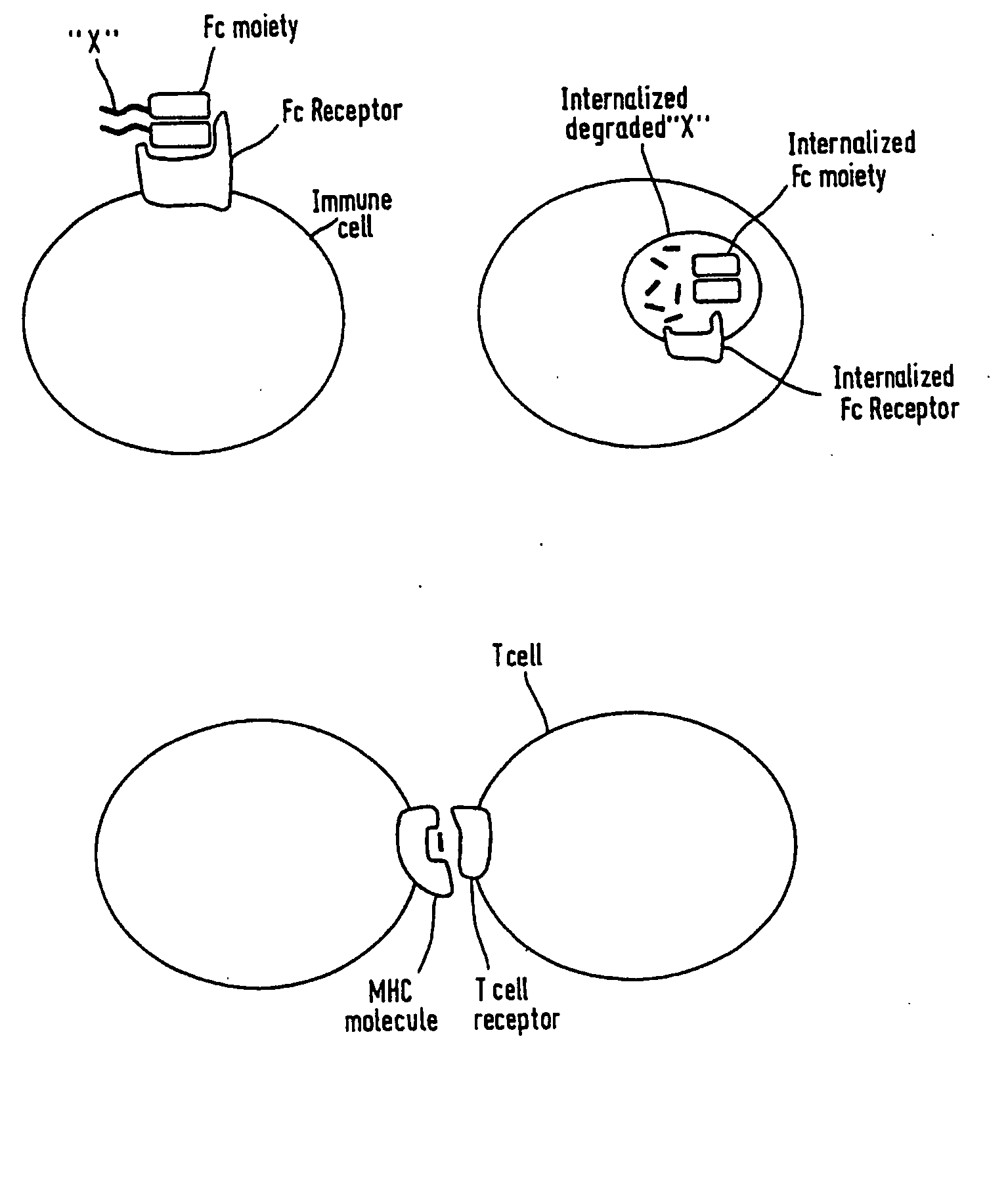
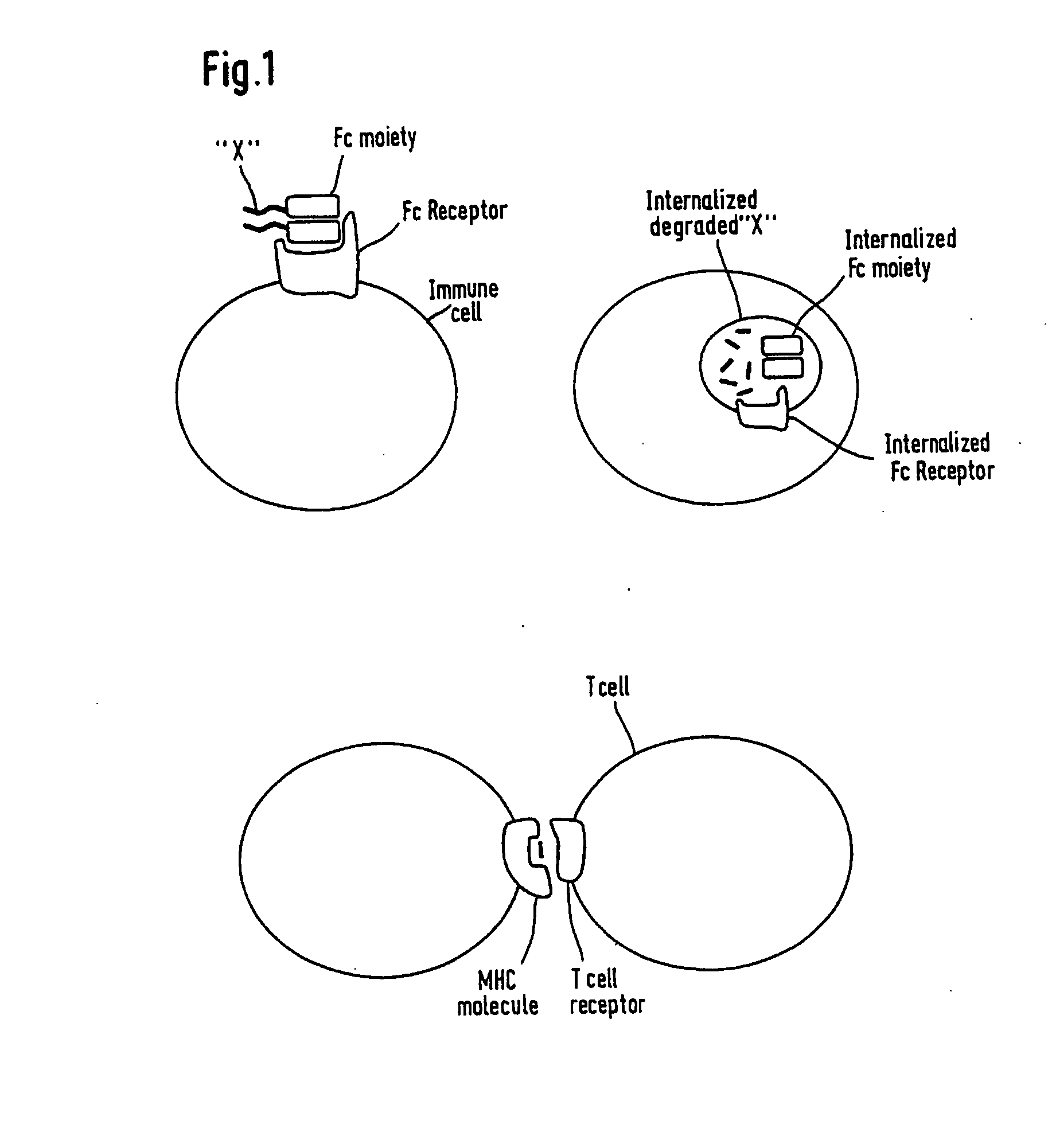
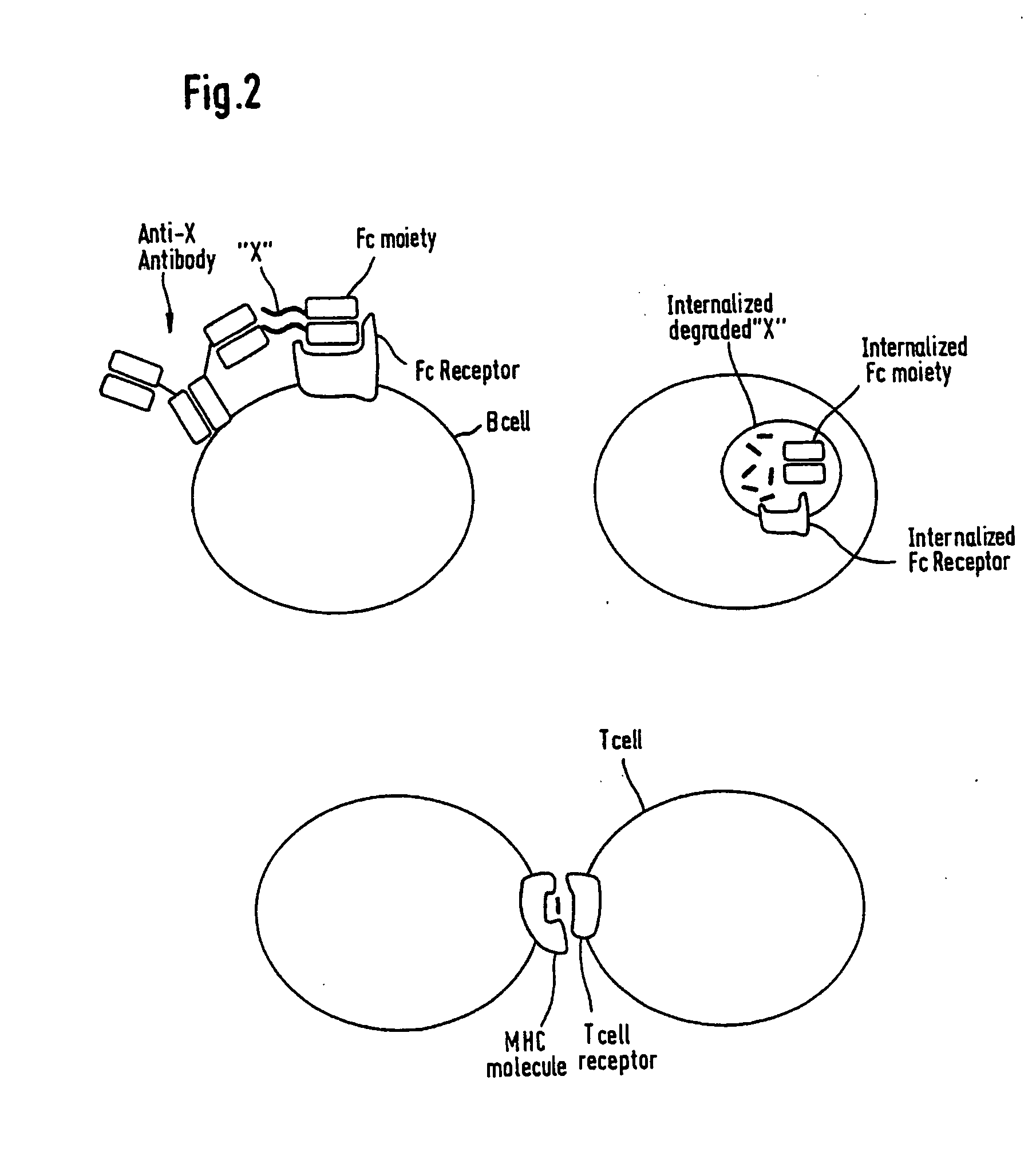
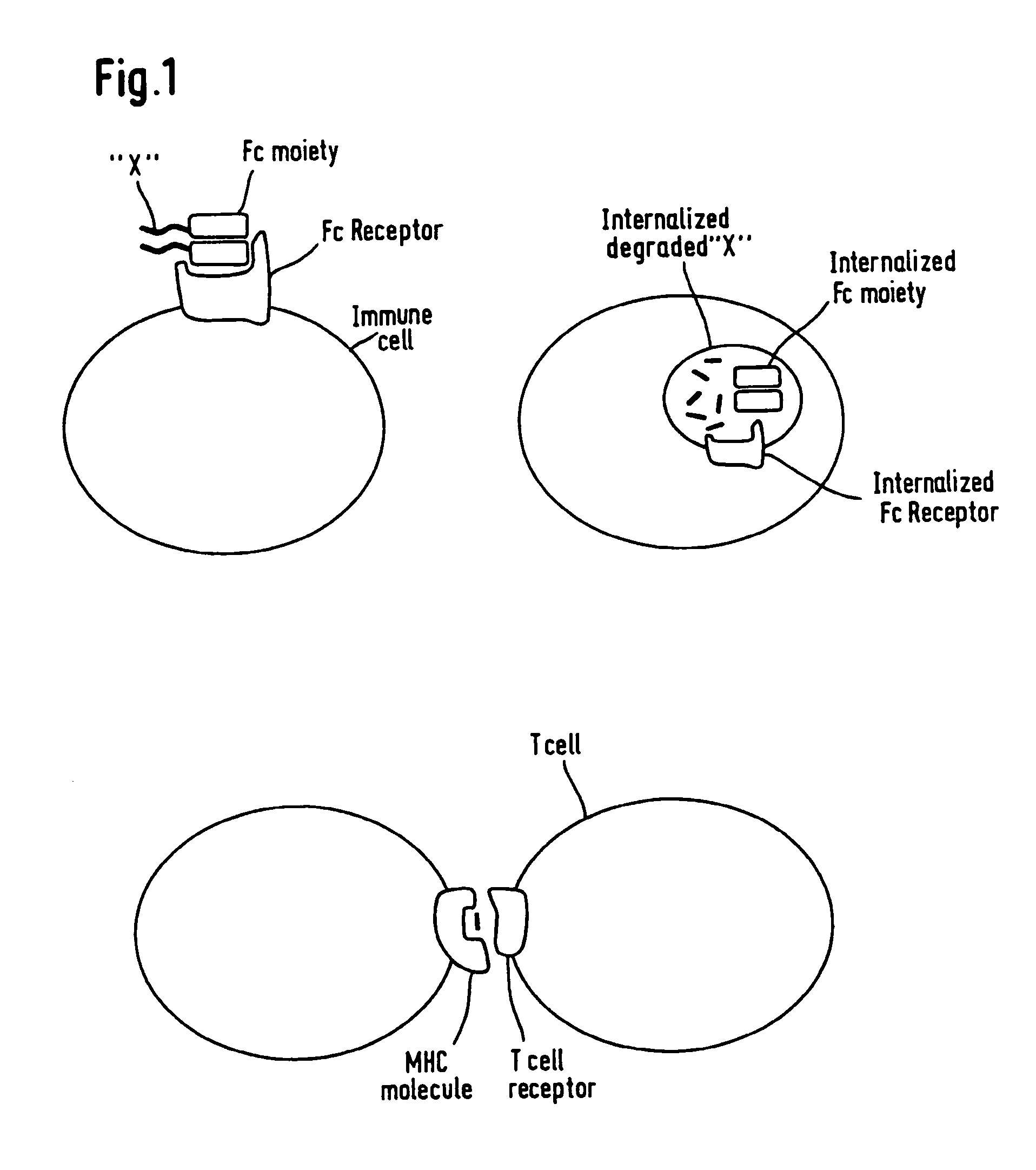
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
80 results about "MHC Class II Molecule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artificial proteins with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS20070269435A1Improve propertiesLow immunogenicitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding sitePharmacometrics
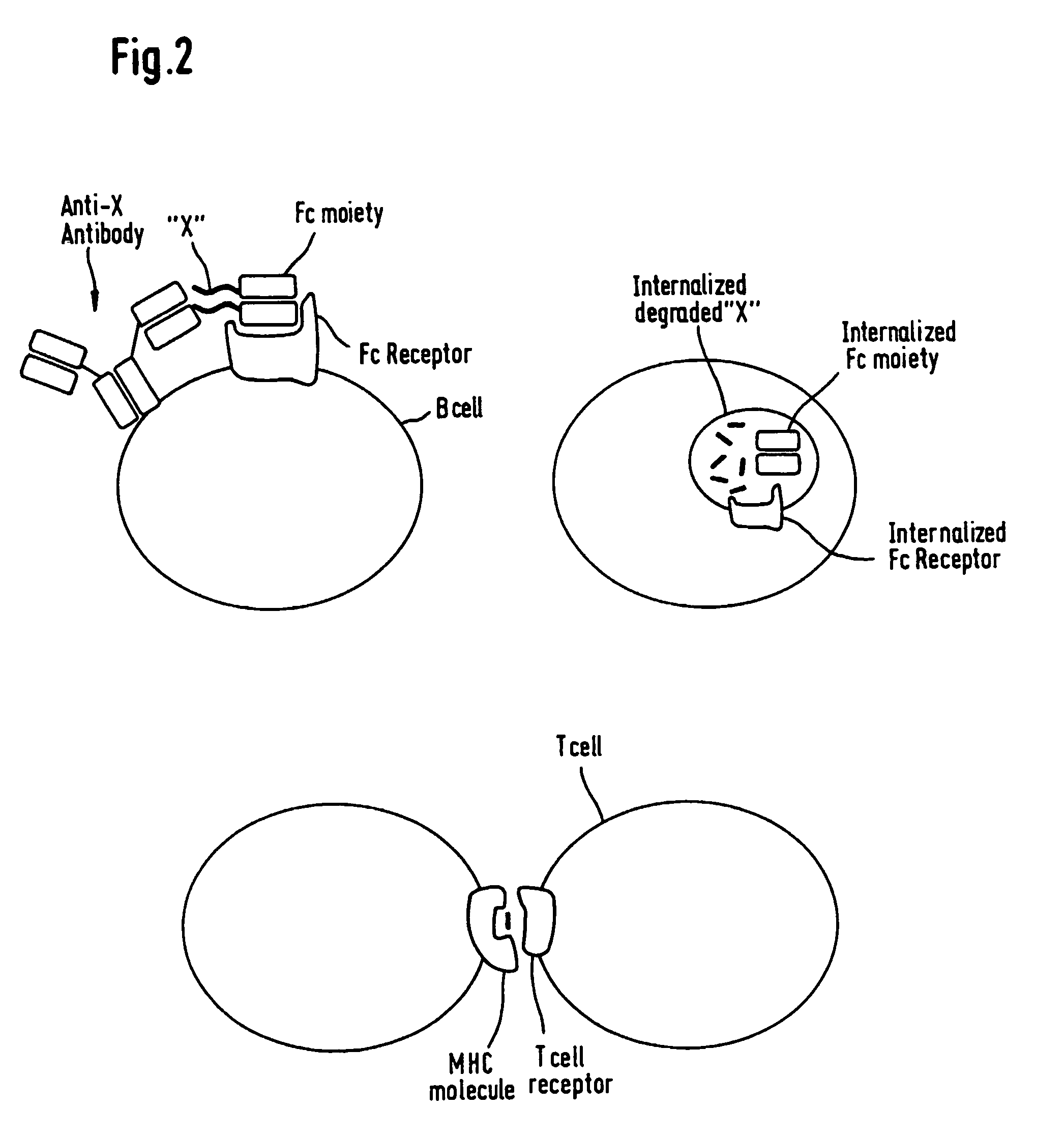
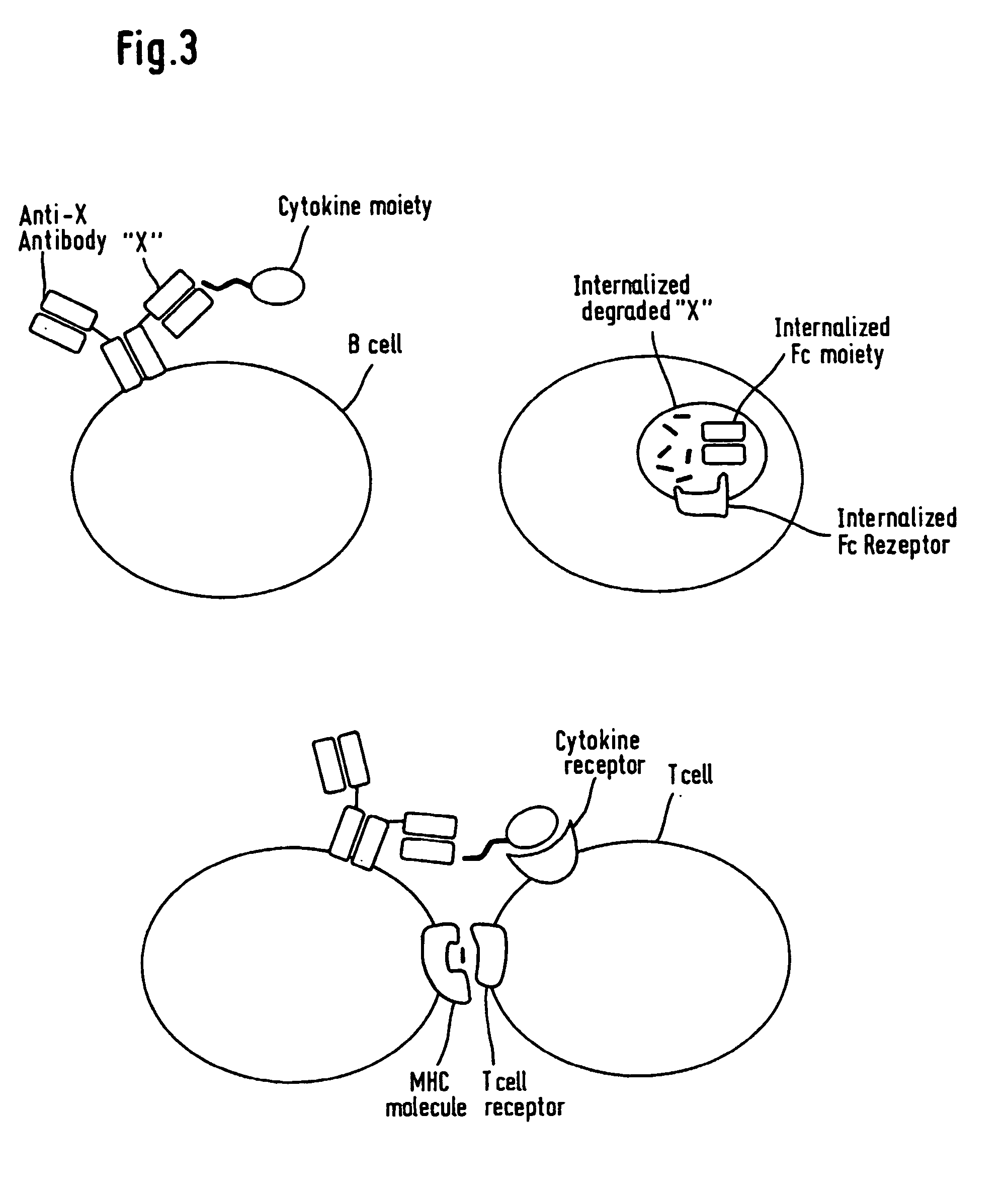
The invention relates to artificial modified proteins, preferably fusion proteins, having a reduced immunogenicity compared to the parent non-modified molecule when exposed to a species in vivo. The invention relates, above all, to novel immunoglobulin fusion proteins which essentially consist of an immunoglobulin molecule or a fragment thereof covalently fused via its C-terminus to the N-terminus of a biologically active non-immunoglobulin molecule, preferably a polypeptide or protein or a biologically active fragment thereof. In a specific embodiment, the invention relates to fusion proteins consisting of an Fc portion of an antibody which is fused as mentioned to the non-immunological target molecule which elicits biological or pharmacological efficacy. The molecules of the invention have amino acid sequences which are altered in one or more amino acid residue positions but have in principal the same biological activity as compared with the non-altered molecules. The changes are made in regions of the molecules which are identified as T-cell epitopes, which contribute to an immune reaction in a living host. Thus, the invention also relates to a novel method of making such fusion proteins by identifying said epitopes comprising calculation of T-cell epitope values for MHC Class II molecule binding sites in a peptide by computer-aided methods.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Anti-KSA/IL-2 fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS7189830B2Simple methodPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBinding siteComputer-aided
The invention relates to artificial modified proteins, preferably fusion proteins, having a reduced immunogenicity compared to the parent non-modified molecule when exposed to a species in vivo. The invention relates, above all, to novel immunoglobulin fusion proteins which essentially consist of an immunoglobulin molecule or a fragment thereof covalently fused via its C-terminus to the N-terminus of a biologically active non-immunoglobulin molecule, preferably a polypeptide or protein or a biologically active fragment thereof. In a specific embodiment, the invention relates to fusion