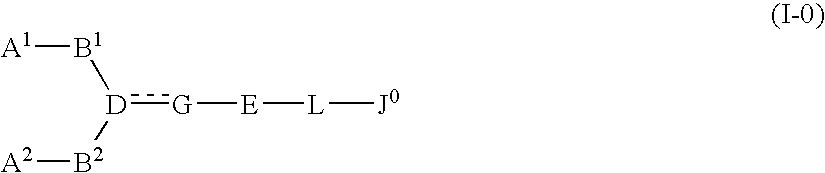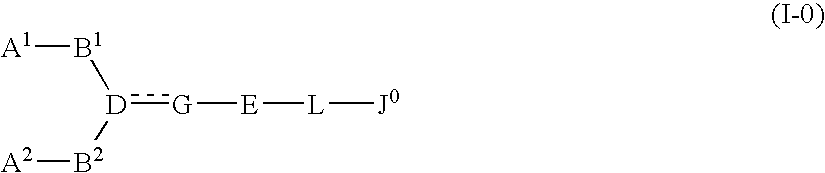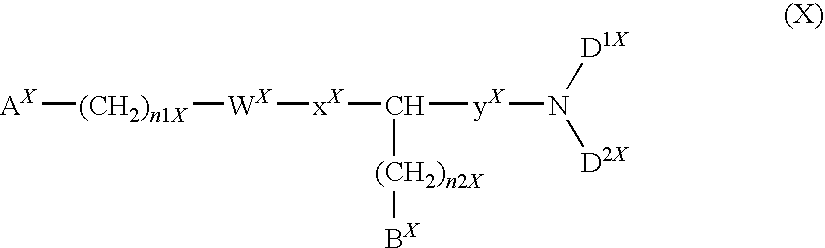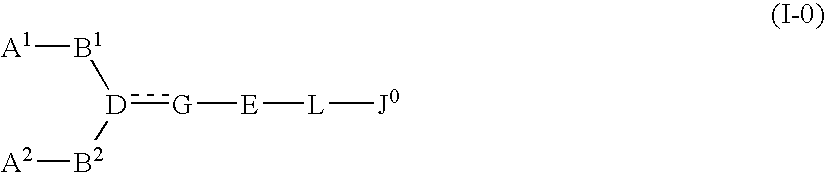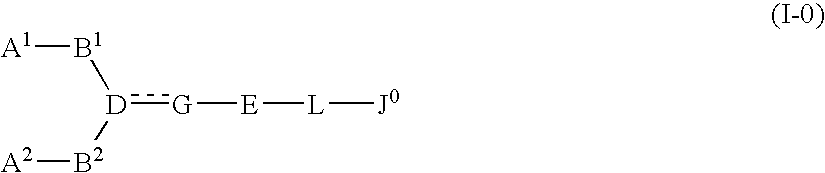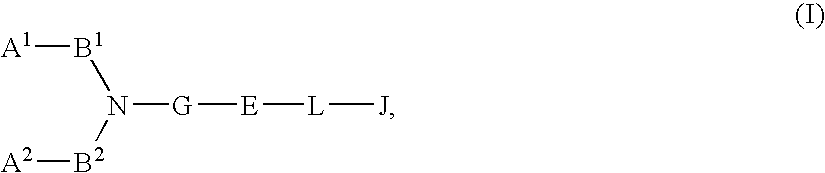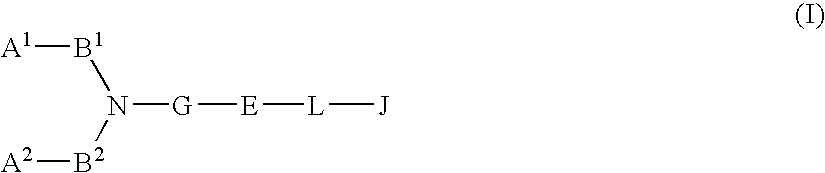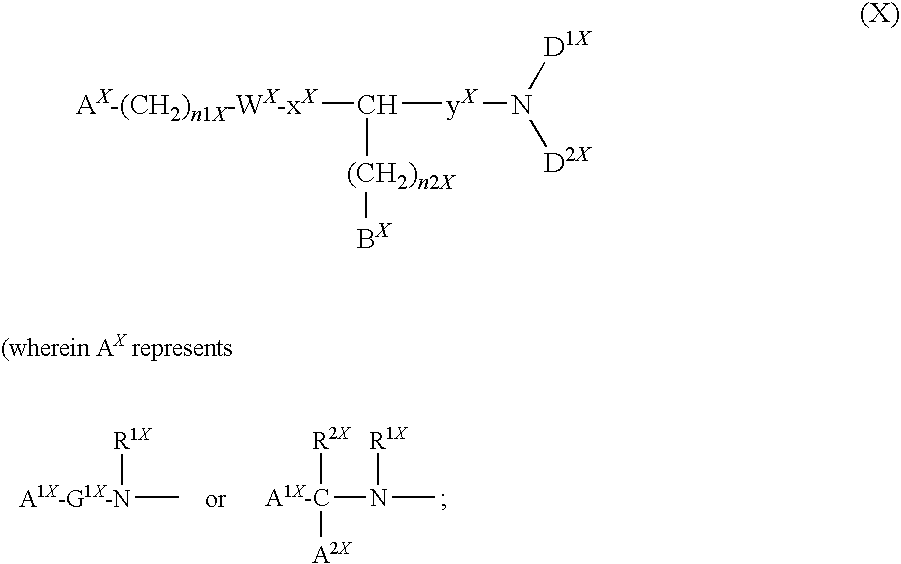Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Organ rejections" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
“Rejection” is a very scary word, but it doesn’t always mean you are losing your transplanted organ. Rejection is when the organ recipient’s immune system recognizes the donor organ as foreign and attempts to eliminate it. It often occurs when your immune system detects things like bacteria or a virus.
Injectable compositions of nanoparticulate immunosuppressive compounds
InactiveUS20060210638A1Improve complianceImprove efficacyPowder deliveryBiocideDepressantCompound (substance)
The invention is directed to an injectable nanoparticulate immunosuppressant composition for the formation of a subcutaneous or intramuscular depot. The invention is also directed to an injectable composition of nanoparticulate tacrolimus and / or sirolimus which eliminates the need to use polyoxyl 60 hydrogenated castor oil (HCO-60) and / or polysorbate 80 as a solubilizer. This invention further discloses a method of making an injectable nanoparticulate tacrolimus and / or sirolimus composition and is also directed to methods of treatment using the injectable nanoparticulate formulations comprising tacrolimus, sirolimus, or combination thereof for a subcutaneous or intramuscular depot for the prophylaxis of organ rejection and for the treatment of psoriasis or other immune diseases
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
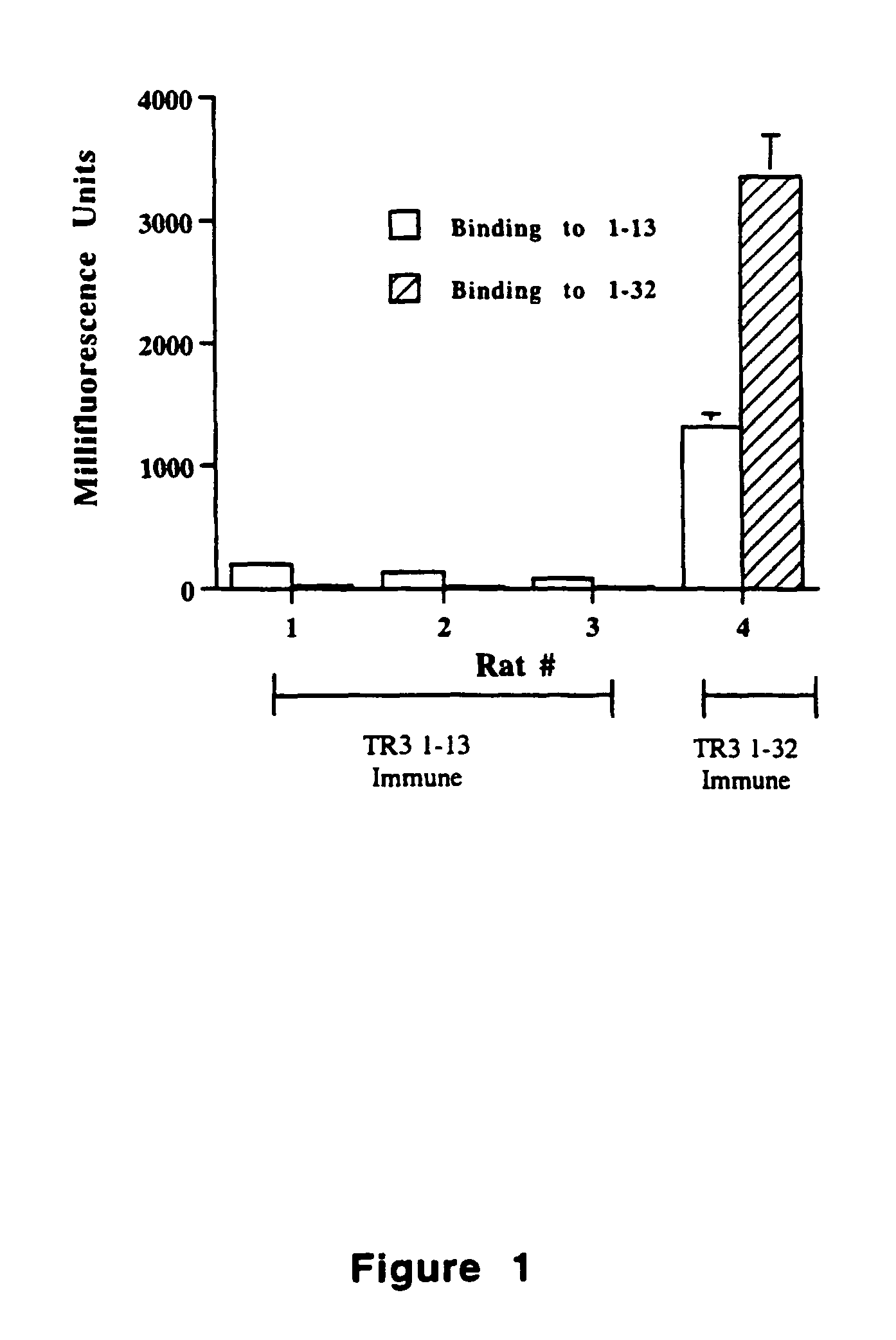
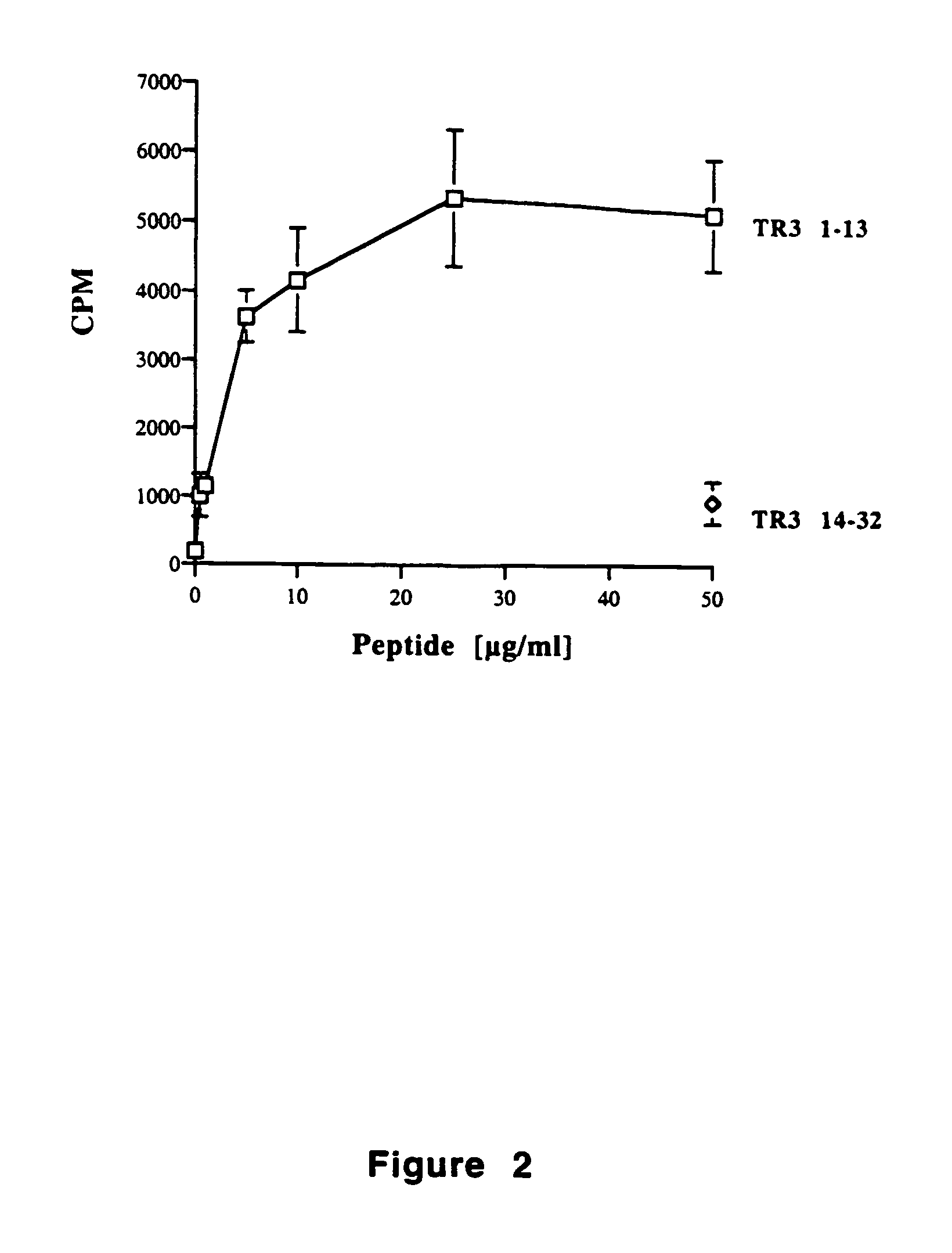
Tr3-specific binding agents and methods for their use
InactiveUS6994976B1Prevent proliferationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody ingredientsAutoimmune responsesActive agent
Biologically active TR3-specific binding agents and methods for their use are disclosed. The biologically active TR3-specific binding agents are useful for inhibiting the proliferation of cells expressing TR3. These biologically active agents are particularly useful for treating T-cell mediated diseases such as graft-versus-host disease, organ rejection, tumor growth, autoimmunity, and inflammation.
