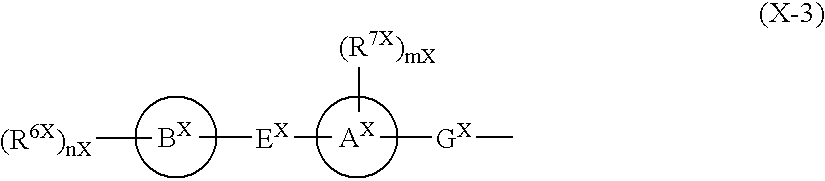Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Solid organ" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solid organ. An internal organ that has a firm tissue consistency and is neither hollow (such as the organs of the gastrointestinal tract) nor liquid (such as blood). Such organs include the heart, kidney, liver, lungs, and pancreas.
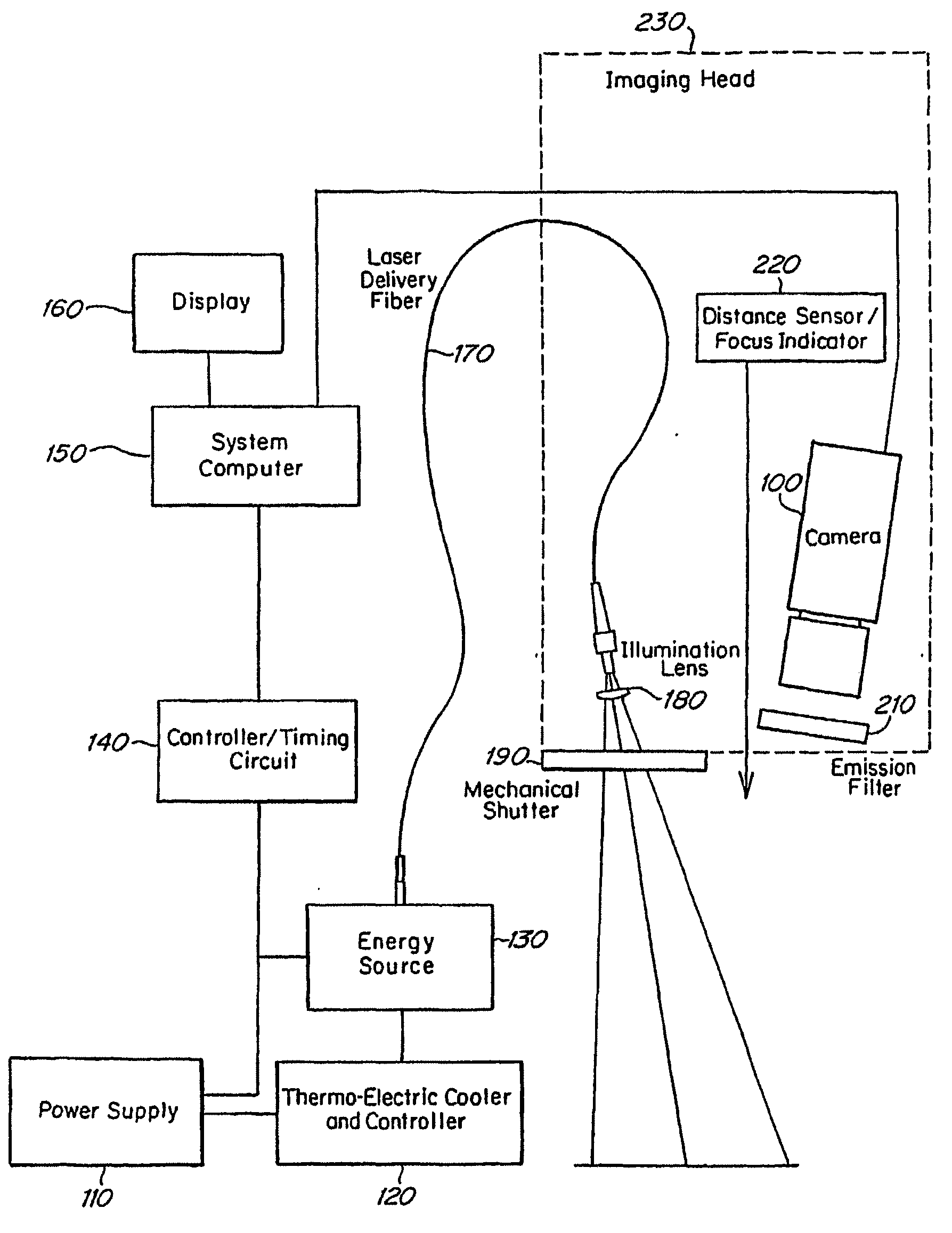
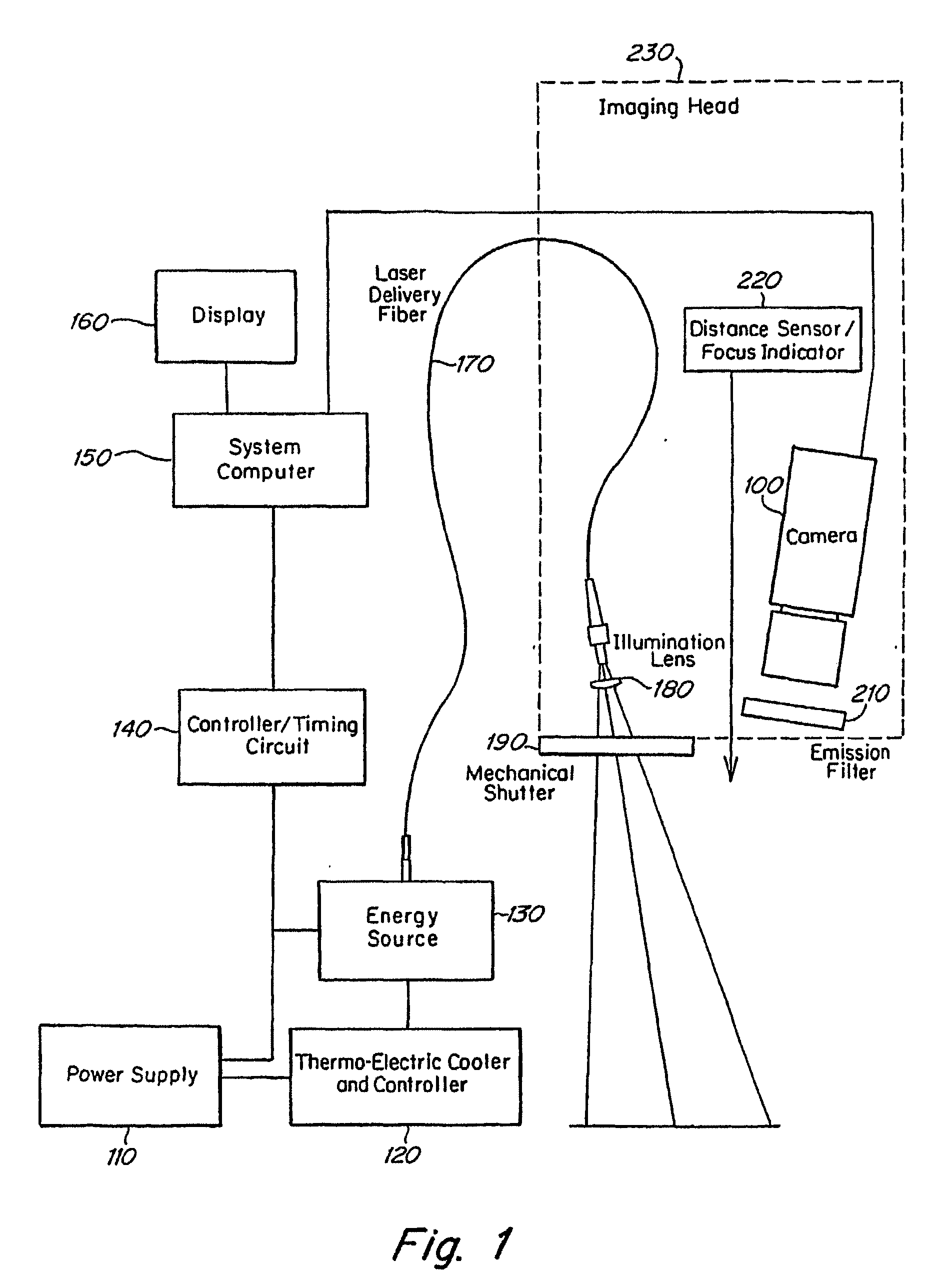
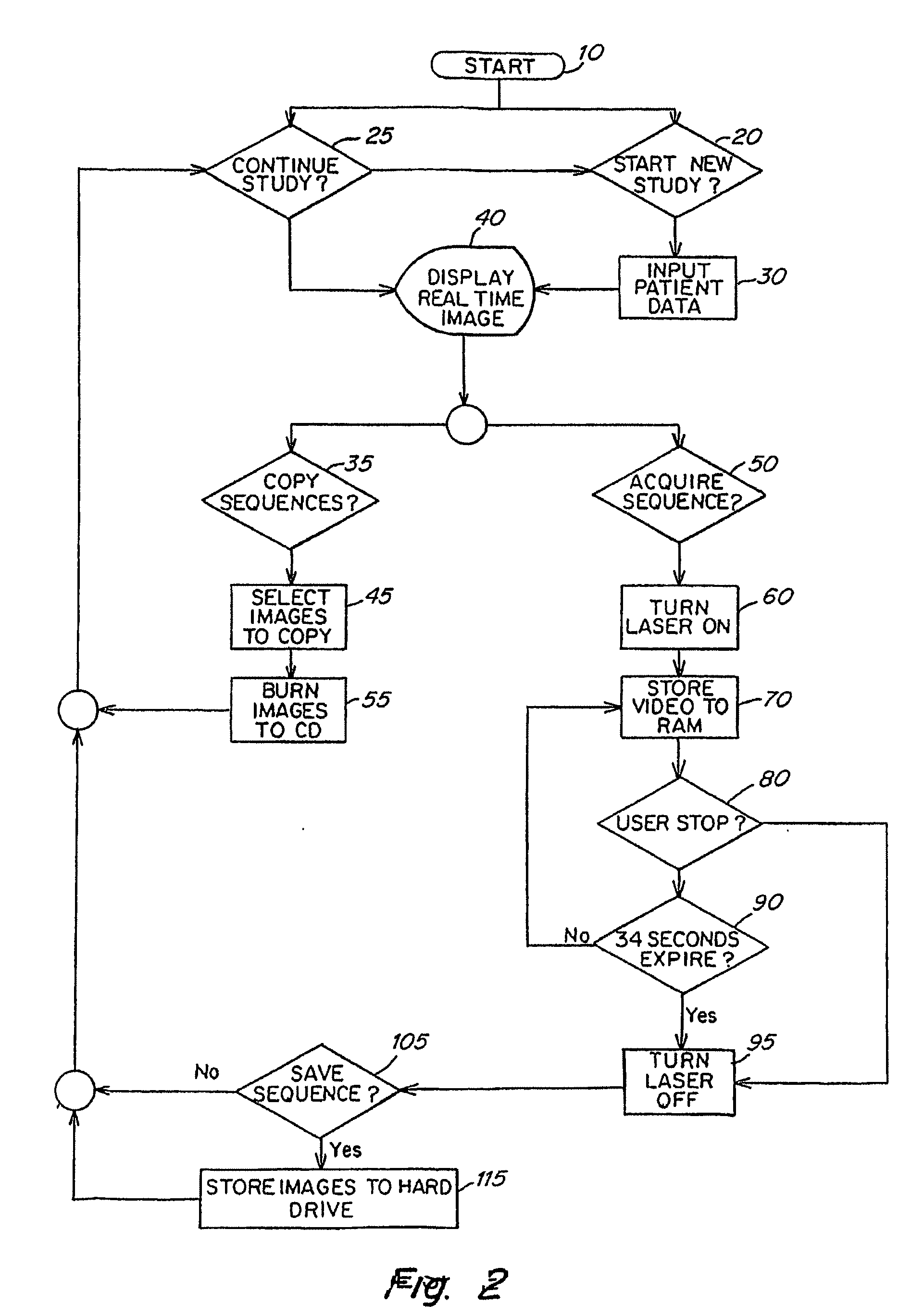
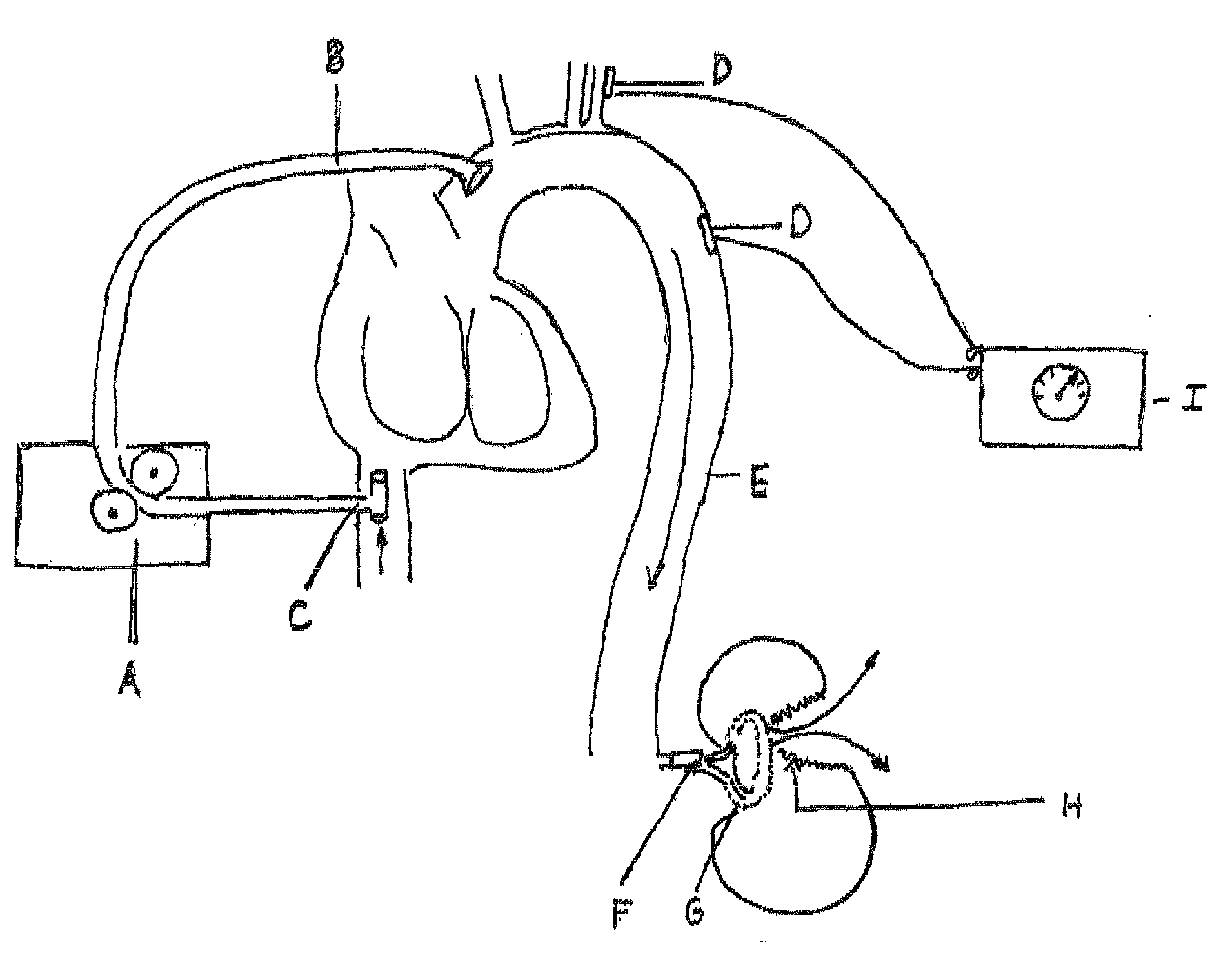
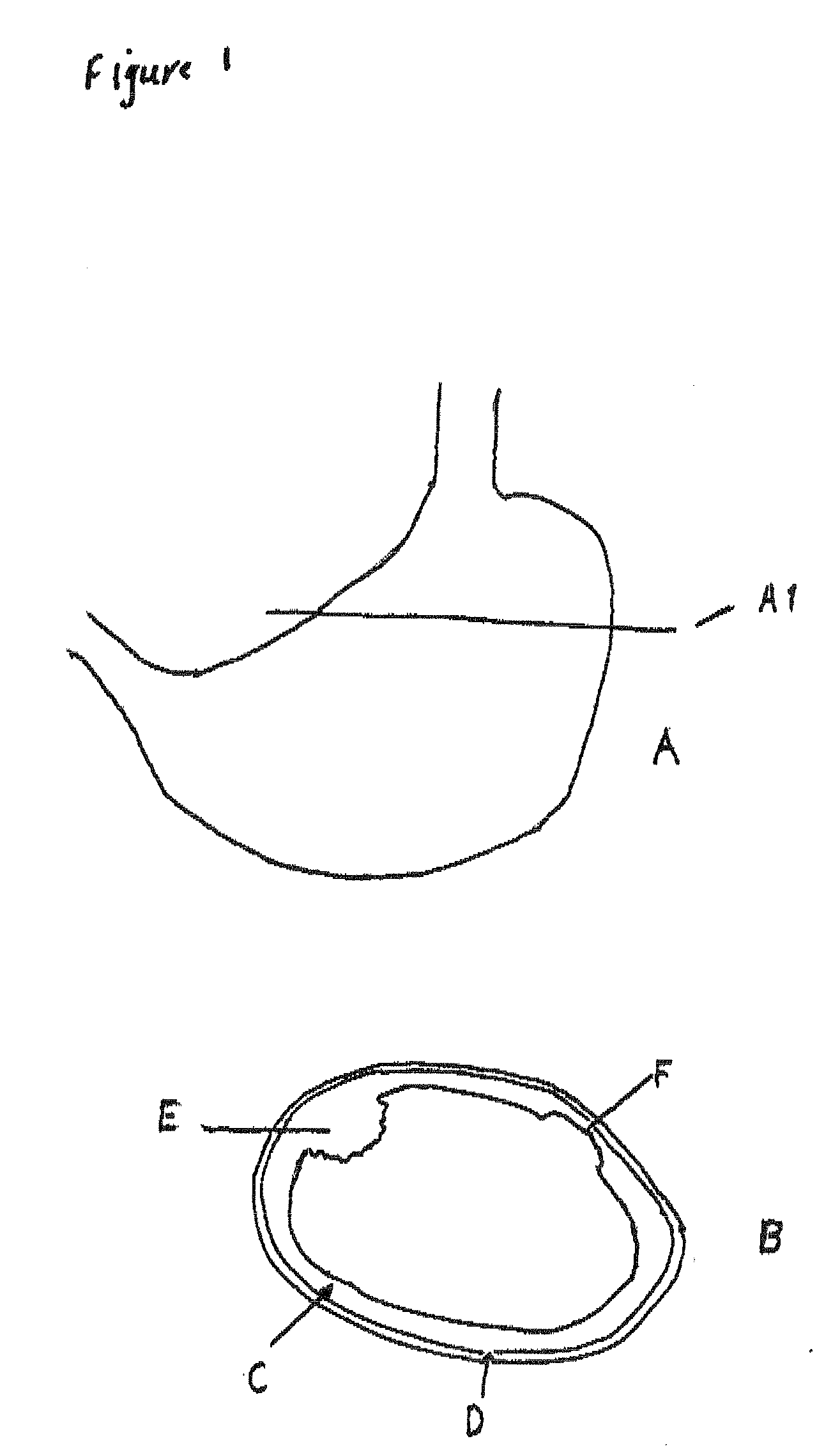
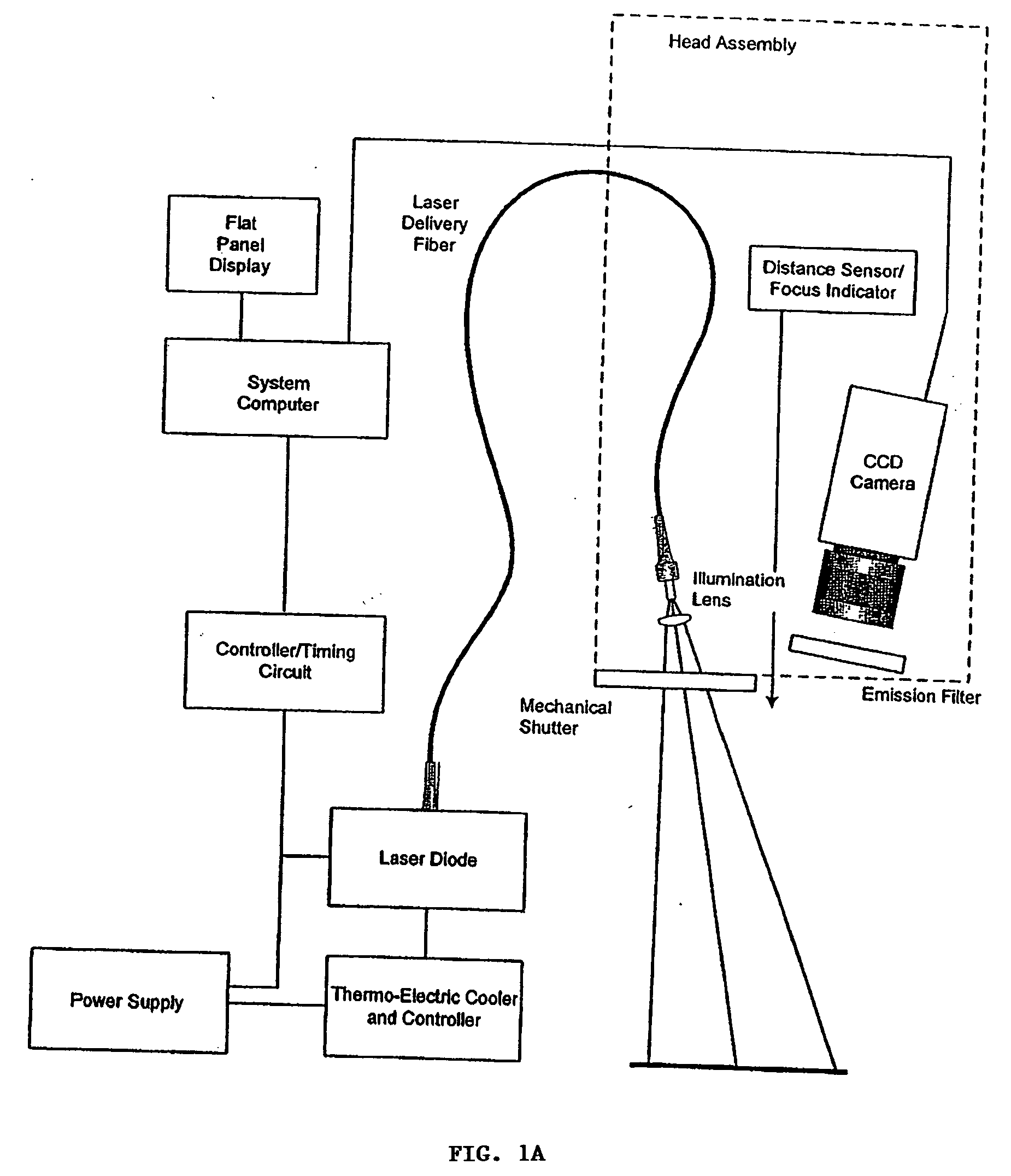
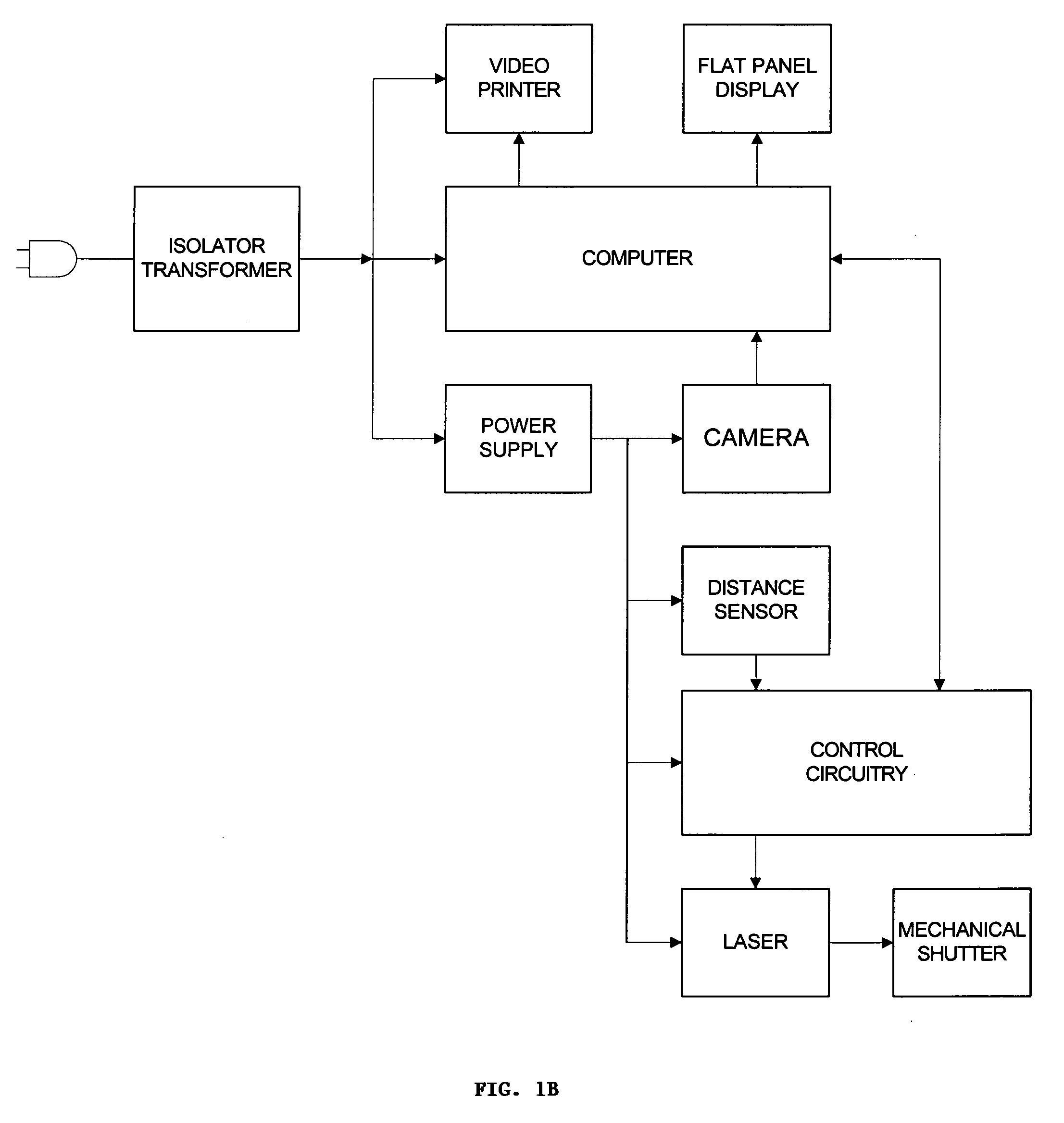
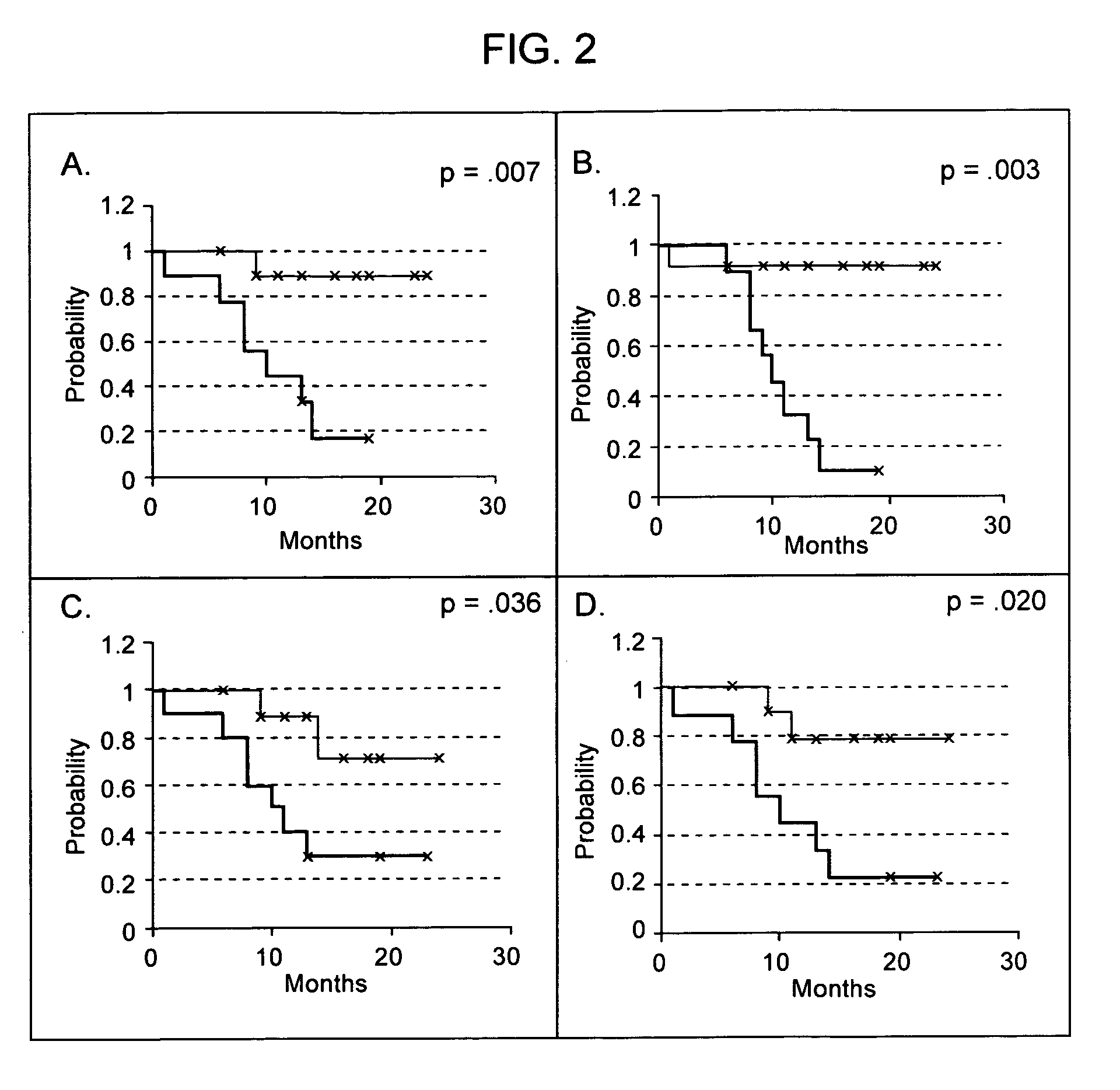
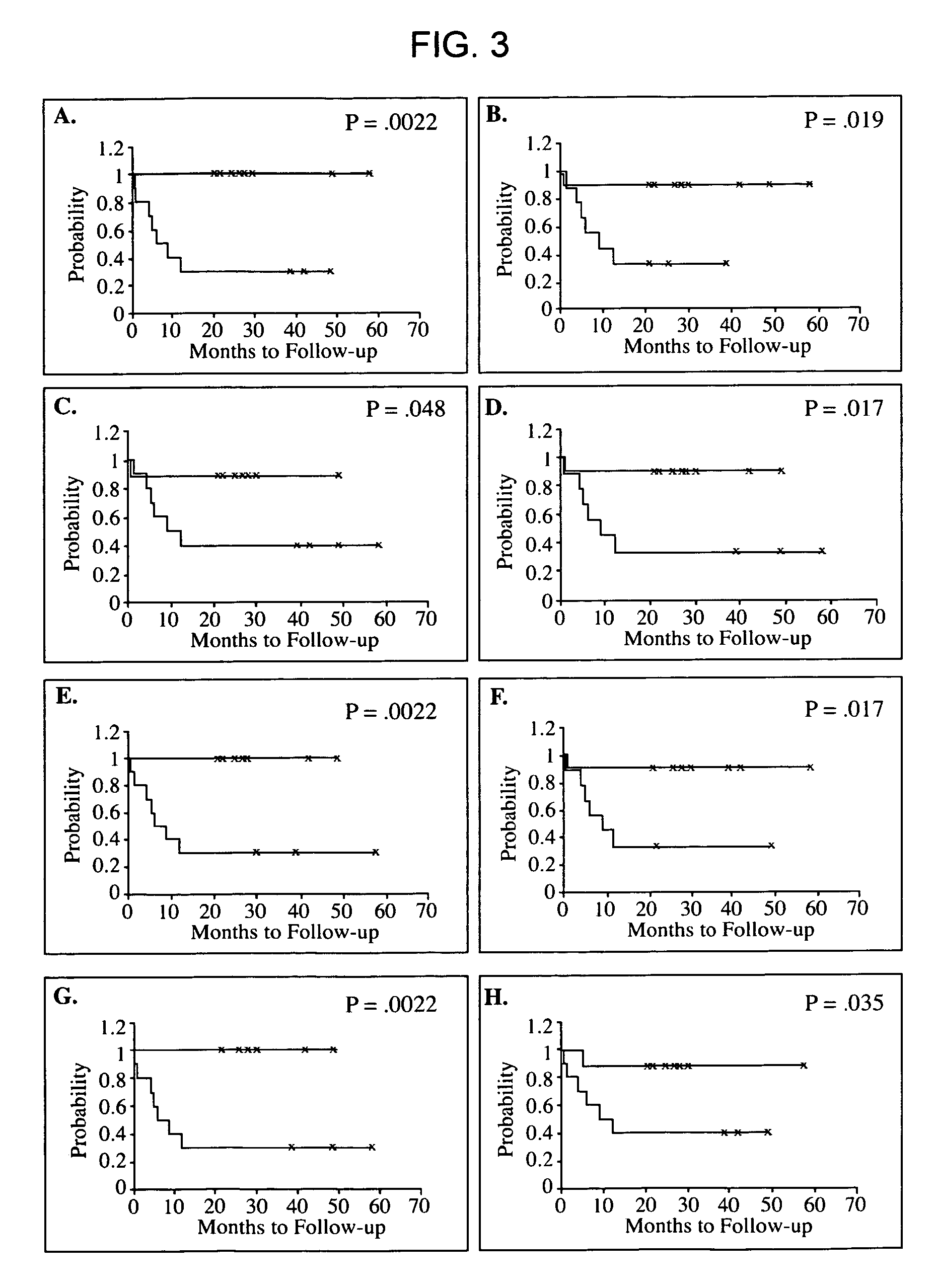
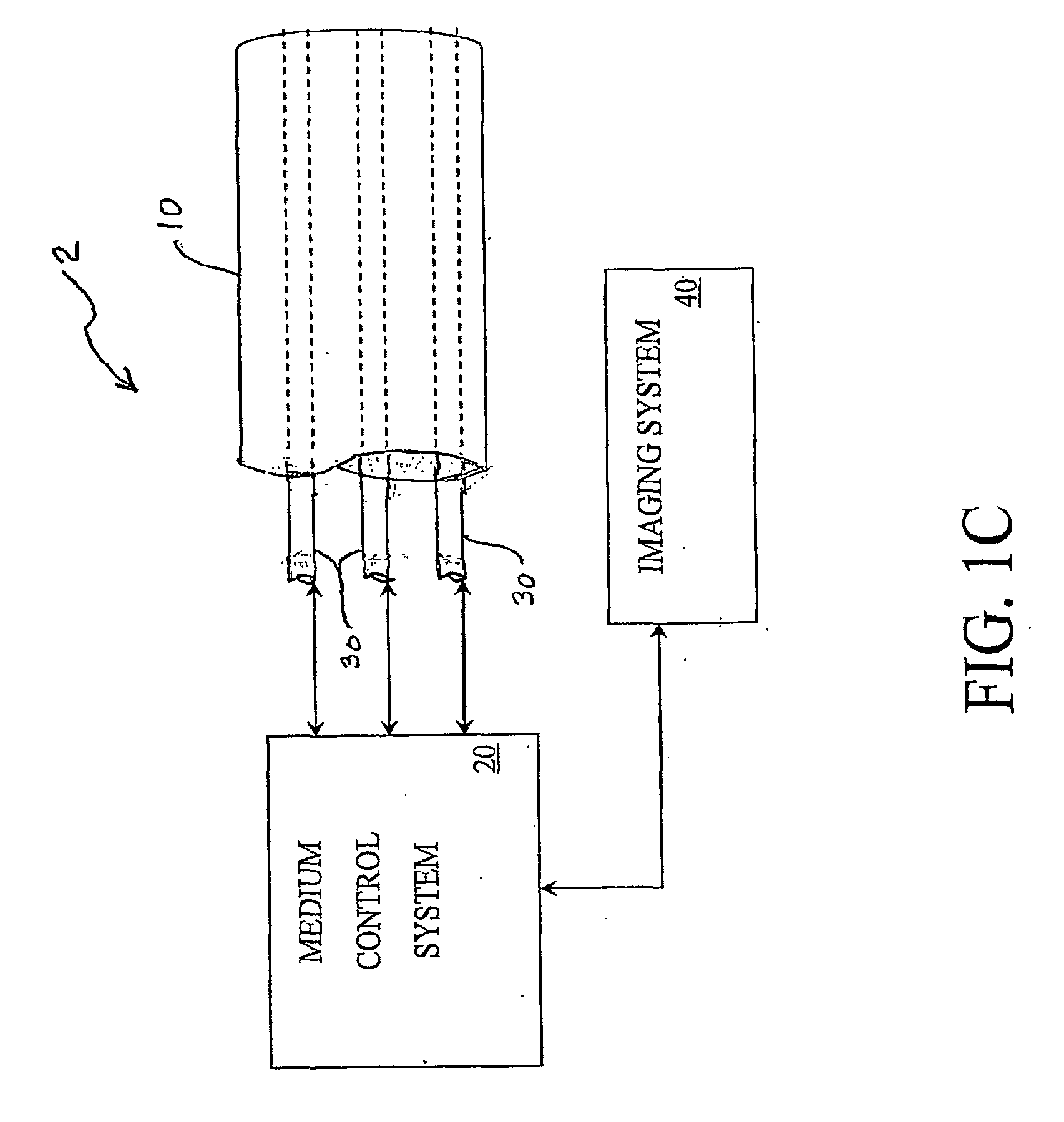
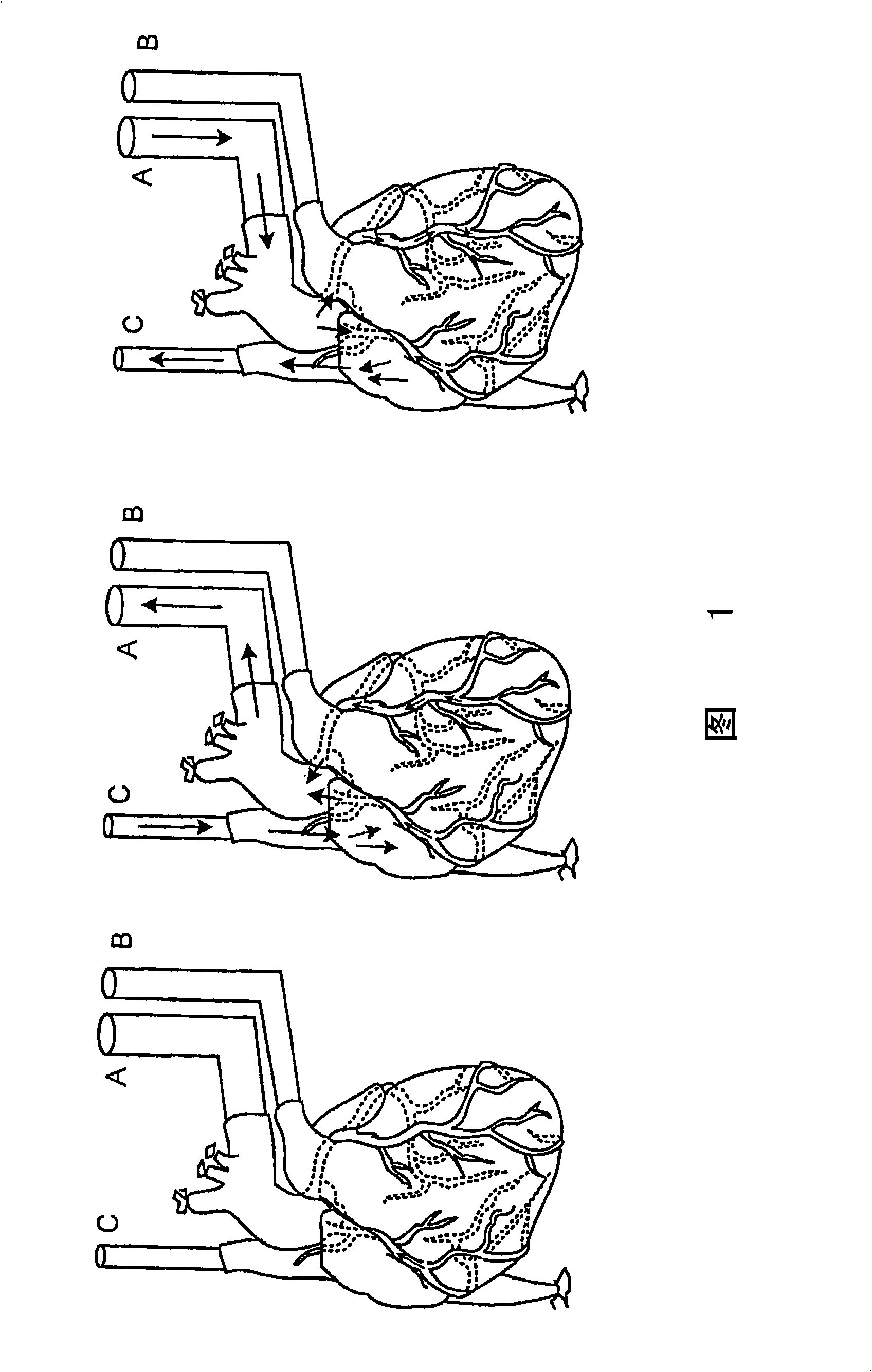
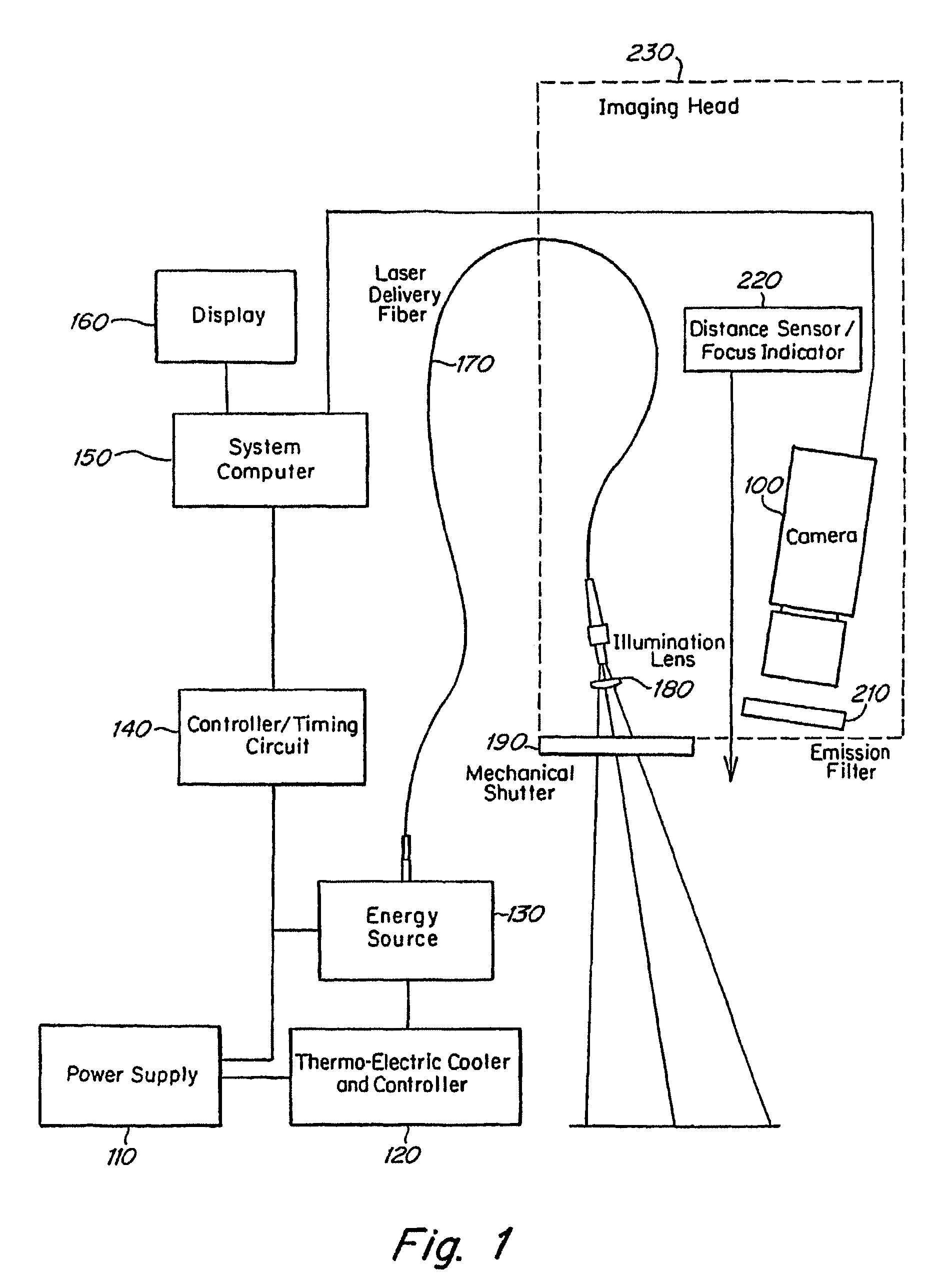
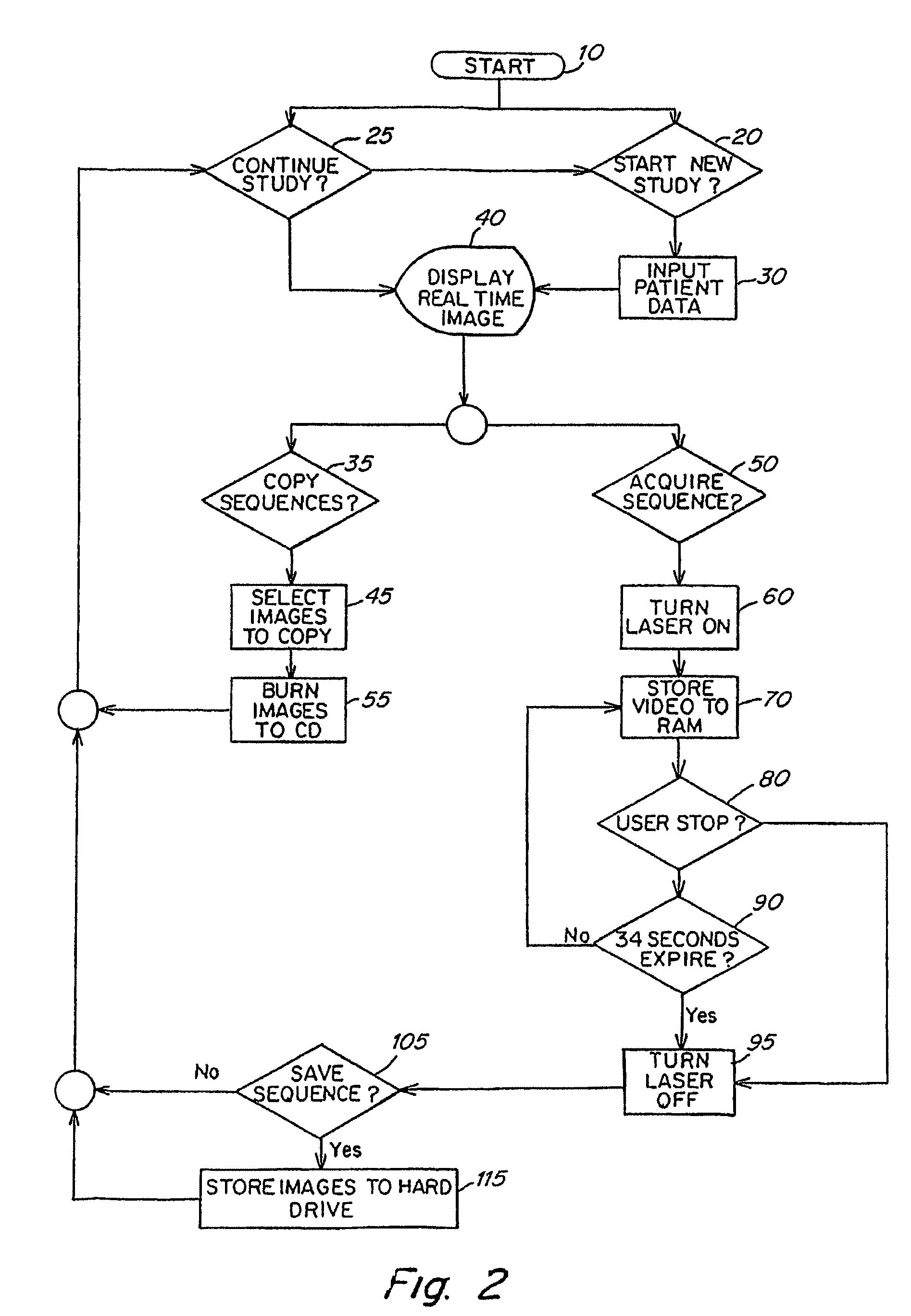
Real time imagining during solid organ transplant
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Simulator for major surgical operations
The invention consists of a hands-on, physically simulated human or animal body interior, containing physically simulated representations of all of the solid organs, hollow viscera, bladders, glands, major ducts, large and medium-sized blood vessels, muscle groups and interstitial tissues. The organs and vessels are life-sized and are composed of molded or sculpted open cell or closed cell foam rubber of varying density and load deformation, matching the physical properties of the specific biologic organs or tissues simulated. The organs, tissues and vessels may be treated with pigments, sealants and / or hardening agents to reflect the contours, appearances, densities, textures, elasticity, and deformability of normal or pathologically-altered internal organs and tissues. Organs contain molded vascular channels, reversibly attached to the larger blood vessels of the simulator. The model has a pressurized, watertight, simulated vascular system, monitored by electronic sensors.
