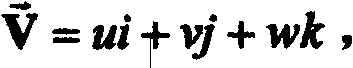Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Viscous dissipation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The viscous dissipation is an effect due to which heat is generated inside the medium. The presence of radiation further complicates the heat transfer behavior inside porous medium.
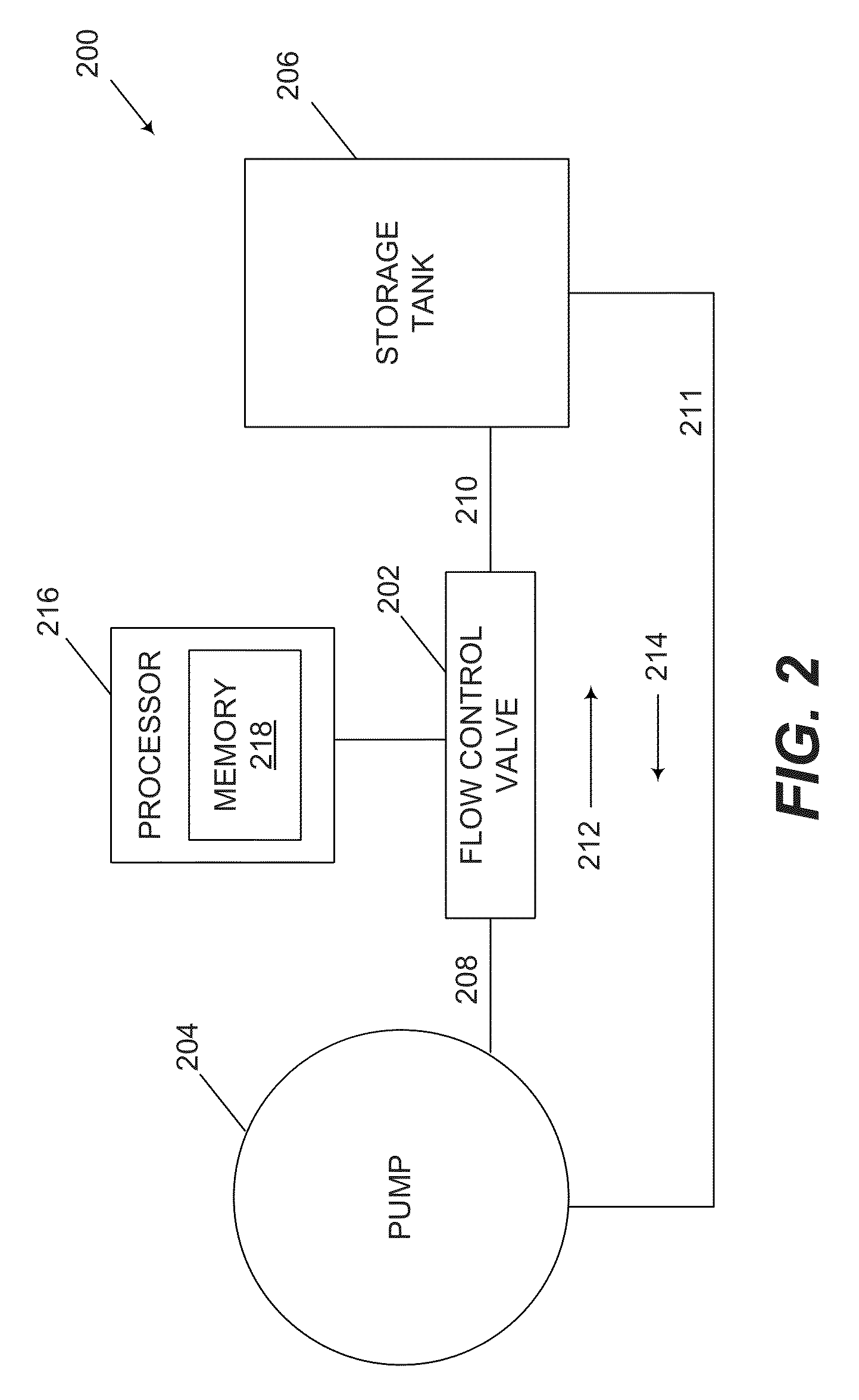
Systems and Methods for a Control Valve
InactiveUS20130247995A1Increasing and decreasing flow rateReduce leakageUsing liquid separation agentValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringViscous dissipation
Embodiments of the invention relate to systems, methods, and apparatuses for a control valve. In one embodiment, a valve can be provided. The valve can include a flow restrictor portion operable to generate a pressure drop in a fluid flow by viscous dissipation; a throttle portion operable to change a flow rate of the fluid; and a guard portion operable to separate the flow restrictor portion from the throttle portion.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Device and method for measuring steady-state extrusion viscous dissipation of micro-scale polymer fused mass
InactiveCN101532939AAccurate temperature controlEasy loading and unloadingDirect flow property measurementTemperature controlViscous dissipation
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring steady-state extrusion viscous dissipation of a micro-scale polymer fused mass. The device and the method are characterized in that on the basis of a capillary rheometer with two material barrels, a temperature sensor is arranged at an outlet of a neck ring mold of a capillary tube in the material barrel through a fixing device, the outlet of the neck ring mold of the capillary tube is aligned with a measuring part of the temperature sensor, and the distance between the neck ring mold of the capillary tube and the sensor is adjusted by additionally mounting a spacer; and the other temperature sensor is arranged at the outlet of the other material barrel through the fixing device for the convenience of measuring the temperature of the fused mass simultaneously by the two sensors. The flow parameters of the fused mass are set on the rheometer, the fused mass flows out of the neck ring mold at certain shearing rate through by the extrusion action of a plunger, and the sensors measure the temperature of the extruded fused mass directly. The temperature difference of the two sensors is calculated out so that the temperature rise of the fused mass caused by the viscous dissipation can be measured. The device and the method has the advantages and benefits that the temperature control of the fused mass is constant, the temperature is measured accurately and quickly, the fixing device is easy to assemble and disassemble, the neck ring mold is convenient to replace, and the range of measuring the shearing rate is higherwider.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Paint spray mist coagulant for circulating water treatment system of paint spray booth
InactiveCN103723812AStrong neutralityWide variety of sourcesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationPotato starchLacquer
The invention relates to a paint spray mist coagulant which shows a good effect on viscous dissipation and coagulation for a solvent-based coating and a water soluble coating. The paint spray mist coagulant is especially applicable to circulating water treatment of a wet type paint spray mist removal system. The paint spray mist coagulant comprises an agent A, an agent B and an agent C, wherein the agent A is a linear high-molecular polymer which has high electric neutrality and can quickly neutralize the paint particle charge and warp the paint particles to realize viscous dissipation; the agent B is an aqueous solution prepared through etherified modified potato starch waste residues with molecular weight of 50,000 to 60,000, which enables the viscosity-free paint particles to be collected; the agent C is used for regulating the pH (Power of Hydrogen) of the circulating water. The invention also provides a preparation method and application of the paint spray mist coagulant. The paint spray mist coagulant is simple in preparation method and convenient in application; the potato starch waste residues are utilized as the raw materials of the agent B, so that the secondary utilization of wastes is realized, and the effect of treatment of wastes with processes of wastes against one another is reached; in addition, the paint spray mist coagulant has the biodegradability so that secondary pollution caused by the application in water can be avoided, and the environmental load can also be reduced effectively.