Owner:TITTLE THOMAS V +1
Anticoagulant fusion protein anchored to cell membrane
InactiveUS6423316B1Prolong clotting timeGood curative effectFungiVirusesCell membraneBlood coagulations
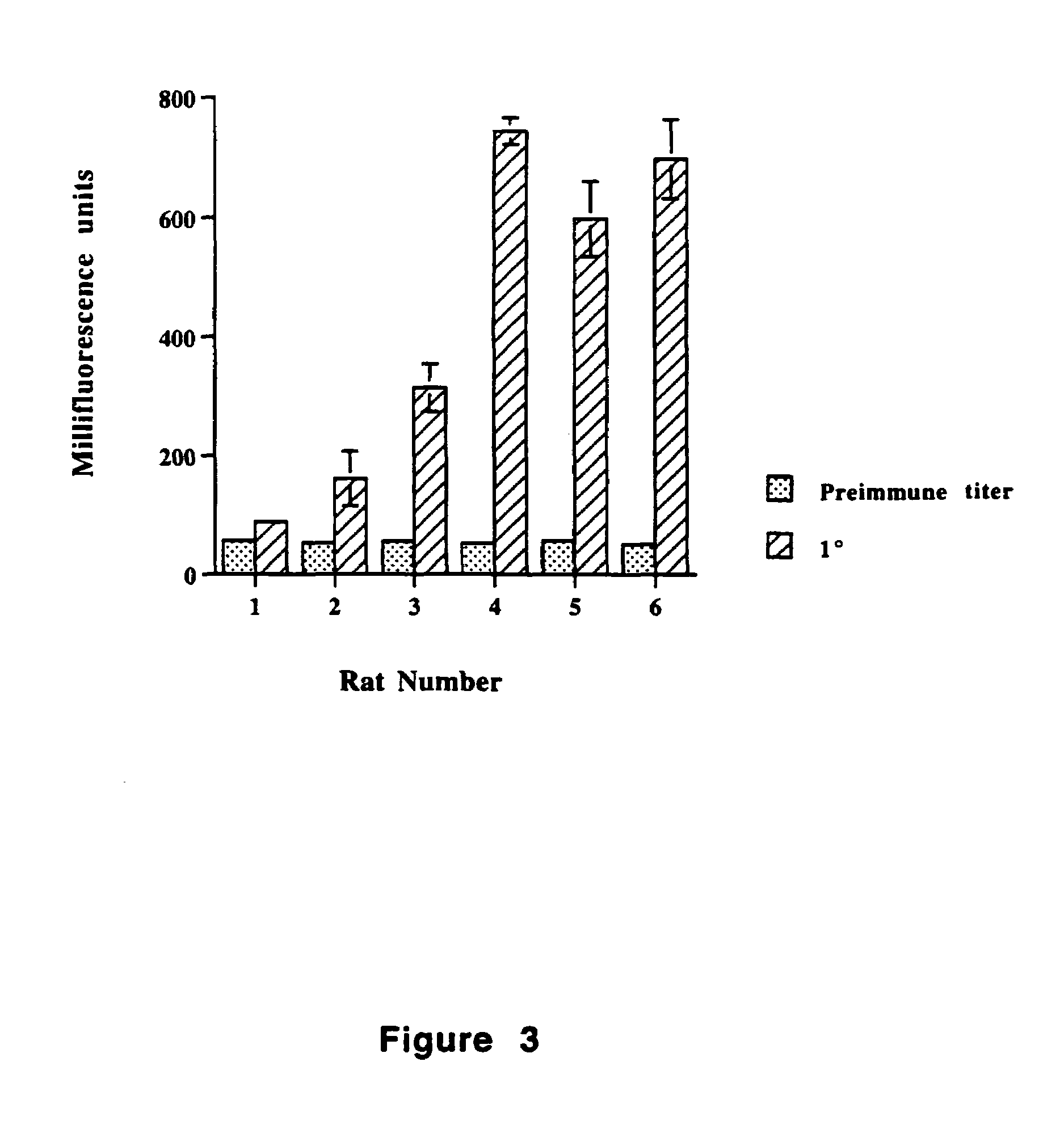
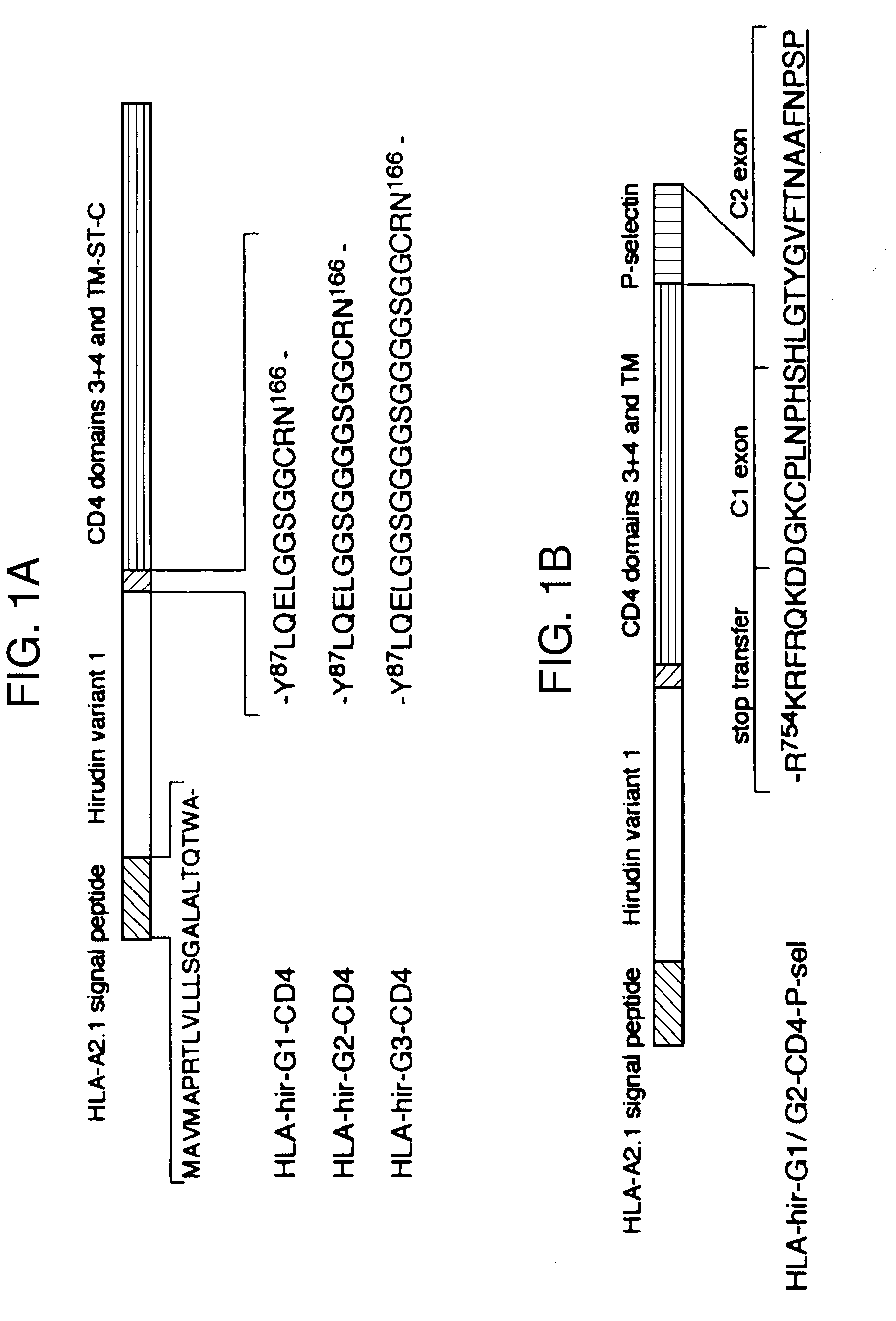
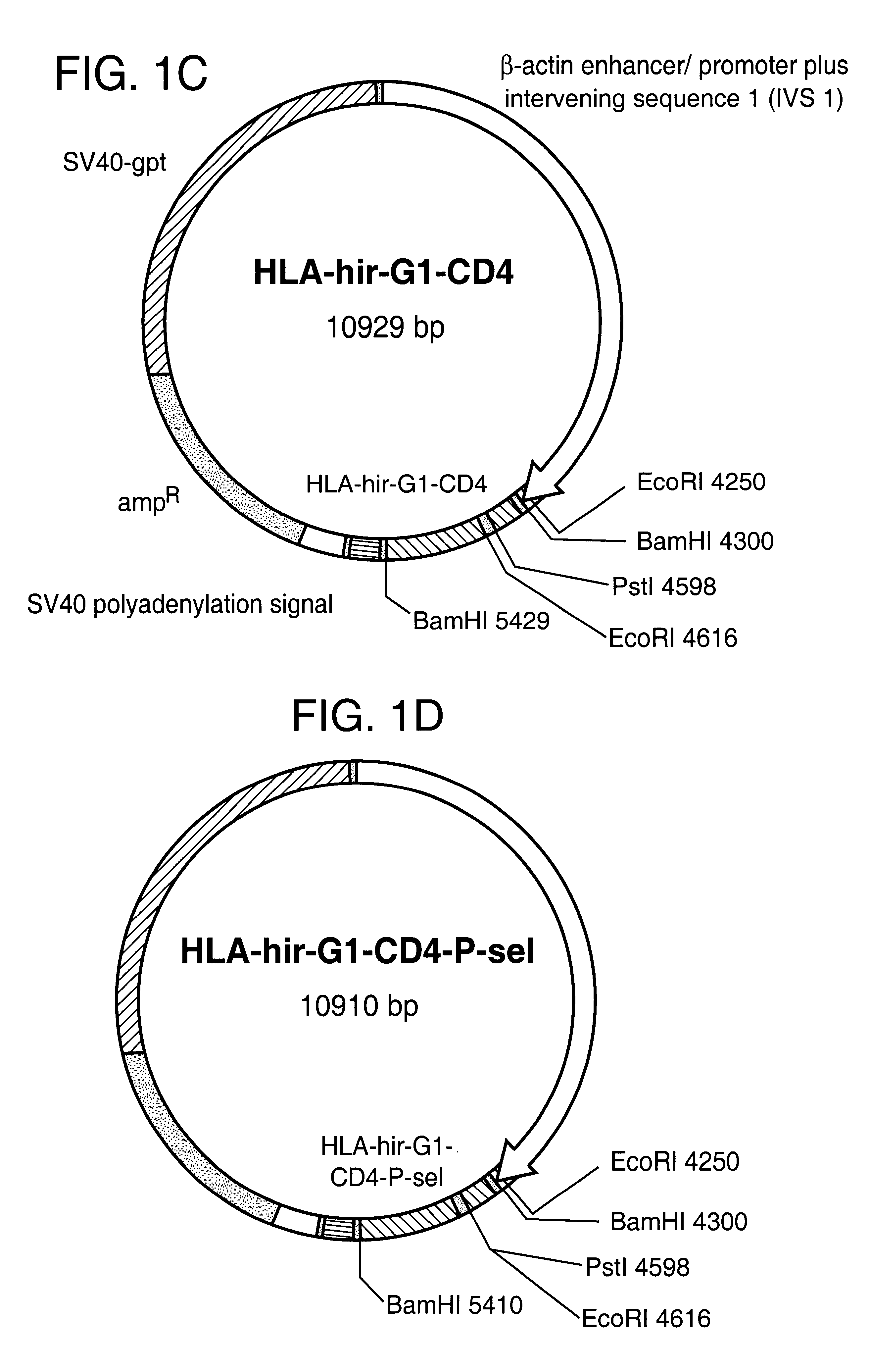
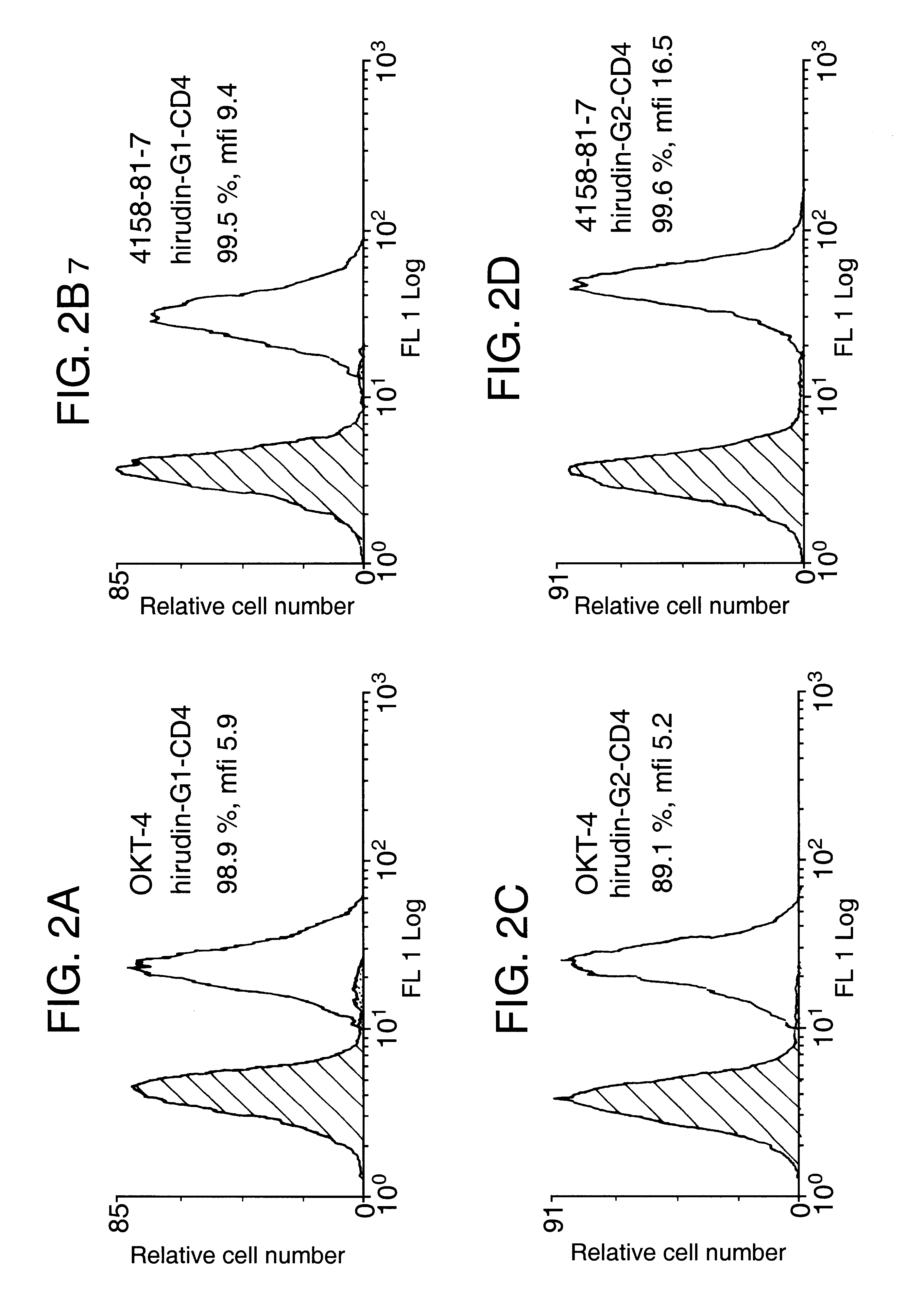
The invention relates to the inhibition of blood coagulation, especially during organ rejection, and in particular the inhibition of delayed vascular rejection. The invention provides anticoagulant proteins which are anchored to cell membranes. The anticoagulant function preferably provided by heparin, antithrombin, hirudin, TFPI, tick anticoagulant peptide, or a snake venom factor. These anticoagulant proteins are preferably prevented from being constitutively expressed at the cell surface. In particular, expression at the cell surface is regulated according to cell activation, for instance by targeting the protein to a suitable secretory granule. Expression of these proteins renders cells, tissues and organs less vulnerable to rejection after transplantation (e.g. after xenotransplantation).
