Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Stopping down" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In photography, stopping down refers to increasing the numerical f-stop number (for example, going from f/2 to f/4), which decreases the size (diameter) of the aperture of a lens, resulting in reducing the amount of light entering the iris of a lens.
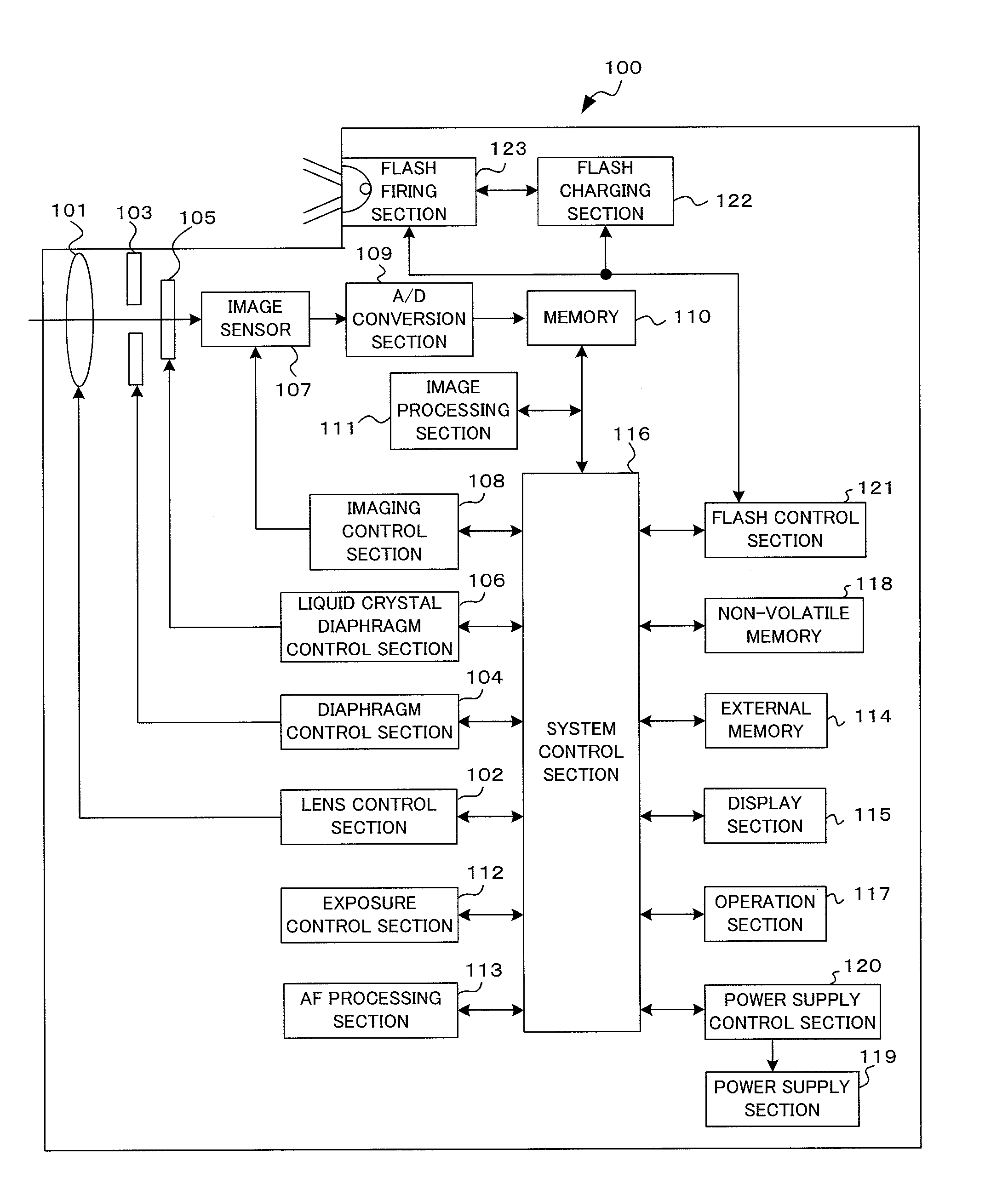
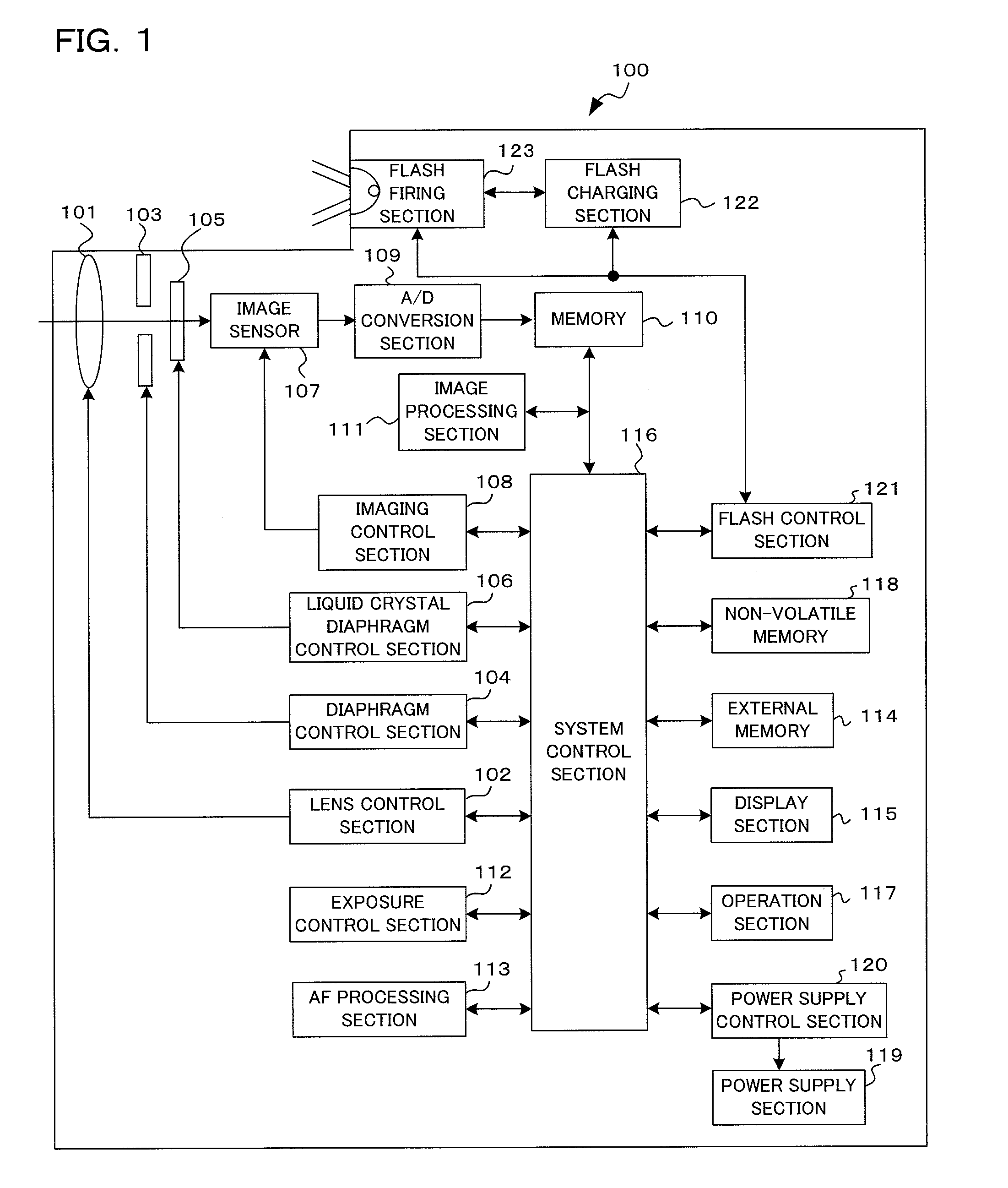
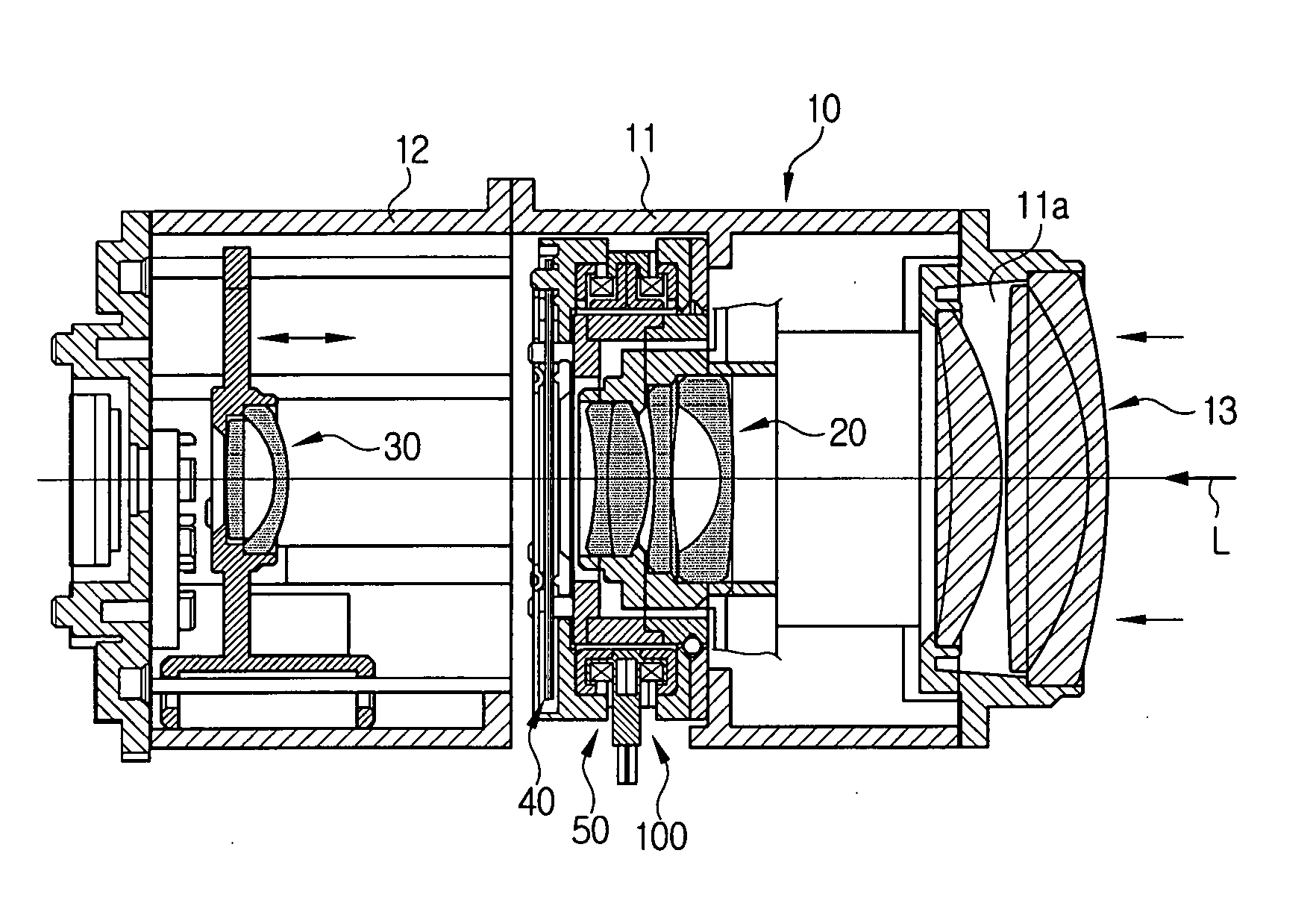
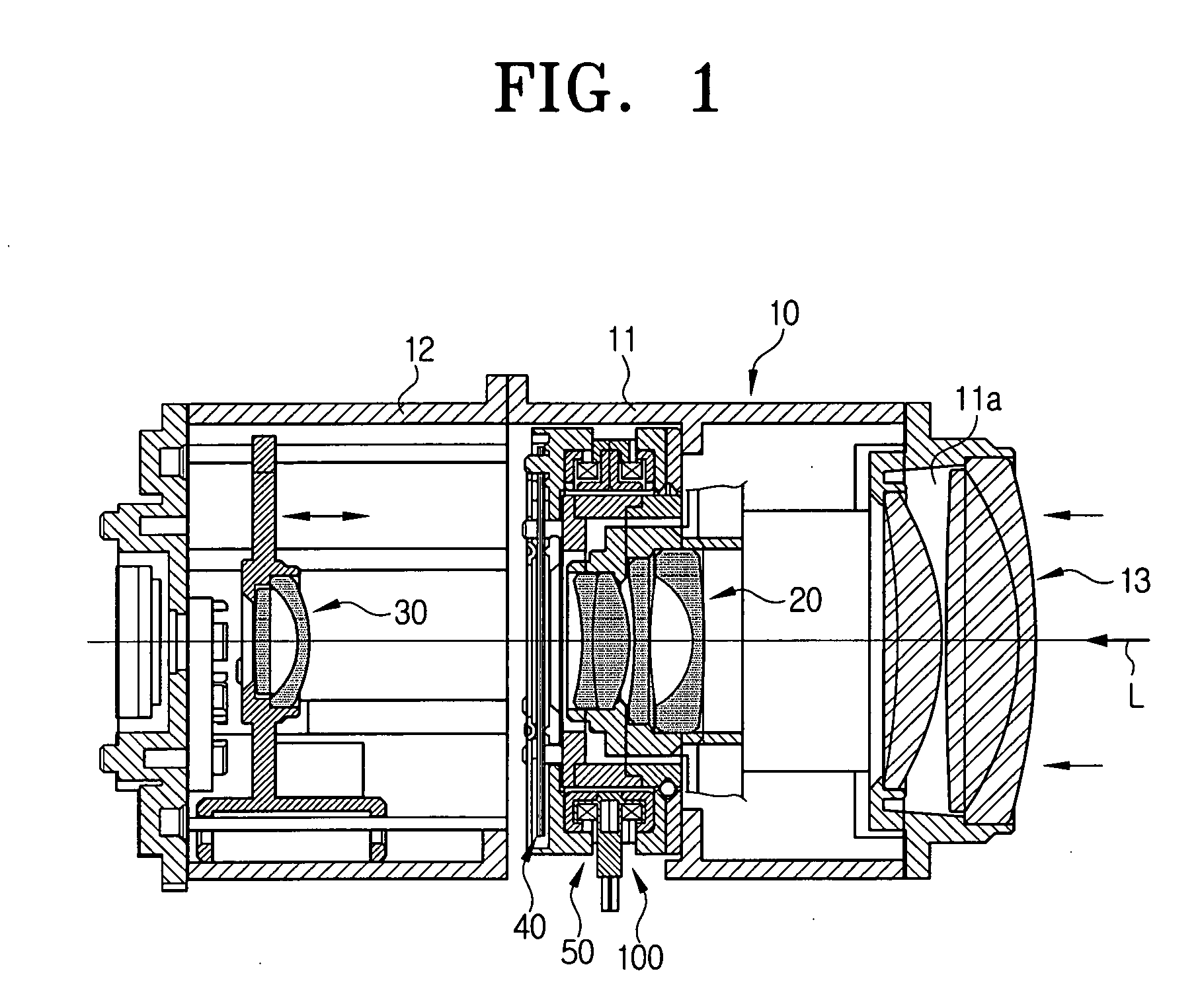
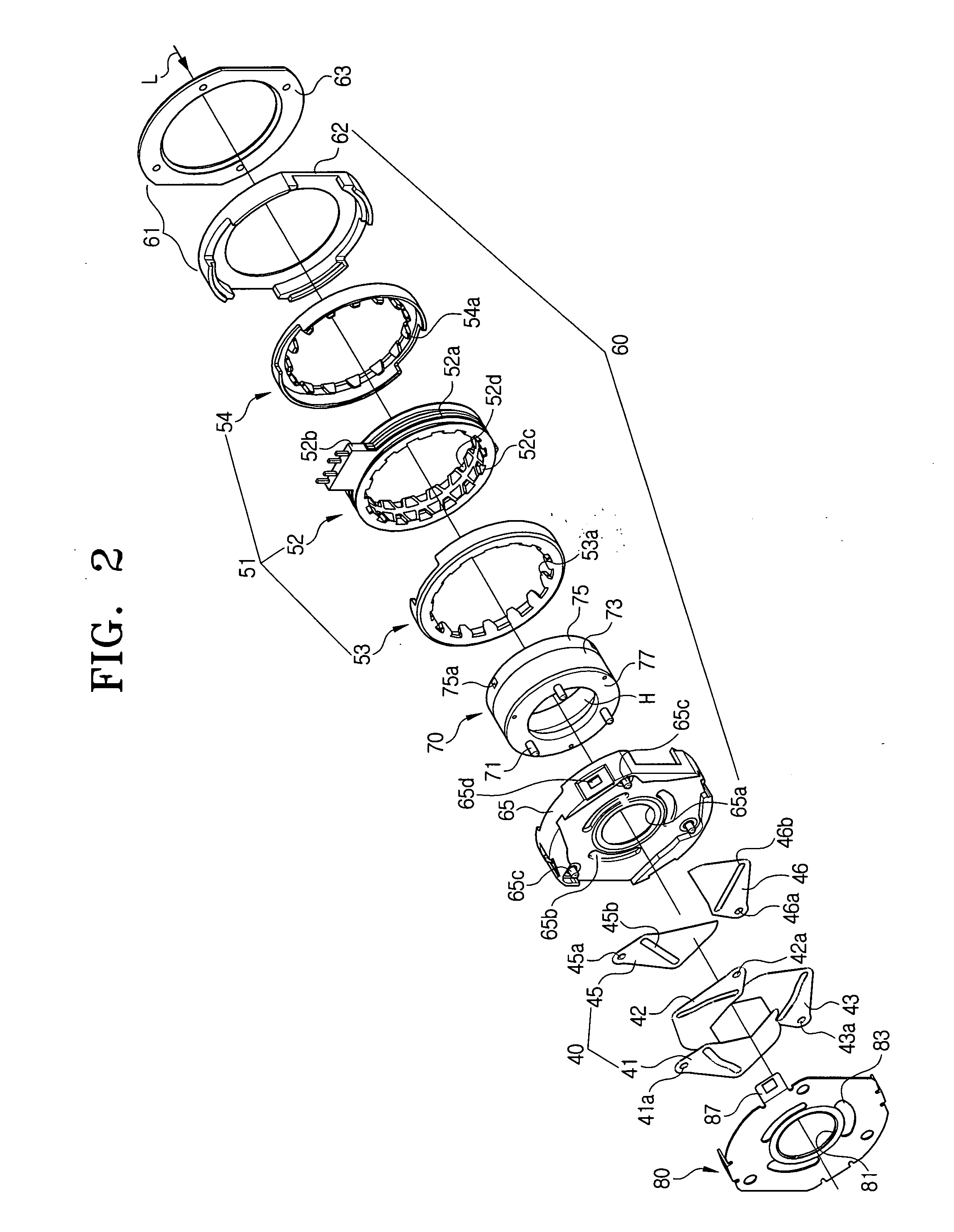
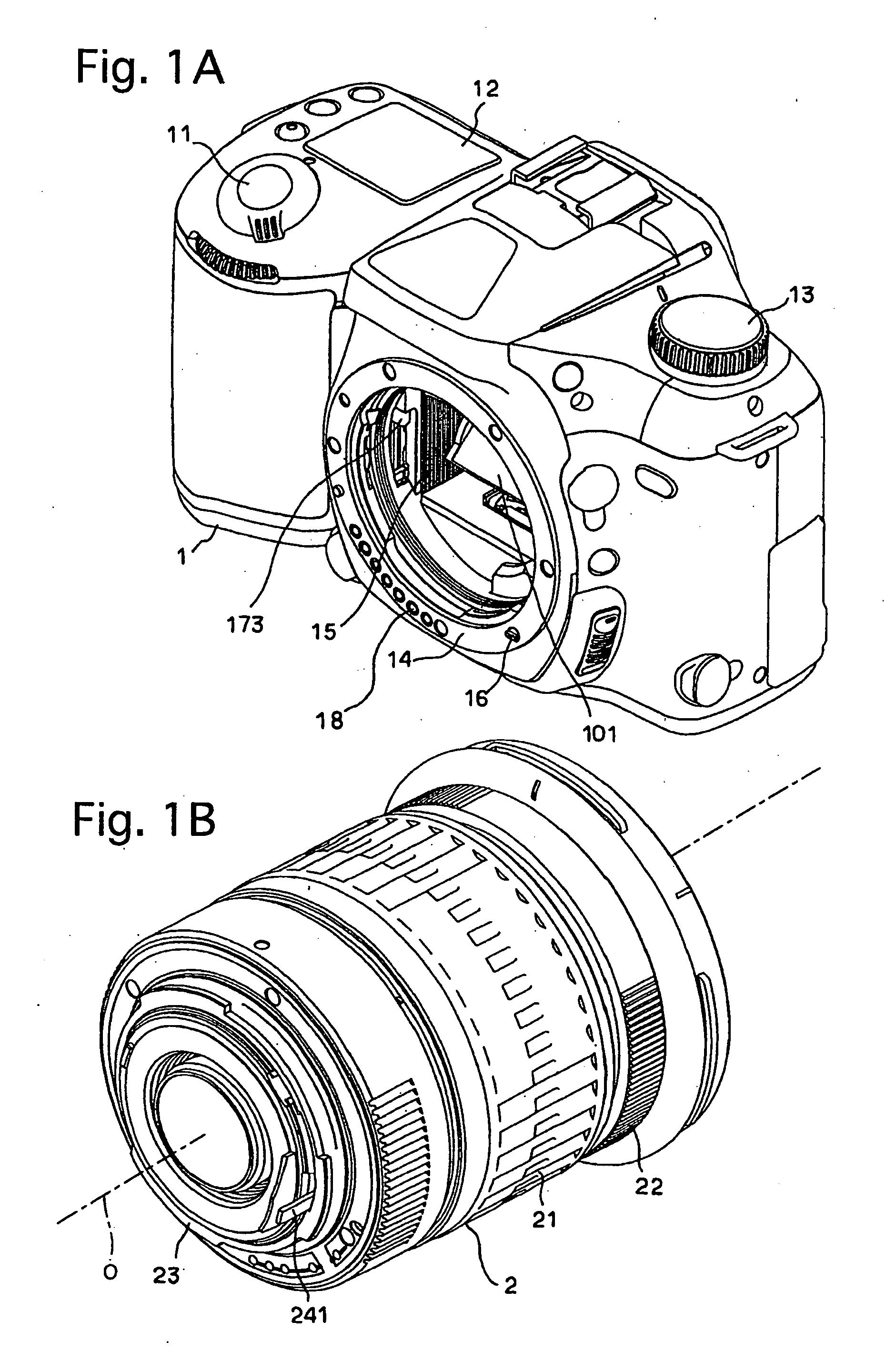
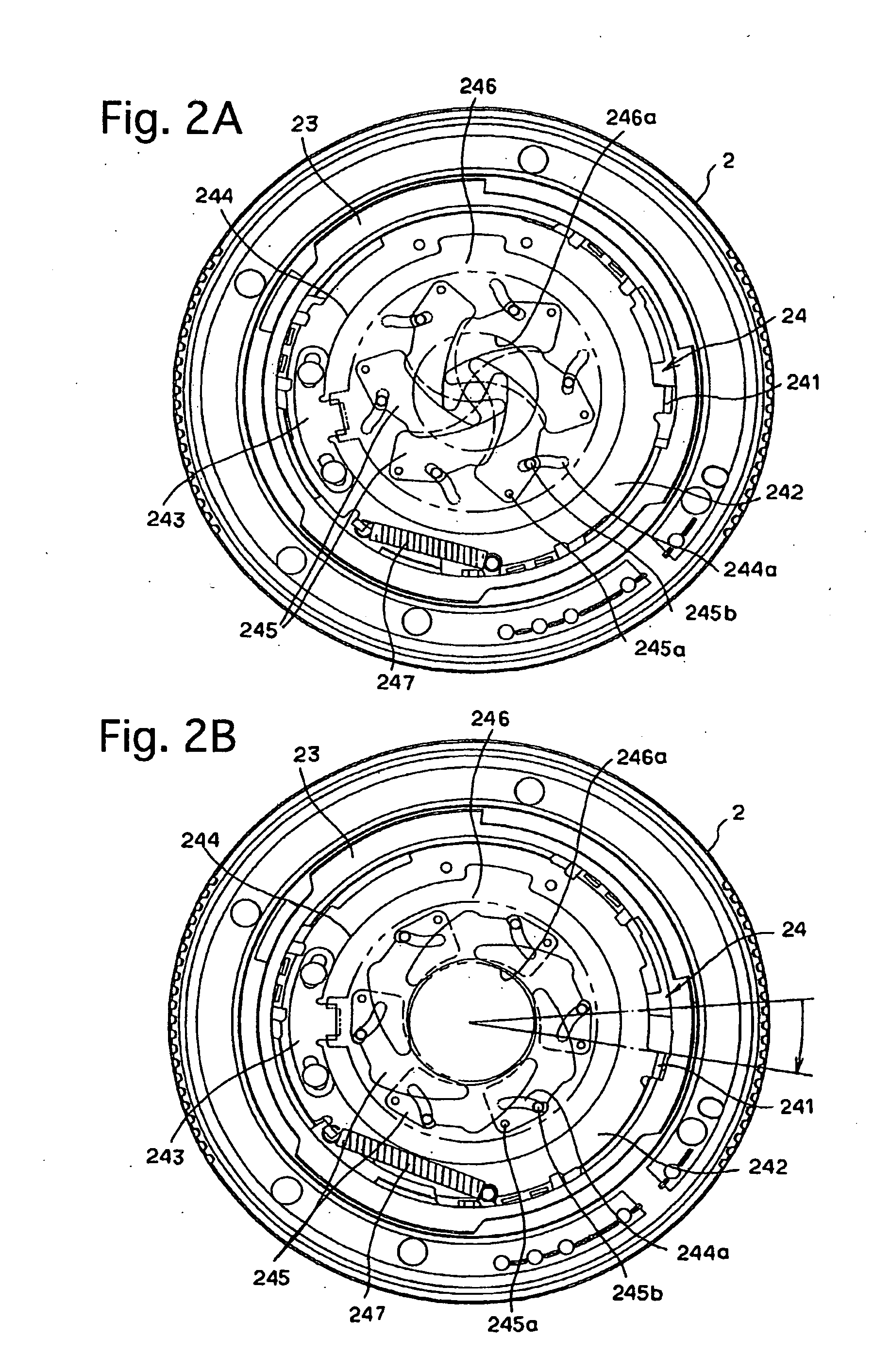
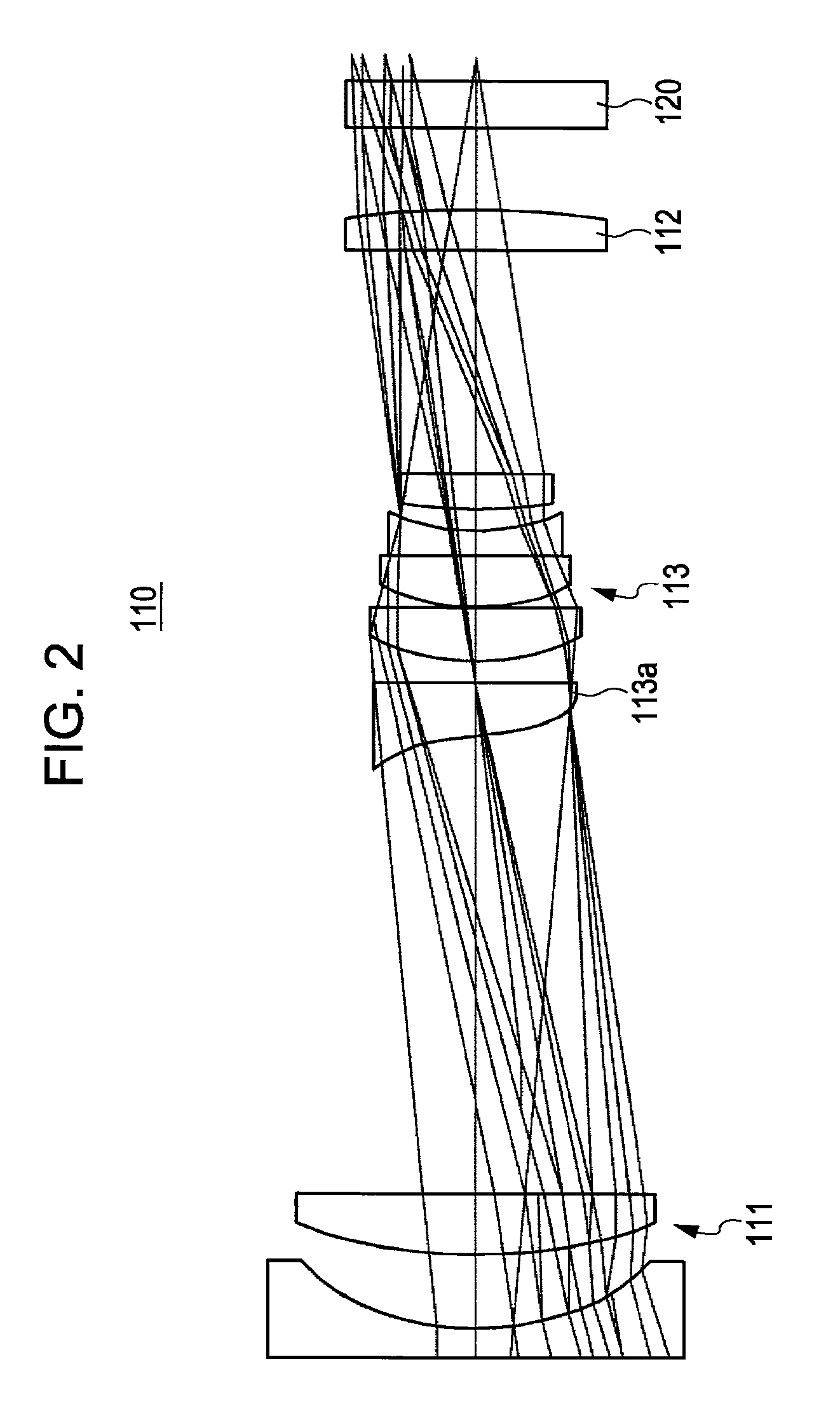
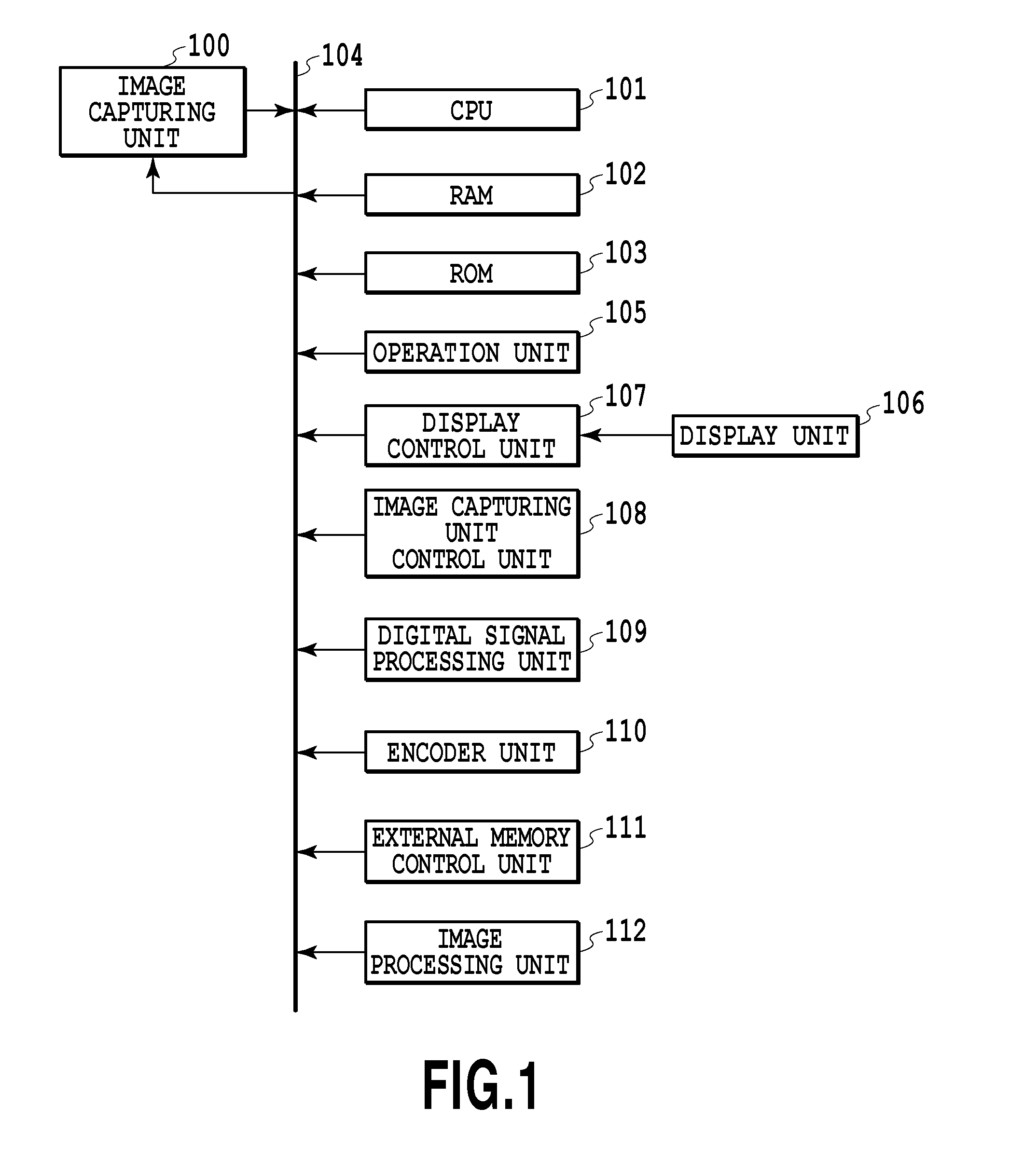
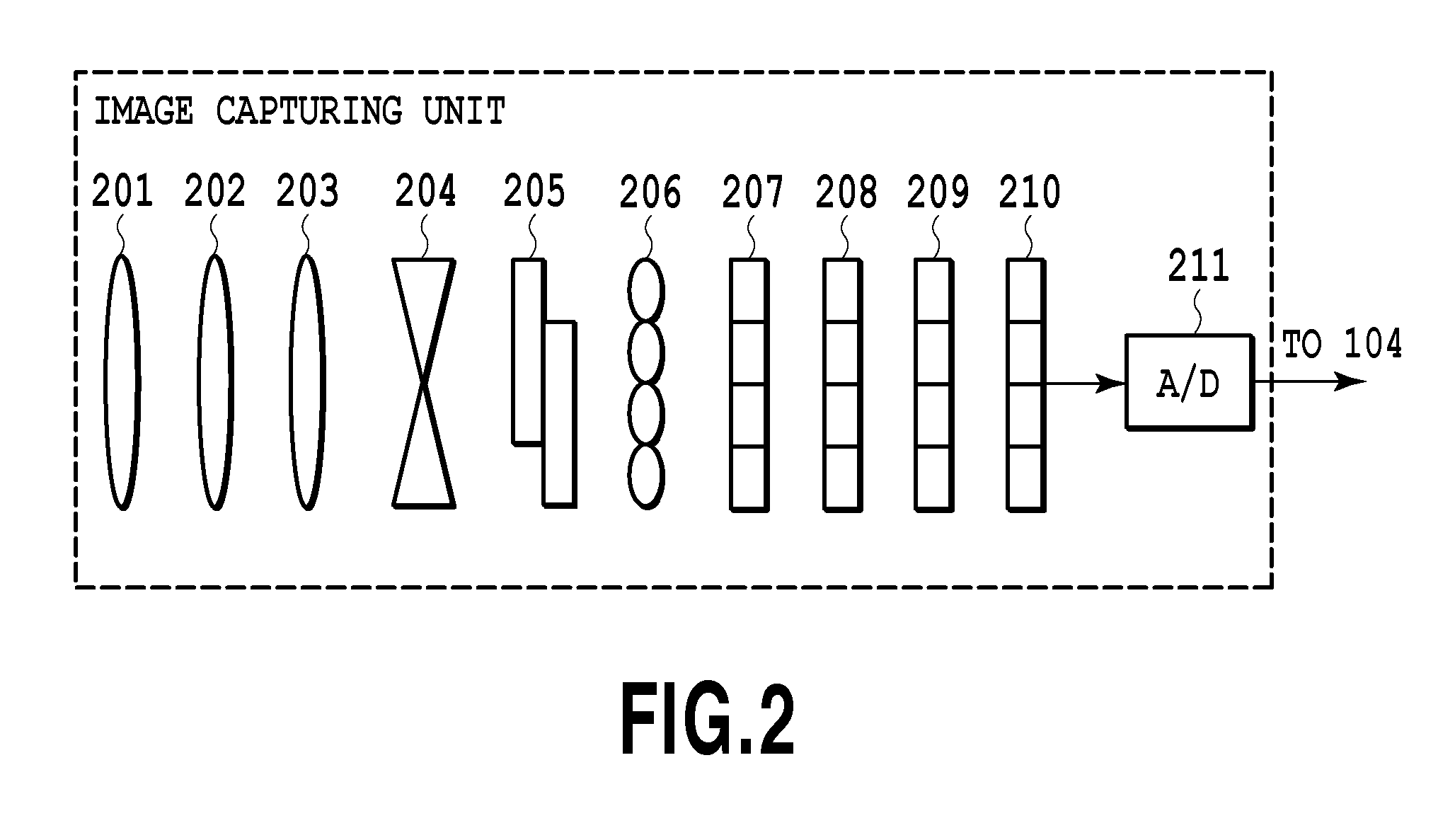
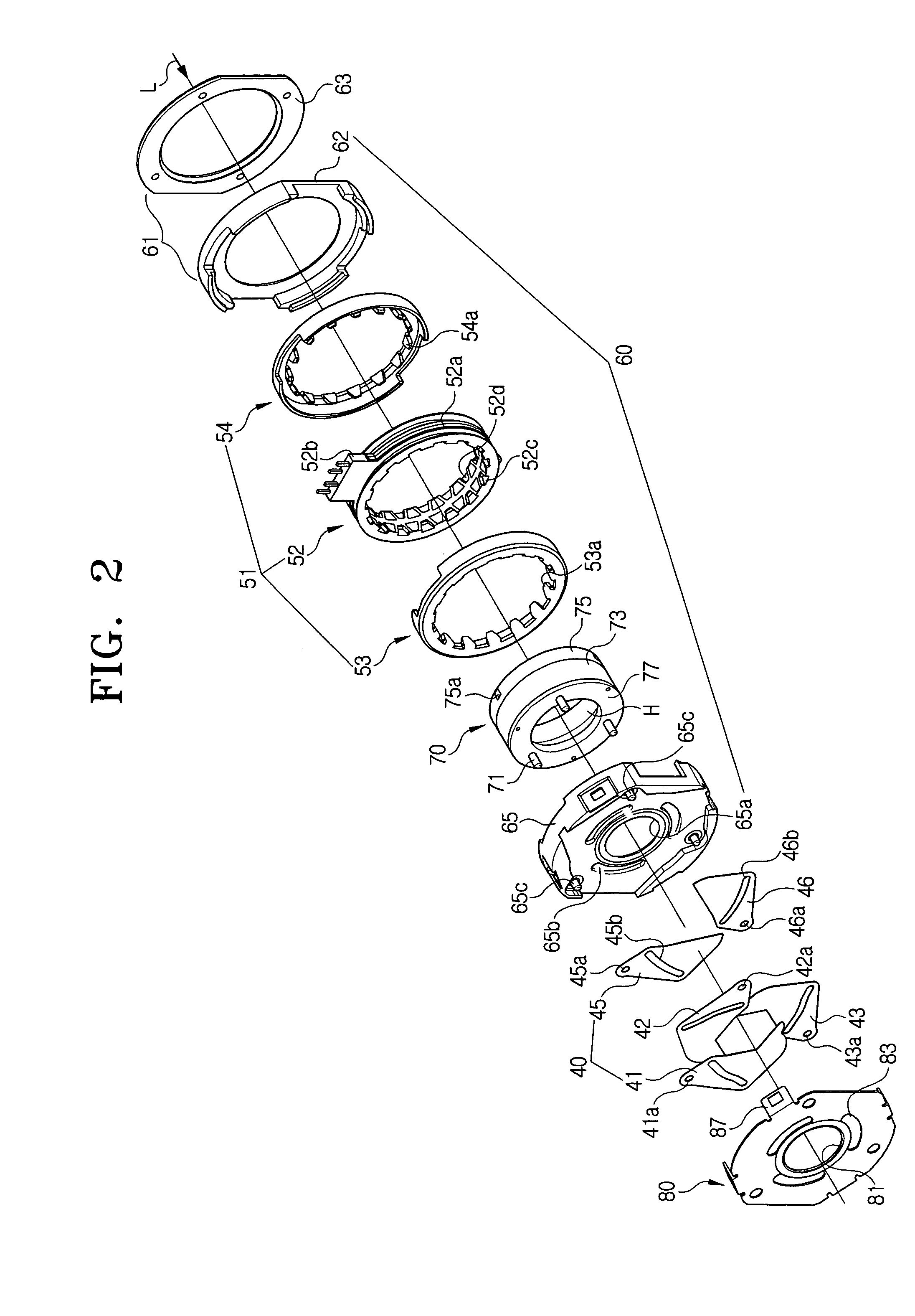
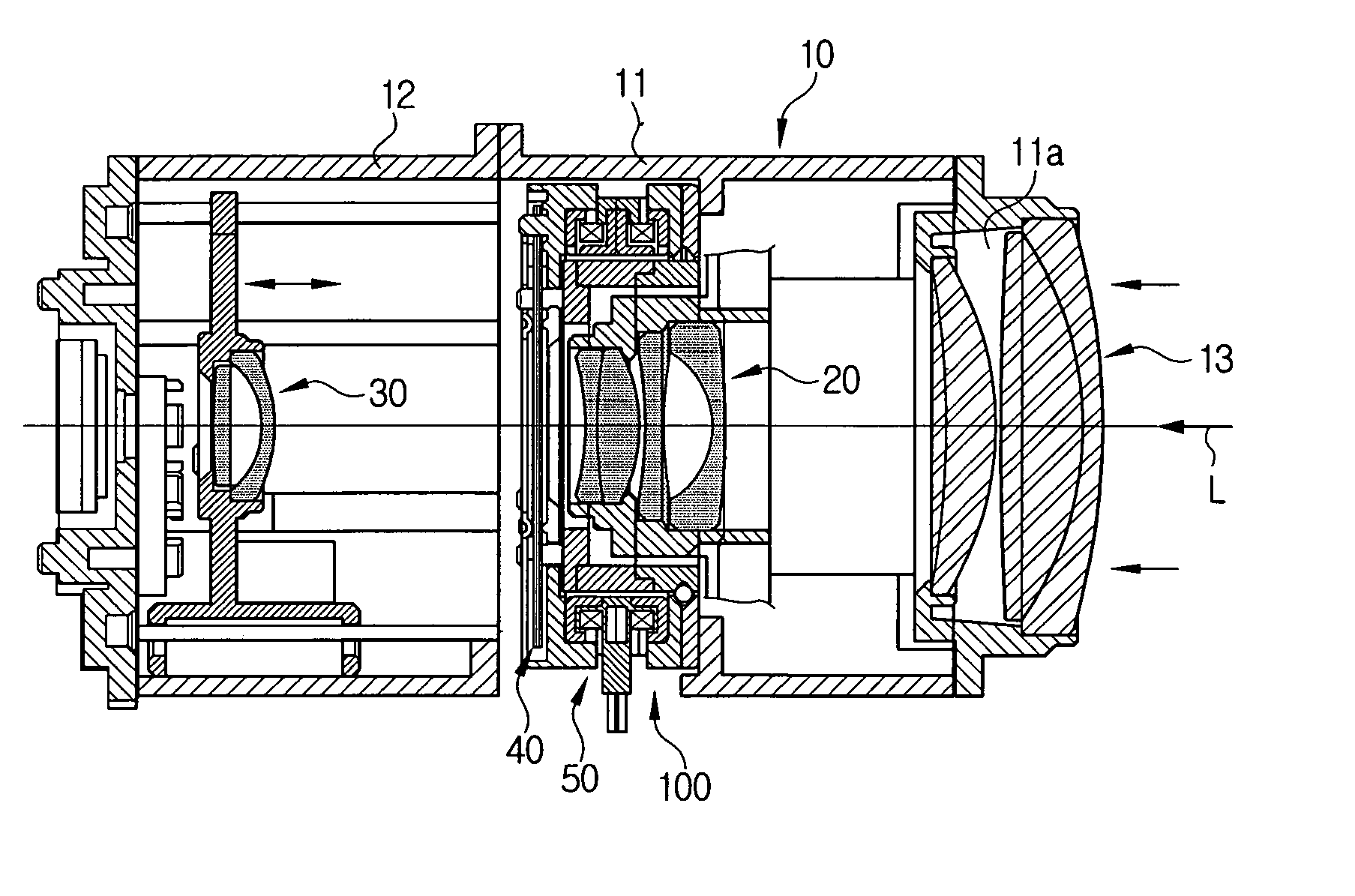
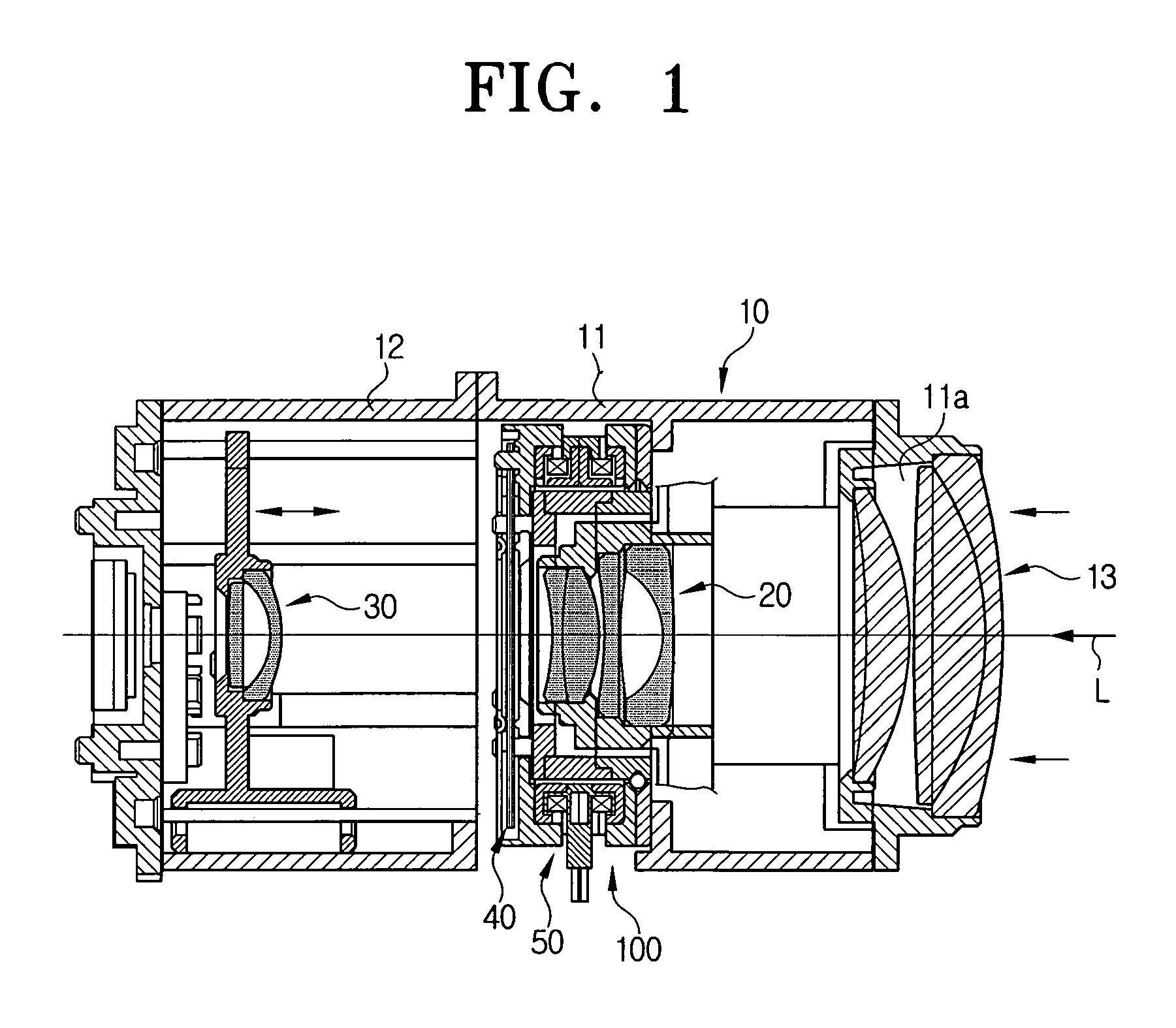
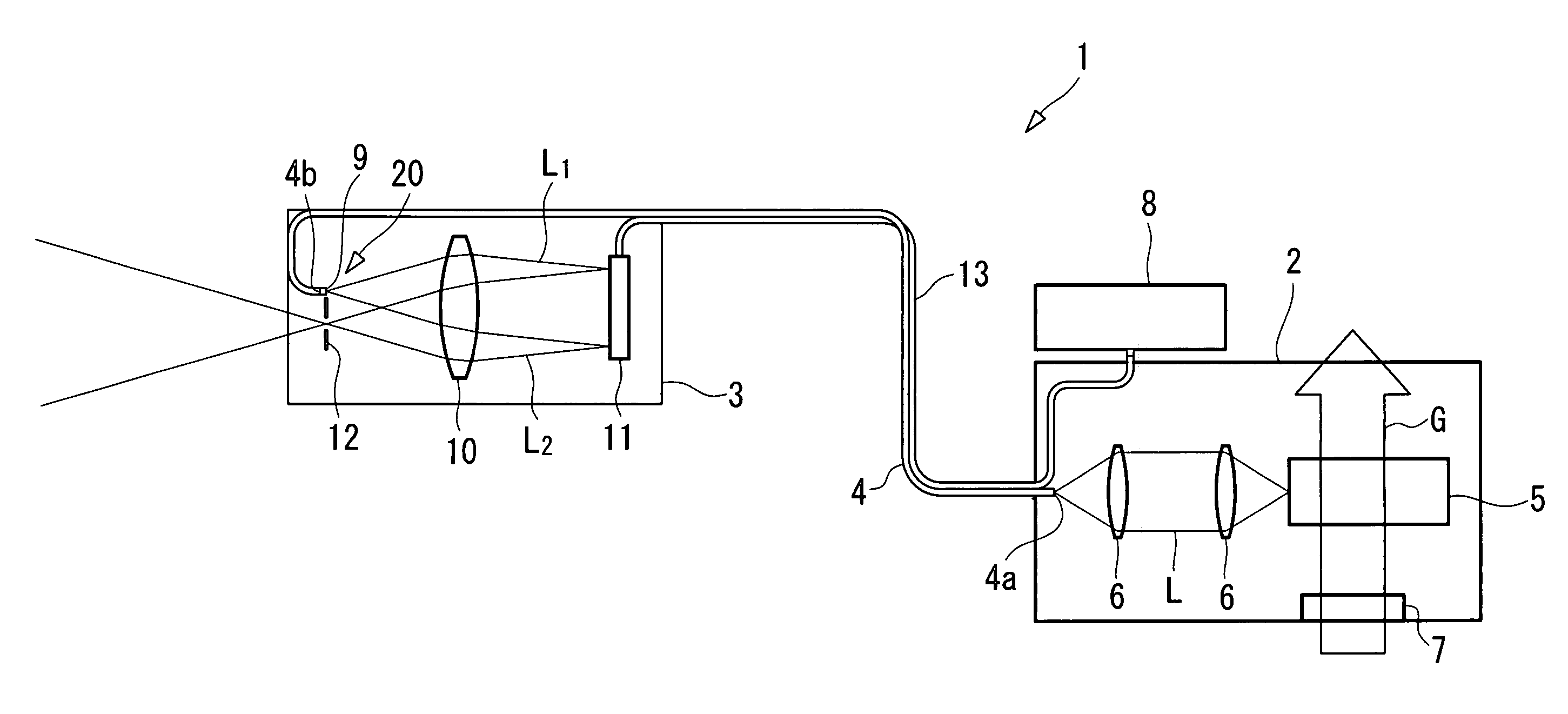
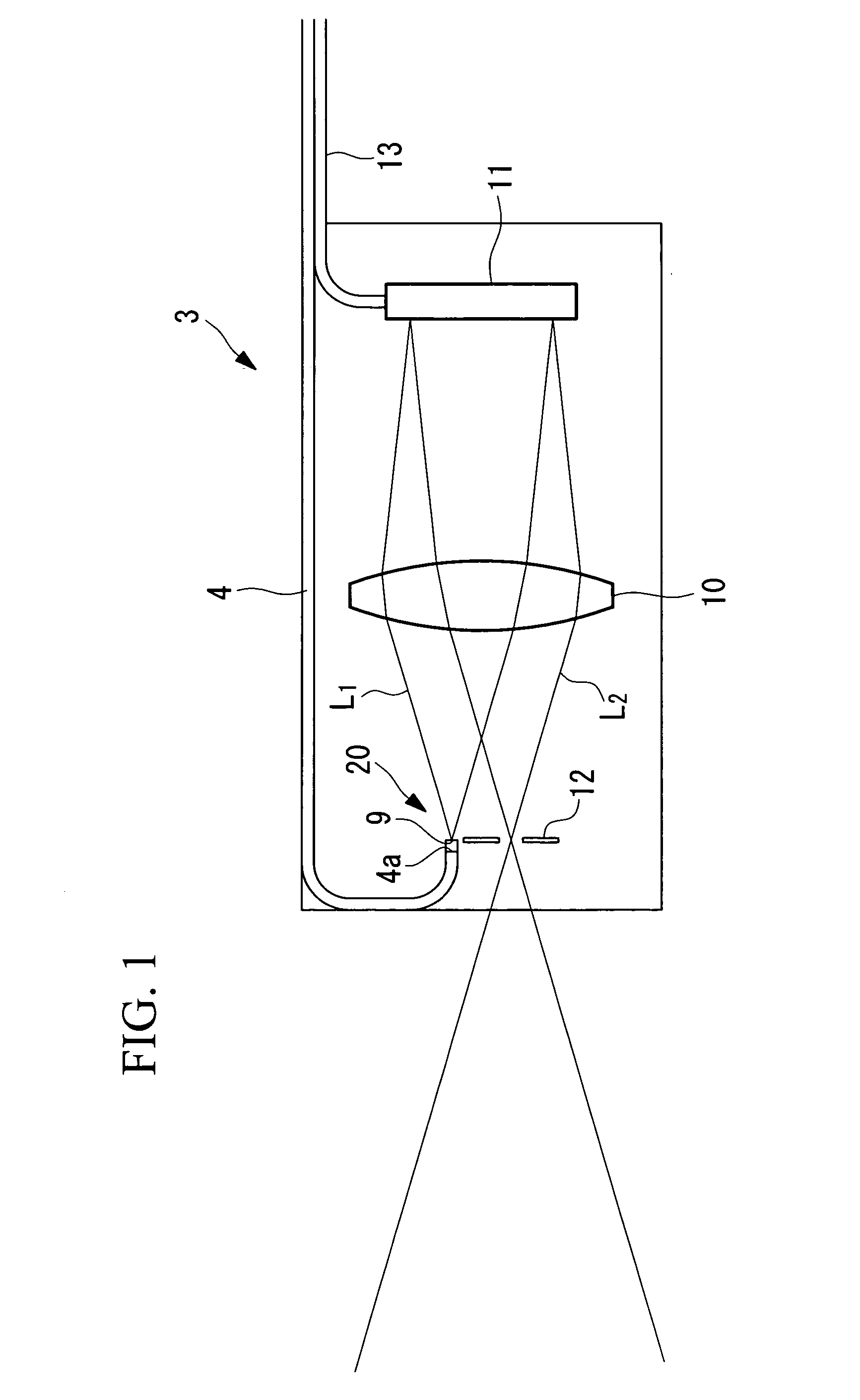
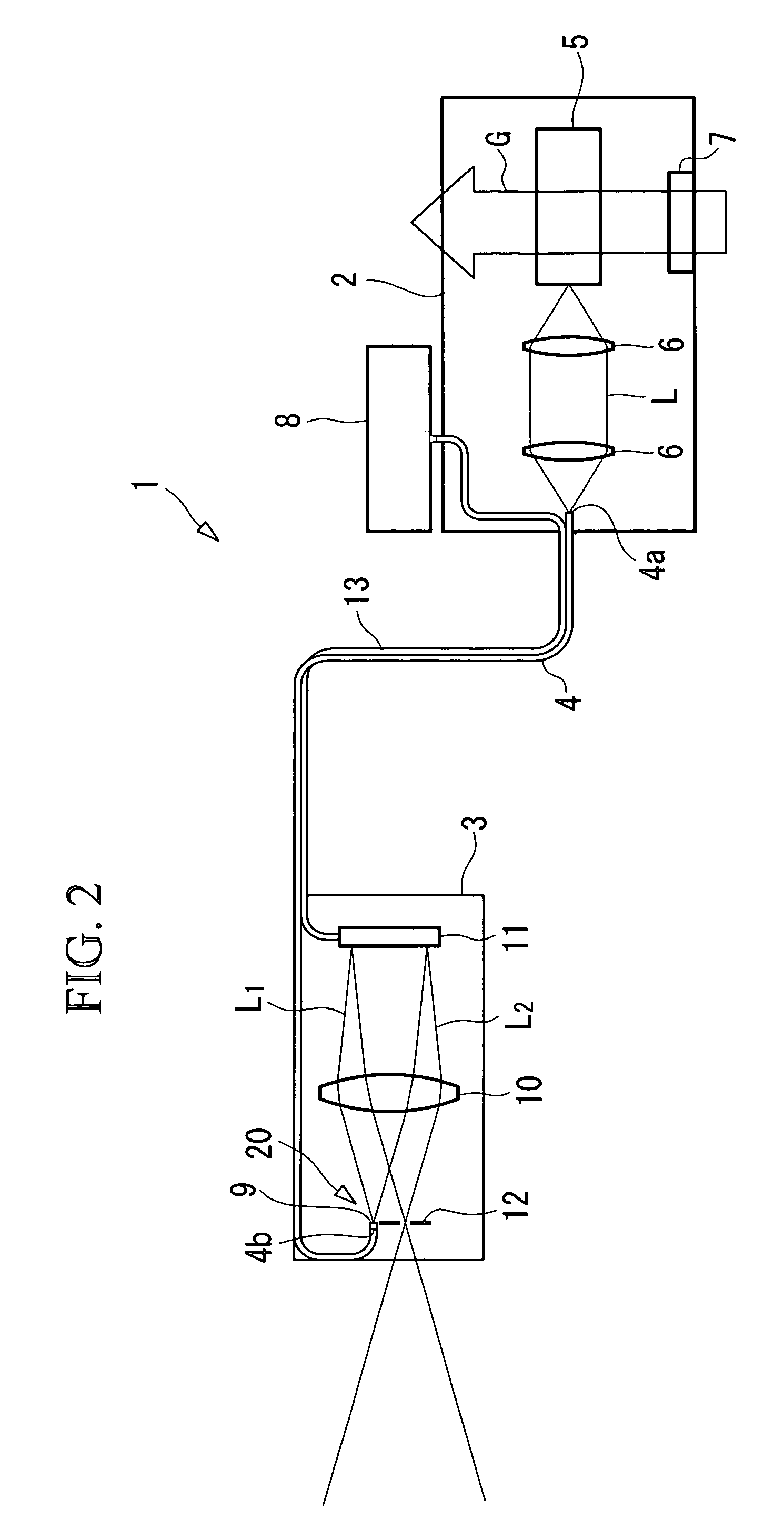
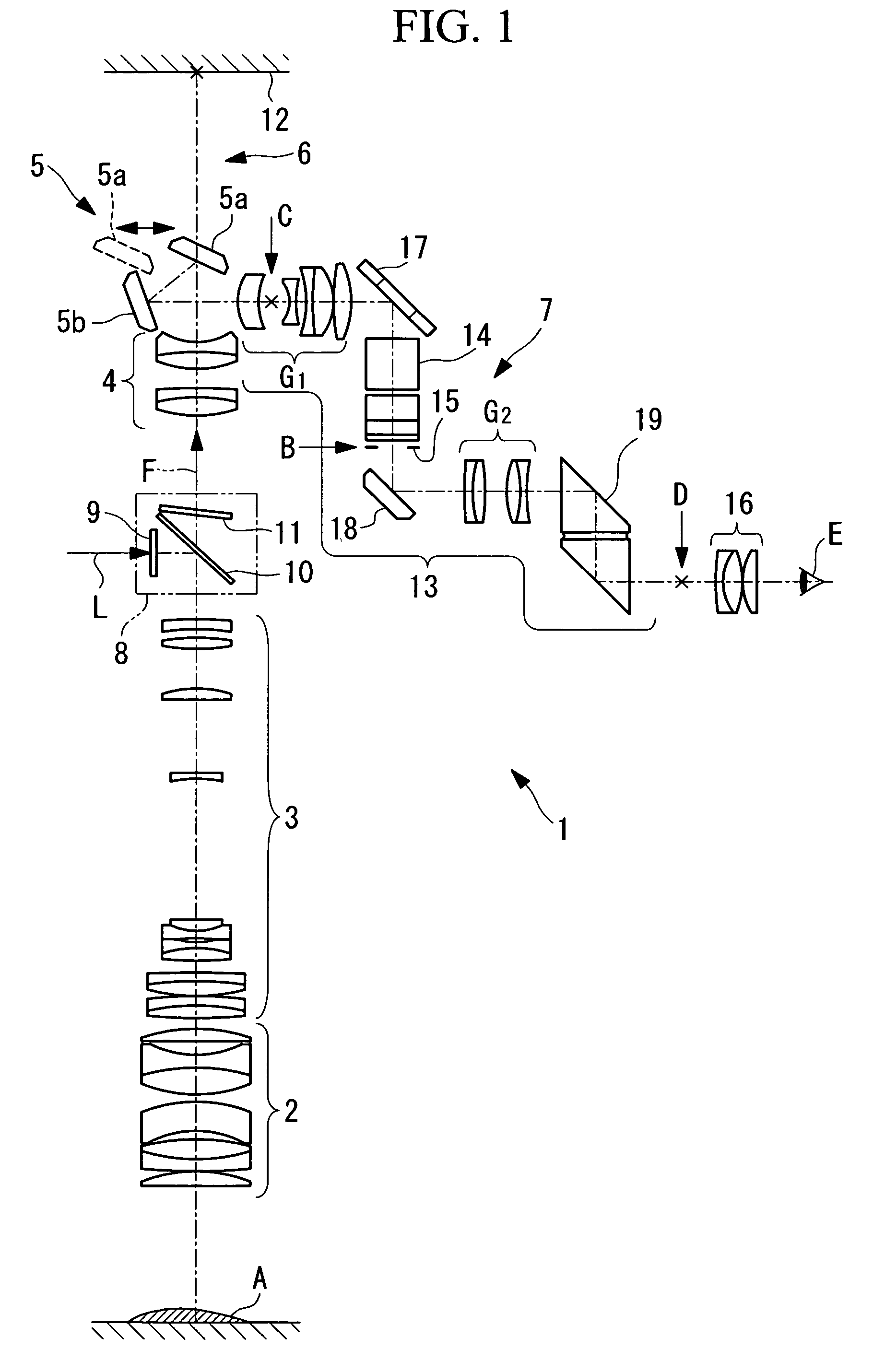
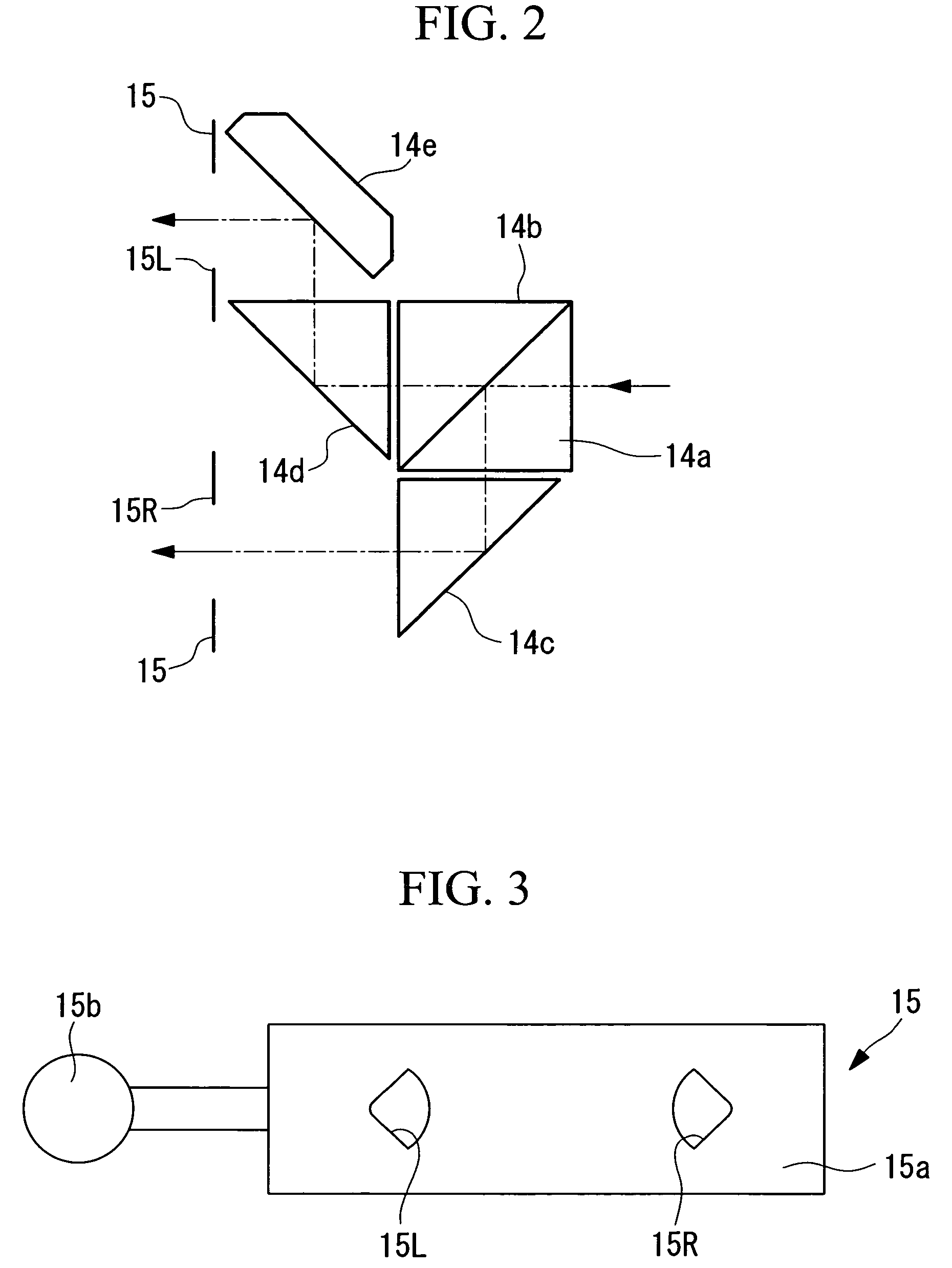
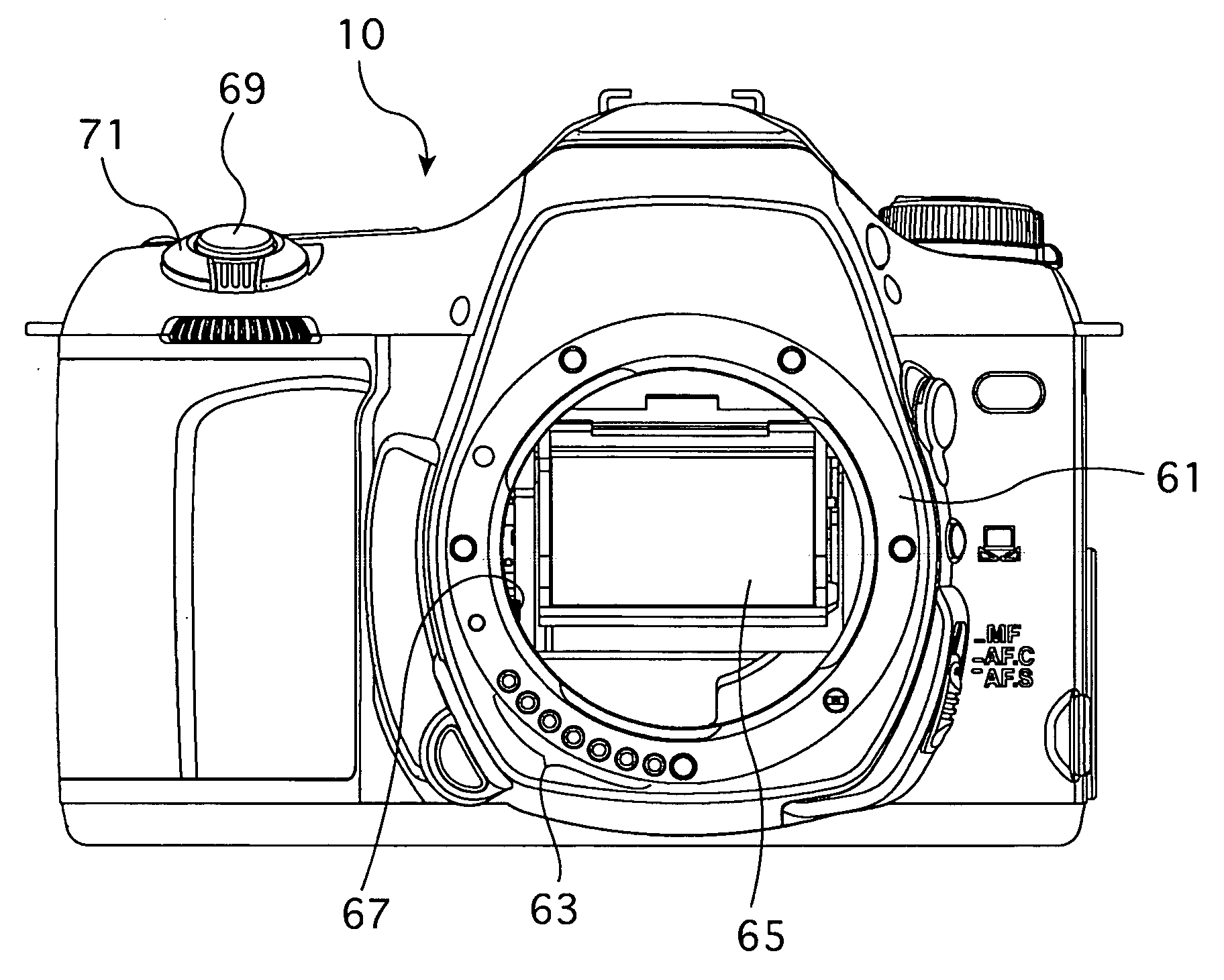
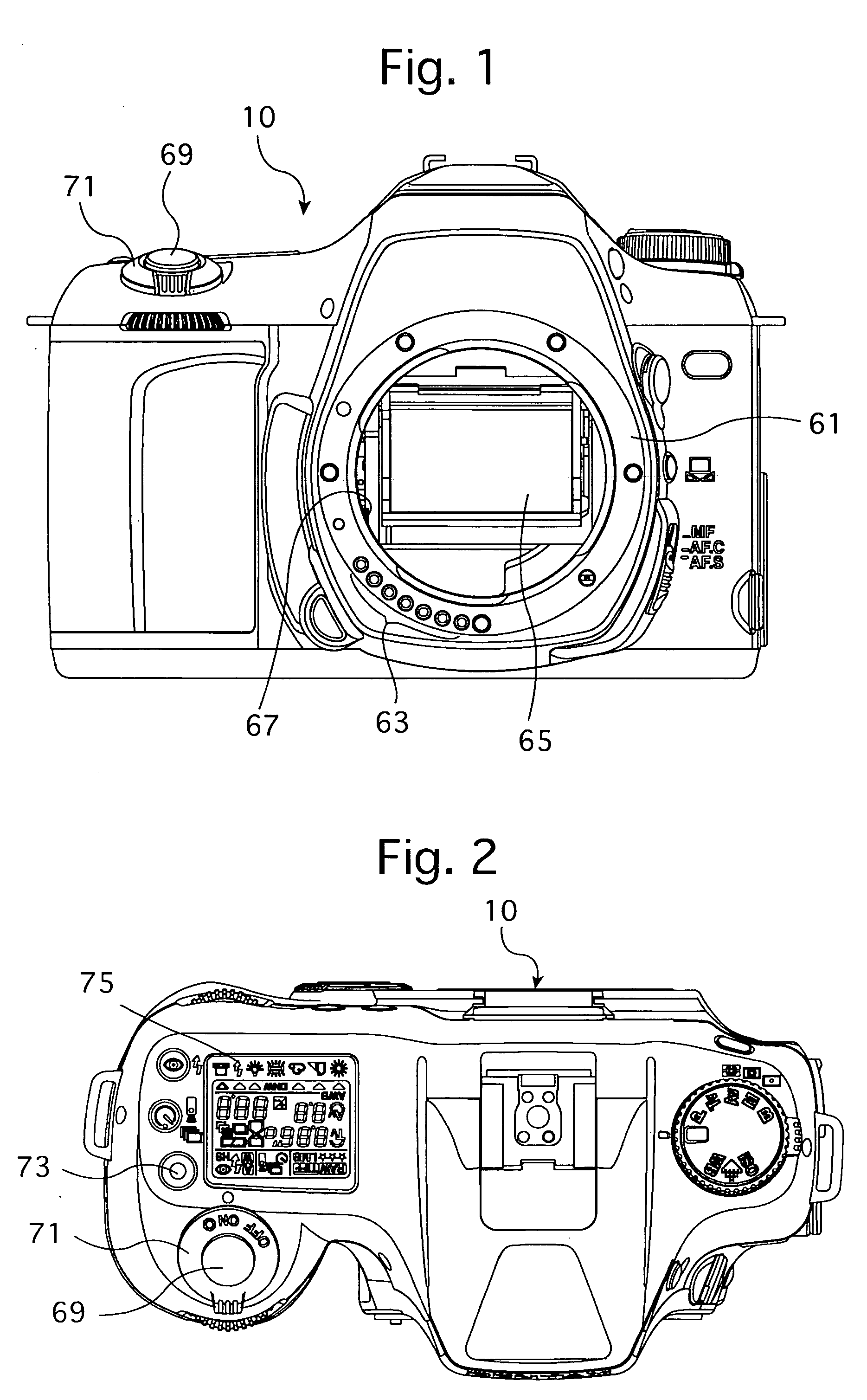
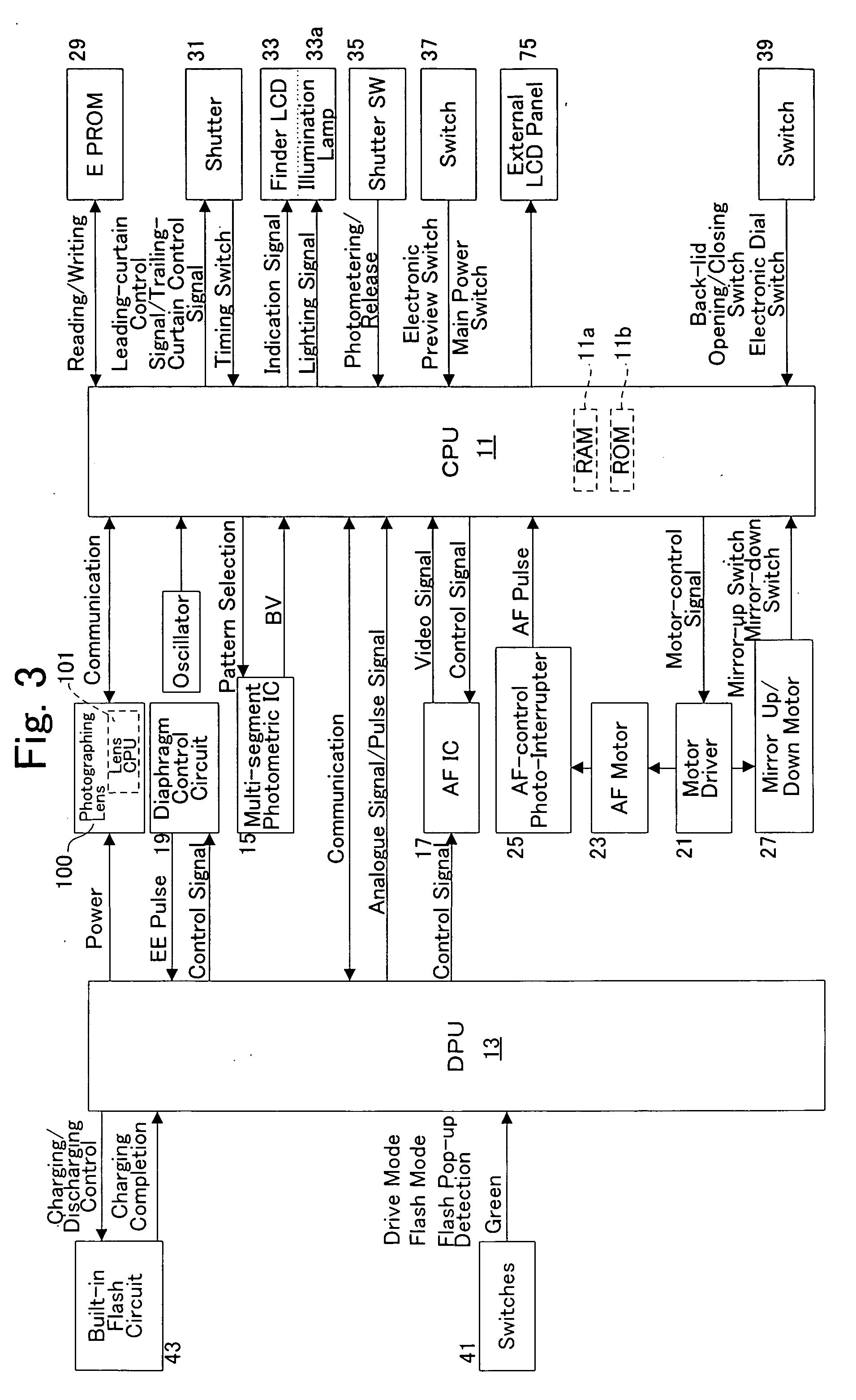
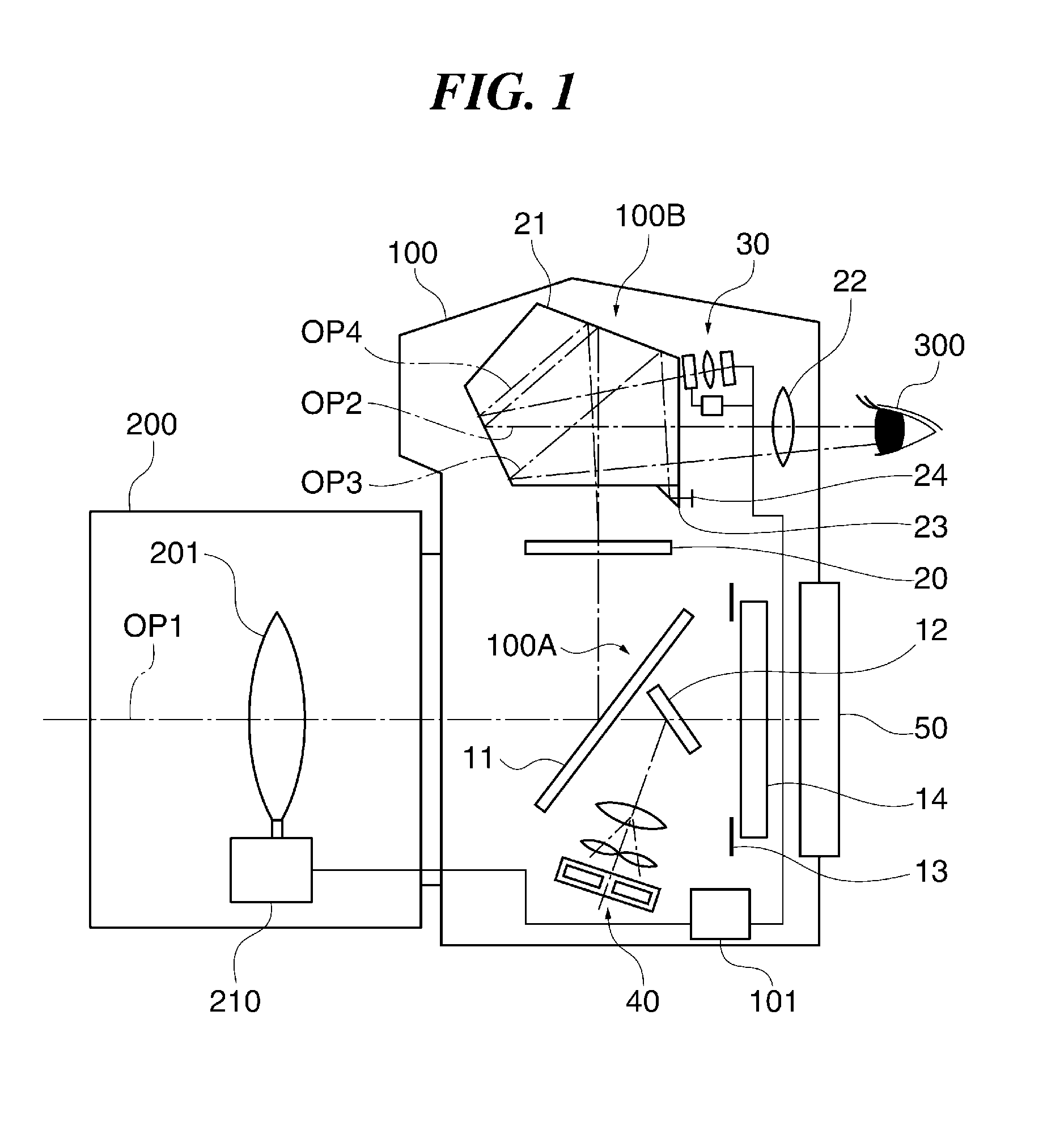
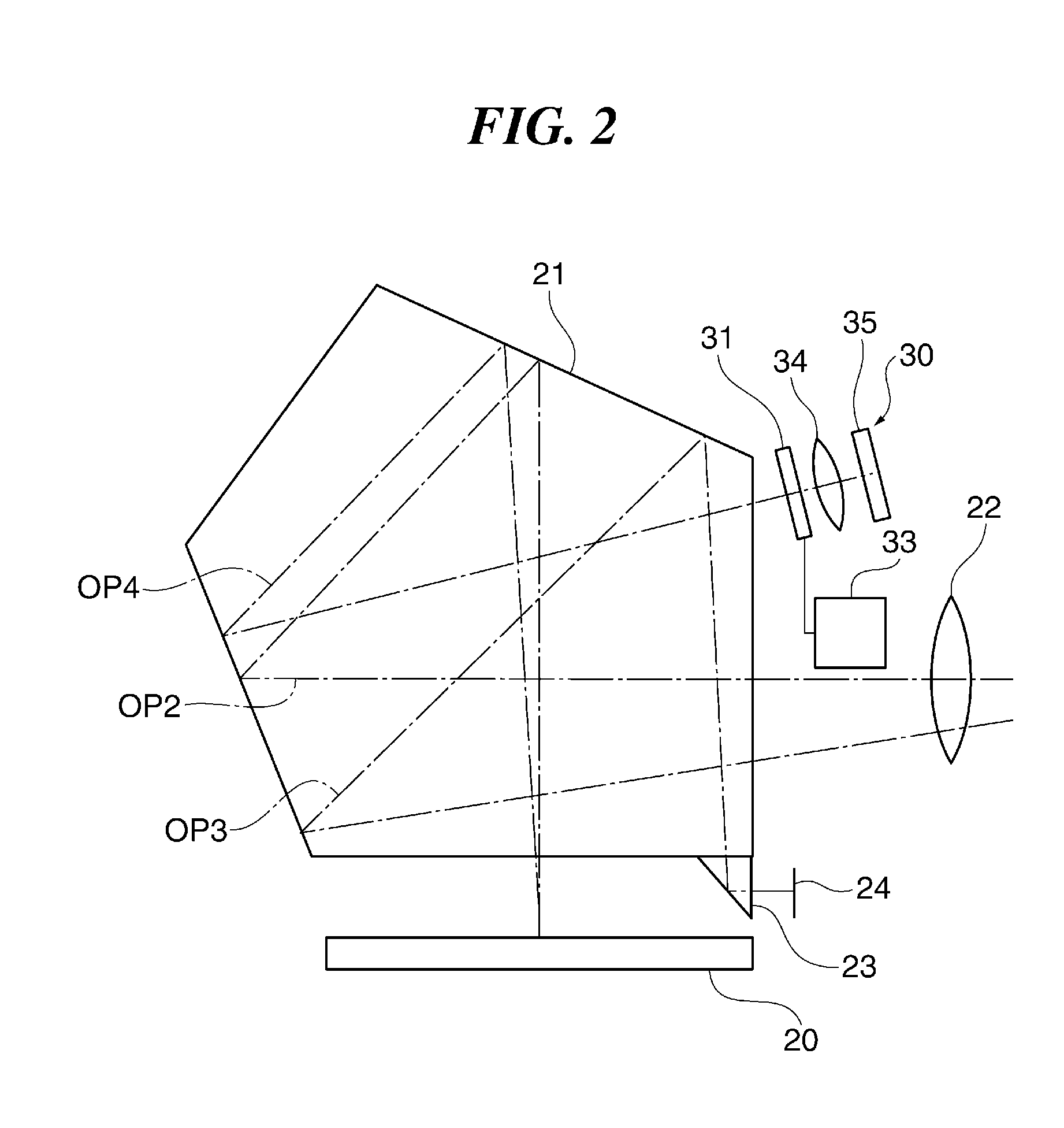
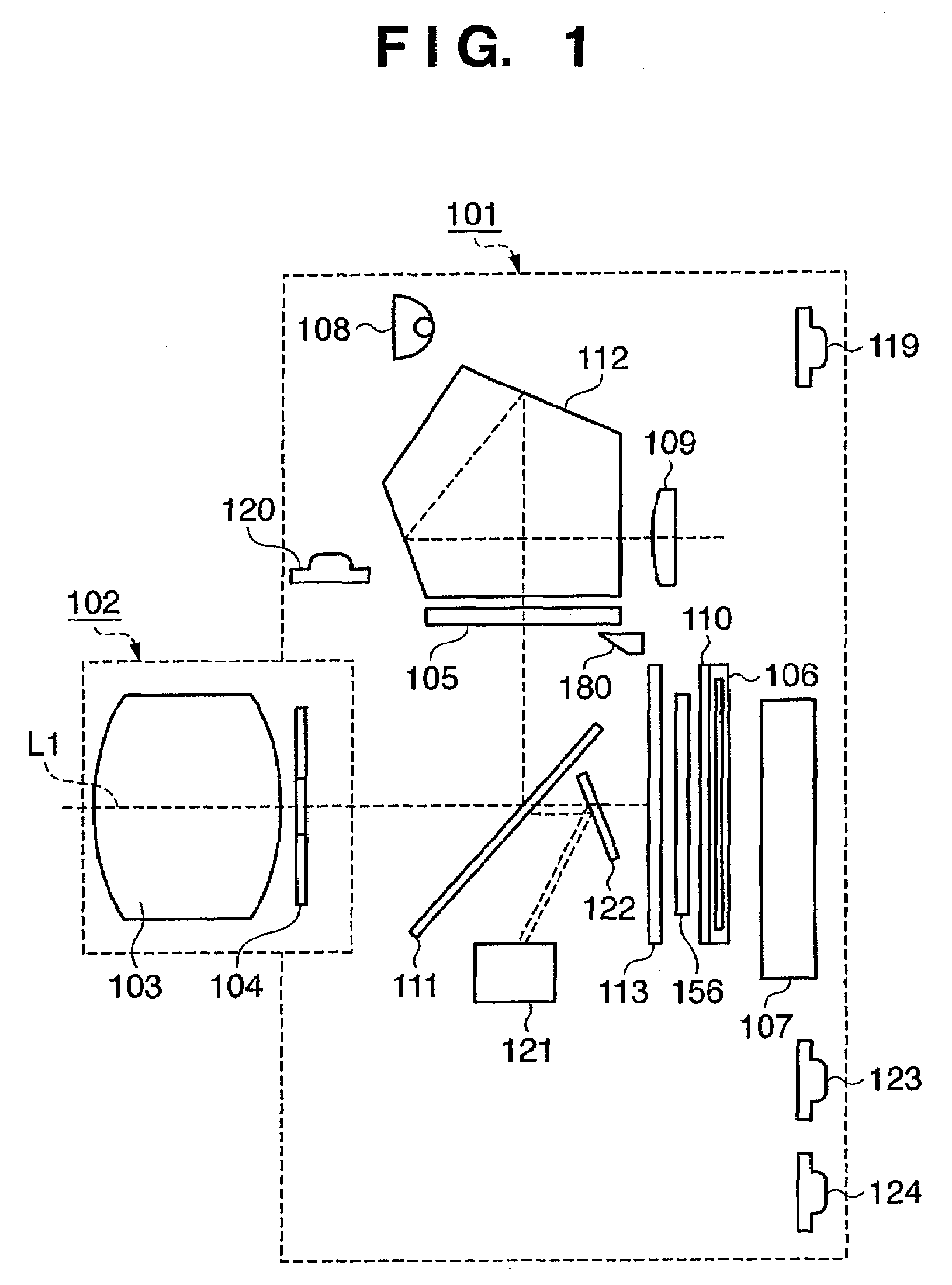
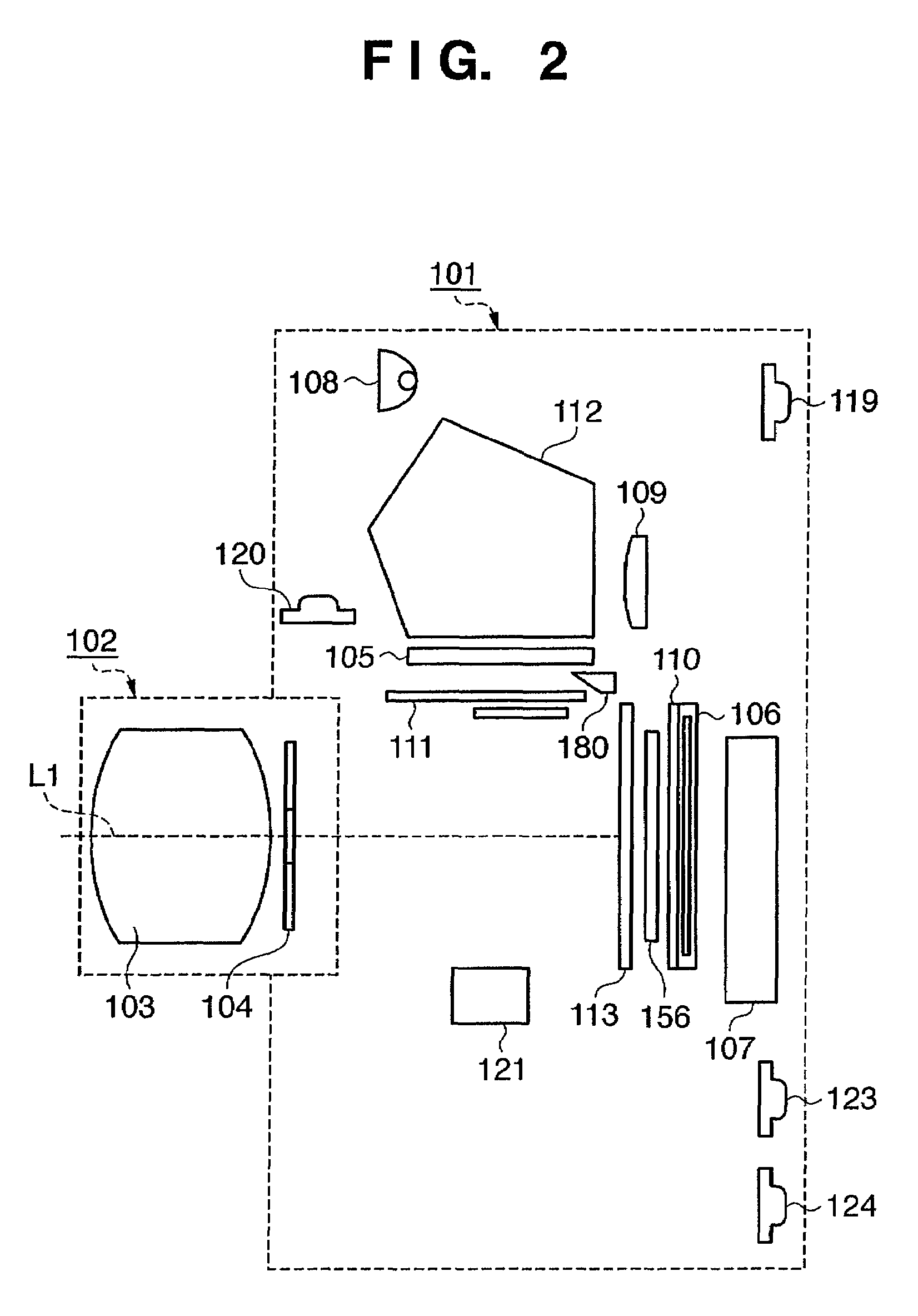
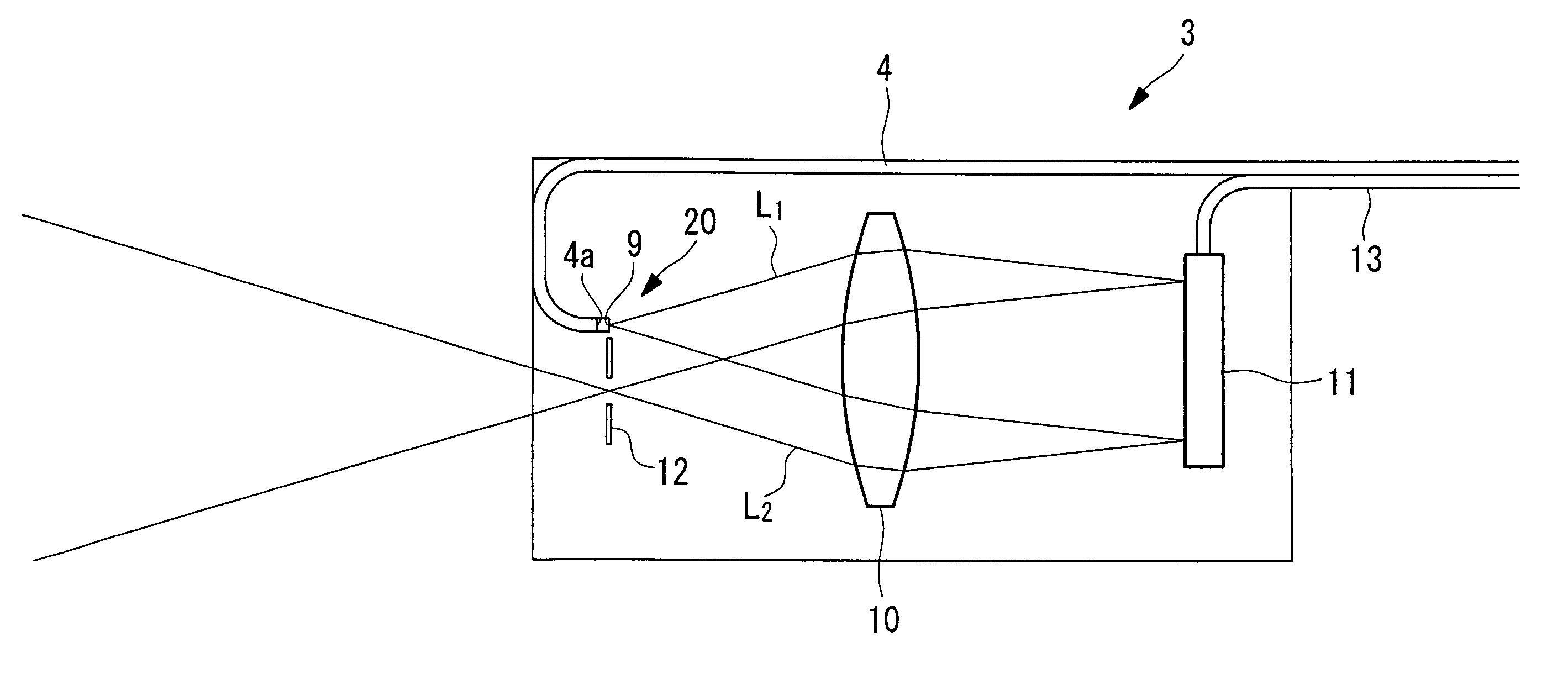
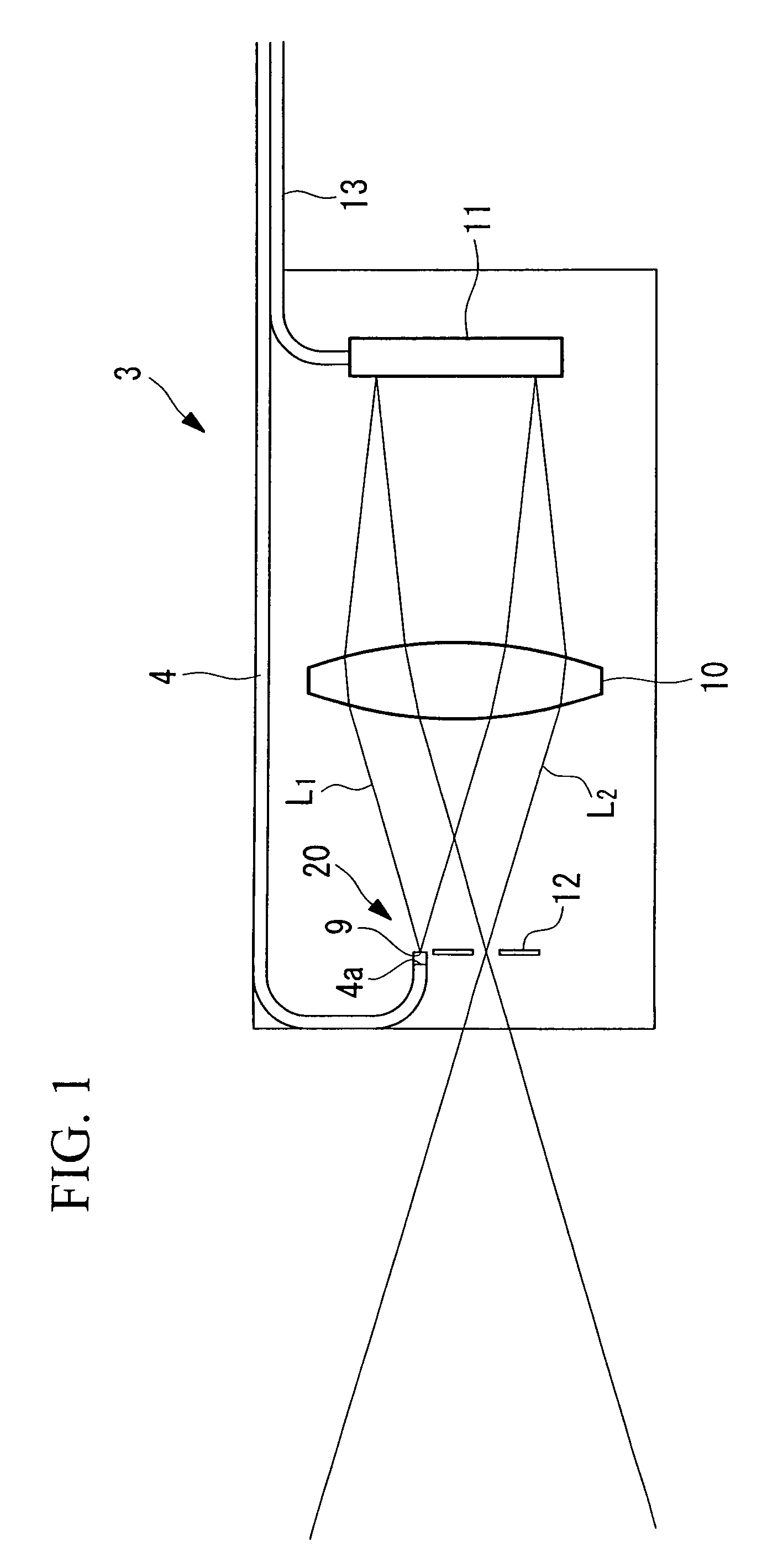
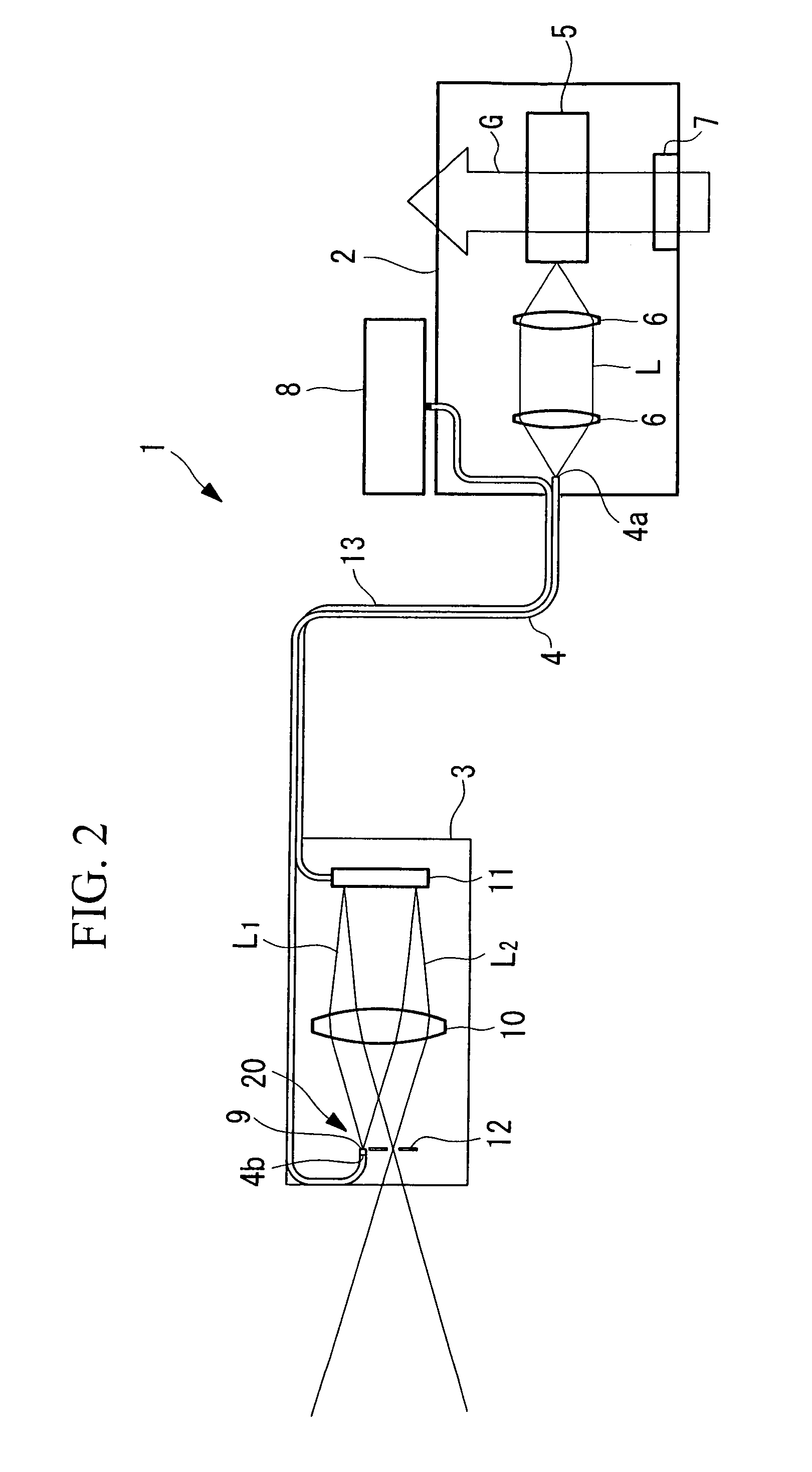
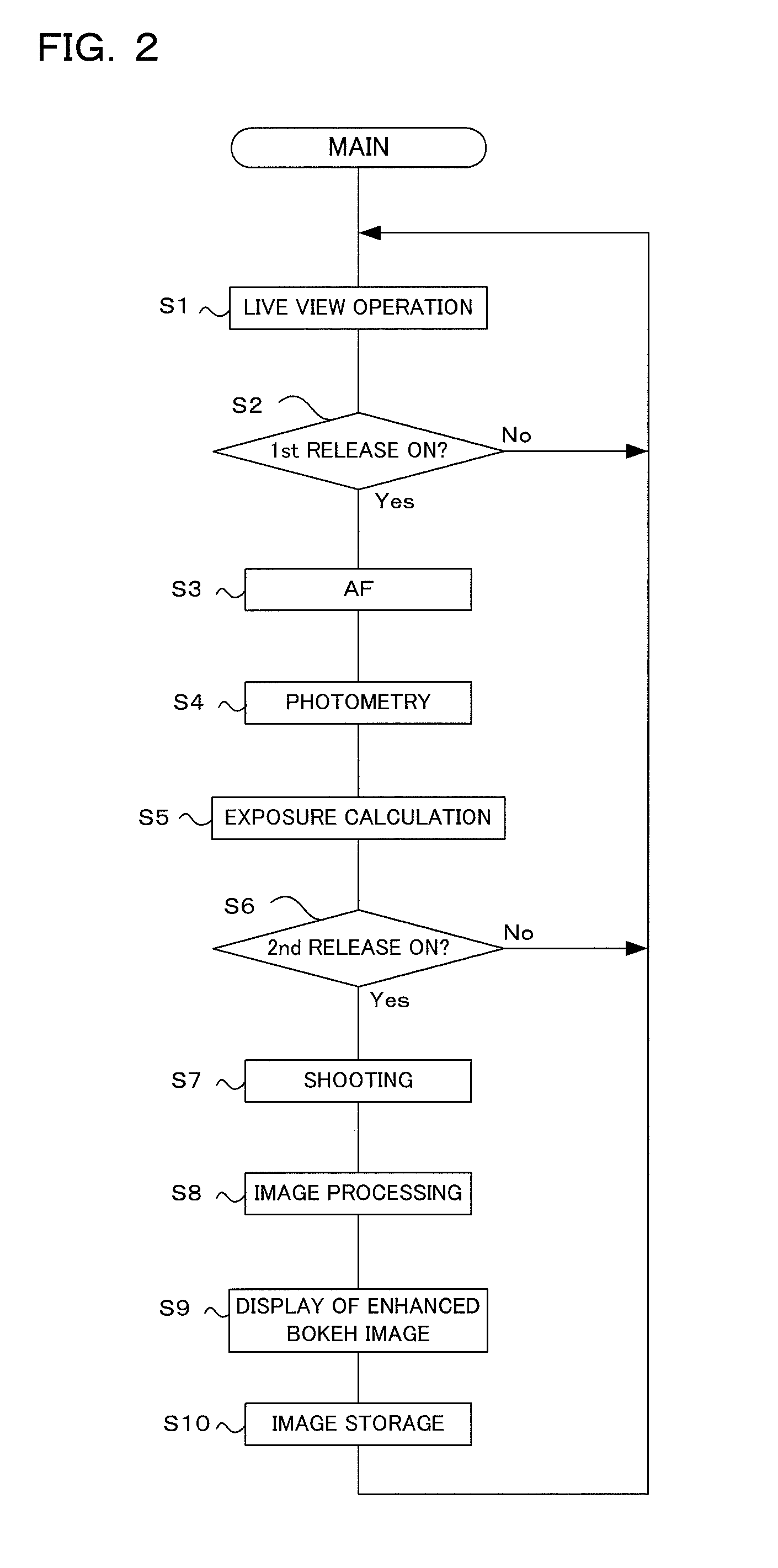
Imaging device and imaging device control method
ActiveUS20110122287A1Natural feelingTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight fluxStopping down
