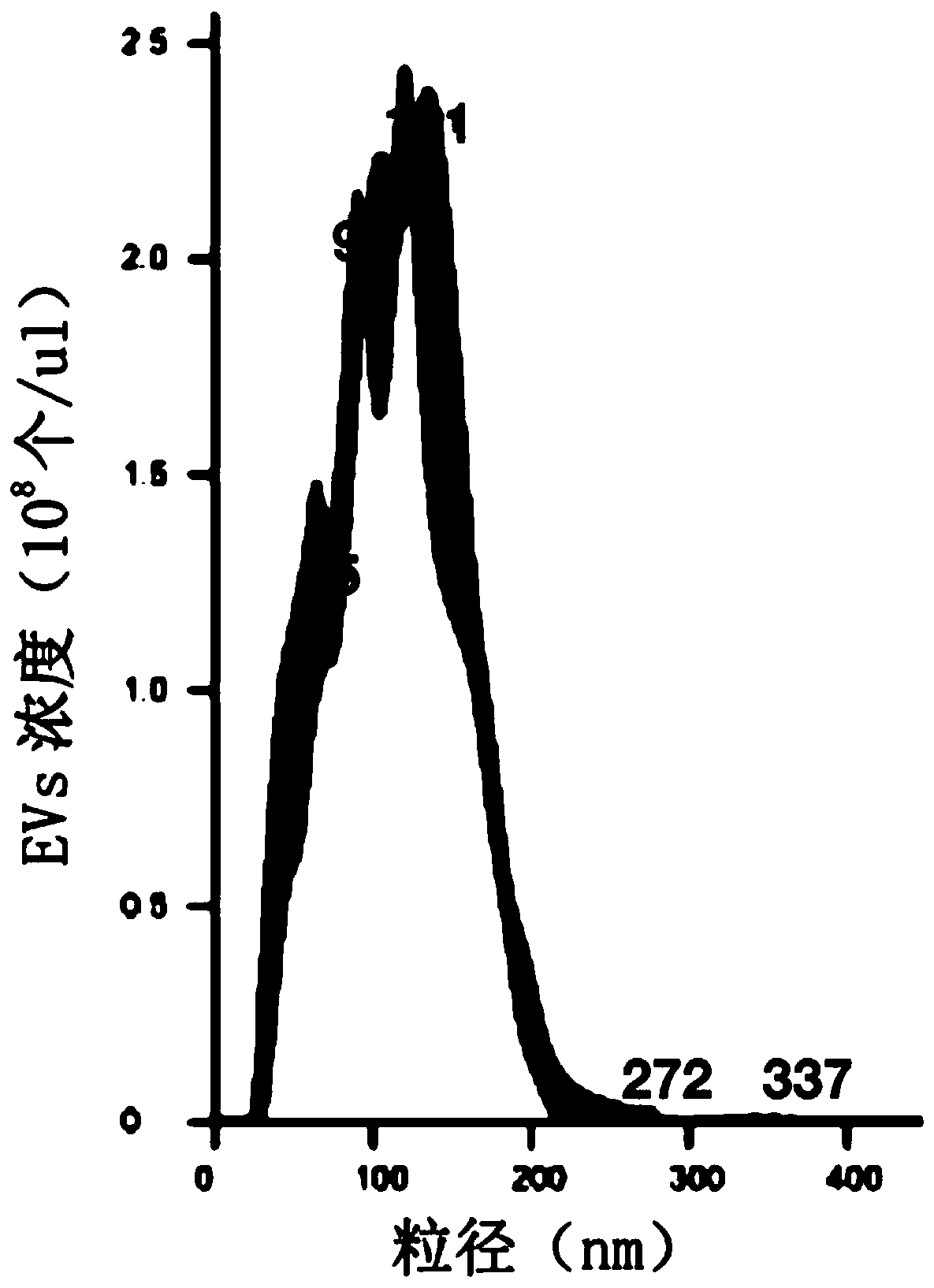
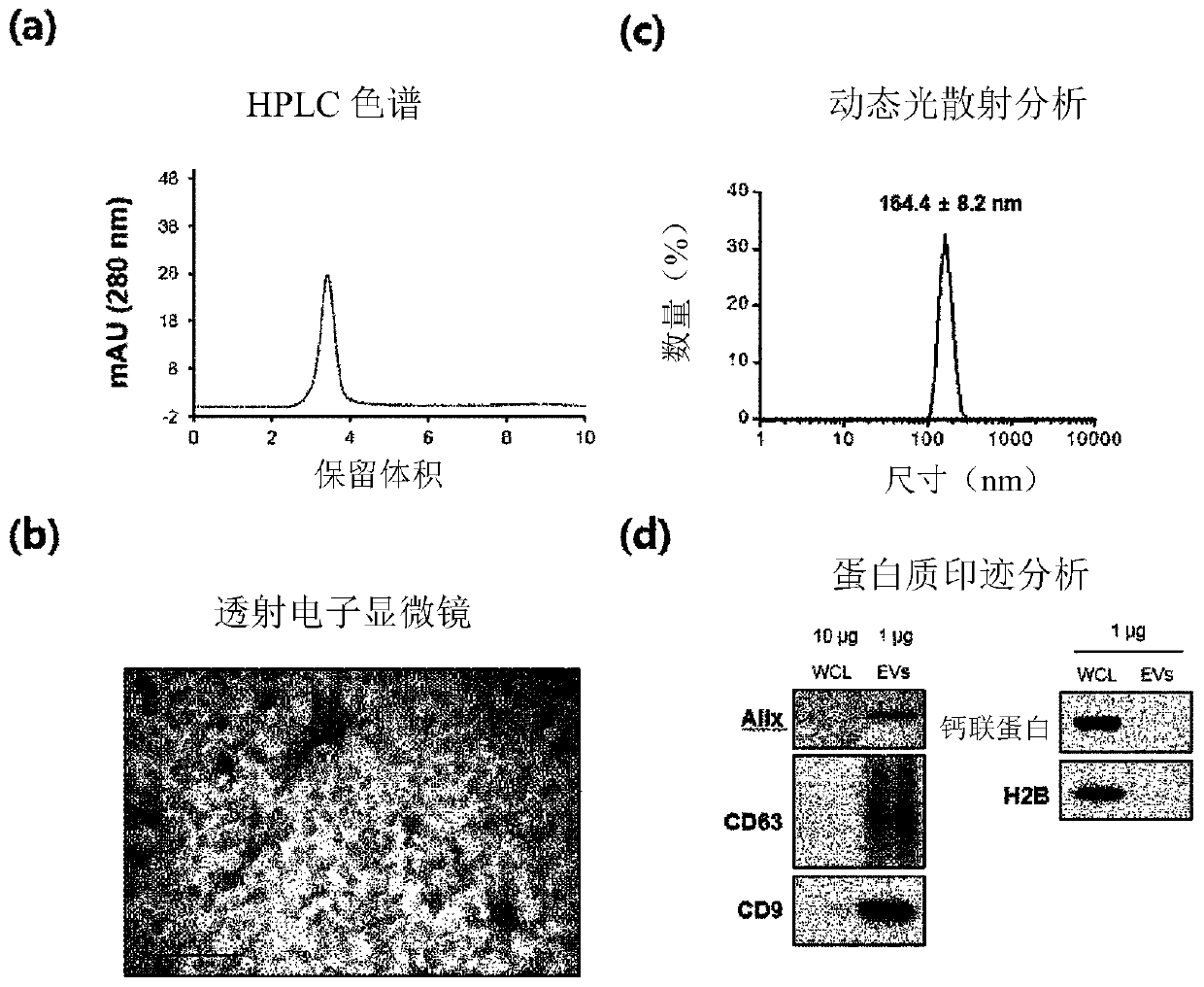
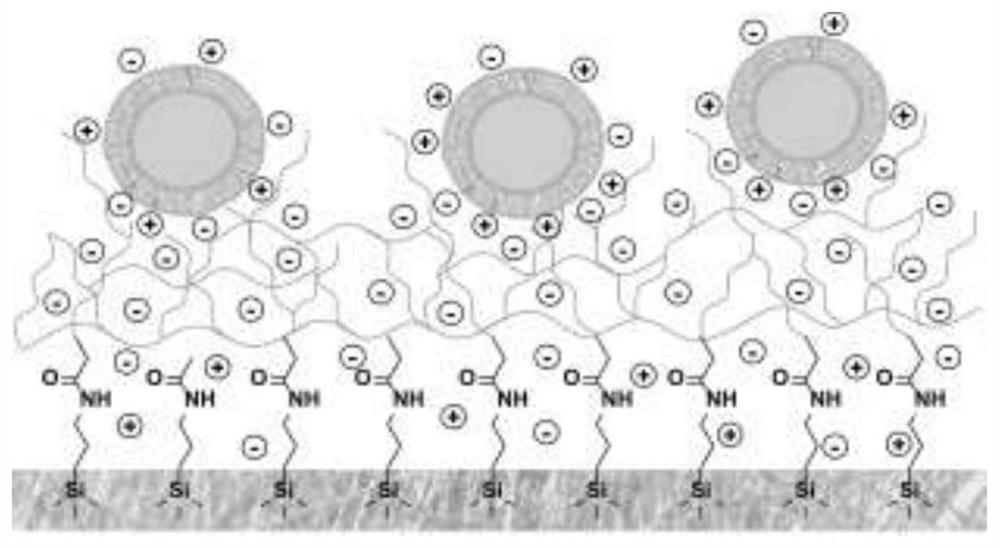
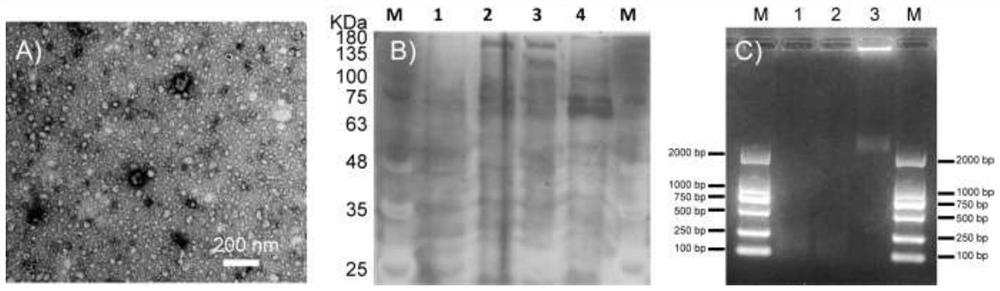
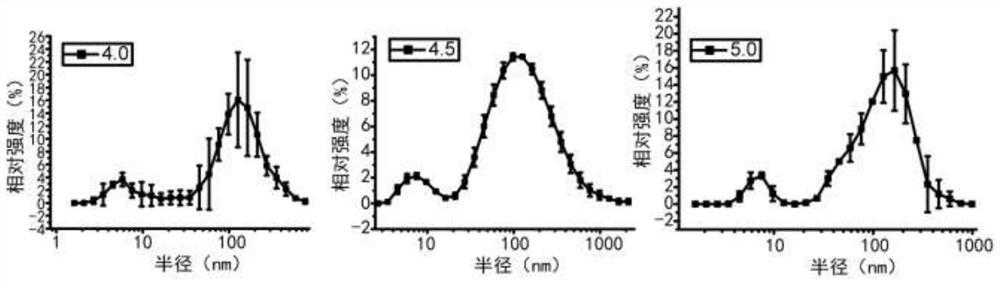
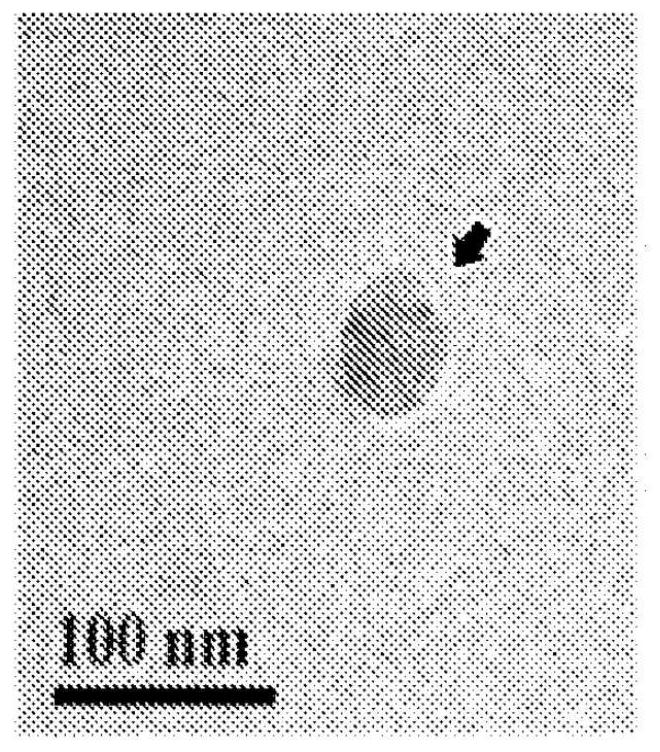
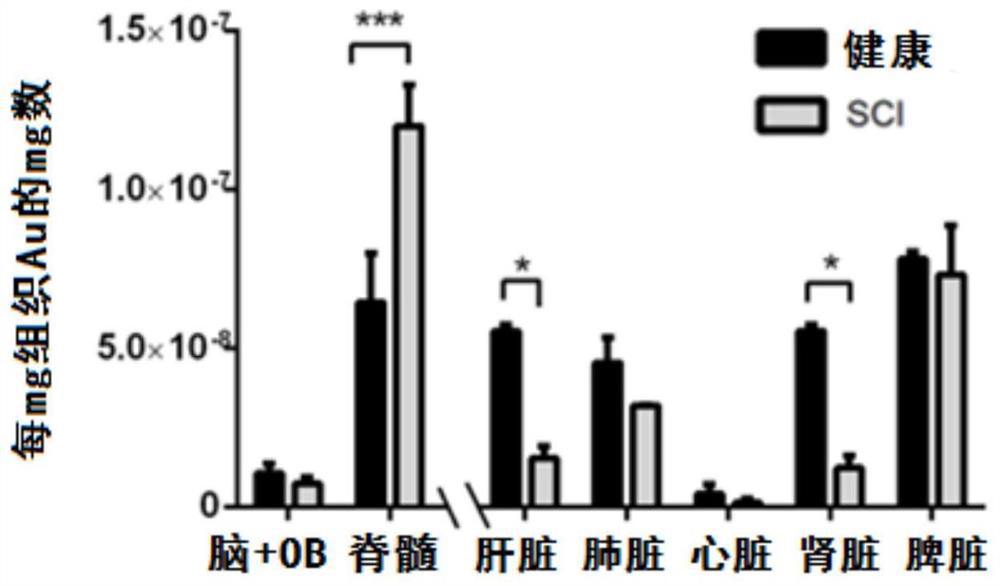
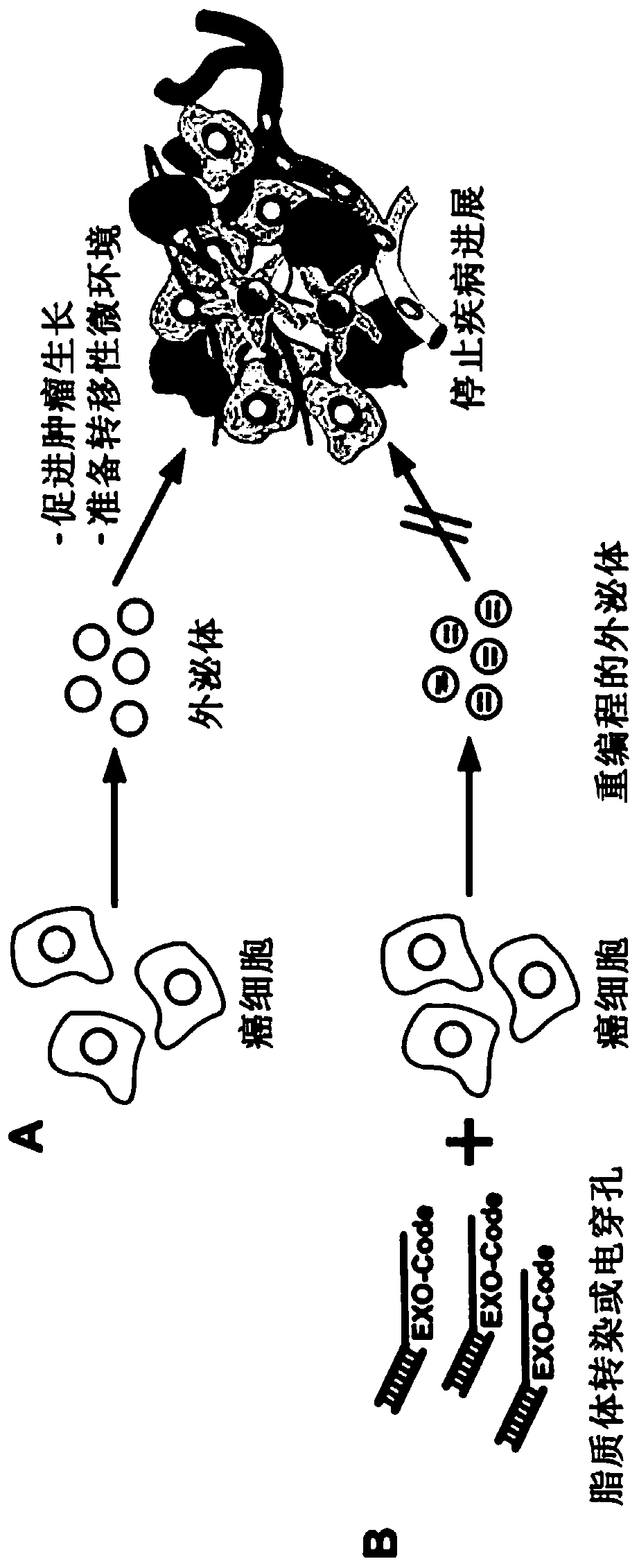
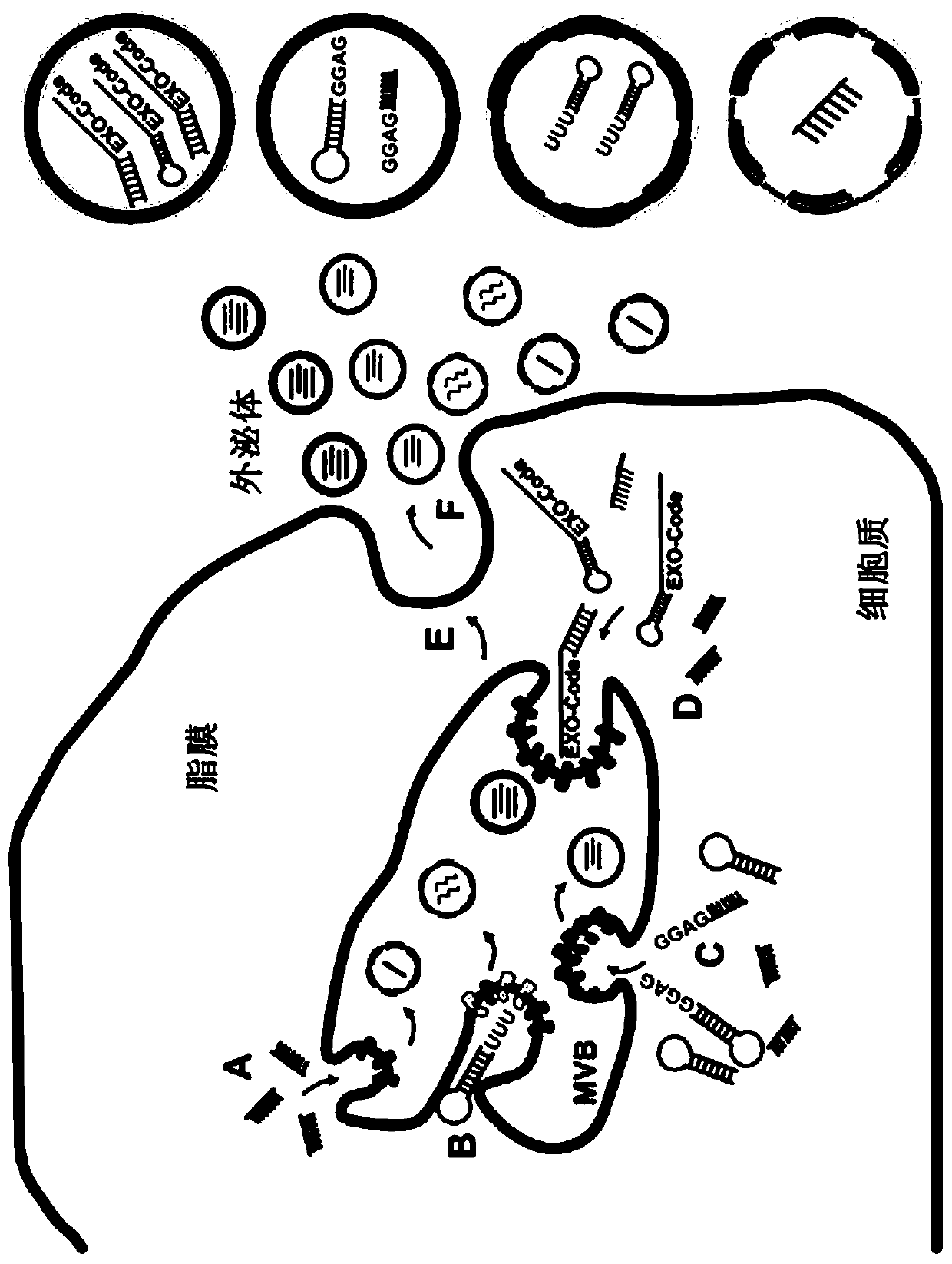
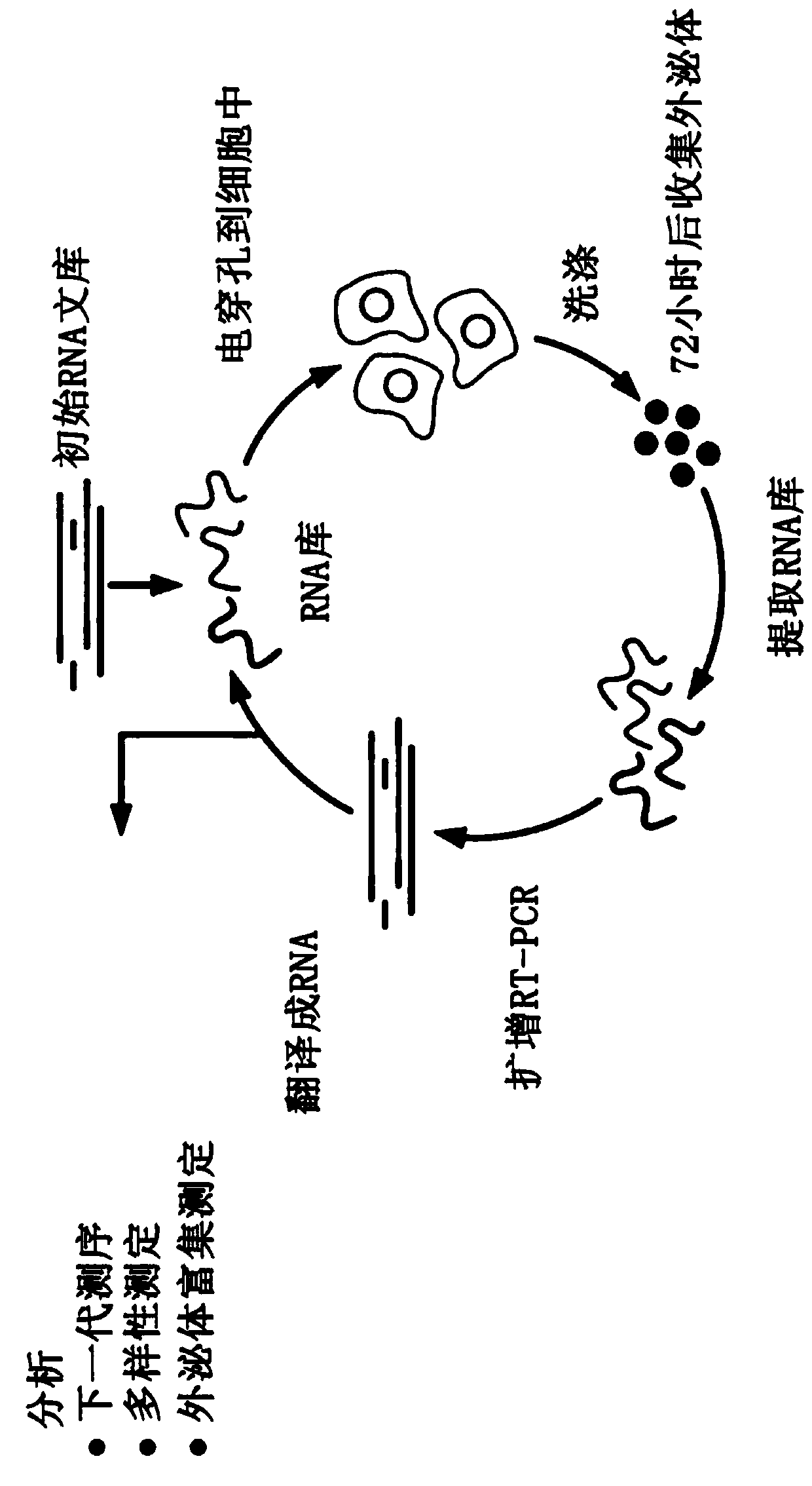
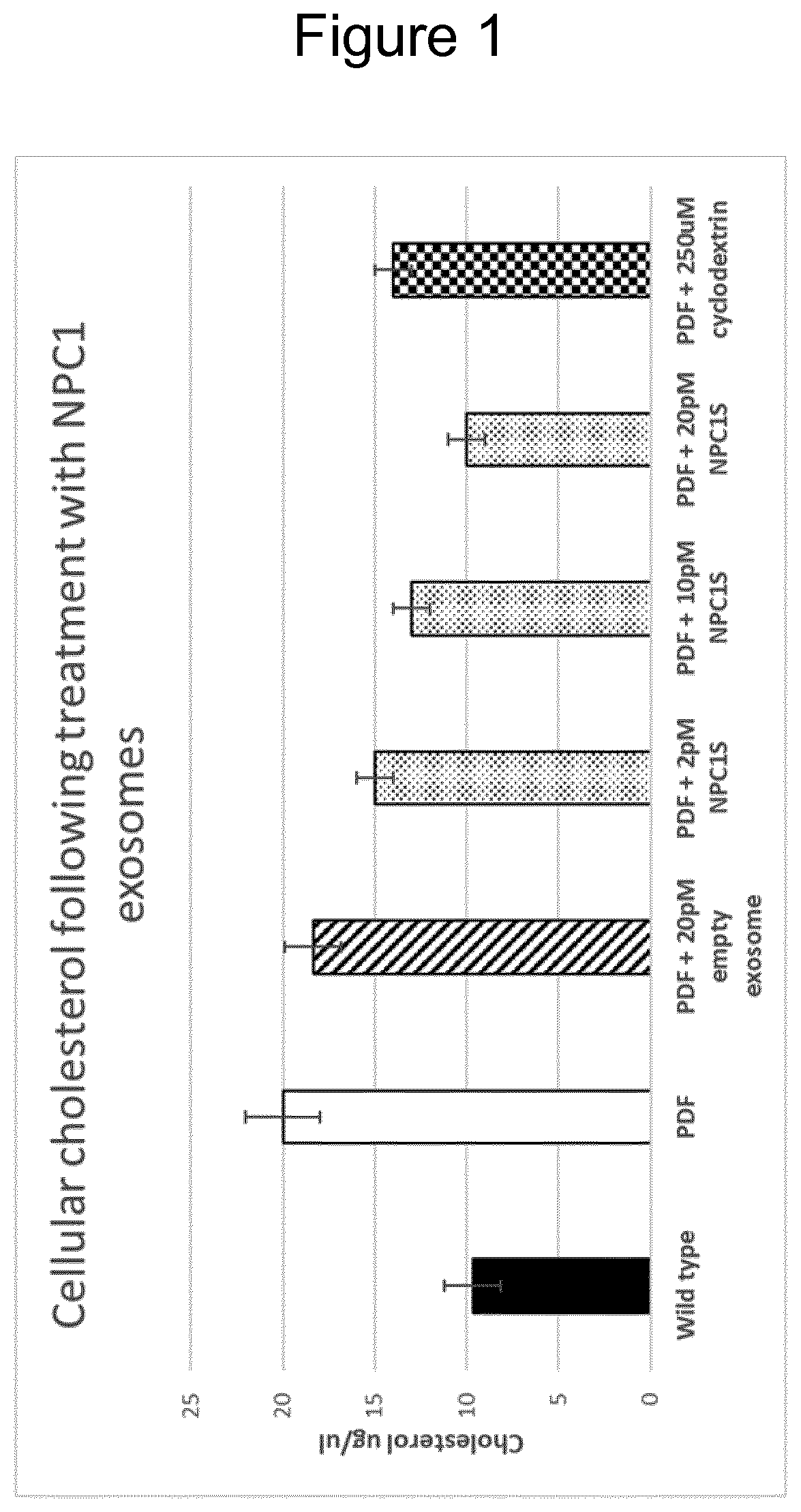
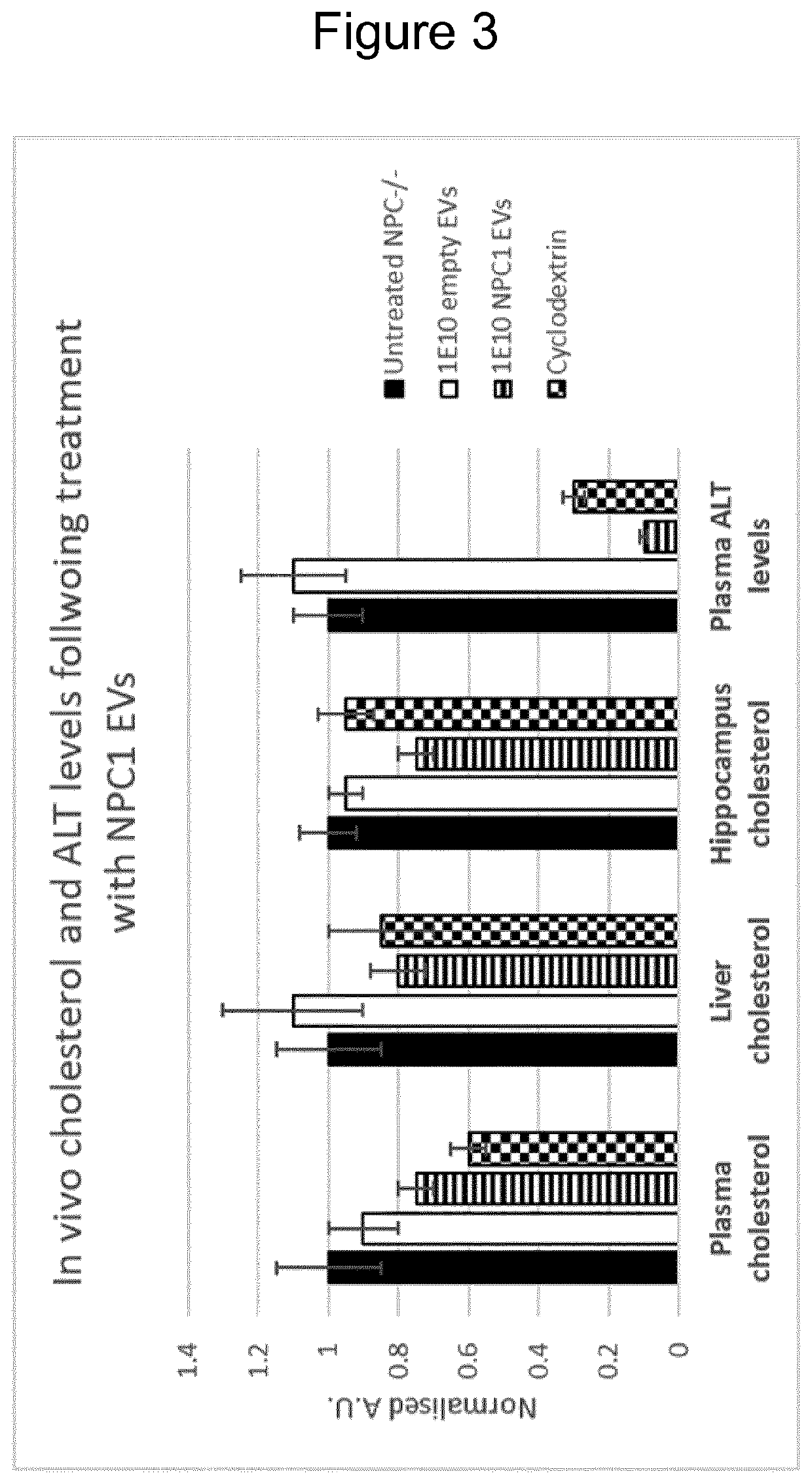
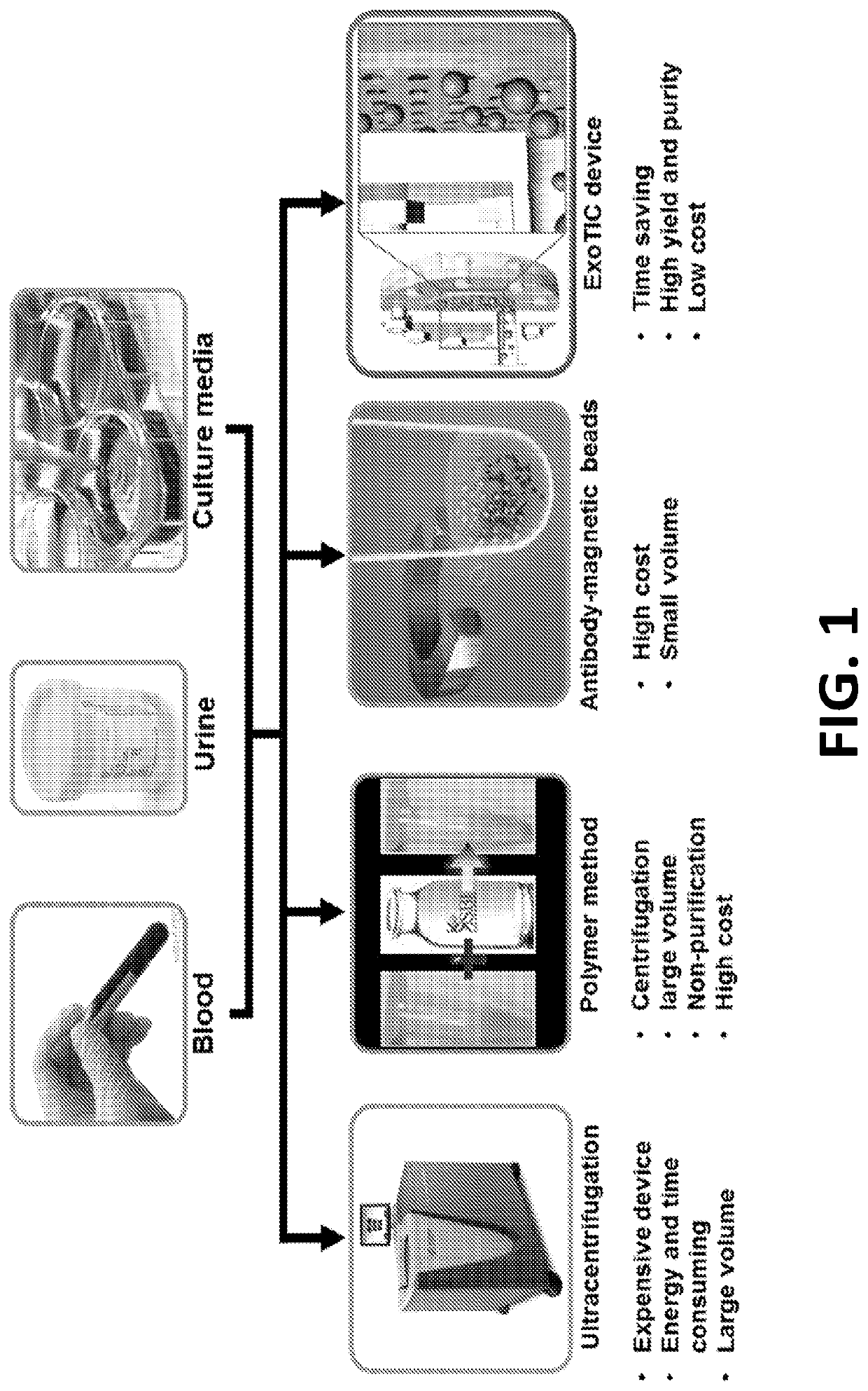
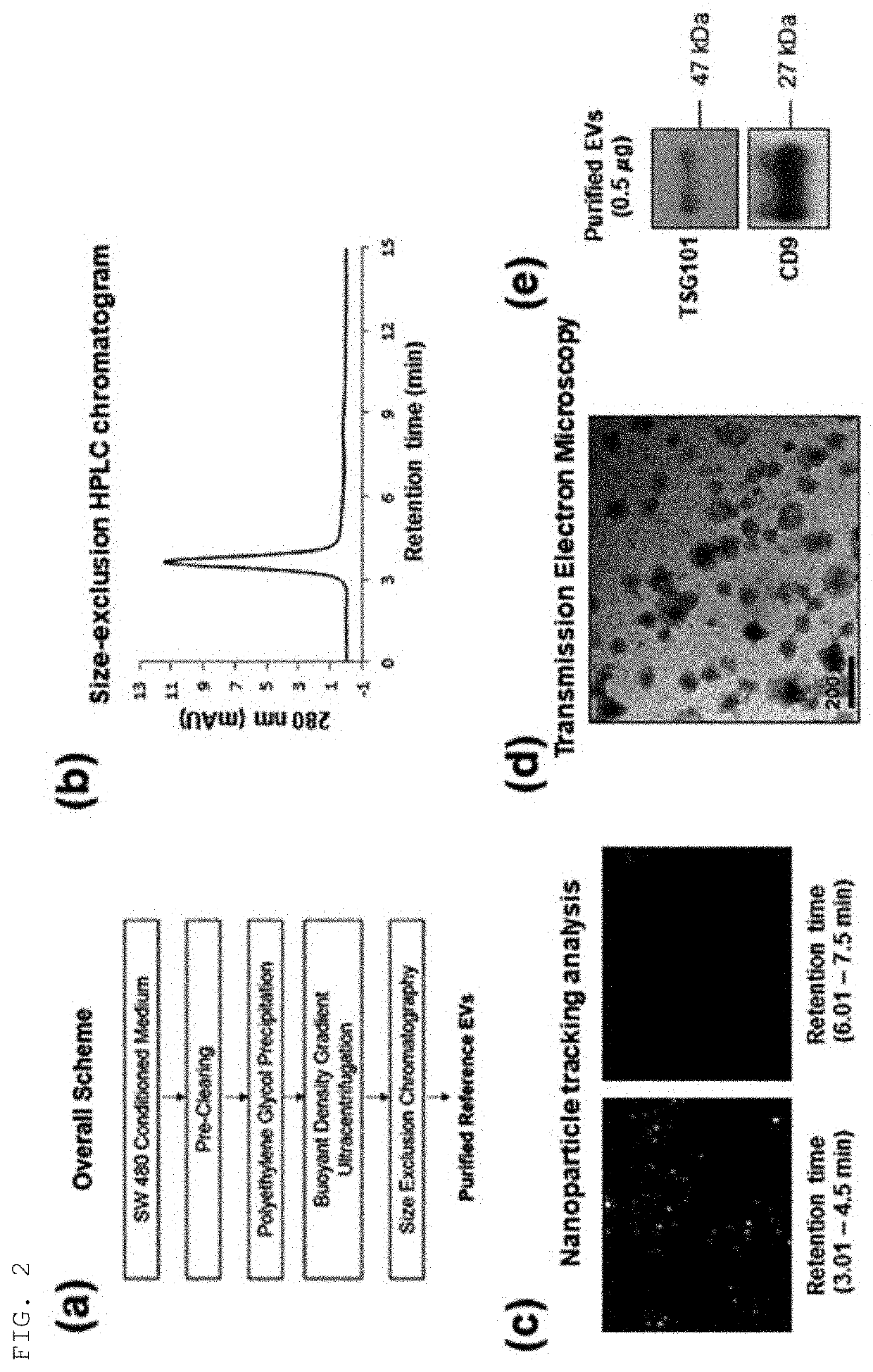
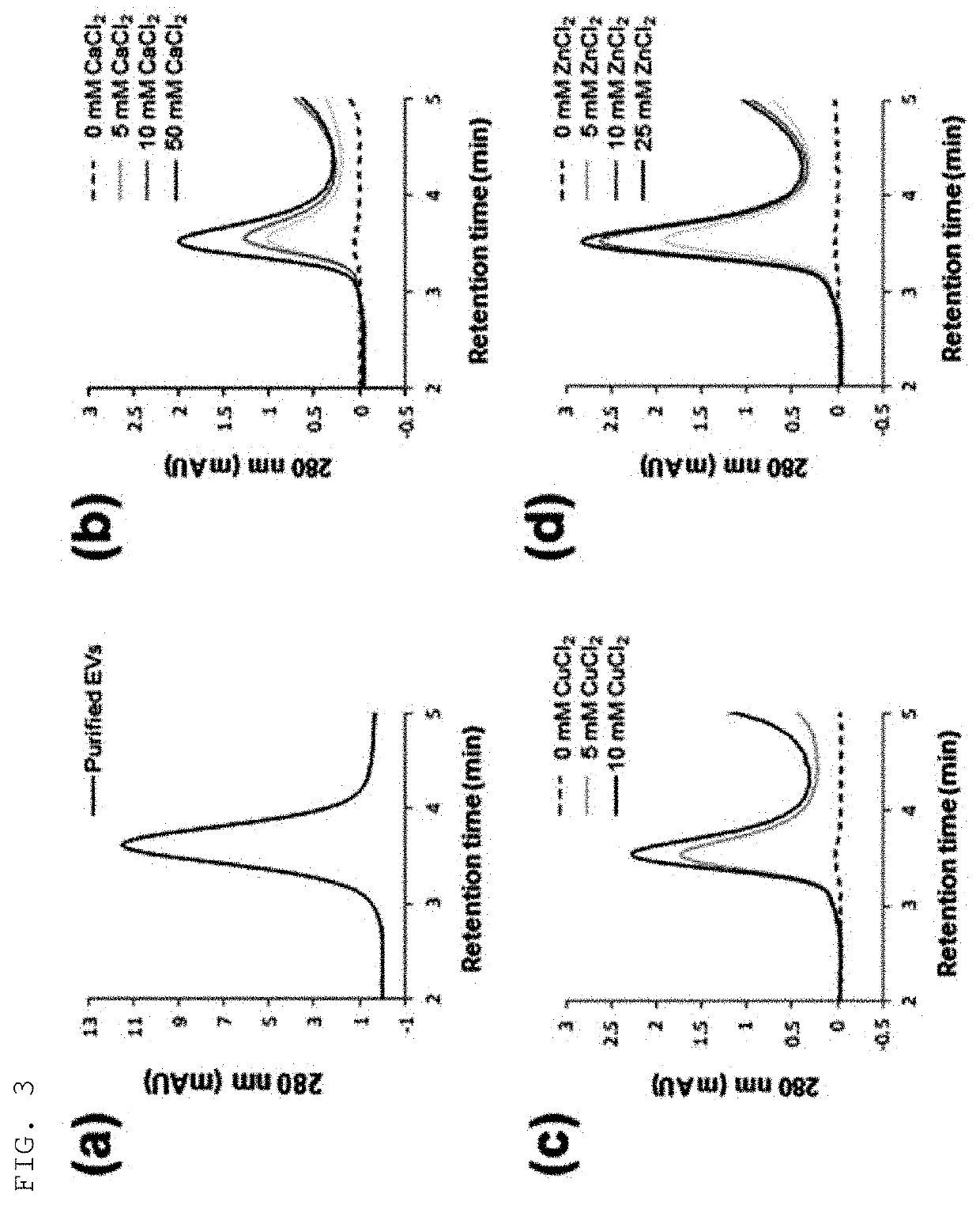
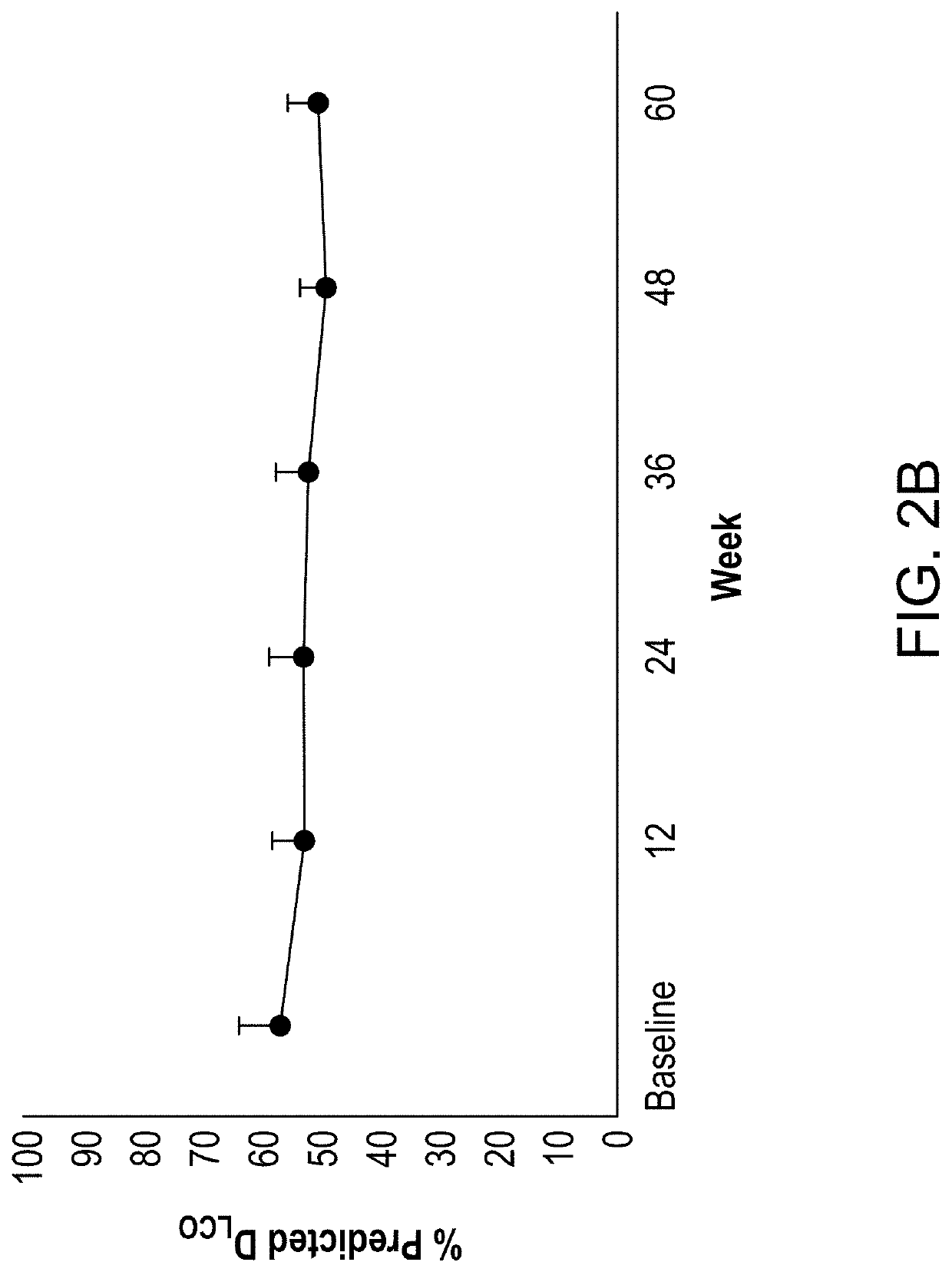
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Exovesicles" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
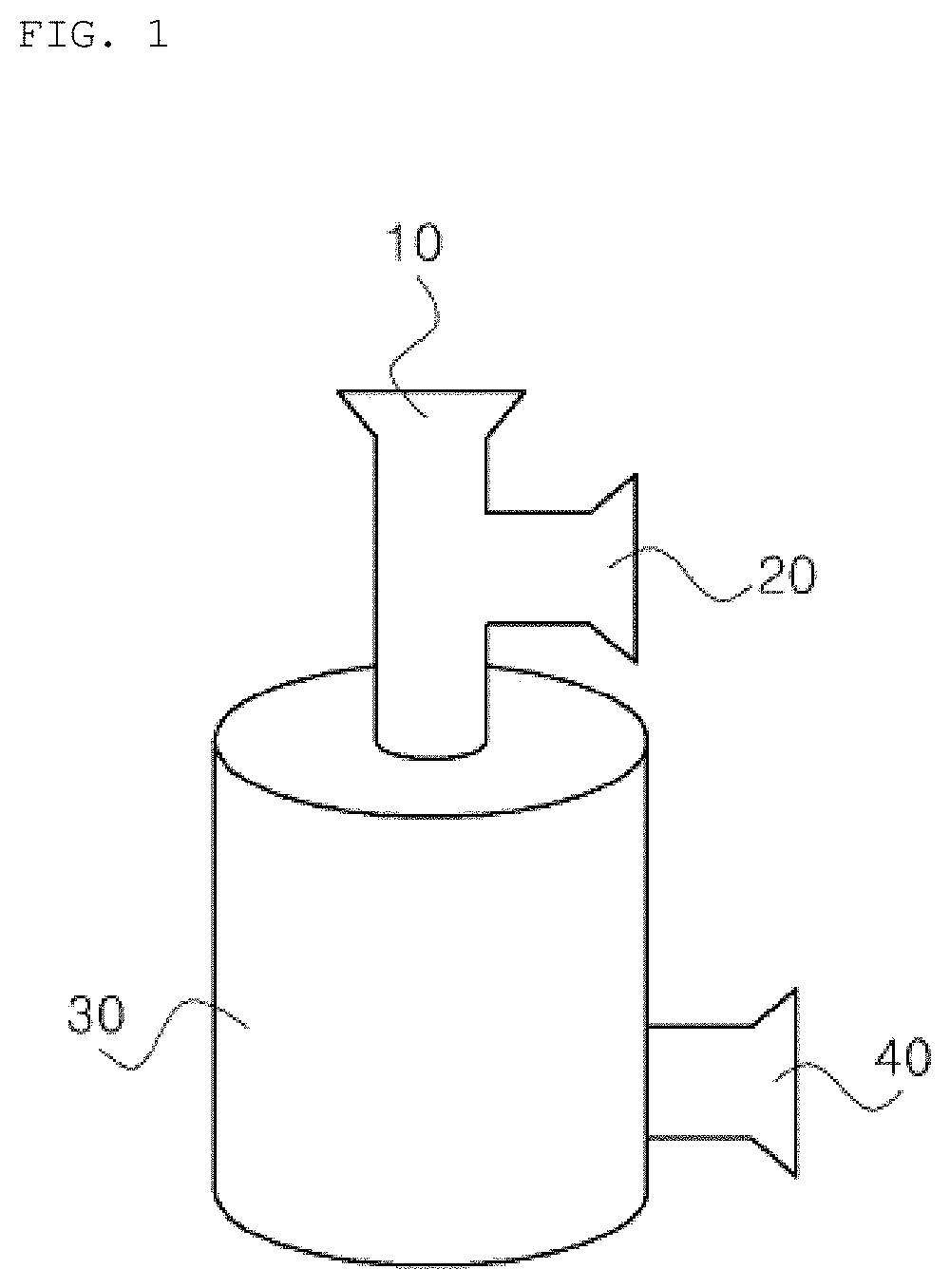
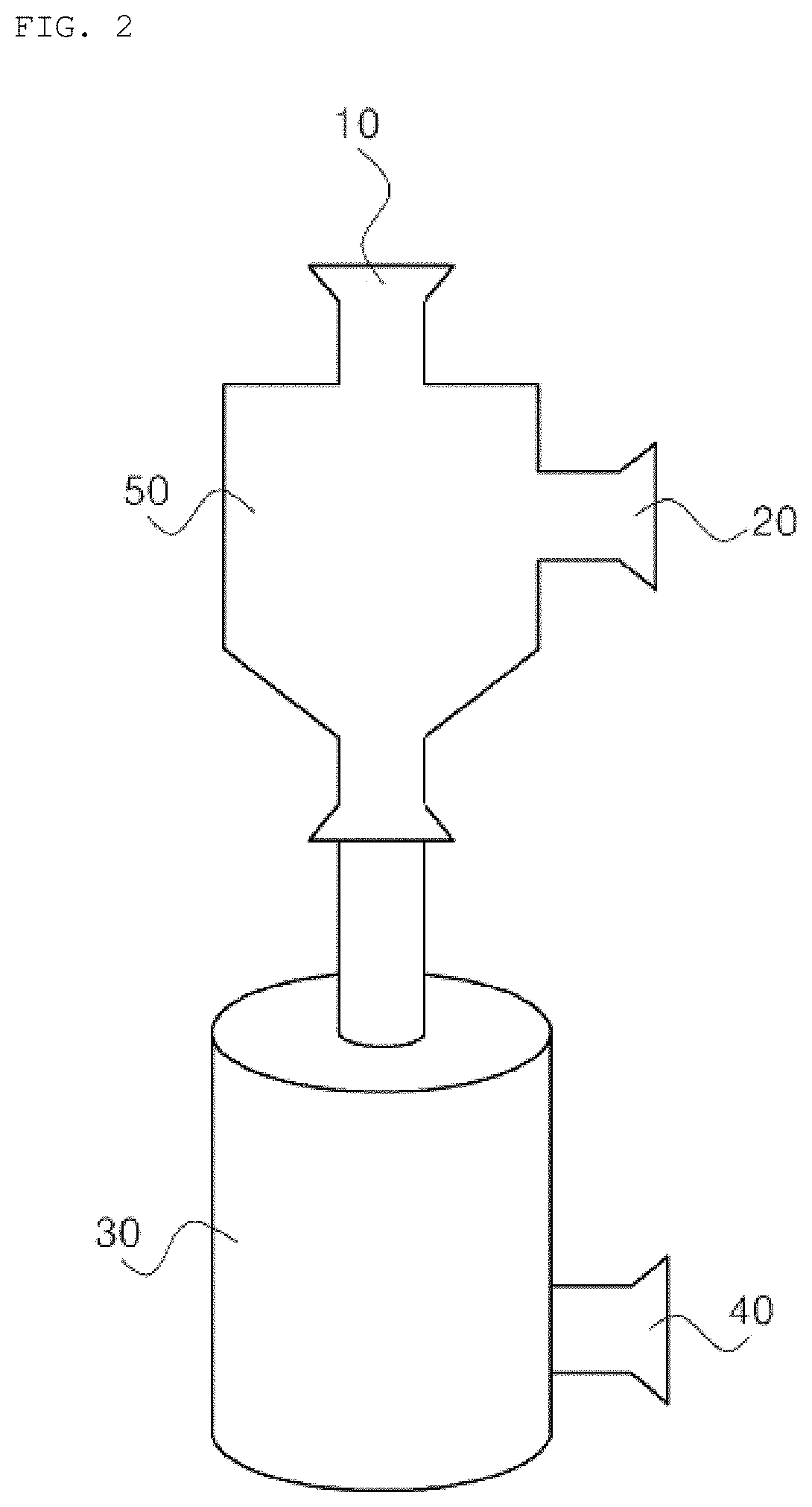
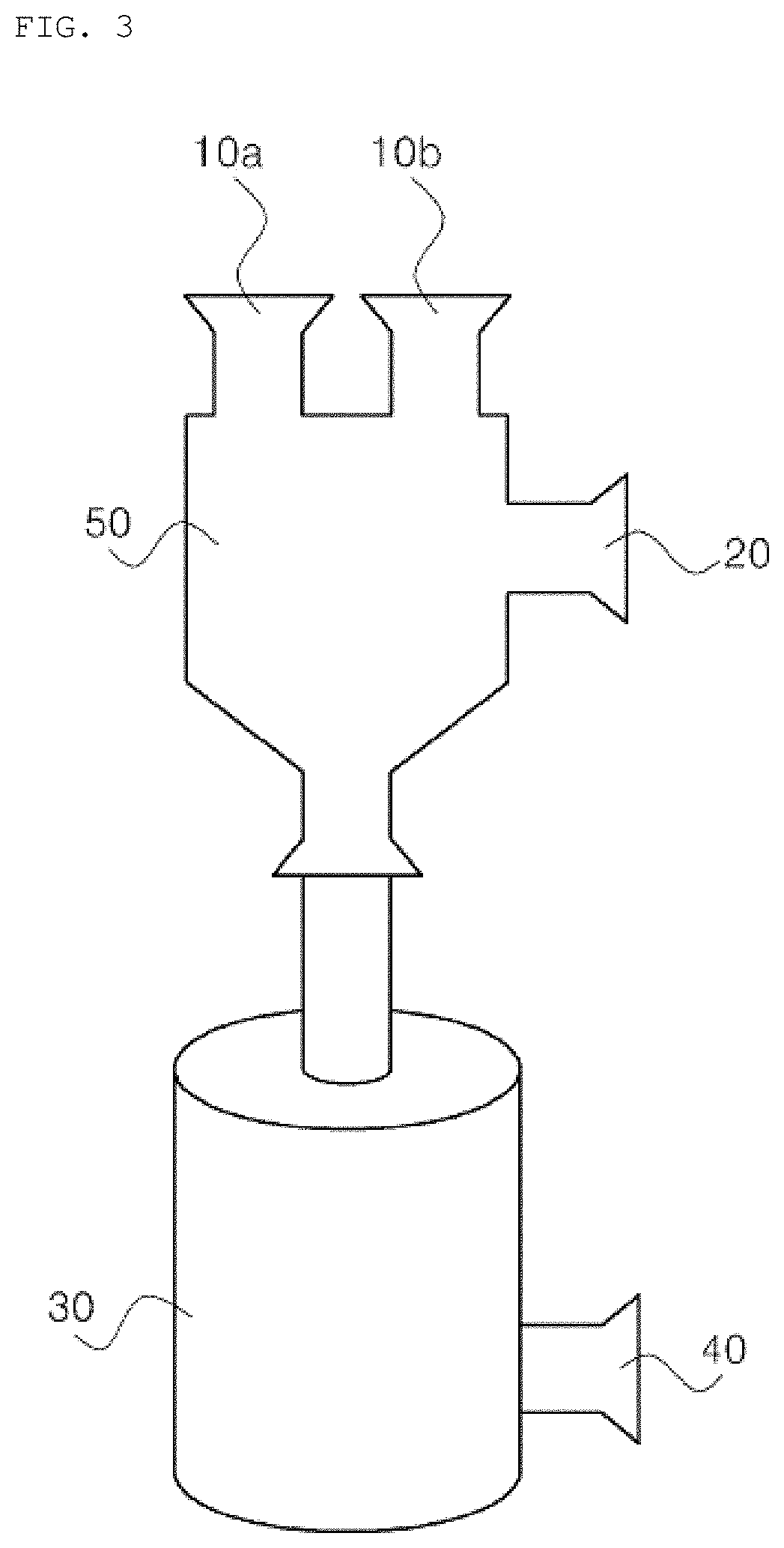
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using aqueous two-phase system
ActiveUS20180164197A1Improve efficiencySimple processSolvent extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
Disclosed is a method of isolating extracellular vesicles using an aqueous two-phase system (ATPS), including (a) preparing an ATPS by mixing a first material and a second material, which are immiscible with each other, with a body fluid or an aqueous solution containing extracellular vesicles and (b) isolating extracellular vesicles concentrated in the second material of the ATPS. This method can exhibit very high isolation efficiency, a simple isolation manner, and a very short isolation time. The isolation of extracellular vesicles using the ATPS requires no ultracentrifuge and achieves almost 100% isolation efficiency within a short time of about 10˜20 min, and thus the method of the invention is practical, is economical due to low costs thereof, can increase the purity of extracellular vesicles contaminated with protein, enables the diagnosis of disease using the isolated extracellular vesicles, and can be applied to various fields using extracellular vesicles.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
Method of detecting membrane protein of extracellular vesicles
The invention relates to the field of biological detection, in particular to a method for detecting membrane protein of extracellular vesicles. The method comprises the following steps: a) co-incubating a composition containing extracellular vesicles (EVs) with a solid phase carrier; wherein the solid phase carrier is coated with a first antibody group of anti-EVs membrane protein; b) washing offnon-specifically bound EVs and other impurities, and c) adding a second antibody group for detection to carry out signal detection, the second antibody group being an antibody of a biomarker of EVs and coupled with a marker for displaying signal intensity. The method is simple and convenient to operate, the detection flux can be flexibly adjusted according to conditions, and the sensitivity is high.
Owner:北京益微生物科技有限公司
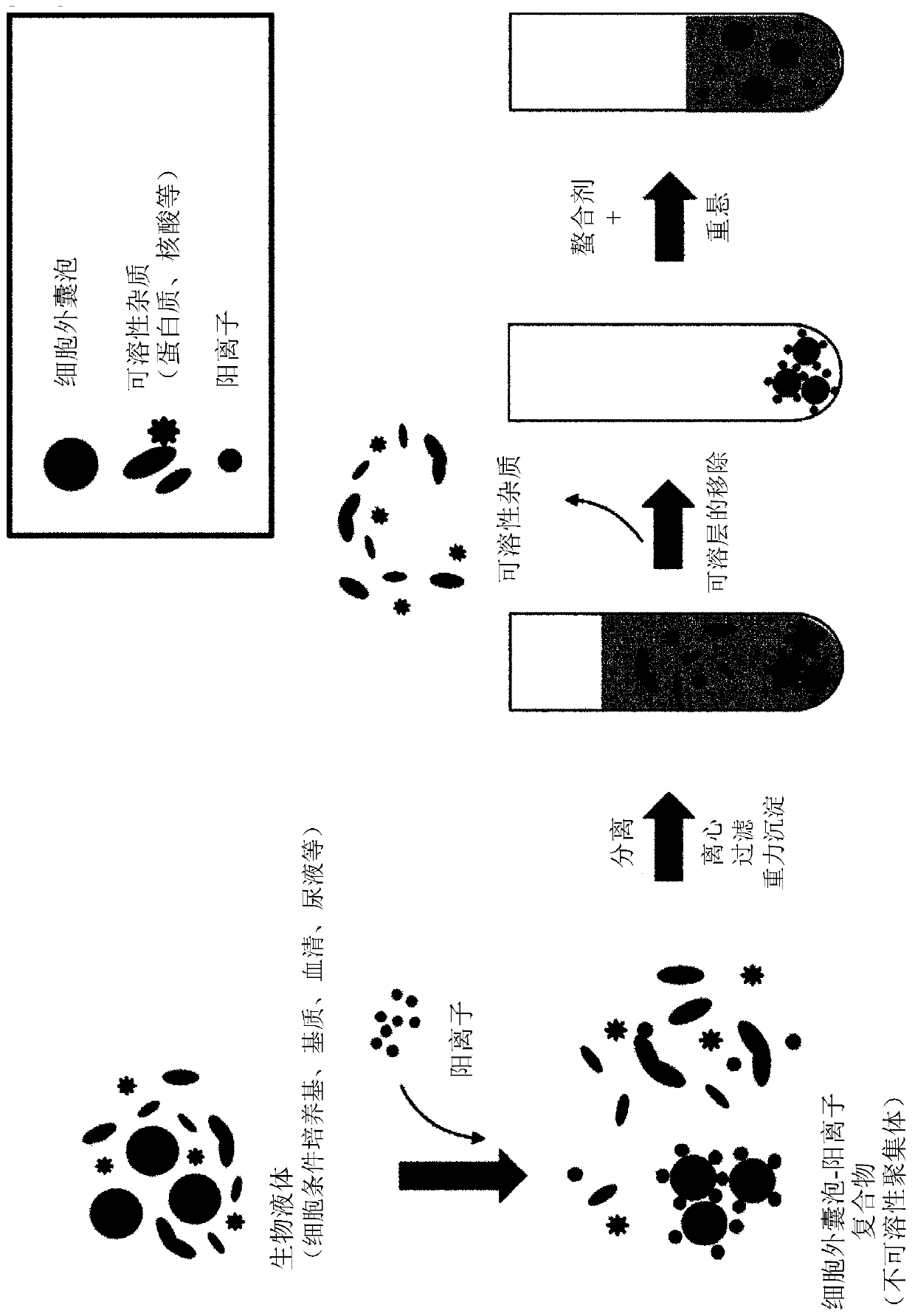
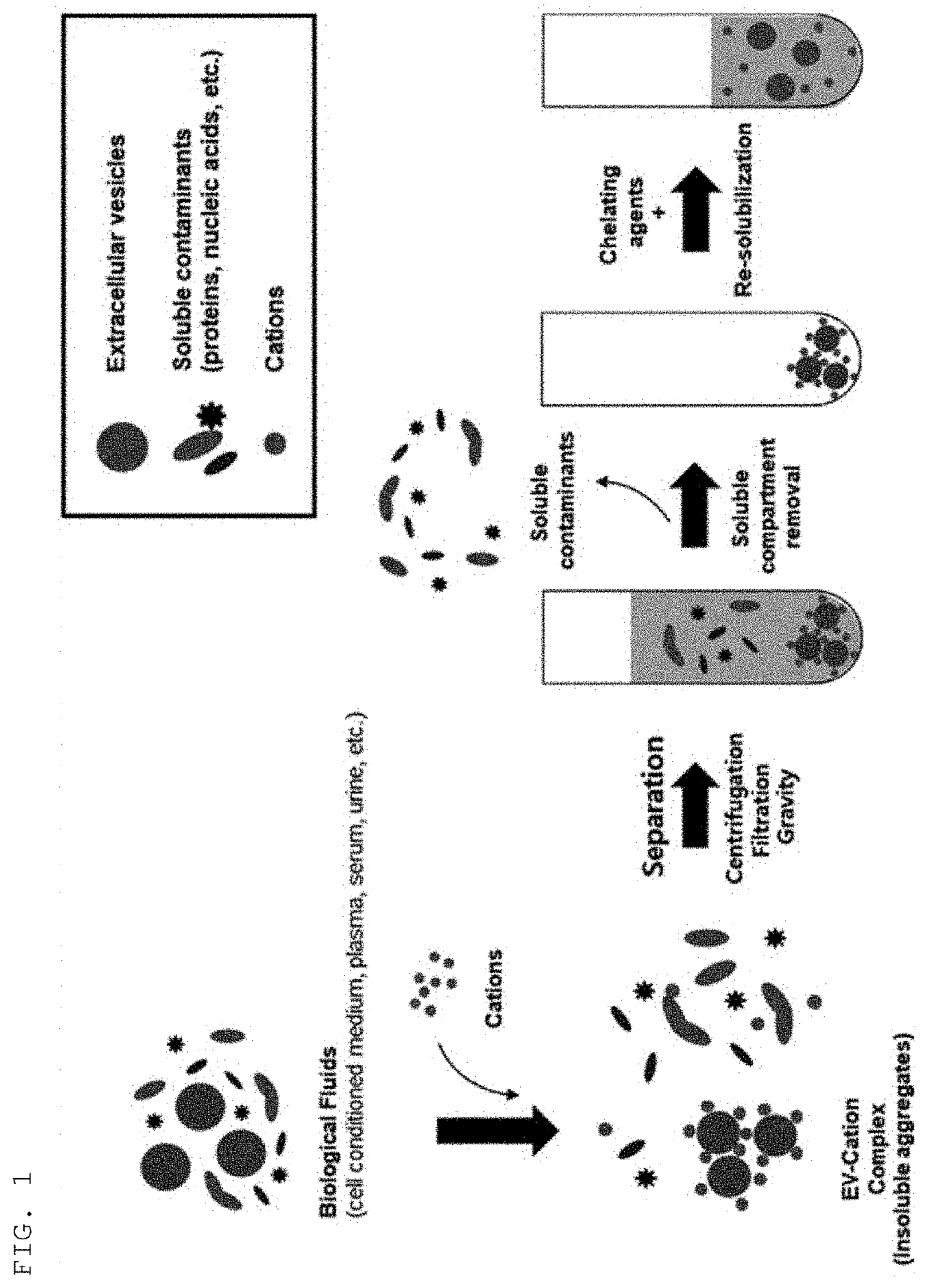
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations
PendingCN111148828AEfficient separationKeep shapeCell dissociation methodsCation exchanger materialsExtracellular vesicleDisease
The present invention relates to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations, and more particularly, to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles from various samples by using theaffinity between the extracellular vesicles and cations. A method for isolating extracellular vesicles according to the present invention does not require expensive equipment, can be applied irrespective of sample amount, and has the advantage of being capable of efficiently isolating the extracellular vesicles while preserving the shape or characteristics thereof. Moreover, the method according to the present invention can be combined with existing isolation methods to maximize extracellular vesicle isolation efficiency, and can be applied to disease diagnosis, disease treatment, and multi-omics research using isolated extracellular vesicles, as well as to research on the properties of extracellular vesicles.
