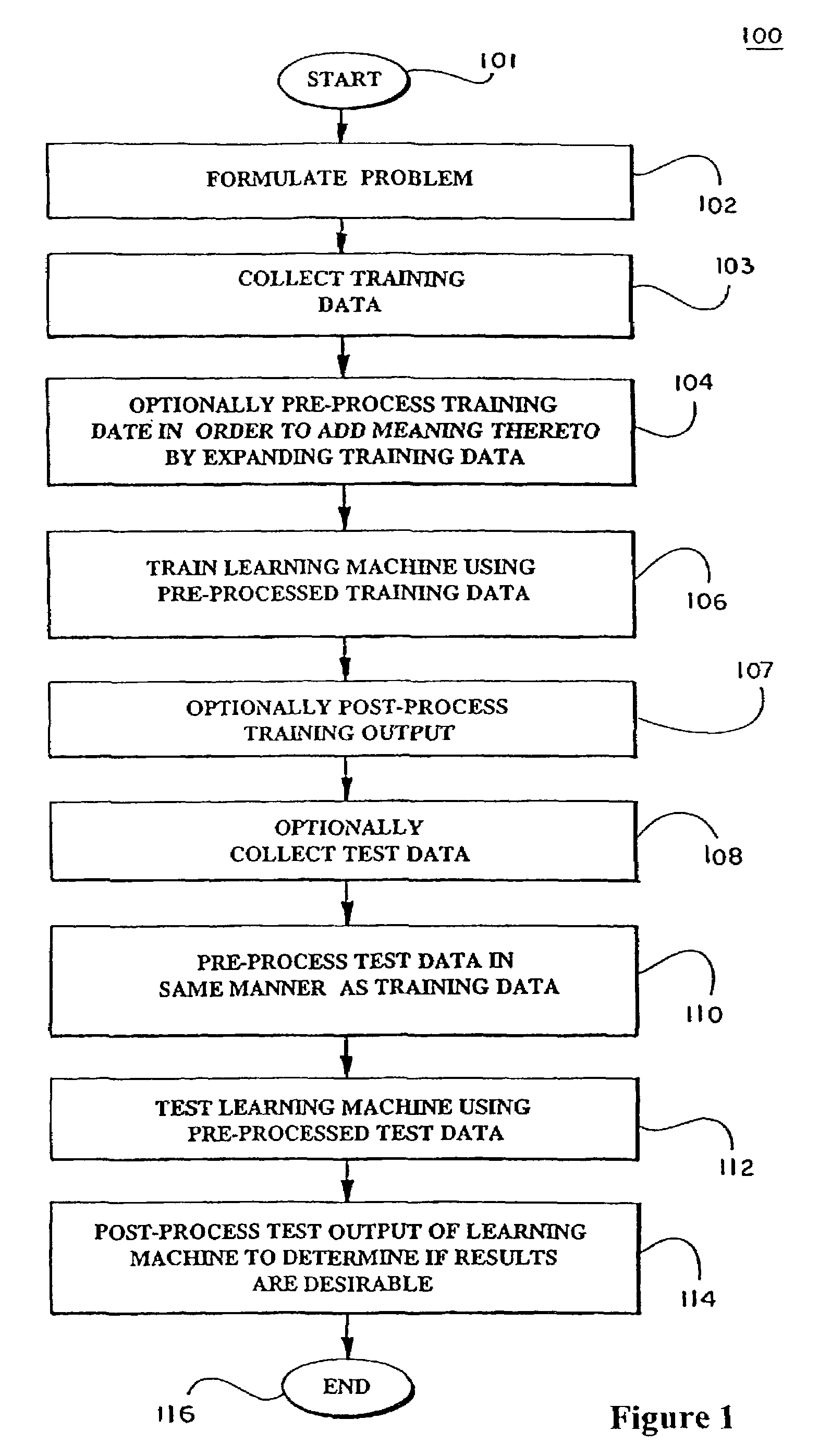
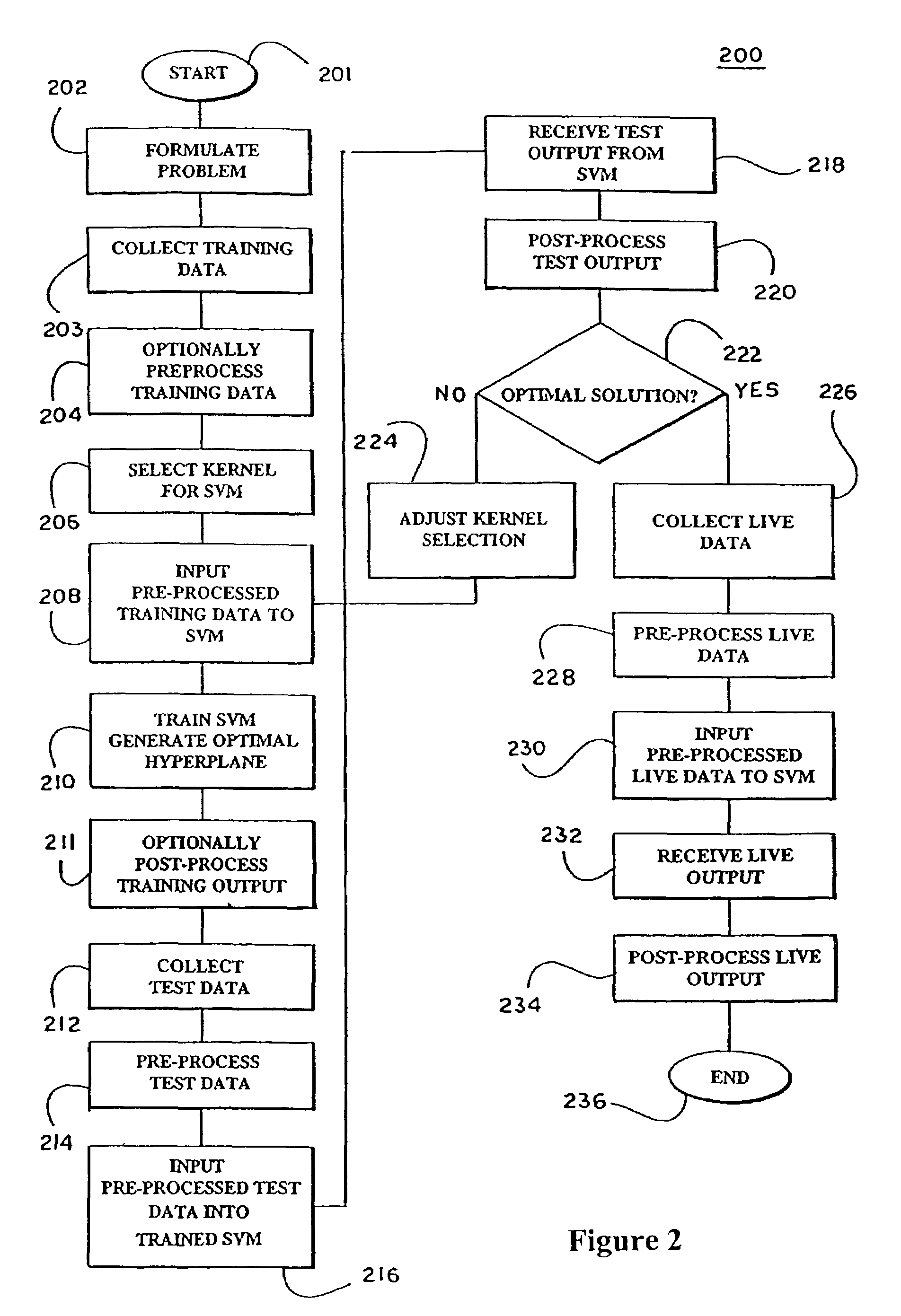
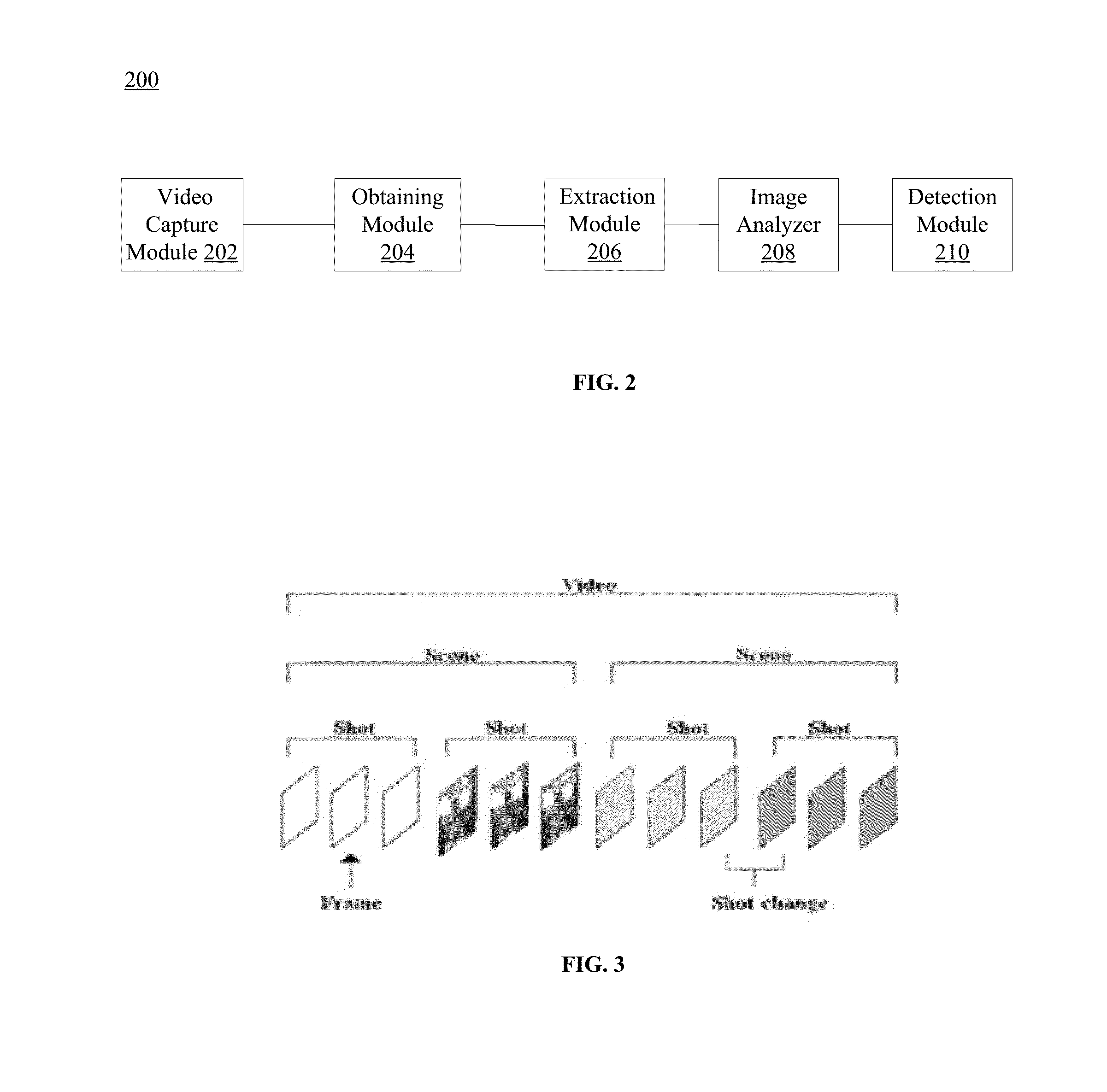
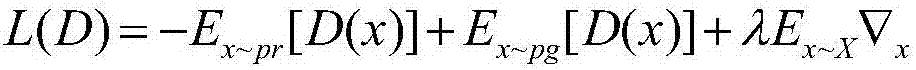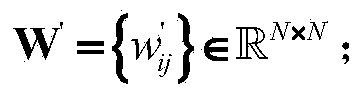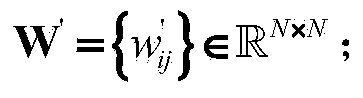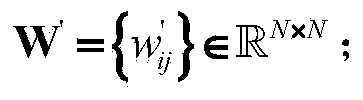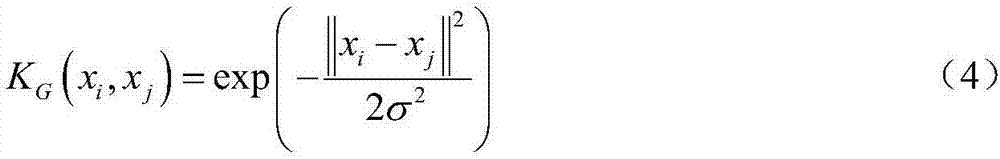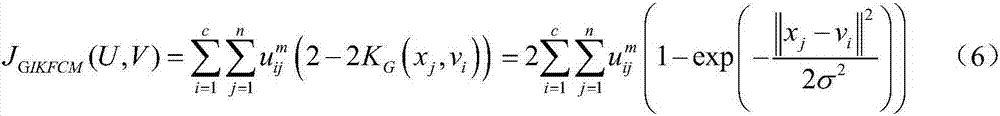Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Kernel method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
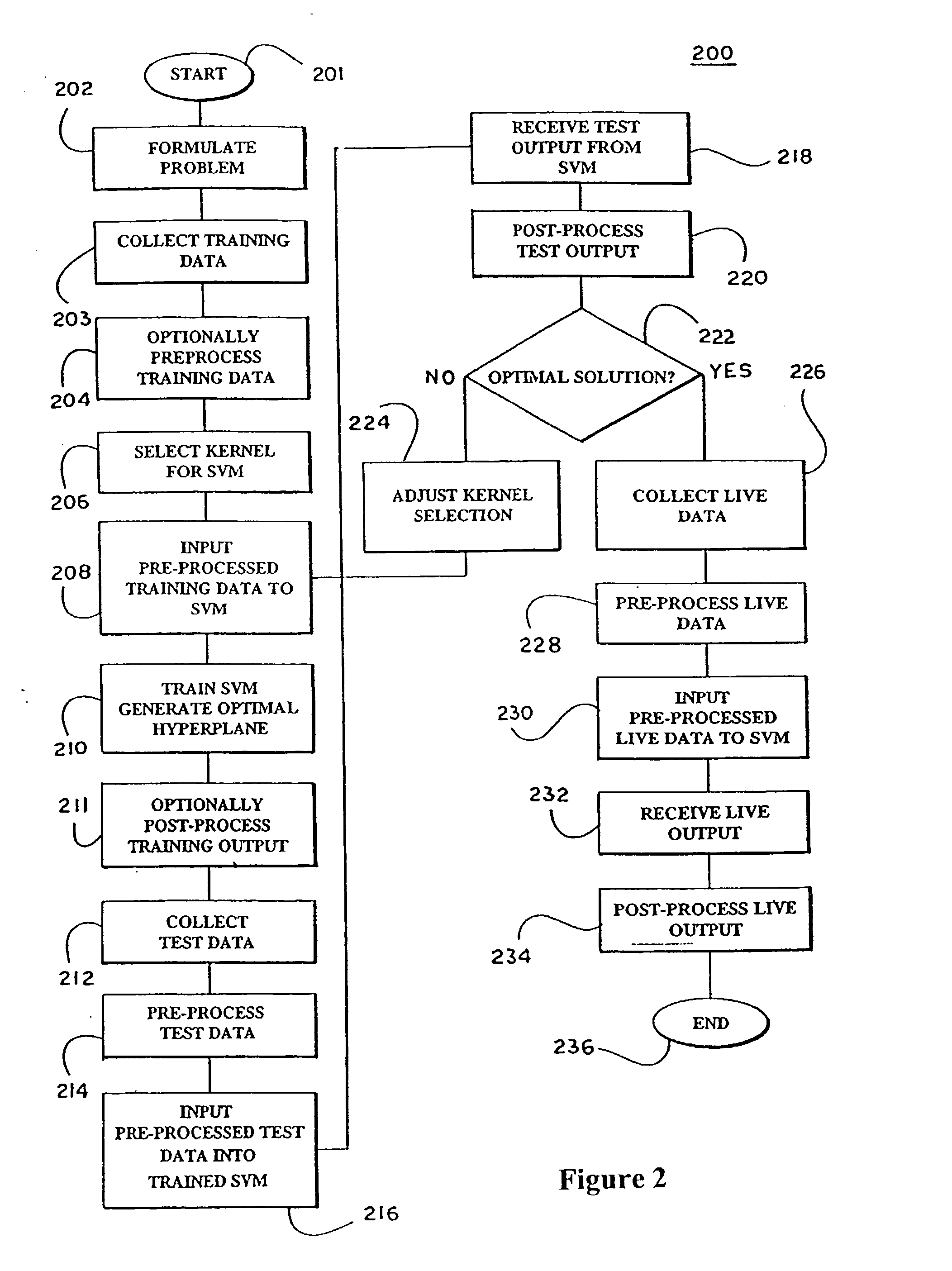
In machine learning, kernel methods are a class of algorithms for pattern analysis, whose best known member is the support vector machine (SVM). The general task of pattern analysis is to find and study general types of relations (for example clusters, rankings, principal components, correlations, classifications) in datasets. For many algorithms that solve these tasks, the data in raw representation have to be explicitly transformed into feature vector representations via a user-specified feature map: in contrast, kernel methods require only a user-specified kernel, i.e., a similarity function over pairs of data points in raw representation.
