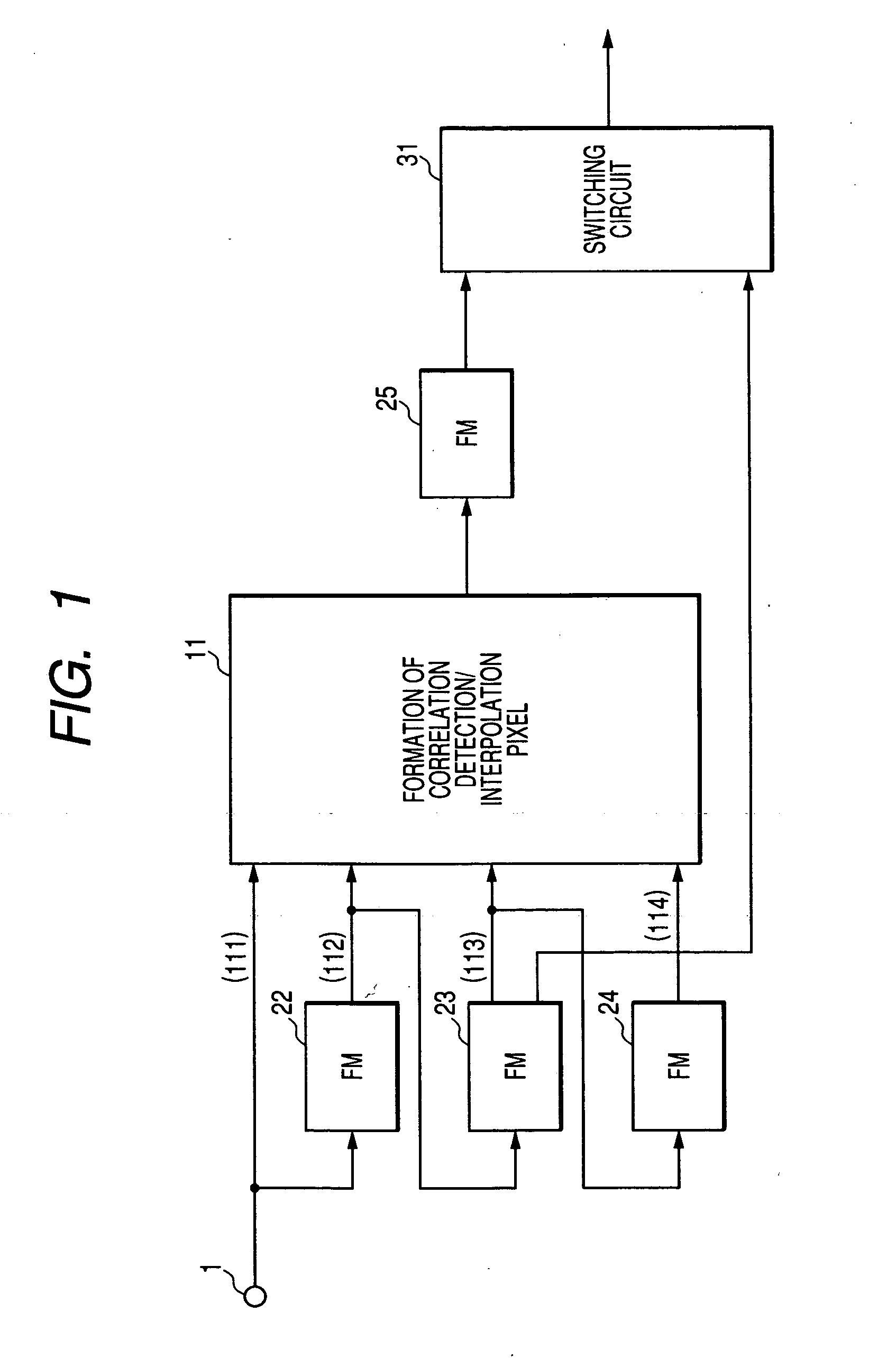
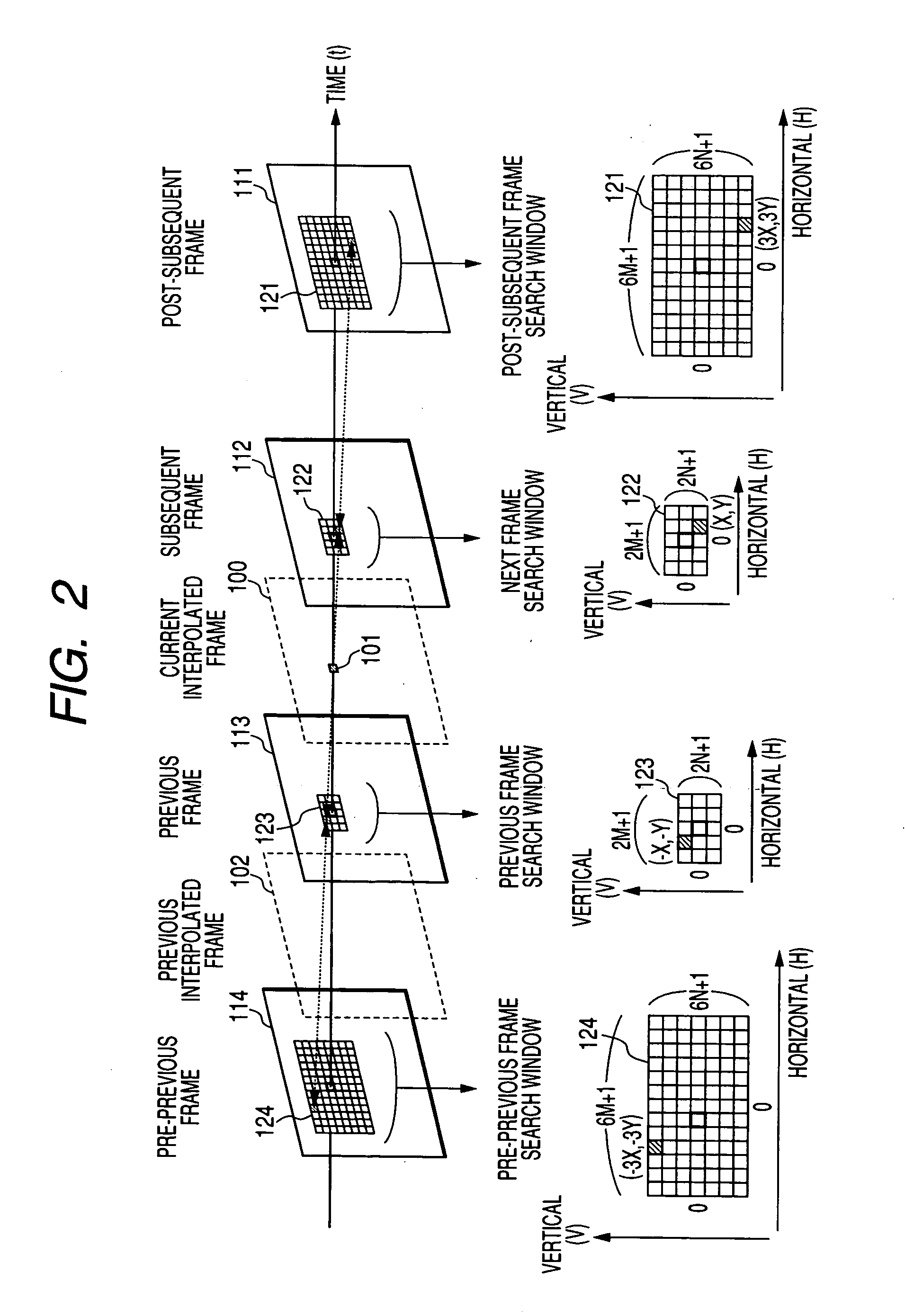
Frame interpolation and apparatus using frame interpolation
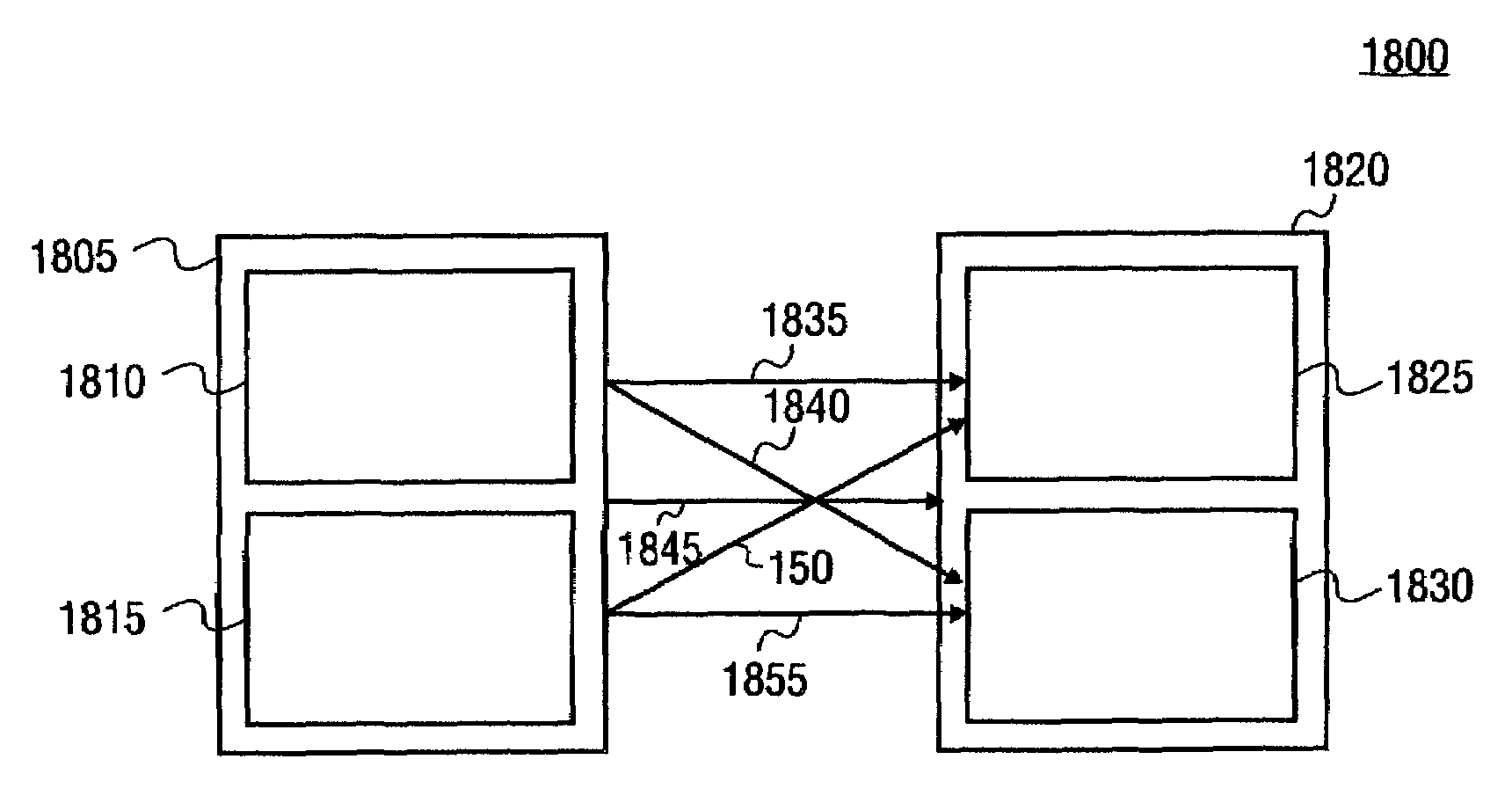
ActiveUS20040046891A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsTight frameMotion vector
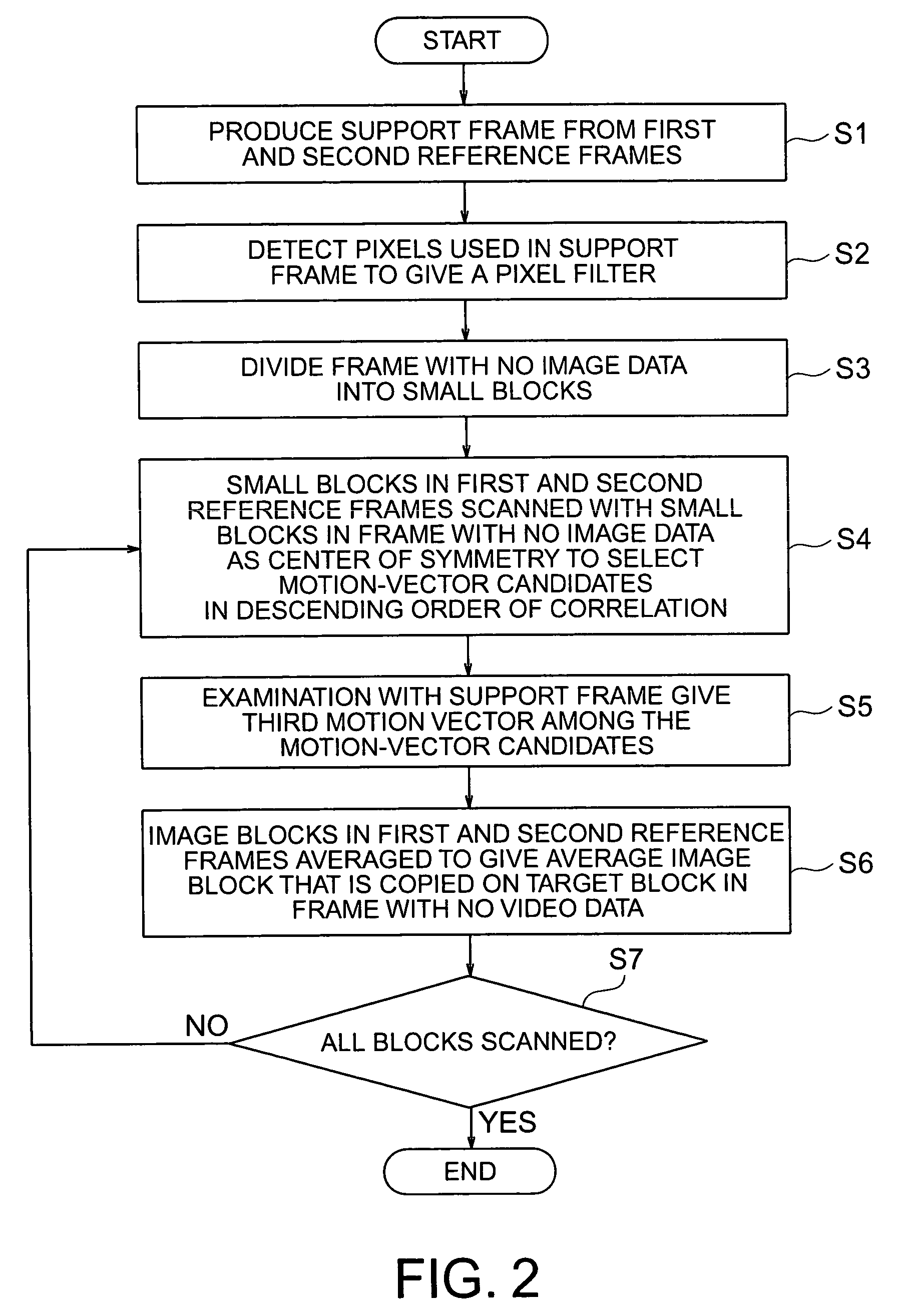
A first motion vector is estimated by using a first frame and a second frame that follows the first frame. A support frame is generated from at least either the first or the second frame by using the first motion vector. The support frame is divided into a plurality of small blocks. Motion vector candidates are estimated by using the first and second frames, in relation to each of the small blocks. A small block on the first frame, a small block on the second frame and the small blocks on the support frame are examined. The small block on the first frame and the small block on the second frame correspond to each of the motion vector candidates. A second motion vector is selected from the motion vector candidates, and points the small block on the first frame and the small block on the second frame which have the highest correlation with each of the small blocks on the support frame. An interpolated frame is generated from at least either the first or the second frame by using the second motion vector.
Owner:FLEXIWORLD TECH
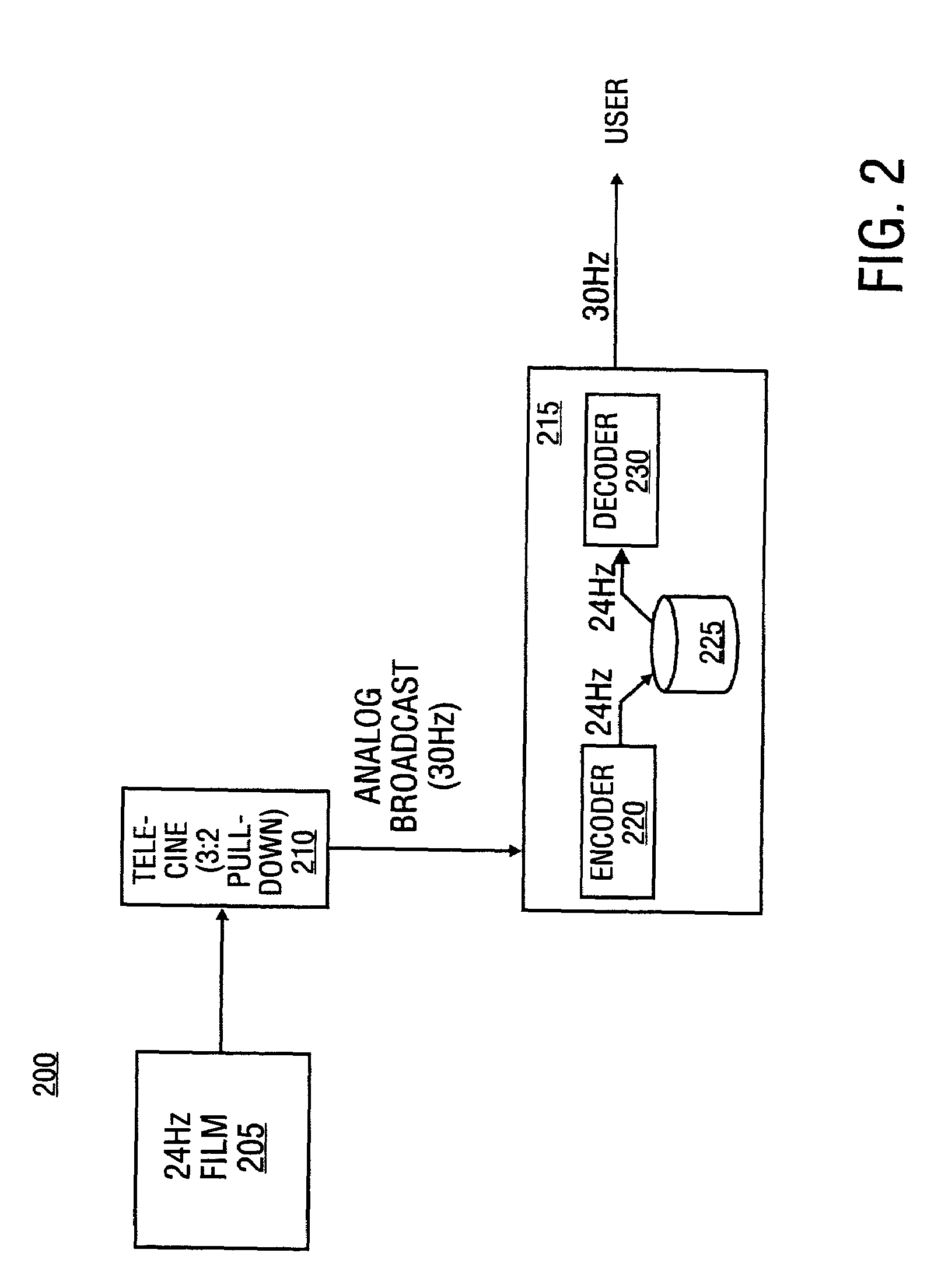
Method, system and article of manufacture for identifying the source type and quality level of a video sequence
InactiveUS6867814B2Reduce Motion ArtifactsAccurately determineTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsQuality levelInterlaced video
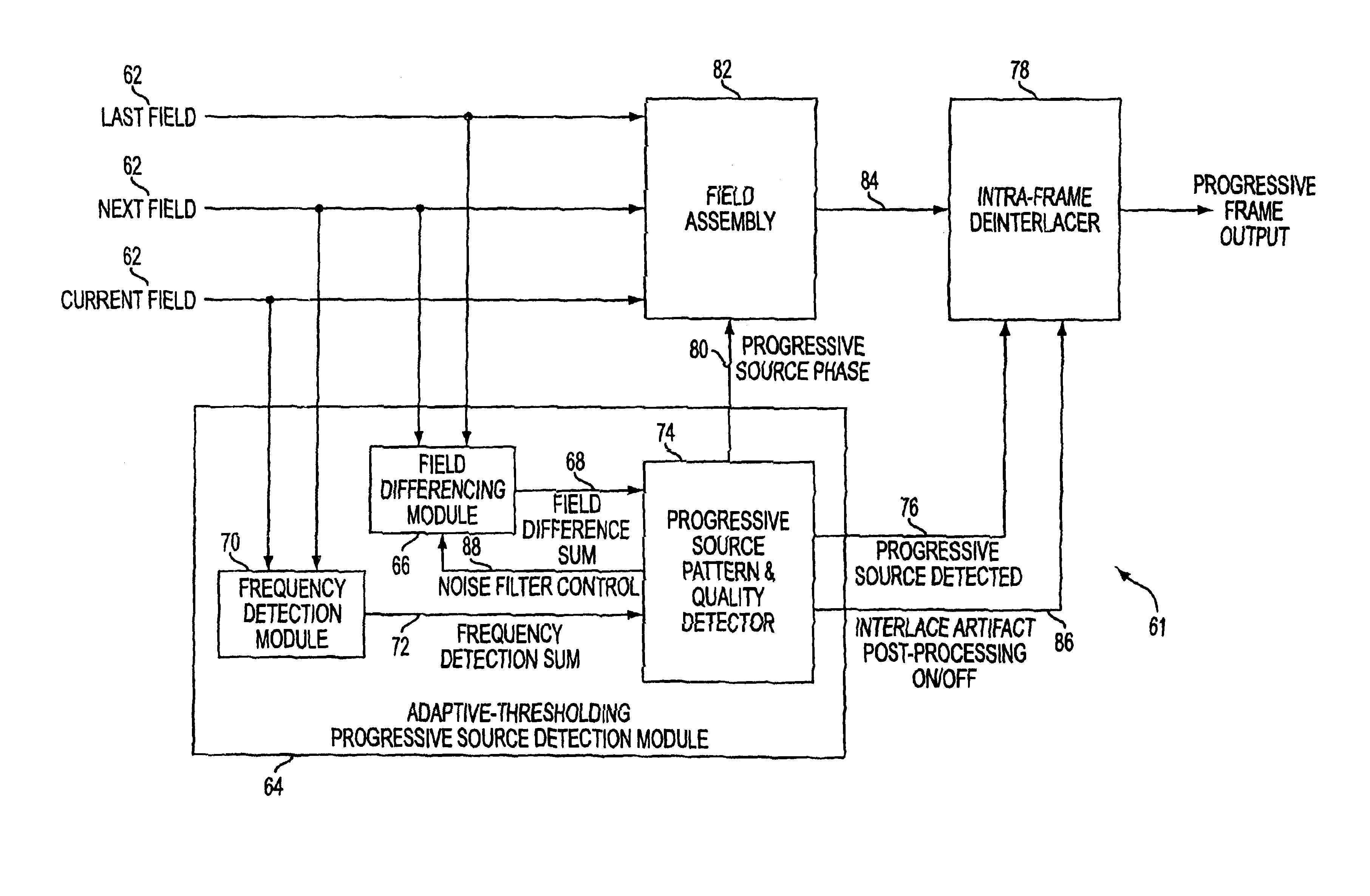
A deinterlacing system which converts an interlaced video stream into a progressive video stream is disclosed. The deinterlacing system includes a field assembly responsive to a last field, a next field, a current field and progressive source phase and operative to develop a progressive output frame, a source detection module responsive to last, next and current fields and operative to develop a progressive source phase and a progressive source detected and an intra-frame deinterlacer responsive to the progressive output frame and the progressive source detected and operative to develop a progressive frame output.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
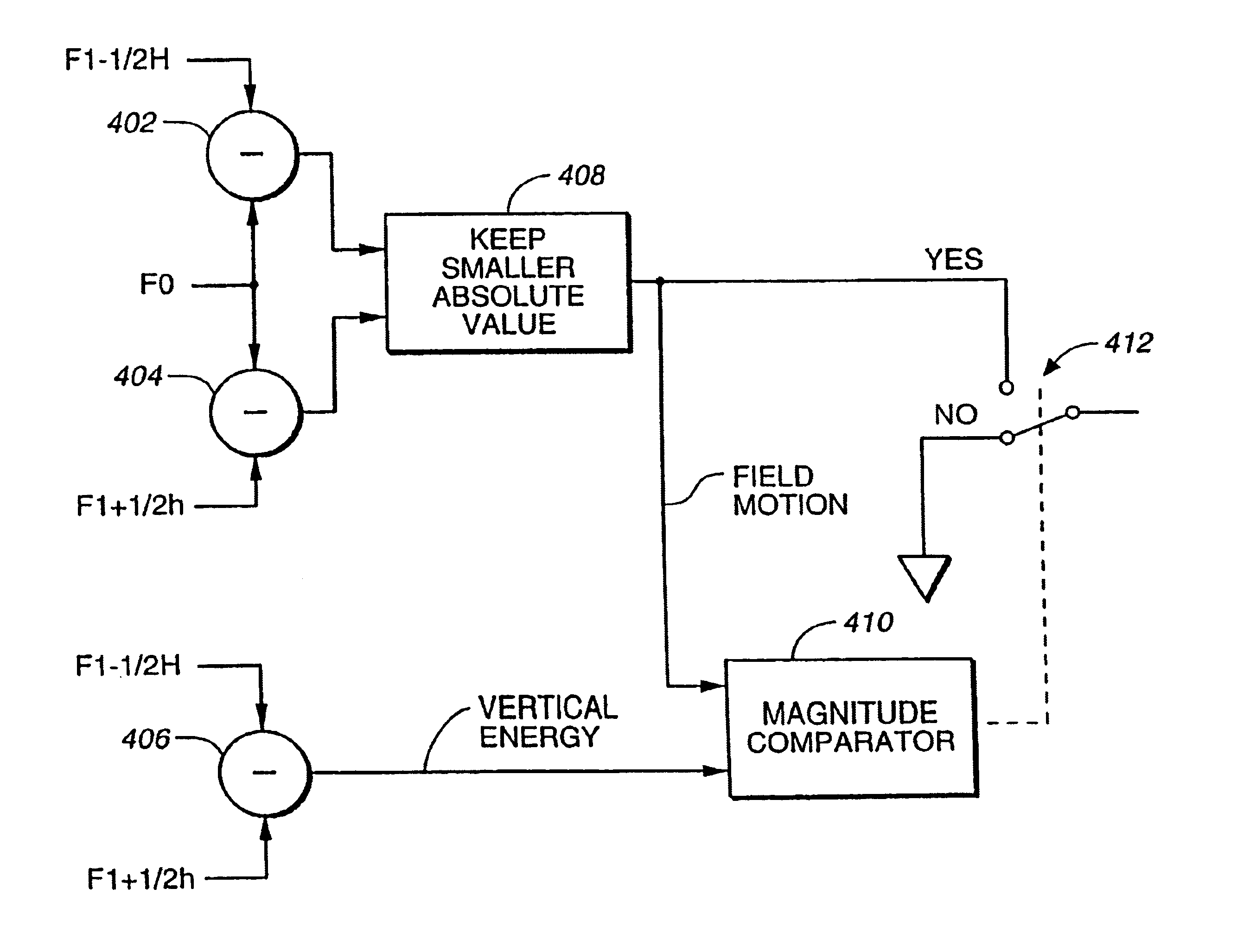
Method and apparatus for eliminating motion artifacts from video
InactiveUS6839094B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsInterlaced videoContinuous field
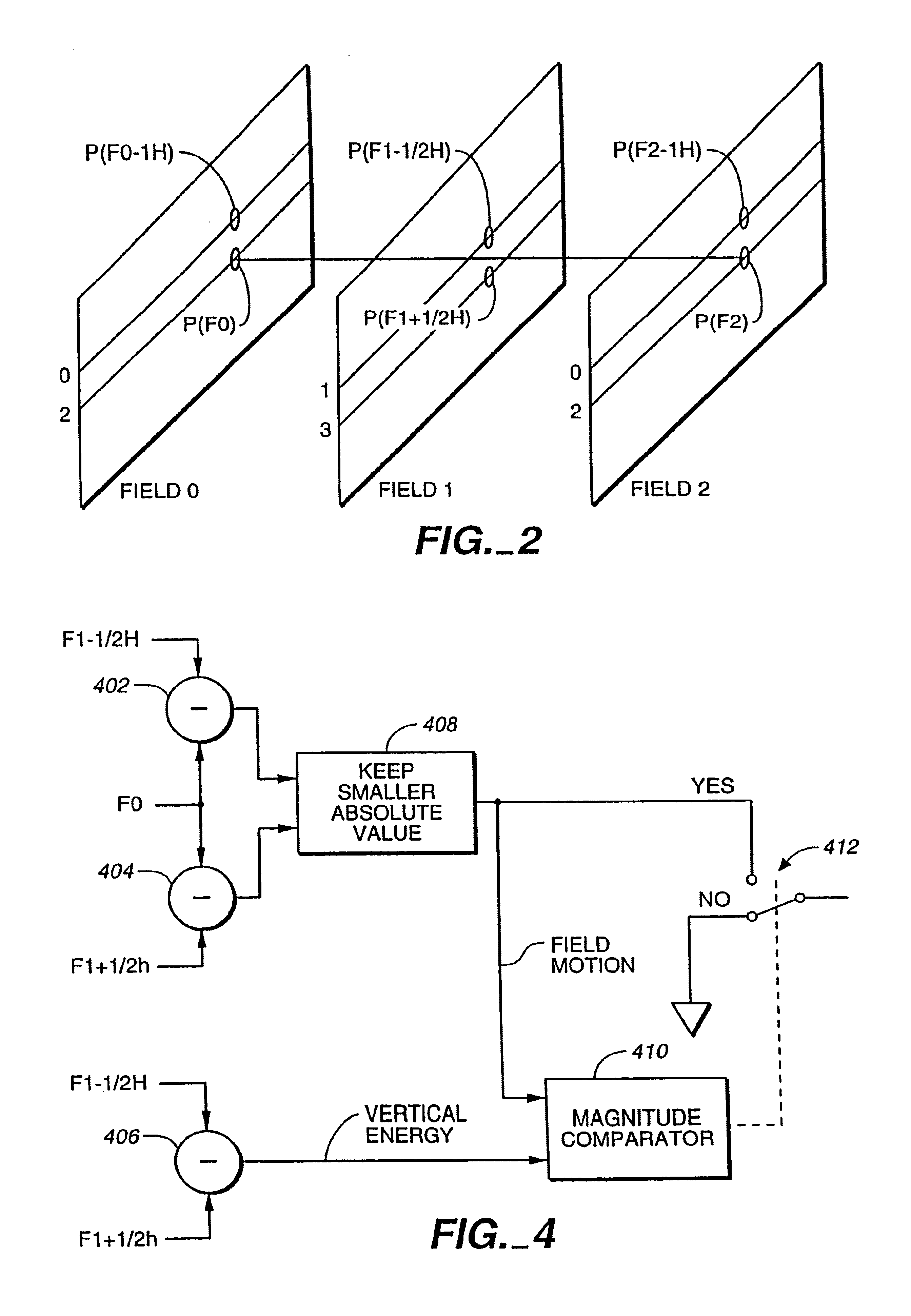
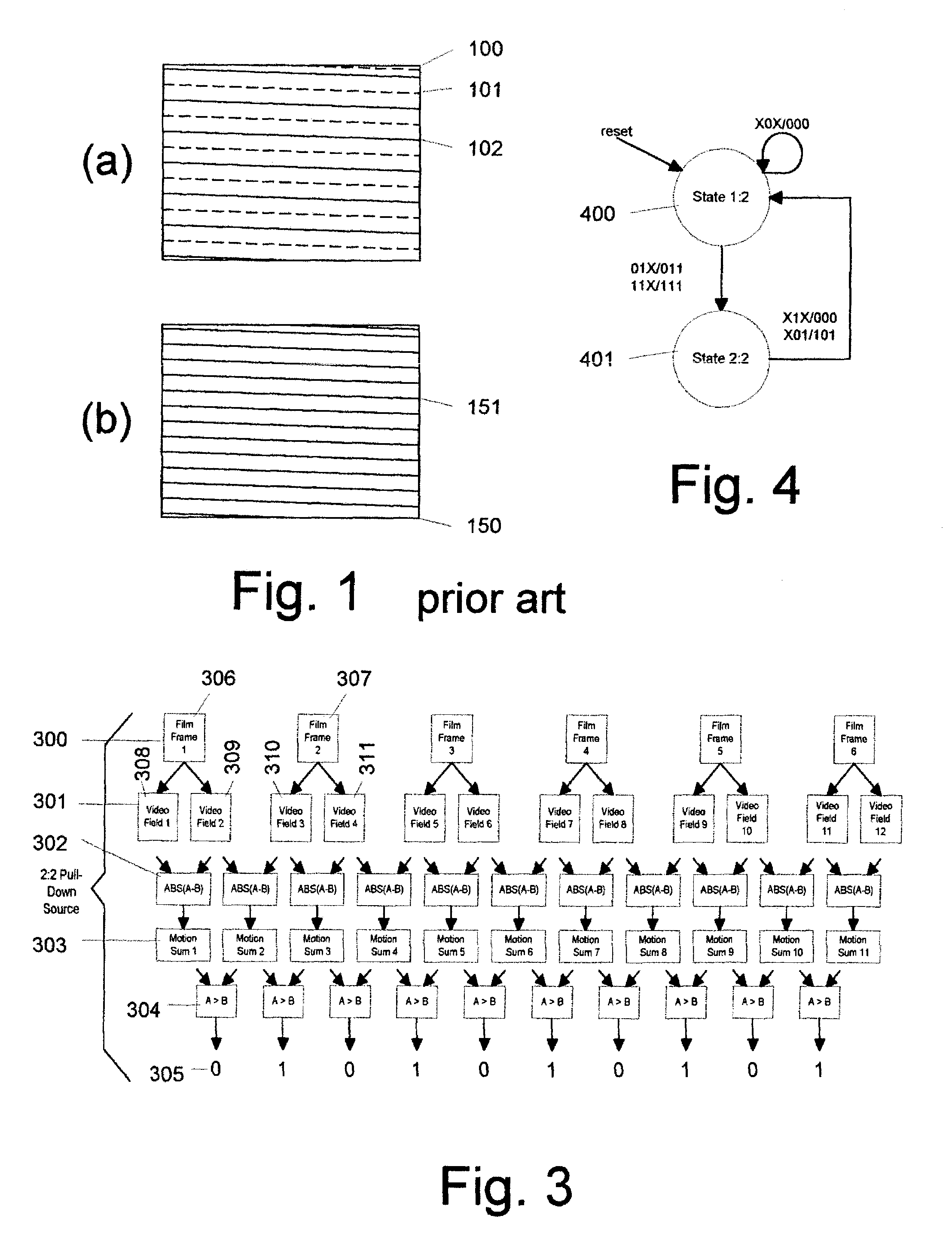
