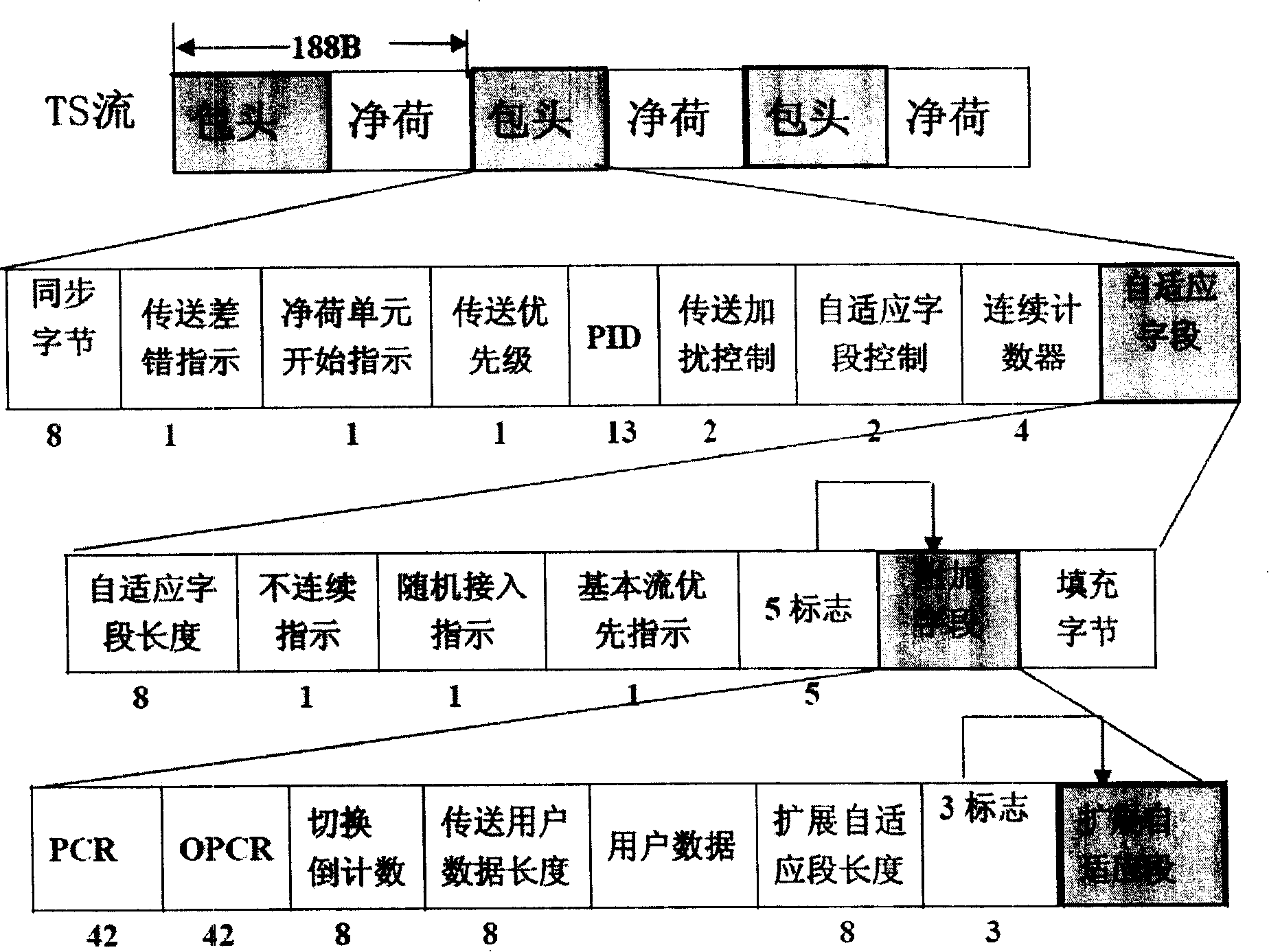
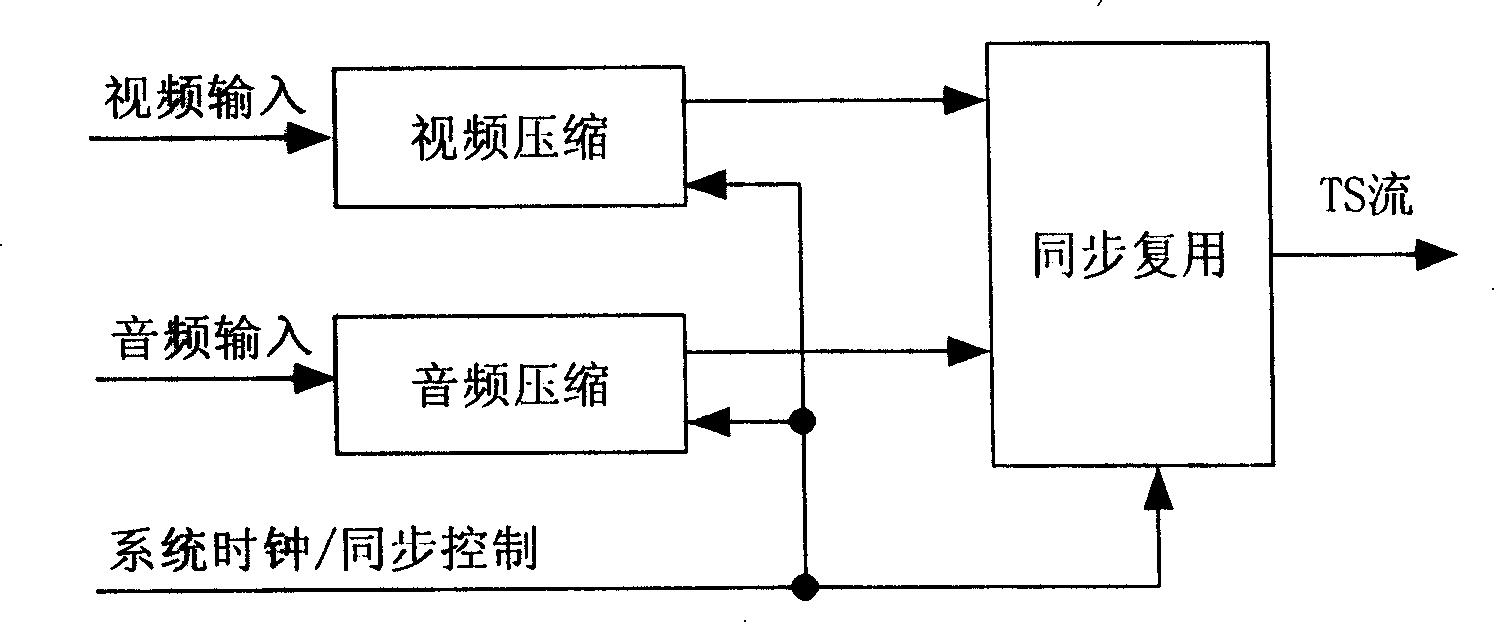
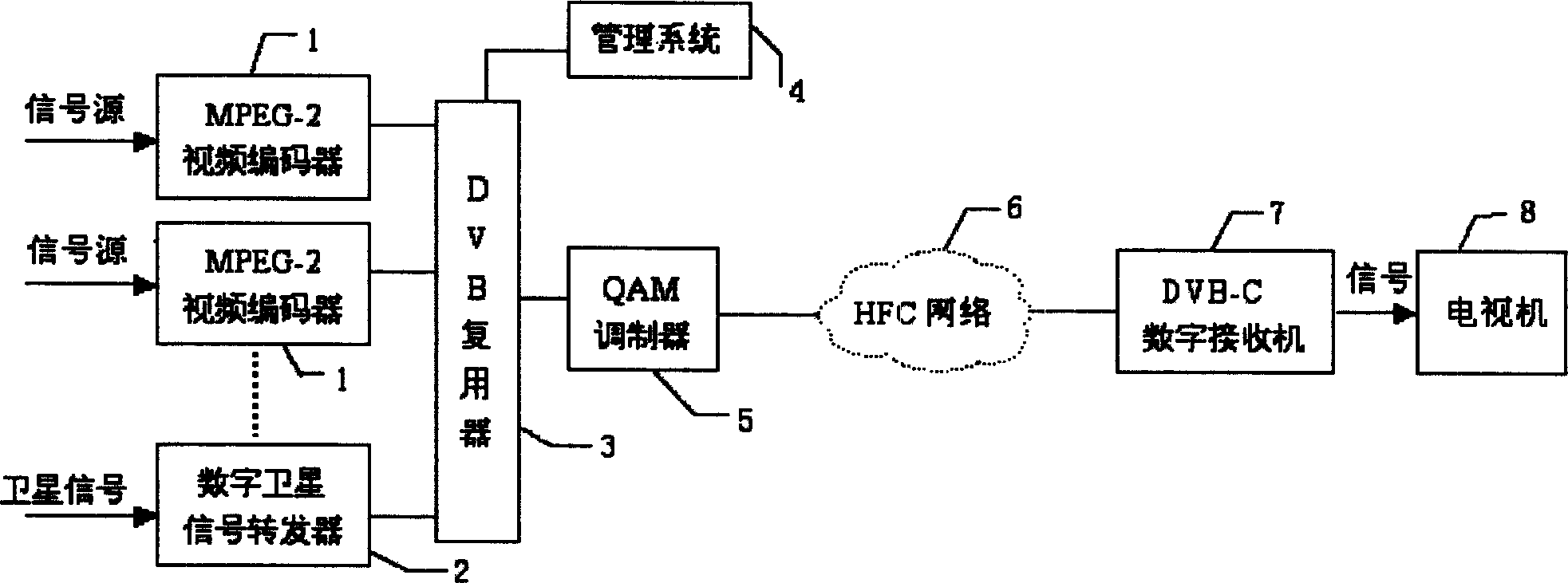
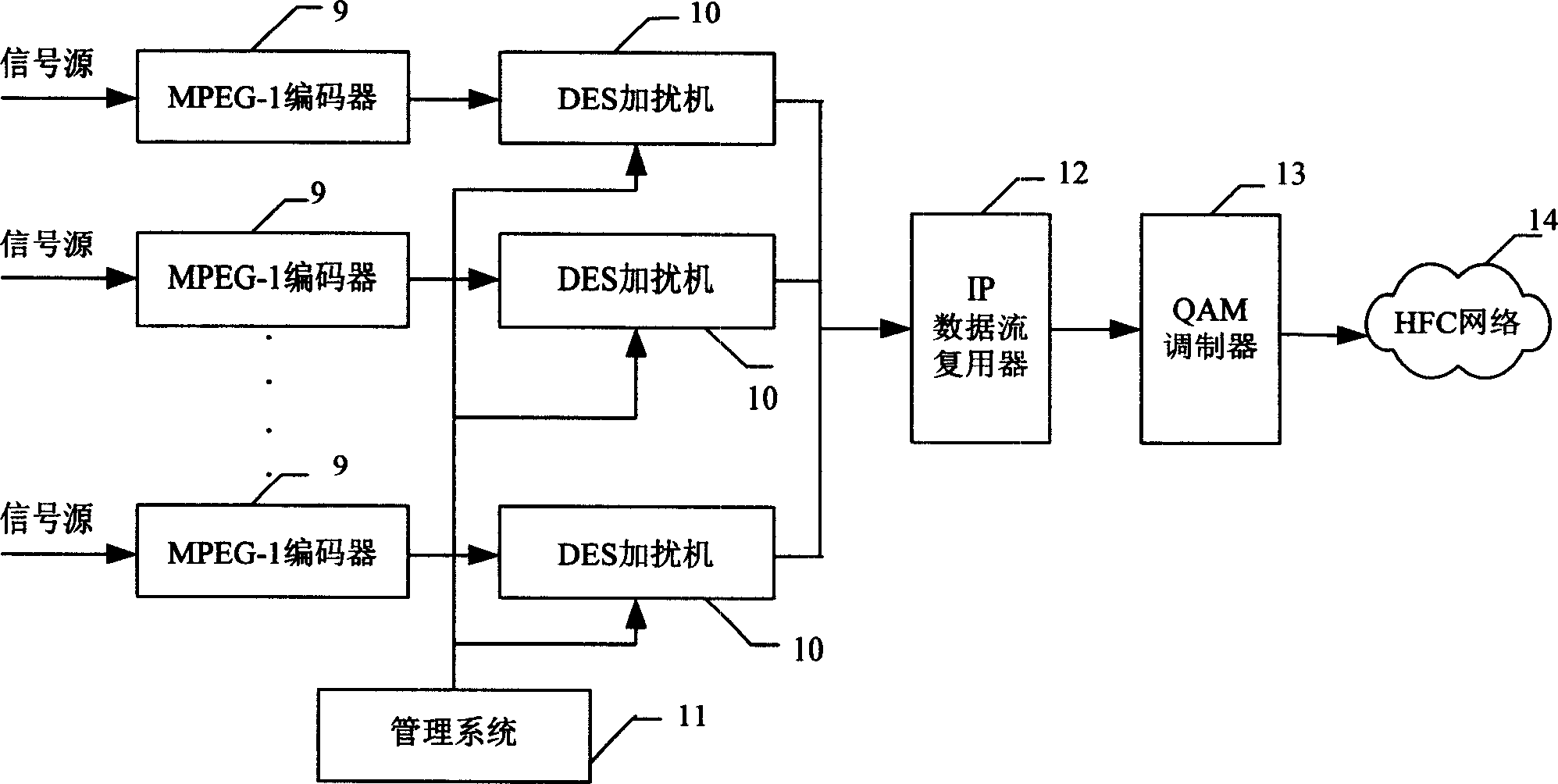
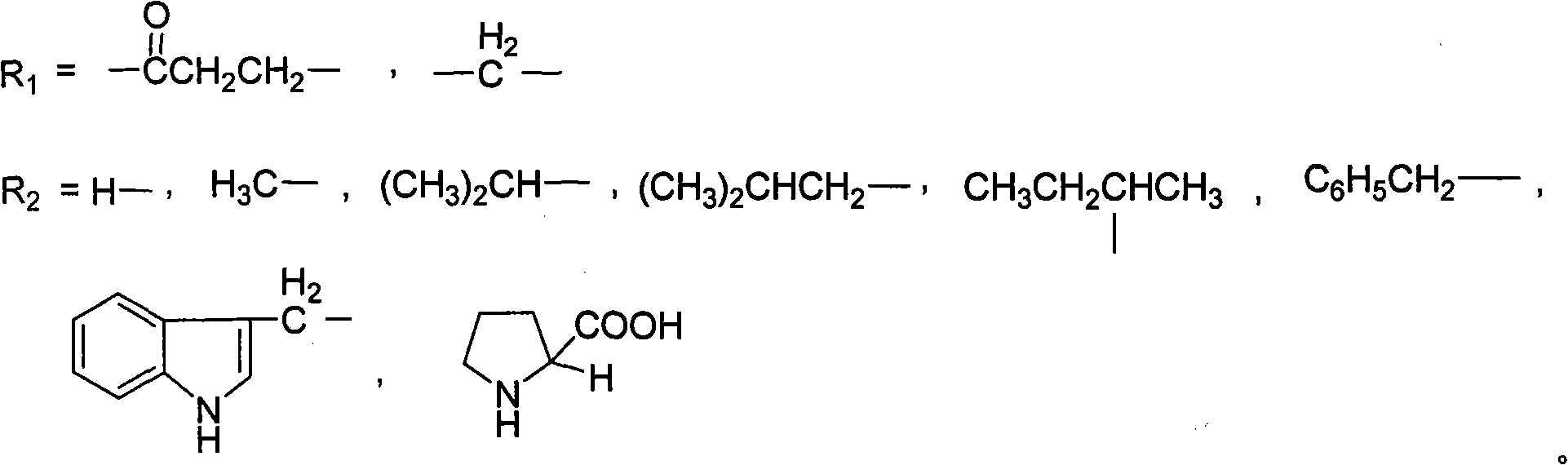Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "MPEG-1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s (26:1 and 6:1 compression ratios respectively) without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting (DAB) possible.
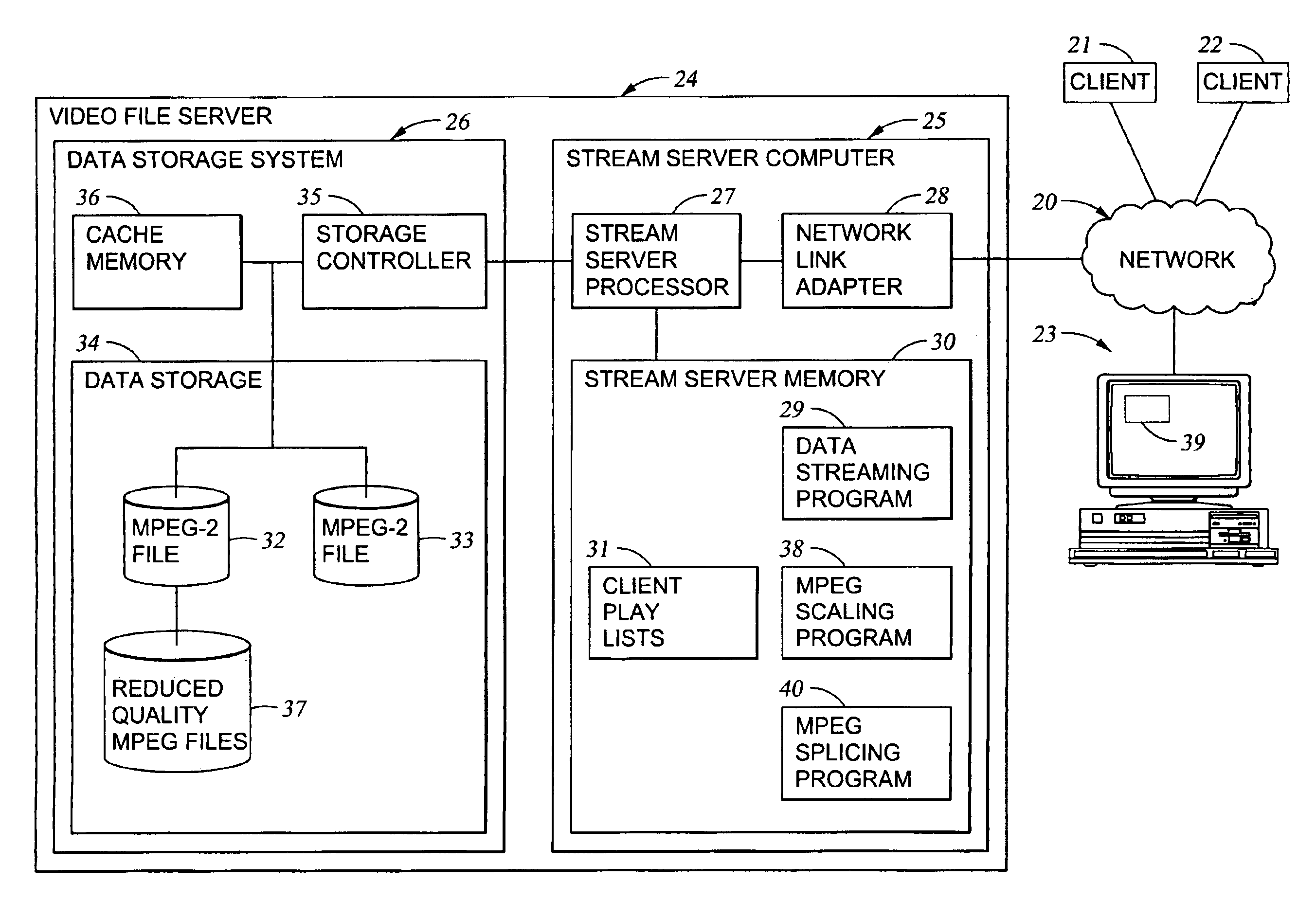
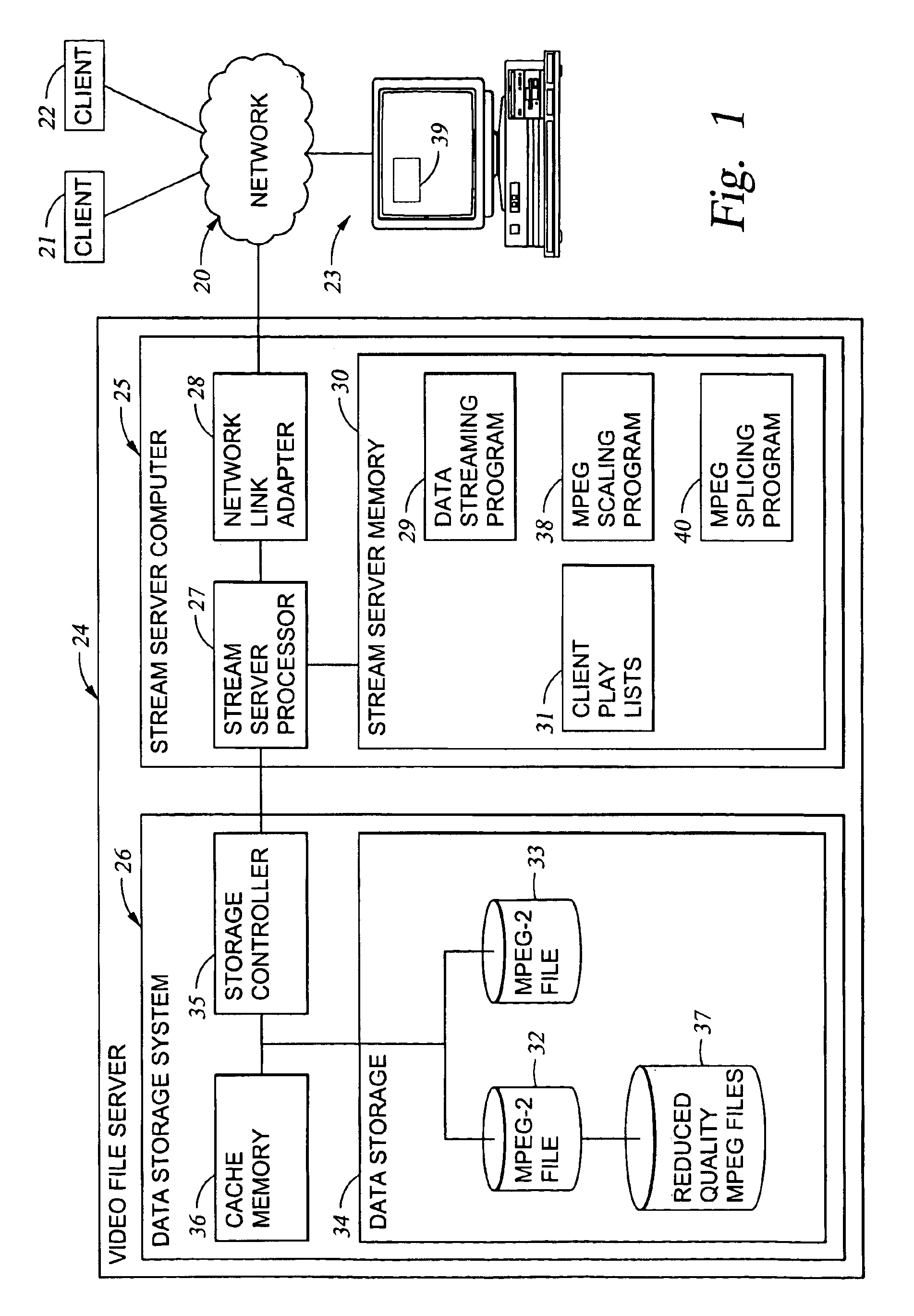
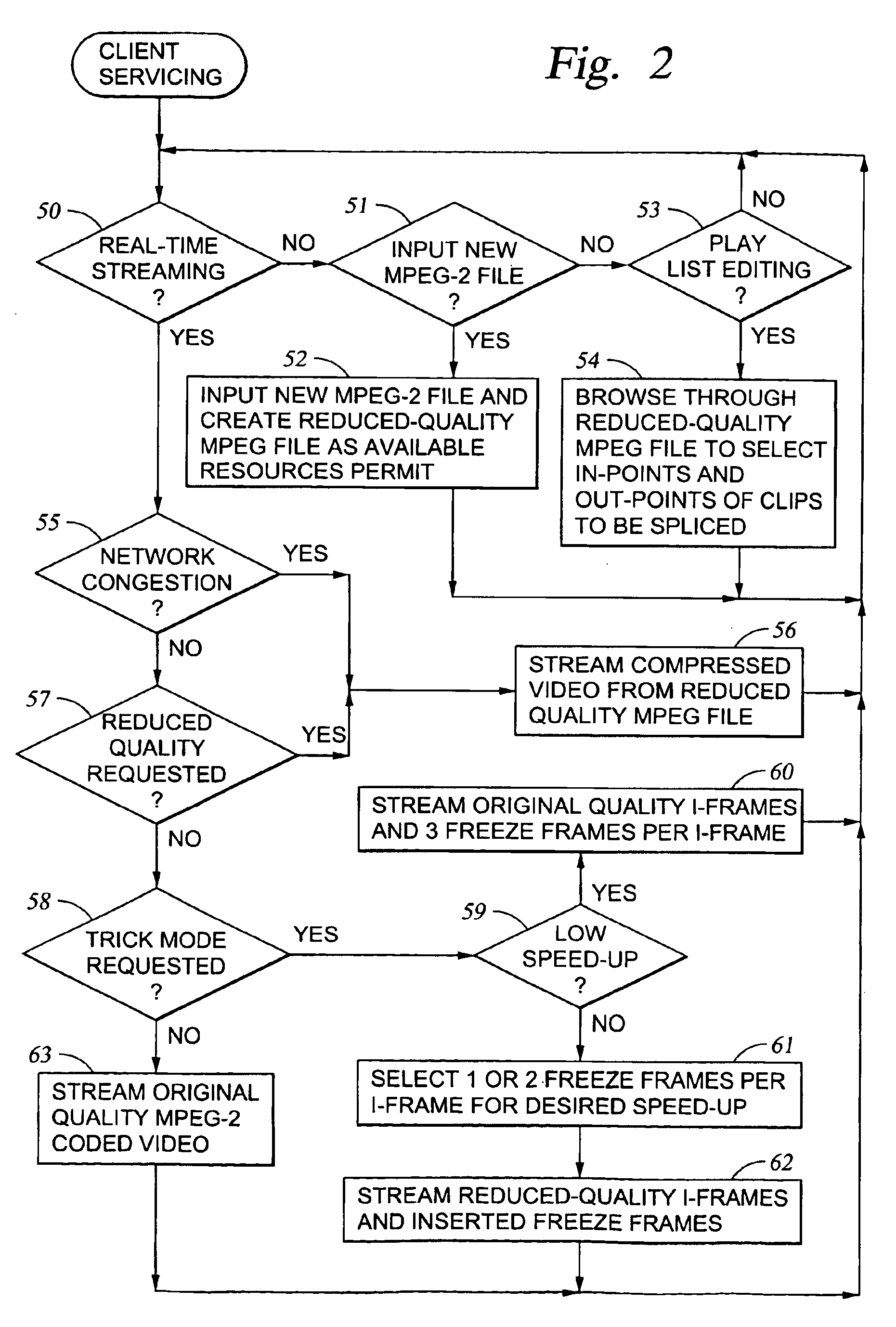
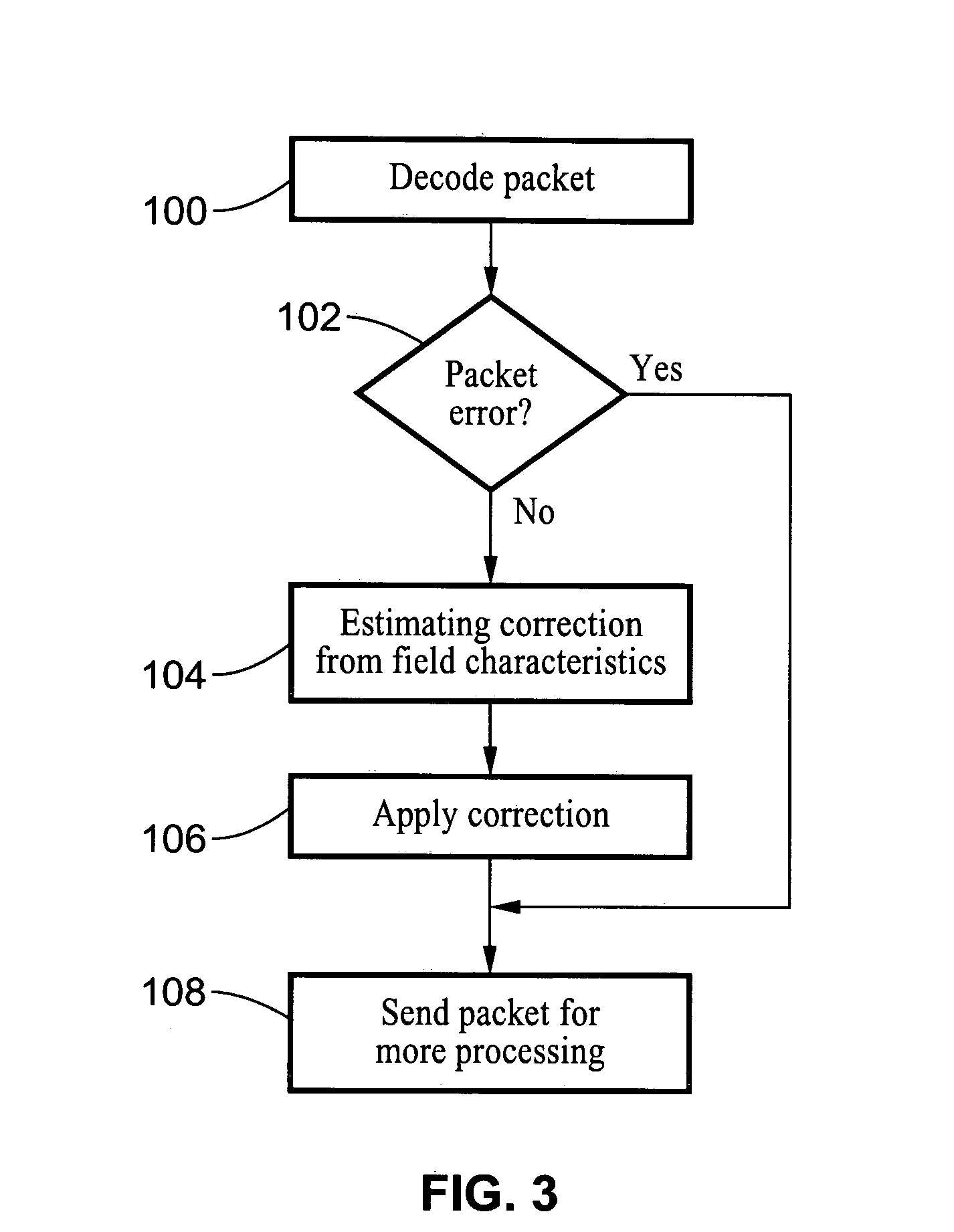
Processing of MPEG encoded video for trick mode operation
InactiveUS6871006B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVisual presentationMPEG transport stream
Original-quality MPEG coded video is processed to produce reduced-quality MPEG coded video for trick mode operation by removing non-zero AC DCT coefficients from the 8×8 blocks of I-frames of the MPEG coded video to produce I-frames of reduced-quality MPEG coded video, and inserting freeze frames in the reduced-quality MPEG coded video. Preferably, the coded video is stored in a main file, a fast-forward file and a fast-reverse file. The fast forward file and the fast reverse files contain reduced-quality I frames corresponding to original-quality I frames in the main file. A reading of the main file produces an MPEG transport stream for an audio-visual presentation at a normal rate, a reading of the fast-forward file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a forward direction at a fast rate, and a reading of the fast-reverse file produces an MPEG transport stream of the audio-visual presentation in a reverse direction at a fast rate. Preferably, the files share a volume that includes at least one GOP index associating the corresponding I frames of the files.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
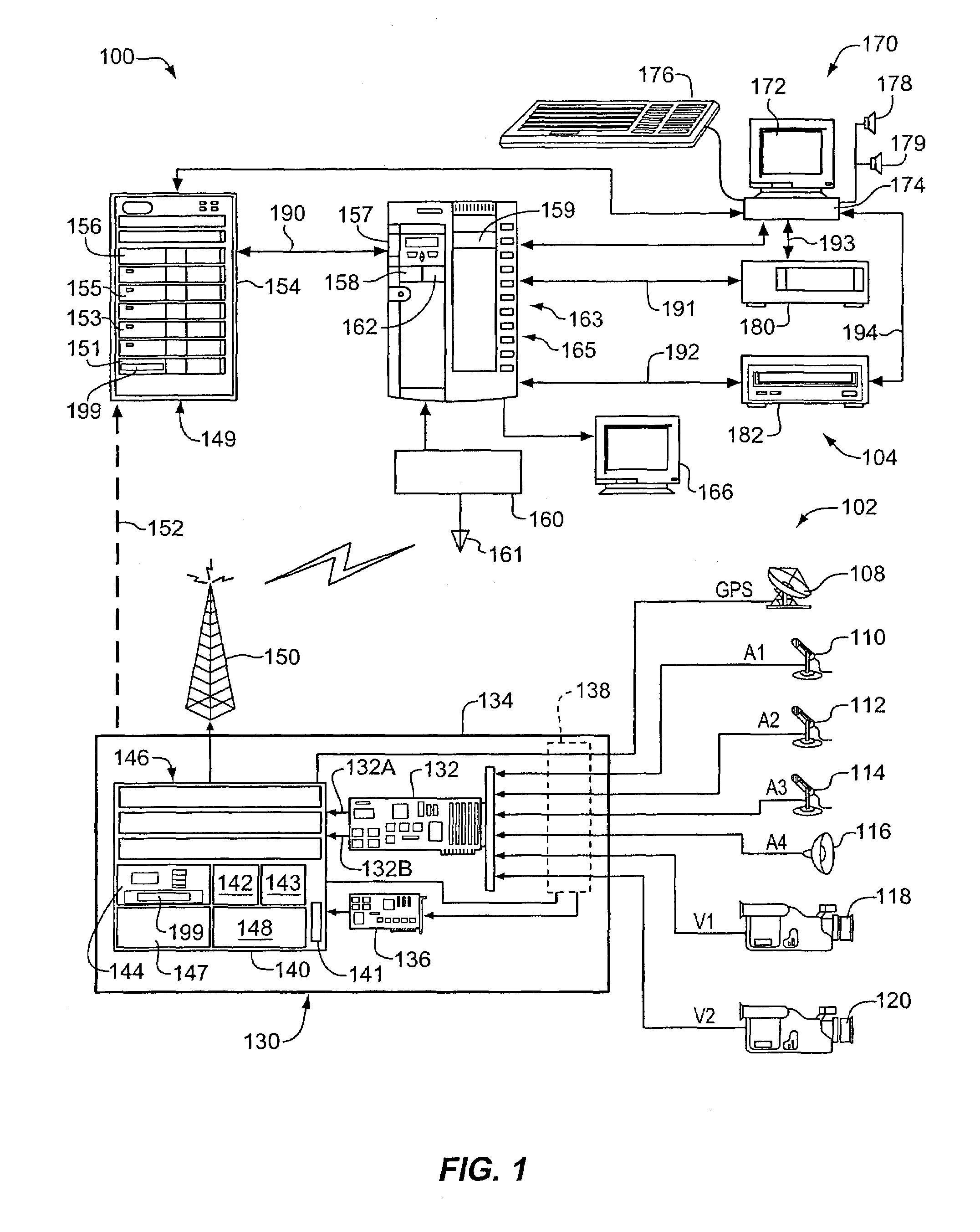
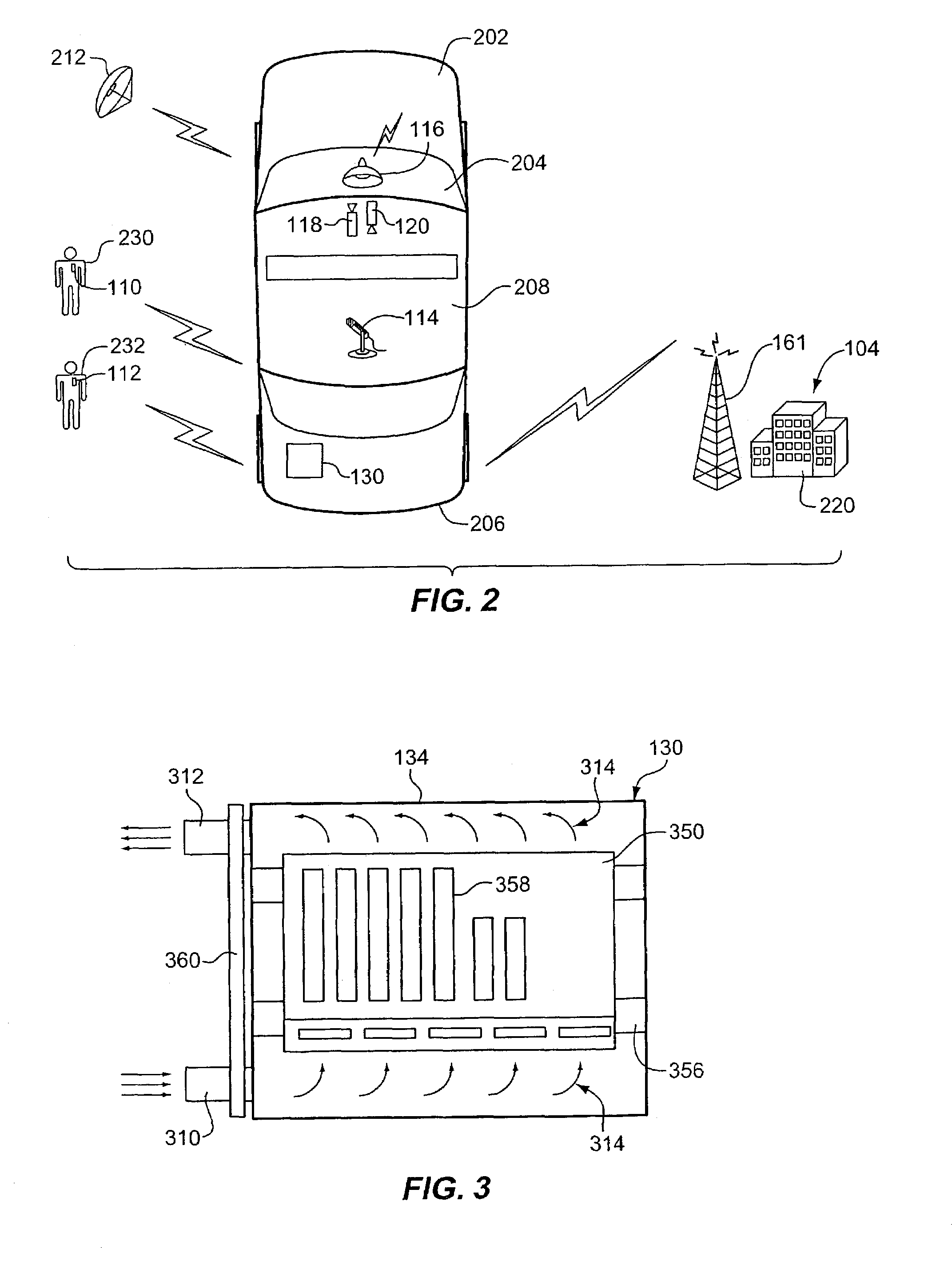
Remote surveillance system
InactiveUS7272179B2Easy retrievalTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMPEG-1Tape recorder
An audio / visual surveillance system for use in mobile vehicles such as patrol cars includes two video cameras producing video signals and four audio sources producing audio signals. The signals are MPEG-2 compressed and streamed in real time with geographic and time data to a digital cartridge-type tape recorder located in the vehicle. A full patrol car shift is recorded on a single tape and, at the end of the shift, the tape is placed in a master sled bay. An MD5 hash authenticates the data for court use. Up to four videos can be synchronized frame-by-frame for simultaneous monitoring. An MPEG-1 stream is sent via wireless to headquarters in real time. One camera captures data external to the vehicle, while the other captures data internal to the vehicle. One audio source captures audio inside the vehicle and another captures dispatcher communications. The other two audio sources are carried by officers.
