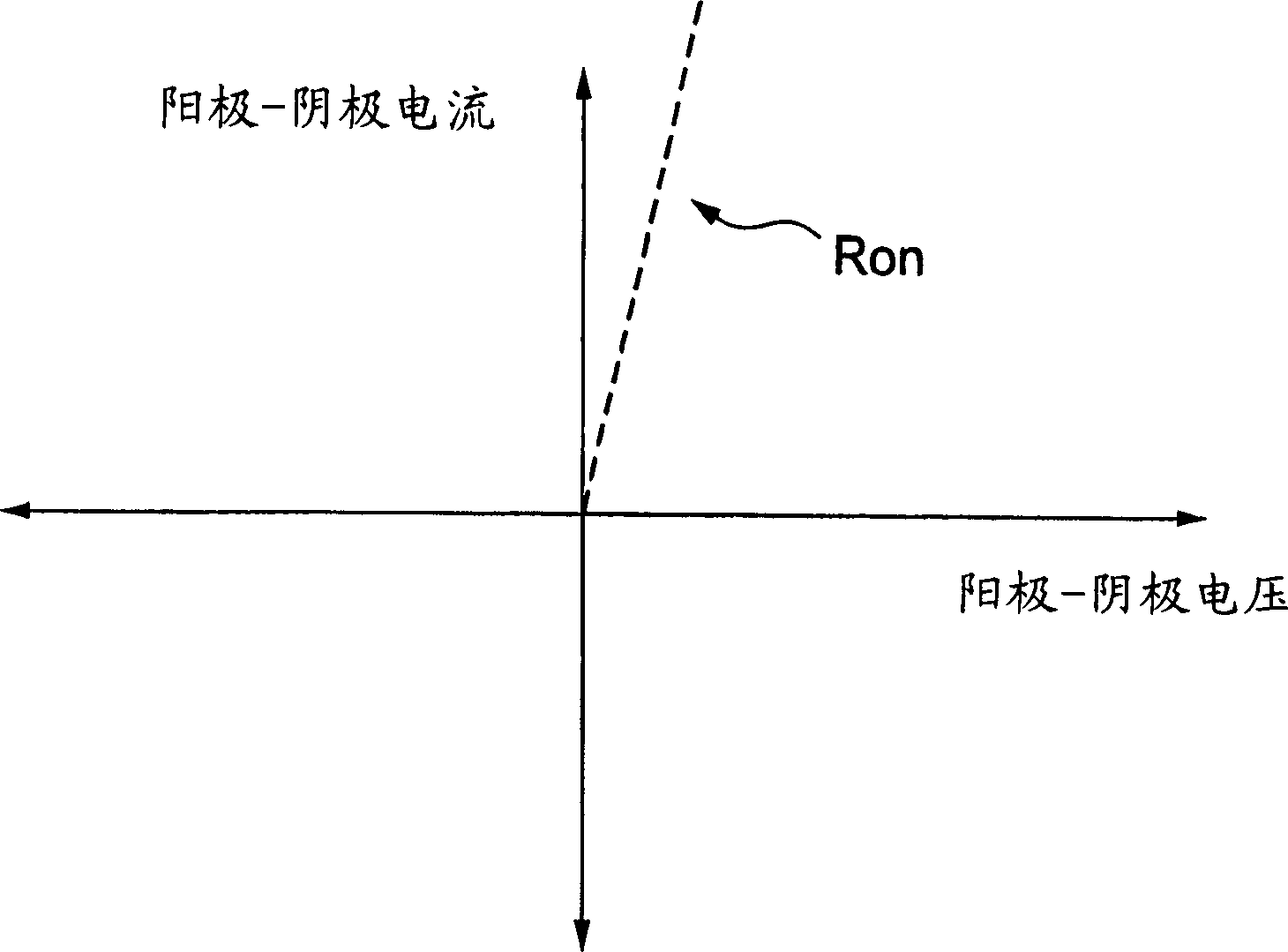
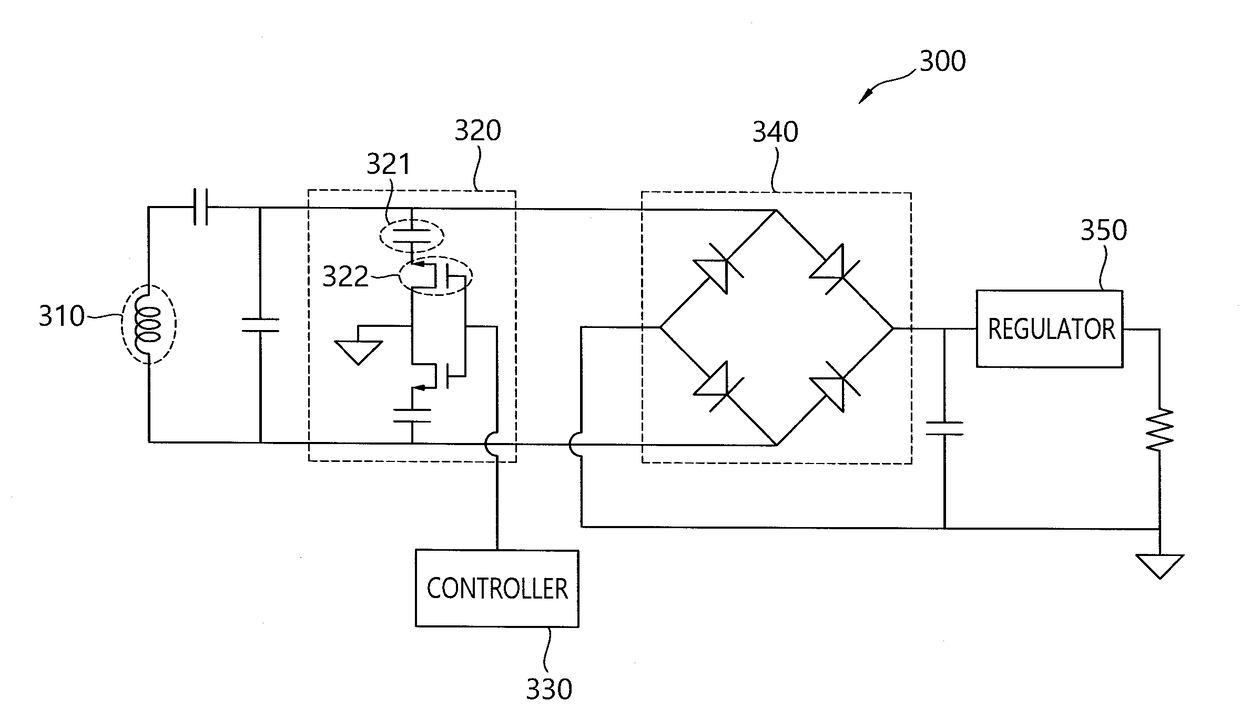
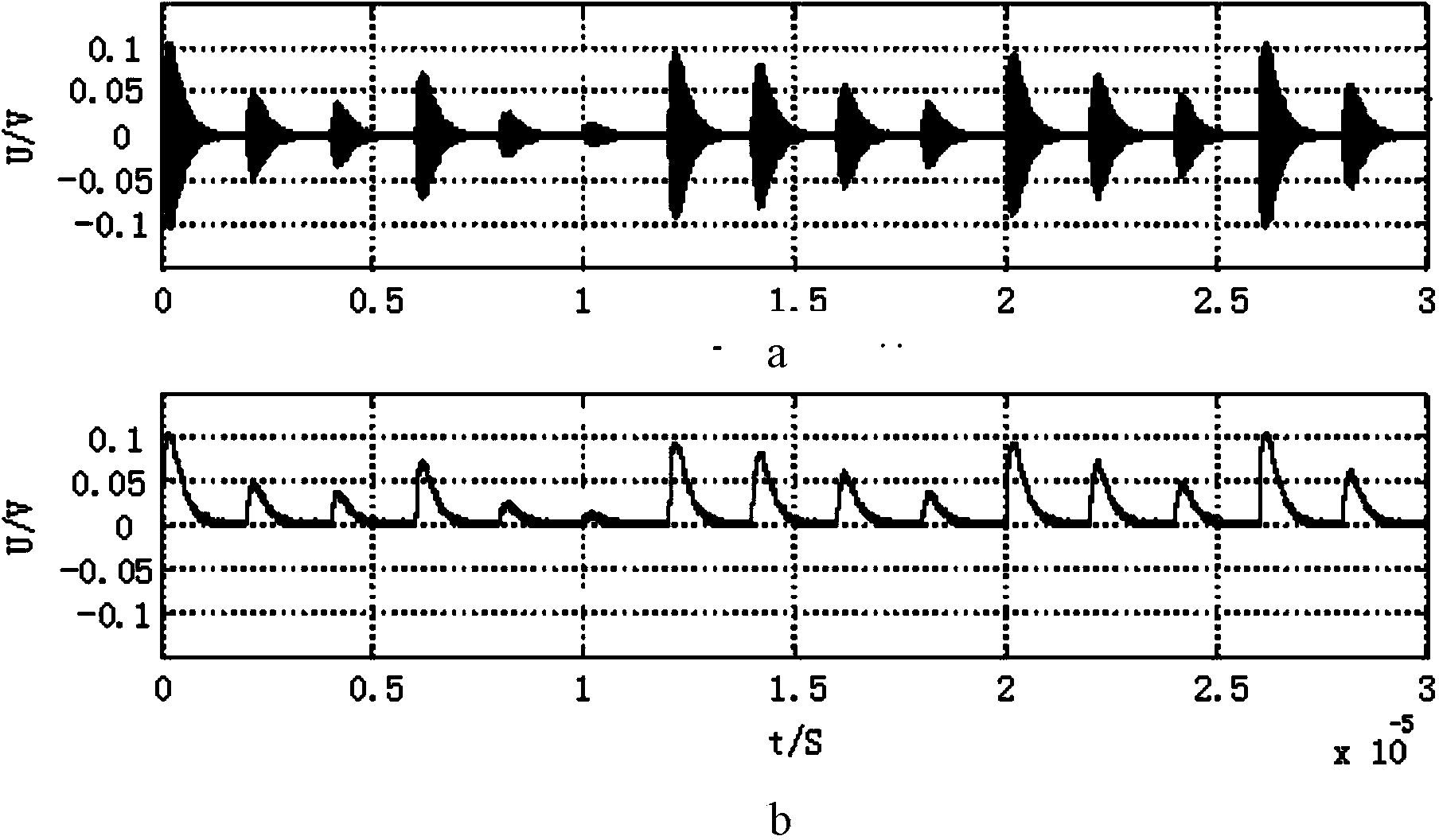
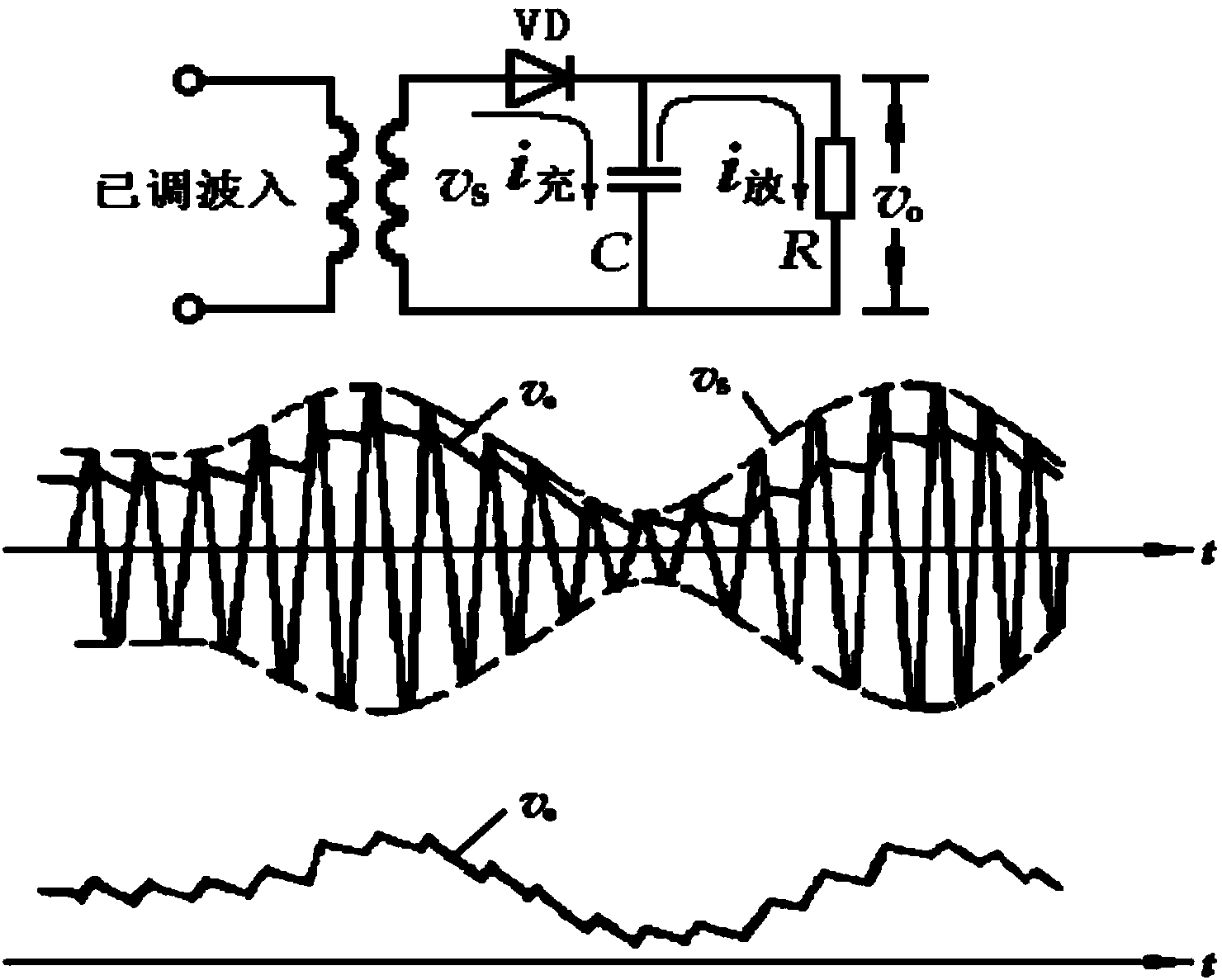
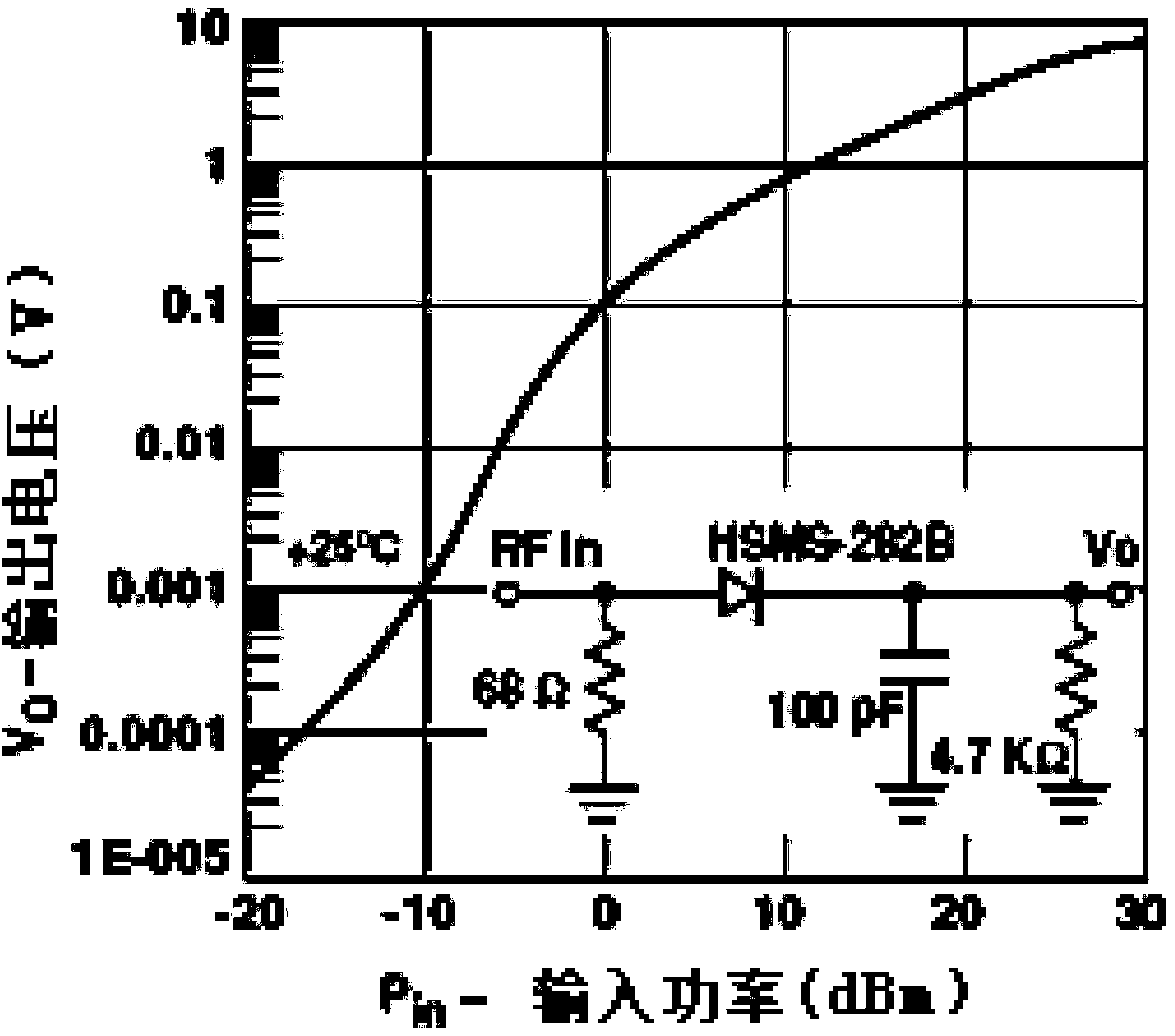
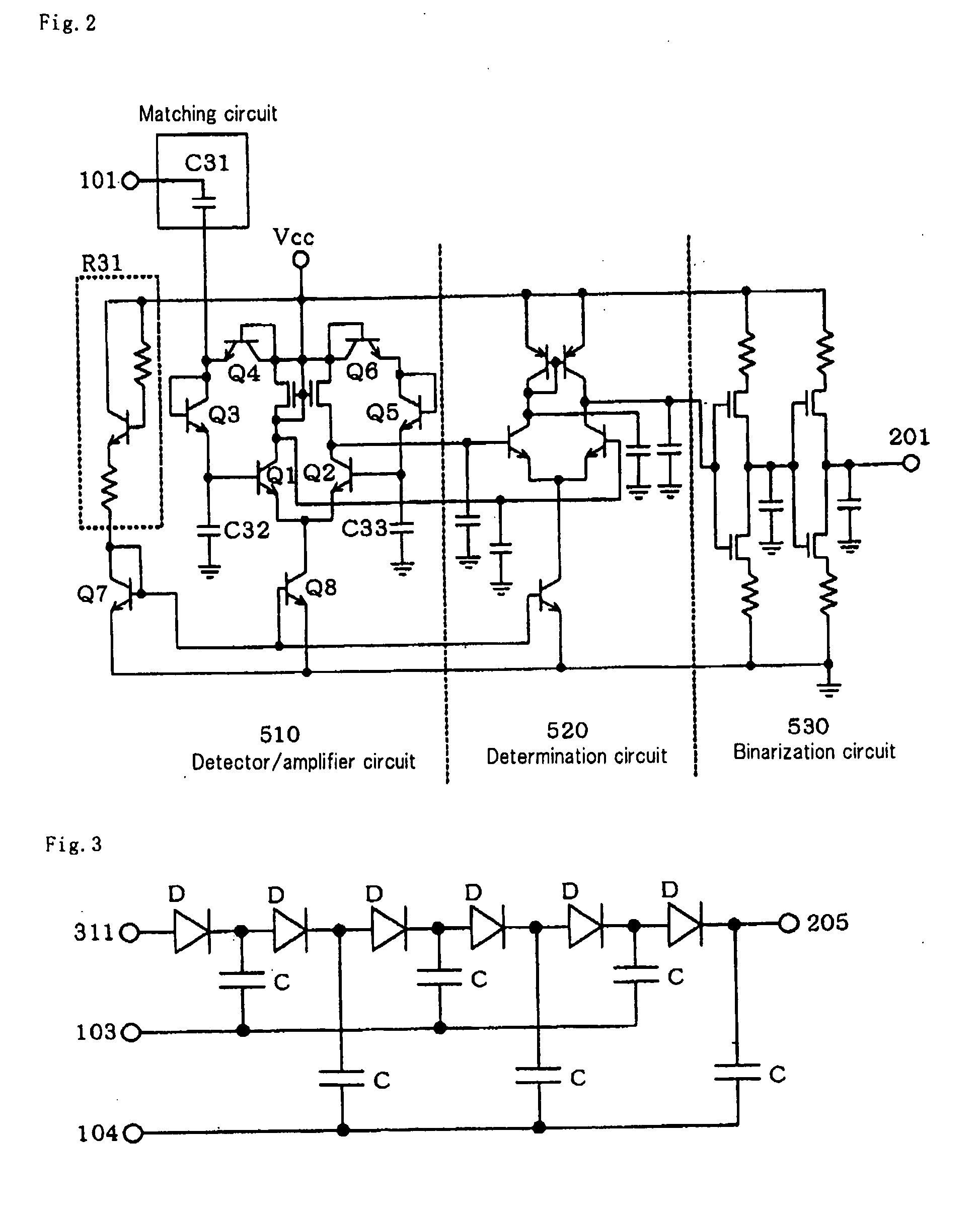
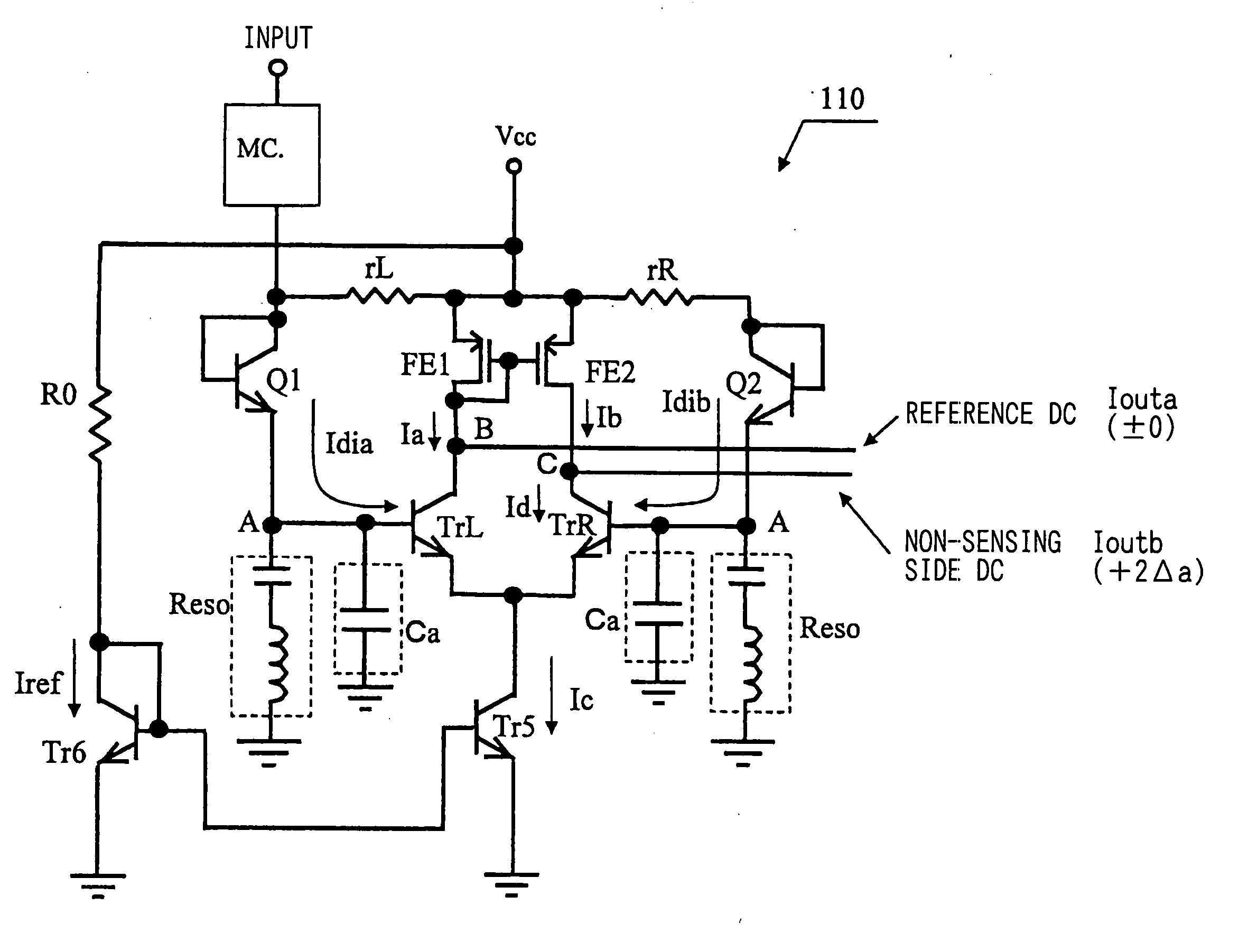
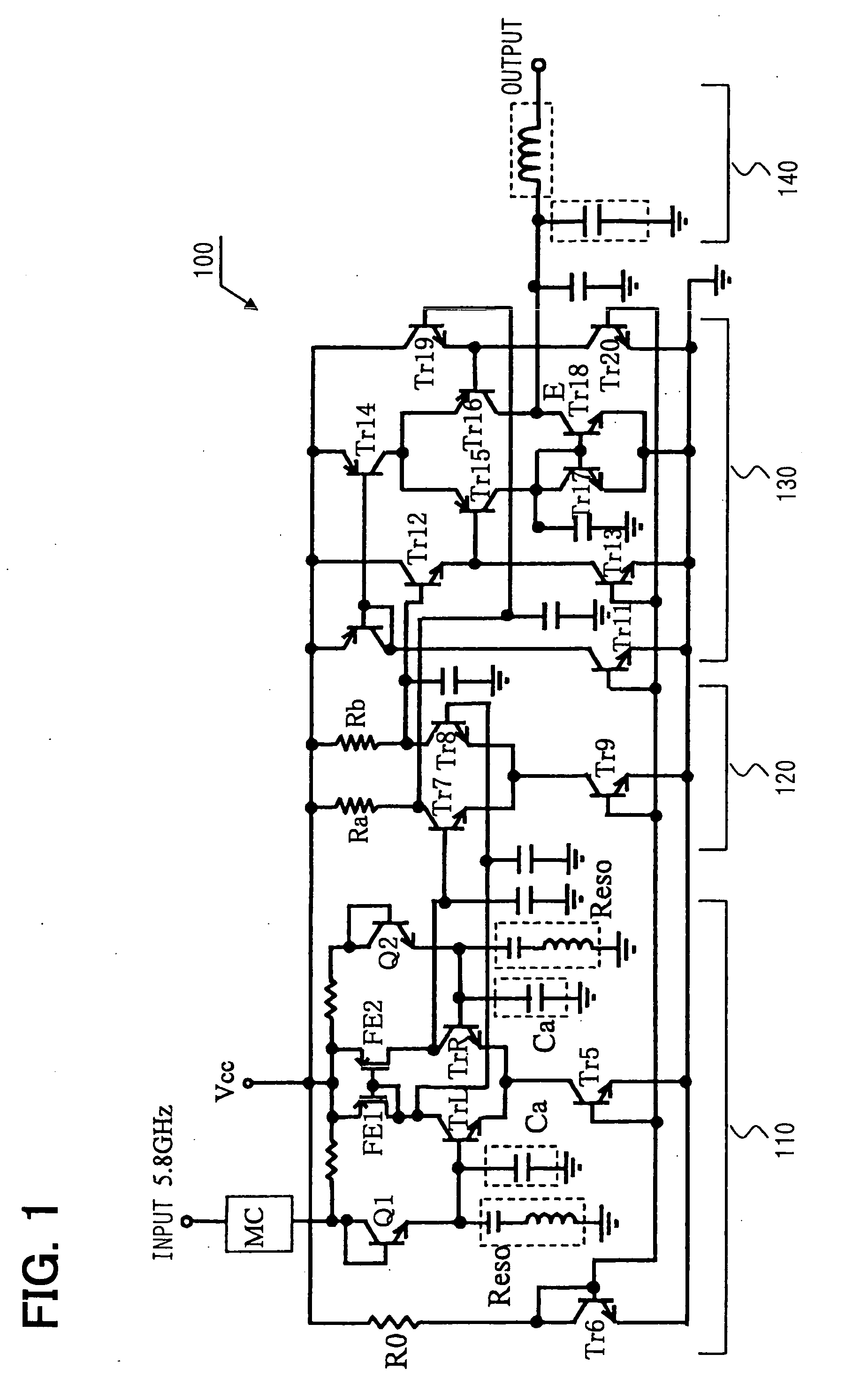
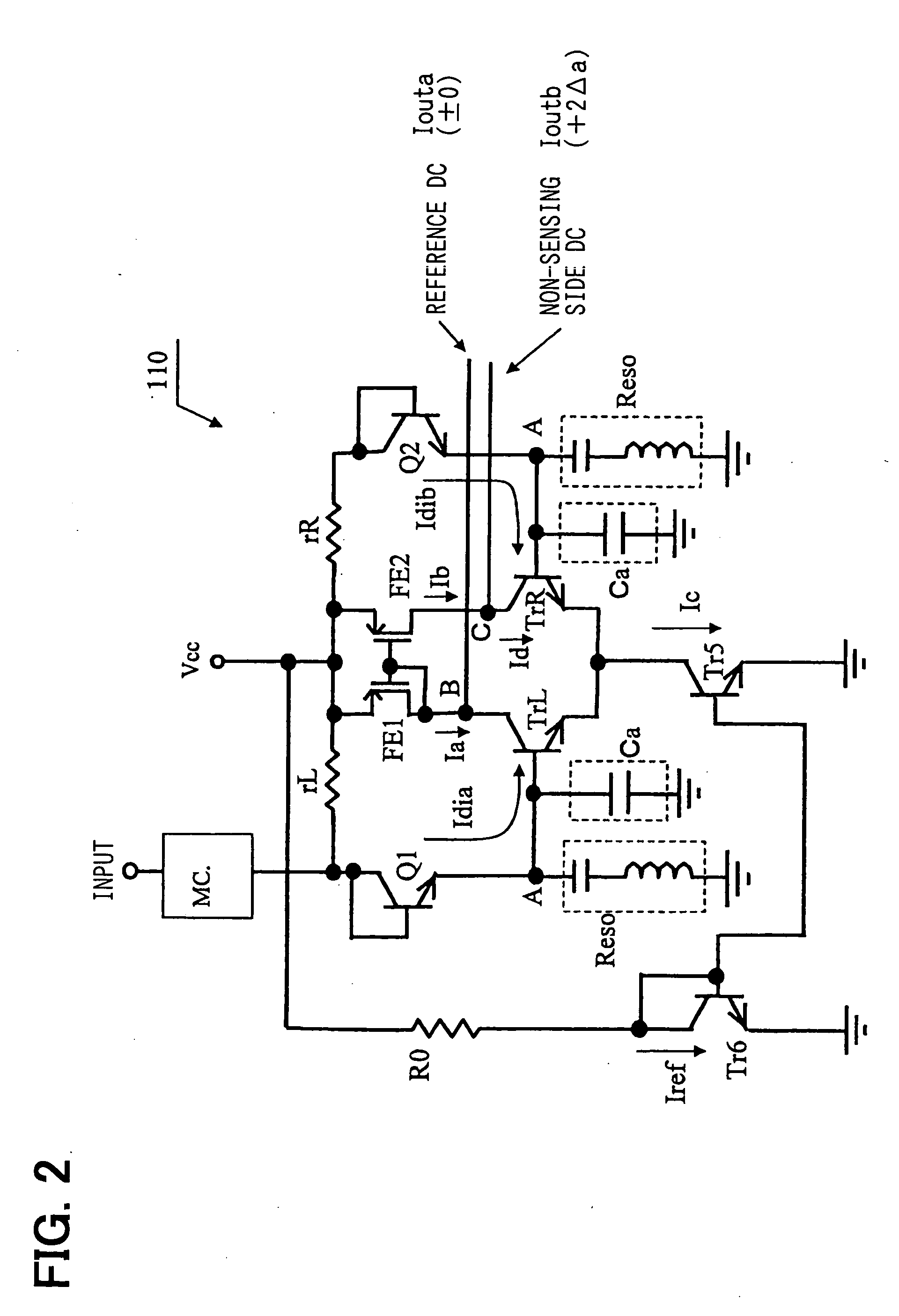
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74results about "Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Sweep method using digital signals
ActiveUS6961370B2High resolutionTelevision system detailsModulated-carrier systemsWeight coefficientDigital signal
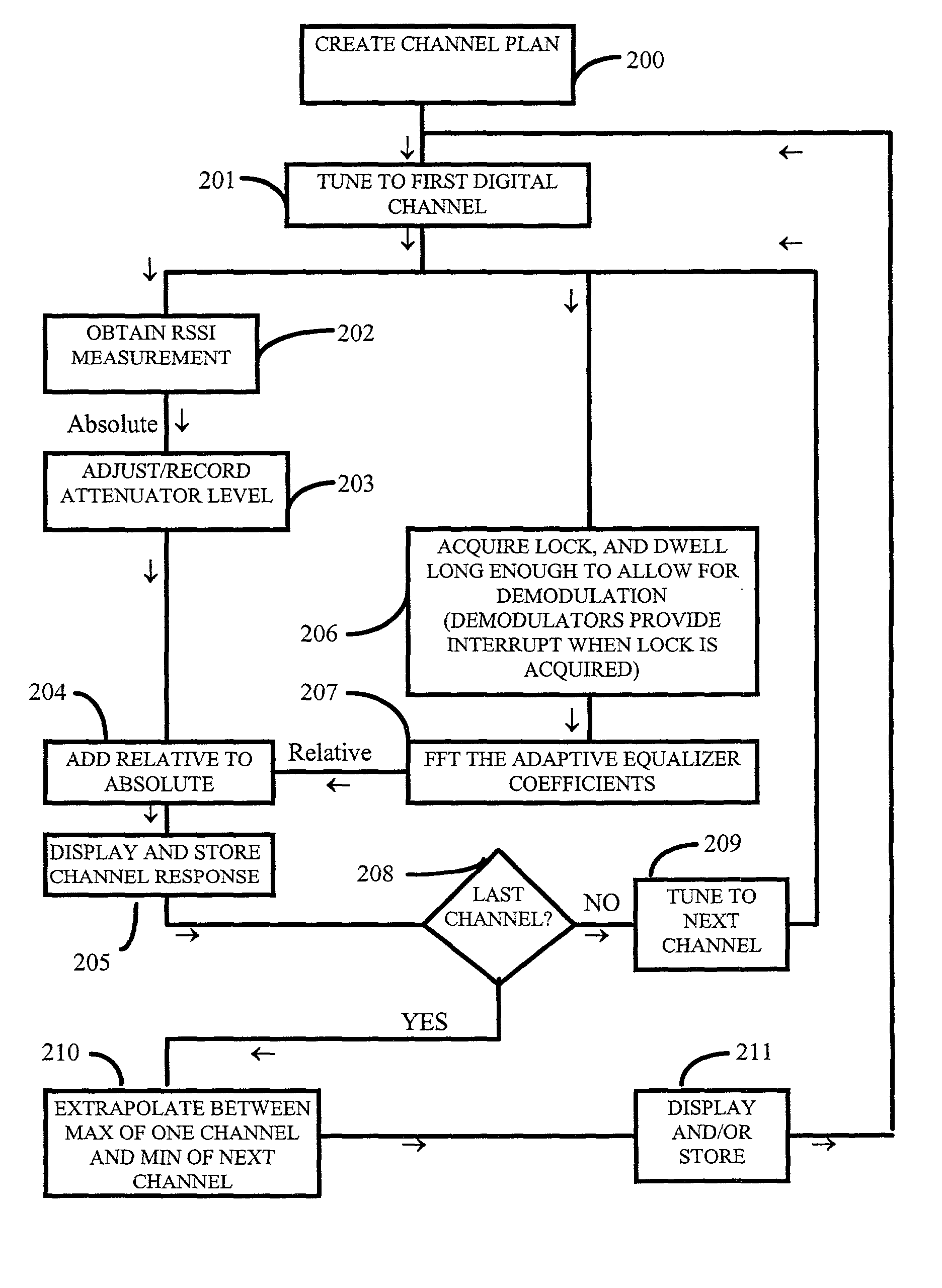
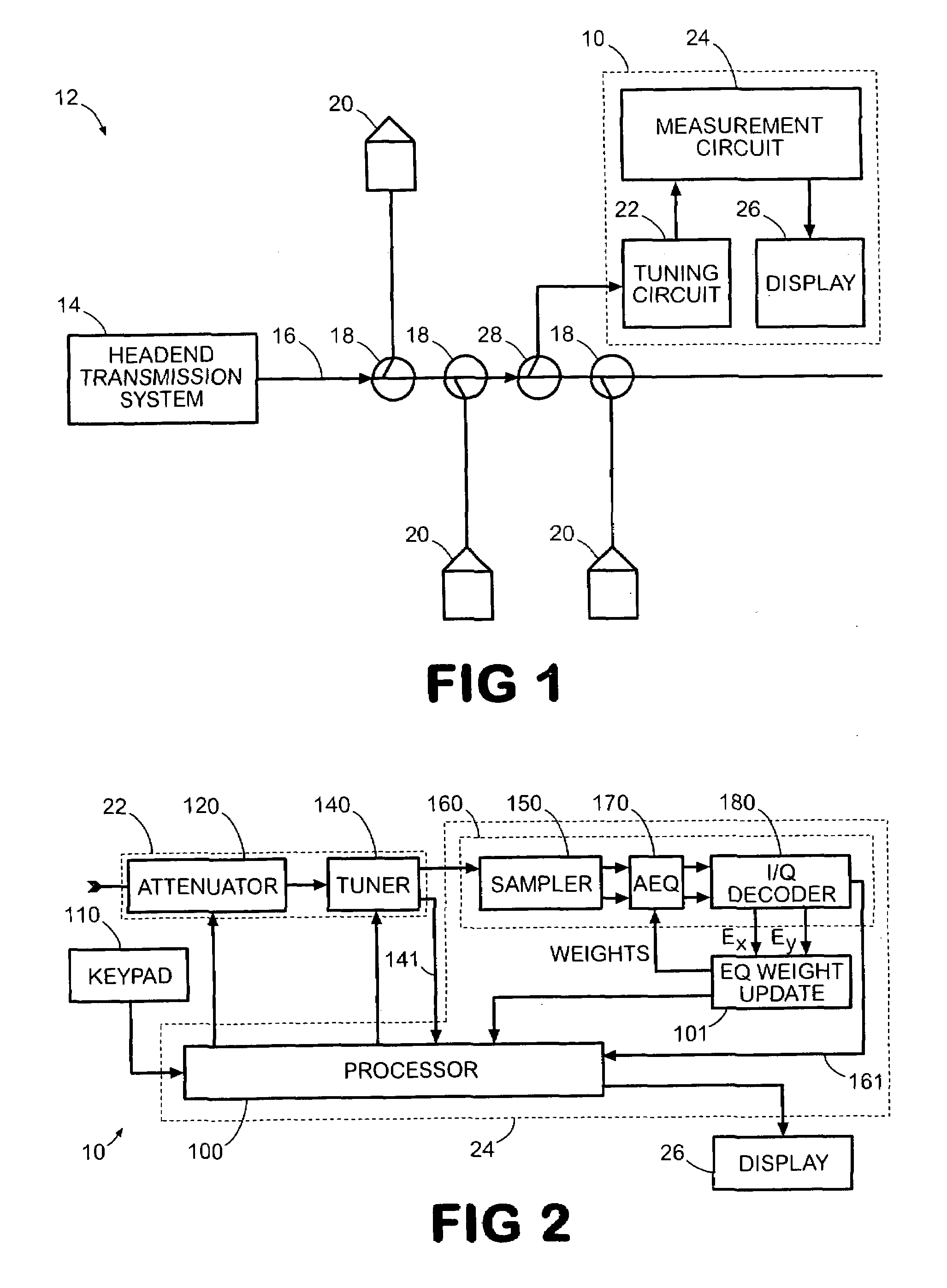
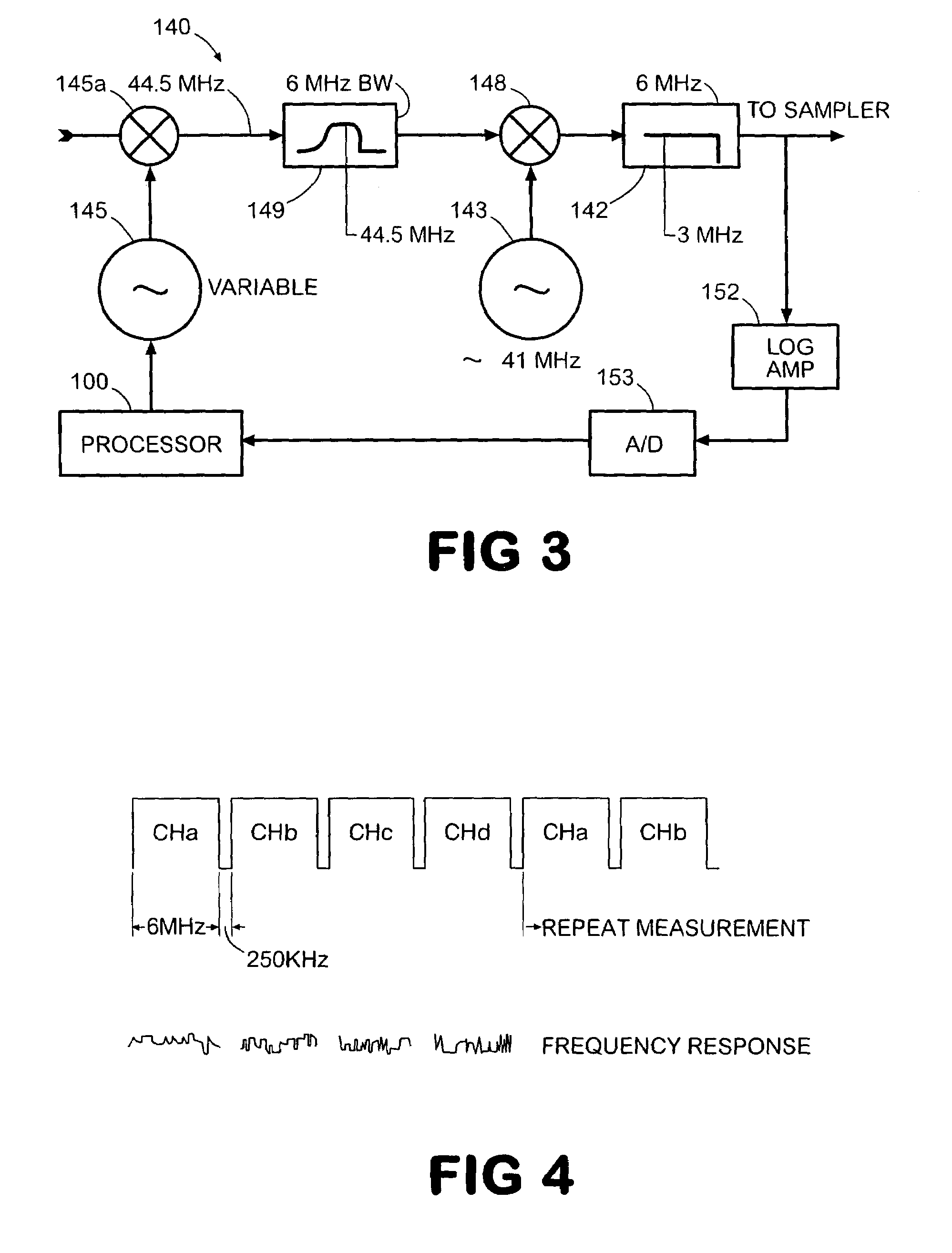
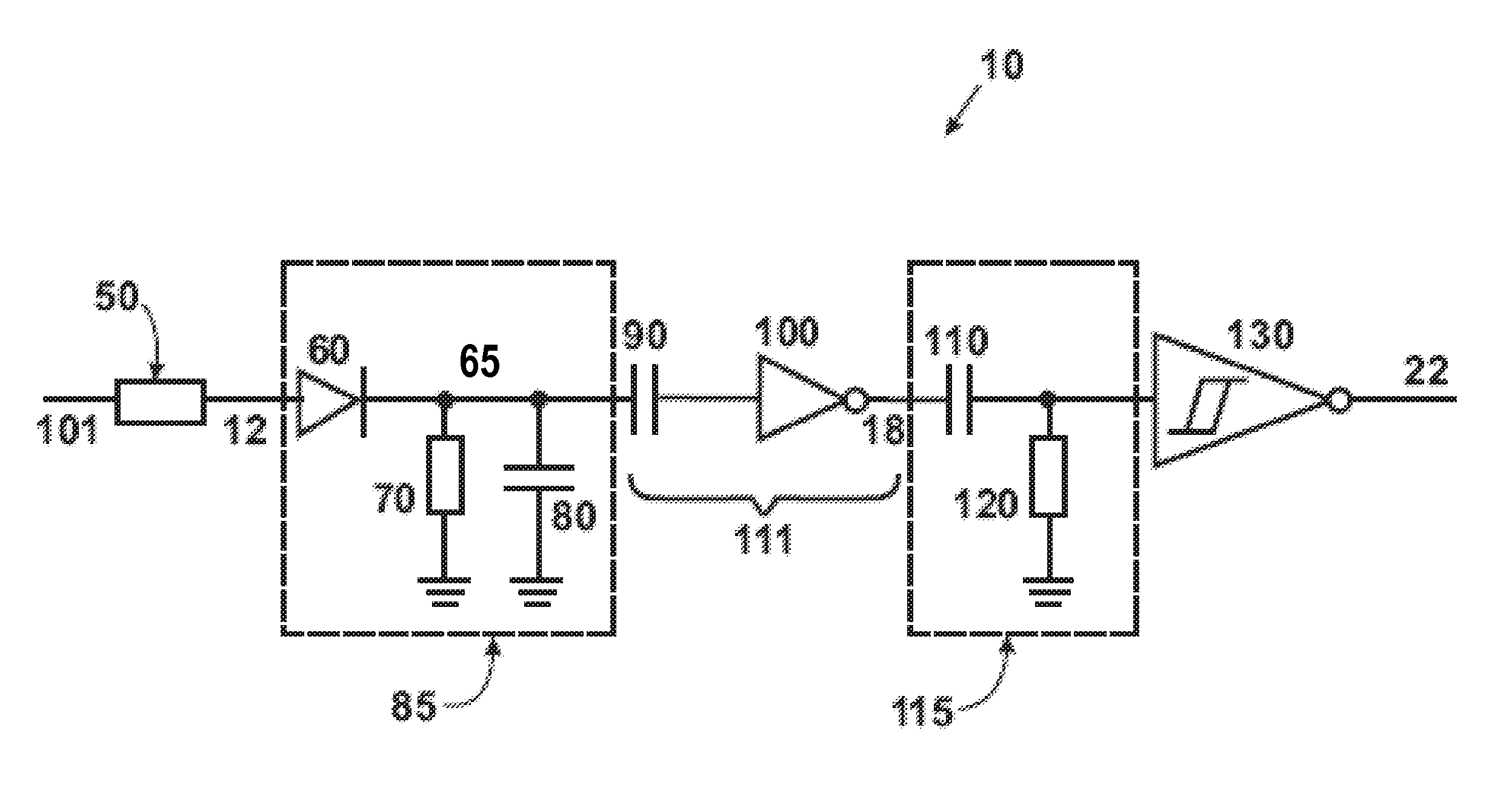
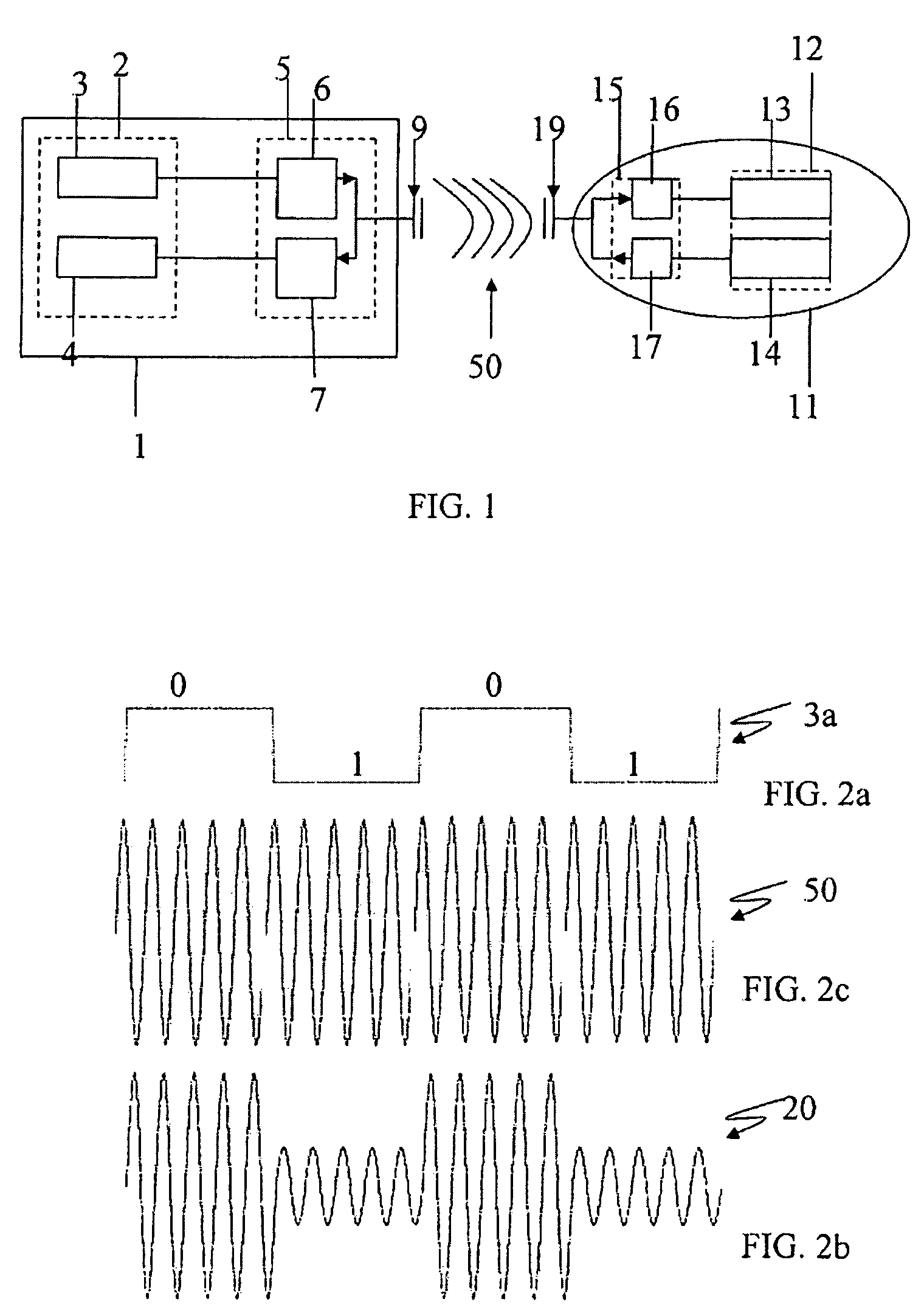
An apparatus, system, and method, for determining the total frequency response of a communication system, include one or more testers each having a tuner, digital demodulation circuitry, and a controller that measures an absolute power level at the tester location for a particular channel and that measures a relative frequency response for the channel based on the tap weight coefficients from the digital demodulation circuitry. The absolute and relative measurements are combined and then recorded by each tester. The combined values of two or more testers are compared to determine the total frequency response of the communication system. The relative response measurements are converted from time domain to frequency domain by fast Fourier transformation. The controllers maintain a channel plan for sequencing the sweeping of consecutive channels.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Amplitude shift keyed (ASK) demodulation pattern and use in radio frequency identification (RFID)
ActiveUS20100189196A1Increase rate of changeReduce sensitivityAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsHysteresisAc components
