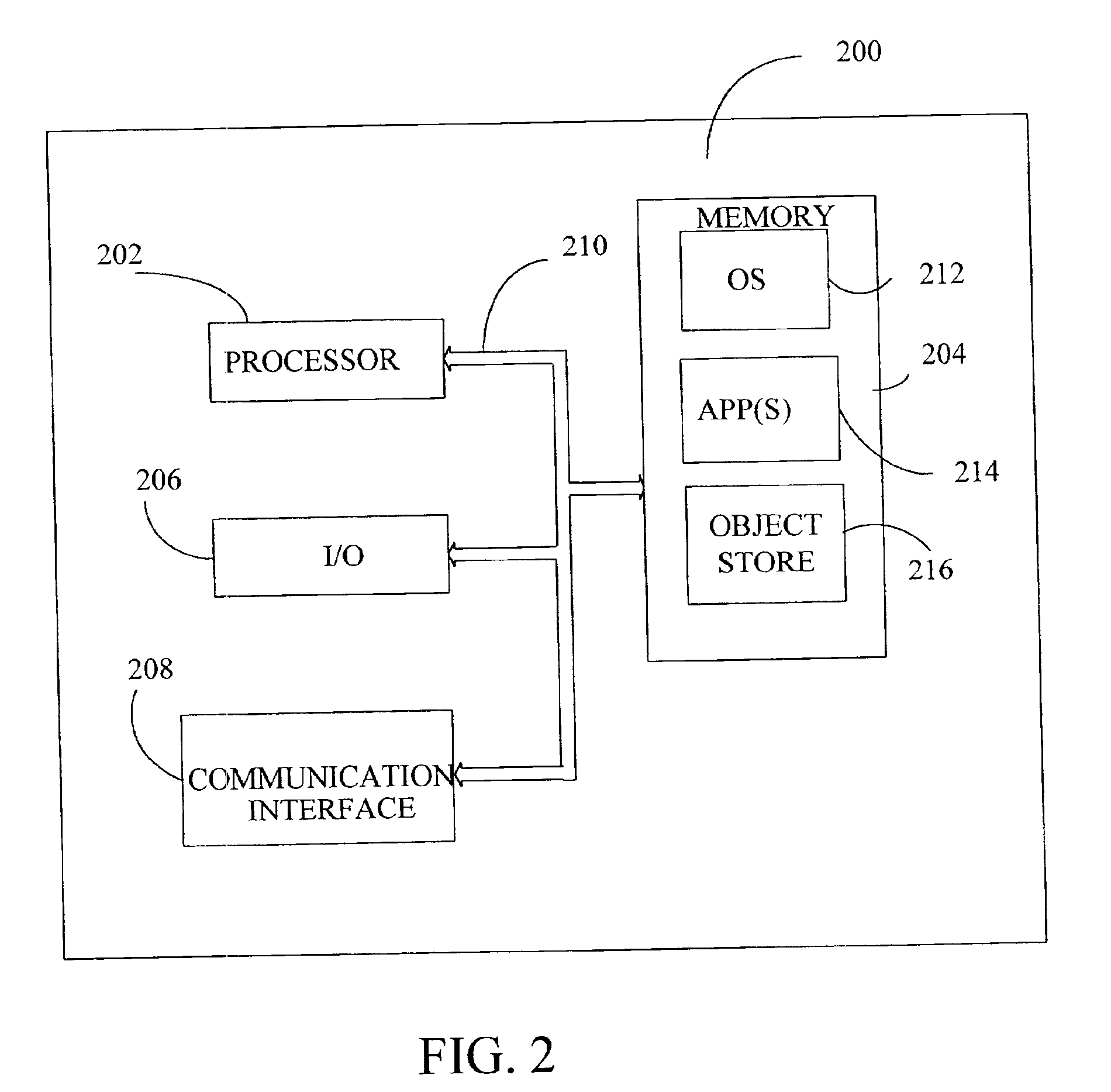
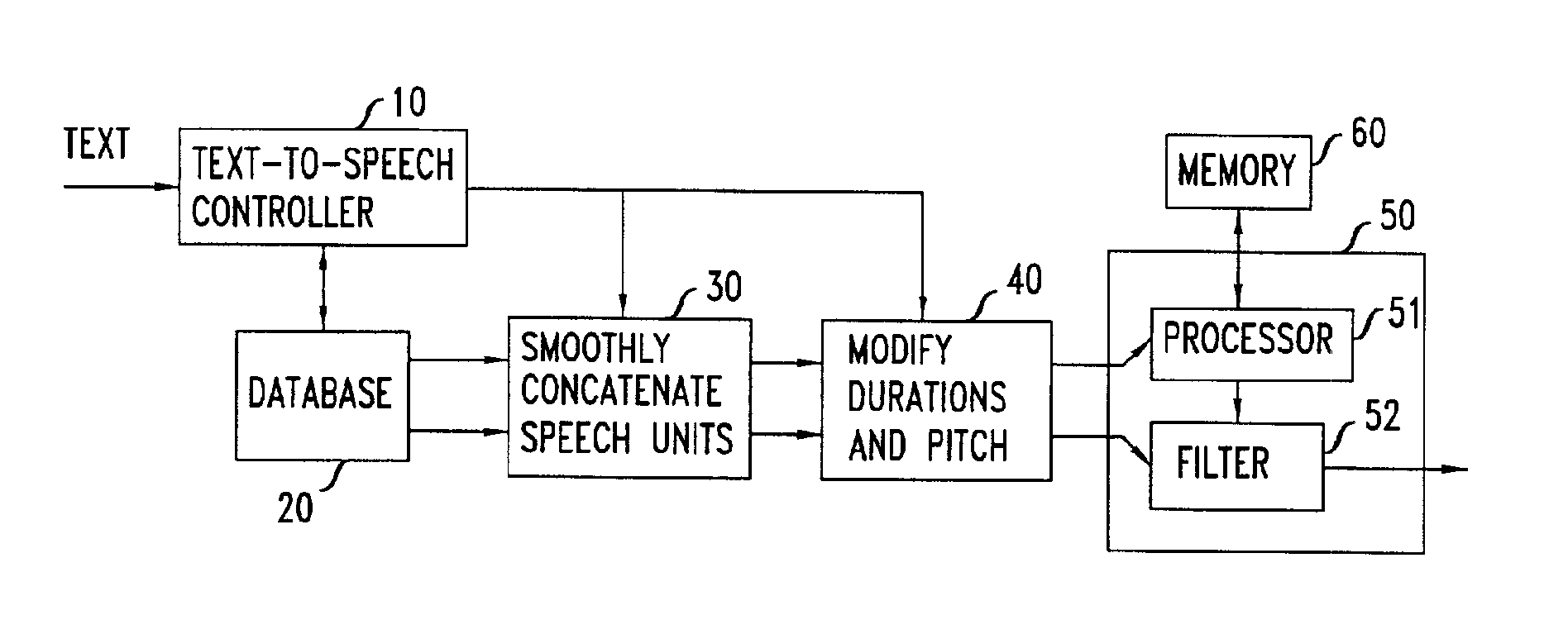
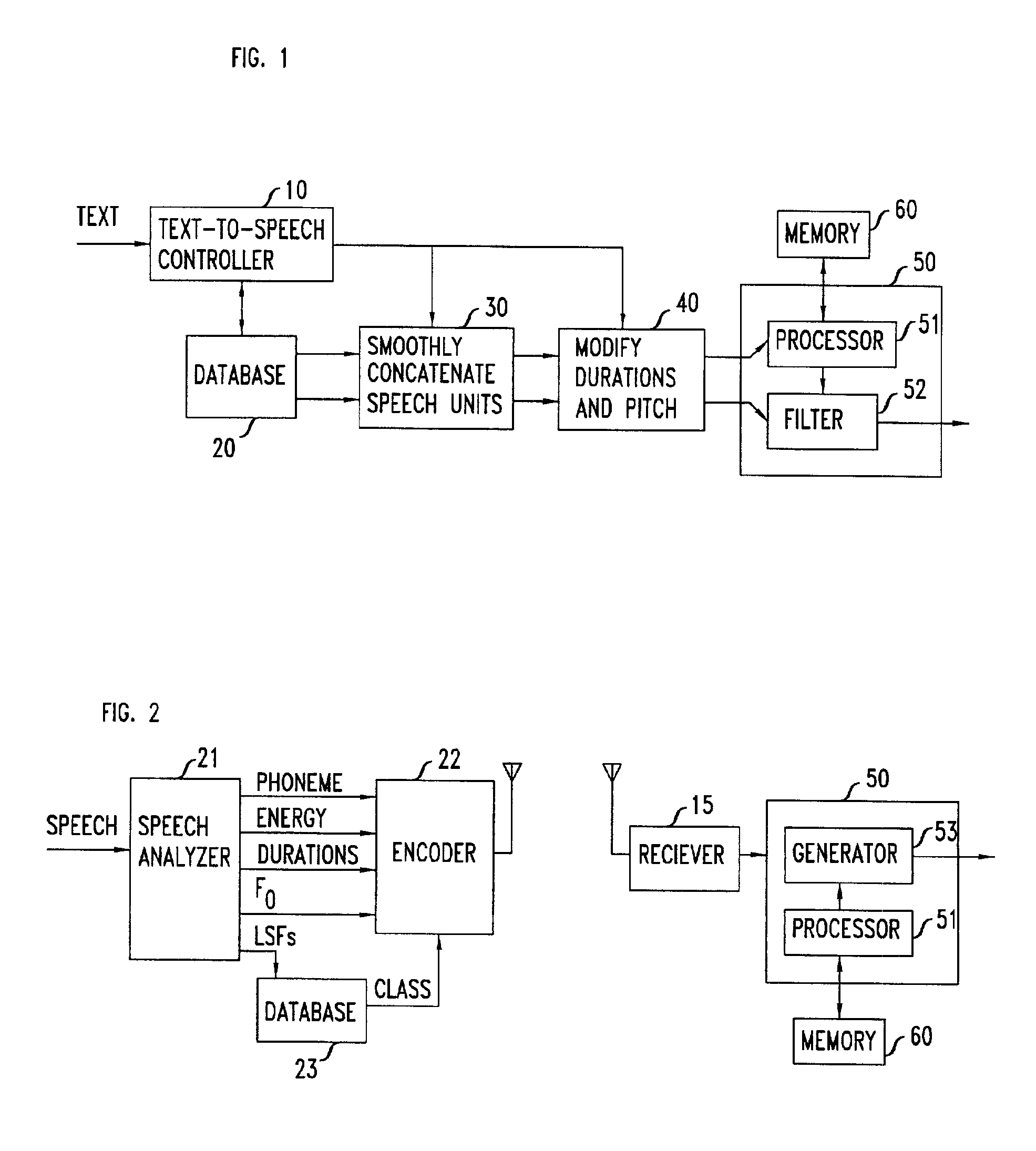
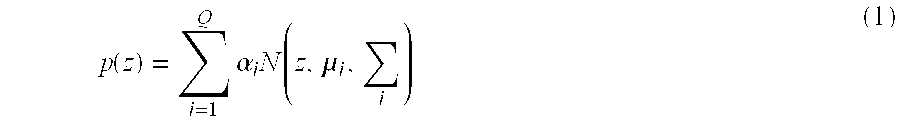Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "Natural sounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Natural sounds are any sounds produced by non-human organisms as well as those generated by natural, non-biological sources within their normal soundscapes. It is a category whose definition is open for discussion. Natural sounds create an acoustic space.
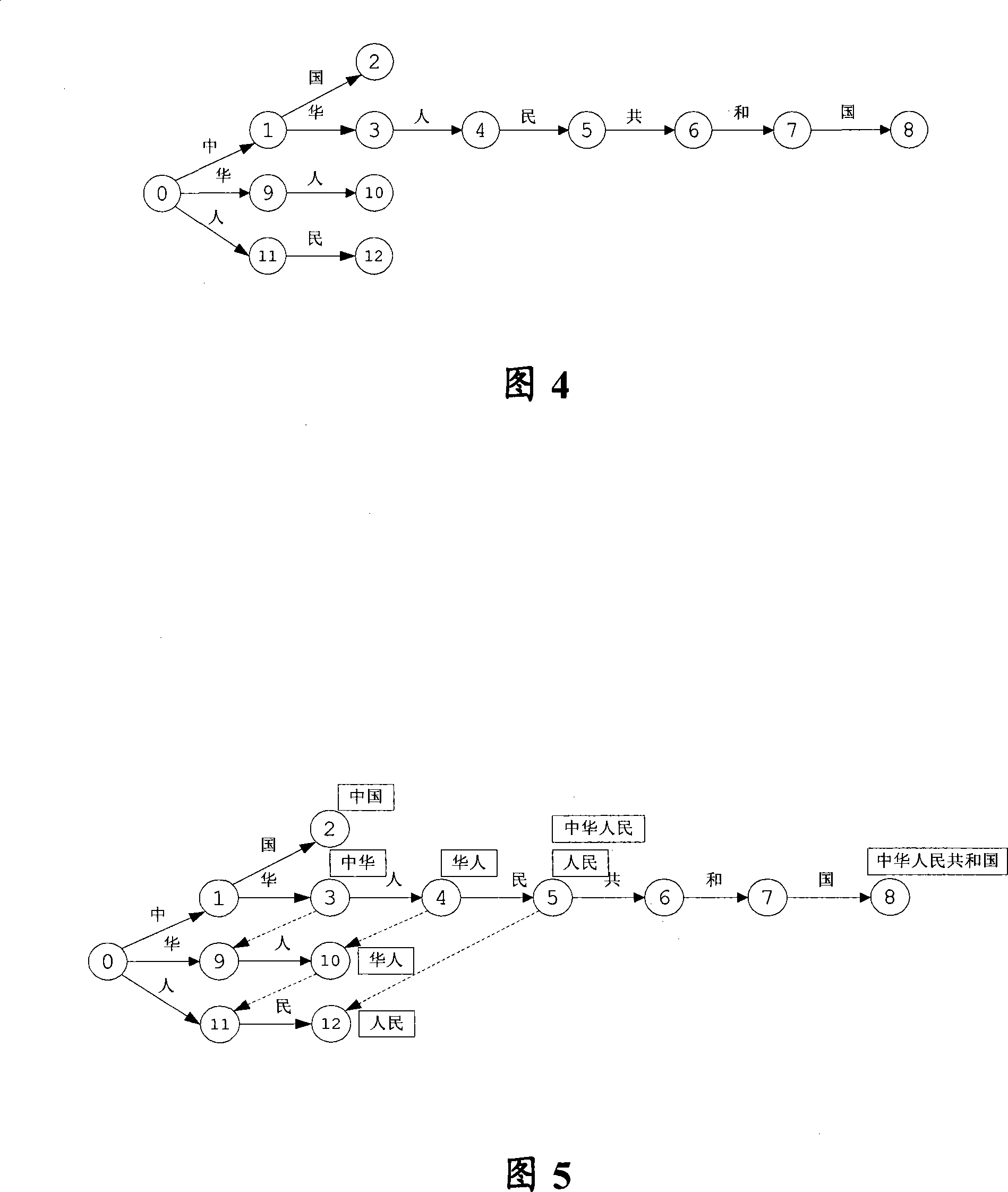
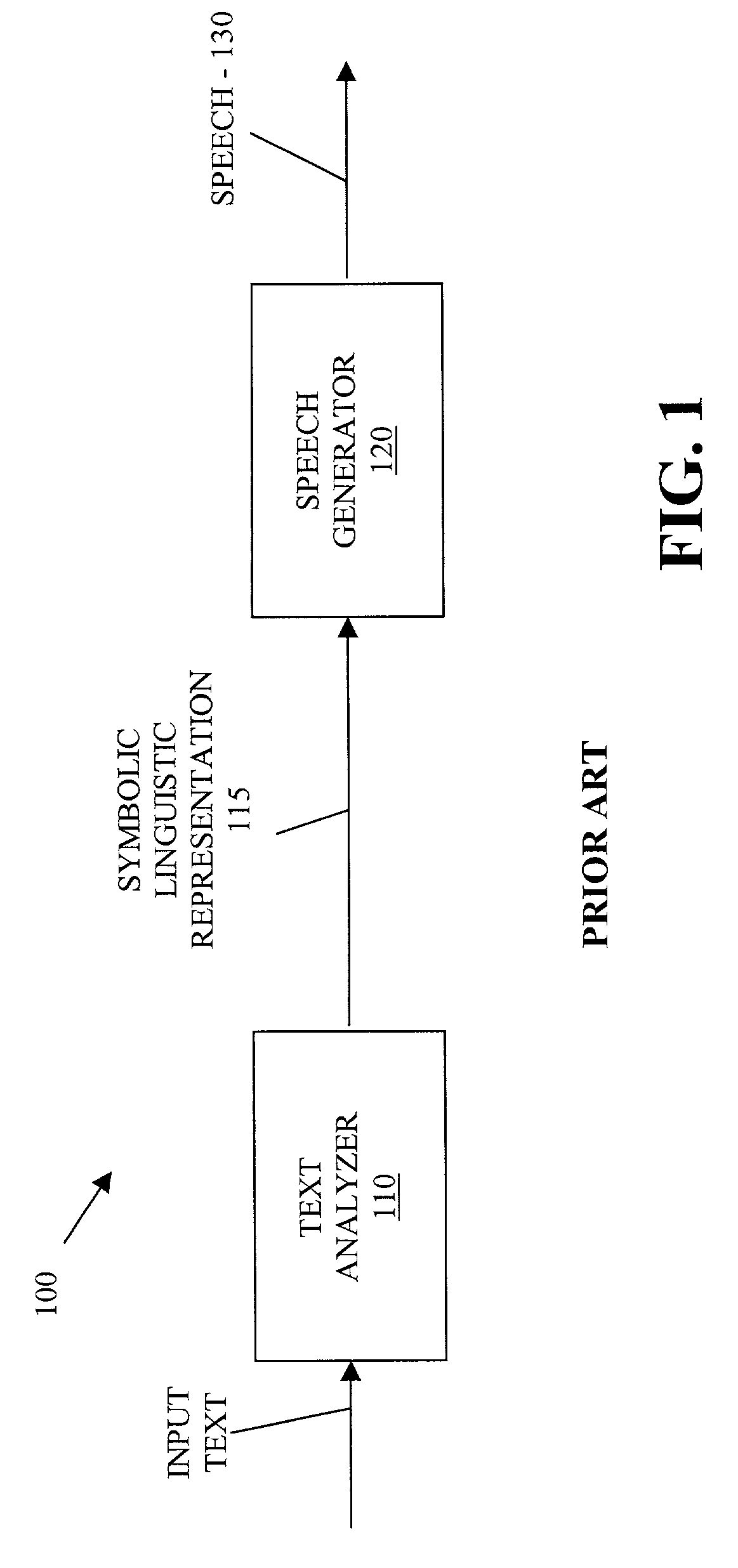
Coarticulated concatenated speech
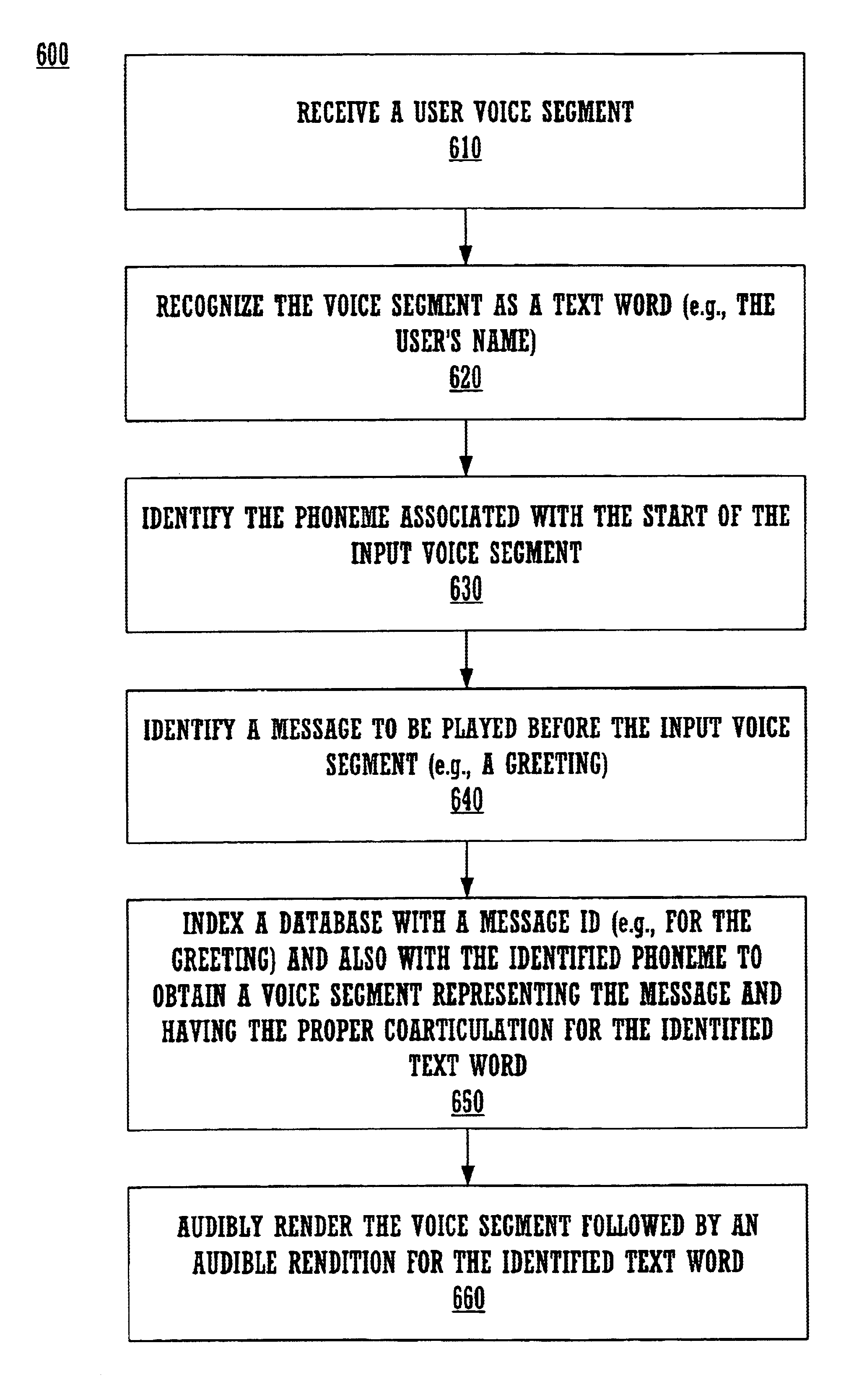
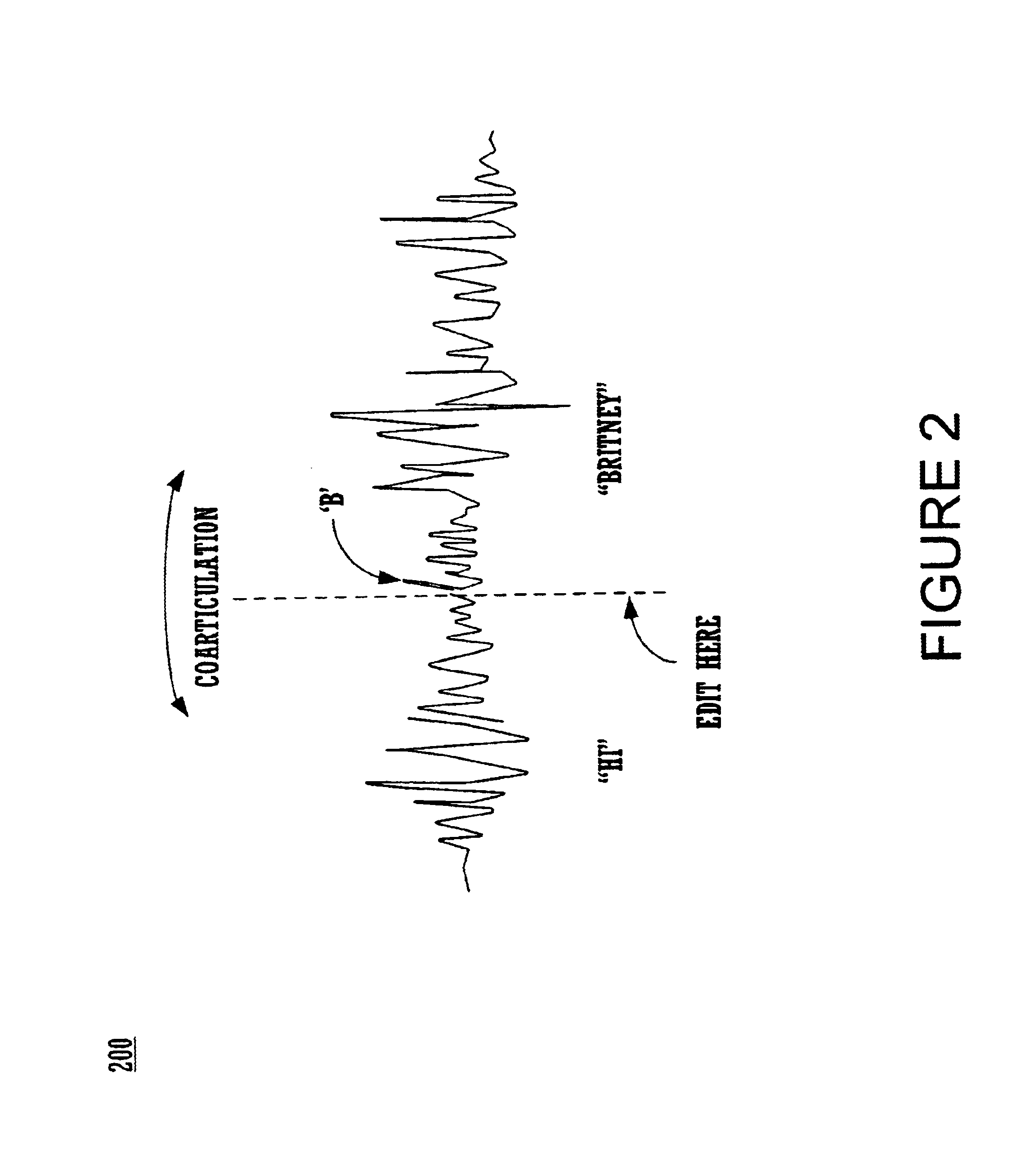
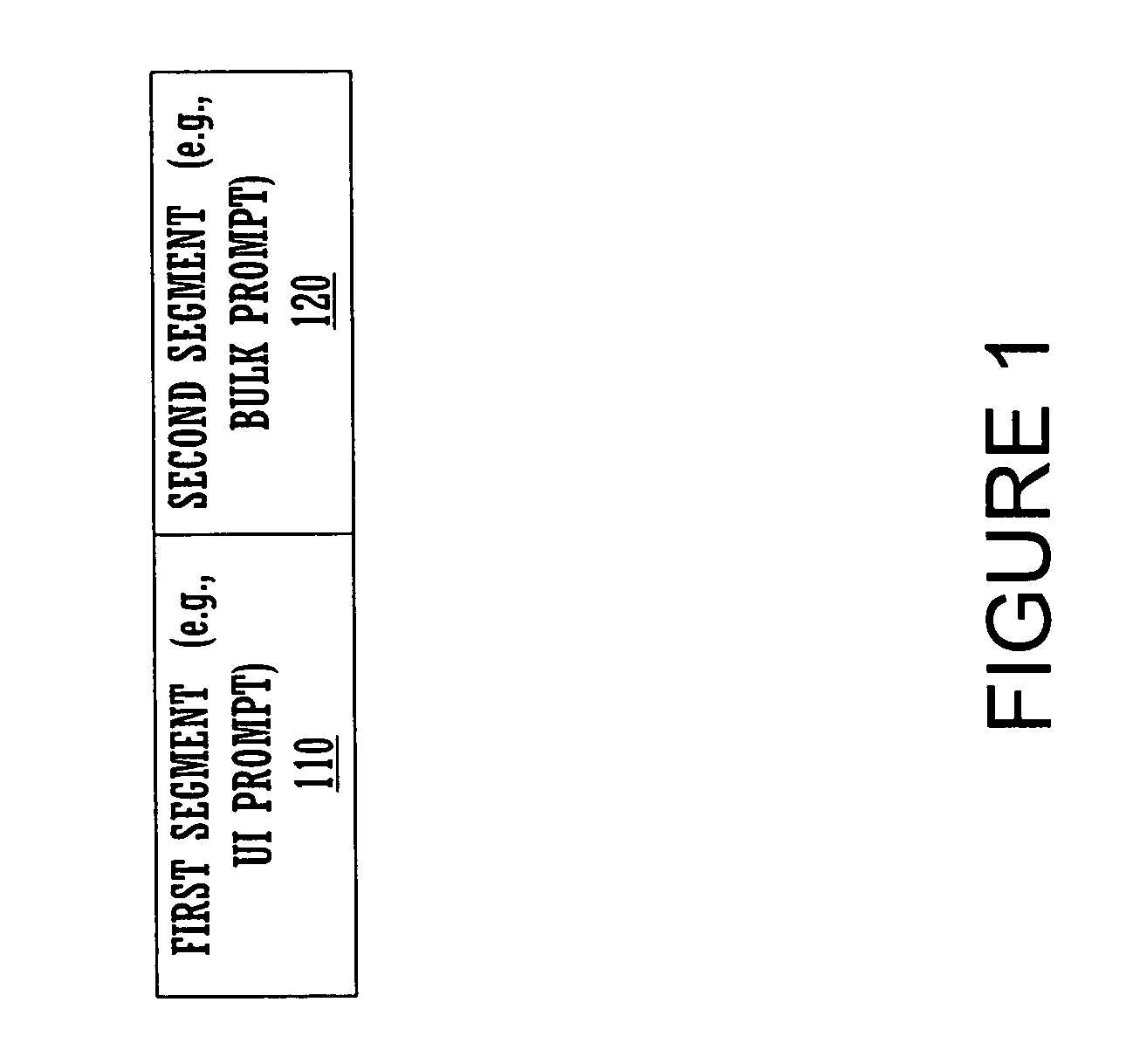
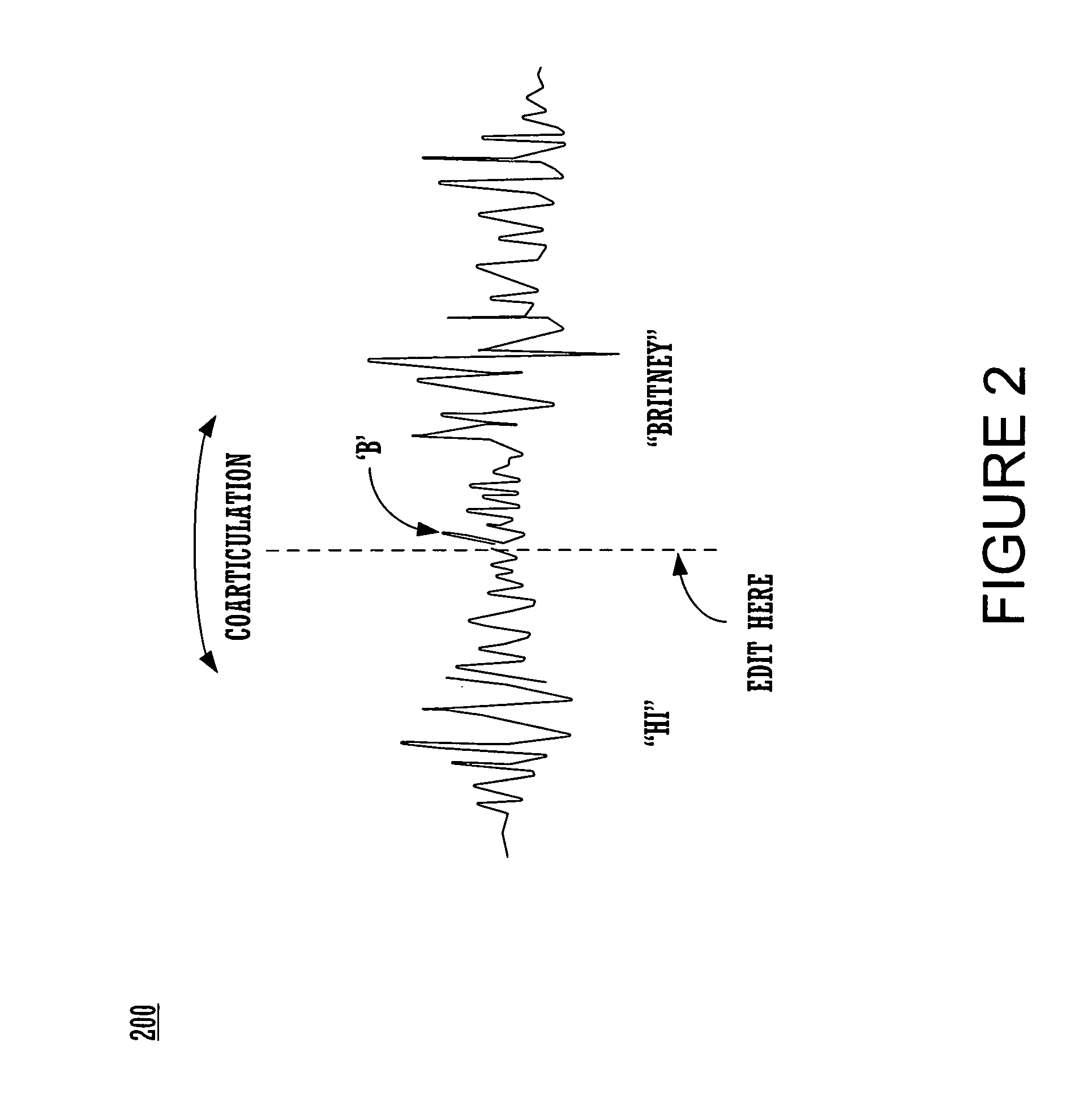
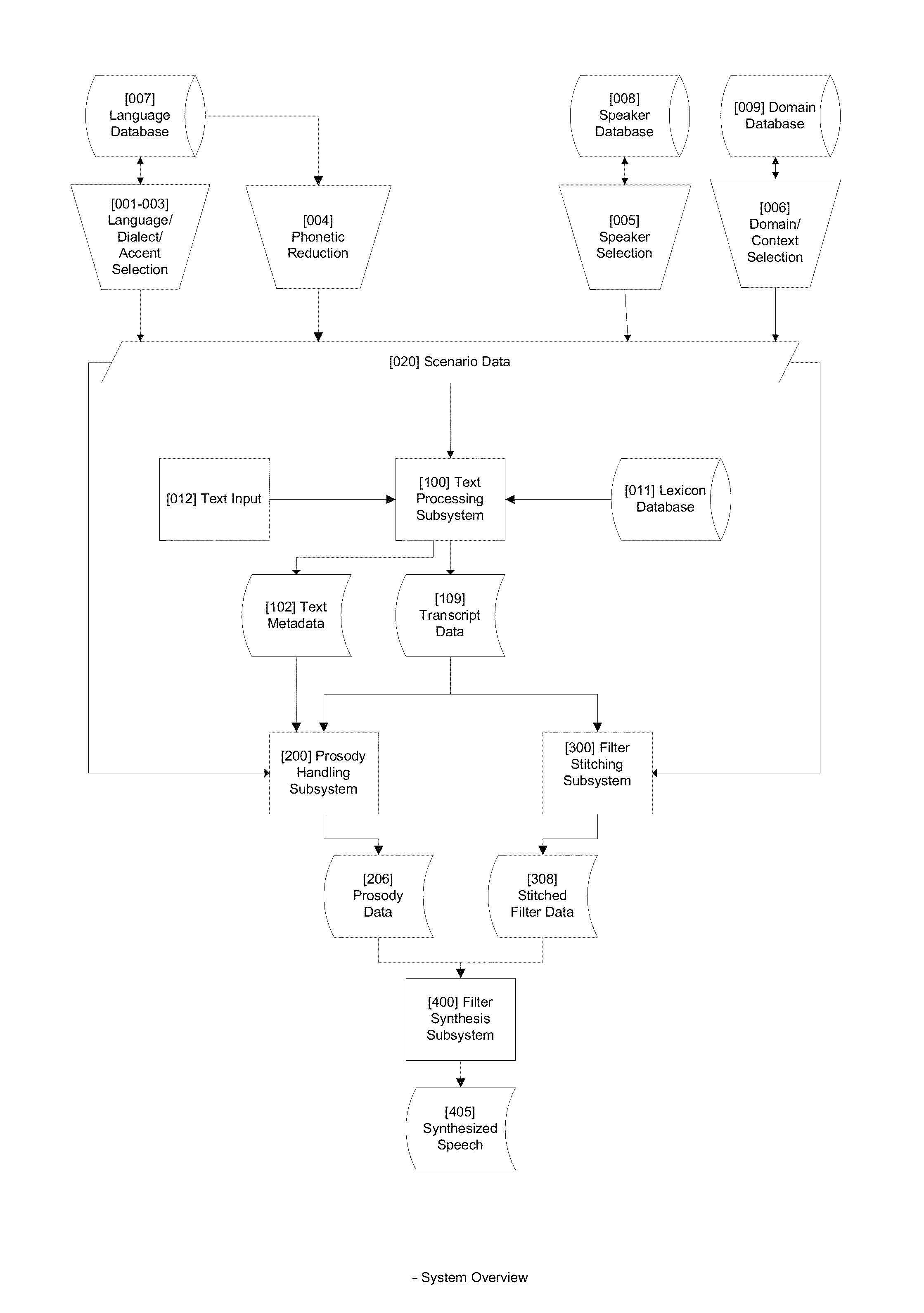
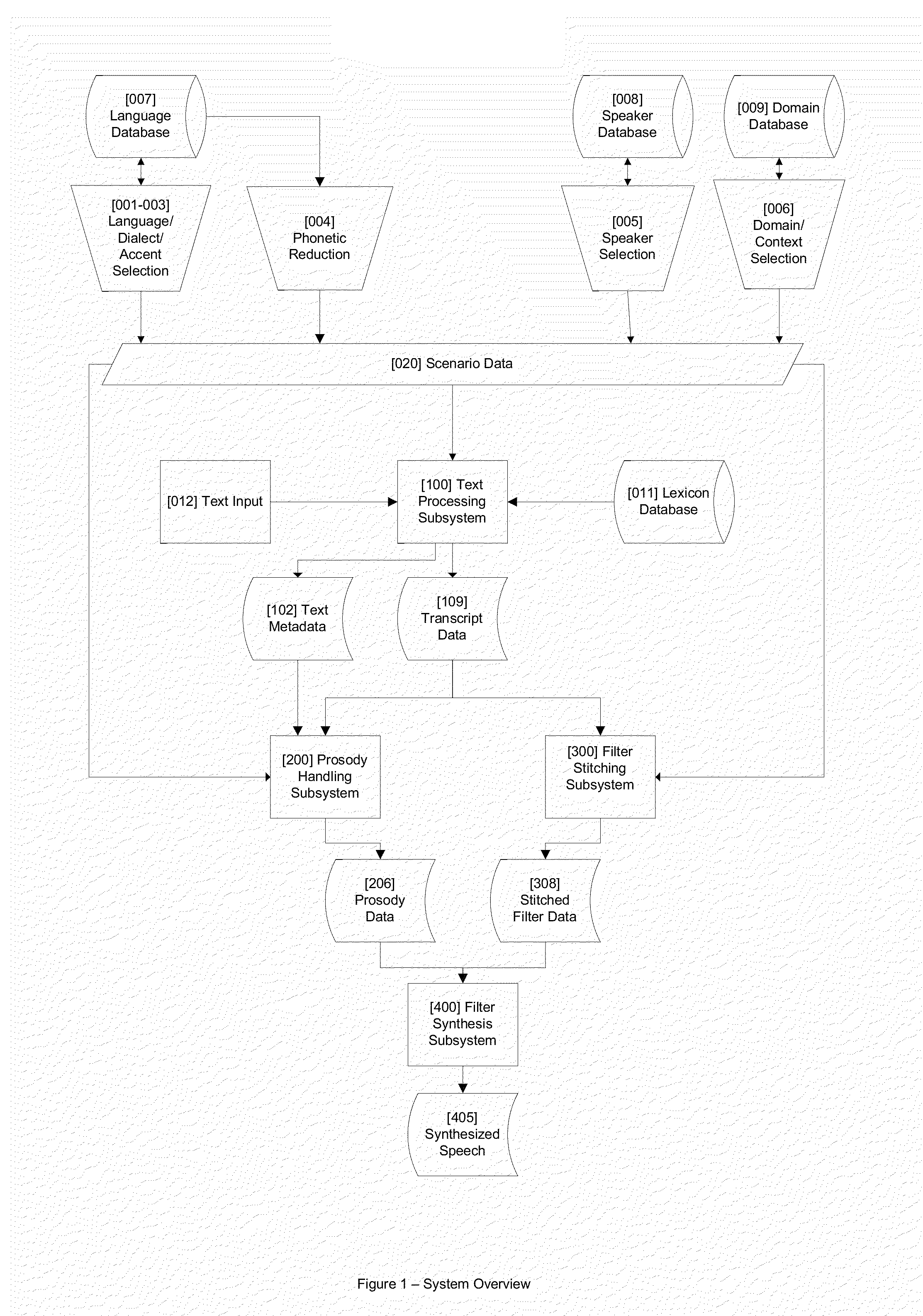
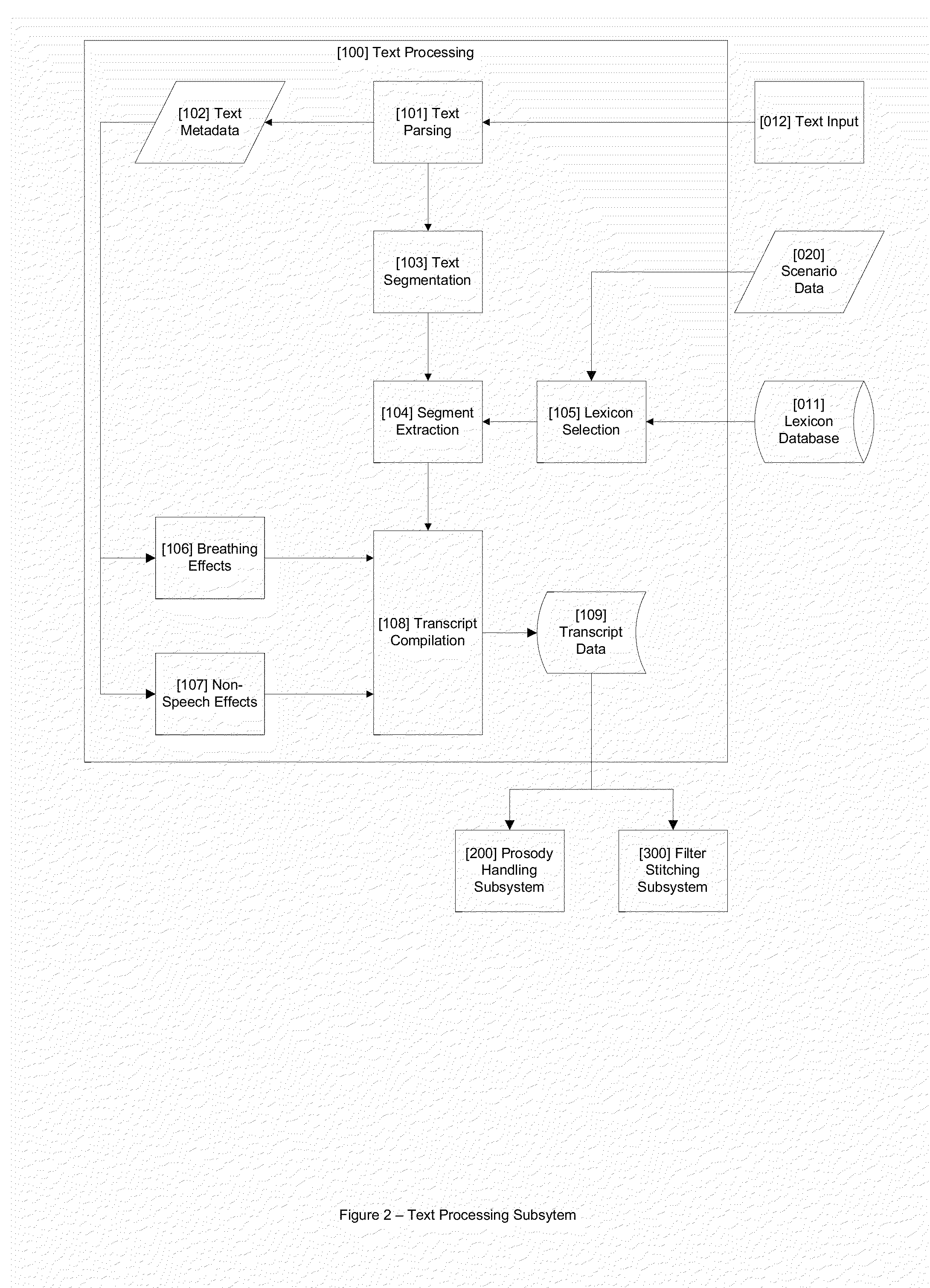
Described are methods and systems for reducing the audible gap in concatenated recorded speech, resulting in more natural sounding speech in voice applications. The sound of concatenated, recorded speech is improved by also coarticulating the recorded speech. The resulting message is smooth, natural sounding and lifelike. Existing libraries of regularly recorded bulk prompts can be used by coarticulating the user interface prompt occurring just before the bulk prompt. Applications include phone-based applications as well as non-phone-based applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Coarticulated concatenated speech
Described are methods and systems for reducing the audible gap in concatenated recorded speech, resulting in more natural sounding speech in voice applications. The sound of concatenated, recorded speech is improved by also coarticulating the recorded speech. The resulting message is smooth, natural sounding and lifelike. Existing libraries of regularly recorded bulk prompts can be used by coarticulating the user interface prompt occurring just before the bulk prompt. Applications include phone-based applications as well as non-phone-based applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for speech synthesis without prosody modification
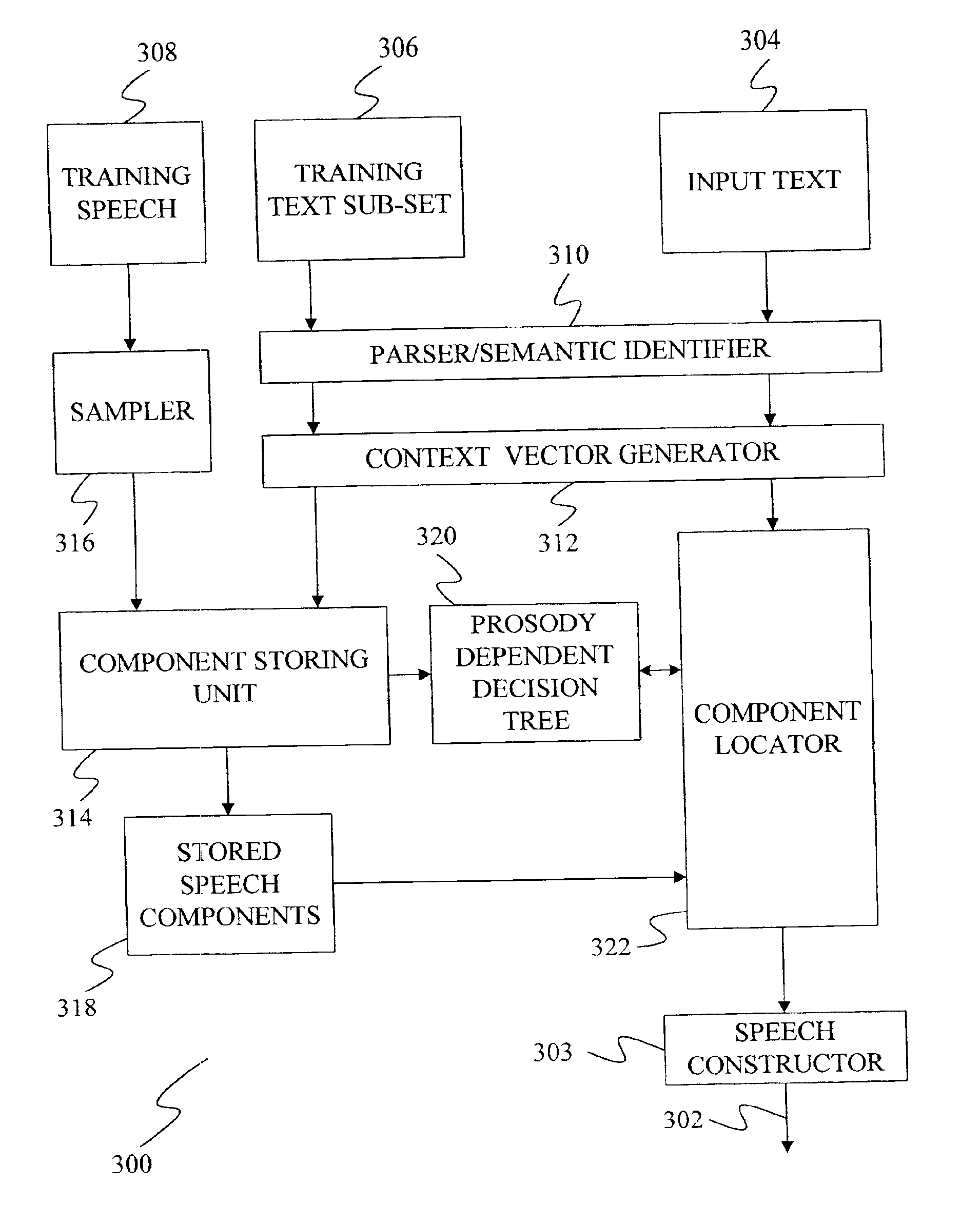
A speech synthesizer is provided that concatenates stored samples of speech units without modifying the prosody of the samples. The present invention is able to achieve a high level of naturalness in synthesized speech with a carefully designed training speech corpus by storing samples based on the prosodic and phonetic context in which they occur. In particular, some embodiments of the present invention limit the training text to those sentences that will produce the most frequent sets of prosodic contexts for each speech unit. Further embodiments of the present invention also provide a multi-tier selection mechanism for selecting a set of samples that will produce the most natural sounding speech.