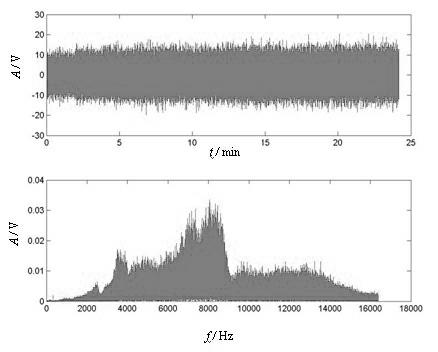
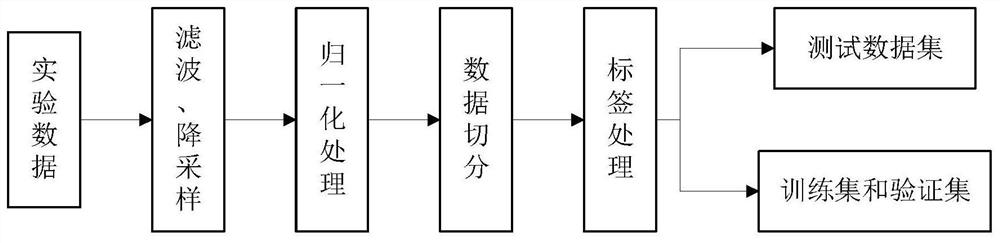
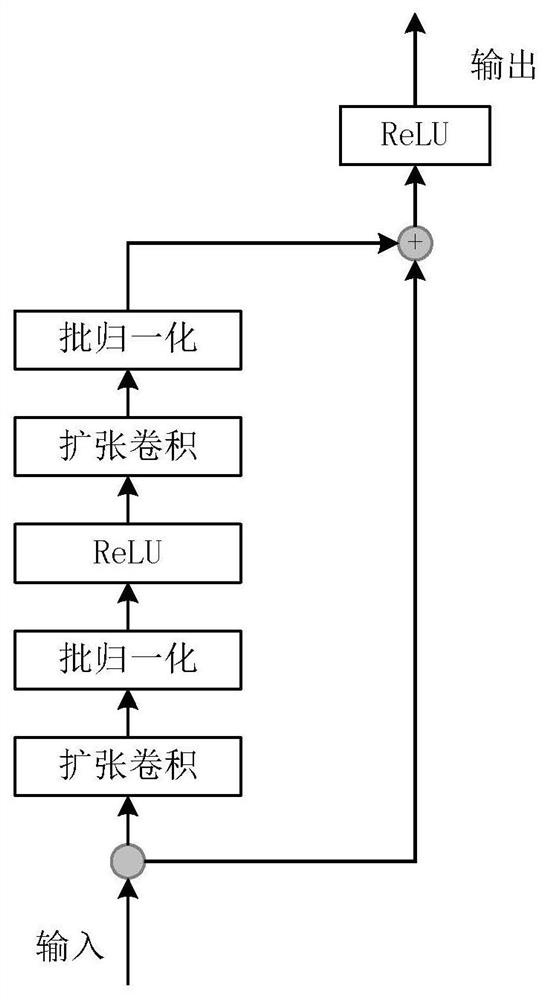
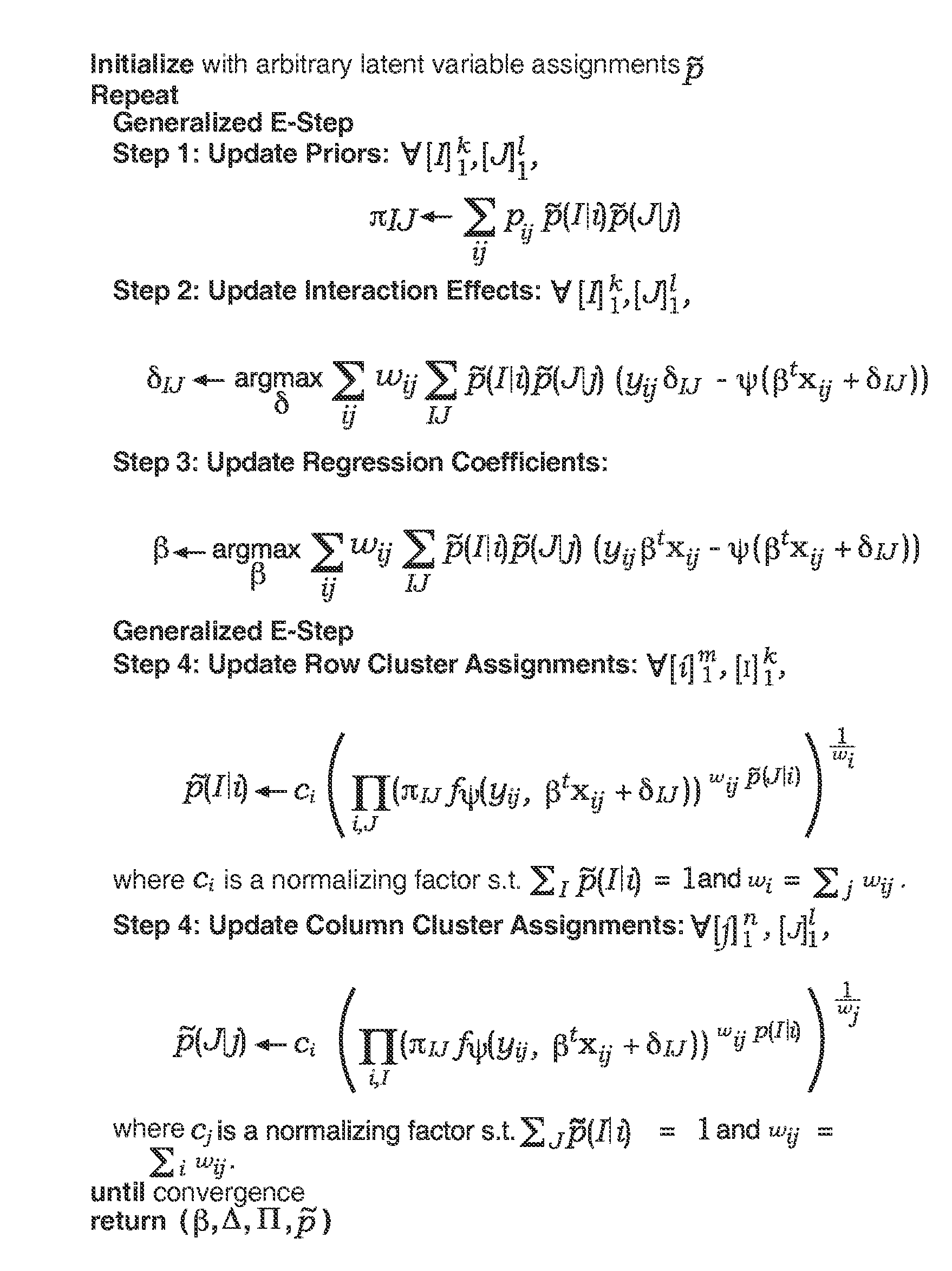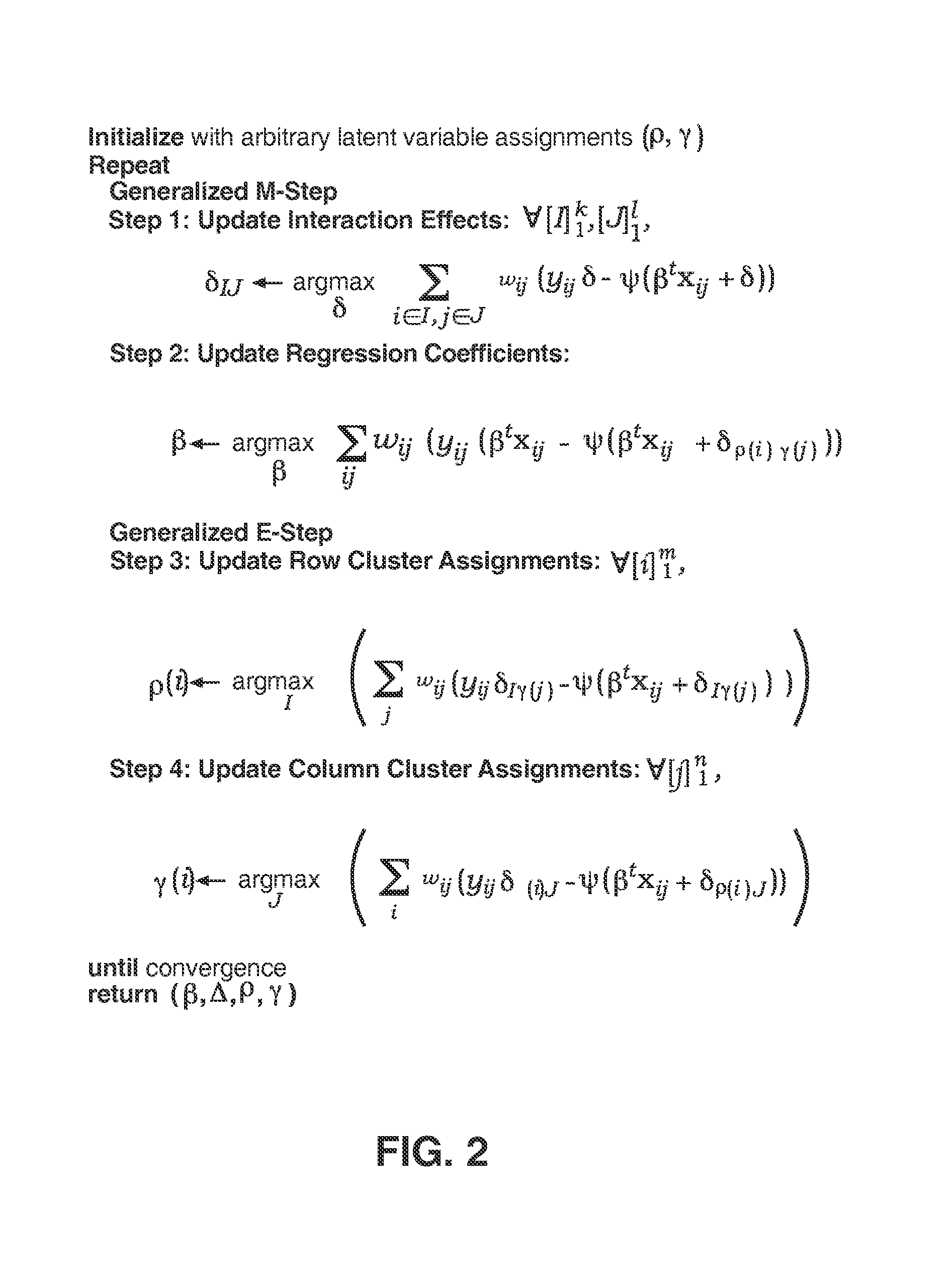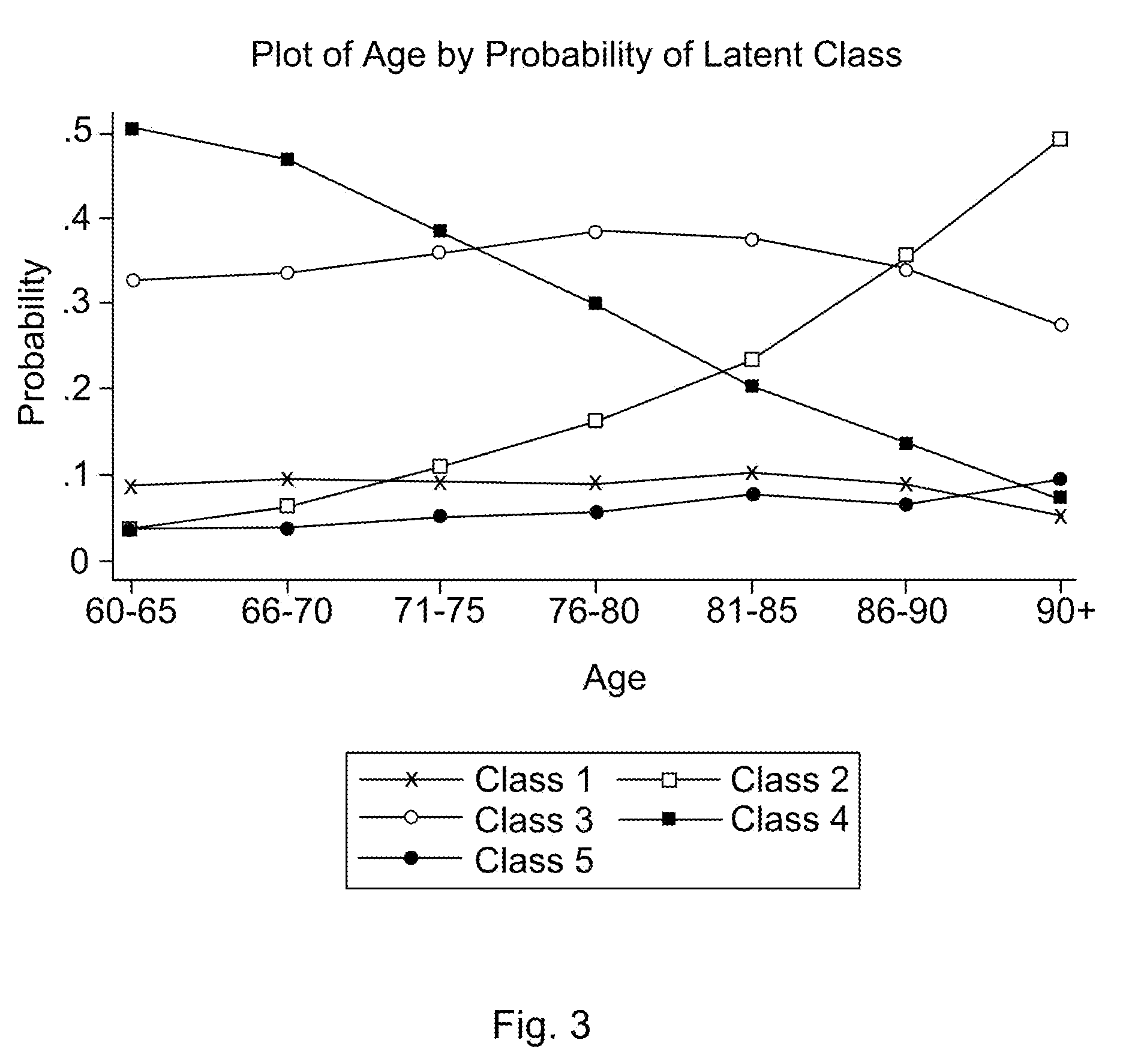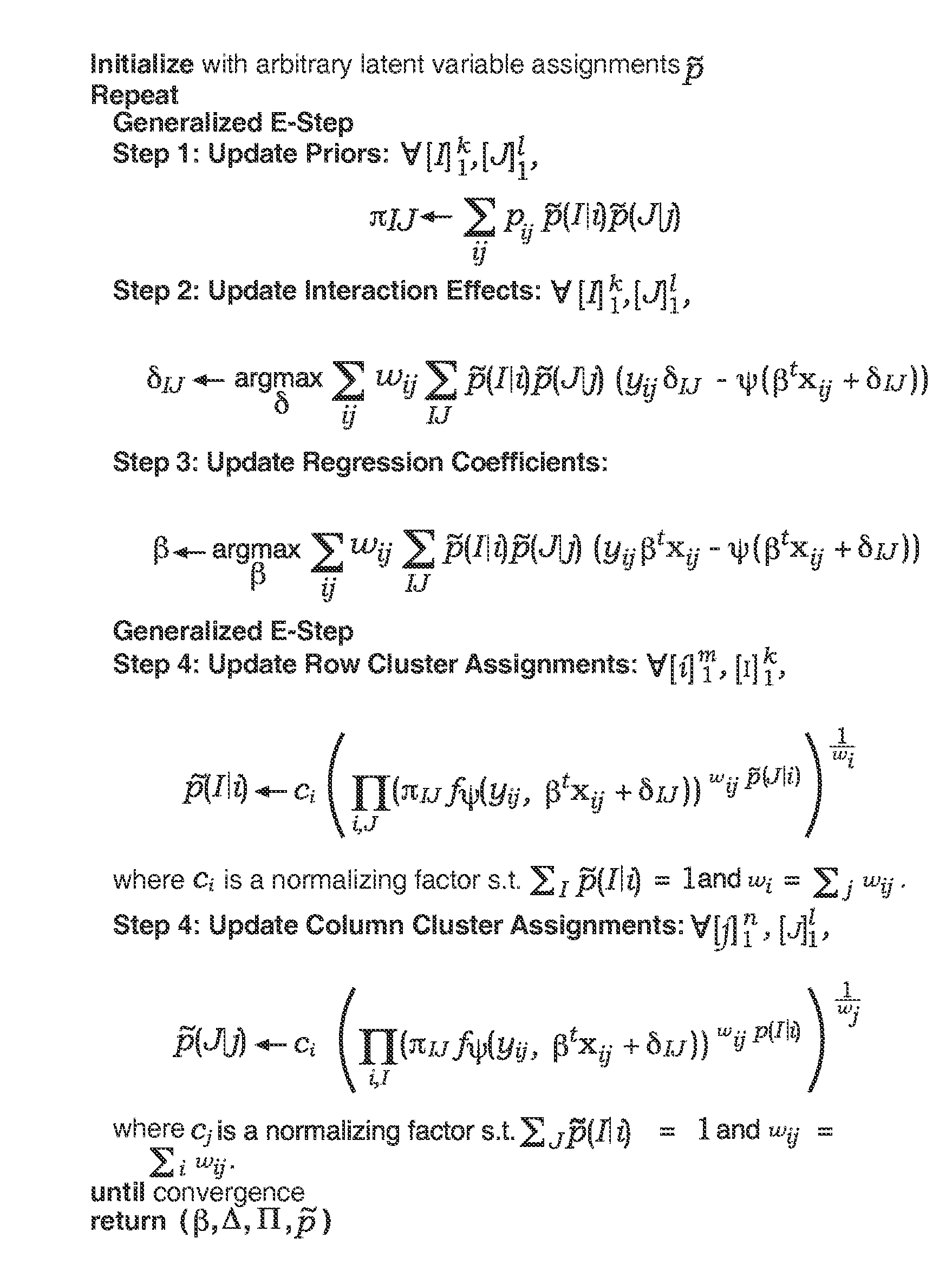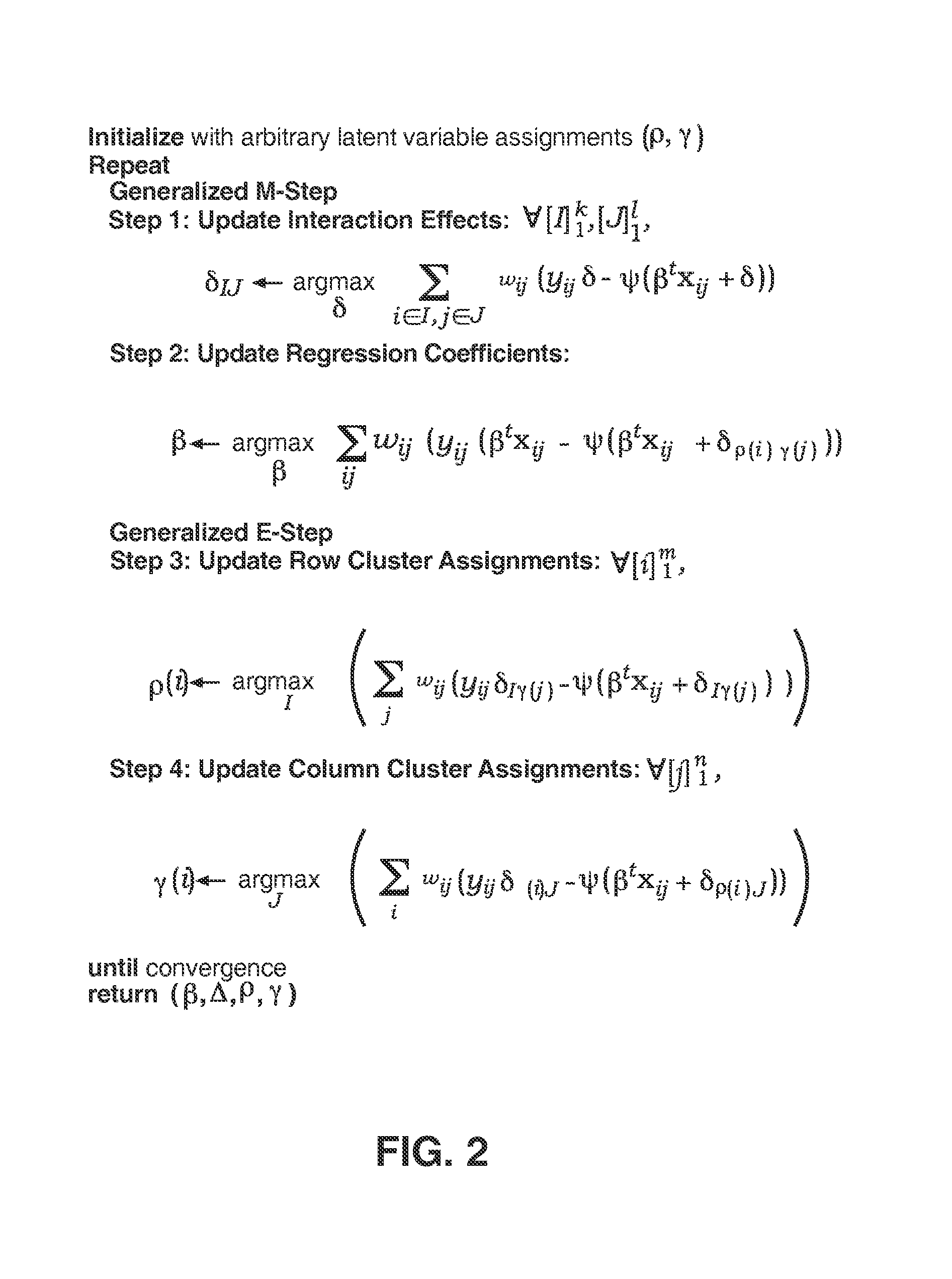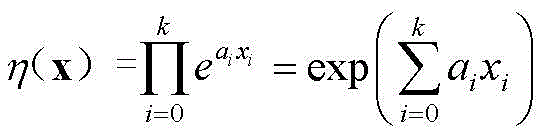