A method and apparatus for detecting and correcting motion artifacts in interlaced video signal converted for progressive video display. A correction is applied where interlaced video material is determined to originate from film source, thereby having been converted to video using a process known as 3-2 pulldown. Where the video material is not a result of the 3-2 pulldown process, a check is made for the presence of “pixel motion” so that corrections may be applied to smooth out the pixel motion. To determine 3-2 pulldown or field motion, a video field is compared to the field prior to the previous field to generate field error. Field errors are generated for five consecutive fields and a local minimum error repeated every five fields indicate the origination of the video material from film source using the 3-2 pulldown process. Upon confirmation of 3-2 pulldown, the video material is modified to correct for the mixing of two film frames into one interlaced video frame by assuring that the two fields of the de-interlaced video frame contain data from the same film frame. Where the video material did not originate from a film source, but pixel motion is detected, the pixel motion is smoothed out by an averaging method. The odd and even fields of the resulting video data are subsequently combined to form a progressive video material.
Owner:RGB SYST INC
System and method for detecting a non-video source in video signals
InactiveUS7129990B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionPattern detection
A system detects a non-video source embedded in a video sequence and provides direction to a deinterlacing algorithm accordingly. The system comprises a signal generator for generating a plurality of signals. The signals are generated in accordance with pixels input from the video sequence. The system further comprises a plurality of pattern detection state machines, each for receiving the signals and for detecting a pattern in the video sequence. The pattern is detected in accordance with a preset threshold, wherein the pattern detection state machine varies the preset threshold in accordance with the received signals. The system further comprises an arbiter state machine coupled with the plurality of pattern detection state machines for governing the pattern detection state machines and for determining whether or not a non-video source is embedded in the video sequence.
Owner:PIXELWORKS SEMICON TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
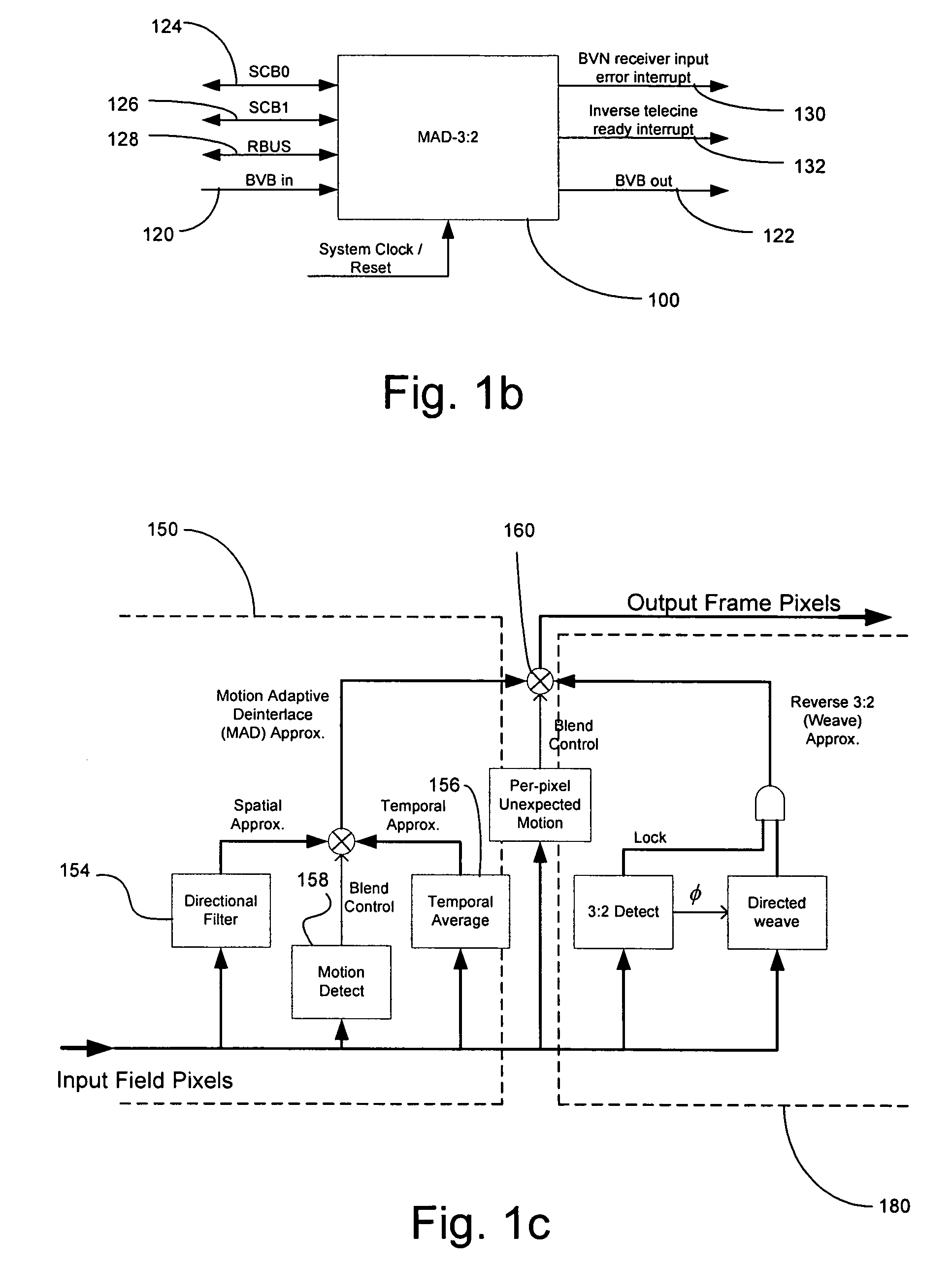
Method and apparatus for motion adaptive deinterlacing
InactiveUS7098958B2Improves feathering detectionTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesAdaptive filterInterlaced video
An adaptive filter calculates a target pixel from an interlaced video signal. The video signal comprises a plurality of frames, each of which comprises an even and an odd field. The filter comprises a quantized motion calculator and a filter selector. The quantized motion calculator estimates an amount of motion about the target pixel. The filter selector selects a filter in accordance with the estimated amount of motion. The filter applies a first weighting factor to a plurality of current field pixels and a second weighting factor to a plurality of previous field pixels for creating the target pixel.