An imaging device of the present invention comprises an imaging section for photoelectrically converting a subject image, and outputting image data, an aperture control section for narrowing subject light flux at a first aperture value and a second aperture value, a shooting control section for, in response to a release instruction, imaging a first image at the first aperture value and, reading out first image data from the imaging section while simultaneously carrying out a stopping down operation to the second aperture value, imaging a second image at the second aperture value and, reading out second image data from the imaging section, and an image processing section for detecting an amount of variation in contrast value for each location in the first image data and the second image data, and carrying out processing to blur at an intensity of blurring according to the amount of variation between each location.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Image pickup apparatus and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080043126A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsWavefrontImage signal
An image pickup apparatus includes an element-including optical system, a variable aperture, a detector, and a converter. The element-including optical system has an optical system and an optical wavefront modulation element which modulates an optical transfer function. The detector picks up an object image that passes through the optical system, the variable aperture, and the optical wavefront modulation element. The converter generates an image signal with a smaller blur than that of a signal of a blurred object image output from the detector. Positions at which the element-including optical system and the detector are attached are adjusted by stopping down a variable aperture included in the element-including optical system.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Iris diaphragm, iris diaphragm driving device and camera unit having the same, and iris diaphragm control method
InactiveUS20050238347A1Simple structureReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsLight filter