Owner:ROSETTA EXOSOME CO LTD
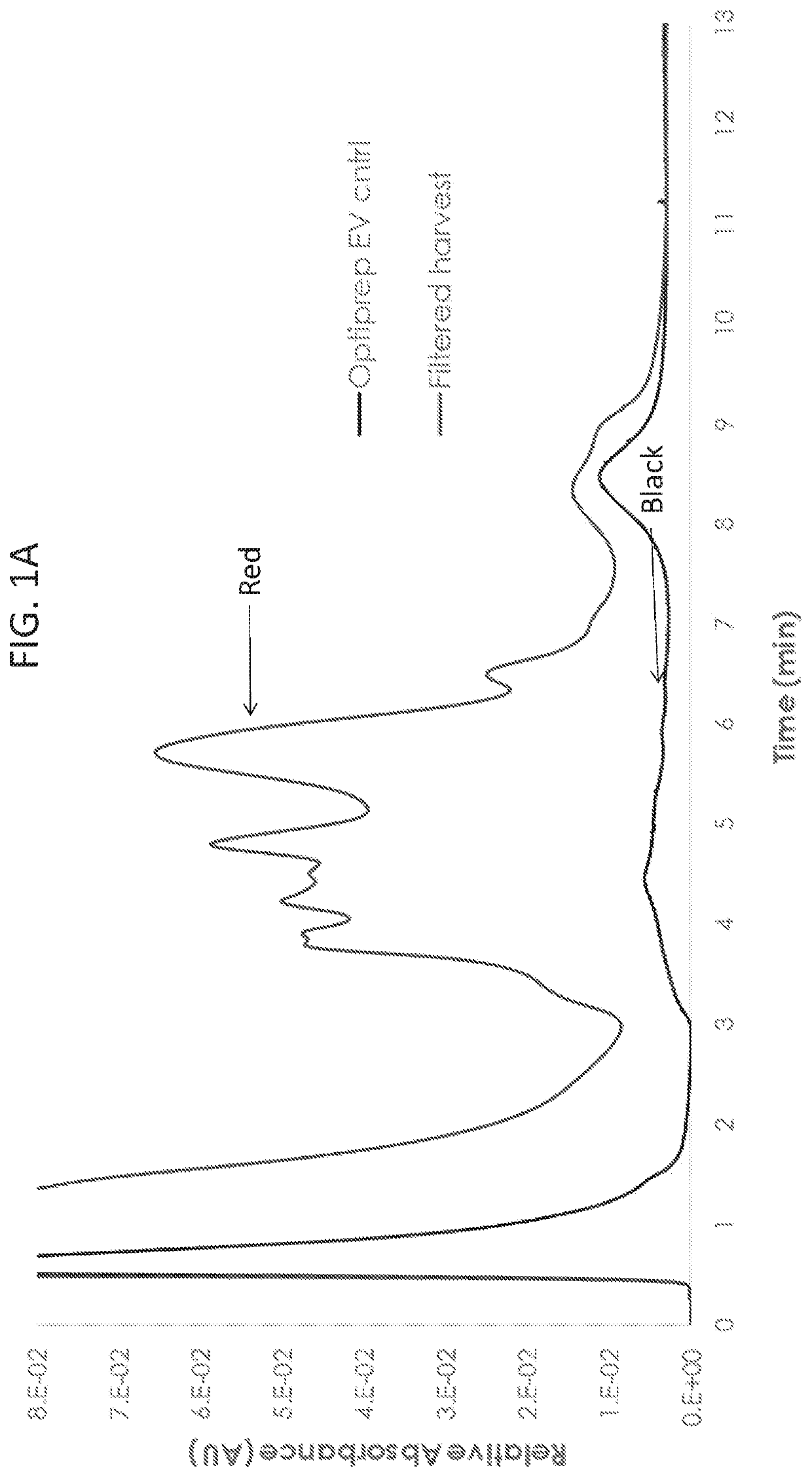
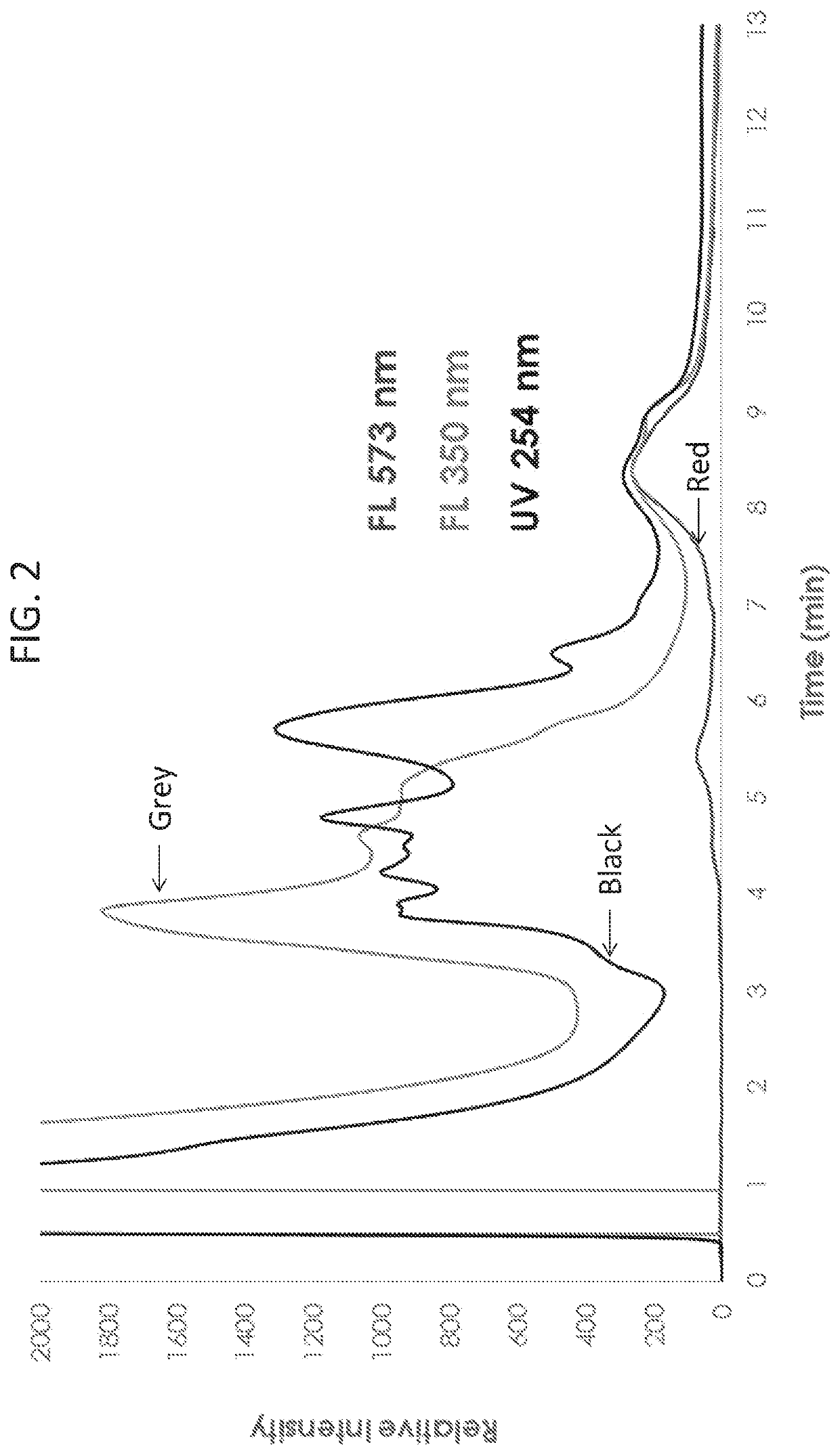
Methods of measuring exosomes using intrinsic fluorescence
InactiveUS20200025685A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceExtracellular vesicleExosome
Described herein are novel rapid and reliable methods of detection of extracellular vesicles and quantifying extracellular vesicle concentrations and absolute number from various sources, including raw cell harvest. The methods described herein comprise detection of intrinsic fluorescence of extracellular vesicles in biological samples. Extracellular vesicles analyzed by the methods of this application have a stereotypical elution profile distinct from known contaminants. The methods described herein are a significant improvement over the state of the art and fulfills an unmet need in the field of extracellular vesicle manufacturing and quality control.
Owner:LONZA SALES AG
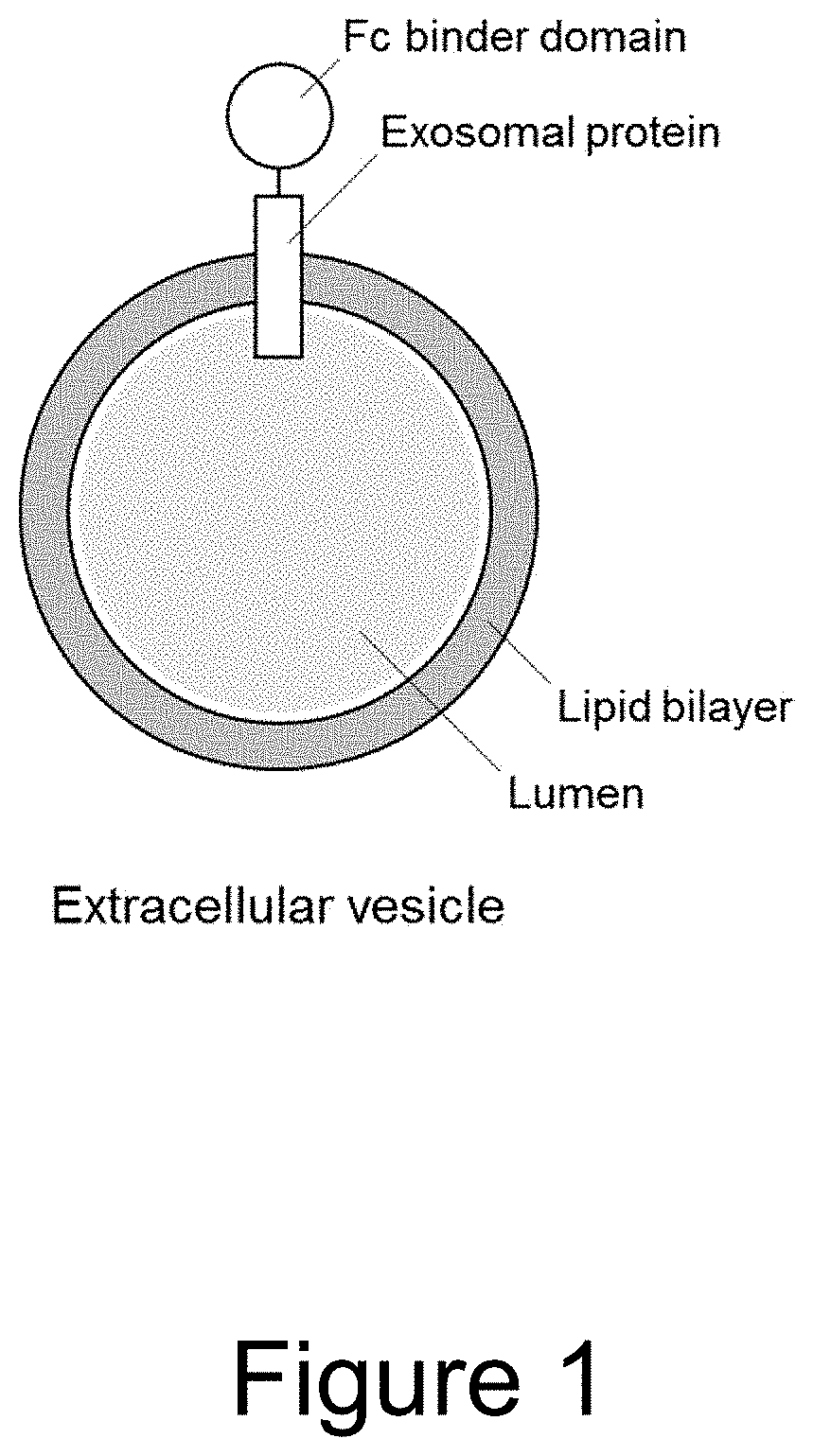
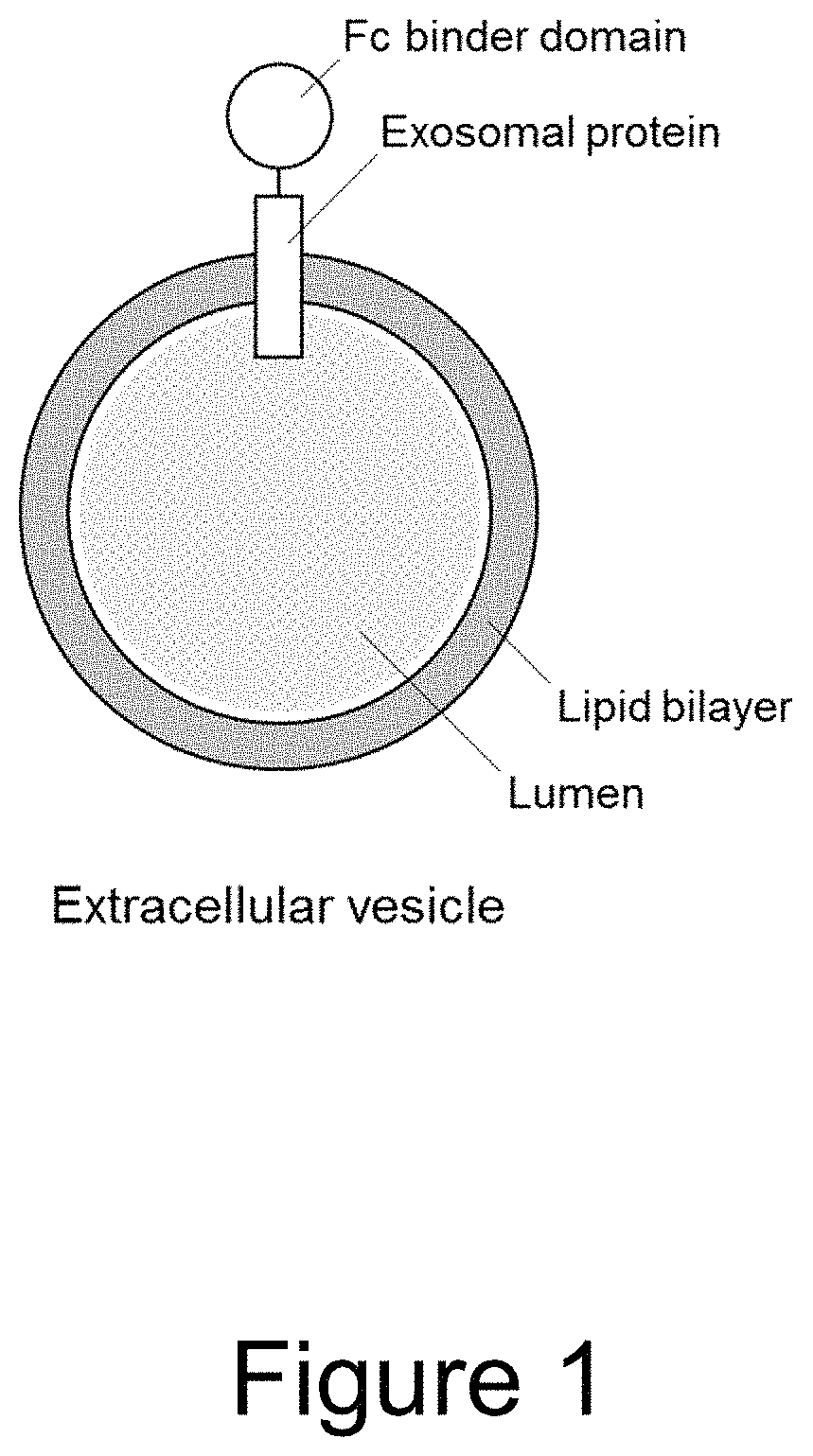
Extracellular vesicle comprising a fusion protein having fc binding capacity
ActiveUS20200109183A1Enhance therapeutic potentialOvercome problemsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs are coated with proteins containing Fc domains (such as antibodies) for i.a. targeting and therapeutic applications. The coating of EVs is achieved through inventive protein engineering of EV polypeptides. The present invention thus relates to methods for coating of EVs, EVs per se, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical applications of such EVs coated with Fc containing proteins.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Method for isolating extracellular vesicle using hydrophobic interaction
PendingCN111065730ASeparation is quick and easyEfficient separationCell dissociation methodsCation exchanger materialsExtracellular vesicleA lipoprotein
The present invention relates to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles and, more particularly, to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles using hydrophobicity of the extracellular vesicles, and extracellular vesicles isolated using the method. When used, the method for isolating extracellular vesicles according to the present invention allows for isolating, from various animal body fluids including blood and urine or various tissues including cancer tissues, extracellular vesicles free of contamination with lipoproteins that are difficult to eliminate using a conventional method,can solve conventional problems caused by lipoprotein contamination, and is expected to be an essential technology that has a great influence on various research using extracellular vesicles isolatedfrom various animal body fluids or tissues, such as characterization and function research, multi-omics research, excavation of novel biomarkers, diagnosis and treatment, etc.
Owner:ROSETTA EXOSOME CO LTD
Extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method based on anionic polymer modified matrix
ActiveCN112048462AAchieve classification separationHigh purityCell dissociation methodsBlood plasmaSaliva
The invention discloses a simple, low-cost and high-universality extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method. The method is characterized in that extracellular vesicles in sample types suchas a culture medium, plasma, serum, urine, saliva, emulsion, pleural effusion and cerebrospinal fluid are separated and enriched through electrostatic interaction. According to the implementation mode of the method, the extracellular vesicles are captured by utilizing an anionic polymer modified matrix material under an acidic condition, and the extracellular vesicles captured in the previous step are eluted under a neutral or alkaline condition, so that the purpose of separating and enriching the extracellular vesicles is finally achieved. Compared with an existing extracellular vesicle separation and enrichment method, the method has the advantages of being simple in separation process, low in cost, good in universality and high in downstream detection compatibility.
