Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
250 results about "Terrain elevation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elevated terrain represents terrain at different levels above the battlefield. Elevated terrain can contain other kinds of terrain like hindering or blocking which would have the properties of both elevated terrain and the other terrain. Elevated terrain itself can’t be destroyed.
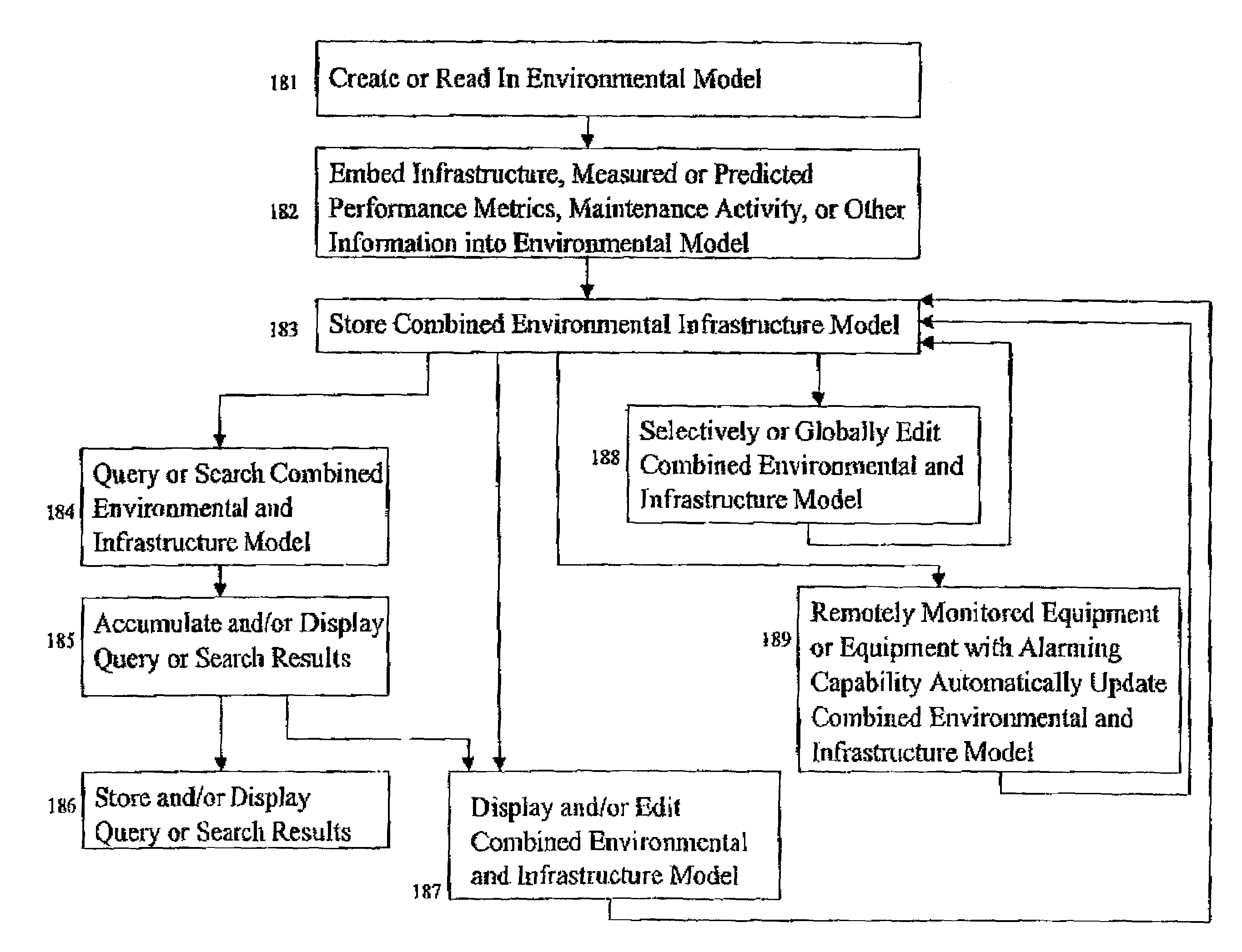
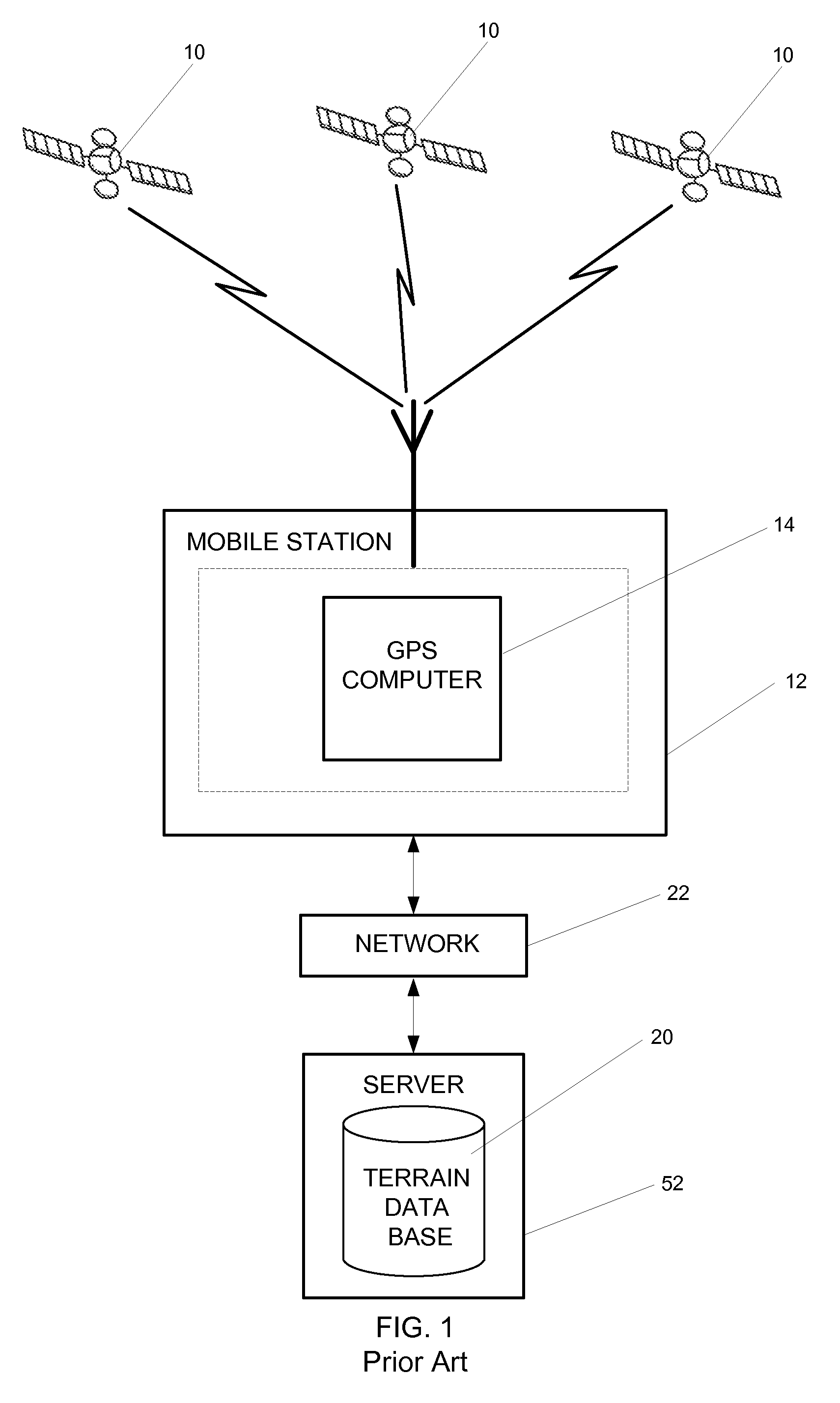
Method and system for modeling and managing terrain, buildings, and infrastructure
ActiveUS7164883B2Enhance on-going managementBroadcast transmission systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSpecific modelEngineering
A method and system for creating, using, and managing a three-dimensional digital model of the physical environment combines outdoor terrain elevation and land-use information, building placements, heights and geometries of the interior structure of buildings, along with site-specific models of components that are distributed spatially within a physical environment. The present invention separately provides an asset management system that allows the integrated three-dimensional model of the outdoor, indoor, and distributed infrastructure equipment to communicate with and aggregate the information pertaining to actual physical components of the actual network, thereby providing a management system that can track the on-going performance, cost, maintenance history, and depreciation of multiple networks using the site-specific unified digital format.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
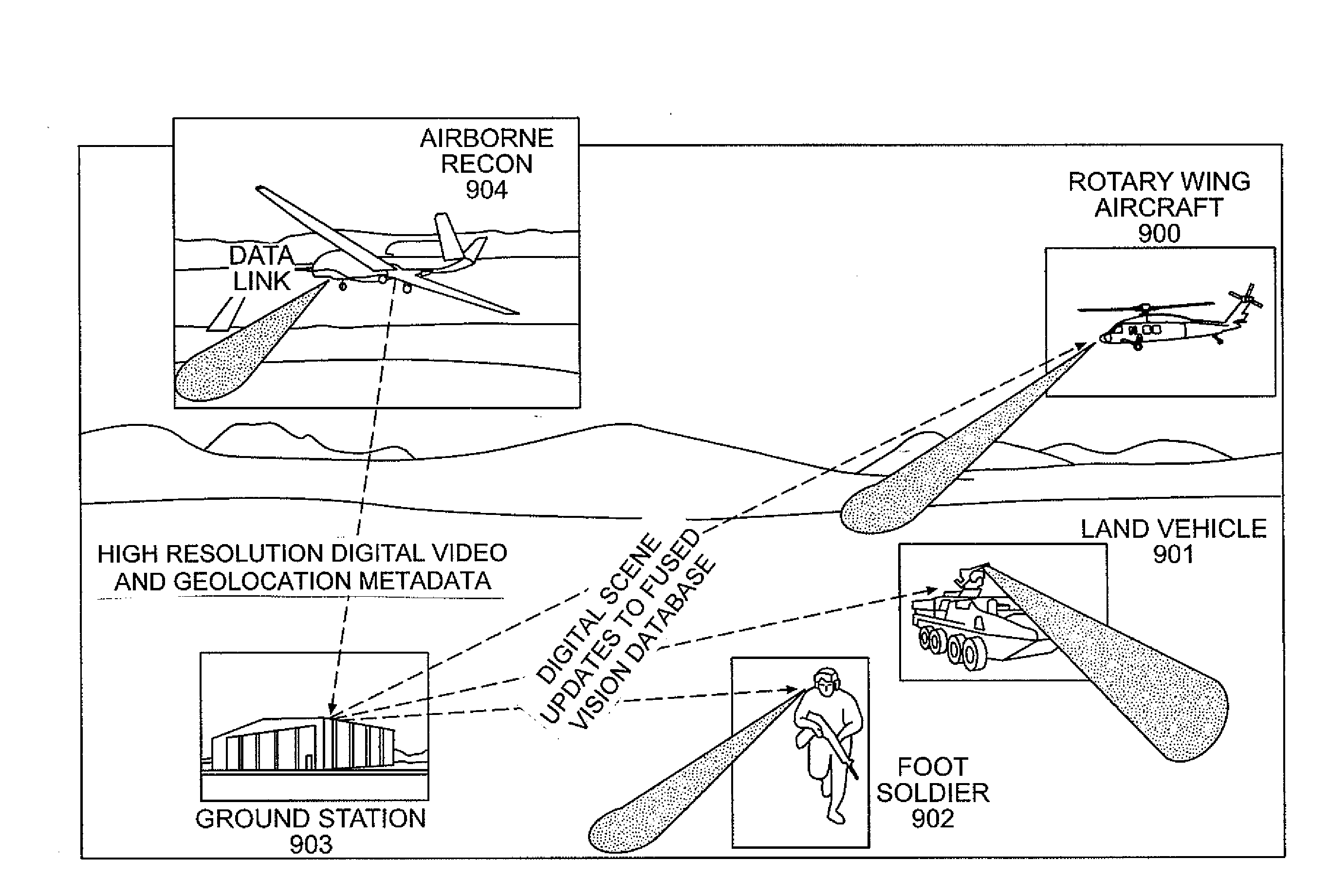
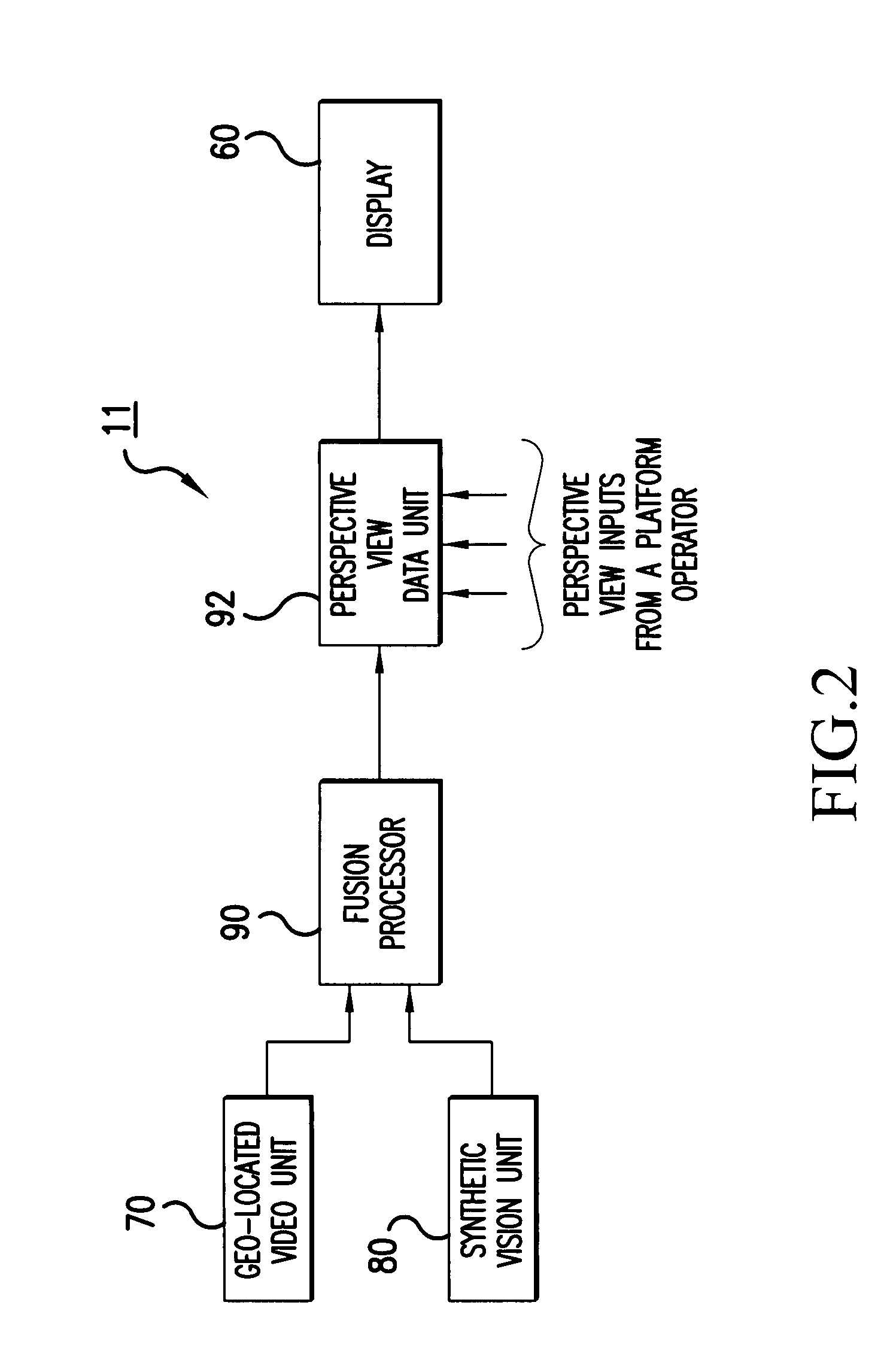
Method and system for providing a perspective view image by intelligent fusion of a plurality of sensor data
A method and system for providing a perspective view image created by fusing a plurality of sensor data for supply to a platform operator with a desired viewing perspective within an area of operation is disclosed. A plurality of sensors provide substantially real-time data of an area of operation, a processor combines the substantially real-time data of the area of operation with digital terrain elevation data of the area of operation and positional data of a platform operator to create a digital cartographic map database having substantially real-real time sensor data, a memory for storing the digital cartographic map database, a perspective view data unit inputs data regarding a desired viewing perspective of the operator within the area of operation with respect to the digital cartographic map database to provide a perspective view image of the area of operation, and a display for displaying the perspective view image to the operator.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for modeling and managing terrain, buildings, and infrastructure
ActiveUS20030023412A1Enhance on-going managementBroadcast with distributionOffice automationSpecific modelLand use
A method and system for creating, using, and managing a three-dimensional digital model of the physical environment combines outdoor terrain elevation and land-use information, building placements, heights and geometries of the interior structure of buildings, along with site-specific models of components that are distributed spatially within a physical environment. The present invention separately provides an asset management system that allows the integrated three-dimensional model of the outdoor, indoor, and distributed infrastructure equipment to communicate with and aggregate the information pertaining to actual physical components of the actual network, thereby providing a management system that can track the on-going performance, cost, maintenance history, and depreciation of multiple networks using the site-specific unified digital format.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
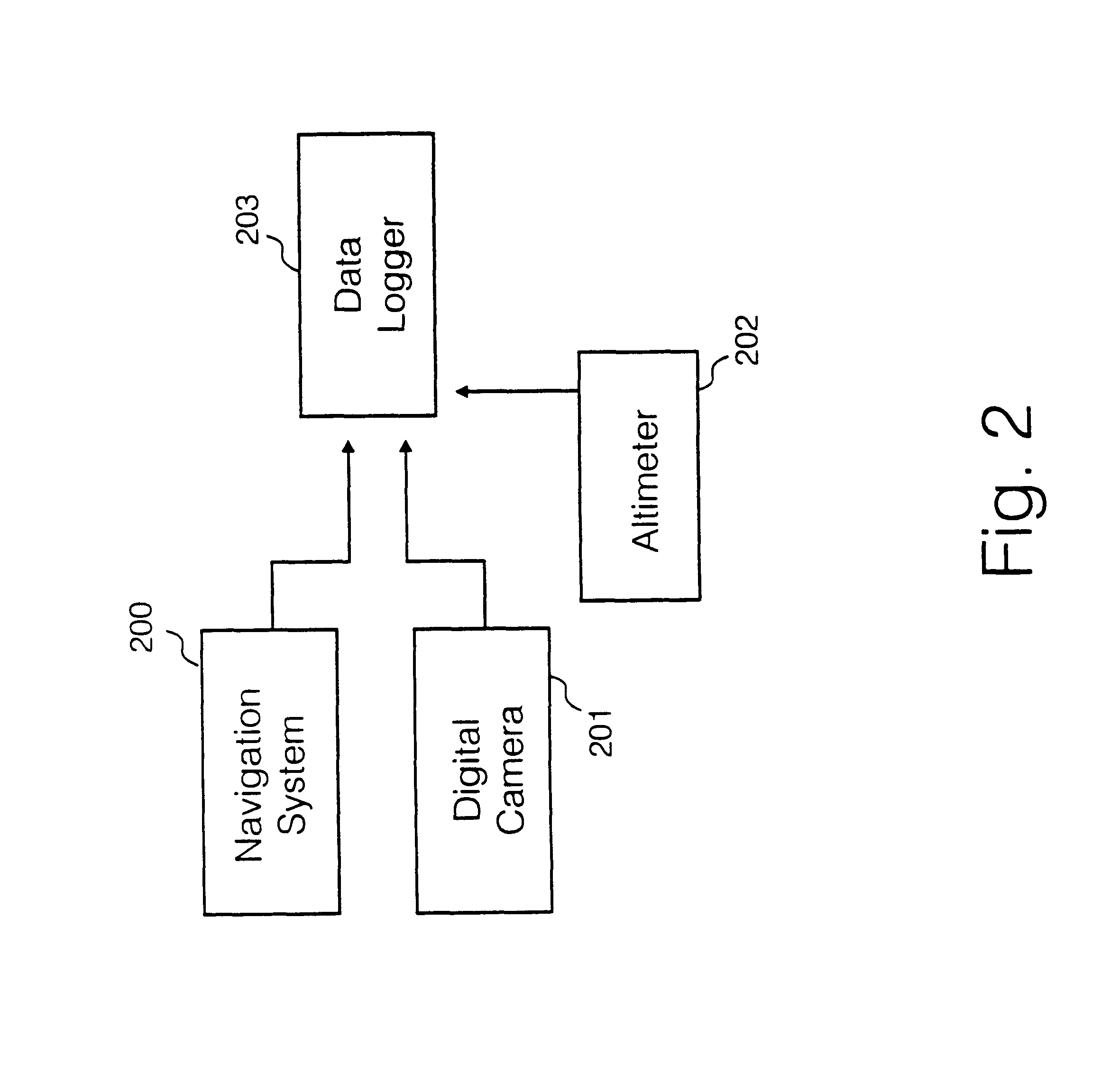
Automatic registration of images in digital terrain elevation data
A method of registering reconnaissance image data with map data is disclosed, comprising recording image data at a plurality of positions, together with the role, pitch and height above mean sea level data from an airborne navigation system and imaging system, and recording altitude of a reconnaissance craft from an altimeter; obtaining a difference between said recorded altitude data, and an altitude calculated from said navigation system data and a map data; selecting a difference data having a lowest standard deviation, and at a position of said selected difference data generating a three dimensional surface data using a bi-quadratic equation; generating a bi-quadratic surface of each of a plurality of positions for which data is recorded; generating a difference data between said bi-quadratic surface data, and height data obtained from said map, and minimising an error between bi-quadratic surface data and said height data by translating said position data relative to said map data, until minimum error is achieved; registering said image data with said map data after applying a said translation of said image data.