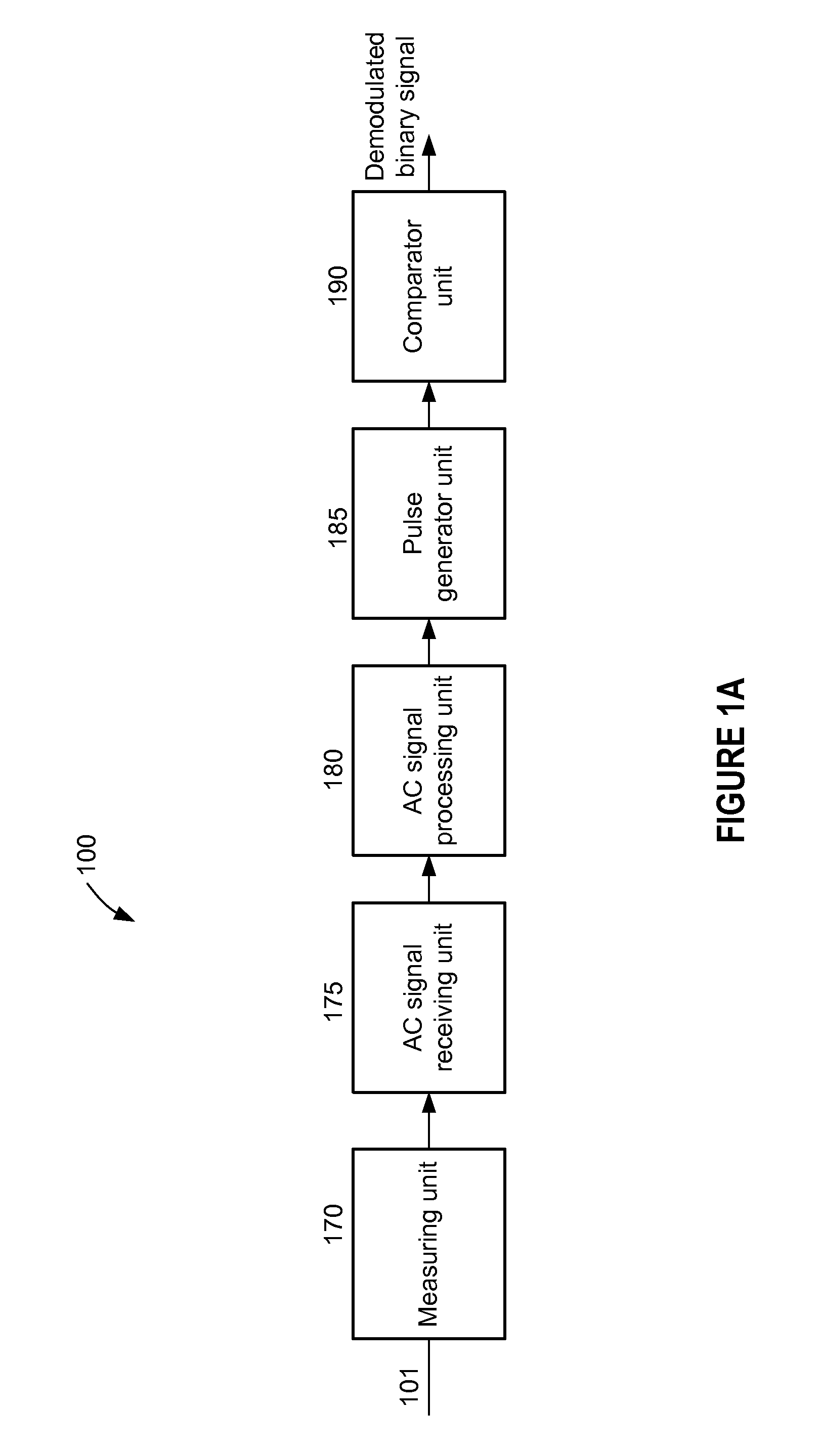
A demodulation circuit for an Amplitude Shift Keyed (ASK) modulated signal includes an envelope detector, an alternating voltage amplifier, a differentiator circuit, and a comparator having a hysteresis connected in series. The envelope detector produces an envelope signal from the received ASK signal. The amplifier blocks the DC component of the envelope signal and amplifies AC components of the envelope signal to obtain a steeper slope of the rising and falling edges. The differentiator circuit then processes the transition edges to provide a differentiated signal having positive and negative electrical pulses. The comparator converts the pulses into a binary data stream which corresponds to the transmitted data stream. The combination of the differentiated signal and comparator having a hysteresis enables better stability and sensitivity of the ASK demodulation circuit.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Dynamic adjusting RFID demodulation circuit
ActiveUS20120313698A1Eliminate the problemAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsRecord carriers used with machinesEngineeringComparator
A dynamic adjusting RFID demodulator circuit includes an envelope detector having an input for receiving a modulated RF signal, a fixed reference generator coupled to the input of an RC filter, an RF level dependent signal path adding to the fixed reference level at higher RF energy levels, a comparator having a first input coupled to an output of the envelope detector, a second input coupled to an output of the RC filter, and an output for providing a data output signal.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
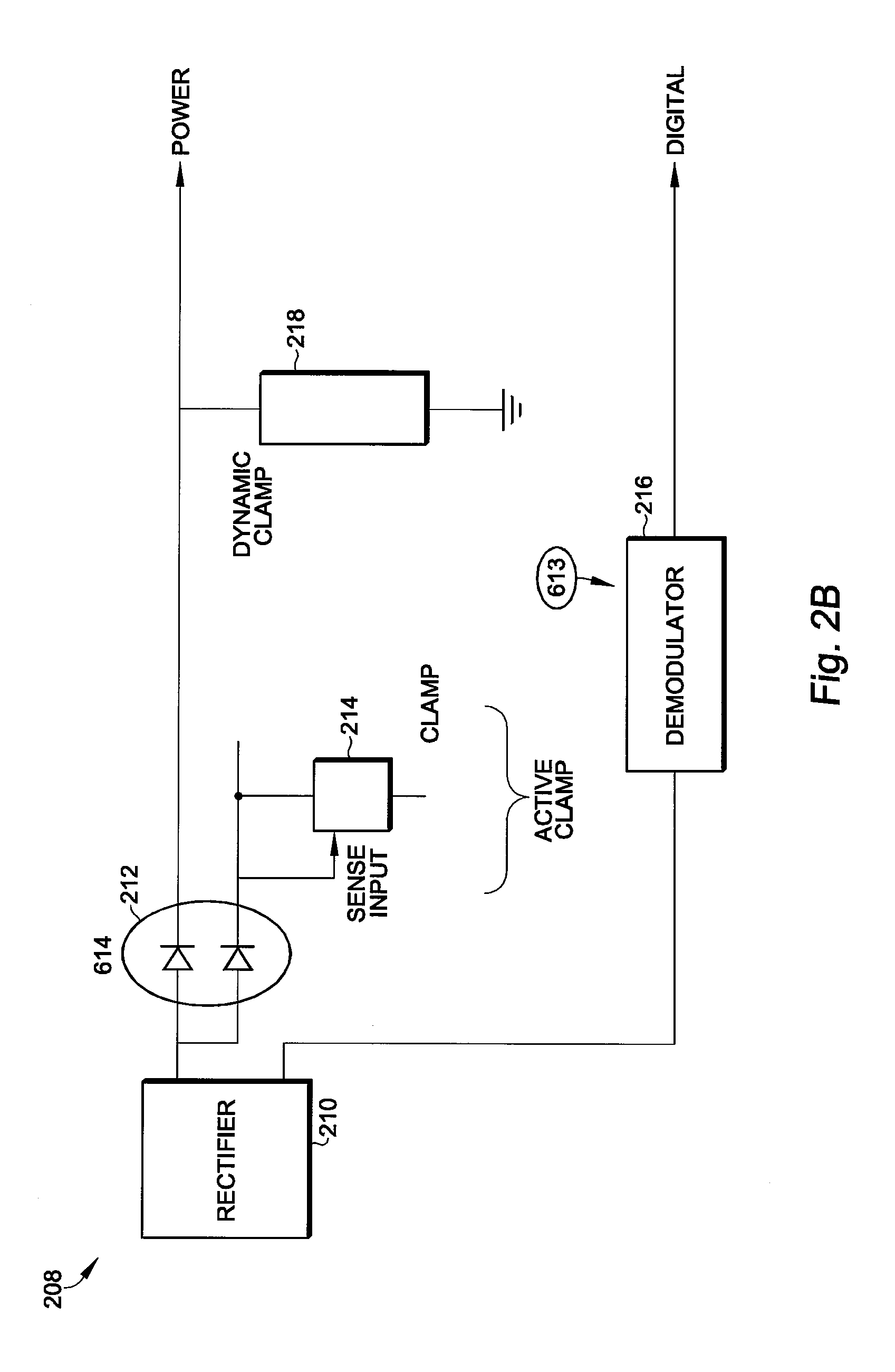
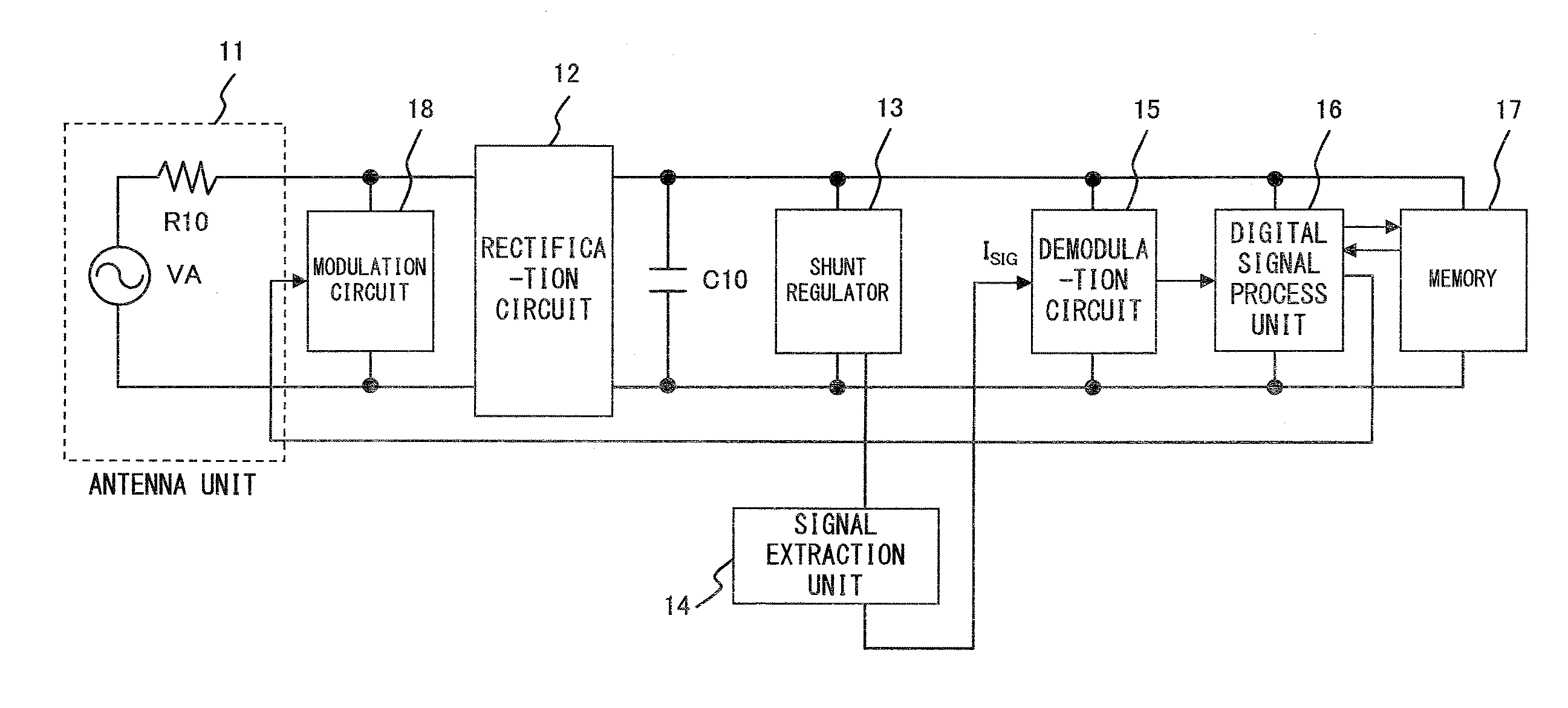
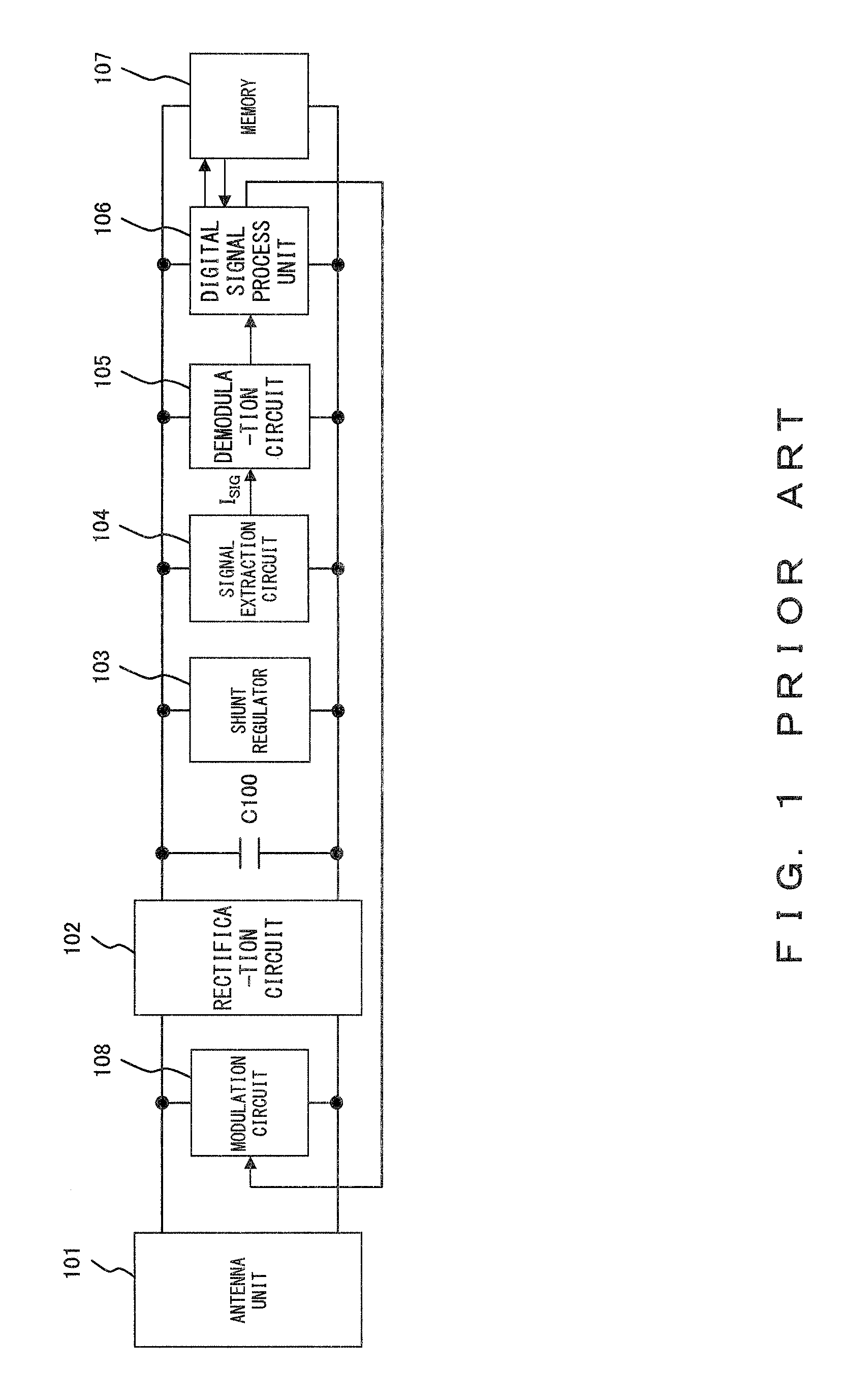
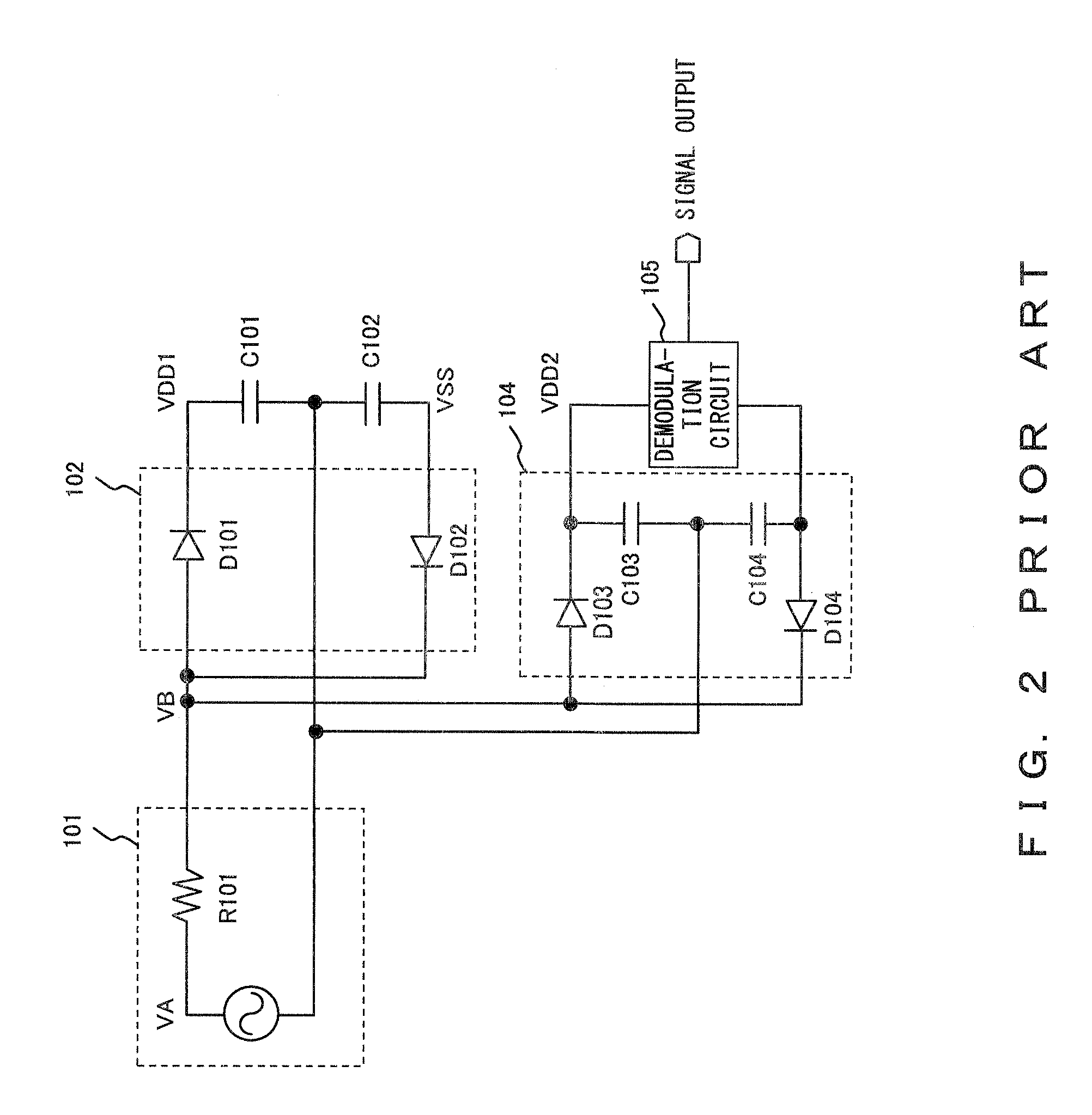
Signal extraction circuit
