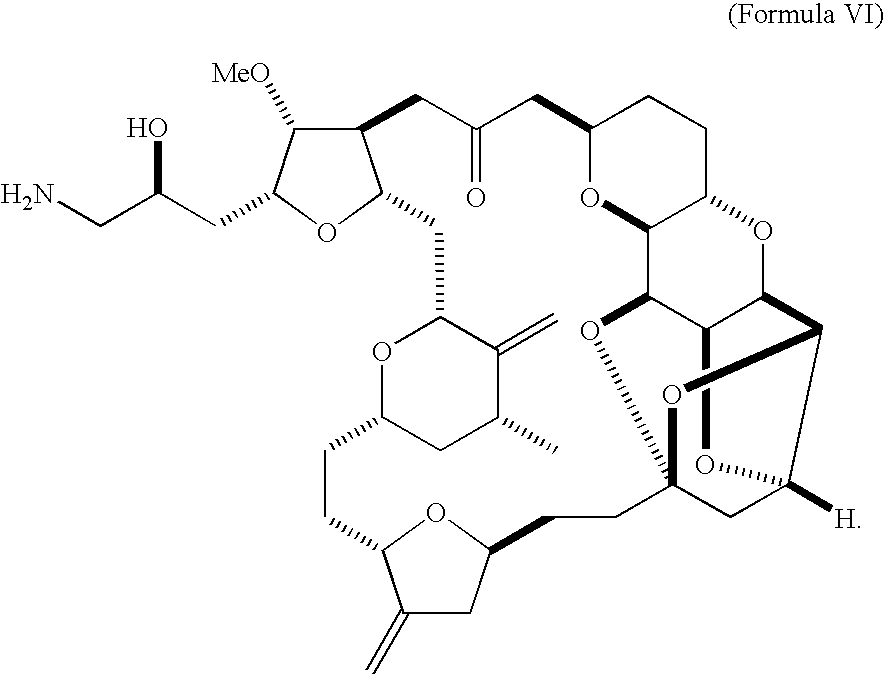
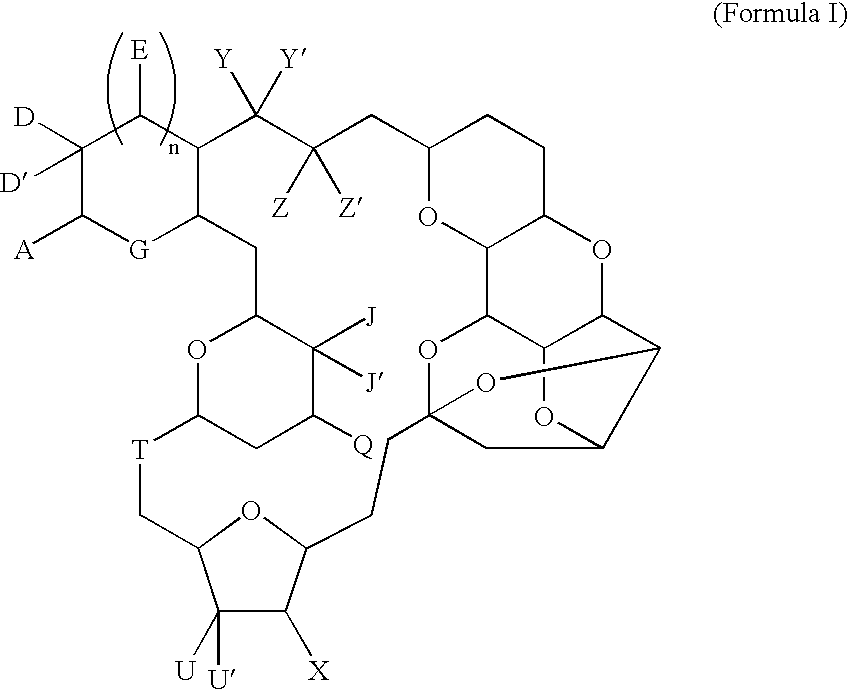
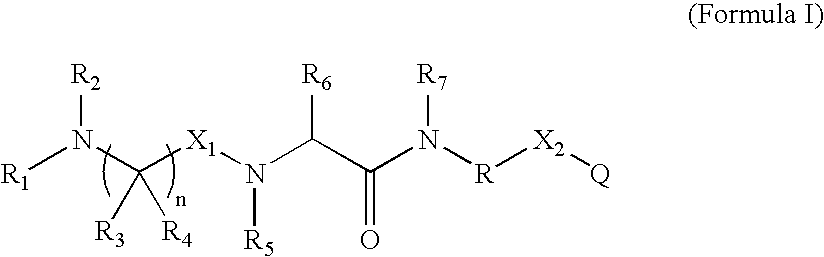
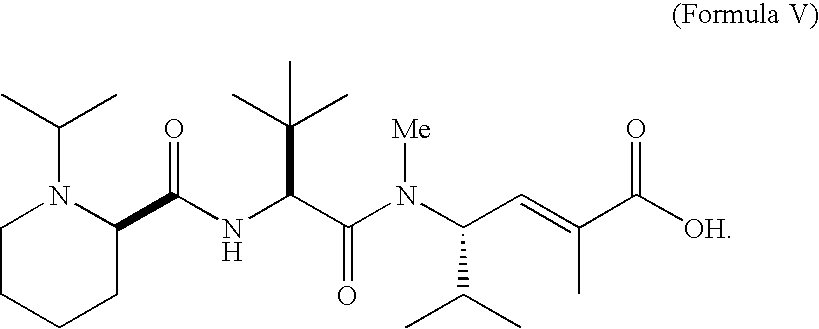
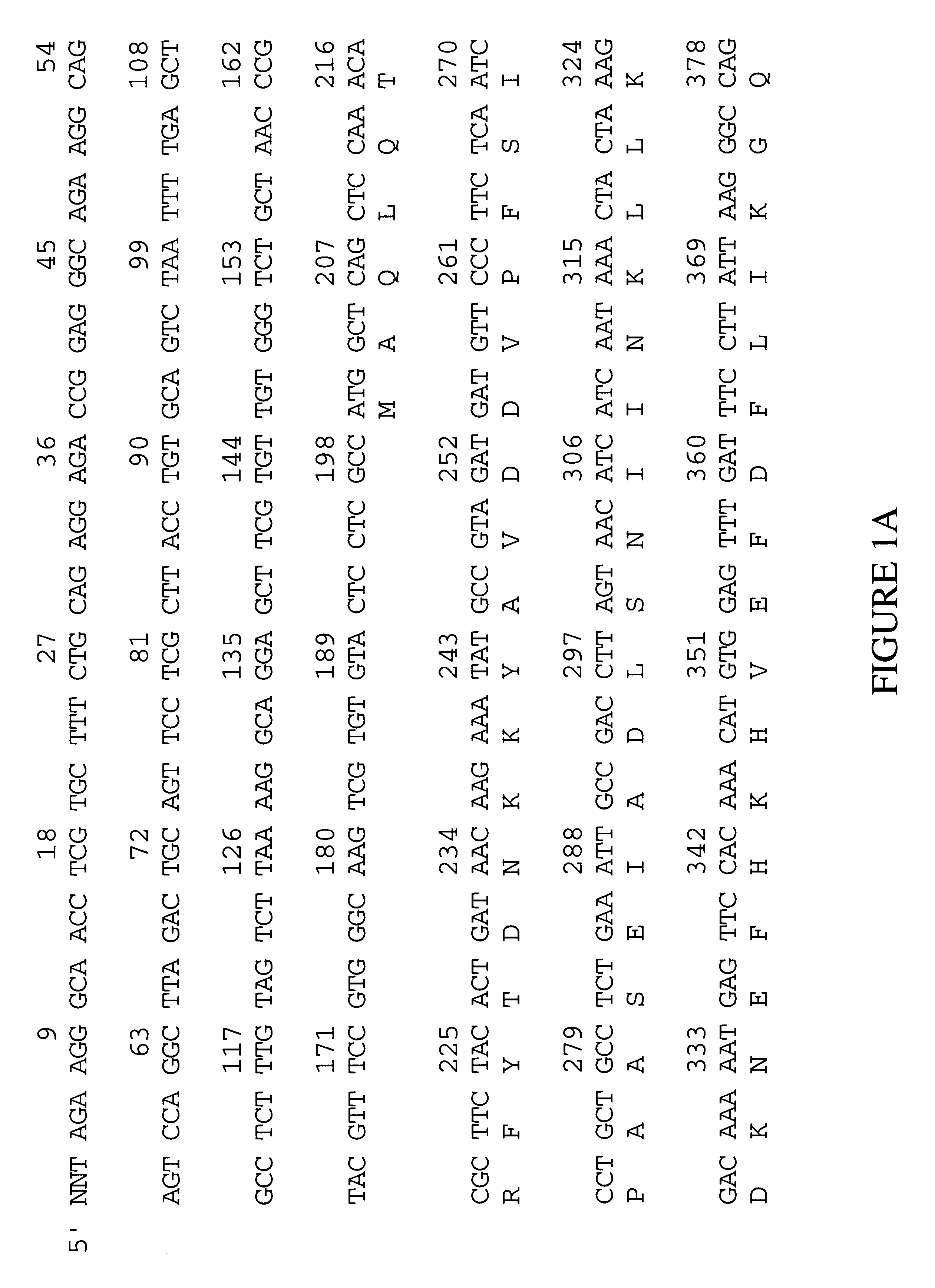
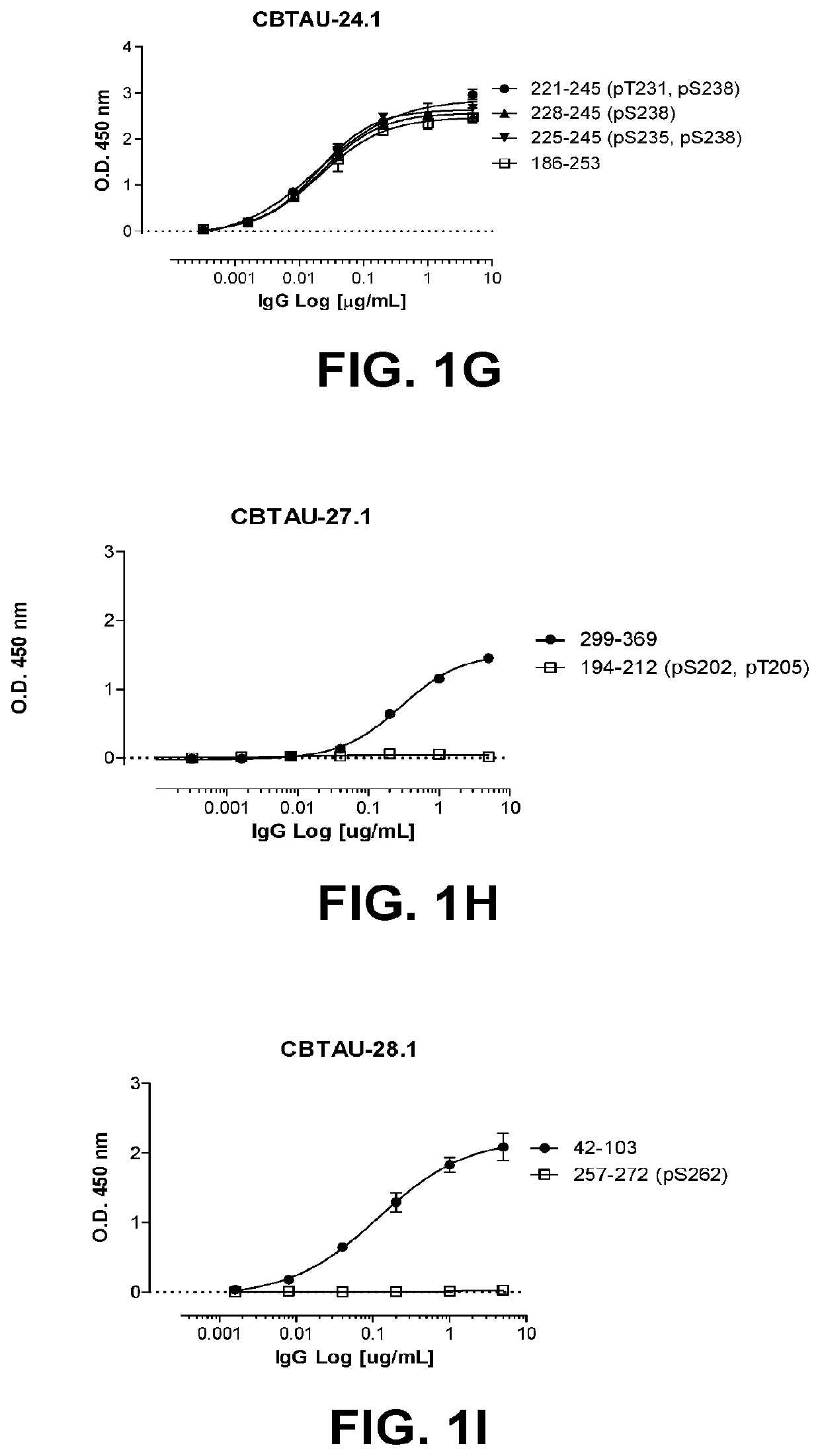
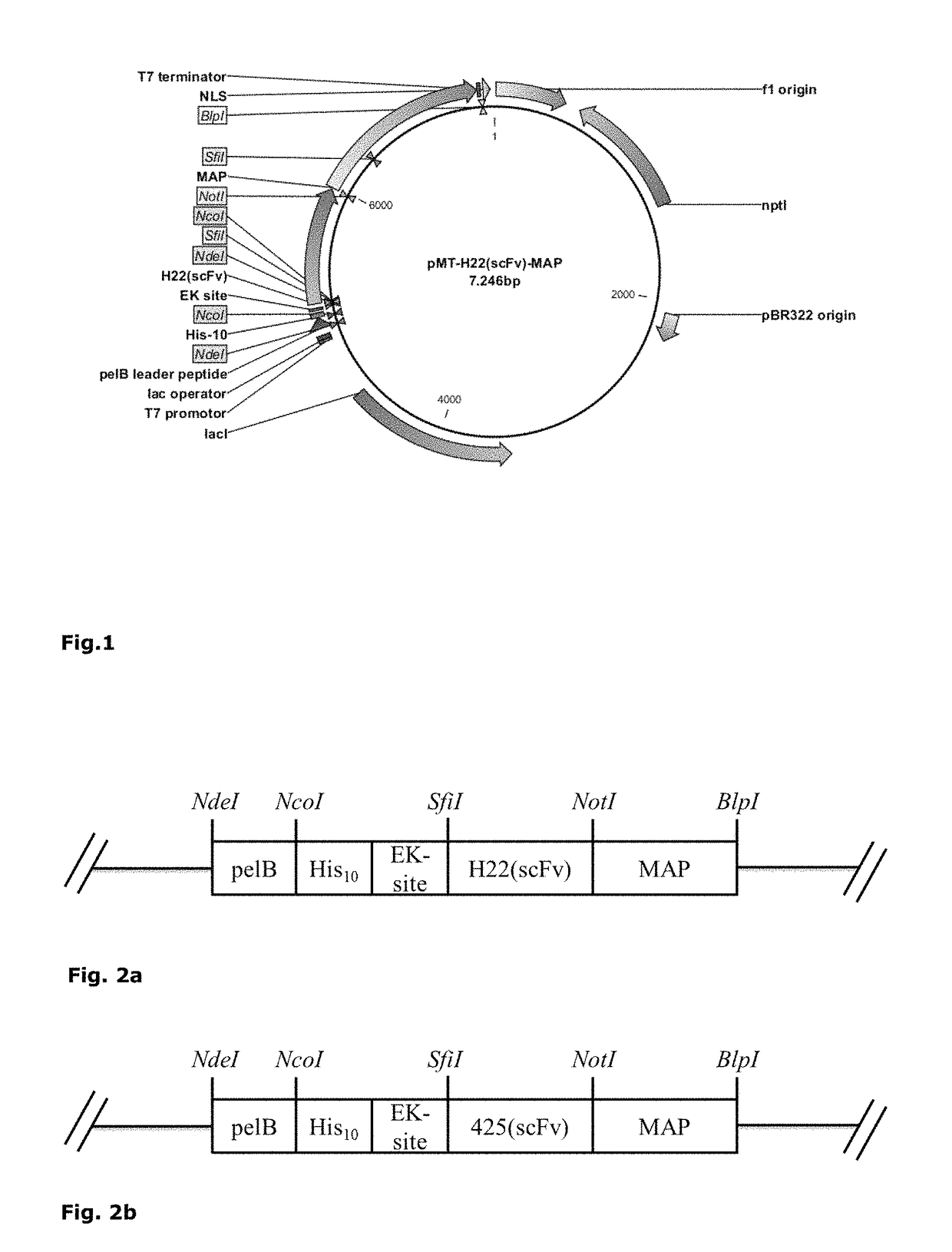
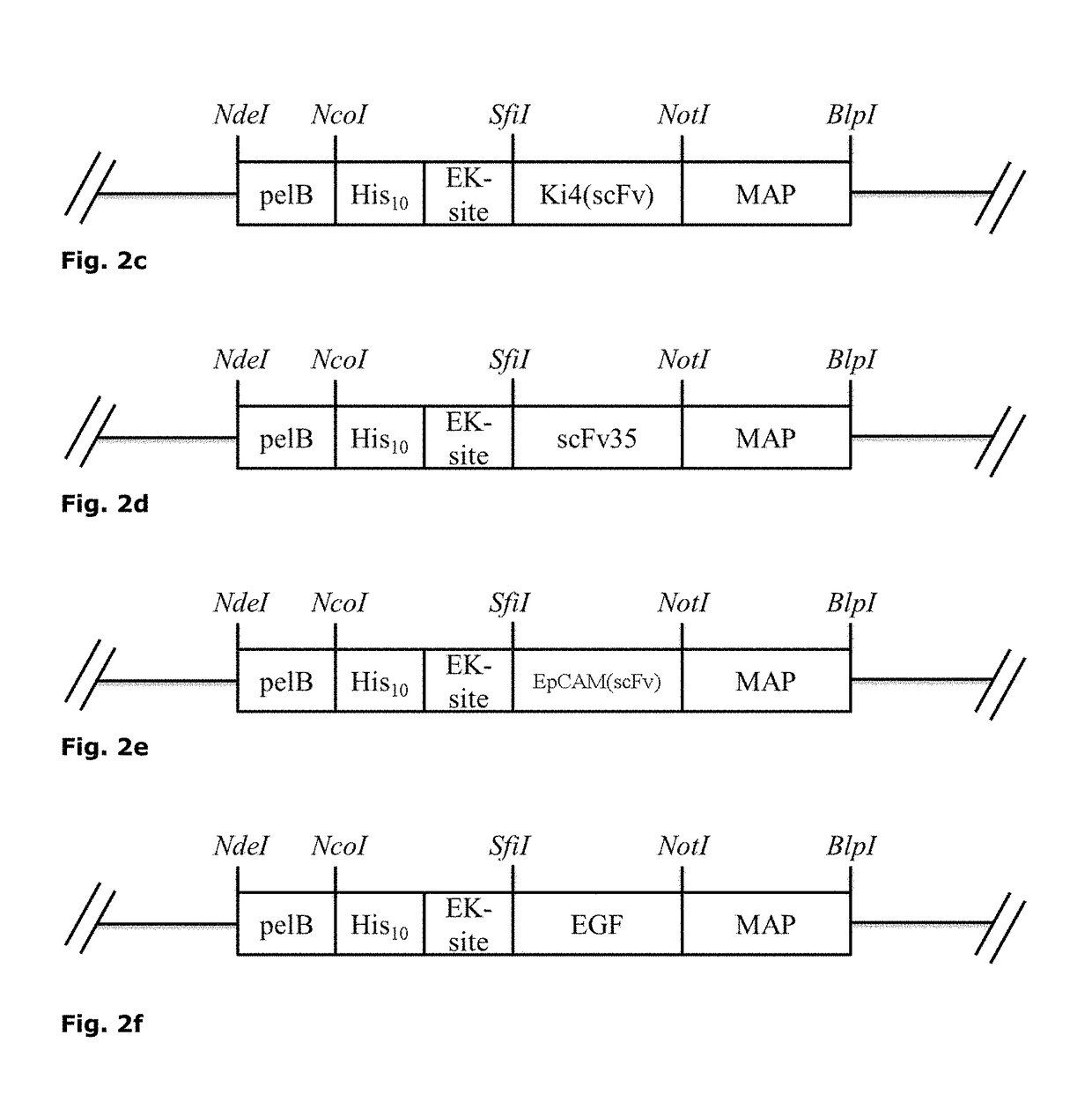
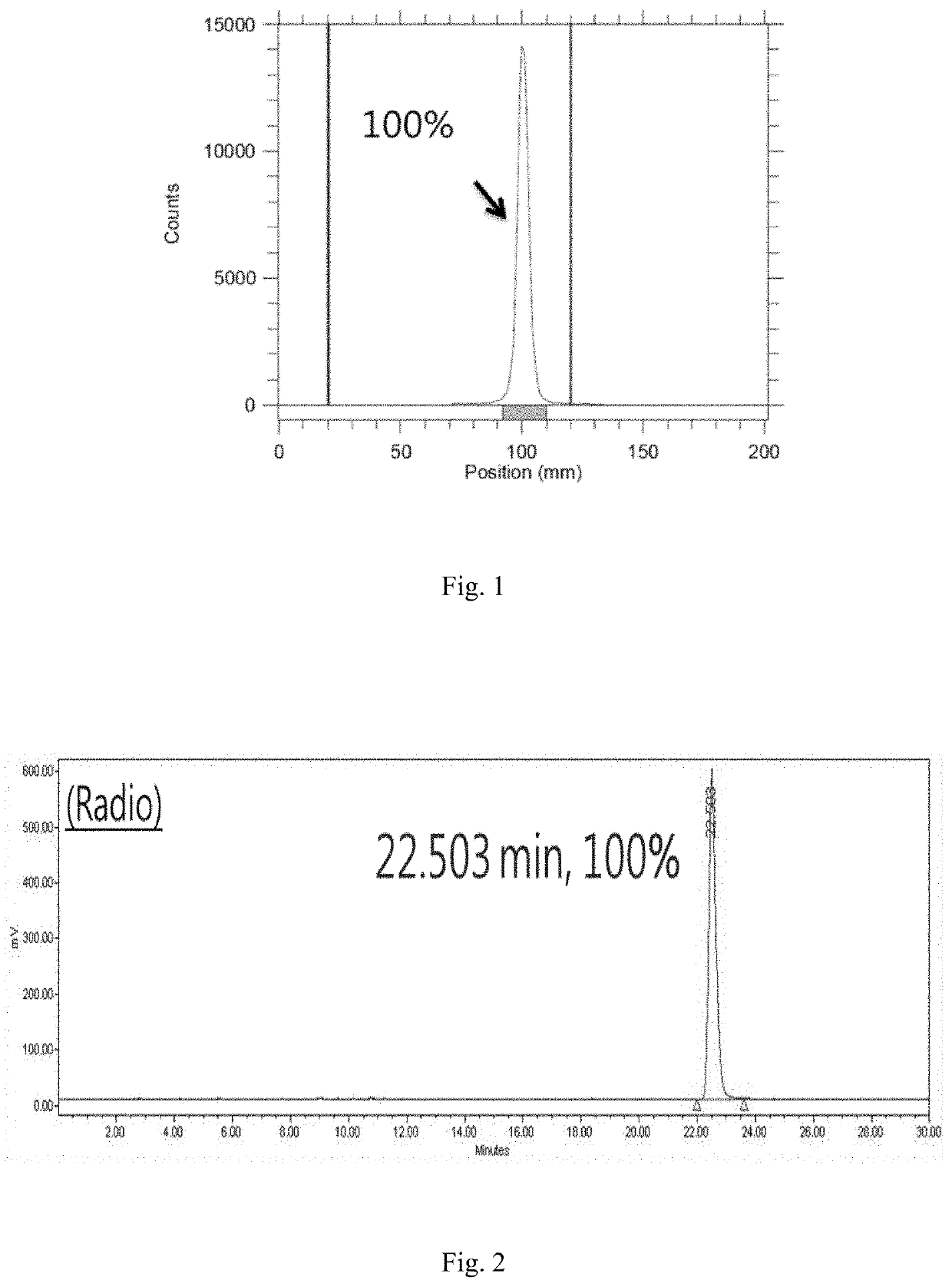
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Microtubule-associated protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cell biology, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton.
