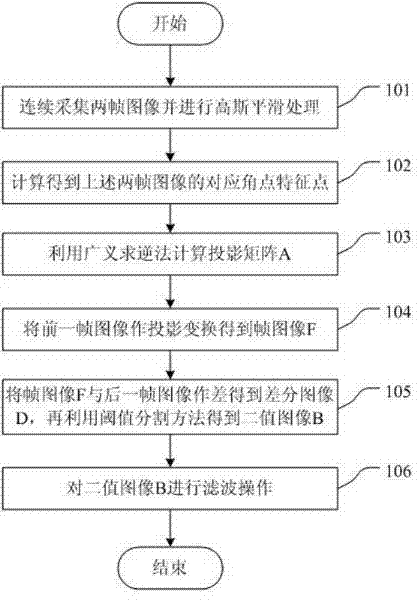
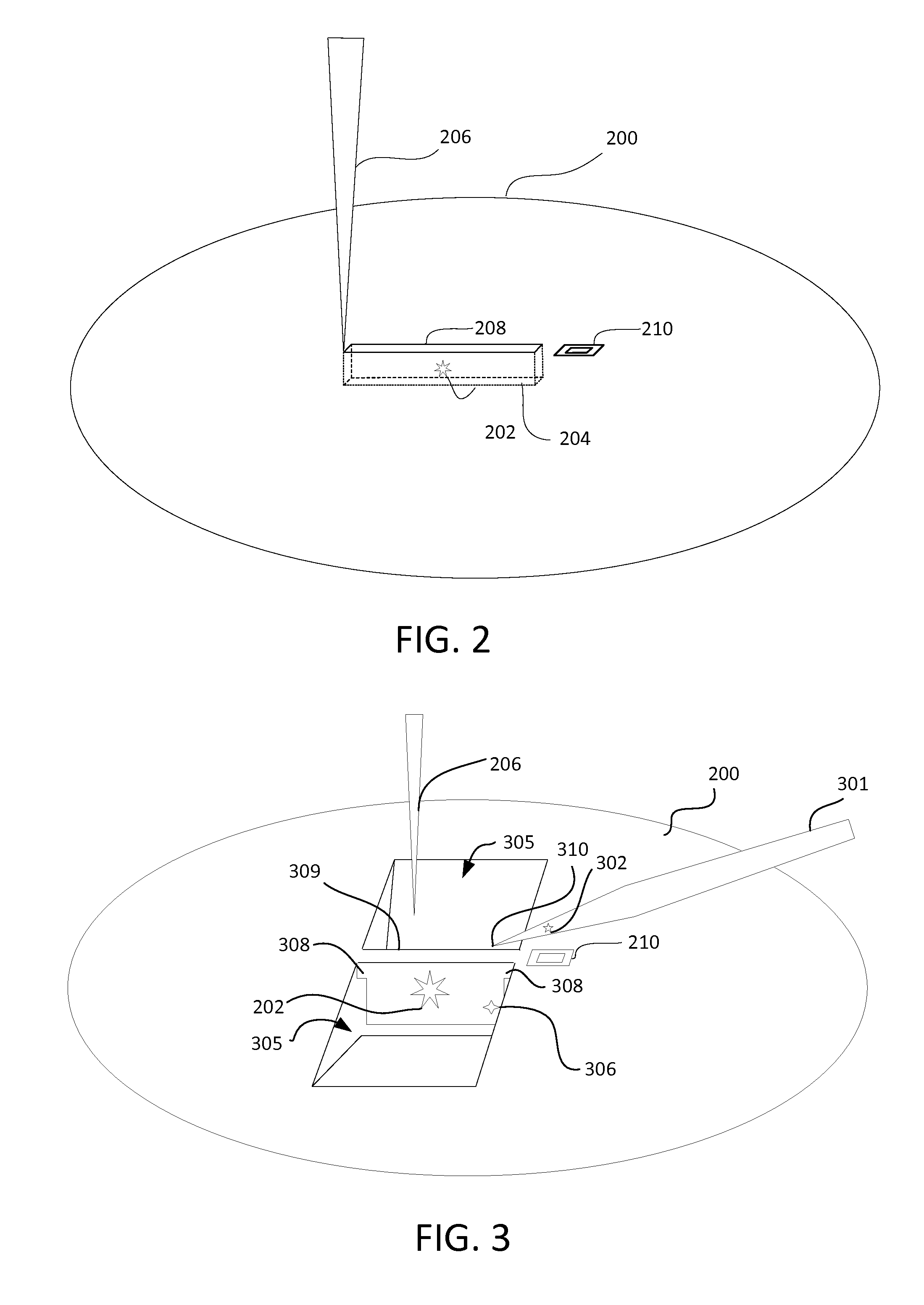
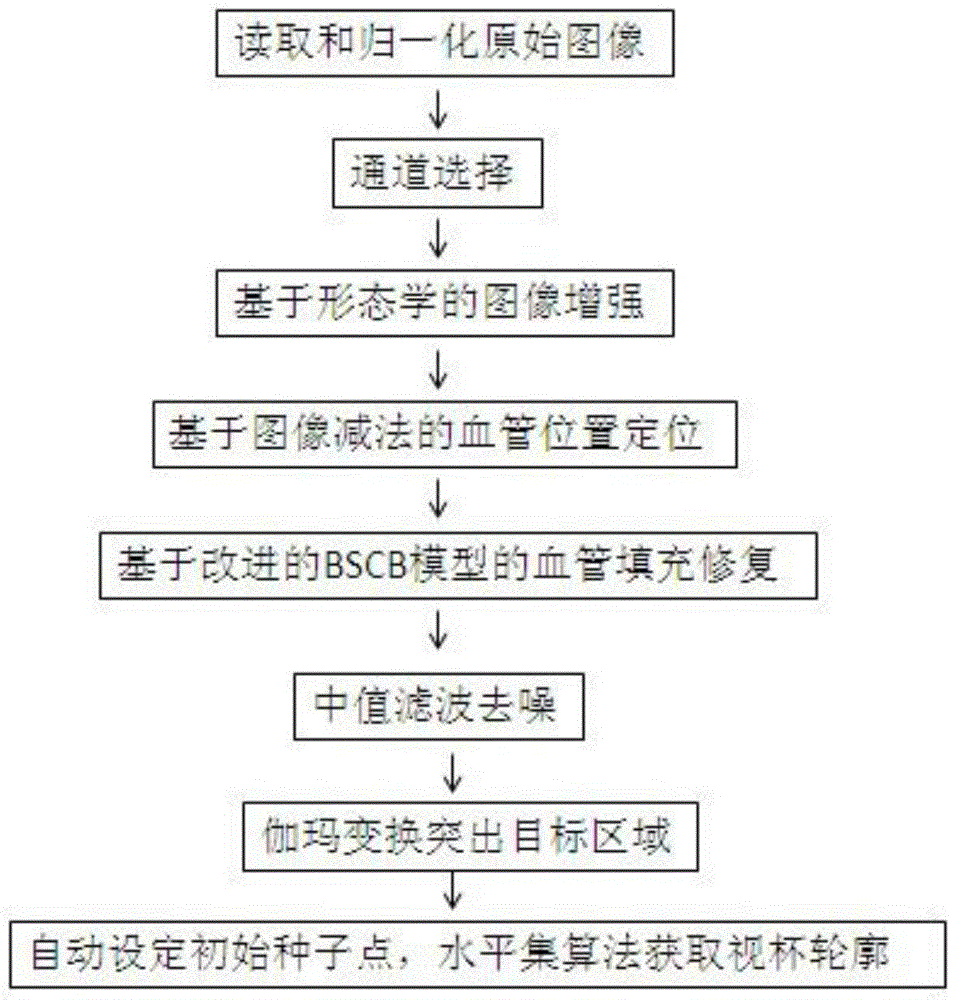
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119 results about "Image subtraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image subtraction or pixel subtraction is a process whereby the digital numeric value of one pixel or whole image is subtracted from another image. This is primarily done for one of two reasons – levelling uneven sections of an image such as half an image having a shadow on it, or detecting changes between two images. This detection of changes can be used to tell if something in the image moved. This is commonly used in fields such as astrophotography to assist with the computerized search for asteroids or Kuiper belt objects in which the target is moving and would be in one place in one image, and another from an image one hour later and where using this technique would make the fixed stars in the background disappear leaving only the target. For an example see.
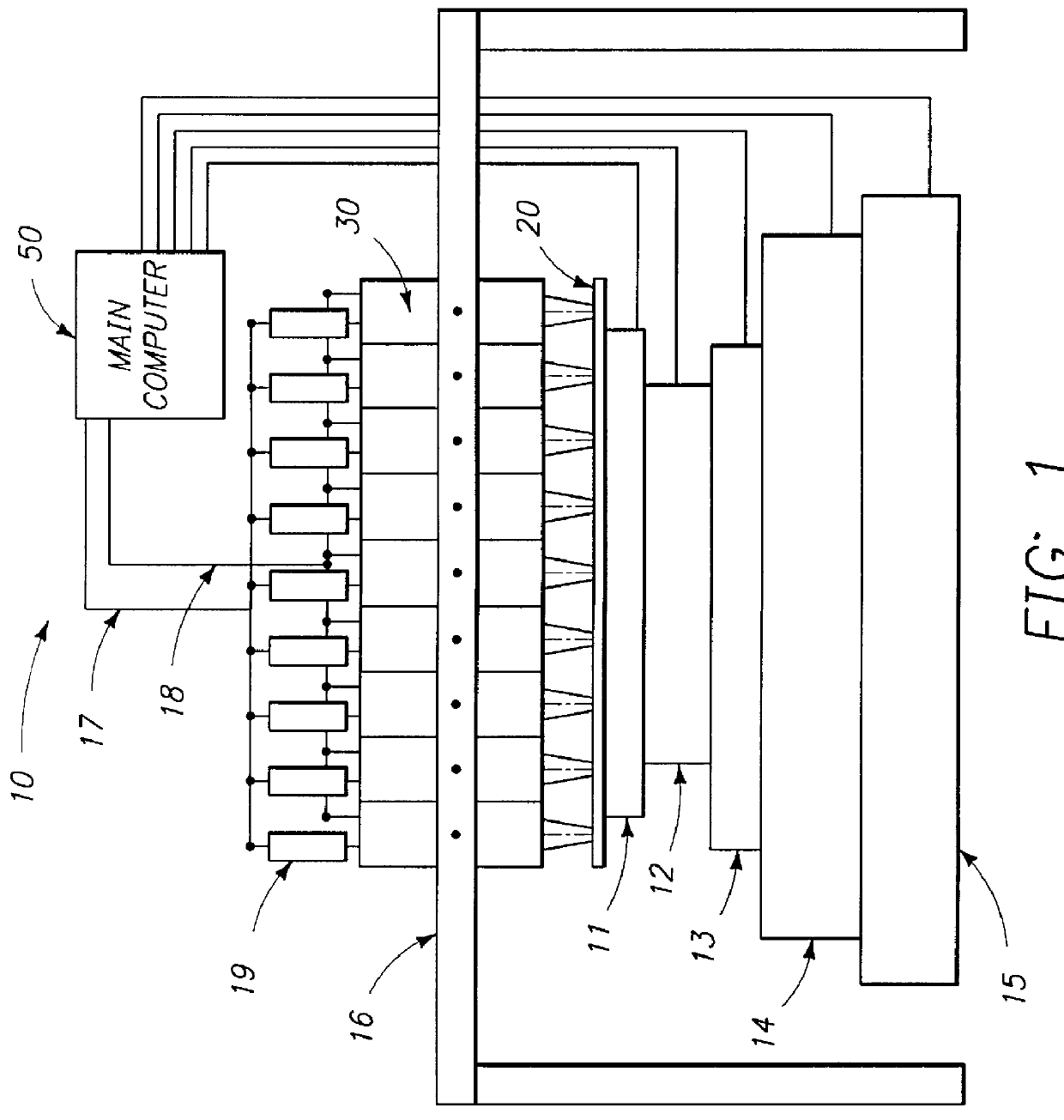
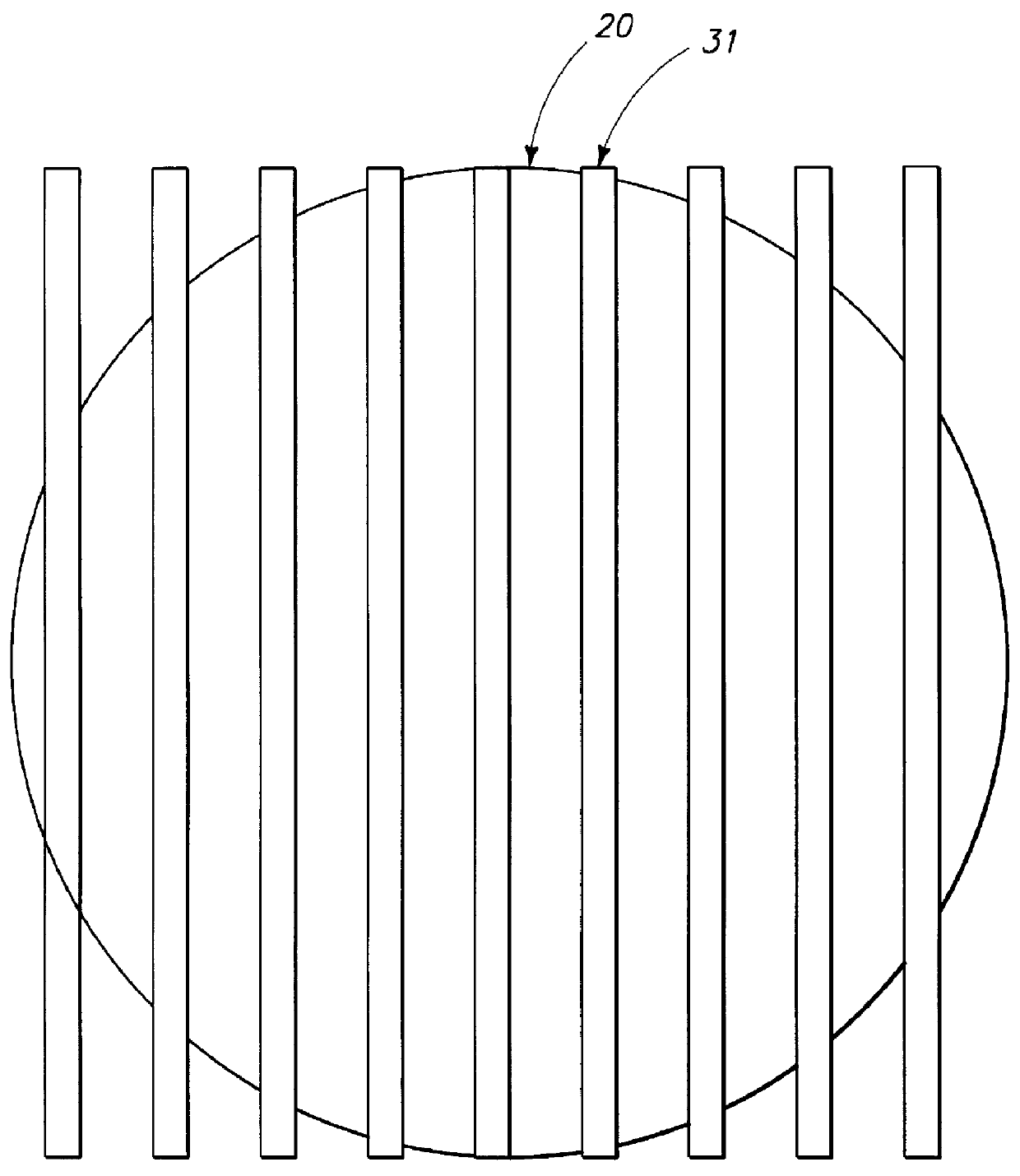
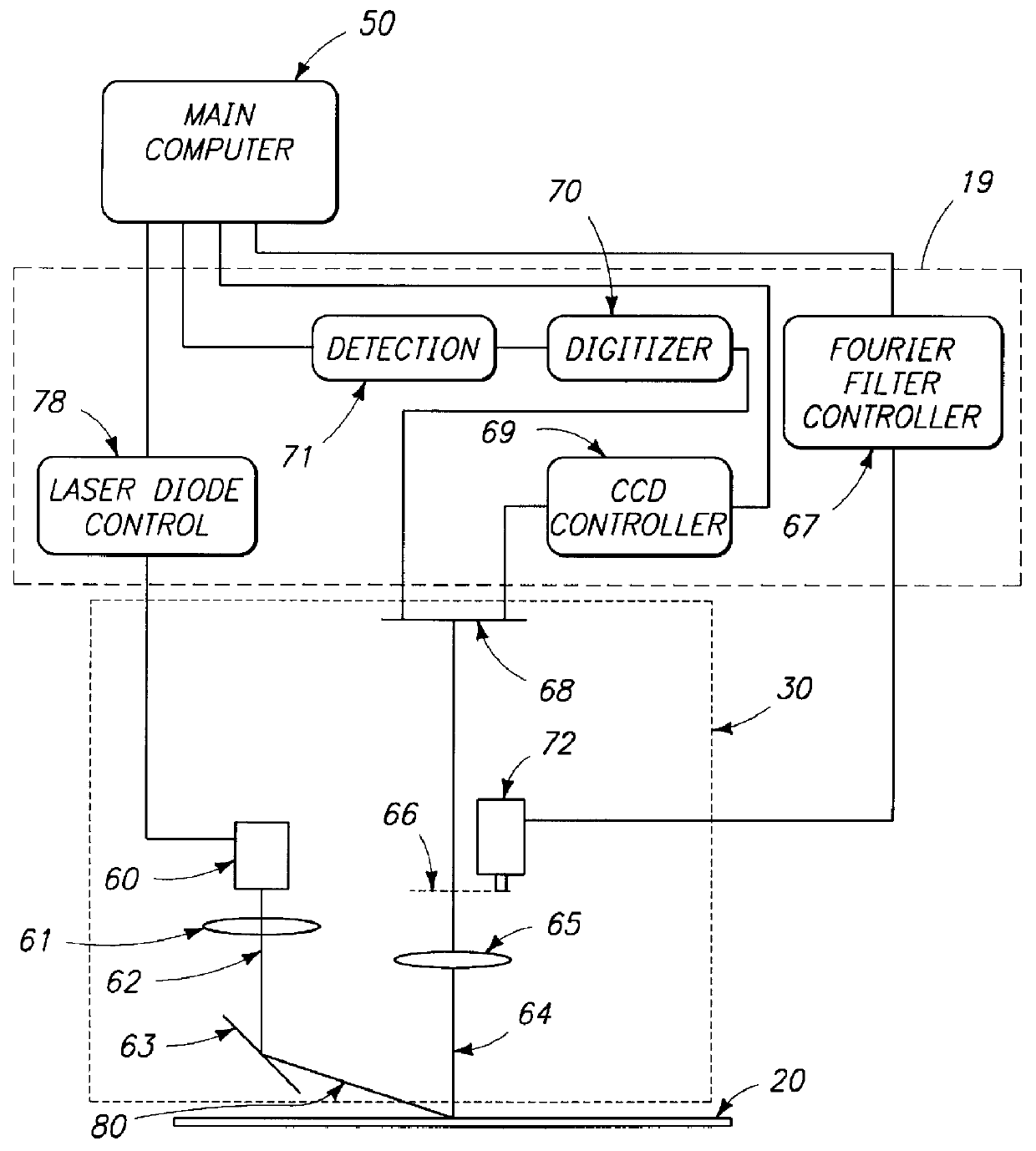
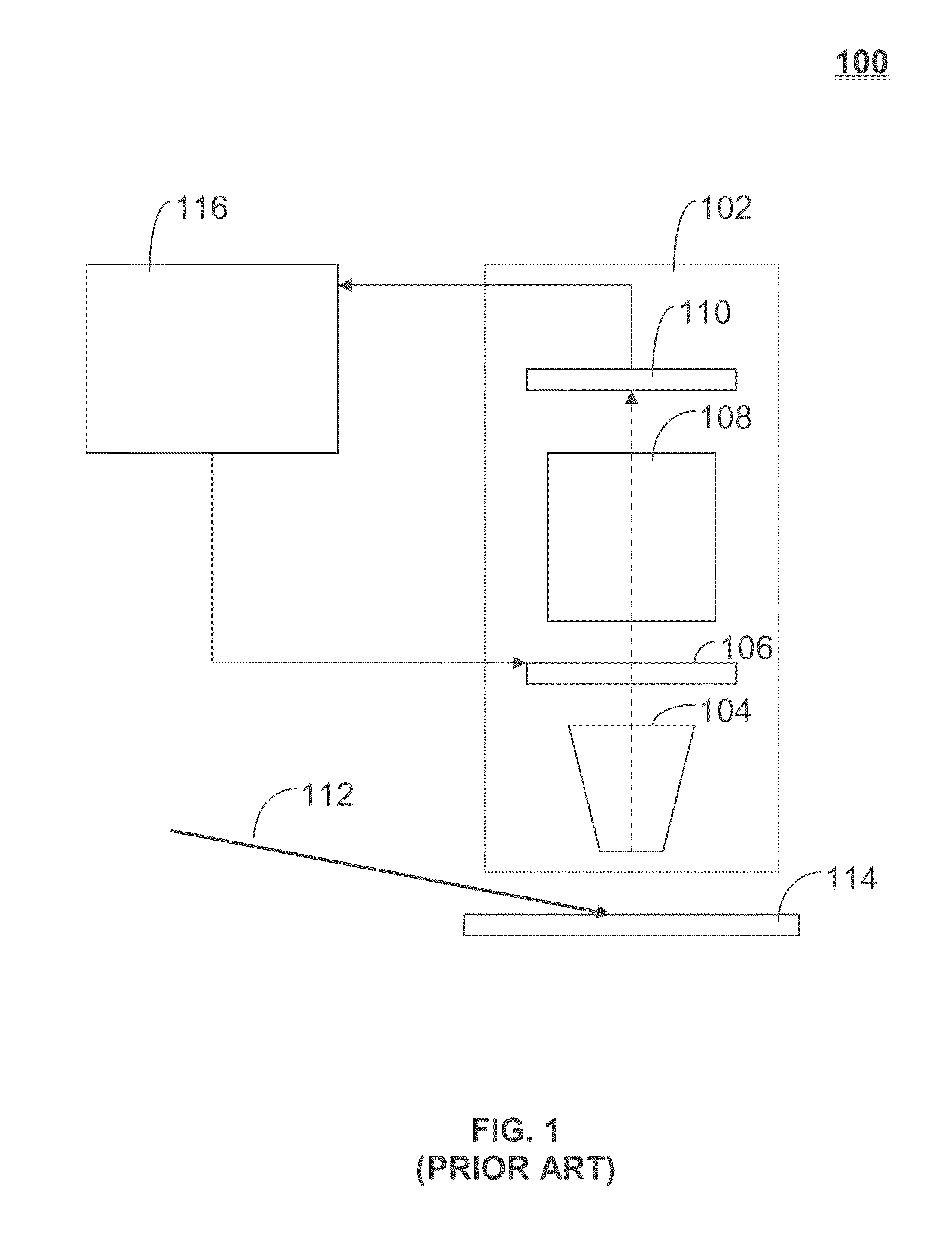
System and method for inspecting semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS6020957ALow costFaster throughputSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingImage subtraction
A method for inspecting semiconductor wafers is provided in which a plurality of independent, low-cost, optical-inspection subsystems are packaged and integrated to simultaneously perform parallel inspections of portions of the wafer, the wafer location relative to the inspection being controlled so that the entire wafer is imaged by the system of optical subsystems in a raster-scan mode. A monochromatic coherent-light source illuminates the wafer surface. A darkfield-optical system collects scattered light and filters patterns produced by valid periodic wafer structures using Fourier filtering. The filtered light is processed by general purpose digital-signal processors. Image subtraction methods are used to detect wafer defects, which are reported to a main computer to aid in statistical process control, particularly for manufacturing equipment.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
Image subtraction to remove ambient illumination
InactiveUS6021210ATelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage subtractionAmbient lighting
In a method of image subtraction a series of frames of a subject are taken using a video camera The subject is illuminated in a manner so that illumination is alternately on then off for successive fields within the image frame. A single frame is grabbed and an absolute difference between the odd field and the even field within that single image frame is determined. The resulting absolute difference image will represent the subject as illuminated by the system illumination only, and not by any ambient illumination, and can then be used to identify the subject in the image.