Owner:ATLANTIC INERTIAL SYST
Methods and systems for measuring terrain height
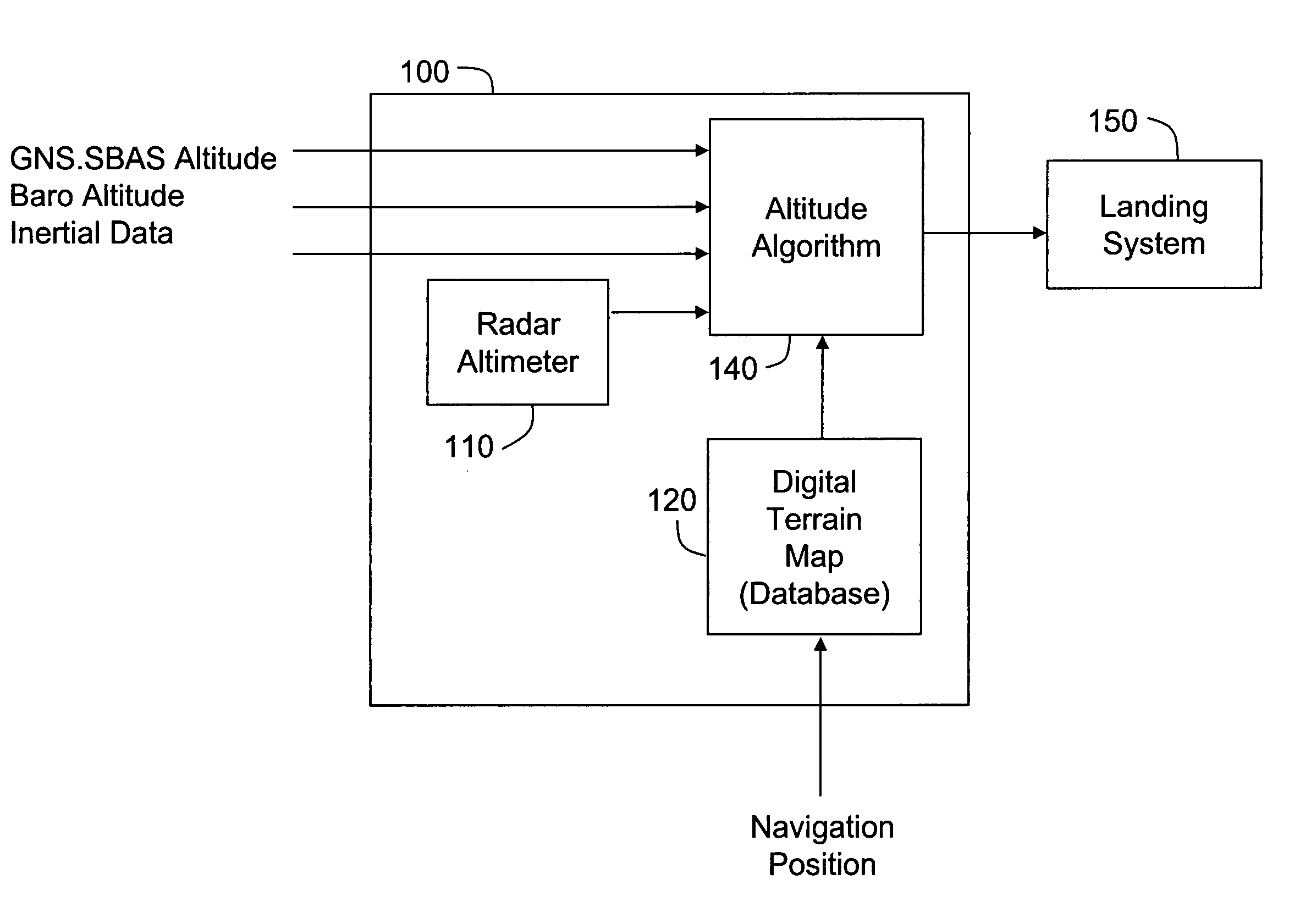
ActiveUS7145501B1Fluid pressure measurement using pressure-sensitive liquidPosition fixationRadarRadar altimeter
An altitude measuring system is described that includes a radar altimeter configured to measure altitude and a digital terrain map database. The database includes data relating to terrain elevation and at least one data parameter relating to an accuracy of the terrain elevation data and the altitude measured by the radar altimeter. The system is configured to weigh an altitude derived from the terrain elevation data and the radar altimeter measurements according to the at least one data parameter.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
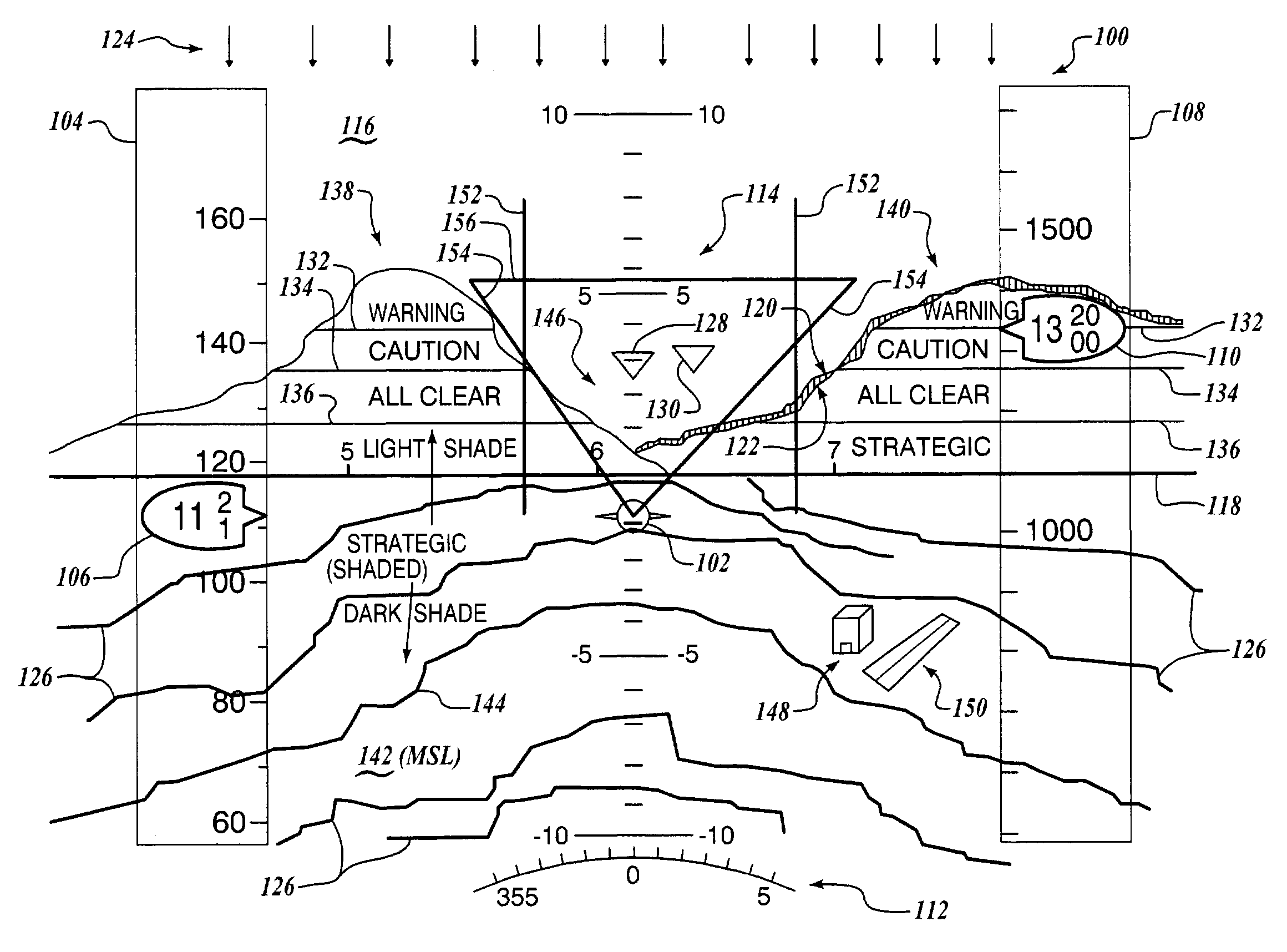
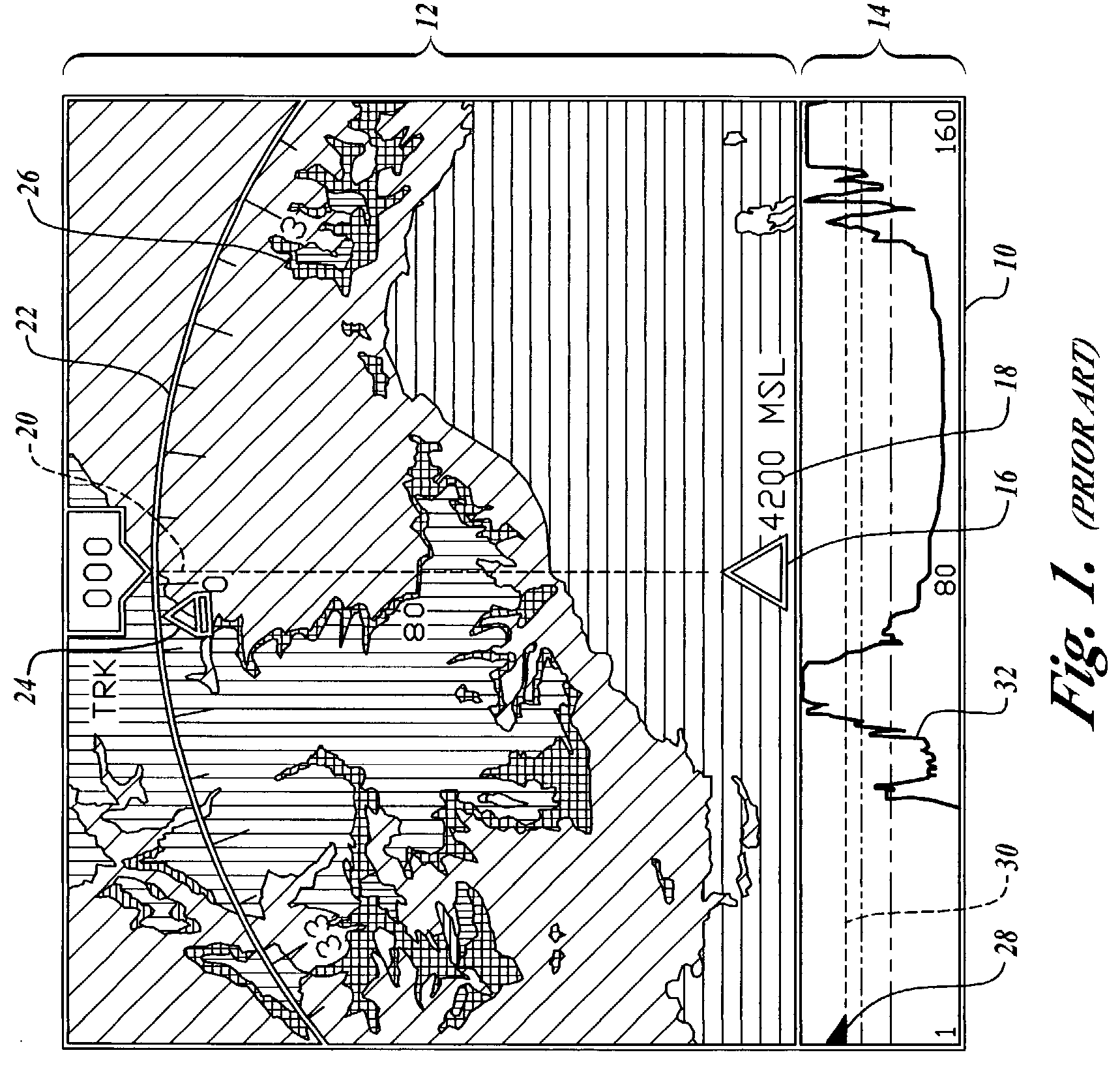
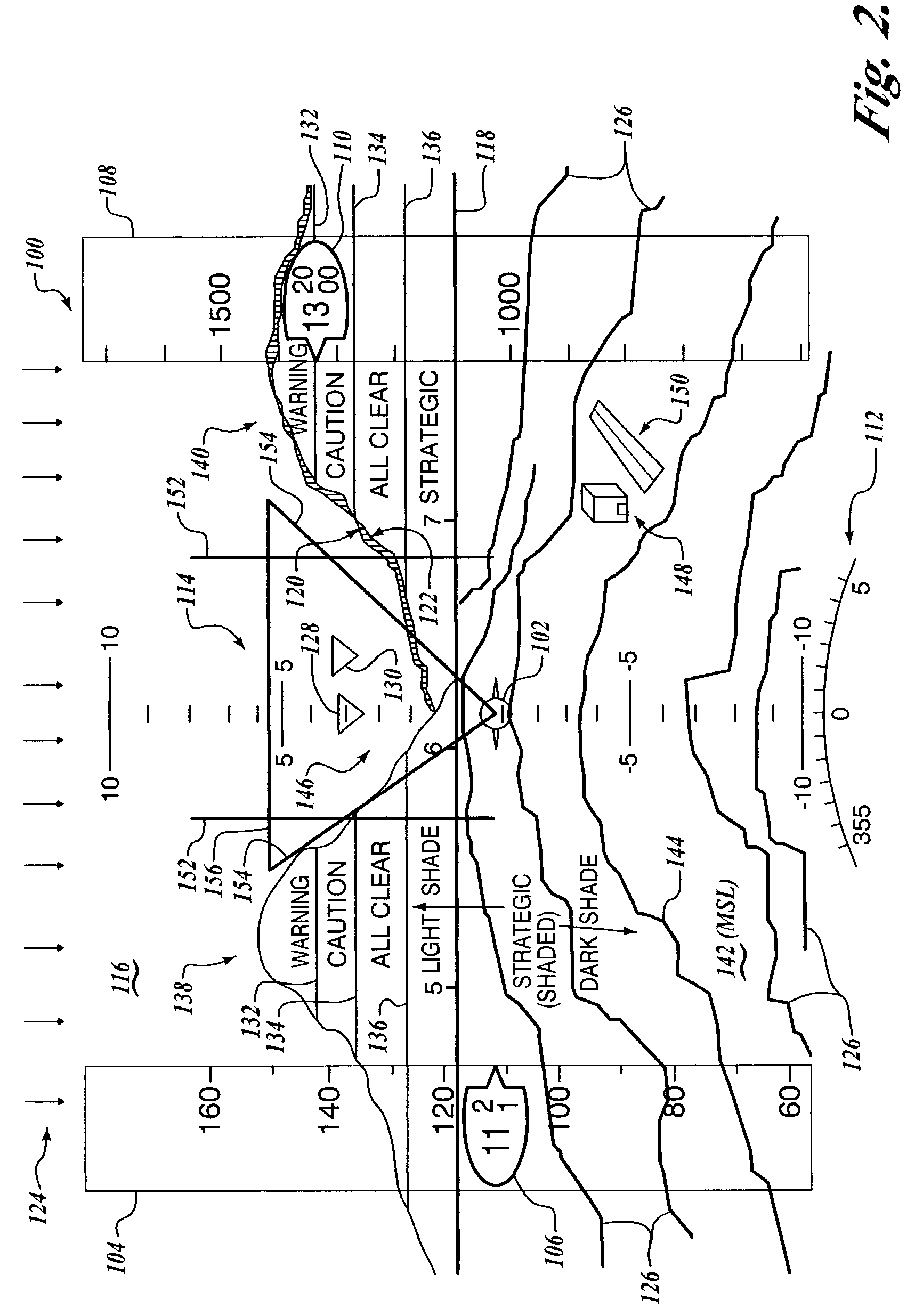
Display methodology for encoding simultaneous absolute and relative altitude terrain data
A display control device, having a processor structured for receiving terrain elevation information and samples of current position and altitude above ground data; and one or more algorithms resident on the processor for generating, as a function of the current position and altitude above ground data, one or more display control signals for causing a display device to display, in a monochromatic scale graduated as a function of terrain elevation relative to mean sea level, a strategic portion of the terrain elevation information extending between a minimum elevation of the strategic portion of the terrain elevation information and a pre-selected strategic altitude threshold less than the altitude above ground data.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
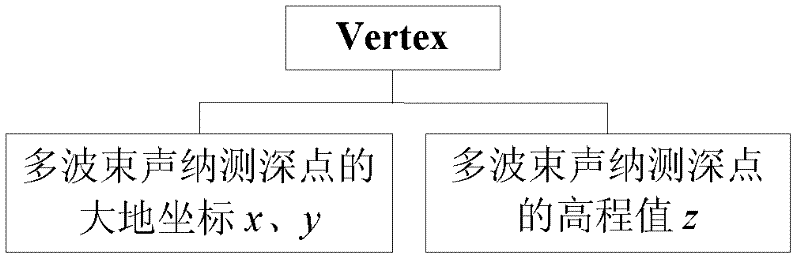
Method for constructing three-dimensional terrain vector model based on multi-beam sonar submarine measurement data
ActiveCN102446367AResolve can only provide discrete terrain elevationSolve the shortcoming of only being able to query the terrain parameters of the survey point3D modellingOcean bottomSonar
The invention discloses a method for constructing a three-dimensional terrain vector model based on multi-beam sonar submarine measurement data, and relates to a method for constructing the three-dimensional vector terrain model with measurement data of multi-beam sonar, which solves the defect that a multi-beam ranging sensor can only provide discrete terrain elevation and can only query terrainparameters at a measurement point. The method is used for non-structural submarine terrain modeling and vector data retrieval. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a horizontal coordinate of a sampling point of the terrain of a submarine area and corresponding elevation data; defining a data structure of a terrain triangular net model according to characteristics of multi-beam sonar terrain measurement data; and finally, establishing a Delaunay triangular net vector model according to elevation data of each point of the multi-beam sonar terrain measurement and the data structure of a Delaunay triangular net.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
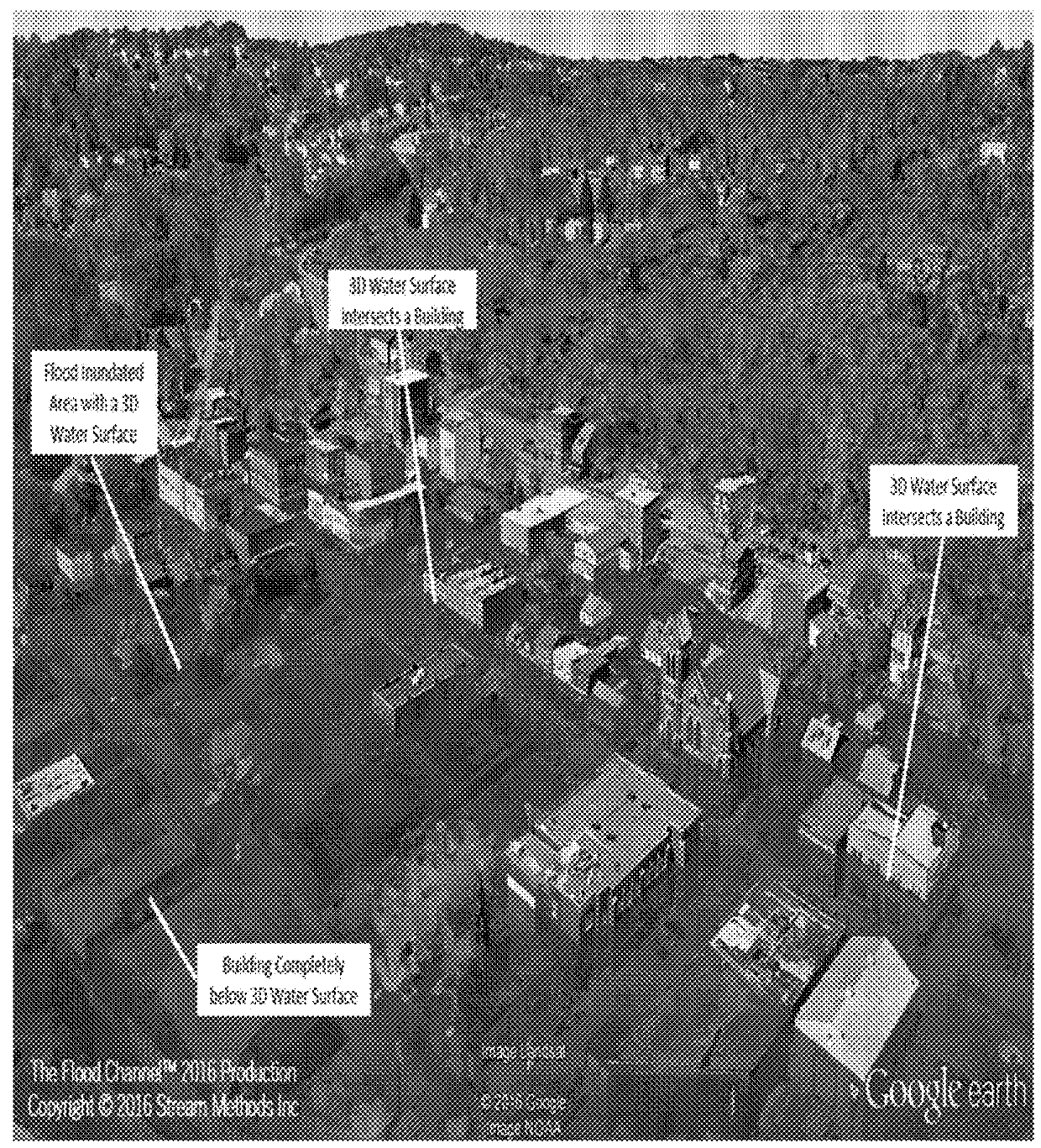
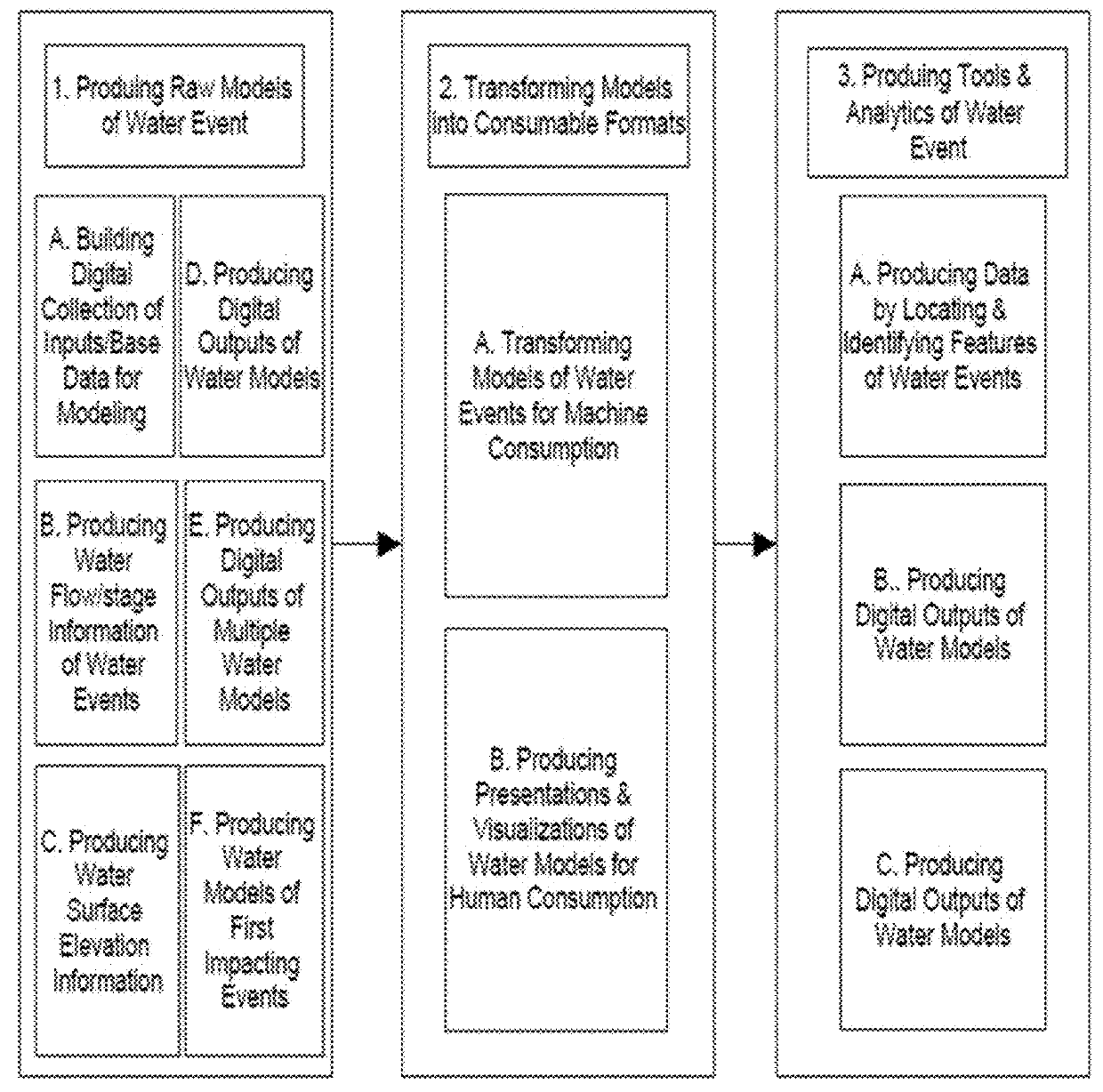
System and Method for Producing and Distributing Information Relevant to Water Events
ActiveUS20180165616A1Cost-effectiveConvenient transactionFinanceClimate change adaptationFlood risk assessmentData set
The present invention relates to water events modeling including flood, the number one natural disaster in the world. Specifically, the present invention generates models of water events consist of one or multiple outputs from various modeling processes. It also generates analytics of water events, and integrating the water models for machine and human-eyes consumption. Further, the present invention produces derivatives, tools, and informational services for various purposes, such as, flood risk assessment; flood determination; and insurance rating. The present invention is the process and systems of producing one or multiple models of water events and derivatives, based on various inputs. For modeling water events at a given location and in a timely fashion, the present invention prepares, aggregates, integrates, and maintains all relevant inputs in one system. The input data include various information, such as, water events' extent, flooded areas, flood plain, inundated areas, and measurement of water condition. The input datasets also include various other data, such as, terrain elevation data, land use land cover data, soil conductivity, water gauge measurements, and hydrologic regression equations for calculating flows. The inputs further include hydrologic modeling algorithms, hydraulic modeling algorithms, geospatial algorithms, and local or remote data of real-time water conditions acquired through machine services.