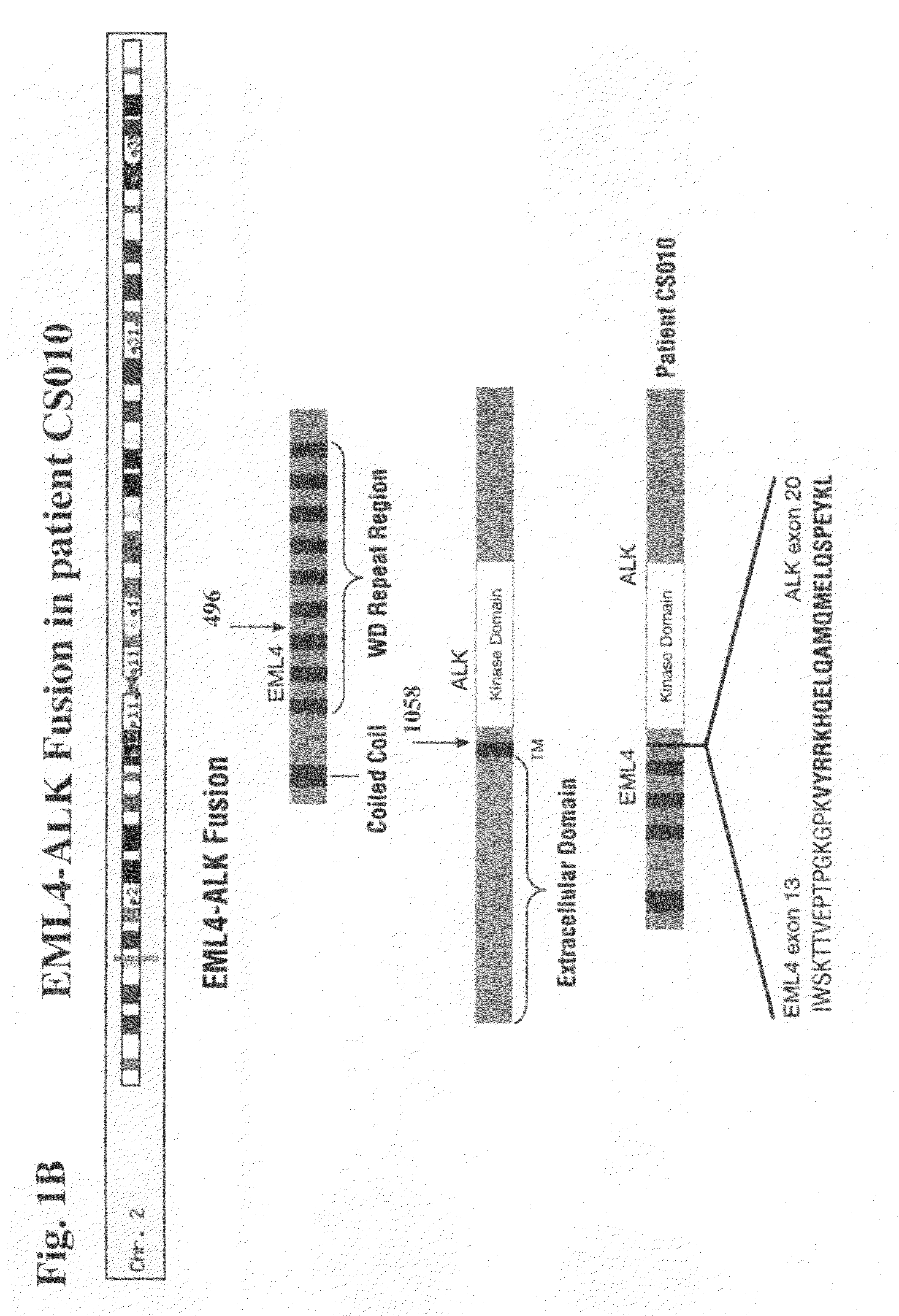
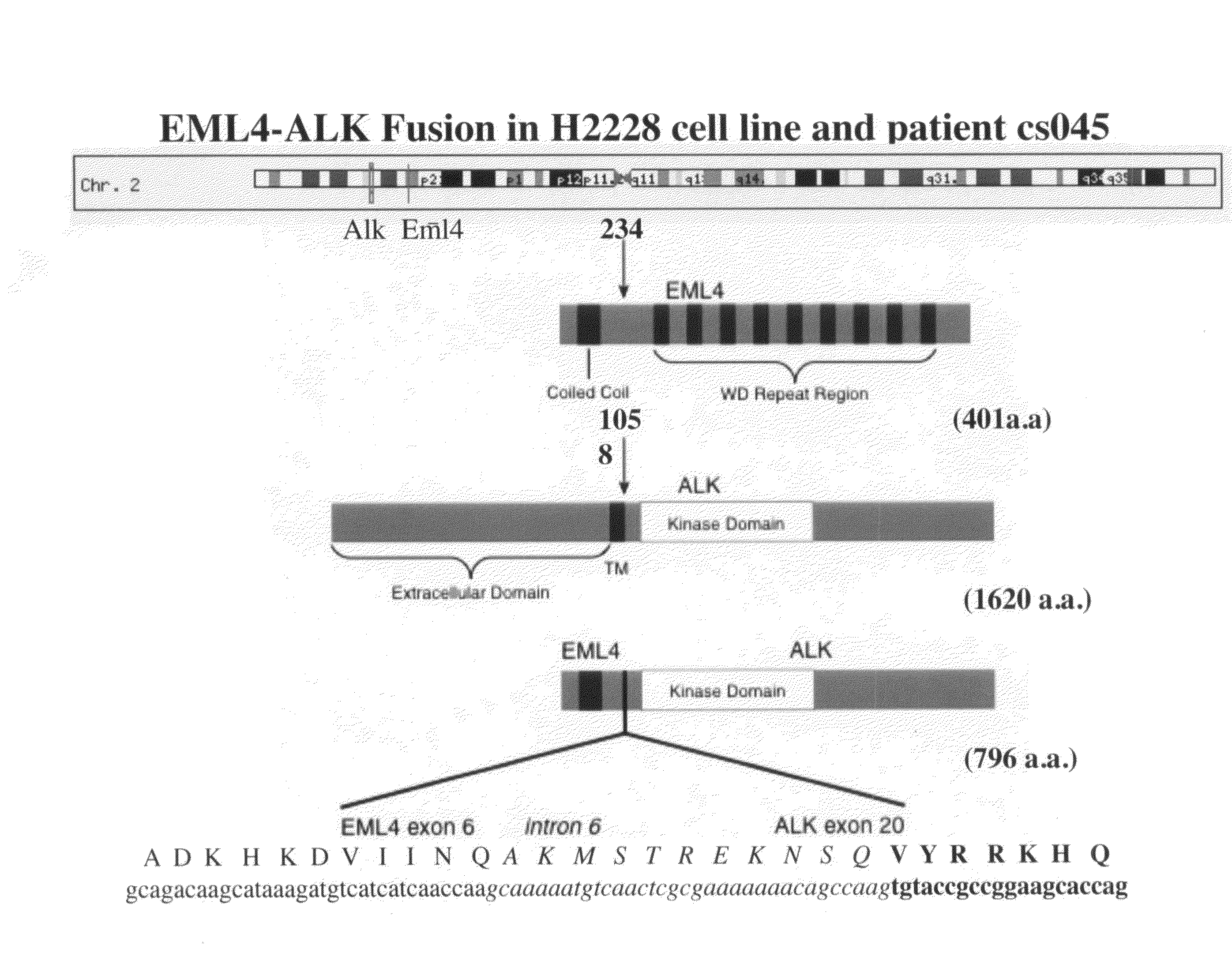
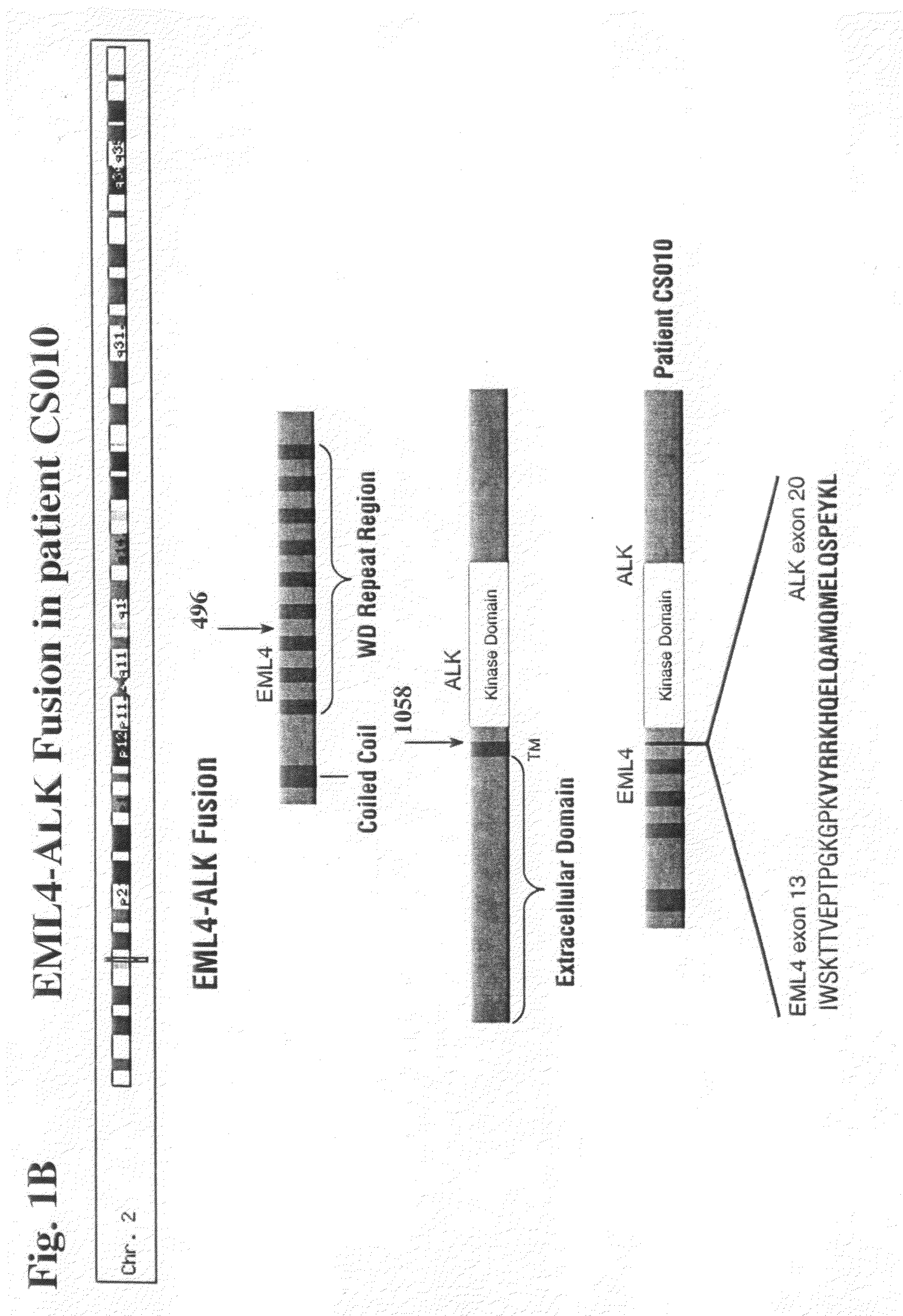
Gene defects and mutant ALK kinase in human solid tumors
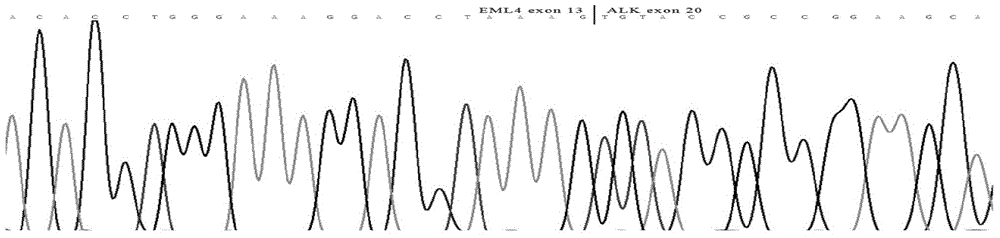
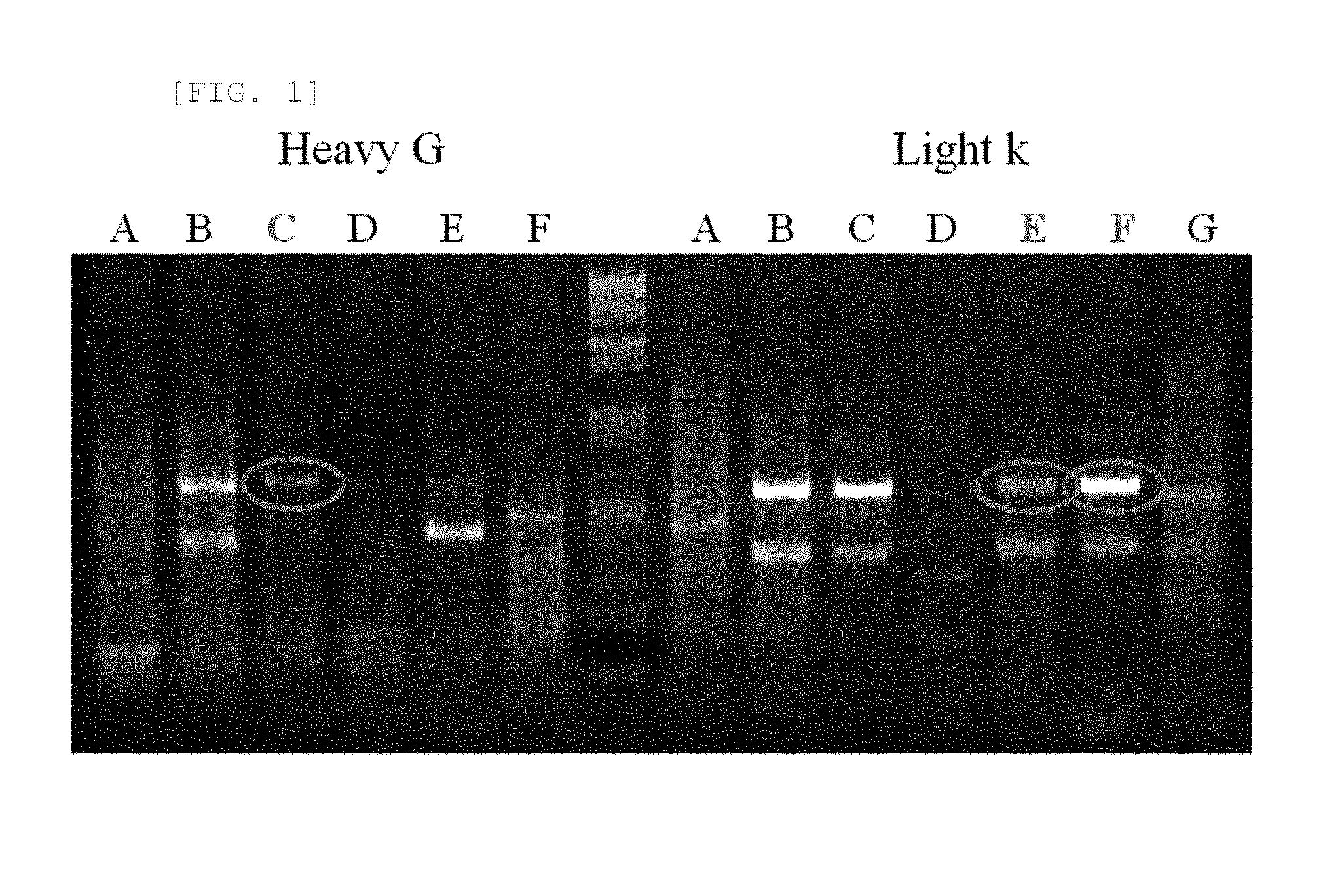
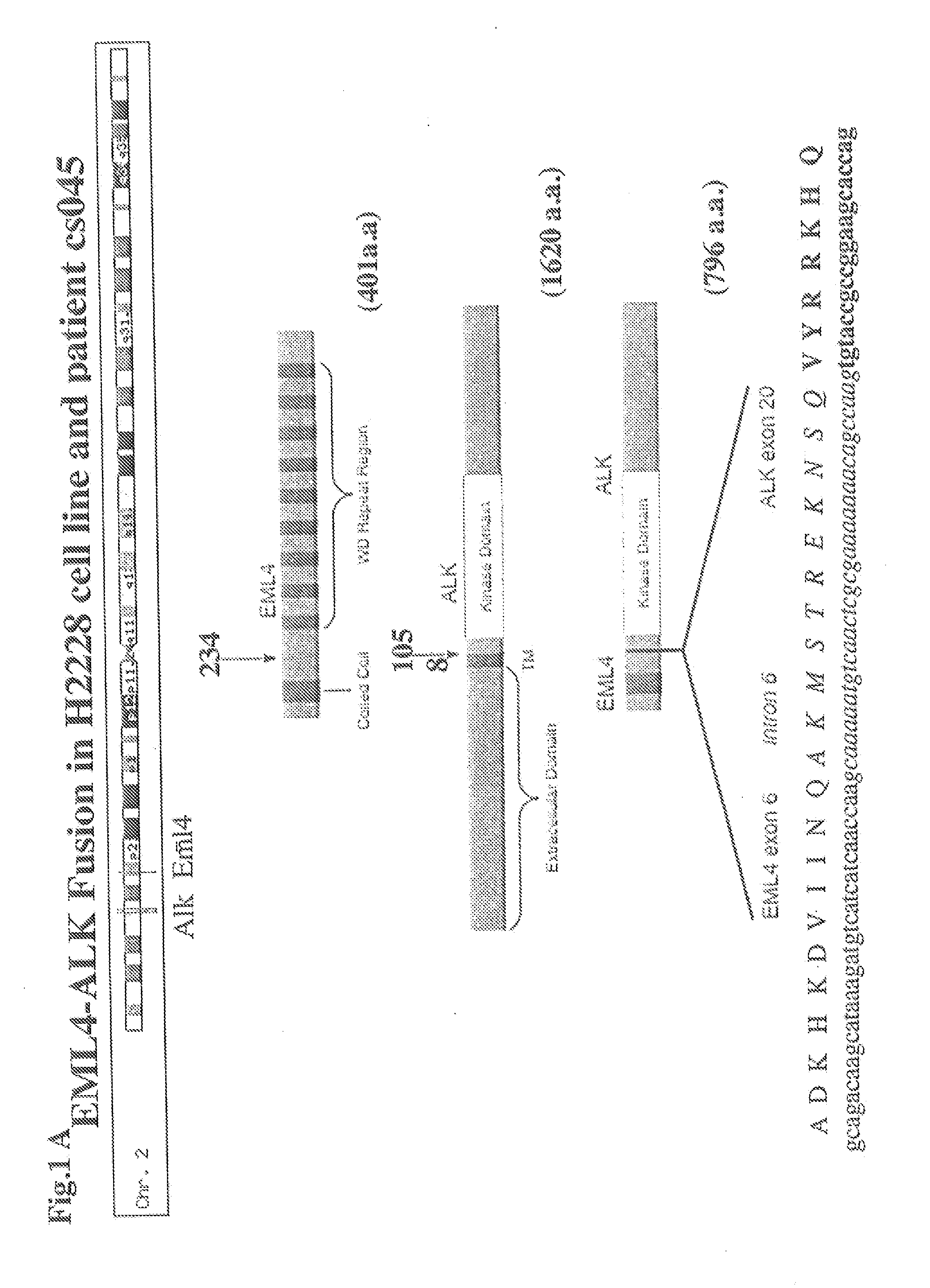
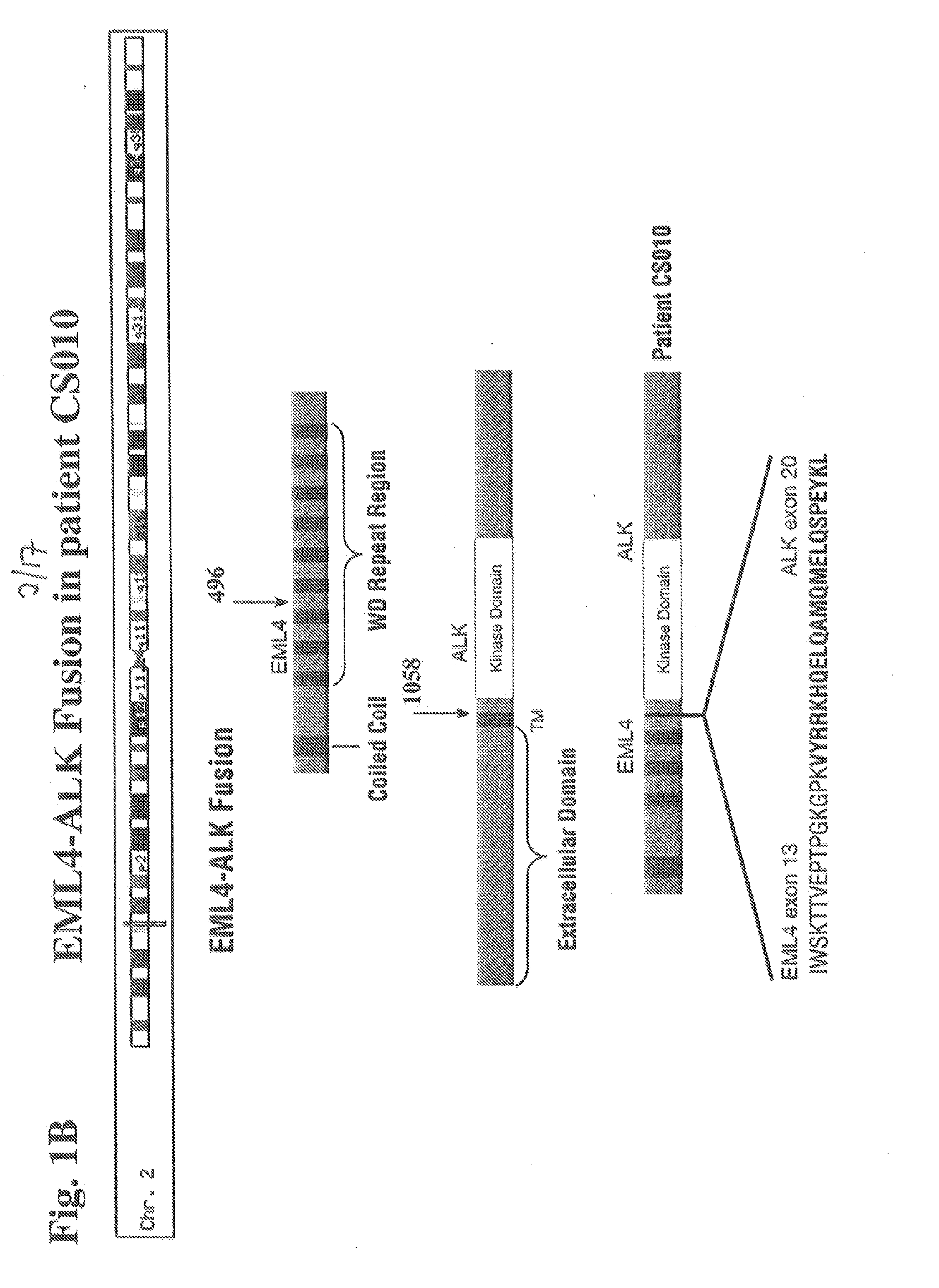
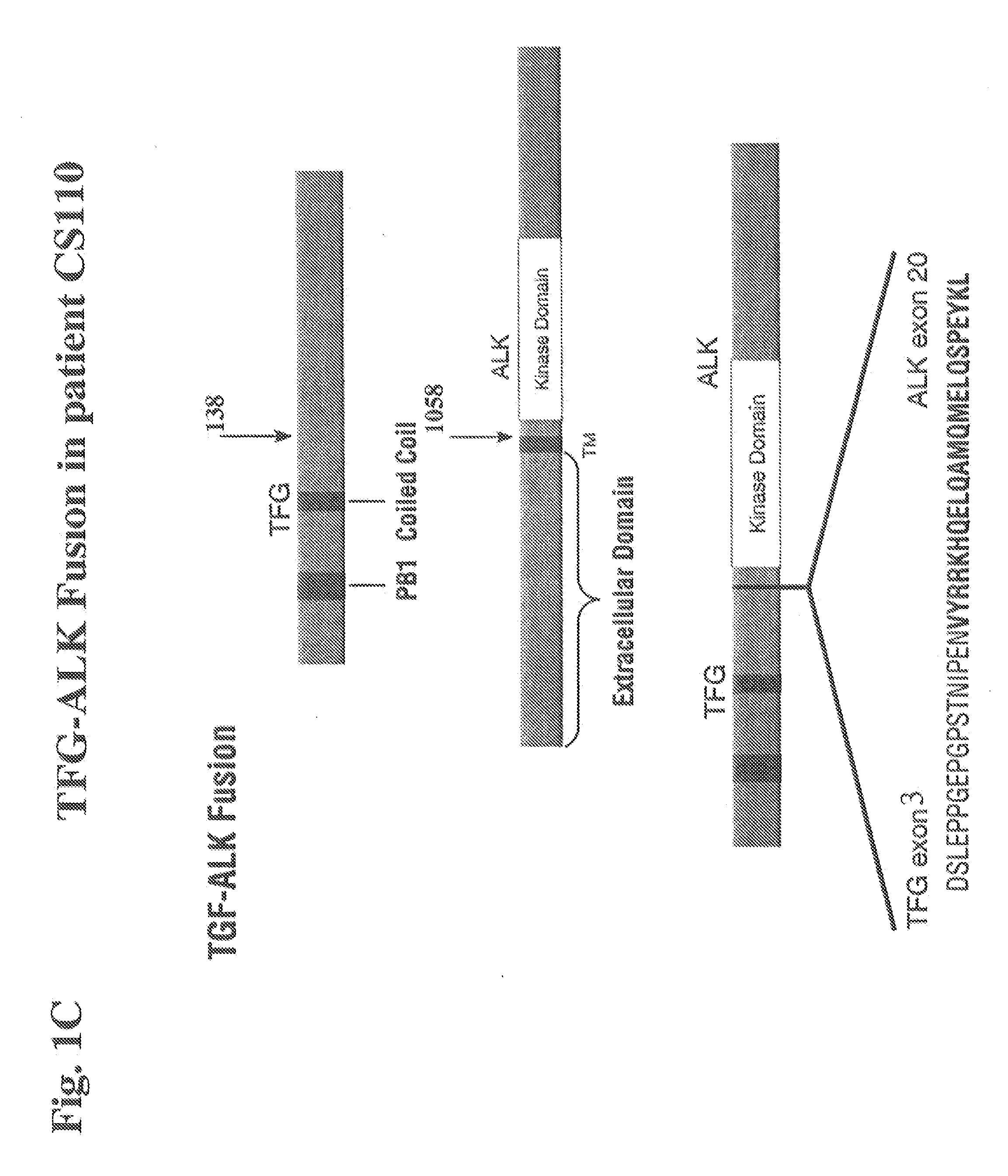
In accordance with the invention, novel gene deletions and translocations involving chromosome 2 resulting in fusion proteins combining part of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) kinase with part of a secondary protein have now been identified in human solid tumors, e.g. non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Secondary proteins include Echinoderm Microtubule-Associated Protein-Like 4 (EML-4) and TRK-Fusion Gene (TFG). The EML4-ALK fusion protein, which retains ALK tyrosine kinase activity, was confirmed to drive the proliferation and survival of NSCLC characterized by this mutation. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ALK kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of this new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ALK kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
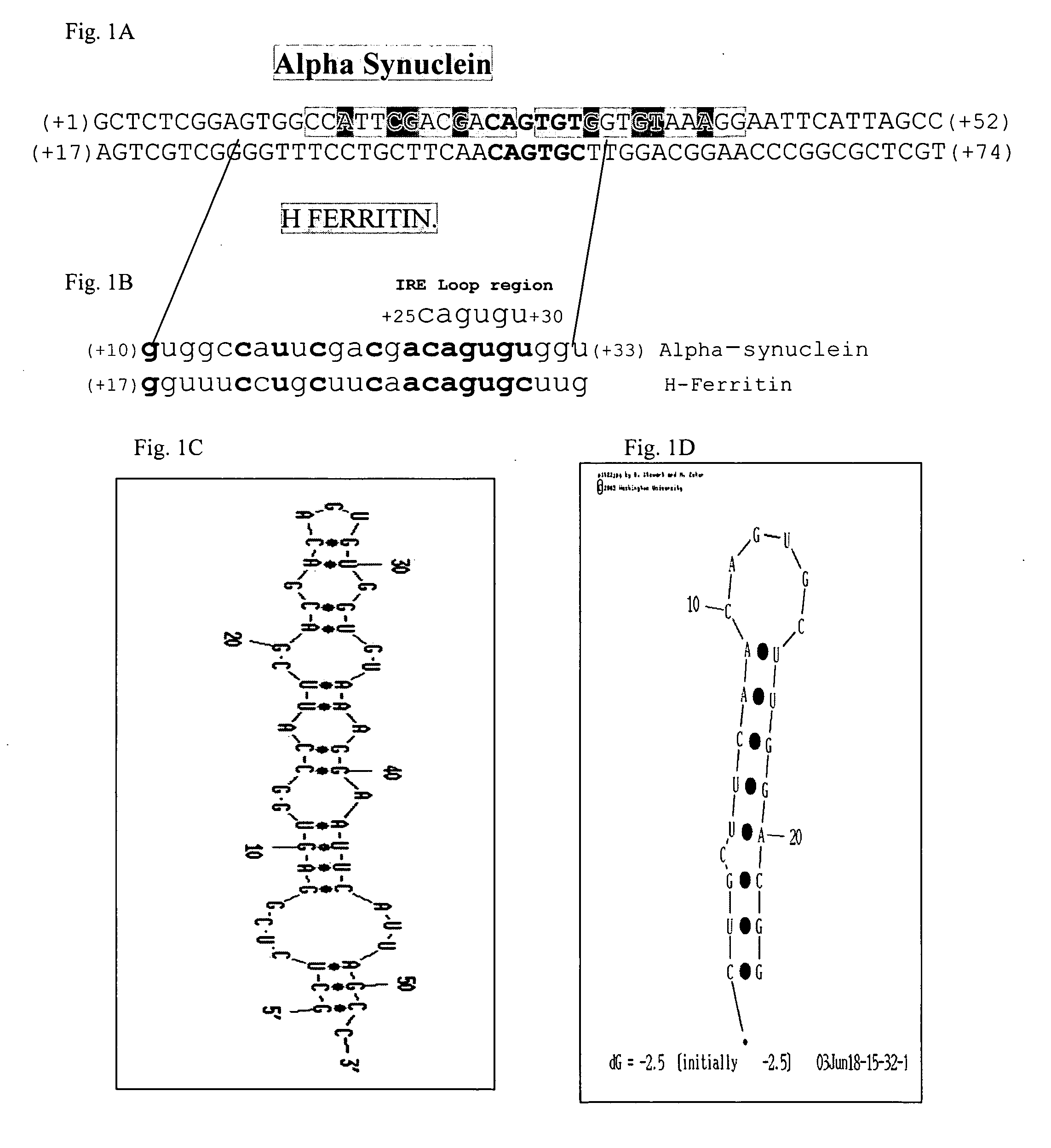
Translation enhancer elements of genes encoding human Tau protein and human alpha-synuclein protein
InactiveUS20080003570A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNeuro-degenerative diseaseEnhancer Elements