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
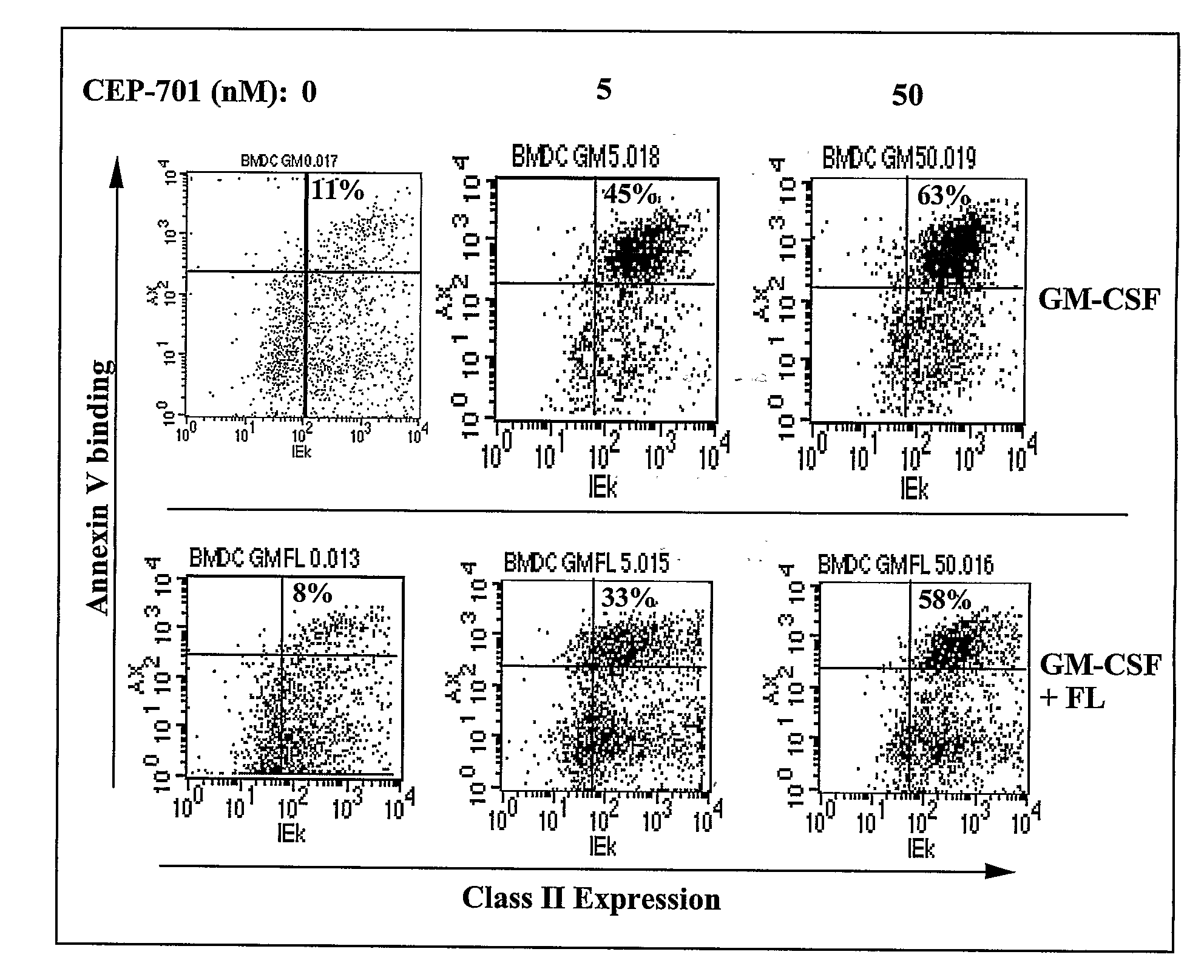
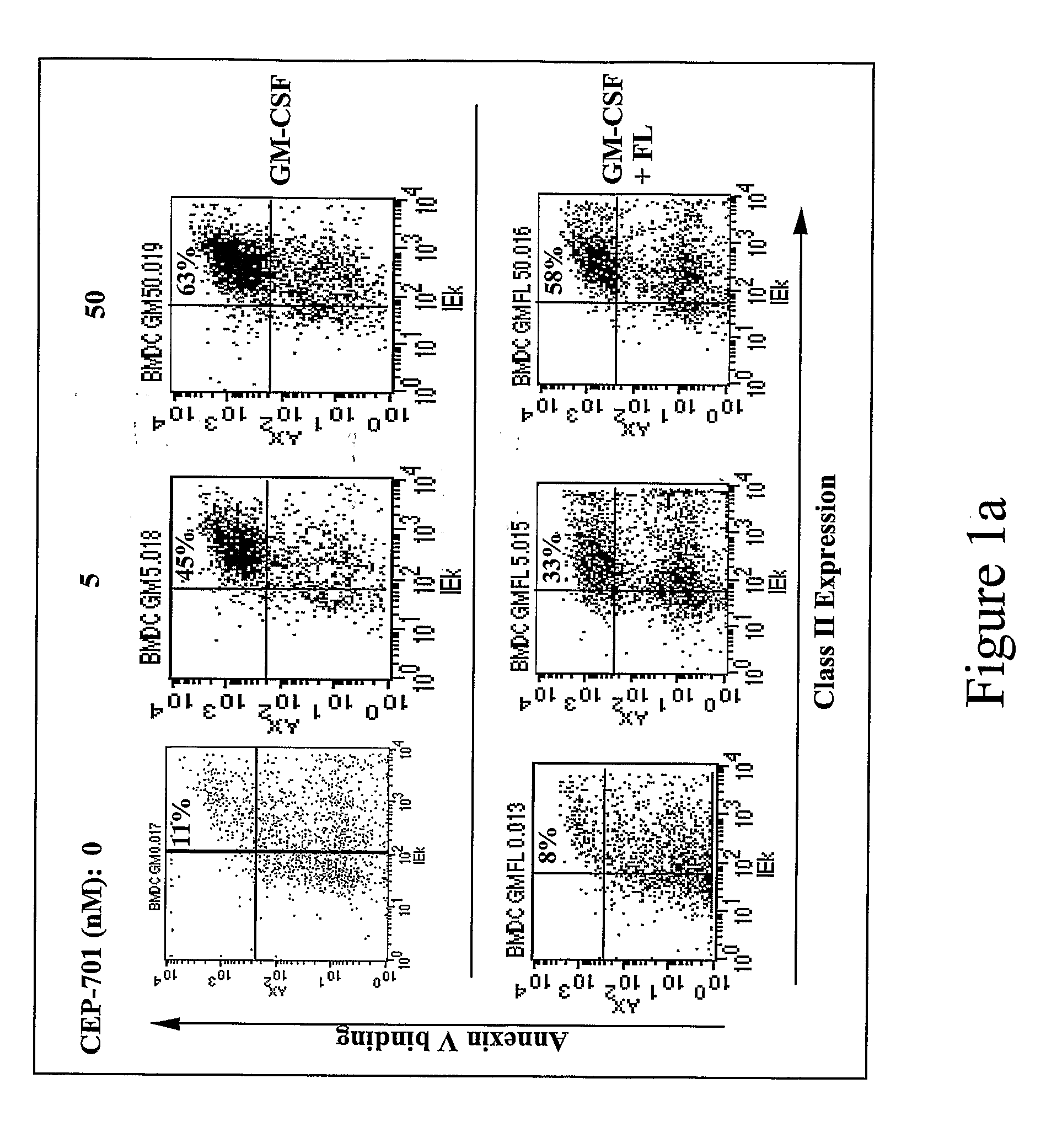
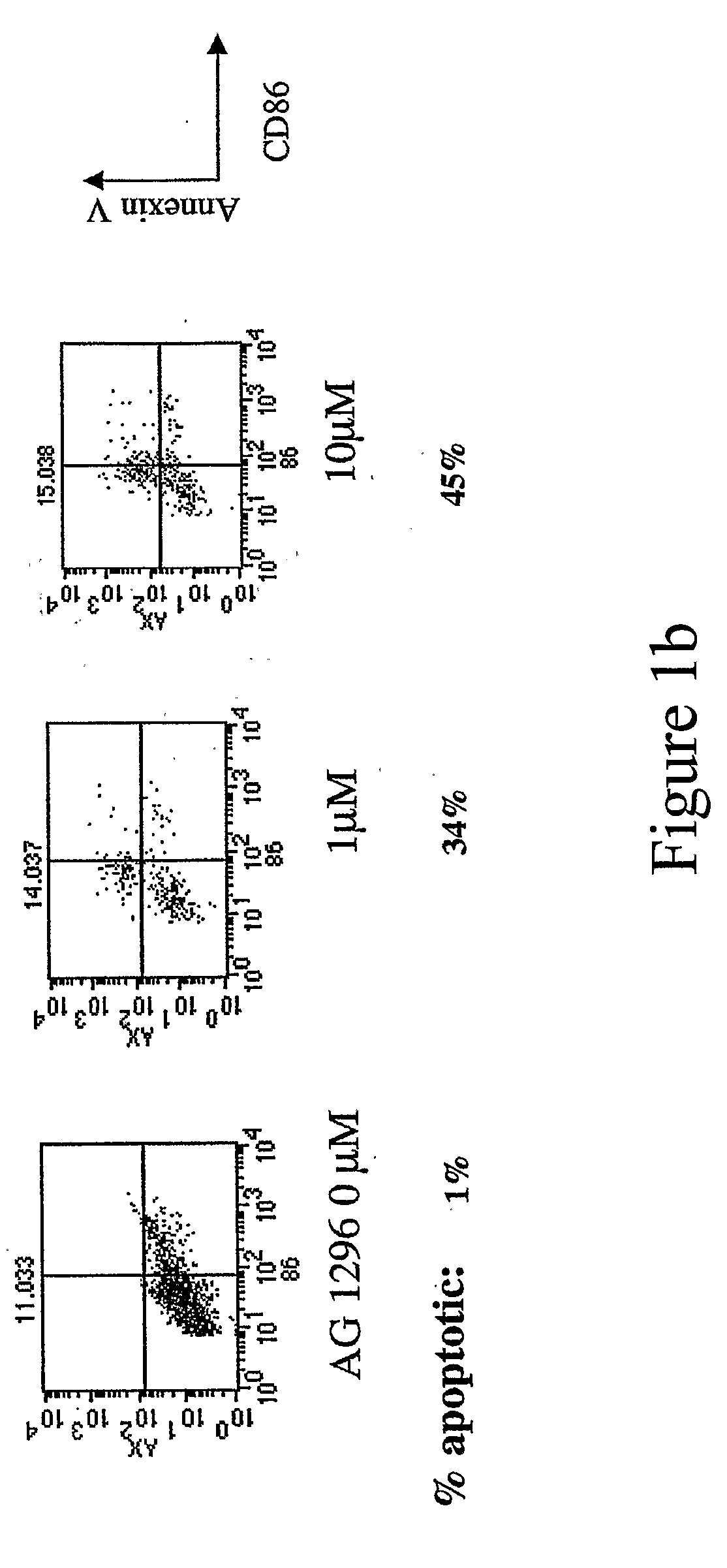
Flt3 inhibitors for immune suppression
InactiveUS20090054358A1Suppressing response of cellReduce in quantityBiocideNervous disorderAcquired immunodeficiencySystemic lupus erythematosus
New methods are provided for suppressing the immune system and for treating immune related disorders. Therapies of the invention include administration of an FLT3 inhibitor compound to a subject in need thereof, such as a subject suffering from organ rejection, bone marrow transplant rejection, acquired immune deficiency syndrome, arthritis, aplastic anemia, graft-versus-host disease, Graves' disease, established experimental allergic encephalitomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, lupus, or a neurological disorder. Methods are also provided for screening therapeutic agents for treating immune disorders, including the use of a mouse having an elevated level of FLT3 receptor activity.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
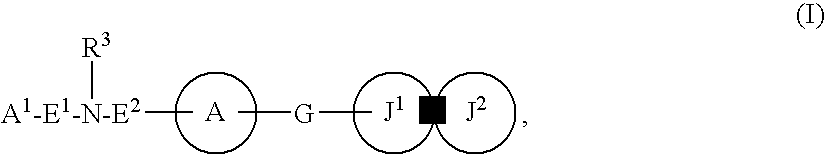
Compound containing basic group and use thereof
The present invention relates to a compound represented by formula (I-0):wherein symbols in formula have the same meanings as described in the present specification, a salt thereof, an N-oxide thereof or a solvate thereof or a prodrug thereof, and medical use thereof. The compound of the present invention has an antagonistic activity against CXCR4 and is therefore useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for CXCR4-mediated diseases, for example, inflammatory and immune diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, retinopathy, pulmonary fibrosis, transplanted organ rejection, etc.), allergic diseases, infections (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), psychoneurotic diseases, cerebral diseases, cardiovascular disease, metabolic diseases, and cancerous disease (for example, cancer, cancer metastasis, etc.), or an agent for regeneration therapy.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for obtaining hematopoietic stem cells derived from embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050221482A1Good conditionMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
