Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
492 results about "Gasoline station" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
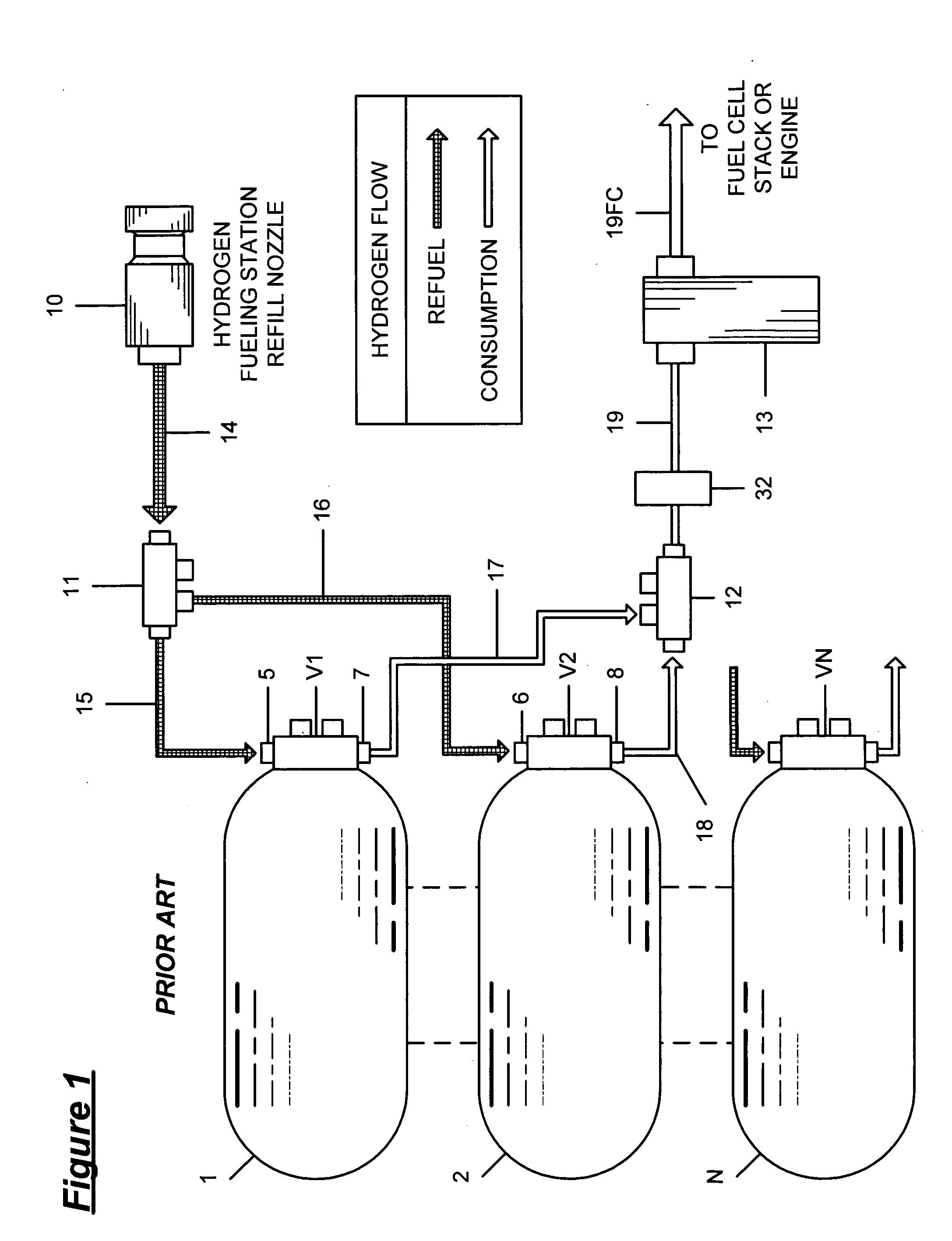
A gas station, also known as a filling station, fueling station, service station or petrol station is a facility which sells fuel and lubricants for motor vehicles. The most common fuels sold are gasoline (petrol) or diesel fuel.
Autonomous vehicle refueling
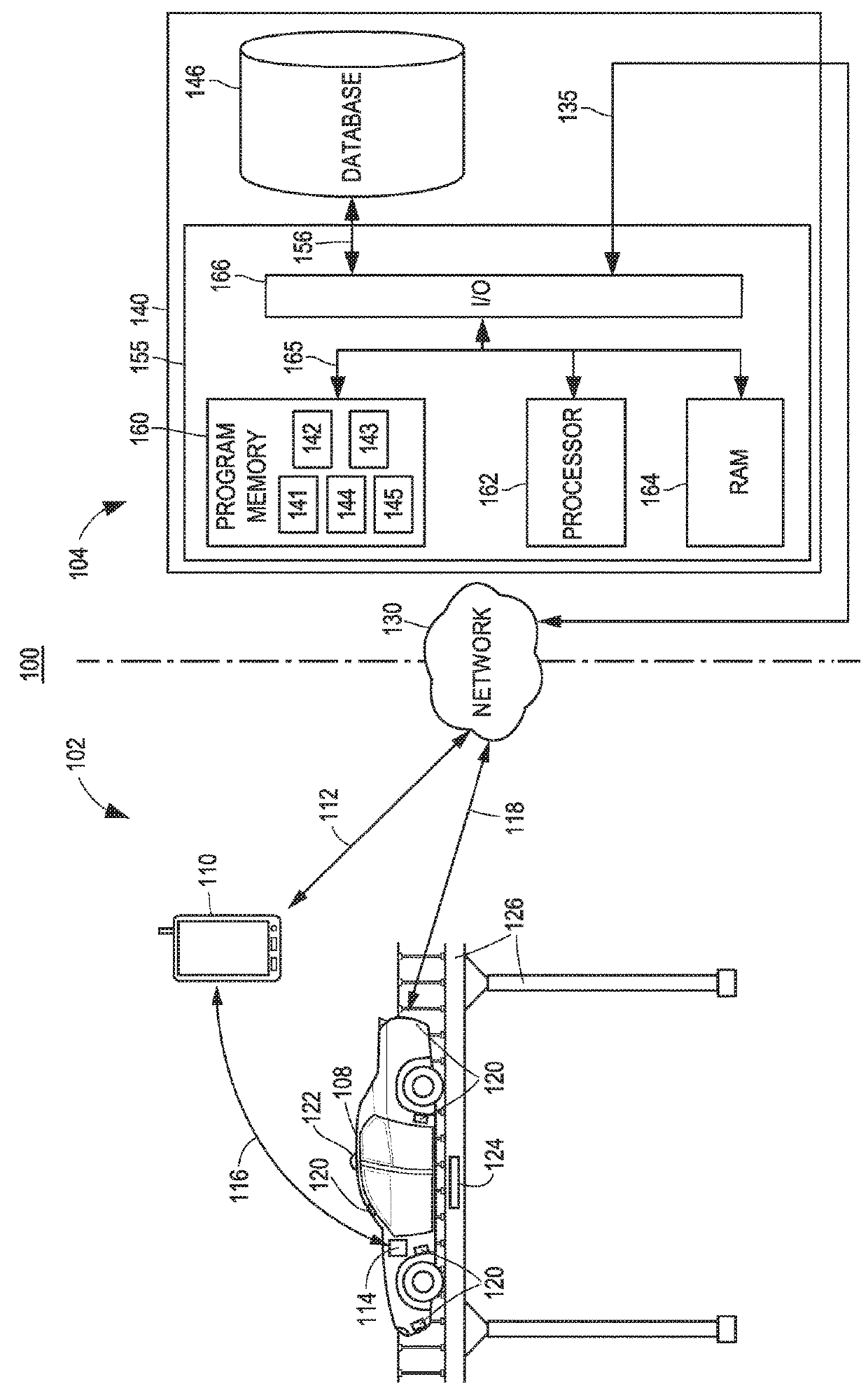
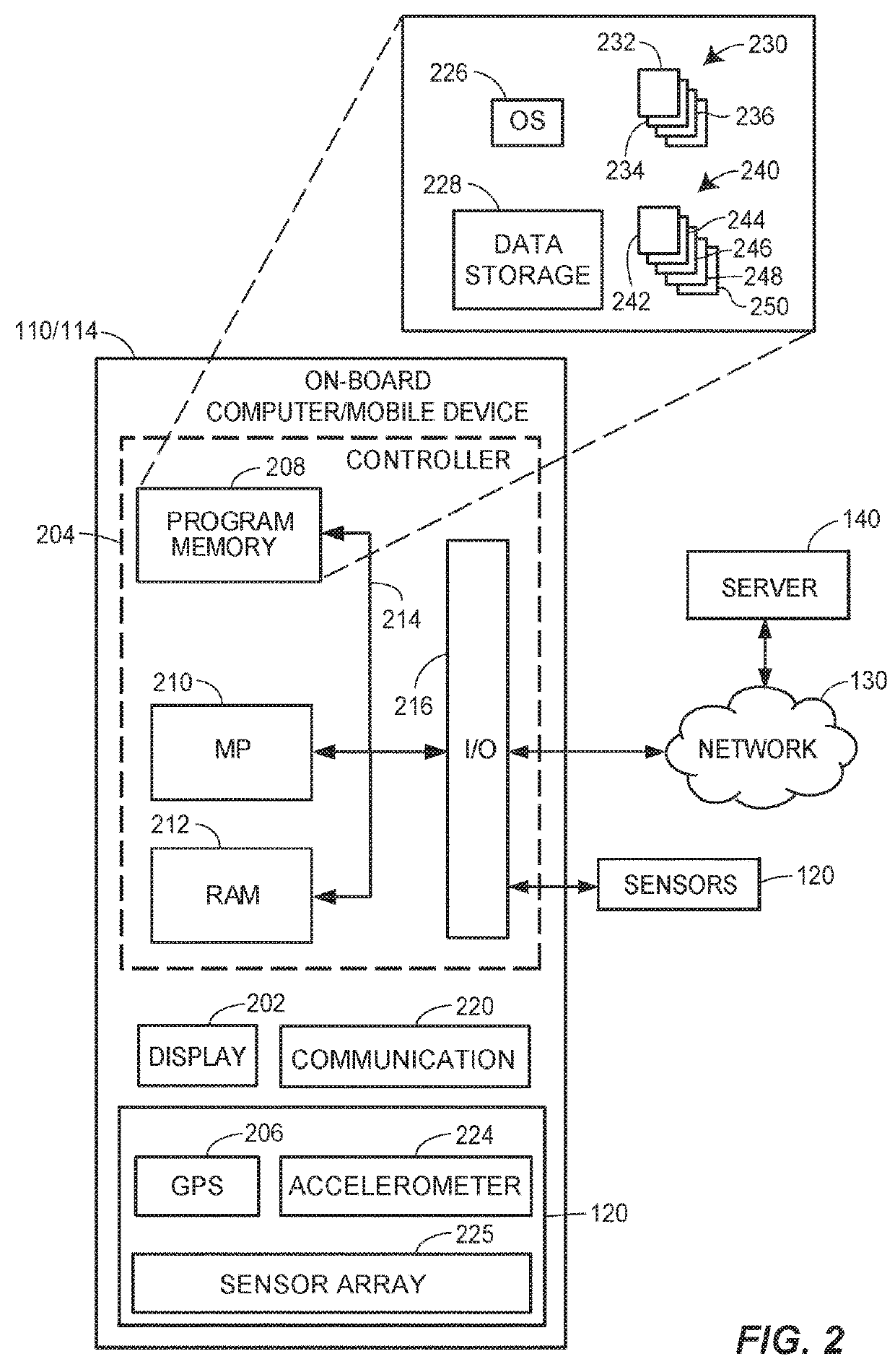
Methods and systems for autonomous vehicle recharging or refueling are disclosed. Autonomous vehicles may be automatically refueled by routing the vehicles to available fueling stations when not in operation, according to methods described herein. A fuel level within a tank of an autonomous vehicle may be monitored until it reaches a refueling threshold, at which point an on-board computer may generate a predicted use profile for the vehicle. Based upon the predicted use profile, a time and location for the vehicle to refuel the vehicle may be determined. In some embodiments, the vehicle may be controlled to automatically travel to a fueling station, refill a fuel tank, and return to its starting location in order to refuel when not in use.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
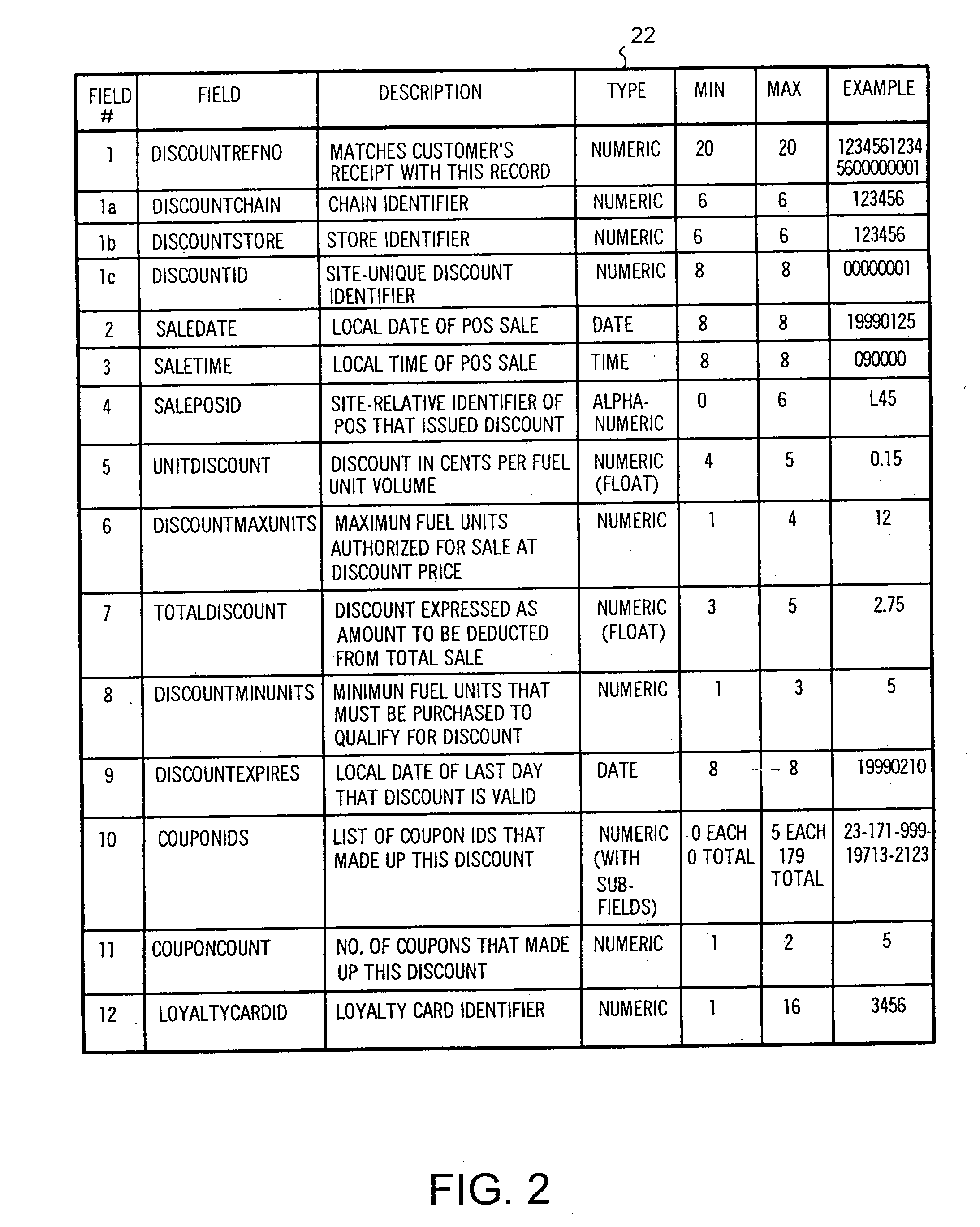
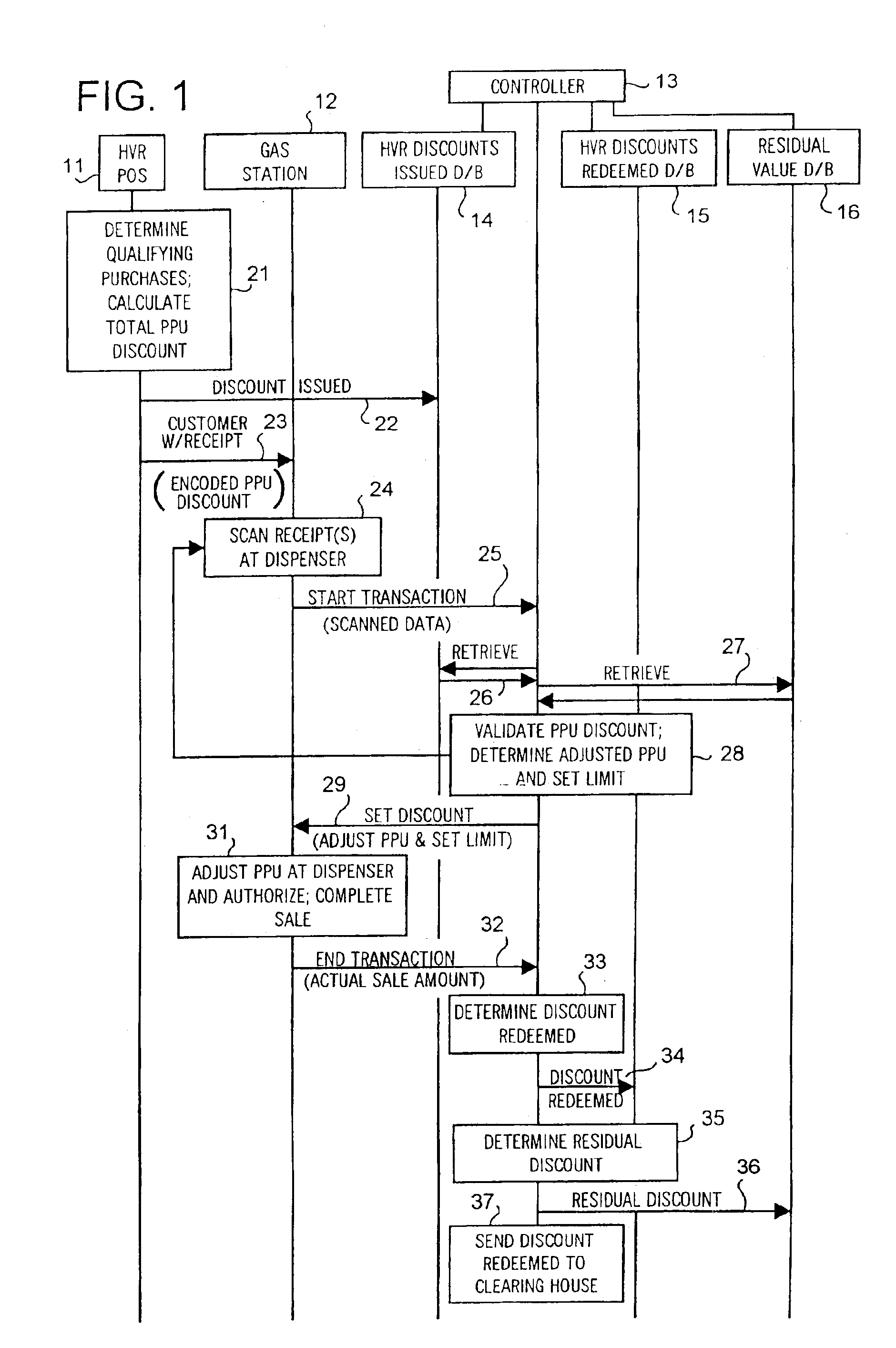
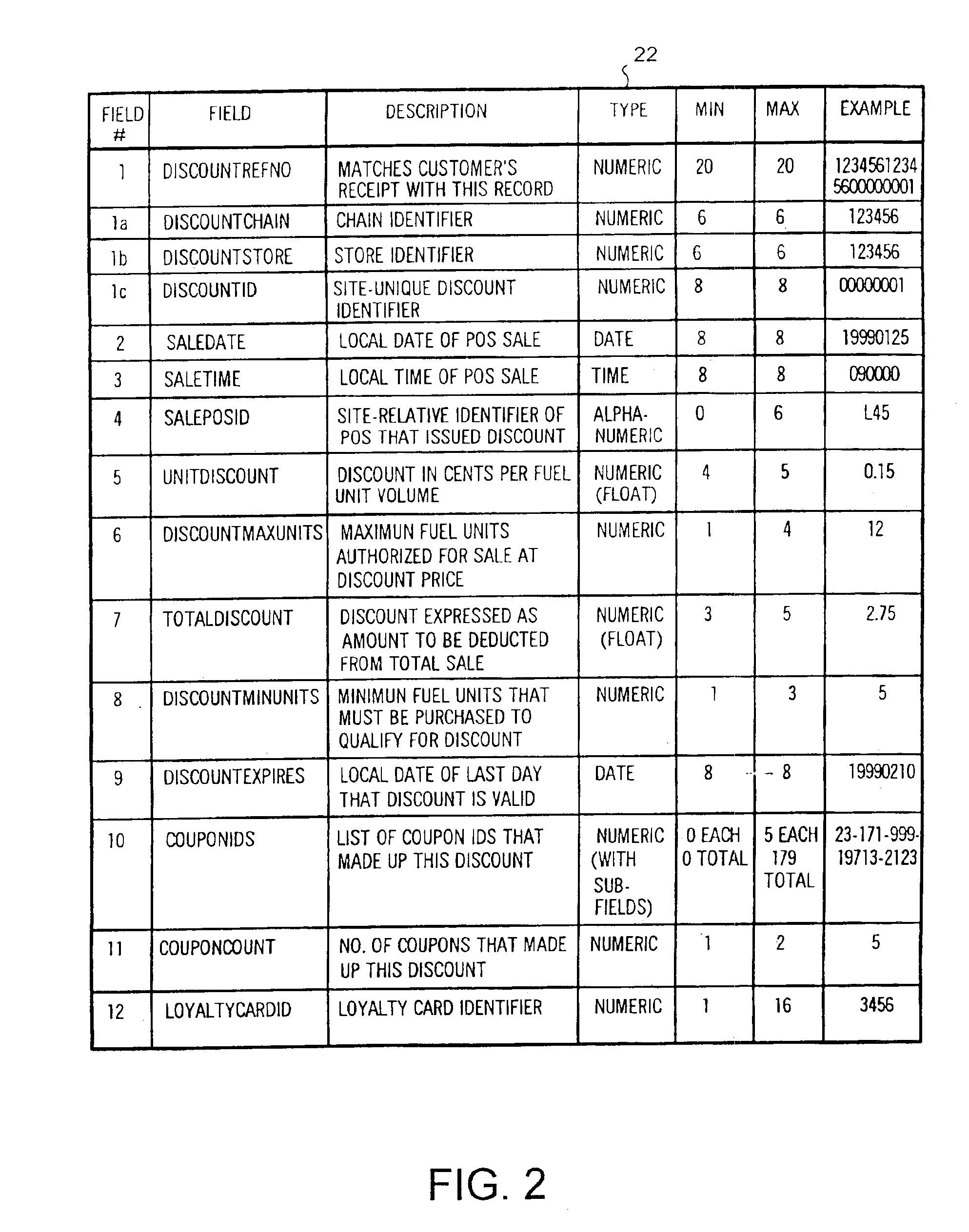
System and method of providing multiple level discounts on cross-marketed products and discounting a price-per-unit-volume of gasoline