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Stochastic modeling of spectral adjustment for high quality pitch modification
Natural-sounding synthesized speech is obtained from pieced elemental speech units that have their super-class identities known (e.g. phoneme type), and their line spectral frequencies (LSF) set in accordance with a correlation between the desired fundamental frequency and the LSF vectors that are known for different classes in the super-class. The correlation between a fundamental frequency in a class and the corresponding LSF is obtained by, for example, analyzing the database of recorded speech of a person and, more particularly, by analyzing frames of the speech signal.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
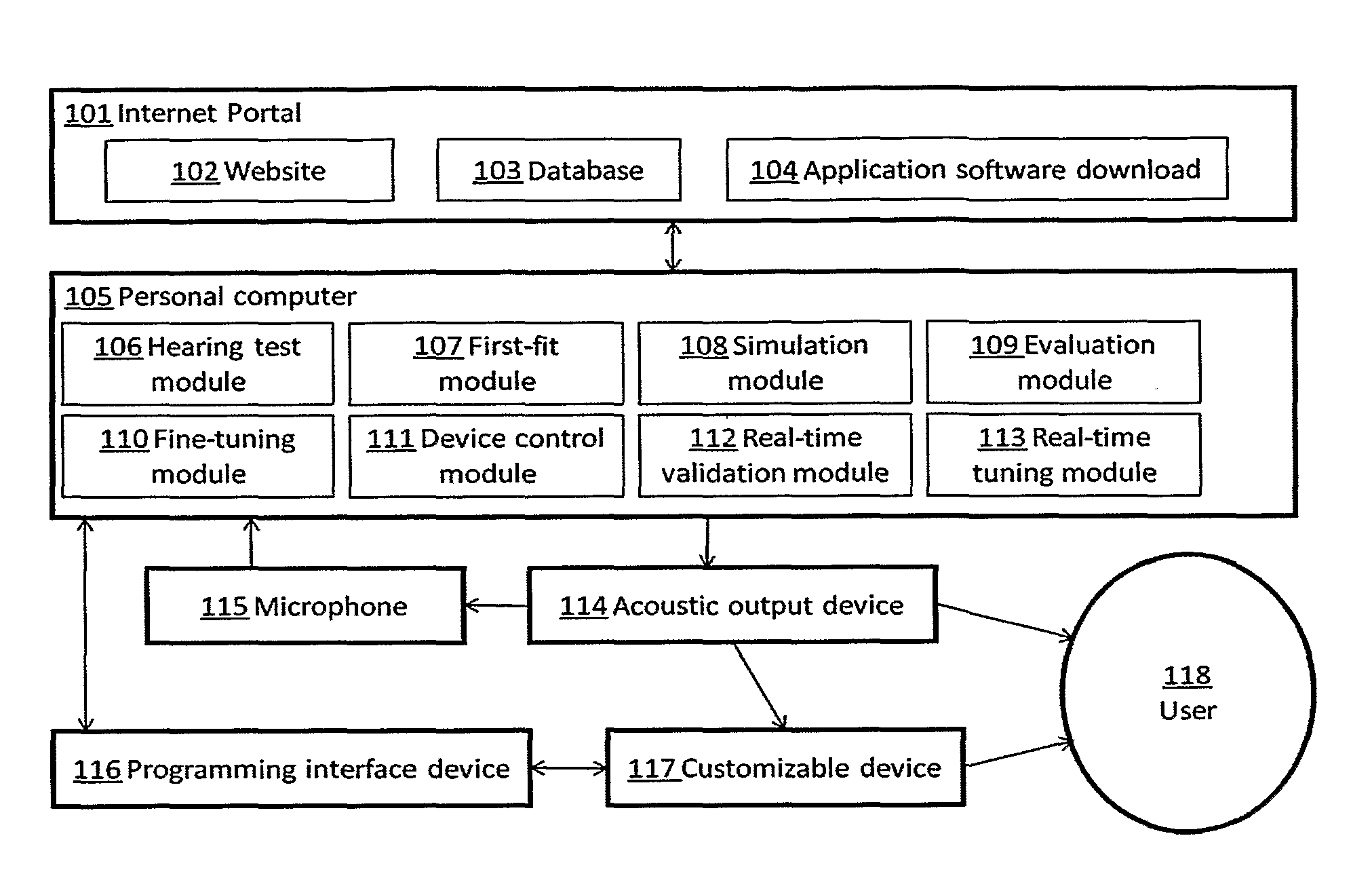
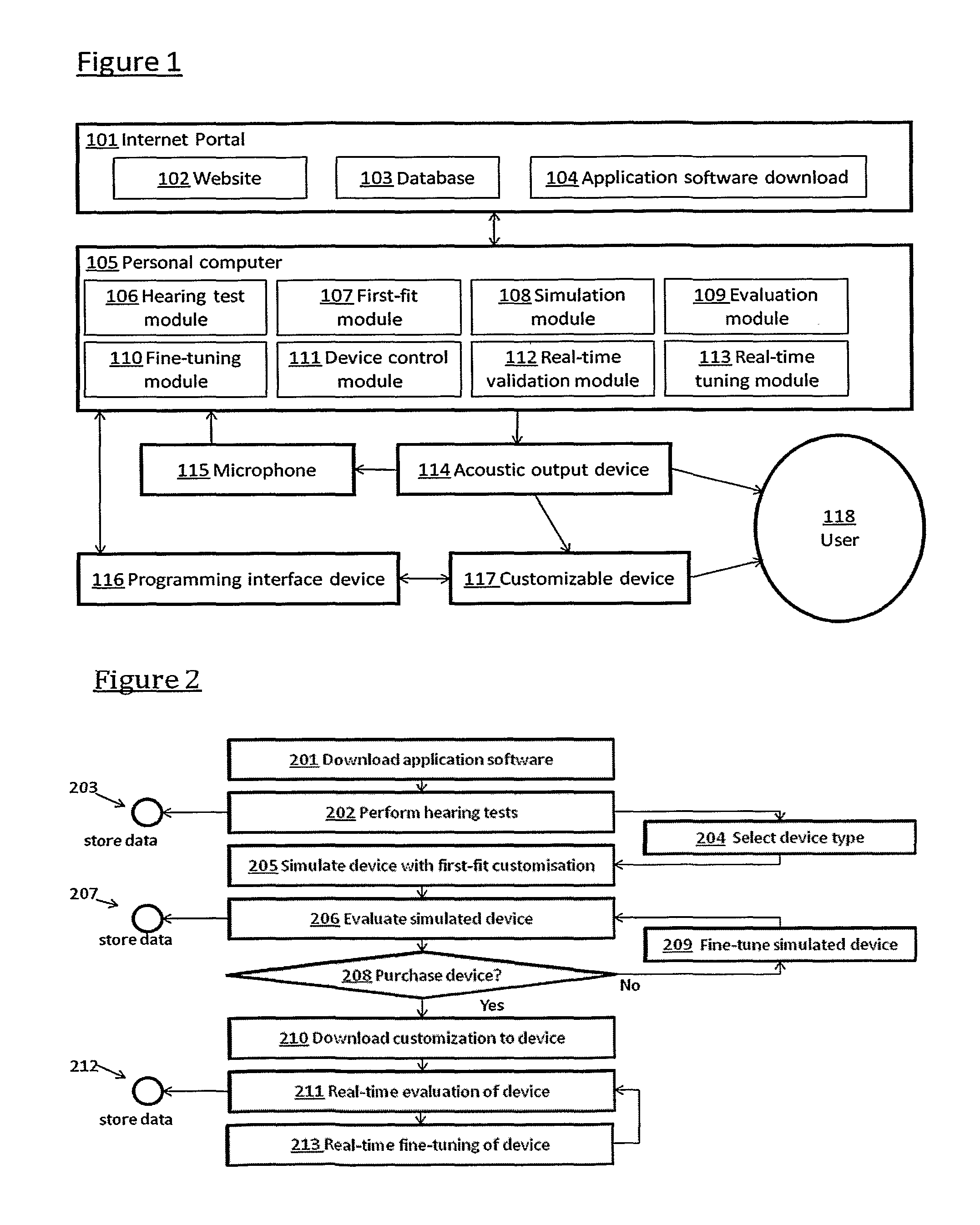
Automated fitting of hearing devices
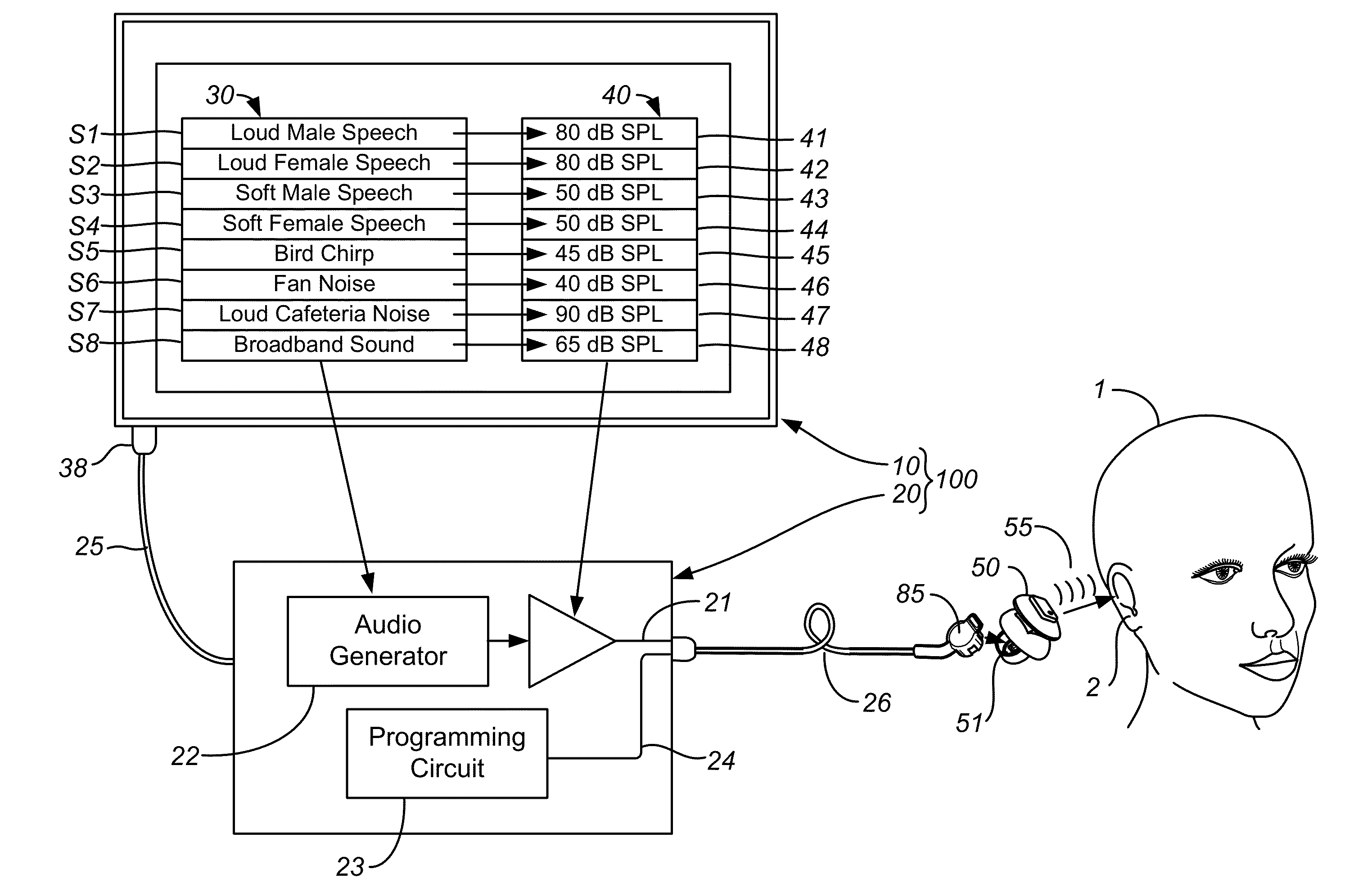
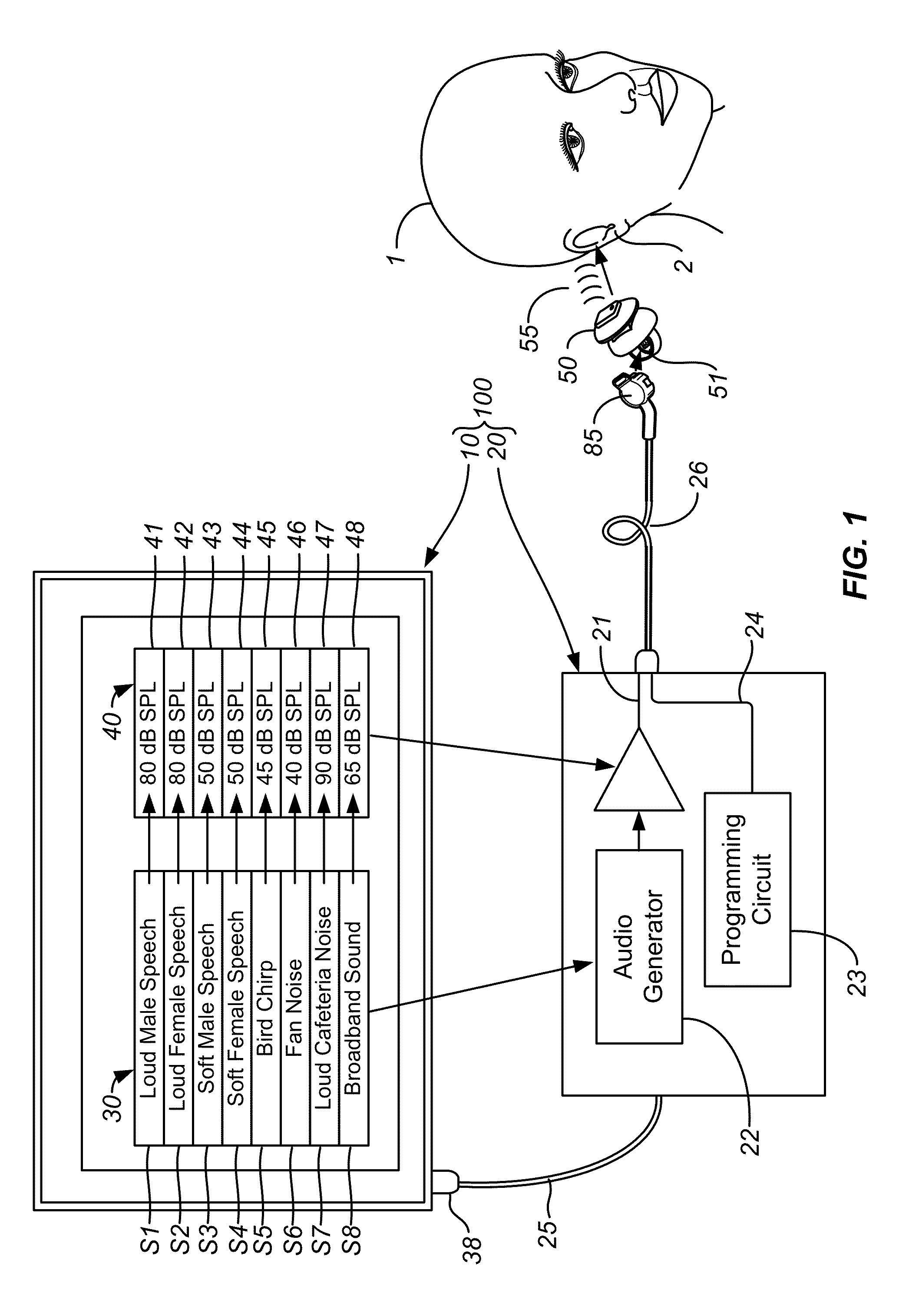
ActiveUS20120051569A1Improve developmentEasy to adjustDeaf aid adaptationUser inputPattern perception
Fitting a sound processing device for an individual is automated using a computer. Fitting and customisation is carried out using natural sounds without specialised audiometric equipment or audiological expertise. Software for this purpose is downloaded from an internet portal. The computer plays back acoustic signals, and obtains user input reflecting the user's perceptions of the acoustic signals, from which a hearing map is derived, representing the user's hearing. An algorithm updates the device fitting based on the hearing map. Also provided is pre-sale virtual device fitting, whereby a virtual signal processing path is established in the computer, reflecting a signal processing function of a sound processing device of interest to the user. An algorithm updates parameters of the virtual processing path, based on the hearing map. Audio signals passed through the virtual processing path are played back to the user, giving the user an acoustic indication of future device performance.
Owner:SONOVA AG
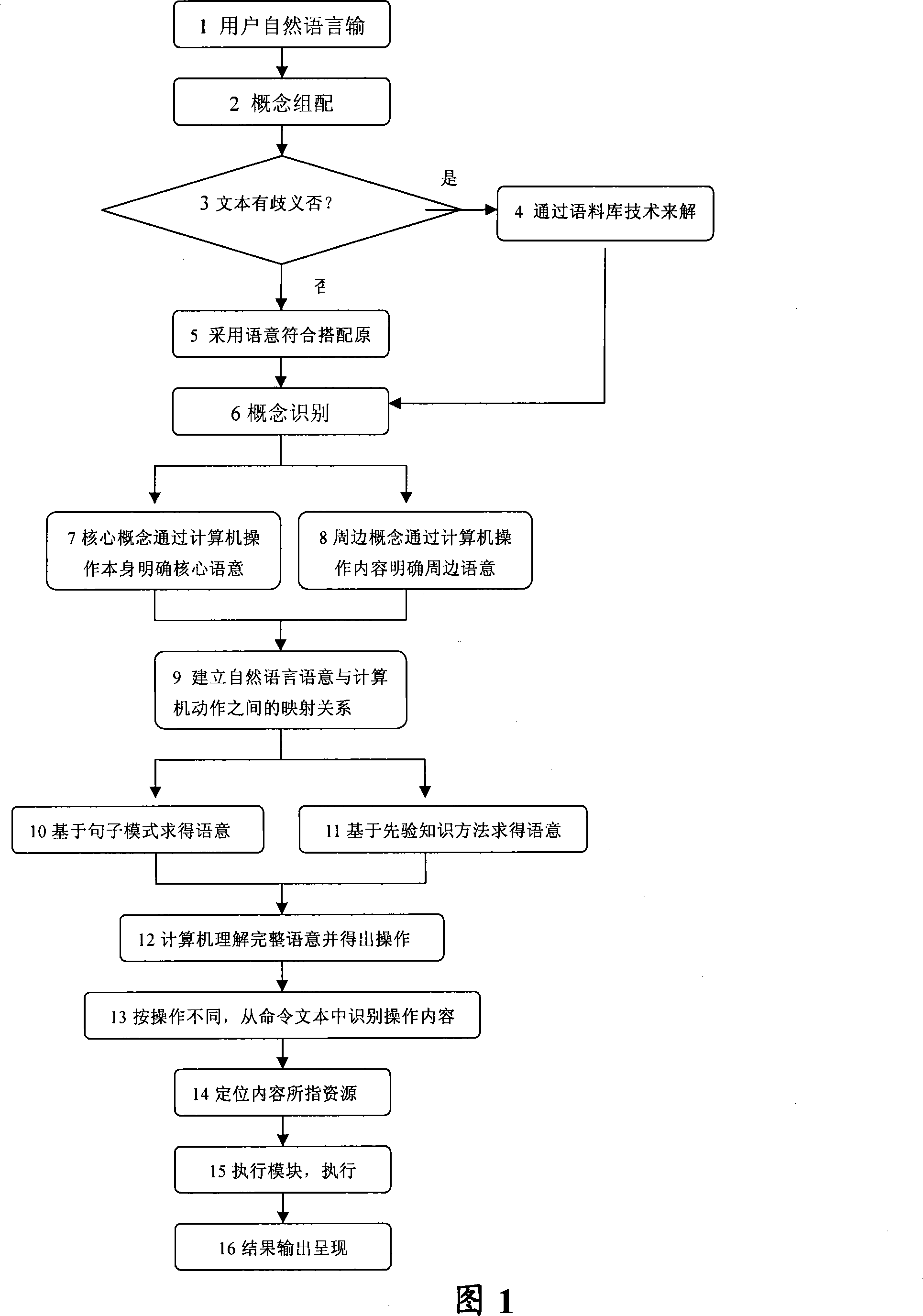
Free-running speech comprehend method and man-machine interactive intelligent system
InactiveCN101178705AEasy to understandCorrect answerSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsNatural language understandingAmbiguity