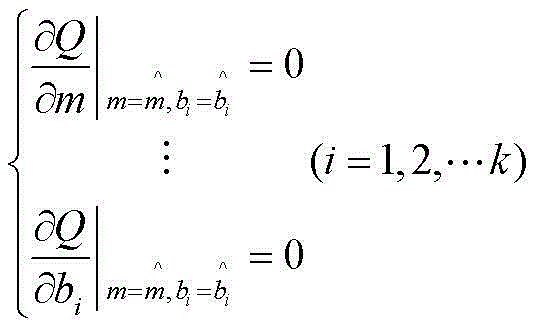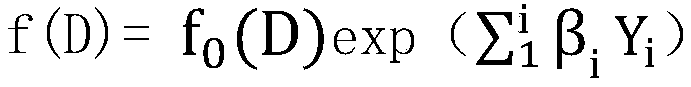Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Covariate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In statistics, a covariate is a variable that is possibly predictive of the outcome under study. A covariate may be of direct interest or it may be a confounding or interacting variable. The alternative terms explanatory variable, independent variable, or predictor, are used in a regression analysis. In econometrics, the term "control variable" is usually used instead of "covariate". In a more specific usage, a covariate is a secondary variable that can affect the relationship between the dependent variable and other independent variables of primary interest. An