Owner:HANGZHOU ZIJING BIOLOGY CO LTD
Extracellular vesicle and preparation method and parting analysis method thereof
PendingCN109652375AHigh affinityImplement typing analysisCell dissociation methodsMicrobiological testing/measurementExtracellular vesicleCulture vessel
The invention provides an extracellular vesicle and a preparation method and a parting analysis method thereof. Surface N-carbohydrate of the extracellular vesicle is removed, so that the taking-in rate of the extracellular vesicle relative to specific cells is increased. According to the method, by adopting co-culture of a living cell and the extracellular vesicle, through a fluorescent mark anda flow cytometry, cells, with fluorescence, in cell suspensions of different cell culture vessels and the fluorescence intensity are detected, and through the interaction relation of the living cell and the extracellular vesicle, parting analysis verification is conducted on the extracellular vesicle; in addition, the invention provides the extracellular vesicle which is prepared to be more efficiently taken in by HCT116.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Vesicles comprising a pten inhibitor and uses of same
PendingCN112236131AOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderExtracellular vesiclePharmaceutical drug
The present invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising membrane vesicles, including extracellular vesicles including those referred to as exosomes, loaded with an exogenous Phosphataseand tensin homolog (PTEN) inhibitor. Methods of treating neurological diseases, disorders or conditions using the extracellular vesicles are provided. Isolated extracellular vesicles loaded with an exogenous Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) inhibitor are provided as well.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Compositions and methods for loading extracellular vesicles with chemical and biological agents/molecules
Presented are RNA nucleotide sequences referred to as EXO-Codes, and longer RNA polynucleotides that contain the EXO-Codes. EXO-Codes provide RNA with the ability to a) be selectively sorted to extracellular vesicles such as exosomes, and b) deliver a variety of cargo types to program or reprogram the extracellular vesicles, and cells that receive the exosomes. Also presented are methods of makingthe EXO-Codes, modifying cells using the EXO-Codes, expression vectors encoding the EXO-Codes, and exosomes and other secreted vessices that include RNA polynucleotides that contain the EXO-Codes.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Protein engineered extracellular vesicles
PendingUS20200399591A1High trafficPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell dissociation methodsExtracellular vesicleLysosome
The present invention relates to extracellular vesicles (EVs) as a novel therapeutic approach to lysosomal storage disorders (LSD). More specifically, the invention relates to the use of various protein engineering strategies for improving loading of hard-to-load LSD-related proteins and targeting of the resultant EVs to tissues and organs of interest.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
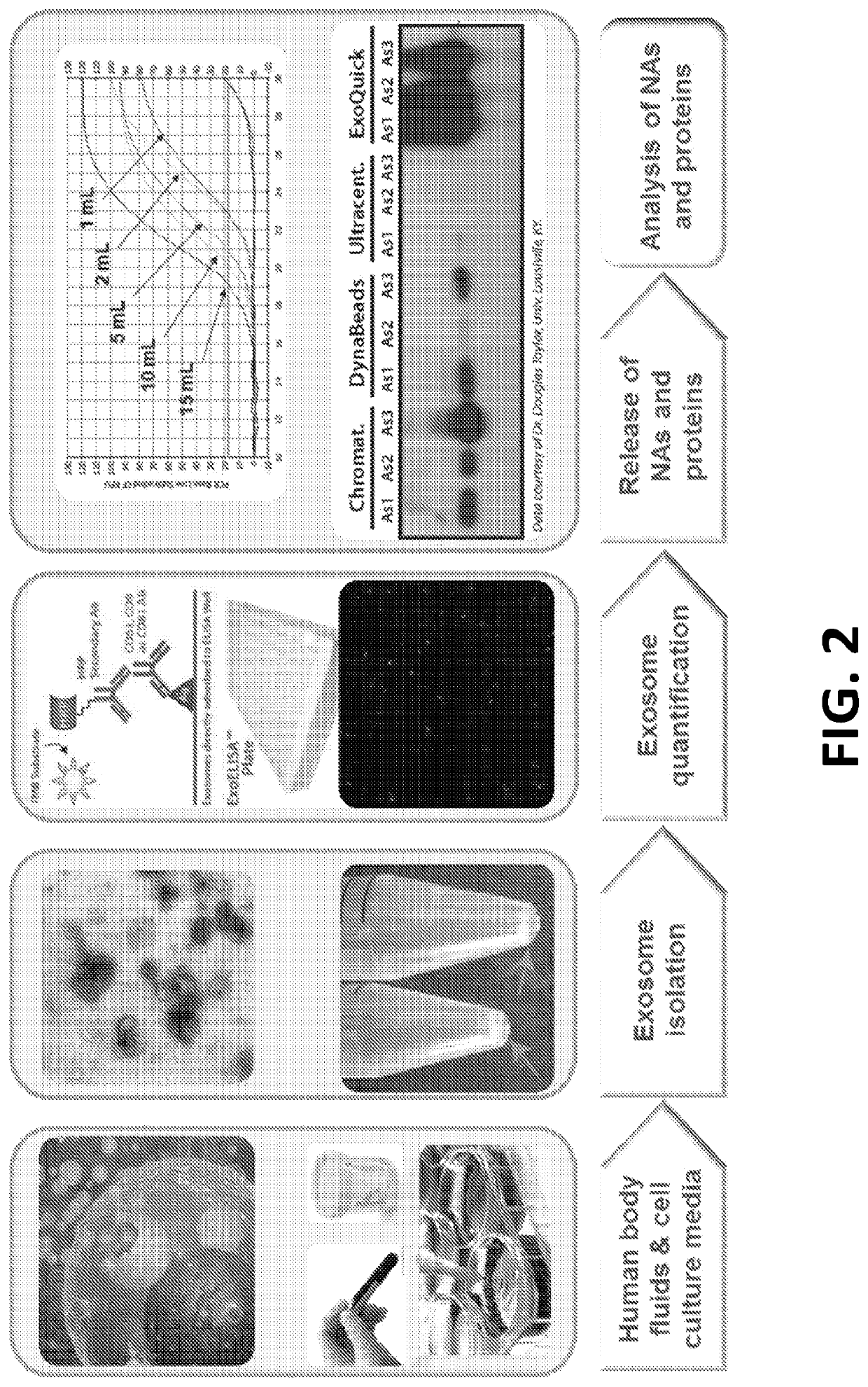
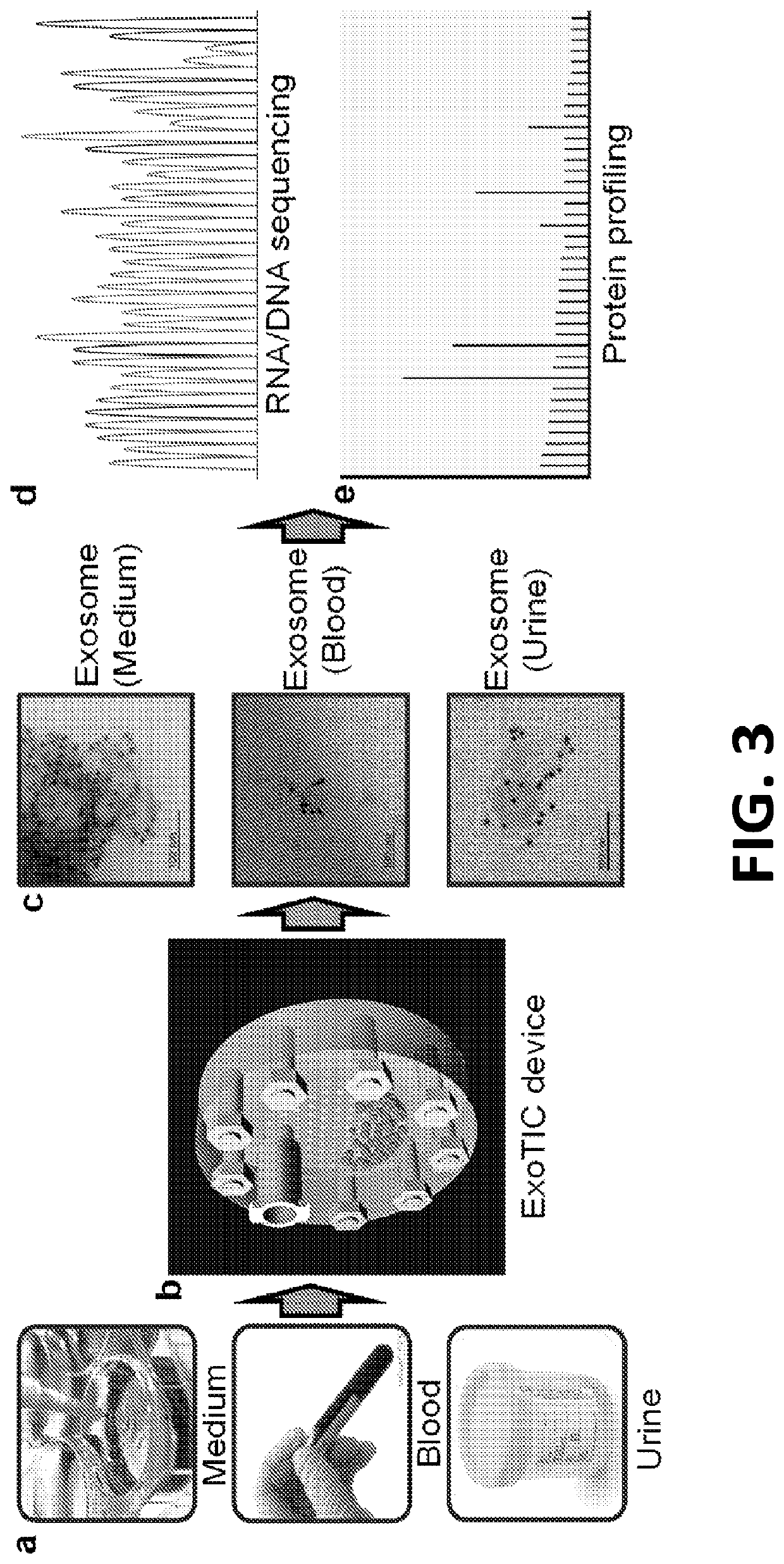
Exosome-Total-Isolation-Chip (ExoTIC) device for isolation of exosome-based biomarkers
ActiveUS11073511B2Facilitate identification of biomarkersRapid and high yield and high purity isolationLaboratory glasswaresDisease diagnosisDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
A device (“the ExoTIC device”) for the isolation of extracellular vesicles from an extracellular vesicle-containing sample in which the sample is flowed through a membrane in a flow chamber to capture and purify the extracellular vesicles on the membrane. The extracellular vesicles may be washed and collected and utilized in any one of a number of ways including, but not limited to, identifying biomarkers of a disease, identifying the presence of a biomarker in a patient to determine whether a patient has a disease, and therapeutically treating existing diseases by re-introducing the extracellular vesicles, potentially modified, back into a body.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using aqueous two-phase system
ActiveUS11016009B2Improve efficiencySimple processSolvent extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementExtracellular vesicleDisease
Disclosed is a method of isolating extracellular vesicles using an aqueous two-phase system (ATPS), including (a) preparing an ATPS by mixing a first material and a second material, which are immiscible with each other, with a body fluid or an aqueous solution containing extracellular vesicles and (b) isolating extracellular vesicles concentrated in the second material of the ATPS. This method can exhibit very high isolation efficiency, a simple isolation manner, and a very short isolation time. The isolation of extracellular vesicles using the ATPS requires no ultracentrifuge and achieves almost 100% isolation efficiency within a short time of about 10˜20 min, and thus the method of the invention is practical, is economical due to low costs thereof, can increase the purity of extracellular vesicles contaminated with protein, enables the diagnosis of disease using the isolated extracellular vesicles, and can be applied to various fields using extracellular vesicles.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND +1
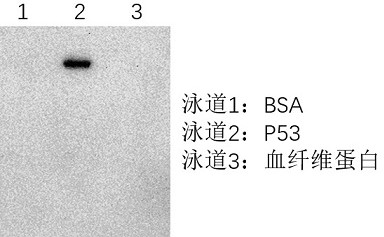
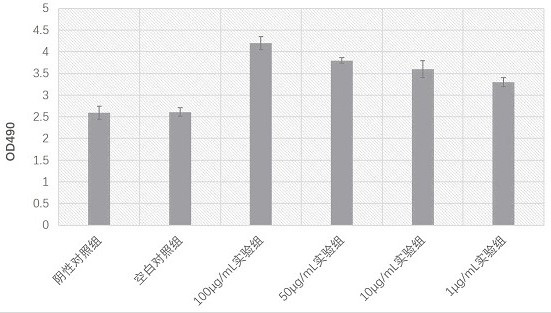
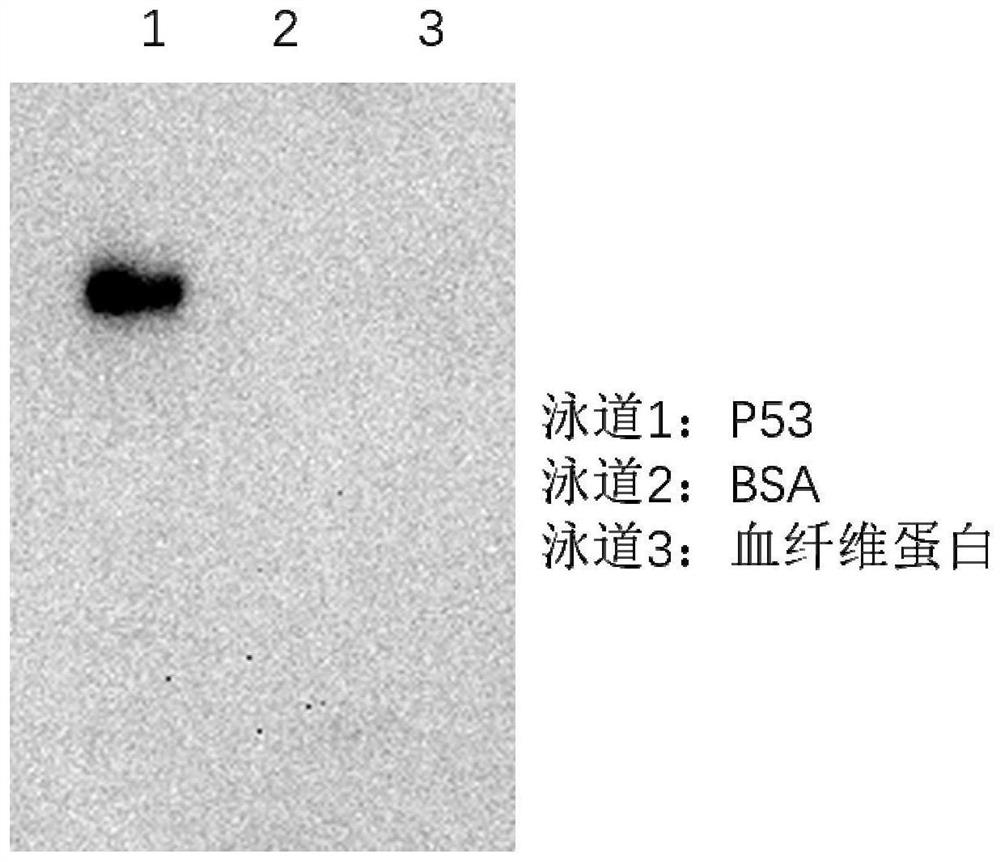
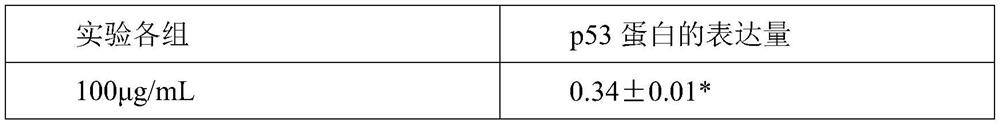
Preparation of fibroblast extracellular vesicles and application of fibroblast extracellular vesicles in beauty and medicines
ActiveCN114349856APrevent agingGood anti aging activityCosmetic preparationsCell dissociation methodsExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to preparation of fibroblast extracellular vesicles and application of the fibroblast extracellular vesicles in beauty and medicines. The effect of the invention is achieved by inhibiting P53 activity to improve fibroblast activity and prevent aging to produce ectovesicles at high yield. A monoclonal antibody is used for inhibiting the activity of P53, after the monoclonal antibody is added into a culture medium of fibroblasts, the aging of the fibroblasts can be inhibited, the content of exovesicles secreted by the fibroblasts can be increased, and the exovesicles are good in anti-aging activity and suitable for preparing anti-aging beautifying or medicine products. Good market application values are realized.