The invention discloses natural language understanding method, comprising the steps that: a natural language is matched with a conceptual language symbol after receiving the natural language input by the customer, and then a conception is associated with the conceptual language symbol; a conception which is most suitable to the current language content is selected by being compared with the preset conception dictionary, and then whether the conception is ambiguous is judged; and if the answer is YES, the conception is obtained by a language data base, entering the next step; and if the answer is NO, the conception is obtained based on the principle of language content matched, entering to the next step; a core conception and a sub conception are obtained by a conception reorganization, wherein, the core language meaning of the core conception is defined by an operation of the computer while the sub language meaning of the sub conception is defined by the operation content of the computer; and the complete language meaning is obtained by combining the core language meaning with the sub language meaning. The invention also provides a human-computer interaction intelligent system based on the method provided by the invention. The invention recognizes the natural sound input by the customer more accurately, thereby providing the customer with more intelligent and perfect services.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
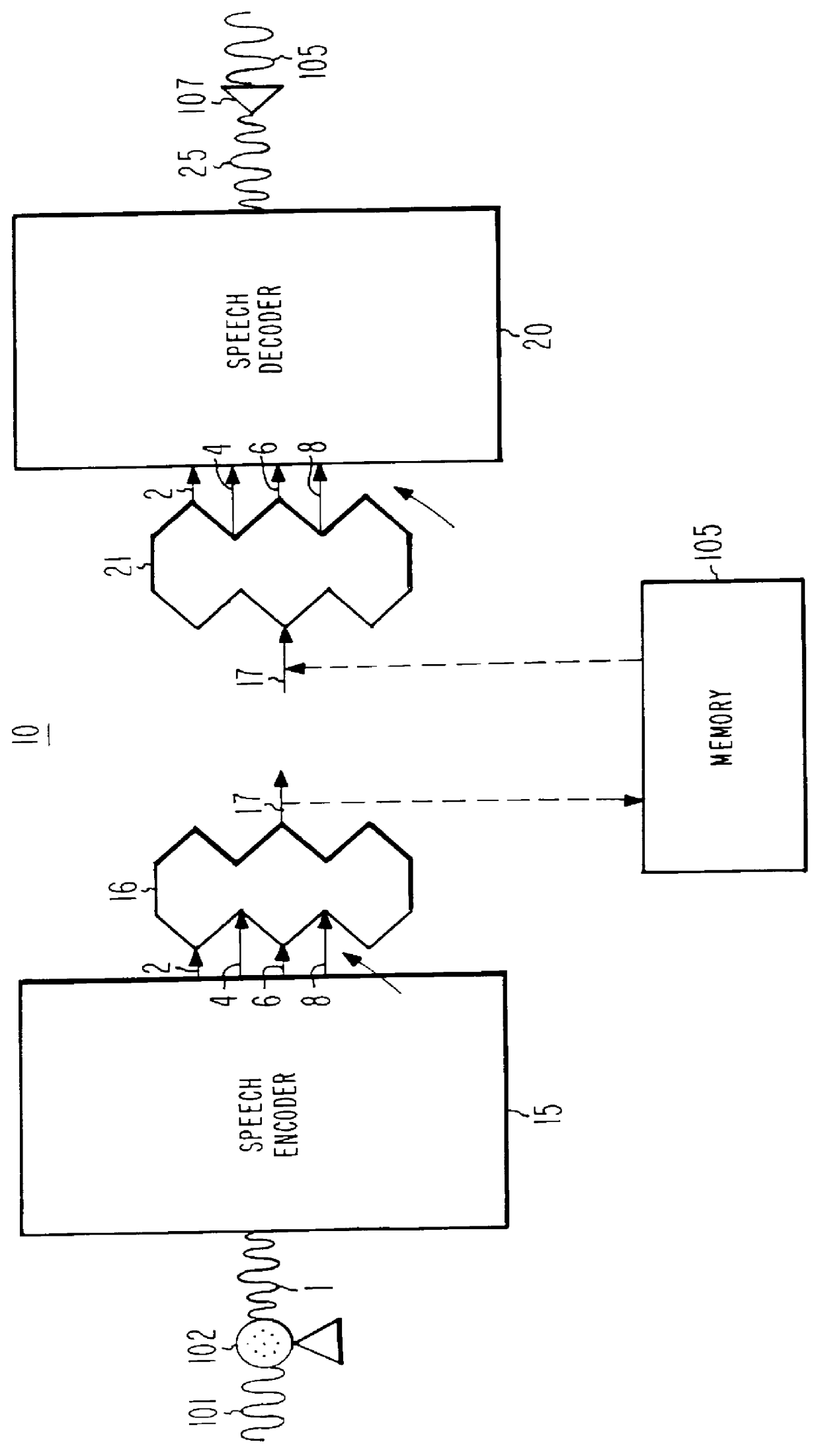
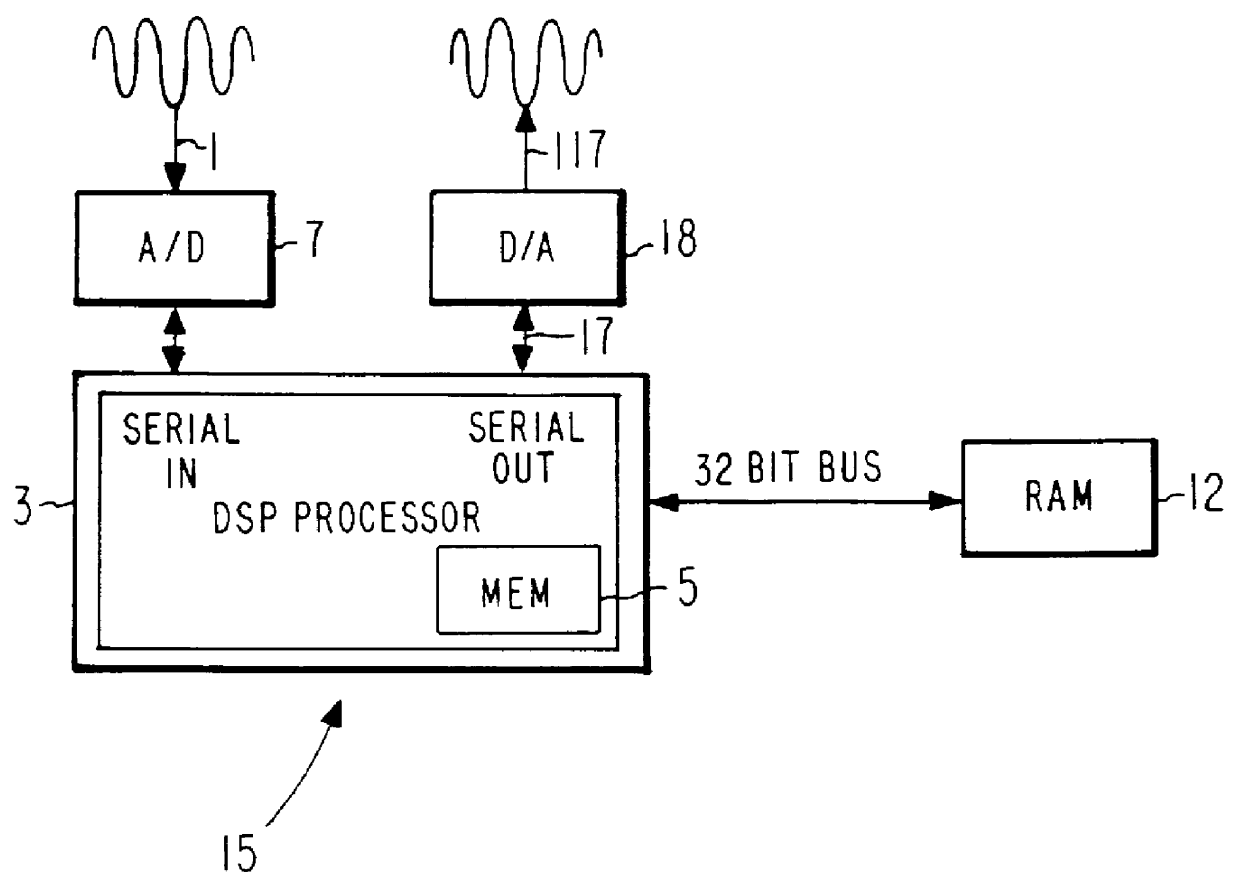
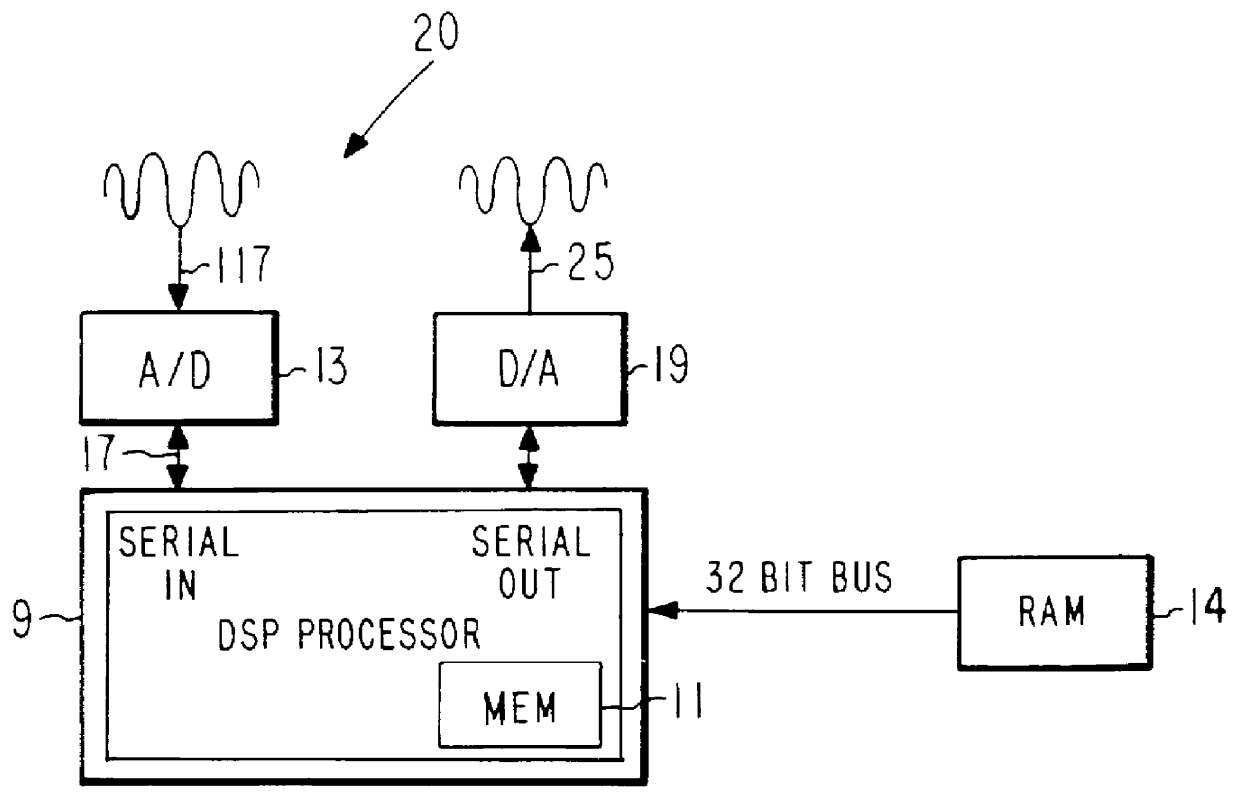
LPC speech synthesis using harmonic excitation generator with phase modulator for voiced speech
A speech coding system (10) and associated method relies on a speech encoder (15) and a speech decoder (20). The speech decoder (20) includes a harmonic generator (70) which modulates the phase of each generated harmonic with a low frequency, low bandwidth signal to remove the buzzy quality of the speech and to produce natural sounding speech. The amplitude of the phase modulating signal is adjusted in accordance with the harmonic magnitude. For harmonics residing in a spectral valley the amplitude of the modulating signal is relatively large and for harmonics residing near spectral peaks, the amplitude of the modulation signal is relatively small.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Realistic Speech Synthesis System
A system and method for realistic speech synthesis which converts text into synthetic human speech with qualities appropriate to the context such as the language and dialect of the speaker, as well as expanding a speaker's phonetic inventory to produce more natural sounding speech.