Owner:尹志华 +3
Vorticity refinement used in numerical simulation of incompressible swirling flow field
InactiveCN102682192AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringViscous dissipation
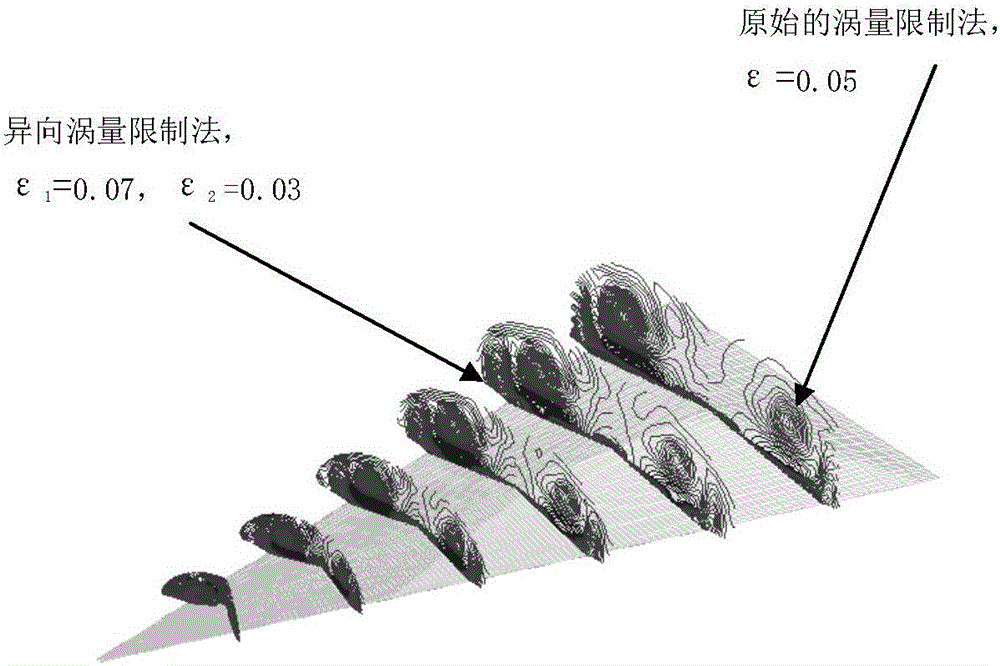
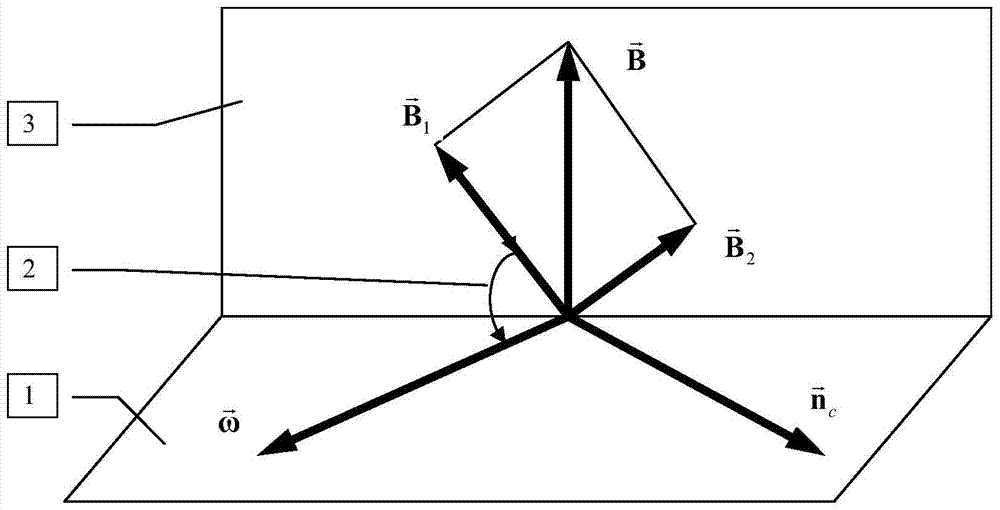
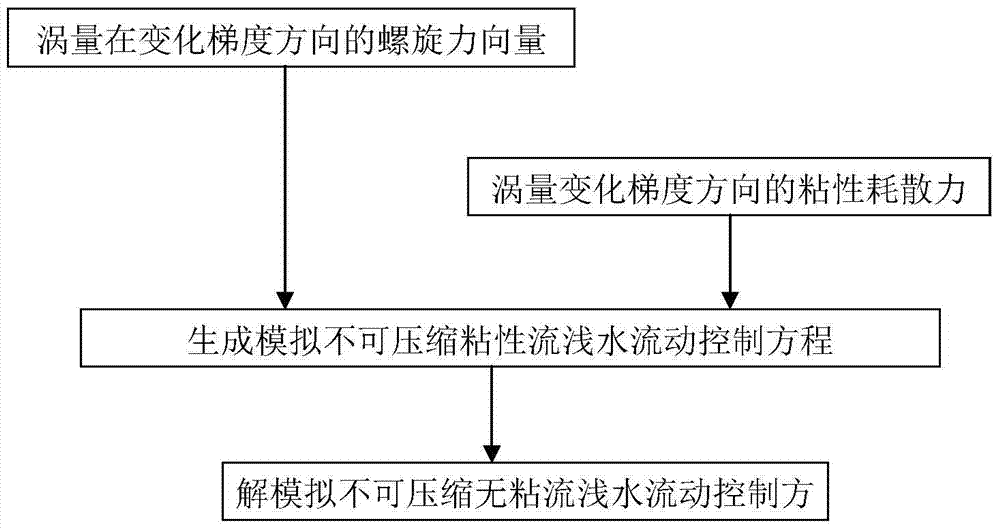
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method for the vortex motion of an incompressible flow, being called as vorticity refinement. According to the characteristics of the incompressible flow, two different forms of forces are added to a momentum equation so that the precision of the numerical simulation of a flow field based on the vortex motion. The two forms of forces are respectively a spiral force and a viscous dissipation force of vorticity in the varying gradient direction. The numerical simulation method leads the integral computation of the spiral force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the varying gradient direction to be converted into the flux computation of a superior force on a boundary of the computational grid and can lead the spatial dispersion of the superior force to have a high-order accuracy format; simultaneously, a source item of the momentum equation reserves the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction for increasing the convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forces adopt different amplification coefficients so that the accuracy of the vorticity can be further remained, and the vortex motion in the flow field can be more accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Composite-film bearings
InactiveUS20070206891A1Superior minimizationImprove protectionBearing componentsSliding contact bearingsFriction reductionComposite film
Hydrodynamic bearings providing reduced friction are provided. The bearings include a load-transferring element and a porous bearing pad spaced from the load-transferring element. The load-transferring element is provided with a high-viscosity lubricant. The porous bearing pad is saturated with a low-viscosity lubricant. The high-viscosity lubricant and the low-viscosity lubricant are drawn into the clearance space by hydrodynamic action to form a bi-component lubricant film. The bi-component lubricant film includes a high-viscosity film layer and a low-viscosity film layer, which provide reduced viscous dissipation as well as proper cooling and lubrication.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
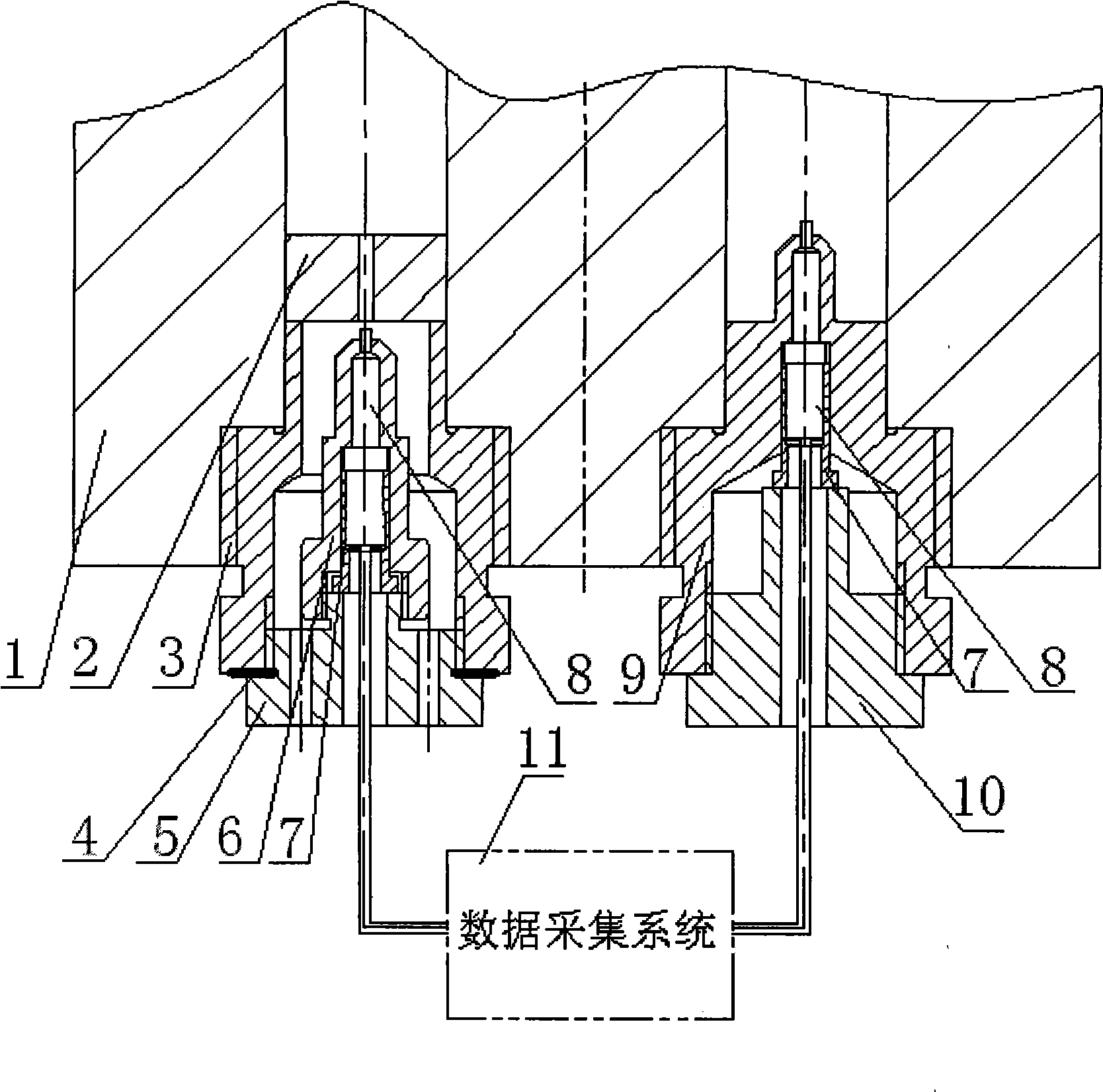
Viscous dissipation measuring device and measuring method
The invention relates to a viscous dissipation measuring device and a measuring method, relating to a micro-scale polymer melt steady state extrusion flowing viscous dissipation measuring device and a measuring method and aiming at solving the problem that the measuring precision is low due to adoption of contact type temperature measurement in the prior art; and the measuring device comprises a rheometer charging barrel, a capillary orifice mould, a temperature sensor I, a temperature sensor II, a fixing device I, a fixing device II and a data acquisition system, wherein an annular groove is arranged at the periphery of a central round hole of the capillary orifice mould and opened downwards, extruded polymer melt is fully filled in the