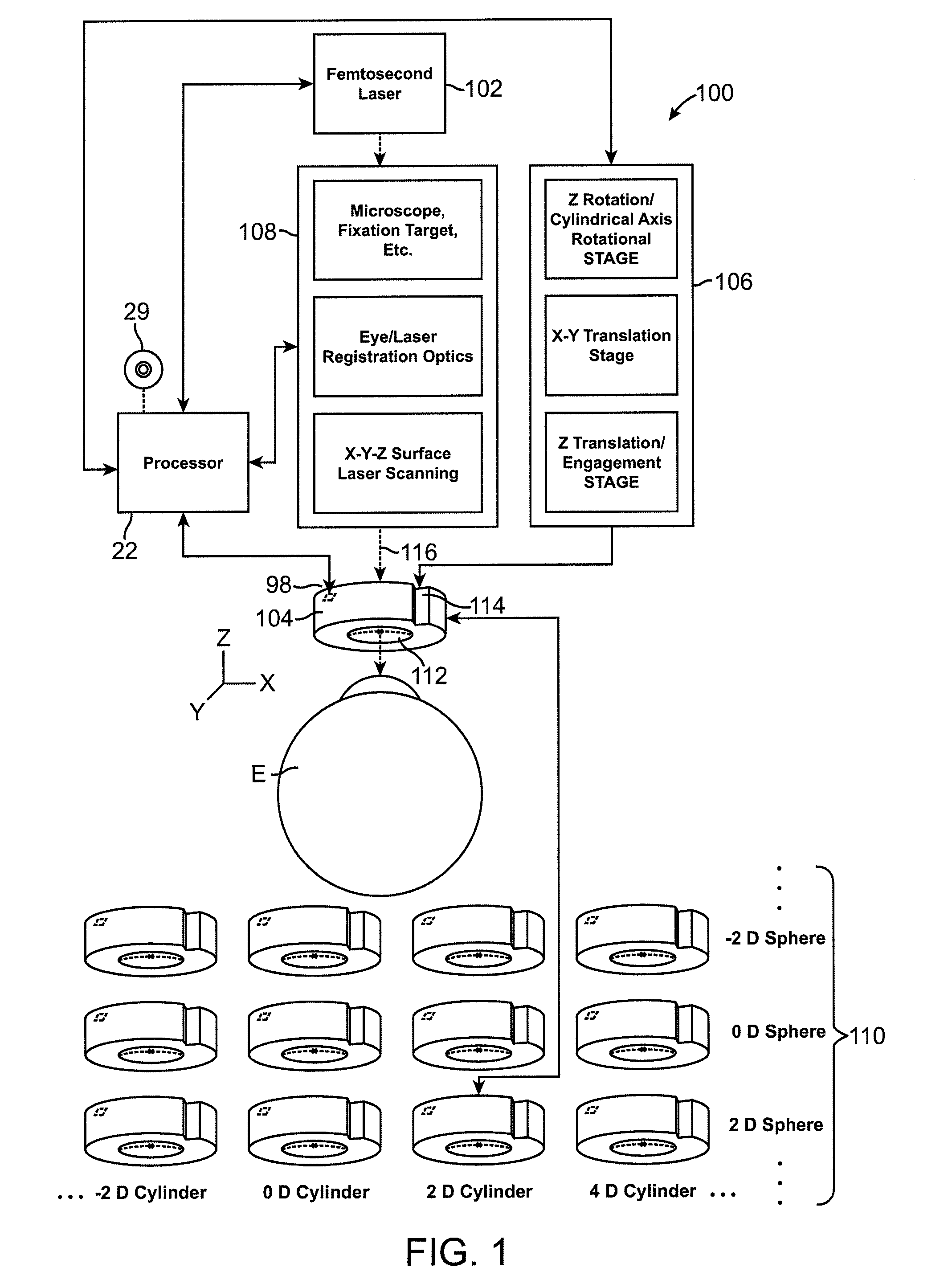
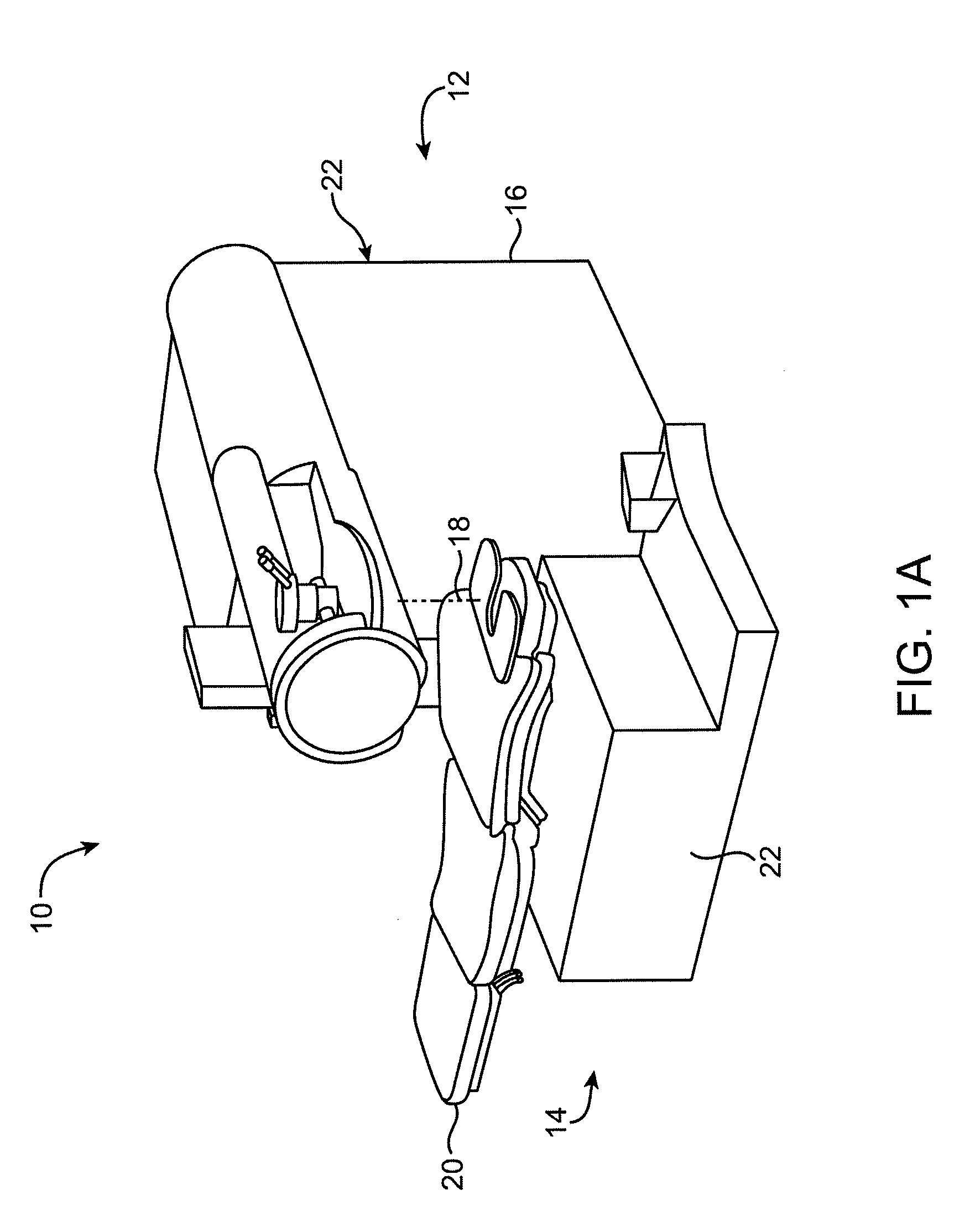
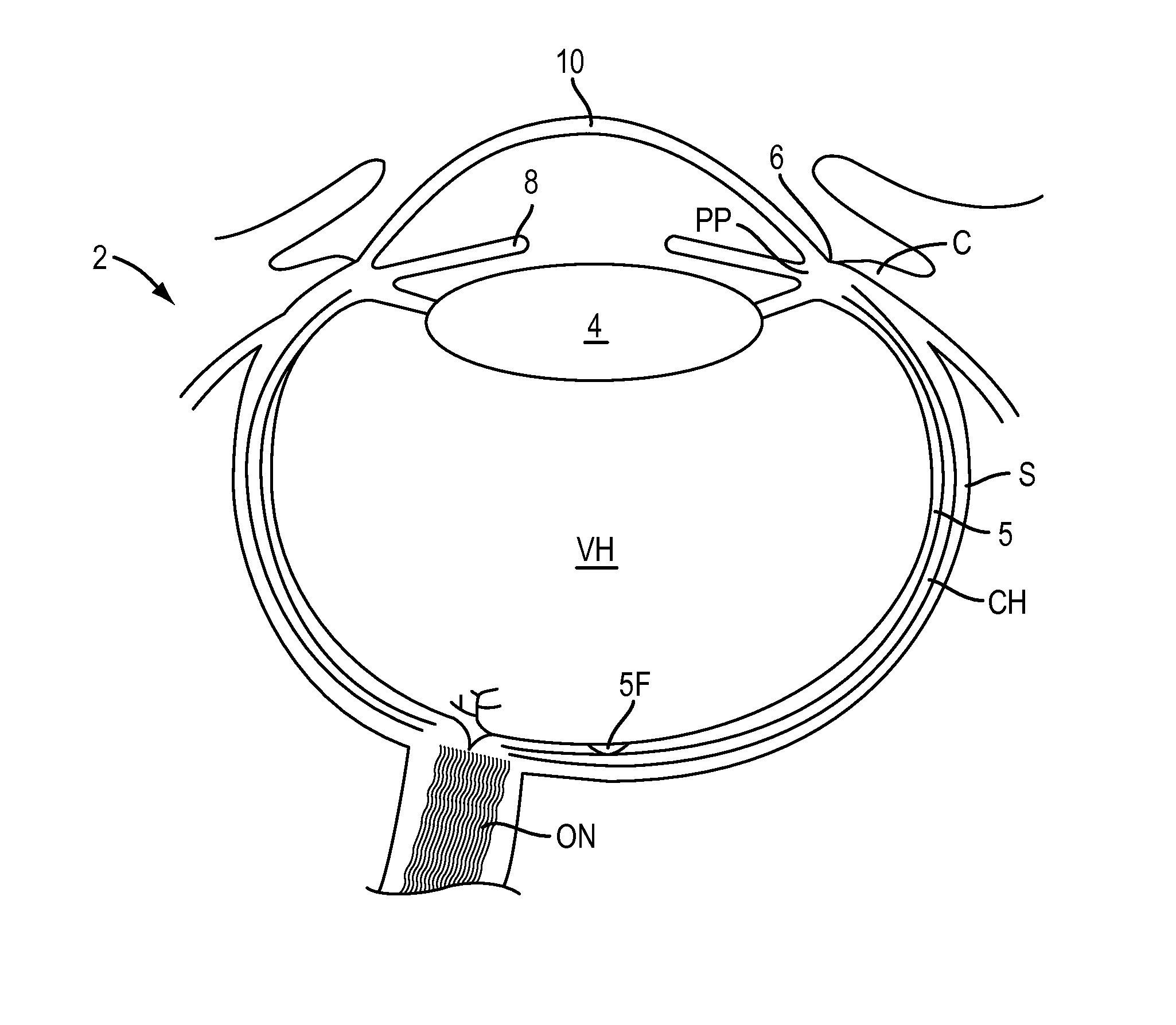
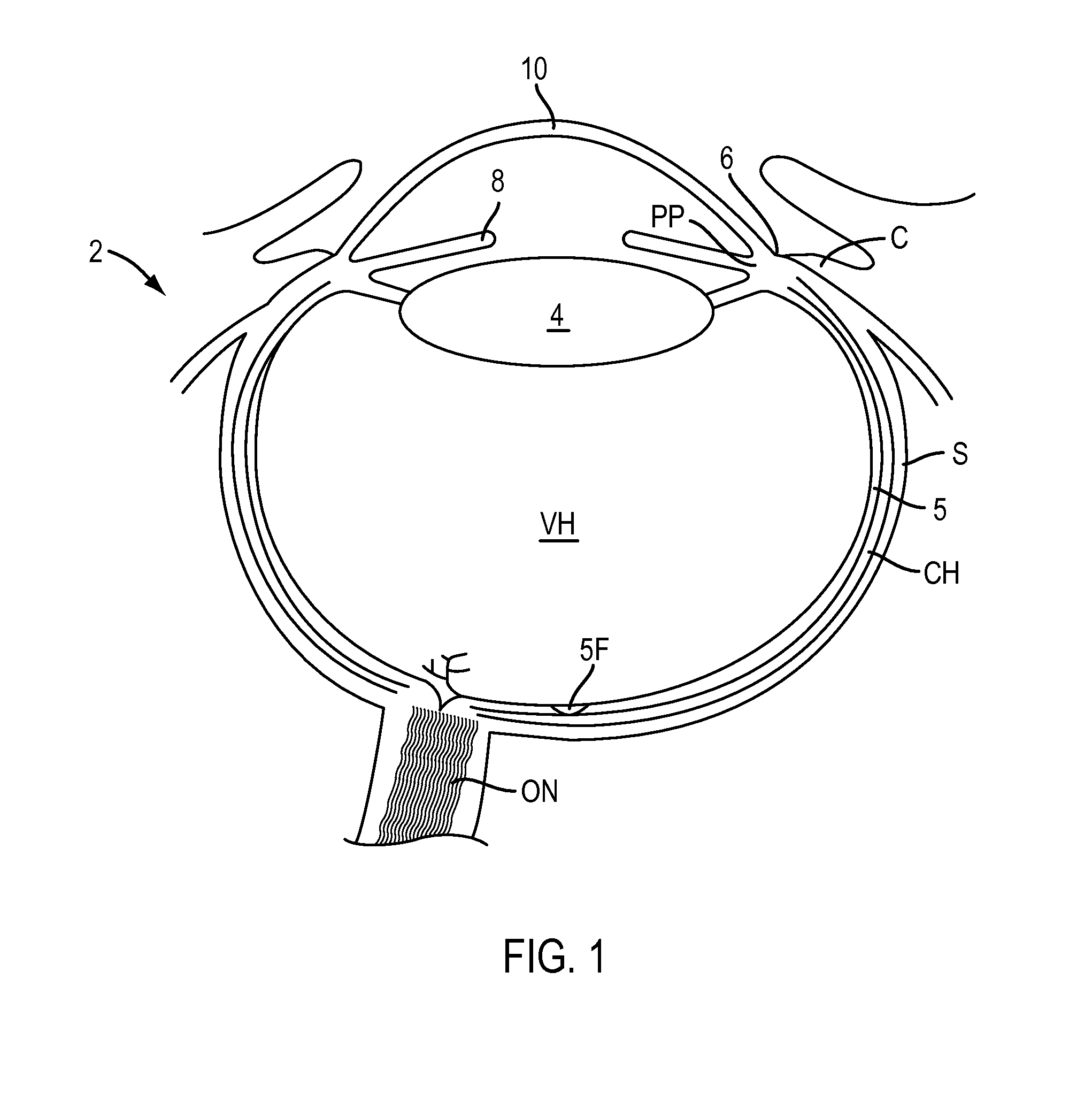
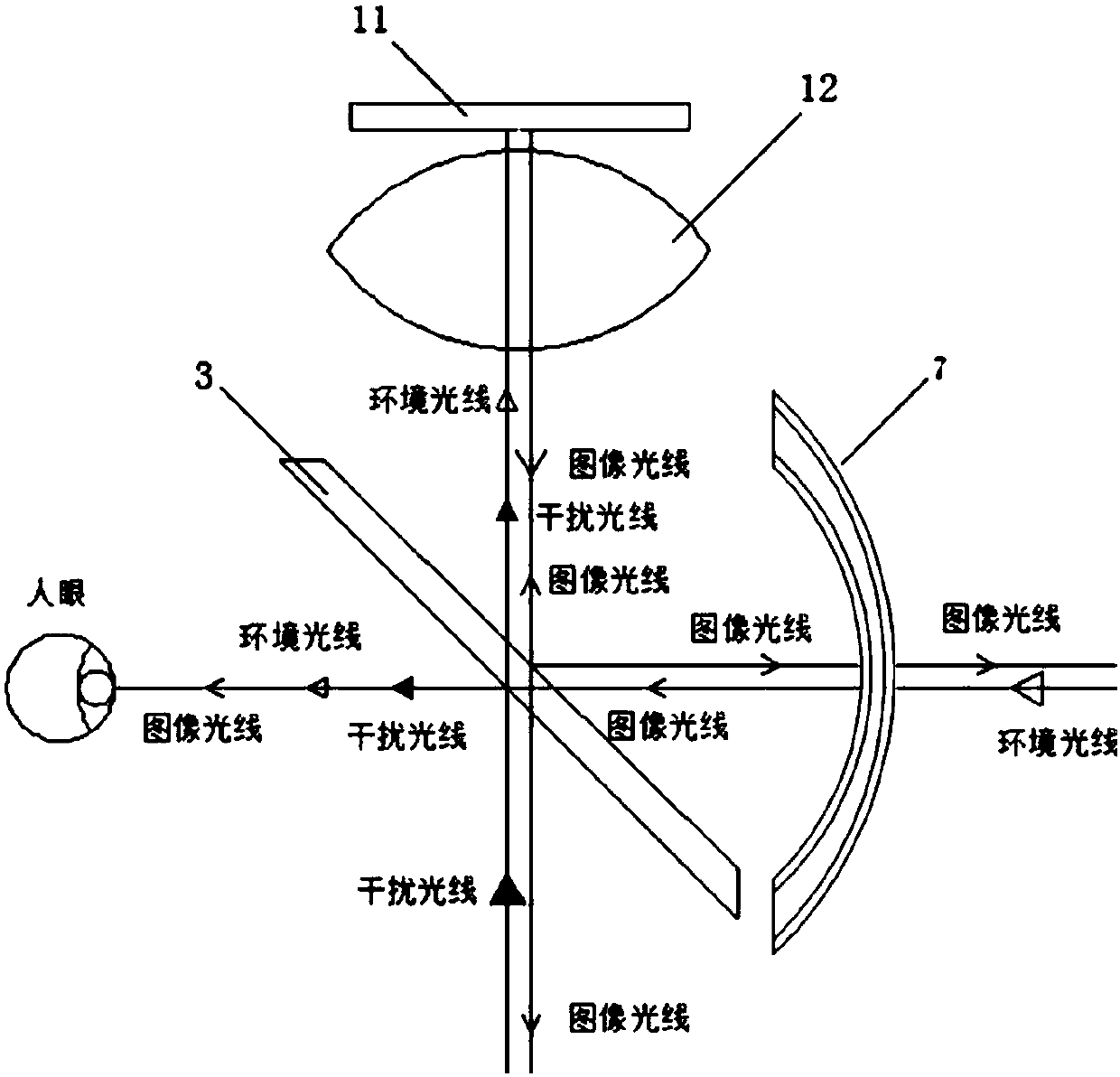
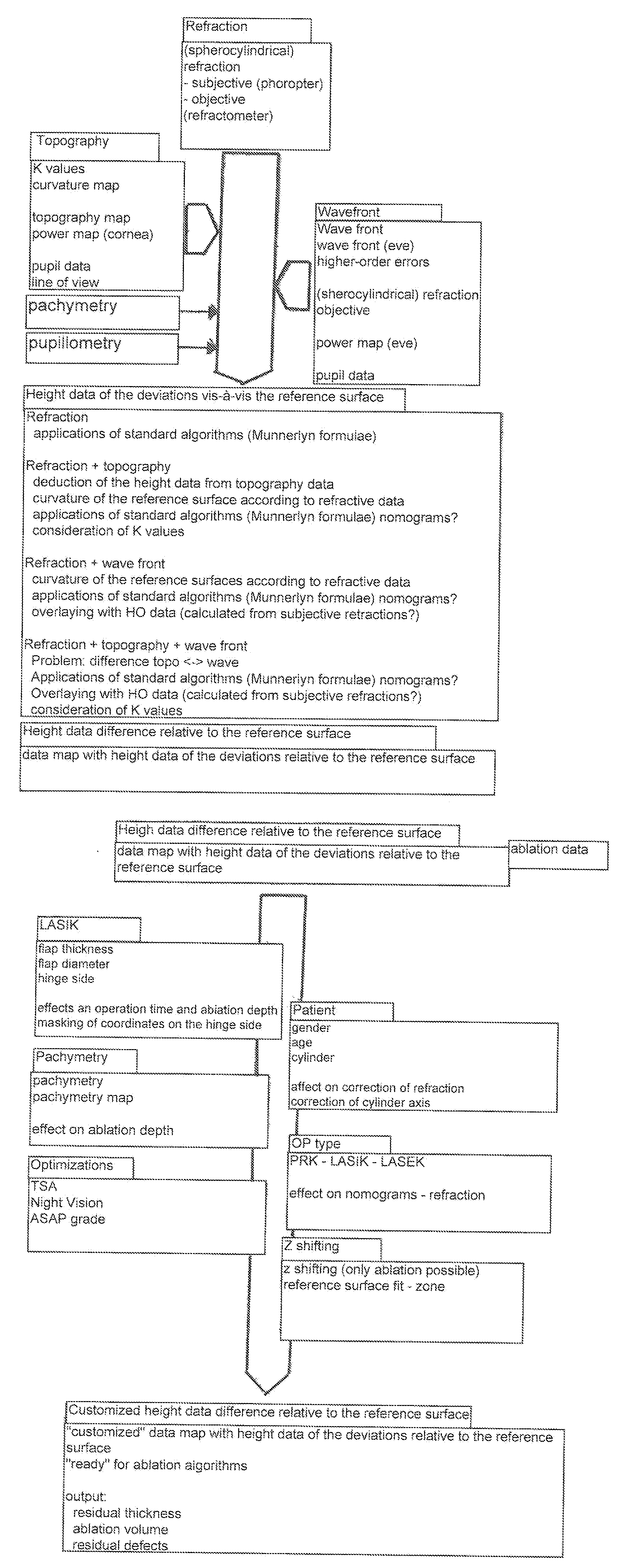
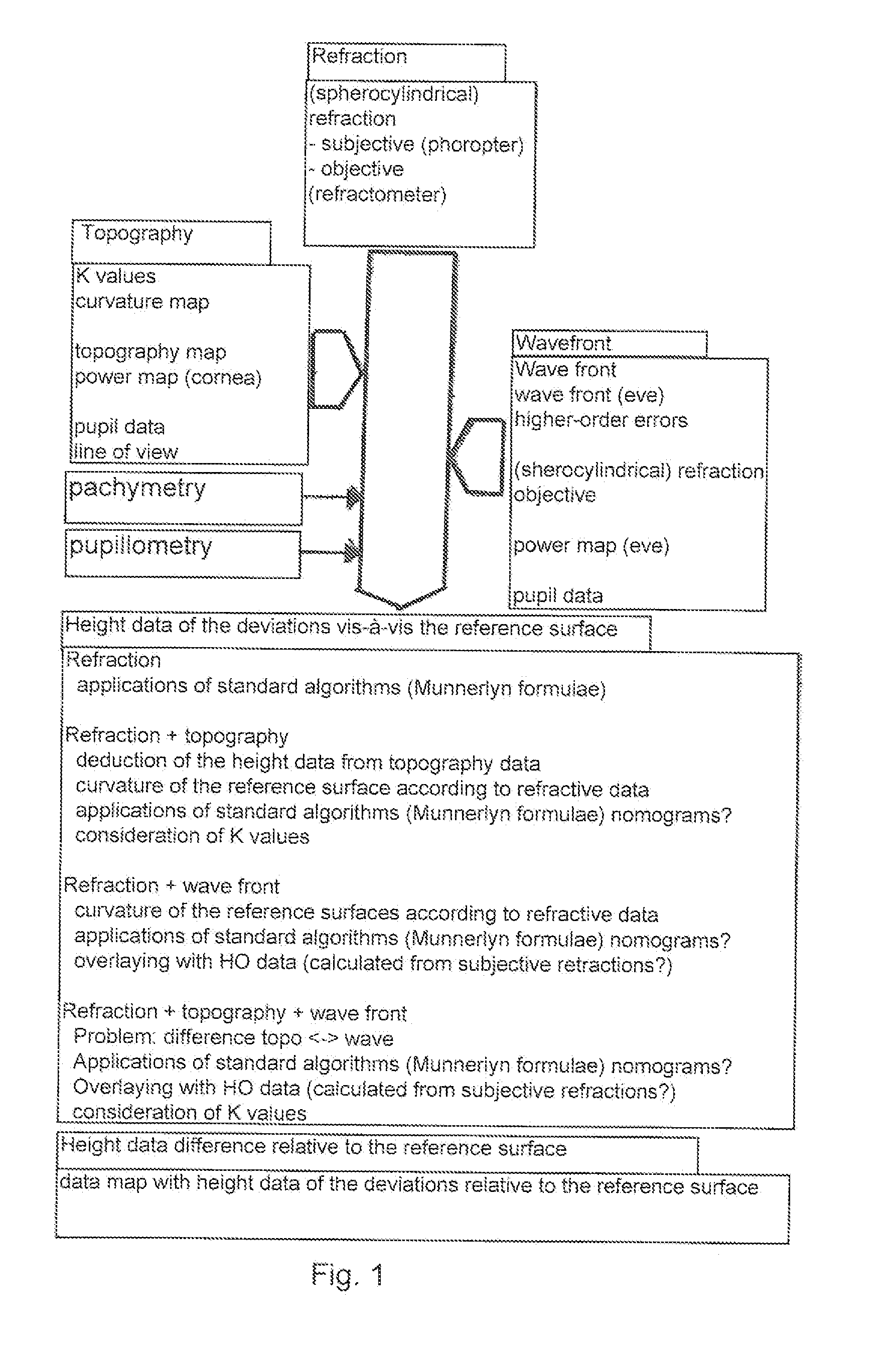
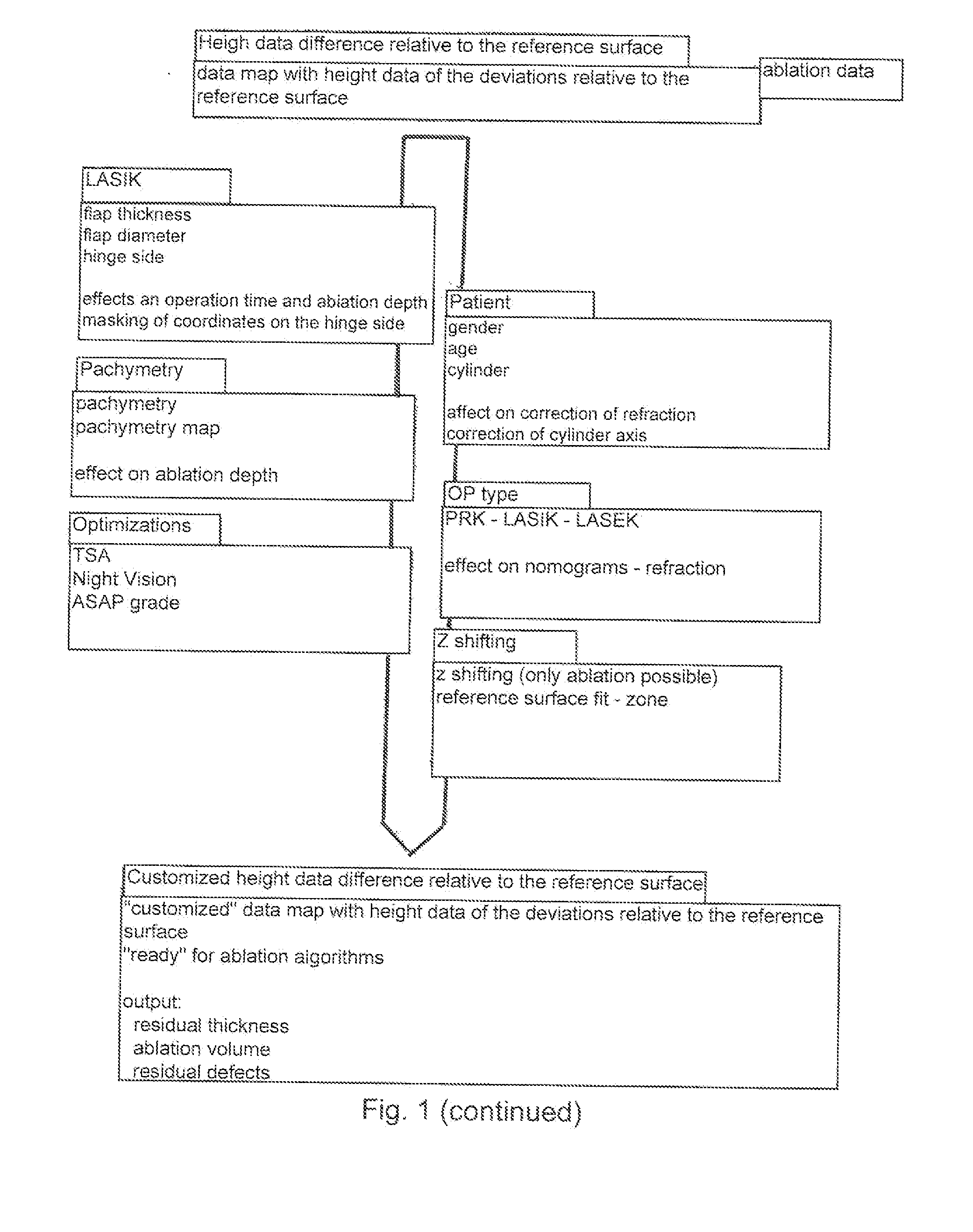
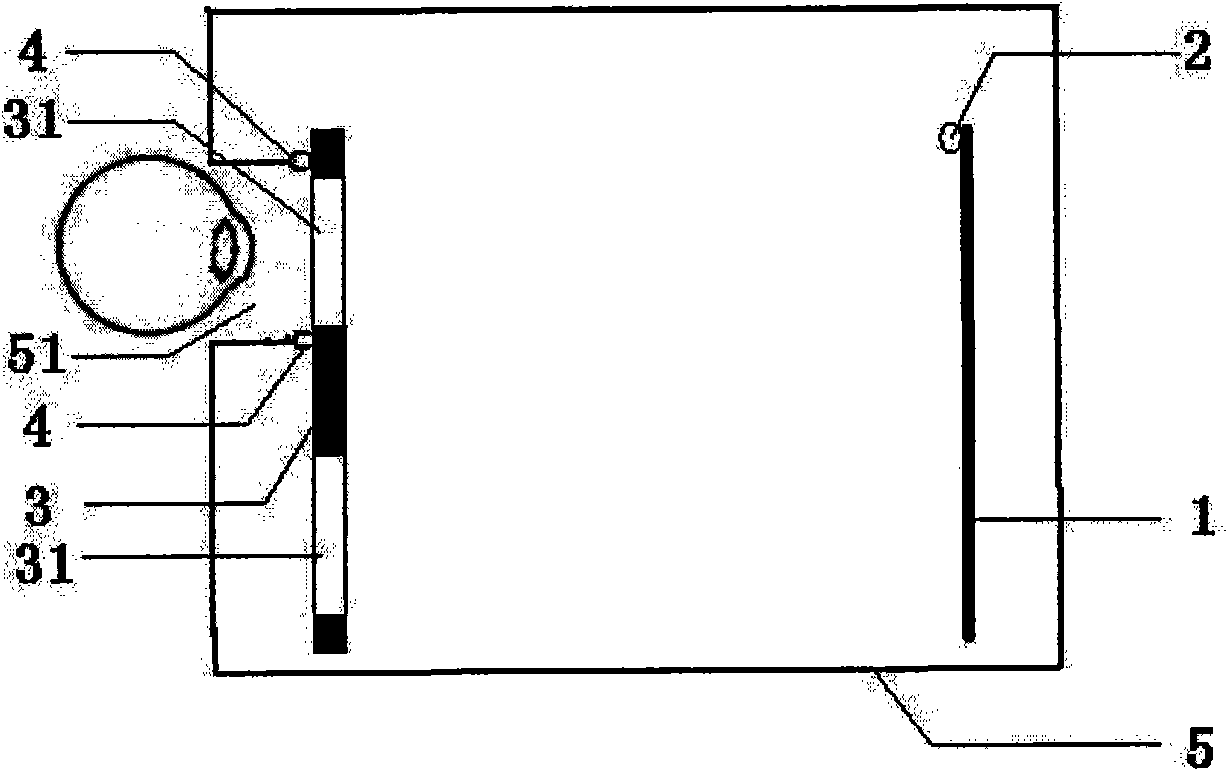
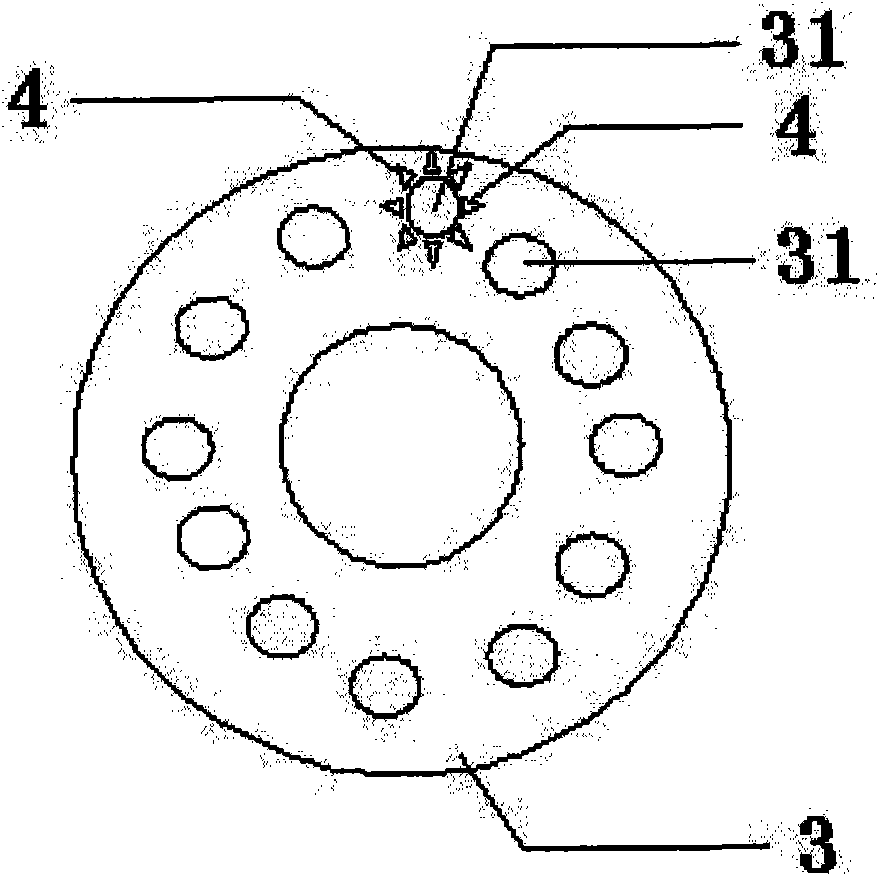
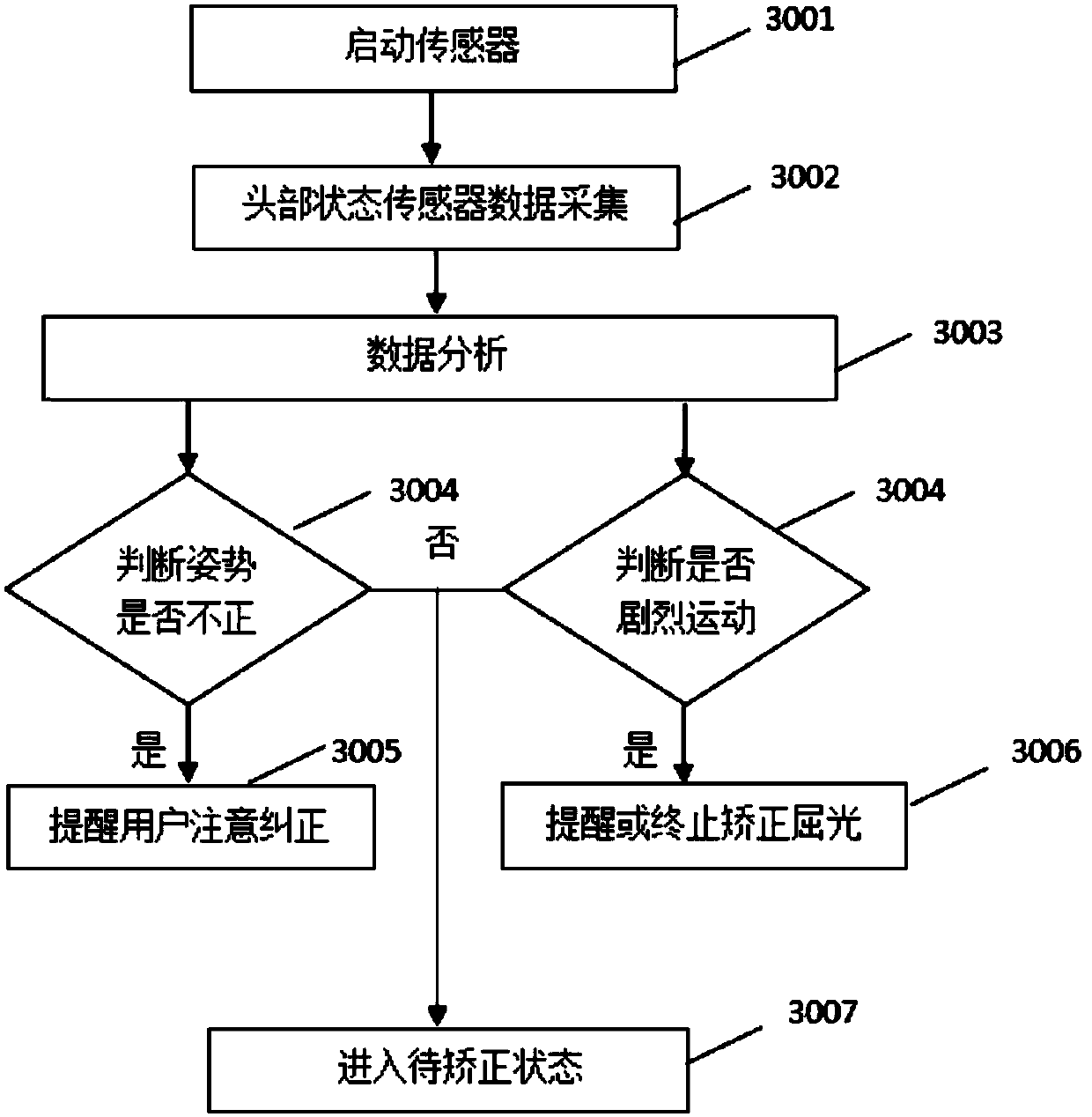
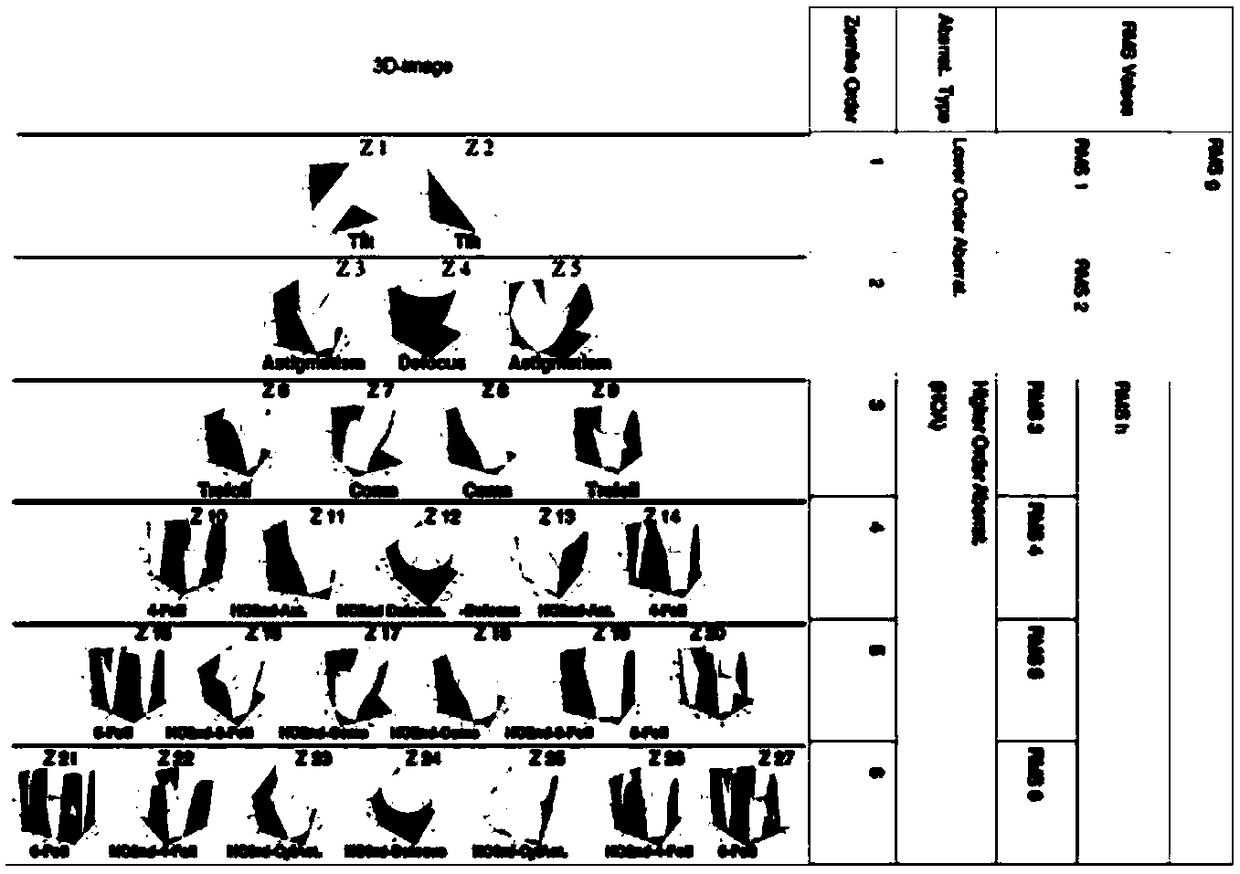
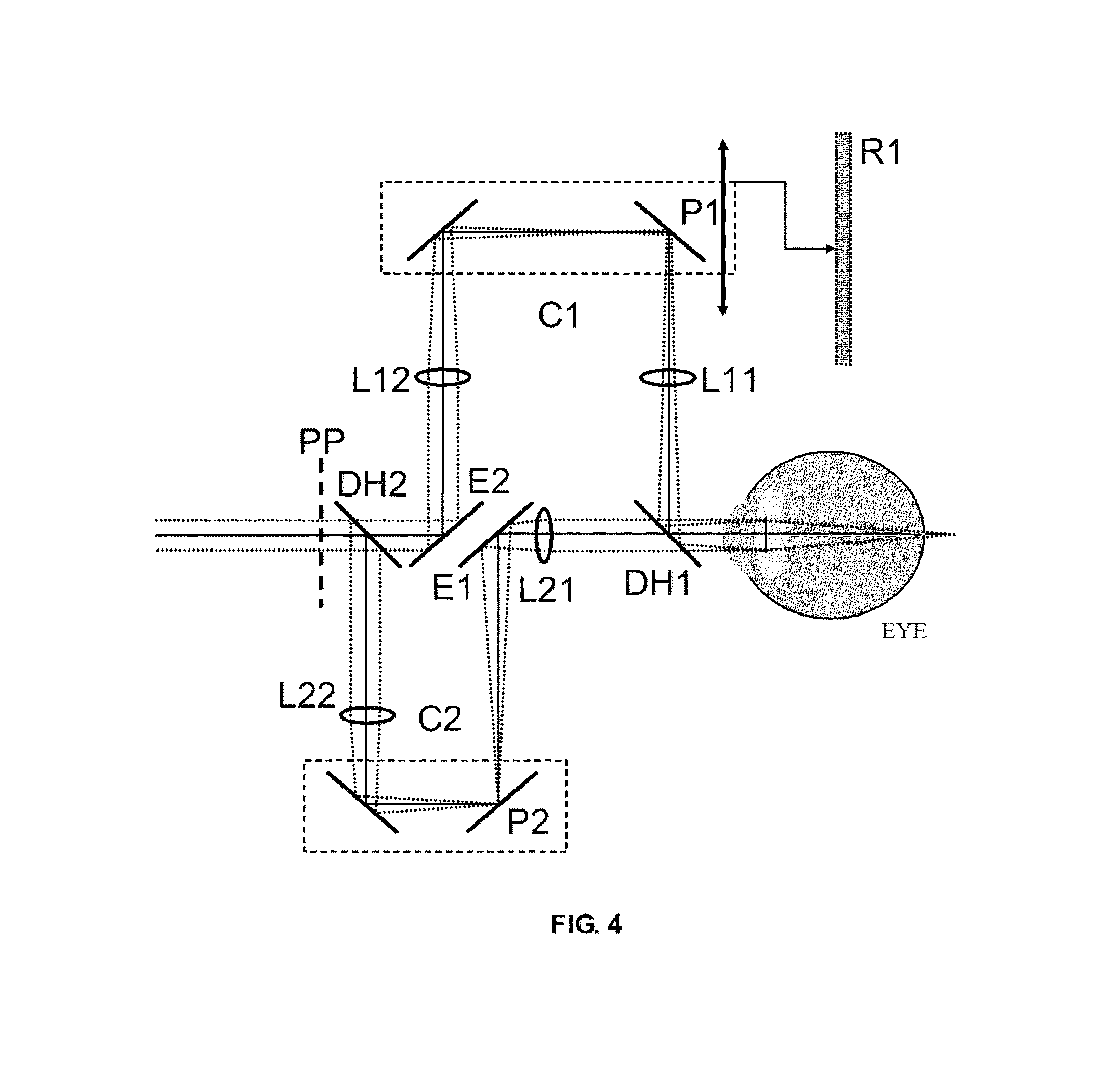
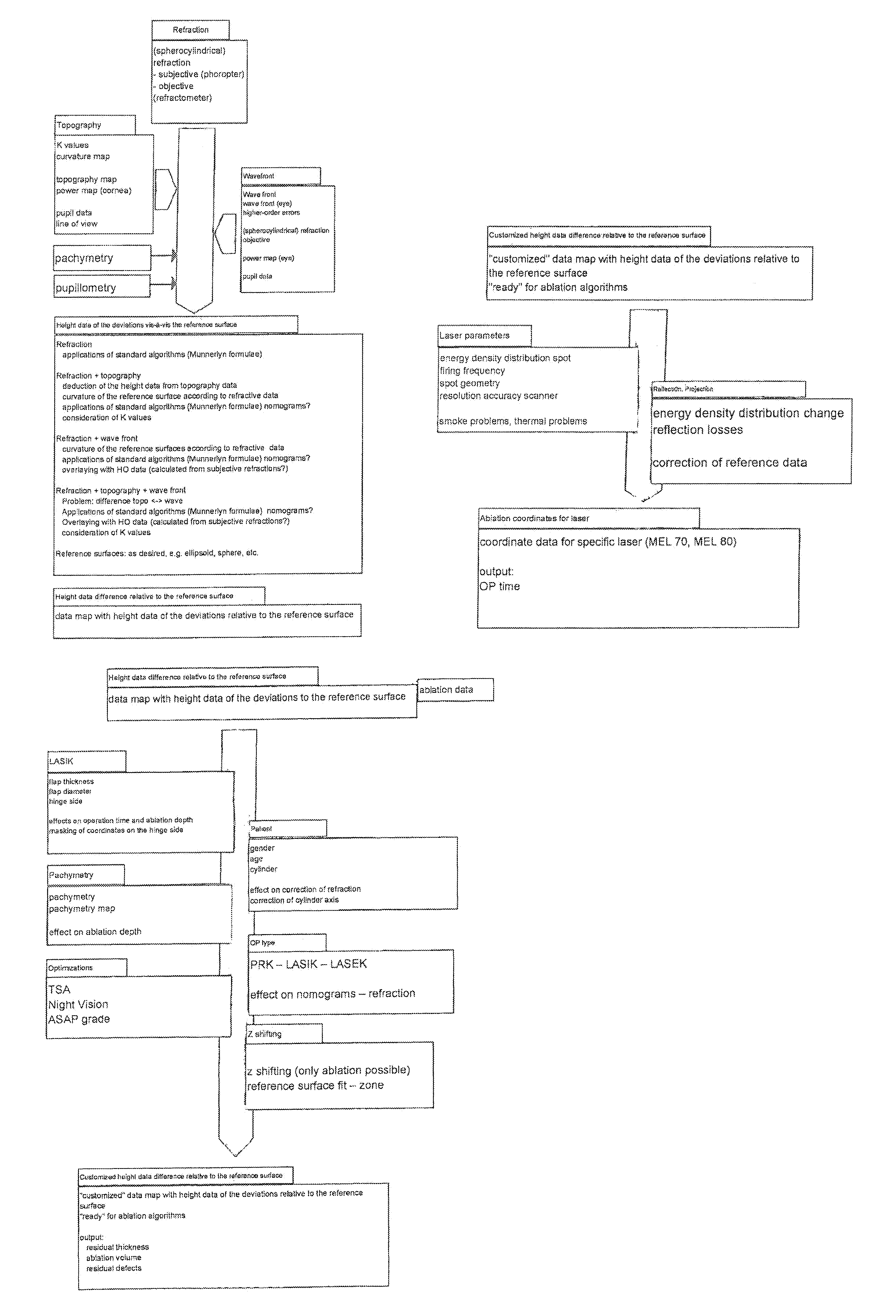
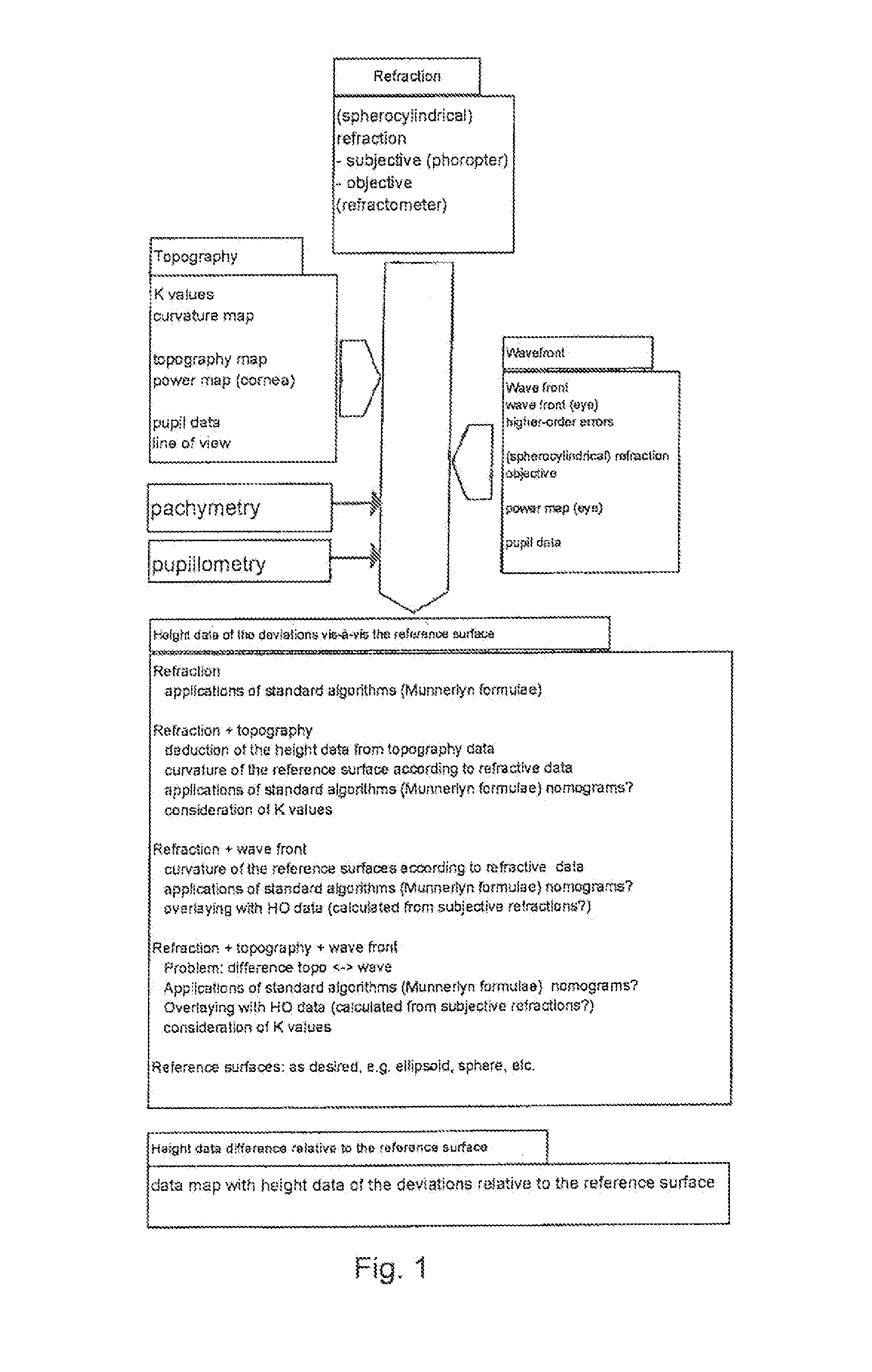
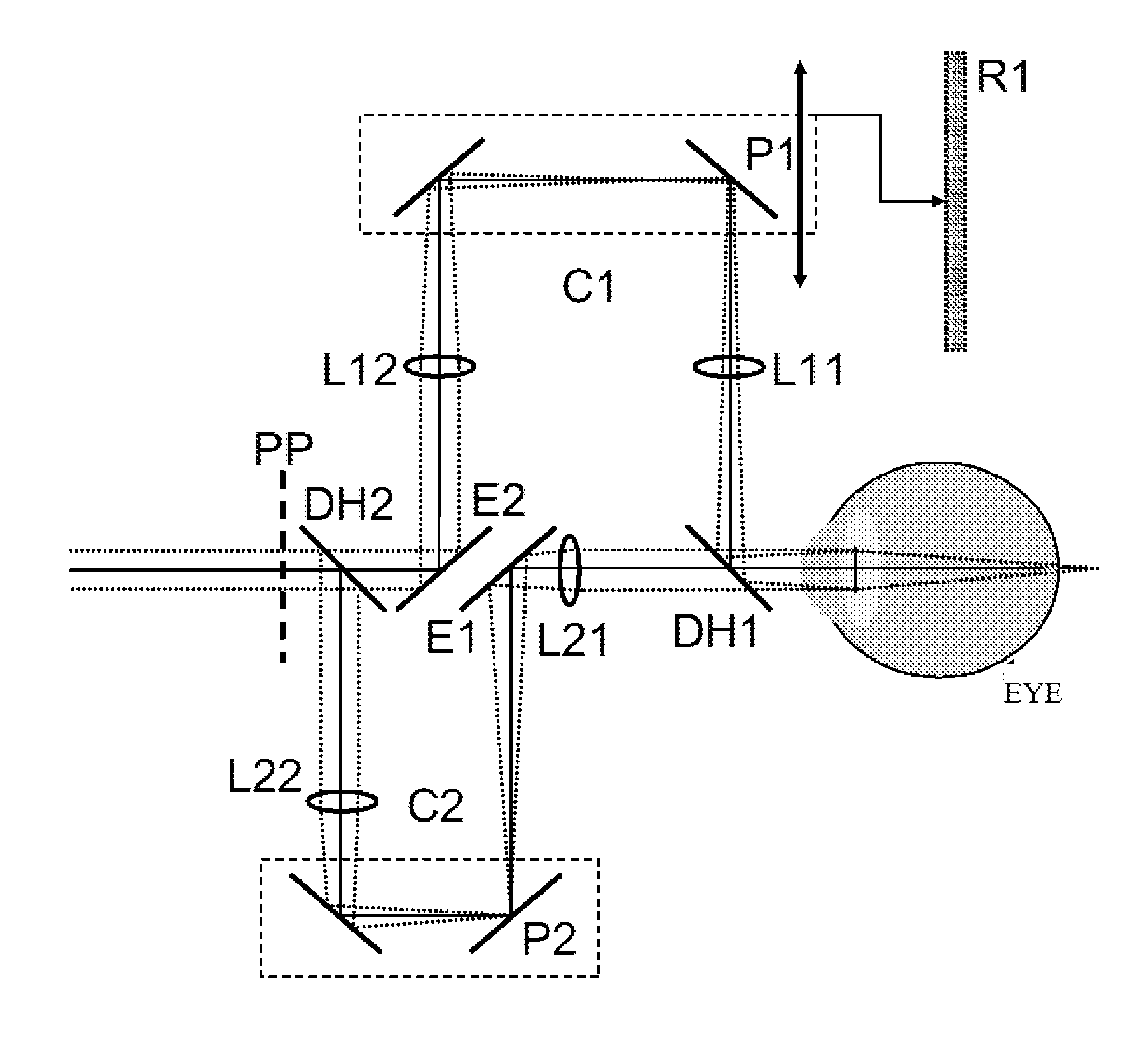
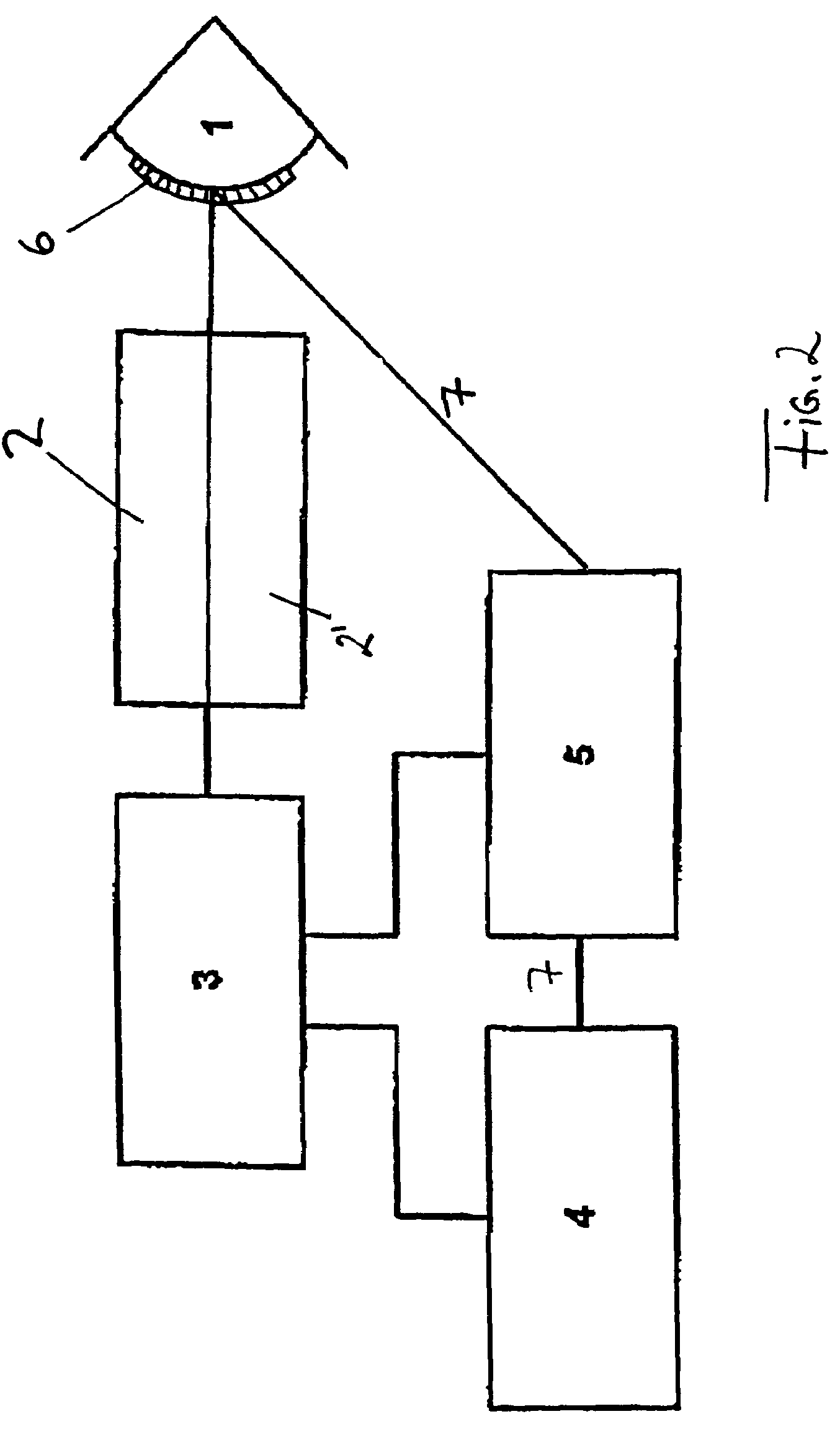
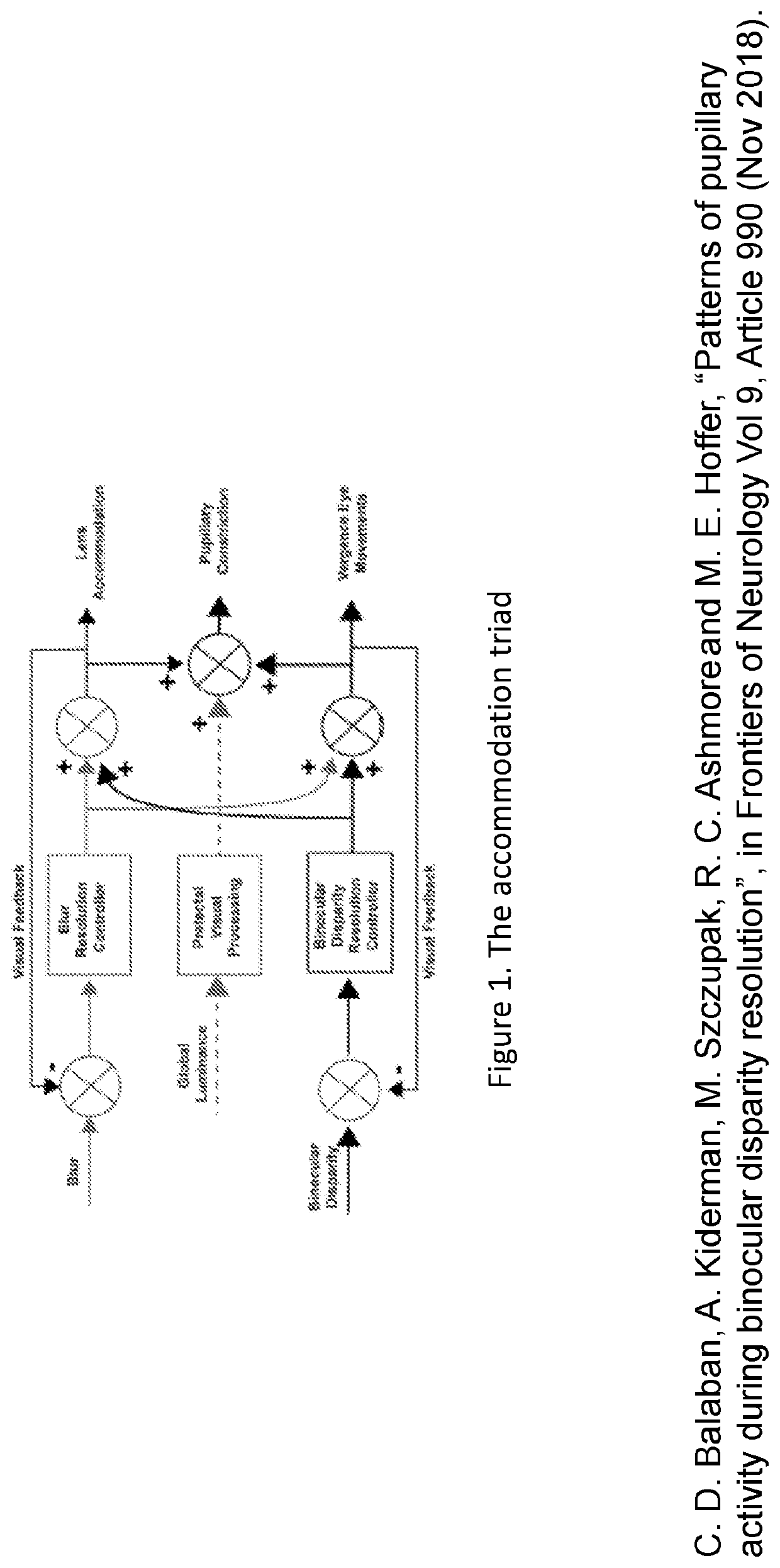
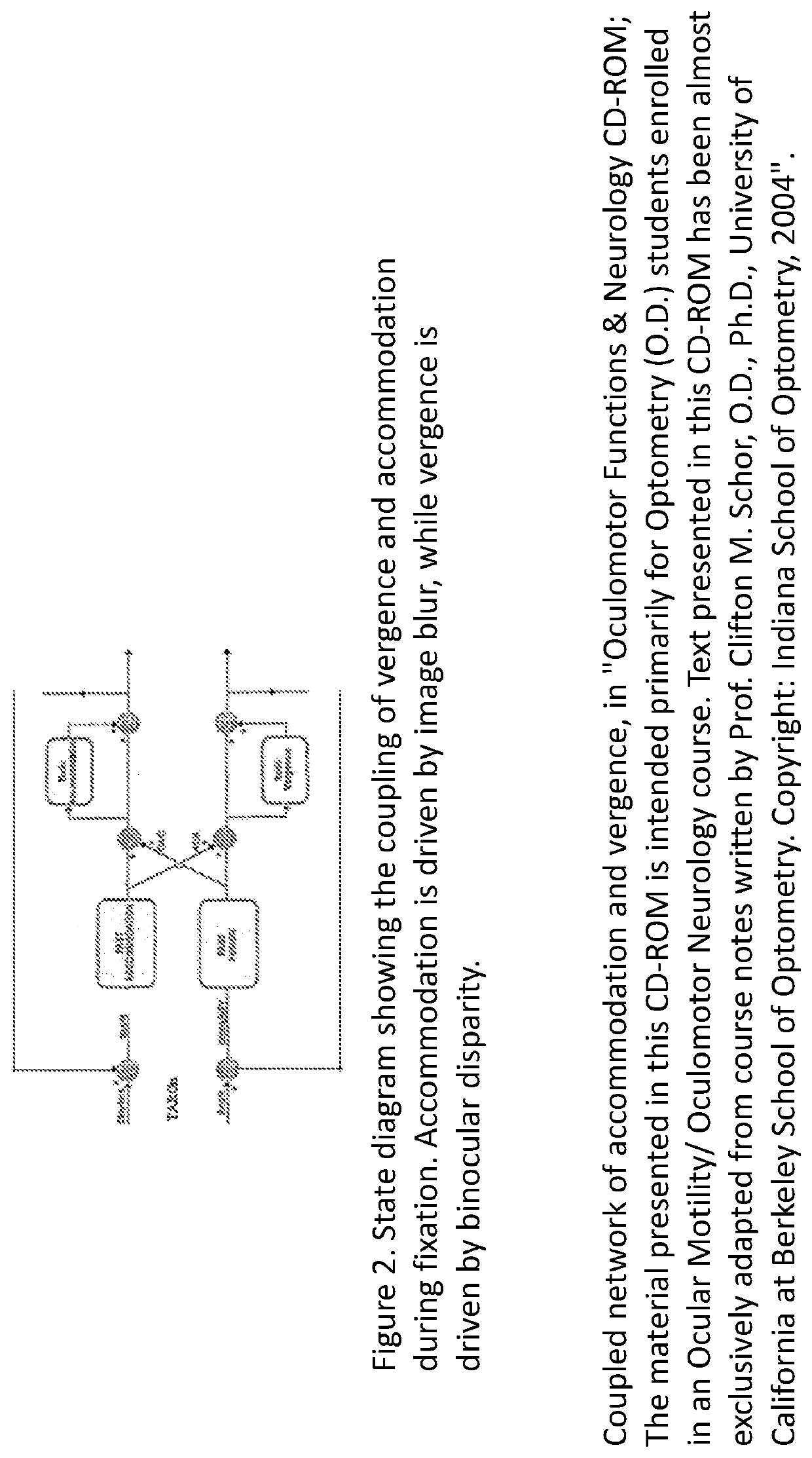
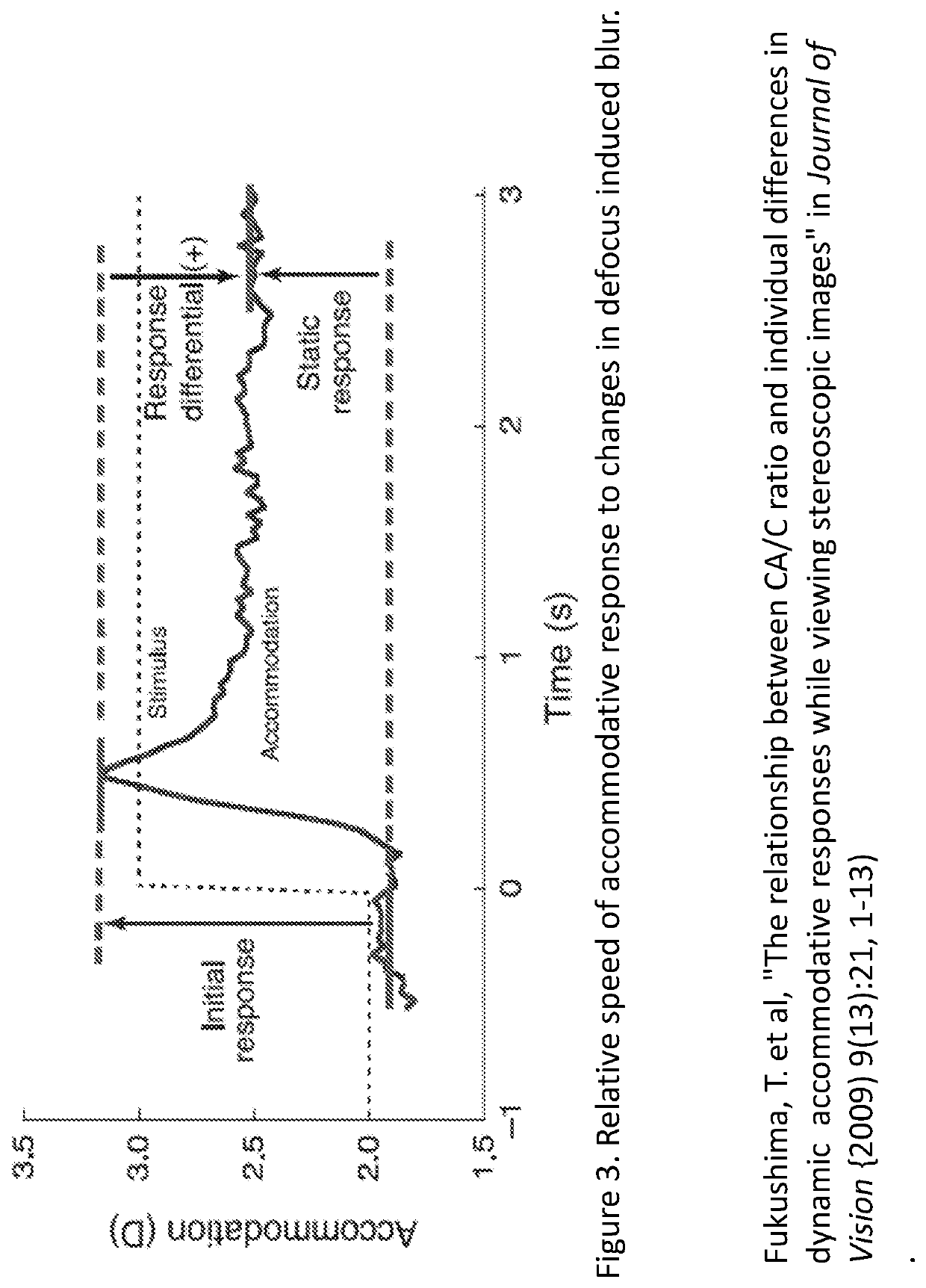
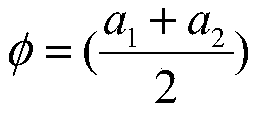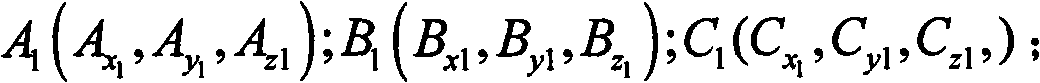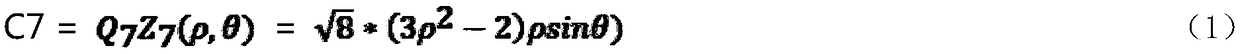Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Dioptric correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
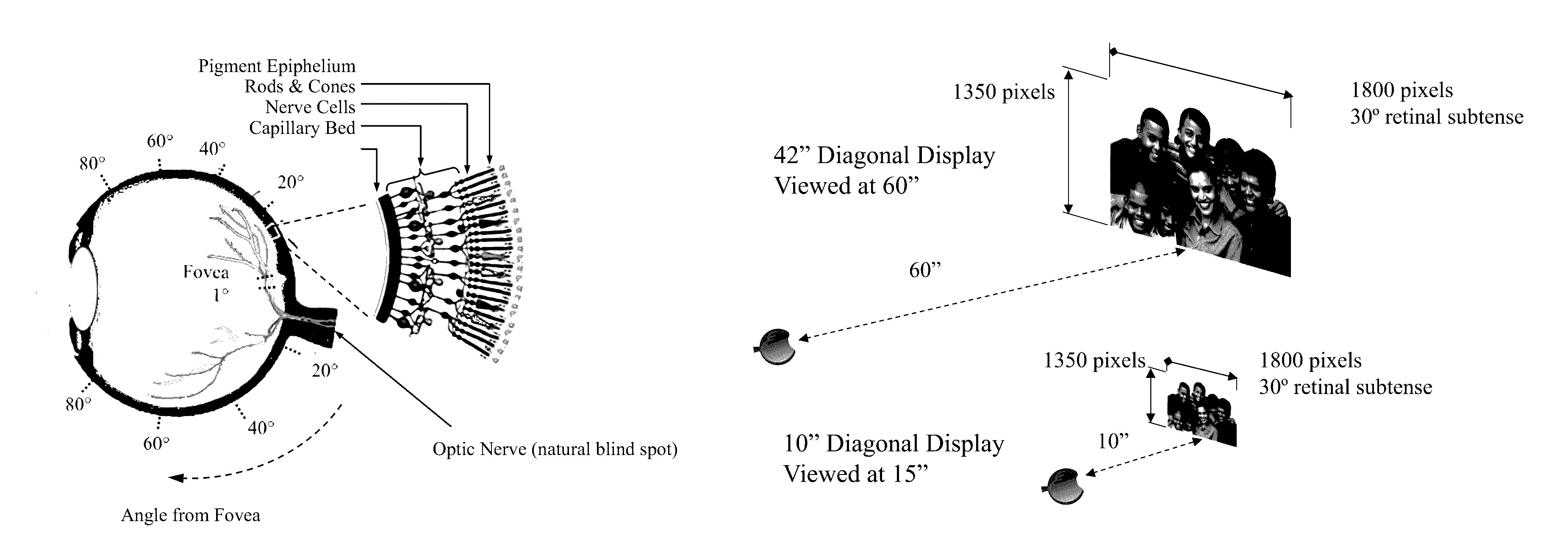
Dioptric correction is the expression for the adjustment of the optical instrument to the varying visual acuity of a person's eyes. It is the adjustment of one lens to provide compatible focus when the viewer's eyes have differing visual capabilities. One result is less strain on the eyes that allow for optimal viewing and depth and contrast focusing when composing a photograph or viewing an item through a device made of lenses or lens elements.
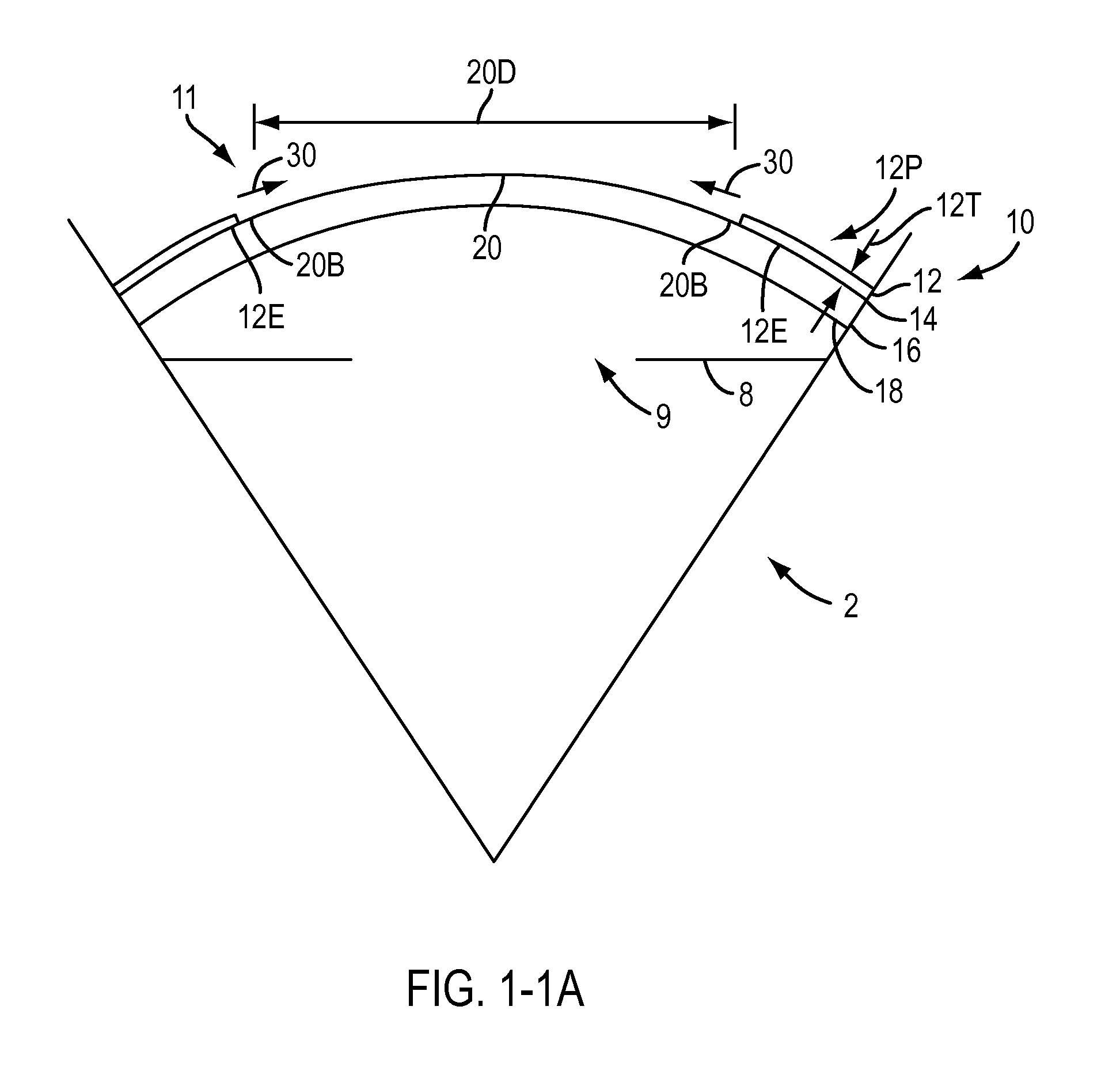
Apparatus and Method for Enhancing Human Visual Performance in a Head Worn Video System
InactiveUS20130215147A1Mitigate such drawbackCathode-ray tube indicatorsEye diagnosticsDisplay deviceRadiology
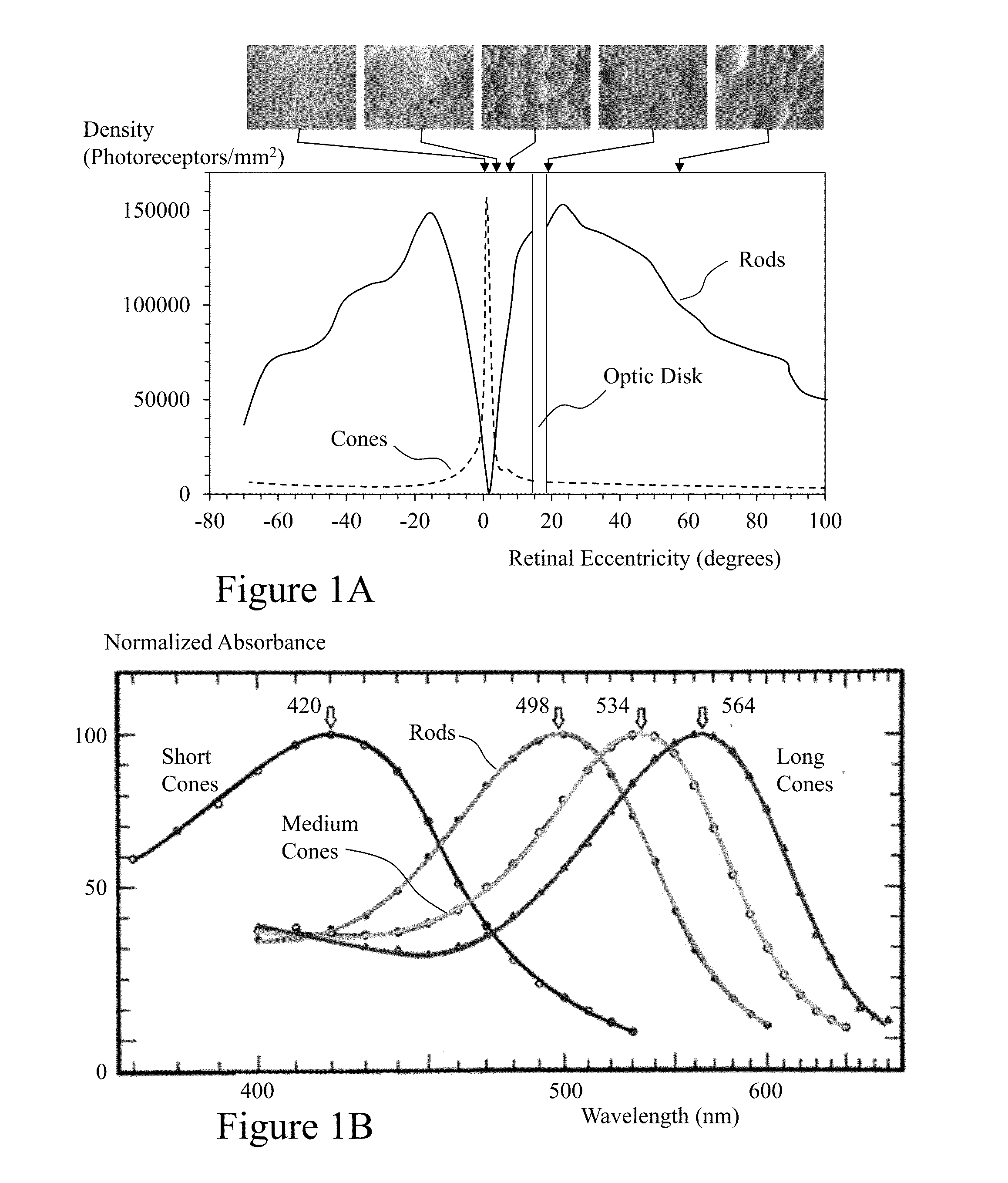
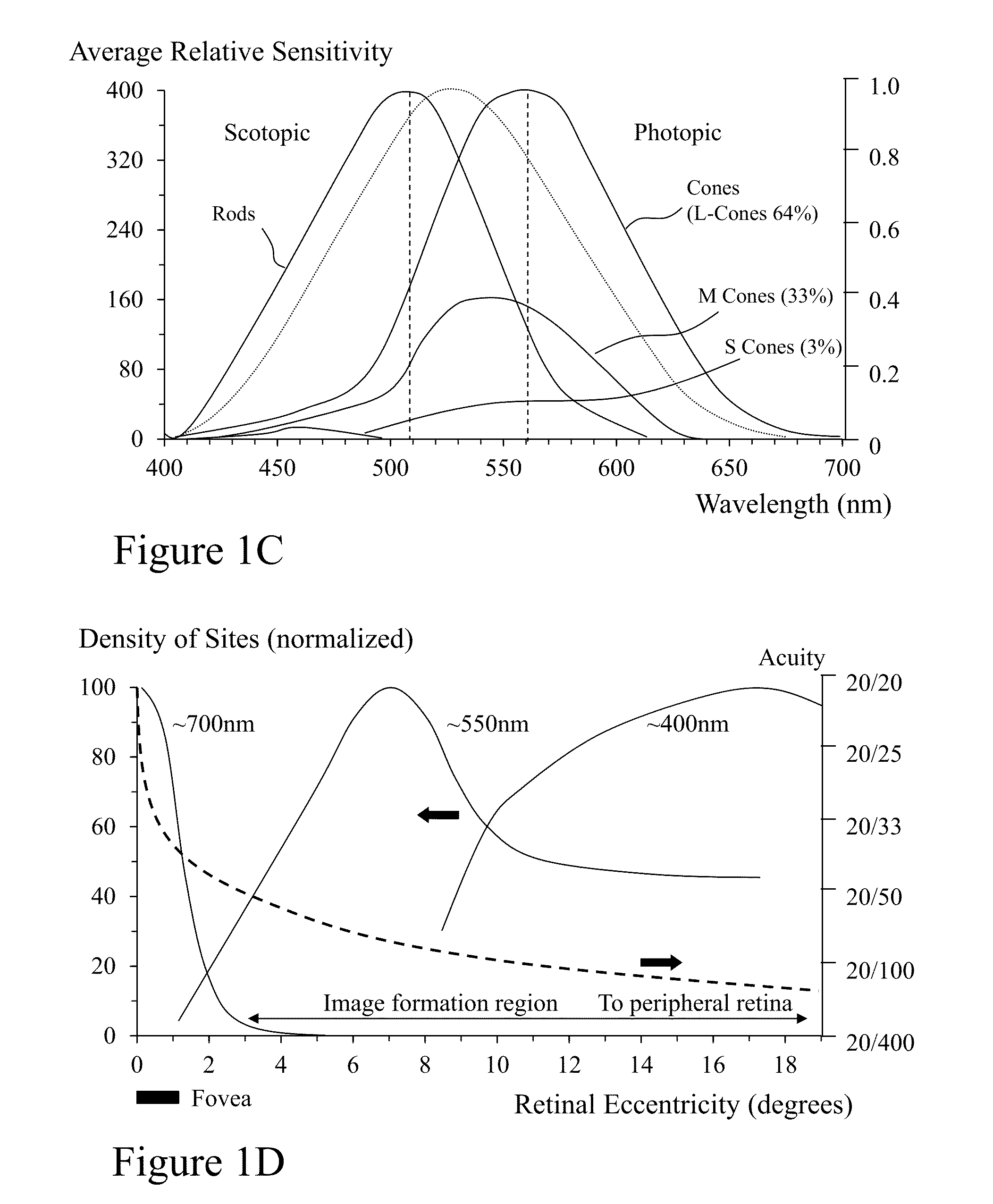
Visual impairment, or vision impairment, refers to the vision loss of an individual to such a degree as to require additional support for one or more aspects of their life. Such a significant limitation of visual capability may result from disease, trauma, congenital, and / or degenerative conditions that cannot be corrected by conventional means, such as refractive correction, such as eyeglasses or contact lenses, medication, or surgery. According to embodiments of the invention a method of augmenting a user's sight is provided