Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Protein design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein design is the rational design of new protein molecules to design novel activity, behavior, or purpose, and to advance basic understanding of protein function. Proteins can be designed from scratch (de novo design) or by making calculated variants of a known protein structure and its sequence (termed protein redesign). Rational protein design approaches make protein-sequence predictions that will fold to specific structures. These predicted sequences can then be validated experimentally through methods such as peptide synthesis, site-directed mutagenesis, or artificial gene synthesis.
Protein design automation for protein libraries
The invention relates to the use of protein design automation (P DA) to generate computationally prescreened secondary libraries of proteins, and to methods and compositions utilizing the libraries.
Owner:XENCOR
Apparatus and method for automated protein design
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for quantitative protein design and optimization.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Apparatus and method for automated protein design
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for quantitative protein design and optimization.
Owner:MAYO STEPHEN +4
Array oligomer synthesis and use
InactiveUS20070059692A1Simple processShorten the timePeptide librariesSugar derivativesOligomerProteomics
The present disclosure provides efficient and reproducible methods for individually synthesizing oligomers in a parallel manner (e.g., oligonucleotides) on a solid support to produce pools of oligomers. Pools of oligonucleotides can be used for a variety of genomic and proteomic applications, including synthesis of genes or long DNA of any arbitrary sequence, PCR template amplification, and to generate primers for multiplexing PCR or transcription. Rapid availability of these oligonucleotide products will greatly accelerate the processes of de novo protein design, vaccine development, production of short RNA fragments, such as siRNA, oligonucleotide-based drug screening, and SNP sample preparation.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
COP protein design tool
The instant invention provides methods and implementing computer software for designing mutant proteins (or “Target Protein or TP”) that will preferentially bind one list of prespecified ligands (Active Ligands or AL) with respect to another list of ligands (The Inactive Ligands or IL).
