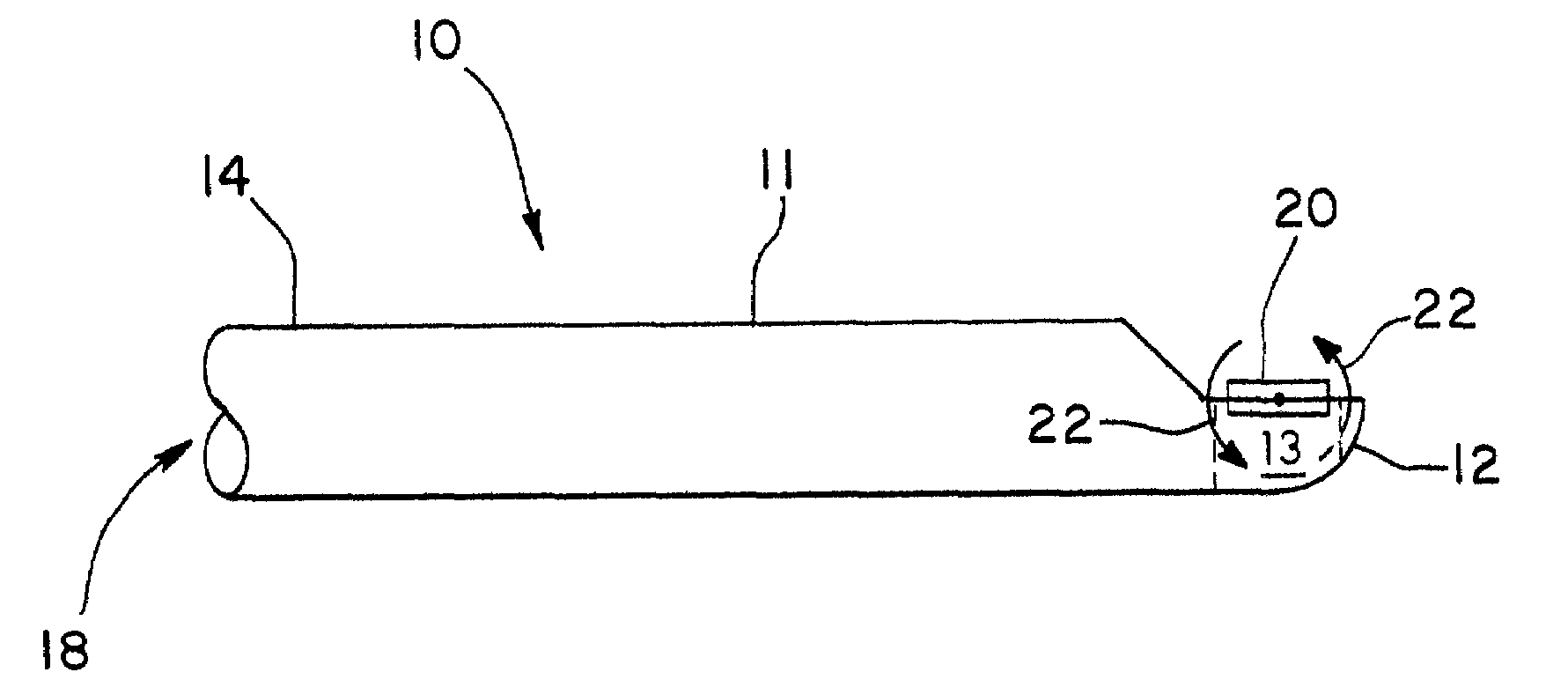
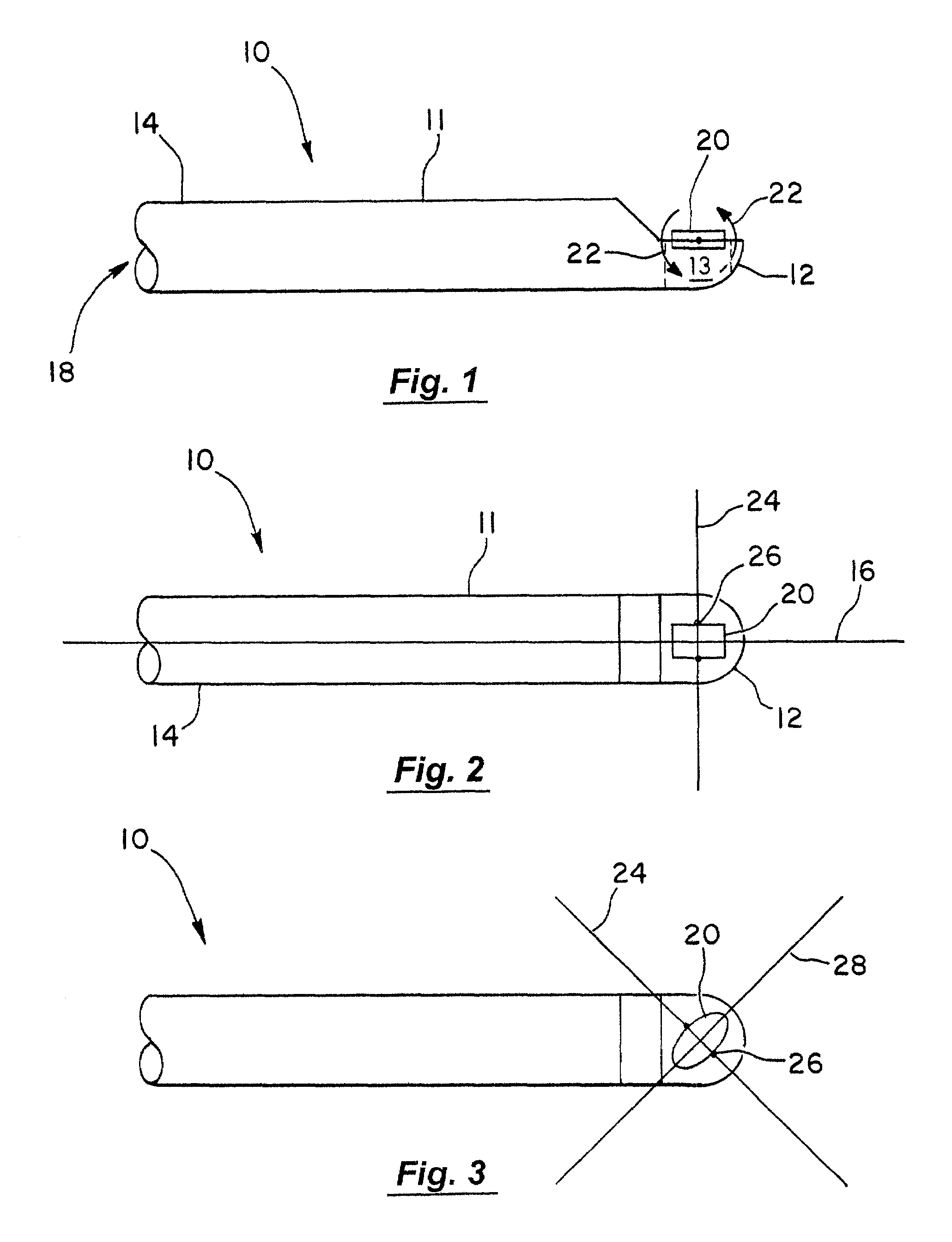
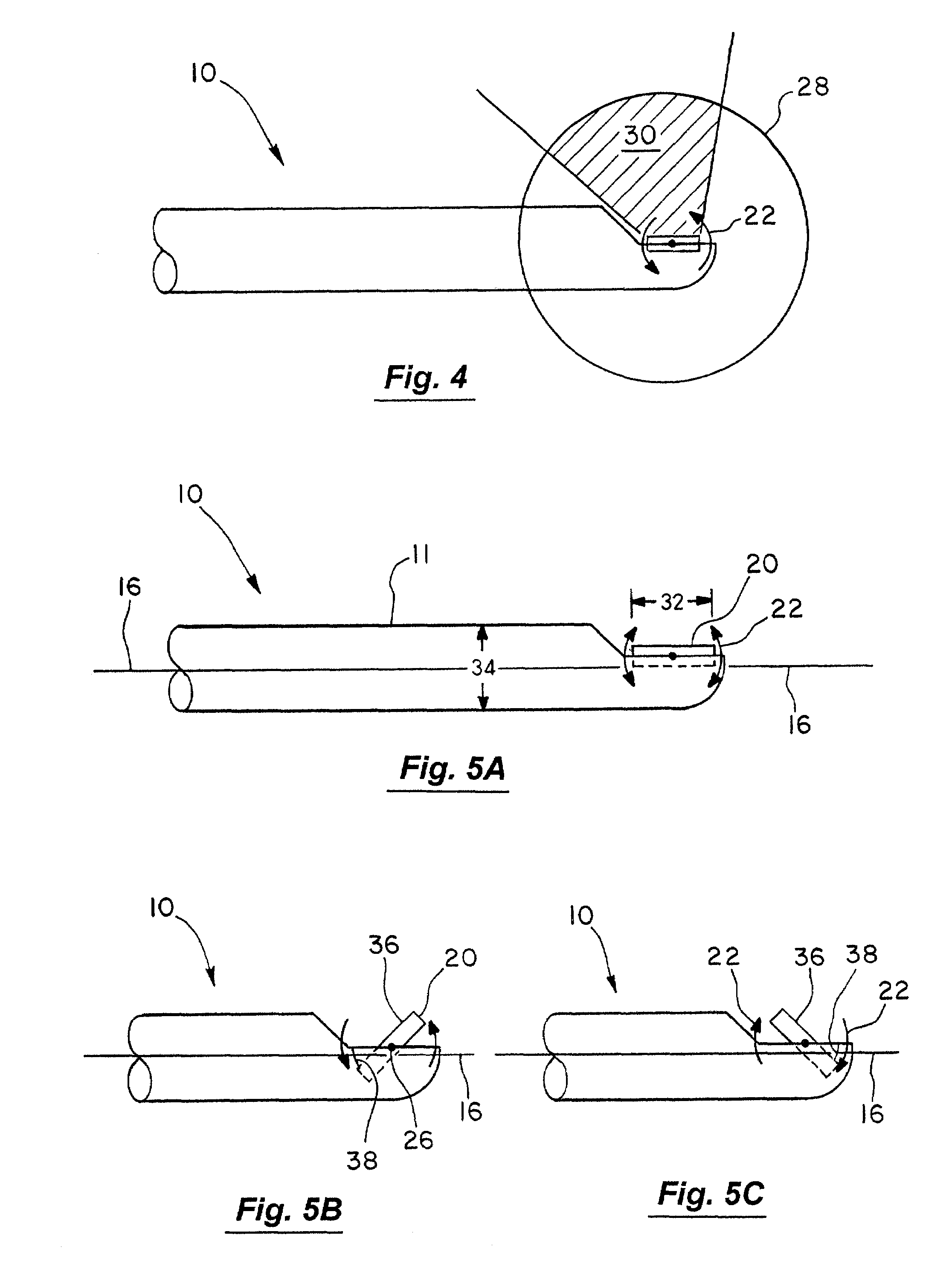
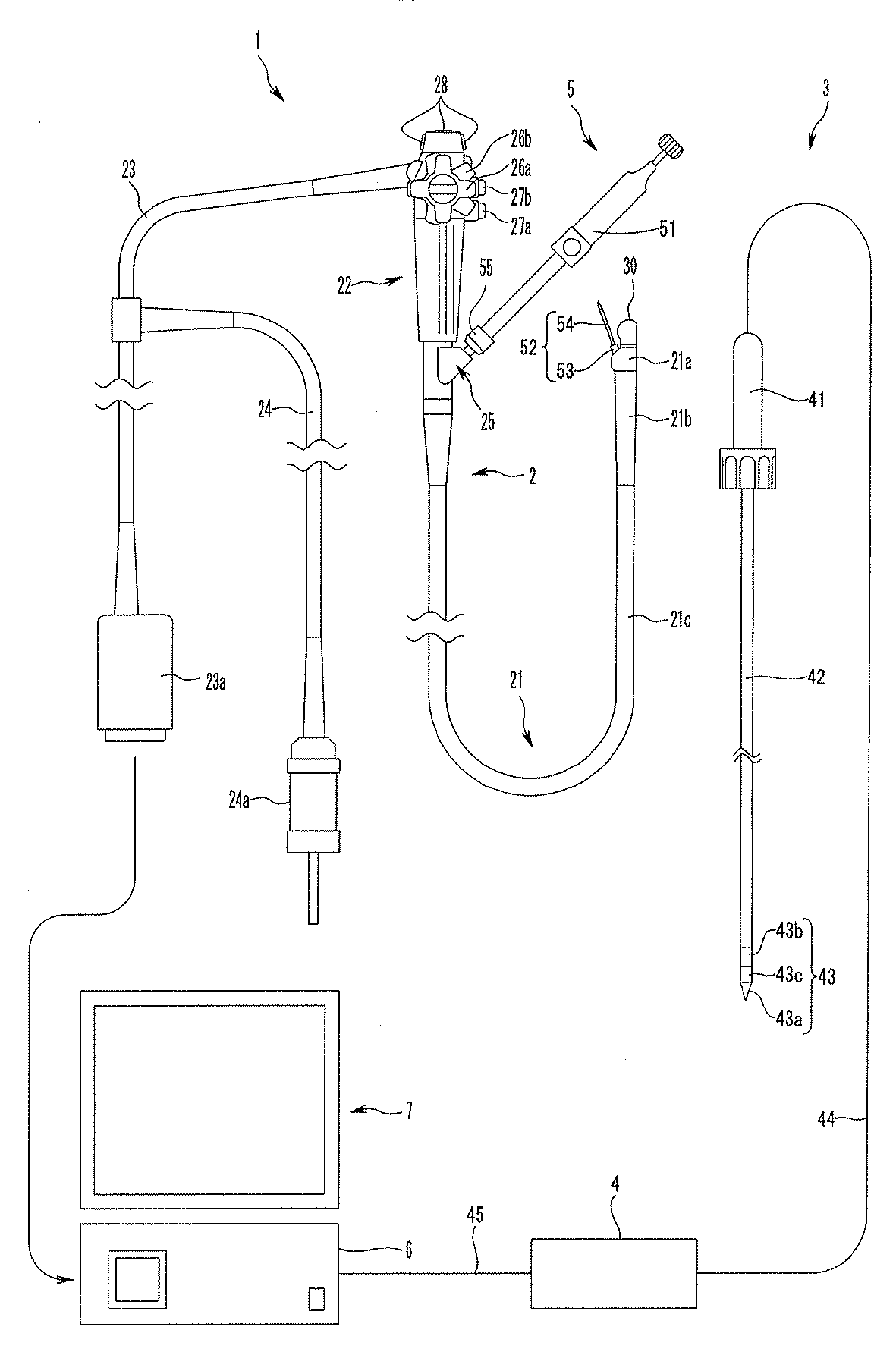
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
267 results about "Ultrasound guided" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
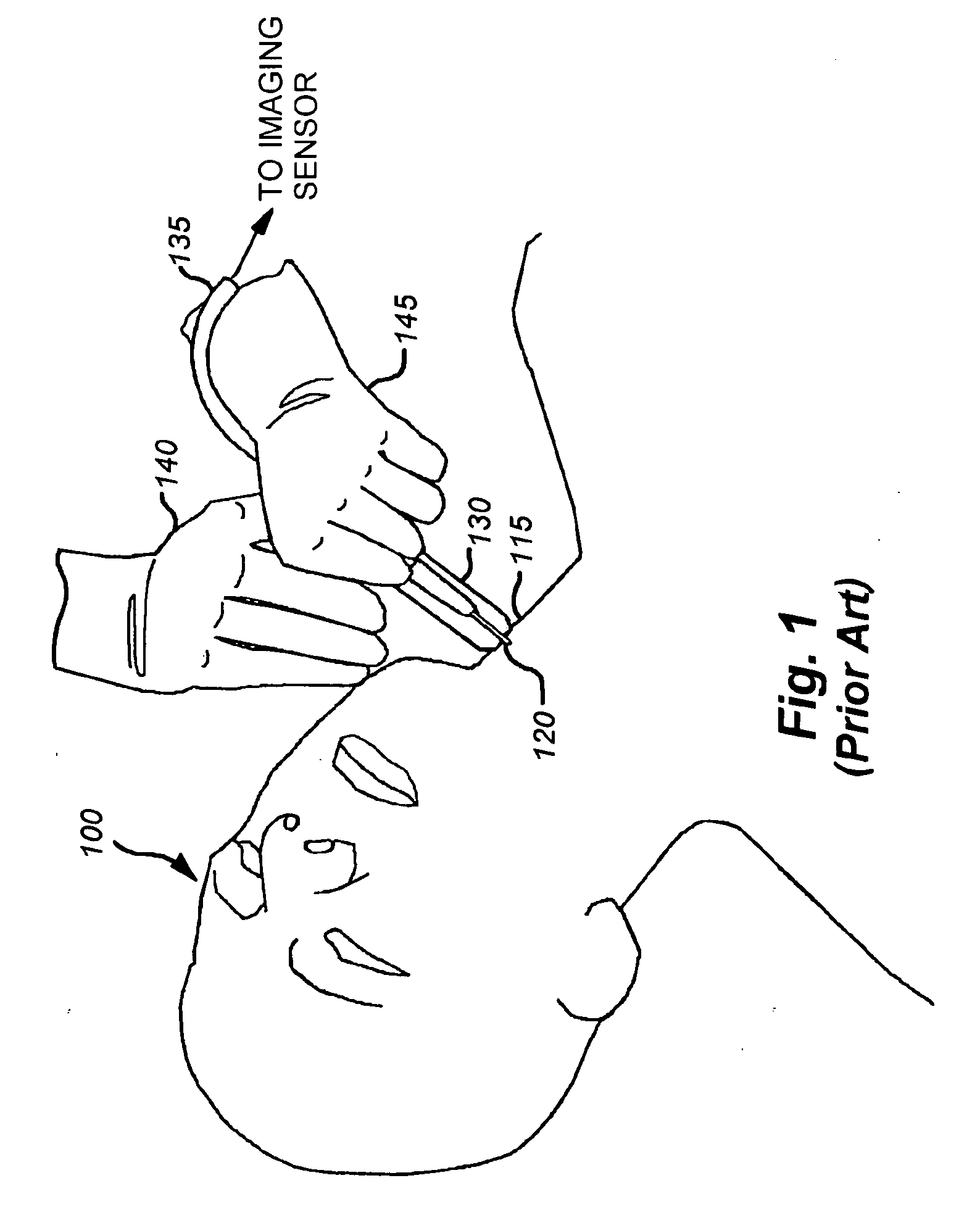
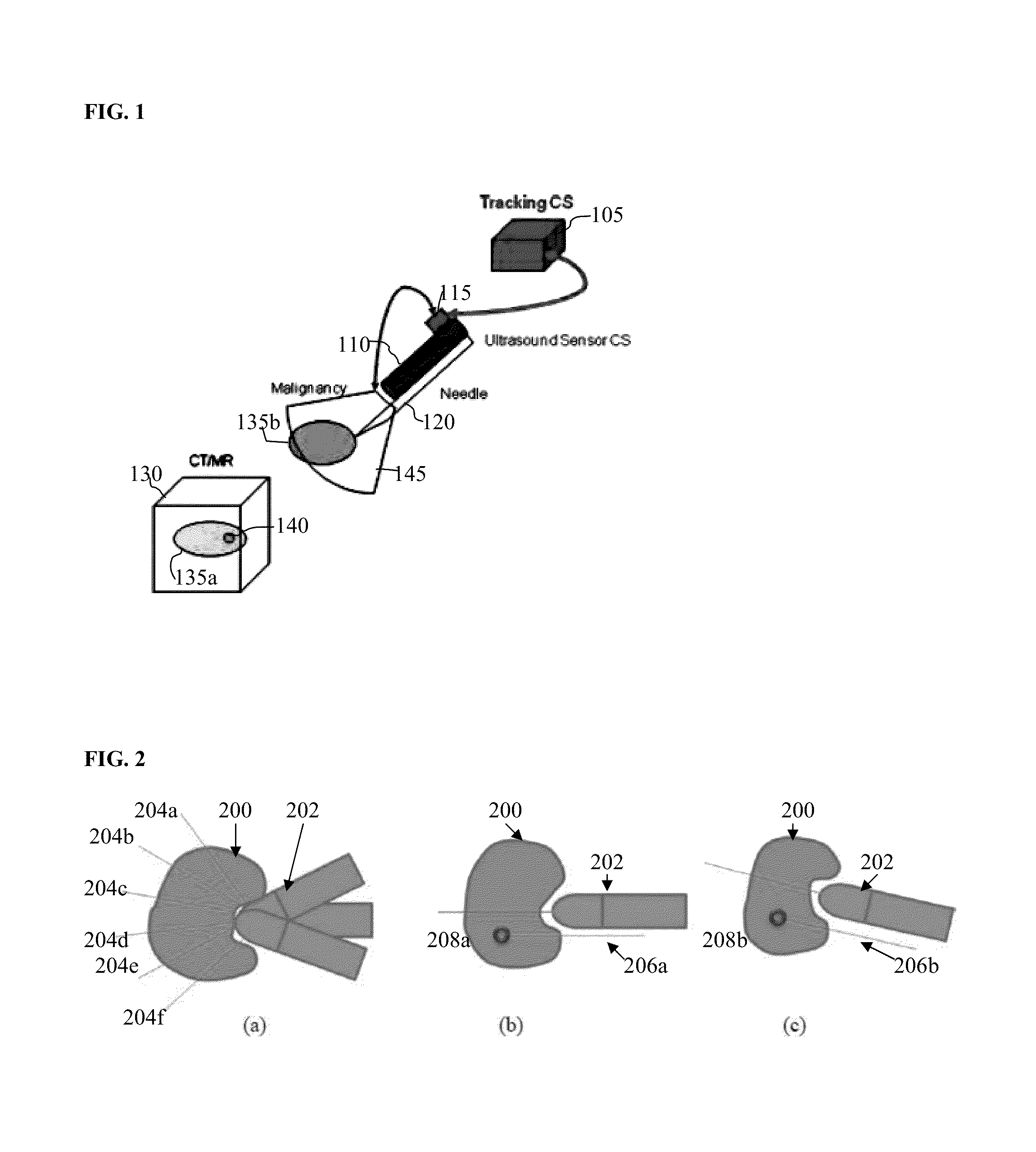
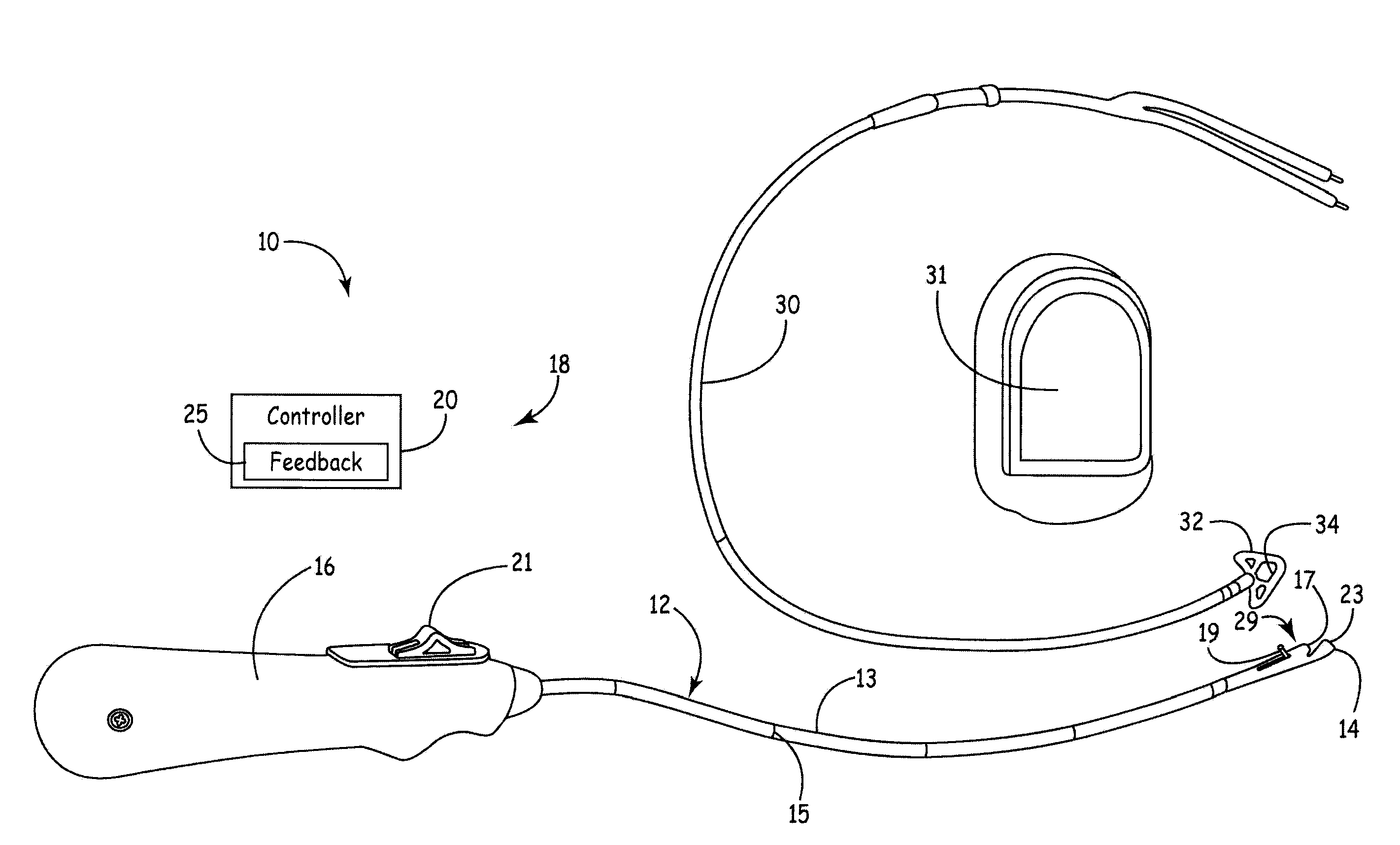
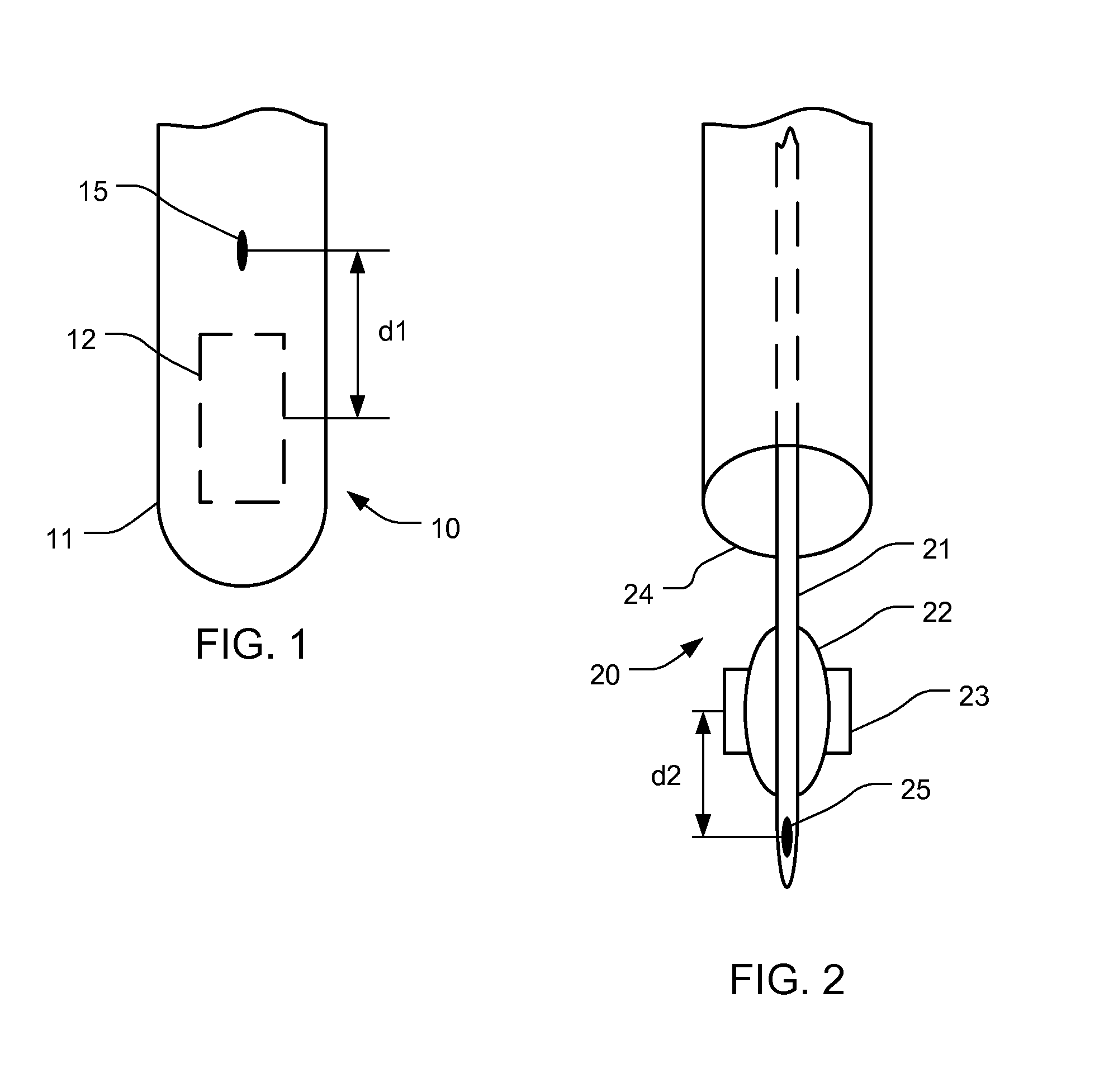
In an ultrasound guided biopsy, the physician uses an ultrasound machine to locate the area where it is best to remove tissue. The ultrasound wand or transducer pulses out waves of sound into the body, and then calculates their return.