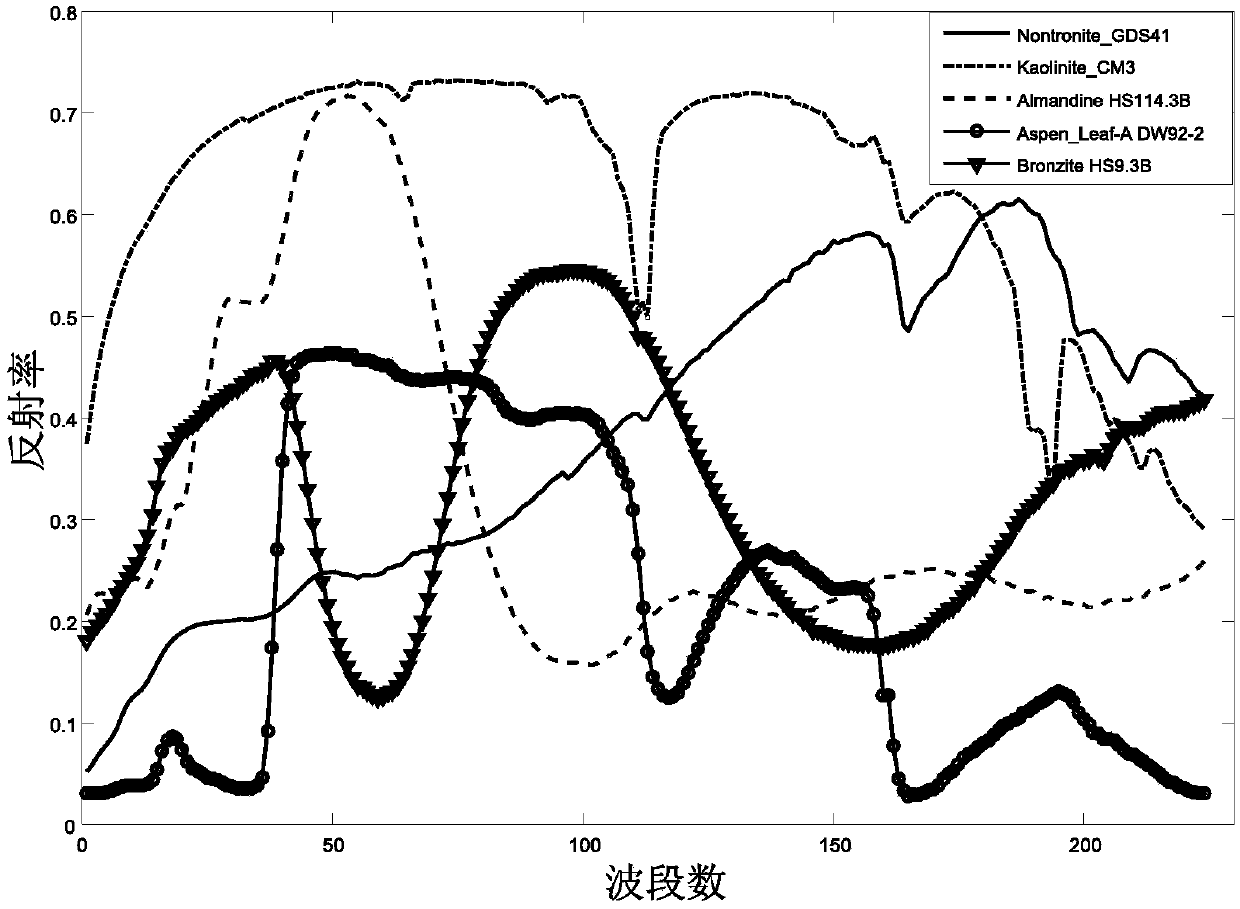
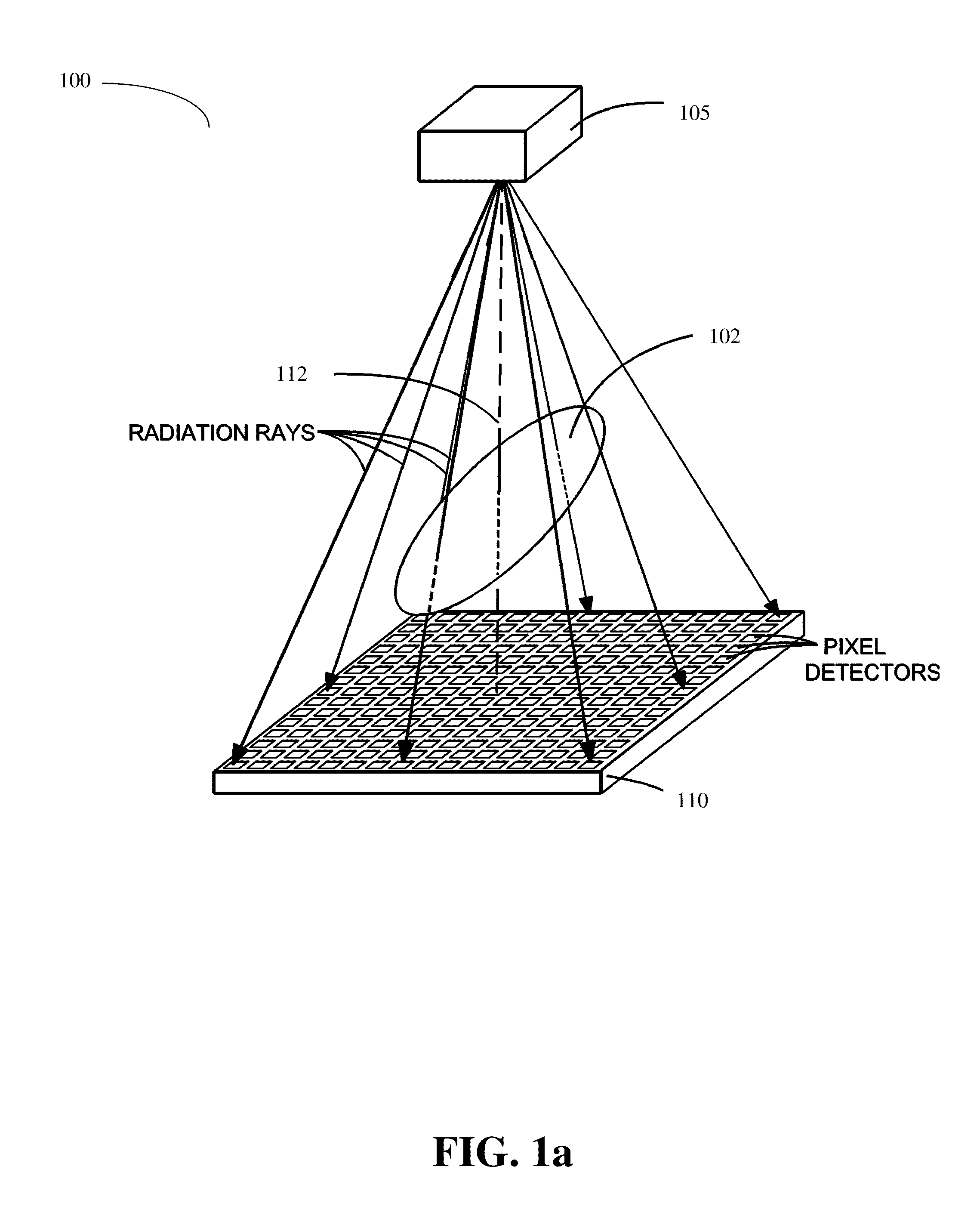
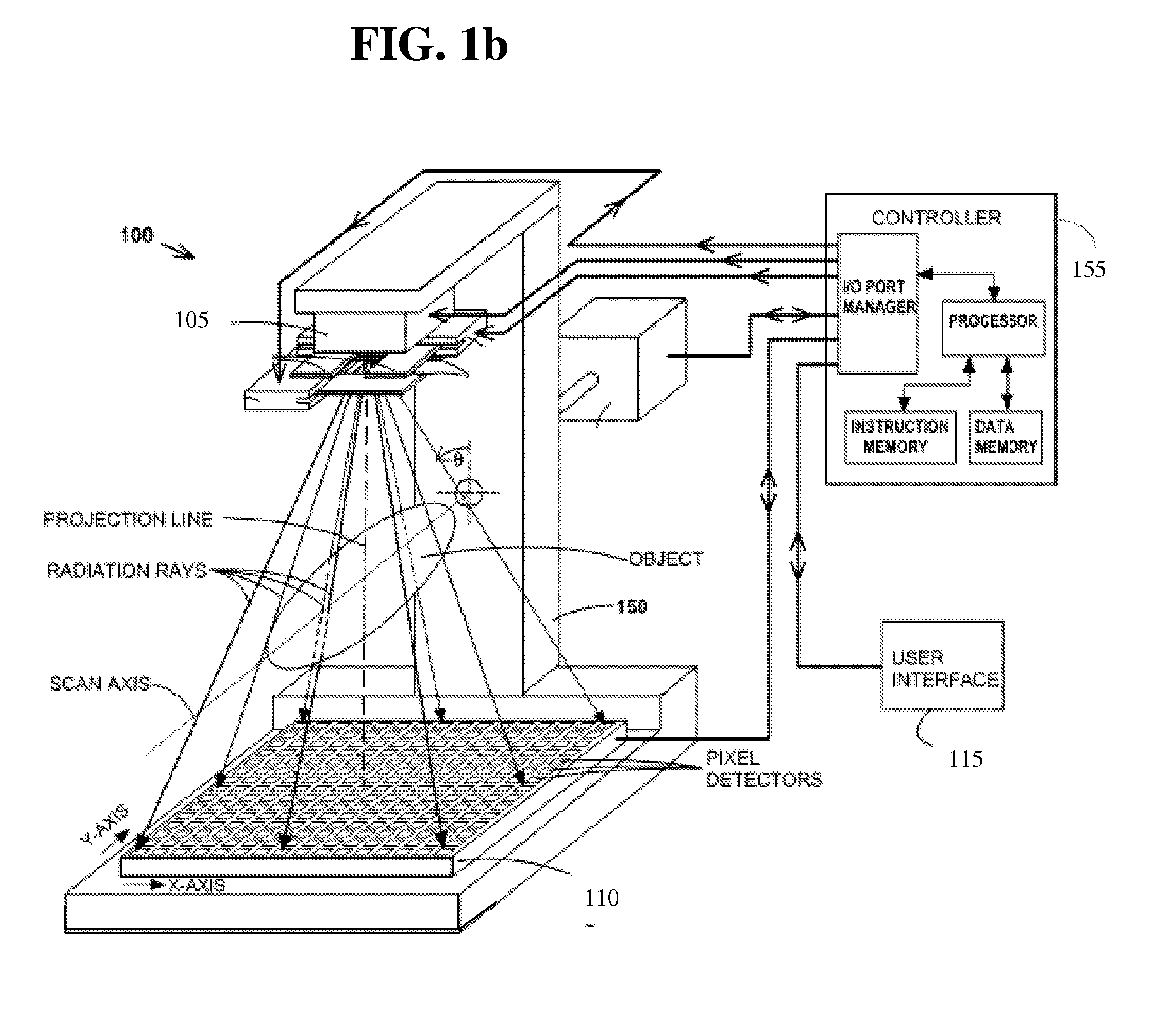
Kernels and kernel methods for spectral data
InactiveUS20050228591A1Enhancing knowledge discoveryBroaden their knowledgeDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpectrum analyzerKernel method
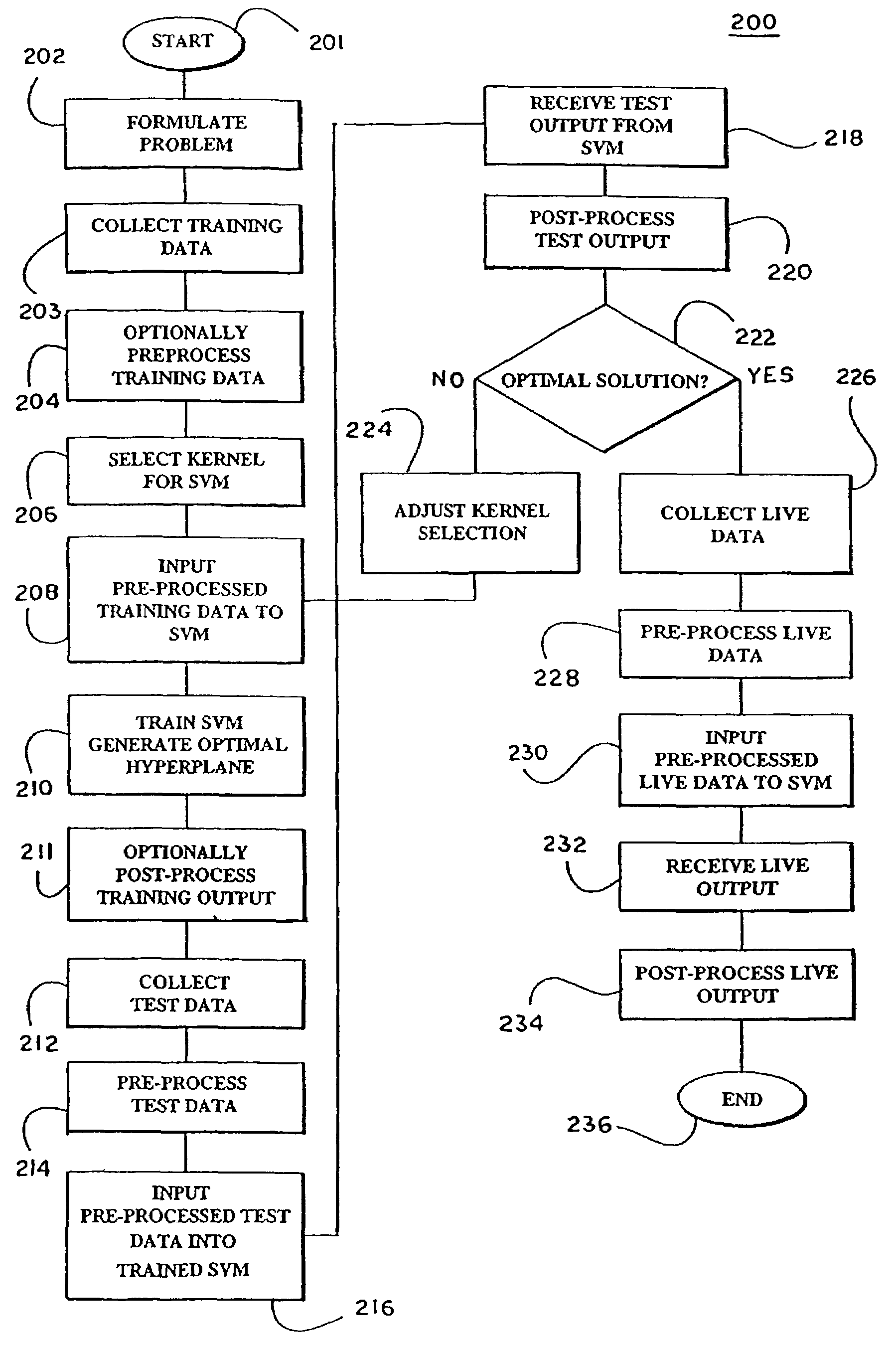
Support vector machines are used to classify data contained within a structured dataset such as a plurality of signals generated by a spectral analyzer. The signals are preprocessed to ensure alignment of peaks across the spectra. Similarity measures are constructed to provide a basis for comparison of pairs of samples of the signal. A support vector machine is trained to discriminate between different classes of the samples. to identify the most predictive features within the spectra. In a preferred embodiment feature selection is performed to reduce the number of features that must be considered.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Use of machine learning for classification of magneto cardiograms
InactiveUS20070167846A1Exceeding quality of classificationCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisMagnetocardiographyKernel method
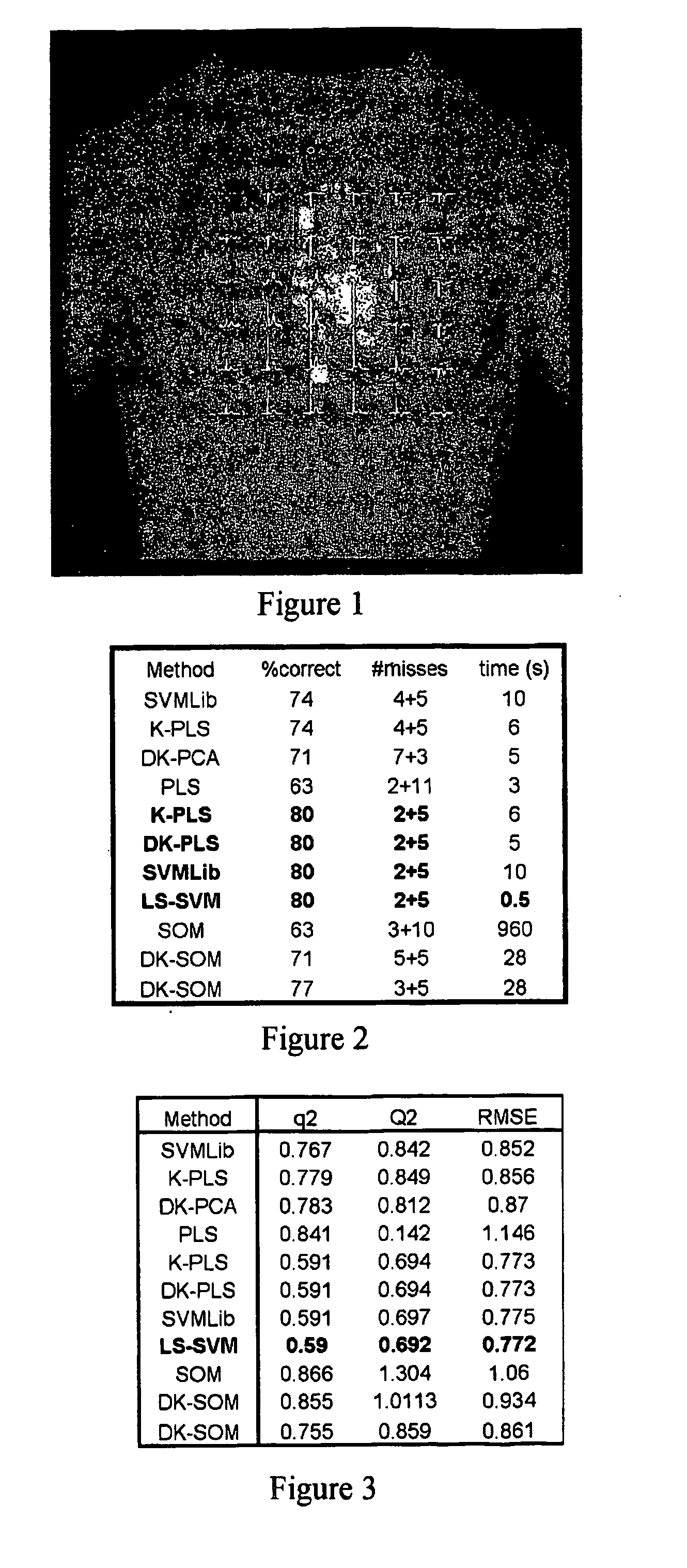
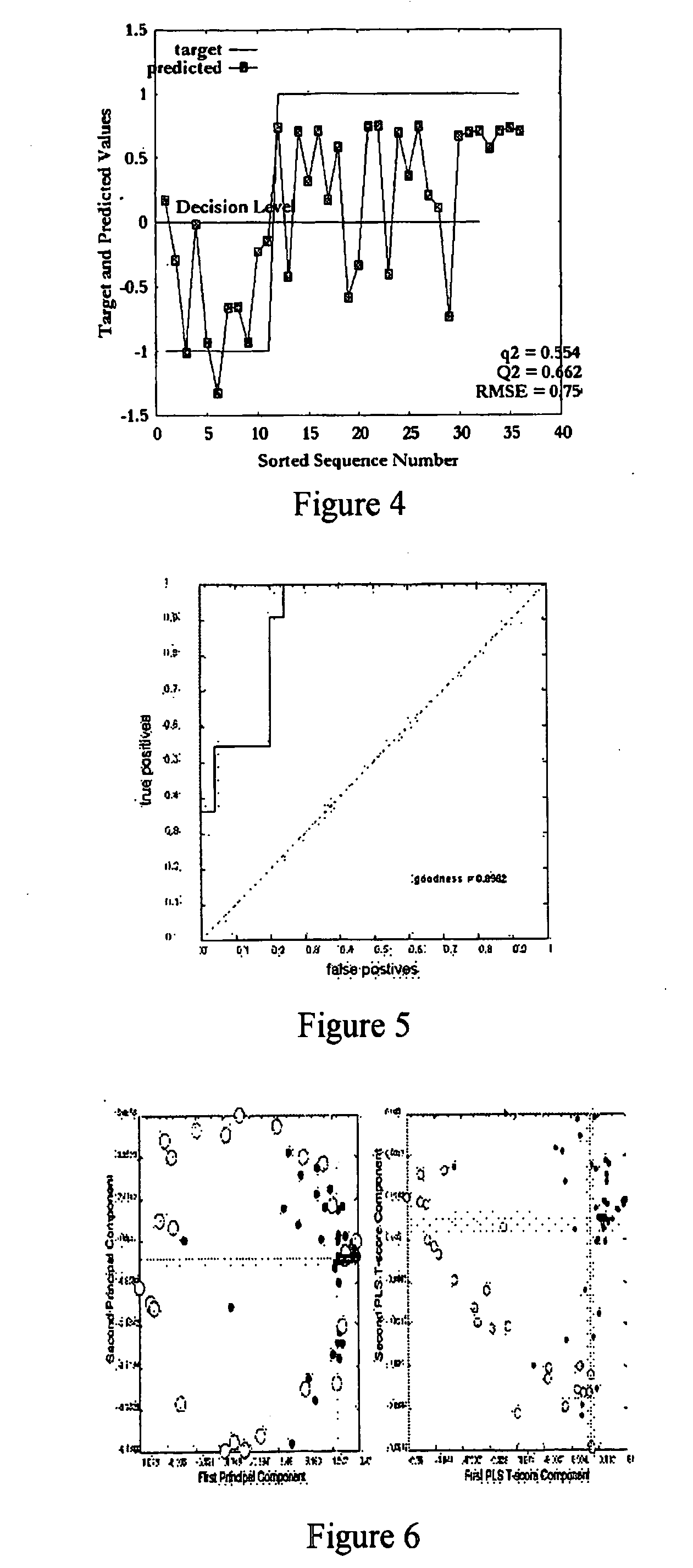
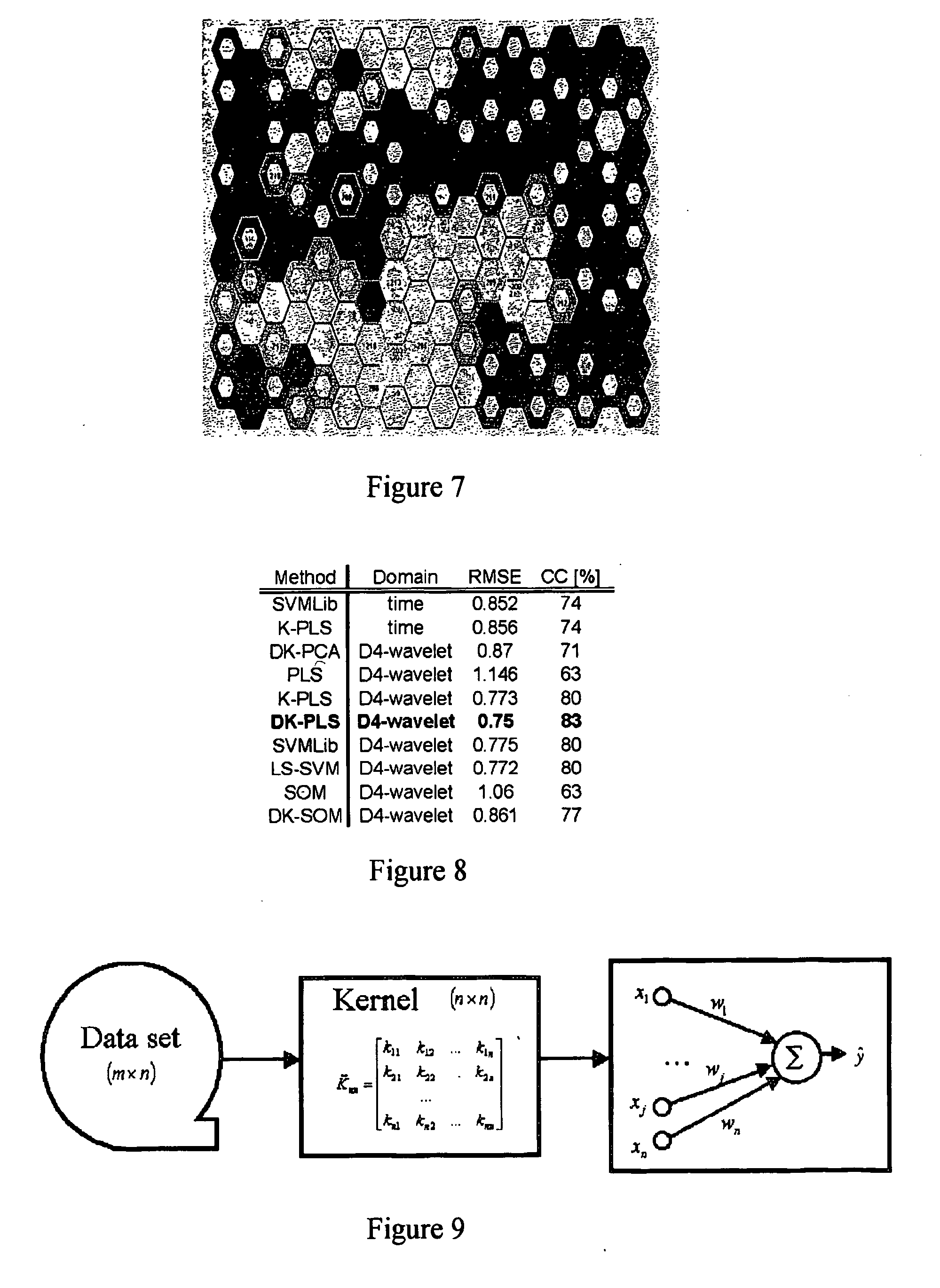
The use of machine learning for pattern recognition in magnetocardiography (MCG) that measures magnetic fields emitted by the electrophysiological activity of the heart is disclosed herein. Direct kernel methods are used to separate abnormal MCG heart patterns from normal ones. For unsupervised learning, Direct Kernel based Self-Organizing Maps are introduced. For supervised learning Direct Kernel Partial Least Squares and (Direct) Kernel Ridge Regression are used. These results are then compared with classical Support Vector Machines and Kernel Partial Least Squares. The hyper-parameters for these methods are tuned on a validation subset of the training data before testing. Also investigated is the most effective pre-processing, using local, vertical, horizontal and two-dimensional (global) Mahanalobis scaling, wavelet transforms, and variable selection by filtering. The results, similar for all three methods, were encouraging, exceeding the quality of classification achieved by the trained experts. Thus, a device and associated method for classifying cardiography data is disclosed, comprising applying a kernel transform to sensed data acquired from sensors sensing electromagnetic heart activity, resulting in transformed data, prior to classifying the transformed data using machine learning.