Owner:SENSAR
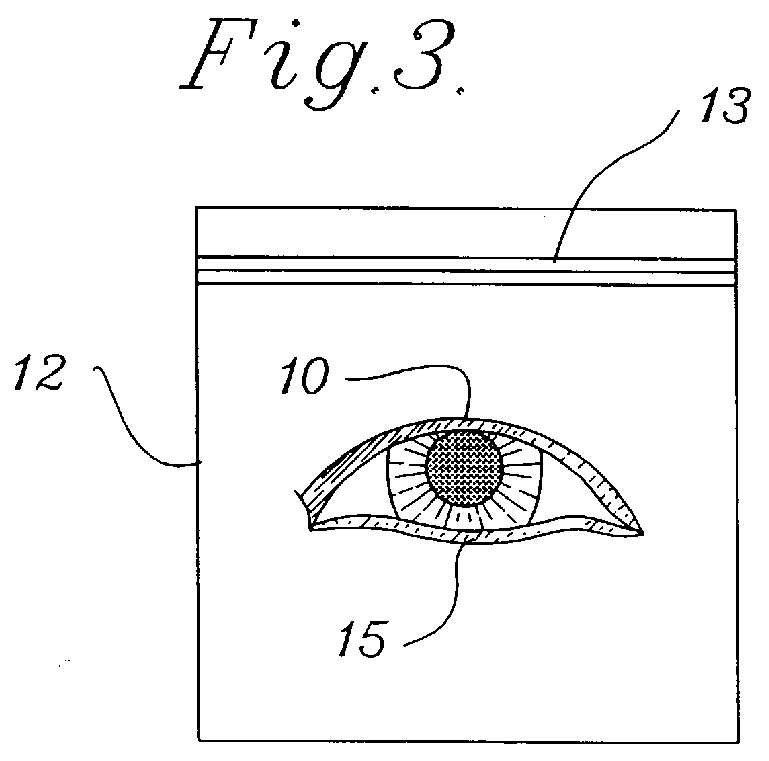
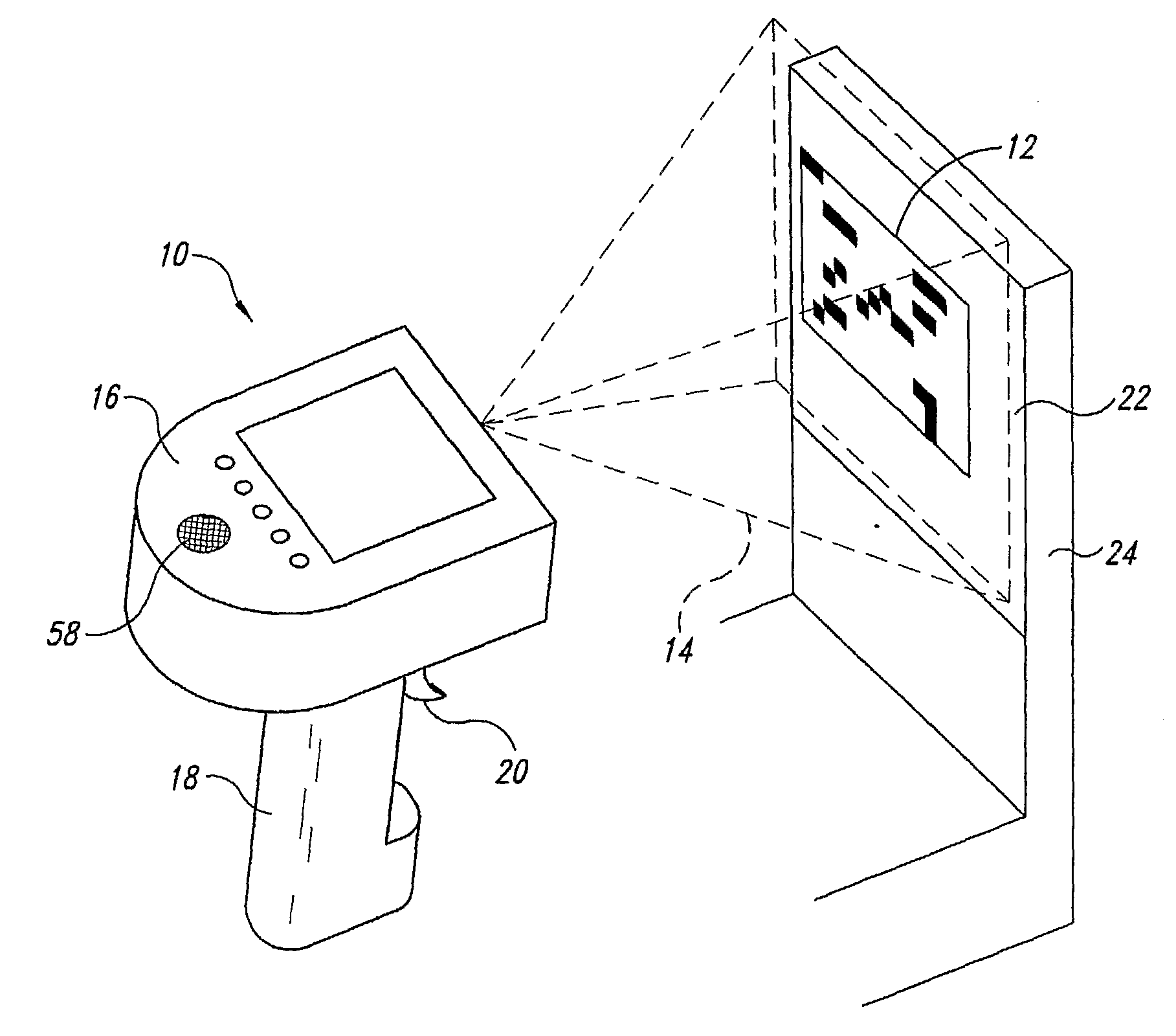
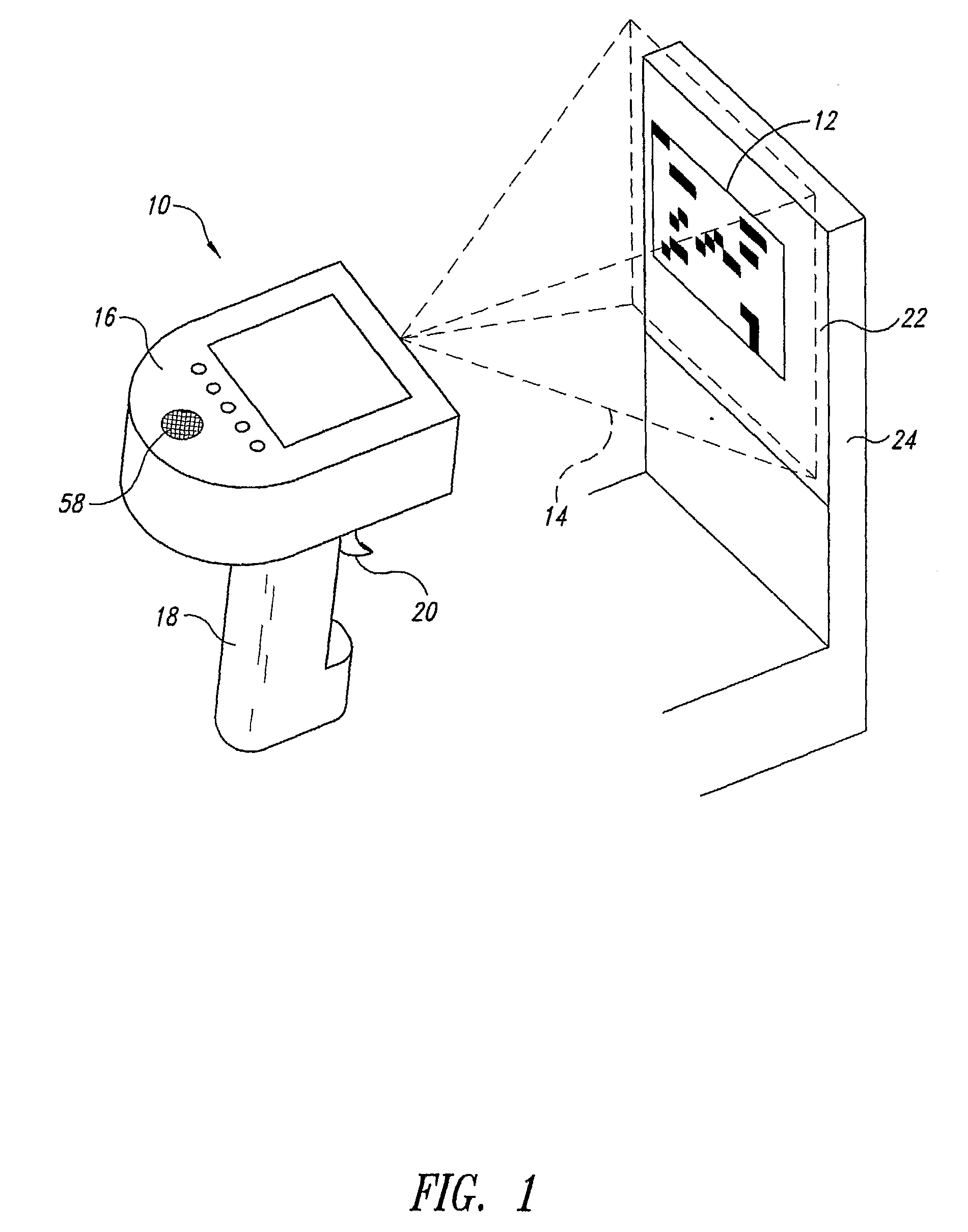
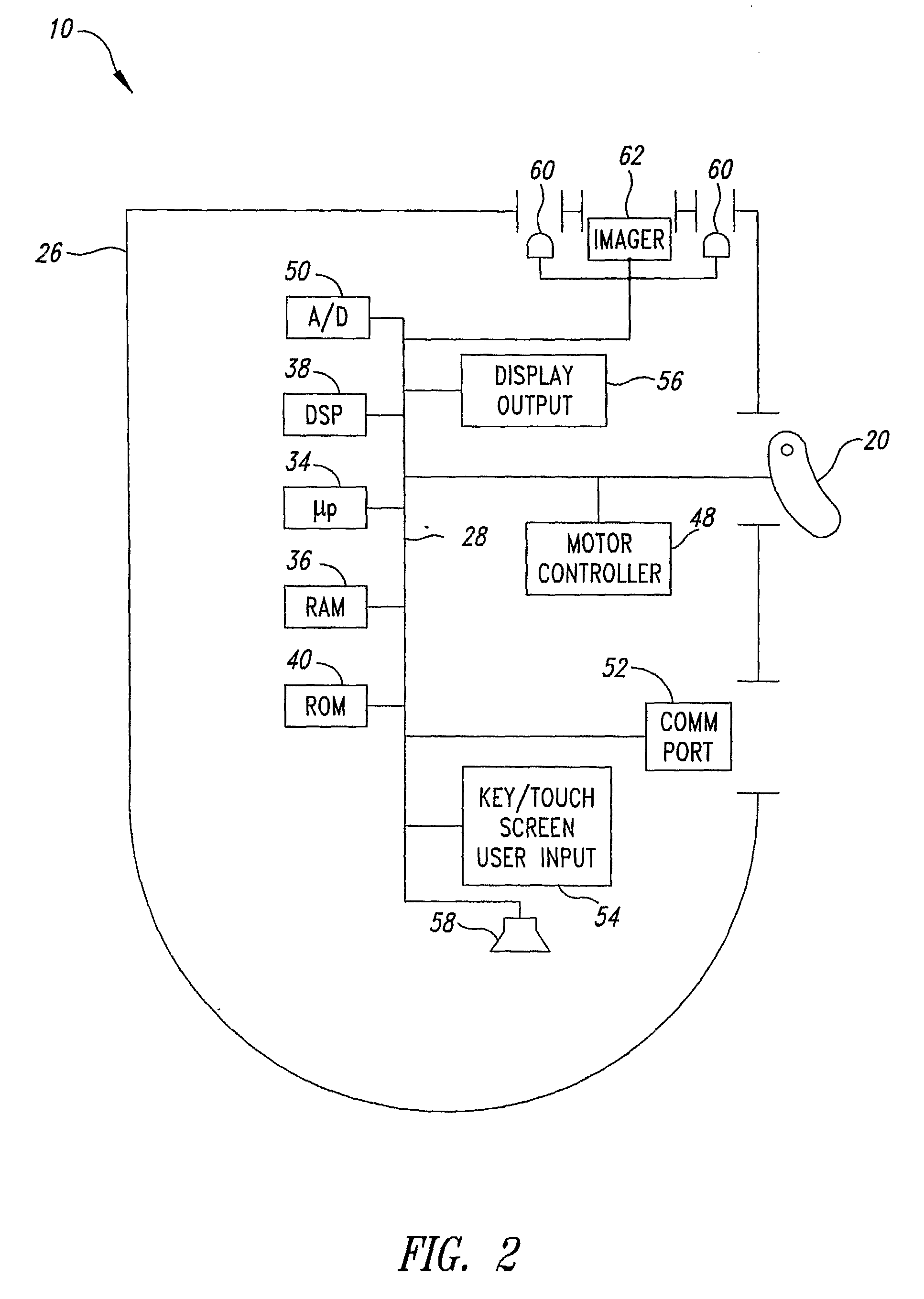
Noise Reduction by Image Subtraction in an Automatic Data Collection Device, Such as an Image Acquisition Device
ActiveUS20080267537A1Character and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage subtractionDisplay device
An automatic data collection device (10) and method reads images from display screen (22) of an electronic display device (24), such as a cellular telephone. The method reads a flashing image of a target machine-readable symbol (12) displayed on the display screen, by obtaining at least two images of the display screen. In the first image, the image of the target machine-readable symbol is present. In the second image, the image of the target machine-readable symbol (12) is absent. The second image of the display screen, when the image of the target machine-readable symbol is absent, comprises noise and other images that are irrelevant to the decoding process. This noise in the second image is subtracted from the first image of the display screen having the image of the target machine-readable symbol displayed thereon the symbol. A resulting image from the image subtraction is an improved image of the target machine-readable symbol.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Motion clutter suppression for image-subtracting cameras
ActiveUS7315324B2Magnitude is minimisedWidth minimizedTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage subtractionElectronic chip
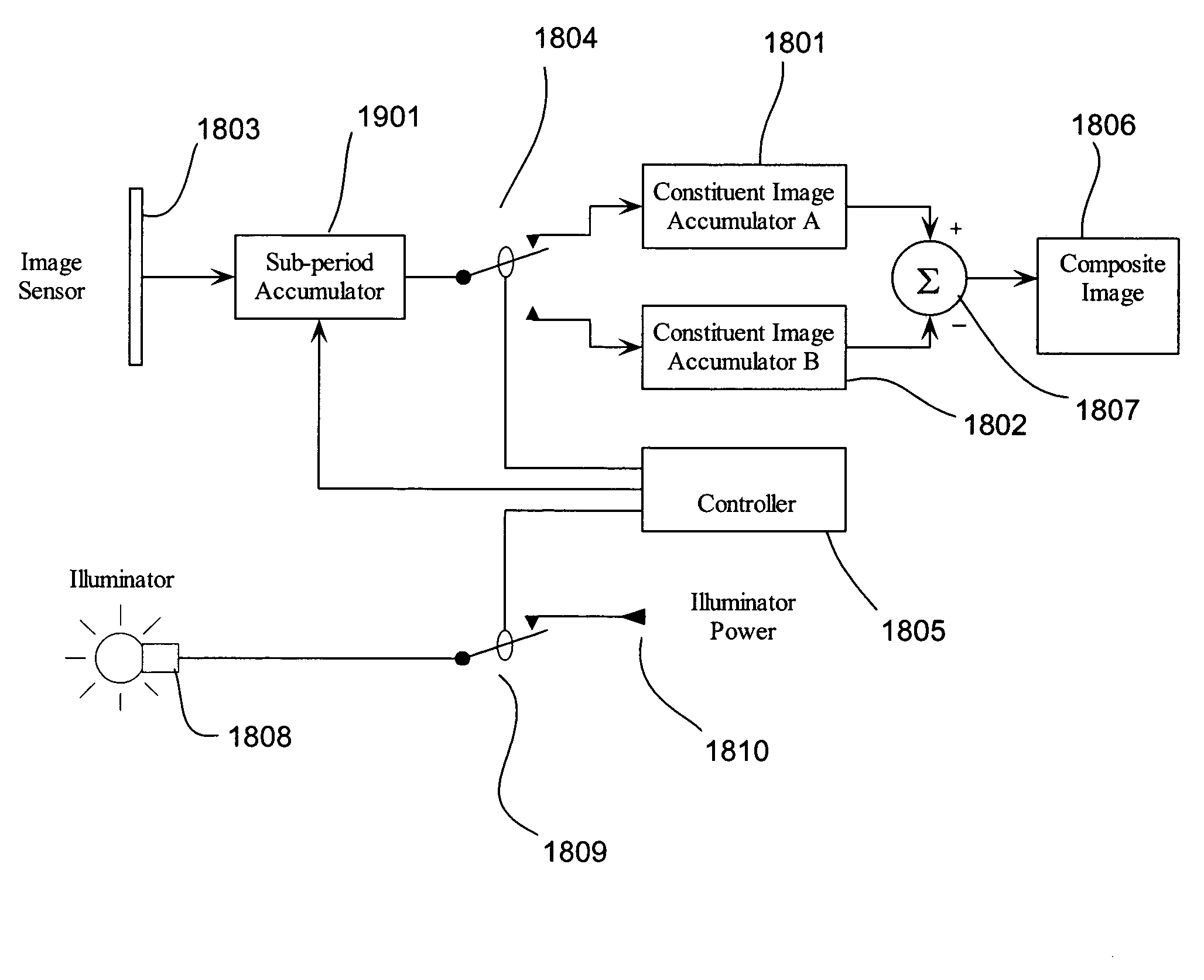
Embodiments of the present invention relate to systems and methods for minimizing motion clutter in image-generation devices. Temporally-interleaved image-subtraction reduces the magnitude of motion clutter and has no adverse effect on the desired ambient-light cancellation of static images. Embodiments of image-generation devices employing temporally-interleaved image-subtraction include single, double, triple, and series accumulator configurations. All four embodiments allow synchronization with scene illuminators and may be implemented on a single electronic chip. Temporally-interleaved image-subtraction is particularly well suited for use in video eyetracking applications where ambient light and scene motion can cause significant problems.
Owner:EYEGAZE INC
Adherent white blood cell segmentation method based on nucleus-marked watershed transformation
ActiveCN104392460AEasy to operateShort timeImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionCell adhesion
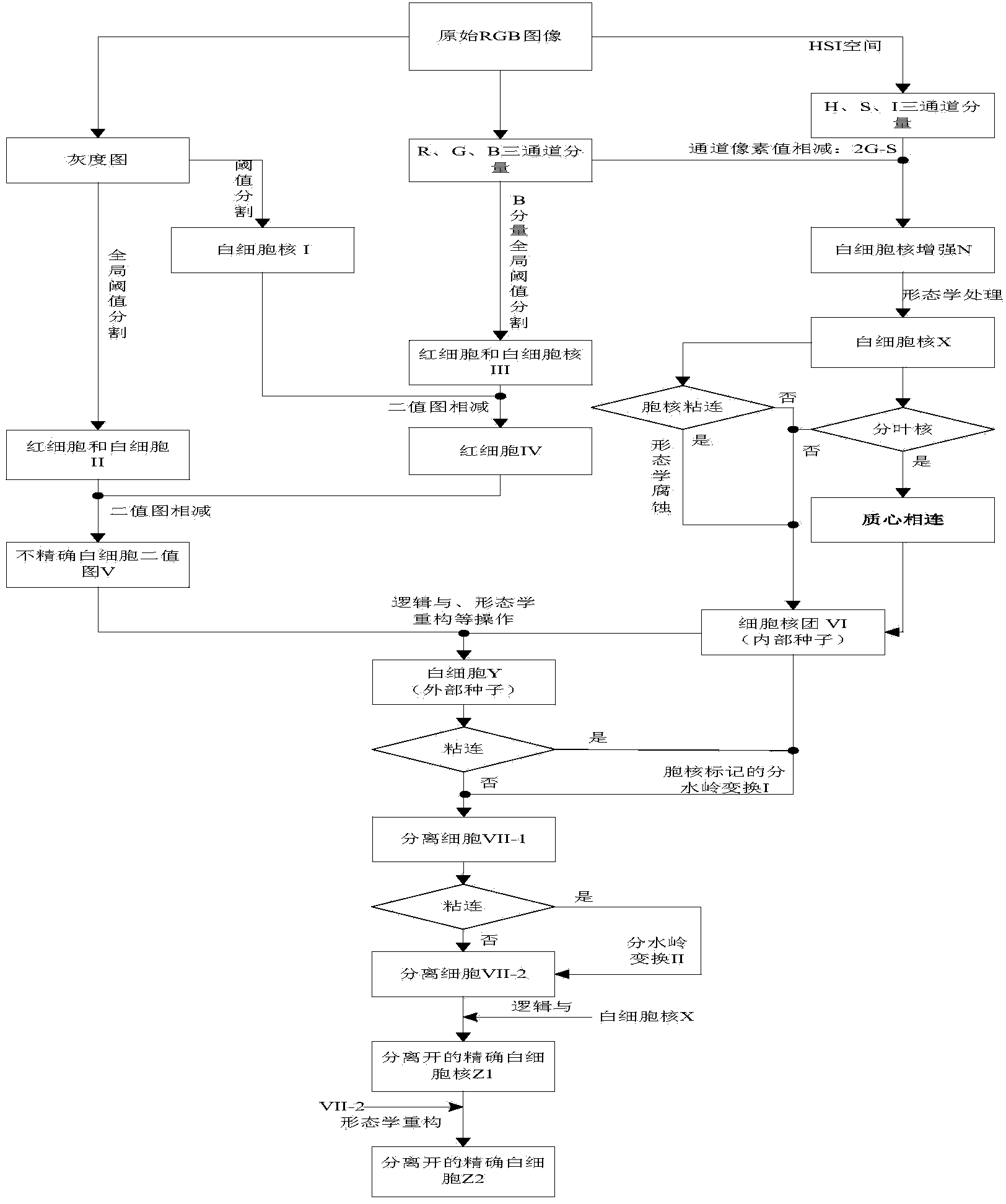
The utility model discloses an adherent white blood cell segmentation method based on nucleus-marked watershed transformation. The adherent white blood cell segmentation method comprises the following steps: firstly inputting original RGB (Red, Green, Blue) images and discovering the generally difficult-to-solve problem of peripheral white blood cells and bone marrow white blood cells in the image processing process; secondly, carrying out HIS (Hue-Saturation-Intensity) and LUV color space and grayscale space conversion on the original images and analyzing the characteristics of each channel component image; thirdly, respectively carrying out threshold value segmentation and image subtraction on components B and grayscale images to obtain white blood cell images containing a part of impurities; fourthly, obtaining a target taking a white blood cell nuclei as a marker through an image enhancement technology; fifthly, carrying out morphological operation and watershed transformation on the white blood cell nuclei and the white blood cell images containing the impurities to remove the impurities, obtain accurate white blood cell images and solve the problem of cell adhesion; finally, cutting the targeted white blood cells, converting the targeted white blood cells into an LUV space, clustering the white blood cell images from the view of space and color and obtaining a white blood cell nucleus.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
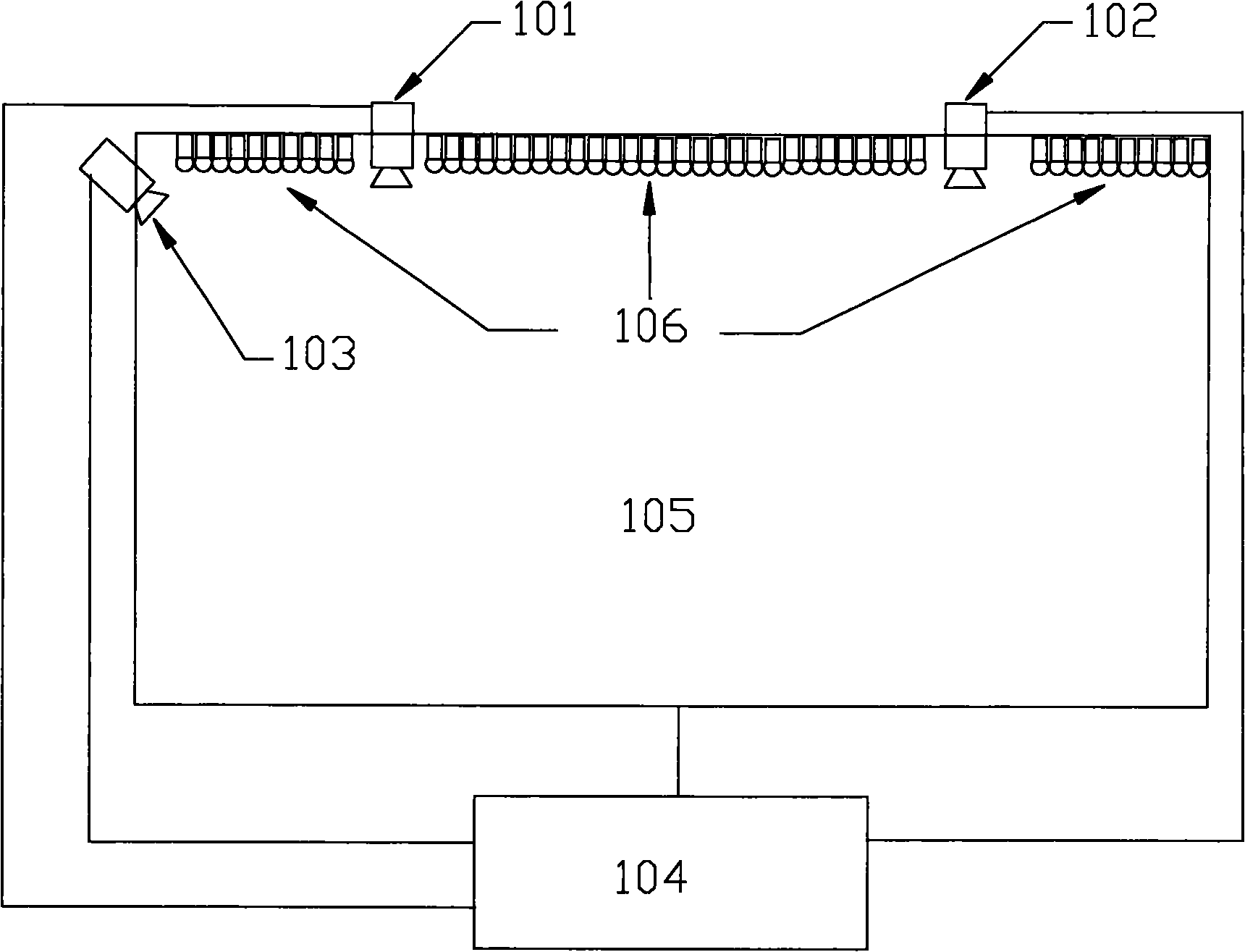
Device and method for discriminating color of touch pen of touch device
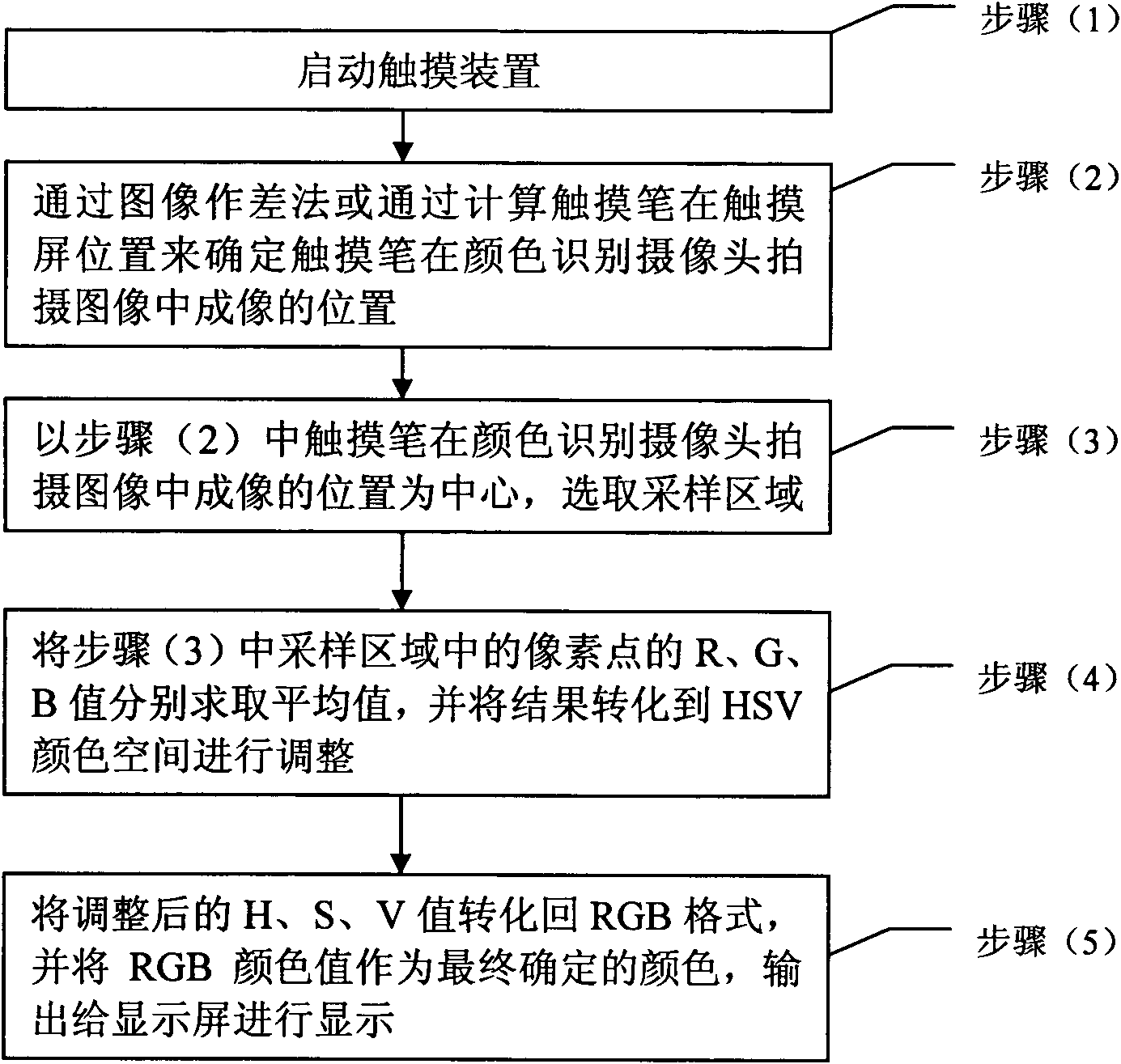
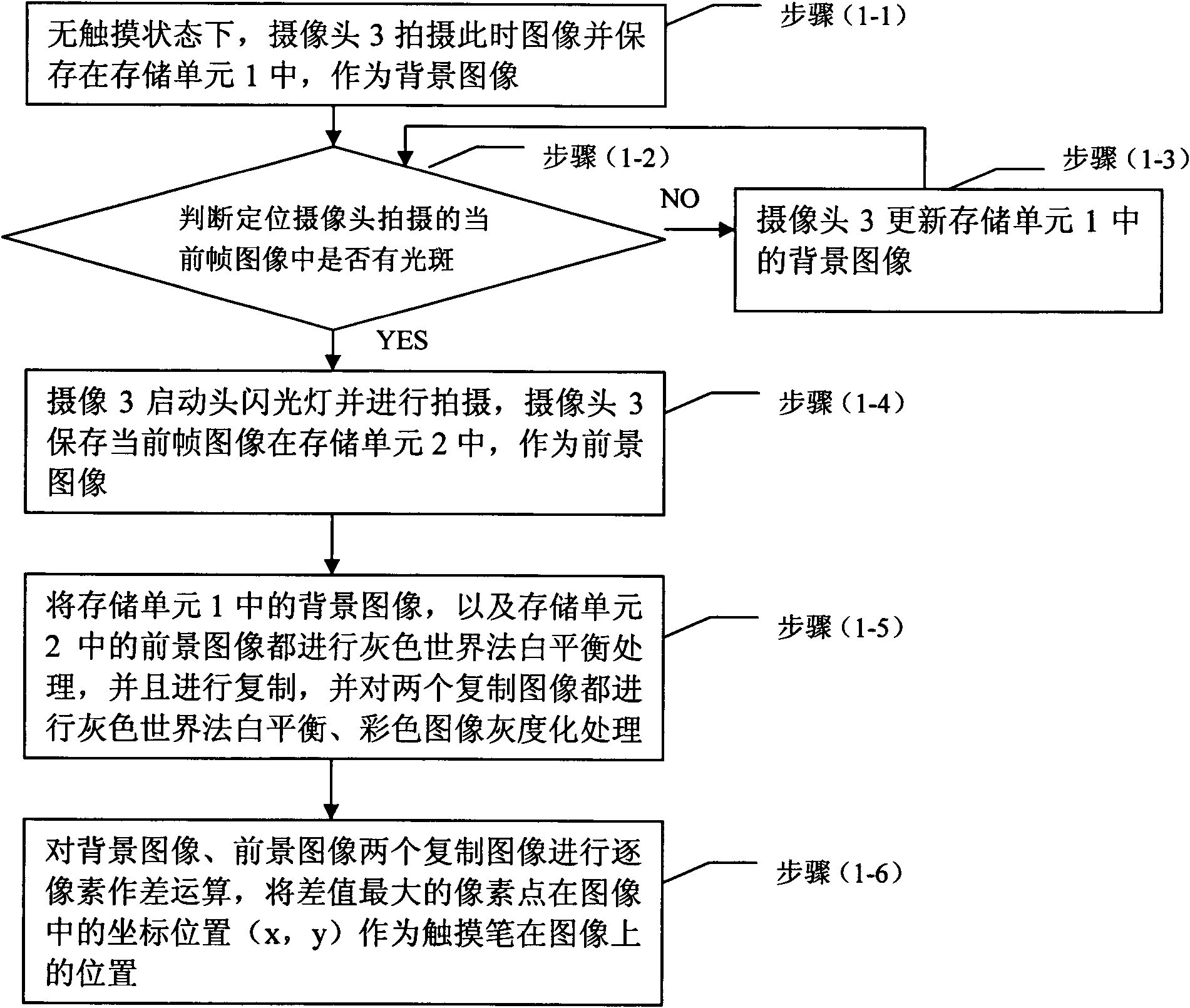
InactiveCN101882034AProcessing speedQuick responseInput/output processes for data processingImage subtractionComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a device and a method for discriminating the color of a touch pen of a touch device. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: determining the imaging position of the touch pen in an image shot by the color discrimination camera through an image subtraction method or by computing the position of the touch pen on a touch screen; selecting a sampling area by taking the position as a center; respectively solving the average values of R, G, B values of pixel points in the sampling area, and converting a result to an HSV (Hue Saturation Value) color space for adjustment; and converting the adjusted H, S V values back to RGB (Red-Green-Blue) formats, and outputting the RGB color values as ultimately determined colors to a display screen for display. The invention can more accurately discriminate the color of the touch pen of the touch device, effectively improves the condition that the display color is slant dark and has easy operation.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