Owner:STREAM METHODS INC
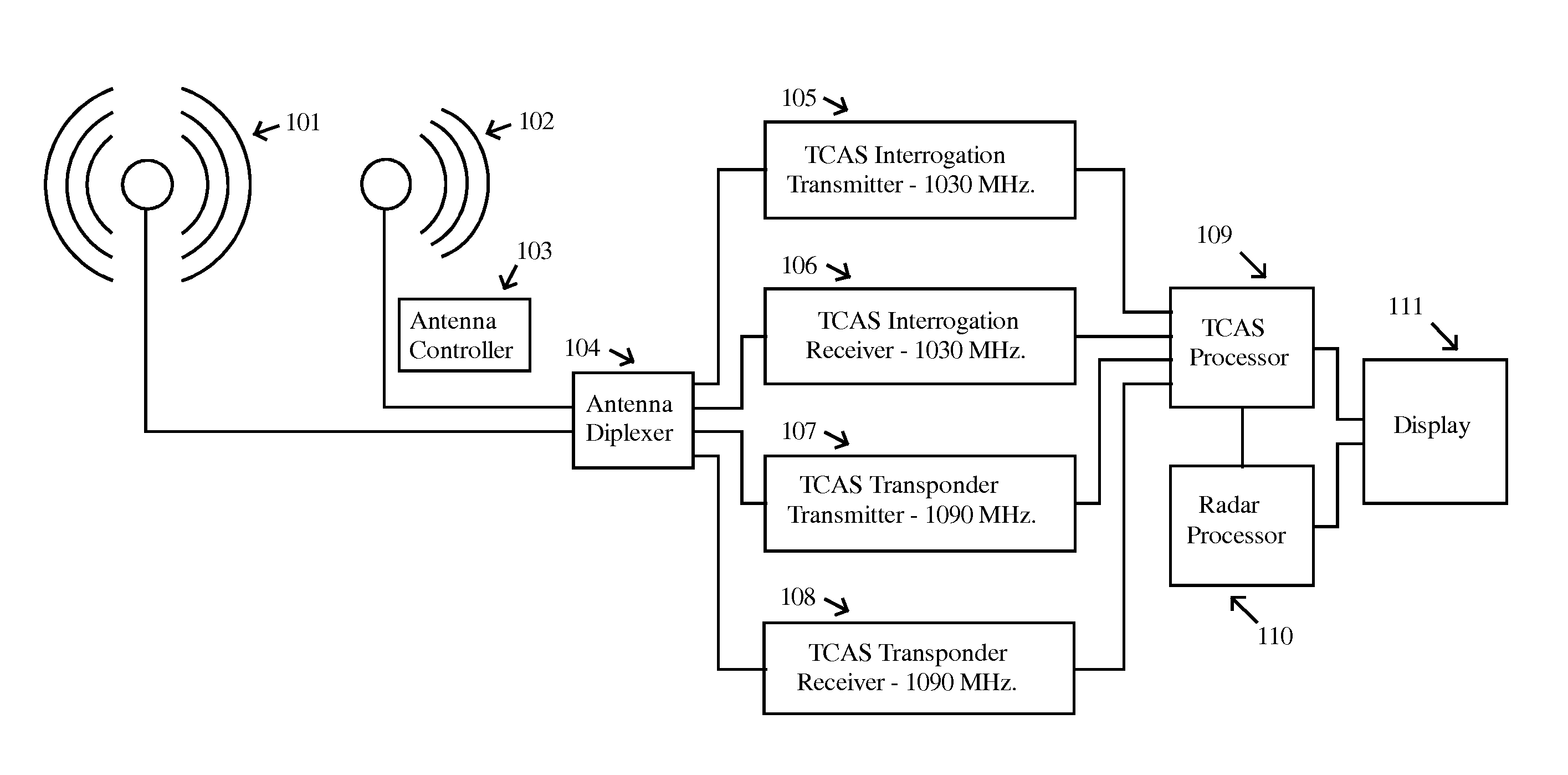
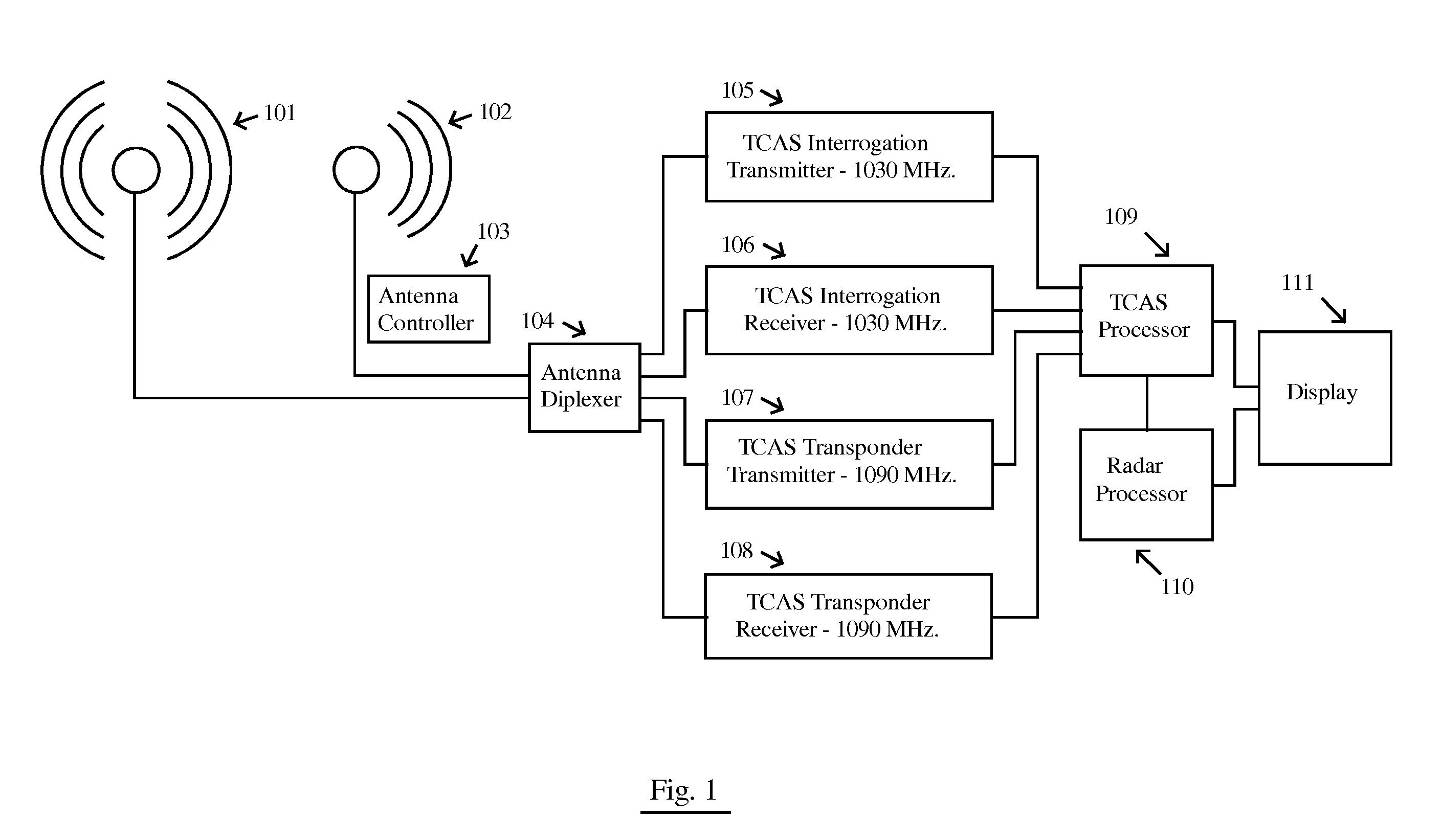
System for sensing aircraft and other objects
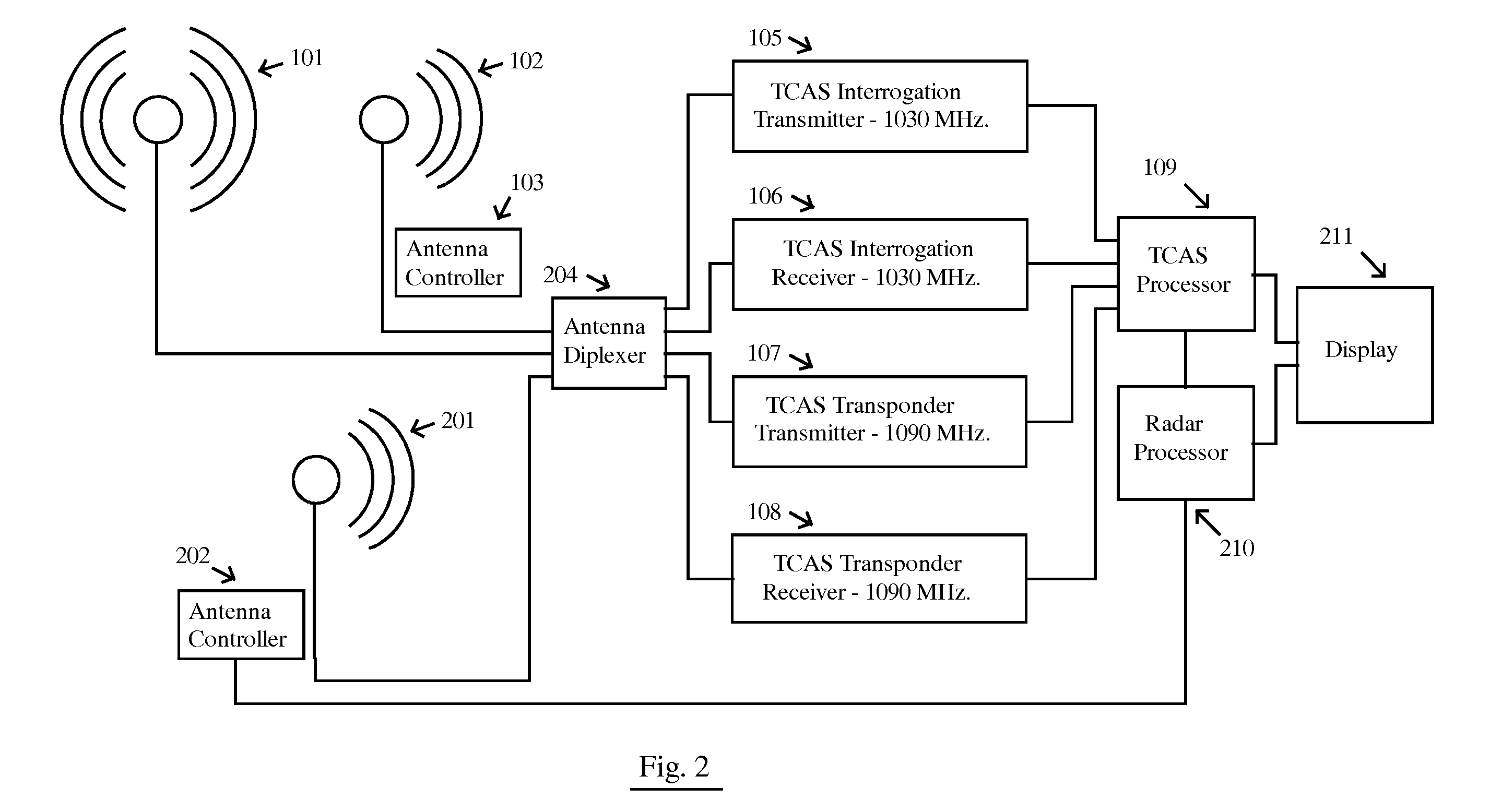
InactiveUS20110169684A1Reduce RF NoiseReduce noisePosition fixationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCommunications systemFlight vehicle
A system for sensing aircraft and other objects uses bistatic radar with spread-spectrum signals transmitted from remotely located sources such as aircraft flying at very high altitudes or from a satellite constellation. A bistatic spread spectrum radar system using a satellite constellation can be integrated with a communications system and / or with a system using long baseline radar interferometry to validate the digital terrain elevation database. The reliability and safety of TCAS and ADS-B are improved by using the signals transmitted from a TCAS or ADS-B unit as a radar transmitter with a receiver used to receive reflections. Aircraft and other objects using spread spectrum radar are detected by using two separate receiving systems. Cross-Correlation between the outputs of the two receiving systems reveals whether a noise signal is produced by the receiving systems themselves or is coming from the outside.
Owner:MARGOLIN JED
Electro-magnetic propagation modeling
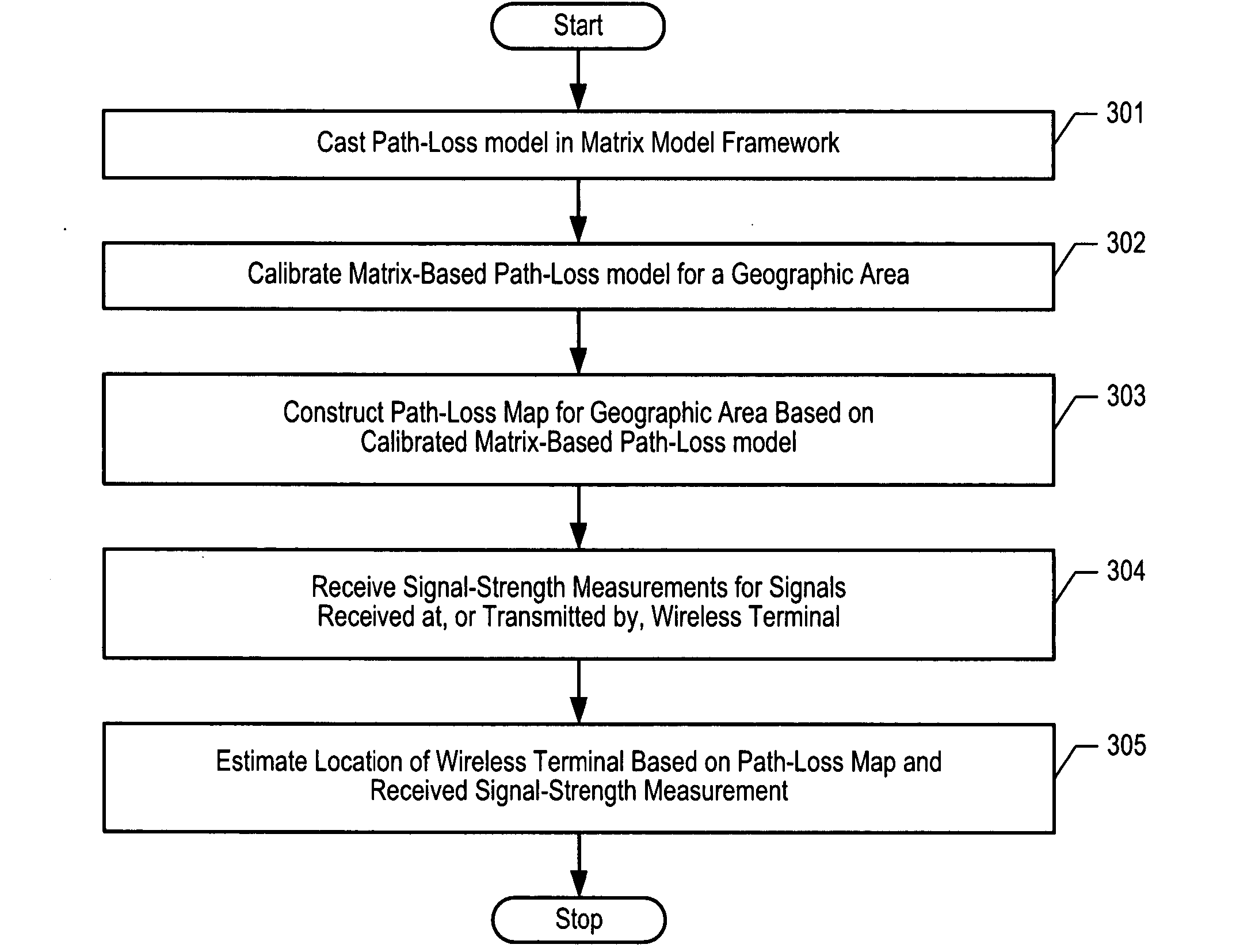
ActiveUS7433652B2Efficient of admissibilityEffective calculationDirection finders using radio wavesTransmission monitoringCommon frameworkData acquisition
A generalized framework is disclosed in which a wide variety of propagation models can be cast in a matrix-based format using arbitrary matrix coefficients. Casting propagation models in the matrix-based framework enables efficient computer implementation and calculation, ease of tuning, admissibility, and aggregating multiple propagation models into a single matrix-based model. Matrix-based propagation models based on transmitter-receiver azimuth orientation, transmitter antenna height, terrain elevation, and clutter are also disclosed. The propagation models can be used in conjunction with automated data acquisition from information sources such as topographic maps, clutter maps, etc.