Owner:SECURITY WITH ADVANCED TECH
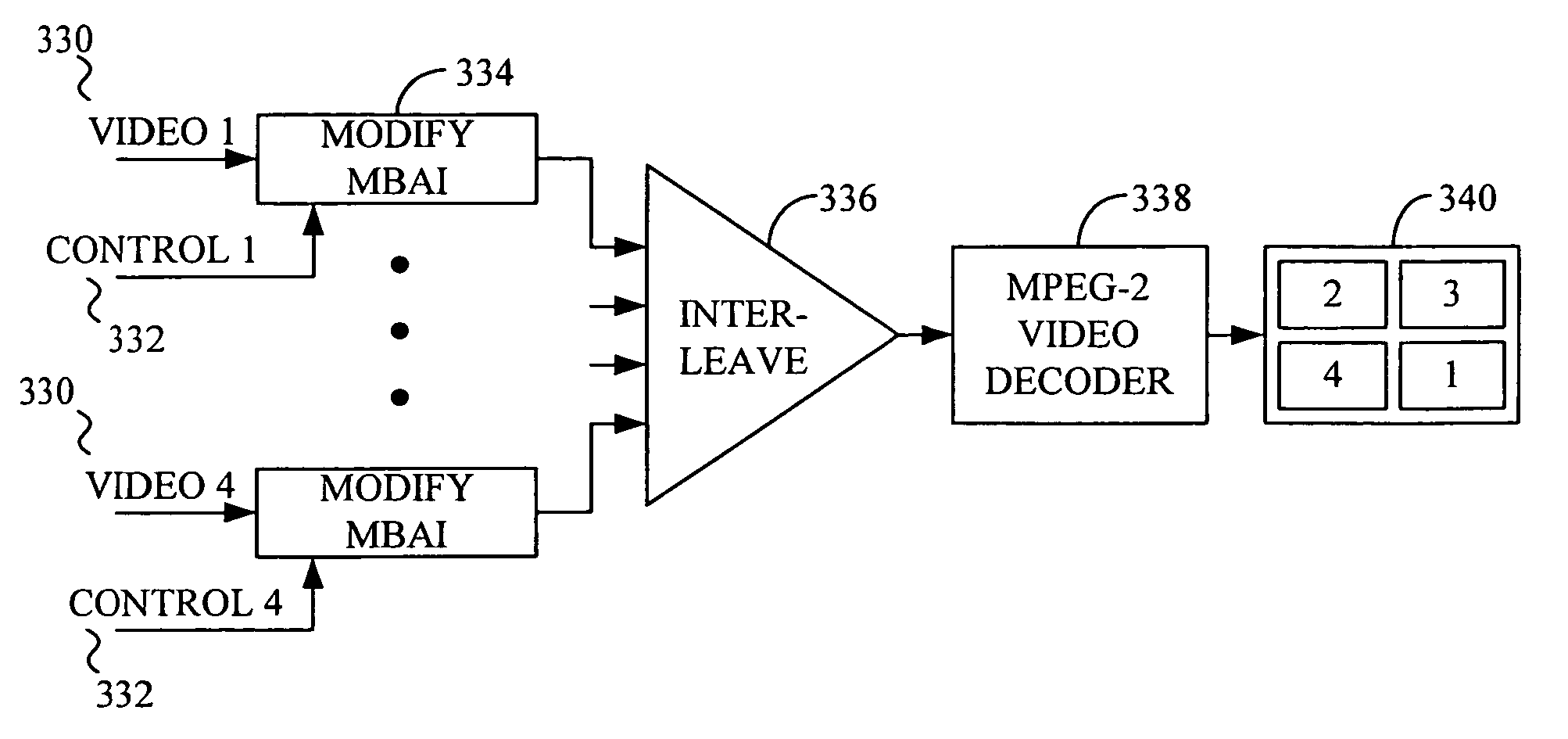
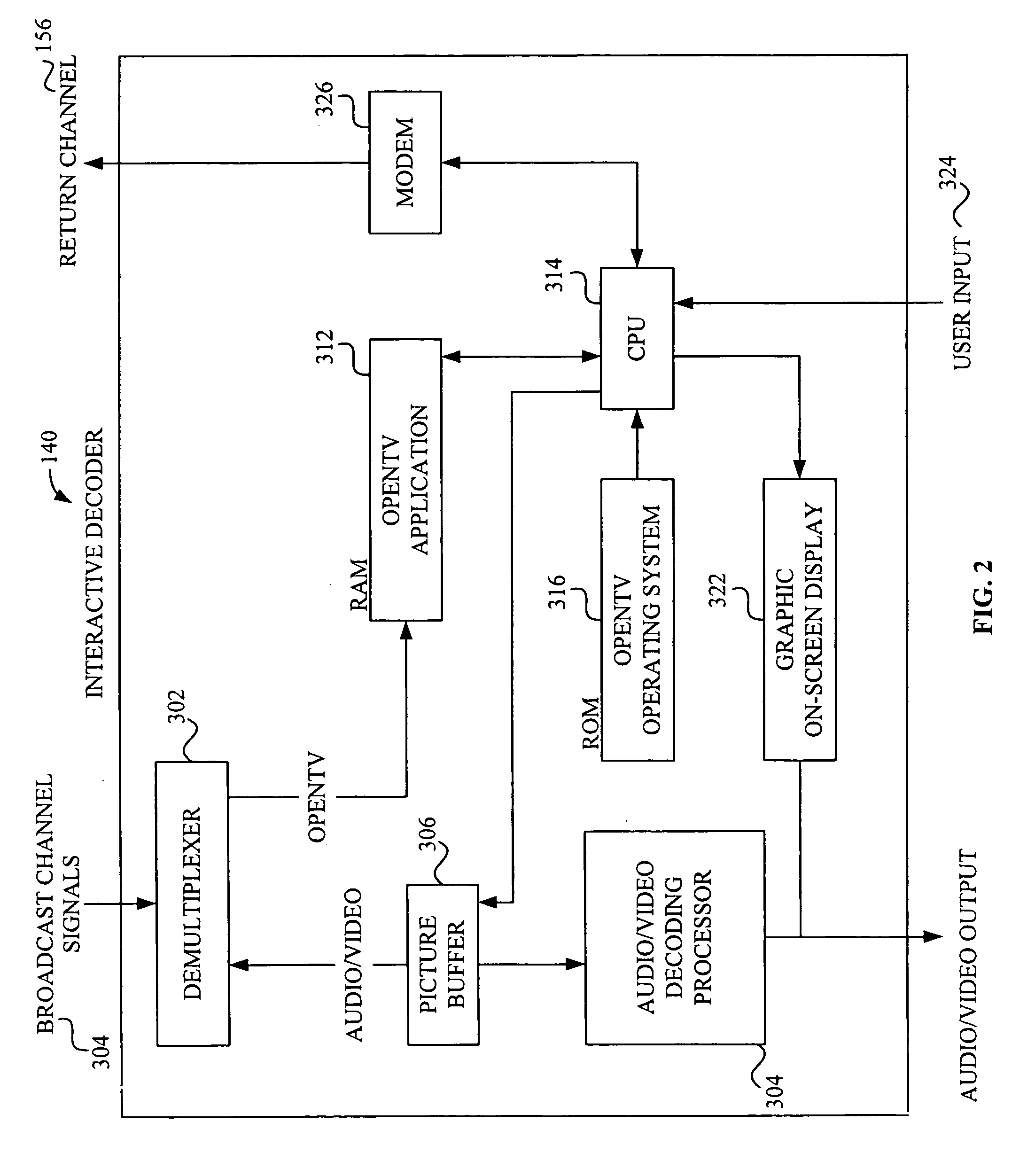
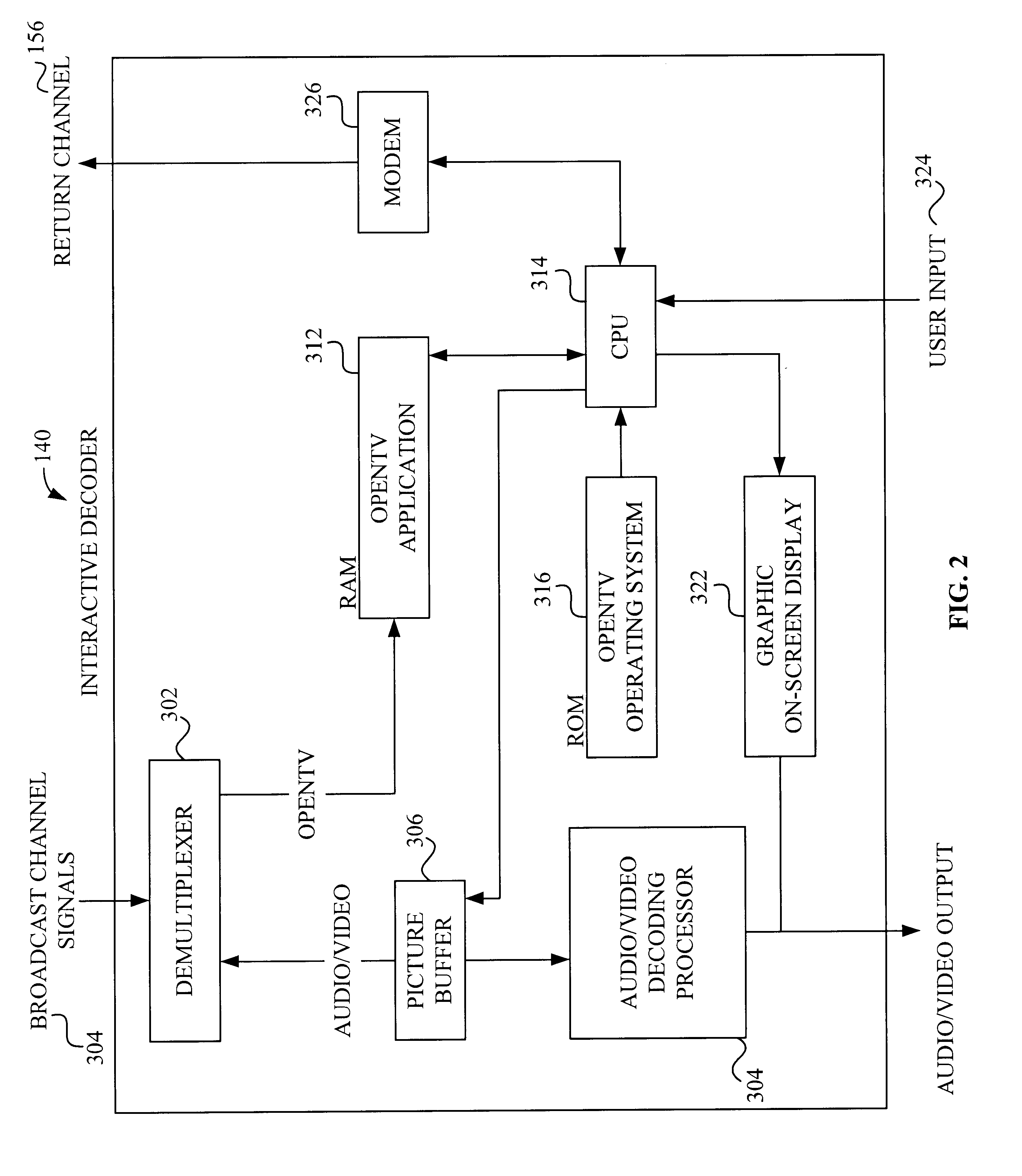
Interactive television system and method for simultaneous transmission and rendering of multiple MPEG-encoded video streams
InactiveUS6931660B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision systemDigital video
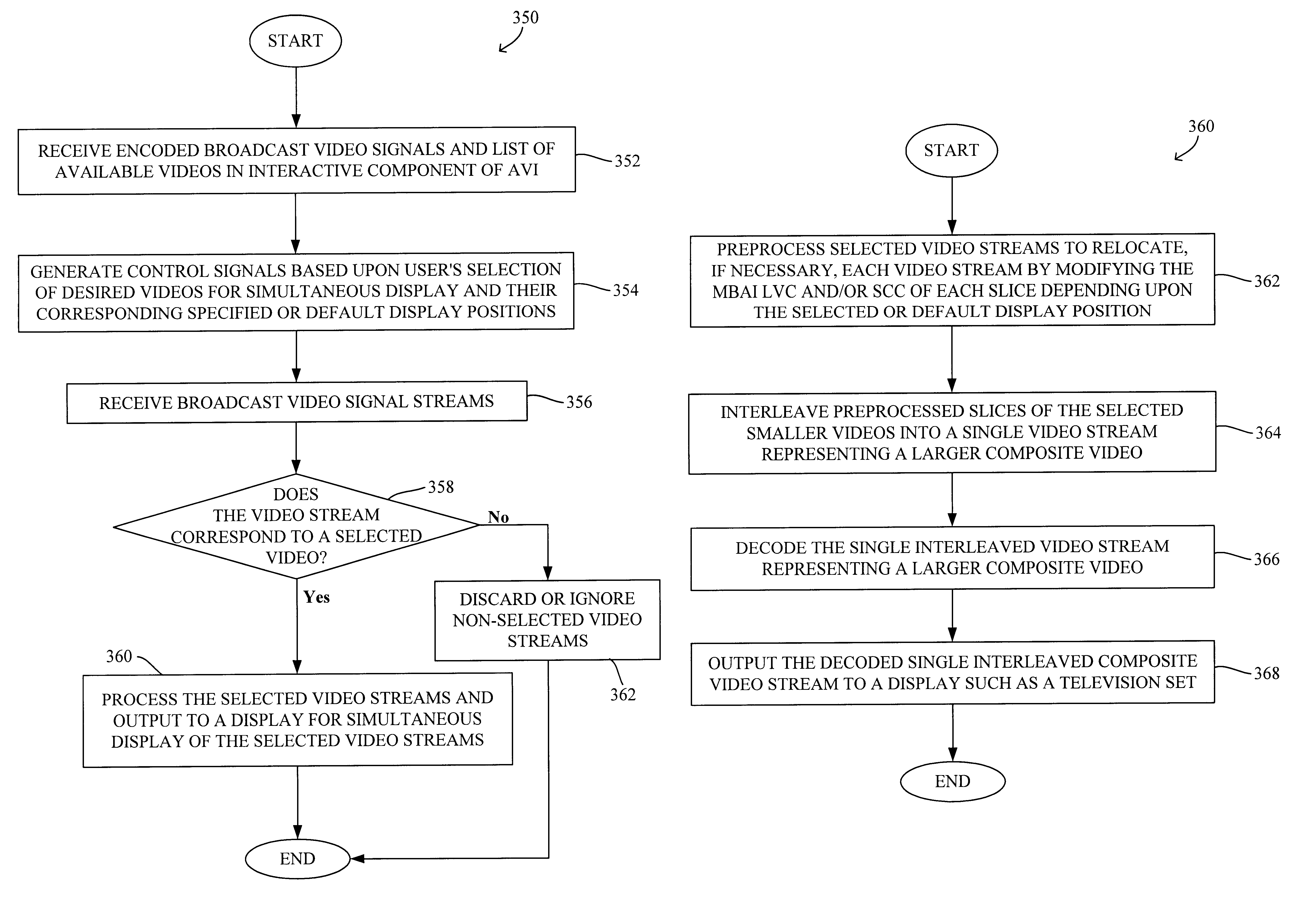
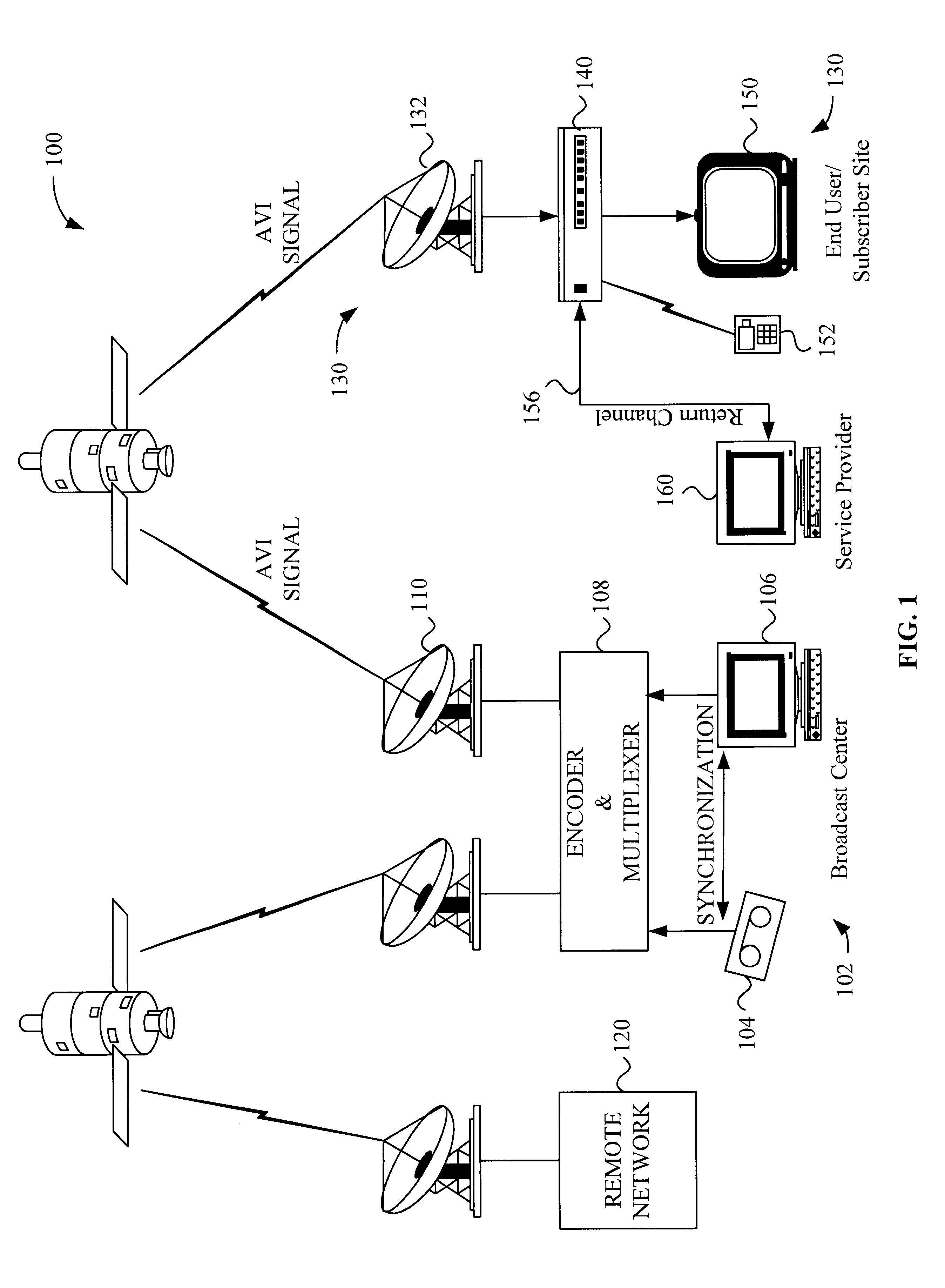
A system and method for the simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple MPEG-encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application are disclosed. Simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple MPEG-encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application generally comprises determining a value for a display position code corresponding to a display position of each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams, modifying the value of the display position code of each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams as necessary, and interleaving each slice of each of the MPEG-encoded video streams as modified into a single composite video stream. The modifying preferably maintains bit-alignment of the display position code within a byte. The MPEG-encoded video streams are optionally MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 encoded video streams and the display position code is optionally a macroblock address increment variable length codeword and / or at least a byte of a slice startcode.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
Interactive television system and method for simultaneous transmission and rendering of multiple encoded video streams
InactiveUS6539545B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionTelevision systemDigital video
A system and method for the simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application are disclosed. Simultaneous transmission and rendition of multiple encoded digital video signal streams in an interactive television application generally comprises modifying at least one of the multiple encoded video streams broadcast from a broadcast center for repositioning the at least one of the multiple encoded video stream for display, interleaving the modified multiple encoded video streams comprising the at least one modified encoded video stream into a single composite interleaved video stream, and outputting the single composite video stream. The method may further comprise receiving the multiple encoded video streams from a broadcast center. Each of the multiple encoded video streams is preferably encoded using MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 compression technology.