proteins consisting of an Fc portion of an antibody which is fused as mentioned to the non-immunological target molecule which elicits biological or pharmacological efficacy. The molecules of the invention have amino acid sequences which are altered in one or more amino acid residue positions but have in principal the same biological activity as compared with the non-altered molecules. The changes are made in regions of the molecules which are identified as T-cell epitopes, which contribute to an immune reaction in a living host. Thus, the invention also relates to a novel method of making such fusion proteins by identifying said epitopes comprising calculation of T-cell epitope values for MHC Class II molecule binding sites in a peptide by computer-aided methods.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Inhibition of li expression in mammalian cells
The present invention is directed toward compositions and methods involving the inhibition of Ii expression in cells for the purpose of altering antigen presentation pathways. More specifically, disclosed are compositions and methods which relate to MHC Class II molecule presentation of antigenic epitopes which, under normal circumstances, would not be presented in association with MHC Class II molecules. The invention relates to presentation in cells which normally express MHC Class II molecules, as well as cells which can be induced to express MHC Class II molecules. Embodiments relating to RNA interference of Ii are specifically disclosed.
Owner:ANTIGEN EXPRESS
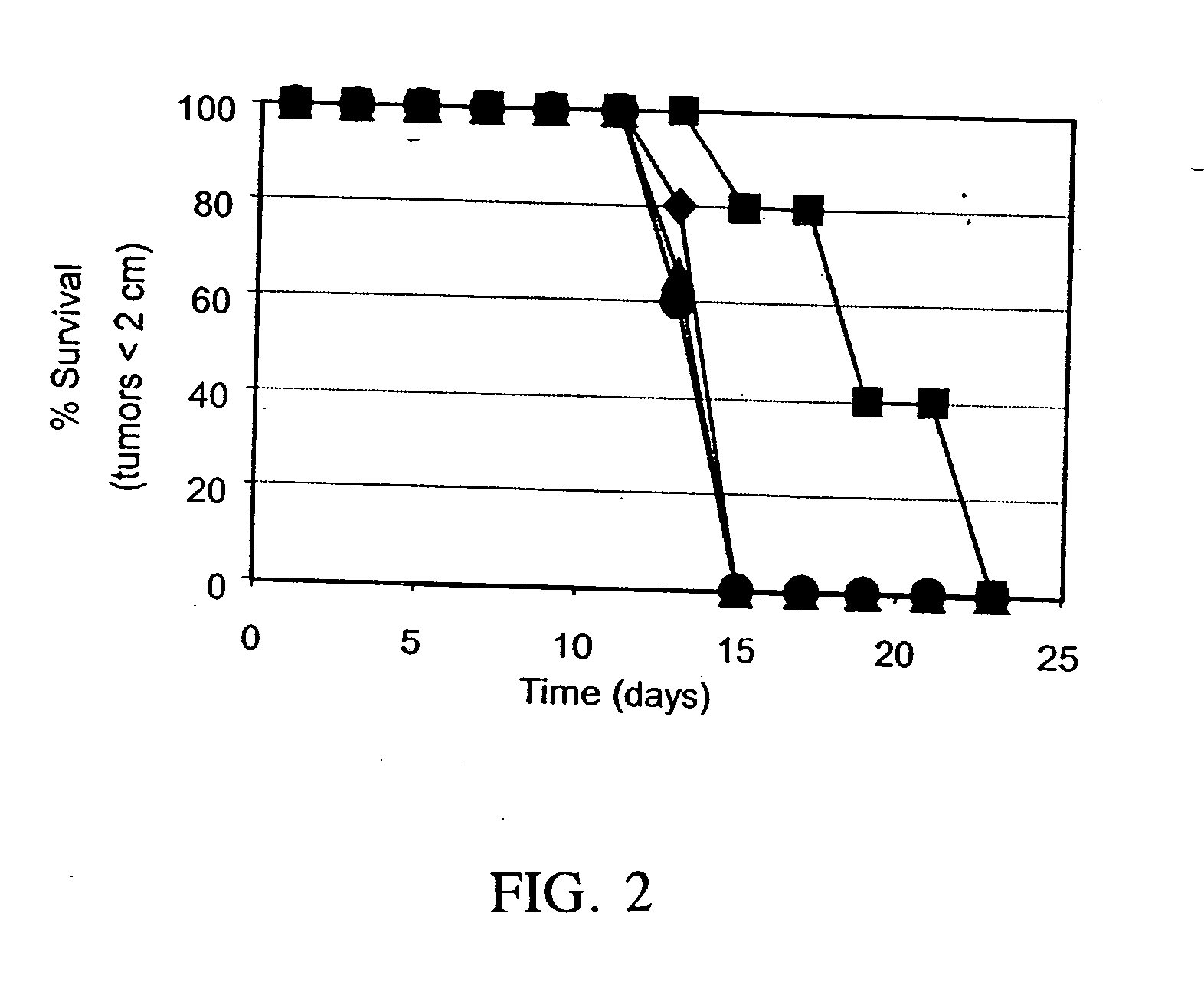
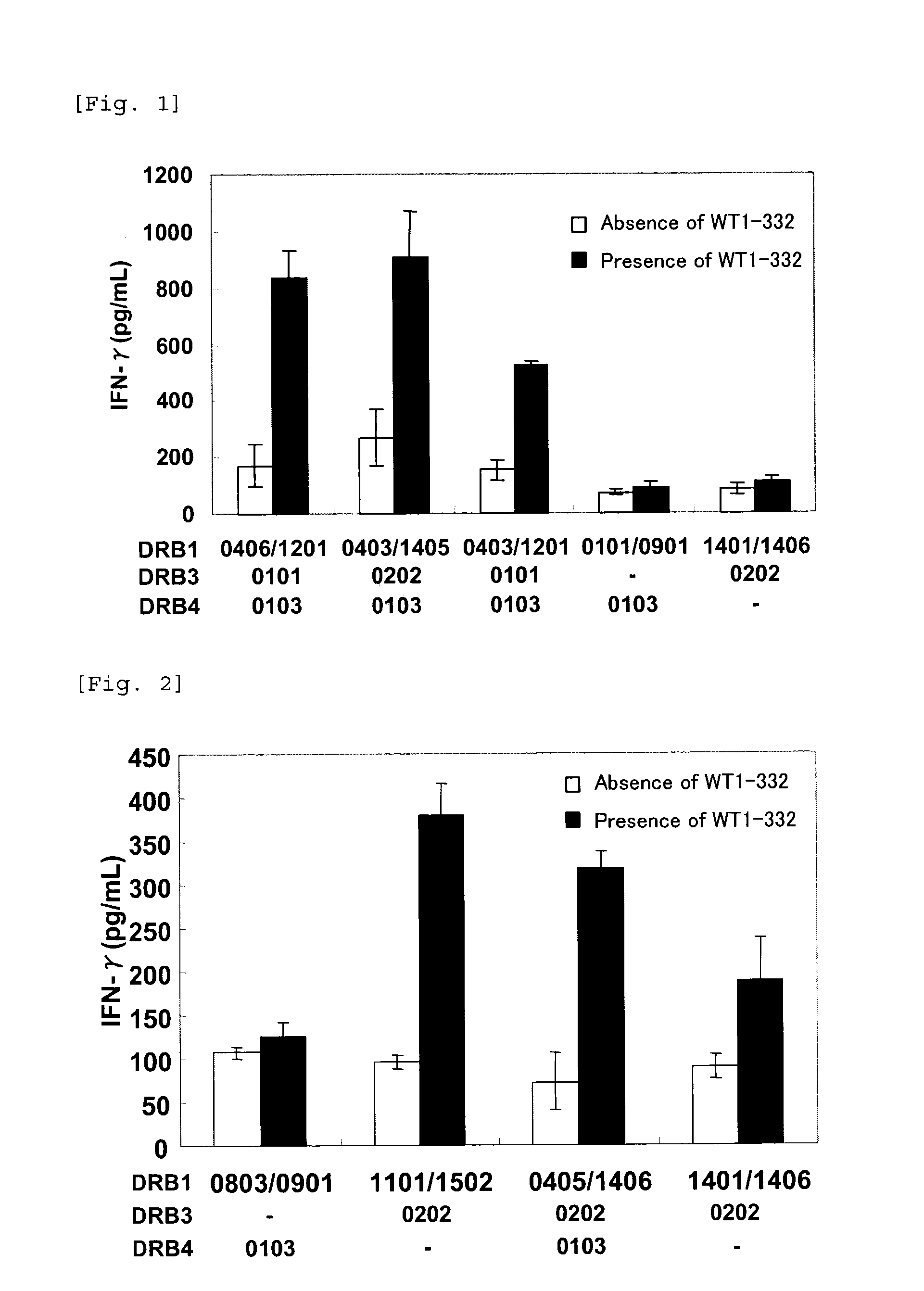
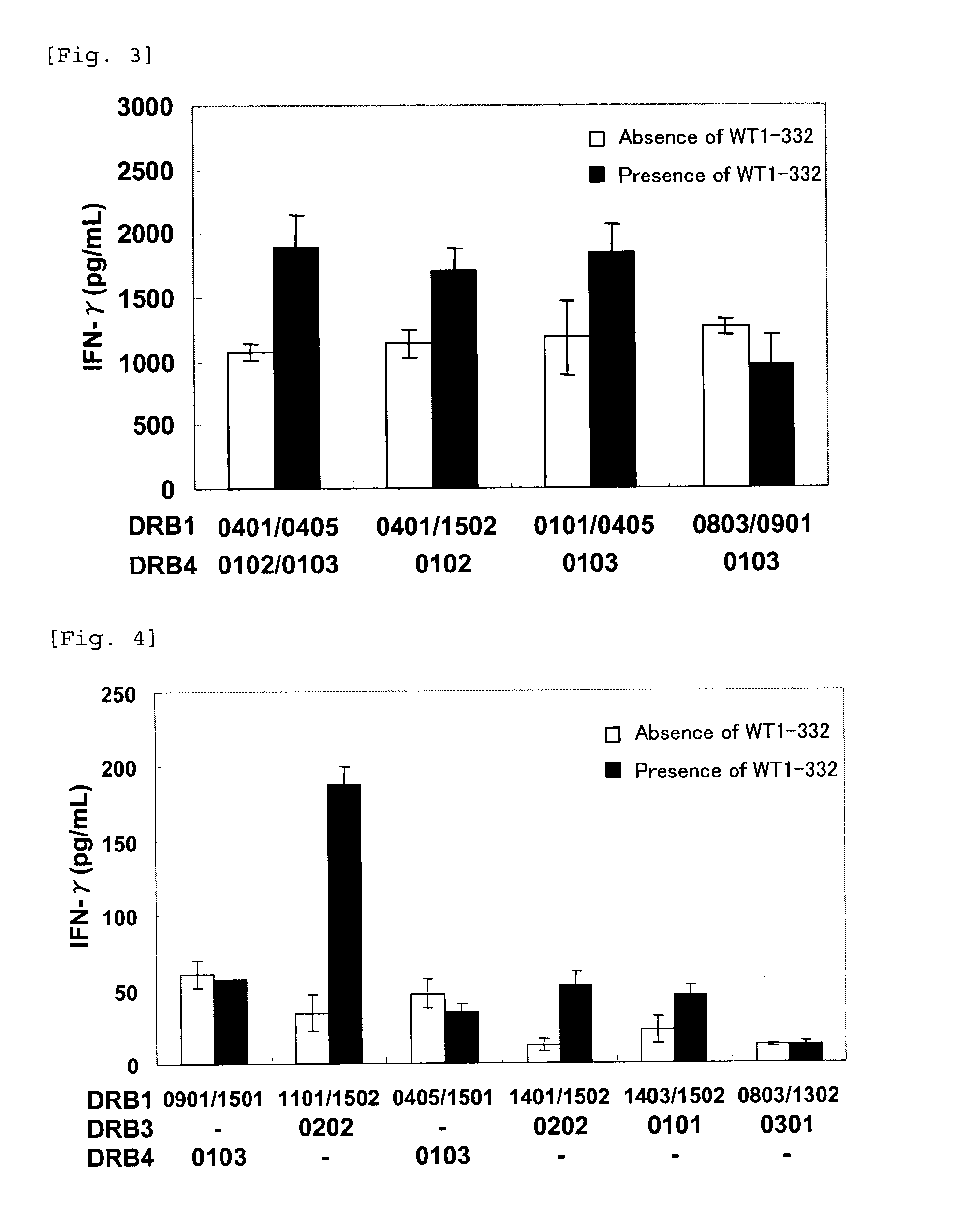
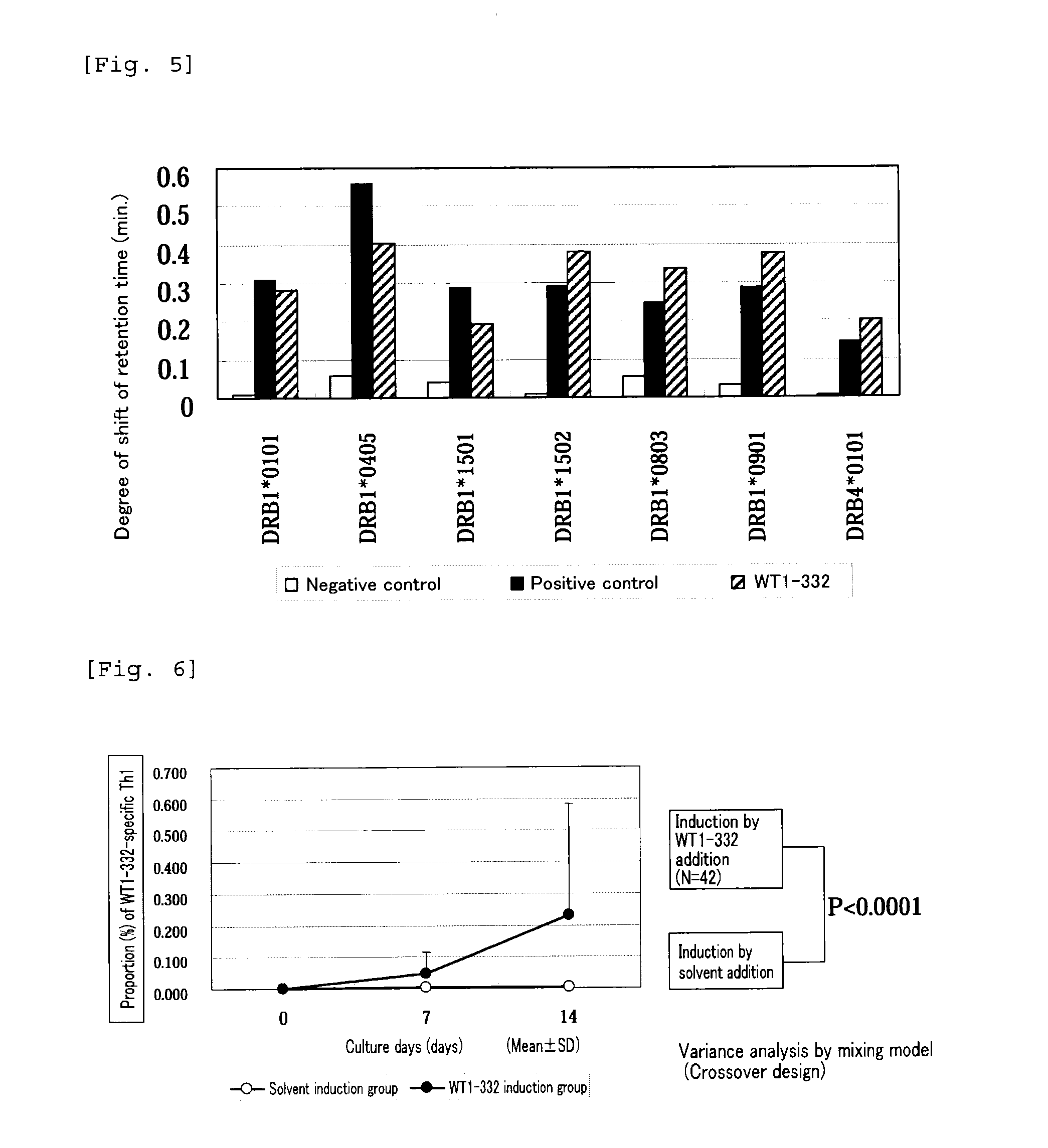
Method for activating helper t cell
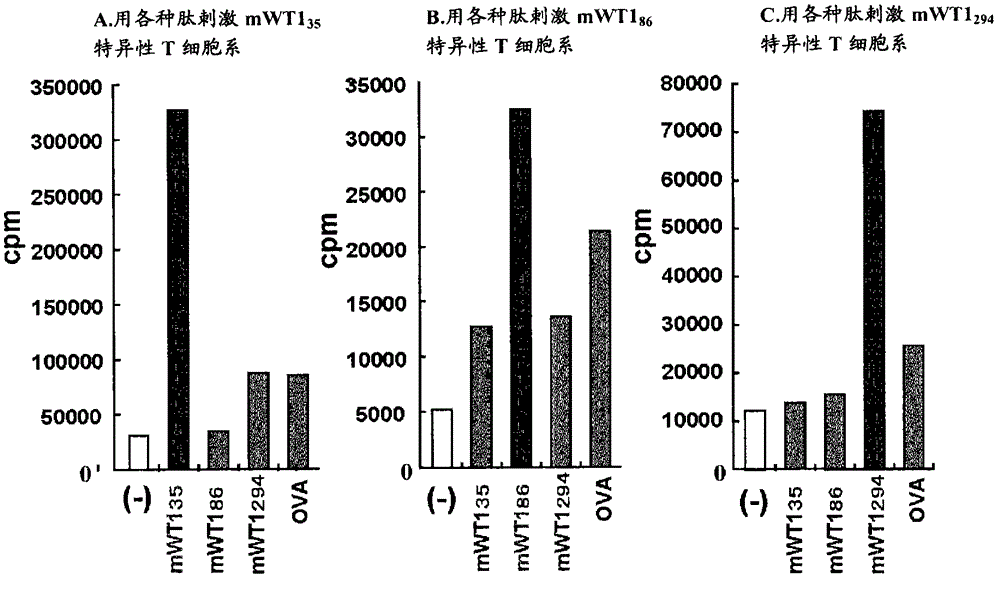
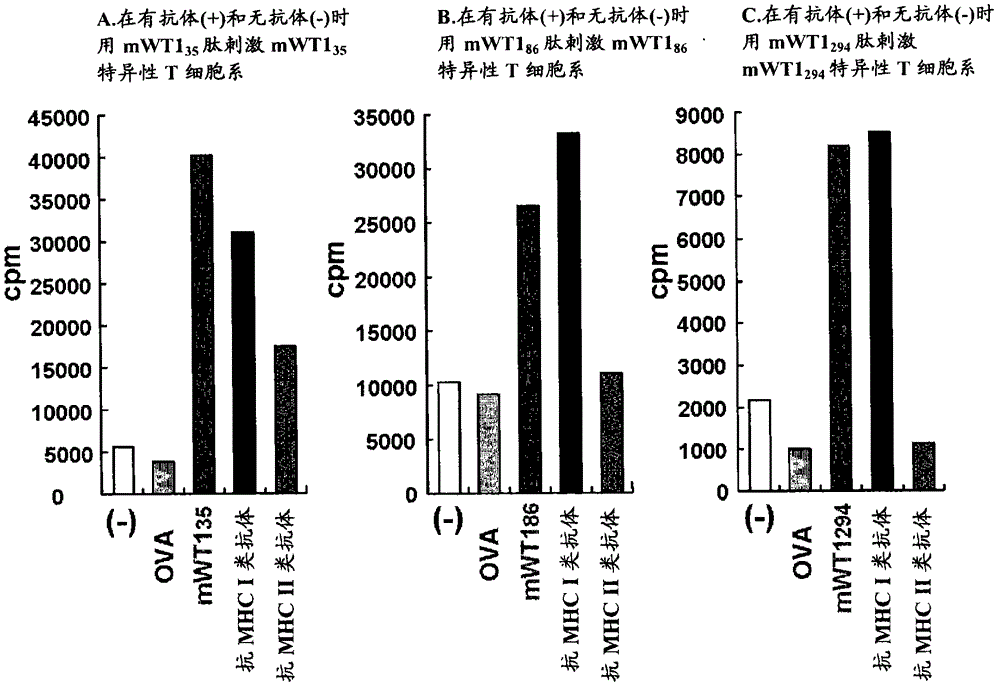
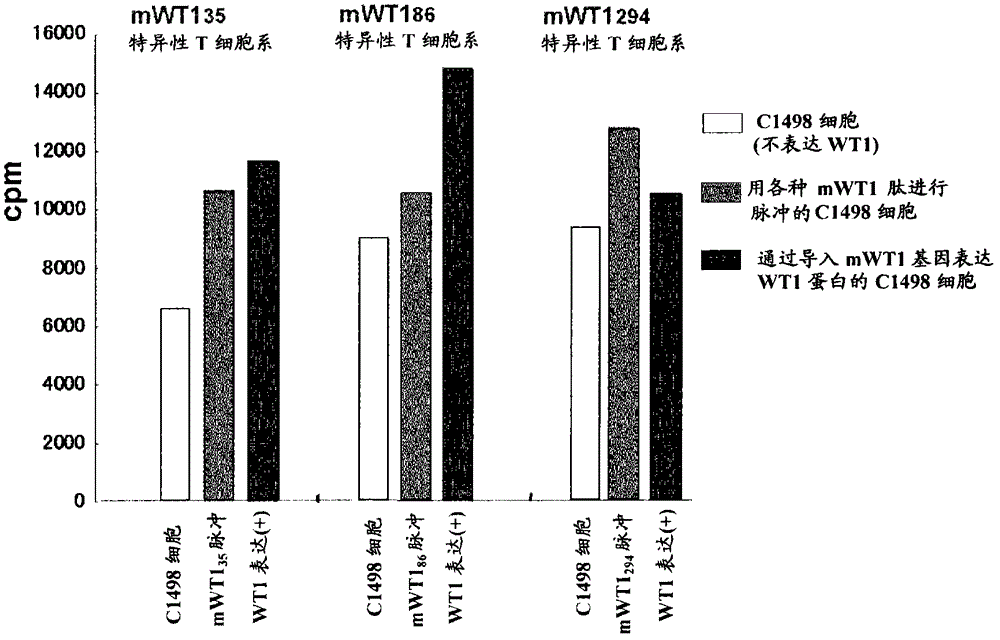
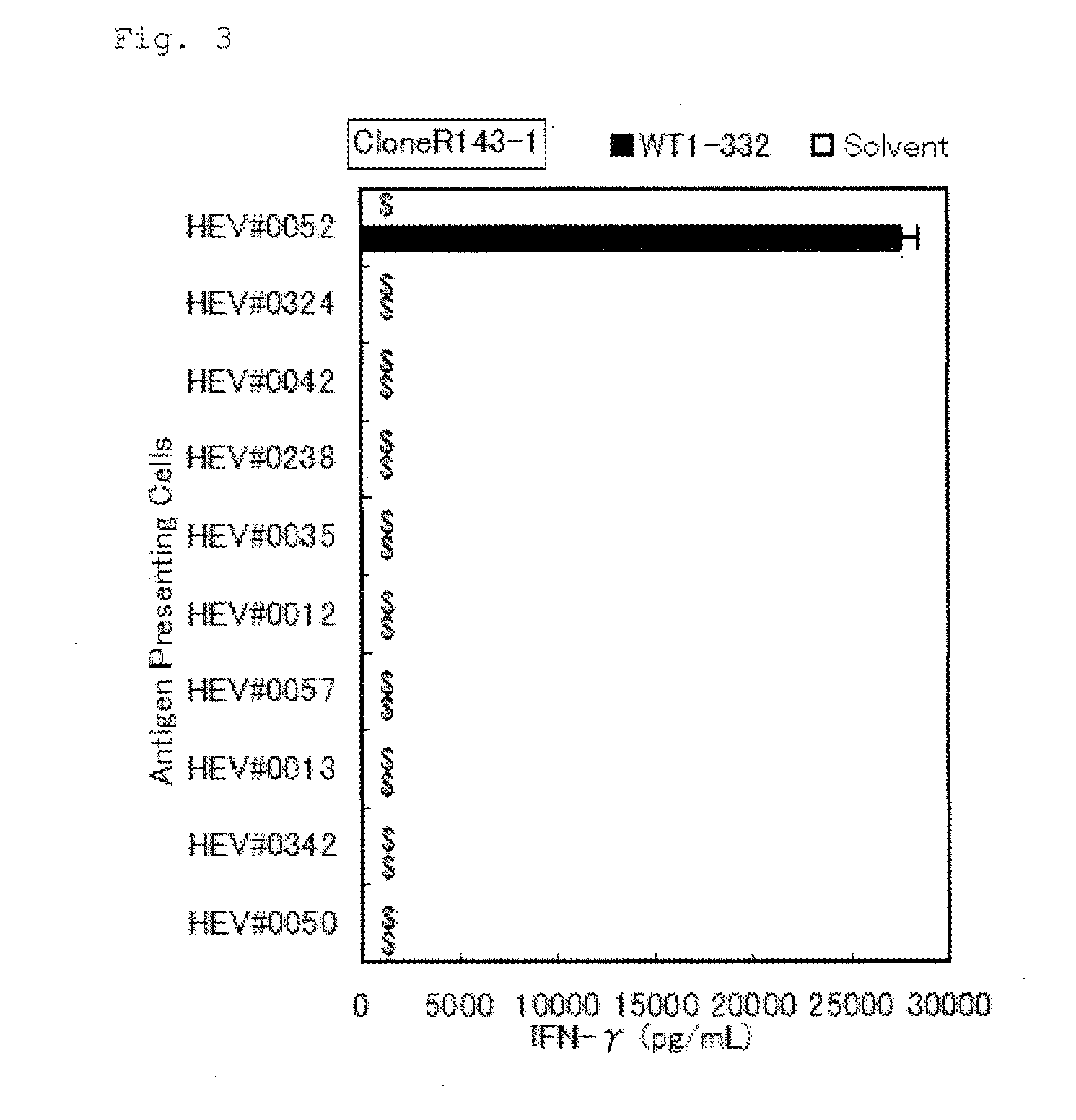
The present invention relates to a method for activating helper T cells, which includes the step of activating helper T cells by adding a WT1 peptide to antigen presenting cells, wherein the WT1 peptide has the ability to bind to any MHC class II molecule of an HLA-DRB1* 0101 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 0401 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 0403 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 0406 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 0803 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 0901 molecule, an HLA-DRB1* 1101 molecule, an HLA-DRB3* 0202 molecule, an HLA-DRB4* 0101 molecule, an HLA-DPB1* 0201 molecule or an HLA-DPB1* 0301 molecule, and the like.
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
Cancer antigen helper peptide