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
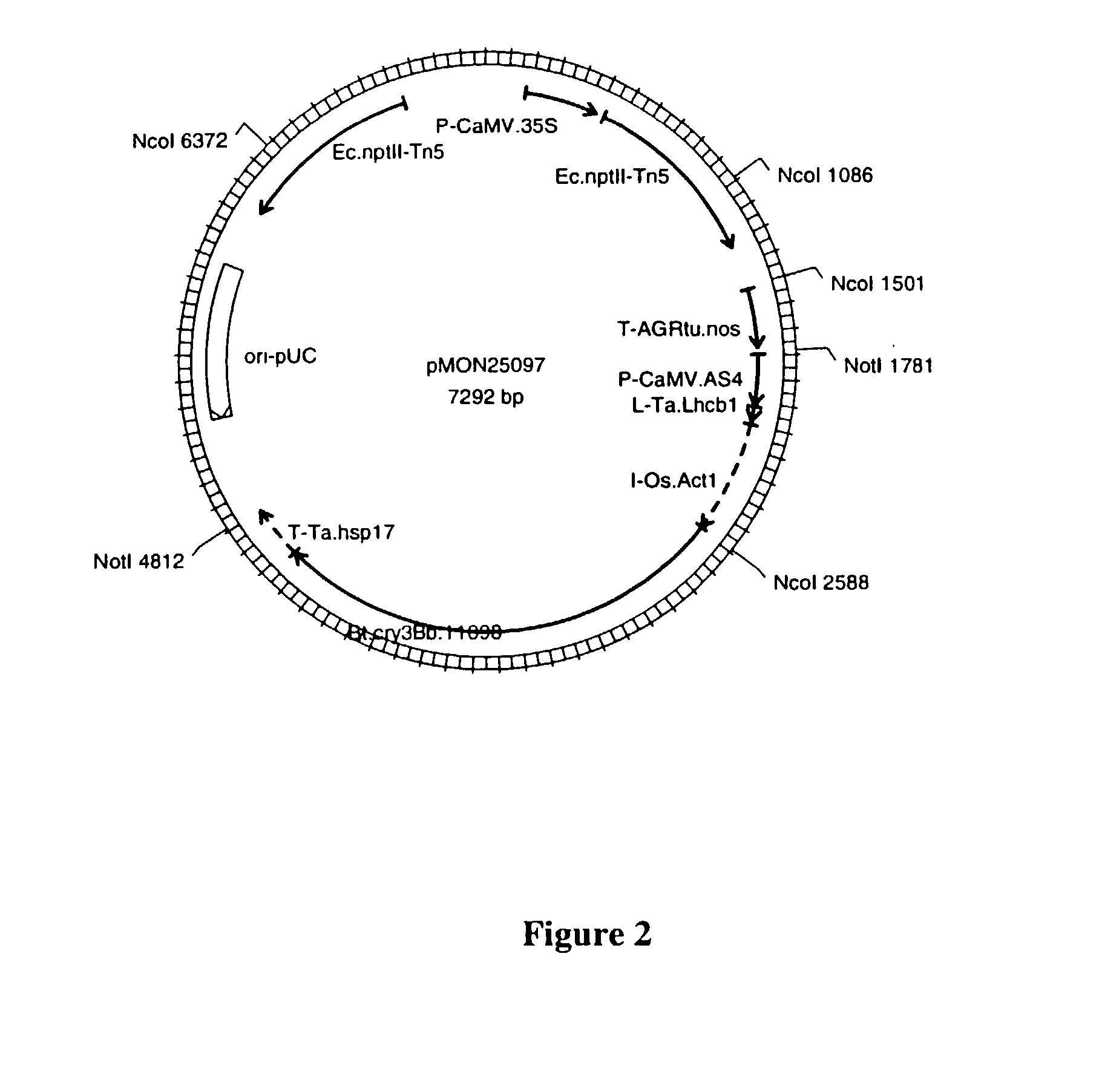
Expression of Cry3B insecticidal protein in plants
InactiveUS6943281B2Easy to controlSeason long protectionBiocideBacteriaActive proteinGenetically modified maize
The present invention discloses methods and compositions comprising a group of novel expression cassettes which provide significantly improved levels of accumulation of Coleopteran inhibitory Cry3B and Cry3B variant amino acid sequences when these are expressed in plants. The preferred embodiments of the invention provide at least up to ten fold higher levels of insect controlling protein relative to the highest levels obtained using prior compositions. In particular, transgenic maize expressing higher levels of a protein designed to exhibit increased toxicity toward Coleopteran pests deliver superior levels of insect protection and are less likely to sponsor development of populations of target insects that are resistant to the insecticidally active protein.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Simplifying residue relationships in protein design
The invention provides a method of determining changes in a first set of residues r1 due to changes in a second set of residues r2 in a protein system comprising one or more proteins comprising n and r2. In exemplary embodiments, the method comprises optimizing a quality function Q by modifying one or more properties of r1 and r2 in a constrained environment in which all degrees of freedom of the system except those directly involved in the potential coupling between r1 and r2 are removed.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
Apparatus and method for designing proteins and protein libraries
InactiveUS7231328B2Increase probabilityPeptide librariesAnalogue computers for chemical processesProteomeComputational biology
Methodology for the automated design of proteins is disclosed. Various methods executed by a computer for generating probability matrices, protein sequences, combinatorial libraries of proteins, and optimization of various parameters related to protein design are disclosed. Methodology is applicable to the design and analysis of protein structures and protein sequences.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Expression of Cry3B insecticidal protein in plants