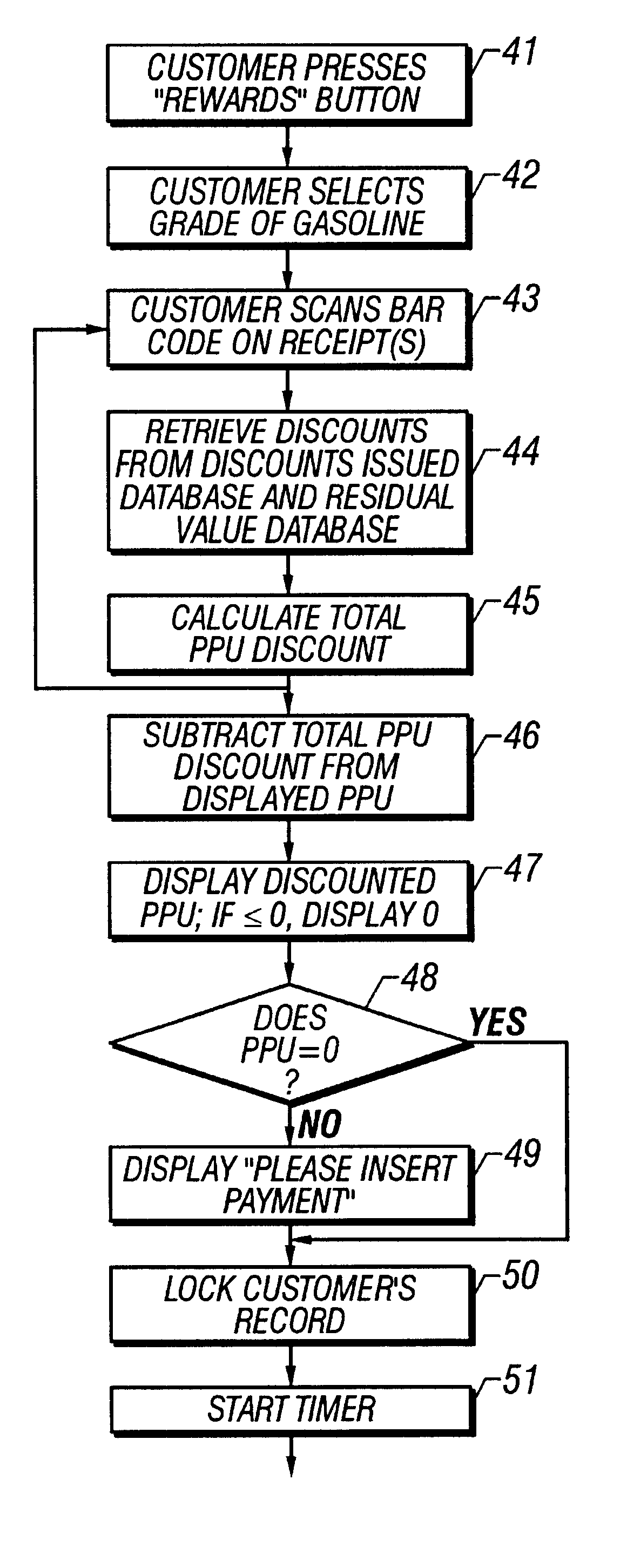
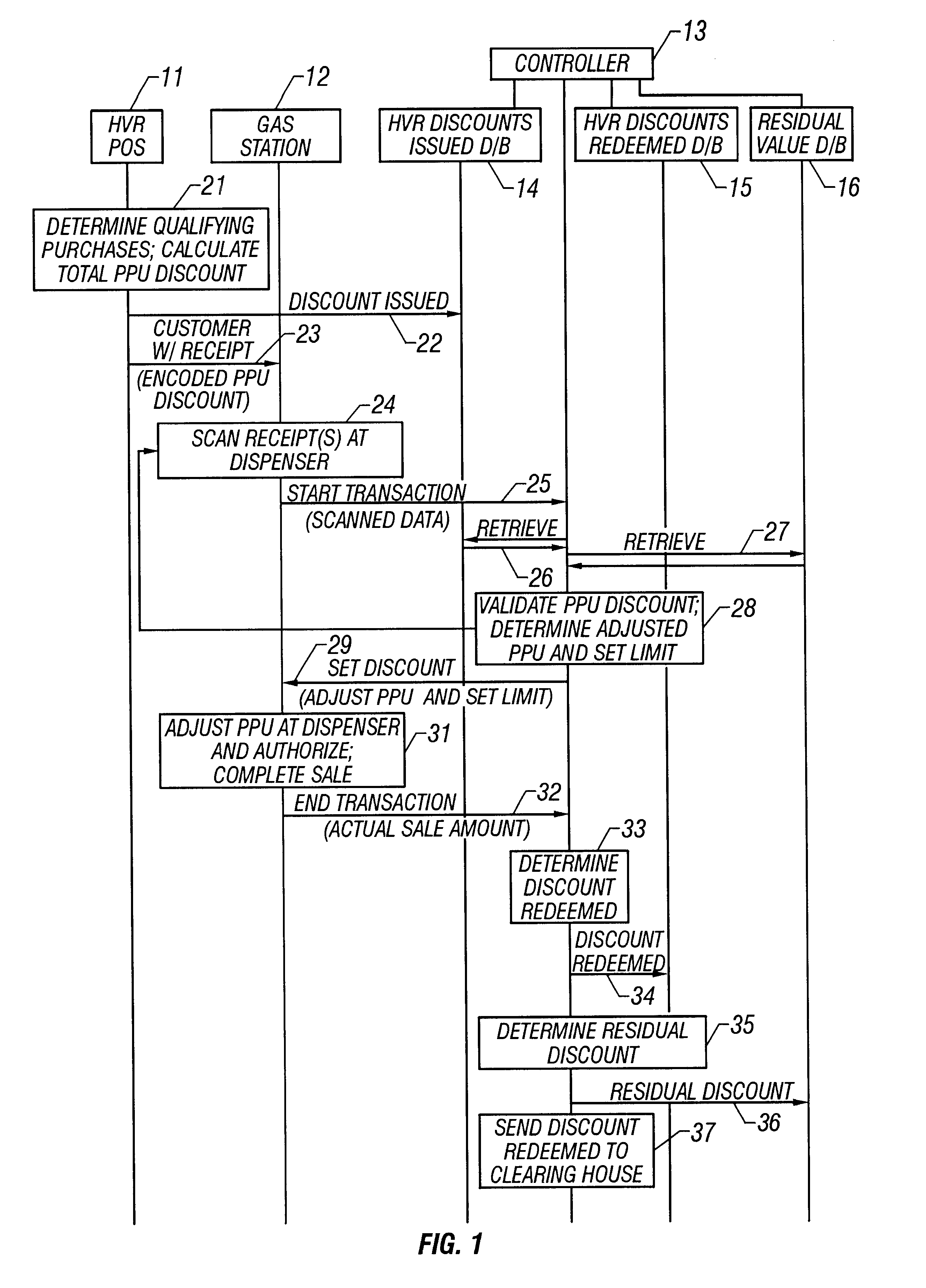
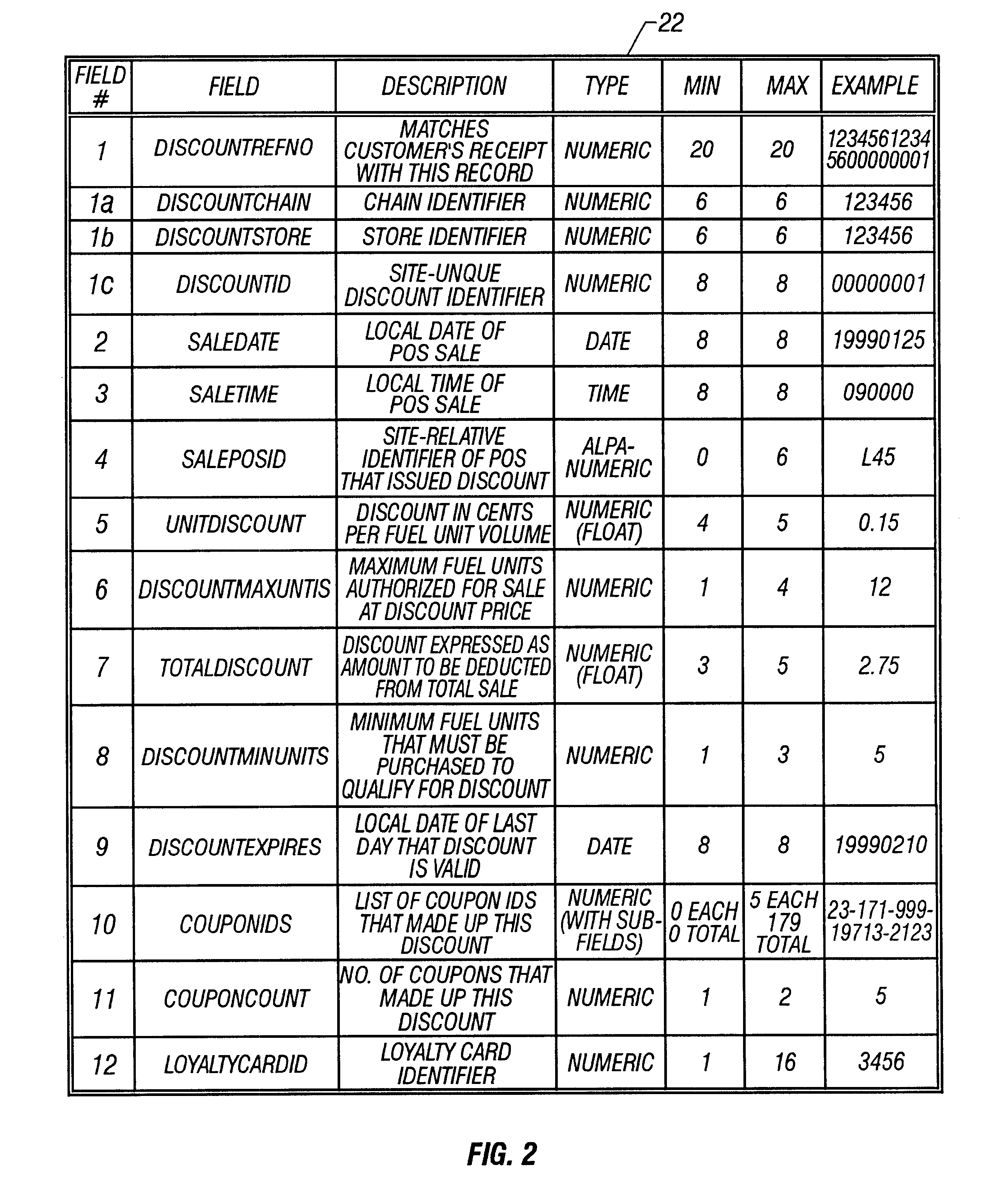
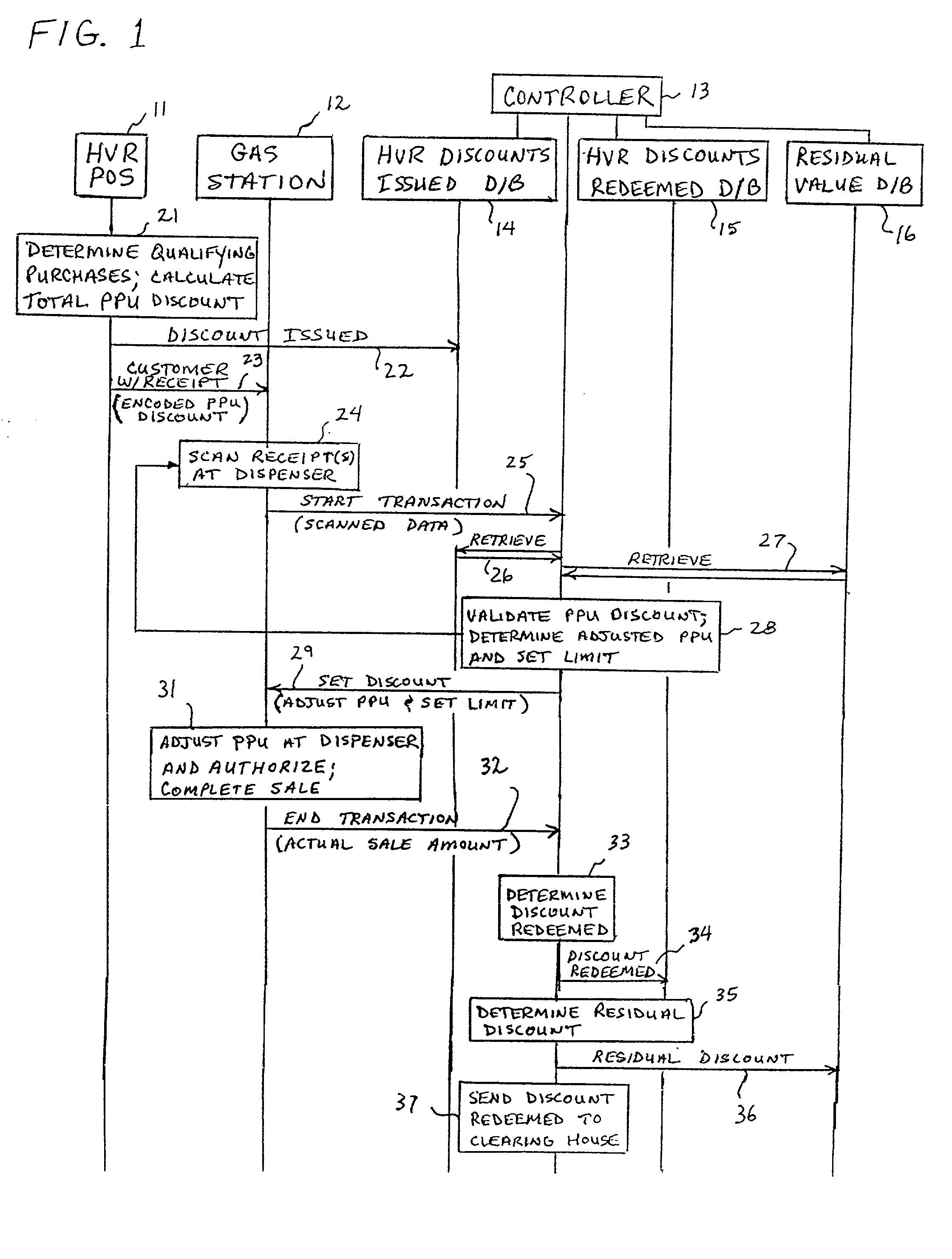
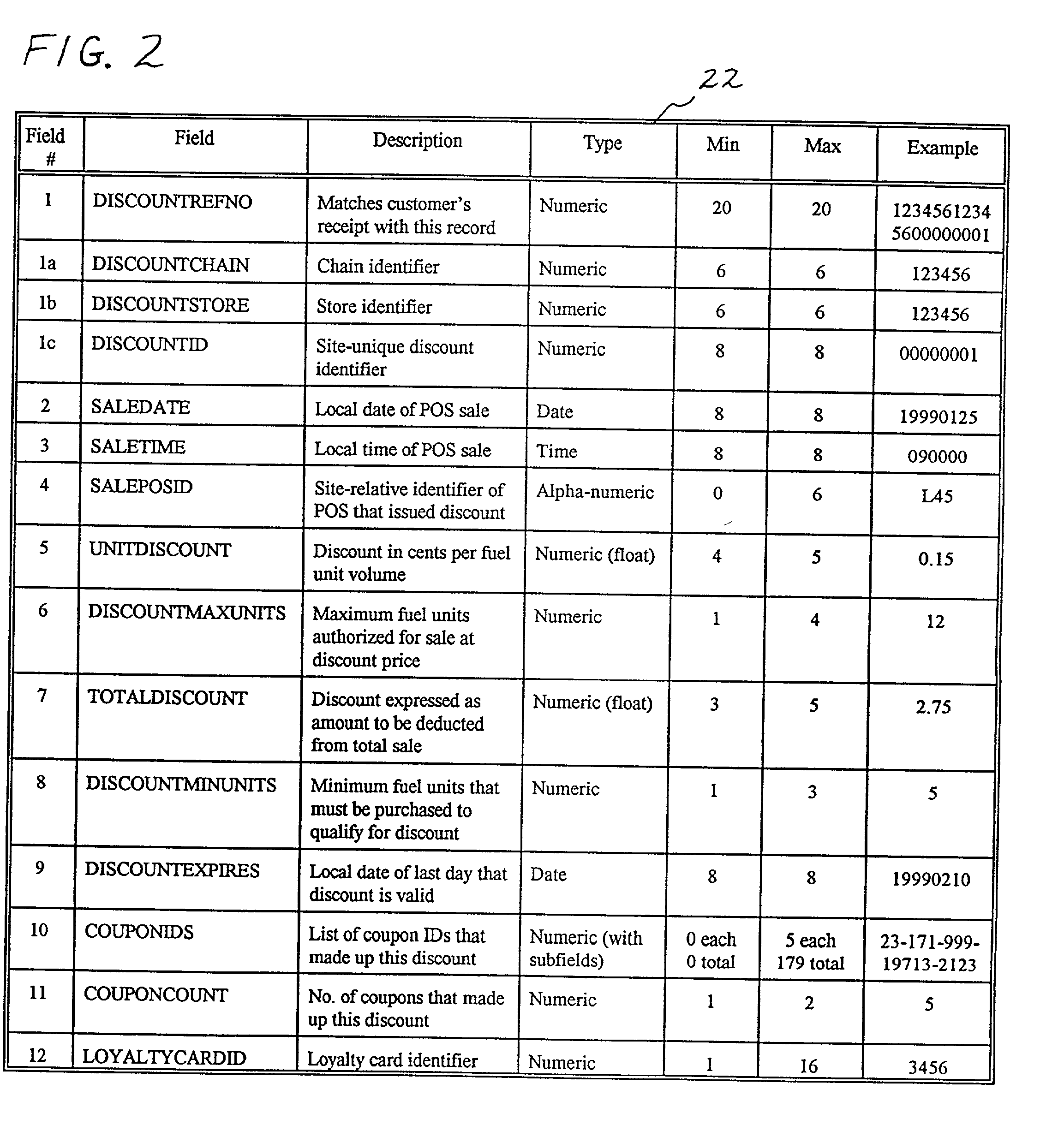
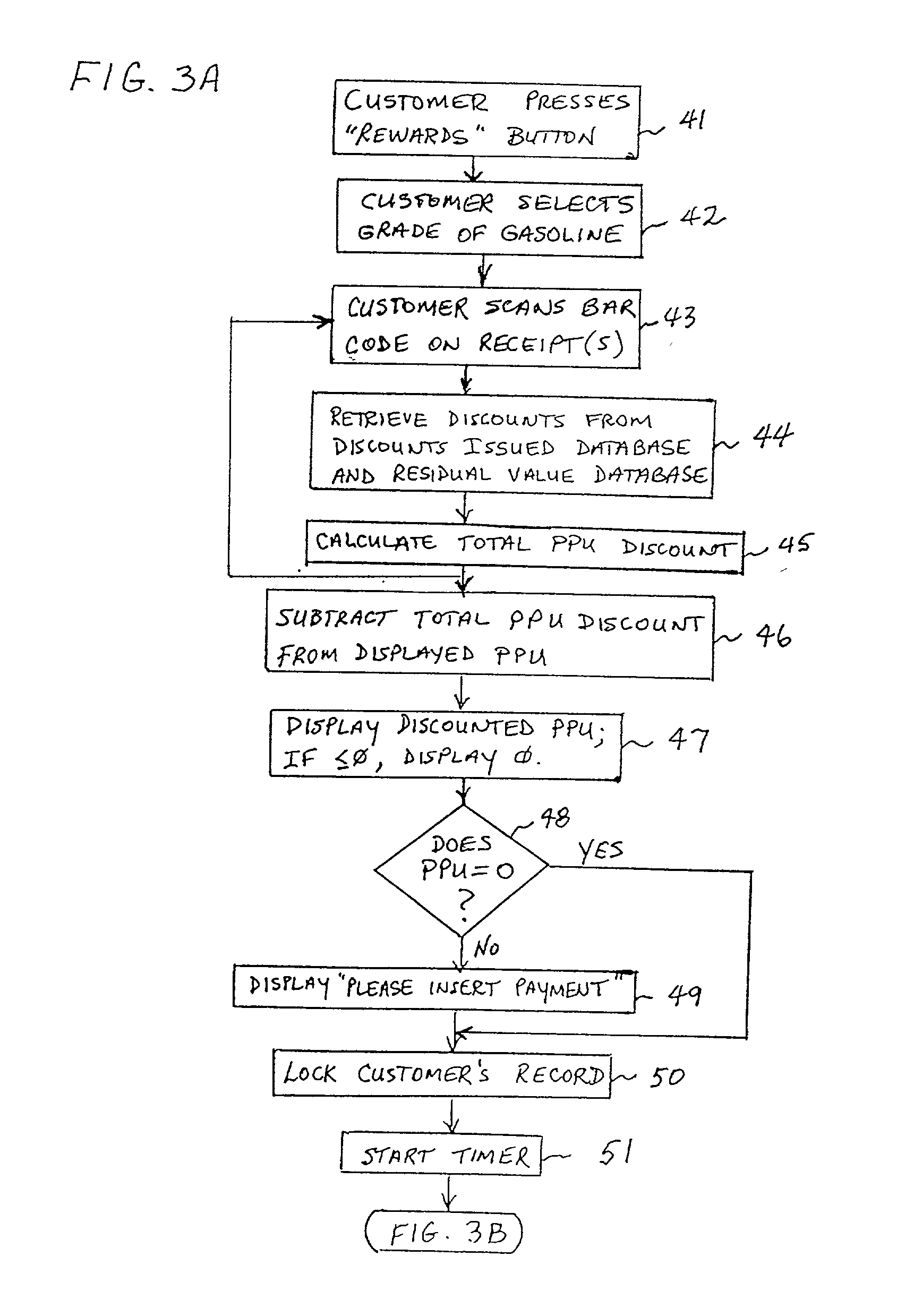
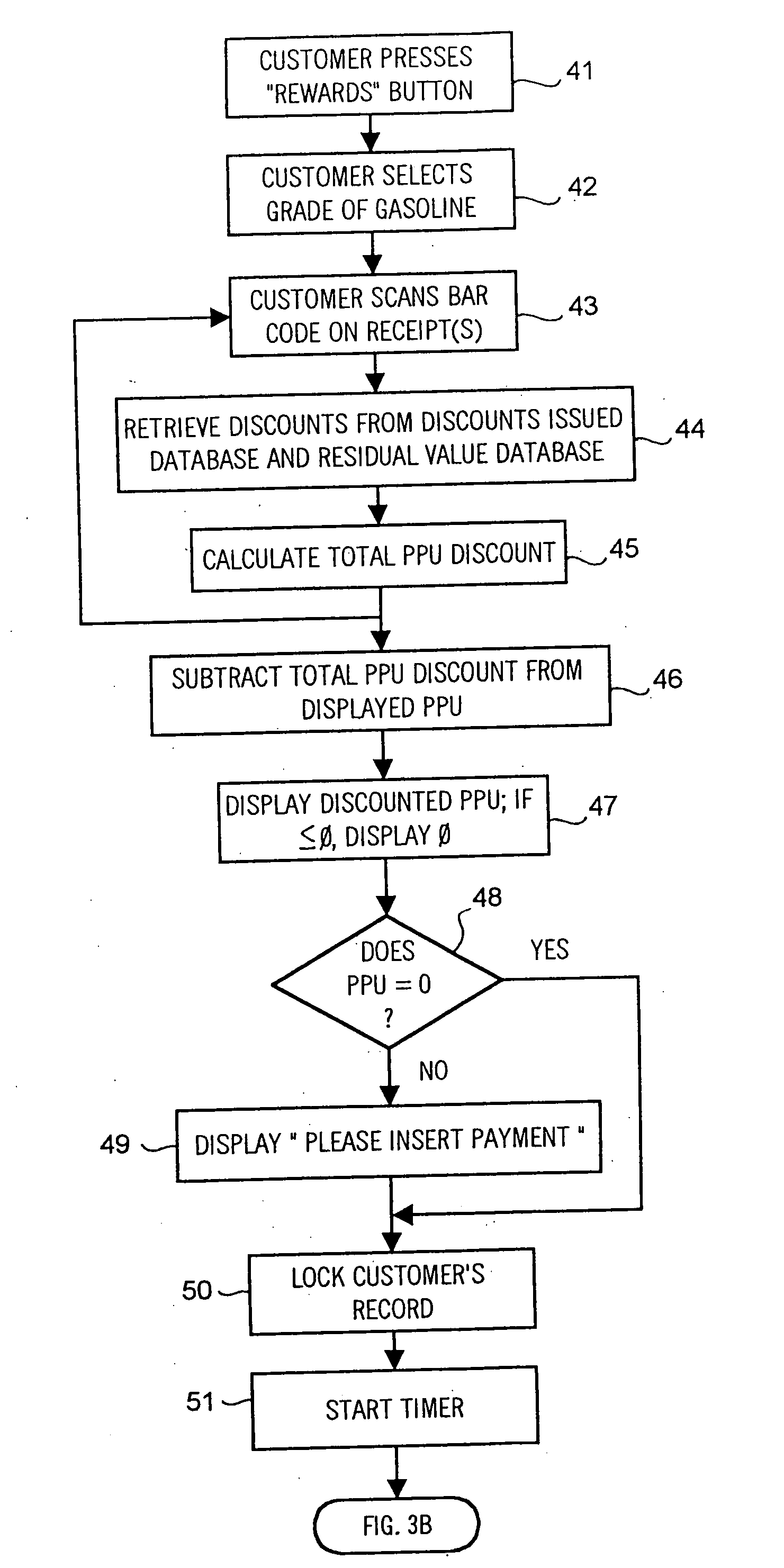
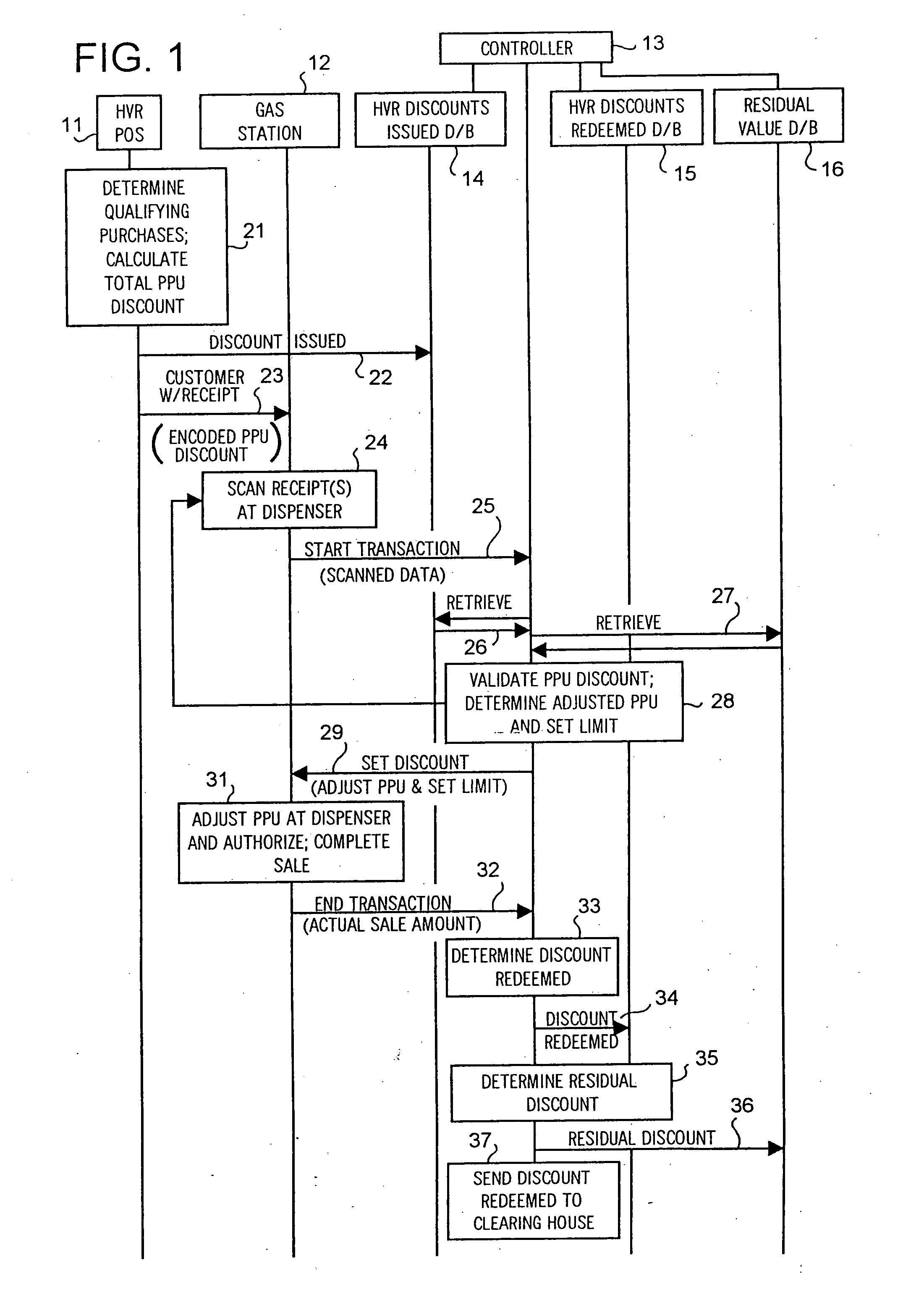
A method of providing multiple level, price-per-unit (PPU) discounts on gasoline to a customer who purchases at least one cross-marketed product. The customer is awarded a first PPU discount on the gasoline based on a purchase by the customer of a first cross-marketed product, and is awarded a second PPU discount based on the purchase of a second cross-marketed product. The first discount is then added to the second discount to determine a total PPU discount, and a paper receipt is printed for the customer with a customer identification and a transaction identification encoded in a bar code thereon. The total discount is stored in a discounts issued database. The customer then scans the encoded bar code with a bar code scanner at a gasoline dispenser to redeem the discount. The total discount is retrieved from the discounts issued database, and the gasoline station then reduces the price-per-unit-volume of the gasoline by an amount equal to the total discount. When the customer completes the gasoline purchase, a value of the total discount redeemed is determined and stored in a discounts redeemed database. Portions of the discount redeemed are then allocated to vendors of the first and second cross-marketed products according to predetermined criteria.