Owner:JALDI SEMICON CORP
Systems and methods for digitally re-mastering or otherwise modifying motion pictures or other image sequences data
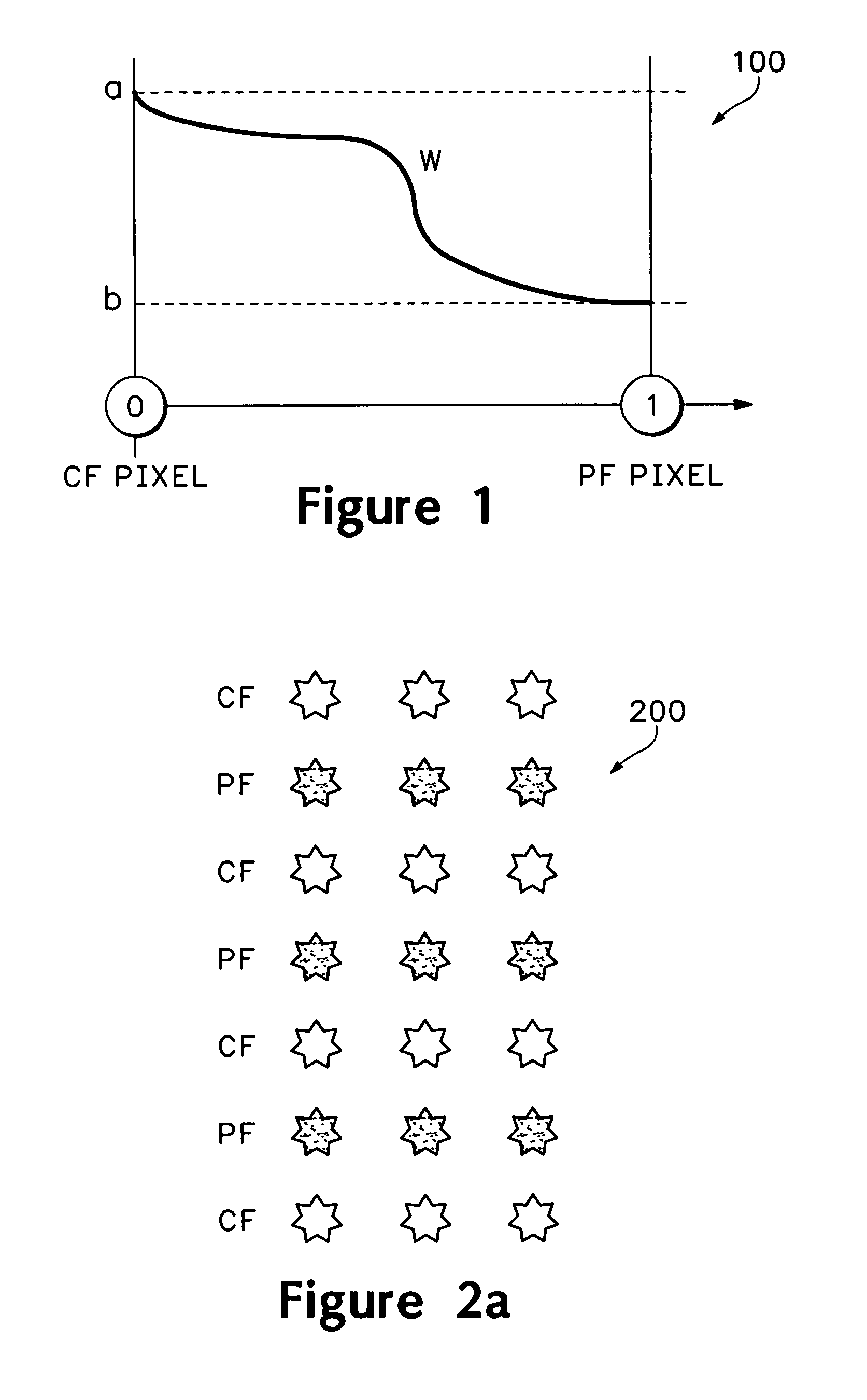
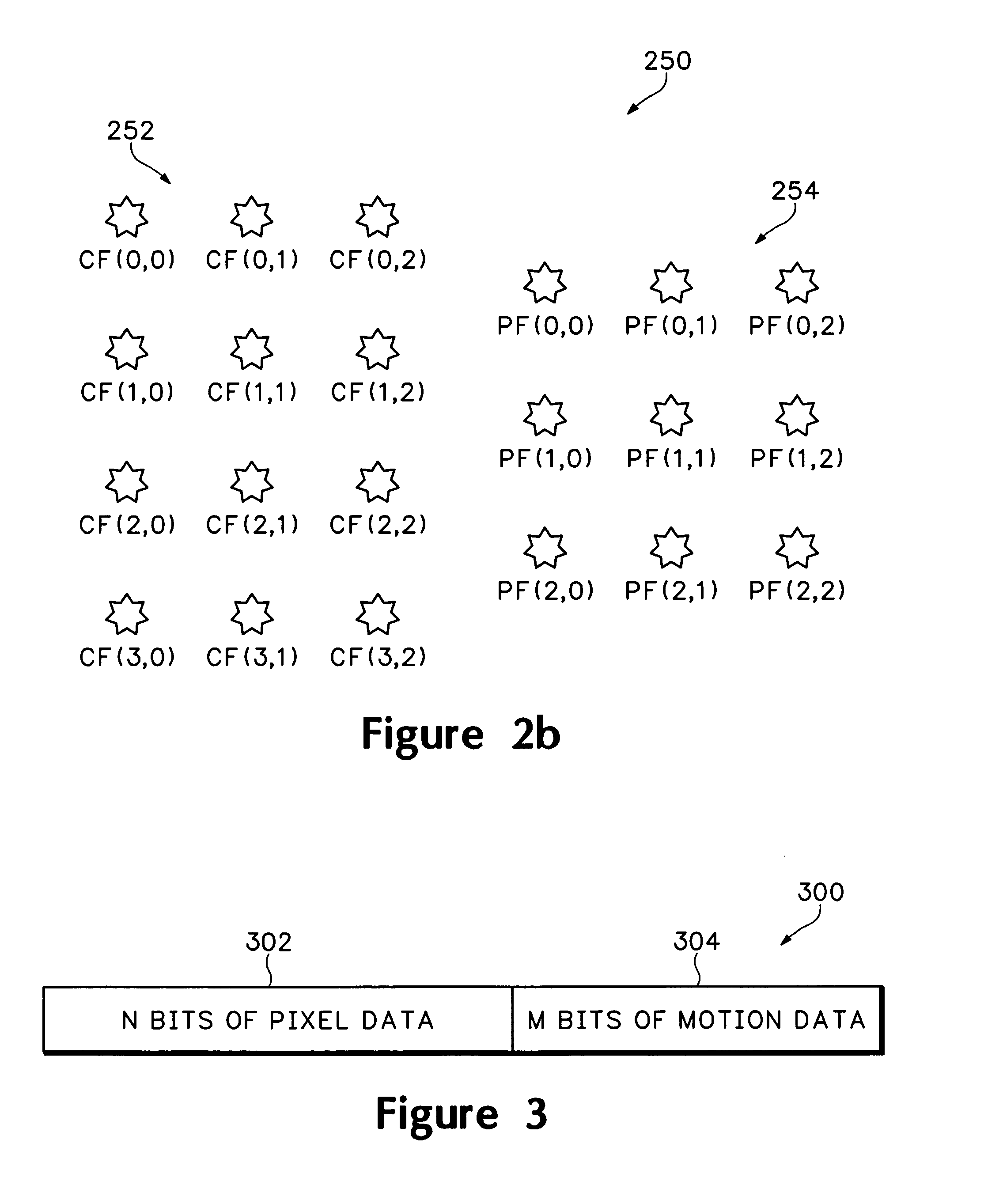
ActiveUS7856055B2Improve spatial resolutionExpands image frequency spectrumTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionStatistical quality
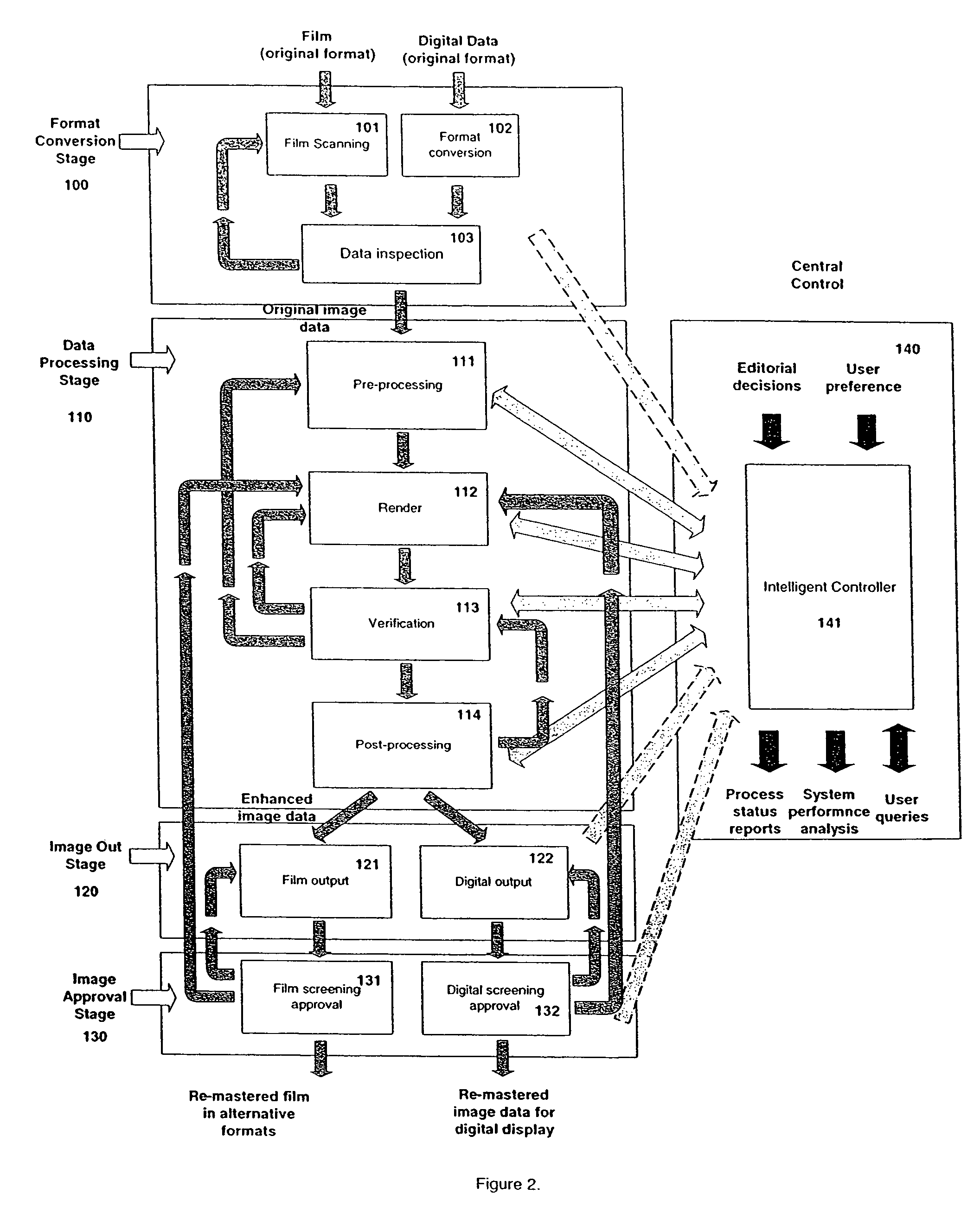
A process and methods of digital enhancement of motion pictures and other moving image sequences for the purpose of being exhibited in an alternative display format including a large format cinema are disclosed. The invention efficiently enhances image resolution and quality through a temporal filtering process and achieves high performance using automated or interactive statistical quality evaluation methods. A system specially designed for efficient temporal computing with a parallel and distributed computing configuration equipped with a variety of optimization schemes is also disclosed. The performance of the process and the system is optimized through an intelligent controller and is scalable to support any throughput requirements demanded for concurrent motion picture releases in the original format as well as in any alternative format.
Owner:IMAX CORP
Video signal converting apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050001929A1Increase frame ratePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningInterlaced videoHigh frame rate
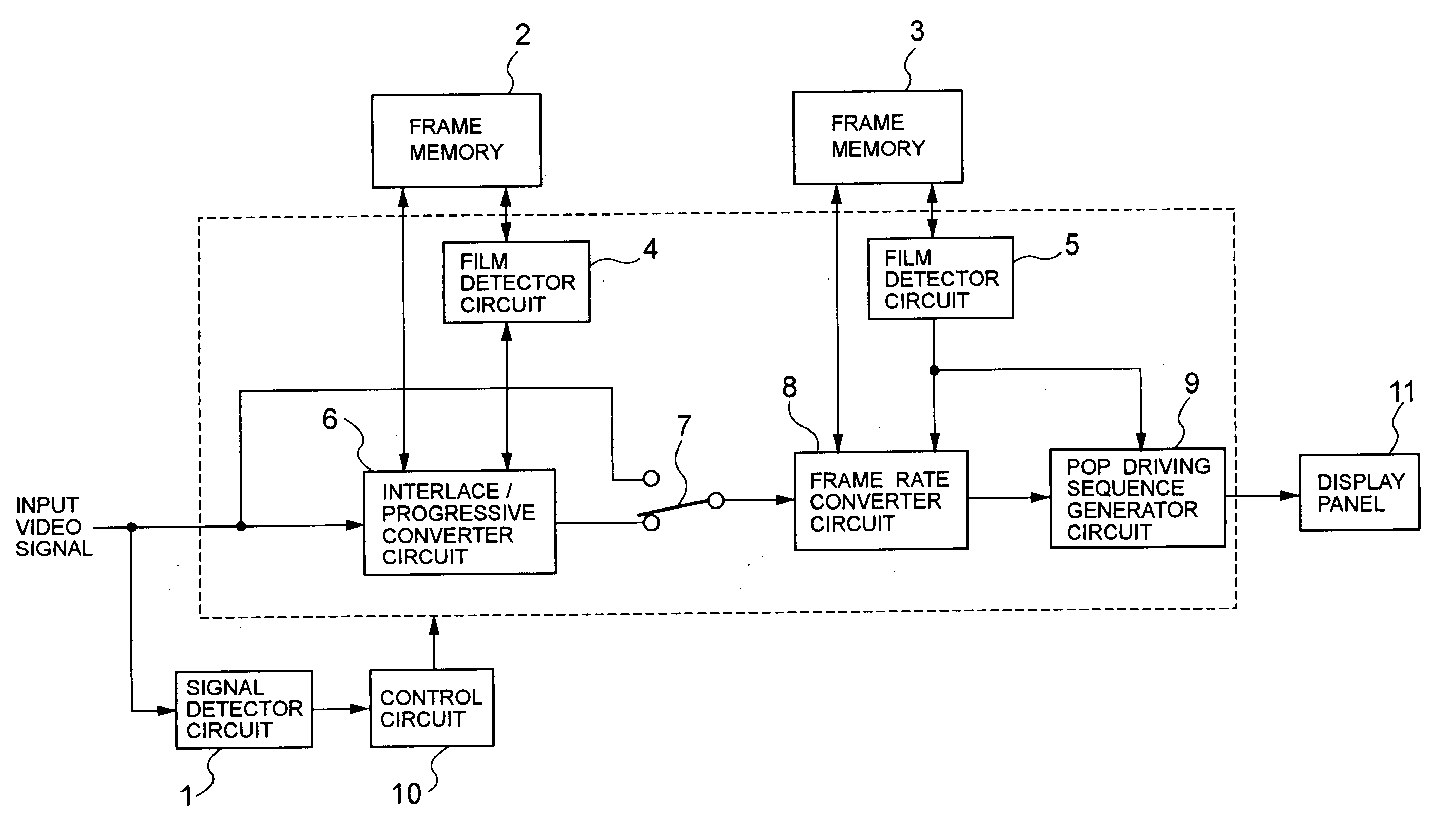
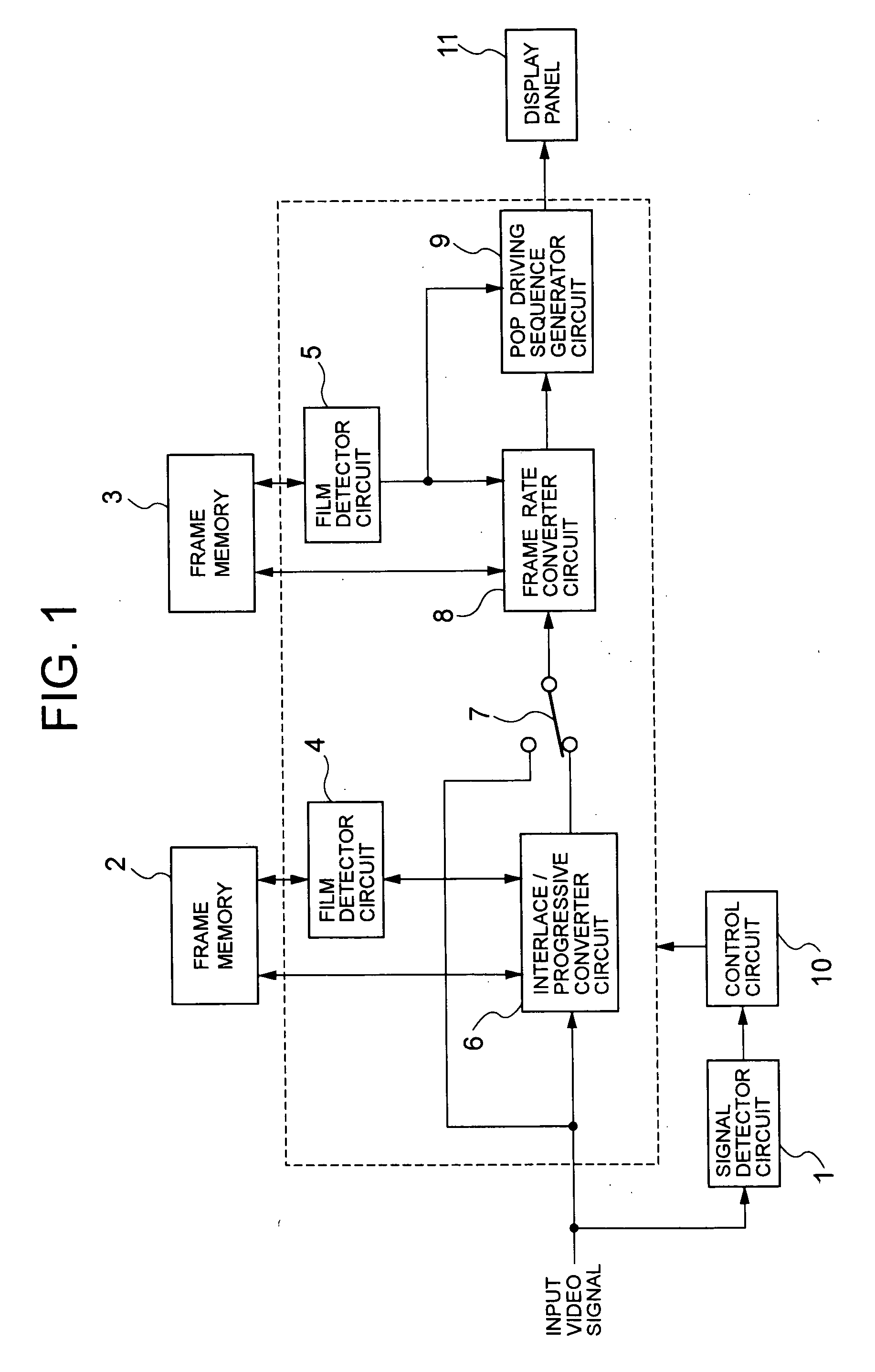
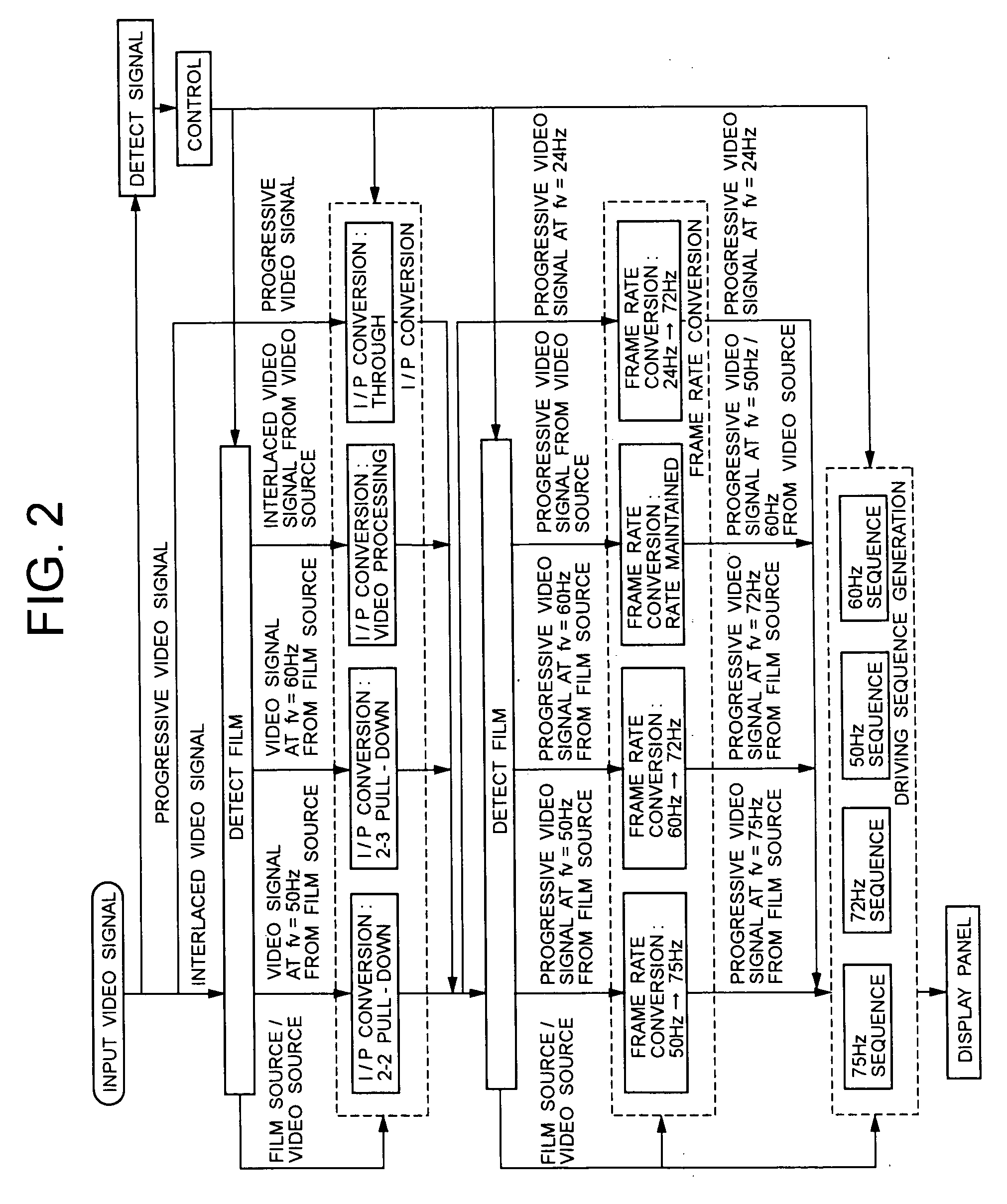
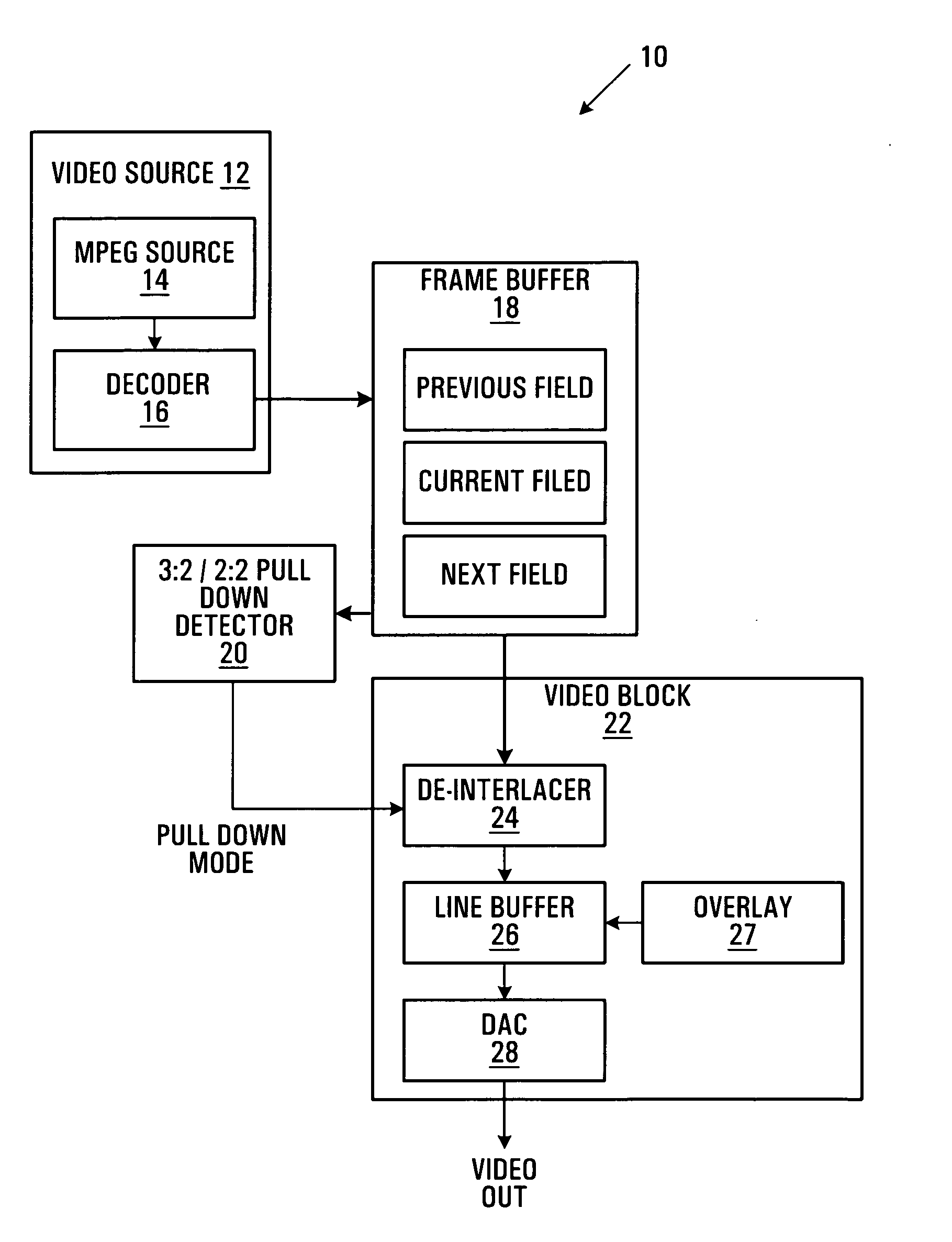
A video signal converting apparatus and method for improving display quality of video signals from both film source and video source. It is discriminated whether the input video signal is an interlaced video signal or not, and it is discriminated whether the input video signal is a video signal from a film source based on a film. If the input video signal is discriminated as interlaced video signals, the input video signal is converted, for outputting, to the progressive video signals by a converting method in accordance with a discrimination result regarding whether the input video signal is a video signal from the film source or not. The converted progressive video signal is converted, for outputting, to a video signal having a high frame rate in accordance with the discrimination result regarding whether the converted progressive video signal is a video signal from the film source or not. If the input video signal is not discriminated as an interlaced video signal, the input video signal is converted to a video signal having a high frame rate in accordance with a discrimination result regarding whether the input video signal is a video signal from the film source or not.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method and apparatus for improving video quality