The present invention discloses methods and compositions comprising a group of novel expression cassettes which provide significantly improved levels of accumulation of Coleopteran inhibitory Cry3B and Cry3B variant amino acid sequences when these are expressed in plants. The preferred embodiments of the invention provide at least up to ten fold higher levels of insect controlling protein relative to the highest levels obtained using prior compositions. In particular, transgenic maize expressing higher levels of a protein designed to exhibit increased toxicity toward Coleopteran pests deliver superior levels of insect protection and are less likely to sponsor development of populations of target insects that are resistant to the insecticidally active protein.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Modified proteins, designer toxins, and methods of making thereof
The present invention concerns methods of reducing the antigenicity of a proteinaceous compound while maintaining the compounds biological activity, as well as proteinaceous compositions with biological activity but reduced antigenicity. These methods and compositions have significant benefits to a subject in need of such compounds and compositions. Also included are modified toxin compounds that are truncated and / or possess reduce antigenicity. Such designer toxins have therapeutic, diagnostic, and preventative benefits, particularly as immunotoxins. Methods of treating cancer using these immunotoxins are provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
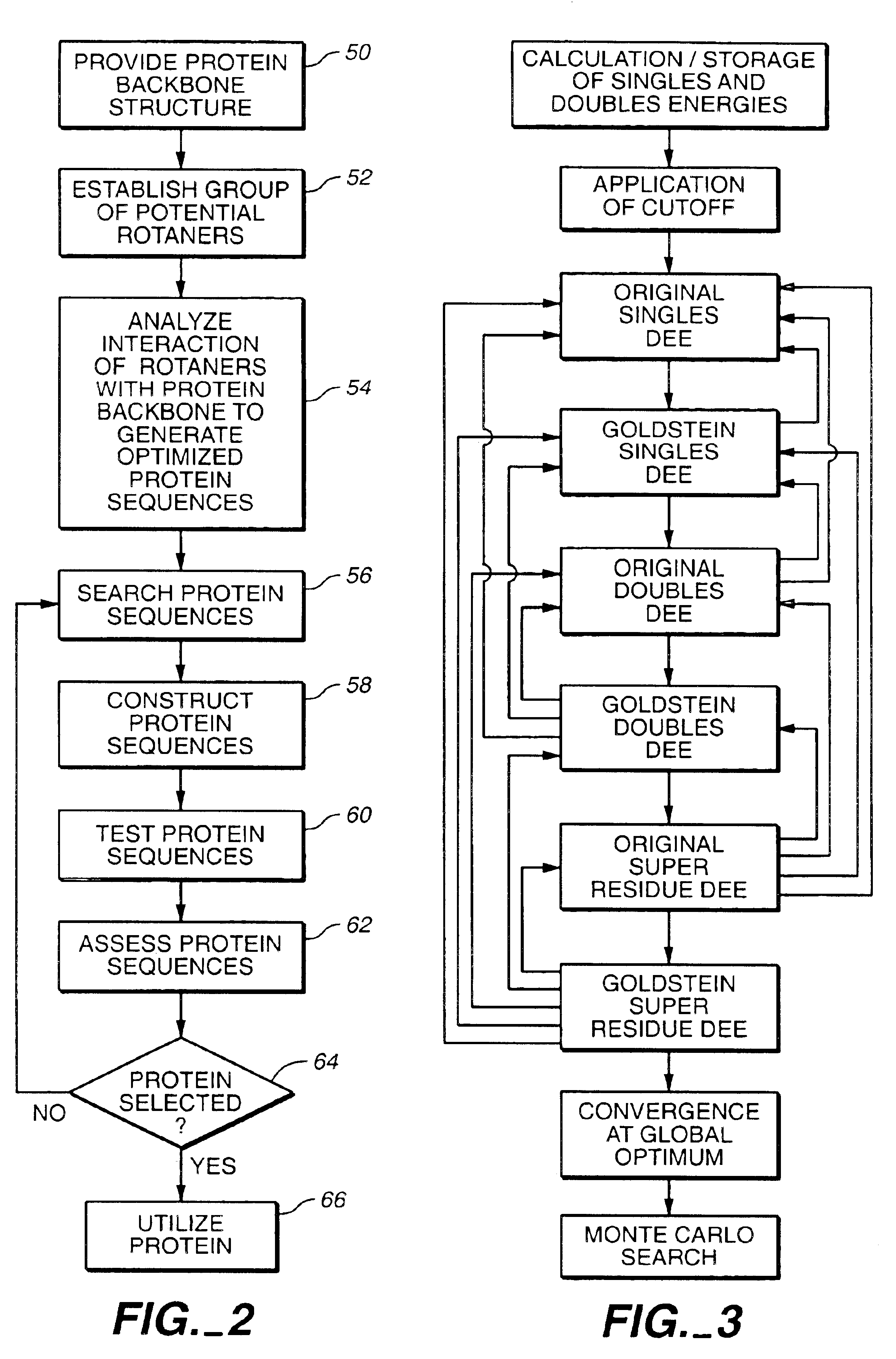
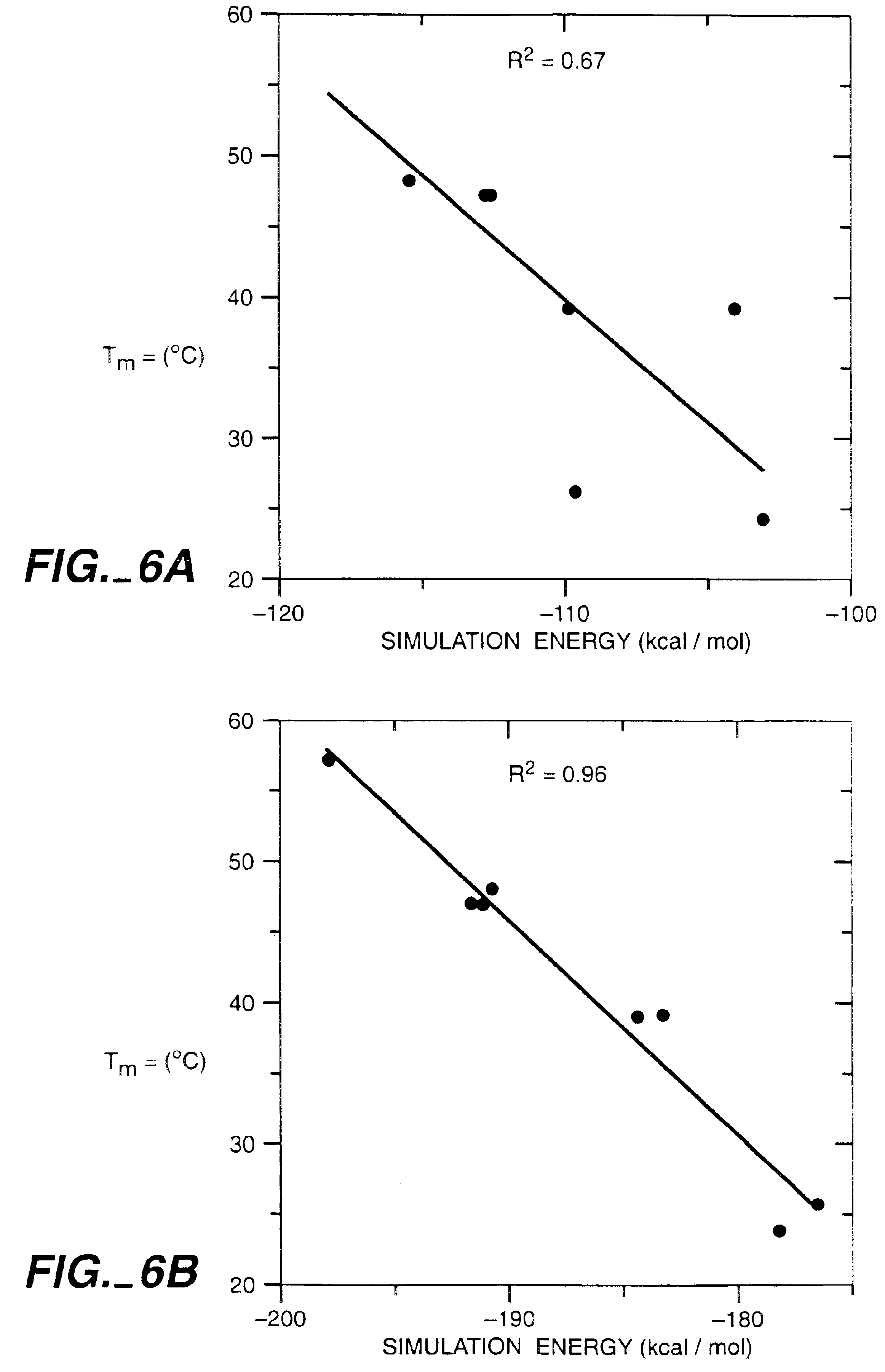
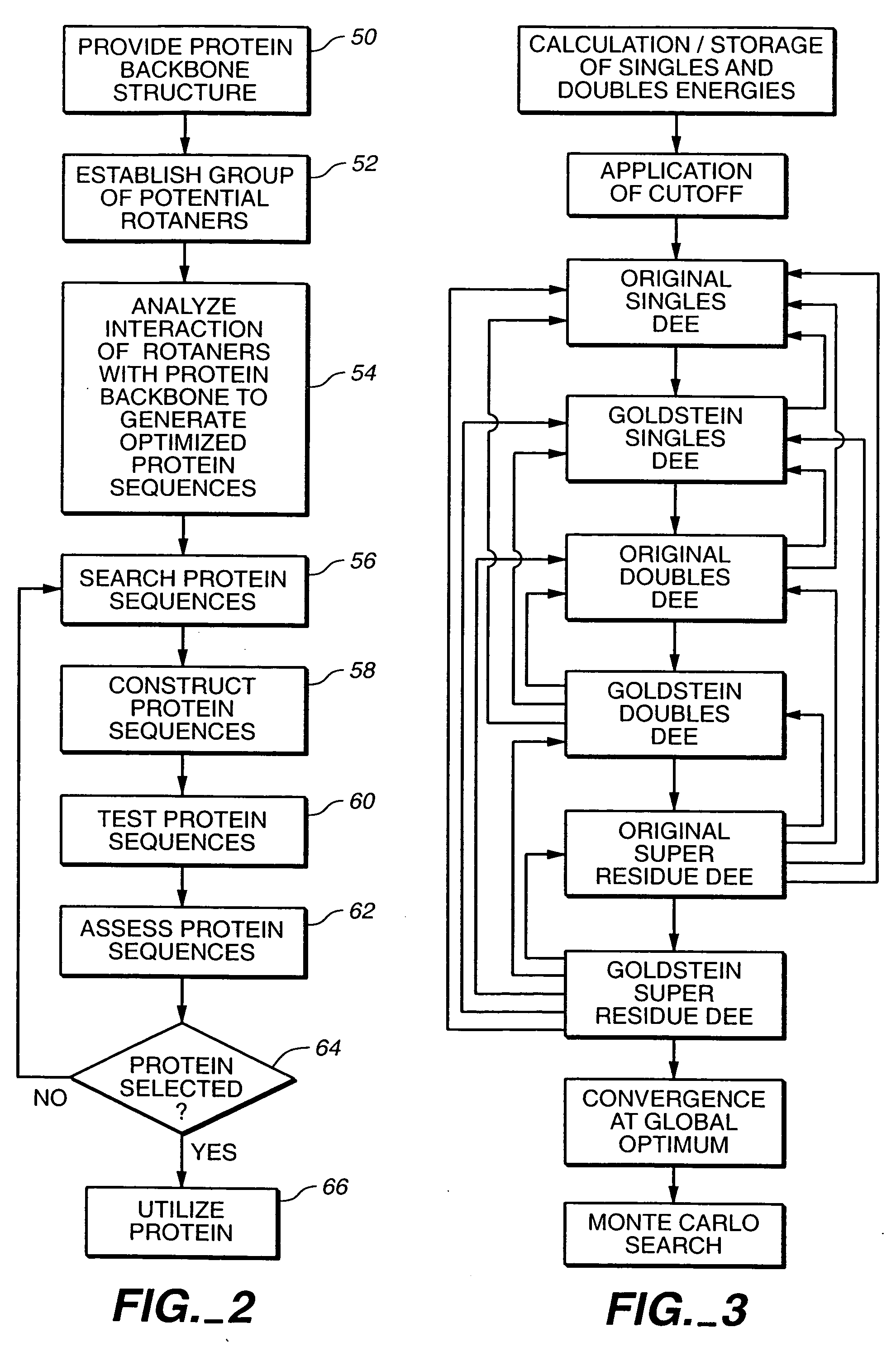
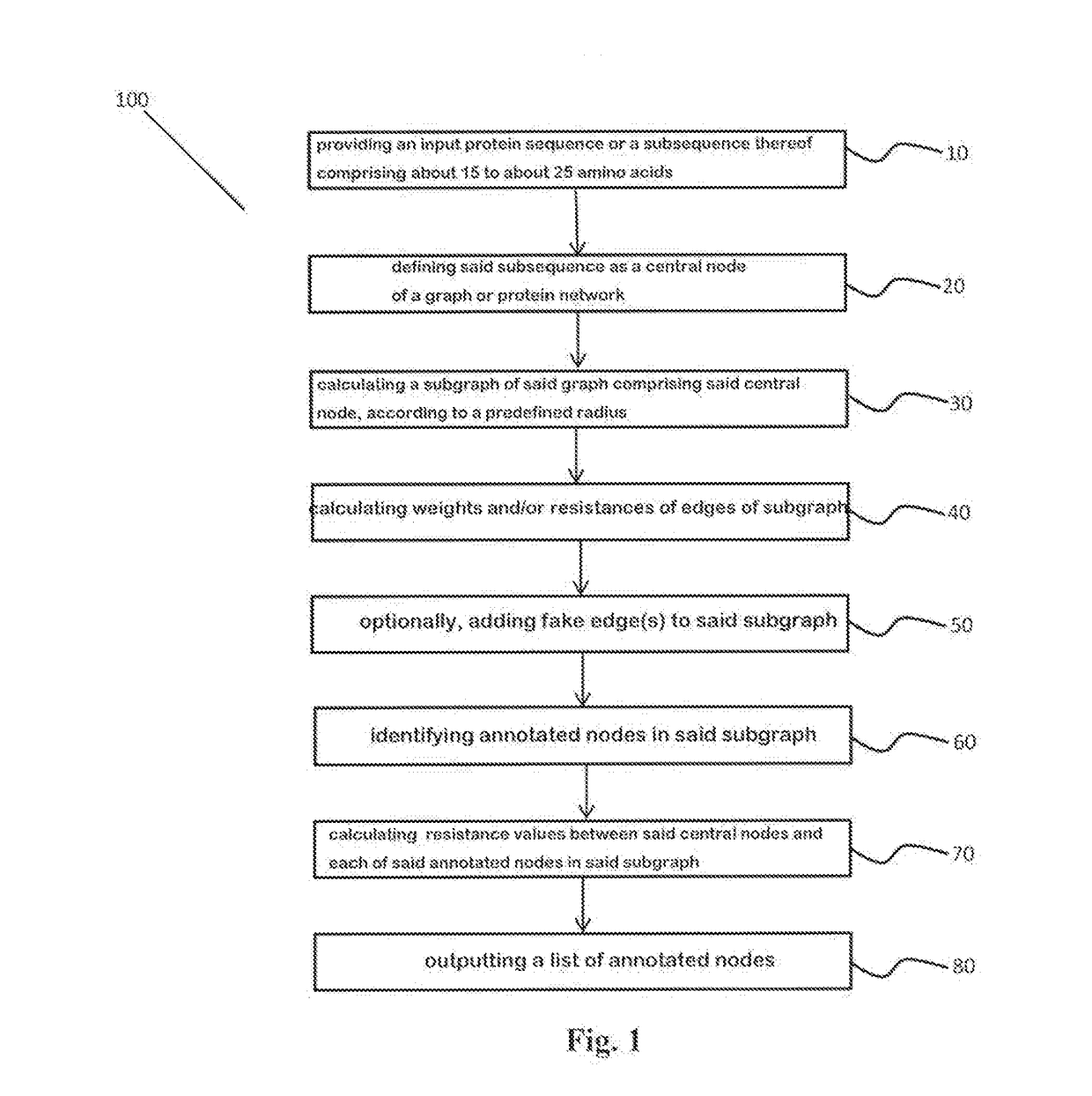
Protein design method and system
A method for annotating a protein sequence or a subsequence thereof includes the steps of providing an input protein sequence or a subsequence thereof. The subsequence is defined as a central node of a graph or protein network. A subgraph of the graph is calculated including the central node, according to a predefined radius and weights and / or resistances of edges of the subgraph are also calculated. Annotated nodes in the subgraph are identified. Resistance values between the central nodes and each of the annotated nodes in the subgraph are calculated and a list of annotated nodes is outputted. Each of the annotated nodes has a characteristic calculated resistance value to the central node of the input protein sequence.