ActiveCN102803487AEfficient activationOrganic active ingredientsTumor rejection antigen precursorsAntigenCancer antigen
Disclosed are: a WT1 peptide which comprises an amino acid sequence composed of contiguous amino acid residues derived from a WT1 protein and can bind to an MHC class-II molecule to induce a WT1-specific helper T cell; a pharmaceutical composition containing the peptide; and others.
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
Isolated peptides which bind to MHC class II molecules, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6800730B1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman leukocyte antigen DRCD4 antigen
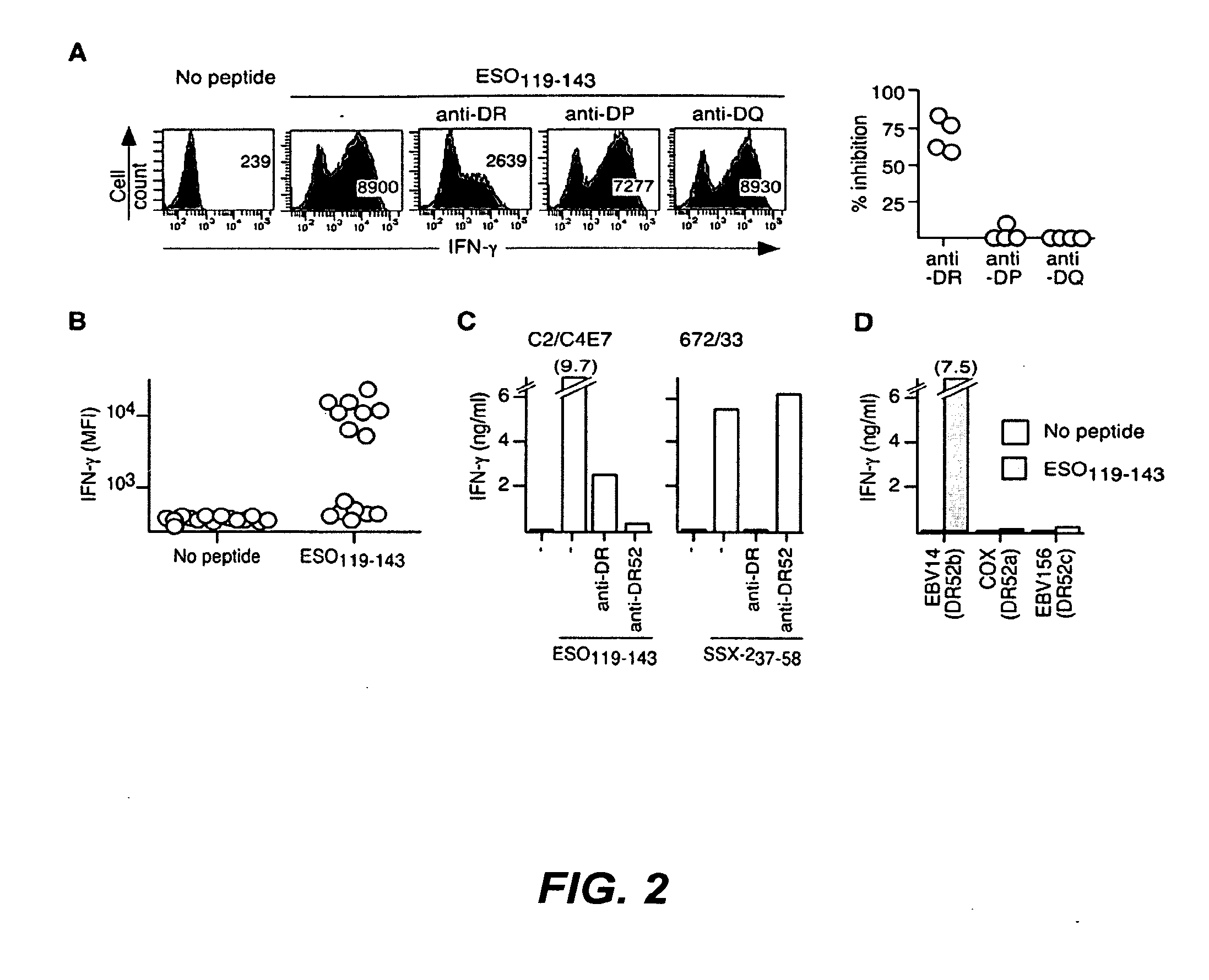
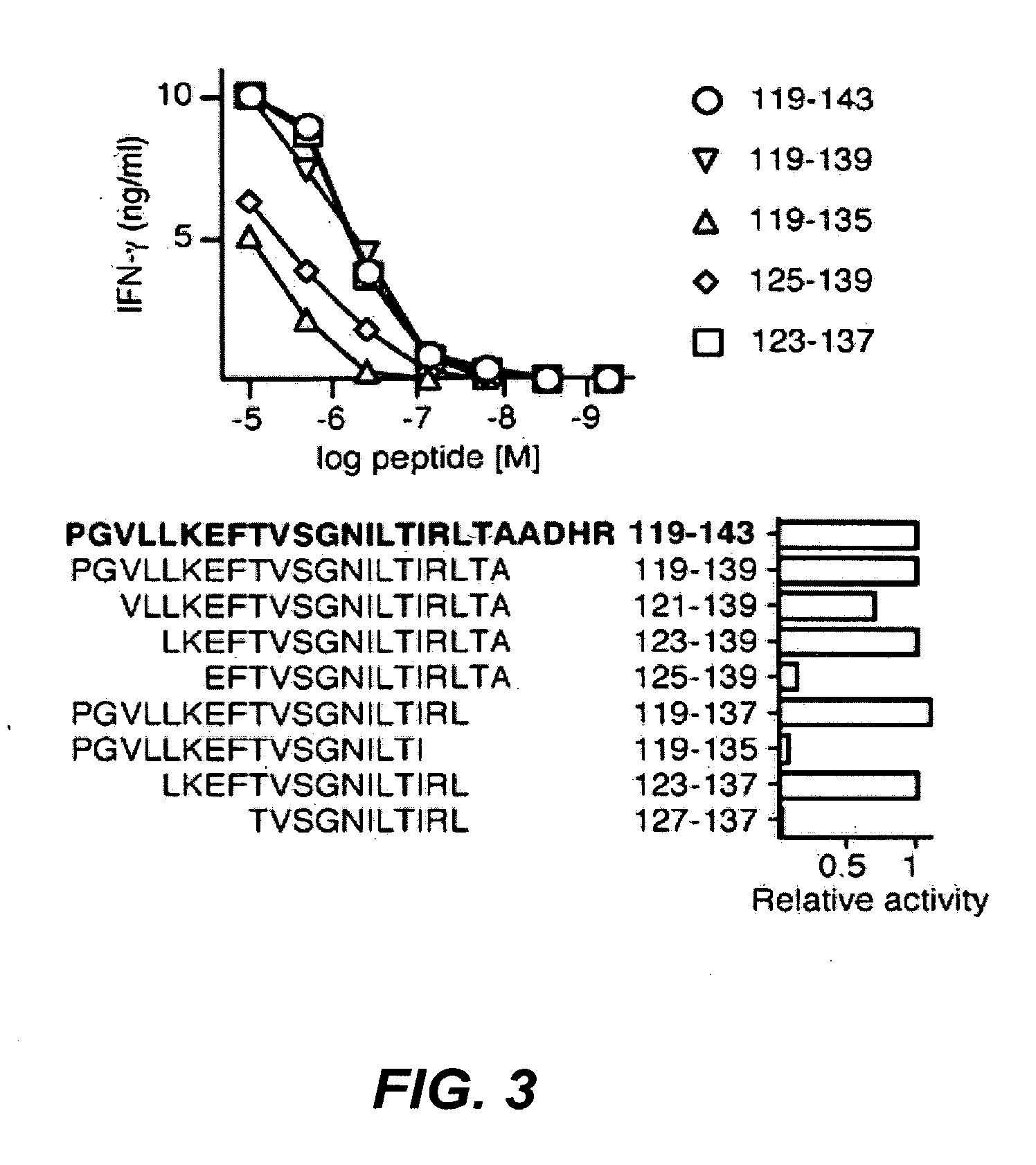
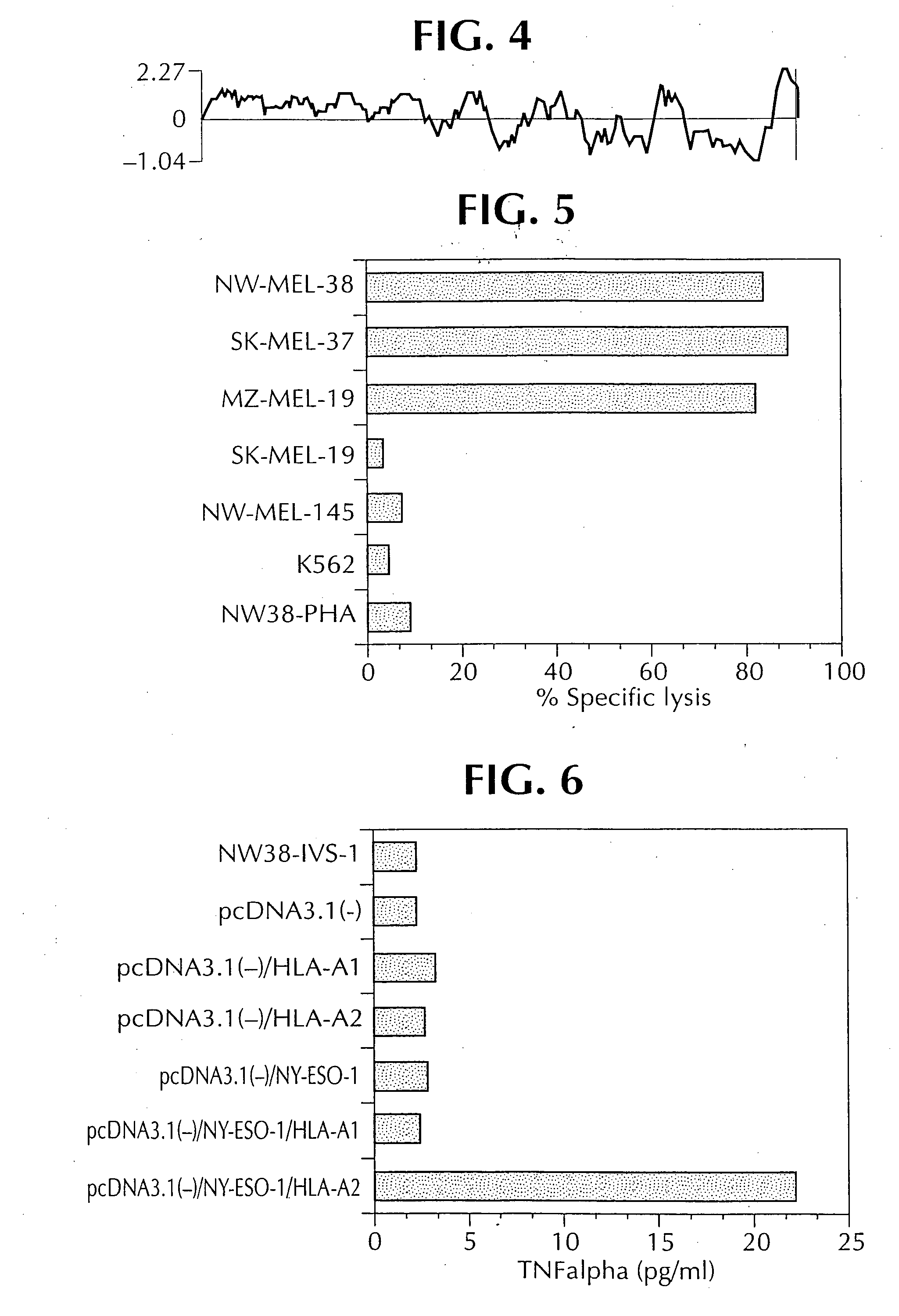
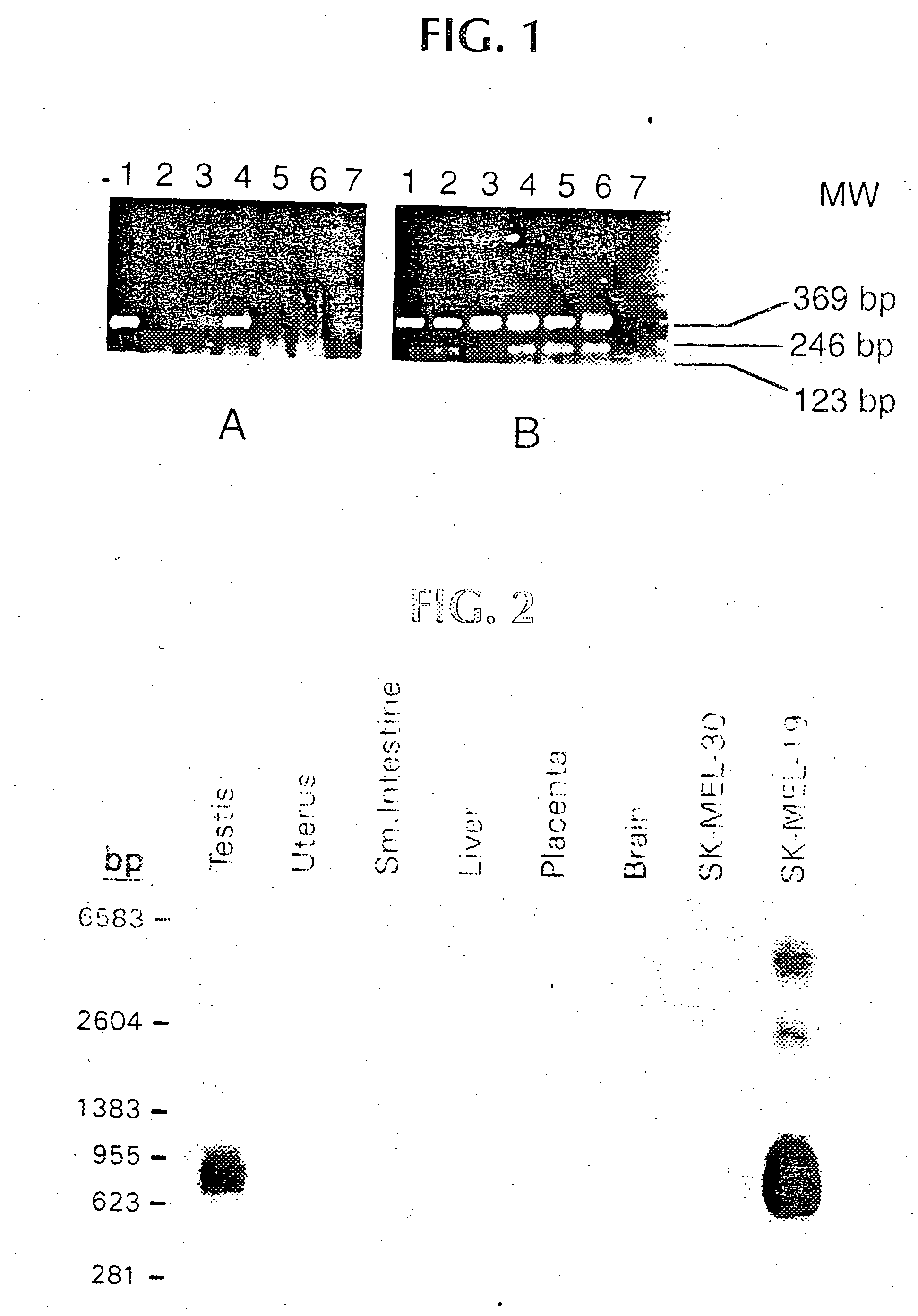
Peptides which have an amino acid sequence identical to sequences found in tumor rejection antigen precursors, such as NY-ESO-1, and SSX-2, are disclosed. These peptides bind to MHC-Class II molecules, such as HLA-DR molecules, and provoke proliferation of CD4+ cells.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Isolated peptides corresponding to amino acid sequences of NY-ESO-1, which bind to MHC Class I and MHC Class II molecules, and uses thereof
The invention relates to peptides which bind to MHC Class I and to MHC Class II molecules. These peptides are useful in different therapeutic and diagnostic contexts.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES +3
Method for activating helper t cell
The present invention relates to a method for activating helper T cells, which includes the step of activating helper T cells by adding a WT1 peptide to antigen presenting cells, wherein the WT1 peptide has the ability to bind to an MHC class II molecule selected from HLA-DRB1*08:02 molecule, an HLA-DRB1*13:02 molecule, an HLA-DRB1*14:03 molecule, an HLA-DRB1*14:05 molecule, an HLA-DQB1*03:02 molecule, and an HLA-DQB1*04:01 molecule.
Owner:INT INST OF CANCER IMMUNOLOGY INC
Cellular telomerase vaccine and its use for treating cancer
InactiveUS20060204483A1Guaranteed monitoring effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsMHC class IDendritic cell
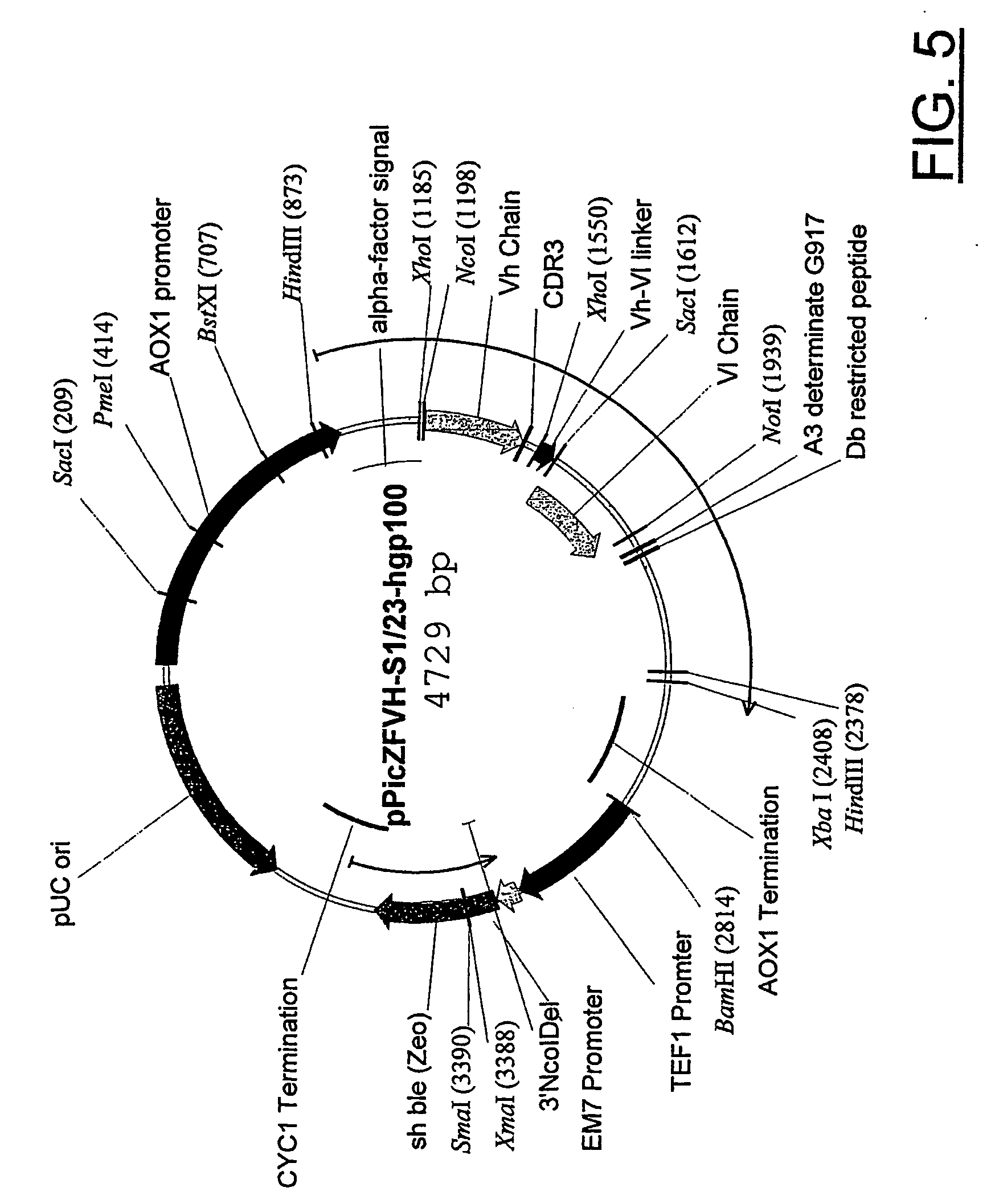
The invention provides dendritic cell (DC) preparations that present a telomerase reverse transcriptase (TRT) peptide in the context of an MHC class I or MHC class II molecule. The DCs may be pulsed with a TRT polypeptide, or may comprise a recombinant polynucleotide encoding TRT. The invention also describes the use of such compositions for the prevention and treatment of cancers and other diseases.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
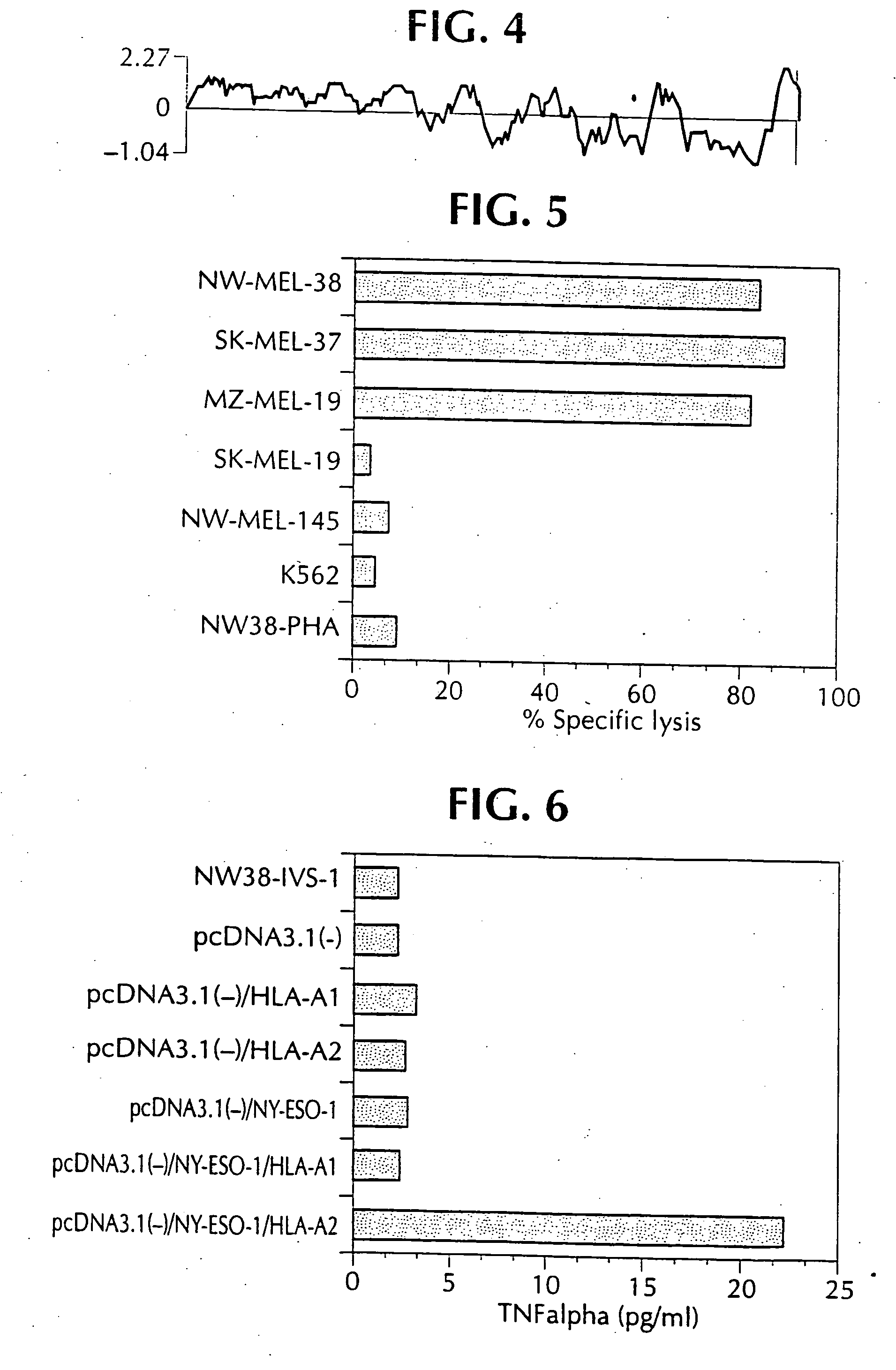
