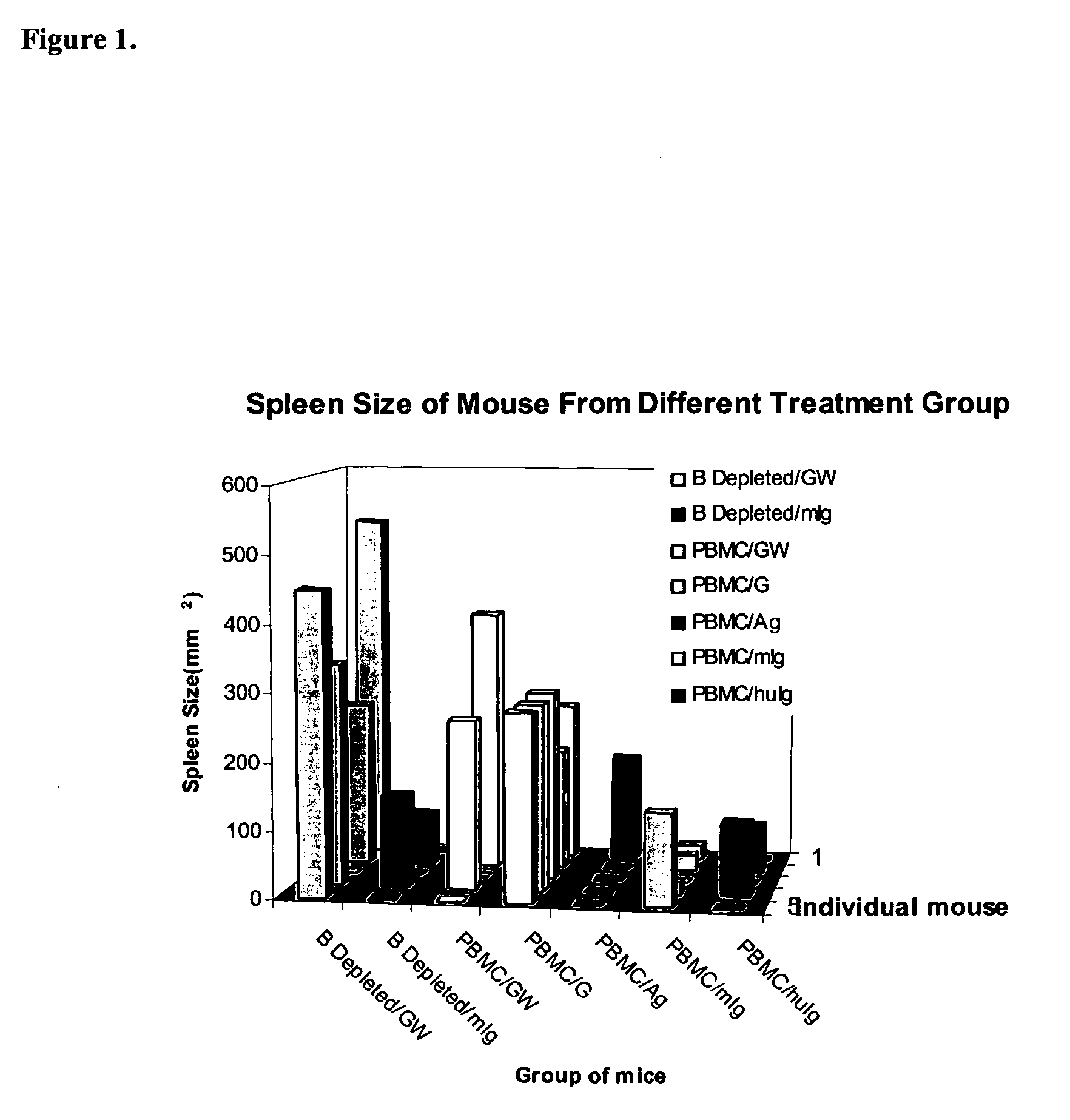
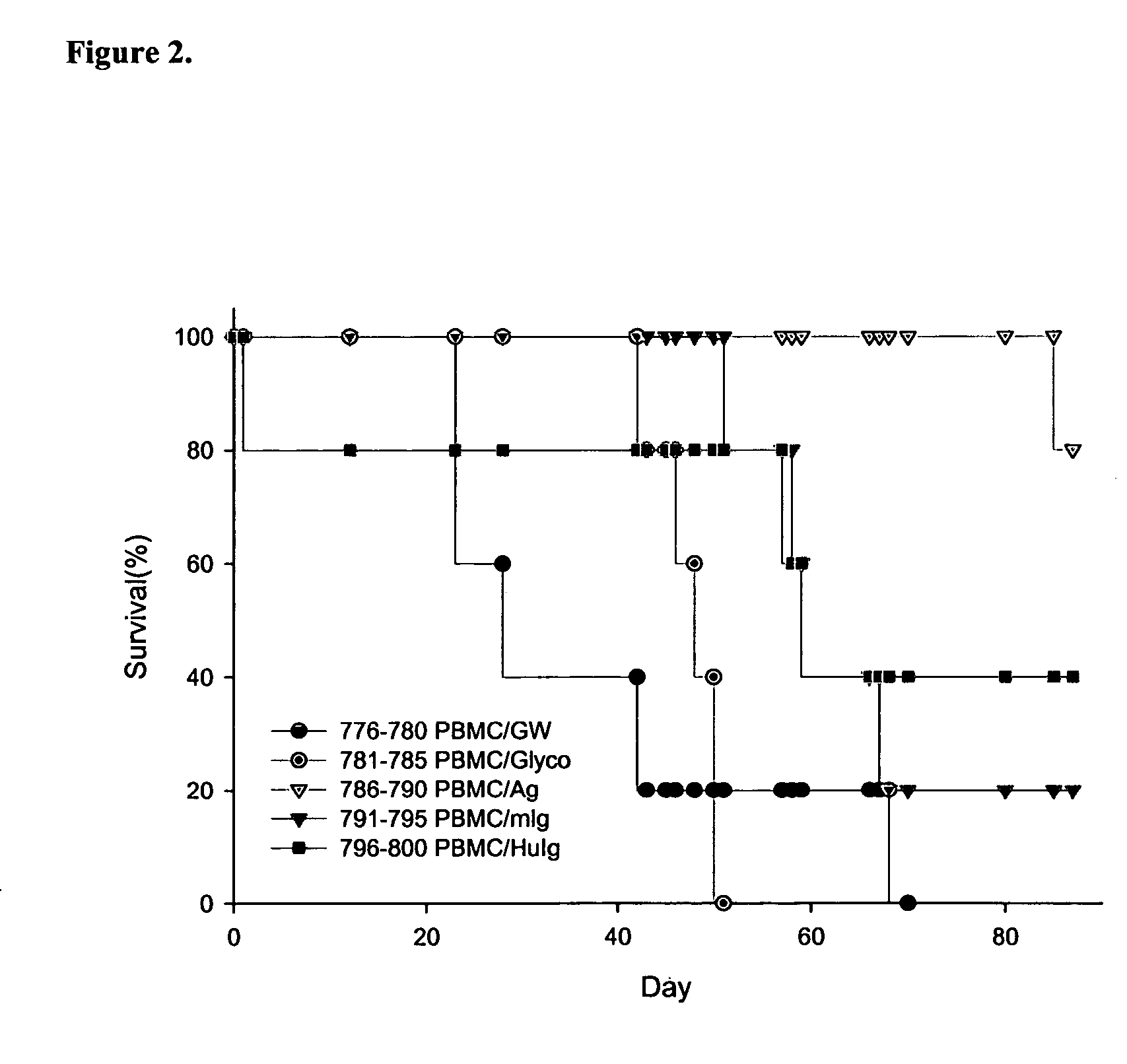
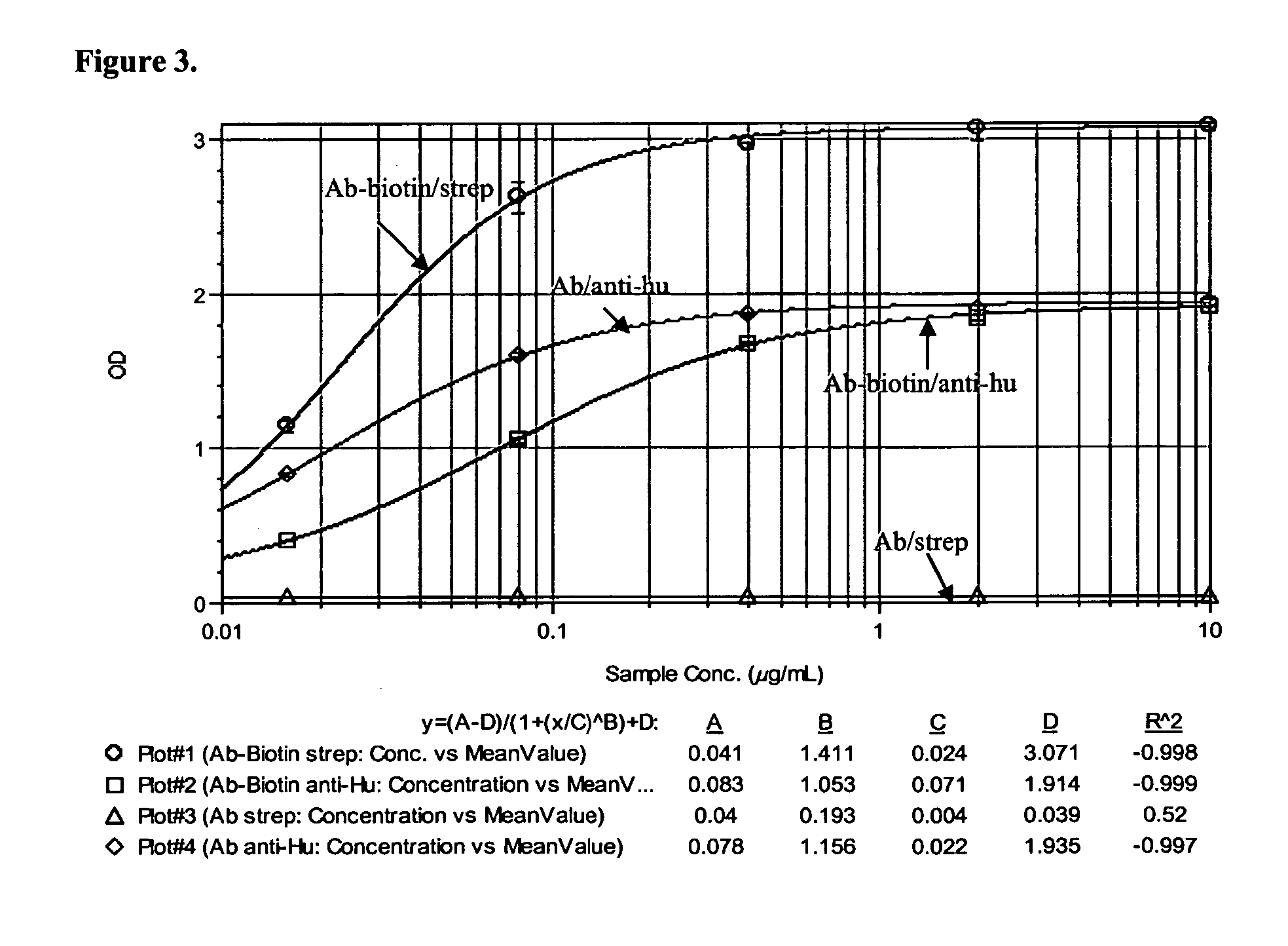
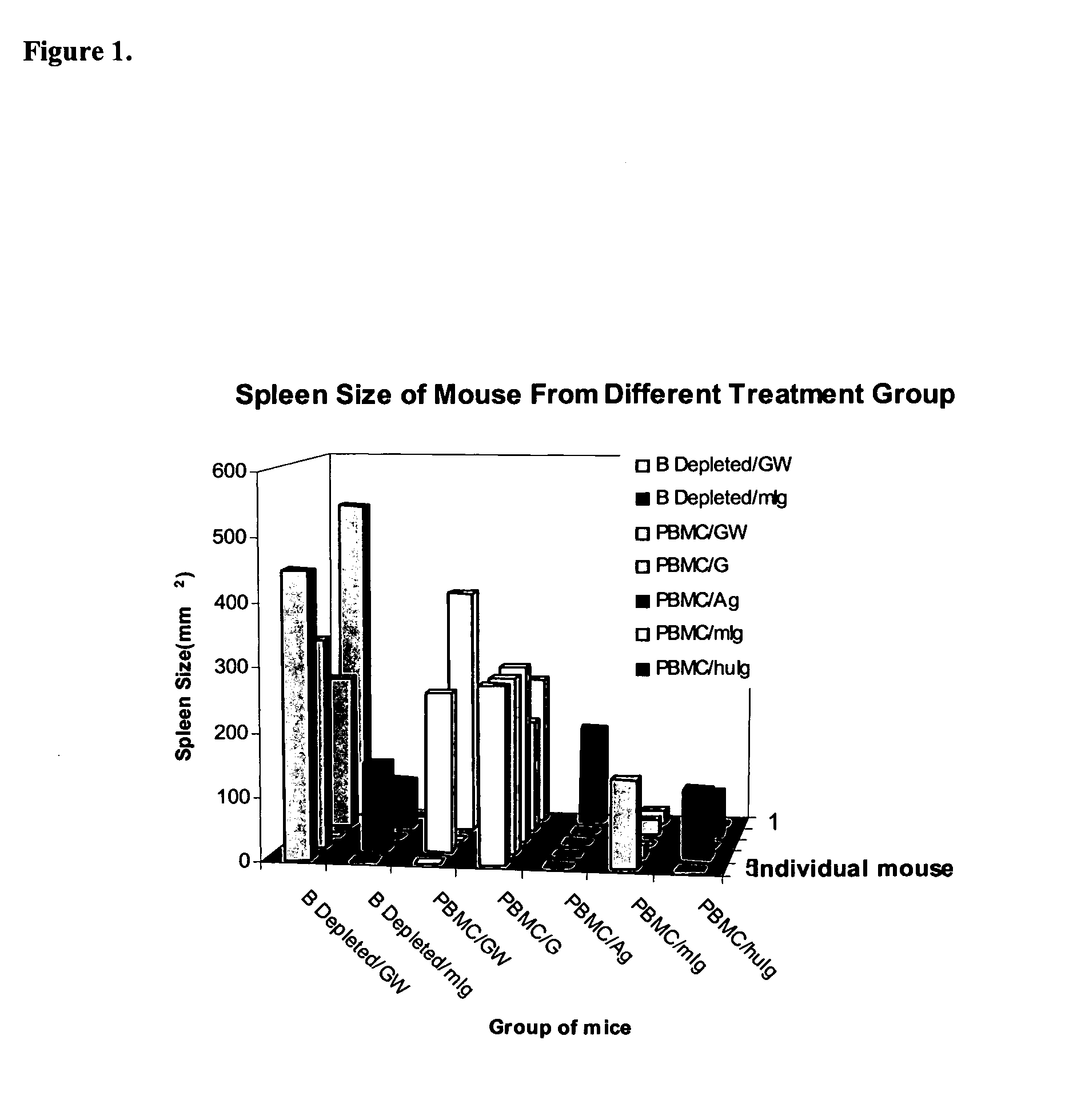
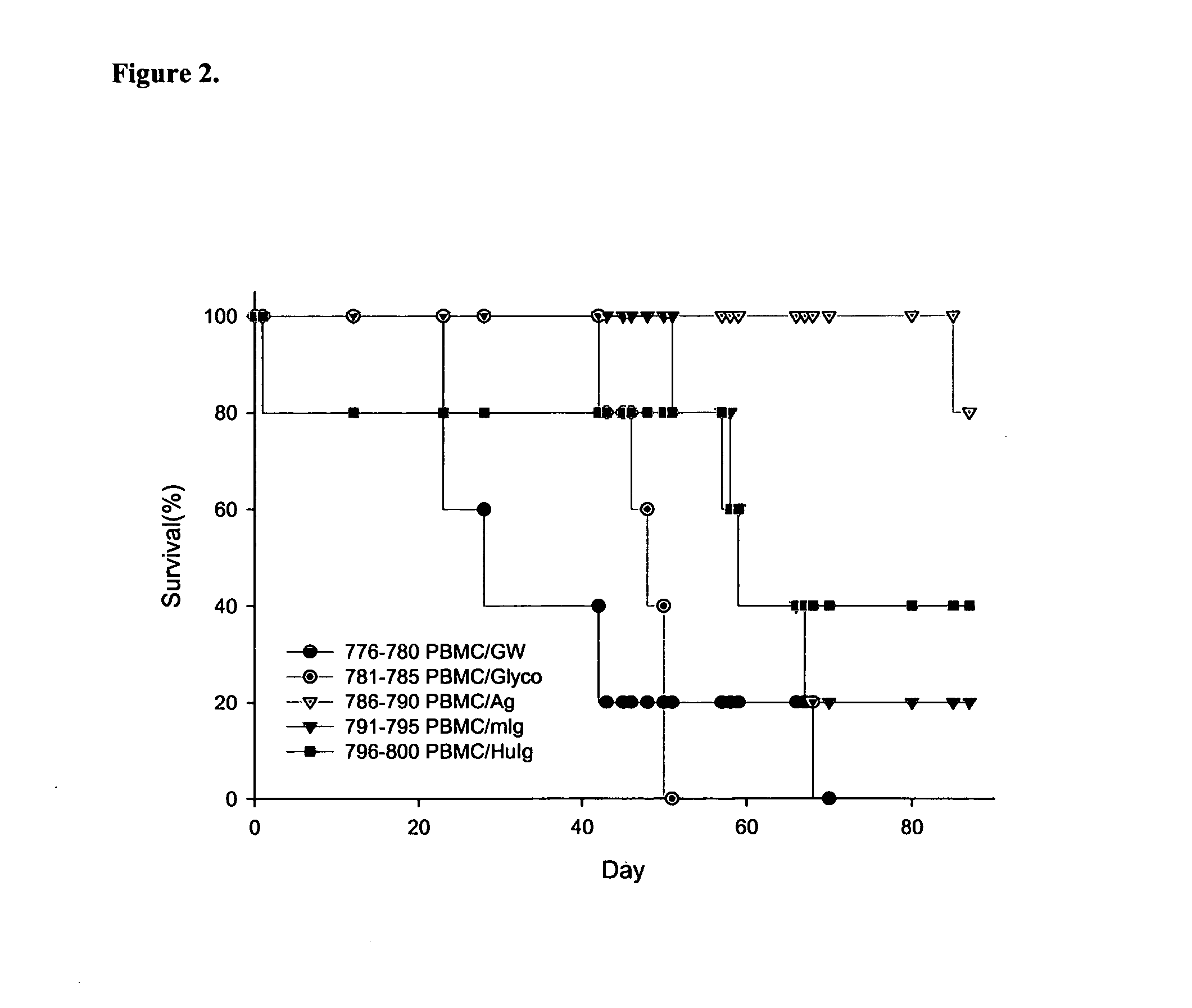
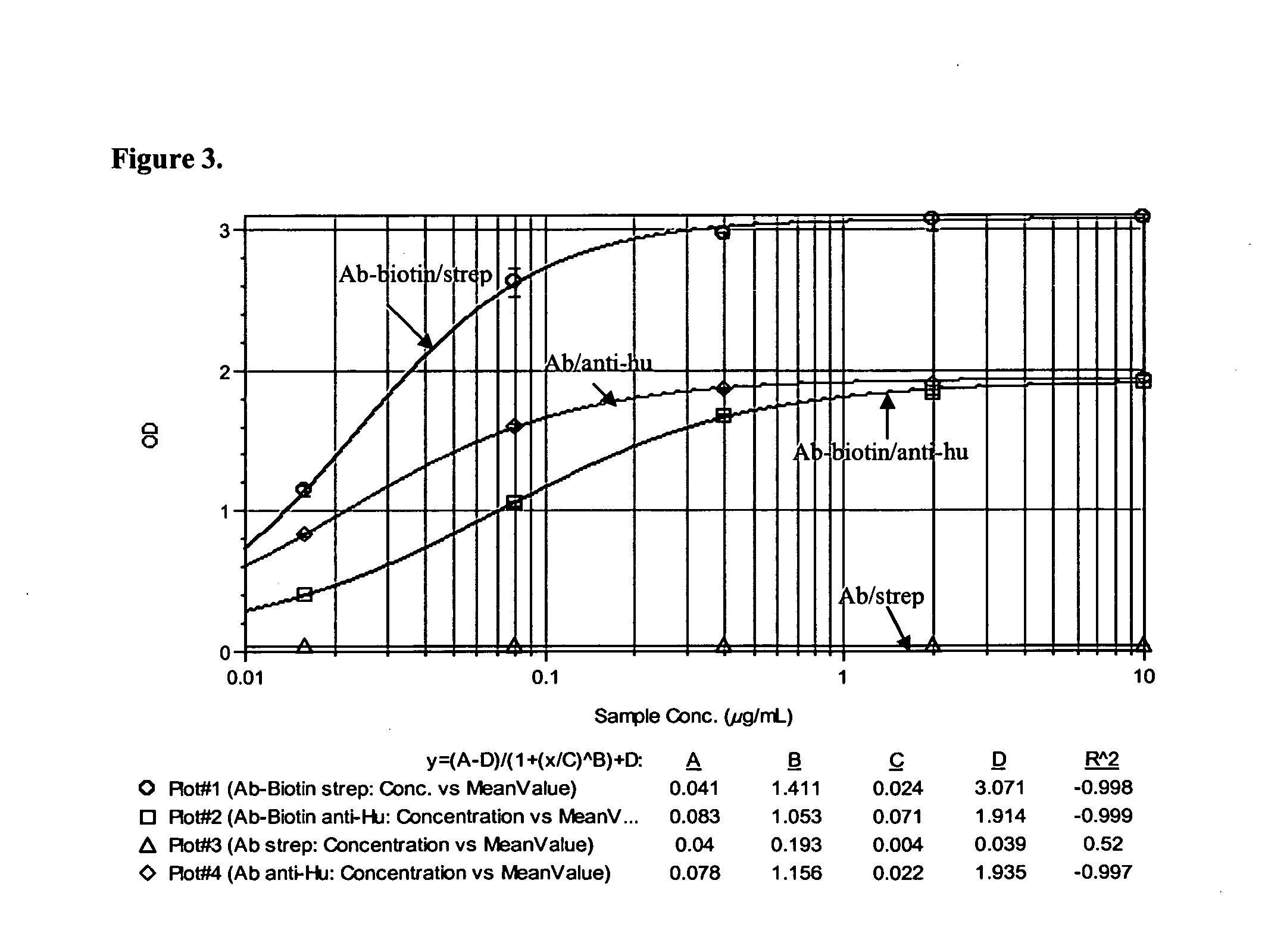
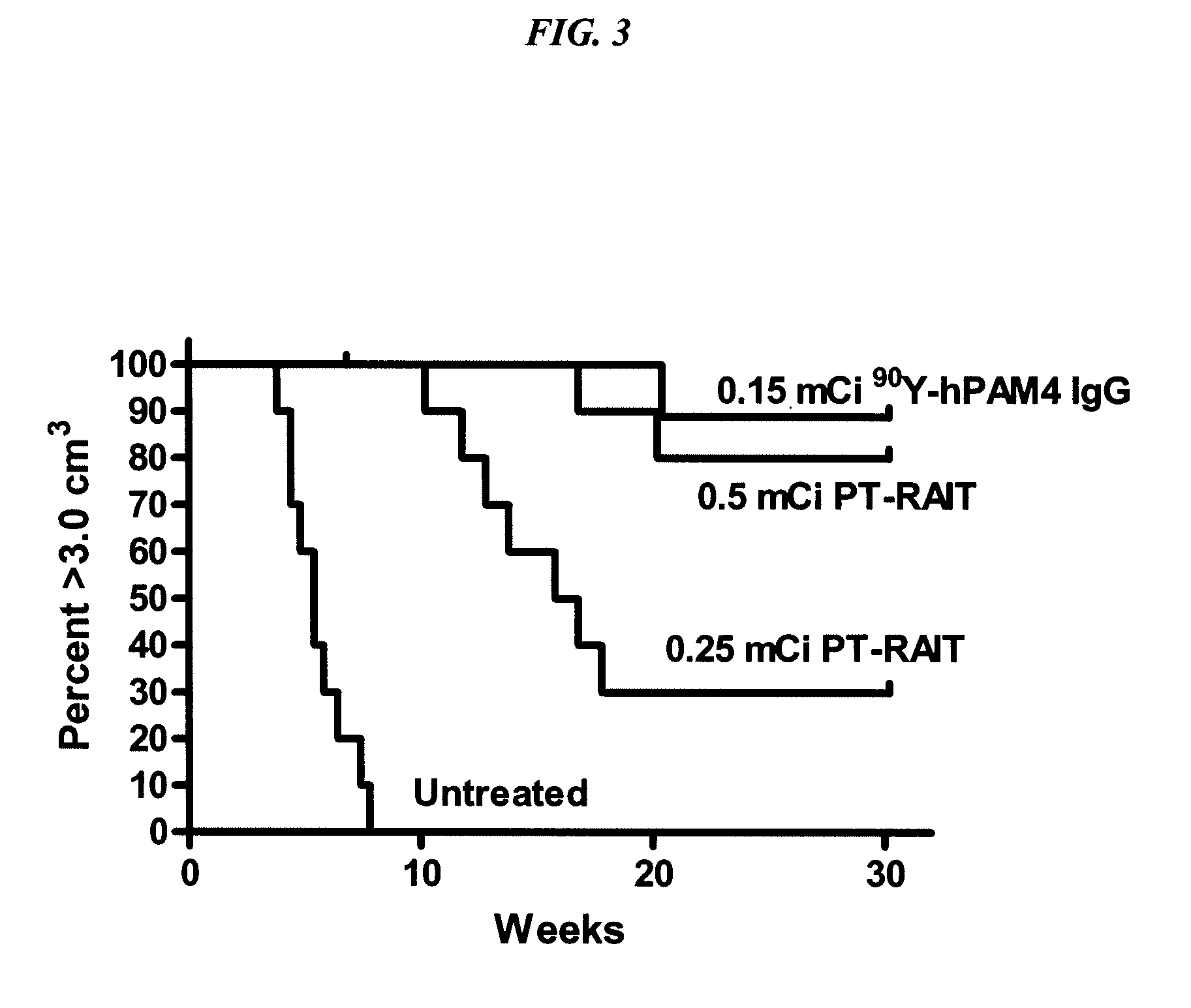
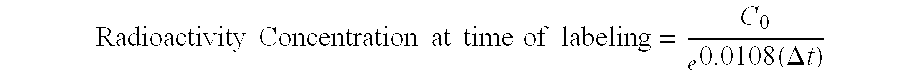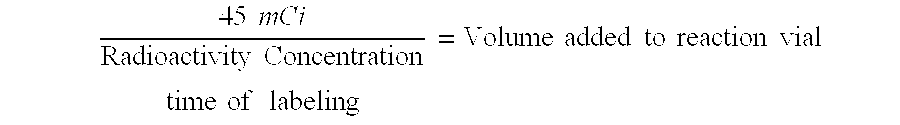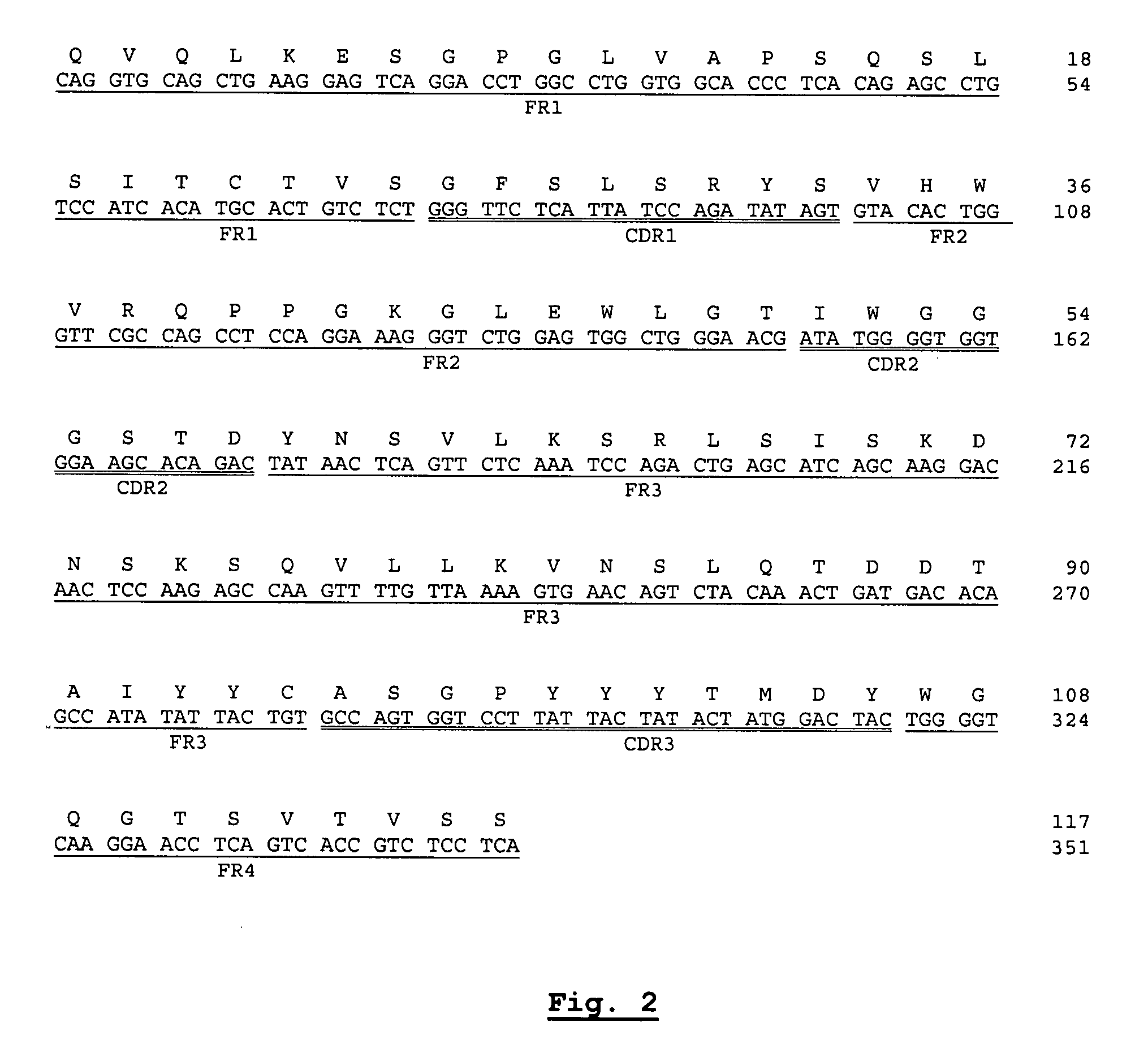Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Radioimmunotherapy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Radioimmunotherapy uses an antibody labeled with a radionuclide to deliver cytotoxic radiation to a target cell. In cancer therapy, an antibody with specificity for a tumor-associated antigen is used to deliver a lethal dose of radiation to the tumor cells. The ability for the antibody to specifically bind to a tumor-associated antigen increases the dose delivered to the tumor cells while decreasing the dose to normal tissues. By its nature, RIT requires a tumor cell to express an antigen that is unique to the neoplasm or is not accessible in normal cells.
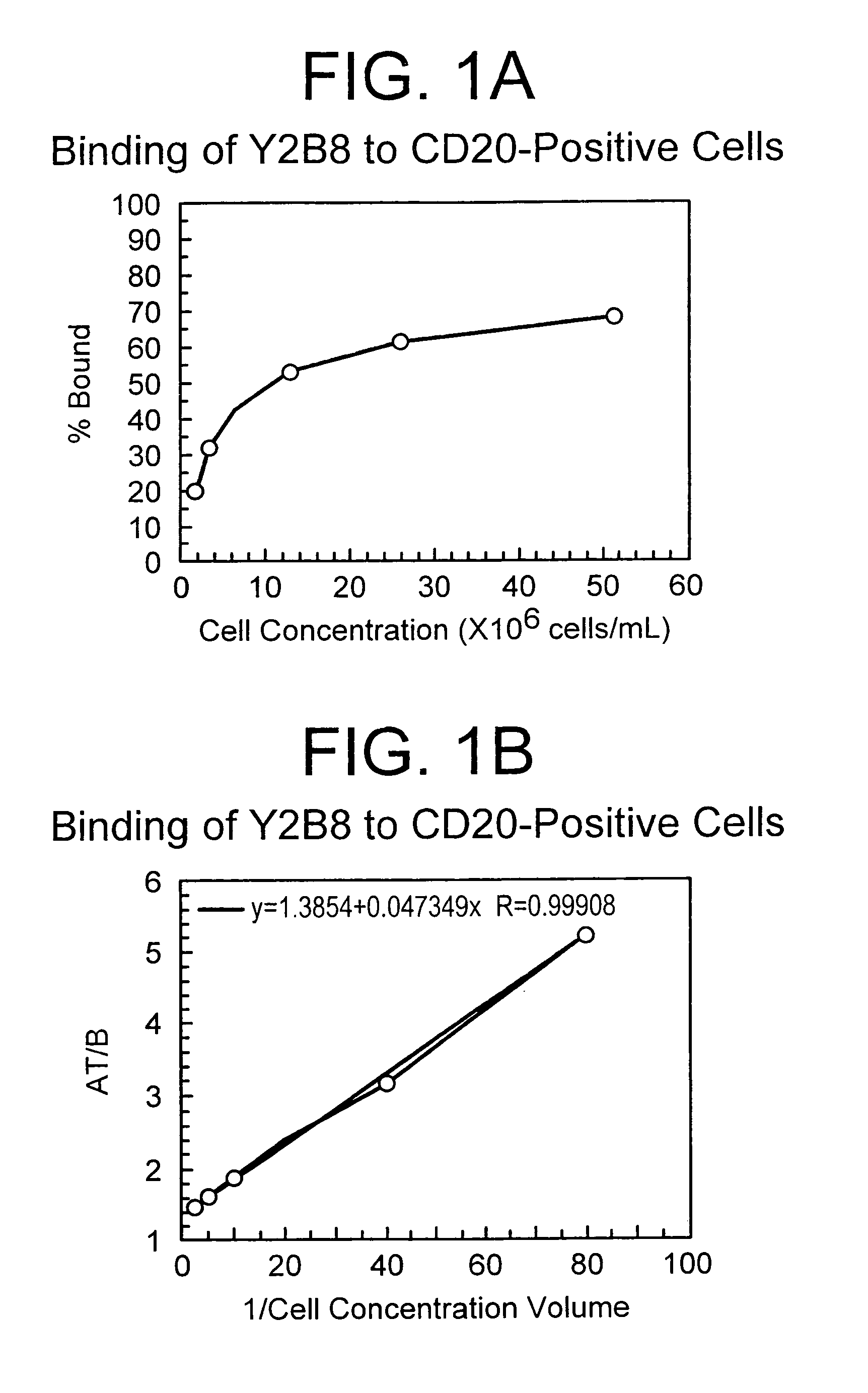
Radioimmunotherapy of lymphoma using anti-CD20 antibodies
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Radioimmunotherapy of lymphoma using anti-CD20 antibodies
Methods for the treatment of lymphoma by administration of a B cell-specific antibody are described. The invention encompasses providing to a patient both unlabeled antibodies and antibodies labeled with a radioisotope. A principal advantage of the method is that tumor responses can be obtained in a radiometric dose range that does not require hematopoietic stem cell replacement as an adjunct therapy also described is a composition useful in the treatment of lymphoma.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +2
Combining Radioimmunotherapy and Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Improved Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20110070156A1Organic active ingredientsHybrid immunoglobulinsParanasal Sinus CarcinomaAntiendomysial antibodies
Described herein are compositions and methods of use of radionuclide-antibody conjugates (for RAIT) and drug-antibody conjugates (ADC). The combination of RAIT and ADC was more efficacious than either RAIT alone, ADC alone, or the sum of effects of RAIT and ADC. The unexpected synergy resulted in decreased tumor growth rate and increased survival, with a high incidence of tumor-free survival in Capan-1 human pancreatic cancer xenografts in nude mice.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
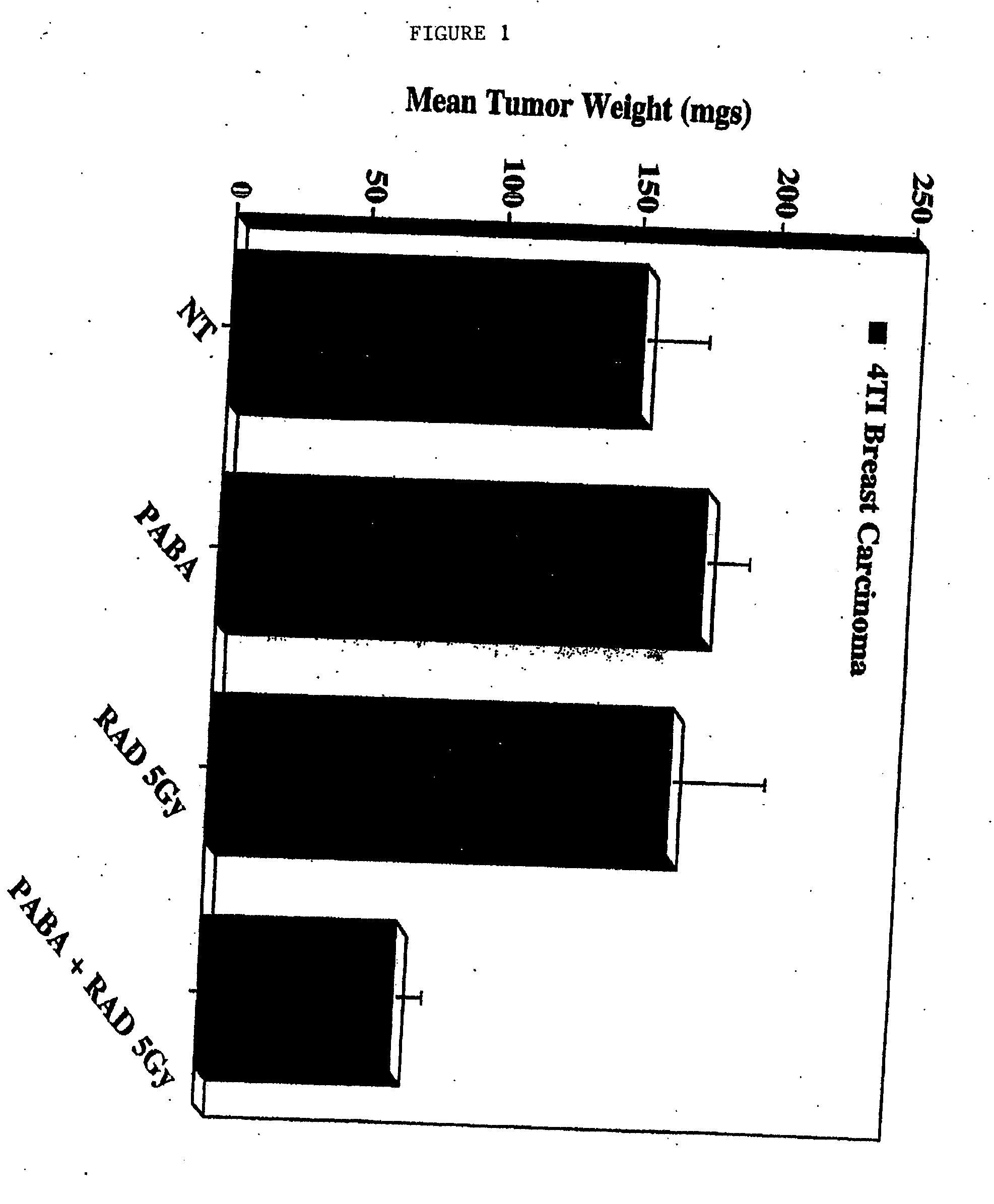
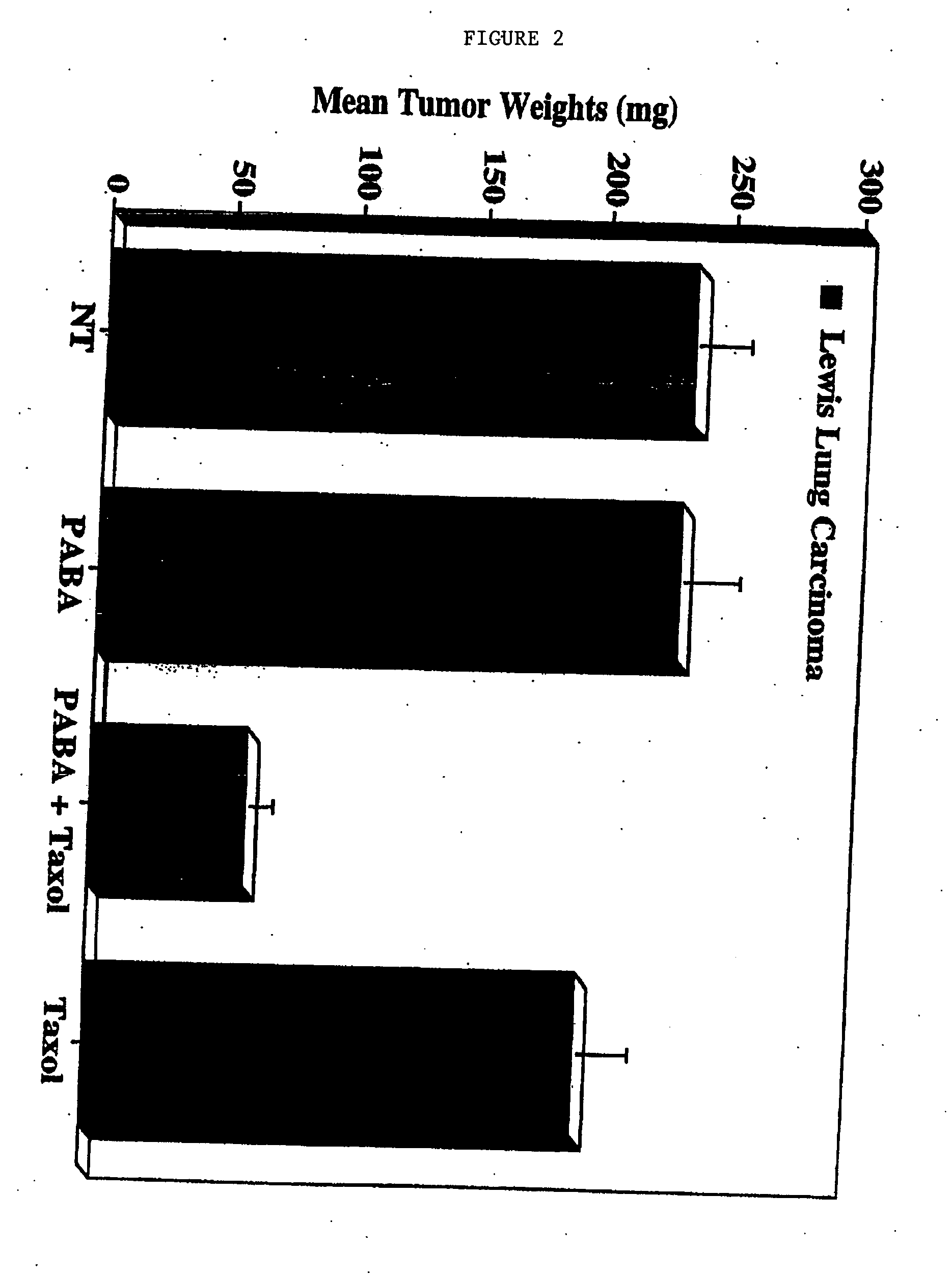
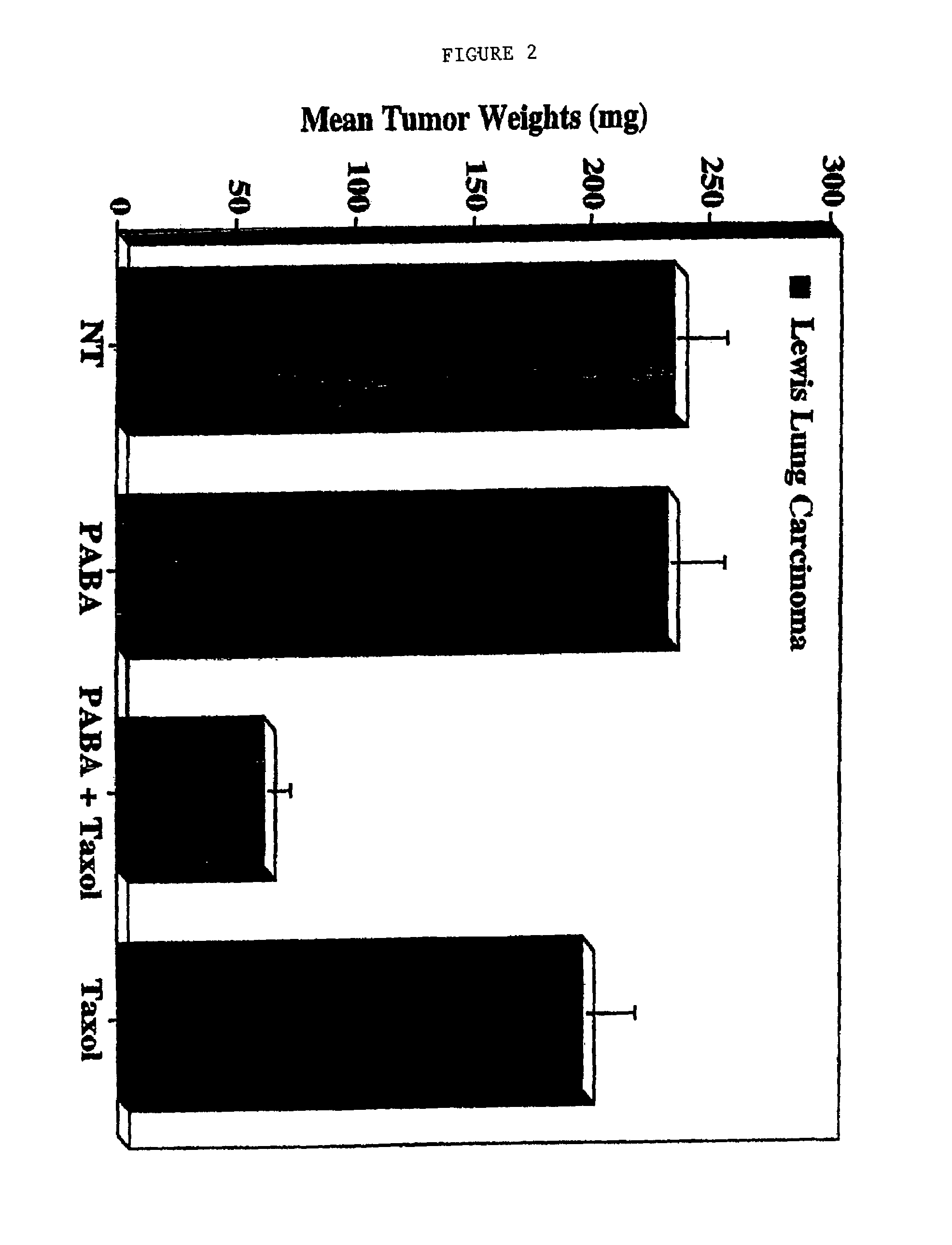
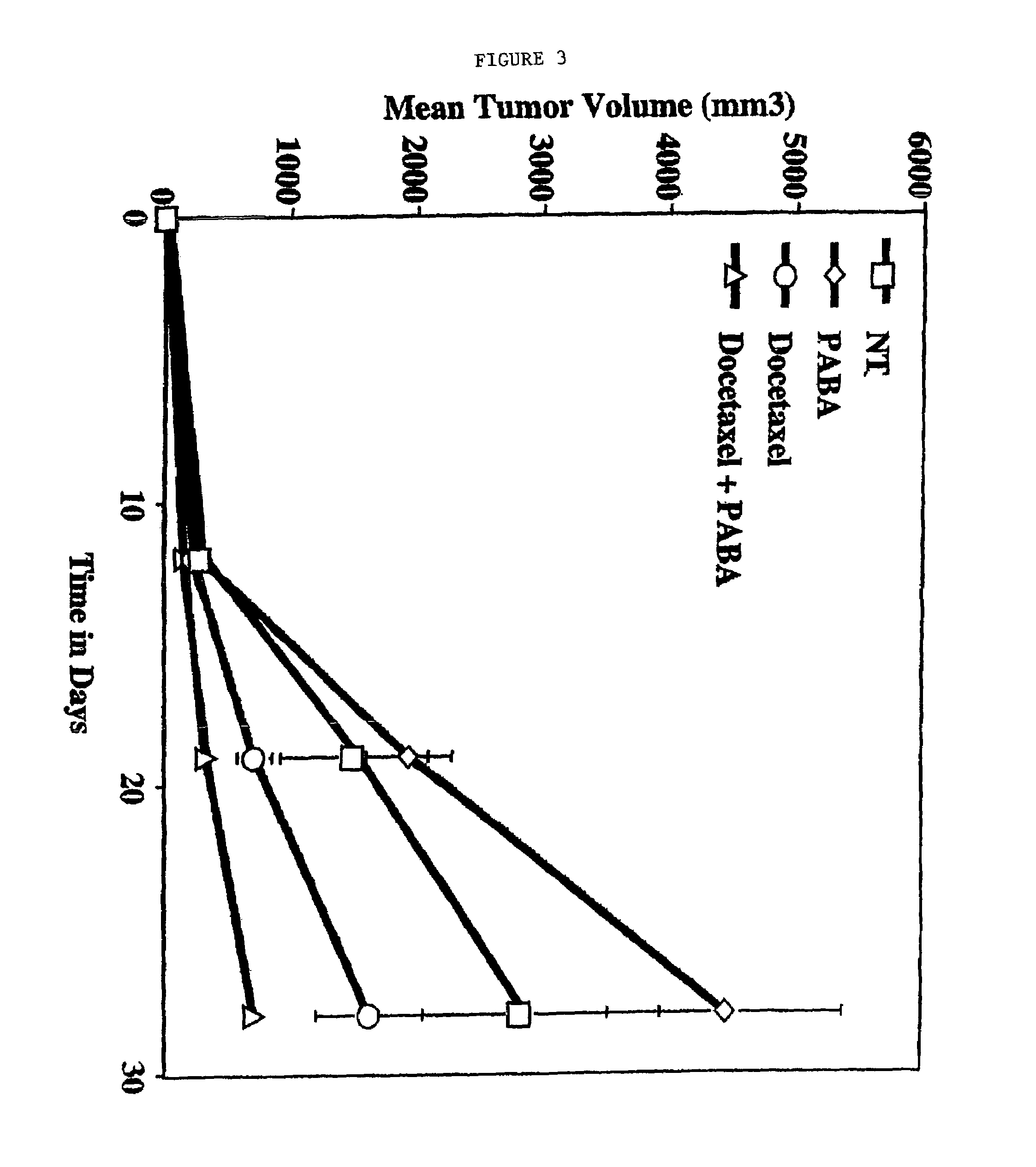
Methods for treating non-melanoma cancers with PABA
The present invention relates to a method for treating non-melanotic cancers by administration of PABA. The present invention also relates to the potentiation of standard cancer treatment of radiation, radioimmunotherapy, and / or chemotherapy using PABA.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Stable radioiodine conjugates and methods of their synthesis