Owner:CARDIOMAG IMAGING
Kernels and kernel methods for spectral data
InactiveUS7617163B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel methodSpectrum analyzer
Support vector machines are used to classify data contained within a structured dataset such as a plurality of signals generated by a spectral analyzer. The signals are pre-processed to ensure alignment of peaks across the spectra. Similarity measures are constructed to provide a basis for comparison of pairs of samples of the signal. A support vector machine is trained to discriminate between different classes of the samples. to identify the most predictive features within the spectra. In a preferred embodiment feature selection is performed to reduce the number of features that must be considered.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
High-speed automatic multi-object tracking method and system with kernelized correlation filters
ActiveUS20160239982A1Increase speedError minimizationImage enhancementImage analysisCorrelation filterMulti target tracking
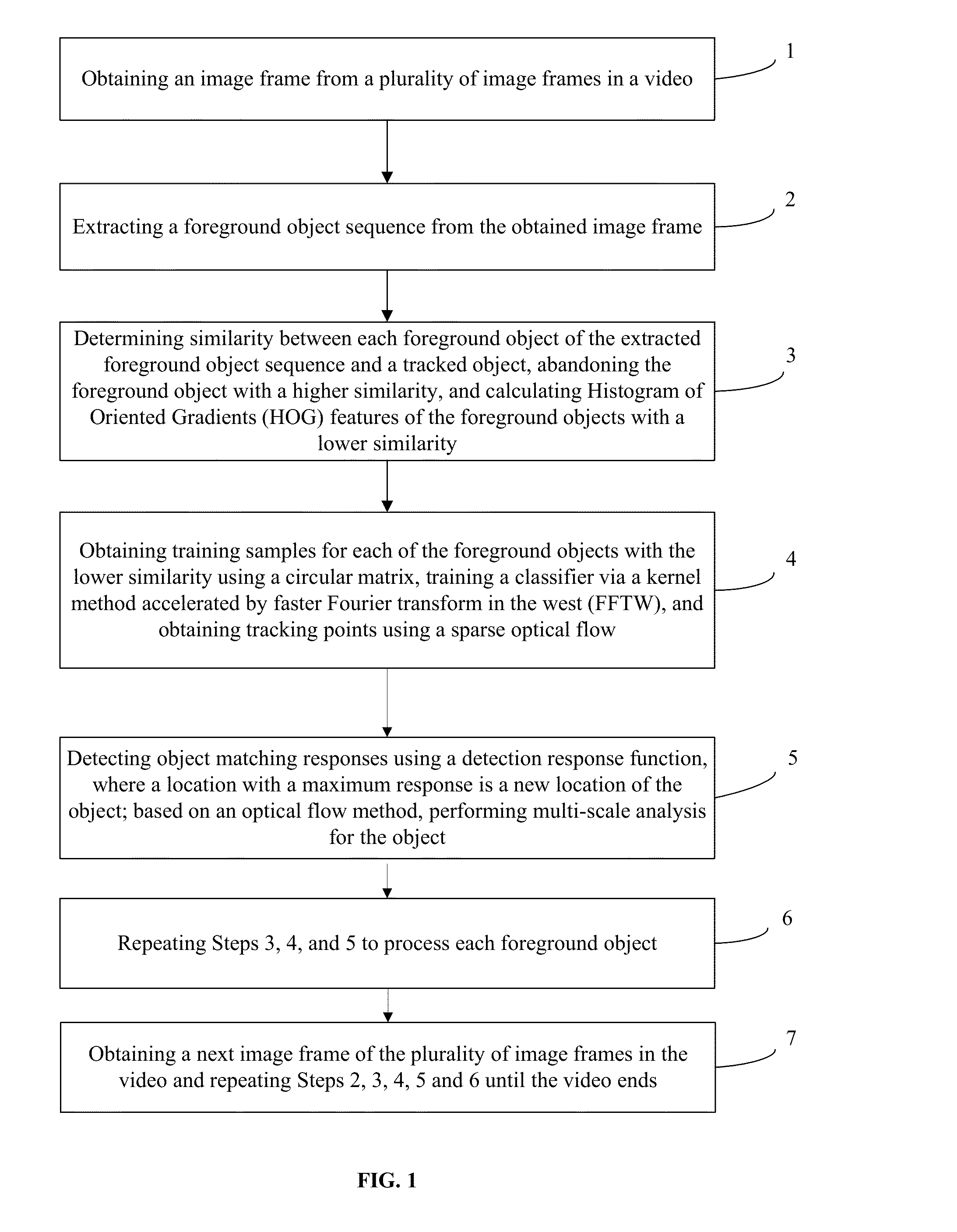
A high-speed automatic multi-object tracking method with kernelized correlation filters is provided. The method includes obtaining an image frame from a plurality of image frames in a video, extracting a foreground object sequence from the obtained image frame, and determining similarity between each foreground object of the extracted foreground object sequence and a tracked object. The method also includes calculating HOG features of the foreground objects with a lower similarity, obtaining training samples for each of the foreground objects with the lower similarity using a circular matrix, obtaining a classifier via a kernel method accelerated by FFTW, and obtaining tracking points using a sparse optical flow. Further, the method includes detecting object matching responses using a detection response function, performing multi-scale analysis for the object based on an optical flow method, and processing a next image frame of the plurality of image frames in the video until the video ends.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENGHUI LIGHTING
System and method for clustering content according to similarity
ActiveUS20110302163A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesIndividual itemDistance matrix
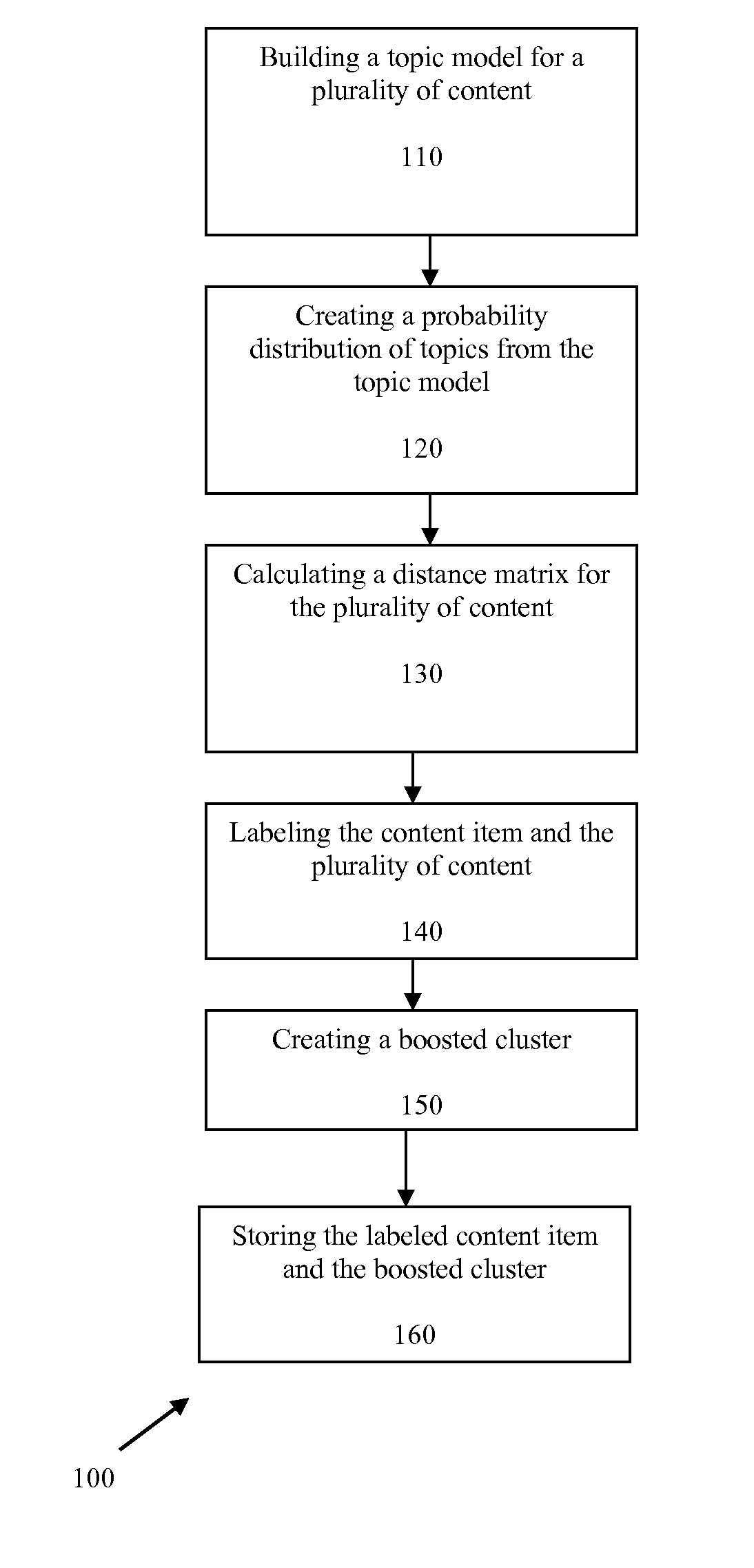
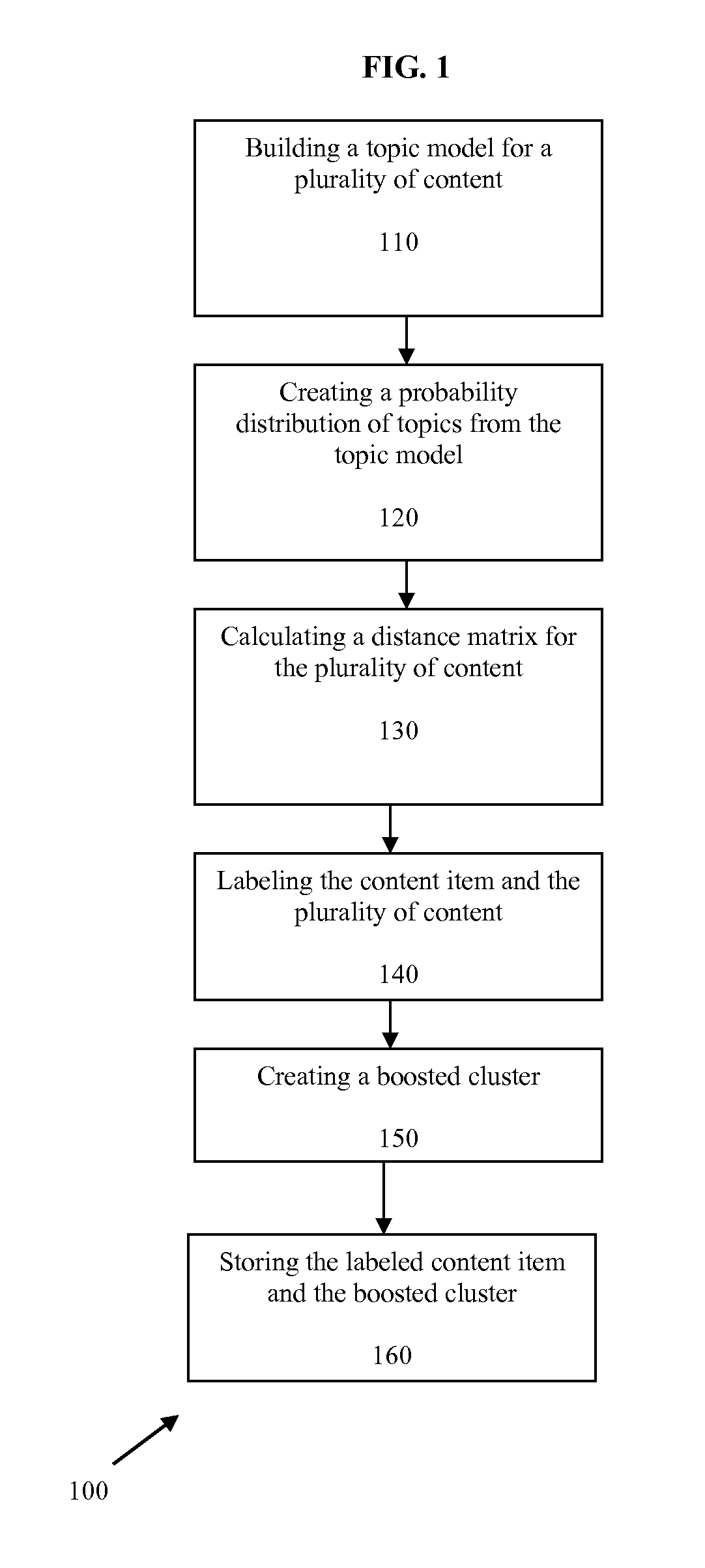
Systems and methods for clustering content according to similarity are provided that identify and group similar content using a set of tags associated with the content. A topic model of a group of content is built, producing a probability distribution of topic membership for the content. Individual items of content are then clustered using a clustering algorithm, and a distance matrix from the probability distribution is built. Based on the distance matrix, individual items of content are labeled as “must-link” or “cannot-link” pairs with the group of content. The topic model is then embedded into successively smaller dimensions using a kernel method, until the clustering is stable with respect to both the behavioral and content domains.
Owner:CBS INTERACTIVE INC
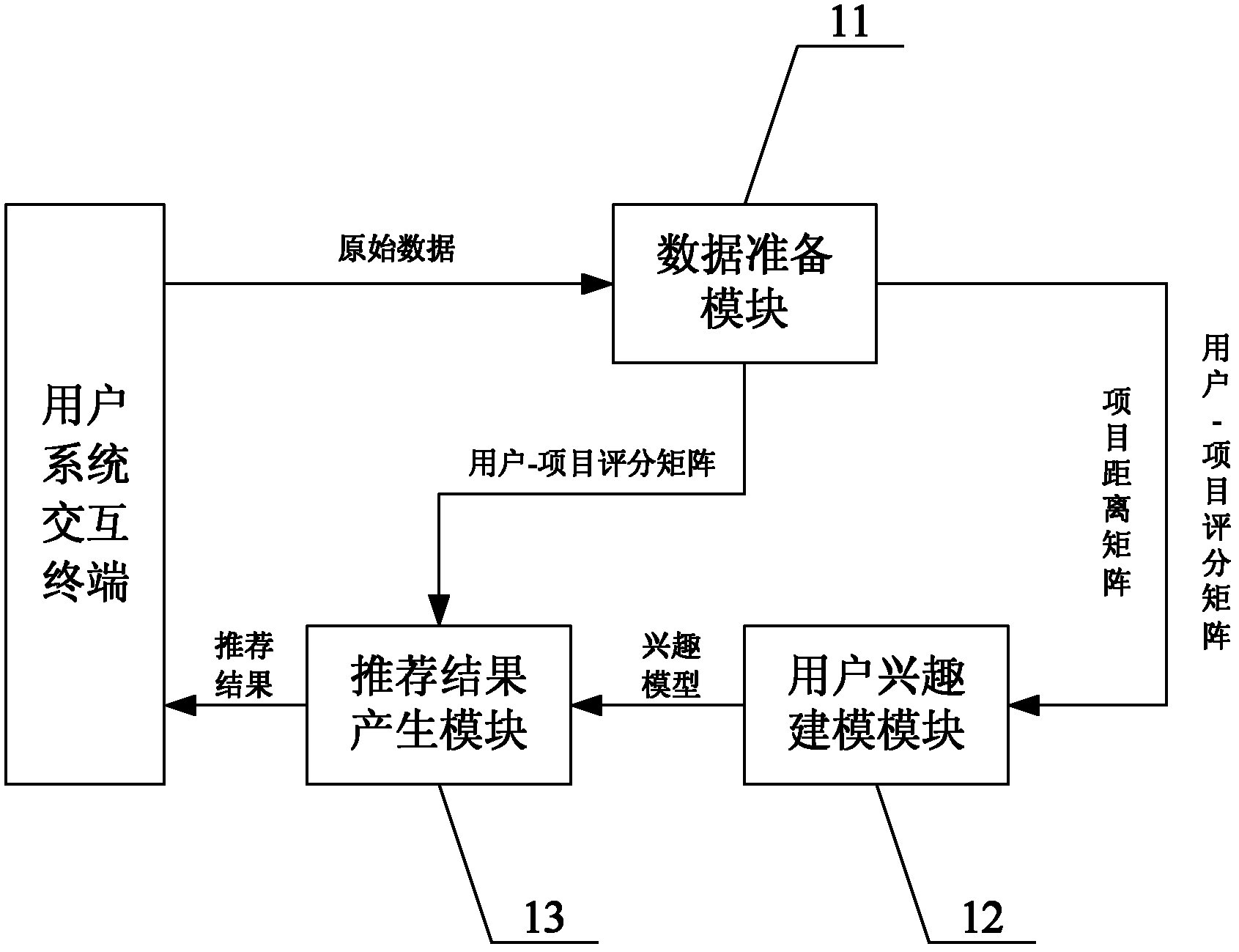
Kernel method-based collaborative filtering recommendation system and method
InactiveCN102609533ASimilarity estimationHigh expressionSpecial data processing applicationsDistance matrixOriginal data
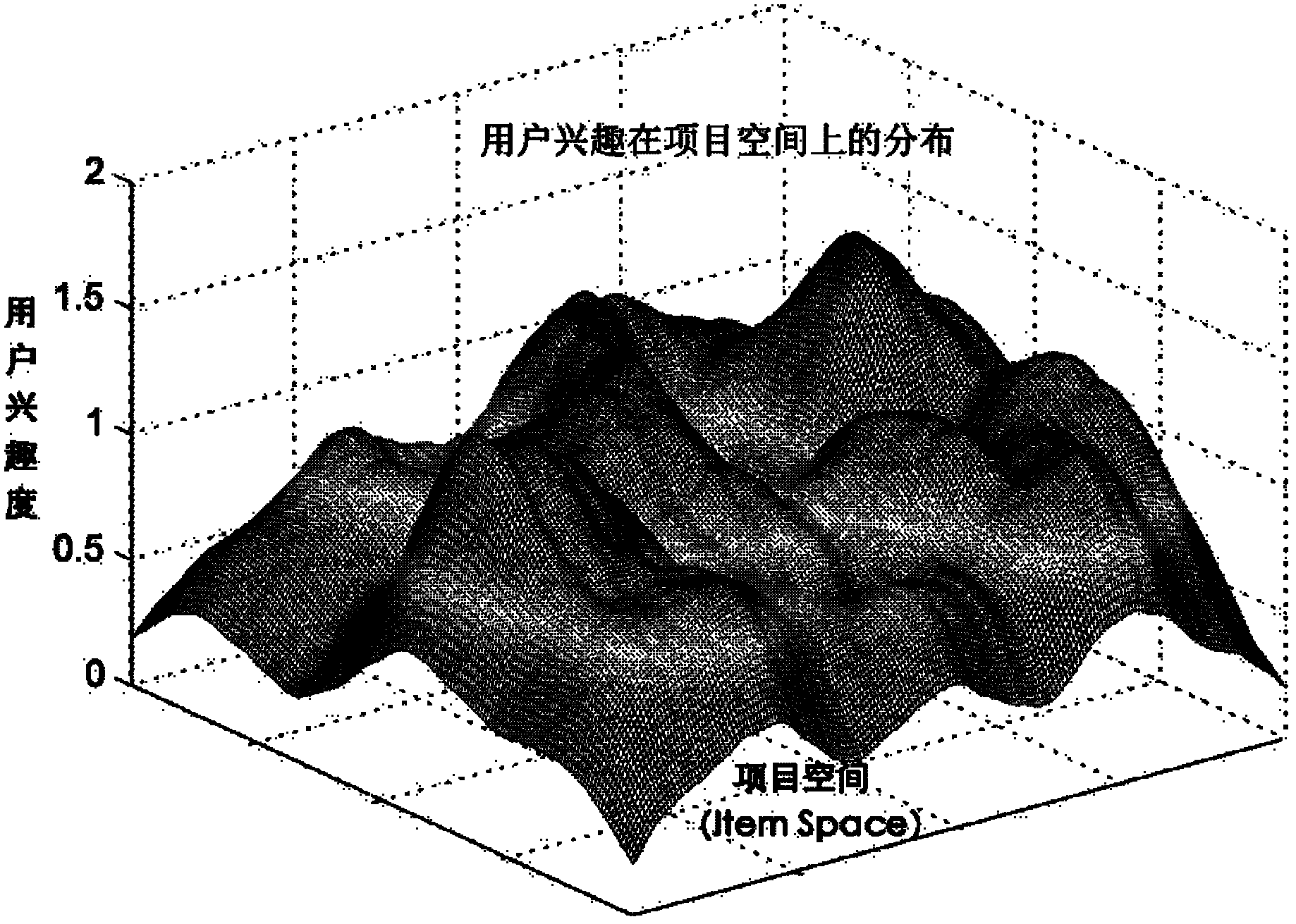
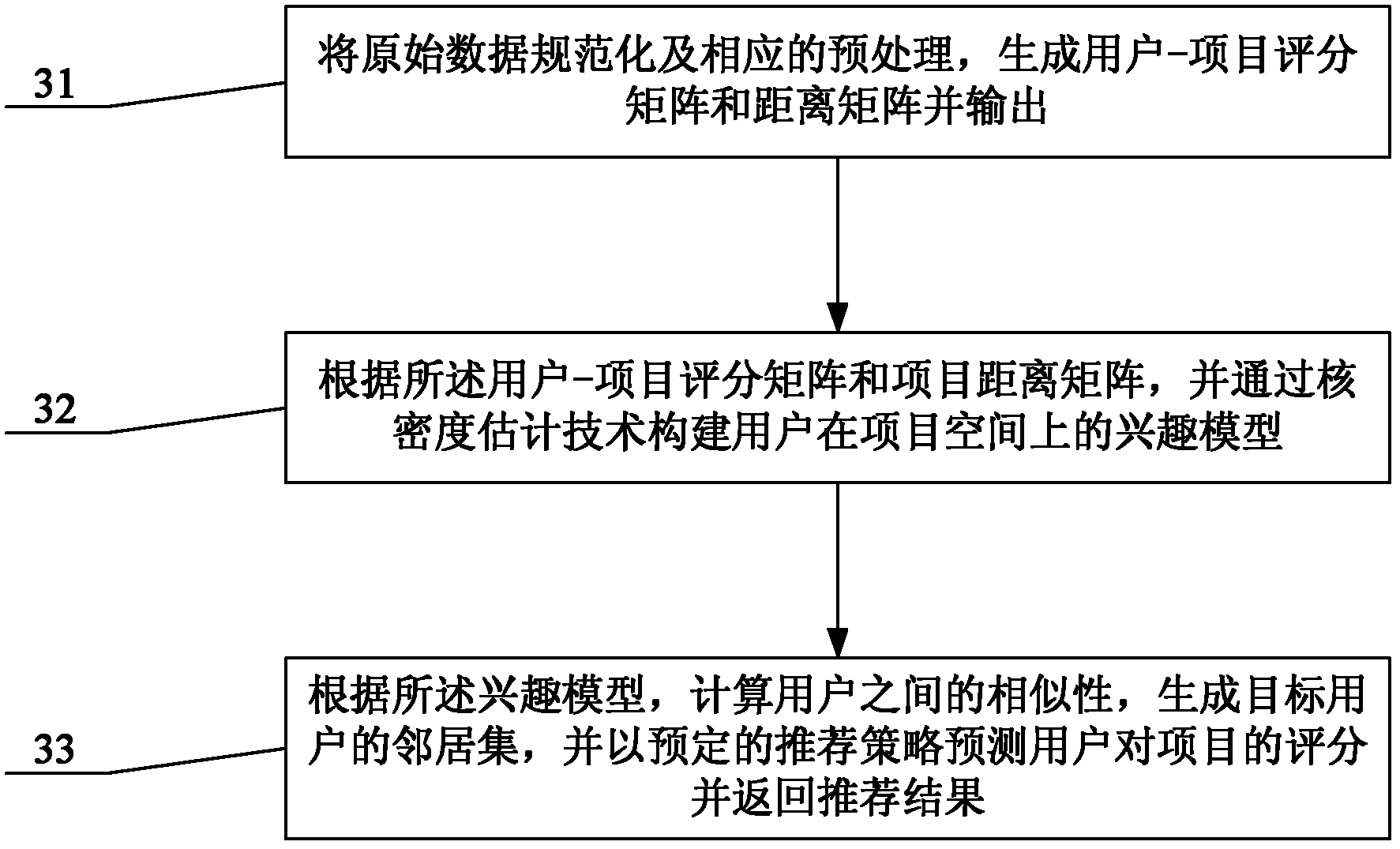
The invention provides a kernel method-based collaborative filtering recommendation system and a kernel method-based collaborative filtering recommendation method. The corresponding system comprises a data preparation module which is used for standardizing the original data and carrying out corresponding preprocessing, generating a user-project rating matrix and a project distance matrix to output; a user interest modeling module which is used for constructing an interest model for a user on a project space according to the user-project rating matrix and the project distance matrix as well as a kernel density estimation technology; and a recommendation result generation module which is used for computing the similarities among the users according to the interest model, generating a neighbor set of a target user, and predicting a score of the project rated by the user according to a predetermined recommendation strategy and returning the recommendation result. Through the recommendation system and the recommendation method provided by the invention, the user interest model can be better presented, the user similarity in the practical application is estimated more accurately, the performance of the recommendation system can be promoted considerably, and more stable recommendation result can be obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and system for matching MR image feature points before and after nonlinear deformation of biological tissue
ActiveCN106530338AReduce in quantityReduce complexityImage enhancementImage analysisNonlinear deformationKernel method
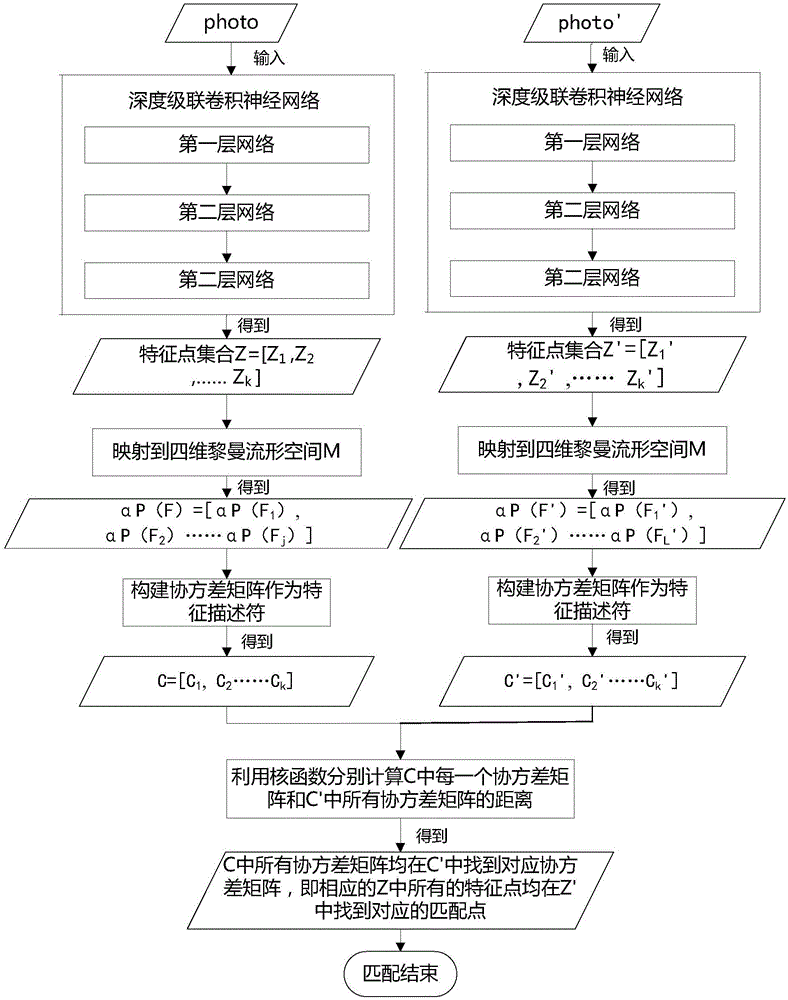
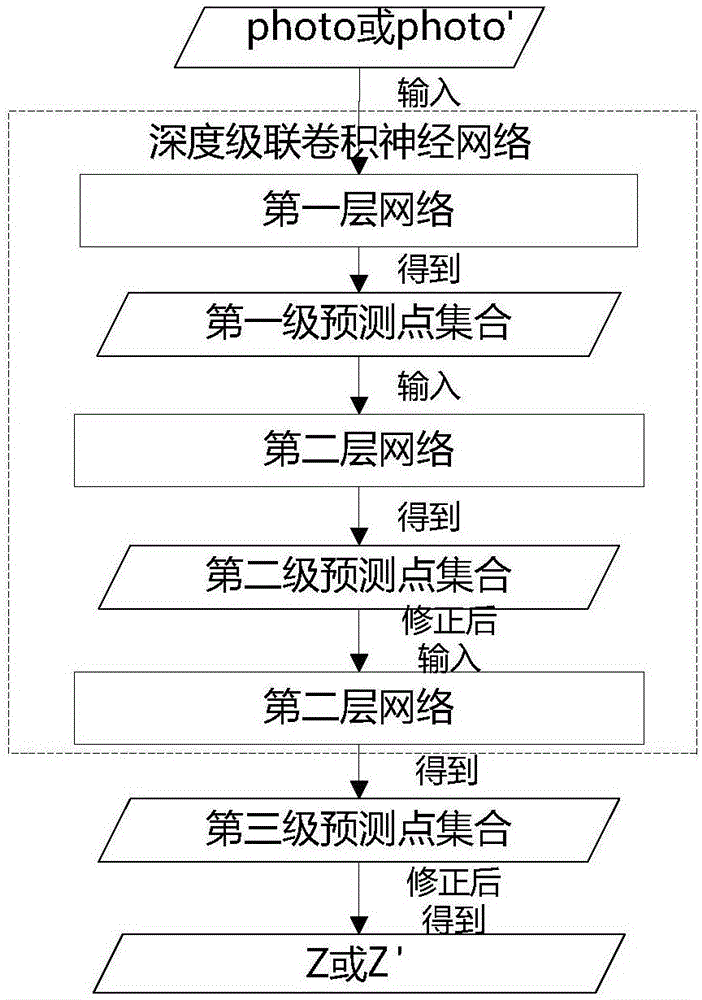
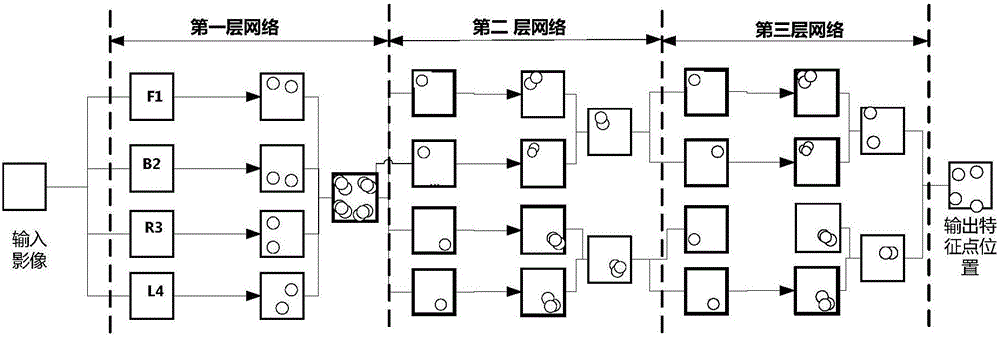
The present invention relates to a method and a system for matching MR image feature points before and after the nonlinear deformation of a biological tissue. According to the technical scheme of the invention, a feature point automatic detection method based on a depth-cascaded convolutional neural network is provided. According to the method, firstly, a general region of feature points is obtained through the first layer of the depth convolutional network. Secondly, the position of a target feature point is approximated step by step in the second and third layers of the cascade convolutional network, so that the detection rate of feature points is further improved. The method aims to solve the problem in the prior art that the feature point distinguishing ability is reduced due to the image nonlinear deformation of existing feature point descriptors. In this way, a Riemannian manifold is combined with the kernel method to construct a nonlinear deformation feature point descriptor for robustness. The three-dimensional feature points of a magnetic resonance image are mapped into a four-dimensional Riemannian manifold space. Meanwhile, the feature points are further mapped into a higher-dimensional Hilbert space based on the kernel method, so that a richer description of data distribution is obtained. Meanwhile, a real geometric distance between feature points is obtained, so that the feature points are matched.