InactiveUS7800436B2Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear multiple-pole elementsRadio frequency signalSignal extraction
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
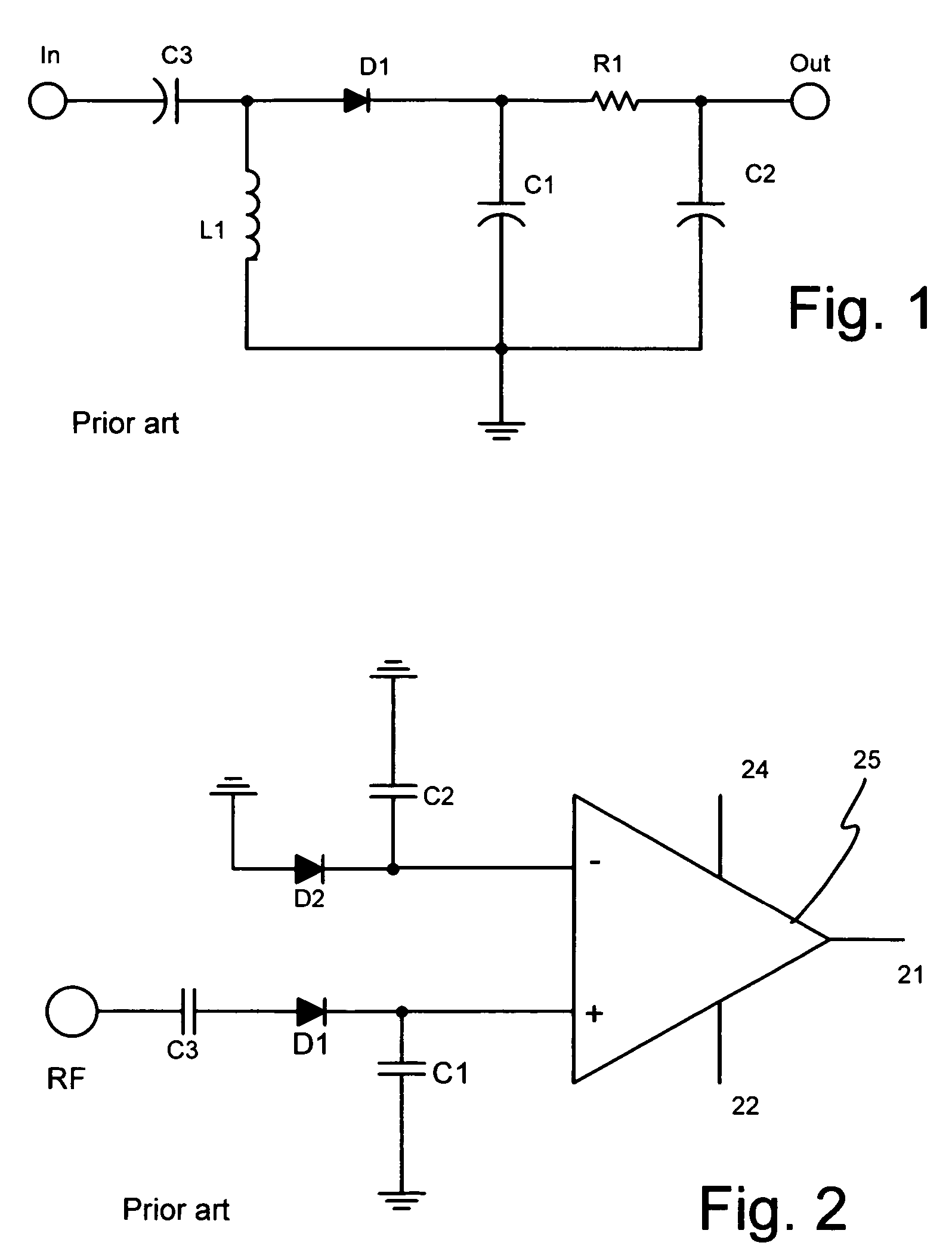
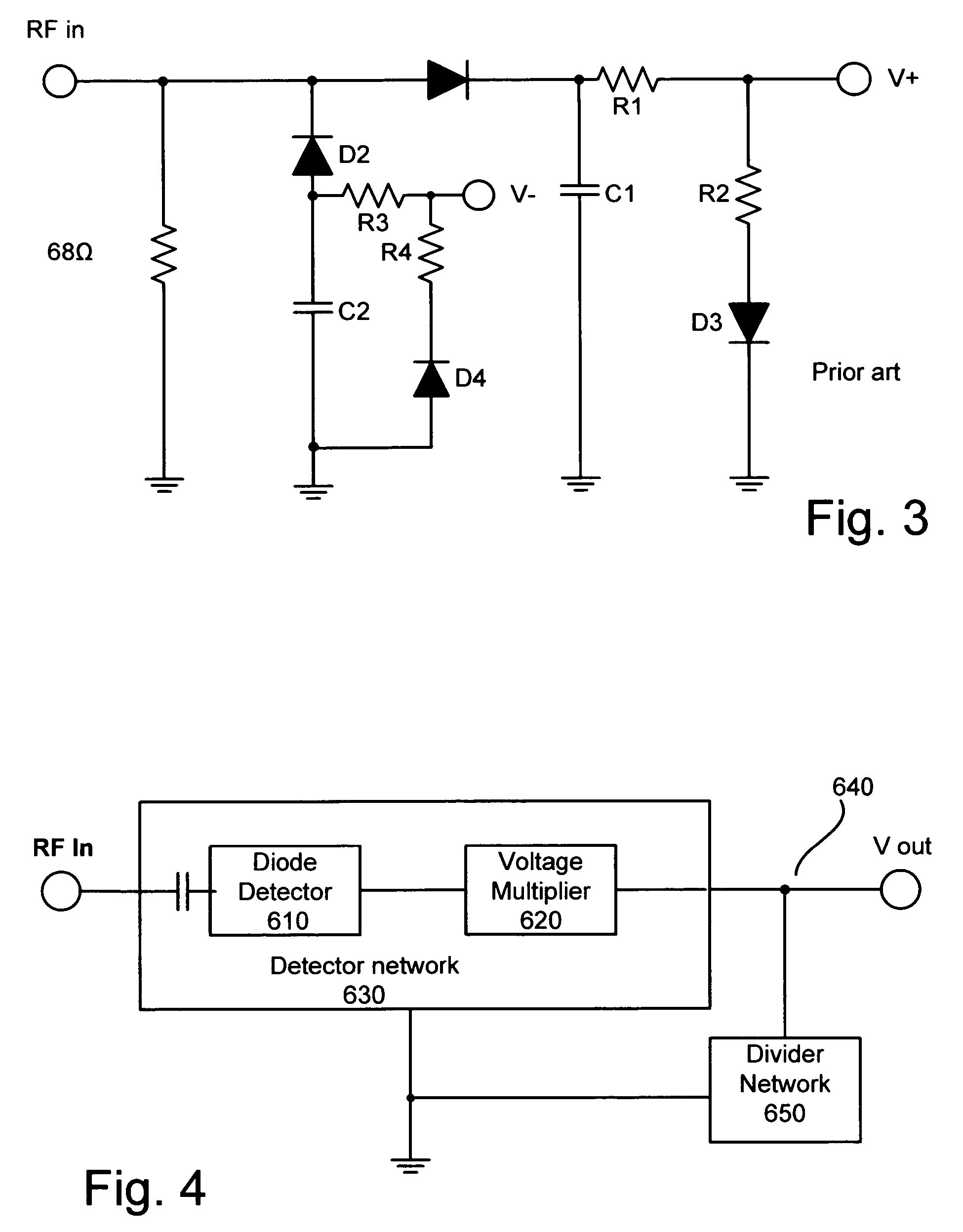
Temperature compensated, high efficiency, controlled input impedance diode detector
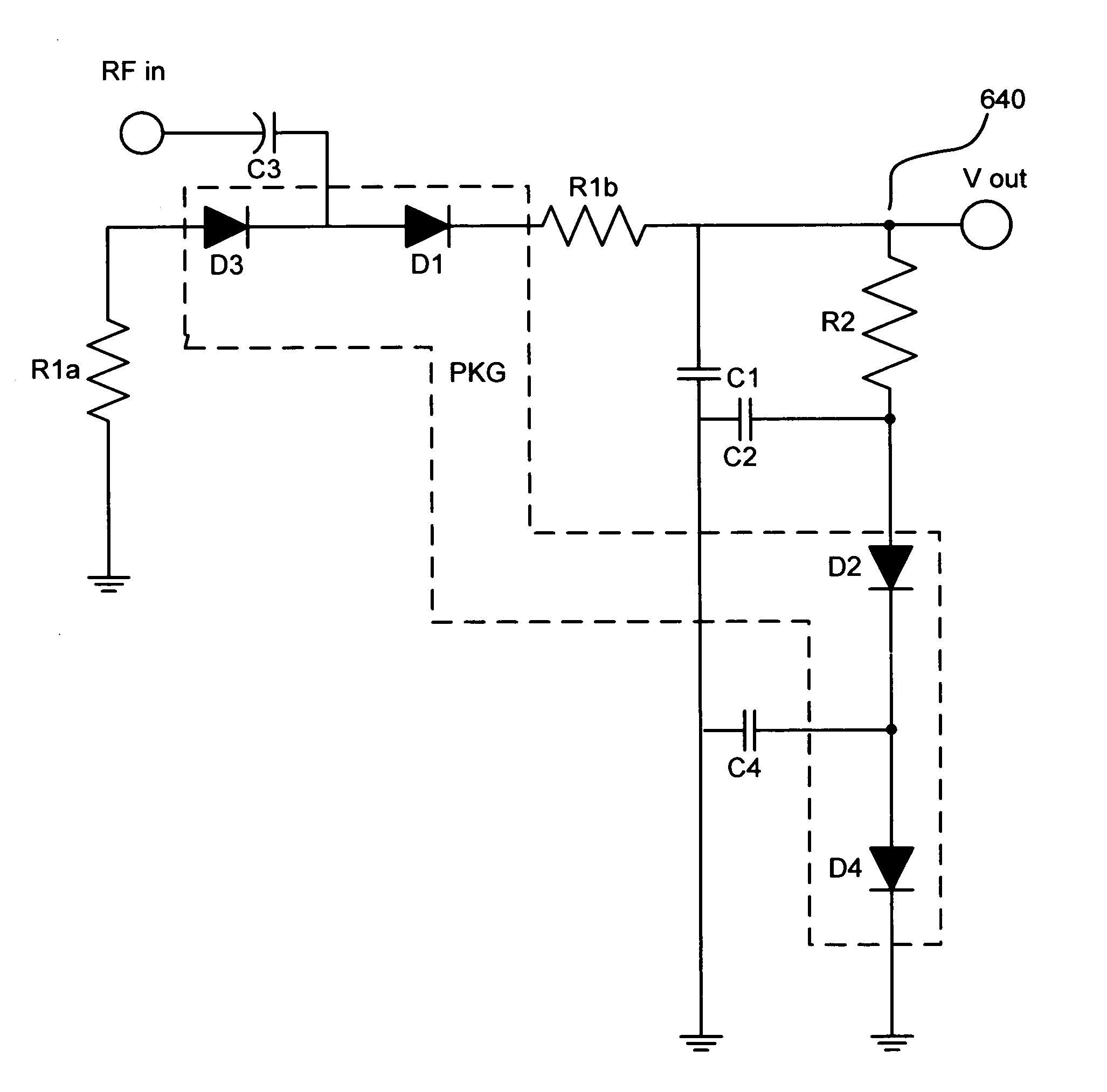
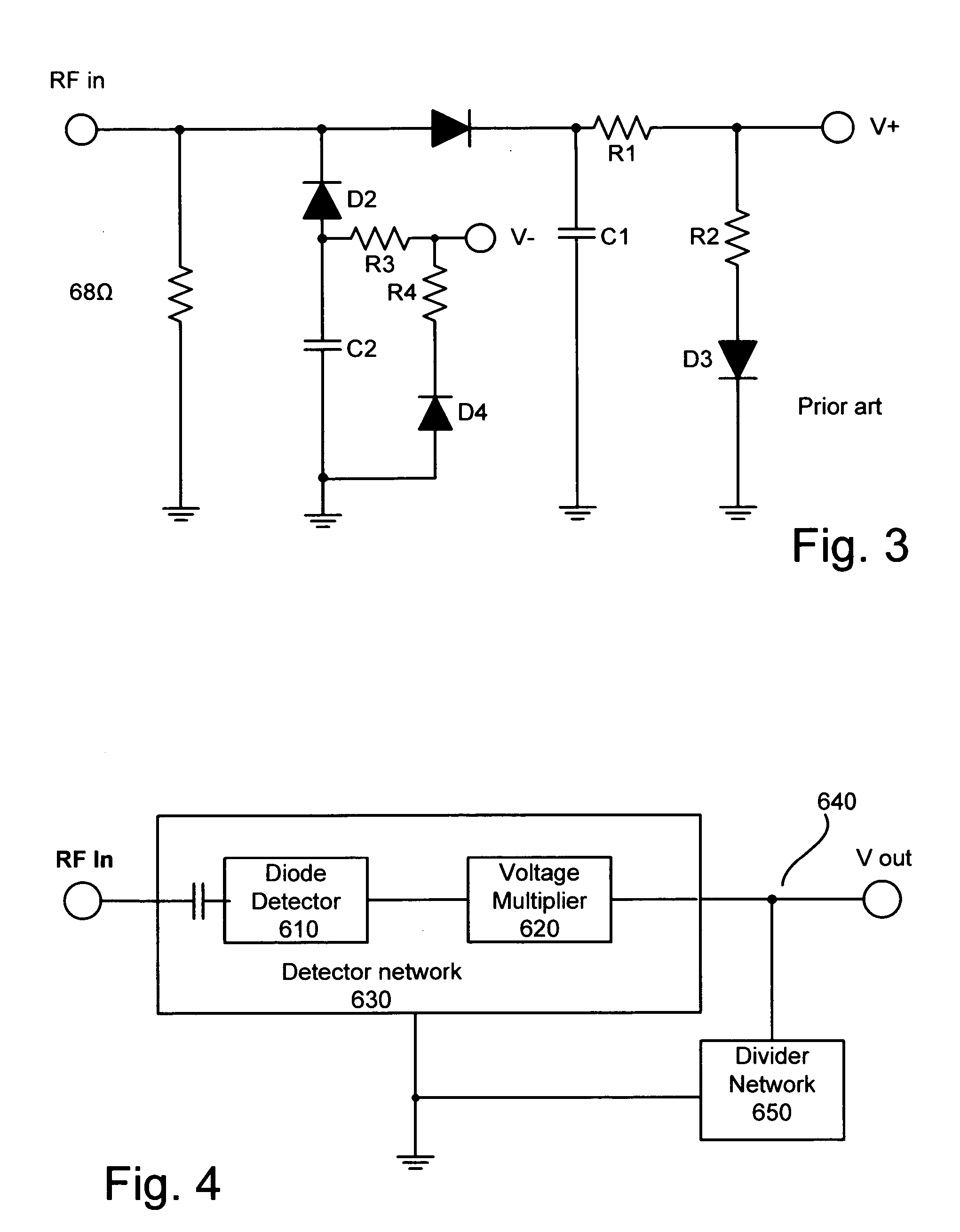
InactiveUS20050057302A1Pulse automatic controlAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsVoltage converterInput impedance
A diode detector comprising a detector network adapted to detect and multiply the detected voltage coupled to a divider network that comprise diodes in equal number to the number of diodes in the detector network, provides a passive detector applicable to any application requiring a small, efficient, high output, inexpensive temperature compensated detector for use as demodulator or as power to voltage converter. Integrating a portion of the divider network in the detector / multiplier network allows control over the minimum input impedance of the detector.
Owner:VECTRON INT INC
Envelope detector circuit
ActiveUS20150136857A1Constructed small and simpleReduce power consumptionInstant pulse delivery arrangementsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsDetector circuitsEngineering
An envelope detector circuit, suitable for use in RFID tags, includes a voltage doubler circuit and a biasing voltage generating circuit which comprises components matched respectively to rectifying components of the voltage doubler circuit. A rectifying component of this voltage doubler circuit is formed by a transistor controlled by the biasing voltage generating circuit which provides a biasing voltage to a control gate of this transistor, the biasing voltage generating circuit being arranged so as to permit a determined forward biasing current to