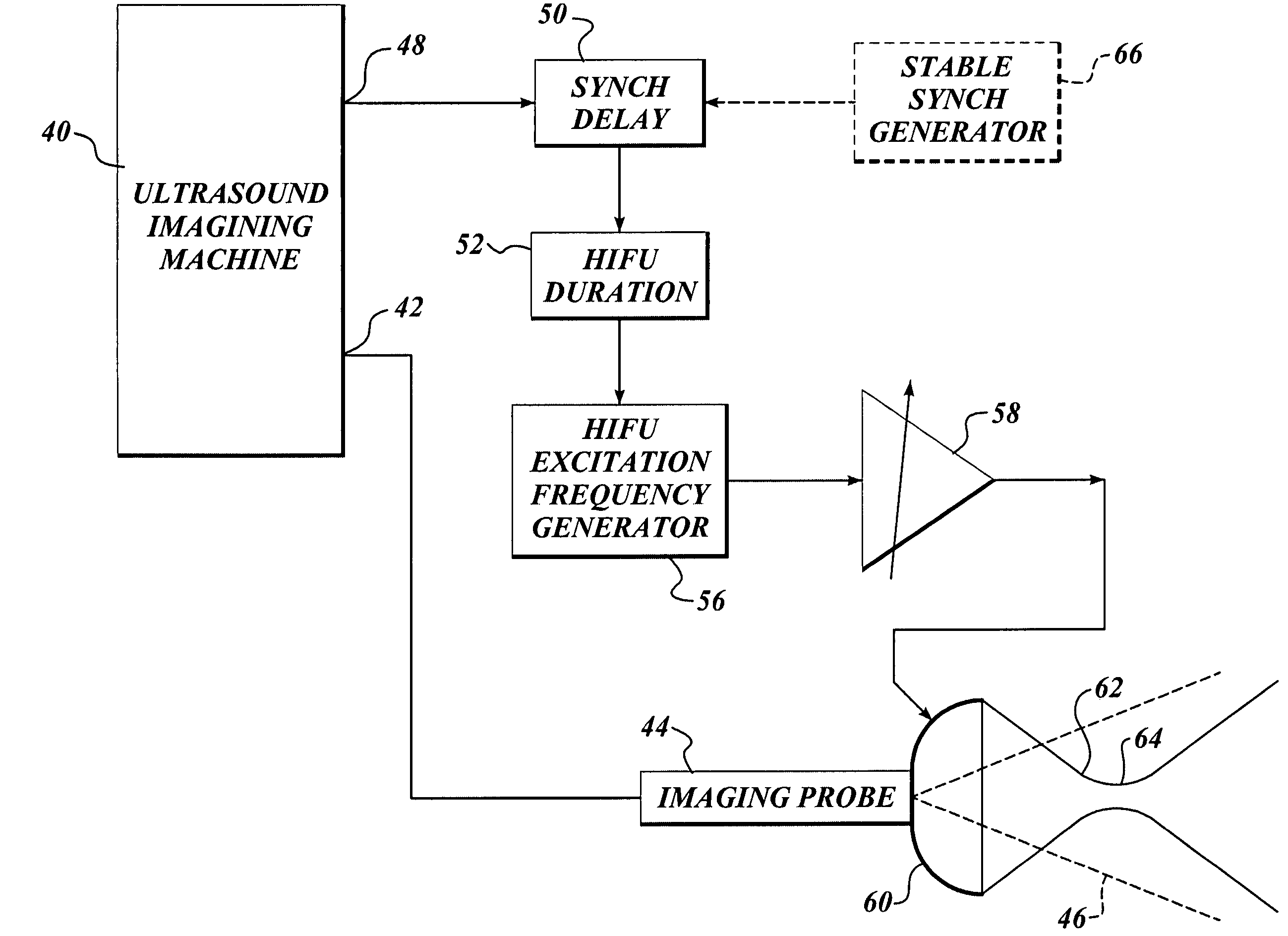
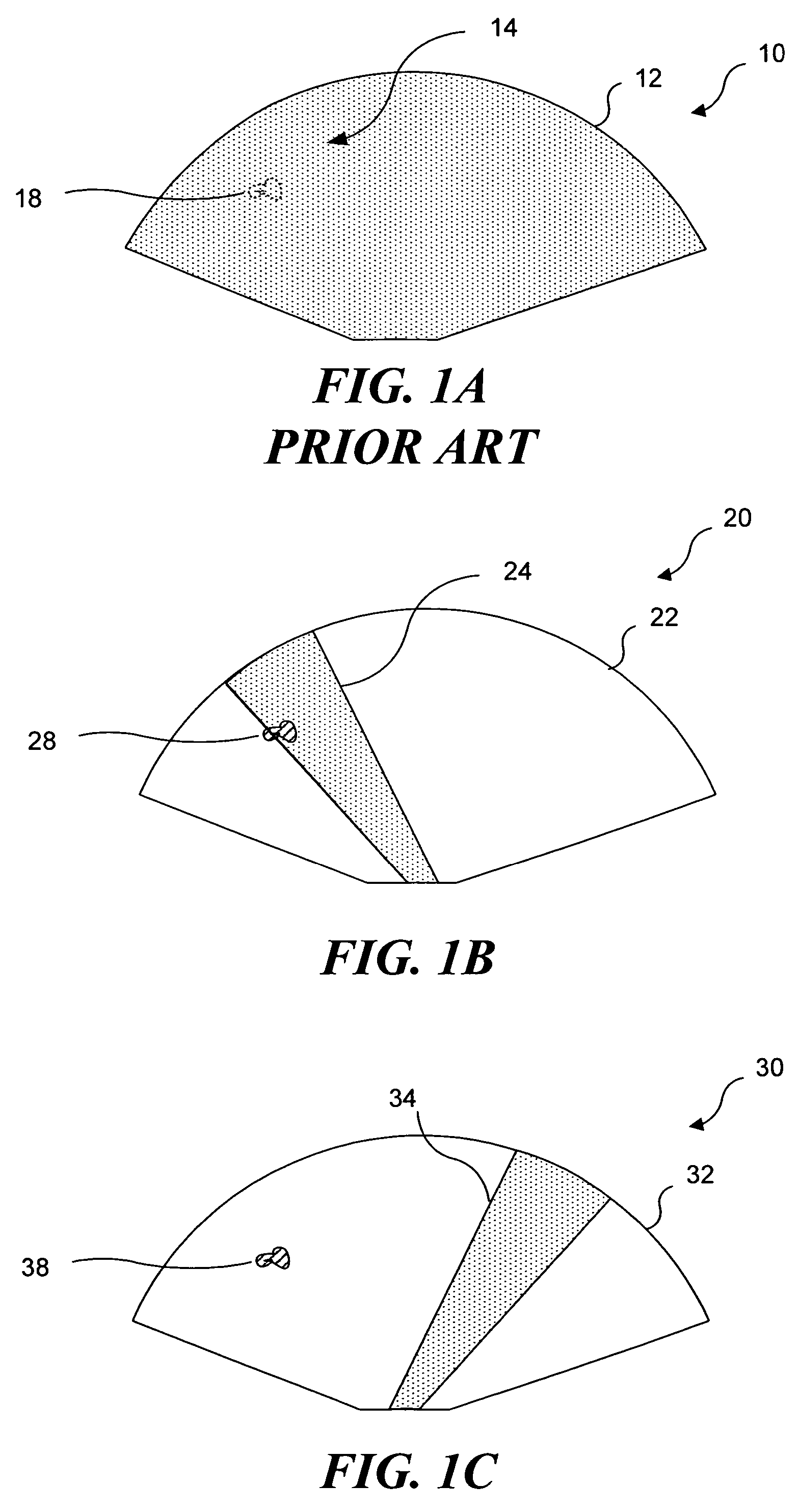
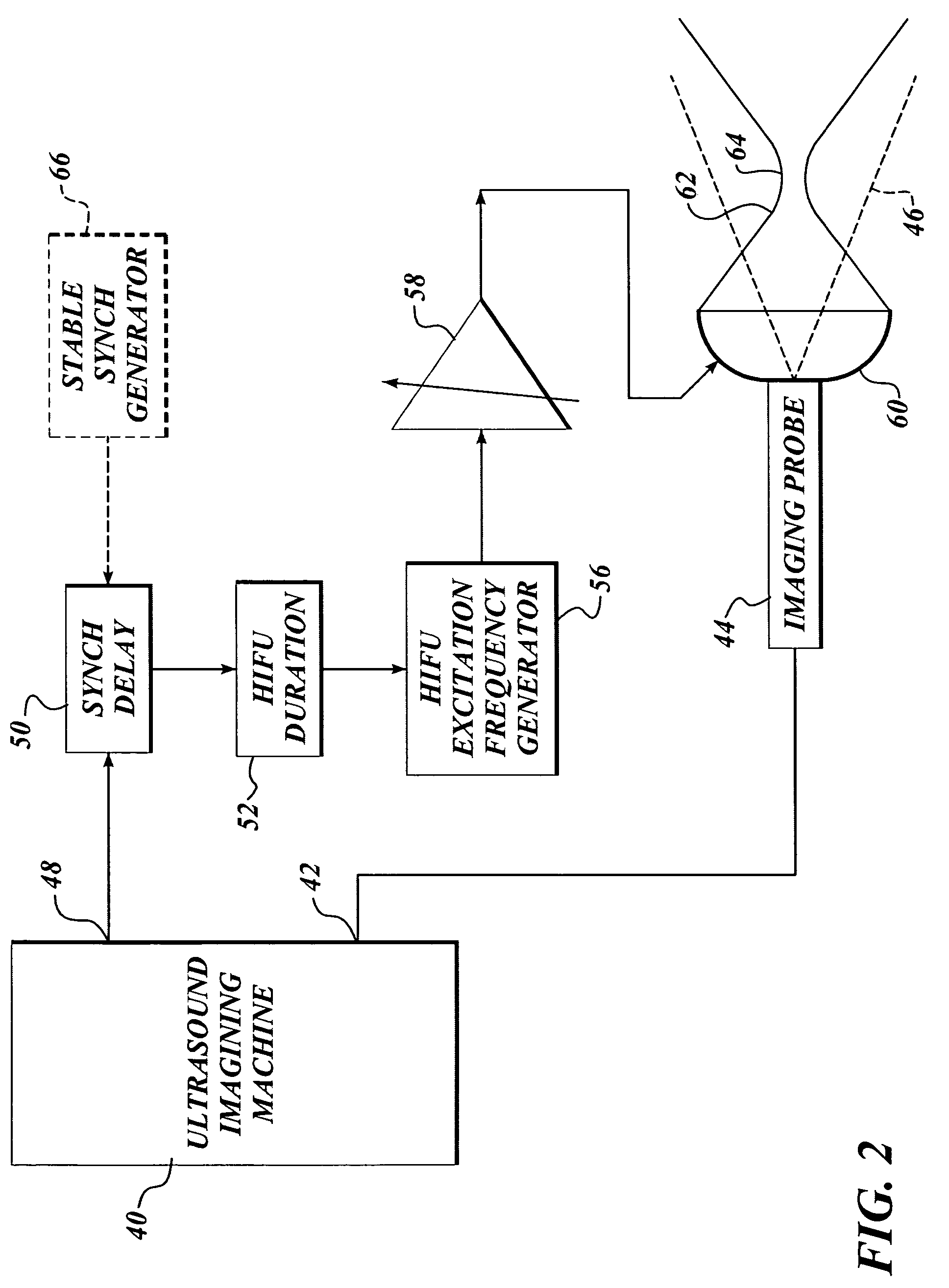
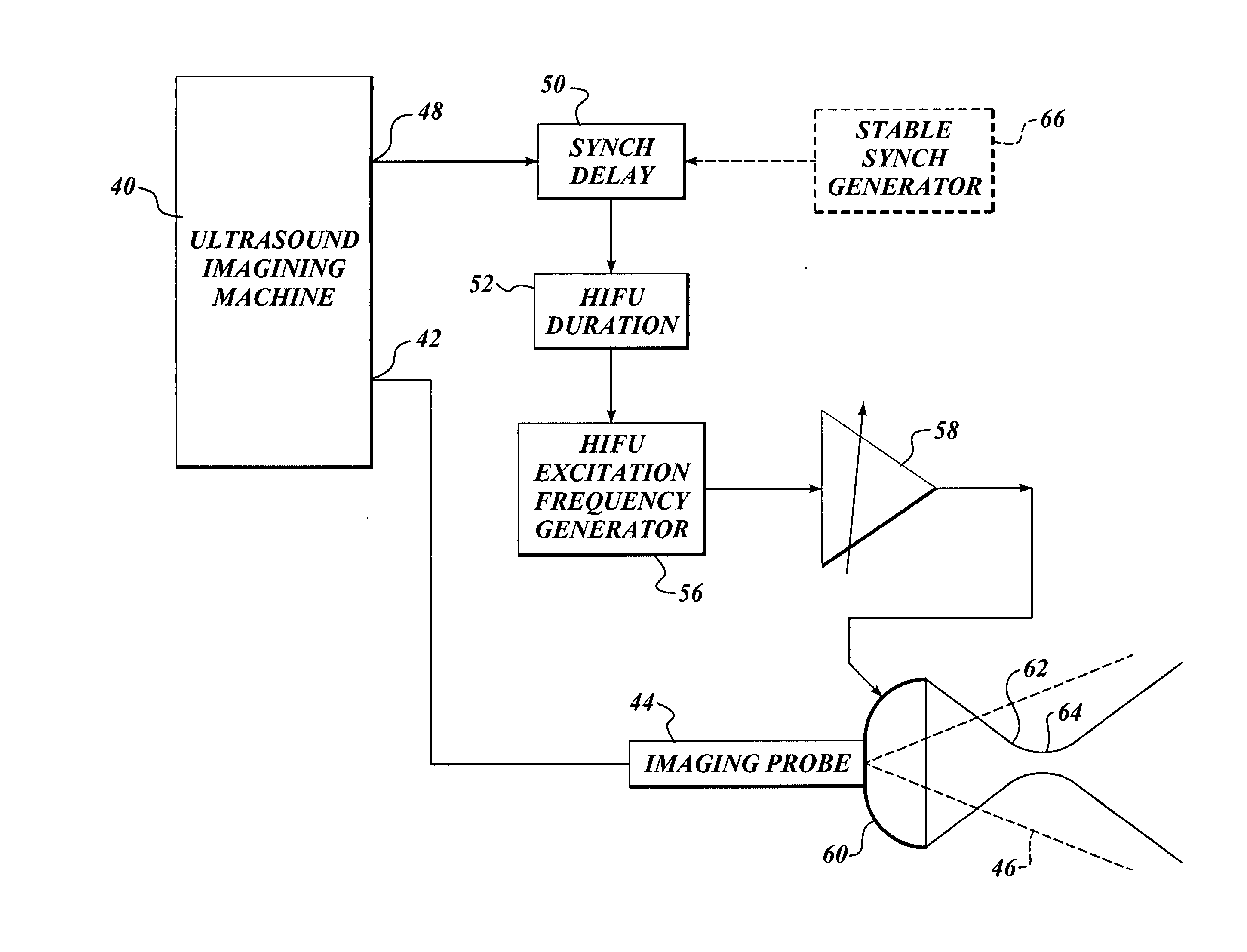
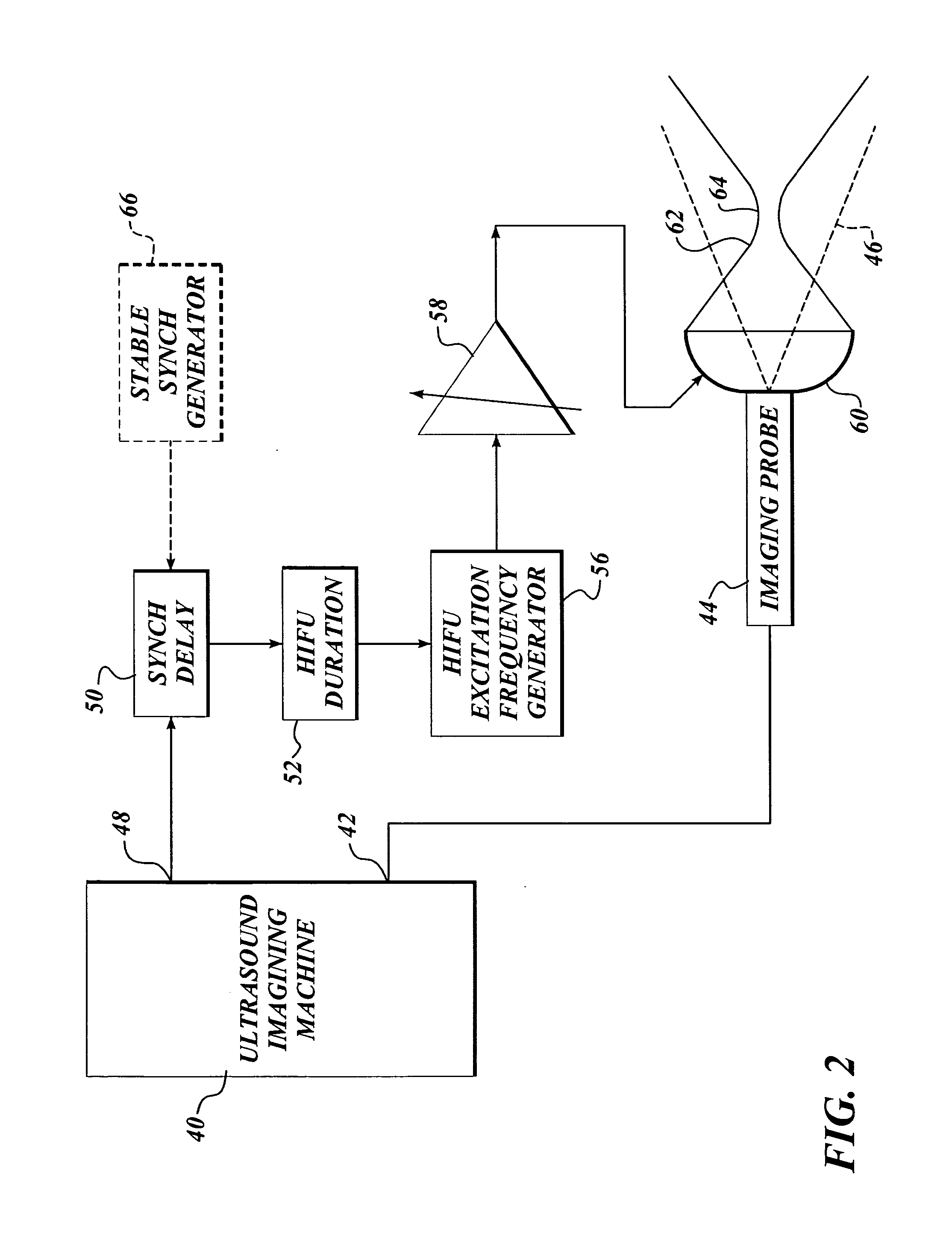
Ultrasound guided high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of nerves
InactiveUS7510536B2Relieve painEasy procedureUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesSonificationHigh doses
A method for using high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to treat neurological structures to achieve a desired therapeutic affect. Depending on the dosage of HIFU applied, it can have a reversible or irreversible effect on neural structures. For example, a relatively high dose of HIFU can be used to permanently block nerve function, to provide a non-invasive alternative to severing a nerve to treat severe spasticity. Relatively lower doses of HIFU can be used to reversible a block nerve function, to alleviate pain, to achieve an anesthetic effect, or to achieve a cosmetic effect. Where sensory nerves are not necessary for voluntary function, but are involved in pain associated with tumors or bone cancer, HIFU can be used to non-invasively destroy such sensory nerves to alleviate pain without drugs. Preferably, ultrasound imaging synchronized to the HIFU therapy is used to provide real-time ultrasound image guided HIFU therapy of neural structures.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Ultrasound guided high intensity focused ultrasound treatment of nerves
InactiveUS20050240126A1Relieve painEasy procedureUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesAbnormal tissue growthHigh doses
A method for using high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) to treat neurological structures to achieve a desired therapeutic affect. Depending on the dosage of HIFU applied, it can have a reversible or irreversible effect on neural structures. For example, a relatively high dose of HIFU can be used to permanently block nerve function, to provide a non-invasive alternative to severing a nerve to treat severe spasticity. Relatively lower doses of HIFU can be used to reversible a block nerve function, to alleviate pain, to achieve an anesthetic effect, or to achieve a cosmetic effect. Where sensory nerves are not necessary for voluntary function, but are involved in pain associated with tumors or bone cancer, HIFU can be used to non-invasively destroy such sensory nerves to alleviate pain without drugs. Preferably, ultrasound imaging synchronized to the HIFU therapy is used to provide real-time ultrasound image guided HIFU therapy of neural structures.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
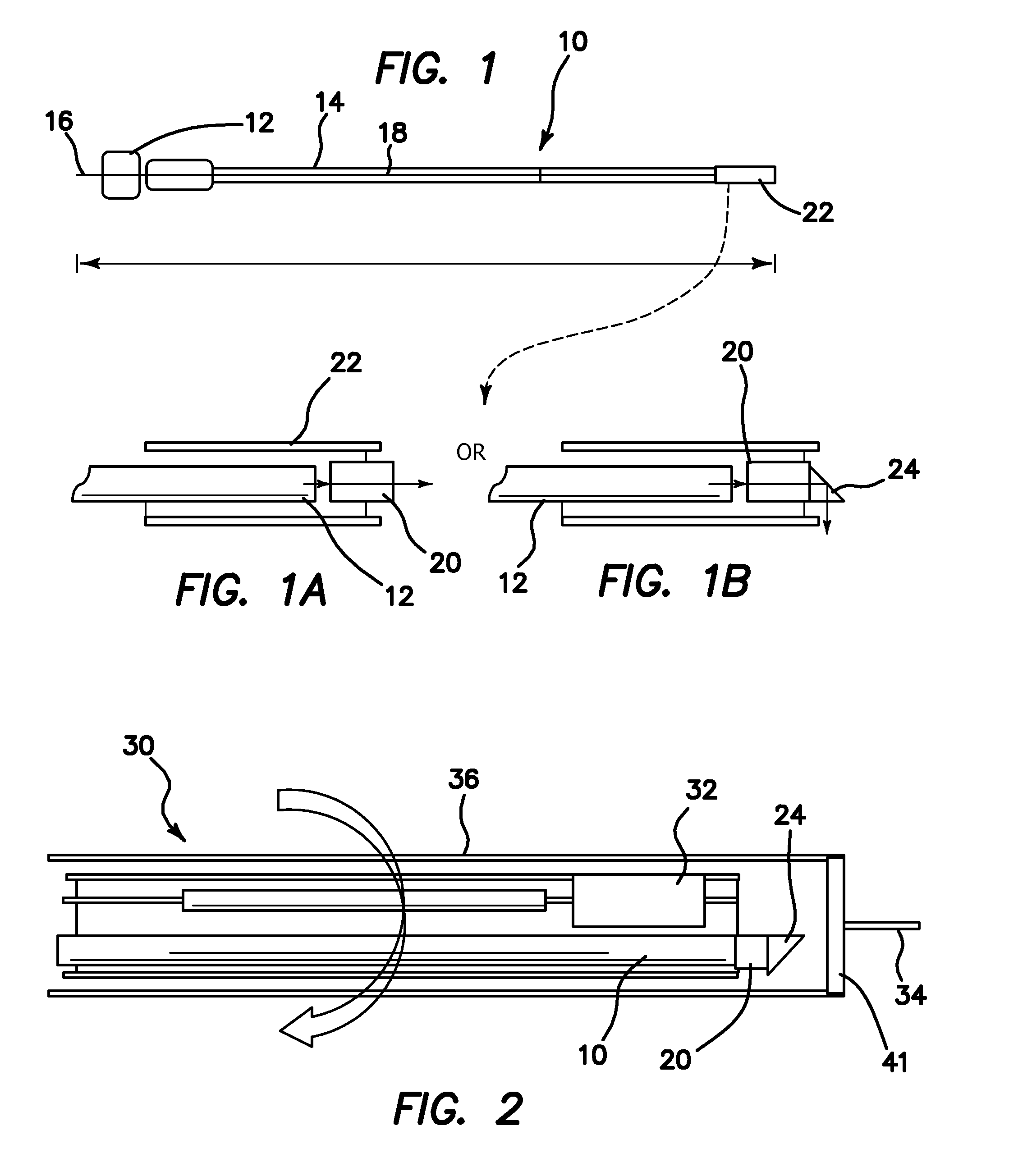
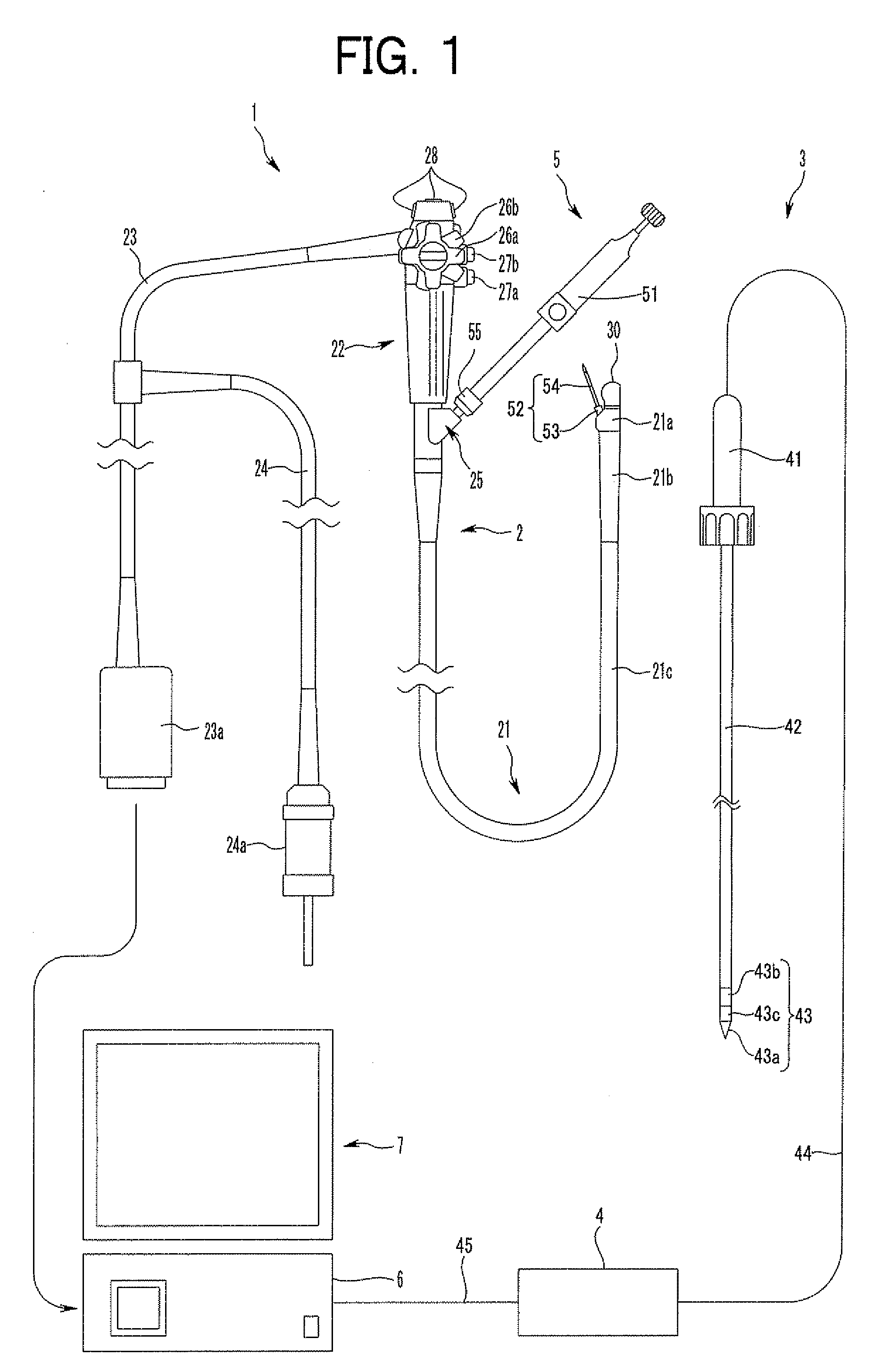
Method and apparatus for ultrasound guided intravenous cannulation
InactiveUS6132379AEasy to operateQuick buildBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionVenous accessDual mode
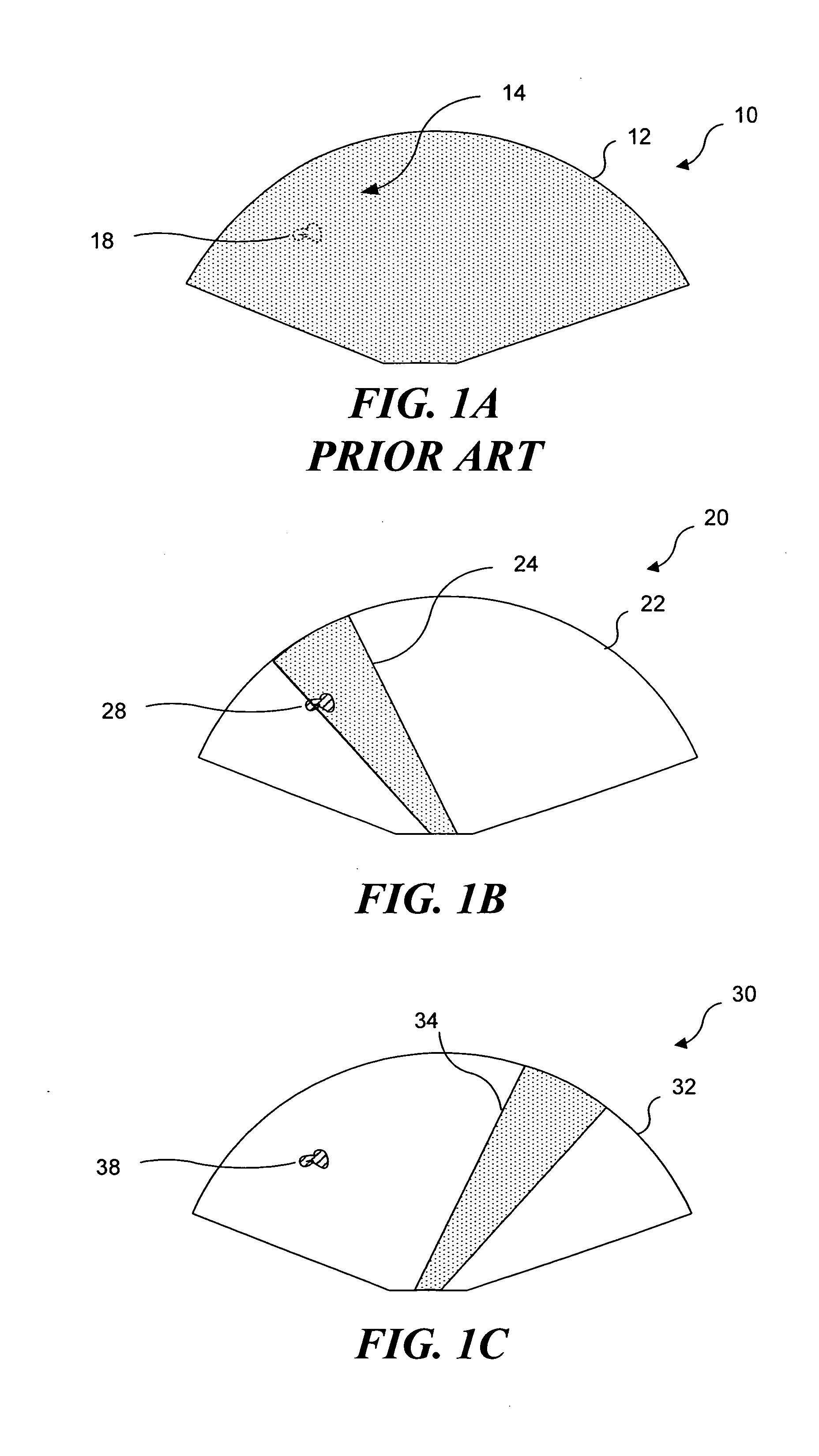
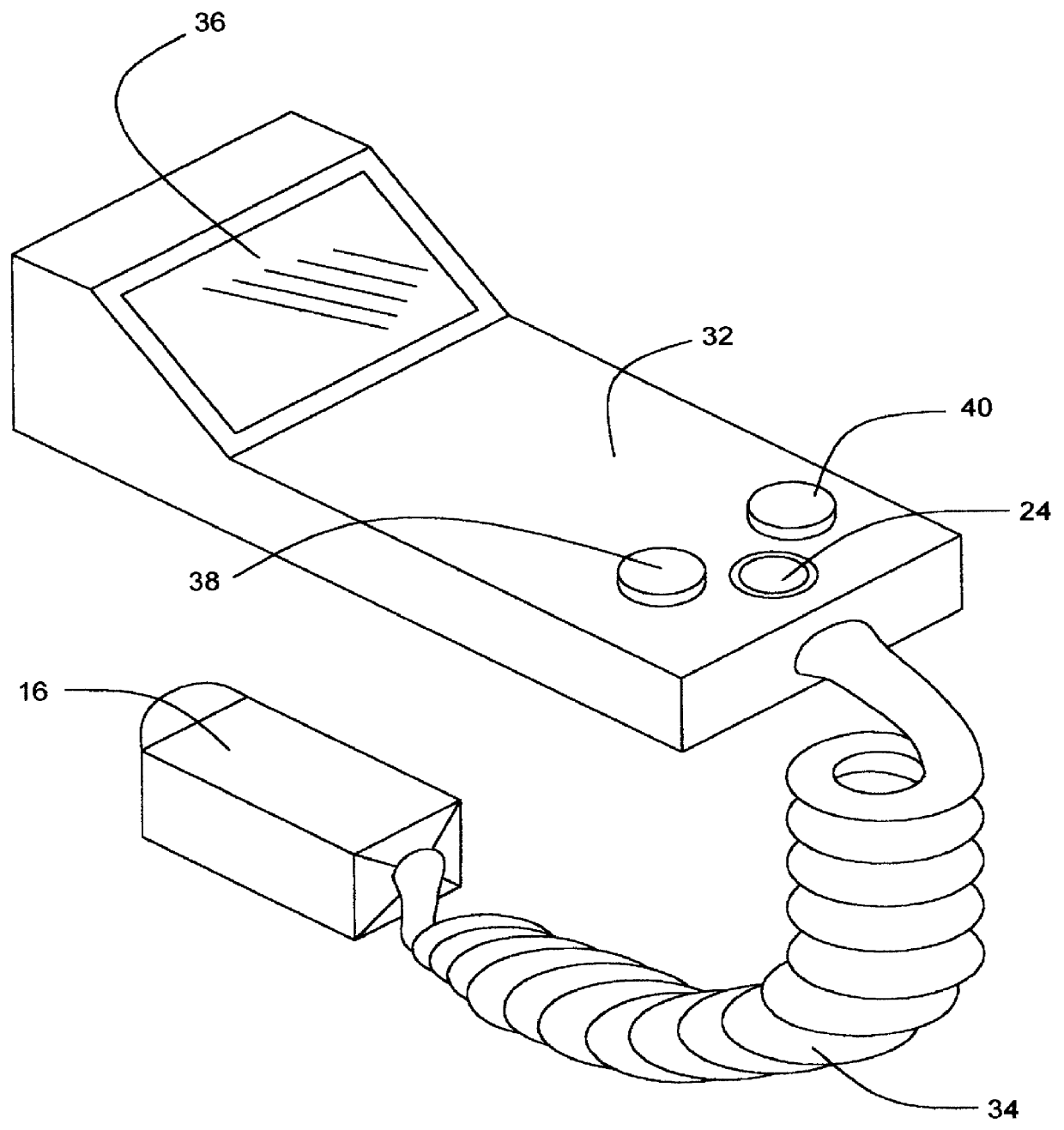
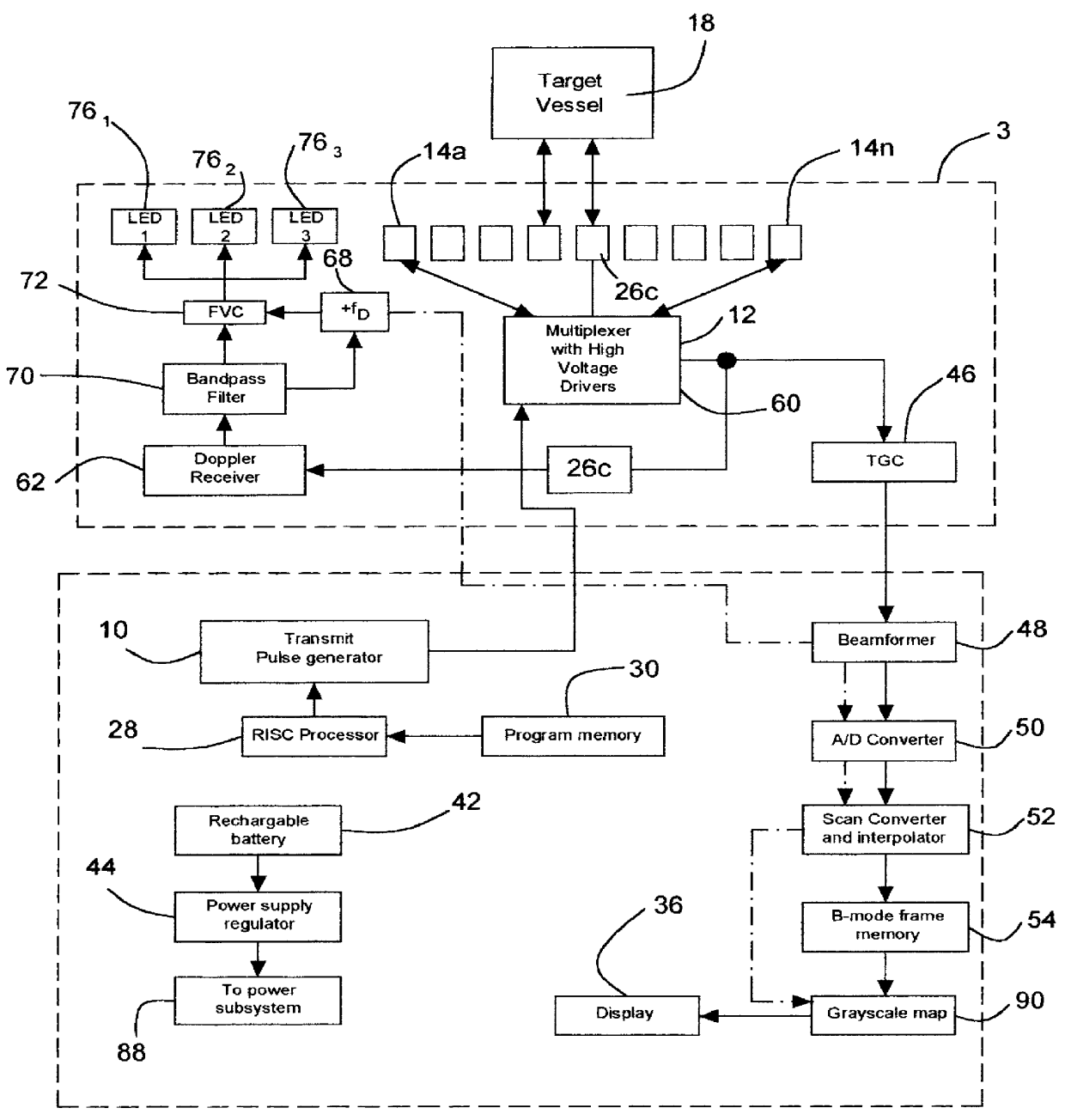
A dual mode handheld ultrasonic device is provided for guiding a venous access catheter into a patient's peripheral vein. It provides B-mode imaging with a predetermined aperture and operating frequency which locates and displays a gray scale cross-sectional image of the target blood vessel. A single doppler beam in a separate mode detects the same blood vessel and creates a single scanline image superimposed to such B-mode cross-sectional image. Simultaneously, the intensity of the positive doppler shift detected by the single doppler beam as it hits the target blood vessel activates a plurality of light emitting diode (LED) indicator lights with varying voltage requirements mounted in the scanhead. Activated LED indicator lights forms an arrow pointing inferiorly perpendicular to the target vessel which guides a physician or a paramedical professional to the precise catheter insertion spot on a patient's extremity while simultaneously viewing the target blood vessel's cross-section on the display screen.