The invention relates to translation enhancer elements that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human microtubule-associated tau protein and nucleic acid molecules that enhance translation of the gene encoding the human α-synuclein protein. The translation enhancer elements of the invention are useful in compositions and methods for identifying compounds for the prevention and / or treatment of neurodegenerative disease. The invention also includes in some aspects, vectors that include a translation enhancer element of the invention. The invention also includes the use of enhancer element containing vectors in methods to produce recombinant protein and in assays to identify compounds that modulate expression of tau protein or α-synuclein protein.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
EML4-ALK (Echinoderm microtubule associated protein like4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) assay kit
ActiveCN103468813AEliminate distractionsHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementEchinodermConserved sequence
The invention relates to an EML4-ALK (echinoderm microtubule associated protein like4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) assay kit, which is applicable to assay of EML4-ALK fusion gene mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. The kit comprises probes, primers and positive controls, which are specially designed for conserved sequences of 9 fusion variations of the EML4-ALK fusion gene. The kit can be used for quickly and accurately assaying 9 most common EML4-ALK fusion gene variations with high sensitivity, namely 9 fusion variations of 7 variant subtypes, which are subtype 1 (E13; A20), subtype 2 (E20; A20), subtype 3 (E6a / b; A20), subtype 4 (E14; A20), subtype 5 (E2a / b; A20), subtype 6 (E18; A20) and subtype 7 (E14; A20), so that a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR system for assaying 9 most common EML4-ALK fusion gene variations can be established.