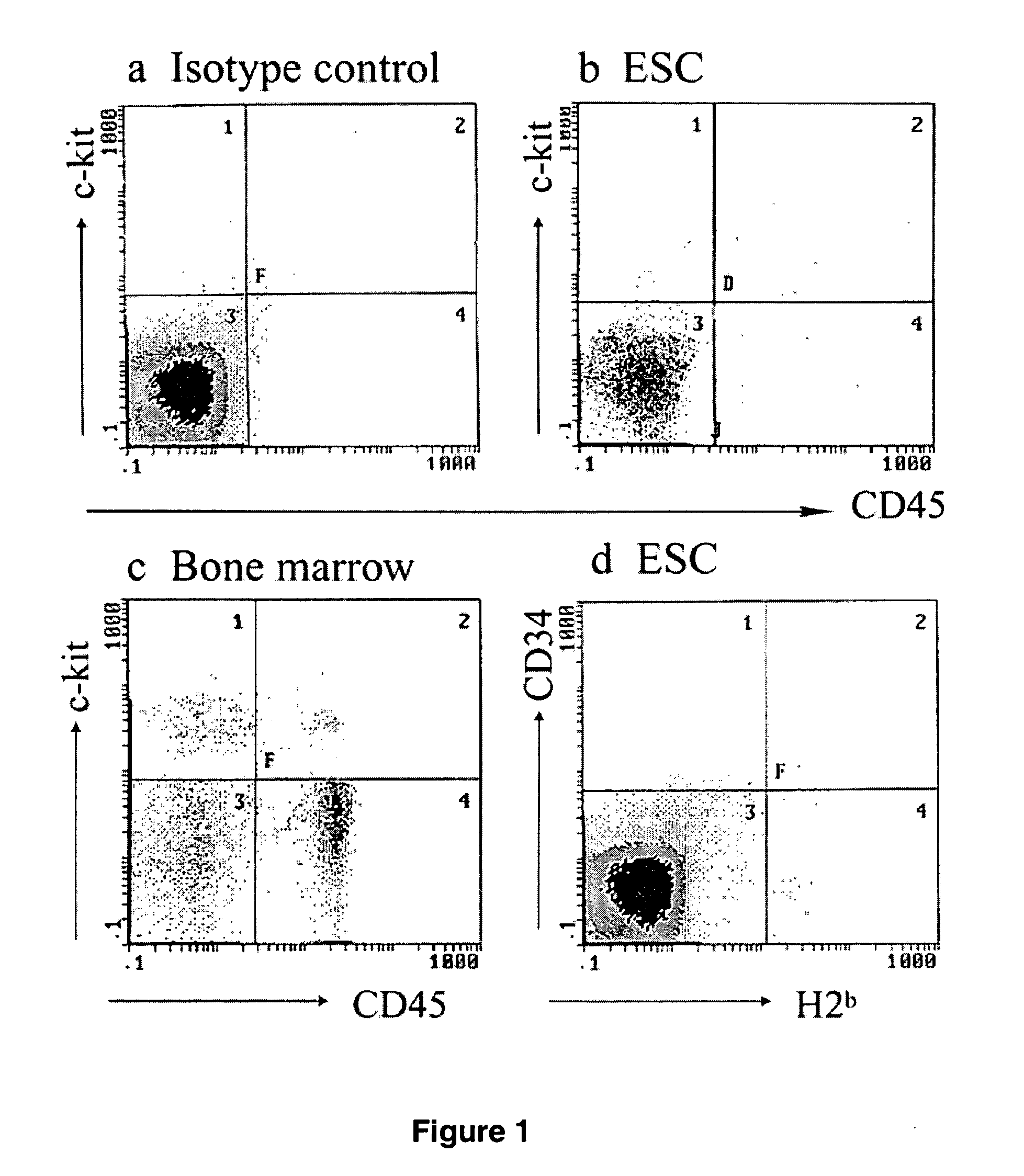
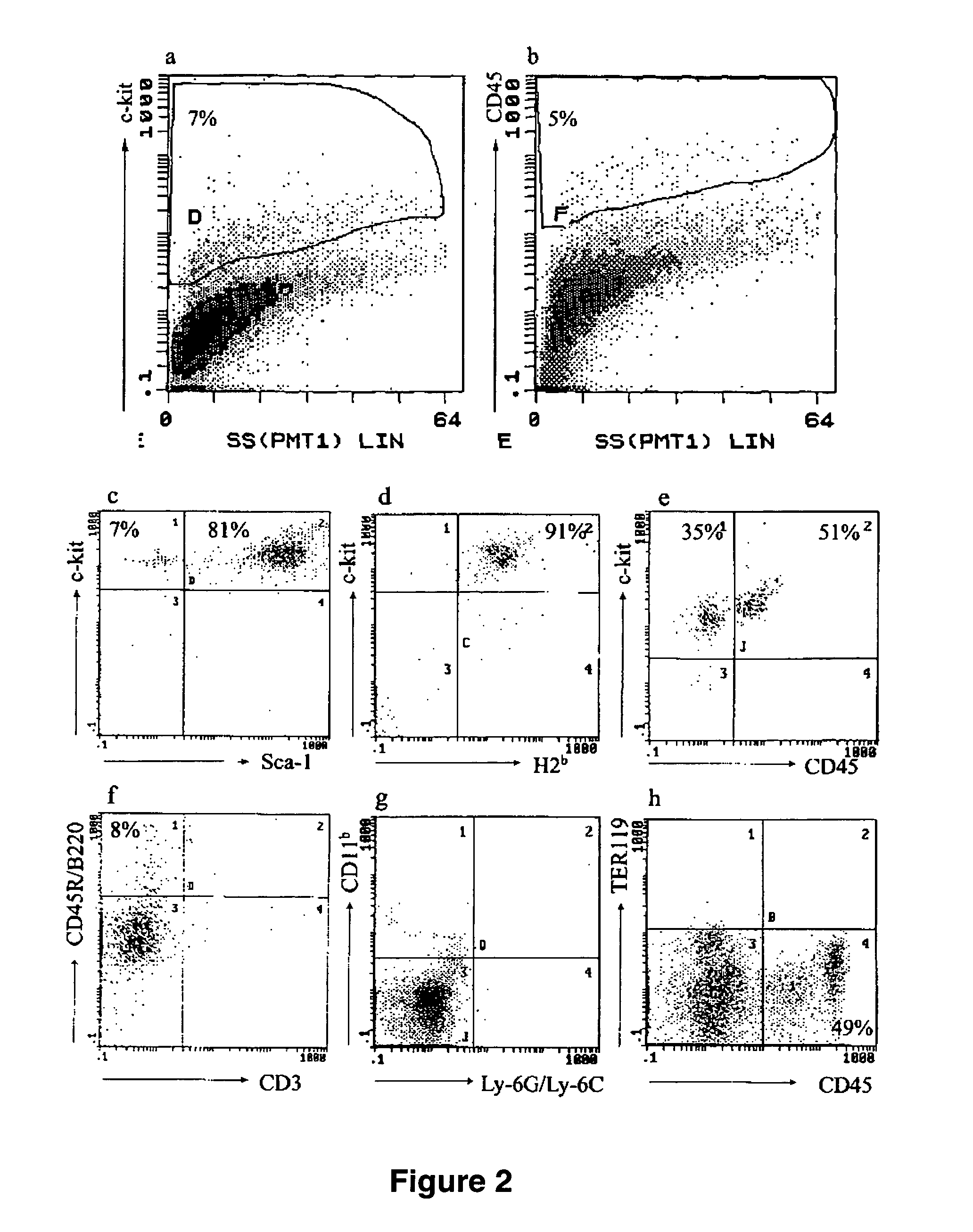
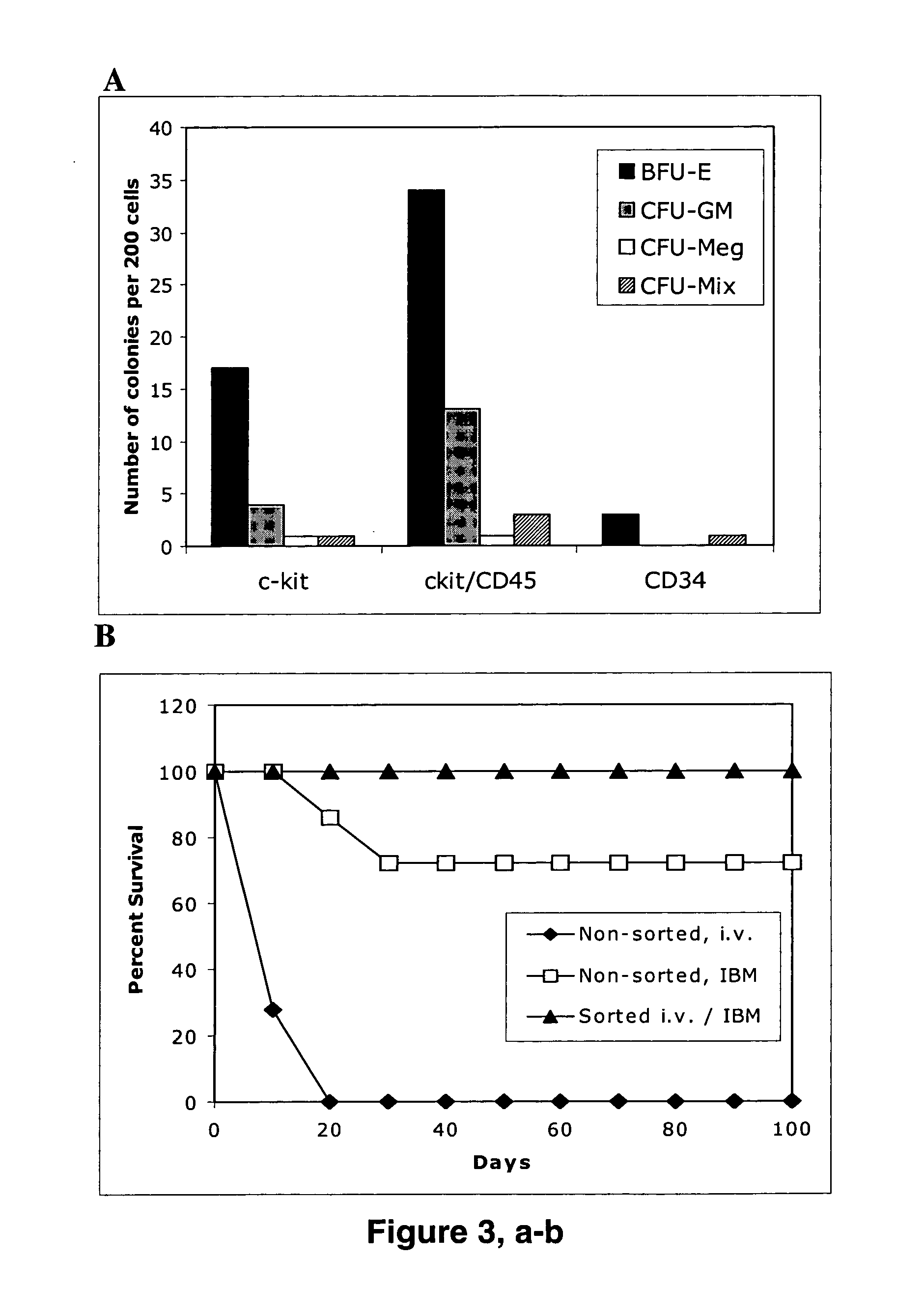
The present invention provides an isolated population of adult hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) derived from embryonic stem cells (ESC) induced to differentiate in vitro by culturing ESCs in a medium with stem cell factor, interleukin (IL)-3, and IL-6. HSC of immunophenotype c-kit+ or c-kit+ / CD45+ from this population are isolated and injected either intra bone marrow or intravenously into myeloablated recipient individuals. This method allows for the establishment of banks of allogeneic ESC-derived adult stem cells for treatments of autoimmune diseases, immune deficiencies and induction of immunotolerance during organ transplantation. These allogeneic ESC-derived adult hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) may be used in reconstituting bone marrow, without the development of teratomas or graft versus host disease, despite crossing histocompatibility barriers. Additionally, allogeneic ESC-derived HSC can be used to prevent the development of autoimmune diseases or organ rejection during transplantation.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS +1
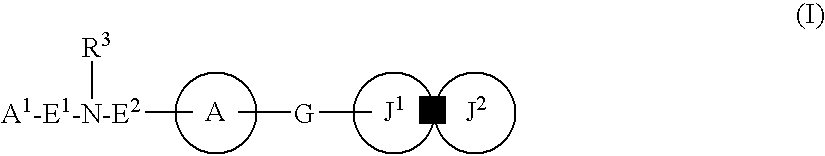
Compound Containing Basic Group and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080009495A1Less effectPrevention and therapyBiocideSenses disorderSolventCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to a compound represented by formula (I-0): wherein symbols in formula have the same meanings as described in the present specification, a salt thereof, an N-oxide thereof or a solvate thereof or a prodrug thereof, and medical use thereof. The compound of the present invention has an antagonistic activity against CXCR4 and is therefore useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for CXCR4-mediated diseases, for example, inflammatory and immune diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, retinopathy, pulmonary fibrosis, transplanted organ rejection, etc.), allergic diseases, infections (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), psychoneurotic diseases, cerebral diseases, cardiovascular disease, metabolic diseases, and cancerous diseases (for example, cancer, cancer metastasis, etc.), or an agent for regeneration therapy.