Owner:EXCENTUS CORP +1
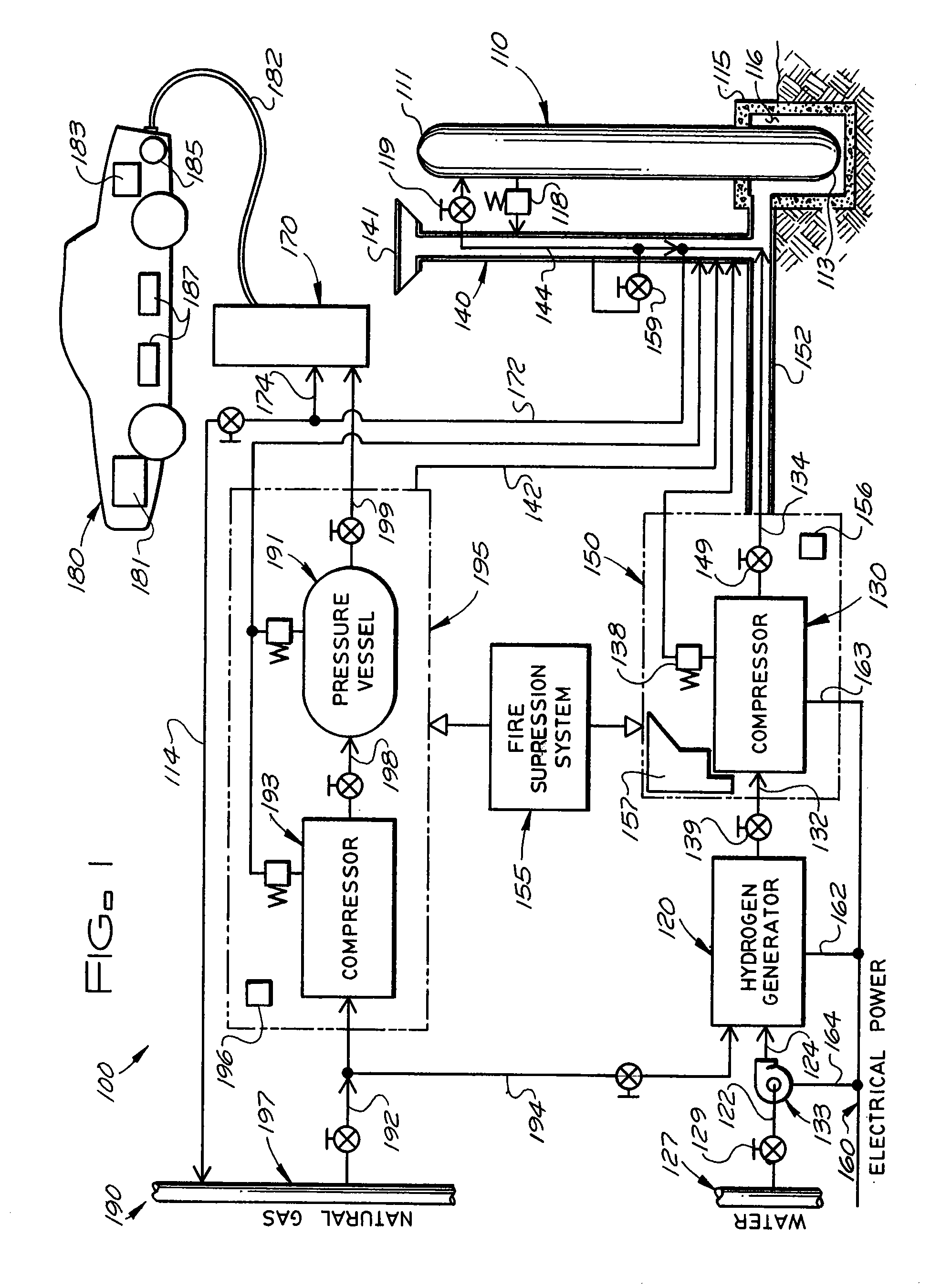
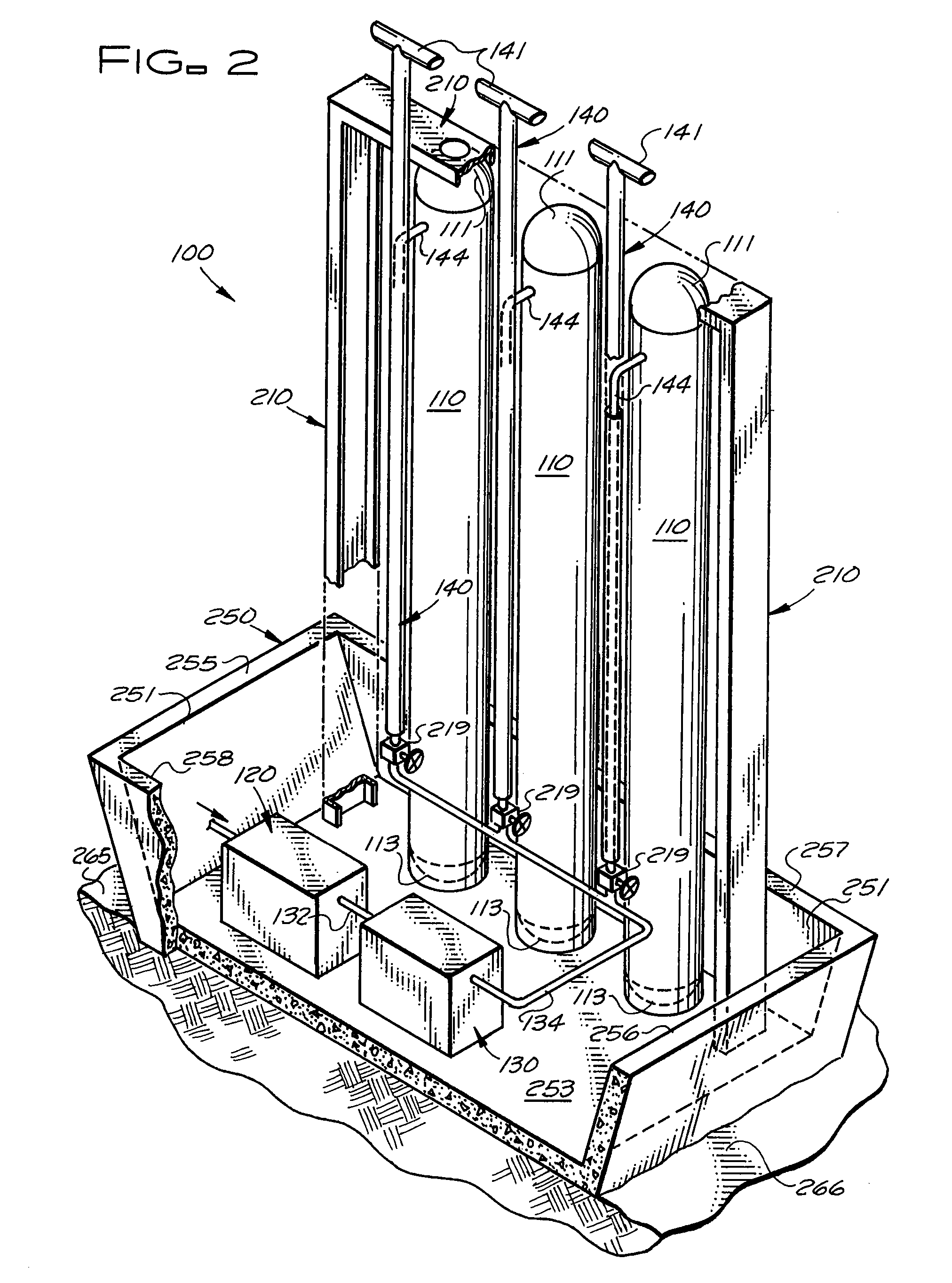
Transportable hydrogen refueling station
InactiveUS6755225B1Easy to monitorReduce riskTank vehiclesGas handling applicationsHigh pressureGaseous hydrogen
A portable hydrogen refueling stations which can dispense gaseous hydrogen from one or more internal high pressure tanks. The refueling station can be refilled with a lower pressure hydrogen gas feed and then compressed for storage within the refueling station.
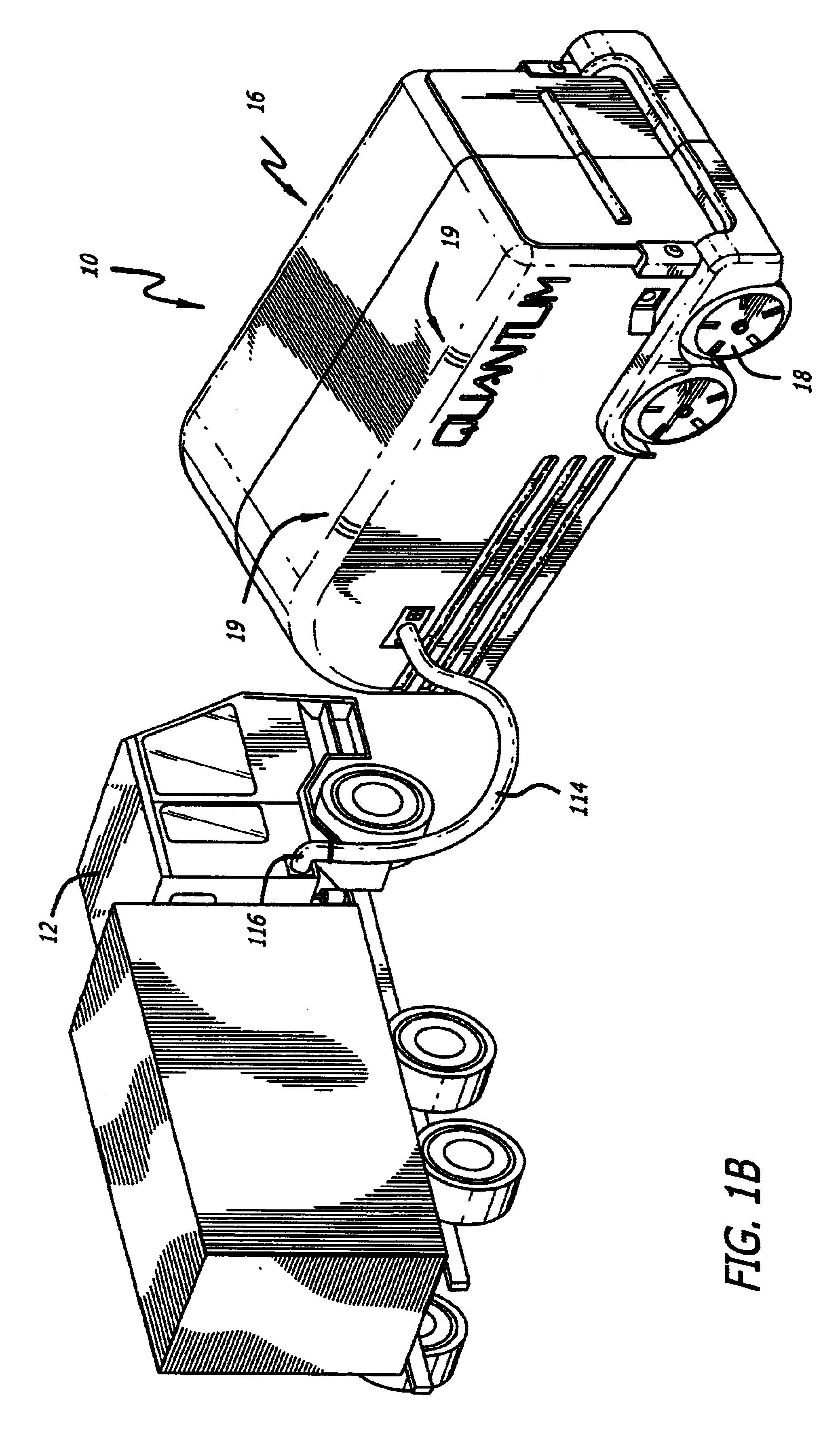
Owner:QUANTUM FUEL SYST TECH WORLDWIDE INC
Built-up synergetic class-A/B water extinguishing agent series
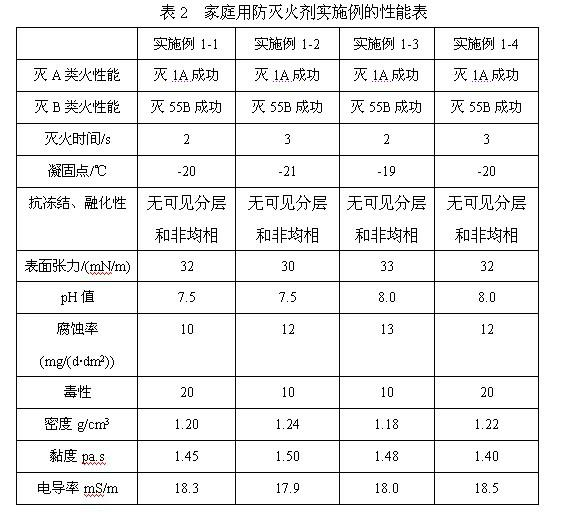
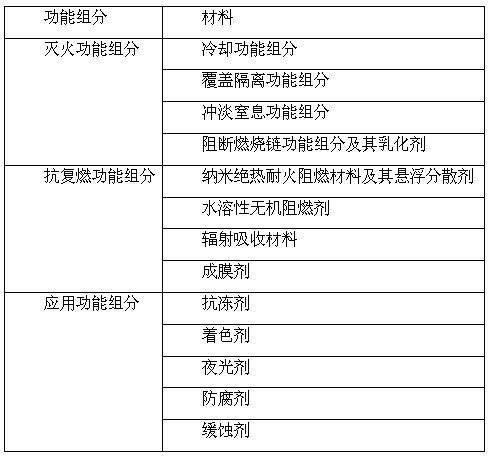
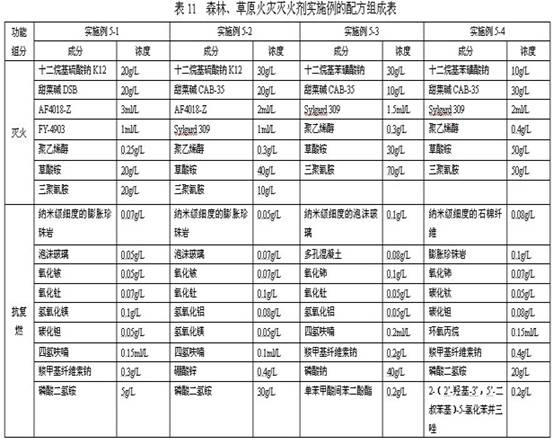
The invention discloses a built-up synergetic class-A / B water extinguishing agent series. Class-A fires caused by solid substances (such as woods, cottons, wools, linens, paper) and products thereof and class-B fires caused by liquid or melted solids such as gasoline, kerosene, diesel oil, crude oil, methanol, ethanol, asphalt, paraffin waxes and the like can be put out rapidly through the functions such as heat absorption and cooling, diluting and smothering, insulating and covering, suppressing and blocking combustion chains, and the like which are synergetically performed by various extinguishing functional components, and a high-temperature-resistant thermal-insulation and fire-retarding covering layer is formed on the surface of an inflammable matter by various after-combustion functional components so as to achieve the effect of after-combustion resistance. Because the class A / B fires relate to multiple occasions of daily life and production activities, the extinguishing agent disclosed by the invention can be used in the fields of home fire prevention and extinguishing, urban architecture fire prevention and extinguishing, oil depot and gasoline station fire prevention and extinguishing, vehicle and ship fire prevention and extinguishing, forest and grassland fire prevention and extinguishing, mine fire prevention and extinguishing, confined spaces (such as civil air-defense architectures) fire prevention and extinguishing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
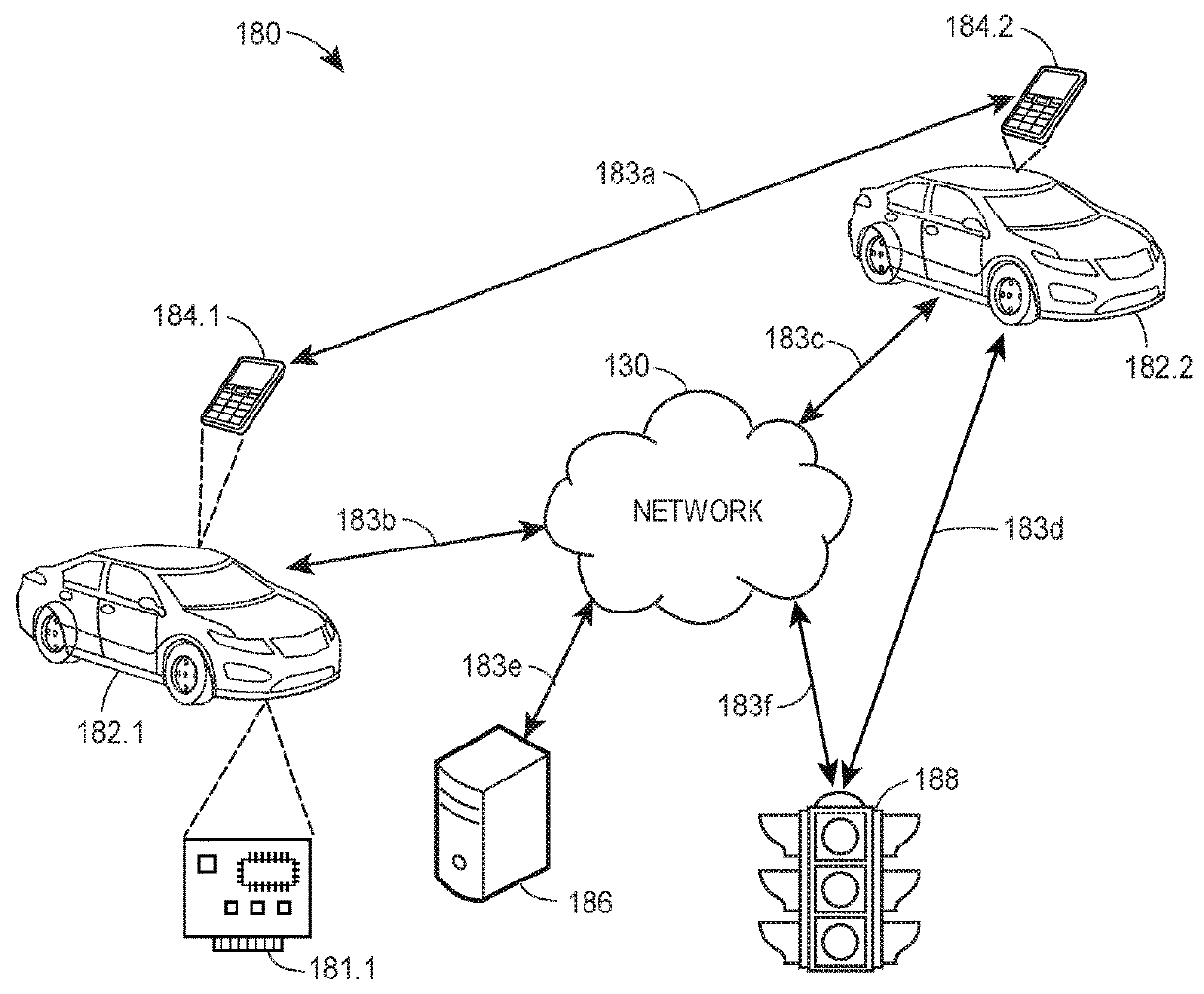
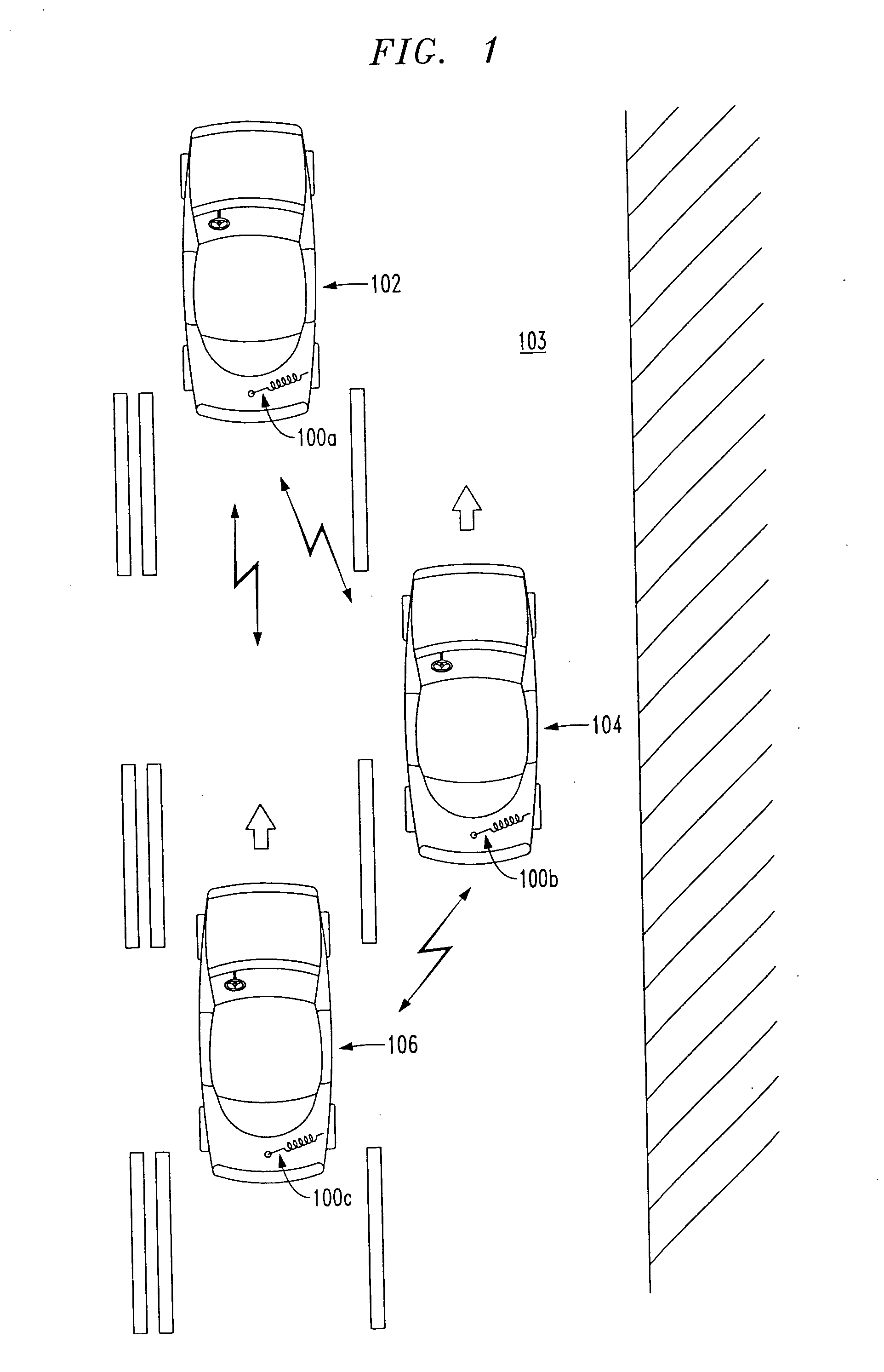
Vehicle interaction communication system
The information available to a driver of a vehicle is greatly expanded using wireless communications (e.g., using Bluetooth wireless communication devices). In one embodiment, information regarding an adjacent vehicle such as a brake light, a turn light, speed, distance, direction, etc., is transmitted from one vehicle to a nearby or adjacent other vehicle. The received information is used in any appropriate manner, such as causing the receiving vehicle to change vehicle speed or brake, to turn to avoid a collision, etc. In a second embodiment, roadside wireless transceivers collect information regarding passing vehicles, and central database is compiled relating to a traffic conditions. The traffic condition information can be passed back to the passing vehicles for appropriate use, e.g., causing the driver to slow down, or even causing a navigation device in the receiving vehicle to manually prompt for or automatically recalculate a best route to an intended destination. In yet another embodiment, broadcast transmitters can be established at signs and other significant locations transmitting information to passing vehicles. The broadcast information may be as simple as indicating the existence of the sign, or depending upon the range of the particular wireless transmitter, the existence of a particular sign, bump in road, curve, etc., can be forewarned far in advance of when the driver will actually see the relevant object. Alternatively, the broadcast information may be quite detailed, e.g., containing a detailed itemization and directions to a large number of gas stations, restaurants, etc., reachable from a particular exit from a highway.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
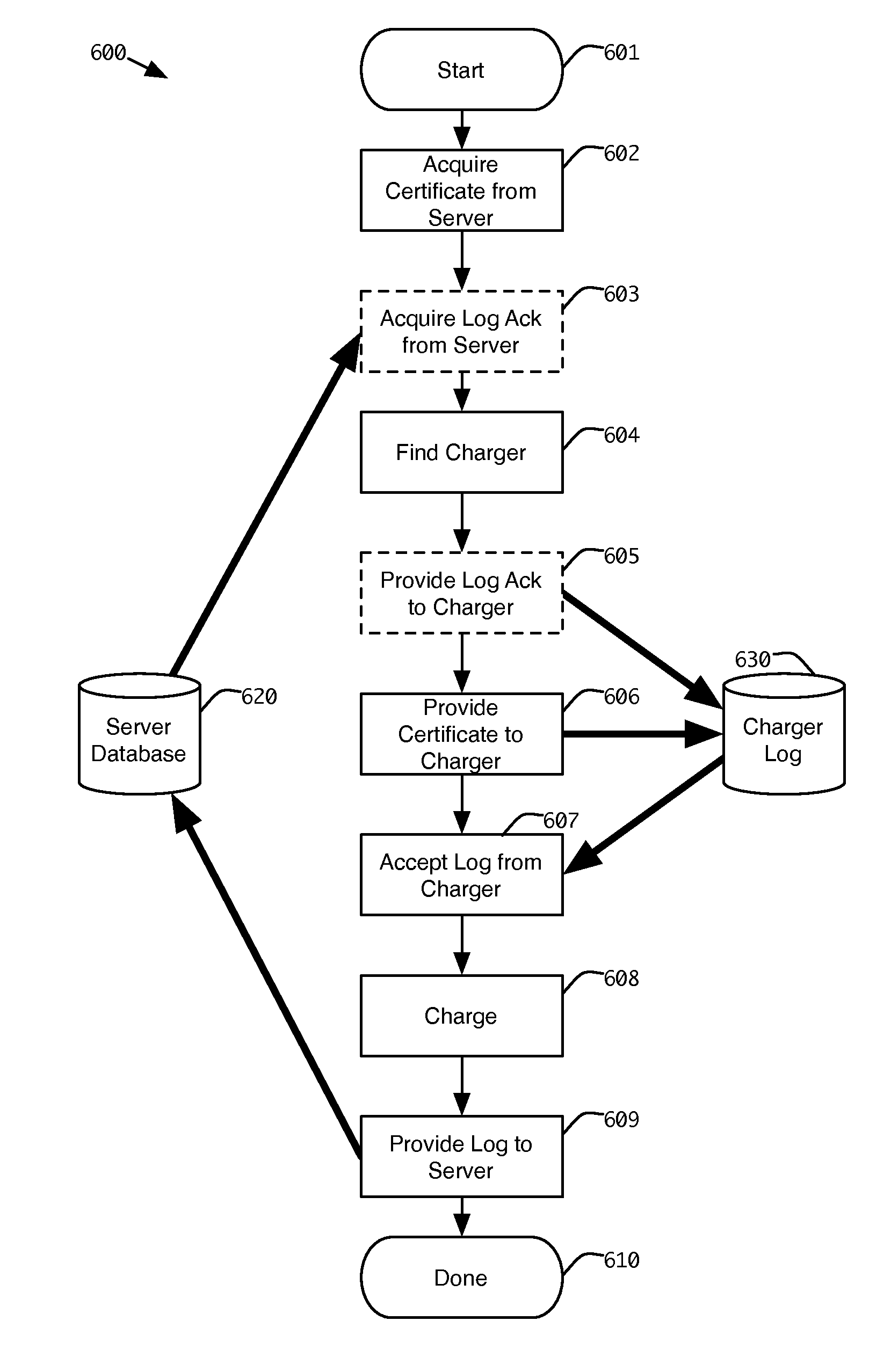
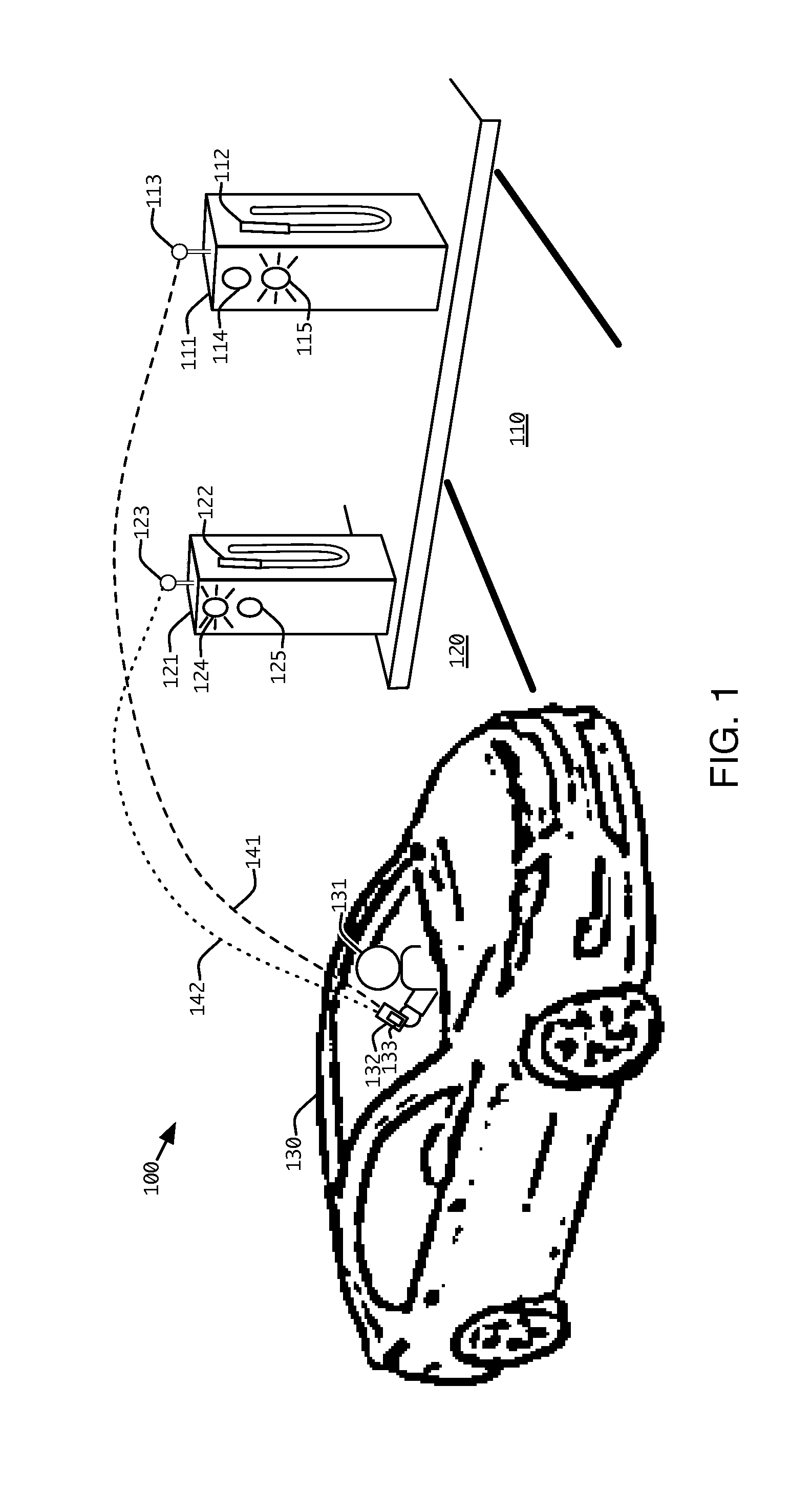
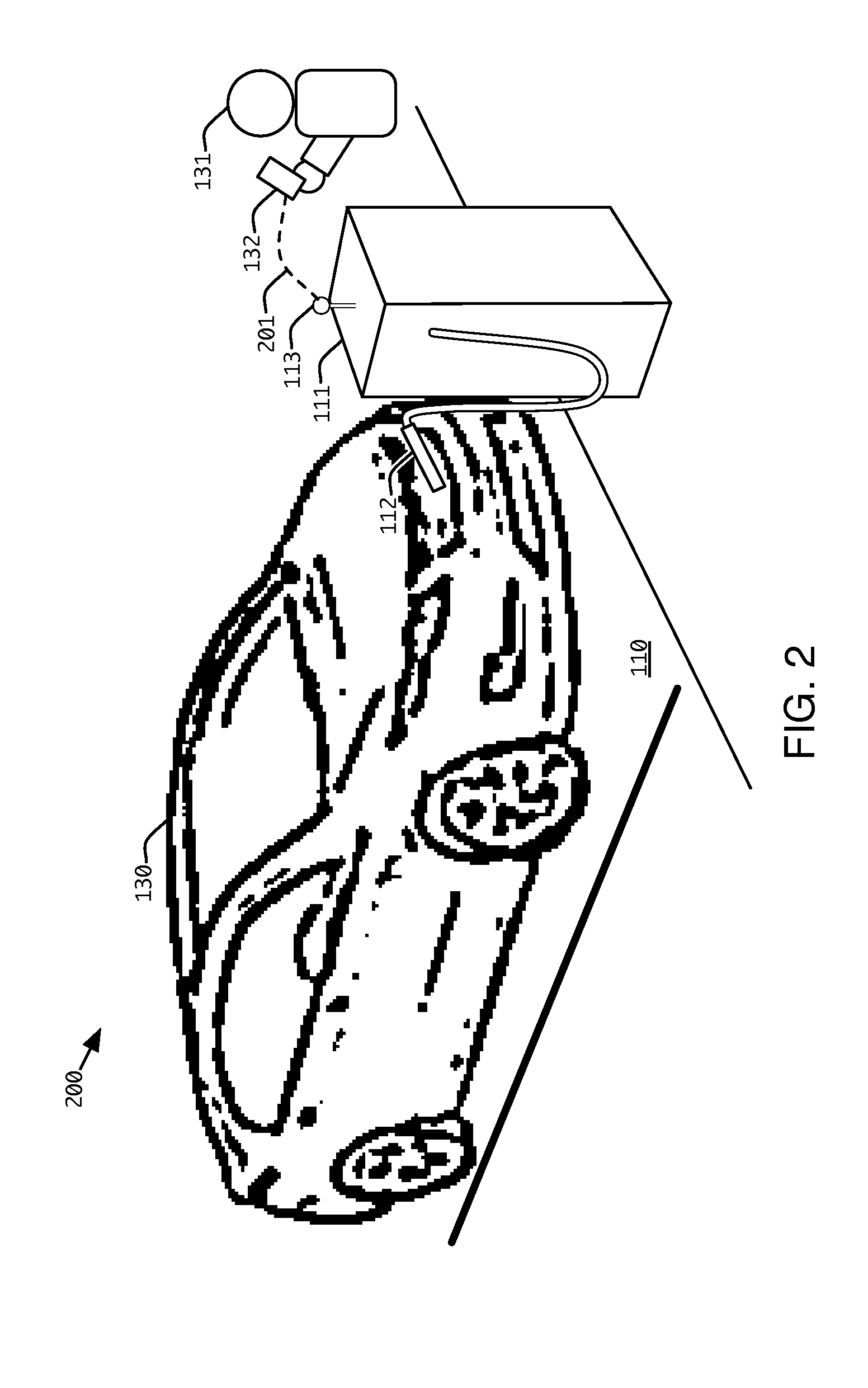
Method and apparatus for finding and accessing a vehicle fueling station, including an electric vehicle charging station
ActiveUS20120191242A1Low costConvenient and robust and secure user experienceInterlocksPayment protocolsDashboardLoad Shedding
A control system and method are provided for a station to dispense fuel to a vehicle, including an electric vehicle, without requiring dedicated access to a communications network, with the advantage that authorization for fleet vehicles or individuals can be obtained from an access management system, using a portable, wireless device, such as a smart phone or a dashboard appliance. The authorization is wirelessly relayed to the station by the wireless device, to enable the dispensing of fuel. Subsequently, a log comprising the transaction is provided to the access management system, through the same or a different wireless, mobile computing device. The log may also report status and other events, such as load shedding.