Owner:广州达健生物科技有限公司
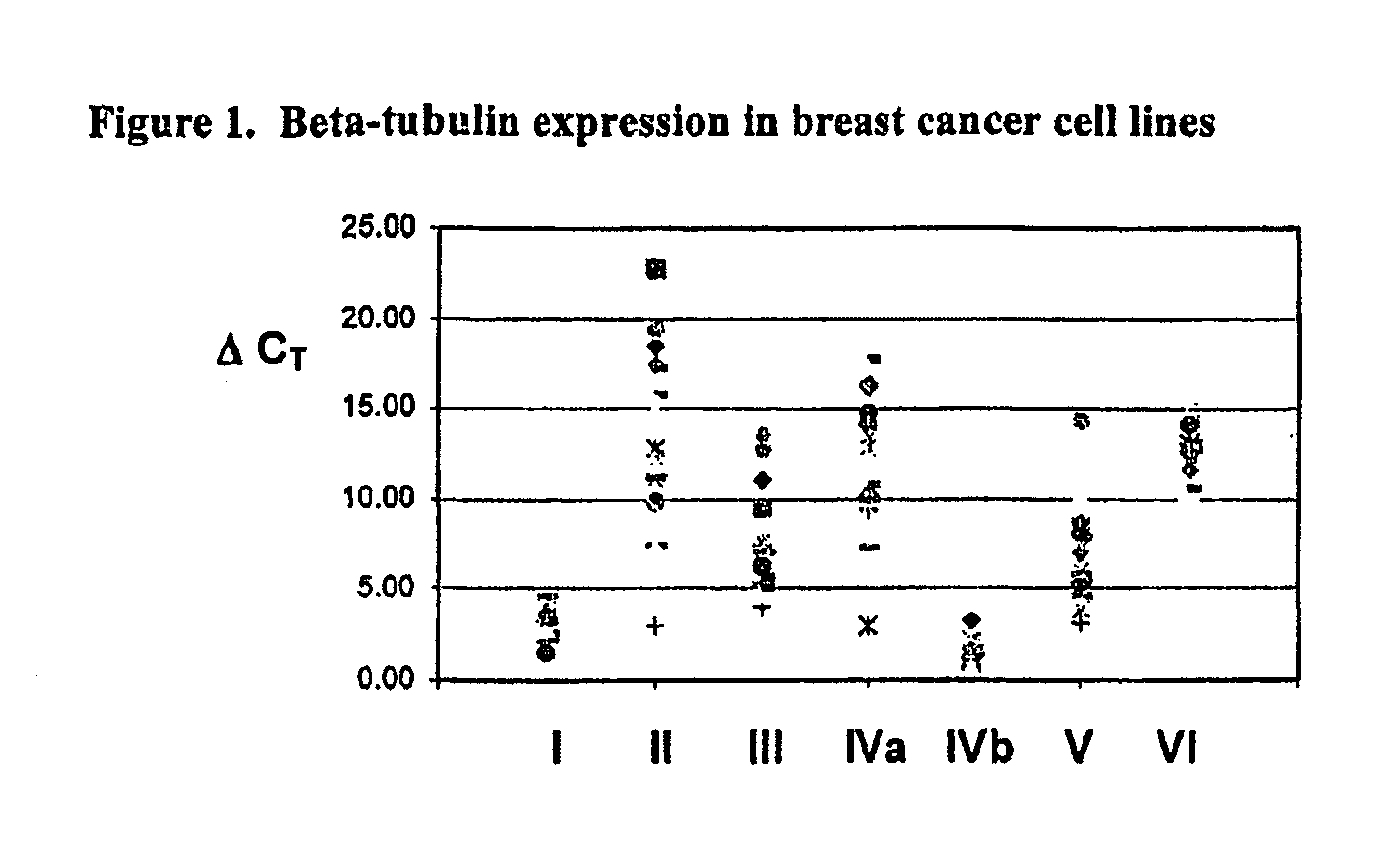
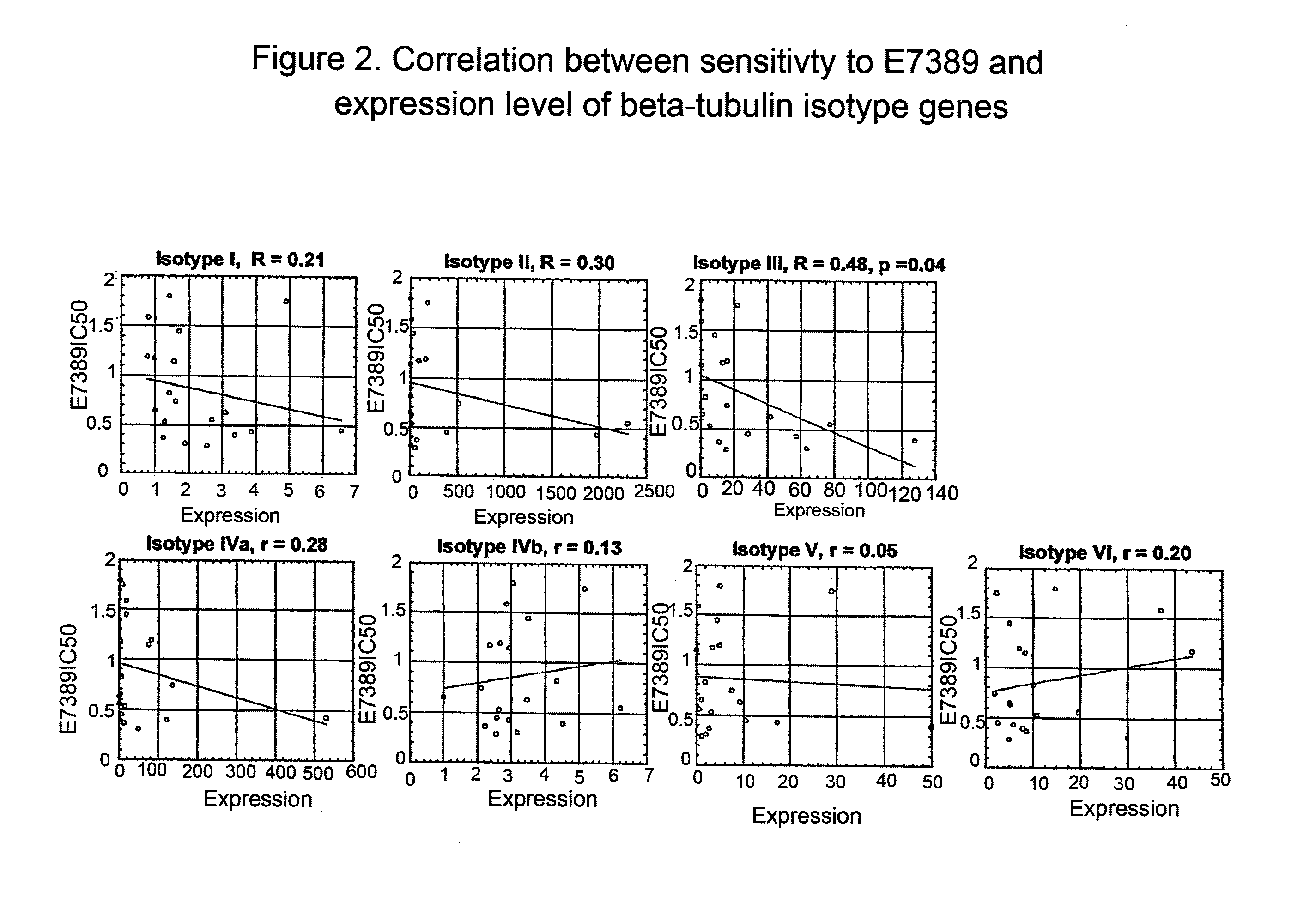
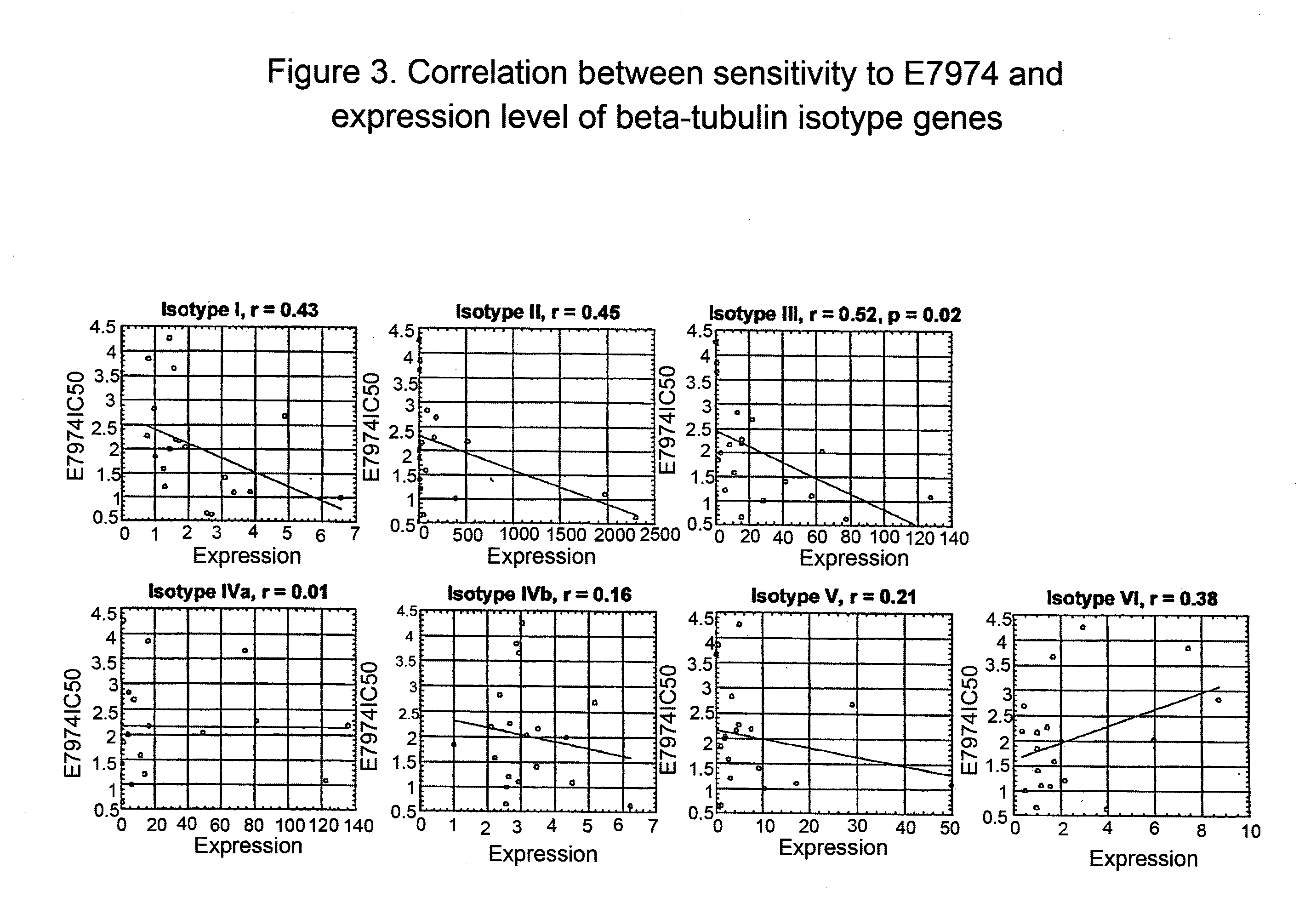
Tubulin isotype screening in cancer therapy using halichondrin B analogs
Chemotherapeutic agents that interfere with microtubule assembly or disassembly in the cell are potent inhibitors of cell replication. Examples of such agents include halichondrin B analogs. It has been shown that the susceptibility of certain cancers to analogs of halichondrin B correlates with the expression of particular tubulin isotypes or other microtubule-associated proteins such as MAP-4 and stathmin. Correlations such as these may be used in identifying patients suitable for treatment using a particular chemotherapeutic agent. Such a system avoids treating patients with cytotoxic compounds where there is a minimal or no effect on the cancer. The invention also provides a system of establishing these correlations for different compounds and cancer types. The system will be particularly useful in establishing correlations between anti-microtubule agents and cancers such as lung, breast, and ovarian cancer. Kits and reagents useful in practicing the invention are also provided.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Tubulin isotype screening in cancer therapy using hemiasterlin analogs
Chemotherapeutic agents that interfere with microtubule assembly or disassembly in the cell are potent inhibitors of cell replication. Examples of such agents include hemiasterlin analogs. It has been shown that the susceptibility of certain cancers to analogs of hemiasterlin correlates with the expression of particular tubulin isotypes or other microtubule-associated proteins such as MAP-4 and stathmin. Correlations such as these may be used in identifying patients suitable for treatment using a particular chemotherapeutic agent. Such a system avoids treating patients with cytotoxic compounds where there is a minimal or no effect on the cancer. The invention also provides a system of establishing these correlations for different compounds and cancer types. The system will be particularly useful in establishing correlations between anti-microtubule agents and cancers such as lung, breast, and ovarian cancer. Kits and reagents useful in practicing the invention are also provided.
Owner:EISAI CO LTD
Diagnostics and Therapeutics of Neurological Disease
InactiveUS20080152589A1Improve accuracyFewer depressive episodesBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmacogeneticsMedicine
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing a neurological disease and / or for determining the predisposition of a subject to a neurological disease and / or for determining a subject at risk of developing a neurological disease, the method comprising detecting a marker in a glycogen synthase kinase 3β gene or expression product thereof and a microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) gene or expression product thereof. The present invention also provides pharmacogenetic methods, e.g., for identifying a subject that will respond to treatment with a therapeutic compound.