Owner:POLARIS WIRELESS
Laser scanning apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160259058A1Avoid it happening againEliminate negative effectsUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationBlind zoneLaser scanning
The disclosed embodiments include an apparatus and method of using a laser to scan the ground or a target from an airborne or ground-based platform. In certain embodiments, the apparatus and method produces a 3-D elevation model of the terrain. In some embodiments, the apparatus includes a pulsed laser, a receiver to detect and amplify the pulse after being reflected by objects on the ground (or the ground itself), and electronics which measures the time of flight of the optical pulse from which the slant range to the target is calculated. Technical advantages of the disclosed embodiments include avoiding blind zones to ensure that no laser shots are wasted. In certain embodiments for airborne applications, the apparatus may also be configured to maintain a constant swath width or constant spot spacing independent of aircraft altitude or ground terrain elevation.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
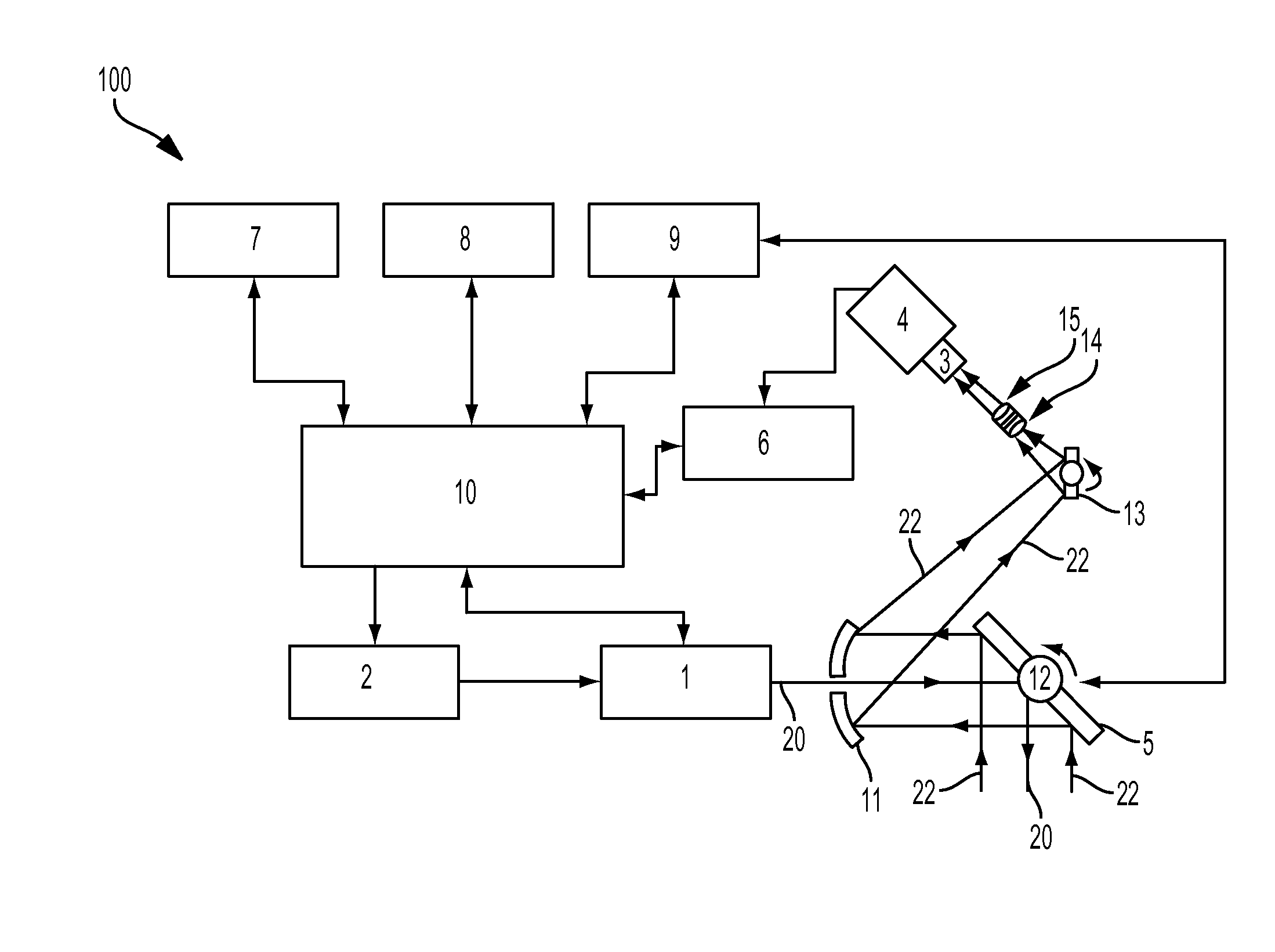
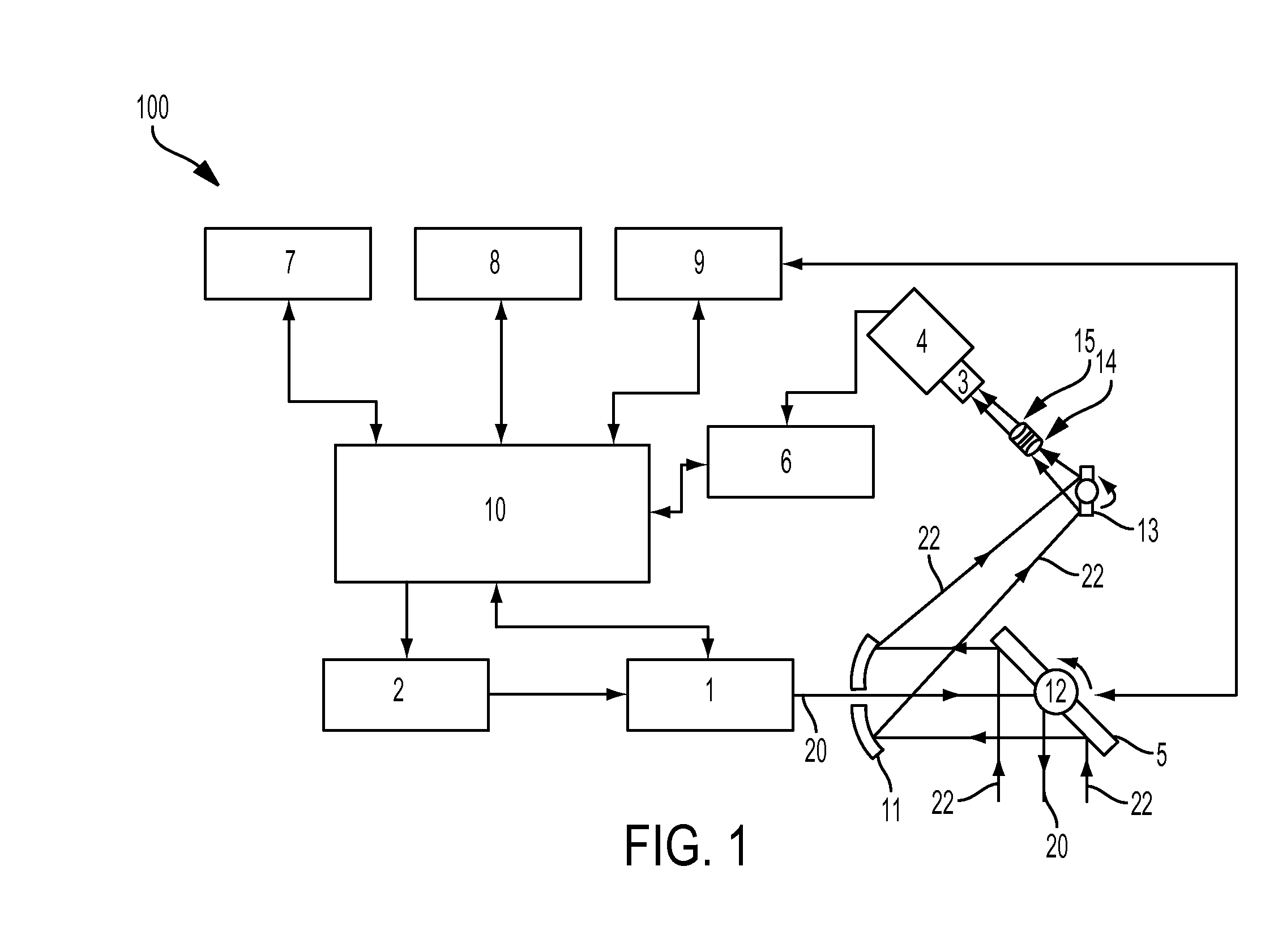
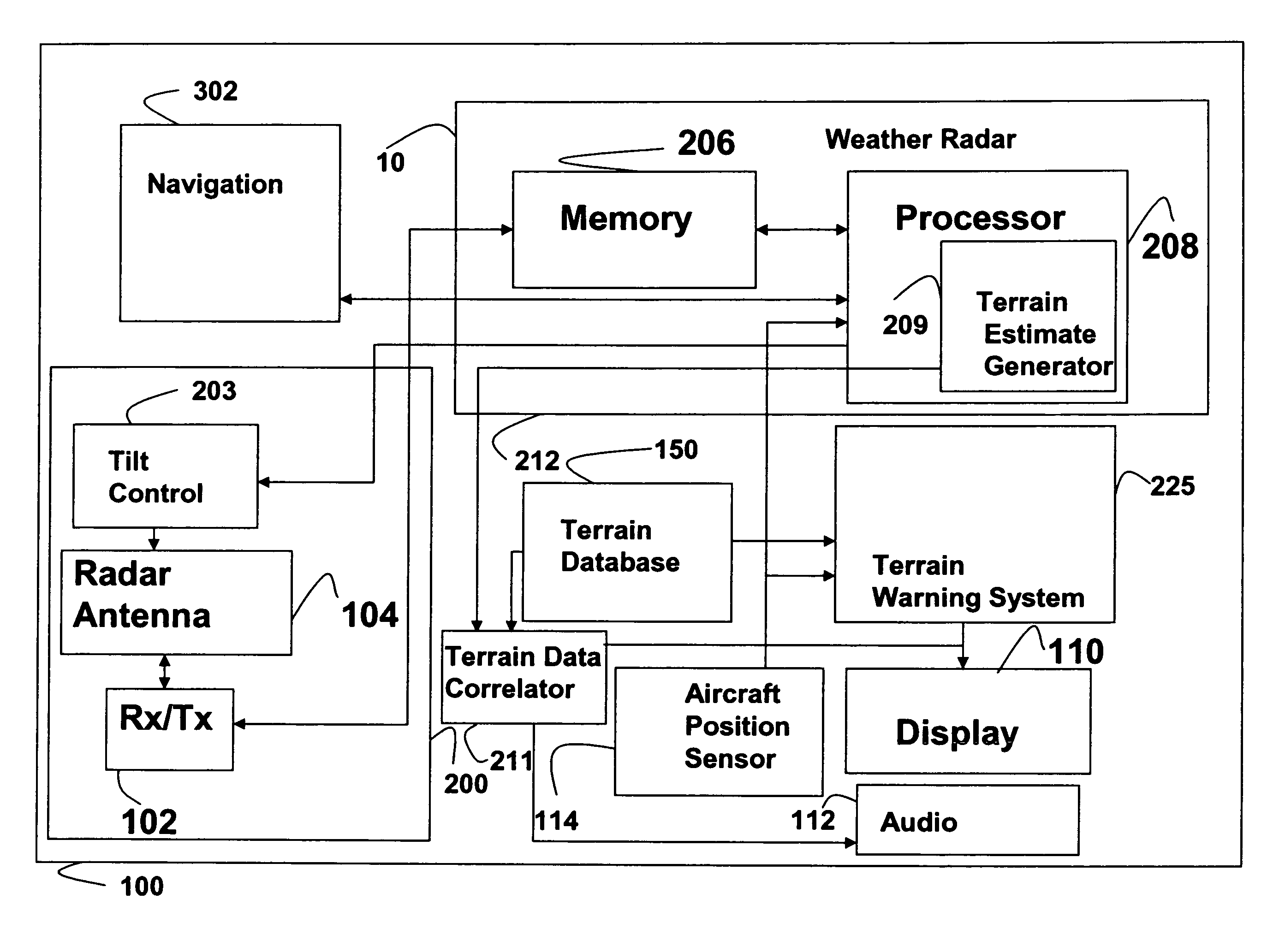
System and method for a terrain database and/or position validation
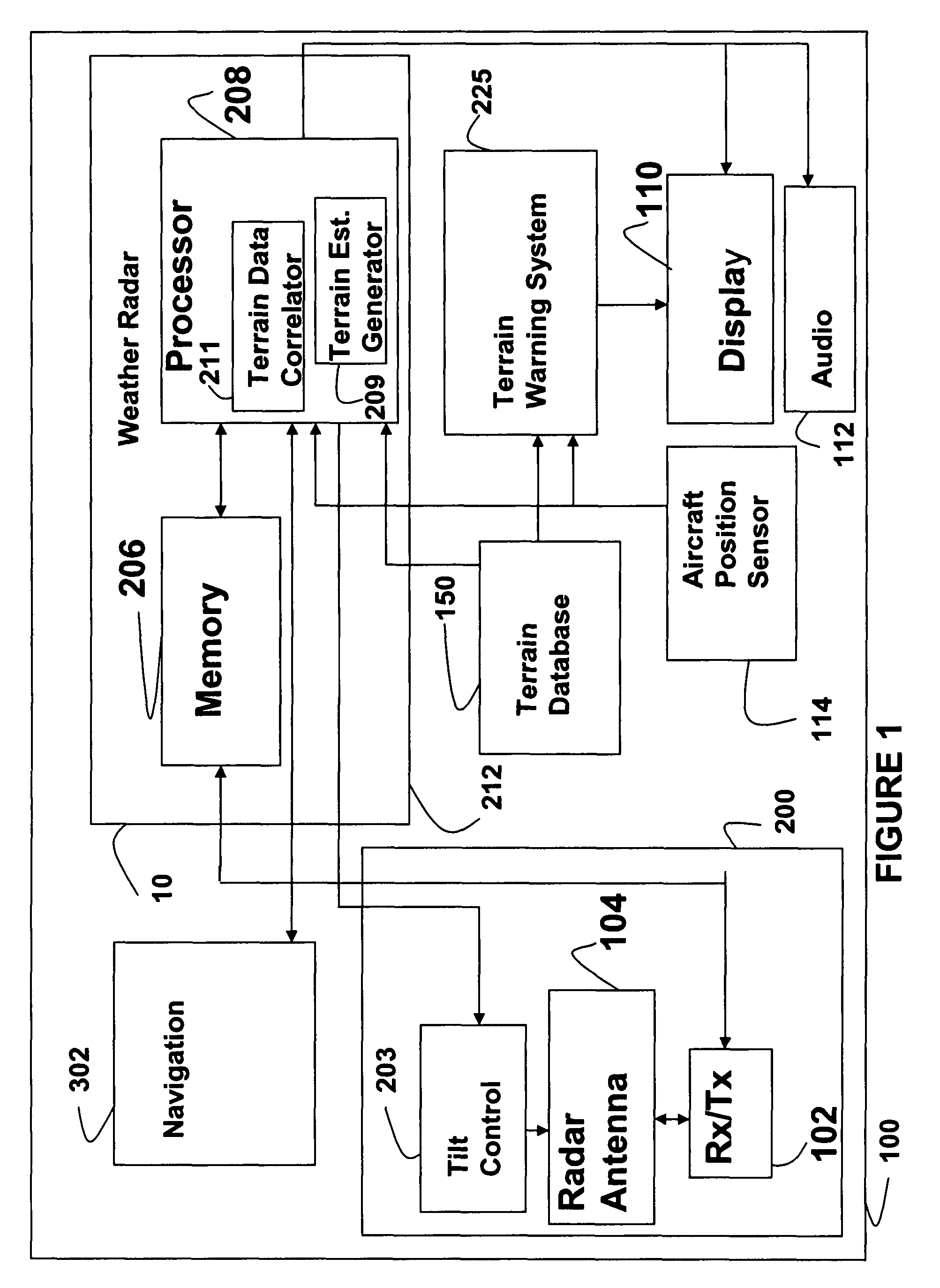
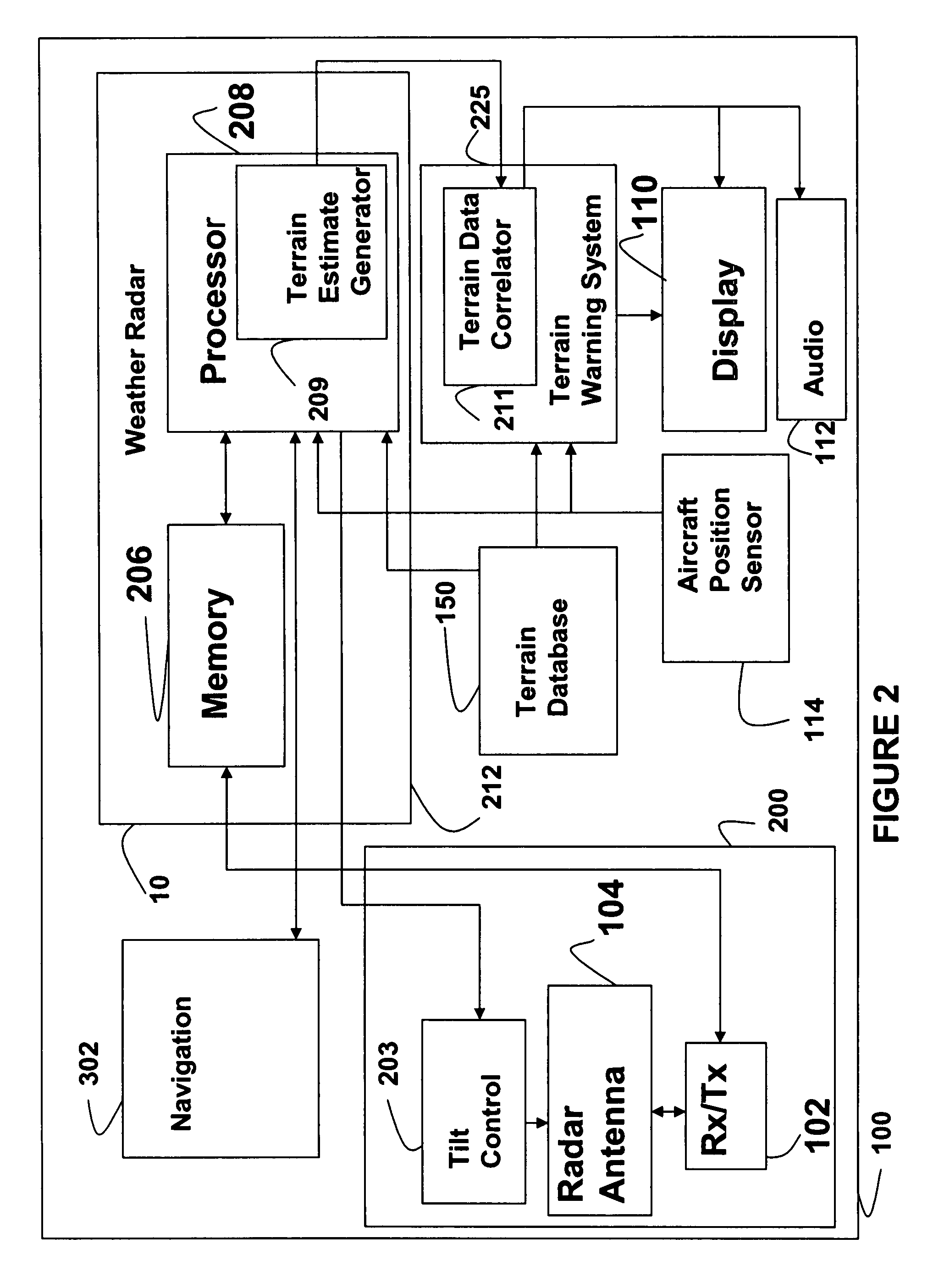
An aircraft weather radar system can be used with a terrain avoidance system. The aircraft weather radar system is coupled to an antenna. A processor receives radar returns received by the antenna. The processor determines terrain elevation estimates for use with the terrain avoidance system from the radar returns. The terrain elevation estimates are compared to stored terrain elevation data used with the terrain avoidance system to verify position or to check the integrity of the stored elevation data. The processor can be part of a terrain avoidance system, a weather radar system, a navigation system, or can be a standalone system.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Electro-magnetic propagation modeling
ActiveUS20060199546A1Tuning is slowEfficient of admissibilityDirection finders using radio wavesTransmission monitoringReal arithmeticLinear matrix
A generalized framework is disclosed in which a wide variety of propagation models can be cast in a matrix-based format using arbitrary matrix coefficients (e.g., real numbers, integers, etc.). Casting propagation models in the matrix-based framework enables efficient computer implementation and calculation, ease of tuning, admissibility (i.e., the tuned parameters of a linear matrix model are guaranteed to be the global optimum), and aggregating multiple propagation models into a single matrix-based model. Matrix-based propagation models based on transmitter-receiver azimuth orientation, transmitter antenna height, terrain elevation, and clutter are also disclosed. The propagation models can be used in conjunction with automated data acquisition from information sources such as topographic maps, clutter maps, etc.
Owner:POLARIS WIRELESS
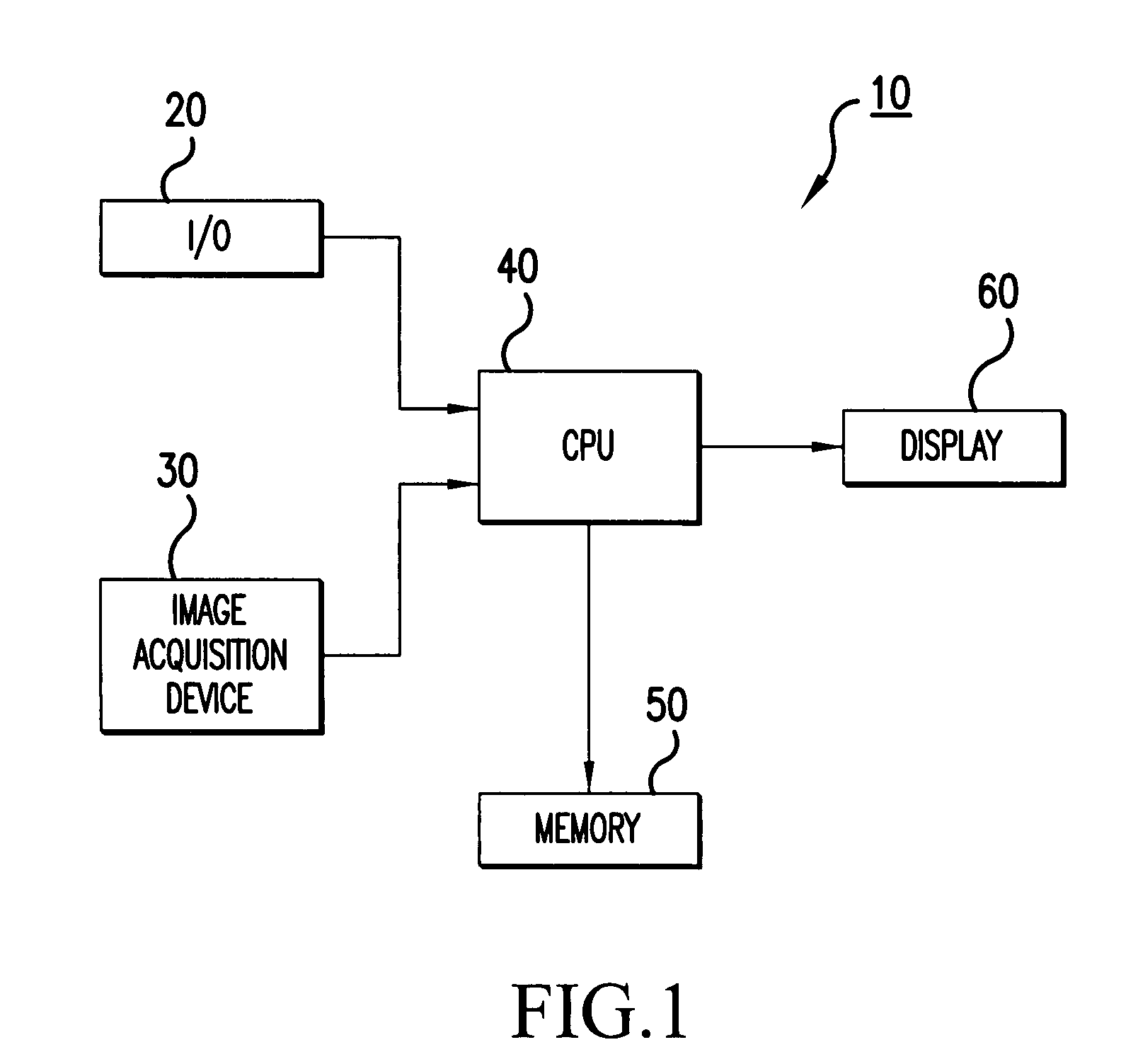
Three dimensional imaging method and apparatus
InactiveUS20100020066A1Increase the areaEnhance detailsImage analysisPicture taking arrangementsComputer visionVisualization methods
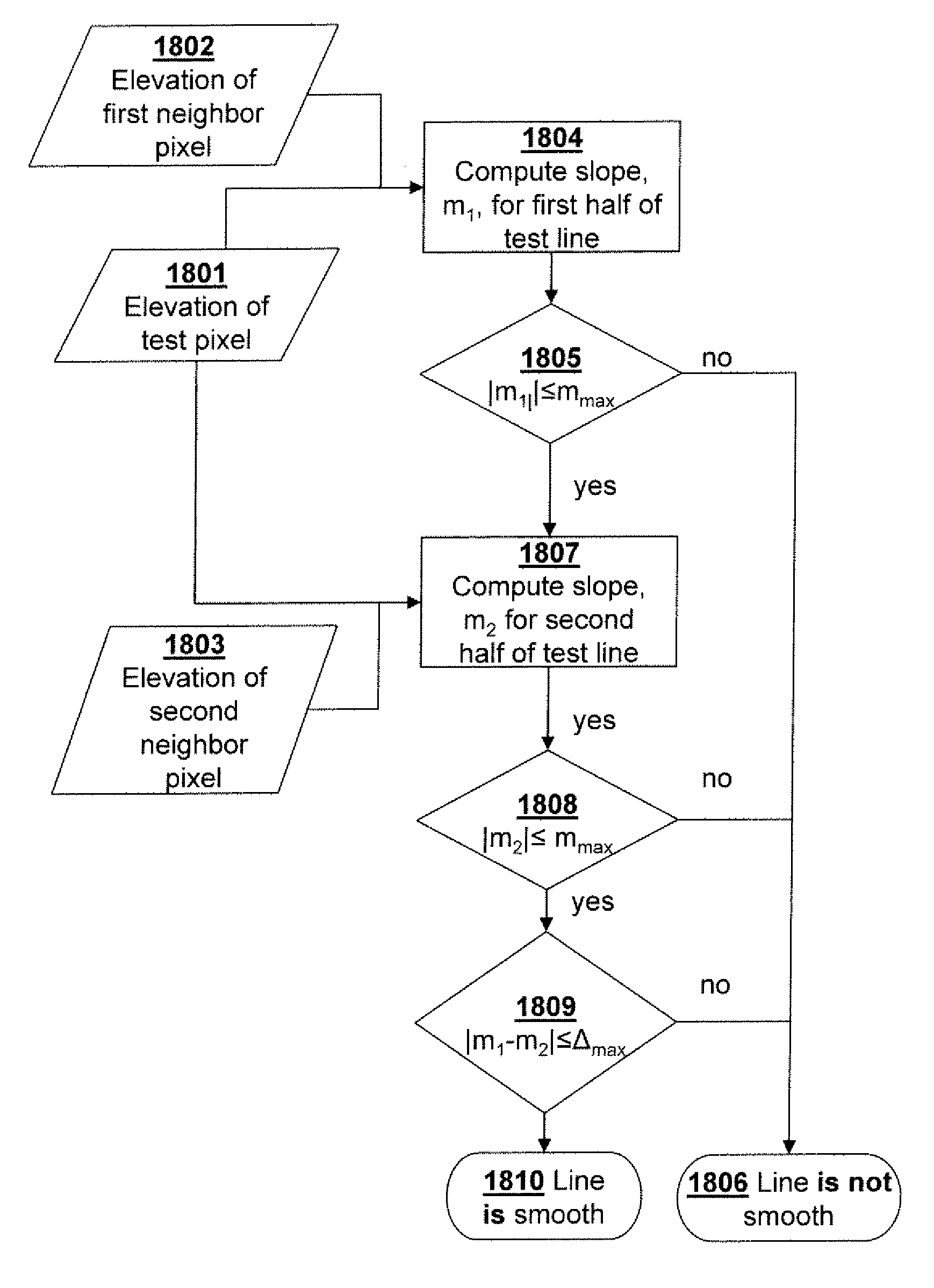
Three-dimensional imaging techniques are used for a visualization method and apparatus. In a preferred embodiment, terrain data is displayed as a series of pixels—areas of terrain elevation data. Individual pixels are analyzed to determine whether they are locally smooth or “warpable” relative to their surrounding neighbor pixels. Those pixels that are locally relatively “smooth,” i.e., those satisfying a given set of criteria, are joined with adjacent neighbor pixels by a process referred to herein as “warping” to create “smooth,” gap-free surfaces. A preferred embodiment includes drawing or generating lines between the centers of two pairs of adjacent pixels to determine a slopes m1 and m2 respectively. The slopes m1 and m2 are then analyzed using the following equations / determinations: |m1∥≦mmax; |m2∥≦mmax; and |m1−m2|≦Δmax; i.e., the slopes m1 and m2 must each be less than or equal to a predetermined threshold mmax and the difference between the slopes must be less than or equal to a predetermined difference Δmax.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
System and method for enhanced situational awareness of terrain in a vertical situation display
ActiveUS7209070B2Efficient use ofHeight/levelling measurementNavigation instrumentsLandformComputer science
A vertical situation display (“VSD”) system according to the invention generates a terrain image that represents a profile view of terrain elevation relative to the position of an aircraft traveling above the terrain. The VSD system generates the VSD image such that the terrain image is biased toward the lower elevation region of the VSD screen, thus making efficient use of the available display area. The VSD image is also generated such that it is continuous across the lateral range of the VSD, thus ensuring that terrain is shown in the VSD at all practical times, depending upon the available range and any priority display rules.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
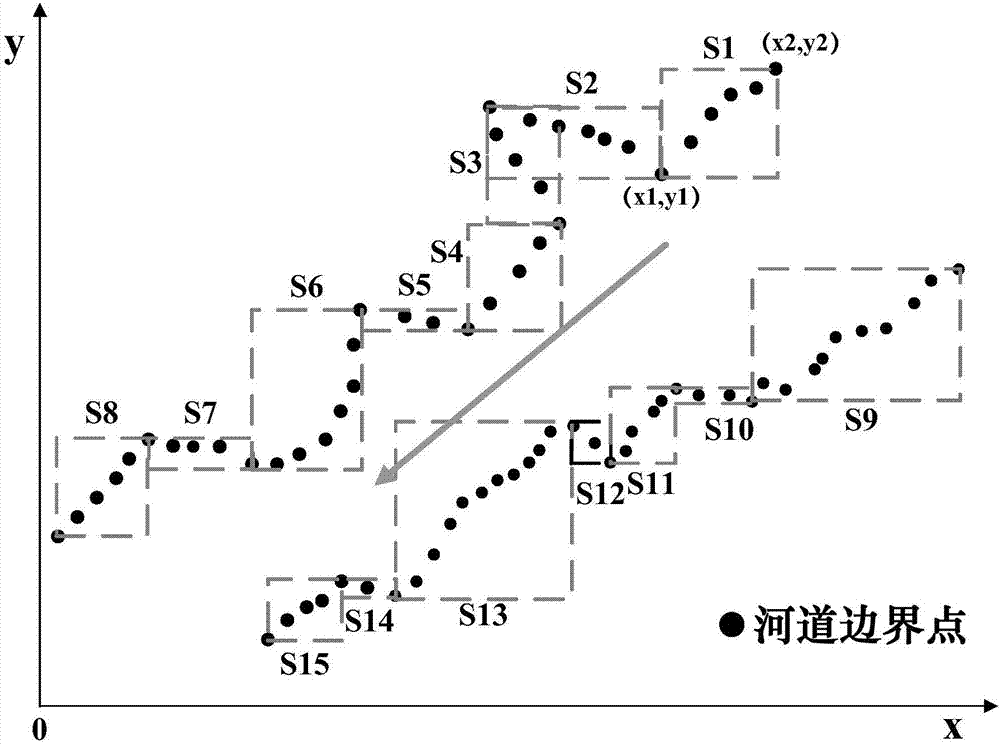
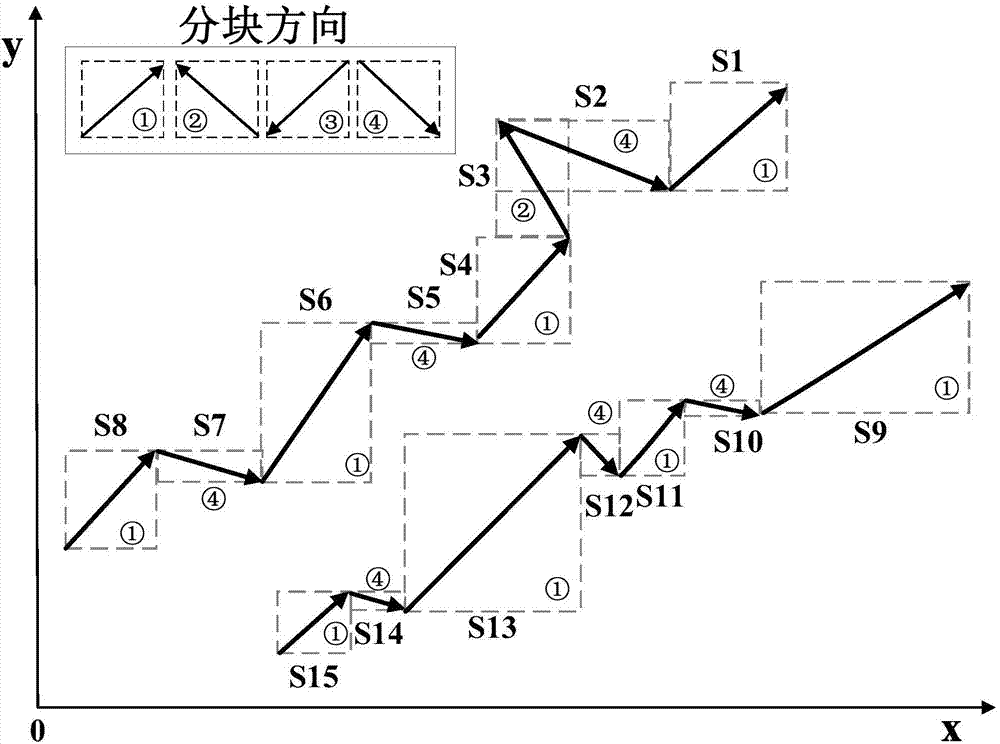