Owner:OPERATIVE EXPERIENCE
Real time vascular imaging during solid organ transplant
The invention provides methods and systems for imaging vessels in a subject. In certain embodiments the vessels may be associated with a solid organ transplant.
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC
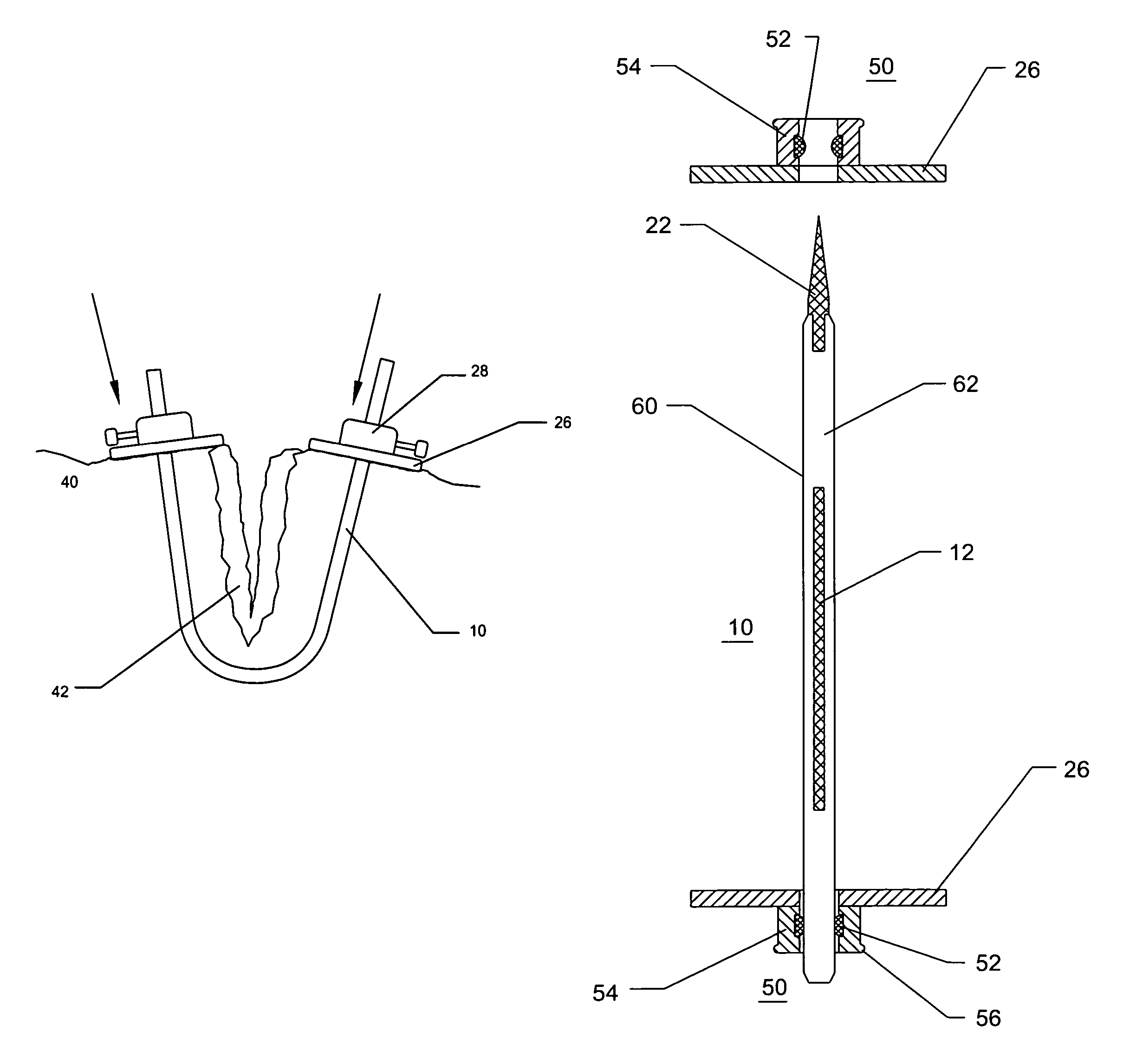
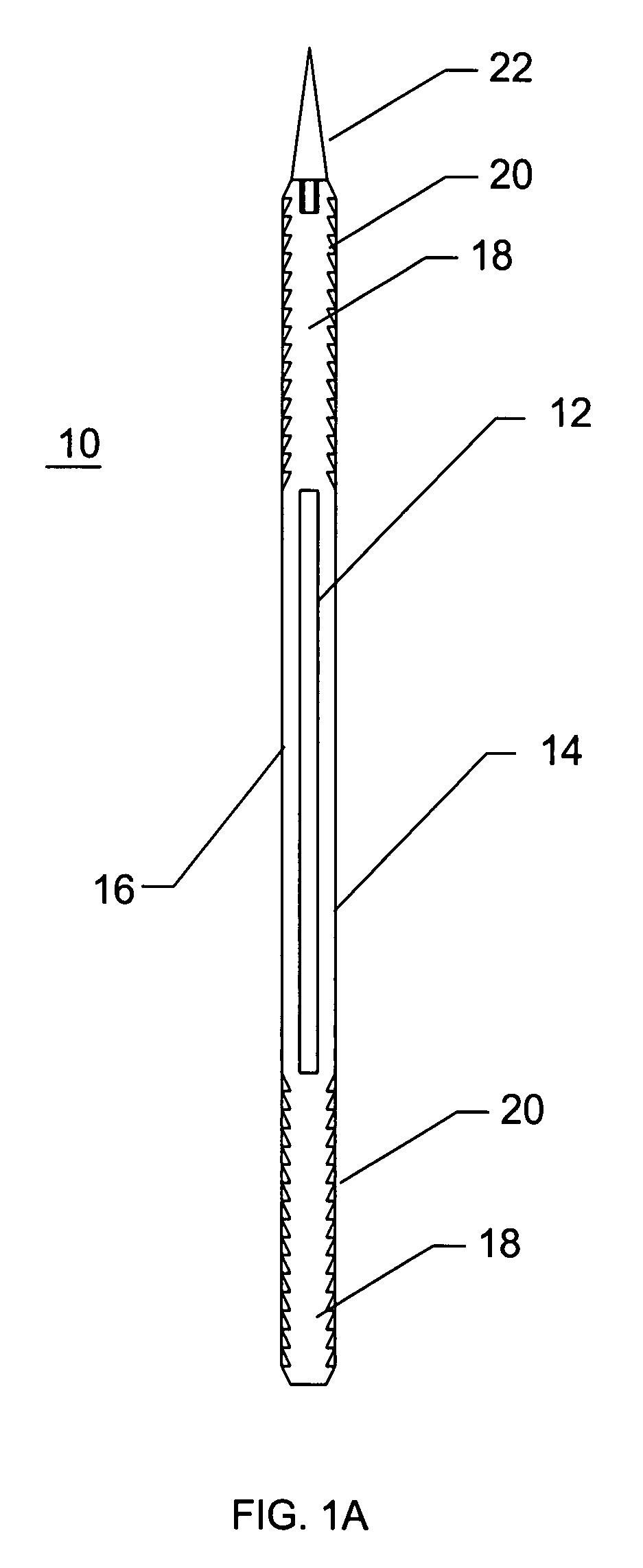
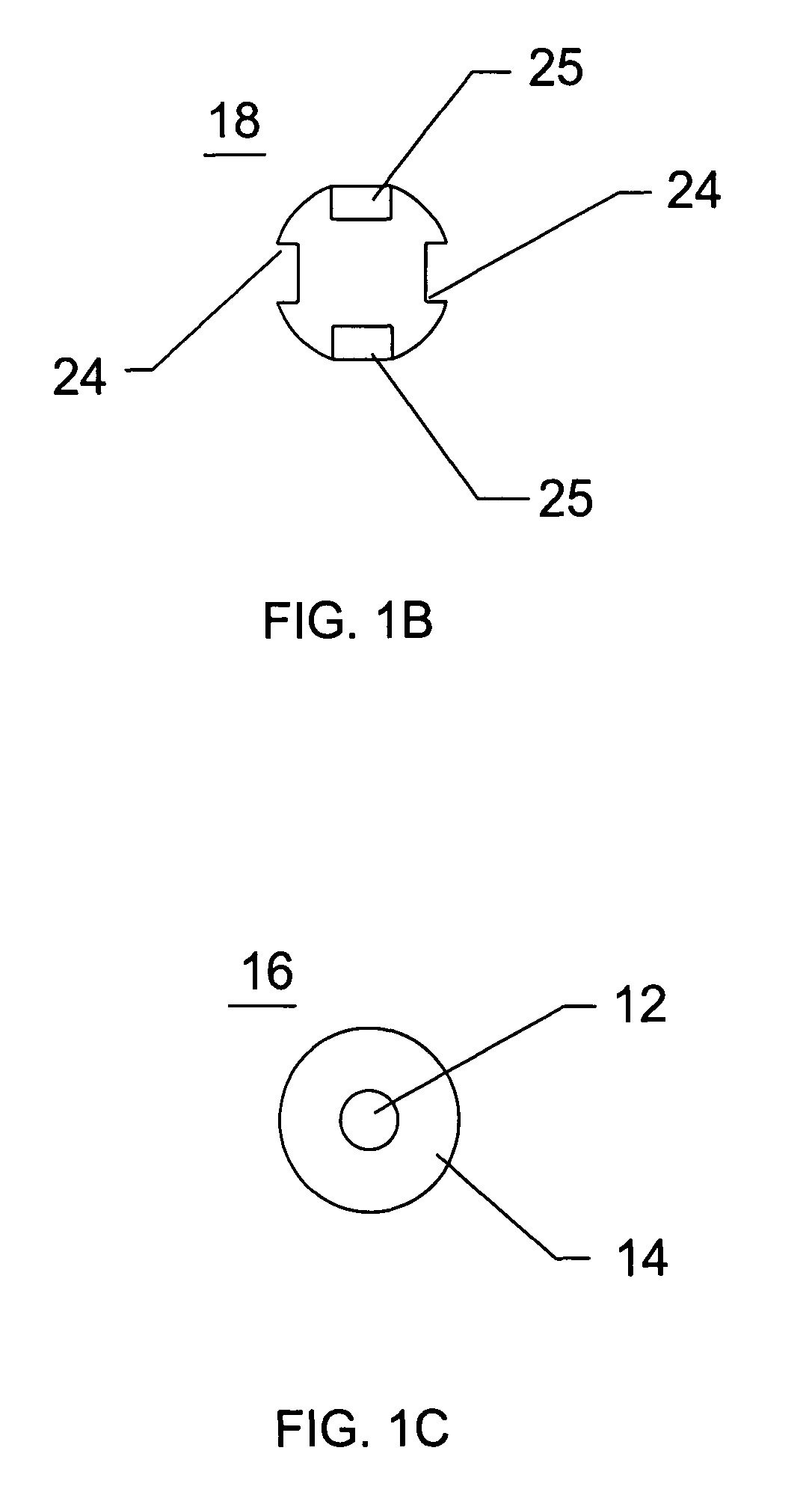
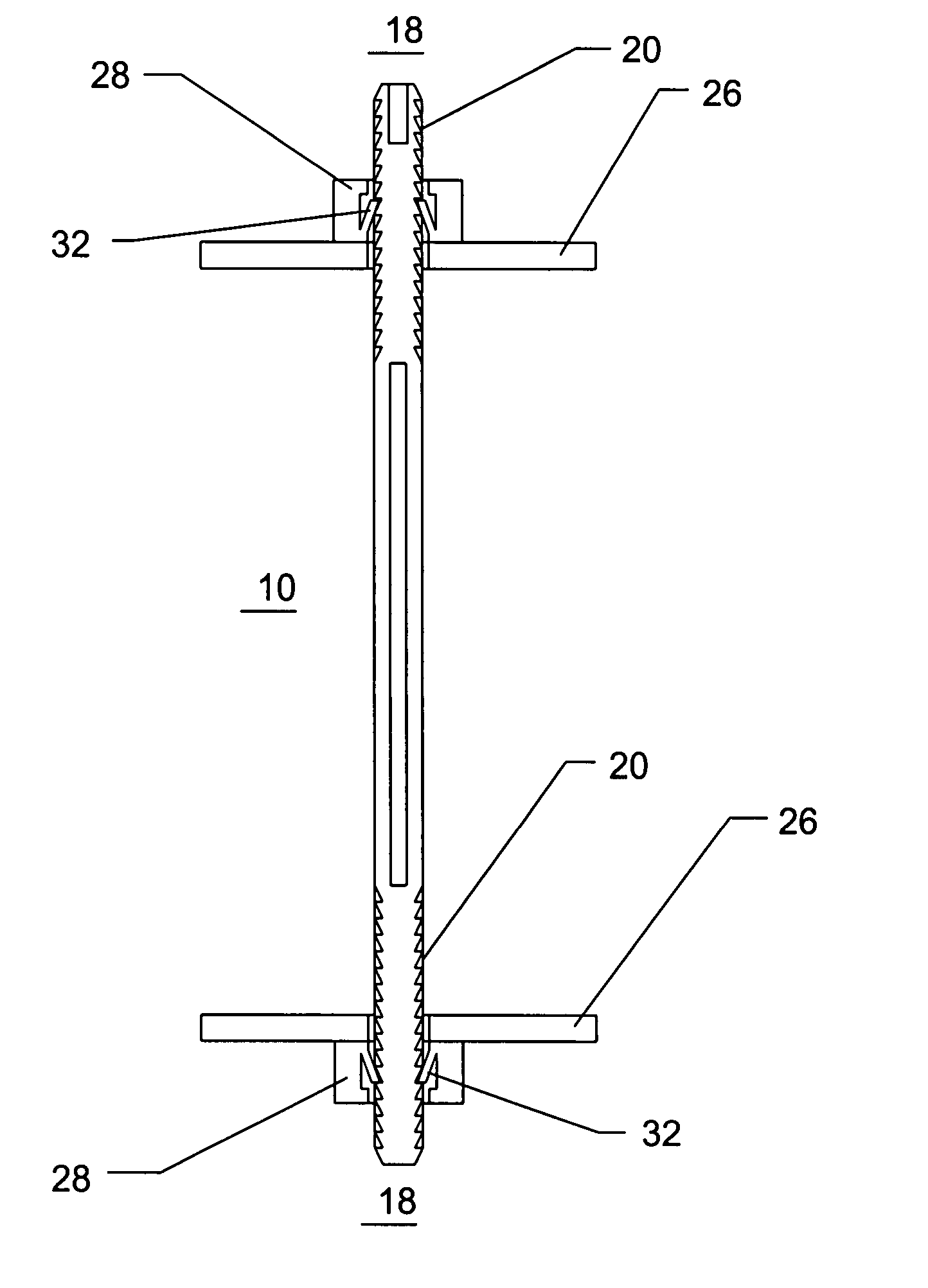
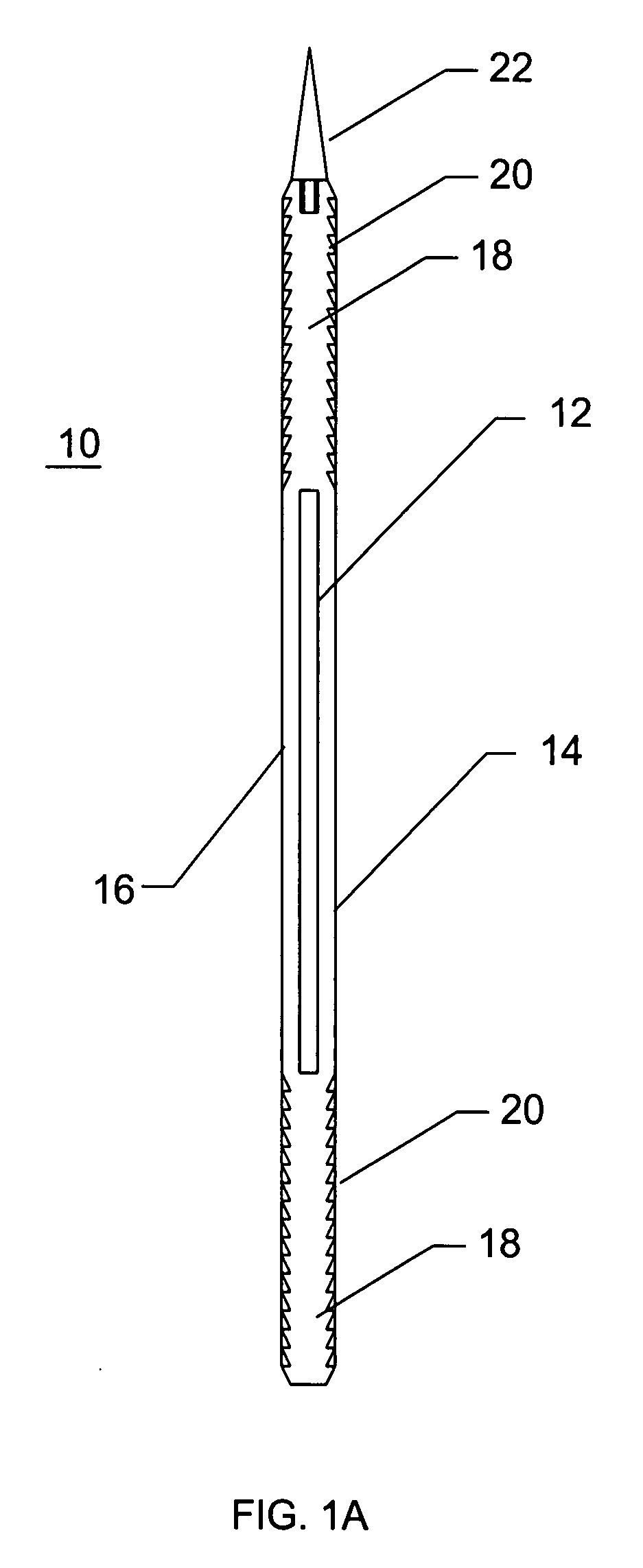
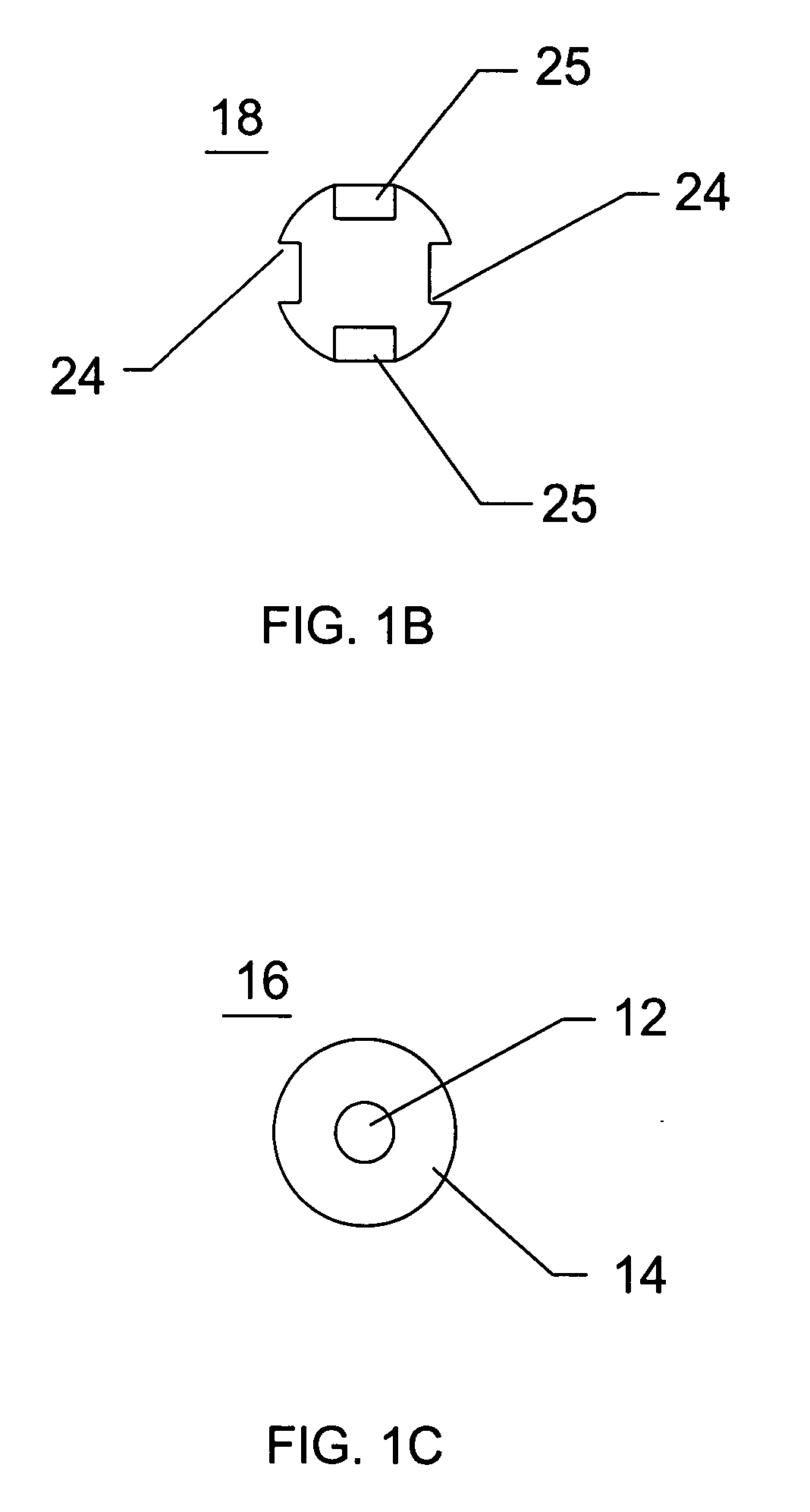
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
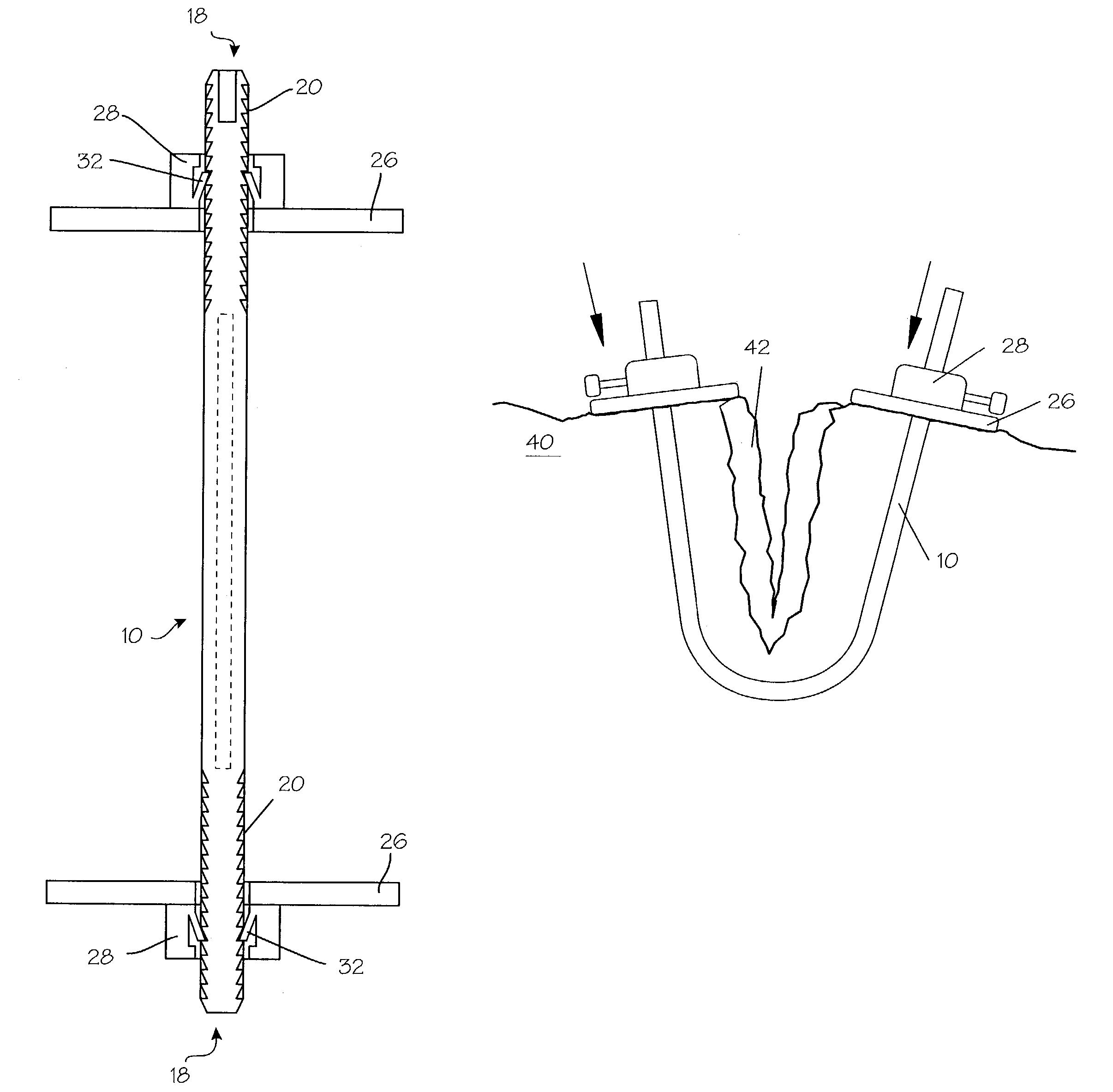
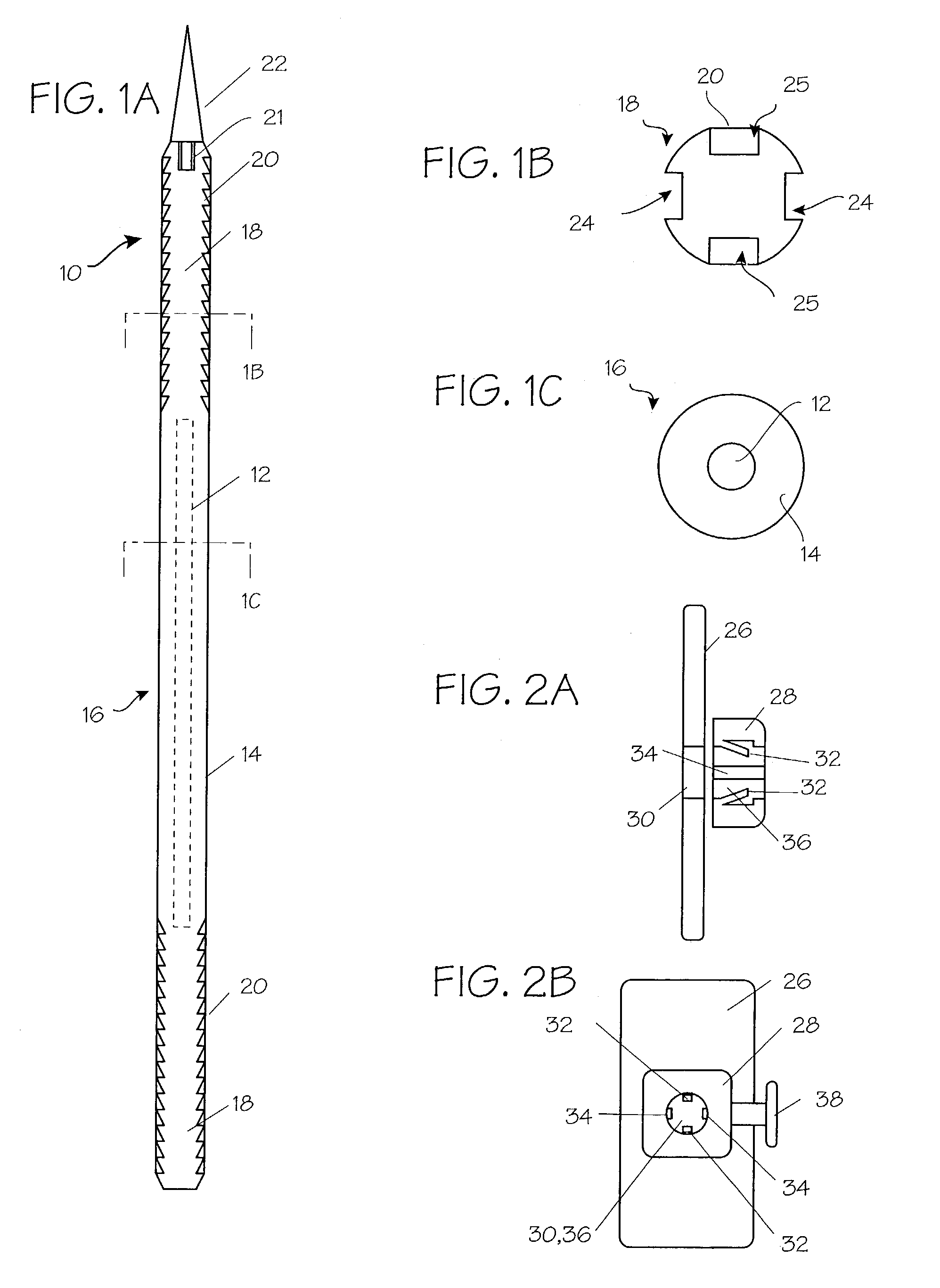
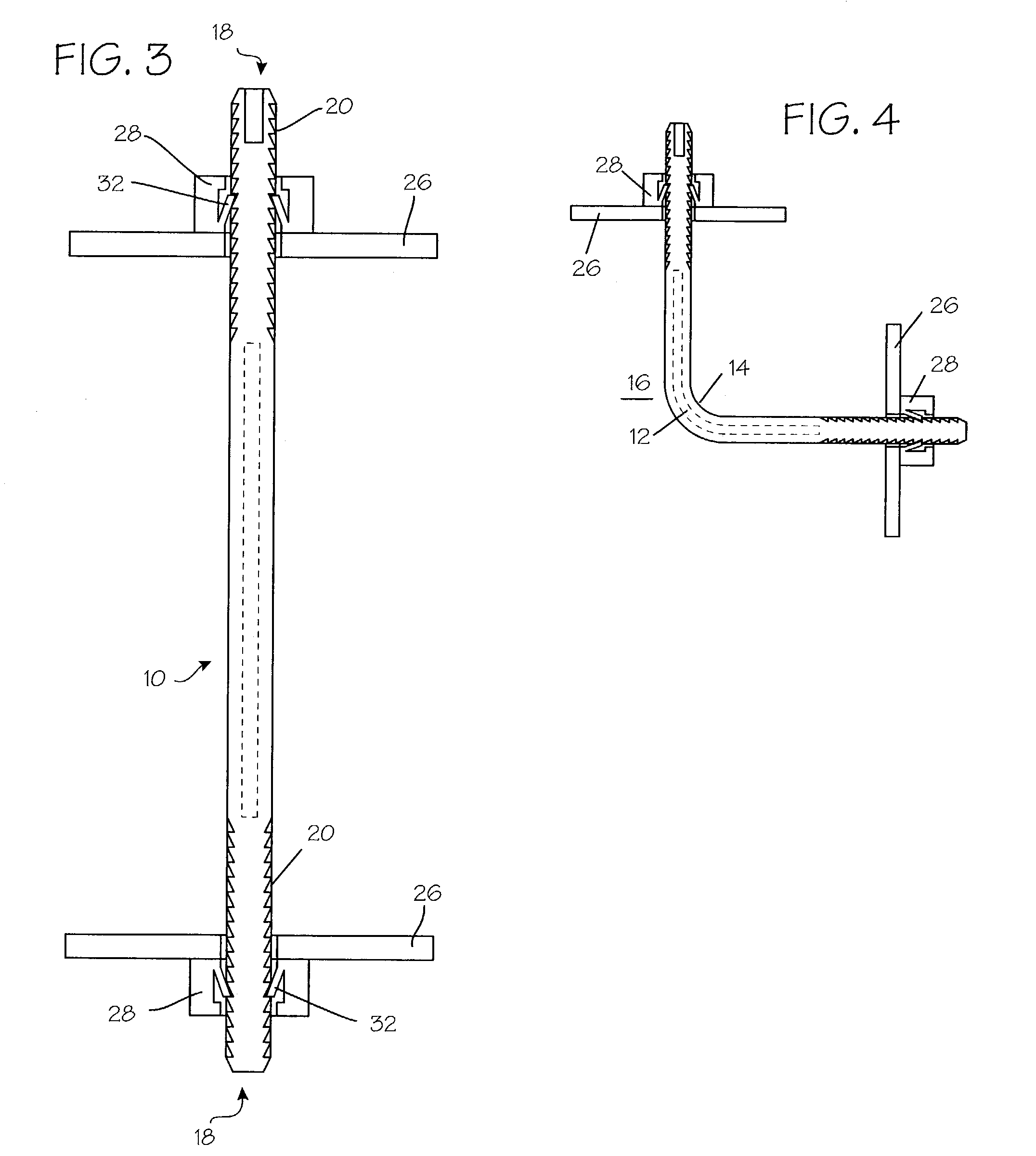
InactiveUS7235090B2Improved haemostatic tissue appositionEasy and fast applicationIntravenous devicesSurgical veterinaryTrauma surgeryParenchyma
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in solid visceral wounds. Such devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdominal viscera. The devices utilize flexible, variable depth transfixing bolts that penetrate the viscera. These bolts are pulled tight to bring the tissue into apposition and hold said tissue in apposition while the wound heals. These bolts overcome the limitations of sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The bolts come in a variety of lengths and diameters. Since the bolts are flexible, the curvature may be adjusted by the surgeon. The devices are flexible, bendable, and conformable in their wet or dry state. They can be used either straight or through a broad range of curvatures to suit the needs of various pathologies. The bolts include pressure plates that are capable of exerting compressive pressure over broad areas of visceral wounds without causing tearing of the friable parenchyma. The bolts may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Methods and compositions for evaluating graft survival in a solid organ transplant recipient
ActiveUS20060246485A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingOrgan transplantationProtein level