Owner:SRC INC
Active non-lethal avian denial infrasound systems and methods of avian denial
An active non-lethal infrasound system for denying all bird species access to critical areas, particularly in areas around aircraft and other high value systems. The system comprises a plurality of infrasound generators broadcasting continuous infrasonic signals to create a bird-free infrasound active zone within the perimeters of the protected critical area and an infrasound-free dead zones for birds being denied access to the critical areas. Further, an active infrasonic barrier is assembled within an exclusion area surrounding the bird-free infrasound active zone to dampen all low frequency sound waves emanating from the critical area and its perimeters. Wherever the situation allows, a wildlife sanctuary is preferably established further from the exclusion area to attract and protect birds, enforced by broadcasting infrasound signals that simulate natural sounds that attract species typical of the geographic location.
Owner:TECH INT INC +1
Hearing aid fitting systems and methods using sound segments representing relevant soundscape
ActiveUS20150023535A1Eliminate the calibration processMinimizing overlap in parameter optimizationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHearing apparatusHearing aid
Disclosed herein are systems and methods enabling hearing aid fitting by a non-expert consumer. The method in one embodiment involves delivering a sequence of test audio signals corresponding to natural sound segments to a non-acoustic input of a programmable hearing device in-situ, while allowing the consumer to adjust fitting parameters based perceptual assessment of hearing device output. The sound segments define a fitting soundscape within the normal human auditory range, with each sound segment corresponding to one or more fitting parameters of the programmable hearing device. The consumer is instructed to listen to the output of the in-situ hearing device and adjust controls related to corresponding fitting parameters. In one embodiment, the fitting system comprises a personal computer and a handheld device providing calibrated test audio signals and programming interface. The systems and methods allow home dispensing of hearing devices without requiring specialized instruments.
Owner:HIMPP
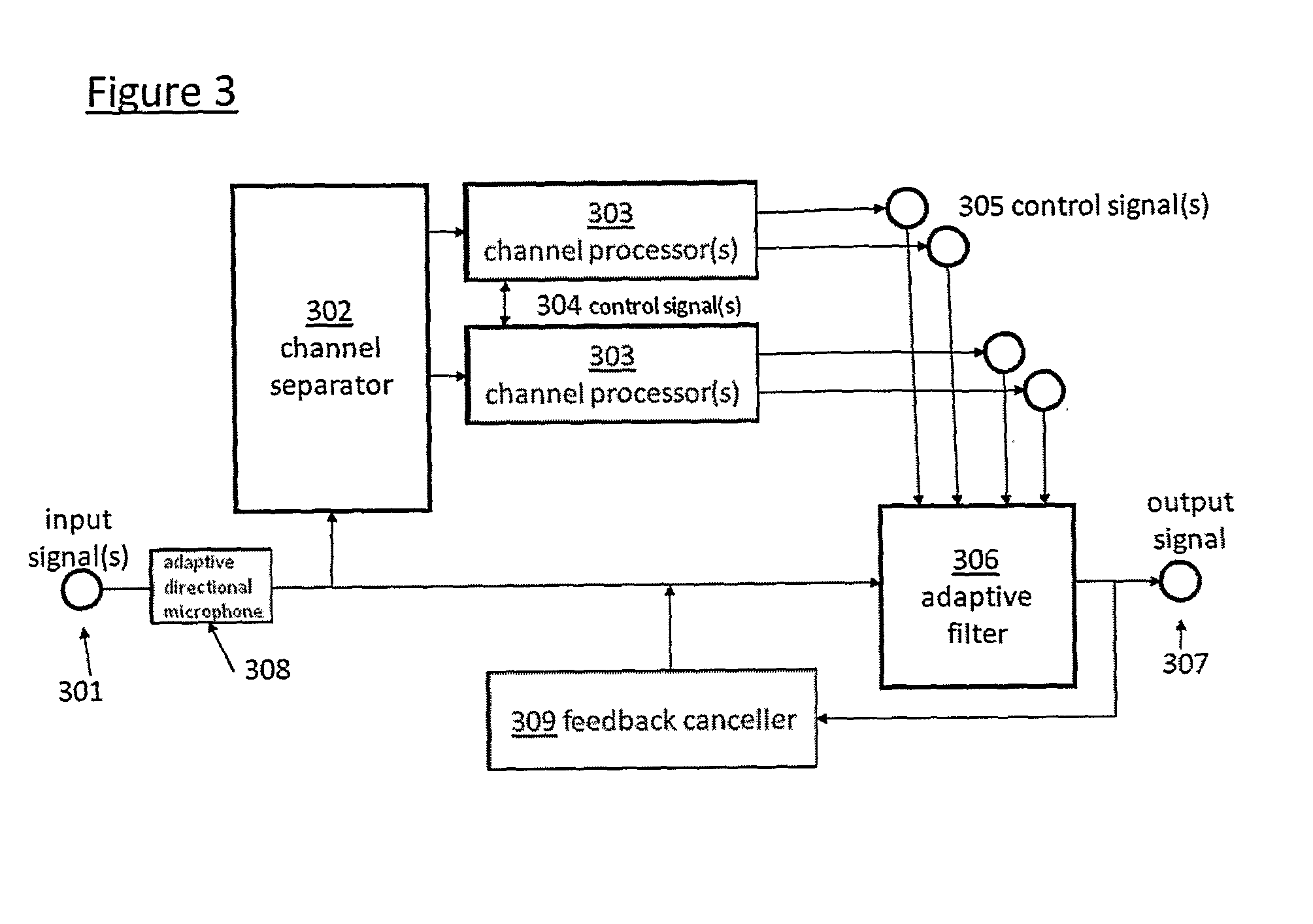
Sound processing method and apparatus
InactiveUS7162045B1High separation precisionSpeech analysisTransmission noise suppressionAudio frequencyComputer science
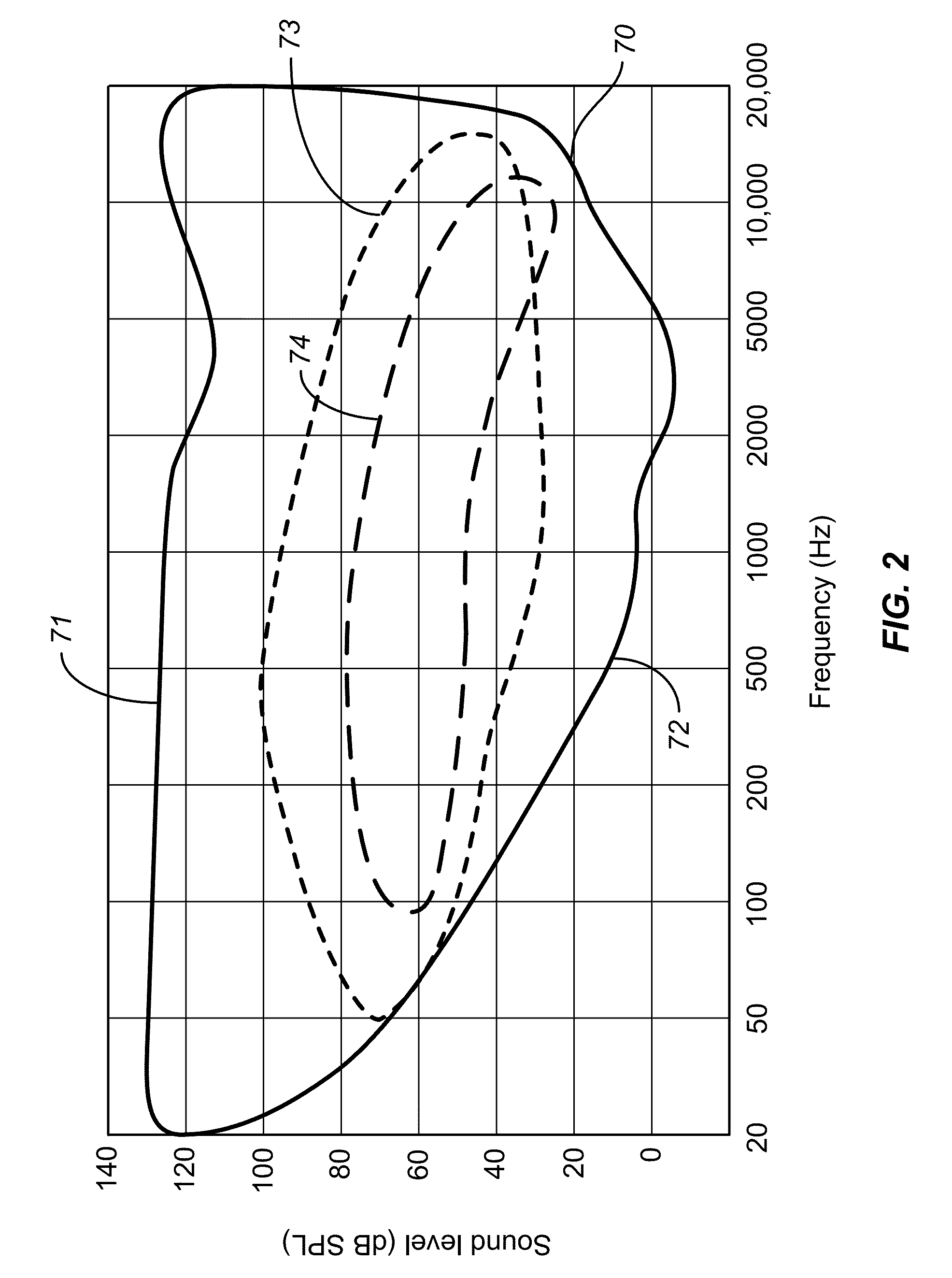
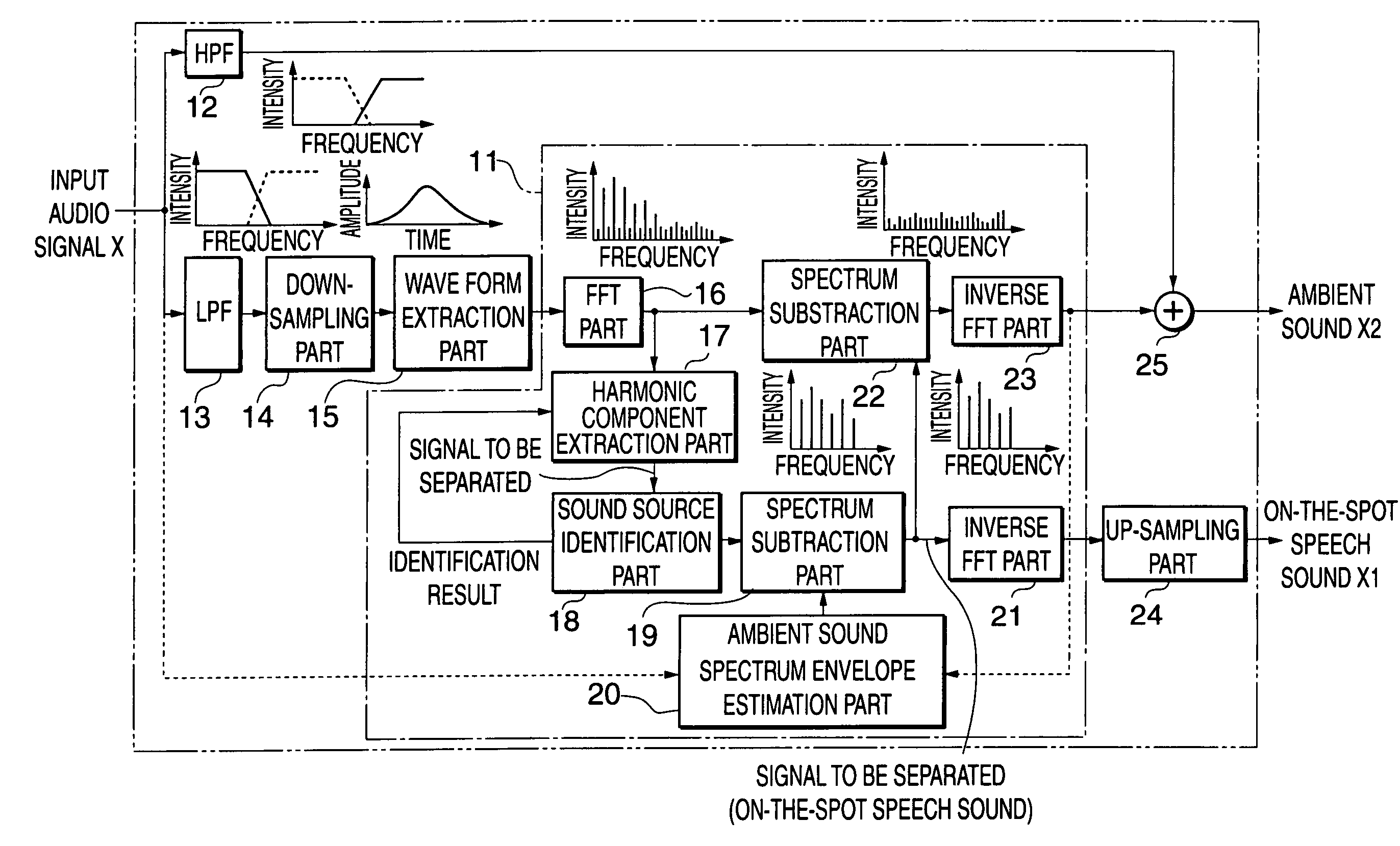
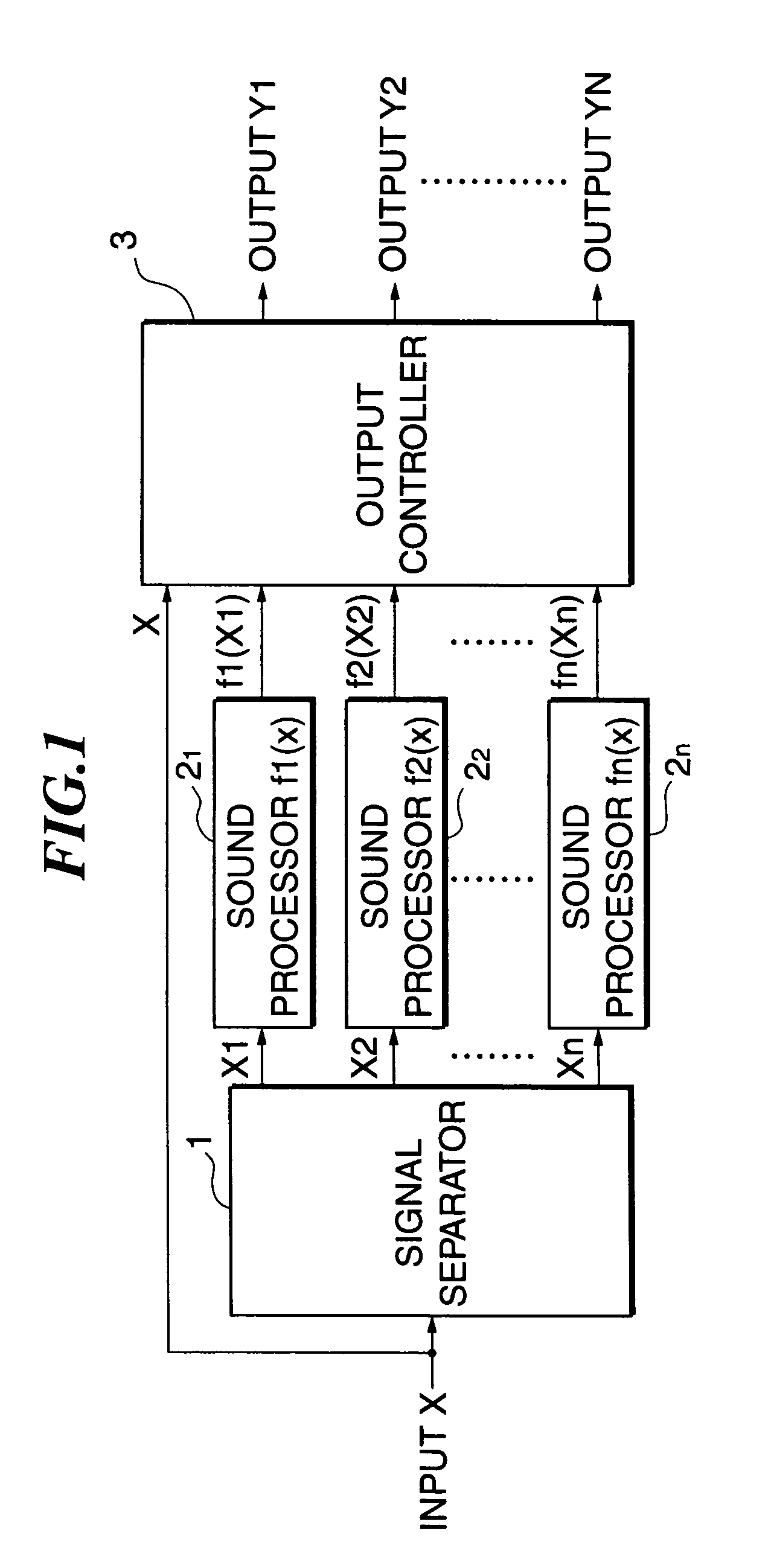
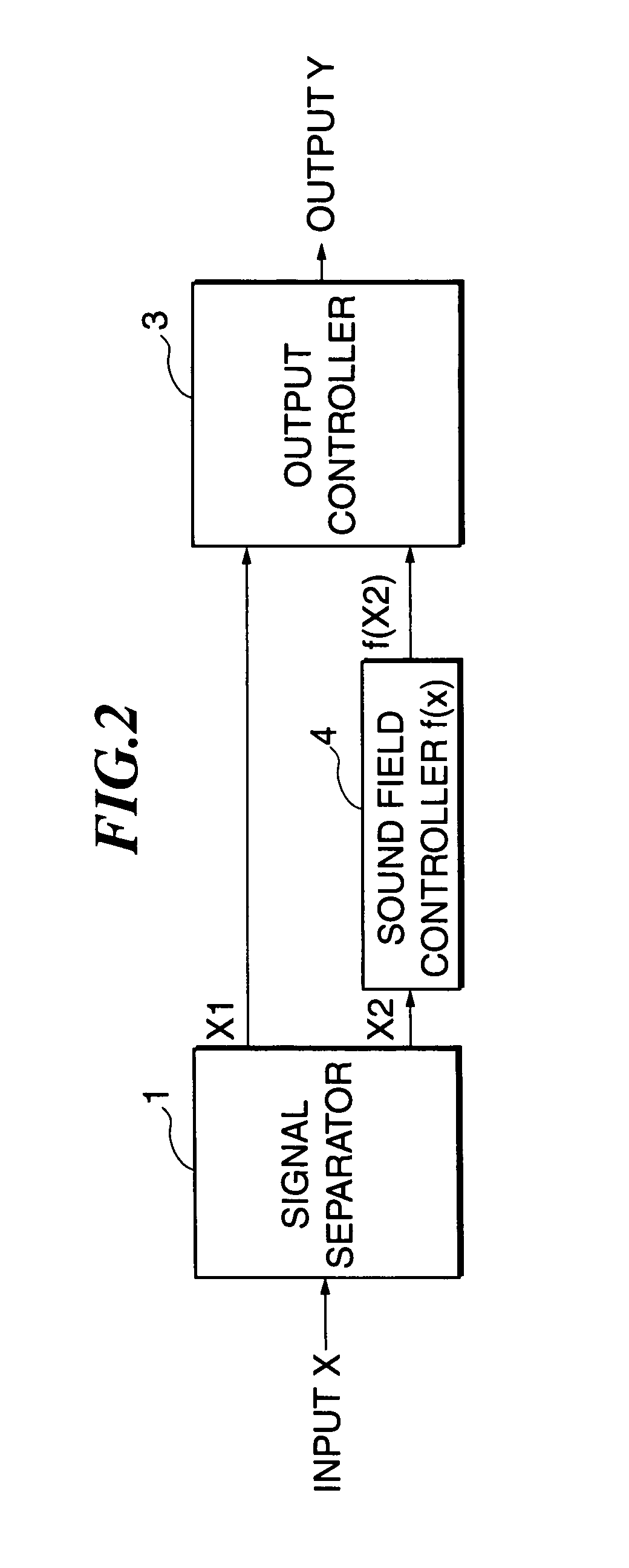
A sound processing method and apparatus are provided, which are capable of performing sound processing on input audio signals containing a plurality of signal components being different in desired sound processing conditions, in a manner that allows natural sound to be reproduced. An input audio signal of at least one system is separated into a plurality of separated signal components, and each signal component of at least part of the plurality of separated signal components is subjected to individual sound processing according to the signal component, and the plurality of separated signal components are outputted as at least one audio signal after each signal component of the at least part thereof is subjected to the individual sound processing. The plurality of separated signal components are synthesized into a synthesized audio signal, which is then outputted, or alternatively, the plurality of separated signal components are outputted separately as audio signals.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Electronic keyboard musical instrument
ActiveUS20070017353A1Sufficient volumeEasy qualityElectrophonic musical instrumentsStringed musical instrumentsMusical toneVibration control
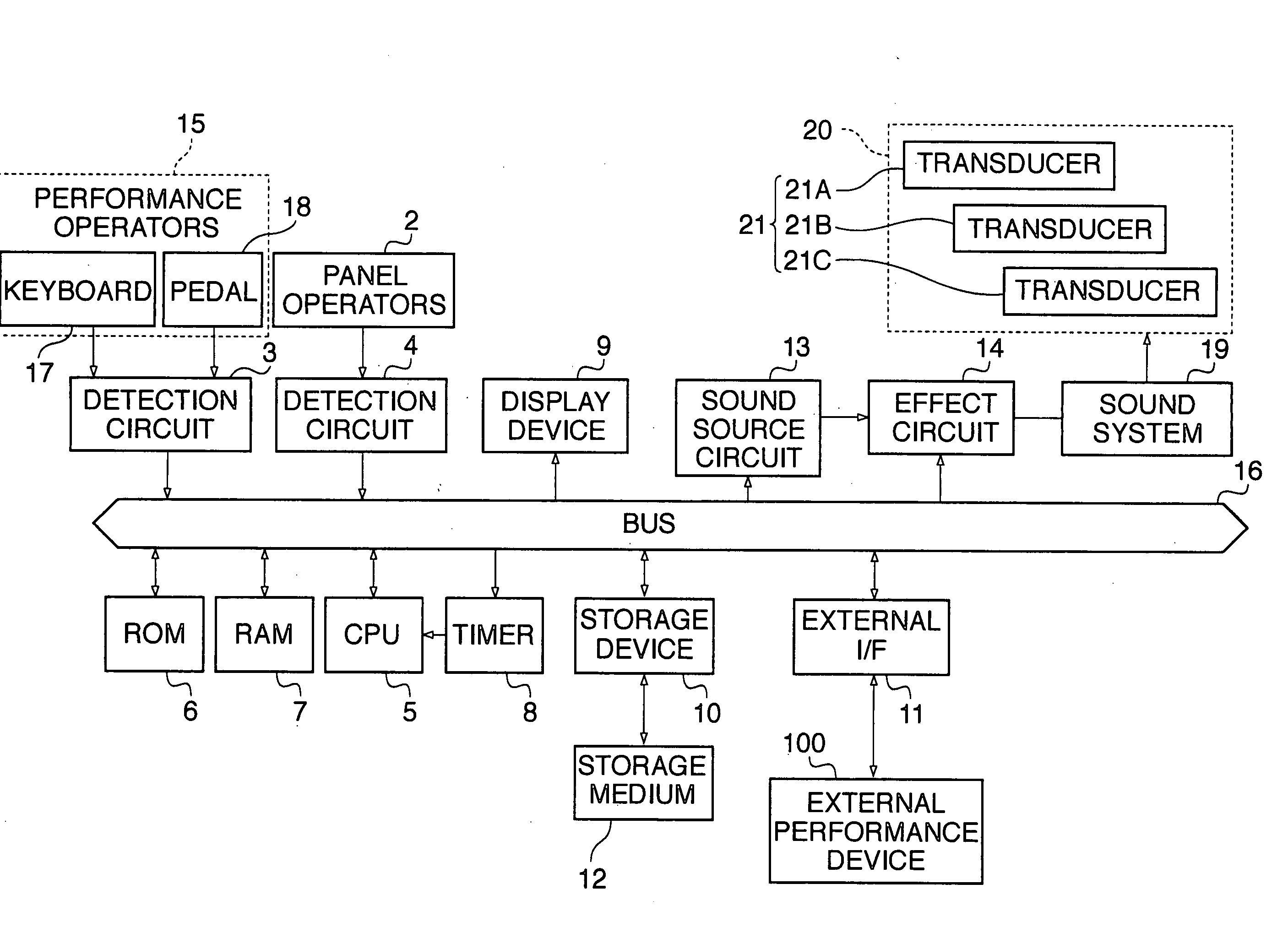
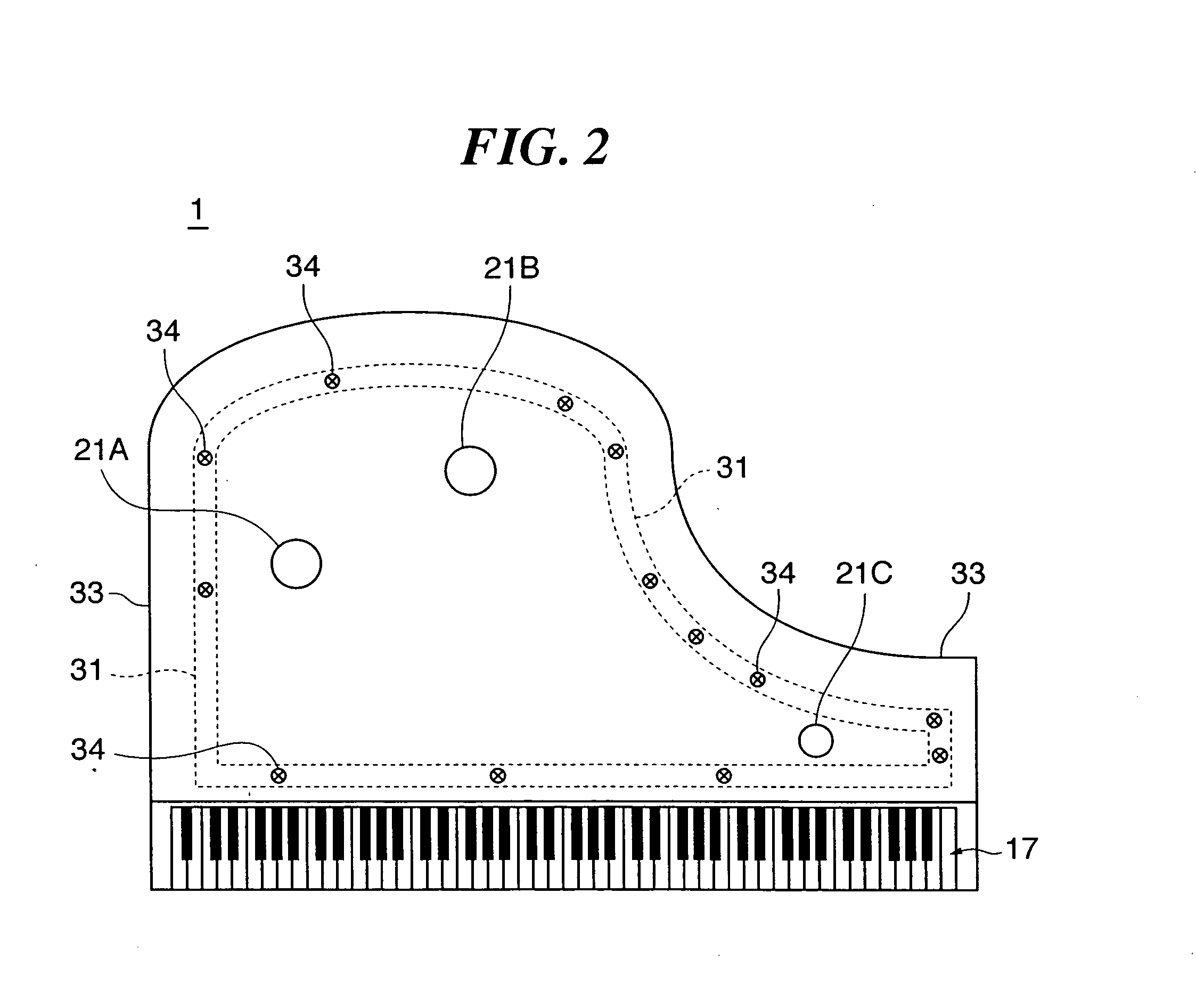
An electronic keyboard musical instrument capable of performing delicate sound board vibration control based on outputs generated individually for respective ones of transducers, thereby realizing production of natural sounds with sufficient volume, and an easy tone quality adjustment. A sound board is fixed to a frame, and the transducers are mounted to the sound board so as to be spaced from one another. In accordance with first and second performance signals generated in response to a key operation of a keyboard and a damper pedal operation, driving signals for the transducers are individually generated in consideration of characteristics and mounting positions of the transducers, and the driving signals are supplied to the transducers. The sound board is thereby caused to vibrate at a frequency varying according to a tone pitch, thus producing a musical tone and / or a damper tone.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Envelope-based amplitude mapping for cochlear implant stimulus