An iris diaphragm includes at least one lens shutter to adjust the size of an aperture that incident light passes through according to movement of the at least one lens shutter. At least one ND filter is installed to move independently of the lens shutter to reduce the amount of incident light by covering the aperture stopped-down by the lens shutter according to the movement of the at least one ND filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Diaphragm driving device of a camera system using an interchangeable lens
InactiveUS20090263120A1Reduce power consumptionTotal current dropCamera diaphragmsDriving currentDrive motor
A diaphragm driving device for a camera including a camera body and an interchangeable lens which is detachably attached to the camera body, wherein the interchangeable lens includes a diaphragm mechanism having an in-lens spring device for performing a stop-down operation, the in-lens-spring device having a spring constant. The camera body includes a diaphragm drive mechanism having a diaphragm drive motor and an in-body spring device, both of which are for making the diaphragm mechanism of the interchangeable lens perform the stop-down operation, anda controller for controlling a driving current which is supplied to the diaphragm drive motor in accordance with the spring constant of the in-lens spring device.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20080037125A1Suppress generationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRegular patternLow-pass filter
An image pickup apparatus which is capable of suppressing generation of shadows even when the aperture of the photographic lens is stopped down. A digital camera as an image pickup apparatus includes a photographic lens, a image pickup element that picks up an image of an object, and an optical low-pass filter disposed between the photographic lens and the image pickup element. The filter includes a liner phase diffraction grating having unit cells which are disposed in a regular pattern at a grating pitch P and