Owner:OFEK ESHKOLOT RES & DEV
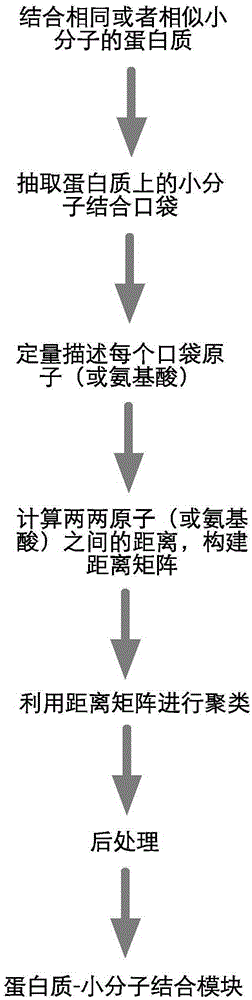
Method for extracting protein-micromolecule interaction module
The invention relates to a method for extracting a protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method specifically comprises: firstly, performing quantitative description on atoms (or amino acids) forming a micromolecular binding pocket on protein according to properties of the atoms (or amino acids); secondly, estimating the distance between the every two pocket atoms (or amino acids), and establishing a distance matrix; thirdly, extracting categories of the pocket atoms (or amino acids) with similar properties by utilizing a clustering algorithm; and finally, performing post-processing to obtain the protein-micromolecule interaction module. The method can be applied to multiple aspects of bioinformatics research, protein design, drug screening, micromolecular chemical synthesis and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for development of a peptide building block useful for de novo protein design
InactiveUS20110224404A1Improve thermal stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide sourcesProtein targetAlternative methods
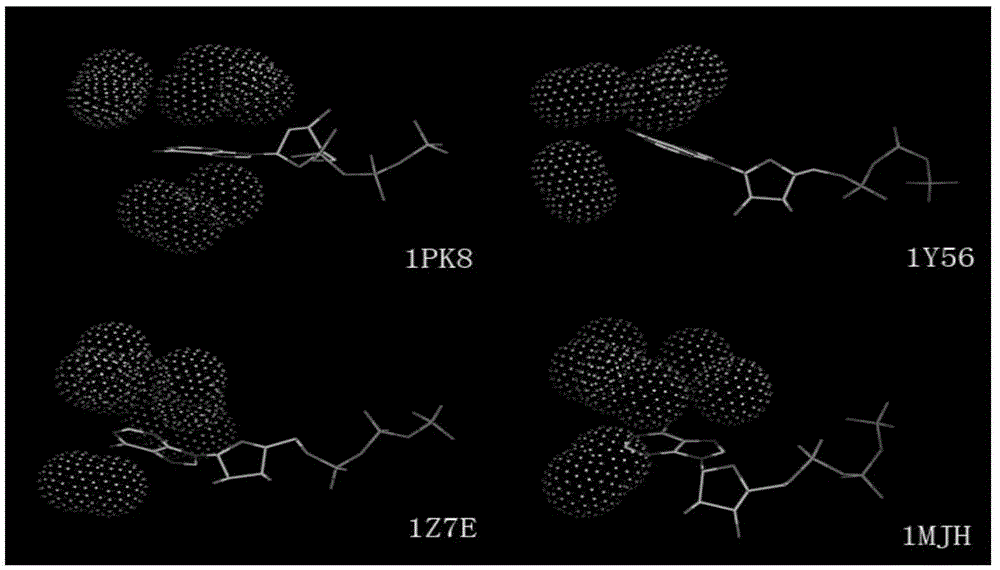
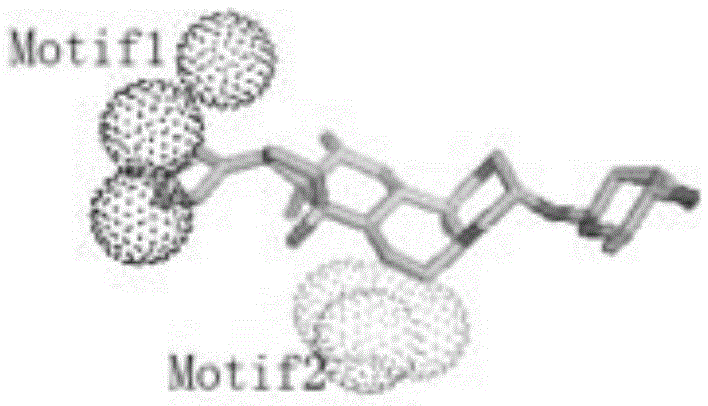
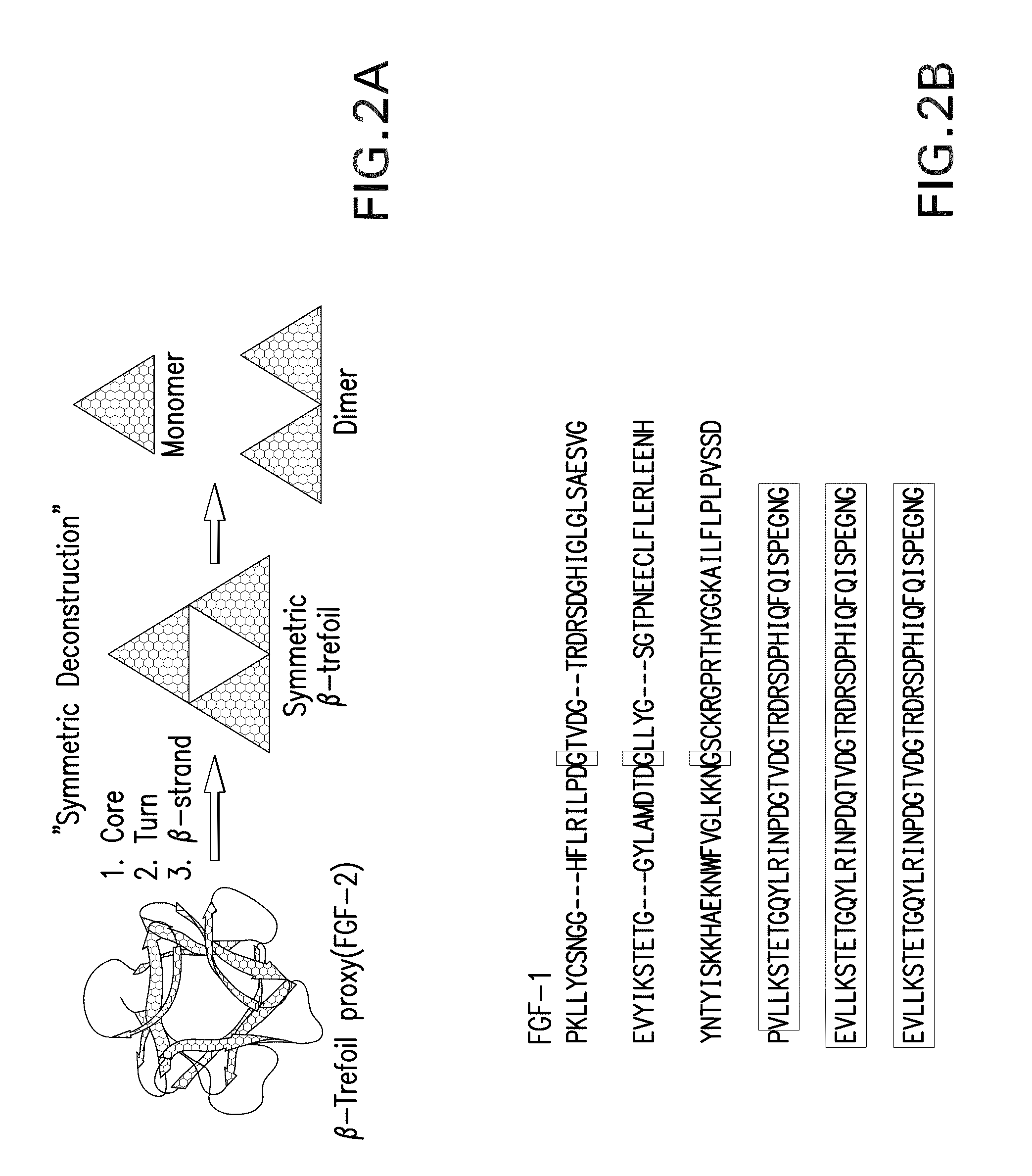
The present invention relates to a top-down symmetric deconstruction approach which provides a novel alternative means to successfully identify a useful polypeptide “building block” for subsequent “bottom-up” de novo design of target protein architecture. The present invention also pertains to a novel peptides isolated by top-down symmetric deconstruction which may be useful for design or directed evolution of novel proteins with novel functionalities.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Protein design automation for protein libraries
InactiveUS7379822B2Microbiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsCell biologyAutomation
The invention relates to the use of protein design automation (PDA) to generate computationally prescreened secondary libraries of proteins, and to methods and compositions utilizing the libraries.