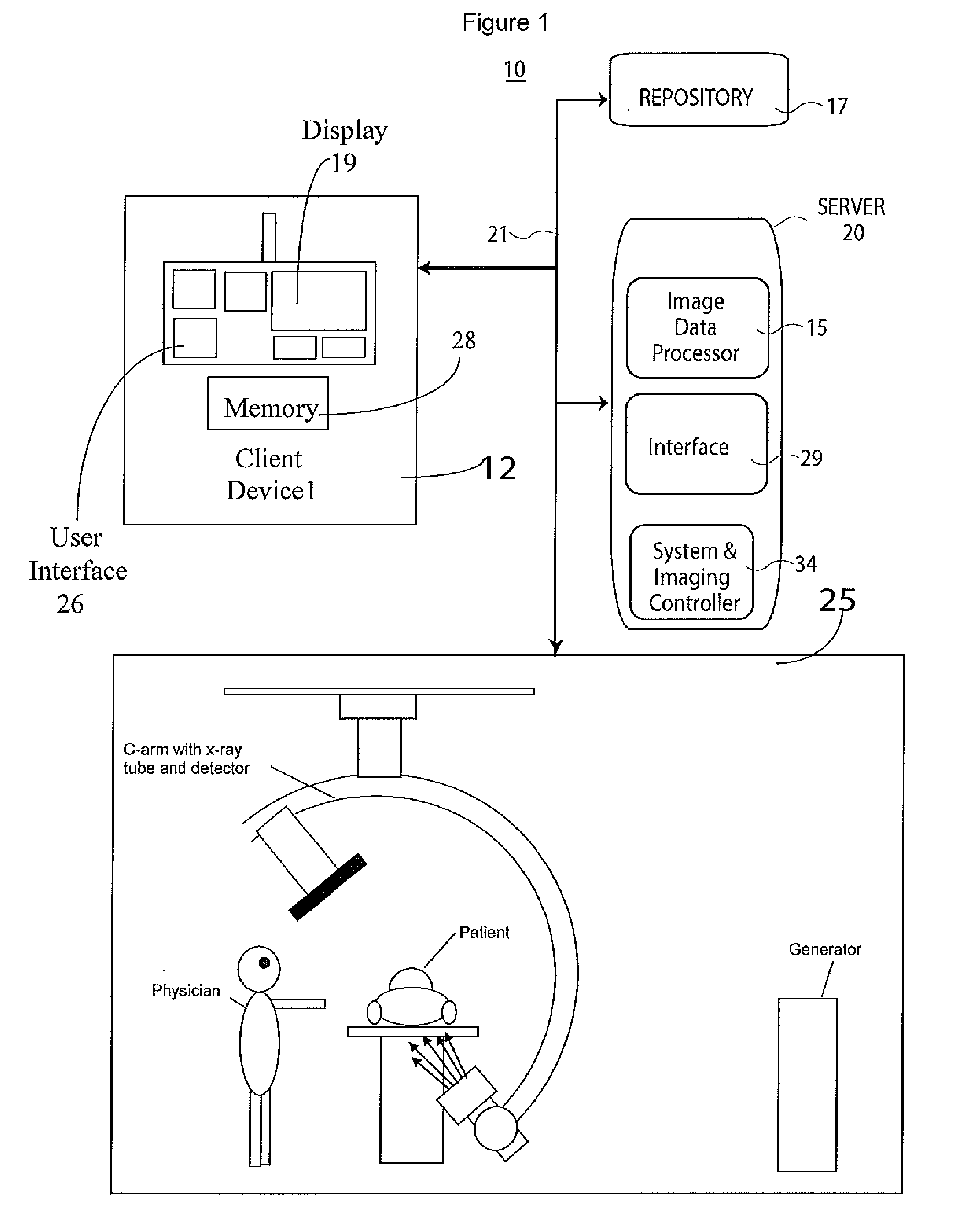
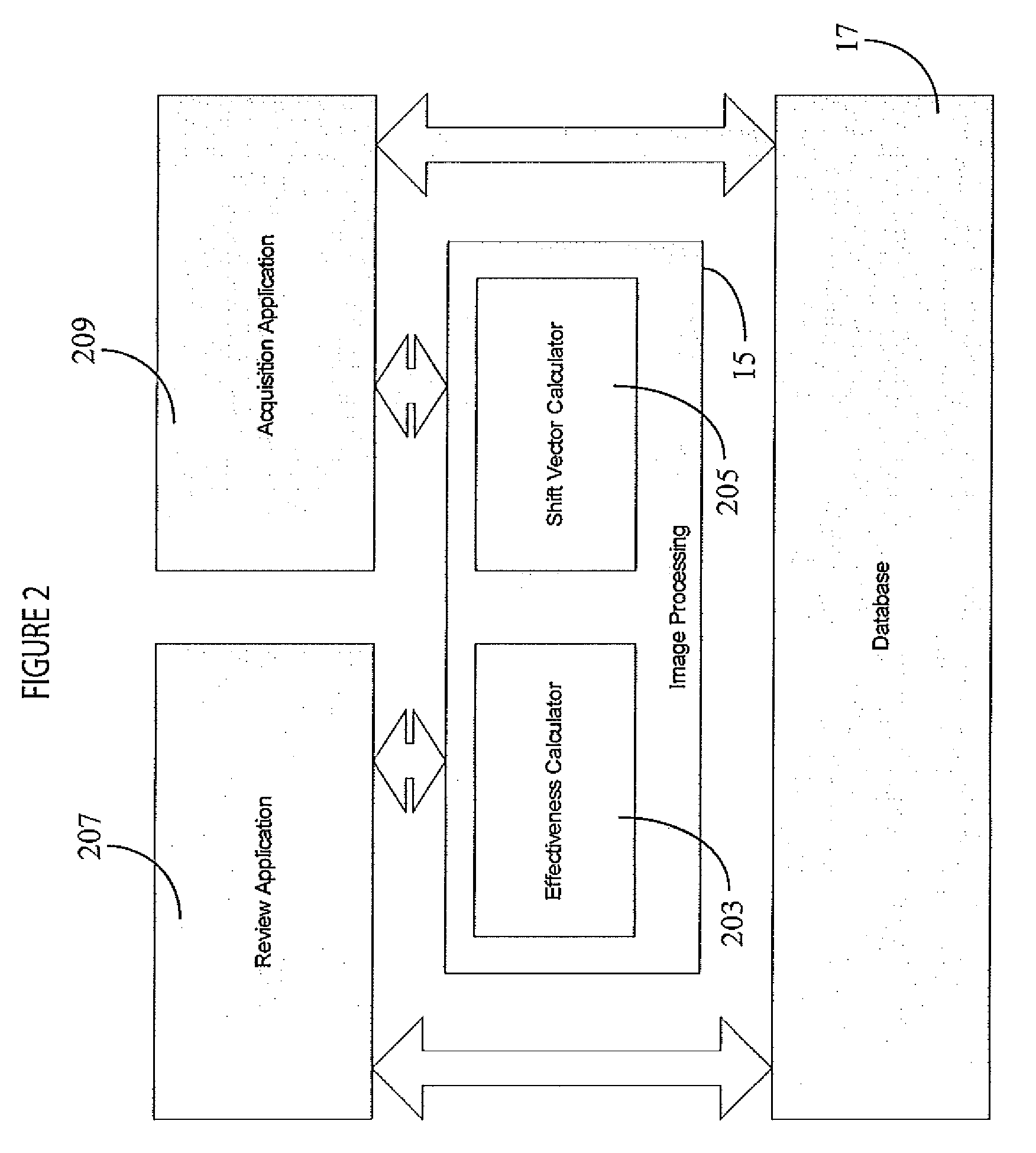
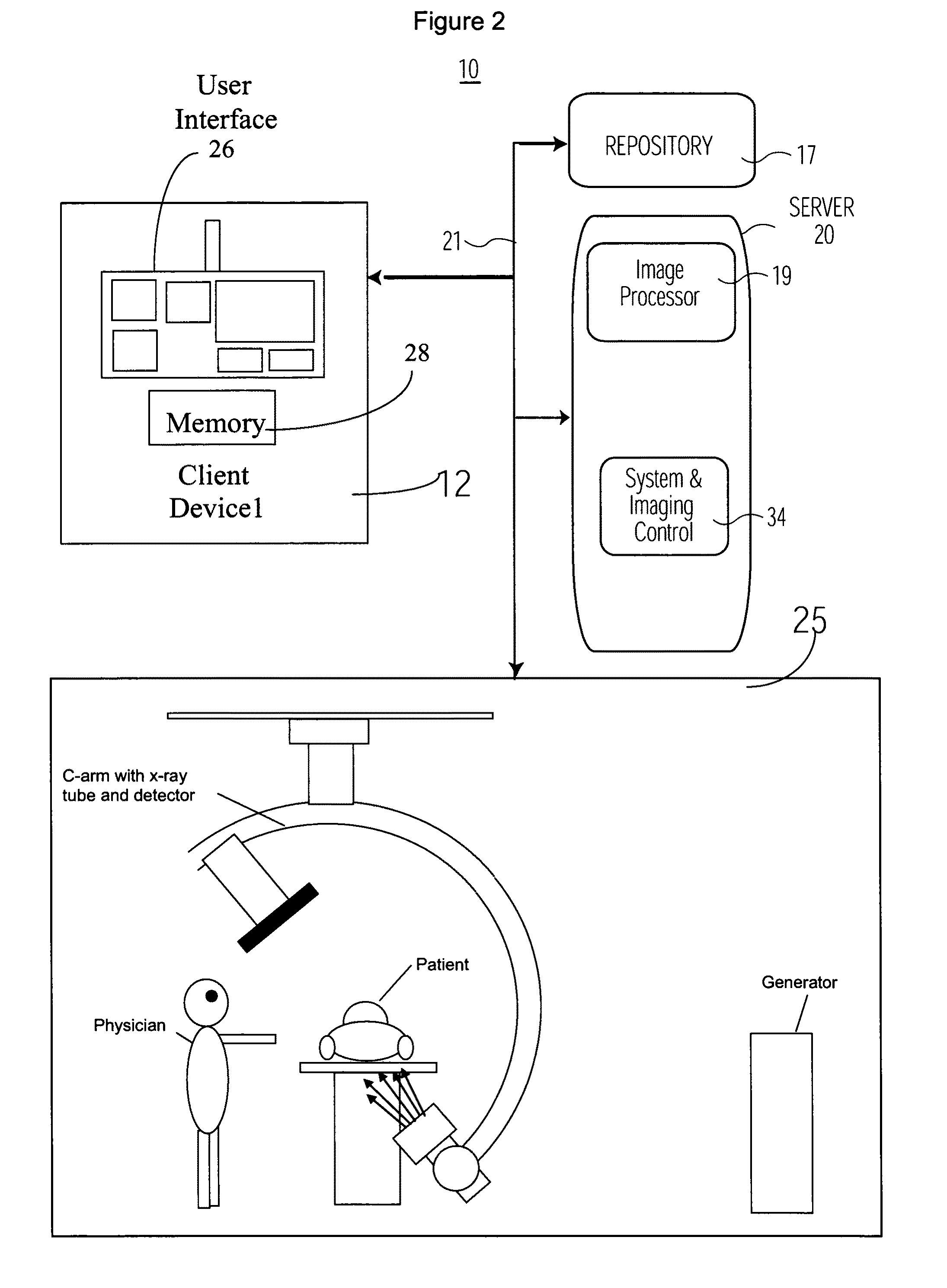
Medical Image Processing and Registration System
InactiveUS20110293162A1Improve visualizationImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionImaging processing
An image data subtraction system enhances visualization of vessels subject to movement using an imaging system. The imaging system acquires data representing first and second anatomical image sets comprising multiple temporally sequential individual mask (without contrast agent) and fill images (with contrast agent) of vessels respectively, during multiple heart cycles. An image data processor automatically identifies temporally corresponding pairs of images comprising a mask image and a contrast enhanced image and for the corresponding pairs, automatically determines a shift of a contrast enhanced image relative to a mask image to compensate for motion induced image mis-alignment. The image data processor automatically shifts a contrast enhanced image relative to a mask image in response to the determined shift. The image data processor subtracts data representing a mask image of a corresponding pair from a shifted contrast enhanced image of the corresponding pair, to provide multiple subtracted images showing enhanced visualization of vessels.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
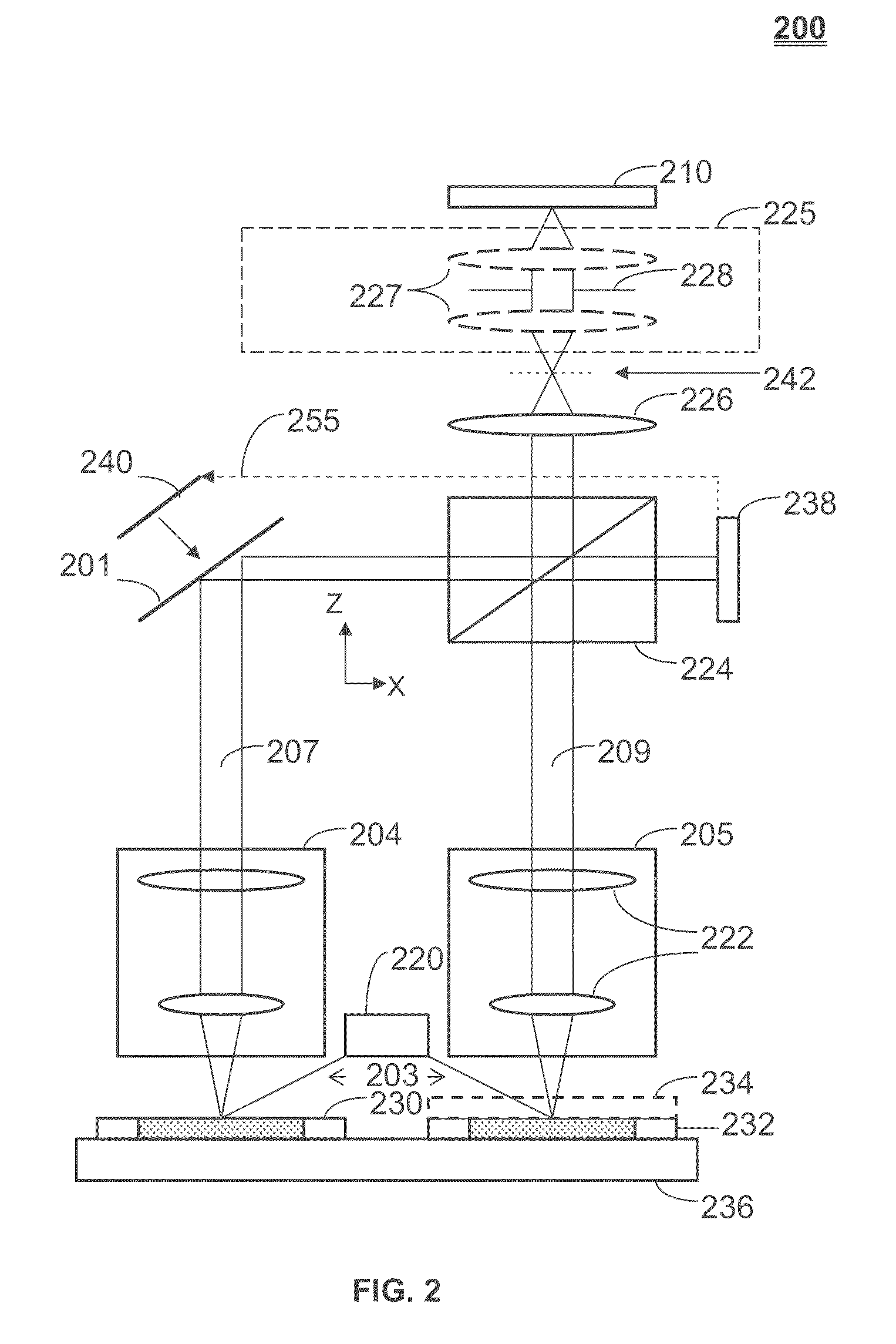
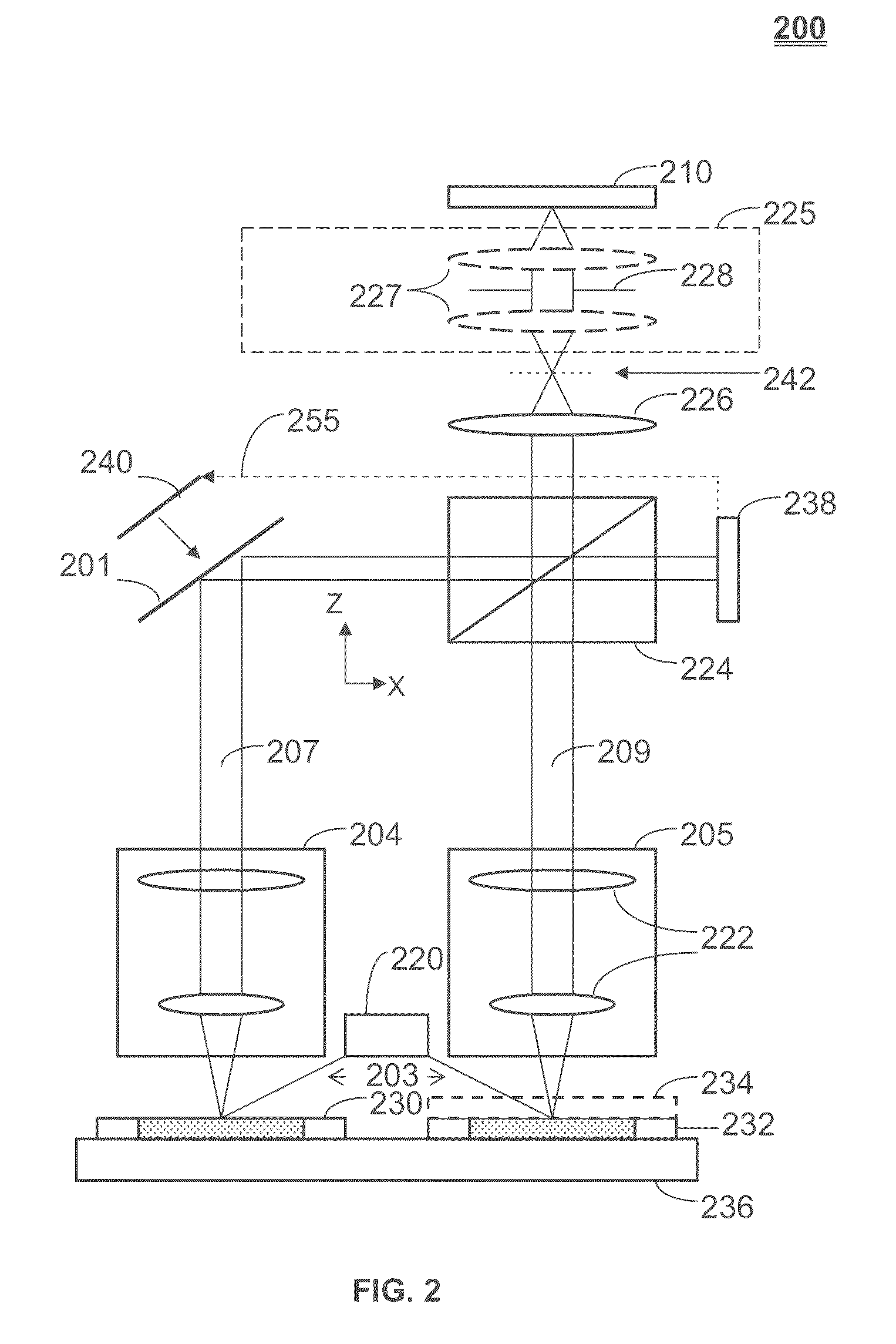
Reticle Inspection Systems and Method
ActiveUS20100149548A1Easy to distinguishPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusImage subtractionPhase difference
A method and systems for reticle inspection. The method includes coherently illuminating surfaces of an inspection reticle and a reference reticle, applying a Fourier transform to scattered light from the illuminated surfaces, shifting the phase of the transformed light from the reference reticle such that a phase difference between the transformed light from the inspection reticle and the transformed light from the reference reticle is 180 degrees, combining the transformed light as an image subtraction, applying an inverse Fourier transform to the combined light, and detecting the combined light at a detector. An optical path length difference between two optical paths from the illumination source to the detector is less than a coherence length of the illumination source. The image detected by the detector represents a difference in amplitude and phase distributions of the reticles allowing foreign particles, defects, or the like, to be easily distinguished.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
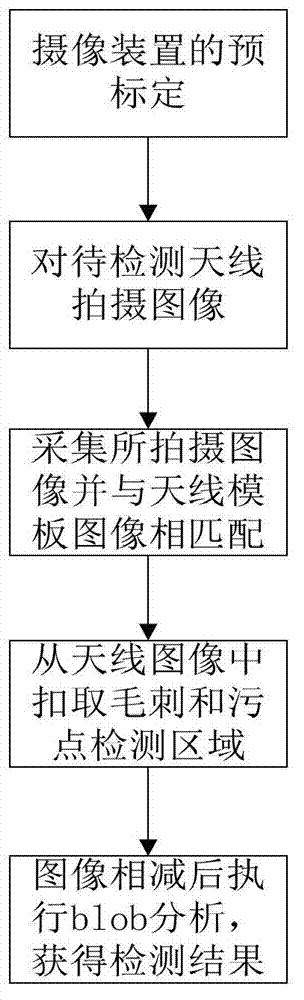
System and method for visual inspection on burrs and stain defects of radio frequency identification (RFID) antennae
ActiveCN103091331AGuaranteed accuracyEnsure consistencyOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPattern recognitionImage subtraction
The invention discloses a method for visual inspection on burrs and stain defects of radio frequency identification (RFID) antennae. The method comprises the following steps of: calibrating a camera device, and then shooting images of each RFID antenna to be inspected through the cooperation of the camera device and a strip-type or backlight source; acquiring the shot images of the antennae, and matching the acquired shot images with images of an antenna template to obtain pre-alignment information; taking off corresponding burrs and stain inspection areas from the images of the antennae according to regions of interest (ROI) on the images of the antenna template and the pre-alignment information; respectively carrying out binary processing on the inspection areas taken off from the images and the ROI, and then carrying out image subtraction; and carrying out blob analysis on residual images subjected to the image subtraction, and determining results of the burrs and the stain defects. The invention also discloses a system for carrying out the corresponding visual inspection. Through the method and the system, the inspection process of the burr / stain quality of the RFID antennae can be carried out efficiently and accurately, and the positions of the defects can be accurately positioned, so that the method and the system are particularly suitable for industrial processing and manufacturing processes of the RFID antennae.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