are formed by equal-width recesses and equal-width protrusions adjacent to each other. When a shortest wavelength of a reference wavelength employed is λS, and a longest wavelength of the reference wavelength is λL, an optical path difference ΔH between lengths of optical paths of light of which a phase is varied by the phase grating is larger than λS / 2 and smaller than λL / 2.
Owner:CANON KK
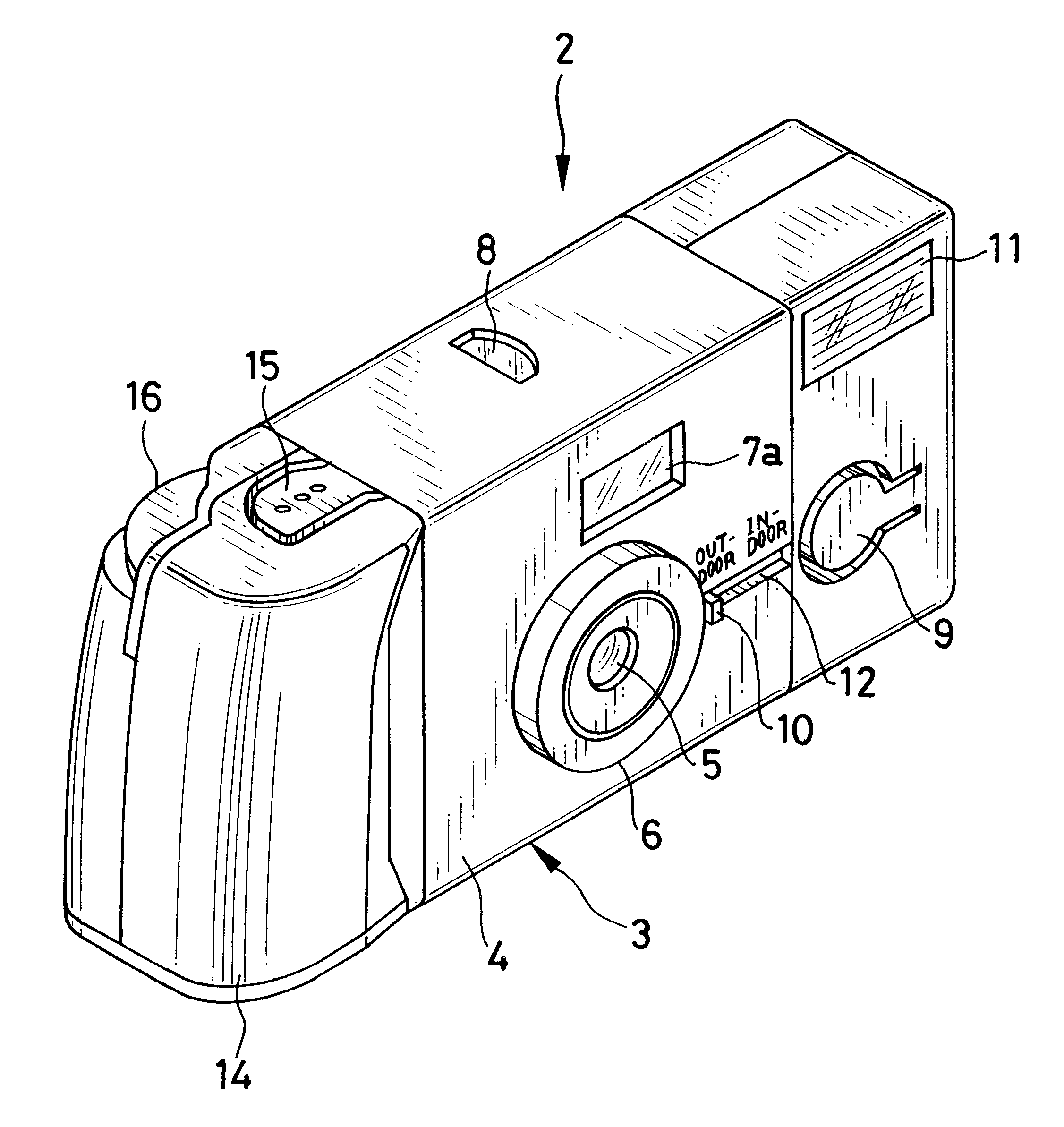
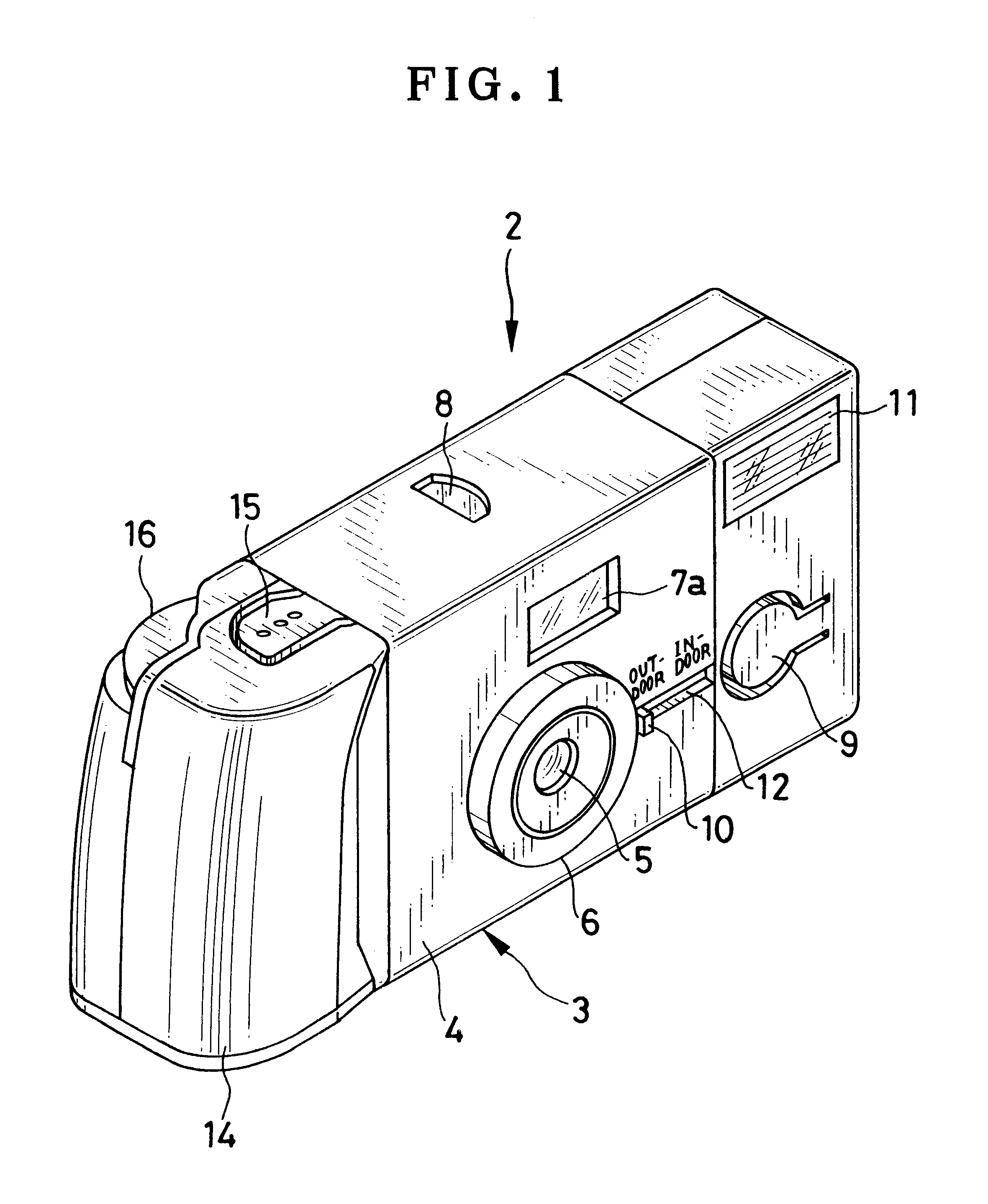
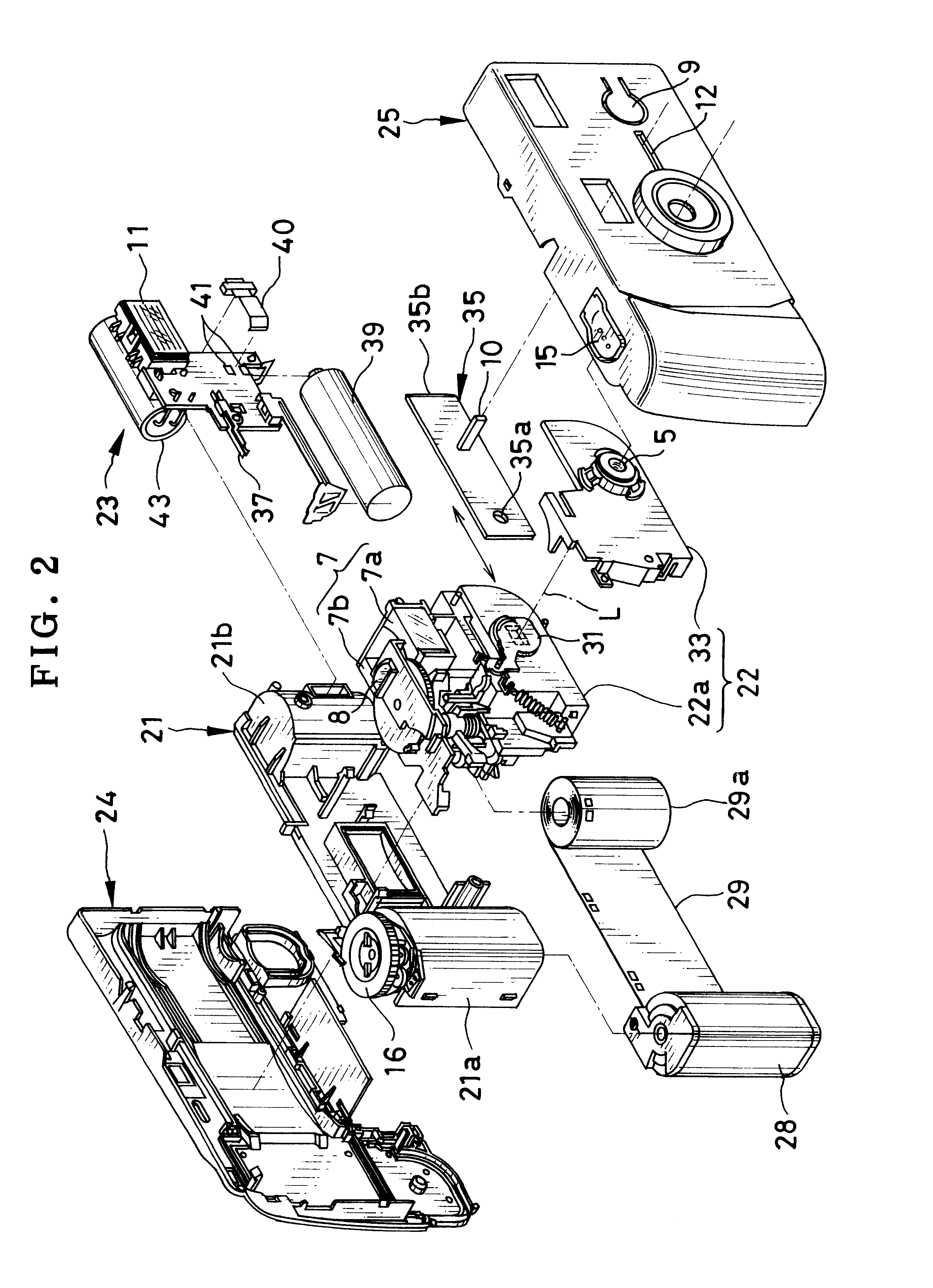
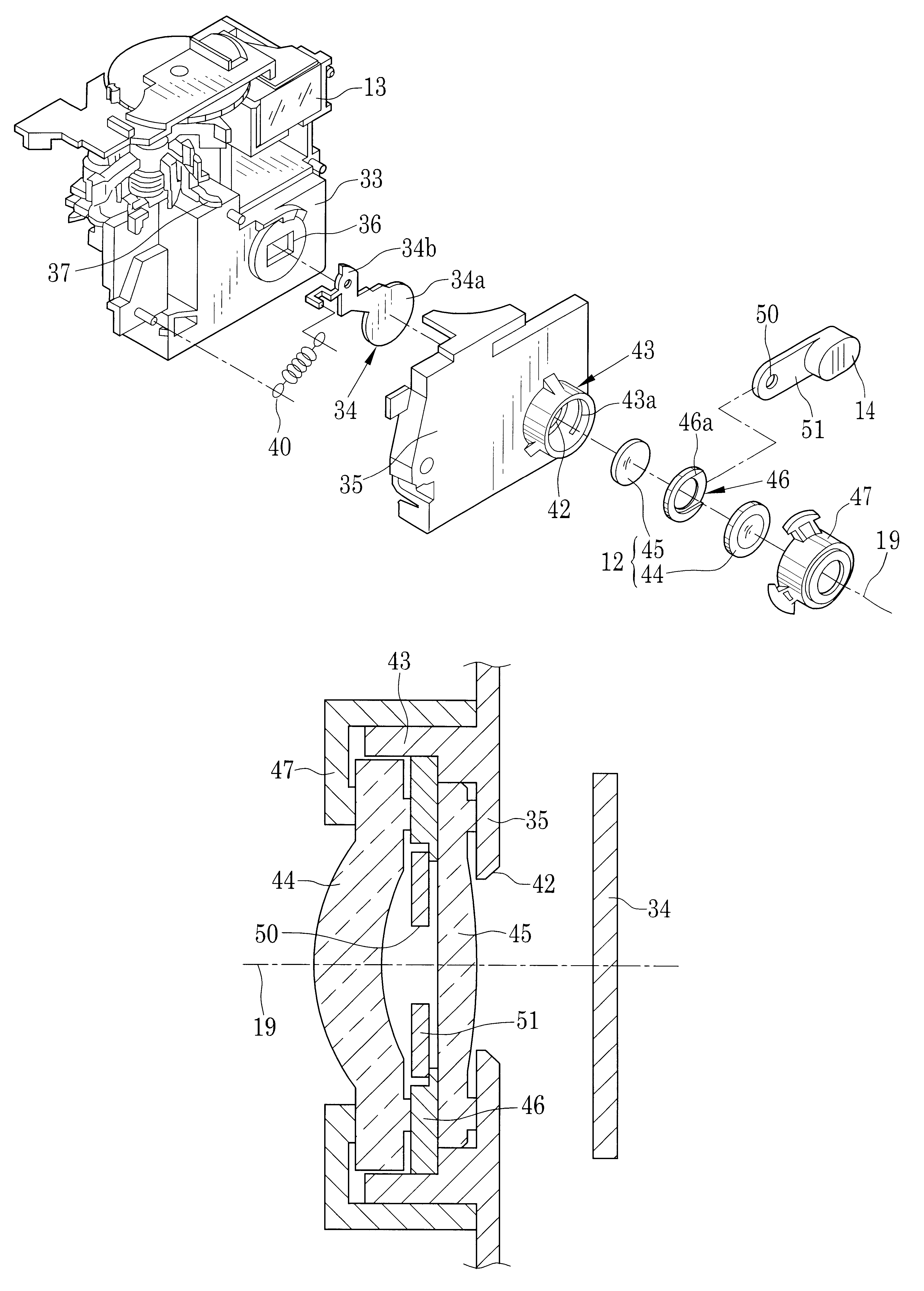
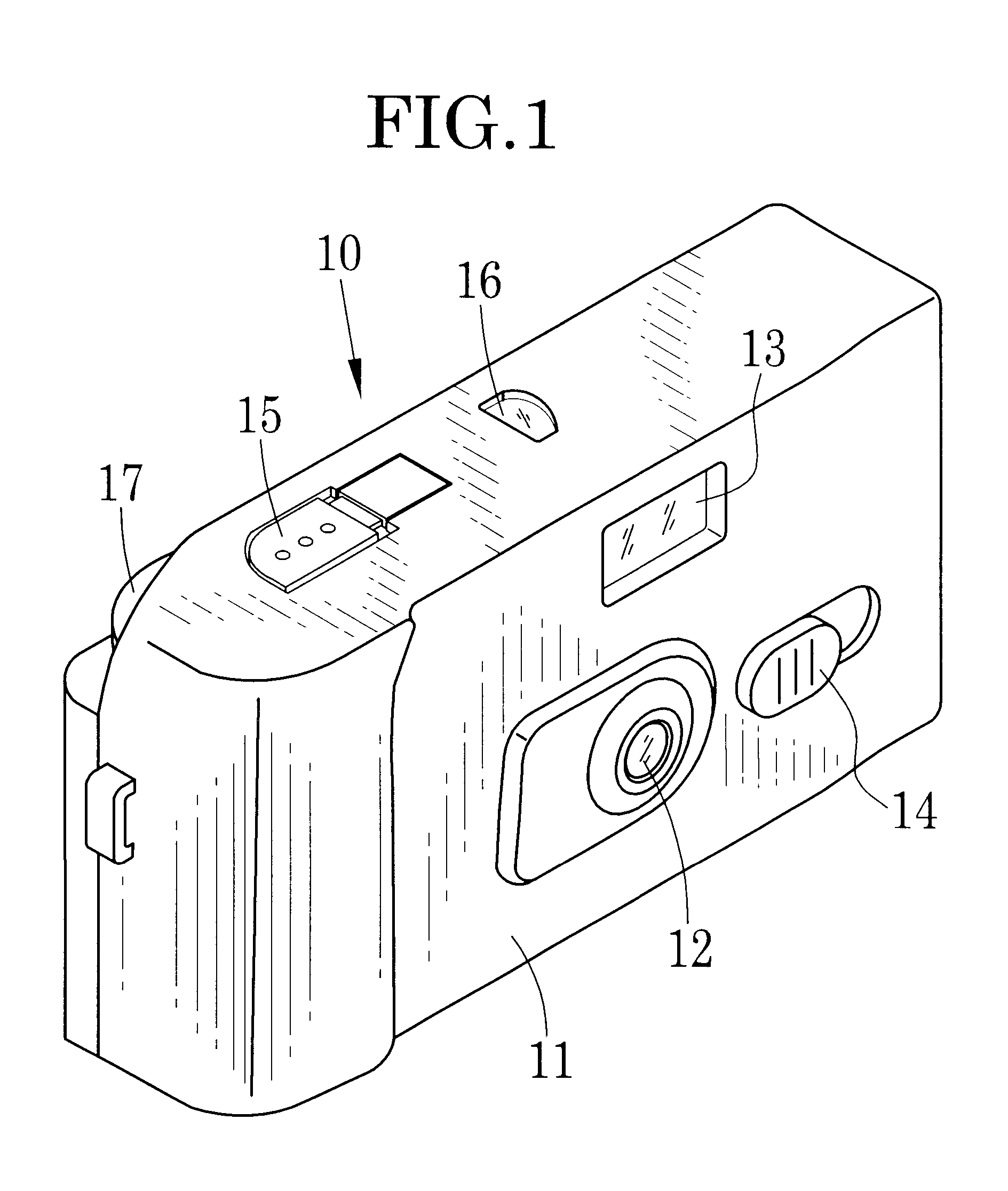
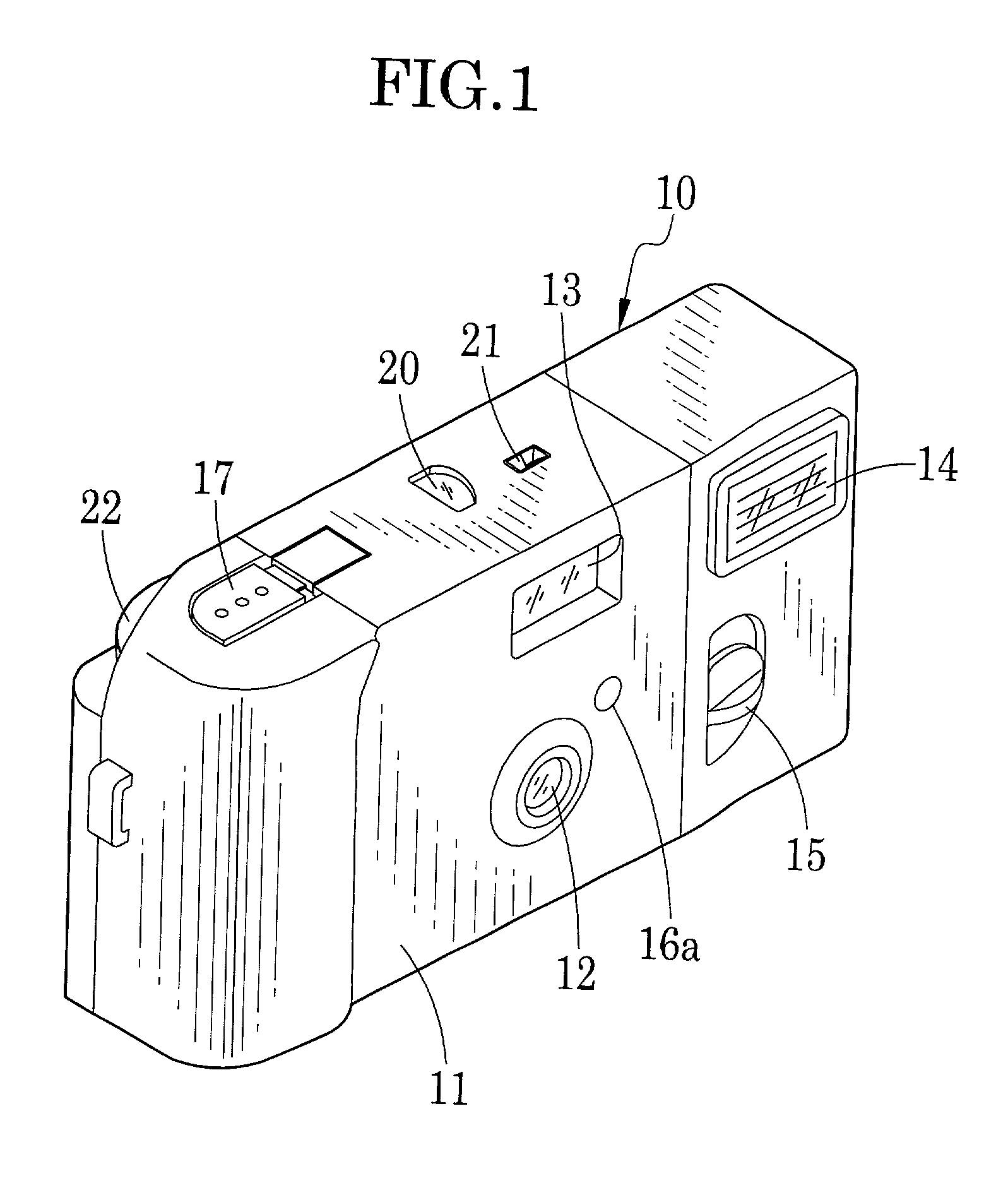
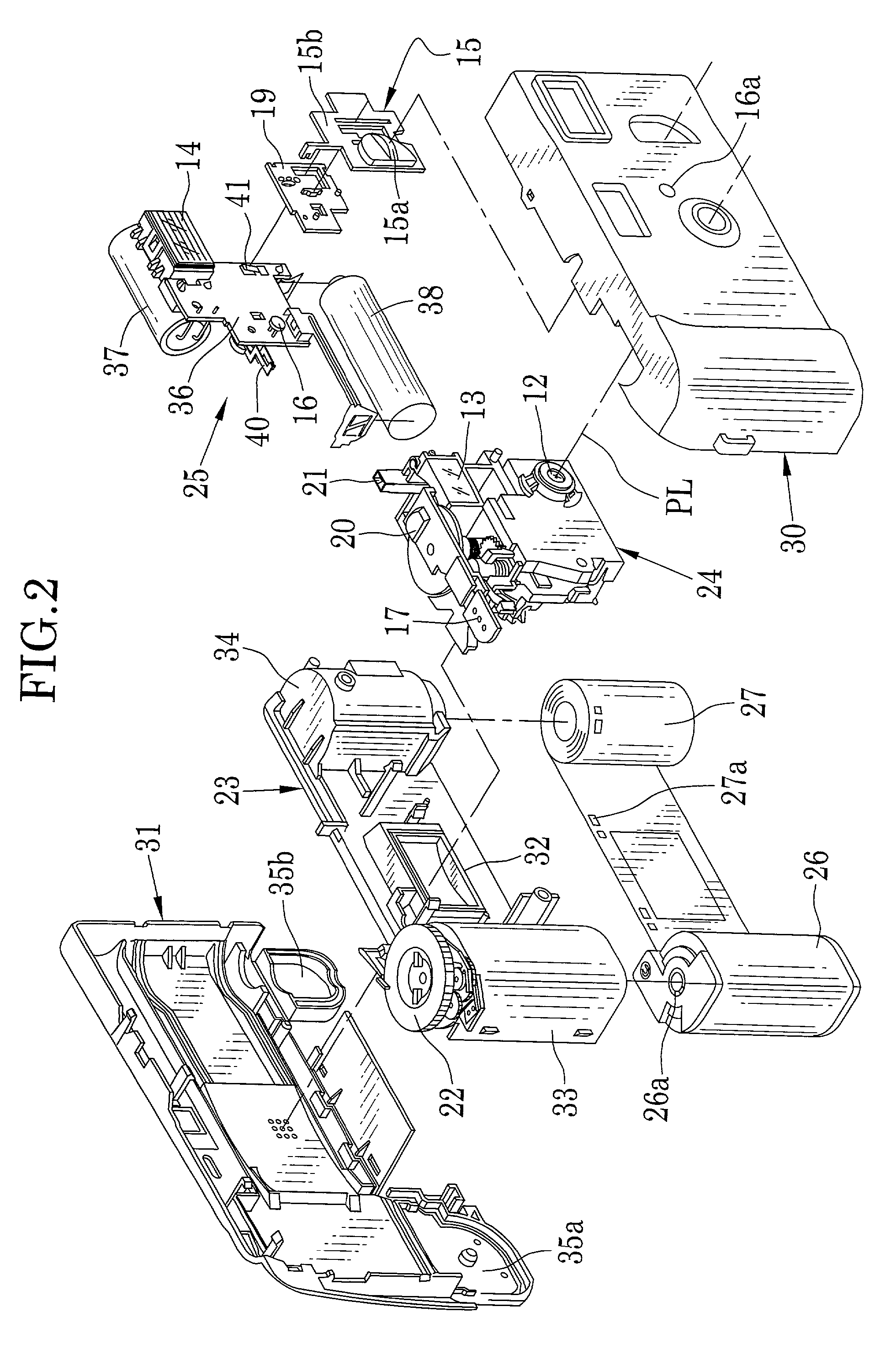
Lens-fitted photo film unit with flash device
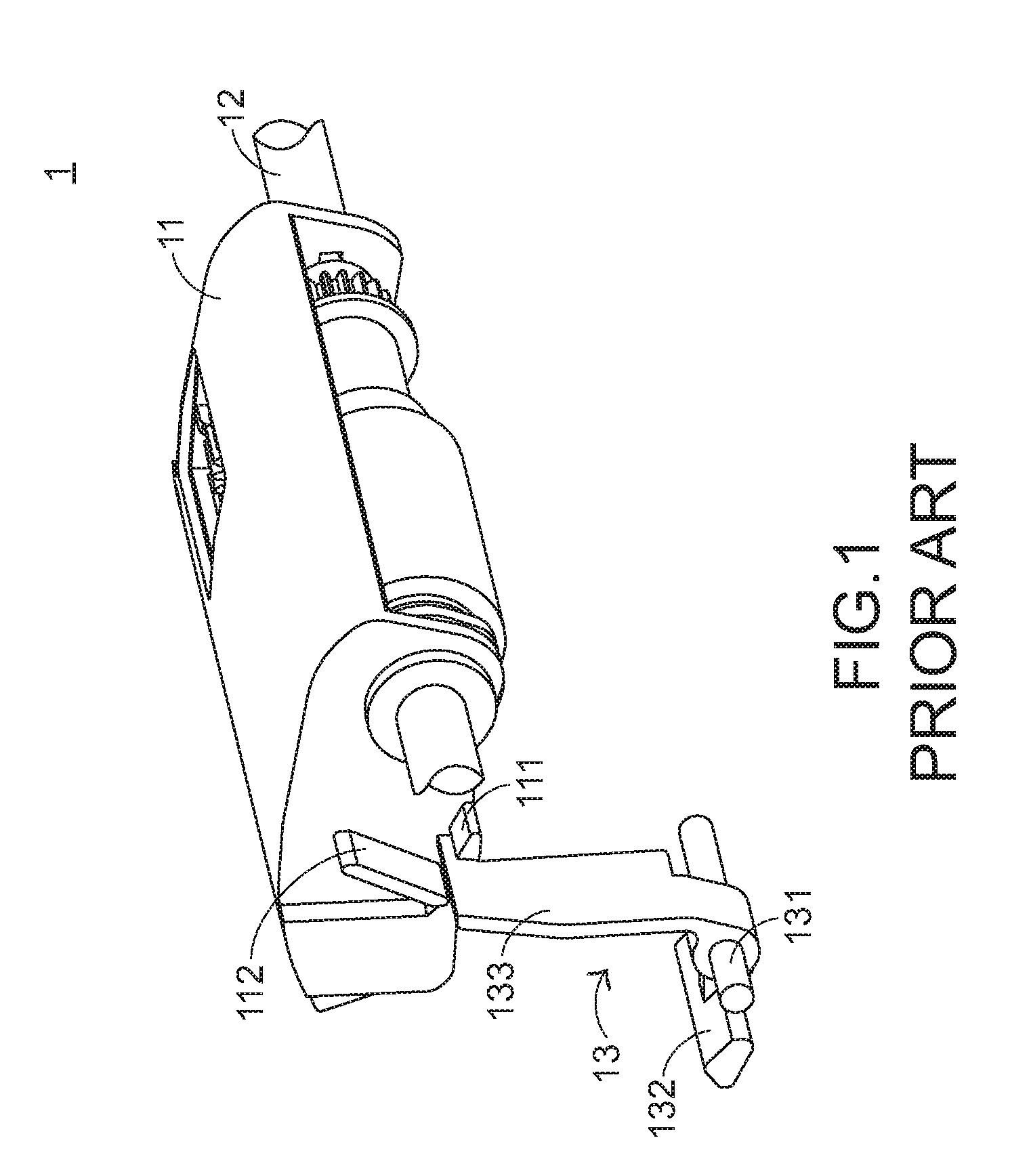
A lens-fitted photo film unit includes a main body pre-loaded with photo film. A flash unit is secured to the main body, and emits flash light to a photographic field. An exposure opening is formed in the main body, and introduces light from the photographic field to the photo film. A shutter mechanism is secured to the main body, and opens and closes the exposure opening. A charger switch causes the flash unit to store charge upon being turned on. A changeover plate with a small diameter opening is movable to first and second set positions, and stops down the exposure opening when in the first set position. One end of the changeover plate allows turning on and off the charger switch when the changeover plate is in the first set position, and forcibly turns on the charger switch when the changeover plate is in the second set position.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Image pickup apparatus and method and apparatus for manufacturing the same