flow through the transistor and further rectifying elements of the voltage doubler circuit. This embodiment provides fast, highly sensitive detection of envelope waveforms in input signals. Thanks to the matched rectifying components, efficiency variations due to variations in manufacturing process can be eliminated. The envelope detector circuit is further arranged for maintaining a stable detection independent of variations in temperature.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Carrier detecting circuit and infrared communication device using same
InactiveUS20050003786A1Reduce capacitanceCancel noiseGain controlAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsCapacitanceIntegrator
A conventional carrier detecting circuit which generates a carrier detection level by integral action based on a reception signal and detects using the carrier detection level whether a carrier exists is arranged to charge and discharge in the following manner, an integration capacitor in an integrator that performs the integral action. Namely, the integration capacitor is (i) either charged or discharged in accordance with a result of the discrimination of the reception signal at the carrier detection level, or (ii) charged in accordance with the result of the discrimination while the integration capacitor is constantly discharged at a constant level. In contrast, a carrier detecting circuit of the present invention is arranged so that the integration capacitor is both charged and discharged constantly at a level that varies in accordance with the result of the discrimination. In other words, the integration capacitor is charged and discharged using a difference current between a current charged from a charging circuit and a current discharged to a discharging circuit. With this, it is possible to reduce the chip area without causing problems due to the reduction of the currents flowing through the transistors.