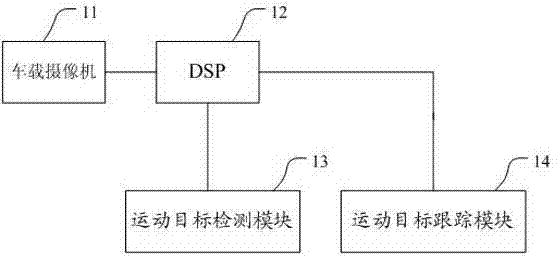
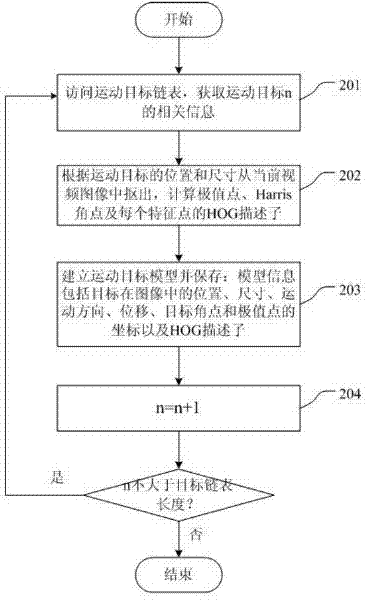
Video monitoring system and moving target detecting and tracking method thereof
ActiveCN102456225AEasy to calculateReal-time computingImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsVideo monitoringImage subtraction
The invention discloses a video monitoring system and a moving target detecting and tracking method thereof. The method is applied to the video monitoring system on the condition that a camera is in a moving state. The method comprises the following steps: a moving target detection step, in which combination of a Harris corner and an HOG descriptor is employed as an image feature as well as processing including image feature extraction, image projection conversion, and image subtraction operation and the like is carried out to obtain a plurality of moving targets; a moving target model establishment step, in which moving target models are established for all the moving targets as well as a combination mode of a Harris corner, an extreme point and an HOG descriptor is employed to express features of the moving targets; and a target tracking step, in which target tracking is carried out according to the moving target models. According to the invention, corner feature matching is employed to reduce the calculated amount and precision of moving target detection is ensured; a corner and an extreme point are employed as target features, so that target identification has high robustness and tracking sustainability is strong; and a target motion estimation method is employed to reduce the calculated amount.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZTE NETVIEW TECH
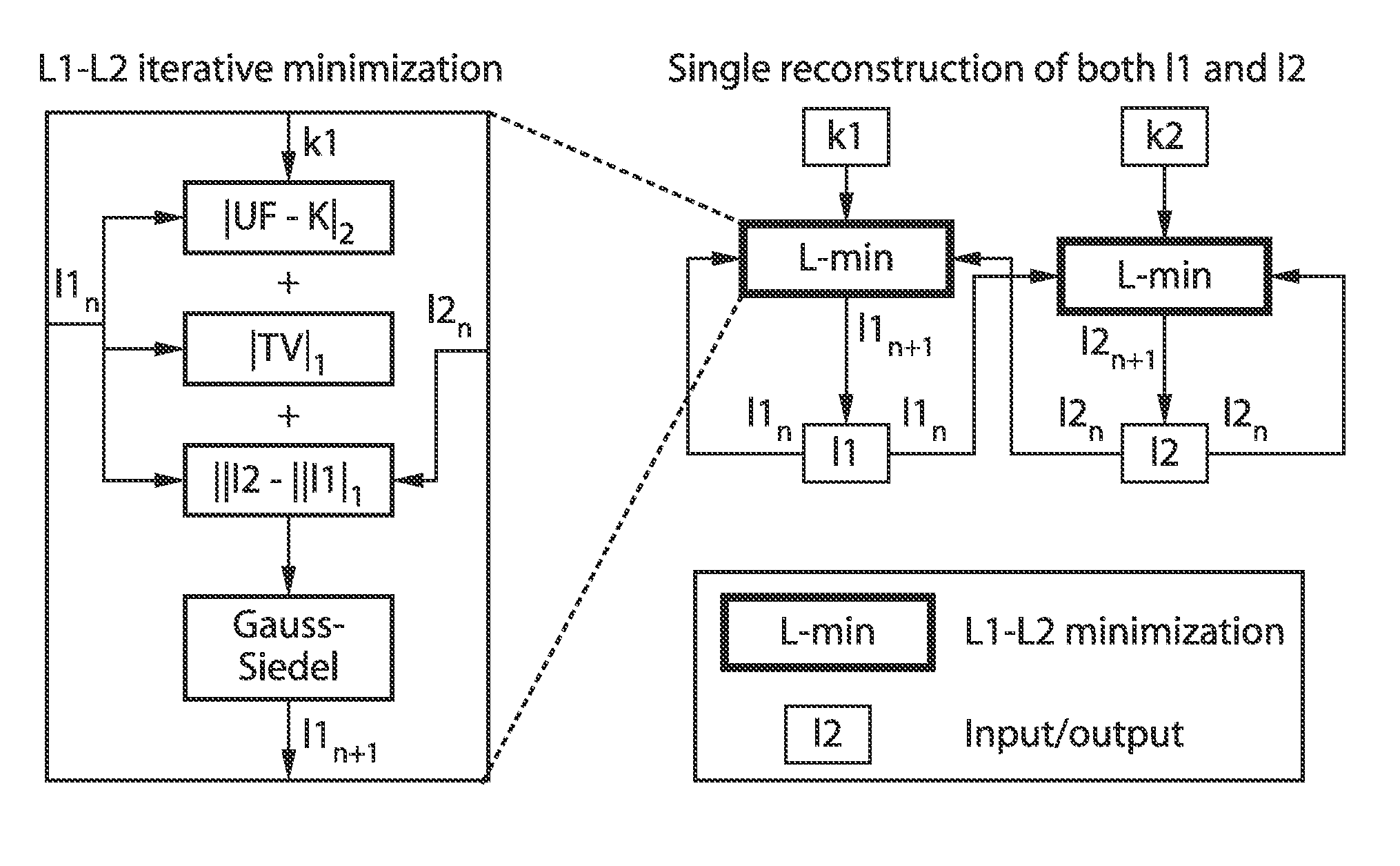
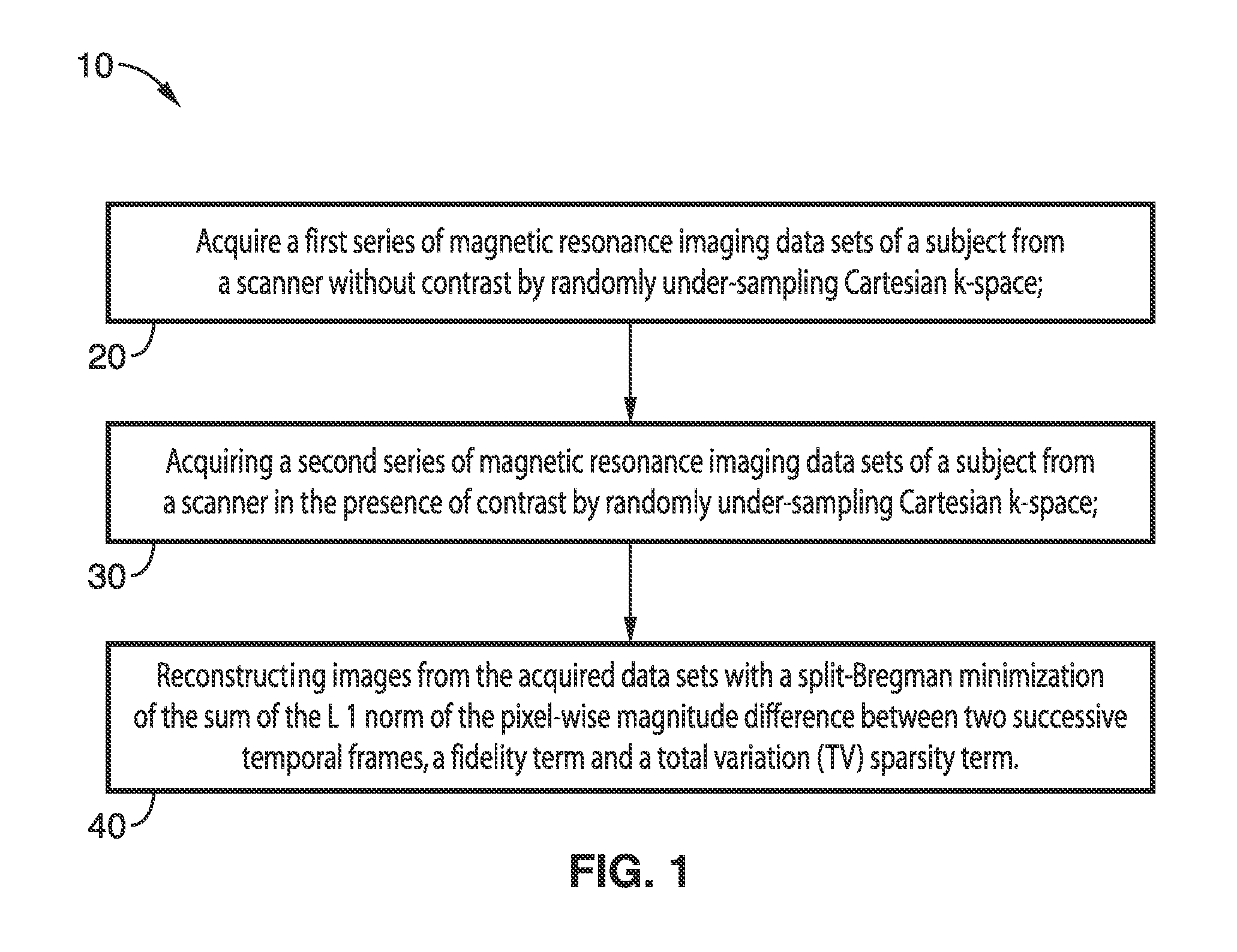
High spatial and temporal resolution dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
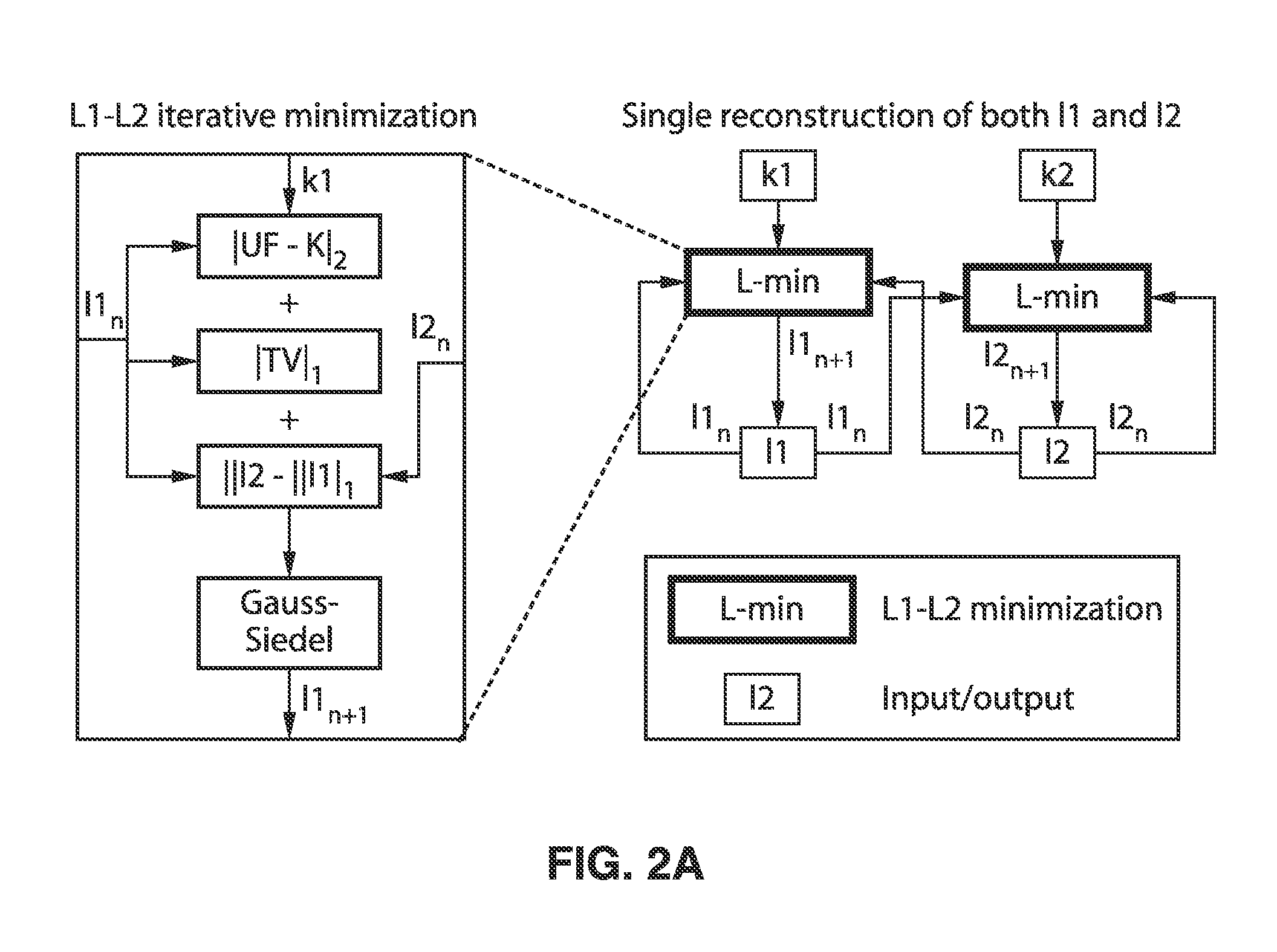
ActiveUS20150346303A1Improve sparsityAccelerate contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiographyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTemporal resolutionDynamic contrast
A method for high spatial and temporal resolution dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using a random subsampled Cartesian k-space using a Poisson-disk random pattern acquisition strategy and a compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm incorporating magnitude image subtraction is presented. One reconstruction uses a split-Bregman minimization of the sum of the L1 norm of the pixel-wise magnitude difference between two successive temporal frames, a fidelity term and a total variation (TV) sparsity term.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for fast positioning license plate
ActiveCN105117727AAchieve positioningHigh speedCharacter and pattern recognitionImage subtractionComputer vision
Provided is a method for fast positioning a license plate. The method comprises steps of: performing image subtraction operation on color channel components of an original color vehicle image to obtain a difference image; performing binary operation on a grayscale image Ibr subjected to channel component subtraction by means of an Otsu method; performing dilation operation in the horizontal direction on a binary image Ibw; performing erosion operation on a dilated image Ibw_dilate; searching a communication area of an image Ibw_imerode; computing the height of each area in the Z; removing areas where Ti is less than 11 from the Z in order to obtain a license plate candidate area set Z'; further filtering the license plate candidate areas on the basis of positioned upper and lower boundaries; positioning the left and right boundaries of the license plate candidate areas; and computing the aspect ratio of each license plate candidate area in the Z'' so as to achieve positioning.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
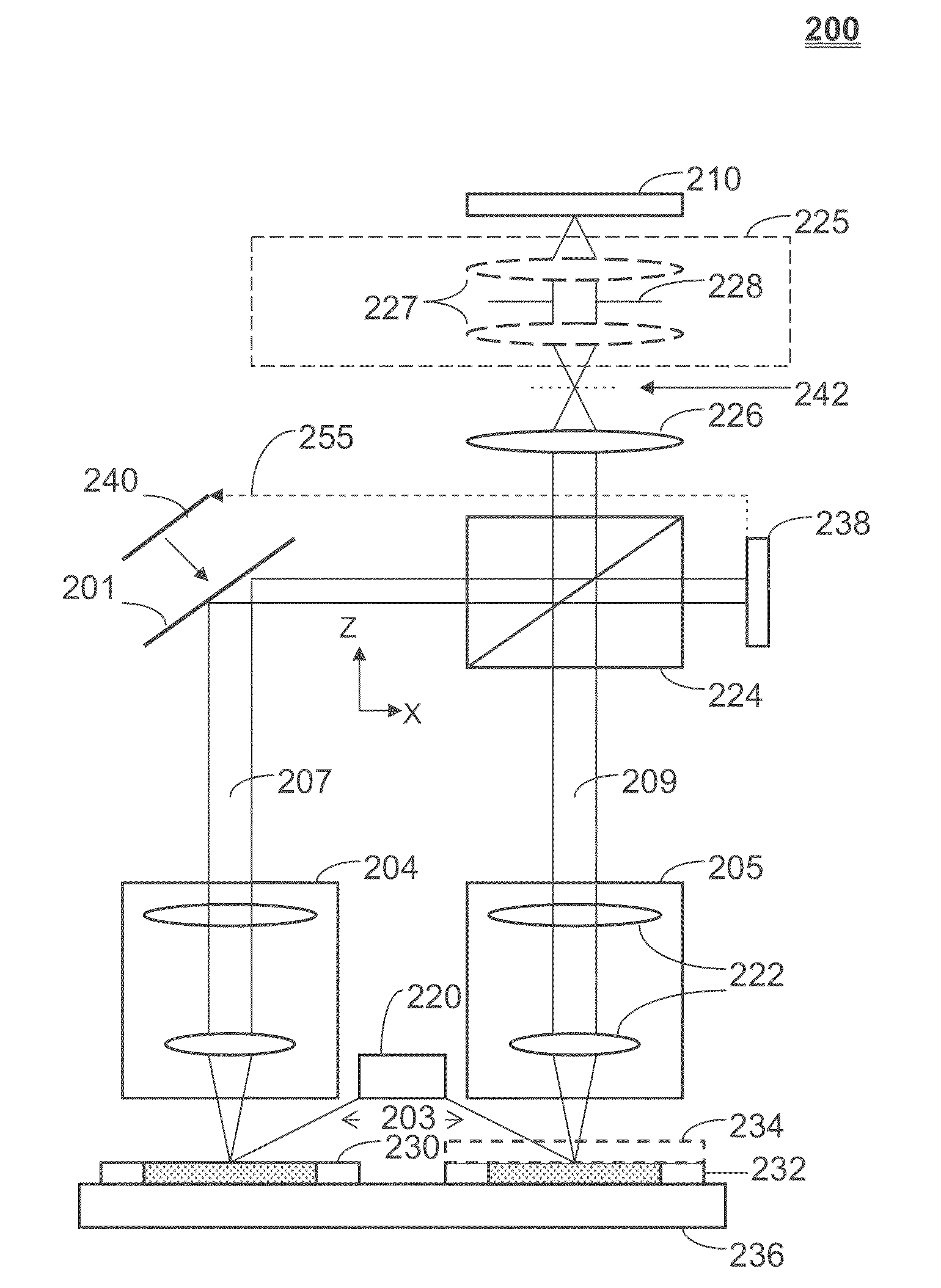
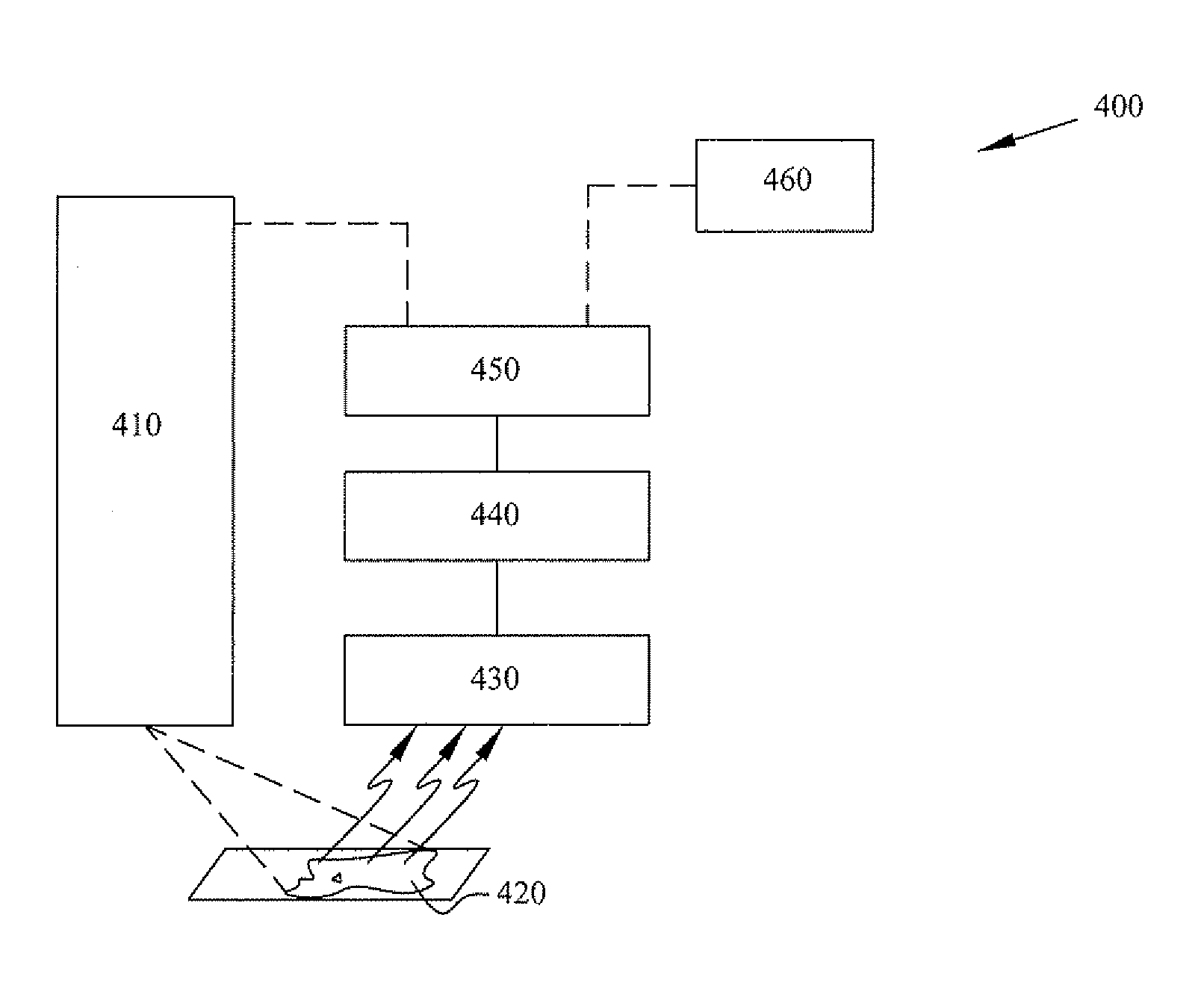
Method and apparatus for interactive hyperspectral image subtraction