An image pickup apparatus includes an element-including optical system, a variable aperture, a detector, and a converter. The element-including optical system has an optical system and an optical wavefront modulation element which modulates an optical transfer function. The detector picks up an object image that passes through the optical system, the variable aperture, and the optical wavefront modulation element. The converter generates an image signal with a smaller blur than that of a signal of a blurred object image output from the detector. Positions at which the element-including optical system and the detector are attached are adjusted by stopping down a variable aperture included in the element-including optical system.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
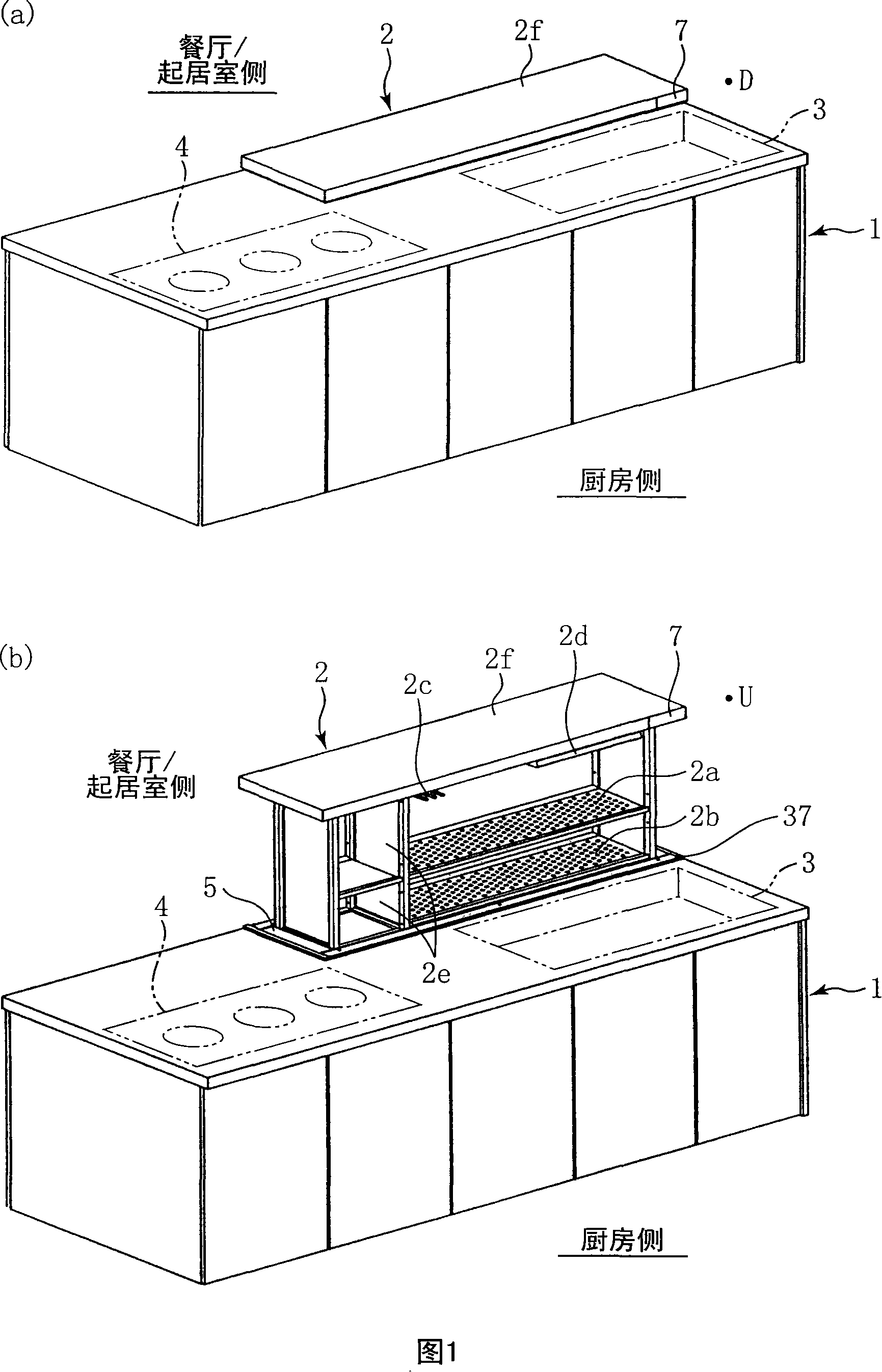
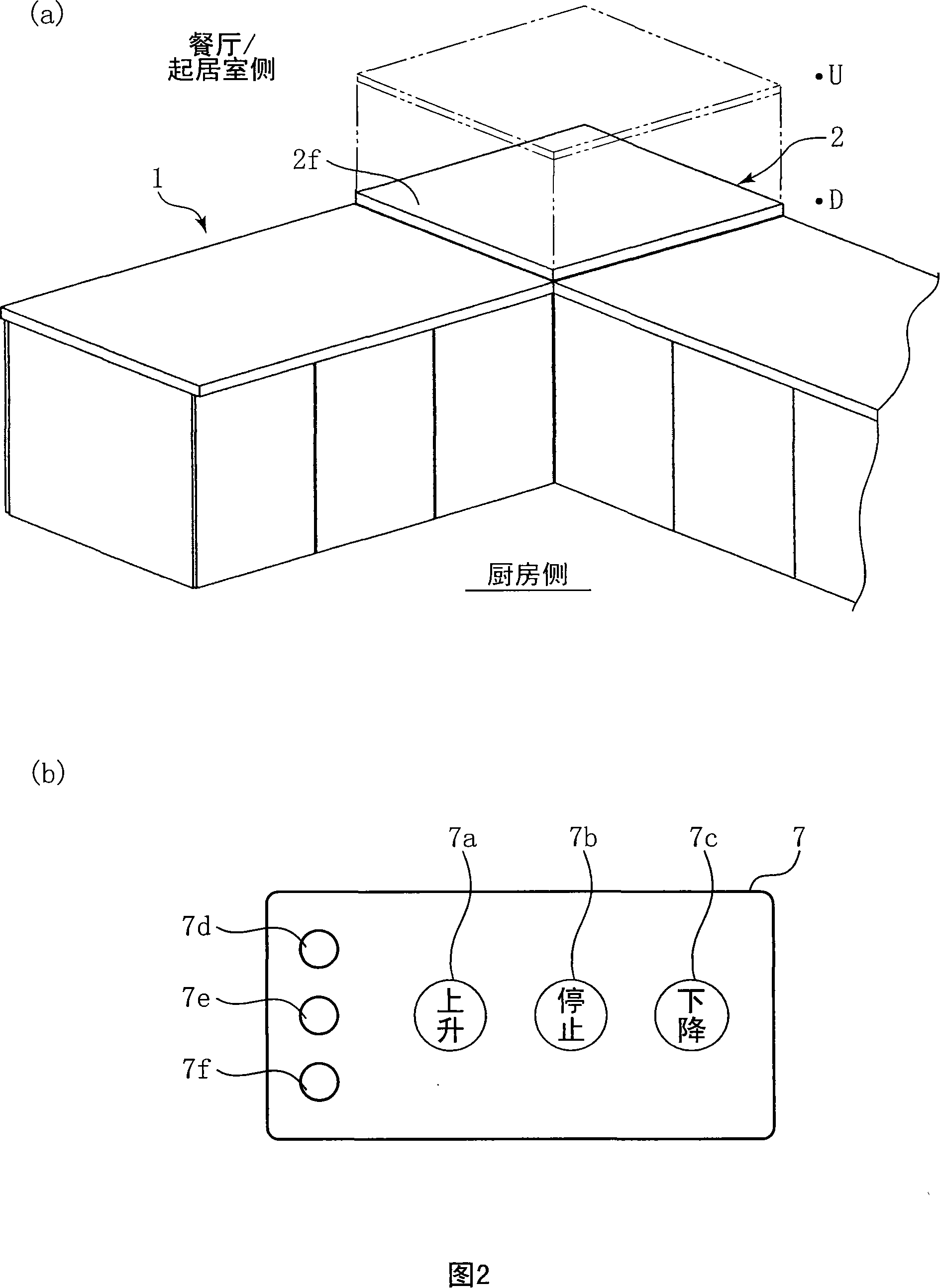
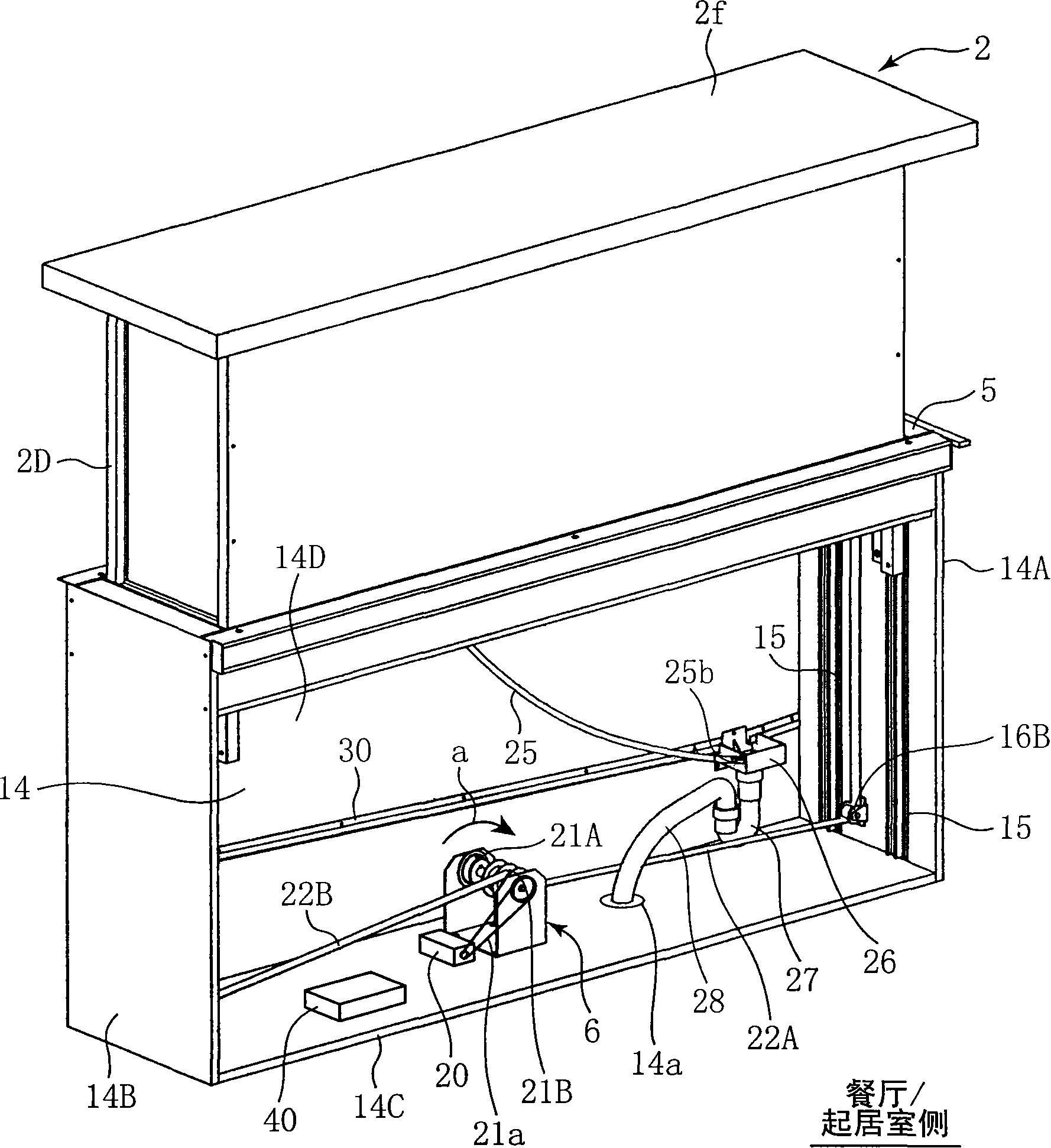
Lifting-type storage device
InactiveCN101155528APrevents problems caused by entrapment of foreign objectsKitchen cabinetsMovable shelf cabinetForeign matterEngineering
The elevating storage device of the present invention is provided with a drain rack (storage rack) (2) arranged in an opening (5) for lifting and lowering formed on a part of the counter of the kitchen floor cabinet (1) and for lowering the drain rack (2). To the storage space (14) under the counter and the lifting mechanism (6) raised to the counter, the lifting type storage device is provided with a foreign object detection part ( 38), (39); when the foreign matter detection part (38), (39) detects the foreign matter, the foreign matter detection stop part (control box) (40) that makes the drain rack (2) stop the lifting action. Thus, problems such as locking of the lifting mechanism (6) and failure to operate or overload (overcurrent) caused by foreign matter can be prevented.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
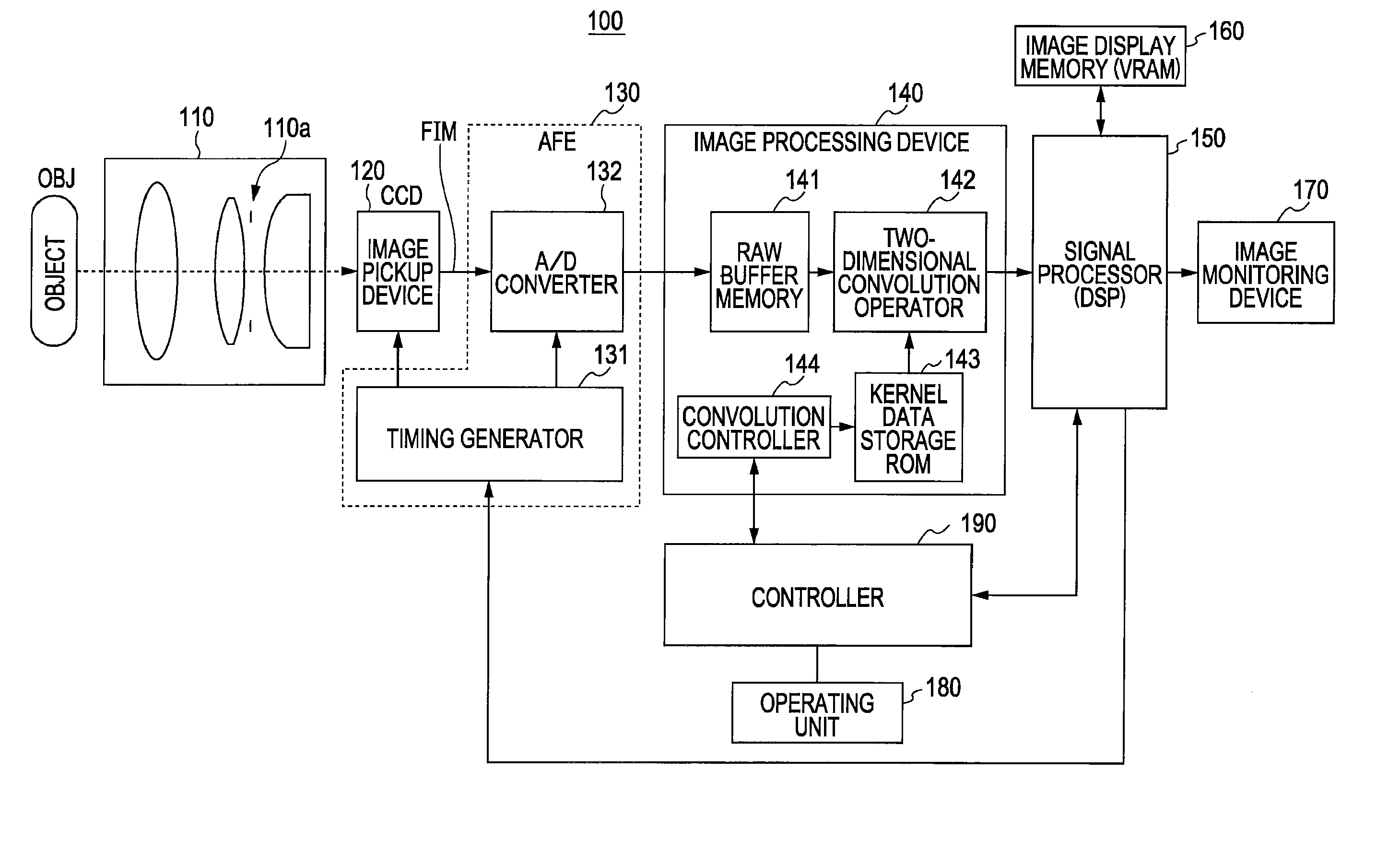
Imaging device and imaging method
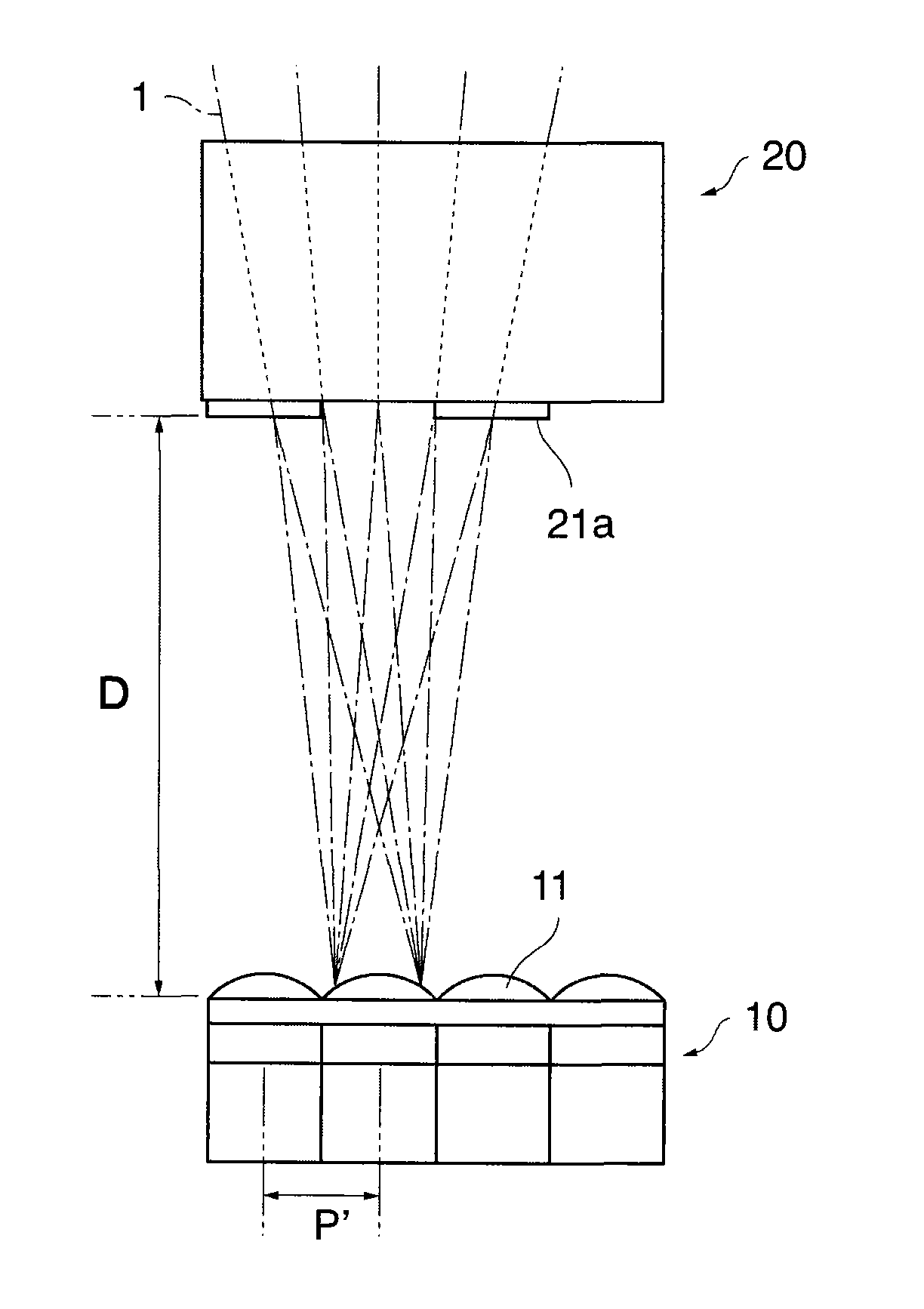
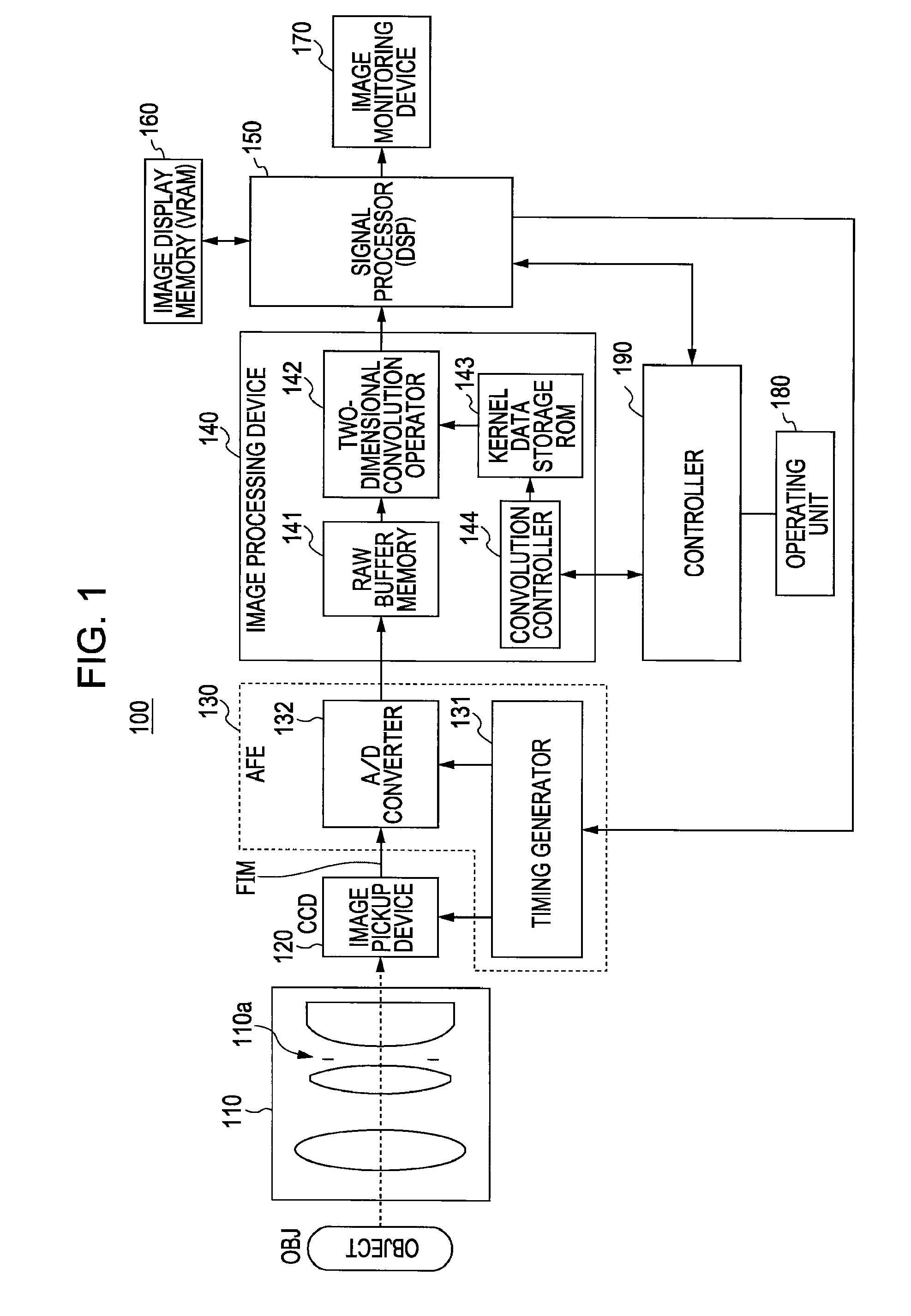
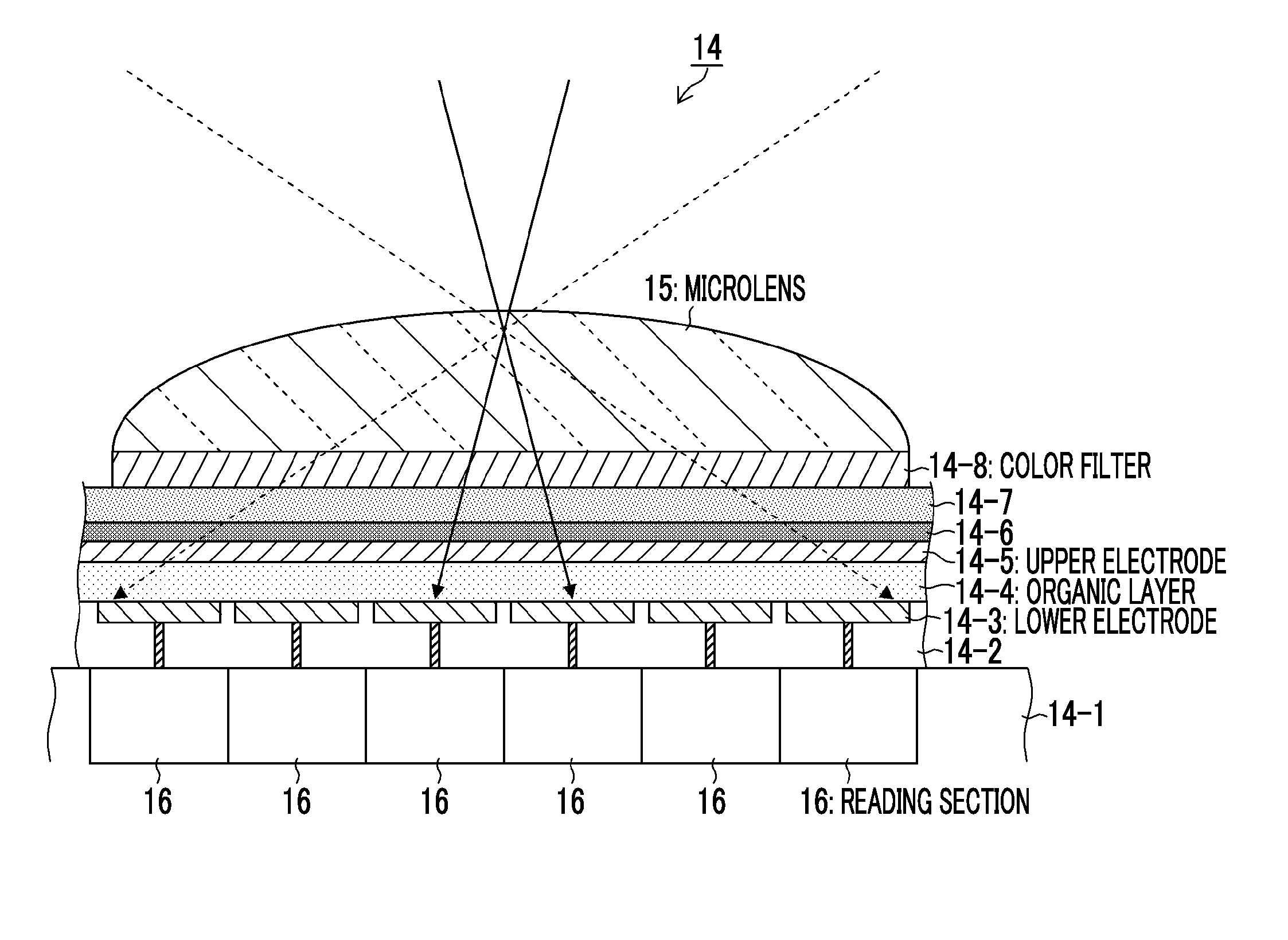
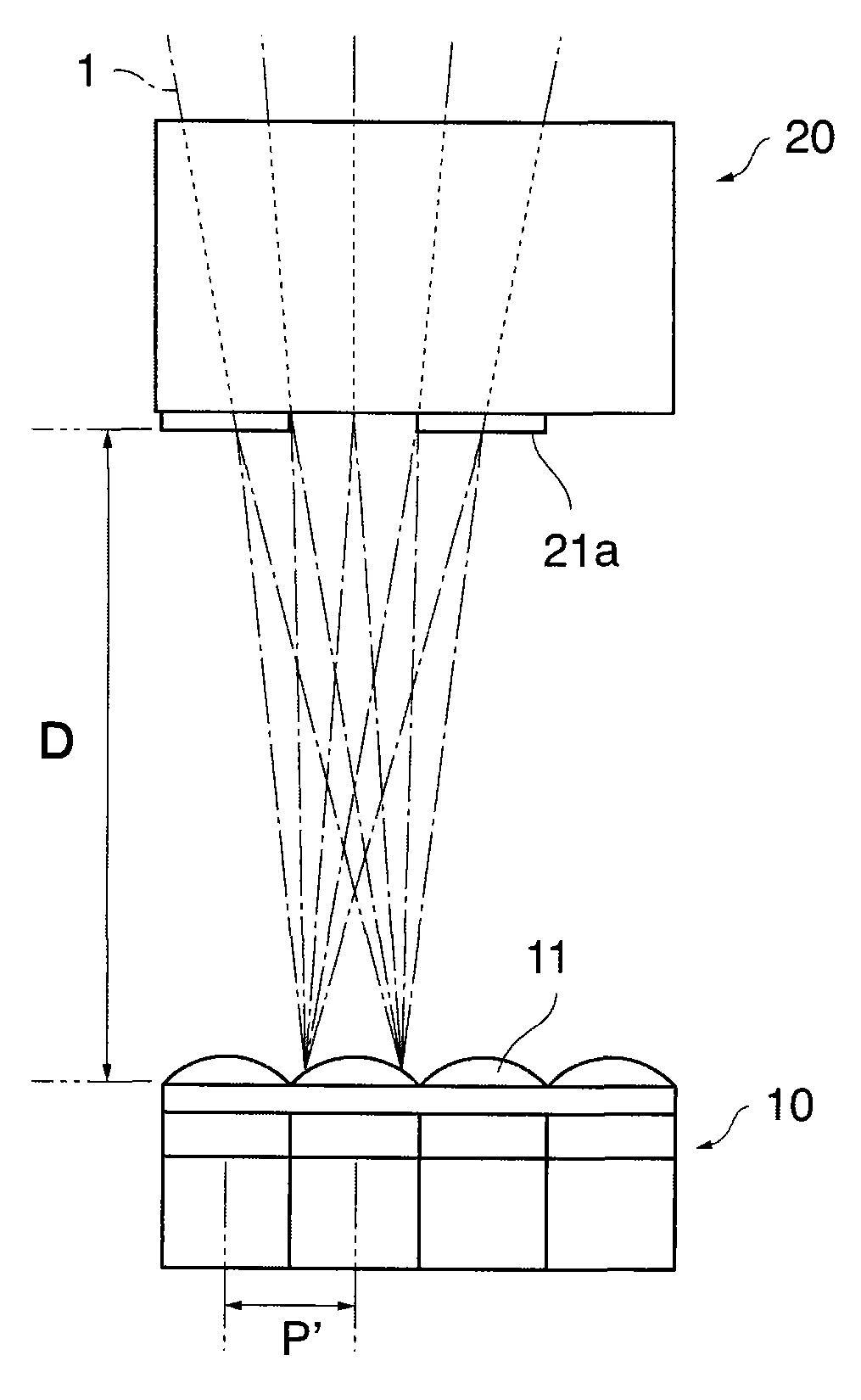
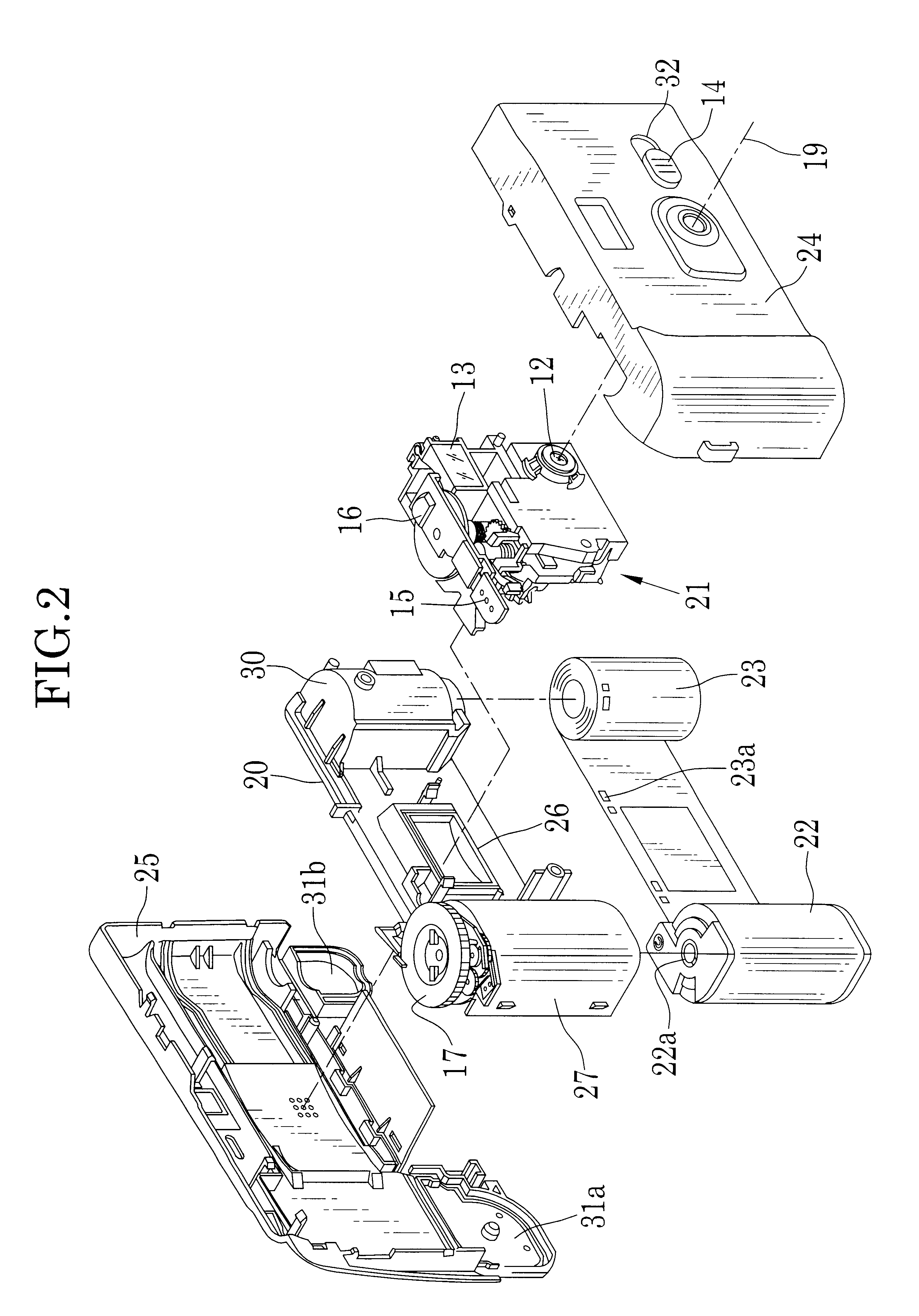