Complex riverway terrain quick and fine generation method
ActiveCN108010103AHigh data accuracyImprove interpolation accuracyDrawing from basic elementsGeographical information databasesLandformComputer science
The invention discloses a complex riverway terrain quick and fine generation method. By performing unified block division, classification and numbering on spatial relationships of complex terrain boundary points, scattered boundary points are fitted with a natural riverway course and a new riverway boundary is generated, so that the problem of disorder of a large amount of boundary points of a riverway is solved; through a finite riverway monitoring section terrain, based on a weight interpolation method, quick generation of a riverway terrain is realized; and the terrain is generated throughriverway interpolation, and accurate supplement of a riverway section is realized by utilizing a distance between a to-be-supplemented section and a known sampling elevation section of the riverway, and a gradient change. According to a characteristic that the scattered boundary points of the riverway and terrain elevation sampling data cannot meet riverway hydrodynamic calculation precision requirements, the modes of riverway boundary fitting, riverway terrain interpolation and riverway sampling elevation section supplement are adopted, the characteristics of the natural riverway course and the terrain change are fully considered, and the terrain interpolation errors are effectively reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS7196653B2Low costFeasible effortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsImaging equipment
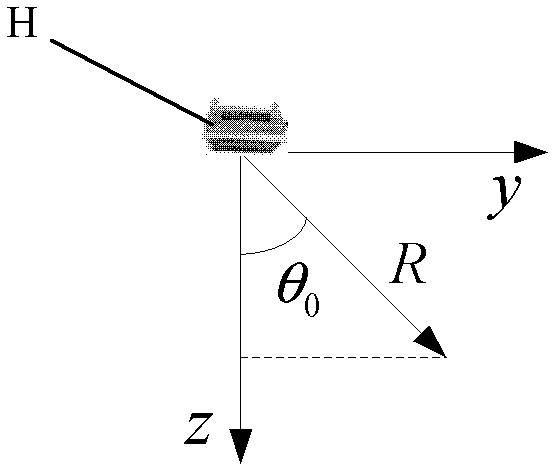
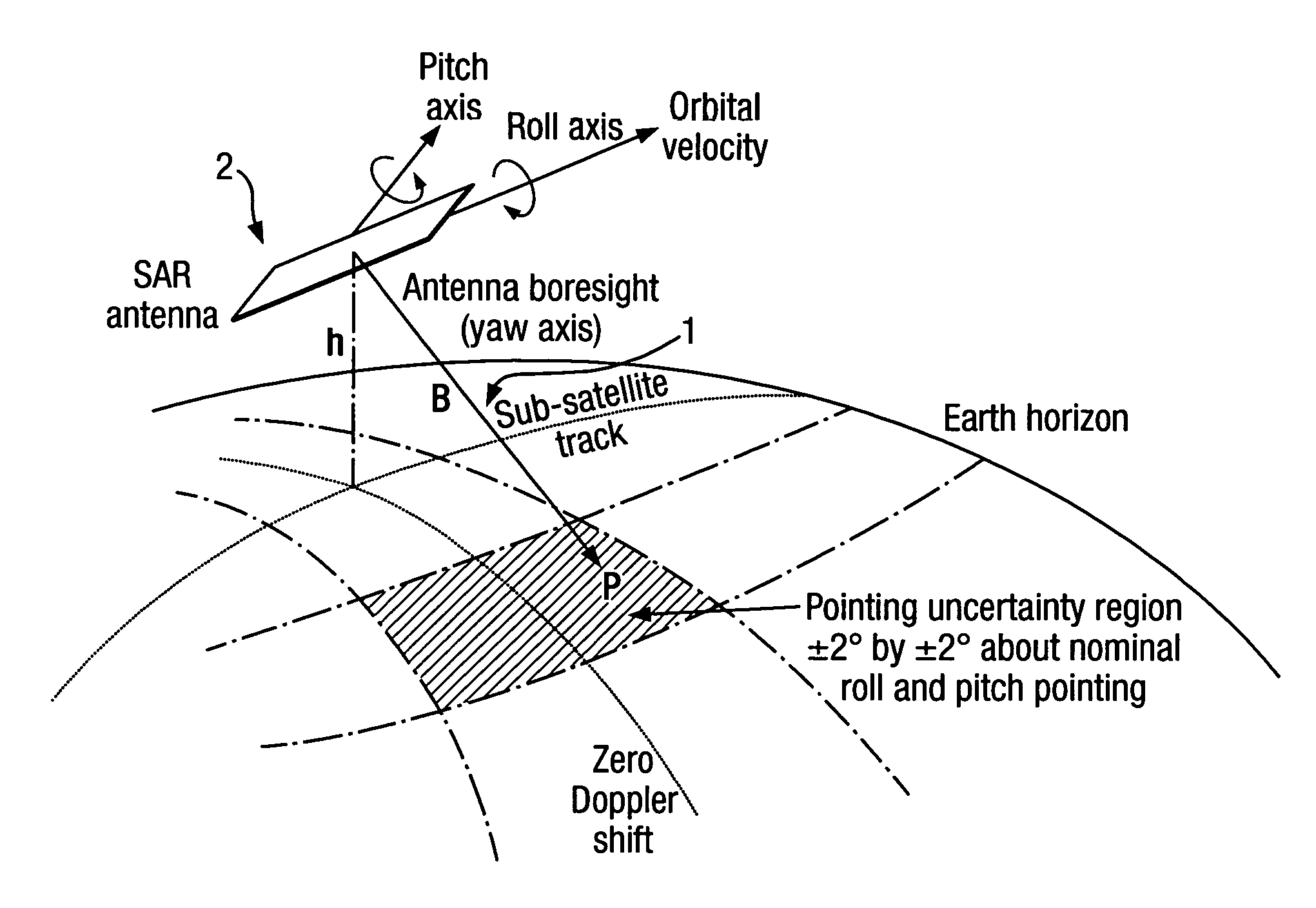
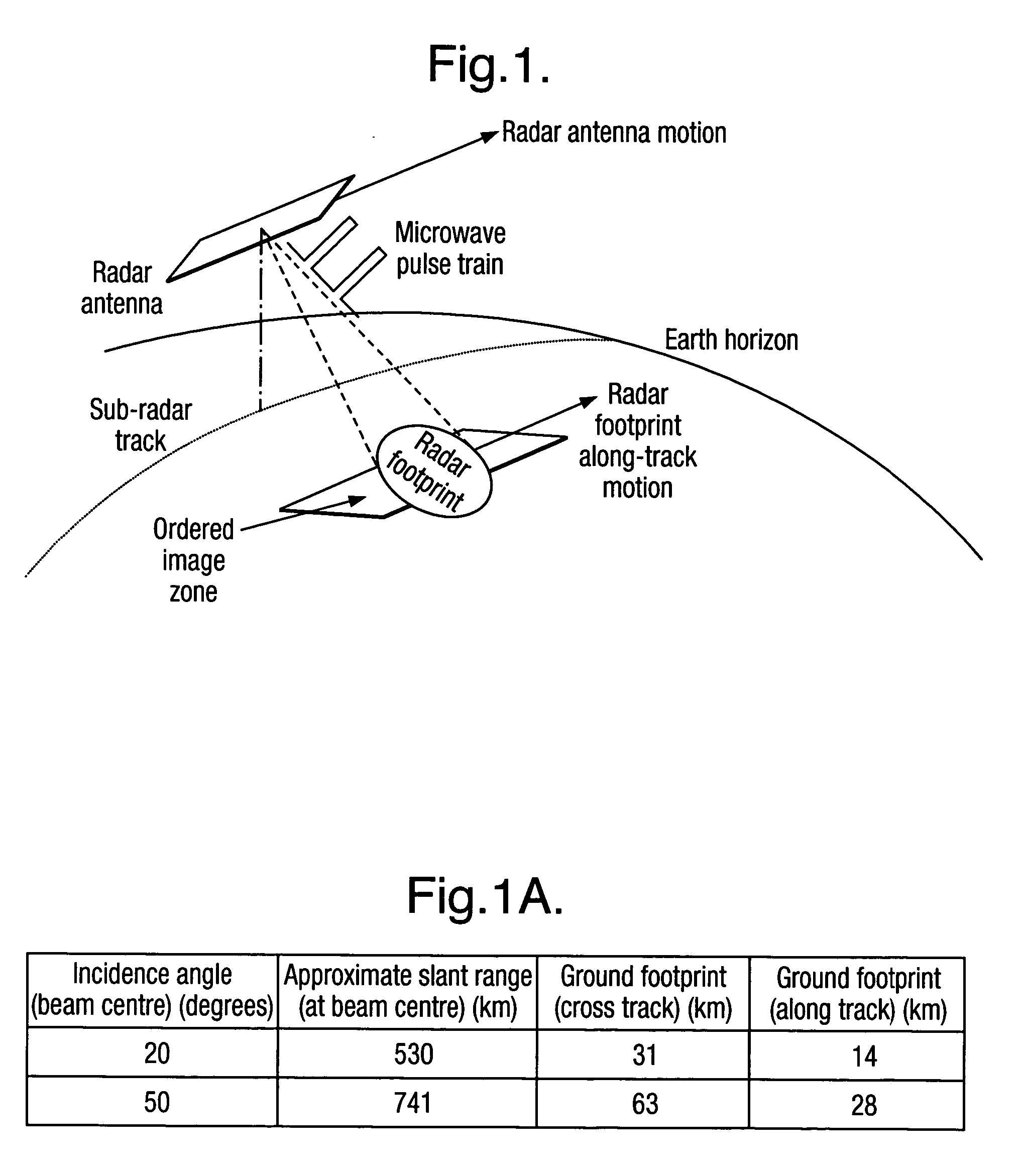
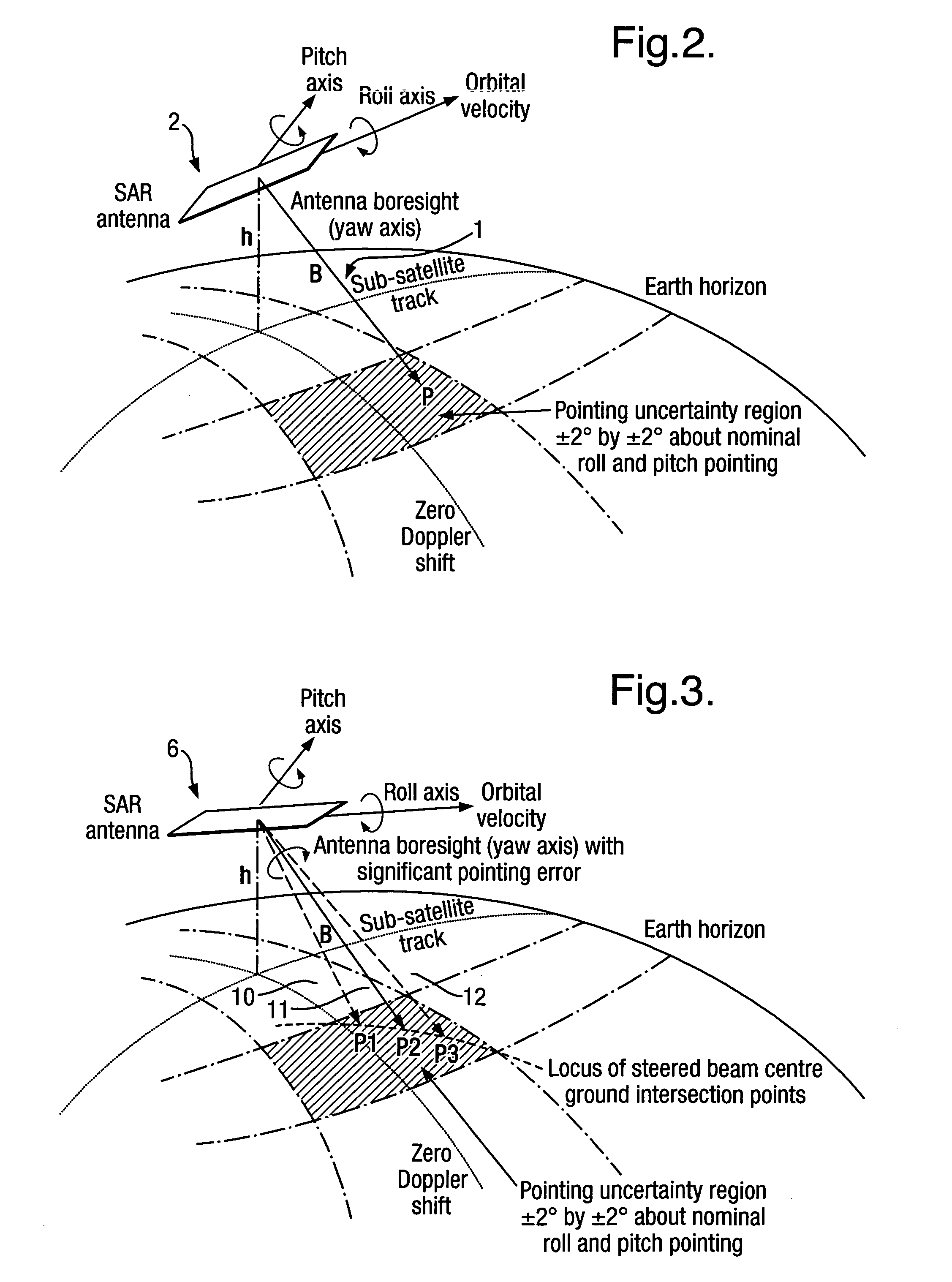
An imaging apparatus has transmitter illuminating a selected surface with a radar beam footprint, and processor for profiling / processing the radar returns so as to derive attitude information in real time about a number of predefined axes associated with the radar which depends upon the relative dispositions of the radar, the selected surface and upon the radar beam footprint characteristics.A plurality of transmit beams image the surface and the processing arrangement has the capability of determining roll, pitch and / or yaw pointing data associated with the radar, such pointing data being determined by derivation of the attitude information and by selective input of terrain elevation data so as to take account of variations in the radar viewing geometry with terrain elevation.This provides a low cost advantage over known radar designs, and retains utility for many applications, for example spaceborne and airborne applications.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
High-fidelity digital modeling method for landform altitude
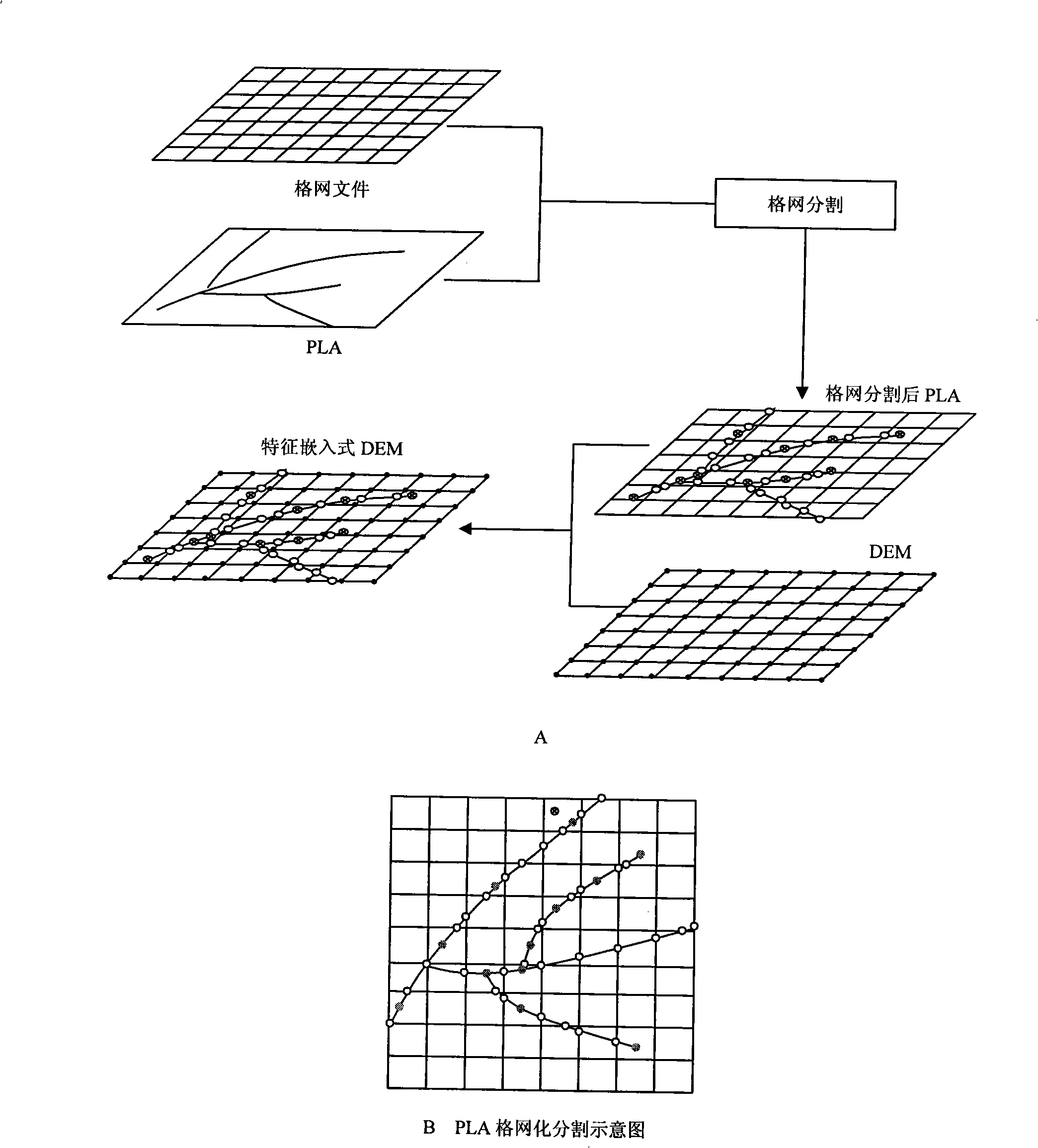
InactiveCN101344390AImprove accuracyImprove integritySpecial data processing applicationsProfile tracingRegular gridData acquisition
The invention discloses a high-fidelity digital modeling method of terrain elevation, the steps are as follows: the first step is to carry out push-broom data acquisition; the second step is to carry out grid segmentation of the acquired vector terrain feature data; the third step is to carry out similar DEM grid data organization of PLA, organization management is carried out to the PLA data after the grid segmentation treatment according to grid data structure; the fourth step is to generate a new digital elevation model file to carry out the seamless embedding of the vector feature data; a feature embedded digital elevation model data structure is composed of three sub-files which comprise a grid file, a feature identification file and a feature file; the grid file is a regular grid data structure; the feature identification file is used for spatial data index of a vector grid integrated organization, the structure thereof is consistent with the current national DEM data structure and only records the grids with the features; the feature file records terrain feature information which is contained in one grid unit, and the information comprises feature points and feature lines.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Distance estimation method for a moving object having a constrained vertical path profile
InactiveUS20080154493A1Road vehicles traffic controlNavigation instrumentsEstimation methodsChamfer distance
This method makes it possible to plot, from a terrain elevation database, a map of the distances of the points accessible to a moving object subject to constraints (inaccessible reliefs, unnegotiable obstacles, weather disturbances, path with an imposed vertical profile, etc.), the distances being measured only along paths that are practical for the moving object. It employs a chamfer distance transform applied to the image consisting of the projection on the horizontal plane of a 3D representation of the flying space of the moving object, which is likened to a mesh of elementary cubes associated with specific negotiation danger levels. It lists the typical paths without exceeding an acceptable danger threshold, going from a target point, the distance of which is to be estimated, to a source point, the origin of the distance measurements, and likens the distance of the target point to the length of the shortest practicable path or paths.