Owner:OPEN TV INC
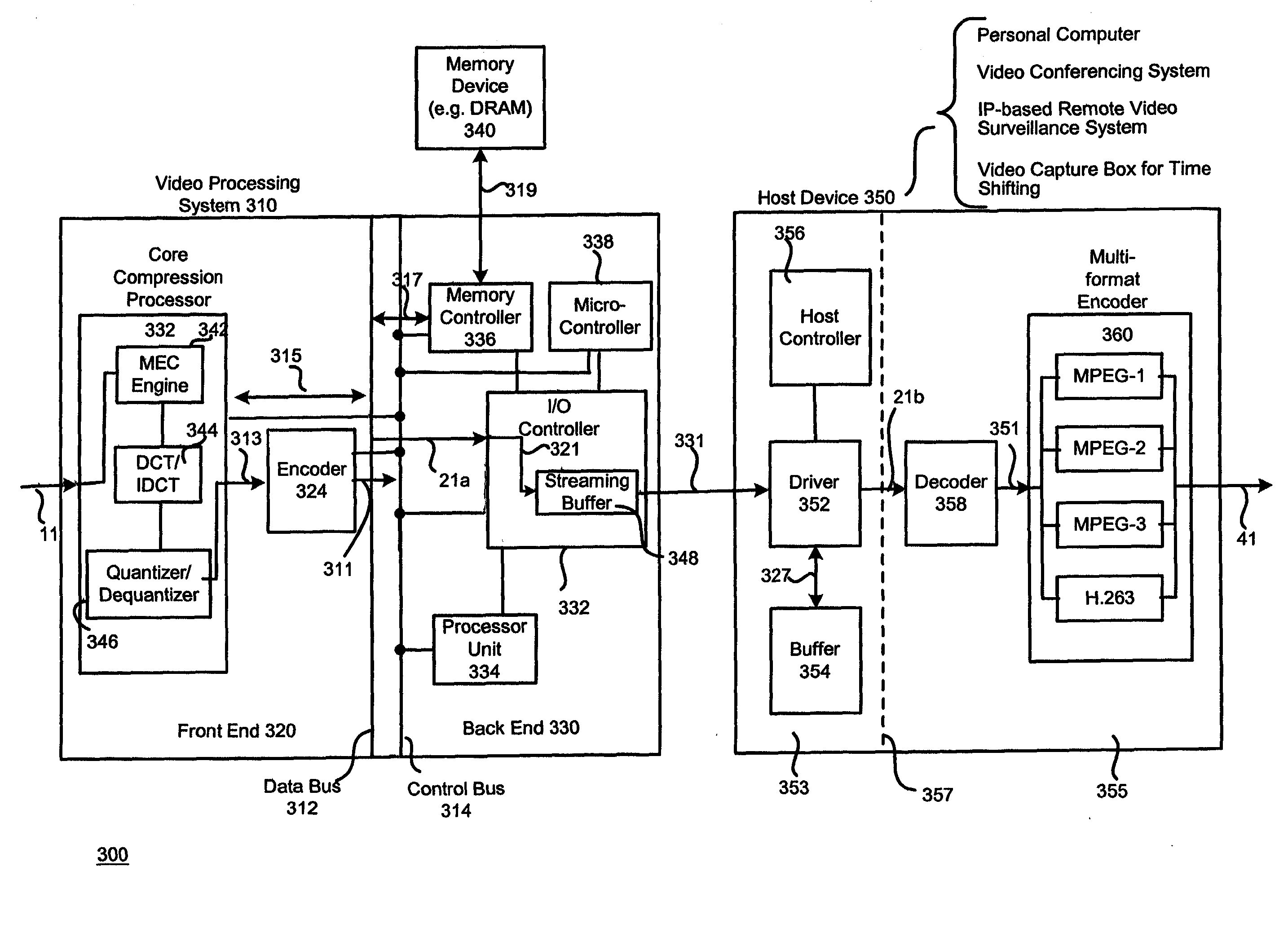
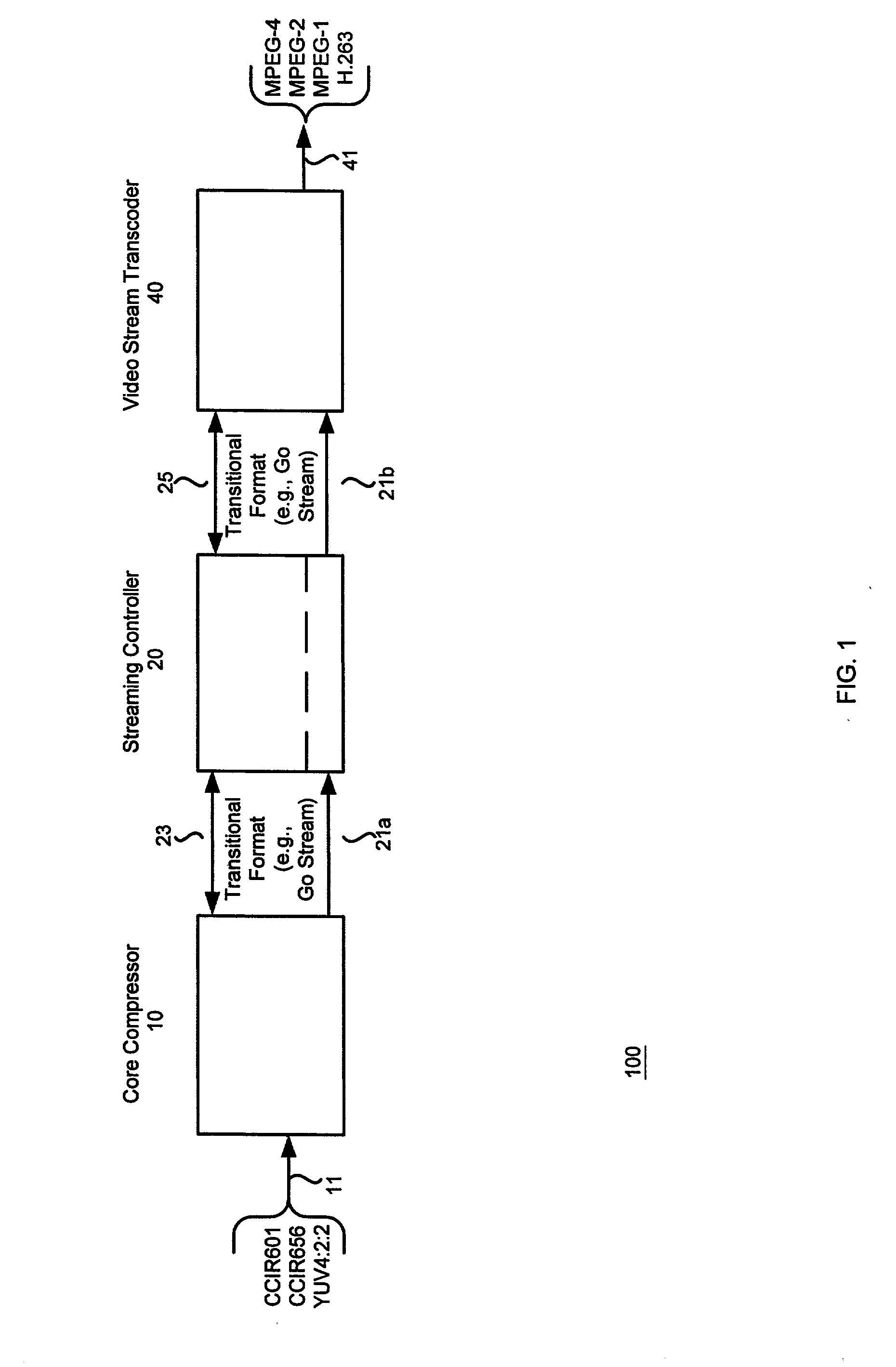
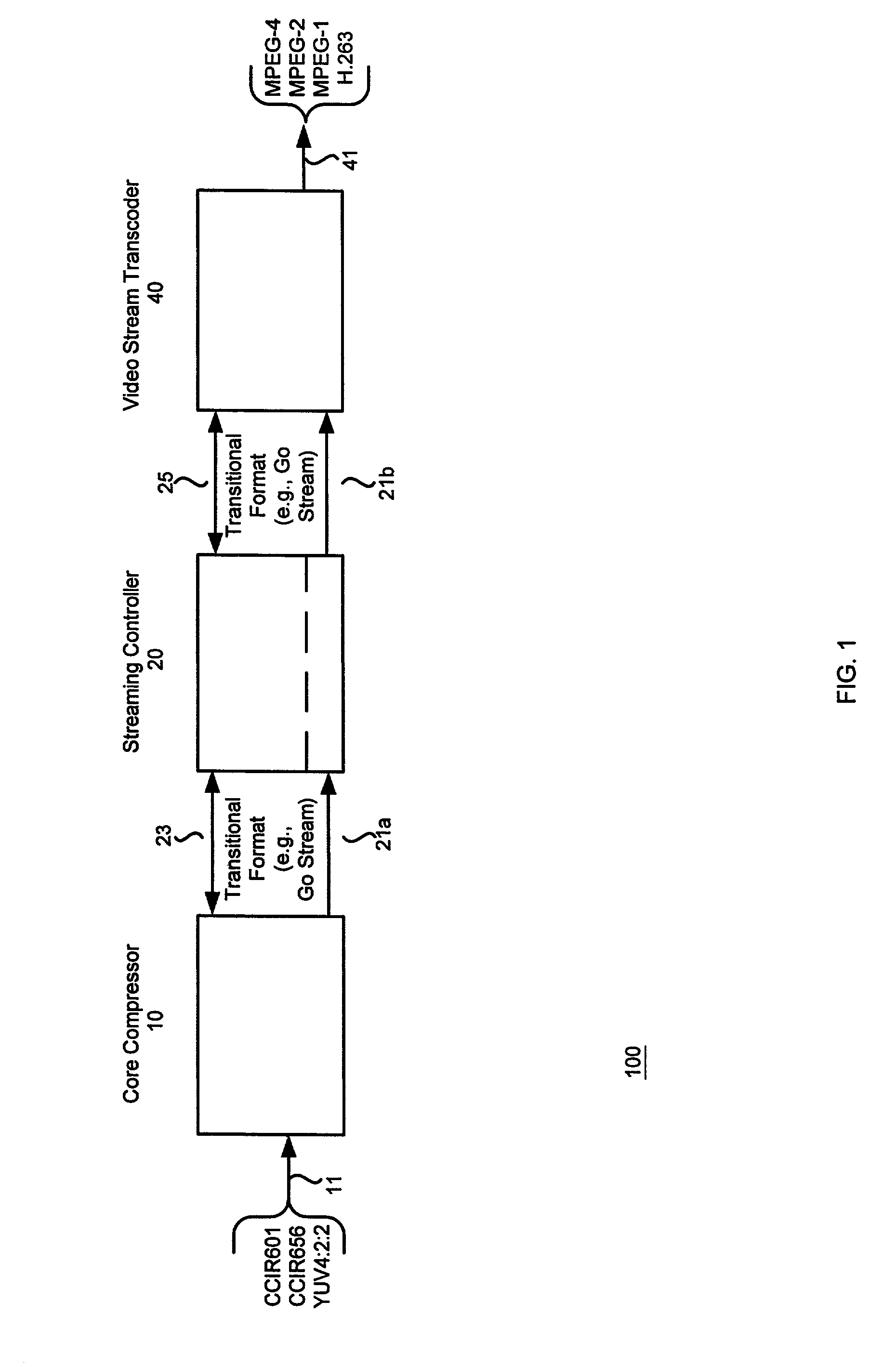
Multiple format video compression
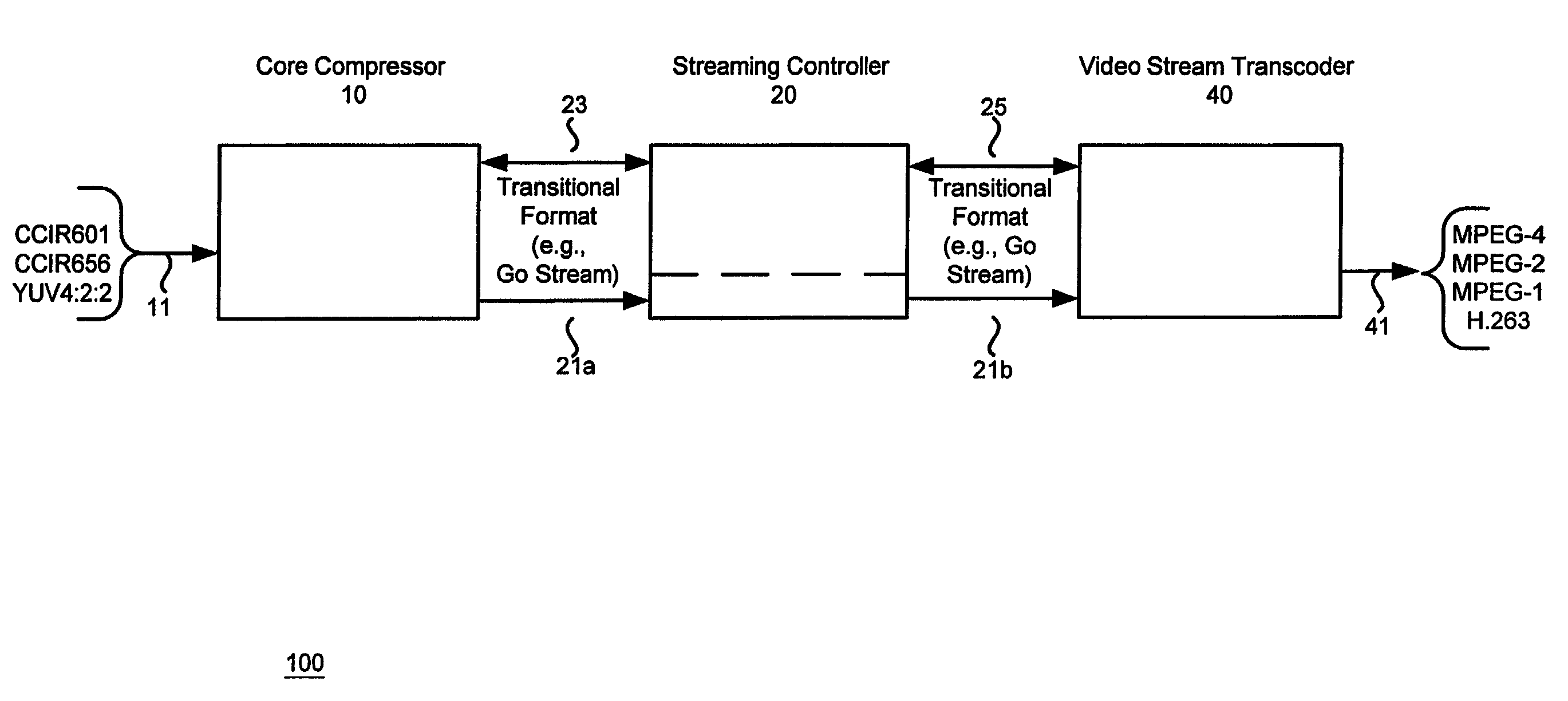
InactiveUS20050226324A1Promote divisionEasy to usePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMPEG-1Dirac (video compression format)
A video compression scheme enables the user to select one of many video compression formats, including the widely-used standard video formats such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 and H.263. In one embodiment, the scheme is implemented as a hardware-software combination, with the hardware portion, preferably implemented as an ASIC chip, performing the core compression and the software portion dealing with the detailed formatting. In another embodiment, a 32-bit aligned transitional data format is used.
Owner:MICRONAS
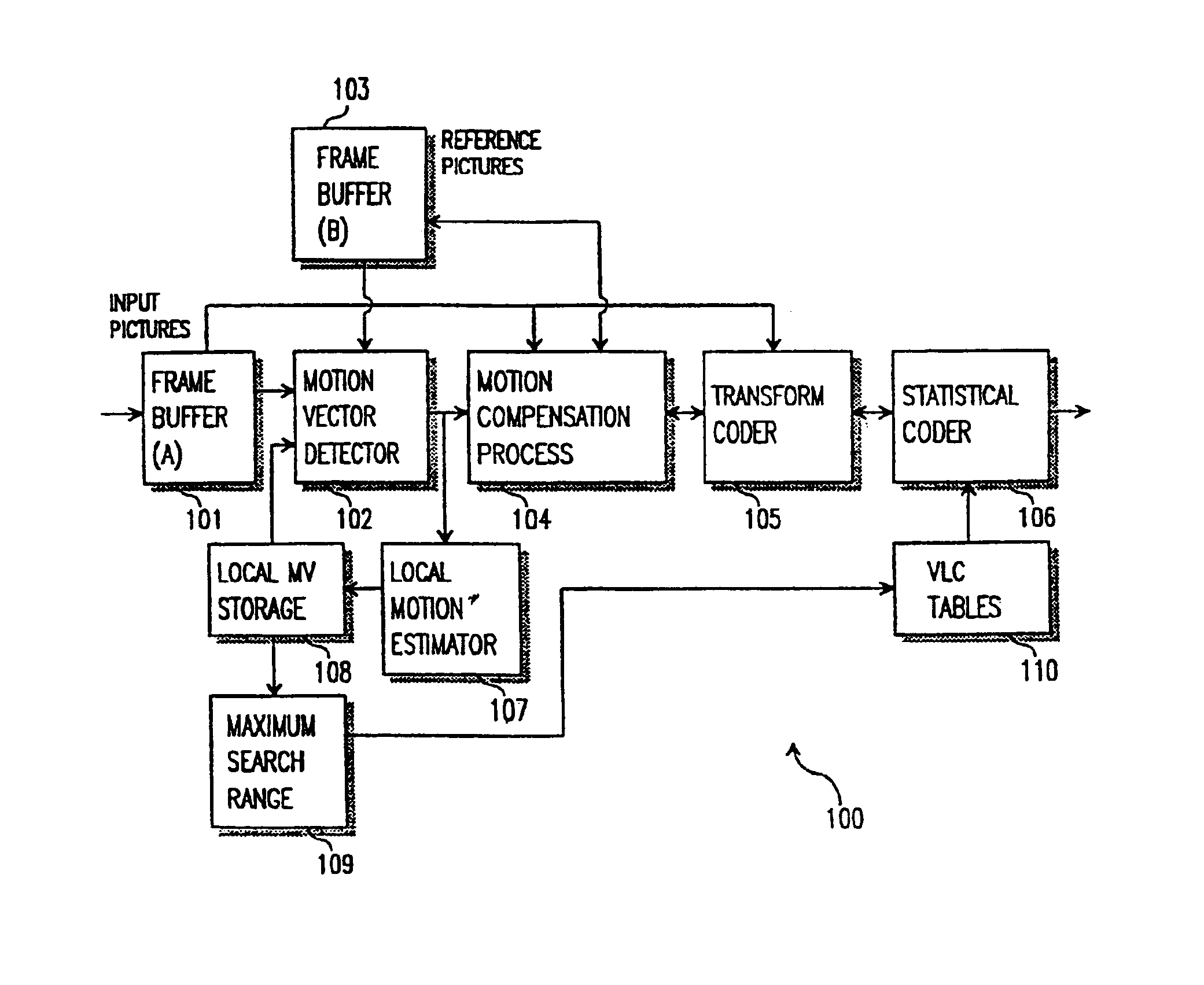
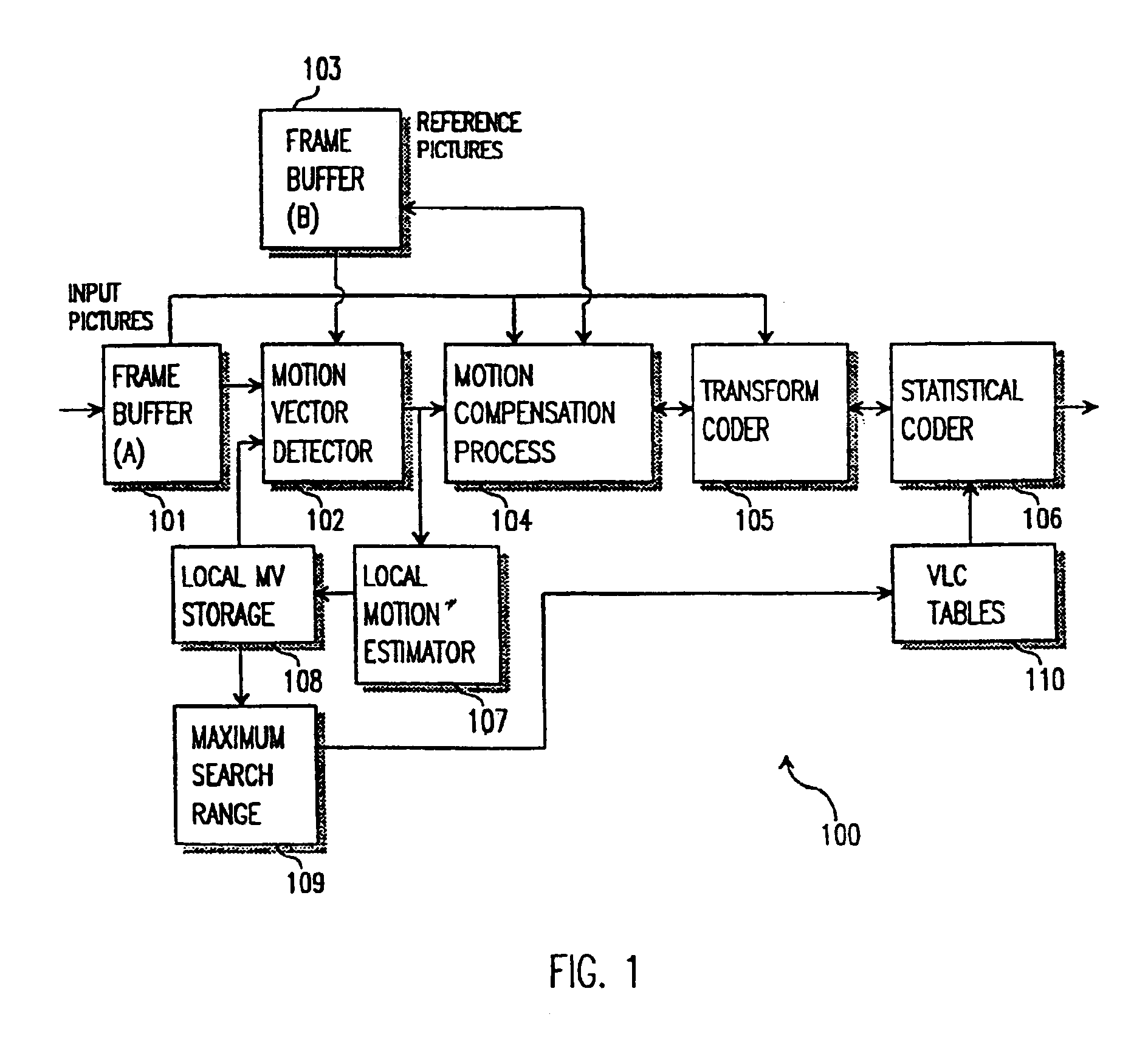
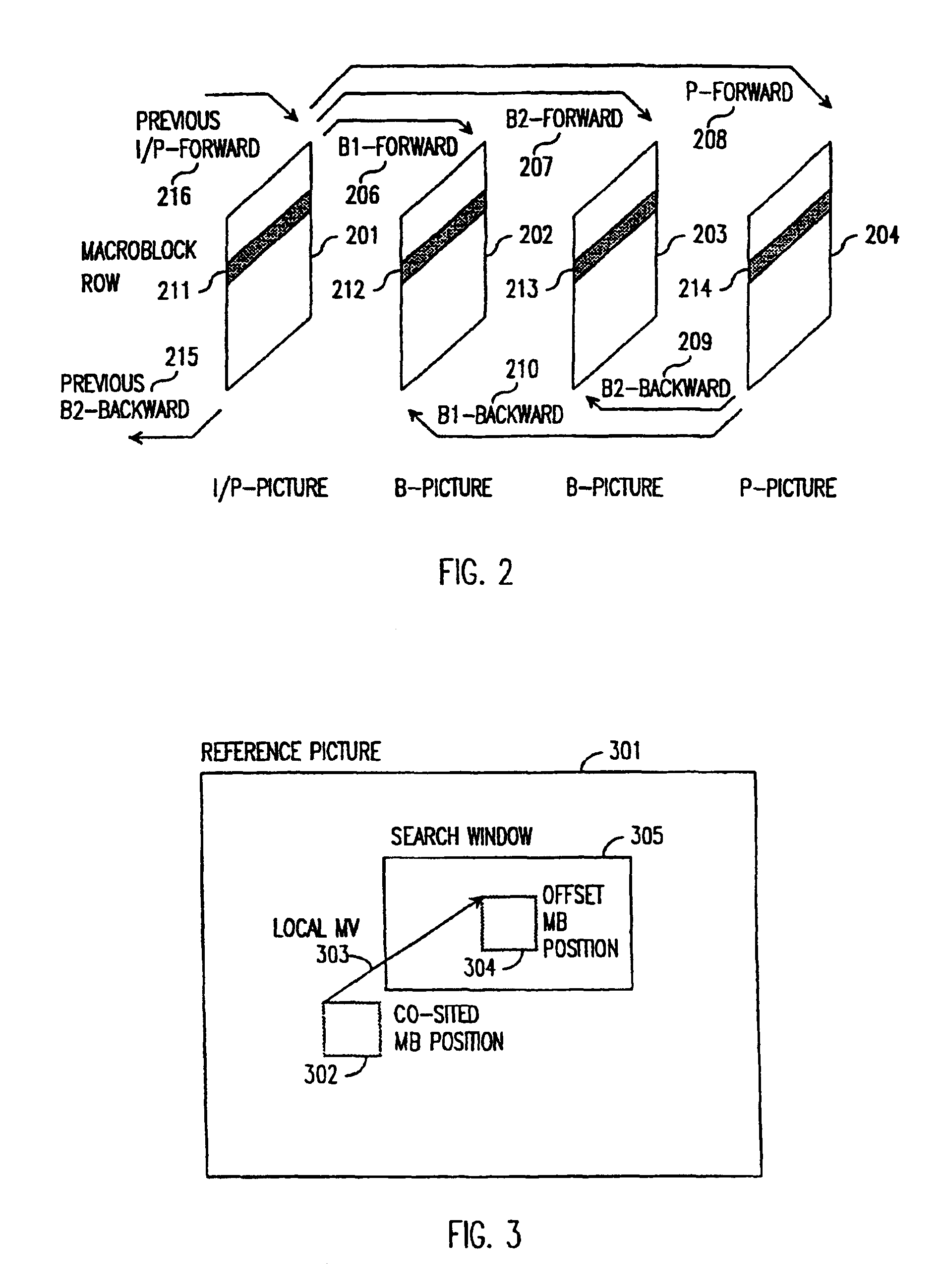
Motion vector detection with local motion estimator
InactiveUS6876702B1Increase the search rangeMinimized search windowColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoMPEG-1
A method and apparatus of encoding digital video, for example according to the ISO / IEC MPEG standards (ISO / IEC 11172-2 MPEG-1 and ISO / IEC 13818-2 MPEG-2), which employs a local motion estimator for determining respective local motion vectors for groups of adjacent macroblocks in a picture. A local motion vector is determined for each row of macroblocks in a picture from the motion vectors of the macroblocks in that row. Then, for macroblocks in the corresponding row of a subsequently coded picture, the local motion vector can be used to select the search window used for determining the motion vectors. The local motion estimator improves search range and accuracy of macroblock motion vector detection without increasing the search window accessing bandwidth and caching requirement, and computation lode of searching.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
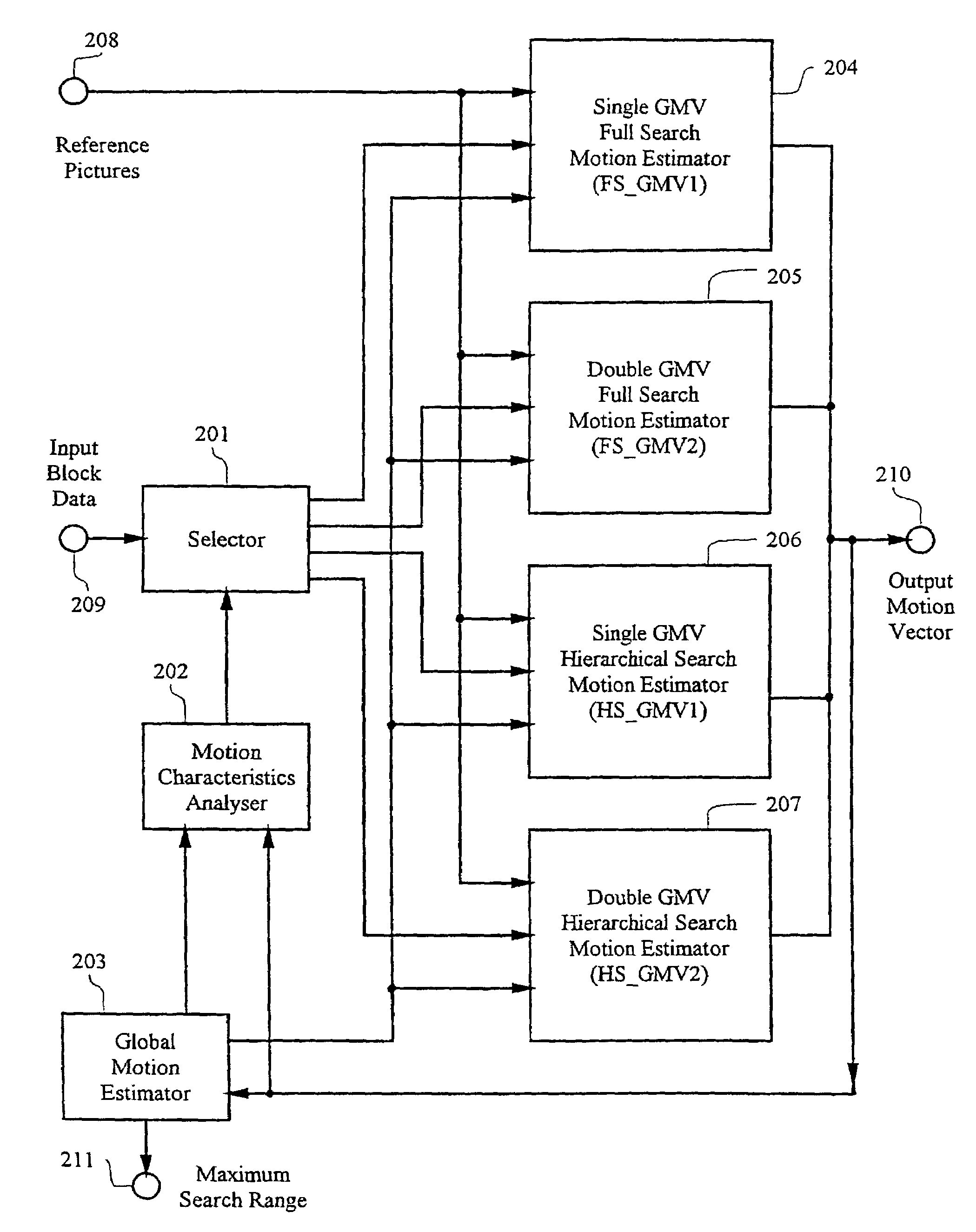
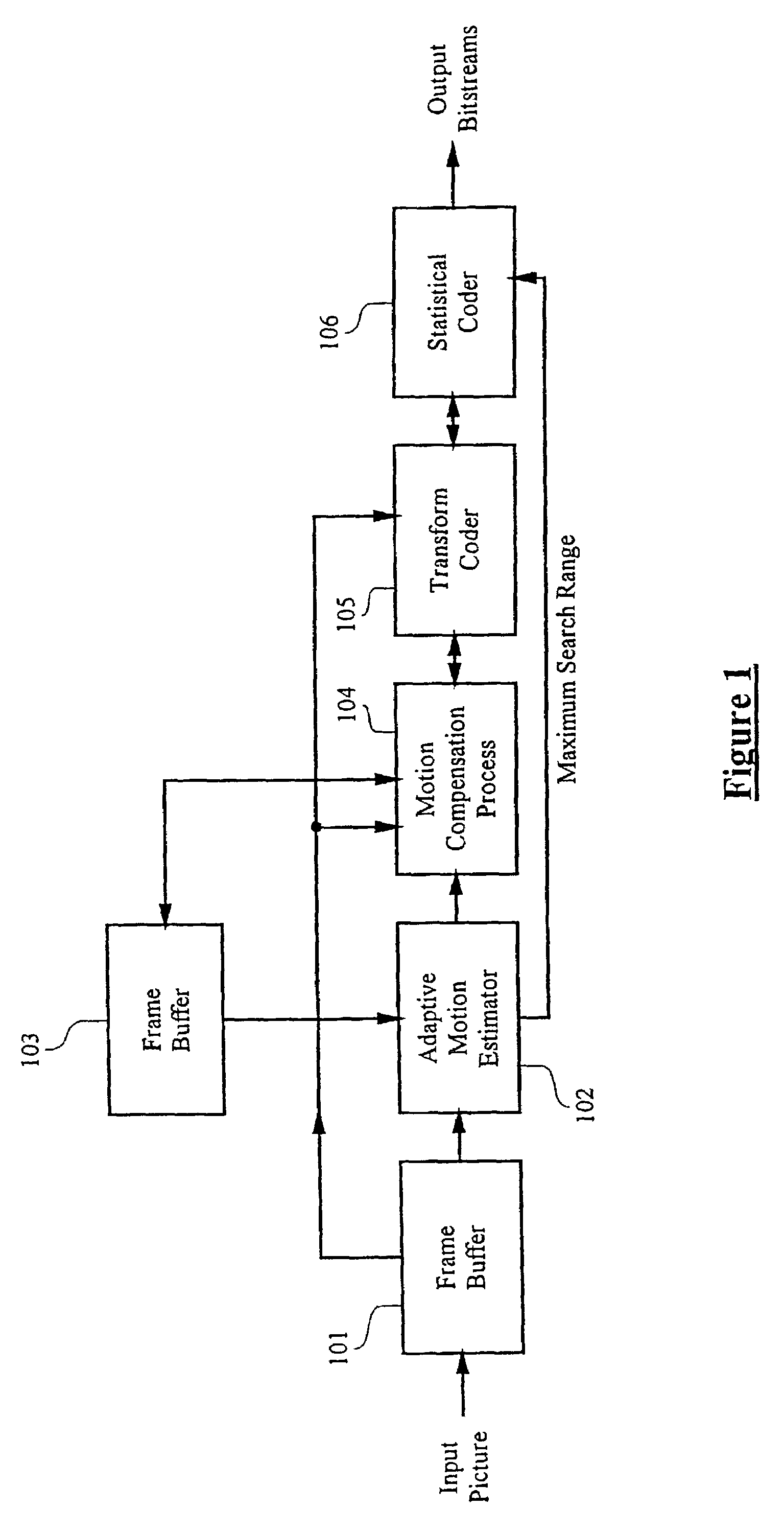
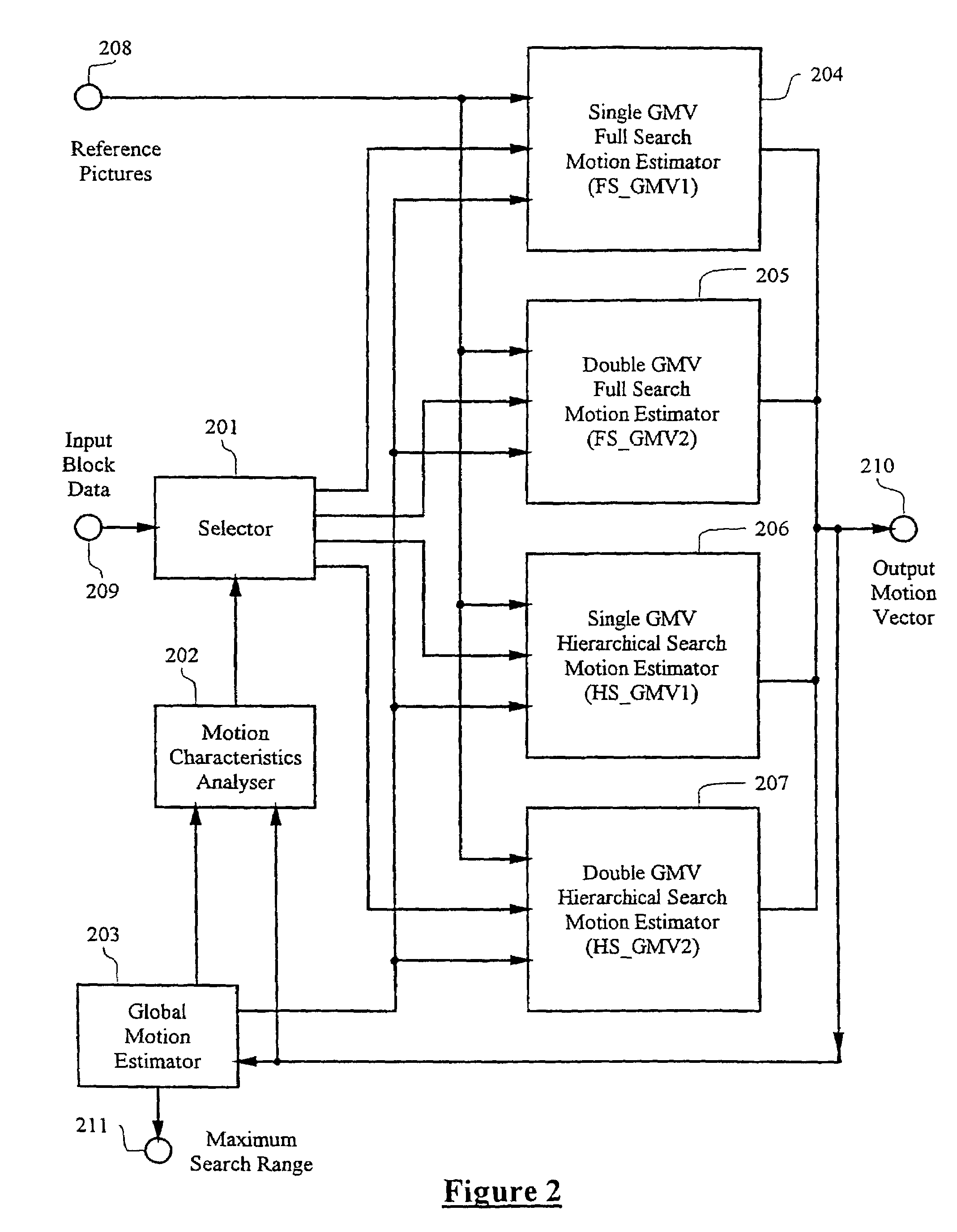
Adaptive motion estimator
InactiveUS7551673B1Expand effective search rangeMeet growth requirementsColor television with pulse code modulationImage analysisDigital videoMPEG-1
A method and apparatus of encoding digital video according to the ISO / IEC MPEG standards (ISO / IEC 11172-2 MPEG-1 and ISO / IEC 13818-2 MPEG-2) using an adaptive motion estimator. A plurality of global motion vectors are derived from the motion vectors of a previous picture in a sequence, and the global motion vectors are analyzed to determine motion characteristics. The video encoding is arranged to enable switching among different types of local motion estimators based on the motion characteristics of the moving pictures sequence. This gives rise to a motion estimation algorithm that can adaptively change its search range, search area and block matching scheme to suit different types of moving sequences.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
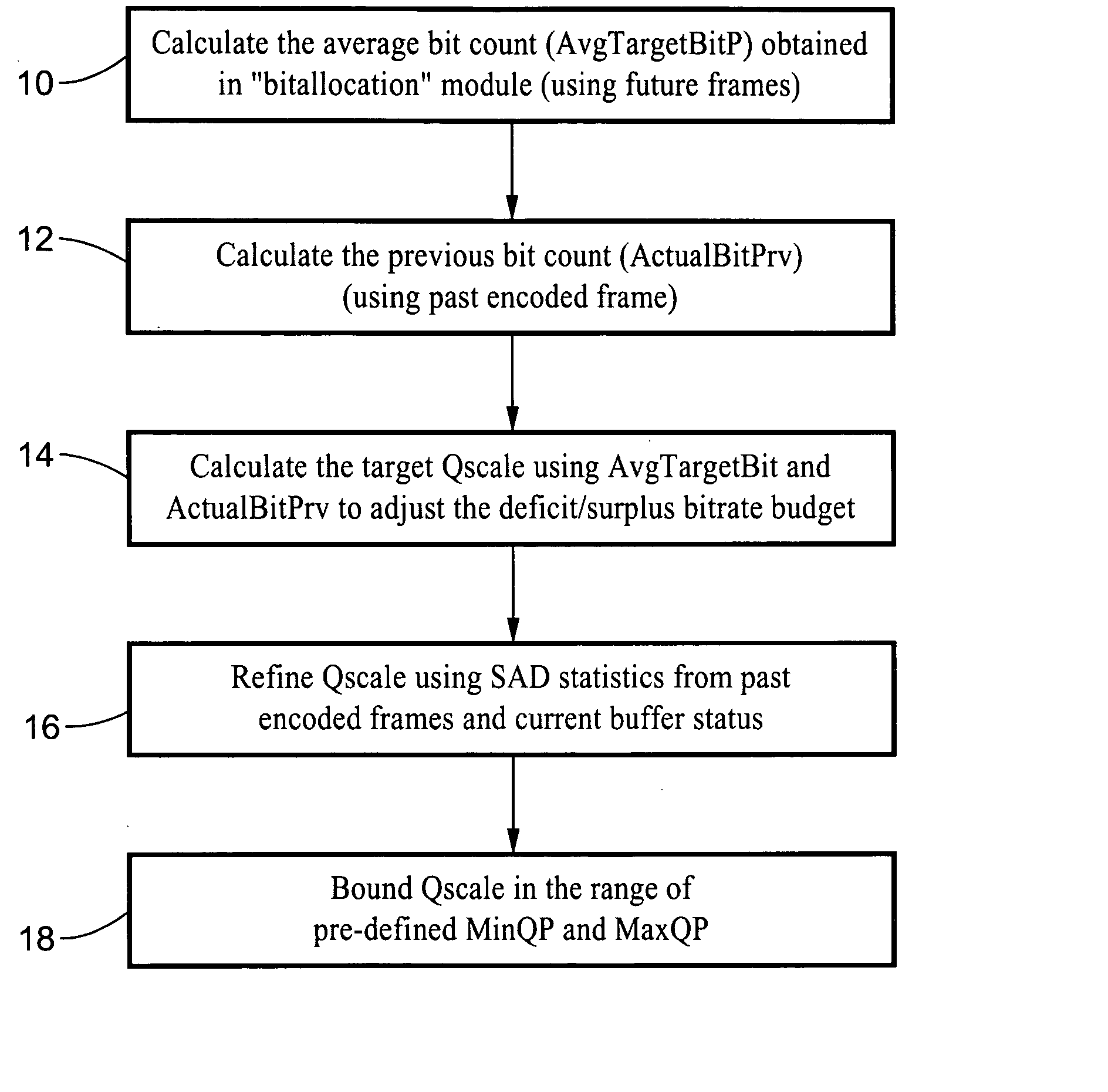
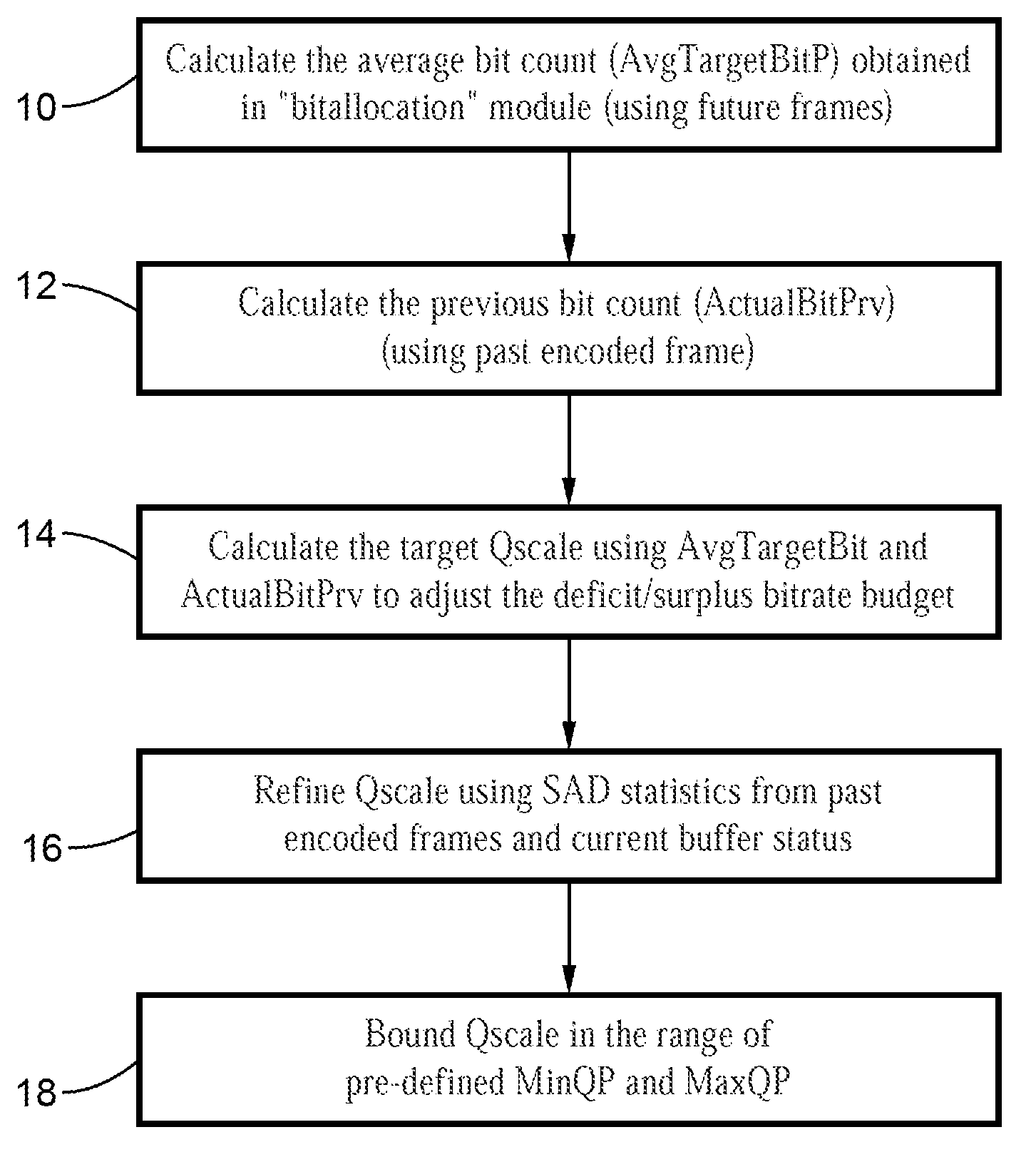
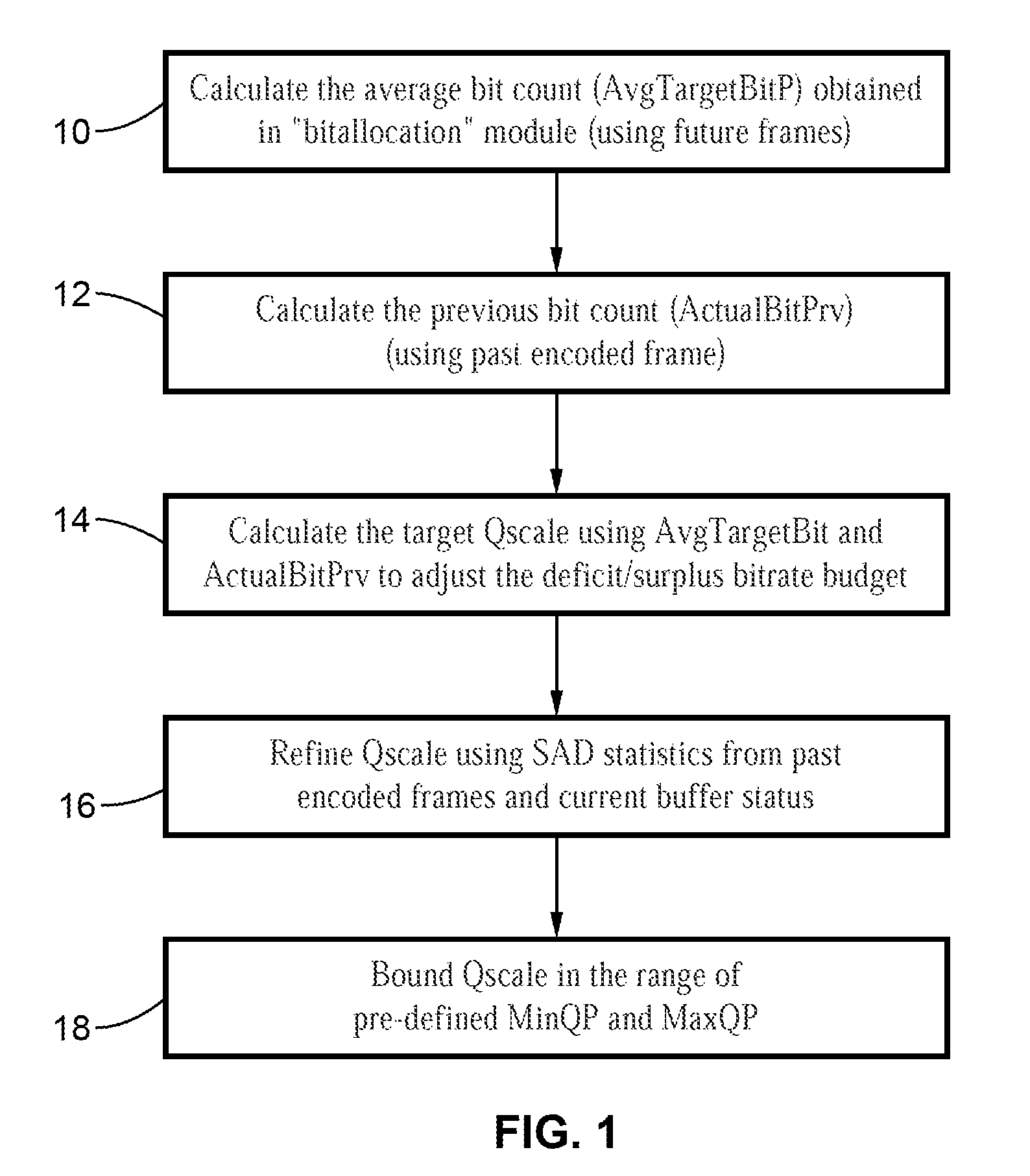
Scalable MPEG video/macro block rate control