comprising obtaining an image of a scene using a camera carried by the individual, transmitting the obtained image to a processor, selecting an algorithm of a plurality of spectral, spatial, and temporal image modification algorithms to be applied to the image by the processor, modifying the using the algorithm substantially in real time, and displaying the modified image on a display device worn by the individual.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Laser method for shaping of optical lenses
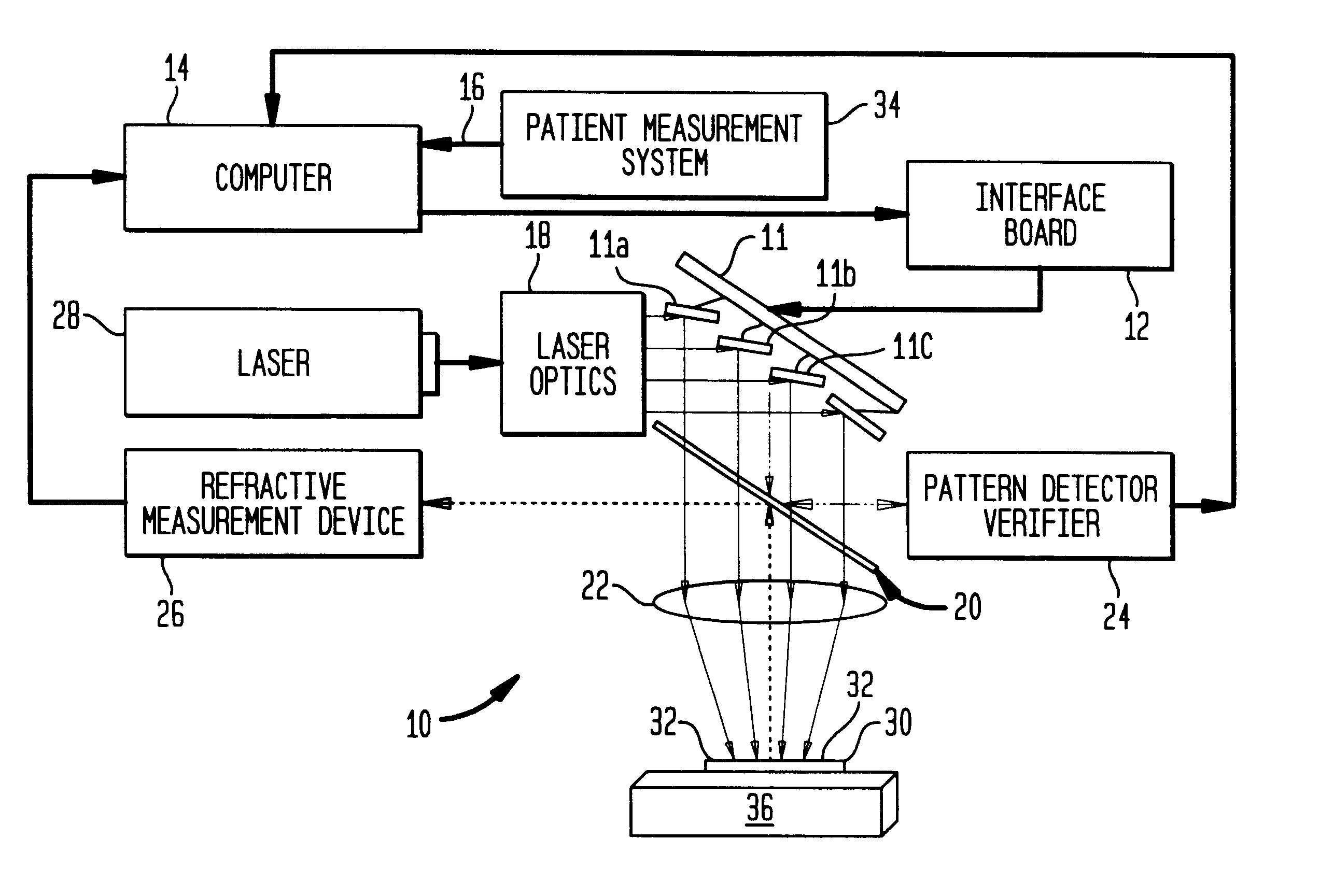
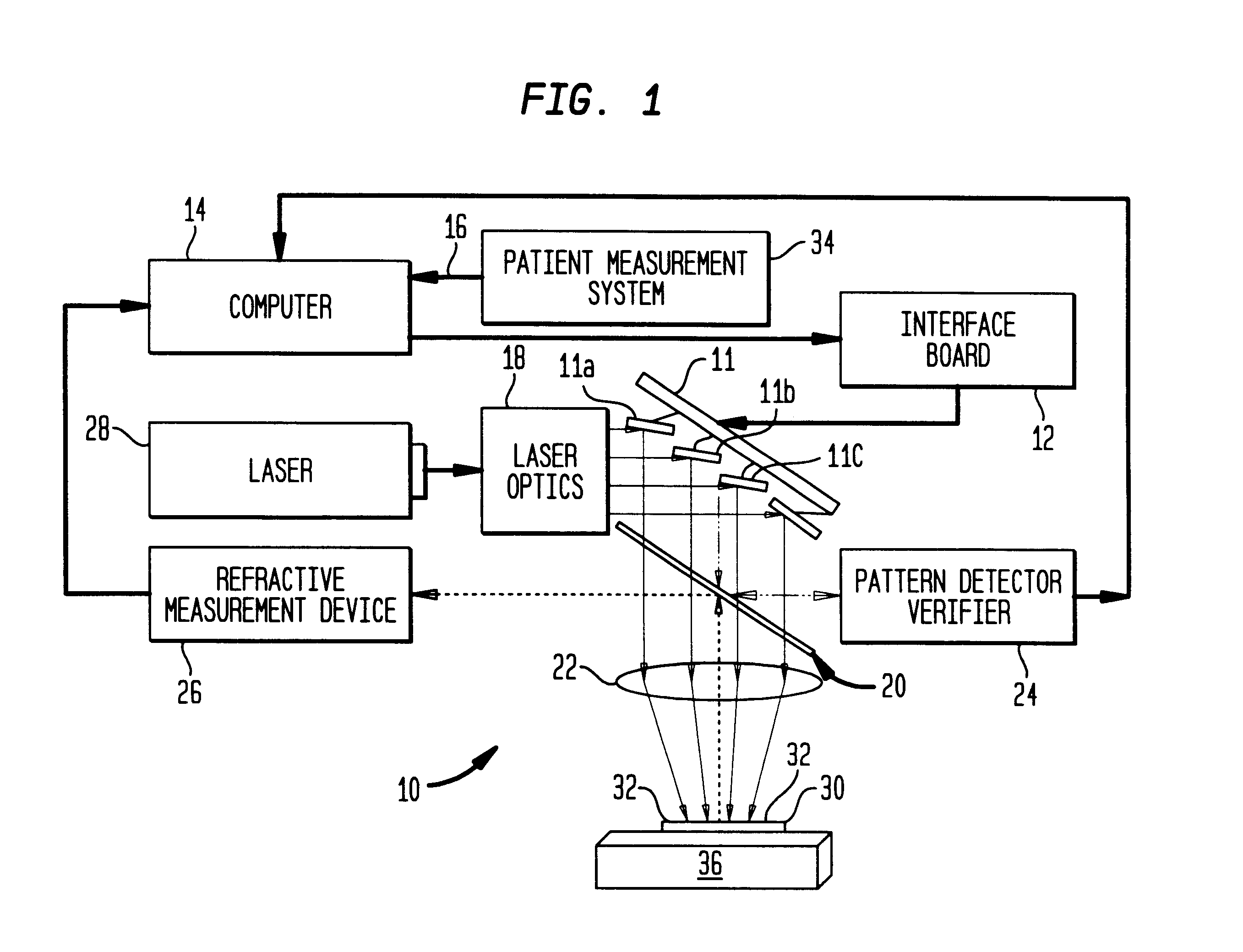
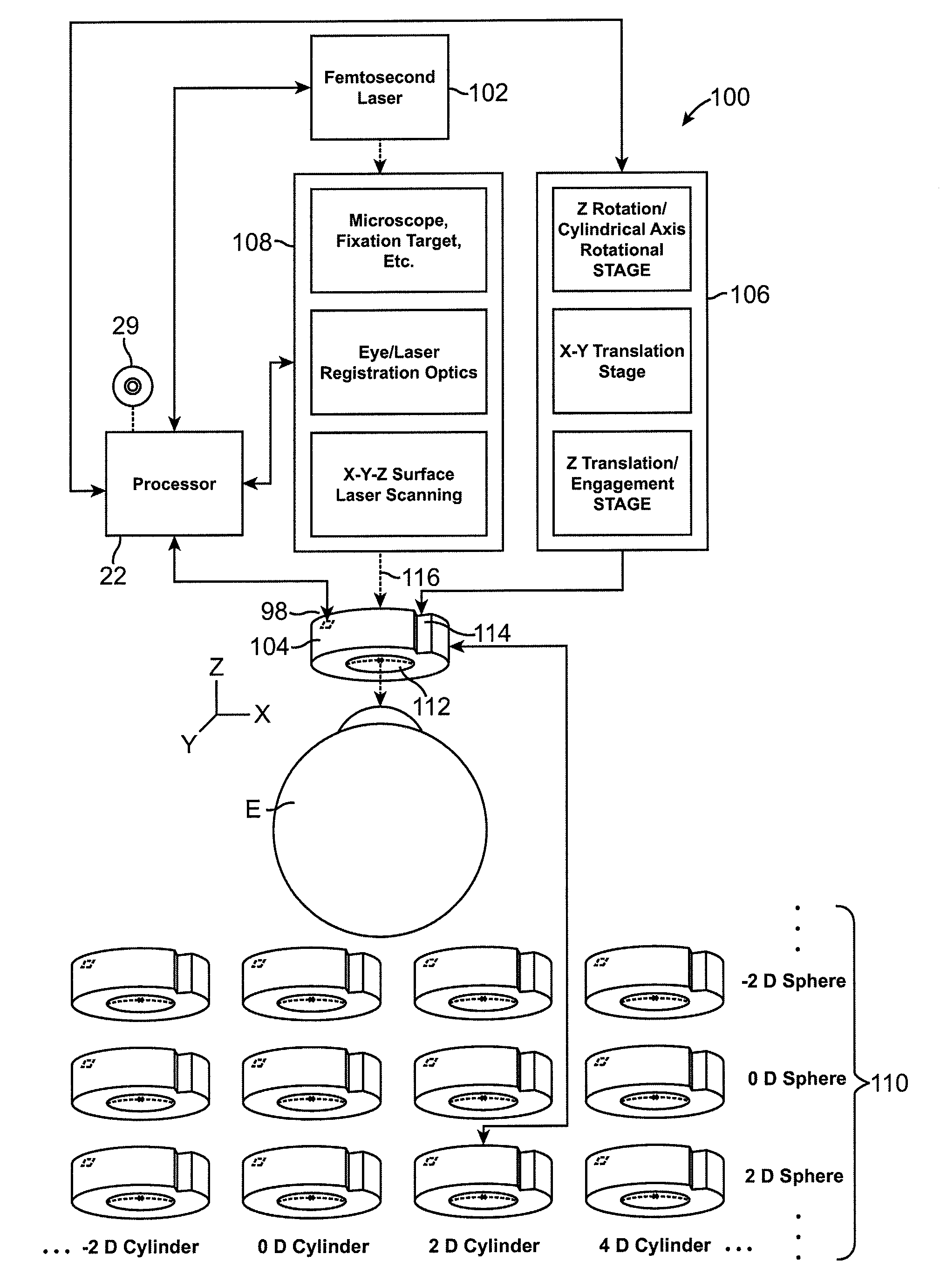
A method for making accurate and precise customized corrections to the surface of an optical lens is described. An electronic correction contour is generated from a measured refractive correction for a patient, and transferred to the surface of the lens by ablation etching with one or more laser pulses. After each of the laser pulses, the refractive properties of the lens are measured and compared to the electronic contour correction derived from a patient's refractive correction. The ablation etching is terminated in localized areas where the refractive properties match the electronic correction contour. End point detection includes monitoring refractive qualities of the lens during the recontouring process, modifying the pattern through changes in the laser pulses.
Owner:WESTAR PHOTONICS
Apparatus and Method for Enhancing Human Visual Performance in a Head Worn Video System
Visual impairment, or vision impairment, refers to the vision loss of an individual to such a degree as to require additional support for one or more aspects of their life. Such a significant limitation of visual capability may result from disease, trauma, congenital, and / or degenerative conditions that cannot be corrected by conventional means, such as refractive correction, such as eyeglasses or contact lenses, medication, or surgery. According to embodiments of the invention a method of augmenting a user's sight is provided comprising obtaining an image of a scene using a camera carried by the individual, transmitting the obtained image to a processor, selecting an algorithm of a plurality of spectral, spatial, and temporal image modification algorithms to be applied to the image by the processor, modifying the image using the algorithm substantially in real time, and displaying the modified image on a display device worn by the individual.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Intrastromal refractive correction systems and methods