Owner:ONO PHARMA
Injectable compositions of nanoparticulate immunosuppressive compounds
The present invention relates to an injectable nanoparticulate immunosuppressant composition for the formation of a subcutaneous or intramuscular depot. The invention is also directed to an injectable composition of nanoparticulate tacrolimus and / or sirolimus which eliminates the need to use polyoxyl 60 hydrogenated castor oil (HCO-60) and / or polysorbate 80 as a solubilizer. This invention further discloses a method of making an injectable nanoparticulate tacrolimus and / or sirolimus composition and is also directed to methods of treatment using the injectable nanoparticulate formulations comprising tacrolimus, sirolimus, or combination thereof for a subcutaneous or intramuscular depot for the prophylaxis of organ rejection and for the treatment of psoriasis or other immune diseases.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
Basic group-containing compound and use thereof
A compound represented by general formula (I):a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof wherein all symbols are as defined in the specification has an antagonistic activity against CXCR4 and is therefore useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for CXCR4-mediated diseases, for example, inflammatory and immune diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, systemic erythematosus, retinopathy, macular degeneration, pulmonary fibrosis, transplanted organ rejection, etc.), allergic diseases, infections (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), psychoneurotic diseases, cerebral diseases, cardiac / vascular disease (for example, arteriosclerosis, myocardial infarction, stenocardia, cerebral infarction, chronic arterial occlusive disease, etc.), metabolic diseases, and cancerous diseases (for example, cancer, cancer metastasis, etc.), a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cancerous diseases or infections, or an agent for regeneration therapy.
Owner:ONO PHARMA
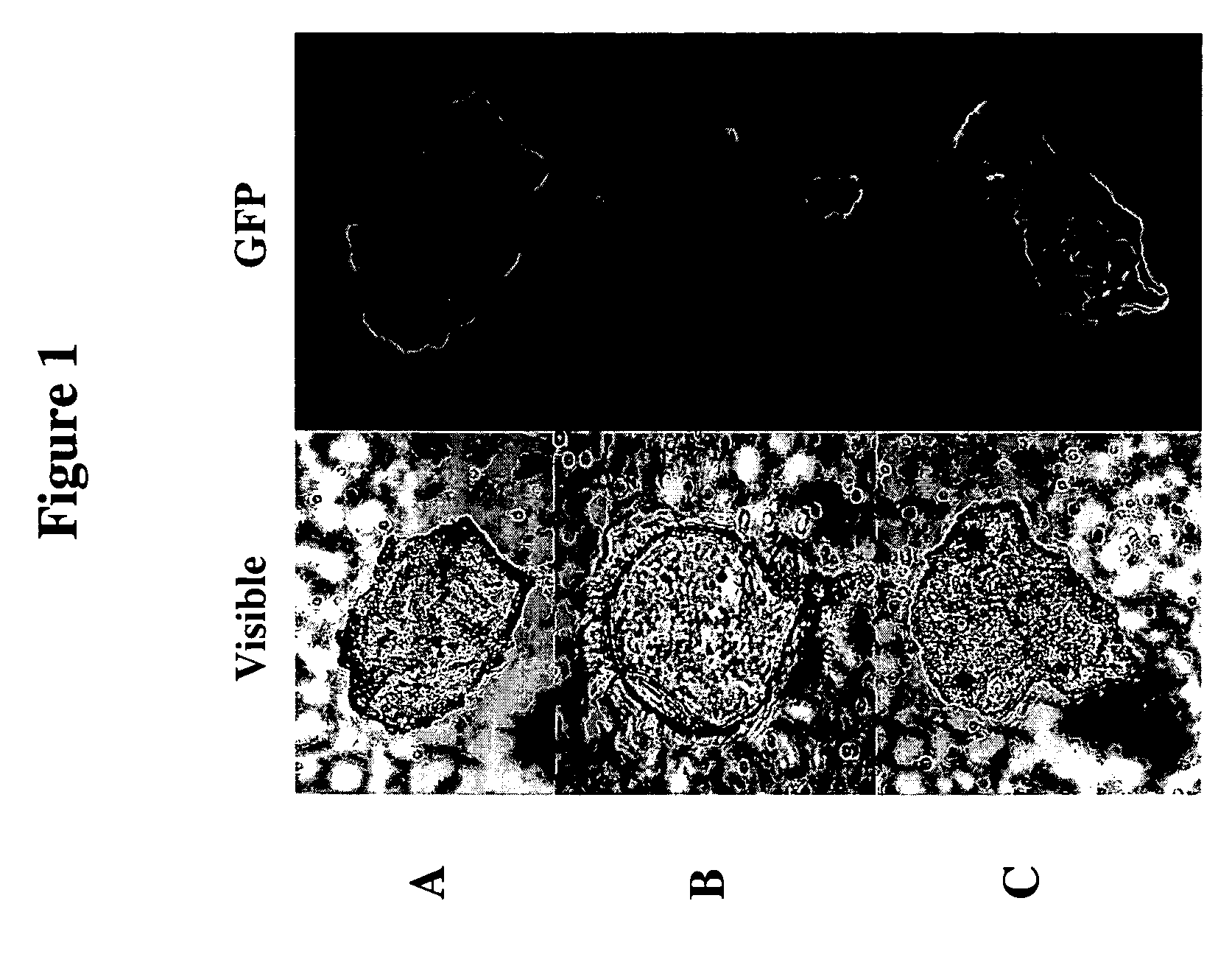
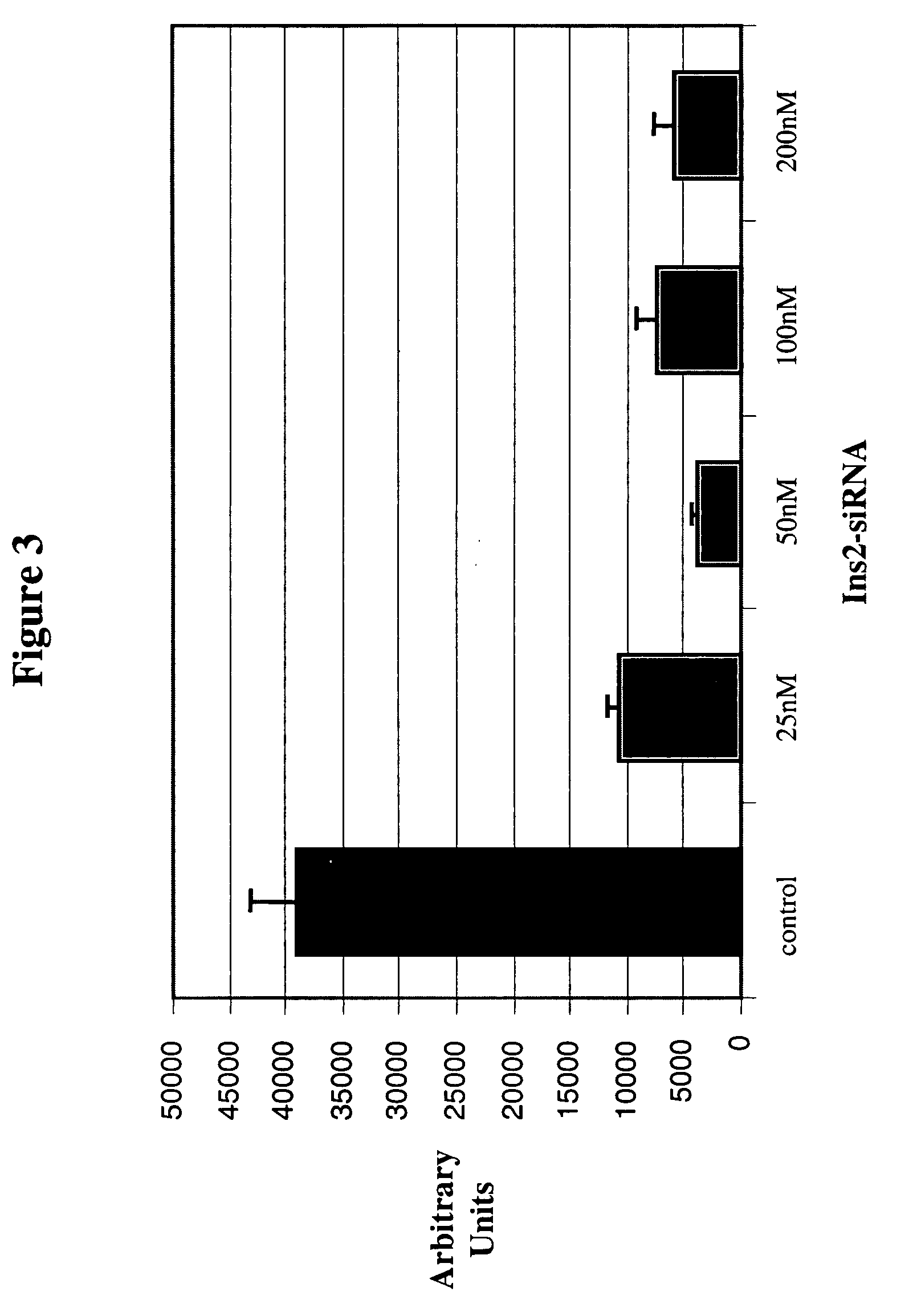
Therapeutic alteration of transplantable tissues through in situ or ex vivo exposure to RNA interference molecules
ActiveUS20060073127A1Prevent immune-mediated rejectionInhibit growthBiocideSugar derivativesApoptosisBiology
The present invention, at least in part, relates to the discovery of efficacious delivery of an RNAi agent (in preferred aspects of the invention, an siRNA) to a transplantable tissue. Organ rejection, transplantation-mediated transmission of viral infection, and triggering of apoptosis in transplanted tissues can each be minimized by the methods and compositions of the instant invention. The RNAi agent(s) of the instant invention can be delivered as “naked” molecules, or using liposomal and other modes of delivery, to transplantable tissues. Such delivery can occur via perfusion of the RNAi agent in solution through the vasculature of a whole or partial organ; or tissues including transplantable cells and cell lines may be bathed, injected or otherwise treated with RNAi agents. Preferred transplantable tissues include, for example, pancreas, liver, kidney, heart, lung, and all cells and cell lines derived from such tissues (e.g., pancreatic islet cells that may, e.g., be transplanted as a treated population).