Methods are provided for evaluating a subject for graft survival, e.g., in terms of predicting graft survival, identifying the presence of a deleterious graft condition, such as CAN and DT, identifying the severity and class of acute rejection, etc, in a subject are provided. In practicing the subject methods, the expression of at least one gene in a sample from the subject, e.g., a blood or biopsy sample, is assayed, e.g., at the nucleic acid and / or protein level, to evaluate the subject. Also provided are compositions, systems and kits that find use in practicing the subject methods. The methods and compositions find use in a variety of applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
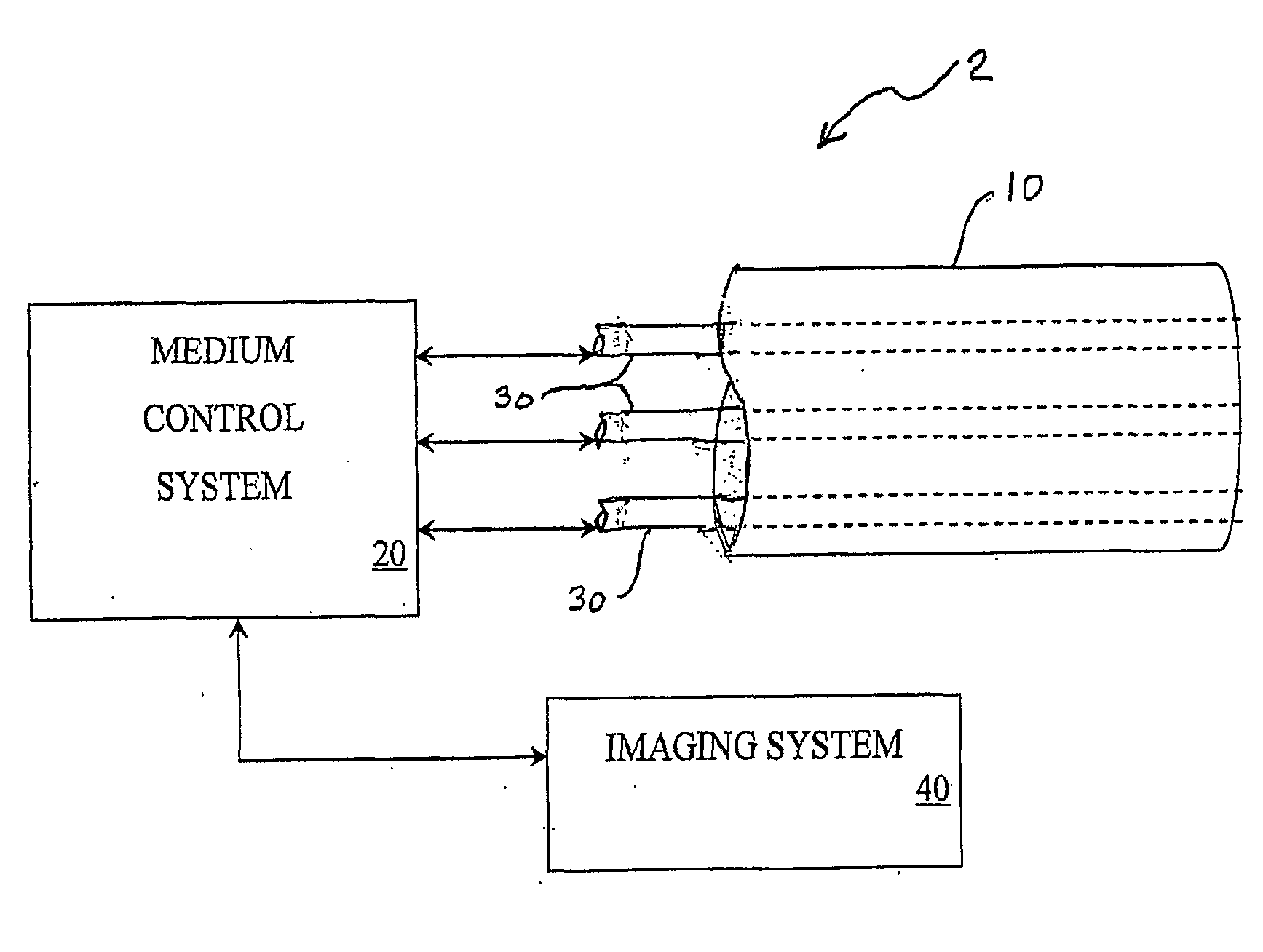
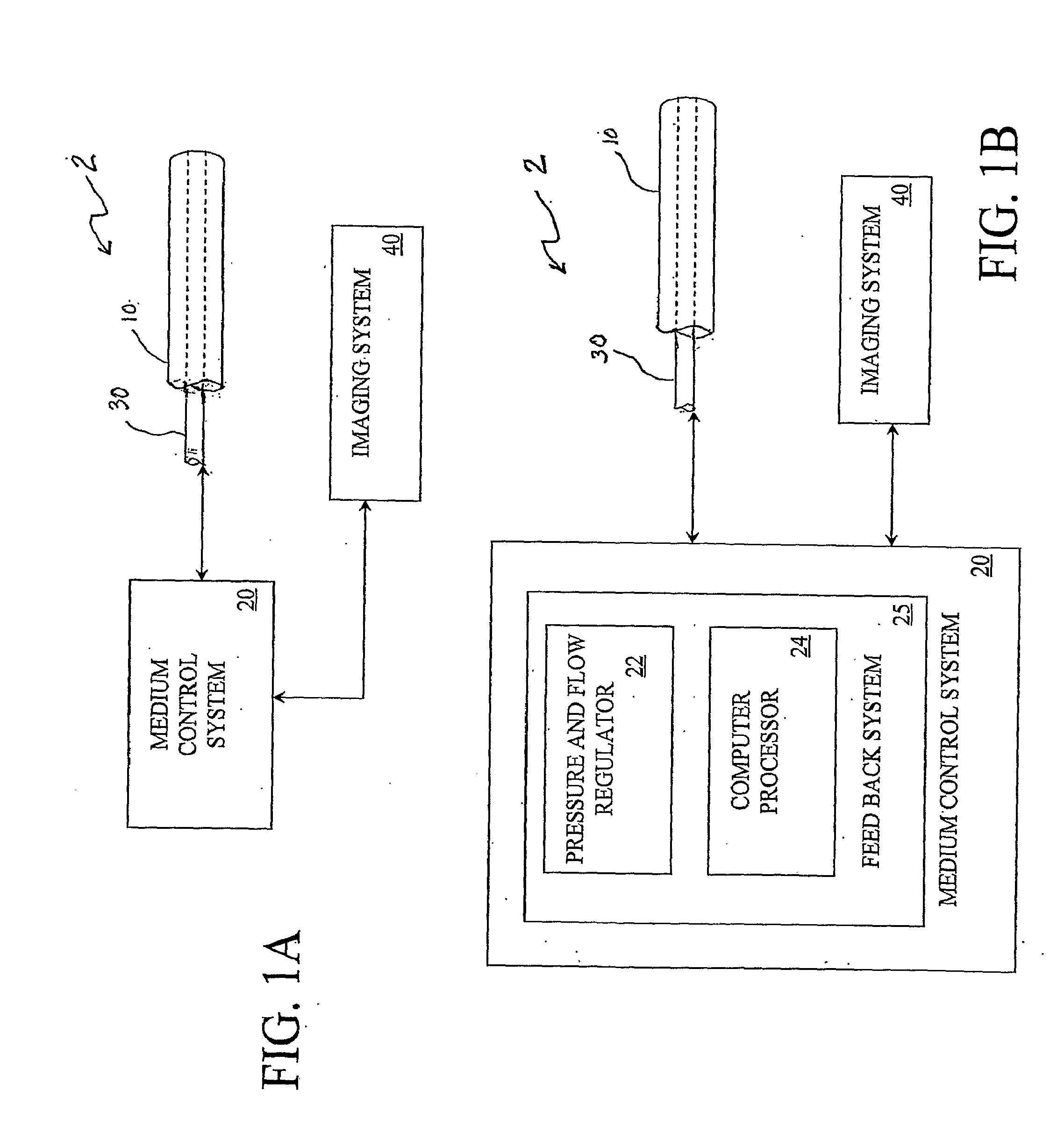
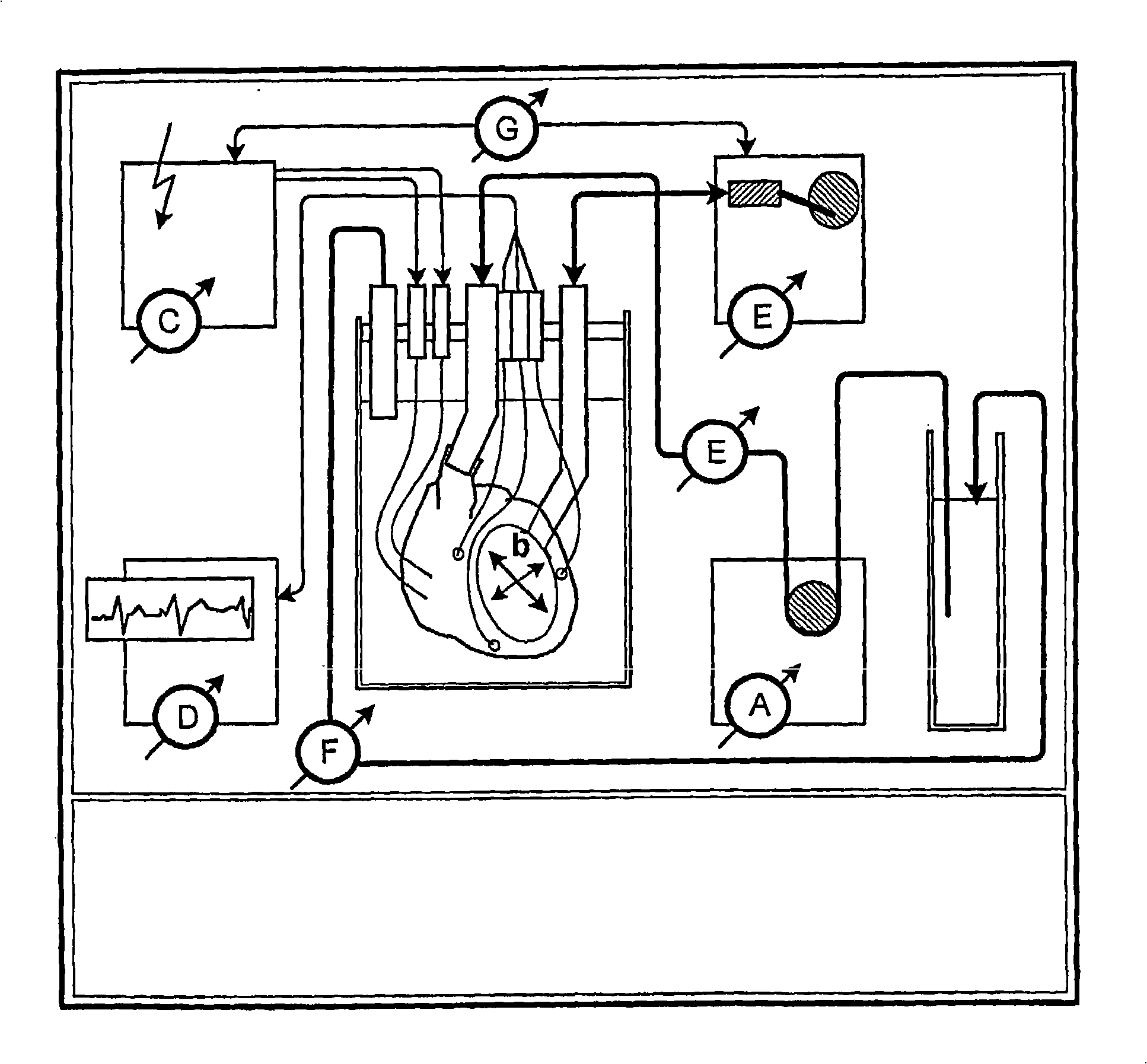
Multi-Port Catheter System with Medium Control and Measurement Systems for Therapy and Diagnosis Delivery
A series of embodiments of multi-lumen, multisegmented (or variable diameter) catheters and associated multi-channel flow control and measurement systems and methods for simultaneous delivery of a medium to a plurality of locations is described. The need for precise, stable reliable, and repeatable flow control in therapy delivery catheters is crucial to the efficacious treatment of the clinical manifestations of peripheral vascular disease (PVD) and other such maladies. Such treatments may involve the placement of multi-lumen catheters into peripheral arterial trees, with the subsequent need to govern the flow dynamics within each individual lumen of the multi-lumen device in such a way that an optimum distribution of the agent is achieved intra-arterially. Combinations of pumps, flow monitors, pressure monitors, feedback loops and related hardware and software collectively capable of achieving this goal are described. In other embodiments, this device and method could be used for infusions into tissues and solid organs, and microcoil systems can be added to the various components of the catheter systems to improve the imaging quality during MR-guided procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Decellularization and recellularization of organs and tissues
ActiveCN101272815APharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsDecellularizationSolid organ
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
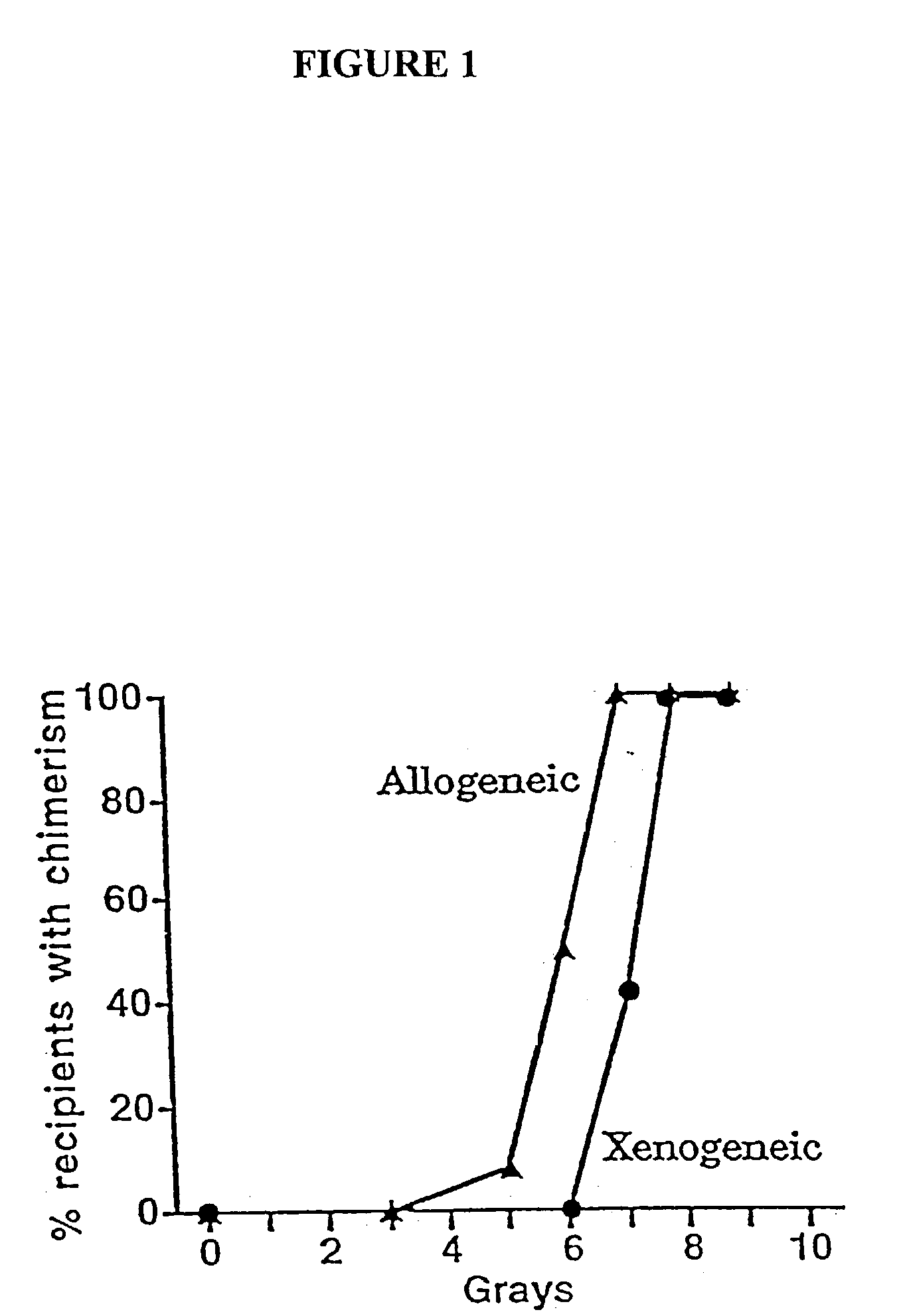
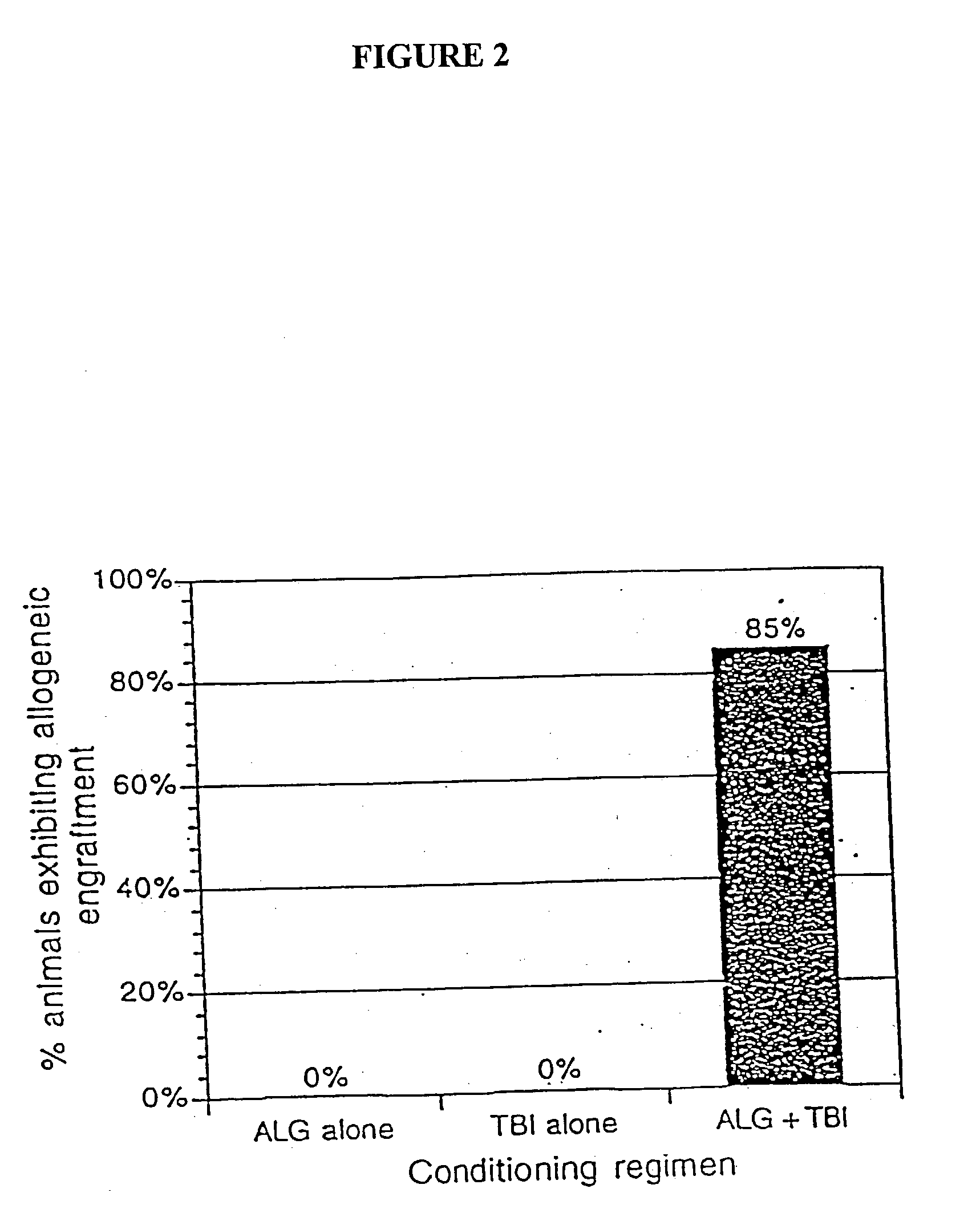
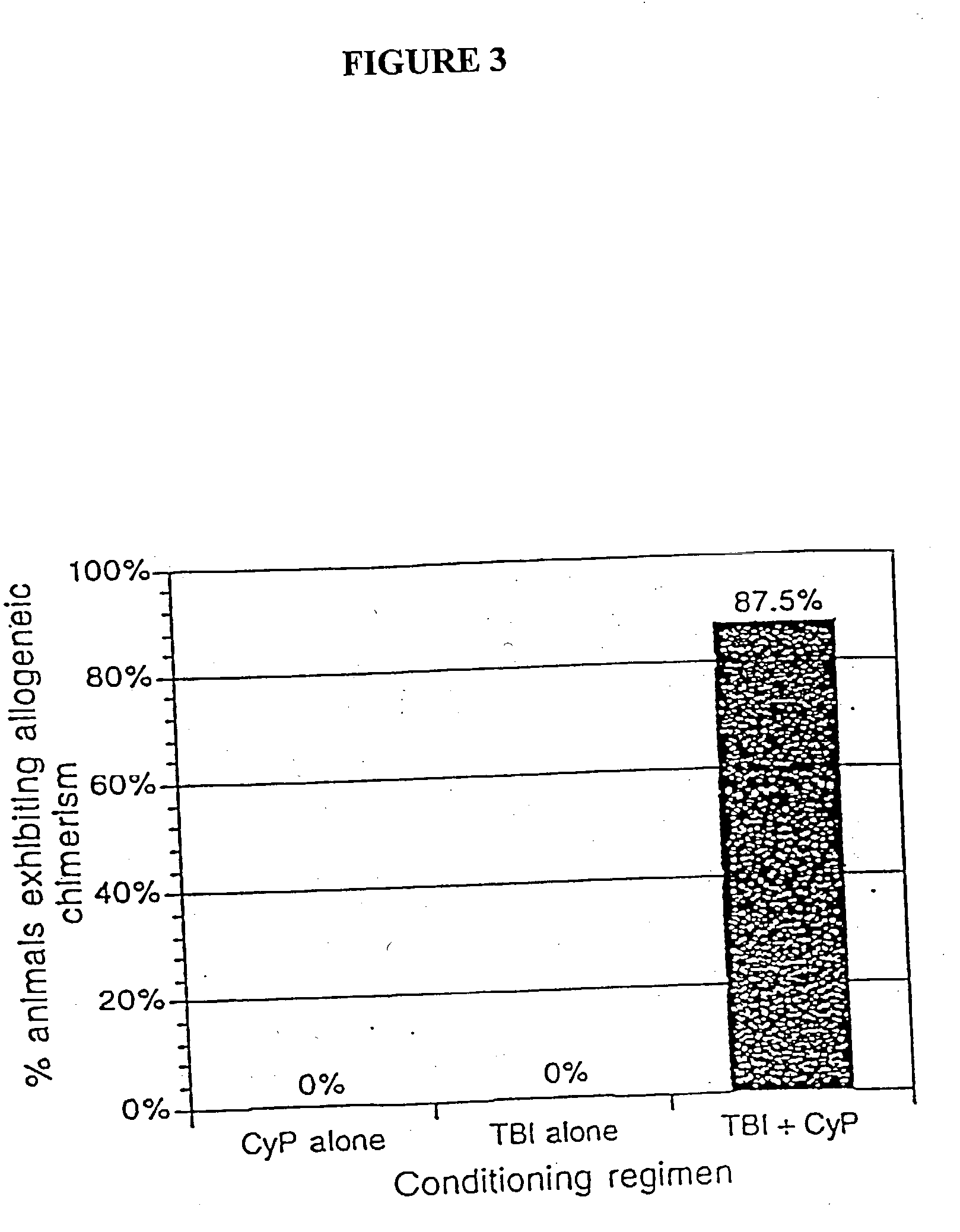
Non-lethal methods for conditioning a recipient for bone marrow transplantation
InactiveUS6217867B1Reduce proliferationDiminished cytotoxic activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsGackstroemiaAcquired immunodeficiency