Owner:诺赛联合(北京)生物医学科技有限公司
Method for the isolation of intact extracellular vesicles
The present invention relates to a method for the isolation of intact extracellular vesicles from biological tissues and fluids. Under a further aspect, the present invention relates intact extracellular vesicles, obtainable from the method herein described, and their use as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Extracellular vesicle enrichment detection method
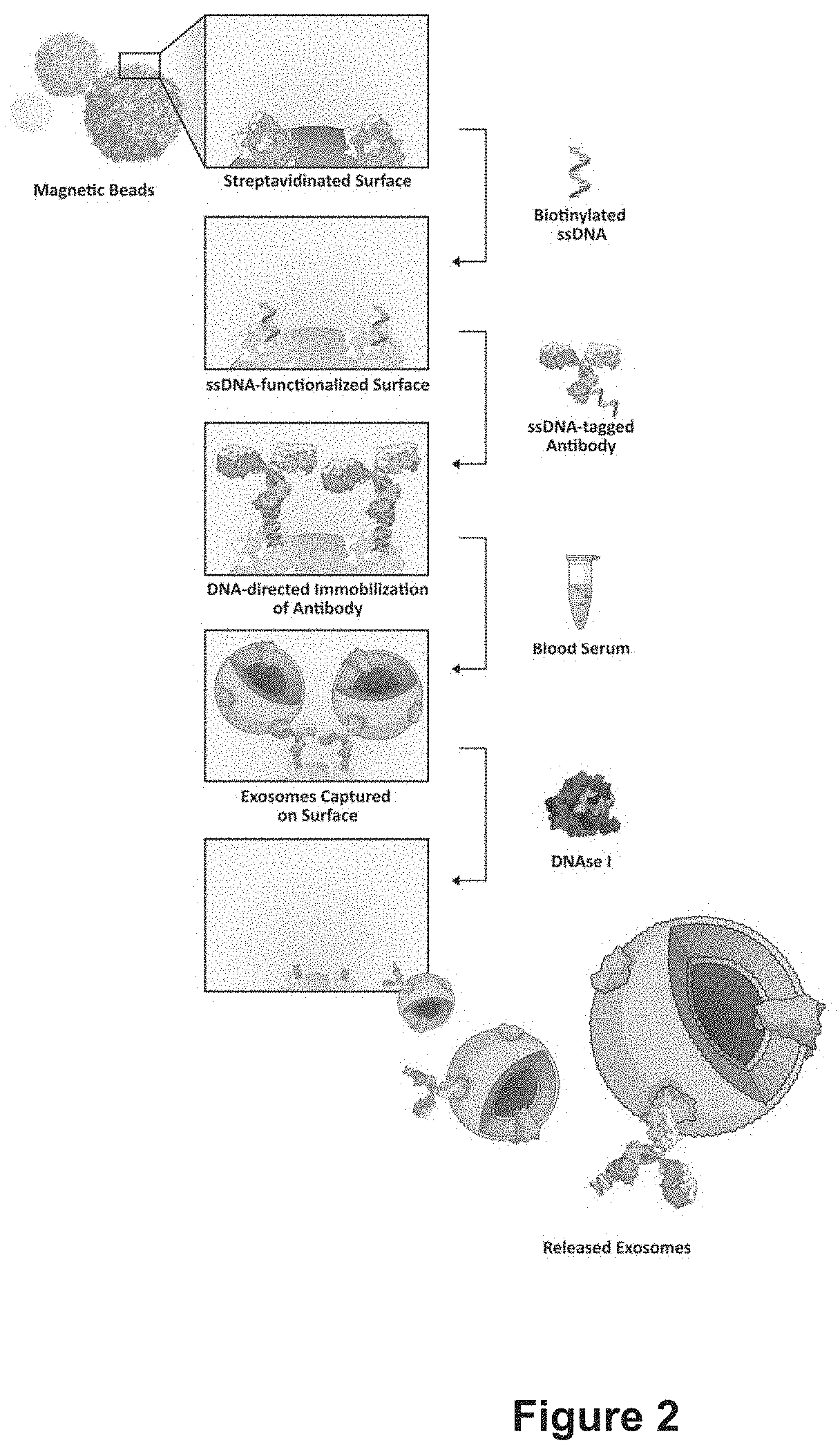
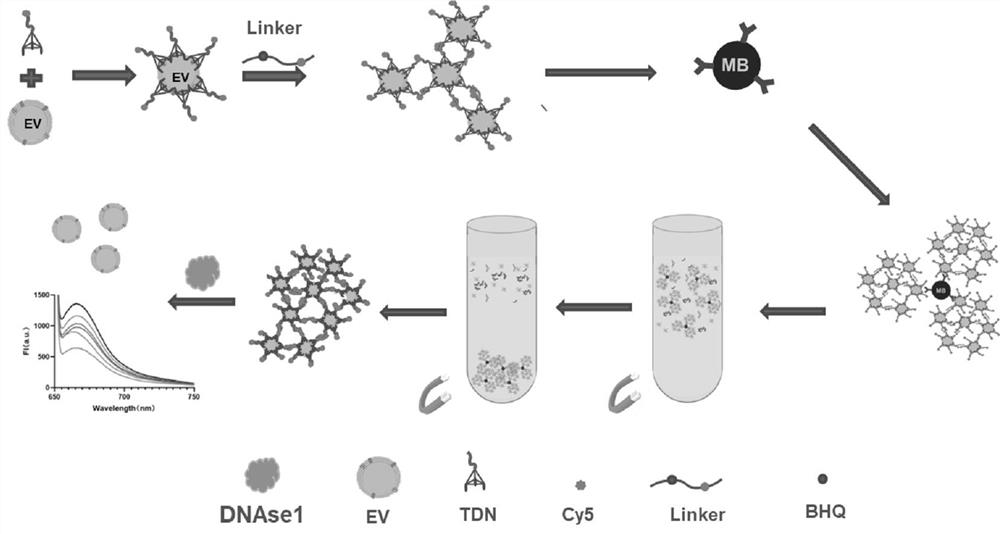
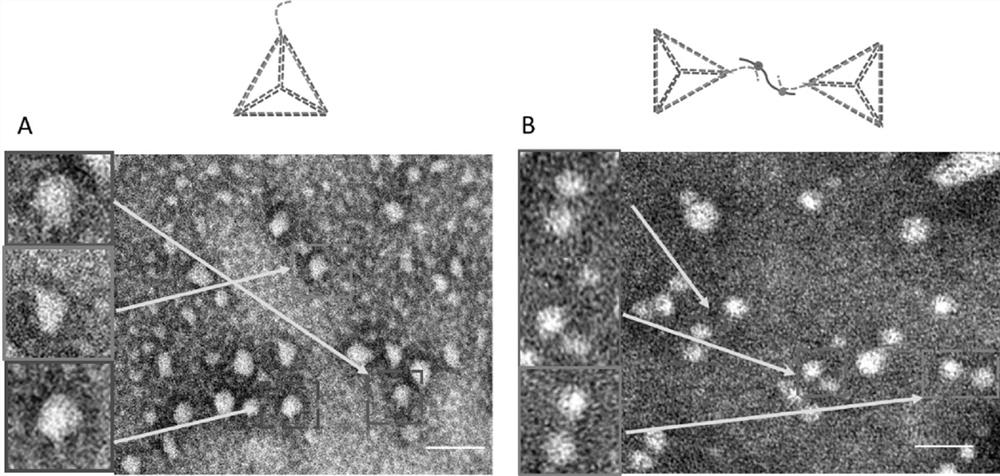
PendingCN113358617AEasy to identifySpecific recognition and bindingFluorescence/phosphorescenceAptamerDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical detection, and discloses an extracellular vesicle enrichment detection method, which is characterized in that exosome enrichment detection is performed after DNA tetrahedron synthesis, magnetic bead combination and exosome extraction. According to the method, exosome surface specific protein is utilized, on the basis of a DNA origami aptamer and immunoaffinity magnetic bead space recognition dual recognition and capture method, a DNA fluorescent probe is further combined, so that rapid separation and capture of the exosome are realized, and the method can be used for quantitatively detecting the exosome. The invention is suitable for being used as a kit to realize enrichment, separation and detection of exosomes, and has very important significance in wide application in the fields of disease diagnosis, pathological research, new drug development and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
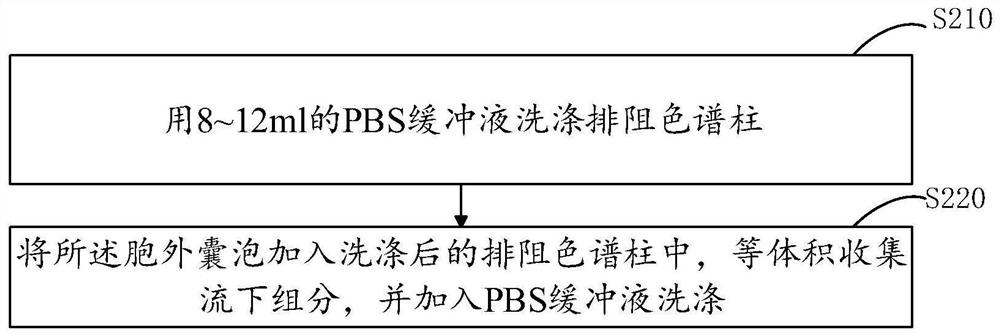
Method for purifying extracellular vesicles
ActiveCN113388520AHigh purityGreat practicabilityMicroorganism separationPlant cellsExtracellular vesicleFree protein
The invention provides a method for purifying extracellular vesicles of a large-volume sample solution. The method comprises the following steps: providing a sample solution of extracellular vesicles to be prepared, and extracting the extracellular vesicles; taking the volume of the sample solution by liter; adding the extracellular vesicles into an exclusion chromatographic column, and collecting flow-down components in an isovolumetric manner; selecting and mixing the flow-down components having a target particle size or a target concentration of free protein; and transferring the mixture into an ultrafiltration tube for centrifugation, and reserving trapped fluid to obtain purified extracellular vesicles. The obtained extracellular vesicles are high in purity, small in soluble impure protein pollution and wide in practicability, and can fulfill subsequent analysis of NTA, electron microscopes, proteomes and the like. The operation is simple and costs short time.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of immunomodulatory extracellular vesicles
ActiveCN111748523AHas immunomodulatory activityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsExtracellular vesicleImmunomodulations
The invention provides a preparation method and application of immunomodulatory extracellular vesicles, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: (a) culturing animal cells subjected to primary separation and purification in a culture system for a period of time so as to accumulate effective concentration of immunomodulatory extracellular vesicles in a culture medium; (b) collecting the medium of step (a); and (c) separating the immunomodulatory extracellular vesicles from the culture medium collected in the step (b). The extracellular vesicle provided by the invention has immunomodulatory activity, can activate macrophages and convert into M1 phenotype, and provides a theoretical basis for prevention or treatment of diseases caused or aggravated by immunosuppression.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
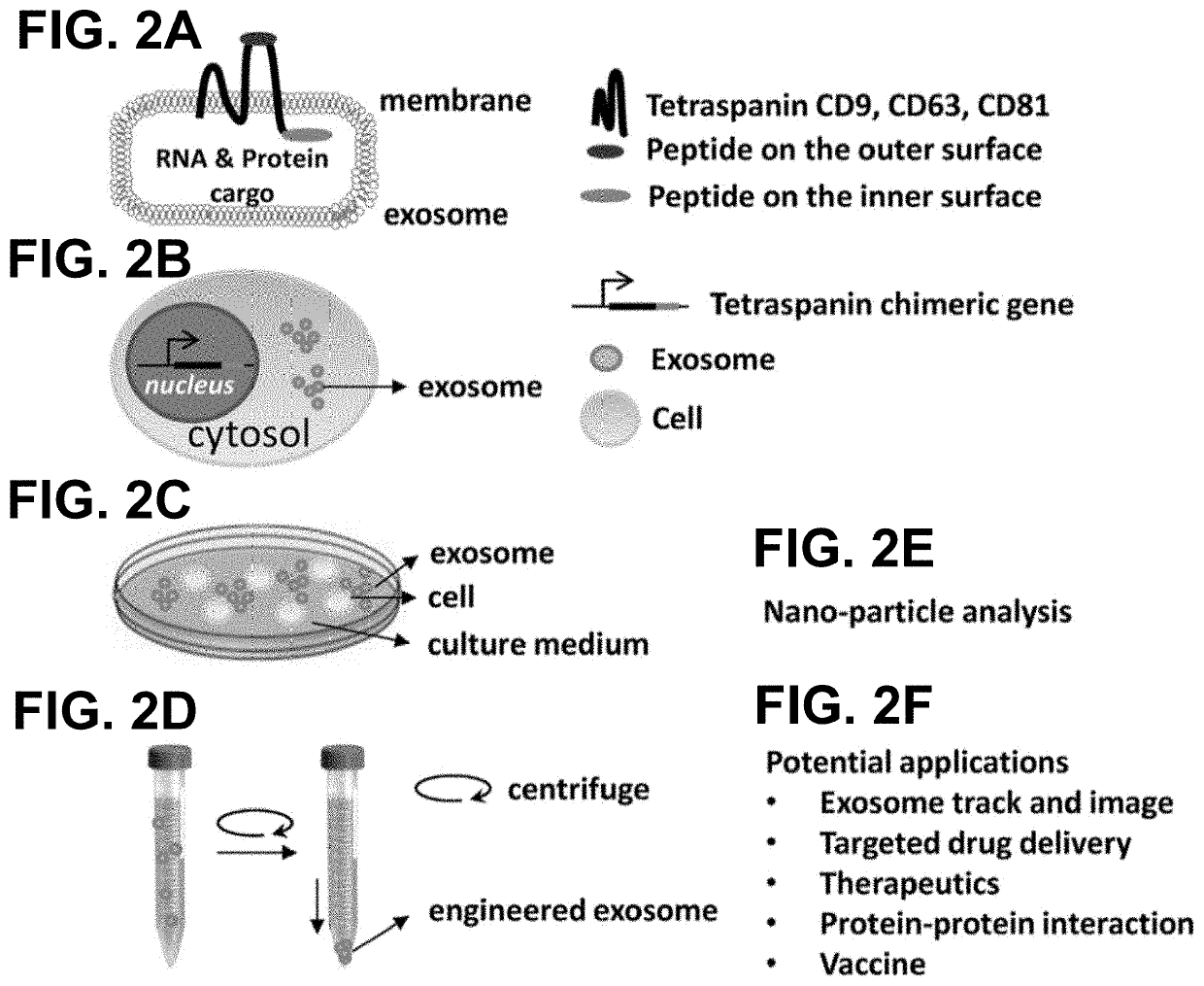
Engineered exosomes for the delivery of bioactive cargo using transmembrane tetraspanins
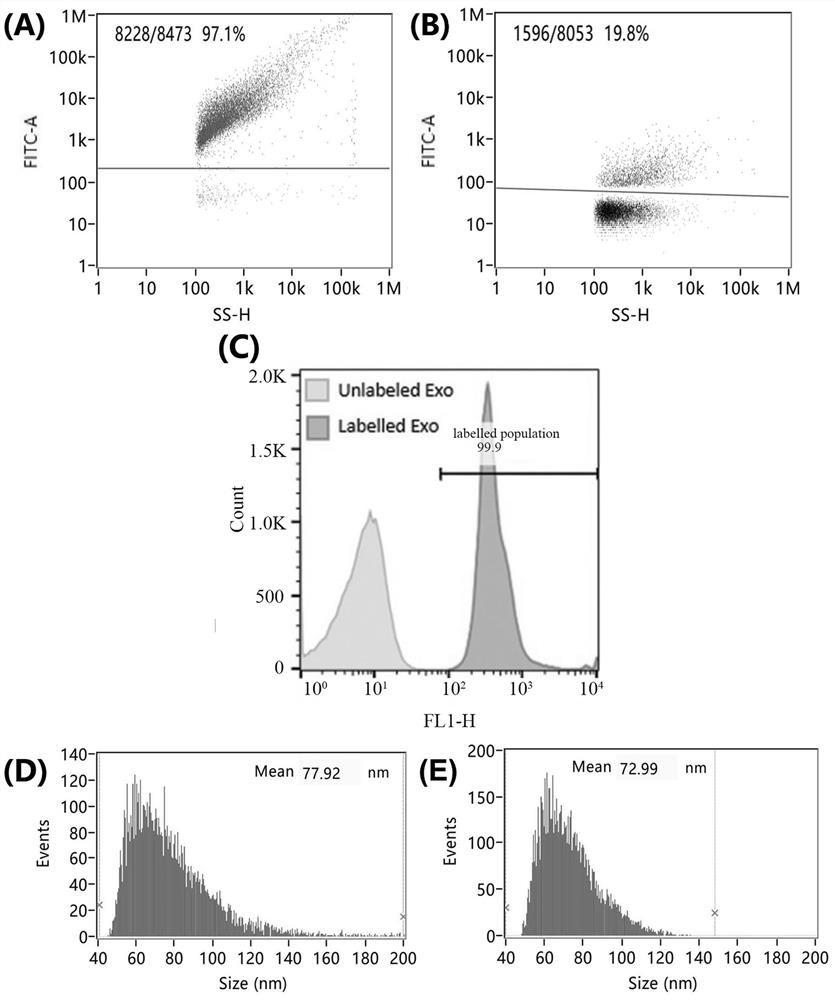
ActiveUS10617768B2Efficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainTetraspaninExosome
Engineered exosomes for the delivery of bioactive cargo are provided. The exosomes incorporate a tetraspanin transmembrane anchoring scaffold onto the membrane of the exosome. The tetraspanin transmembrane anchoring scaffold has a C-terminal attachment site in the inner-vesicle space of the exosome, a N-terminal attachment site in the inner-vesicle space or the outer-vesicle space, and / or a loop attachment site in the outer-vesicle space. Peptides can be attached to the different attachments sites in any form or combination. Tetrapanins naturally anchor on the exosome membrane, are biocompatible, and allow for robust loading and delivery of bioactive cargos in mammalian system.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
Extracellular vesicle comprising a fusion protein having Fc binding capacity
ActiveUS11236143B2Enhance therapeutic potentialDirection easyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs are coated with proteins containing Fc domains (such as antibodies) for i.a. targeting and therapeutic applications. The coating of EVs is achieved through inventive protein engineering of EV polypeptides. The present invention thus relates to methods for coating of EVs, EVs per se, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical applications of such EVs coated with Fc containing proteins.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations
PendingUS20200164284A1Avoid contactEffective isolationCell dissociation methodsCation exchanger materialsExtracellular vesicleDisease
The present invention relates to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles using cations, and more particularly, to a method for isolating extracellular vesicles from various samples by using the affinity between the extracellular vesicles and cations. A method for isolating extracellular vesicles according to the present invention does not require expensive equipment, can be applied irrespective of sample amount, and has the advantage of being capable of efficiently isolating the extracellular vesicles while preserving the shape or characteristics thereof. Moreover, the method according to the present invention can be combined with existing isolation methods to maximize extracellular vesicle isolation efficiency, and can be applied to disease diagnosis, disease treatment, and multi-omics research using isolated extracellular vesicles, as well as to research on the properties of extracellular vesicles.
Owner:ROSETTA EXOSOME
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles and uses thereof for treating and diagnosing fibrotic diseases
ActiveUS20210052657A1Improve the level ofUpregulate expressionSpecial deliveryMicroencapsulation basedDiseaseFibrosis
The described invention provides compositions and methods for treating a fibrotic condition in a subject. The methods include administering a therapeutic amount of a pharmaceutical composition comprising synthetic extracellular vesicles (EVs) and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:SPIRITUS THERAPEUTICS INC
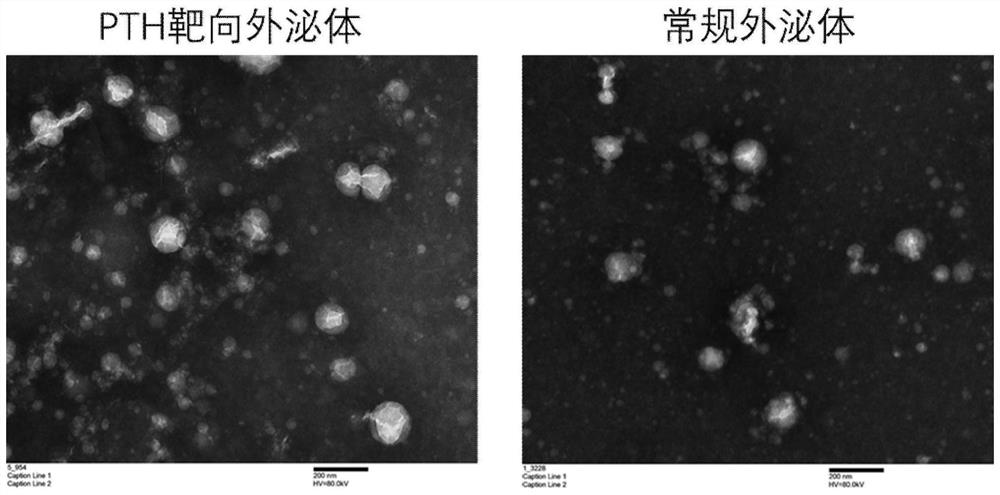
Bone and bone tissue targeted exosome as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111876388AHighly toxicDid not significantly affect secretion capacityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifMicrobiological testing/measurementExtracellular vesicleMedicine
The invention relates to a bone and bone tissue targeted exosome and a preparation method and application thereof. The method adopts a molecule comprising a PTH (parathyroid hormone) domain and an extracellular vesicle obtained from or obtainable from the method disclosed herein, the method comprises the step of introducing a molecule comprising a parathyroid hormone-associated protein component (PTH component), into a fluid that possibly comprises the extracellular vesicle, wherein the PTH component comprises a PTH domain or an active fragment thereof.