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
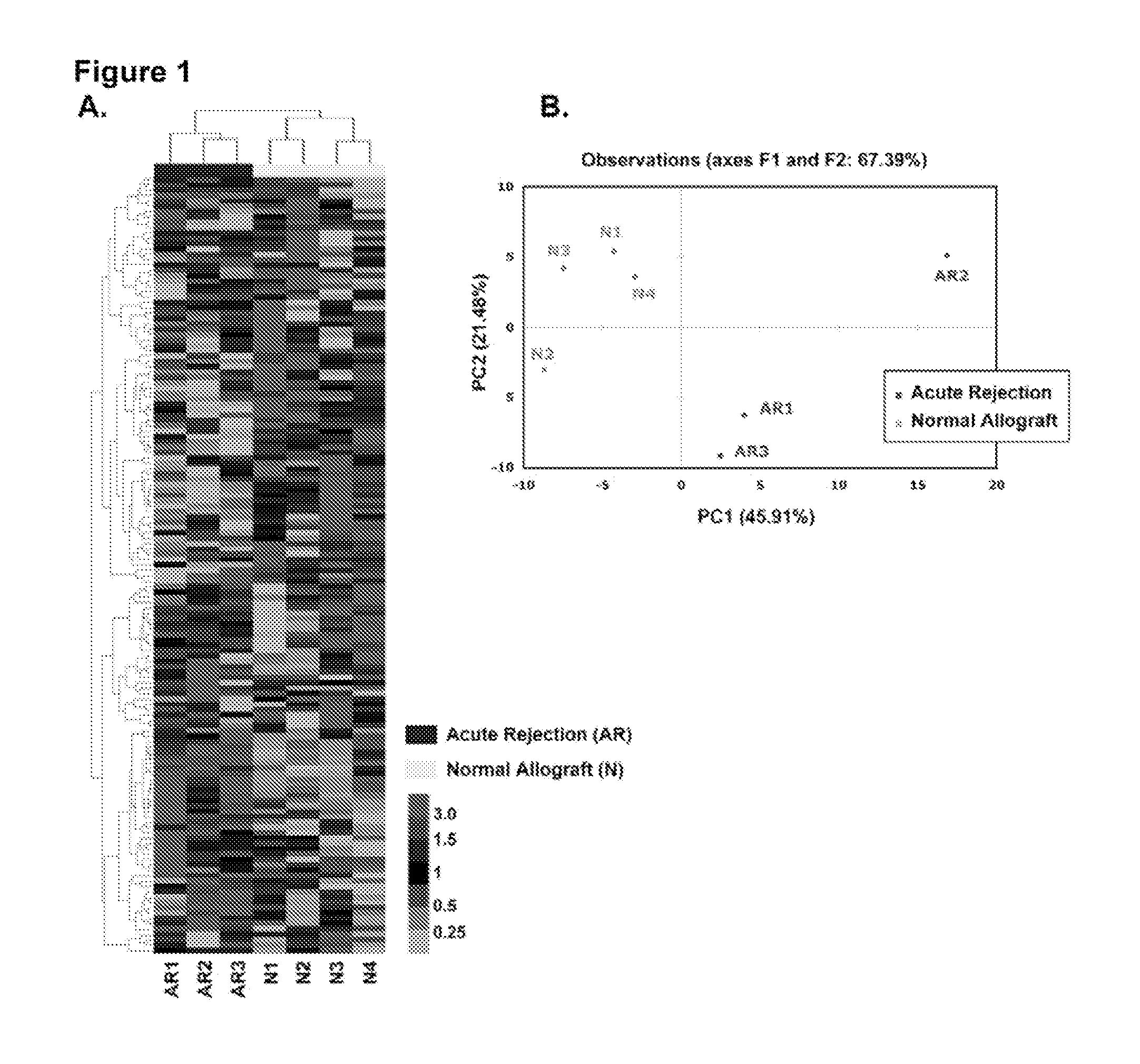
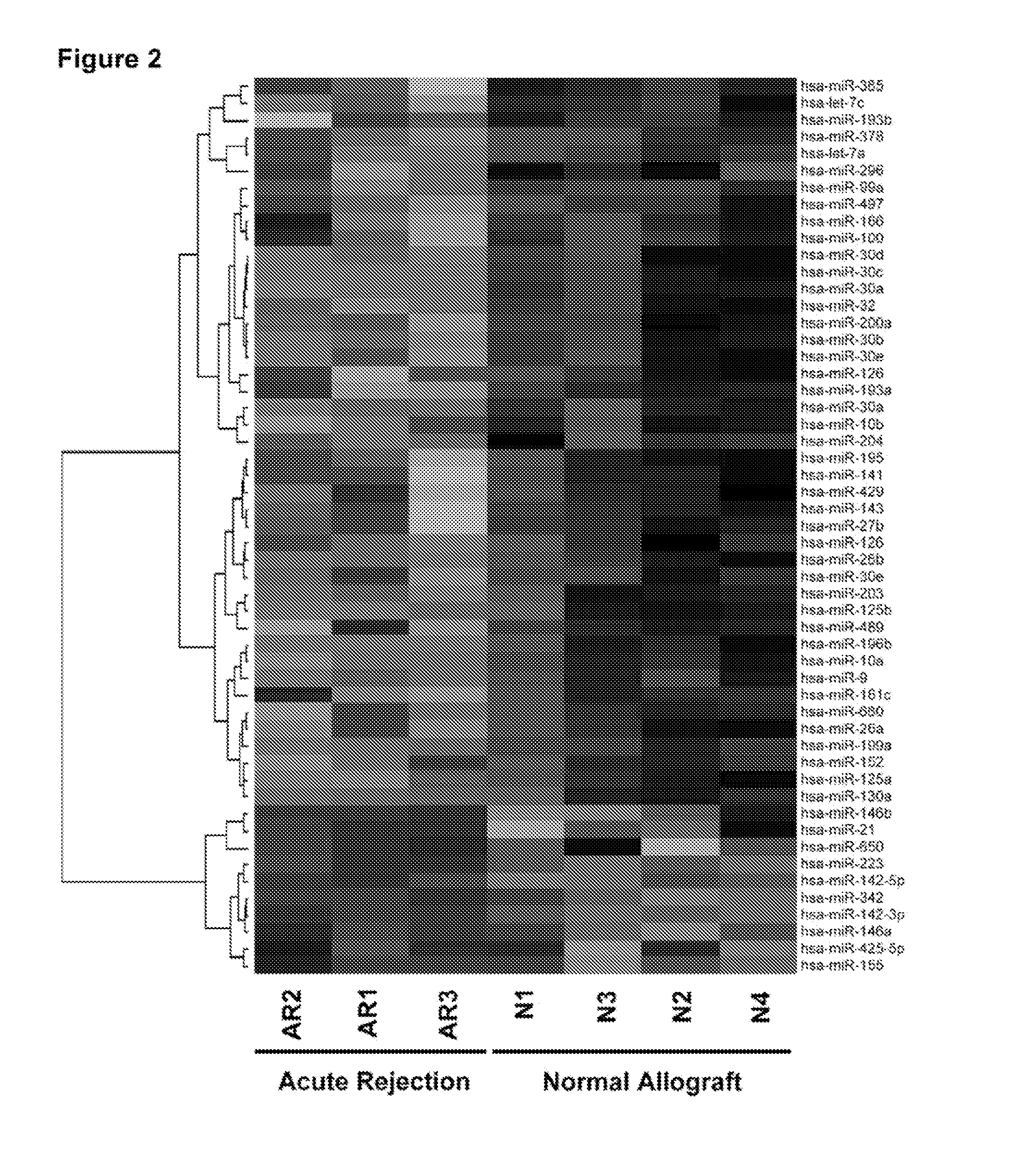
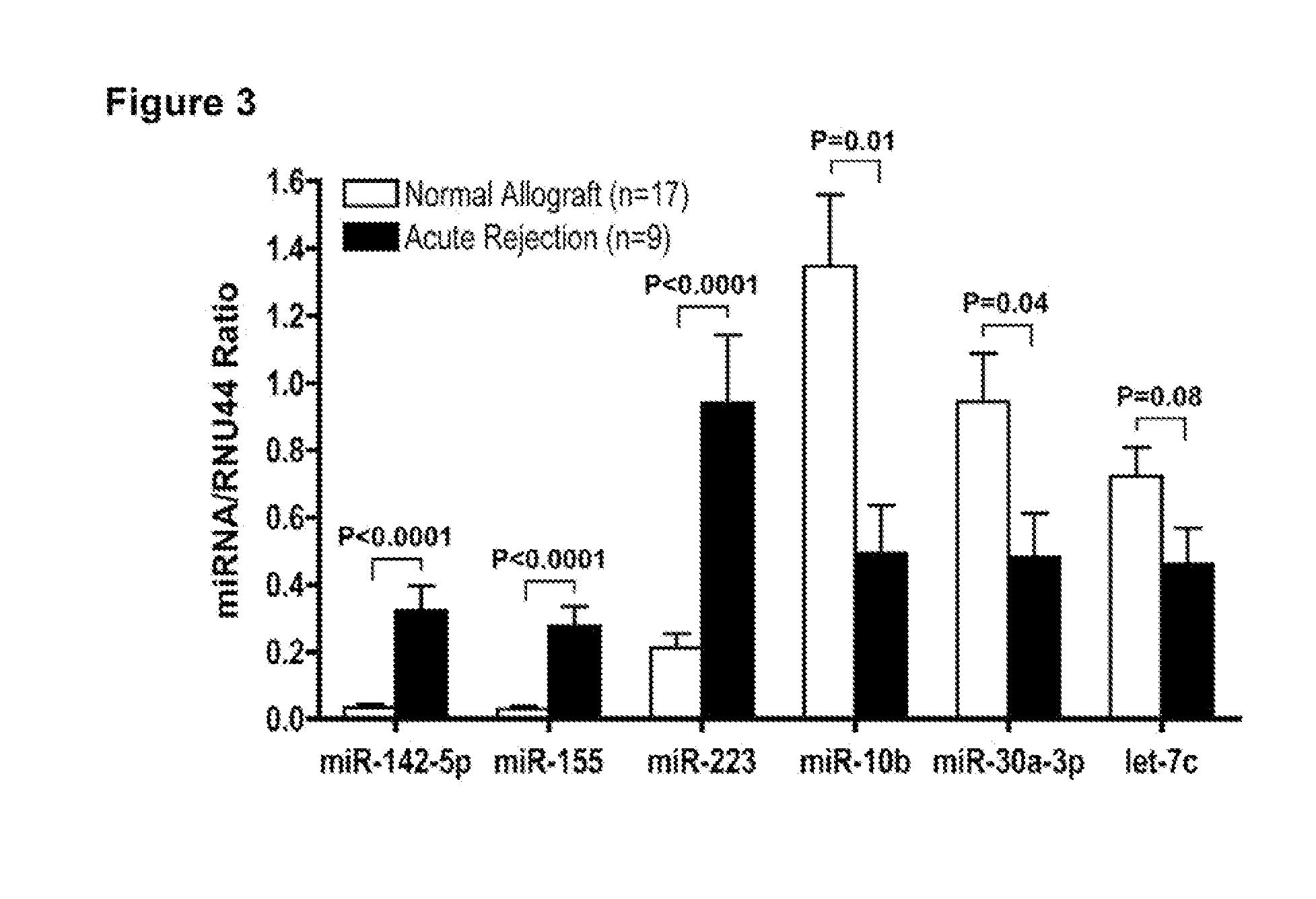
Method to assess human allograft status from microrna expression levels
ActiveUS20120101001A1Increased riskRisk assessmentMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMicroRNACvd risk
The invention relates to, among other things, a method for assessing risk of organ rejection in a patient having a transplanted organ. The method includes measuring an amount of expression of a small non-coding marker RNA in a biological sample from the patient. The method further includes comparing the measured amount of expression of the small non-coding marker RNA in the patient to a reference amount of expression of the small non-coding marker RNA. In another aspect, the invention relates to kits for assessing risk of organ rejection in a patient having a transplanted organ.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
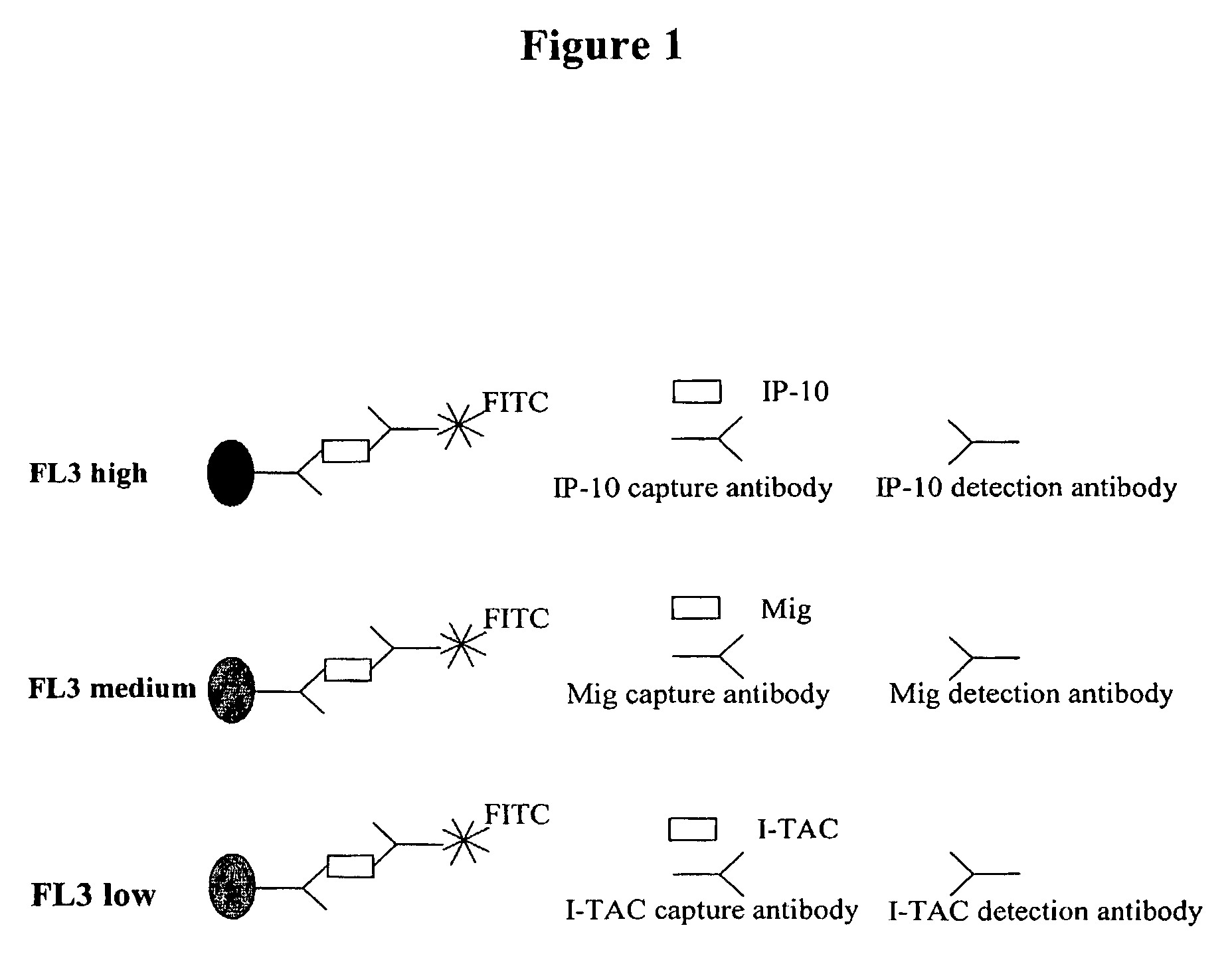
Anaphylatoxins for detecting clinical conditions
InactiveUS20090226374A1Compounds screening/testingMicrobiological testing/measurementVasculitisBasophilia
Non-allergic hypersensitivity reactions can be observed in a sample of cells from a subject in response to anaphylatoxins. Accordingly, methods are provided for detecting clinical conditions such as cellular hyper-reactivity, non-allergic hypersensitivity, asthma, inflammation, chronic or acute infection, bacterial infection, viral infection, parasite infection, adverse drug reaction, organ rejection, vasculitis, mastocytosis, eosinophilia, basophilia, leukemia, and / or C3a or C5a receptor defects in a subject. Also provided are kits for detecting such clinical conditions in a subject.
Owner:HEALTH AIRE
TR3-specific binding agents and methods for their use
Biologically active TR3-specific binding agents and methods for their use are disclosed. The biologically active TR3-specific binding agents are useful for inhibiting the proliferation of cells expressing TR3. These biologically active agents are particularly useful for treating T-cell mediated diseases such as graft-versus-host disease, organ rejection, tumor growth, autoimmunity, and inflammation.