Disclosed is a method of obtaining a spectral image of each of a plurality of predetermined chemical species in a sample, comprising: (a) illuminating the sample with a first plurality of photons to produce a second plurality of photons; (b) collecting the second plurality of photons and producing a plurality of images of the sample therefrom, each of said images comprising a frame consisting essentially of a plurality of pixels; (c) for each of the predetermined chemical species, identifying at least one wavelength range at which the chemical specie exhibits a unique absorption of radiation; (d) identifying at least one wavelength range at which none of the predetermined chemical species exhibits an absorption of radiation; (e) in each of the image frames, identifying which of the pixels do not contain any of the predetermined chemical species; (f) in each of the image frames, identifying which of the pixels contain only a first the predetermined chemical species; (g) repeating the previous step for each of the predetermined chemical species; (h) in each of the image frames, identifying which of the pixels contain more than one of the predetermined chemical species; (i) for each pixel that contains more than one of the predetermined chemical species, separating the contribution of each predetermined chemical species; and (j) composing separate spectral images of each of the predetermined chemical species in the sample. Also disclosed are apparati for performing these methods, comprising: (a) an illumination source for illuminating the sample with a first plurality of photons to form a second plurality of photons; (b) an optical device for receiving and directing the second plurality of photons to an imaging device; (c) an imaging device for forming a plurality of images of the sample; and (d) a processor in communication with the imaging device.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Bone inhibition method in chest X-ray image
InactiveCN103824281AThe result is obviousImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionImaging processing
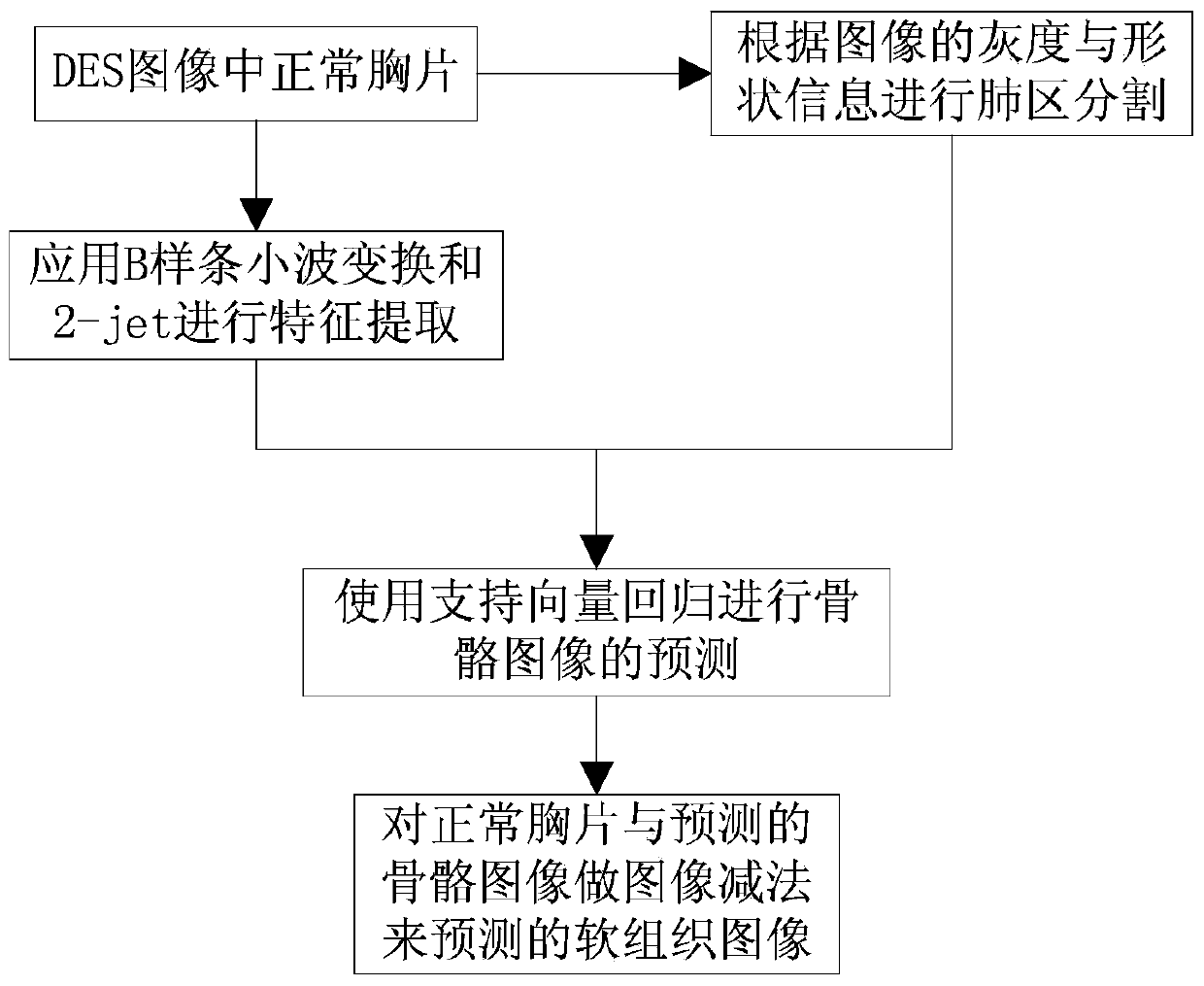
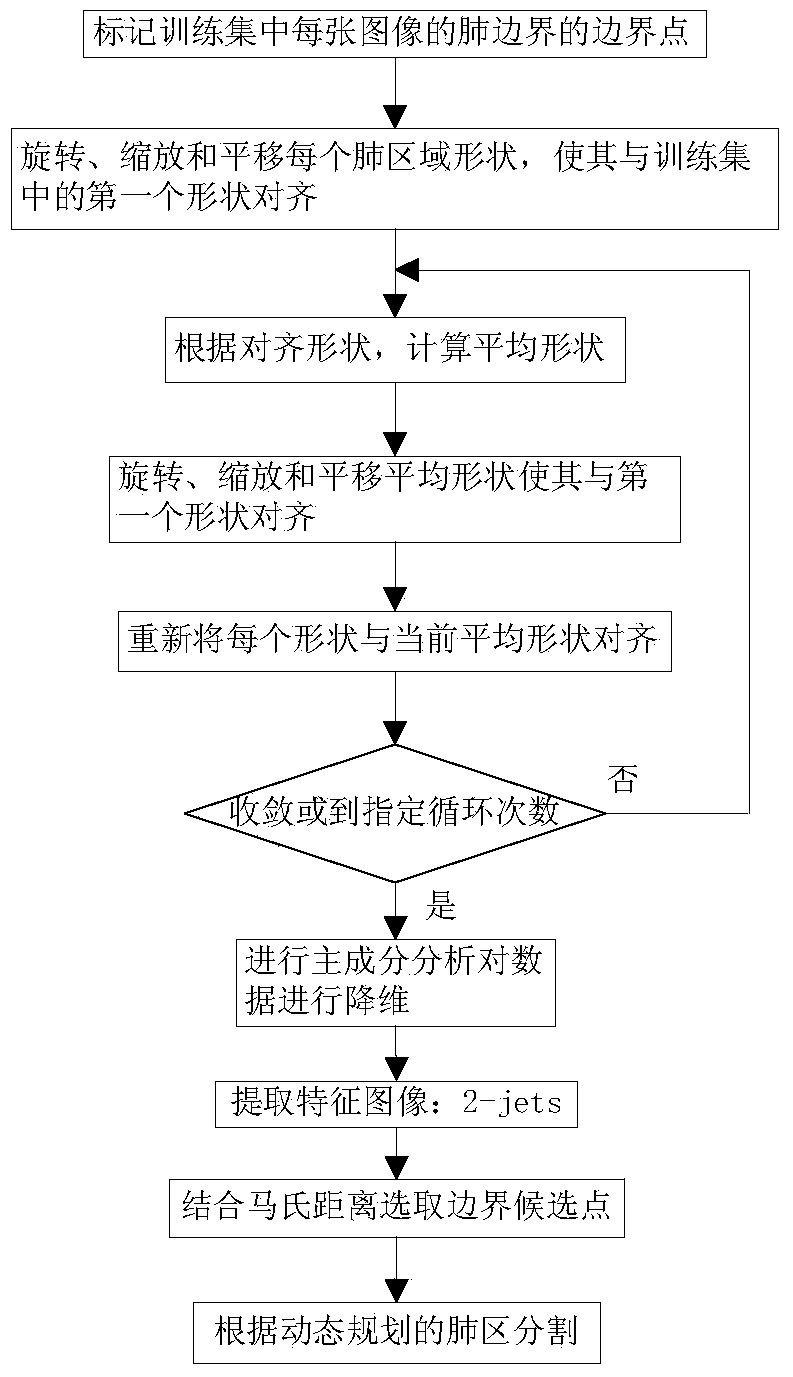
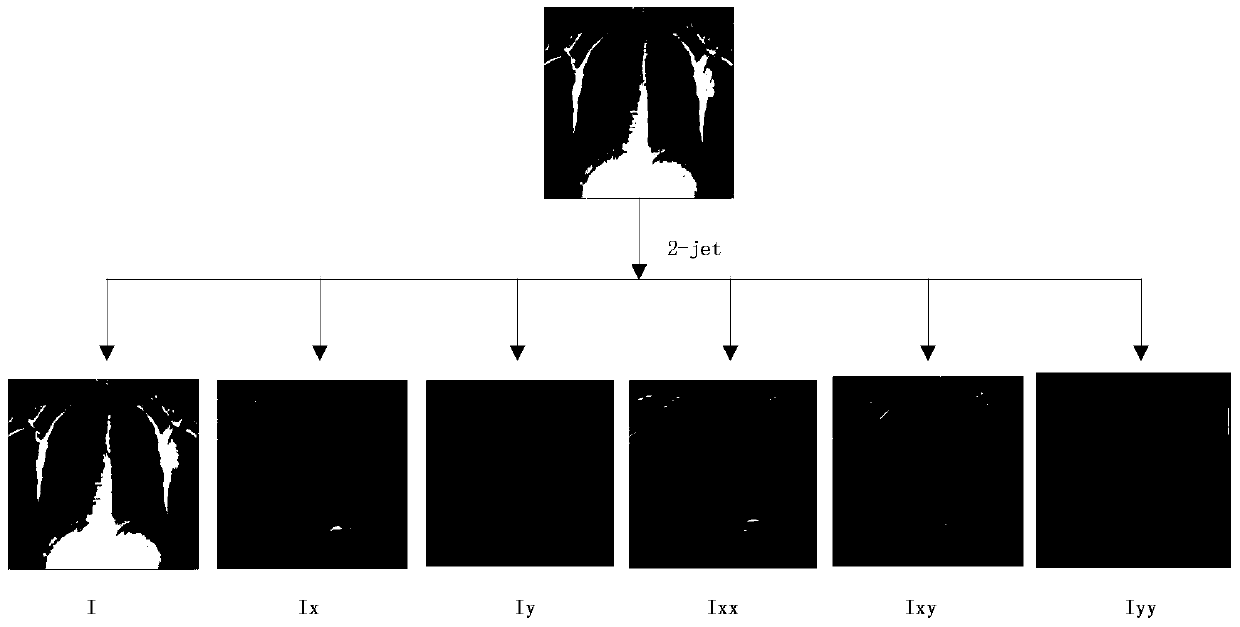
The invention belongs to the technical field of X-ray image processing, and specifically relates to a bone inhibition method in a chest X-ray image. A lung contour model is established for a normal chest image in a dual-energy silhouette image, three-order B batten wavelet transformation is then applied to perform three-scale wavelet decomposition on the image, a characteristic image is extracted by use of a 2-jet method from the decomposed image, then a bone model is established by use of a support vector regression machine, the bone model is applied to an X-ray image for extracting a corresponding prediction bone image, and finally, image subtraction is carried out on the X-ray image and the predicted bone image so as to obtain a predicted soft tissue image. Because most of bone inhibition methods employ a nerve network method, the method is liable to local optimum and the training result is not yet stable. Therefore, the method provided by the invention employs the support vector regression machine to carry out bone prediction, and a better result is obtained.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and storage medium
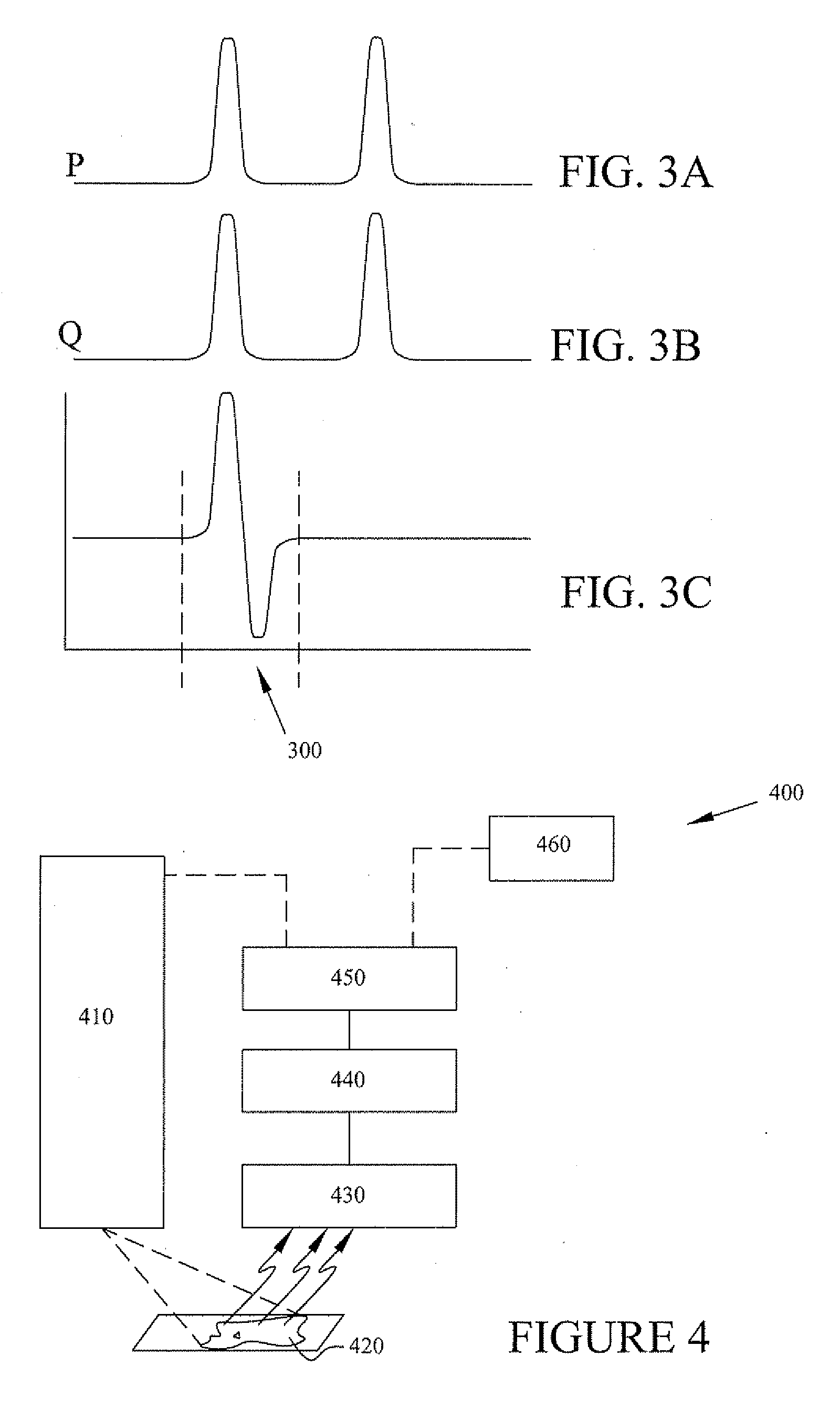
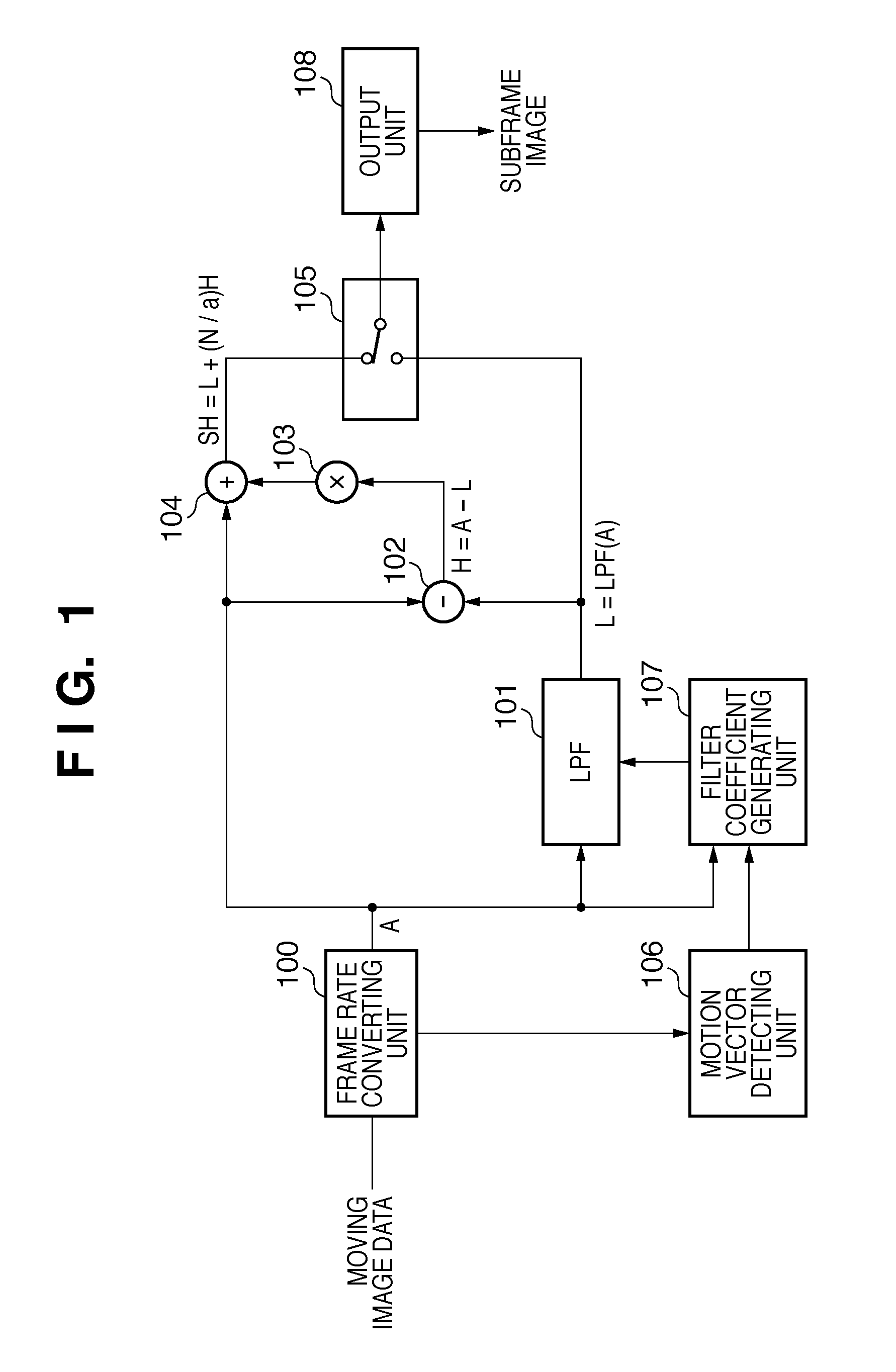
InactiveUS20100303374A1Reduce image lagSmall amount of calculationTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesImaging processingImage subtraction
According to one aspect of the invention, an image processing apparatus comprises: a unit configured to obtain an input image and a subsequent image; a unit configured to obtain N replicated images from the input image; a generating unit configured to generate a low-frequency enhanced image; a subtraction unit configured to generate a high-frequency enhanced image; a synthesizing unit configured to generate a high-frequency output image; and an output unit configured to select and output one of the low-frequency enhanced image and the high-frequency output image. The generating unit comprises a unit configured to obtain a motion vector of an object, and a filter unit configured to apply the filter to pixels around a specified pixel position Q in the replicated image, to obtain a pixel value at a pixel position P in the low-frequency enhanced image.
Owner:CANON KK
Automated tem sample preparation
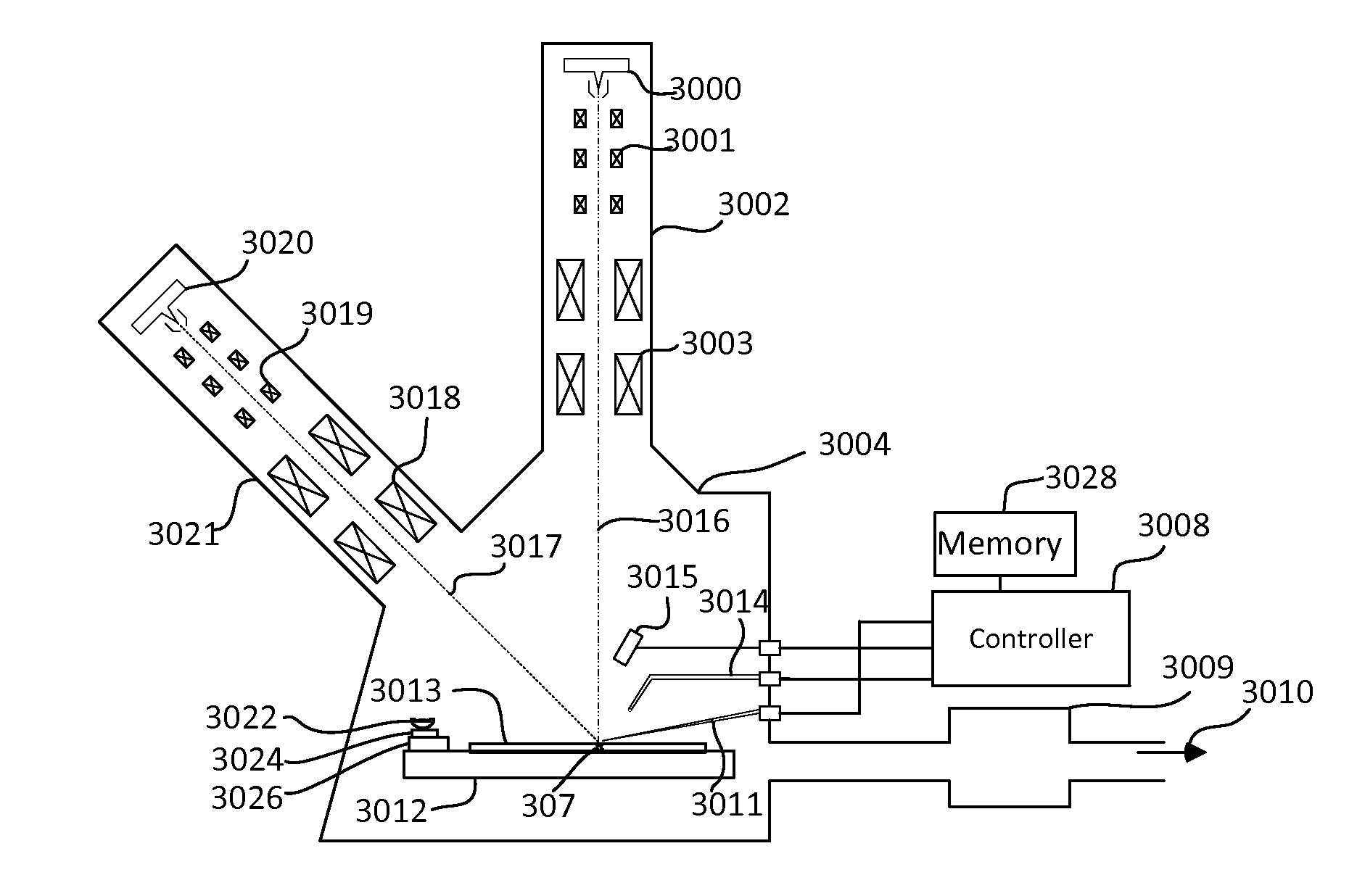
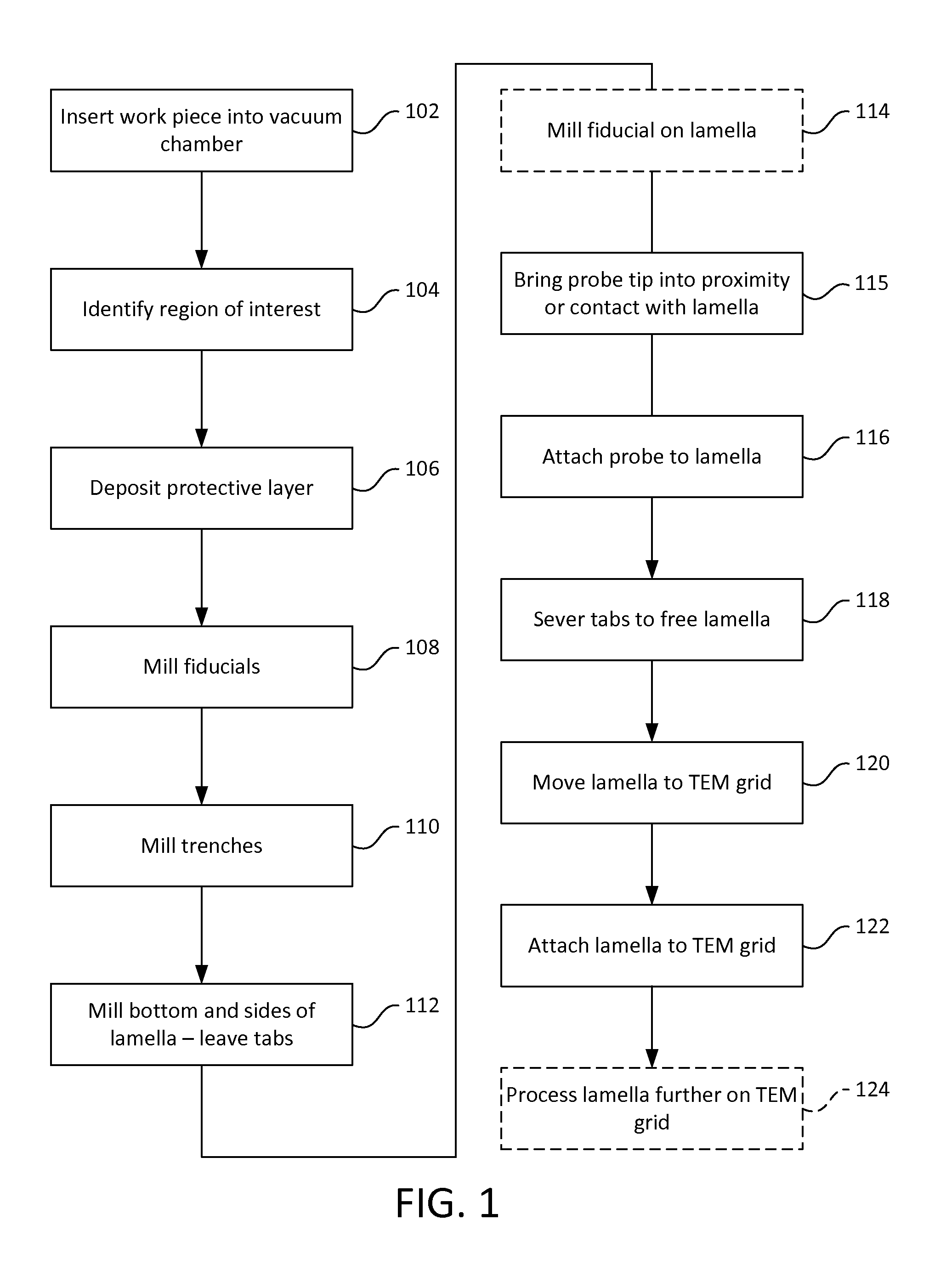
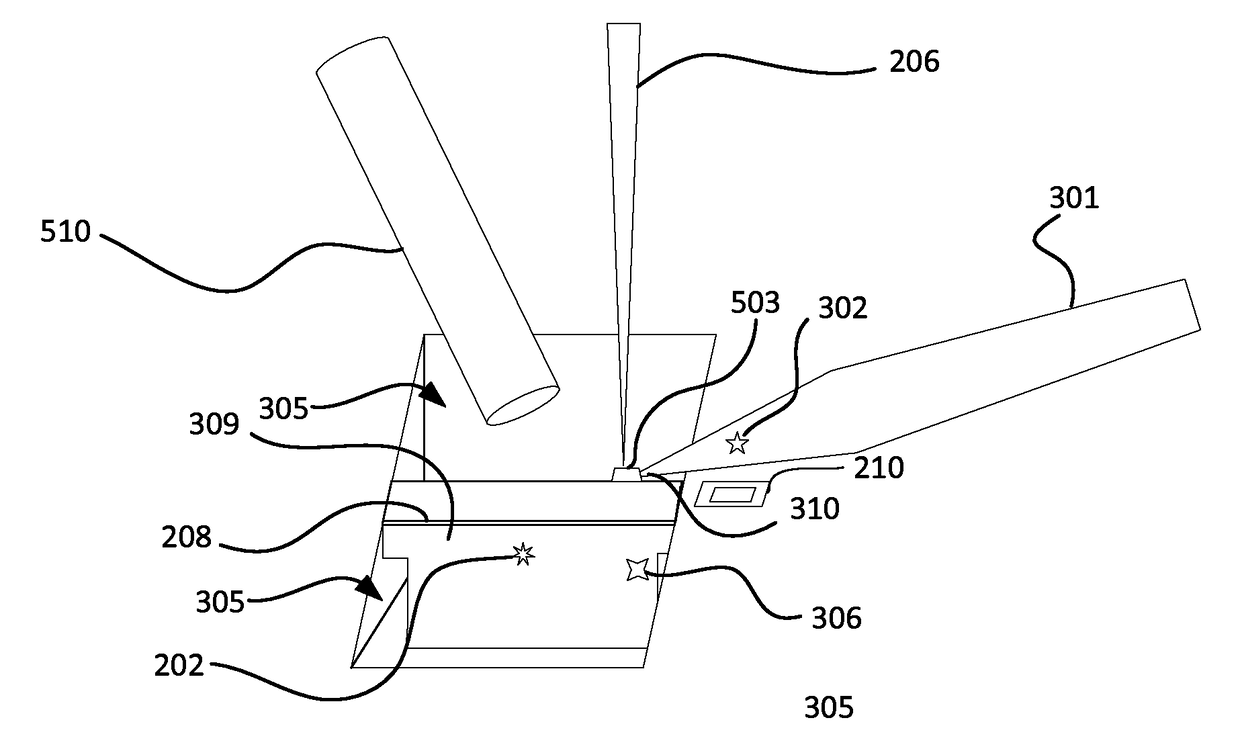
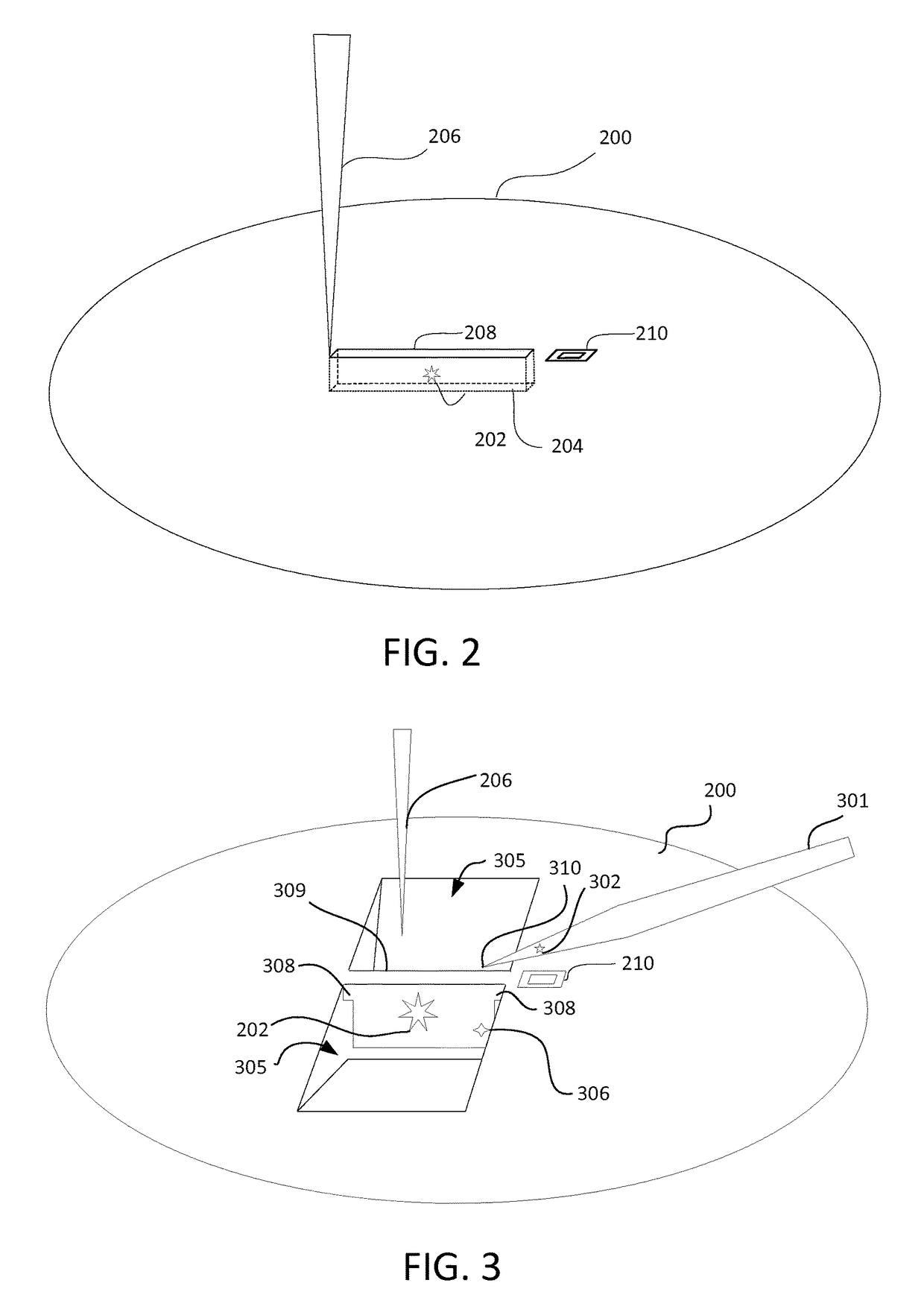
ActiveUS20160141147A1Improve performanceDifficult to automateSamplingElectric discharge tubesImage subtractionMachine vision
Techniques are described that facilitate automated extraction of lamellae and attaching the lamellae to sample grids for viewing on transmission electron microscopes. Some embodiments of the invention involve the use of machine vision to determine the positions of the lamella, the probe, and / or the TEM grid to guide the attachment of the probe to the lamella and the attachment of the lamella to the TEM grid. Techniques that facilitate the use of machine vision include shaping a probe tip so that its position can be readily recognized by image recognition software. Image subtraction techniques can be used to determine the position of the lamellae attached to the probe for moving the lamella to the TEM grid for attachment. In some embodiments, reference structures are milled on the probe or on the lamella to facilitate image recognition.