Owner:WUHAN TEXTILE UNIV
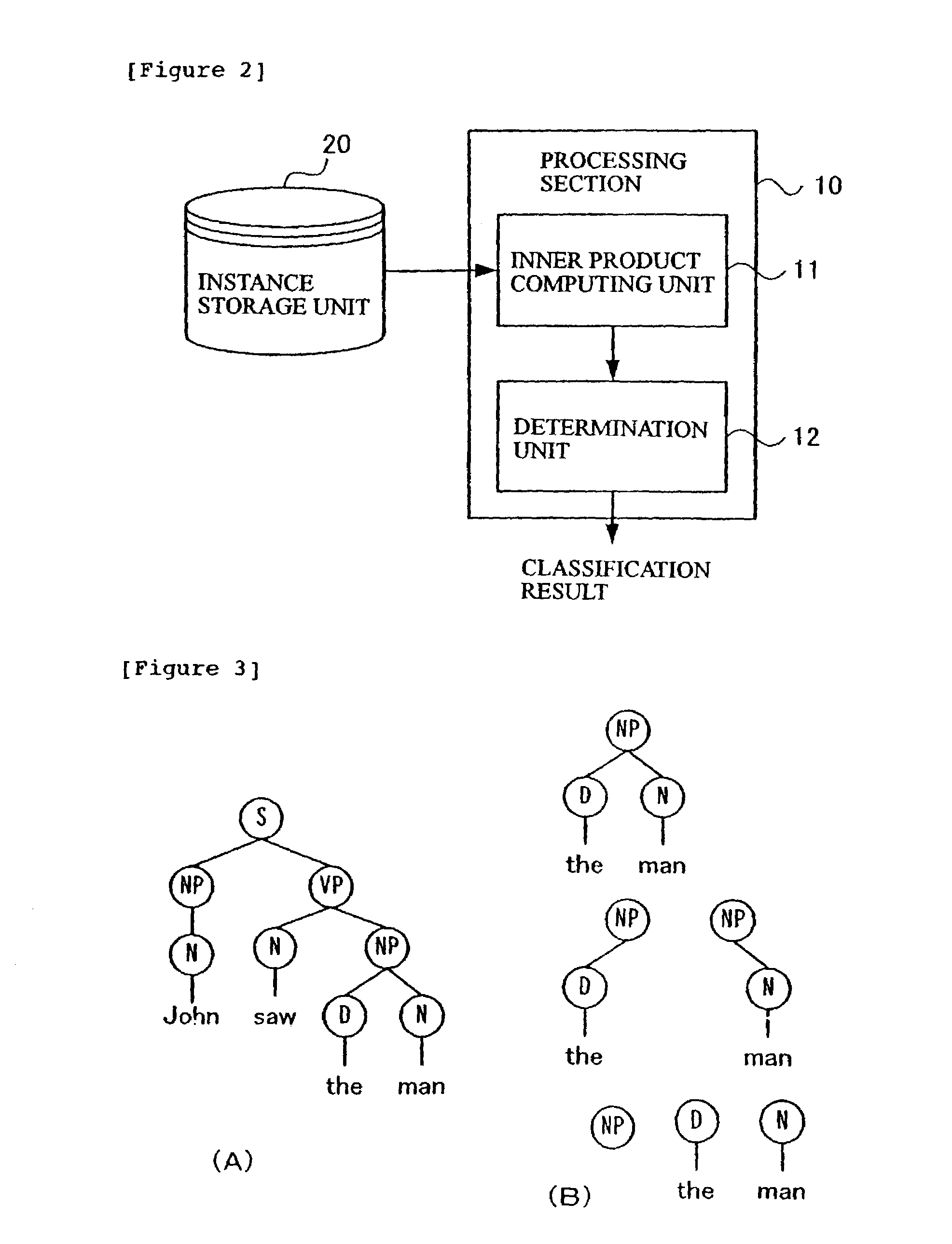
Classification method of labeled ordered trees using support vector machines
InactiveUS7130833B2Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionSemi-structured dataKernel method
To achieve classification of semistructured data with a Kernel method for labeled ordered trees, instances having a labeled ordered tree structure are input and their inner product is computed, the result of which is used for classification learning of the instances. In the inner product computation, a sum of matches is computed for descendant nodes of non-leaf nodes of the labeled ordered trees by applying dynamic programming based on correspondence in which order of the nodes is maintained.
Owner:IBM CORP
Use of machine learning for classification of magneto cardiograms
InactiveUS7742806B2Medical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel methodMagnetocardiography
The use of machine learning for pattern recognition in magnetocardiography (MCG) that measures magnetic fields emitted by the electrophysiological activity of the heart is disclosed herein. Direct kernel methods are used to separate abnormal MCG heart patterns from normal ones. For unsupervised learning, Direct Kernel based Self-Organizing Maps are introduced. For supervised learning Direct Kernel Partial Least Squares and (Direct) Kernel Ridge Regression are used. These results are then compared with classical Support Vector Machines and Kernel Partial Least Squares. The hyper-parameters for these methods are tuned on a validation subset of the training data before testing. Also investigated is the most effective pre-processing, using local, vertical, horizontal and two-dimensional (global) Mahanalobis scaling, wavelet transforms, and variable selection by filtering. The results, similar for all three methods, were encouraging, exceeding the quality of classification achieved by the trained experts. Thus, a device and associated method for classifying cardiography data is disclosed, comprising applying a kernel transform to sensed data acquired from sensors sensing electromagnetic heart activity, resulting in transformed data, prior to classifying the transformed data using machine learning.
Owner:CARDIOMAG IMAGING
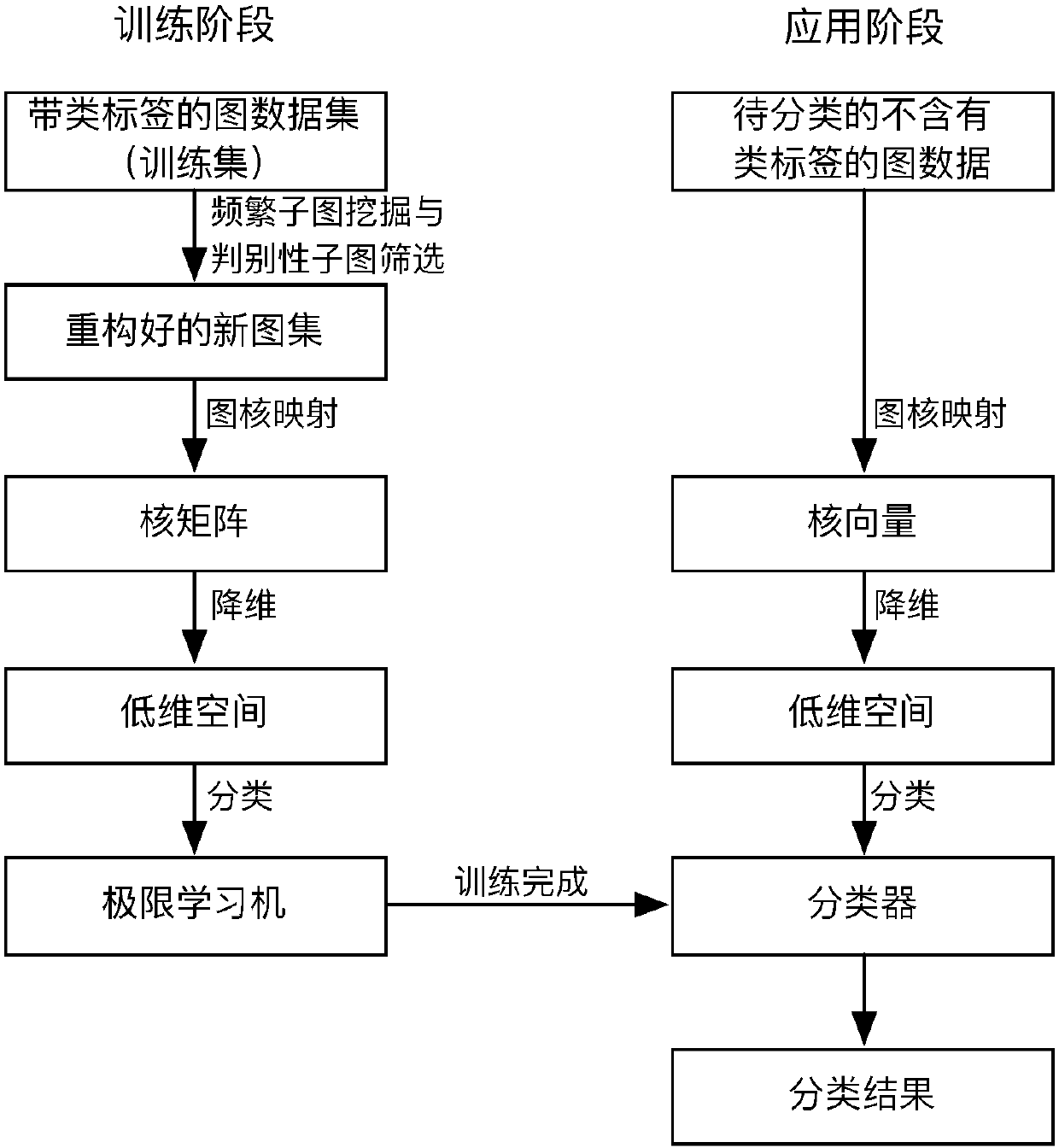
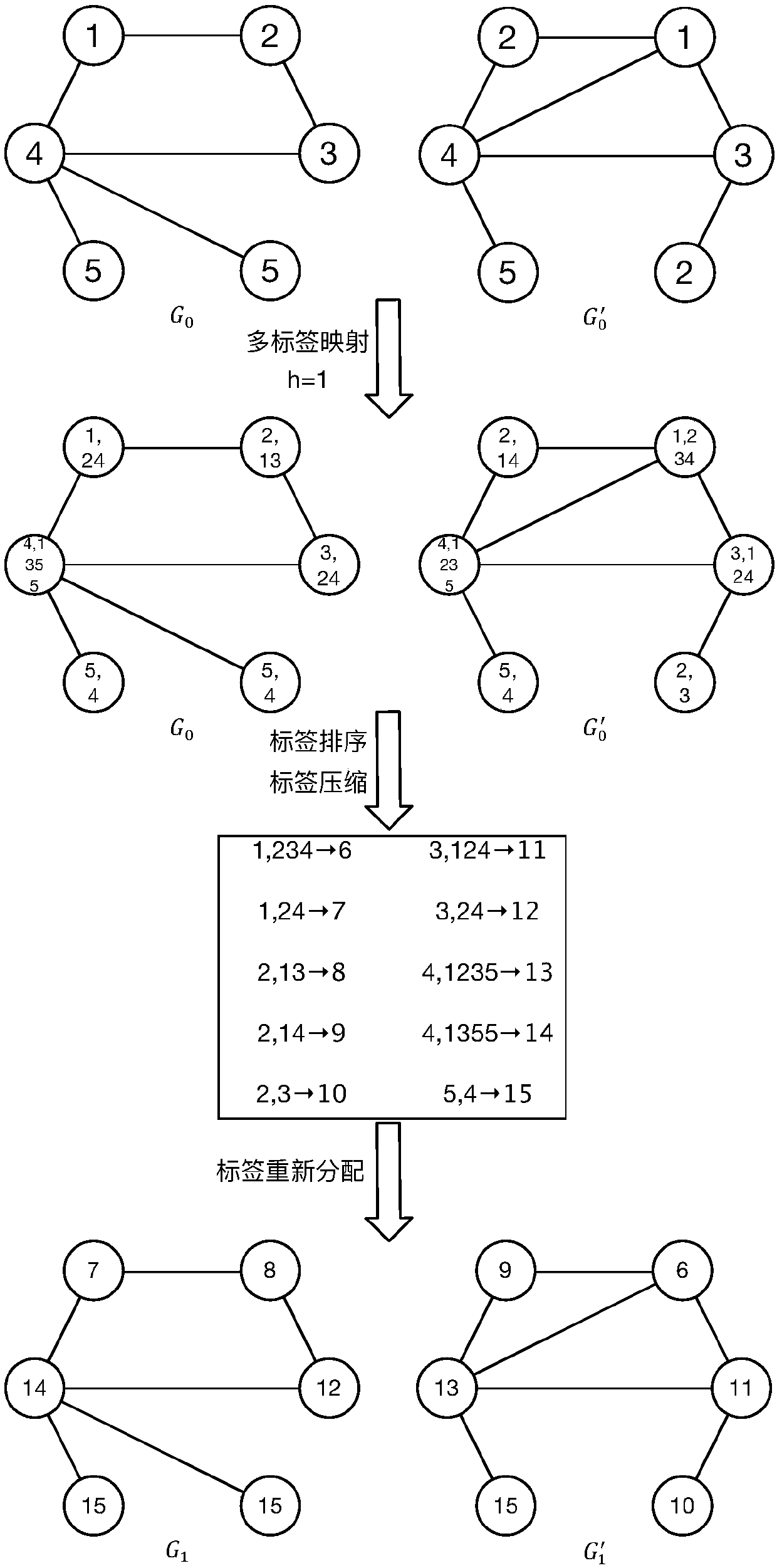
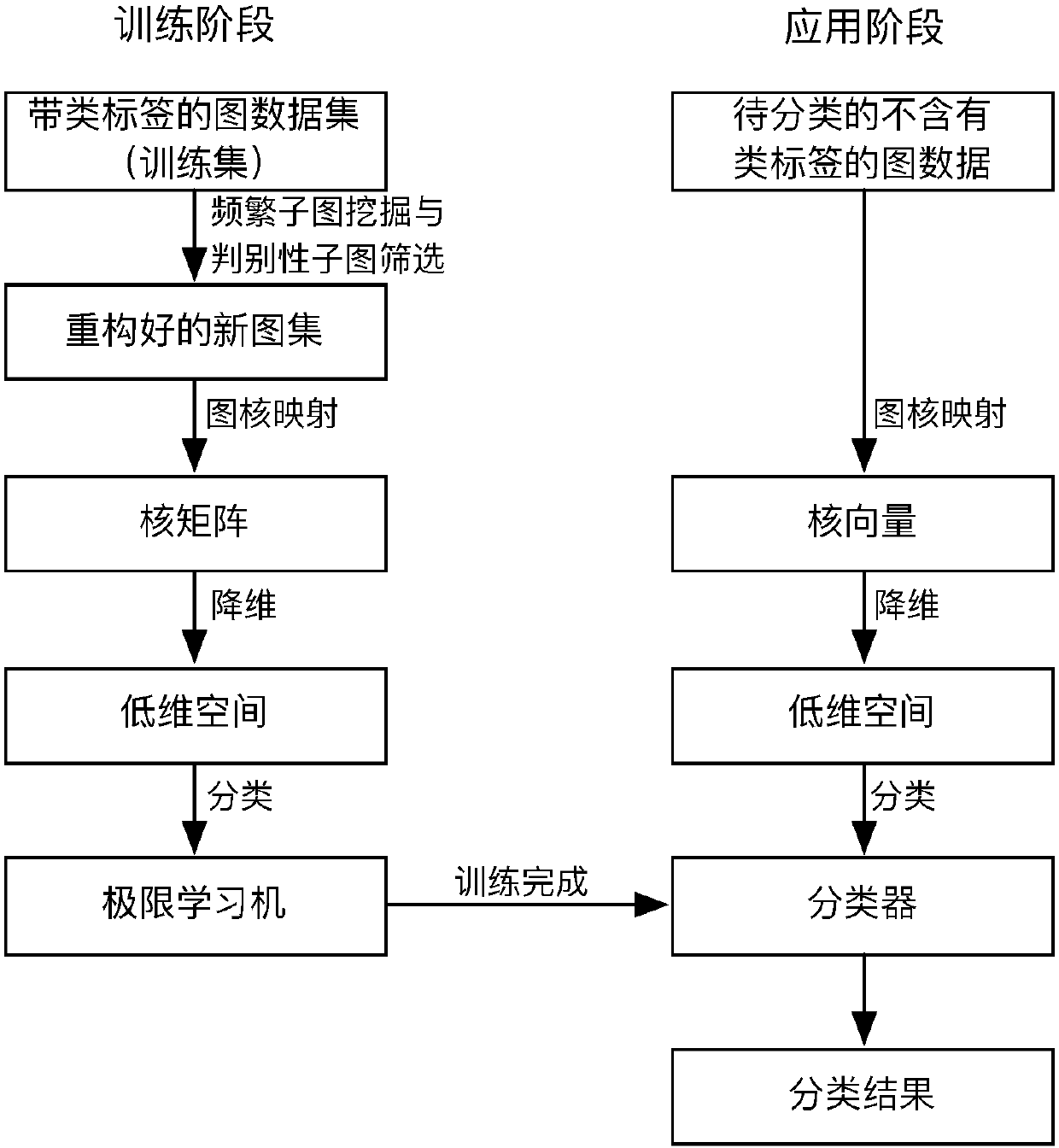
A graph classification method based on graph set reconstruction and graph kernel dimensionality reduction
InactiveCN106991132ASmall scaleImprove performanceSpecial data processing applicationsLearning machineData set
The invention provides a graph classification method based on graph set reconstruction and graph kernel dimensionality reduction. The method comprises the steps of: 1) performing frequent sub-graph mining on a graph data set used for training, and performing discriminative sub-graph screening on obtained frequent sub-graphs with the emerging frequentness differences of the sub-graphs in a positive class and a negative class; 2) reconstructing the original graph set with selected discriminative frequent sub-graphs; 3) obtaining a kernel matrix for describing the similarity between every two graphs in the newly-reconstructed graph set by using a Weisfeiler-Lehman shortest path kernel method, and based on class label information of training graphs, performing dimensionality reduction on high-dimensionality kernel matrixes by using a KFDA method; 4) training graph data projected to a low-dimensionality vector space based on an extreme learning machine to build a classifier; 5) standardizing graph data requiring classification, projecting the data to a low-dimensionality space obtained through training and inputting the projected data to the classifier to obtain a classification result. The method can directly classify graph data without class labels and guarantee high classification accuracy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
A nonlinear de-mixing method for hyperspectral images considering spectral variability
ActiveCN109035154AOvercoming Spectral Variability IssuesOvercoming the Variability ProblemImage enhancementImage analysisNonlinear spectroscopyKernel method
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing image processing, in particular to a nonlinear de-mixing method for hyperspectral images considering spectral variability. At first, original data are mapped to a high-dimensional characteristic space by a kernel method, and the spectral variation coefficient is considered in the high-dimensional space to perform linear unmixing; at the same time, according to the spatial continuity of object distribution, local smoothing constraint is added to abundance and coefficient of variation, which makes them have spatial smoothness. This method can be used for unsupervised nonlinear spectral unmixing in the presence of spectral variability in Hapke and GBM nonlinear mixing models. The invention can overcome the problem of spectral variability existing in different nonlinear mixing scenes and improve the precision of spectral unmixing, and has important significance in practical application.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition
InactiveCN104392243ASolve nonlinear unmixingOvercoming the Insufficiency of Linear UnmixingCharacter and pattern recognitionMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
The invention relates to a nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition. The nonlinear un-mixing method comprises the following steps: estimating the number of end members for hyperspectral images by utilizing a dimension virtual method; then, popularizing the conventional un-mixing algorithm based on a linear mixing model to a nonlinear characteristic space by utilizing a kernel method, and solving a nonlinear spectrum un-mixing problem by using an alternative iterative optimization method. The nonlinear un-mixing method of hyperspectral images based on kernel sparse nonnegative matrix decomposition has the beneficial effects that from a mixing model of hyperspectral observation pixels, the sparsity of the hyperspectral abundance is added into a sparse model, and the linear mixing model is mapped into a nonlinear mixing model by virtue of the kernel method, so that the defects of linear un-mixing are effectively overcome, and good noise resistances are simultaneously achieved, and therefore, the nonlinear un-mixing method can be used as an effective means for solving the un-mixing of hyperspectral remote sensing images.