InactiveUS7147856B2Low efficiencyAggregate formationPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersCarbohydrate structureSynthesis methods
Methods are described for conjugating radioiodinated peptides or carbohydrate structures to proteins with improved yields and qualities of conjugates. In one method, specially designed radioiodinated bifunctional peptides containing nonmetabolizable amide bonds are coupled to antibodies. In a second method, radioiodinated nonmetabolizable bifunctional peptides, which also contain aminopolycarboxylates, are coupled to antibodies. In a third method, radioiodinated bifunctional aminopolycarboxylates are coupled to antibodies. In a fourth method, a hydrazide-appended antibody is coupled to a radioiodinated carbohydrate or a thiolated antibody is coupled to a hydrazide-appended and radioiodinated carbohydrate. In a fifth method a monoderivatized cyanuric chloride is used to conjugate thiolated antibody. Radioiodinated residualizing antibody conjugates made by these methods are particularly stable in vivo and are suitable for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Method of using an anti-CD137 antibody as an agent for radioimmunotherapy or radioimmunodetection
InactiveUS20060188439A1Reduce and prevent inactivationEasy to manufactureHybrid immunoglobulinsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAnticarcinogenImmune modulator
The current invention relates to the development and methods of use of a recombinant agonistic antibody anti-human CD137, and glycosylation variants thereof. These antibodies act as anti-cancer agents and / or immune modulators that are effective in shrinking solid tumors or other cancerous indications and preventing their recurrence. The types of cancer for which the contemplated antibody is effective in treating also include leukemia and lymphoma. In a preferred imbodiment the recombinant antibodies of the current invention were produced in and purified from the milk of transgenic animals. In another preferred embodiment of the current invention the agonistic anti-CD137 antibodies of the invention can be conjugated to radionuclides for radioimmunodetection or radioimmunotherapeutic purposes, or conjugated to a toxin for enhanced therapeutic treatment of various cancers.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Method of using an anti-CD137 antibody as an agent for radioimmunotherapy or radioimmunodetection
InactiveUS20080019905A9Reduce and prevent inactivationEasy to manufactureHybrid immunoglobulinsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAnticarcinogenImmune modulator