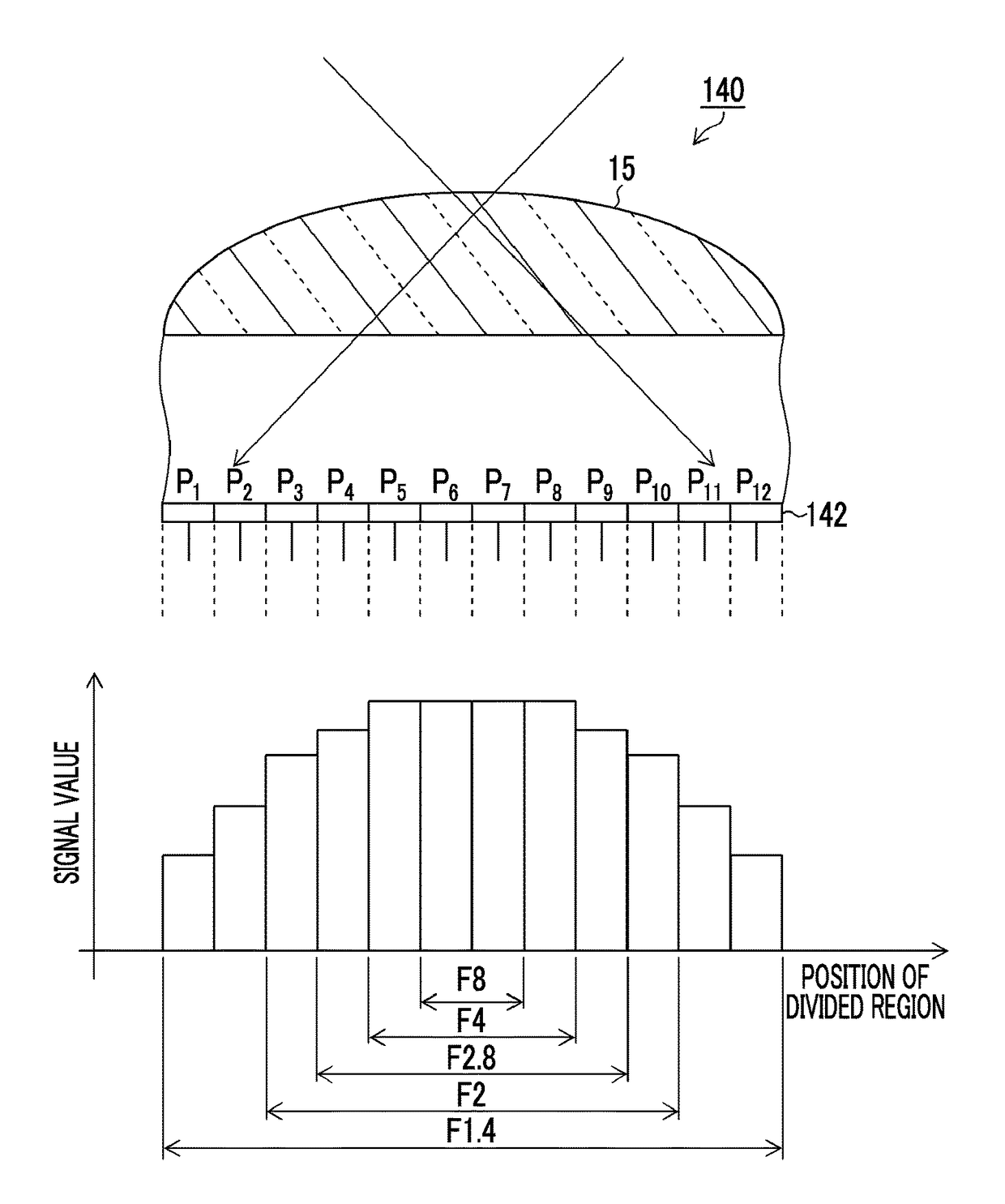
The imaging device of the present invention includes: an image sensor 14 that is configured such that a plurality of pixels having an organic layer (14-4) for photoelectric conversion is two-dimensionally arranged, and each pixel of the image sensor (14) is divided into a plurality of regions, and has an on-chip microlens (15), which forms a pupil image of a optical imaging system on the plurality of regions, and reading sections (16) which respectively read photoelectrically converted signals of the plurality of divided regions; an optical diaphragm that mechanically stops down rays which are incident into the image sensor 14; and an electronic diaphragm section that electronically controls an aperture value, and that selects signals of the divided regions corresponding to the aperture value from the signals of the plurality of divided regions, on the basis of the aperture value which is controlled by the optical diaphragm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image processing device, image processing method, and program
InactiveUS20130229532A1Improve accuracySuppress blurTelevision system detailsImaging processingImaging data
By a conventional technique, it is not possible to provide an image refocused accurately at a desired subject distance. An image processing device is characterized by including an image data acquiring unit configured to acquire calibration image data obtained by an image capturing device including an aperture to adjust an amount of incident light, a lens array in which a plurality of lenses is arranged, and an image sensing element to photoelectrically convert an image of a subject via the lens array and obtained in a state where the aperture is stopped down in accordance with an instruction of calibration; and a unit configured to acquire a position of an image on the image sensing element corresponding to each of the lenses based on the calibration image data.