Owner:THALES SA
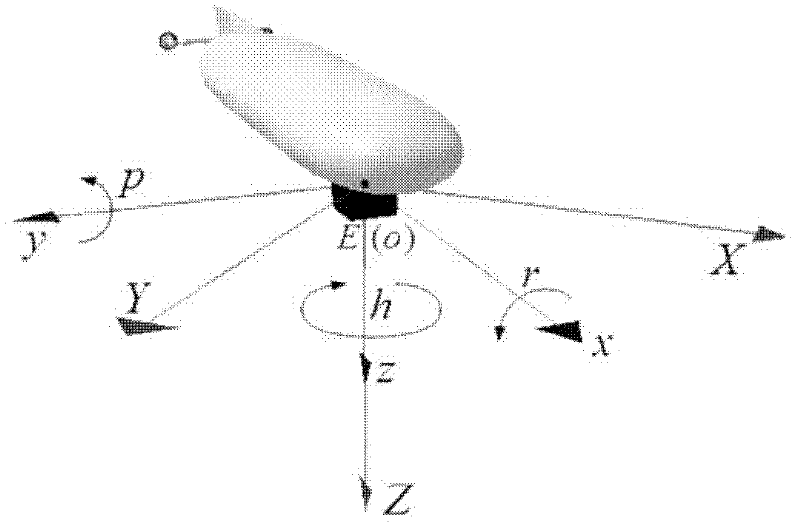
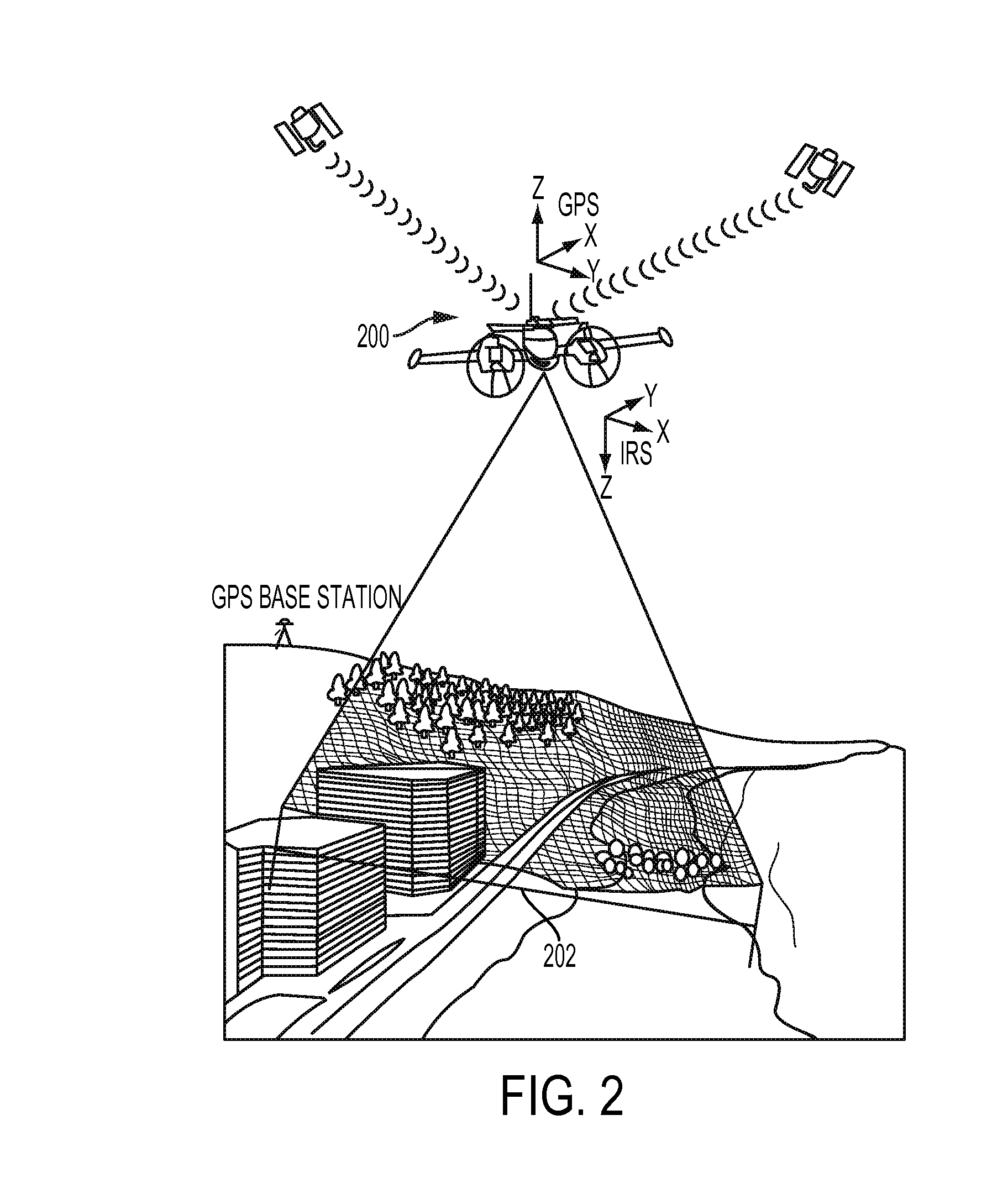
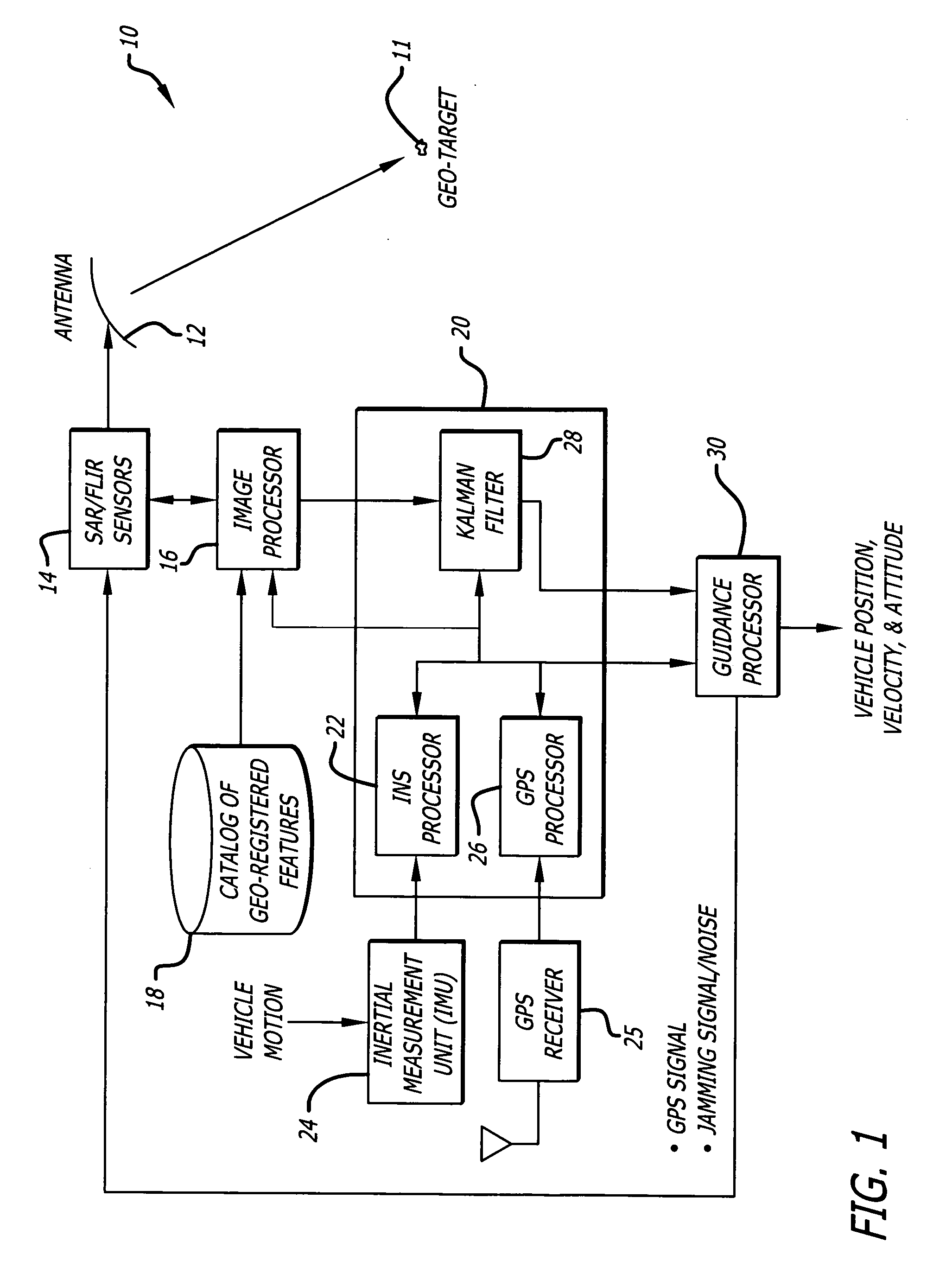
System and method for geo-registration with global positioning and inertial navigation
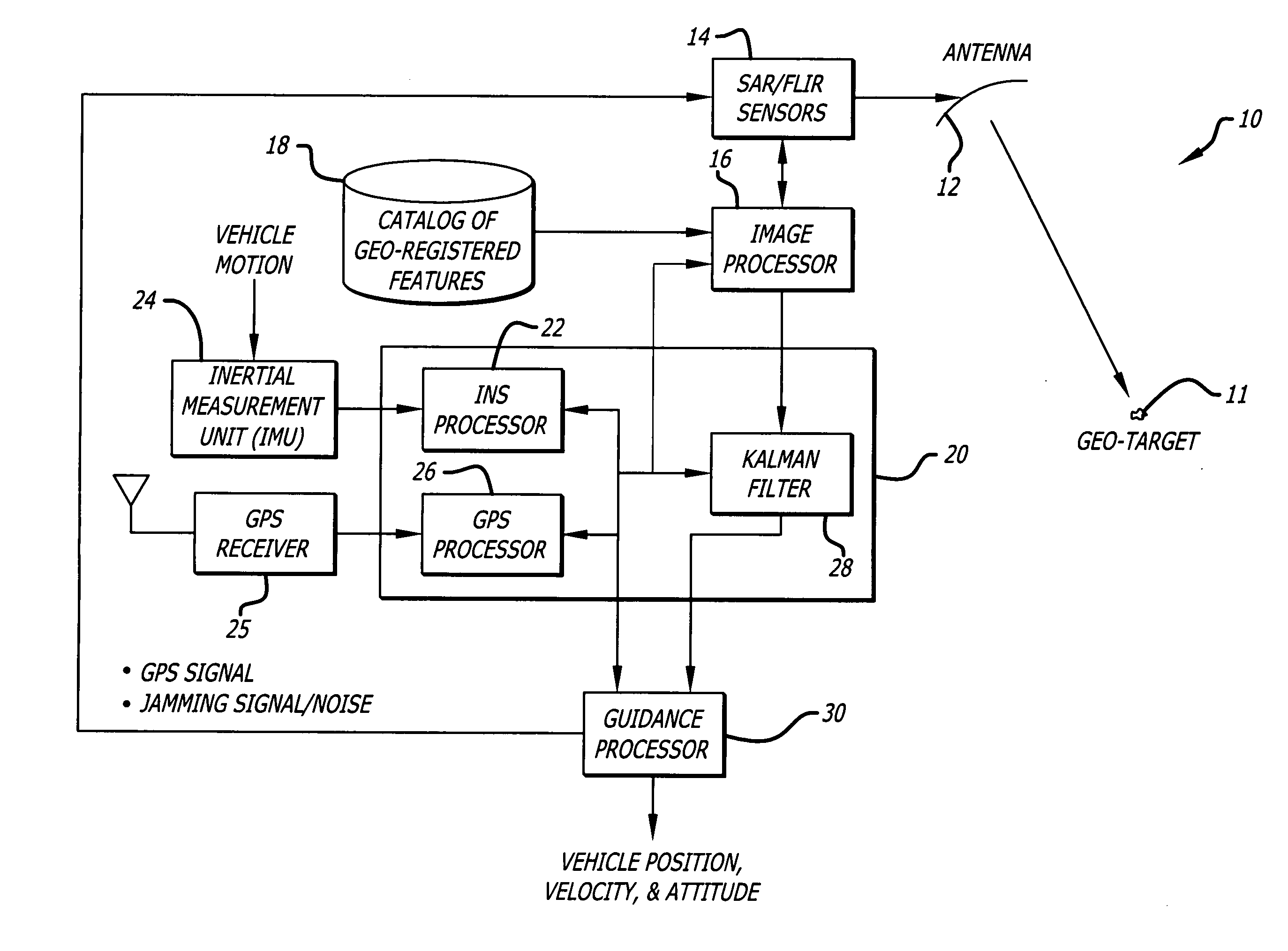
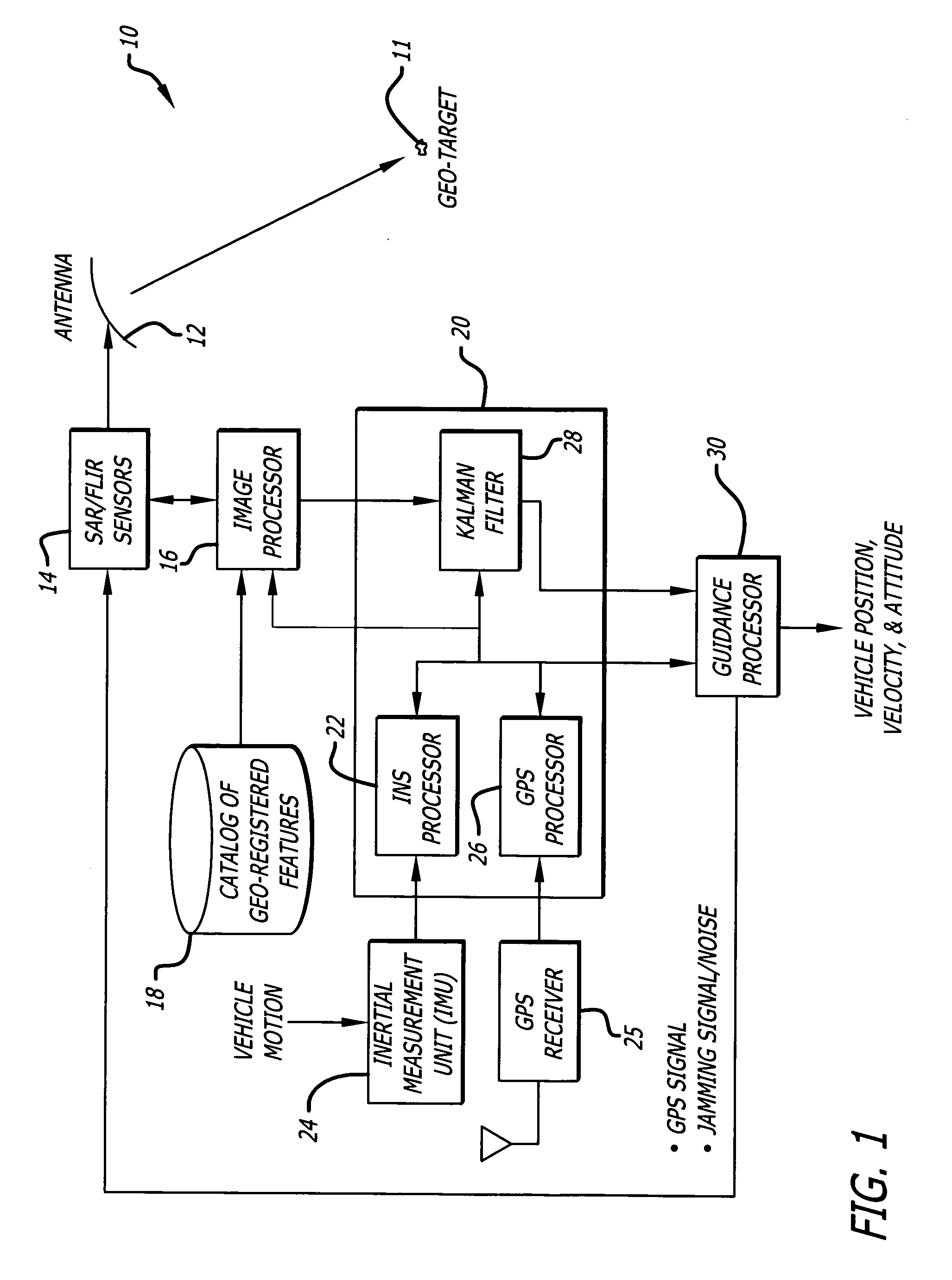
ActiveUS20060293854A1Improve navigation accuracyAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarForward looking
A position estimation system including a first arrangement for providing an image with a known target in a known reference frame. A second arrangement correlates the image with a stored image. The correlation is used to compute an error with respect to a position estimate. In a specific embodiment, the error is referenced with respect to first (x), second (y) and third (z) directions. A target location error is computed with respect to a stored image provided by a target image catalog. The target image catalog includes target geo-locations and digital terrain elevation data. In an illustrative application, the image data is provided by synthetic aperture radar and forward-looking infrared systems. An observation model and a measure noise matrix are Kalman filtered to ascertain a position error in navigation data generated by an integrated inertial navigation and Global Positioning system. In the illustrative application, geo-registered SAR / FLIR imagery is used to track targets and to determine a target location error (TLE). This TLE information is a set of error equations that describe the relationship between vehicle navigation information and target data. In accordance with the invention, this relationship is used to form an observation model for vehicle navigation with respect to target locations. Using Kalman filtering and the observation model, vehicle navigation errors can be bound and the navigation accuracy of the vehicle can be improved.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Compensation of flight path deviation for spotlight SAR
ActiveUS7277042B1Enhance the imageRadio wave reradiation/reflectionArray data structureFourier transform on finite groups
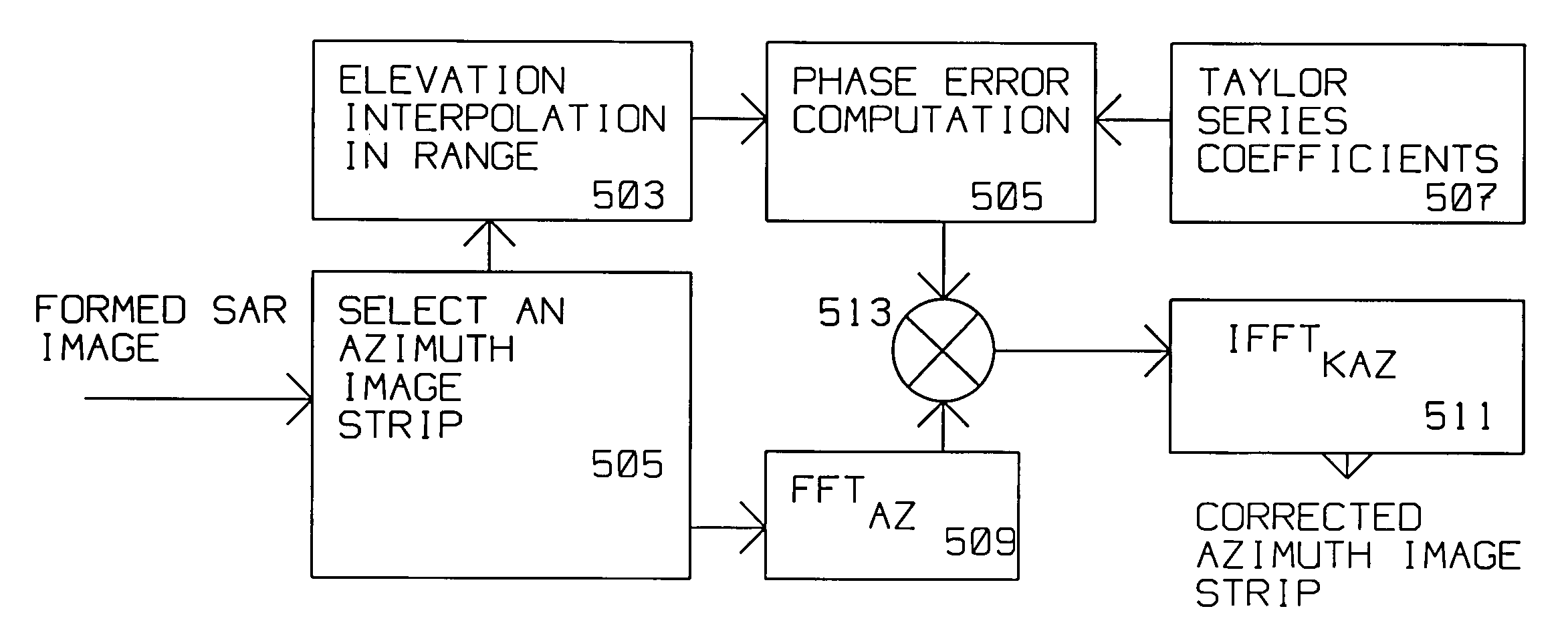
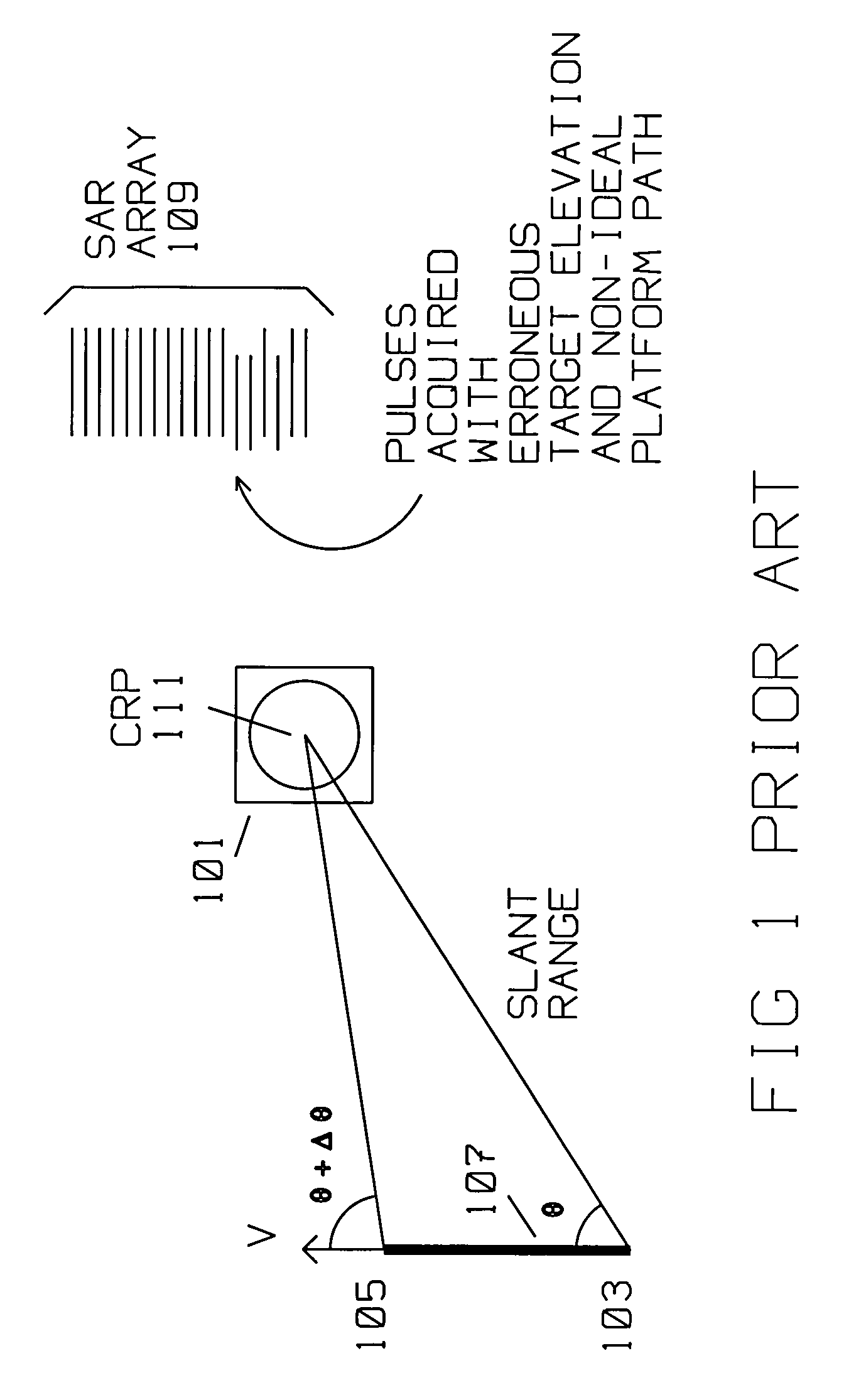
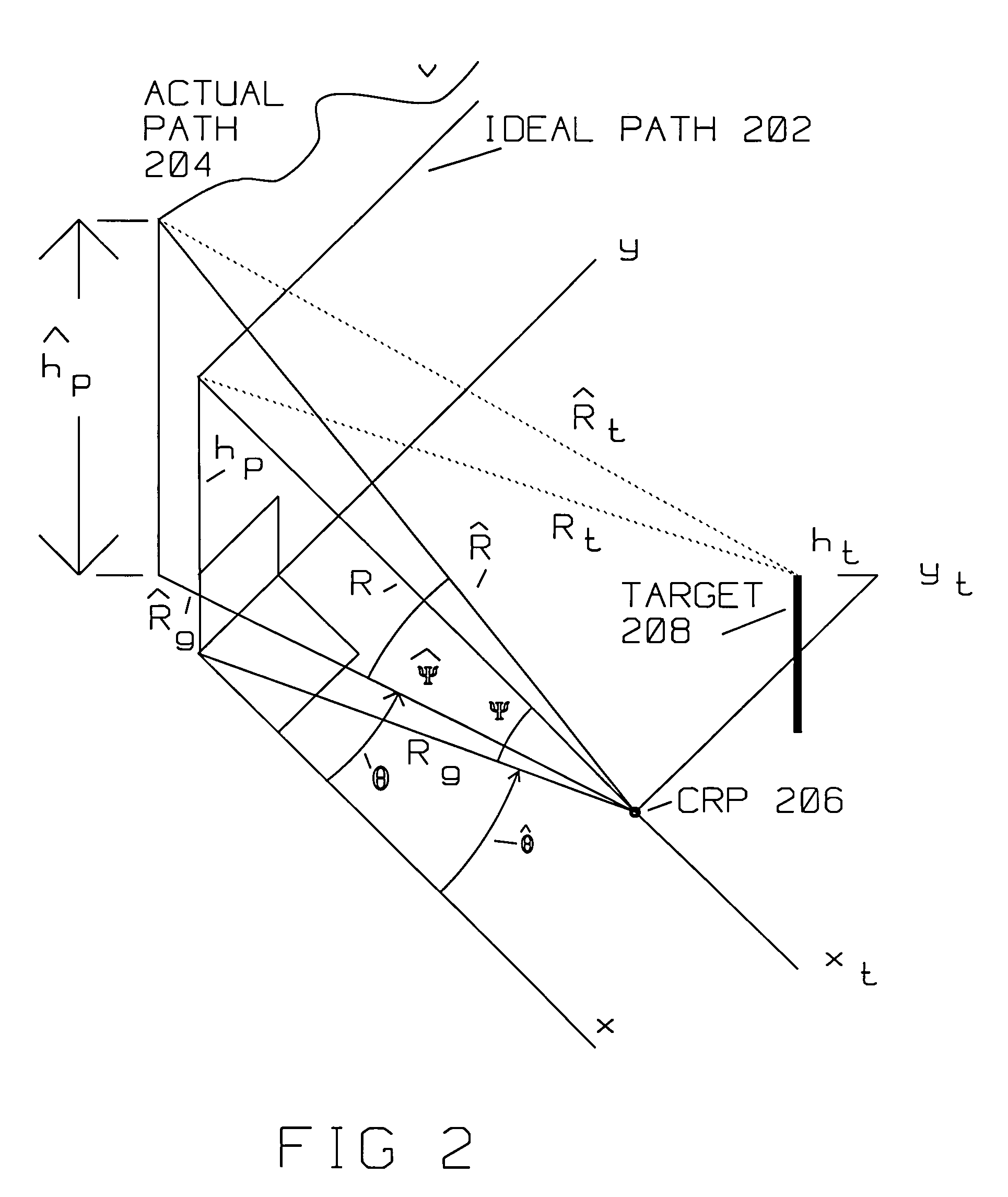
A radar acquires a formed SAR image of radar scatterers in an area around a central reference point (CRP). Target(s) are within the area illuminated by the radar. The area covers terrain having a plurality of elevations. The radar is on a moving platform, where the moving platform is moving along an actual path. The actual path is displaced from an ideal SAR image acquisition path. The radar has a computer that divides the digital returns descriptive of the formed SAR image into multiple blocks, such as a first strip and an adjacent strip. The first strip is conveniently chosen, likely to generally align with a part of the area, at a first elevation. An adjacent strip covers a second part of the area at a second elevation. The first strip is overlapping the adjacent strip over an overlap portion. The first and second elevation are extracted from a terrain elevation database (DTED). Horizontal displacement of returns (range deviation) is computed for each strip using the elevation information from the terrain elevation database. Taylor series coefficients are computed for the horizontal displacement due to terrain elevation using the ideal path, the actual path and central reference point. Actual flight path deviation is available at each pulse position while azimuth frequency is given in azimuth angle off mid angle point. Remapping between indices in two arrays is also computed. Phase error compensation and compensation in azimuth (spacial frequency) is computed using the Taylor series coefficients, a Fast Fourier Transform and an inverse Fast Fourier Transform for each strip. Phase error compensation is applied to the digital returns from each strip to obtain the SAR image. The SAR image is further improved by having the first strip corrected data and the second strip corrected data merged over the overlap portion to generate a relatively seamless SAR image.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Imaging apparatus and method
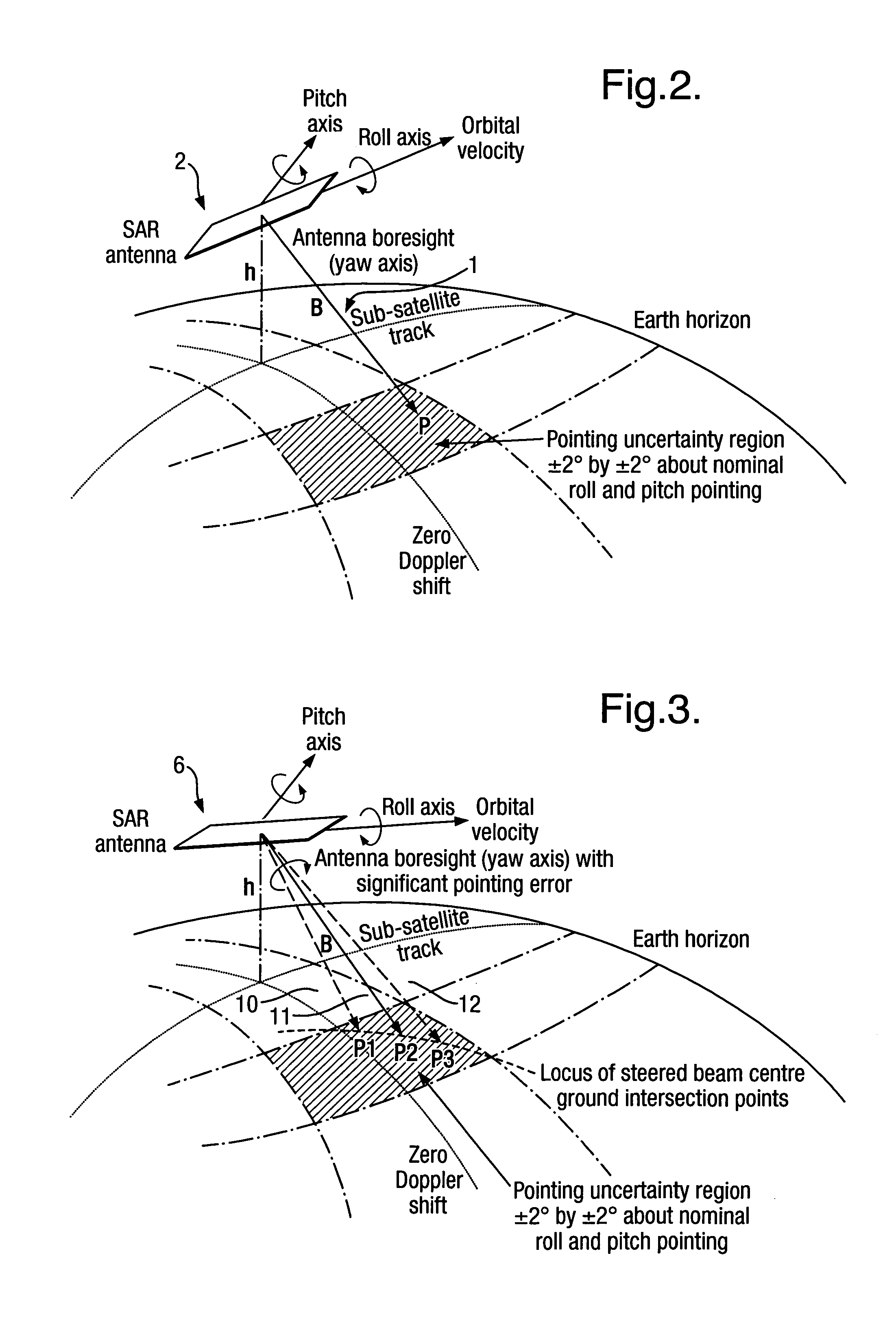
InactiveUS20050104763A1Low costFeasible effortRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar observationsContour analysis