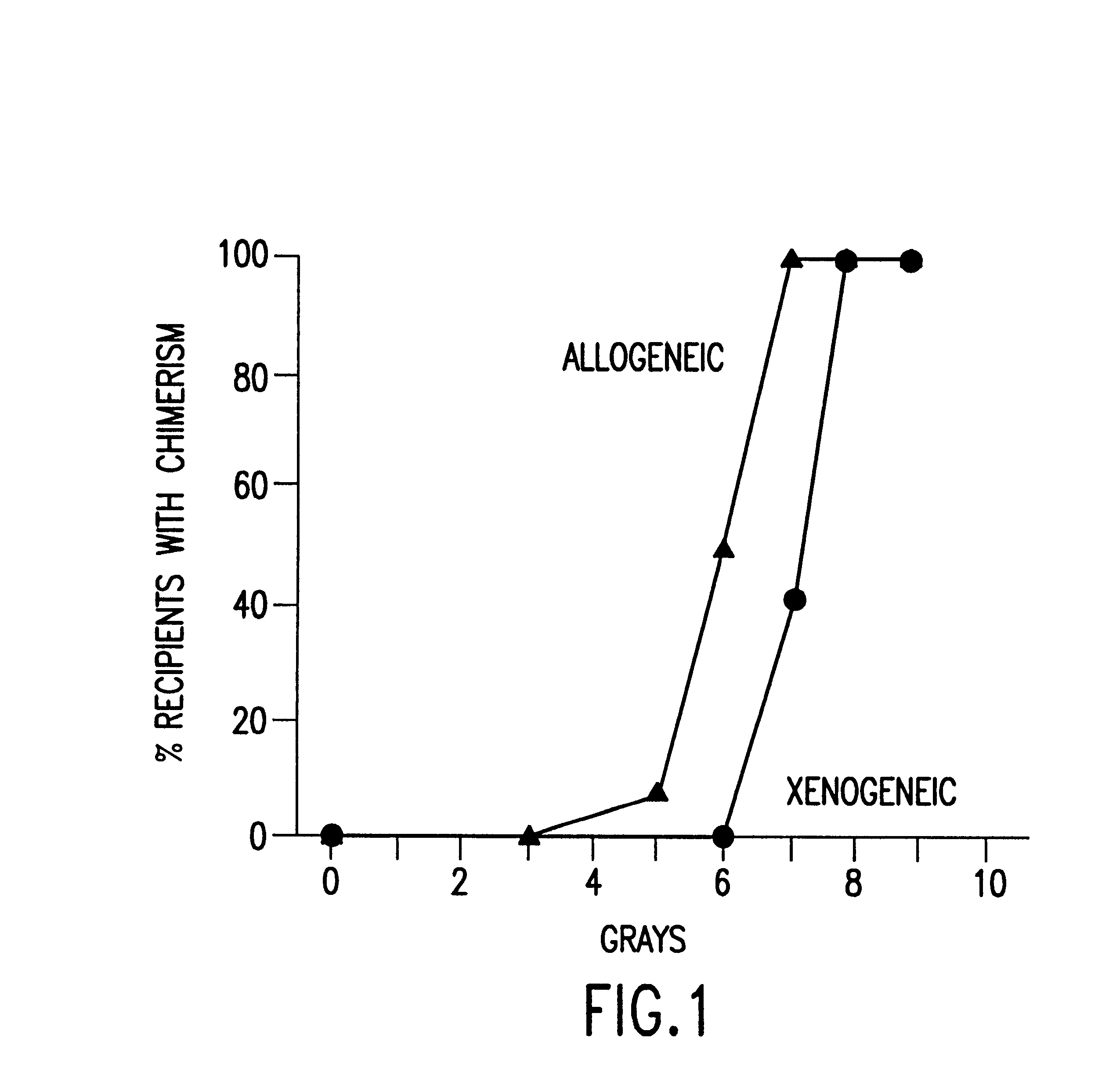
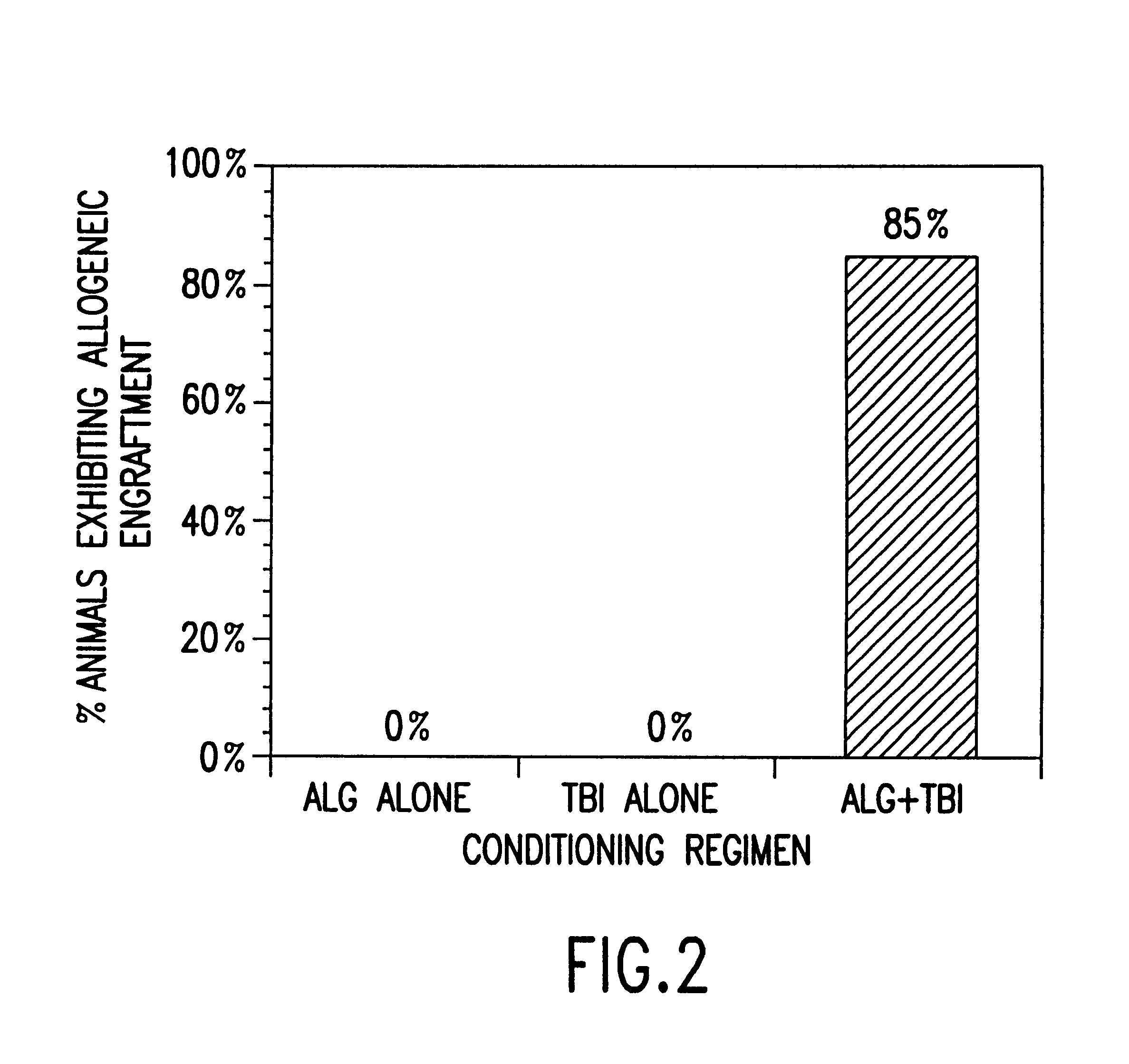
The present invention relates to non-lethal methods of conditioning a recipient for bone marrow transplantation. In particular, it relates to the use of nonlethal doses of total body irradiation, total lymphoid irradiation, cell type-specific or cell marker-specific antibodies, especially antibodies directed to bone marrow stromal cell markers, NK cells, or the CD8 cell marker, cytotoxic drugs, or a combination thereof. The methods of the invention have a wide range of applications, including, but not limited to, the conditioning of an individual for hematopoietic reconstitution by bone marrow transplantation for the treatment of hematologic malignancies, hematologic disorders, autoimmunity, infectious diseases such as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and the engraftment of bone marrow cells to induce tolerance for solid organ, tissue and cellular transplantation.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF
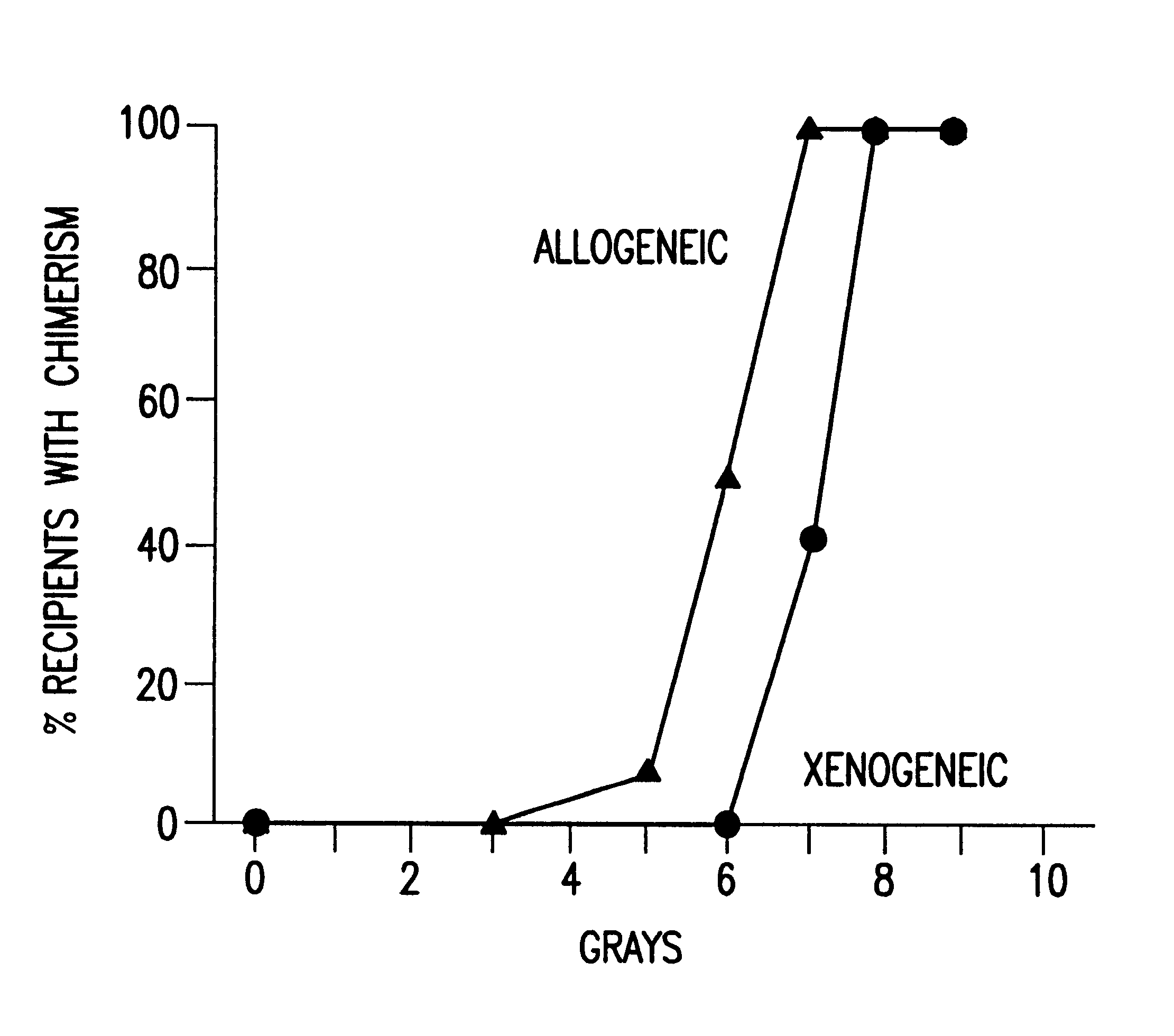
Combined organ and hematopoietic cells for transplantation tolerance of HLA mismatched grafts
ActiveUS9504717B2Organic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsImmunosuppressive drugHematopoietic cell
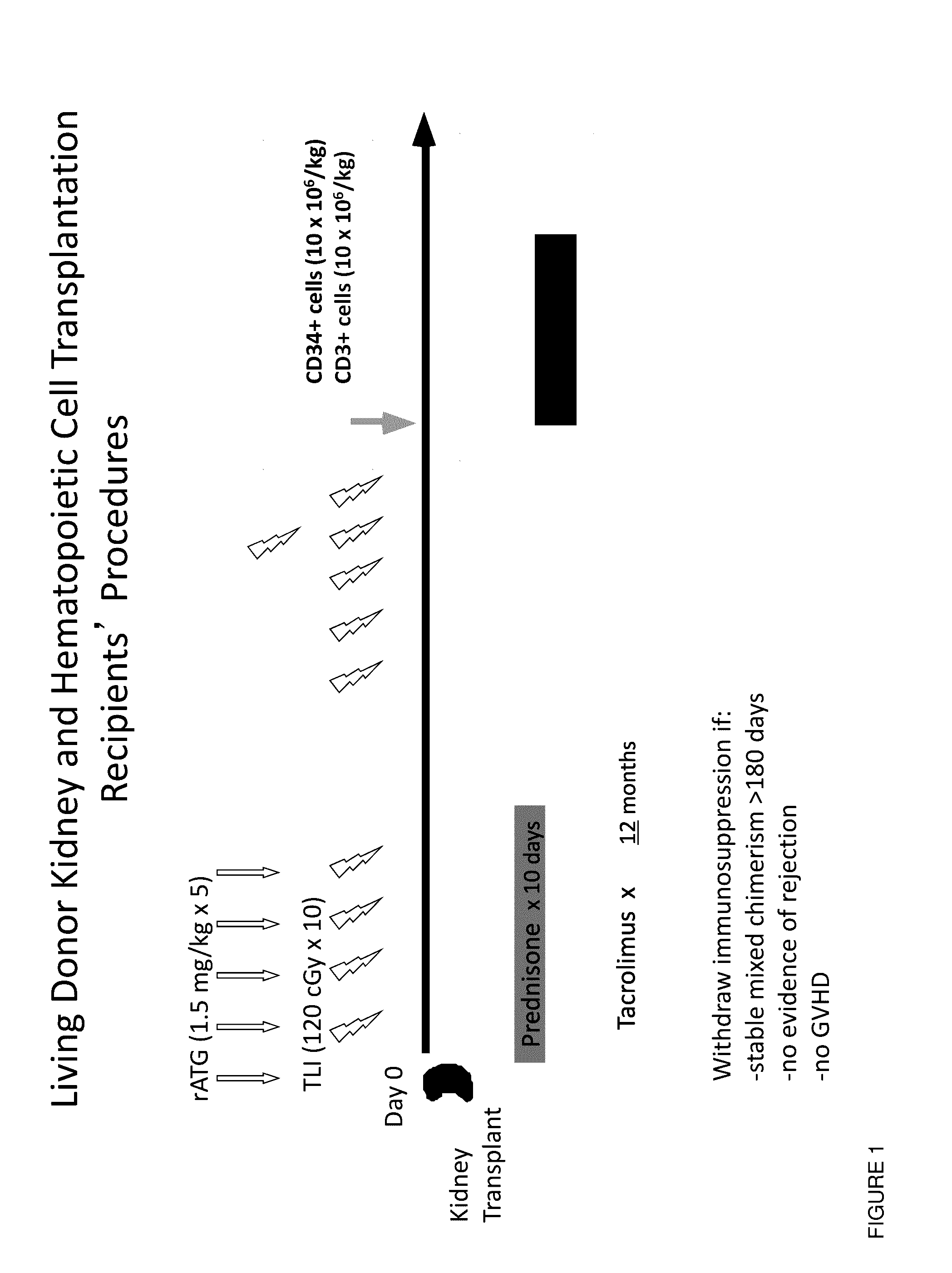
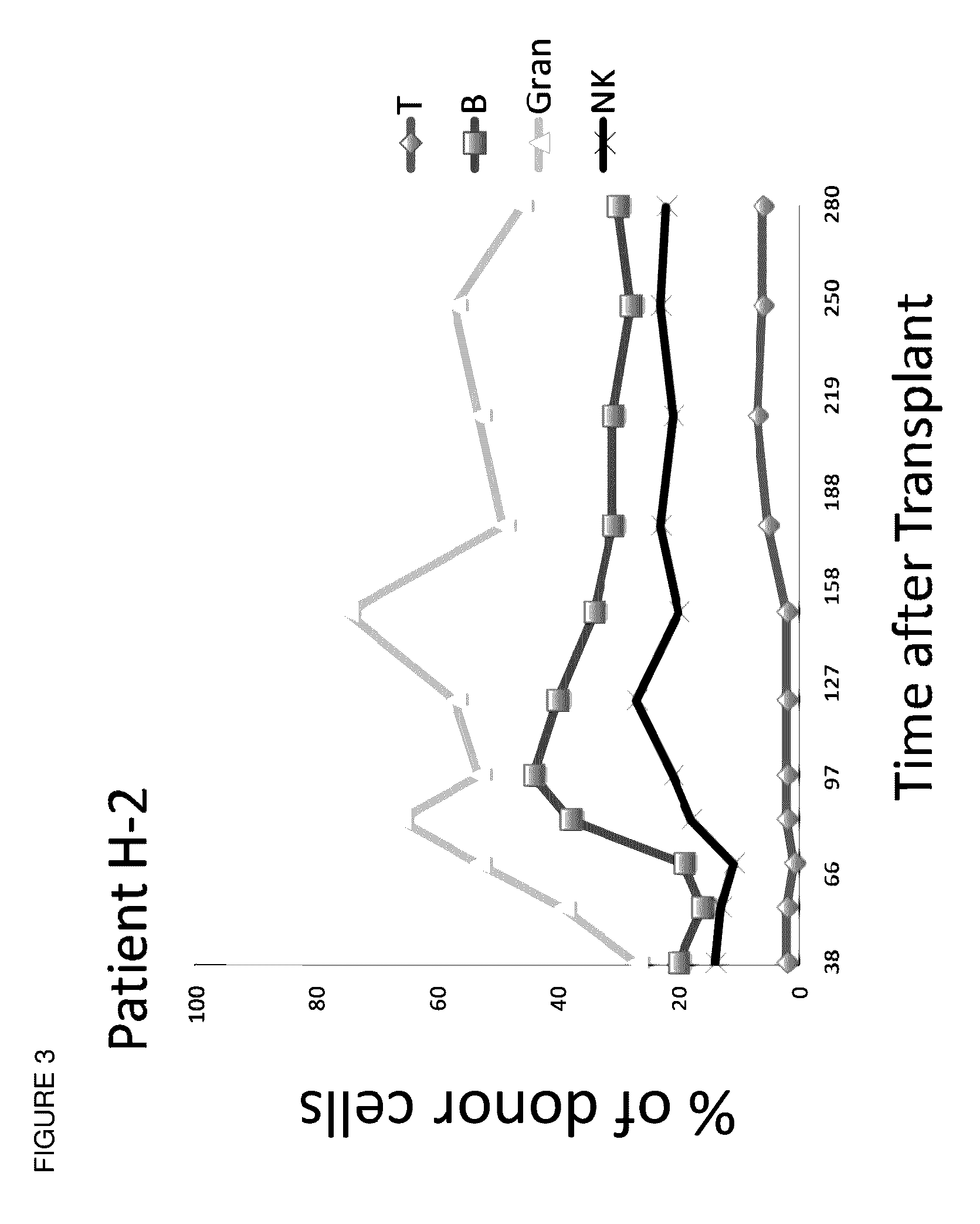
Methods and compositions are provided for combined transplantation of a solid organ and hematopoietic cells to an HLA mismatched recipient, where tolerance to the graft is established through development of a persistent mixed chimerism. An individual with persistent mixed chimerism, usually for a period of at least six months, is able to withdraw from the use of immunosuppressive drugs after a period of time sufficient to establish tolerance.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Real time imaging during solid organ transplant
The invention provides methods and systems for imaging vessels in a subject. In certain embodiments the vessels may be associated with a solid organ transplant.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Combined organ and hematopoietic cells for transplantation tolerance of HLA mismatched grafts
ActiveUS20170106086A1Organic active ingredientsEnergy modified materialsImmunosuppressive drugHematopoietic cell