Owner:CANON KK
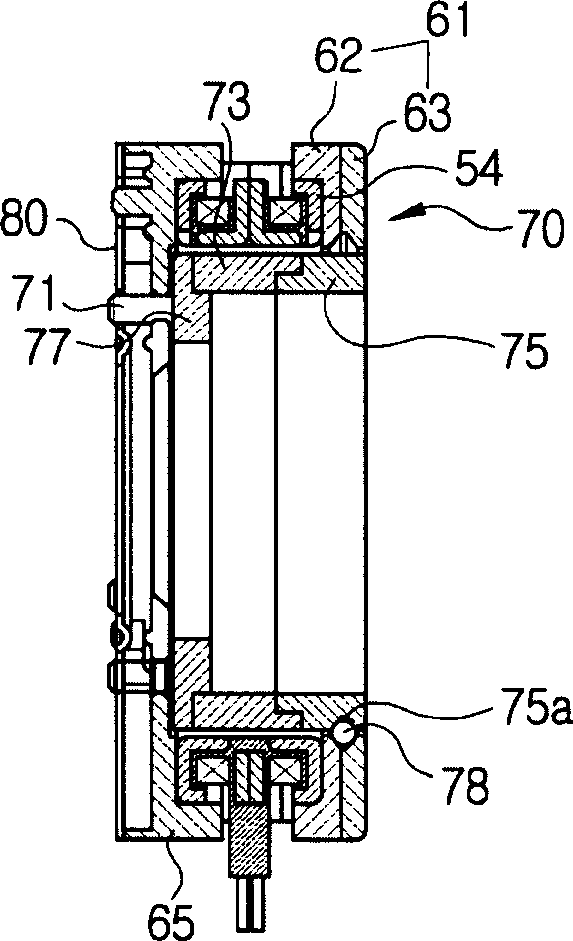
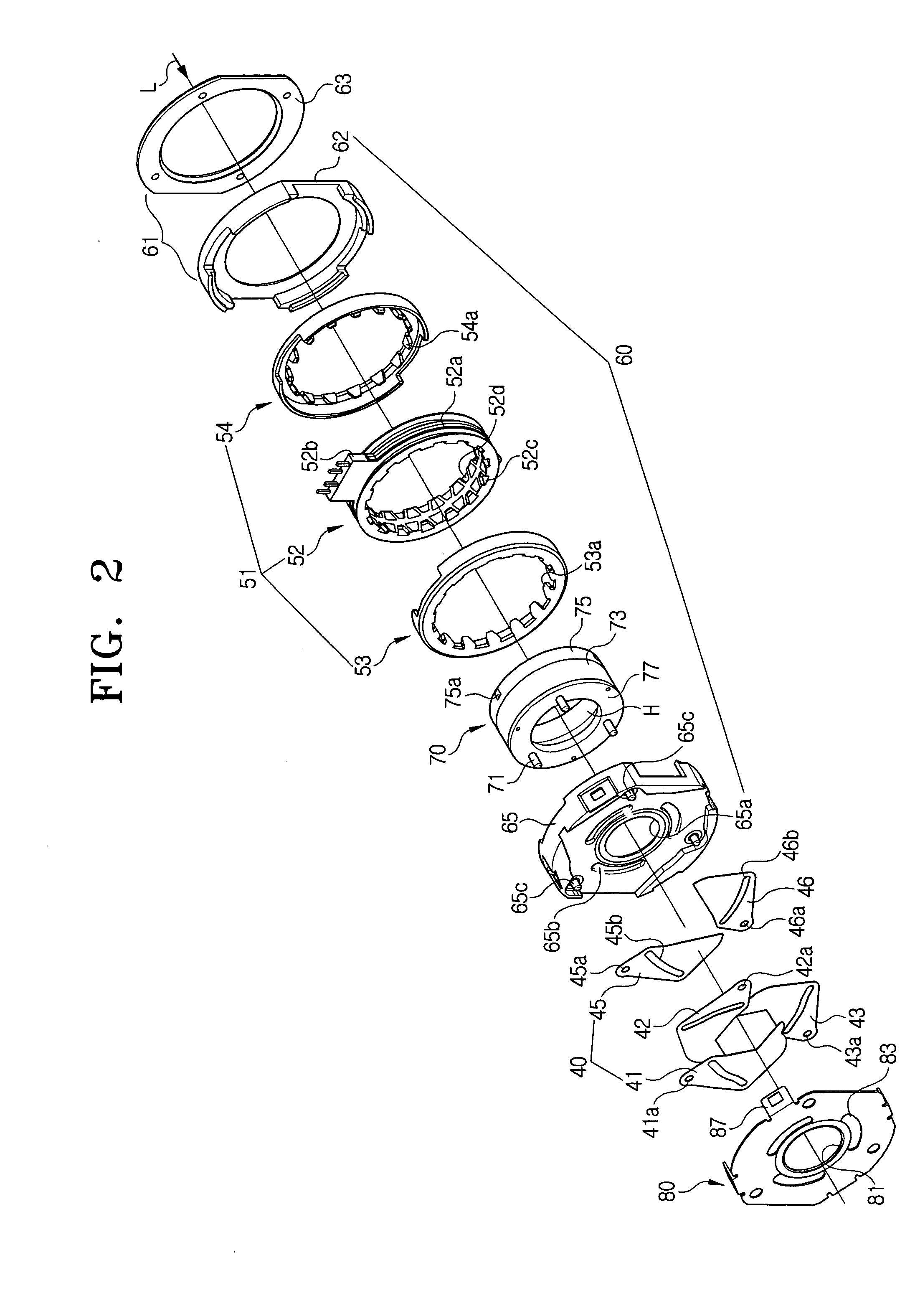
Iris diaphragm device, diaphragm driving device and camera unit including the same, and diaphragm control method
InactiveUS7559709B2Simple structureReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsStopping down
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
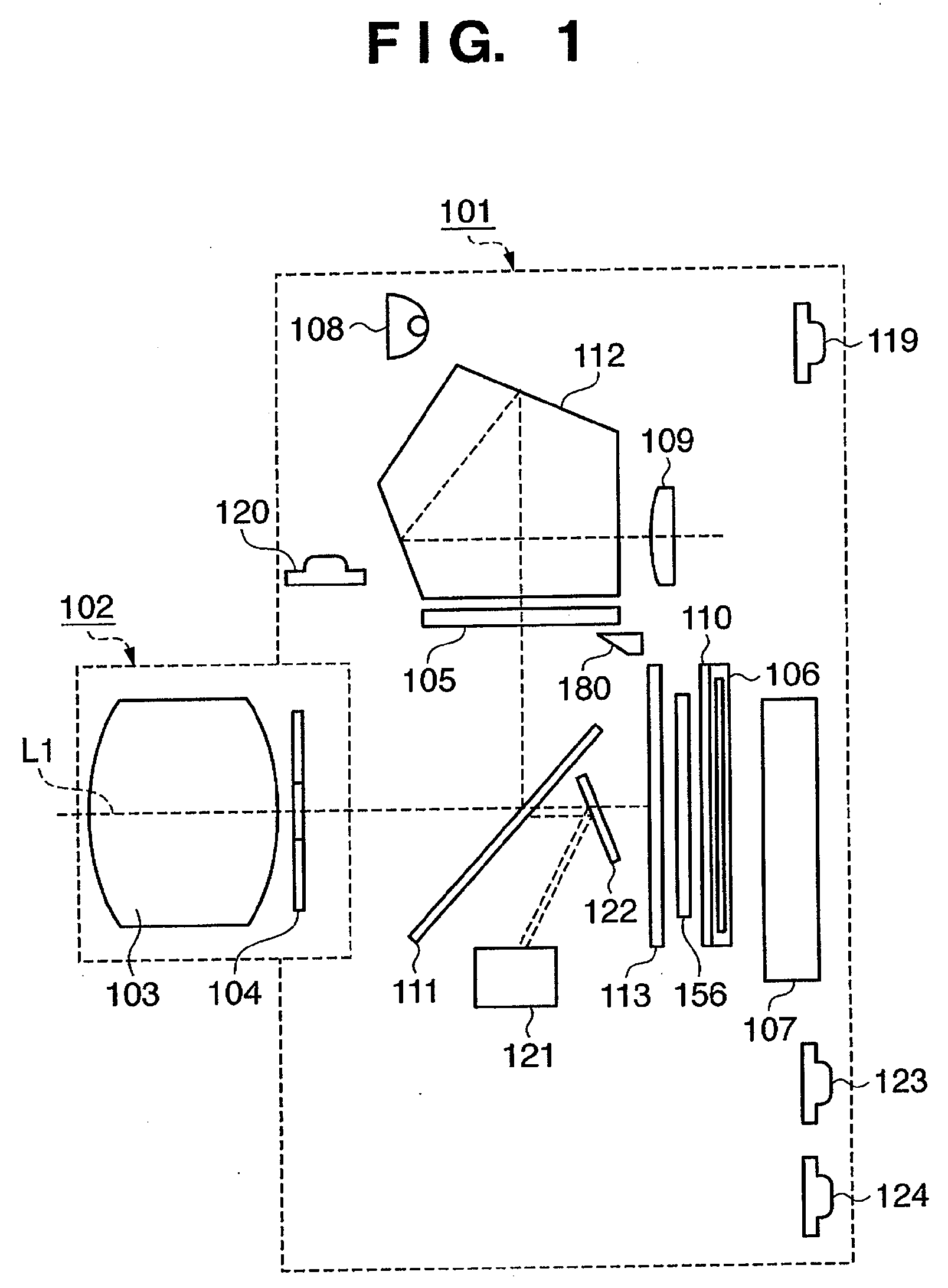
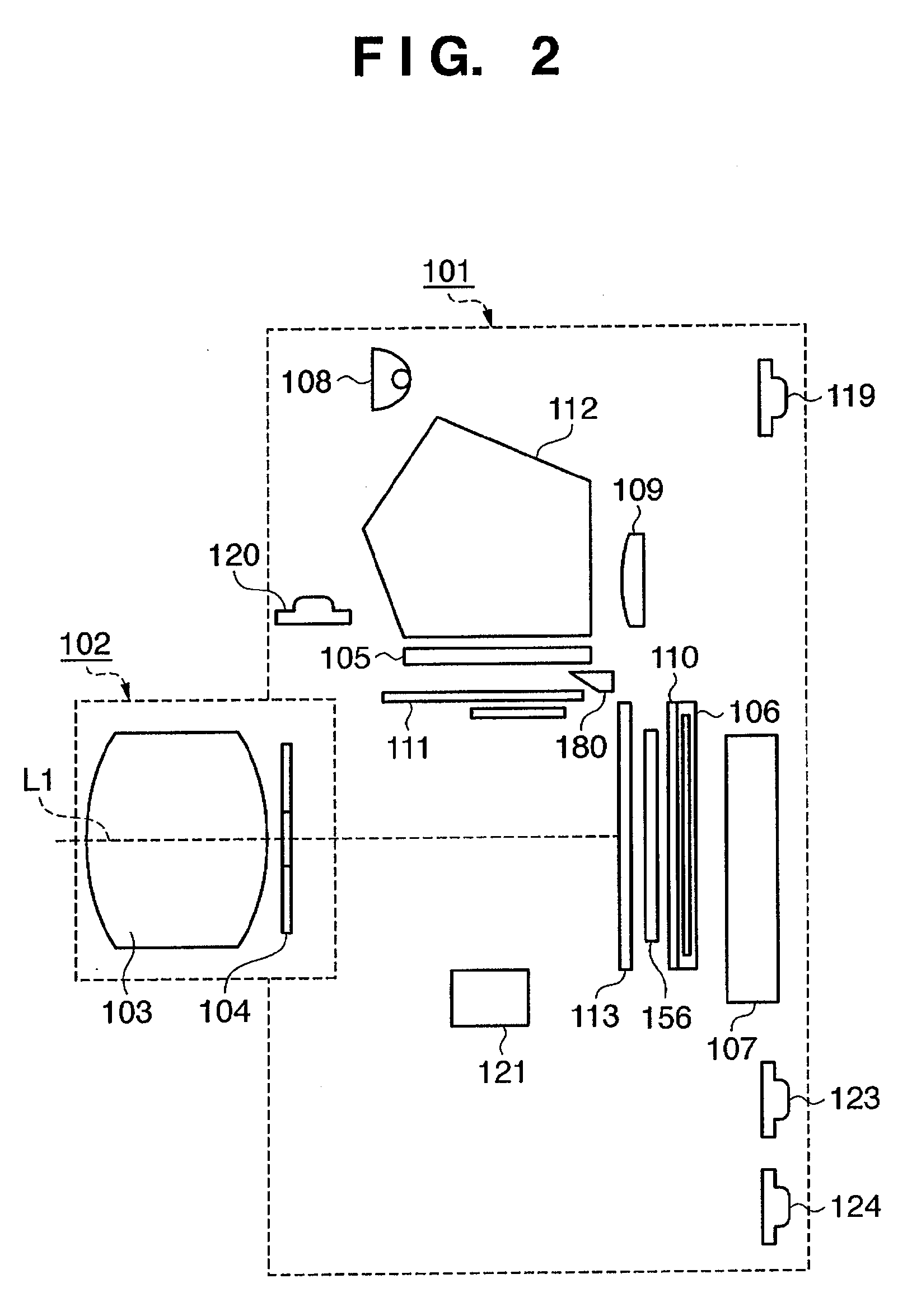
Image sensing apparatus and control method
InactiveUS20080292301A1Return quicklyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamElectric signal
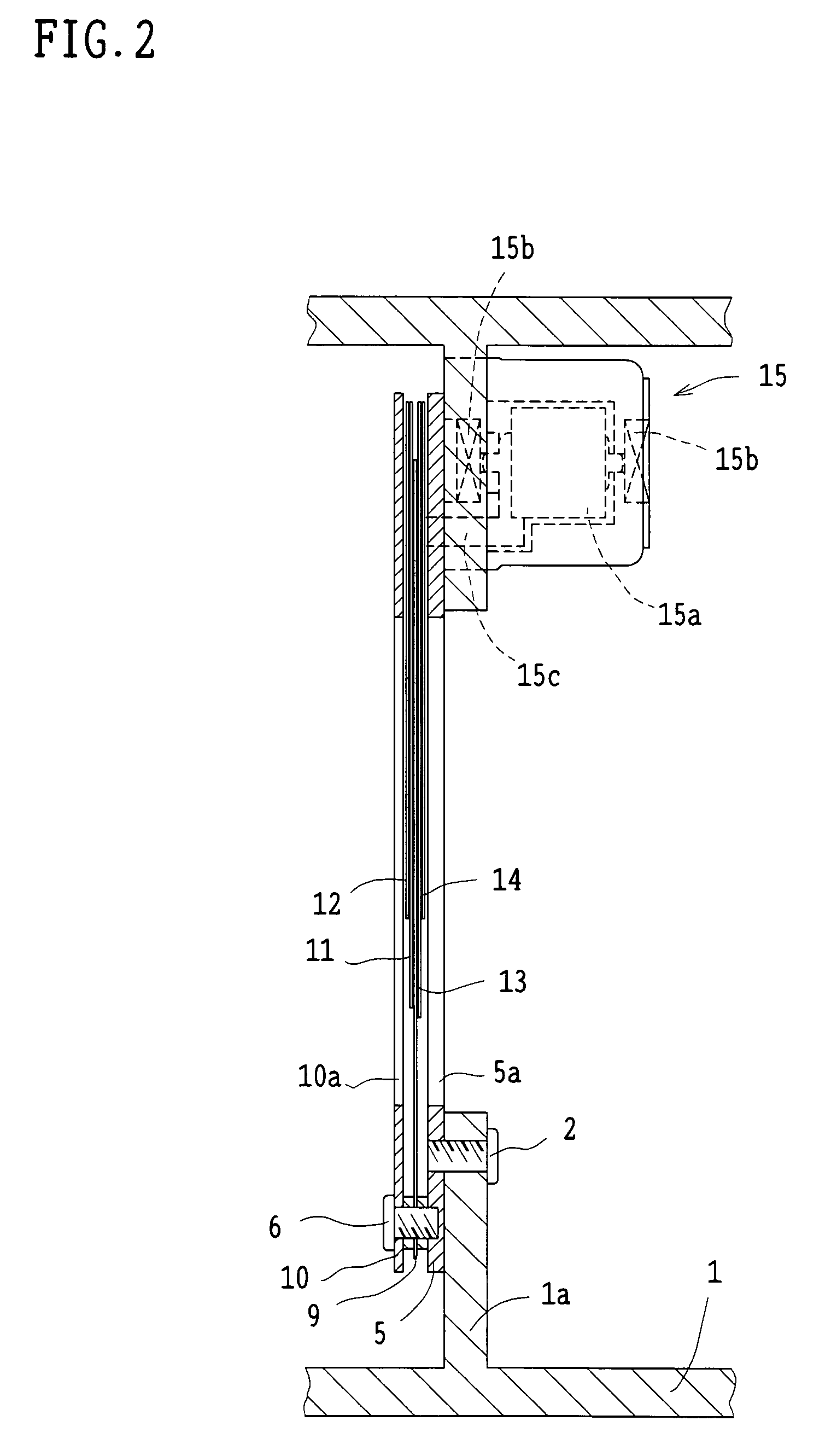
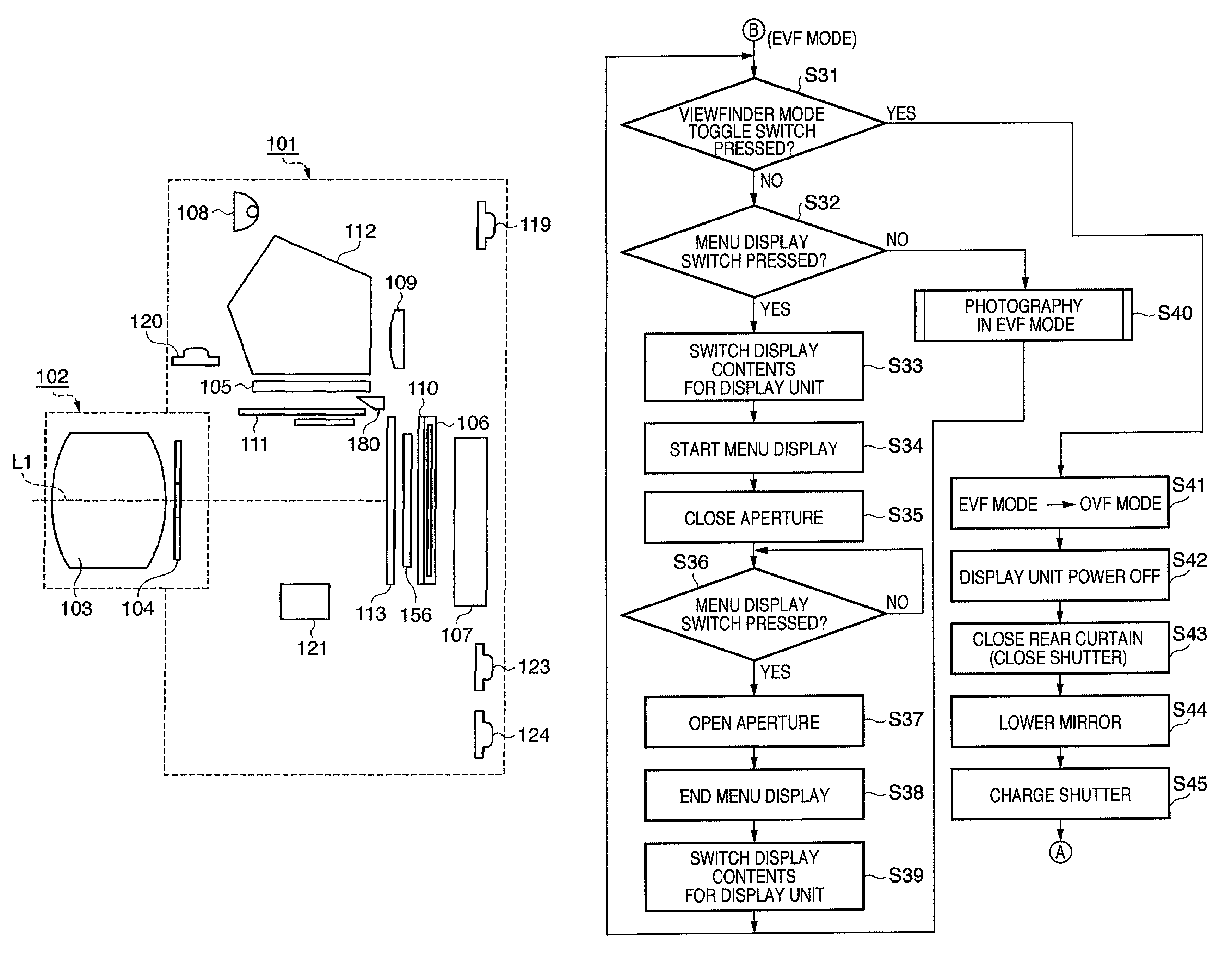
An image sensing apparatus is provided with an aperture unit (104), an image sensor (106) that converts light beams entering through a photographing lens (103) and the aperture unit into electrical signals, and a display unit (107), including an electronic viewfinder mode to continuously display on the display unit images based on the electrical signals obtained by the image sensor. The image sensing apparatus has a control unit (135) that causes the aperture unit to stop down, when there is an instruction to display on the display unit an image other than the image based on the electrical signals obtained by the image sensor while in the electronic viewfinder mode.
Owner:CANON KK
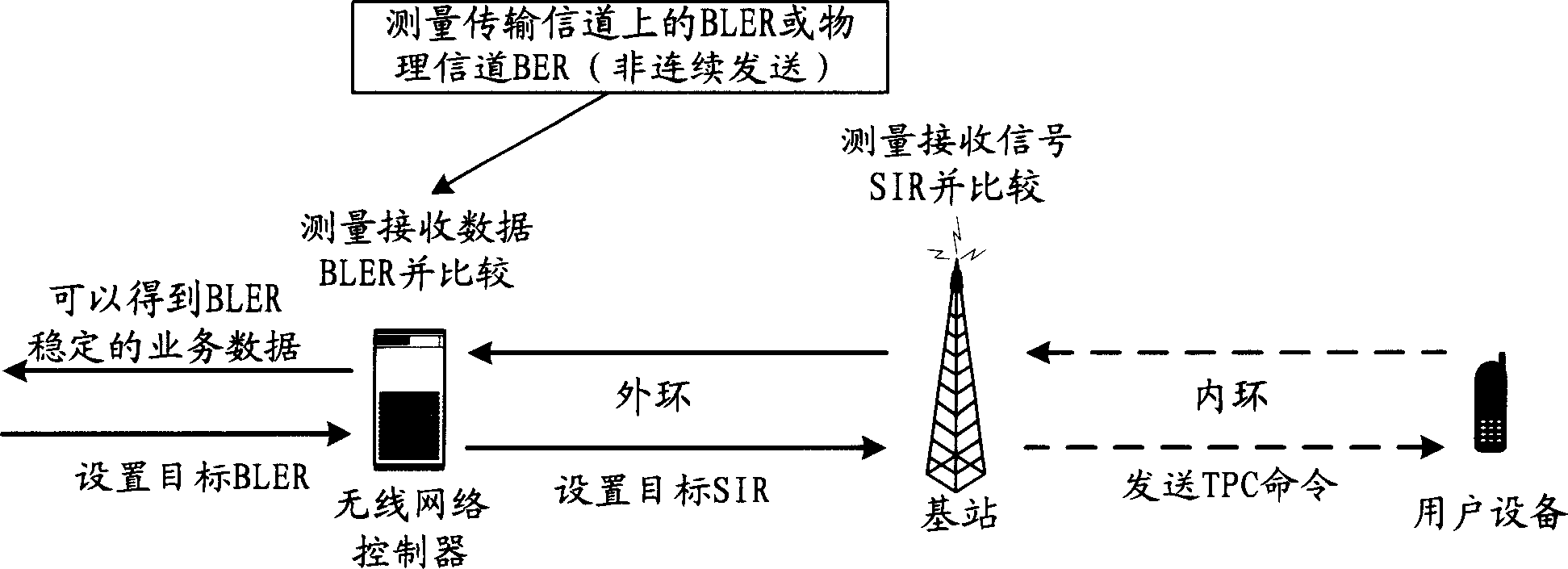
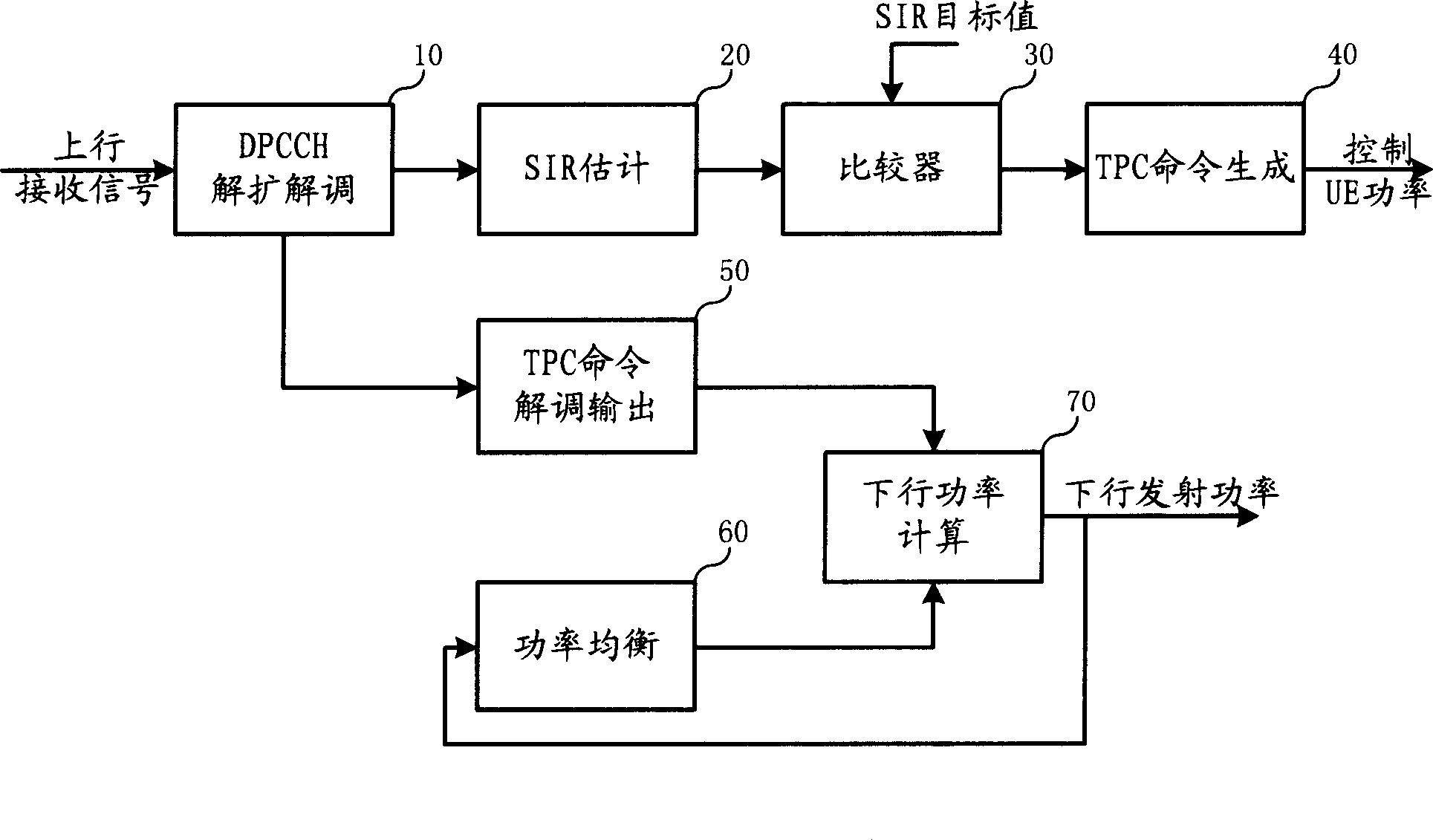
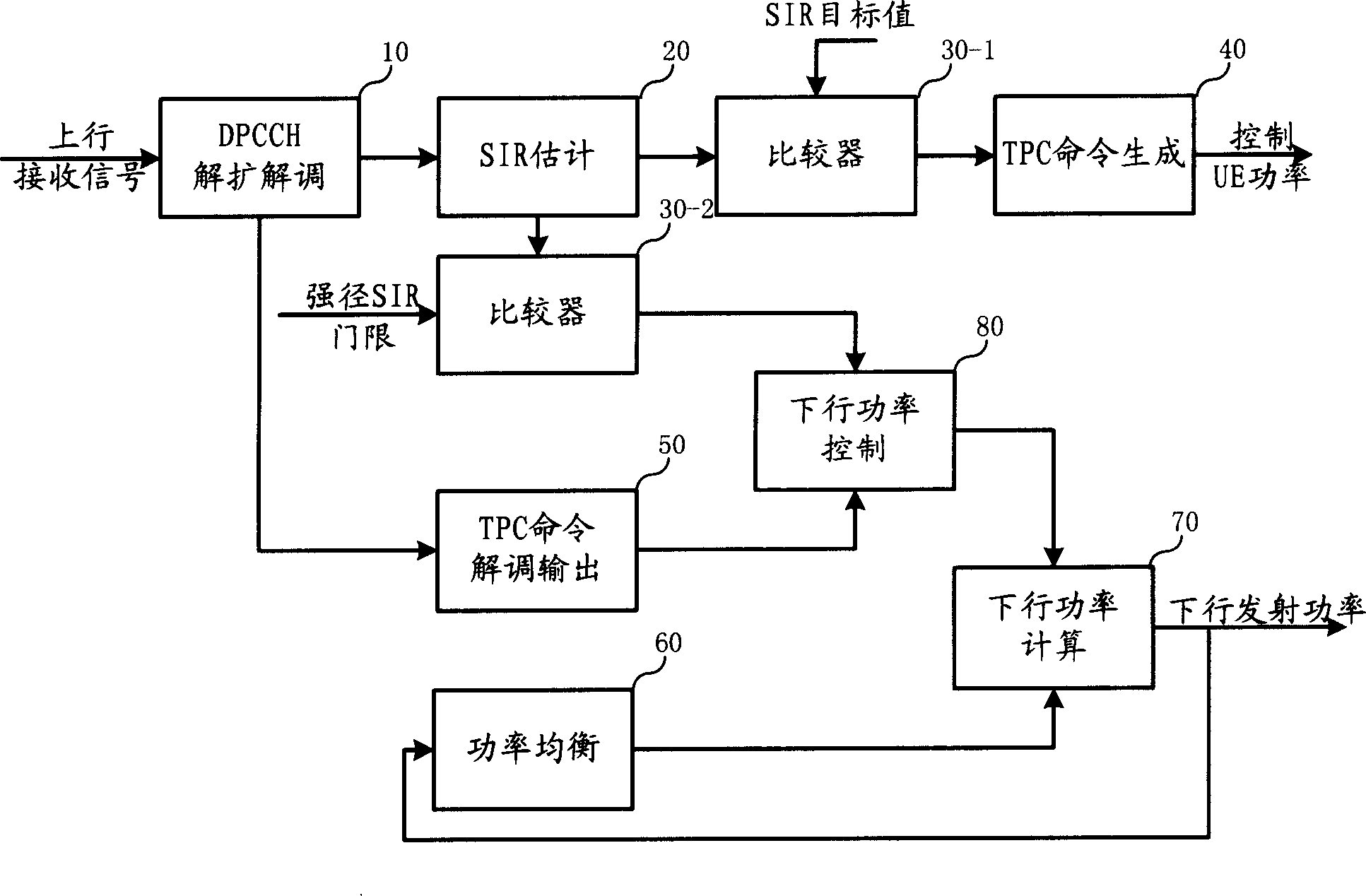
Soft handover downlink power control system and its method
InactiveCN1885732AMinor changesEasy to upgradeTransmission control/equalisingHigh level techniquesCoupling lossControl system
The related control system to soft switch down power can make a compromise for up and down link to avoid linkage couple and receiving SIR fluctuation, wherein for weak up signal, it stops down inner power control as up TPC, and changes into down inner power control as DPB algorithm. This invention also set the down minimal emission power as mean value minus an offset.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Iris diaphragm device, diaphragm driving device and camera unit including the same, and diaphragm control method
InactiveCN1690831ASimple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensStopping down
An iris diaphragm includes at least one lens shutter to adjust the size of an aperture that incident light passes through according to movement of the at least one lens shutter. At least one ND filter is installed to move independently of the lens shutter to reduce the amount of incident light by covering the aperture stopped-down by the lens shutter according to the movement of the at least one ND filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Iris diaphragm device, diaphragm driving device and camera unit including the same, and diaphragm control method
InactiveUS20050238348A1Simple structureReduce the amount requiredTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsStopping down
An iris diaphragm device has at least one lens shutter for adjusting the size of an aperture through which incident light passes. At least one ND filter is installed to move independently of the lens shutter, and reduces the amount of incident light by covering the aperture stopped down by the lens shutter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Projector
InactiveUS20070153237A1Reduce aberrationReduce the overall diameterProjectorsFluorescenceDisplay device
There is provided a projector having a point light source disposed to an edge of an optical fiber for transmitting exciting light and including a fluorescent illuminant for emitting fluorescence by being exited by the exiting light, a light collecting optical system for collecting the fluorescence emitted from the point light source, a reflective display device for reflecting the fluorescence collected by the light collecting optical system and overlapping the fluorescence with an image signal, an outgoing aperture for stopping down the fluorescence overlapped with the image signal by the reflective display device, wherein the outgoing aperture and the point light source are disposed side by side in the vicinity of the front focusing surface of the light collecting optical system. With this arrangement, a bright projected image can be obtained while disposing the outgoing aperture and the point light source sufficiently near to each other, reducing aberration, and reducing the diameter of a collecting lens so that the overall size of the projector can be reduced.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Sheet stopping structure
InactiveUS8096547B1Minimize the possibilityReduce layout spacingArticle separationEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:PRIMAX ELECTRONICS LTD
Aperture stop changing device for camera
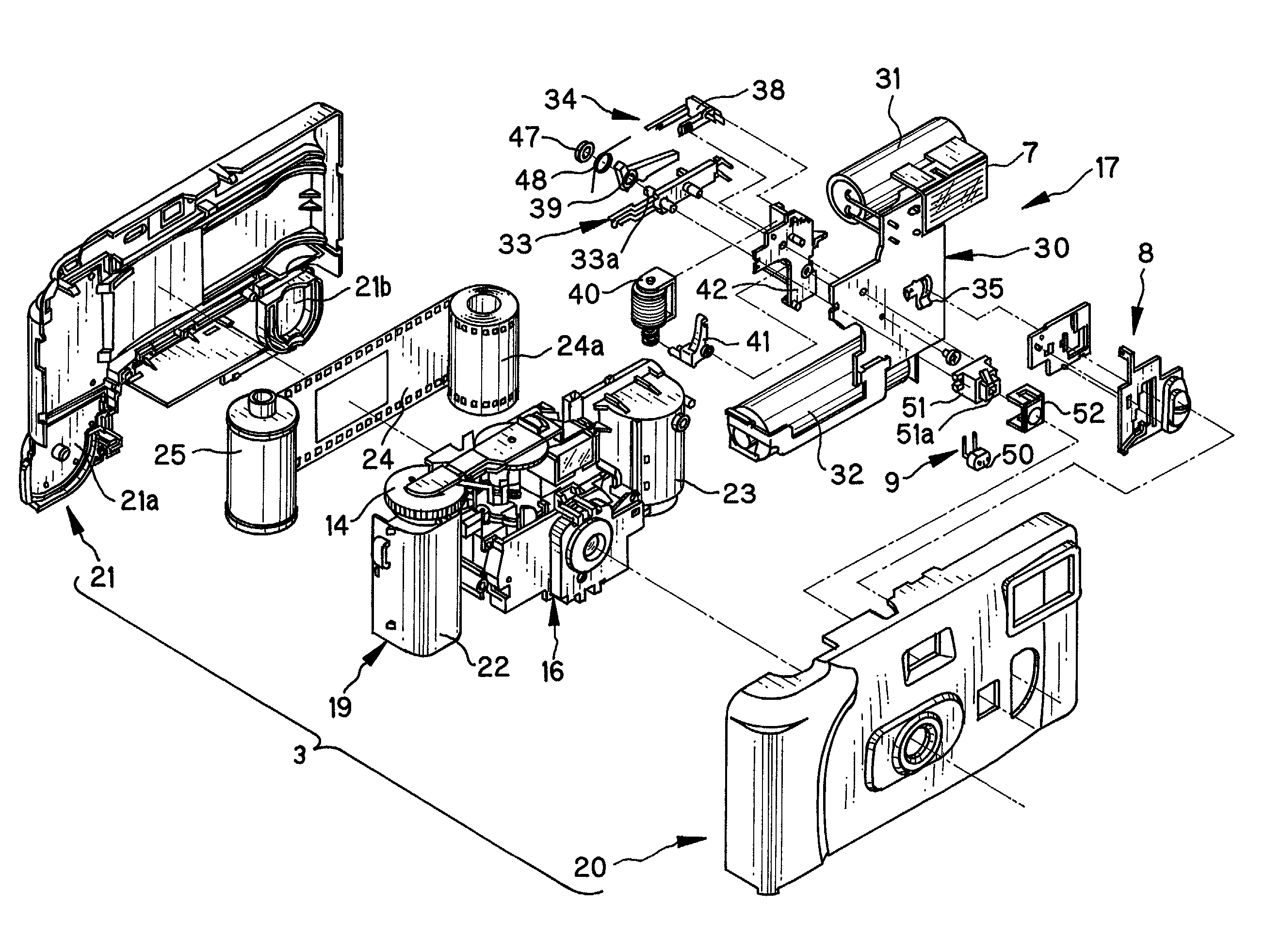
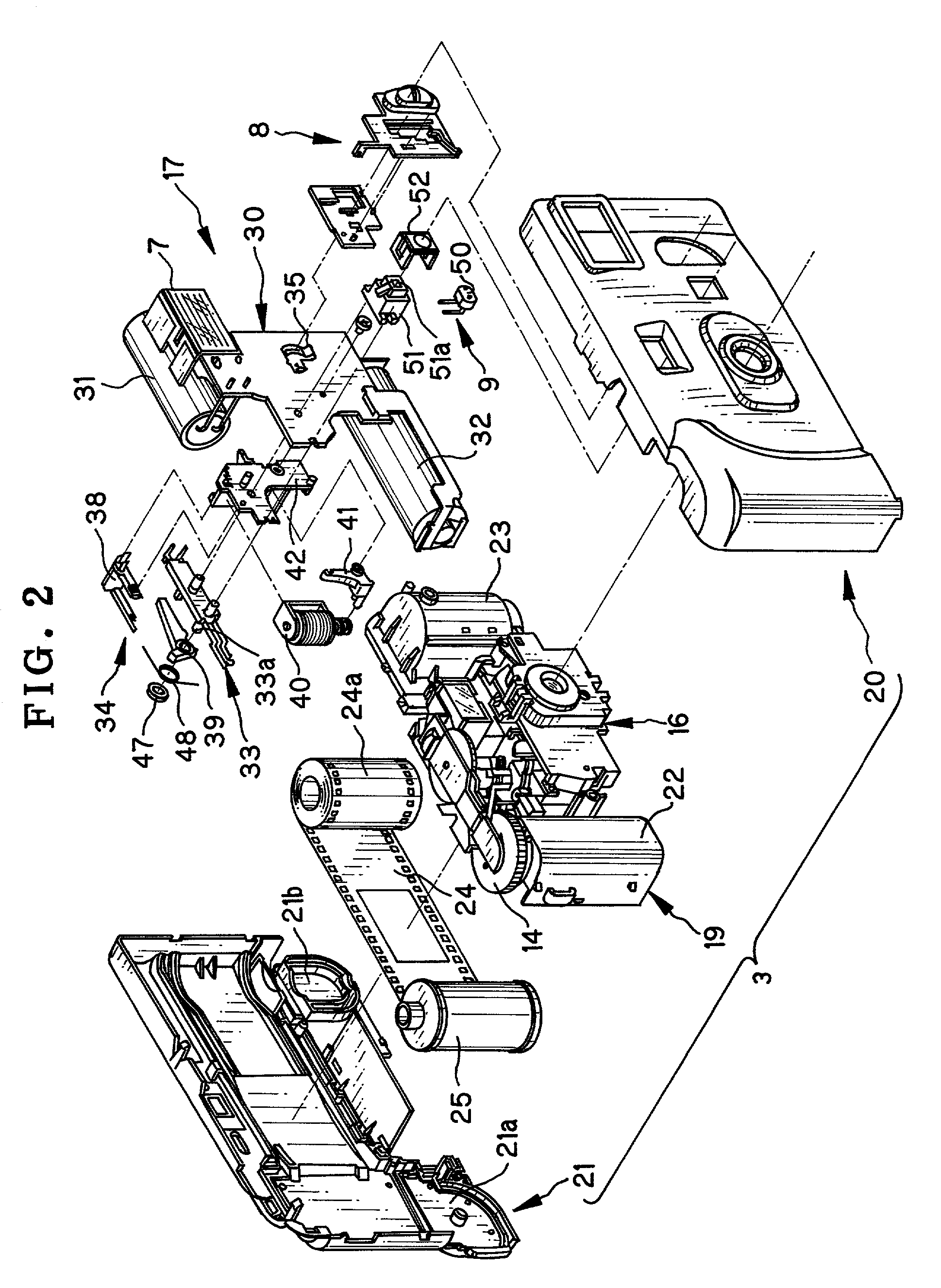
A camera includes a preset open aperture for introducing object light to photo film. A taking lens is disposed in a light path of the object light, and has two lens elements. In the camera, an aperture stop changing device is provided. An aperture changing plate includes a stop-down opening having a small diameter, is disposed close to the taking lens, is movable between a small diameter position and a large diameter position. The stop-down opening, when the aperture changing plate is in the small diameter position, is set in the light path for stopping down the preset open aperture, and when the aperture changing plate is in the large diameter position, is set away from the light path. A spacer is secured to a partial section of a peripheral portion of the taking lens, for defining a passage gap or cutout at a remaining partial section of the peripheral portion of the taking lens. The passage cutout allows passage of the aperture changing plate moving between the small and large diameter positions.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
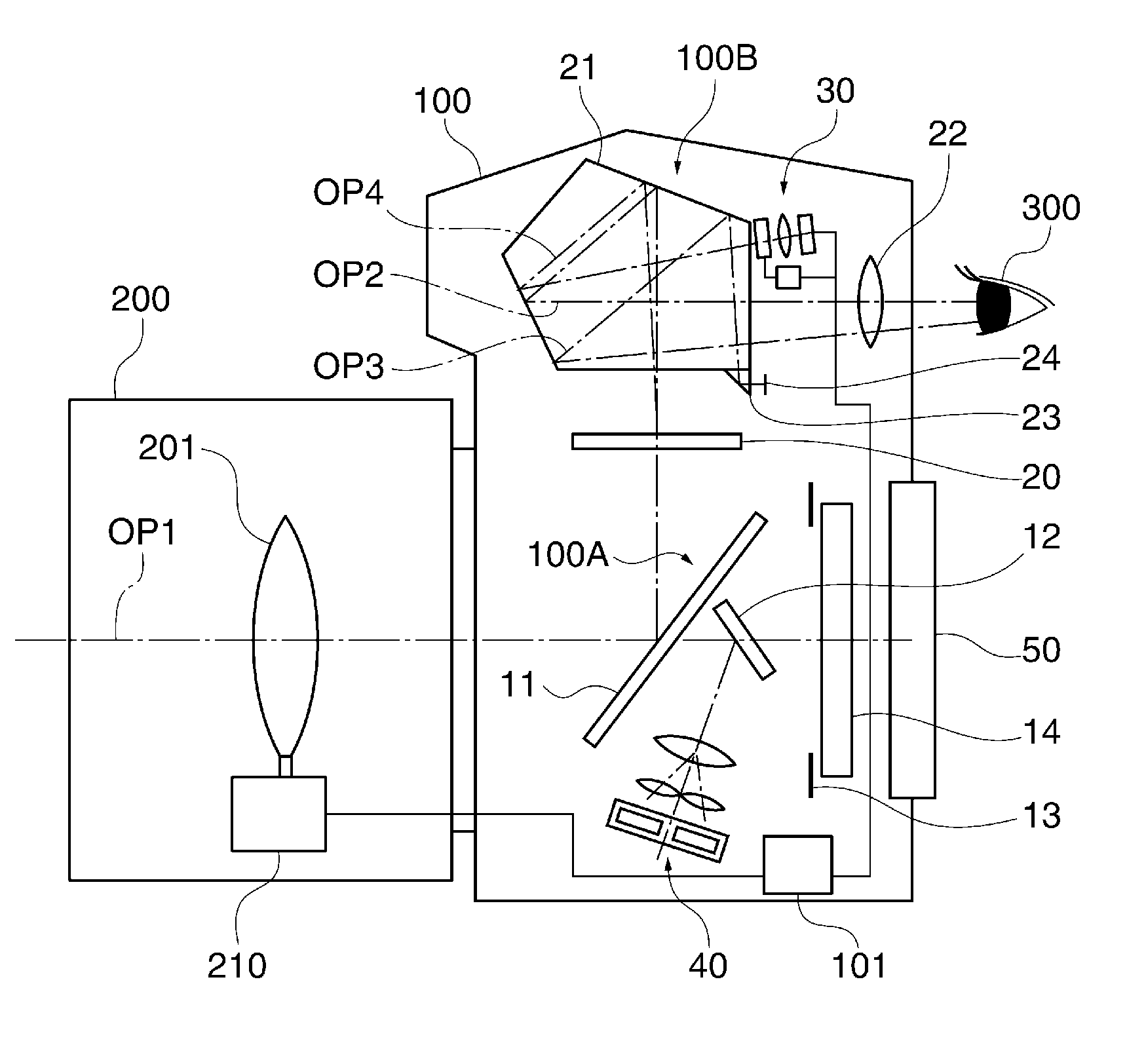
Zoom microscope including an image-acquisition optical path and an observation optical path
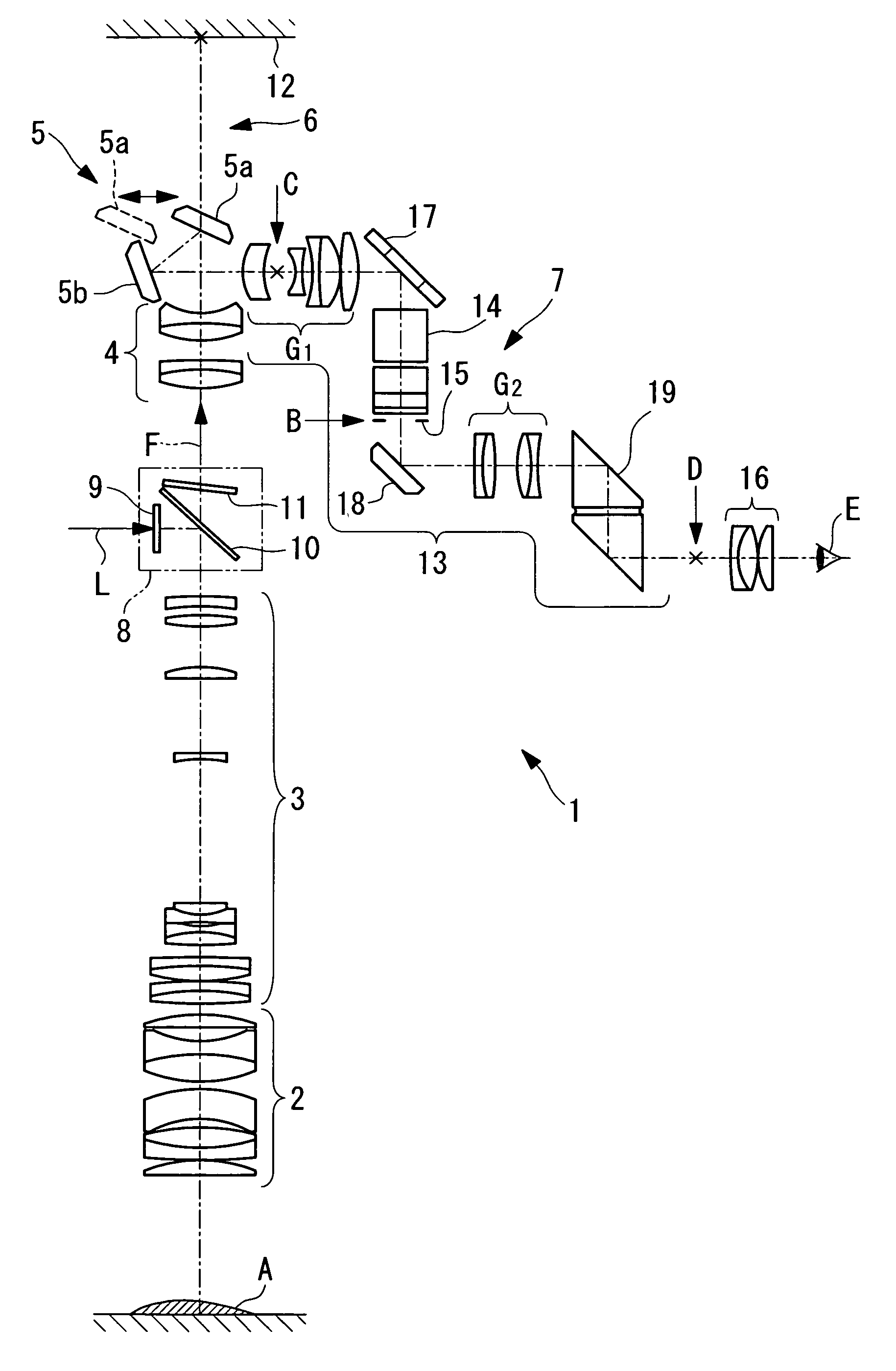
ActiveUS7821705B2Avoid image shiftStable observationMicroscopesTelescopesOptic systemNumerical aperture
The exposure time for obtaining a bright image in an image-acquisition optical system can be reduced, and shifting of an image visually observed in an observation optical system is prevented, thus enabling stable observation. A microscope including an image-acquisition optical path for recording an image focused by an objective lens and an observation optical path for visually observing an image split-off from the image-acquisition optical path; and including an aperture stop, in the observation optical path, for stopping down the numerical aperture thereof to smaller than the numerical aperture of the image-acquisition optical path.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Automatic exposure control device for a camera
InactiveUS6363222B2Prevents changing over sizeReduce stepsExposure controlCamera diaphragmsPotential differenceOptical axis
A photo diode and a resistor are connected to each other in series. A gate of a FET is connected to the connection of the photo diode and the resistor. When a photometry switch is turned on, the photo diode generates a photo current according to a subject brightness. A potential difference is generated between the both terminal of the resistor. When the subject brightness is less than a threshold level, the FET is not turned on because of low potential difference of the resistor. When a subject brightness is equal to or more than the threshold level, the FET is turned on because of high potential difference of the resistor. A first transistor turned to be in a state opposite to the FET and a second transistor turned on and off according the state of the first transistor are provided. When the FET is turned off, the second transistor is turned on, and a solenoid is powered. The solenoid moves a stop plate out of an optical axis such that an exposure is taken through a large stop opening. When the FET is turned on, the second transistor is turned off, so the solenoid is not driven. Since the stop plate is set on the optical axis, an exposure is taken through a stop-down opening.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Camera system
A camera system includes a camera body including a photometering device and an external operating device, and a photographing lens which is detachably attached to the camera body, the photographing lens including an aperture setting device for selecting an auto aperture setting and at least one fixed aperture setting. A full-aperture photometering operation is performed when the aperture setting device is positioned at the auto aperture setting, and a stop-down photometering operation is performed in response to an operation of the external operating device when the aperture setting device is positioned at the fixed aperture setting.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20140293064A1Performing object recognition with accuracyHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight fluxObject detection