Owner:URBAN INTEL INC
System and method of maintaining a posted street price for fuel while offering different prices to identified customers
InactiveUS20010039512A1Address rising pricesSpecial data processing applicationsMarketingBarcodeMarketed products
A method of providing multiple level, price-per-unit (PPU) discounts on gasoline to a customer who purchases at least one cross-marketed product. The customer is awarded a first PPU discount on the gasoline based on a purchase by the customer of a first cross-marketed product, and is awarded a second PPU discount based on the purchase of a second cross-marketed product. The first discount is then added to the second discount to determine a total PPU discount, and a paper receipt is printed for the customer with a customer identification and a transaction identification encoded in a bar code thereon. The total discount is stored in a discounts issued database. The customer then scans the encoded bar code with a bar code scanner at a gasoline dispenser to redeem the discount. The total discount is retrieved from the discounts issued database, and the gasoline station then reduces the price-per-unit-volume of the gasoline by an amount equal to the total discount. When the customer completes the gasoline purchase, a value of the total discount redeemed is determined and stored in a discounts redeemed database. Portions of the discount redeemed are then allocated to vendors of the first and second cross-marketed products according to predetermined criteria.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO +1
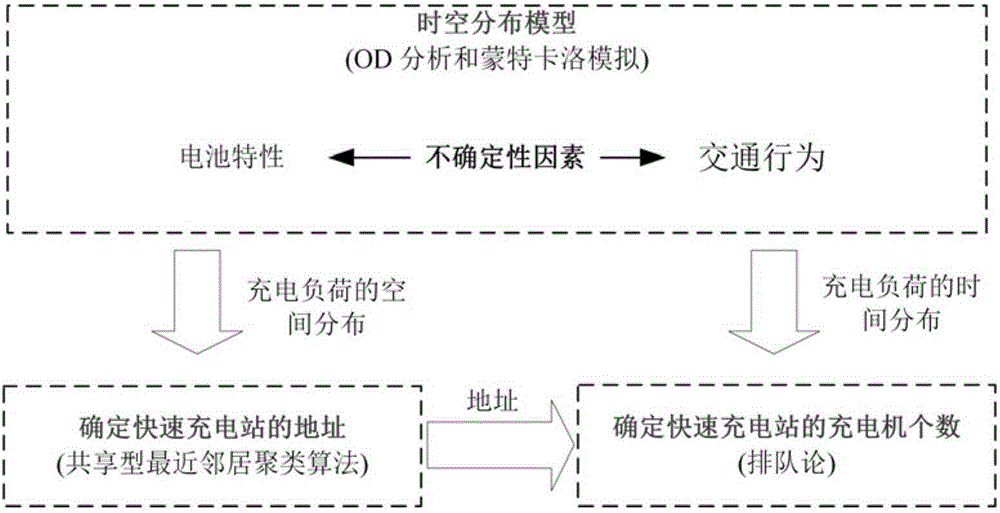
Planning method of electric vehicle fast-charging station on expressway
InactiveCN105160428AMeet charging needsCharging stationsForecastingSimulationNearest neighbor clustering
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of cross-marketing utilizing electronic coupons
InactiveUS20040158493A1Address rising pricesOther washing machinesPayment architectureBarcodeMarketed products
A method of providing multiple level, price-per-unit (PPU) discounts on gasoline to a customer who purchases at least one cross-marketed product. The customer is awarded a first PPU discount on the gasoline based on a purchase by the customer of a first cross-marketed product, and is awarded a second PPU discount based on the purchase of a second cross-marketed product. The first discount is then added to the second discount to determine a total PPU discount, and a paper receipt is printed for the customer with a customer identification and a transaction identification encoded in a bar code thereon. The total discount is stored in a discounts issued database. The customer then scans the encoded bar code with a bar code scanner at a gasoline dispenser to redeem the discount. The total discount is retrieved from the discounts issued database, and the gasoline station then reduces the price-per-unit-volume of the gasoline by an amount equal to the total discount. When the customer completes the gasoline purchase, a value of the total discount redeemed is determined and stored in a discounts redeemed database. Portions of the discount redeemed are then allocated to vendors of the first and second cross-marketed products according to predetermined criteria.
Owner:EXCENTUS CORP
Hydrogen vehicle gas utilization and refueling system
InactiveUS20060118175A1Minimize mechanical energy lossMinimize compression energyGas handling applicationsBottling operationsMobile vehicleOn board
A system for increasing the overall efficiency of a hydrogen fueled vehicle and refilling station infrastructure wherein the process of (1) consuming pressurized hydrogen gas that is stored in on board tanks used to power hydrogen fueled motor vehicles and (2) refueling the vehicle tanks at a hydrogen refilling station after the available on board fuel supply in the tanks is consumed is controlled according to a predetermined sequence involving the utilization of the hydrogen in the on board tanks.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
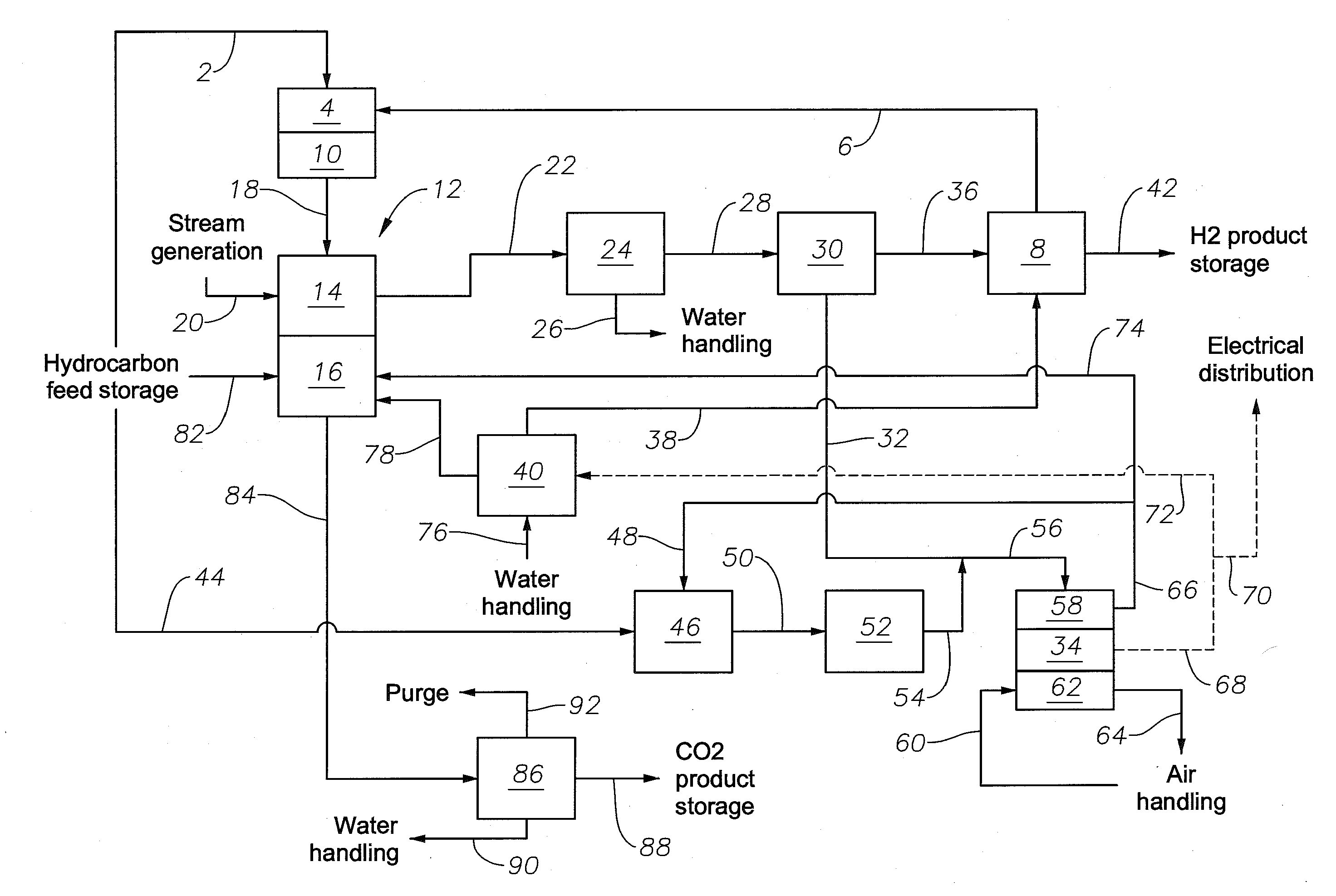
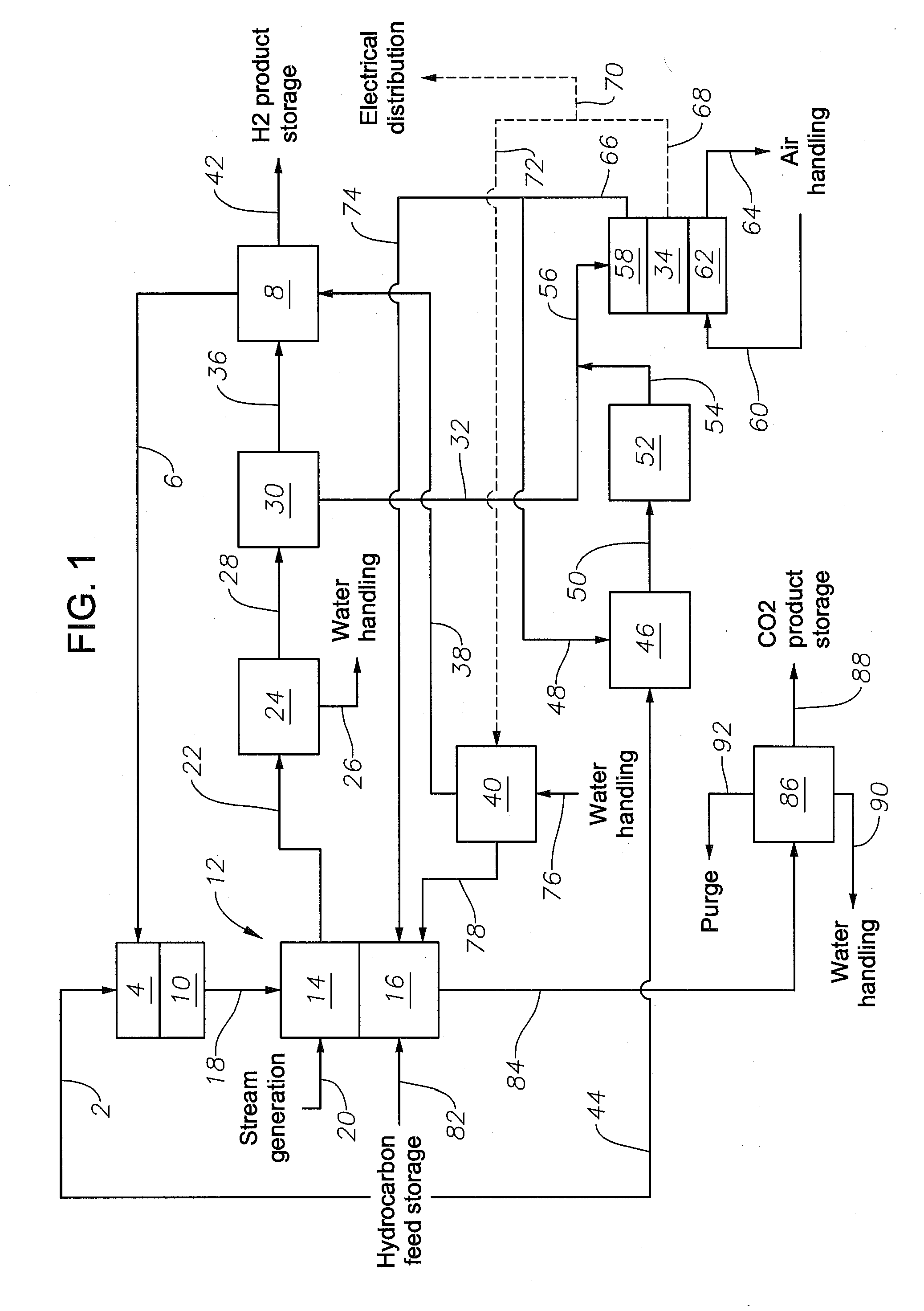
Method and a system for combined hydrogen and electricity production using petroleum fuels
ActiveUS20130126038A1Reduce decreasePrevents carbon dioxide emissionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionVehicular energy storageElectricityCombustion chamber
A SOFC system for producing a refined carbon dioxide product, electrical power and a compressed hydrogen product is presented. Introducing a hydrocarbon fuel and steam to the SOFC system, operating the SOFC system such that the steam-to-carbon molar ratio in the pre-reformer is in a range of from about 3:1 to about 4:1, the oxygen in the reformer combustion chamber is in excess, greater than 90% of the carbon dioxide produced during the process forms the refined carbon dioxide product are steps in the process. An alternative fueling station having a SOFC system is useful for fueling both electrical and hydrogen alternative fuel vehicles. Introducing steam and a hydrocarbon fuel, operating the alternative fueling station, coupling the alternative fuel vehicle to the alternative fueling station, introducing an amount of alternative fuel and decoupling the alternative fuel vehicle are steps in the method of use.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Hydrogen vehicle gas utilization and refueling system
InactiveUS7325561B2Minimize mechanical energy lossMinimize compression energyGas handling applicationsBottling operationsMobile vehicleOn board
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method of providing price-per-unit discounts for fuel to a customer
InactiveUS6885996B2Address rising pricesOther washing machinesPayment architectureMarketed productsEngineering
Owner:EXCENTUS CORP
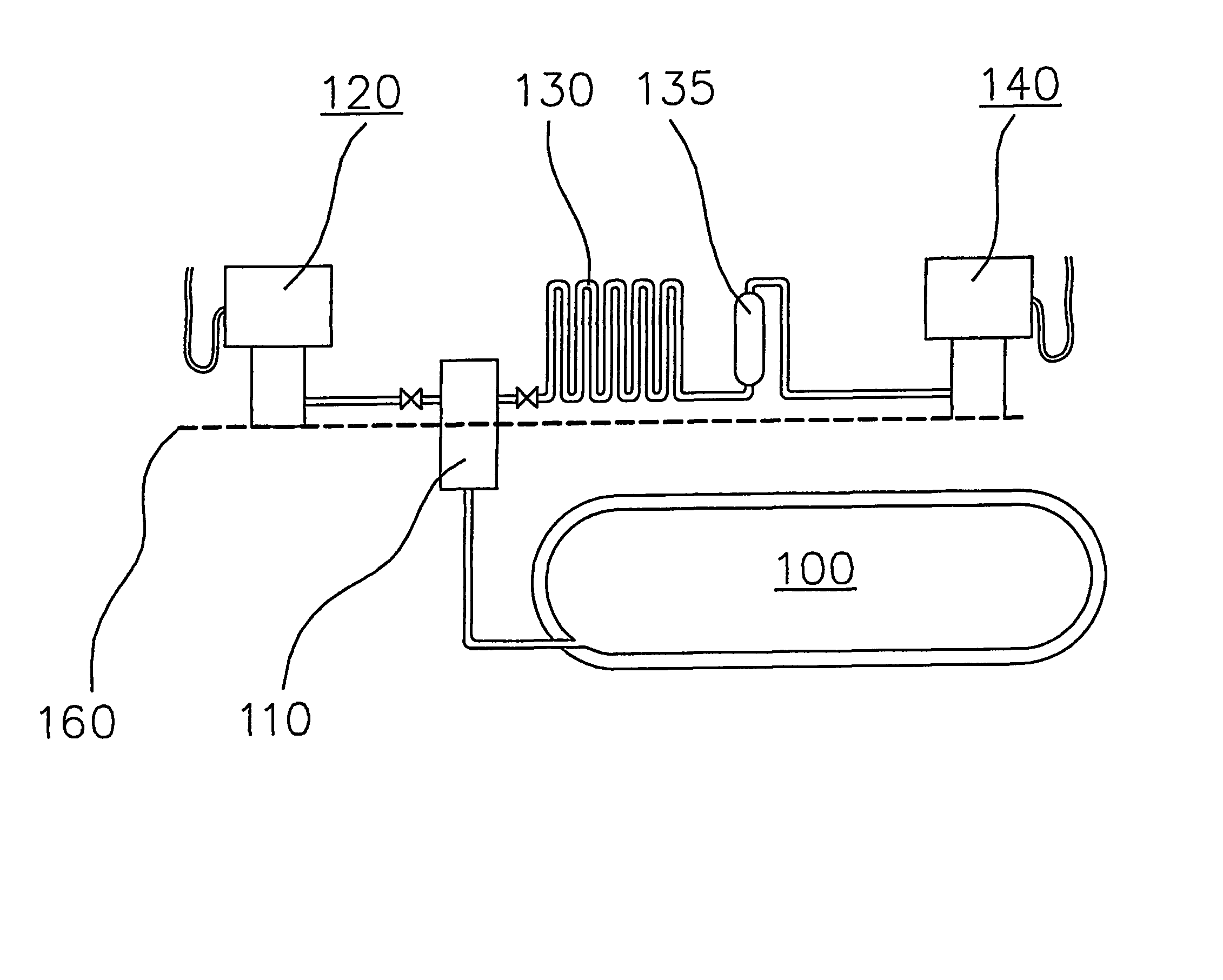
Self-contained mobile fueling station
InactiveUS20050103400A1Increase ratingsReduce pressureLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsPower stationHydrogen
A mobile self-contained self-powered station having a plurality of vessels delivers a pressurized fluid to a receiving tank (e.g., a fuel tank of a hydrogen-powered vehicle) without using mechanical compression, external electric power, or other external utilities. The station includes first and second vessels, a conduit in fluid communication with the receiving tank and each of the first and second vessels, means for transferring at least a portion of a quantity of the pressurized fluid from the first vessel to the receiving tank, means for measuring continuously a pressure differential between the increasing pressure in the receiving tank and the decreasing pressure in the first vessel, means for discontinuing the transfer from the first vessel when a predetermined limit value is reached, and means for transferring at least a portion of a quantity of the pressurized fluid from the second vessel to the receiving tank.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Displacement safety system for electrical charging stations
A safety circuit for disconnecting the power feed to an EV (electrical vehicle) charging enclosure or gasoline station fuel pump enclosure in the event that the enclosure is partially or totally dislodged from the foundation and dangerously high voltage has been exposed due to underground conduits being torn apart and electrical cables being exposed and in contact with sheet metal cabinets and other metal parts, thus creating the possibility of an explosion or the electrocution of a user or bystanders. The safety circuit comprises at least two proximity sensors, each of which transmits a signal into a control circuit which causes the power feed to the enclosure to be disconnected at the source when either or both of the proximity sensors inform the control circuit that the station has moved either vertically or horizontally more than a few thousandths of an inch.