Owner:扬州匠新精密数控设备有限公司
Image segmentation method based on multi-kernel local information FCM algorithm
InactiveCN106846326AReduce the impactAccurate segmentationImage analysisPattern recognitionKernel method
The invention discloses an image segmentation method based on a multi-kernellocal information FCM algorithm. The image segmentation method is characterized by including the steps that 1, optimal division is carried out on a pixel set, so that the value of a target function is made minimum; 2, an initial membership grade matrix and an initialized clustering center are obtained; 3, a membership grade value and the clustering center are obtained through iteration; 4, a target function after a weight index is introduced is obtained. The image segmentation method can accurately avoid that an FCM is sensitive to noise points, and in implementation of a common kernel method, selection of a kernel function is not determined, meanwhile can find the most appropriate weight value and a current membership grade value to improve the reliability and astringency of the algorithm, is applied to image segmentation, and can achieve a good image segmentation effect.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
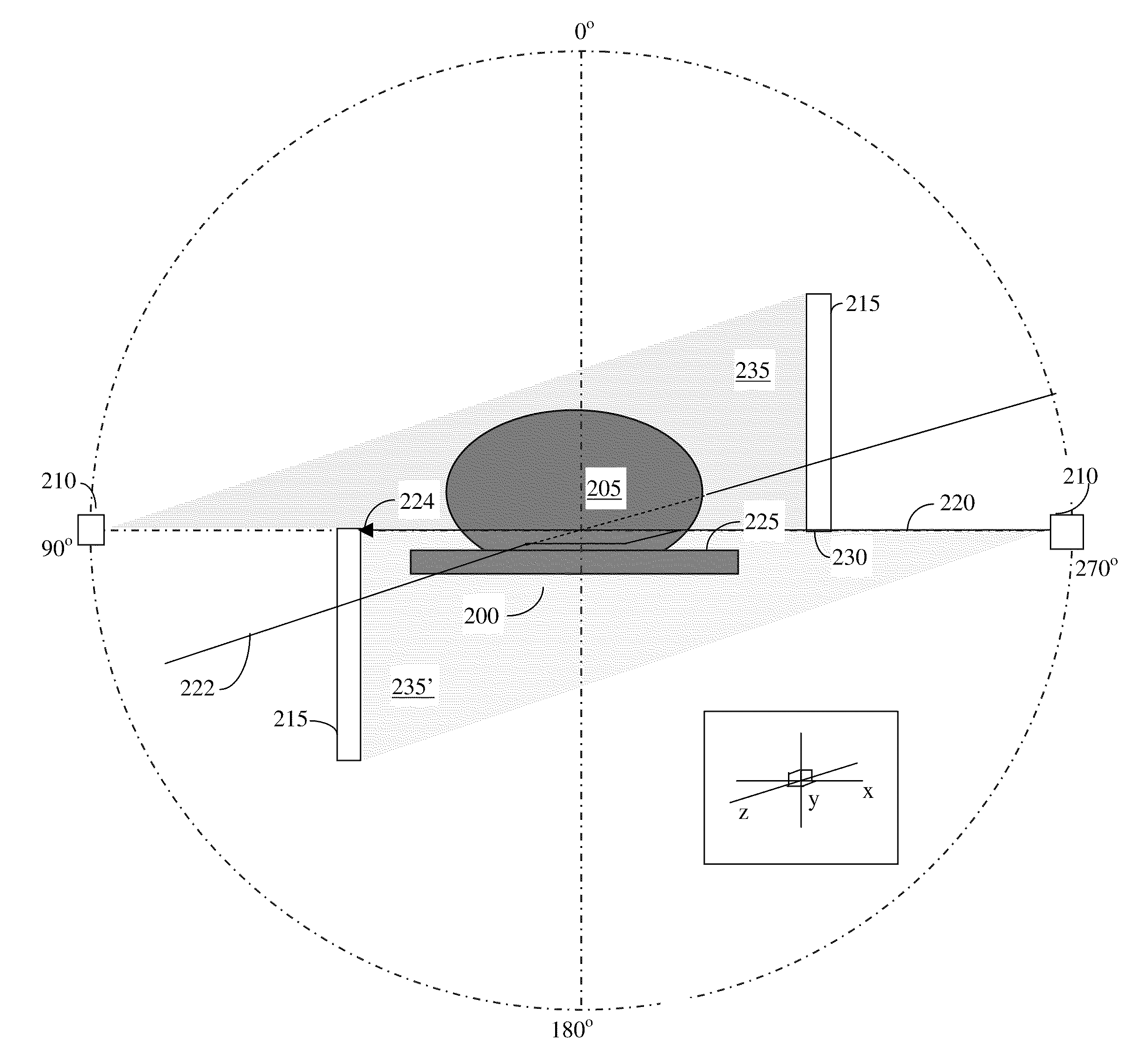
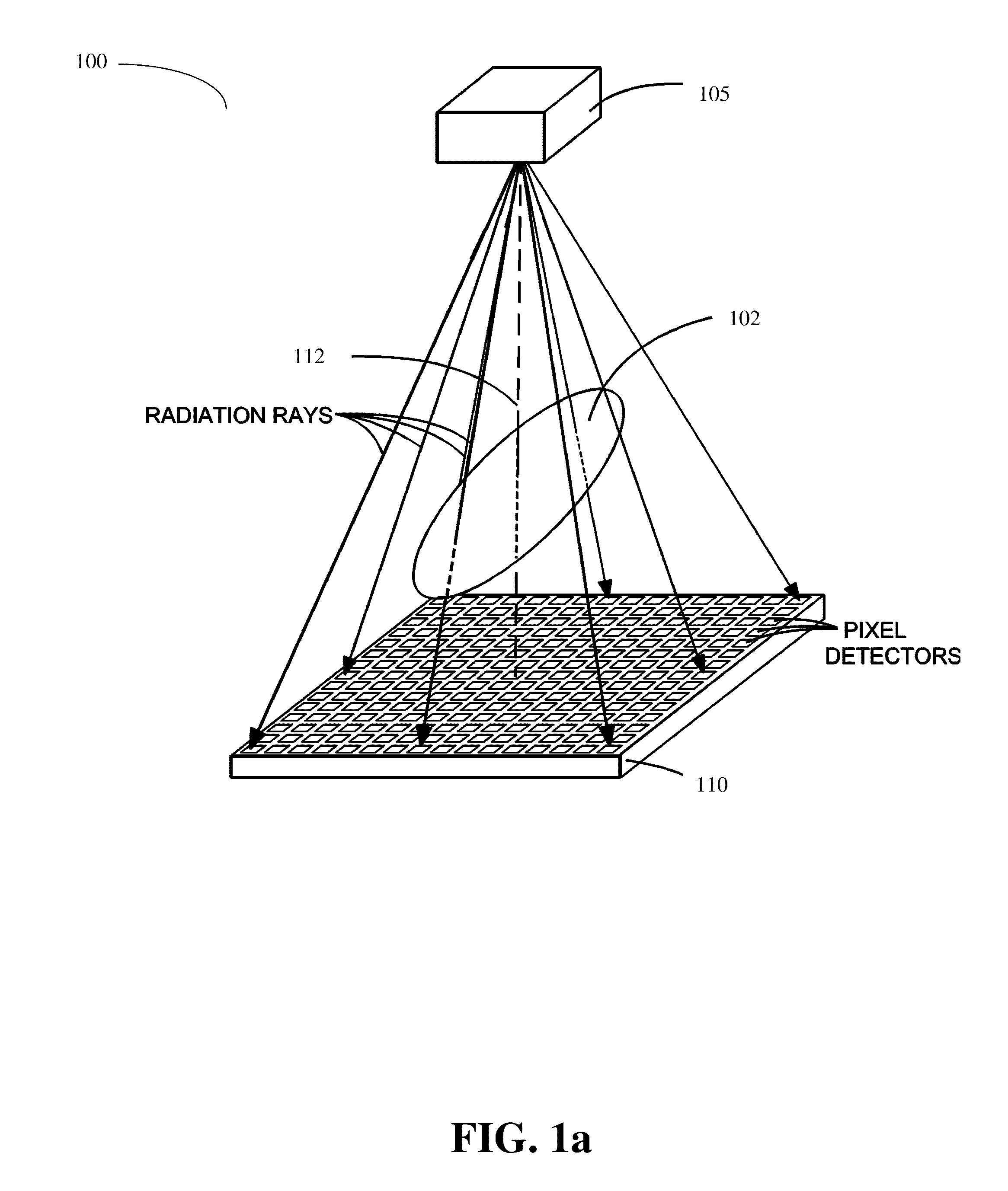
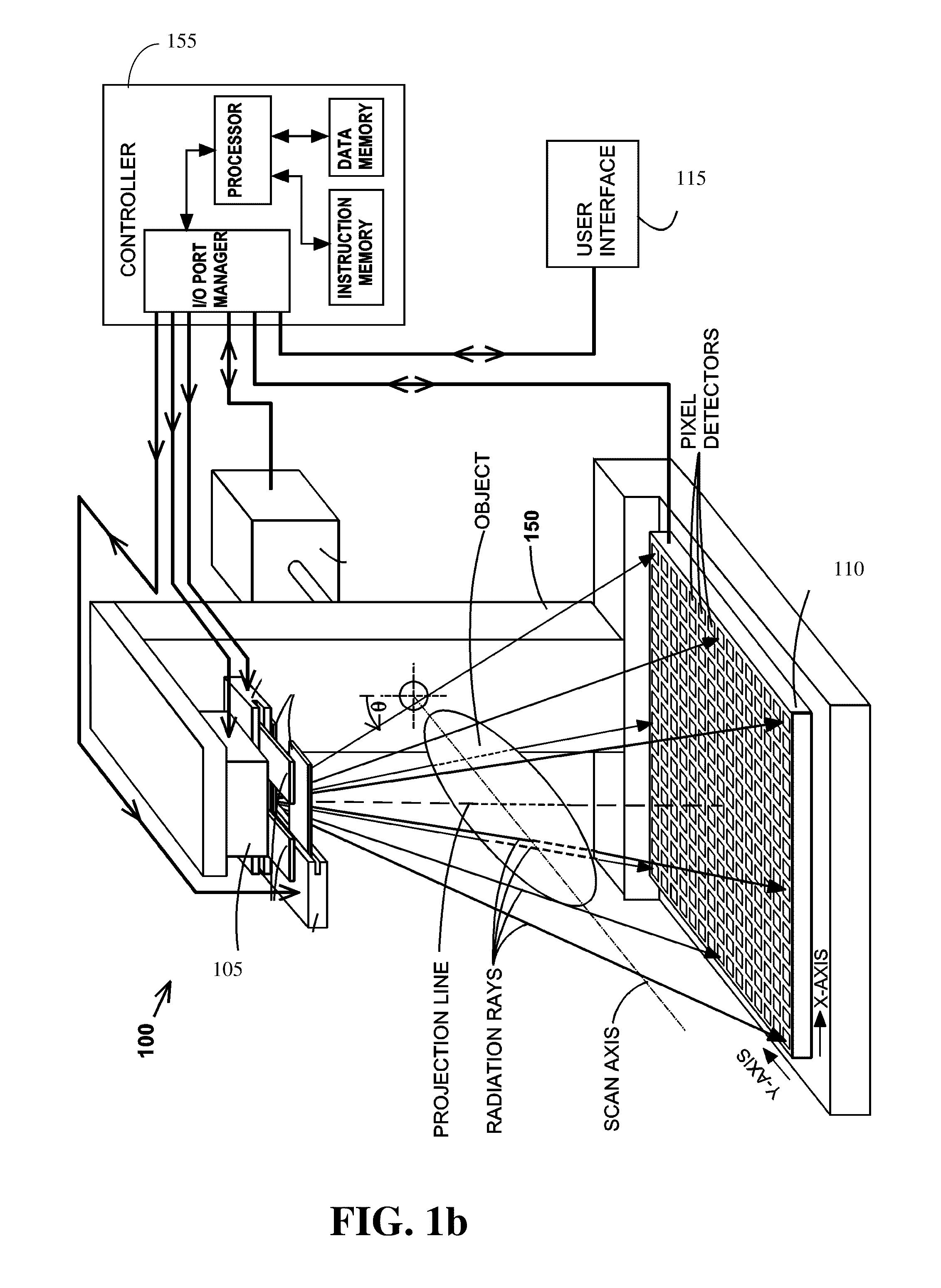
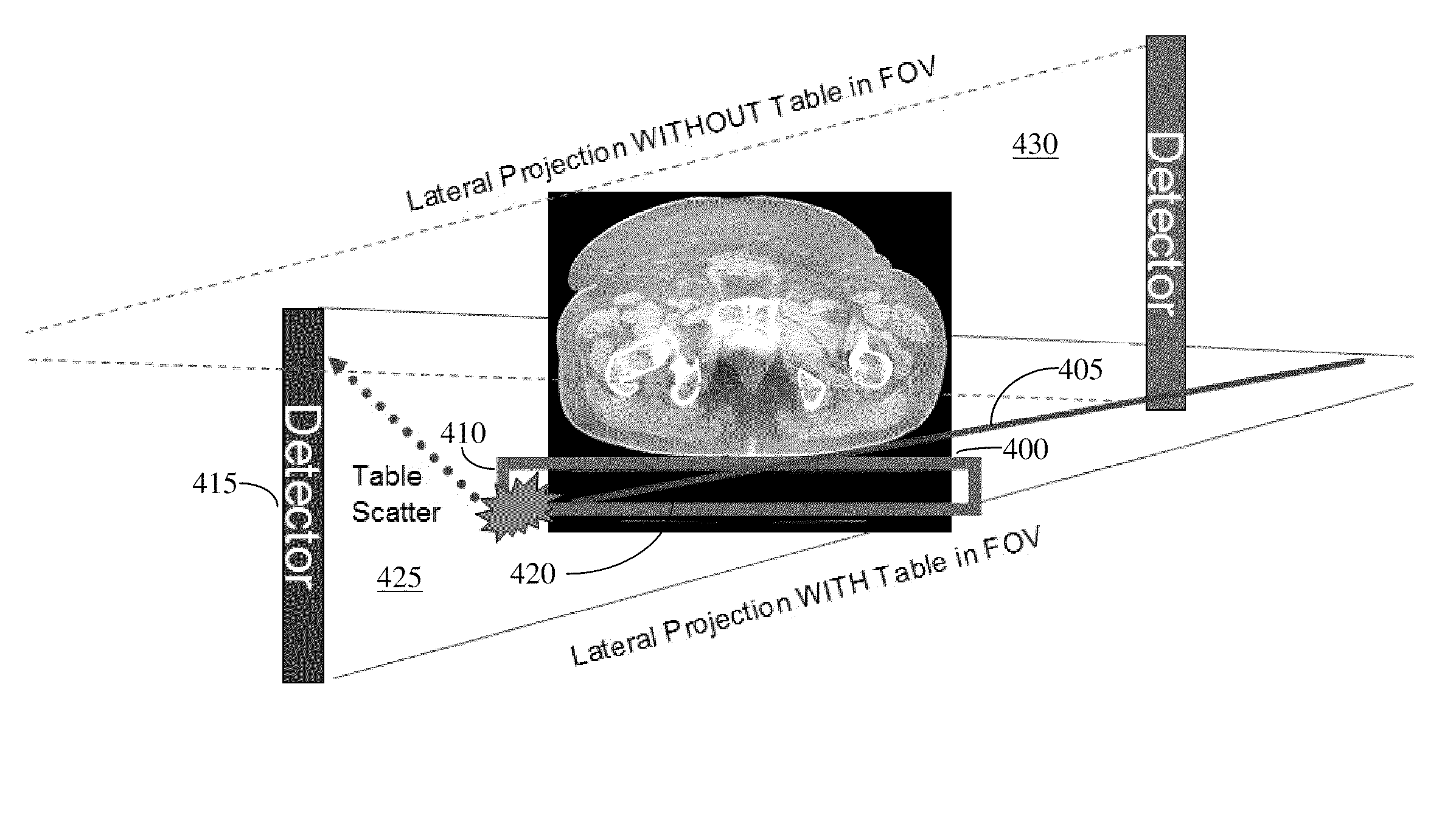
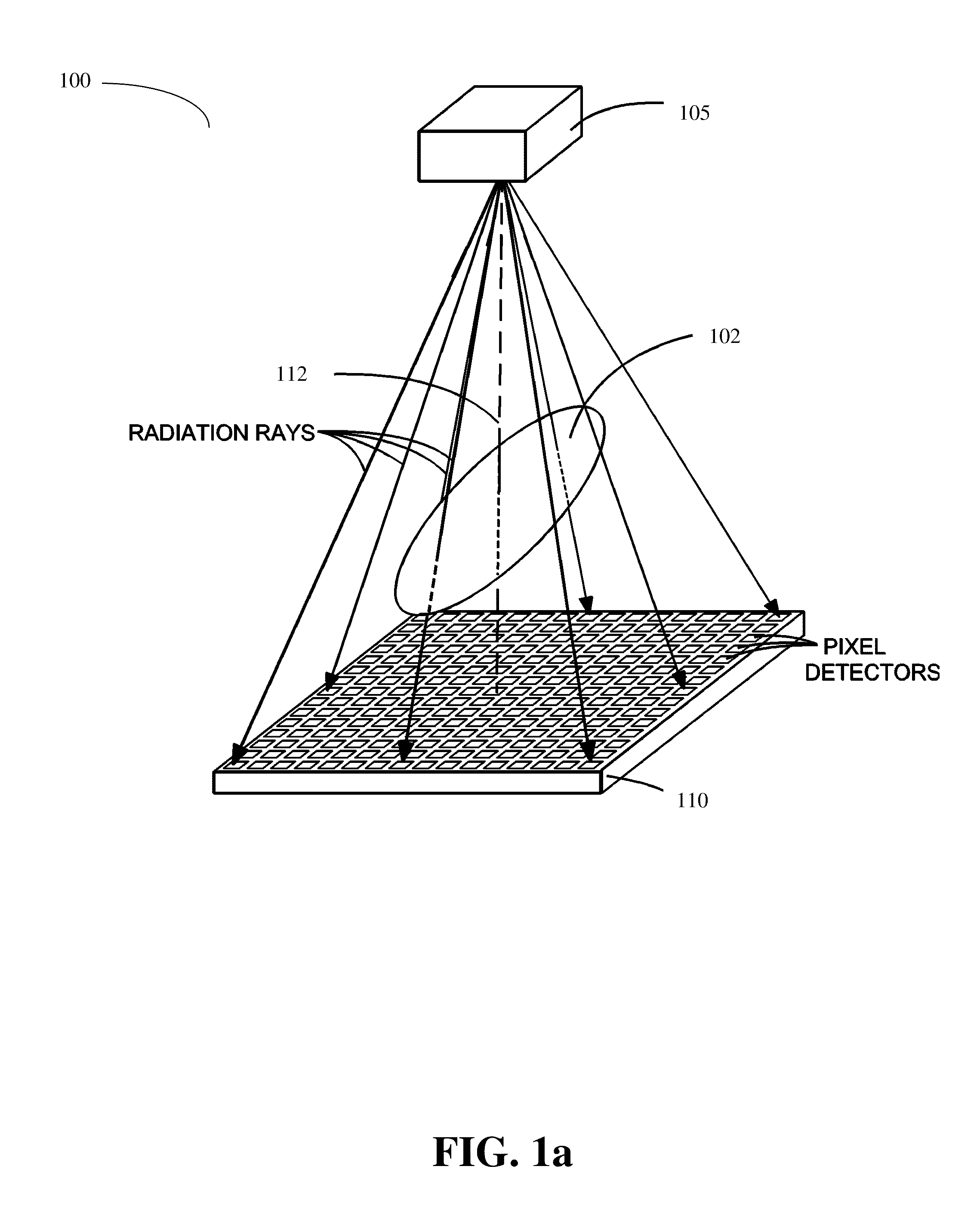
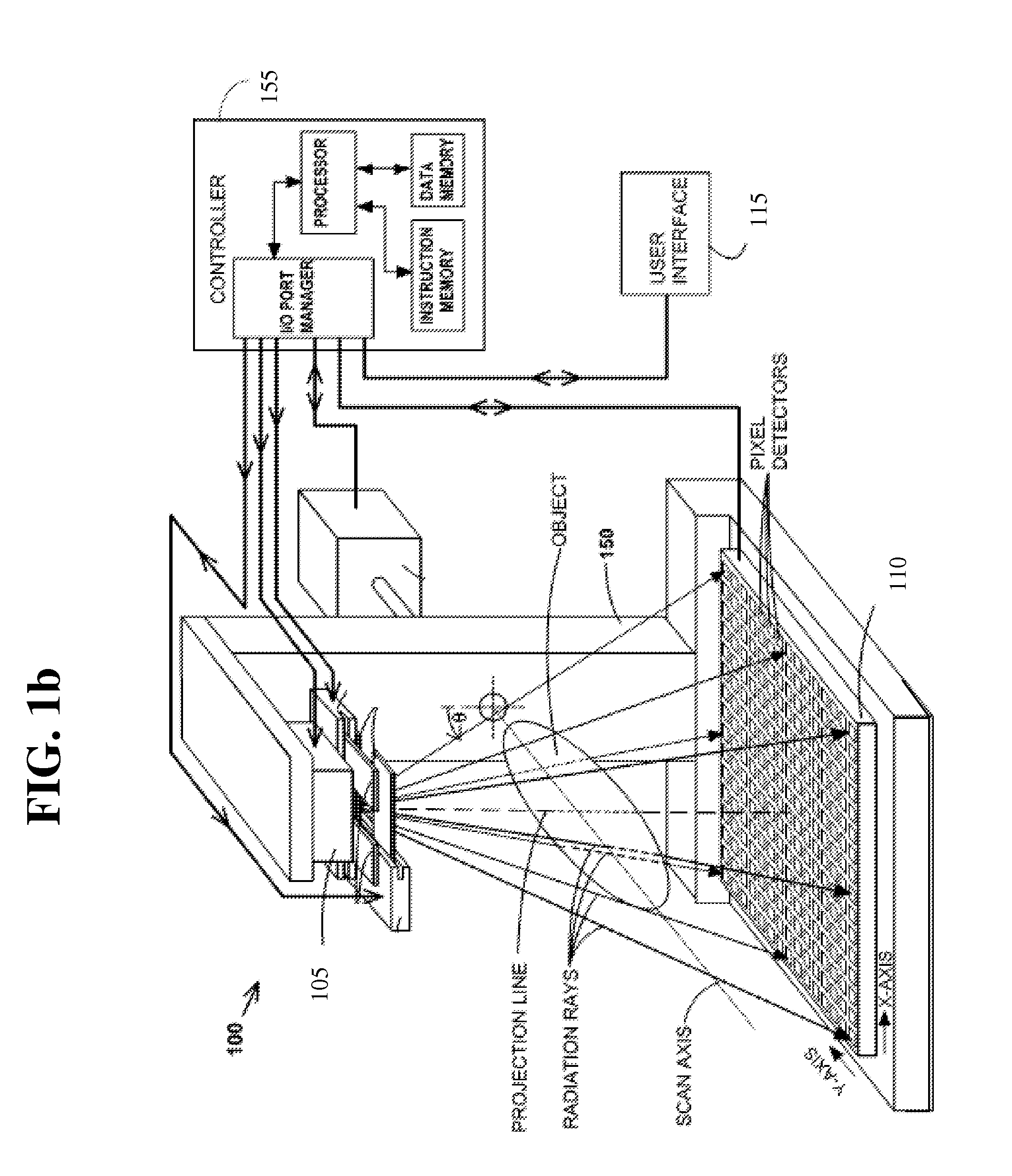
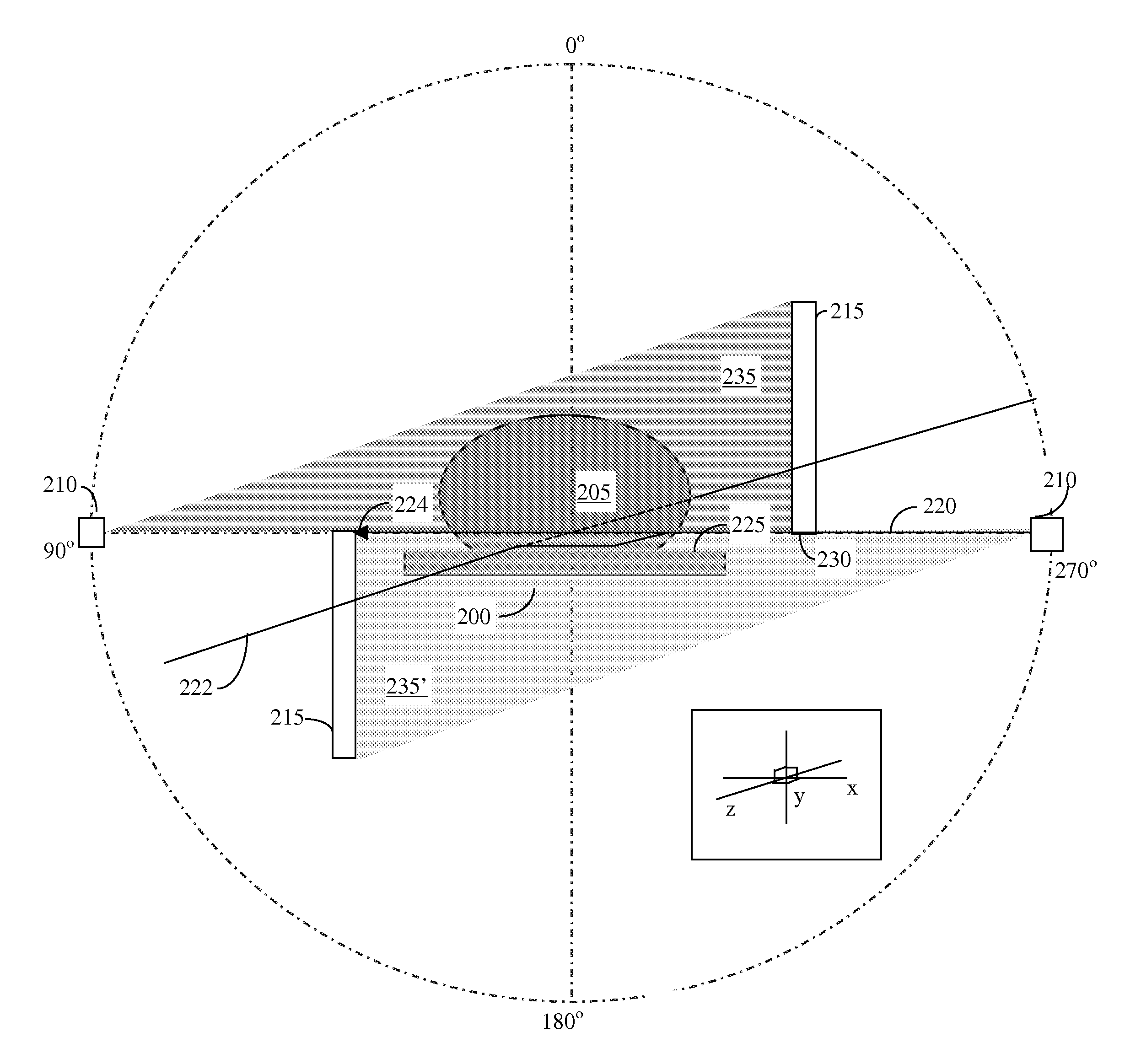
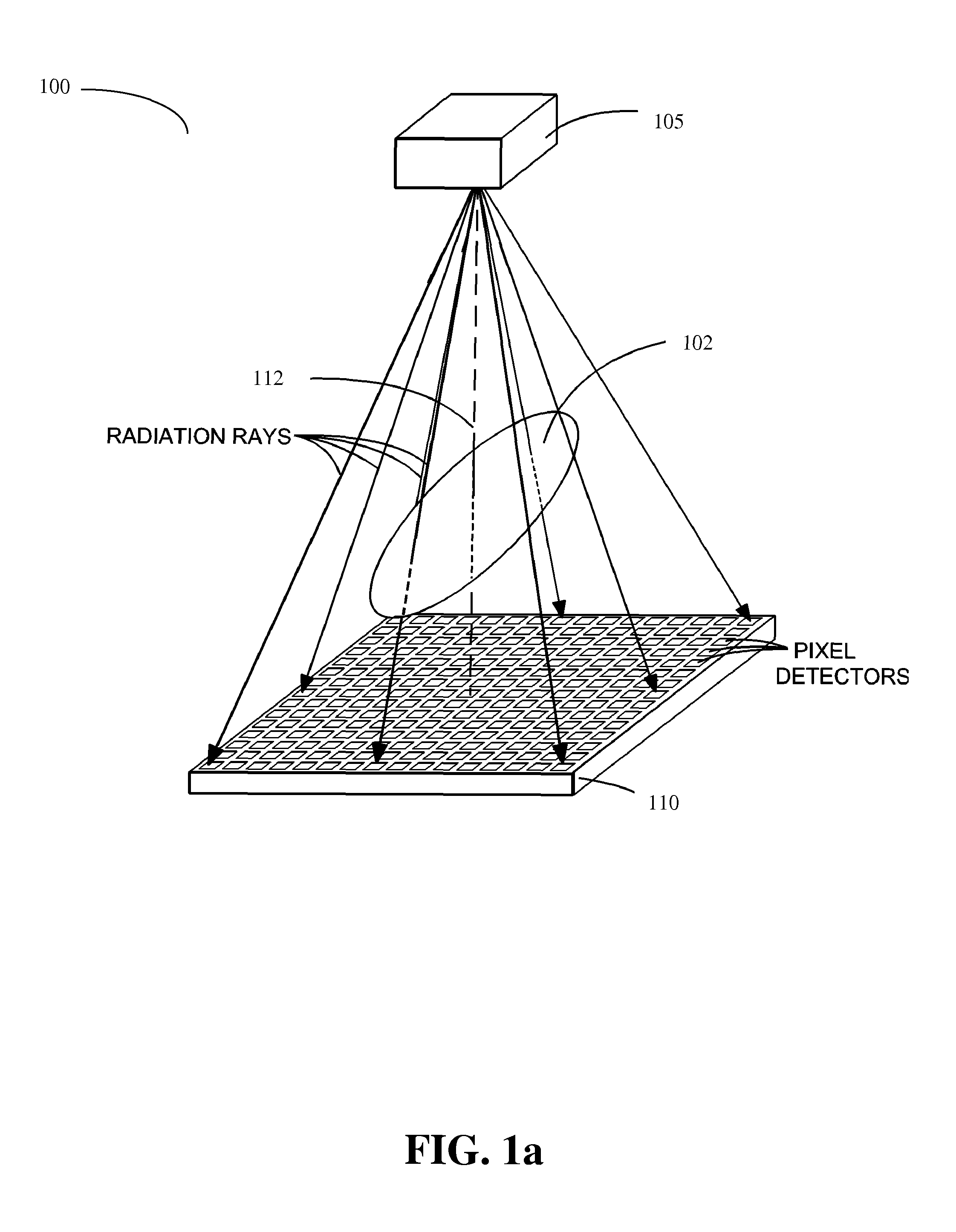
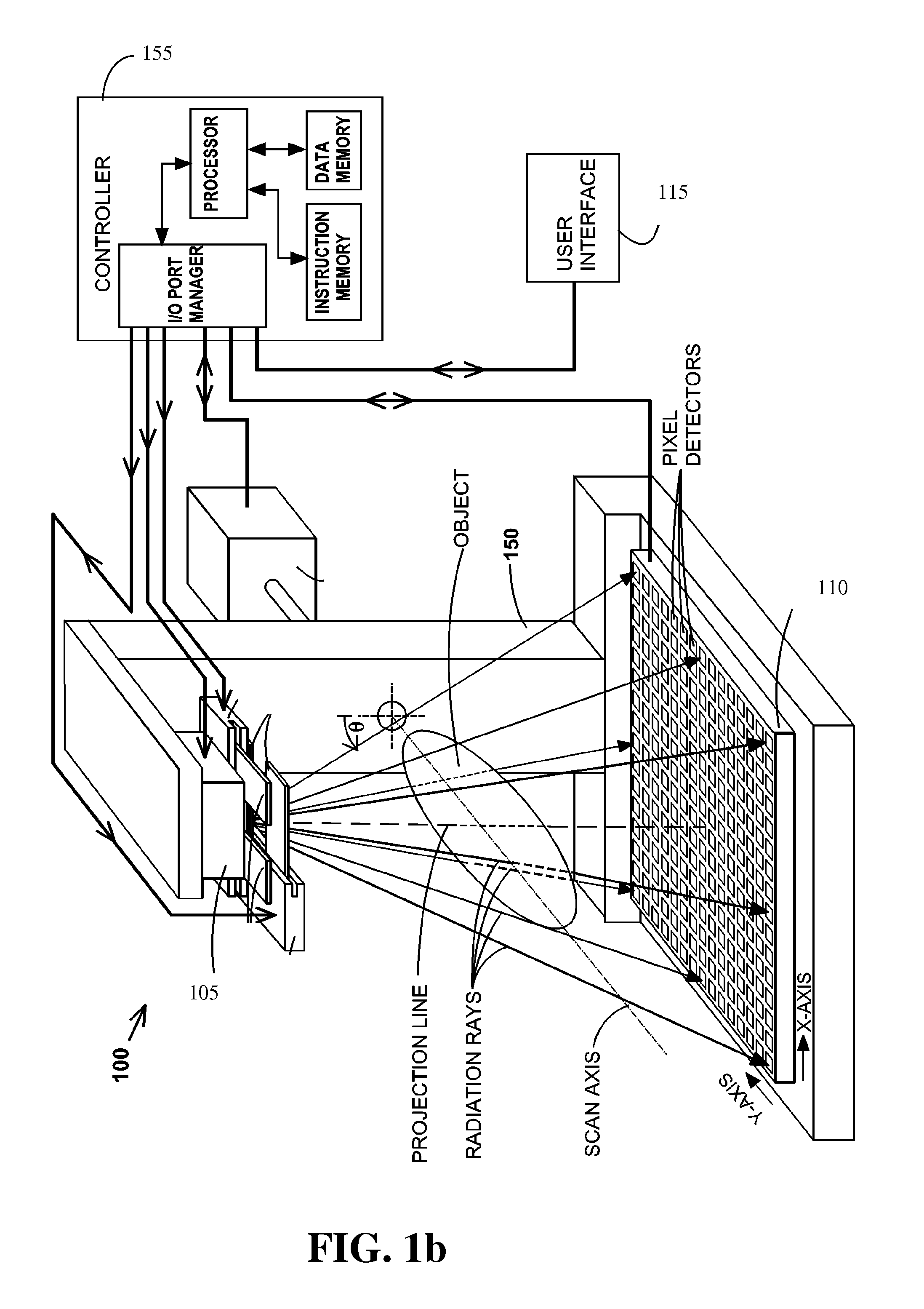
Methods of scatter correction of x-ray projection data 2
ActiveUS20110255656A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPiercing pointKernel method
A system and method for forming an adjusted estimate of scattered radiation in a radiographic projection of a target object, which incorporates scattered radiation from objects adjacent to the target object, such as a patient table. A piercing point equalization method is disclosed, and a refinement of analytical kernel methods which utilizes hybrid kernels is also disclosed.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
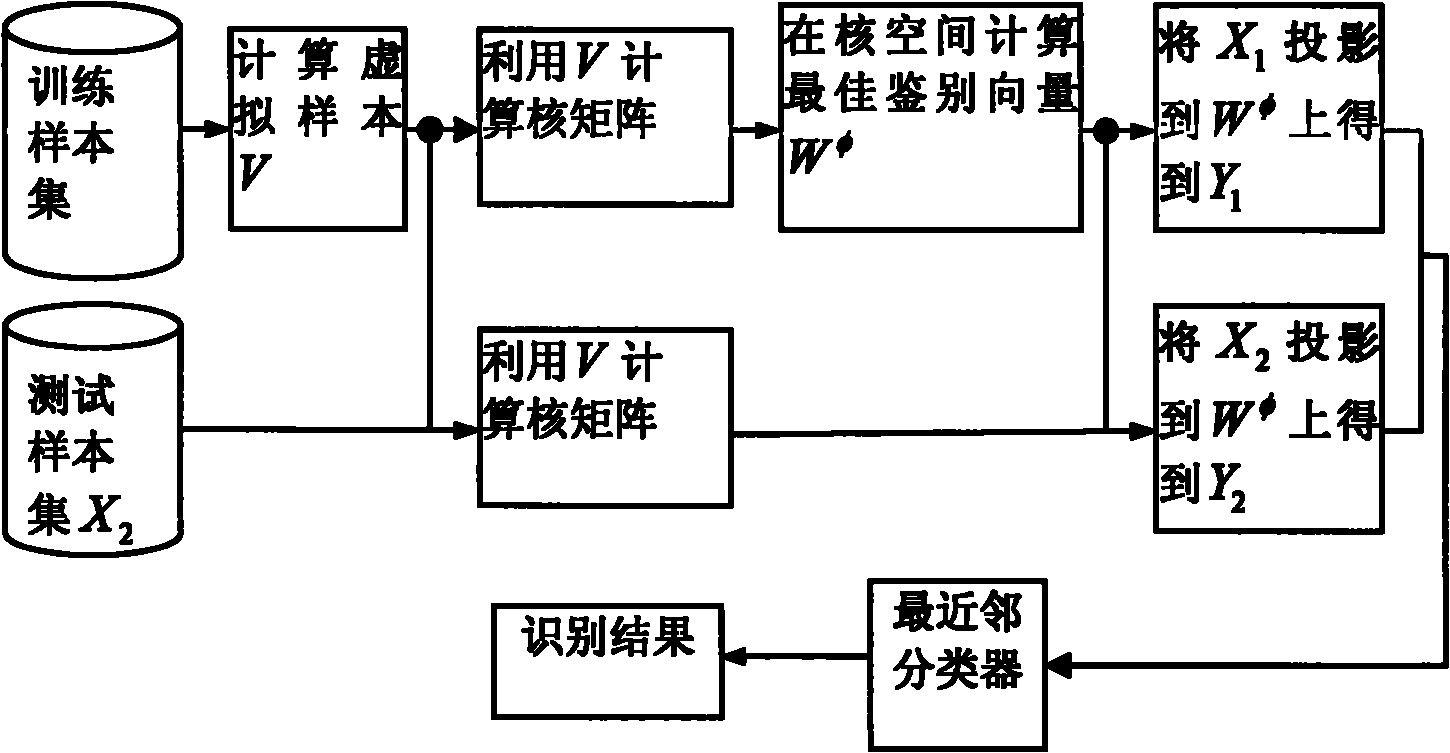
Virtual sample based kernel discrimination method for face recognition
InactiveCN102142082AStrong descriptive abilityQuick and effective recognition effectCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionFERET database
The invention discloses a virtual sample based kernel discrimination method for face recognition, which is a virtual sample based quick kernel method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a virtual sample set for a training sample set at one time before constructing a kernel matrix for the training sample set; and training / testing through a kernel matrix theory based on the virtual sample set. Since the virtual sample set is an aggregate of a characteristic sample set (MES) and a public vector sample set (MCS) of the training sample set, the virtual sample set has extremely high description capacity for both a known training sample set and an unknown test sample set. Experimental verification of the method on an FERET database shows that the method is quick and effective; the computation speed of the kernel method is greatly increased by using the method; and meanwhile, compared with the conventional kernel method, the recognition rate is also increased.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINASUN COMM
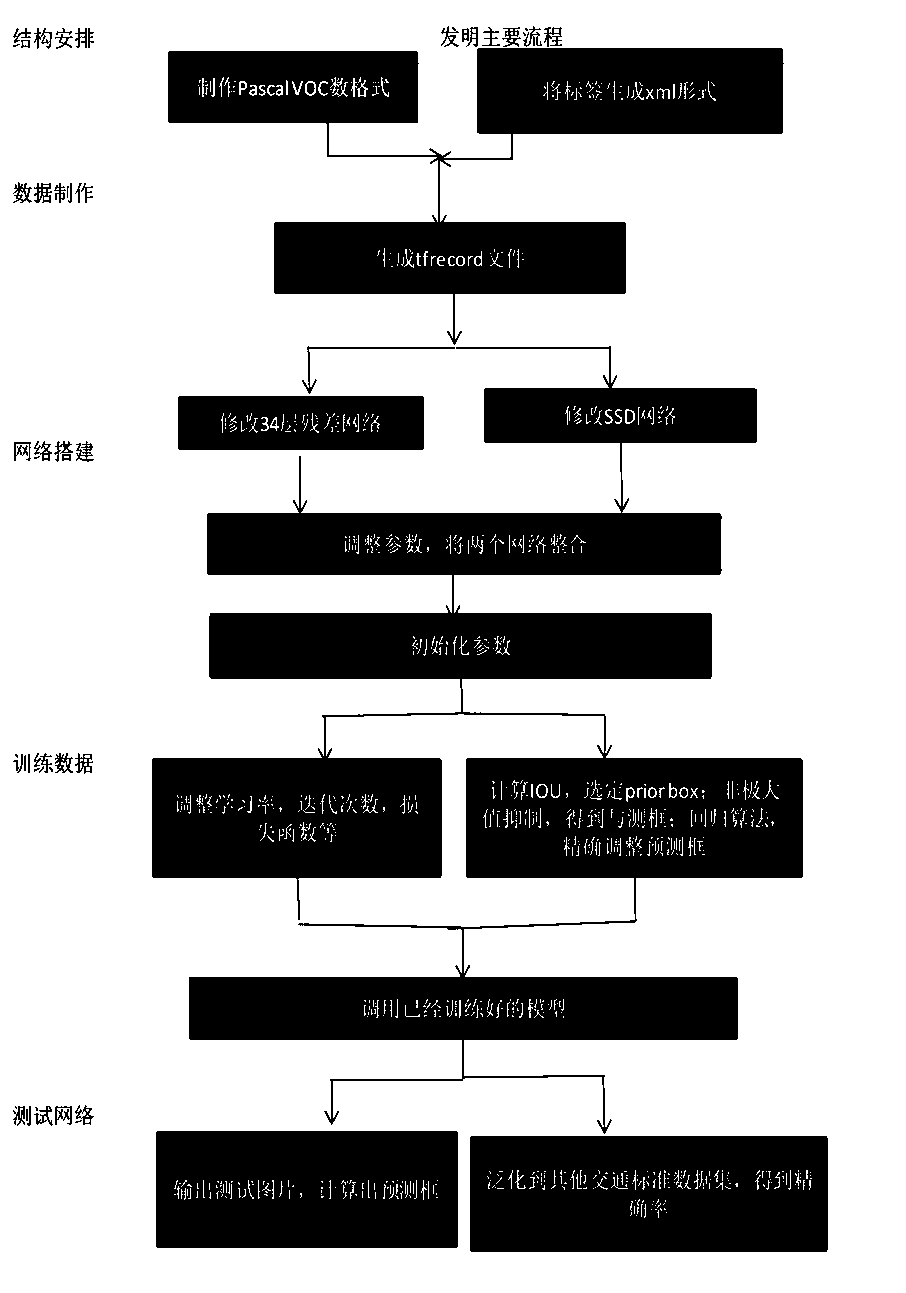
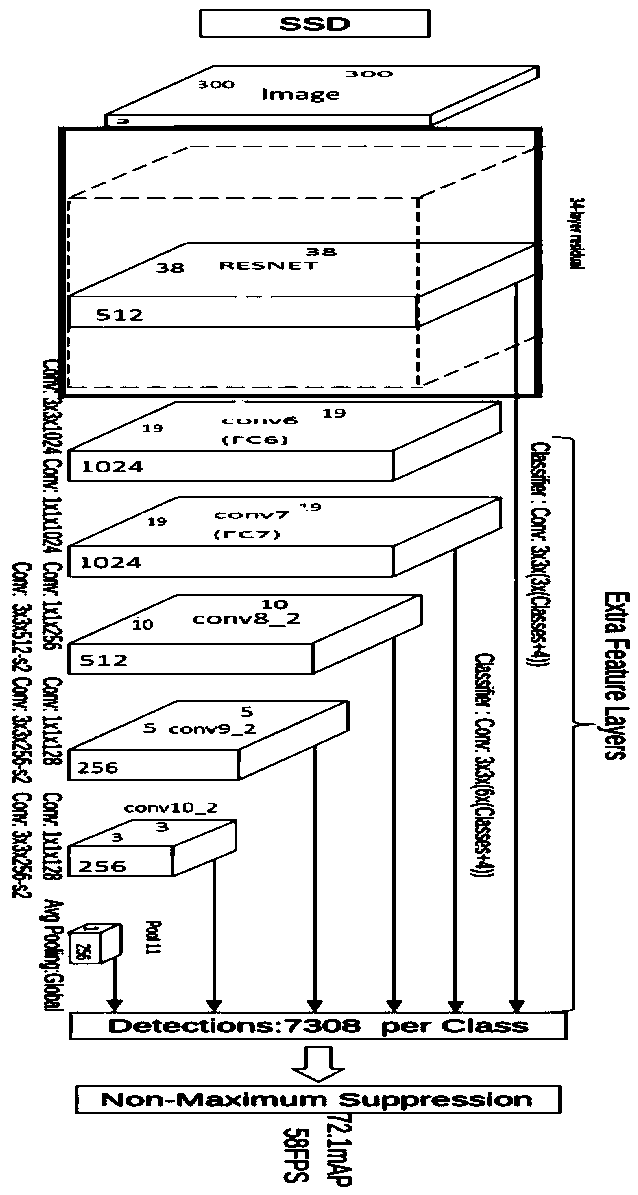
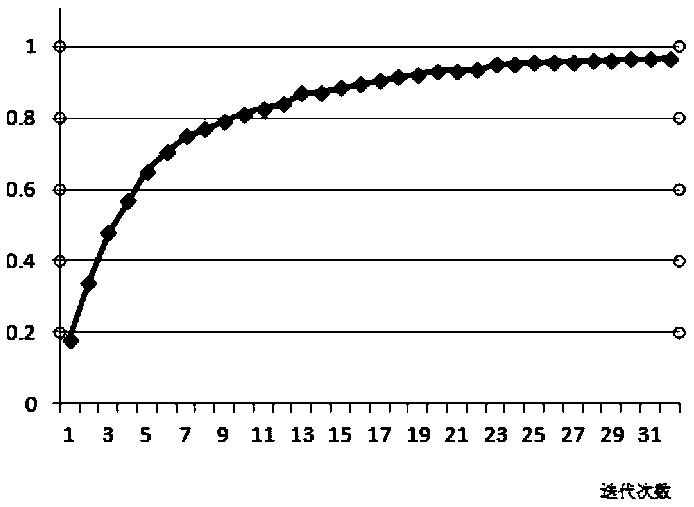
Traffic sign recognition method based on improved SSD network
InactiveCN110287806AReduce consumptionLow costCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesTraffic sign recognitionAlgorithm
The invention discloses a deep learning target detection and recognition algorithm based on an improved SSD. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, modifying a residual error network, using a series convolution kernel method to be equivalent to a large-size convolution kernel, sending the pictures to 34 layers of residual error networks to obtain the feature maps of different sizes, obtaining the feature map of the last layer of the residual error network, and obtaining the feature map of each convolution layer at the same time. The improved SSD network method provided by the invention aims to improve the detection rate of the SSD network on the small targets and realize the detection of the SSD algorithm on the small traffic signs. Due to the fact that the end-to-end network is adopted, the extra storage equipment are not needed, the consumption of the hardware is reduced, the cost is saved, and meanwhile under the improvement of the residual network, the improved SSD network has better accuracy for the small target detection.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
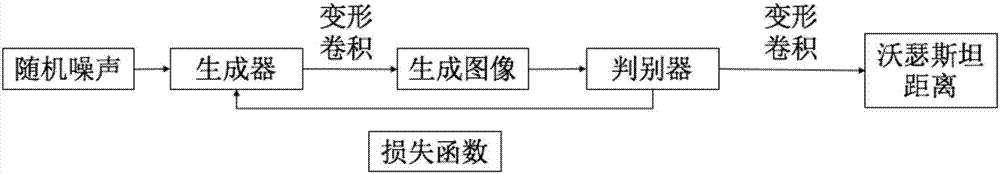
Deformable convolution kernel method based on WGAN (Wasserstein-Generative Adversarial Network) model