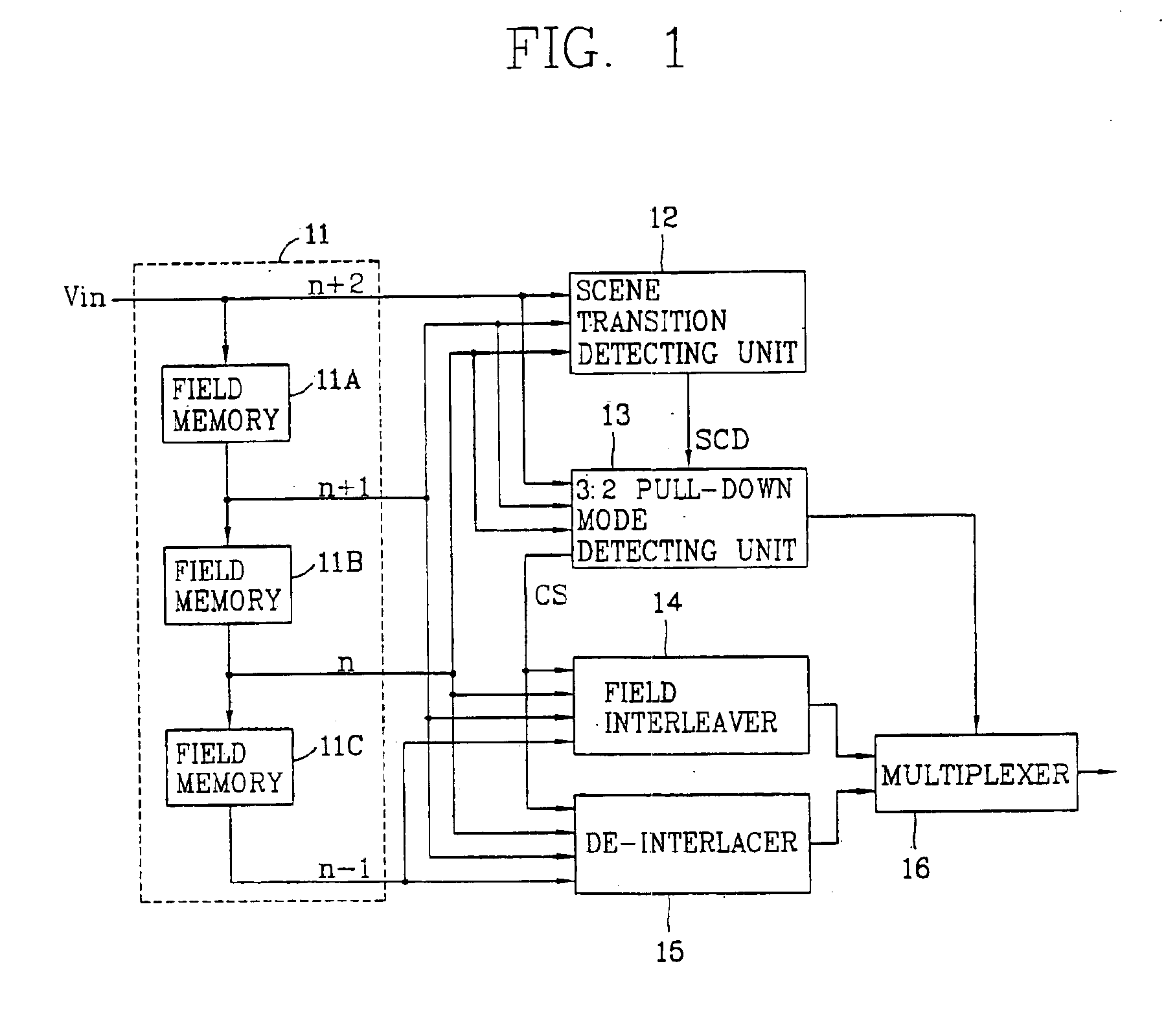
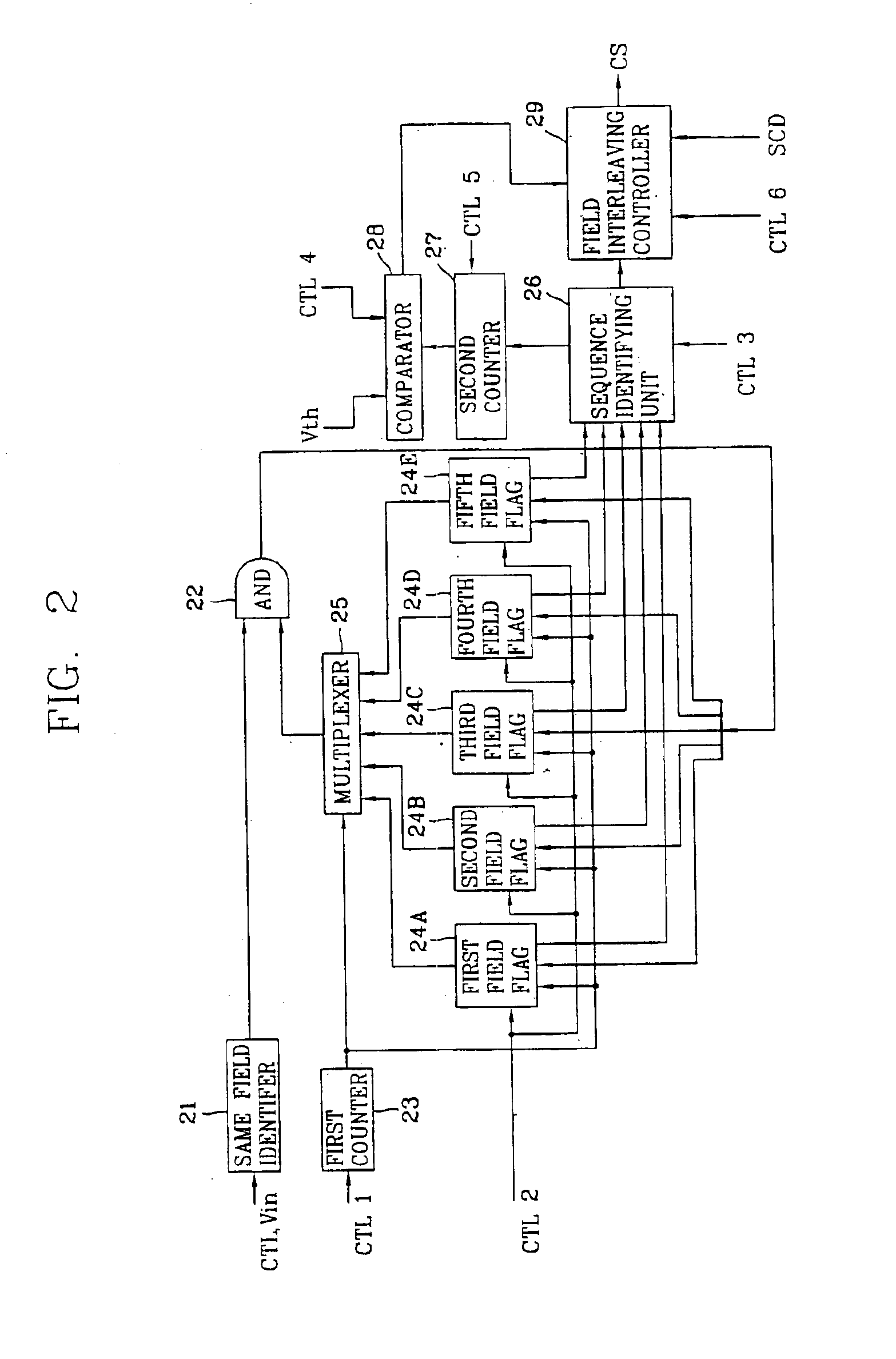
InactiveUS6891571B2Simple structureTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsVideo qualityField data
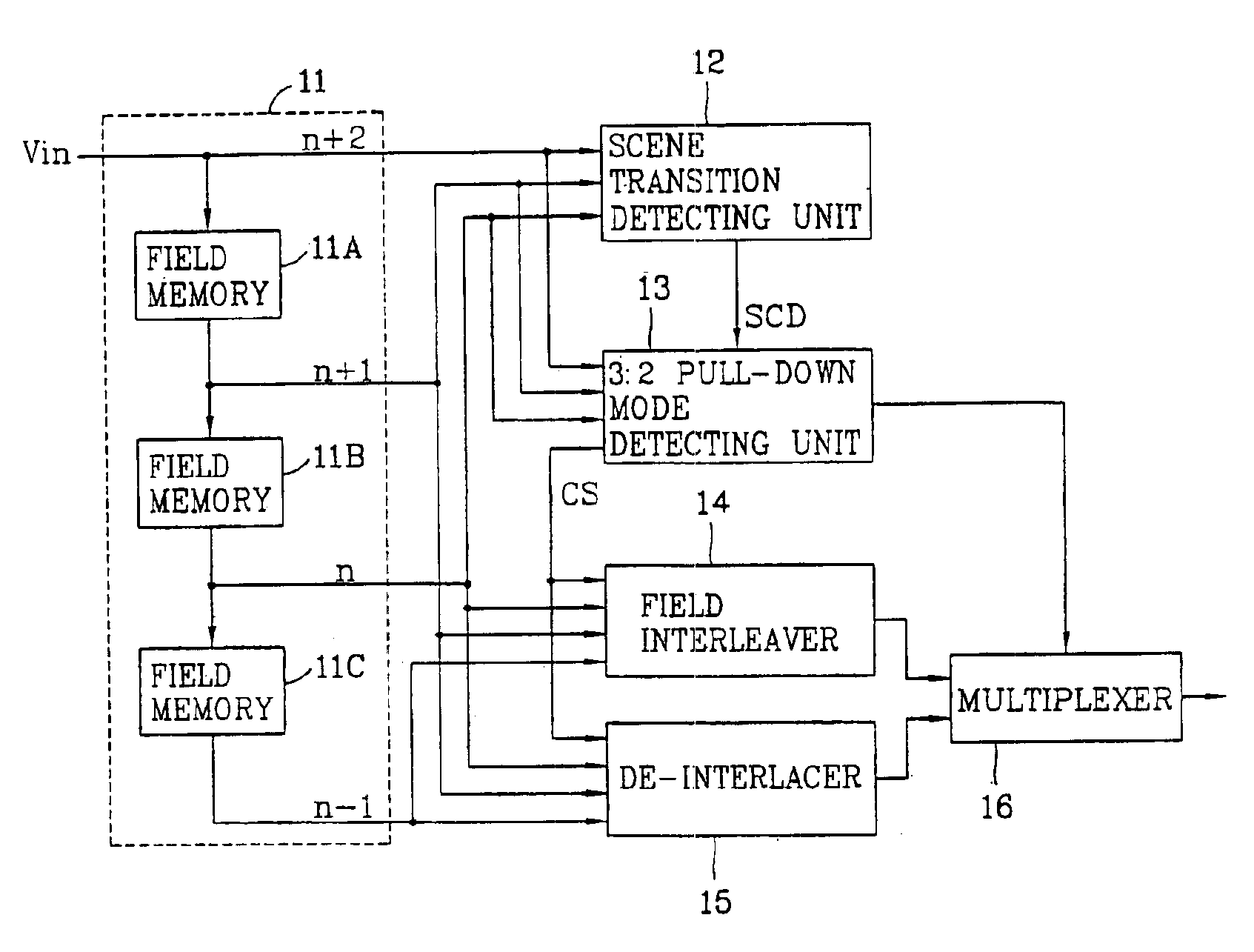
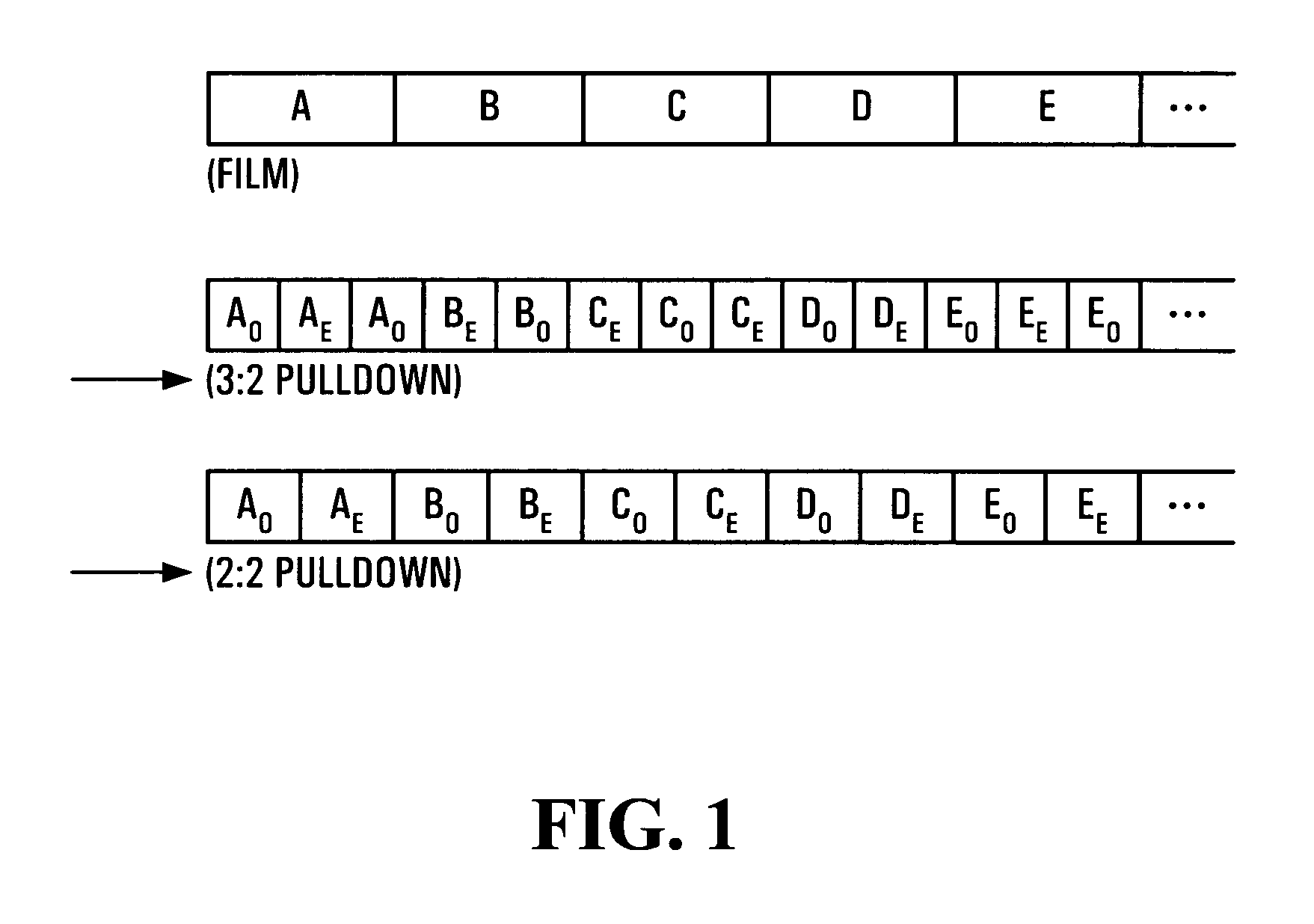
Disclosed is a video restoring apparatus and method thereof enabling to improve a video mode by interpolating field data. The present invention includes the steps of: identifying whether a scene on an image sequence is changed by receiving field data; detecting whether a 3:2 pull-down mode exists in the image sequence; generating a first interpolated frame by interleaving a field to be interpolated and adjacent fields each other when there is the 3:2 pull-down mode; generating a second interpolated frame by de-interlacing the field to be interpolated and the adjacent fields each other when there is not the 3:2 pull-down mode, and selectively outputting one of the first and second interpolated frames.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
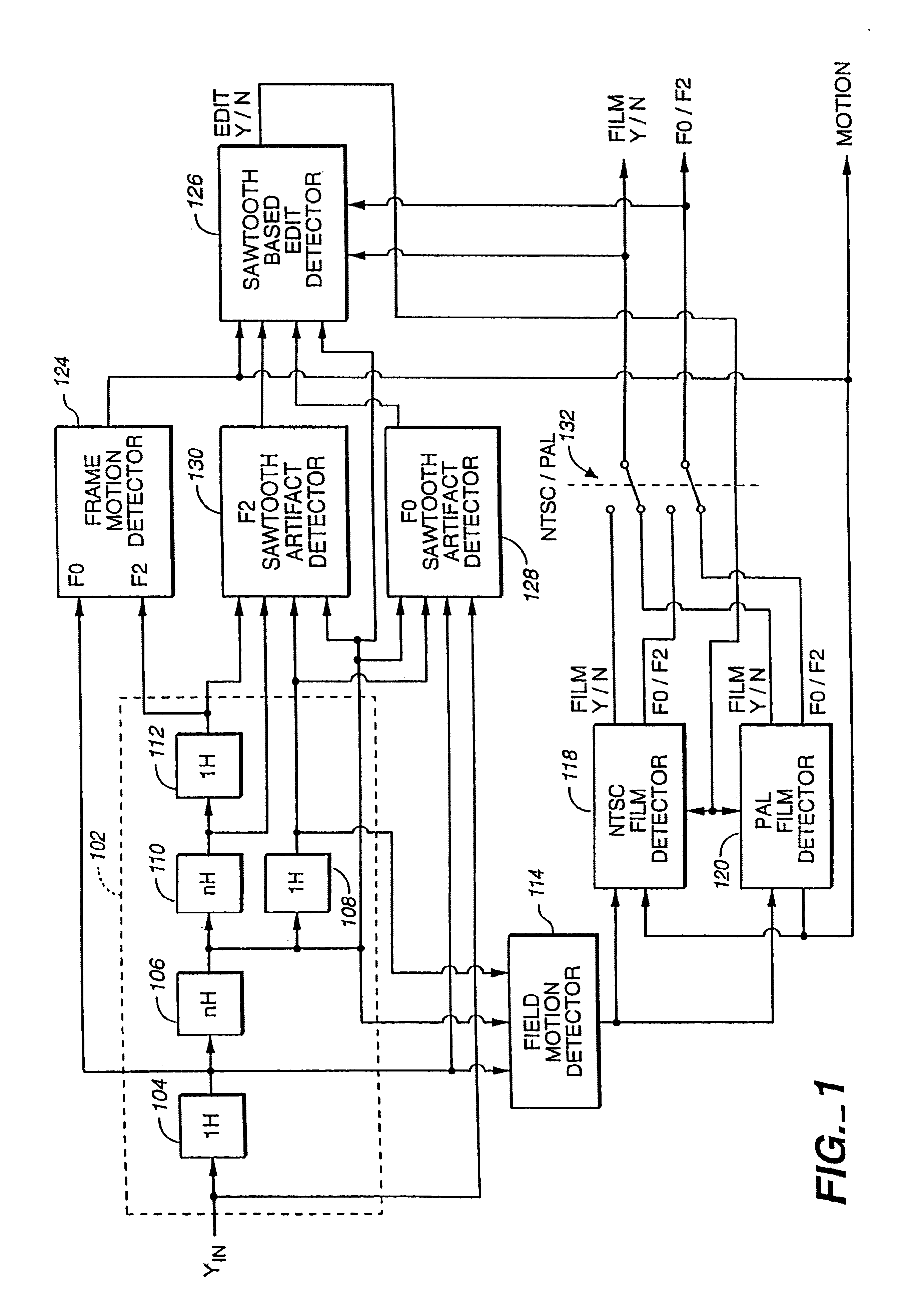
Film source video detection
InactiveUS6859237B2Improve abilitiesIncrease differentiationTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMotion detectorPattern sequence
A television line doubler (interlaced to progressive scan converter) incorporating the following aspects—an improved field motion detector which does not treat low frequency vertical transitions as motion; a frame motion detector having an improved ability to differentiate motion from subcarrier signal components; a sawtooth artifact detector; a sawtooth artifact detector in combination with a film pattern detector, such that the artifact detector can take the film pattern detector out of film mode earlier than it would if it only were responsive to a break in the film pattern; tandem field motion detectors; an improved field based film detector; film pattern detectors and motion detectors used therewith which operate by performing end-of-field calculations; the combination of a field motion detector and a frame motion detector such that the frame motion detector provides a motion signal used as a verification by the field motion detector; an improved NTSC film detector requiring a minimum number of NTSC film pattern sequences; and an improved PAL film detector employing a minimum motion threshold detector.