InactiveUS6996438B1Reduce in quantityHigh processing loadElectrotherapyArtificial respirationBandpass filteringWaveform shaping
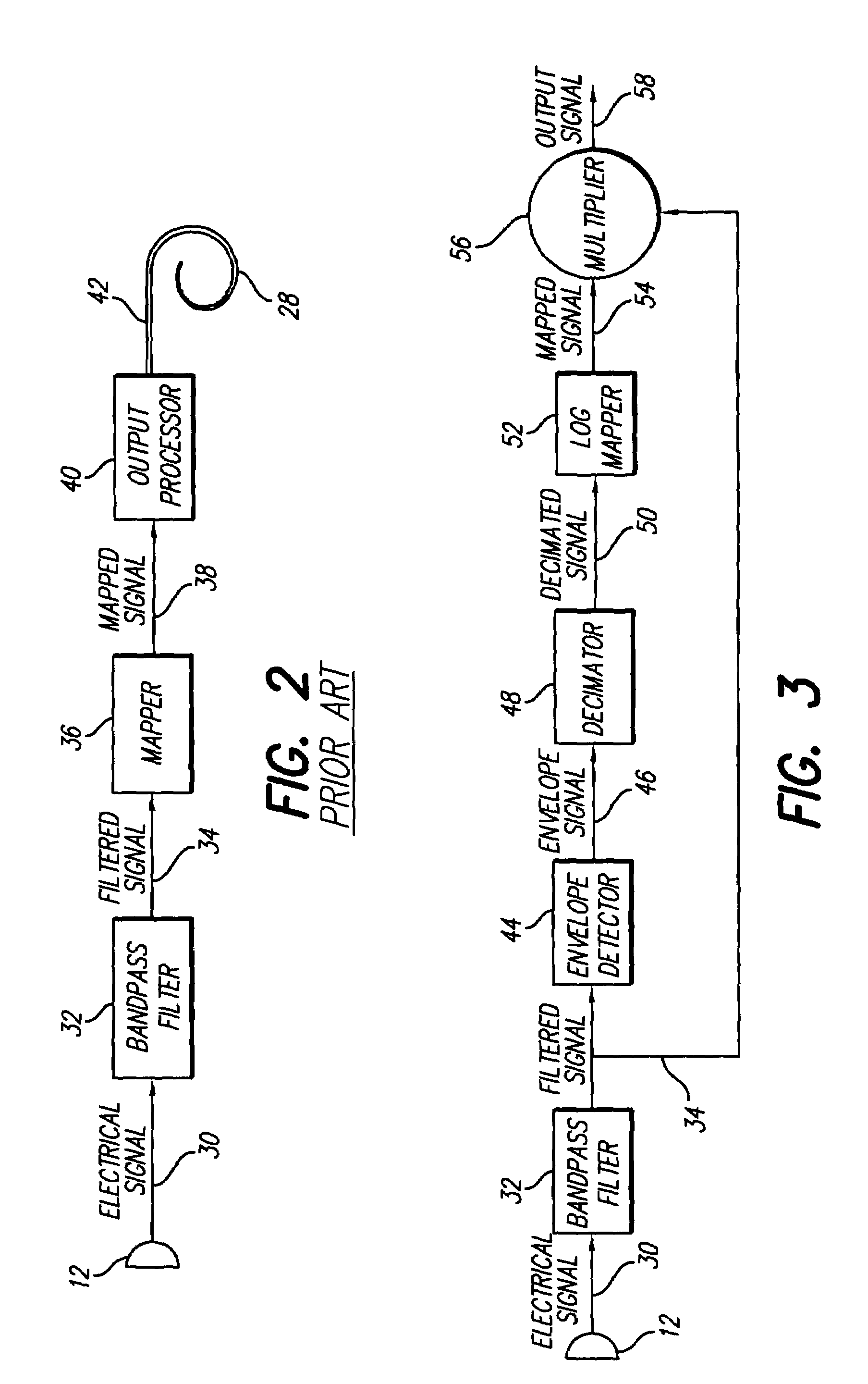
An envelope based amplitude mapping achieves the signal compression required to provide a natural sound level without the high processor loading or waveform alteration. In a preferred embodiment, the output of a family of parallel bandpass filters is processed by an envelope detector, followed by decimation. The resulting reduced data rate envelope is log mapped to produce a scaling factor for the original high data rate bandpass filter output sequence. The resulting scaled signal determines the current level for stimulation of the cochlea for each frequency band, which stimulation achieves a log mapping of the sound amplitude effect similar to natural hearing, while reducing processor load, and preserving waveform shape.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
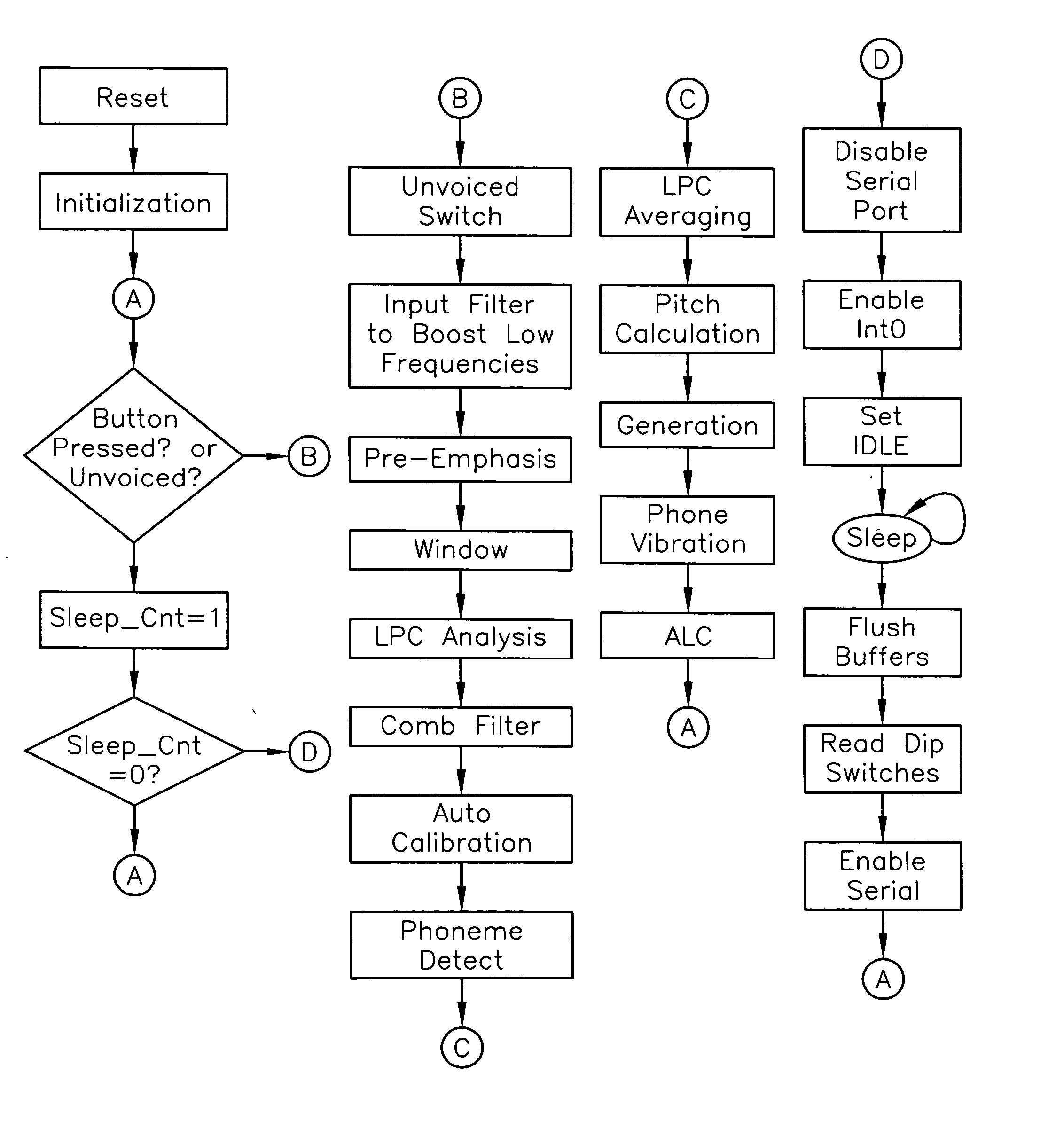
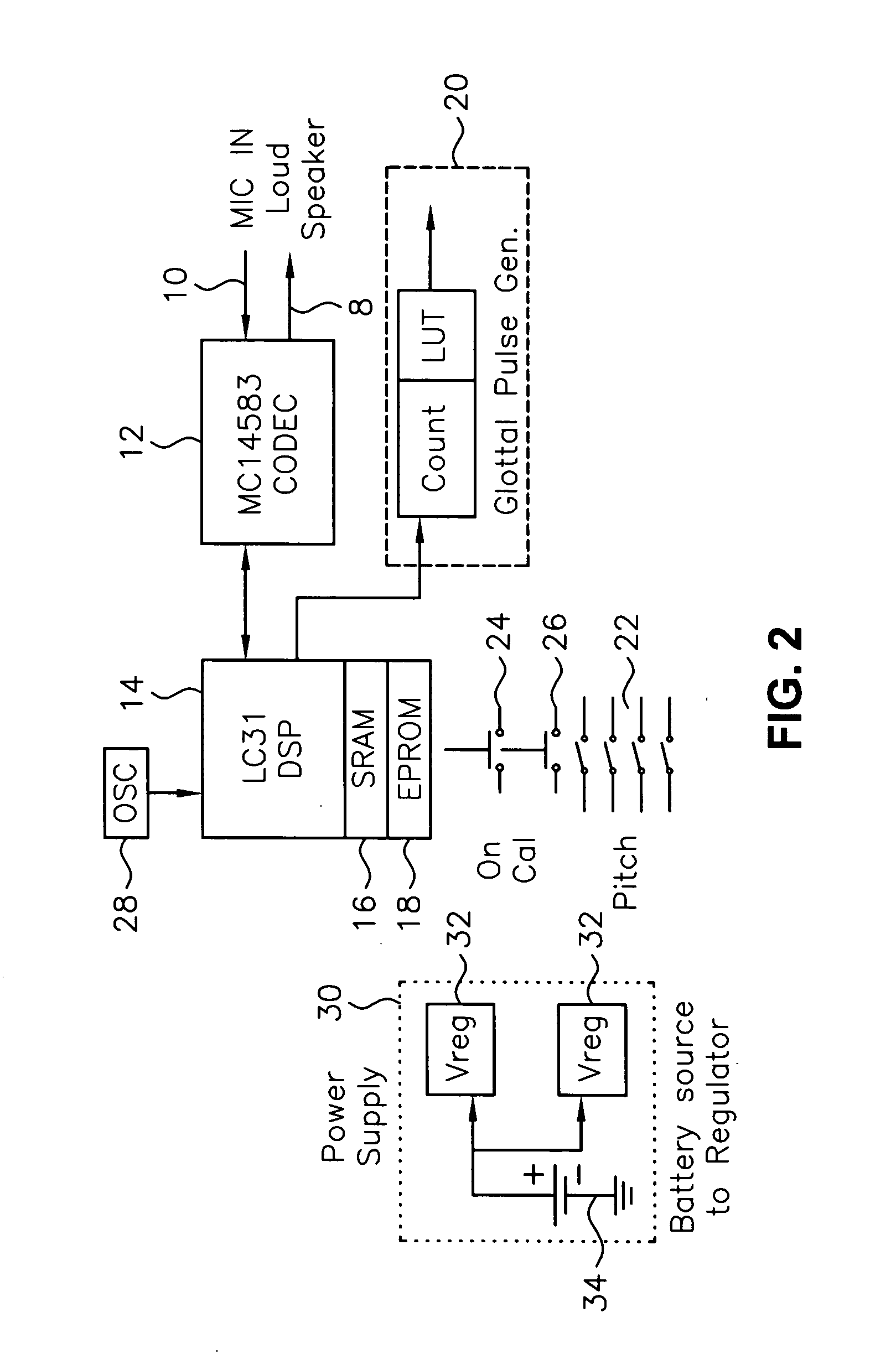
Method and means for creating prosody in speech regeneration for laryngectomees
InactiveUS20050049856A1Improve naturalnessAssist in intelligibilitySpeech synthesisFrequency spectrumGlottis
A device and a method to be used by laryngeally impaired people to improve the naturalness of their speech. An artificial sound creating mechanism which forms a simulated glottal pulse in the vocal tract is utilized. An artificial glottal pulse is compared with the natural spectrum and an inverse filter is generated to provide an output signal which would better reproduce natural sound. A digital signal processor introduces a variation of pitch based on an algorithm developed for this purpose; i.e. creating prosody. The algorithm uses primarily the relative amplitude of the speech signal and the rise and fall rates of the amplitude as a basis for setting the frequency of the speech. The invention also clarifies speech of laryngectomees by sensing the presence of consonants in the speech and appropriately amplifying them with respect to the vowel sounds.
Owner:BARAFF DAVID R
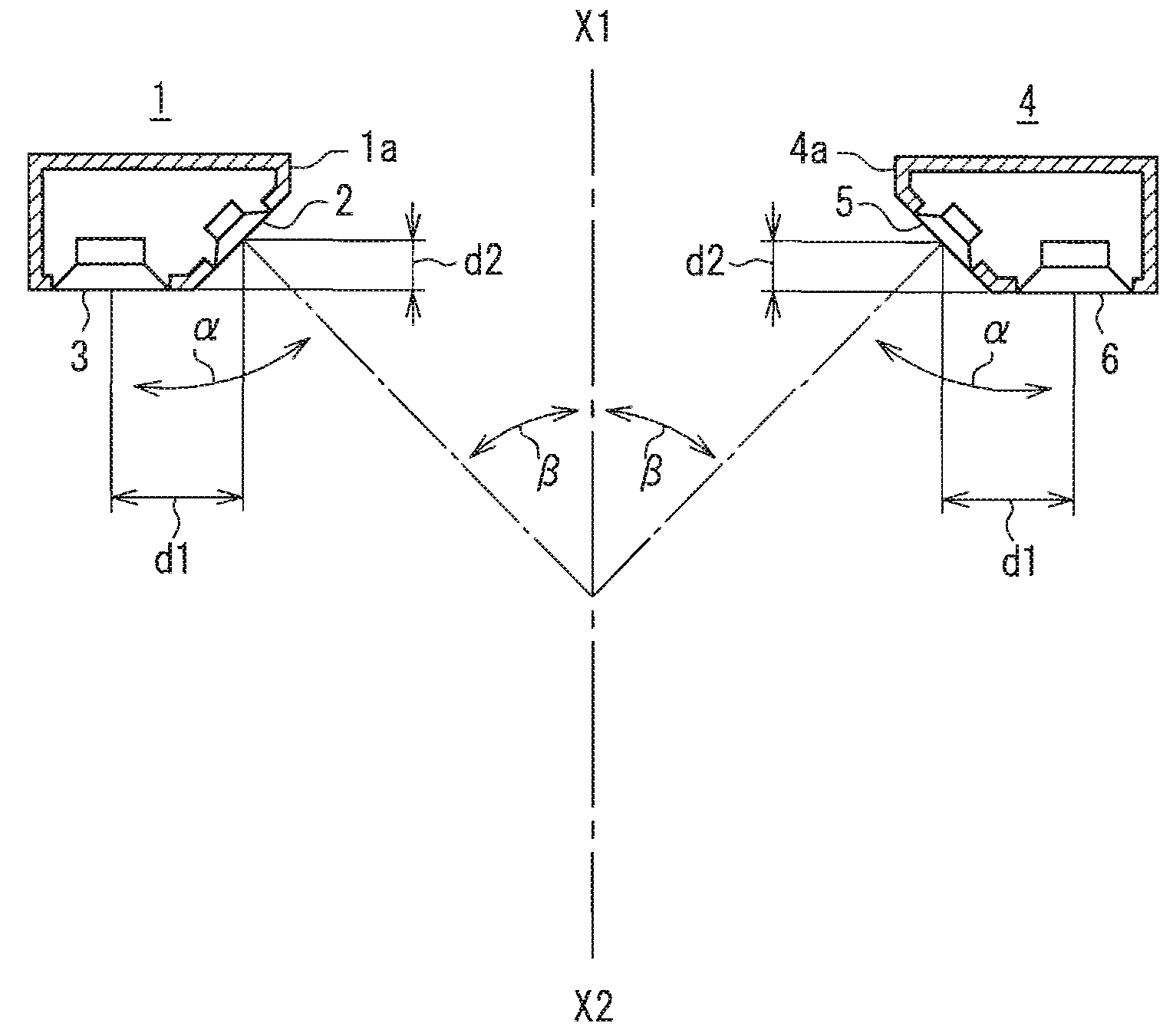
Speaker device
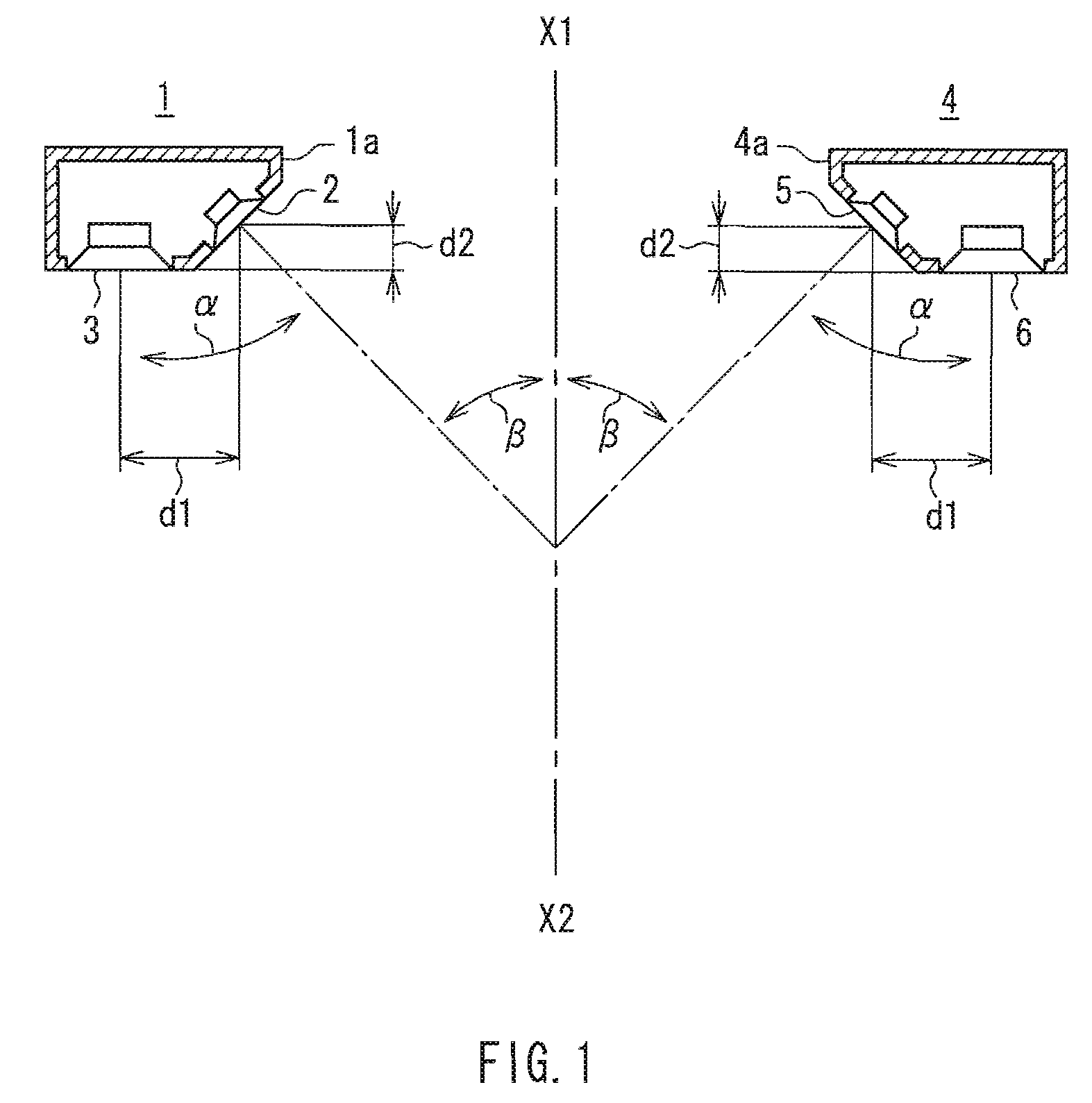
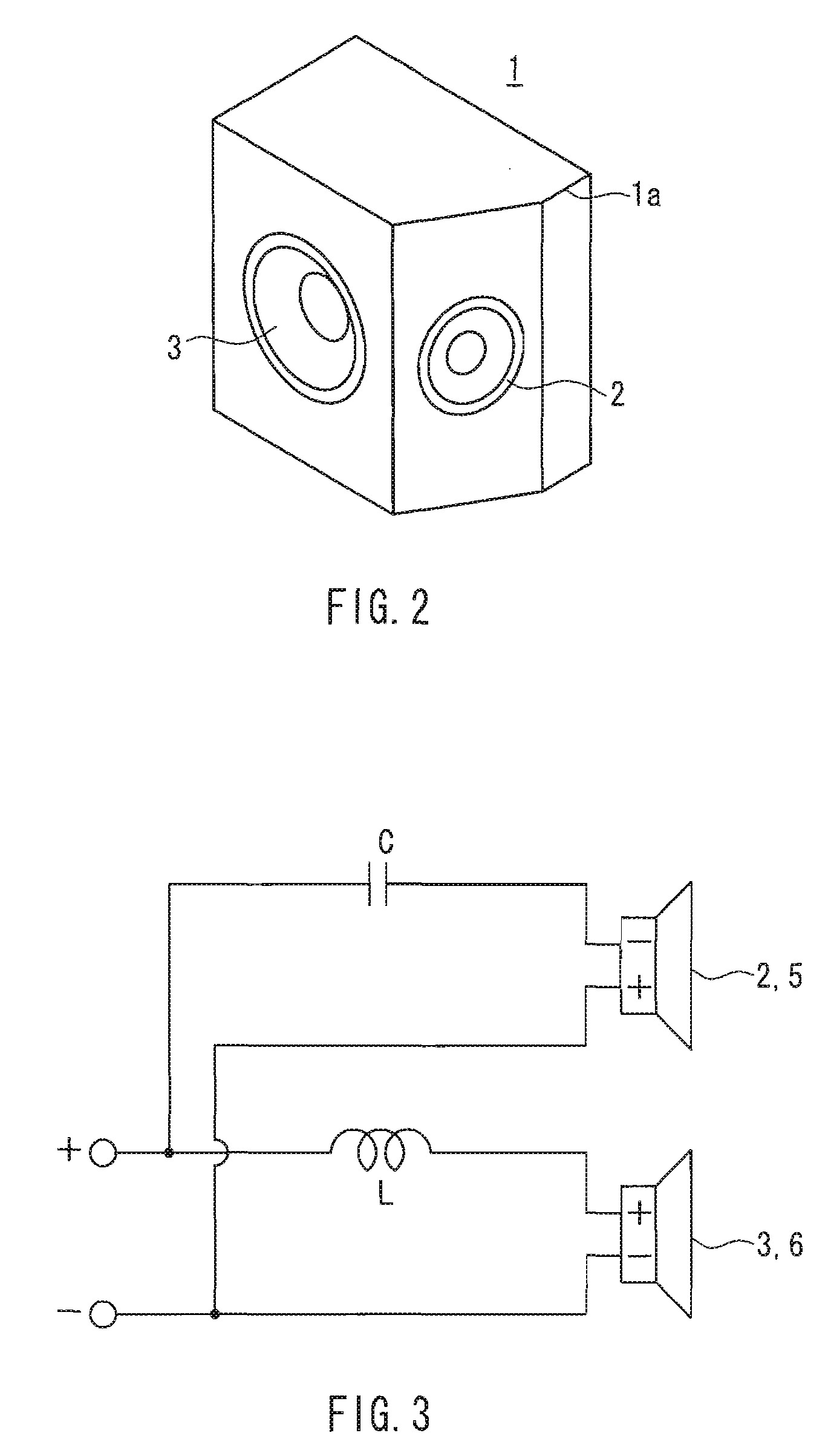
InactiveUS20090279721A1Good effectReduce sound pressureLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSound imagePhase difference
A speaker device includes first speaker units 2 and 5 and second speaker units 3 and 6 that are arranged symmetrically as viewed from a listening center axis X1-X2. The first speaker units 2 and 5 emit sounds in inward directions and reproduces at least the mid-range and above, and the second speaker units 3 and 6 emit sounds in a front direction and attenuates the treble range. With respect to a listening position in a front direction of one of the speaker systems 1 and 4, a sound arriving to the listening position from the first speaker unit of the speaker system located closer to the listening position, and a sound arriving thereto from the second speaker unit of the same speaker system, are destructive to each other in the mid-range due to a phase difference, whereby a sound pressure in the mid-range arriving from the speaker system located closer to the listening position is attenuated more, as compared with a sound pressure in the mid-range arriving from the speaker system located farther from the listening position. It is possible to achieve an excellent effect of expanding a listening position range for obtaining the center sound image localization, the natural sound quality without sense of discomfort, the large sound pressure reproduction, and the downsizing.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Wild game call
A wild game call has a single inlet passage into which a user blows to generate sounds that simulate the natural sounds produced by the particular animal being called or attracted. The call includes a splitter that splits the single air inlet passage into a plurality of outlet passages. The sound either is generated in the single air passage or passes into the single air passage from the user and is directed into the plurality of outlet passages to produce the final output sound from the call. The plurality of outlet passages can be configured to produce subtle differences in the sound passing through a passage to provide a combination of sounds more closely simulating the natural animal sound than can be produced in only a single outlet passage. Various sound chamber can be added to the outlet passages to modify the sound emanating from that passage in a desired manner.