Owner:XENCOR INC
Method for designing proteins on basis of polarizable force fields and pso (particle swarm optimization)
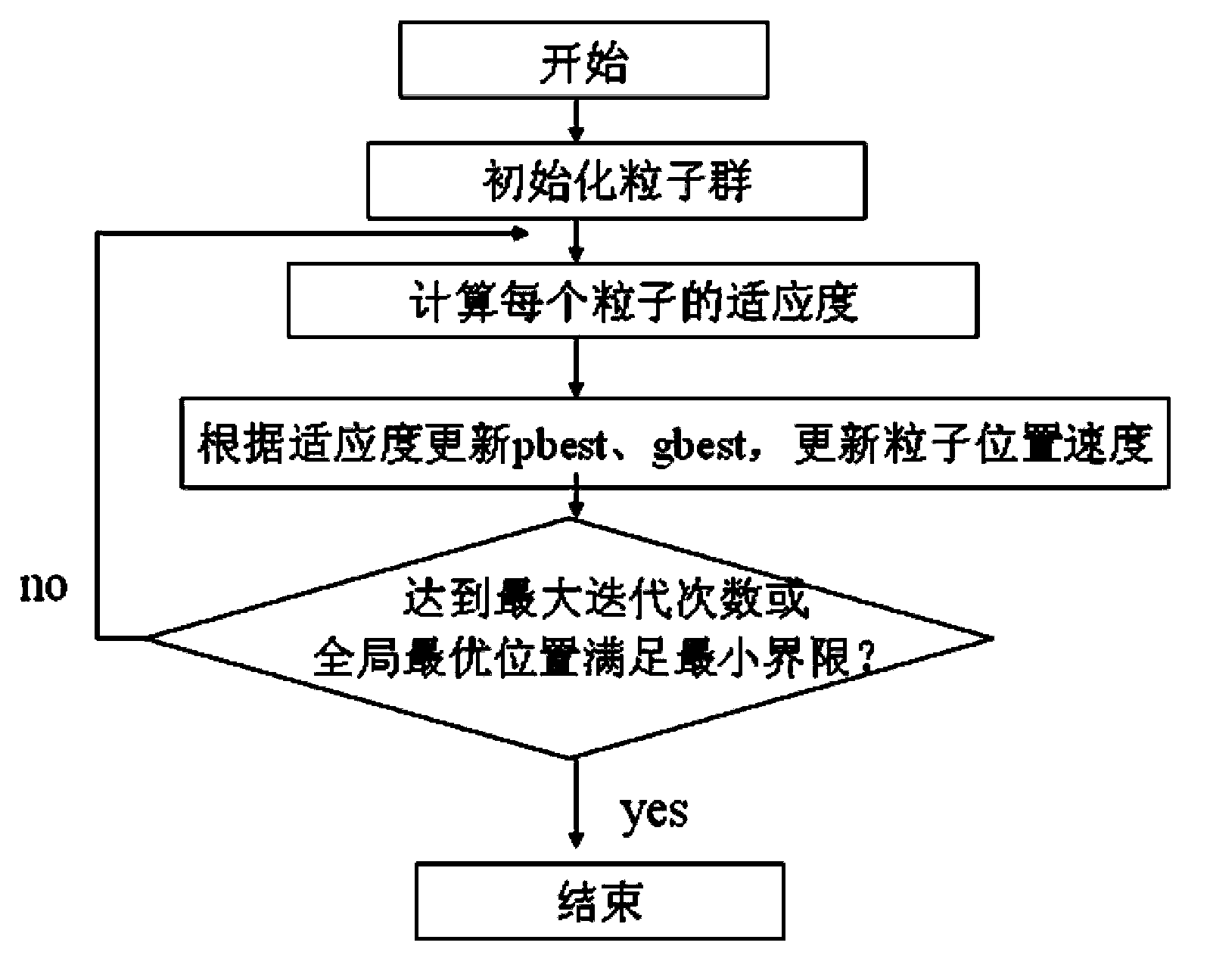
The invention relates to a method for designing proteins on the basis of polarizable force fields and pso (particle swarm optimization). The method includes steps of acquiring a plurality of proteins by the aid of a protein design template; optimizing each protein, in other words, searching certain rotamers in a rotamerlib, and creating a temporary particle by the aid of each found rotamer; computing the fitness of each temporary particle, and updating local optimal particles and neighbor optimal particles according to the fitness of each temporary particle; updating positions and speeds of all non-temporary particles; comparing the positions of all the neighbor optimal particles to acquire the global optimal positions; searching side-chain conformation combined spaces by the aid of particle swarms to acquire the optimized proteins. Each certain rotamer is the closest to sub-vectors of the corresponding particle which continuously moves in a 4n (four-dimensional) space. The method has the advantages that discrete problems are solved by the aid of pso, and the polarizable force fields are used as evaluation foundations by the aid of the high efficiency of pso; modification on the proteins can be predicted theoretically, and the proteins can be screened theoretically.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Protein structure design method and device based on deep learning
ActiveCN112289372AReduce screeningReduce adsorptionBiostatisticsDesign optimisation/simulationProtein targetGraph neural networks
The invention relates to a protein structure design method and device based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: determining a gene sequence or molecular crystal structure information of a targeted protein according to a biomarker; inputting the gene sequence or molecular crystal structure information of the targeted protein into a geometric graph neural network model; generating an amino acid sequence by using the trained geometric graph neural network model; constructing a protein skeleton model according to the generated amino acid sequence and the homologous protein;and optimizing the protein skeleton model according to proteomics and molecular dynamics. According to the method, protein data is bound with corresponding DNA sequences and mRNA sequences, so that the interpretability and effectiveness of the generated amino acid sequences are improved, the screening, repeated adsorption, elution and amplification processes of protein design or verification arereduced, and the calculation amount of the model is reduced through a geometric graph neural network.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Individualized cancer therapy
In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods for treating cancer, comprising: (a) obtaining a specimen of cancer tissue and normal tissue from a patient; (b) extracting total protein and RNA from the cancer tissue and normal tissue; (c) obtaining a protein expression profile of the cancer tissue and normal tissue; (d) identifying over-expressed proteins in the cancer tissue; (e) comparing the protein expression profile to a gene expression profile; (f) identifying at least one prioritized protein target by assessing connectivity of each said over-expressed protein to other cancer-related or stimulatory proteins; (g) designing a first RNA interference expression cassette to modulate the expression of at least one gene encoding the prioritized target protein; (h): designing a first RNA interference expression cassette to modulate the expression of at least one gene encoding a protein of higher priority in the signaling pathway in which the first protein is a component; (i) incorporating the first cassette into a first delivery vehicle; (j) providing a patient with an effective amount of the first delivery vehicle; (k) extracting total protein and RNA from the treated cancer tissue; (l) identifying over-expressed proteins in the treated cancer tissue; (m) designing a second RNA interference expression cassette to modulate the expression of a second prioritized protein in the treated tissue; (n) incorporating the second cassette into a second delivery vehicle; (o) providing the previously treated patient with an effective amount of the second delivery vehicle; (p) identifying a novel protein signal following prior treatment with protein specific knockdown; (q) identifying a gene mutation provided by gene sequencing / microarray on assessment of other protein signals; and (r) identifying of a novel protein signal as a result of determination of the gene mutation and assessment of other protein signals to, directly or indirectly, modify the expression (i.e., production) of such proteins.
Owner:GRADALIS
Blocking ELISA kit for detecting neutralizing antibody of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and application of blocking ELISA kit
ActiveCN112979789AObvious negative reactionStrong specificityBiological material analysisImmunoglobulins against virusesElisa kitInfectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus
The invention relates to detection of a neutralizing antibody of an infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus, in particular to a blocking ELISA kit for detecting the neutralizing antibody of the infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus and application of the blocking ELISA kit. The invention provides a monoclonal antibody with neutralizing activity for resisting infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. The monoclonal antibody is secreted by hybridoma cells with the preservation number of CGMCC No.21015. The invention further provides a kit for detecting the neutralizing antibody of the infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus. The kit comprises the monoclonal antibody. Based on the monoclonal antibody and truncated gD protein designed in the invention, a blocking ELISA method for detecting a neutralizing antibody of the infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus is established, and the blocking ELISA method has the advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity and good repeatability.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for improving biological functions of protein
InactiveCN1763227AIncrease biological functionImprove thermal stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyGene engineeringProtein evolution
The present invention relates to method for raising biological function of protein. The method includes reasonable conventional protein design to determine the functional region related to the biological function of protein; substituting the gene in the functional region related to the biological function of protein with randomly changed primer segment and constituting mutant gene library in conventional gene engineering method; and the final directional protein evolution to screen out from the mutant gene library the protein with raised biological function. The method of the present invention can obtain protein with raised biological function, and is simple, practical and efficient.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Protein Design Automation for Protein Libraries
The invention relates to the use of protein design automation (PDA) to generate computationally prescreened secondary libraries of proteins, and to methods and compositions utilizing the libraries.