InactiveUS20050169370A1Easy to exportColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG-1Absolute difference
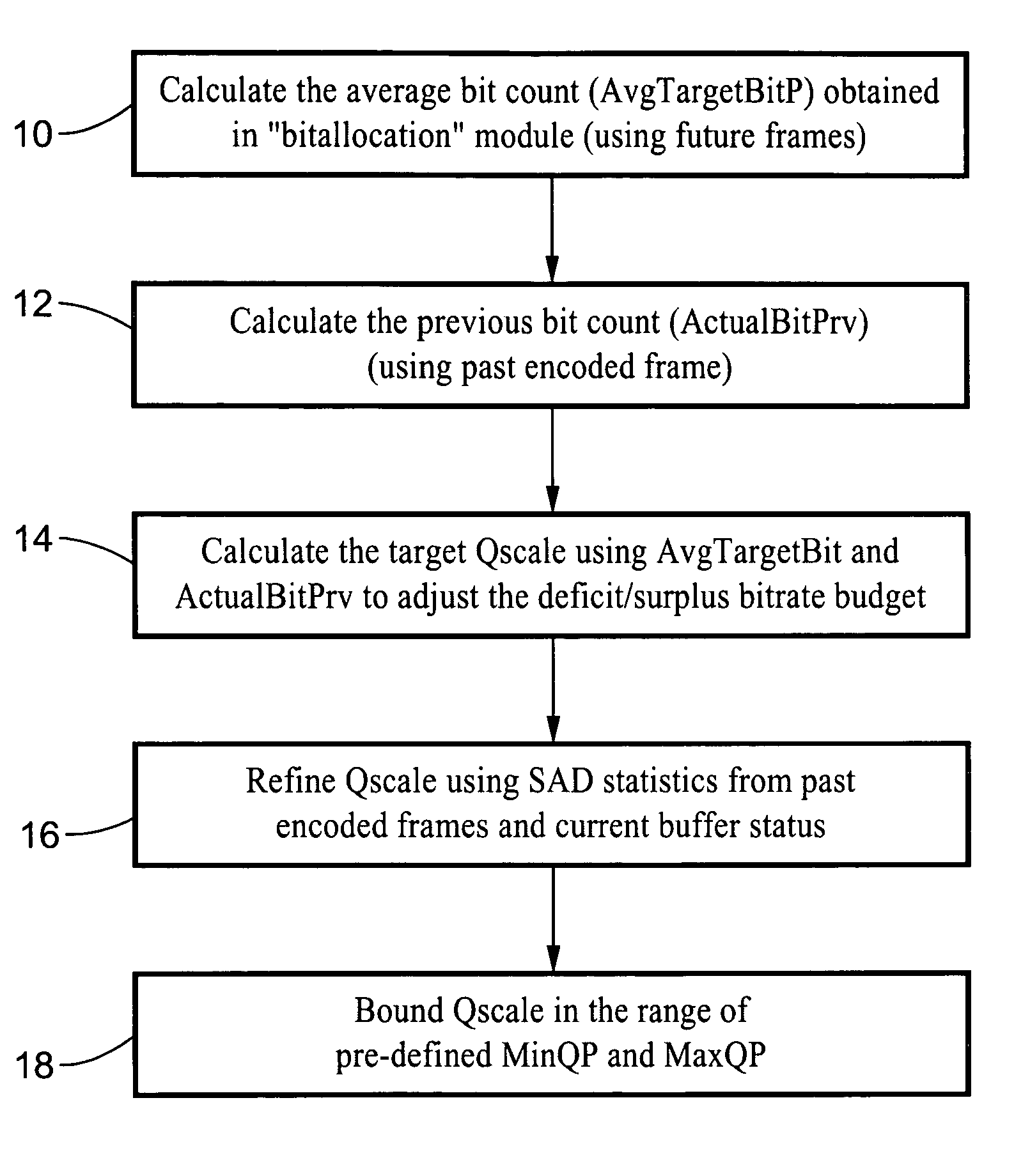
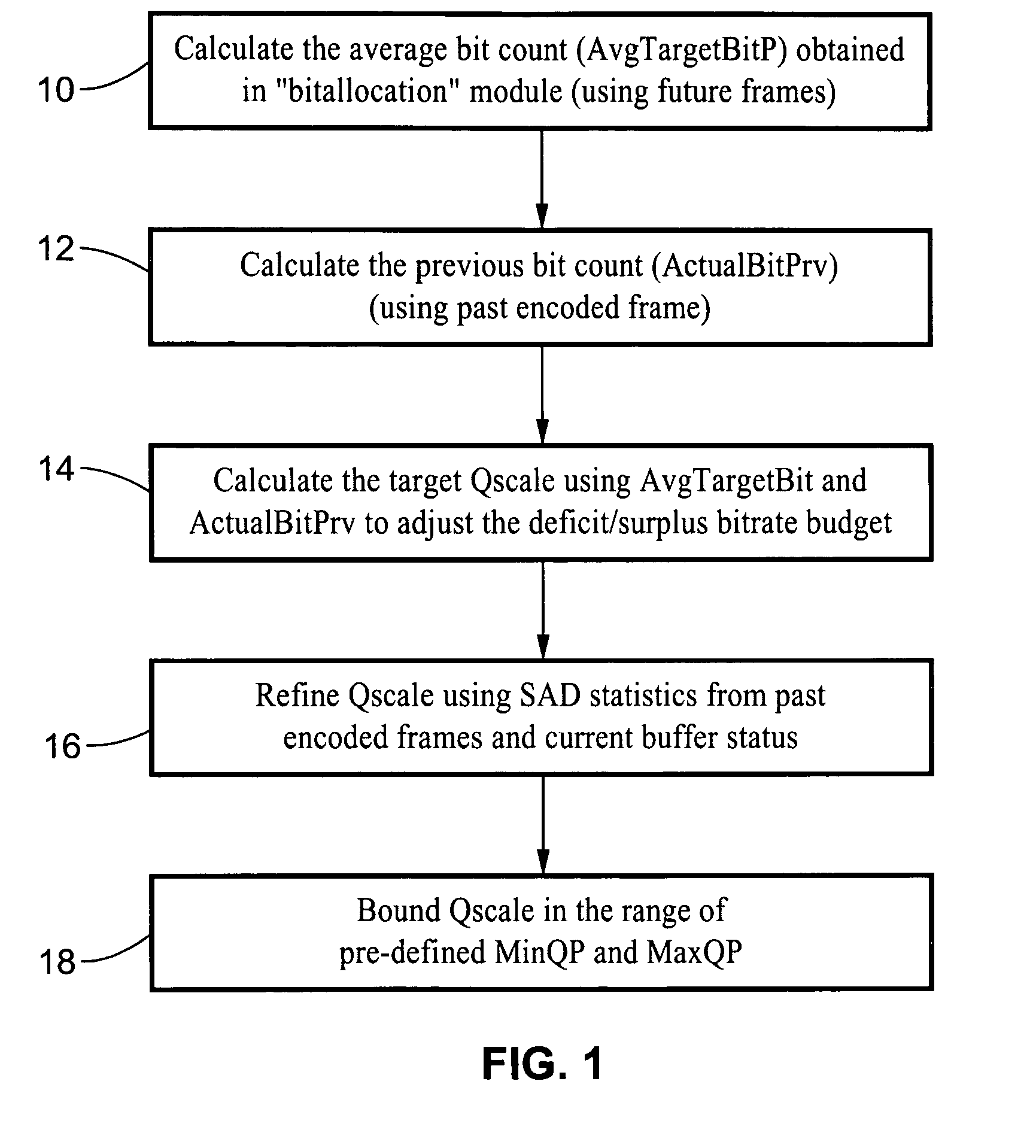
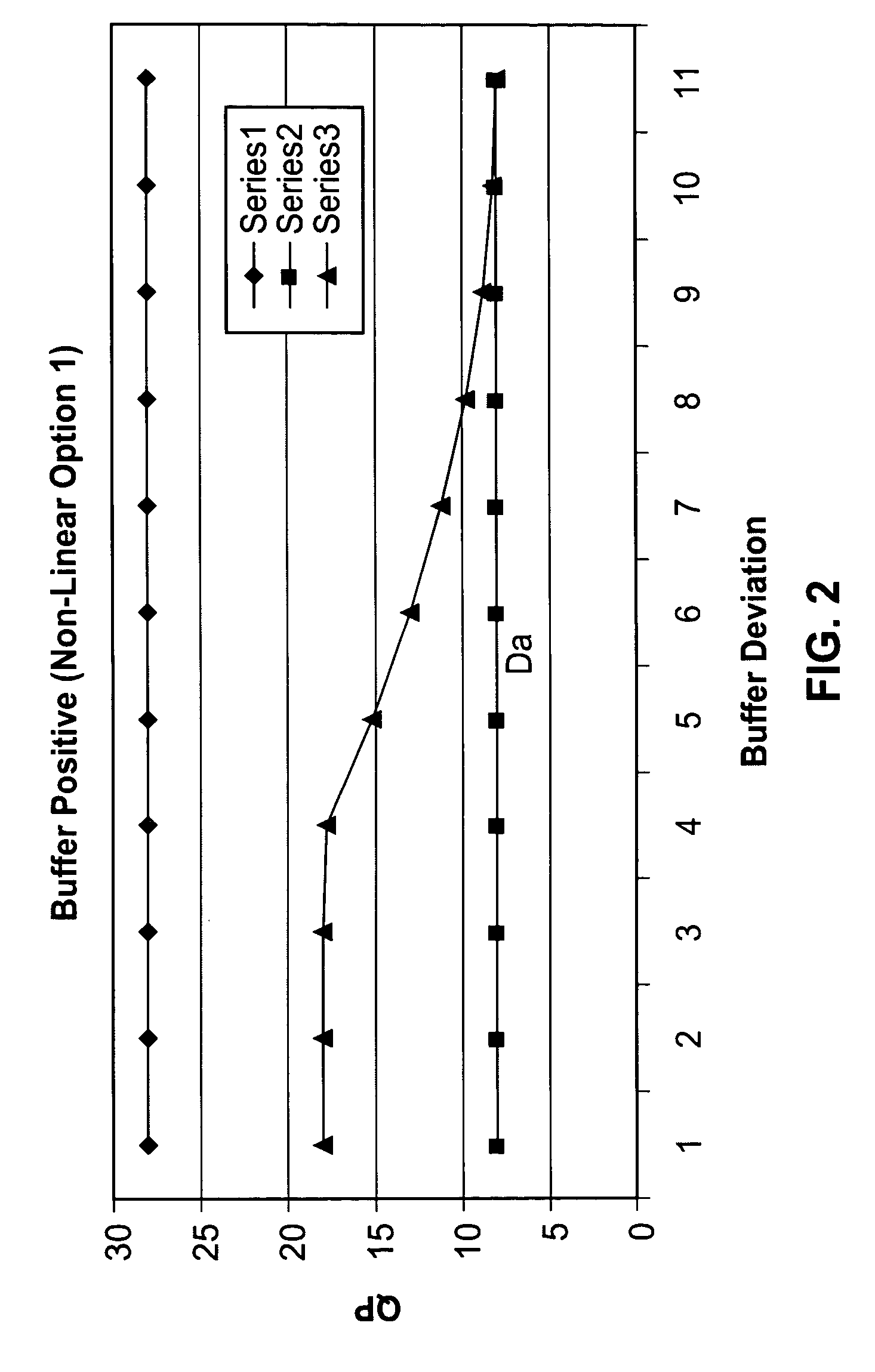
A scaleable macro block rate control method particularly well-suited for MPEG video. There is provided a method to easily derive a quantization parameter (QP) value using information such as bit usage, previous QP values and SAD values from the past encoded and future frames. The method utilizes quantization estimation techniques based on statistical relationships between different intensity measures, such as distortion intensity, absolute difference intensity and mean of absolute difference intensity. The method is well-suited to applications utilizing MPEG video such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, JVT / H.264 standards and so forth.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
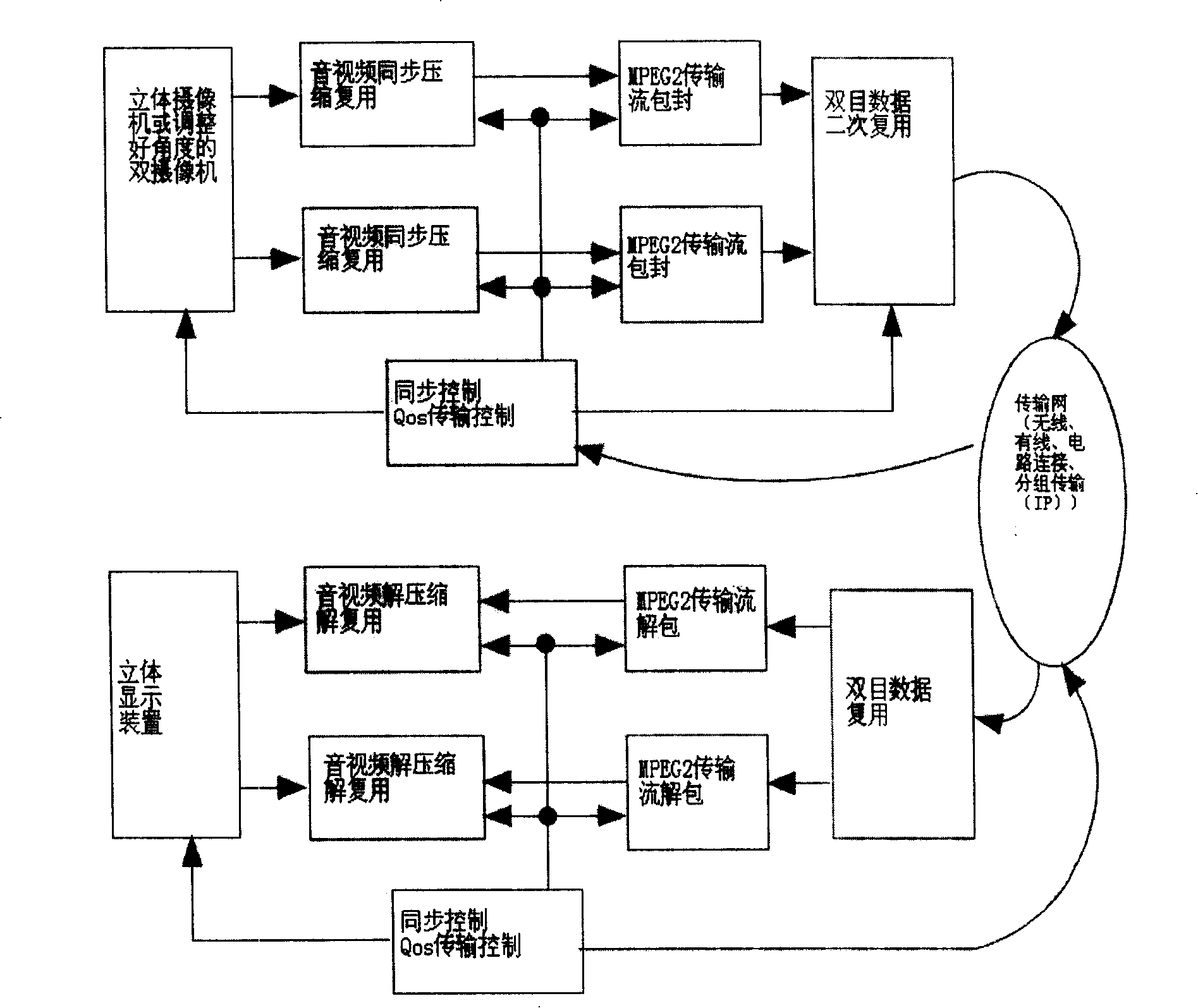
System and method for transmitting stereo audio and video numerical coding based on transmission stream
InactiveCN101232623AResolve synchronizationSolve the problem of congestion and packet lossPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationStreaming dataMPEG-1
The invention relates to a stereo audio and video stream data coding transmission method and system based on transmission streams. The invention comprises: a. Perform camera picking up to gain binocular audio and video data before synchronous compression and multiplex respectively in synchronous control; b. respectively perform envelopment in the synchronous control for transmission stream; c. perform secondary multiplex coding in transmission stream synchronous control, so as to gain single data stream; d. follow real-time transmission protocols to perform envelopment transmission and receive feedback adjusting; f. in the transmission service quality control, the invention can perform real-time transmission protocol de-envelopment and feedback information; g. de-multiplex to gain transversal binocular audio and video data; h. in synchronous monitoring condition, perform audio and video data de-compression and de-multiplexing; i. A display apparatus realizes stereo playing. The invention supports audio and video coding, such as MPEG-1 / 2 / 4, VC1, H263, H.264 and etc, as well as such transmission methods as wireless, cable, time division multiplex, block transmission and so on. The invention can realize remote stereophonical reoccurrence of local audio / video, and is simple, universal and reliable.
Owner:李会根 +3
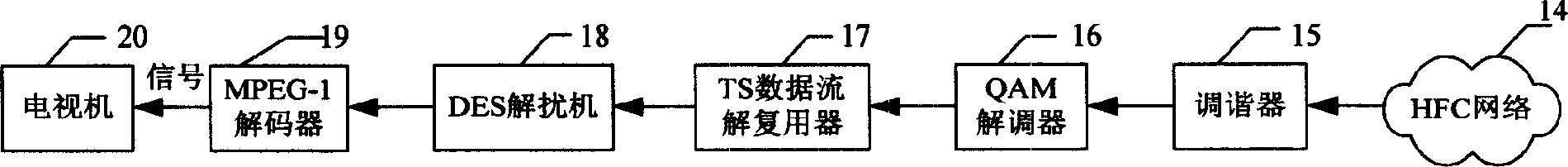
Digital television broadcasting system based on MPEG-1
ActiveCN1595975ALow costTelevision system detailsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesMPEG-1Resonance
The invention is a digital television broadcasting system based on MPEG-1, the system is made up of network, digital television broadcasting system based on MPEG-1 through the network and digital television broadcasting receiving system based on MPEG-1. The transmitting system includes MPEG-1 coder, disturber, IP data flow complex device and modulator, the receiving system includes resonance device, demodulator, TS data flow demultiplexing device, and MPEG-1 decoder. The cost is low, and it can display program source with MPEG-1 format with IP mode.