Owner:赛瑞诚(苏州)生物科技有限公司
Extracellular vesicle comprising a fusion protein having fc binding capacity
PendingUS20220098267A1Enhance therapeutic potentialDirection easyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs are coated with proteins containing Fc domains (such as antibodies) for i.a. targeting and therapeutic applications. The coating of EVs is achieved through inventive protein engineering of EV polypeptides. The present invention thus relates to methods for coating of EVs, EVs per se, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and medical applications of such EVs coated with Fc containing proteins.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
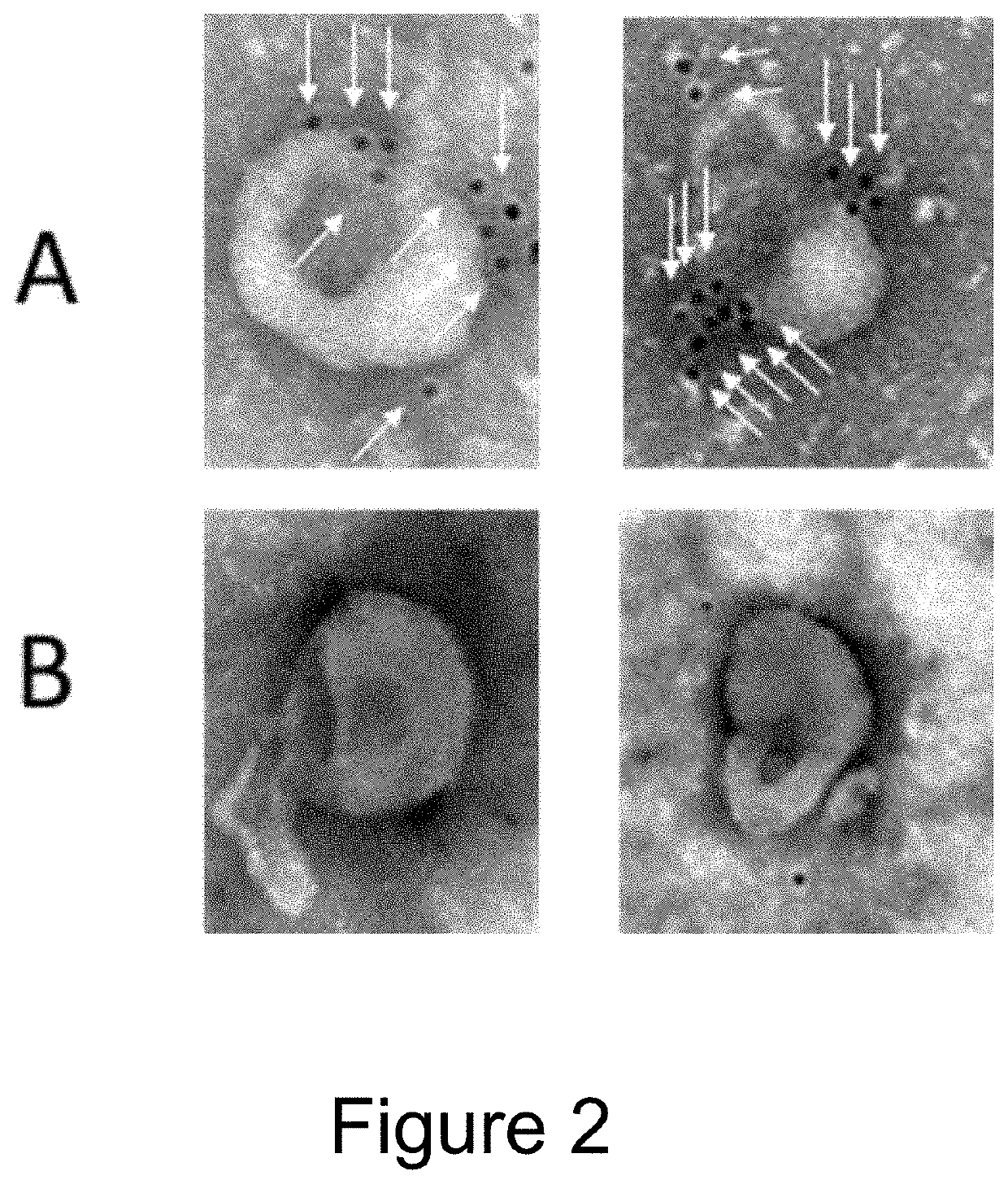
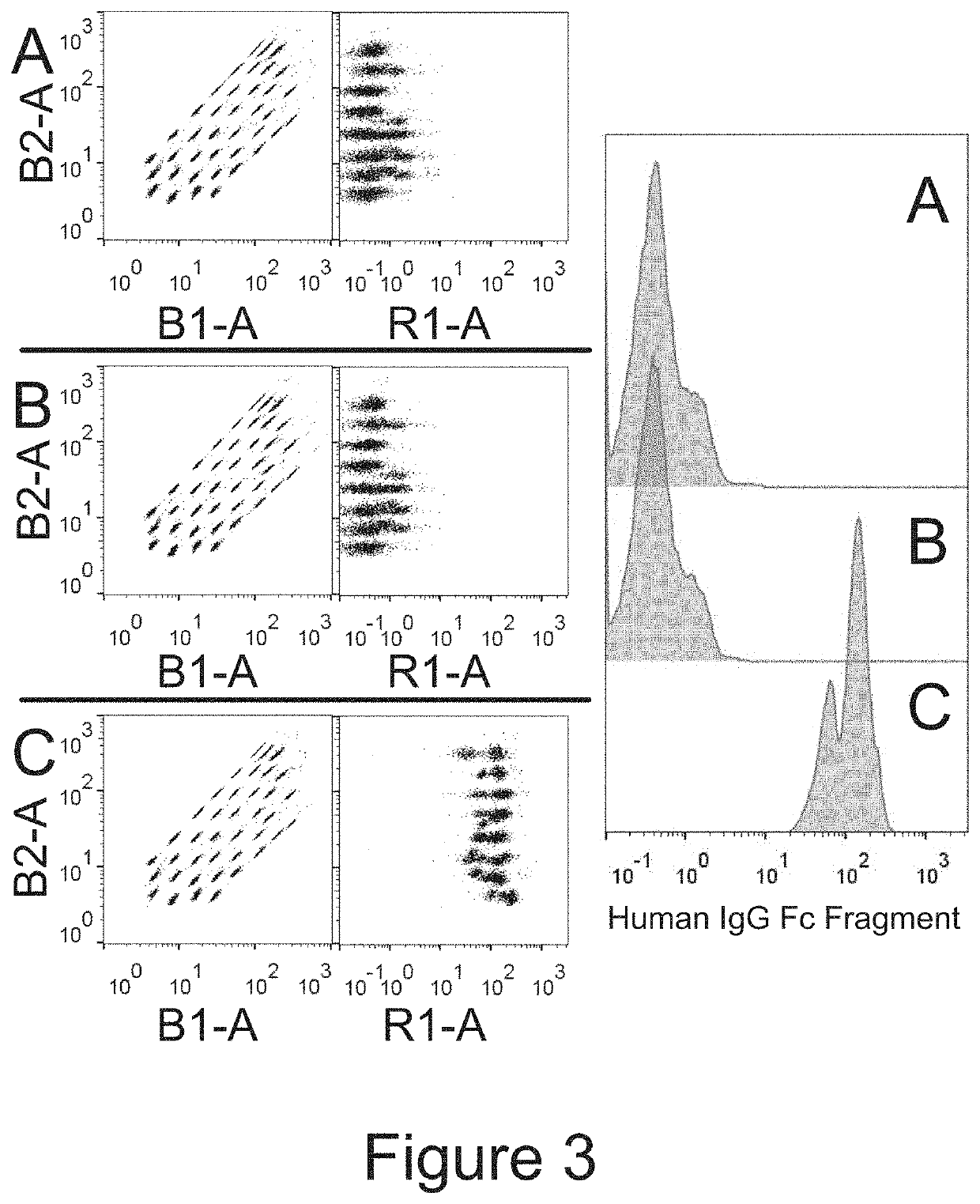
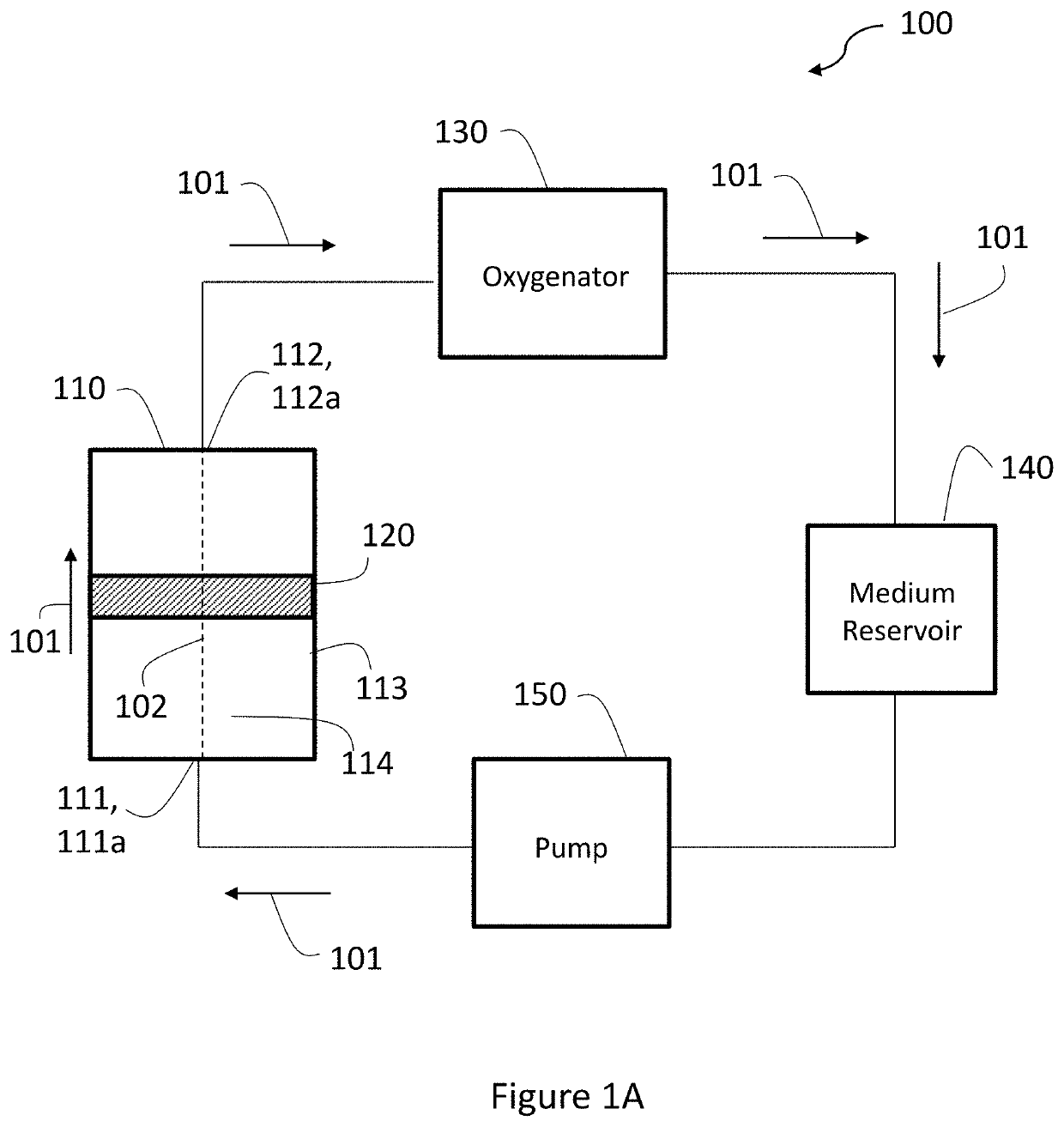
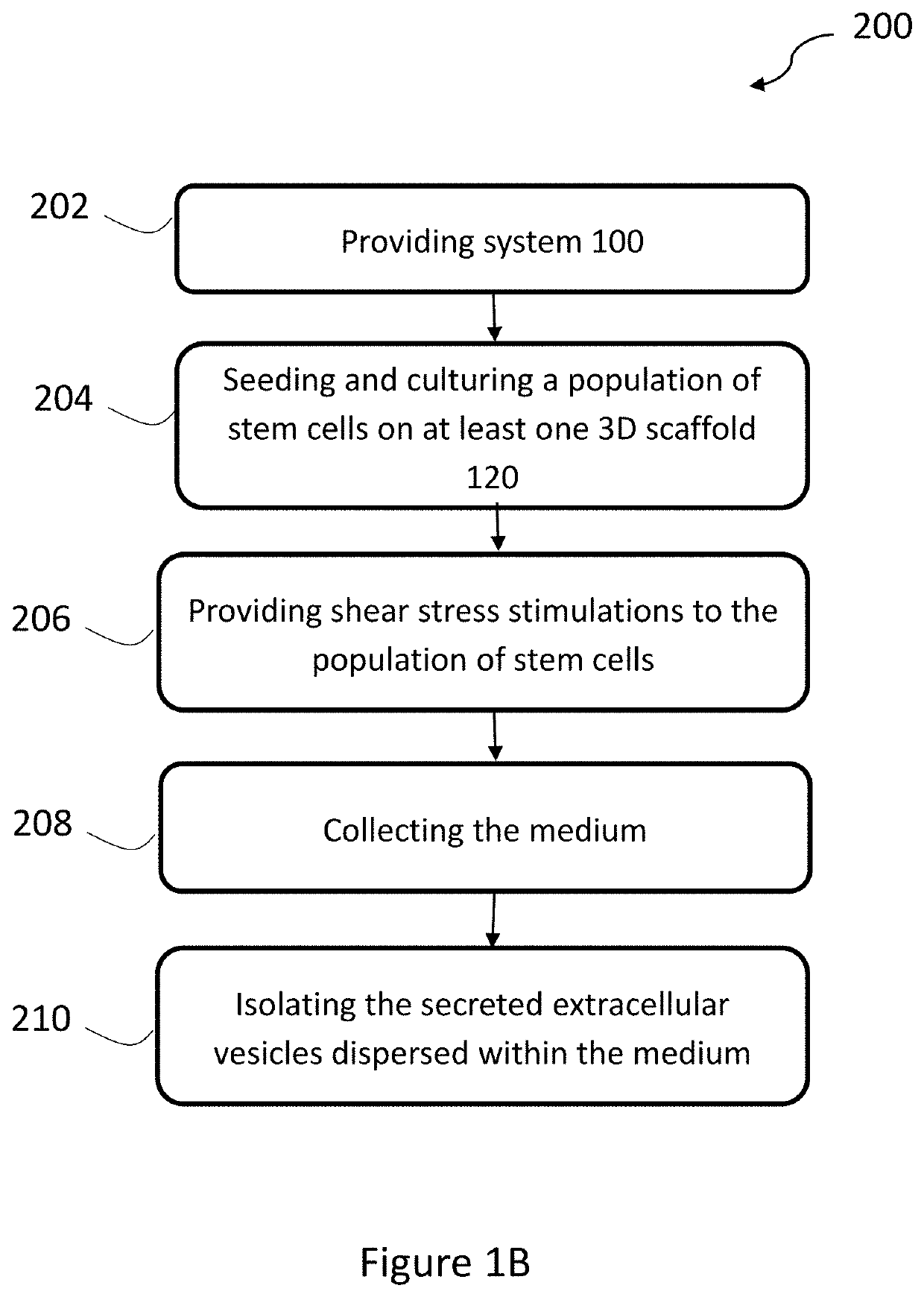
Production of extracellular vesicles from stem cells
PendingUS20210189329A1Increase secretionImprove biological effectCulture processVertebrate cellsExtracellular vesicleSecretion
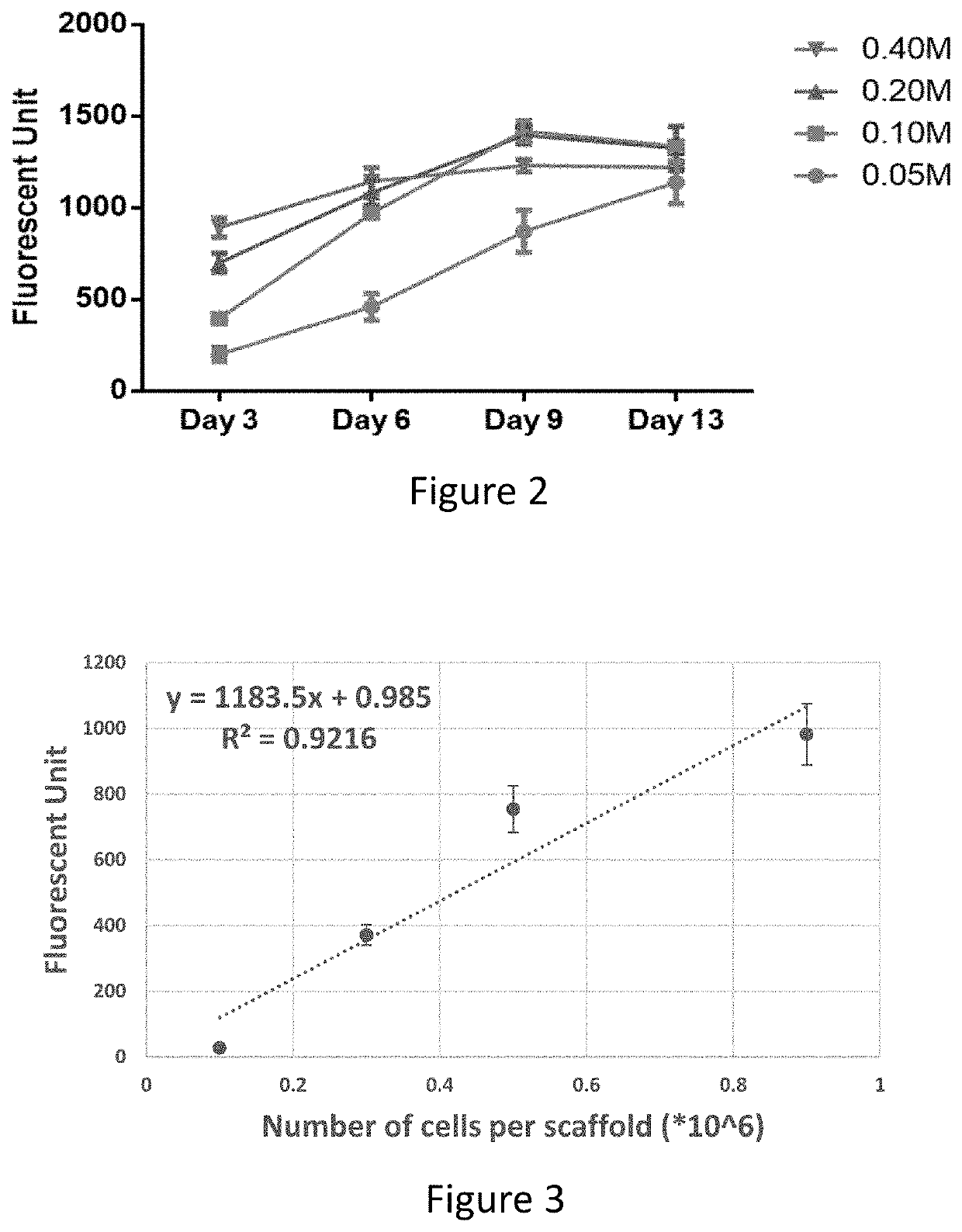
The present invention provides methods and systems for enhanced production and / or secretion of extracellular vesicles from at least one three-dimensional porous scaffold having a population of stem cells cultured thereon, utilizing various shear stress conditions on a variety of stem cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Targeting extracellular vesicle as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113528580AHigh drug loading rateAccurate targetPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCell dissociation methodsTherapeutic effectPharmaceutical Substances
The invention relates to the technical field of biological drug carrier preparation, and particularly discloses a targeting extracellular vesicle as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: constructing an LV-Lc-PDGFA fusion expression lentiviral vector, infecting neural stem cells, constructing a stably transfected cell line NSC-LV-Lc-PDGFA, and positioning an expressed exogenous ligand PDGFA on the surface of an extracellular vesicle membrane, so that the targeting capability of the extracellular vesicles on the oligodendroglia lineage cells is improved. The extracellular vesicle with the membrane surface expressing the PDGFA small peptide has high targeting property, can be used as a drug carrier, and has a good treatment effect on demyelination diseases.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Reagent for modifying extracellular vesicles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN114225044AModified stabilizationGrooming is efficient and controllableOrganic active ingredientsLuminescence/biological staining preparationFluoProbesExtracellular vesicle
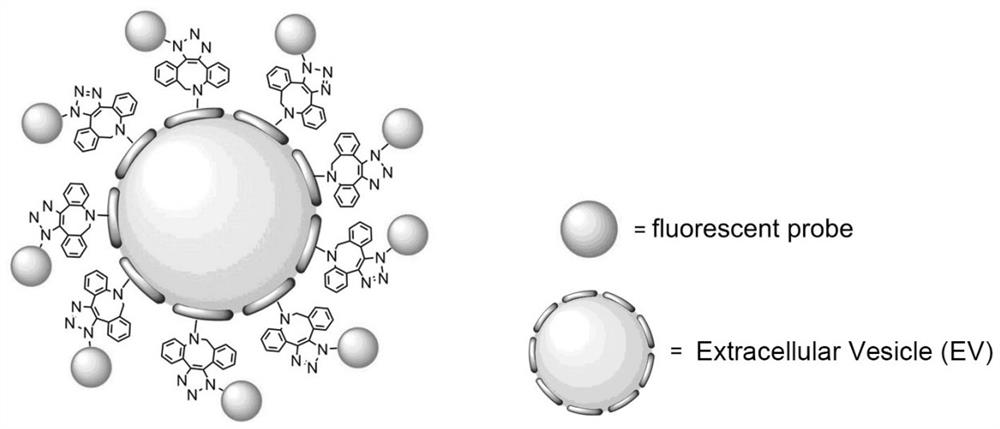
The invention discloses a reagent for modifying extracellular vesicles and a preparation method thereof, and the reagent for modifying the extracellular vesicles, which has a modifier functional group and an active ester group at the same time, is formed by carrying out click chemical coupling on an azido-modified modifier and carboxyl-activated dibenzene ring octynoic acid. The method has the beneficial effects that the morphology and structural composition of the extracellular vesicles are not changed, the biological functions of the extracellular vesicles are not influenced, and the extracellular vesicles can be stably, efficiently and controllably modified; for example, when the modifier is a fluorescent probe, the extracellular vesicles can be efficiently and controllably modified, a good visualization effect of the extracellular vesicles is achieved, and a new strategy can be provided for developing an extracellular vesicle in-vivo tracing method and an extracellular vesicle tracing drug.
Owner:天津外泌体科技有限公司
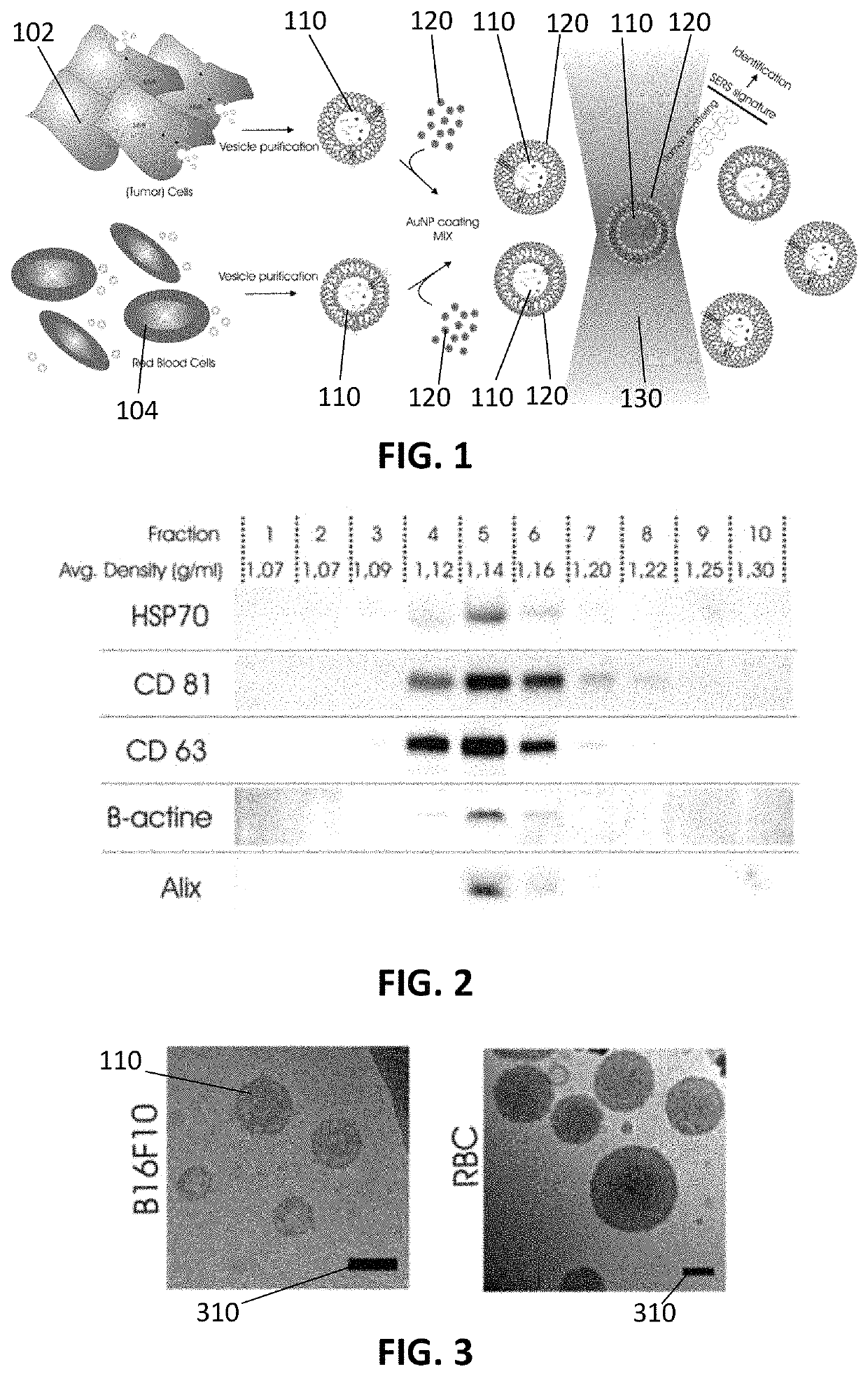
Method and system for characterizing extracellular vesicles
ActiveUS10746730B2Well representedRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringExtracellular vesicleSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
A method for characterizing extracellular vesicles at an individual level is described. It comprises obtaining a sample comprising extracellular vesicles to be characterized and functionalizing the extracellular vesicles with plasmonic nanoparticles or a plasmonic coating. The method further comprises irradiating the individual extracellular vesicles with a laser beam and detecting a surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy signal from said individual extracellular vesicle.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Medicine or cosmetic prepared from fibroblast extracellular vesicles
ActiveCN114736296APrevent agingGood anti aging activityCell dissociation methodsCosmetic preparationsExtracellular vesicleAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention relates to a medicine or a cosmetic prepared from fibroblast extracellular vesicles. The effect of the invention is achieved by inhibiting P53 activity to improve fibroblast activity and prevent aging to produce ectovesicles at high yield. A monoclonal antibody is used for inhibiting the activity of P53, after the monoclonal antibody is added into a culture medium of fibroblasts, the aging of the fibroblasts can be inhibited, the content of exovesicles secreted by the fibroblasts can be increased, and the exovesicles are good in anti-aging activity and suitable for preparing anti-aging beautifying or medicine products. Good market application values are realized.