Owner:TOG IP LLC
Electronic keyboard musical instrument
ActiveUS7432428B2Sufficient volumeEasy qualityElectrophonic musical instrumentsStringed musical instrumentsVibration controlOn board
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Sound-based method and apparatus for generating AR content and storage medium
ActiveCN109065055ASmart serviceSmart experienceSound input/outputSpeech recognitionSound source locationSound sources
The invention provides a sound-based method and apparatus for generating an AR content and a storage medium. The method comprises: step 11, acquiring real-time voice data in a current AR environment;S131, determining whether the real-time voice data include a speaker; and if so, converting a speech content of the speaker in the real-time voice data into a text and extracting key semantic information; S132, extracting an artificial non-speaking sound or natural sound in the real-time voice data; S133, locating sound source locations of the speaker and the artificial non-speaking voice or natural sound; S15, carrying out scene matching based on the key semantic information and artificial non-speaking voice or natural sound; and S17, generating an AR content according to the key semantic information, the sound source locations, the scene or a real scene image in the AR environment and displaying the AR content. With the method provided by the invention, the AR content can be dynamicallygenerated based on the input voice and the AR intelligent display of the auditory information can be realized; and thus the convenient and intelligent services and experience can be provided for users.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CHINA R&D CENT +1
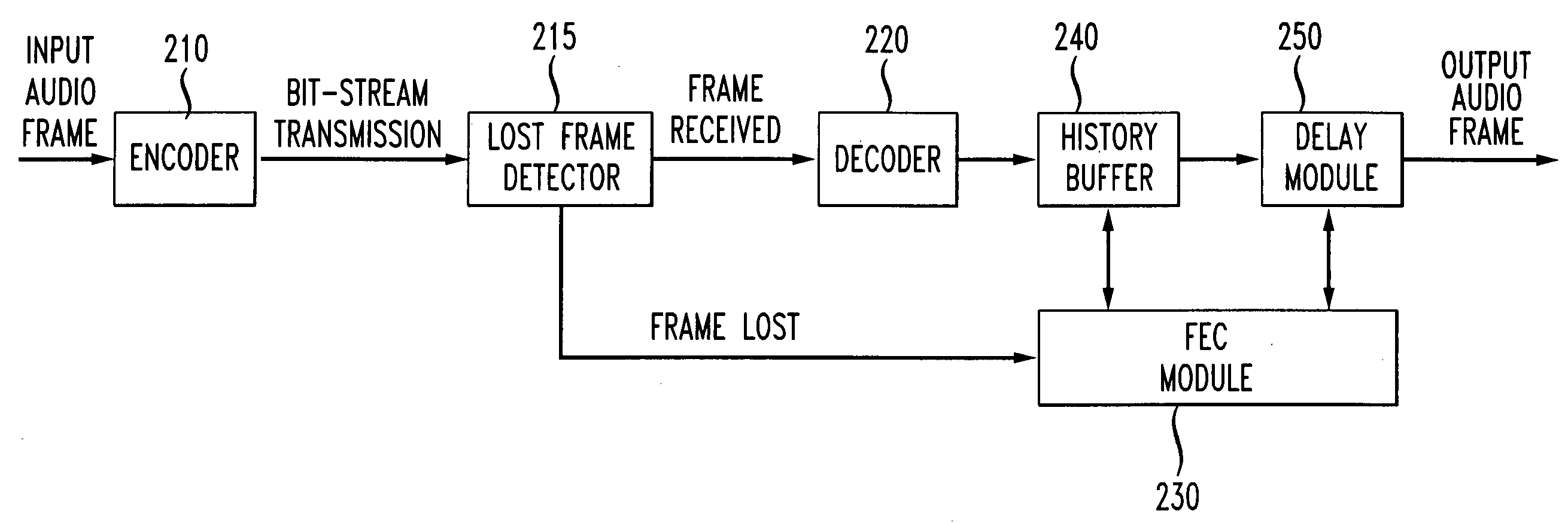
Method and apparatus for performing packet loss or frame erasure concealment
The invention concerns a method and apparatus for performing packet loss or Frame Erasure Concealment (FEC) for a speech coder that does not have a built-in or standard FEC process. A receiver with a decoder receives encoded frames of compressed speech information transmitted from an encoder. A lost frame detector at the receiver determines if an encoded frame has been lost or corrupted in transmission, or erased. If the encoded frame is not erased, the encoded frame is decoded by a decoder and a temporary memory is updated with the decoder's output. A predetermined delay period is applied and the audio frame is then output. If the lost frame detector determines that the encoded frame is erased, a FEC module applies a frame concealment process to the signal. The FEC processing produces natural sounding synthetic speech for the erased frames.
Owner:AT & T INTPROP II LP
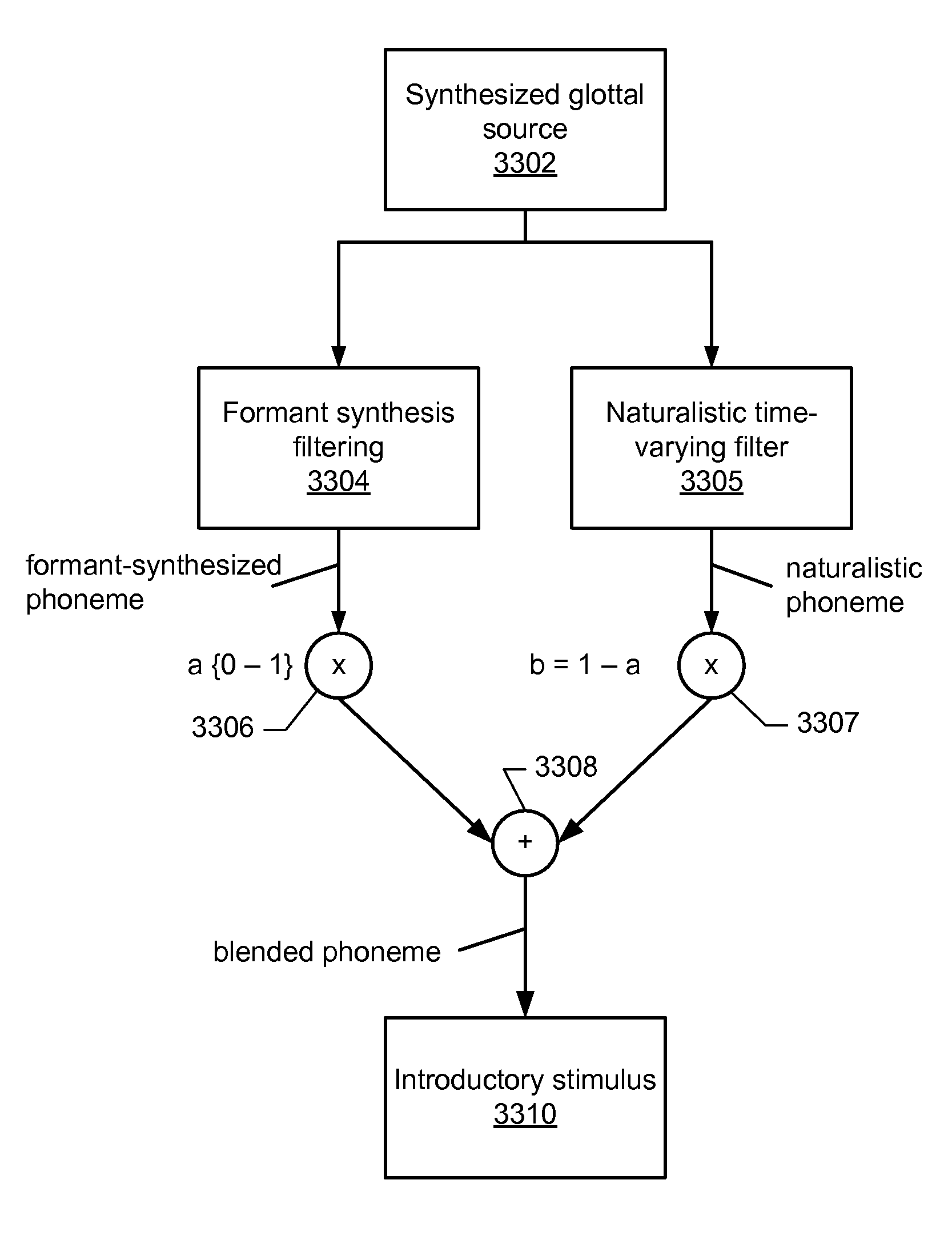
Method for modulating listener attention toward synthetic formant transition cues in speech stimuli for training
ActiveUS8210851B2Increase salienceImprove accuracyReadingElectrical appliancesSpeech soundNormal speech
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult, such as processing the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, stretching the portions, and / or separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech. Introductory phonemes may each include a blend of a formant-synthesized phoneme and an acoustically naturalistic phoneme that substantially replicates the spectro-temporal aspects of a naturally produced phoneme, with the blends progressing from substantially natural-sounding to substantially formant-synthesized.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
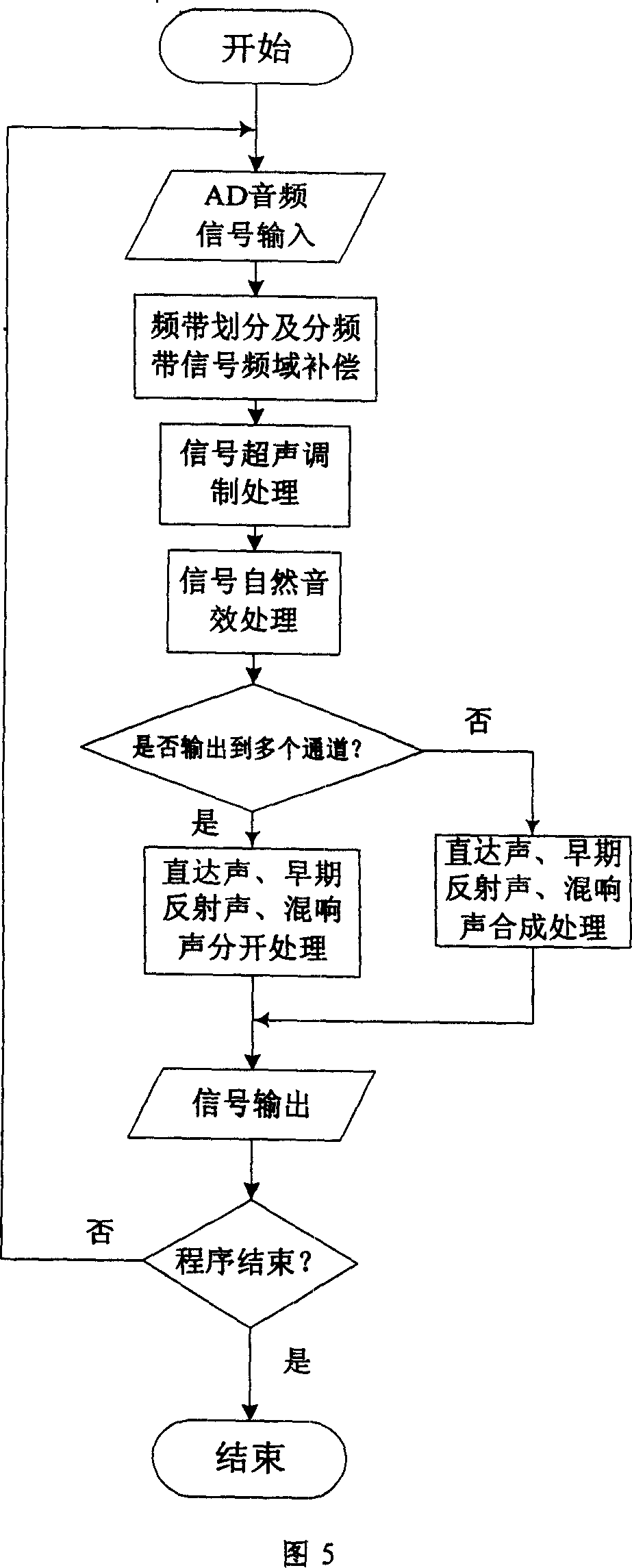
Full band natural sound effect audio directional loudspeaker
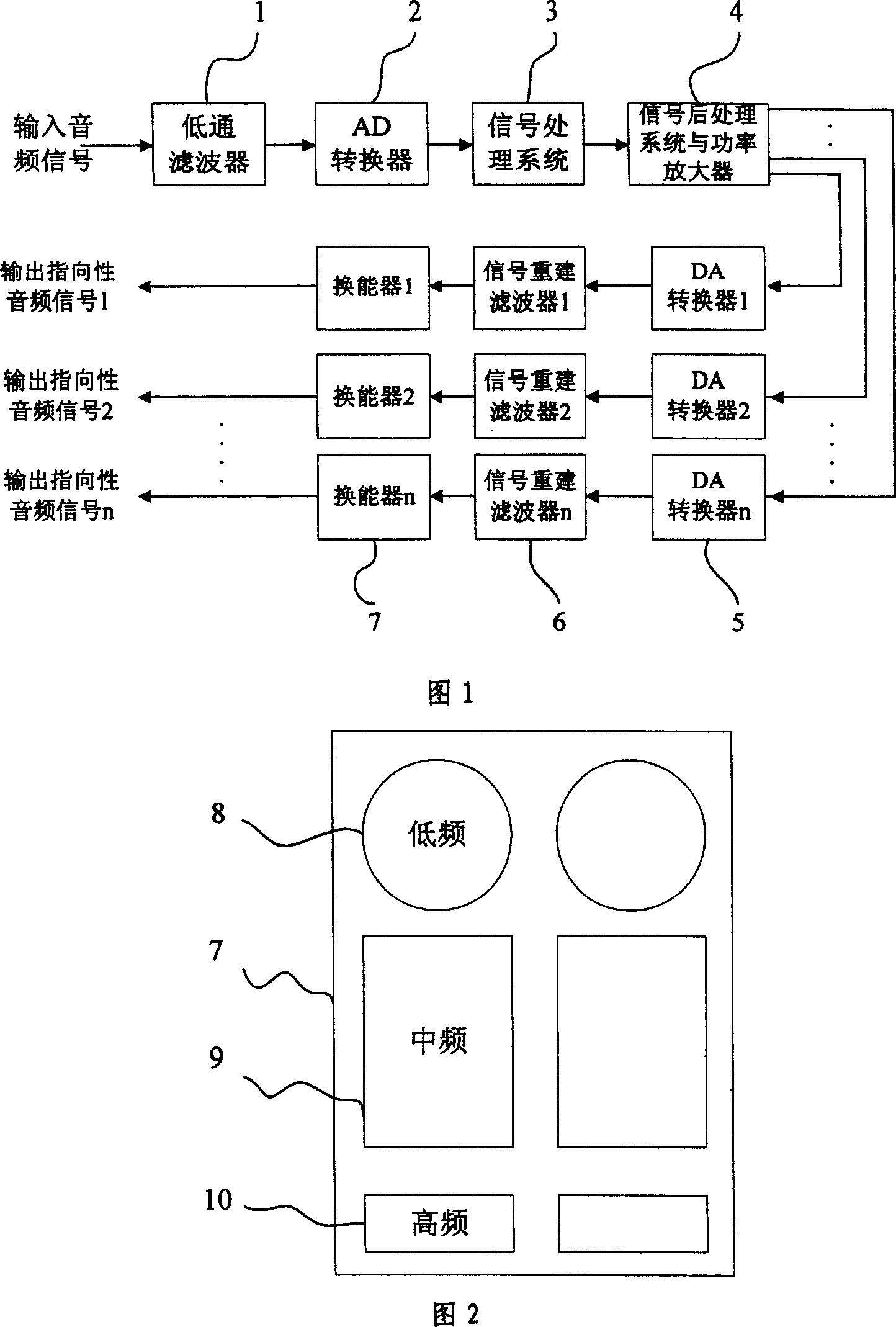
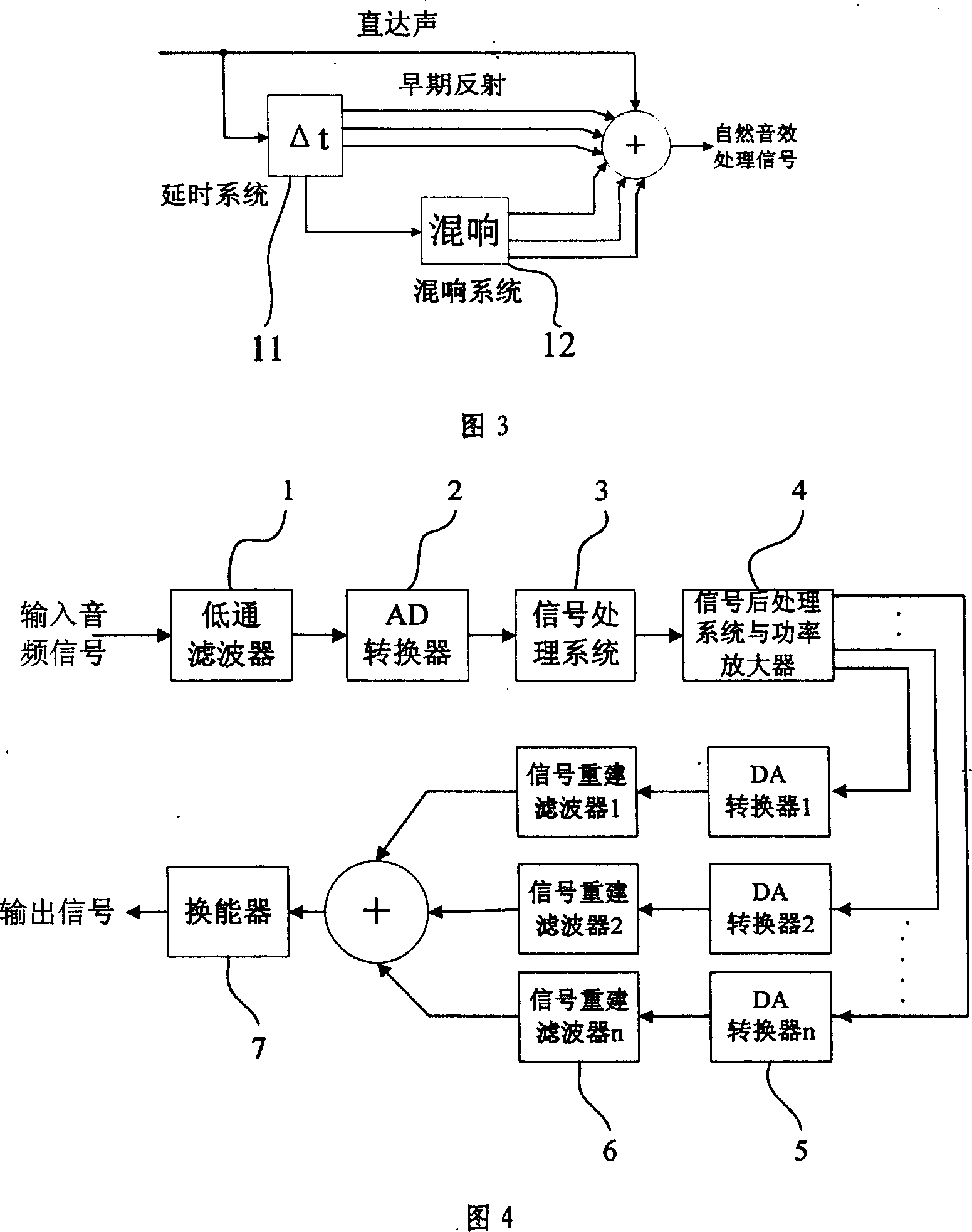
ActiveCN101014209AFlexible implementation of full-band audio outputWith natural sound effectsFrequency response correctionProcess systemsLow-pass filter
The invention relates to one whole frequency band natural audio direction microphone, which comprises low pass filter, AD converter, signal process system, signal back process system and power amplifier, DA conversion set, re-set filter sets and energy conversion, wherein, the above signal process system comprises more than three frequency division digital filter and more than three filters with inclination and supersonic modulation. The invention can compensate audio signals in whole frequency band range for natural audio effect program to realize whole frequency output.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for simulating a 3D sound environment
InactiveUS7391876B2High simulationHeadphones for stereophonic communicationTwo-channel systemsTime domainVocal tract
The invention provides a method for simulating a 3D sound environment in an audio system using an at least two-channel reproduction device, the method including generating first and second pseudo head-related transfer function (HRTF) data, first using at least one speaker and then using headphones; dividing the first and second frequency representation of the data or using a deconvolution operator on the time domain representation of the first and second data, or subtracting the cepstrum representation of the first and second data, and using the results of the division or subtraction to prepare filters having an impulse response operable to initiate natural sounds of a remote speaker for preparing at least two filters connectable to the system in the audio path from an audio source to sound reproduction devices to be used by a listener.
Owner:BE4
Electroacoustic transducer and ear speaker device
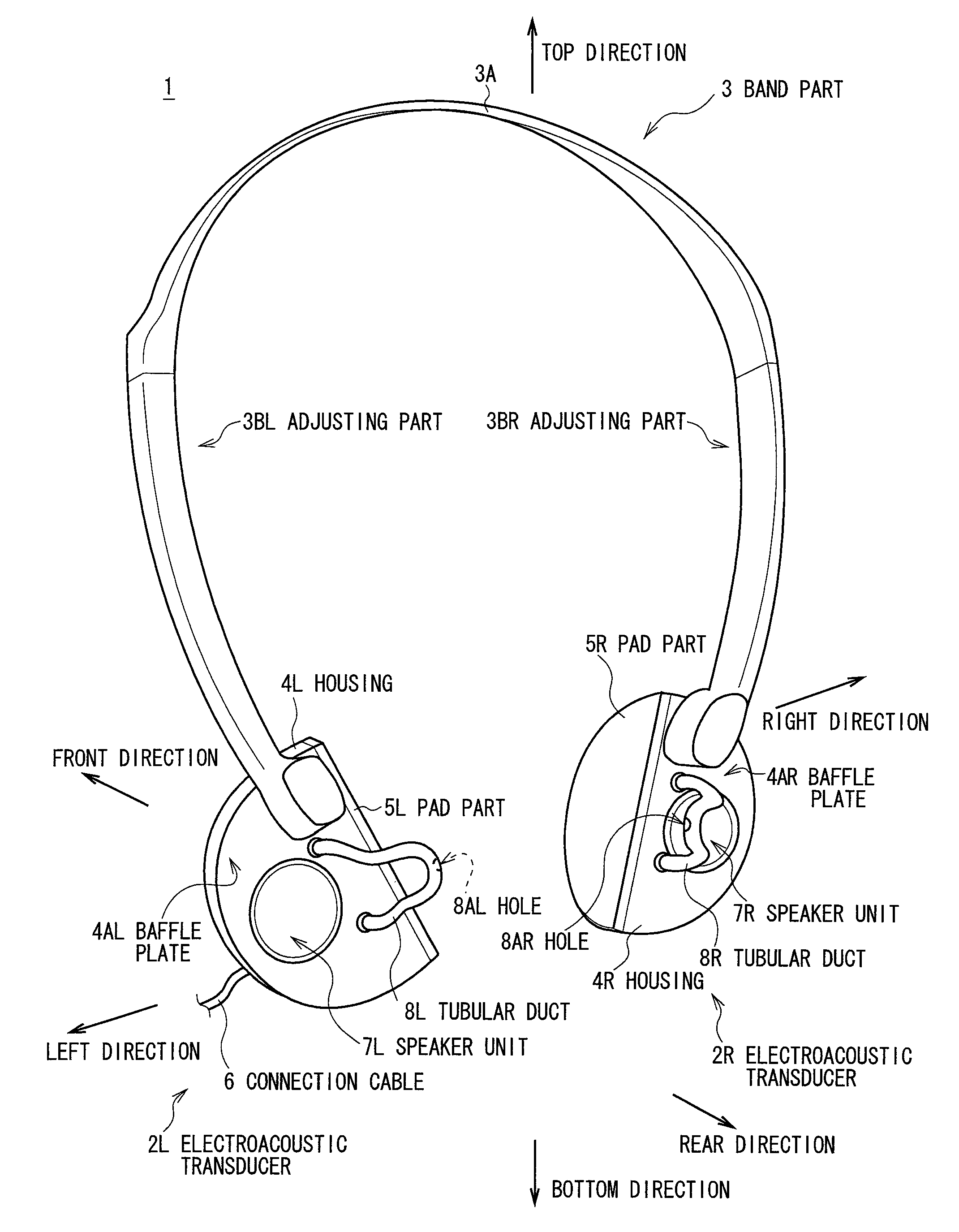
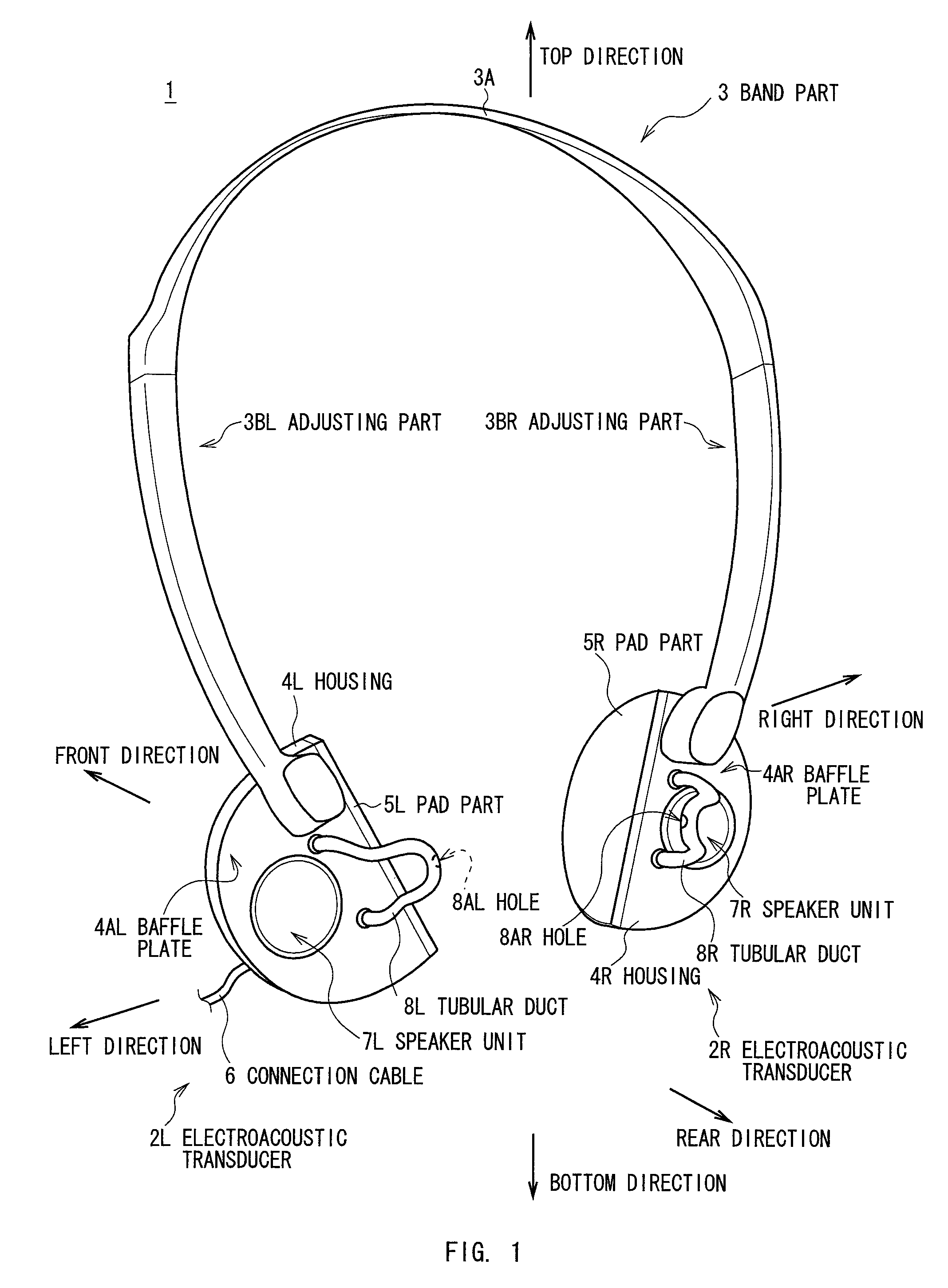
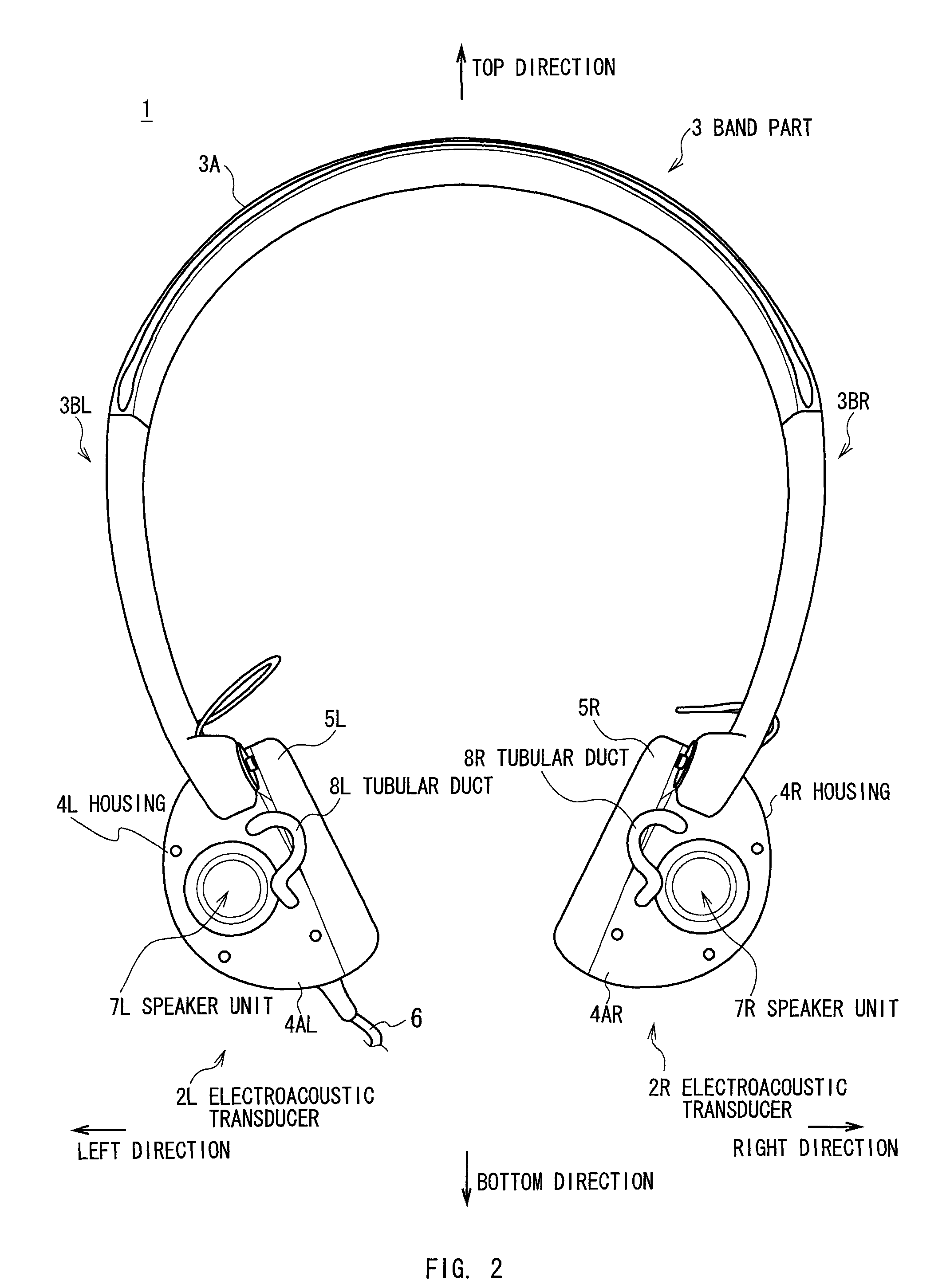
InactiveUS8213632B2Quality improvementIncrease the sound pressure levelHeadphones for stereophonic communicationBone conduction transducer hearing devicesTransducerExternal Acoustic Meatus
A reproduced sound of high quality is allowed to be listened to by a listener while natural sound image localization is provided. By providing a housing 4L having internal space mounted at a predetermined position of the head of the listener, a speaker unit 7L mounted on one surface of the housing 4L and positioned away from an entrance of an external acoustic meatus of the listener for a predetermined distance when the housing 4L is mounted on the head 100 of the listener, and a tubular duct 8L extended so as to allow a sound generated by the housing 4L to reach the vicinity of the entrance of the external acoustic meatus of the listener, the sound generated by the housing 4L can be directly reached to an eardrum 103L in the inside of the external acoustic meatus from the vicinity of the entrance of the external acoustic meatus of the listener via a tubular duct 8L. In this manner, a sound at an sufficient level can be listened to by the listener while the natural sound image localization is provided as an open type.