Owner:南通研祥智能科技有限公司
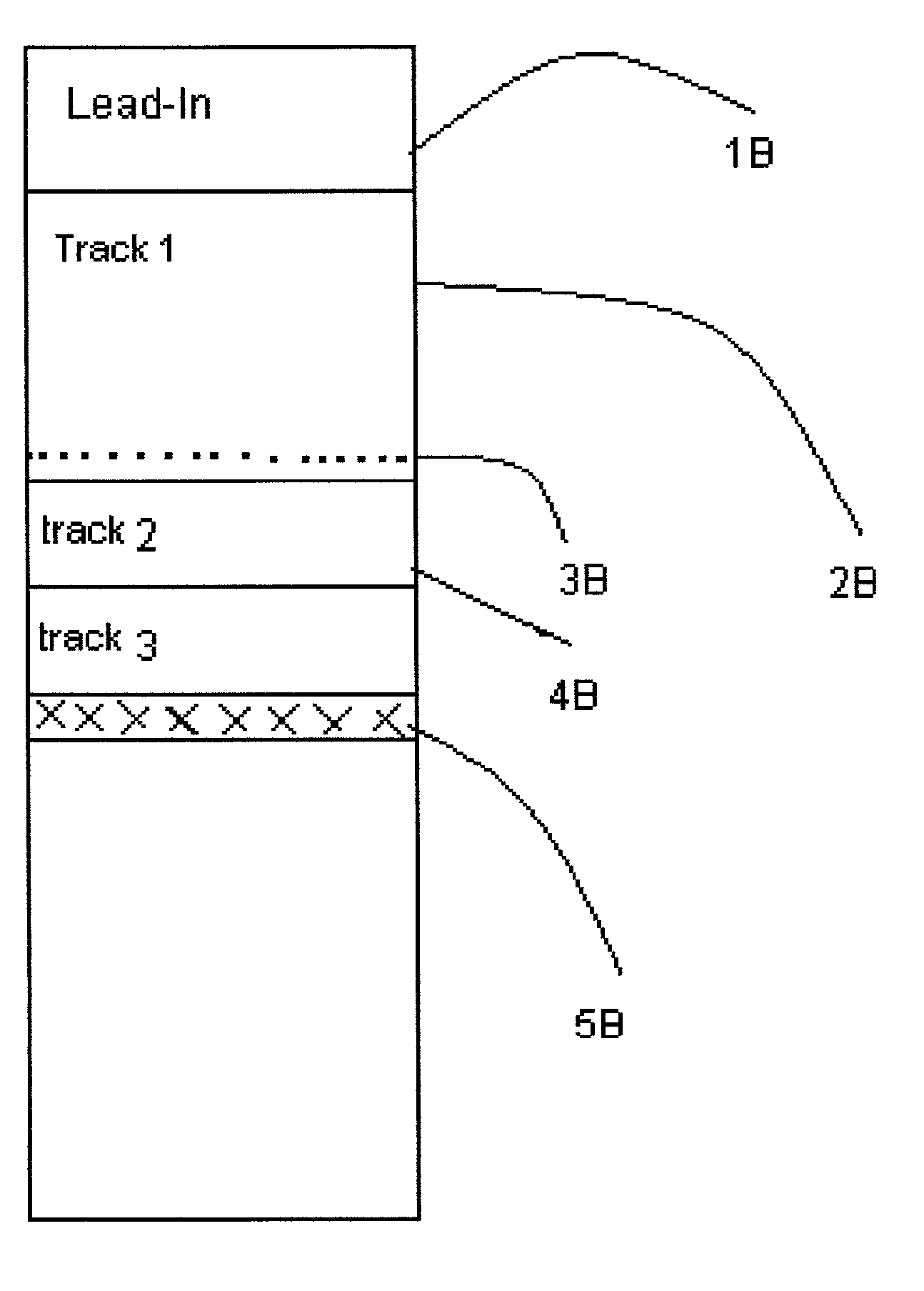
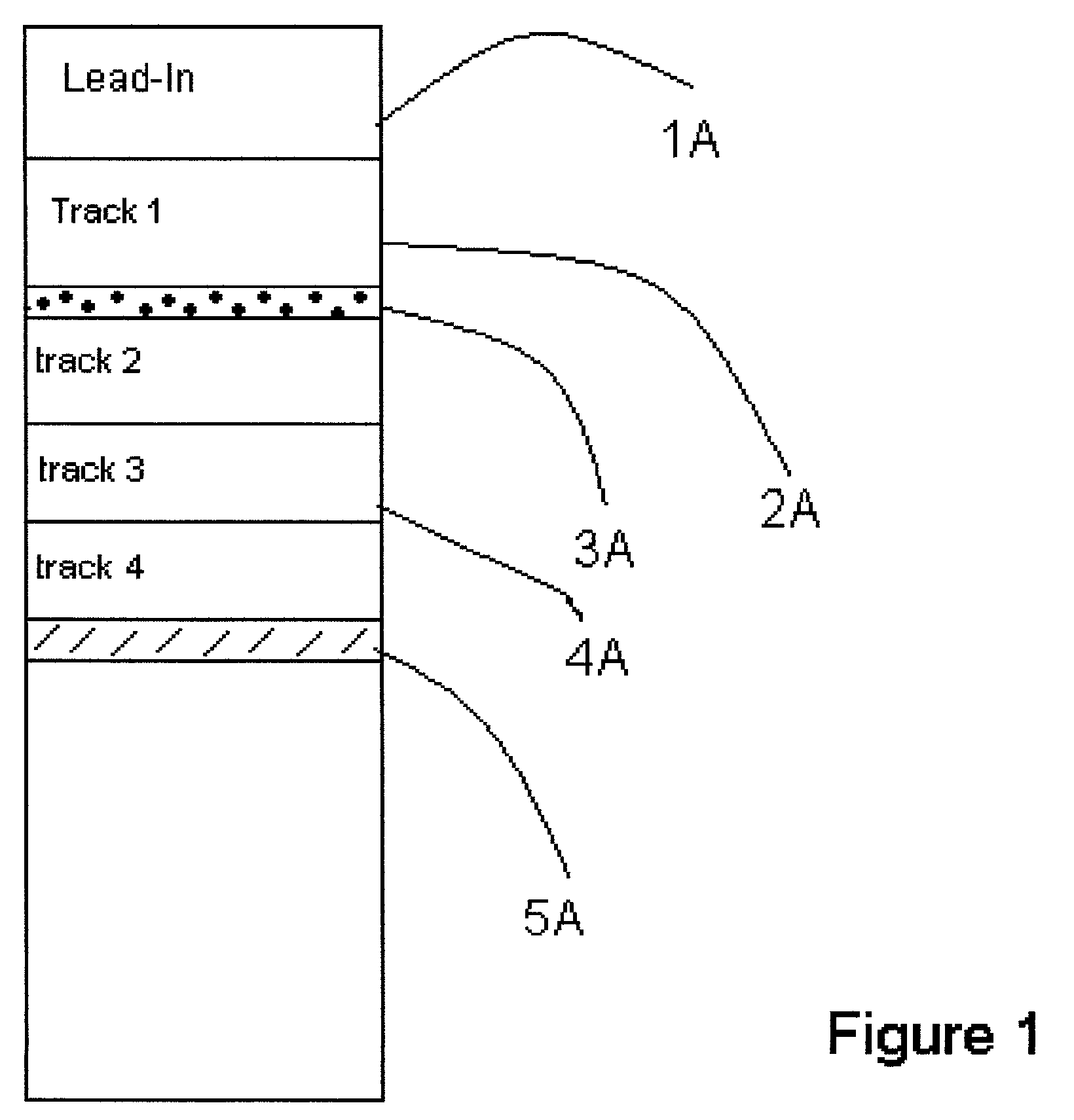
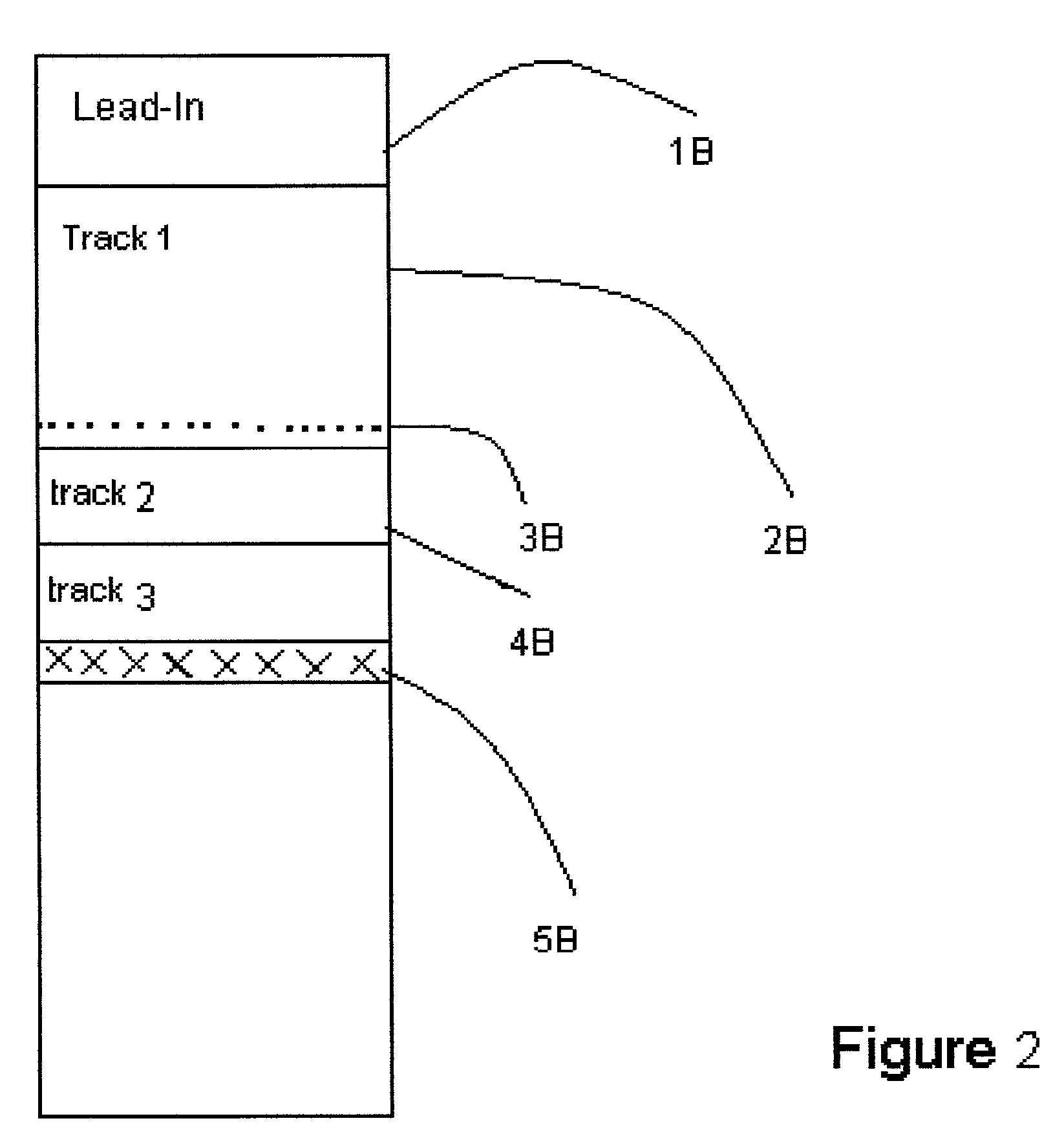
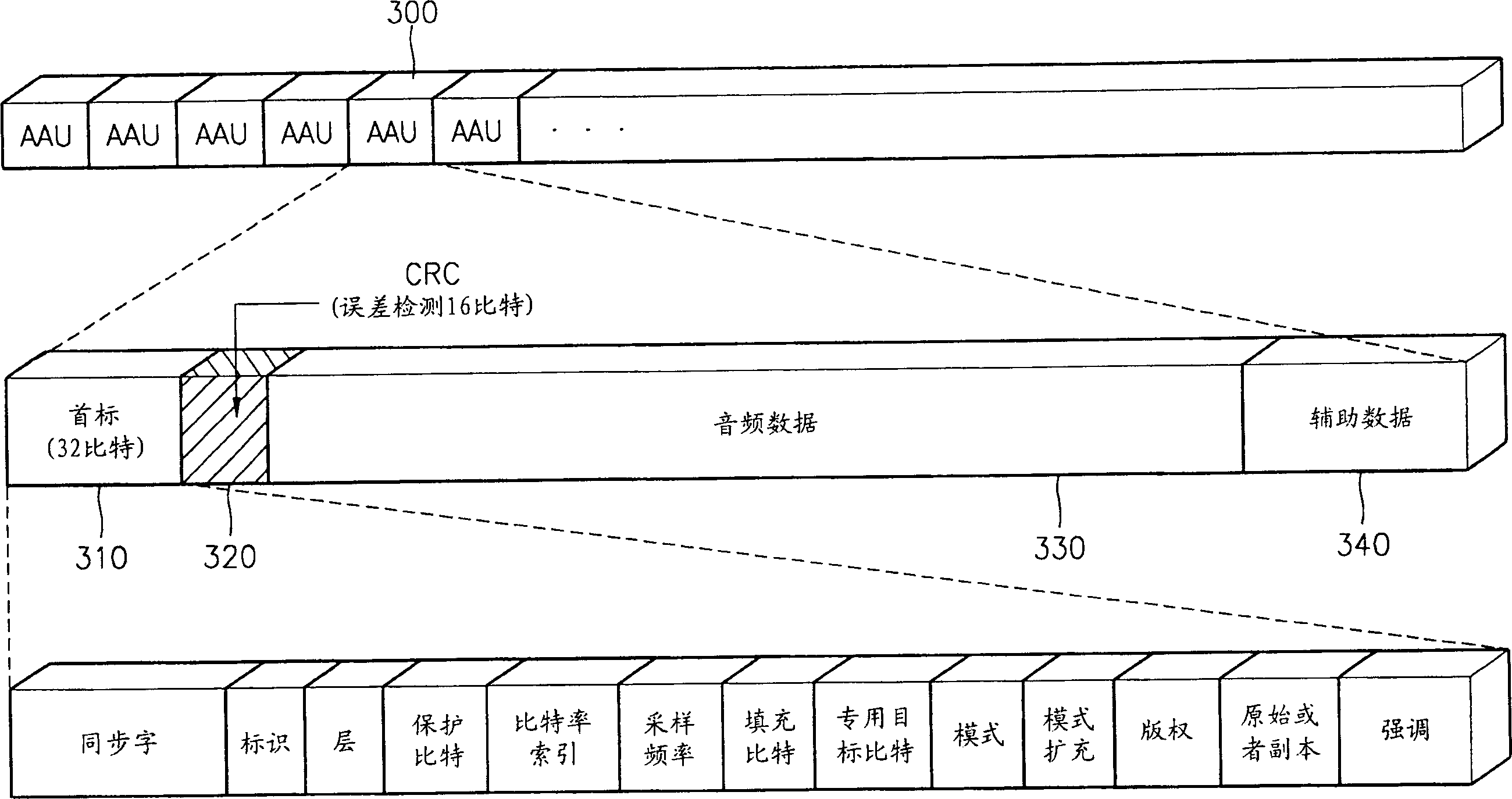
Consumer friendly error correcting formating method for white book 2.0 video compact disc with CD-DA red book audio tracks
InactiveUS7103261B2Take advantage ofTelevision system detailsDisc-shaped record carriersMPEG-1CD player
Consumer friendly compact disc which employ MPEG 1 video data for DVD players, computers, and CD-DA tracks for Compact Disc players with traditional playback identified by these independent machines. DVD playable MPEG 1 video time will not alter CD audio playability in CD players due to a 4-second track 1 Table of Contents time. Playback of disc in DVD players allows Play Back Control (PBC) of MPEG 1 data without interaction of CD-DA tracks. The method employed ensure a compact disc free from digital E32 type sector errors associated with PRE GAP and untrue lead out point now true with current white book 2.0 spec when including CD-DA tracks. This specially authored formatted disc derived from a previous unperfected white book spec allow the bridging of three of the most popular consumer products of our time, the DVD player, CD player and the home computer.
Owner:GRECIA WILLIAM
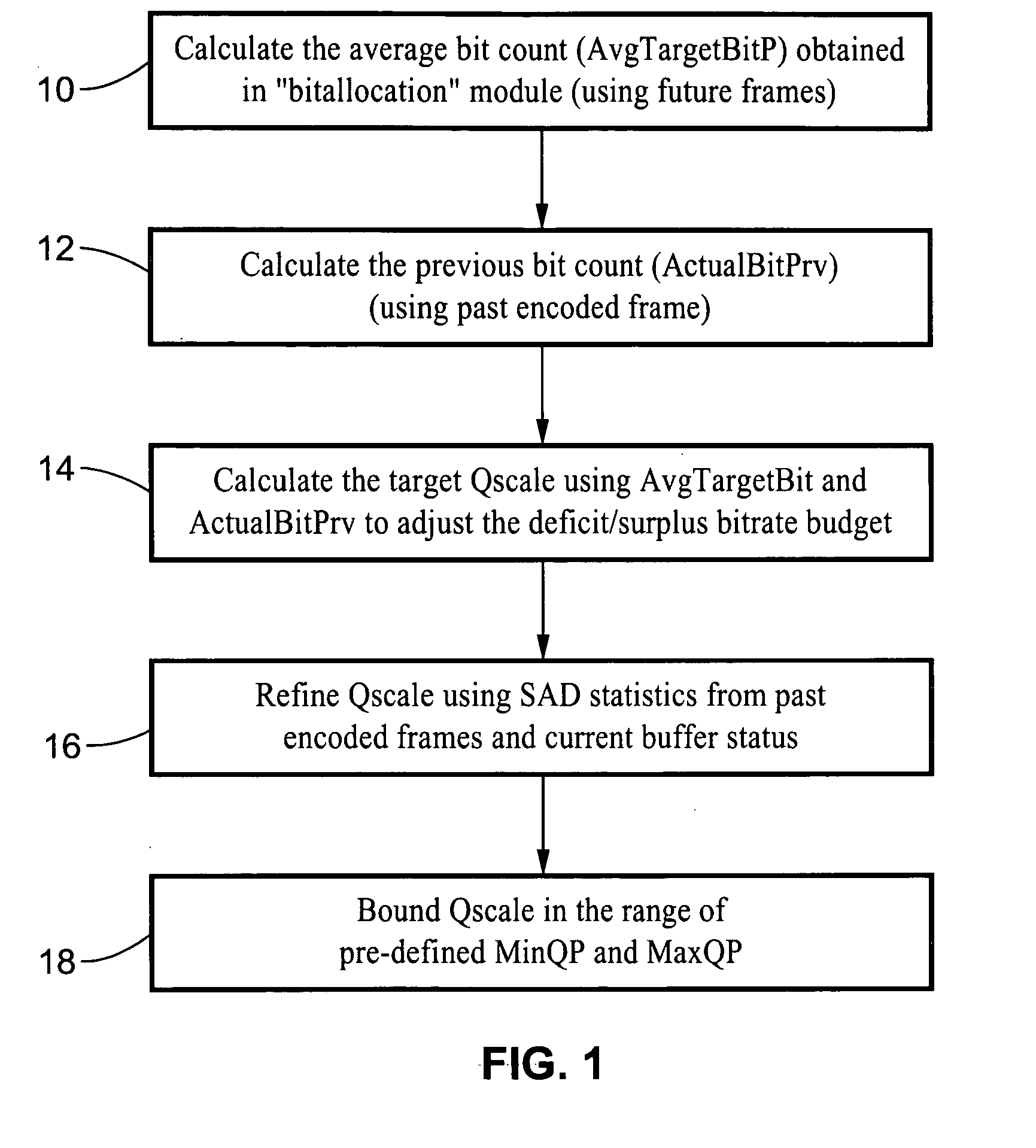
Scalable MPEG video/macro block rate control
InactiveUS7697608B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG-1Absolute difference
A scaleable macro block rate control method particularly well-suited for MPEG video. There is provided a method to easily derive a quantization parameter (QP) value using information such as bit usage, previous QP values and SAD values from the past encoded and future frames. The method utilizes quantization estimation techniques based on statistical relationships between different intensity measures, such as distortion intensity, absolute difference intensity and mean of absolute difference intensity. The method is well-suited to applications utilizing MPEG video such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, JVT / H.264 standards and so forth.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Multiple format video compression
InactiveUS7085320B2Promote divisionEasy to useFrequency diversityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMPEG-1Dirac (video compression format)
Owner:MICRONAS
Scalable MPEG video/macro block rate control
InactiveUS20050169369A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG-1Absolute difference
A scaleable macro block rate control method particularly well-suited for MPEG video. There is provided a method to easily derive a quantization parameter (QP) value using information such as bit usage, previous QP values and SAD values from the past encoded and future frames. The method utilizes quantization estimation techniques based on statistical relationships between different intensity measures, such as distortion intensity, absolute difference intensity and mean of absolute difference intensity. The method is well-suited to applications utilizing MPEG video such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, JVT / H.264 standards and so forth.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Scalable MPEG video/macro block rate control
InactiveUS20100150227A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMPEG-1Absolute difference
A scaleable macro block rate control method particularly well-suited for MPEG video. There is provided a method to easily derive a quantization parameter (QP) value using information such as bit usage, previous QP values and SAD values from the past encoded and future frames. The method utilizes quantization estimation techniques based on statistical relationships between different intensity measures, such as distortion intensity, absolute difference intensity and mean of absolute difference intensity. The method is well-suited to applications utilizing MPEG video such as MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, JVT / H.264 standards and so forth.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP +1
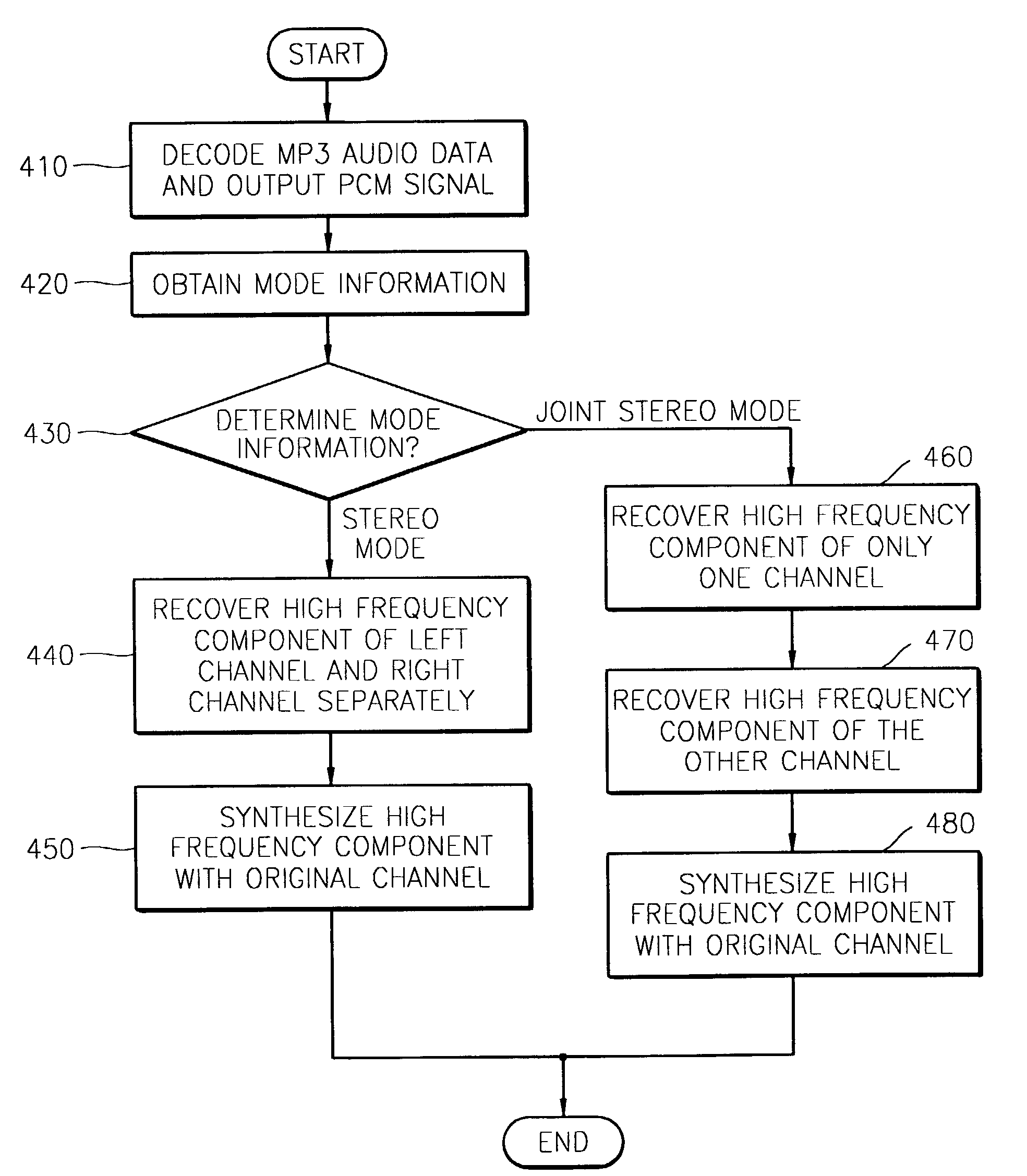
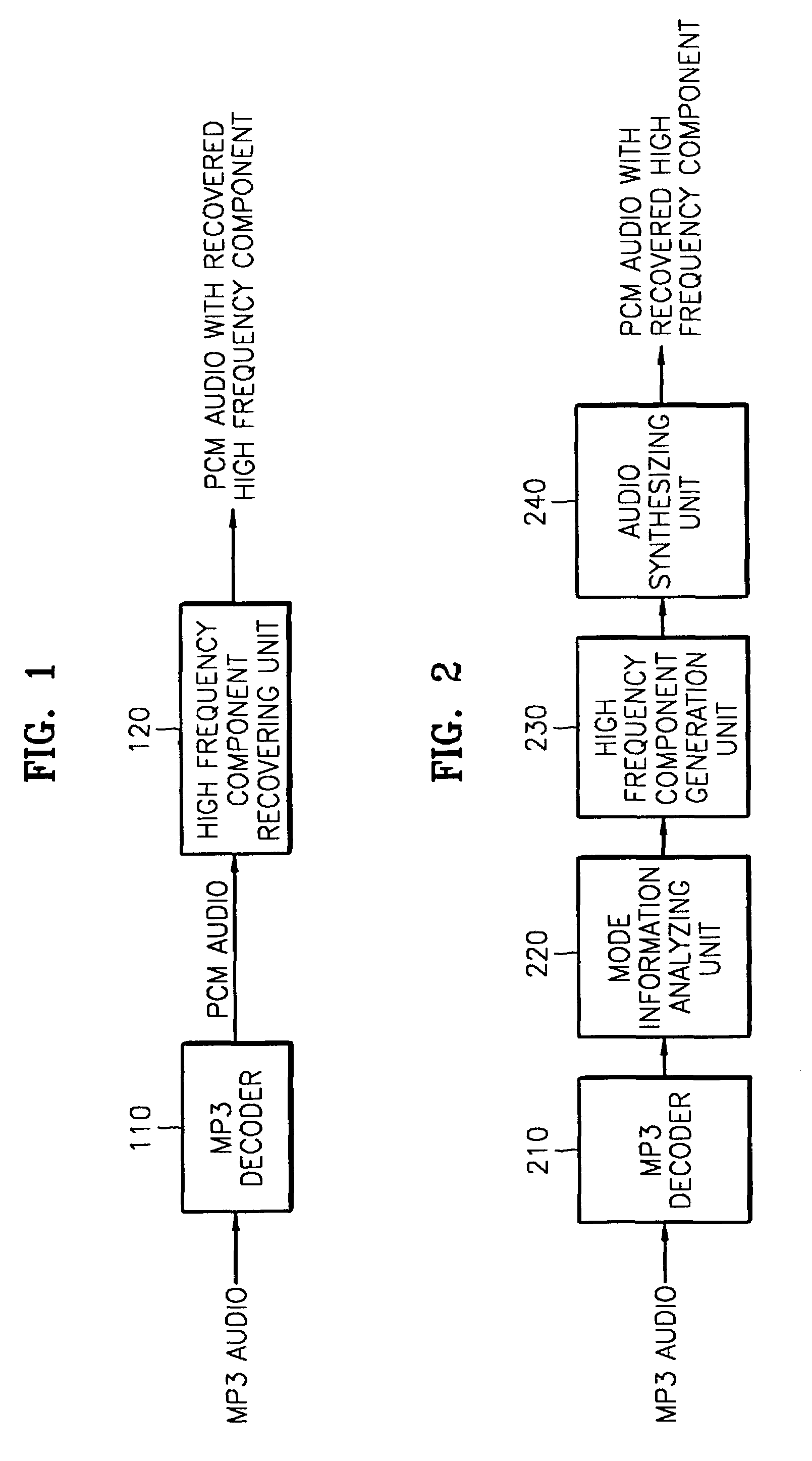
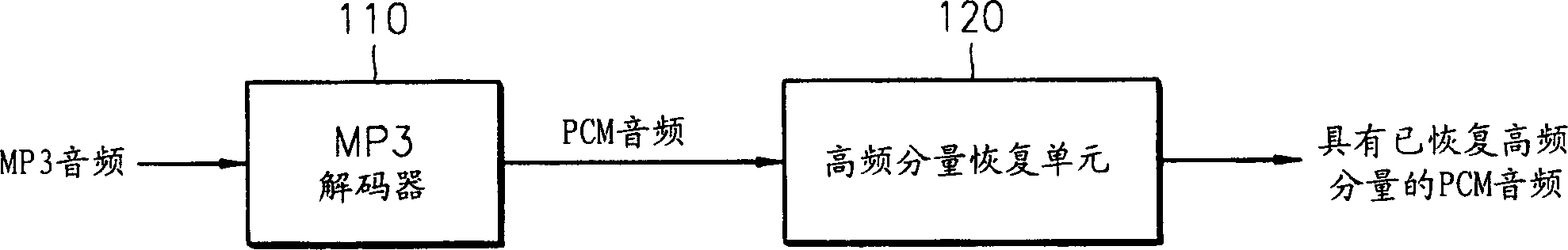
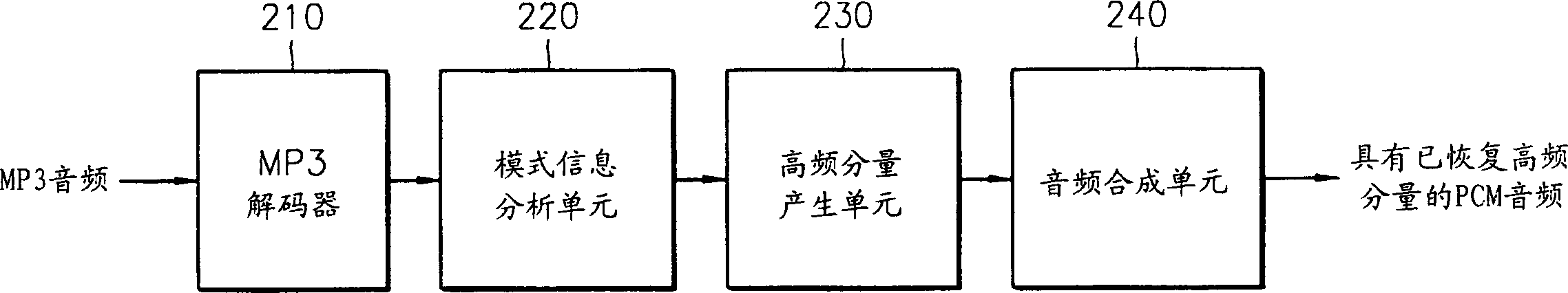
Audio decoding method and apparatus which recover high frequency component with small computation
InactiveUS7328161B2Reduce the amount presentElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsDecoding methodsMPEG-1
A method and apparatus for performing audio post processing using mode information that indicates the degree of similarity between a right channel signal and a left channel signal in MPEG-1 layer 3 audio data, are provided. If the difference between the two channel signals is small, a first mode is used in which the high frequency component of only one channel is recovered and the recovered high frequency component is used to recover the high frequency component of the other channel. If the difference between the two channel signals is large, a second mode is selected in which the high frequency component in only one of every two frames is recovered alternately in the left channel and the right channel and the high frequency component of each of the skipped frames is interpolated based on the high frequency components of the previous frame and the next frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Audio decoding method and apparatus which recover high frequency component with small computation