InactiveUS20090234335A1Quickly and accurately inciseSignificant changeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorTarget surface
Devices, systems, and methods for laser eye surgery selectively ablate tissues within the cornea of an eye along one or more target surfaces, so that corneal tissue bordered by the laser incision surface(s) can be mechanically removed. An appropriate tissue-shaping surface can be selected based on the regular refractive error of the eye, and a shape of the target laser surface(s) can be calculated so as to correct irregular refractive errors of the eye, impose desired additional sphero-cylindrical and / or irregular alterations.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Eye covering and refractive correction methods and apparatus having improved tear flow, comfort, and/or applicability
An eye covering such as a contact lens may comprise one or more structures to pump tear liquid under the covering such that the covering can remain in the eye and correct vision for an extended amount of time. In many embodiments, the covering comprises a material having fenestrations to draw tear liquid under the covering and an outer portion shaped to contact the conjunctiva over the sclera, such that when the eye closes pressure of one or more eyelids urges tear liquid through one or more fenestrations and under the outer portion shaped to contact the conjunctiva. When the eye blinks, the pressure of the one or more eyelids can urge the covering toward the cornea such that tear liquid can pass through the fenestrations.
Owner:JOURNEY1 INC
Intrastromal Refractive Correction Systems and Methods
InactiveUS20070219543A1Quickly and accurately inciseSignificant changeLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsRefractive errorTarget surface
Devices, systems, and methods for laser eye surgery selectively ablate tissues within the cornea of an eye along one or more target surfaces, so that corneal tissue bordered by the laser incision surface(s) can be mechanically removed. An appropriate tissue-shaping surface can be selected based on the regular refractive error of the eye, and a shape of the target laser surface(s) can be calculated so as to correct irregular refractive errors of the eye, impose desired additional sphero-cylindrical and / or irregular alterations.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Apparatus and method for enhancing human visual performance in a head worn video system