Owner:SHARP KK
Envelope detector with DC level shifting
InactiveUS20060046674A1Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsAc/pulses peak value measurementsLevel shiftingPeak value
An envelope detector that does not generate an undesirable DC offset at its DC output signal. An envelope detector according to the present teachings includes a circuit for performing a DC level shift on an AC input signal applied to the envelope detector such that a magnitude of the DC level shift is proportional to a peak envelope of the AC input signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Demodulator for an amplitude-modulated alternating signal
ActiveUS7215723B2Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsMemory record carrier reading problemsPeak valueEngineering
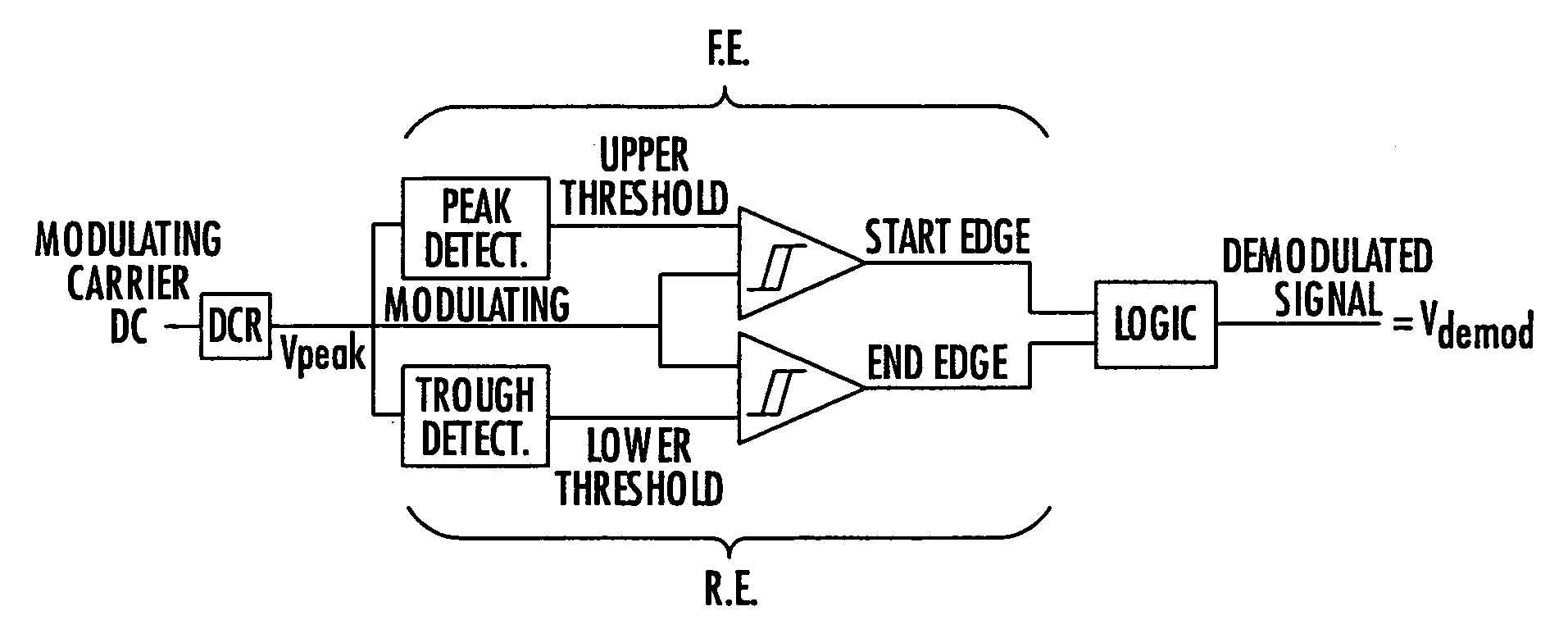
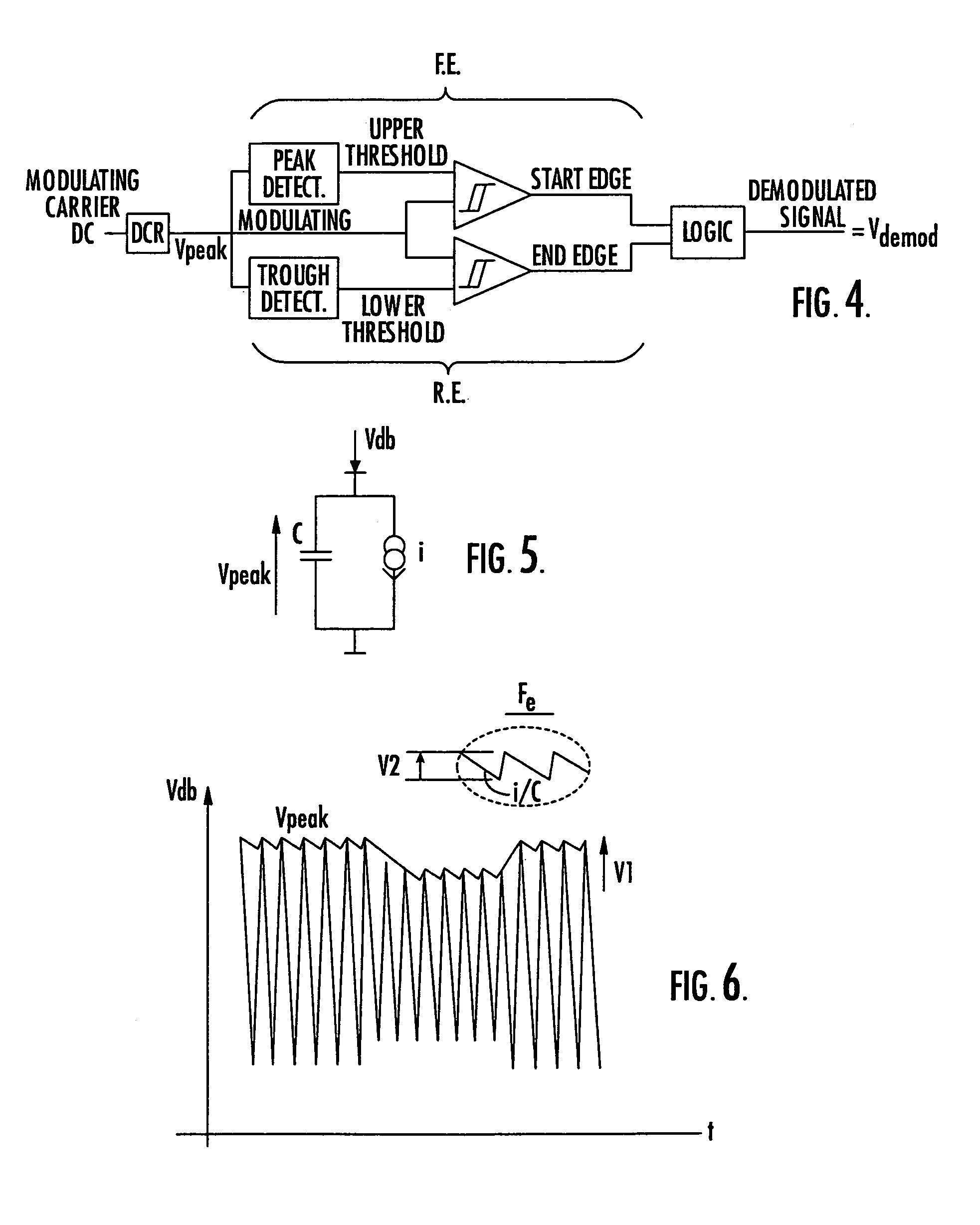
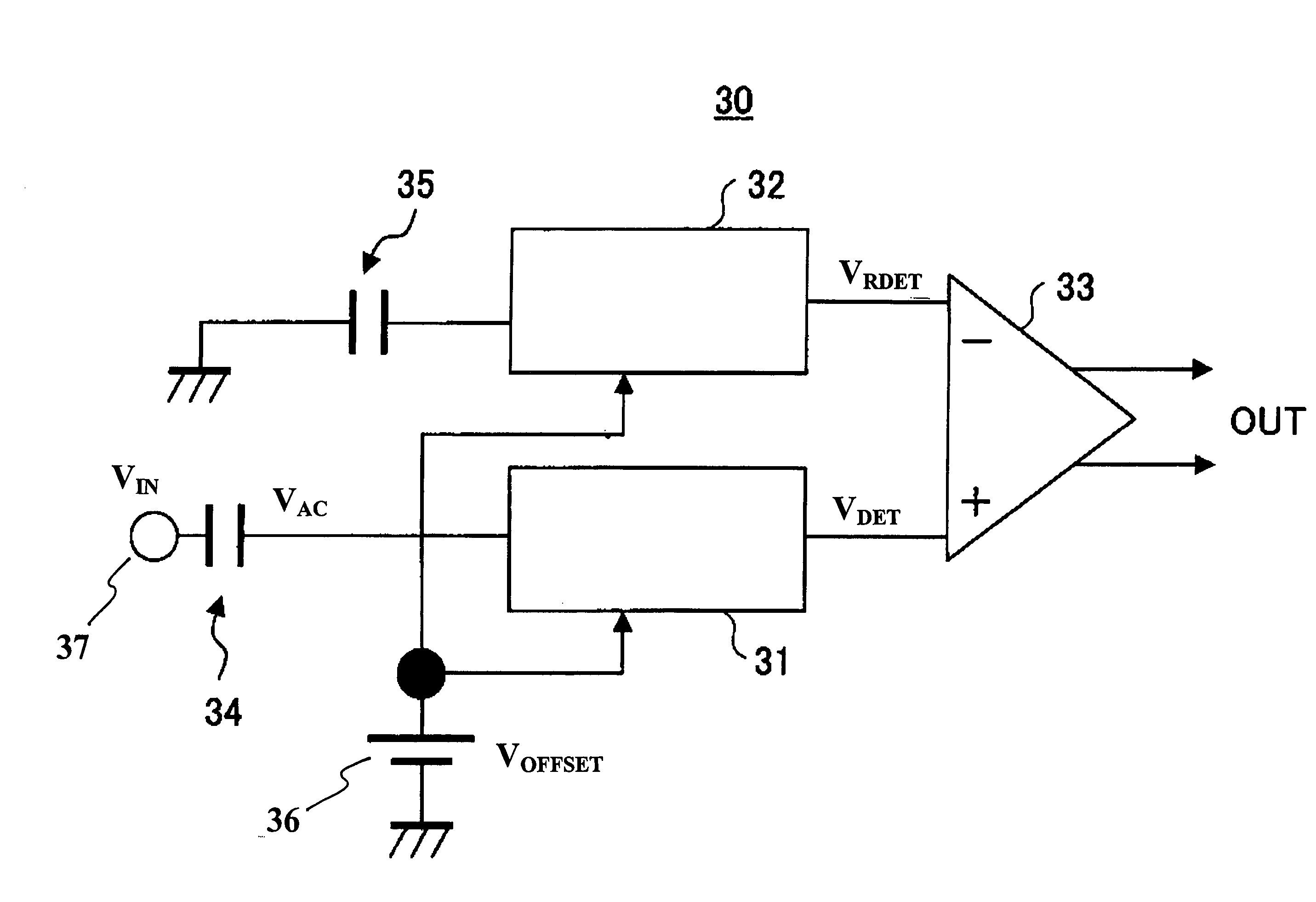
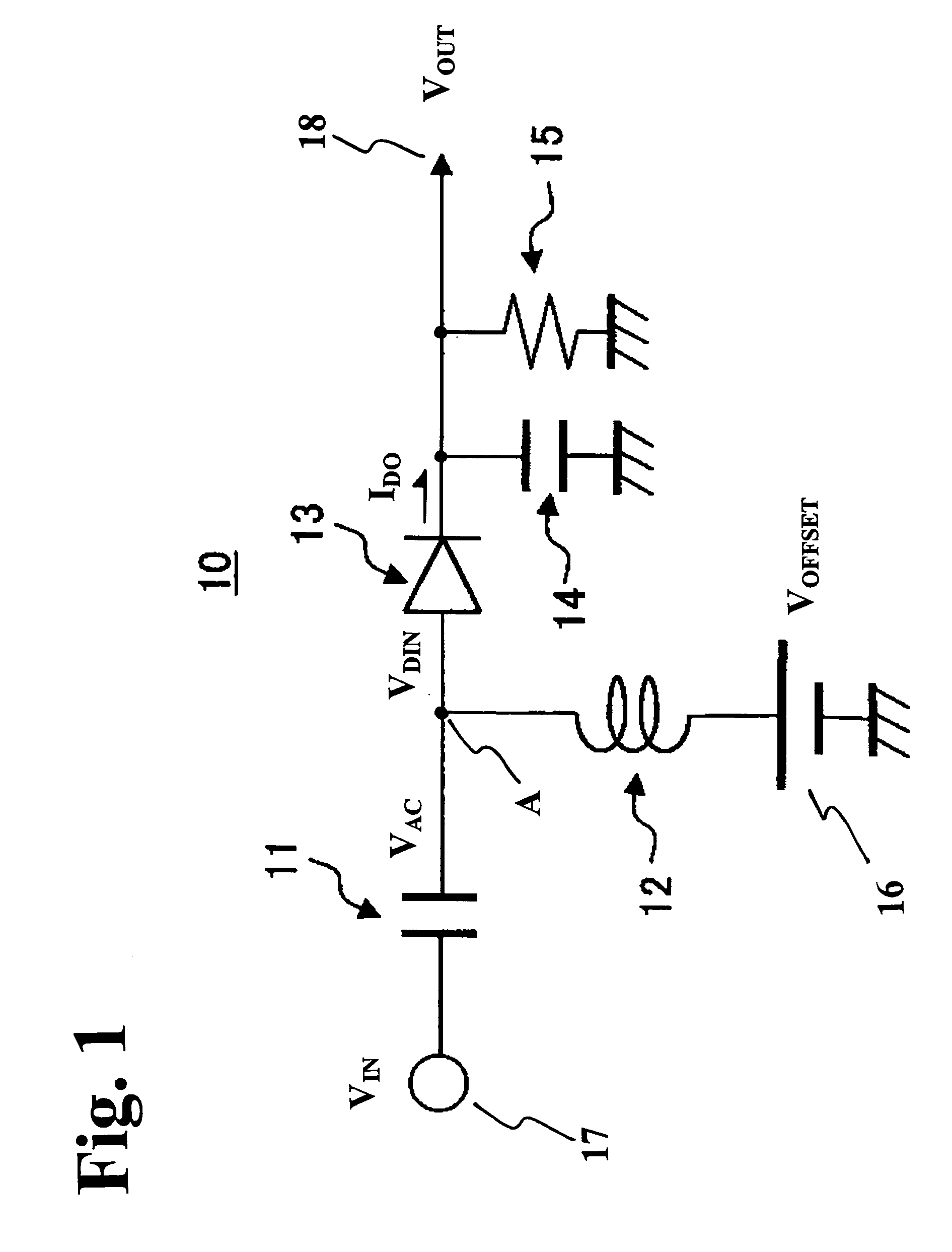
The invention concerns a demodulator of an amplitude-modulated signal (Vdb), characterised in that it comprises a peak detecting cell (DCR) capable of extracting the reference modulating signal (Vpeak1) of the modulated signal (Vdb); a first demodulator (FE) adapted to detect the peak of the reference modulating signal (Vpeak1) to generate a high comparison threshold and locate the start of the modulation, a second demodulator (RE) adapted to detect a trough of the reference modulating signal (Vpeak1) to generate a low comparison threshold and locate the end of the modulation; a logic processing unit capable of supplying the demodulated signal (Vdemod).
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Diode circuit
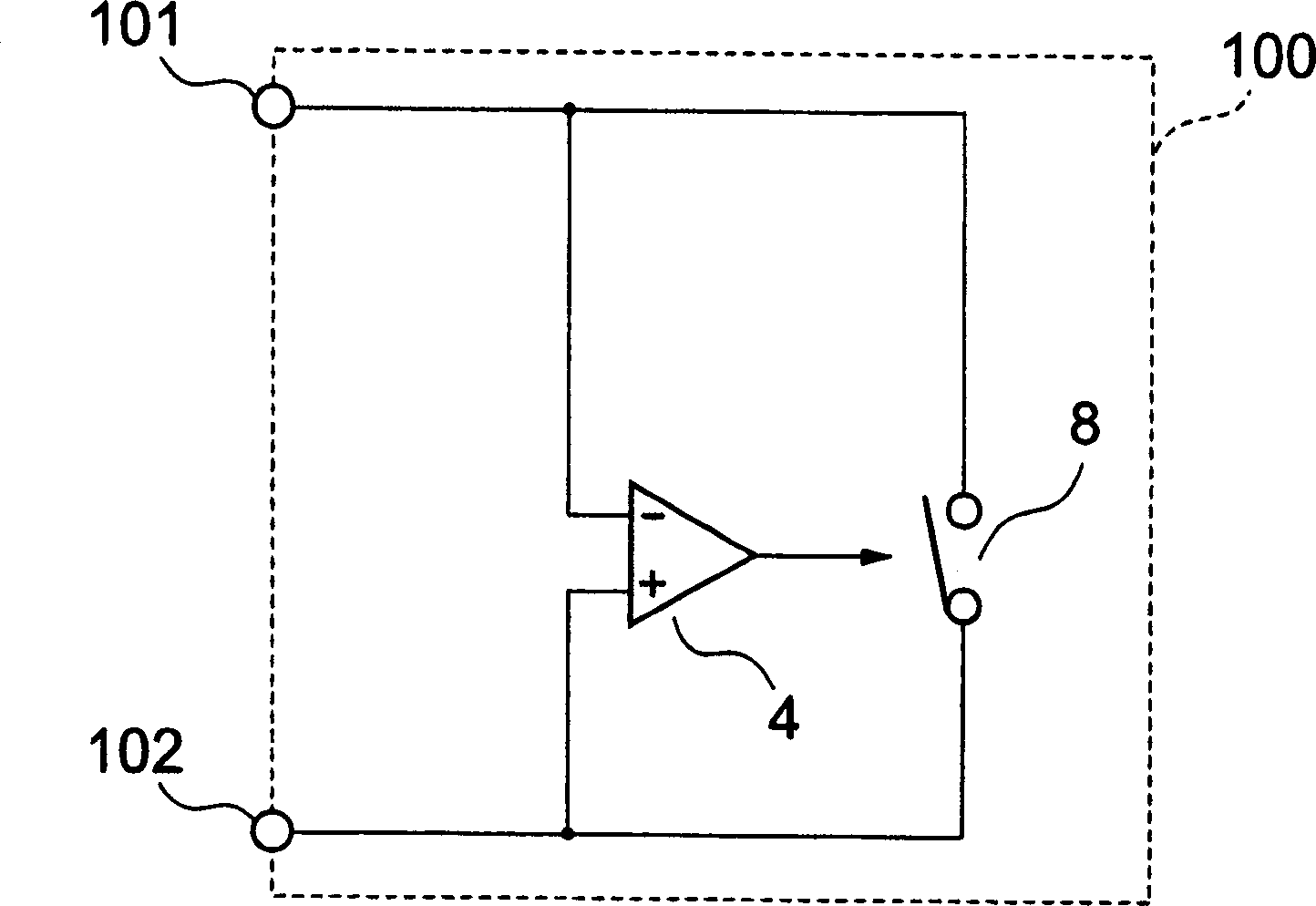
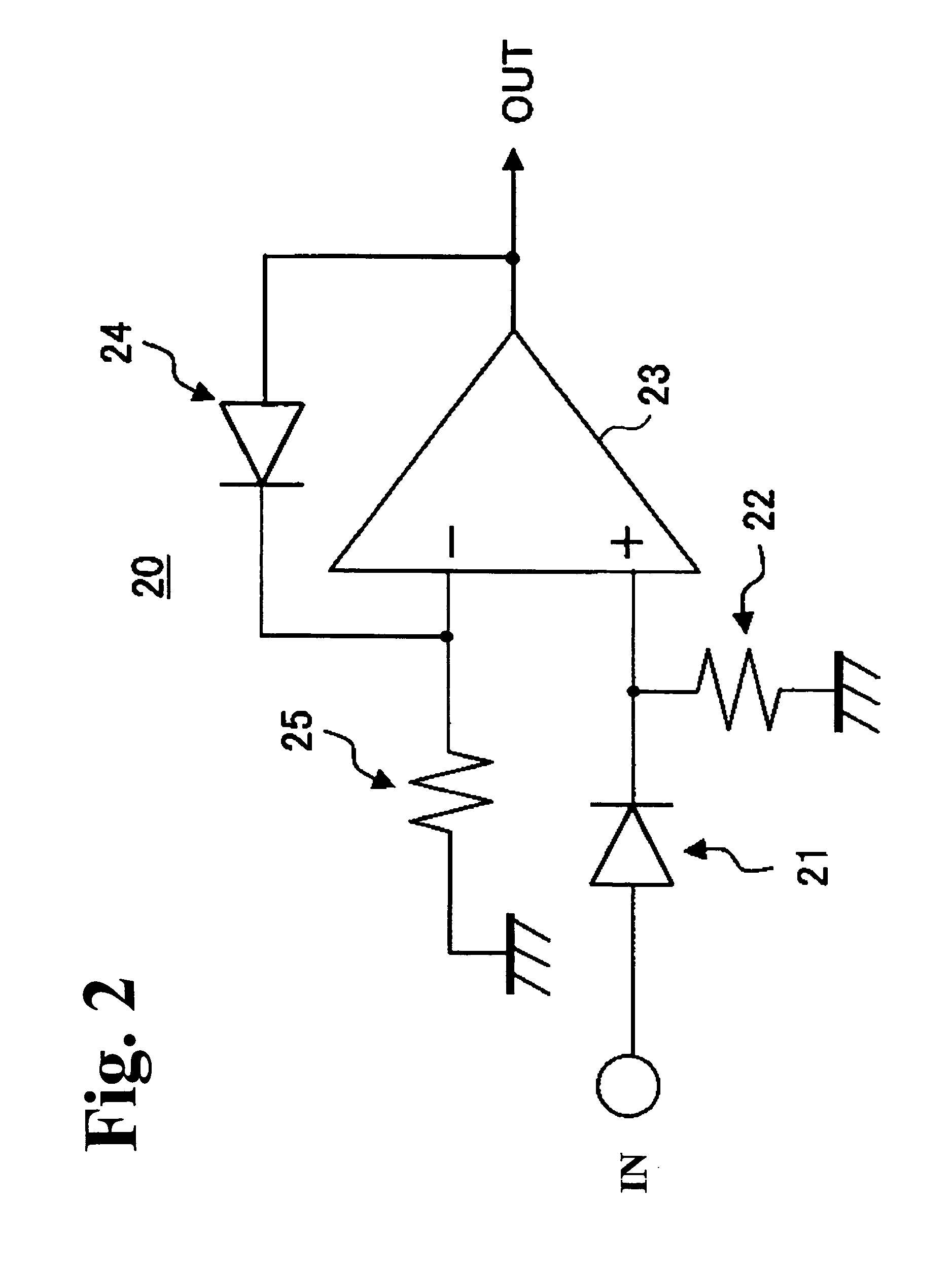
Provided is a diode circuit with small power consumption. A first voltage comparator (4) compares a voltage at a cathode terminal (101) with a sum of a voltage at an anode terminal (102) and a voltage across a first voltage source (10) to output a reset signal, and a second voltage comparator (5) compares a voltage at the anode terminal (102) with a sum of a voltage at the cathode terminal (101) and a voltage across the second voltage source (11) to output a set signal. A first latch circuit (20) outputs an L signal when the reset signal from the first voltage comparator (4) is inputted, and outputs an H signal when the set signal from the second voltage comparator (5) is inputted. An n-channel MOS transistor (2) turns off upon receiving the L signal, and turns on upon receiving the H signal, to thereby limit an output current.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Wireless power reception device and wireless communication method
ActiveUS20170201127A1Smooth communicationBatteries circuit arrangementsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsIntensity modulationElectric power
A wireless power reception device and a wireless communication method thereby are provided. The wireless communication method by the wireless power reception device may comprise the steps of: receiving a wireless power signal from a wireless power transmission device; measuring the strength of the wireless power signal; modulating the amplitude of the wireless power signal according to the measured strength of the wireless power signal; and performing communication with the wireless power transmission device by using the signal having the amplitude modulated.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
Demodulation circuit and RFID tag including the demodulation circuit
ActiveUS8258862B2DistanceEnergy of electromagnetic wavesAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsSolid-state devicesPower flowSemiconductor materials
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Amplitude demodulator for an electromagnetic transponder
ActiveUS7439800B2Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCapacitanceAmplitude demodulation
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Activation signal output circuit and determination circuit
InactiveUS7209842B2Efficient inputHigh sensitivityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFrequency analysisDetector circuitsEngineering
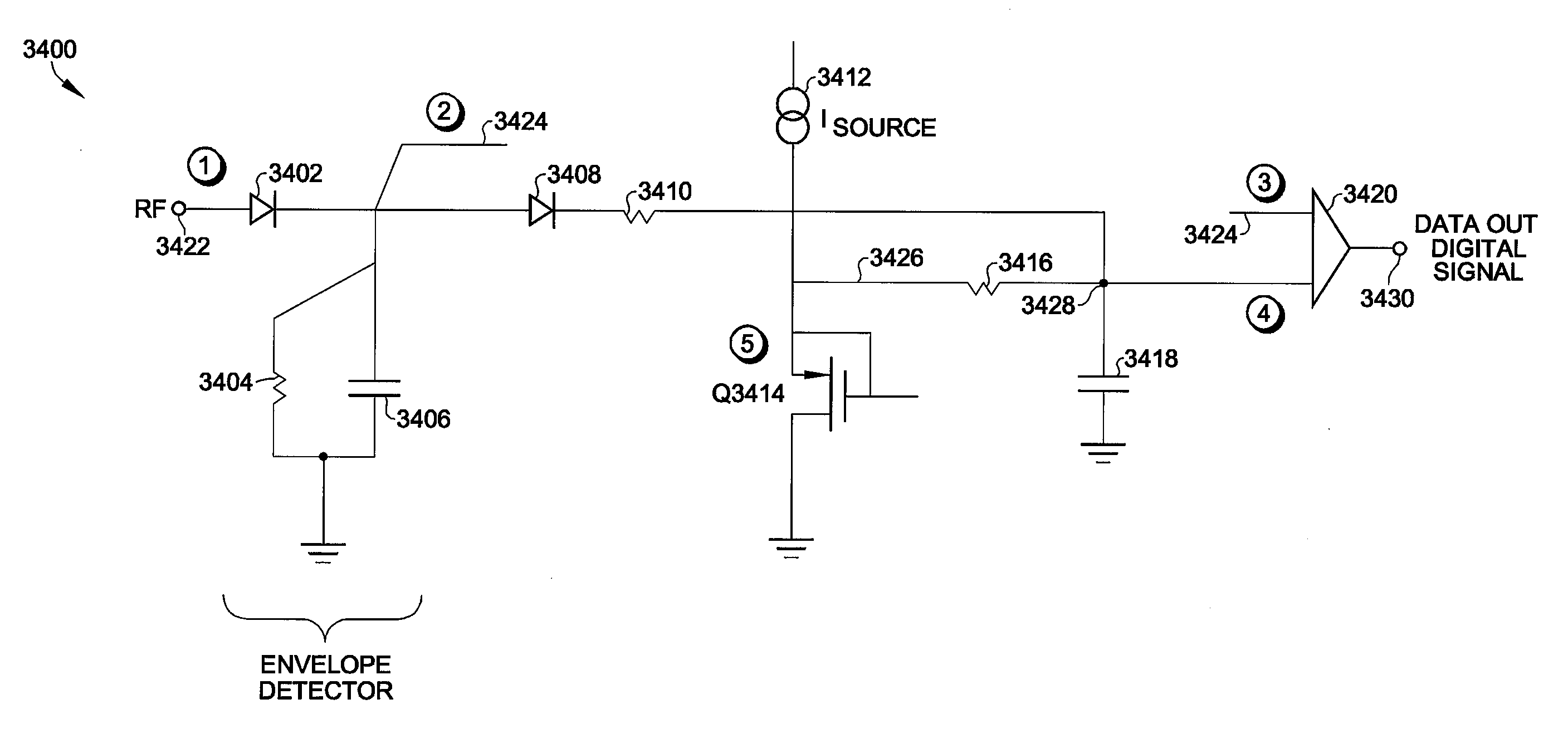
A start signal output circuit having an RF / DC conversion circuit to which radio frequency power (RF) of specified frequency is inputted and from which a direct current potential (DC) is outputted, comprises a detection / amplification circuit 210 which includes a voltage doubler wave-detector circuit 10 configured including a sensing diode Q1 (Tr34) for sensing the RF power, a differential amplifier including differential pair transistors Tr31 and Tr32, and a current mirror circuit. A base current of one Tr31 of the differential pair transistors is brought into substantial agreement with a DC component of a current flowing through the sensing diode Q1 (Tr34). A total of currents flowing through the differential pair transistors Tr31 and Tr32 is regulated to a substantially constant value by the current mirror circuit. Thus, the start signal output circuit which is small in size, high in sensitivity and low in power consumption can be realized.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Partial-discharge ultrahigh-frequency-signal detection conditioning circuit