InactiveCN1467703ASmall amount of calculationElectrophonic musical instrumentsStereophonic/quadraphonic recording circuitsDecoding methodsMPEG-1
A method and apparatus for reducing the amount of computation in audio post processing, and more particularly, a method and apparatus for performing audio post processing using mode information that indicates the degree of similarity between a right channel signal and a left channel signal in MPEG-1 layer 3 audio data, are provided. If the difference between the two channel signals is small, a first mode is used in which the high frequency component of only one channel is recovered and the recovered high frequency component is used to recover the high frequency component of the other channel, and if the difference between the two channel signals is large, a second mode is selected in which the high frequency component in only one of every two frames is recovered alternately in the left channel and the right channel and the high frequency component of each of the skipped frames is interpolated based on the high frequency components of the previous frame and the next frame. By doing so, the new audio decoding method and apparatus recover high frequency components with a small amount of computation. The method reduces the amount of computation to less than half the amount of computation used in the prior art in recovering high frequency components.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and process for encoding audio data
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
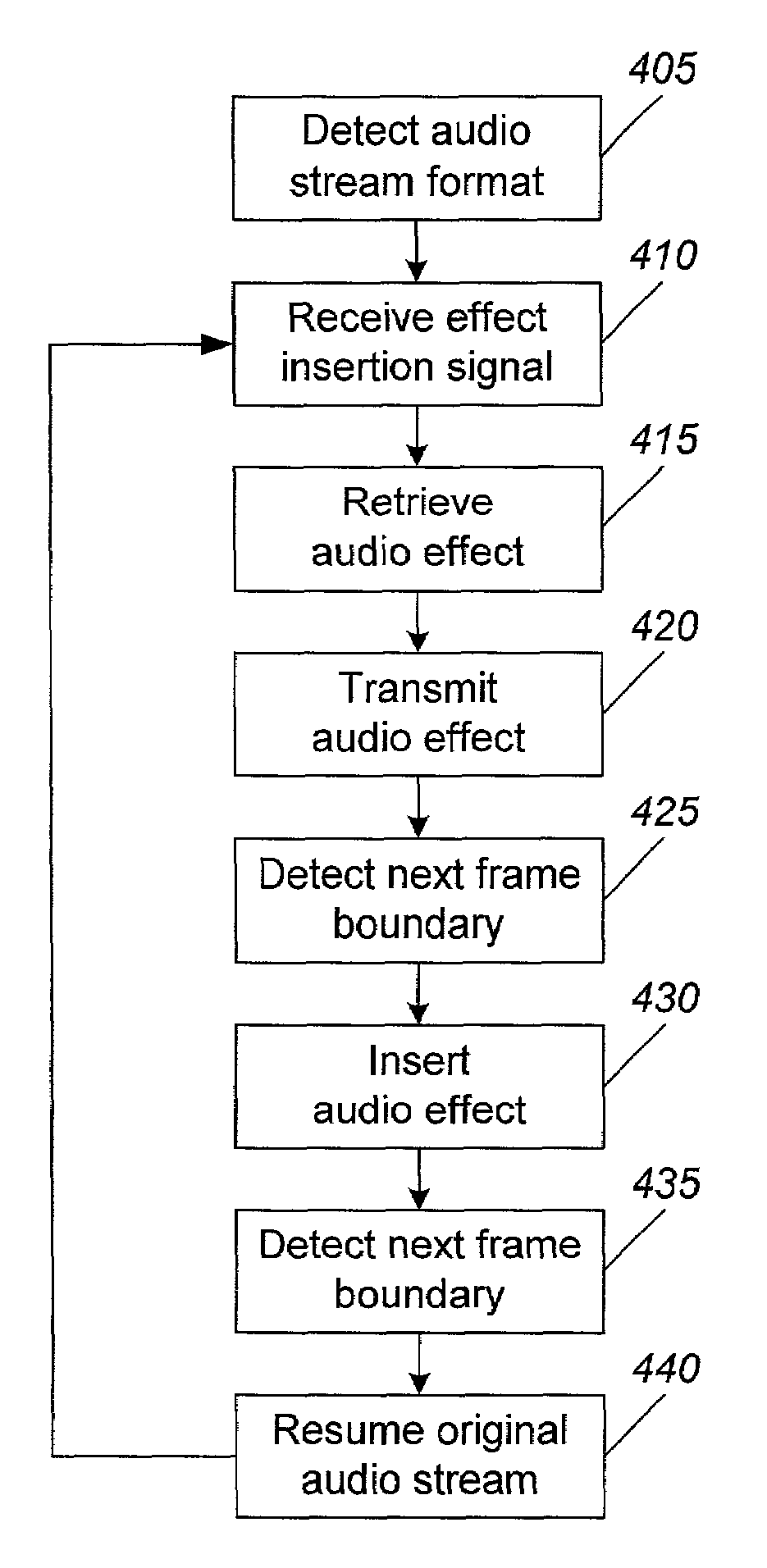
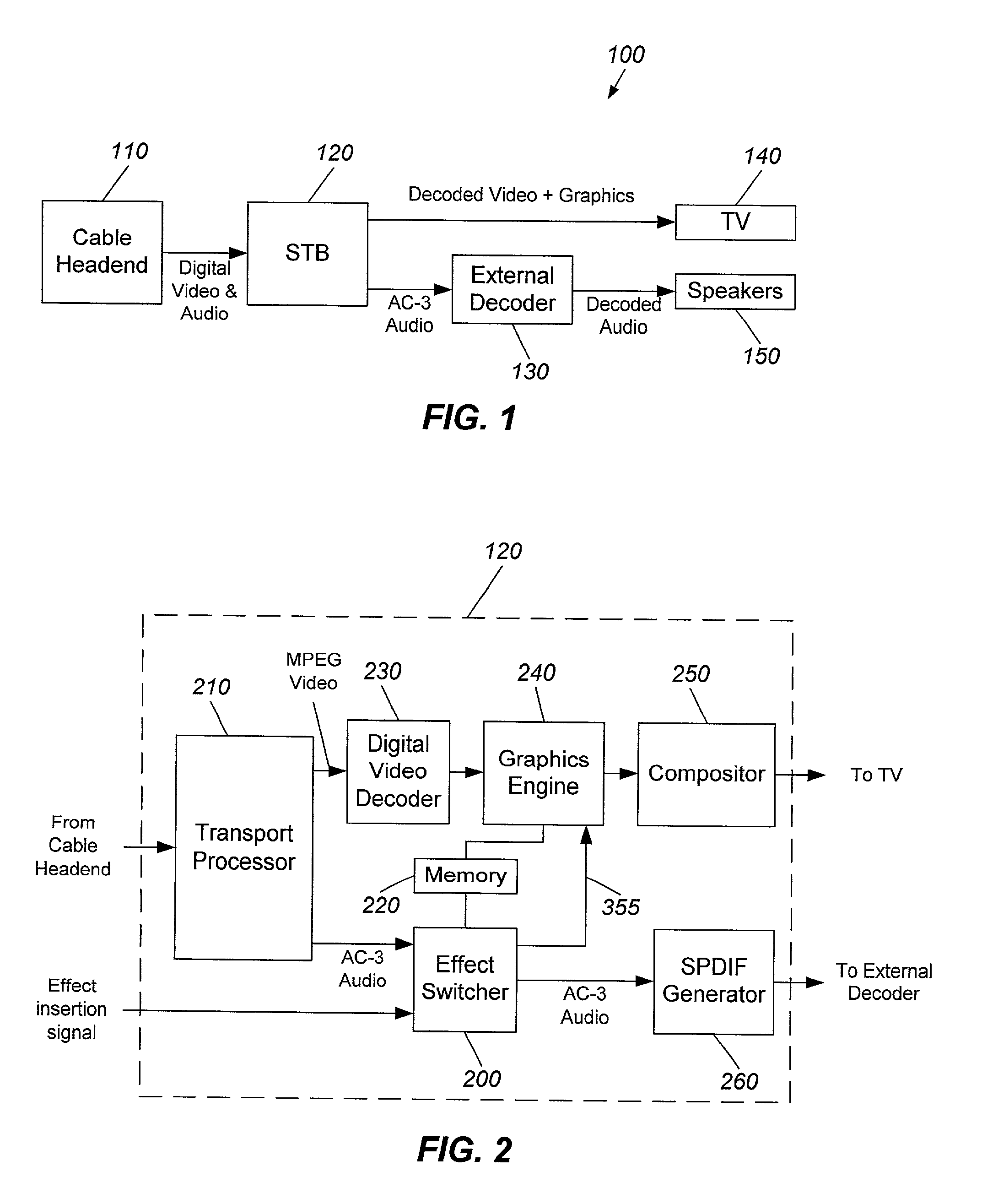
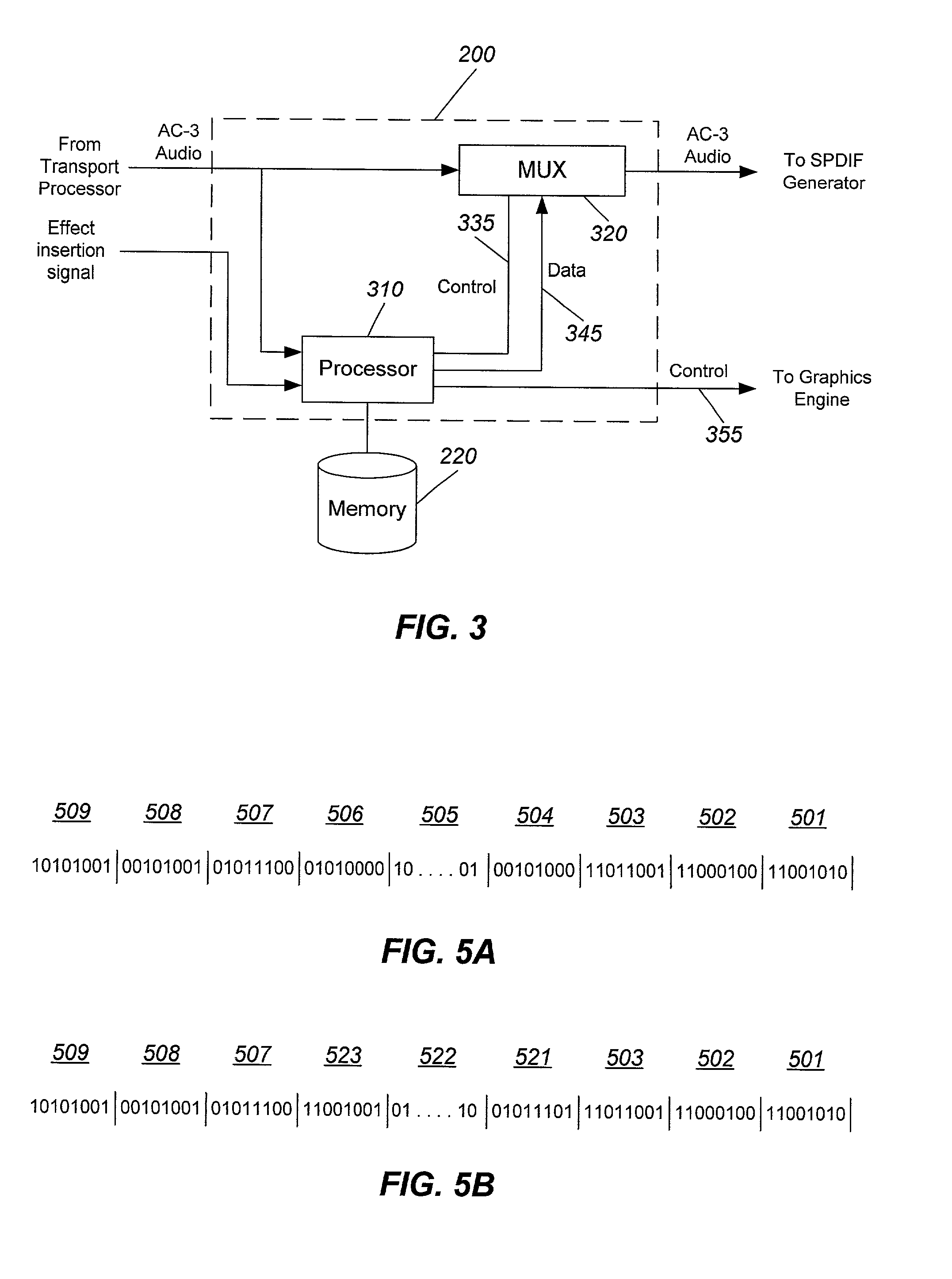
Apparatus and method for inserting data effects into a digital data stream
ActiveUS7006976B2Quality improvementLoss of synchronizationTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital dataData stream
The method includes receiving a signal to insert a data effect into a digitally encoded, framed data stream, retrieving a data effect having the same format as that of the data stream, detecting a first data stream frame boundary, inserting the data effect into the data stream at the first data stream frame boundary, detecting a second data stream frame boundary, and resuming the data stream at the second data stream frame boundary. If the data stream can be of more than one format, the format of the data stream can first be determined. The apparatus includes a processor and a multiplexor. The multiplexor is used for inserting the data effect into the data stream. The processor is used for detecting data stream frame boundaries, retrieving from a memory a data effect having the format of the data stream, and transmitting the formatted data effect to the multiplexor. The data stream may be an audio stream formatted in MPEG format (including MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MP3, MPEG-4), AC-3 format (including 2-channel, 5.1-channel, and 7.1-channel), or DTS format. The data effects may be stored in a plurality of formats. Synchronization between the video and audio streams is maintained by dropping frames that are replaced by the data effect. Another method generates a video signal by retrieving a video effect corresponding to an audio effect, inserting the video effect into a video stream associated with an audio stream, and resuming the video stream and audio stream.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
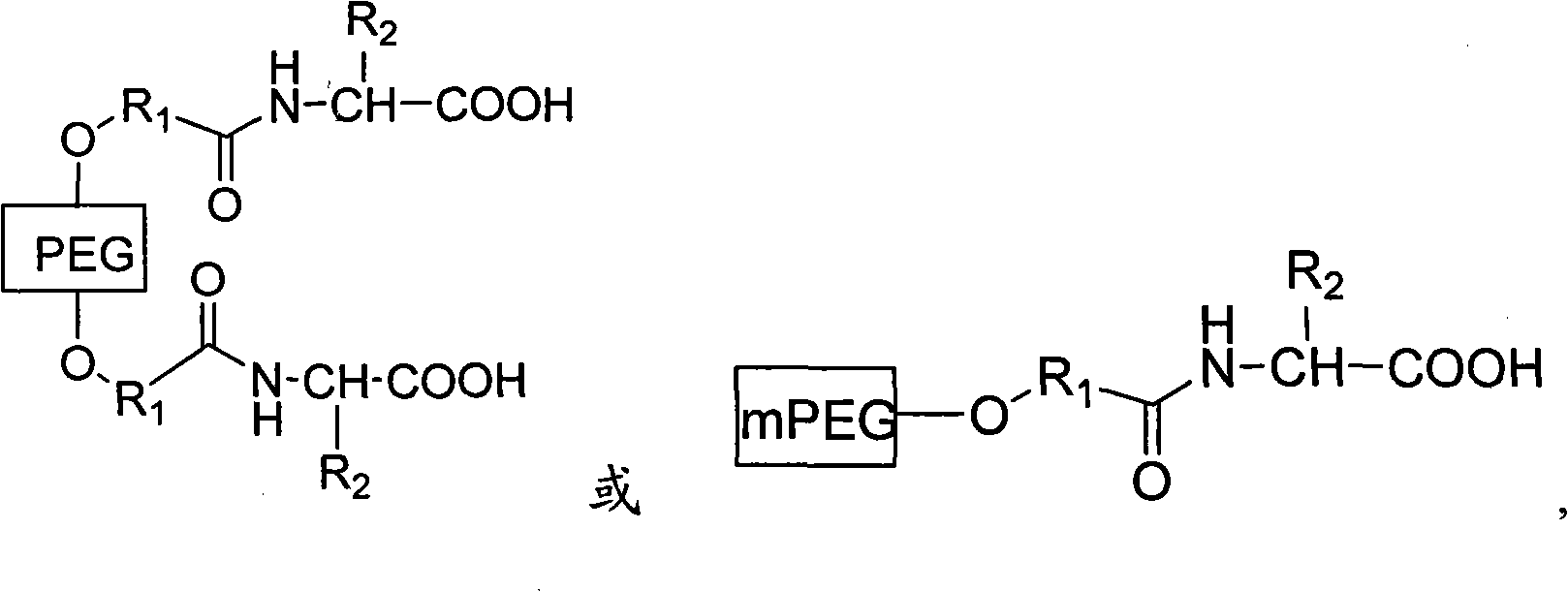
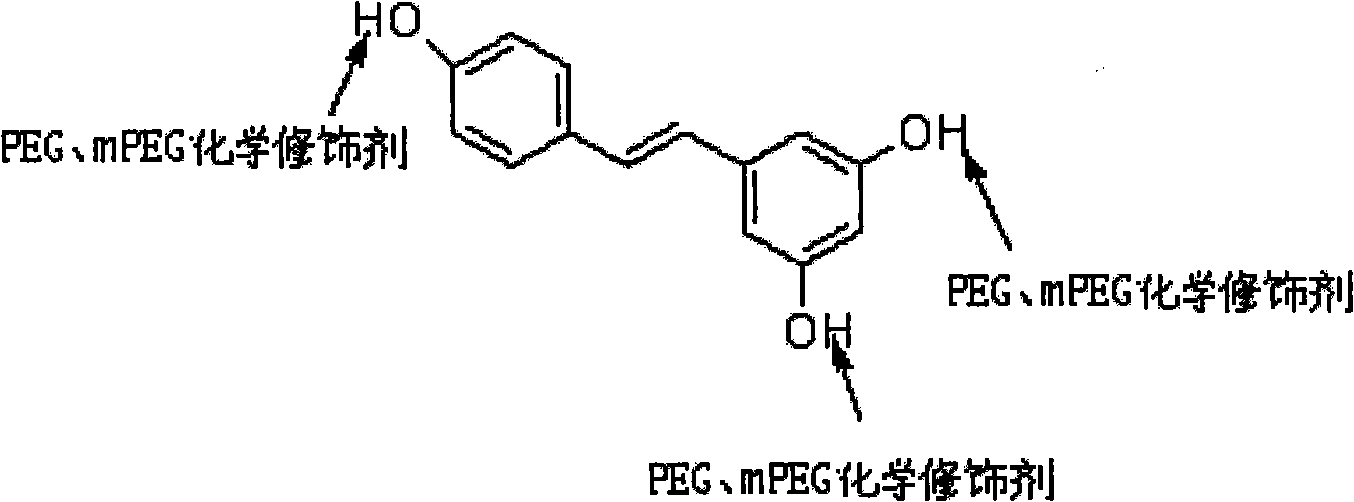
PEG (Polyethylene Glycol), mPEG (Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol) chemical modifier and method thereof for preparing water-soluble resveratrol prodrug
The invention discloses a PEG (Polyethylene Glycol) / mPEG (Methoxy Polyethylene Glycol) chemical modifier and a method thereof for preparing a water-soluble resveratrol prodrug. In the PEG / mPEG chemical modifier, PEG or mPEG is used as a vector, and the chemical modifier is prepared through reacting succinic anhydride, bromoacetate or isobutyl bromoacetate with amino acid. The preparation conditions and steps of the chemical modifier are simple. The chemical modifier is used for modifying the resveratrol to prepare the resveratrol prodrug, can change the water solubility and the stability of the resveratrol, is convenient to use and improves the bioactivity. When the prodrug is decomposed in vivo, amino acid required by the human body is also released while the resveratrol is released, thus the application scope of the prodrug is wider than that of the resveratrol.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
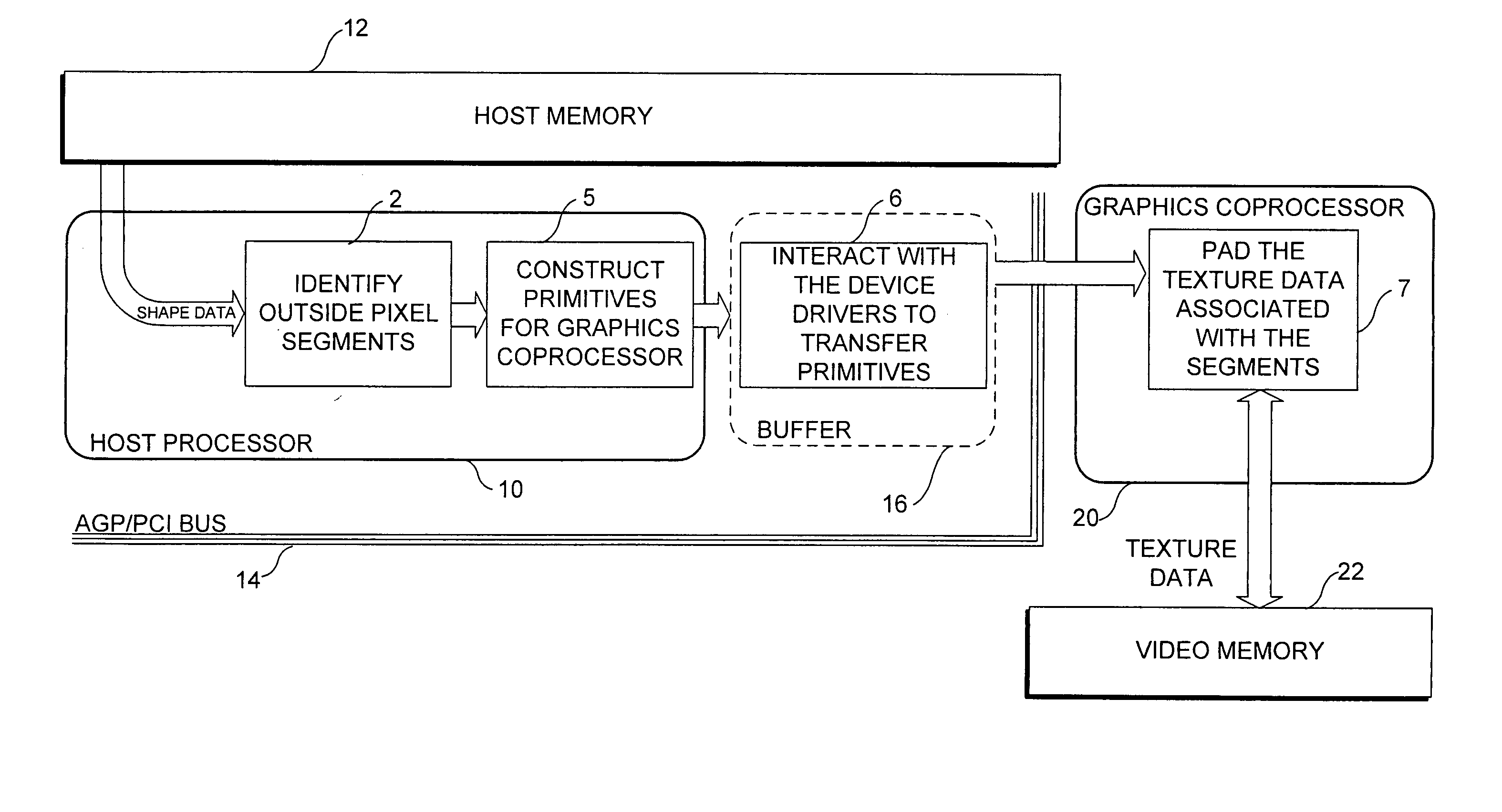
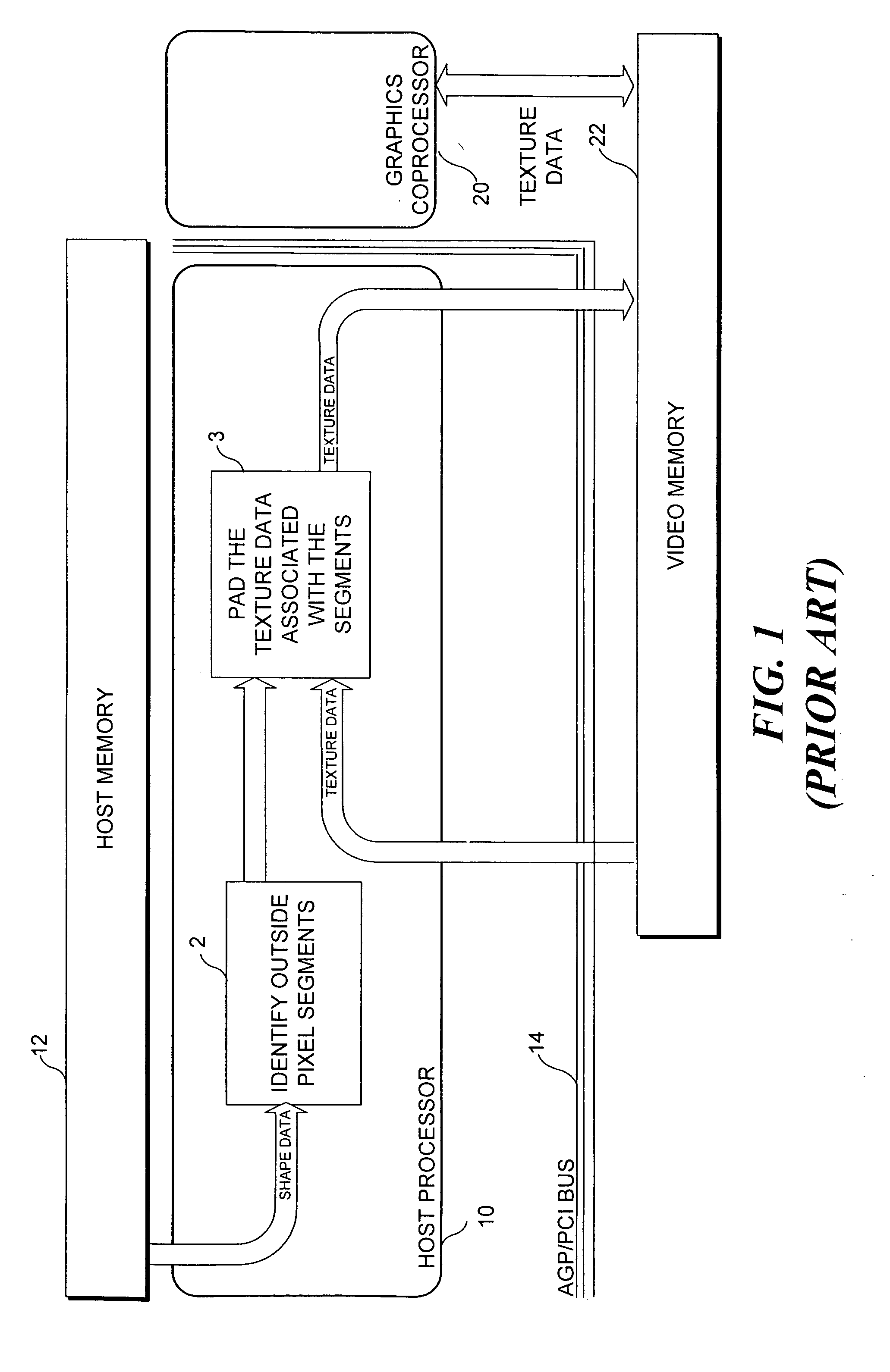
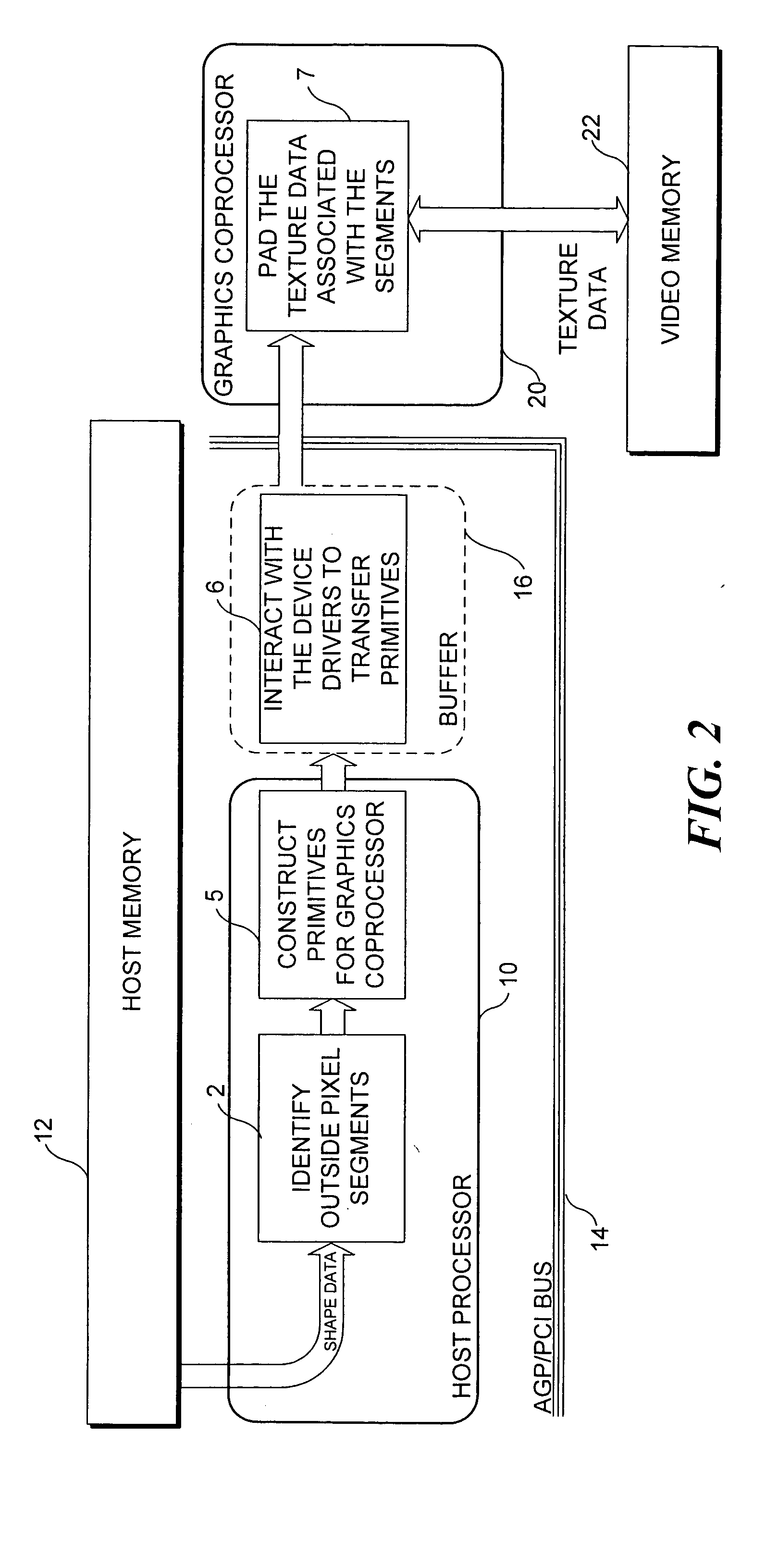
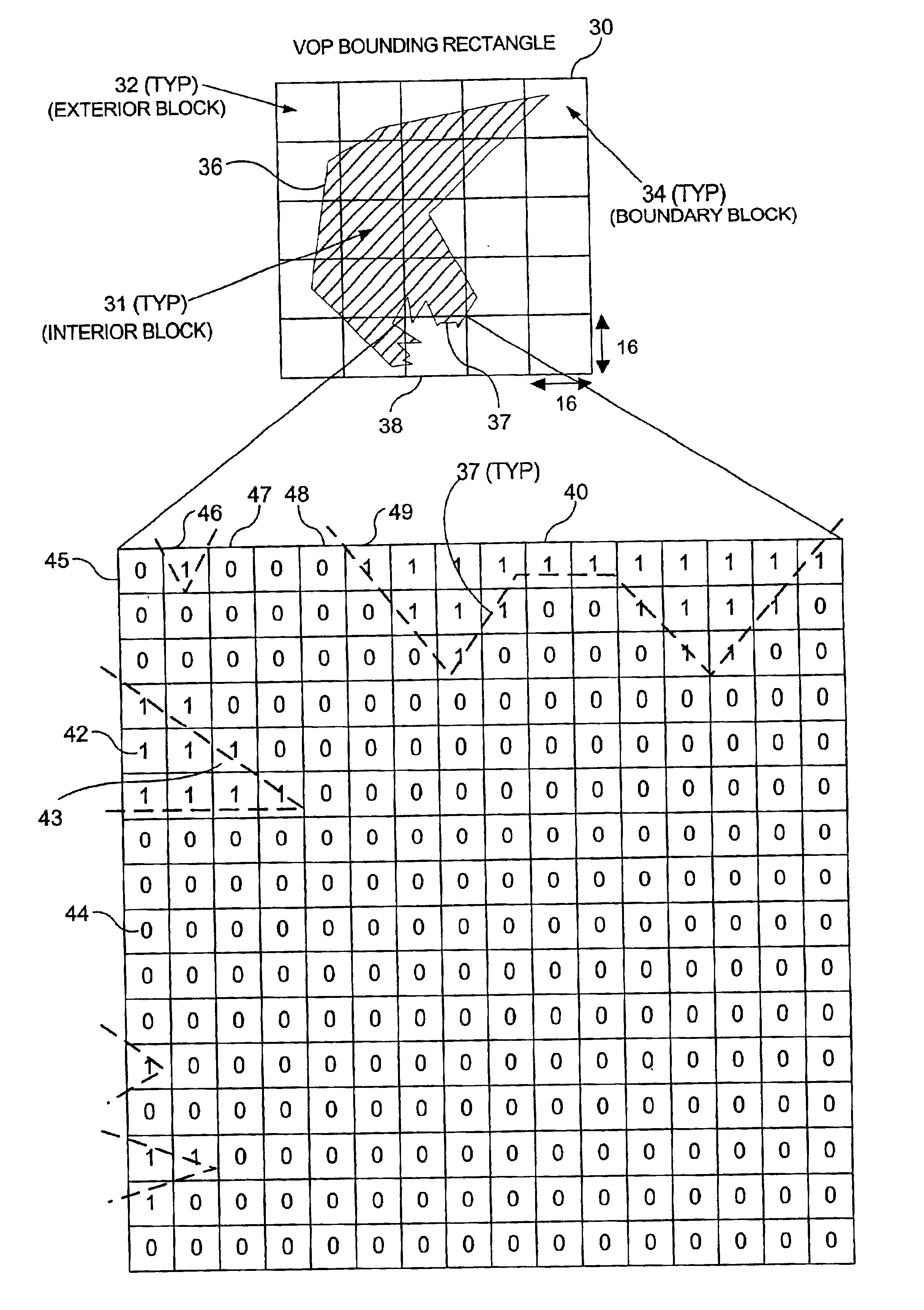
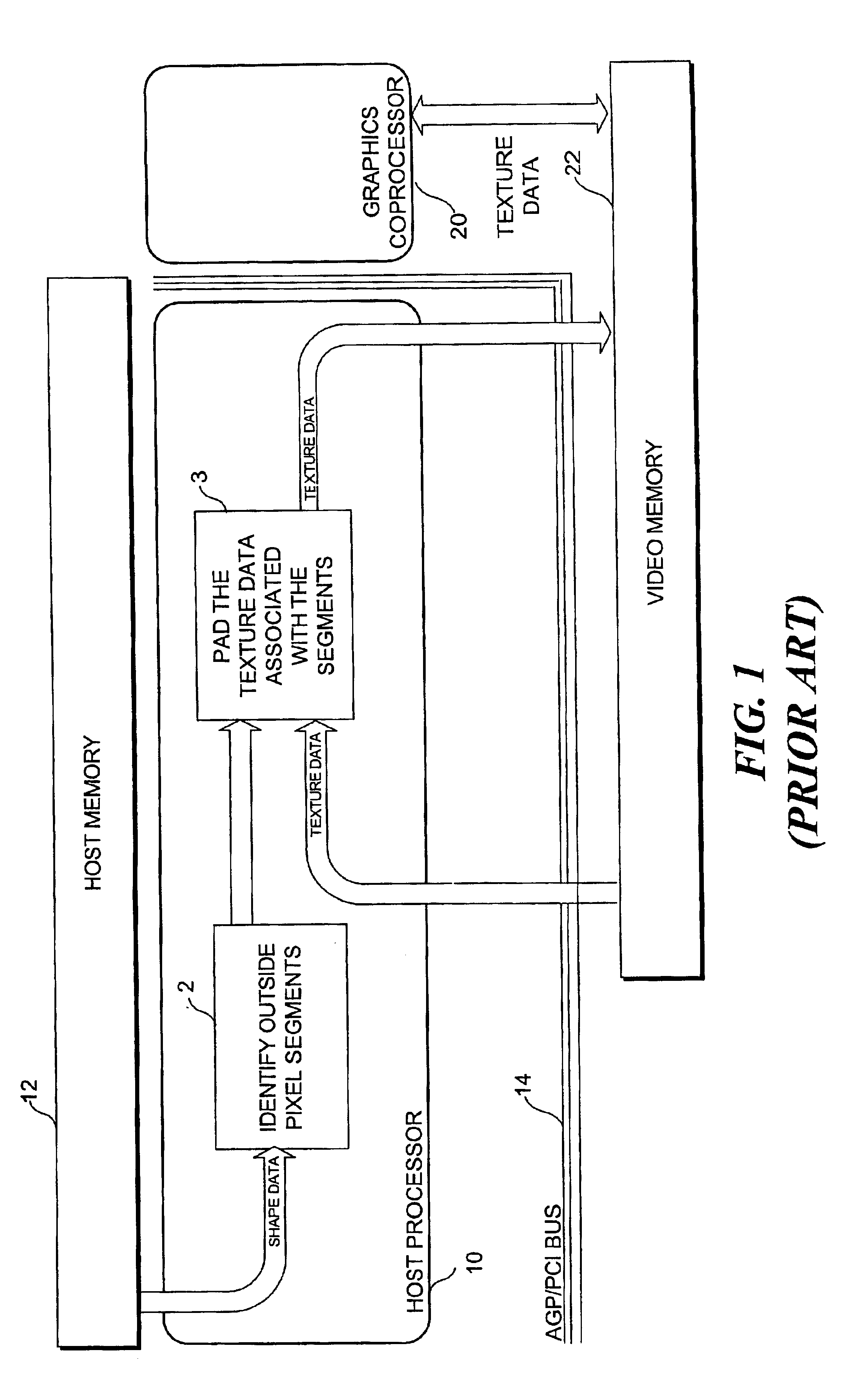
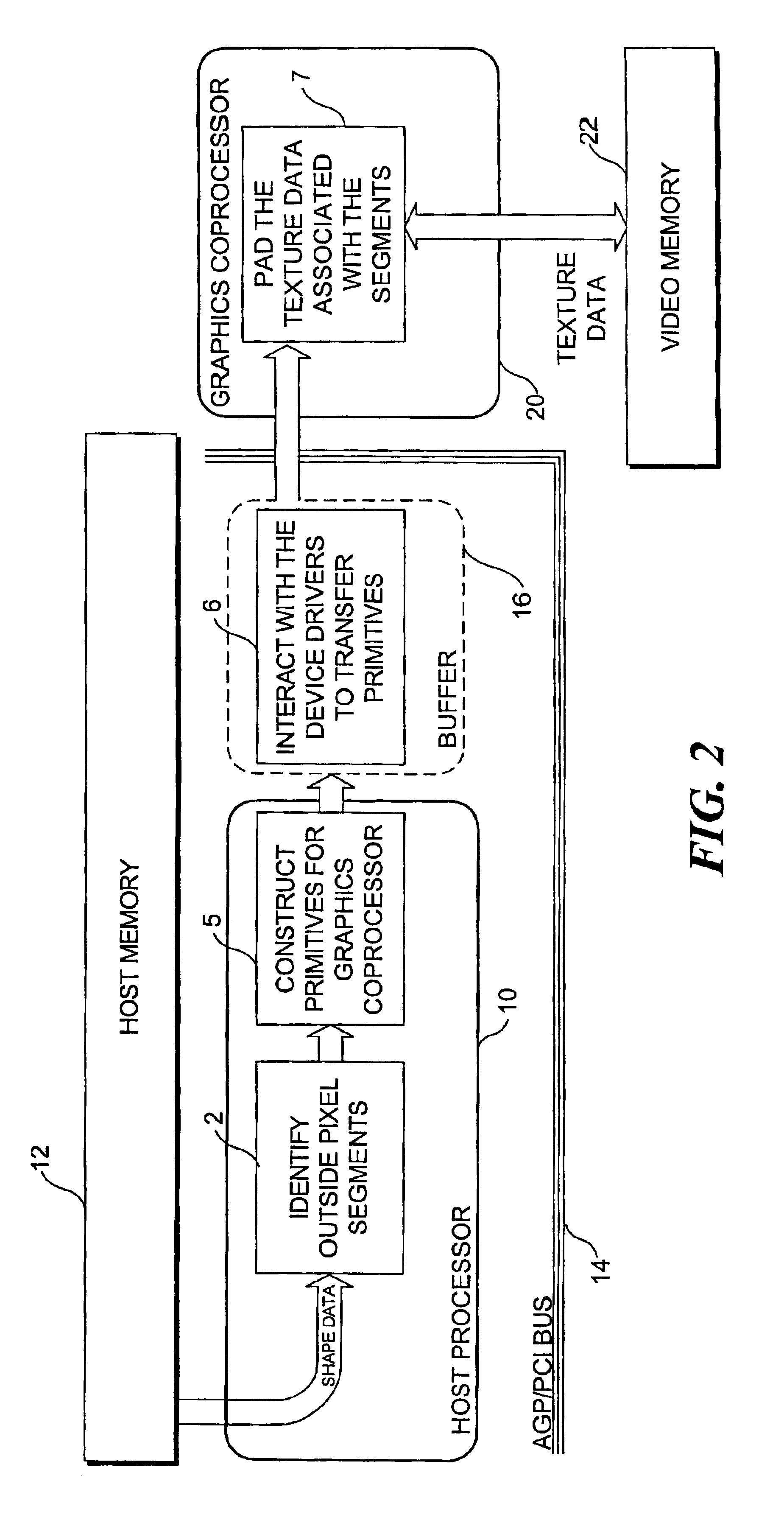
Macroblock padding
InactiveUS20050035968A1Significant synchronization overheadDrawing from basic elementsDigital computer detailsVideo memoryMPEG-1