example is provided by the analysis of trend in sea-level by Woodworth. Here the dependent variable was the annual mean sea level at a given location for which a series of yearly values were available. The primary independent variable was "time". Use was made of a "covariate" consisting of yearly values of annual mean atmospheric pressure at sea level. The results showed that inclusion of the covariate allowed improved estimates of the trend against time to be obtained, compared to analyses which omitted the covariate.
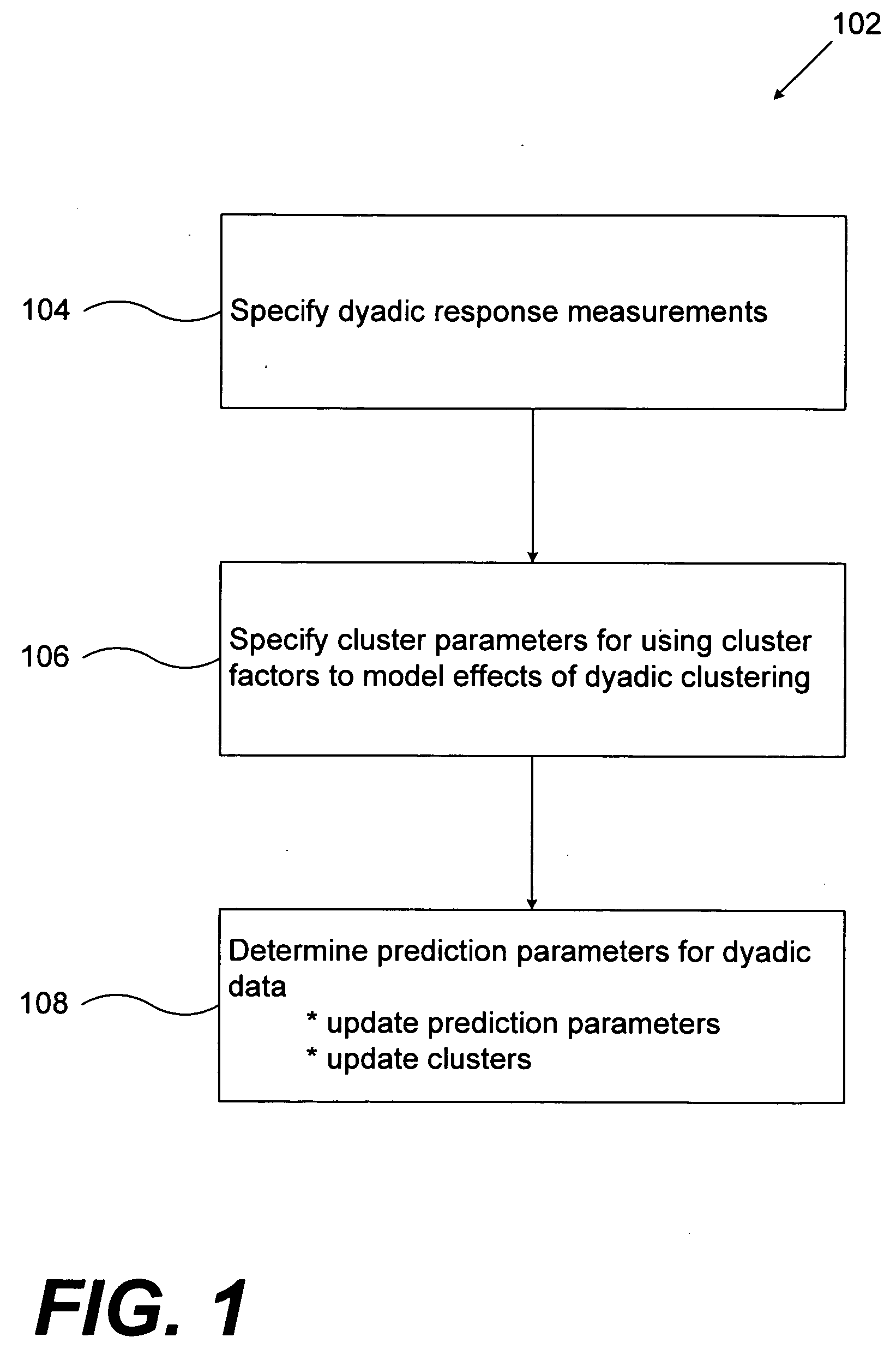
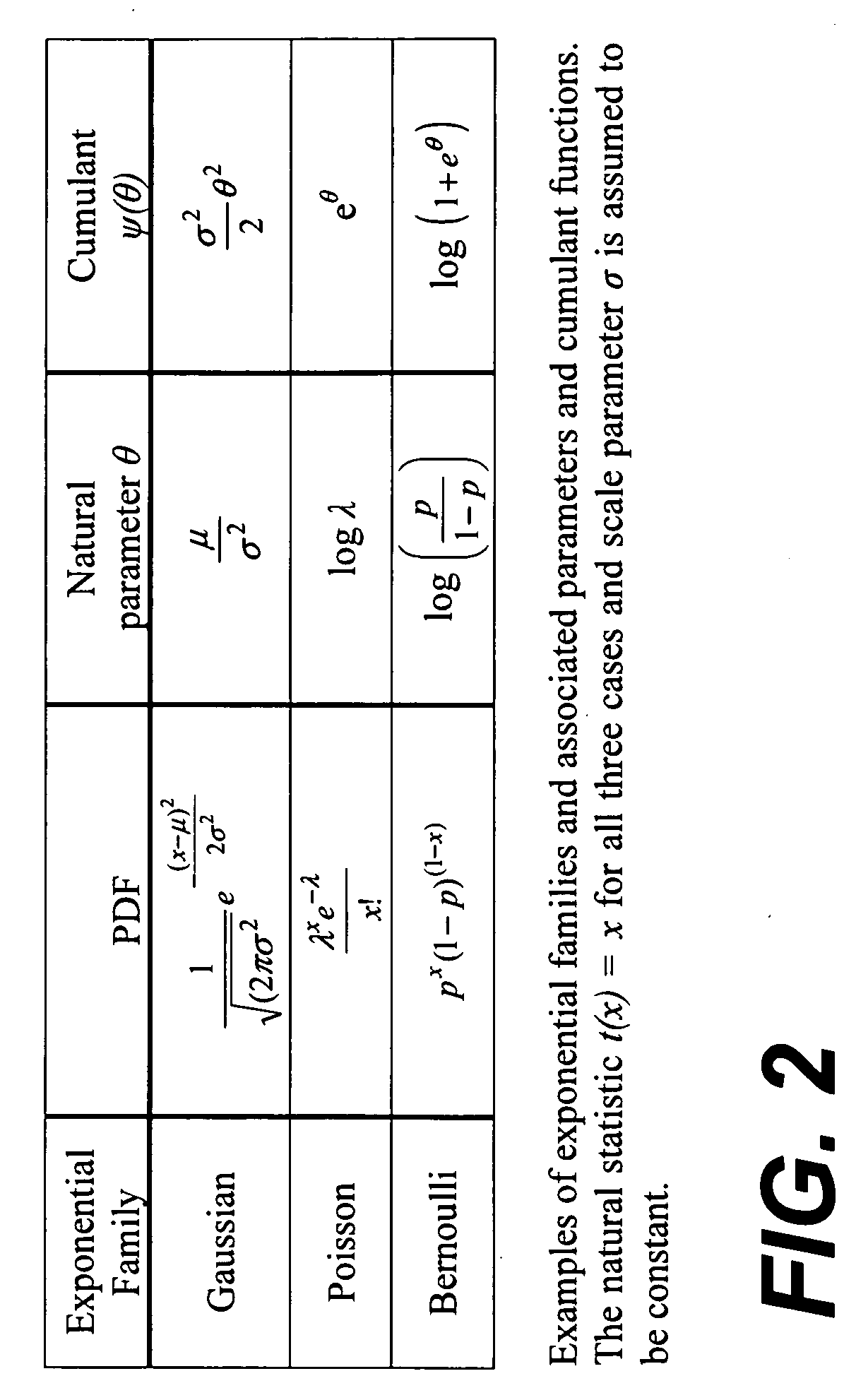
Predictive discrete latent factor models for large scale dyadic data
InactiveUS20090055139A1Accurate and interpretable predictive modelPrecision