The current invention relates to the development and methods of use of a recombinant agonistic antibody anti-human CD137, and glycosylation variants thereof. These antibodies act as anti-cancer agents and / or immune modulators that are effective in shrinking solid tumors or other cancerous indications and preventing their recurrence. The types of cancer for which the contemplated antibody is effective in treating also include leukemia and lymphoma. In a preferred imbodiment the recombinant antibodies of the current invention were produced in and purified from the milk of transgenic animals. In another preferred embodiment of the current invention the agonistic anti-CD137 antibodies of the invention can be conjugated to radionuclides for radioimmunodetection or radioimmunotherapeutic purposes, or conjugated to a toxin for enhanced therapeutic treatment of various cancers.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Combining radioimmunotherapy and antibody-drug conjugates for improved cancer therapy
InactiveUS8435529B2Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody conjugateWilms' tumor
Described herein are compositions and methods of use of radionuclide-antibody conjugates (for RAIT) and drug-antibody conjugates (ADC). The combination of RAIT and ADC was more efficacious than either RAIT alone, ADC alone, or the sum of effects of RAIT and ADC. The unexpected synergy resulted in decreased tumor growth rate and increased survival, with a high incidence of tumor-free survival in Capan-1 human pancreatic cancer xenografts in nude mice.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
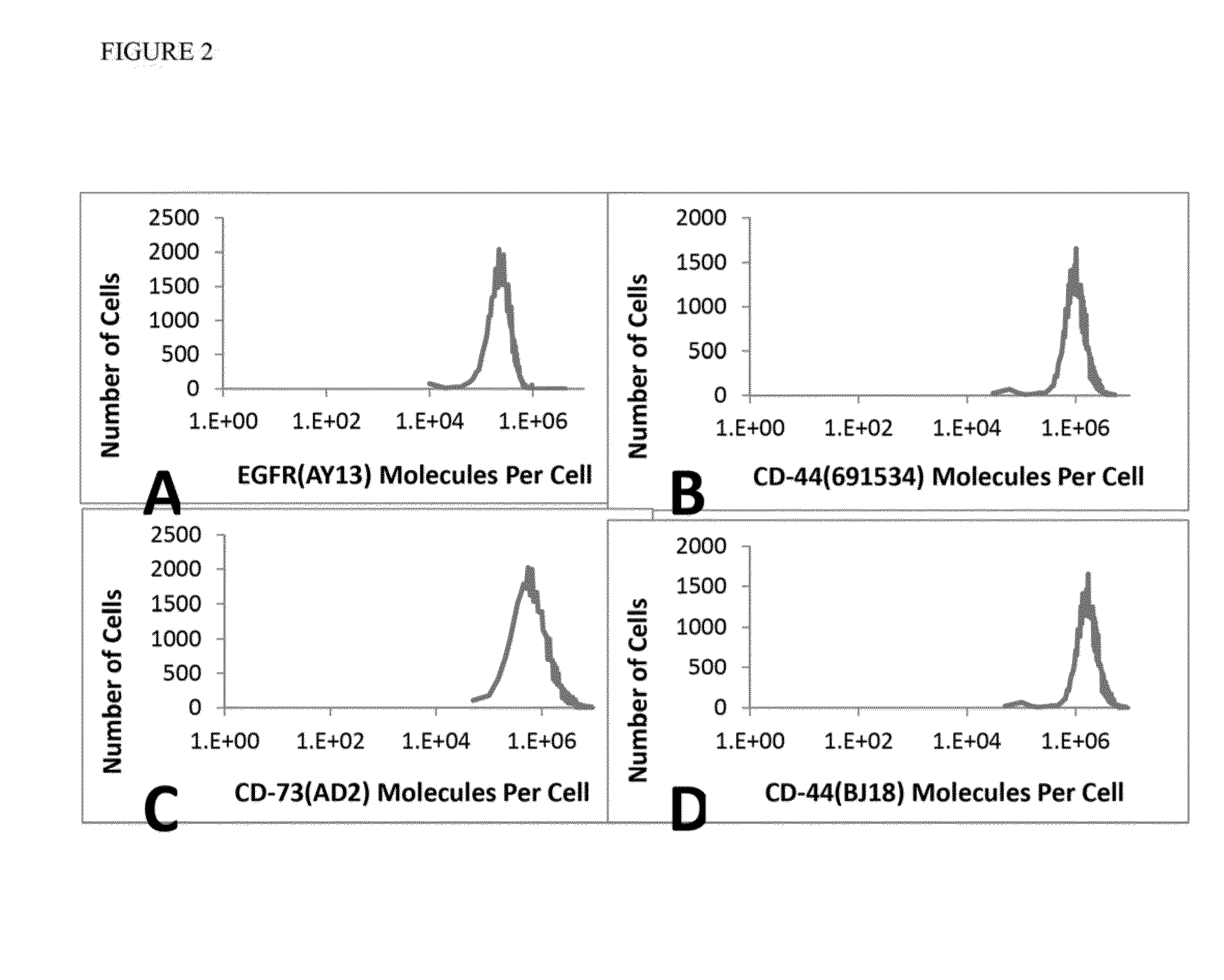
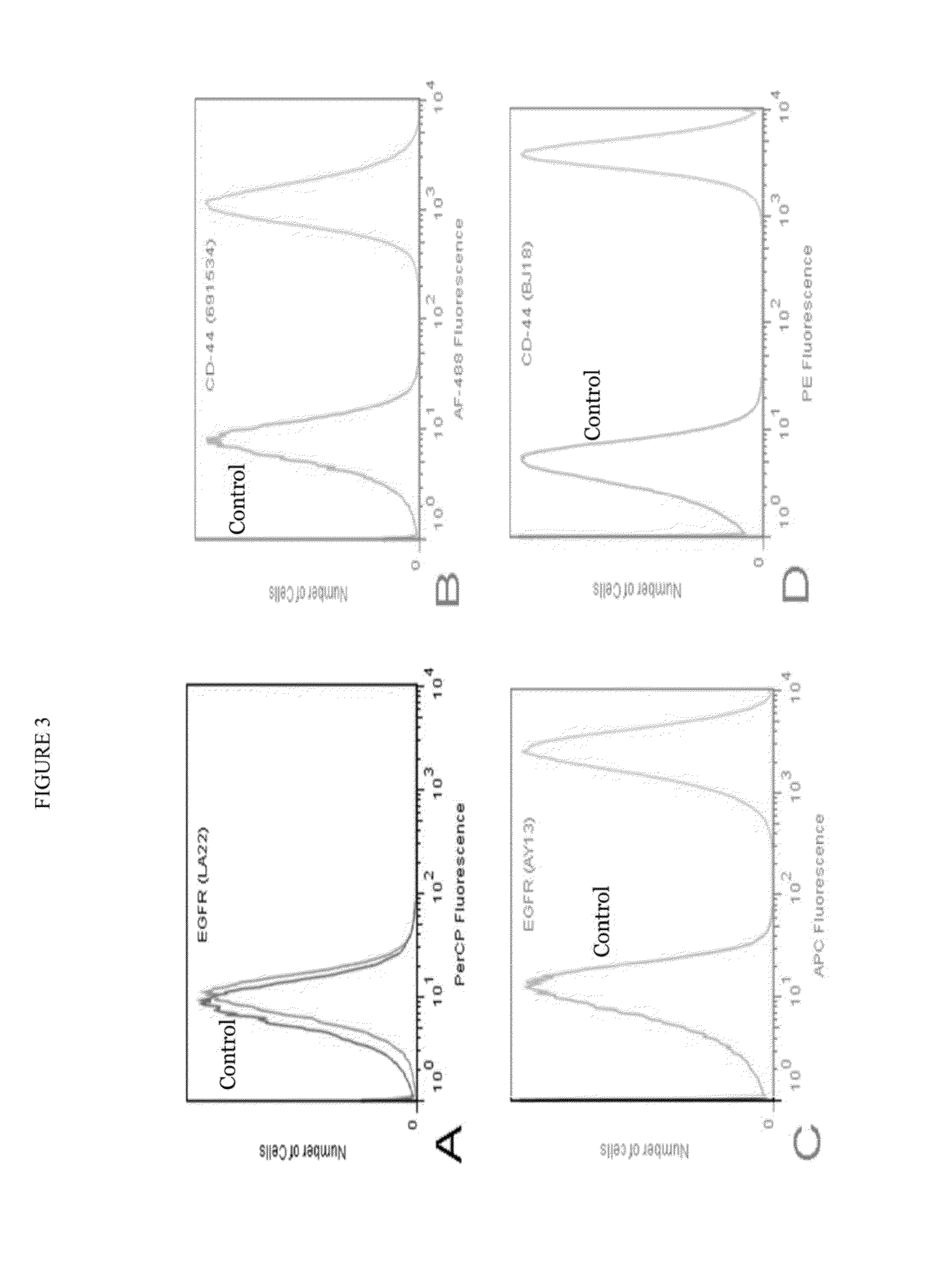
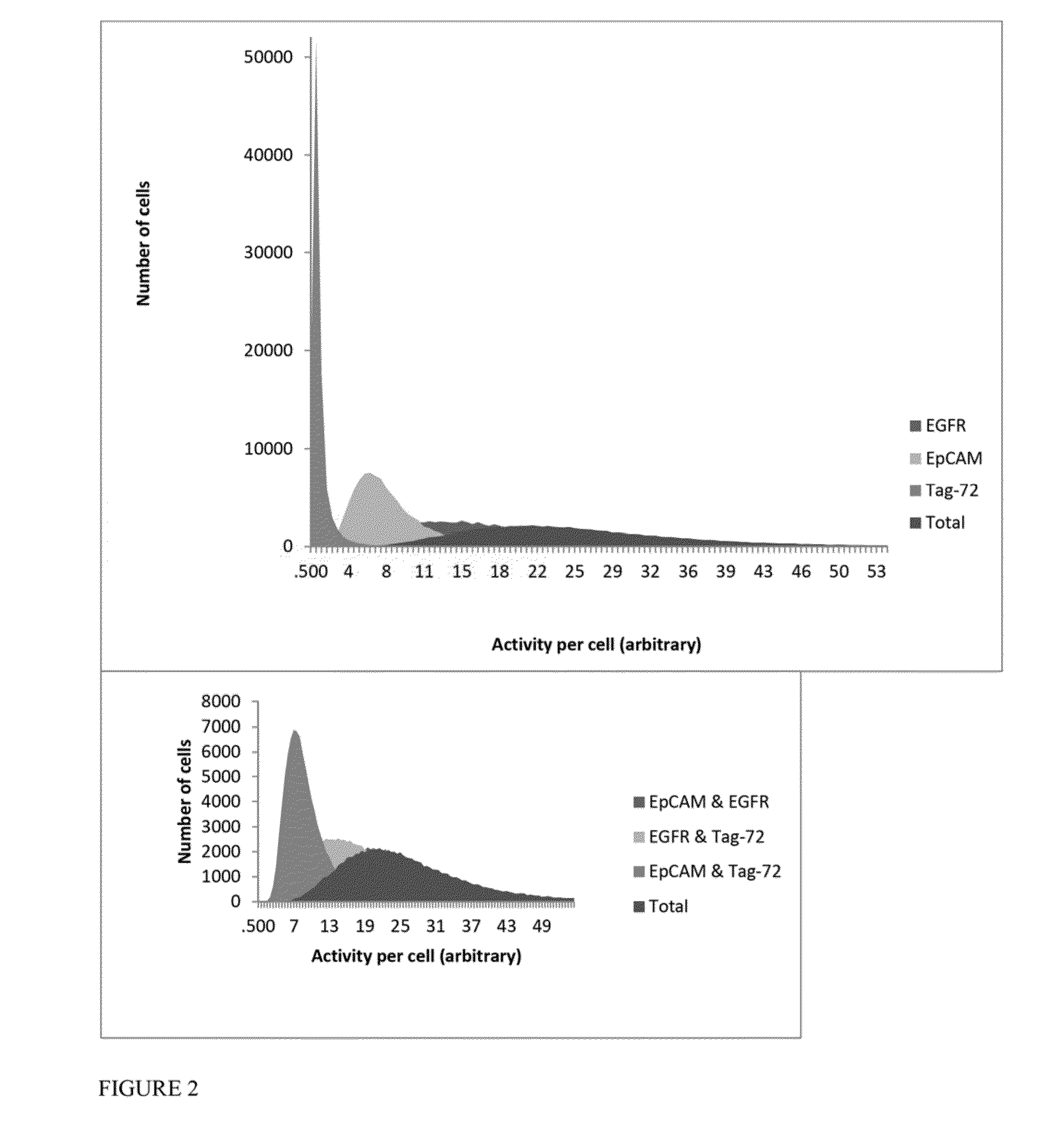
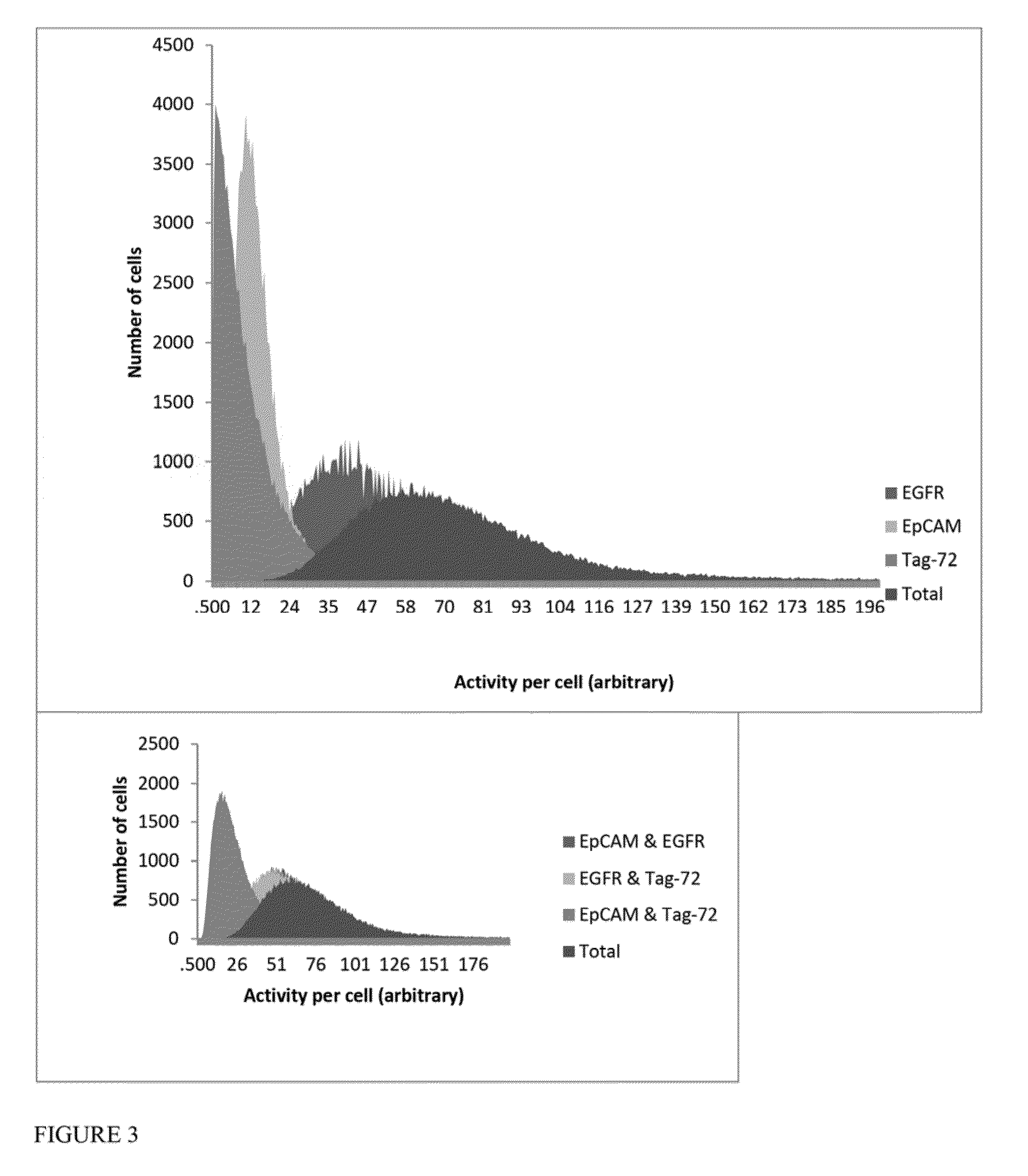
Antibody cocktails for breast cancer radioimmunotherapy
InactiveUS20150030534A1Radioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyAntigen bindingImmune therapy
The present invention provides compositions comprising a therapeutically effective combination of at least two of radionuclide-labeled anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (anti-EGFR), radionuclide-labeled anti-CD-44, and radionuclide-labeled anti-CD-73. or their respective antigen binding portions, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of use thereof for the treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Kit for radiolabeling ligands with yttrium-90
InactiveUS6994840B1Simplifying kitAvoid insufficient purityRadioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsIsotopeOutpatient setting
Methods and kits for radiolabeling proteins, peptides and ligands with radiolytic isotopes, particularly yttrium-90, are disclosed, whereby sufficient purity, specific activity and binding affinity are achieved such that the radiolabeled protein may be directly administered to a patient without further column purification. Such kits and methods will be particularly useful in bringing radioimmunotherapy to the hospital and outpatient setting for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:RIT ONCOLOGY
Methods for treating non-melanoma cancers with PABA
The present invention relates to a method for treating non-melanotic cancers by administration of PABA. The present invention also relates to the potentiation of standard cancer treatment of radiation, radioimmunotherapy, and / or chemotherapy using PABA.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
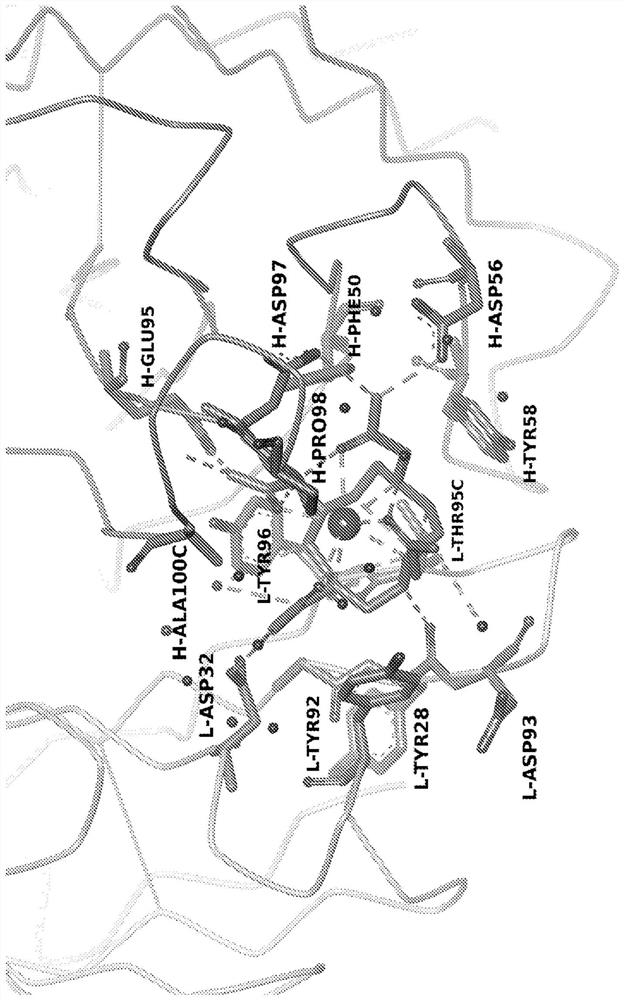