A boundary macroblock of a video object is padded without significant synchronization overhead between a host processor and an existing coprocessor. The host processor determines horizontal and vertical graphics primitives as a function of shape data stored in a host memory. The shape data determine whether a dot, a line, or a rectangle primitive should be used to pad transparent pixels in the macroblock. The host processor communicates the primitives to a coprocessor, which renders the primitives in an interleaved pipeline fashion to pad transparent pixels of the macroblock based on texture data stored in video memory. The flow of primitives is in one direction from the host processor to the graphics coprocessor, and the texture data is not transferred back and forth between the host processor and coprocessor. This technique is especially useful for enabling acceleration of MPEG-4 video decoding utilizing existing coprocessors capable of accelerating MPEG-1 / 2 video decoding.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
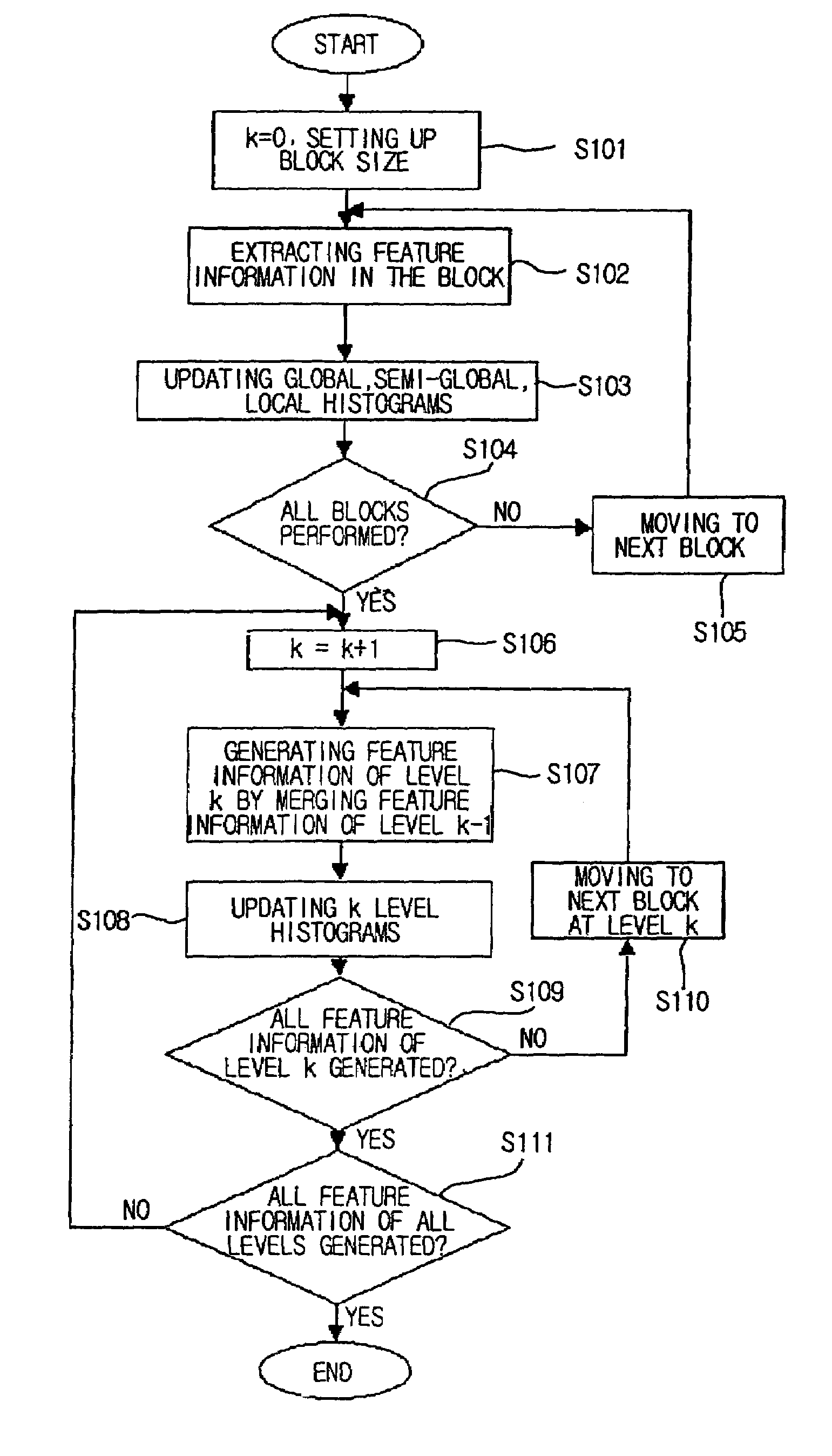
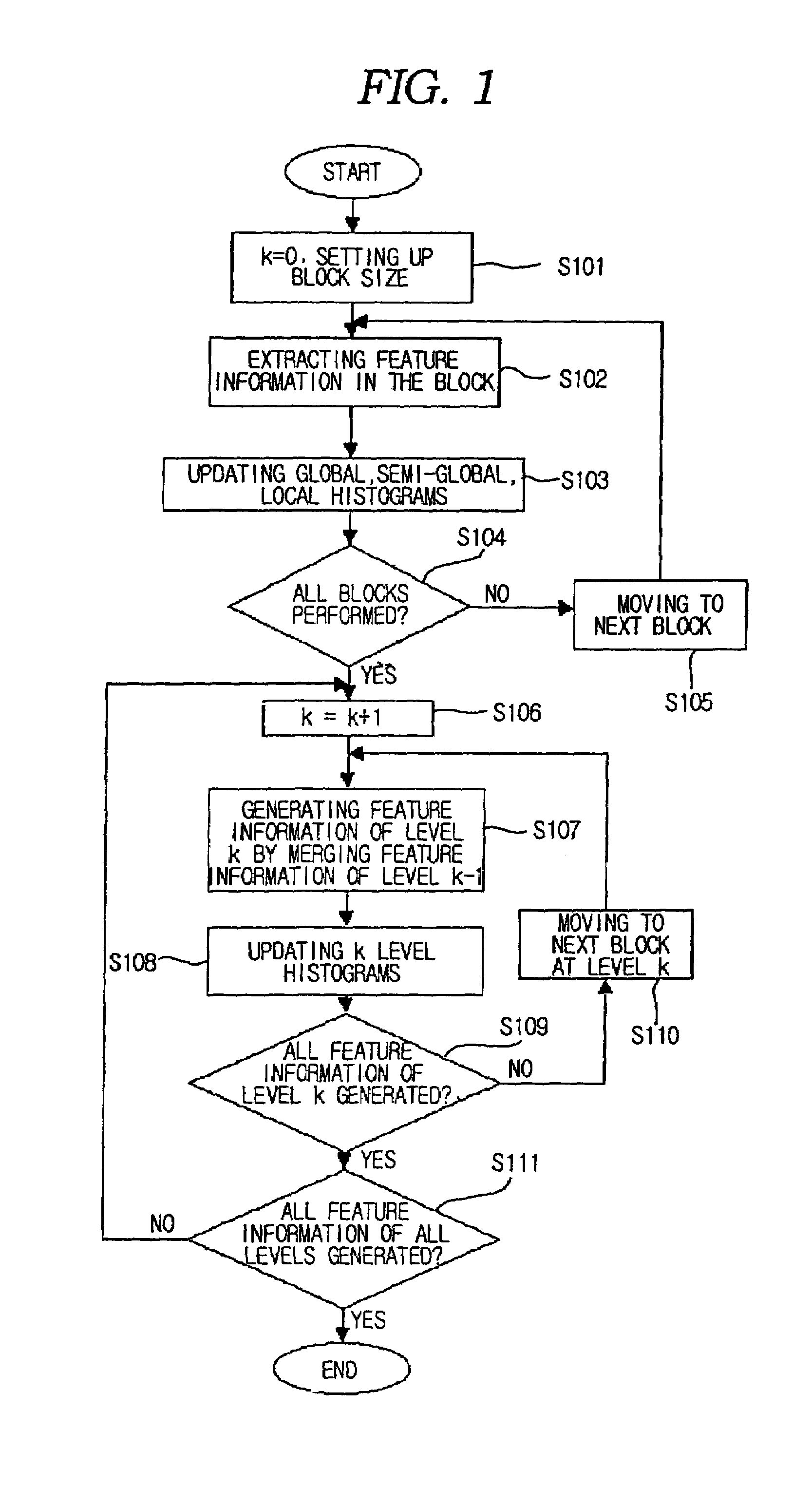
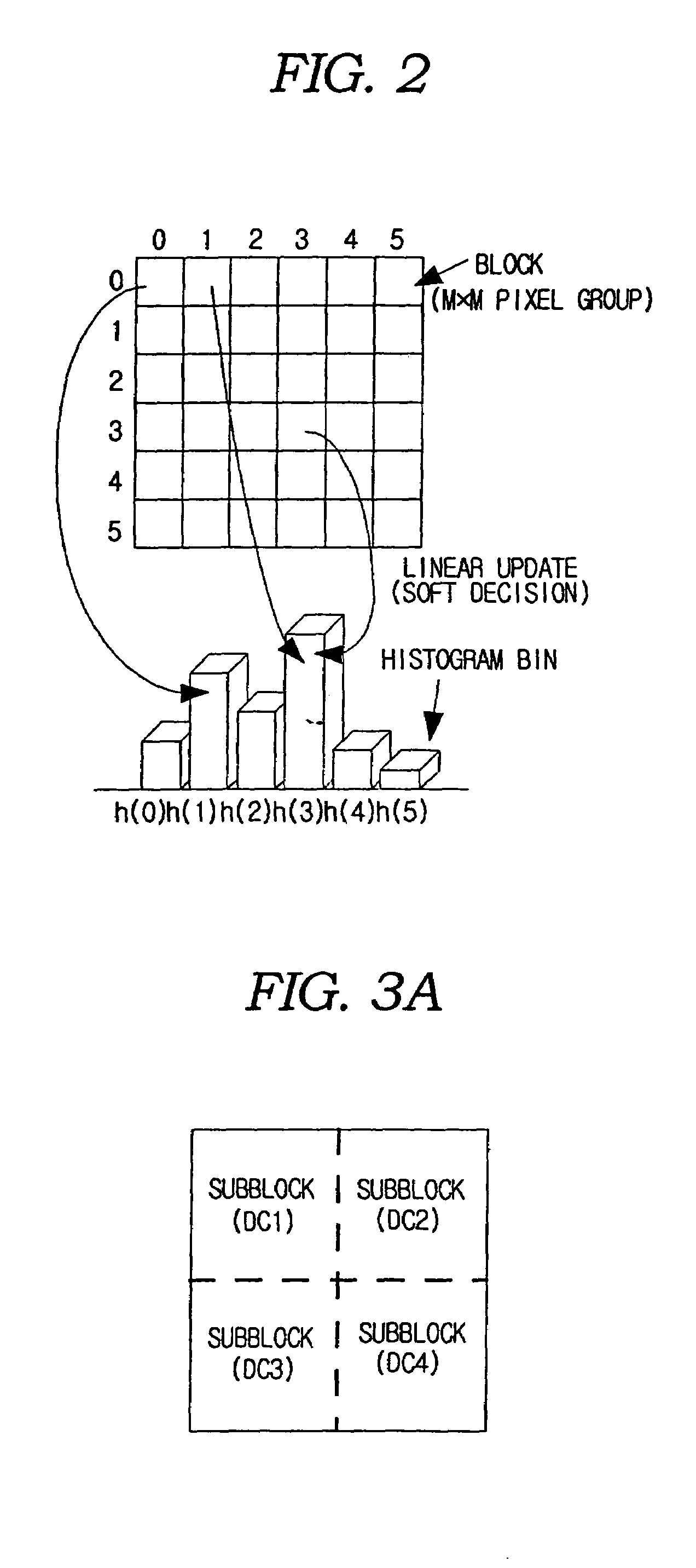
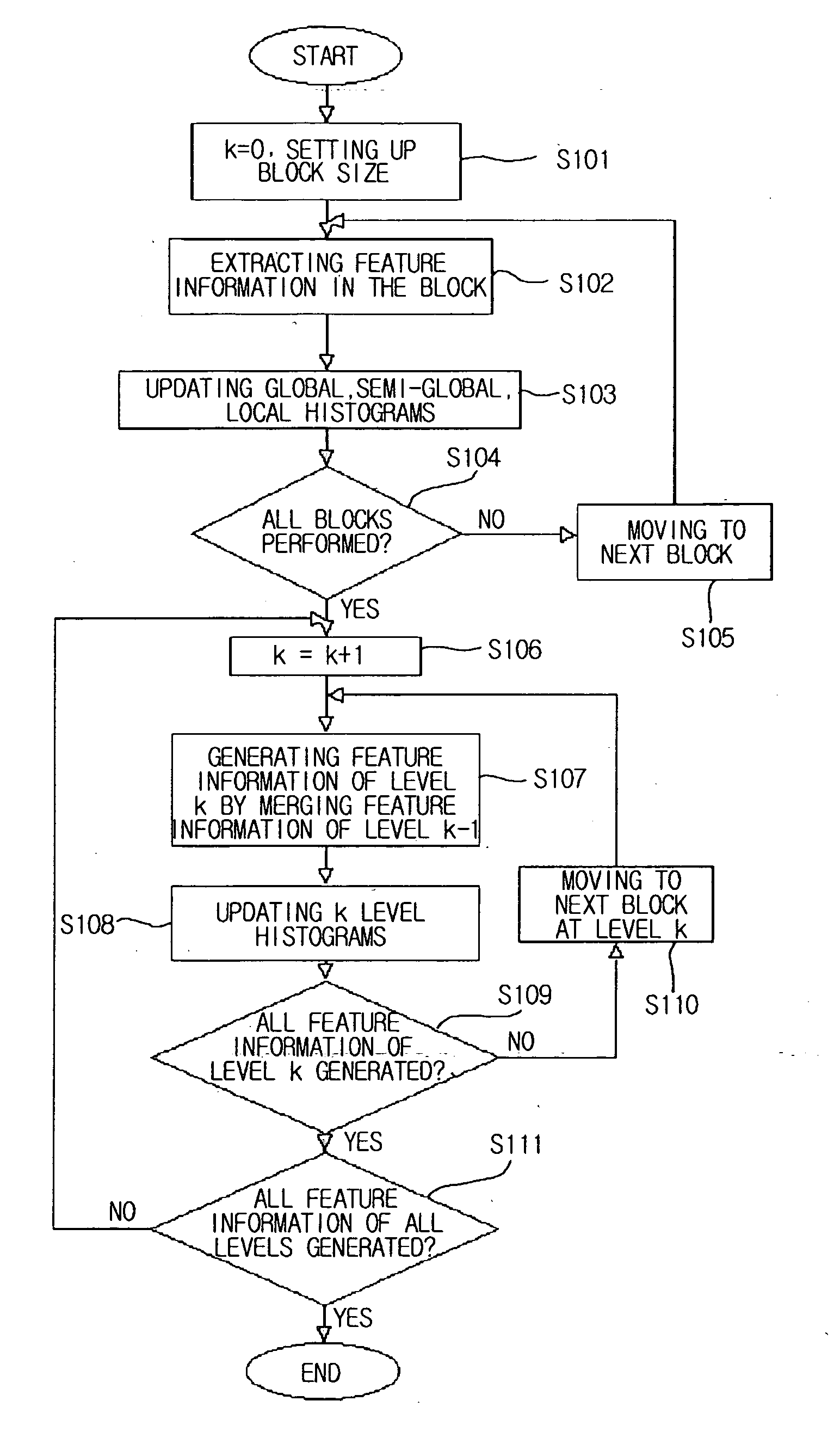
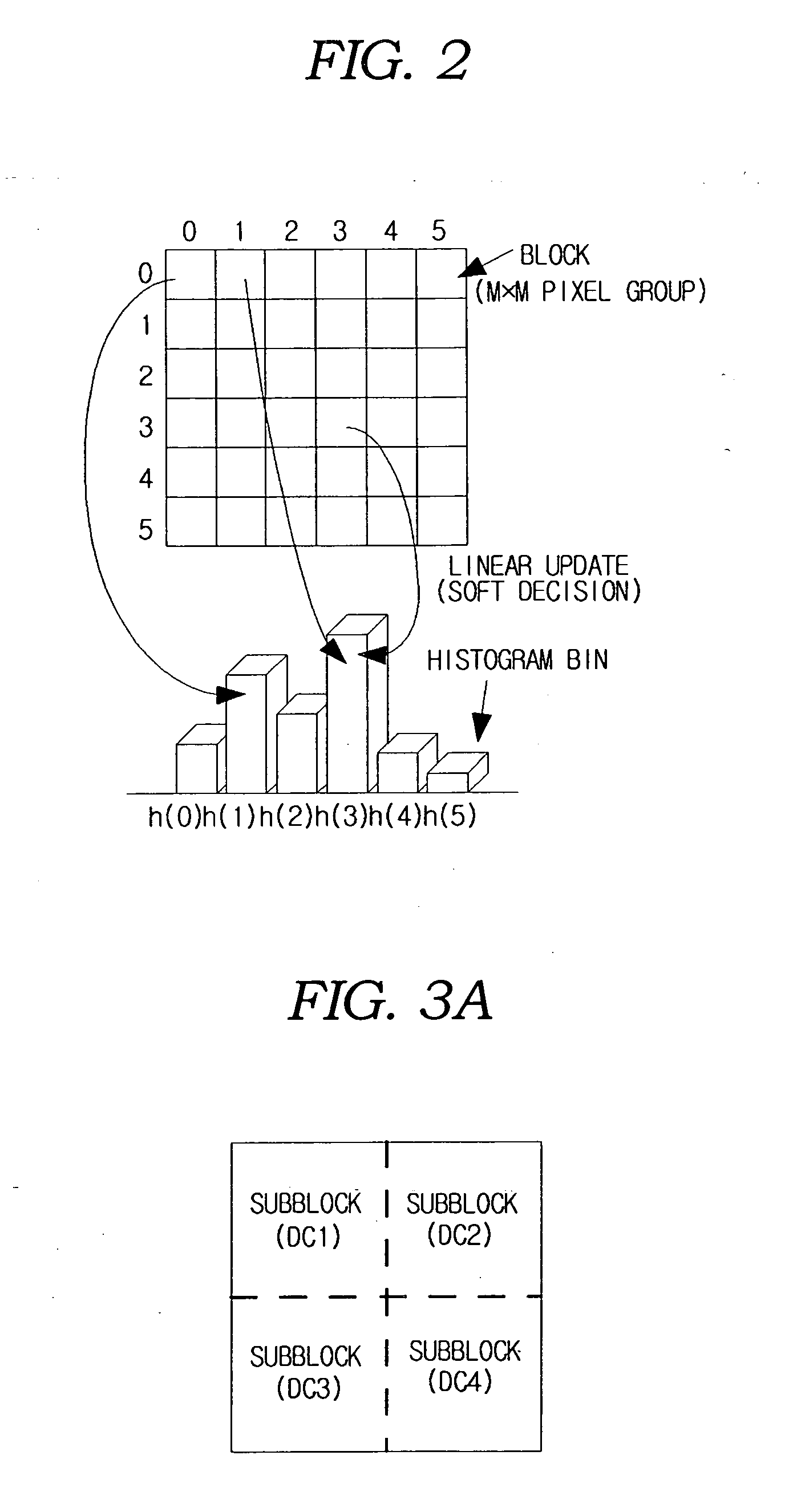
Method for generating a block-based image histogram
A method for generating a block-based image histogram from data compressed by JPEG, MPEG-1, and MPEG-2, or uncompressed image data employing block-based linear quantization to generate histograms that include color, brightness, and edge components. The edge histogram, in particular, includes the global edge features, semi-global edge features, and local edge features. The global edge histogram is based on image blocks of the entire image space. The local edge histogram is based on a group of edge blocks. The semi-global edge histogram is based on the horizontally and the vertically grouped image blocks. A method for generating block-based image histogram with color information and brightness information of image data in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention extracts feature information of an image in terms of the block and updates global histogram bins on the basis of the feature information. The method for generating block-based image histogram with color information and brightness information of image data minimizes quantization error by employing linear weight and updates values of histogram bins. The error that occurs at a boundary between bins of the histograms and the linear weight depends on the distance between the histogram bins.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Remote surveillance system
InactiveUS20050232352A1Easy to useReliably and routinely transferredTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMobile vehicleMPEG-1
An audio / visual surveillance system for use in mobile vehicles such as patrol cars includes two video cameras producing video signals and four audio sources producing audio signals. The signals are MPEG-2 compressed and streamed in real time with geographic and time data to a digital cartridge-type tape recorder located in the vehicle. A full patrol car shift is recorded on a single tape and, at the end of the shift, the tape is placed in a master sled bay. An MD5 hash authenticates the data for court use. Up to four videos can be synchronized frame-by-frame for simultaneous monitoring. An MPEG-1 stream is sent via wireless to headquarters in real time. One camera captures data external to the vehicle, while the other captures data internal to the vehicle. One audio source captures audio inside the vehicle and another captures dispatcher communications. The other two audio sources are carried by officers.
Owner:SECURITY WITH ADVANCED TECH
MPEG multi-format compatible decoding method based on software and hardware coprocessing and device thereof
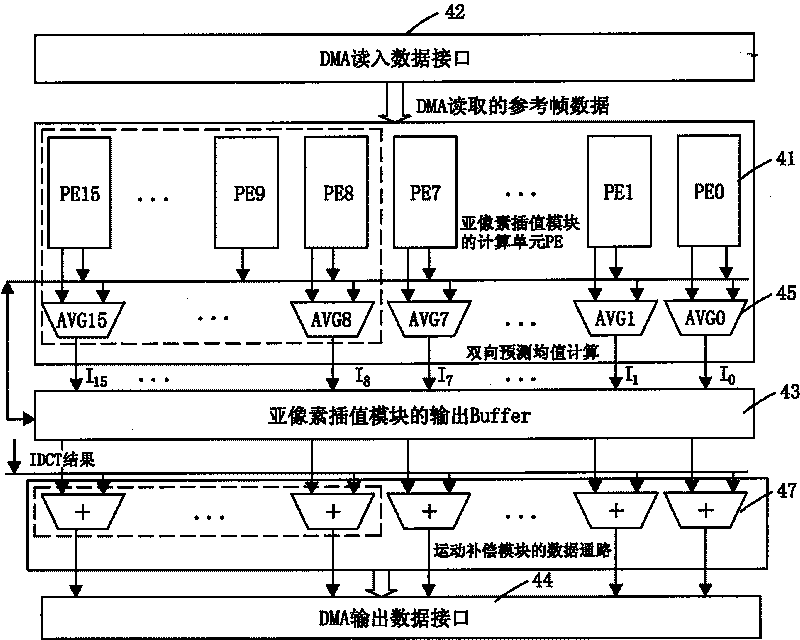
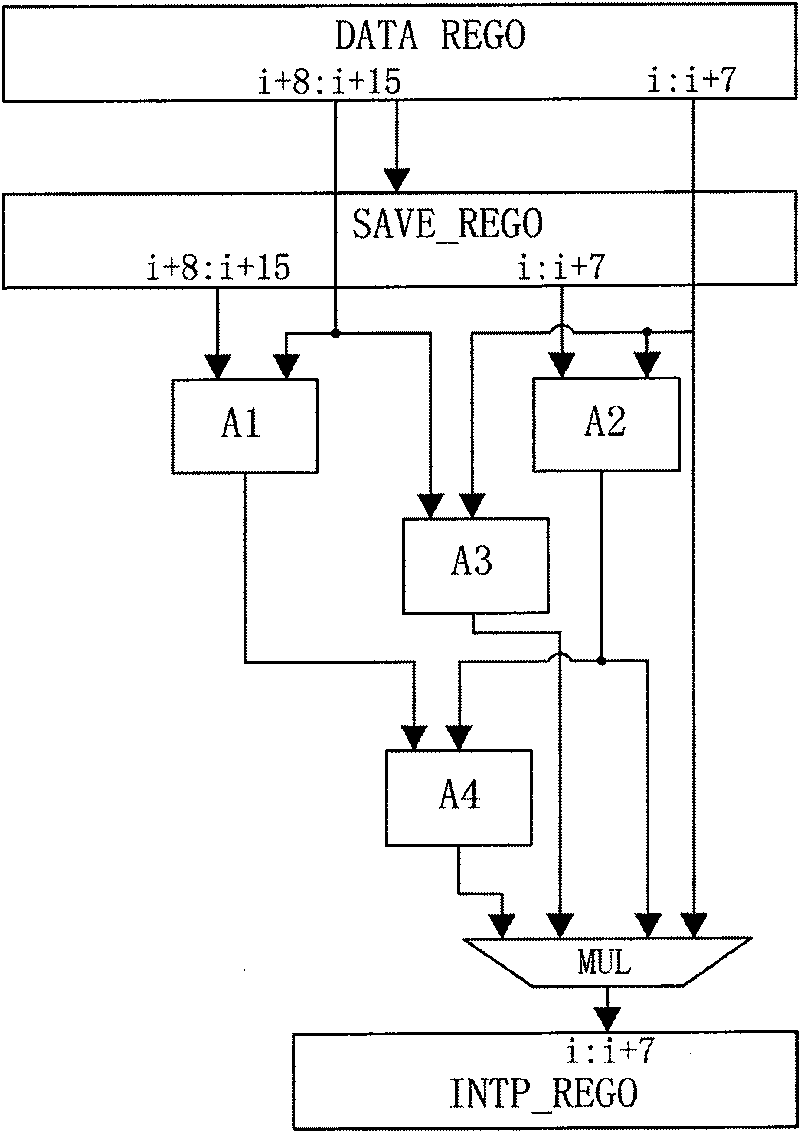
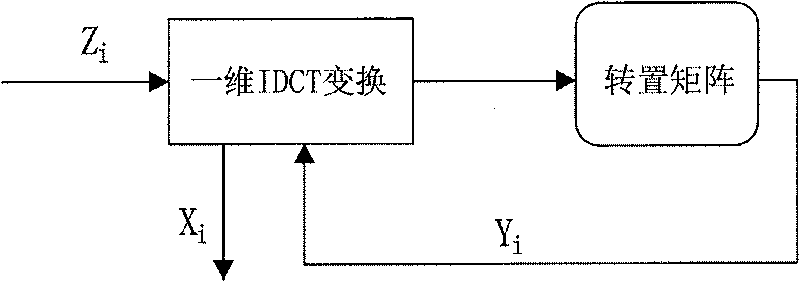
ActiveCN101729893AReduce areaReduce power consumptionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationRegister allocationMPEG-1
The invention discloses an MPEG multi-format compatible decoding method based on software and hardware coprocessing and a device thereof. The device comprises a processor and a hardware accelerator, wherein a register configuration interface between the processor and the accelerator supports the MPEG-1 / 2 / 4 standard. The hardware accelerator comprises a sub-pixel interpolation module, a discrete cosine inverse transformation module, a motion compensation module and a DMA controller module, wherein the sub-pixel interpolation module is used for carrying out sub-pixel interpolation operation to read-in reference macro block data; the discrete cosine inverse transformation module is used for carrying out two-dimensional discrete cosine inverse transformation treatment on residual data; the motion compensation module is used for reconstructing a decoding macro block by a sub-pixel interpolation operation result and treated residual data; and the DMA controller module is used for calculating the reference block data reading position, reading the reference block data from a reference frame and writing the reconstructed macro block into the corresponding position address of a reconstructed frame. The invention realizes MPEG multi-format compatible decoding.