ActiveCN104035012AAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsAmplitude demodulation detailsCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Disclosed is a partial-discharge ultrahigh-frequency-signal detection conditioning circuit which includes an input capacitor C0, a first capacitor C1, a second capacitor C2, a third capacitor C3, a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2, a third resistor R2, a forth resistor R4, a fifth resistor R5, a first diode D1, a second diode D2, a negative bias voltage UB and an amplifier A1. The partial-discharge ultrahigh-frequency-signal detection conditioning circuit improves defects of poor small-signal sensitivity, serious nonlinearity, low response speed and sensitivity to temperature and the like of a basic diode detector circuit through application of DC negative voltage bias and design of a balance-type topological structure on the basis of the basic diode detector circuit so that balance-type negative bias voltage diode detection is finally designed and realized.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Start signal detector circuit
ActiveUS20110121864A1Improve rectification efficiencyStable signalMultiple input and output pulse circuitsElectrical controlDetector circuitsAudio power amplifier
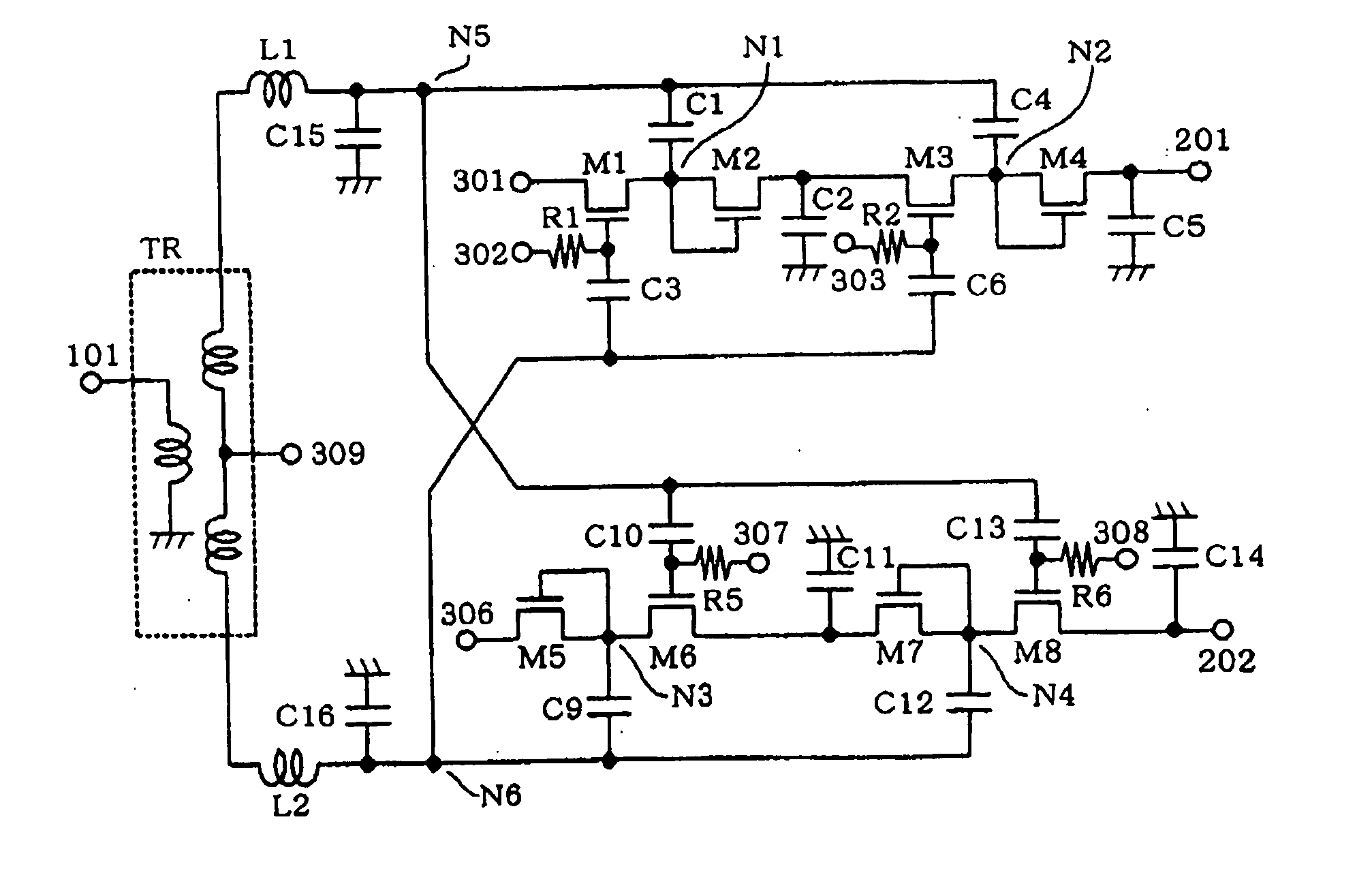
The nonlinearity effect of a rectifying element is enhanced, and further a resonant circuit is used to enlarge the input amplitude. Furthermore, the rectifying efficiency of a detection rectifier circuit is enhanced, thereby allowing the gain of an amplifier circuit in the following stage to be set to a low value. Signals having mutually opposite phases are inputted to RF input terminals (101,102). The signal at the terminal (102) is then inputted to the gate of a transistor (M1) via a capacitor (C3), while the signal at the terminal (101) is then inputted, via a capacitor (C1), to a node (N1) to which the source of the transistor (M1) and the gate and drain of a transistor (M2) are connected, whereby a capacitor (C2) is charged with a half-wave voltage-doubled rectified current. DC biases are inputted to terminals (301,302). There are formed series resonant circuits (L1,C15;L2,C16). A plurality of half-wave voltage-doubled rectifier circuits (M1,M2,C1-C3,R1) are connected in cascade.
Owner:NEC CORP
Activation signal output circuit and determining circuit
InactiveUS20060071654A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFrequency analysisDetector circuitsEngineering
A start signal output circuit having an RF / DC conversion circuit to which radio frequency power (RF) of specified frequency is inputted and from which a direct current potential (DC) is outputted, comprises a detection / amplification circuit 210 which includes a voltage doubler wave-detector circuit 10 configured including a sensing diode Q1 (Tr34) for sensing the RF power, a differential amplifier including differential pair transistors Tr31 and Tr32, and a current mirror circuit. A base current of one Tr31 of the differential pair transistors is brought into substantial agreement with a DC component of a current flowing through the sensing diode Q1 (Tr34). A total of currents flowing through the differential pair transistors Tr31 and Tr32 is regulated to a substantially constant value by the current mirror circuit. Thus, the start signal output circuit which is small in size, high in sensitivity and low in power consumption can be realized.
Owner:DENSO CORP
AM (amplitude modulation) demodulation system for RFID reader device
ActiveUS7791409B2Improve filtering effectSimple and cheap configurationAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsRope driveEngineeringDemodulation
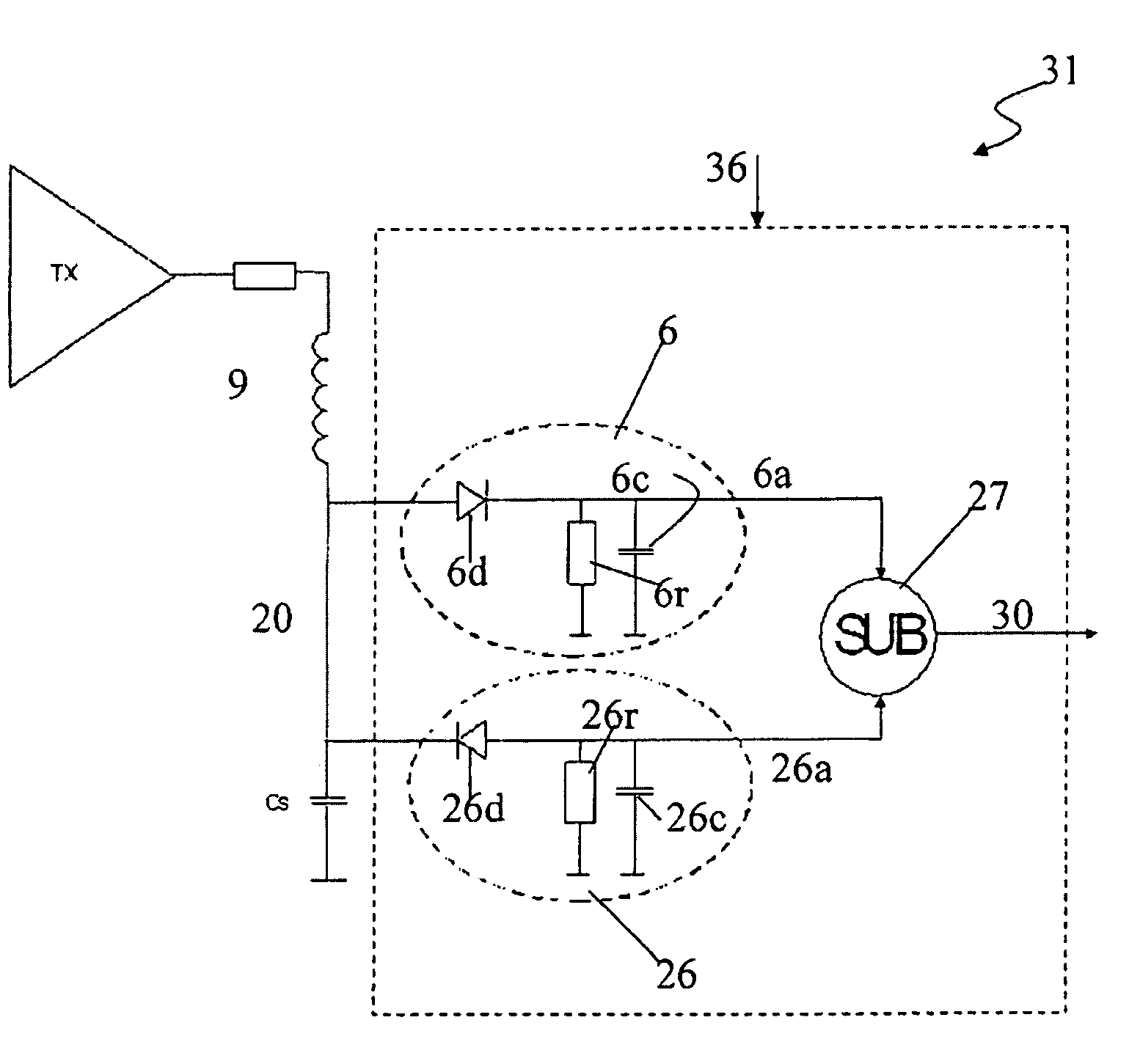
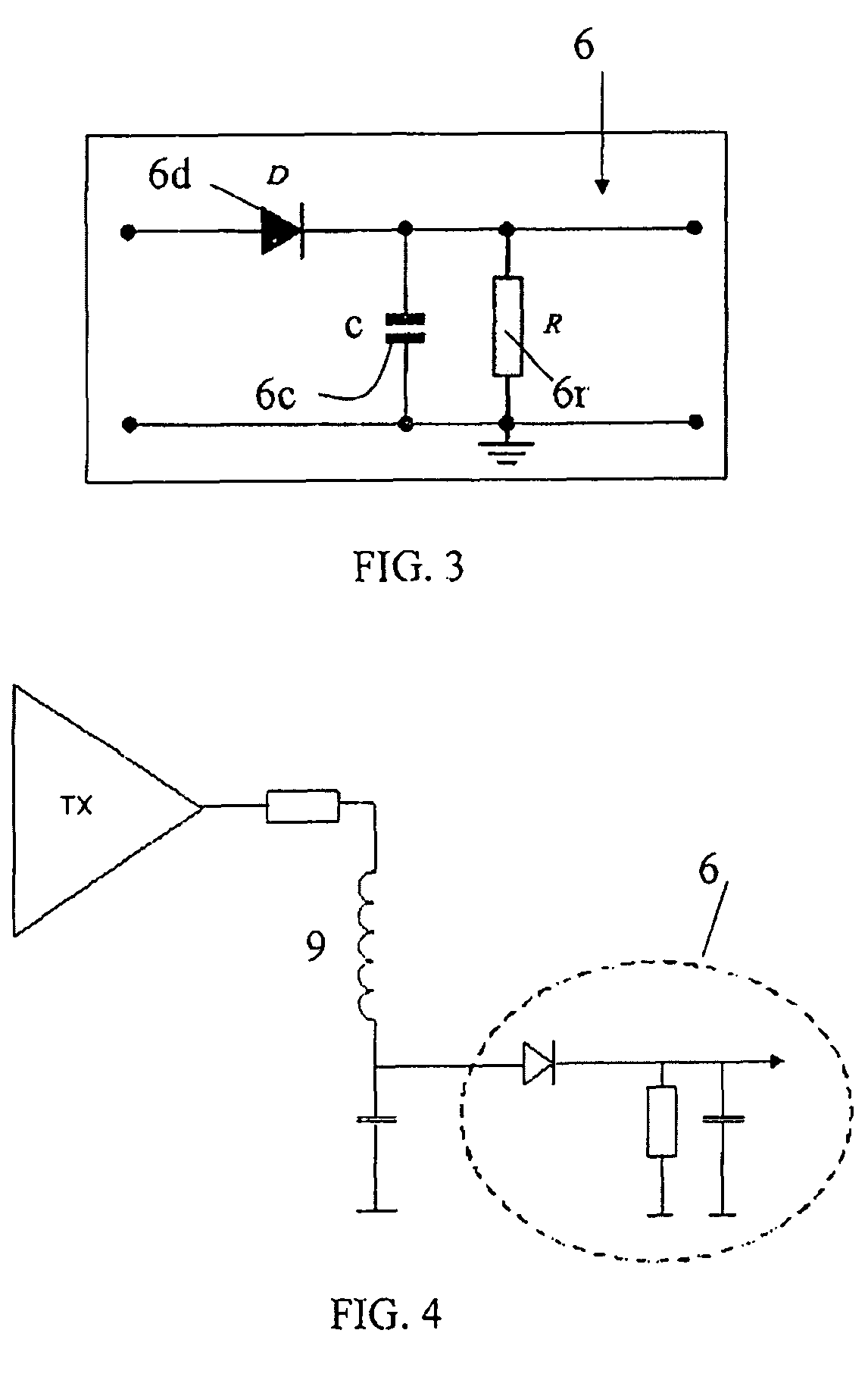
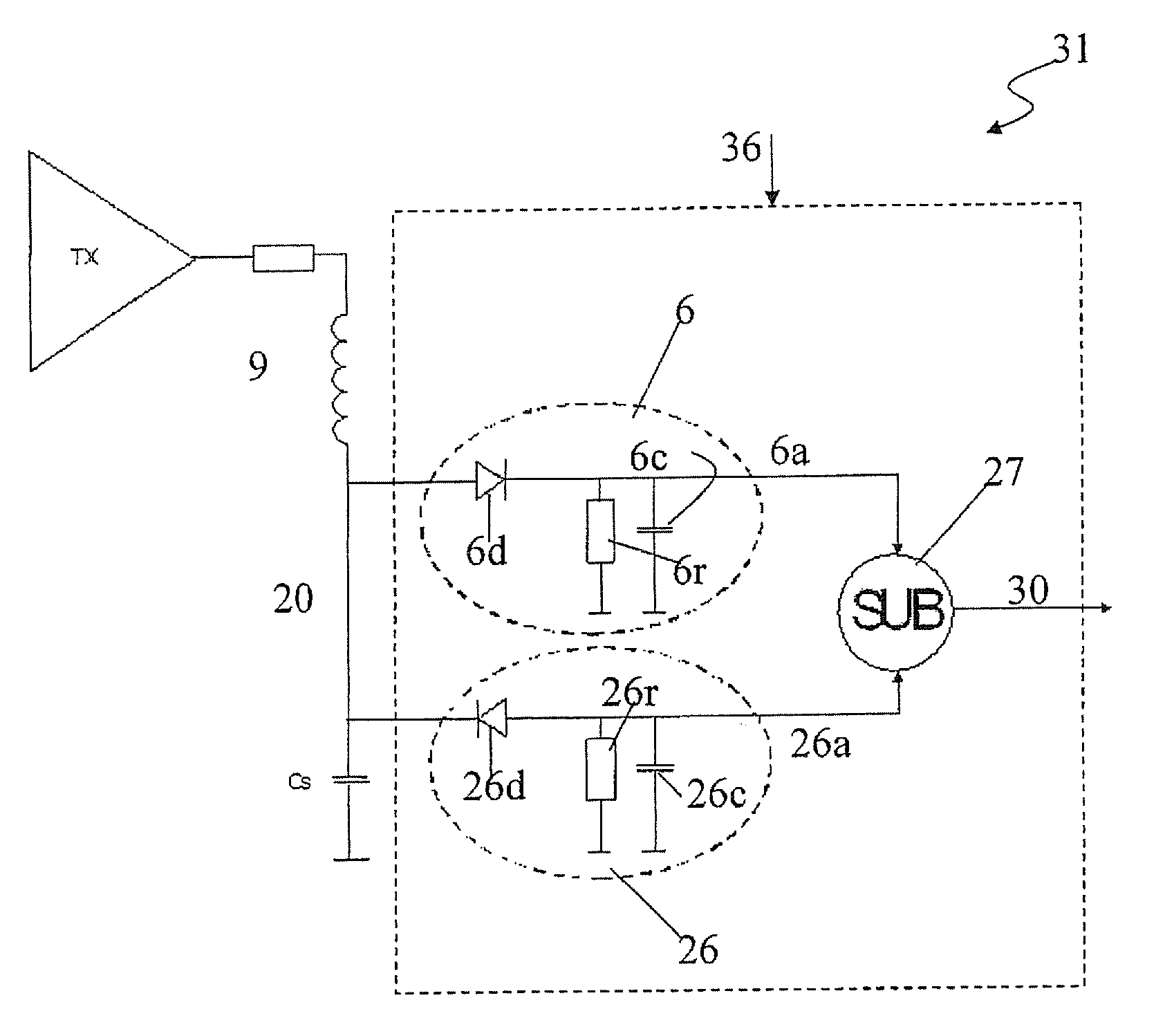
AM (Amplitude Modulation) demodulation system (36) for an RFID reader device (31), of the type comprising a demodulator (6) for receiving from a RFID tag (11) an AM (Amplitude Modulation) wave (20) having a predetermined frequency (f) and for retrieving, from the AM wave (20), a demodulated output (6a) associated to predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes of said AM wave (20). The AM demodulation system comprises at least a second demodulator (26) for receiving the AM wave (20) and retrieving a second demodulated output (26a) associated to Amplitudes opposite to the predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes and a block (27) having, in input, the demodulated output (6a) and the second demodulated output (26a) and returning, in output, an enforced demodulated output (30) with a frequency (f1) greater than the predetermined frequency (f).