Nucleotide and protein sequences of an antibody directed against an epitope common to human acidic and basic ferritins, monoclonal antibodies or antibody-like molecules comprising these sequences and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to monoclonal, chimeric or humanized, antibodies or antibody-like molecules that recognize an epitope common to human acidic and basic isoferritins. The anti-ferritin antibodies or antibody-like molecules can be used in pharmaceutical compositions for immunotherapy or radioimmunotherapy to target various cancer cells in a mammal. A method for delivering anti-ferritin antibodies or antibody-like molecules to cancerous lymph cells, pancreatic cells, lymphatic endothelium cells, and liver cells is also disclosed, as well as methods for treating pancreatic cancer, hepatocellular carcinomas, Kaposi's sarcoma and Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Owner:IMMUNE PHARMA
Stable radioiodine conjugates and methods for their synthesis
InactiveUS6858705B2Increase productionEasy to oxidizeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsRadioimmunodetectionAntibody conjugate
Methods are described for conjugating radioiodinated non-metabolizable peptides to proteins and antibodies with improved yields and qualities of conjugates. Radioiodinated residualizing antibody conjugates comprising any aminopolycarboxylate-appended peptide, or any carbohydrate-appended peptide, are also provided. Additionally, methods are described for conjugating radioiodinated aminopolycarboxylates to proteins and antibodies, as well as for conjugating radioiodinated non-metabolizable carbohydrates to proteins and antibodies by a variety of chemical approaches. The instant radioiodinated residualizing antibody conjugates are particularly stable in vivo and are suitable for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
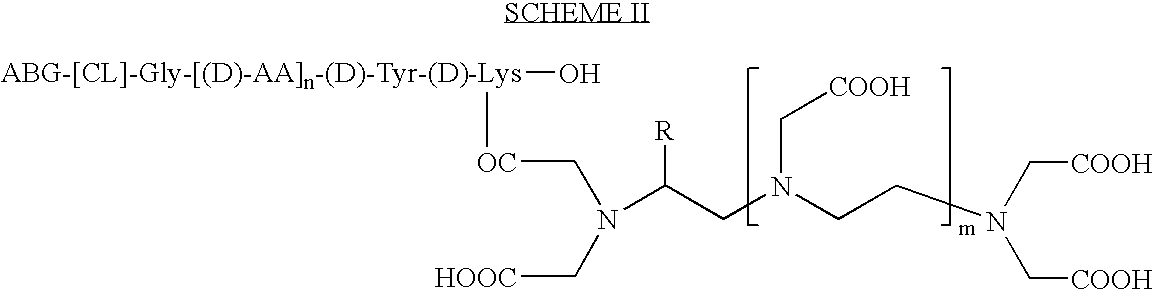
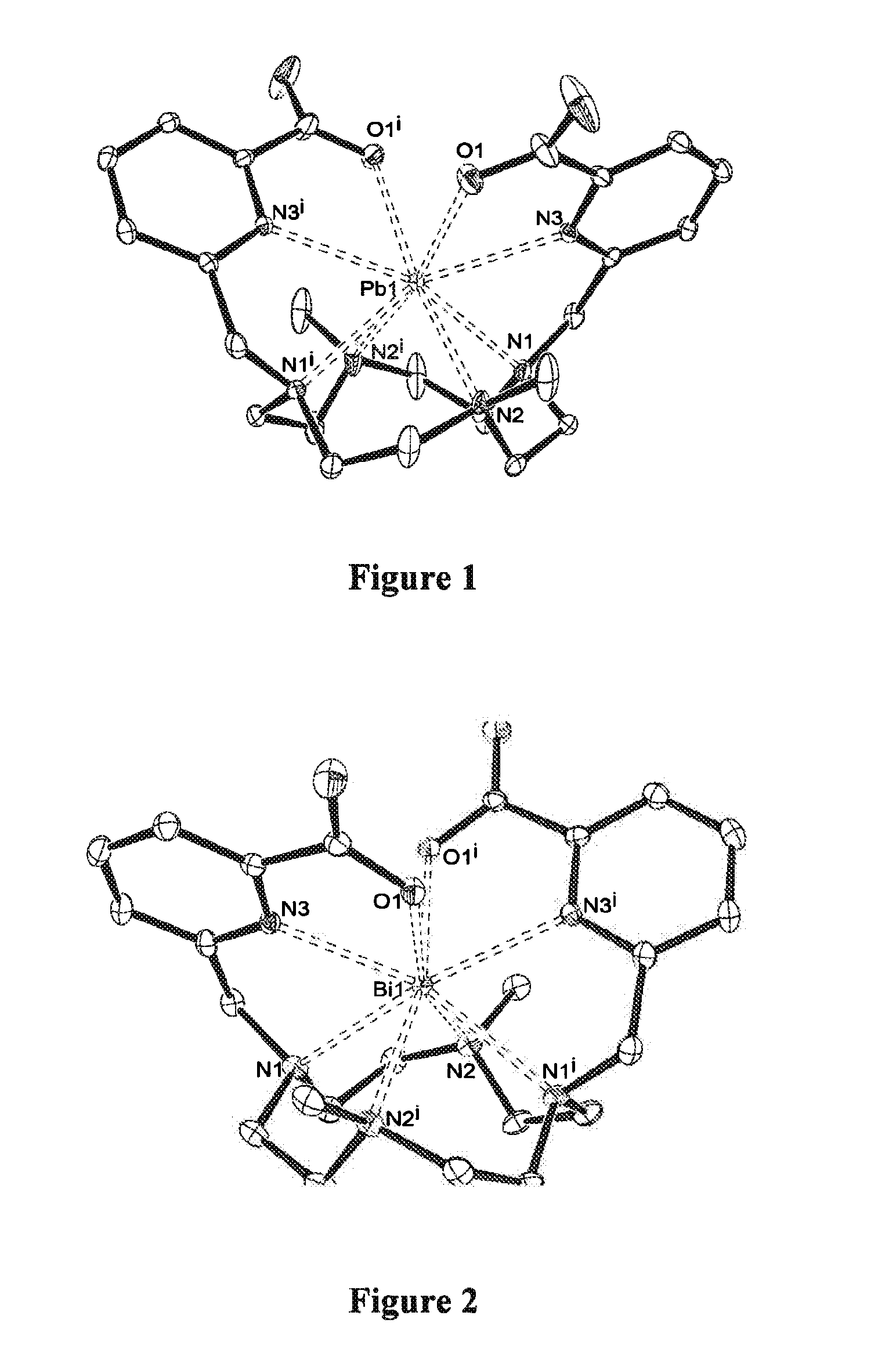
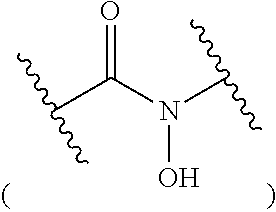
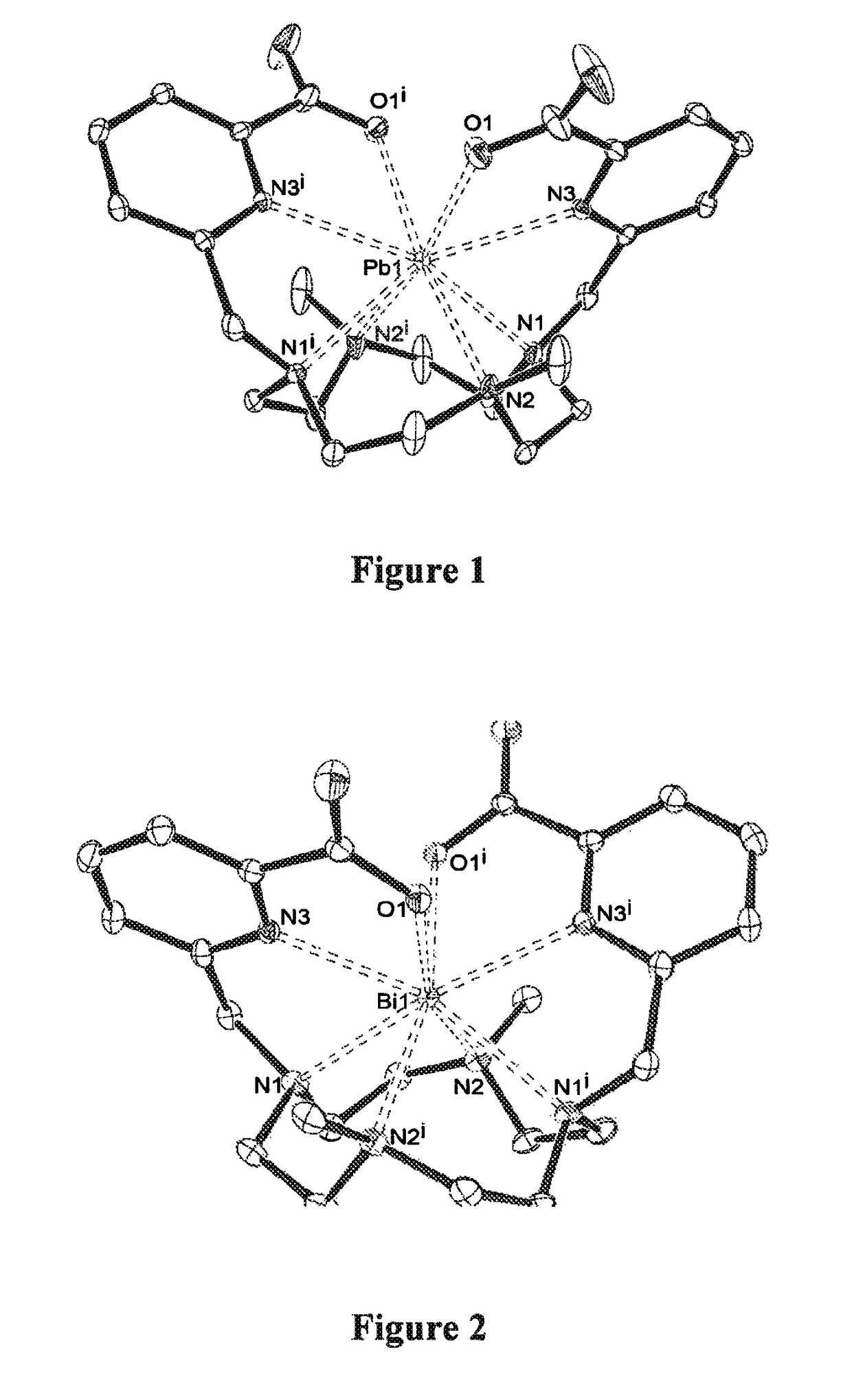
Chelates of Lead (II) and Bismuth (III) Based on Trans-Di-N-Picolinate Tetraazacycloalkanes
ActiveUS20160115187A1Efficient complexationAntinoxious agentsRadioactive preparation carriersCrystallographyPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a chelate resulting from the complexing of a trans-di-N-picolinate tetraazacycloalkane ligand with a metal cation, said ligand corresponding to formula (A) wherein n is equal to 0 or to 1, R is H or a C1-C18 alkyl radical, and R′ is H or a C1 -C18 alkyl radical, said metal cation being a cation of a metal selected from the group consisting of lead (II) and bismuth (III). The invention is applicable in the field of lead trapping and alpha-radioimmunotherapy.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Radiation dosimetry and blocking antibodies and methods and uses therefor in the treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20060127311A1Less costlyLong half-lifeNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSurgically-Created Resection CavityWilms' tumor
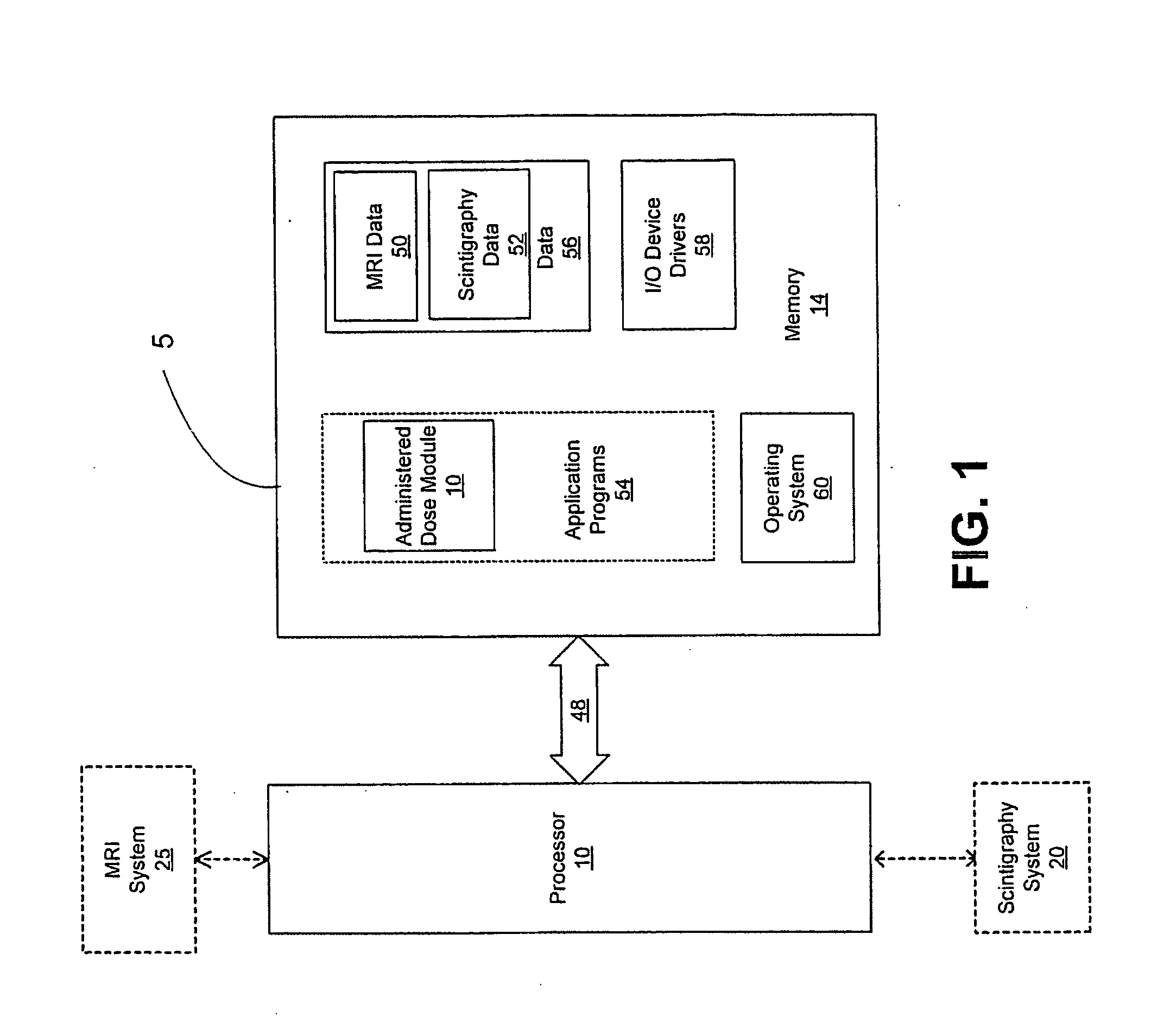
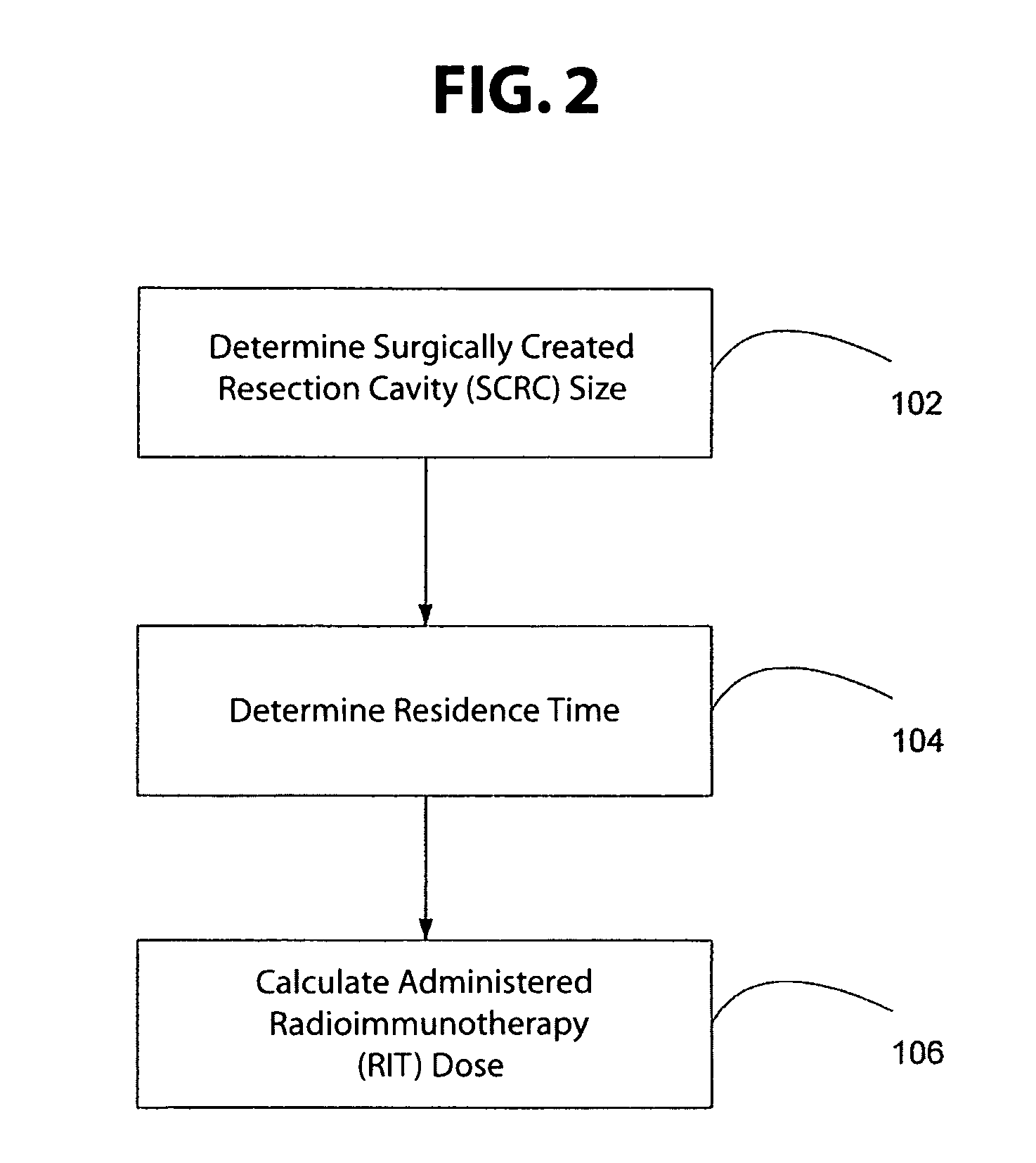