InactiveCN107886162ATraining accuratelyTraining in the right directionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a deformable convolution kernel method based on a WGAN (Wasserstein-Generative Adversarial Network) model, and belongs to the field of the deep learning neural network. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: constructing an original generative adversarial network model; S2: constructing a Wasserstein distance as the judgment index of the adversarial network model; S3: initializing random noise, and inputting the random noise into a generator; S4: in the WGAN model, utilizing a deformable convolution kernel to carry out convolution on an image; and S5: inputting a loss function obtained by a deformable convolution operation into the generator for subsequent training. By use of the deformable convolution kernel method, which is constructed by the invention, based on the WGAN model, a convolution way generated after a discriminator and the generator receive a picture is changed, the discriminator and the generator can automatically change the size of the convolution kernel according to a training situation, so that the characteristics of a dataset image can be adaptively learnt, and the robustness of whole network training is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
Methods of Scatter Correction of X-Ray projection data 1
ActiveUS20110255655A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationKernel methodPiercing point
A system and method for forming an adjusted estimate of scattered radiation in a radiographic projection of a target object, which incorporates scattered radiation from objects adjacent to the target object, such as a patient table. A piercing point equalization method is disclosed, and a refinement of analytical kernel methods which utilizes hybrid kernels is also disclosed.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Methods of scatter correction of x-ray projection data 2
ActiveUS8199873B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPiercing pointKernel method
A system and method for forming an adjusted estimate of scattered radiation in a radiographic projection of a target object, which incorporates scattered radiation from objects adjacent to the target object, such as a patient table. A piercing point equalization method is disclosed, and a refinement of analytical kernel methods which utilizes hybrid kernels is also disclosed.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
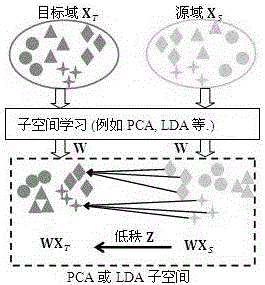
Image classification method based on sparse nonlinear subspace migration
InactiveCN106326935AImprove accuracyApplicable conversionThree-dimensional object recognitionKernel methodHilbert space
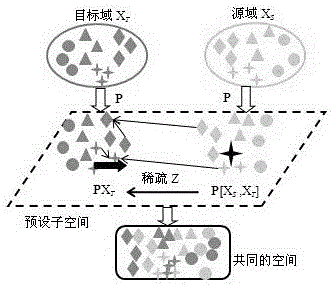
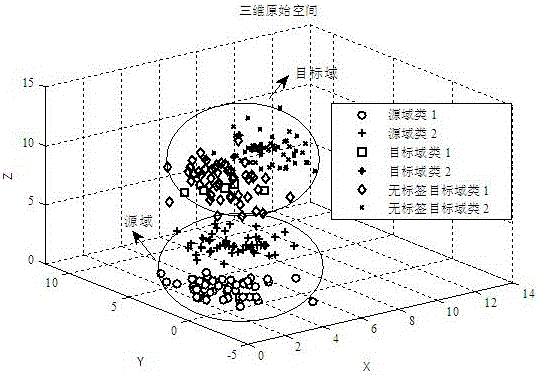
The invention discloses an image classification method based on sparse nonlinear subspace migration. The method comprises the steps of mapping data from an original space to a regenerated kernel Hilbert space via a kernel method, mapping target domain training data XT to a preset subspace via predefined fundamental transformation P in the kernel Hilbert space to obtain target data PXT, mapping source domain training data XS to the preset subspace via the fundamental transformation P to obtain P[XS, XT], transforming the source domain data P[XS, XT] via a spare matrix Z, and distributing the P[XS, XT] and the PXT in the preset subspace in a sharing mode. The method has the advantages of improving the migration accuracy of image data in the preset subspace and being applicable to transformation of nonlinear data.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Nonlinear channel equalization method in Alpha stable distribution noise environment
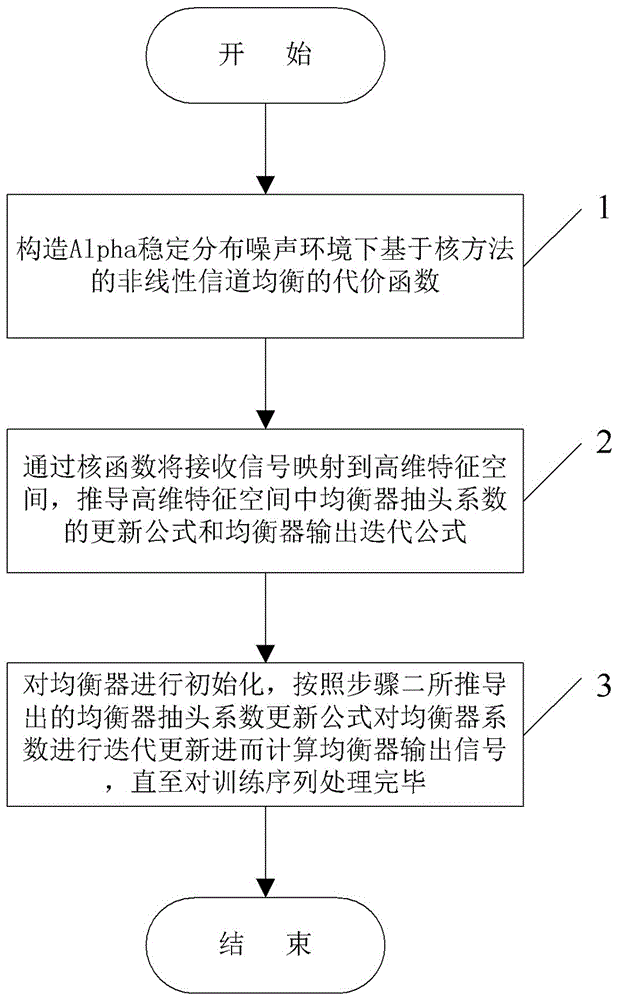
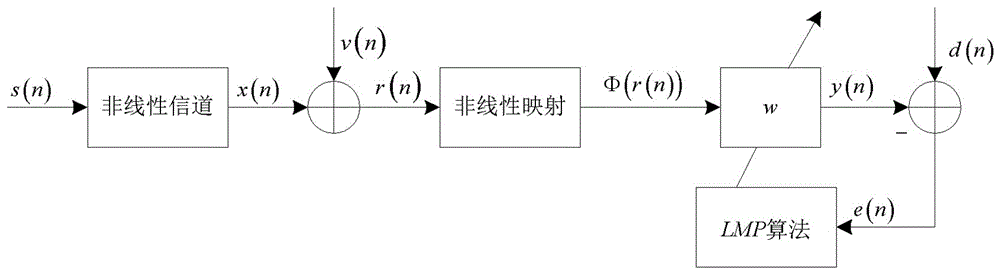
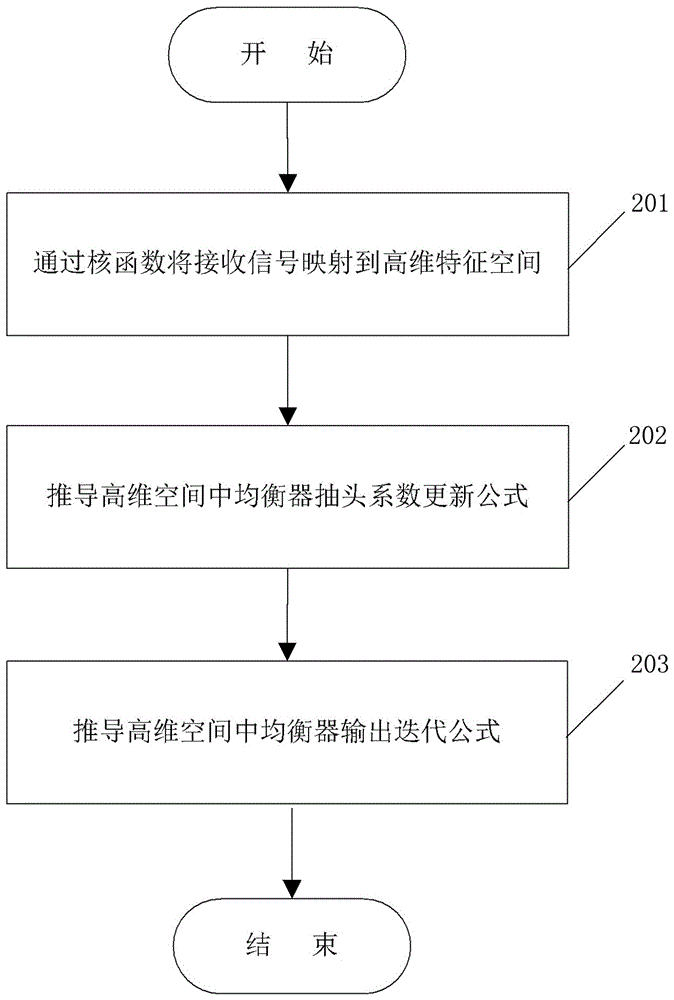
ActiveCN106130936AMake up for distortionImprove uniformityEqualisersChannel estimationKernel methodAlgorithm
The invention relates to a channel equalization problem in an Alpha stable distribution noise environment, and in particular relates to a nonlinear channel equalization method in an Alpha stable distribution noise environment. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), constructing a cost function in the Alpha stable distribution noise environment; (2), mapping a received signal into a high-dimensional feature space through a kernel function, and deducing an equalizer tap coefficient updating formula in the high-dimensional feature space and an equalizer output iterative formula; and (3), performing iterative updating of the equalizer coefficient by using the equalizer tap coefficient updating formula till a training sequence is completely processed. According to the nonlinear channel equalization method disclosed by the invention, a kernel method is successfully applied in nonlinear channel equalization under Alpha stable distribution noise; a KLMP algorithm is provided; distortion generated by a nonlinear channel under the Alpha stable distribution noise can be made up better; and, on the premise that the convergence speed of the algorithm is ensured, the better equalization performance can be obtained through low steady-state error.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
Mechanical state monitoring method based on CELMDAN and SSKFDA