Owner:PATACSIL ESTELITO G +1
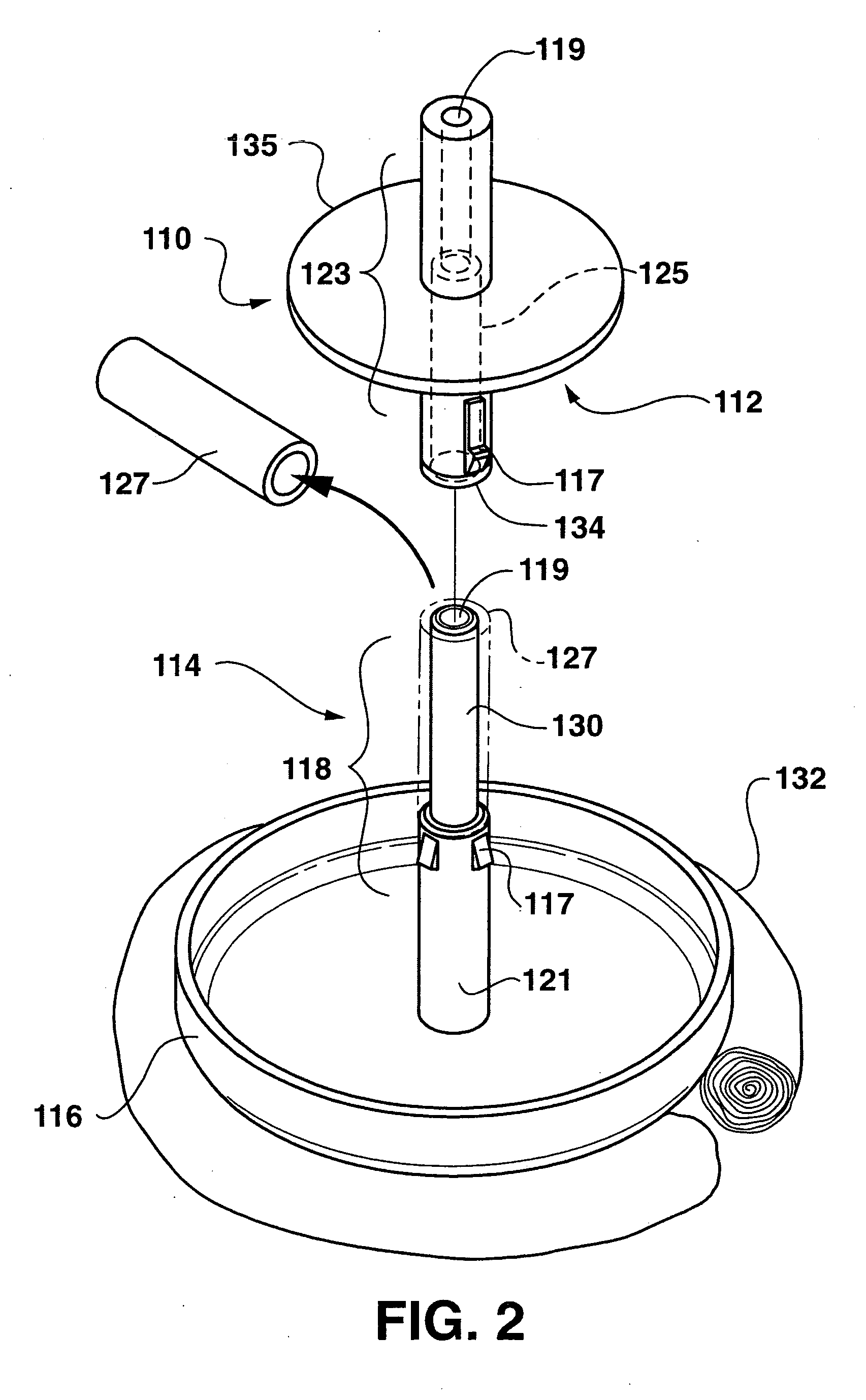
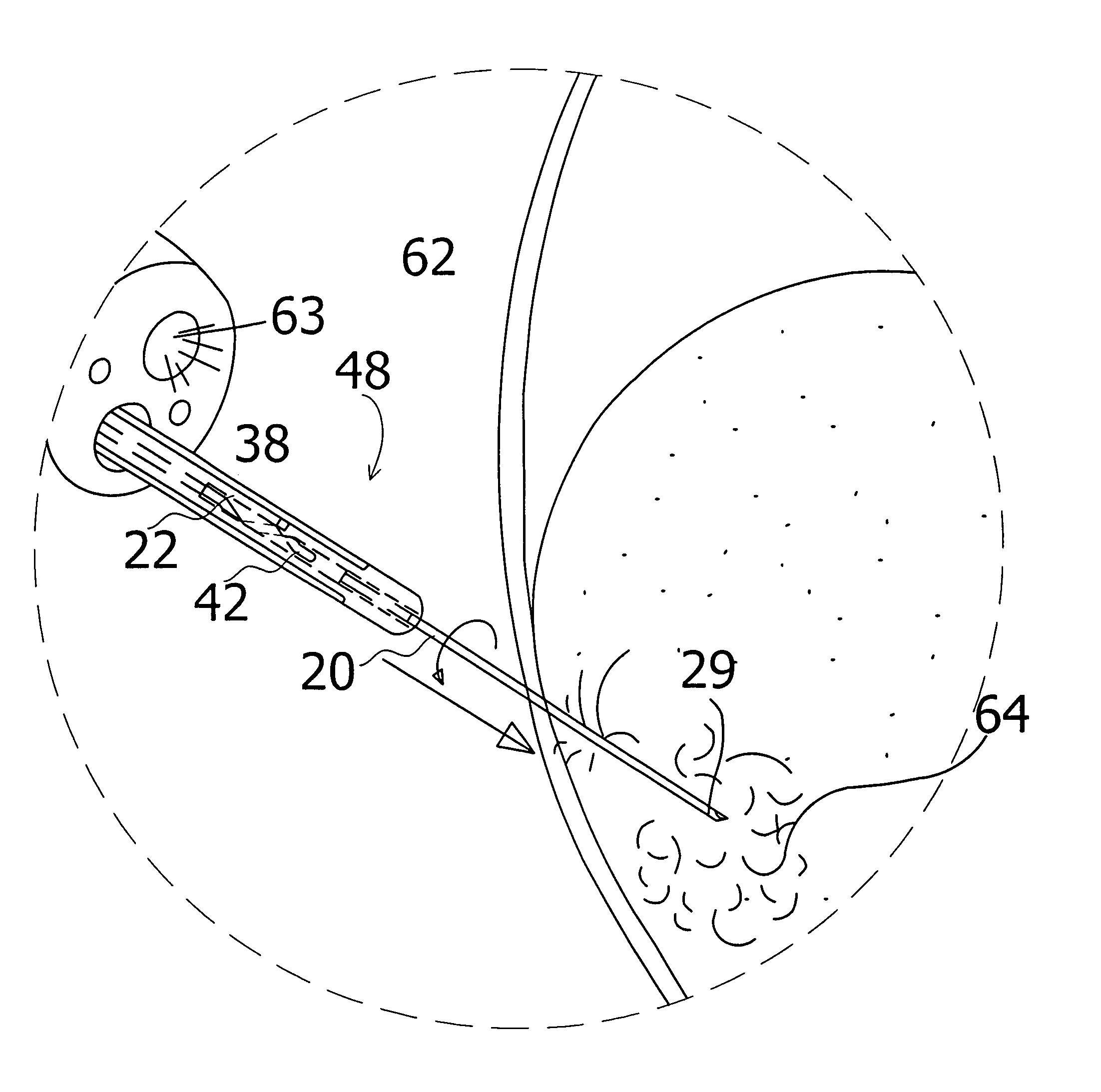
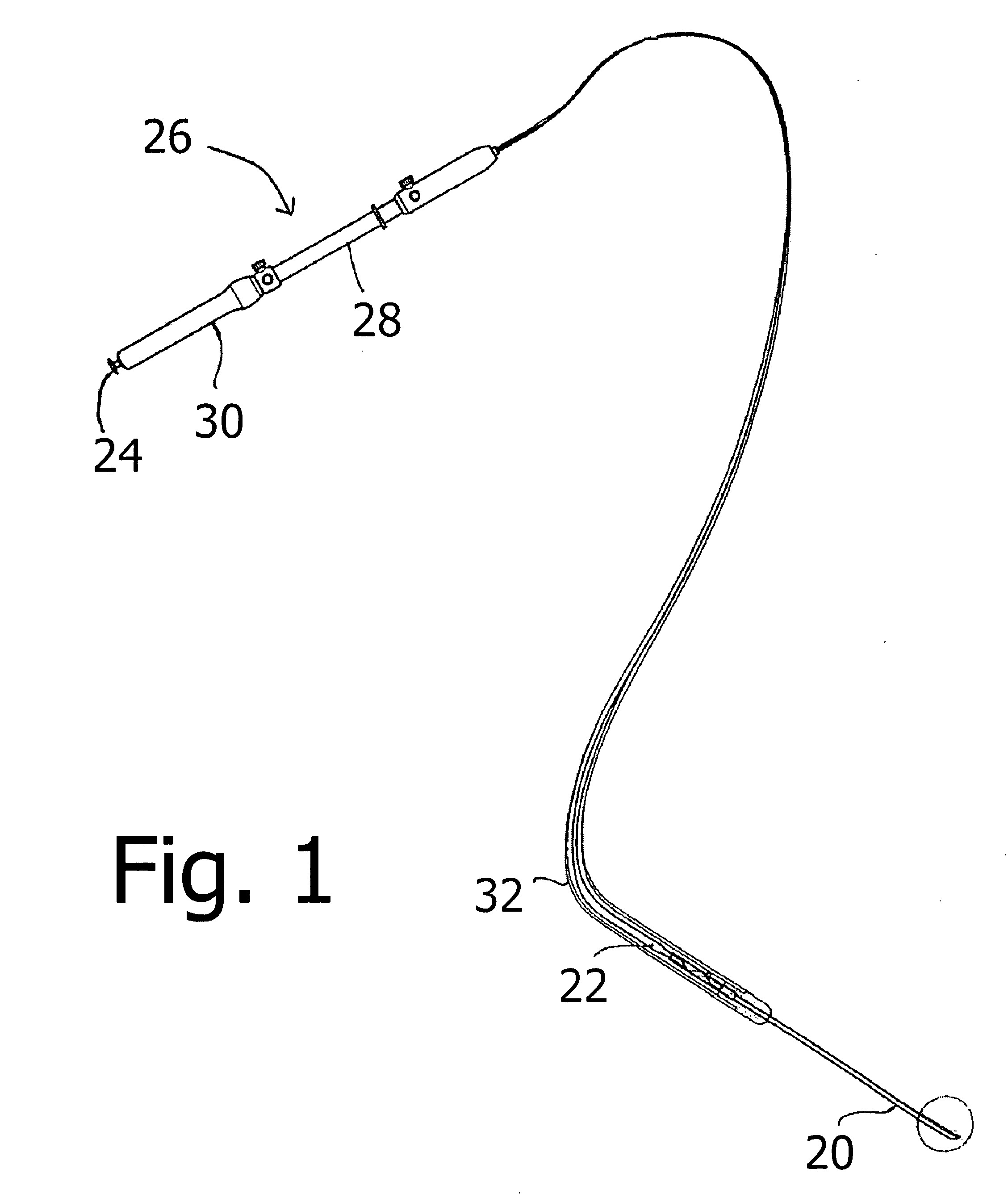
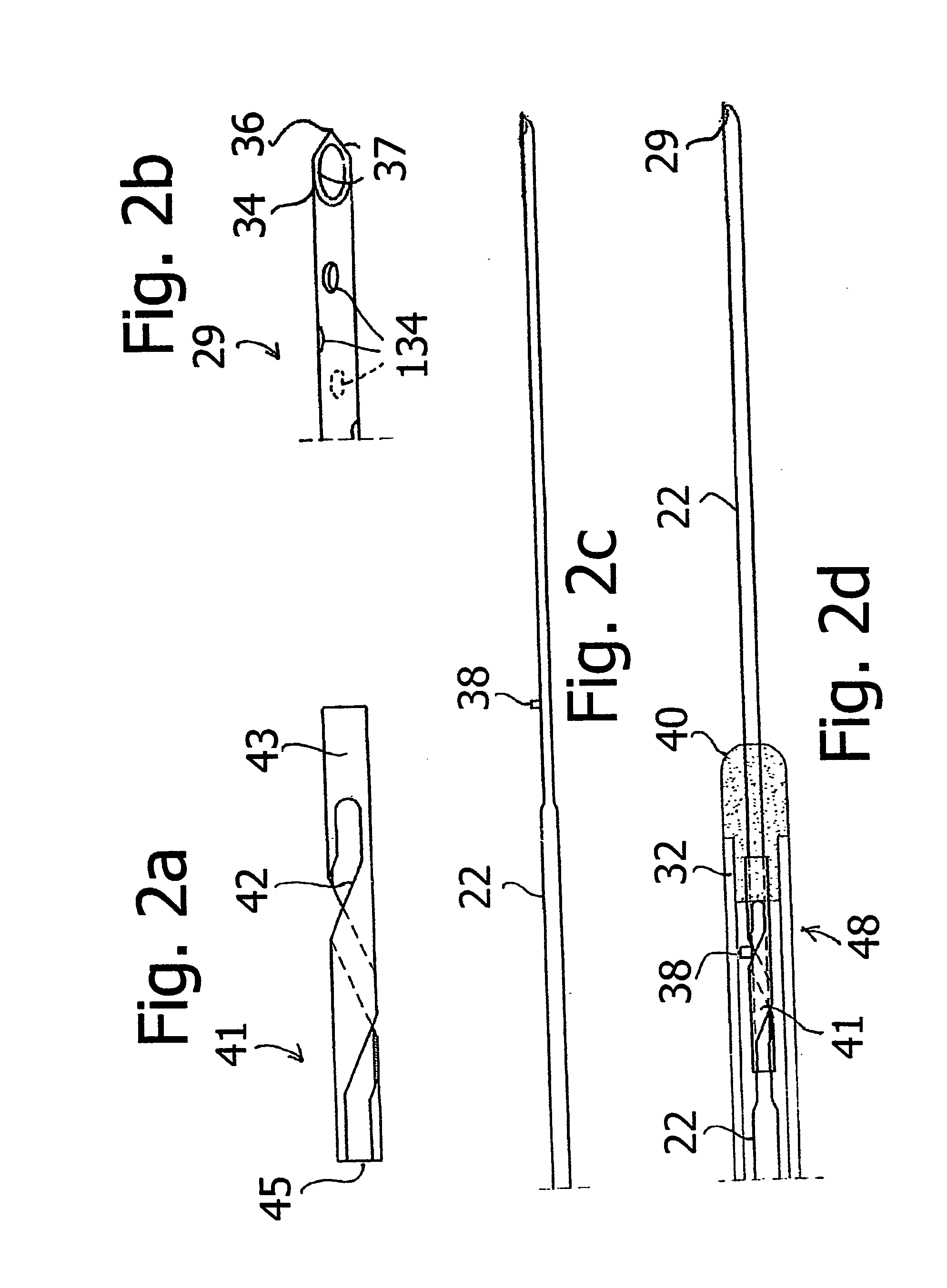
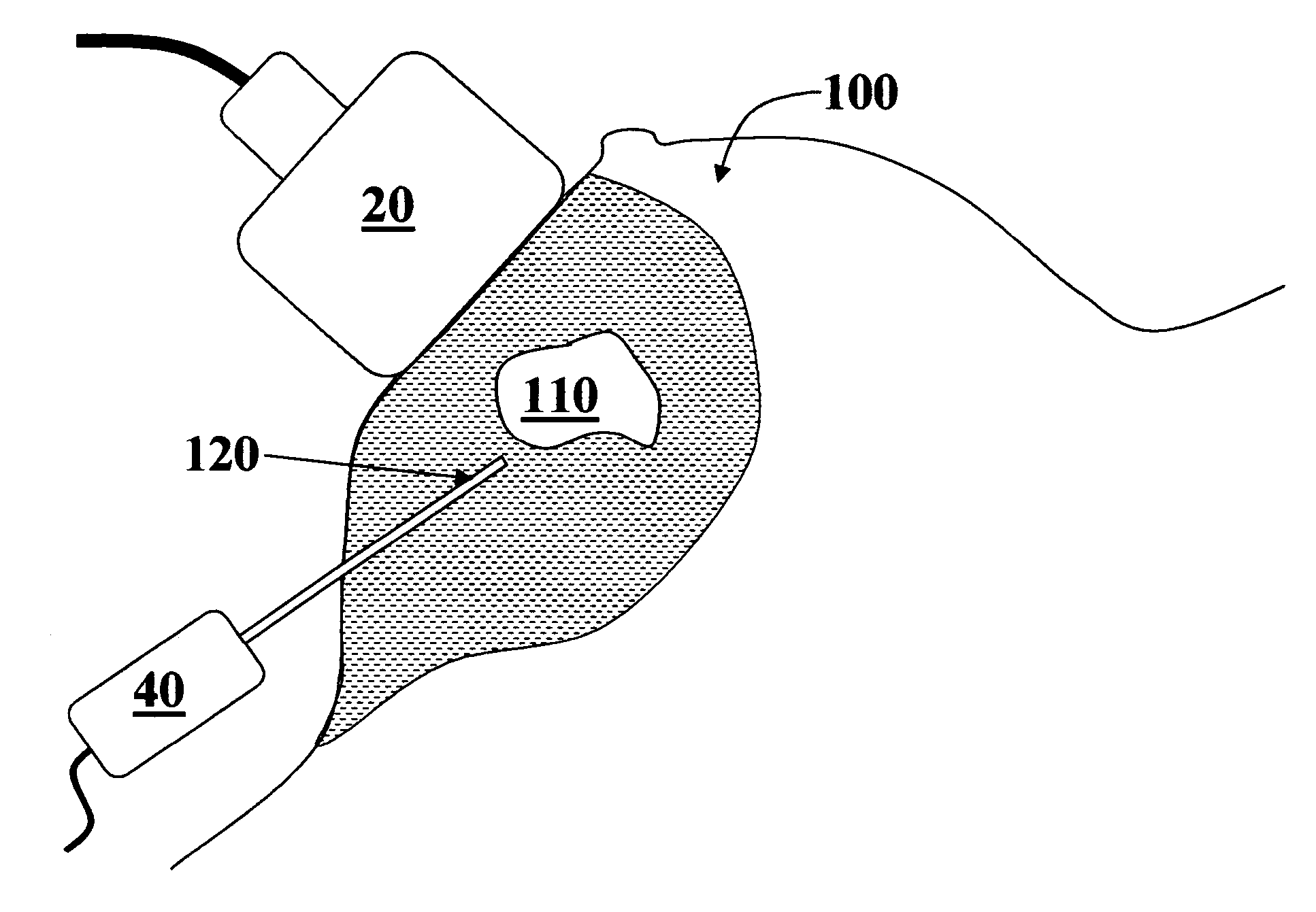
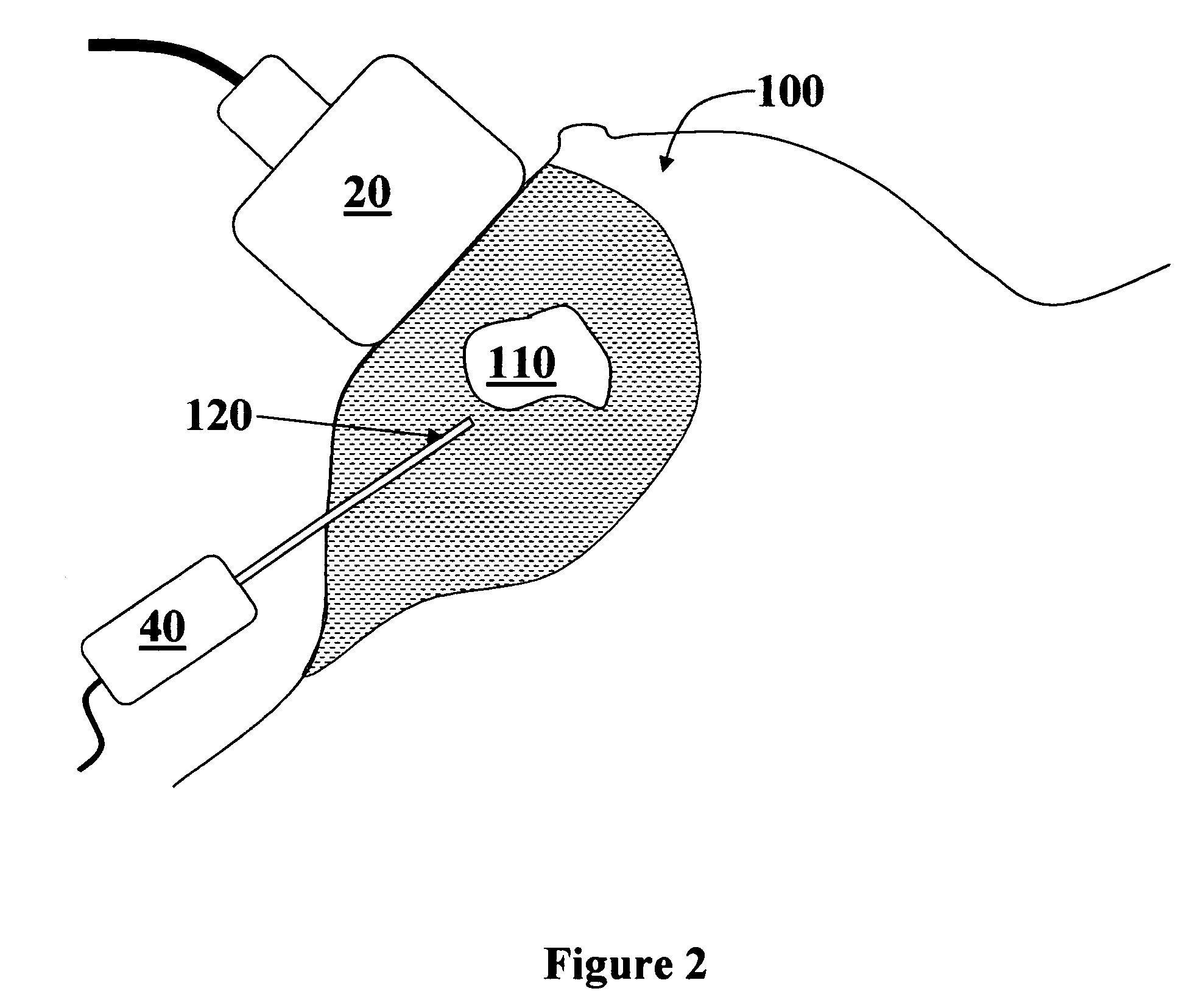
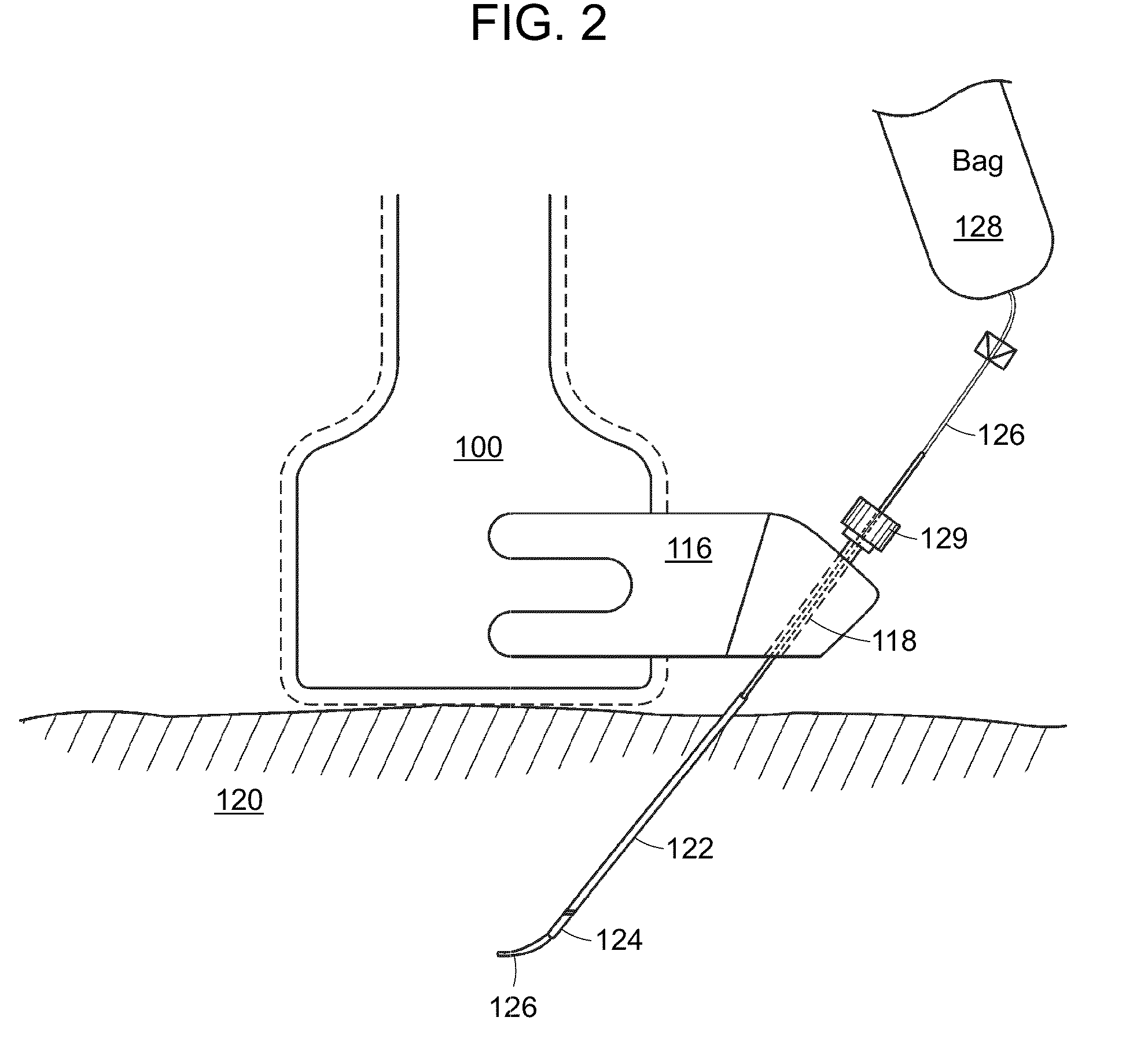
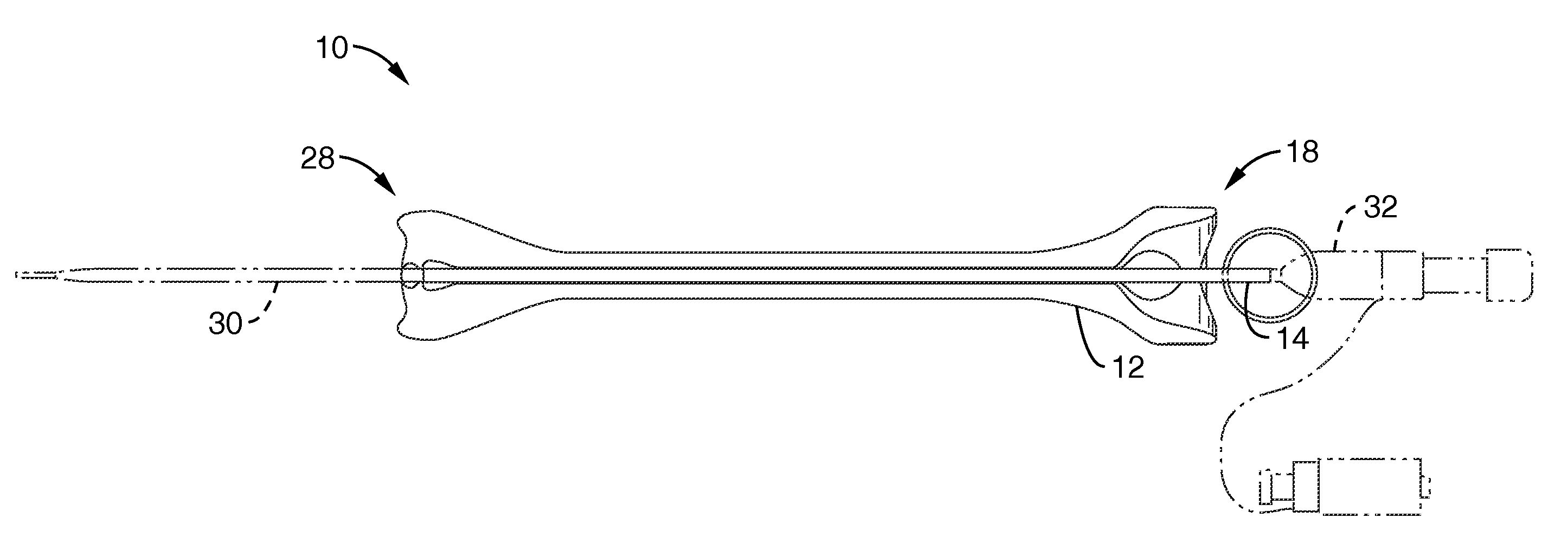
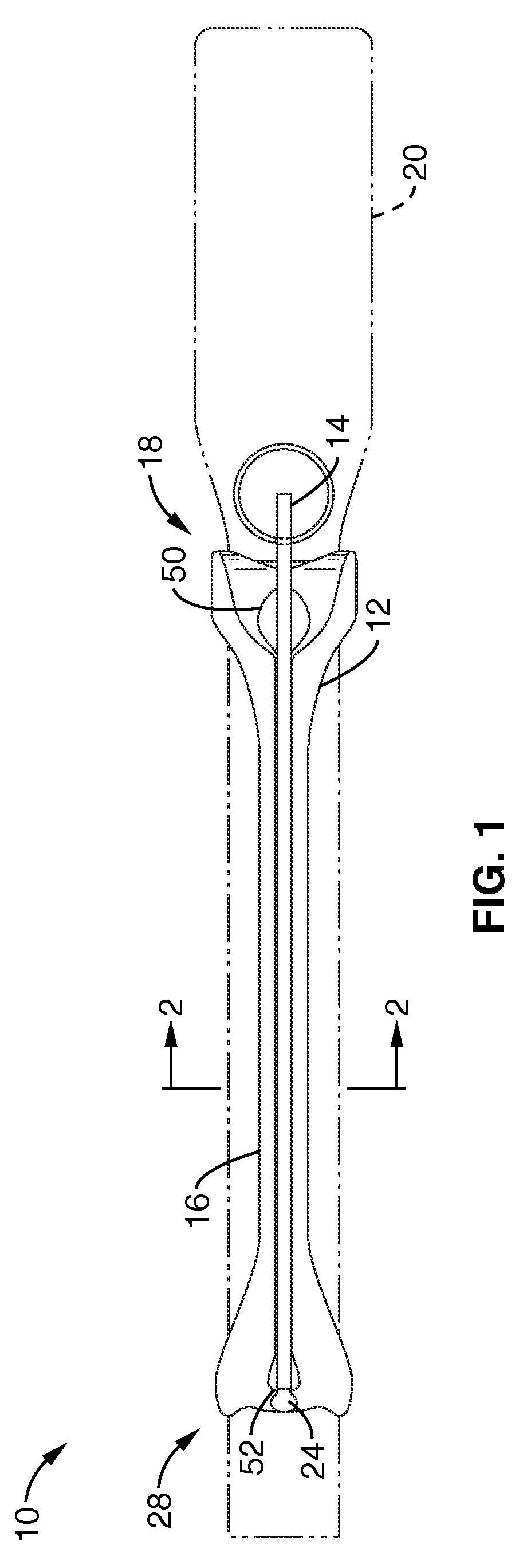
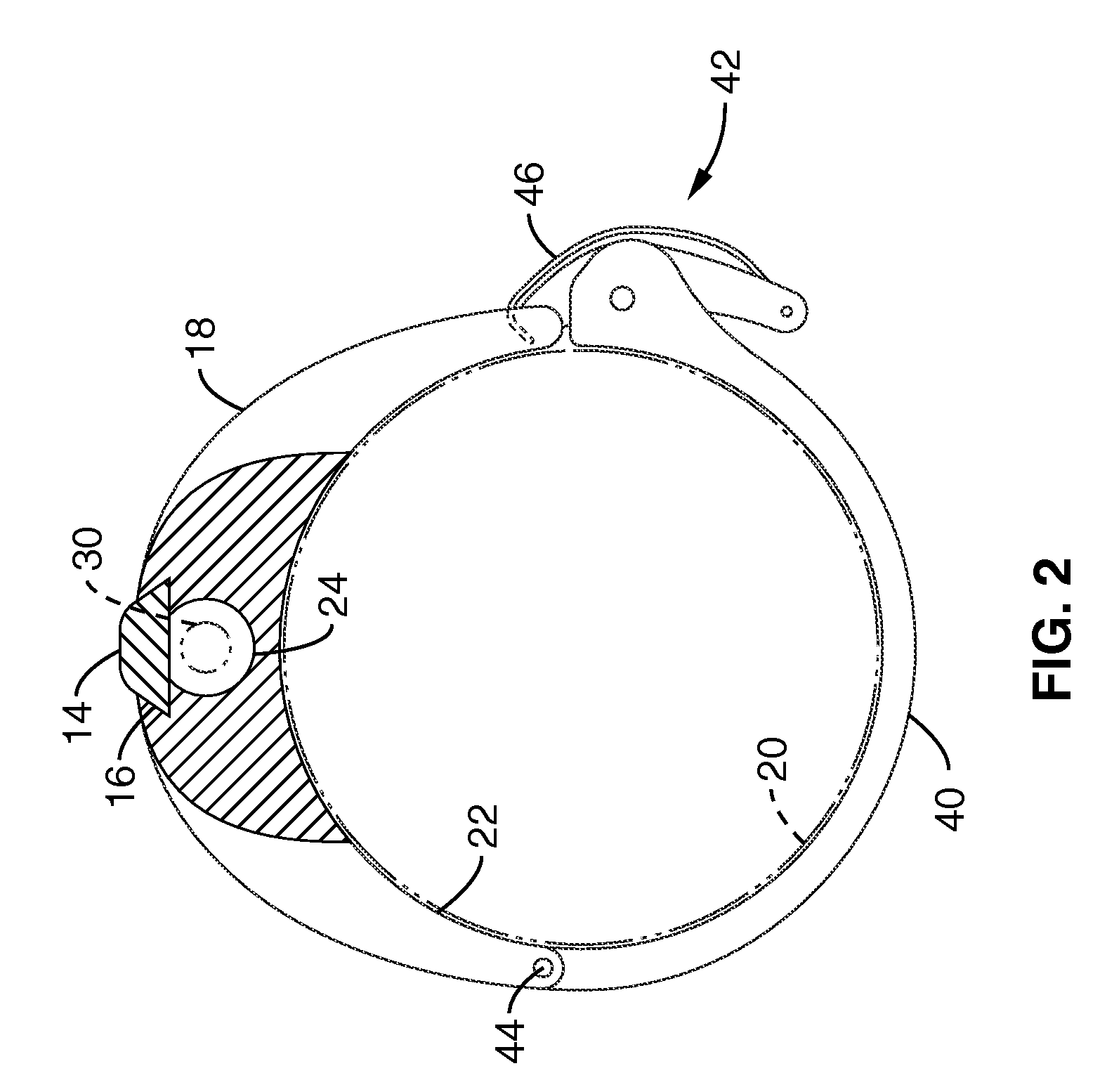
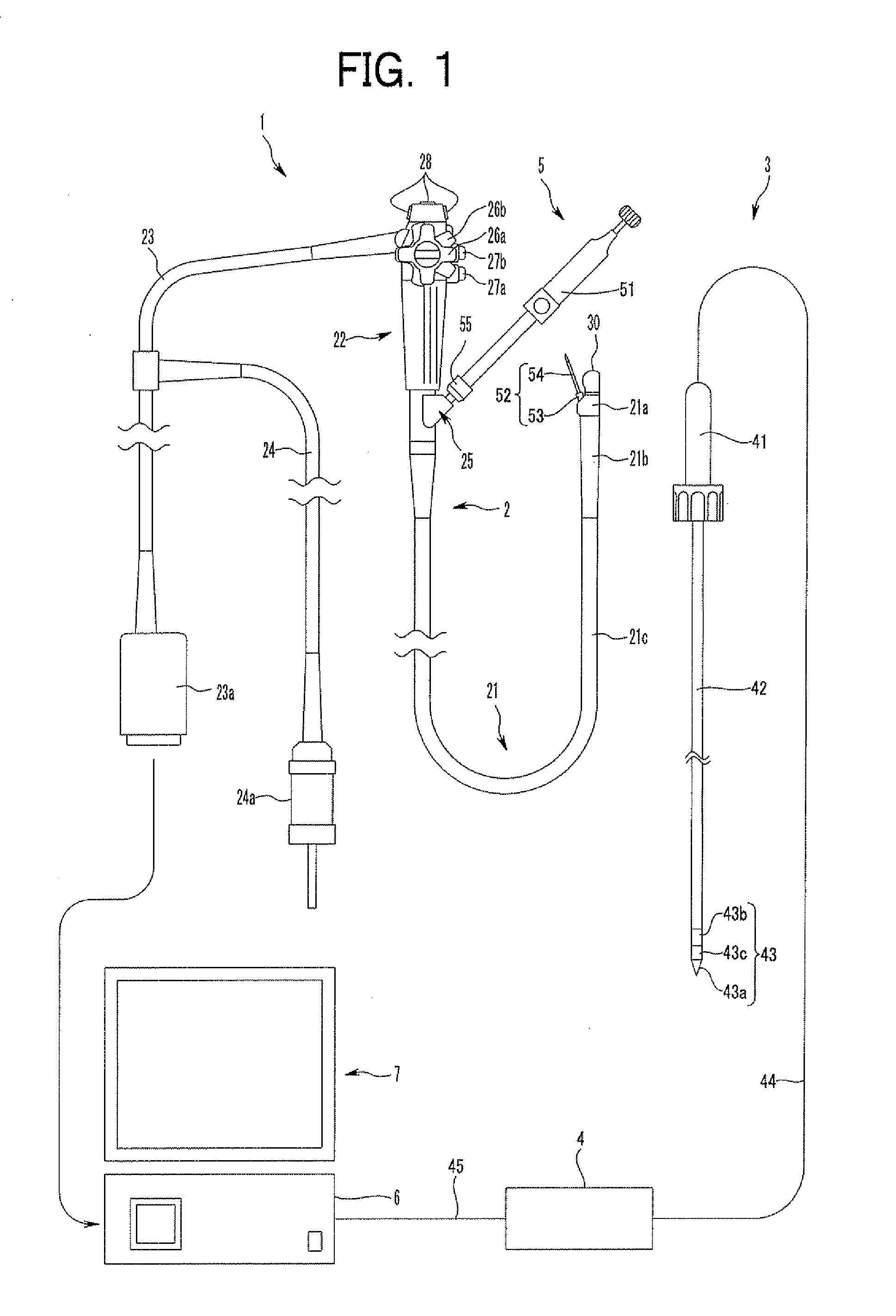
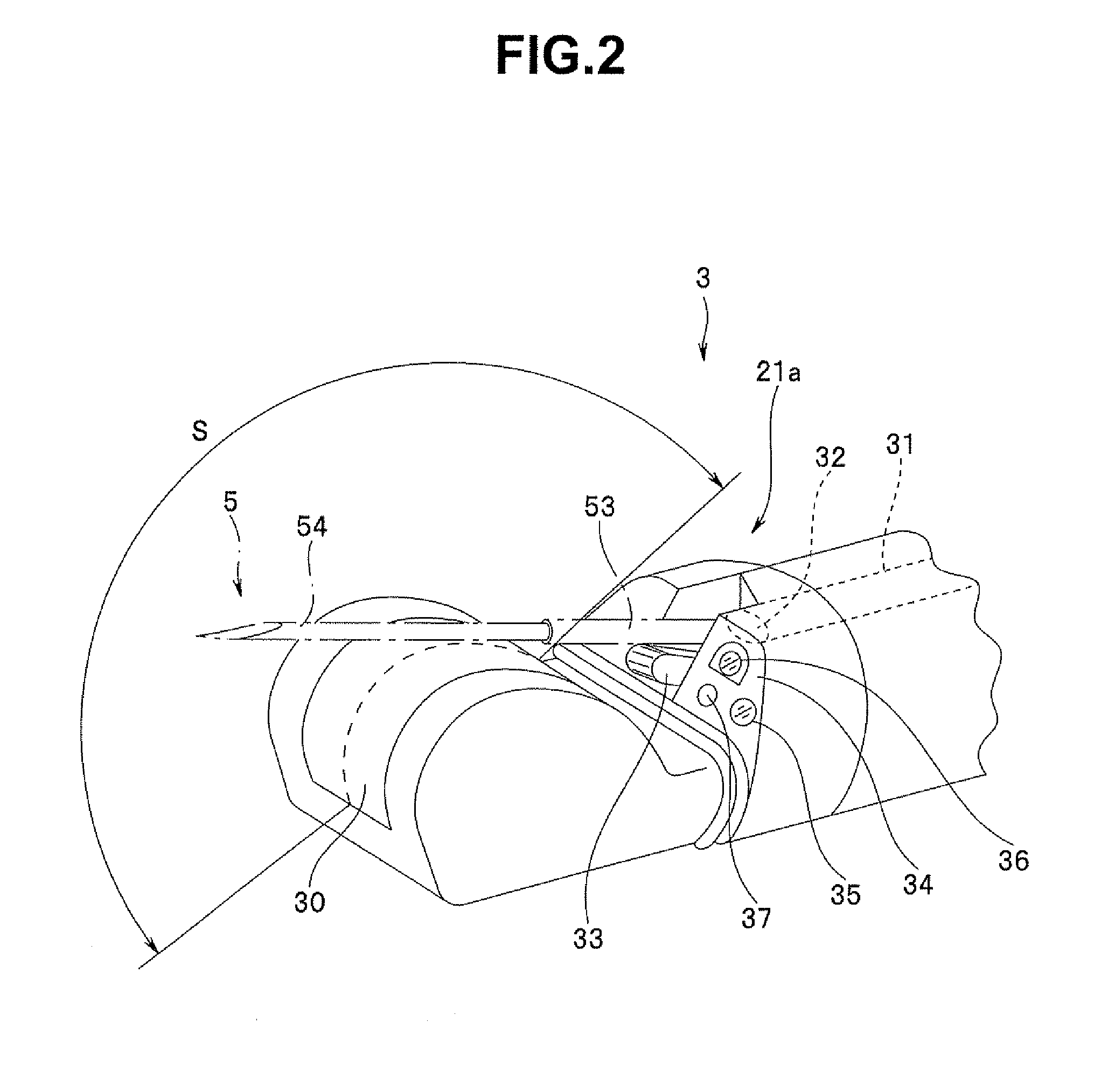
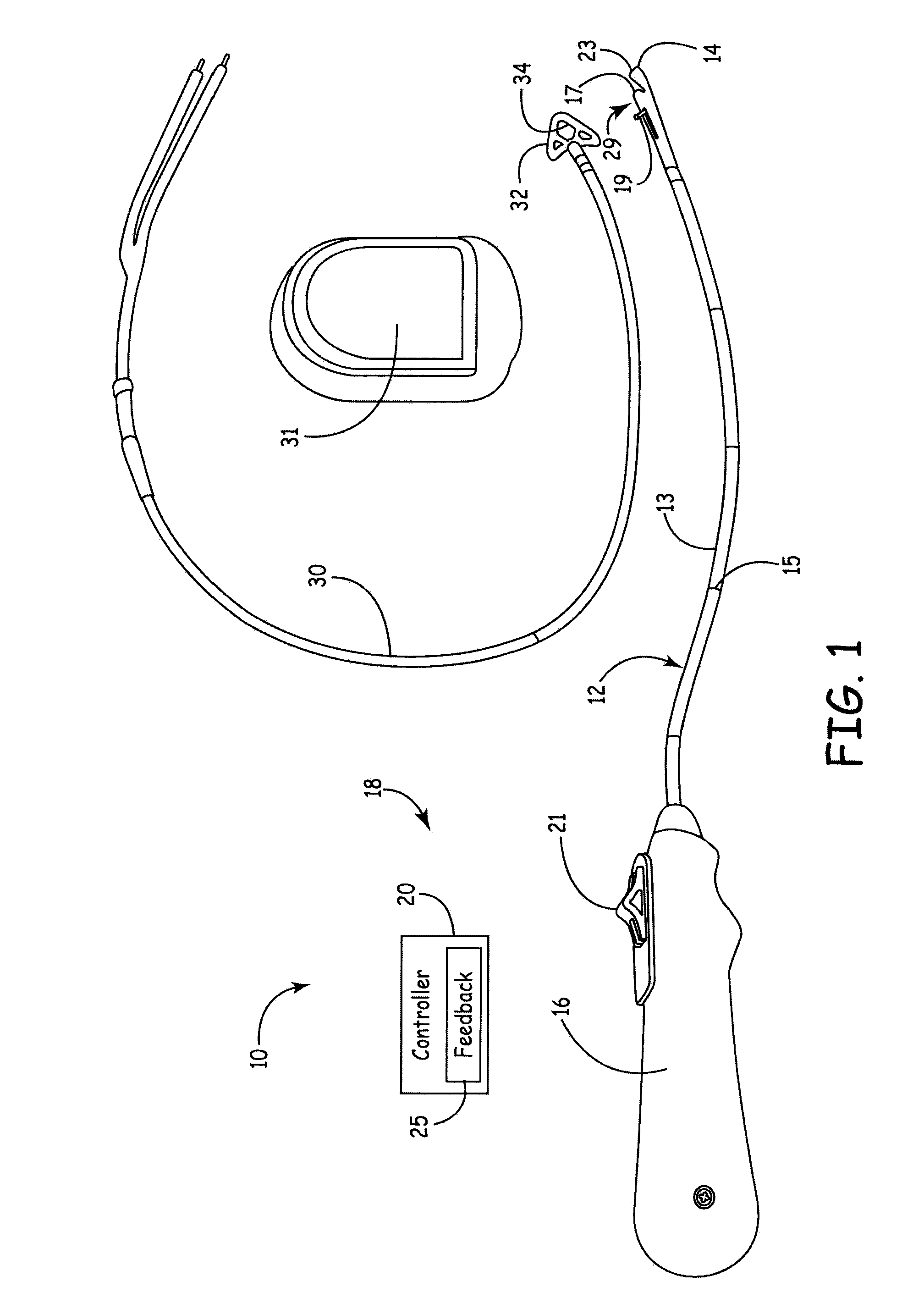
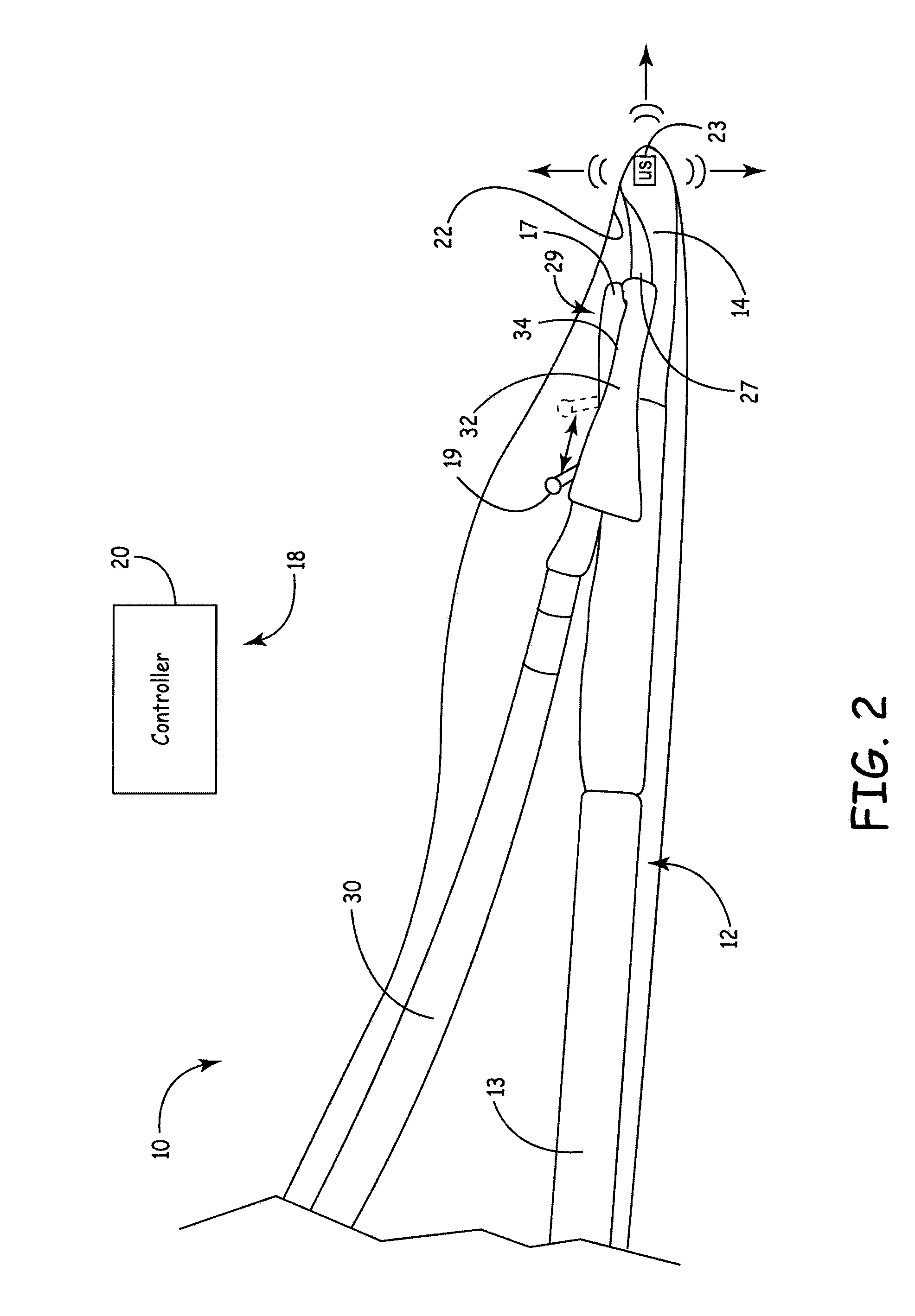
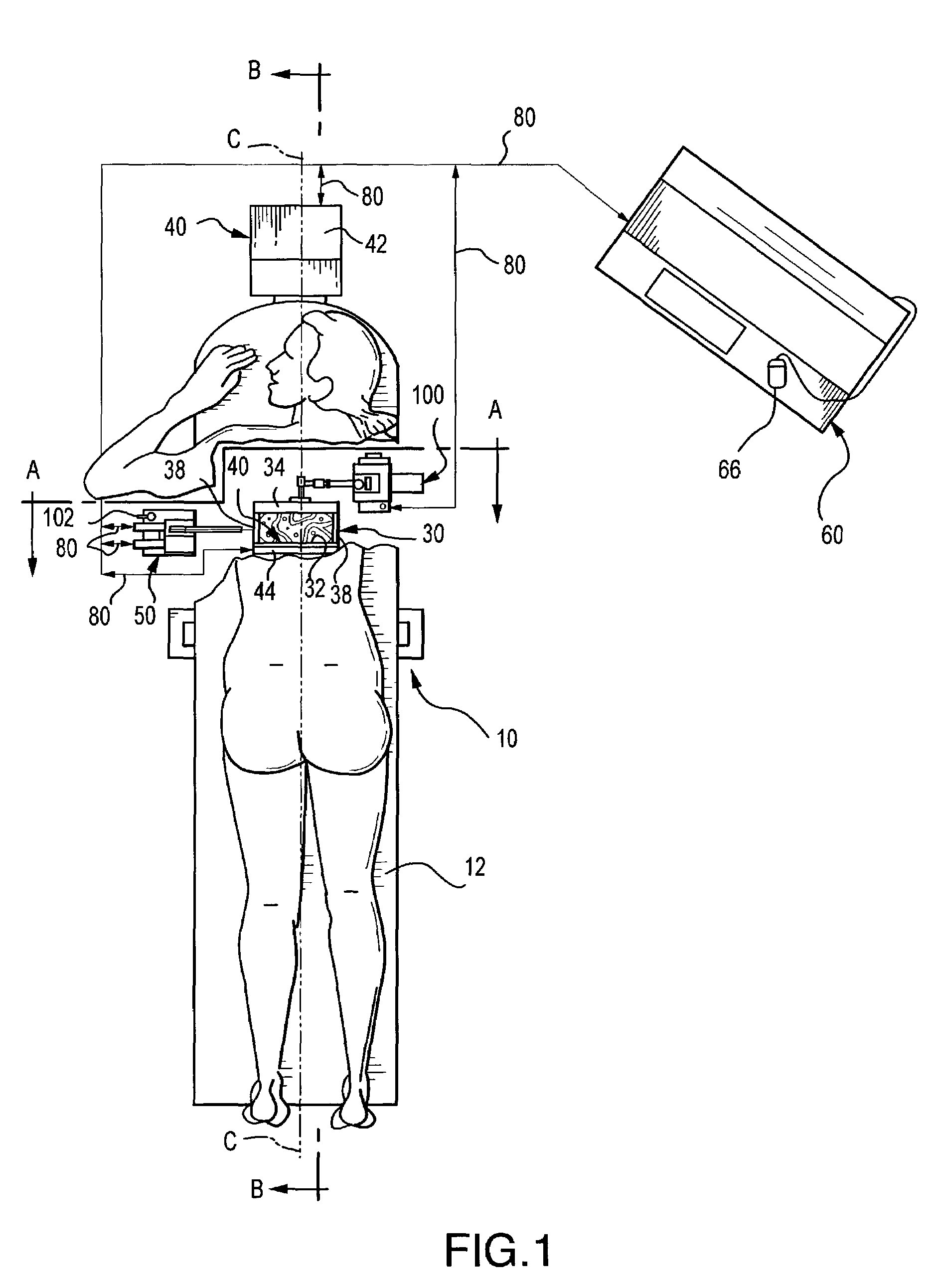
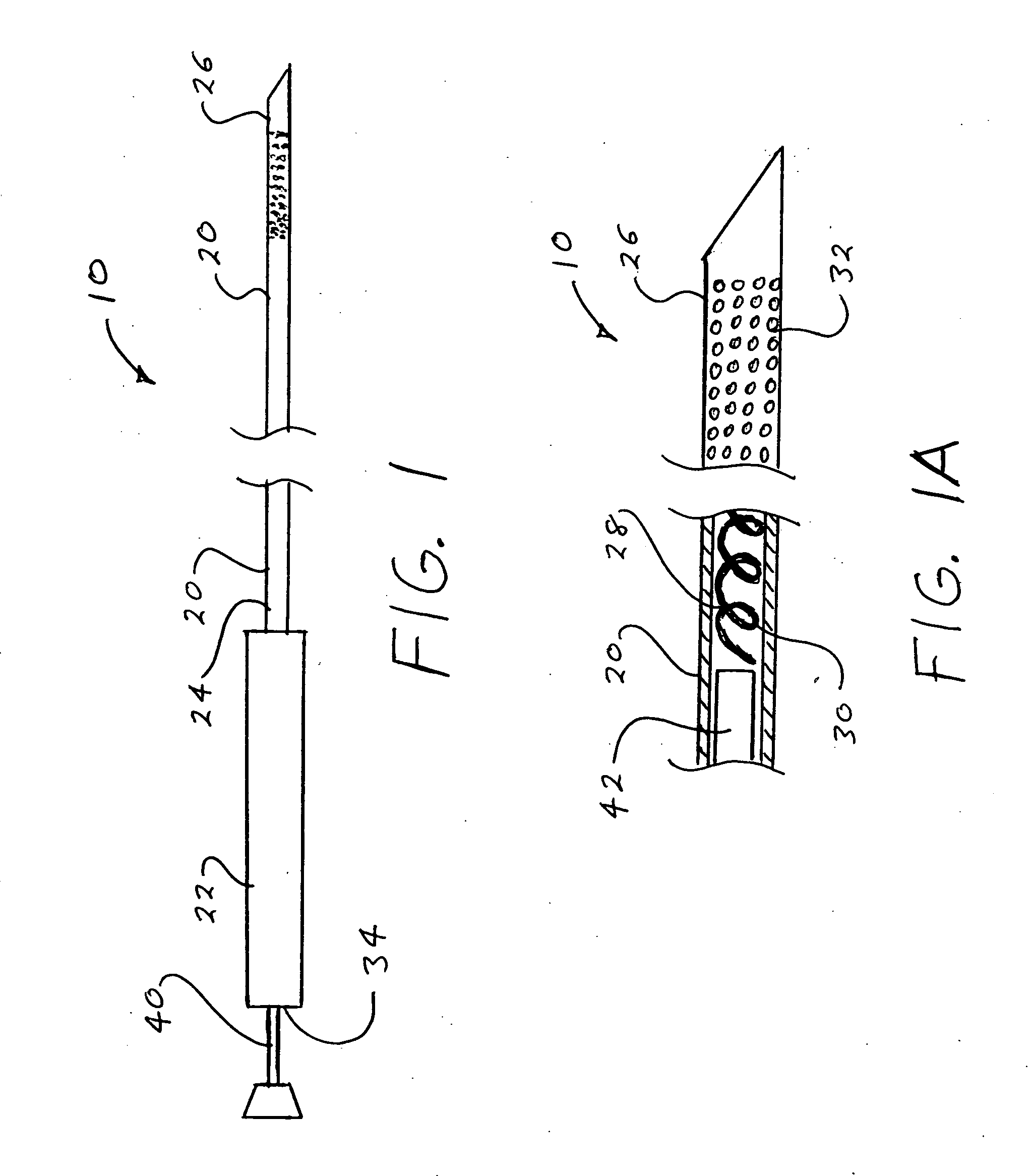
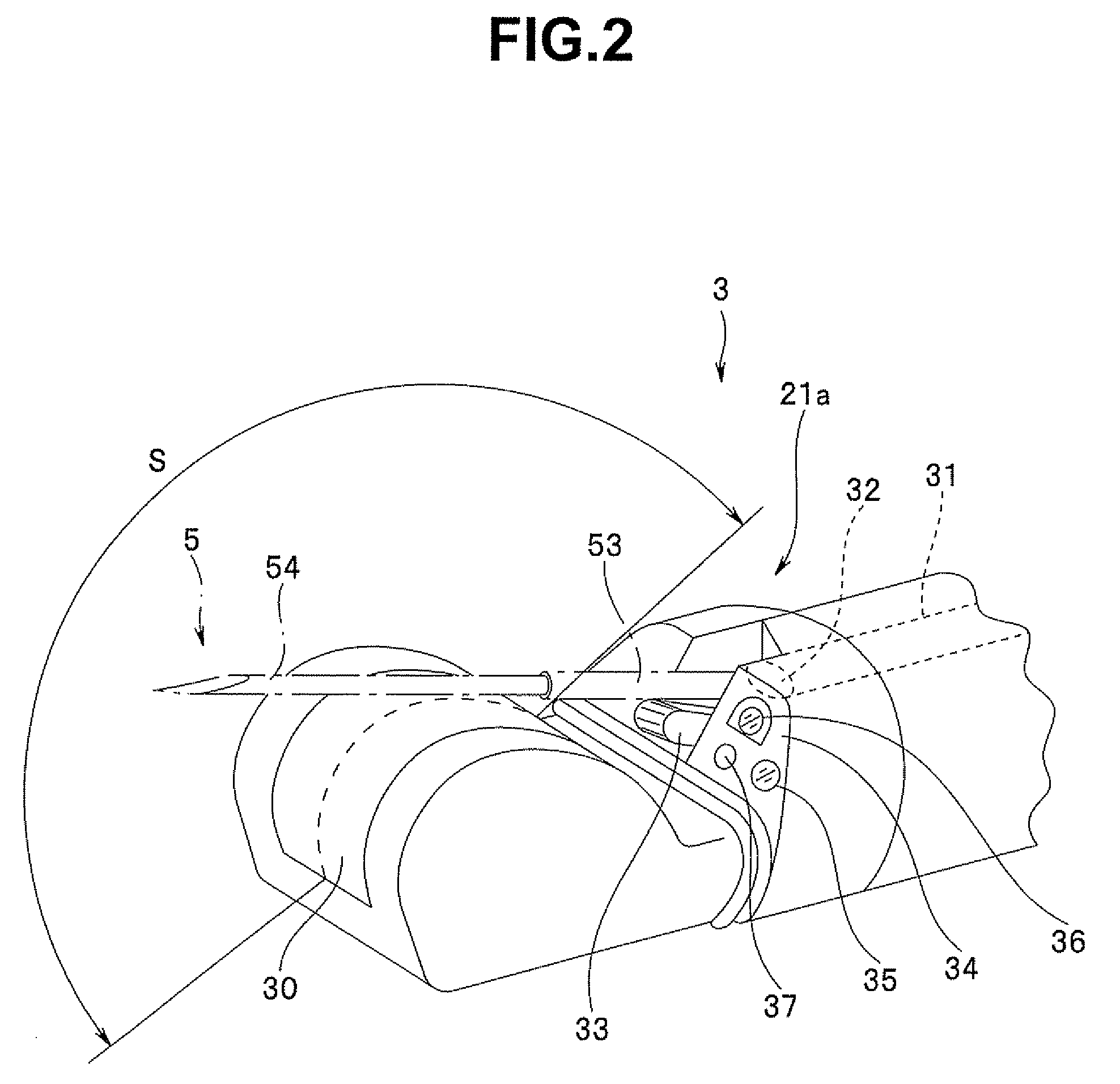
Ultrasound guided probe device and method of using same
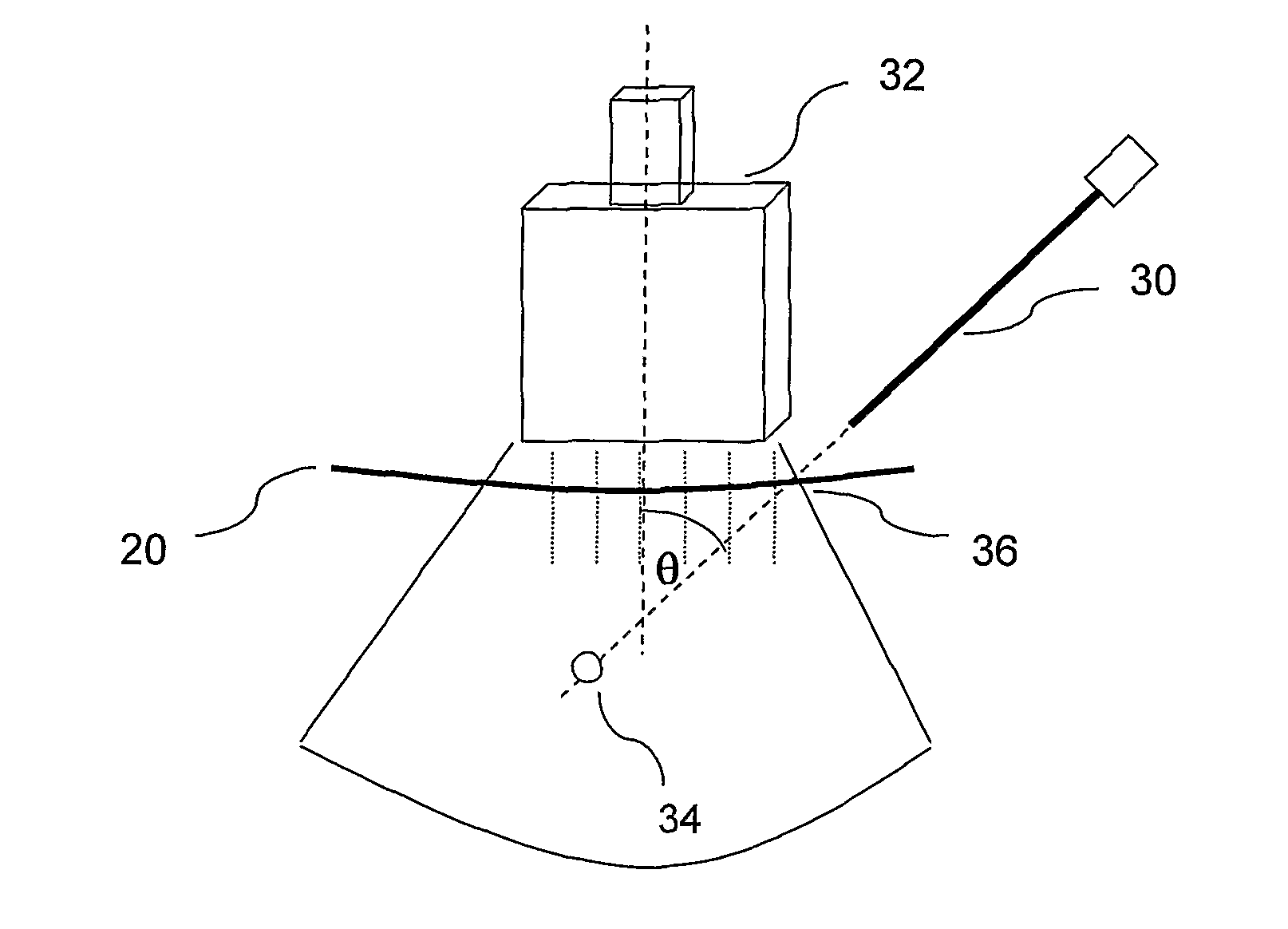
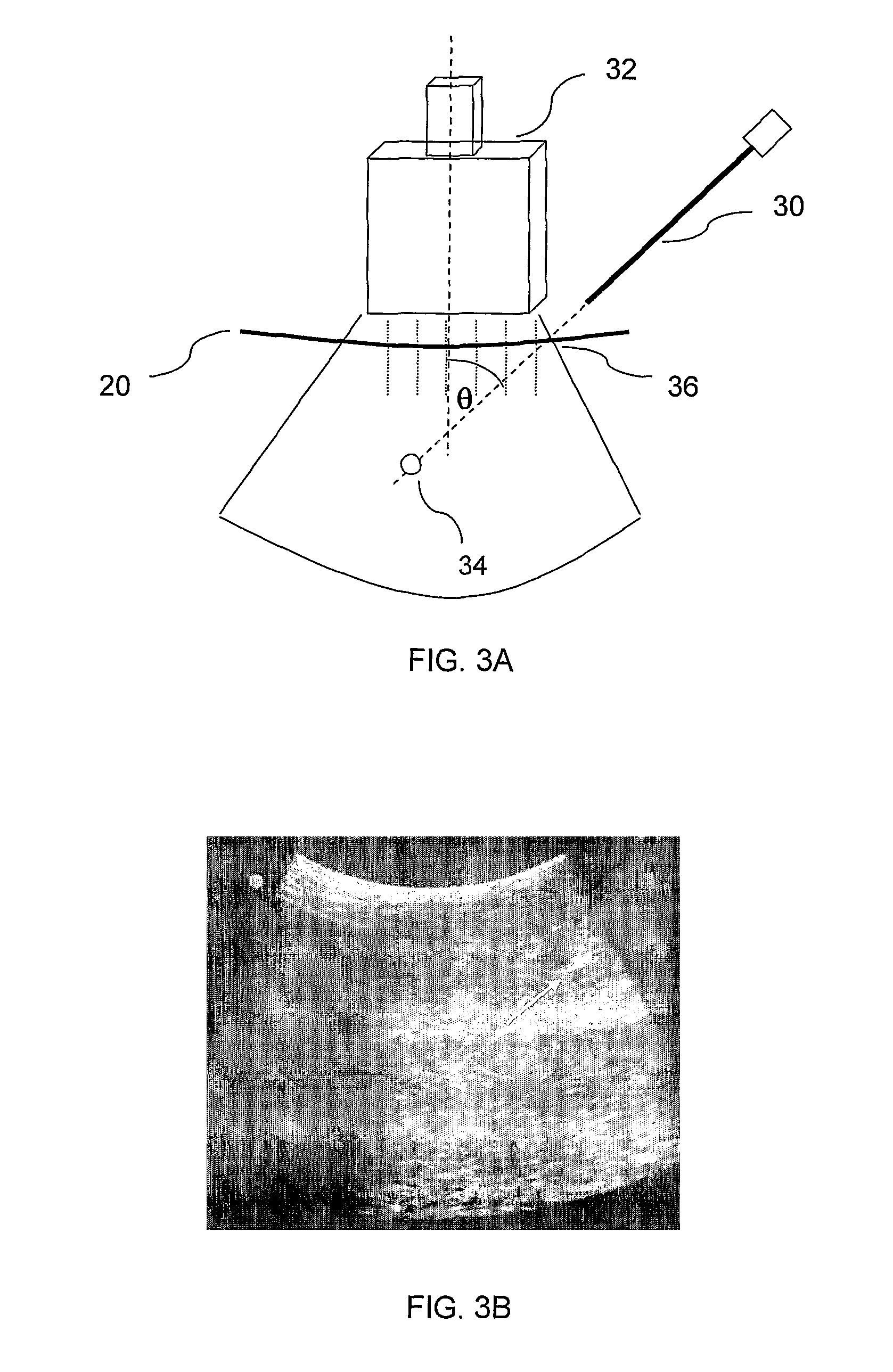
The present invention is directed to improved devices and methods for use in ultrasound guiding of percutaneous probes during medical procedures. The ultrasound devices of the present invention include an ultrasound transducer housing having a passage therethrough configured to accommodate a probe. The devices can be utilized to guide a probe through the probe guide in the passage of the transducer housing, and along a path extending from the ultrasound transducer housing to a target at a known angular relationship to the ultrasound transducer. In this manner, the path of the advancing probe and hence the location of the probe tip can be more clearly known in relation to a target imaged by the ultrasound device. In addition, the devices can include a sterile sleeve including a sterile probe guide such that the transducer housing itself, including the integral probe guide opening, can be separated from the patient by a sterile barrier. The devices can also include a clamp for clamping the probe in the probe guide. The devices can also include means and methods for imaging a virtual probe overlaying the sonogram formed by the ultrasound device such that a real time image of the probe approach to the target may be observed during and after probe placement.