Disclosed is a method for dosimetry estimation for a region of interest at or around a surgically created resection cavity in a subject. These methods enable medical practitioners to estimate the amount of administered Radioimmunotherapy (RIT) agent needed to safely and effectively achieve a final Radiation Absorbed Dose (RAD). Furthermore, computer hardware and software are provided herein, so that the methods according to the invention may be automated for more efficient use. Also disclosed is a method of enhancing delivery of therapeutic antibodies that specifically bind to an extracellular stromal constituent of a tumor in a mammalian subject. The method comprises administering to a subject an effective dosage of a blocking antibody, said blocking antibodies specifically binding to said extracellular stromal constituent and blocking the binding of therapeutic antibodies to non-target tissue.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Radioimmunotherapy and imaging of tumor cells that express viral antigens
InactiveUS20120003148A1Less toxicityRadioactive preparation carriersAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellVirus-Related Carcinoma
Owner:DADACHOVA EKATERINA +3
Antibody cocktails for breast cancer radioimmunotherapy
InactiveUS20140037539A1Radioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyAntigen bindingImmune therapy
The present invention provides compositions comprising a therapeutically effective combination of radionuclide-labeled anti-EpCAM, radionuclide-labeled anti-EGFR, and radionuclide labeled anti-Tag-72, or their respective antigen binding portions, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, and method of use thereof for the treatment of breast cancer.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
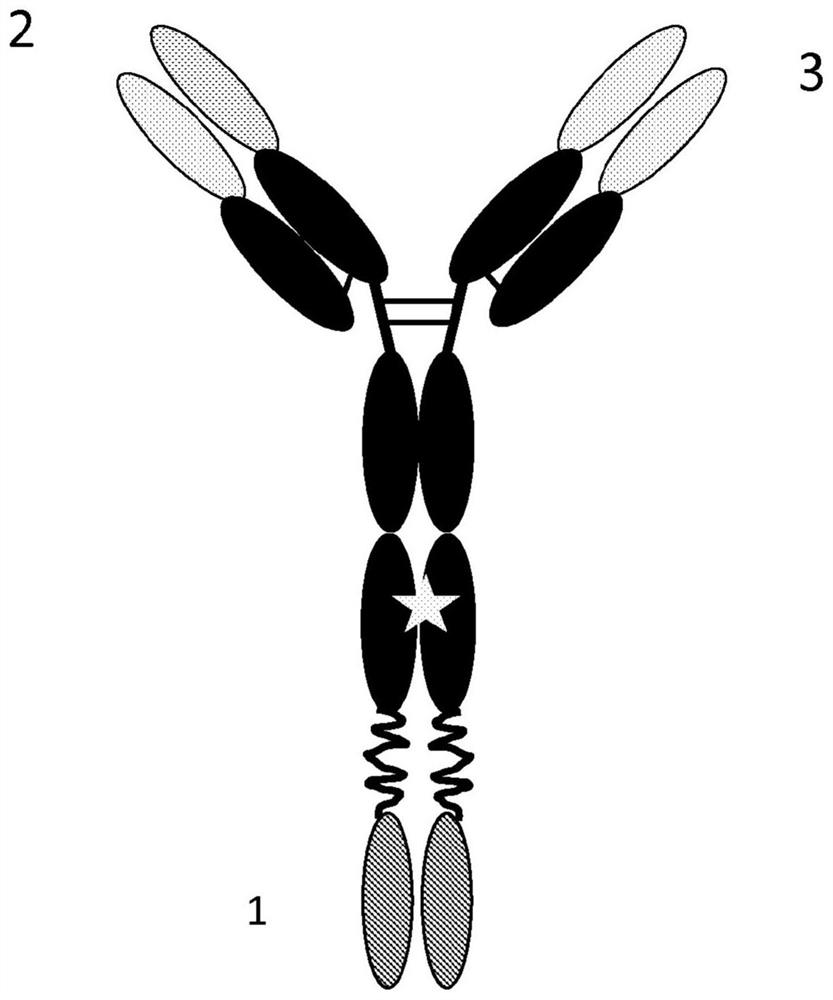
Dimerization strategies and compounds for molecular imaging and/or radioimmunotherapy
PendingUS20190134240A1High sensitivityStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysMolecular imaging
The present invention provides a multivalent compound for targeted molecular imaging and / or targeted drug delivery, wherein two components or targeting molecules each interacts with one or more biomarkers on a cell. The present invention further provides a multifunctional chelator to combine the targeting molecules. The present invention also provides an in vitro high-throughput screening assay to determine the length of the spacer molecules. The present invention also relates to compounds / probes, kits and methods for use in targeted molecular imaging and / or targeted drug delivery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Antibodies for chelated radionuclides and clearing agents
PendingCN112638416ARadioactive preparation carriersImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
The present application relates to antibodies which bind specifically to chelated radionuclides, including bispecific antibodies, It further relates to the use of such bispecific antibodies in applications such as radioimmunoimaging and radioimmunotherapy. It additionally relates to clearing agents and useful in such methods.