Owner:XENCOR INC
Method of computational protein design
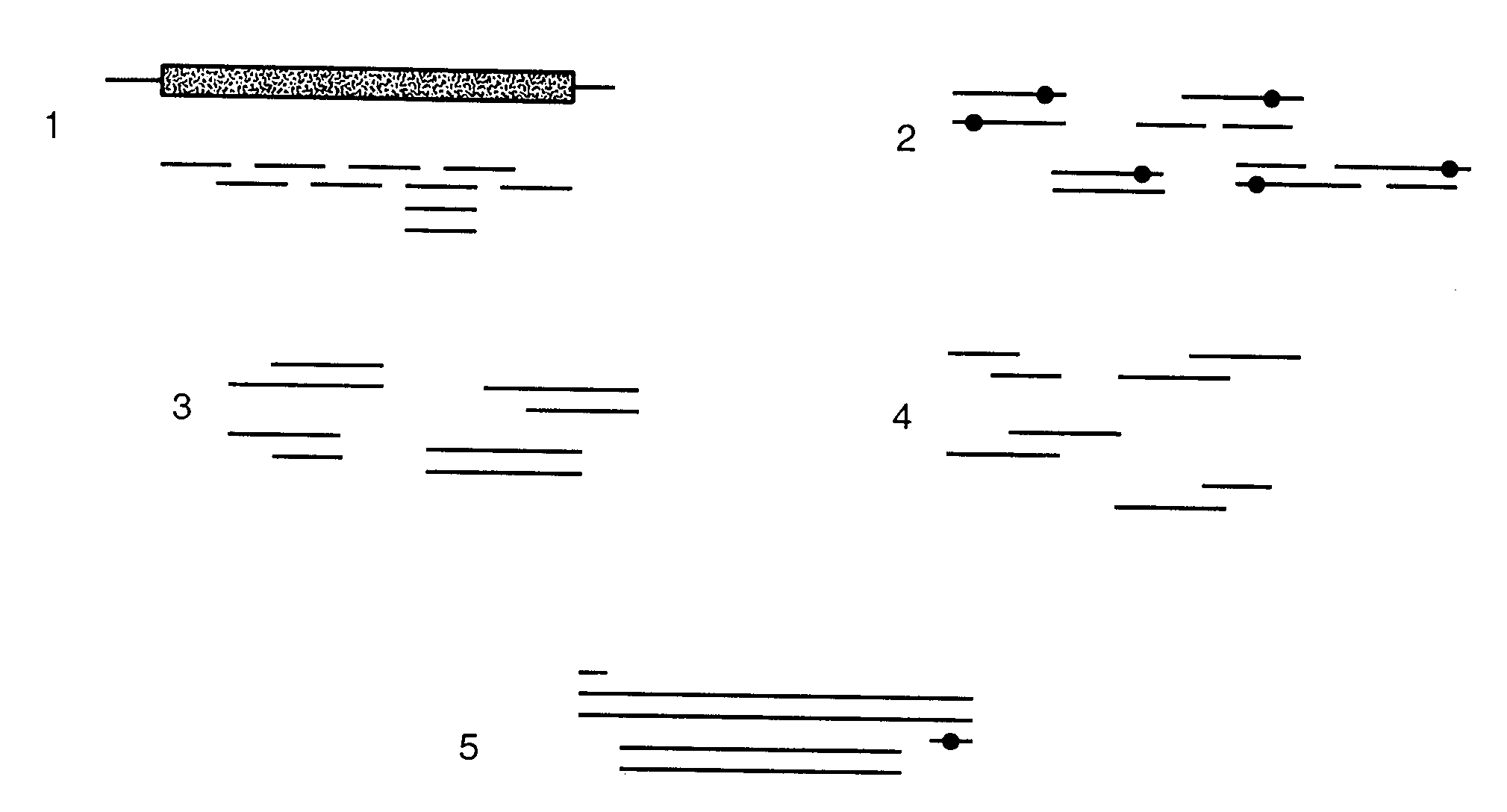
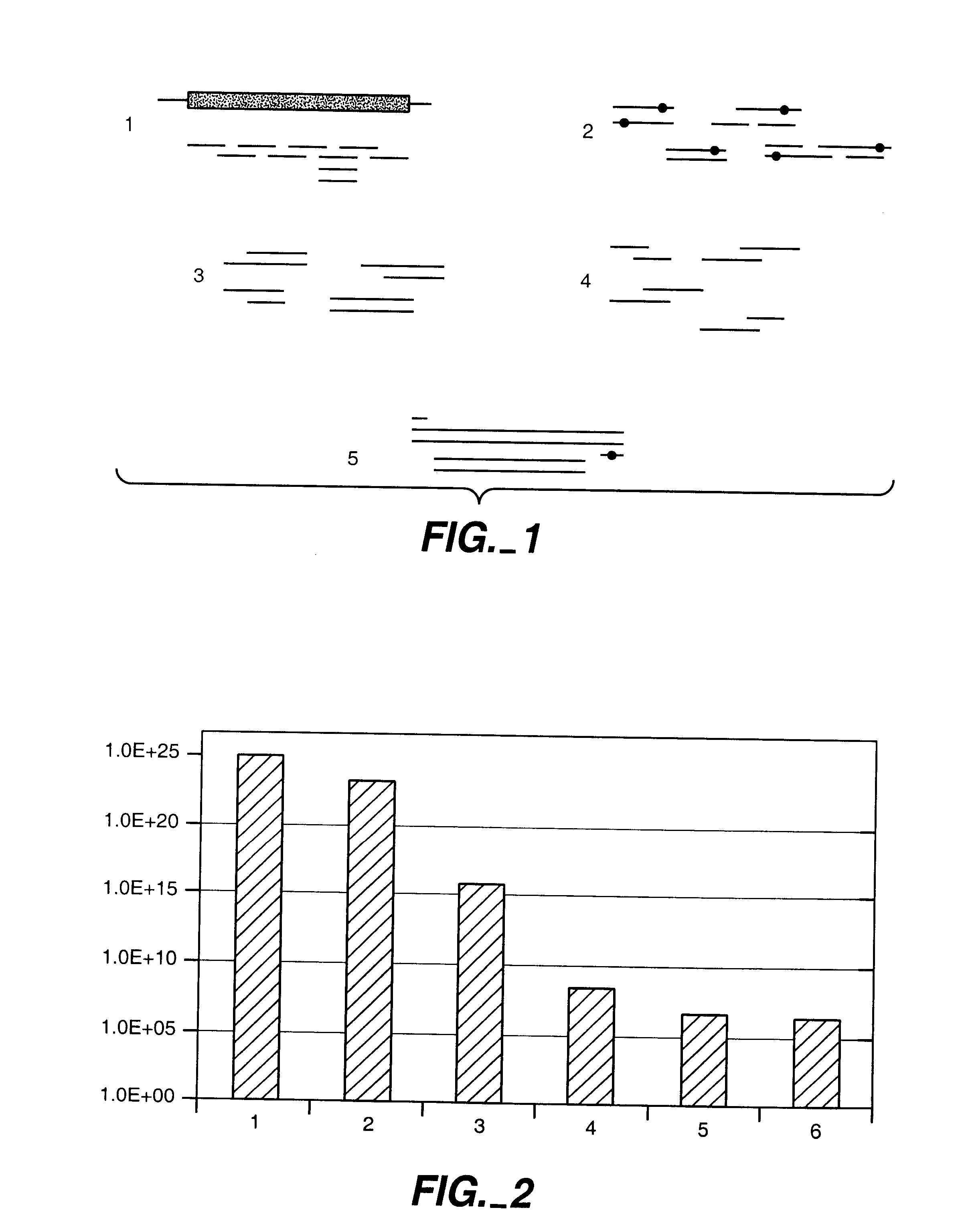
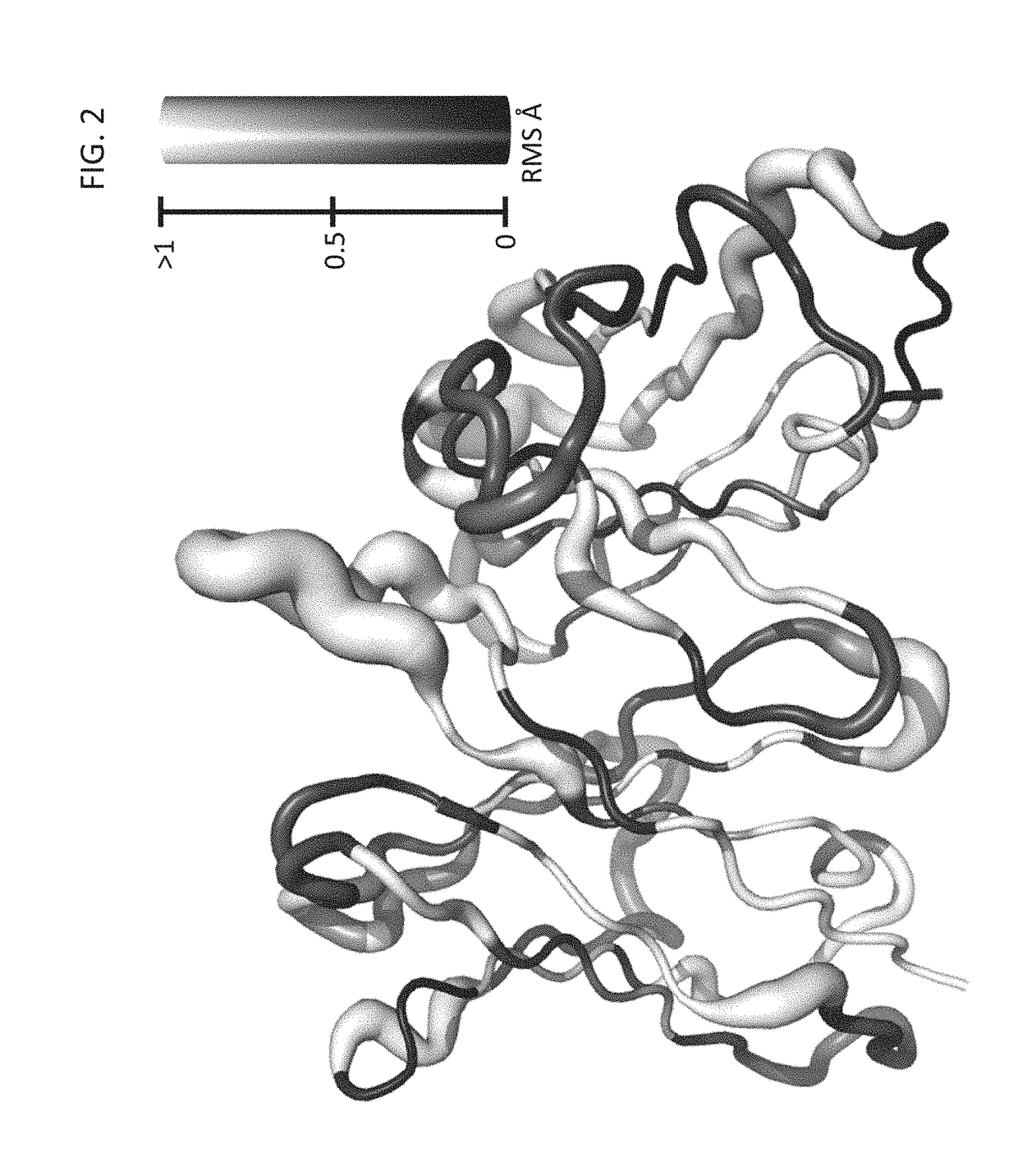
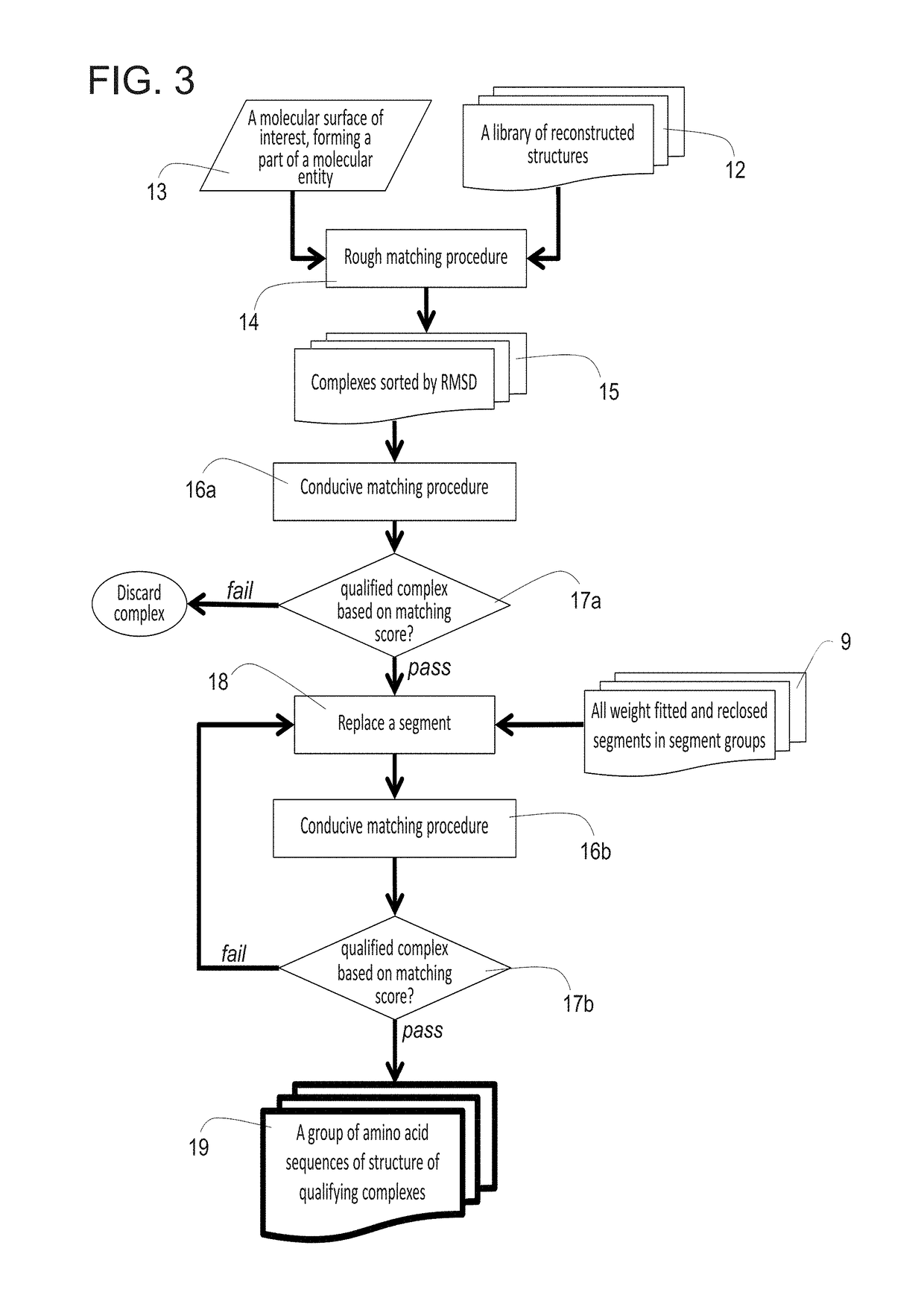
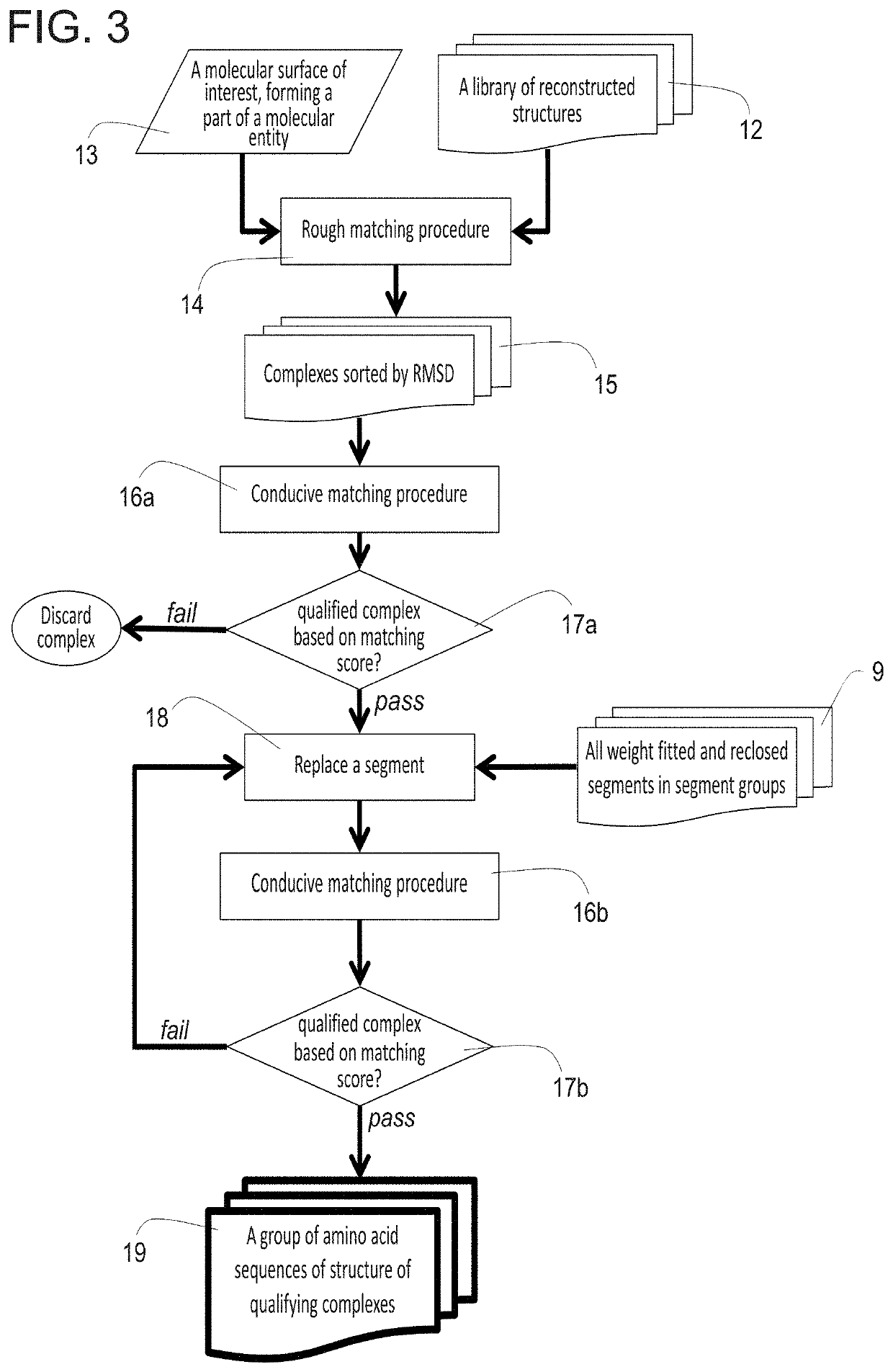
A method for constructing a library of amino-acid sequences having a common structural fold, and a method for designing and selecting an amino-acid sequence having a desired affinity to a molecular surface of interest of a molecular entity, using the library, are provided herein. The methods are based on a stochastic sampling of backbone conformations and amino acid conservation patterns observed in experimentally available protein structures having the common structural fold.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Process for Generating Synthetic Engineered Recombinant Proteins for Vaccination, Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease
A process for generating a synthetic engineered recombinant protein has been performed by providing an original protein design and the necessary probabilistic priors for random in silico assembly. Once the in silico synthetic protein is assayed using mathematic modeling, the proteins are then reverse translated into DNA. The DNA fragment, modifying the original DNA to obtain a first DNA fragment, wherein the modifying step comprising adding an antigen optimization sequence to the original DNA fragment, purifying the first DNA fragment, performing a DNA self-assembly or a ligation, adding an amplification linker to obtain a second DNA fragment, purifying the second DNA fragment, transferring the second DNA fragment into an expression vector, expressing the second DNA fragment into a synthetic engineered recombinant protein, as well as purifying the synthetic engineered recombinant protein.
Owner:OLLE ERIC WILLIAM
Method for development of a peptide building block useful for de novo protein design
ActiveUS20150361149A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAnalogue computers for chemical processesProtein targetAlternative methods
The present invention relates to a top-down symmetric deconstruction approach which provides a novel alternative means to successfully identify a useful polypeptide “building block” for subsequent “bottom-up” de novo design of target protein architecture. The present invention also pertains to a novel peptides isolated by top-down symmetric deconstruction which may be useful for design or directed evolution of novel proteins with novel functionalities.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
TAL-mediated transfer DNA insertion