Owner:TAMIRAS PER PTE LTD LLC
Integrated multi-format audio/video production system
InactiveUS20080030614A1Improve compatibilityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoMass storage
Owner:SCHWAB BARRY H +1
Apparatus and method for deinterlace video signal
InactiveUS7170562B2Improve picture qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningInterlaced videoImaging processing
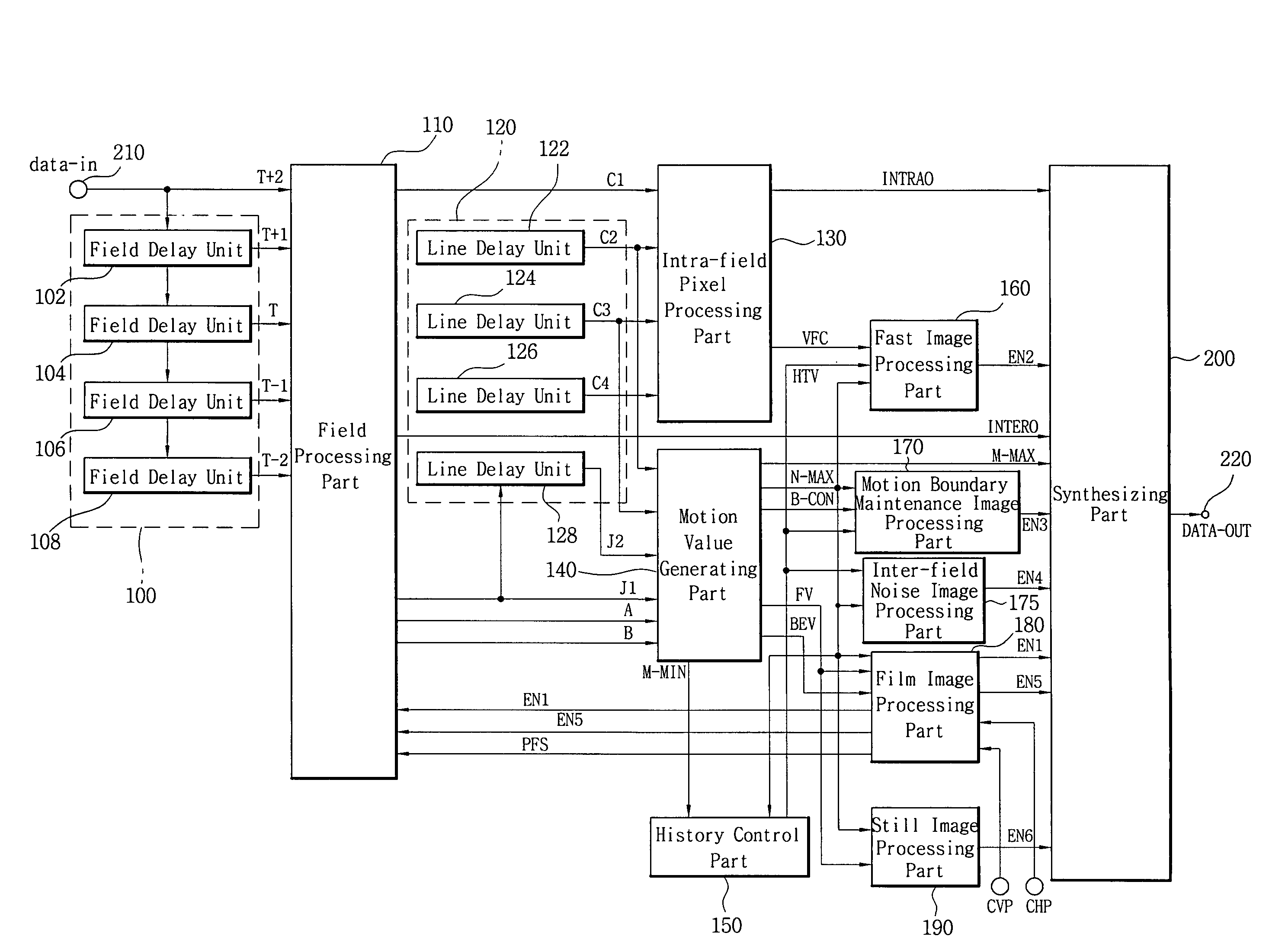
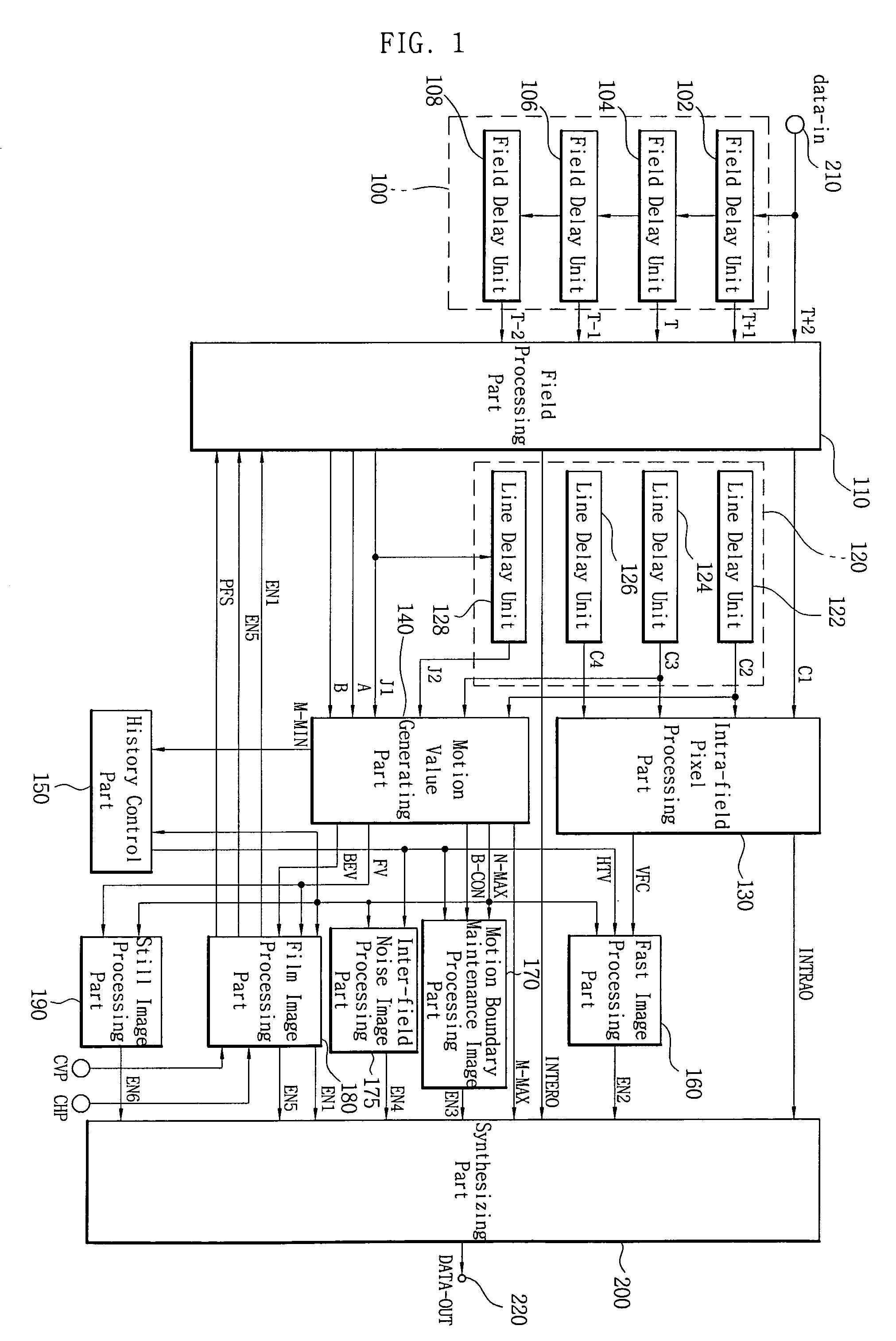
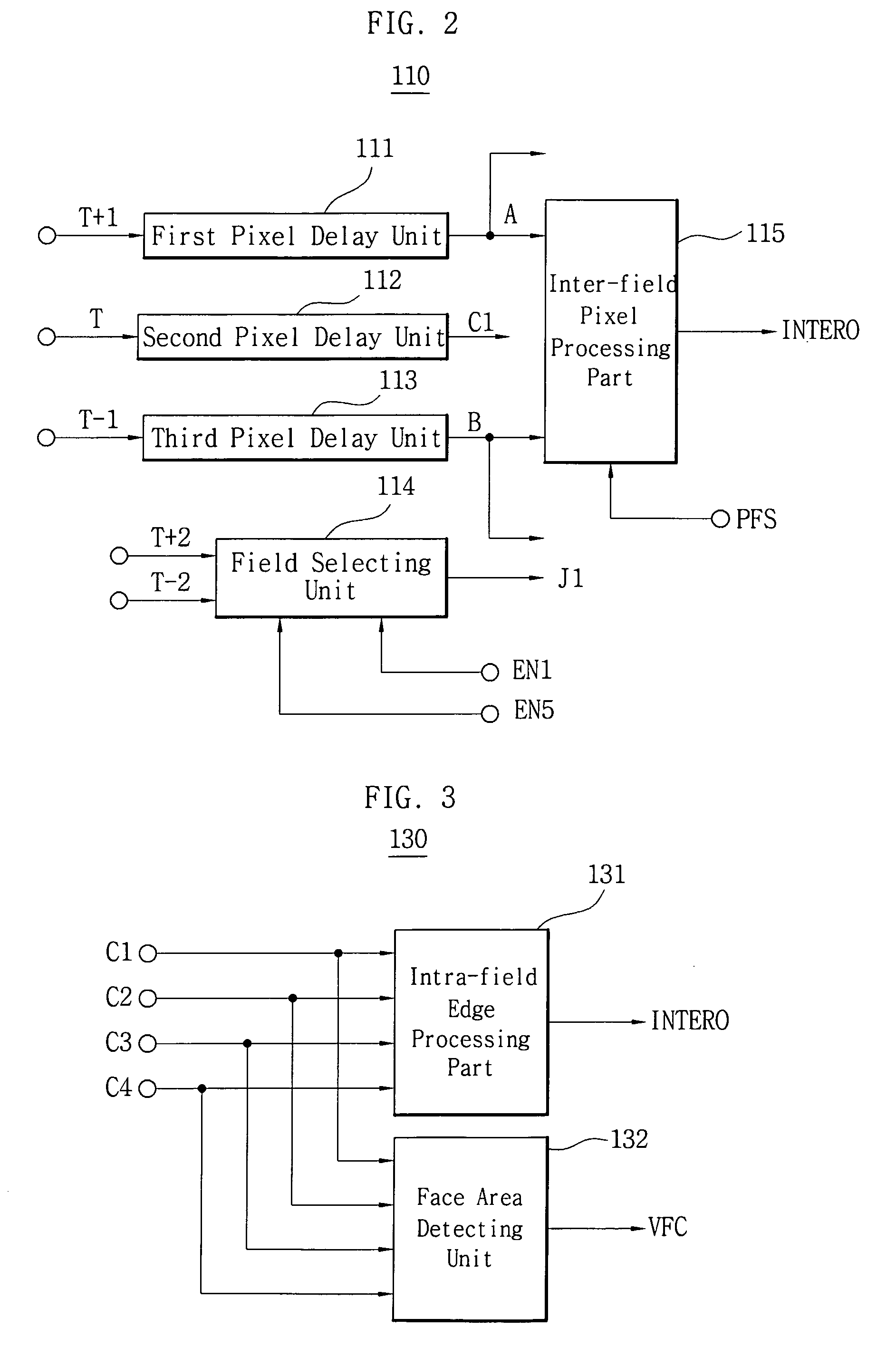
There is provided an image signal deinterlacing apparatus for converting an interlaced scanning image into a progressive scanning image. The deinterlacing apparatus includes: an intra-field pixel processing unit for detecting a face area and a to-be-interpolated data within a field by using pixels of a field disposed before two field from a current field; a motion value generating unit for detecting first to third motion values and first and second motion degree values; a history control unit for detecting a history value; a fast image processing unit for detecting a fast motion image; a film image processing unit for detecting a film image and a caption area and determining a to-be-interpolated field data; a still image processing unit for accumulating the first motion value and the second motion degree value to detect a still image; an inter-field noise image processing unit for detecting an adjacent inter-field noise image; a motion boundary maintenance image processing unit for detecting a motion boundary maintenance image; and a synthesizing unit for selectively interpolating the intra-field to-be-interpolated data, the before-one-field inter-field data and the before-three-field inter-field data according to the detection result.
Owner:MACRO IMAGE TECH
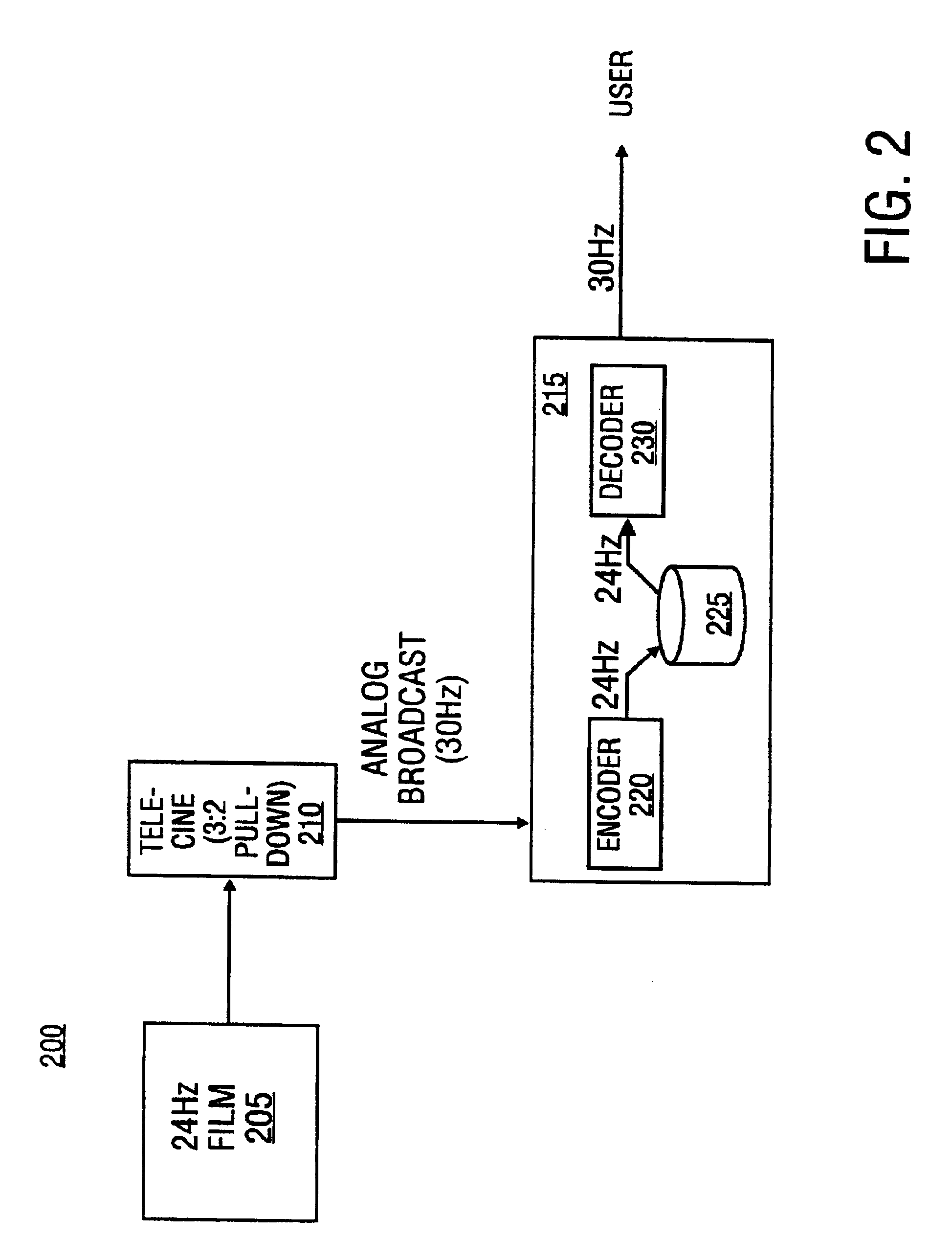
Edit decision list for identifying the pull down phase of a video signal
InactiveUS6871003B1Easy to optimizeFacilitate the processTelevision system detailsElectronic editing analogue information signalsRecording durationDownstream processing
The invention provides an editing system for editing and combining media material into a resulting media composition. The media may be film or video based material, and also may include audio material. The video may adhere to either NTSC or PAL timing. In response to editing instructions, an Edit Decision List (EDL) is produced that specifies the material that makes up the edited composition, and the order of presentation of this material in the output composition. The EDL specifies the input clips that are taken from the source material using source timecode and similarly defines the output order again according to a new time code, the record time code. The editing system produces an extended EDL that facilitates the downstream processing (after the editing has been completed) for post production tasks requiring the need to know accurately where edit points occur.
Owner:AVID TECHNOLOGY
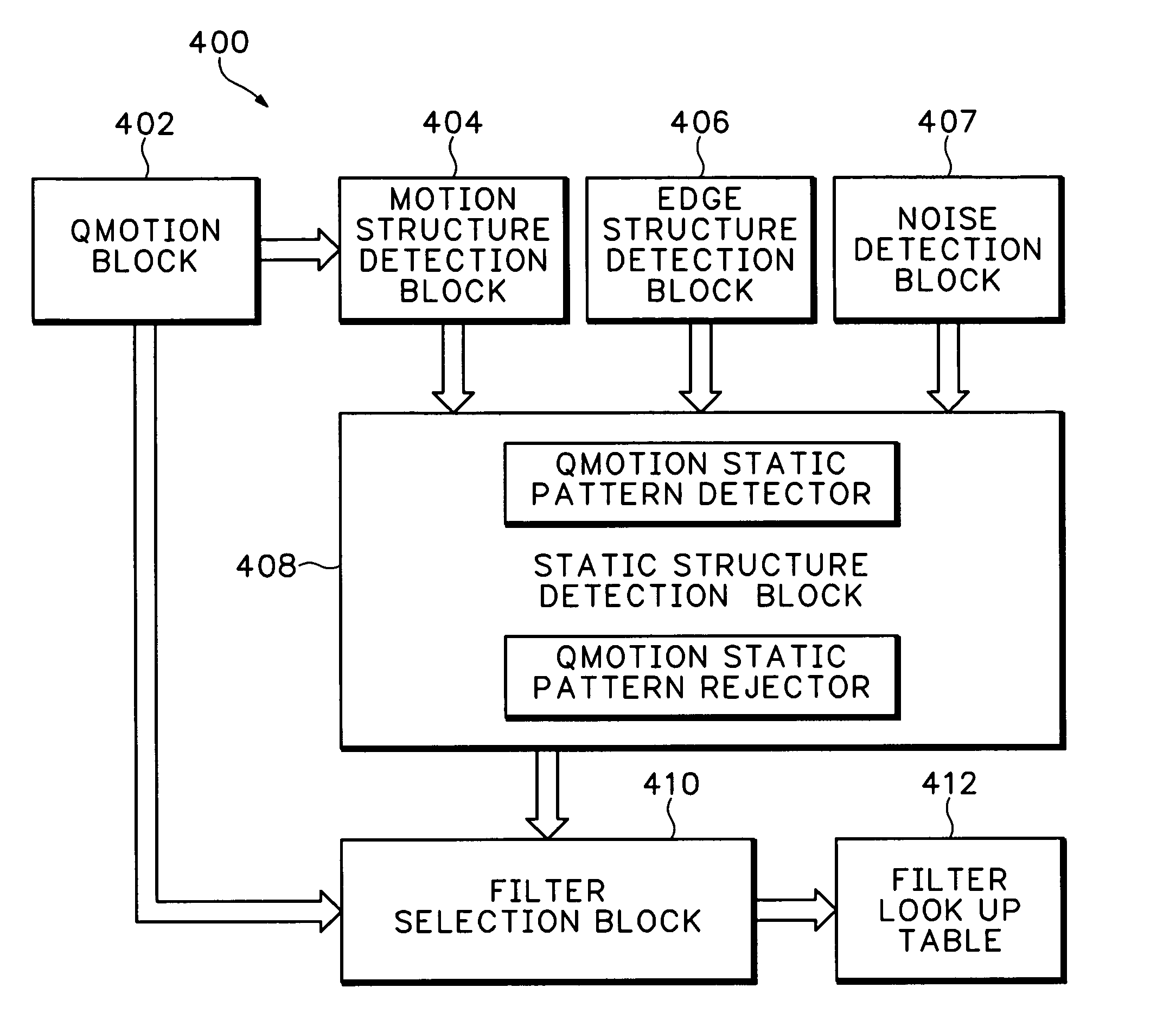
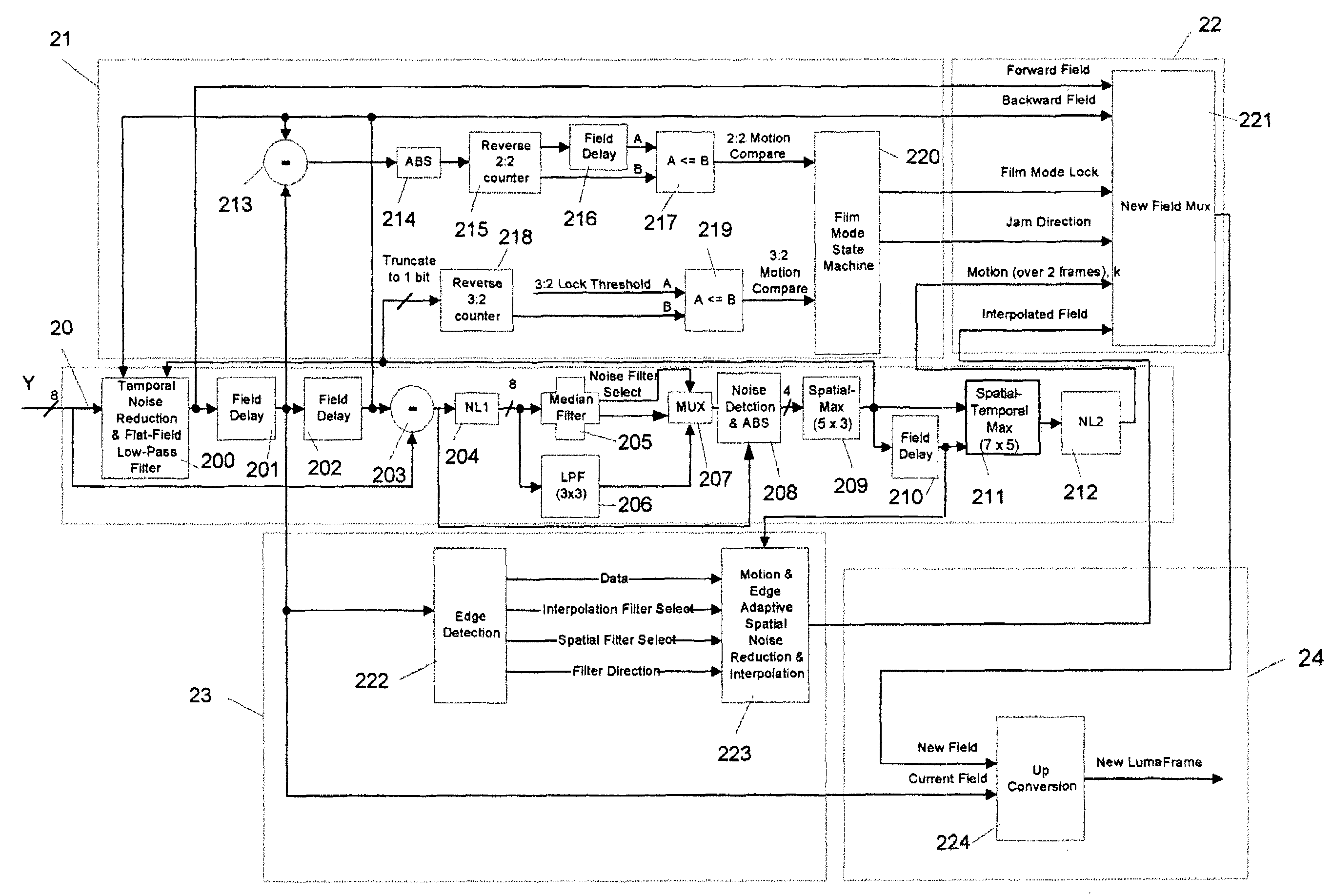
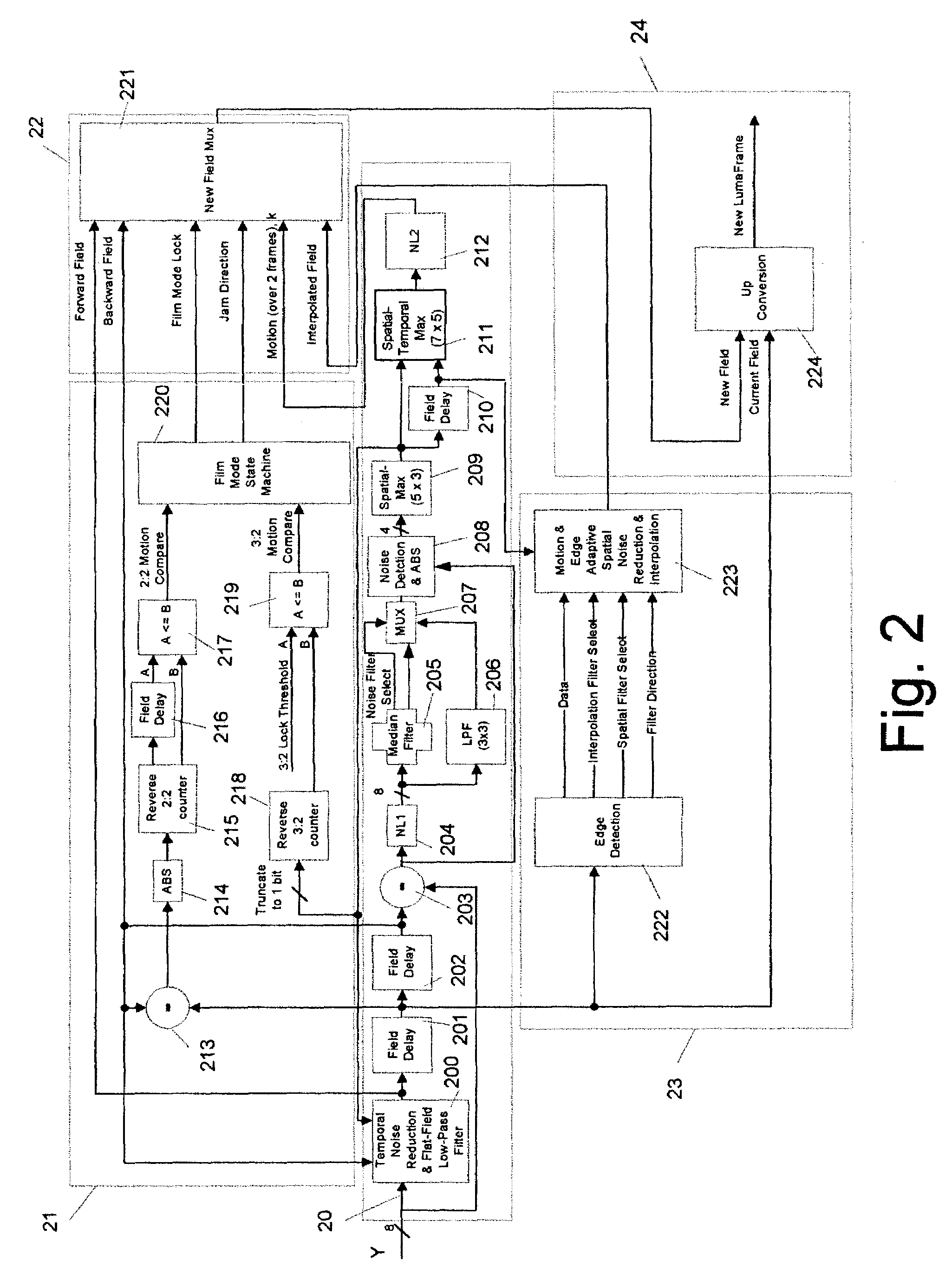
Content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction
ActiveUS7375760B2Quantity minimizationReduce noiseTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionLow-pass filter
A content-dependent scan rate converter with adaptive noise reduction that provides a highly integrated, implementation efficient de-interlacer. By identifying and using redundant information from the image (motion values and edge directions), this scan rate converter is able to perform the tasks of film-mode detection, motion-adaptive scan rate conversion, and content-dependent video noise reduction. Adaptive video noise reduction is incorporated in the process where temporal noise reduction is performed on the still parts of the image, thus preserving high detail spatial information, and data-adaptive spatial noise reduction is performed on the moving parts of the image. A low-pass filter is used in flat fields to smooth out Gaussian noise and a direction-dependent median filter is used in the presence of impulsive noise or an edge. Therefore, the selected spatial filter is optimized for the particular pixel that is being processed to maintain crisp edges.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
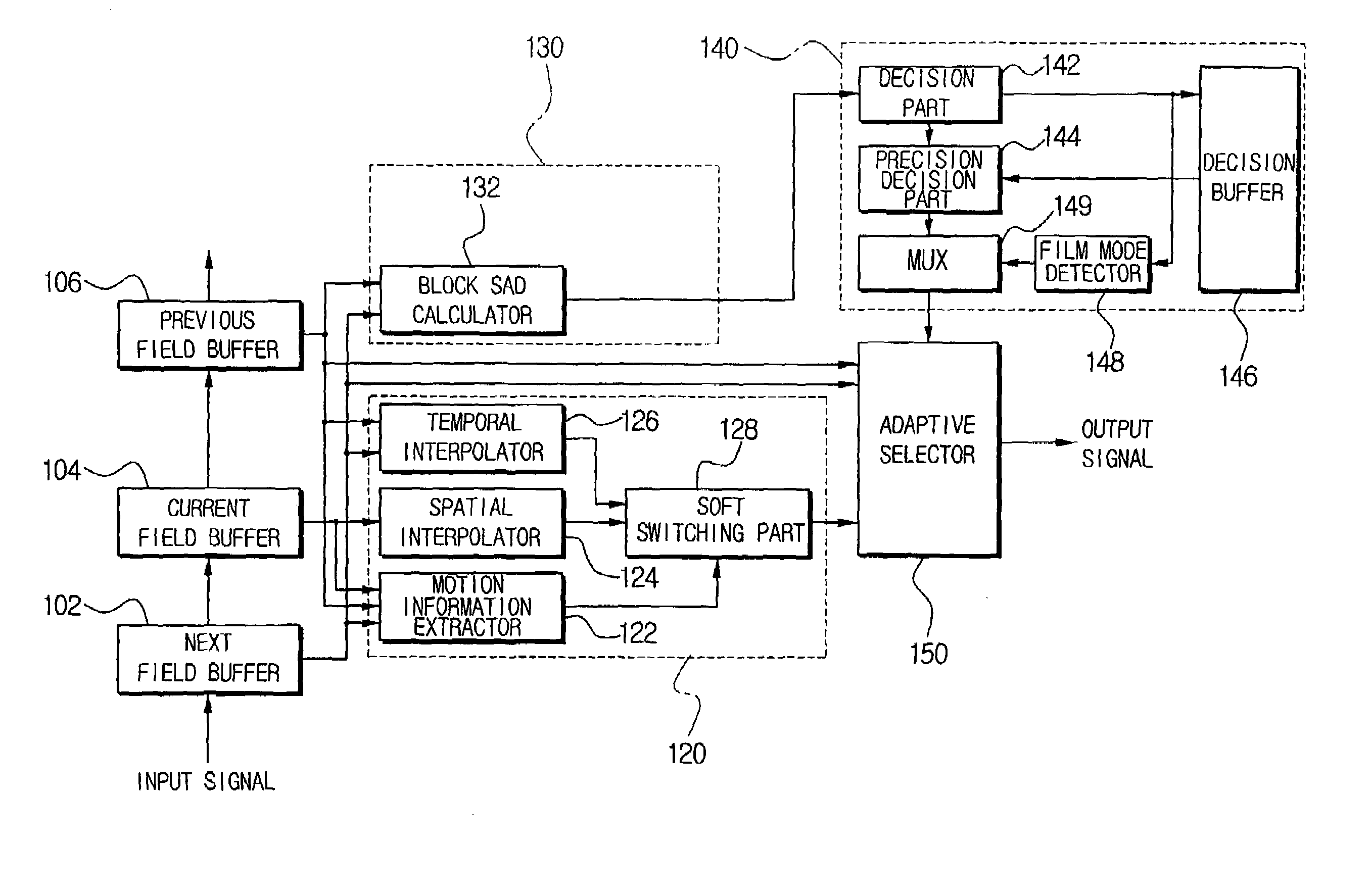
Deinterlacing apparatus and method