Owner:DATAMARS
Diode detecting circuit
InactiveUS7183839B2Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsElectronic switchingHighly sensitiveVoltage
A diode detecting circuit which cancels temperature dependence of a detecting diode so as to obtain highly sensitive detection. The diode detecting circuit has a first diode detecting unit in which a first diode detects an input signal biased by a bias voltage, a second diode detecting unit in which a second diode receives the bias voltage, and an output unit which compares an output from the first diode detecting unit with an output from the second diode detecting unit.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
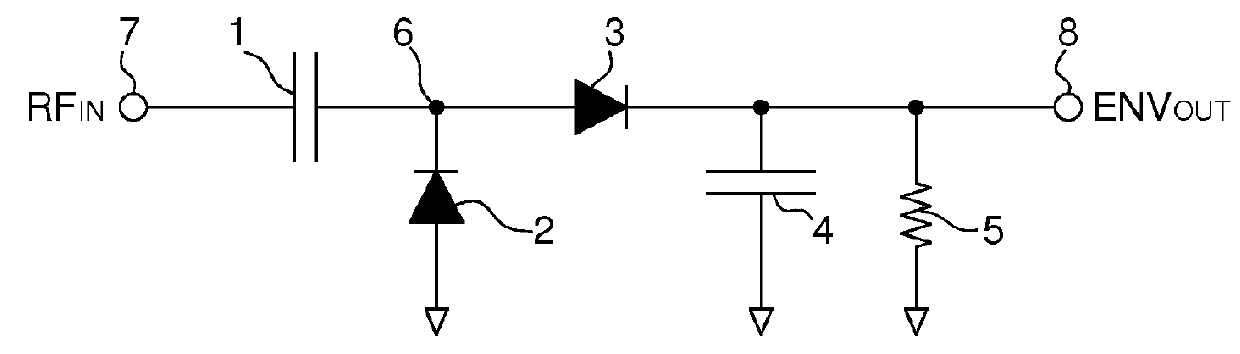
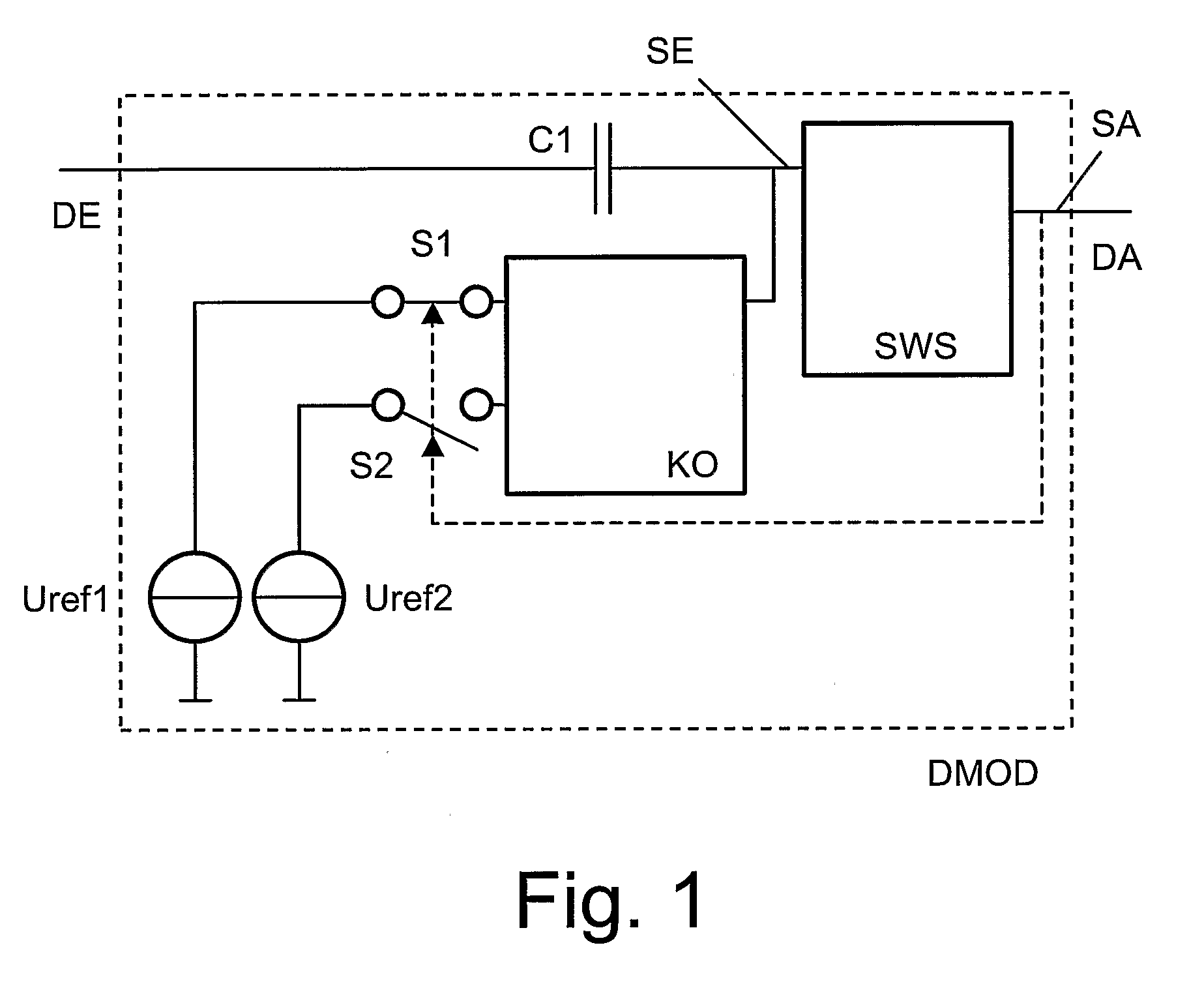
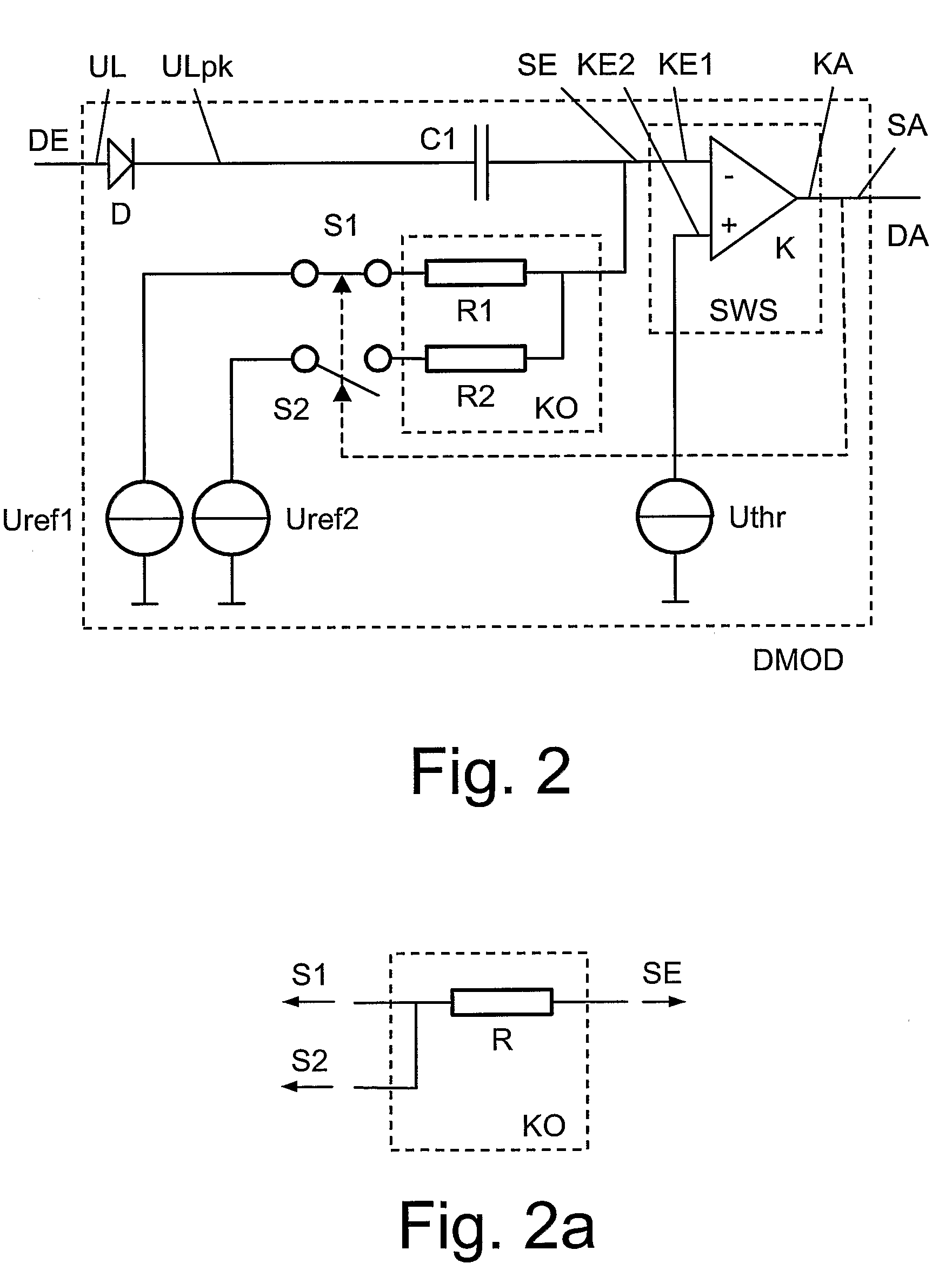
Demodulator for amplitude-modulated signals
ActiveUS7847627B2Reduce areaSeparate componentAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsMemory record carrier reading problemsCouplingCapacitor
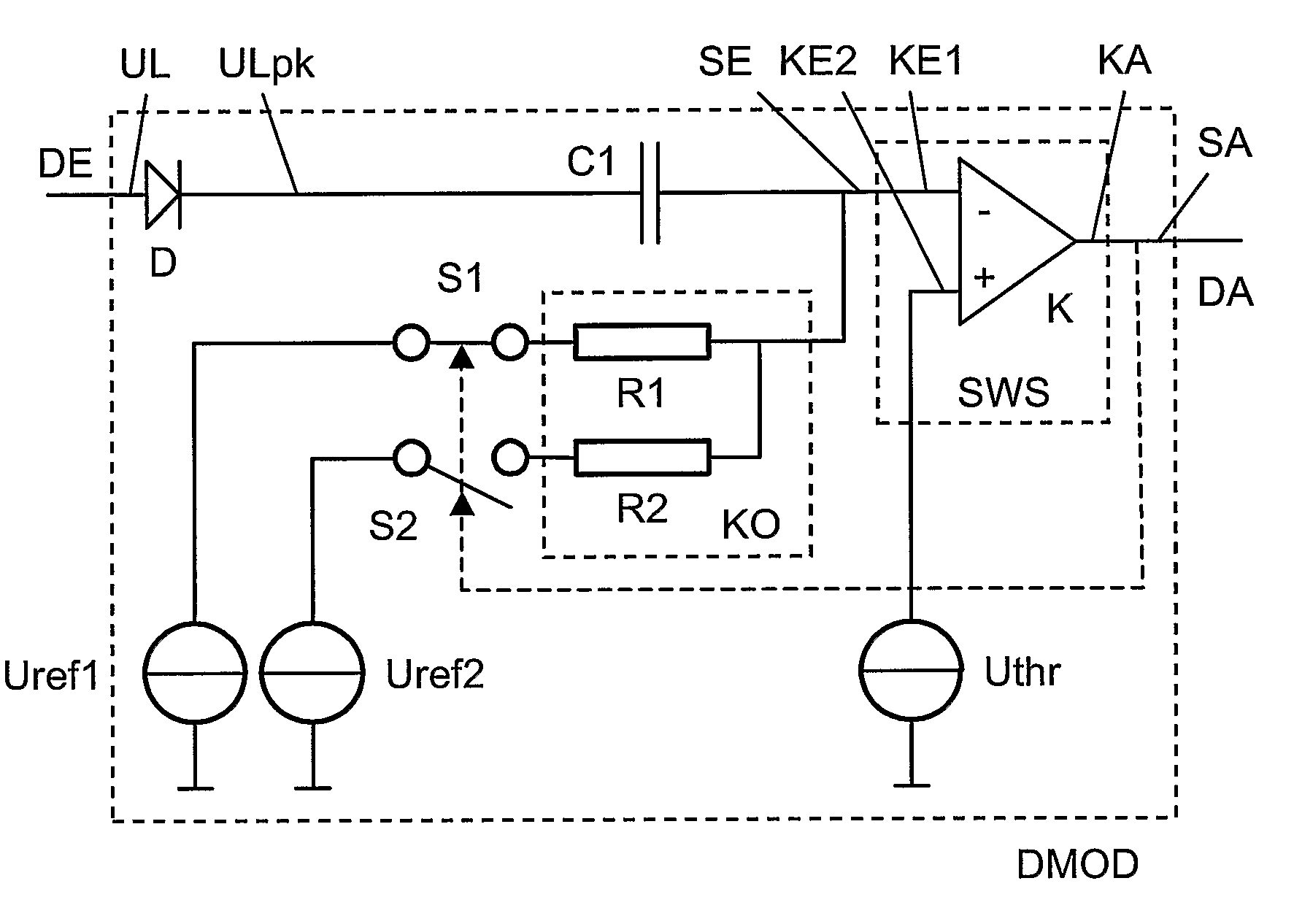
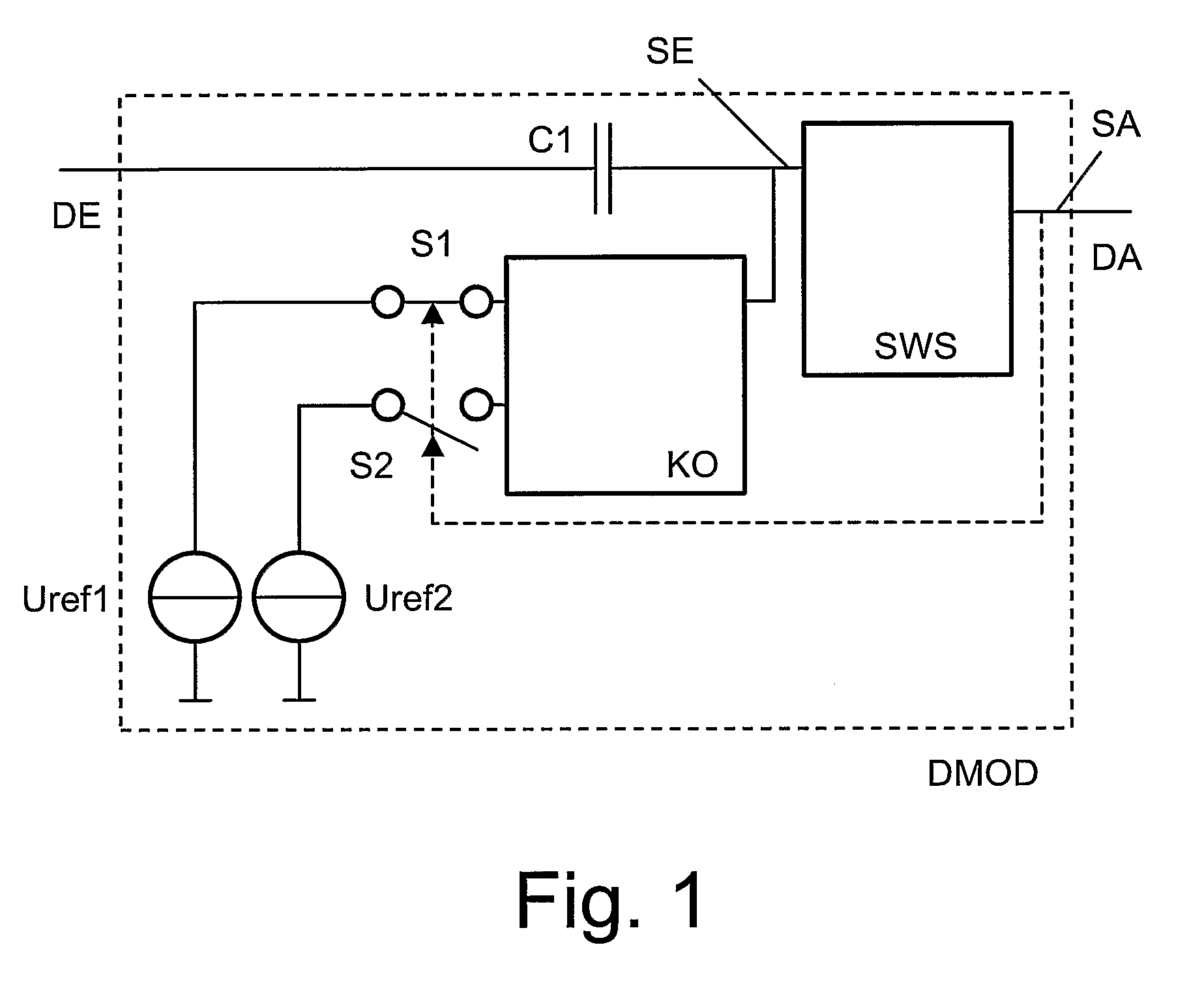
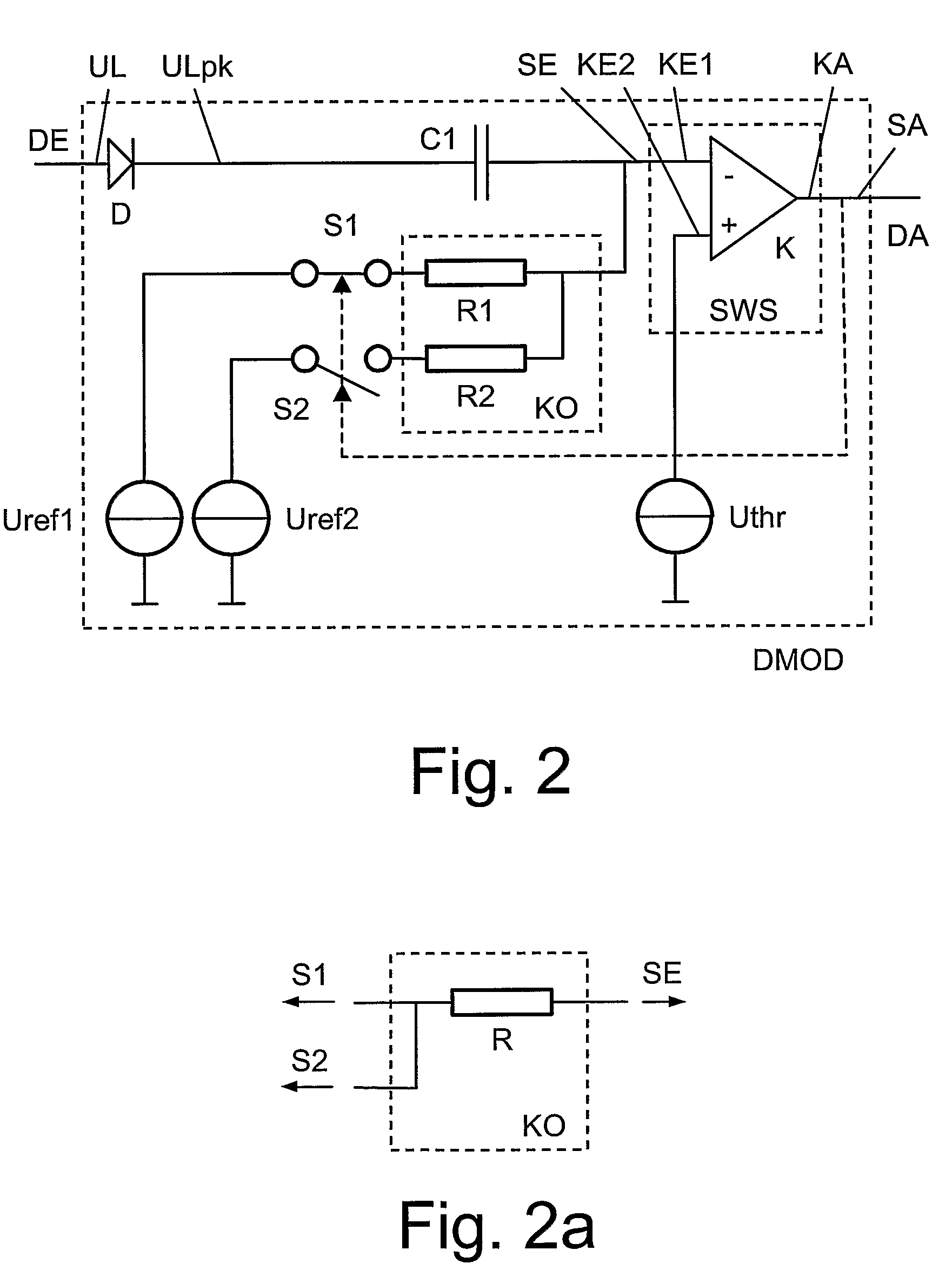
A demodulator circuit (DMOD) for amplitude-modulated signals is defined which comprises a threshold switch module (SWS), wherein a signal output (SA) of the threshold switch module (SWS) is connected to the output (DA) of the demodulator circuit (DMOD) and a signal input (SE) of the threshold switch module (SWS) is connected via a first capacitor (C1) to the input (E) of the demodulator circuit (DMOD). In addition, the signal input (SE) can be connected via a coupling element (KO) to a first or alternatively a second.