annular groove of the capillary orifice mould under the action of pressure, and the extruded polymer melt is utilized to fill the annular groove, so that the heat loss of viscous dissipation is reduced. The device and the method provided by the invention utilize a novel design of the capillary orifice mould, the heat generated by the melt viscous dissipation is not carried away by the capillary orifice mould, and therefore, the precision of measuring the average temperature rise of the viscous dissipation is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in swirling flow field
InactiveCN103064996AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention provides a numerical method for simulating pollutant dispersion in a swirling flow field. According to characteristics of incompressible flows, two forms of force are added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation accuracy of the vortical-motion-oriented flow field. The two forms of force are respectively vortical force and viscous dissipation force of a vorticity in the changing gradient direction. The numerical method enables integral calculation of the vortical force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the changing gradient direction to be converted into flux calculation of force on a boundary of the computational grid and can enable spatial dispersion to have a high-order accuracy form. In addition, the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the changing gradient direction is retained by a source item of the momentum equation so as to improve convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forms of force adopt different amplification coefficients, the accuracy of the vorticity can be further kept, and pollutant dispersion movement in the swirling flow field can be accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Numerical method for simulating wingtip vortex flow of aircraft
InactiveCN102930134AHigh precisionFast convergenceAerodynamics improvementSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumEngineering
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Sandwich energy absorption device
InactiveCN104441802AImprove vibration resistanceImprove impact resistanceCeramic layered productsEnergy absorptionAbsorbed energy
The invention provides a sandwich energy absorption device which comprises an upper panel, a lower panel, side plates and a core plate layer, wherein enclosed space defined by the upper panel, the lower panel and the side plates is filled with the core plate layer. The sandwich energy absorption device is characterized in that the core plate layer comprises a brittle blasting layer and core materials inlaid in the brittle blasting layer; and space between the core materials and the brittle blasting layer is filled with a shear thickening fluid. When the energy absorption device is penetrated by a bullet, the panels and the side plates absorb energy firstly, then the bullet penetrates through the brittle blasting layer, the brittle blasting layer is cracked, and bullet energy is further absorbed; and meanwhile, the shear thickening fluid flows rapidly in the brittle blasting layer deformation process, and energy is dissipated through viscosity; and shock resistance and impact resistance of the sandwich energy absorption device are improved.