ActiveUS7057665B2Improve image qualityLow costPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern detectionSelf adaptive
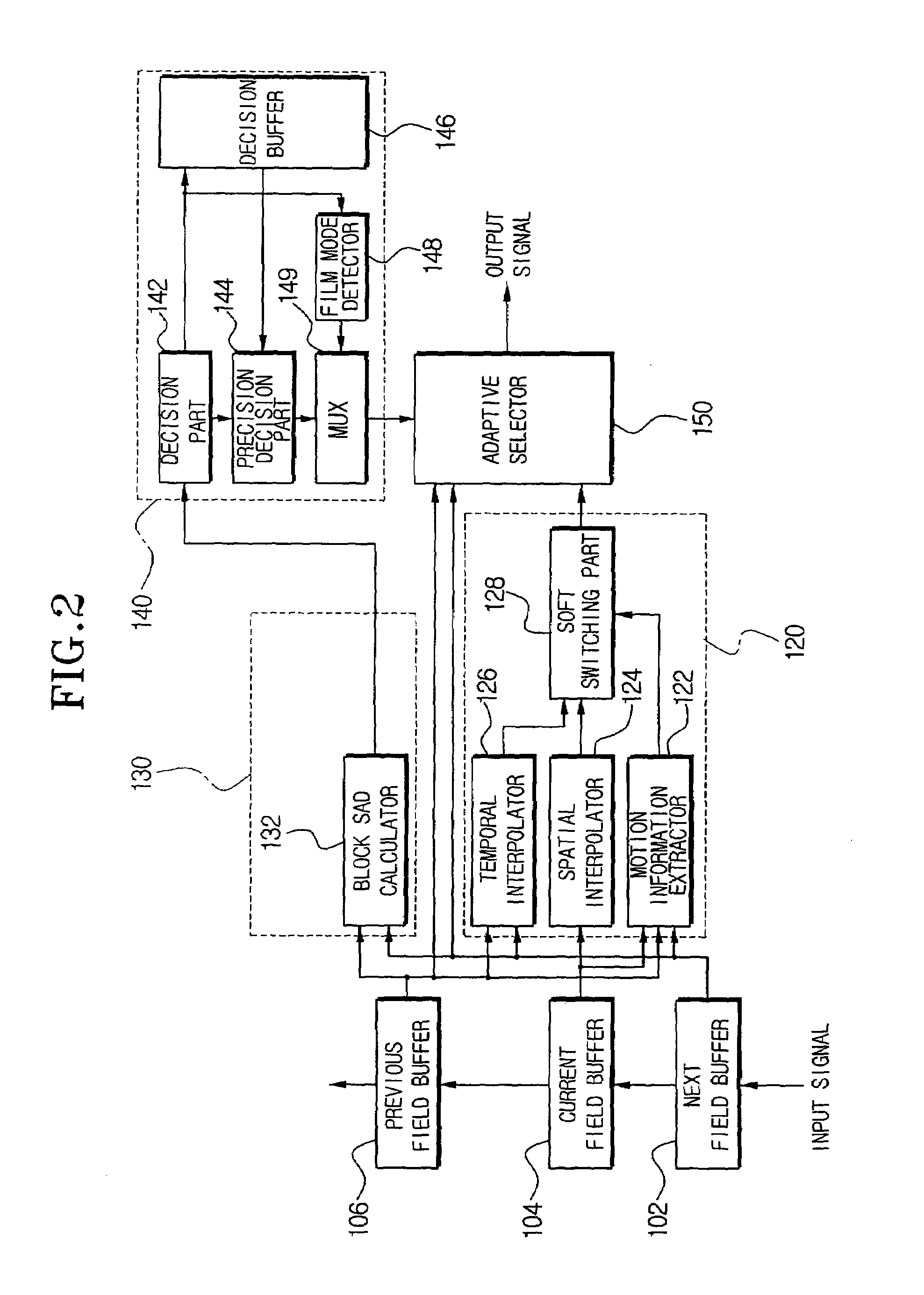
A deinterlacing apparatus and method use a buffer unit having a previous field buffer, a current field buffer, and a next field buffer to store, sequentially, individual fields of an image signal; calculate a Sum of Absolute Difference (SAD) value of a predetermined search region unit with reference to a next field stored in the next field buffer and a previous field stored in the previous field buffer; determine whether the predetermined search region is a still region and whether a source of the image signal is a film based on the SAD value; uses a 3D interpolation unit to output adaptively a temporal interpolation value and a spatial interpolation value based on motion information; and adaptively select a deinterlacing result based on the previous field, the next field, and an output of the 3D interpolation unit according to a signal outputted from the still region / film mode detection unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Film-mode (3:2/2:2 Pulldown) detector, method and video device
InactiveUS20050243215A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhysicsFilm (photographic)
A film mode detector detects film mode of a series of fields of video by comparing pixels in a field adjacent the current field, with corresponding pixels directly above and directly below the pixels in an adjacent field. The number of pixels in the adjacent in time to the current field having (or not having) a value approximately between values of the pixels above and below in the current field is assessed. Film mode for a current field may be detected by monitoring the assessment from field to field. Alternatively or additionally, the detector may detect film mode by assessing for each current field, whether a relatively large or relatively small number of pixels in the immediately previous field have values outside a specified distance of values of a corresponding pixel in the immediately subsequent field, for at least a portion of the immediately previous and subsequent fields. Again, film mode may be detected by monitoring this second assessment from field to field.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Frame interpolation and apparatus using frame interpolation
A first motion vector is estimated by using a first frame and a second frame that follows the first frame. A support frame is generated from at least either the first or the second frame by using the first motion vector. The support frame is divided into a plurality of small blocks. Motion vector candidates are estimated by using the first and second frames, in relation to each of the small blocks. A small block on the first frame, a small block on the second frame and the small blocks on the support frame are examined. The small block on the first frame and the small block on the second frame correspond to each of the motion vector candidates. A second motion vector is selected from the motion vector candidates, and points the small block on the first frame and the small block on the second frame which have the highest correlation with each of the small blocks on the support frame. An interpolated frame is generated from at least either the first or the second frame by using the second motion vector.
Owner:FLEXIWORLD TECH
Single chip multi-function display controller and method of use thereof
ActiveUS7420618B2Cancel noiseBandwidthTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMulti-function displayInterlaced video
A multi-function display controller that includes a source detector unit for determining if the source of an input stream is either film originated source originated or video source originated. A source converter unit for converting the input image stream to a common signal processing format is coupled to the source detector unit. Once converted to the common signal processing format, a determination is made if the input image stream is interlaced or non-interlaced (progressive scan). If the input image stream is interlaced, a de-interlace unit converts the interlaced signal to progressive scan using either motion adaptive or motion compensated de-interlacing techniques. It should be noted that in the described embodiment, motion vectors generated for use by the motion compensated de-interlace can be optionally stored in a memory unit for use in subsequent operations, such as motion compensated frame rate conversion or noise reduction (if any).