Owner:NXP BV
Semiconductor device
InactiveCN101548286AStable jobReduce the impact of noiseTransistorAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsElectrical polarityEngineering
A demodulation signal is generated by provision of a demodulation signal generation circuit to the semiconductor device capable of wireless communication and by obtainment of a difference between voltages having opposite polarities by the demodulation signal generation circuit. Alternatively, a plurality of demodulation signal generation circuits and a selective circuit which selects a demodulation signal generation circuit depending on characteristics of a received signal are provided, where operation of a second demodulation signal generation circuit stops when a first demodulation signal generation circuit is operated. The selective circuit includes an inverter circuit, a flip-flop circuit, and a selector circuit. When the second demodulation signal generation circuit has a comparator and the like, power consumption thereof is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
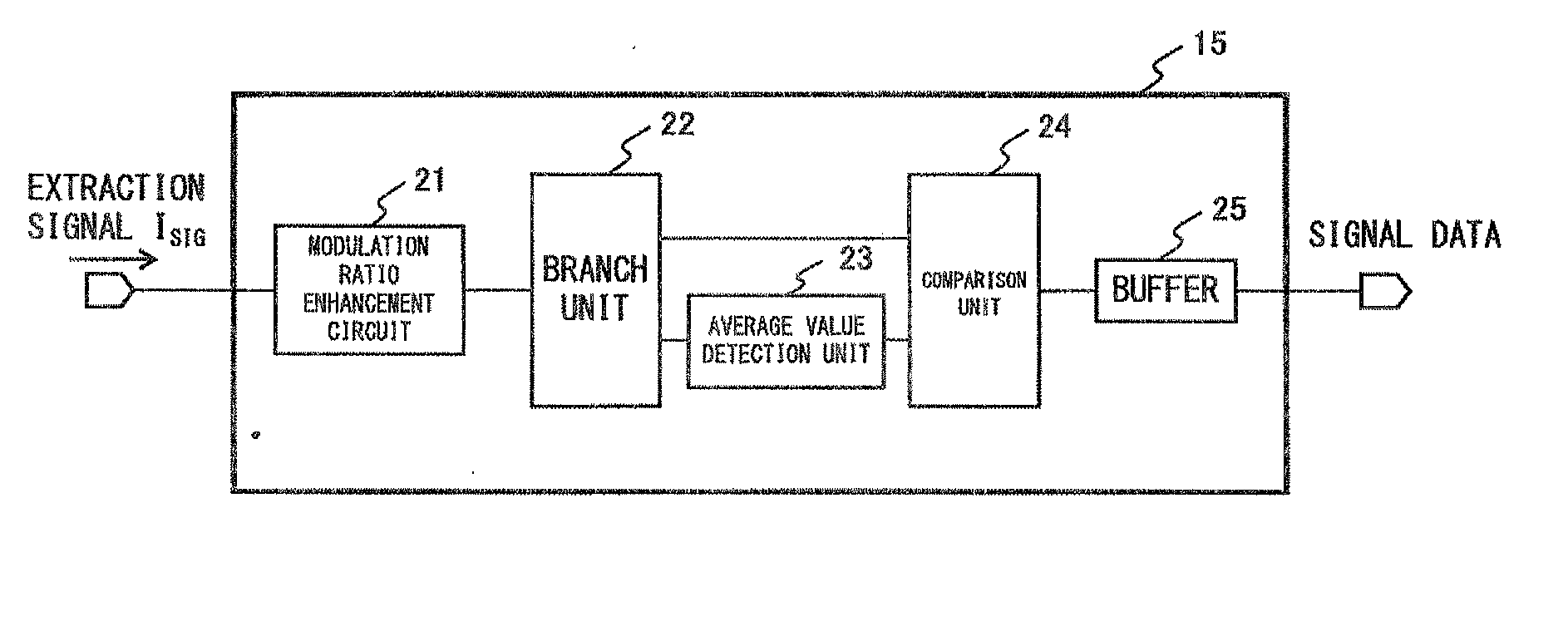
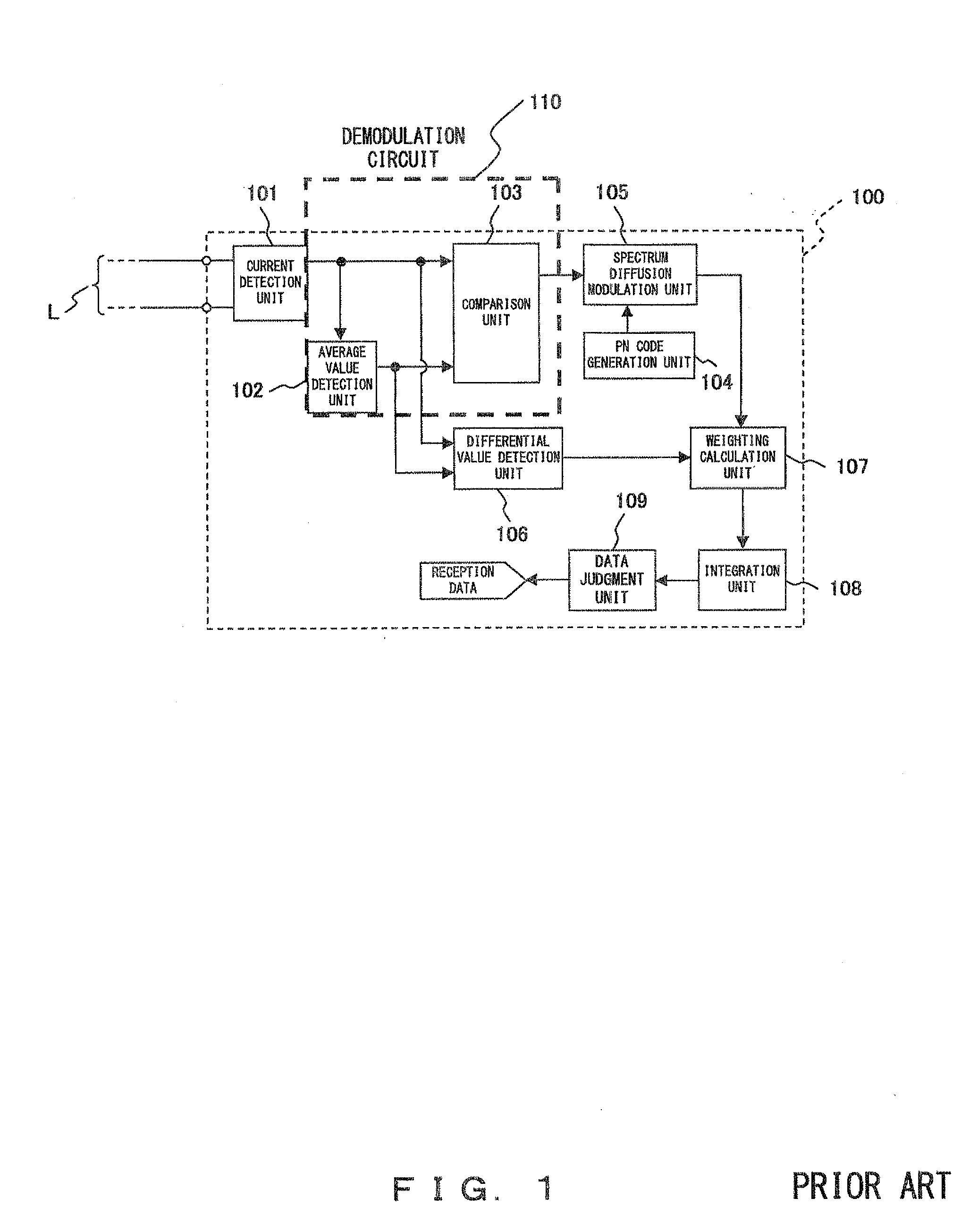
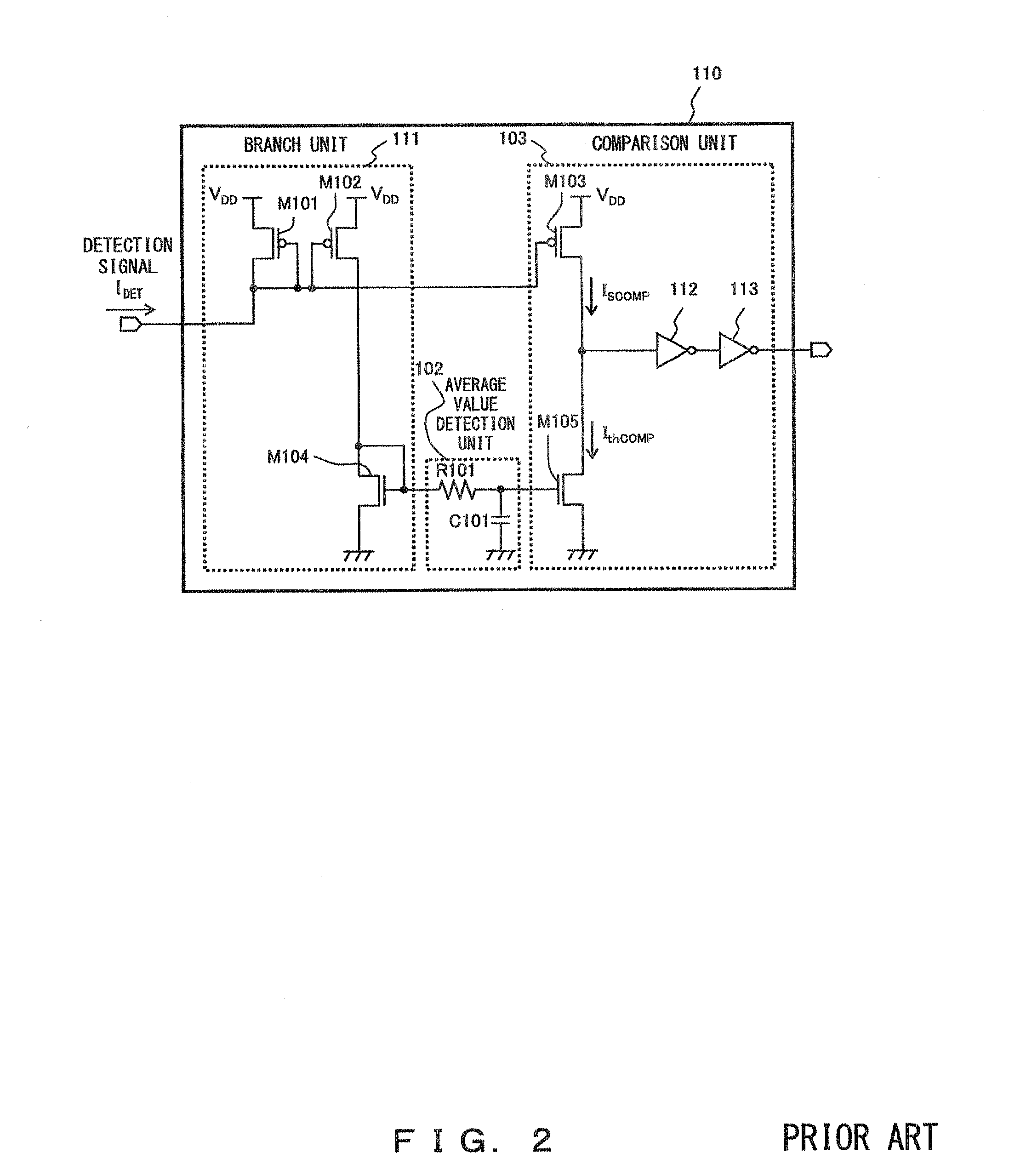
Demodulation circuit
InactiveUS20080224766A1Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsEngineeringComparator
A modulation ratio enhancement circuit increases the modulation ratio of a current signal which is ASK-modulated with signal data. A branch unit, an average value detection unit, a comparator and a buffer constitute a demodulation unit so that the signal data is demodulated from a current signal of which the modulation ratio is increased by the modulation ratio enhancement circuit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Envelope detector circuit
ActiveUS9360504B2Constructed small and simpleSensitive highAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsMemory record carrier reading problemsDetector circuitsEngineering
An envelope detector circuit, suitable for use in RFID tags, includes a voltage doubler circuit and a biasing voltage generating circuit which comprises components matched respectively to rectifying components of the voltage doubler circuit. A rectifying component of this voltage doubler circuit is formed by a transistor controlled by the biasing voltage generating circuit which provides a biasing voltage to a control gate of this transistor, the biasing voltage generating circuit being arranged so as to permit a determined forward biasing current to flow through the transistor and further rectifying elements of the voltage doubler circuit. This embodiment provides fast, highly sensitive detection of envelope waveforms in input signals. Thanks to the matched rectifying components, efficiency variations due to variations in manufacturing process can be eliminated. The envelope detector circuit is further arranged for maintaining a stable detection independent of variations in temperature.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Demodulator for Amplitude-Modulated Signals
ActiveUS20080246541A1Reduce areaSeparate componentAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsMemory record carrier reading problemsCouplingCapacitor
A demodulator circuit (DMOD) for amplitude-modulated signals is defined which comprises a threshold switch module (SWS), wherein a signal output (SA) of the threshold switch module (SWS) is connected to the output (DA) of the demodulator circuit (DMOD) and a signal input (SE) of the threshold switch module (SWS) is connected via a first capacitor (C1) to the input (E) of the demodulator circuit (DMOD). In addition, the signal input (SE) can be connected via a coupling element (KO) to a first or alternatively a second
Owner:NXP BV
Am (amplitude modulation) demodulation system for RFID reader device
ActiveUS20100328041A1Improve filtering effectSimple and cheap configurationAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsAmplitude demodulation detailsEngineeringDemodulation
An RFID reader device (31), of the type comprising a demodulator (6) for receiving from a RFID tag (11) an AM (Amplitude Modulation) wave (20) having a predetermined frequency (f) and for retrieving, from the AM wave (20), a demodulated output (6a) associated to predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes of said AM wave (20), said demodulated output having a portion with a frequency F. The AM demodulation system comprises at least a second demodulator (26) for receiving the AM wave (20) and retrieving a second demodulated output (26a) associated to Amplitudes opposite to the predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes, said second demodulated output having a portion with said frequency F; the RFID reader includes a block (27) having, in input, the demodulated output (6a) and the second demodulated output (26a) and returning, in output, an enforced demodulated output (30) with a portion with frequency (f1) doubled with respect to said frequency (F).
Owner:DATAMARS
Demodulator
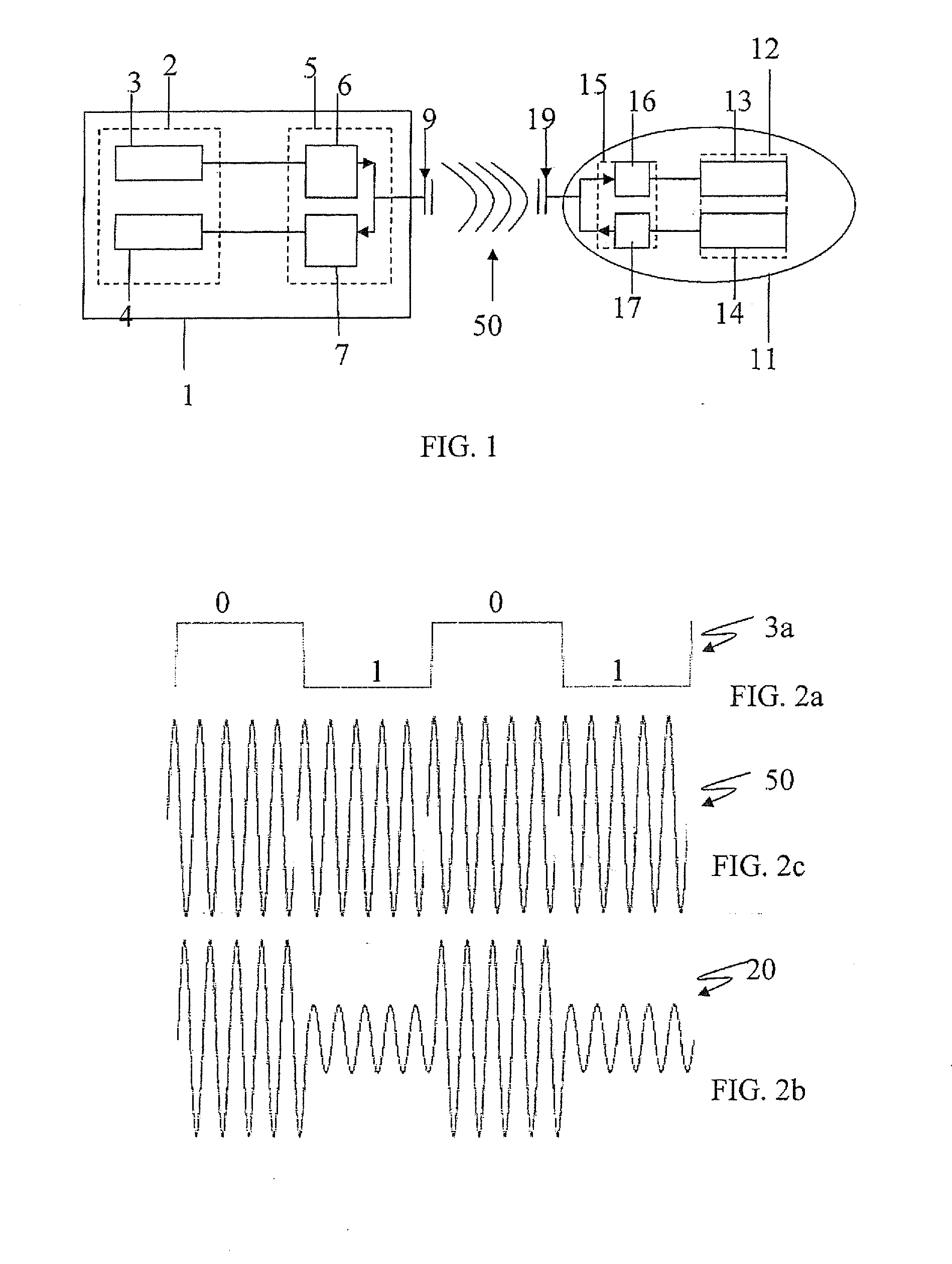
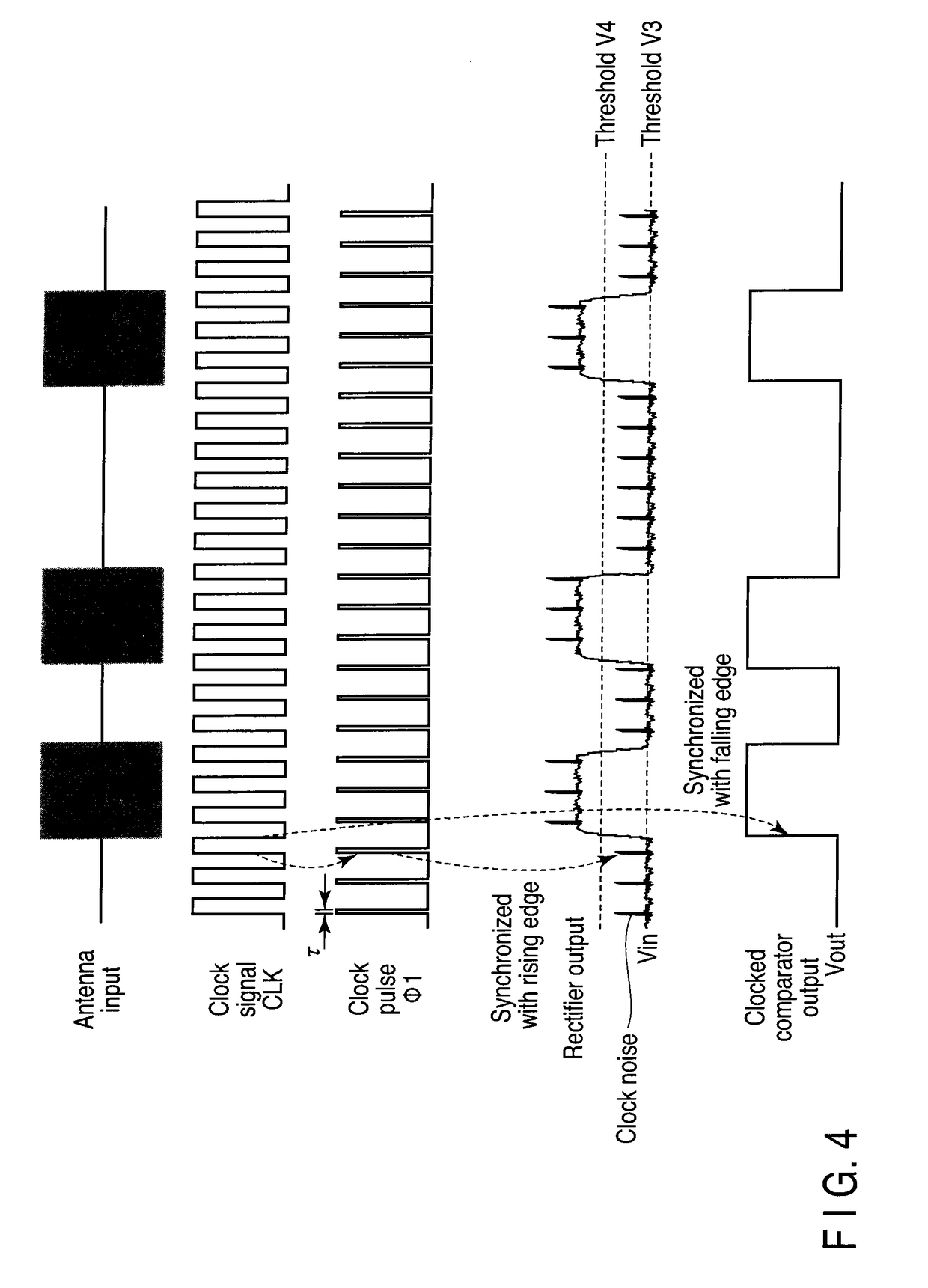
InactiveUS7907006B2Pulse automatic controlAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsEngineeringComparator
According to one embodiment, a threshold adjusting apparatus for a clocked comparator, the clocked comparator comparing an input signal with a threshold in accordance with a clock, the threshold adjusting apparatus comprises an output detection module configured to detect an output from the clocked comparator with the threshold while changing the threshold and a setting module configured to set the threshold when the output detection module detects a change in the output from the clocked comparator as an adjusted threshold.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
AM (amplitude modulation) demodulation system for RFID reader device
ActiveUS8159291B2Improve filtering effectSimple and cheap configurationAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsRope driveEngineeringDemodulation
An RFID reader device (31), of the type comprising a demodulator (6) for receiving from a RFID tag (11) an AM (Amplitude Modulation) wave (20) having a predetermined frequency (f) and for retrieving, from the AM wave (20), a demodulated output (6a) associated to predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes of said AM wave (20), said demodulated output having a portion with a frequency F. The AM demodulation system comprises at least a second demodulator (26) for receiving the AM wave (20) and retrieving a second demodulated output (26a) associated to Amplitudes opposite to the predetermined positive or negative Amplitudes, said second demodulated output having a portion with said frequency F; the RFID reader includes a block (27) having, in input, the demodulated output (6a) and the second demodulated output (26a) and returning, in output, an enforced demodulated output (30) with a portion with frequency (f1) doubled with respect to said frequency (F).
Owner:DATAMARS
Differential input circuit with process variation and temperature compensation
InactiveUS7611066B2Amplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsRecord carriers used with machinesFoundryPower semiconductor device
Systems with semiconductor devices that are DC-biased at either their weak inversion (i.e., sub-threshold) region or their strong inversion region. In a preferred embodiment using semiconductor devices (e.g., NMOS, PMOS, etc.), a gate to source voltage (Vgs) is slightly below the threshold voltage (Vtn) of the device. These weakly turned-on semiconductor devices increase the receiving AC sensitivity of an AM-Detector compared to that of a conventional AM-Detector without any DC-biasing. Further, the compensating bias voltage (Vbias) compensates for one or both of the ambient temperature change and the foundry's process variation of the various semiconductor devices.
Owner:ZEST LABS INC
Temperature compensated, high efficiency, controlled input impedance diode detector
A diode detector comprising a detector network adapted to detect and multiply the detected voltage coupled to a divider network that comprise diodes in equal number to the number of diodes in the detector network, provides a passive detector applicable to any application requiring a small, efficient, high output, inexpensive temperature compensated detector for use as demodulator or as power to voltage converter. Integrating a portion of the divider network in the detector / multiplier network allows control over the minimum input impedance of the detector.
Owner:VECTRON INT INC
Wireless power reception device and wireless communication method
ActiveUS10615643B2Smooth communicationAmplitude demodulation by non-linear two-pole elementsElectric powerTelecommunicationsSignal strength
A wireless power reception device and a wireless communication method thereby are provided. The wireless communication method by the wireless power reception device may comprise the steps of: receiving a wireless power signal from a wireless power transmission device; measuring the strength of the wireless power signal; modulating the amplitude of the wireless power signal according to the measured strength of the wireless power signal; and performing communication with the wireless power transmission device by using the signal having the amplitude modulated.
Owner:GE HYBRID TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com