Visual impairment, or vision impairment, refers to the vision loss of an individual to such a degree as to require additional support for one or more aspects of their life. Such a significant limitation of visual capability may result from disease, trauma, congenital, and / or degenerative conditions that cannot be corrected by conventional means, such as refractive correction, such as eyeglasses or contact lenses, medication, or surgery. According to embodiments of the invention a method of augmenting a user's sight is provided comprising obtaining an image of a scene using a camera carried by the individual, transmitting the obtained image to a processor, selecting an algorithm of a plurality of spectral, spatial, and temporal image modification algorithms to be applied to the image by the processor, modifying the image using the algorithm substantially in real time, and displaying the modified image on a display device worn by the individual.
Owner:ESIGHT CORP
Methods and devices for refractive correction of eyes
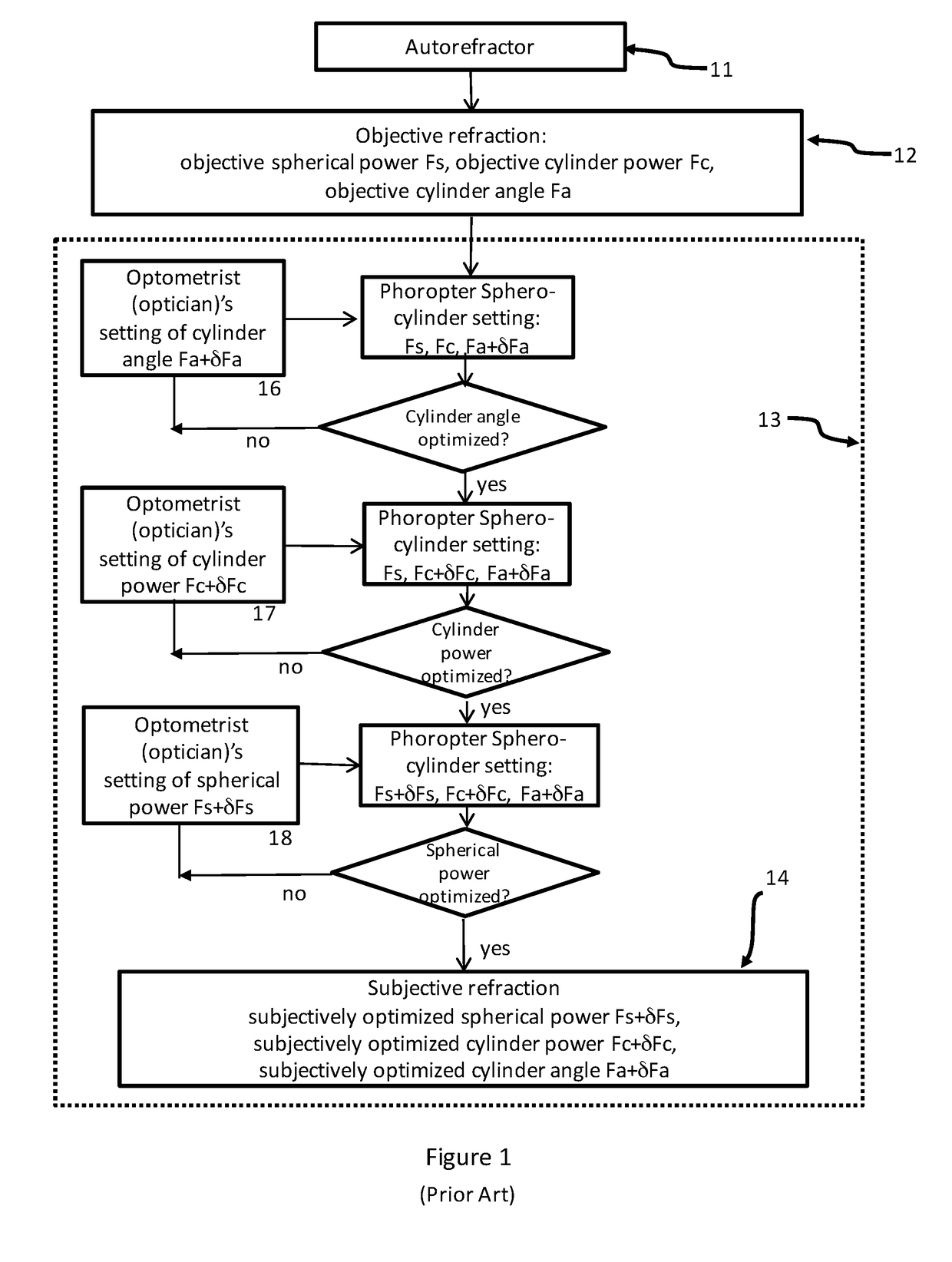
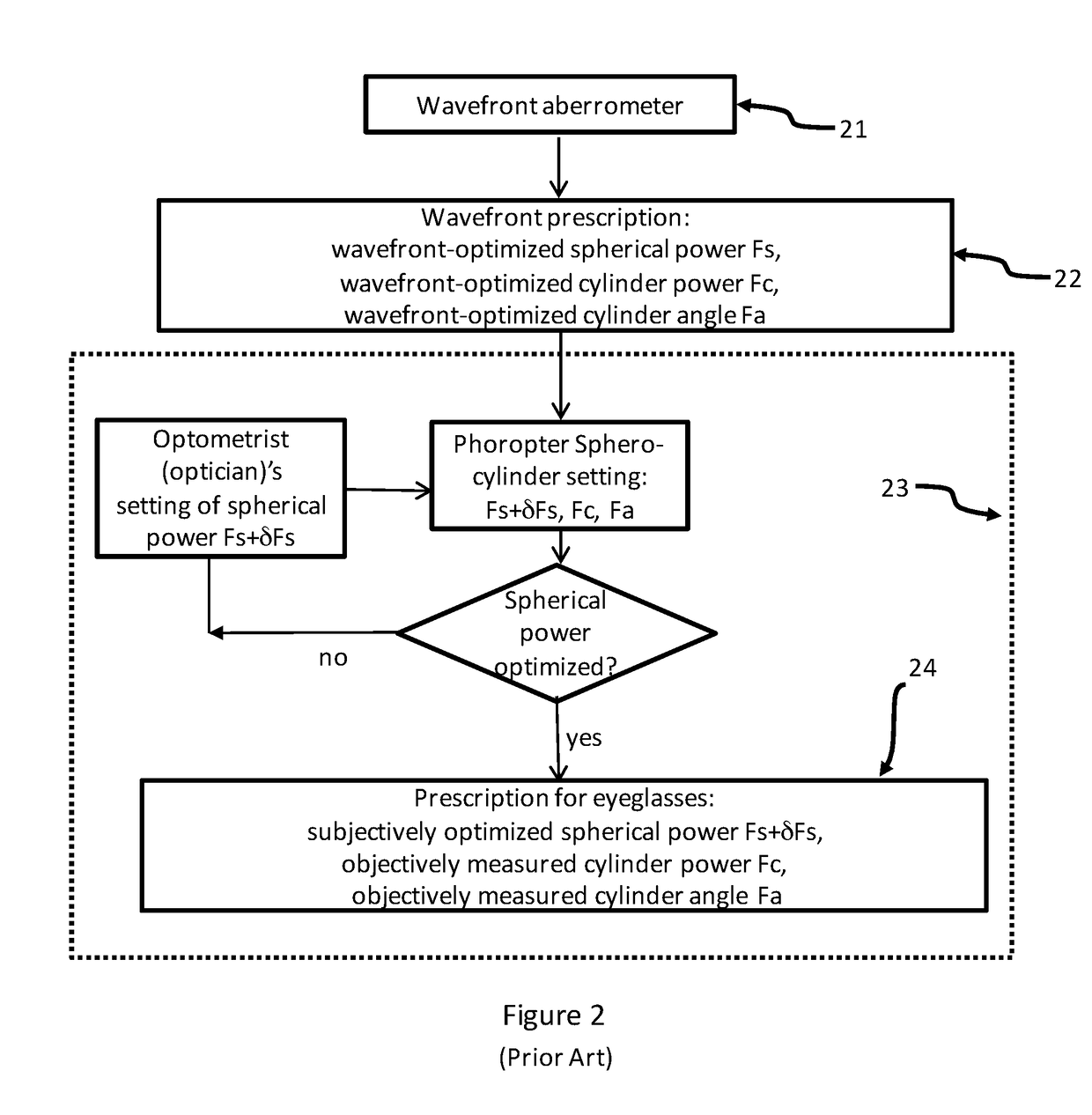
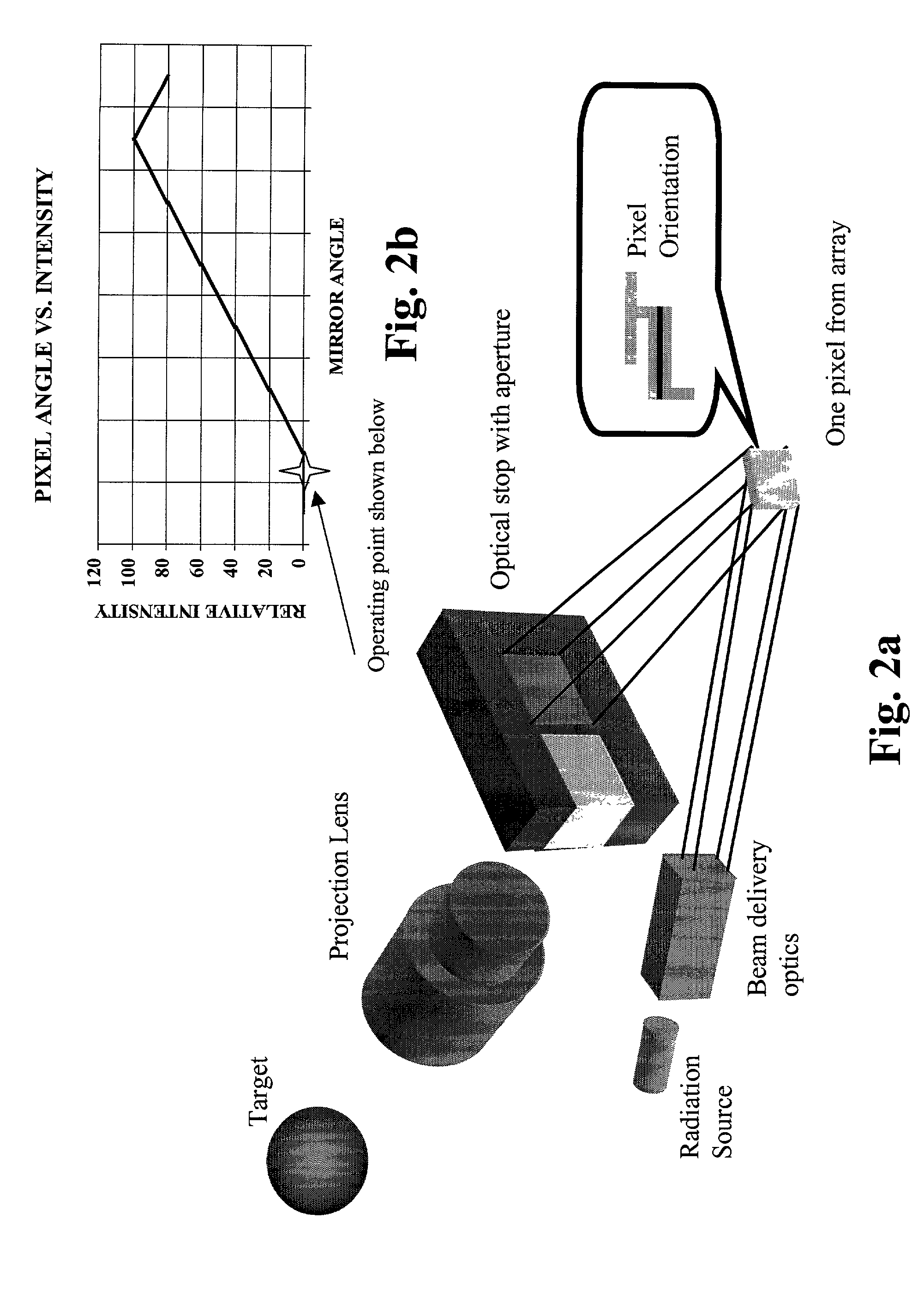
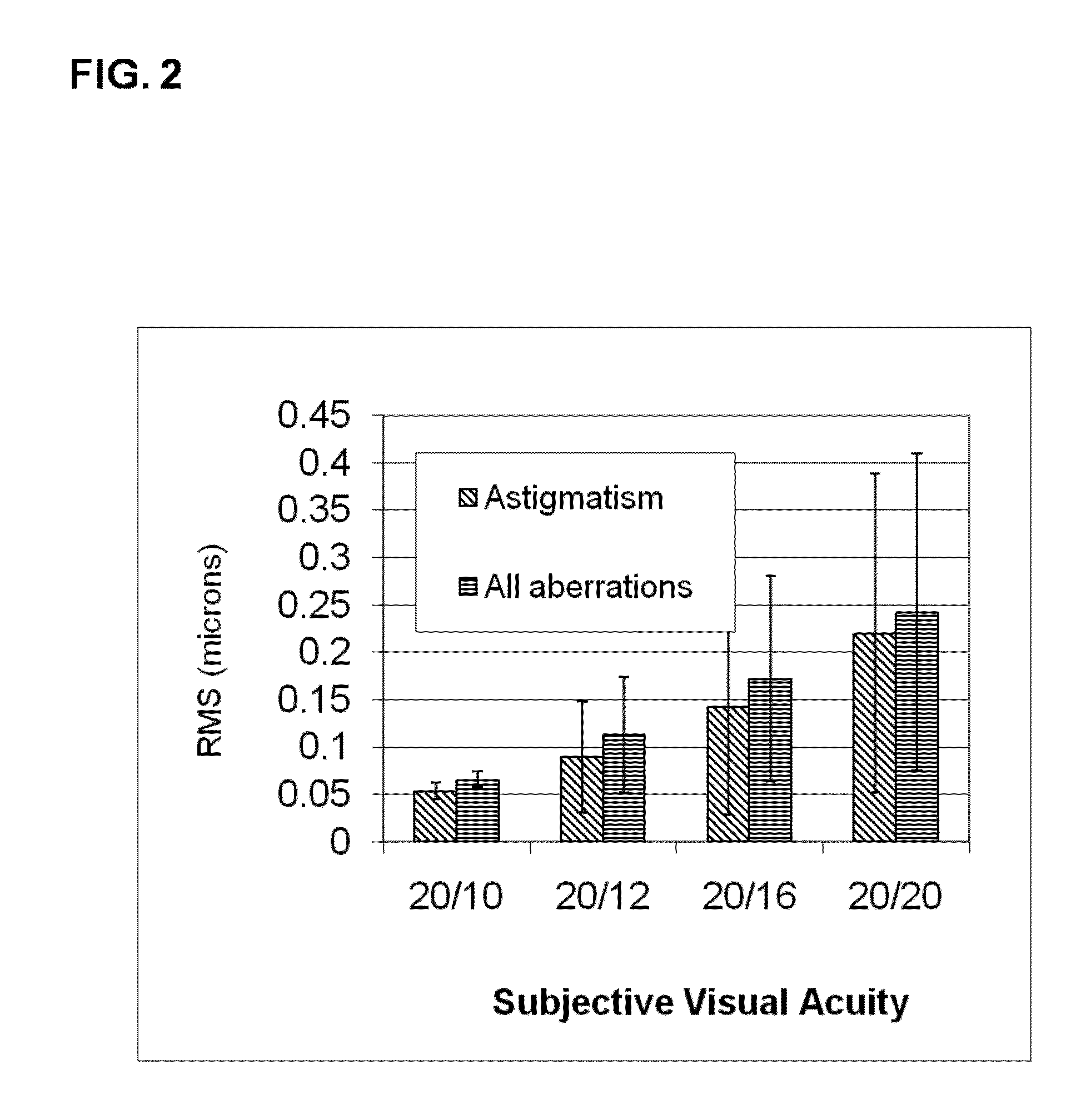
Methods and devices are provided to obtain refractive correction with superior visual acuity (e.g., 20 / 10) by achieving an astigmatism-free customized refractive correction. The astigmatism-free customized refractive correction involves obtaining an objective and precise measurement of cylindrical power in a resolution between 0.01 D and 0.10 D in an eye using an objective aberrometer, reliably relating the cylindrical axis obtained from the objective aberrometer to that in a phoroptor, determining an optimized focus error of an eye through subjective refraction with a phoroptor, generating a customized refraction by combining the objective measured cylindrical power, the objective measured cylindrical axis, and the subjectively measured focus power, fabricating a custom lens with a tolerance finer than 0.09 D based on the generated customized refraction, and delivering an ophthalmic lens that can provide an astigmatism-free refractive correction for an eye.