Owner:诺赛联合(北京)生物医学科技有限公司
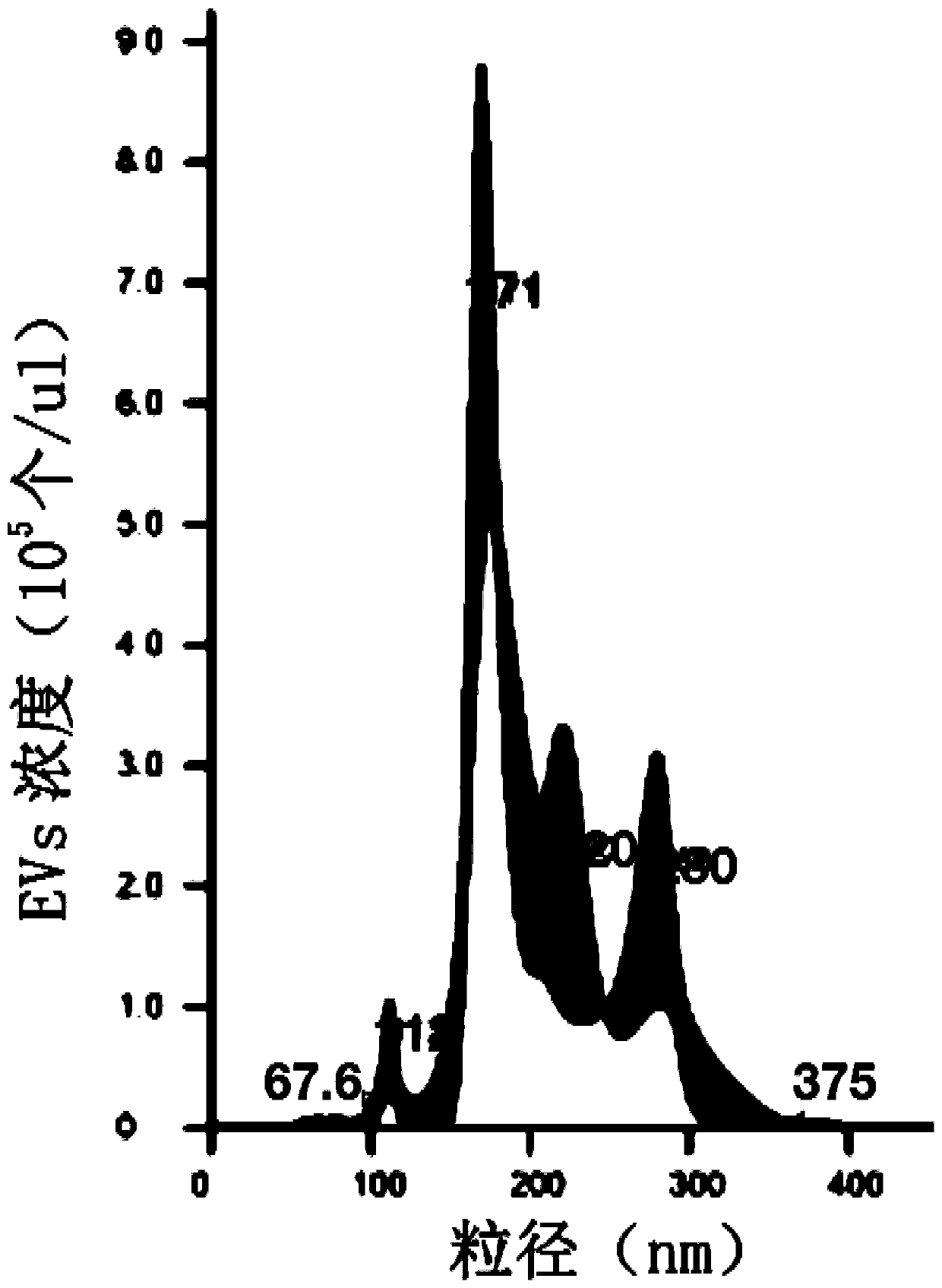
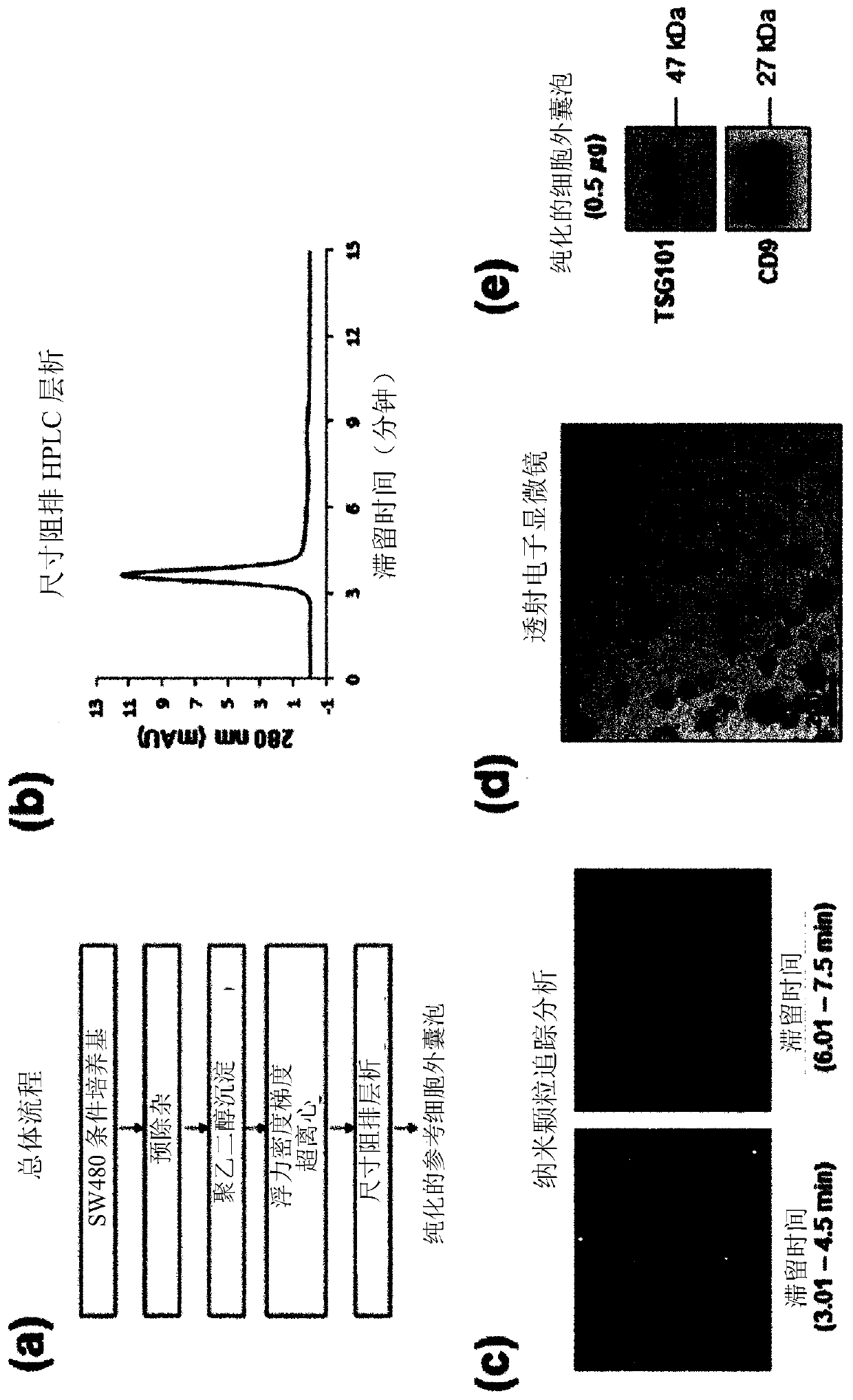
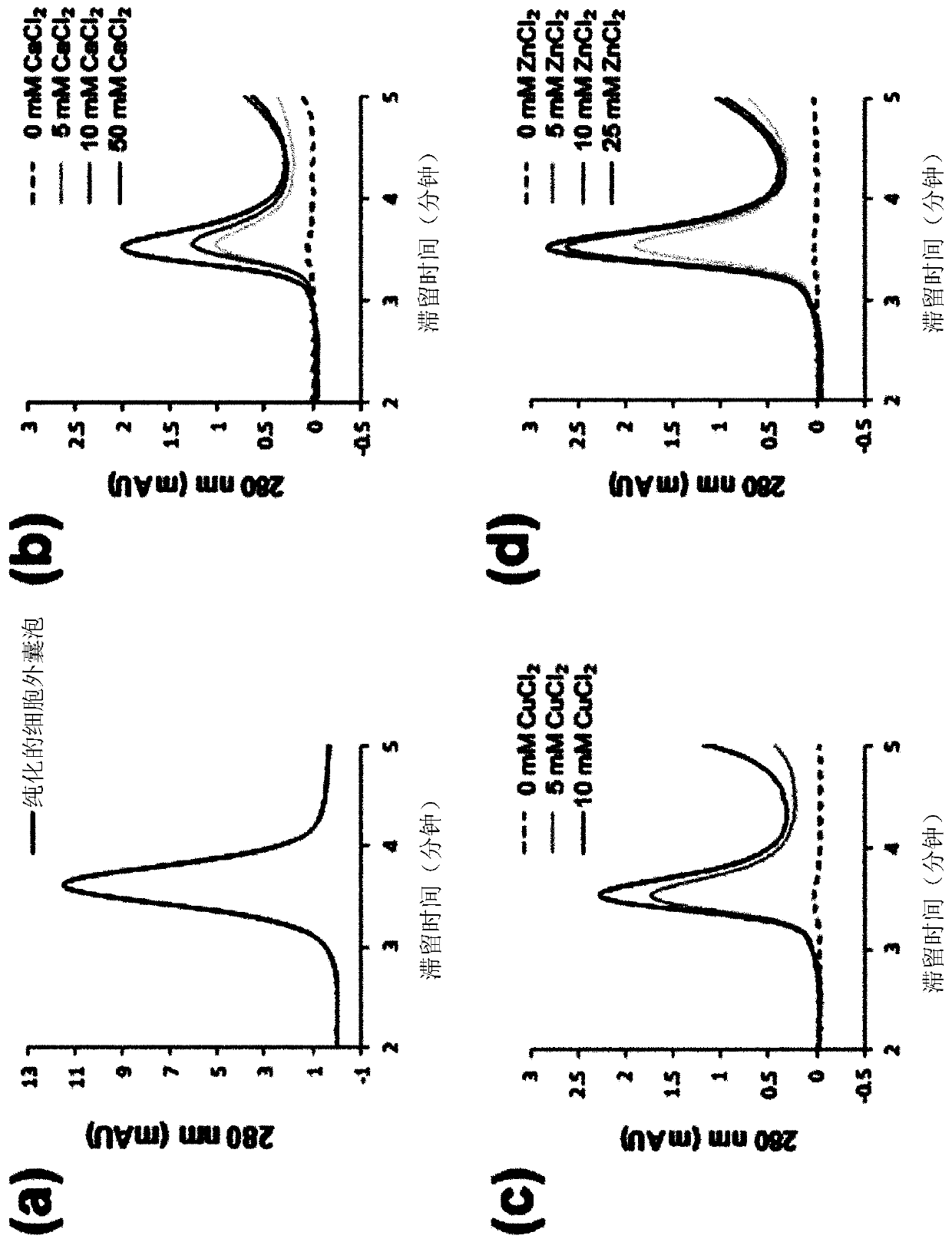
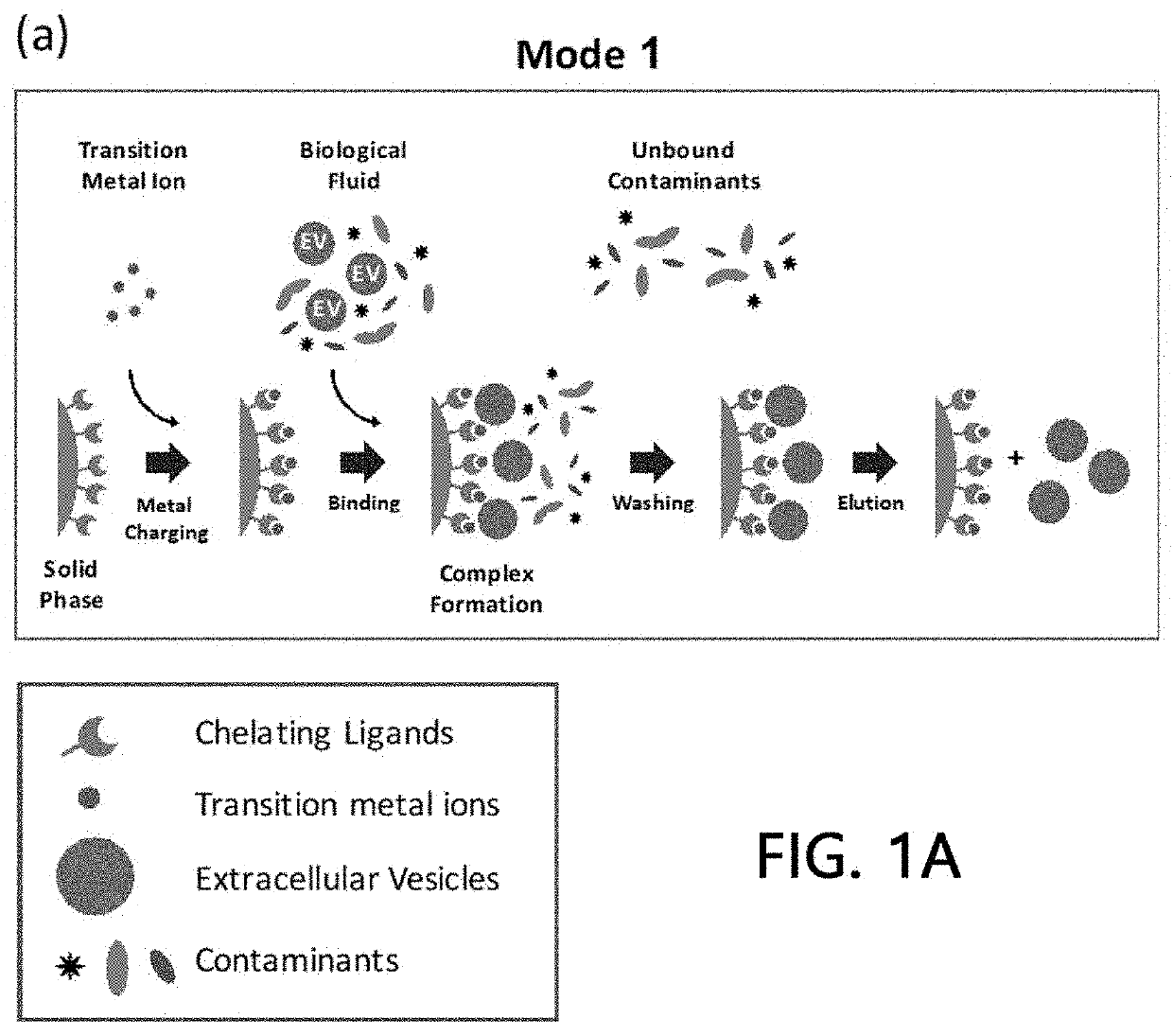
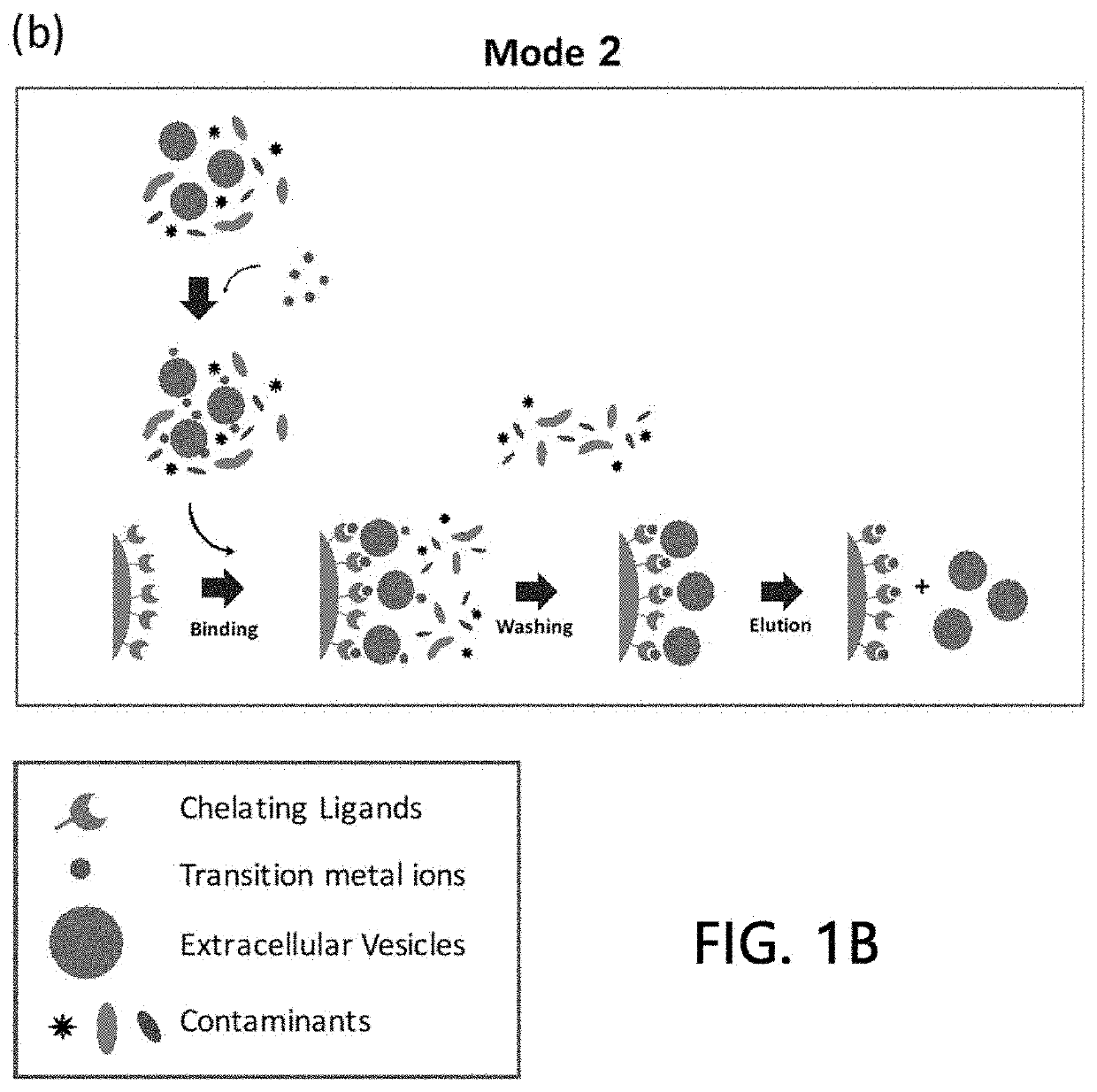
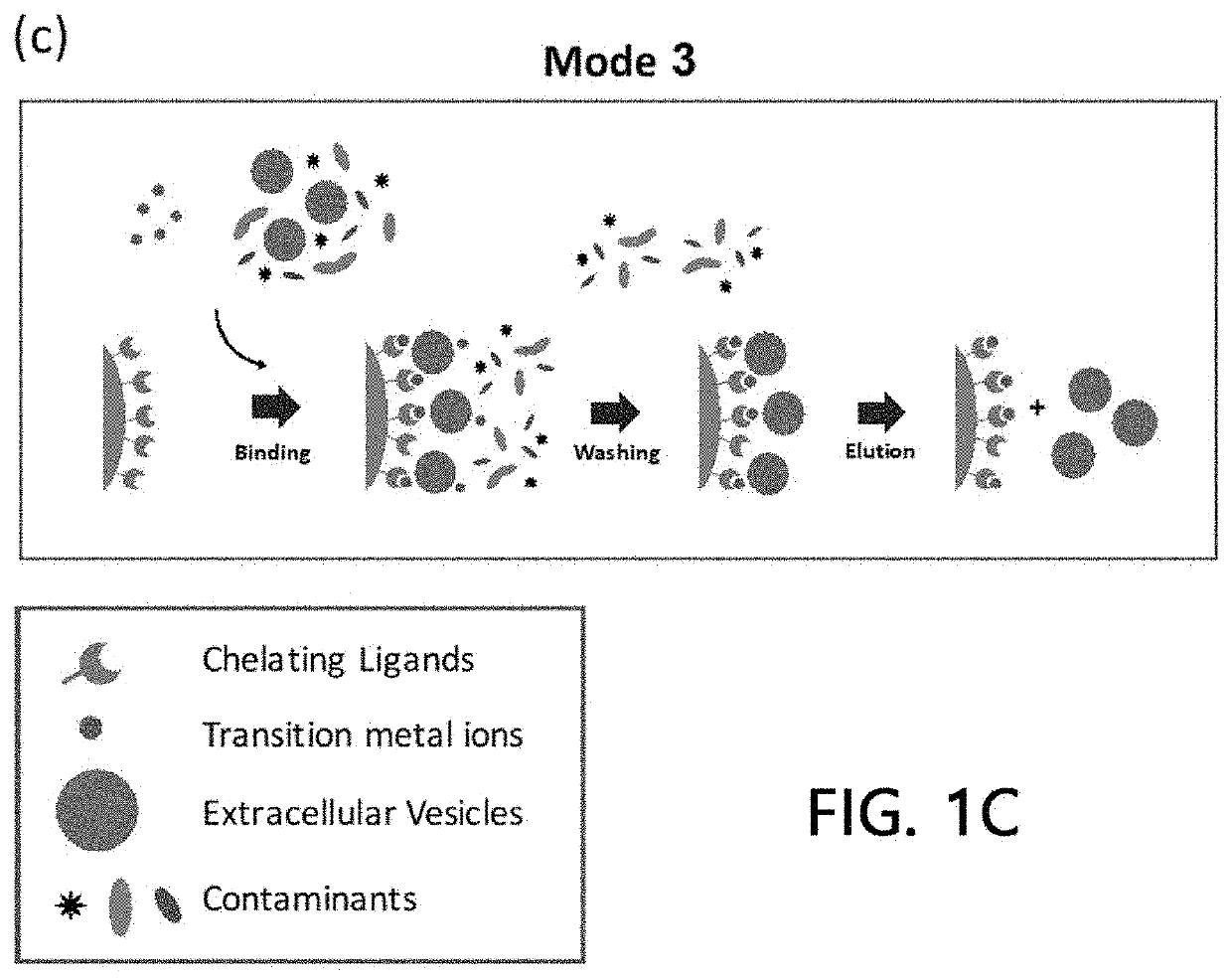
Extracellular vesicle isolation method using metal
ActiveUS11135528B2Effective isolationMaximize efficiencyFungiCation exchanger materialsExtracellular vesicleDisease
Owner:ROSETTA EXOSOME
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com