Owner:SONY CORP
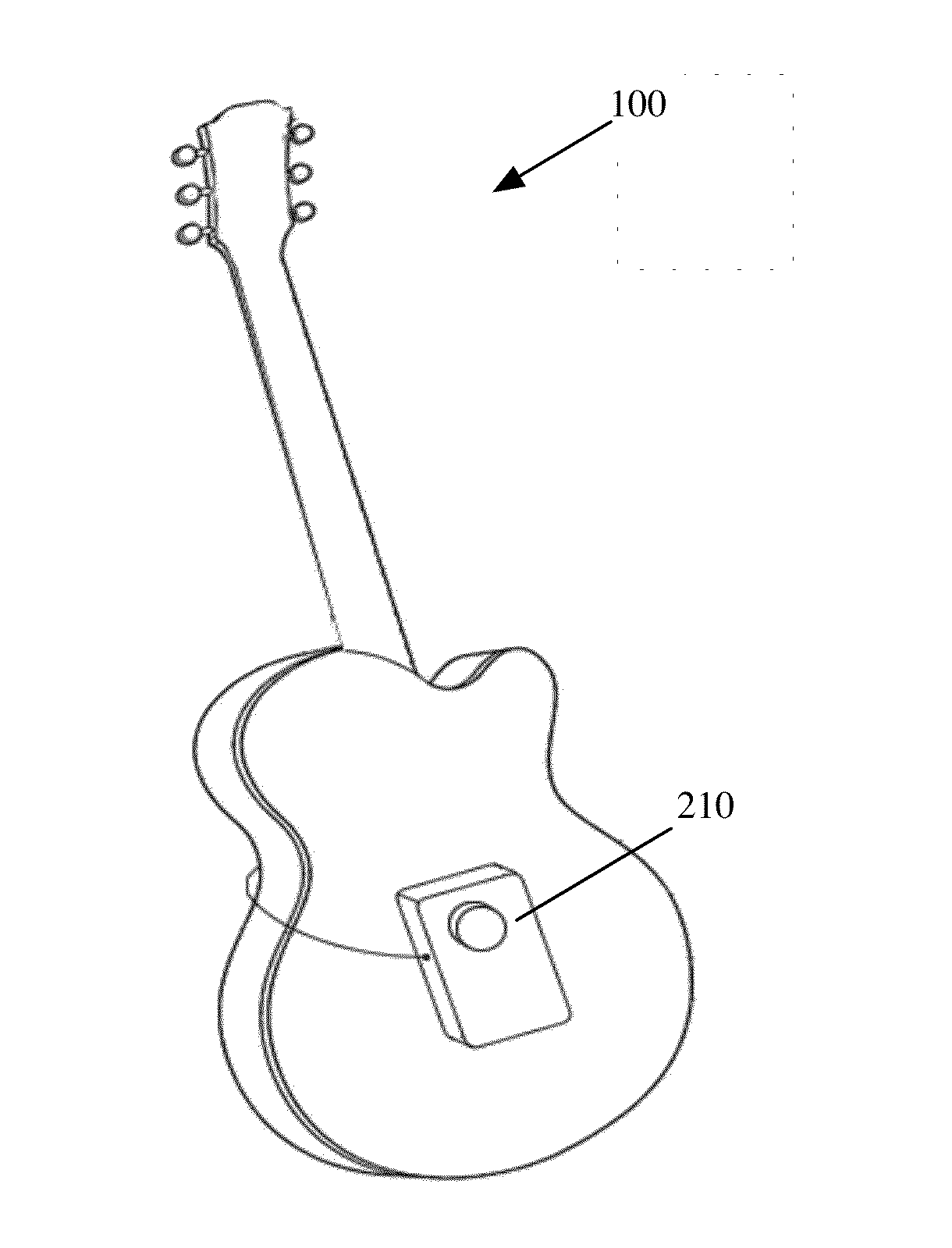
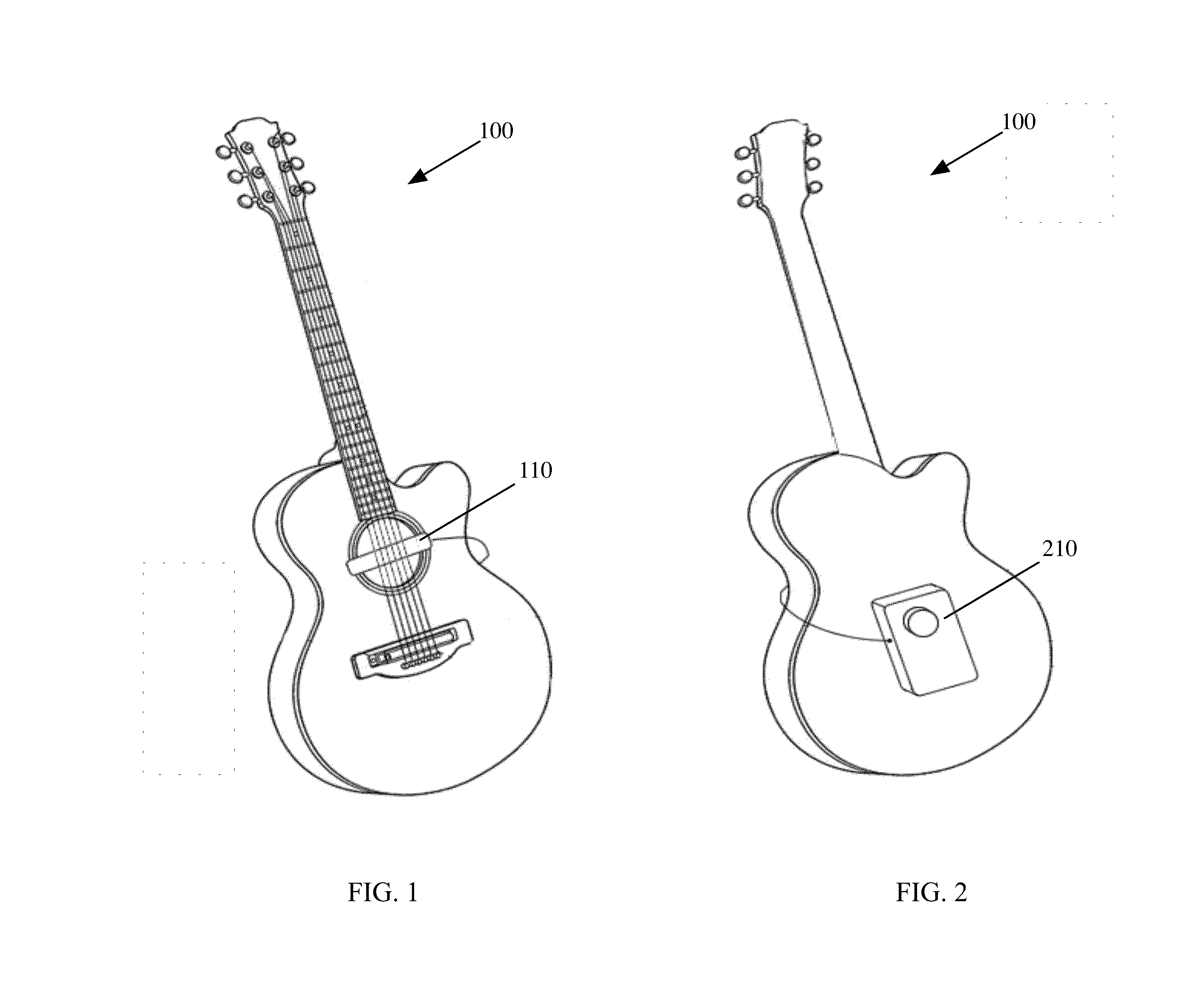
System and method for sound augmentation of acoustic musical instruments
ActiveUS20140224099A1Improve soundImprove sound outputElectrophonic musical instrumentsGNSS augmentationEngineering
A sound capture device is affixed to an acoustic instrument to capture the natural sound output of the instrument. The captured sound signal is routed to an electronic sound augmentation system that is configured to augment the captured sound with spatial sound effects such as reverb, echo, delay, etc. The processed and augmented sound is then reproduced via a vibrating driver that has been affixed to the body of the acoustic instrument. This creates a situation where the body of the musical instrument, responding to a series of vibrations produced by the vibrating driver, acts as a speaker component, reproducing a rich augmented sound output that comprises the sum of the sound produced by the original sound production capabilities of the acoustical instrument plus the added augmented or enhanced sound effects.
Owner:WEBMAN OFER
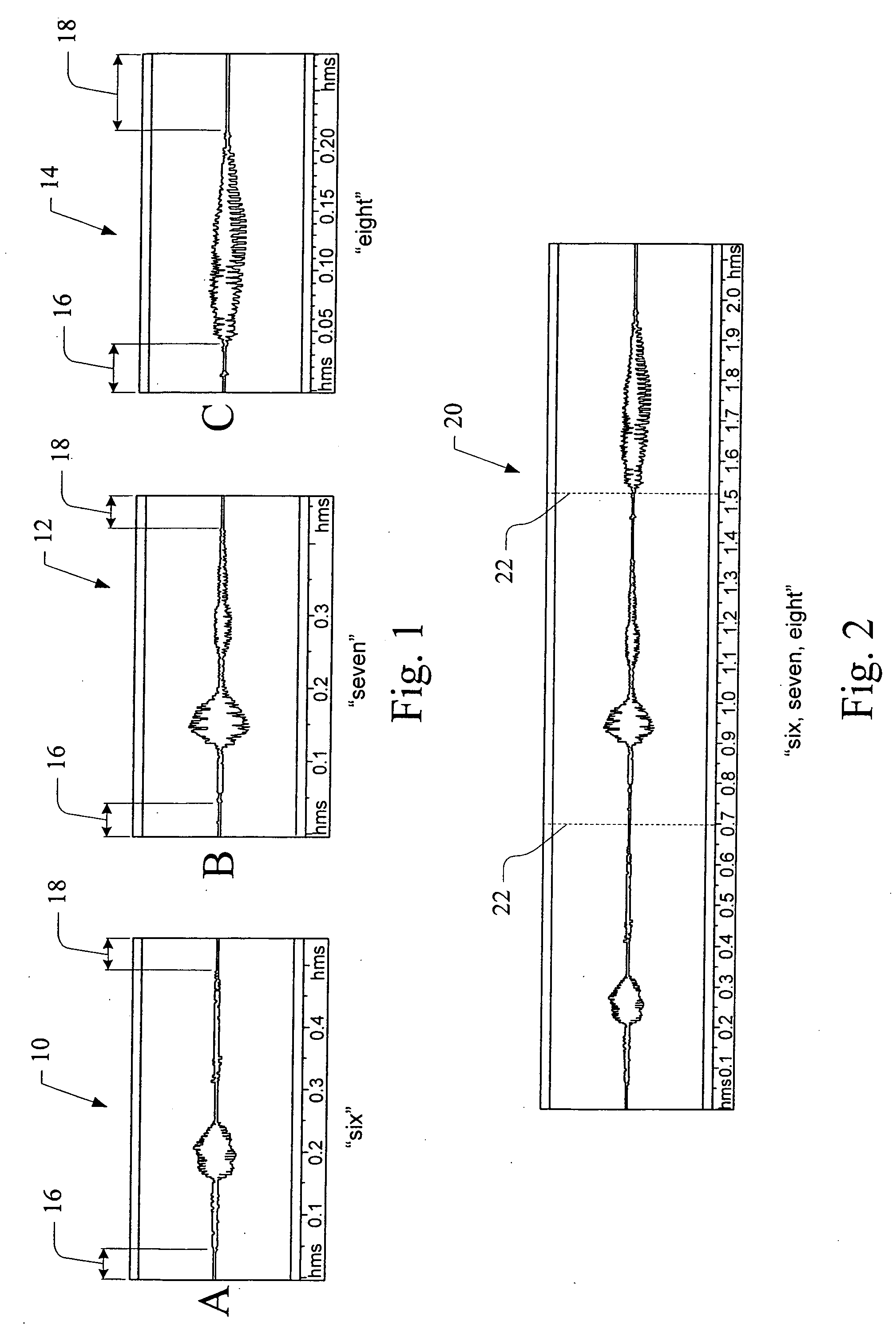
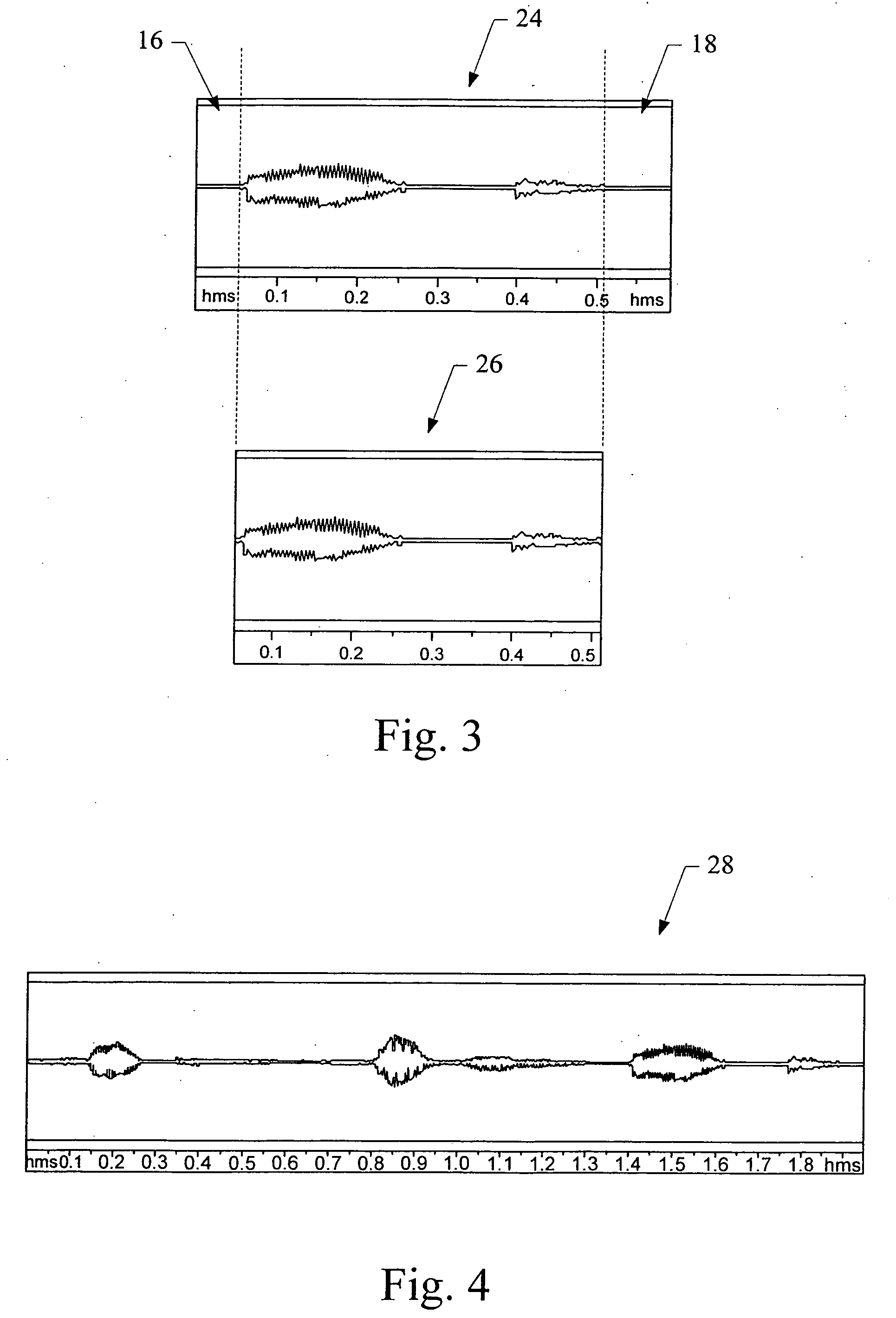
Dynamic real-time cross-fading of voice prompts
ActiveUS20060271372A1Shorten the length of timeElectronic editing digitised analogue information signalsAutomatic exchangesEngineeringSpeech sound
A system and method are provided for creating shorter more natural sounding voice messages and prompts from a plurality of pre-recorded sound segments, the prerecorded sound segments are dynamically cross faded in order to produce a more natural blended sound, various cross fade parameters such as the fade length and the shape of the cross fade amplitude envelopes are determined based on characteristics of the various sound segments being combined.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
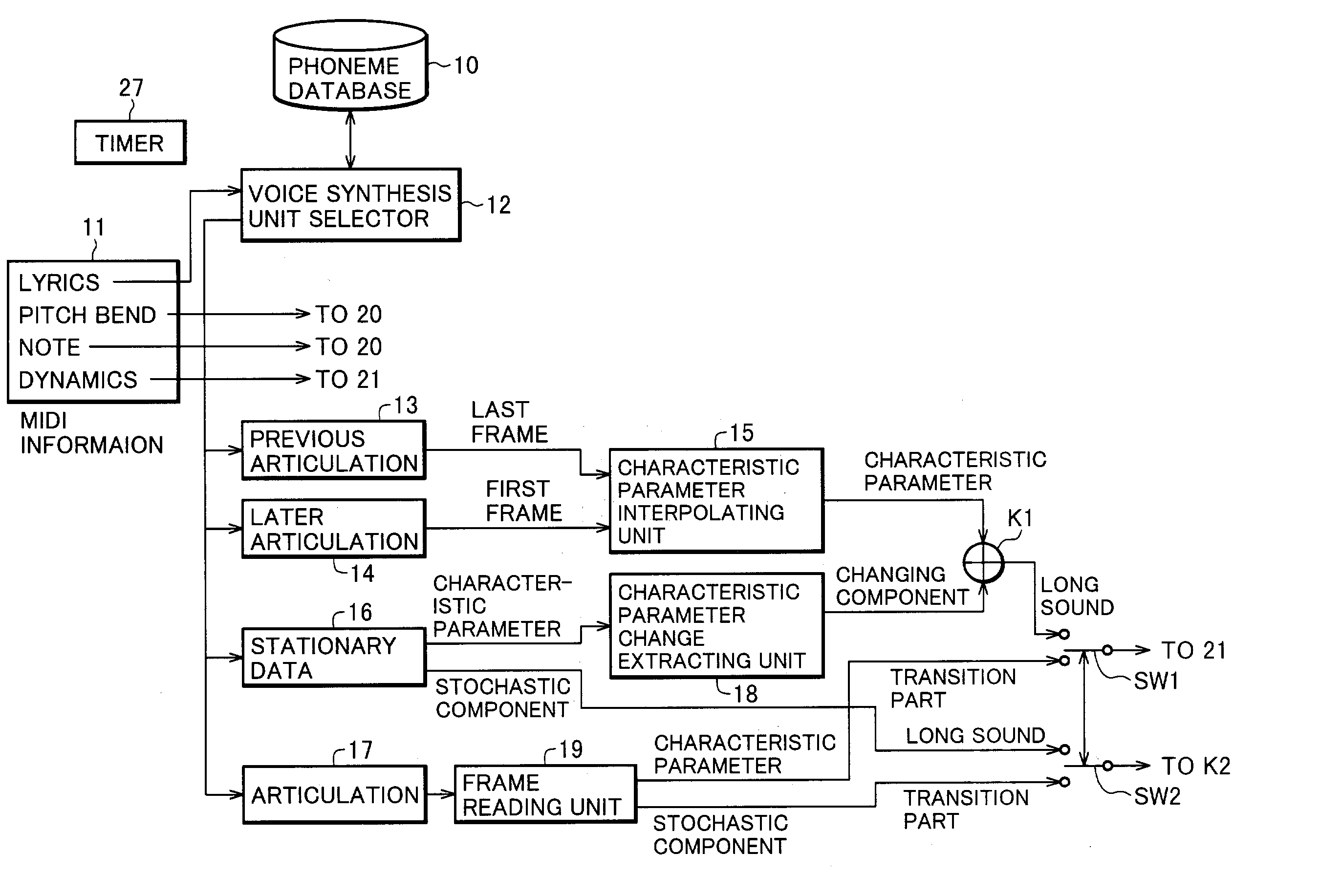
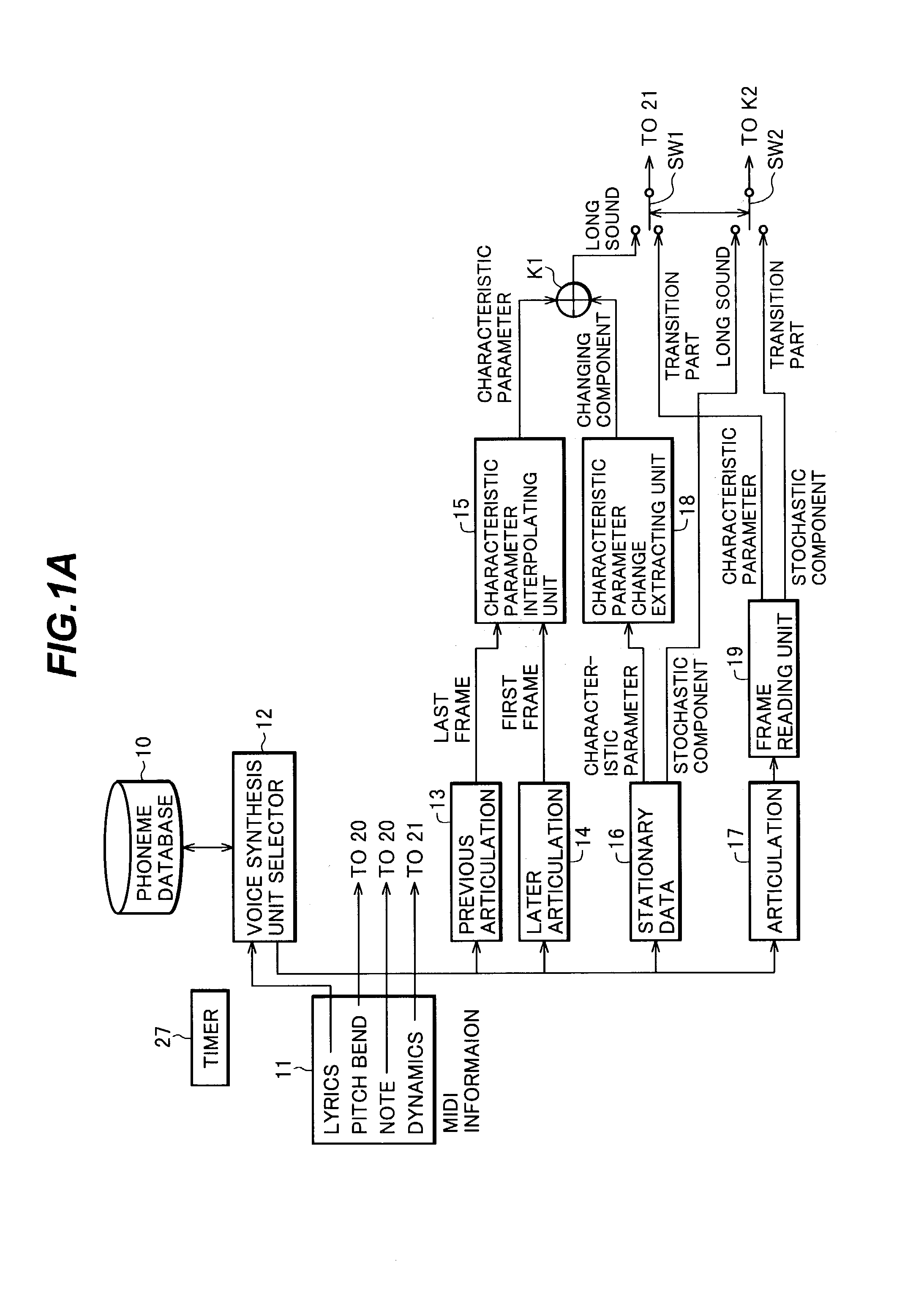
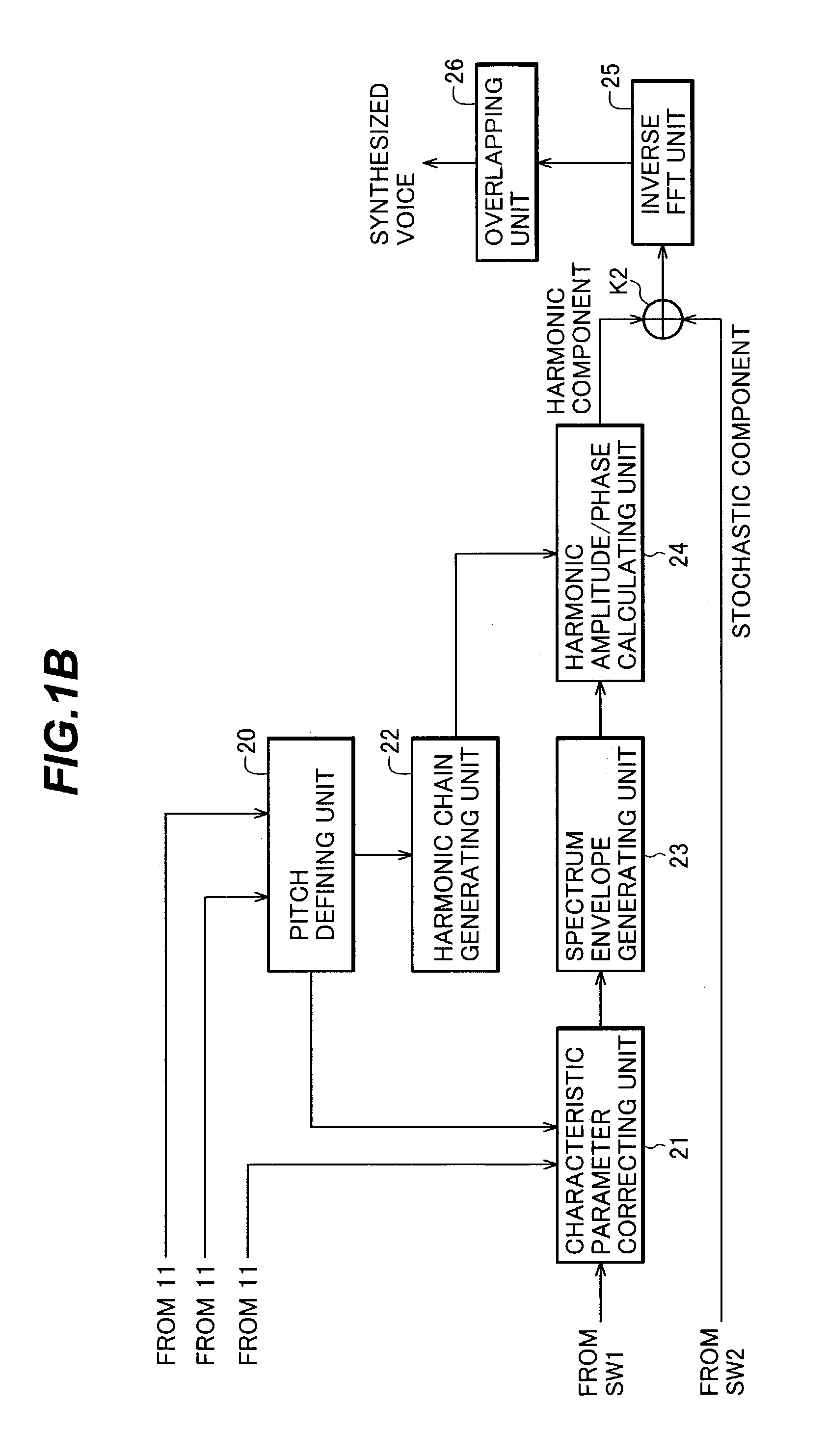
Singing voice synthesizing apparatus, singing voice synthesizing method and program for singing voice synthesizing
InactiveUS7135636B2Improve natureQuality improvementGearworksMusical toysFeature parameterNatural sounds
A method for synthesizing a natural-sounding singing voice divides performance data into a transition part and a long sound part. The transition part is represented by articulation (phonemic chain) data that is read from an articulation template database and is outputted without modification. For the long sound part, a new characteristic parameter is generated by linearly interpolating characteristic parameters of the transition parts positioned before and after the long sound part and adding thereto a changing component of stationary data that is read from a constant part (stationary) template database. An associated apparatus for carrying out the singing voice synthesizing method includes a phoneme database for storing articulation data for the transition part and stationary data for the long sound part, a first device for outputting the articulation data, and a second device for outputting the newly-generated characteristic parameter of the long sound part.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
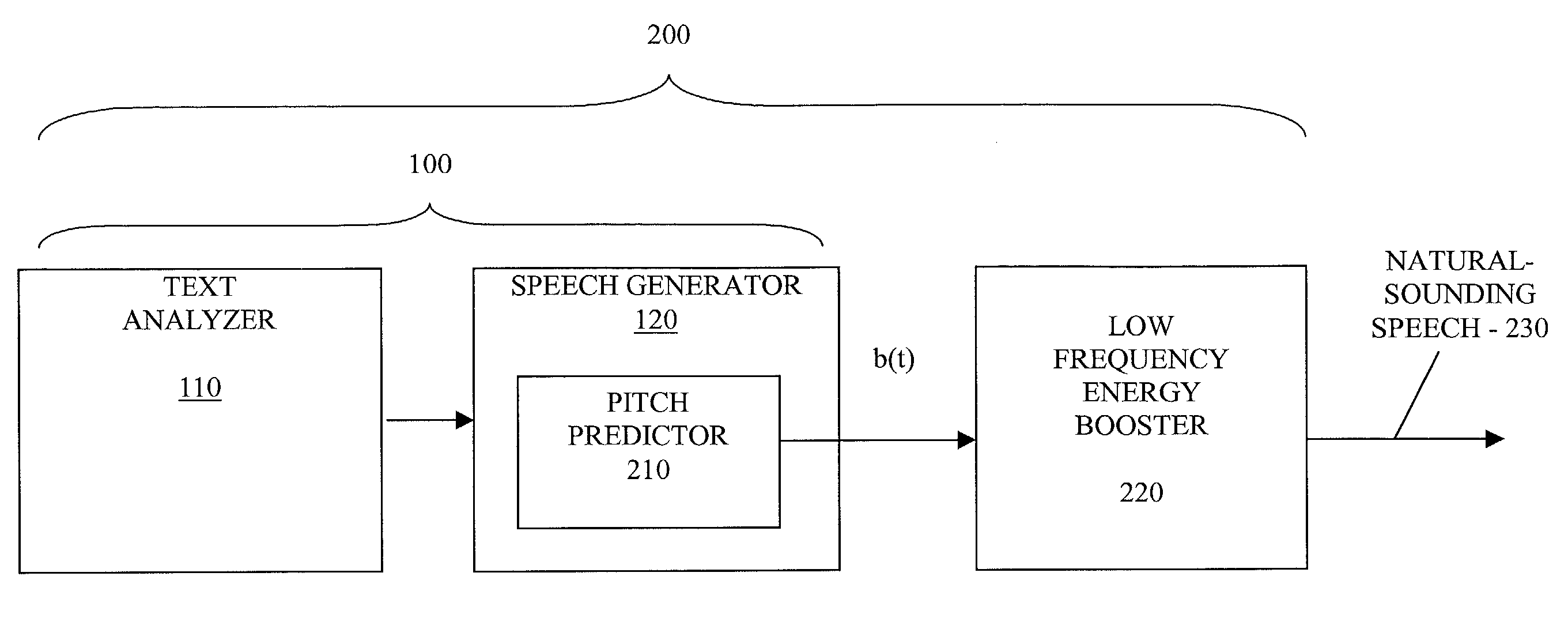
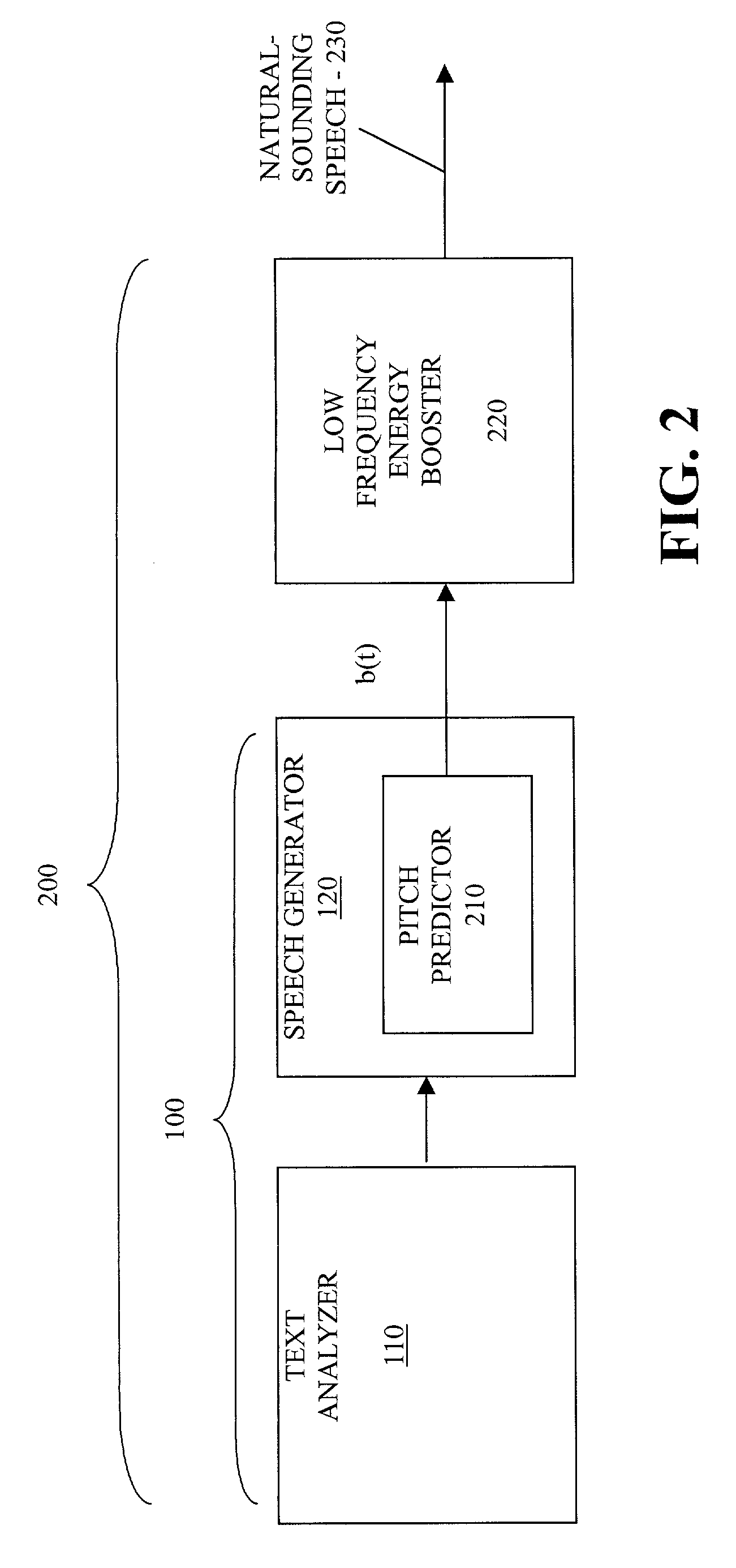
Method and apparatus for producing natural sounding pitch contours in a speech synthesizer