Owner:SOMA RES LLC
Biomedical positioning and stabilization system
InactiveUS20070129634A1Minimal effortGood flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesAnatomical structuresPrimary operation
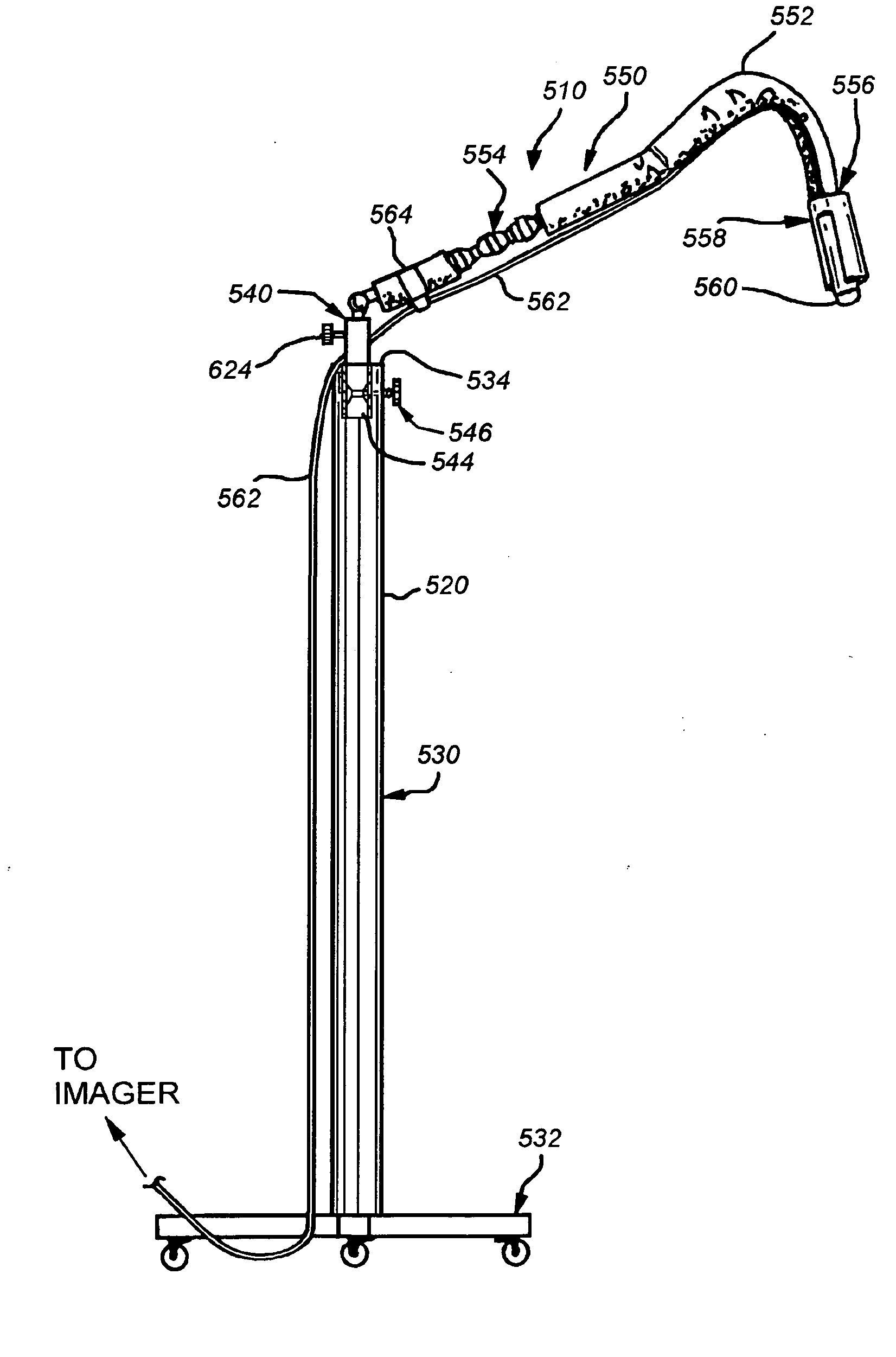
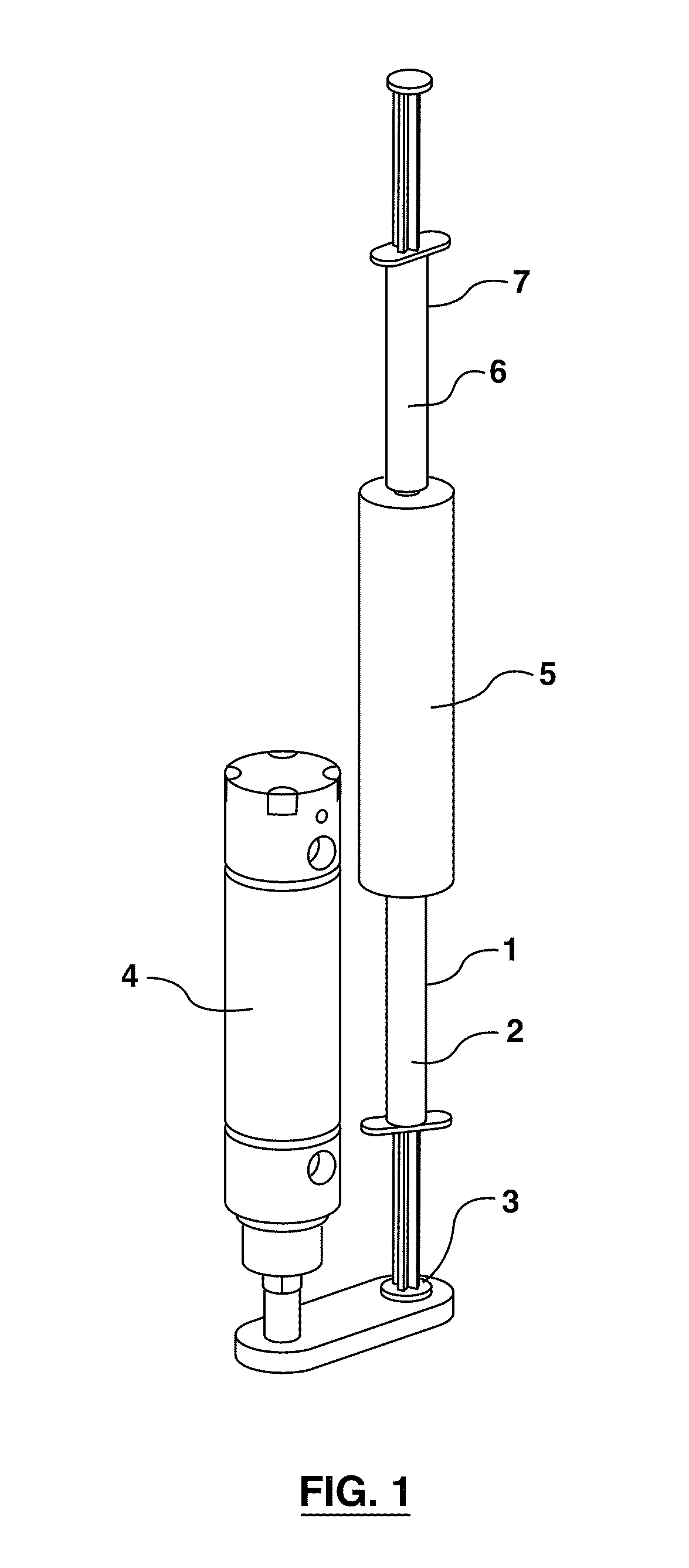
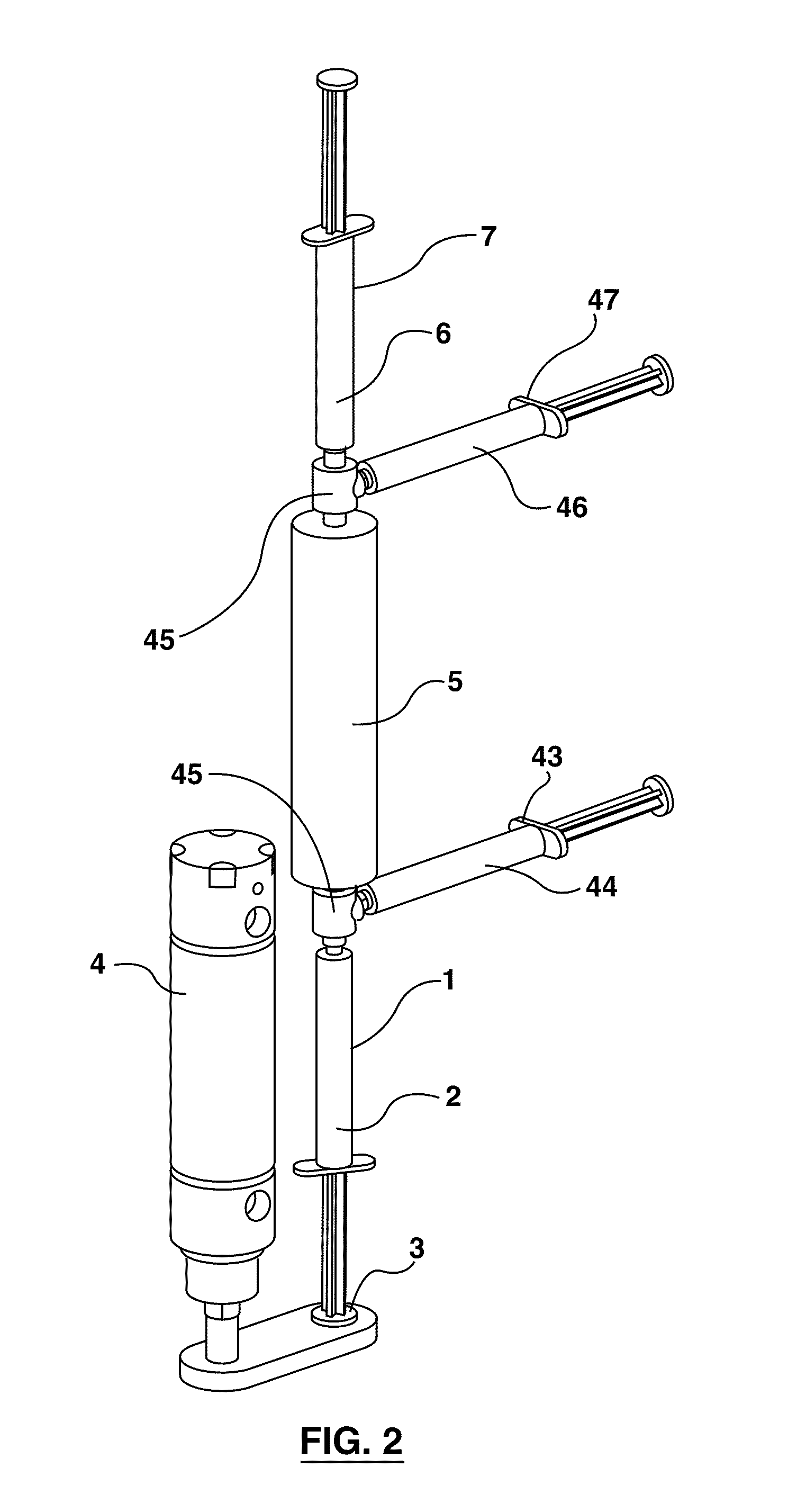
This invention provides a support device that allows the adjustable, yet rigid placement of a probe or other medical instrument against a region of interest / treatment on a patient. The system and method of rigid fixation, positioning, and adjustment contemplated herein is useful for a broad array of medical procedures including, but not limited to, ultrasound-guided anesthetic delivery. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a flexible armature is attached to a rigid stand placed upon the floor, or attached to another stable surface such as a bed rail, wall, ceiling or piece of equipment. A joint connects the armature to an instrument holder able to accommodate and rigidly attach an ultrasound sensing probe or other medical device. The medical device then remains rigidly attached to the described invention during the procedure. Furthermore, this set position is resistant to minor patient motion or other disturbances. If required, small alterations can be made by the operator during the procedure with minimal effort. Such adjustment may be desirable, for example, if access to a new anatomical structure is needed. In this manner, the primary operator is able to maintain a ‘hands-free’ approach.
Owner:WELLAN MEDICAL SOLUTIONS +1
Microbubble medical devices
ActiveUS20100228122A1Enhance heat ablation effectSimple procedureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersFocus ultrasoundLight activation
Method and medical devices for generating and stabilizing micro- or nano-bubbles, and systems and methods for therapeutic applications using the bubbles, are provided. The micro-bubbles may be used to enhance therapeutic benefits such as ultrasound-guided precision drug delivery and real-time verification, acoustic activation of large tumour masses, enhanced acoustic activation through longer retention of therapeutic agents at the point of interest, enhancement of high intensity focused ultrasound treatments, light activation of photodynamic drugs at a depth within a patient using extracorporeal light sources, probes, or sonoluminescence, and initiation of time reversal acoustics focused ultrasound to permit highly localized treatment.
Owner:ARTENGA
Ultrasound guided probe device and method of using same
The present invention is directed to improved devices and methods for use in ultrasound guiding of percutaneous probes during medical procedures. The ultrasound devices of the present invention include an ultrasound transducer housing having a passage therethrough configured to accommodate a probe. The devices can be utilized to guide a probe through the probe guide in the passage of the transducer housing, and along a path extending from the ultrasound transducer housing to a target at a known angular relationship to the ultrasound transducer. In this manner, the path of the advancing probe and hence the location of the probe tip can be more clearly known in relation to a target imaged by the ultrasound device. In addition, the devices can include a sterile sleeve including a sterile probe guide such that the transducer housing itself, including the integral probe guide opening, can be separated from the patient by a sterile barrier. The devices can also include a clamp for clamping the probe in the probe guide. The devices can also include means and methods for imaging a virtual probe overlaying the sonogram formed by the ultrasound device such that a real time image of the probe approach to the target may be observed during and after probe placement.
Owner:SOMA RES LLC
Ultrasound guided optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic probe for biomedical imaging
ActiveUS20110098572A1High resolution imagingEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHigh resolution imaging
An imaging probe for a biological sample includes an OCT probe and an ultrasound probe combined with the OCT probe in an integral probe package capable of providing by a single scanning operation images from the OCT probe and ultrasound probe to simultaneously provide integrated optical coherence tomography (OCT) and ultrasound imaging of the same biological sample. A method to provide high resolution imaging of biomedical tissue includes the steps of finding an area of interest using the guidance of ultrasound imaging, and obtaining an OCT image and once the area of interest is identified where the combination of the two imaging modalities yields high resolution OCT and deep penetration depth ultrasound imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Rotating fine needle for core tissue sampling
ActiveUS20060116605A1Easy to collectSmall diameterSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSurgical siteEcho endoscopie
A medical instrument usable with an ultrasound-endoscope for performing a needle biopsy on a patient's internal body tissues usable at a surgical site not visible to the unaided eye or viewed endoscopically, comprises an elongate tubular member with a hollow needle element connected at its distal end, a sheath member housing said tubular member and needle element, an actuator subassembly with a shifter member operatively connected to elongate tubular member's proximal end, and a distal camming subassembly, said subassembly enabling a rotating motion of said needle member while handle actuator is moved in the forward direction. Upon inserting an ultrasound-endoscope into a patient and locating a mass, the fine needle with sharply pointed spoon shaped distal end is inserted into the mass aided by endoscopic and ultrasonographic guidance. Once in the mass, a camming action is initiated, causing rotation of the fine needle within the mass, resulting in a scooped out core biopsy. This instrument enables the performance of a fine needle aspiration requiring only one or two needle introductions, with a resultant core biopsy substantial enough for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
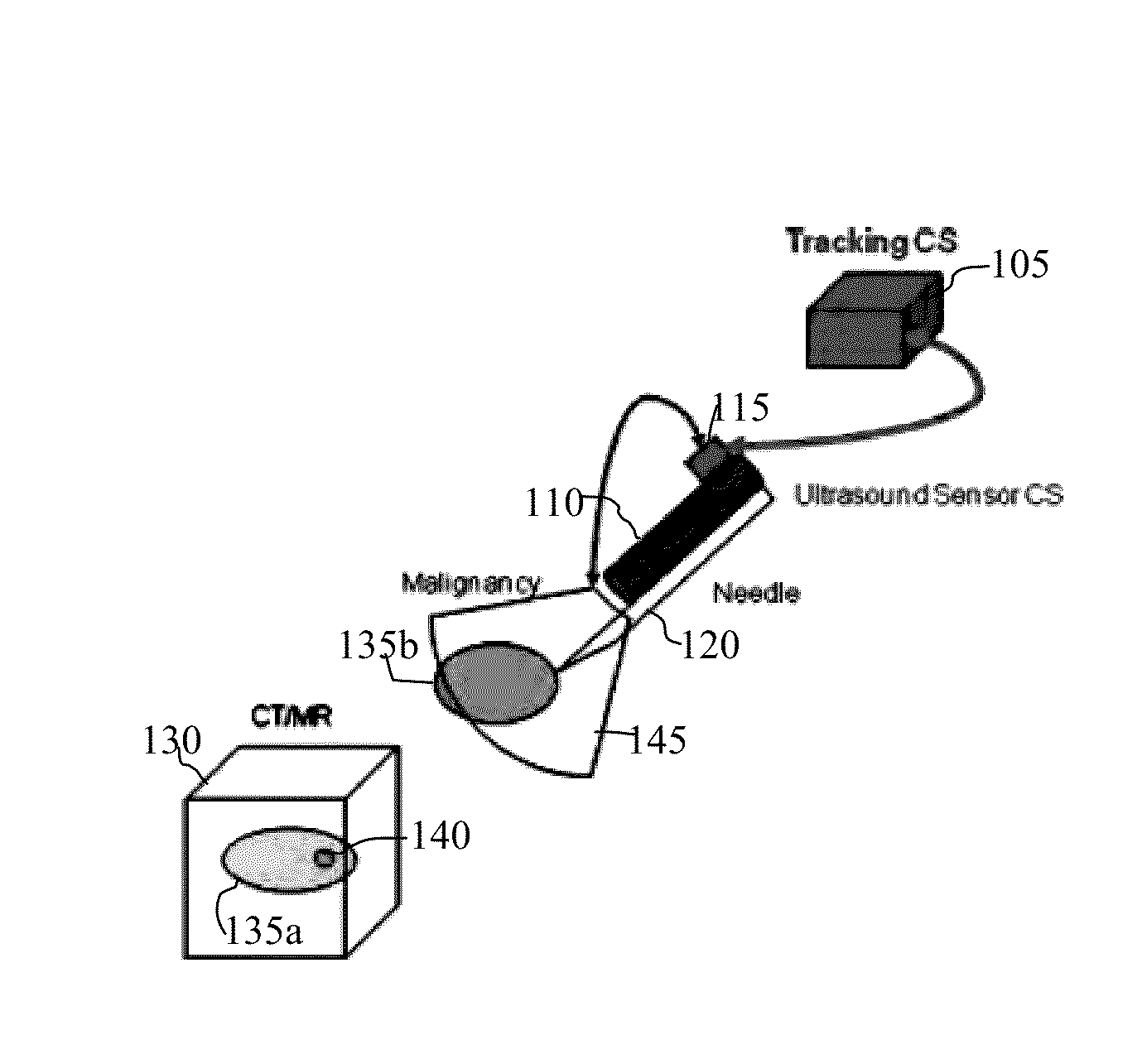
System and Method for Real-Time Ultrasound Guided Prostate Needle Biopsy Based on Biomechanical Model of the Prostate from Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data
A method and system for real-time ultrasound guided prostate needle biopsy based on a biomechanical model of the prostate from 3D planning image data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, is disclosed. The prostate is segmented in the 3D ultrasound image. A reference patient-specific biomechanical model of the prostate extracted from planning image data is fused to a boundary of the segmented prostate in the 3D ultrasound image, resulting in a fused 3D biomechanical prostate model. In response to movement of an ultrasound probe to a new location, a current 2D ultrasound image is received. The fused 3D biomechanical prostate model is deformed based on the current 2D ultrasound image to match a current deformation of the prostate due to the movement of the ultrasound probe to the new location.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
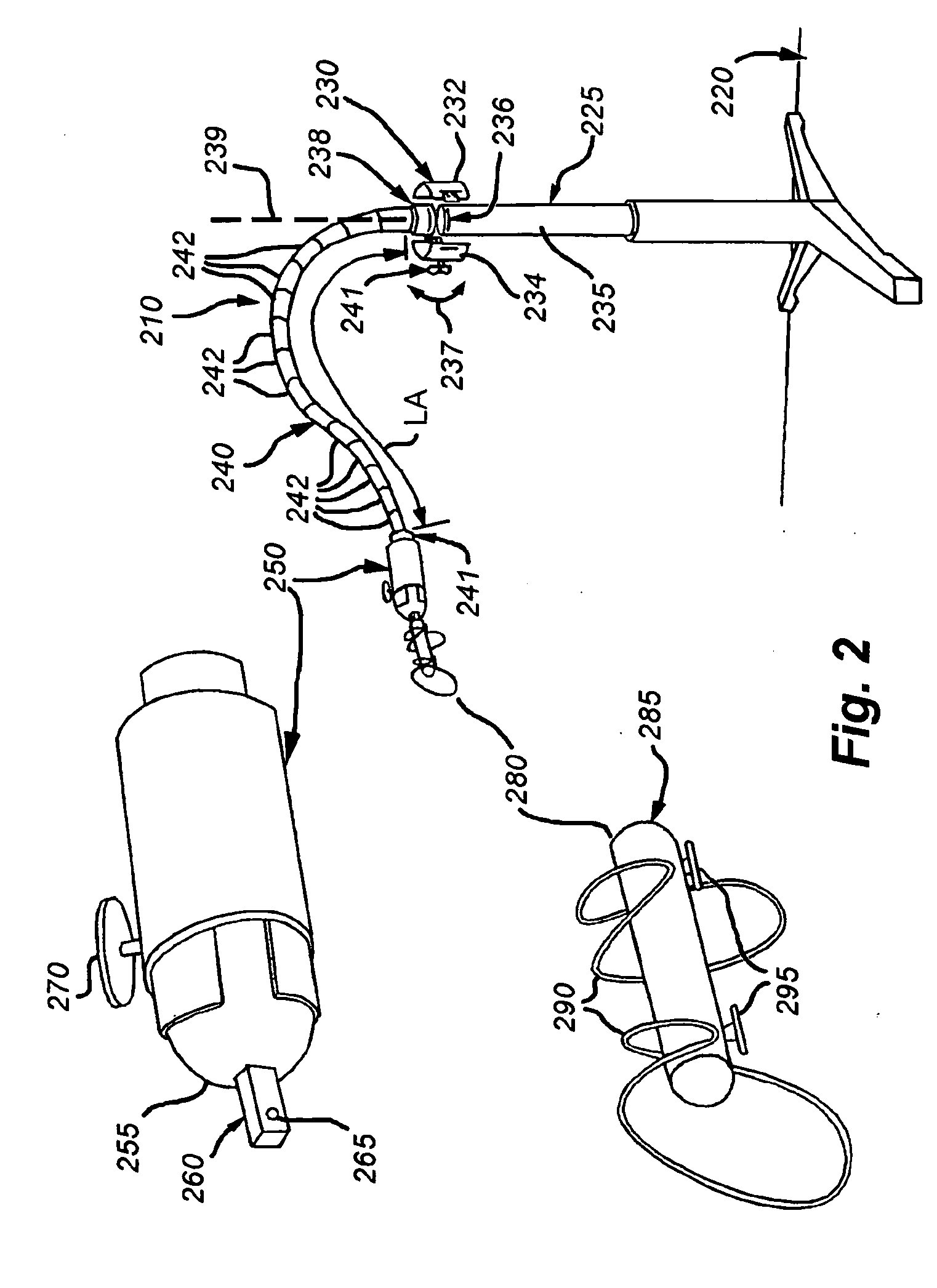
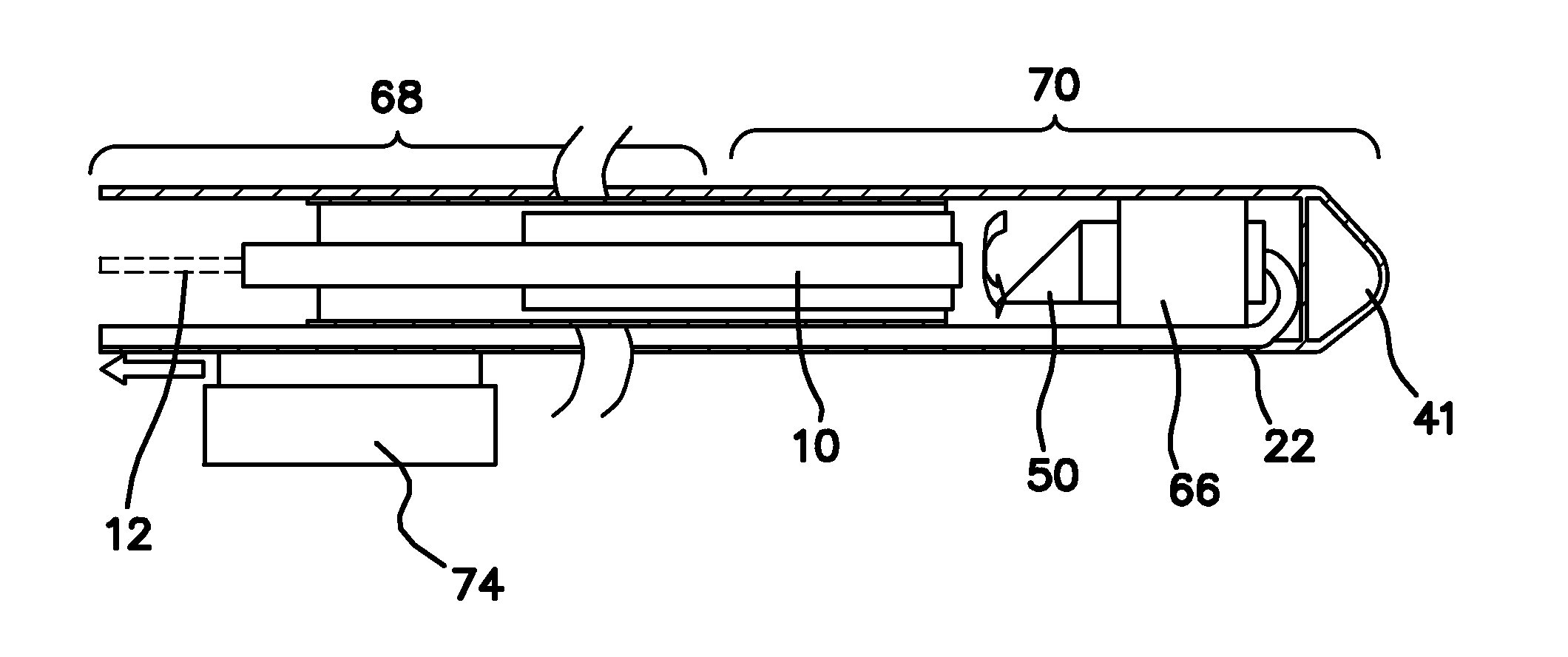
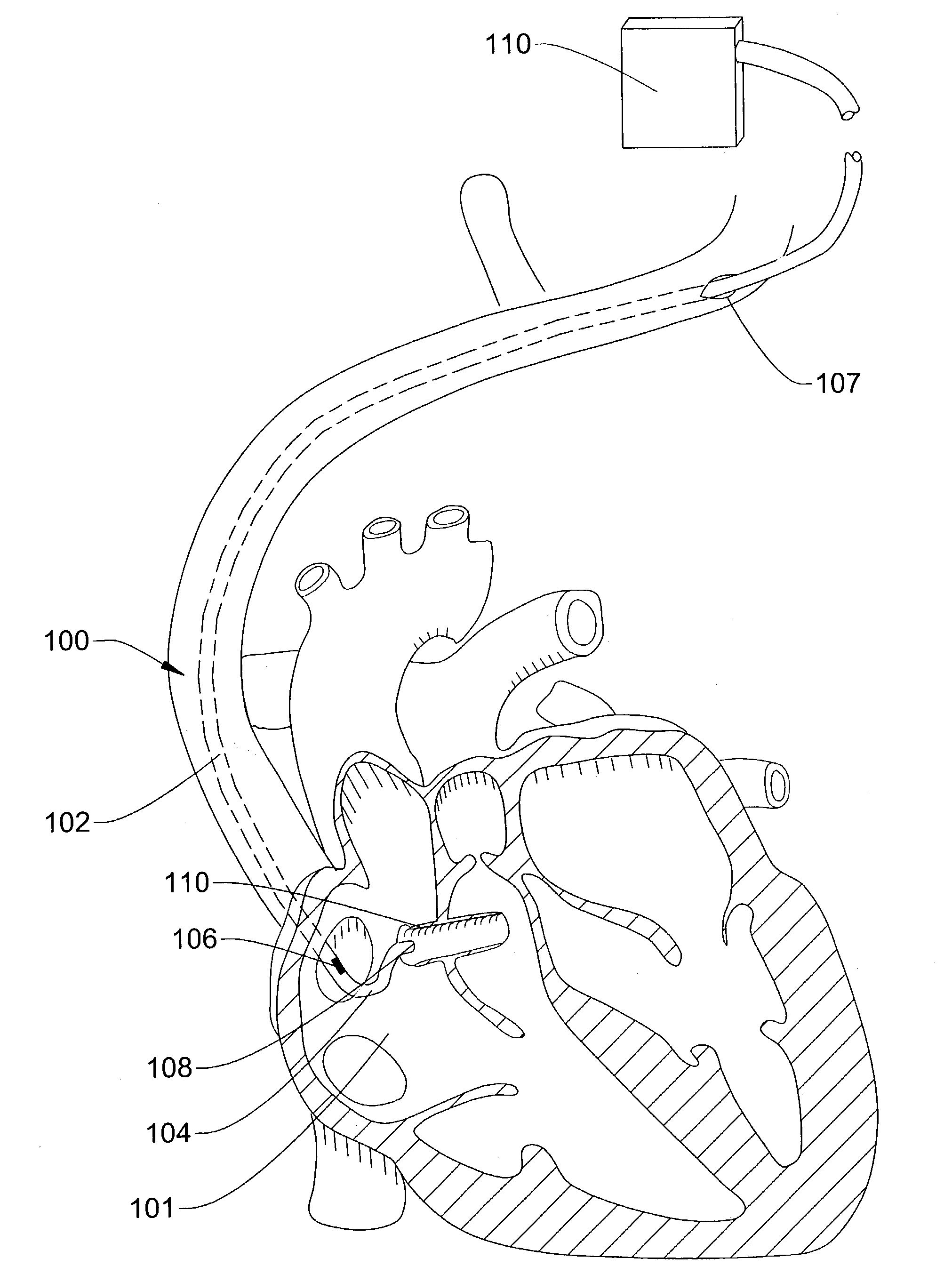
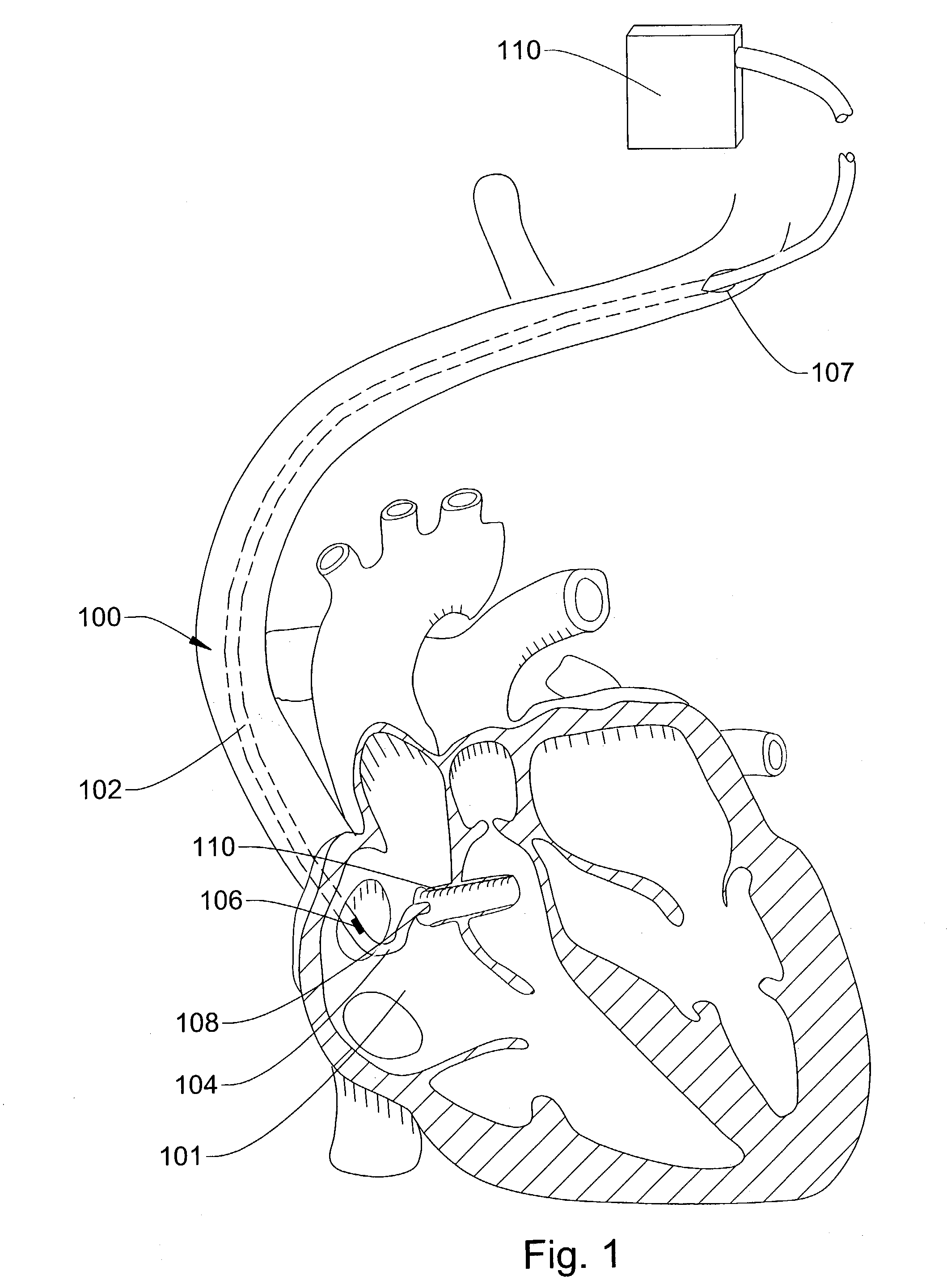
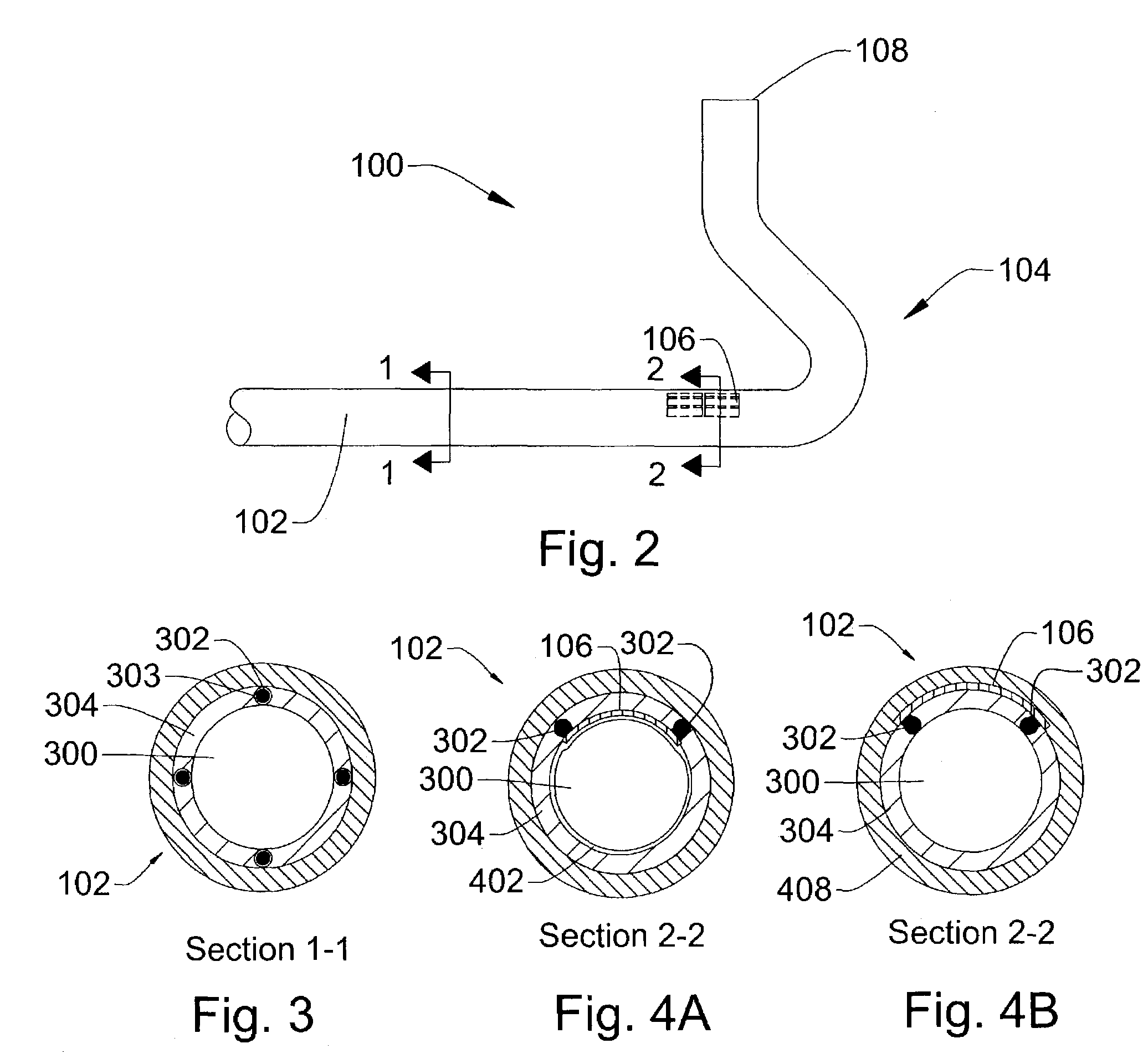
Ultrasound directed guiding catheter system and method
A guiding catheter system employs a flexible shaft having a preformed bend at a distal end. An ultrasound transducer is mounted proximal to the pre-formed bend. The ultrasound transducer has a field of view directed to a distal tip of the guiding catheter. The guiding catheter includes an open lumen adapted for the introduction of payloads through the catheter system. The guiding catheter system can be used to direct a smaller guiding catheter or guide wire into a destination vessel from a heart chamber. In one application, the guiding catheter system is used to introduce a guiding catheter into the coronary sinus ostium from the right atrium.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
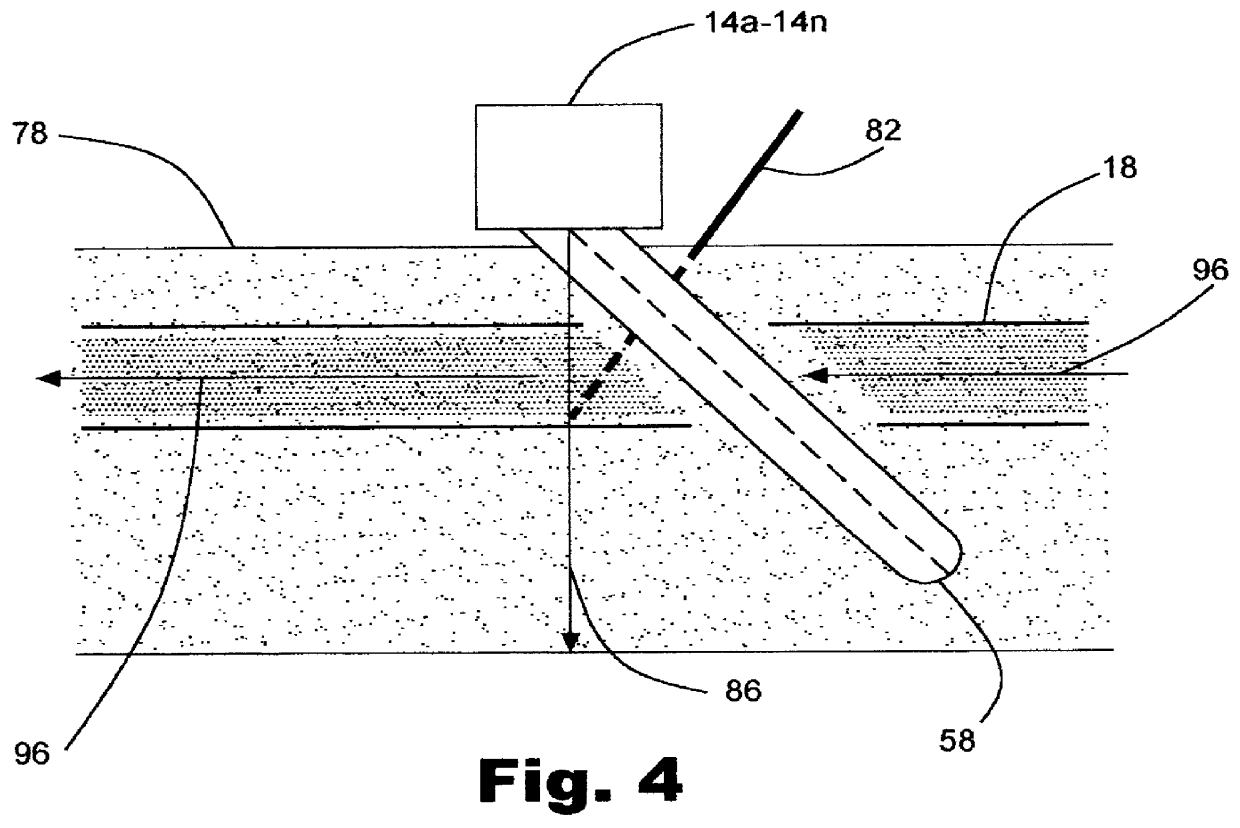
Ultrasound guided tissue measurement system
InactiveUS20060241450A1Uniform mannerPrecise positioningUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingGuidance system
A tissue guidance system integrates an ultrasound imaging device with a tissue diagnostic probe. Ultrasound imaging is used to guide the tissue probe to the target area. Measurements made by the probe can then be analyzed to determine tissue type or state (e.g., malignant or benign).