Immunodominant mhc dr52b restricted ny-eso-1 epitopes, mhc class ii monomers and multimers, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130029358A1Long-term outcome is improvedPrevent relapseTumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsEpitopeNY-ESO-1
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Antigen presenting cell targeting conjugate, an antigen presenting cell contacted with such conjugate, their use for vaccination or as medicament, and methods for their production or generation
InactiveUS20060088520A1Expand selectionImprove bindingNervous disorderTumor rejection antigen precursorsMHC class IVaccination
The invention relates to a conjugate for targeting antigen presenting cells comprising: at least one antigenic moiety conjugated to a targeting moiety that is capable of binding to a cell surface structure of an antigen presenting cell, wherein the conjugate is capable of being internalized and processed by said antigen presenting cells such as to cause processed antigenic moiety fragments thereof to be presented via MHC class I and MHC class II molecules of the antigen presenting cell, to nucleic acid sequence comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding the antigenic moiety and a nucleic acid sequence encoding the targeting moiety, to a host cell to a method for producing a conjugate, and for generating an antigen presenting cell capable of eliciting an immune response to such antigen presenting cell, to a pharmaceutical composition comprising a conjugate or an antigen presenting cell and their use for vaccination, and as a medicament.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method for the detection, preparation and depletion of cd4+ t lymphocytes
InactiveUS20160091492A1Synapse formation is increasedExtended durationImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCD4 antigenAntigenic protein
The present invention relates an in vitro method for detecting class II restricted CD4+ T cells in a sample. Herein a sample is contacted with an isolated complex of an MHC class II molecule and a peptide. This peptide comprises an MHC class II restricted T cell epitope of an antigenic protein and immediately adjacent thereof, or separated by a linker of at most 7 amino acids a sequence with a [CST]-xx-C or C-xx-[CST] motif. CD4+ T cells are detected by measuring the binding of the complex with cells in the sample, wherein the binding of the complex to a cell is indicative for the presence of CD4+ T cells in the sample. The present invention further relates to an isolated complex of an MHC Class II molecule and a peptide comprising an MHC class II restricted T cell epitope of an antigenic protein and immediately adjacent thereof, or separated by a linker of at most 7 amino acids a sequence with a [CST]-xx-C or C-xx-[CST] motif.