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
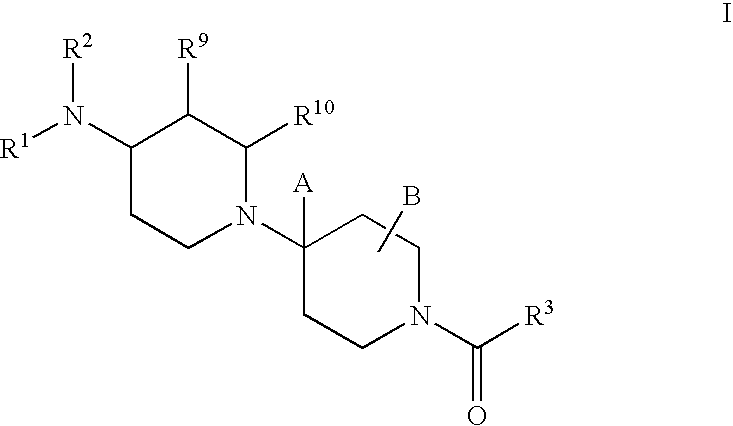
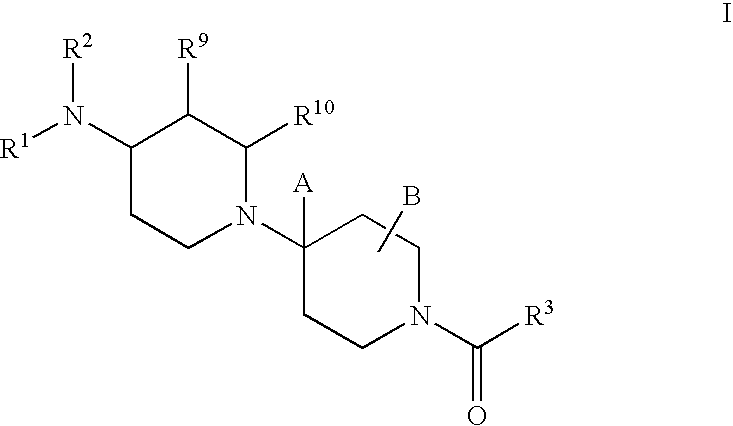
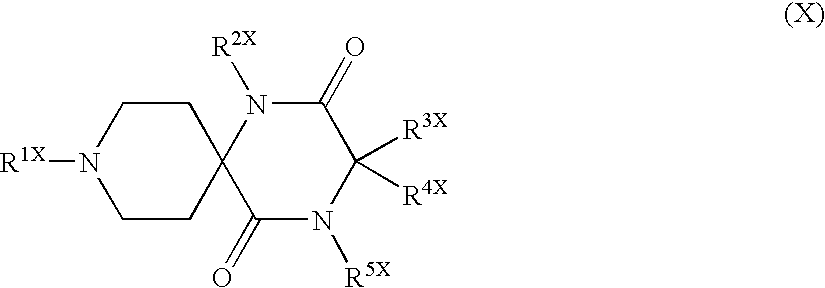
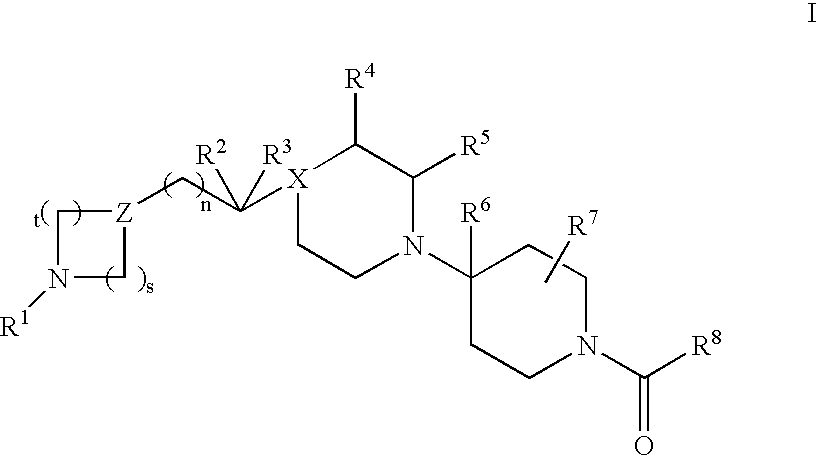
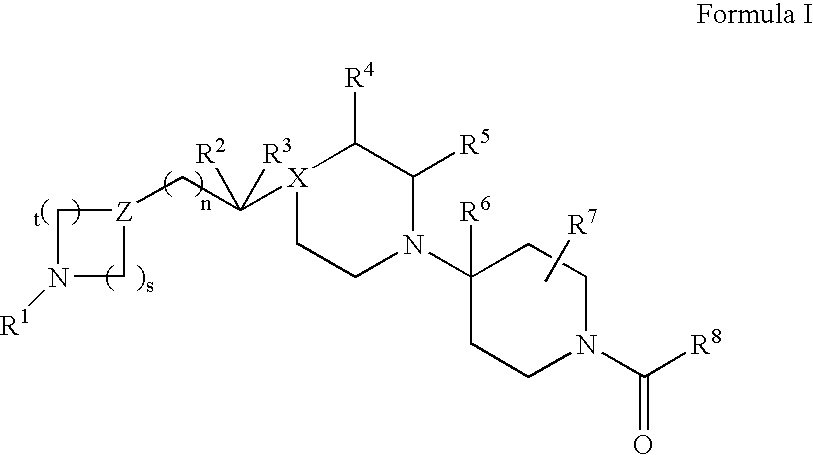
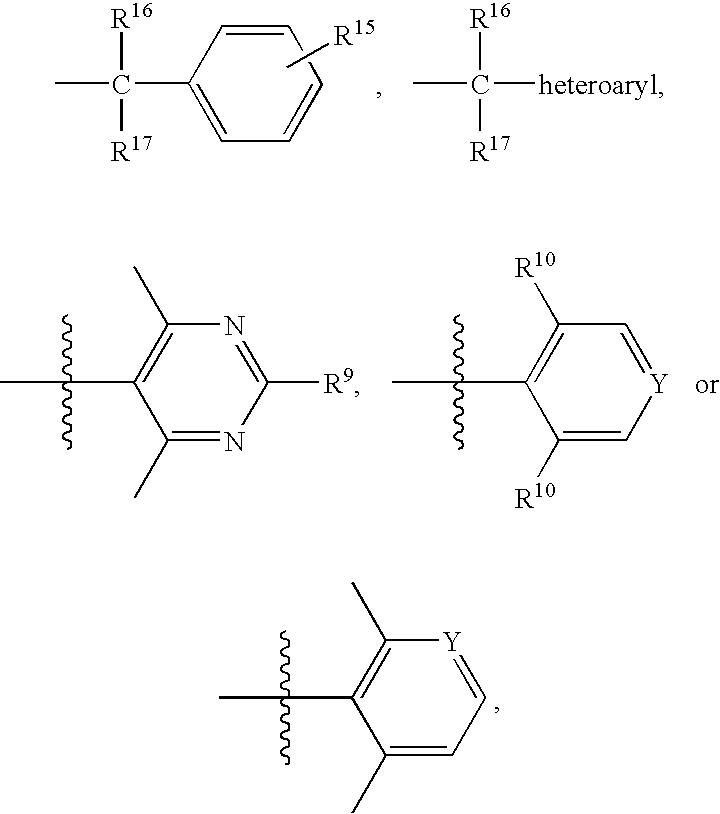
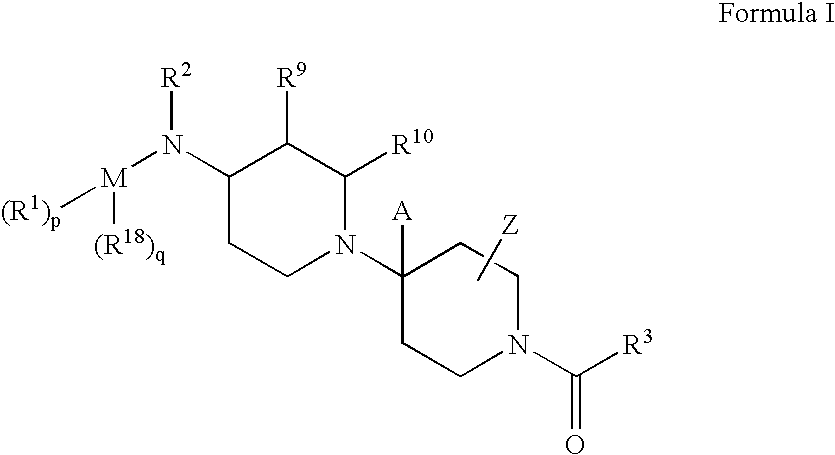
Piperidine derivatives useful as CCR5 antagonists
The present invention provides a compound of the formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, R<9>, R<10>, A and B are as defined in the specification. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing the compound of this invention, and methods of treatment using the compound of this invention. The invention also relates to the use of a combination of a compound of this invention and one or more antiviral or other agents useful in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The invention further relates to the use of a compound of this invention, alone or in combination with another agent, in the treatment of solid organ transplant rejection, graft v. host disease, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, asthma, allergies or multiple sclerosis.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Non-lethal methods for conditioning a recipient for bone marrow transplantation
InactiveUS20030165475A1Diminished proliferative and cytotoxic activityDosage of TBI can be further reducedBiocideEnergy modified materialsAcquired immunodeficiencyGackstroemia
The present invention relates to non-lethal methods of conditioning a recipient for bone marrow transplantation. In particular, it relates to the use of nonlethal doses of total body irradiation, total lymphoid irradiation, cell type-specific or cell marker-specific antibodies, especially antibodies directed to bone marrow stromal cell markers or the CD8 cell marker, cytotoxic drugs, or a combination thereof. The methods of the invention have a wide range of applications, including, but not limited to, the conditioning of an individual for hematopoietic reconstitution by bone marrow transplantation for the treatment of hematologic malignancies, hematologic disorders, autoimmunity, infectious diseases such as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and the engraftment of bone marrow cells to induce tolerance for solid organ, tissue and cellular transplantation.