Owner:BIOTELLIGENT
Ultrasound guided automated wireless distraction osteogenesis
InactiveUS20130138017A1Promote healingOvercome problemsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasonic sensorSonification
A bone distraction device applies guided incremental forces to opposing bone segments for the purpose of generating native bone in an osteotomy site (distraction osteogenesis). The bone distraction device automatically adjusts the rate of the distraction utilizing feedback received from the ultrasound transducer and other sensors, using an adaptive decision algorithm(s). A wireless transmitter allows for remote guidance, feedback and monitoring.
Owner:JUNDT JONATHON +1
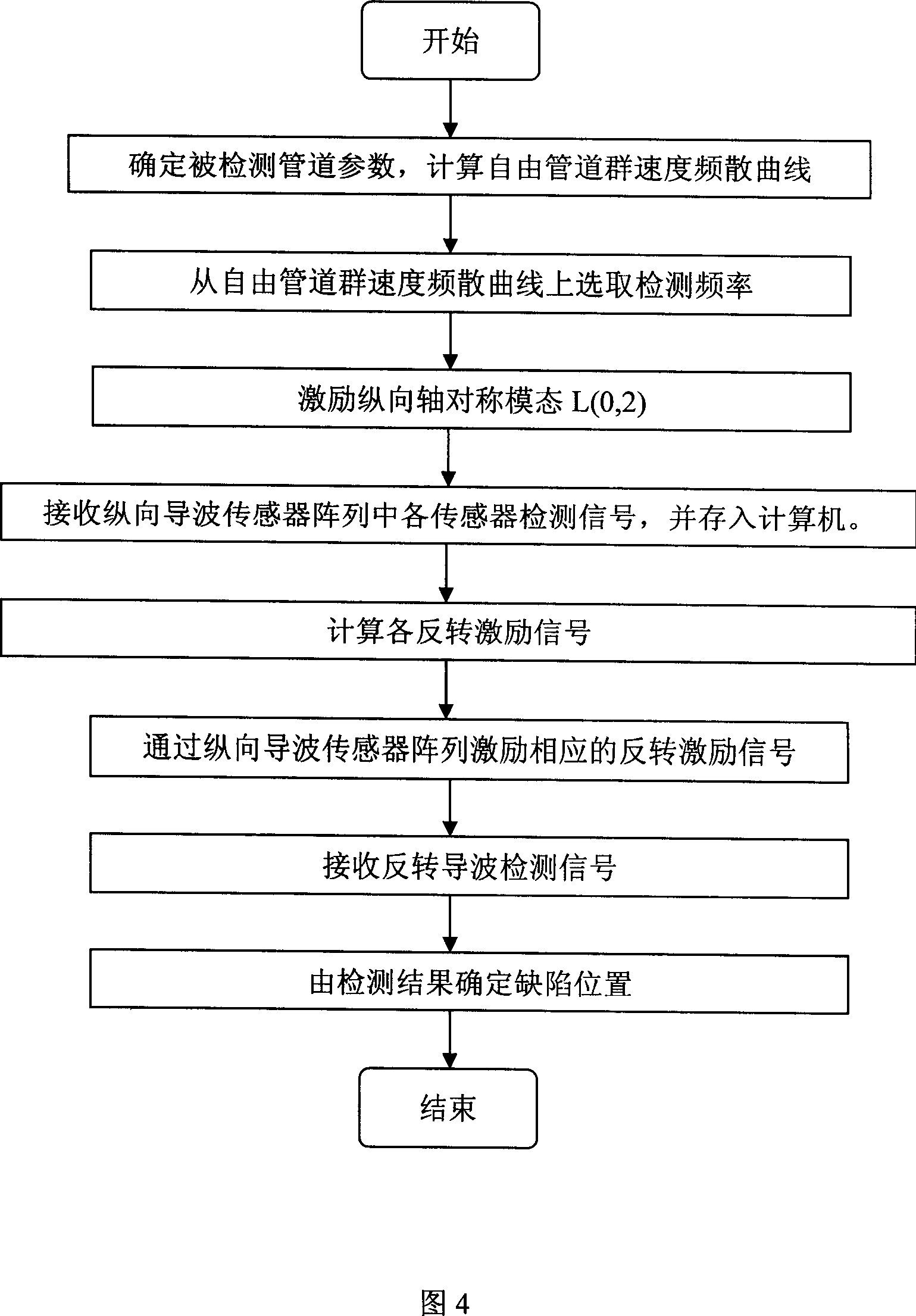
Supersonic guide-wave time reversion detection apparatus and method for defect of pipeline
ActiveCN1978977AImprove readabilityImprove detection abilityPipeline systemsSonificationWave detection
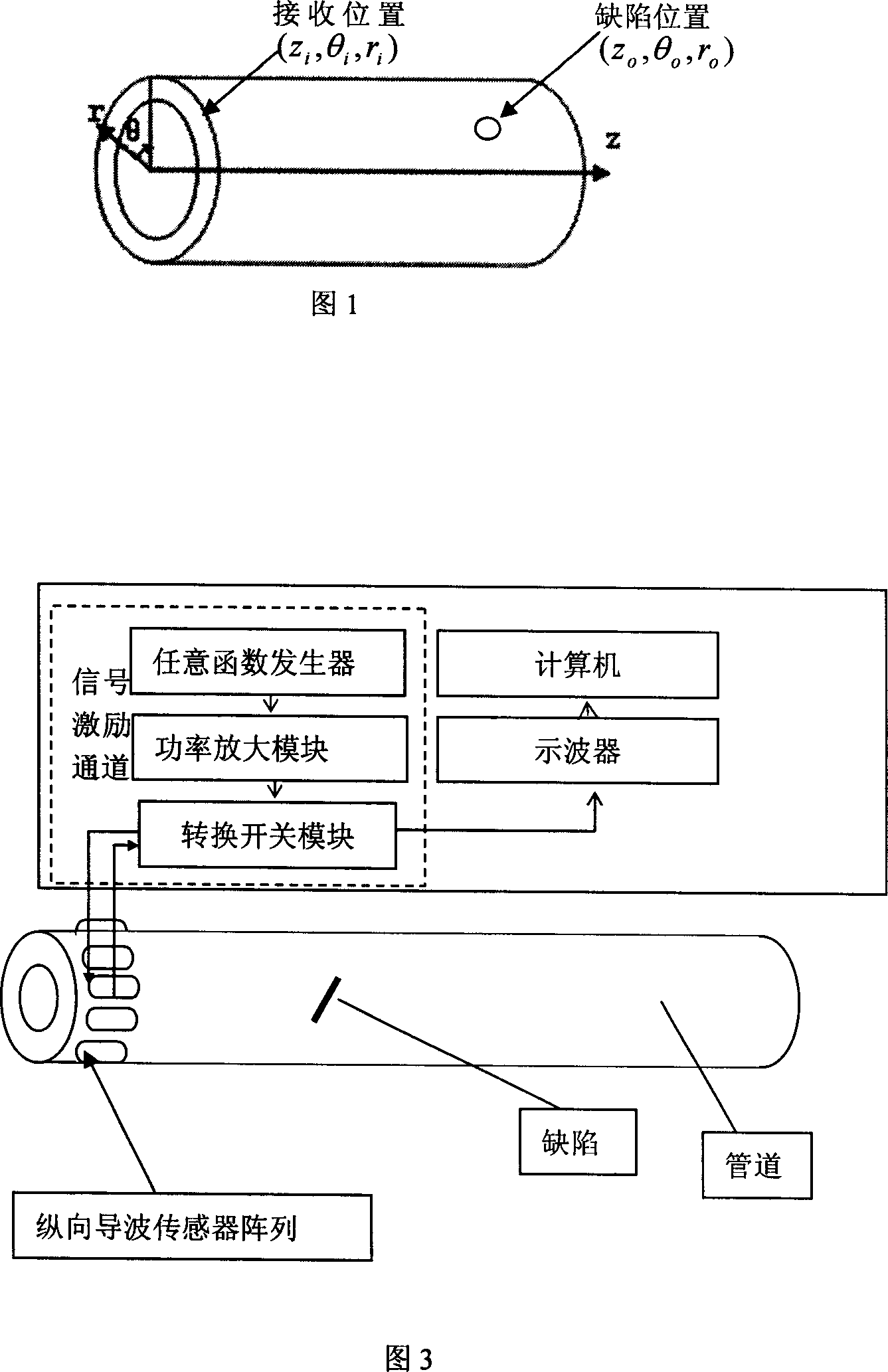
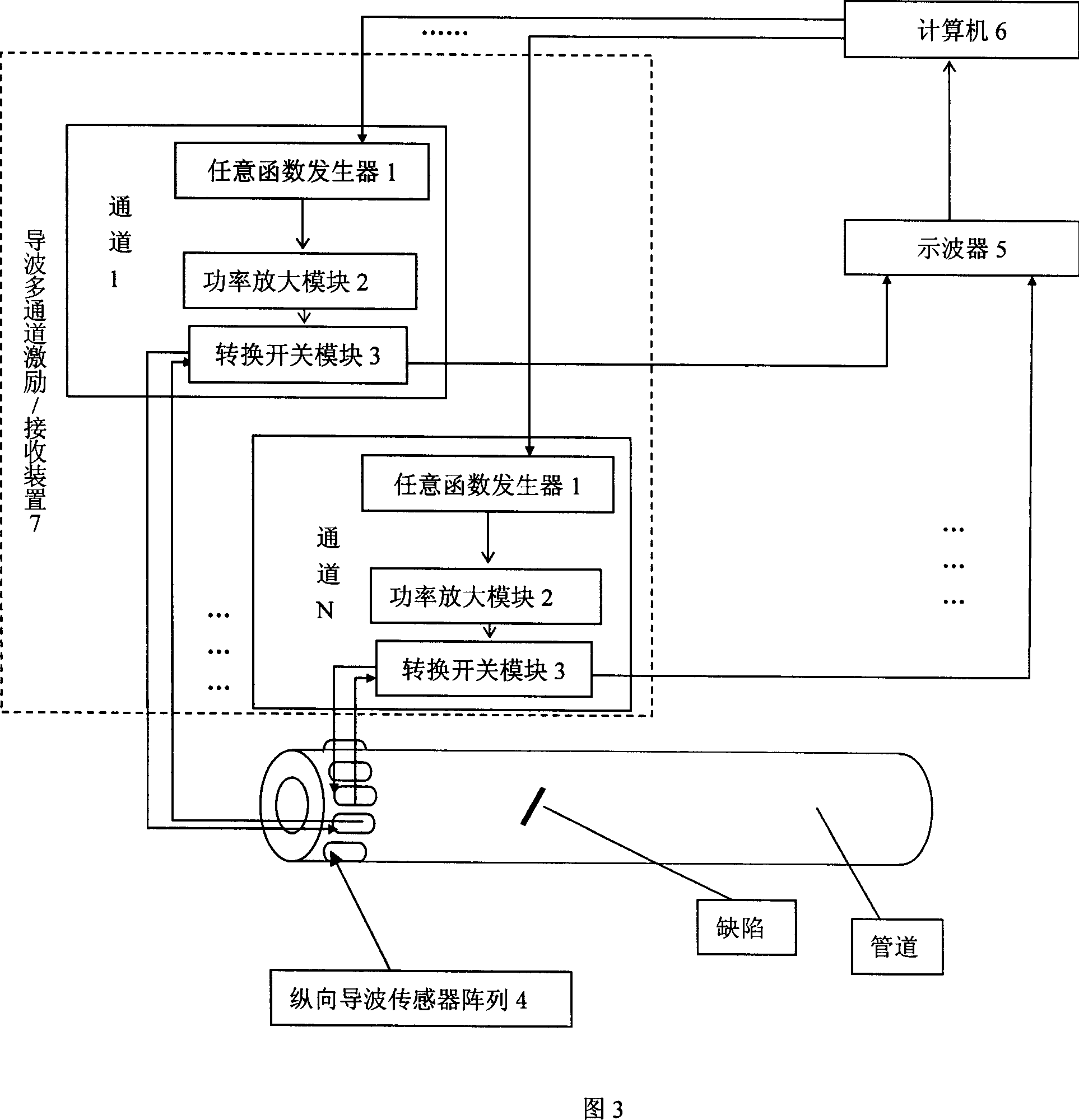
The invention relates to pipeline defect ultrasound guided wave time reversal detection device and method. The method includes the following steps: selecting detecting frequency according to the detected pipeline corresponding free hollow column structure group velocity dispersion curve; inputting the frequency into the arbitrary function generator to generate center frequency used as single sound signal; sending the signal to each passage of exciting / receiving set to transducer unit; exciting longitudinal axis symmetry guided wave modal; sending the reflected signal to the computer and gaining reversal excitation signal by time reversal; repeatedly exciting guided signal to detect. The invention realize space and time focus for guided wave detection, greatly improve detection capability for little defect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
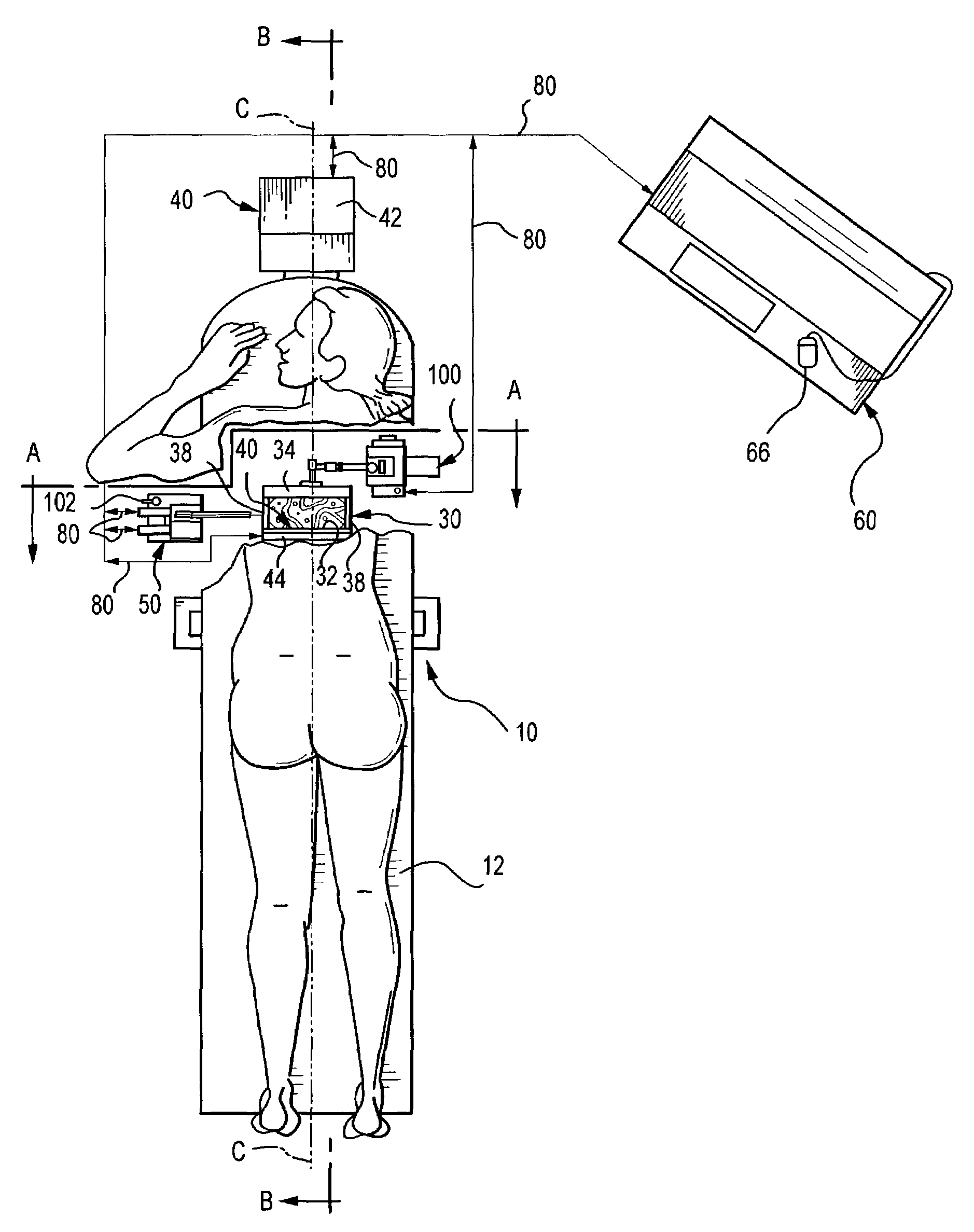
User interface system for mammographic imager
InactiveUS20090143674A1Reduce trained medical personnel time requirementEasy to useOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesBody contactX-ray
The present invention provides for x-ray imaging and ultrasound imaging of a body region of interest in a spatially correlatable manner. The resultant x-ray and ultrasound images may be combinatively employed to provide three-dimensional information regarding a location of interest within the body, and is particularly apt for use in the analysis / biopsy of potential lesions and suspicious masses in a female breast. The invention provides for direct body contact by an ultrasound imaging head, as well as targeted ultrasound imaging of a selected portion of the region from which x-ray images are obtained. A user interface system facilitates various procedures including ultrasound guided needle biopsy procedures.
Owner:NIELDS MORGAN W +2
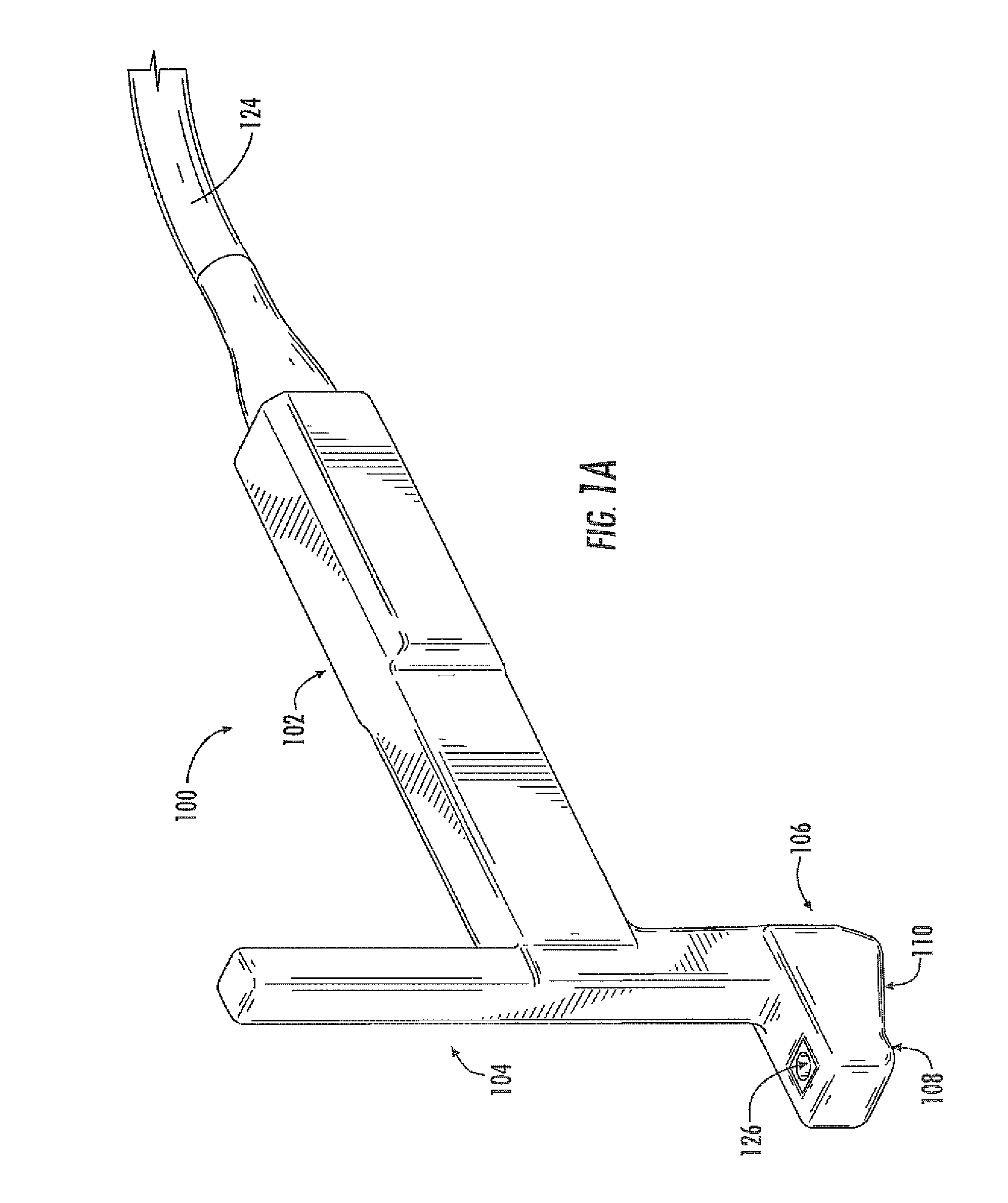
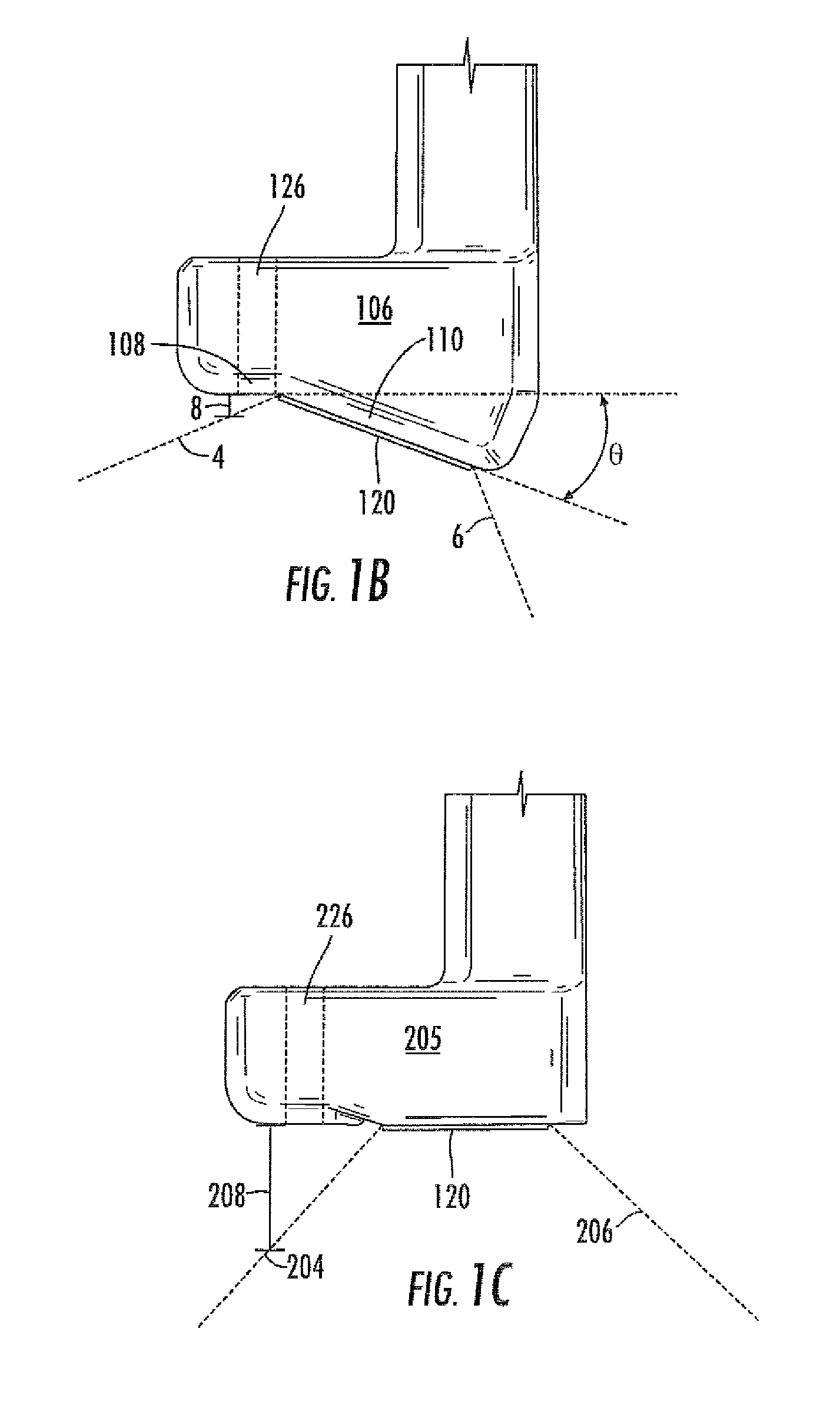
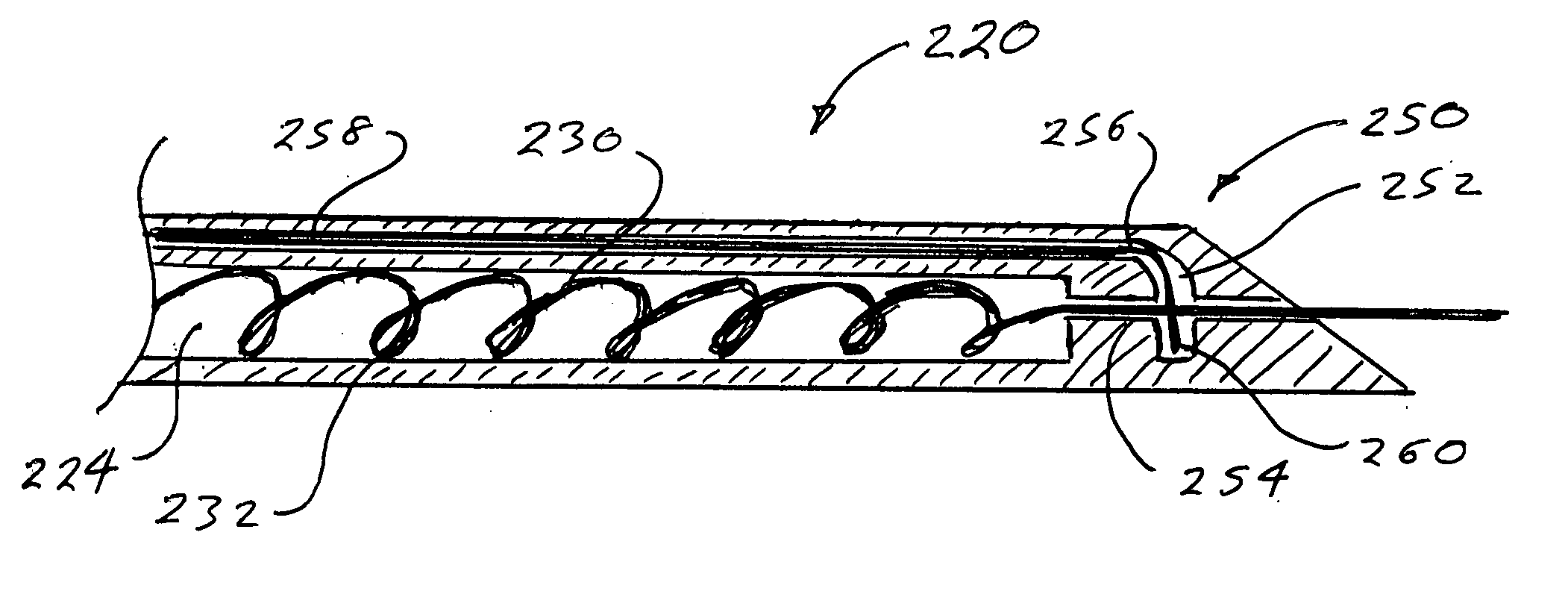
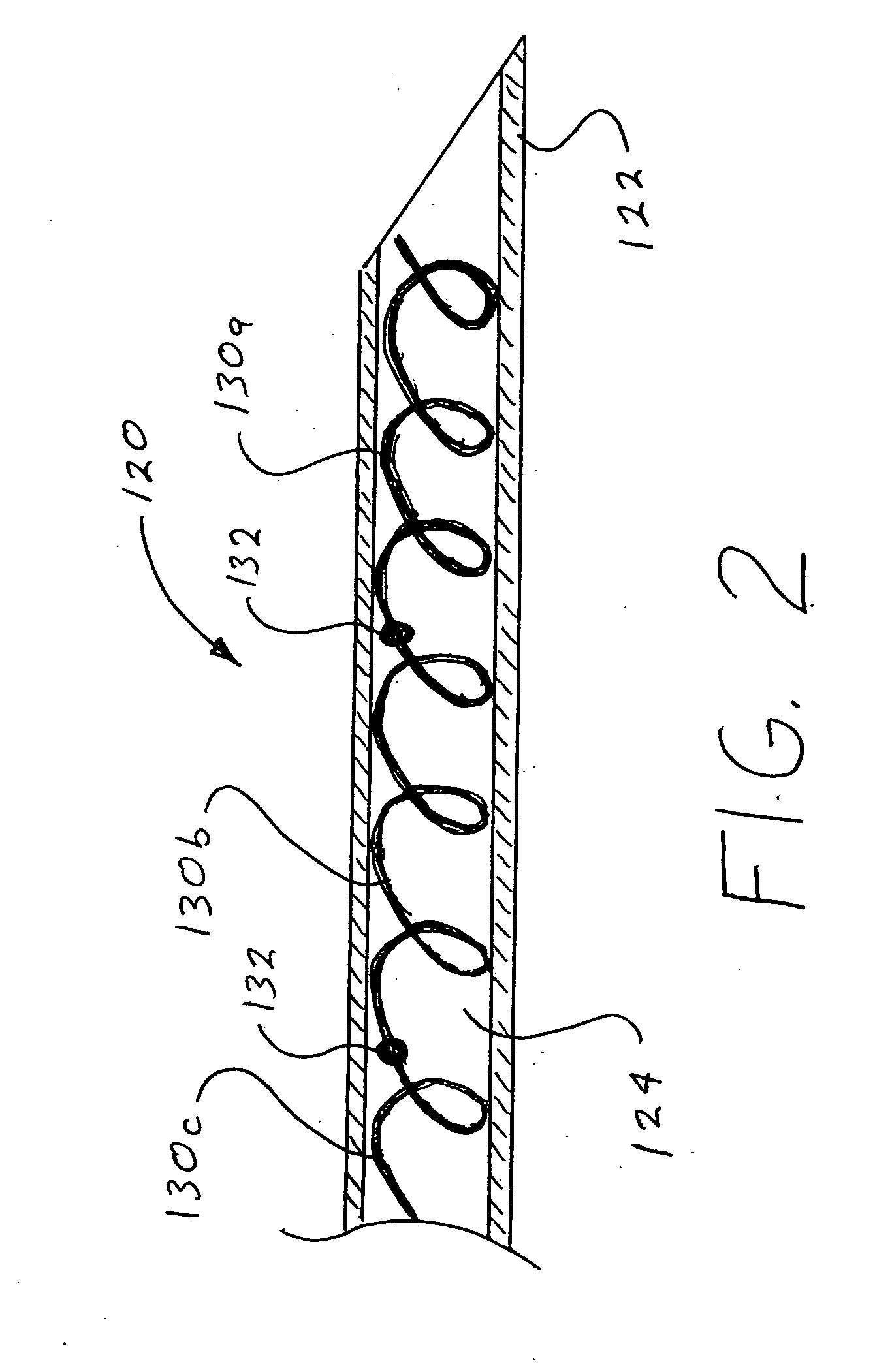
Ultrasound Guided Probe Device and Sterilizable Shield for Same
ActiveUS20110087105A1Enhanced couplingImprove visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorSkin surface
Disclosed are medical probe devices and methods for use guiding of percutaneous probes during medical procedures. The probe devices include an ultrasound transducer housing having a passage therethrough configured to accommodate a probe. The devices can be utilized to guide a probe through the probe guide to a percutaneous target with real time visualization of the probe during the procedure. In addition, the devices can include a sterilizable shield including a sterile probe guide such that the transducer housing itself can be separated from a subject by a sterile barrier. The sterilizable shield can be a single-use shield that can prevent contamination and re-use of the shield. The devices can define a beneficial geometry conducive to use by a single operator that can be utilized for percutaneous targets near the skin surface and can enable excellent contact between the device and the skin surface of a subject.