An imaging apparatus 6 has means for illuminating a selected surface with a radar beam footprint, and means for profiling / processing the resultant radar returns in an efficient and logical fashion such as to derive radar attitude information in real time about a number of predefined axes associated with the radar which depends upon the relative dispositions of the radar and the selected surface and upon the radar beam footprint characteristics. Advantageously, a plurality of transmit beams 10,11,12 are used to image the surface and the processing arrangement has the capability of determining roll, pitch and / or yaw pointing data associated with the radar, such pointing data being determined by derivation of the attitude information and by selective input of terrain elevation data so as to take account of variations in the radar viewing geometry with terrain elevation. The inventive radar bears a definite low cost advantage over known radar designs, and retains utility for many applications, for example spaceborne and airborne applications.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
System and method for geo-registration with global positioning and inertial navigation
ActiveUS7395156B2Improve navigation accuracyAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarForward looking
A position estimation system including a first arrangement for providing an image with a known target in a known reference frame. A second arrangement correlates the image with a stored image. The correlation is used to compute an error with respect to a position estimate. In a specific embodiment, the error is referenced with respect to first (x), second (y) and third (z) directions. A target location error is computed with respect to a stored image provided by a target image catalog. The target image catalog includes target geo-locations and digital terrain elevation data. In an illustrative application, the image data is provided by synthetic aperture radar and forward-looking infrared systems. An observation model and a measure noise matrix are Kalman filtered to ascertain a position error in navigation data generated by an integrated inertial navigation and Global Positioning system.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
GPS based terrain referenced navigation system
InactiveUS20020188386A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsAbove groundGeolocation
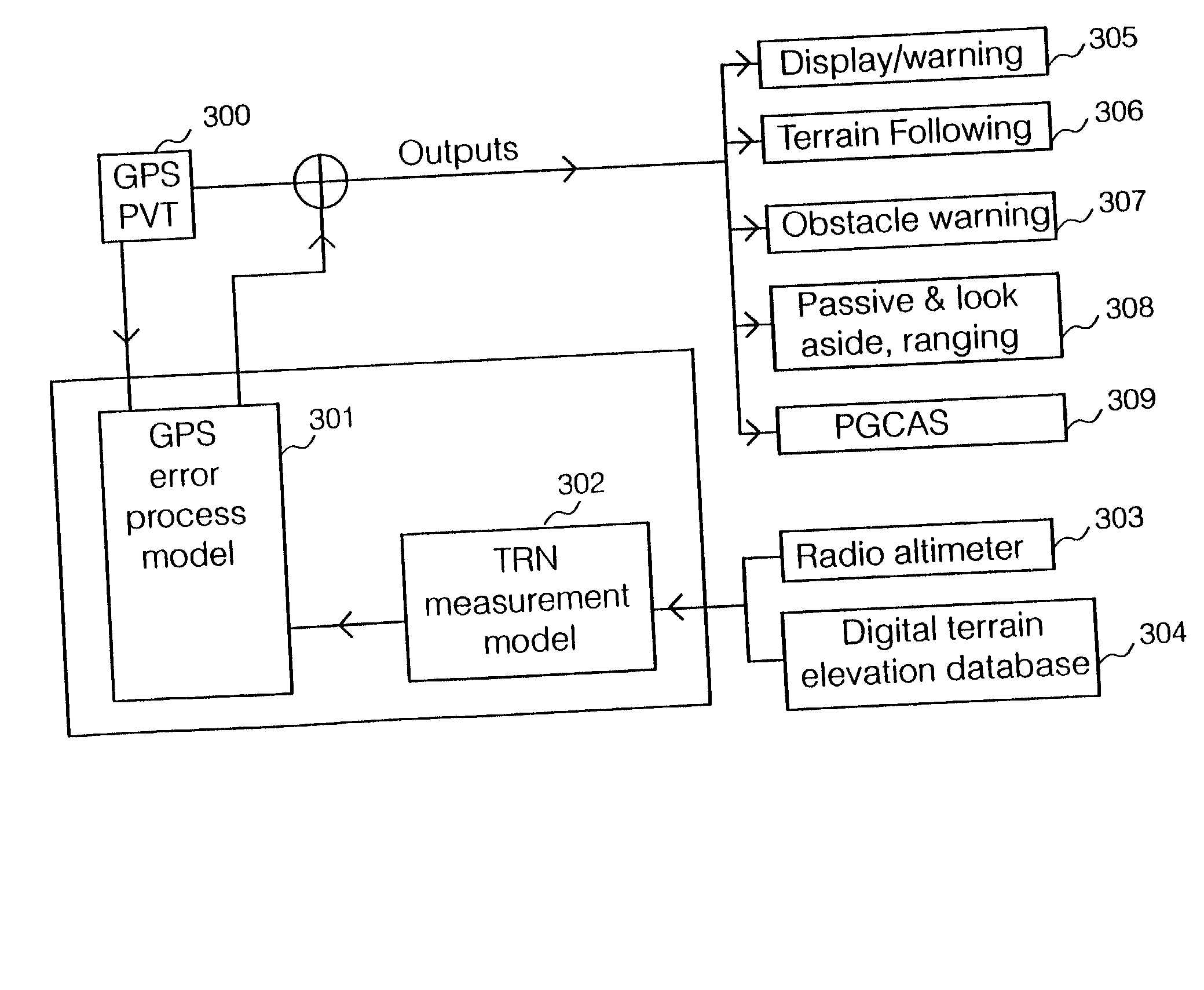
The terrain referenced navigation system uses data from a global positioning system (GPS) to determine a vehicles position, velocity and height above ground. The system uses input data from an altimeter device, a digital terrain elevation data, and a GPS position, velocity and time data. The system applies a GPS error process model in addition to a TRN measurement model, to obtain a state vector which includes estimates of current errors in the GPS data. The PVT data input from a GPS receiver is used to determine a current vehicle position and height in geographic axis. Using specifically constructed Kalman filter states, a geographical position and height of the vehicle is reference to the digital terrain elevation data, and an estimated ground clearance at the vehicle position is determined. The ground clearance is differenced with a radar altimeter output, and the residual is processed by Kalman filter to determine a new state vector, including estimates of current errors in the GPS data. The output can be configured to be either referenced to navigation axis, or to the digital terrain database for use by other digital terrain system functions.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Method and apparatus for displaying terrain elevation information
ActiveUS20090024311A1Instruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficHigh elevationDisplay device
A method, apparatus, and computer usable program code for presenting terrain elevation information on a vehicle display. In one advantageous embodiment, a swath representing an area ahead of the vehicle is identified, wherein the swath has a length and a width. A two dimensional elevation view is presented on the vehicle display, wherein a vertical axis of the two dimensional elevation view represents a highest elevation along a width of a swath for a particular point along the length of the swath. The width of the swath is updated in response to vehicle movement to form an updated swath width. The two dimensional elevation view is updated using the updated swath width.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Apparatus and method of image rendering
A method of image rendering includes representing a height map of terrain elevation data as a virtual texture; sampling a portion of the height map terrain elevation data on a uniform grid corresponding to render nodes used for rendering a terrain mesh, wherein a correspondence of the grid to the render nodes results in the sampled terrain elevation data for a render node being entirely contained within one physical page of memory, and wherein the equivalent position of a height map virtual co-ordinate in a page of physical memory is obtained based upon an offset to a physical page co-ordinate, rather than by reference to an indirection texture; and rendering terrain mesh for a render node according to terrain elevation data obtained from a single physical page of memory corresponding to respective virtual co-ordinates.