Owner:WMK SAFETY SOLUTIONS LLC
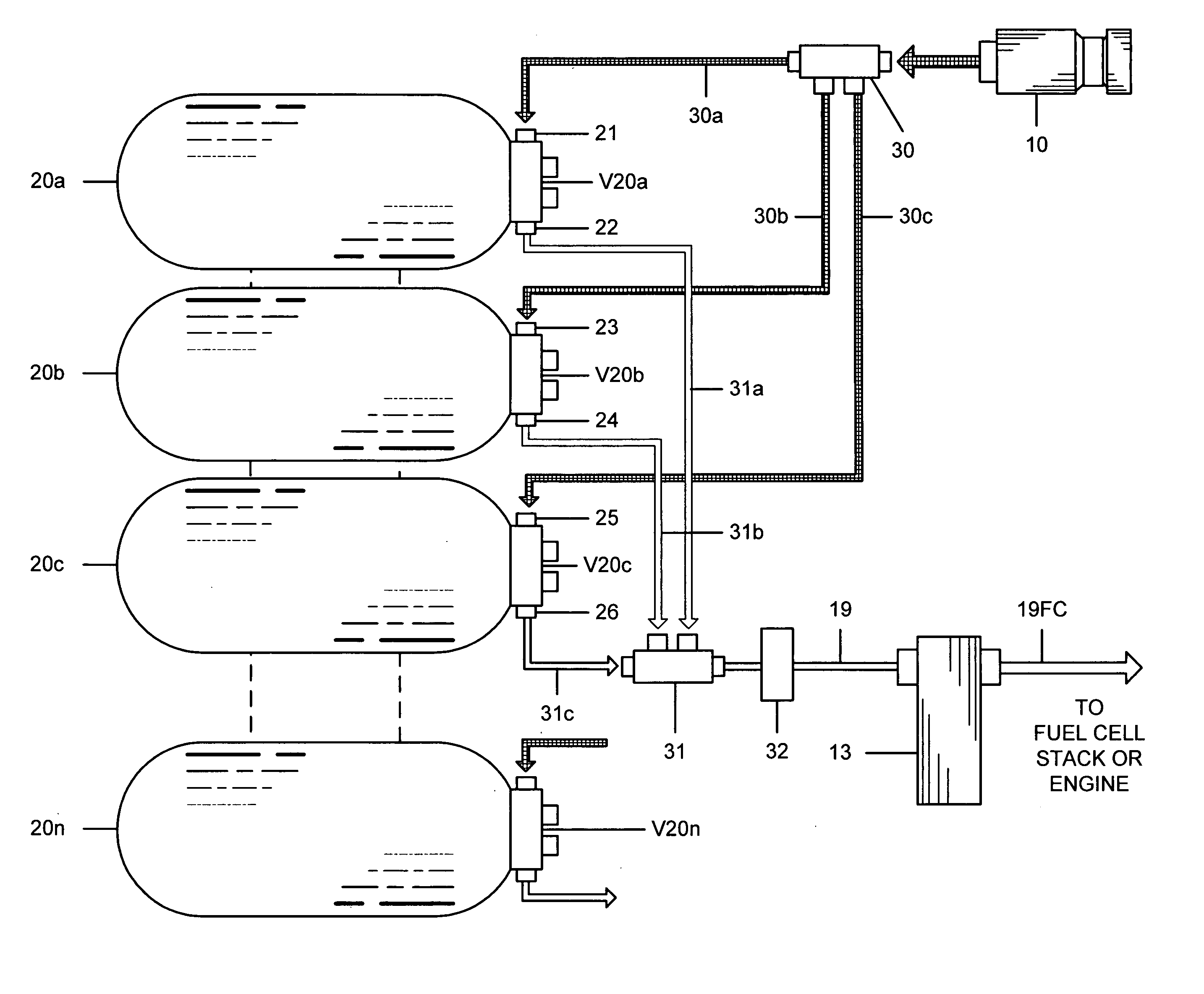
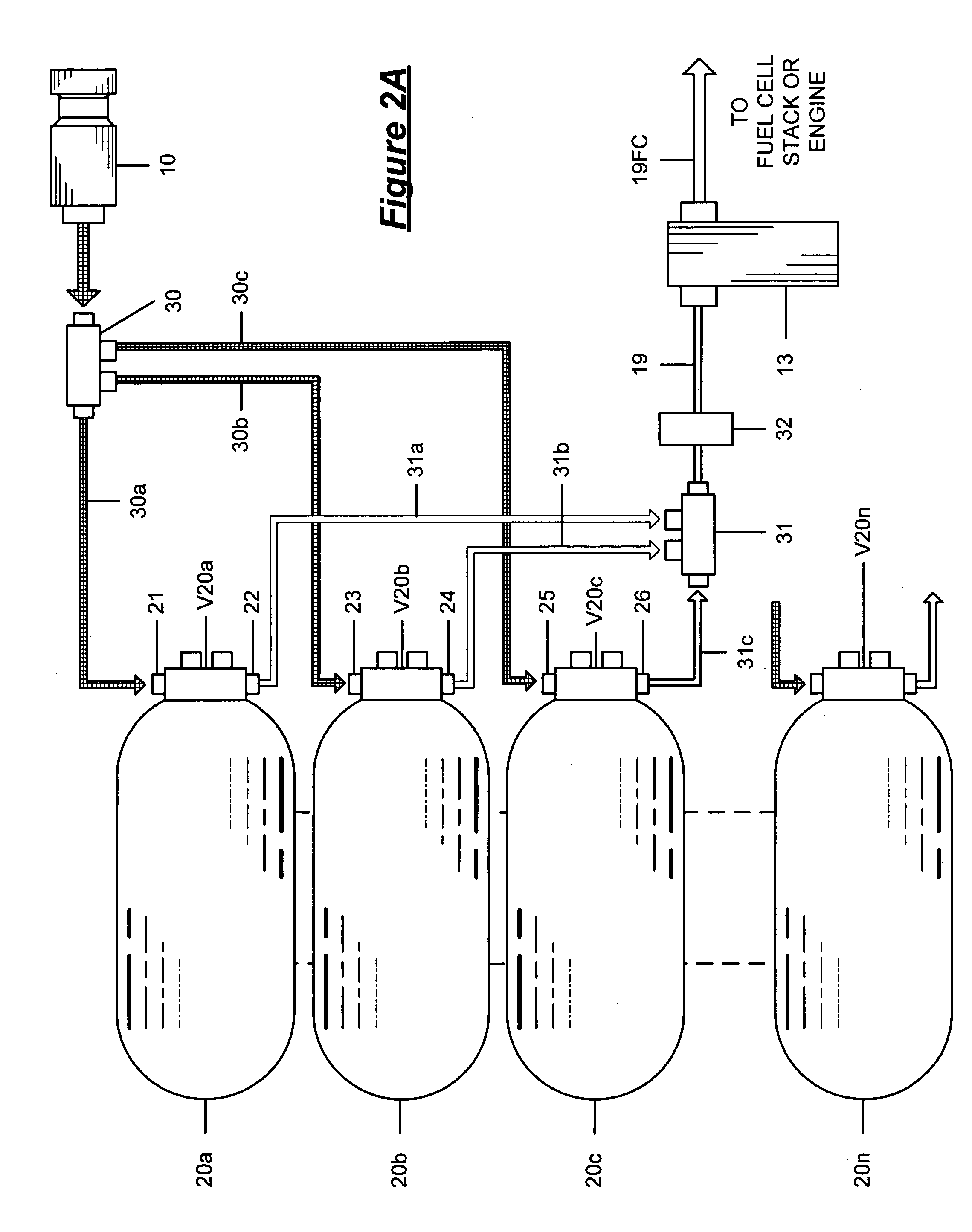
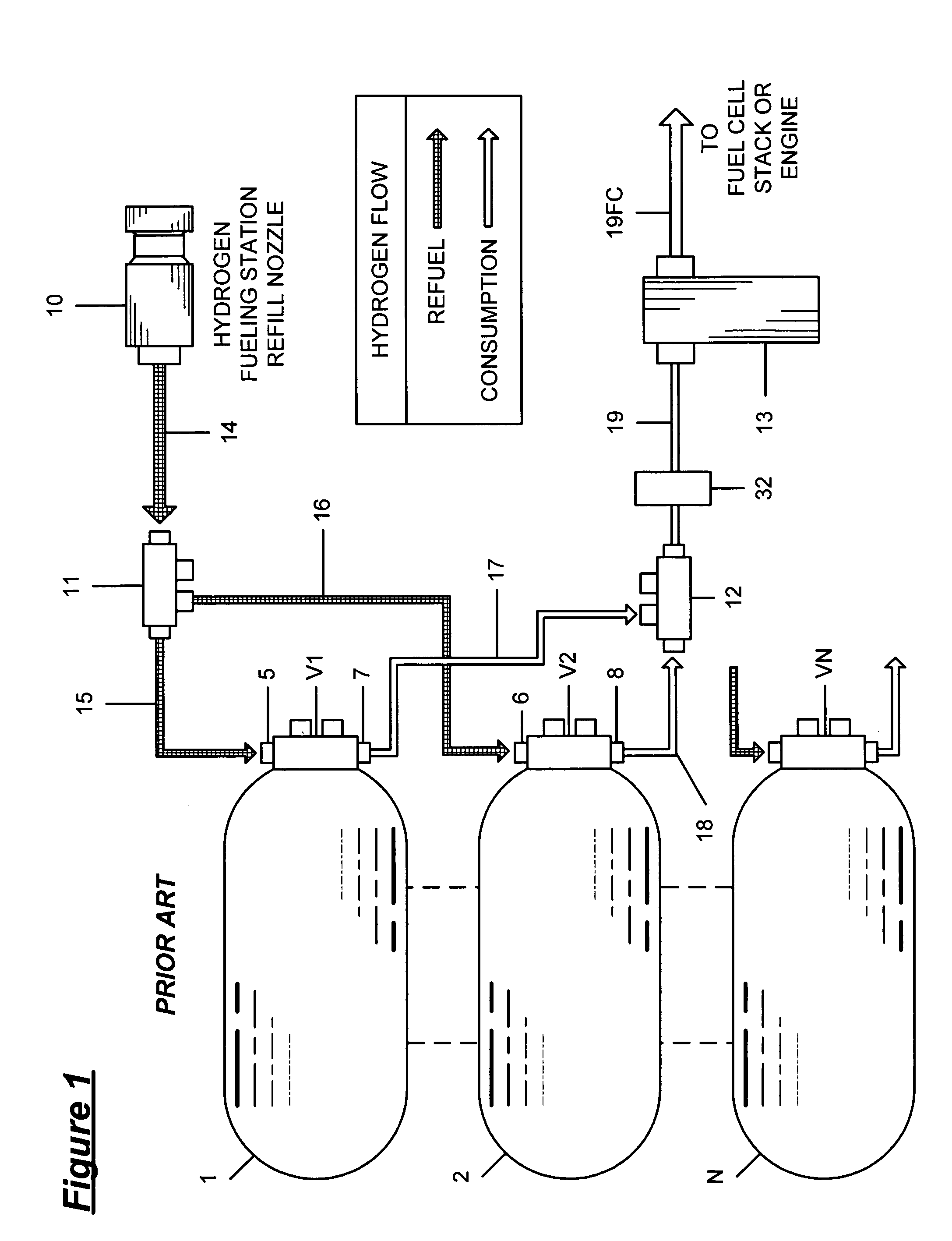
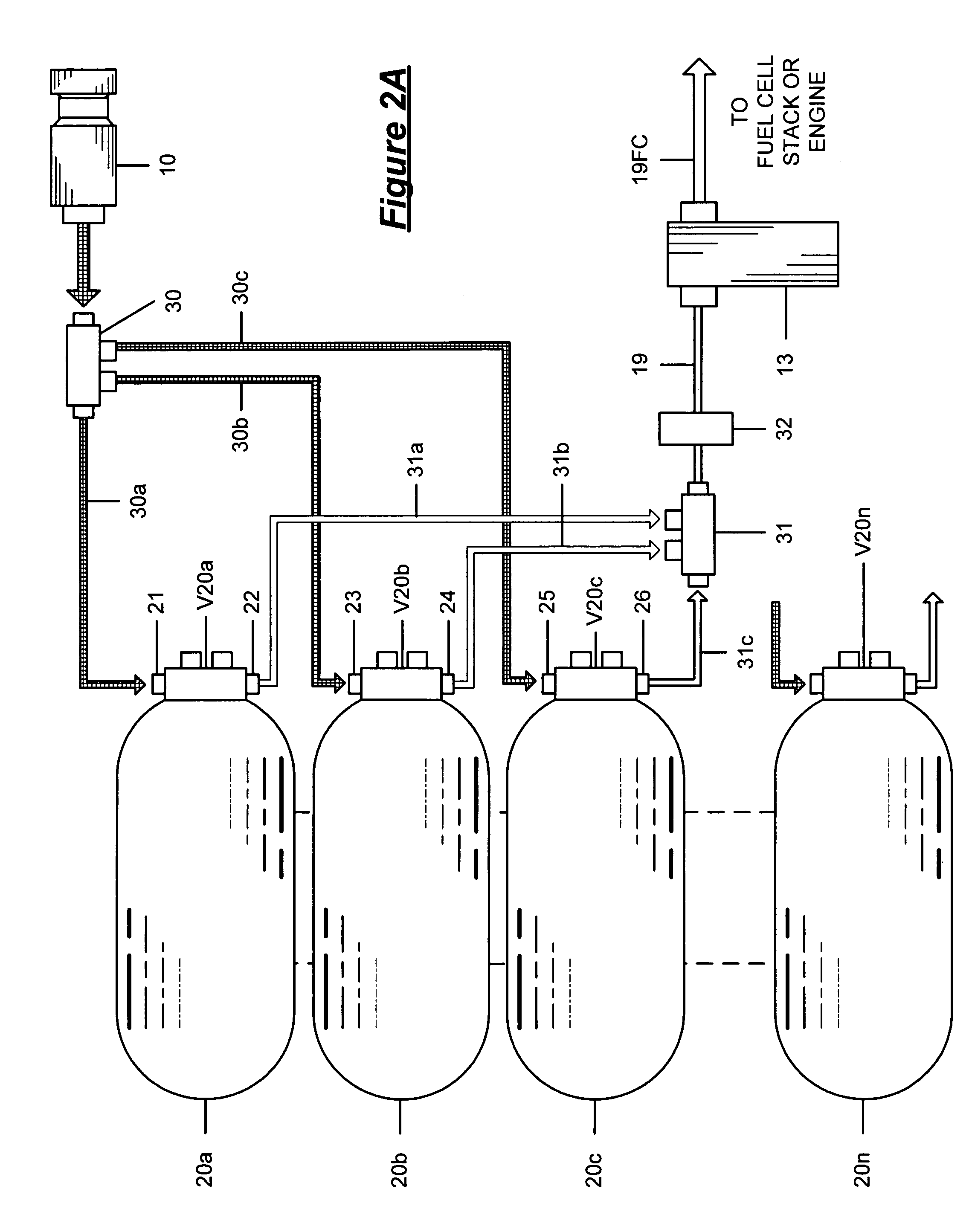
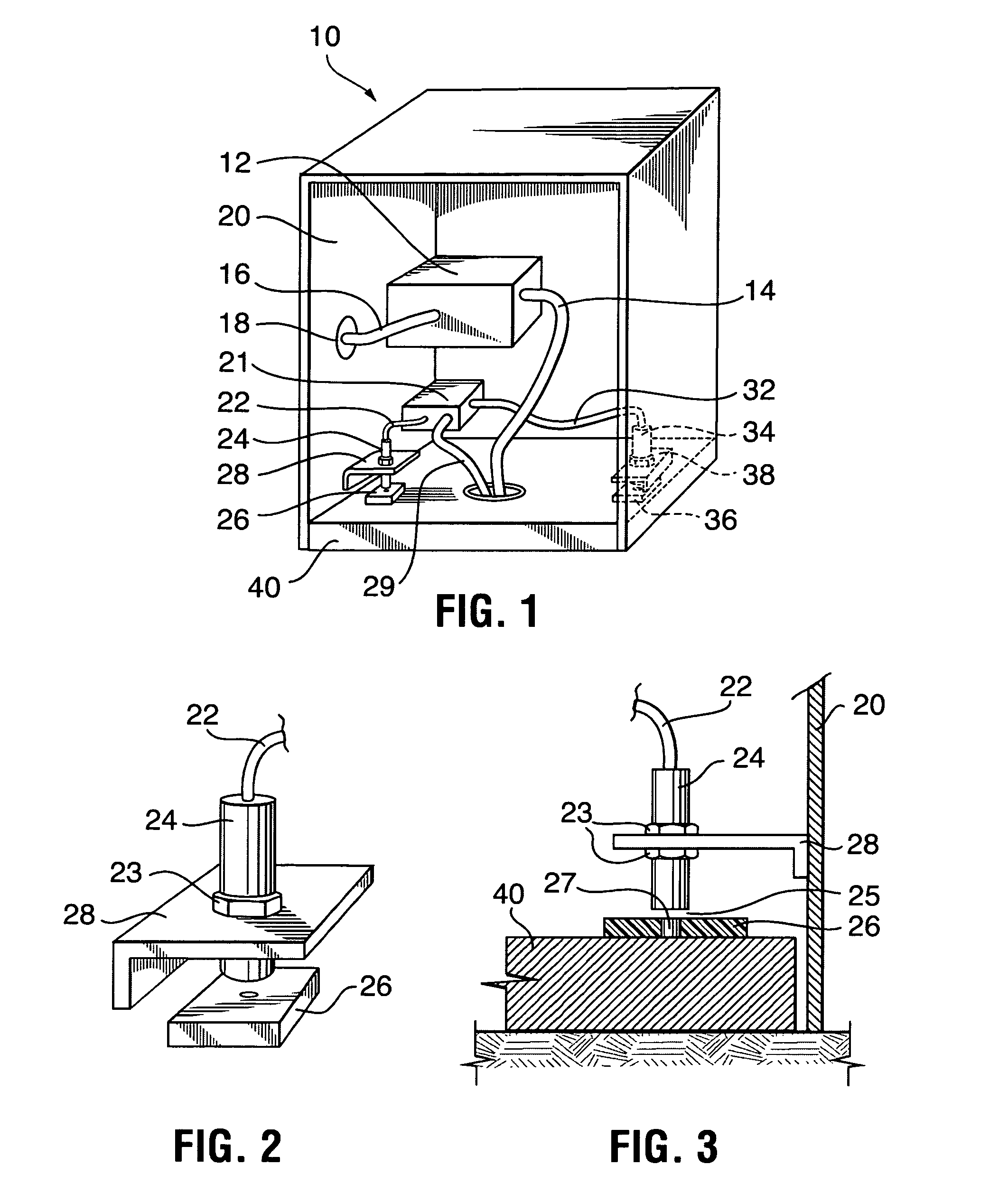
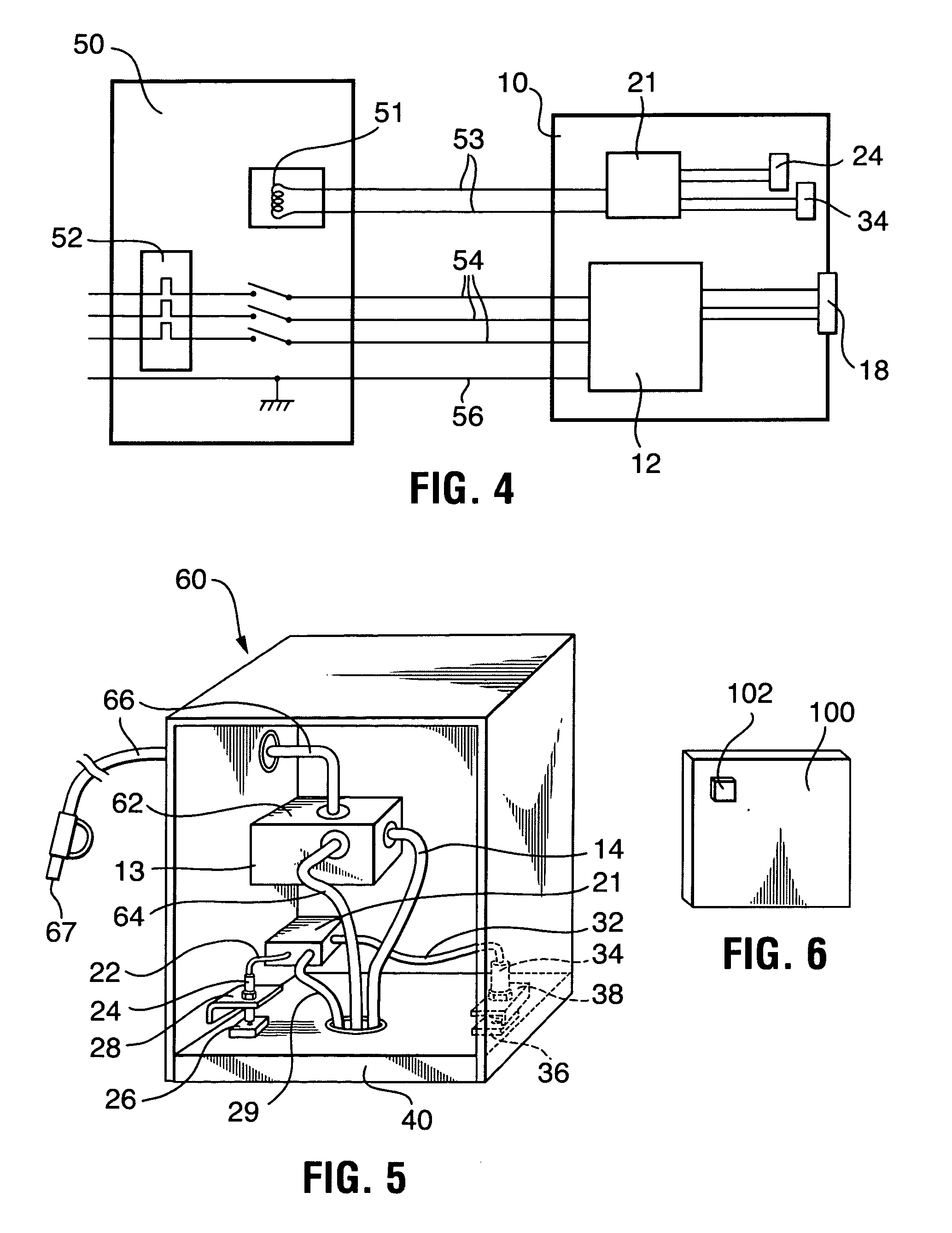
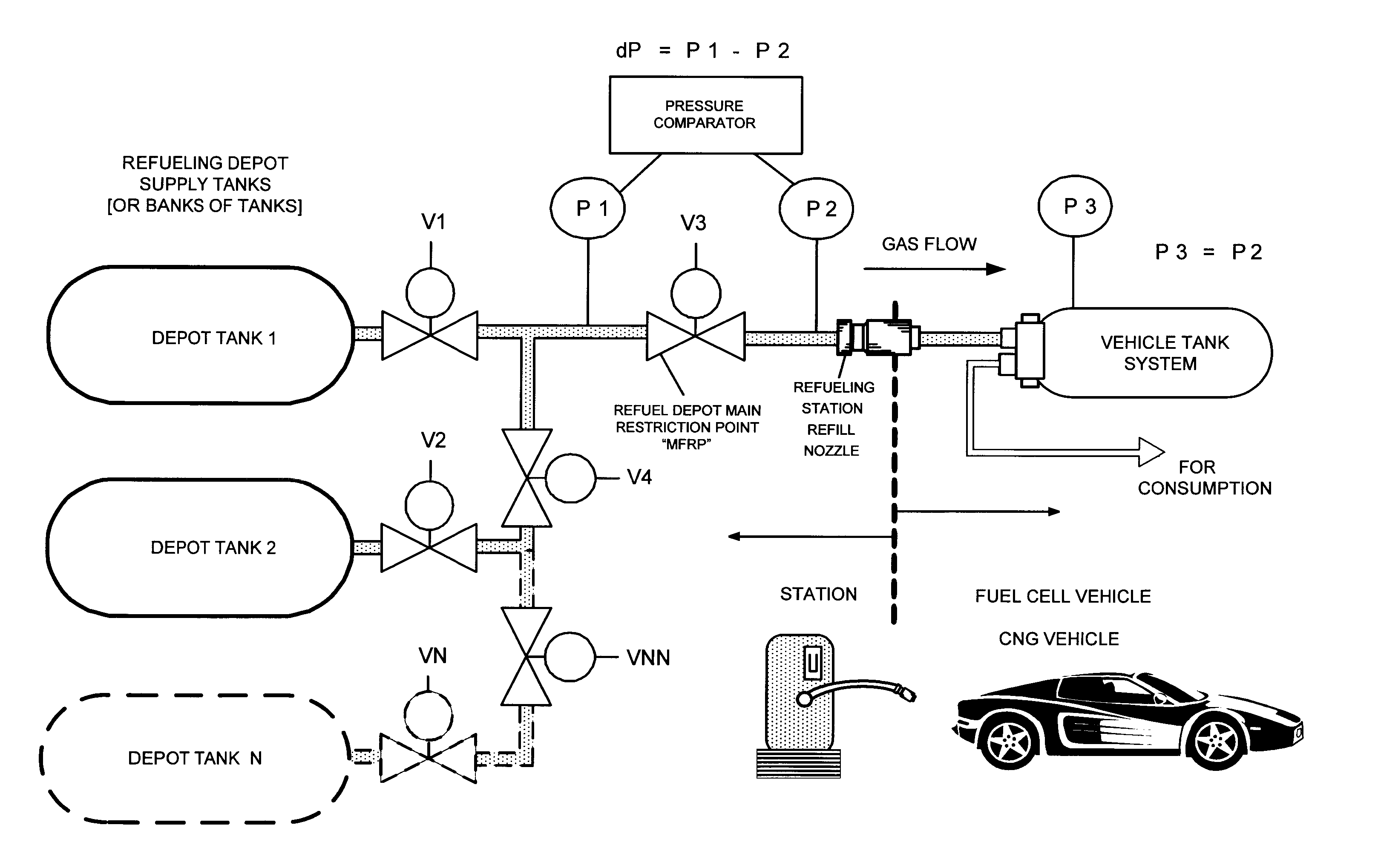
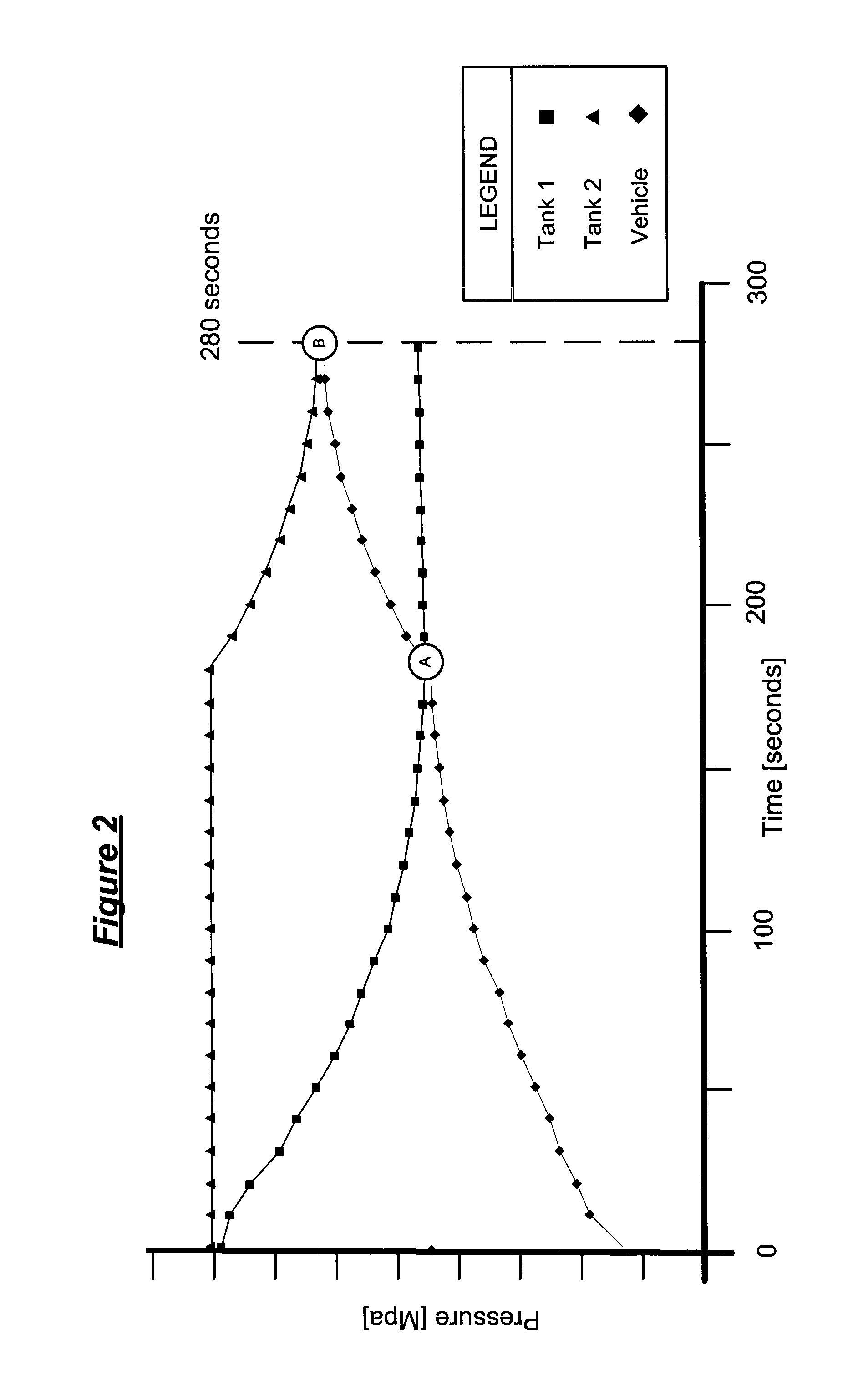
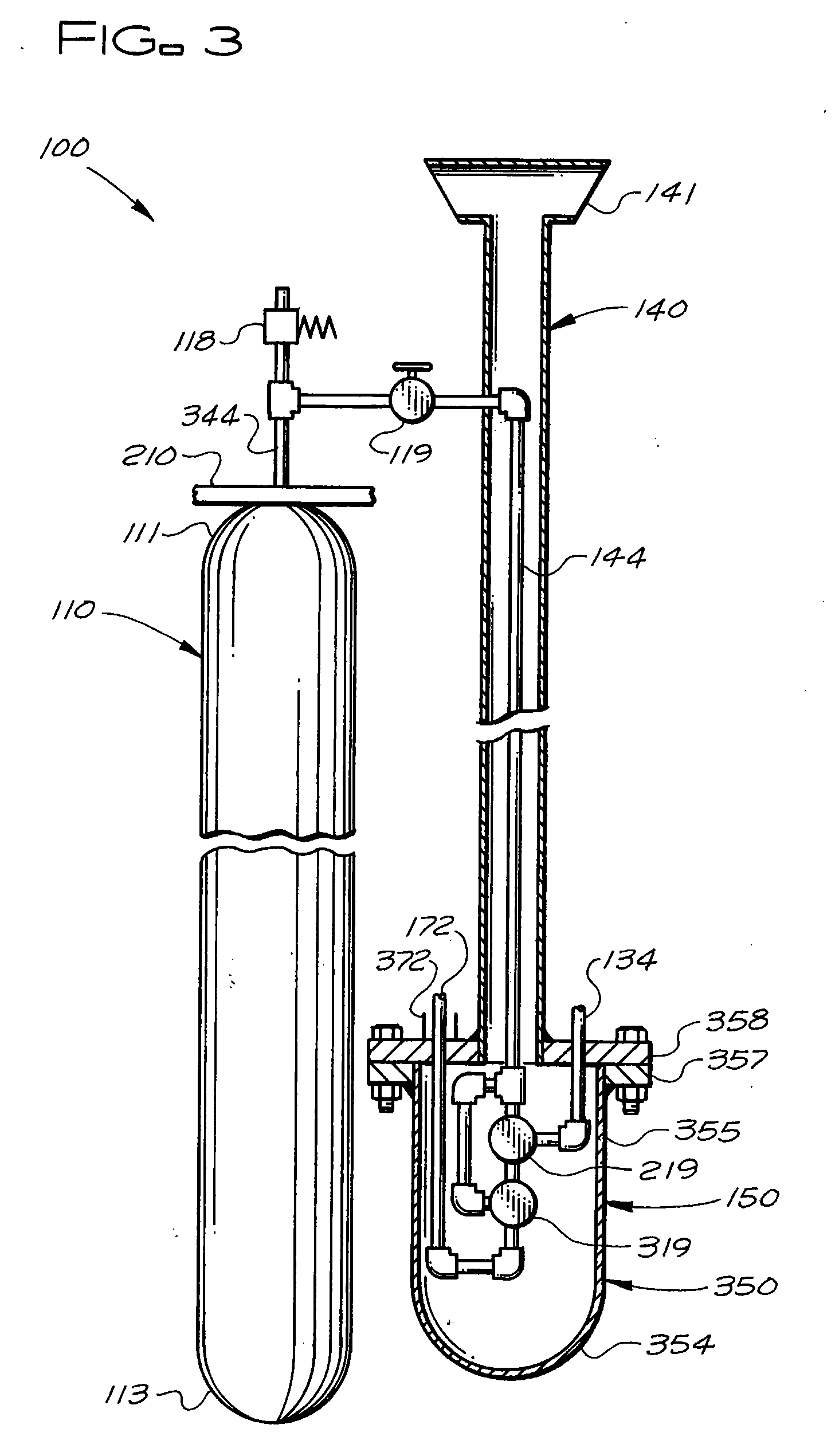
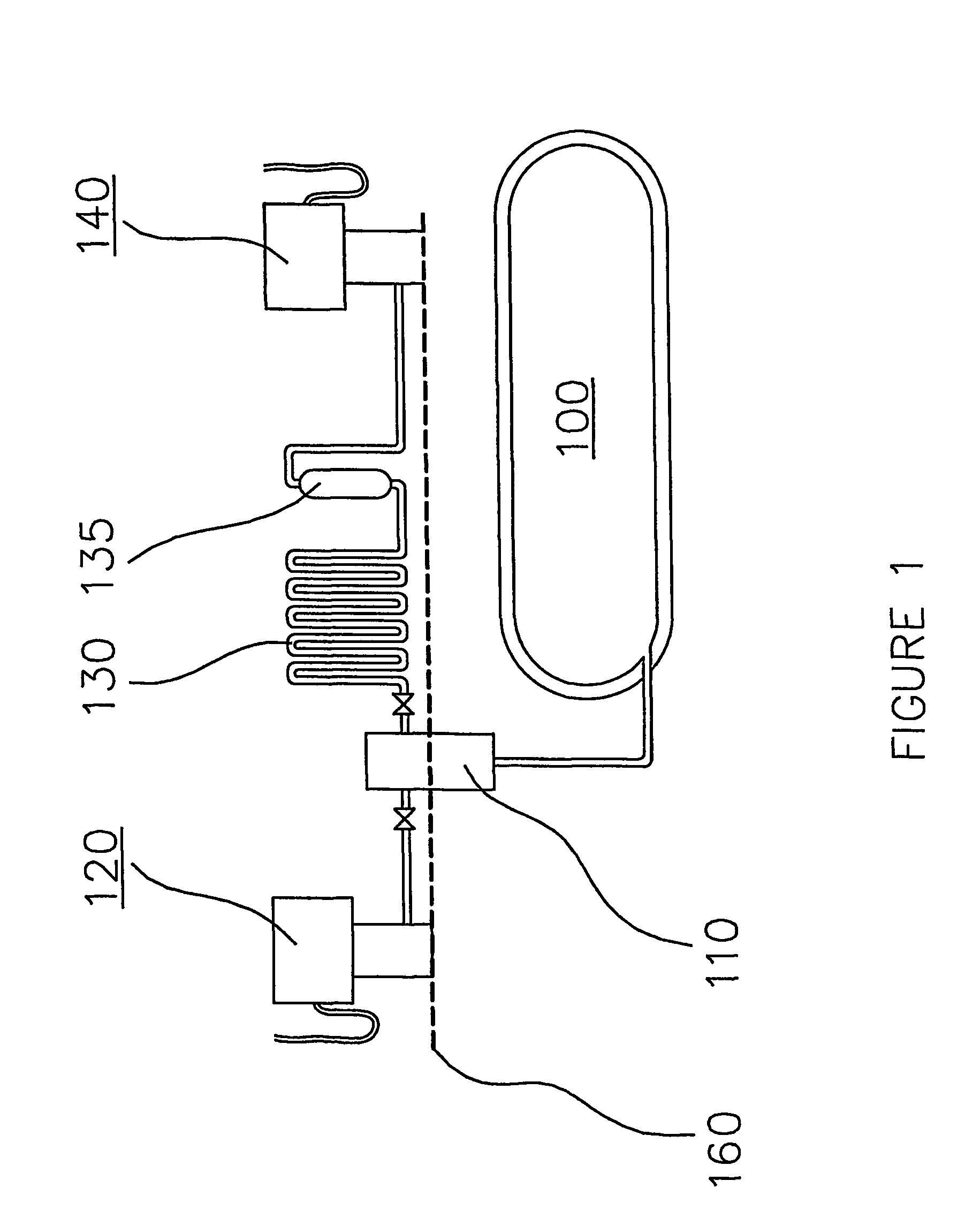
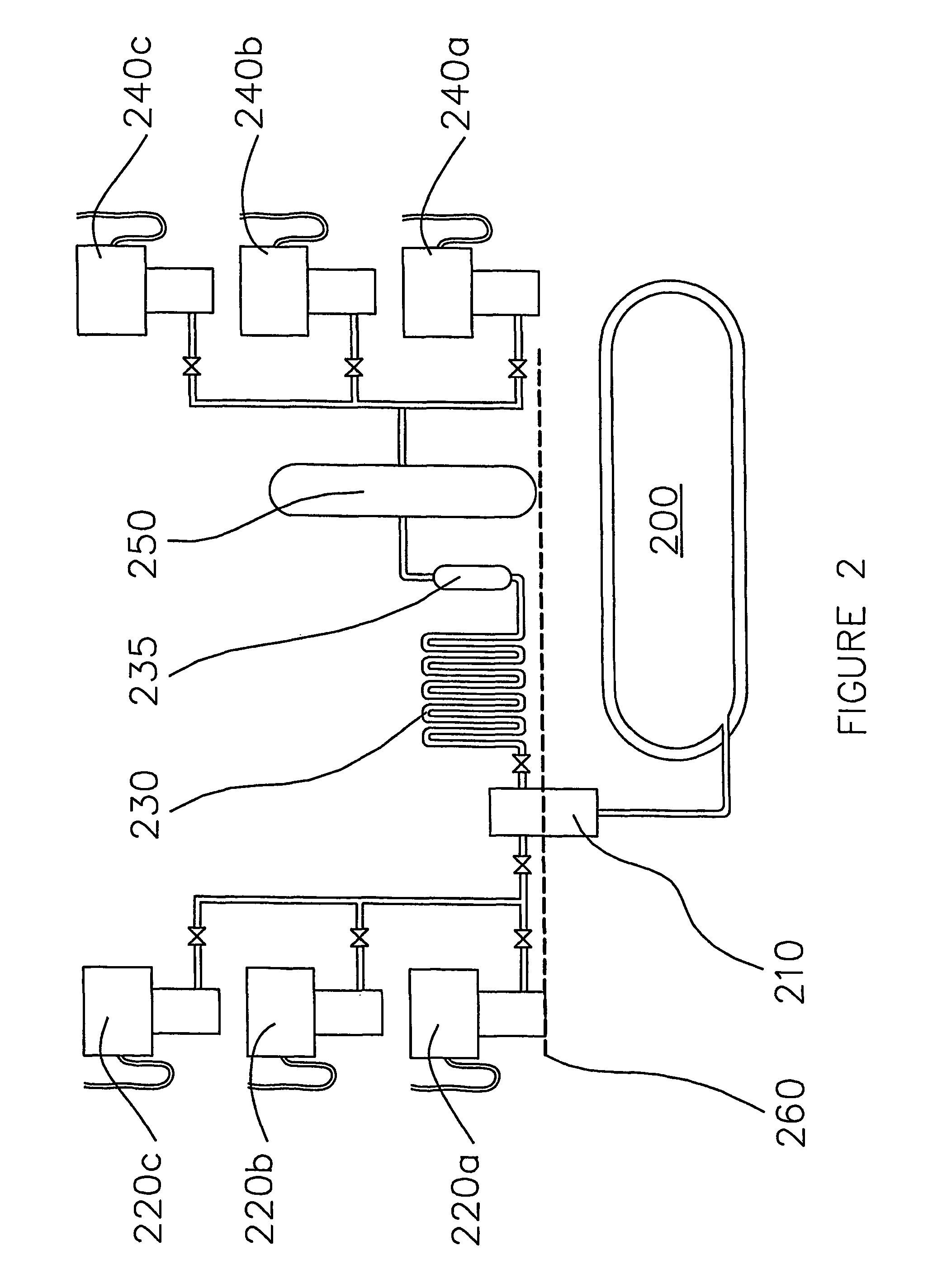
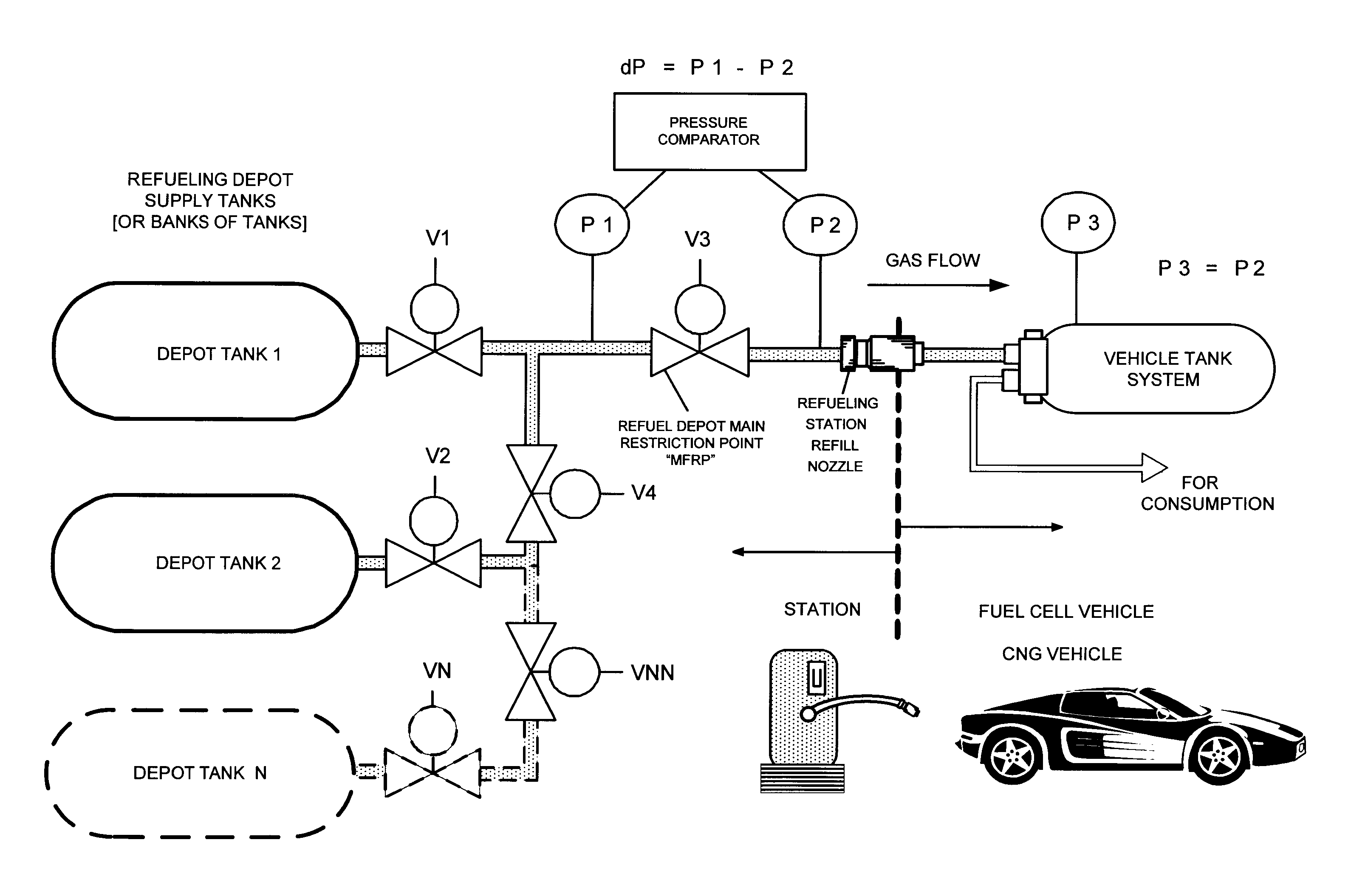
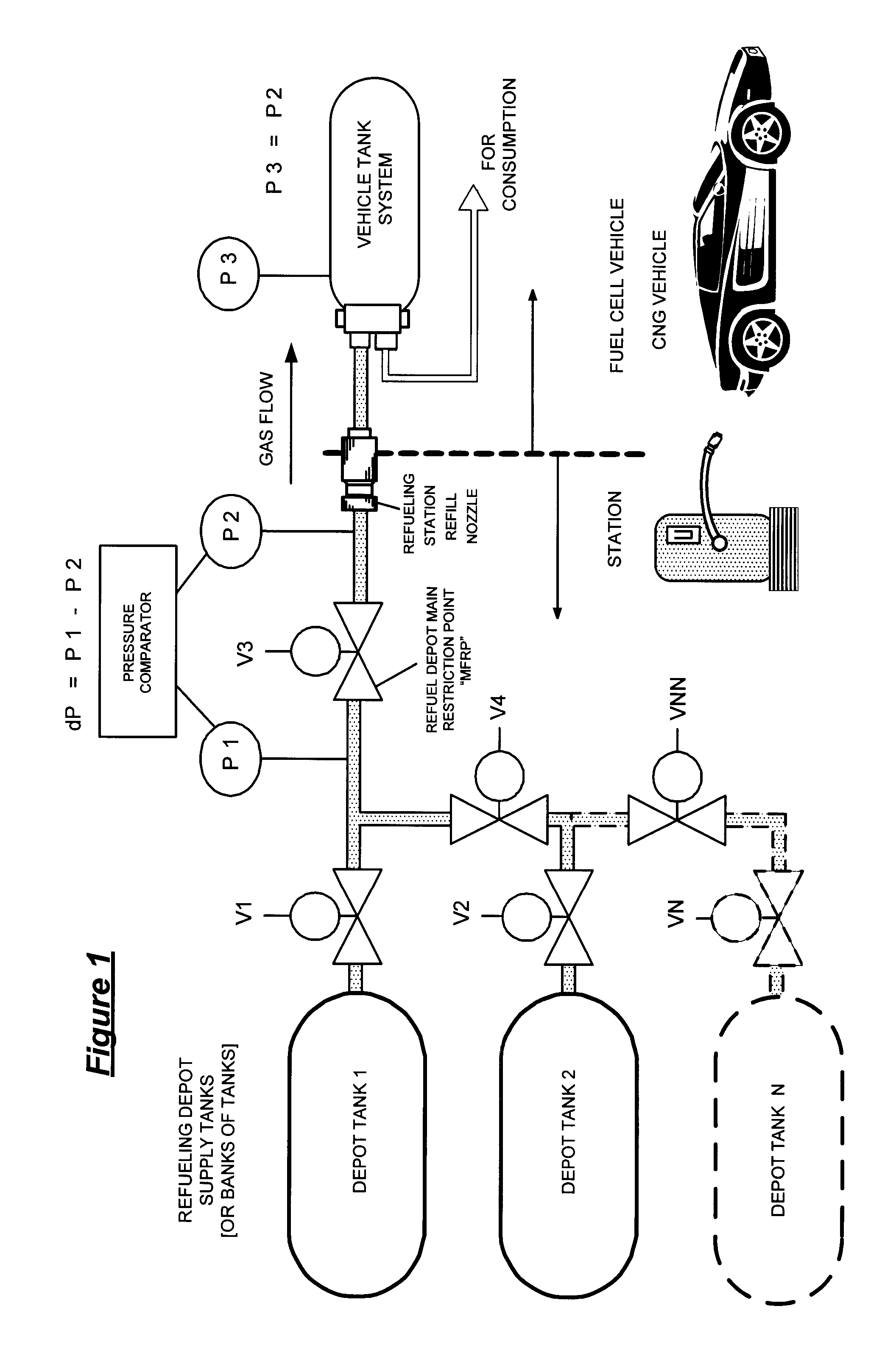
Pressure Differential System for Controlling High Pressure Refill Gas Flow Into On Board Vehicle Fuel Tanks
ActiveUS20070051423A1Reduce refueling timesStable and accurate operationLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsIn vehicleOn board
A high pressure fuel flow control device wherein pressure sensors are interposed on either side of the main restriction point of a refueling depot when the vehicle tank(s) to be refilled are interconnected in a flow circuit that connects the refilling depot and the vehicle tanks. The sensors measure pressure on the side of the depot tank[s] and pressure on the side of the vehicle tank at a restriction point in the gas flow circuit. Flow from a tank is complete and a tank is switched when the difference in the pressures sensed on opposite sides of the restriction point approaches zero or slightly greater than zero.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hydrogen handling or dispensing system
InactiveUS20060174965A1Cheap manufacturingQuantity minimizationLiquid fillingFuel cell auxillariesHydrogenPetrol station
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
E85 gas station locator applications using v2x peer-to-peer social networking
InactiveUS20100245124A1Arrangements for variable traffic instructionsRadio transmissionPeer-to-peerReal-time computing