Owner:FEI CO
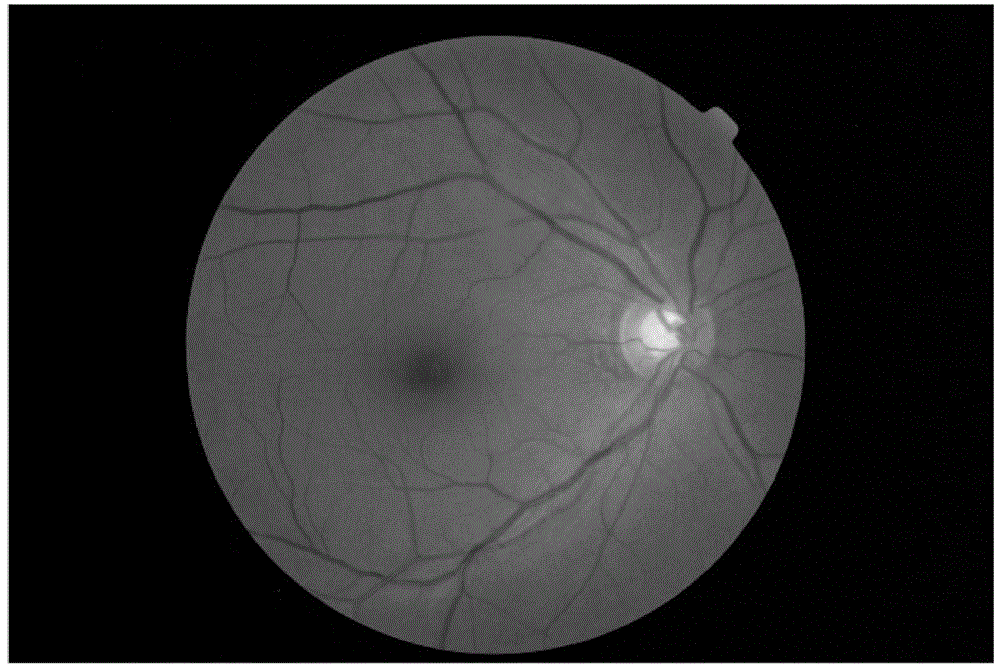
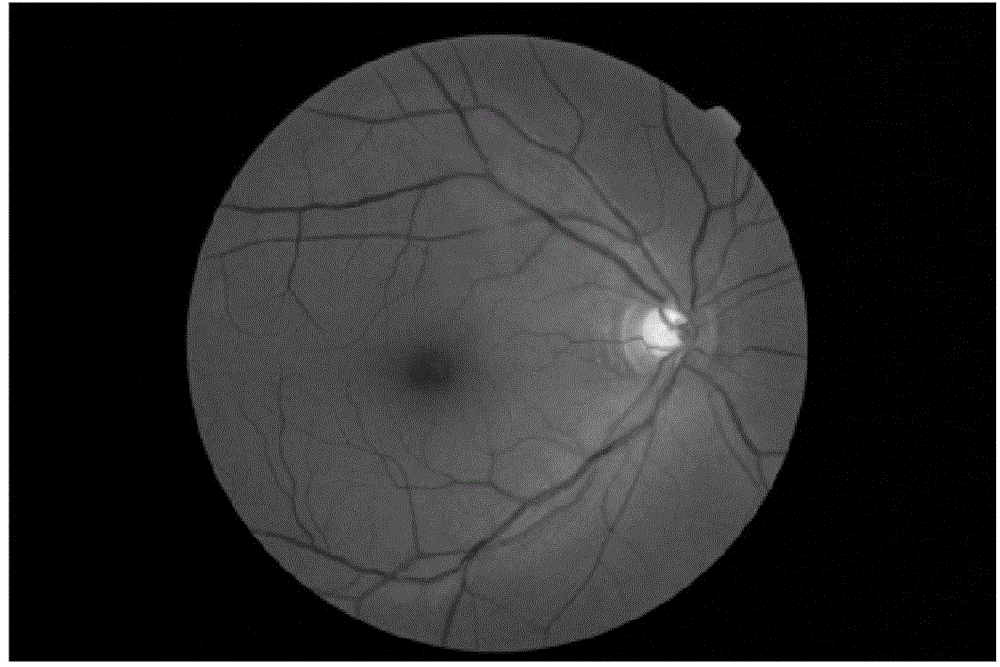
Eye fundus image optical cup automatic segmentation method based on improved PDE image repairing
InactiveCN104835157AEliminate the effects of segmentationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationImage subtraction
The invention discloses an eye fundus image optical cup automatic segmentation method based on improved PDE image repairing. The method is carried out with following steps: reading and normalizing an original image; selecting channels for the original image; enhancing the image based on a morphological principle; positioning blood vessels based on an image subtraction; filling and repairing blood vessel areas by the use of an improved BSCB model; performing median filtering and noise reduction for the image and highlighting object areas through gamma transformation; and preliminarily obtaining an optical cup contour through a level set algorithm under a condition that the mass center of the brightest pixel point set on the image serves as an initial seed point. According to the invention, the image in which the blood vessels are filled and repaired eliminate the influence on optical cup segmentation by the blood vessel areas to a certain extent; the accuracy of optical disk segmentation is improved; the seed point is automatically selected as the contour of an optical cup is obtained through the level set algorithm; and manual intervention in a conventional semi-automatic method is reduced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
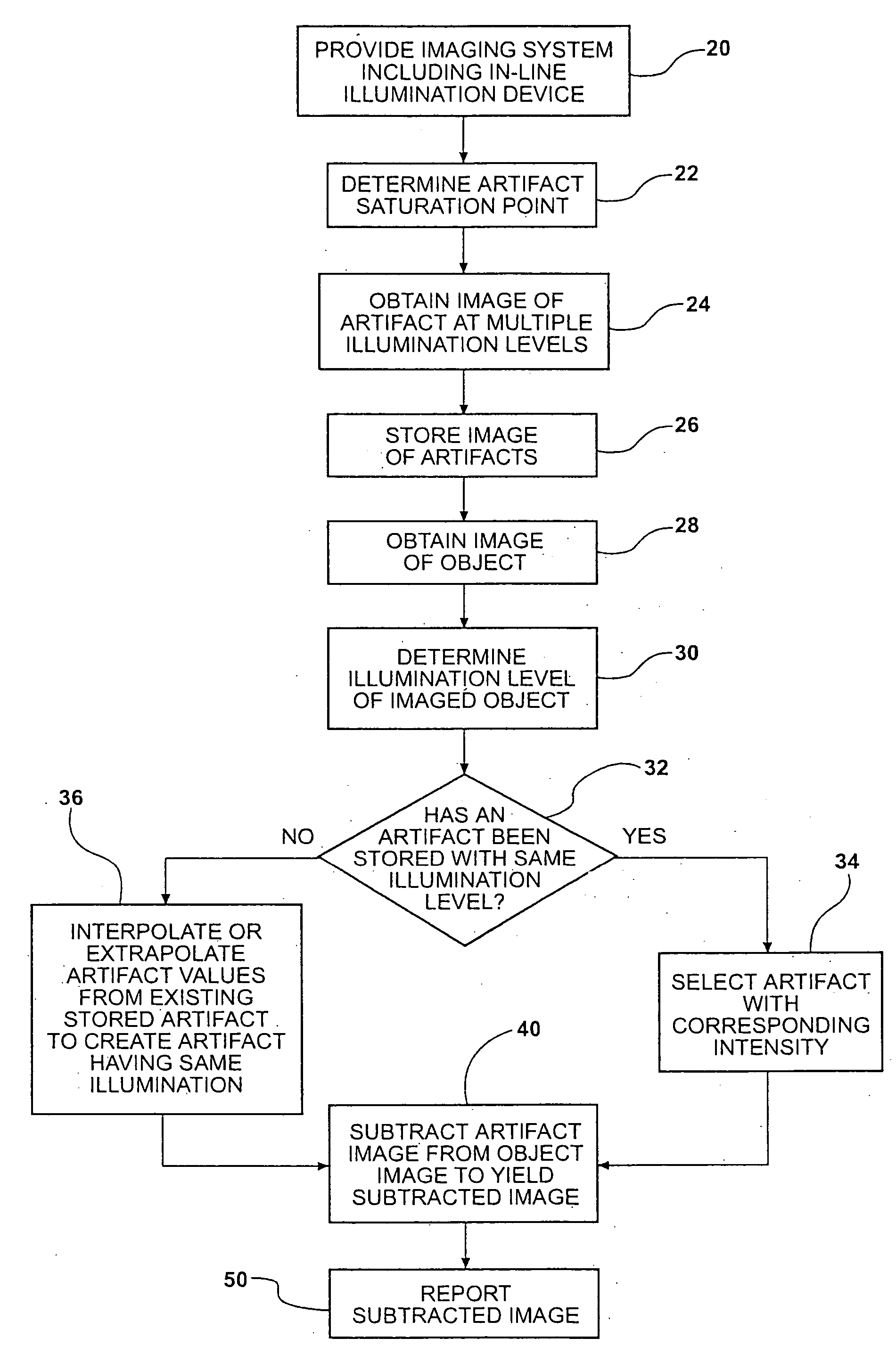
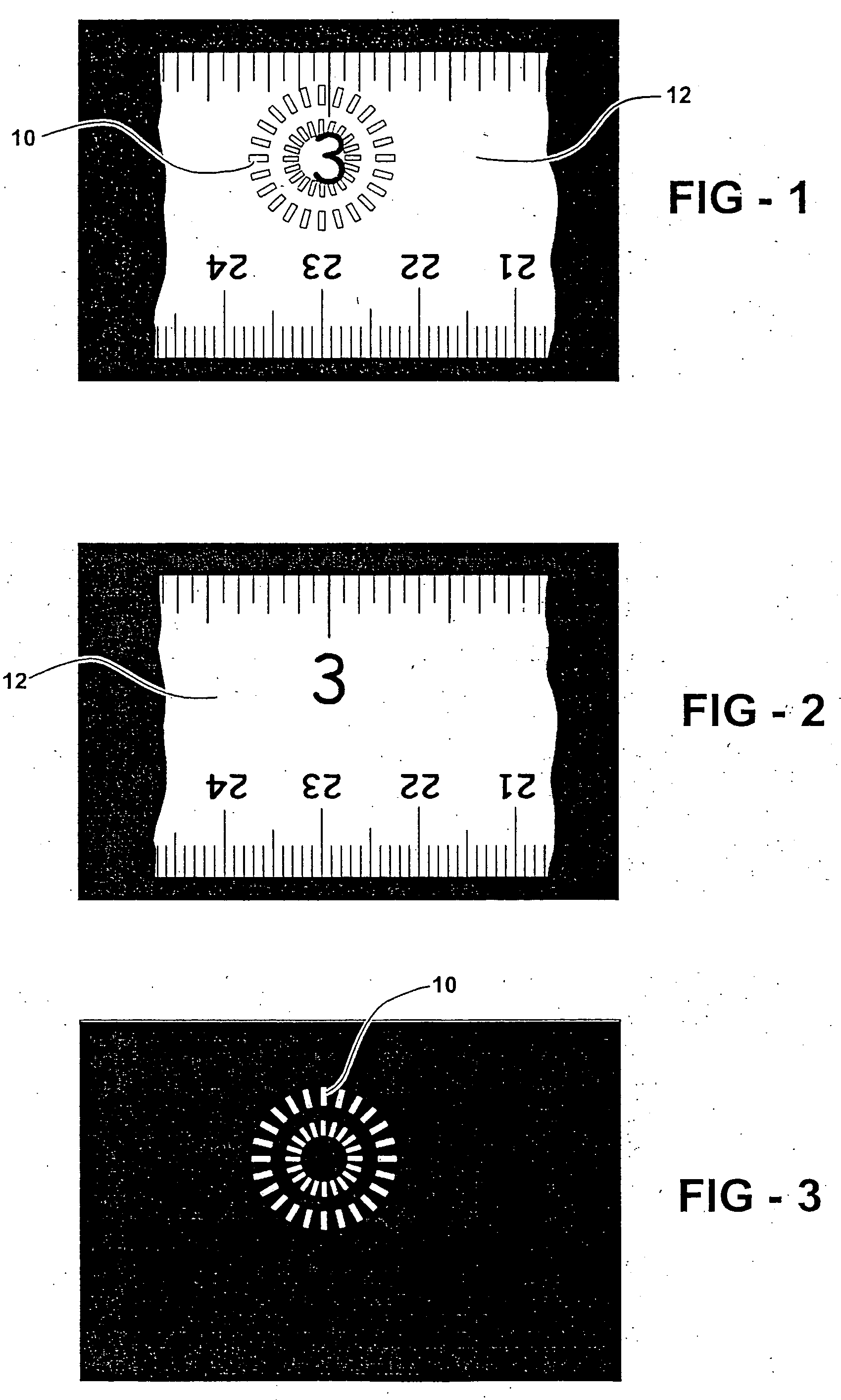
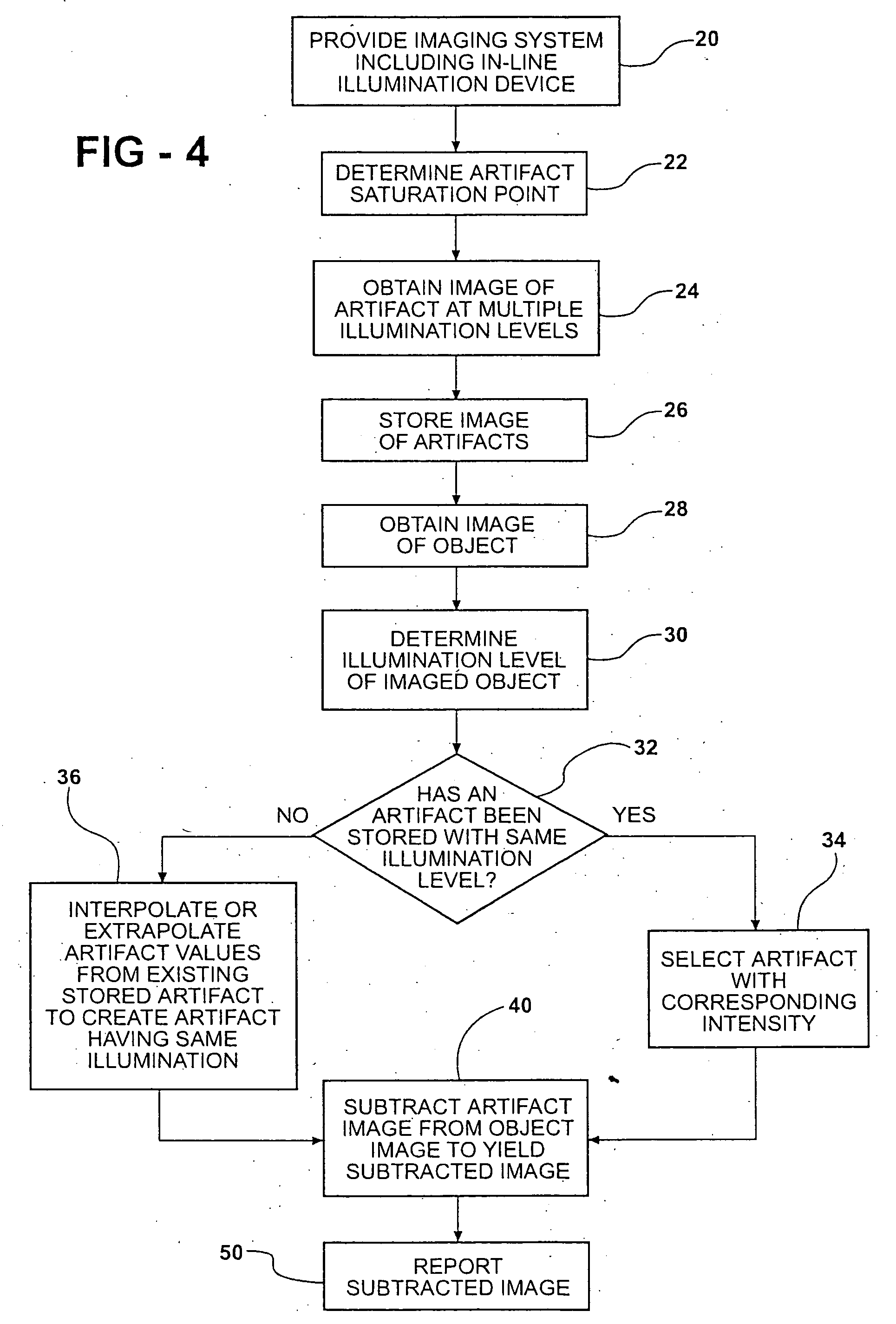
Image subtraction of illumination artifacts
InactiveUS20050163397A1Less interferenceIncrease illuminationImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionImage subtractionImage system
A method of removing an artifact resulting from an in-line illumination device of an imaging system from an object image. It includes obtaining a first image of the artifact using a first artifact illumination level and imaging the object using the imaging system wherein the illumination device is using an object illumination level. An artifact image is independent of the object and has pixel values related to the illumination level. Thus, the artifact can be removed by subtracting respective pixel values of an artifact image from respective values of the object image on a pixel address-by-pixel address basis. Various illumination levels can be used to create more than one artifact image. The artifact image for the subtraction can be one of the images taken or can be a scaled image where an artifact image is scaled to the object illumination level.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
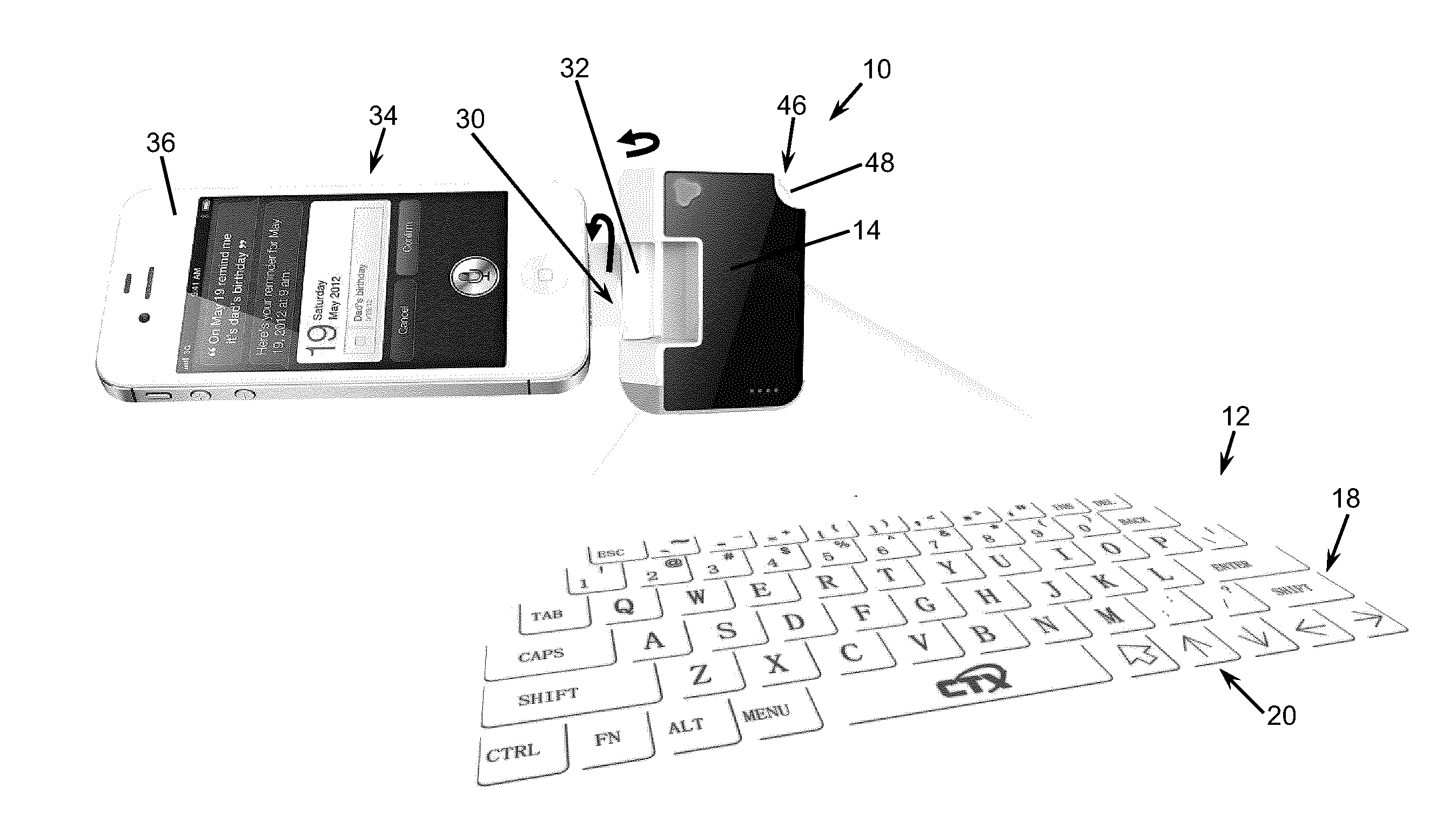
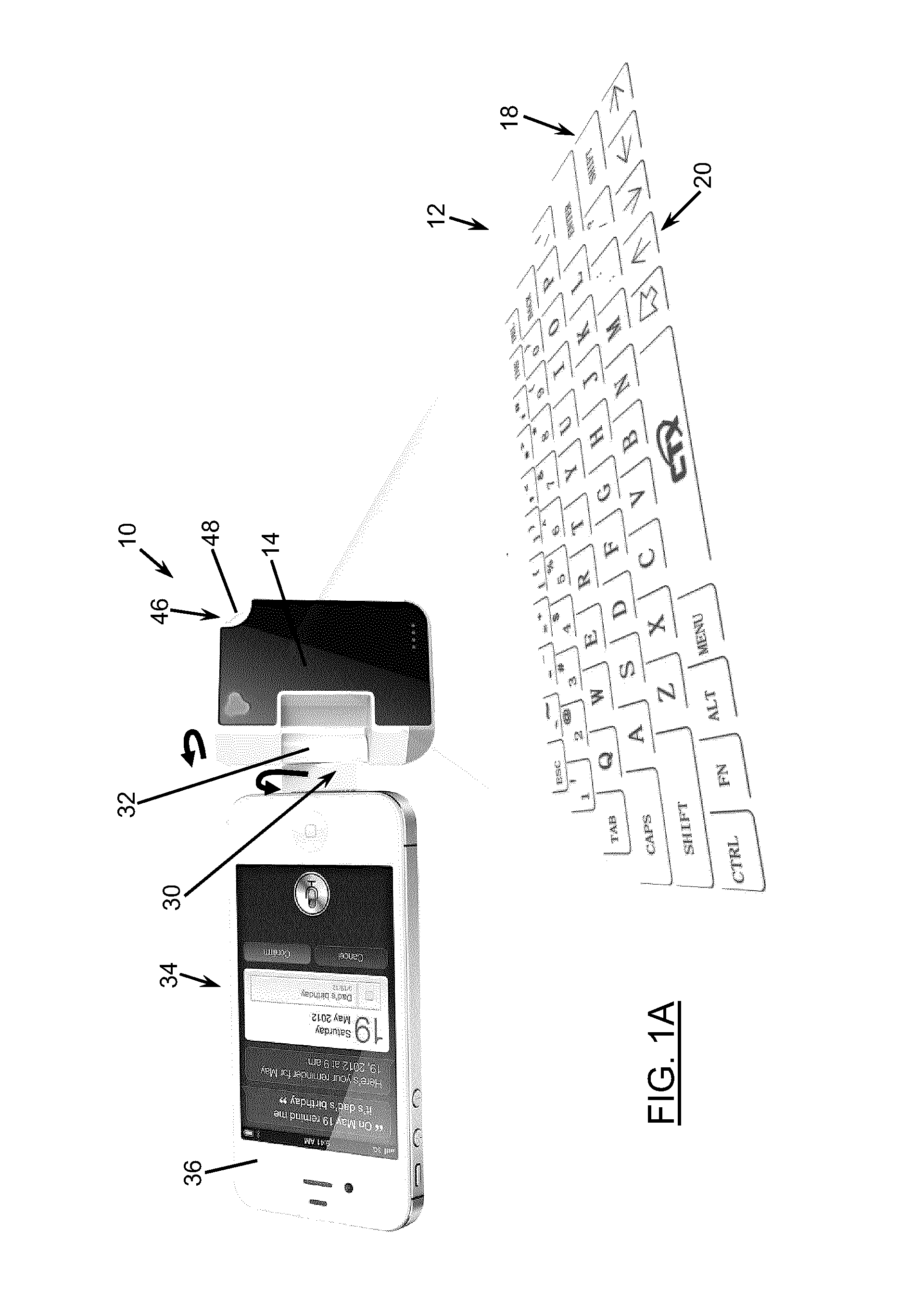
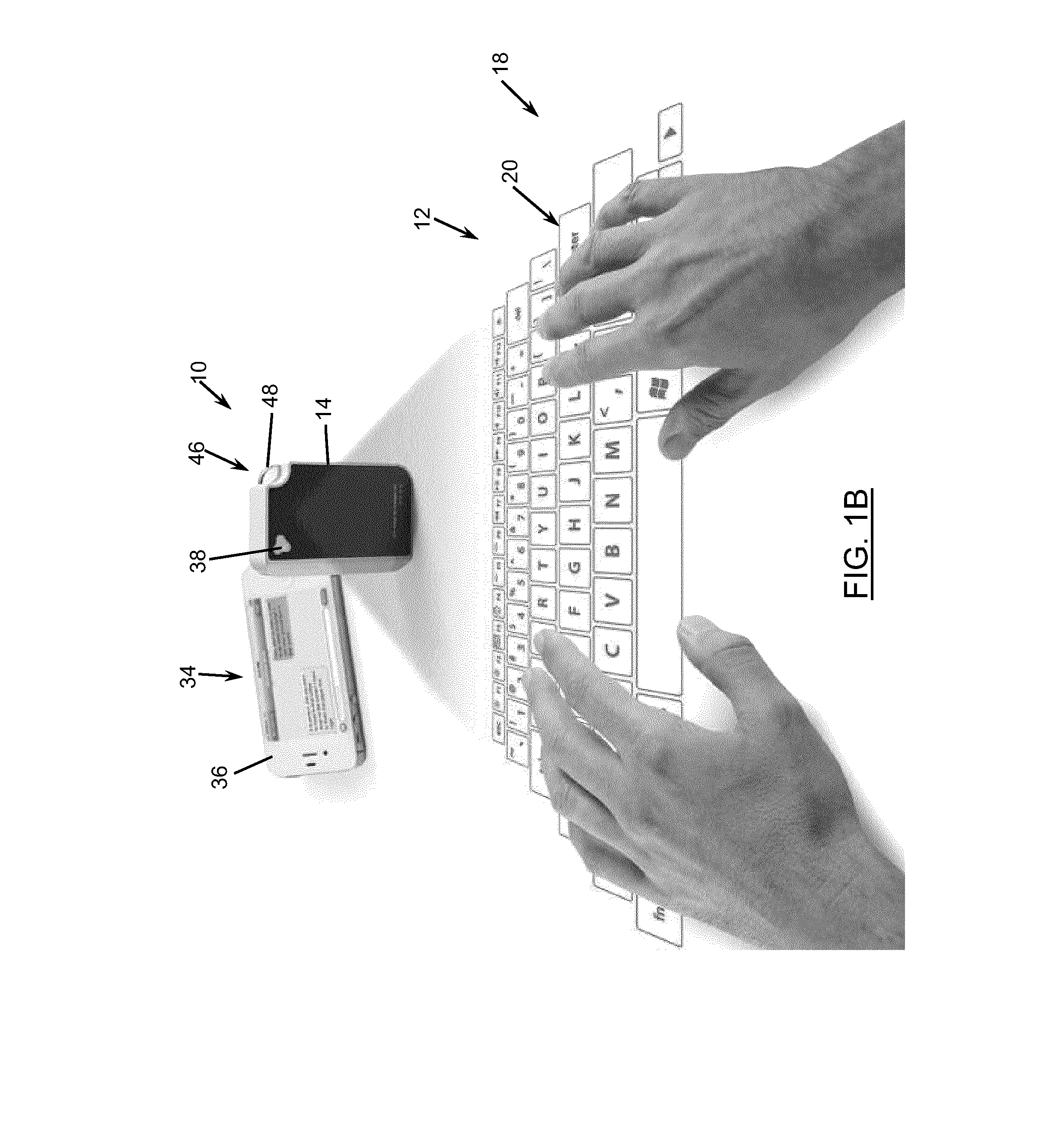
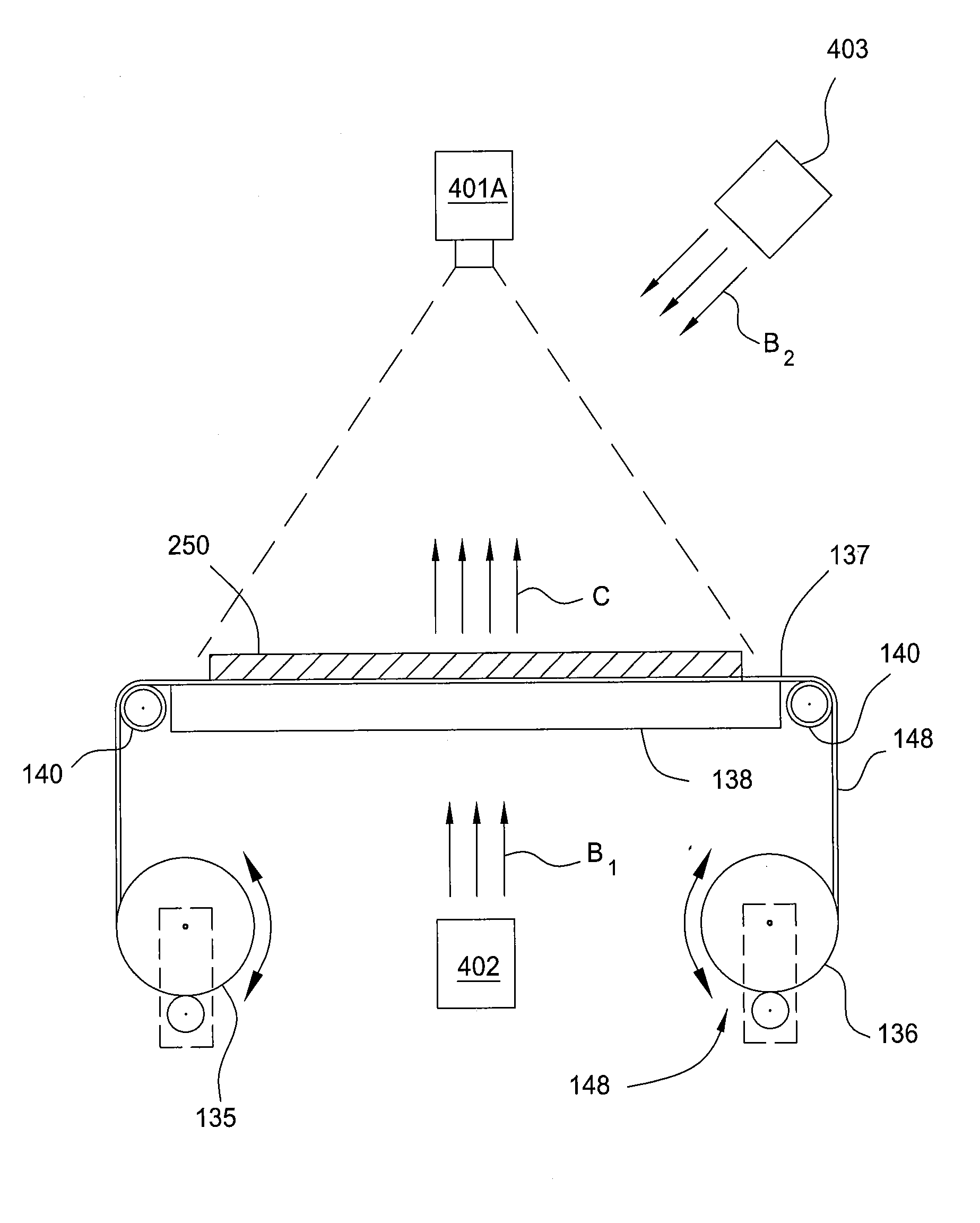
Keyboard projection system with image subtraction
InactiveUS20150160738A1Satisfies needInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsImage subtractionLight beam
A method for detecting a keystroke operated on a projected keyboard, and an associated device are disclosed. A first image and a second image of the projected keyboard are captured. Preferably, while the first image is taken, an infrared (IR) beam is projected on the keyboard, and while the second image is taken, the IR beam is switched off. The second image is subtracted from the first image to remove noise and detect a difference between the first and second image. The location where the difference is detected is associated with the keystroke. The location of the keystroke is determined in relation to the projected image of the keyboard. The location is then associated with a key of the keyboard based on a keyboard layout stored in a memory. A command signal corresponding to the key is then generated for transmittal to the computing device.