Owner:IMCYSE
Peptides associated with HLA-DR MHC class II molecule and involved in Rheumatoid arthritis
InactiveUS20090010943A1Improve usabilityInhibition of activationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticShared epitopeEpitope
Owner:LONDON HEALTH SCI CENT RES
Isolated Ny-Eso-1 Peptides Which Bind To Hla Class II Molecules And Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080139464A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsNY-ESO-1 peptideHla class ii
The invention relates to peptides which consist of amino acid sequences found in the NY-ESO-1 molecule, which bind to MHC-Class II molecules. These can be used alone, or in combination with other peptides.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
Compounds that modulate autoimmunity and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20120195929A1Improve bindingPrevent diabetesMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsDiseaseAntigen
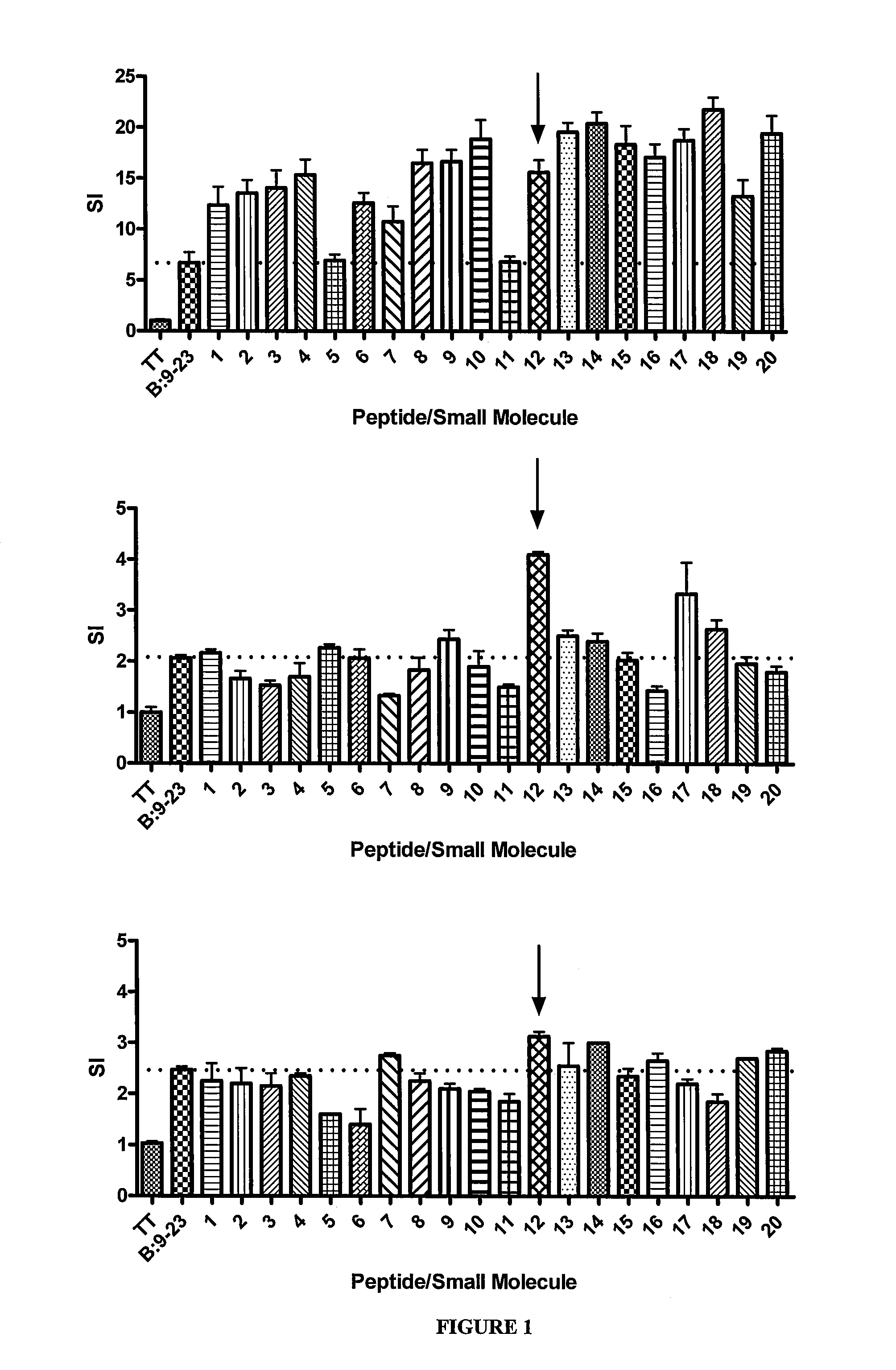
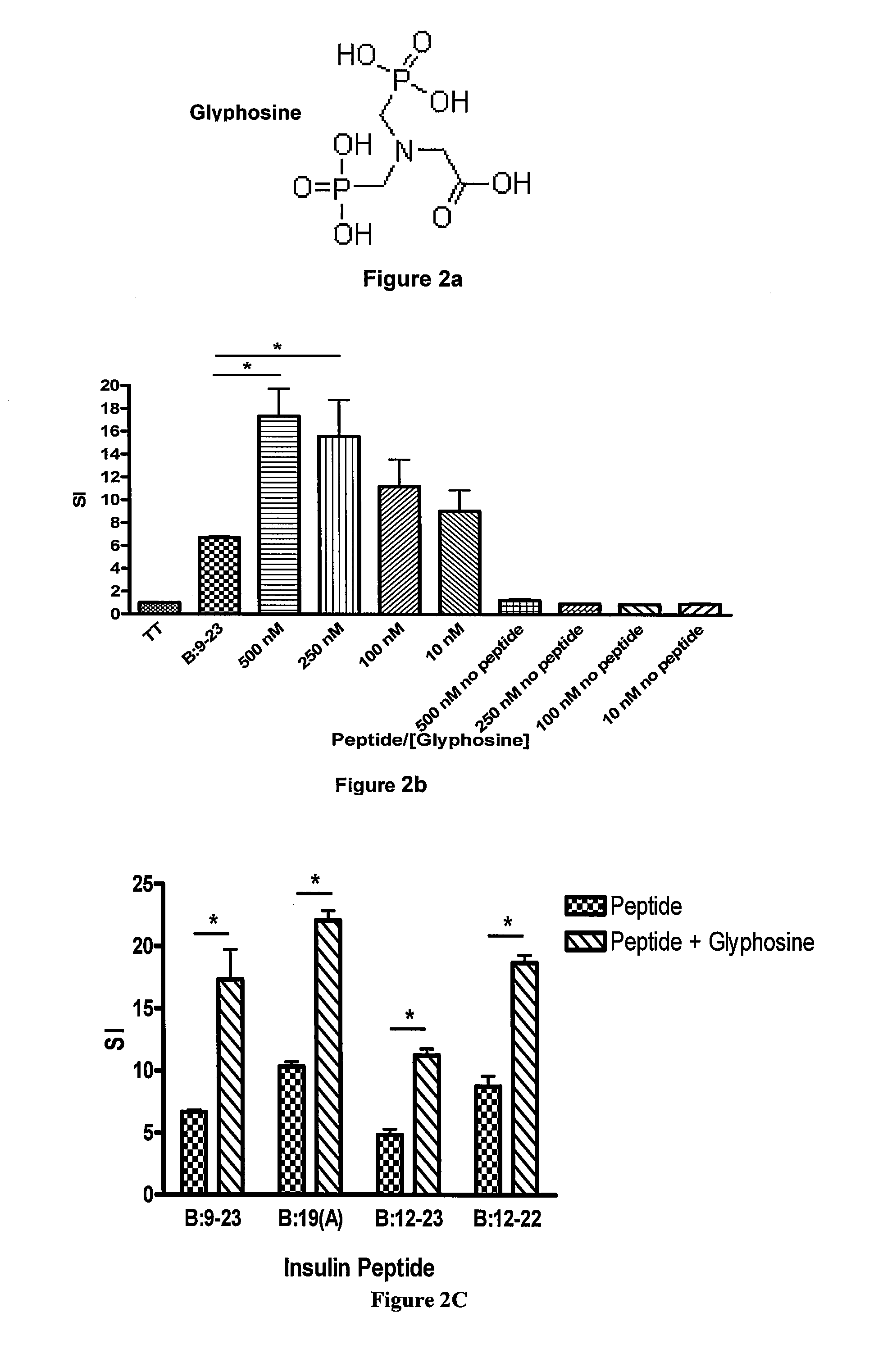
The invention provides methods of preventing, treating or ameliorating autoimmune diseases such as diabetes by modulating the binding of MHC class II molecules to antigenic peptides or fragments of antigenic peptides of the autoimmune disease by the administration of small organic compounds. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the therapeutically effective small organic compounds and methods of using the same.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Therapeutic compositions and methods for the prevention of autoimmune diseases
ActiveUS20120171212A1Therapeutic effectMetabolism disorderAntibody ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune disease
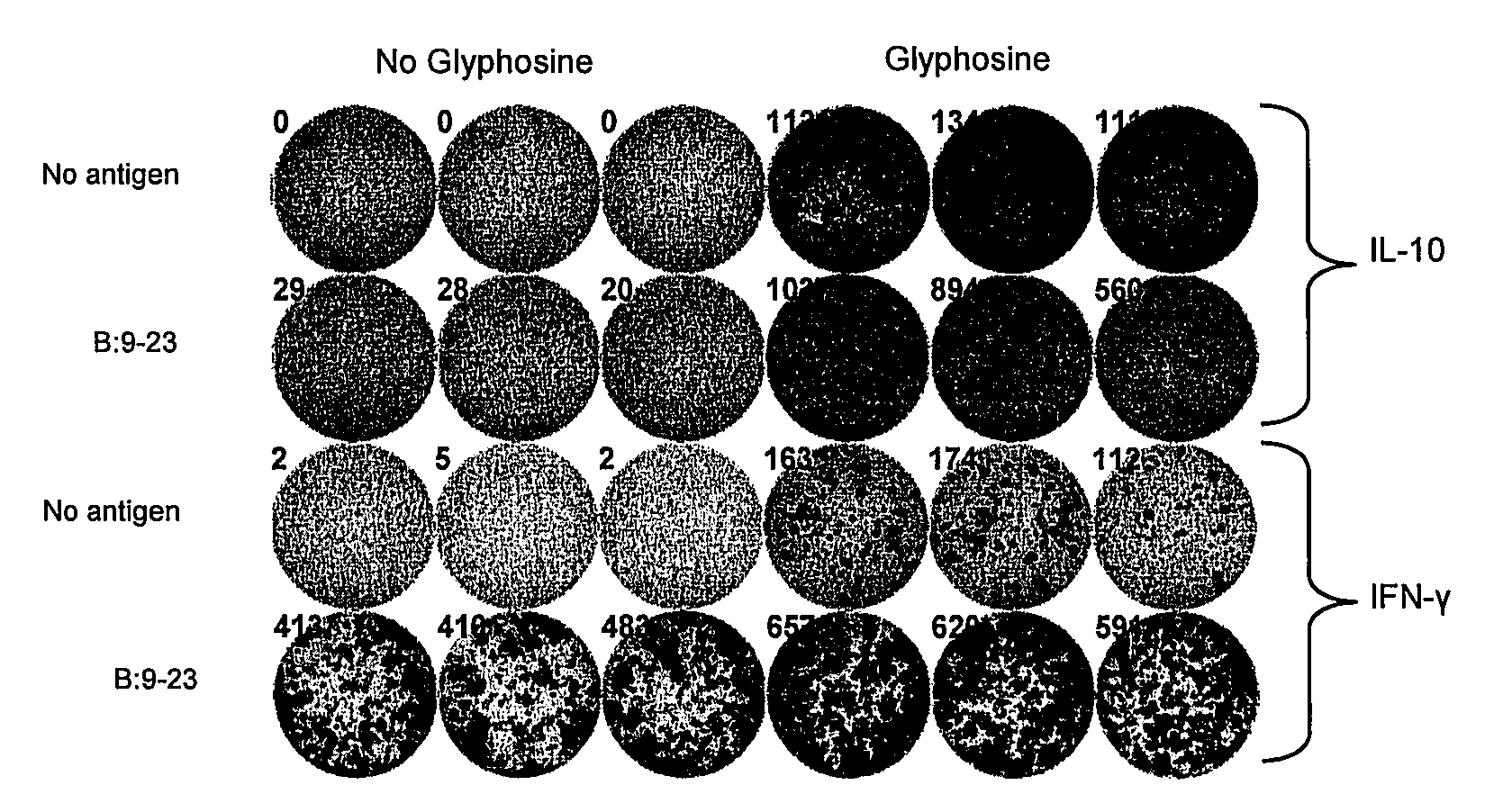
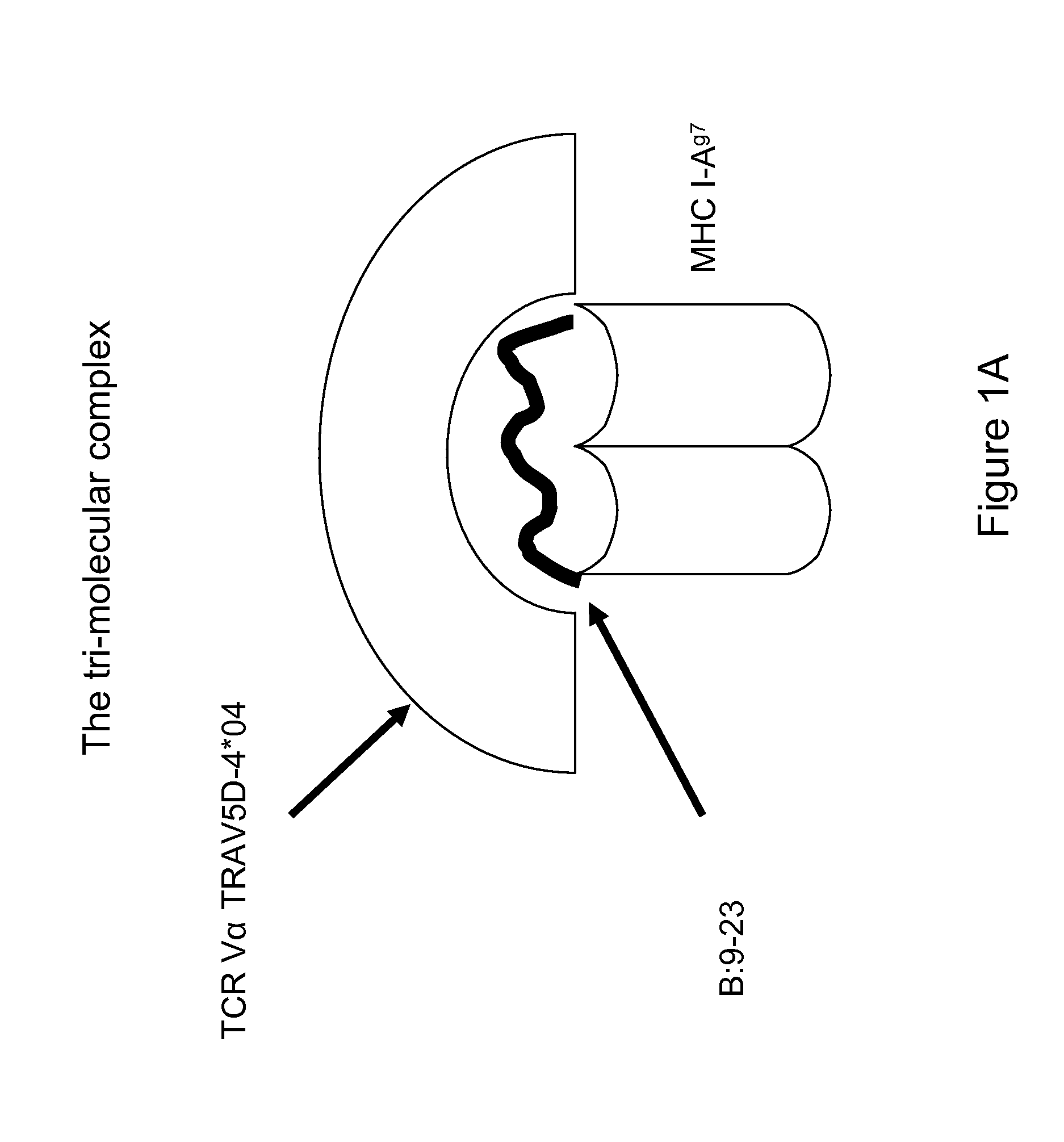
The present invention is directed to therapeutic compositions and methods for the prevention or treatment of autoimmune diseases, comprising molecules that disrupt or prevent the assembly of the trimolecular complex required for the T cell immune response comprising the autoantigen, the MHC class II molecule, and the T cell receptor implicated in the autoimmune disease.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Compounds that modulate autoimmunity and methods of using the same
ActiveUS9629848B2Decreases cell receptor responseDecrease T cell responsePeptide/protein ingredientsSulfonylurea active ingredientsAntigenDiabetes mellitus
The invention provides methods of preventing, treating or ameliorating autoimmune diseases, such as diabetes and celiac disease, by decreasing the binding of MHC class II molecules to antigenic peptides or fragments of antigenic peptides of the autoimmune disease by the administration of small organic compounds. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising the therapeutically effective small organic compounds and methods of using the same.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Dendritic cell compositions and methods
ActiveUS8153425B2Good flexibilityImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsSnake antigen ingredientsMHC class IDendritic cell
Methods are provided for the production of dendritic cells from monocytes that have been incubated at a temperature of 1° C.-34° C. for a period of approximately 6 to 96 hours from the time they are isolated from a subject. After the incubation period, the monocytes can then be induced to differentiate into dendritic cells. Mature dendritic cells made by the methods of the invention have increased levels of one or more of CD80, CD83, CD86, MHC class I molecules, or MHC class II molecules as compared to mature dendritic cells prepared from monocytes that have not been held at 1° C.-34° C. for at least 6 hours from the time they were isolated from a subject. Dendritic cells made by the methods of the invention are useful for the preparation of vaccines and for the stimulation of T cells.