InactiveUS20140154397A1Lower Level RequirementsSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to methods for stably integrating a desired polynucleotide into a plant genome, comprising transforming plant material with a first vector comprising nucleotide sequences encoding TAL proteins designed to recognize a target sequence; transforming the plant material with a second vector comprising (i) a marker gene that is not operably linked to a promoter (“promoter-free marker cassette”) and which comprises a sequence homologous to the target sequence; and (ii) a desired polynucleotide; and identifying transformed plant material in which the desired polynucleotide is stably integrated.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
Compositions and methods for design of non-immunogenic proteins
InactiveUS20070184487A1Peptide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic intentPeptide fragment
Provided are methods for de novo design of proteins that are non-immunogenic when administered for therapeutic purposes. The methods involve protein design based on combinations of peptide fragments naturally encountered by the immune system.
Owner:CODON DEVICES
Method of computational protein design
A method for constructing a library of amino-acid sequences having a common structural fold, and a method for designing and selecting an amino-acid sequence having a desired affinity to a molecular surface of interest of a molecular entity, using the library, are provided herein. The methods are based on a stochastic sampling of backbone conformations and amino acid conservation patterns observed in experimentally available protein structures having the common structural fold.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
A protein structure design method and device based on deep learning
ActiveCN112289372BImprove interpretabilityImprove effectivenessBiostatisticsDesign optimisation/simulationProtein targetGraph neural networks
The present invention relates to a protein structure design method and device based on deep learning, the method comprising: determining the gene sequence or molecular crystal structure information of the targeted protein according to biomarkers; inputting the gene sequence or molecular crystal structure information of the targeted protein into the geometric graph neural network model; use the trained geometric graph neural network model to generate an amino acid sequence; construct a protein skeleton model based on the generated amino acid sequence and homologous proteins; optimize the protein skeleton model according to proteomics and molecular dynamics. The present invention binds protein data to corresponding DNA sequences and mRNA sequences, on the one hand, improves the interpretability and effectiveness of amino acid sequences, and on the other hand reduces the time and effort of screening, repeated adsorption, elution, and amplification for protein design or verification. In the process, the calculation amount of the model is reduced through the geometric graph neural network.