Owner:TITTLE THOMAS +1
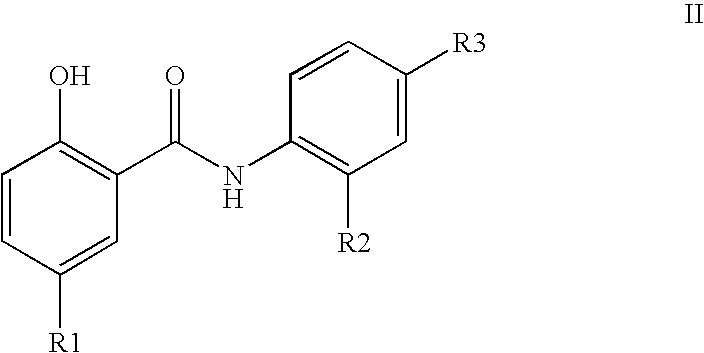
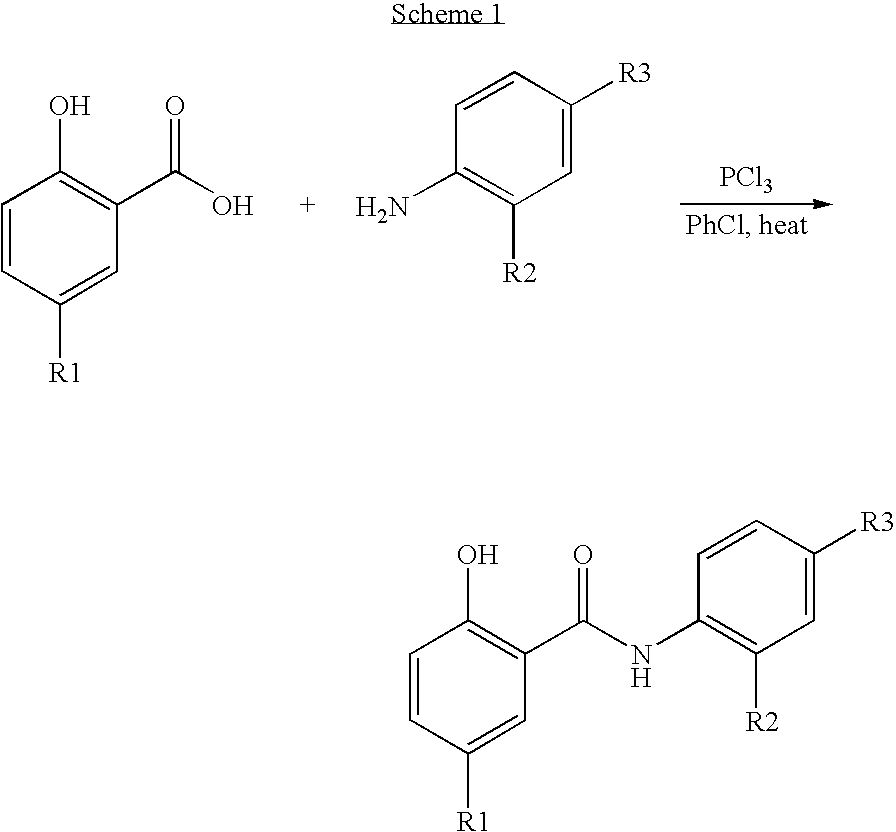
Inhibitors of transcription factor NF-kappaB
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions of salicylanilide inhibitors of transcription factor NF-κB, and methods for treating diseases in which activation of NF-κB is implicated. More specifically, the present invention provides methods of treatment of a variety of diseases associated with NF-κB activation including inflammatory disorders; particularly rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma; dermatosis, including psoriasis and atopic dermatitis; autoimmune diseases; tissue and organ rejection; Alzheimer's disease; stroke; atherosclerosis; restenosis; cancer, including Hodgkin's disease; certain viral infections, including AIDS; osteoarthritis; osteoporosis; and Ataxia Telangiestasia by administering to a patient in need thereof a compound of the present invention.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Detection of organ rejection
InactiveUS20100086928A1Regulate the stability or translational efficiency of target mRNAsNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroRNABioinformatics
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Systems and methods for identifying organ transplant risk
InactiveUS20070287188A1Disease diagnosisBiological testingOrgan transplant rejectionOrgan transplanting
Owner:RENOVAR
Treatment of graft rejection by administering a complement inhibitor to an organ prior to transplant
InactiveUS20160184391A1Easily penetrate organMinimize impactPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSAntiendomysial antibodies
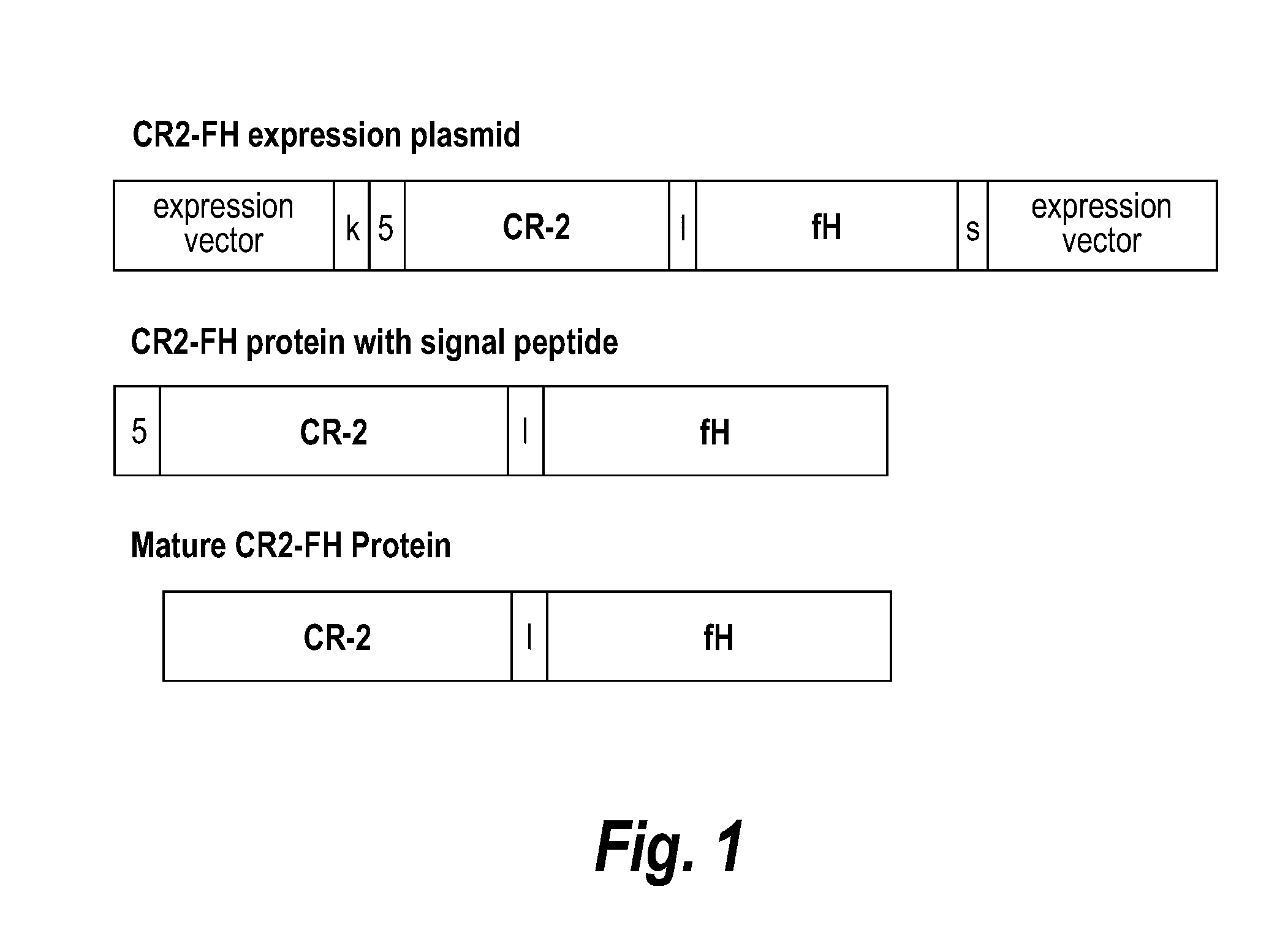
Methods of prolonging survival of a transplanted organ, as well as methods of preventing or attenuating rejection of a transplanted organ are provided. These methods involve contacting the organ with an inhibitor of complement activity (e.g., a complement inhibitor that has a maximum molecular weight of 70 kDa and / or a half-life shorter than 10 days, such as a CR2-FH fusion protein or a single chain anti-C5 antibody), prior to transplantation The methods also include administering to the allotransplant recipient an inhibitor of complement activity together with one or more immunosuppressants. A pretreatment with an alternative complement inhibitor was found to be effective in improving graft survival and decreasing ischemia-reperfusion injury in animal.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Biomarkers for lung disease monitoring
InactiveUS20110250589A1High expressionIncrease pressureMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInterstitial lung diseaseOrganizing pneumonia
The present invention pertains to the monitoring and treatment of lung transplant recipients. In particular, the invention pertains to the use of biomarkers to predict or detect post-lung transplantation complications (e.g., organ rejection, acute organ rejection, organ injury, bronchiolitis obliterans, bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome, organizing pneumonia), fibroproliferative repair responses, interstitial lung diseases (e.g., idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic lung diseases), and other immune-mediated lung diseases (e.g., graft versus host disease, scleroderma).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Compound having cyclic group bound thereto through spiro binding and use thereof
InactiveUS20090325992A1Prevention and therapyTreatment safetyAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseMental nerve
A compound represented by general formula (I):a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof wherein all symbols are as defined in the specification has an antagonistic activity against CXCR4 and is therefore useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for CXCR4-mediated diseases, for example, inflammatory and immune diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, retinopathy, macular degeneration, pulmonary fibrosis, transplanted organ rejection, etc.), allergic diseases, infections (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), psychoneurotic diseases, cerebral diseases, cardiovascular disease, metabolic diseases, cancerous diseases (for example, cancer, cancer metastasis, etc.), a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for cancerous diseases or infections, or an agent for regeneration therapy.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Anticoagulant fusion protein anchored to cell membrane
The invention relates to the inhibition of blood coagulation, especially during organ rejection, and in particular the inhibition of delayed vascular rejection. The invention provides anticoagulant proteins which are anchored to cell membranes. The anticoagulant function preferably provided by heparin, antithrombin, hirudin, TFPI, tick anticoagulant peptide, or a snake venom factor. These anticoagulant proteins are preferably prevented from being constitutively expressed at the cell surface. In particular, expression at the cell surface is regulated according to cell activation, for instance by targeting the protein to a suitable secretory granule. Expression of these proteins renders cells, tissues and organs less vulnerable to rejection after transplantation (e.g. after xenotransplantation).