Owner:PERFECT VISION TECH HK
Optimization of ablation correction of an optical system and associated methods
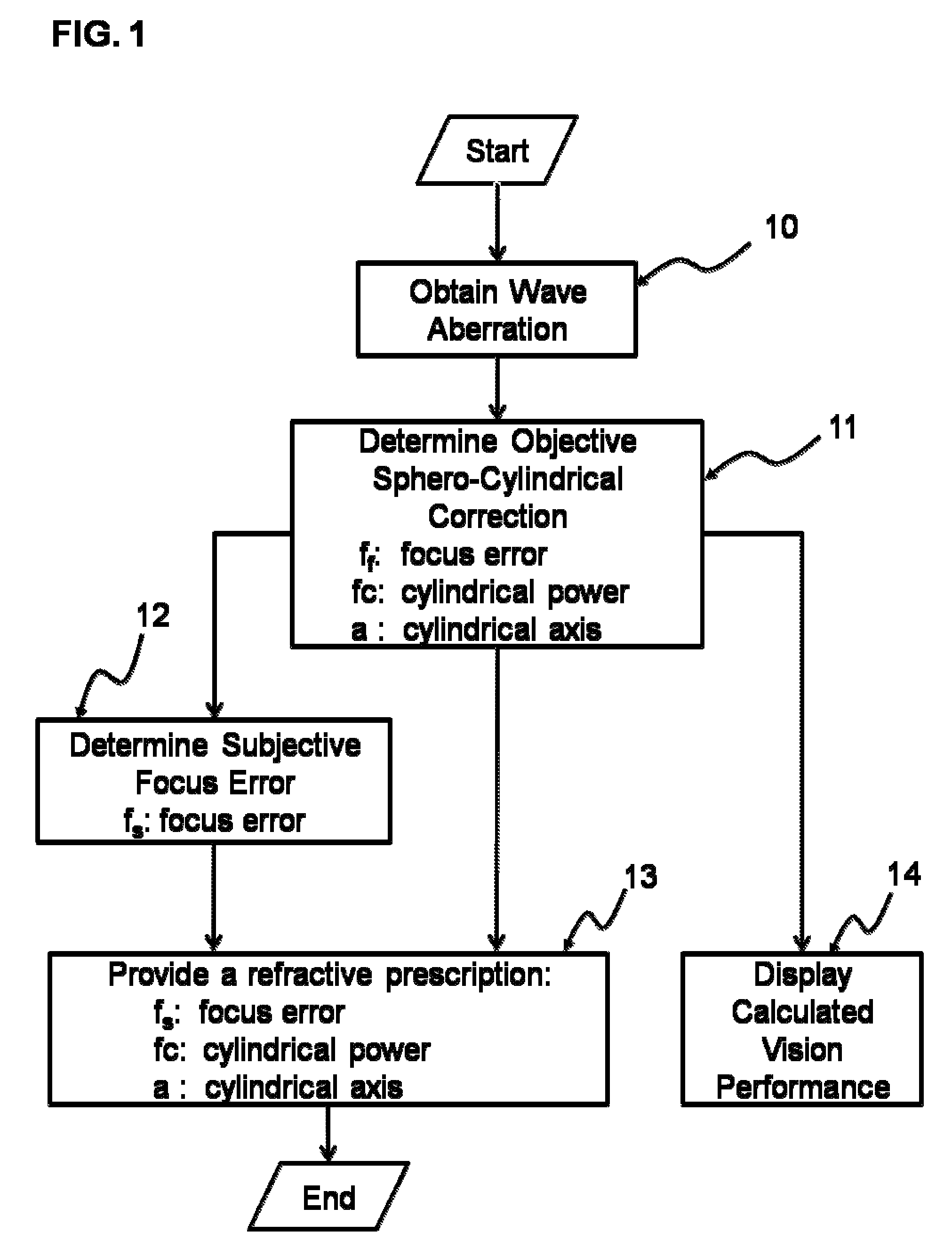
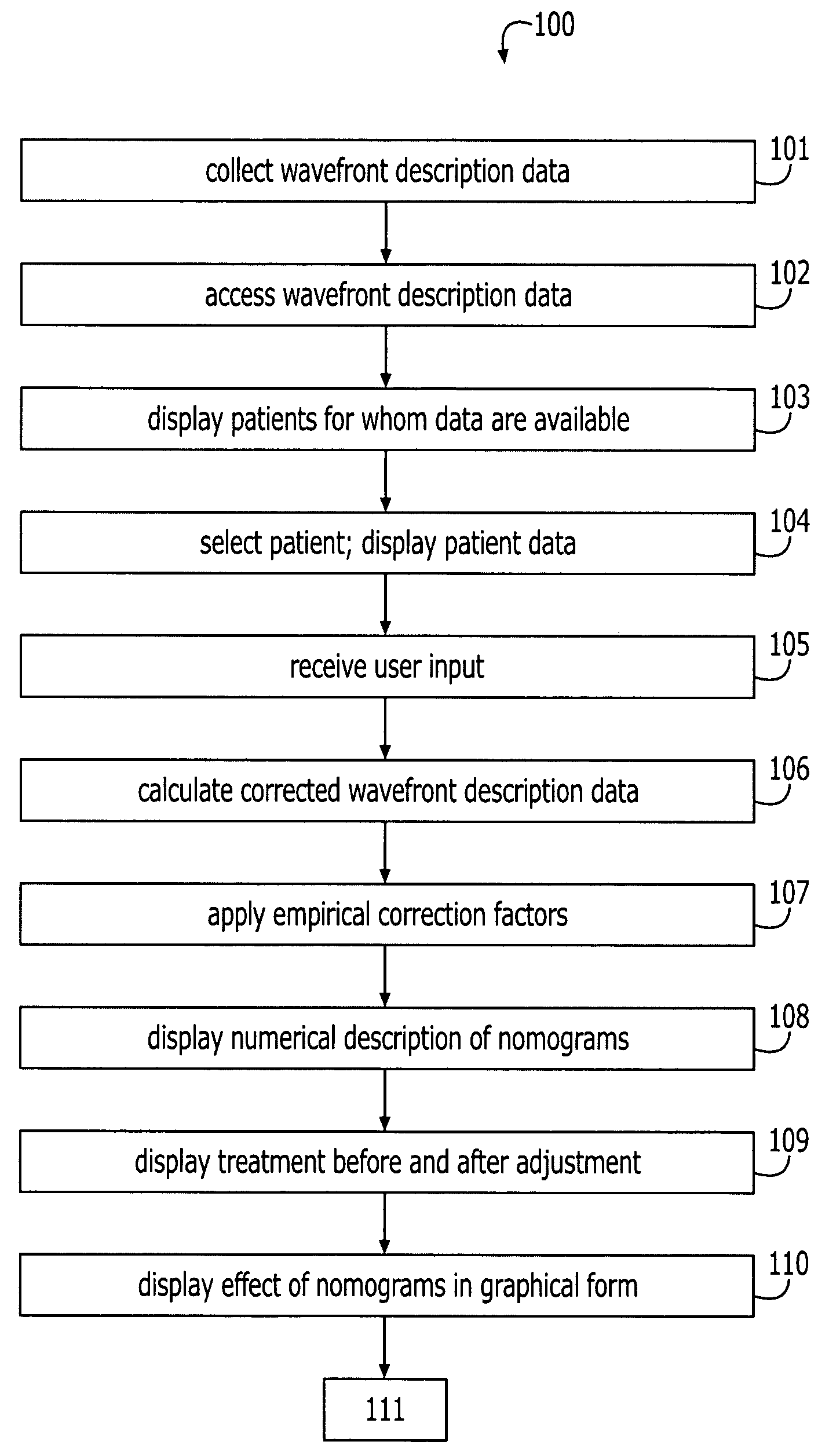
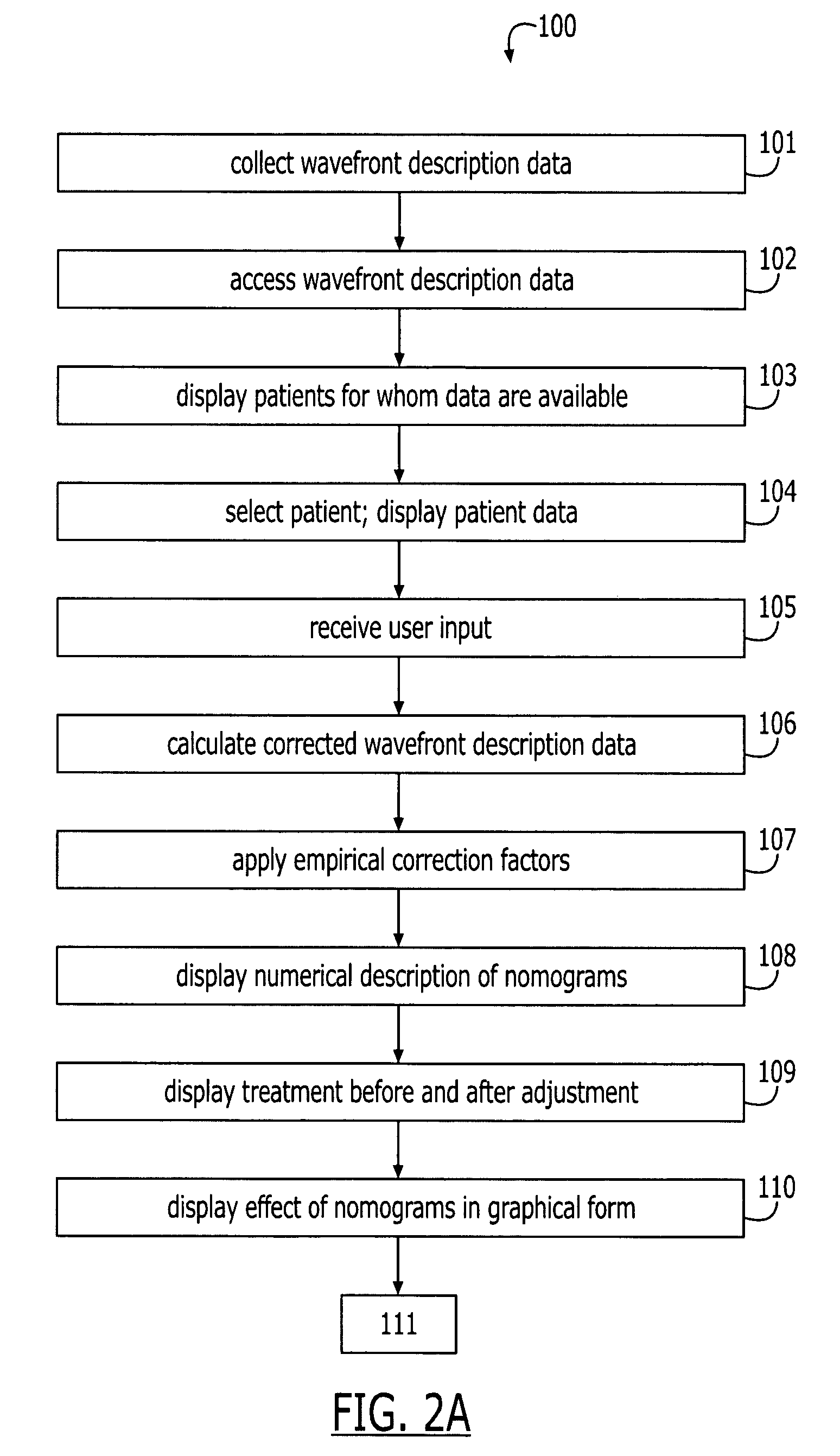
A method for optimizing a prescription for laser-ablation corneal treatment achieves the modification of wavefront-based refractive correction data with the use of user / doctor-input nomograms. Data comprising a wavefront description of a patient eye are received and displayed to a user, who can then make modifications to these treatment data. A modification is calculated based upon the desired correction to yield corrected wavefront description data, which are displayed to the user. A system includes a processor and a device for transmitting a wavefront description of a patient eye to the processor. An input device is adapted to receive a desired correction to the wavefront description data. Software is resident on the processor having code segments for implementing the calculations as described.
Owner:ALCON INC
Methods and Systems for Determining Refractive Corrections of Human Eyes for Eyeglasses
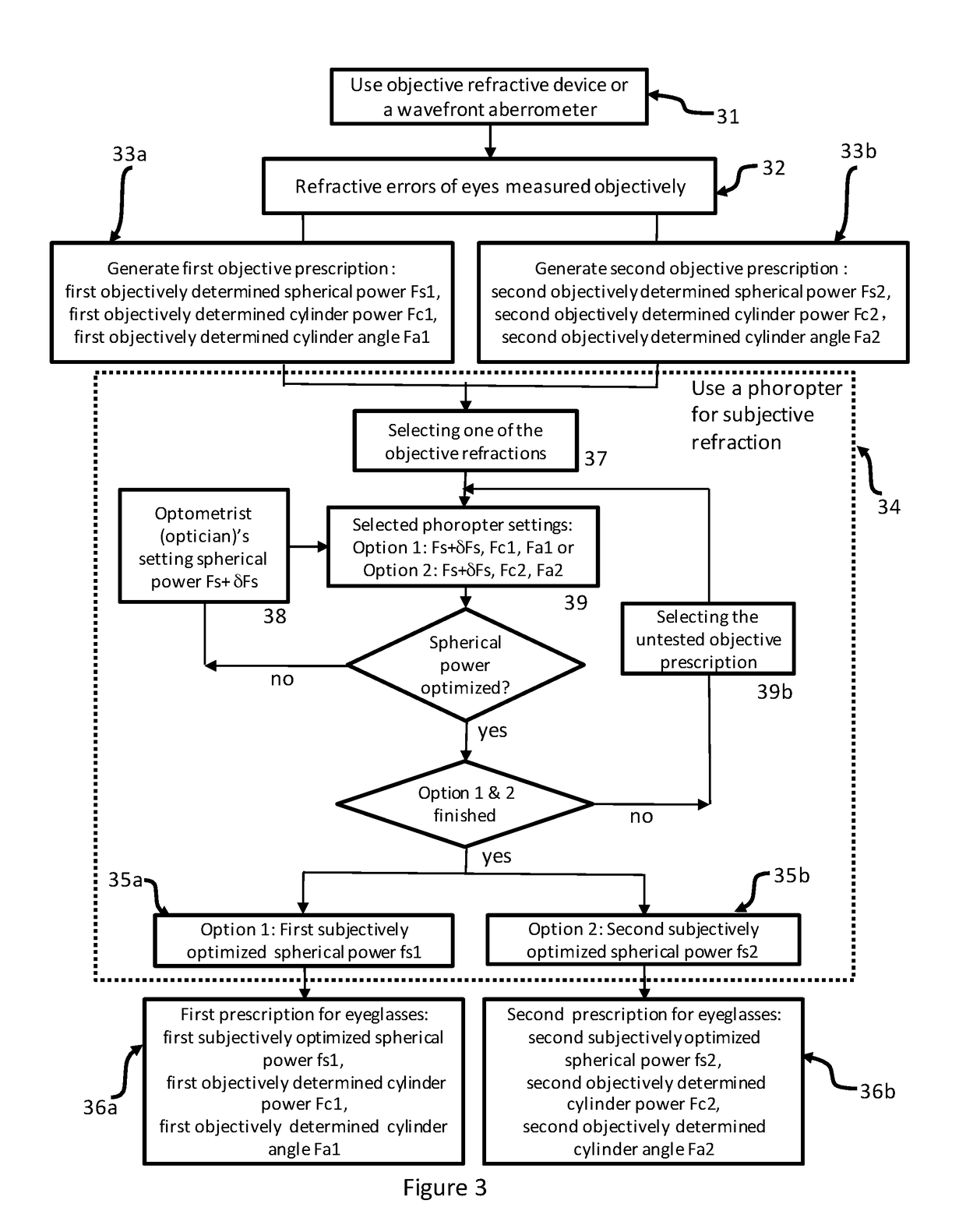
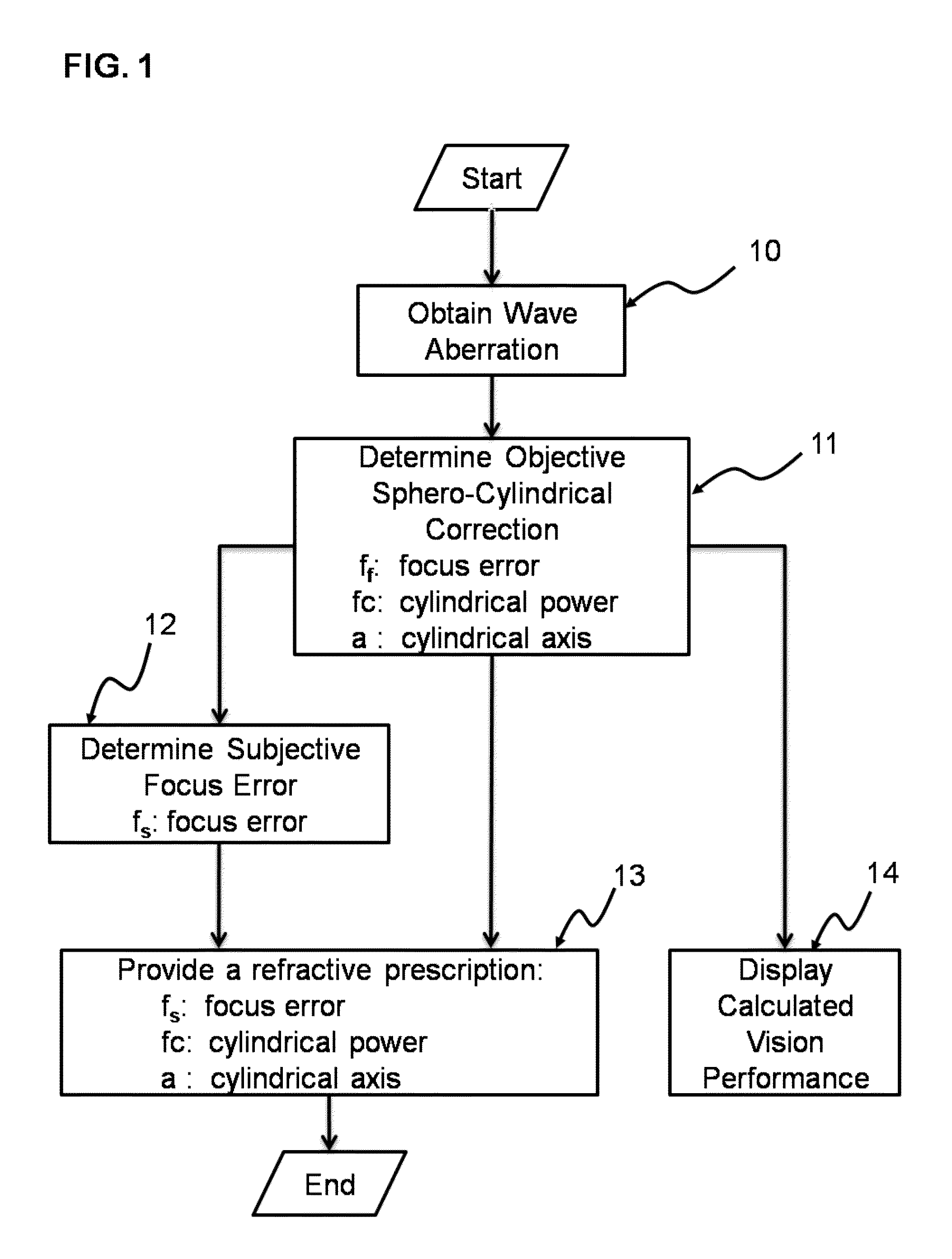
Methods, devices, and systems are disclosed for determining refractive corrections of human eyes to reduce and eliminate image distortion associated with eyeglasses. In some embodiments, an objective refraction module is configured to measure refractive errors of an eye objectively, without subjective feedback from a tested subject. A computation module is configured to generate a plurality of objective prescriptions. A phoropter module is configured to perform a subjective refraction for determining a plurality of subjective spherical powers based on the plurality of objective prescriptions. An output module is configured to generate a plurality of prescriptions for eyeglasses, the plurality of prescriptions comprising (a) a first prescription having a first subjective spherical power f.sub.s1, a first objective cylinder power F.sub.c1, and a first objective cylinder angle F.sub.a1, and (b) a second prescription having a second subjective spherical power f.sub.s2, a second objective cylinder power F.sub.c2, and a second objective cylinder angle F.sub.a2.
Owner:PERFECT VISION TECH HK
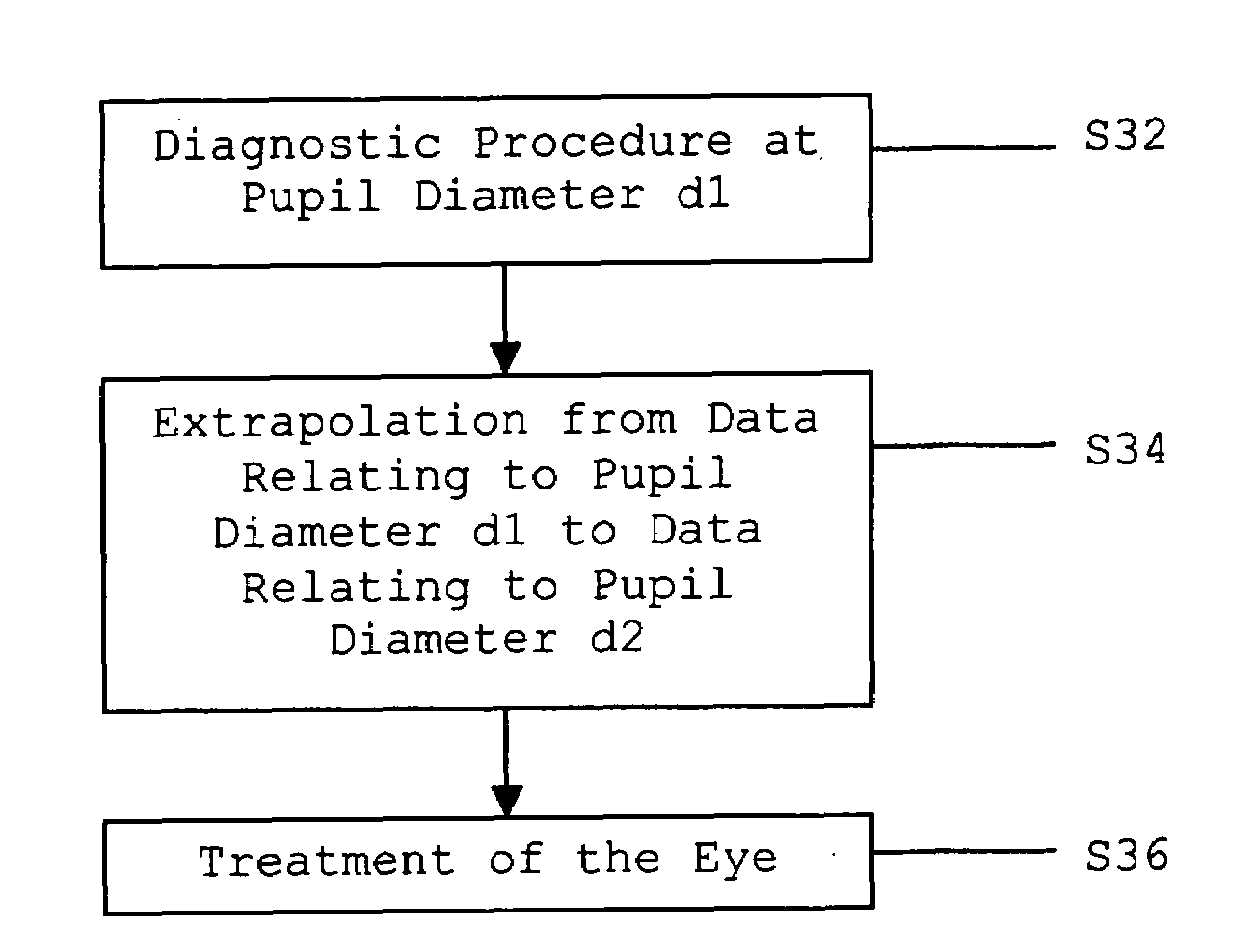
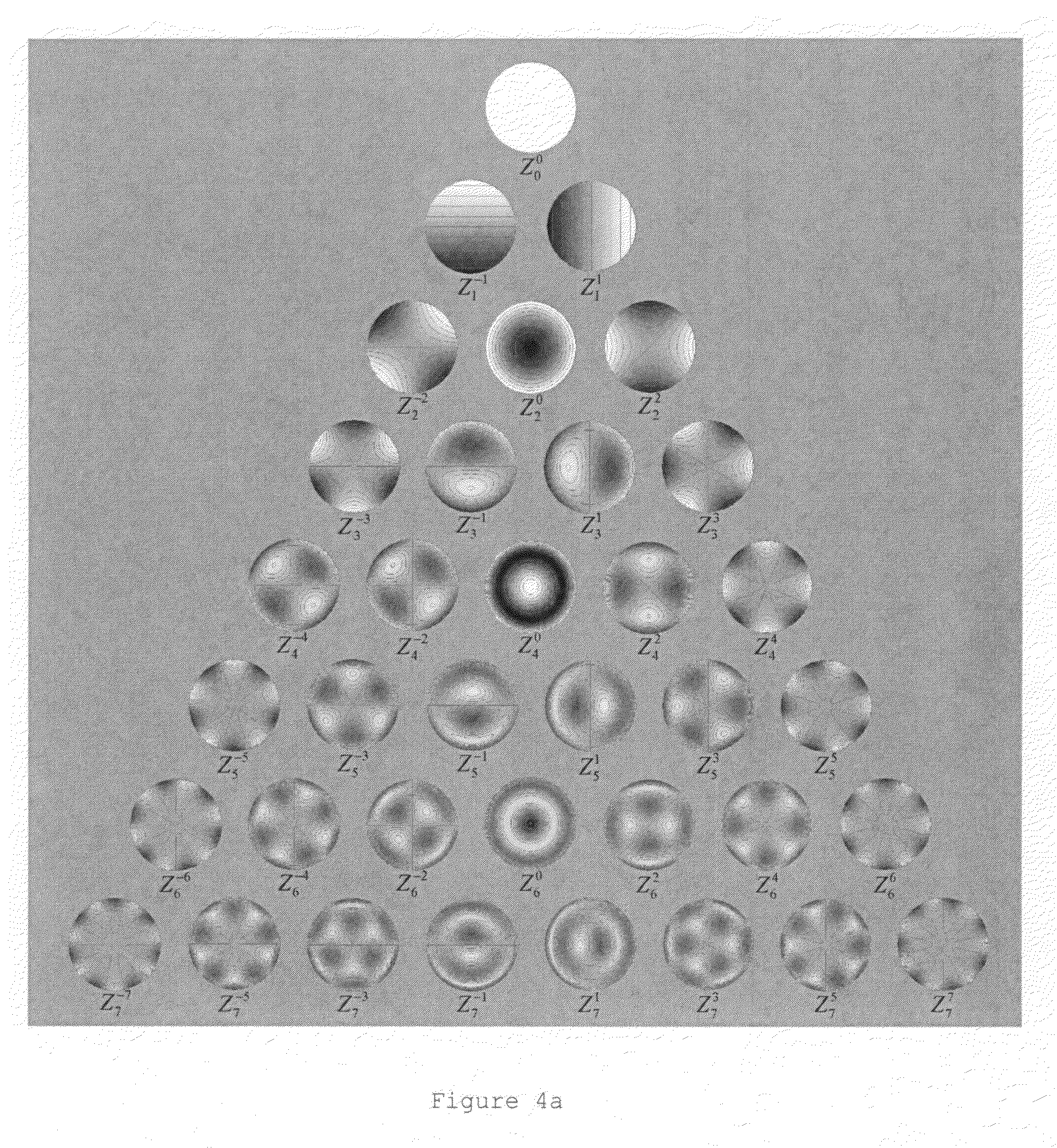
Method and apparatus for extrapolating diagnostic data
ActiveUS20090006508A1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsDiagnostic programPupil diameter
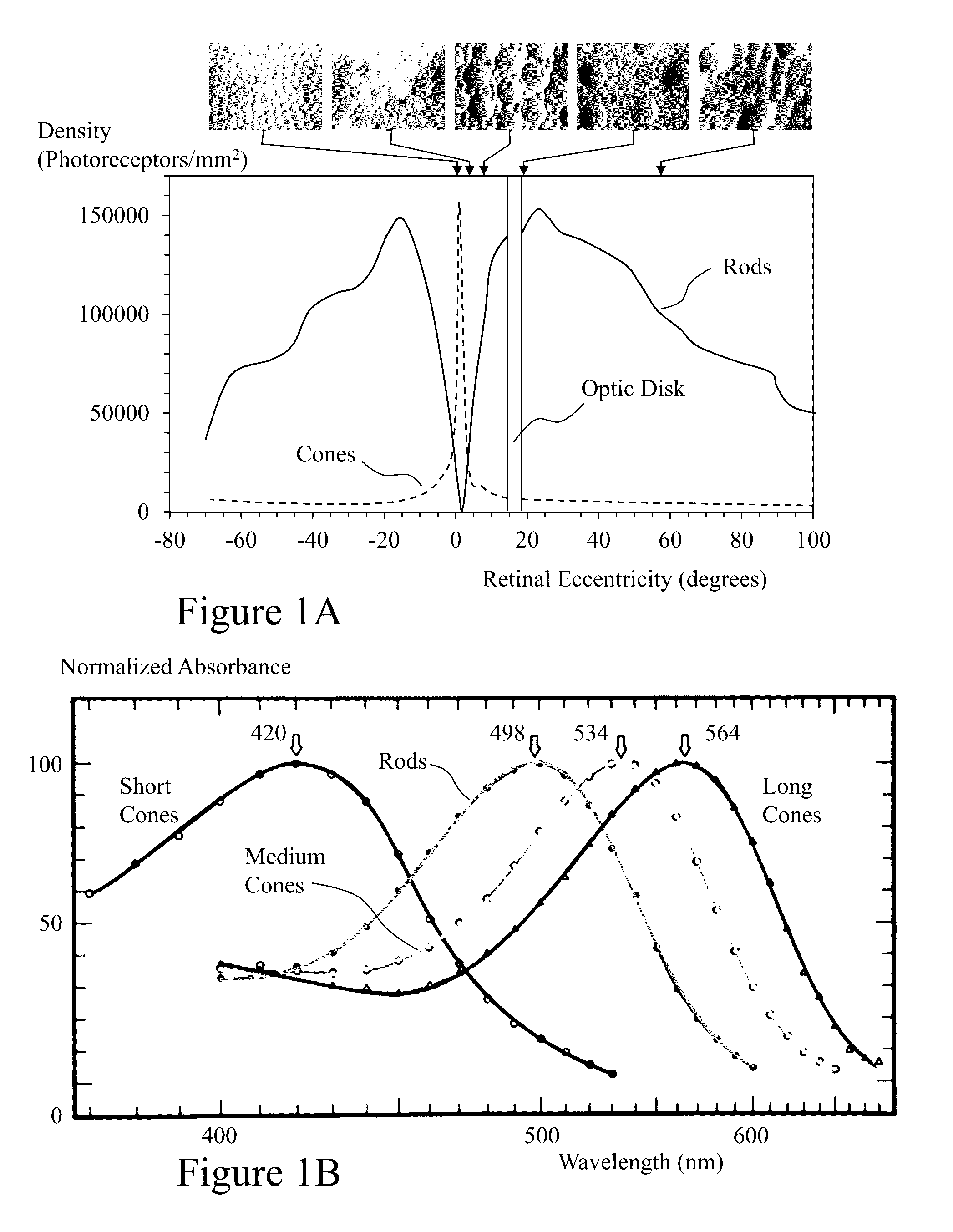
A method and an apparatus for extrapolating diagnostic data relating to one pupil diameter to another pupil diameter. Embodiments according to the invention are more particularly directed to extrapolating wavefront aberration data, for example, in the form of Zernike polynomial data, obtained from a smaller pupil diameter, d1, to a larger pupil diameter, d2. Data relating to the first pupil diameter d1 may be obtained in a diagnostic procedure. In the extrapolation, a conversion matrix M is utilized. The conversion matrix M can be generated from a static matrix and a dynamic matrix, the latter taking the pupil diameter d1 into consideration. Data relating the first pupil diameter d1 and wavefront aberration data can be ordered via a permutation matrix P. If necessary, Extrapolated data can be re-ordered via a transposed permutation matrix PT. The extrapolated data relating to the pupil diameter d2 can be processed to obtain an ablation profile, a shot file, or other data for a refractive vision correction treatment.