Owner:オラノメッド +1
Method and means for site directed therapy
InactiveUS7374936B2Reduce the amount requiredGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFermentationTreatment fieldEffective treatment
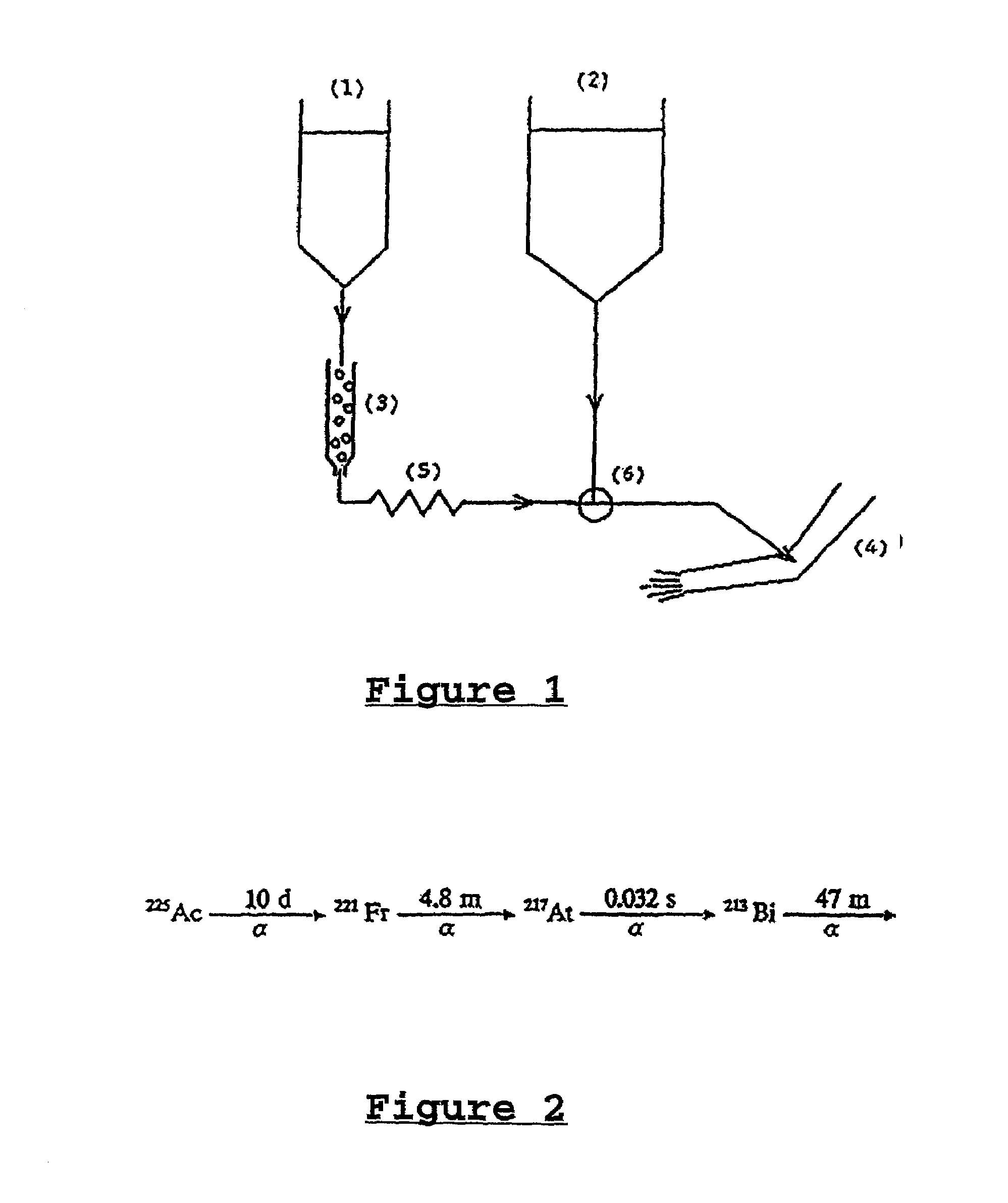
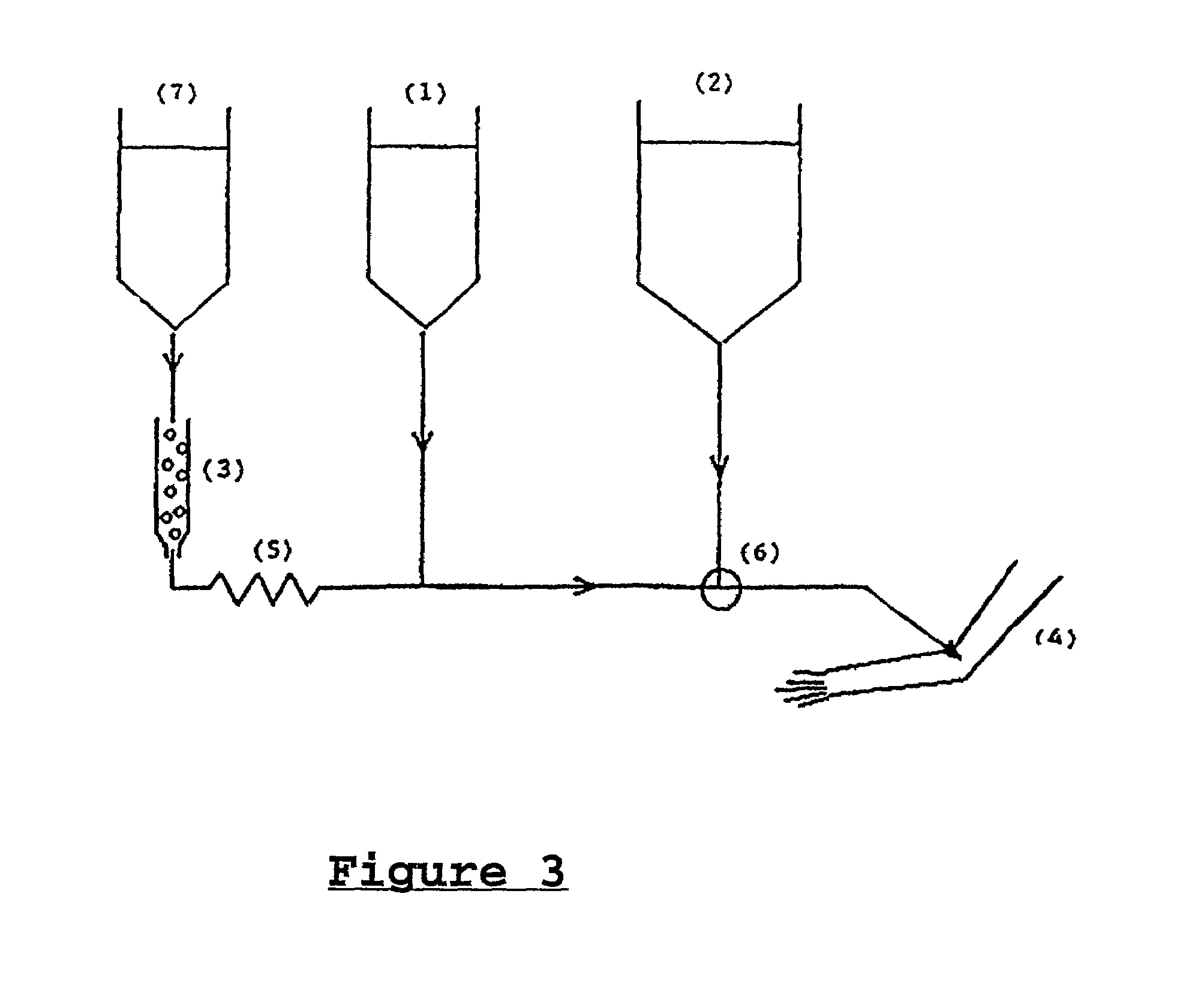
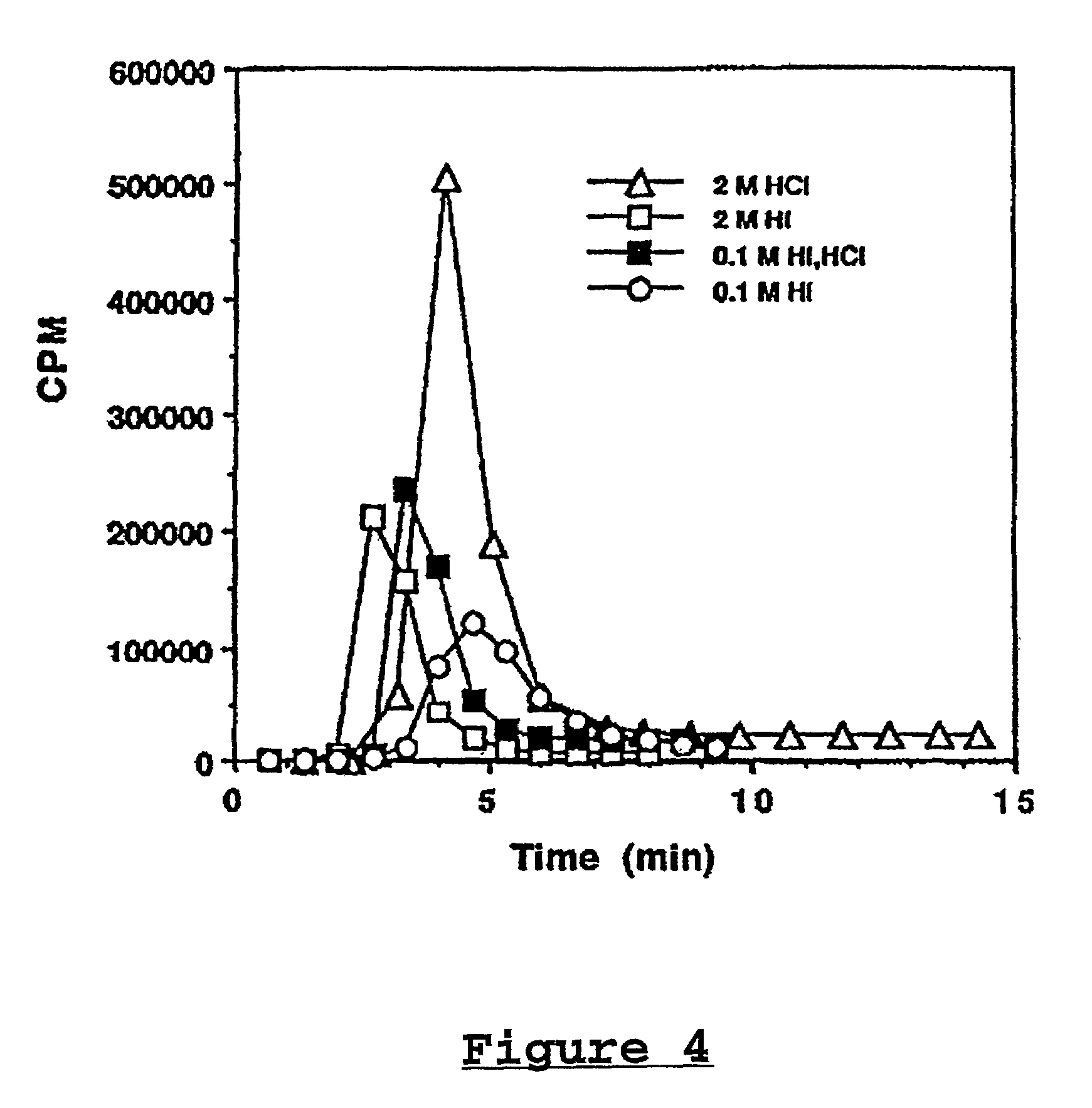
The present invention relates to the field of site directed therapy. More specifically the invention relates to site directed radio therapy, and provides a method for production of radioconjugates and an apparatus for radioimmunotherapy. The method, conjugates and apparatus can be practicalized without the need for radioactive shielding and / or airtight facilities. Without these restrictions the invention provides a simple and efficient means of therapy at the bed-side of the patient.
Owner:ACTINIUM PHARMA
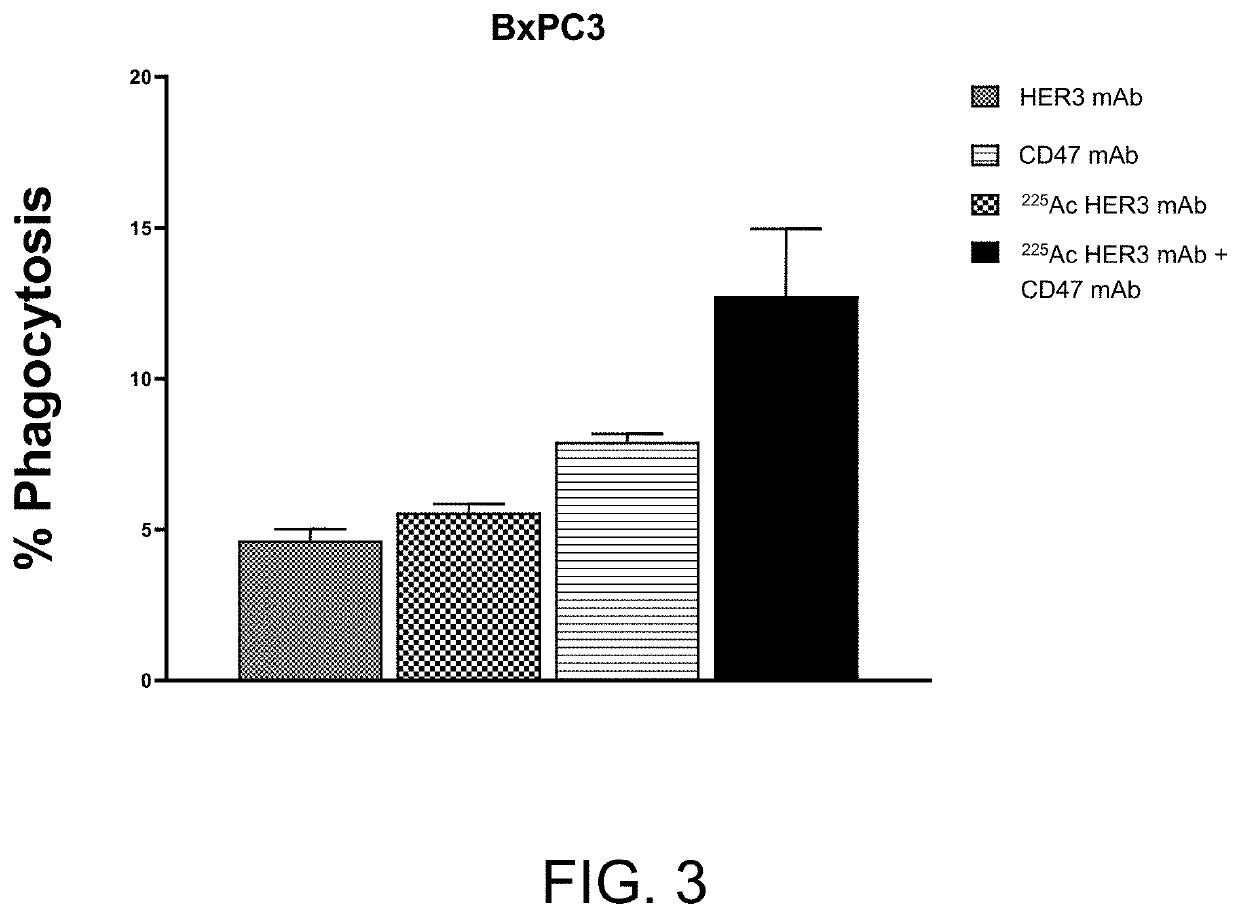
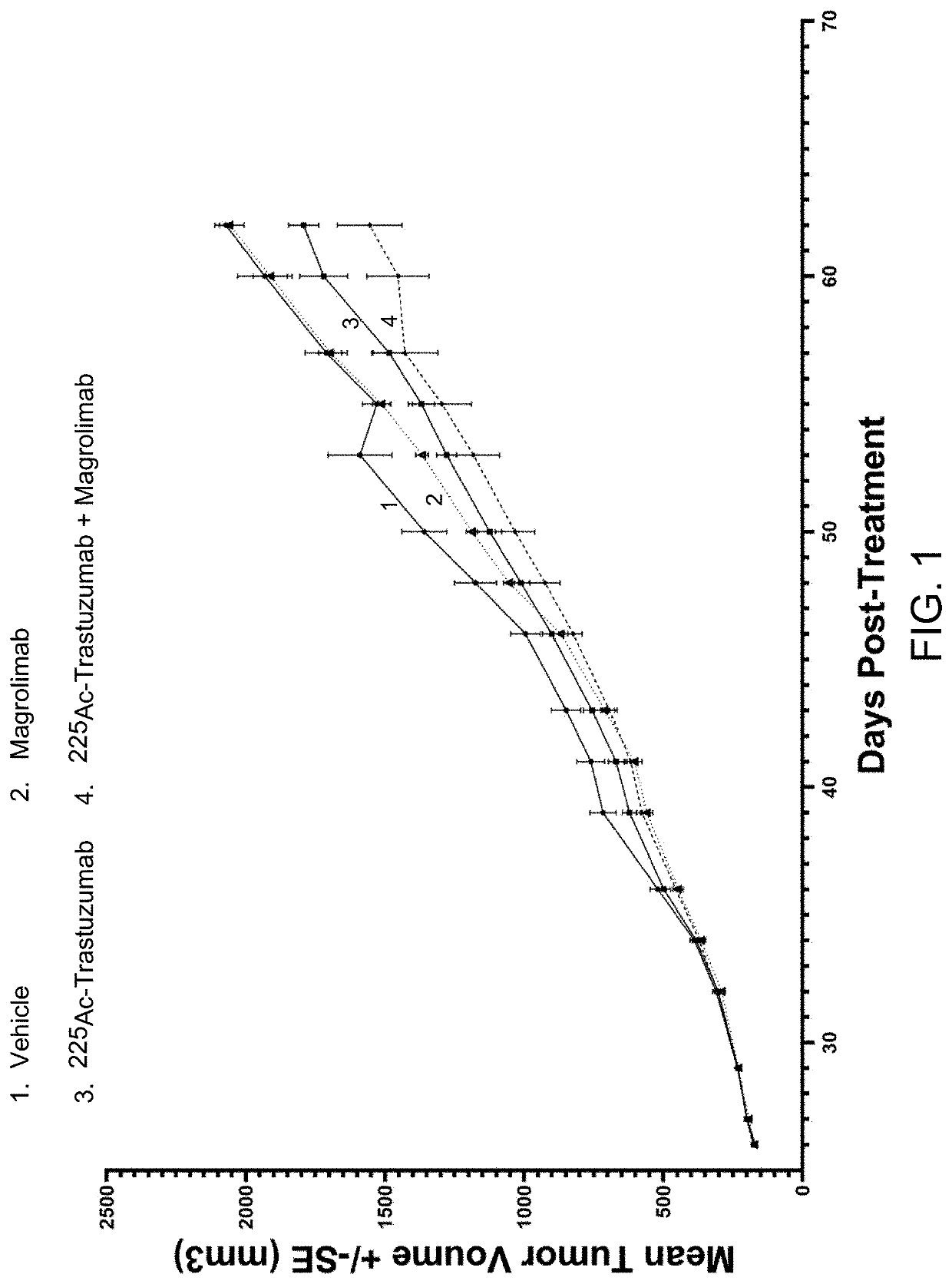
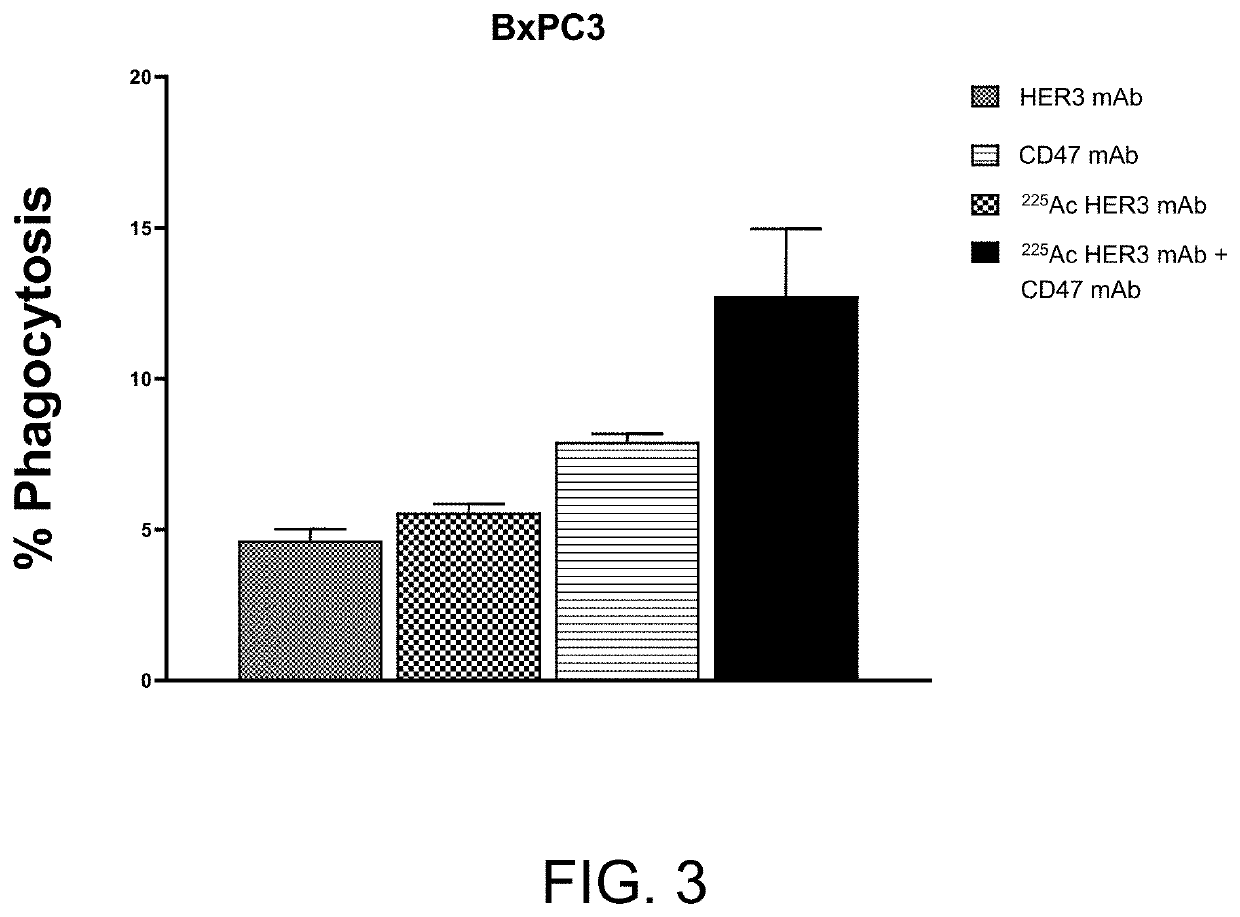
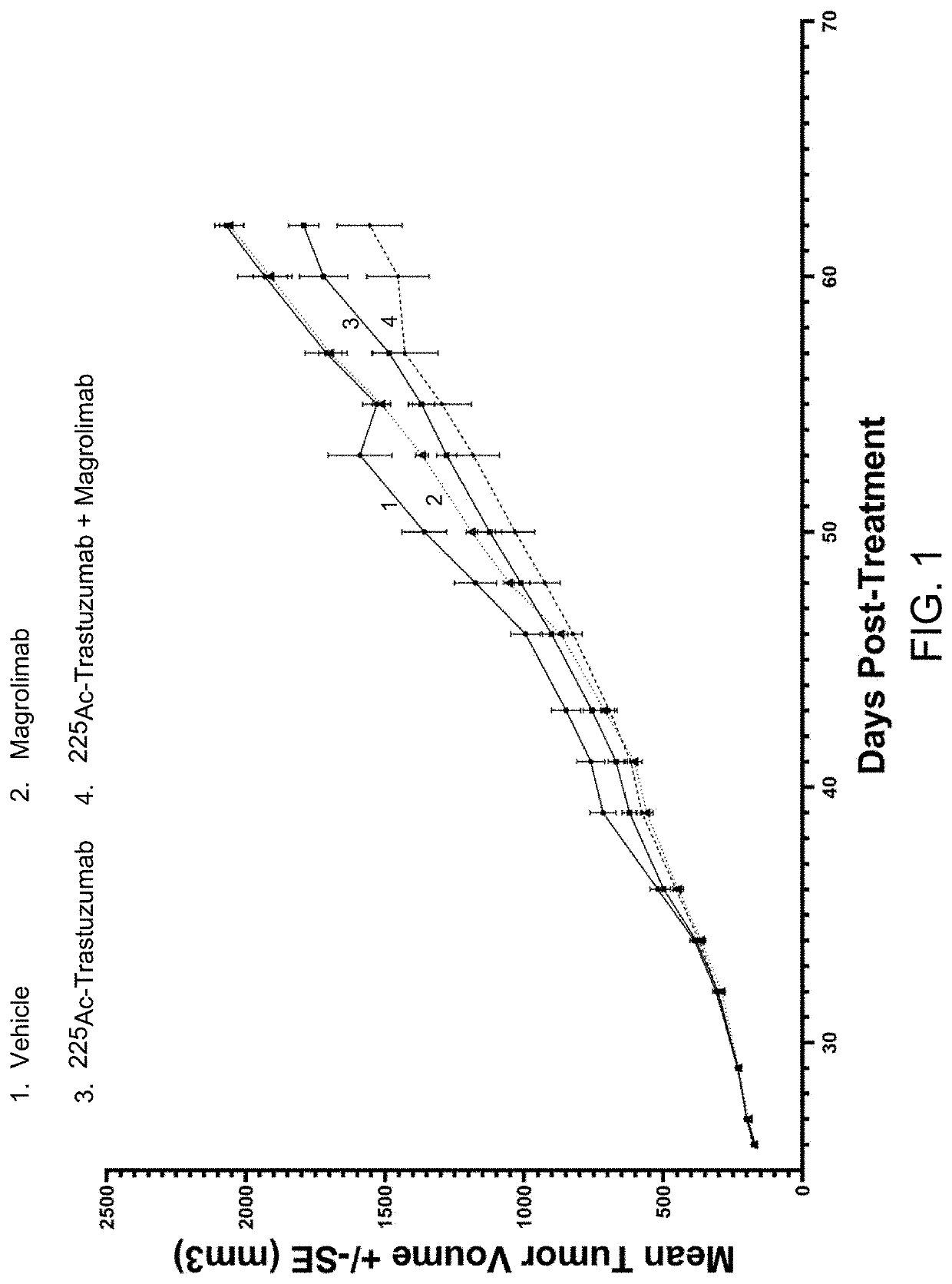
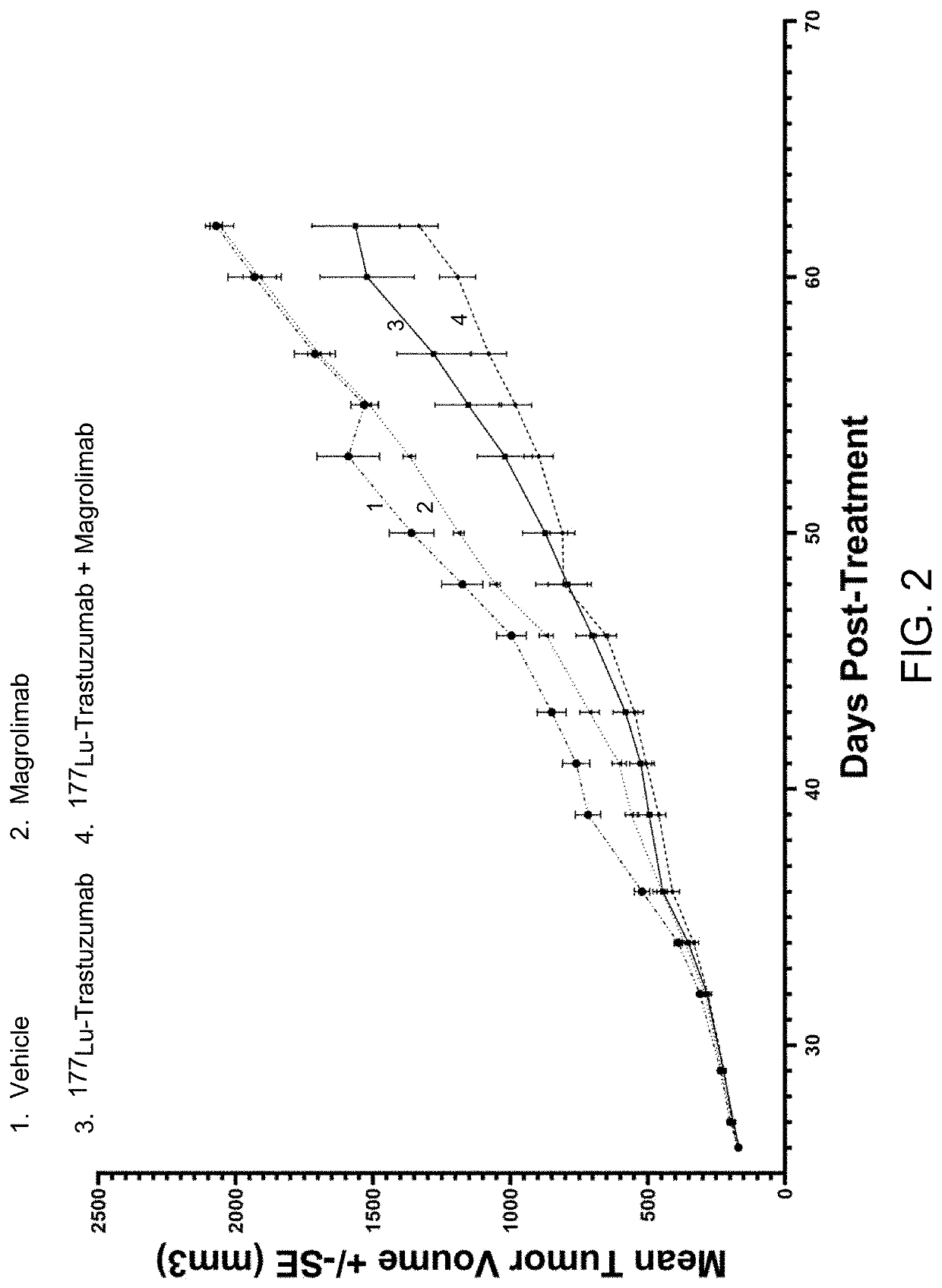
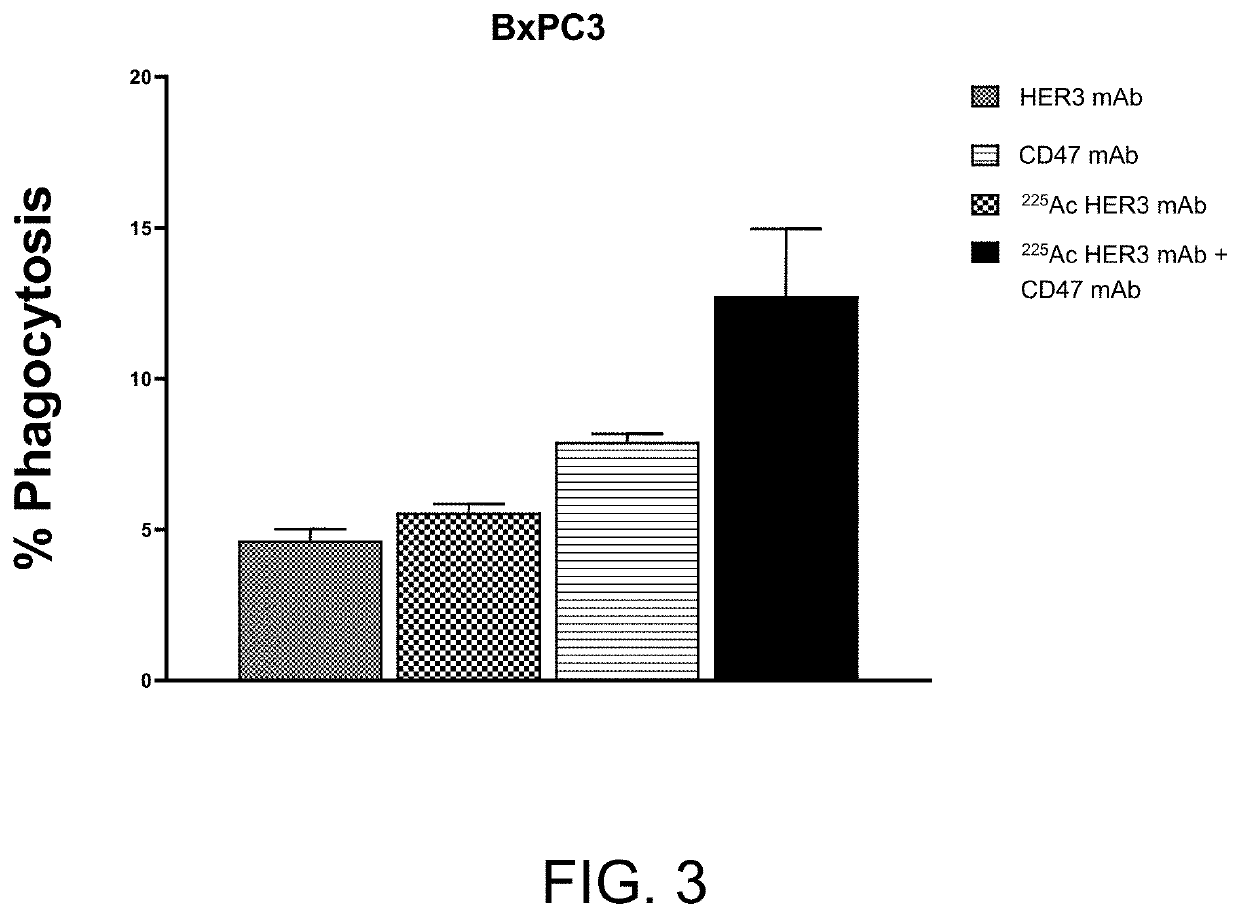
Combination radioimmunotherapy and cd47 blockade in the treatment of cancer
PendingUS20220288244A1Improve clinical outcomesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Provided are compositions and methods for treating cancers and precancerous proliferative disorders in a mammalian subject that involve the combination use of a radiotherapeutic agent, such as a radiolabeled CD33, DR5, 5T4, HER2, HER3, or TROP2 targeting agent, and a CD47 checkpoint inhibitor, such as a SIRPα-IgG Fc fusion protein or a monoclonal antibody against CD47 or SIRPα.
Owner:ACTINIUM PHARMA
Combining Radioimmunotherapy and Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Improved Cancer Therapy
InactiveUS20130209356A1Organic active ingredientsNanomedicineParanasal Sinus CarcinomaAntiendomysial antibodies
Described herein are compositions and methods of use of radionuclide-antibody conjugates (for RAIT) and drug-antibody conjugates (ADC). The combination of RAIT and ADC was more efficacious than either RAIT alone, ADC alone, or the sum of effects of RAIT and ADC. The unexpected synergy resulted in decreased tumor growth rate and increased survival, with a high incidence of tumor-free survival in Capan-1 human pancreatic cancer xenografts in nude mice.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Antibodies for chelated radionuclides
PendingCN112261952AIn-vivo radioactive preparationsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesBispecific antibody