A speech synthesis system is disclosed that utilizes a pitch contour resulting in a more natural-sounding speech. The present invention modifies the predicted pitch, b(t), for synthesized speech using a low frequency energy booster. The low frequency energy booster interpolates the discrete pitch values, if necessary, and increase the amount of energy of the pitch contour associated with low frequency values, such as all frequency values below 10 Hertz. The amount of energy of the pitch contour associated with low frequency values can be increased, for example, by adding band-limited noise (a carrier signal) to the pitch contour, b(t), or by filtering the pitch values with an impulse response filter having a pole at the desired low frequency value. The present invention serves to add vibrato to the to the original pitch contour, b(t), and thereby improves the naturalness of the synthetic waveform.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
Traffic control using sound signals
InactiveUS20180286232A1Digital data information retrievalControl with pedestrian guidance indicatorTraffic sign recognitionMobile vehicle
Methods for vehicle to vehicle communication, vehicle detection, and vehicle to traffic sign communication are devised. Such methods can involve the use of one or a plurality of speakers to emit artificial sound signals, as well as the use of one or a plurality of sound detectors to record artificial or natural sound signals emitted by nearby vehicles or traffic signs. The use of an active sonar system will also allow autonomous vehicles to detect nearby surroundings. The Doppler Effect can also be used to determine the speeds of moving vehicles. These methods allow autonomous vehicles to drive and respond to their surroundings, and also allow traffic signs to respond to various traffic situations by detecting the presence of nearby vehicles.
Owner:SHAU DAVID
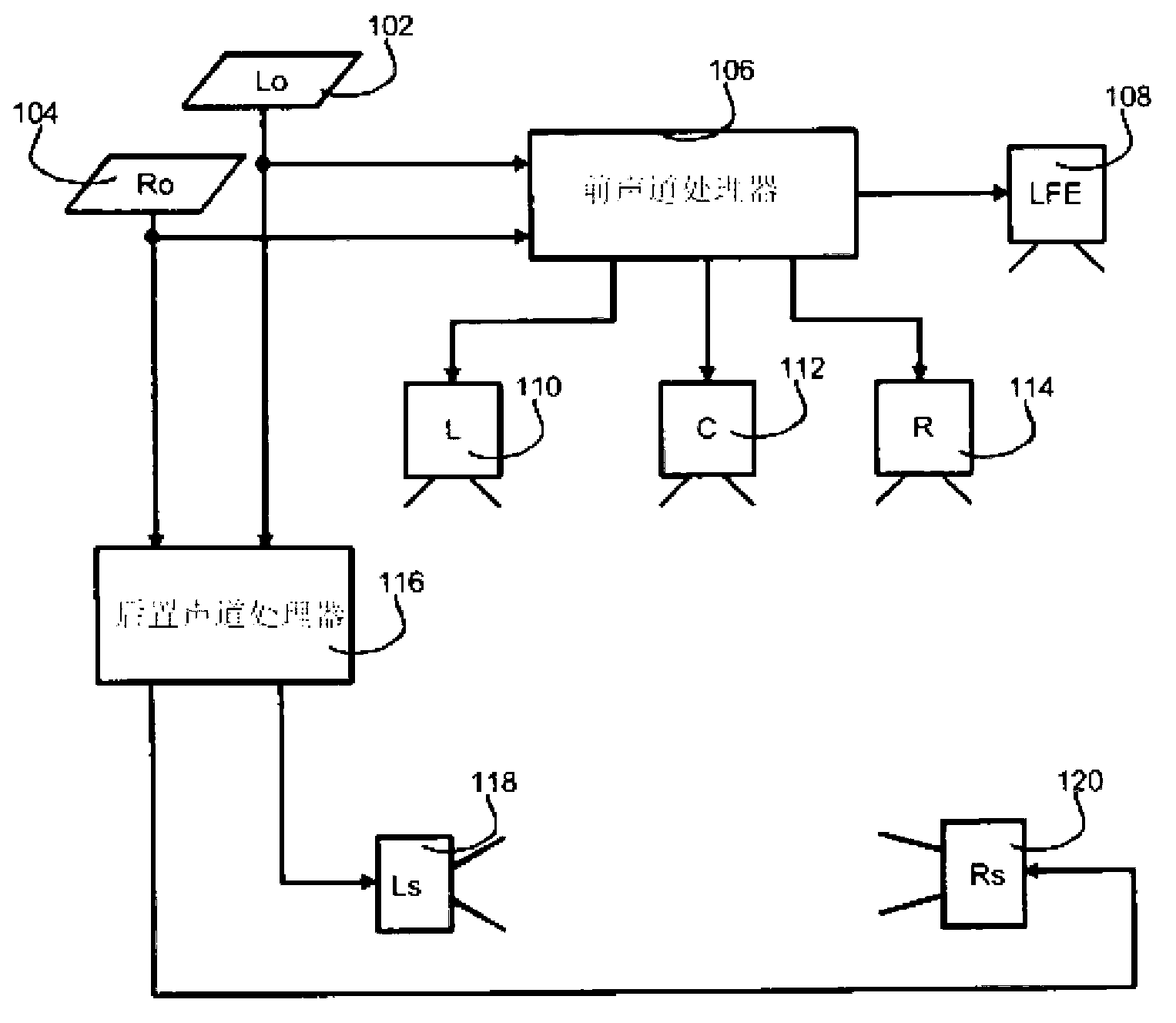
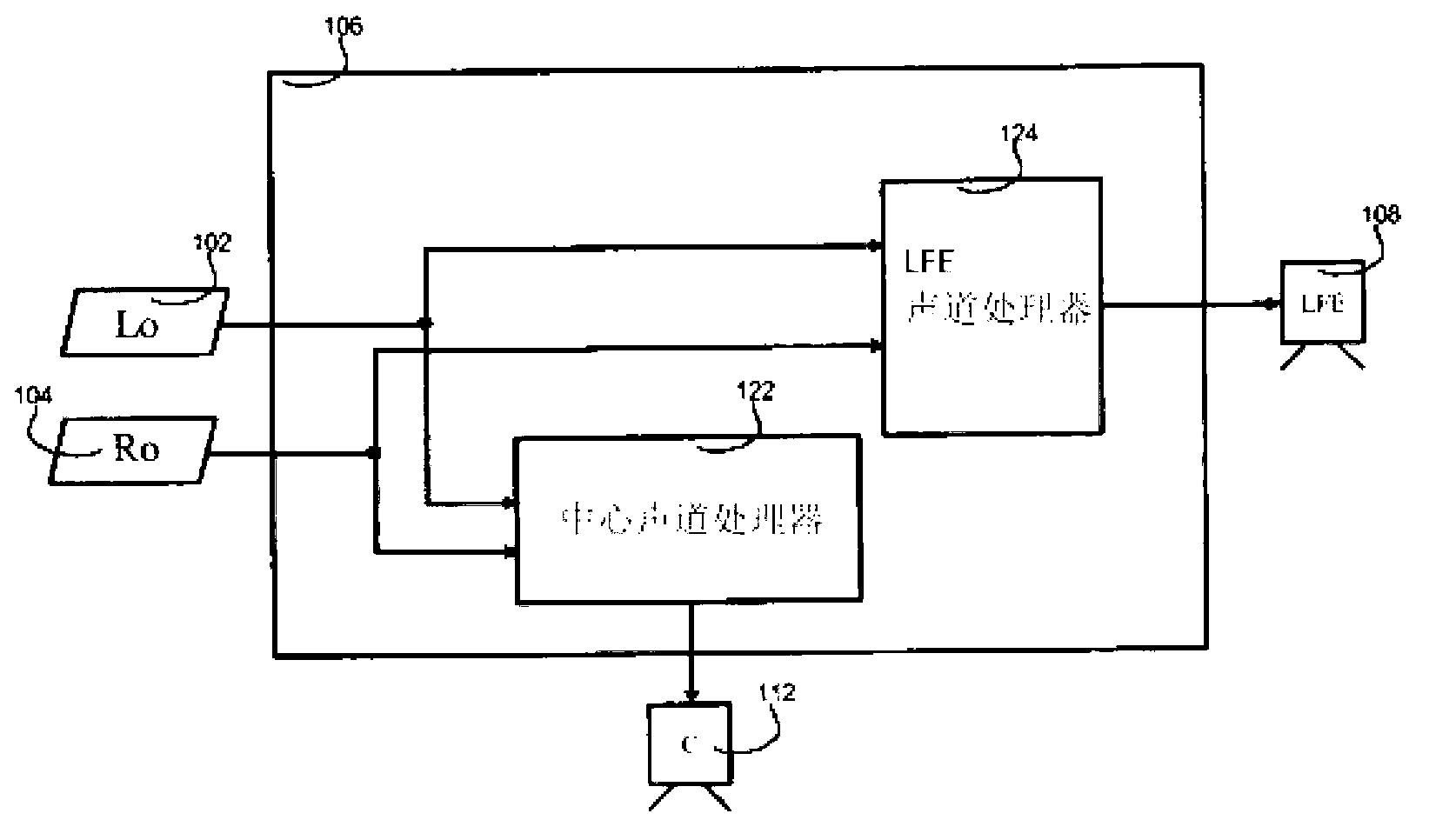
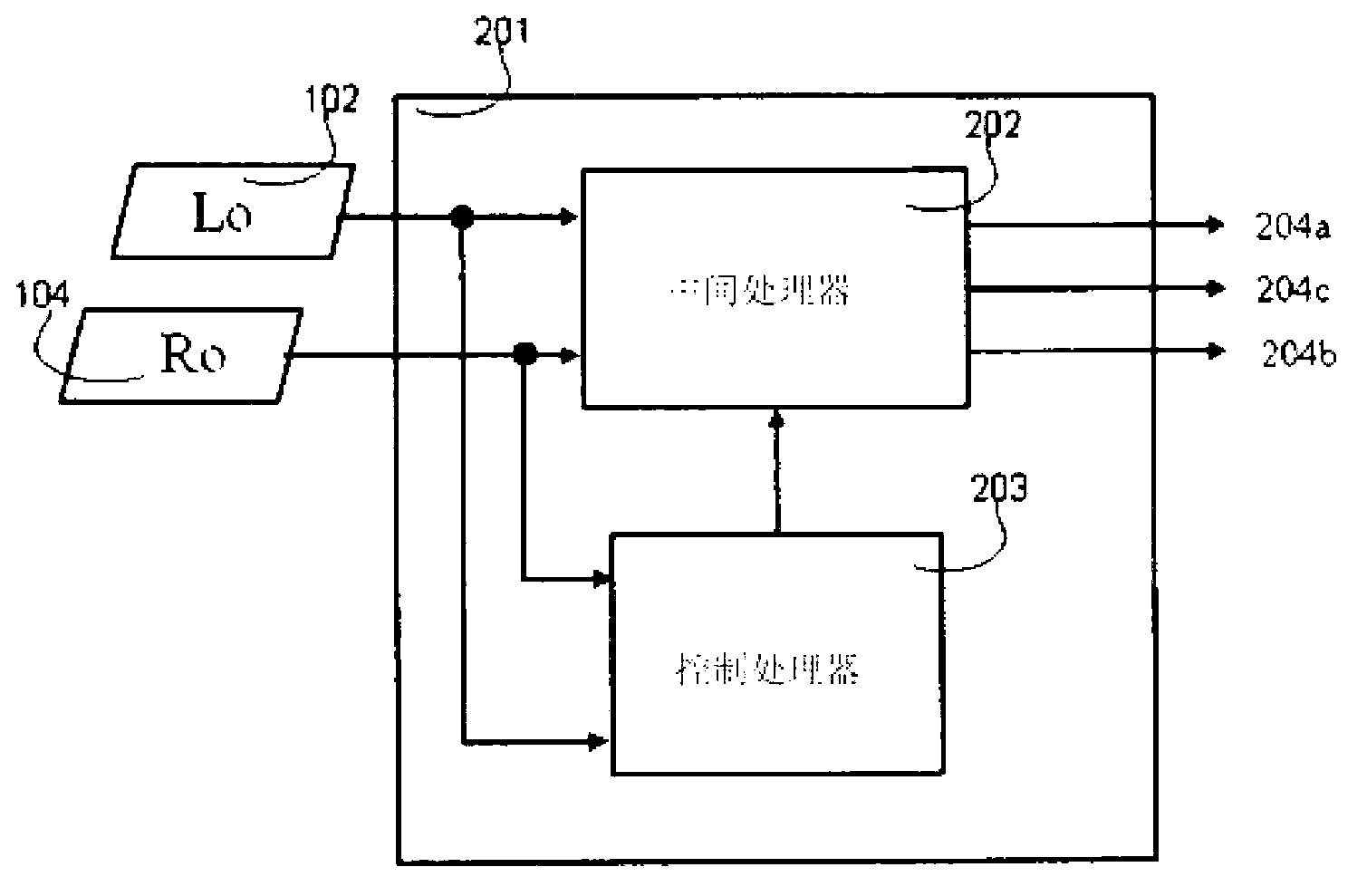
Upmixing method and system for multichannel audio reproduction
An audio signal enhancing device, and a corresponding method of enhancing stereophonic signals, is provided which generates an enhanced signal with improved spatial sound image quality for upmixing a stereophonic input signal. When used in combination with a centre channel processor or LFE processor, an improved processing of the input signals is provided resulting in final centre channel and at least one LFE sub-woofer channel wherein the problems and disadvantages of the prior art are resolved. The result is a centre and LFE signal that contains a stable, non time-smeared image with a high quality natural-sounding fidelity. These advantages are achieved especially for time-delayed or phase-panned stereo input signals, independently of whether they are matrix encoded or non-matrix encoded input signals.
Owner:DOLBY INTERNATIONAL AB
Method for modulating listener attention toward synthetic formant transition cues in speech stimuli for training
InactiveUS20070111173A1Increase salienceImprove accuracyElectrical appliancesTeaching apparatusFormantSpeech sound
A method on a computing device for enhancing the memory and cognitive ability of an older adult by requiring the adult to differentiate between rapidly presented stimuli. The method utilizes a sequence of phonemes from a confusable pair which are systematically manipulated to make discrimination between the phonemes less difficult or more difficult based on the success of the adult, such as processing the consonant and vowel portions of the phonemes by emphasizing the portions, stretching the portions, and / or separating the consonant and vowel portions by time intervals. As the adult improves in auditory processing, the discriminations are made progressively more difficult by reducing the amount of processing to that of normal speech. Introductory phonemes may each include a blend of a formant-synthesized phoneme and an acoustically naturalistic phoneme that substantially replicates the spectro-temporal aspects of a naturally produced phoneme, with the blends progressing from substantially natural-sounding to substantially formant-synthesized.
Owner:POSIT SCI CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com