A system and method for wirelessly exchanging information concerning the location of E85 gas stations between E85 vehicles. The method includes transmitting messages from an E85 gas station that identifies the location of the E85 gas station, the time of the transmission and the price of the E85 gas, and receiving the messages by E85 vehicles that pass within a certain distance of the E85 gas station. The method also includes identifying that two E85 vehicles pass close to each other, where the vehicles periodically broadcast an E85 beacon identifying them as E85 vehicles. When two E85 vehicles are identified, the vehicles exchange information concerning a list of the E85 gas stations that they have stored from messages received from E85 gas stations and / or other E85 vehicles. The two vehicles update their lists to include those E85 gas stations that one vehicle may have that the other does not.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Combined liquefied gas and compressed gas re-fueling station and method of operating same
InactiveUS7284575B2Cost-effectiveness and versatilityConvenient ArrangementLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsLow speedNuclear engineering
A re-fueling station is provided for selectively dispensing fuel in the form of liquefied gas or compressed gas. The re-fueling station comprises a storage tank for storing liquefied gas; a positive displacement fuel pump operable to draw fuel from the storage tank and discharge fuel to a flow diverter, which is operable to selectively direct fuel through one of a first outlet or a second outlet; and conduits through which fuel may flow from the first outlet to a heat exchanger and then to a first dispenser for dispensing compressed gas, or from the second outlet to a second dispenser for dispensing liquefied gas. A method is provided comprising operating the fuel pump in a low speed mode when fuel is directed to the first dispenser and operating the fuel pump in a high speed mode when fuel is directed to the second dispenser.