Owner:SONY INTERACTIVE ENTERTAINMENT INC
Efficient use of expected user altitude data to aid in determining a position of a mobile station
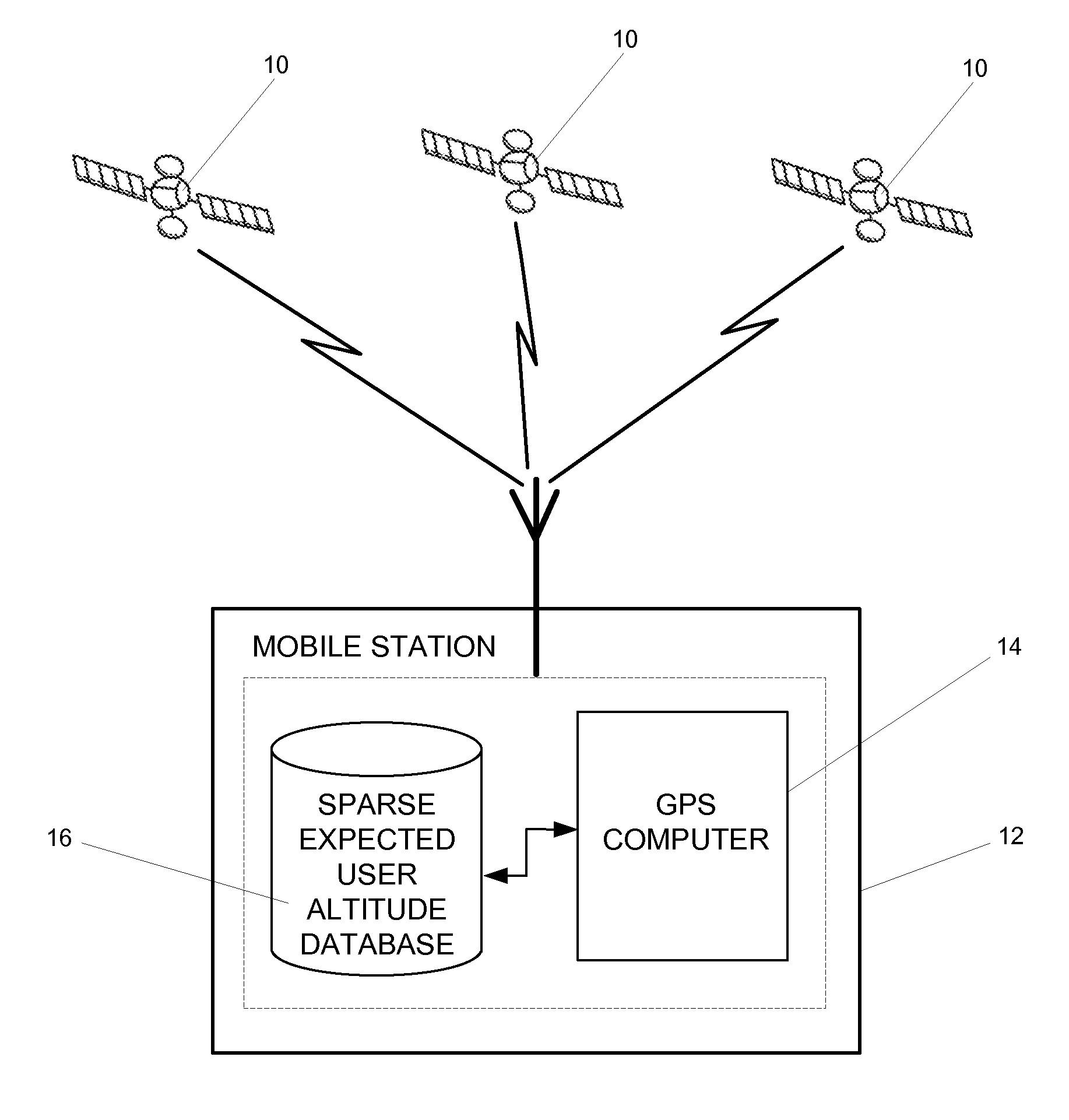
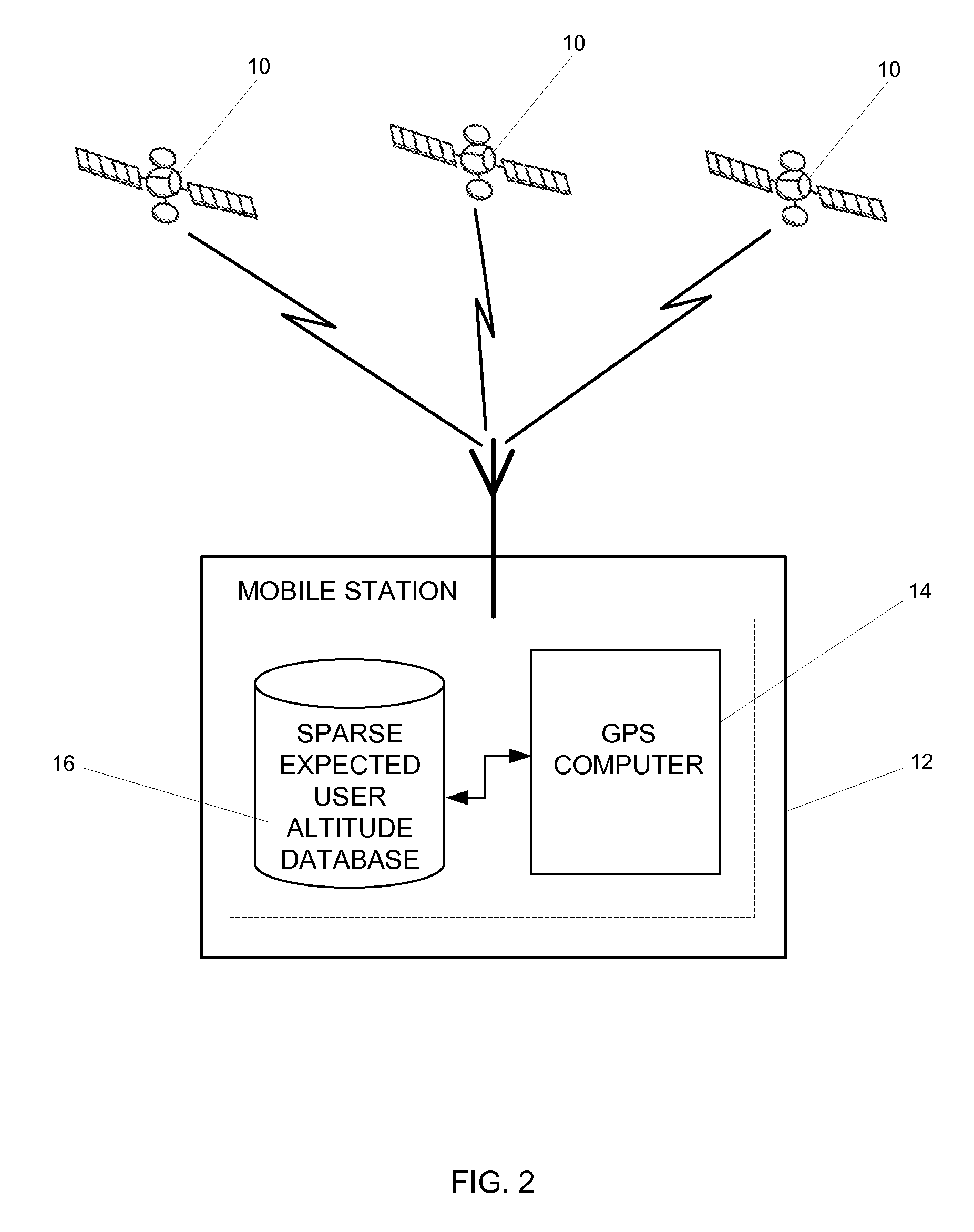
ActiveUS20090210156A1Less memoryHigh yieldPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsHeight mapMobile station
A method and apparatus for using a predetermined portion of terrain elevation maps in a database for aiding in computing a three-dimensional position of a wireless station. Instead of using the entire terrain model of the earth or an entire country, the database consists of an incomplete model, which includes only the most populous areas or specific regions. This reduces the size of the information in the database, which in turn reduces the amount of time to compute the positions of the wireless device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
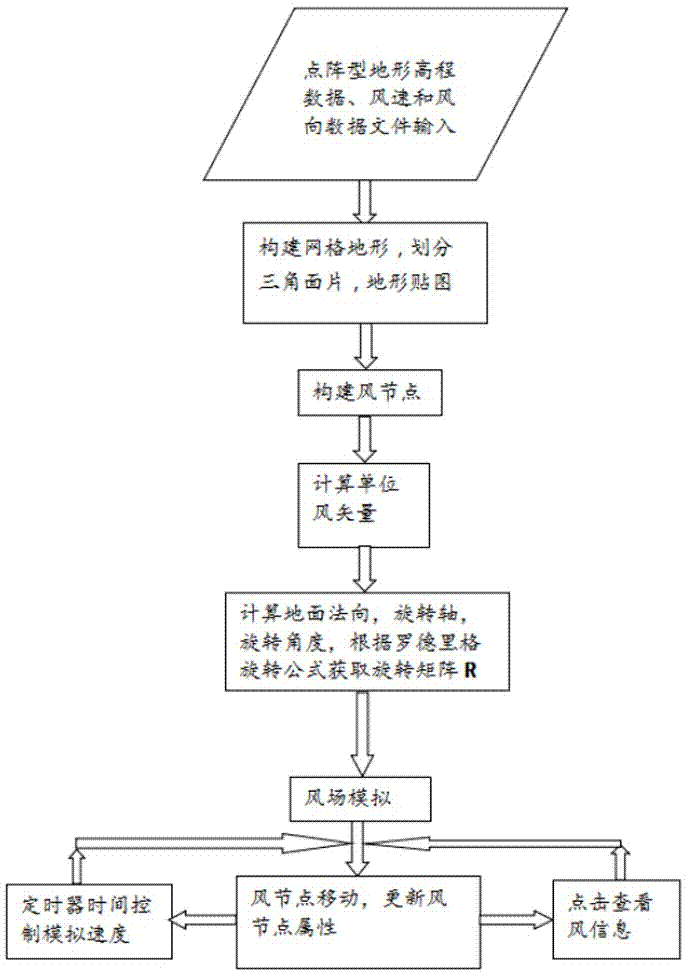
Three-dimensional-terrain-based dynamic visualization method for wind
The invention relates to a three-dimensional-terrain-based dynamic visualization method for wind. The method comprises steps of data inputting and virtual scene construction, three-dimensional wind vector field construction, and dynamic wind field displaying. To be specific, dot-matrix type terrain elevation, wind speed and wind direction data files are inputted; a three-dimensional grid terrain is constructed; a wind node is constructed and a wind node direction is initialized; a wind node parallel to an XY plane is rotated to enable the node to express a correct two-dimensional wind direction, a terrain normal vector is calculated, and a rotation matrix R is obtained; a unit three-dimensional wind vector is calculated and the calculated vector is multiplied by a wind speed to obtain a next position point; when the wind node moves to the next position point, the wind vector, the rotation matrix R, the color, and the size of the wind node are updated; and when the wind node is located at an end position, the wind node moves to a starting position at a next step. Therefore, wind flowing at a three-dimensional terrain is simulated dynamically at a computer under the circumstance that the wind speed and wind direction data of a study region are calculated by inputted elevation data and wind field calculation models.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
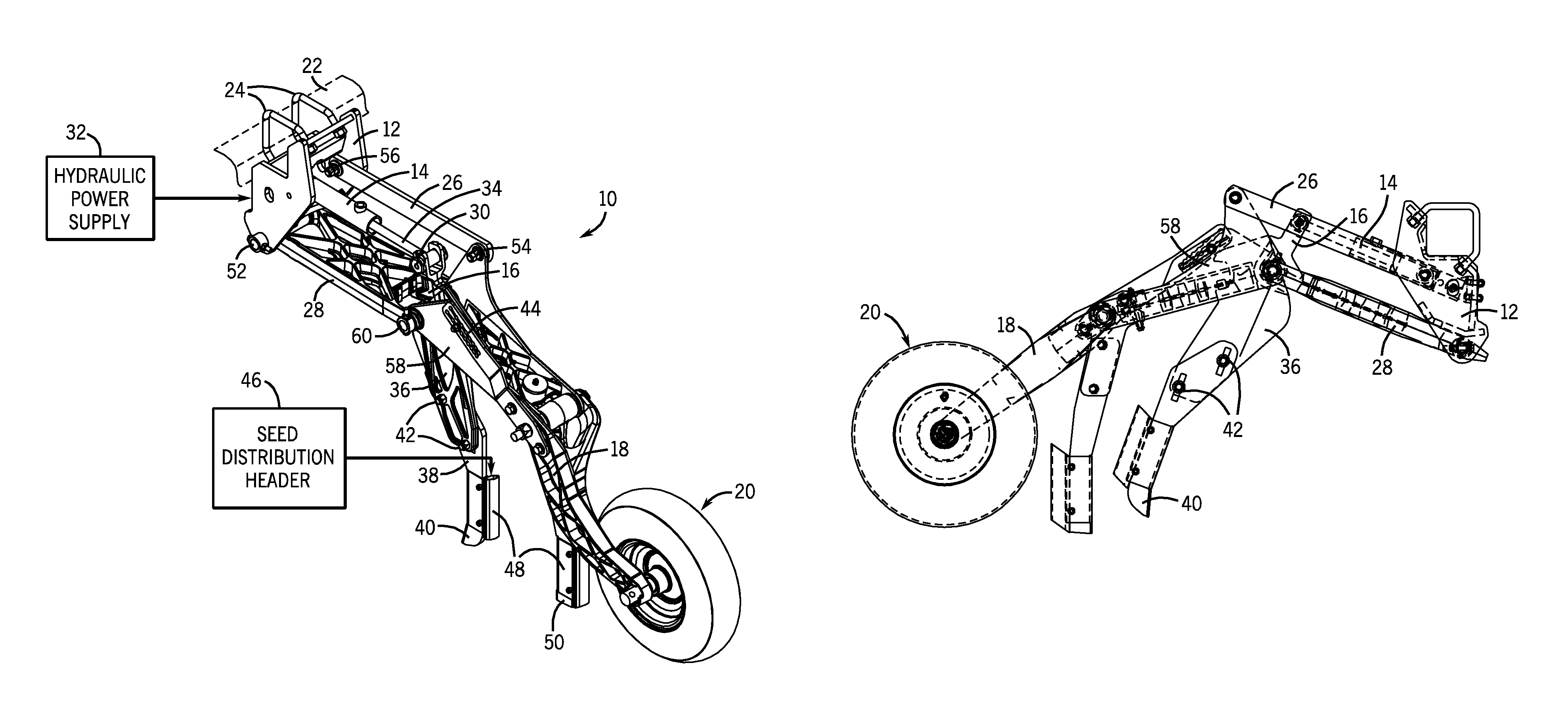
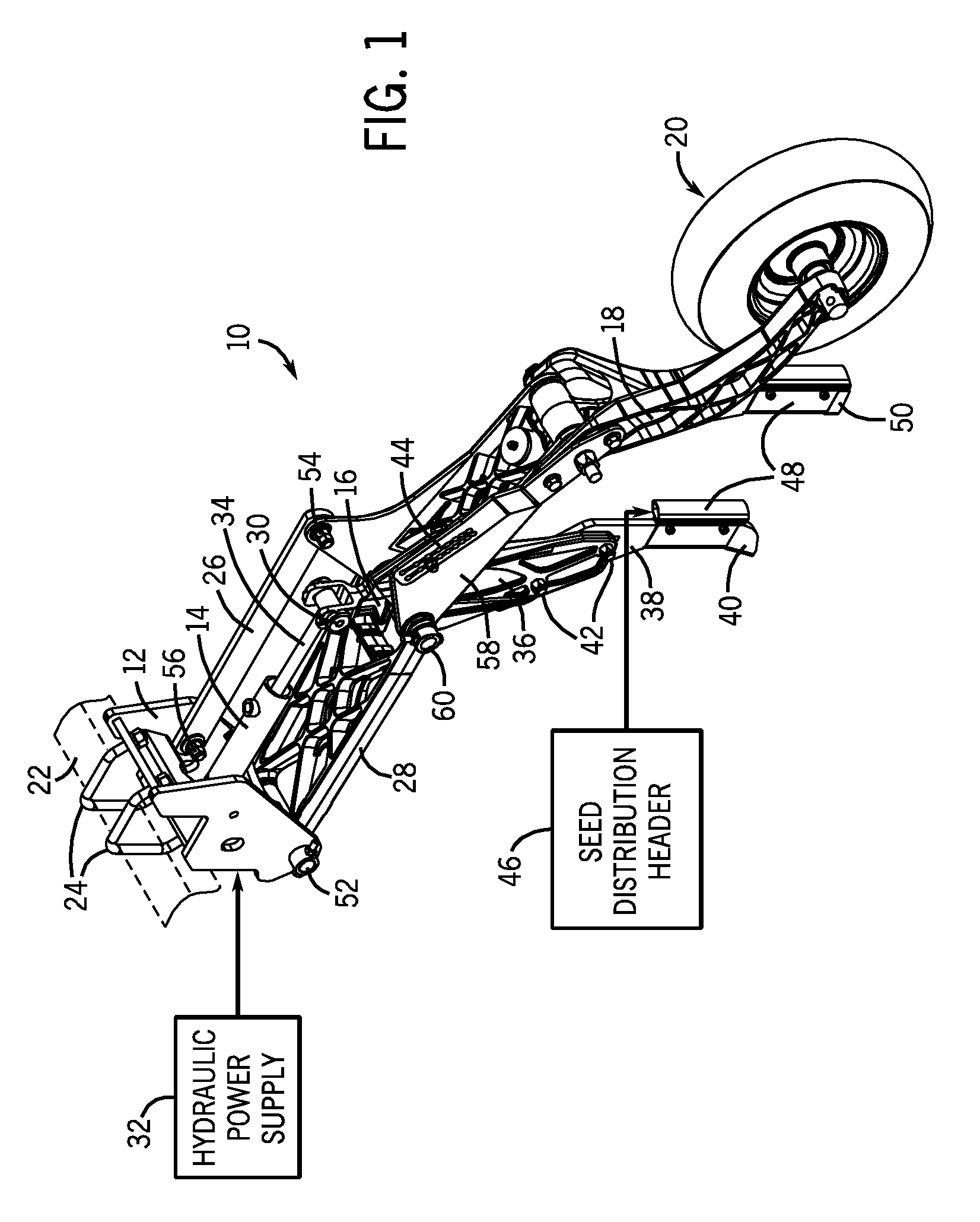
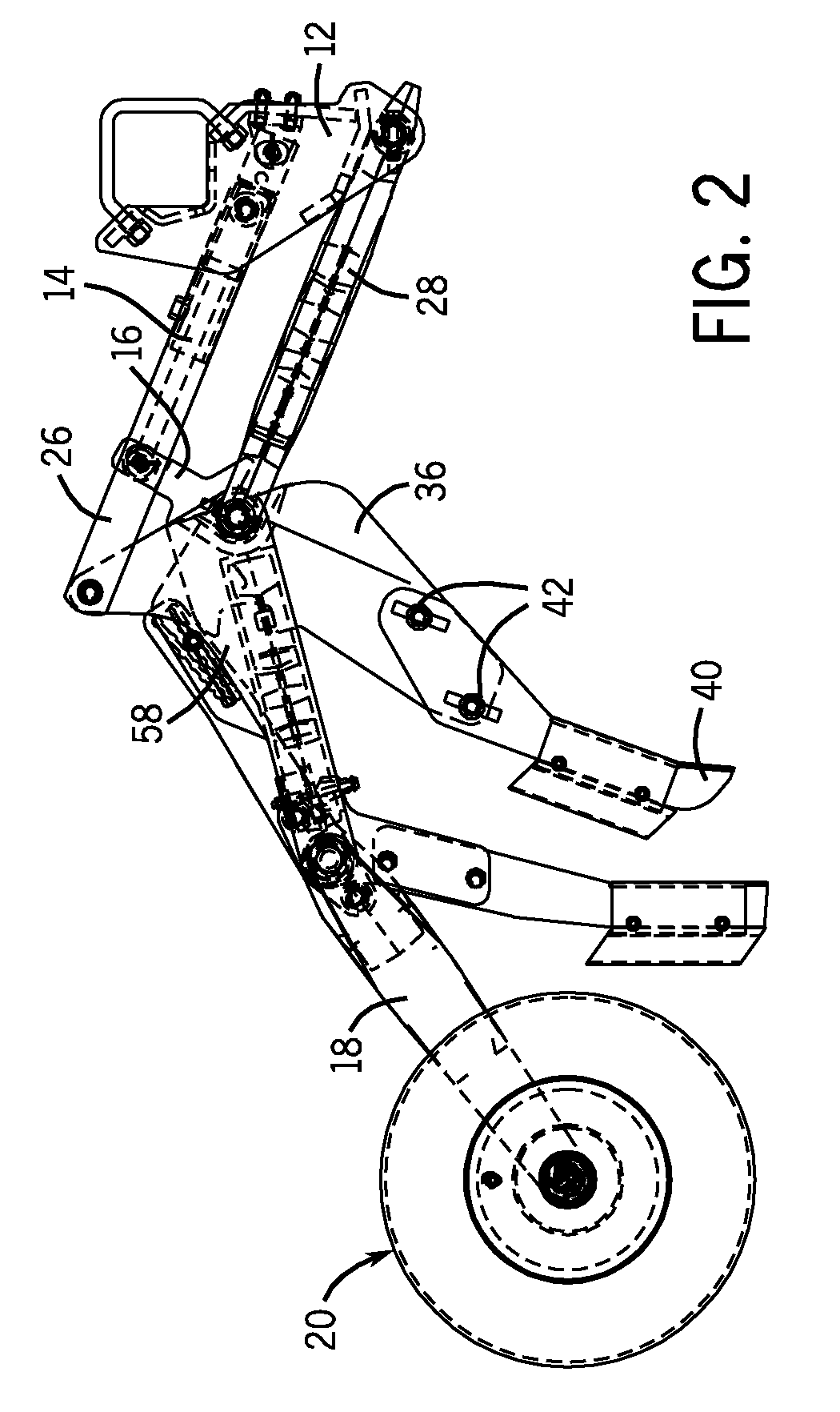
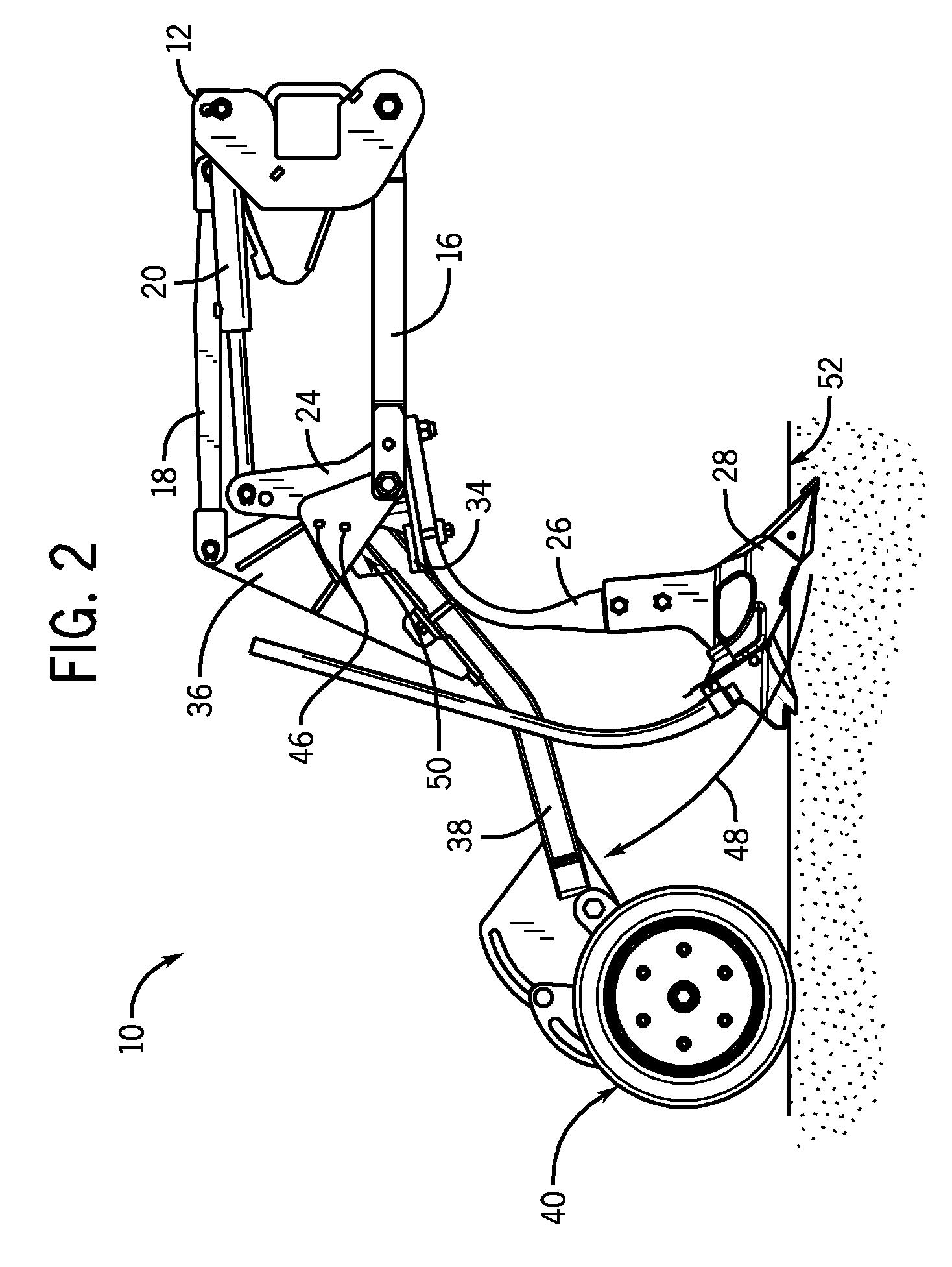
Precision hoe opener with draft force compensation
InactiveUS7578246B2Increase relative motionConstant pressureSpadesPlantingMechanical engineeringTerrain elevation
A precision hoe opener assembly is provided with improved accuracy of seeding as well as improved control over the opener and packer wheel assemblies. The opener assembly includes a hydraulically-driven parallel linkage assembly, a swing link, a ground engaging tool, and a packer wheel. The design provides improved seeding accuracy, by compensating for changes in draft force caused by changes in terrain elevation. The swing link allows the cylinder to compensate for the forces applied to the ground engaging tool, thereby providing a substantially constant packing force to the soil beneath the packing wheel.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
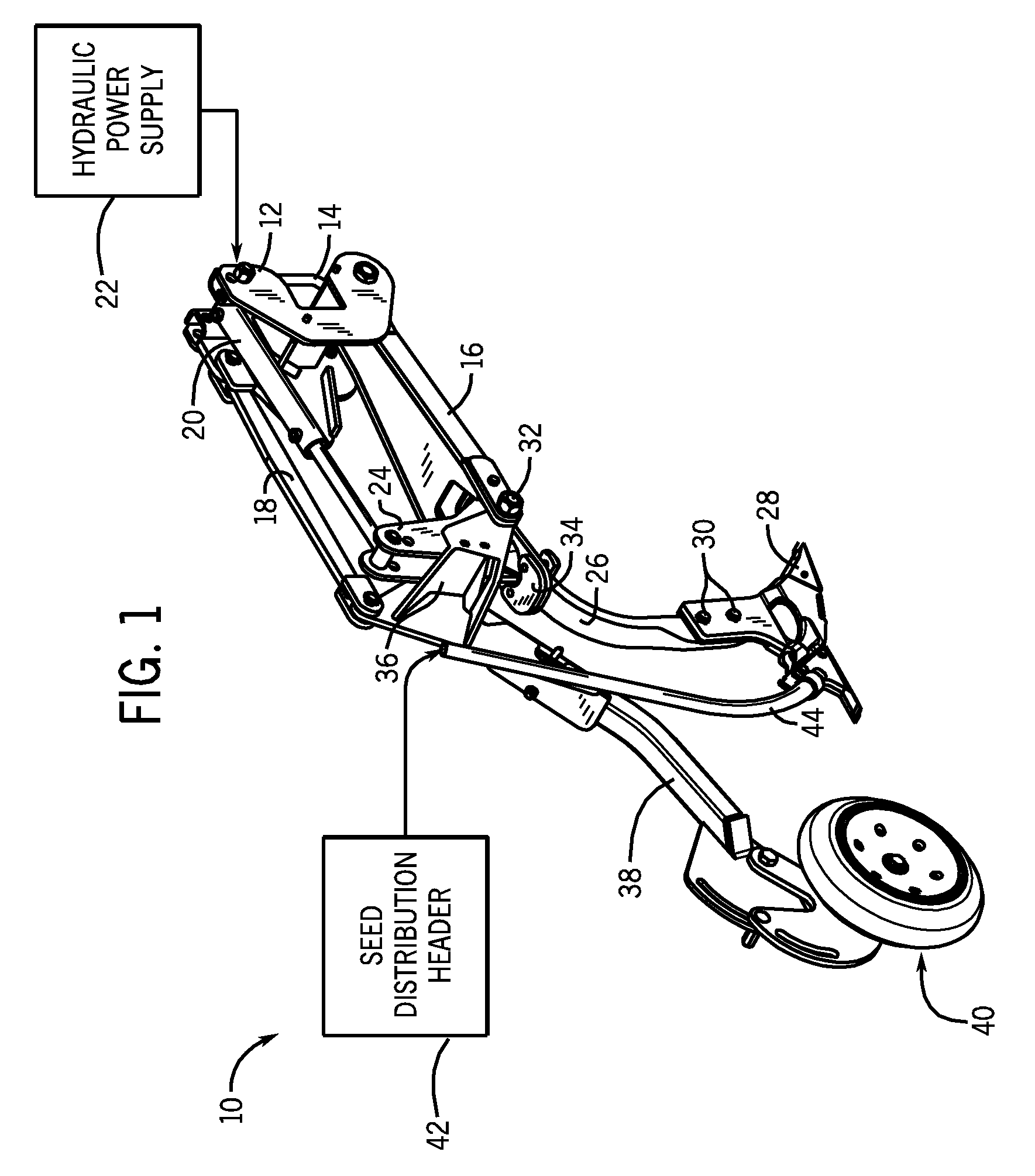
Precision hoe opener and packer wheel assembly
ActiveUS7574969B1Improve seeding accuracyEasy to assemblePlantingSoil-working equipmentsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A precision hoe opener assembly is provided with improved accuracy of seeding as well as improved control over the opener and packer wheel assemblies. The opener assembly includes a hydraulically-driven parallel linkage assembly, hoe opener, and a packer wheel. The design provides improved seeding accuracy, especially during changes in terrain elevation.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com