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
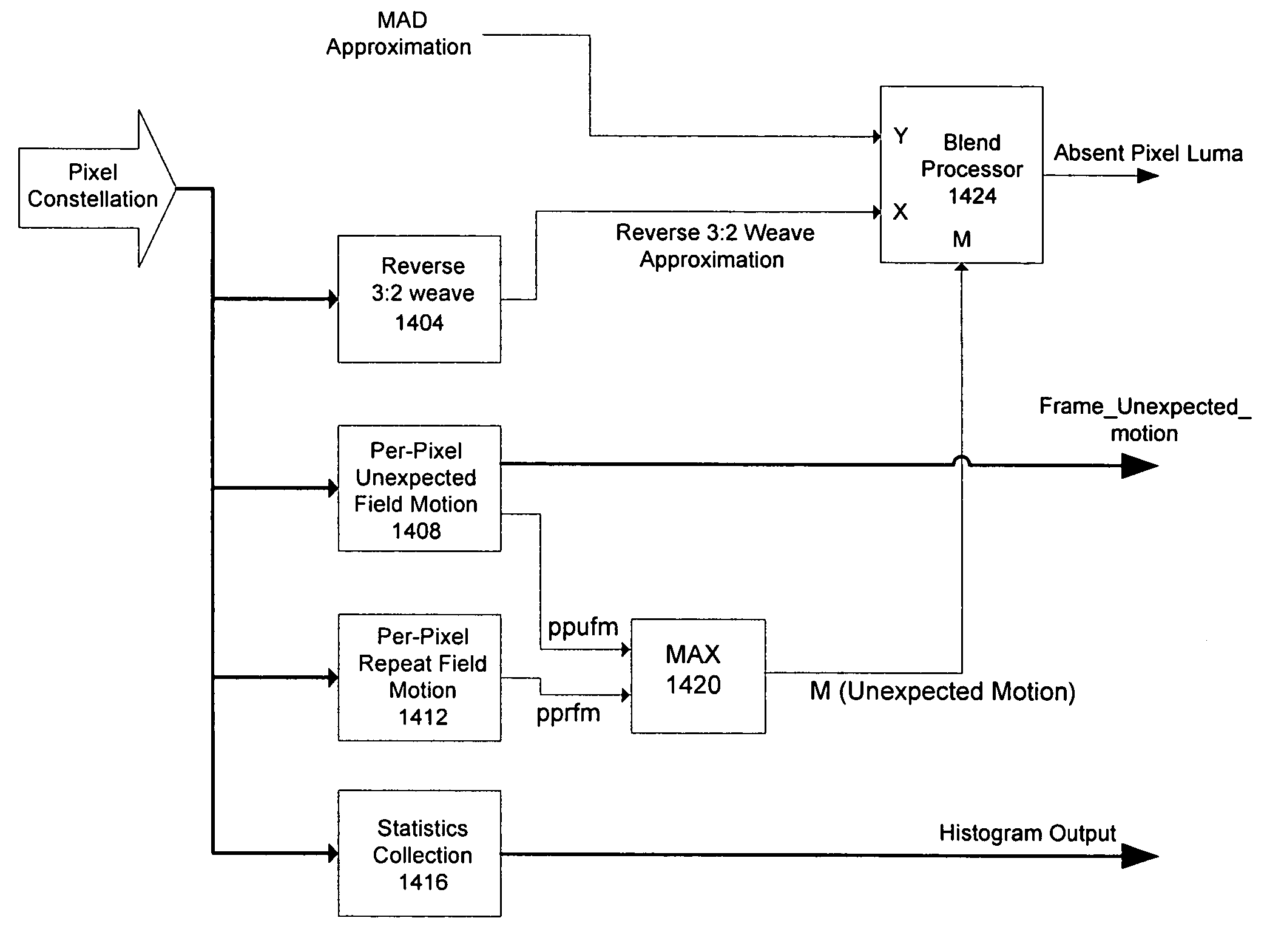
Reverse pull-down video using corrective techniques
InactiveUS7557861B2Effectively detect and correctTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer visionComputer science
Aspects of the present invention may be found in a system and method to more effectively detect and correct irregularities of video in a pull-down video signal, such as a 3:2 (or 2:2) pull-down video signal. Various aspects of the present invention provide a system and method to determine when the cadence of pull-down video has changed. This may occur, for example, when a bad-edit is encountered in the pull-down video. Other aspects of the present invention may be found in a system and method of detecting and correcting distortion or artifacts occurring at the pixel level. The distortion or artifacts are detected and corrected at a per-pixel level while performing a reverse pull-down of the video signal. Finally, aspects of the invention allow the automatic enabling of per-pixel correction when performing a reverse 3:2 directed weave. A computed variable is used to automatically activate the per-pixel correction.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
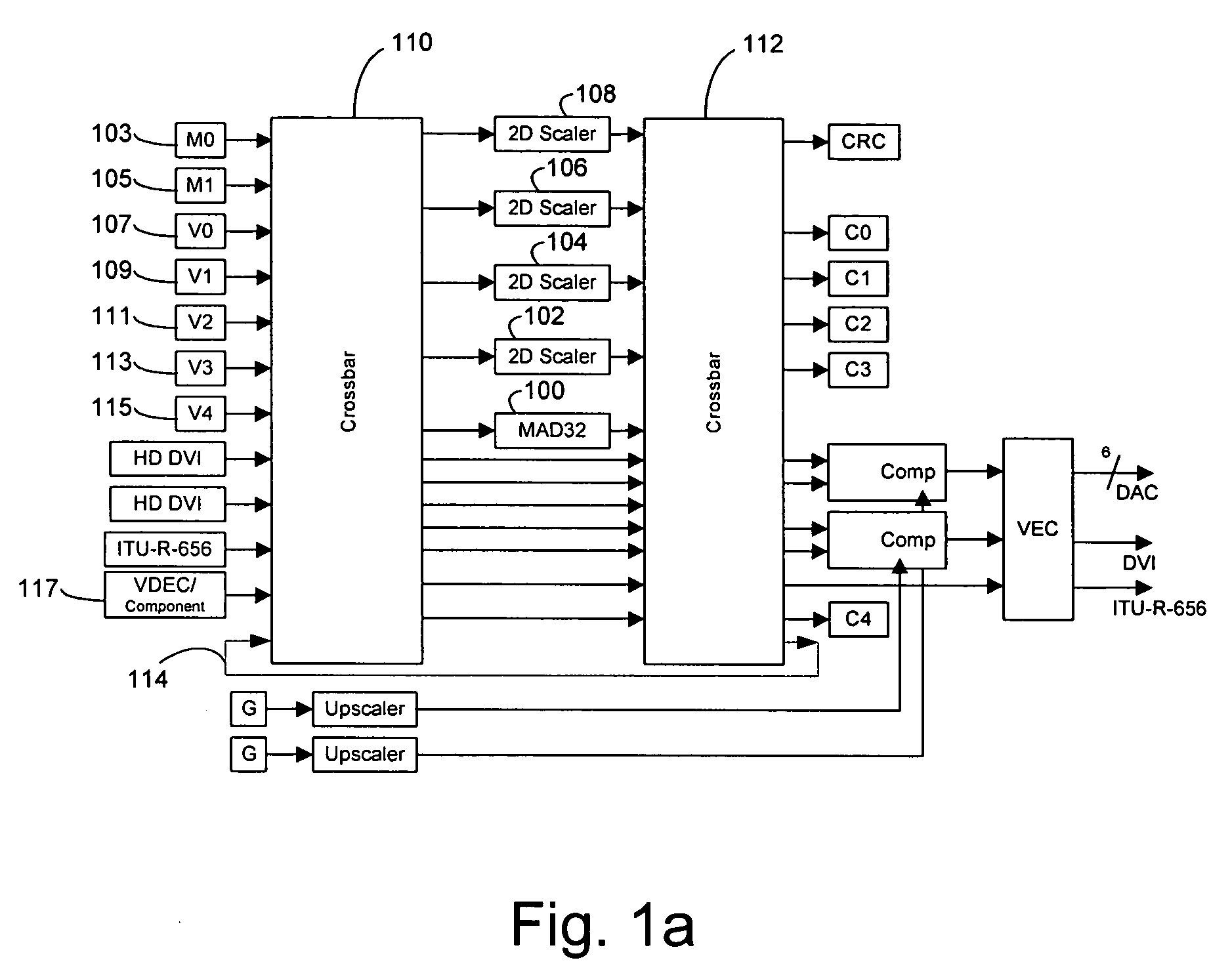
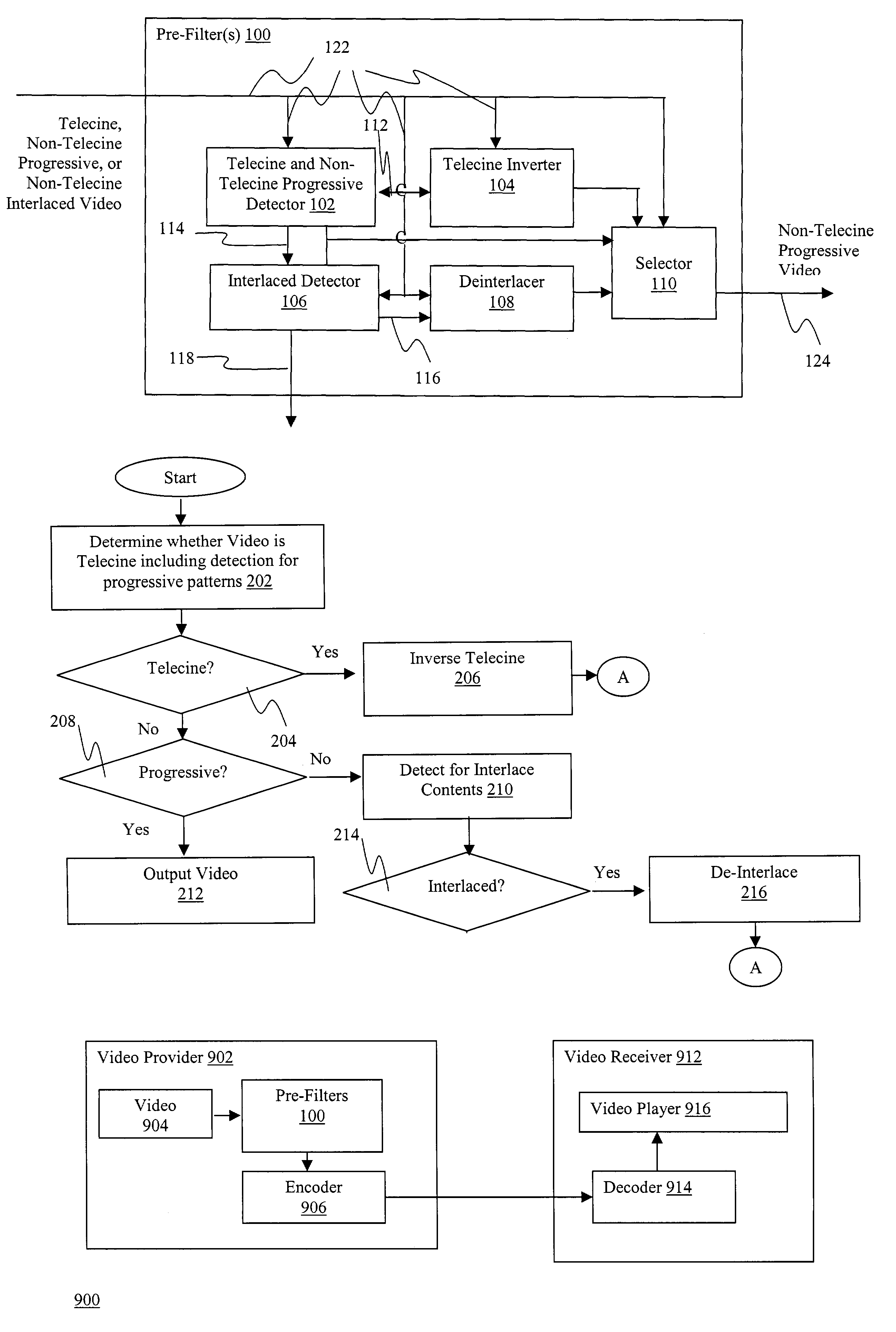
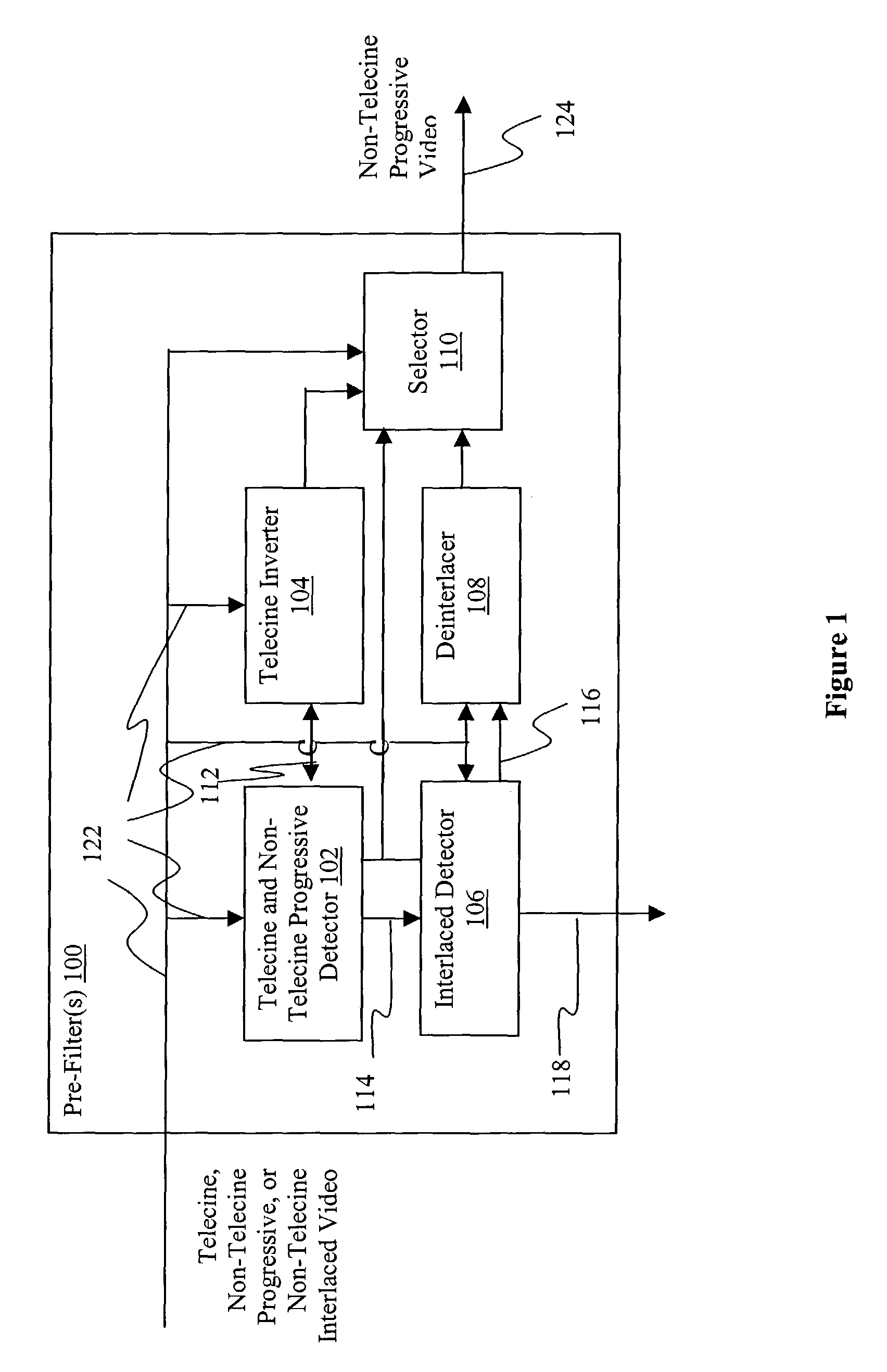
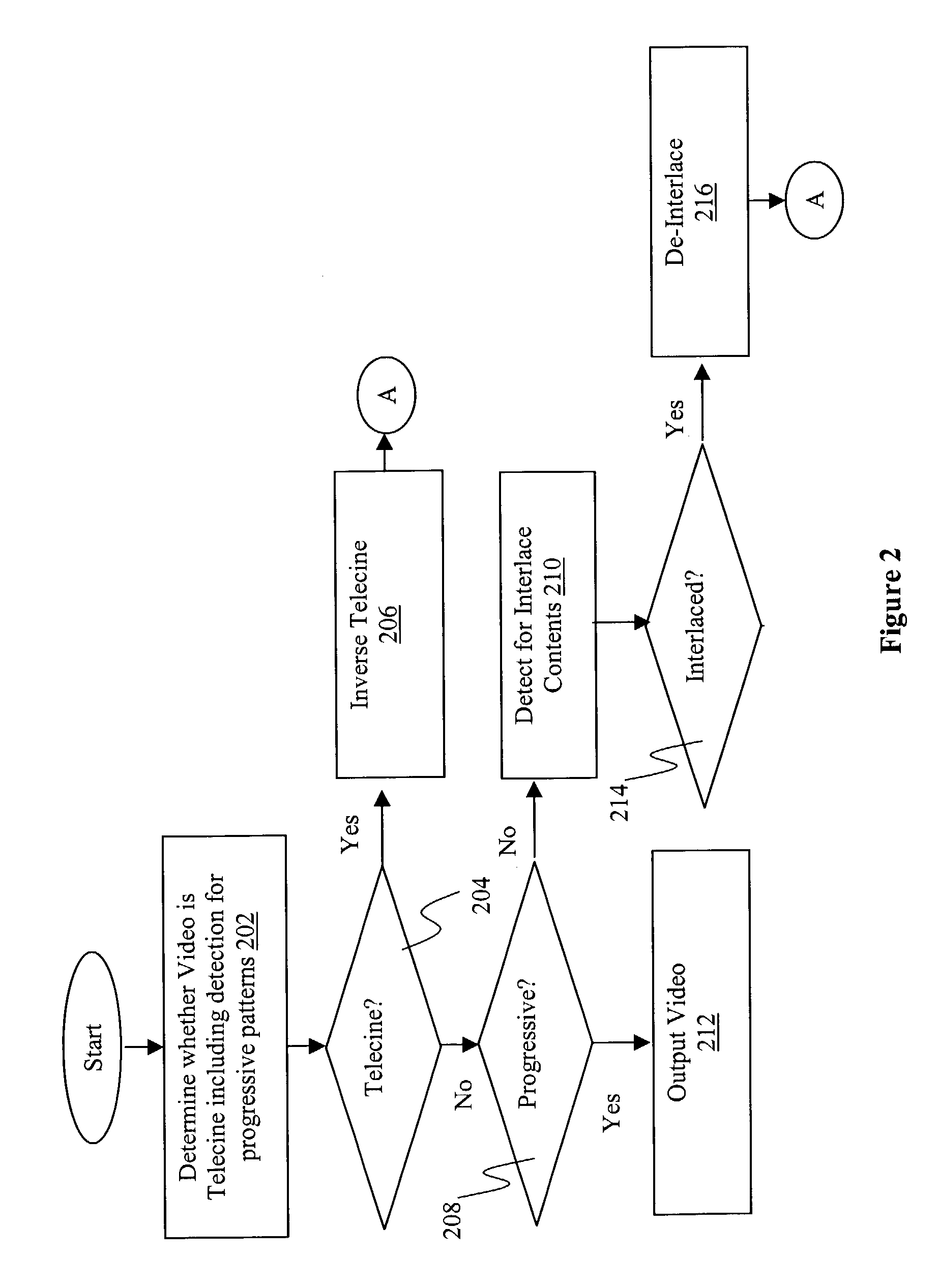
Automatic deinterlacing and inverse telecine
A video apparatus is provided with automatic deinterlacing and inverse telecine pre-filtering capability to automatically analyze the frames of the video to determine at least whether the video is one of telecine, non-telecine progressive and non-telecine interlaced formatted, and to automatically reformat the video into a non-telecine progressive format if the video is determined to be one of telecine and non-telecine interlaced formatted.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Video system with de-motion-blur processing
ActiveUS7262818B2Short response timeQuality improvementTelevision system detailsImage enhancementProgressive scanDisplay device
A video system that performs TV signal decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blurring for progressive scan flat panel display is introduced. The system embeds a frame buffer and a scaler for conducting format and resolution conversions for display panels of different sizes. The output of the scaler is sent to a de-motion-blur processor for reducing the blurriness due to the motion of image objects and the slow response time of flat panel display devices. The de-motion-blur processor gets the motion and noise indication signal from scaler or the pre-frame-buffer video processor. Based on the motion and noise information and the information of temporal difference, the de-motion-blur processor performs over driving for the display panel interface and improves the rising and falling response time of the flat panel display. The decoding, deinterlacing, and de-motion-blur processing share the same frame buffer controller so the entire system can be optimized in cost and performance.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
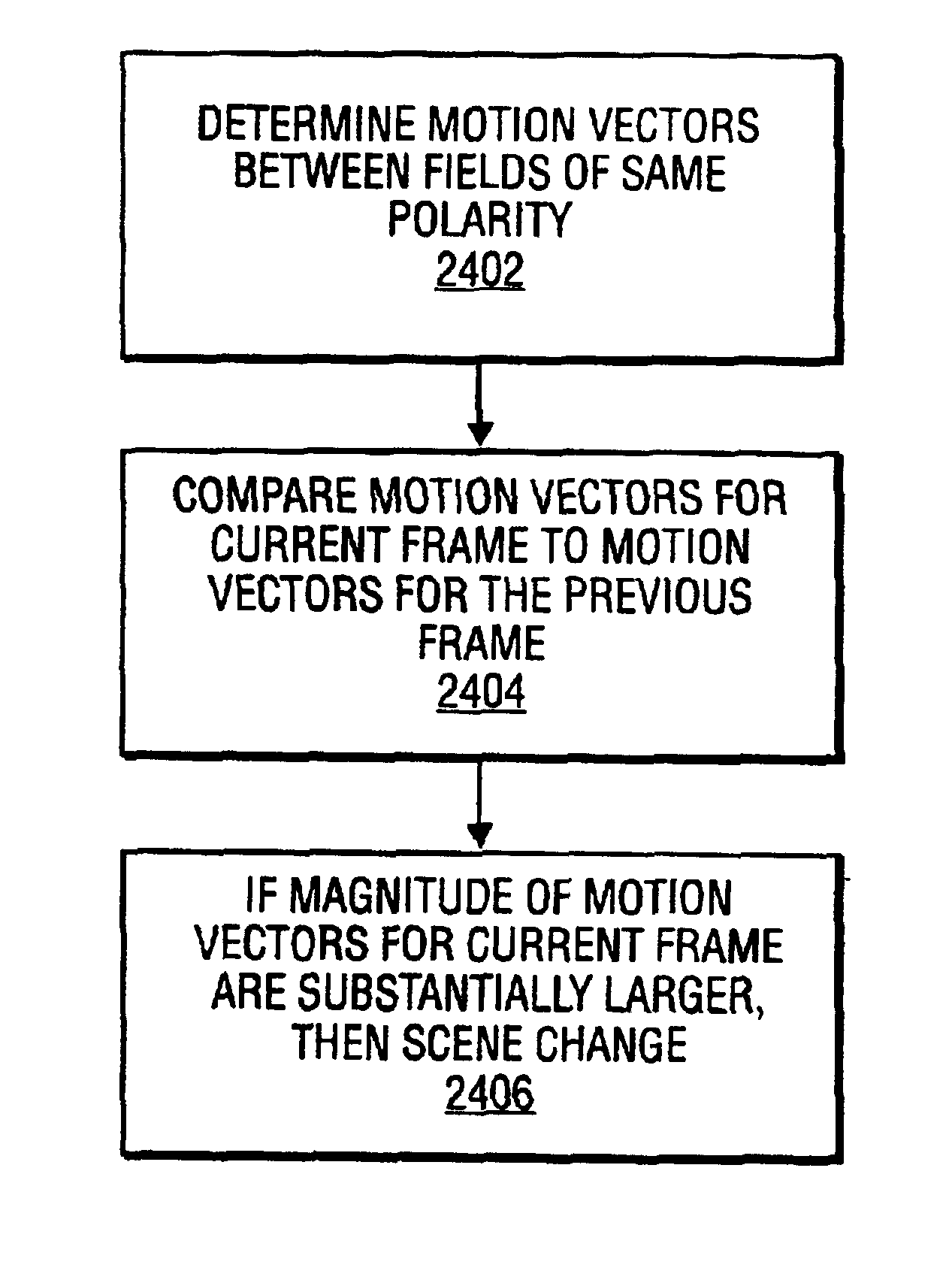
3:2 Pull-down detection
InactiveUS7203238B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorVideo sequence
In one embodiment, a 3:2 pull-down detection component of a video encoder uses motion vectors to determine whether a repeated field exists in a video sequence. The 3:2 pull-down detection component uses field motion vectors determined by a motion estimator and compares the field motion vectors to a threshold to determine whether a repeated field exists. If a repeated field exists, a video encoder can then eliminate the repeated field.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Real-time film effects processing for digital video
InactiveUS20080204598A1Avoid stutter artifactAvoid artifactsColor signal processing circuitsElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsDigital videoComputer graphics (images)
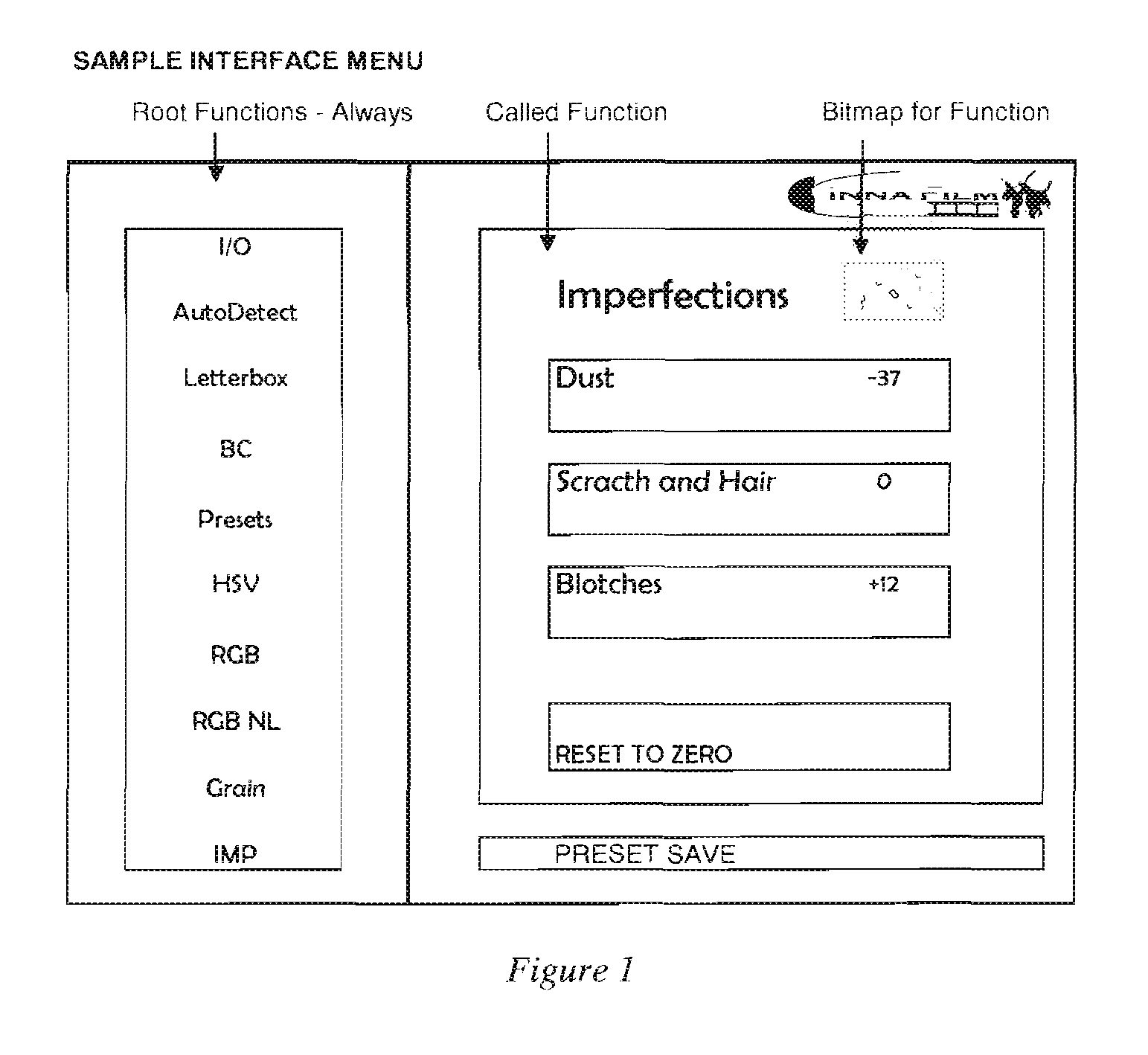
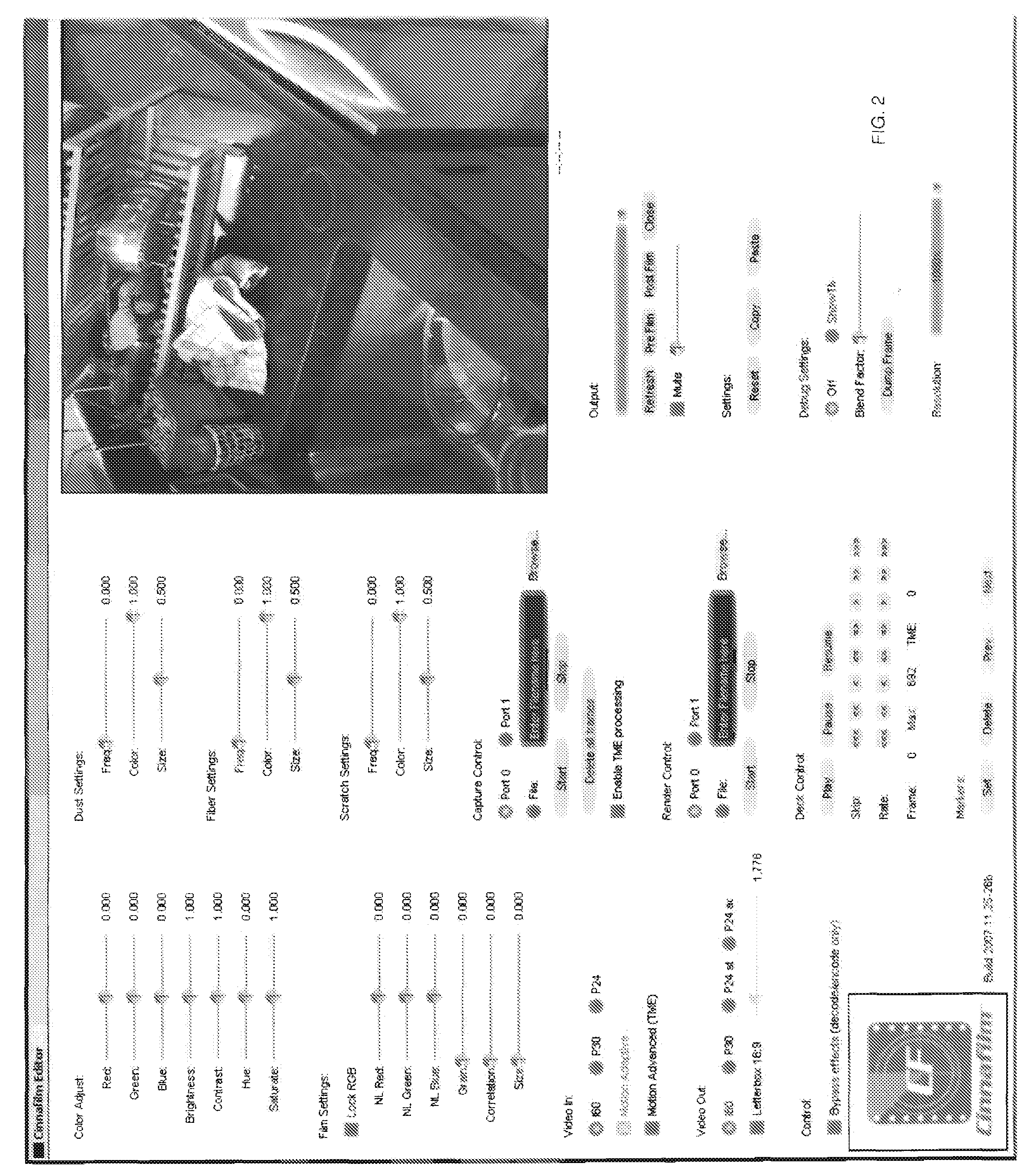
A method, apparatus, and computer software for applying in real time imperfections to streaming video which causes the resulting digital video to resemble cinema film.