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Antigen presenting cell assay
Disclosed herein are methods for diagnosing or predicting acute cellular and / or humoral rejection in a subject. In one example, a method of assessing organ rejection includes contacting a first sample comprising antigen presenting cells (APCs) obtained from a subject in need of or having received an organ transplant with a donor antigen from a donor under conditions sufficient to induce uptake of the donor antigen; contacting a second sample comprising APCs obtained from the subject in need of or having received an organ transplant with a third-party antigen under conditions sufficient to induce uptake of the third-party antigen; and determining an antigen presenting index by determining a ratio of uptake of the donor antigen in the first sample to uptake of the third-party antigen in the second sample, wherein the ratio of greater than one indicates organ rejection and the APCs are monocytes or monocyte-derived cells.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), compositions and methods thereof
Owner:ICELL GENE THERAPEUTICS LLC
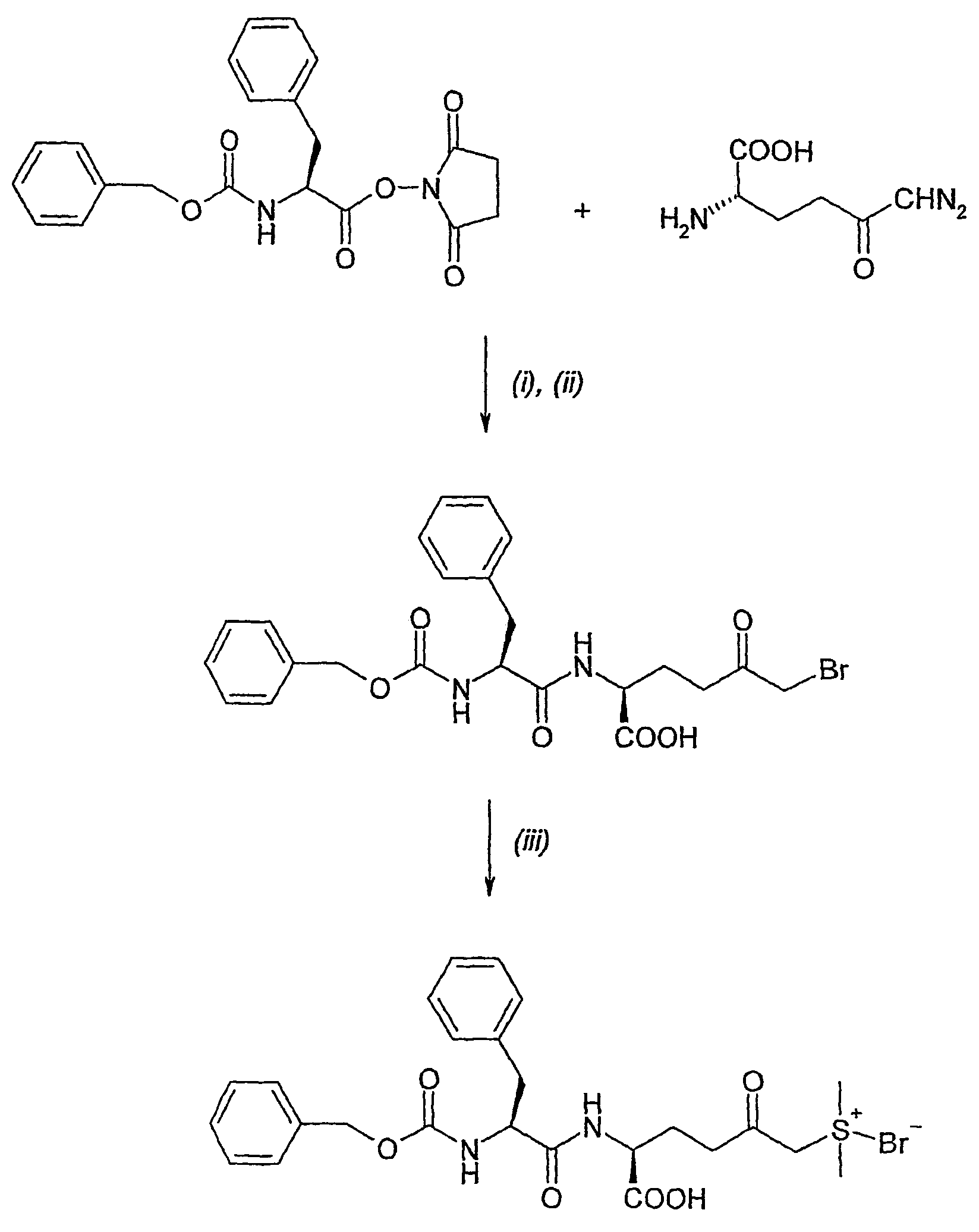
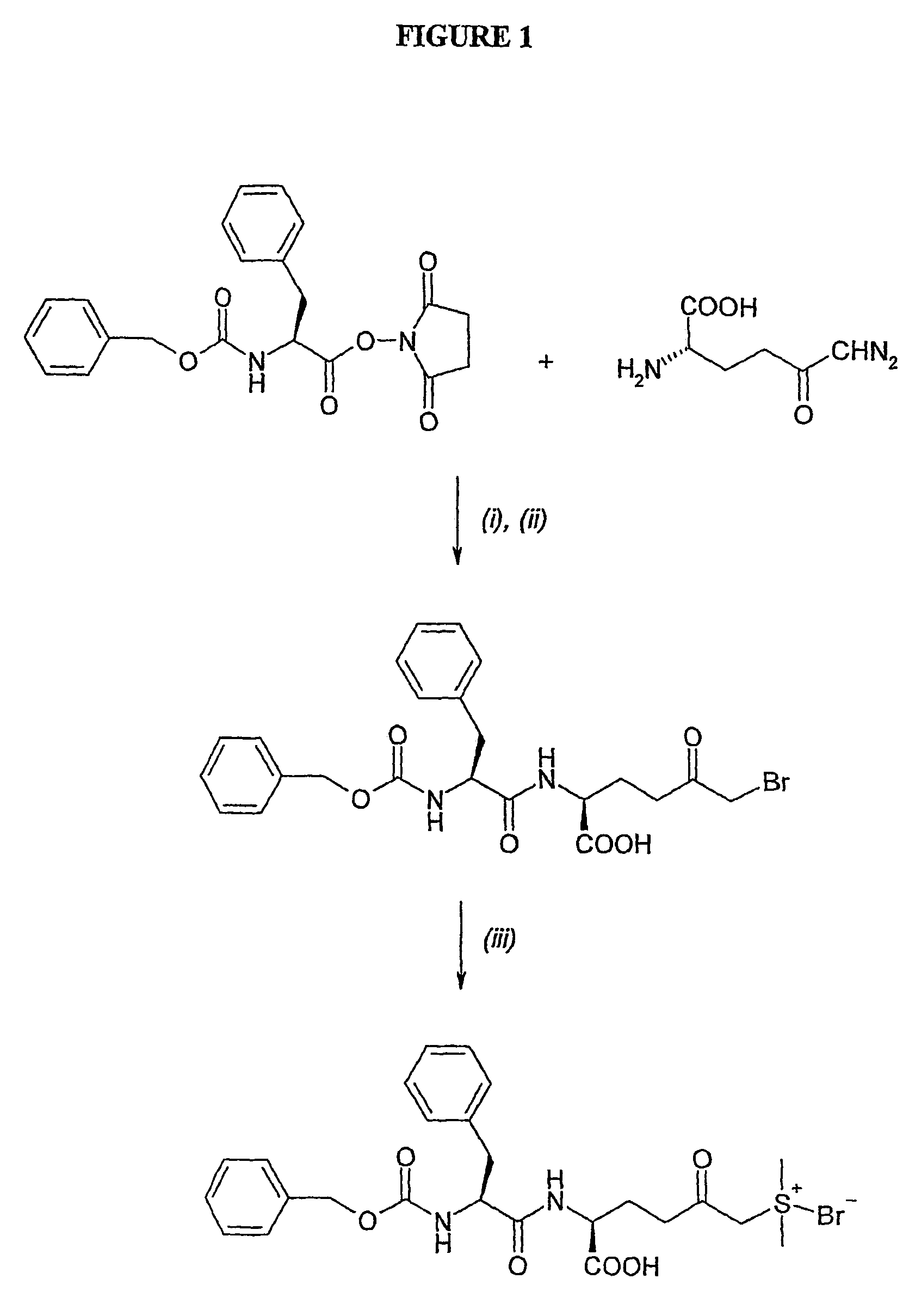
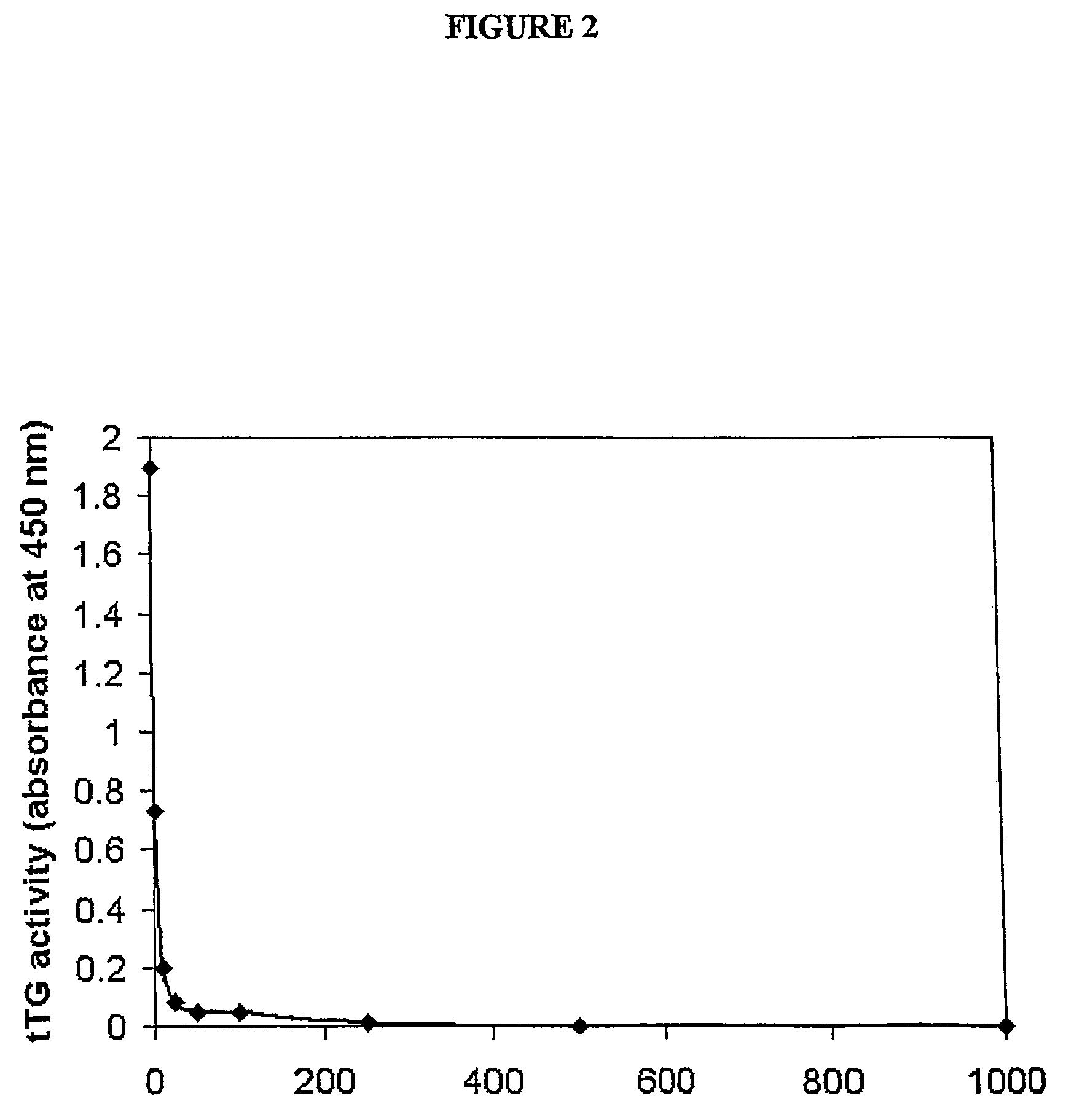
Amino acid derivatives and pharmaceutical uses thereof
InactiveUS7723307B2ExcessivePrevent degenerationCarbamic acid derivatives preparationDipeptide ingredientsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Owner:ASTON UNIV
Supperssor of the endogenous interferon-gamma
InactiveUS20110135602A1Suppressing hIFN-γ activityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune responses
The invention relates to suppressor of the endogenous human interferon-gamma (hlFN-γ) applicable in treatment of diseases associated with impaired activity of endogenous hlFN-γ, especially autoimmune diseases and for prevention of graft arteriosclerosis and rejection of organs in allograft transplanted patients. It is based on inactive analogues of the hlFN-γ with pre-served affinity to the hlFN-γ receptor, genetically modified in the domain responsible for triggering the signal transduction pathway.
Owner:MILLICOM
Amines that inhibit a mammalian anandamide transporter, and methods of use thereof
One aspect of the present invention relates to amines. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the use of the amines as inhibitors of a mammalian anandamide transporter. The compounds of the present invention will also find use in the treatment of numerous ailments, conditions and diseases which afflict mammals, including but not limited to asthma, neuropathic pain, persistent pain, inflammatory pain, hyperactivity, hypertension, brain ischemia, Parkinson's disease, spasticity, Tourette's syndrome, schizophrenia, hemorrhagic shock, septic shock, cardiac shock, migrane, Horton's headache, multiple sclerosis, anorexia, AIDS wasting syndrome, organ rejection, autoimmune diseases, allergy, arthritis, Crohn's disease, malignant gliomas, neurodegenerative diseases, Huntington's chorea, glaucoma, nausea, anxiety, psychosis, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, premature ejaculation, and stroke. Another aspect of the present invention relates to combinatorial libraries of amines, and methods for preparing the libraries.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Regimen for suppressing organ rejection
ActiveUS9168246B2Low fluctuation and swingSuppression of rejectionAntibody ingredientsPill deliveryOral treatmentRegimen
The present invention relates to a method of suppressing organ rejection in a patient receiving an organ transplant by initiating oral treatment with a once-daily extended release tacrolimus dosage form, for example, at an initial dose of from about 0.15 to about 0.20 mg / kg / day within 24 or 48 hours following transplantation. The once-daily extended release tacrolimus dosage form (i) provides low fluctuation and / or swing of tacrolimus, (ii) provides a significantly lower Cmax than an immediate release formulation of tacrolimus while providing the same or greater area under the curve (AUC), (iii) releases the tacrolimus substantially in the colon and / or the lower ileum, (iv) releases at most 63.5% of the tacrolimus in the dosage form at the 12 hour time point, or (v) any combination of any of the foregoing.
Owner:VELOXIS PHARM INC
Therapeutic alteration of transplantable tissues through in situ or ex vivo exposure to RNA interference molecules
The present invention, at least in part, relates to the discovery of efficacious delivery of an RNAi agent (e.g., an siRNA) to a transplantable tissue. The agent may be used to minimize organ rejection, transplantation-mediated transmission of viral infection, and triggering of apoptosis in transplanted tissues. The RNAi agent(s) can be delivered as “naked” molecules, or using liposomal and other modes of delivery, to transplantable tissues. Such delivery can occur via perfusion of the RNAi agent in solution through the vasculature of a whole or partial organ; or tissues including transplantable cells and cell lines may be bathed, injected or otherwise treated with RNAi agents. Preferred transplantable tissues include, for example, pancreas, liver, kidney, heart, lung, and all cells and cell lines derived from such tissues (e.g., pancreatic islet cells that may, e.g., be transplanted as a treated population).
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Systems and methods for identifying organ transplant risk
InactiveUS7244555B2Reduce the amount requiredMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisOrgan transplant rejectionImproved method
The present invention relates to methods of diagnosing and predicting organ transplant rejection. In particular, the present invention relates to the detection and prediction of kidney transplant rejection by detection of CXCR3 and CCL chemokines in urine. The present invention provides improved methods of diagnosing organ rejection and determining the efficacy of anti-rejection drugs.
Owner:RENOVAR
Compound containing basic group and use thereof
InactiveUS20090118279A1Preventive therapeuticAvoid prolonged useBiocideSenses disorderMental nerveArthritis
The present invention relates to a compound represented by formula (I):wherein all symbols are as defined here, a salt thereof, a solvate thereof, or a prodrug thereof.The compound of the present invention has an antagonistic activity against CXCR4 and is therefore useful as a preventive and / or therapeutic agent for CXCR4-mediated diseases, for example, inflammatory and immune diseases (for example, rheumatoid arthritis, arthritis, retinopathy, pulmonary fibrosis, rejection of transplanted organ, etc.), allergic diseases, infections (for example, human immunodeficiency virus infection, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, etc.), psychoneurotic diseases, cerebral diseases, cardiovascular disease, metabolic diseases, and cancerous diseases (for example, cancer, cancer metastasis, etc.), or an agent for regeneration therapy.
Owner:ONO PHARMA CO LTD
Flt3 inhibitors for immune suppression
The invention refers to an FLT3 inhibitors for immune suppression. New methods are provided for suppressing the immune system and for treating immune related disorders. Therapies of the invention include administration of an FLT3 inhibitor compound to a subject in need thereof, such as a subject suffering from organ rejection, bone marrow transplant rejection, acquired immune deficiency syndrome, arthritis, aplastic anemia, graft-versus-host disease, Graves' disease, established experimental allergic encephalitomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, lupus, or a neurological disorder. Methods are also provided for screening therapeutic agents for treating immune disorders, including the use of a mouse having an elevated level of FLT3 receptor activity.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com