Owner:COIMMUNE INC
Autoantibody detection method, method for testing possibility of autoimmune disease contraction, autoantibody detection reagent, and autoimmune disease test reagent
The present invention provides an autoantibody detection method that can detect an autoantibody causing an autoimmune disease with high accuracy. The autoantibody detection method of the present invention includes the steps of; causing a sample and an antigen reagent comprising a denatured protein presented by an MHC class II molecule to come into contact with each other; and detecting a complex of an autoantibody in the sample and the denatured protein in the antigen reagent. By detecting a complex of the autoantibody and the denatured protein in a biological specimen isolated from a subject according to this detection method, it is possible to test the possibility of the autoimmune disease in the subject from the detection result.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Isolated peptides which bind to MHC class II molecules, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040214284A1Tumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsCD4 antigenHuman leukocyte antigen DR
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES LTD
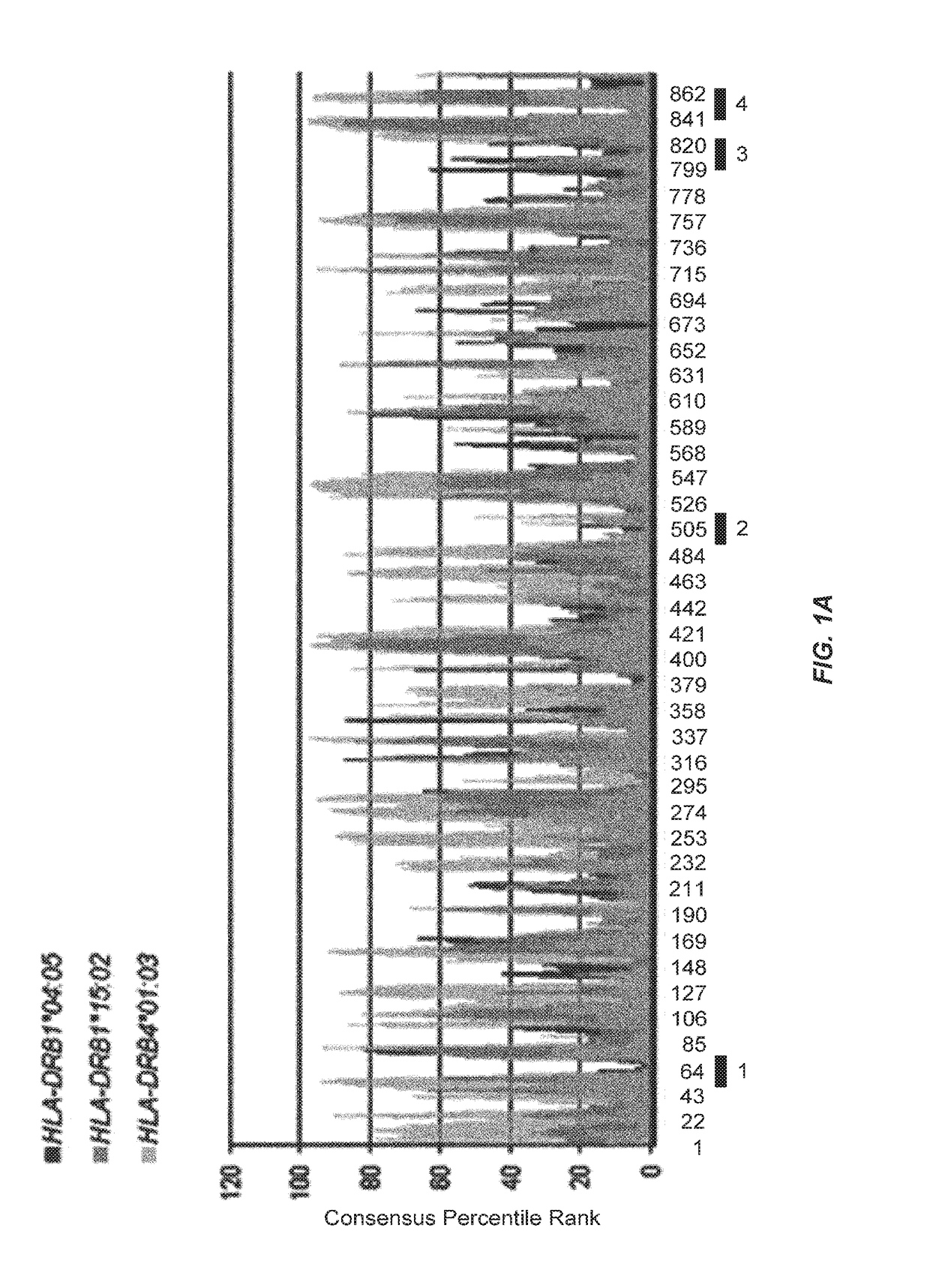
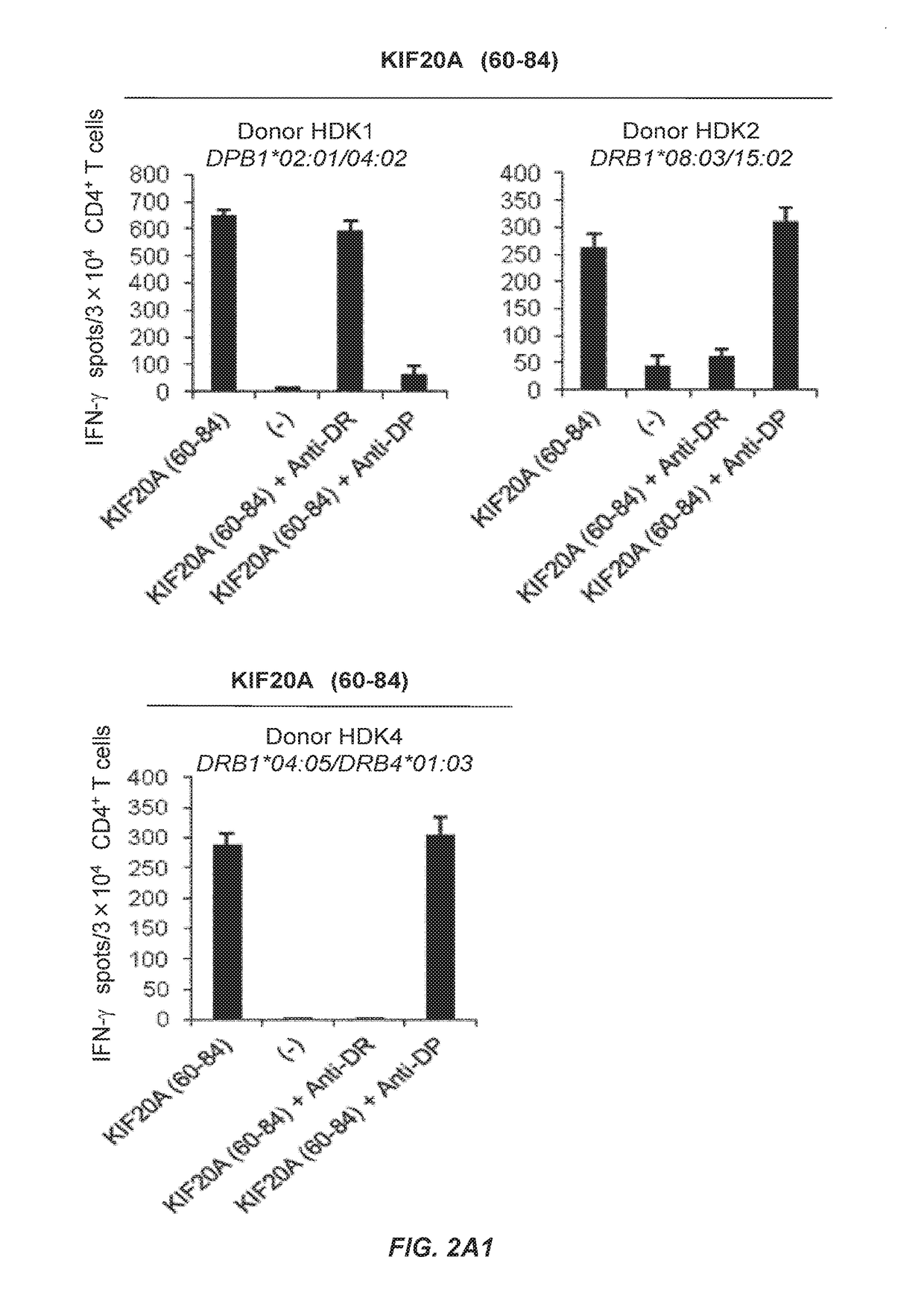
KIF20A Epitope Peptides for TH1 Cells and Vaccines Containing the Same
Isolated KIF20A-derived epitope peptides having Th1 cell inducibility are disclosed herein. Such peptides can be recognized by MHC class II molecules and induce Th1 cells. In preferred embodiments, such a peptide of the present invention can promiscuously bind to MHC class II molecules and induce KIF20A-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in addition to Th1 cells. Such peptides are thus suitable for use in enhancing immune response in a subject, and accordingly find use in cancer immunotherapy, in particular, as cancer vaccines. Also disclosed herein are polynucleotides that encode any of the aforementioned peptides, APCs and Th1 cells induced by such peptides and methods of induction associated therewith. Pharmaceutical compositions that comprise any of the aforementioned components as active ingredients find use in the treatment and / or prevention of cancers or tumors.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Method of amplifying a population of antigen-specific memory cd4+ t cells using artificial presenting cells expressing HLA class ii molecules
InactiveUS20180355316A1Mammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsHla class iiAccessory molecule
The present invention relates to method of amplifying a population of antigen-specific memory CD4+ T cells using artificial presenting cells expressing HLA class II molecules. In particular, the present invention relates to a method of amplifying a population of antigen-specific memory CD4+ T cells comprising the steps of i) providing a population of artificial antigen presenting cells consisting host cells that are genetically modified to stably express at least one MHC class II molecule along with at least one accessory molecule ii) loading the population of artificial antigen presenting cells of step i) with an amount of at least one antigen of interest and iii) coculturing the suitable population of a T cells with the population of artificial antigen presenting cells of step ii).