Owner:INST OF MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
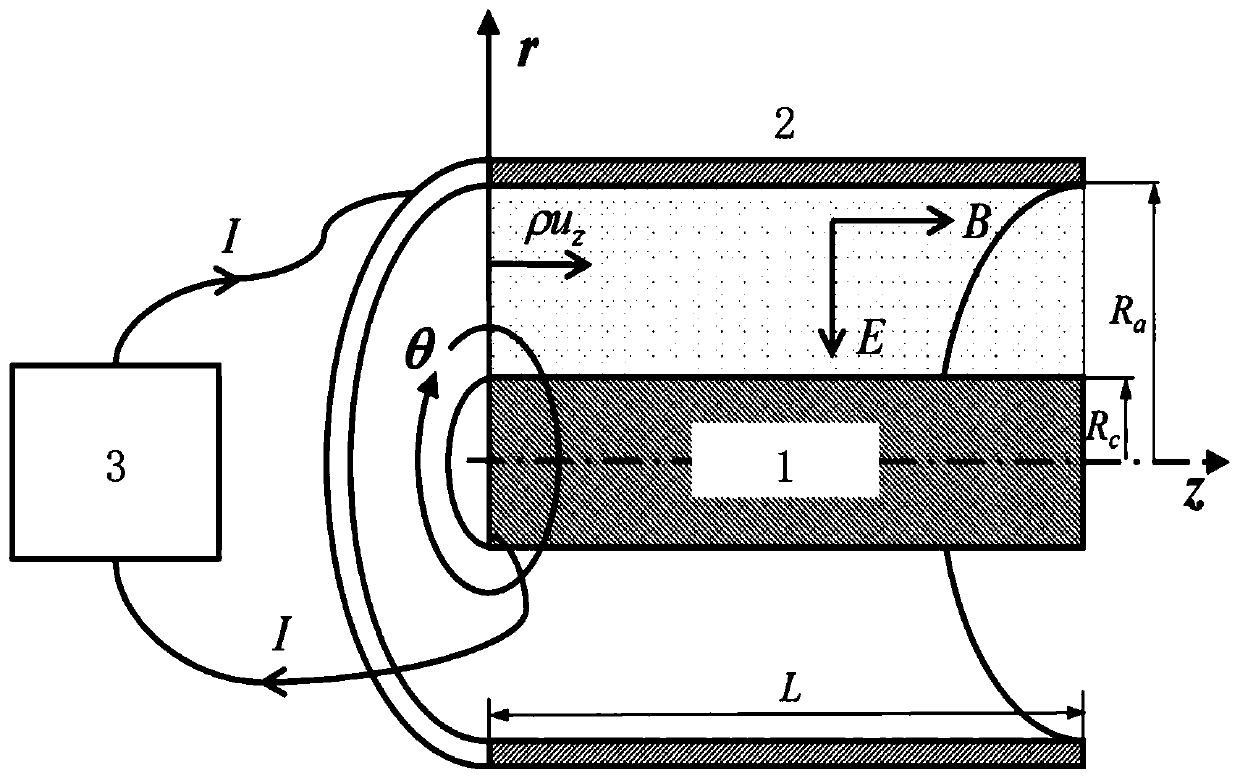
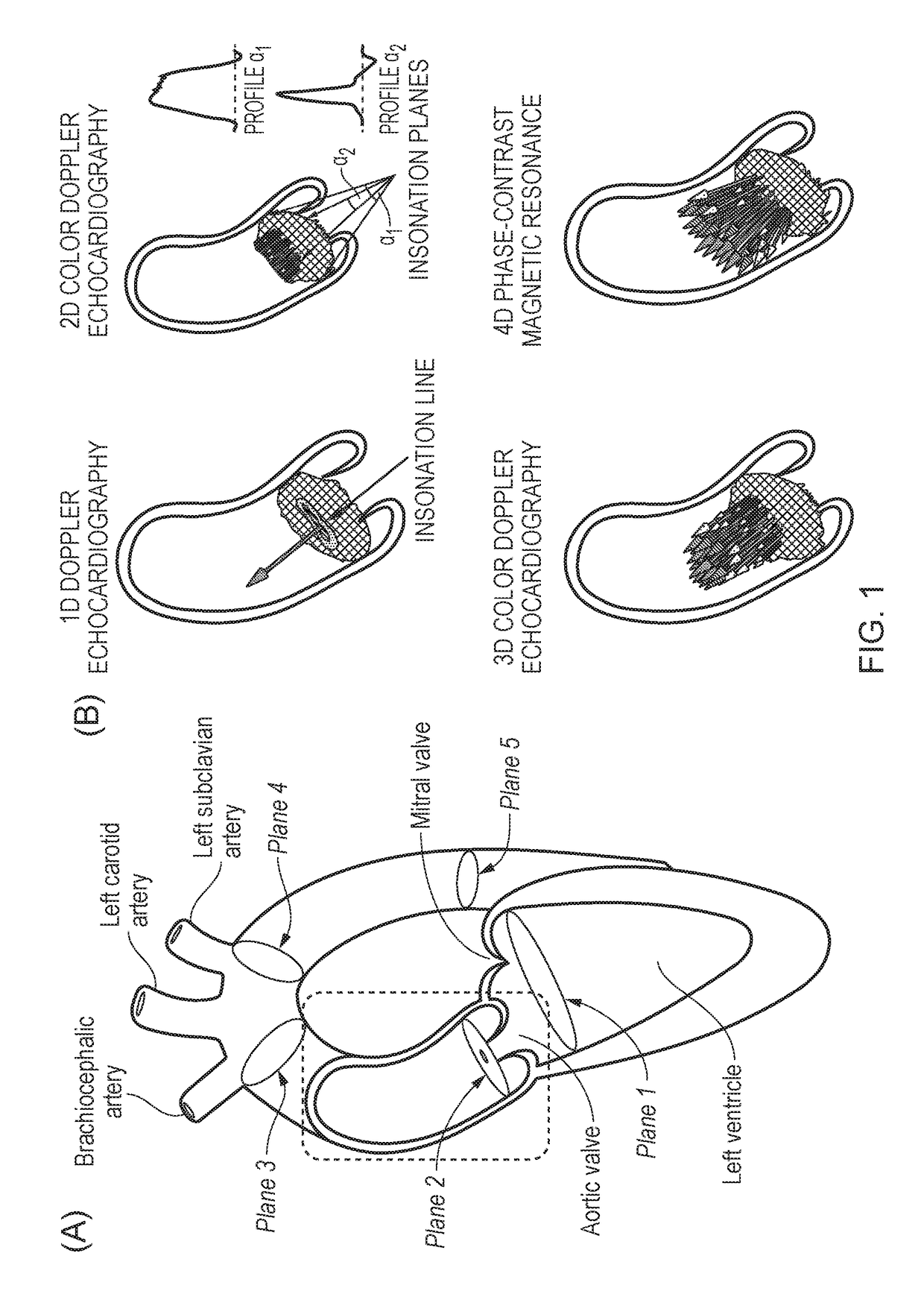
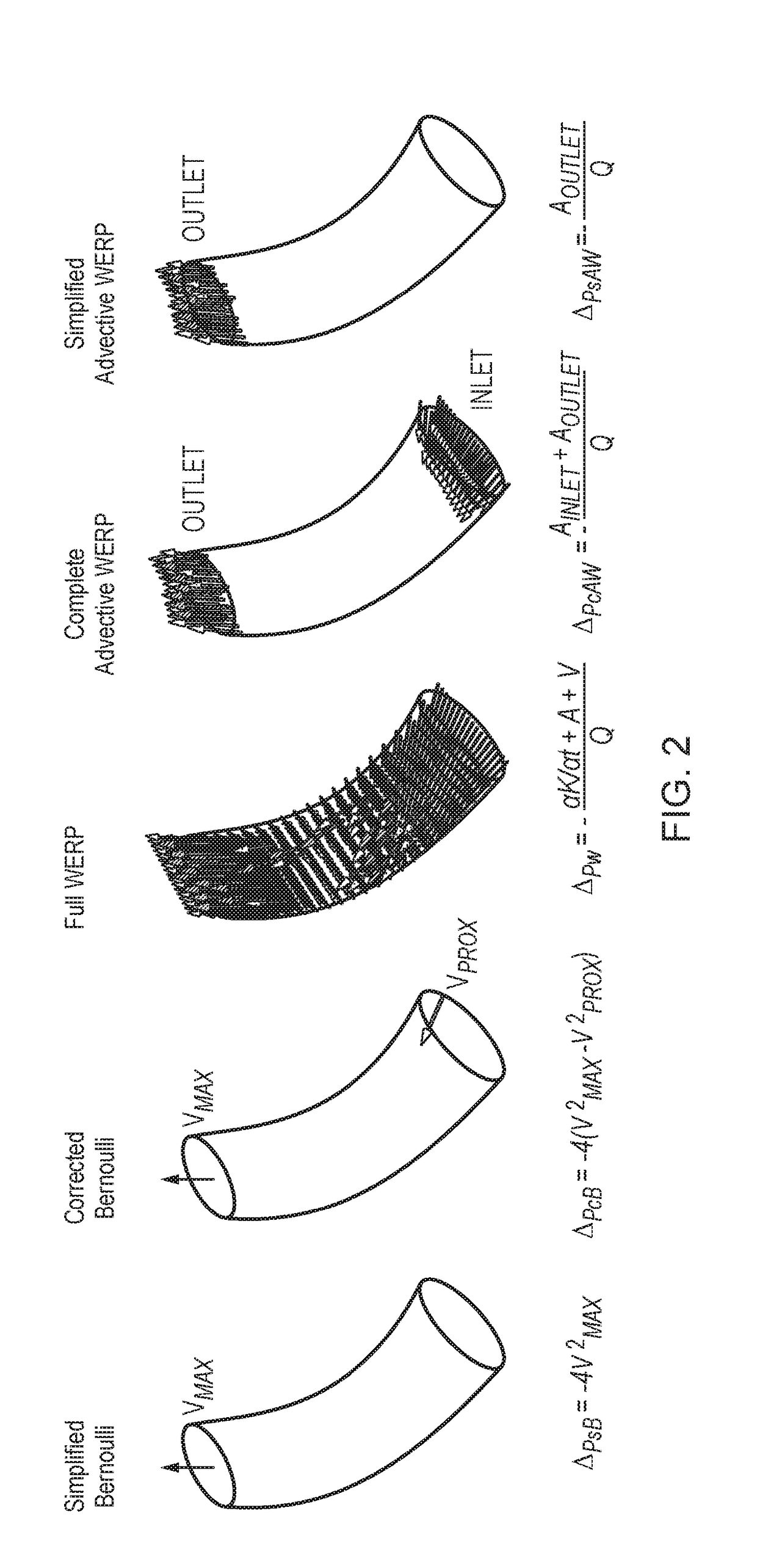
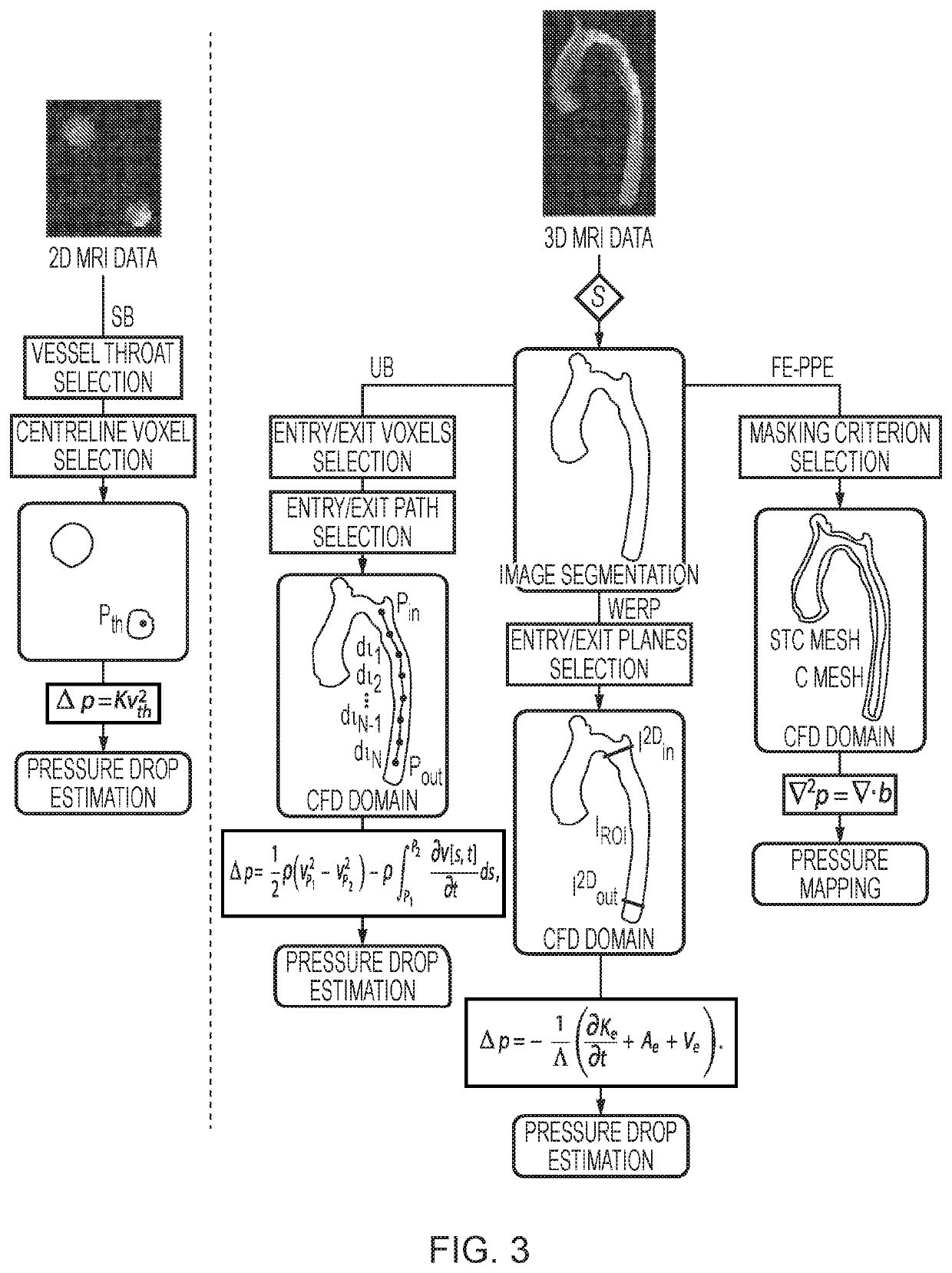
Method and system for pressure drop estimation
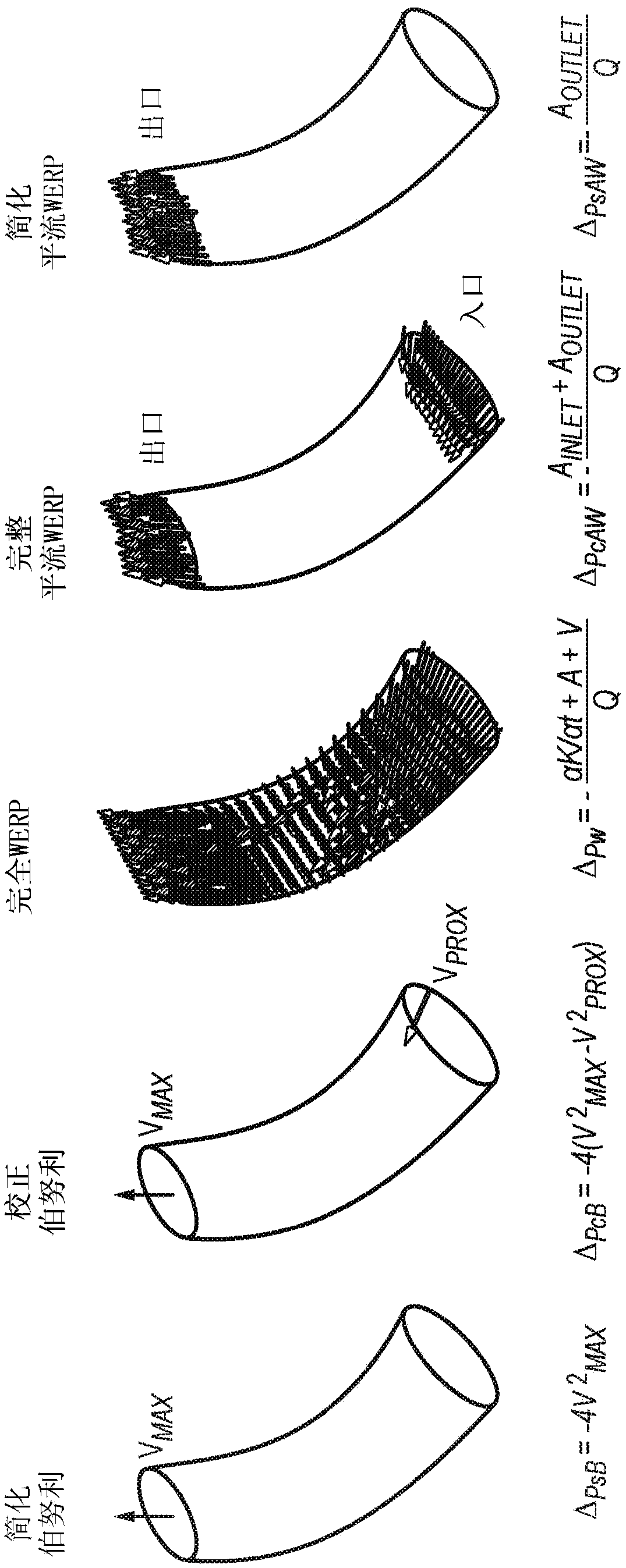
Embodiments of the invention provide a method of determining pressure difference across a tube arising from fluid flow within the tube, comprising: obtaining three- dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data at a plurality of points along the tube; processing the three-dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data to determine: i) a flow rate (Q) of the fluid through the tube; ii) the kineticenergy (K) of the fluid flow through the tube; iii) an advective energy rate (A) of the fluid flow through the tube; and iv) a viscous dissipation rate (V) pertaining to the fluid flow; and calculating the pressure difference in dependence on all of the flow rate (Q), kinetic energy (K), advective energy rate (A), and viscous dissipation rate (V). Further embodiments are also described.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Numerical method for simulating incompressible swirl flow field of aircraft with low span-chord ratio
InactiveCN106326514AGuaranteed accuracySimulation is accurateSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention discloses a numerical method for simulating an incompressible swirl flow field of an aircraft with a low span-chord ratio. Two forces in different forms are added