The present application relates to antibodies which bind specifically to chelated radionuclides, including bispecific antibodies. It further relates to the use of such bispecific antibodies in applications such as radioimmunoimaging and radioimmunotherapy. It additionally relates to clearing agents useful in such methods.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Multidentate bifunctional chelating agents for radionuclide complexation in diagnostics and therapy
ActiveUS20170106106A1Improve versatilityReduce deliveryGroup 4/14 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesRadioactive preparation carriersNanoparticleChemistry
The invention relates to octadentate ligands of a general formula R1-D-X-D-X-D-X-D-E-R2, wherein D is C(O)N(OH) or N(OH)C(O), pyrimidinone or pyridinone, each X independently of any other X is a saturated or partially unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted linker comprising 8-11 atoms selected from any of N, C, O; R1 is alkyl, cycloalkyl, arene, or heteroarene, E is a saturated or partially unsaturated, substituted or unsubstituted chain comprising 1-50 atoms and R2 is a moiety capable of selectively binding to a biomolecule, or a nanoparticle. The invention further relates to complexes of the ligand, particularly radionuclides and their use in radioimmunotherapy and imaging.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Chelates of lead (II) and bismuth (III) based on trans-di-N-picolinate tetraazacycloalkanes
ActiveUS9884881B2Efficient complexationAntinoxious agentsRadioactive preparation carriersCrystallographyCycloalkane
The invention relates to a chelate resulting from the complexing of a trans-di-N-picolinate tetraazacycloalkane ligand with a metal cation, said ligand corresponding to formula (A) wherein n is equal to 0 or to 1, R is H or a C1-C18 alkyl radical, and R′ is H or a C1-C18 alkyl radical, said metal cation being a cation of a metal selected from the group consisting of lead (II) and bismuth (III). The invention is applicable in the field of lead trapping and alpha-radioimmunotherapy.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Combination radioimmunotherapy and cd47 blockade in the treatment of cancer
PendingUS20220211886A1Improve clinical outcomesOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Owner:ACTINIUM PHARMA
Combination radioimmunotherapy and cd47 blockade in the treatment of cancer
PendingUS20220251239A1Improve clinical outcomesImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseAntiendomysial antibodies
Provided are compositions and methods for treating cancers and precancerous proliferative disorders in a mammalian subject that involve the combination use of a radiotherapeutic agent, such as a radiolabeled CD33, DR5, 5T4, HER2, HER3, or TROP2 targeting agent, and a CD47 checkpoint inhibitor, such as a SIRPα-IgG Fc fusion protein or a monoclonal antibody against CD47 or SIRPα.