Owner:BAUSCH & LOMB INC
Laser method for shaping of optical lenses
A method for making accurate and precise customized corrections to the surface of an optical lens is described. An electronic correction contour is generated from a measured refractive correction for a patient, and transferred to the surface of the lens by ablation etching with one or more laser pulses. After each of the laser pulses, the refractive properties of the lens are measured and compared to the electronic contour correction derived from a patient's refractive correction. The ablation etching is terminated in localized areas where the refractive properties match the electronic correction contour. End point detection includes monitoring refractive qualities of the lens during the recontouring process, modifying the pattern through changes in the laser pulses.
Owner:WESTAR PHOTONICS
Flexible refractive film patch with microstructure
InactiveCN109633925AAlleviate the effect of peripheral defocusVarious designsOptical partsLensEye lensSpectacle lenses
The invention relates to a flexible refractive film patch with a microstructure. Besides having the performance of a conventional film patch, the flexible refractive film patch has a certain refractive effect in a prescribed area; after being attached onto the spectacle lens of a spectacle frame, the flexible refractive film maintains a good refractive correction effect at the central region of the spectacle lens; and the flexible refractive film patch can also realize peripheral defocusing, and therefore, the flexible refractive film patch can alleviate the peripheral defocusing effect of theretina of a person who wears glasses. The film patch of the invention can be applied to various spectacle lenses, and is flexible and variable in shape; and the micro-structured ring zone distribution area of the film patch can be designed into various forms, and therefore, the correction needs of different groups can be met.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Methods And Devices For Refractive Correction Of Eyes
Methods and devices are provided to obtain refractive correction with superior visual acuity (e.g., 20 / 10) by achieving an astigmatism-free customized refractive correction. The astigmatism-free customized refractive correction involves obtaining an objective and precise measurement of cylindrical power in a resolution between 0.01 D and 0.10 D in an eye using an objective aberrometer, reliably relating the cylindrical axis obtained from the objective aberrometer to that in a phoroptor, determining an optimized focus error of an eye through subjective refraction with a phoroptor, generating a customized refraction by combining the objective measured cylindrical power, the objective measured cylindrical axis, and the subjectively measured focus power, fabricating a custom lens with a tolerance finer than 0.09 D based on the generated customized refraction, and delivering an ophthalmic lens that can provide an astigmatism-free refractive correction for an eye.
Owner:PERFECT VISION TECH HK
Systems and methods for refractive correction in visual field testing
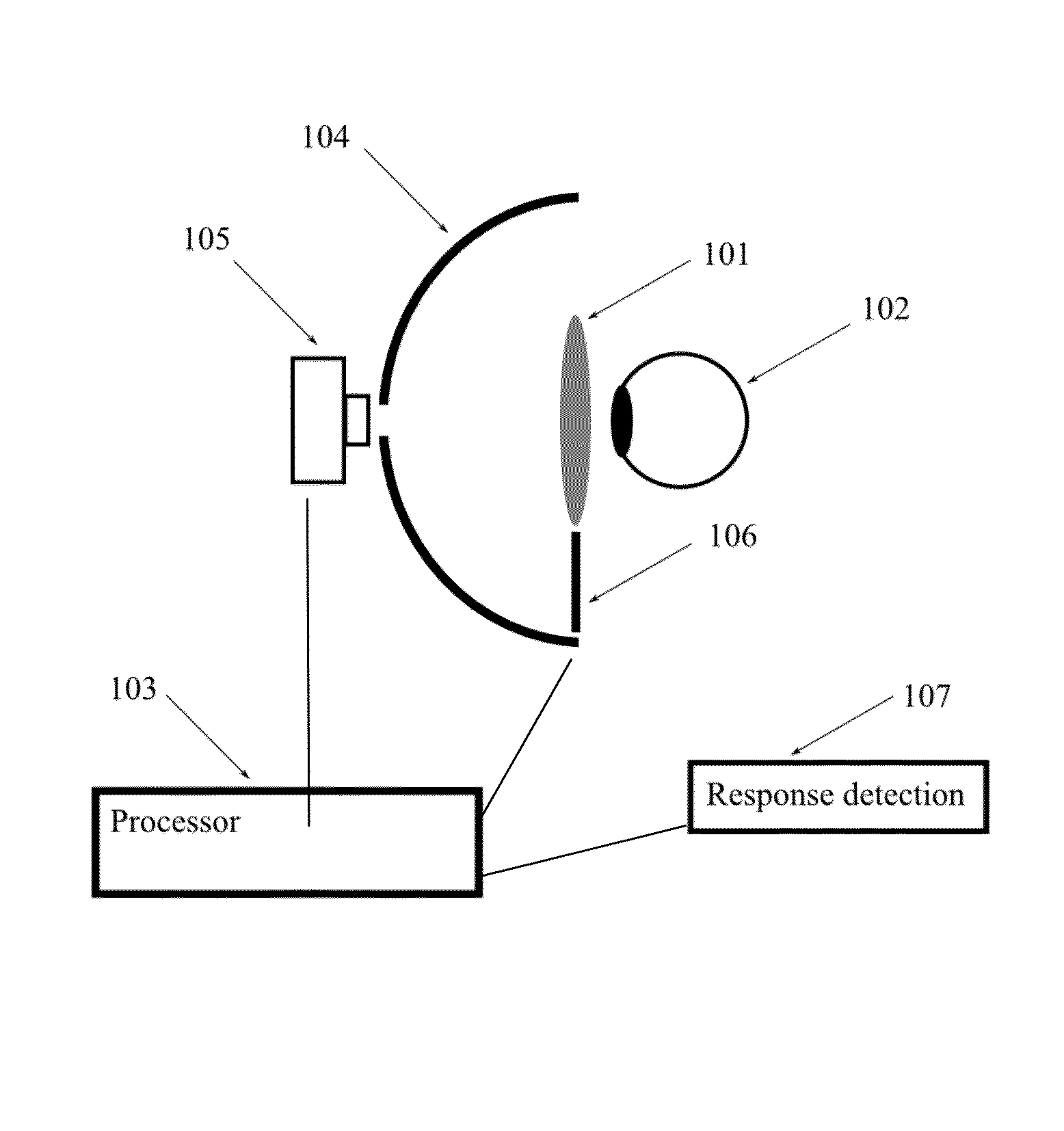
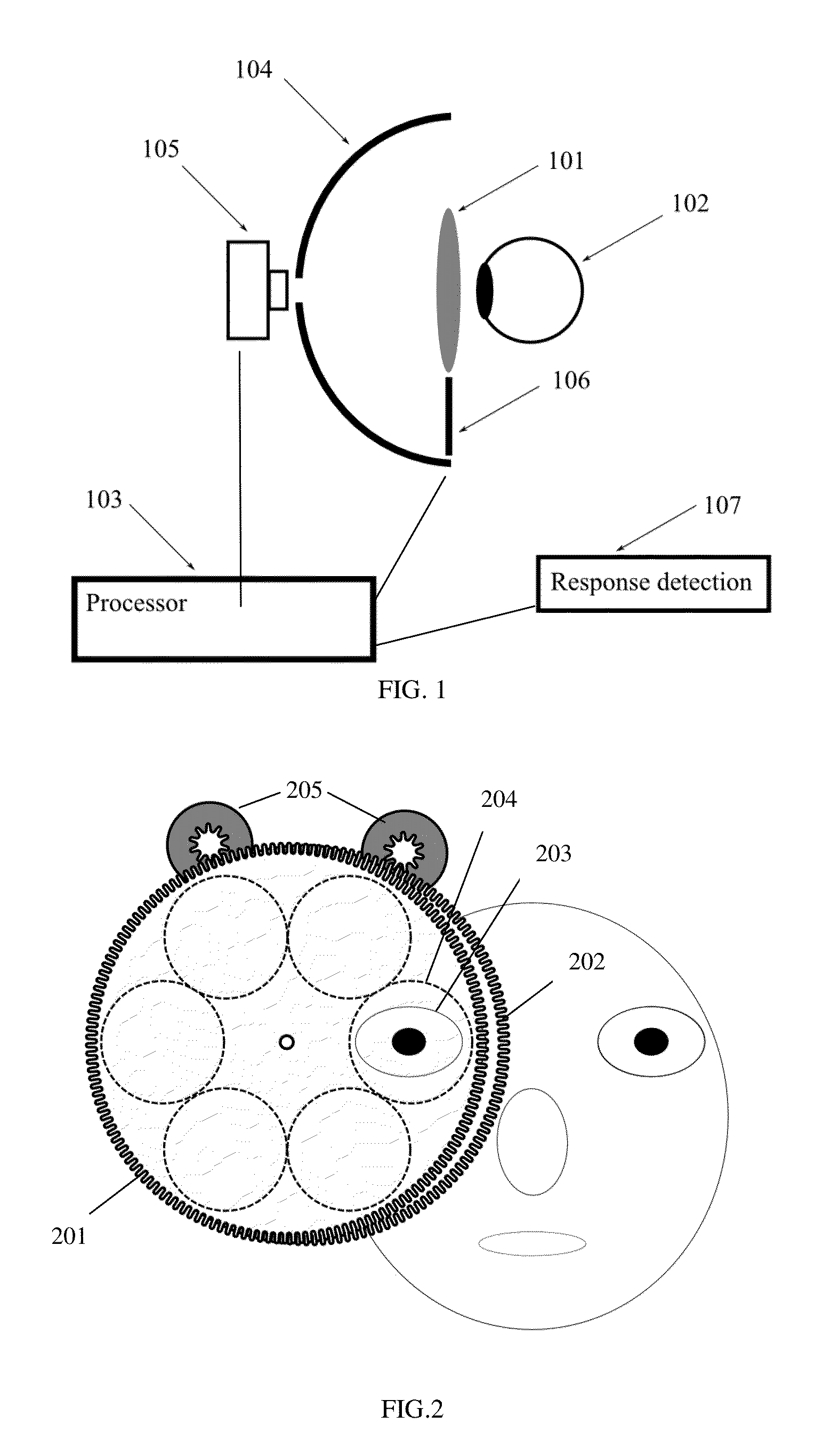
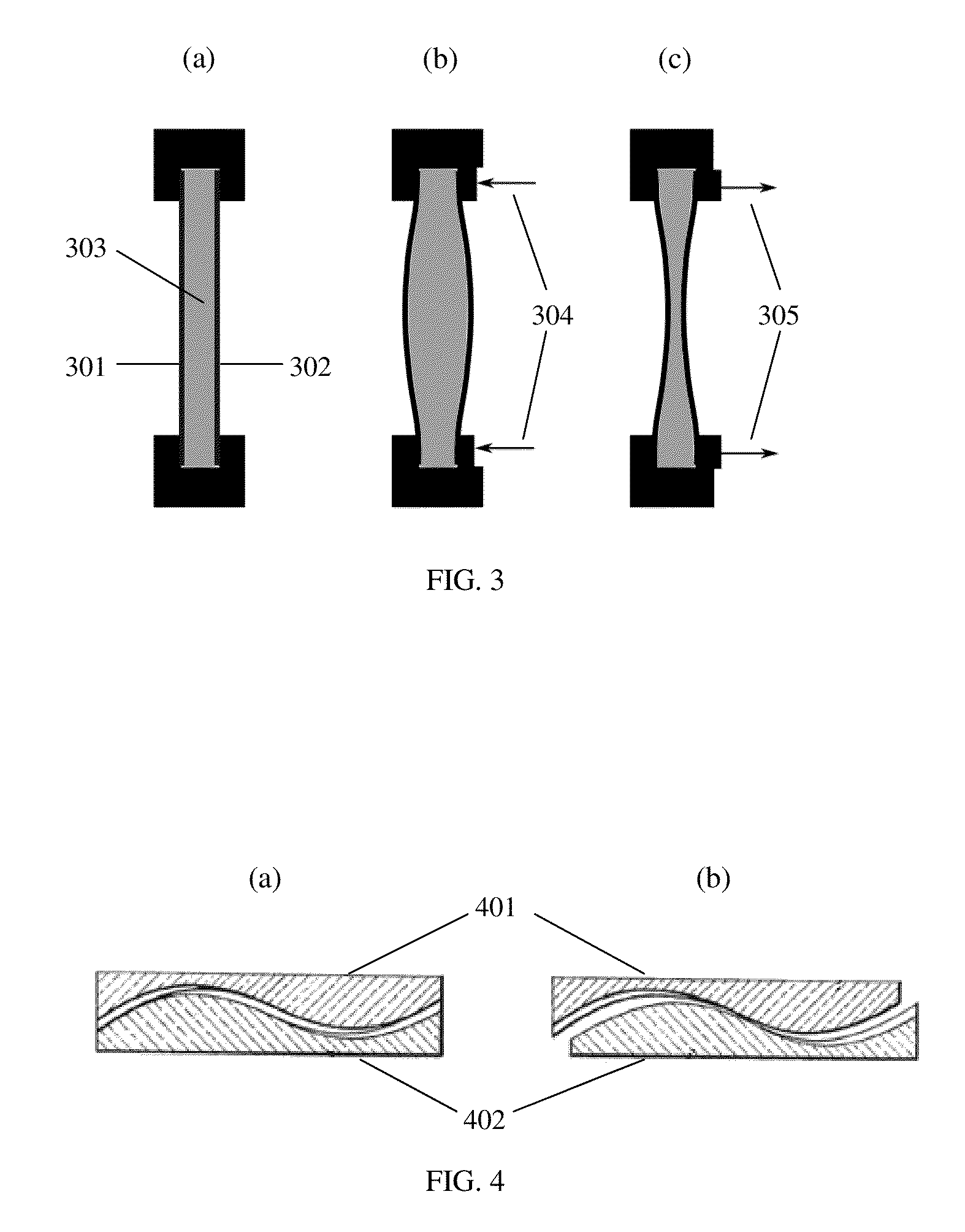
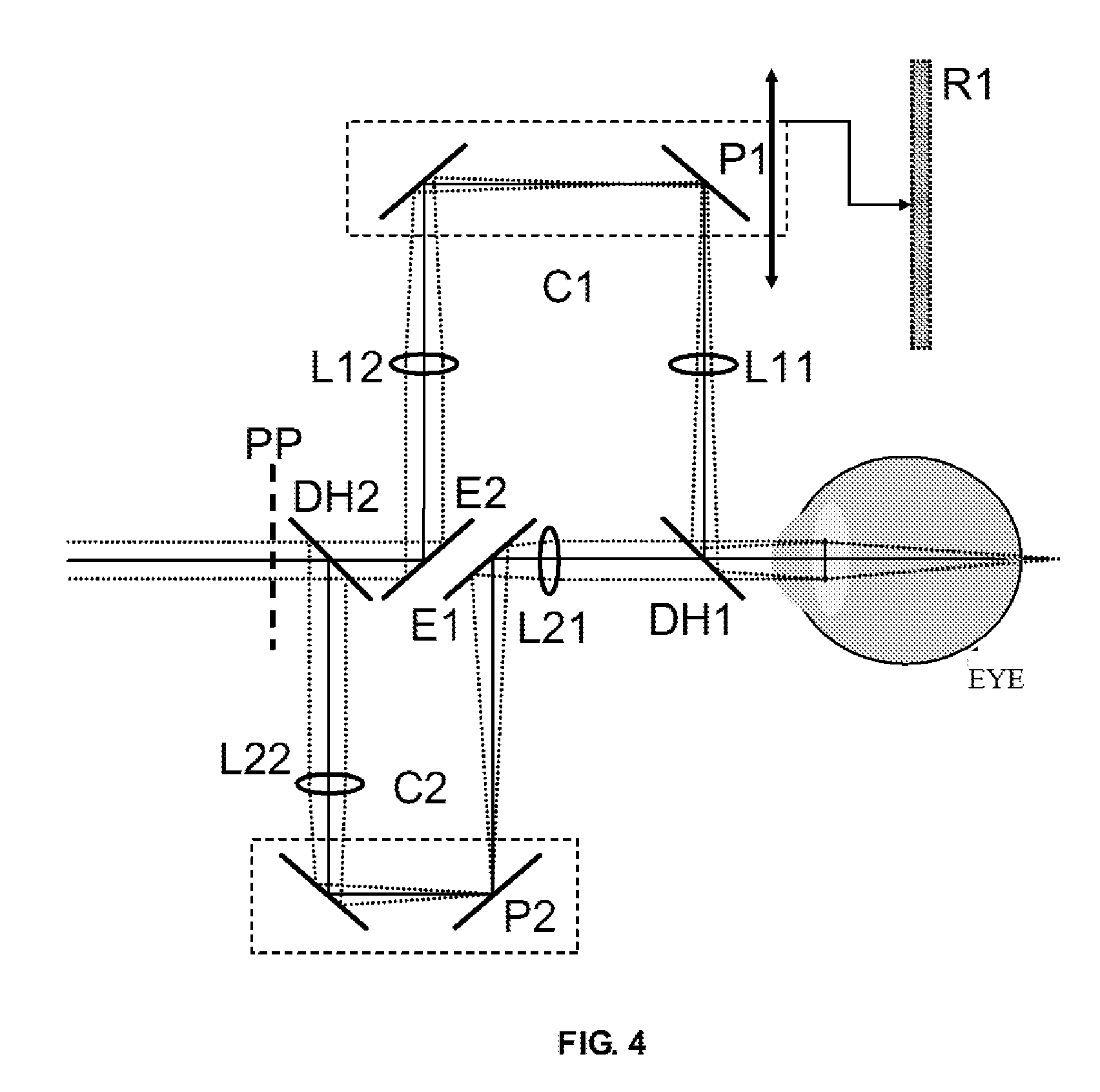
Systems and methods for providing variable refractive correction in a visual field testing device are presented. One embodiment of the variable refractive correction involves two or more aligned transmissive plates arranged to produce changes in refractive power by translation or rotation of the plates relative to each other. Several alternative designs for providing variable refractive correction are described. The refractive correction can be set manually or automatically based on knowledge of the refractive error of a specific patient and spherical and cylindrical refractive correction are possible. Additional lens systems can be used to extend the range of refractive correction to accommodate a larger patient population.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Subjective and objective integrated precision optometry device and method
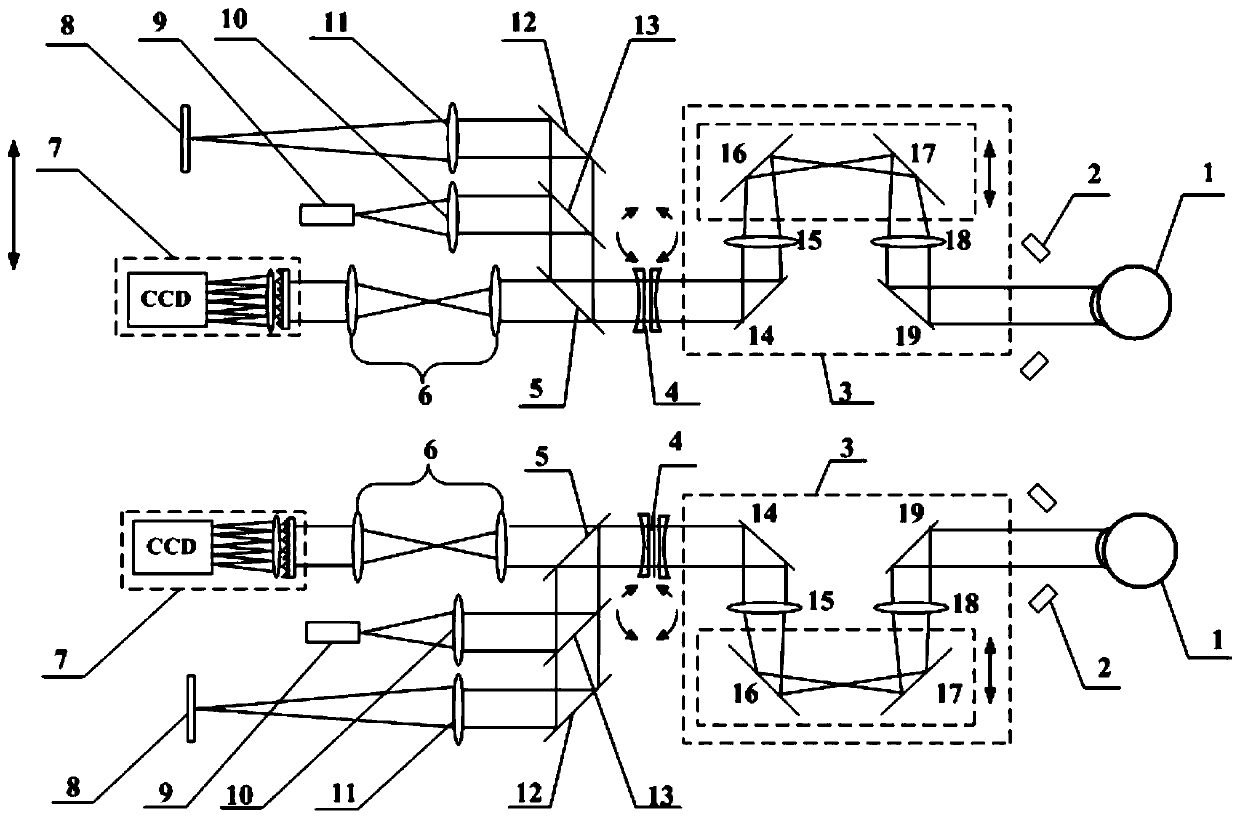
ActiveCN110367924APrecise Refractive Correction PrescriptionRefractometersSkiascopesPupillary distancePupil
Disclosed are a subjective and objective integrated precision optometry device and method. The device is composed of a left eye light path and a right eye light path. Each monocular eye light path comprises a human eye refraction objective measurement subsystem, a human eye refraction correction subsystem, an eyeball positioning subsystem and a subjective visual function test subsystem; each humaneye refraction objective measurement subsystem objectively measures the refractive power of the corresponding human eye to guide an inner focusing device in moving front and back along an optical axis to correct myopia or hyperopia and rotating a cylindrical mirror pair to correct astigmatism; an examinee observes a built-in sighting target through the device and moves a double-dot scribing framepart as a whole to finely tune the out-of-focus value according to subjective visual experience, the relative angle of the rotating cylindrical mirror pair is finely tuned to synthesize a light-scattering degree and an axial direction until the best subjective corrected visual quality is obtained, and the monocular subjective refraction optometry is completed. After the subjective refraction optometry of the left and right eyes is completed, the left and right eye light paths are moved in the direction perpendicular to the optical axis as a whole to adjust the pupil distance, the red-green and binocular adjustment balance process is carried out, and finally, the best precision refraction correction prescription for both eyes is given.