in a momentum equation according to the characteristics of incompressible flow, so that the numerical simulation precision of a swirl motion-based flow field is improved. The forces in two forms are a helical force with vorticity in a changed gradient direction and a viscous dissipation force with vorticity in the changed gradient direction respectively. According to the method, the integral computation for computing the helical force with the vorticity in the changed gradient direction in a grid is converted into the flux computation for calculating a force on the boundary of the grid, and the spatial discretization can be enabled to have a format of high-order precision. The two forces adopt different amplification coefficients, so that the precision of the vorticity can be further kept and the swirl motion in the flow field can be simulated more accurately.
Owner:成都金景盛风科技有限公司
Thermoacoustic heat regenerator based on surface acoustic wave generator
InactiveCN106338164AImprove ferroelectric propertiesImprove photoelectric performanceMachines/enginesSuperheatersThermoacousticsNatural convection
The invention relates to a novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator capable of improving thermoacoustic heat regenerator heat regenerating and thermoacoustic transition efficiency; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator can supplement partial viscosity loss energy in the heat regenerator heat exchange process, and can use oscillations formed by surface acoustic waves to convert nature convection on a stack surface into forced convection, thus enhancing heat exchange capability, and improving efficiency; the thermoacoustic heat regenerator comprises a stacked structure heat regenerator and a surface acoustic wave generator, wherein the stacked structure is formed by combining a pres-stamping forming thin plate with a heat regenerator sleeve; the surface acoustic wave generator is formed by using an electron beam to etch a PZT piezoelectric material; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator fully uses the thermoacoustic transition principle, and employs the mature technology, simple structure and low cost features of the stack heat regenerator, thus solving the problems that a conventional heat regenerator is large in viscosity dissipation, not obvious in heat exchange, and poor in efficiency; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator has excellent application values.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Numerical method for simulating rotor flow field of water turbine
InactiveCN106934197AHigh precisionFast convergenceInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumWater turbine
The invention discloses a numerical method for simulating a rotor flow field of a water turbine. According to characteristics of incompressible flow, force in two different forms is added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation precision of a type of flow field based on a vortex motion. The force in the two forms is spiral force and viscous dissipation force of vorticity in a varying gradient direction respectively.