Owner:ACTINIUM PHARMA
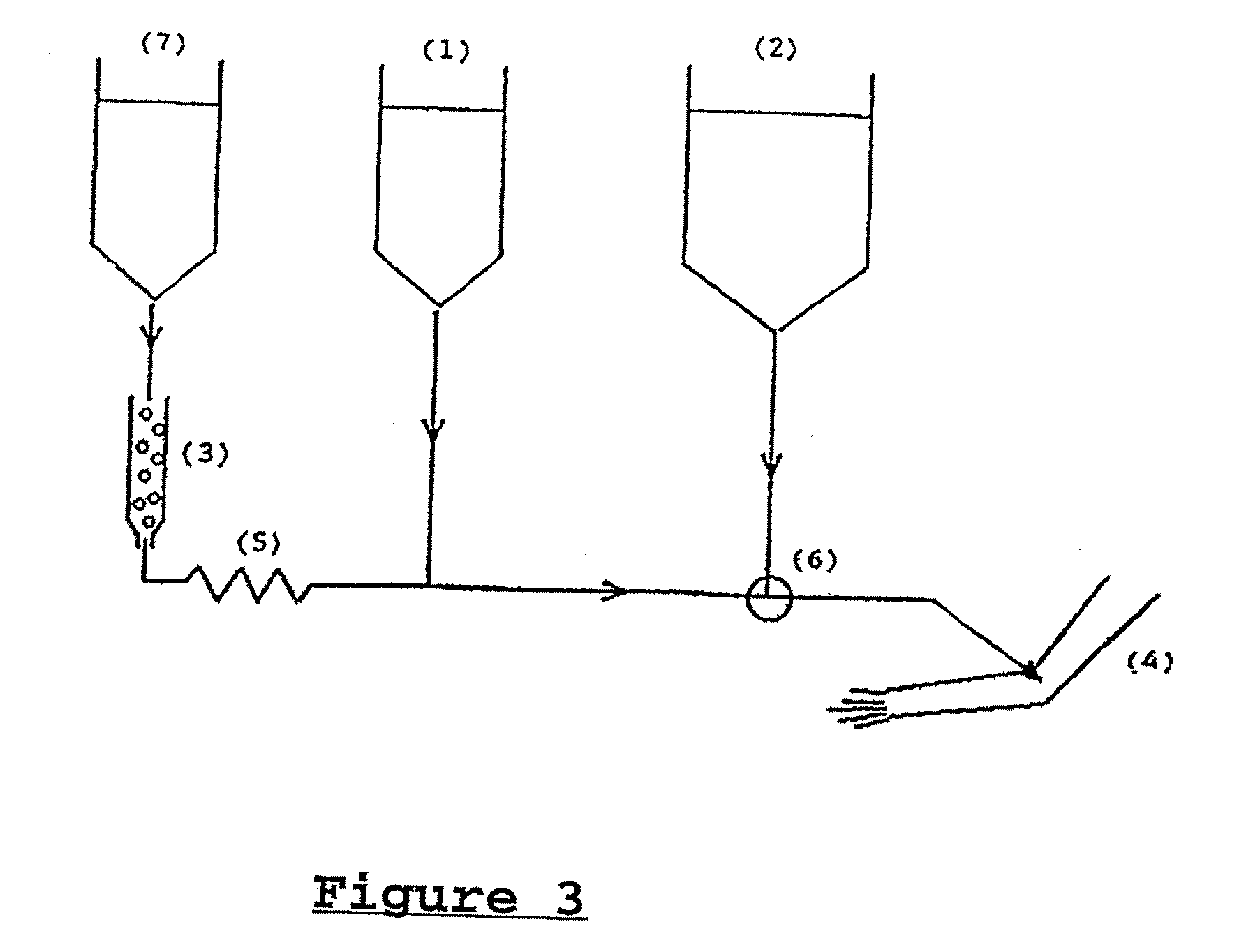
Brief radioimmunotherapy
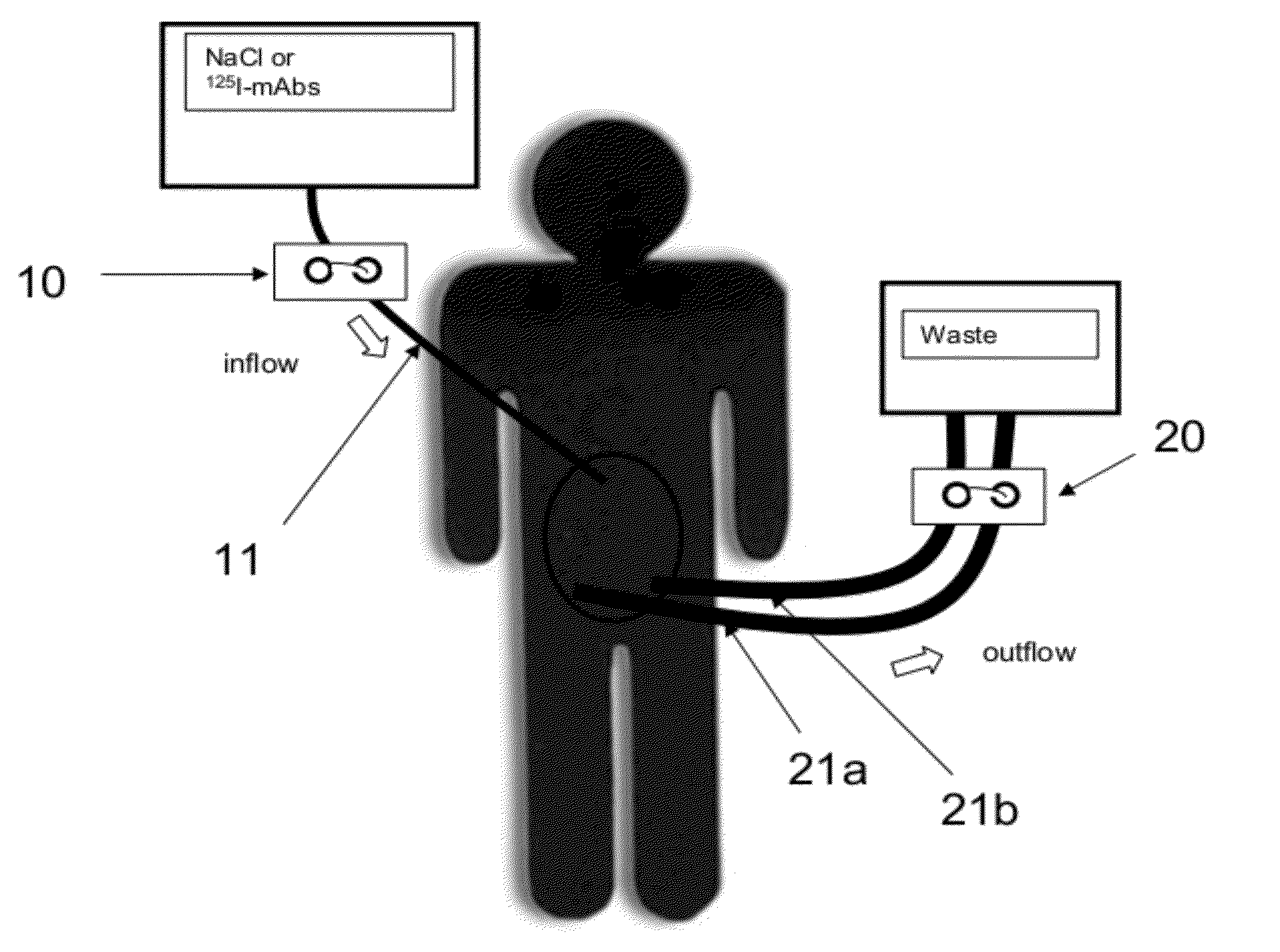
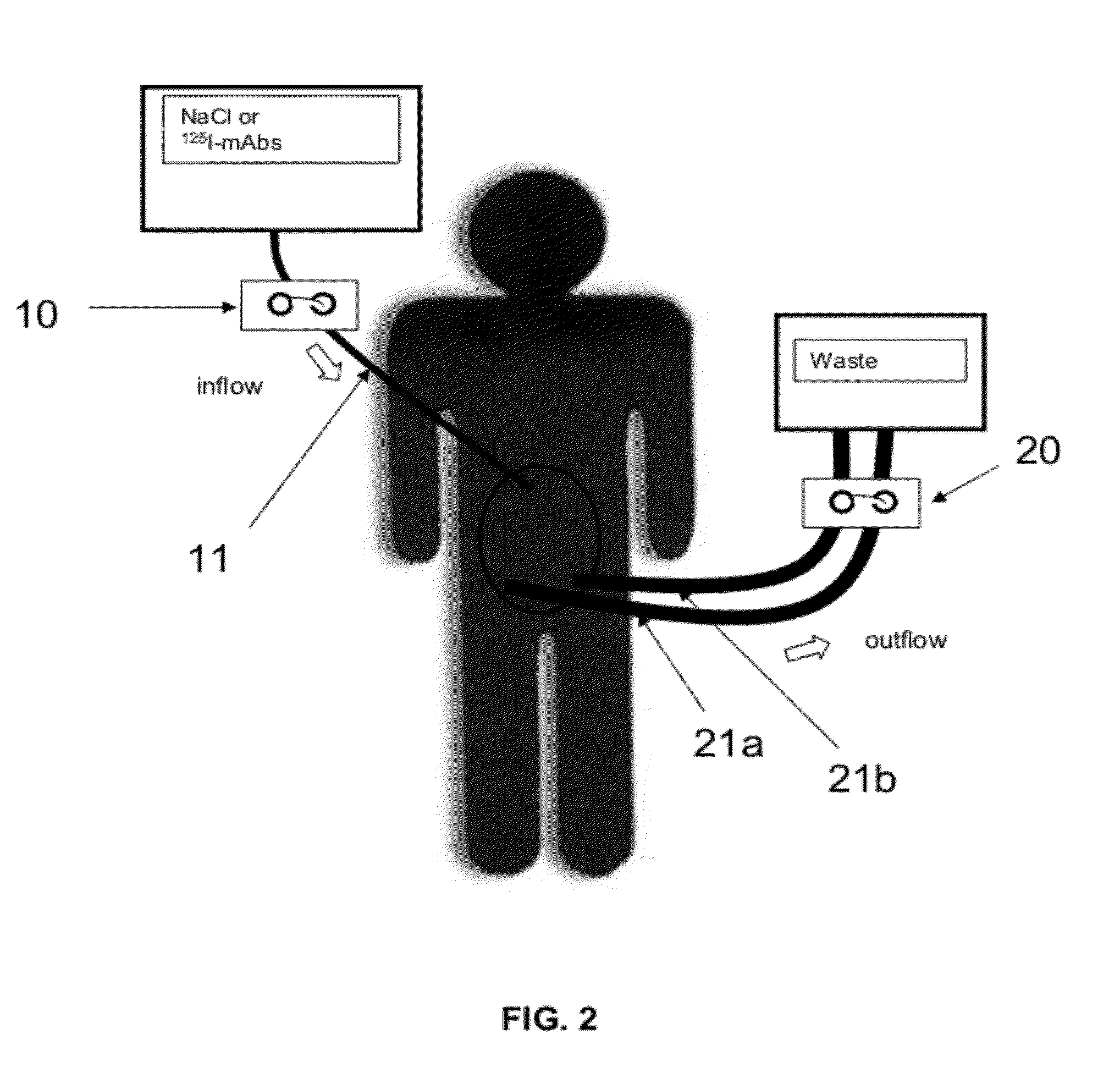
The present invention relates to a method of treating a subject having a cancer in a body cavity characterized in that it comprises the steps of:administering in said body cavity of the subject radiolabeled binding molecules which bind to an antigen expressed by cancerous cells;washing the body cavity to remove unbound radiolabeled molecules.The present invention also relates to a body cavity perfusing system for carrying out said method.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALER UNIV NIMES +1
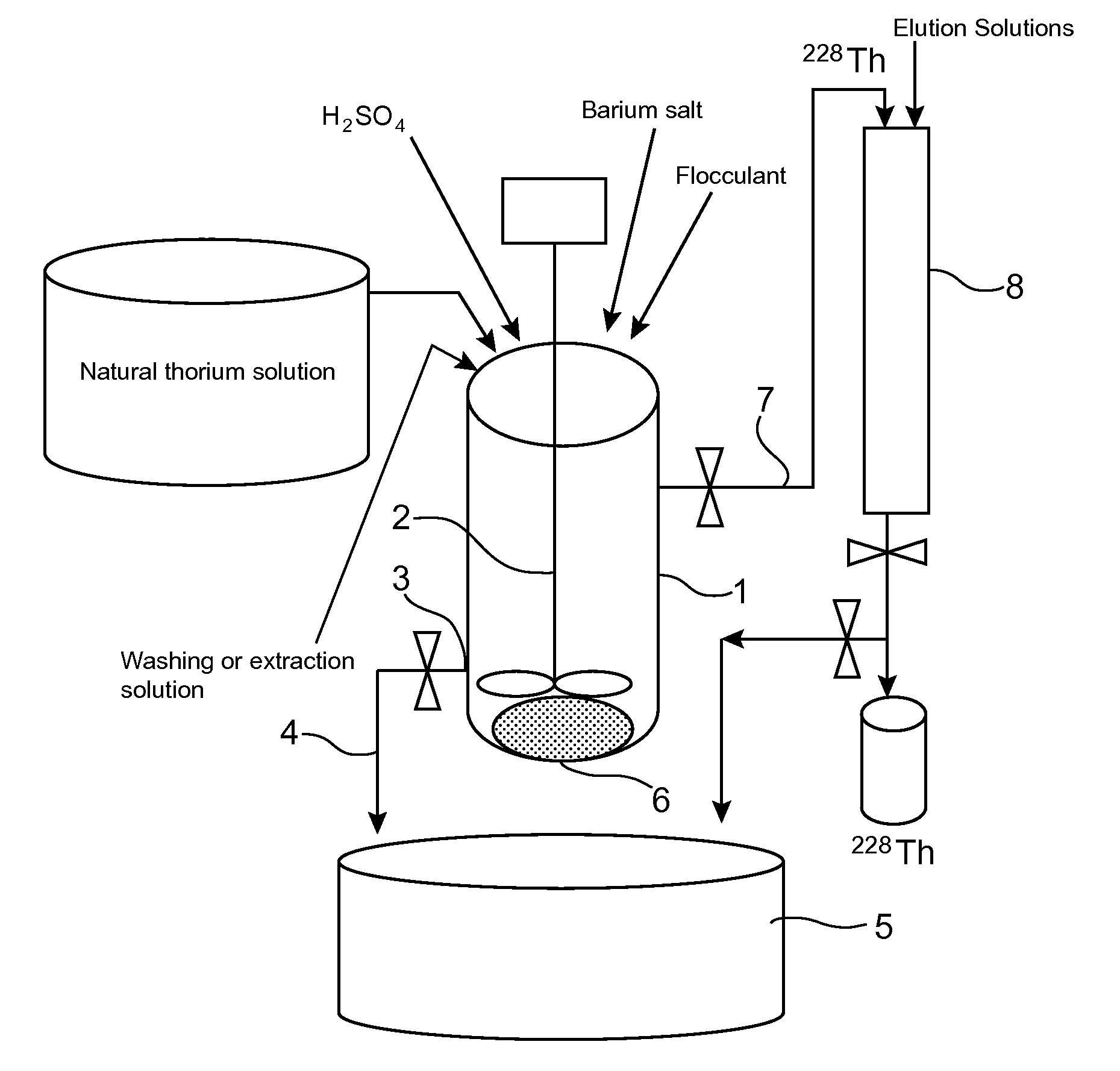
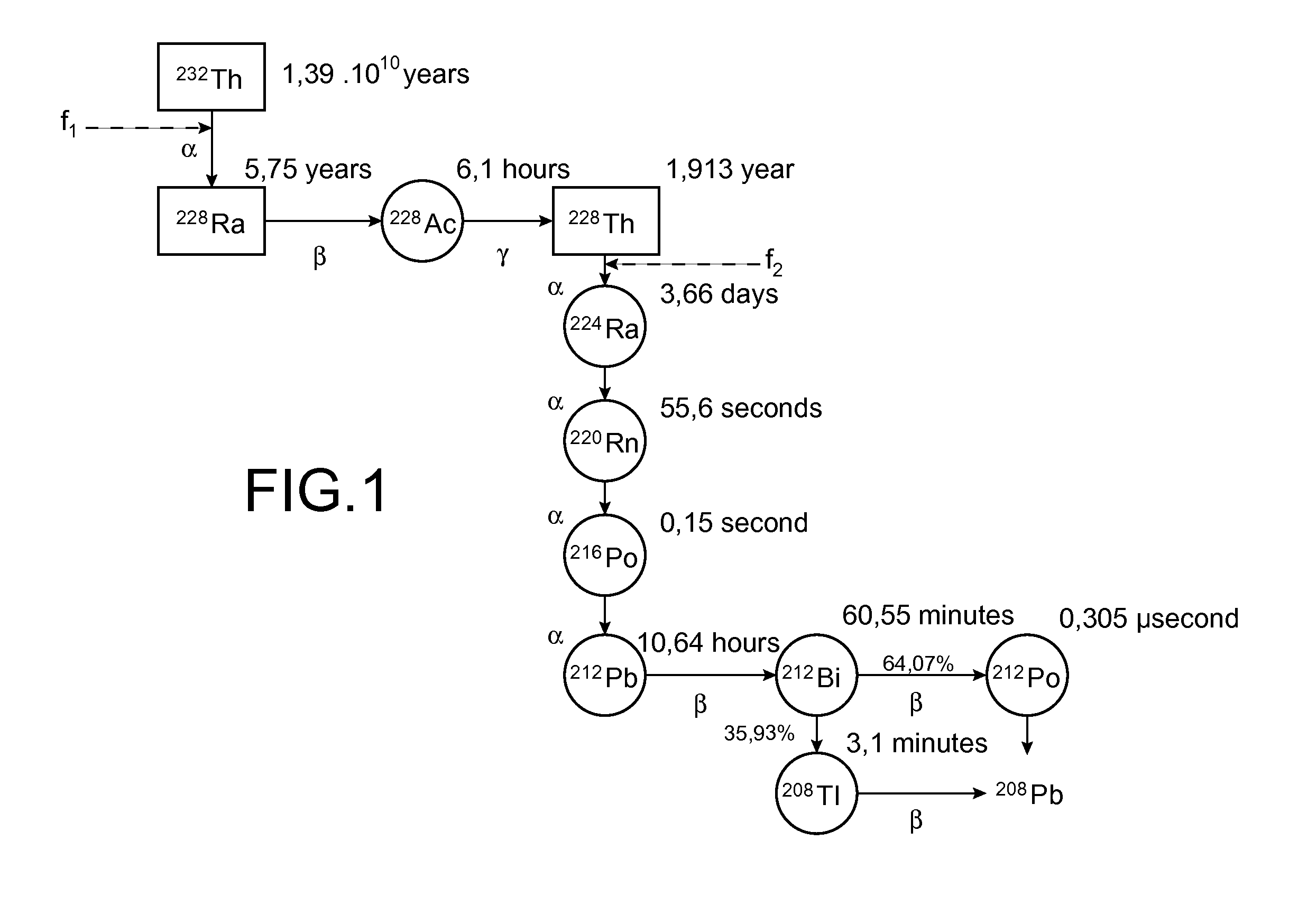
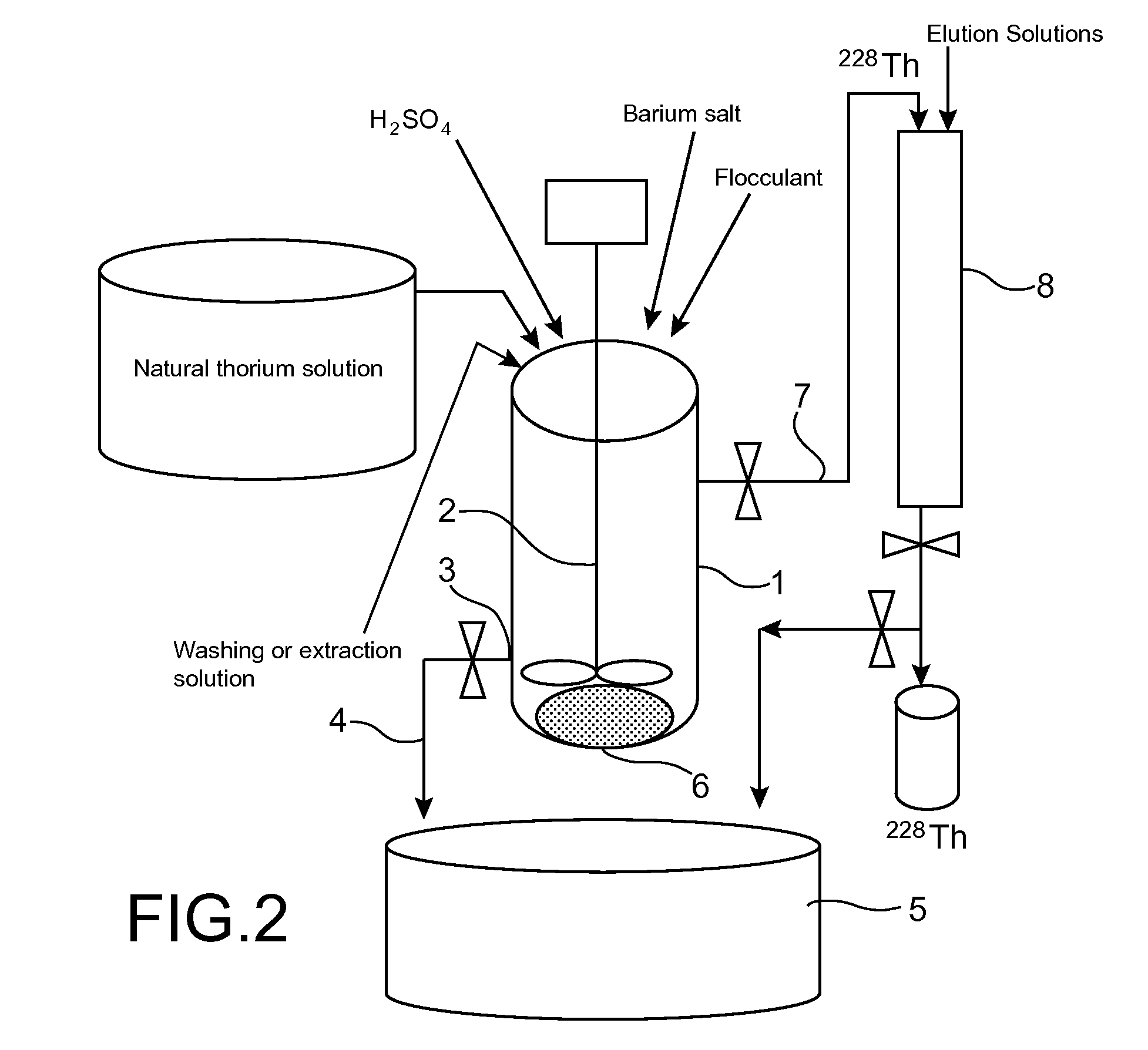
Production of thorium 228 starting from a natural thorium salt
ActiveUS20100104467A1High purityMinimize dilution effectRadium compoundsRadioactive preparation carriersBarium saltCoprecipitation
The invention relates to a process for producing 228Th from a natural thorium salt, which comprises in succession: a) the separation of the radium from the other radioelements present in this salt, by at least one coprecipitation of the radium by barium sulphate, this coprecipitation comprising: i) the addition of sulphuric acid and a barium salt to an aqueous solution of said natural thorium salt in order to form a barium-radium sulphate coprecipitate and ii) the separation of the coprecipitate from the medium in which it has formed; b) the extraction of the thorium 228 coming from the decay of radium 228 from the coprecipitate thus separated; and, optionally c) the purification and concentration of the 228Th thus extracted. Applications: manufacture of radiopharmaceutical products useful in nuclear medicine, in particular in radioimmunotherapy for the treatment of cancers and AIDS.
Owner:AREVA MED
Methods for detecting pathological sites
InactiveUS20080279772A1Reduce the amount requiredHybrid immunoglobulinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMedicineTreatment field
The present invention relates to the field of site directed therapy. More specifically the invention relates to site directed radio therapy, and provides a method for production of radioconjugates and an apparatus for radioimmunotherapy. The method, conjugates and apparatus can be practicalized without the need for radioactive shielding and / or airtight facilities. Without these restrictions the invention provides a simple and efficient means of therapy at the bed-side of the patient.
Owner:ACTINIUM PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com