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
Simplifying residue relationships in protein design
The invention provides a method of determining changes in a first set of residues r1 due to changes in a second set of residues r2 in a protein system comprising one or more proteins comprising r1 and r2. In exemplary embodiments, the method comprises optimizing a quality function Q by modifying one or more properties of r1 and r2 in a constrained environment in which all degrees of freedom of the system except those directly involved in the potential coupling between r1 and r2 are removed.
Owner:ZYMEWORKS INC
TAL-mediated transfer DNA insertion
InactiveUS9756871B2Vector-based foreign material introductionFood scienceNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to methods for stably integrating a desired polynucleotide into a plant genome, comprising transforming plant material with a first vector comprising nucleotide sequences encoding TAL proteins designed to recognize a target sequence; transforming the plant material with a second vector comprising (i) a marker gene that is not operably linked to a promoter (“promoter-free marker cassette”) and which comprises a sequence homologous to the target sequence; and (ii) a desired polynucleotide; and identifying transformed plant material in which the desired polynucleotide is stably integrated.
Owner:J R SIMPLOT
Streptococcus suis vaccine recombinant protein GSE and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN112410310AEfficient preparationPracticalAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigen epitopeProtective antigen
The invention relates to a recombinant protein GSE used as a streptococcus suis vaccine. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is SEQ ID NO. 1. Aiming at the problems that the cross protection effect between an inactivated vaccine and a low virulent vaccine of streptococcus suis is poor, and certain biosecurity exists, the recombinant protein designed on the basis of screening of streptococcus suis protective antigen epitopes can be used for preparing the streptococcus suis vaccine. The recombinant protein can be efficiently prepared under the safe condition and has good practicability.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com