Owner:MAURER LANCE +2
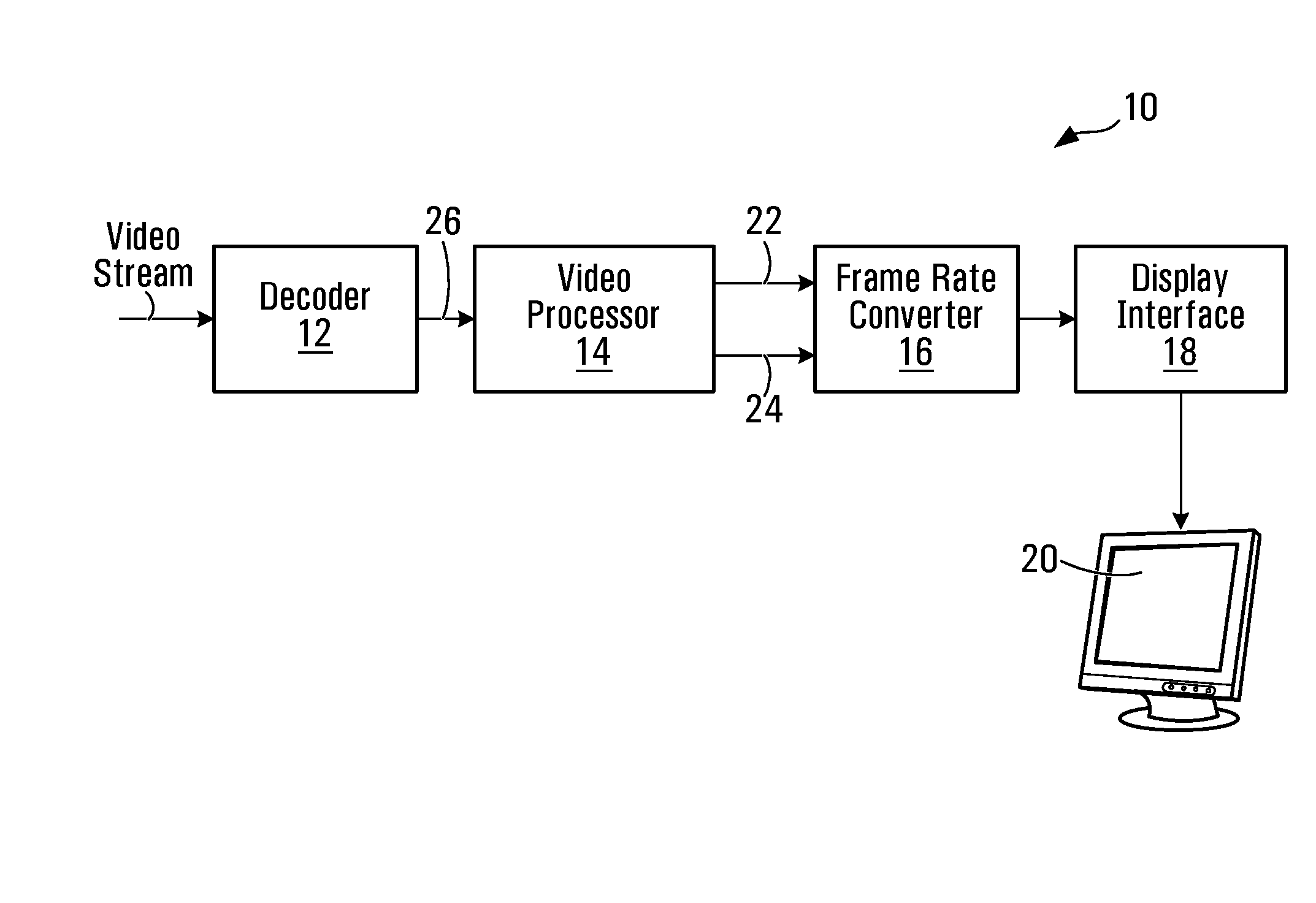
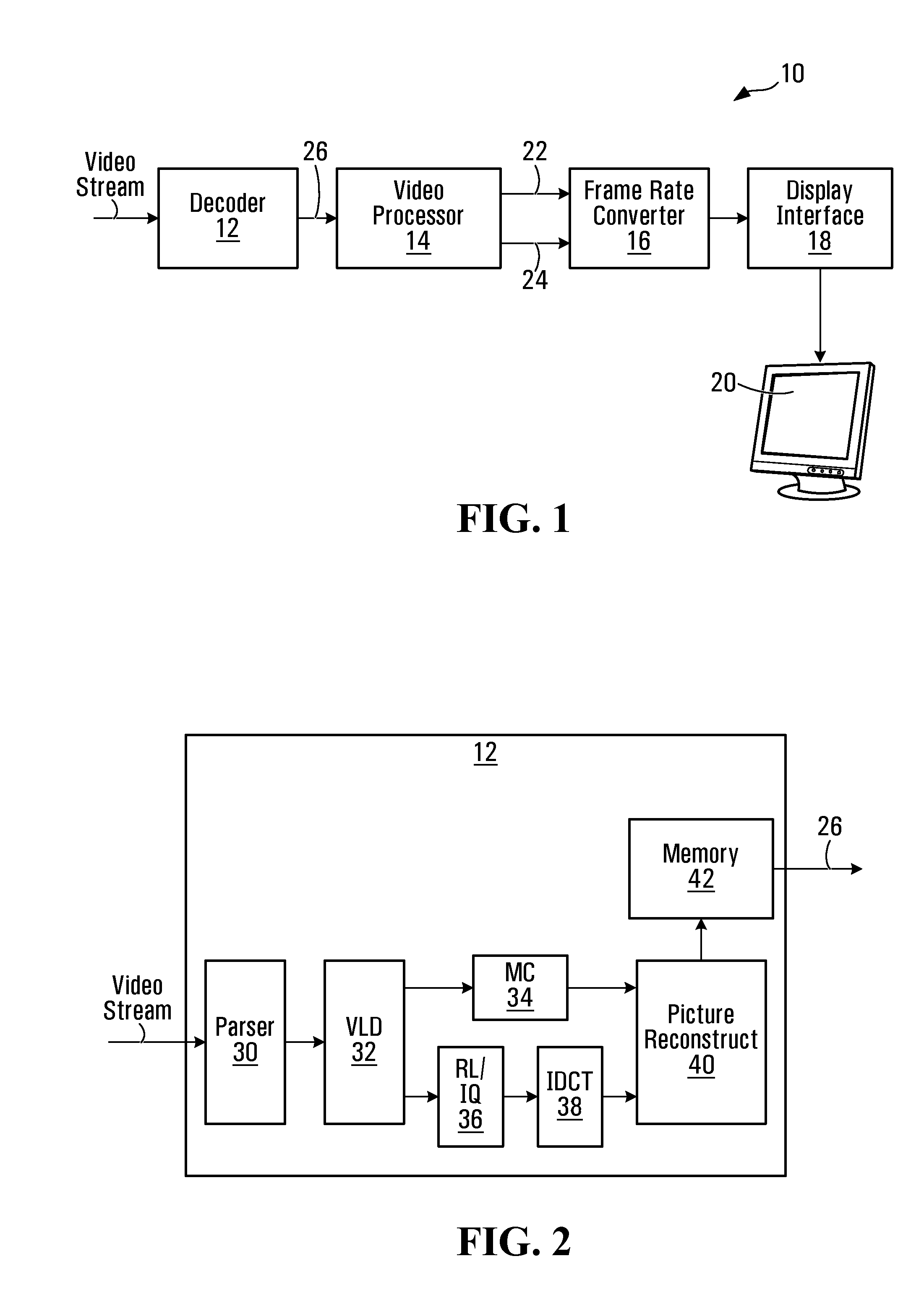
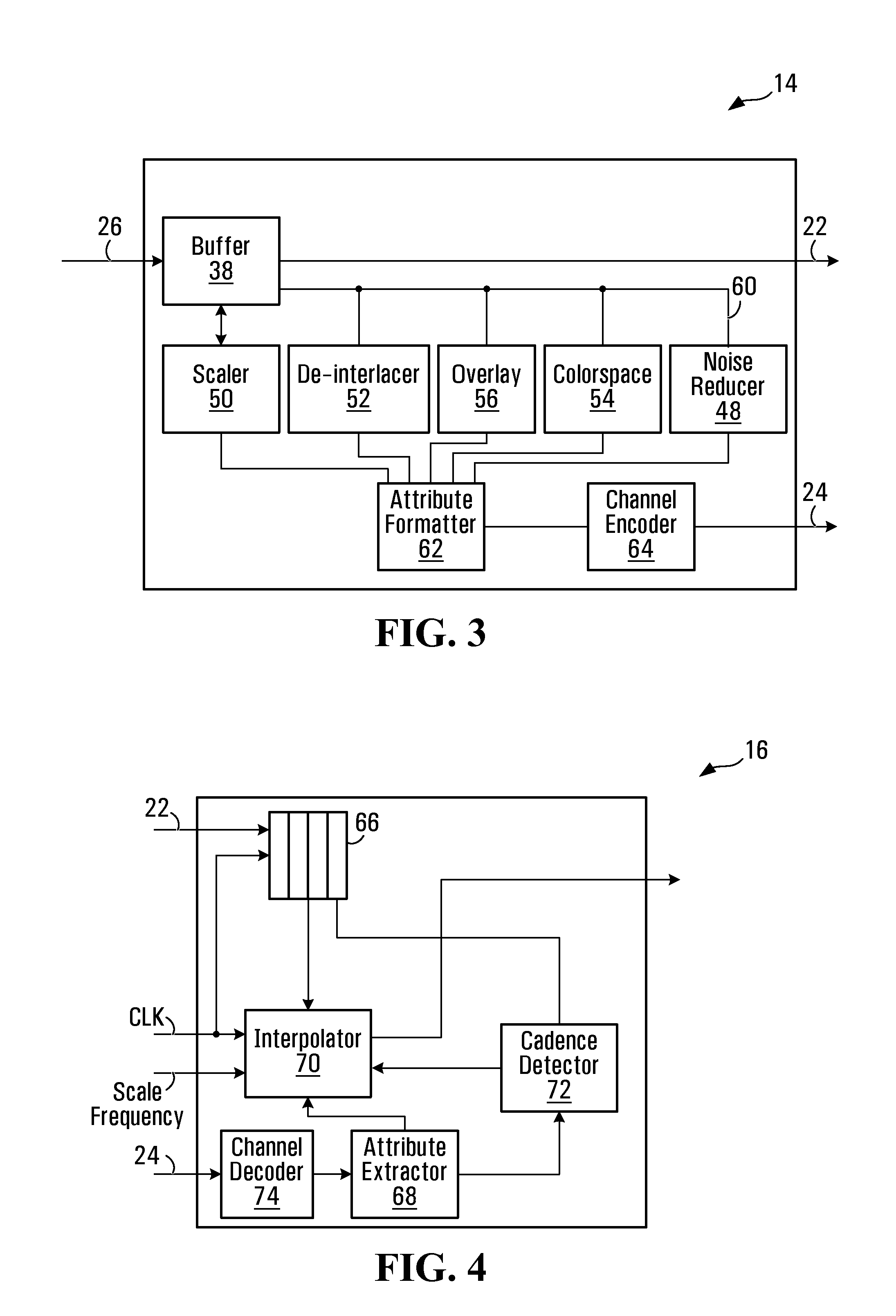
Video processor architecture and method for frame rate converstion
InactiveUS20080151108A1Lower latencyPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningVideo processingComputer science
A video processor, upstream of a frame rate converter determines video attribute data. This attribute data is formatted and passed along a channel to the frame rate converter. The frame rate converter extracts the attribute data from the channel for use in frame rate conversion. The frame rate converter may thus rely on attribute data obtained by the video processor, and need not re-analyze video frames.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
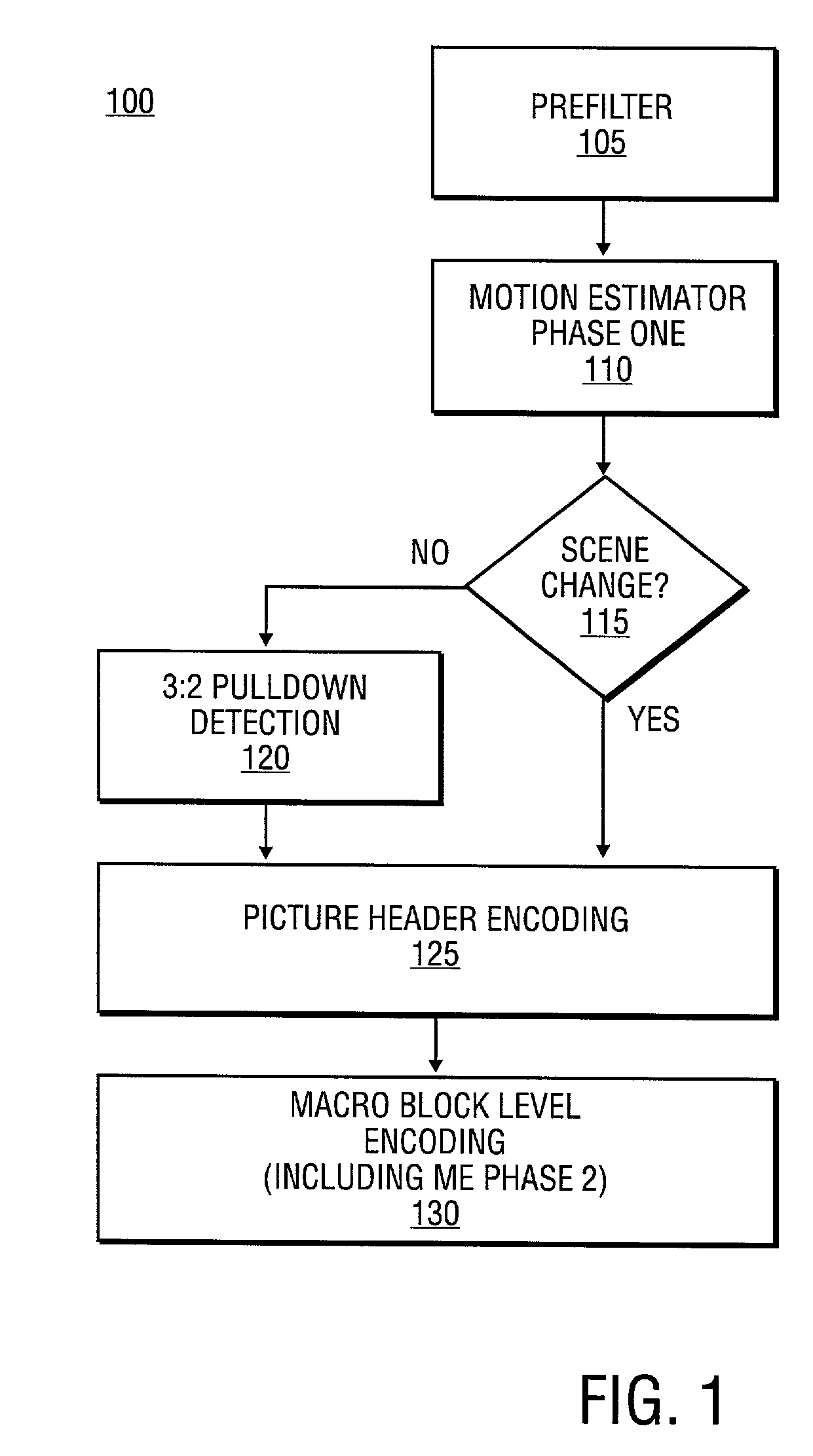
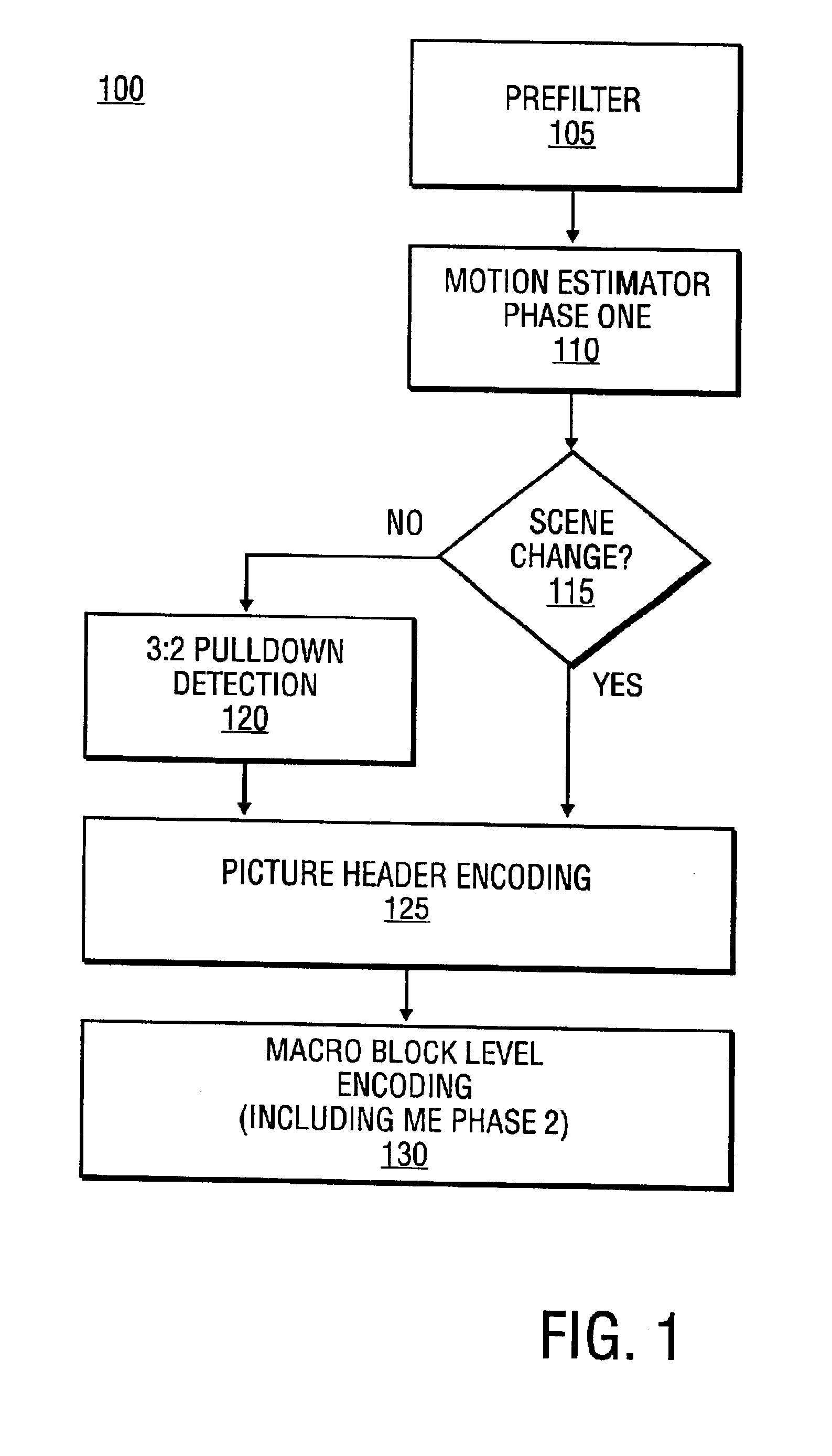
Video encoder with embedded scene change and 3:2 pull-down detections
InactiveUS6934335B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMotion vectorComputer science
In one embodiment, a video encoder having a first and second phase of motion estimation, and scene change and 3:2 pull-down detection components is provided. In another embodiment, the first phase of motion estimation determines a set of field motion vectors to execute the scene change and 3:2 pull-down detection components. In another embodiment, the scene change and 3:2 pull-down detection component, and the second phase of the motion estimation occur after the first phase of motion estimation.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Frame rate conversion device, image display apparatus, and method of converting frame rate
ActiveUS20080007614A1Extended definition imageSmoothing imagePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningInsertion timeImage signal
The present invention provides a technique relating to a frame rate conversion which enables display of an image of extended definition by smoothening the movement of the image. Therefore, the invention fixes the direction of interpolation using information on a first frame which appeared before the insertion time of the interpolated frame, a second frame appeared before the first frame, a third frame appeared after the insertion time, and a fourth frame appeared after the third frame, based on the insertion time of the interpolated frame. The interpolated pixel is generated from pixels of the second frame and the third frame located in the direction of interpolation, and generates the interpolated frame. Then, the interpolated frame is inserted into the inputted image signal to convert the frame rate.
Owner:MAXELL HLDG LTD
Popular searches
Conversion with cinematograph film standard Geometric image transformation Digital video signal modification Steroscopic systems Conversion by changing video signal frequency 3D modelling Picture reproducers using projection devices Cathode-ray tube indicators Picture reproducers using solid-state color display Color motion picture films scanning
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com