Owner:ILDSTAD SUZANNE T
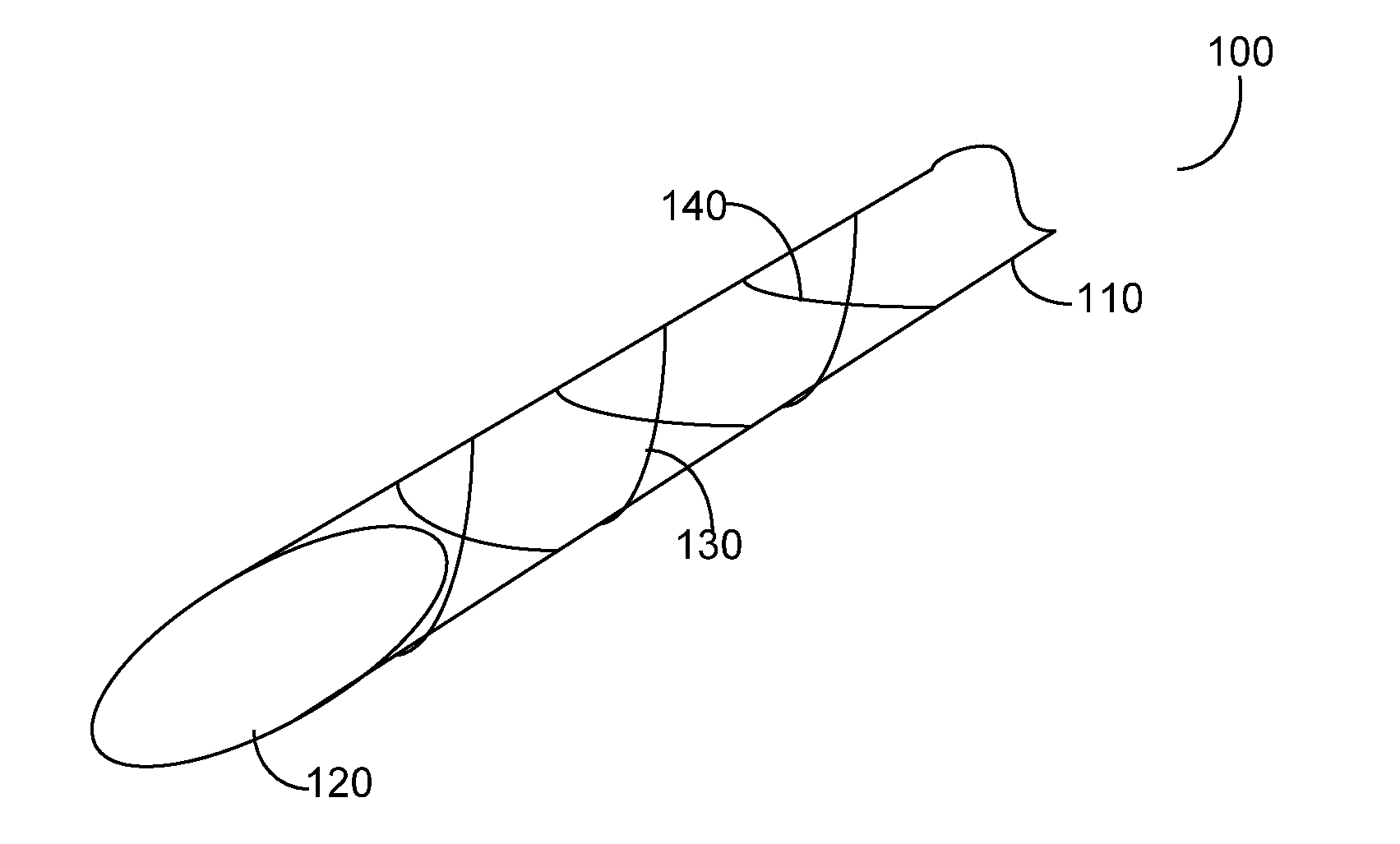
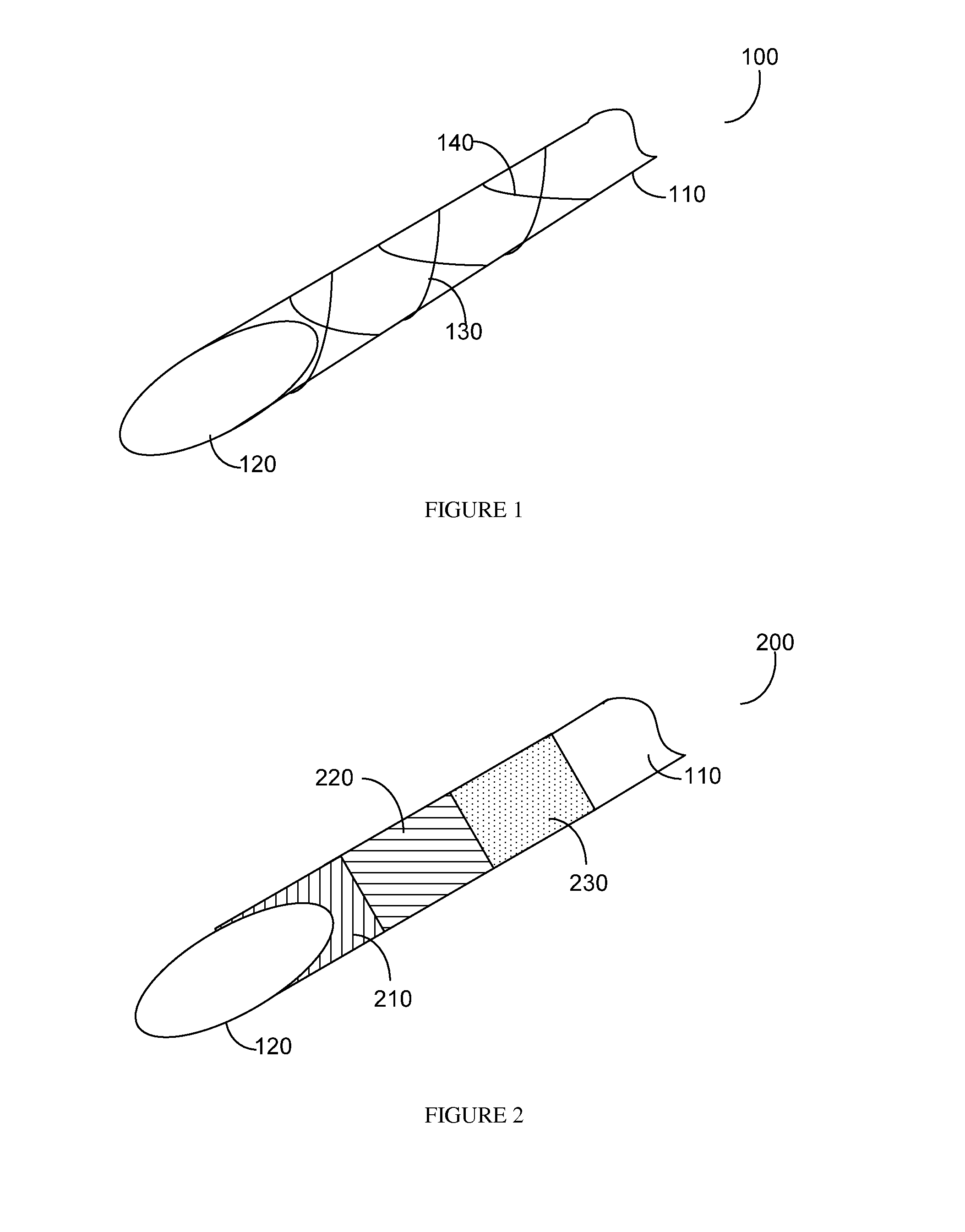
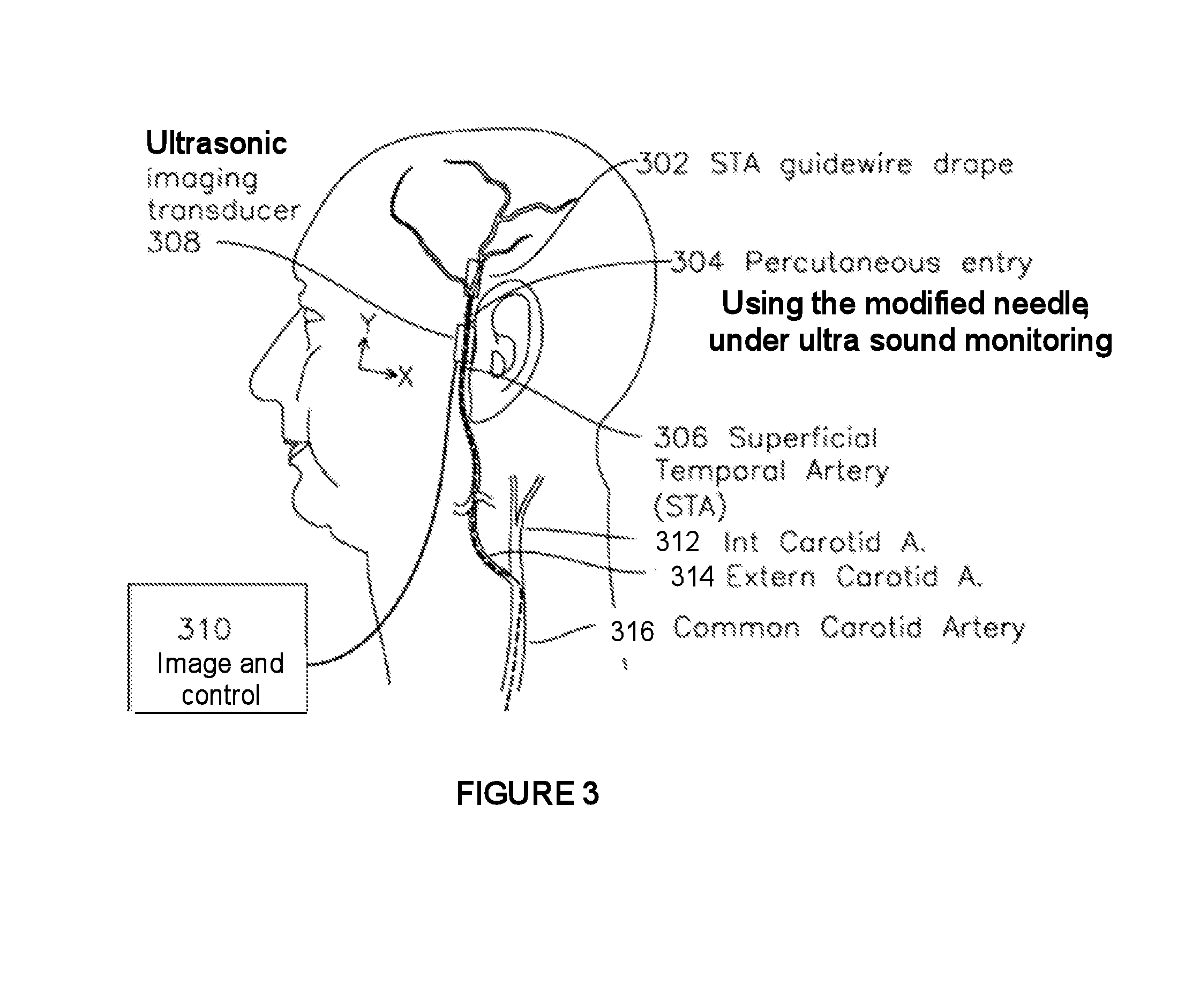
Hypodermic needle with enhanced ultrasound signature for carotid artery stenting
A hypodermic needle outer surface deflects ultrasound signals hitting the surface. The reflected signals depend on the surface which the ultrasound signal hits. According to the invention the outer surface of the needle, beginning at the tip or cutting edge of the needle featuring any one or more of: a) dimples having one or more distinct patterns; b) pits, randomly scattered; and, c) double helix, i.e., two grooves starting at an angle apart, preferably 180 degrees, and spiraling backwards in a helical fashion from the tip. By periodically repeating different pattern(s) for a predetermined length of the needle the position of the needle can be accurately identified using ultrasound imaging. The needle, in different lengths and gauges, can be used to facilitate stenting of the carotid artery as well as other ultrasound guided procedures such as biopsies, drainages / aspirations, solid organ tumor ablations and vascular access in general.
Owner:SYED MUBIN I
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS8114124B2Easy and fast applicationCompression of tissueForeign body detectionSurgical veterinaryWound healingParenchyma
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Function Inhibitor of Effector Cell
InactiveUS20070270429A1Inhibit functioningBiocideOrganic chemistryAutoimmune conditionIslet cell transplantation
The present invention relates to a function inhibitor of an effector cell comprising a CCR5 antagonist. Since the function inhibitor of an effector cell comprising a CCR5 antagonist inhibits the function of effector cells which play an important role in formation of diseases and the like, it is effective for the prevention and / or treatment of, for example, a transplant rejection (e.g., rejection of a solid organ graft, rejection of islet cell transplantation in diabetes mellitus, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), etc.), an autoimmune disease (e.g., arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, ulcerative colitis, etc.), an allergic disease (e.g., asthma, etc.), an ischemic disease (e.g., ischemia-reperfusion injury, etc.), cancer or a metastatic disease or the like.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions and methods for biodegradable microspheres as carriers of bioactive substances
InactiveUS6962716B1Cost-effective and scalablePowder deliveryLiquid surface applicatorsActive matterPolymer solution
A cost-effective, scalable technique for producing microspheres loaded with biologically active solid proteins is provided. The microspheres degrade over time and release biologically active VEGF, as demonstrated by the proliferation of HUVECs in vitro compared to negative controls. A defined concentration of microspheres can deliver a quantifiable level of VEGF with known release kinetics. The invention can be used with other growth factors and applied to tissue engineering applications such as the regeneration of peripheral nerve, bone, adipose tissue, and solid organs. The method of the invention includes the steps of dissolving a polymer with an organic solvent to produce a polymer solution; adding a biologically effective amount of a bioactive substance to the solution to produce a mixture of the polymer and the bioactive substance; vibrating the mixture to produce a bioactive substance-polymer complex; emulsifying the mixture to produce an emulsion comprising the bioactive substance-polymer complex; and extracting the organic solvent from the emulsion to produce microspheres comprising the polymer-bioactive substance complex, wherein the bioactivity of the bioactive substance is usefully preserved.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
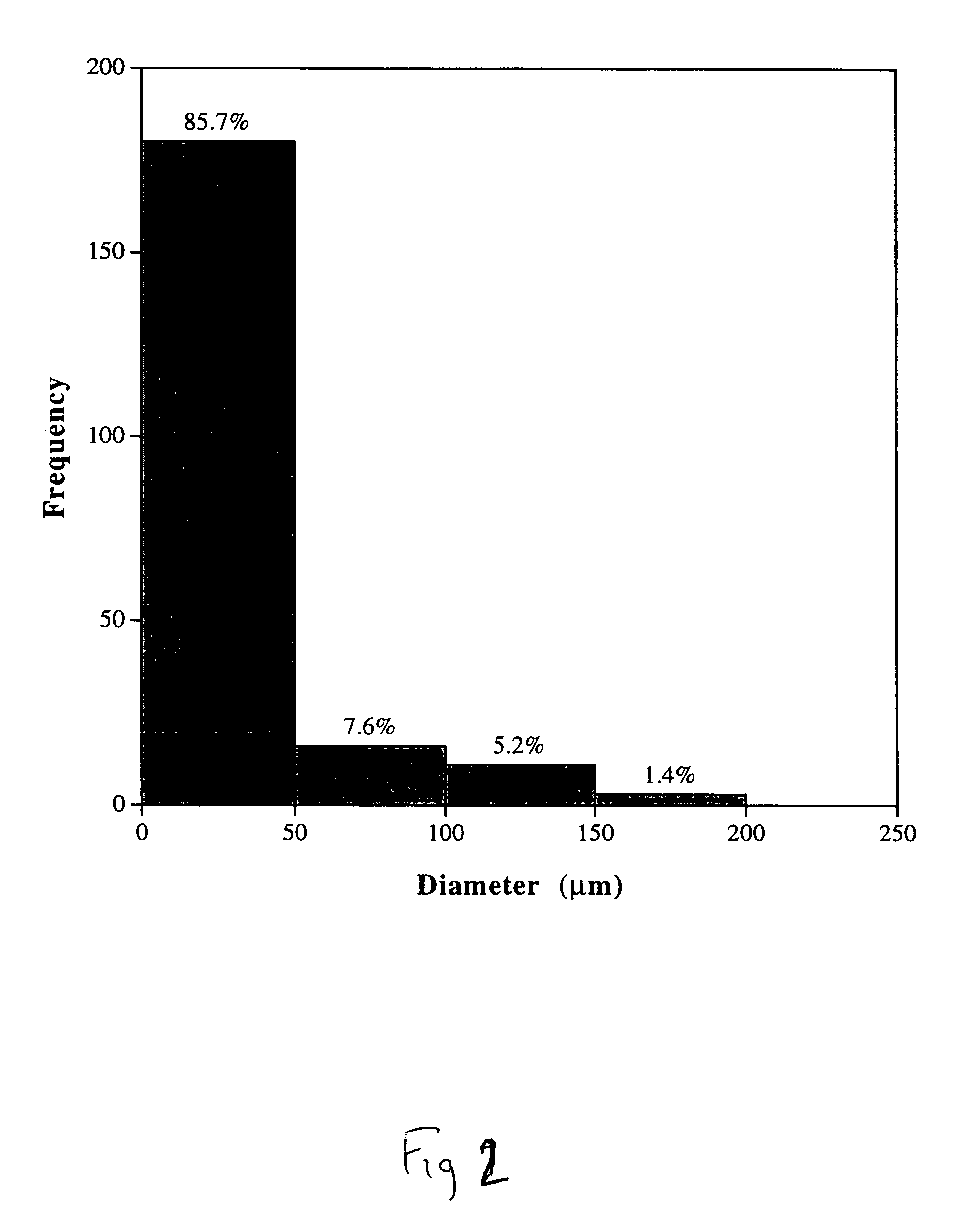
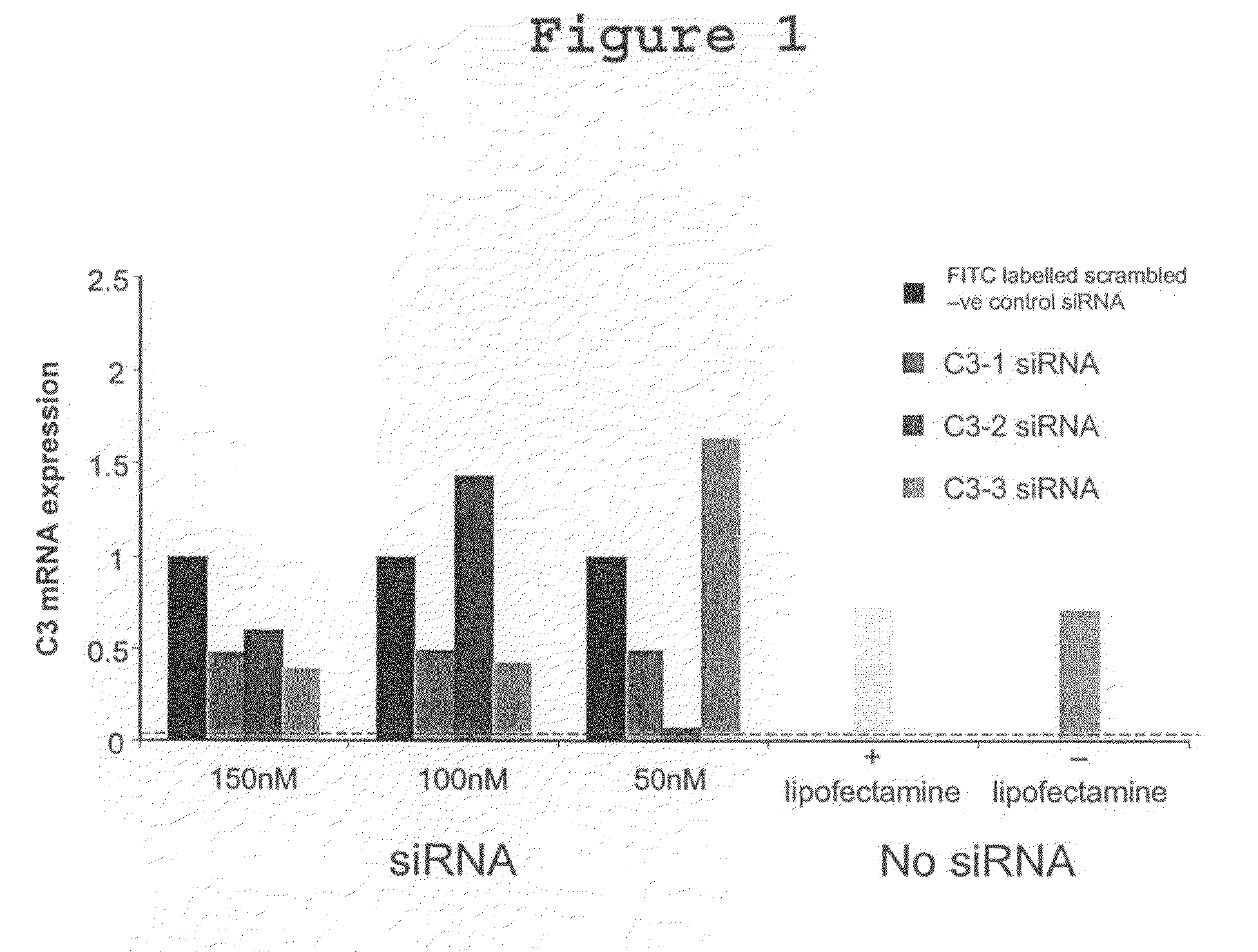
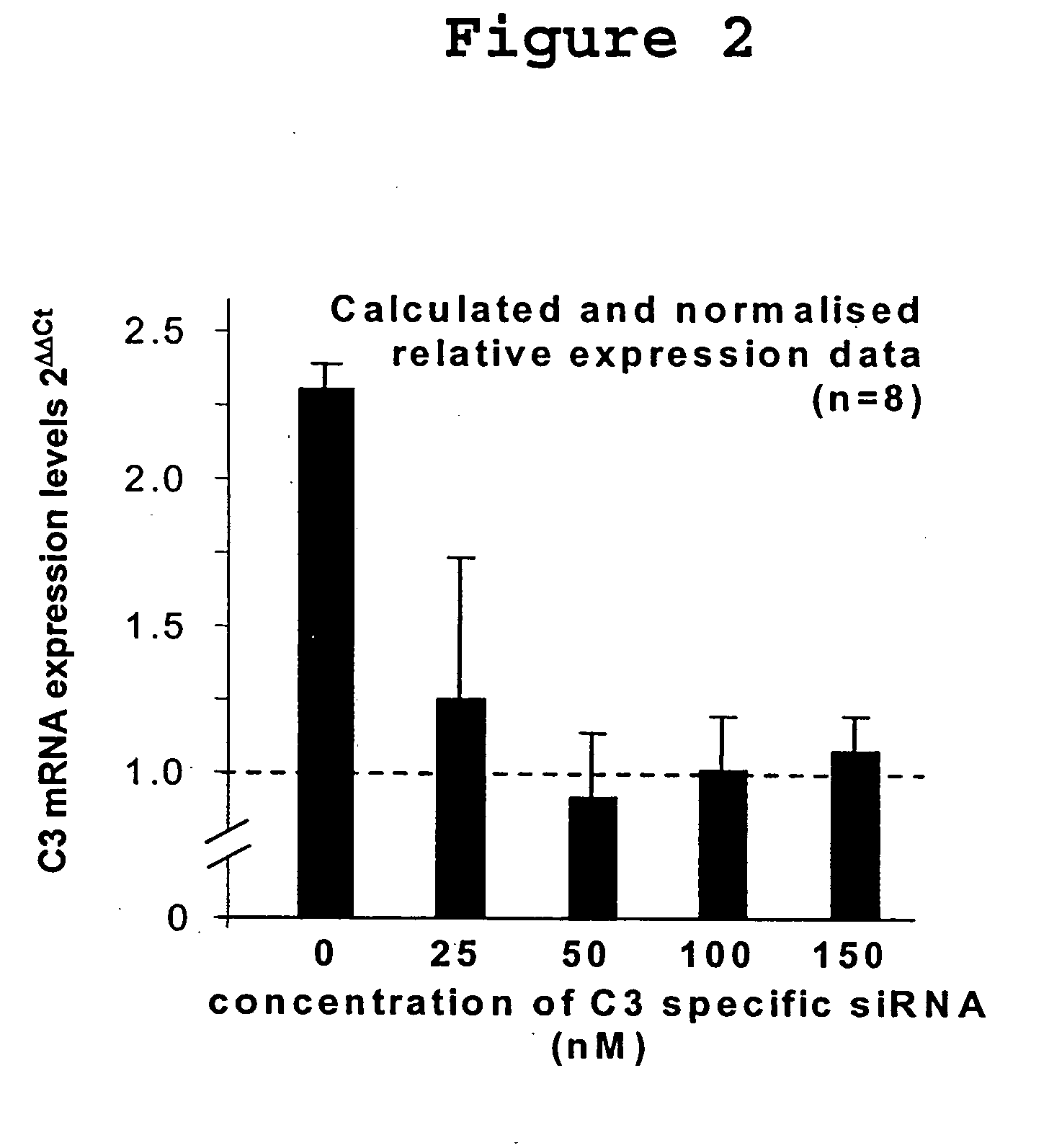
Compositions and Methods of Using siRNA to Knockdown Gene Expression and to Improve Solid Organ and Cell Transplantation
InactiveUS20100028848A1Suppression of rejectionInhibit expressionSugar derivativesSpecial deliveryTransplanted OrgansSolid organ
This invention describes compositions and methods using siRNA to target various genes expressed in cells of transplanted organs or tissues and / or genes expressed in the host to improve the success of the transplantation.
Owner:INTRADIGM CORP +1
Method, an optical probe and a confocal microscopy system for inspecting a solid organ
ActiveUS20120184842A1Enhancing ultrasound visualizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryFiber bundleConfocal microscopy
A method to inspect a solid organ in a subject includes introducing a needle in a predetermined area of the solid organ, inserting an optical probe through a lumen of the needle, and imaging the predetermined area using the optical probe. An optical probe to inspect a solid organ in a subject, the optical probe being intended to be positioned in the solid organ through a needle, the optical probe includes an optical fiber bundle, a ferule to protect the distal tip of the optical fiber bundle, the ferule comprising a shank and a head, and a sheath wrapping the fiber bundle and the shank, wherein the head of the ferule has a length adapted for the optical probe to image the solid organ while keeping the sheath inside the needle.
Owner:MAUNA KEA TECHNOLOGIES
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS20070255315A1Easy to optimizeEasy and fast applicationForeign body detectionSurgical veterinaryTrauma surgeryParenchyma
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in solid visceral wounds. Such devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdominal viscera. The devices utilize flexible, variable depth transfixing bolts that penetrate the viscera. These bolts are pulled tight to bring the tissue into apposition and hold said tissue in apposition while the wound heals. These bolts, or soft tissue rivets, overcome the limitations of sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The bolts come in a variety of lengths and diameters. Since the bolts are flexible, the curvature can be adjusted by the surgeon. The devices are flexible, bendable, and conformable in their wet or dry state. They can be used either straight or configured in a broad range of curvatures to suit the needs of various pathologies. The bolts include pressure plates that are capable of exerting compressive pressure over broad areas of visceral wounds without causing tearing of the friable parenchyma. The bolts may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access. The bolts can be placed into tissue where both sides of the bolt are exposed, or the bolts can be placed blindly into tissue where the bolt does not protrude out of the tissue at its distal end.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Systemic gene delivery vehicles for the treatment of tumors
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
Piperidine derivatives useful as CCR5 antagonists
The present invention provides a compound of the formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein the various moieties are as defined in the specification. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing the compound of this invention, and methods of treatment using the compound of this invention. The invention also relates to the use of a combination of a compound of this invention and one or more antiviral or other agents useful in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The invention further relates to the use of a compound of this invention, alone or in combination with another agent, in the treatment of solid organ transplant rejection, graft v. host disease, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, asthma, allergies or multiple sclerosis.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Production of typed human cells, tissues and organs
InactiveUS20020100065A1High yieldNew breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsCord blood stem cellMammal
A method of obtaining a high yield of differentiated human cells and organs includes the steps of providing typed human bone marrow or cord blood stem cells, providing pre-immune non-human mammalian fetuses, implanting the cells into the fetuses, permitting the fetuses to grow for a sufficient time to produce differentiated cells in hybrid organs, and harvesting the differentiated cells from the mammals. A method is presented to produce hybrid functioning human-animal solid organs for clinical transplantations. The method includes obtaining bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMNC) from the patient, obtaining enriched populations of HSC from the BMNC, and transplanting the enriched cells into Preimmune fetal sheep or pigs intraperitoneally to produce functioning donor (patient)-animal hybrid organs. A method is also presented in which enriched HSC isolated from pre-HLA typed normal human fetal liver / bone marrow, cord blood, or bone marrow will be transplanted into preimmune fetal sheep or pigs in order to create functioning human-animal hybrid organs that can be transplanted into compatible patients. Methods are also presented to obtain high yield of different types (e.g. hepatocytes) of donor (patient or HLA-typed normal donors) cells from the human-animal hybrid organs that can be used either for transplant into patients and / or treatment of the patient. Also disclosed is a method of producing purified human proteins that includes providing a non-human, pre-immune mammal into which human bone marrow or cord blood cells has been implanted into the mammal at the pre-immune state, obtaining blood from the non-human mammal, and isolating the human proteins from the mammalian blood.