An image pickup apparatus capable of performing object recognition with accuracy even when an object image formed on a focusing screen becomes out of focus on a photometric sensor. A light flux of the object image formed on the focusing screen is captured by the photometric sensor through a variable photometric aperture, and object recognition is performed by an object recognition unit based on image information contained in photometric information output from the photometric sensor. If determined that the object recognition cannot be achieved based on an object recognition operation of the object recognition unit performed according to the image information, the variable photometric aperture is stopped down under the control of a photometric control unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Diaphragm device for light source light adjustment
A diaphragm device has a first base plate and a second base plate that are installed with a predetermined interval therebetween and formed into a unit. The diaphragm device is installed to a mounting portion of a lens frame such that the second base plate is disposed adjacently to a light source. The two base plates are partitioned with an intermediate plate to form two accommodating chambers, a stopping-down blade and a covering blade being disposed in each accommodating chamber. A motor is attached to the first base plate to relatively rotate a set of plate members and another set of plate members so as to restrict optical path apertures by the stopping-down blades. Portions directly exposed to light source light are provided with gray or white heat-resistant painting.
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
Image pickup element unit with an image pickup element on a substrate for picking up an image and an optical low pass filter spaced from the image pickup element
InactiveUS8199231B2Suppress generationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsRegular patternPhase grating
An image pickup apparatus which is capable of suppressing generation of shadows even when the aperture of the photographic lens is stopped down. A digital camera as an image pickup apparatus includes a photographic lens, a image pickup element that picks up an image of an object, and an optical low-pass filter disposed between the photographic lens and the image pickup element. The filter includes a liner phase diffraction grating having unit cells which are disposed in a regular pattern at a grating pitch P and are formed by equal-width recesses and equal-width protrusions adjacent to each other. When a shortest wavelength of a reference wavelength employed is λS, and a longest wavelength of the reference wavelength is λL, an optical path difference ΔH between lengths of optical paths of light of which a phase is varied by the phase grating is larger than λS / 2 and smaller than λL / 2.
Owner:CANON KK
Image sensing apparatus and control method
InactiveUS7729609B2Return quicklyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensLight beam
An image sensing apparatus is provided with an aperture unit (104), an image sensor (106) that converts light beams entering through a photographing lens (103) and the aperture unit into electrical signals, and a display unit (107), including an electronic viewfinder mode to continuously display on the display unit images based on the electrical signals obtained by the image sensor. The image sensing apparatus has a control unit (135) that causes the aperture unit to stop down, when there is an instruction to display on the display unit an image other than the image based on the electrical signals obtained by the image sensor while in the electronic viewfinder mode.
Owner:CANON KK
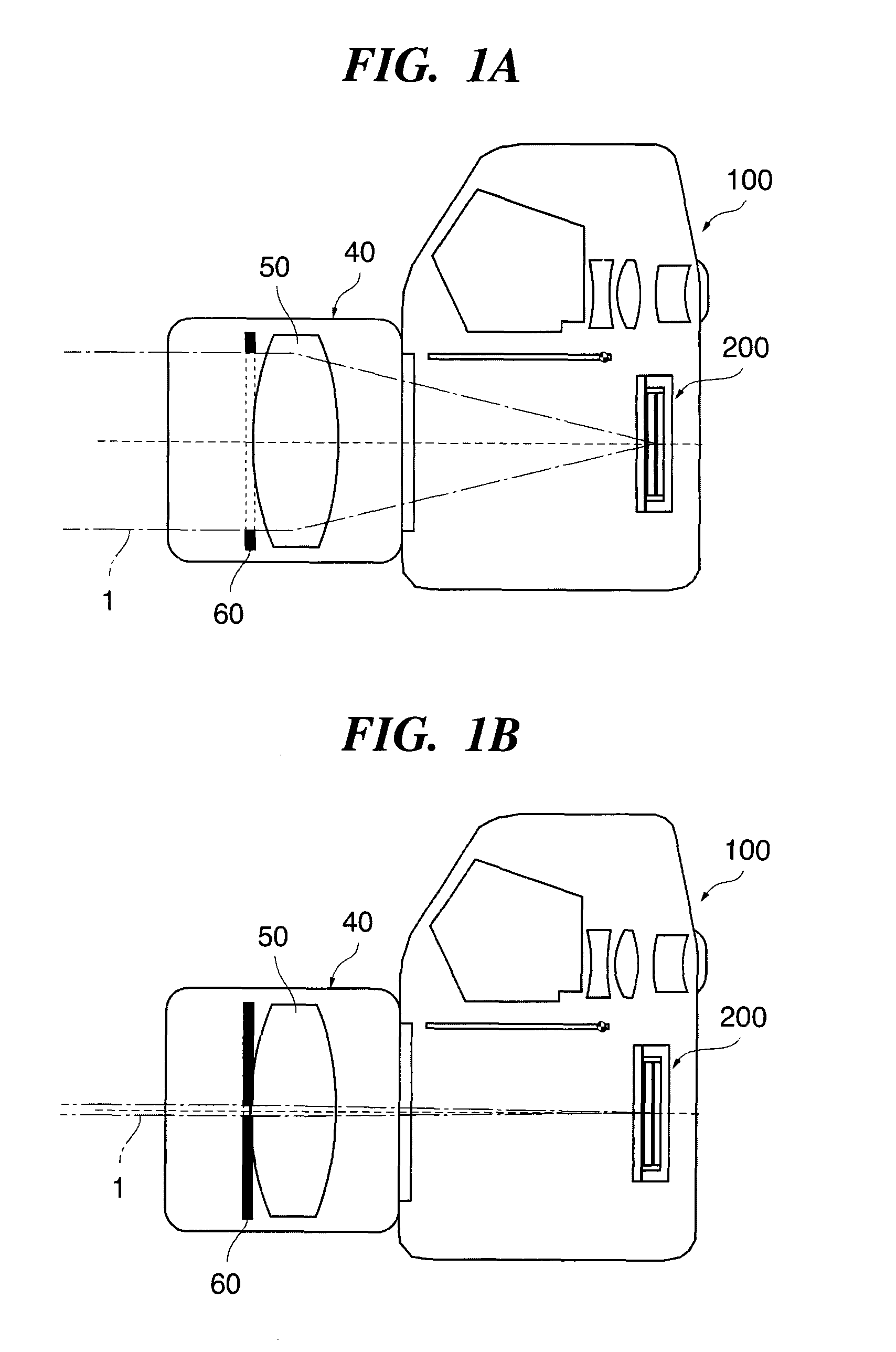
Lens-fitted photo film unit capable of changing over aperture stop
A first lens element and a second lens element for comprising a photographic lens, and a stop opening are arranged on an optical axis in this order. A stop plate has a stop-down opening. The stop plate is movable between a first position where the stop-down opening is inserted on an optical axis between the first and the second lens elements for making an f-number of the photographic lens f1, and a second position where the stop-down opening is retracted from the optical axis for making the f-number f2. The photographic lens is constructed to satisfy the following conditions:wherein L(%) represents a proportion of brightness in a marginal portion of a frame to brightness in a central portion of the frame at the time when the stop-down opening is inserted, and E(EV) represents the difference between the maximum exposure amount and the minimum exposure amount in the marginal portion of the frame.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Imaging device and imaging method
The imaging device of the present invention includes: an image sensor 14 that is configured such that a plurality of pixels having an organic layer (14-4) for photoelectric conversion is two-dimensionally arranged, and each pixel of the image sensor (14) is divided into a plurality of regions, and has an on-chip microlens (15), which forms a pupil image of a optical imaging system on the plurality of regions, and reading sections (16) which respectively read photoelectrically converted signals of the plurality of divided regions; an optical diaphragm that mechanically stops down rays which are incident into the image sensor 14; and an electronic diaphragm section that electronically controls an aperture value, and that selects signals of the divided regions corresponding to the aperture value from the signals of the plurality of divided regions, on the basis of the aperture value which is controlled by the optical diaphragm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Projector
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Imaging device and imaging device control method
ActiveUS8648926B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImaging processingLight flux
An imaging device of the present invention comprises an imaging section for photoelectrically converting a subject image, and outputting image data, an aperture control section for narrowing subject light flux at a first aperture value and a second aperture value, a shooting control section for, in response to a release instruction, imaging a first image at the first aperture value and, reading out first image data from the imaging section while simultaneously carrying out a stopping down operation to the second aperture value, imaging a second image at the second aperture value and, reading out second image data from the imaging section, and an image processing section for detecting an amount of variation in contrast value for each location in the first image data and the second image data, and carrying out processing to blur at an intensity of blurring according to the amount of variation between each location.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
Automatic exposure control device for a camera
InactiveUS20010002949A1Prevents changing over sizeReduce stepsExposure controlCamera diaphragmsOptical axisPotential difference
A photo diode and a resistor are connected to each other in series. A gate of a FET is connected to the connection of the photo diode and the resistor. When a photometry switch is turned on, the photo diode generates a photo current according to a subject brightness. A potential difference is generated between the both terminal of the resistor. When the subject brightness is less than a threshold level, the FET is not turned on because of low potential difference of the resistor. When a subject brightness is equal to or more than the threshold level, the FET is turned on because of high potential difference of the resistor. A first transistor turned to be in a state opposite to the FET and a second transistor turned on and off according the state of the first transistor are provided. When the FET is turned off, the second transistor is turned on, and a solenoid is powered. The solenoid moves a stop plate out of an optical axis such that an exposure is taken through a large stop opening. When the FET is turned on, the second transistor is turned off, so the solenoid is not driven. Since the stop plate is set on the optical axis, an exposure is taken through a stop-down opening.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com