Owner:CHANGXING AIZHITONG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Systems and Methods for Evaluating Contrast Sensitivity and Other Visual Metrics
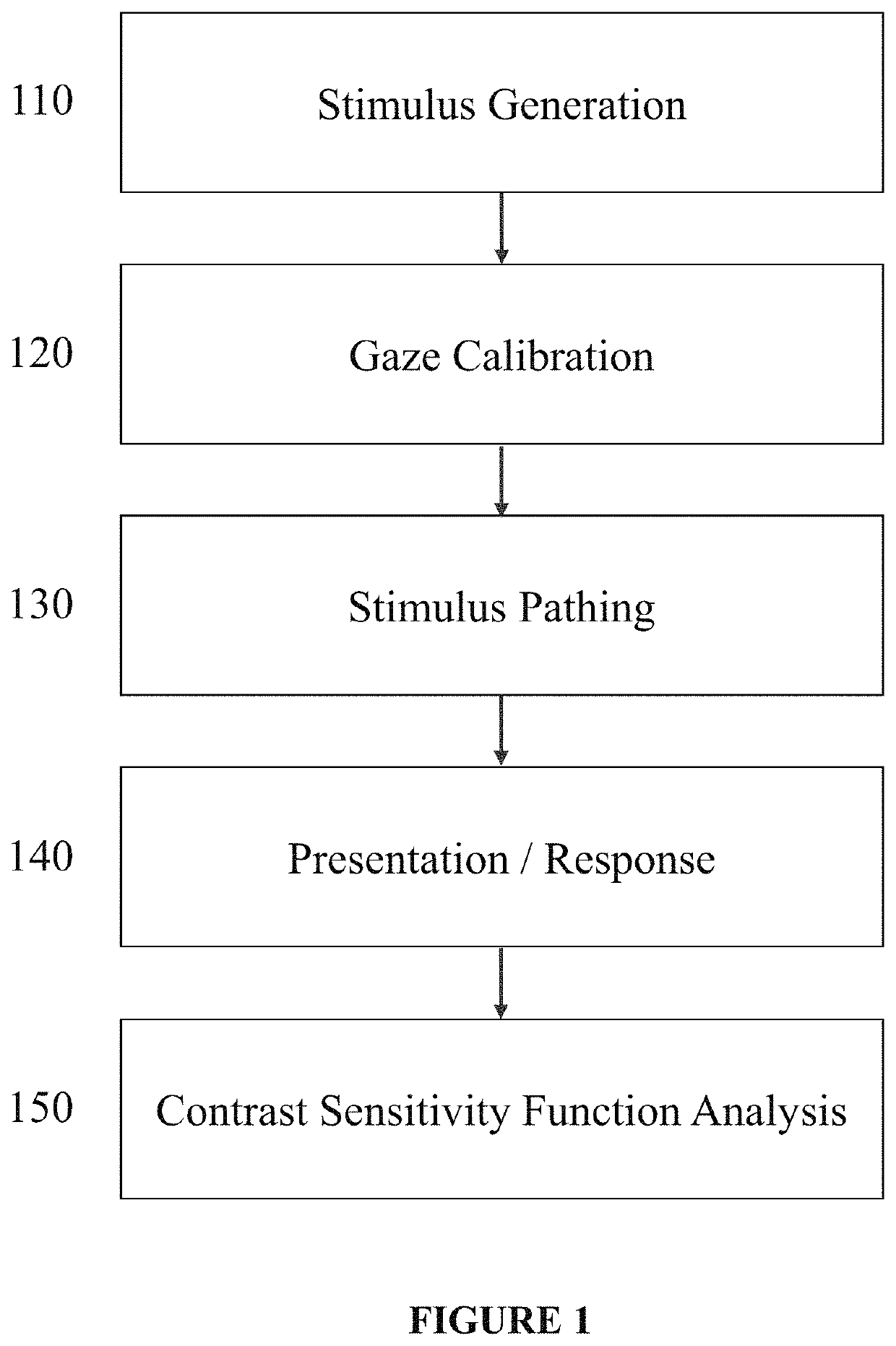
ActiveUS20200121179A1Improve forecastReduce in quantityEye diagnosticsImpaired visual acuityContrast level
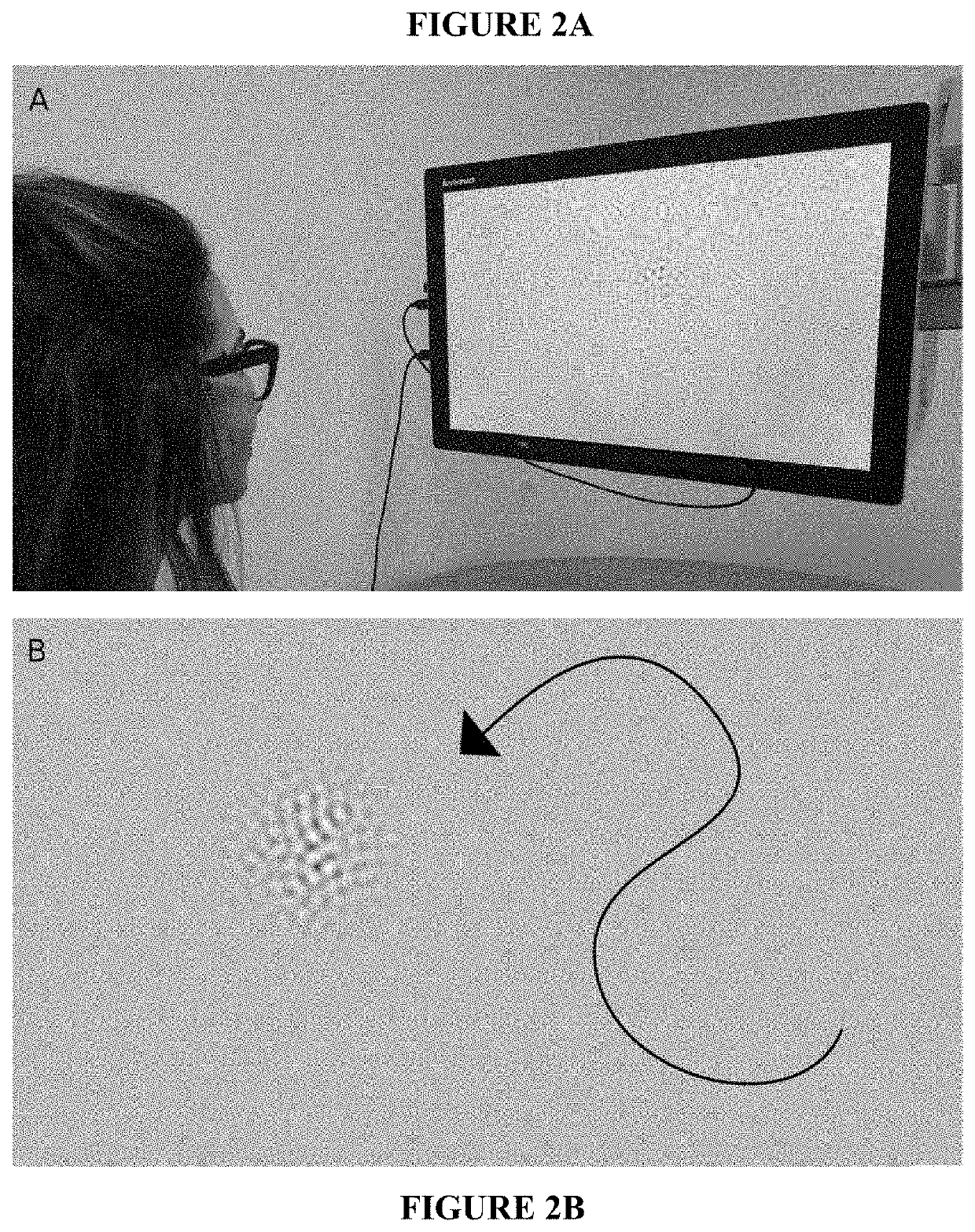
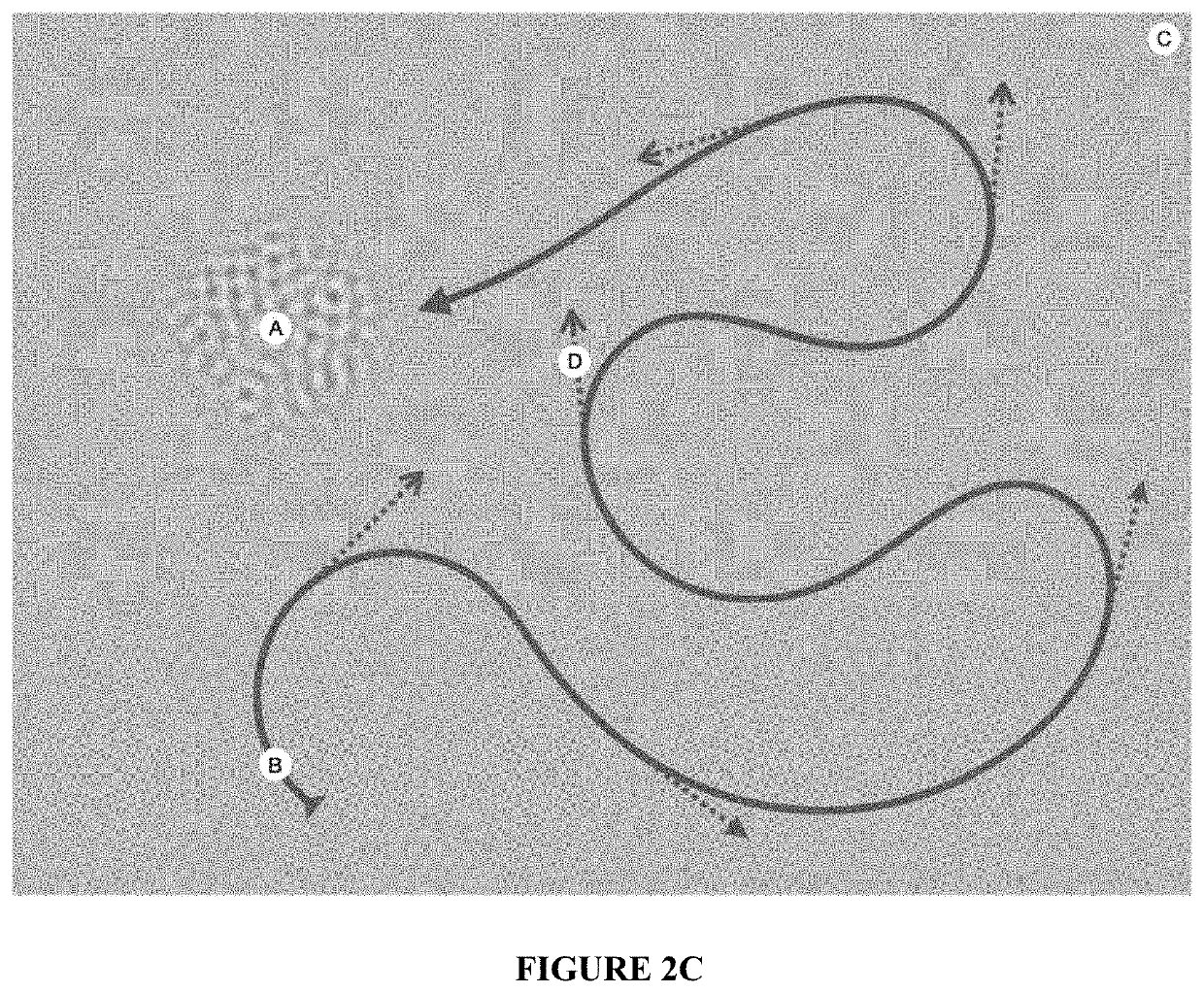
Contrast sensitivity is an informative measure of visual function, but current tools for assessing it are limited by the attentional, motor, and communicative abilities of the participant. These participants are often less able to engage with psychophysical tasks or follow an experiment's instructions, and alternative approaches have disadvantages that limit their usefulness in clinical settings. Here, we describe an efficient new measure of contrast sensitivity—‘Curveball’—that continuously infers stimulus visibility through smooth eye tracking instead of perceptual report. The procedure rapidly lowers stimulus contrast in real time until the threshold is found. The task is repeatable, well-correlated with results from conventional psychophysical methods, and sensitive to improvements in visual acuity from refractive correction. The procedure requires minimal instruction to administer and takes only five minutes to estimate a full contrast sensitivity function (CSF), which is comparable to the best existing methods available for healthy adults. Our technique relies on a minimum level of smooth tracking ability, which could limit its usefulness for participants with specific visual impairments, and we discuss potential solutions to this problem. Overall, our findings indicate that Curveball is a promising means of accurately assessing contrast sensitivity in previously neglected populations.A method to measure gaze tracking behavior comprising, displaying, on a display, one or more variable-contrast, variable-spatial-frequency stimuli each moving from a first location to a second location. Generating ordered sequences of stimuli (“sweeps”) that are incremented upon detected tracking behavior. Generating, by an eye-tracking monitor, a gaze position signal as the visual stimulus moves from the first position to the second position, the gaze position signal detecting a position of one or both eyes. Filtering the gaze position signal by identifying gaze position samples that are not consistent with the limitations of the human eye and / or visual system. Calculating a trajectory-match score for each stimulus on each frame from comparison of that stimulus's position to the gaze position signal over a time window. Identifying the visual function of the subject in response to the trajectory-match scores. Wherein the variable-contrast stimulus increases in contrast. Wherein the variable-contrast stimulus decreases in contrast. Wherein the variable-contrast stimulus alters in a step-wise manner by multiplying the current contrast by a variable between 0.5-1.5 on each frame. Wherein the variable-contrast stimulus is exchanged for the next stimulus in that sweep sequence. Wherein indirect progress along similar sweeps is inferred and recorded. Interpolating a contrast sensitivity function (CSF) from a set of one or more sweep sequences. Detecting, empirically, the subset of one or more sweep sequences that is most informative about the CSF for a given population.
Owner:BURKE NEUROLOGICAL INST
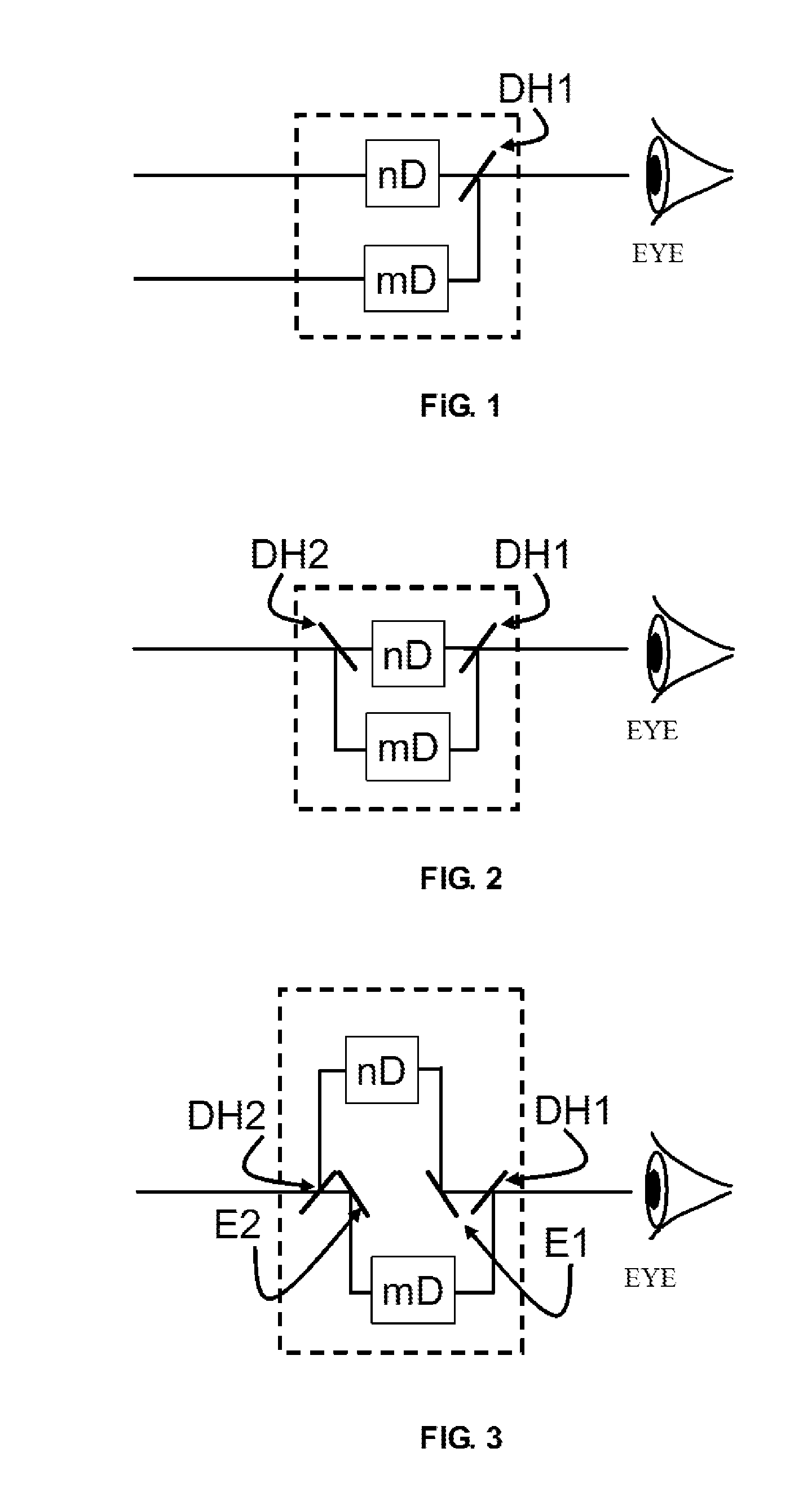
Refractive correction AR display device and wearable AR equipment
The invention provides a refractive correction AR display device and wearable AR equipment. The display device includes an image projection device and an optical path assembly; the image projection device includes an image source; and the optical path assembly includes a spectroscope and a refractive correction lens which are in successive arrangement. Through the technical schemes, the integratedlevels of a system can be enhanced, the complex degree of the system can be reduced, the weight of the system can be decreased, the number of lenses through which human eyes observe extraneous environments can be decreased, light transmittance can be enhanced, stray light can be decreased, and requirements of the system on exit pupil distances can be reduced; a curved mirror which is only reflected once originally can increase refraction and reflection through the design; and the number of refraction surfaces can be increased under the premise that the system volume remains unchanged, so thatdegrees of freedom of design can be enhanced, bases can be provided for reducing aberration and enhancing optical performance, and the definition of an imaging system can be higher and viewing anglescan be larger while the volume is decreased.
Owner:BEIJING UNICORN TECH CO LTD
Method for controlling a device for treating the human eye
A method for controlling a device for the treatment or refractive correction of the human eye using an electronic data processing system provides a simple overview of the influence of all of the parameters. To this end, once the operating parameters have been determined, a graphical simulation of the operating procedure is carried out in the form of a graphical visualization.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Electronic diopsimeter with functions of eyeball tracking and refraction compensation
ActiveCN101601577ARealize the combinationOvercoming the problem of decreased visual field sensitivityEye diagnosticsInfraredVisual field loss
The invention relates to an electronic diopsimeter with the functions of eyeball tracking and refraction compensation, which comprises a shell and a plane electronic visual field screen, wherein the shell is provided with a cylindrical peeping channel; the cylindrical lateral surface of the peeing channel is provided with an infrared illuminating lamp for emitting infrared rays to the eyeball of a subject; the inside of the peeping channel is connected with a refractive error correction system so as to close the inside of the shell; the refractive error correction system is provided with a non-spherical aspheric surface lens with refractive error correction; and an infrared camera for shooting the infrared ray reflected by the eyeball of the subject is also arranged in the shell. The electronic diopsimeter has the advantages of shell closure, eye ball tracking, refractive error correction and the like so that the accuracy is high. Besides, the invention also relates to a method for quantizing and evaluating the cooperation degree of the subject.
Owner:EYE & ENT HOSPITAL SHANGHAI MEDICAL SCHOOL FUDAN UNIV
Use method of refractive correction instrument
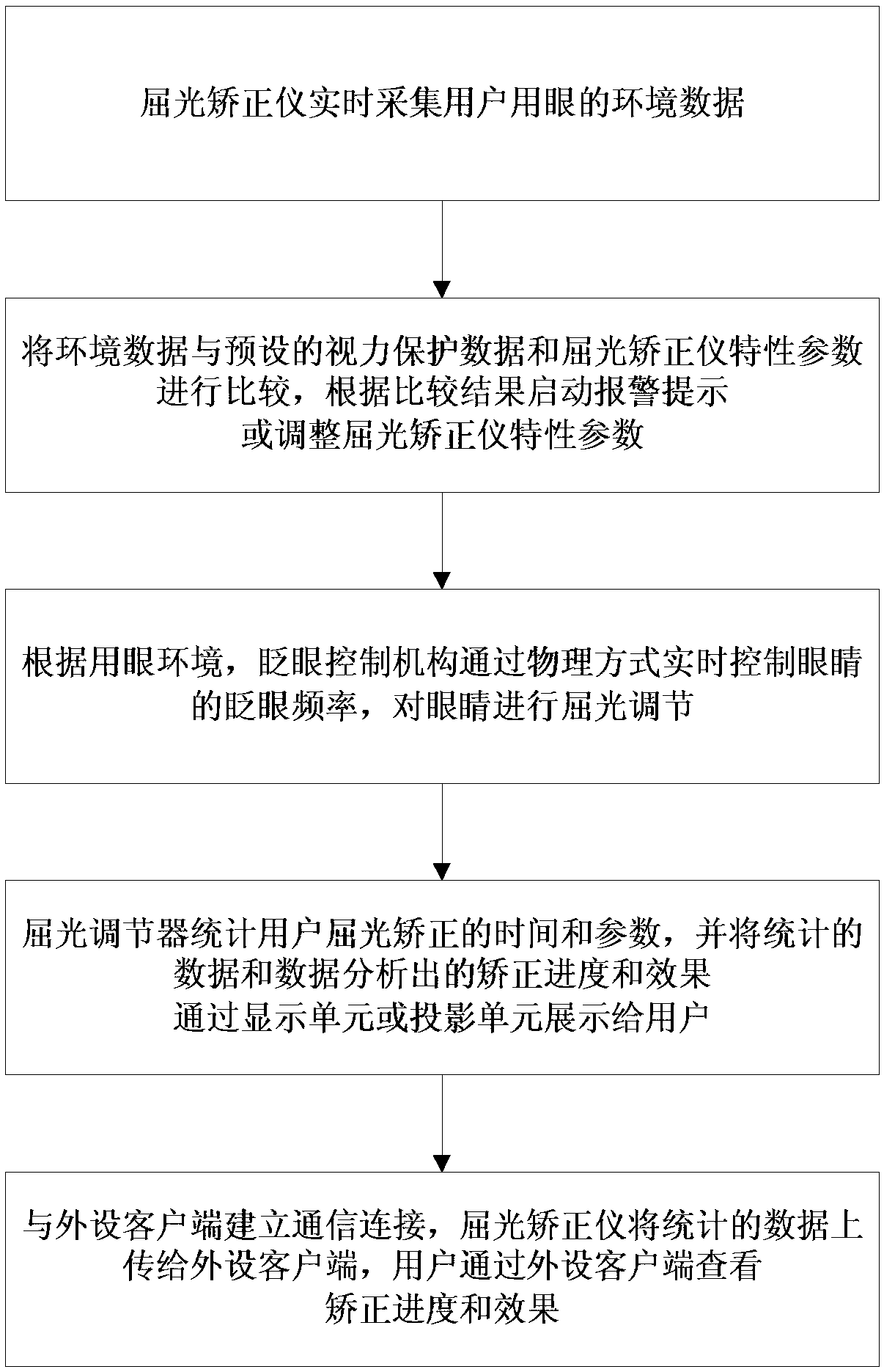
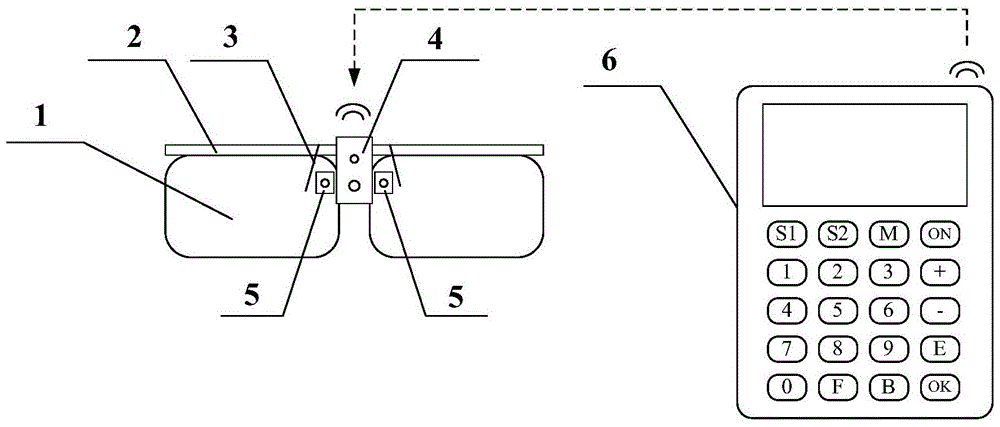
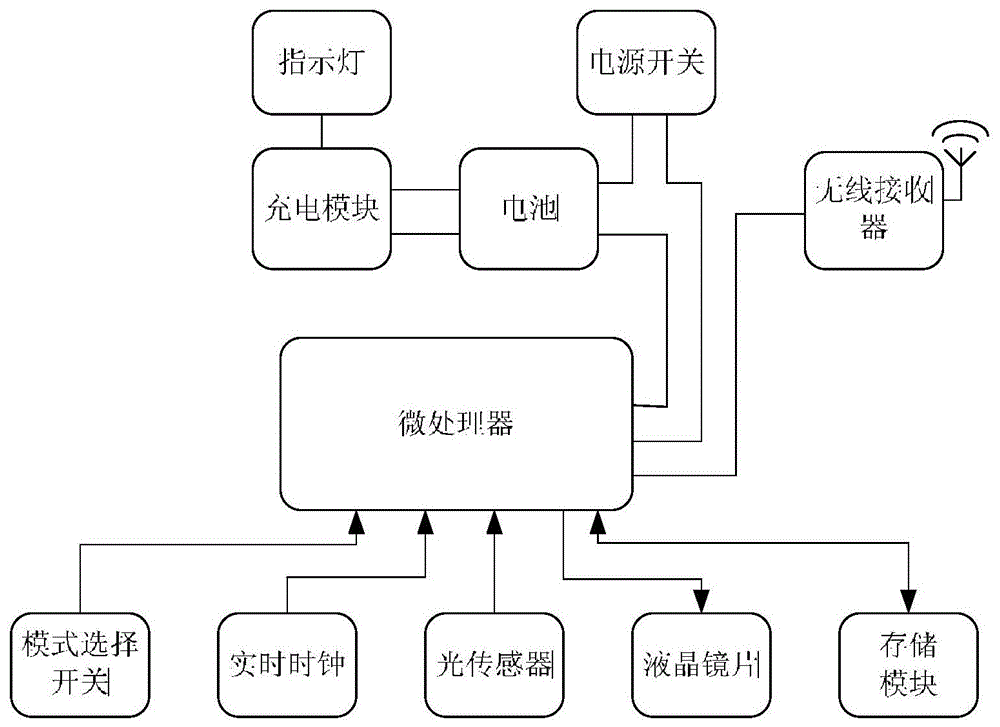
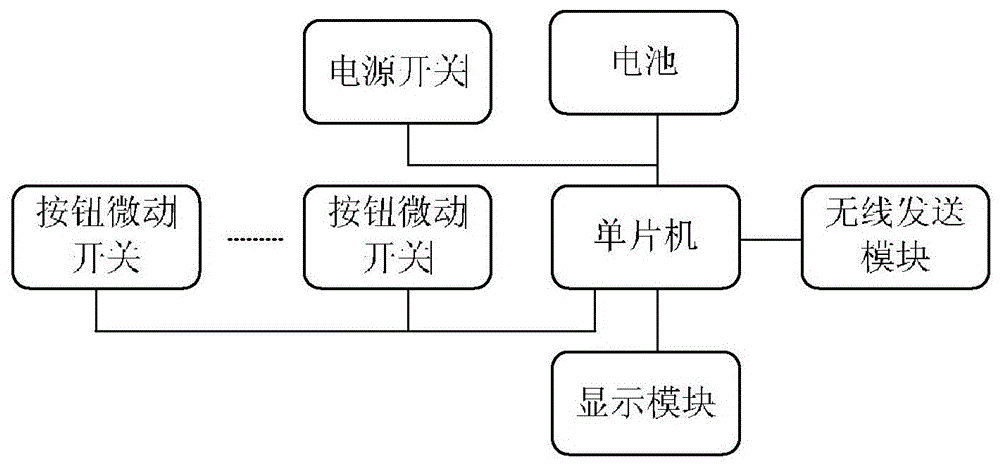
ActiveCN107811640AGood eye environmentWill not harmDiagnostic recording/measuringEye treatmentComputer scienceBand counts
The invention discloses a use method of a refractive correction instrument. The refractive correction instrument collects eye use environment data of a user in real time; the collected environment data is compared with preset eyesight protection data and characteristic parameters of the refractive correction instrument, according to comparison results, an alarming reminding part is started or thecharacteristic parameters of the refractive correction instrument are adjusted, and a good eye use environment is provided for the user in real time; according to the eye use environment, the blinkingfrequency of eyes is controlled by a blinking control mechanism in a physical mode in real time to conduct refractive adjustment on the eyes; refractive correction time and parameters of the user arecounted by a refractive corrector, and the counted data and the correction progress and effect which are obtained through analysis according to the counted data are displayed to the user through a display unit or a projection unit; communication connection is built between the refractive correction instrument and an external client, the counted data is uploaded to the external client, and the correction progress and effect can be checked through the external client. By means of the method, the deflects which exist in the prior art are overcome, and damage caused by refractive correction to the eyes of the human body is reduced.
Owner:李迎
Amblyopia correction and detection device
ActiveCN104207876BAvoid inhibitionAvoid the problem of binocular stereo disparity after healingEye treatmentPhoroptersEngineeringMode selection
Owner:吉林省世光科技有限公司
Film-coated lens with refraction correcting function
The invention provides a film-coated lens with a refraction correcting function and belongs to eyeglasses or an eyeglass lens. The film-coated lens comprises a lens and a coated film, wherein the lens is a plano lens (1); the coated film is a refraction coated film (2) made of flexible and transparent plastic; and one face of the refraction coated film (2) is a plane which is attached to the plano lens (1), and the other face of the refraction film (2) is at least provided with a concave circular surface or a convex circular surface. Two types of eyeglasses with different degrees can be formed by combining the coated film on front and back sides of the plano lens (1) so as to bring convenience to diopter adjustment and conveniently meet the visual requirement on frequent change of sight distances. The film-coated lens has the advantages of convenient use, rapid replacement, high comfortableness, capability of changing coated films with different diopters according to the position change of a student in a classroom and the demand of horizontal change of vision correction, simple structure, low manufacturing cost, remarkable refraction correcting effect and wide application prospect.
Owner:余思成
High-order aberration compensation method for corneal refractive correction
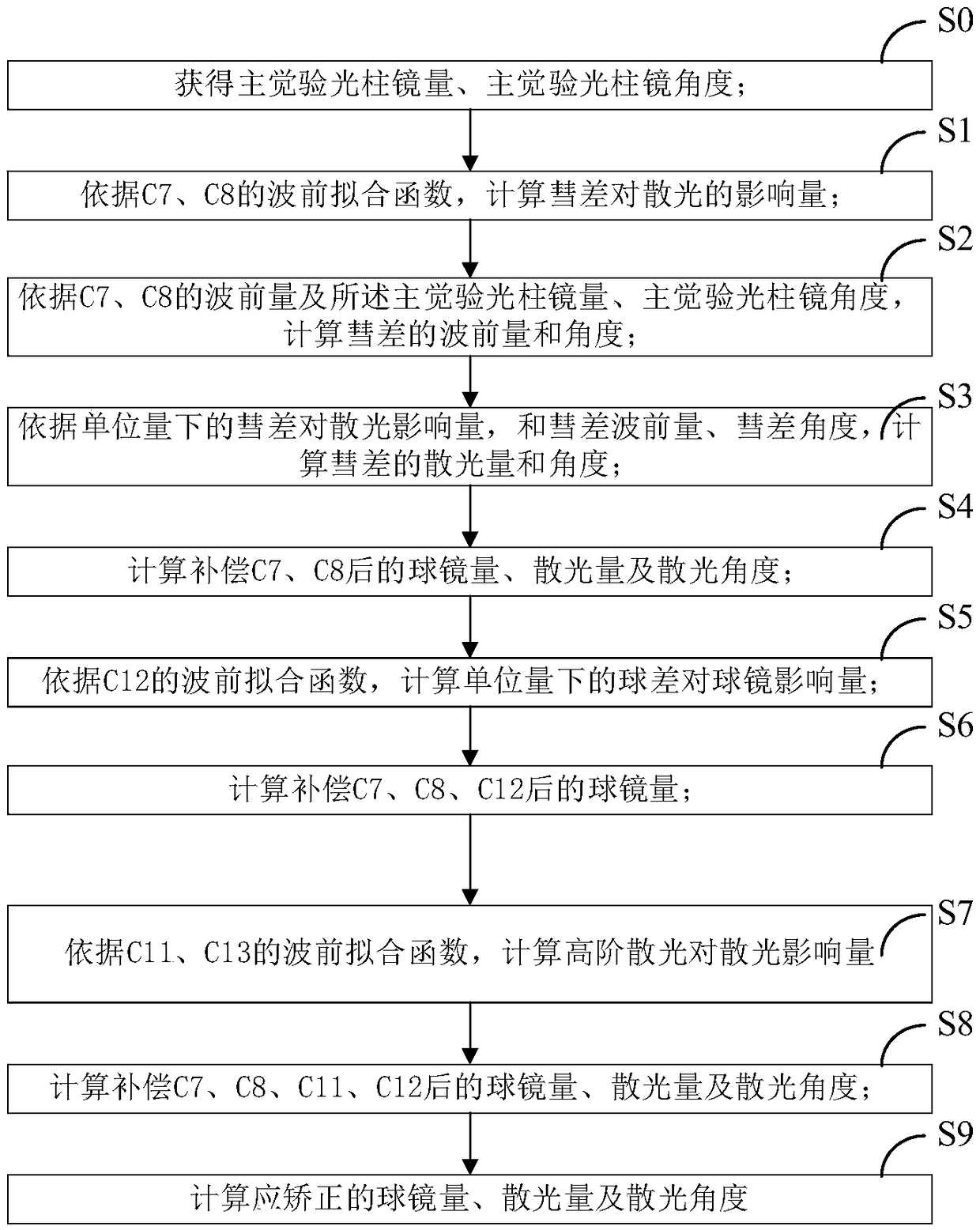
ActiveCN109491083AGood compensationImprove visual qualityOptical elementsStigmatismVisual perception
The invention provides a high-order aberration compensation method for corneal refractive correction. The compensation method is used for solving the problem that high-order aberration compensation methods in the prior art cannot meet requirements and comprises the steps that according to a wavefront fitting function of C7 and C8, the concave-sphere amount, astigmatism amount and the astigmatism angle after compensation of C7 and C8 are calculated; according to a wavefront fitting function of C12, the concave-sphere amount after compensation of C7, C8 and C12 is calculated; according to a wavefront fitting function of C11 and C13, the concave-sphere amount, astigmatism amount and the astigmatism angle after compensation of C7, C8, C11 and C12 are calculated. According to the method, a representation method of a Zernike polynomial and the low-order aberration diopter are converted, and the unit is unified; the comatic aberration, spherical aberration and second-order astigmatism are subjected to conversion of a qualitative and quantitative relationship, the high-order aberration for the corneal refractive correction of the human eyes is better compensated for, the compensation accuracy is improved, the better visual quality is obtained, and meanwhile the statistical difference is taken into account.