Owner:成都金景盛风科技有限公司
Numerical method for simulating ship propeller wake field
InactiveCN102945293AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumPropeller
The invention relates to a numerical method for simulating a ship propeller wake field. The numerical simulation accuracy of a type of flow fields predominant in vortex motion is improved by forces of two different forms in a momentum equation according to the feature of incompressible flows. The forces of two different forms include a spiral force whose vorticity is in a variable gradient direction and a viscous dissipation force whose vorticity is in the variable gradient direction. The method converts an integral calculation of the spiral force in the calculation grid, of which the vorticity is in the variable gradient direction, into a flux calculation of a force on the boundary of the calculation grid, so that the spatial discretization of the force has a format of higher order accuracy. Meanwhile, the source item of the momentum equation maintains the viscous dissipation force whose vorticity is in the variable gradient direction, so as to improve the convergence and stability of numerical solution. The two forces have different amplification coefficients, so that the accuracy of vorticity can be further maintained, and as a result, the vortex motion of the ship propeller wake field is simulated more accurately.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Vorticity maintaining technology used in numerical simulation of incompressible swirling flow fields
InactiveCN103914608AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention relates to a method for numerical simulation for vortical motion of an incompressible flow. The method is called as a vorticity maintaining technology. According to the characteristics of the incompressible flow, two forces in different forms are added in a momentum equation so as to improve numerical simulation precision of flow fields taking the vortical motion as the main thing. The forces in the two forms are respectively a spiral force of vorticity in the change gradient direction and a viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the change gradient direction. According to the method, integral computation of the spiral force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the change gradient direction is converted into flux computation of force on a computational grid boundary, spatial dispersion of the vorticity can be in a high order precision format, and a source item of the momentum equation retains the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the change gradient direction for improving convergence and stability of a numerical solution. Different amplification coefficients are adopted for the two forces, vorticity precision can be further maintained, and the vortical motion in the flow fields can be simulated more precisely.
Owner:西安远景动力模拟技术有限公司
Method for simulating numerical value of wind power wake
InactiveCN106934202AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsMomentumEngineering
The invention discloses a method for simulating a numerical value of a wind power wake. According to the characteristics of icompressible flows, in a momentum equation, two different forms of force are added to improve the numerical value simulation accuracy of one class of flow field which gives priority to vortex movement. The two forms of force are respectively the spiral force of vorticity in a varying gradient direction and the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction. By use of the method, the integral computation of the spiral force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction in a computational grid is converted into the flux computation of the force on the boundary of the computational grid, and meanwhile, the source item of the momentum equation keeps the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction.
Owner:成都金景盛风科技有限公司
Numerical method for simulating helicopter rotor wakes
InactiveCN103065034AHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention provides a numerical method for simulating helicopter rotor wakes. According to characteristics of incompressible flows, two forms of force are added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation accuracy of the vortical-motion-oriented flow field. The two forms of force are respectively vortical force and viscous dissipation force of a vorticity in the changing gradient direction. The numerical method enables integral calculation of the vortical force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the changing gradient direction to be converted into flux calculation of force on a boundary of the computational grid and can enable spatial dispersion to have a high-order accuracy form. In addition, the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the changing gradient direction is retained by a source item of the momentum equation so as to improve convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forms of force adopt different amplification coefficients, the accuracy of the vorticity can be further kept, and vortical motion of the helicopter rotor wakes can be accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
Novel clean environment-friendly coagulant and production method thereof
InactiveCN106348411ADissolve evenlyAbsorbs a lot of paintWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationEnvironmental resistanceSodium Bentonite
The invention belongs to the field of sewage treatment and particularly relates to a novel clean environment-friendly coagulant and a production method thereof. Given the problems of slow coagulation, bad viscous dissipation effect, water pollution and the like of existing coagulant, the invention provides a novel clean environment-friendly coagulant and a production method thereof. The novel clean environment-friendly coagulant consists of the following components in percentage by weight: 10-15% of organic modified bentonite, 15-20% of modified chitosan, 10-12% of modified starch, 3-5% of sodium carbonate, 1-2% of baking soda and the balance of water. The production method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding the baking soda, sodium carbonate, modified starch, modified chitosan and organic modified bentonite into the water; and adjusting the pH to obtain the novel clean environment-friendly coagulant. In the invention, the coagulation speed of the coagulant is high, the viscous dissipation effect is good, and water pollution is avoided; and moreover, the production raw materials are easily available, the operation is easy, and the production cost is saved.
Owner:王家财 +1
Efficiency evaluation method of plasma vortex generator
ActiveCN110705007AFast and accurate calculationFast convergenceElectrical testingDesign optimisation/simulationJoule dissipationViscous dissipation
According to the efficiency evaluation method for the plasma vortex driving device, the effects of viscous force, Lorentz force and inertia force on plasmas in a two-dimensional space are comprehensively considered, and the relation among viscous dissipation, joule dissipation and output vortex kinetic energy can be measured; the two-dimensional infinite series analytic expression convergence of the evaluation method is rapid, the convergence speed is irrelevant to the plasma physical property parameters, the device current and the magnetic field intensity, the efficiency of the vortex drivingdevice can be accurately and rapidly calculated, and then guidance can be provided for device efficiency optimization under wide working conditions.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and System for Pressure Drop Estimation
Embodiments and aspects described herein provide a method of determining pressure difference across a tube arising from fluid flow within the tube, comprising: obtaining three-dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data at a plurality of points along the tube; processing the three-dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data to determine: i) a flow rate (Q) of the fluid through the tube; ii) the kinetic energy (K) of the fluid flow through the tube; iii) an advective energy rate (A) of the fluid flow through the tube; and iv) a viscous dissipation rate (V) pertaining to the fluid flow; and calculating the pressure difference in dependence on all of the flow rate (Q), kinetic energy (K), advective energy rate (A), and viscous dissipation rate (V). Further embodiments and aspects are also described.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Numerical method for simulating cycle stress of bridge pier
InactiveCN106934203AHigh precisionFast convergenceInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsViscous dissipationGradient direction
The invention discloses a numerical method for simulating a cycle stress of a bridge pier. According to characteristics of incompressible flow, force in two different forms is added in a momentum equation to improve numerical simulation precision of a type of flow field based on a vortex motion. The force in the two forms is spiral force and viscous dissipation force of vorticity in a varying gradient direction respectively. According to the method, integral computation of the spiral force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction in a computational grid is converted into flux computation of force on a boundary of the computational grid; and meanwhile, a source item of the momentum equation reserves the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction.