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES OF C ST VINCENTS HOSPITAL
Microtubule-associated protein
InactiveUS6503708B1Avoid developmentPreventing further progressionSugar derivativesBacteriaENCODEAgonist
The invention provides a human microtubule-associated protein (HMAP) and polynucleotides which identify and encode HMAP. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for treating or preventing disorders associated with expression of HMAP.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
Microtubule-associated protein and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN101812127APositioning does not affectReduce positioningPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsWAS PROTEINMicrotubule Depolymerization
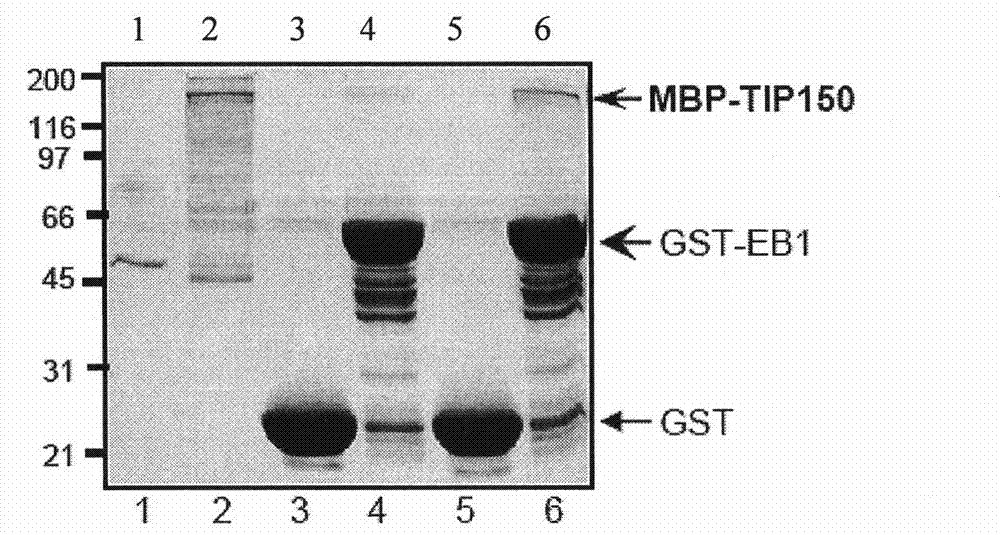
The invention discloses a microtubule-associated protein and coding genes and application thereof. The microtubule-associated protein is protein of (a) or (b): (a) protein formed by an amino acid sequence as shown by a sequence one in a sequence table; and (b) protein derived by the sequence one, related to the inhibition of the microtubule de-polymerization activity of MCAK protein and formed ina way the amino acid sequence of the sequence one is substituted and / or deleted and / or added by one to ten amino acid residues. The protein of the invention participates in the regulation and the control of the forward end dynamics of microtubules through the mutual effect with EB1 and MCAK and stabilizes the microtubules through inhibiting the microtubule de-polymerization activity of the MCAK protein. After the coding genes of the low-interference RNA of microtubule-associated protein genes are introduced into a host, the microtubule positioning of the MCAK is seriously affected. The protein and the coding genes thereof play a great role in the medical field and the pharmaceutical field and thereby the application prospect is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and device to detect, monitor and promote neural regeneration and improvement of cognitive function in a subject suffering from neural injury
InactiveUS20140018299A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderCognitive skillClinical evaluation
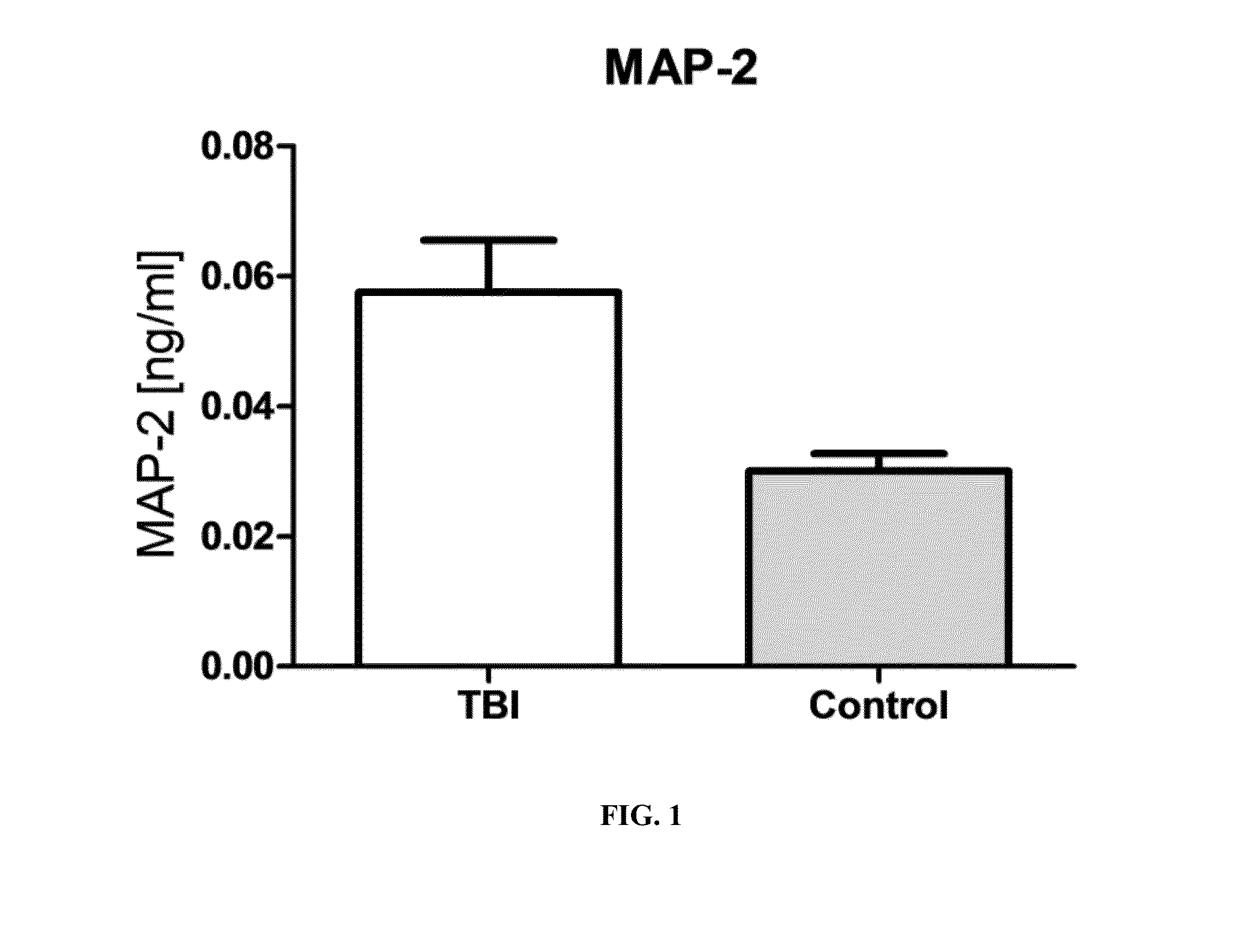
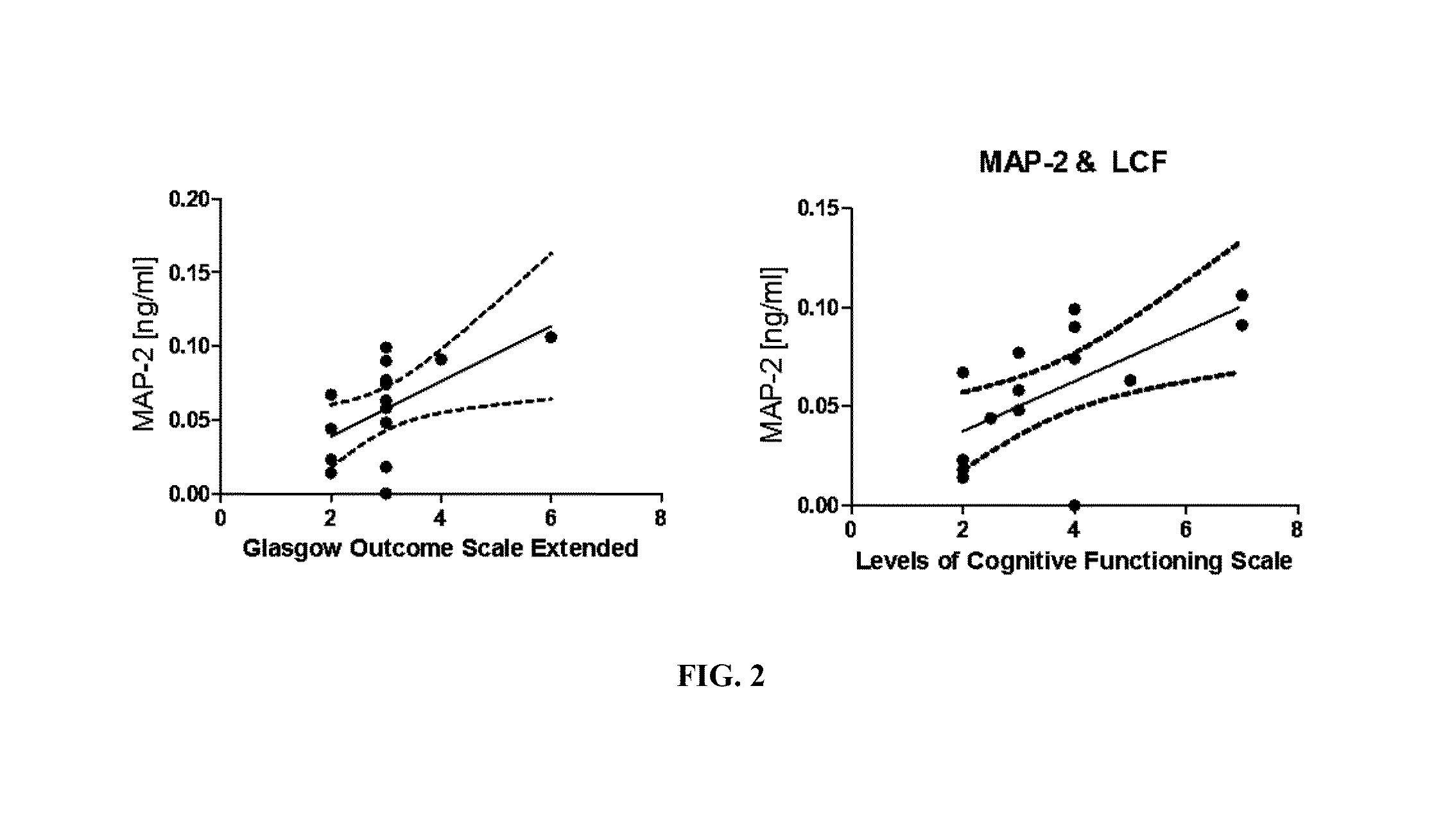
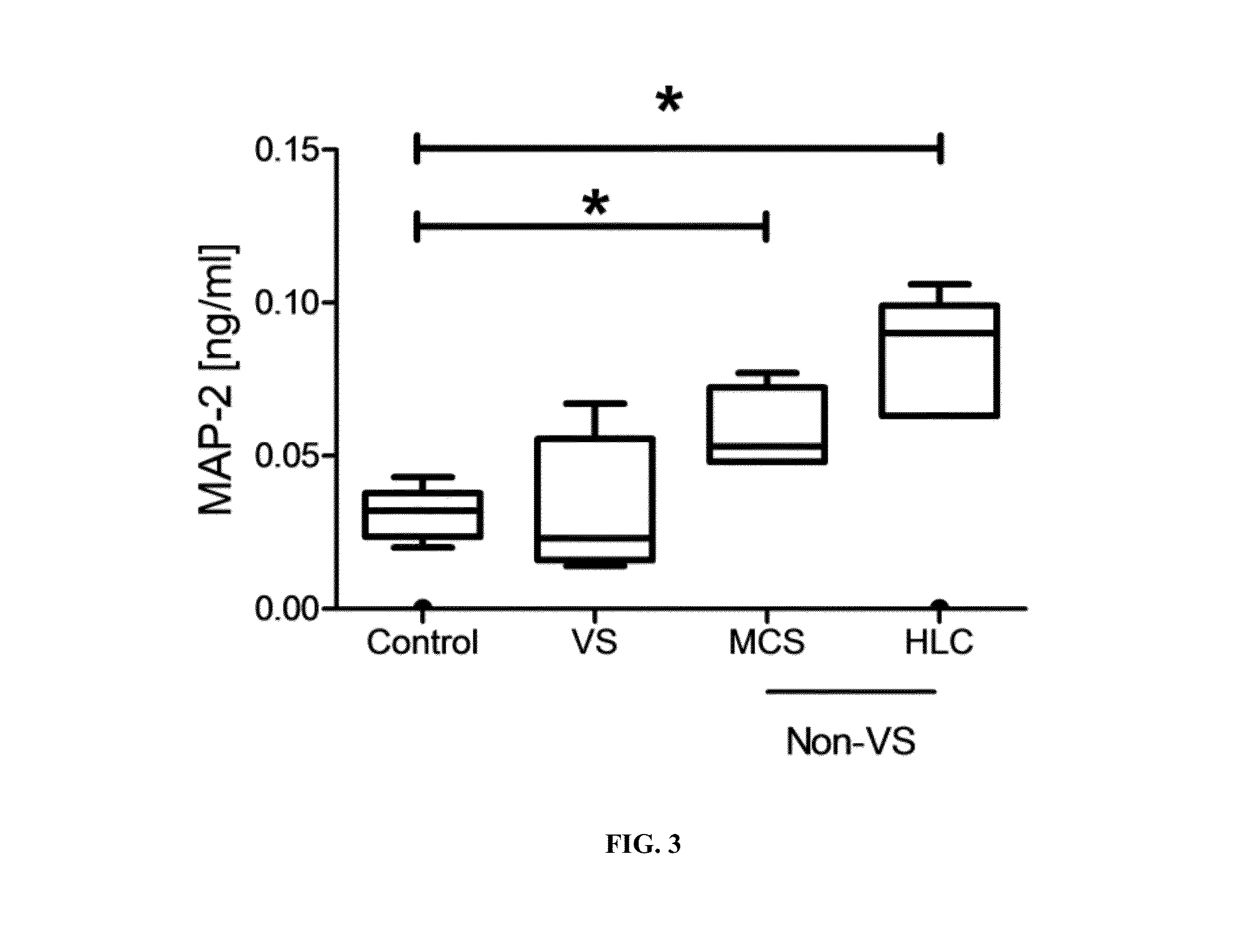
Severe traumatic brain (TBI) injuries are often associated with long-term and disabling consequences. Prognosis and chronic treatment planning following severe TBI remain challenging. The discovery of specific brain biomarkers could create new opportunities for more accurate clinical assessments identifying groups that may experience better outcomes when exposed to an intervention. The present invention provides a method of detection of Microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP-2), a marker of dendritic damage, in a biological sample of survivors after TBI and evaluates the recovery of the patient, including an improvement in cognitive abilities and function.
Owner:BANYAN BIOMARKERS INC
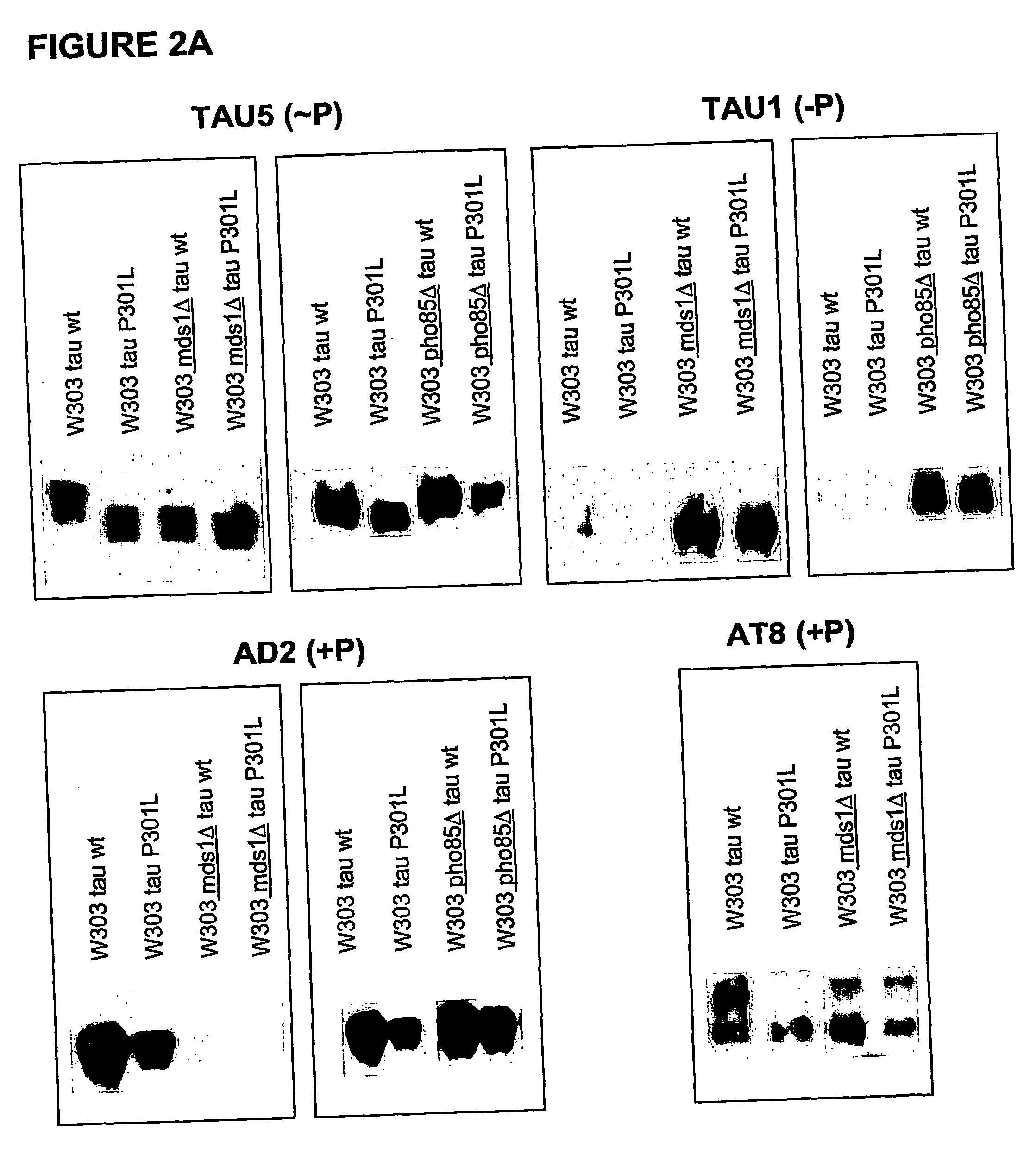
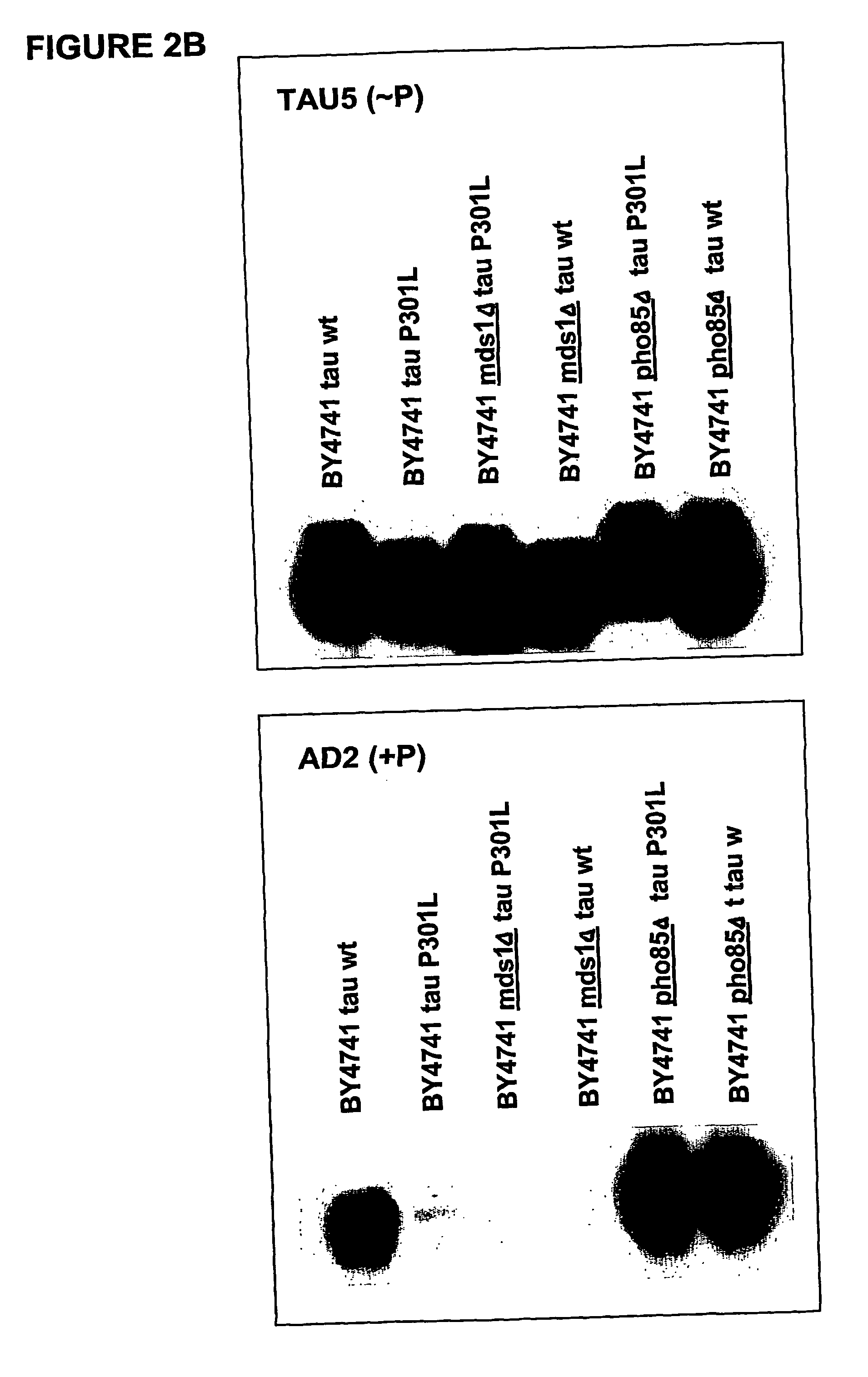
Tau-opathy model
InactiveUS20050009019A1Integrated precisionCompound screeningFungiPhosphorylationMicrotubule associated protein tau
The present invention relates to cell models of Alzheimer's disease. Transgenic yeast cells are described as models for the tau-opathy in Alzheimer's disease. These cell models comprise recombinant DNA constructs comprising control sequences and a cDNA sequence encoding a human tau-isoform and another similar construct comprising a protein kinase that is capable, directly or indirectly, of modulating the phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau. The transgenic cells are useful for high-throughput testing for potential therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Owner:REMYND NV
Miniaturization cucumber plant associated protein and coding gene thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN107254455AInhibition of developmentAbnormal arrangementHydrolasesFermentationNormal growthWild type
The invention discloses a miniaturization cucumber plant associated protein and a coding gene thereof and an application thereof. An amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as a sequence table 2, which belongs to AAA ATP enzyme family, and is related with microtubule associated protein; the coding gene of the protein has a base sequence shown as a sequence table 1, if the mutation is generated on the base sequence, such as cytosine (C) with 1058 bp bit is substituted by thymidine (T), serine (Ser) with 353 bit for coding the protein is changed to phenylalanine (Phe), the protein inhibits the normal growth of the microtubule cell, the microtubule cytoskeleton is lost, the arrangement is abnormal, concretely, the plant phenotype is plant miniaturization, the height of the mutant plant is about 20% of the height of a normal wild type plant, the fruit length is about 10% of the length of normal wild type fruit, and the leaves and the seeds are obviously shortened. The application of the protein and the coding gene can create condition for cucumber strain-type improvement and cross breeding or exploitation of transgene plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene defects and mutant ALK kinase in human solid tumors
ActiveUS20100240034A1Inhibit expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
In accordance with the invention, novel gene deletions and translocations involving chromosome 2 resulting in fusion proteins combining part of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) kinase with part of a secondary protein have now been identified in human solid tumors, e.g. non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Secondary proteins include Echinoderm Microtubule-Associated Protein-Like 4 (EML-4) and TRK-Fusion Gene (TFG). The EML4-ALK fusion protein, which retains ALK tyrosine kinase activity, was confirmed to drive the proliferation and survival of NSCLC characterized by this mutation. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ALK kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of this new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ALK kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Conjugated protein Tau of microtubule of earthworm, its coding gene, and application