Owner:SOMA RES LLC
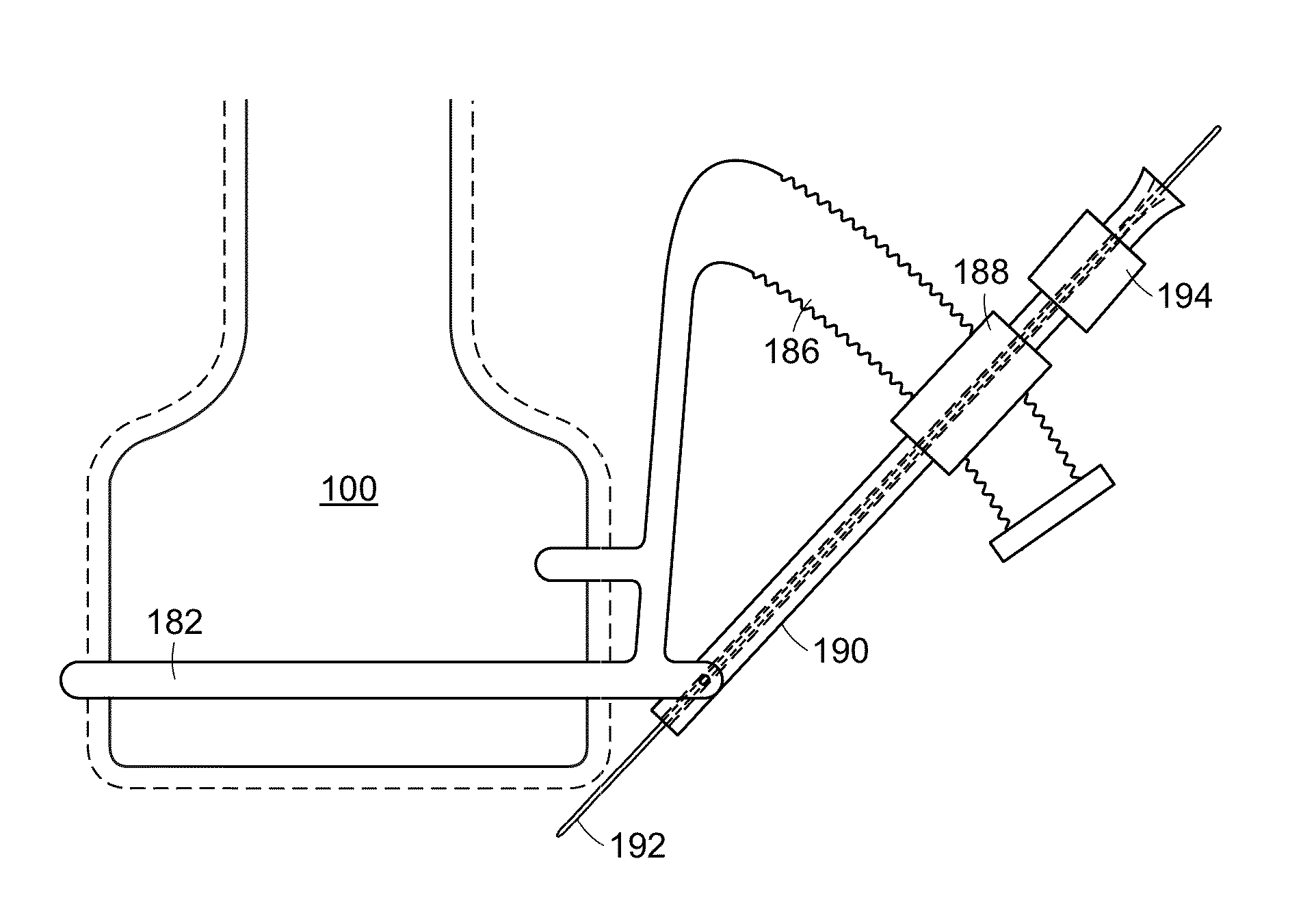
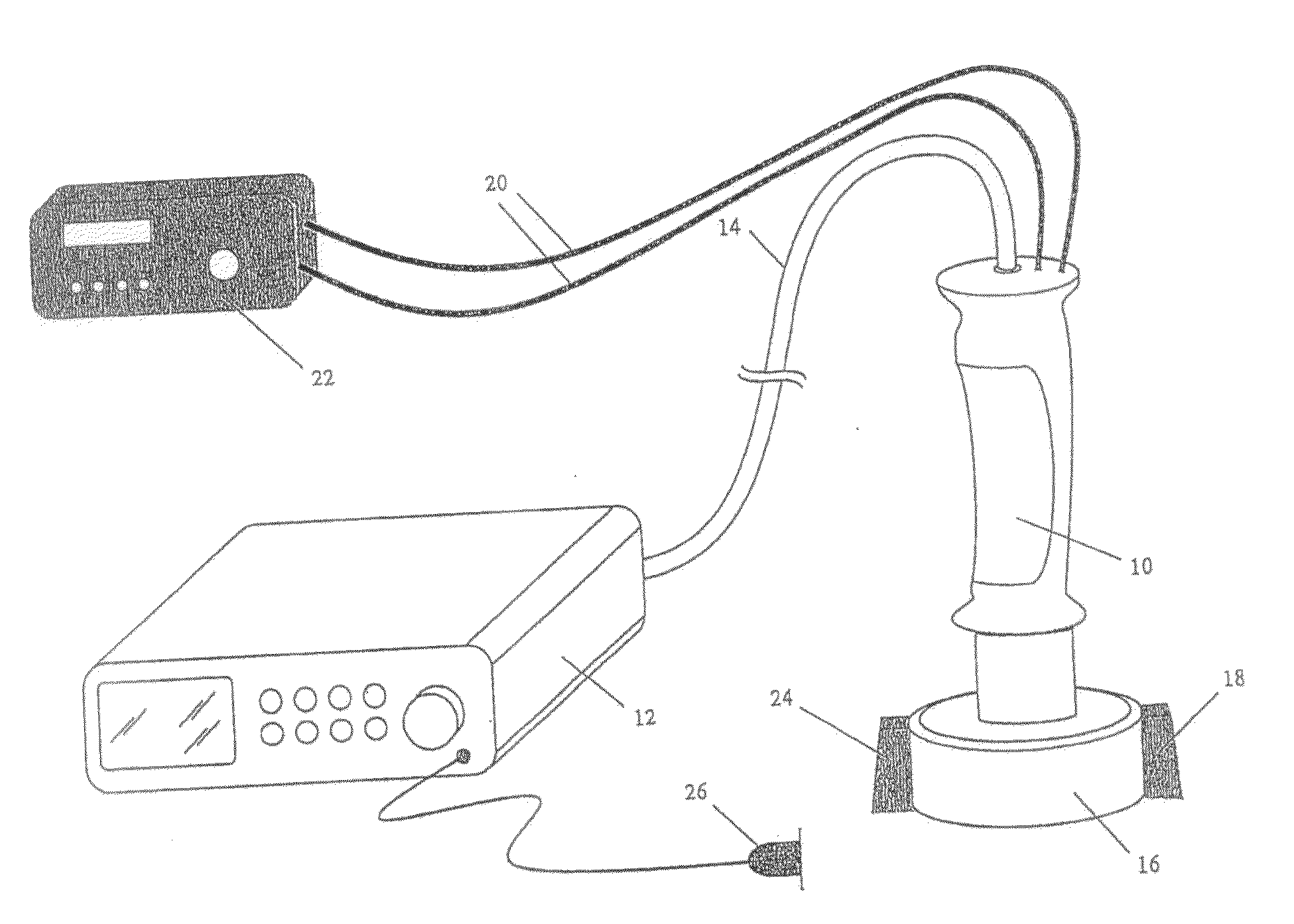
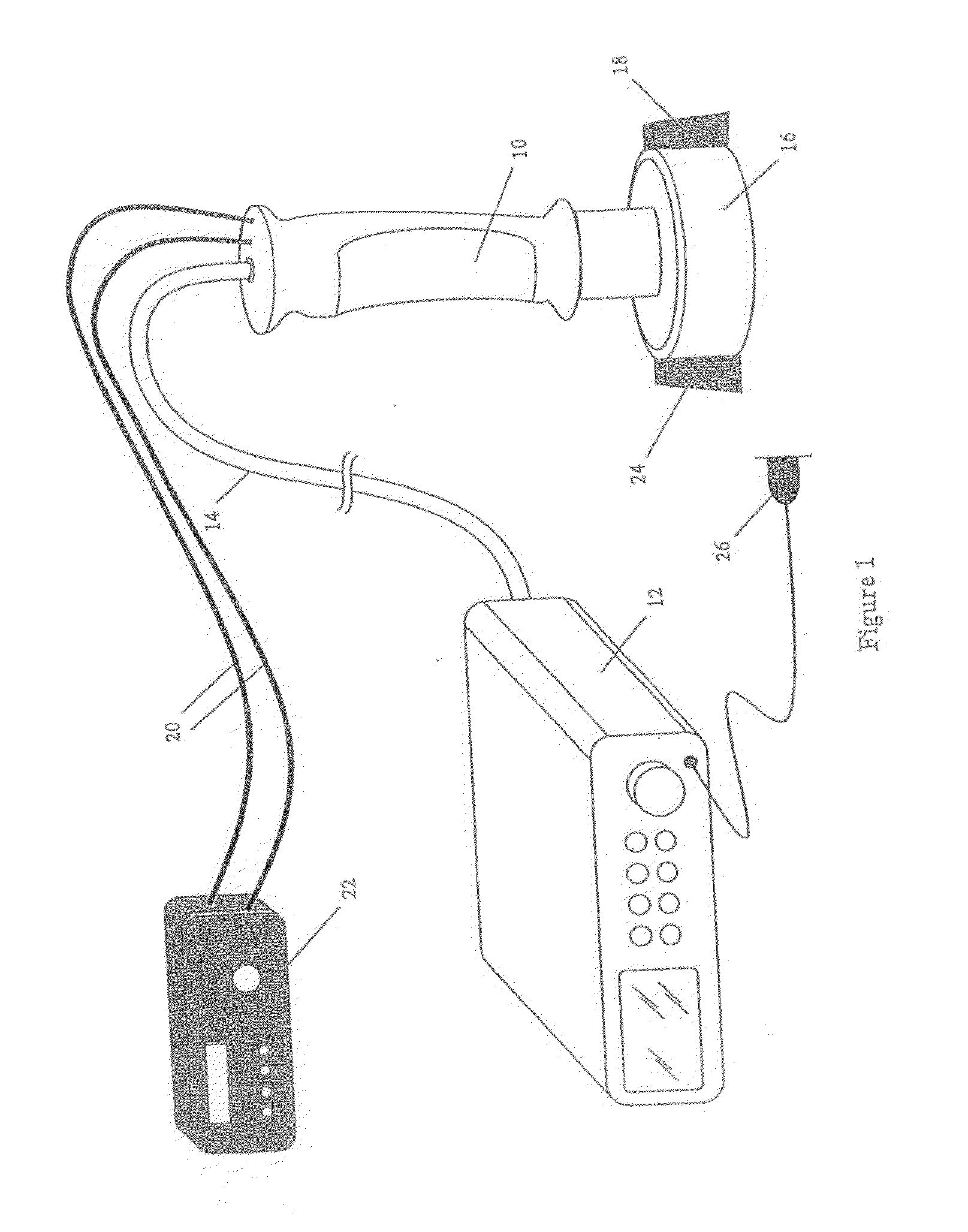
Needle Guides for Catheter Delivery
InactiveUS20100041990A1Improve visualizationOvercome limitationsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasVeinInvasive Procedure
Provided are needle locks and methods of using the same for ultrasound guided catheter insertion. The needle locks hereof substantially immobilizes a needle relative to an ultrasound probe to permit manipulation of a catheter or other device through the needle. The needle locks of the present invention may be used in nerve block, venous catheter insertion procedures or other invasive procedures.
Owner:ANES VENTURES
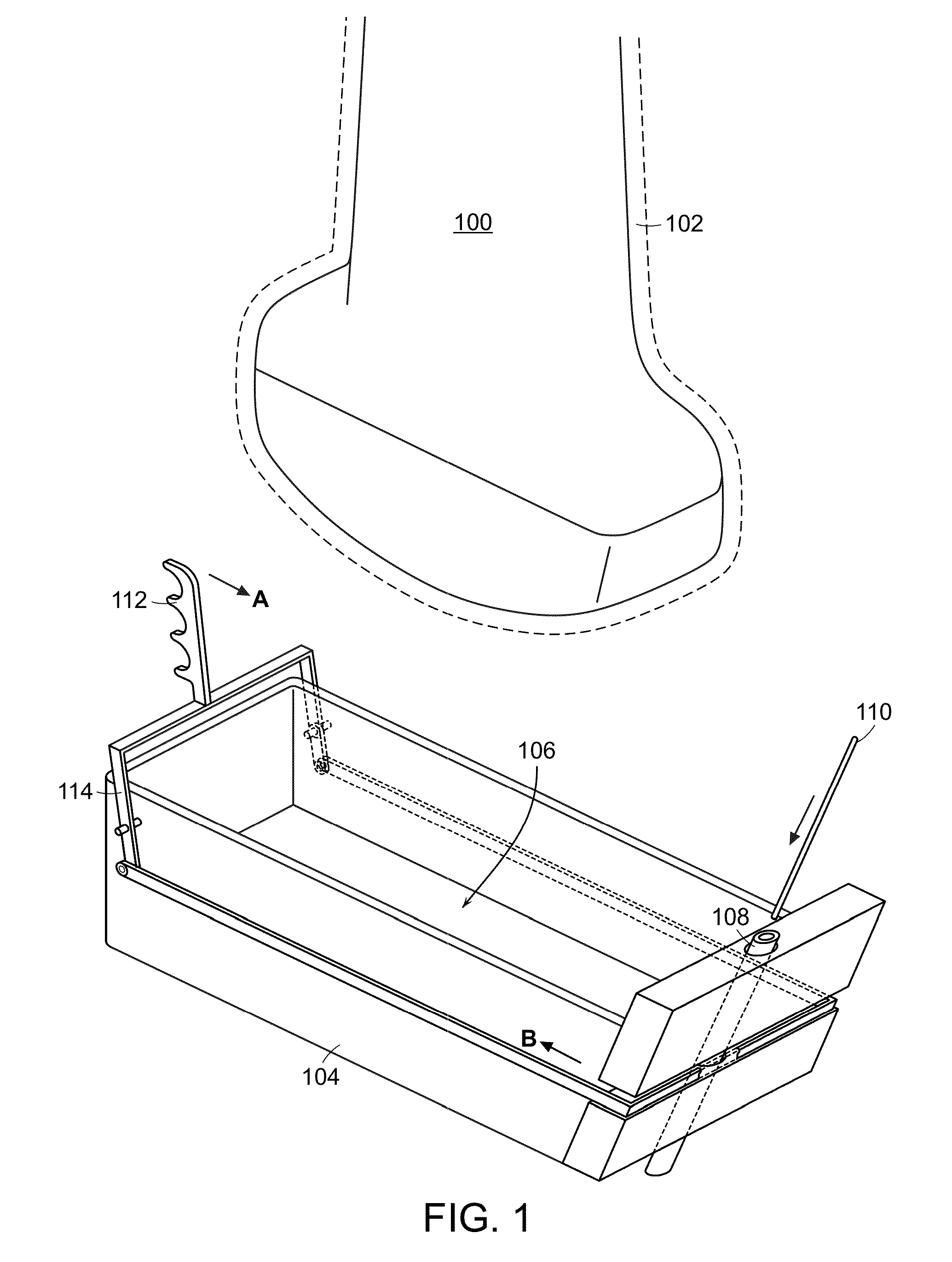
Sonographically guided transvaginal or transrectal pelvic abscess drainage using trocar method and biopsy guide attachment
ActiveUS7981041B2Avoid relative motionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound probeInstrumentation
A needle biopsy guide system is disclosed for attachment to an endoluminal ultrasound probe or like sonographic instrument. The device includes a biopsy-guide attachment that allows for trocar catheter placement for abscess drainage or like procedures, using the transvaginal or transrectal route under sonographic control. The device has a base portion, which is attachable to an ultrasound probe. A removable retainer is provided that slides into the base unit to hold a biopsy needle in place. A physician may locate the target area in the body with the ultrasound probe, insert the biopsy needle into the target area, and then remove the insert (retainer) from the base unit and ultrasound probe, and leave the biopsy needle in place in the body.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ultrasound guided robot for flexible needle steering
ActiveUS8663130B2Absence of hazardMore availabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingRobotic systems
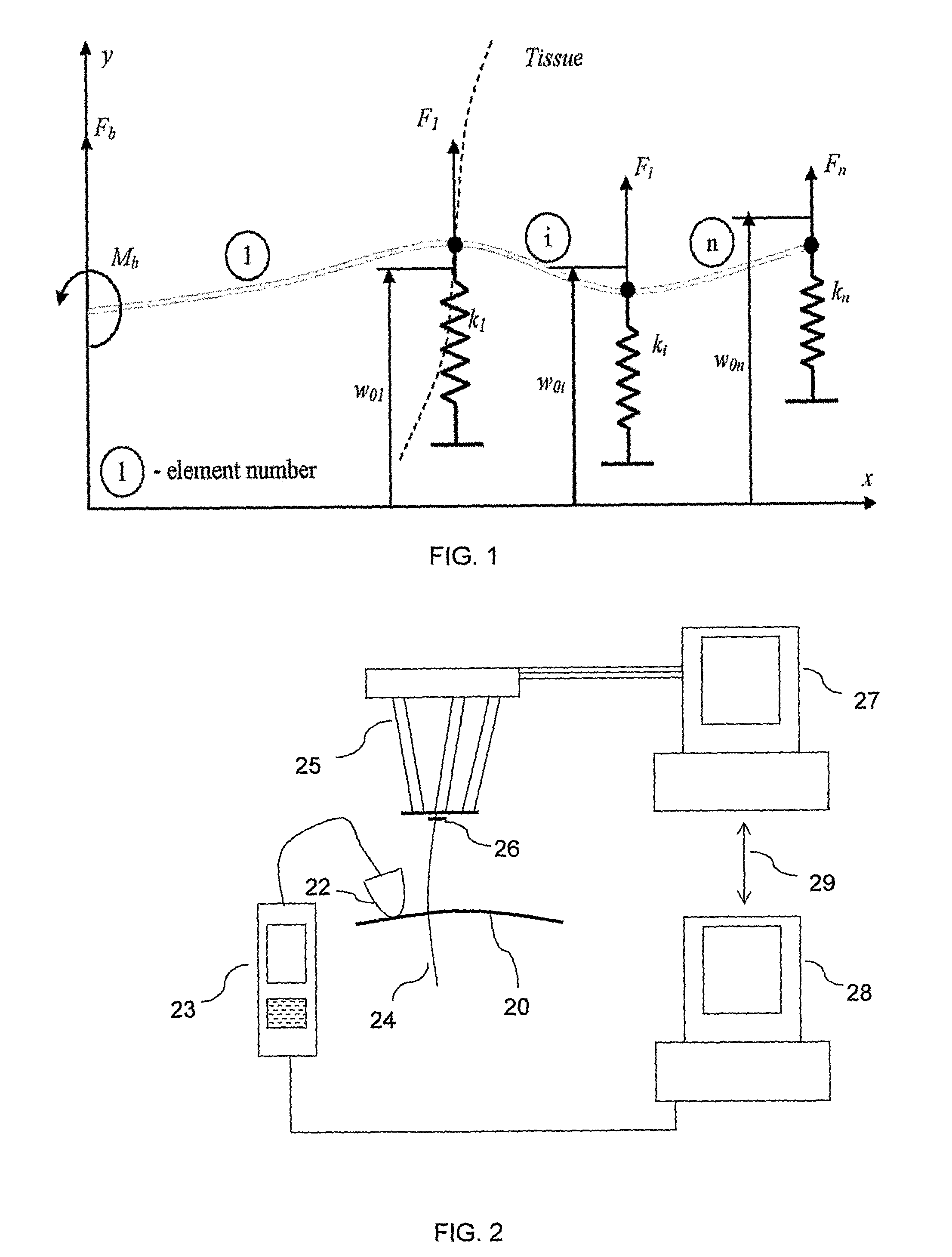
A robotic system for flexible needle steering under ultrasound imaging. A robot is used to steer the needle along a predetermined curved trajectory by maneuvering the needle base. The needle tip position is detected by an ultrasound sensor and the tracking error of the needle tip from a predetermined needle path is input to a controller which solves the inverse kinematic based on the needle position, and the needle and tissue properties. The control algorithm uses a novel method to detect the elastic properties of the tissue by analyzing tissue motion at the region in front of the needle tip. The inverse kinematic solution may be performed on a model of the needle as a flexible beam having laterally connected virtual springs to simulate lateral forces exerted by the tissue elasticity. The system is able to direct the needle to a target within the tissue while circumventing forbidden regions.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Ultrasound-Guided Ablation Method and Ultrasound-Guided Ablation System
InactiveUS20120078094A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorDisplay device
An ultrasound-guided ablation method captures an objective area to be ablated in an ultrasound scan area of an ultrasound transducer and delineates the objective area on an ultrasound image; specifies an ablation target area to display the ablation target area with a margin necessary for ablating the objective area on the ultrasound image processed by an ultrasound observation device and displayed on a display device; ablates, by an ablation device, the ablation target area displayed on the ultrasound image; and checks, on the ultrasound image, that an ablated area ablated by the ablation device has reached the ablation target area displayed on the ultrasound image.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Devices and methods for non-invasive ultrasound-guided body contouring using skin contact cooling
InactiveUS20100198064A1Improve power efficiencyBeneficial therapeutic resultUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySkin contactMedicine
The present invention discloses devices and methods, for non-invasive ultrasound-guided body contouring, including: a variable-frequency treatment applicator having at least one variable-frequency ultrasound emitter; and a control unit for adjusting an output frequency of at least one ultrasound emitter. Devices and methods including: a variable-frequency treatment applicator having at least one variable-frequency ultrasound emitter; a resonance sensor for determining a resonant frequency of a treatment area; and a control unit for adjusting an output frequency, of at least one ultrasound emitter, to the resonant frequency based on a signal from the resonance sensor. Devices and methods including: a variable-frequency treatment applicator having at least one variable-frequency ultrasound emitter; a cooling mechanism located in the treatment applicator; and a control unit for applying an output frequency to at least one ultrasound emitter. Preferably, the output frequency is within a frequency range from 25 kHz to 60 kHz.
Owner:PERL PAUL K +1
Ultrasound guided robot for flexible needle steering
ActiveUS20110112549A1Absence of radiation hazardLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingRobotic systems
A robotic system for flexible needle steering under ultrasound imaging. A robot is used to steer the needle along a predetermined curved trajectory by maneuvering the needle base. The needle tip position is detected by an ultrasound sensor and the tracking error of the needle tip from a predetermined needle path is input to a controller which solves the inverse kinematic based on the needle position, and the needle and tissue properties. The control algorithm uses a novel method to detect the elastic properties of the tissue by analyzing tissue motion at the region in front of the needle tip. The inverse kinematic solution may be performed on a model of the needle as a flexible beam having laterally connected virtual springs to simulate lateral forces exerted by the tissue elasticity. The system is able to direct the needle to a target within the tissue while circumventing forbidden regions.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
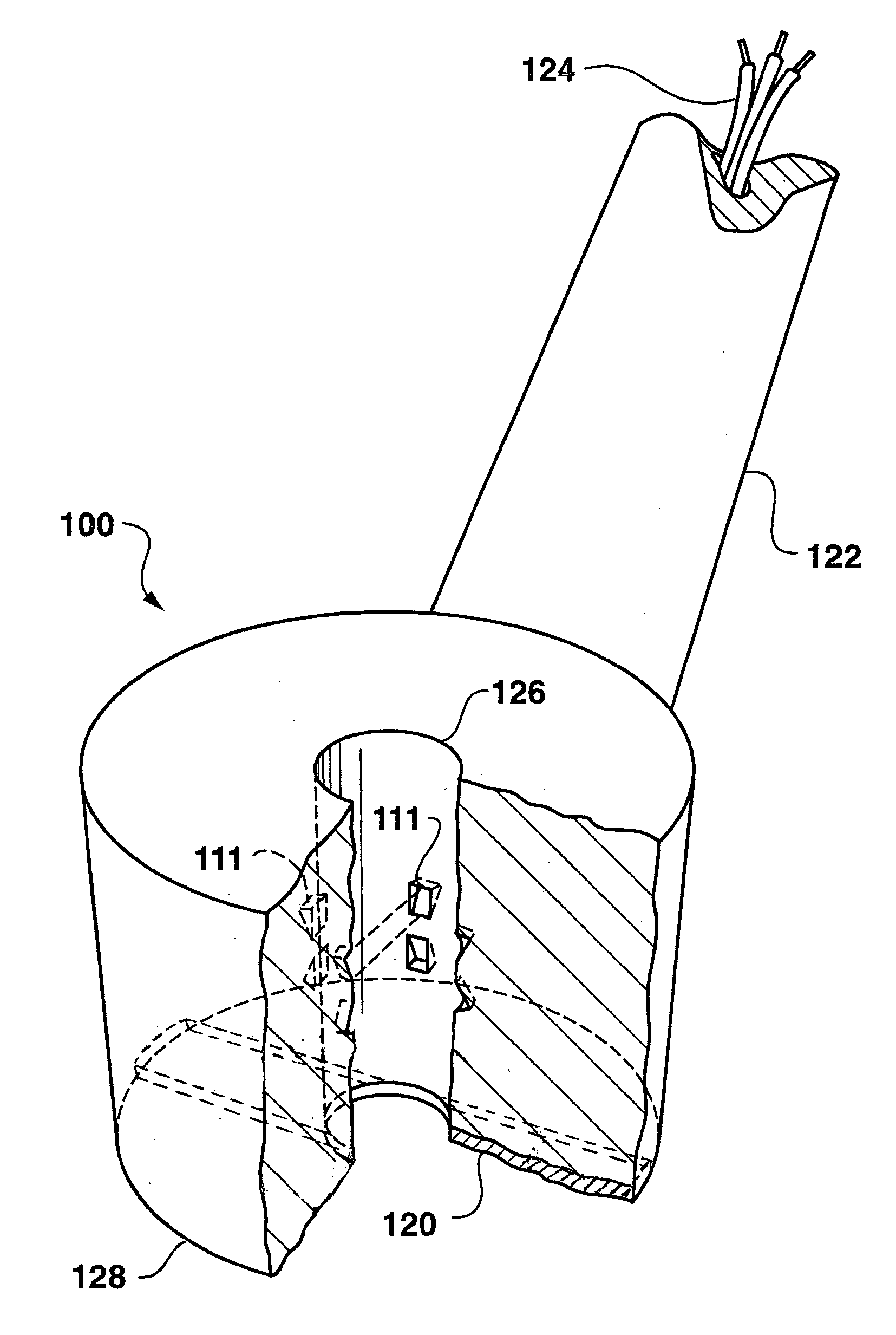
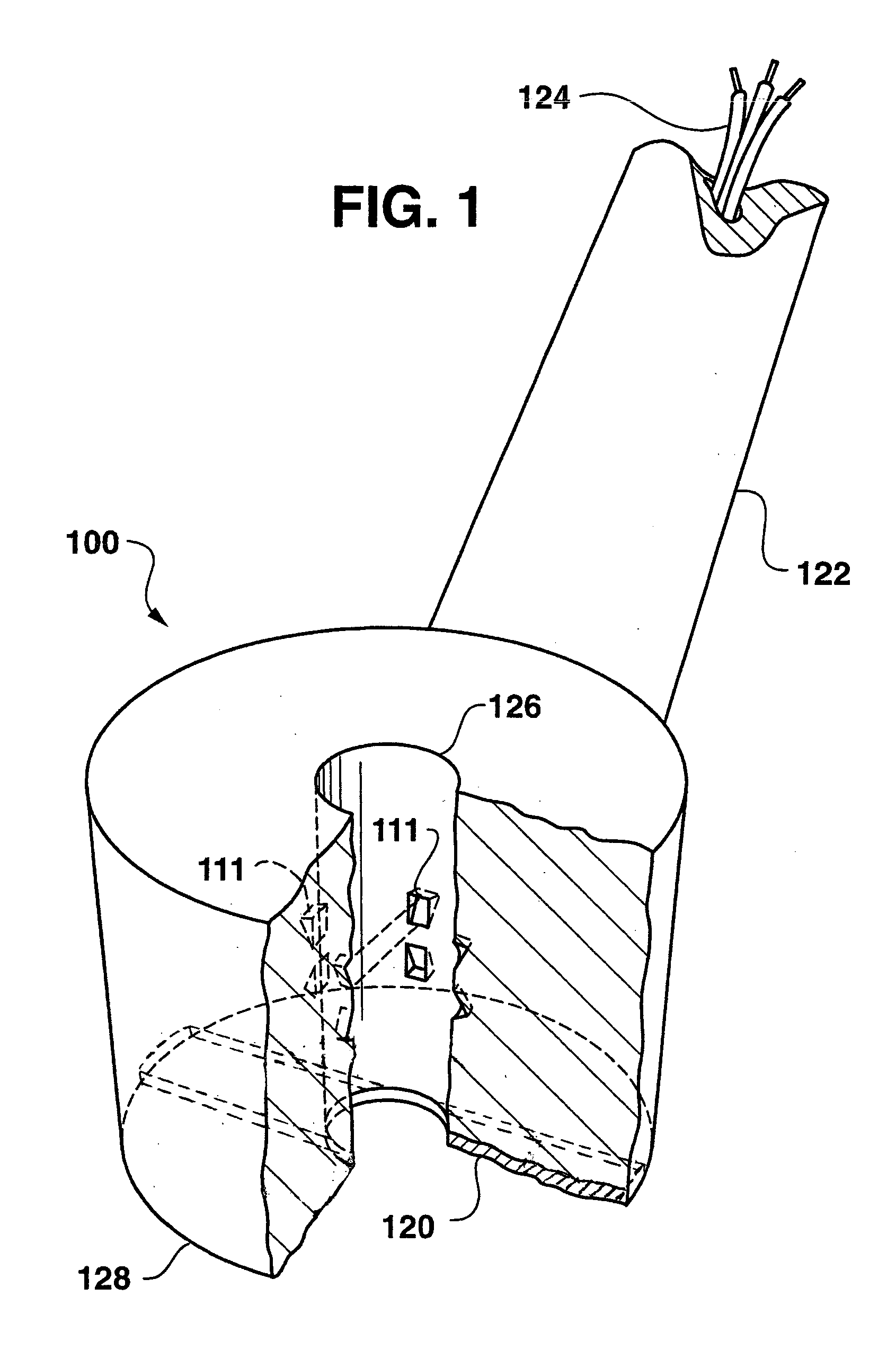
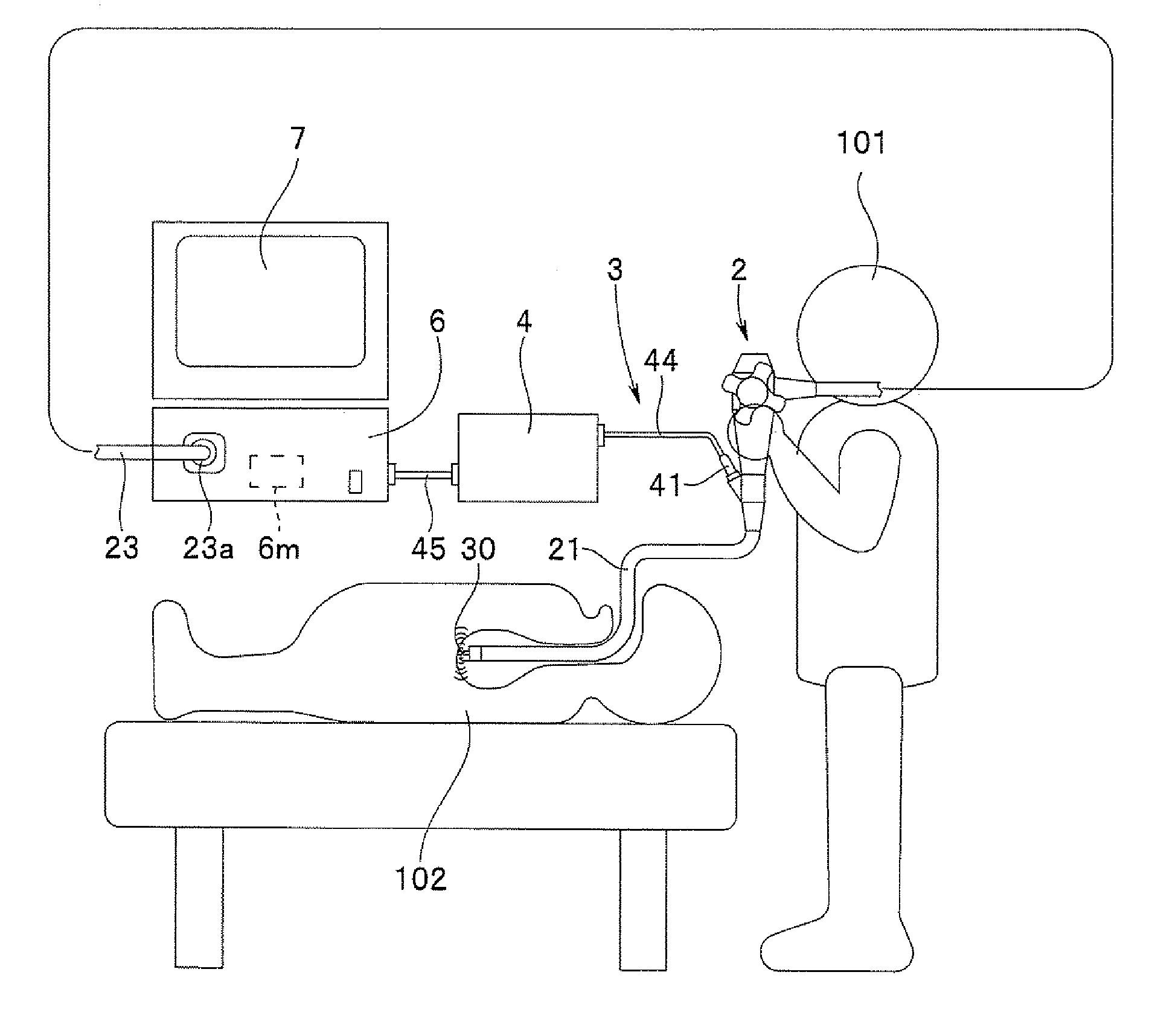
Ultrasonic guidance of subcutaneous tunneling
A method of tracking a medical device in a body includes inserting the medical device into a body and emitting a sonic signal from a transceiver coupled to the medical device. The method further includes receiving an echo of the sonic signal with the transceiver and detecting a location of the medical device in the body based on the received echo.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Spatially correlated x-ray and ultrasound mammographic imaging systems and method
InactiveUS7496398B2Avoids acquisitionAvoid storageOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical needlesUltrasound imagingSoft x ray