Owner:WESTPORT POWER
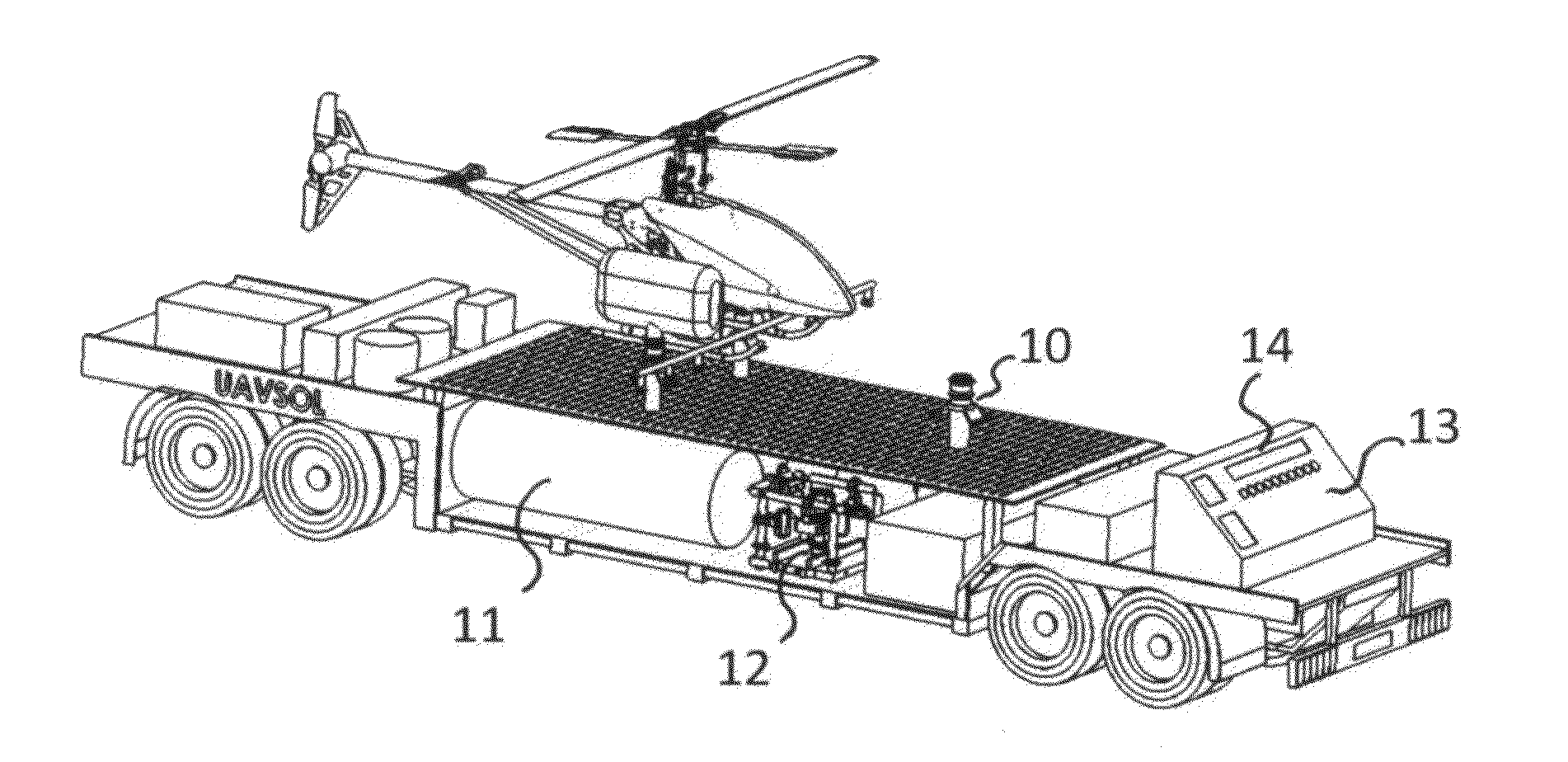
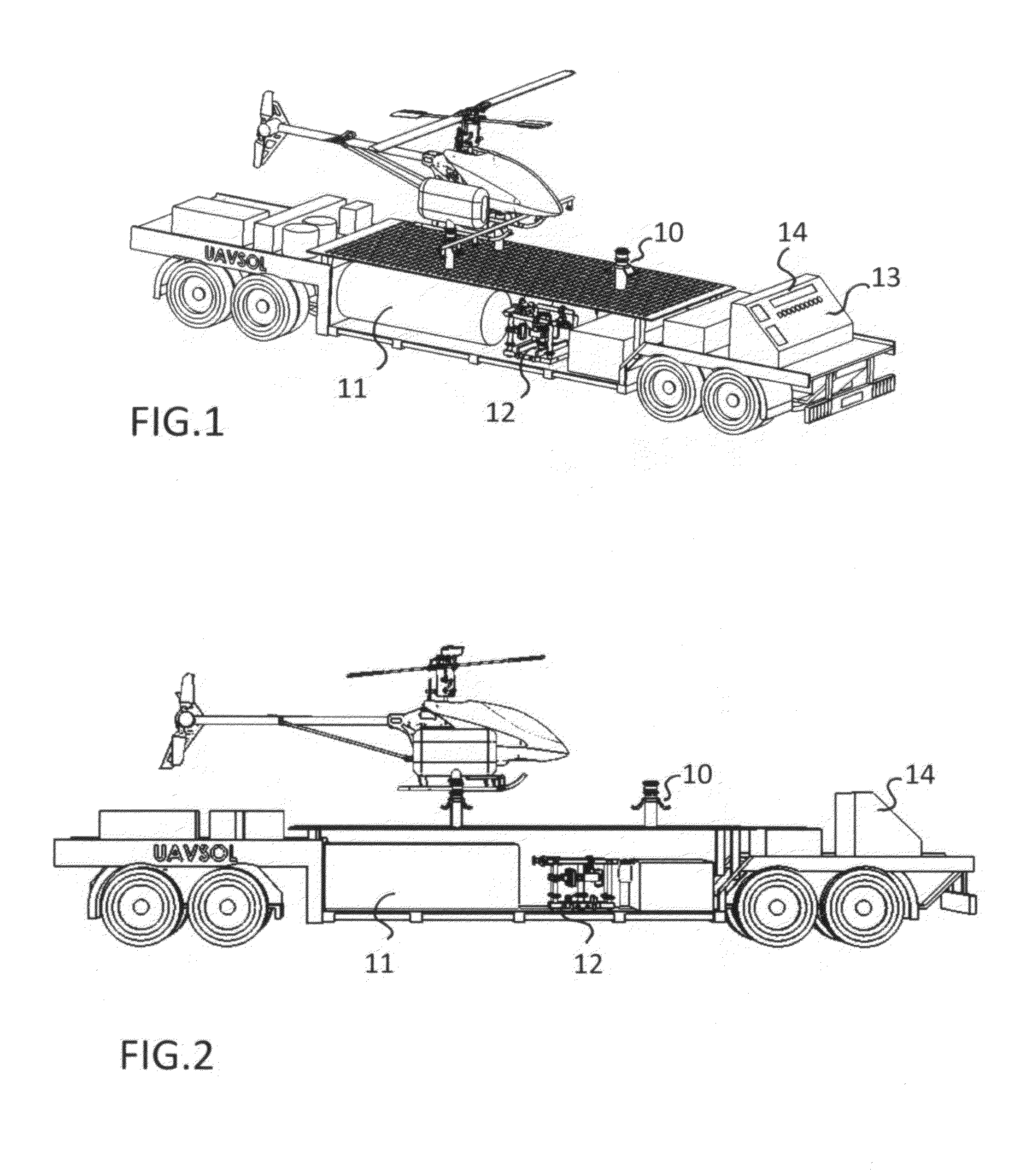
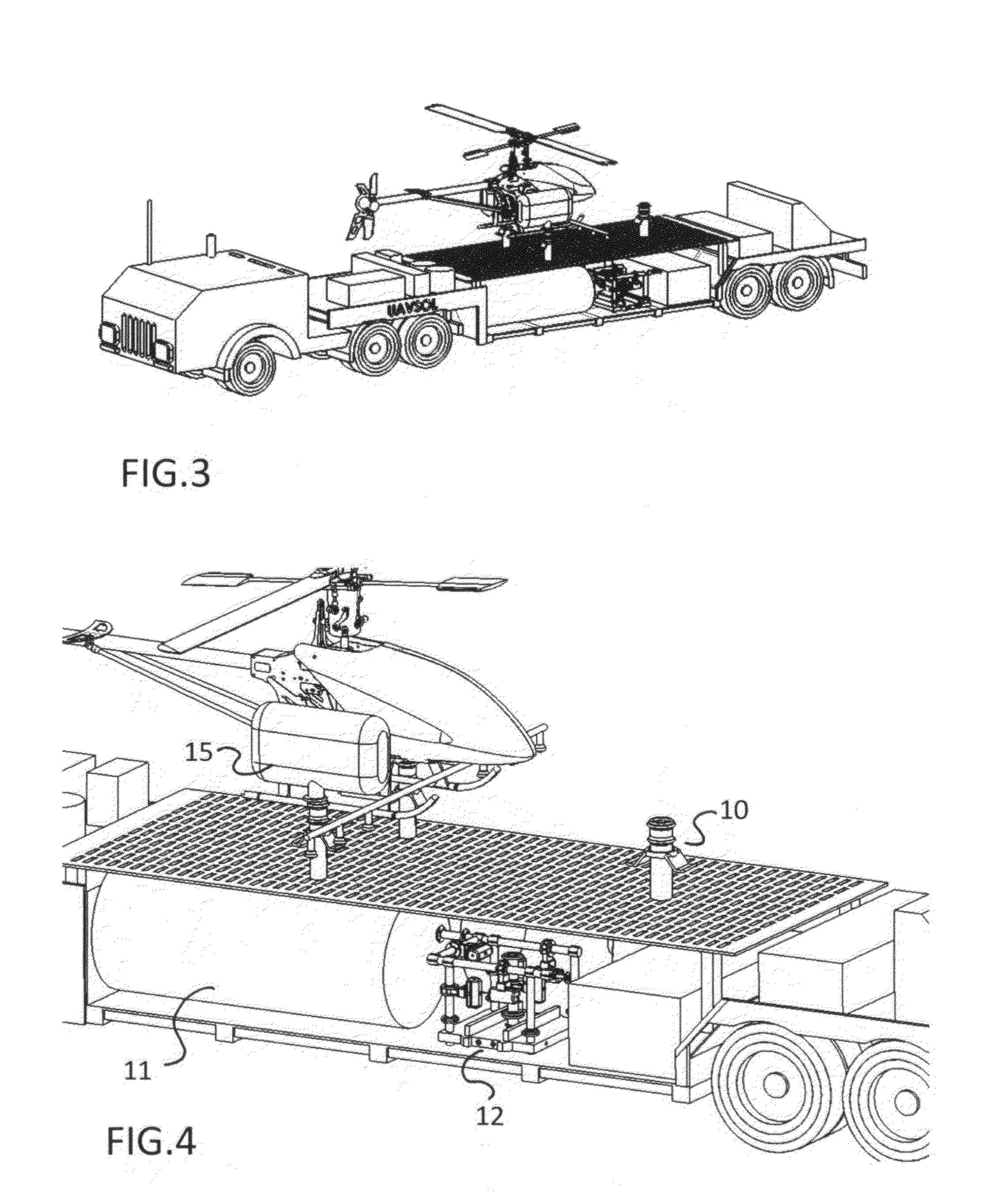
Fueling station for unmaned arial vehicle of the vertical takeoff types
ActiveUS20150123462A1Sufficient powerLiquid fillingRemote controlled aircraftTelecommunications linkEngineering
An unmanned self-sustained fuel dispensing station for fuels of all sorts (gasoline, pesticides, water, fertilizers etc.) a tank, docking, and coupling system for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) of the vertical takeoff types. The station can be independent of public power and communication utilities and can operate by remote control without an on-site attendant. The preferred system has a central command center with a control computer in communication with a station control computer located at one or more satellite stations through a communications link. The station control computer can be controlled remotely by the command center. The station control computer programming has control over the activities of the station through an electrical generation subsystem with a solar array, battery bank, battery charger and standby generator; a fuel dispensing subsystem; a security subsystem with video cameras; a communications link and a status sensor subsystem.
Owner:KAMRADT BRIAN +1
Single use collapsible liquid containment vessel
An expandable single use liquid containment vessel that can fit into restricted spaces such as the trunk or glove compartment of a passenger transport vehicle. The vessel contains a top and bottom wall integrally connected via an outer wall embodying accordion type pleats to allow for vessel compression and expansion. A single piece pouring nozzle is permanently attached to the containment vessel subsequent to introduction of a fluid the containment vessel's interior portion. One end of the filling nozzle secures the nozzle to the containment vessel. At the second end of the nozzle is an exiting orifice which has been dimensioned to preclude insertion therein of publicly accessible fueling nozzles commonly associated with motor vehicle refueling stations.
Owner:HUDKINS BRUCE ERIC
Tire filing method and apparatus adaptable to different sizes of tires
InactiveUS6467524B2Check valvesPackaging under special atmospheric conditionsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A pneumatic tire filling station includes a support and seal arrangement on which one side wall of the tire is supported and sealed, and a tire filling bell that presses and seals against the opposite side wall of the tire and then supplies pressurized air into the tire. The filling bell includes outer and inner rings that are concentrically slidable relative to each other. One of the rings is selected for the filling operation depending on the size of the tire. The support and seal arrangement includes plural plate members that are joined and sealed together to form a continuous support and seal surface, or moved laterally apart to allow a transport apparatus to carry and support the mounted tire from underneath. The tire filling station is adaptable to different models and sizes of mounted tires even in a mixed process flow, in an automated manner.
Owner:SCHENCK ROTEC GMBH
Fuel oil additive and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101671584ASimple preparation processEasy to operateLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlcoholAntioxidant
The invention relates to a fuel oil additive which comprises the components based on parts by weight: 50-65 parts of surface active agent, 15-20 parts of alcohol auxiliary surface active agent, 2-5 parts of antioxidant, 2-5 parts of corrosion inhibitor and 15-30 parts of deionized water. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the fuel oil additive. The fuel oil additive has simple preparation technique, convenient operation and lower cost, and can generate the comprehensive effects such as saving fuel oil, increasing power, cleaning up sediment, reducing emission and the like; furthermore, the gasoline compound added with the fuel oil additive has good stability and strong applicability, is applicable to both gasoline stations and individual users, and can save the gasolineby 8%-15% in the comprehensive effect.
Owner:重庆泰壹环保新能源开发股份有限公司
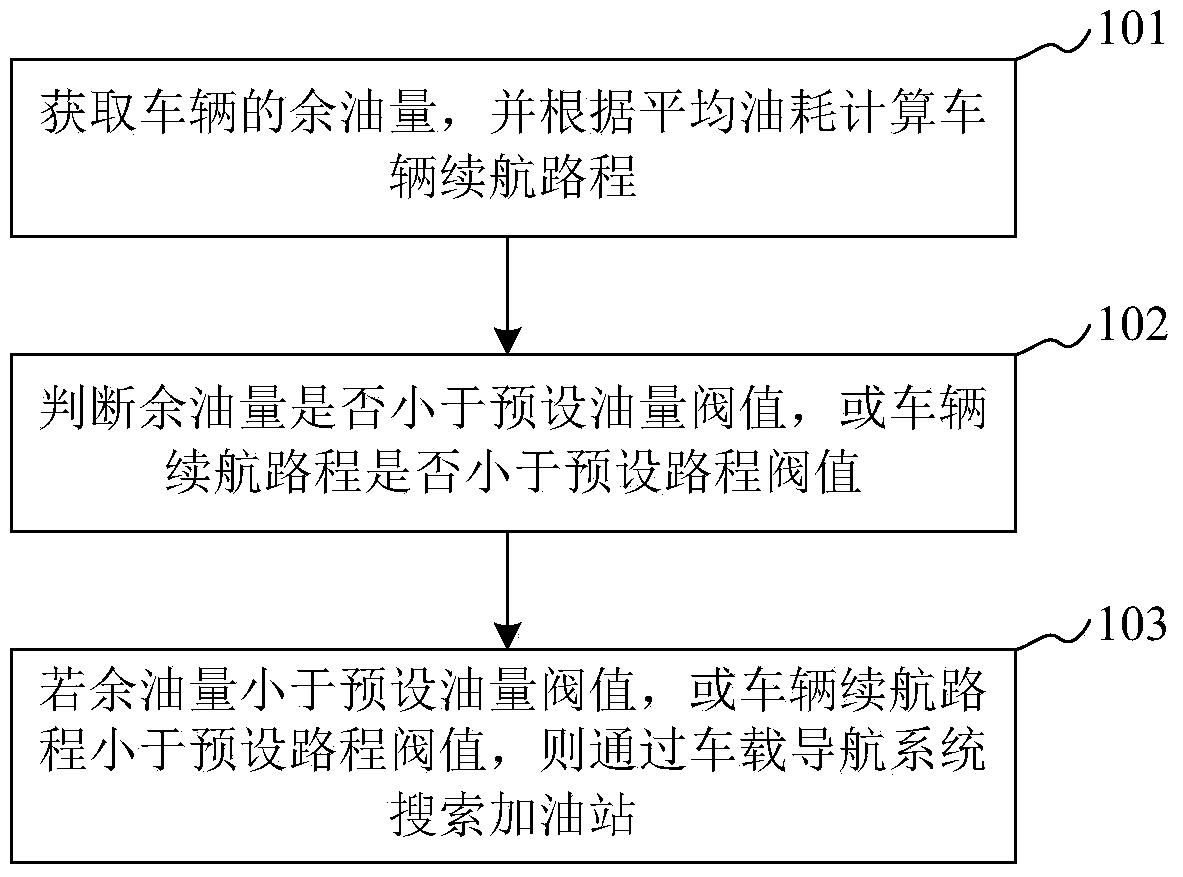
Refueling reminding method
InactiveCN104236574AReduce the risk of stopping halfwayInstruments for road network navigationNavigation systemDistance threshold
The invention discloses a refueling reminding method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a residual fuel amount value of a vehicle and calculating a cruising distance of the vehicle according to average fuel consumption; judging whether the residual fuel amount value is less than a preset fuel amount threshold or the cruising distance value of the vehicle is less than a preset distance threshold; and searching gasoline stations by virtue of a vehicle-mounted navigation system if the residual fuel amount value is less than the preset fuel amount threshold or the cruising distance value of the vehicle is less than the preset distance threshold. Due to the adoption of the technical scheme, the method is capable of reminding a user of searching the gasoline stations for refueling; the risk of parking the vehicle in halfway can be reduced.
Owner:HUIZHOU KAIYUE ELECTRONICS
Vehicle identification method used for gas station
InactiveCN105741560AEasy to manageTo offer comfortRoad vehicles traffic controlClosed circuit television systemsTime informationLicense
The present invention discloses a vehicle identification method used for a gas station. The vehicle identification method used for the gas station comprises the steps of locking a target vehicle via a camera, and obtaining the characteristic information of the target vehicle; obtaining the time information when the target vehicle drives in and drives out the gas station; obtaining the refueling information of the target vehicle; matching the obtained characteristic information, the time information and the refueling information of the target vehicle and then sending to a background server, and displaying the matched target vehicle information in a display screen in a rolling playing manner, wherein the displayed vehicle information comprises the vehicle type, the license plate number, the gas station driving-in time and the refueling type. A vehicle identification system comprises a shooting unit, an identifying and analyzing unit, a sensor unit, a server unit and the display screen, and is used for realizing the vehicle identification method. According to the present invention, the information of the vehicles driving in the gas station can be shot and recorded, the license plate number, the vehicle type and the driver information of the vehicles can be extracted from the shot images and can be played via an outdoor display screen, and the problems that the daily vehicle refueling information in the gas station can not be gathered, and the stolen and robbed vehicles and the vehicles carrying the hazardous chemical substances can not be identified, are avoided.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
System and method for determining and brokering fuel emission offsets
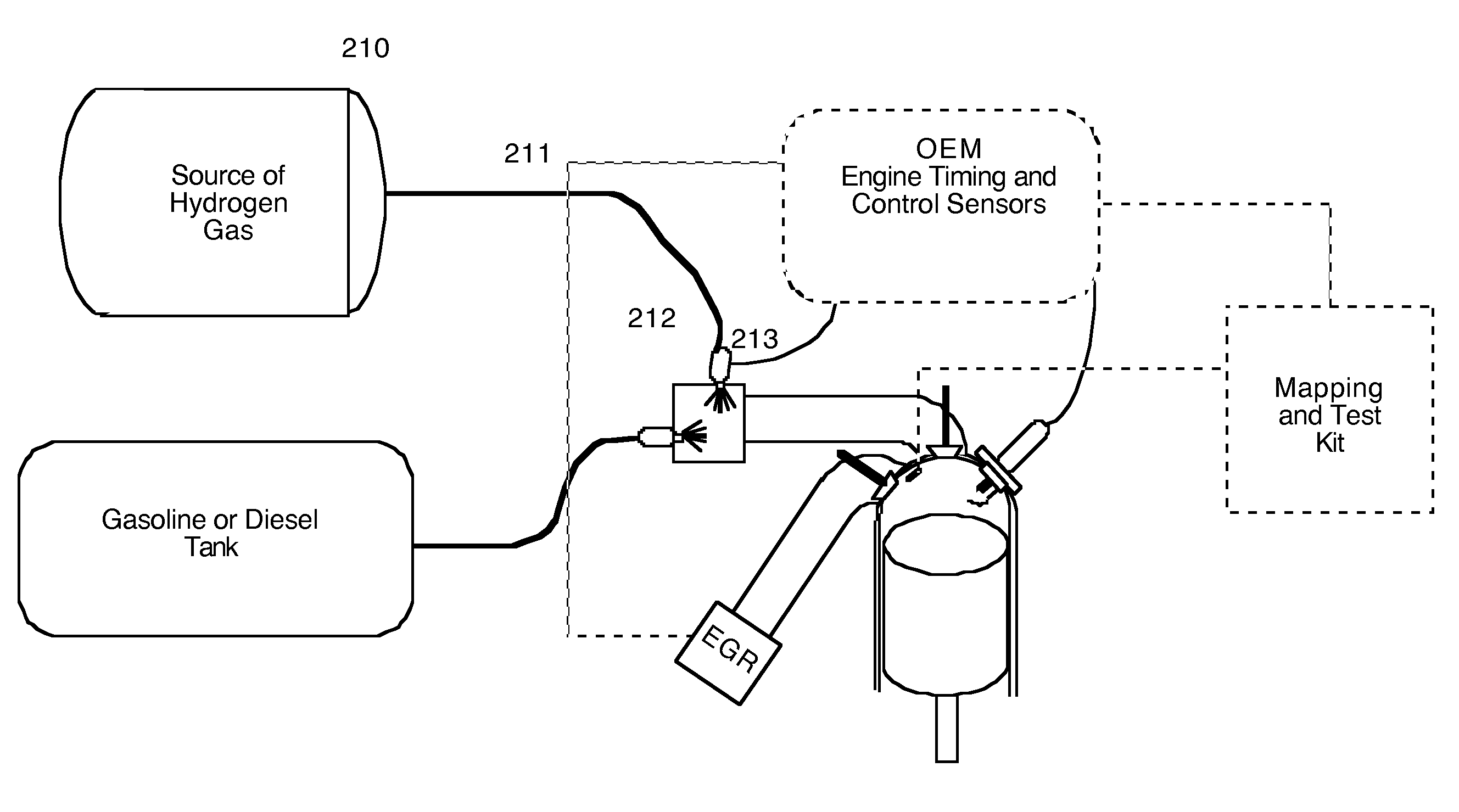
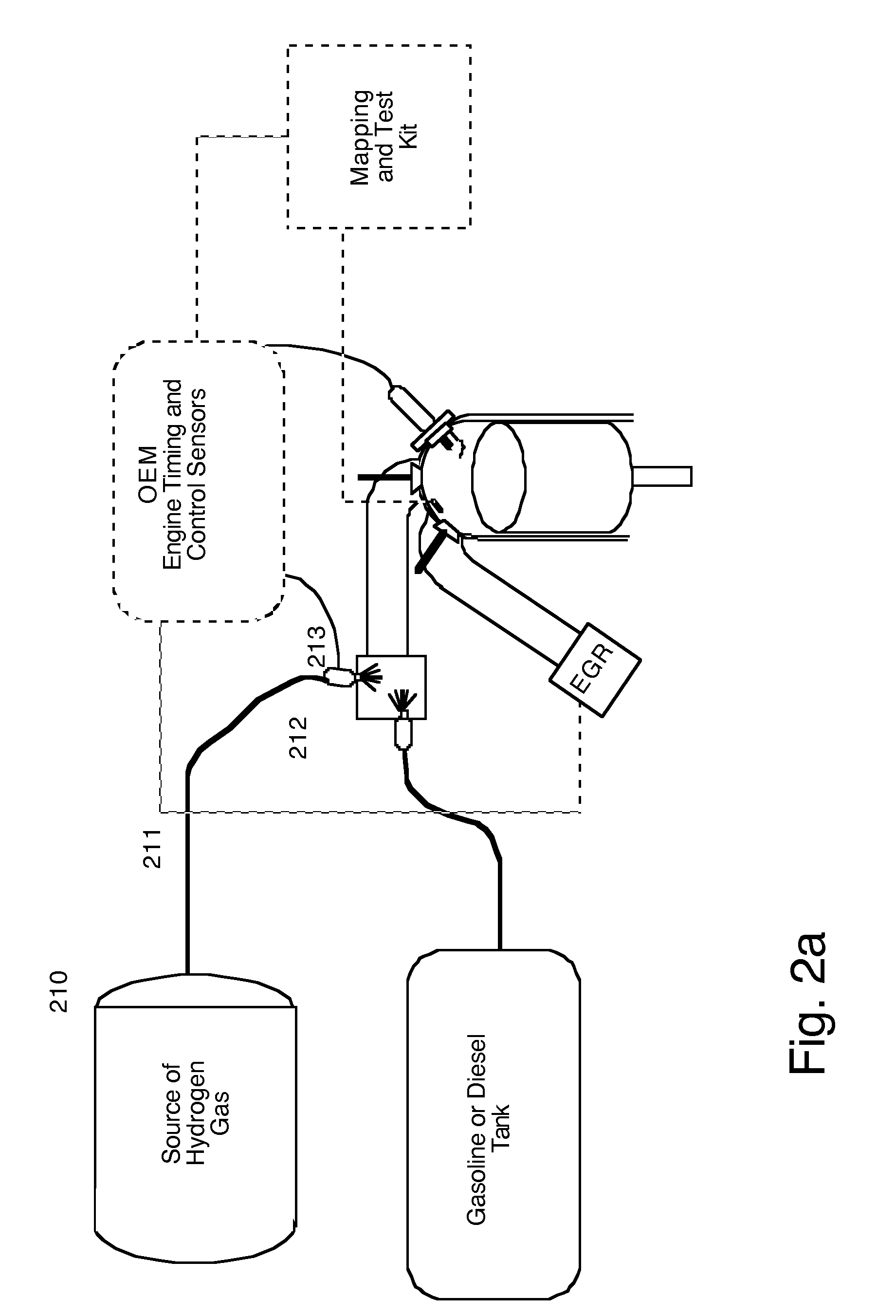
A brokering system and method for providing an incentive for use of more efficient internal combustion engines and hydrogen retrofit kits is disclosed. End users of retrofitted vehicles are provided with discounted fuel costs at authorized fueling stations. The vehicle owner's savings include: a) a reduction in fueling charges because of the vehicle's new reliance on 30% less fossil fuel (which is displaced by hydrogen in the engine), and b) by the purchase of methanol which can be set at a lower cost per calorific equivalent than a barrel of oil while also earning emission offsets to be sold for cash to the end users / creators of carbon credits. In this manner, retrofitted existing internal combustion engines linked to a trust for trading emission offsets will create a consumer-driven hydrogen economy which governments as well as the automotive and petroleum sectors will endorse. Hydrogen, which is substituted for fossil fuel in a retrofitted IC engine result in emission offsets (i.e., the quantum of emissions that are no longer there) which are converted by a regulated emissions trust into cash. This income, which is deposited into the vehicle owner's bank account via the telephone network by using a dedicated hydrogen fueling card and master engine sensor linked to a specific vehicle provided with an engine retrofit kit and an on board source of hydrogen gas. The present method provides a mapping and test kit that relies on OEM engine timing and control sensors to compare engine emissions produced by fossil fuel with emissions eliminated by substituting hydrogen. This method creates consumer demand for cleanly produced sources of hydrogen (beginning with green methanol) to fuel existing OEM engines, which will in turn, induce automobile manufacturers to build more efficient IC engines until, finally, they will all be fueled by 100% hydrogen.