This invention provides E-Tau protein expressed by E-tau gene produced from Lumbricus terrestris total RNA by RT-PCR, recombinant vector containing E-tau gene and its subclones, recombinant microorganisms, eukaryotic expression vector containing E-tau gene and relevant transfected cell lines. E-tau gene is a new type of microtubule-associated gene, which is closely related to Alzheimer's disease. E-Tau protein can accelerate microtubule assembly and stabilize microtubule net. This invention also relates to the application of E-tau gene in neurodegenerative disease treatment.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
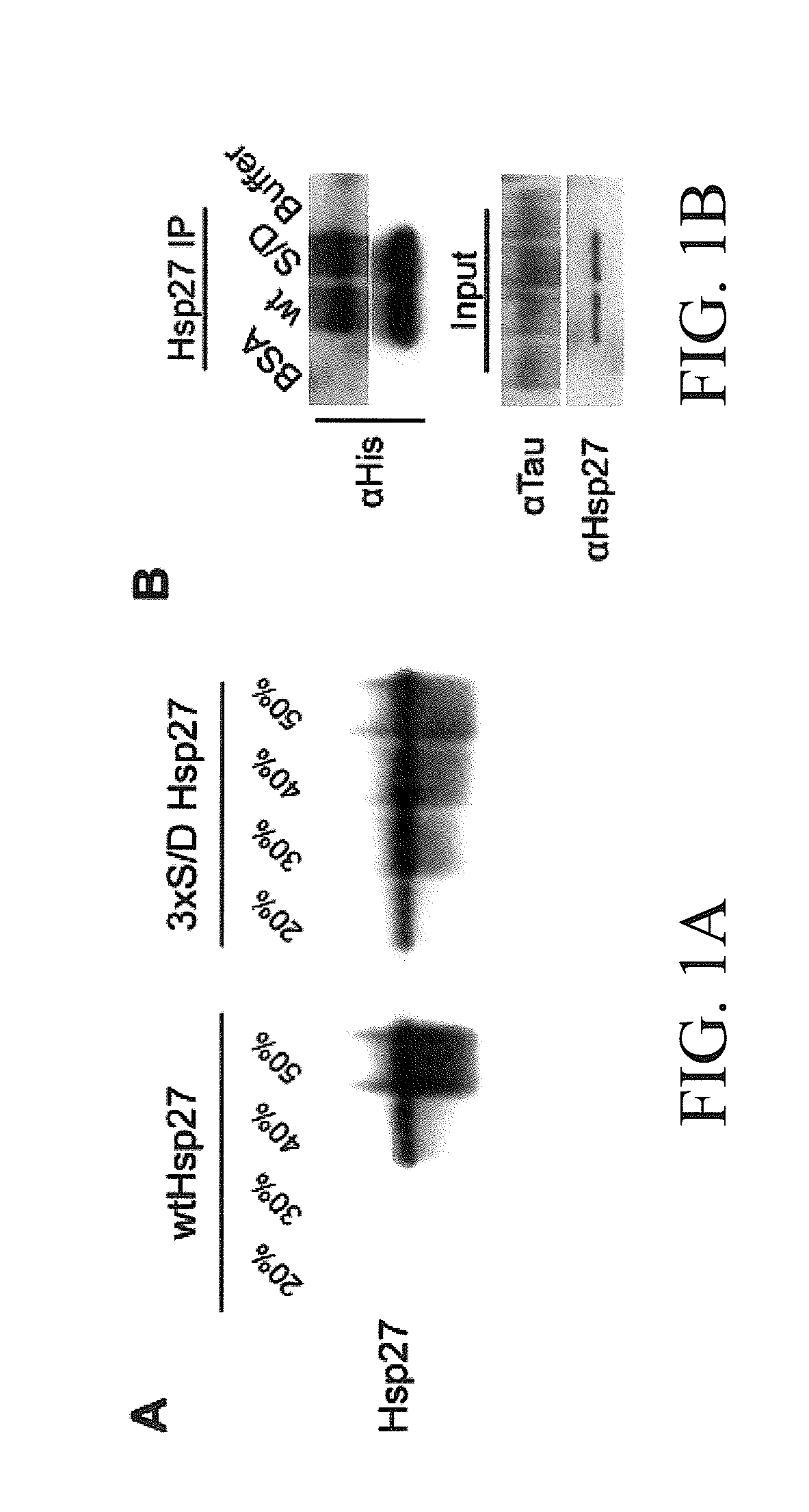
Materials and methods for treating neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20130209549A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderNeuro-degenerative diseaseProtein tau
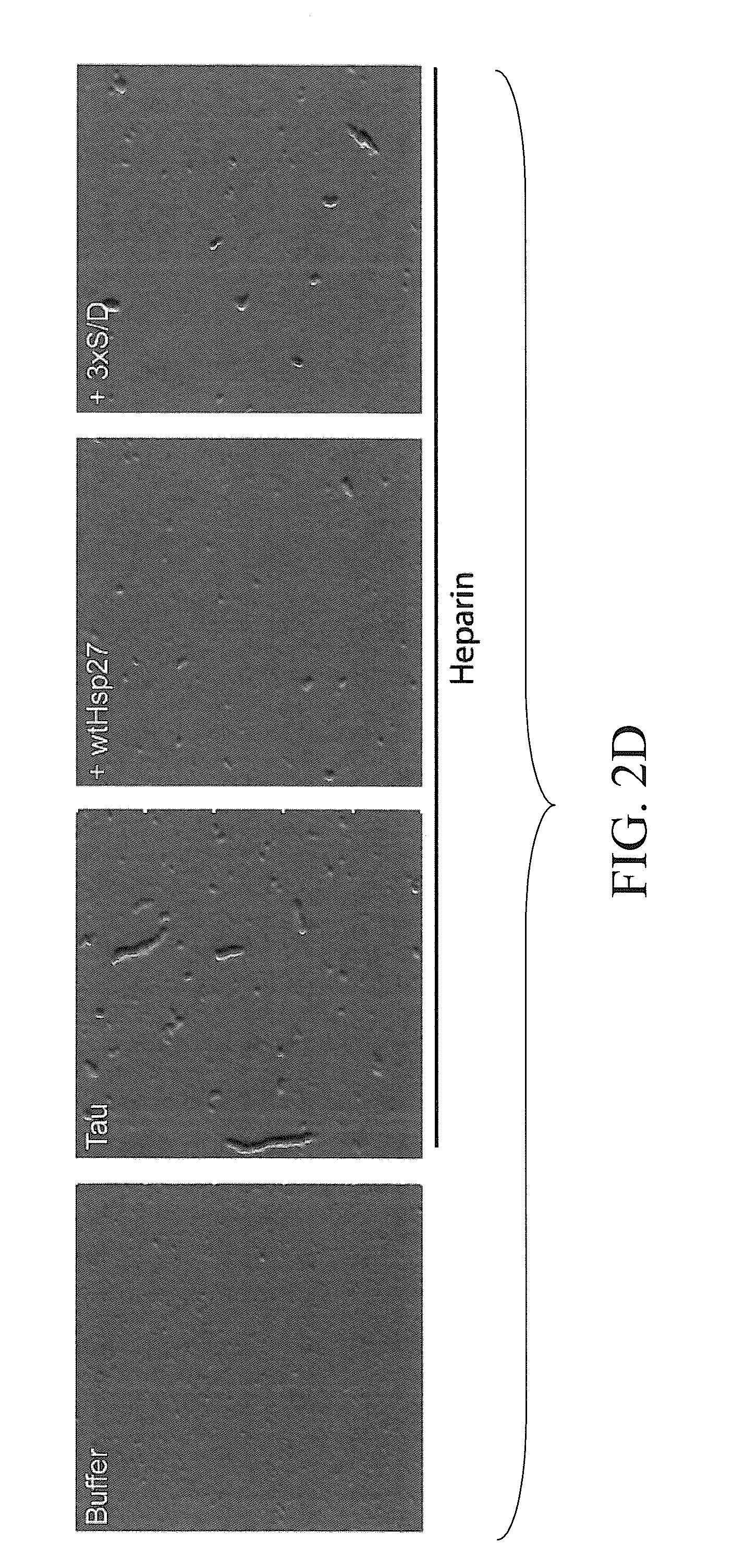
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for treating neurodegenerative diseases and conditions associated with aggregation of the microtubule-associated protein tau. A method of the invention comprises administering an effective amount of a heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27), or a biologically-active fragment or variant thereof, or a polynucleotide encoding the same, to a person or animal in need of treatment. In one embodiment, a heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27), or a biologically-active fragment or variant thereof, is contacted with or provided to a target cell. The target cell can be a neuron. In a specific embodiment, an Hsp27 is delivered to the target cell via a polynucleotide encoding an Hsp27 protein, or a biologically-active fragment or variant thereof. In one embodiment, a method of the invention comprises injecting (e.g., via stereotaxic injection) a polynucleotide expression construct of the invention comprising a polynucleotide encoding an Hsp27 protein directly into neural tissue of a person or animal. The subject invention also concerns compositions comprising i) a heat shock protein 27, or a biologically-active fragment or variant thereof, and / or ii) a polynucleotide encoding an Hsp27, or a biologically-active fragment or variant thereof. The polynucleotide can be an expression construct that provides for expression of an Hsp27 in a target cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
EML4-ALK (Echinoderm microtubule associated protein like4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) assay kit
ActiveCN103468813BEliminate distractionsHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementConserved sequencePositive control
The invention relates to an EML4-ALK (echinoderm microtubule associated protein like4-anaplastic lymphoma kinase) fusion gene fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) assay kit, which is applicable to assay of EML4-ALK fusion gene mutation in lung adenocarcinoma. The kit comprises probes, primers and positive controls, which are specially designed for conserved sequences of 9 fusion variations of the EML4-ALK fusion gene. The kit can be used for quickly and accurately assaying 9 most common EML4-ALK fusion gene variations with high sensitivity, namely 9 fusion variations of 7 variant subtypes, which are subtype 1 (E13; A20), subtype 2 (E20; A20), subtype 3 (E6a / b; A20), subtype 4 (E14; A20), subtype 5 (E2a / b; A20), subtype 6 (E18; A20) and subtype 7 (E14; A20), so that a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR system for assaying 9 most common EML4-ALK fusion gene variations can be established.
Owner:广州达健生物科技有限公司
Tubulin Isotype Screening in Cancer Therapy Using Halichondrin B Analogs
Chemotherapeutic agents that interfere with microtubule assembly or disassembly in the cell are potent inhibitors of cell replication. Examples of such agents include halichondrin B analogs. It has been shown that the susceptibility of certain cancers to analogs of halichondrin B correlates with the expression of particular tubulin isotypes or other microtubule-associated proteins such as MAP-4 and stathmin. Correlations such as these may be used in identifying patients suitable for treatment using a particular chemotherapeutic agent. Such a system avoids treating patients with cytotoxic compounds where there is a minimal or no effect on the cancer. The invention also provides a system of establishing these correlations for different compounds and cancer types. The system will be particularly useful in establishing correlations between anti-microtubule agents and cancers such as lung, breast, and ovarian cancer. Kits and reagents useful in practicing the invention are also provided.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Microtubule-associated proteins and tubulins
The invention provides human microtubule-associated proteins and tubulins (MICAPTUB) and polynucleotides which identify and encode MICAPTUB. The invention also provides expression vectors, host cells, antibodies, agonists, and antagonists. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing, treating, or preventing disorders associated with aberrant expression of MICAPTUB.
Owner:INCYTE CORP
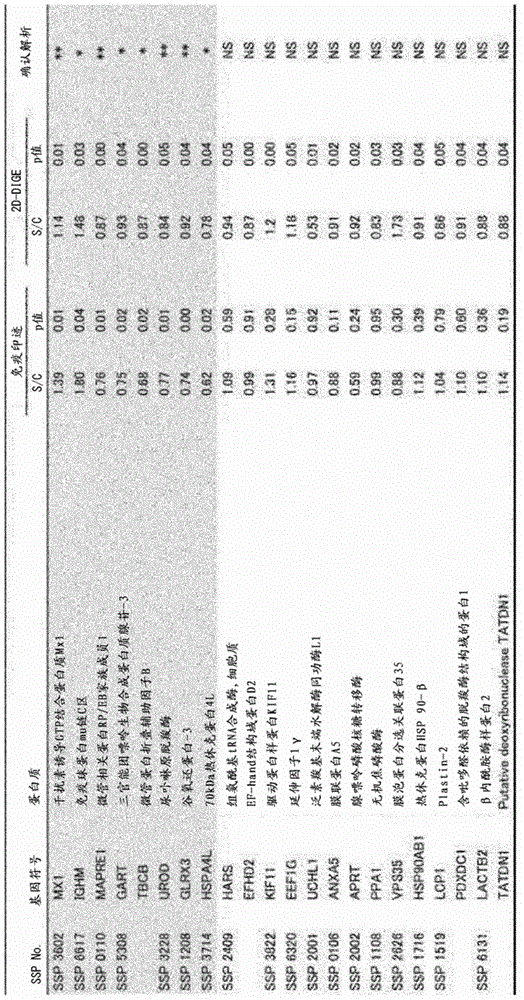
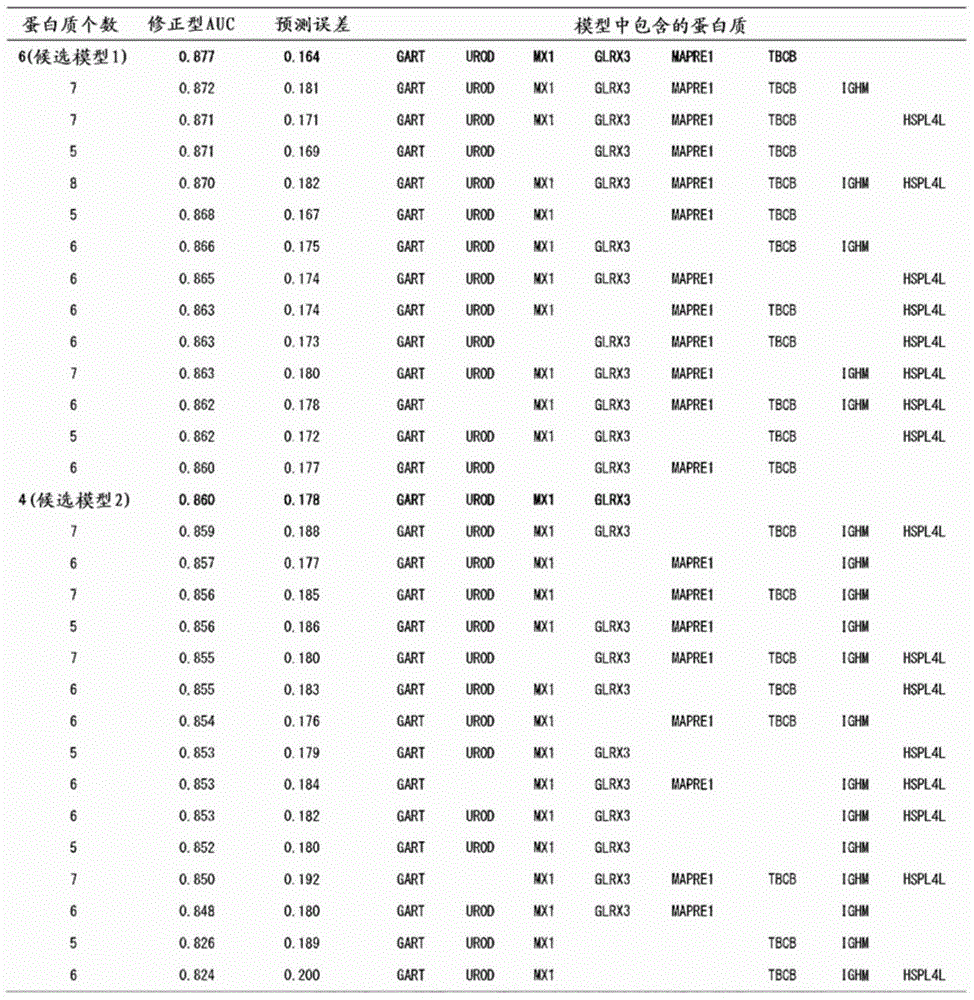
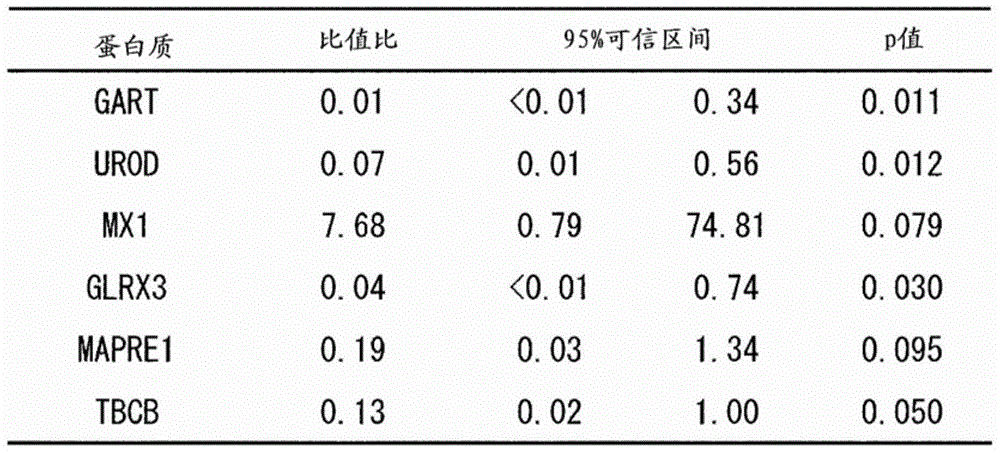
Integration dysfunction syndrome marker set and utilization thereof
The present invention addresses the problem of providing a combination of biomarkers, whereby integration dysfunction syndrome can be highly accurately diagnosed, and the utilization thereof. Provided is an integration dysfunction syndrome marker set which comprises two or more protein molecules combined together, said protein molecules being selected from the group consisting of trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3, uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, interferon-induced GTP-binding protein Mx1, glutaredoxin-3, microtubule-associated protein RP / EB family member 1, tubulin folding cofactor B, immunoglobulin mu chain C region and heat shock 70 kDa protein 4L. Also provided is a method for examining integration dysfunction syndrome with the use of the level of the aforesaid marker set in a specimen as an index.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
Antibodies and antigen-binding fragments that specifically bind to microtubule-associated protein tau
InactiveUS10400034B2Nervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigen Binding FragmentMicrotubule associated protein tau