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +5
Ii-Key hybrid polypeptide and preparation method and application of tumor vaccine of Ii-Key hybrid polypeptide
InactiveCN111040038AImprove anti-cancer effectAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPeptide preparation methodsMolecular bindingTGE VACCINE
The invention discloses an Ii-Key hybrid polypeptide. LRMK tetrapeptide in the amino acid sequence of a stable polypeptide chain (Ii) of MHC class II molecules can be linked by polypeptide recognizedby TH cells, shows MHC class II molecule binding efficacy greater than 250 times in vitro, and is easier to recognize and present by antigen presenting cells. The invention provides a preparation method of a hybrid polypeptide tumor vaccine and application of a combination of the hybrid polypeptide tumor vaccine and an immunologic adjuvant, namely granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) to treatment of cancers. The hybrid polypeptide tumor vaccine disclosed by the invention is an efficient cancer immunotherapy vaccine for activating an autoimmune system with a latest mechanism. The Ii-Key hybrid polypeptide tumor vaccine provided by the invention has the advantage of improved anti-cancer effect.
Owner:深圳市博圣康生物科技有限公司
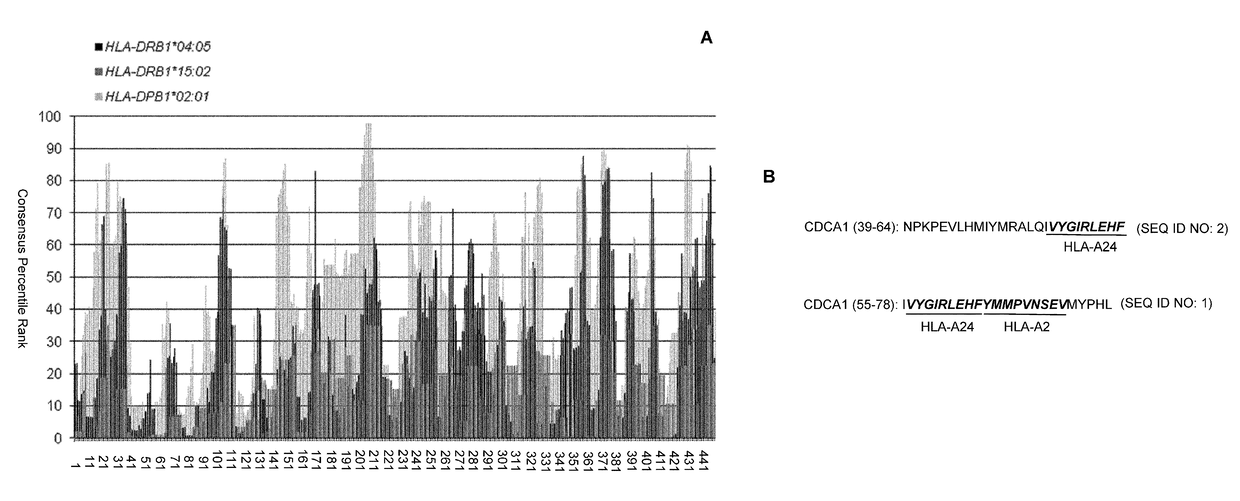
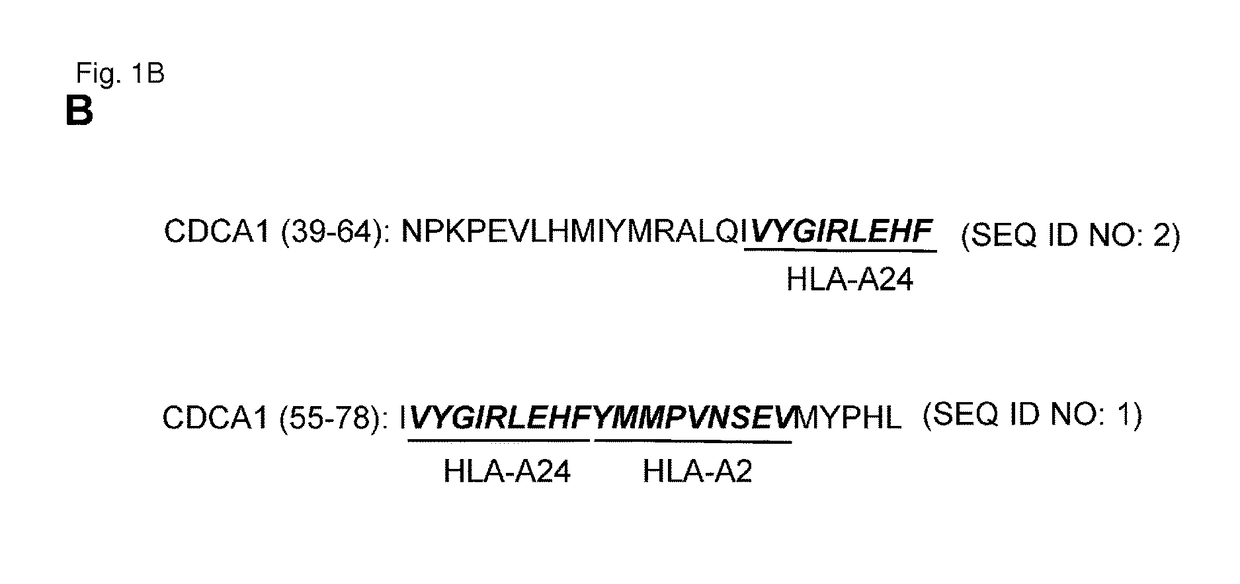
CDCA1 epitope peptides for Th1 cells and vaccines containing the same
InactiveUS9687538B2Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsEpitopeT lymphocyte
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Isolated peptides corresponding to amino acid requirements of NY-ESO-1, which bind to MHC Class I and MHC Class II molecules, and uses thereof
The invention relates to peptides which bind to MHC Class I and to MHC Class II molecules. These peptides are useful in different therapeutic and diagnostic contexts.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +2
Human monoclonal antibodies against lag3 and uses thereof
ActiveUS20210115135A1Stimulate immune responseHigh-affinity bindingImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesMolecular binding
The present disclosure provides isolated monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to LAG3 with high affinity, particularly human monoclonal antibodies. Preferably, the antibodies bind human LAG3. In certain embodiments, the antibodies bind both human and monkey LAG3 but do not bind mouse LAG3. The invention provides anti-LAG3 antibodies that can inhibit the binding of LAG3 to MHC Class II molecules and that can stimulate antigen-specific T cell responses. Nucleic acid molecules encoding the antibodies of the invention, expression vectors, host cells and methods for expressing the antibodies of the invention are also provided. Immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies of the invention are also provided. This disclosure also provides methods for stimulating an immune response, as well as methods for treating cancer using an anti-LAG3 antibody of the invention.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHIMAI PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