The present invention provides for x-ray imaging and ultrasound imaging of a body region of interest in a spatially correlatable manner. The resultant x-ray and ultrasound images may be combinatively employed to provide three-dimensional information regarding a location of interest within the body, and is particularly apt for use in the analysis / biopsy of potential lesions and suspicious masses in a female breast. The invention provides for direct body contact by an ultrasound imaging head, as well as targeted ultrasound imaging of a selected portion of the region from which x-ray images are obtained. A user interface system facilitates various procedures including ultrasound guided needle biopsy procedures.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Embolization coil delivery systems and methods
A system and method for ultrasonically guided endoscopic (EUS) delivery of one or more embolization coils to an internal body site. The embolization coil delivery devices are preferably ultrasonically guided to the selected internal body site after being advanced through the working channel of an endoscope with its distal end located near the selected internal body site. In one aspect, the system and method may be utilized to deploy an embolization coil into a lesion to promote thrombosis and / or prevent bleeding.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
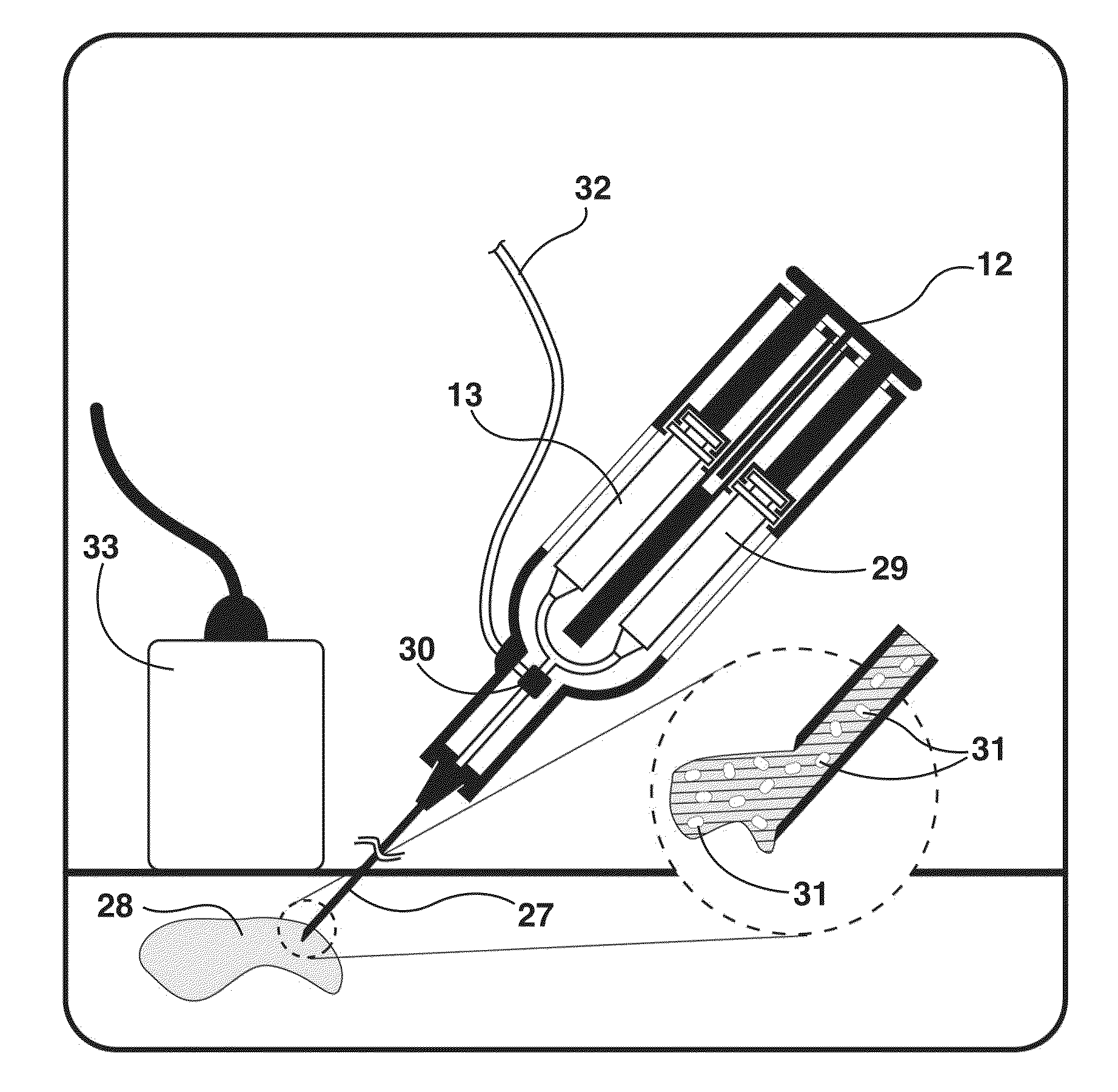
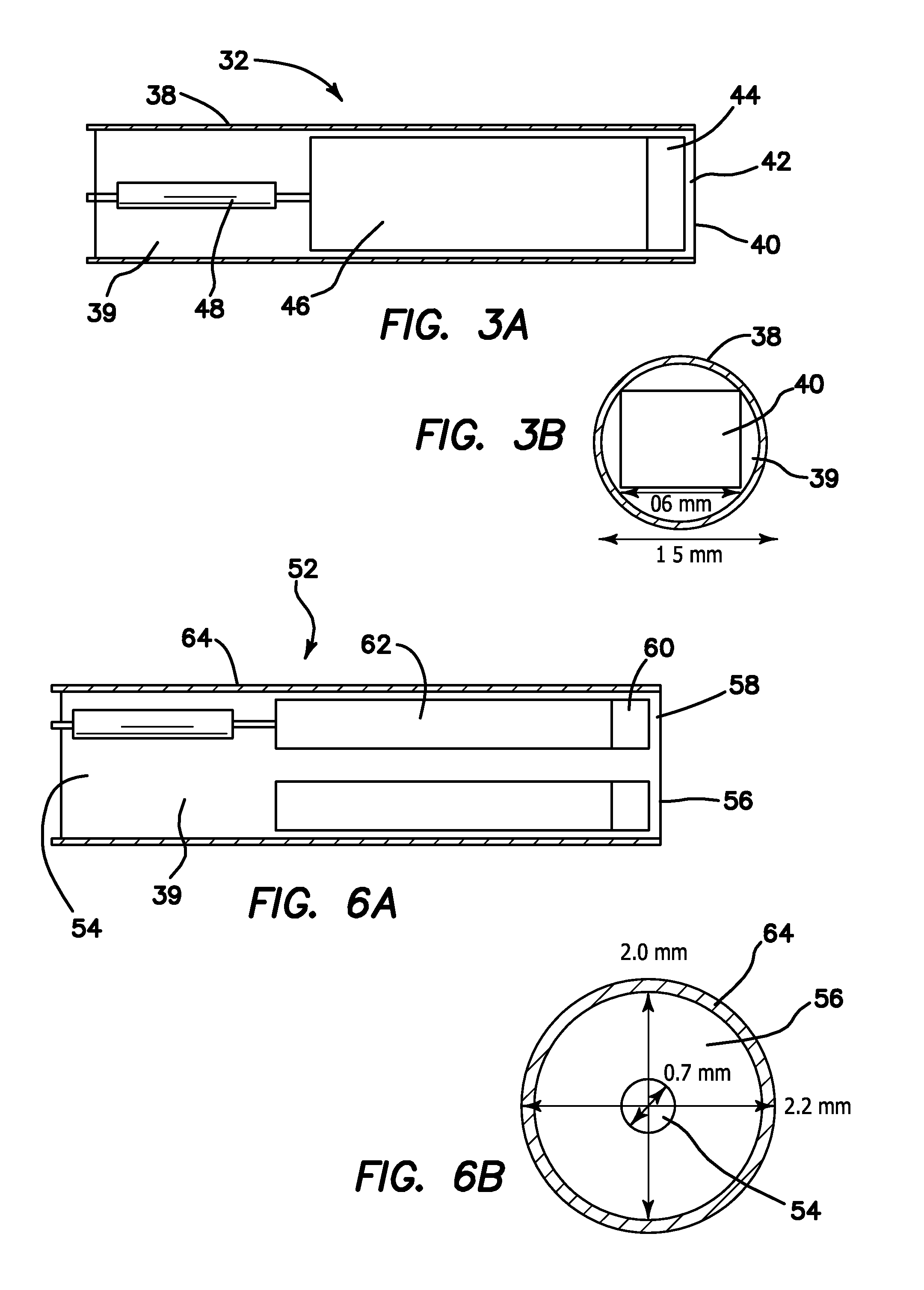
Imaging catheter and methods of use for ultrasound-guided ablation
InactiveUS7488289B2Simple and inexpensiveSimple and inexpensive apparatusUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterUltrasound imagingTransducer
The present invention provides ultrasound imaging catheters, systems and methods for their use which will be particularly useful to monitor the positioning of ablation catheters. In one embodiment, an imaging catheter (10) includes a catheter body (11) having a distal end (12), a proximal end (14) and a longitudinal axis (16). A transducer (20) is rotatably coupled to the distal end. The transducer has an axis of rotation (24) that is at a non-zero angle relative to the catheter body longitudinal axis. Such a configuration provides an exemplary side-looking imaging catheter.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Ultrasound-guided ablation method and ultrasound-guided ablation system
InactiveUS20100063392A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesUltrasonic sensorDisplay device
An ultrasound-guided ablation method captures an objective area to be ablated in an ultrasound scan area of an ultrasound transducer and delineates the objective area on an ultrasound image; specifies an ablation target area to display the ablation target area with a margin necessary for ablating the objective area on the ultrasound image processed by an ultrasound observation device and displayed on a display device; ablates, by an ablation device, the ablation target area displayed on the ultrasound image; and checks, on the ultrasound image, that an ablated area ablated by the ablation device has reached the ablation target area displayed on the ultrasound image.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
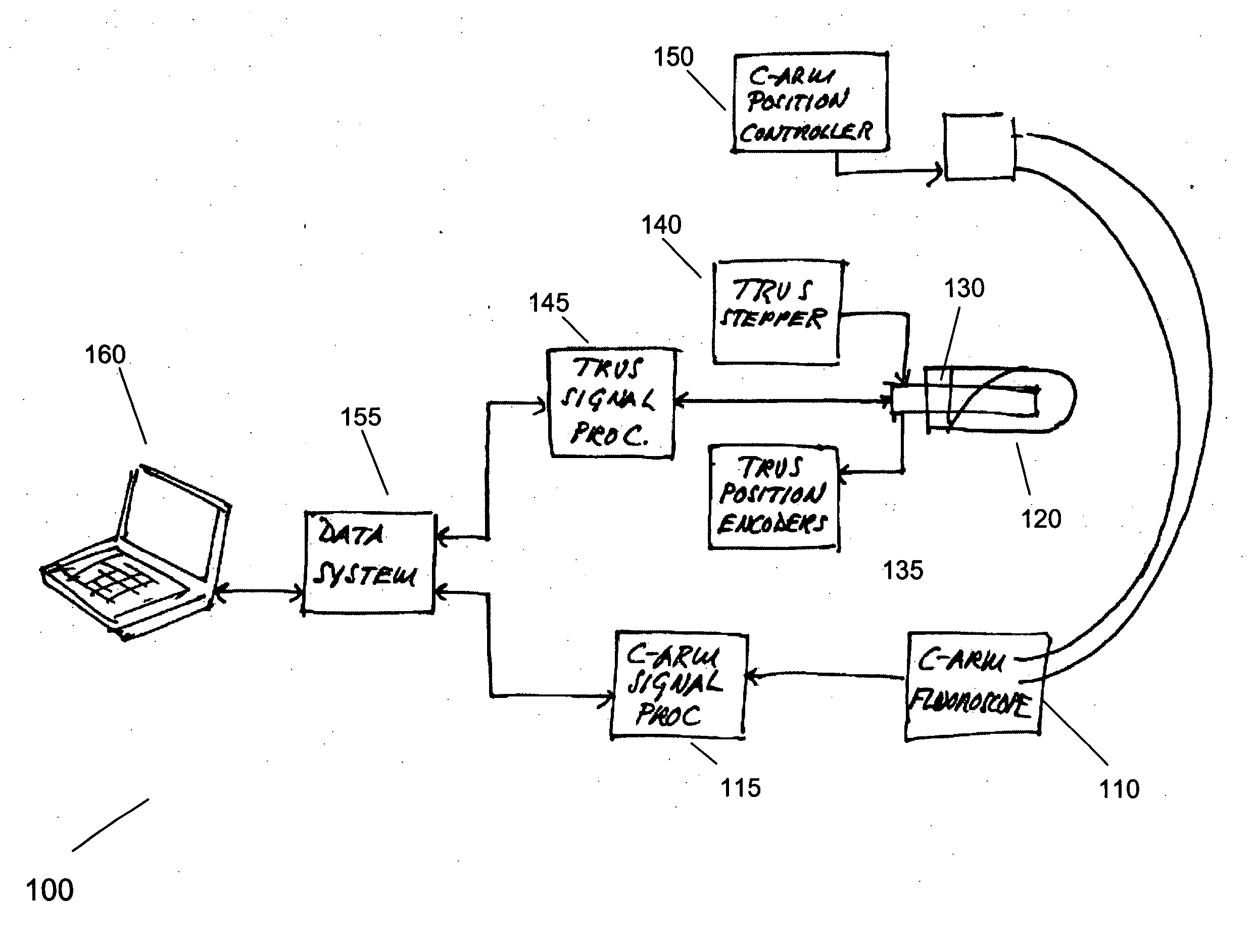
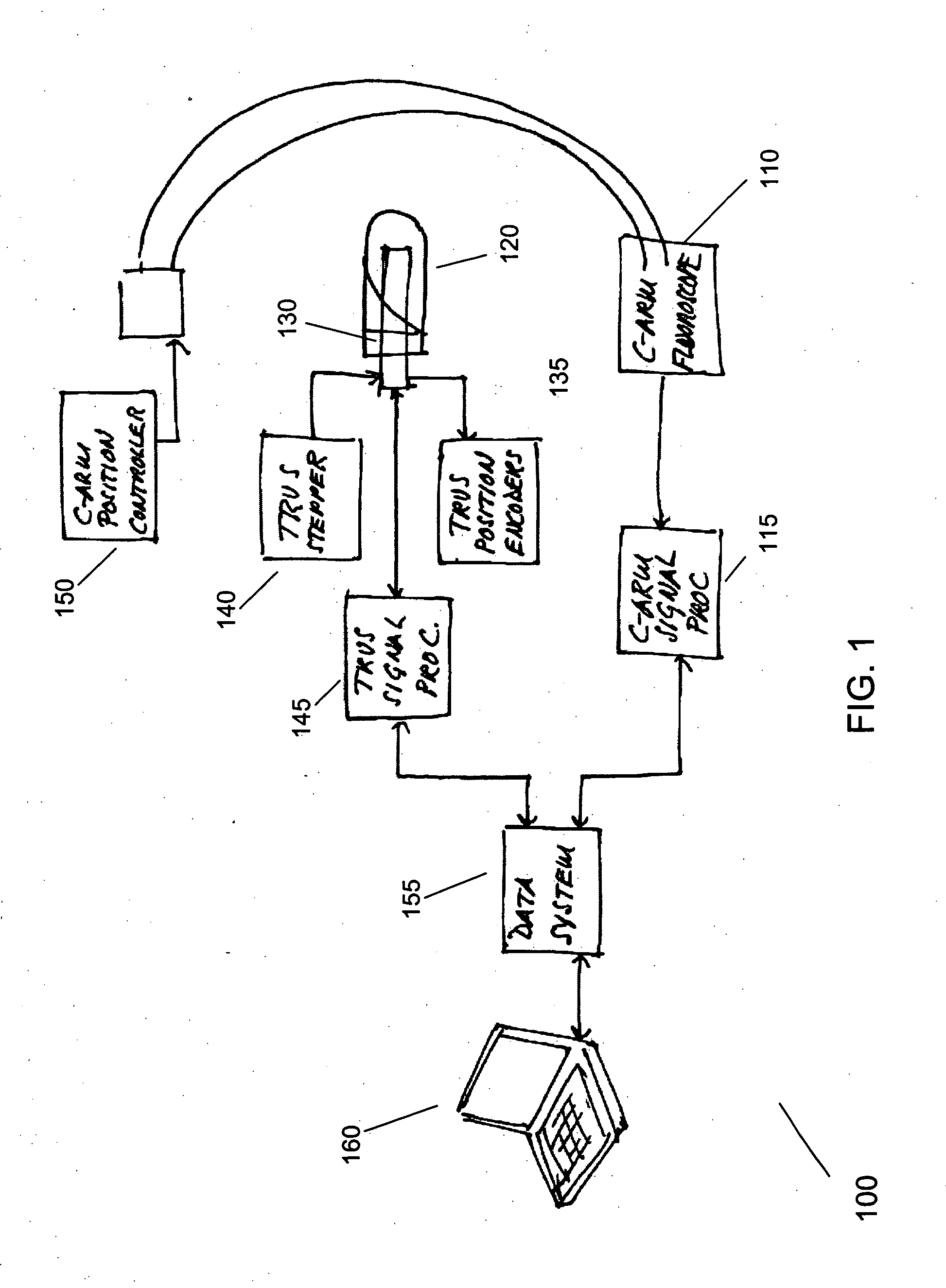
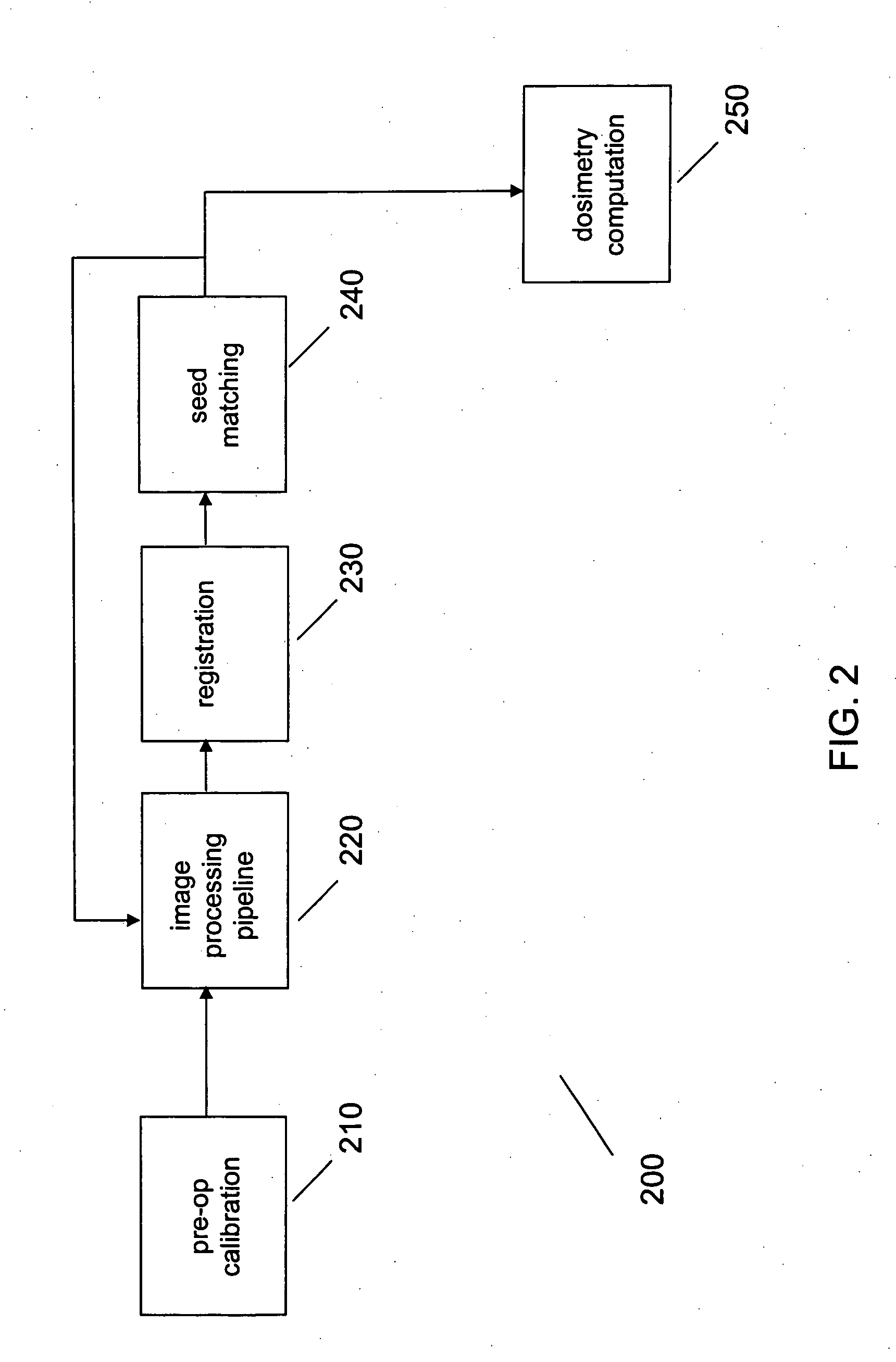
Registration of ultrasound to fluoroscopy for real time optimization of radiation implant procedures
InactiveUS20050171428A1Easy to controlImprove visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonificationFluorescence
Transrectal ultrasound guided transperineal low dose-rate brachytherapy has been emerged as one of the definitive treatments of low-risk prostate cancer. Ultrasound has been an excellent tool in guiding the implant needles with respect to prostate anatomy, yet it cannot show reliably the location of radioactive seeds after they are released in the prostate. Intraoperative C-arm fluoroscopy can show the implanted seeds, but it cannot detect prostate anatomy. Intra-operative fusion of these two complementary modalities offers significant clinical benefit by allowing for real-time optimization of the brachytherapy implant as the procedure progresses in the operating room. Disclosed is a system and method for mitigating this problem and providing registration of seeds seen by fluoroscopy with live prostate anatomy visualized by transrectal ultrasound.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
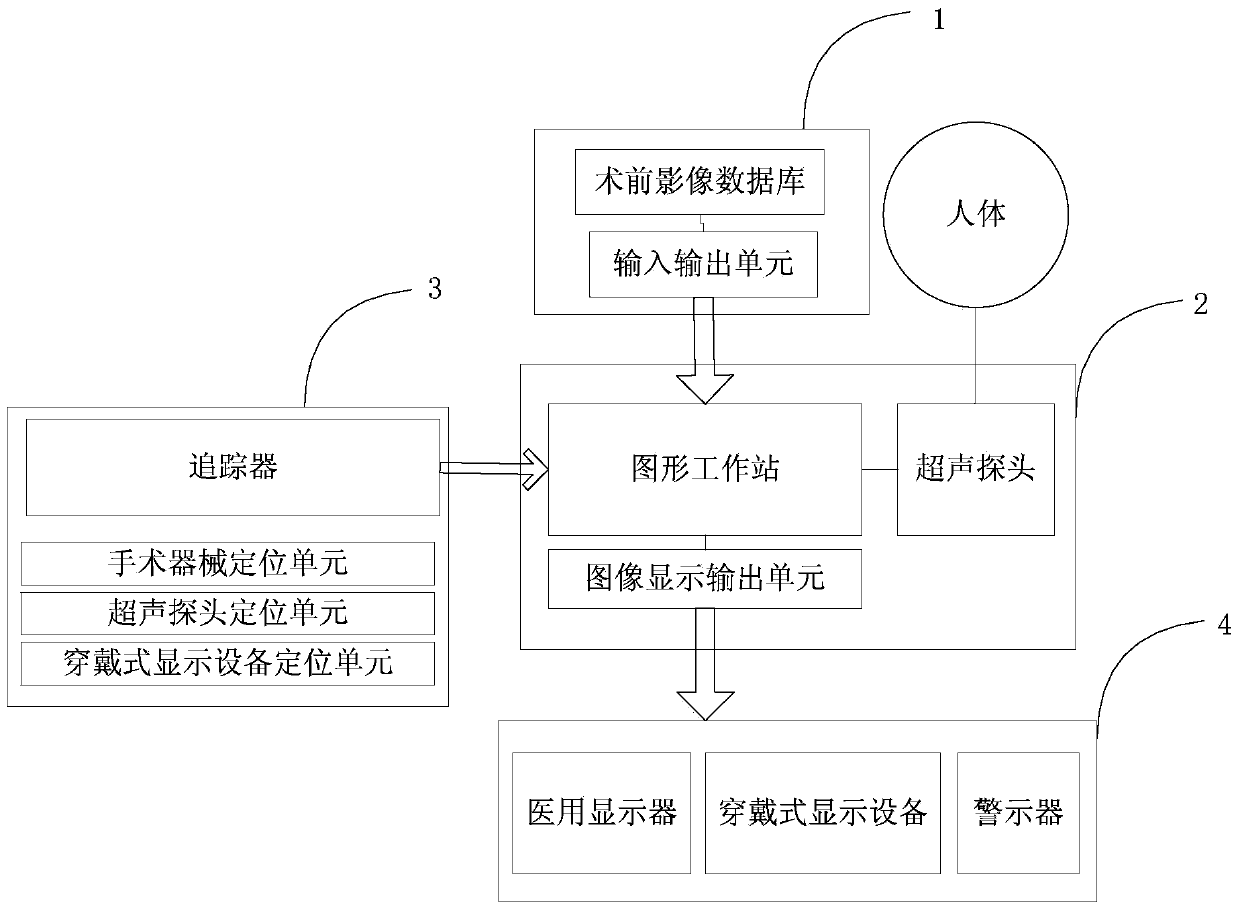
Multimode image navigation system for ultrasonic guidance operation
ActiveCN103735312AReal-time image presentationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryData matchingSonification
The invention discloses a multimode image navigation system for an ultrasonic guidance operation. An ultrasonic image system acquires preoperative image data and stores the preoperative image data to a preoperative data module, and the ultrasonic image system extracts the preoperative image data to construct human three-dimensional model data and stores the human three-dimensional model data to a preoperative data module. A locating module acquires position information of an ultrasonic probe in an operative instrument and the ultrasonic image system and transmits the position information to the ultrasonic image system. The ultrasonic image system extracts the human three-dimensional model data stored in the preoperative data module and matches the position information with the human three-dimensional model data. A display module acquires and displays the information matched by the ultrasonic image system. Images are presented in real time in an operation by locating an operative area through real-time ultrasonic data according to the preoperative image data and the human three-dimensional model data, the operative instrument is accurately located according to the locating module, and the position of the operative instrument in a human model is presented.
Owner:珠海中科先进技术研究院有限公司
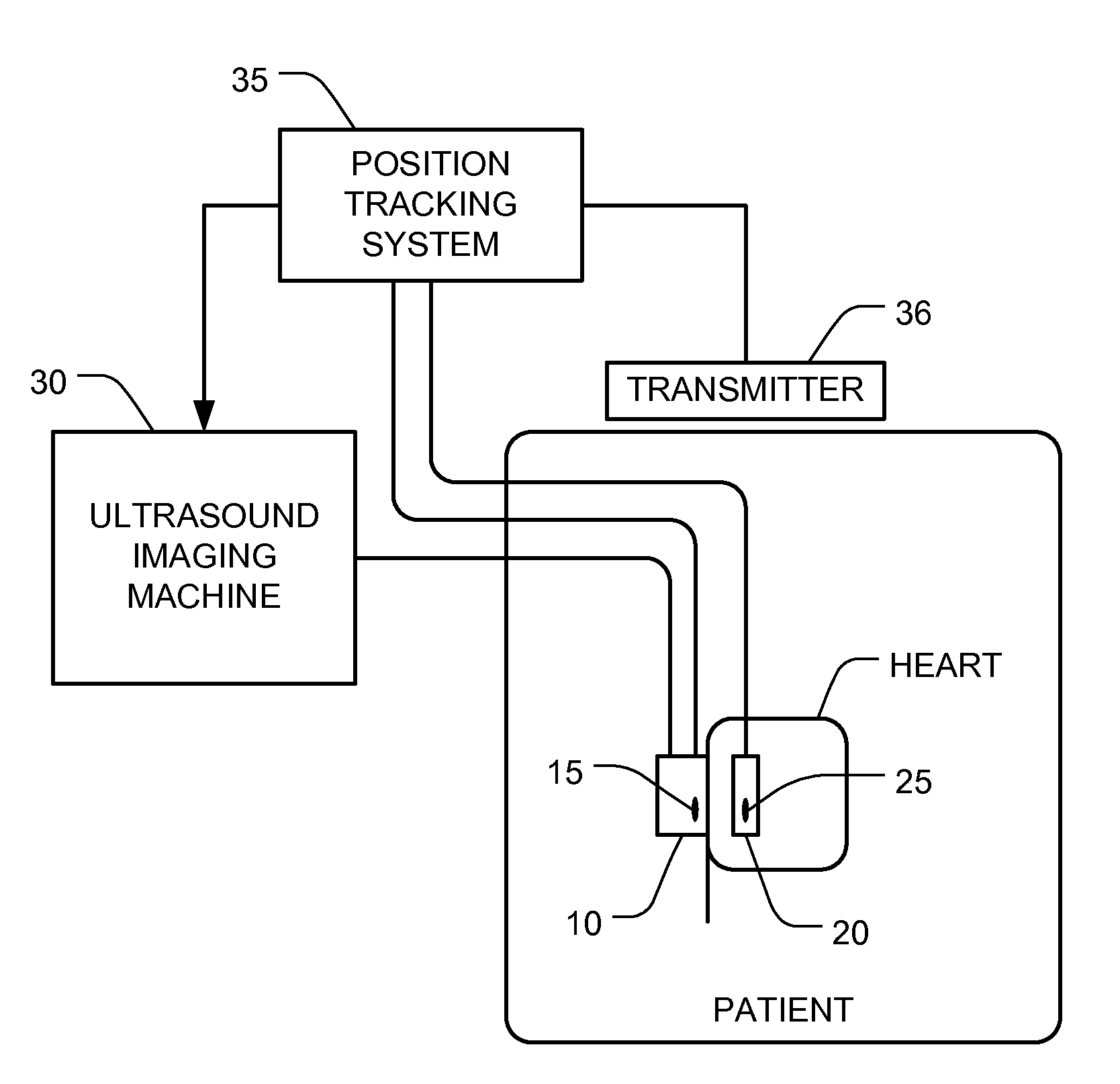
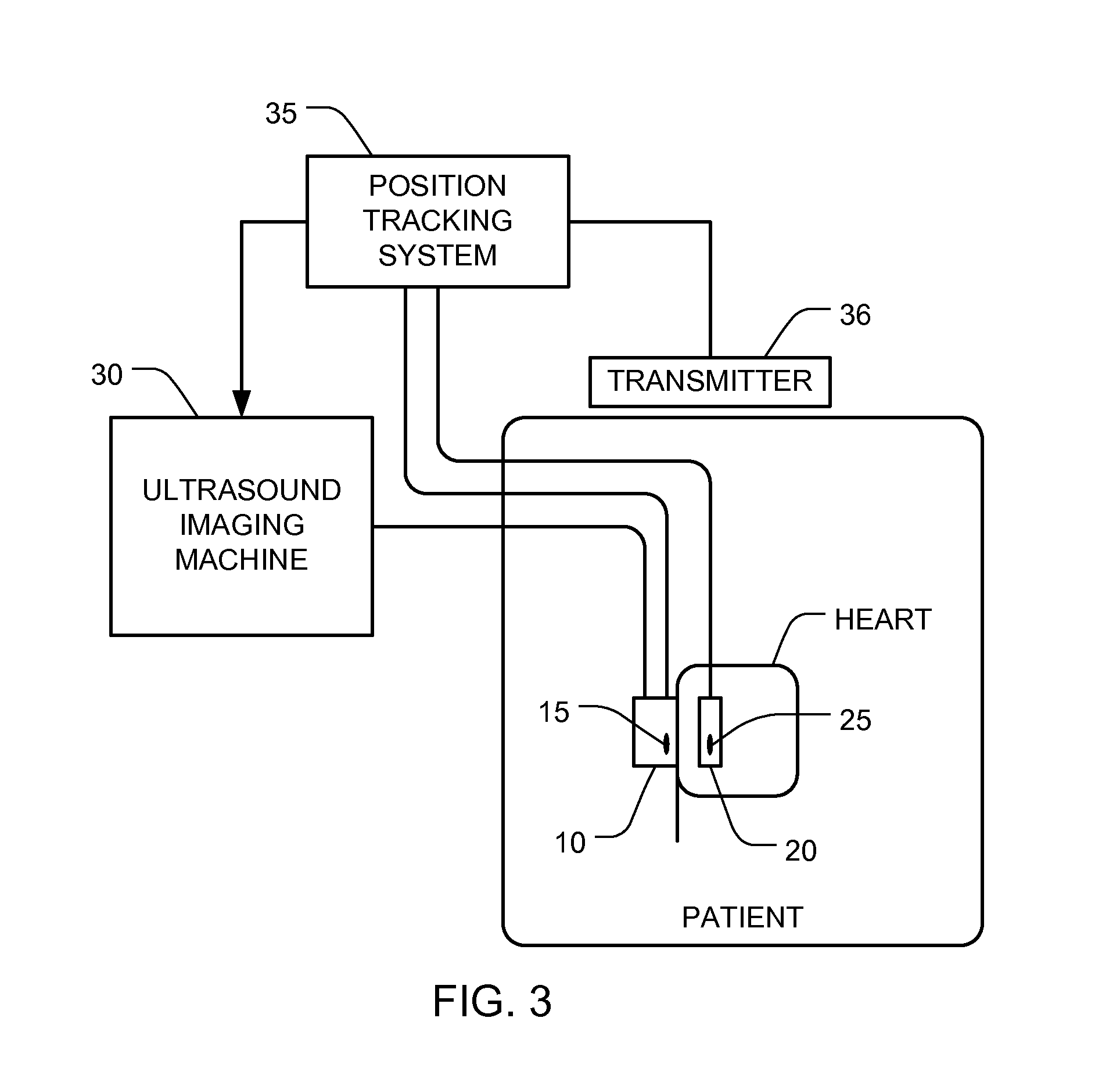
Ultrasound guided positioning of cardiac replacement valves with 3D visualization
InactiveUS20120259210A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesHeart valvesRadiologyComputer vision
A device (e.g., a valve) can be visualized in a patient's body (e.g., in the patient's heart) using an ultrasound system with added position sensors. One position sensor is mounted in the ultrasound probe, and another position sensor is mounted in the device installation apparatus. The device's position with respect to the imaging plane is determined based on the detected positions of the position sensors and known geometric relationships. A representation of the device and the imaging plane, as viewed from a first perspective, is displayed. The perspective is varied to a second perspective, and a representation of the device and the imaging plane, as viewed from the second perspective, is displayed. Displaying the device and the imaging plane from different perspectives helps the user visualize where the device is with respect to the relevant anatomy.
Owner:IMACOR INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com