Owner:CTX VIRTUAL TECH
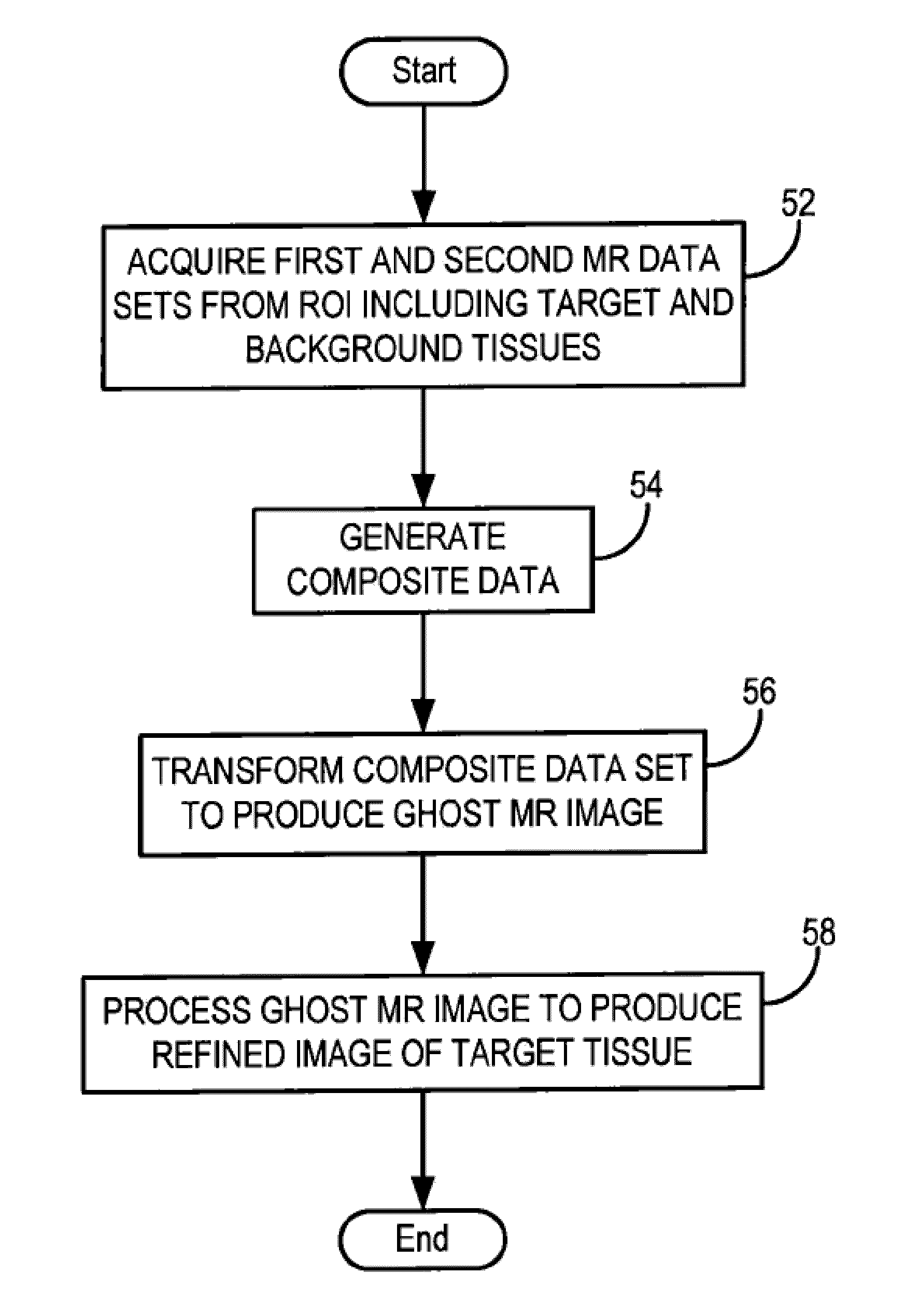
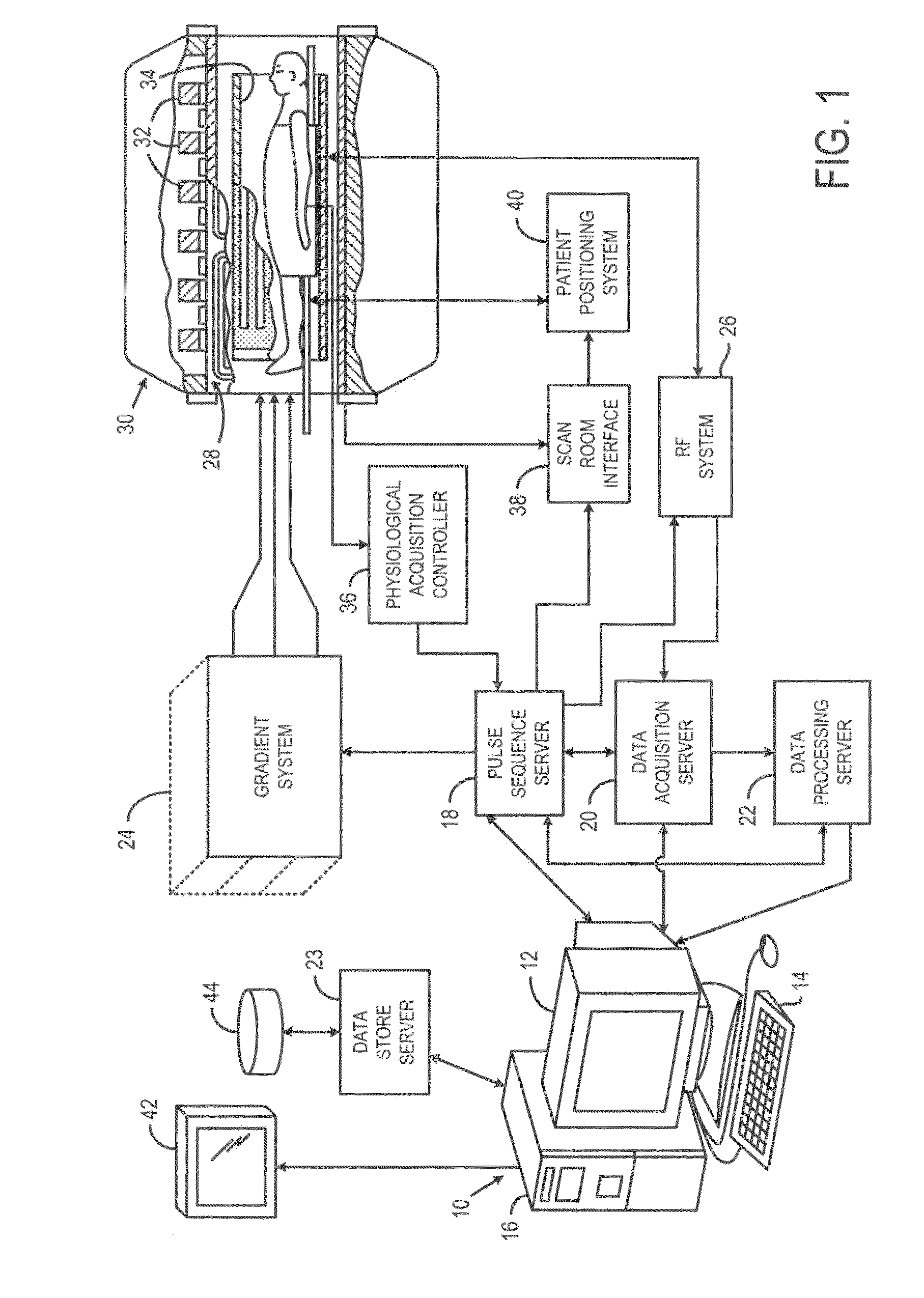
System and Method For Ghost Magnetic Resonance Imaging
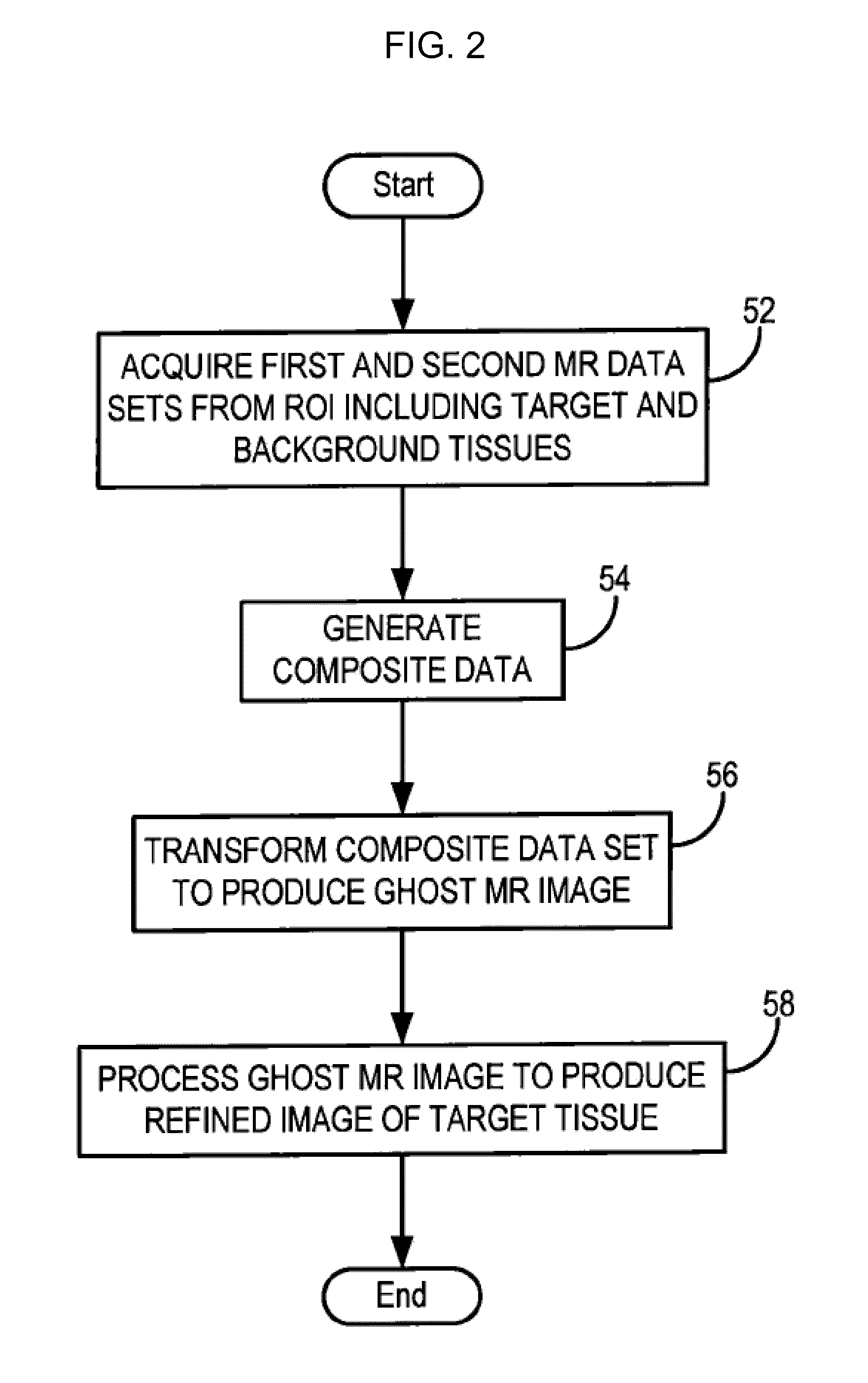
ActiveUS20100134103A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setImage subtraction
A system and method enables the creation of medical images using data related to ghost artifacts. The method thus allows components of an imaged subject to be segmented based on state changes in the components that lead to the controlled production of ghost artifacts. This is achieved in MR by performed a pulse sequence so that multiple sets of MR data are acquired in which the signals from a target tissue vary across the data sets while the signals from a background tissue do not vary across the data sets. A composite data set is generated by populating selected k-space lines of the composite data set with information from a first MR data set and populating the remaining k-space lines of the composite data set with information from a second MR data set. An MR image is then reconstructed from the composite data set. The MR image contains ghost artifacts that faithfully reproduce the 2D or 3D anatomic detail of the target tissues without signal contributions from the background tissues, allowing for background-suppressed or segmented MR images of a target tissue without the need for image subtraction.
Owner:NORTHSHORE UNIV HEALTHSYST
Automated TEM sample preparation
Techniques are described that facilitate automated extraction of lamellae and attaching the lamellae to sample grids for viewing on transmission electron microscopes. Some embodiments of the invention involve the use of machine vision to determine the positions of the lamella, the probe, and / or the TEM grid to guide the attachment of the probe to the lamella and the attachment of the lamella to the TEM grid. Techniques that facilitate the use of machine vision include shaping a probe tip so that its position can be readily recognized by image recognition software. Image subtraction techniques can be used to determine the position of the lamellae attached to the probe for moving the lamella to the TEM grid for attachment. In some embodiments, reference structures are milled on the probe or on the lamella to facilitate image recognition.
Owner:FEI CO
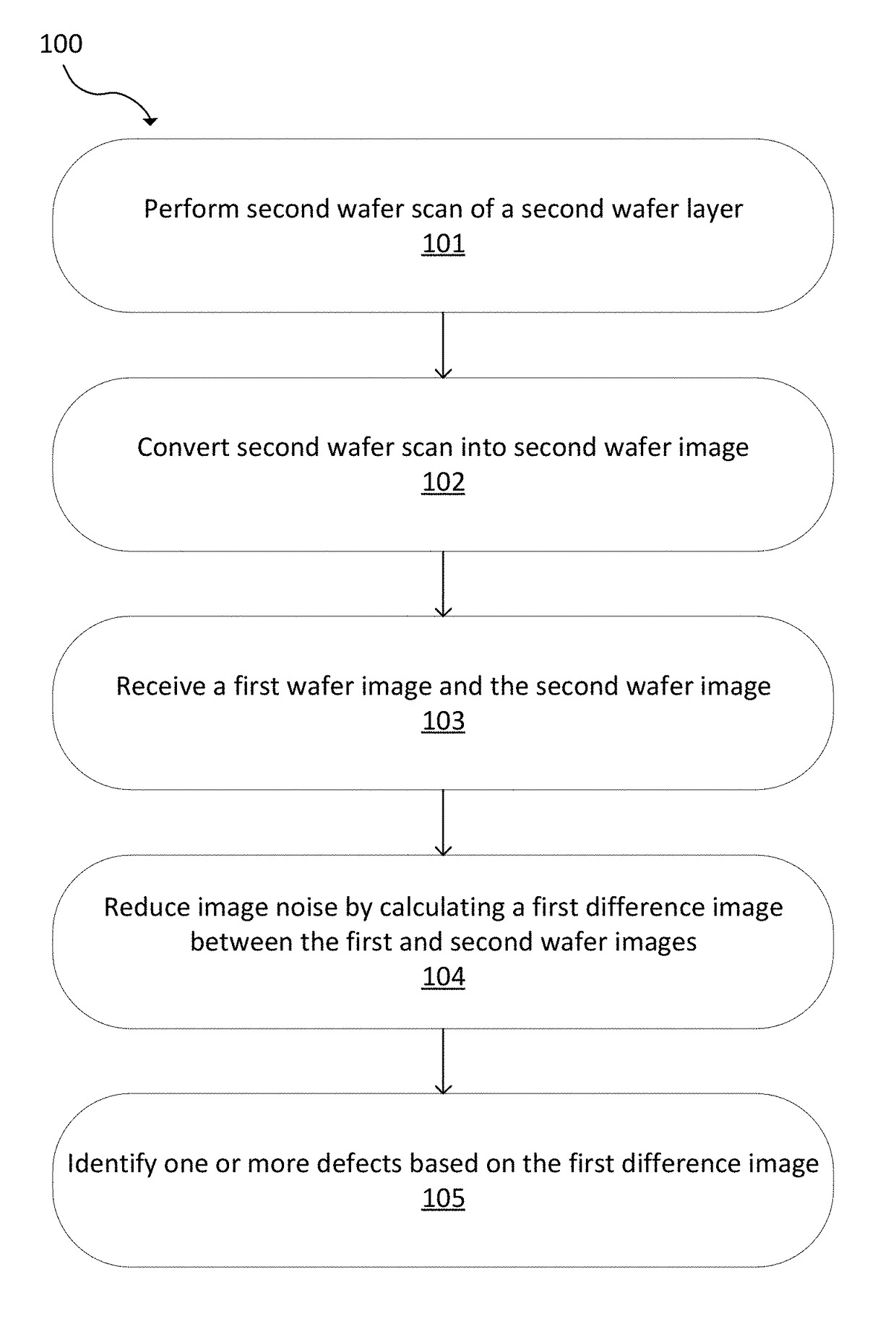
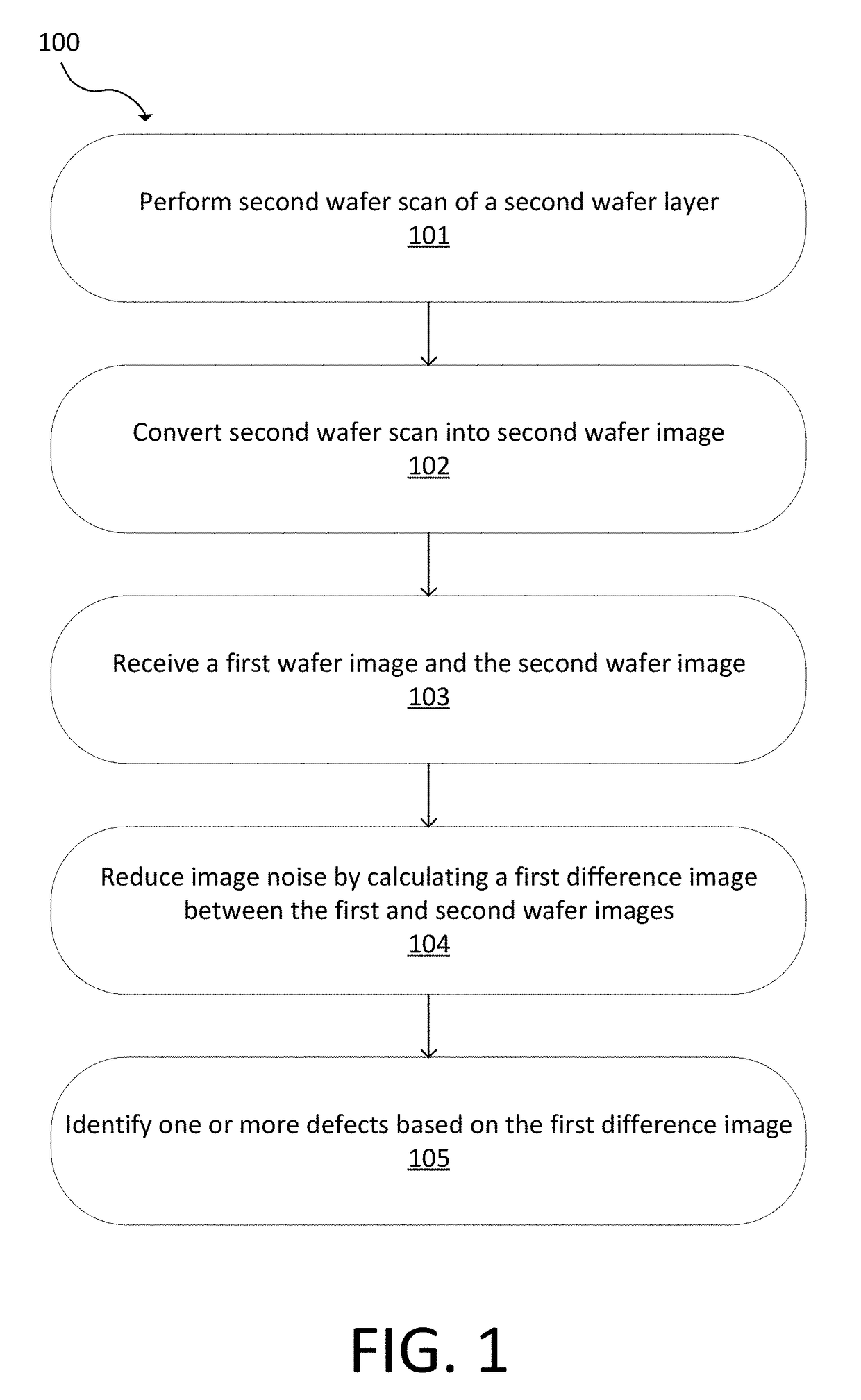
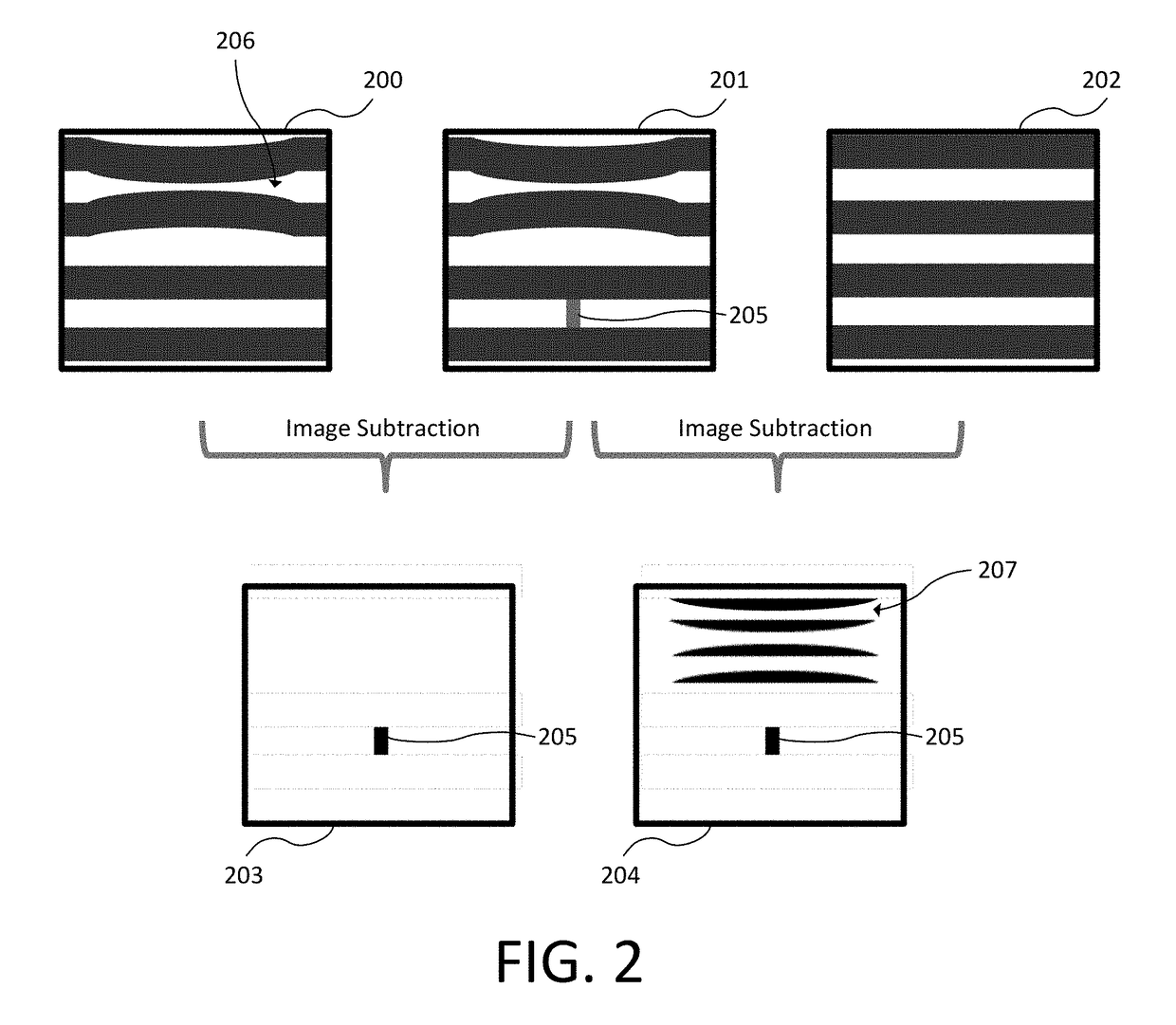
Wafer noise reduction by image subtraction across layers
ActiveUS20180144442A1Reduce noiseReduce image noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionData acquisition
Noise reduction in a difference image of an optical inspection tool is provided by calculating a difference image across layers of a multi-layered wafer. A first wafer image of a first wafer layer and a second wafer image of a second wafer layer are used. The first wafer image and the second wafer image are at a same planar location on the multi-layered wafer, but of different layers and / or after different process steps. A first difference image is calculated between the first wafer image and the second wafer image to reduce wafer noise. Defects can be identified using the first difference image. A system with an image data acquisition subsystem can be used to perform this technique.