Owner:杭州明视康眼科医院有限公司
Instrument for simulating multifocal ophthalmic corrections
The invention relates to an instrument for simulation of multifocal ophthalmic corrections, comprising two optical channels with different optical power values in the beams coming from the object observed, wherein at least one channel comprises a Badal system. This instrument simultaneously provides images of objects near and far focused. The system provides the same optical magnifications for each channel, regardless of the optical power thereof, and produces superimposed retinal images with different degrees of focus which, unlike other devices, are all of the same size. The instrument allows simulating different optical powers for near vision and different refractive corrections for distant vision.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Method for controlling a device for treating the human eye
A method for controlling a device for the treatment or refractive correction of the human eye using an electronic data processing system. The method provides a simple overview of the influence of all of the parameters. To this end, once the operating parameters have been determined, a graphical simulation of the operating procedure is carried out in the form of a graphical visualization.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Instrument for simulating multifocal ophthalmic corrections
The invention relates to an instrument for simulation of multifocal ophthalmic corrections, comprising two optical channels with different optical power values in the beams coming from the object observed, wherein at least one channel comprises a Badal system. This instrument simultaneously provides images of objects near and far focused. The system provides the same optical magnifications for each channel, regardless of the optical power thereof, and produces superimposed retinal images with different degrees of focus which, unlike other devices, are all of the same size. The instrument allows simulating different optical powers for near vision and different refractive corrections for distant vision.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
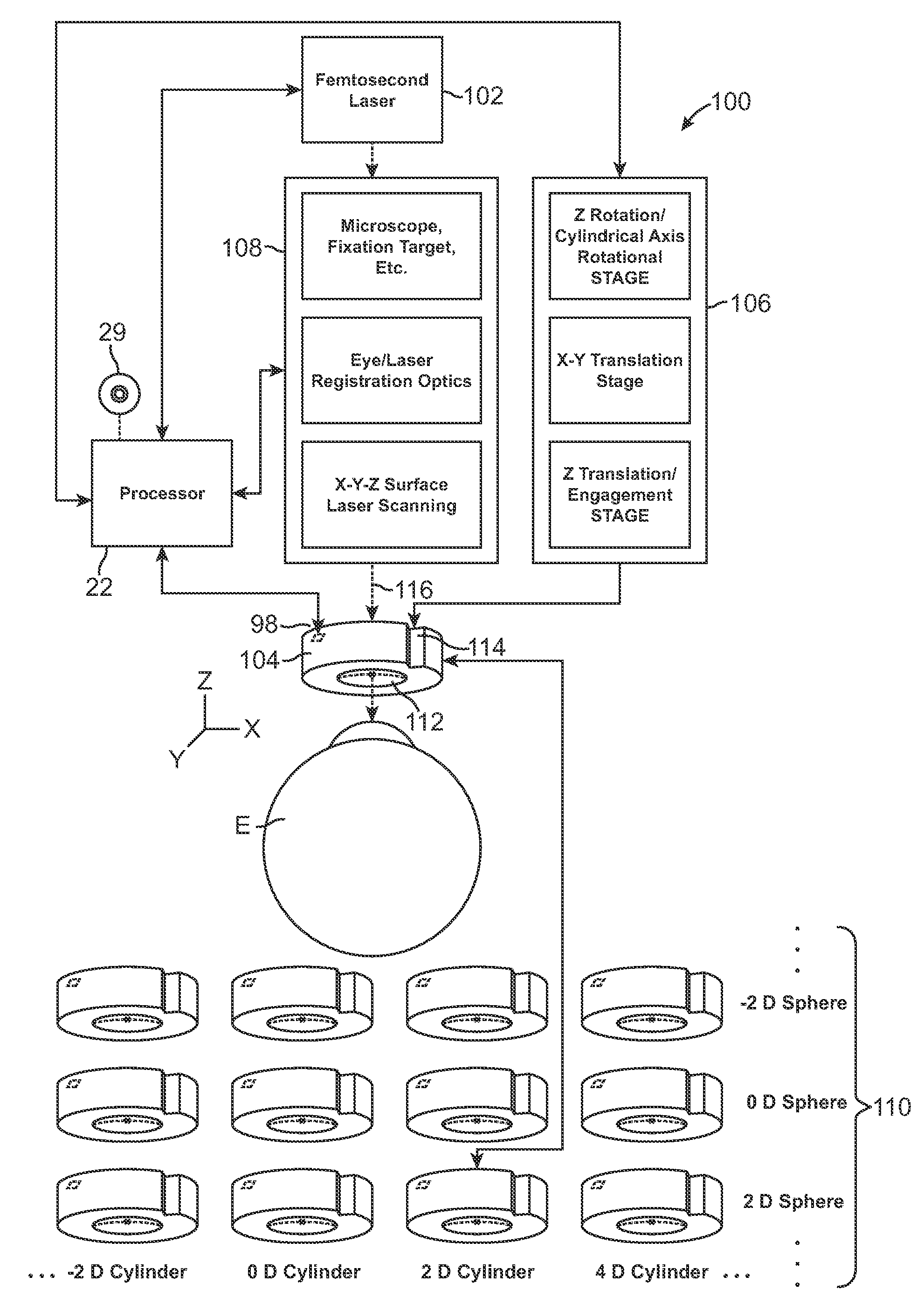
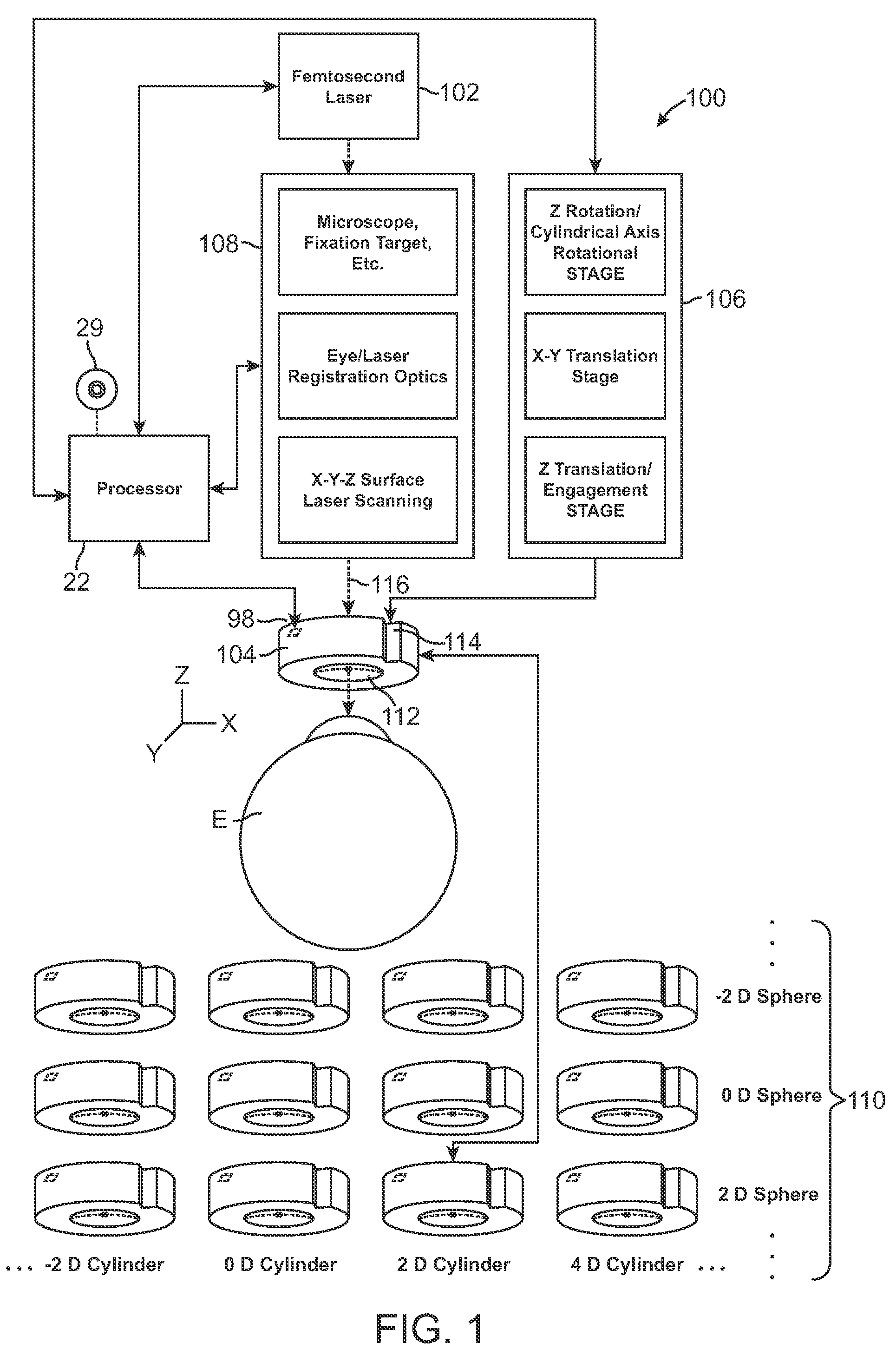
Method and device for performing online aberrometry in refractive eye correction
This invention relates to a method and a device for the complete correction of sight defects in the human eye. Combinations of measuring, and processing methods are described which when applied as disclosed in the invention, make it possible to fully correct sight defects in the human eye. Measuring methods are used which can precisely scan the surface of the cornea and also register other imaging defects in the light path up to the retina. Computer-aided of said measuring results determined when combined with calculation of ideally corrected ocular lenses (for example after cataract operations) or ideally corrected surfaces of the cornea opens up the possibility of manufacturing a patient-specific lens and / or achieving ideal correction of the cornea using preferably a topography-supported spot-scanning-excimer laser system.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Near eye display and related computer-implemented software and firmware
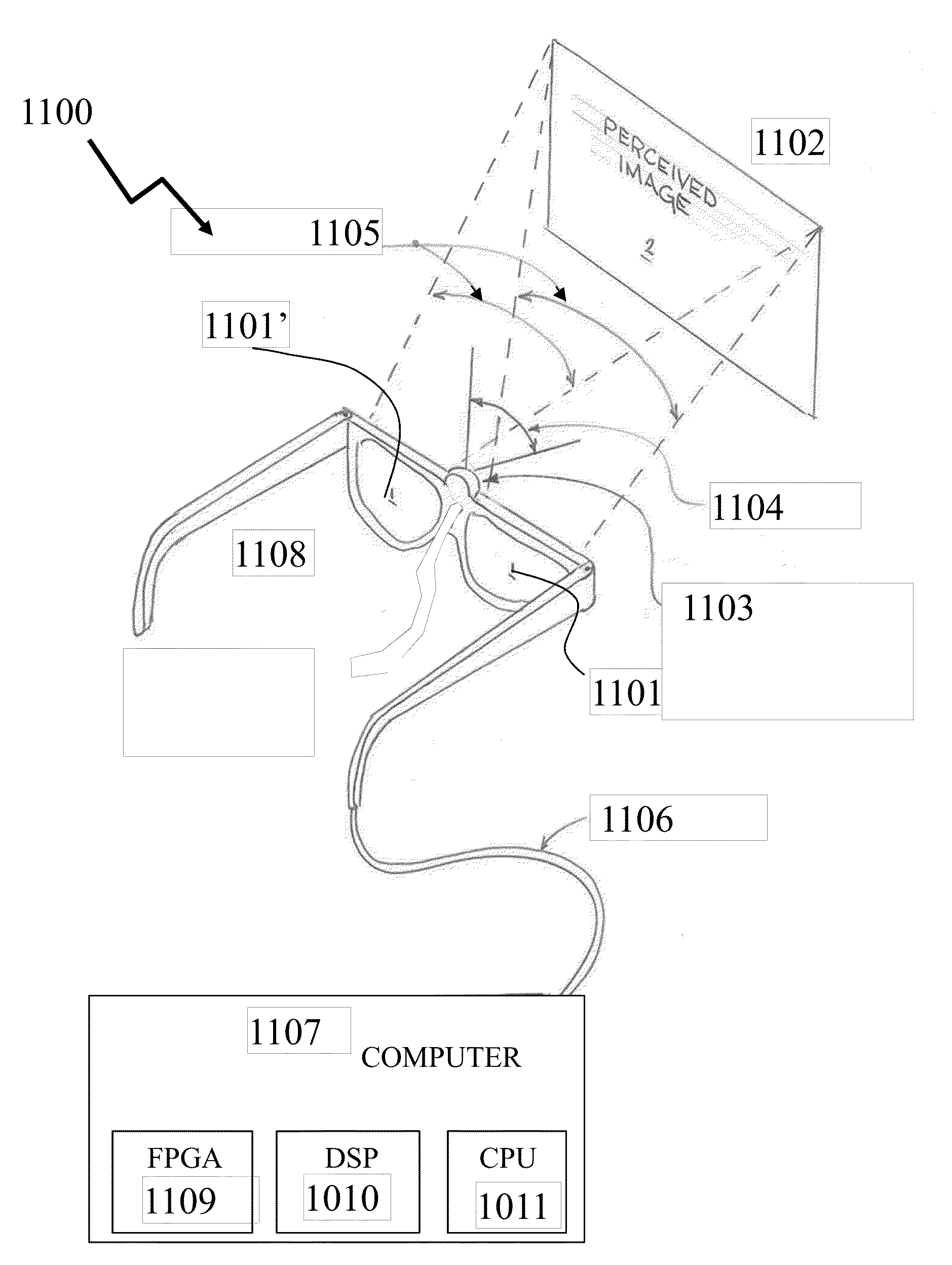
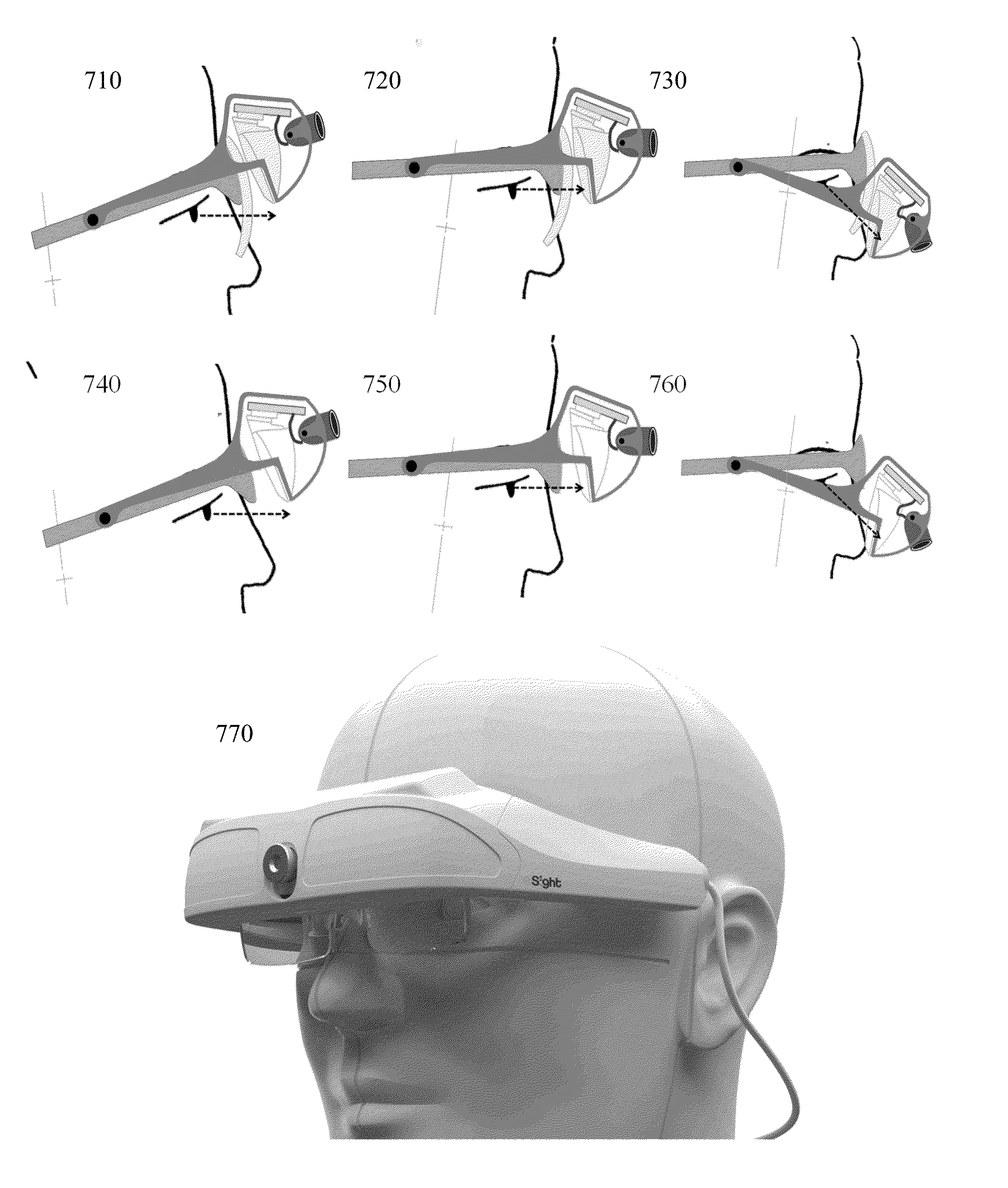
A near-eye display for operation of an augmented or mixed reality system that integrates the virtual image generated by the near eye display to the real environment taking account of the visual processes of the retina, the visual cortex and the oculomotor system. The near eye display is provided in the form of a transparent optical module attached to and aligned with a pair of eyeglasses providing the refractive correction required by the wearer. The effect of the light field created by the eyeglass optic and the transparent optical module are used as inputs to the software or firmware program that drive the micro-display in the transparent optical module and control the location of the content as well as the fixation point being displayed on the micro-display. The near eye display acts as the master and the wearer's or user's eyes as the slave. Thus, the light emitters of the near eye display cause the eye(s) of the user to move and be positioned.
Owner:NEWSIGHT REALITY INC
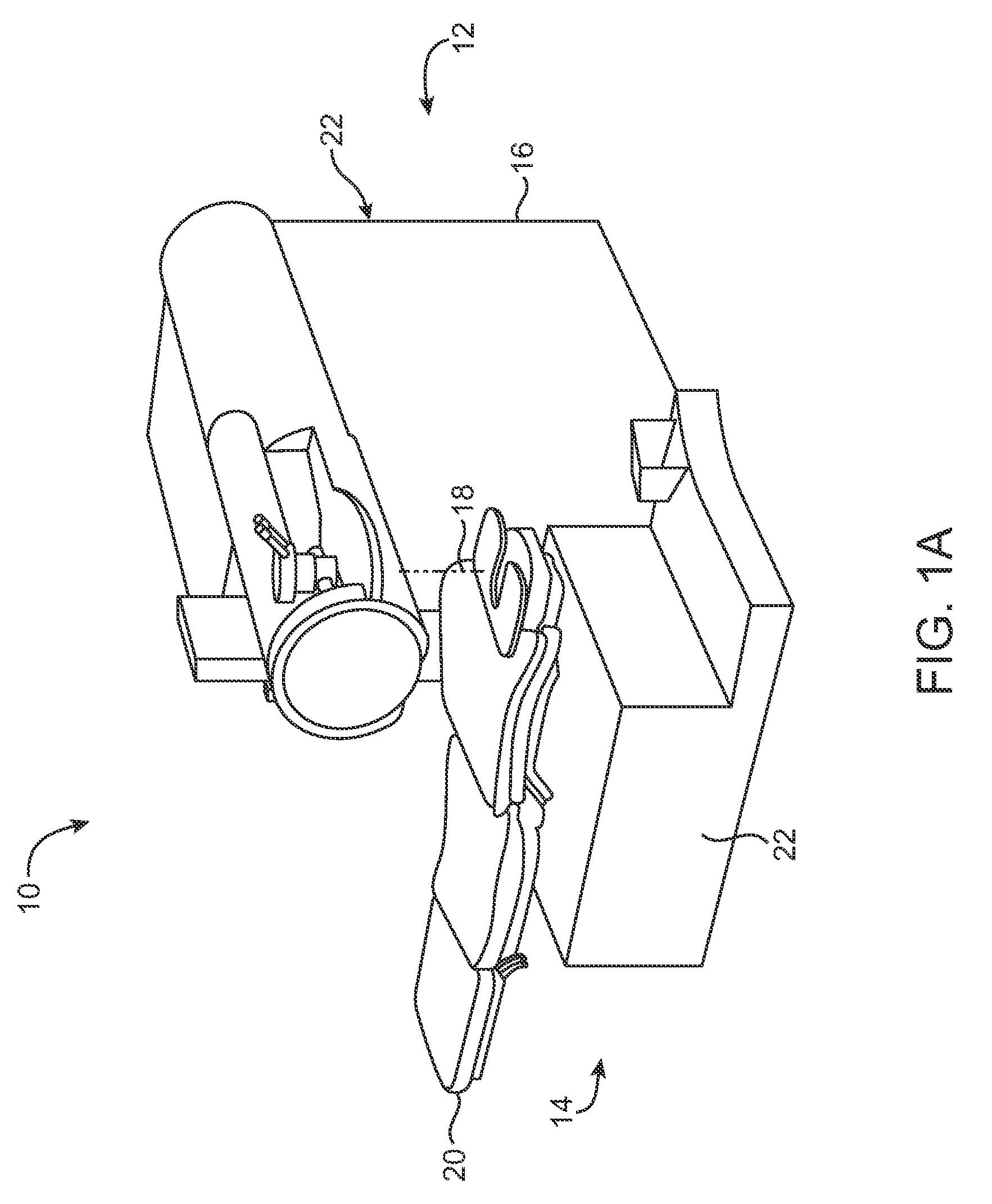
Mazaheri LASIK method for visual enhancement
ActiveUS9192517B2Less potential for eye drynessReduce chanceLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsCorneal surfaceVisual perception
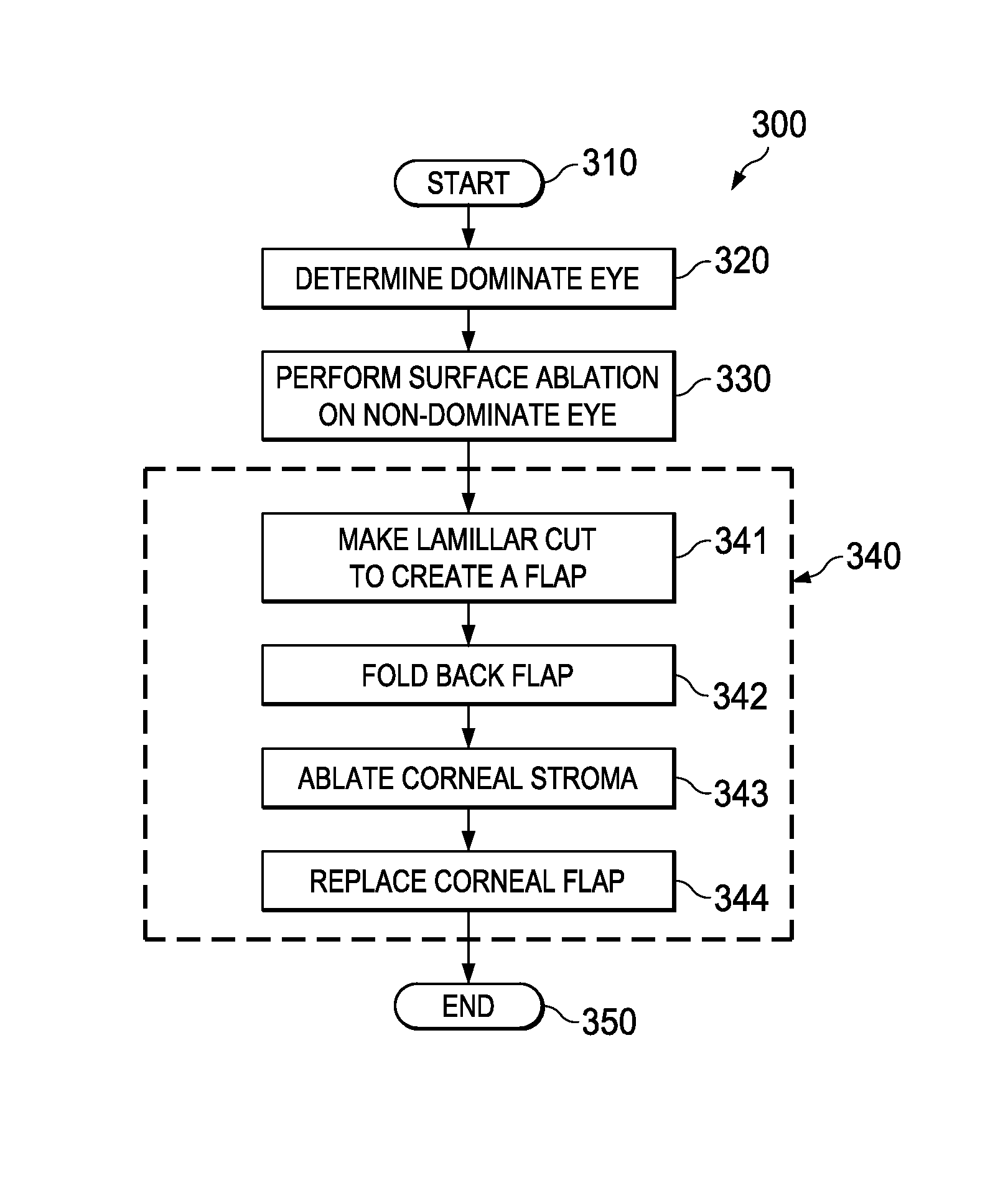
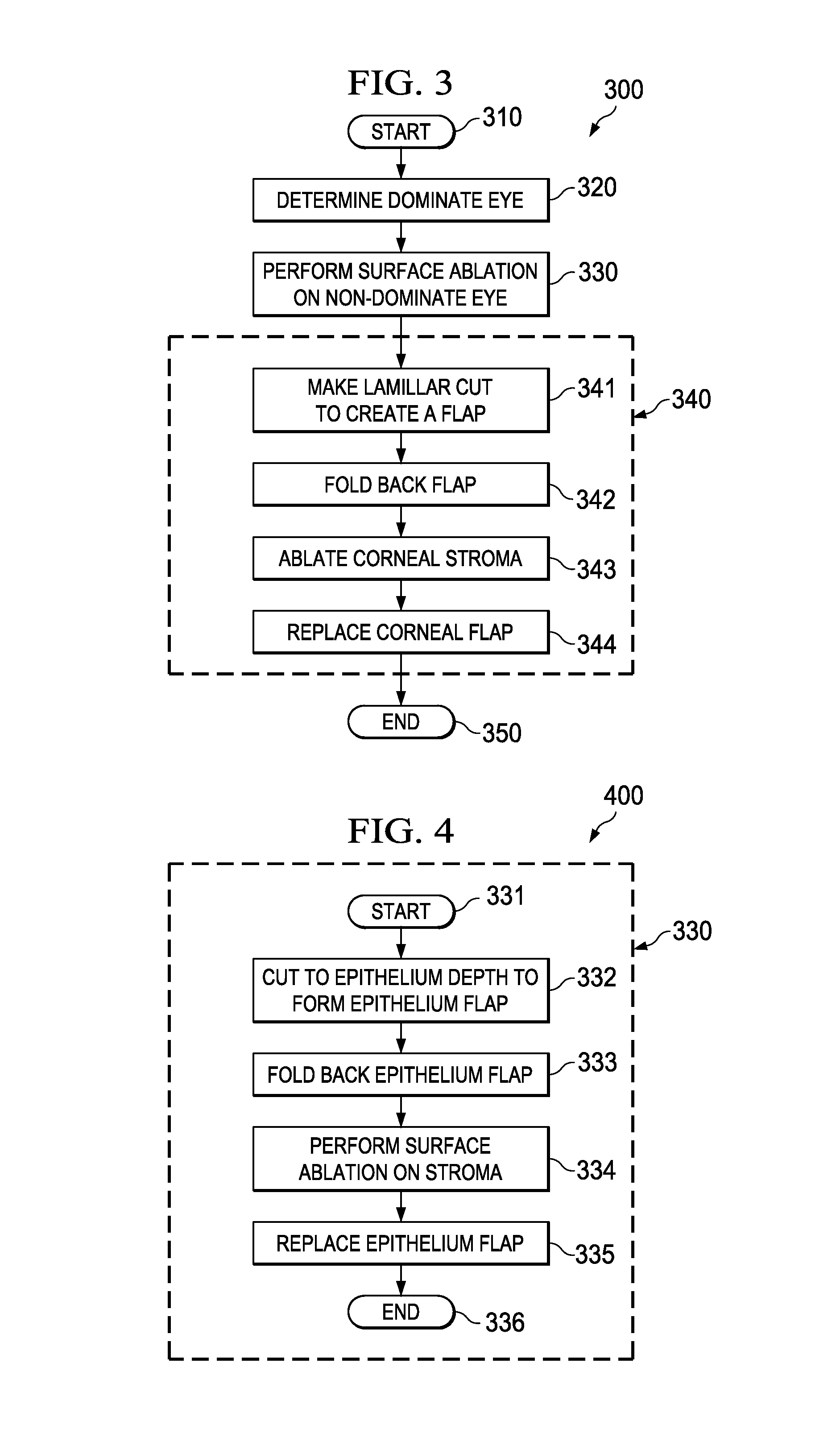
A new and novel method for performing refractive correction on a patient's eyes is introduced. In one embodiment the method includes (1) performing a surface ablation corrective procedure on a corneal surface of the patient's non-dominant eye; and (2) reshaping a corneal stroma of the patient's dominant eye, where the reshaping includes the making of a lamillar cut in the surface of the dominant eye to create a flap; folding the flap back to reveal the corneal stroma and ablating a portion of the corneal stroma, after which the flap is replaced.
Owner:MAZAHERI MICHAEL M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com