Owner:LANGE DAVID
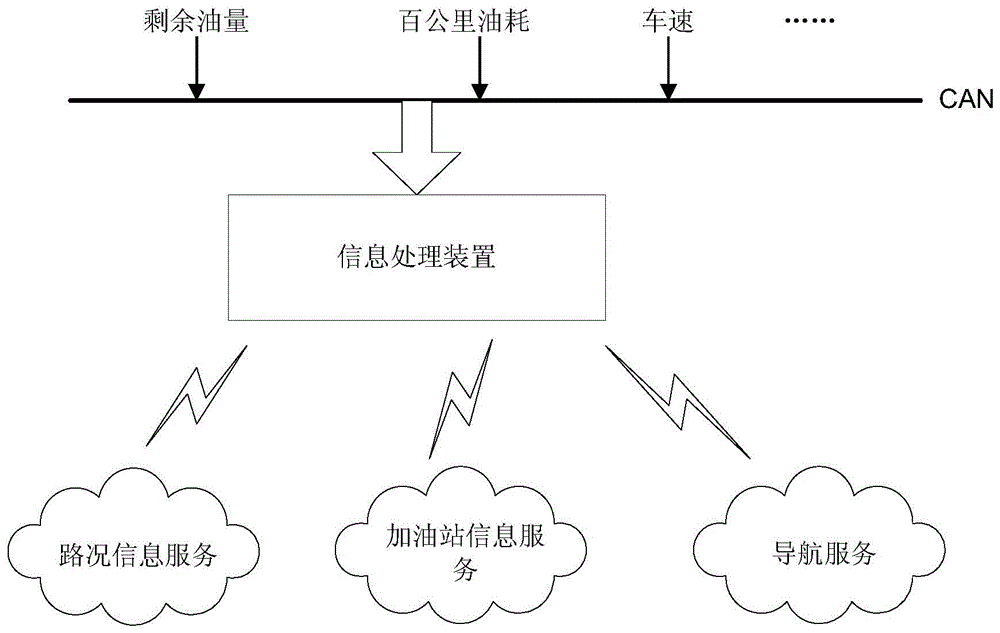
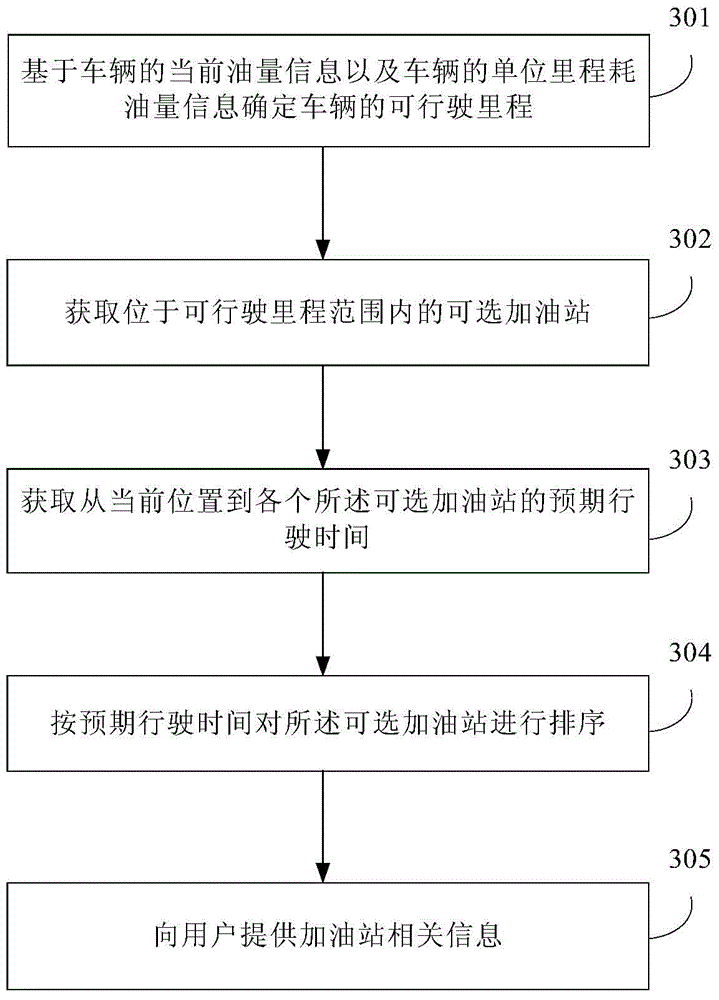
Method for providing gasoline station information, information processing device and vehicle navigation system
InactiveCN104697540AAvoid breaking downAvoider refueling problem too earlyInstruments for road network navigationGasoline stationOil consumption
The invention discloses a method for providing gasoline station information and a corresponding information processing device. The method comprises the following steps: determining the drivable mileage of a vehicle according to the current remaining oil quantity information and the unit mileage oil consumption information of the vehicle; acquiring optional gasoline stations within the drivable mileage; acquiring the anticipated driving time from the current position to each optional gasoline station; sequencing the optional gasoline stations according to the anticipated driving times; and providing gasoline station related information for a user.
Owner:CONTINENTAL HOLDING CHINA CO LTD
Pressure differential system for controlling high pressure refill gas flow into on board vehicle fuel tanks
A high pressure fuel flow control device wherein pressure sensors are interposed on either side of the main restriction point of a refueling depot when the vehicle tank(s) to be refilled are interconnected in a flow circuit that connects the refilling depot and the vehicle tanks. The sensors measure pressure on the side of the depot tank[s] and pressure on the side of the vehicle tank at a restriction point in the gas flow circuit. Flow from a tank is complete and a tank is switched when the difference in the pressures sensed on opposite sides of the restriction point approaches zero or slightly greater than zero.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Oil gas recovery method and device of fuel station
InactiveCN1994858ASimple structureCompact structureLarge containersLiquid transferring devicesRecovery methodPetroleum engineering
The invention relates to a method for using low-temperature condensation and adsorption to recycle oil from fuel station, and relative device, wherein said method comprises that: oil collection, oil low-temperature condensation recycle, and oil deep adsorption recycle. The invention has advantages that: the oil collection can collect the oil generated in underground oil pot collection and oil feeding; using fuel feeding gun of fuel feeder to feedback the discharged oil in fuel feeding into the fuel collecting tube; the recycle device first uses low-temperature condensation and later adsorption, to make the tail gas fuel content lower than 120mg / 3, and fuel recycle ration higher than 99. 9%; the invention only uses one absorber and uses itself vacuum desorber, with adjustable desorbing time.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
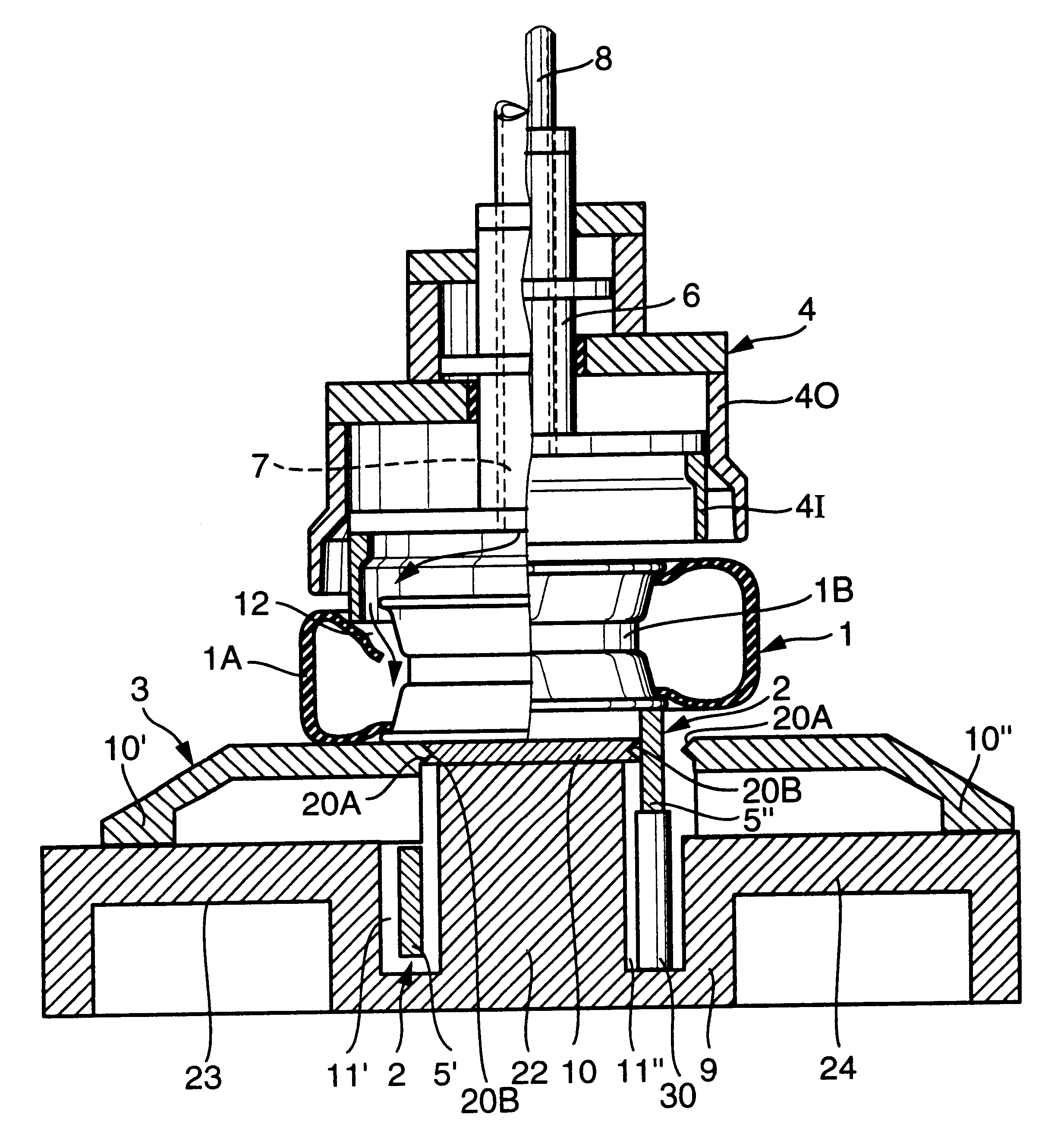
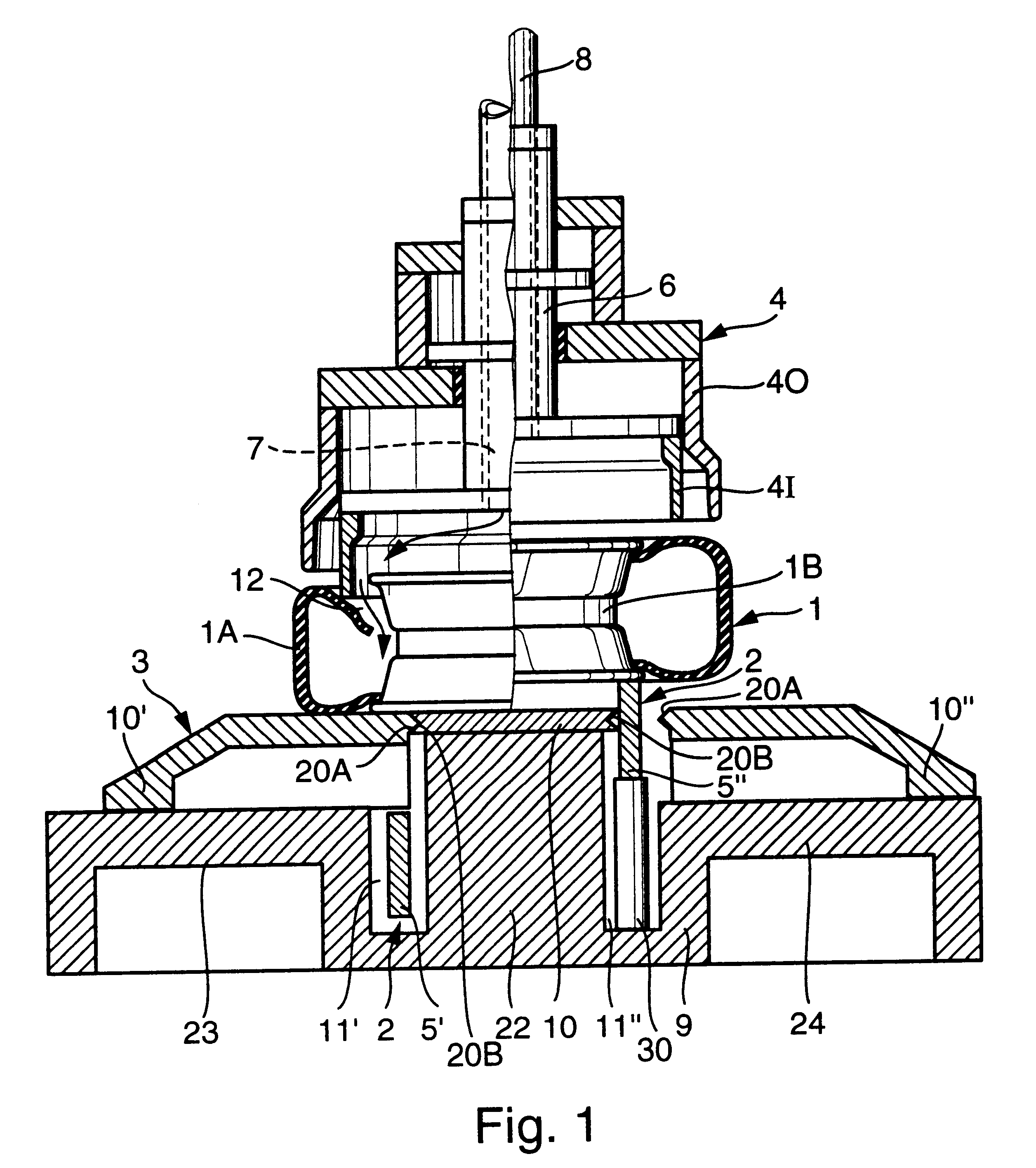
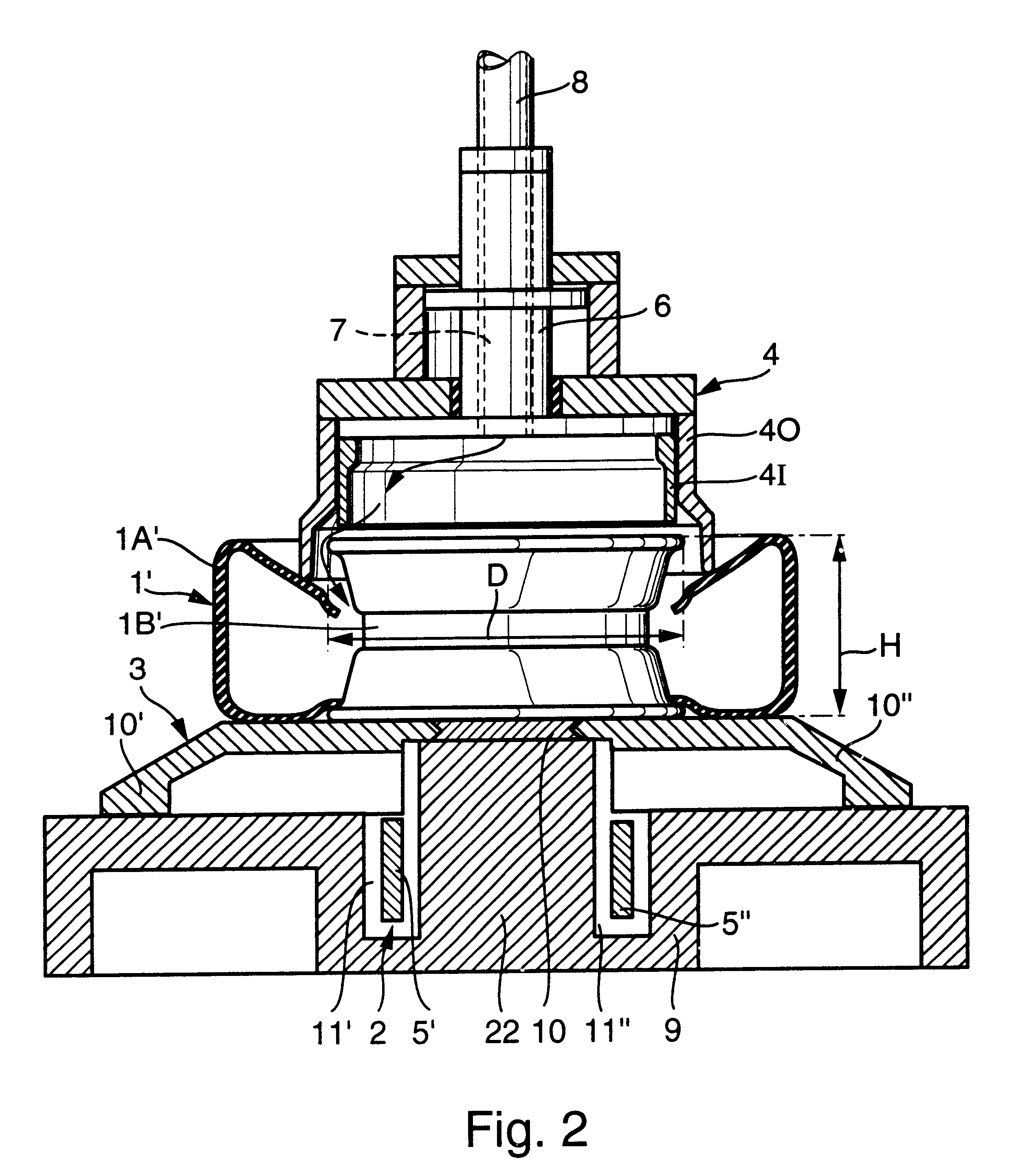
Method and machine for producing blister packs
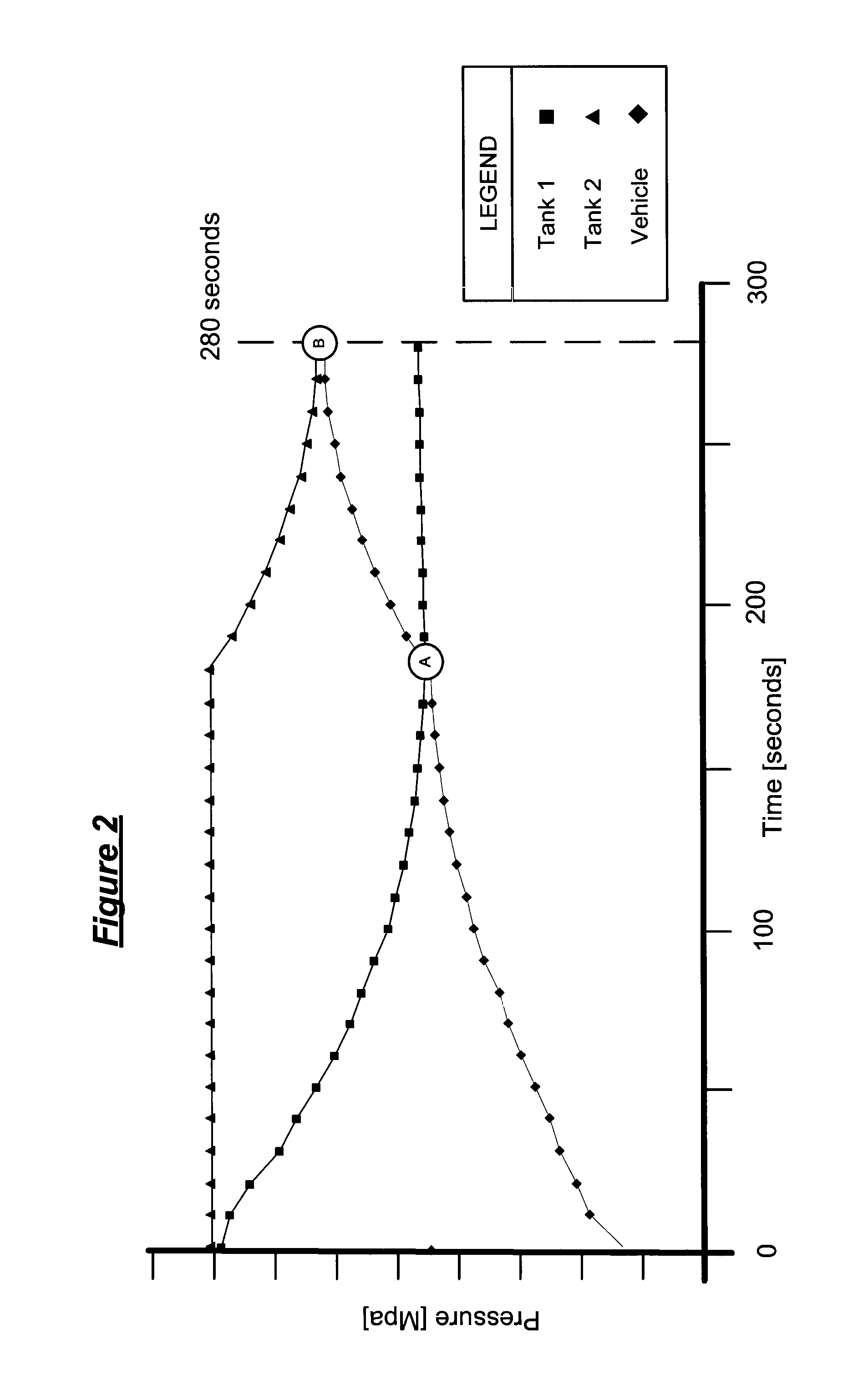
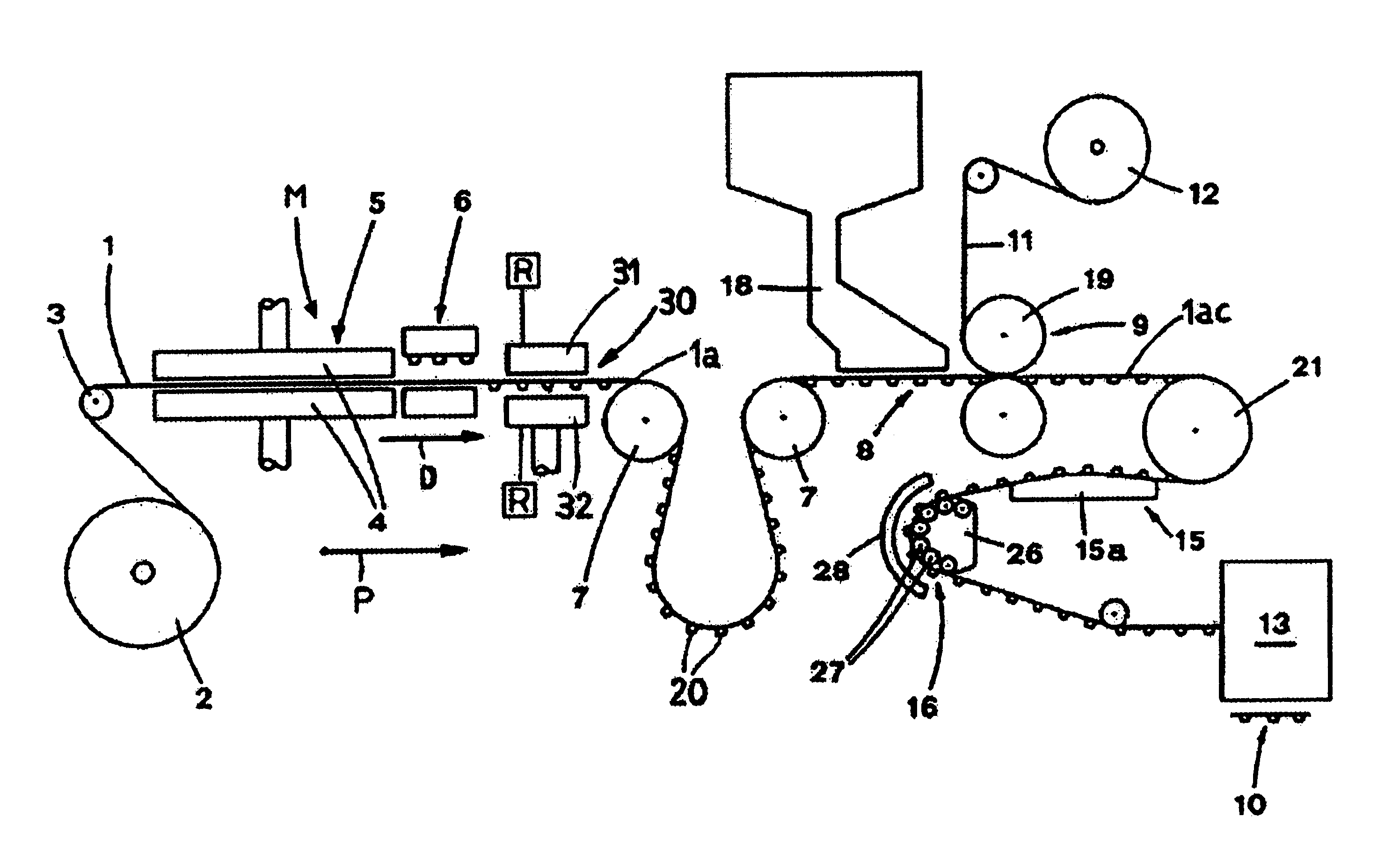
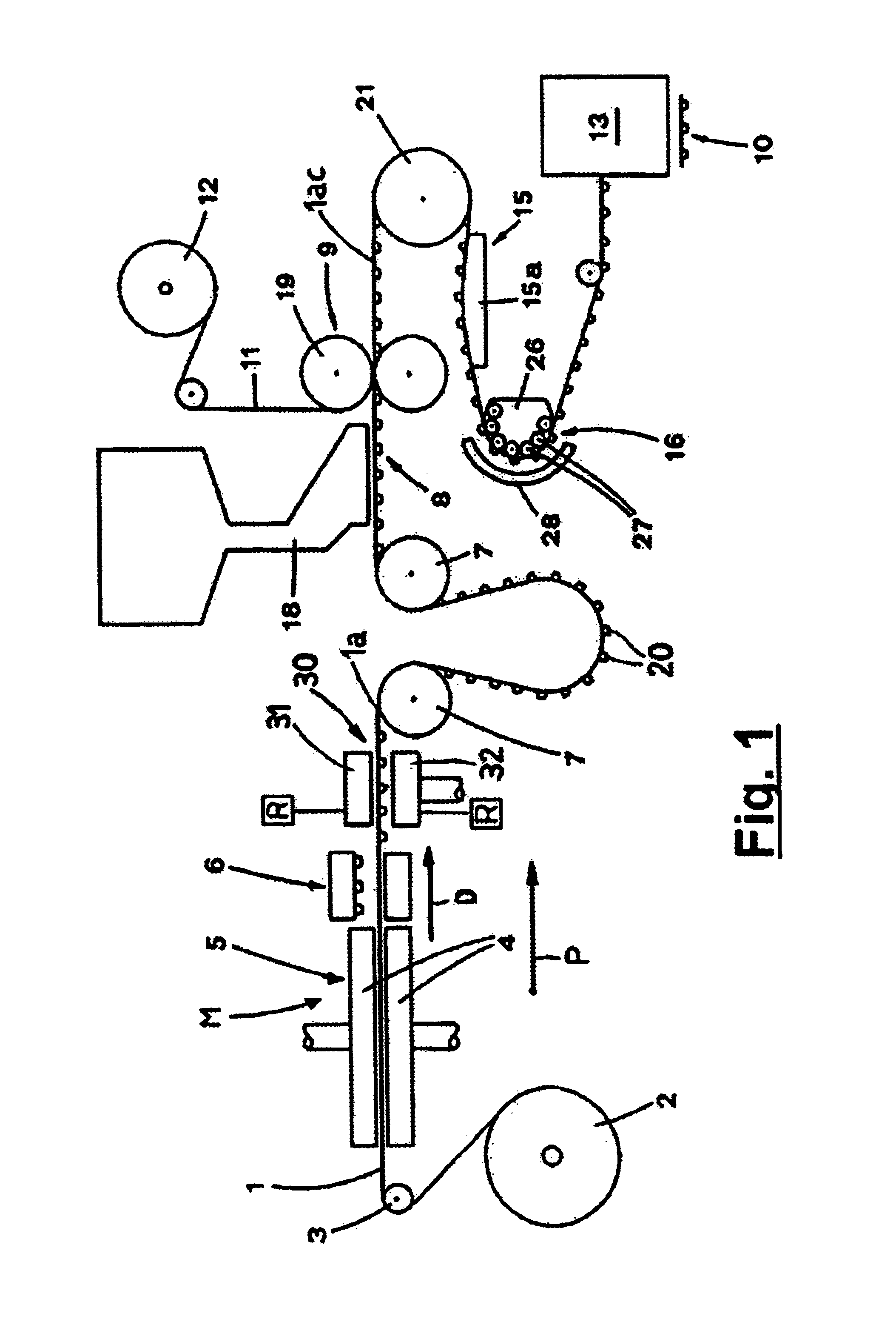
A machine (M) for producing blister packs (10) includes unrolling means (3,7,21) for unrolling a band of heat-formable material from a bobbin (2) and for feeding the band (1) along a predetermined path (P) extending through subsequent stations (5,6,30,8,9,13), in which the band (1) is processed. The above-mentioned stations include a heating station (5), where the band (1) of heat-formable material is heated, a forming station (6), where a plurality of blisters (20) are formed on the band (1), a filling station (8), where the blisters (20) are filled with products, a sealing station (9), where the blister band (1a) is closed with a sealing band (11), and a cutting station (13), where the closed blister band (1ac) is cut into blister packs (10). A further heating station (30) is provided for heating the blister band (1a) along the path (P) upstream of the filling station (8), so as to heat the band (1a) to cause a thermal stabilization treatment of the blister band (1a).
Owner:IMA IND MASCH AUTOMATICHE SPA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com