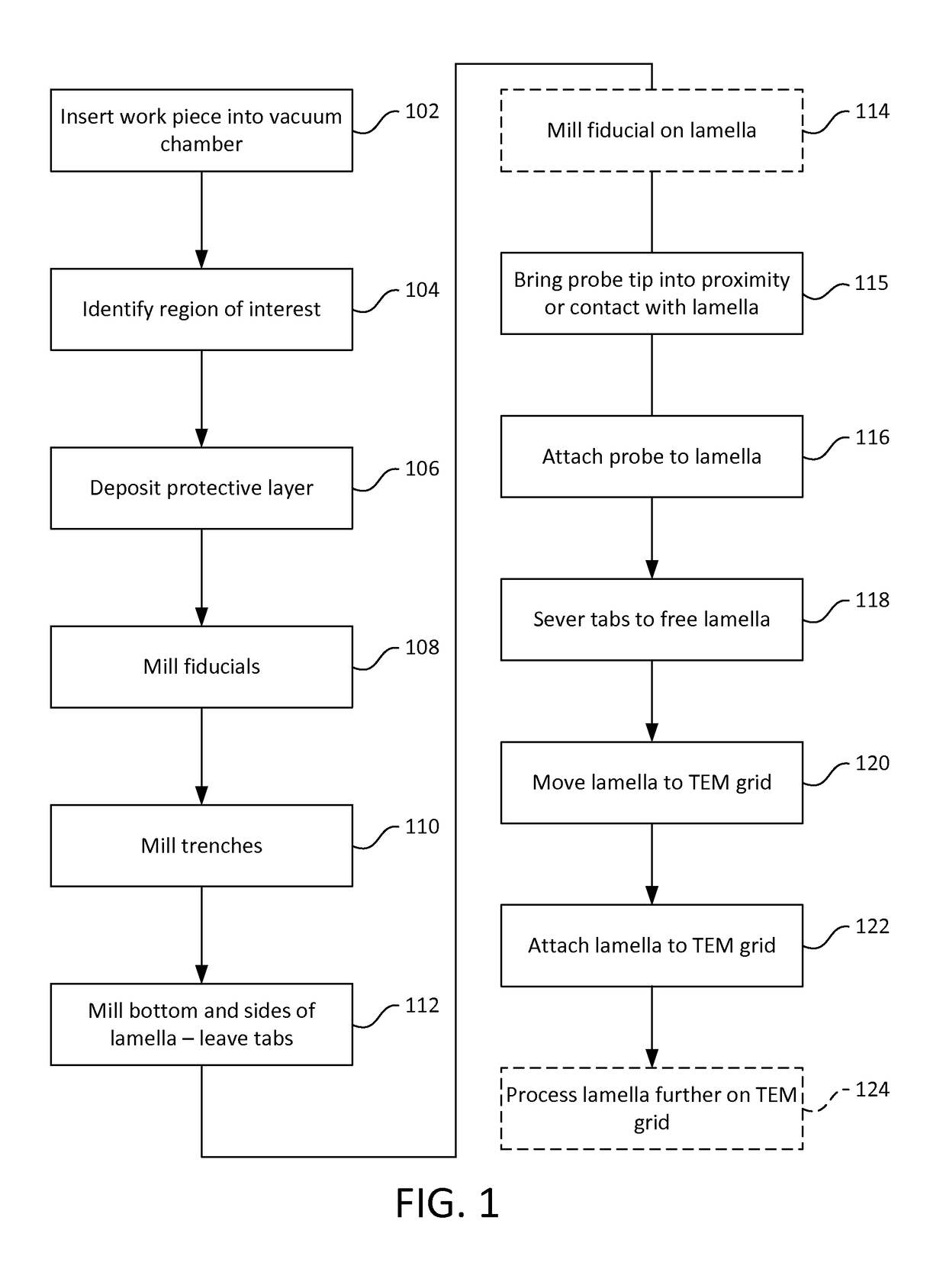
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
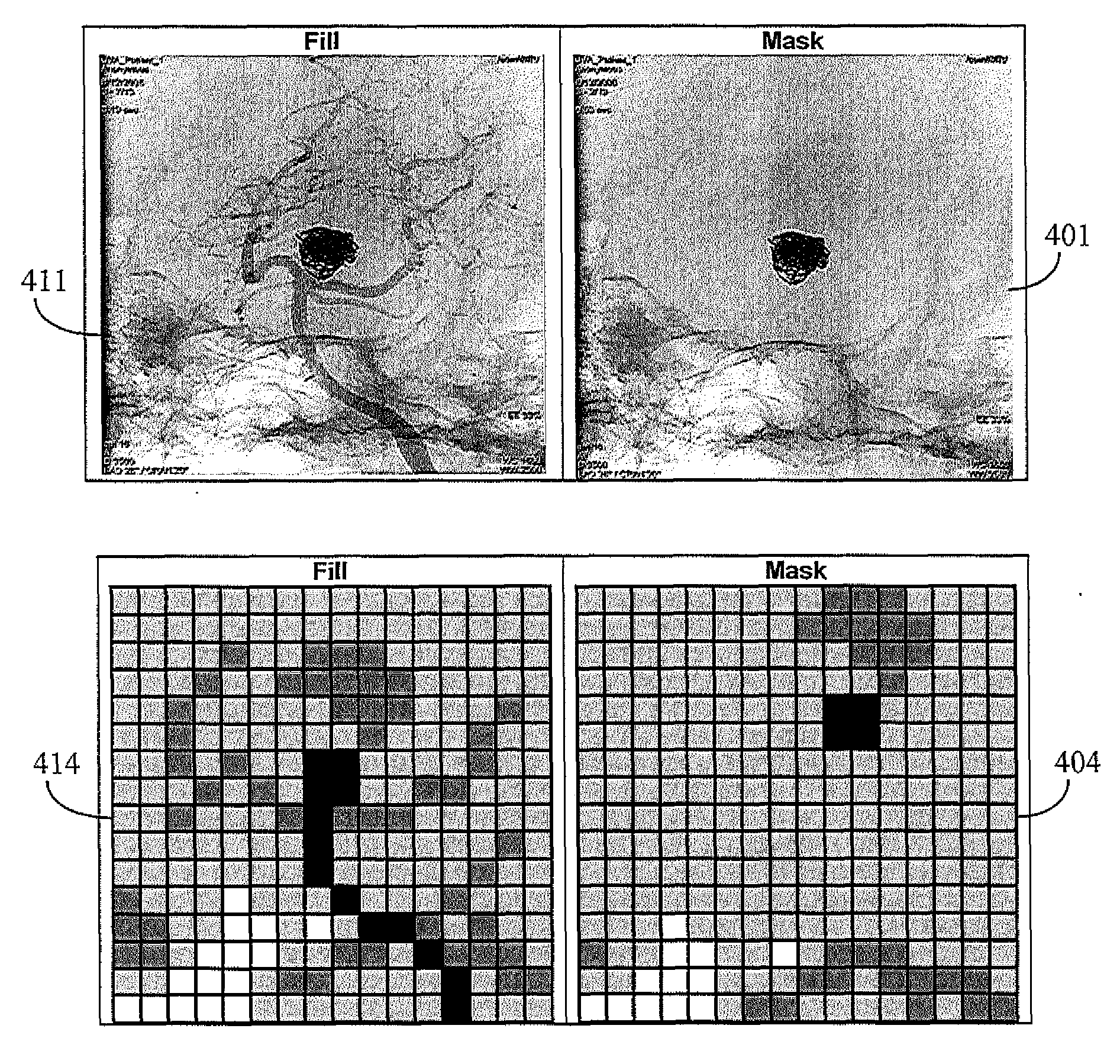
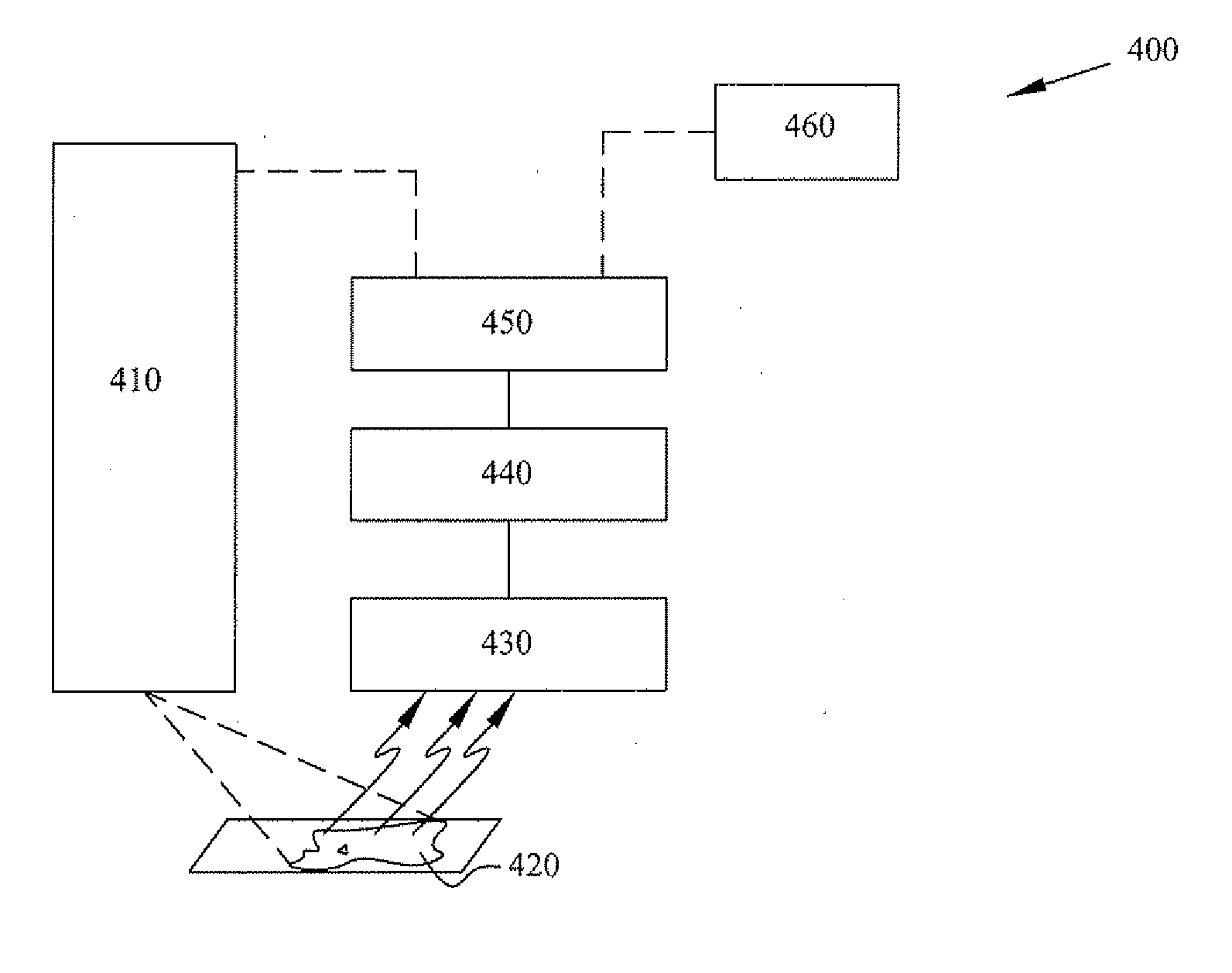
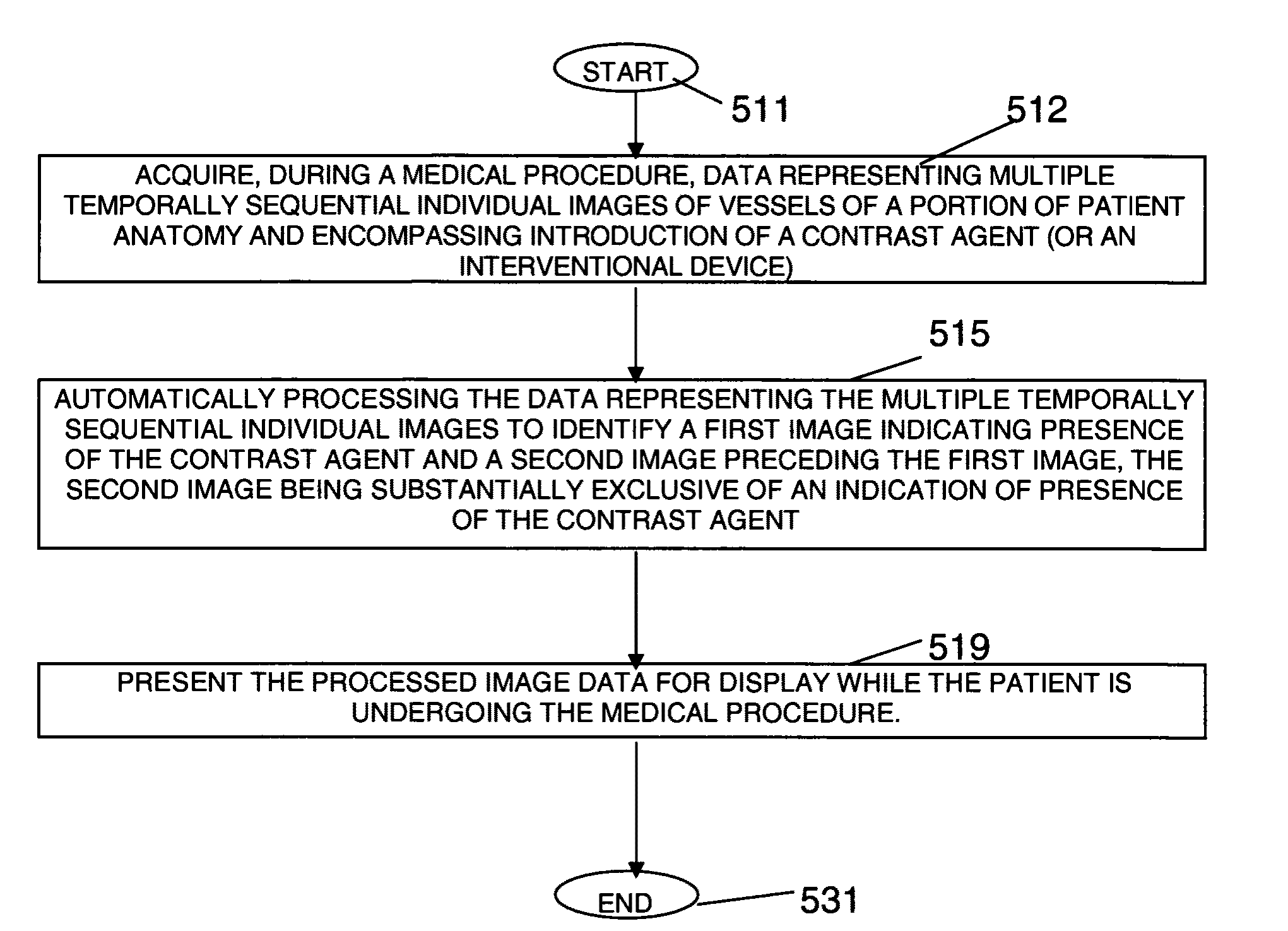
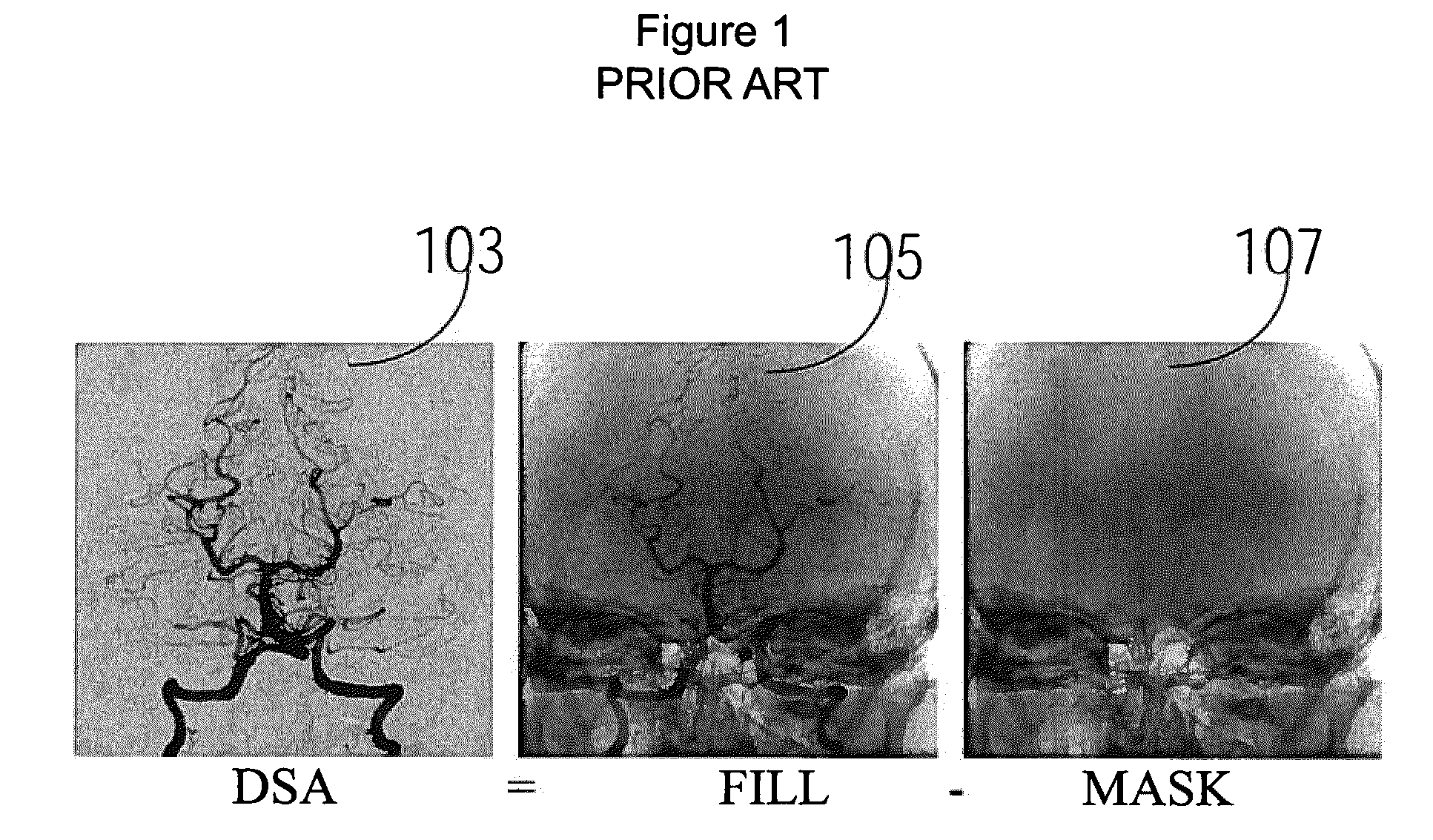
Image data subtraction system suitable for use in angiography
ActiveUS8090171B2Improve visualizationRemove image detailImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage subtractionBackground image
An image data subtraction system suitable for use in Angiography or other medical procedure enhances vessel visualization. The system comprises an imaging system for acquiring, during a medical procedure, data representing multiple temporally sequential individual images of vessels of a portion of patient anatomy. The sequential individual images encompass introduction of a contrast agent. An image processor automatically processes the data representing the multiple temporally sequential individual images to identify a first image indicating presence of the contrast agent and a second image preceding the first image by comparing a difference between measures representative of luminance content of the first and second image, with a threshold. The second image is substantially exclusive of an indication of presence of the contrast agent. The image processor, in response to the difference exceeding the threshold, automatically selects the second image as a mask image and subtracts data representing the mask image from data representing images of the temporally sequential individual images to remove background image detail and emphasize vessel structure in providing processed image data for display. A user interface presents the processed image data for display while the patient is undergoing the medical procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for printing a multilayer pattern
The present invention provides a control method and apparatus for printing a multilayer pattern on a substrate. In one embodiment, a method for printing a multilayer pattern includes a first printing operation comprising depositing a first patterned layer on a region of a surface of the substrate, a second printing operation comprising depositing a second patterned layer over the region of the surface or first patterned layer, and verifying the precision of the alignment of the second patterned layer relative to the first patterned layer. Verifying comprises acquiring a first optical image of the first patterned layer after the first printing operation, acquiring a second optical image of the second patterned layer after the second printing operation, and determining the position of the second patterned layer by performing an image subtraction process to form a first subtracted optical image and comparing the subtracted optical image with the first image.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS ITALIA SRL
Fault detection method, system and device for LED traffic guiding screen
InactiveCN107749055ATo overcome the shortcomings of requiring a lot of manpower and material resourcesSmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionMaterial resources
The invention discloses a fault detection method, system and device for an LED traffic guiding screen. The method comprises steps that a template image is generated according to a standard traffic guiding screen image; a to-be-detected image is generated according to a to-be-detected traffic guiding screen image; an image subtraction method is employed to carry out damaged area detection on the to-be-detected image according to the generated template image; blurred screen detection on the to-be-detected image is carried out according to the generated template image; the system comprises a first generation module, a second generation module, a damaged area detection module and a blurred screen detection module; the device comprises a memory and a processor. The method is advantaged in the image subtraction method is utilized to carry out damaged area detection on the to-be-detected image, computational complexity is substantially reduced, work efficiency is improved, moreover, the blurred screen detection function is newly added, a disadvantage of manpower and material resource consuming existing in a traditional manual inspection mode is solved, efficiency is higher, maintenance cost is reduced, the method can be widely applied to the digital image processing field.
Owner:GUANGDONG FUNDWAY TECH
Subtraction computer body-layer perfusion functional imaging method
InactiveCN101779963ANo pollution in the processExpand the scope of applicationComputerised tomographsTomographyImage subtractionFunctional imaging
The invention provides a subtraction computer body-layer perfusion functional imaging method. The method comprises the following steps: performing single-single or multi-layer dynamic continuous reinforced spiral CT scan on local tissue in order to get image data of each layer of tissue before and after contrast agent blood perfusion; transmitting images to an image workstation; using image subtraction software to create a novel digital image sequence of a group of contrast agent blood perfusion images of protruding tissue; and utilizing CT perfusion imaging (CTP) software of the image workstation to process and analyze the data of the novel digital image sequence in order to produce a group of color level images and values of parameters reflecting tissue blood perfusion states after subtraction. The method has the advantages of economical efficiency, practicability, no need for radioisotope, high image space and time resolution, short scanning and imaging time, few influencing factors, excellent repeatability, wide popularization, low examination cost and the like, and solves the problem that the prior art cannot effectively realize CTP evaluation and non-invasive examination of bone tissue or other high-density tissue and lesions.
Owner:上海市第八人民医院
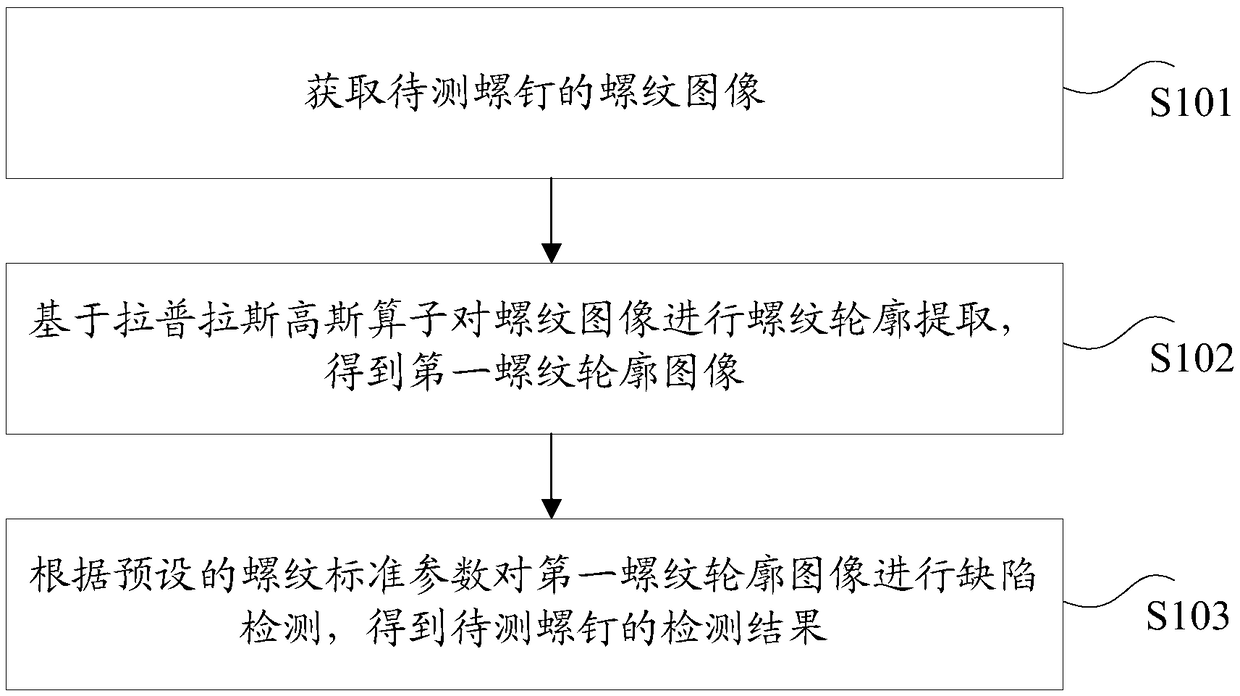
Screw thread detecting method and device
InactiveCN109102507AAchieve precise positioningSolve the technical problems of low detection accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisImage subtractionScrew thread
The invention discloses a screw thread detecting method and a device. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a screw thread image to be tested, extracting a screw thread contour based ona Laplacian Gaussian operator to obtain a first screw thread contour image, and then performing defect detection on the first screw thread contour image to obtain a detection result of the screw to betested, so as to achieve the purpose of accurately positioning the screw thread edge. The invention solves the technical problem that the screw thread detection is carried out by the local measurement and the image subtraction method in the related art, and the screw thread detection accuracy is low.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE INTELLIGENT EQUIP CO LTD +1
Rapid measurement method of LED light distribution curve
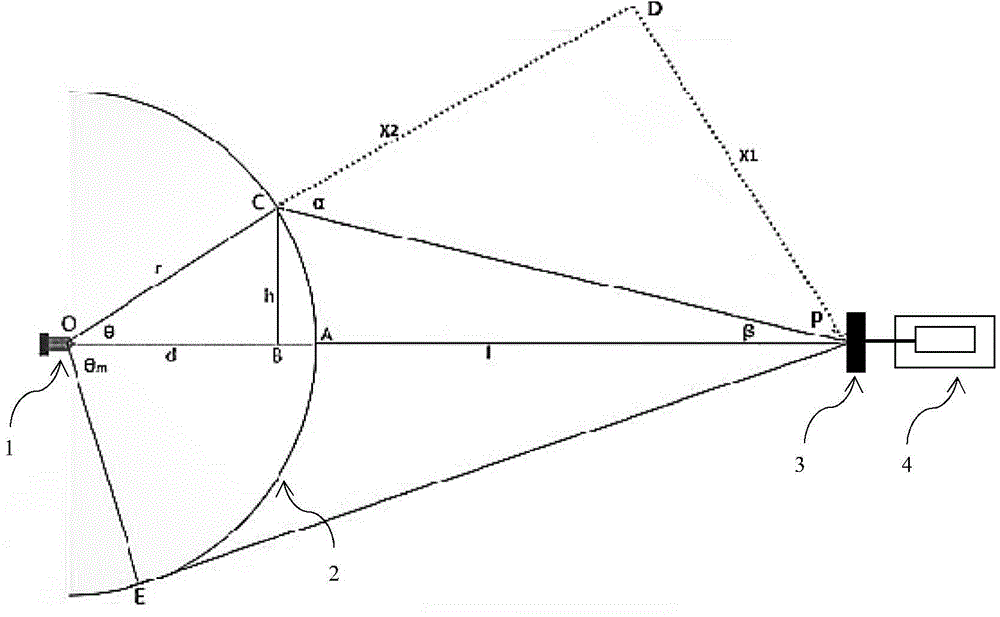
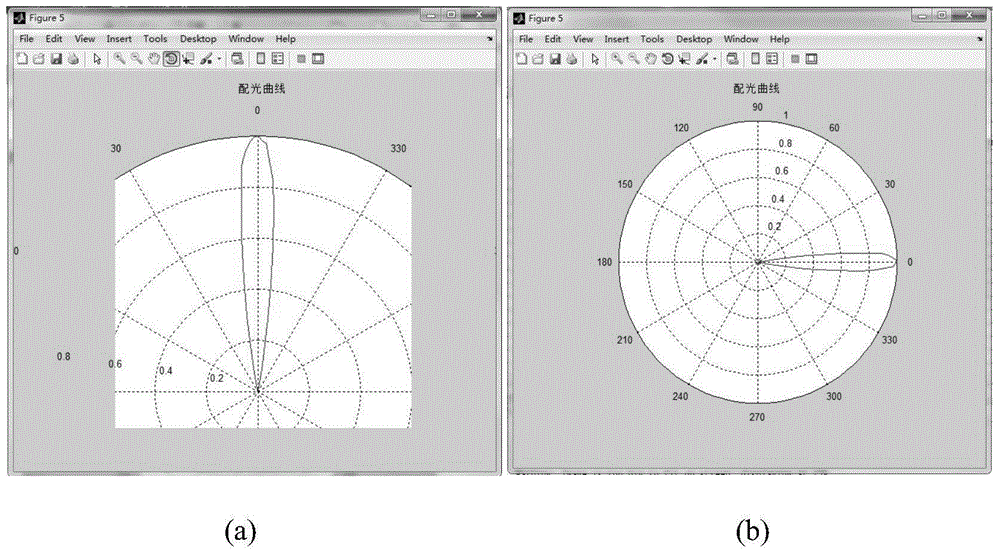
InactiveCN104977155AFastQuick measurementPhotometryTesting optical propertiesImage subtractionLuminous intensity
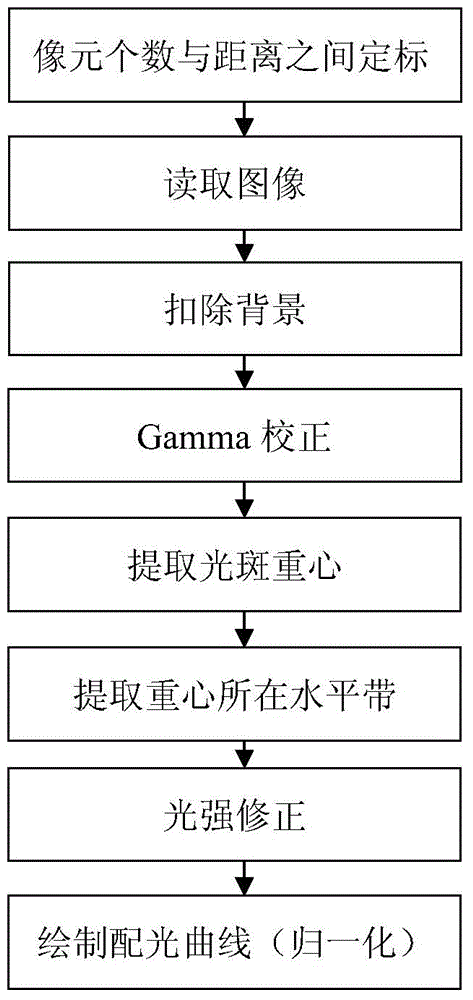
The invention discloses a rapid measurement method of an LED light distribution curve. The method comprises the following steps that: (1), a pixel coordinate of an image formed by an image sensor and an LED luminous intensity space coordinate are calibrated, thereby realizing one-to-one mapping of LED luminous intensities and exit angles; (2), the image sensor shoots an LED light spot image formed on a receiving screen and a non-LED-light-spot receiving screen background image and a computer reads the images to light distribution curve measurement software; (3), image subtraction is carried out to deduct background interference information; (4), Gamma correction is carried out on images with background deduction; (5), gravity center marking is carried out on the images after Gamma correction; (6), pixel point gray values of horizontal bands where the image gravity centers are located are extracted; (7), light intensity correction is carried out; (8), a light distribution curve is drawn automatically according to a light intensity correction formula obtained by the step (7). The method has advantages of high operability, fast measurement speed, high environmental adaptation, and visual measurement result.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Reticle inspection systems and method
ActiveUS8189203B2Easy to distinguishPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotomechanical apparatusImage subtractionPhase difference
A method and systems for reticle inspection. The method includes coherently illuminating surfaces of an inspection reticle and a reference reticle, applying a Fourier transform to scattered light from the illuminated surfaces, shifting the phase of the transformed light from the reference reticle such that a phase difference between the transformed light from the inspection reticle and the transformed light from the reference reticle is 180 degrees, combining the transformed light as an image subtraction, applying an inverse Fourier transform to the combined light, and detecting the combined light at a detector. An optical path length difference between two optical paths from the illumination source to the detector is less than a coherence length of the illumination source. The image detected by the detector represents a difference in amplitude and phase distributions of the reticles allowing foreign particles, defects, or the like, to be easily distinguished.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Method and apparatus for interactive hyperspectral image subtraction
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com