Owner:BEIJING PKUNITY MICROSYST TECH +1
Method for generating a block-based image histogram
A method for generating a block-based image histogram from data compressed by JPEG, MPEG-1, and MPEG-2, or uncompressed image data employing block-based linear quantization to generate histograms that include color, brightness, and edge components. The edge histogram, in particular, includes the global edge features, semi-global edge features, and local edge features. The global edge histogram is based on image blocks of the entire image space. The local edge histogram is based on a group of edge blocks. The semi-global edge histogram is based on the horizontally and the vertically grouped image blocks. A method for generating block-based image histogram with color information and brightness information of image data in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention extracts feature information of an image in terms of the block and updates global histogram bins on the basis of the feature information. The method for generating block-based image histogram with color information and brightness information of image data minimizes quantization error by employing linear weight and updates values of histogram bins. The error that occurs at a boundary between bins of the histograms and the linear weight depends on the distance between the histogram bins.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Macroblock padding
InactiveUS6842177B2Significant synchronization overheadDrawing from basic elementsImage codingVideo memoryMPEG-1
A boundary macroblock of a video object is padded without significant synchronization overhead between a host processor and an existing coprocessor. The host processor determines horizontal and vertical graphics primitives as a function of shape data stored in a host memory. The shape data determine whether a dot, a line, or a rectangle primitive should be used to pad transparent pixels in the macroblock. The host processor communicates the primitives to a coprocessor, which renders the primitives in an interleaved pipeline fashion to pad transparent pixels of the macroblock based on texture data stored in video memory. The flow of primitives is in one direction from the host processor to the graphics coprocessor, and the texture data is not transferred back and forth between the host processor and coprocessor. This technique is especially useful for enabling acceleration of MPEG-4 video decoding utilizing existing coprocessors capable of accelerating MPEG-1 / 2 video decoding.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
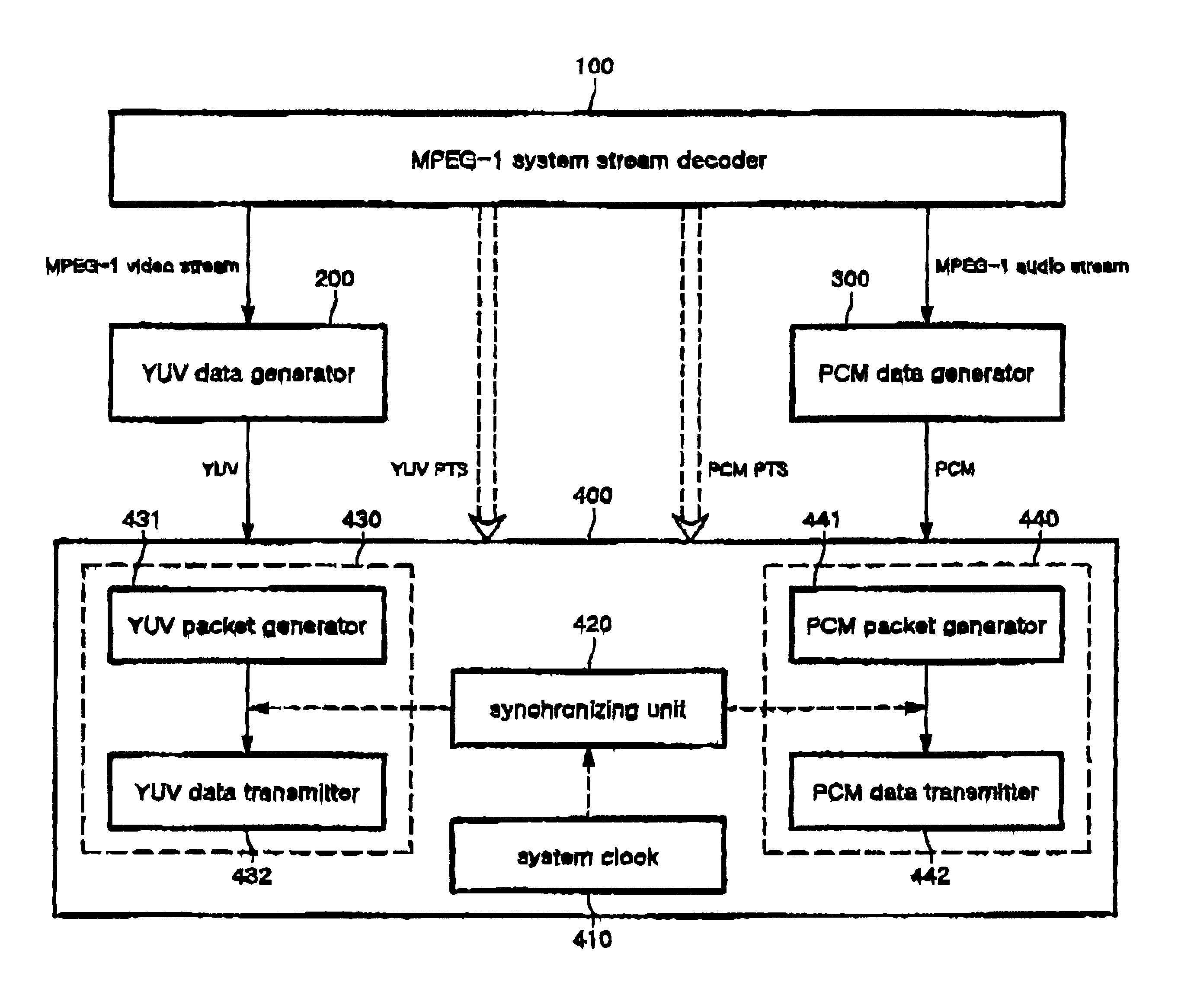
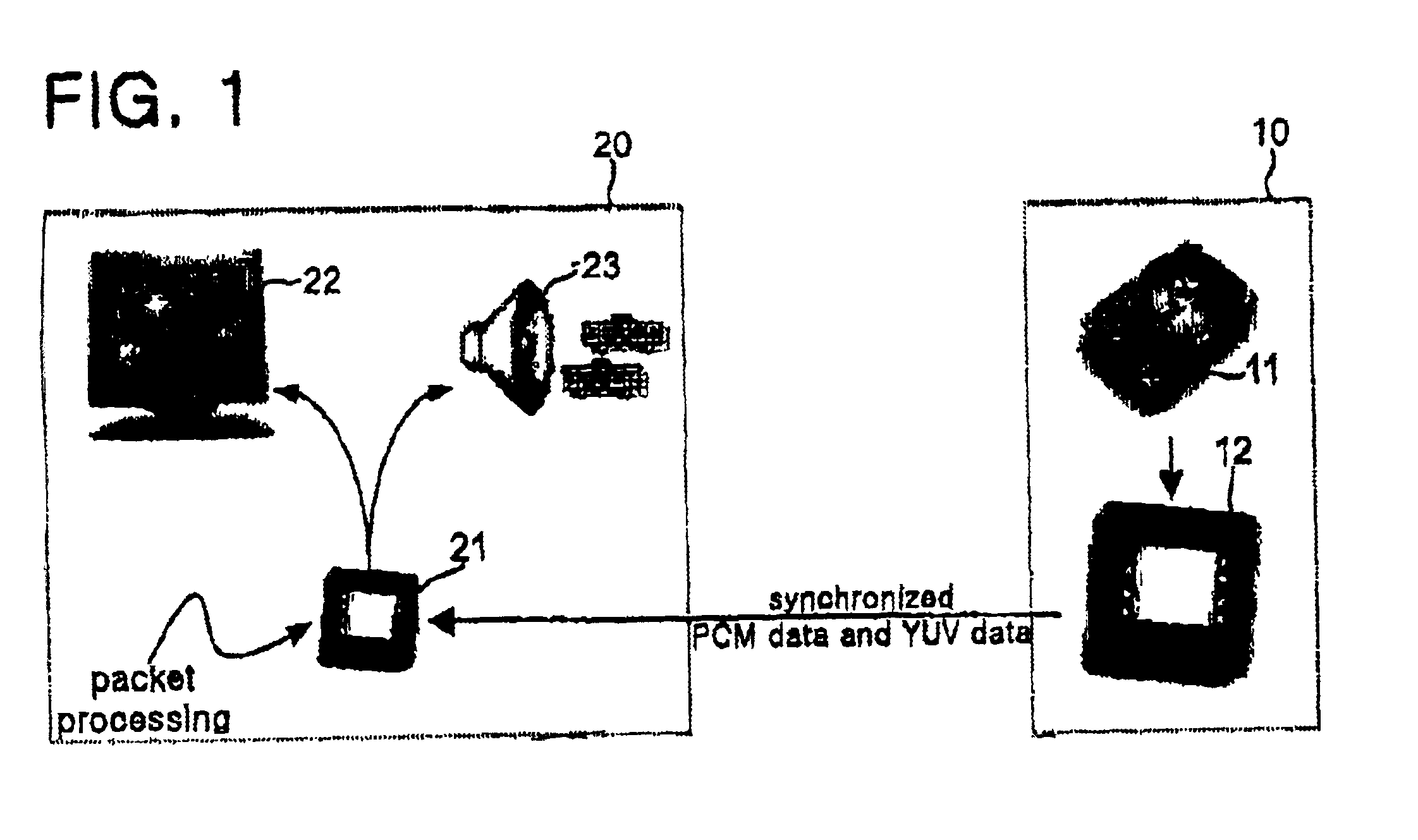
Apparatus and method for streaming MPEG-1 data
InactiveUS6779041B1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesMPEG-1Client-side
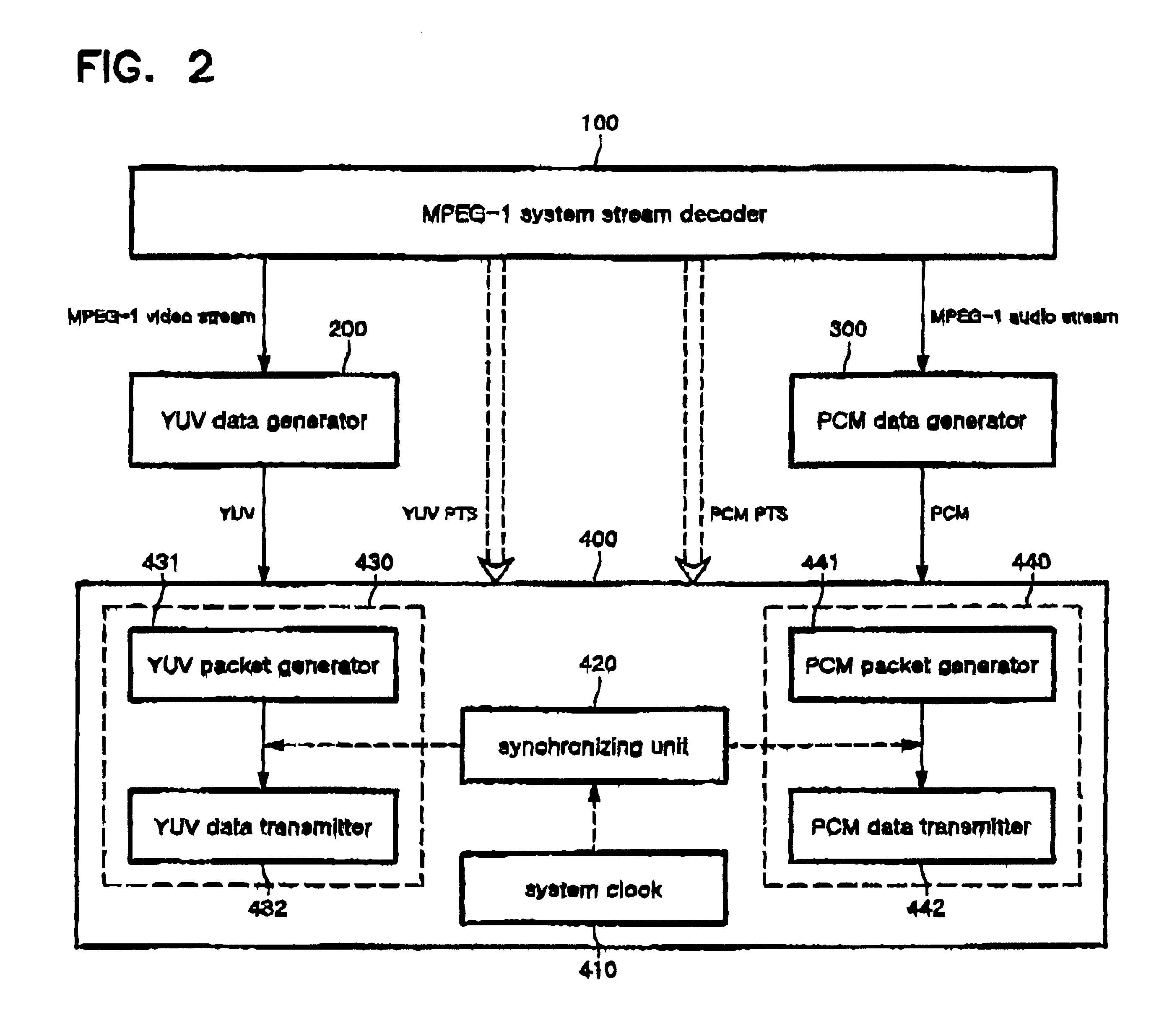
There is provided an apparatus and method for streaming MPEG-1 data in which, when the MPEG-1 data is transmitted through the network, the MPEG-1 data is converted into intermediate data, a server transfers the intermediate data in the form of packet with synchronizing video intermediate data and audio intermediate data with each other, thereby allowing a client to be able to receive and process the intermediate data with a simple conversion. The apparatus includes: an MPEG-1 system stream decoder for decoding the system stream of an MPEG-1 file; a YUV data generator for converting a videos stream transmitted from the MPEG-1 system stream decoder into YUV data as intermediate data; a PCM data generator for converting an audio stream transmitted from the MPEG-1 system stream decoder into PCM data; and an MPEG-1 intermediate data server for synchronizing the YUV data and PCM data, respectively generated by the YUV data generator and PCM data generator, with a YUV PTS and PCM PTS obtained from the MPEG-1 system stream decoder and a system clock, to transmit them to the client.
Owner:THIN MULTIMEDIA
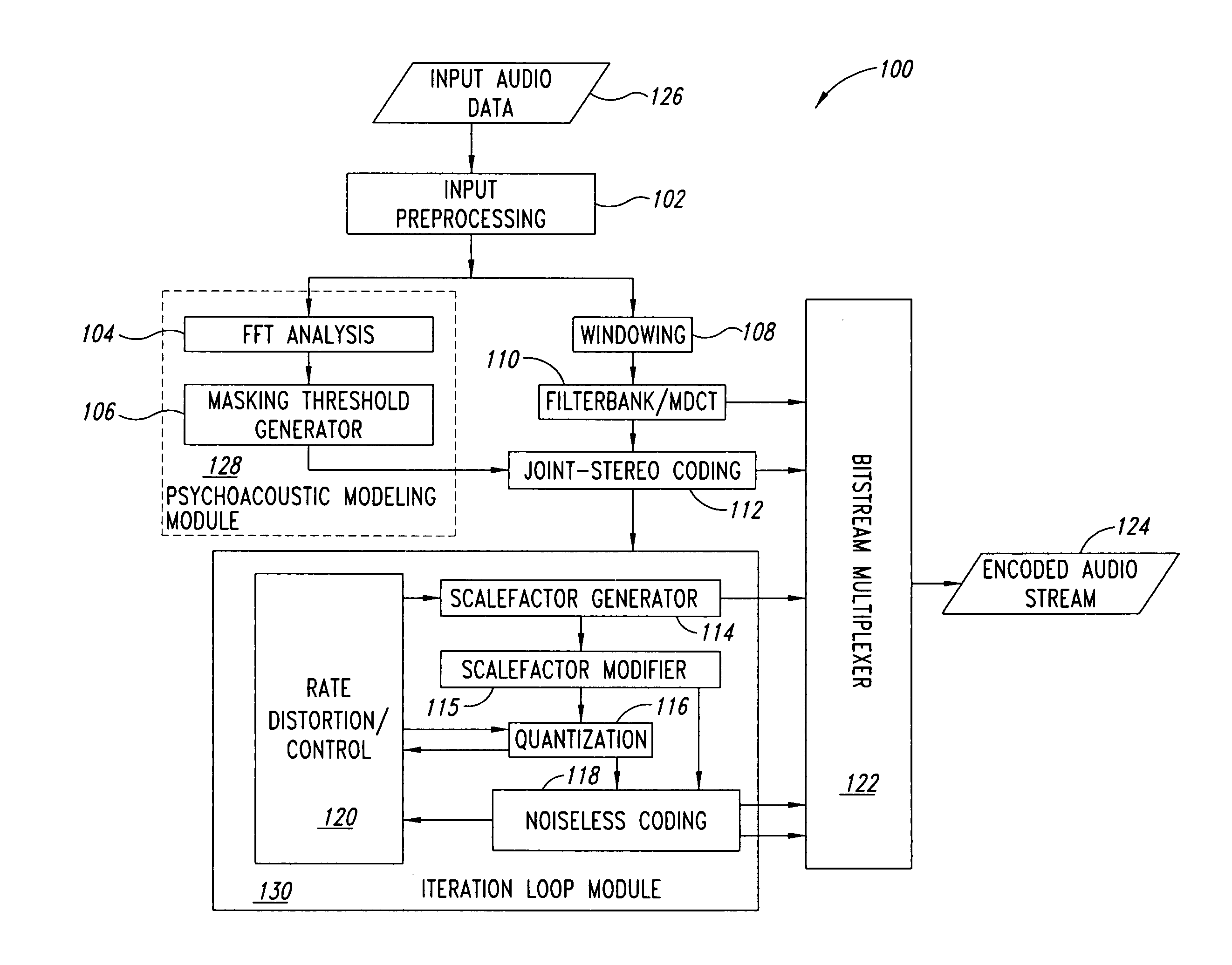
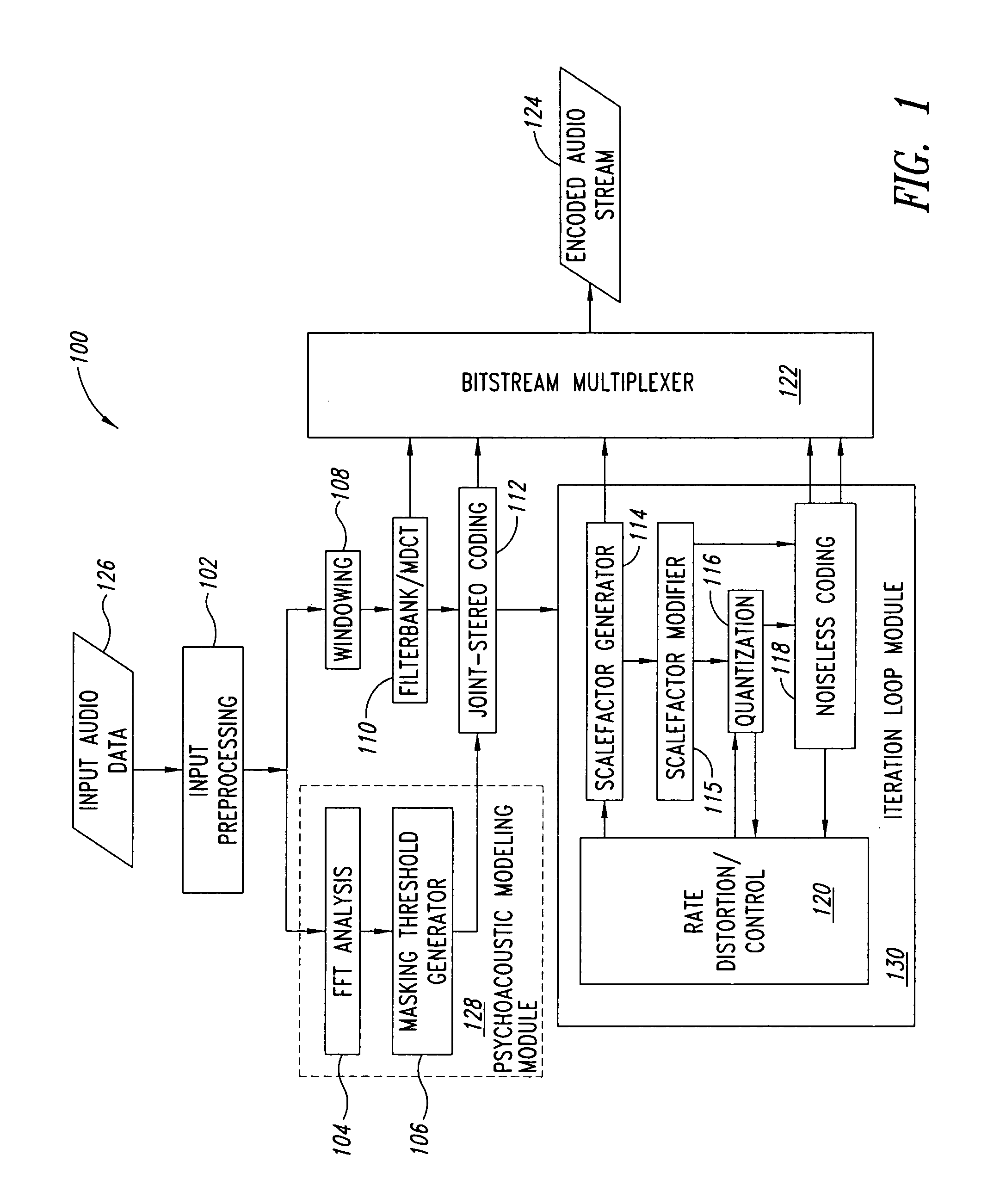
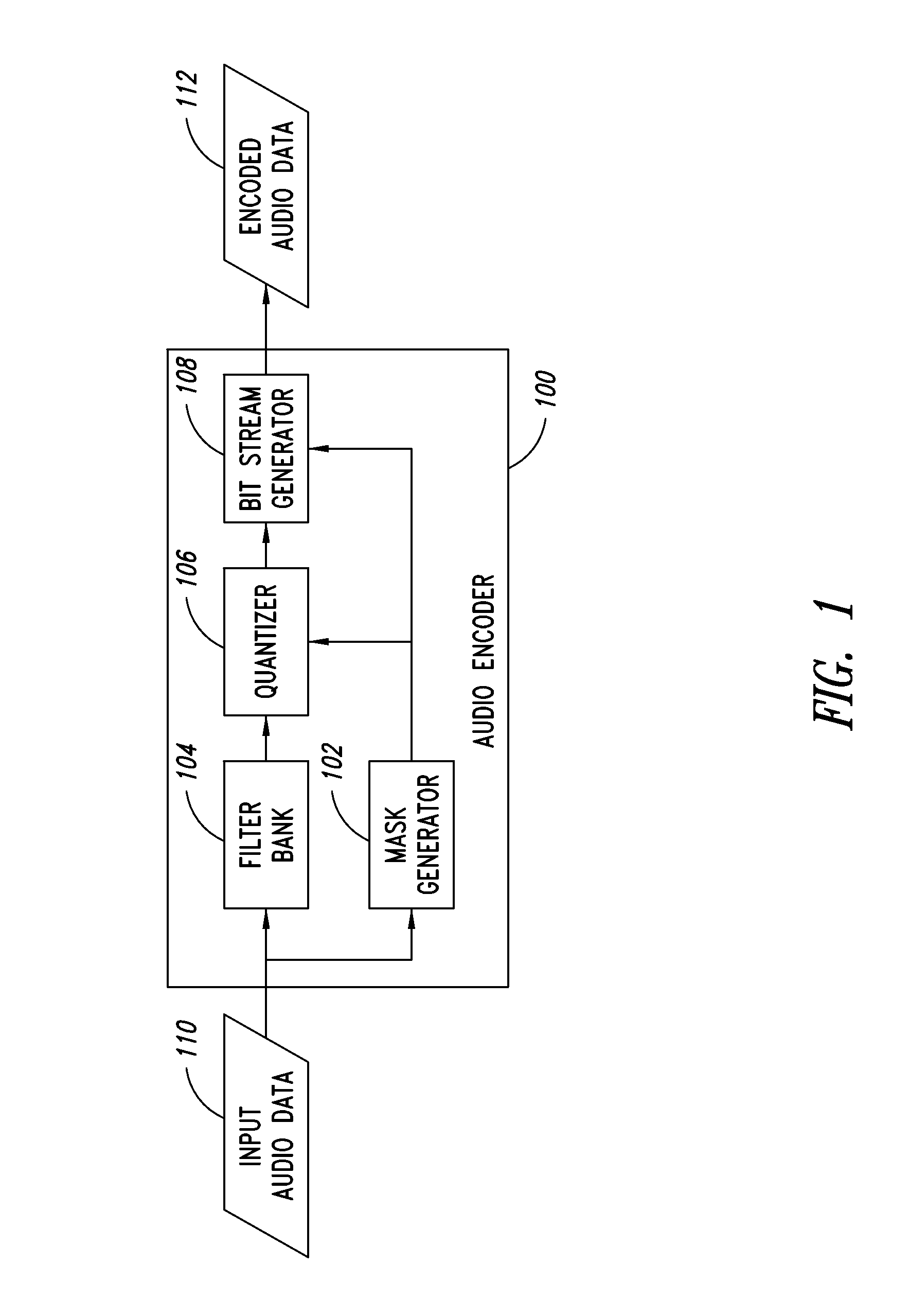
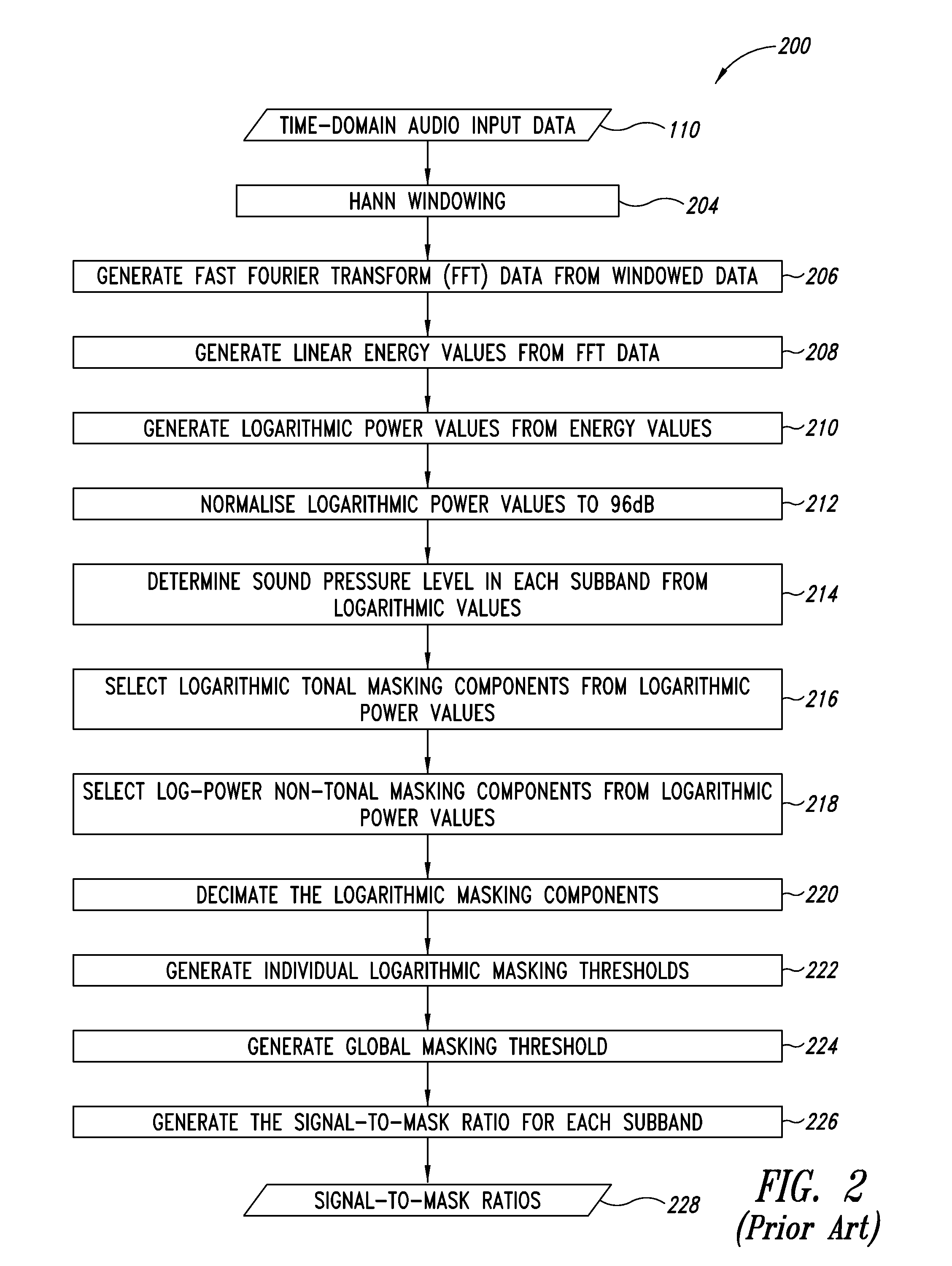
Device and process for use in encoding audio data
A mask generation process for use in encoding audio data, including generating linear masking components from the audio data, generating logarithmic masking components from the linear masking components, and generating a global masking threshold from the logarithmic masking components. The process is a psychoacoustic masking process for use in an MPEG-1-L2 encoder, and includes generating energy values from a Fourier transform of the audio data, determining sound pressure level values from the energy values, selecting tonal and non-tonal masking components on the basis of the energy values, generating power values from the energy values, generating masking thresholds on the basis of the masking components and the power values, and generating signal to mask ratios for a quantizier on the basis of the sound pressure level values and the masking thresholds.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS ASIA PACIFIC PTE
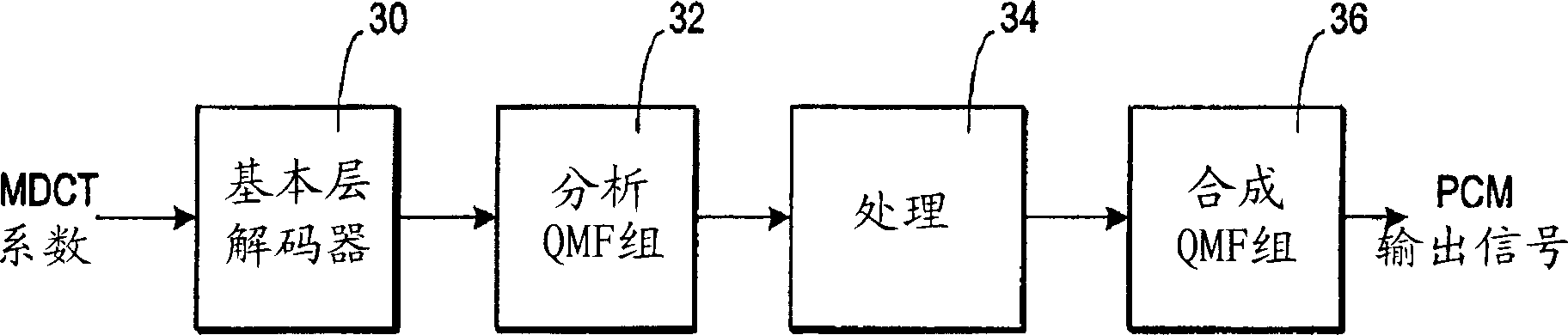
Audio signal decoding using complex-valued data
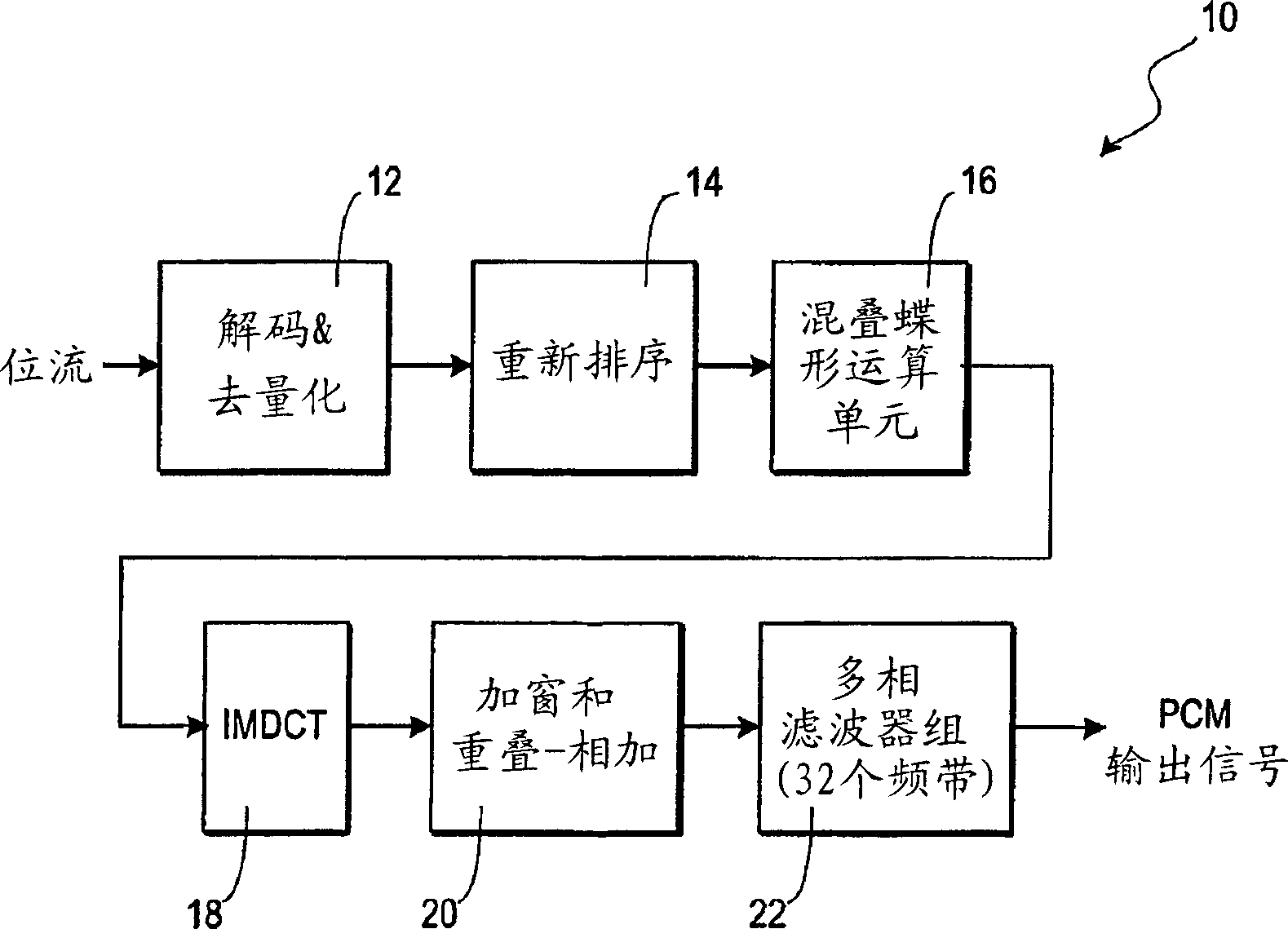
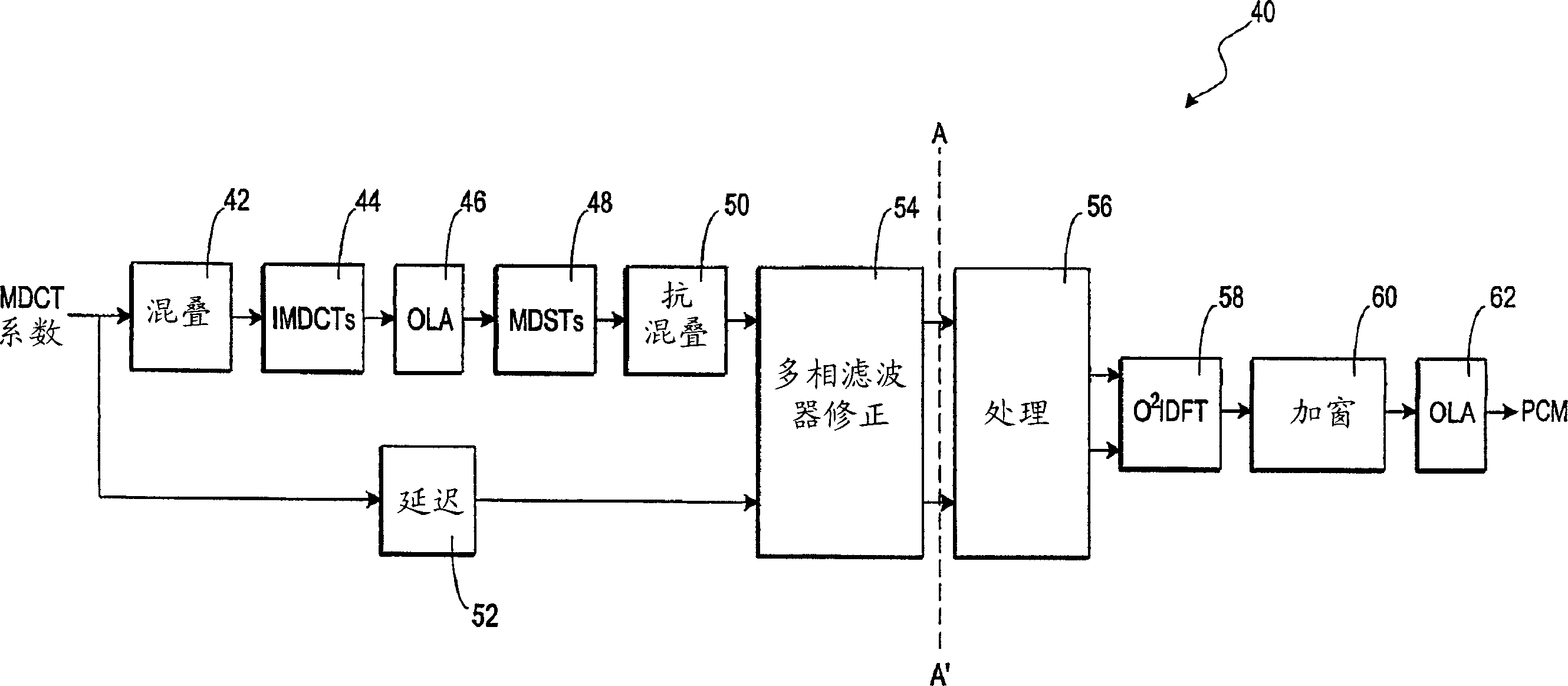
A decoder particularly, but not exclusively, for MPEG-1 layer III data signals, in which recovered spectral coefficients are transformed into time domain signal components, the time domain signal components then being transformed, using a forward transform which is orthogonally modulated with respect to the forward transform that was used at the encoder, to produce a set of second spectral coefficients. In this way, the first and second spectral coefficients may be used as complex-valued spectral coefficients which are amenable to post-processing. In the preferred embodiment, the complex-valued frequency components are, after post-processing, transformed to the time domain using an odd-frequency modulated Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com