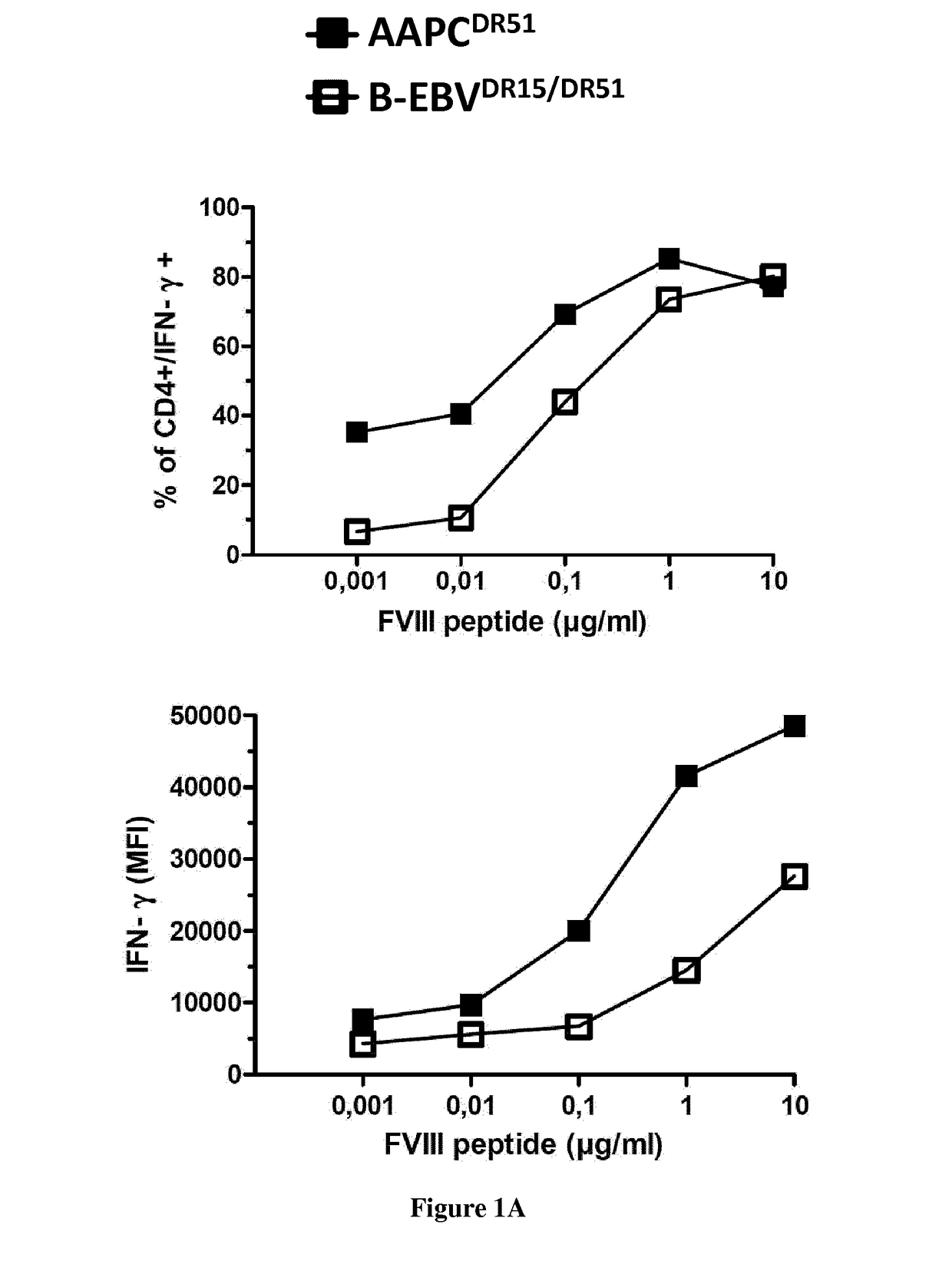
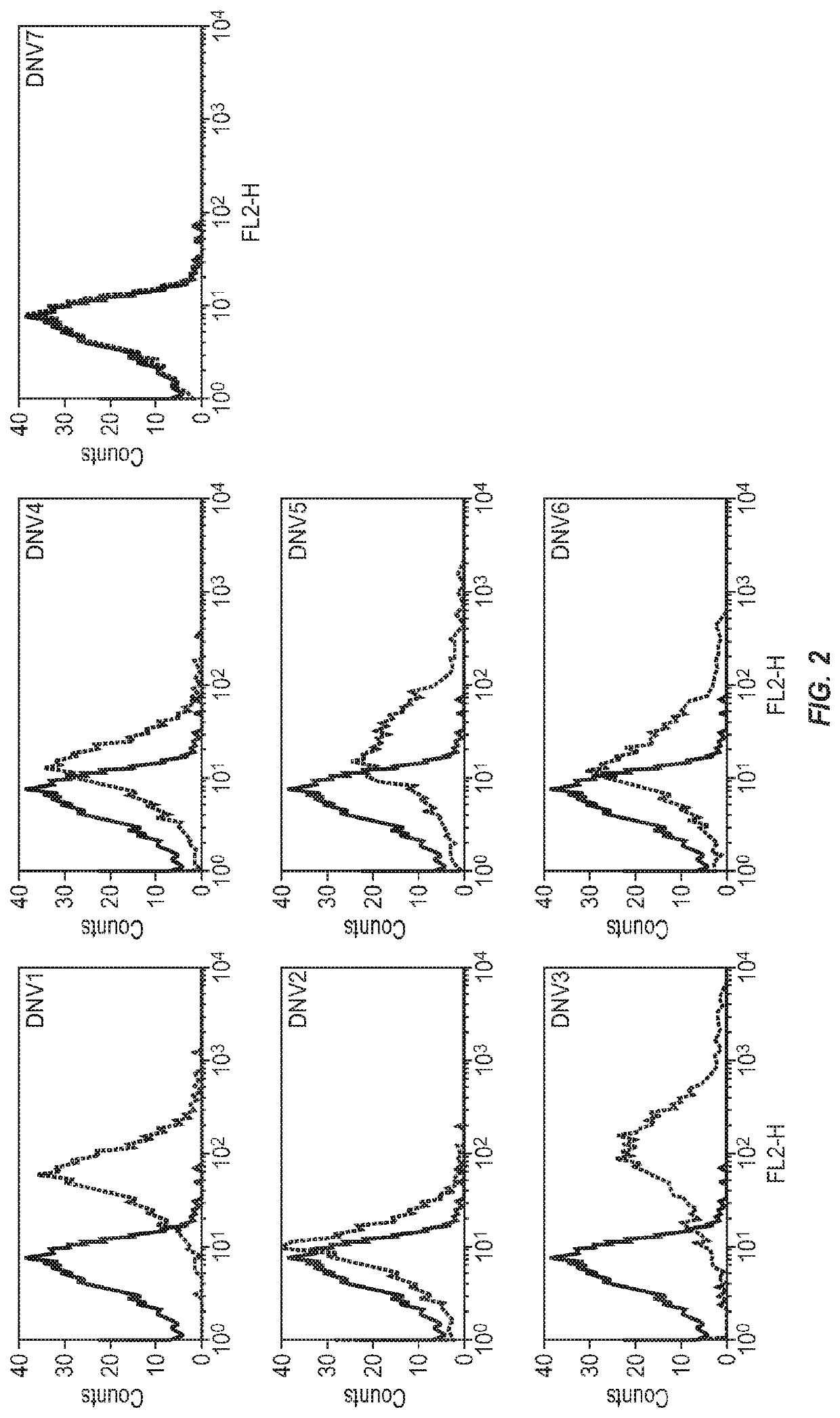
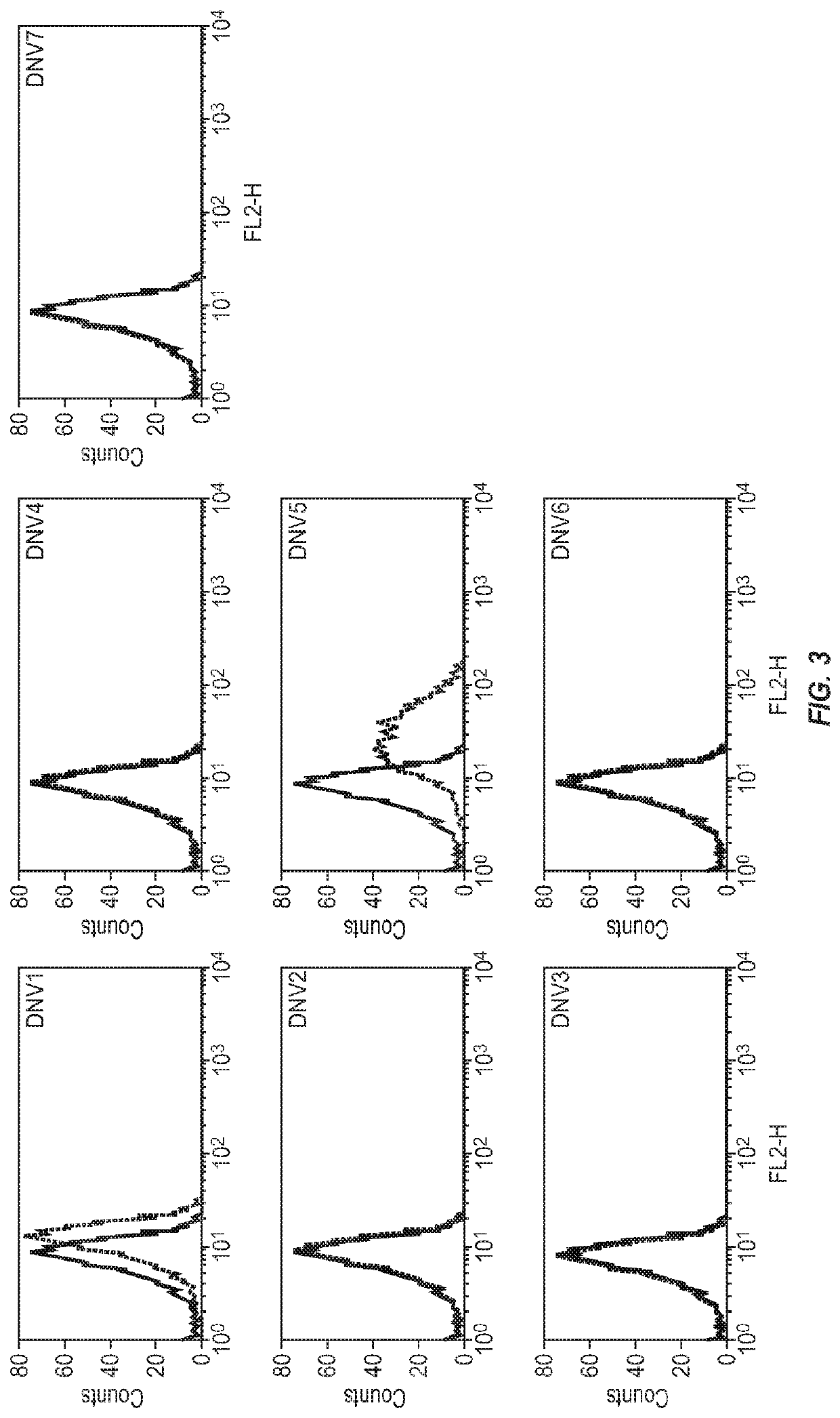
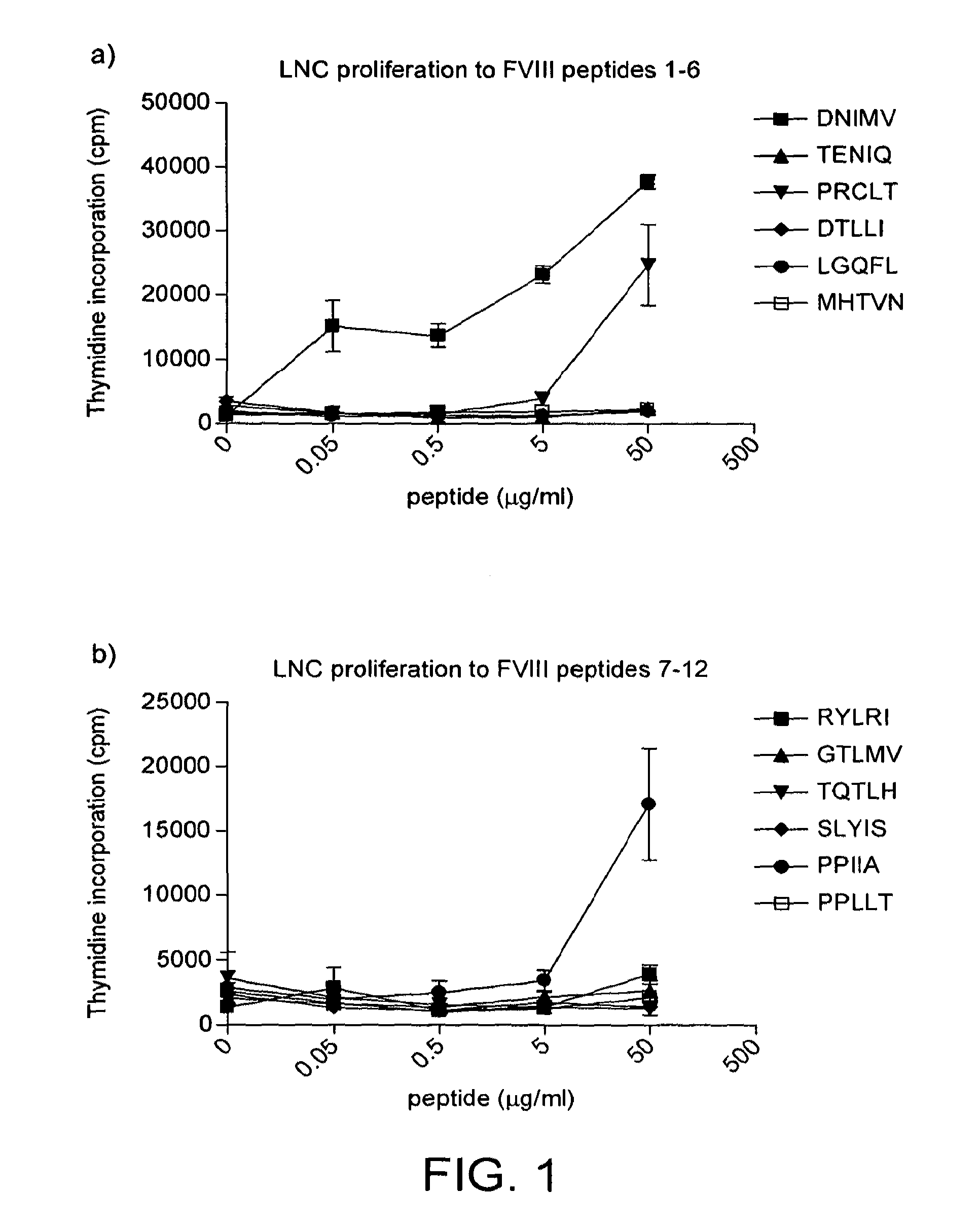
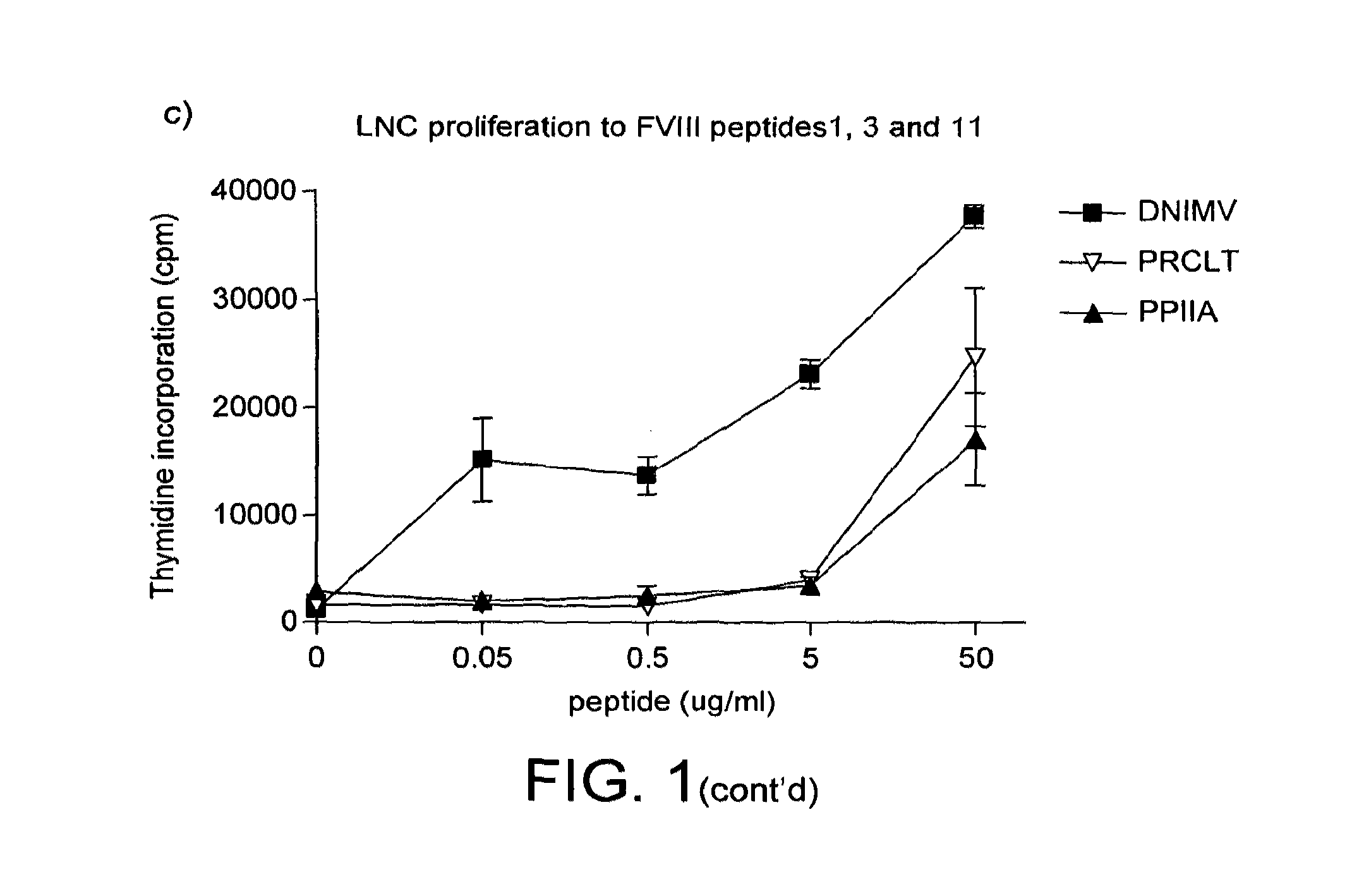
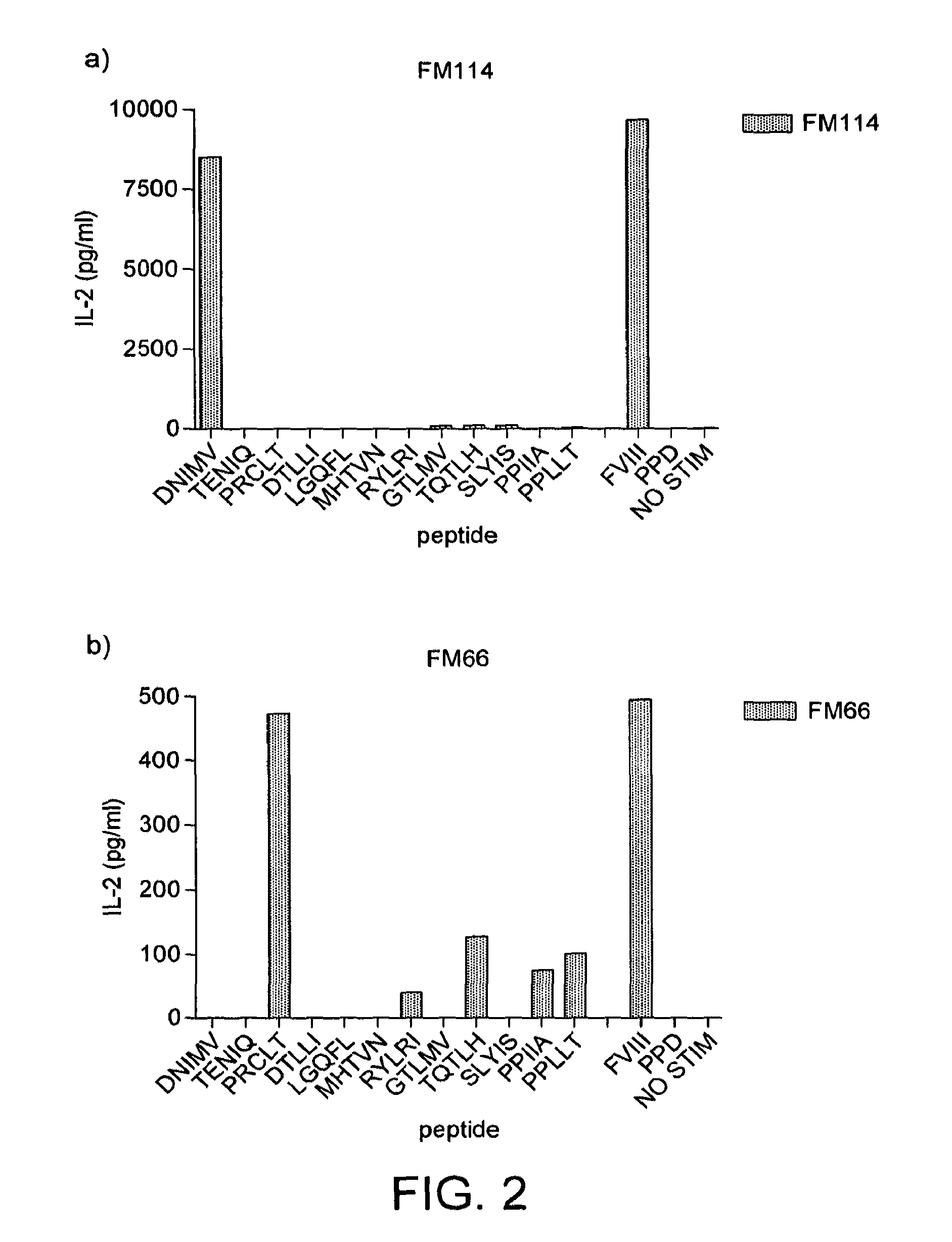
Modified factor VIII peptides
InactiveUS8703705B2Suppressing and preventing and reducing developmentFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigen processingT cell
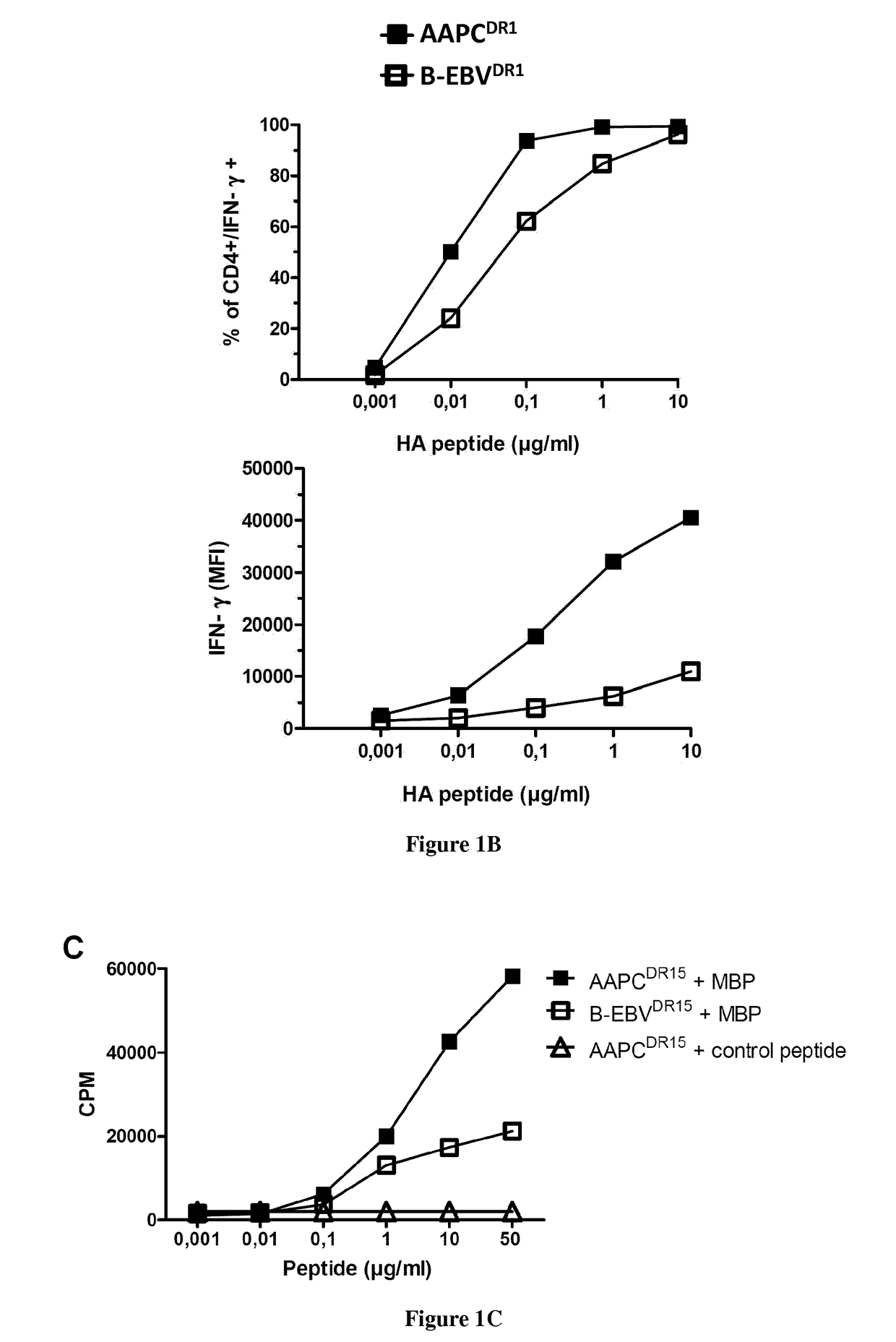
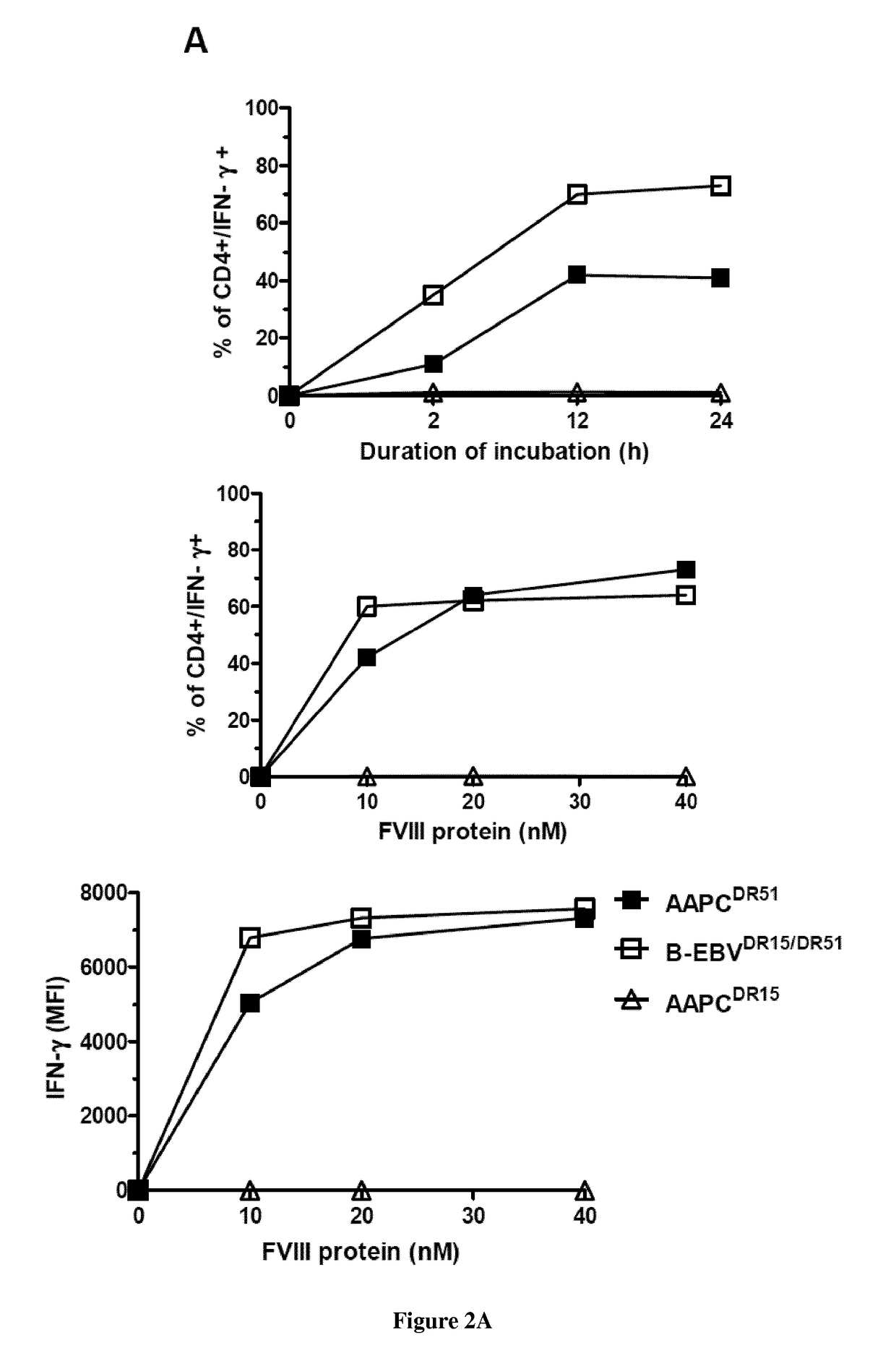
The present invention provides peptides at least partly derivable from FVIII which are capable of binding to an MHC class II molecule without further antigen processing and being recognized by a factor VIII specific T cell. In particular, the present invention provides a peptide comprising or consisting of the sequence EDNIMVTFRNQASR. The present invention also relates to the use of such a peptide for the prevention or suppression of inhibitor antibody formation in haemophilia A and / or acquired haemophilia.
Owner:APITOPE INT
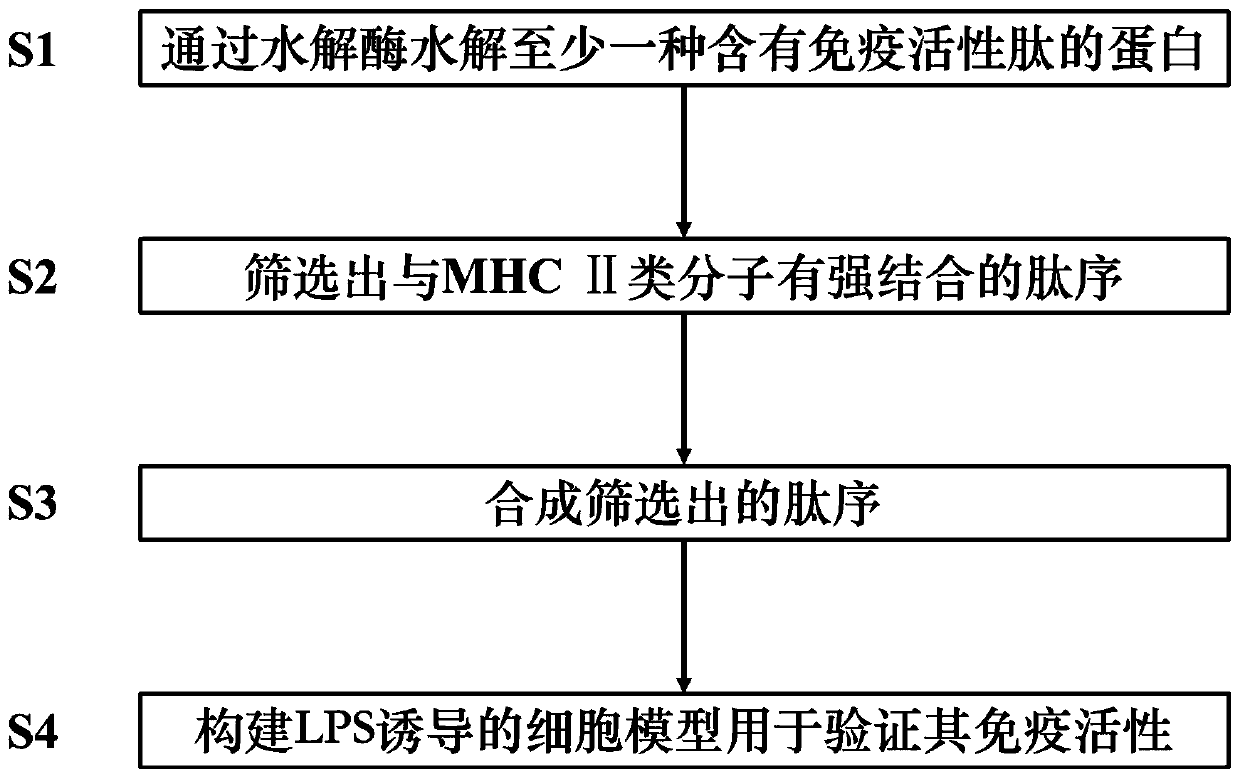
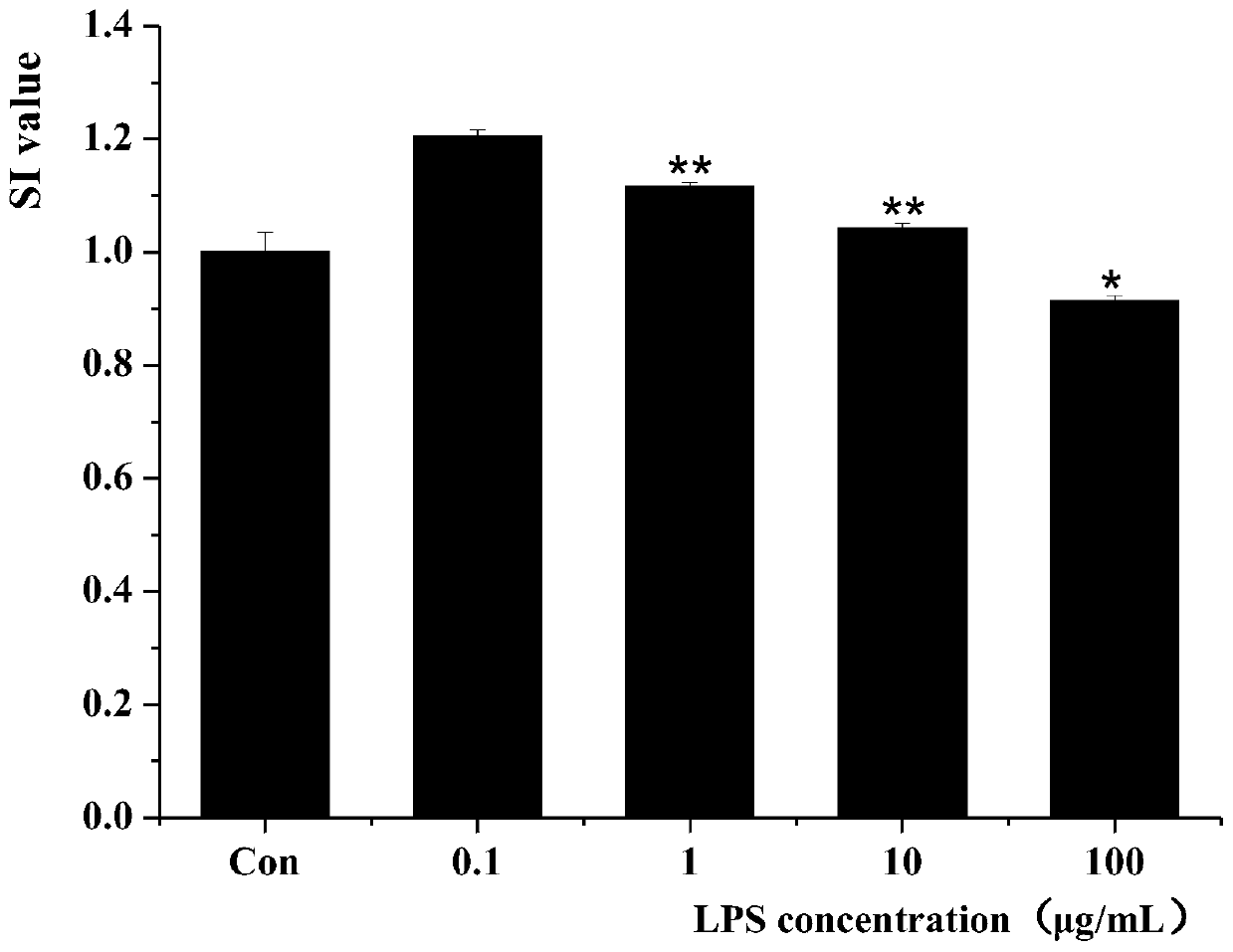
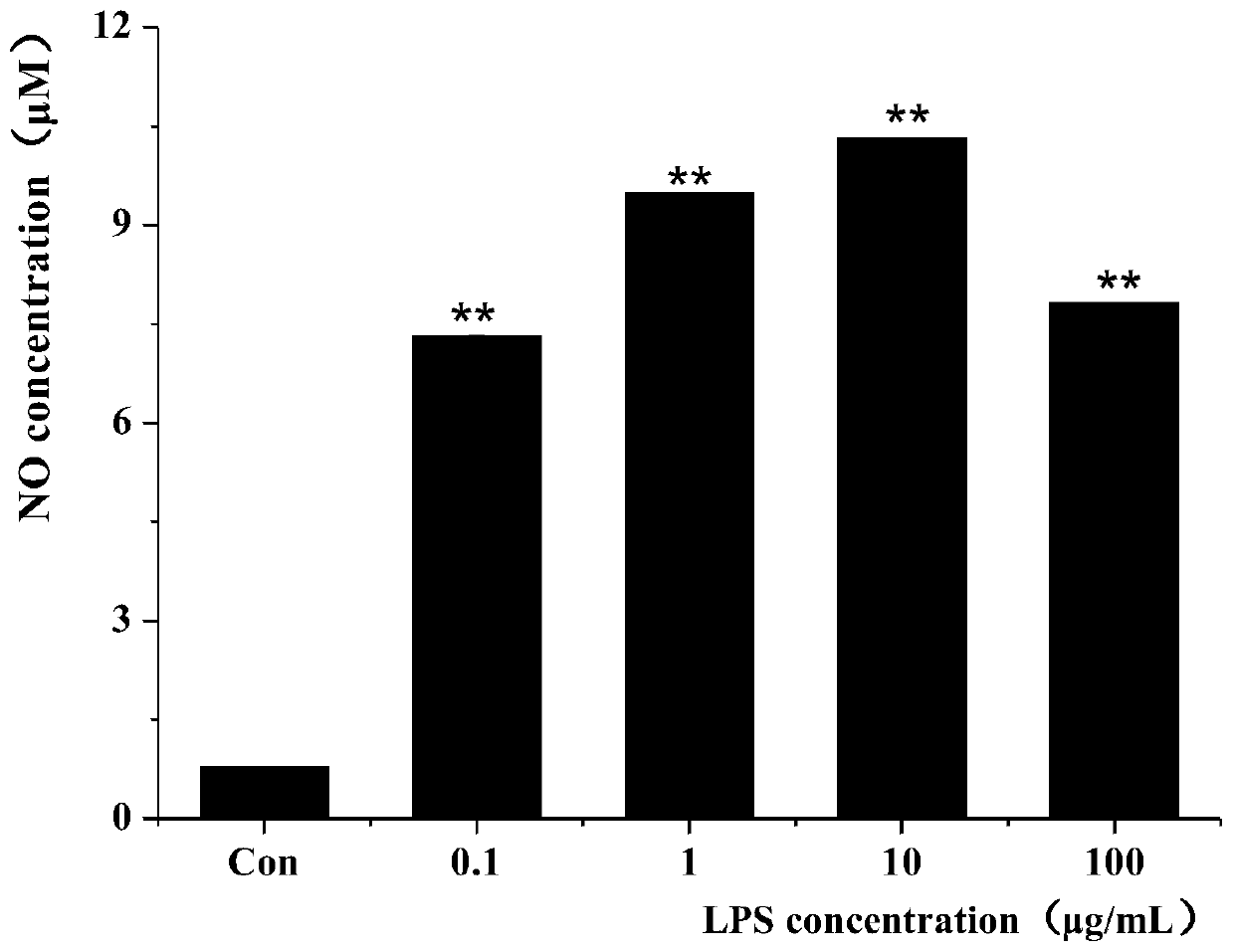
Screening method for immunoactive peptides
ActiveCN110161253AImprove accuracyReactogenic shrinkageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBinding siteScreening method
The invention relates to a screening method for immunoactive peptides. The screening method comprises the following steps of S1, hydrolyzing at least one protein containing the immunoactive peptides through hydrolase in order to obtain a peptide library formed by the immunoactive peptide, wherein peptide sequences of polypeptides in the peptide library are obtained through a mass spectrometry technology; S2, screening out the peptide sequences strongly bound with MHC class II molecules; S3, synthesizing the peptide sequences screened out in S2; and S4, constructing an LPS-induced cell model for verifying the immune activity of the polypeptides synthesized by S3. According to the method, the complex identification of the subsequent peptide sequences and binding sites can be avoided, and thepolypeptides combined with the MHC class II molecules can be directly obtained; and furthermore, the reactogenicity and the immunogenicity of binding of the polypeptides and MHC class II molecules can be simultaneously described, so that data is more complete, a process of obtaining the polypeptides is more rapid, and the efficiency is higher.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Isolated nucleic acid molecules which encode peptides which bind to MHC class II molecules, such as HLA-DR53
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +2
Inhibitors of antigen presentation by MHC class II molecules and methods of use thereof
The present invention relates to compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing such compounds and methods for their use. In particular, the compounds of the invention are useful for the treatment or prevention of diseases associated with T cell proliferation such as autoimmune diseases and disorders.
Owner:PROVID PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com