The disclosure relates to antibodies and antigen-binding fragments that specifically bind to microtubule-associated protein tau. The disclosure also relates to diagnostic, prophylactic and therapeutic methods using anti-tau antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
In vitro Screening Assay of TCPase Modulators
PendingUS20210285024A1Reduce presenceImprove throughputCompound screeningApoptosis detectionChemical compoundTyrosine
The present invention concerns an in vitro screening assay for identification of modulators of tubulin carboxypeptidase (TCPase) activity comprising the steps of: (i) Contacting (a) a substrate of TCPase enzyme comprising an amino acids sequence having at least the last 4 amino acids residues of the C-terminal sequence of an α-tubulin and / or a Microtubule Associated Protein (MAP) and, as ultimate C-terminal amino acid residue, an aromatic amino acid residue, preferably a tyrosine (Y), and b) an isolated or recombinant TCPase enzyme; in the presence or absence (control) of the modulator compound to be tested, and under conditions for substrate cleavage, preferably detyrosination, and / or liberation of a C-terminal free aromatic amino acid residue, preferably a C-terminal free tyrosine; (ii) Using reagents for detecting and measuring the signal related to substrate cleavage, preferably detyrosination, and / or liberation of the C-terminal free aromatic amino acid residue, preferably the C-terminal free tyrosine; (iii) Measuring and comparing the level of substrate cleavage, preferably detyrosination and / or the level of the C-terminal free aromatic amino acid residue, preferably the C-terminal free tyrosine in presence and in absence (control) of the compound to be tested, and (iv) Selecting the modulators of TCPase for which the level of substrate cleavage, preferably detyrosination or liberation of the C-terminal aromatic amino acid residue, preferably C-terminal free tyrosine is increased in the presence of the compound to be tested (activators of TCPase) or decreased in the presence of the compound to be tested (inhibitors of TCPase). The present invention also concerns kits for performing such in vitro screening assay.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI +1
Microtubule-associated protein and coding genes and application thereof
InactiveCN101812127BPositioning does not affectReduce positioningPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsWAS PROTEINMicrotubule Depolymerization
The invention discloses a microtubule-associated protein and coding genes and application thereof. The microtubule-associated protein is protein of (a) or (b): (a) protein formed by an amino acid sequence as shown by a sequence one in a sequence table; and (b) protein derived by the sequence one, related to the inhibition of the microtubule de-polymerization activity of MCAK protein and formed in a way the amino acid sequence of the sequence one is substituted and / or deleted and / or added by one to ten amino acid residues. The protein of the invention participates in the regulation and the control of the forward end dynamics of microtubules through the mutual effect with EB1 and MCAK and stabilizes the microtubules through inhibiting the microtubule de-polymerization activity of the MCAK protein. After the coding genes of the low-interference RNA of microtubule-associated protein genes are introduced into a host, the microtubule positioning of the MCAK is seriously affected. The protein and the coding genes thereof play a great role in the medical field and the pharmaceutical field and thereby the application prospect is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
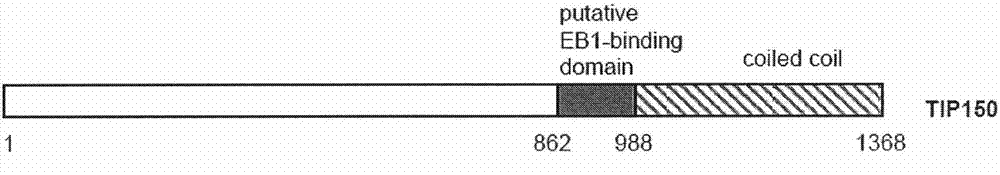
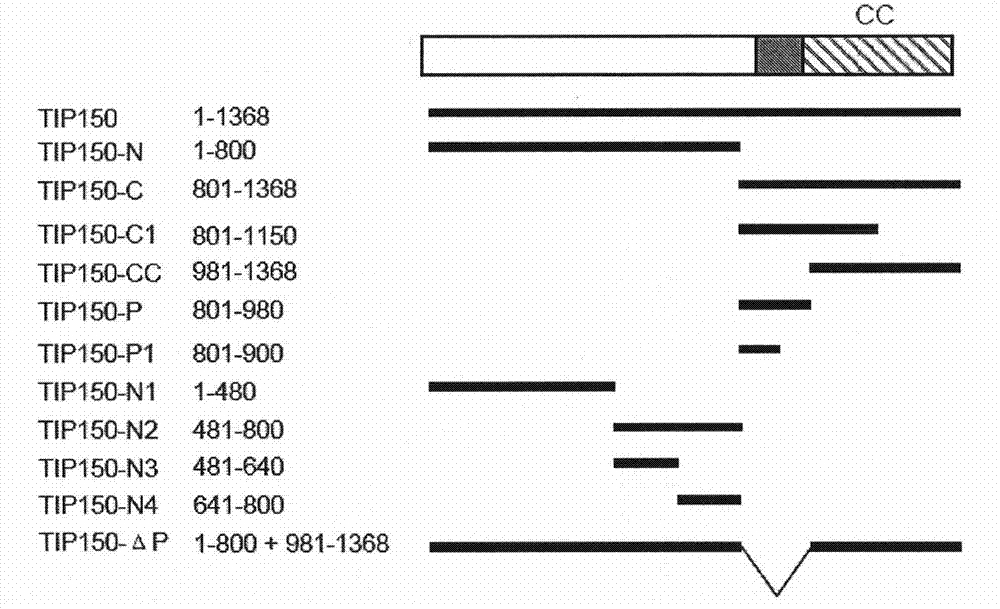
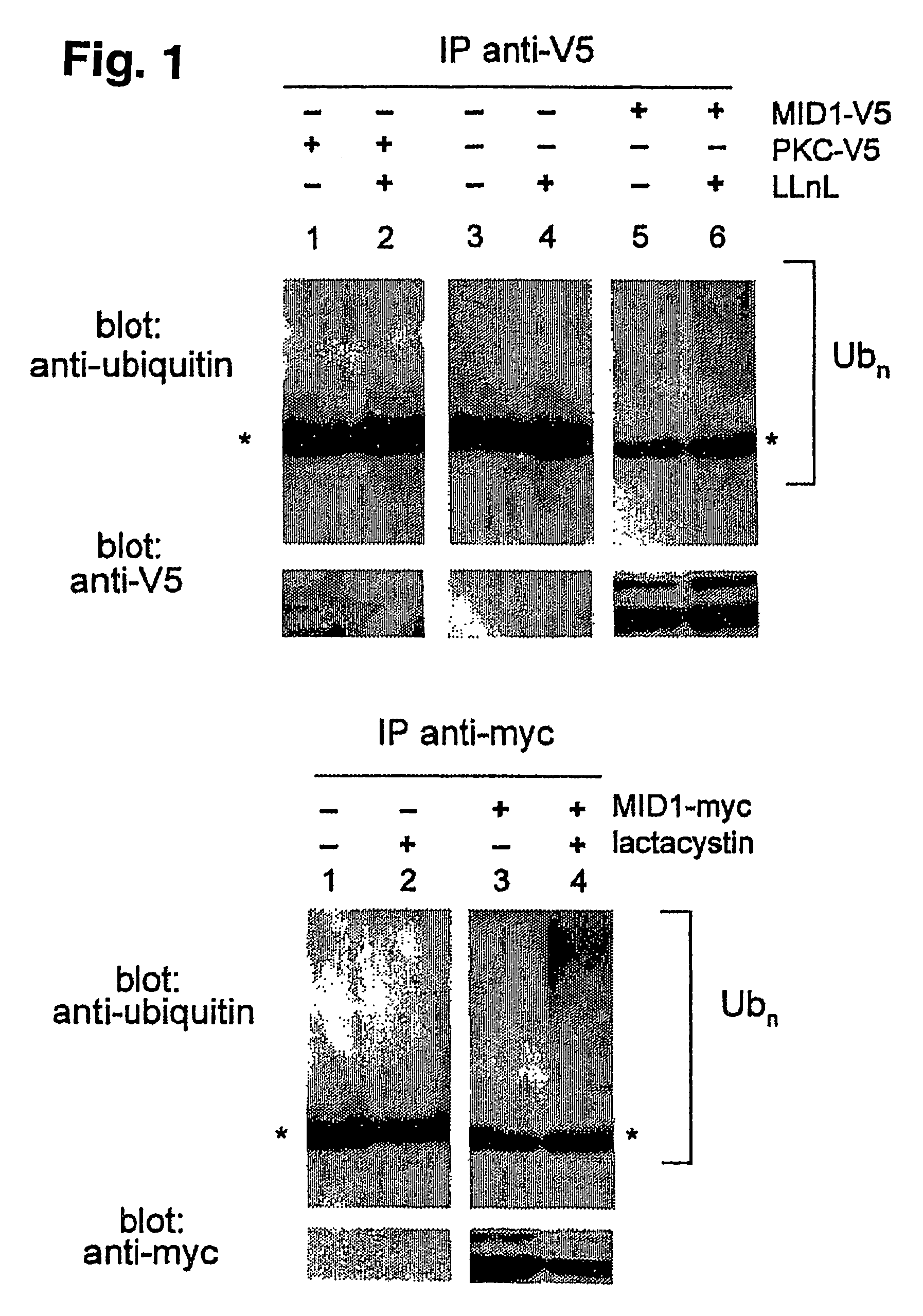
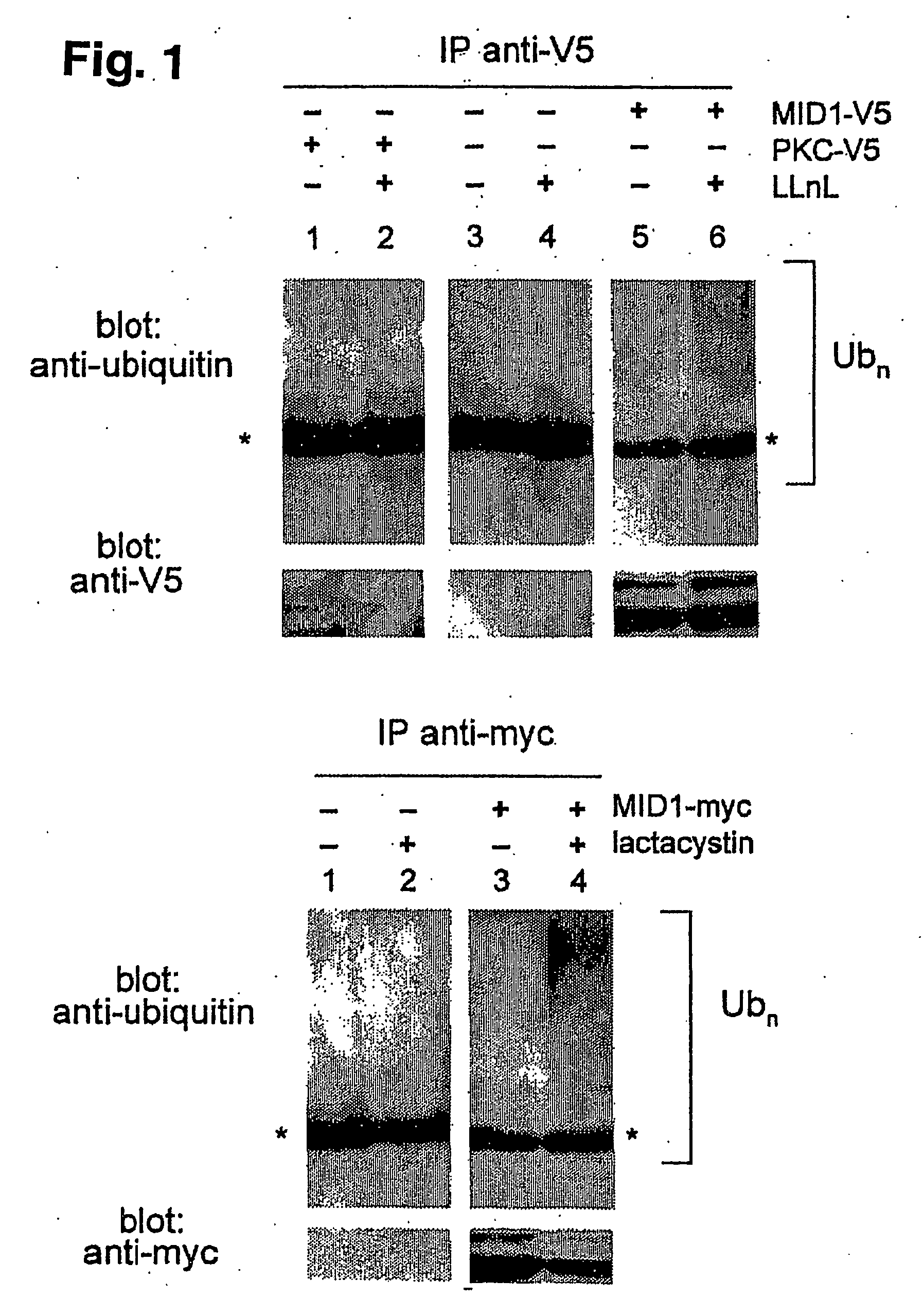
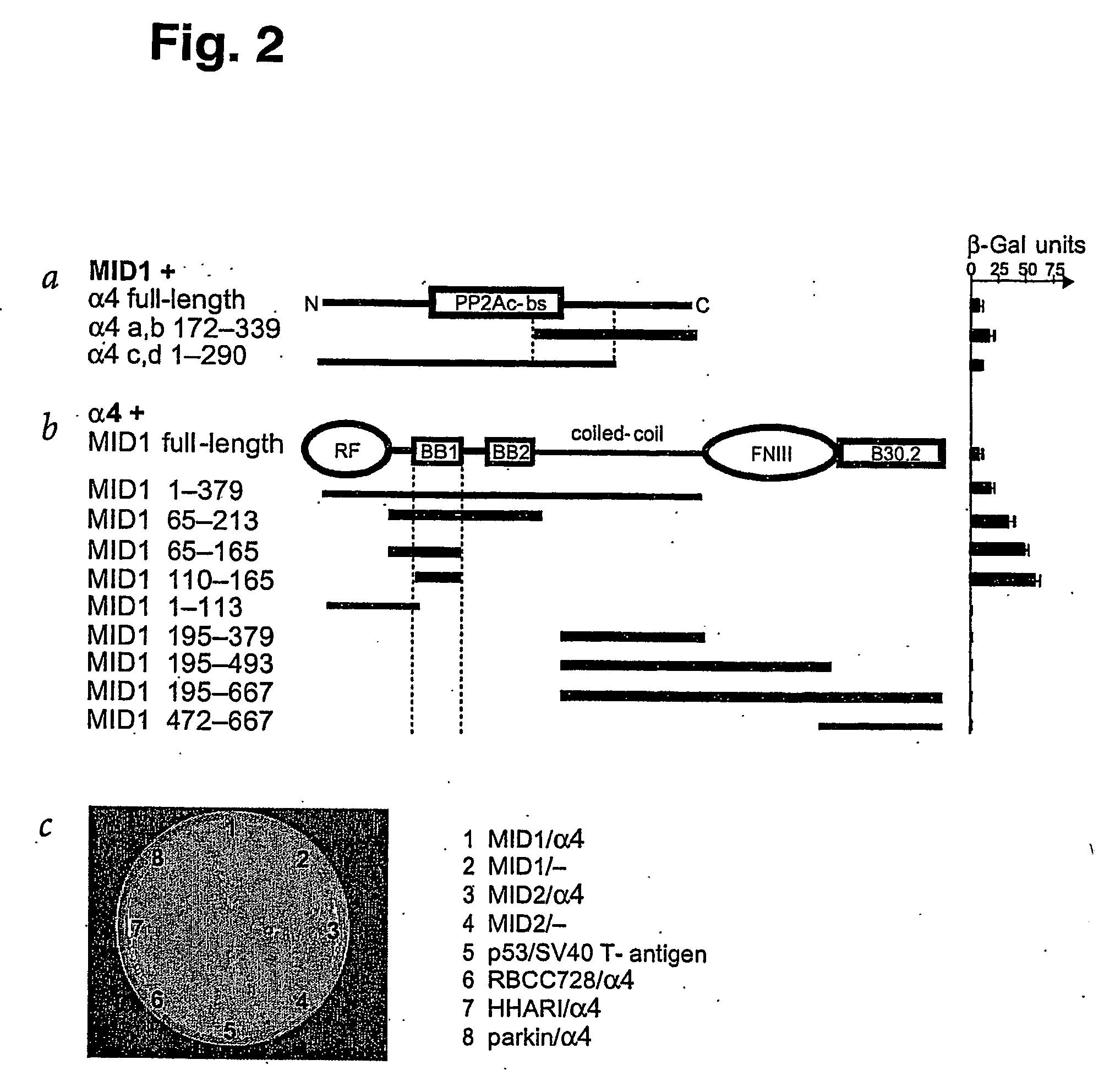
Means for use in treating diseases correlated with or caused by non-physiological levels of microtubule-associated PP2Ac
The present invention relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease correlated with or caused by non-physiologically increased intracellular levels of the catalytic subunit of microtubule-associated protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) comprising administering to a subject affected by said disease or in danger of developing said disease a pharmaceutically effective amount of a protein selected from the group of MID1 or MID2 or a nucleic acid encoding said protein. The invention further relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease correlated with or caused by non-physiologically decreased intracellular levels of the catalytic subunit of microtubule-associated protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) comprising administering to a subject affected by said disease or in danger of developing said disease a pharmaceutically effective amount of a peptidic fragment of MID1 or MID2 wherein said peptidic fragment comprises amino acids 108-165 (preferably 110-165) of MID1, amino acids 108-165 (preferably 110-165) of MID2 or with an effective amount of a fragment of PP2Ac wherein said fragment comprises the binding site to a4 or of a peptide fragment of a4 comprising amino acids 236-279 or with an effective amount of a nucleic acid molecule encoding said peptide fragment or with an effective amount of a molecule interfering with the interaction of MID1 with a4 or with an effective amount of a molecule interfering with the expression or activity of MID1 and / or a 4.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Means for use in treating diseases correlated with or caused by non-physiological levels of microtubule-associated pp2ac
InactiveUS20070134654A1Negative effectHigh activityCompound screeningNervous disorderBinding sitePeptide fragment