Owner:成都金景盛风科技有限公司
Microscale polymer melt extrusion viscous dissipation measuring method
InactiveCN108469397AReduced viscous dissipative heat lossHigh measurement accuracyDirect flow property measurementPolymer scienceViscous dissipation
The invention discloses a microscale polymer melt extrusion viscous dissipation measuring method, relates to the technical field of polymer polymer rheology testing, in particular relates to the microscale polymer melt extrusion viscous dissipation measuring method, and aims to solve the technical problems that a measuring method is low in accuracy since viscous dissipation heat loss can be causedat an inlet section of a mouth mold when a conventional method is used. The method comprises the following steps: I, mounting a microscale polymer melt extrusion viscous dissipation measuring device;II, putting polymer granules, and setting up a rheometer; III, measuring a primary viscous dissipation temperature; IV, replacing a capillary tube mouth mold, and mounting the measuring device for another time; V, repeating operation of the step II and the step III, and measuring a secondary viscous dissipation temperature; and VI, performing calculation. By adopting a differential method, and through differential calculation, viscous dissipation errors caused at the inlet section of the mouth mold can be eliminated, and the measurement precision of average temperature increase of viscous dissipation can be improved. The method is applied to measurement on polymer melt extrusion viscous dissipation.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A Differential Measurement Method of Viscous Dissipation in Microscale Polymer Melt Extrusion
InactiveCN108469397BReduced viscous dissipative heat lossHigh measurement accuracyDirect flow property measurementPolymer scienceDifferential measurement
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Viscous dissipation measuring device and measuring method
The invention relates to a viscous dissipation measuring device and a measuring method, relating to a micro-scale polymer melt steady state extrusion flowing viscous dissipation measuring device and a measuring method and aiming at solving the problem that the measuring precision is low due to adoption of contact type temperature measurement in the prior art; and the measuring device comprises a rheometer charging barrel, a capillary orifice mould, a temperature sensor I, a temperature sensor II, a fixing device I, a fixing device II and a data acquisition system, wherein an annular groove is arranged at the periphery of a central round hole of the capillary orifice mould and opened downwards, extruded polymer melt is fully filled in the annular groove of the capillary orifice mould under the action of pressure, and the extruded polymer melt is utilized to fill the annular groove, so that the heat loss of viscous dissipation is reduced. The device and the method provided by the invention utilize a novel design of the capillary orifice mould, the heat generated by the melt viscous dissipation is not carried away by the capillary orifice mould, and therefore, the precision of measuring the average temperature rise of the viscous dissipation is high.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Vorticity refinement used in numerical simulation of incompressible swirling flow field
InactiveCN102682192BHigh precisionFast convergenceSpecial data processing applicationsMomentumViscous dissipation
The invention relates to a numerical simulation method for the vortex motion of an incompressible flow, being called as vorticity refinement. According to the characteristics of the incompressible flow, two different forms of forces are added to a momentum equation so that the precision of the numerical simulation of a flow field based on the vortex motion. The two forms of forces are respectively a spiral force and a viscous dissipation force of vorticity in the varying gradient direction. The numerical simulation method leads the integral computation of the spiral force of the vorticity in a computational grid in the varying gradient direction to be converted into the flux computation of a superior force on a boundary of the computational grid and can lead the spatial dispersion of the superior force to have a high-order accuracy format; simultaneously, a source item of the momentum equation reserves the viscous dissipation force of the vorticity in the varying gradient direction for increasing the convergence and stability of a numerical solution. The two forces adopt different amplification coefficients so that the accuracy of the vorticity can be further remained, and the vortex motion in the flow field can be more accurately simulated.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROCODE ENG APPL SOFTWAREDEV
A Method for Evaluating Efficiency of Plasma Vortex Generator
ActiveCN110705007BFast and accurate calculationFast convergenceElectrical testingDesign optimisation/simulationJoule dissipationEngineering
According to the efficiency evaluation method for the plasma vortex driving device, the effects of viscous force, Lorentz force and inertia force on plasmas in a two-dimensional space are comprehensively considered, and the relation among viscous dissipation, joule dissipation and output vortex kinetic energy can be measured; the two-dimensional infinite series analytic expression convergence of the evaluation method is rapid, the convergence speed is irrelevant to the plasma physical property parameters, the device current and the magnetic field intensity, the efficiency of the vortex drivingdevice can be accurately and rapidly calculated, and then guidance can be provided for device efficiency optimization under wide working conditions.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and system for pressure drop estimation
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Thermoacoustic regenerator based on surface acoustic wave generating device
InactiveCN106338164BImprove vibrationImprove heat transfer effectMachines/enginesSuperheatersThermoacousticsNatural convection
The invention relates to a novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator capable of improving thermoacoustic heat regenerator heat regenerating and thermoacoustic transition efficiency; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator can supplement partial viscosity loss energy in the heat regenerator heat exchange process, and can use oscillations formed by surface acoustic waves to convert nature convection on a stack surface into forced convection, thus enhancing heat exchange capability, and improving efficiency; the thermoacoustic heat regenerator comprises a stacked structure heat regenerator and a surface acoustic wave generator, wherein the stacked structure is formed by combining a pres-stamping forming thin plate with a heat regenerator sleeve; the surface acoustic wave generator is formed by using an electron beam to etch a PZT piezoelectric material; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator fully uses the thermoacoustic transition principle, and employs the mature technology, simple structure and low cost features of the stack heat regenerator, thus solving the problems that a conventional heat regenerator is large in viscosity dissipation, not obvious in heat exchange, and poor in efficiency; the novel thermoacoustic heat regenerator has excellent application values.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Pressure Drop Estimation
ActiveUS20220000372A1Satisfactory performance of methodBenefit of simplicityMedical imagingMedical imagesEnergy rateStream flow
Embodiments and aspects described herein provide methods and systems for determining pressure difference across a tube arising from fluid flow within the tube, comprising: obtaining three-dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data at a plurality of points along the tube; processing the three-dimensional time dependent fluid velocity data to determine: i) a flow rate (Q) of the fluid through the tube; ii) the kinetic energy (K) of the fluid flow through the tube; iii) an advective energy rate (A) of the fluid flow through the tube; and iv) a viscous dissipation rate (V) pertaining to the fluid flow; and calculating the pressure difference in dependence on all of the flow rate (Q), kinetic energy (K), advective energy rate (A), and viscous dissipation rate (V). Further embodiments are also described.
Owner:KING'S COLLEGE LONDON
A two-dimensional magnetic liquid vibration absorber with nonlinear energy trap
ActiveCN113719573BCapture vibrational energyFast deliverySpringsNon-rotating vibration suppressionViscous dissipationCopper coil
The invention discloses a two-dimensional magnetic liquid vibration absorber with a non-linear energy trap, comprising four vibration damping units in the directions of two moving degrees of freedom, and its structure is composed of a casing, a dynamic mass and a stator; wherein, the casing is composed of Left end cover, coil lead inlet, cylindrical shell, heat dissipation hole, right end cover, coil lead outlet, sealing ring; dynamic mass consists of left end nut, permanent magnet ring, magnetic conductive block, permanent magnet ring cage, right end nut, micro-nano It is composed of magnetic composite fluid; the stator is composed of a coil cage, a coil winding and a copper coil; the guide component includes a left limit block, a guide shaft, a right limit block and a lubrication groove. Based on the second type of suspension characteristics of the magnetic liquid, the invention realizes the vibration-targeted energy transfer between the nonlinear energy trap and the flow pipeline, and finally dissipates the vibration energy of the flow pipeline through the viscosity of the magnetic liquid.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com