InactiveCN112101227AWell representedEliminate schema confusion issuesCharacter and pattern recognitionData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a CELMDAN and SSKFDA-based mechanical state monitoring method. The CELMDAN and SSKFDA-based mechanical state monitoring method includes the following steps that: (1) a CELMDANmethod is adopted to decompose complex vibration signals into a plurality of product functions with physical significance; (2) a method of taking a periodic modulation intensity PMI as a PFs selectioncriterion is provided, so that effective PFs can be accurately selected. (3) an SSKFDA dimension reduction method is provided, geometrical information of a label sample and an unlabeled sample set isfully utilized, a kernel method, sparse representation, manifold learning and an FDA method are fused, a low-dimensional subspace data set embedded in a high-dimensional sparse space is better disclosed, and the problem of dimension reduction of high-dimensional, sparse and nonlinear data is solved. (4) a rapid SSKFDA model selection method is proposed, according to the method, optimal model parameters are solved based on the criterion of minimum intra-class local structure measurement and maximum full-local structure measurement. and (5) a mechanical known and unknown state detection methodbased on global monitoring statistics and Bayesian posteriori reasoning is proposed, and the problem that most mechanical monitoring systems cannot detect unknown abnormal states is well solved.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
SAR ATR method based on multicore optimization
ActiveCN104050489AImprove recognition rateOvercome the problem that the recognition effect is greatly affectedCharacter and pattern recognitionTest sampleKernel method
The invention discloses an SAR ATR method based on multicore optimization. The SAR ATR method based on multicore optimization includes the following steps that 1, SAR images are preprocessed; 2, a kernel function weight vector beta is fixed, a projection matrix coefficient vector alpha is optimized, and an optimized target equation J alpha is obtained; 3, the projection matrix coefficient vector alpha is fixed, the kernel function weight vector beta is optimized, and a target function J beta is obtained; 4, the step 2 and the step 3 are carried out repeatedly until the J alpha and the J beta are equal and keep changeless, and the alpha and the beta are obtained; 5, samples in a high-dimensional space are mapped into a feature space through projection, and image features of a training sample set and image features of a test sample set are obtained respectively; 6, a nearest neighbor classifier is adopted for classification and recognition. Coefficients of a kernel function are obtained according to the optimization method, the problem that selection of different kernel function parameters largely affects a recognition effect in a kernel method is solved, the recognition rate of the SAR images is improved, and the SAR ATR method based on multicore optimization has good stability and higher practical value.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Gauss induction kernel based fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm
ActiveCN107247969AImprove convenienceAccurate Clustering PerformanceCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmAlgorithm
The invention discloses a Gauss induction kernel based fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm, which comprises the steps of 1, performing optimized classification on a sample set according to an objective function minimization principle; 2, initializing a fuzzy membership degree or initializing a clustering center; 3, performing parameter estimation on the fuzzy membership degree and the clustering center according to an iterative calculation formula in a Gauss induction kernel clustering algorithm; and 4, acquiring an optimized objective function. The clustering performance of a kernel clustering algorithm can be improved by effectively utilizing the nonlinear expression ability of a kernel method in the clustering algorithm. The clustering center iteration formula does not contain the clustering center itself, conditions of the clustering algorithm for iterating a convergence proof are met, and thus the convergence of the algorithm is ensured theoretically.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Kernels and kernel methods for spectral data
InactiveUS20080097940A1Digital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setKernel method
Support vector machines are used to classify data contained within a structured dataset such as a plurality of signals generated by a spectral analyzer. The signals are pre-processed to ensure alignment of peaks across the spectra. Similarity measures are constructed to provide a basis for comparison of pairs of samples of the signal. A support vector machine is trained to discriminate between different classes of the samples. to identify the most predictive features within the spectra. In a preferred embodiment feature selection is performed to reduce the number of features that must be considered.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Image enhancement method based on all 1*1 convolution neural network
ActiveCN109255758ACompact structurePrevent overfittingImage enhancementImage analysisNerve networkKernel method
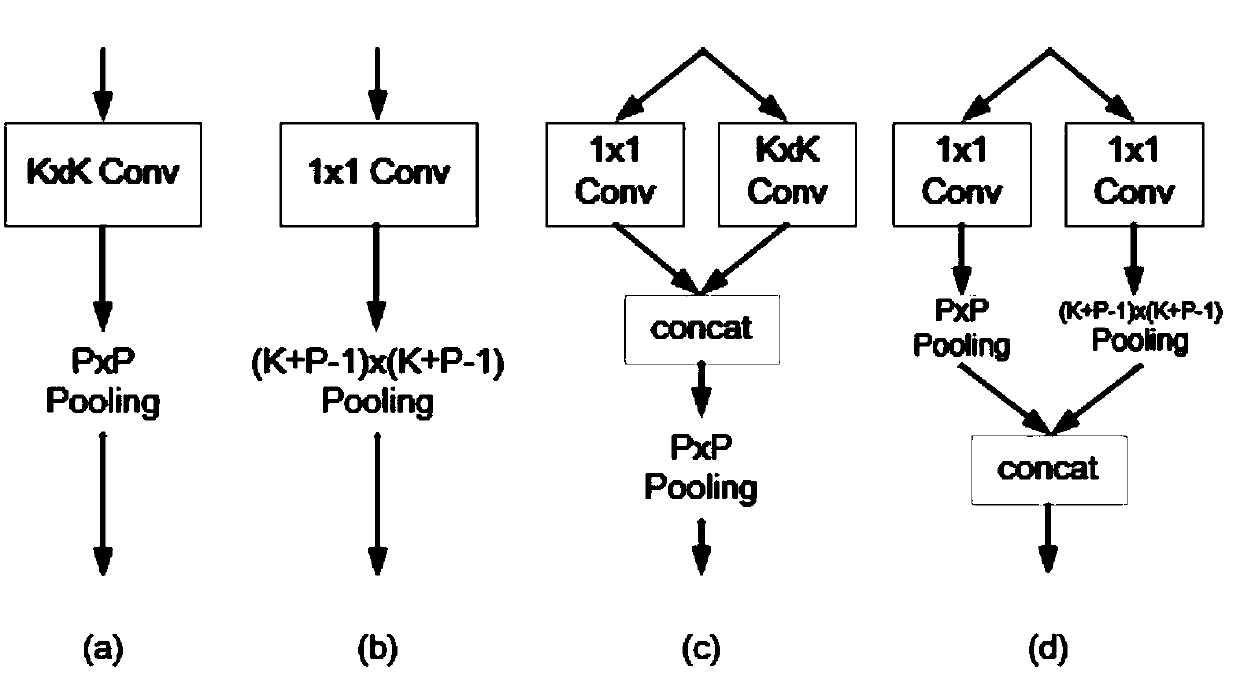
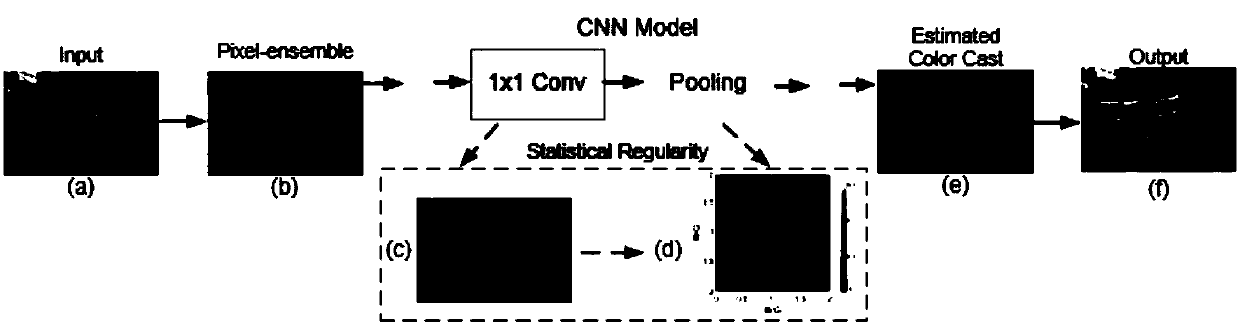
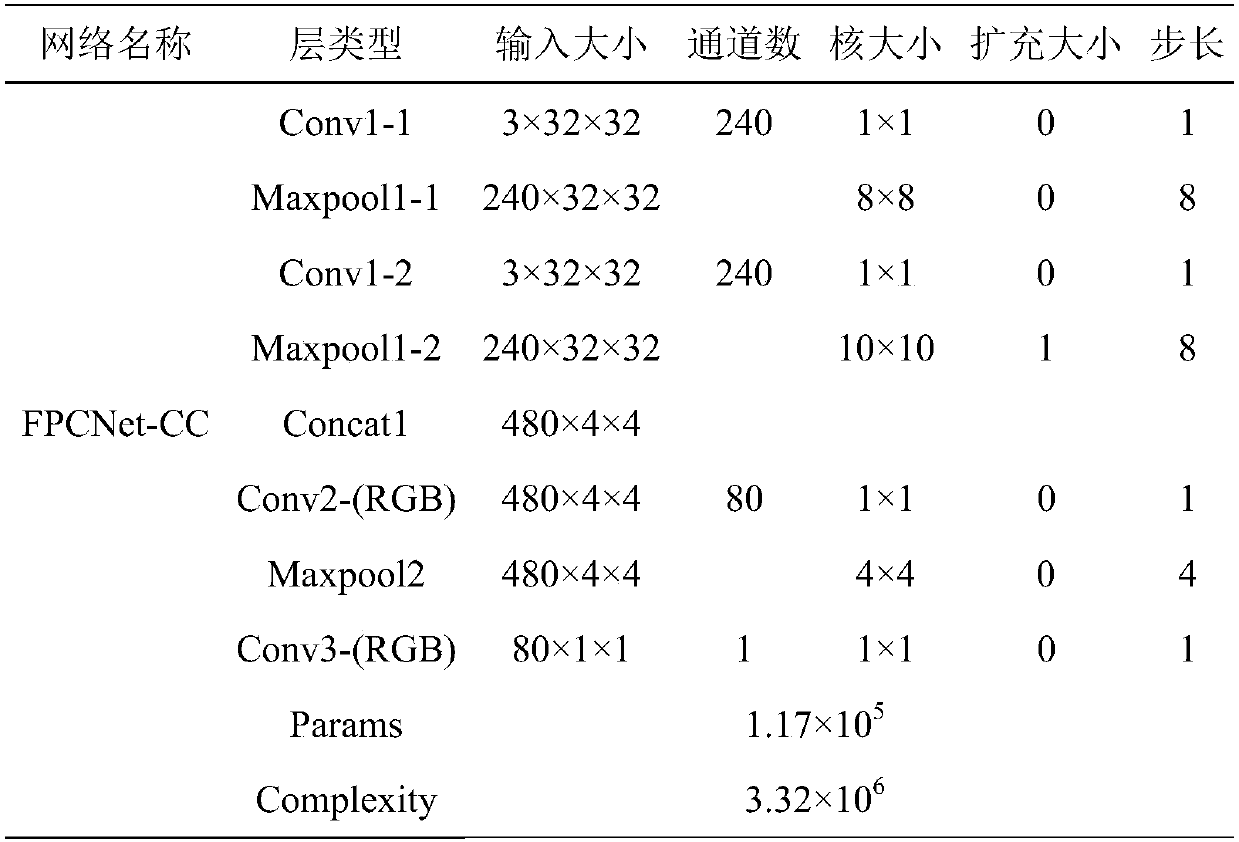