The present invention relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease correlated with or caused by non-physiologically increased intracellular levels of the catalytic subunit of microtubule-associated protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) comprising administering to a subject affected by said disease or in danger of developing said disease a pharmaceutically effective amount of a protein selected from the group of MID1 or MID2 or a nucleic acid encoding said protein. The invention further relates to a method of preventing or treating a disease correlated with or caused by non-physiologically decreased intracellular levels of the catalytic subunit of microtubule-associated protein phosphatase 2A (PP2Ac) comprising administering to a subject affected by said disease or in danger of developing said disease a pharmaceutically effective amount of a peptidic fragment of MID1 or MID2 wherein said peptidic fragment comprises amino acids 108-165 (preferably 110-165) of MID1, amino acids 108-165 (preferably 110-165) of MID2 or with an effective amount of a fragment of PP2Ac wherein said fragment comprises the binding site to a4 or of a peptide fragment of a4 comprising amino acids 236-279 or with an effective amount of a nucleic acid molecule encoding said peptide fragment or with an effective amount of a molecule interfering with the interaction of MID1 with a4 or with an effective amount of a molecule interfering with the expression or activity of MID1 and / or a 4.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Binding molecules that specifically bind to tau
ActiveUS20210047393A1Avoid spreadingMediating uptakeNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigenAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention relates to binding molecules and antigen-binding fragments that specifically bind to microtubule-associated protein tau. The invention also relates to diagnostic, prophylactic and therapeutic methods using the binding molecules or antigen-binding fragments.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Composition for Cancer Prognosis Prediction Comprising Anti-TMAP/CKAP2 Antibodies
InactiveUS20130045486A1Improved prognosisPoor prognosisImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingBinding siteCell division cycle
The present invention relates to an antibody which specifically binds to TMAP (tumor associated microtubule associated protein) / CKAP2 (cytoskeleton associated protein 2) or a fragment thereof, and a method for identifying the presence or absence of mitosis and a method for diagnosing cancer prognosis using the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a composition for diagnosing cancer prognosis comprising an anti-TMAP / CKAP2 antibody or an antigen-binding site thereof, a method for detecting TMAP / CKAP2 using the composition, an anti-TMAP / CKAP2 antibody for diagnosing cancer prognosis, a method for providing information for diagnosing cancer prognosis using the composition, a method for screening a cancer therapeutic agent comprising the step of determining changes in the level of TMAP / CKAP2 antigen-antibody reaction by the treatment of a candidate substance, and a composition for determining cell-division cycles using the composition.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV +1
Gene Defects And Mutant ALK Kinase In Human Solid Tumors
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
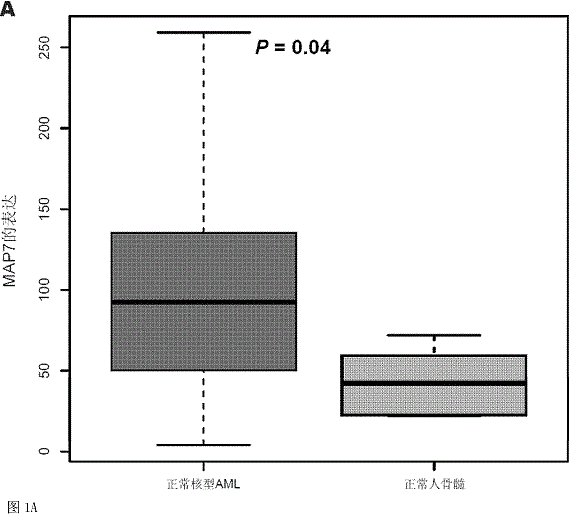
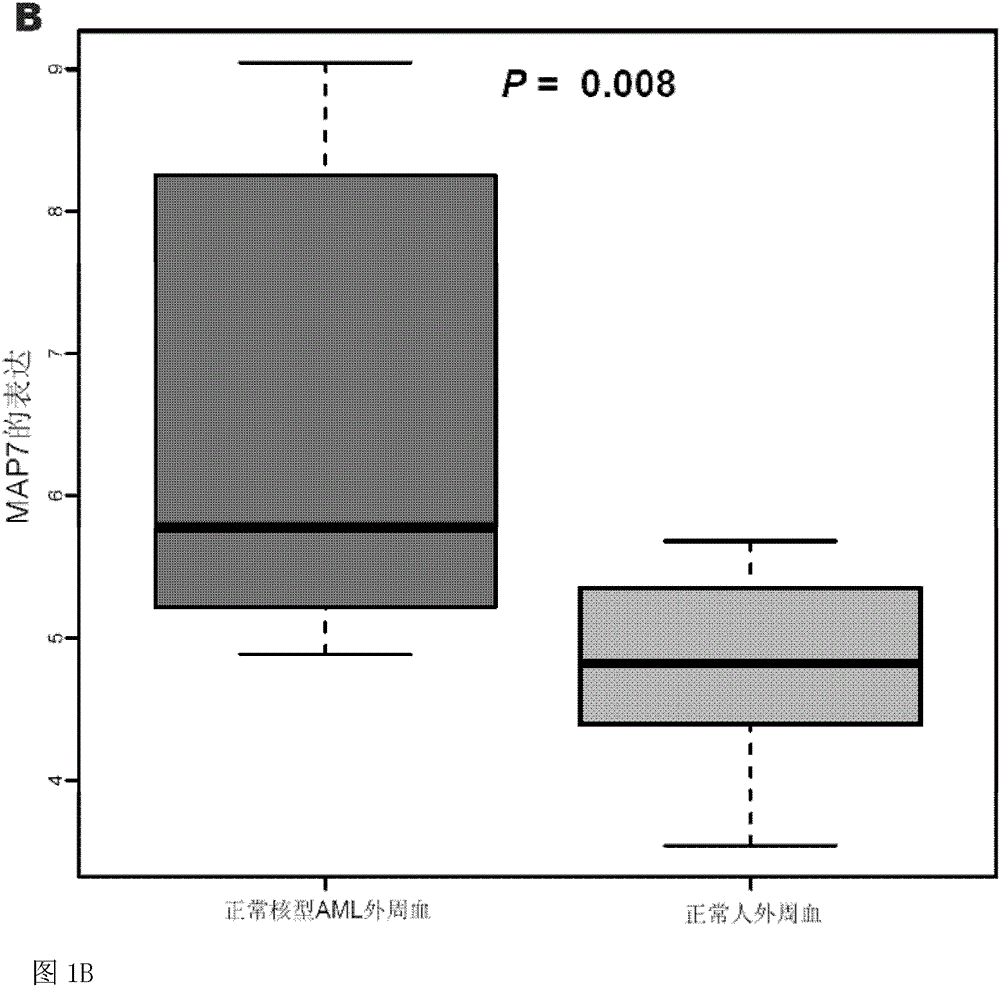
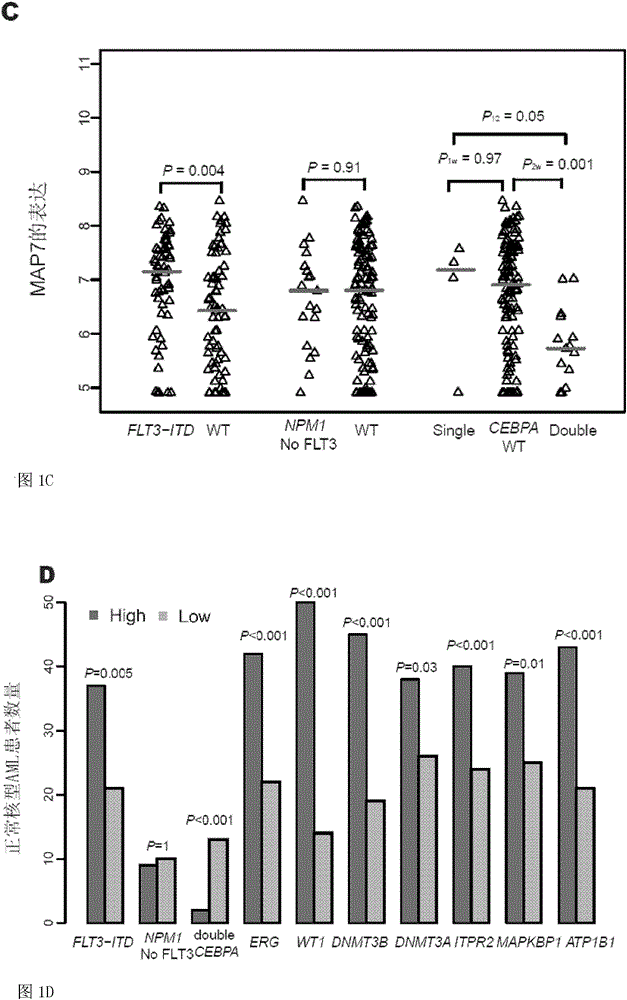
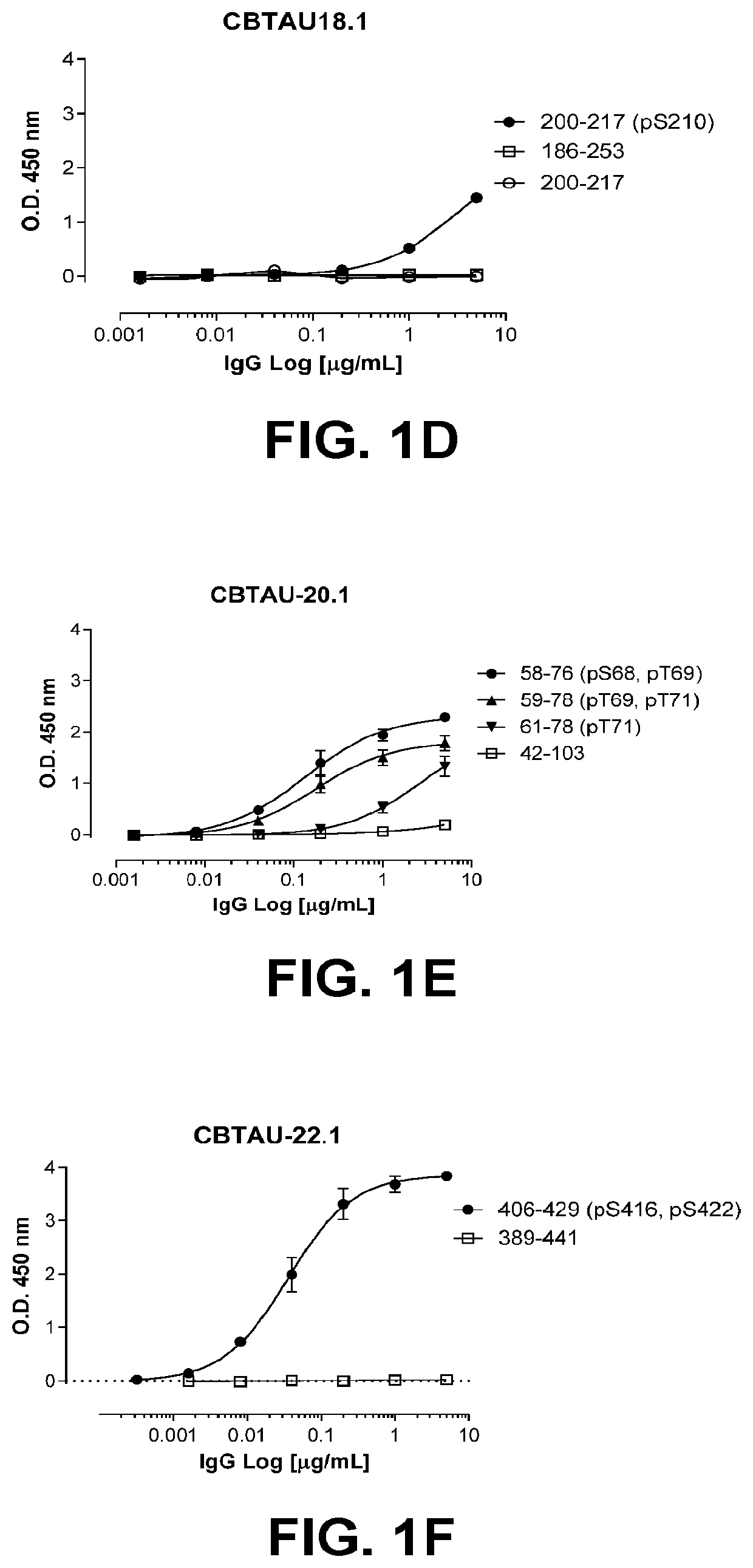
Method for detecting expression level of MAP7 in CN-AML tissue sample and application thereof
ActiveCN105969868AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationClinical prognosisKaryotype
The invention discloses a method for detecting the expression level of MAP7 in a CN-AML tissue sample and an application thereof. The invention provides primer pairs of a microtubule-associated protein 7 gene, wherein the sequences of one primer pair are tcctgggagctgcaattaca (SEQ ID NO:2) and gggtgcttttggtcttctgg (SEQ ID NO:3) or complementary sequences thereof. In the invention, the primer pairs are used for performing risk stratification or clinical prognosis evaluation for patients suffering normal karyotype acute myelogenous leukemia by detecting the expression level of microtubule-associated protein 7. The invention also provides a gene chip and a kit comprising the primer pairs.
Owner:PEKING UNIV THIRD HOSPITAL
Antibodies and antigen-binding fragments that specifically bind to microtubule-associated protein tau
ActiveUS20200399350A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsAntigen Binding FragmentBiochemistry
The invention relates to antibodies and antigen-binding fragments that specifically bind to microtubule-associated protein tau. The invention also relates to diagnostic, prophylactic and therapeutic methods using anti-tau antibodies.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Microtubule-modifying compound
ActiveUS9695239B2Eliminate side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCompound aBinding domain
A compound formed from at least one component A comprising a binding domain for extra-cellular surface structures of a diseased proliferating cell that internalized upon binding of component A of said compound, and at least one component B, characterized in that component B is a polypeptide which amino acid sequence comprises a microtubule-associated protein (MAP) or comprises at least a partial sequence of the MAP, the partial sequence having maintained the binding function of the MAP to a microtubule.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN
Microtubule-associated protein Tau imaging compounds for Alzheimer's disease and precursors thereof
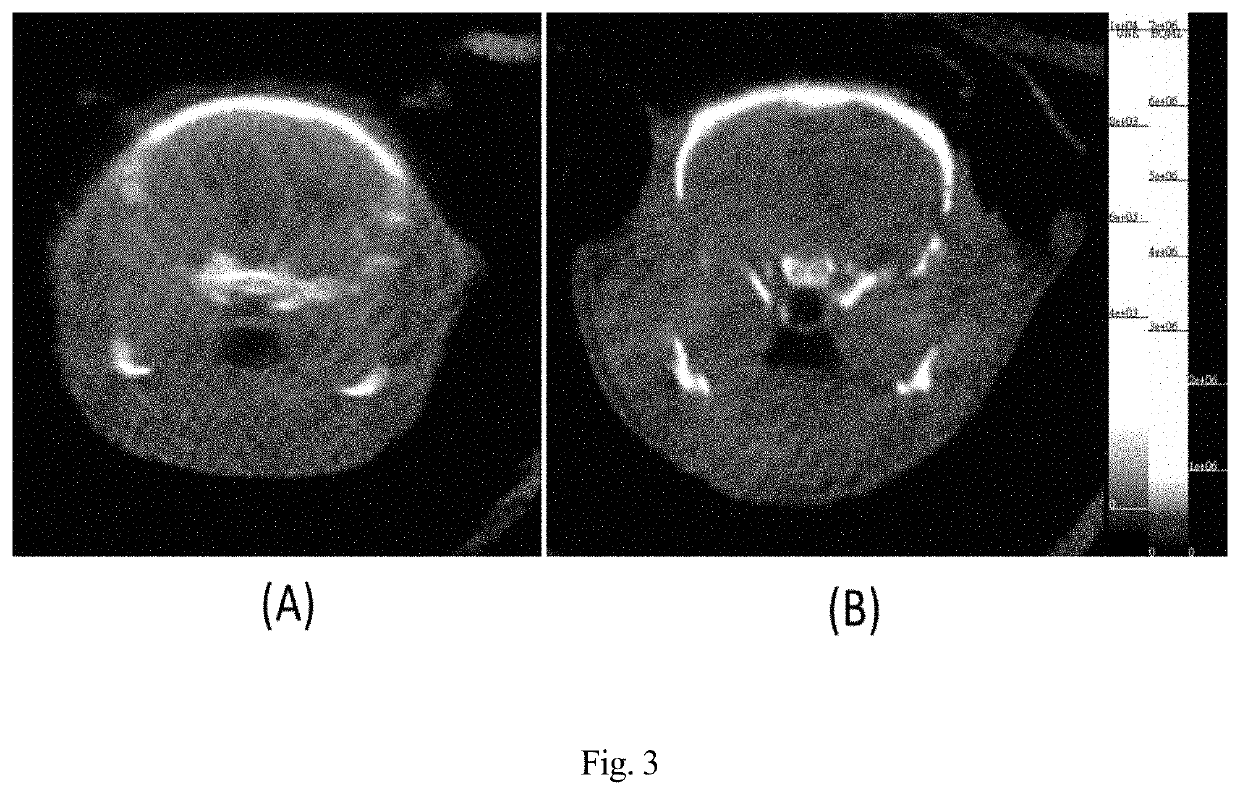
PendingUS20220227728A1Not easily affectedReduce the difficulty of synthesisRadioactive preparation carriersIsotope introduction to organic compoundsDiseaseEfficacy
The present invention discloses a series of nuclear medicine tracers that are combined with brain microtubule-associated protein Tau targeting compounds to produce a group of compounds of nuclear medicine that can be utilized for imaging of microtubule-associated protein Tau. When the positrons released by the decay encounter the electrons of the cells in the sample, utilizing the positron decay characteristics of fluorine-18 or iodine-124 isotope to generate mutual destruction reactions, a pair of opposite gamma rays is formed which are imaged by positron emission tomography. The compounds can be applied for the in vivo detection of microtubule-associated protein Tau deposits in the brain. The invention provides a strategy for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and a method to measure the efficacy of therapeutic drugs targeting microtubule-associated protein Tau.
Owner:LI MING HSIN +5
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com