Owner:ZANJANI ESMAIL D
Organ regeneration method utilizing blastocyst complementation
An object of the present invention is to produce a mammalian organ having a complicated cellular composition composed of multiple kinds of cells, such as kidney, pancreas, thymus and hair, in the living body of a non-human animal. The inventors of the present invention applied the chimeric animal assay described above, to a novel solid organ production method. More specifically, the inventors has shown that a model mouse which is deficient of kidney, pancreas, thymus or hair due to the dysfunction of the metanephric mesenchyme that is differentiated into most of an adult kidney, is rescued by blastocyst complementation by the chimeric animal assay, and whereby a kidney, a pancreas, thymus or hair can be newly produced.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Compositions and methods for diagnosis and prediction of solid organ graft rejection
Owner:IMMUCOR GTI DIAGNOSTICS
Decellularization and recellularization of organs and tissues
ActiveCN101272815BPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsDecellularizationBiology
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Bipiperidinyl derivatives useful as inhibitors of chemokine receptors
In its many embodiments, the present invention provides a novel class of bipiperidinyl compounds as inhibitors of the CCR5 receptors, methods of preparing such compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing one or more such compounds, methods of preparing pharmaceutical formulations comprising one or more such compounds, and methods of treatment, prevention, inhibition, or amelioration of one or more diseases associated with CCR5 using such compounds or pharmaceutical compositions. The invention also relates to the use of a combination of a compound of this invention and one or more antiviral or other agents useful in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The invention further relates to the use of a compound of this invention, alone or in combination with another agent, in the treatment of solid organ transplant rejection, graft v. host disease, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, asthma, allergies or multiple sclerosis.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
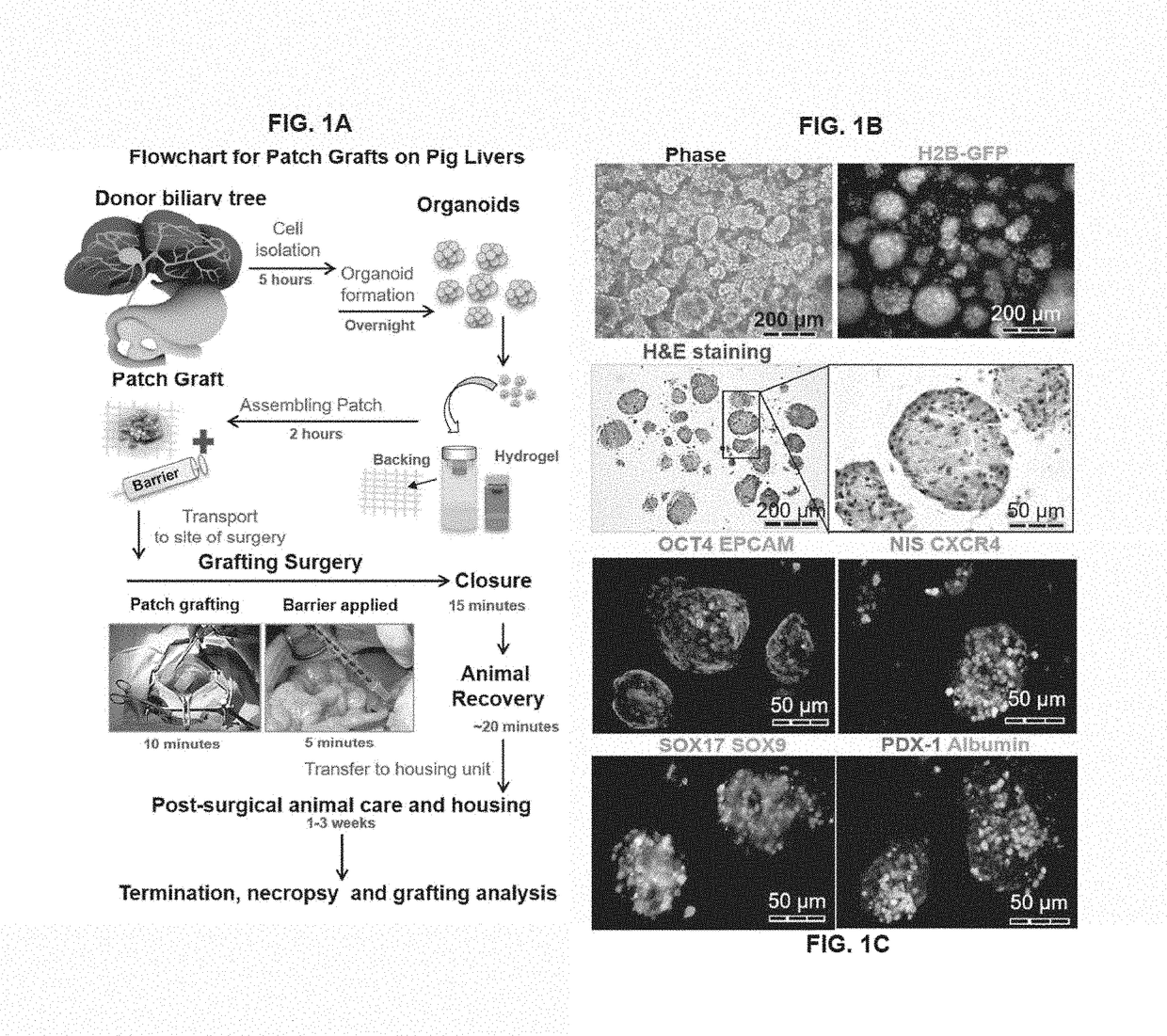
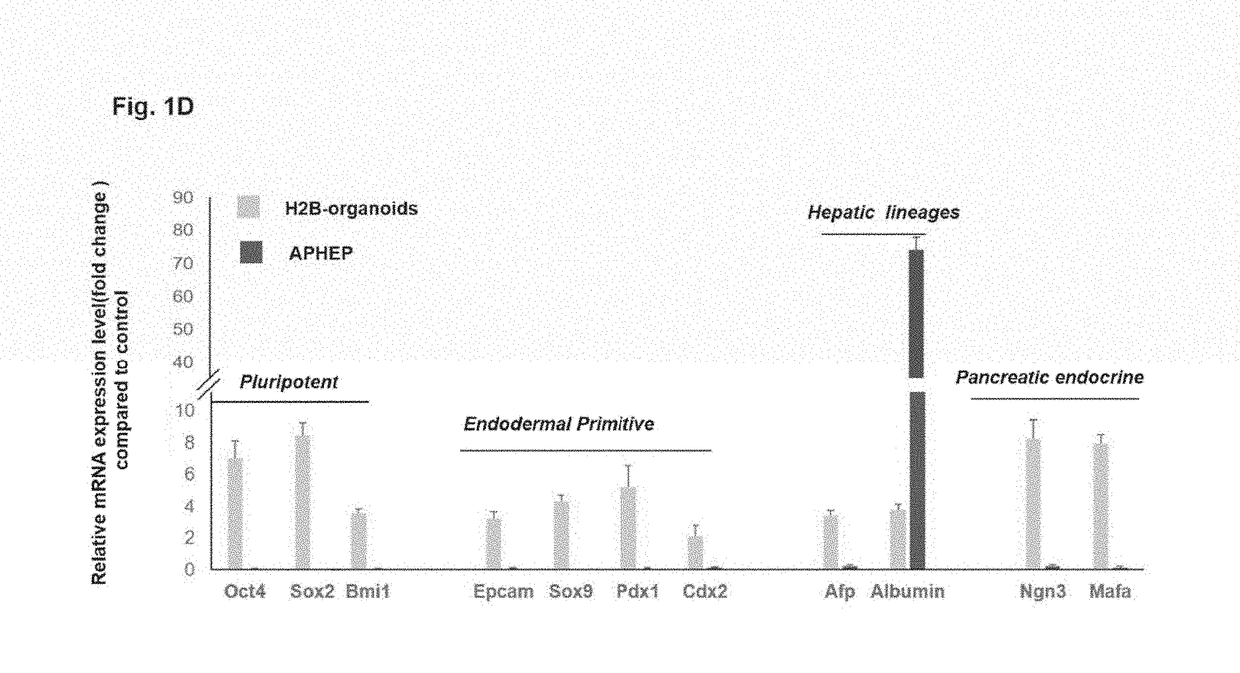
Patch graft compositions for cell engraftment
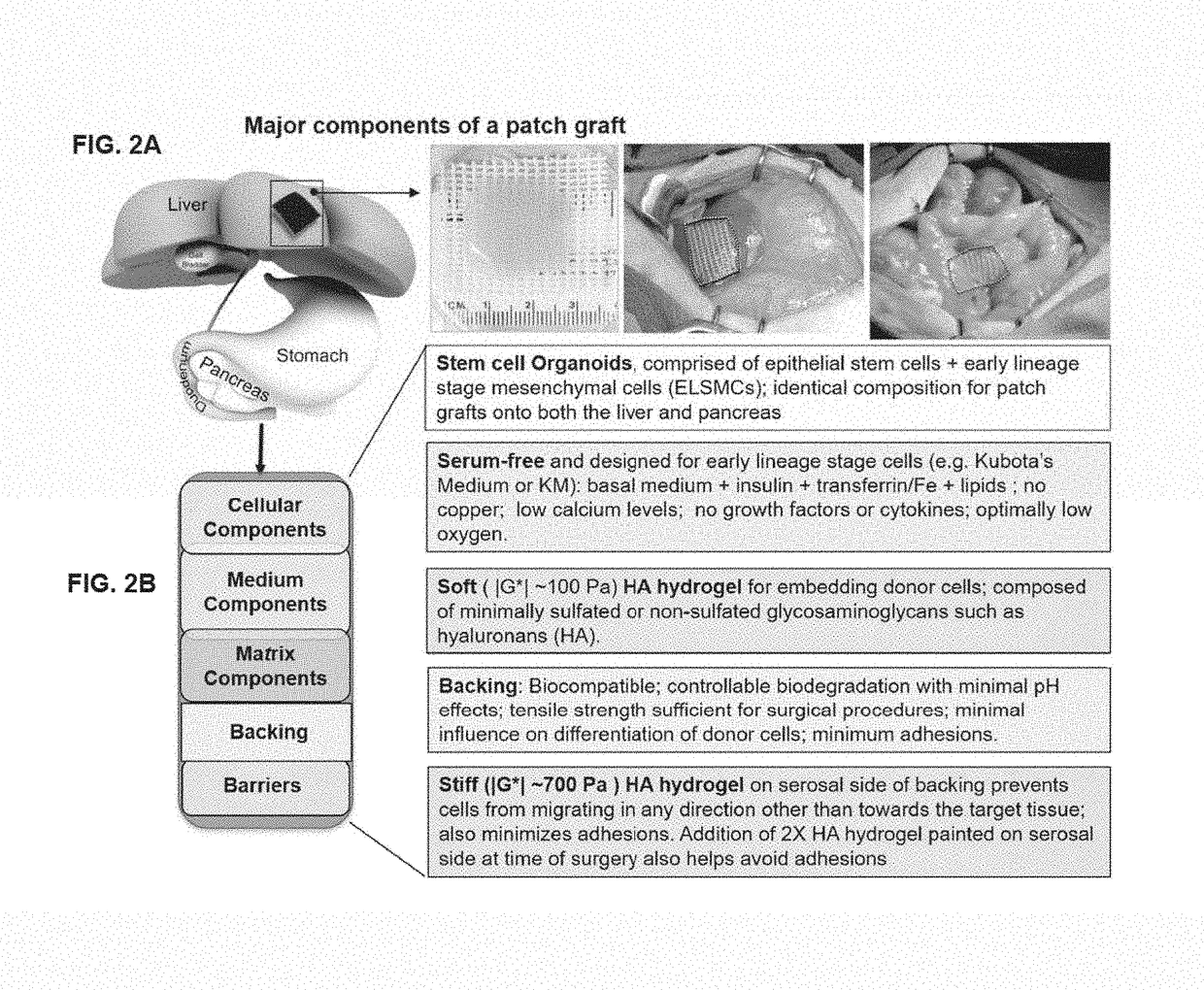
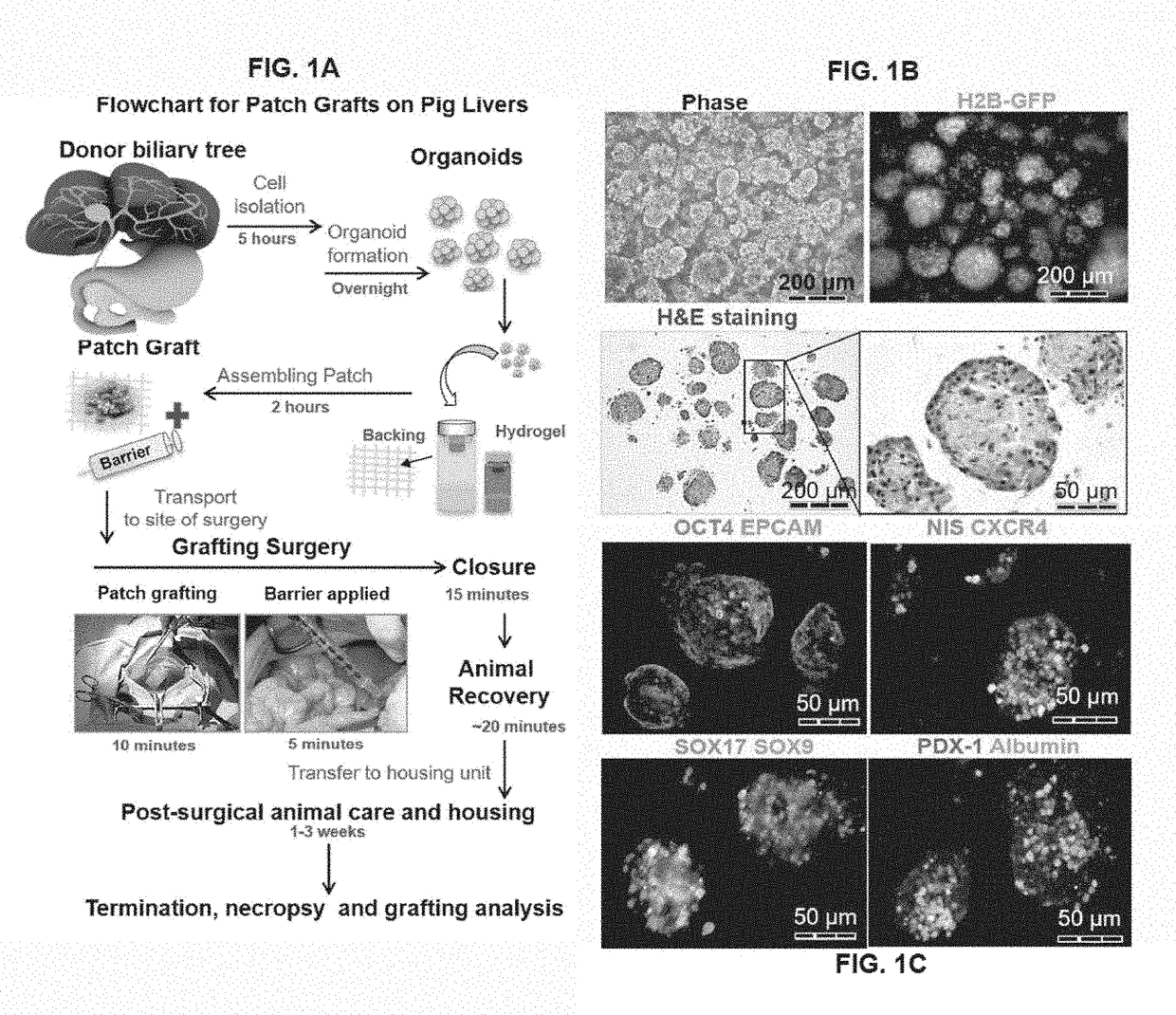
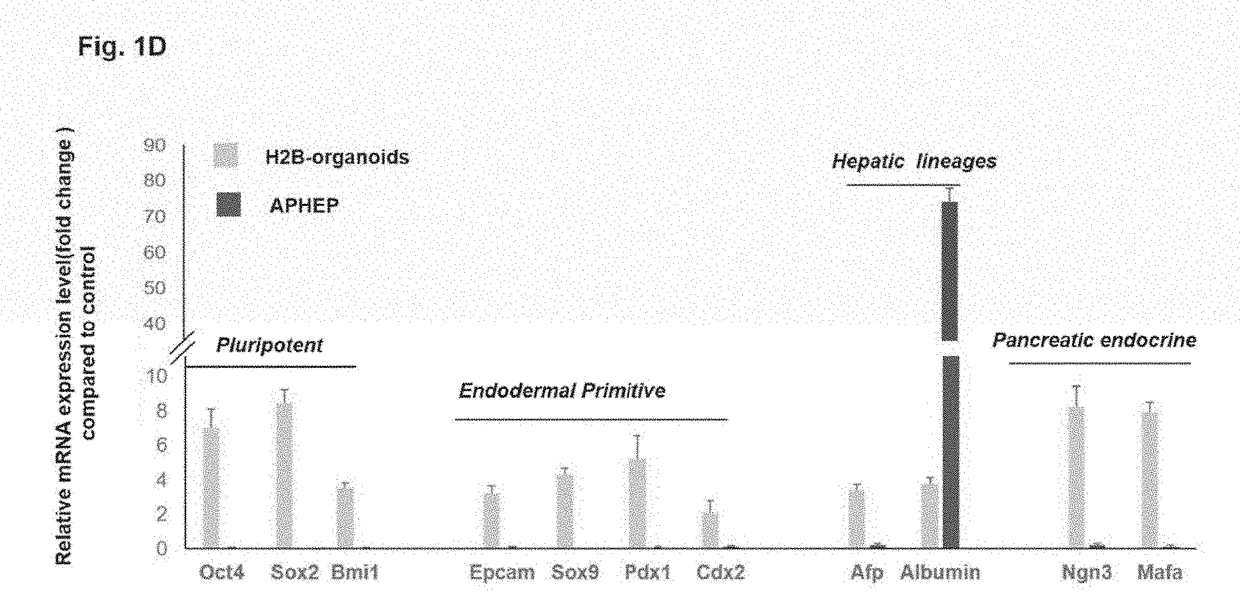
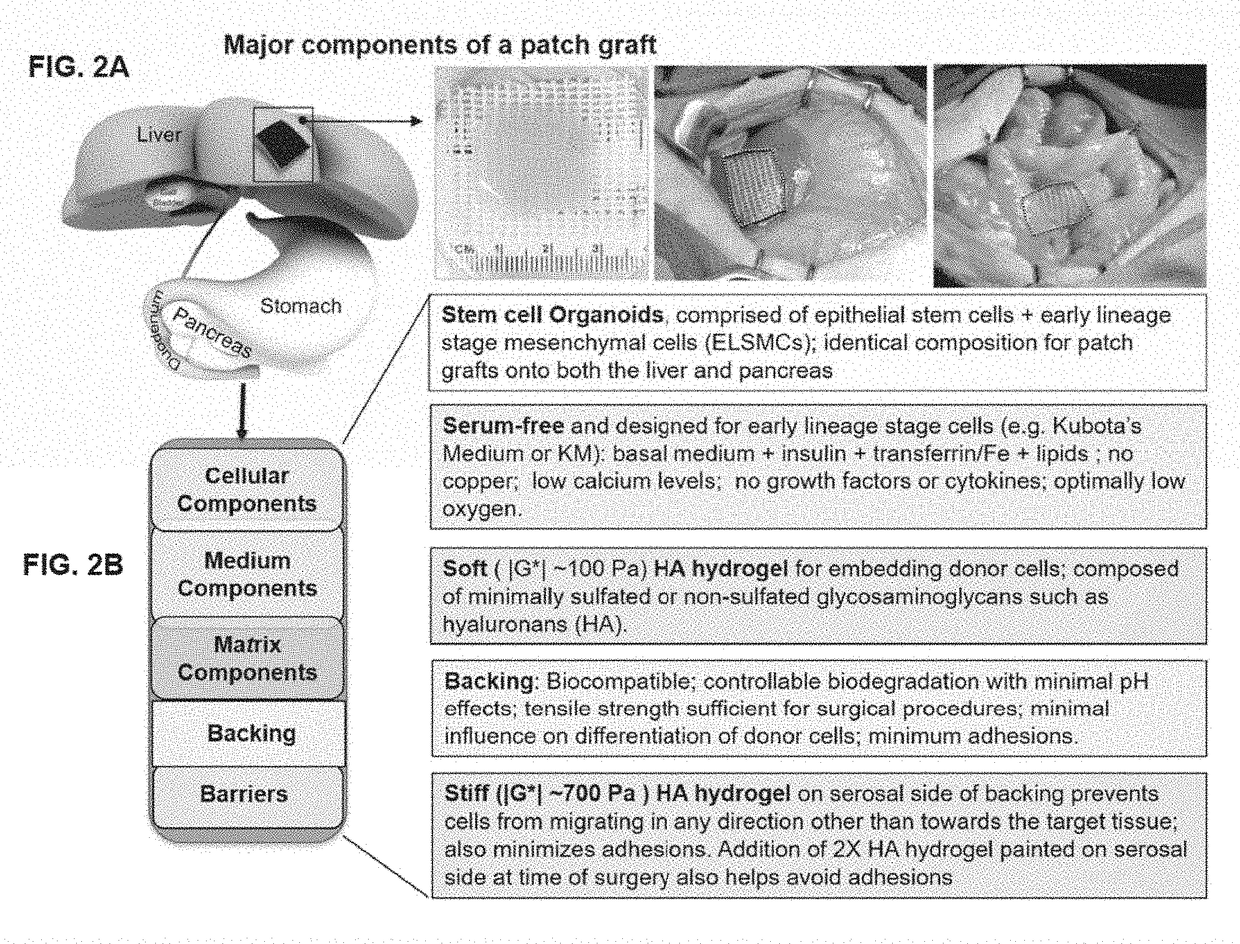
Compositions and methods of transplanting cells by grafting strategies into solid organs (especially internal organs) are provided. These methods and compositions can be used to repair diseased organs or to establish models of disease states in experimental hosts. The method involves attachment onto the surface of a tissue or organ, a patch graft, a “bandaid-like” covering, containing epithelial cells with supporting early lineage stage mesenchymal cells. The cells are incorporated into soft gel-forming biomaterials prepared under serum-free, defined conditions comprised of nutrients, lipids, vitamins, and regulatory signals that collectively support stemness of the donor cells. The graft is covered with a biodegradable, biocompatible, bioresorbable backing used to affix the graft to the target site. The cells in the graft migrate into and throughout the tissue such that within a couple of weeks they are uniformly dispersed within the recipient (host) tissue. The mechanisms by which engraftment and integration of donor cells into the organ or tissue involve multiple membrane-associated and secreted forms of MMPs.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Patch graft compositions for cell engraftment
Compositions and methods of transplanting cells by grafting strategies into solid organs (especially internal organs) are provided. These methods and compositions can be used to repair diseased organs or to establish models of disease states in experimental hosts. The method involves attachment onto the surface of a tissue or organ, a patch graft, a “bandaid-like” covering, containing epithelial cells with supporting early lineage stage mesenchymal cells. The cells are incorporated into soft gel-forming biomaterials prepared under serum-free, defined conditions comprised of nutrients, lipids, vitamins, and regulatory signals that collectively support stemness of the donor cells. The graft is covered with a biodegradable, biocompatible, bioresorbable backing used to affix the graft to the target site. The cells in the graft migrate into and throughout the tissue such that within a couple of weeks they are uniformly dispersed within the recipient (host) tissue. The mechanisms by which engraftment and integration of donor cells into the organ or tissue involve multiple membrane-associated and secreted forms of MMPs.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Immunologic activity measures for t helper on-associated conditions
InactiveUS20060216716A1Accurately reflectAddressing slow performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesWhite blood cellStimulant
A method of providing a reproducible and clinically relevant disease activity measurement for a group of immunologic disorders that share features of a T “helper” 1 (Th1) immune activation phenotype is disclosed. Th1 responses are characterized by the release of a set of pro-inflammatory substances by white blood cells (WBC) By evaluating the ex vivo activation response of whole blood in terms of the extent of release of Th1 produced pro-inflammatory substances in blood (i.e., WBC activity) following activation with a Th1-associated stimulant, the level of, e.g., disease activity or immunosuppression in a specific individual can be determined. The method of the invention provides a disease activity marker for a wide variety of Th1 inflammatory responses, including Crohn's Disease, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis and solid organ transplant rejection.
Owner:SAUBERMANN LAWRENCE J +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com