The invention discloses an image enhancement method based on an all 1*1 convolution neural network. A 1*1 convolution neural network is constructed, and pixels in a local image block in a low-qualityimage or an entire image are rearranged randomly (Pixel shuffle), and that rearranged image blocks or images are used as inputs. Then the latent variables estimated by the network are processed. Basedon the imaging model corresponding to the latent variable, the mathematical expression of the clear image estimated from the low-quality image and the latent variable is obtained, and the enhanced result is calculated. Compared with the convolution kernel method which is widely used in traditional convolution neural networks, it achieves the purpose of maintaining the model representation abilitywith fewer parameters and less computational load, so as to estimate the potential variables in image enhancement quickly and accurately.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Methods of scatter correction of x-ray projection data 1
ActiveUS8199879B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPiercing pointKernel method
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
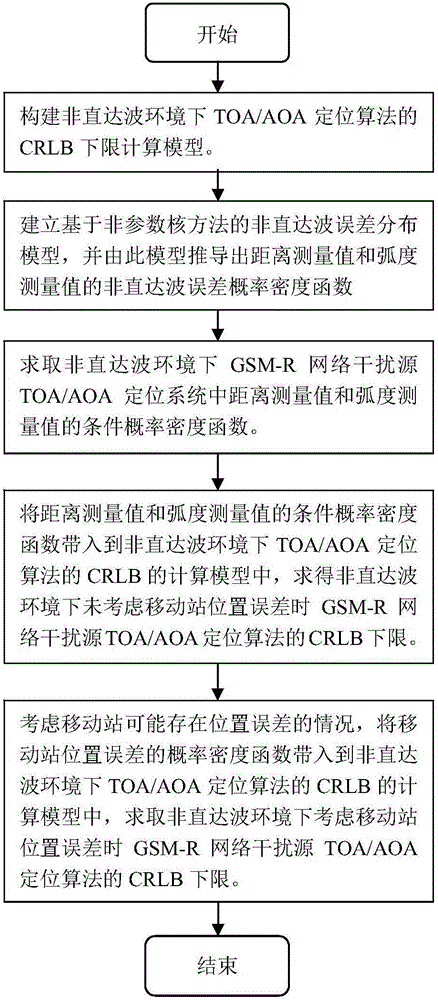
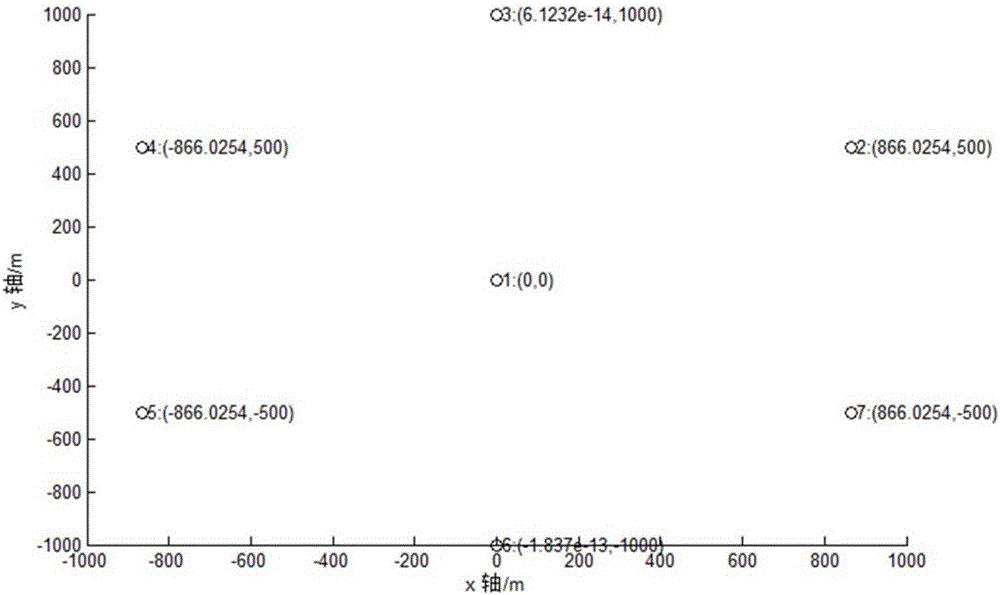
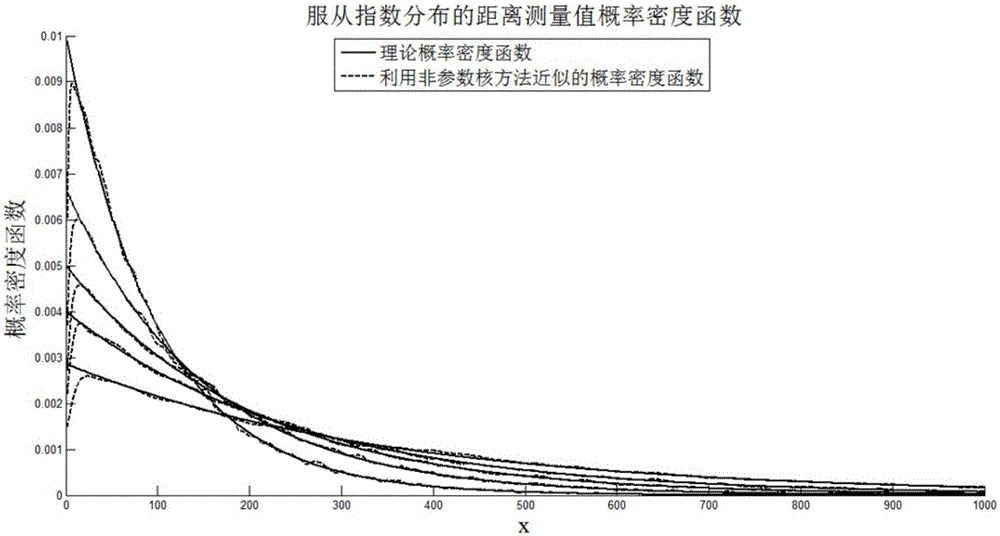
GSM-R interference source positioning algorithm evaluation method in non-line-of-sight environment
The invention belongs to the field of railway wireless communication network interference source positioning technology, and relates to a GSM-R interference source positioning algorithm evaluation method in a non-line-of-sight environment. The GSM-R interference source positioning algorithm evaluation method mainly comprises the steps of firstly constructing a CRLB lower-limit calculation model for a TOA / AOA positioning algorithm in the non-line-of-sight environment; establishing a non-line-of-sight error distribution model based on a non-parameter kernel method, calculating a condition probability density function for a measured distance value and a measured radian value in a positioning system according to a probability density function of a direct wave measurement error, and calculating a CRLB lower limit of an interference source TOA / AOA positioning algorithm in the non-line-of-sight environment. The GSM-R interference source positioning algorithm evaluation method is beneficial in that the GSM-R interference source positioning algorithm evaluation method is suitable for random distribution; the CRLB lower-limit of the GSM-R network interference source TOA / AOA positioning algorithm in the non-line-of-sight environment is derived based on the model; a position error which may exists in a mobile station is considered; and a defect of no evaluation index for the TOA / AOA hybrid positioning algorithm in the non-line-of-sight environment on the condition that the position error may exist in the mobile station is settled.
Owner:NORTH ENG OF THE ELECTRIFICATION BUREAU GROUP CRCC +1
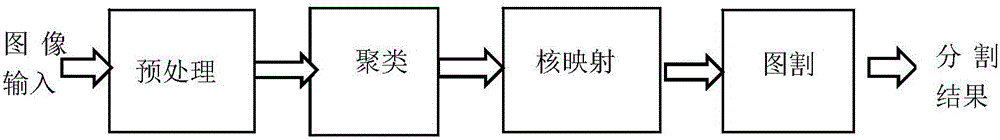
Hyperspectral image segmentation method based on kernel method
InactiveCN106355588AImplement hyperspectral image segmentationElimination of the Haghes phenomenonImage enhancementImage analysisDimensionality reductionImage segmentation algorithm
The invention relates to a hyperspectral image segmentation method based on kernel method and is intended to solve the problems of the prior art that image classification precision is low and Haghes phenomena easily occurs. The method comprises the steps of first, preprocessing hyperspectral image data; second, clustering the preprocessed hyperspectral image data; third, mapping the preprocessed hyperspectral image data and a clustering center to a high-dimensional space through a kernel function; fourth, performing image segmentation on a kernel function mapping space according to image segmentation algorithm. The algorithm provides hyperspectral image segmentation, Haghes phenomena is eliminated by dimensional reduction, the method is suitable for visual analysis and mode recognition and allows hyperspectral image segmentation; the method is applicable to the field of image segmentation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
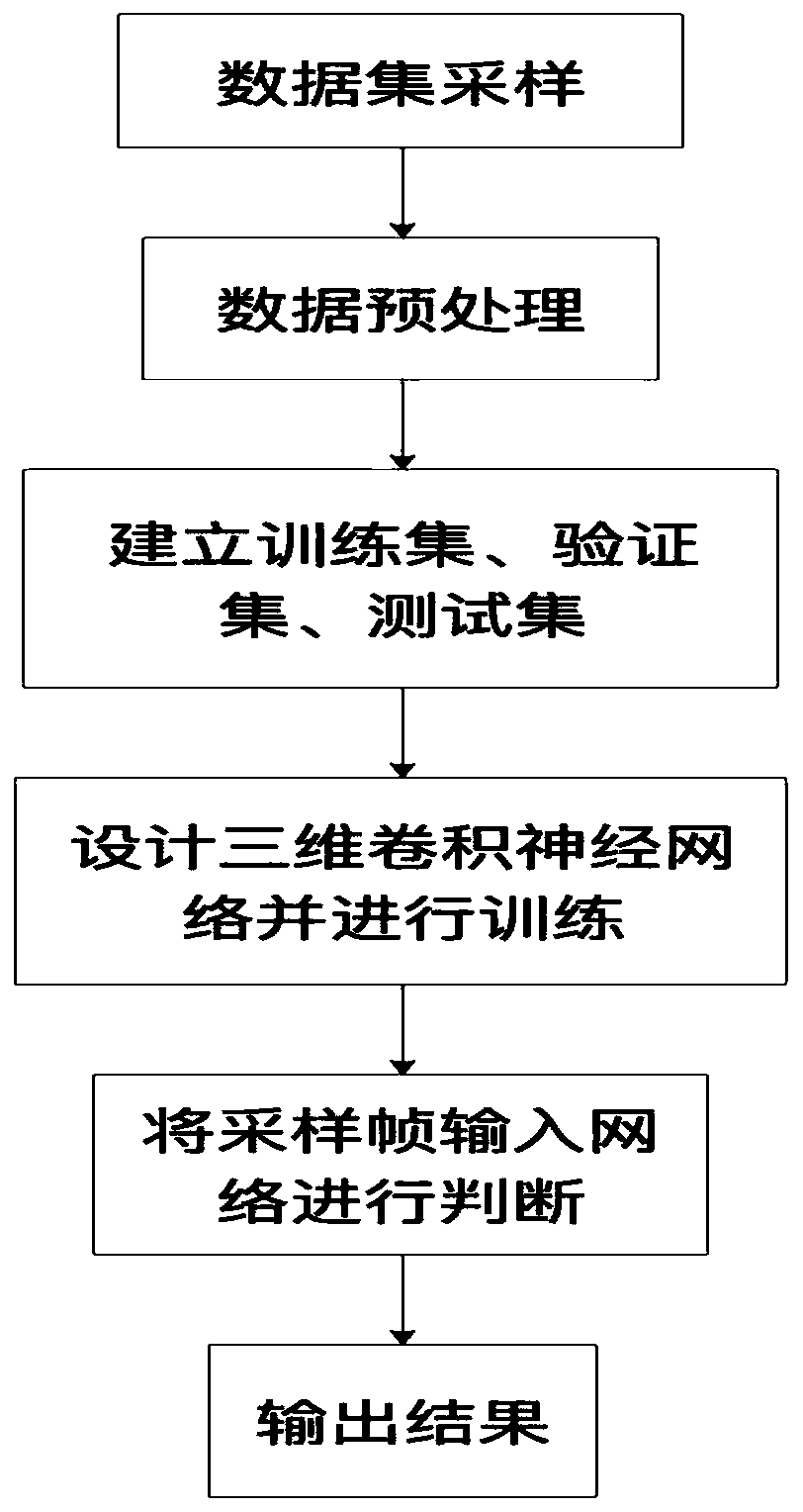
Underground space pipeline abnormality detection method based on 3D convolutional neural network
InactiveCN110032961ASolve the problem of abnormal inefficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesKernel methodAlgorithm
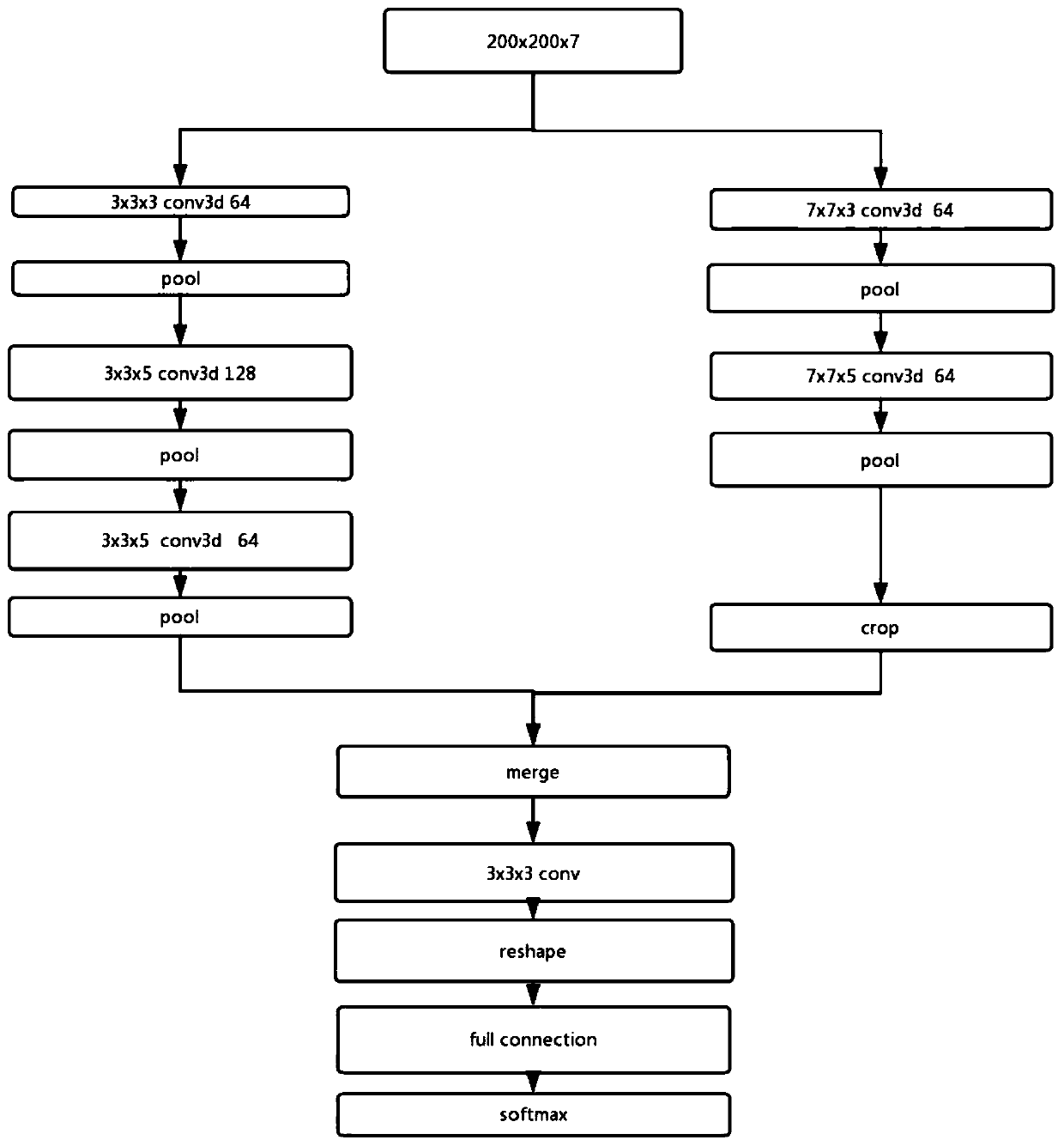
The invention provides a computer vision-based underground space pipeline abnormality detection method. The method is characterized in that the sampled video data is marked, the video frames are extracted, a three-dimensional convolution kernel method (3D CNN) in deep learning is adopted to train a sample set needed by a convolutional neural network, the sample set is preprocessed, and the size ismodified to be 200*200 in batches. By designing a three-dimensional convolution kernel network structure, and training, aiming at the adopted video data, roughly selecting a defect frame, then sampling a video at every 15ms time interval, and inputting a sampling frame into a neural network, whether an abnormal condition exists or not can be detected.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com