productionDigital computer detailsForecastingCovariate
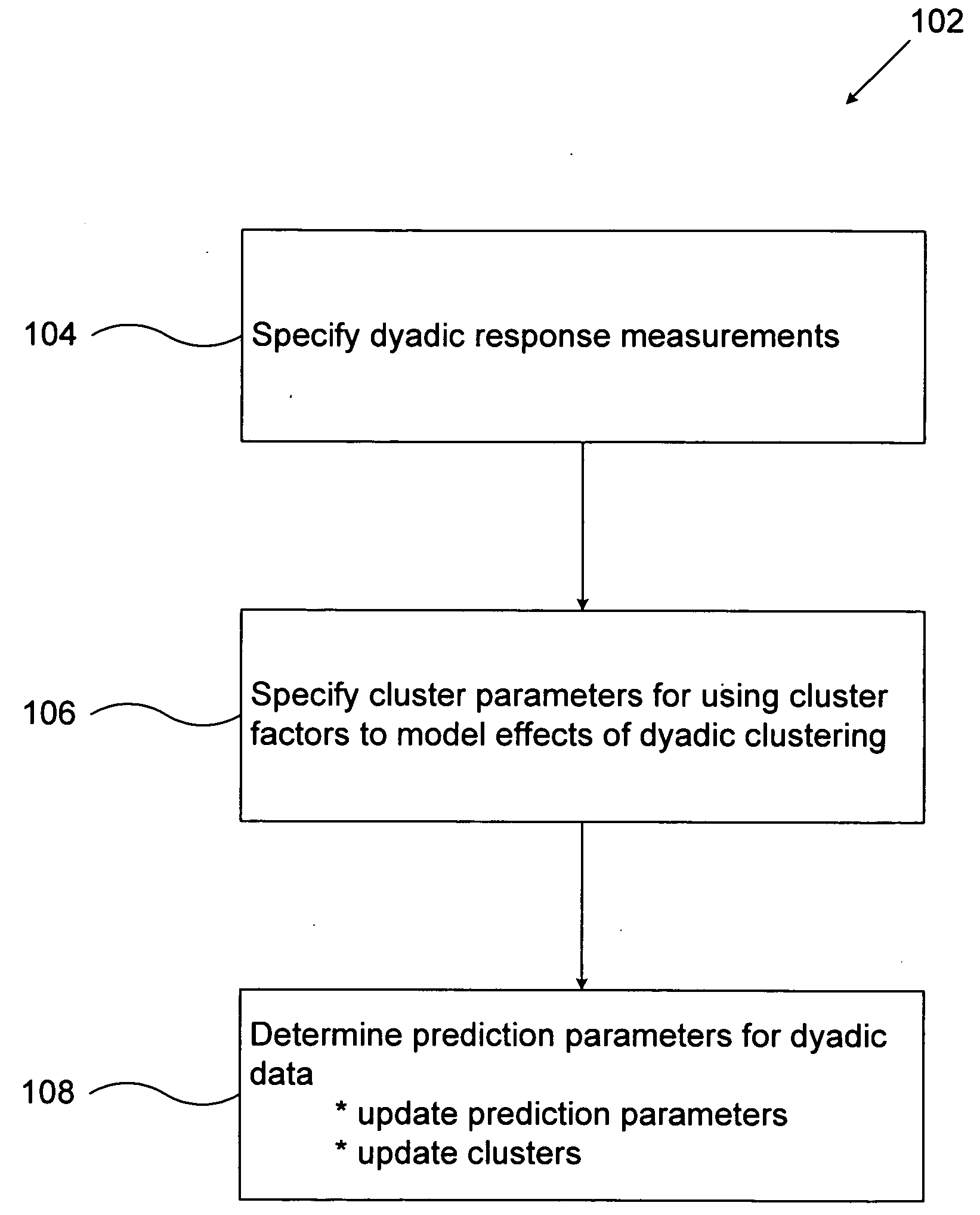
A method for predicting future responses from large sets of dyadic data includes measuring a dyadic response variable associated with a dyad from two different sets of data; measuring a vector of covariates that captures the characteristics of the dyad; determining one or more latent, unmeasured characteristics that are not determined by the vector of covariates and which induce local structures in a dyadic space defined by the two different sets of data; and modeling a predictive response of the measurements as a function of both the vector of covariates and the one or more latent characteristics, wherein modeling includes employing a combination of regression and matrix co-clustering techniques, and wherein the one or more latent characteristics provide a smoothing effect to the function that produces a more accurate and interpretable predictive model of the dyadic space that predicts future dyadic interaction based on the two different sets of data.
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
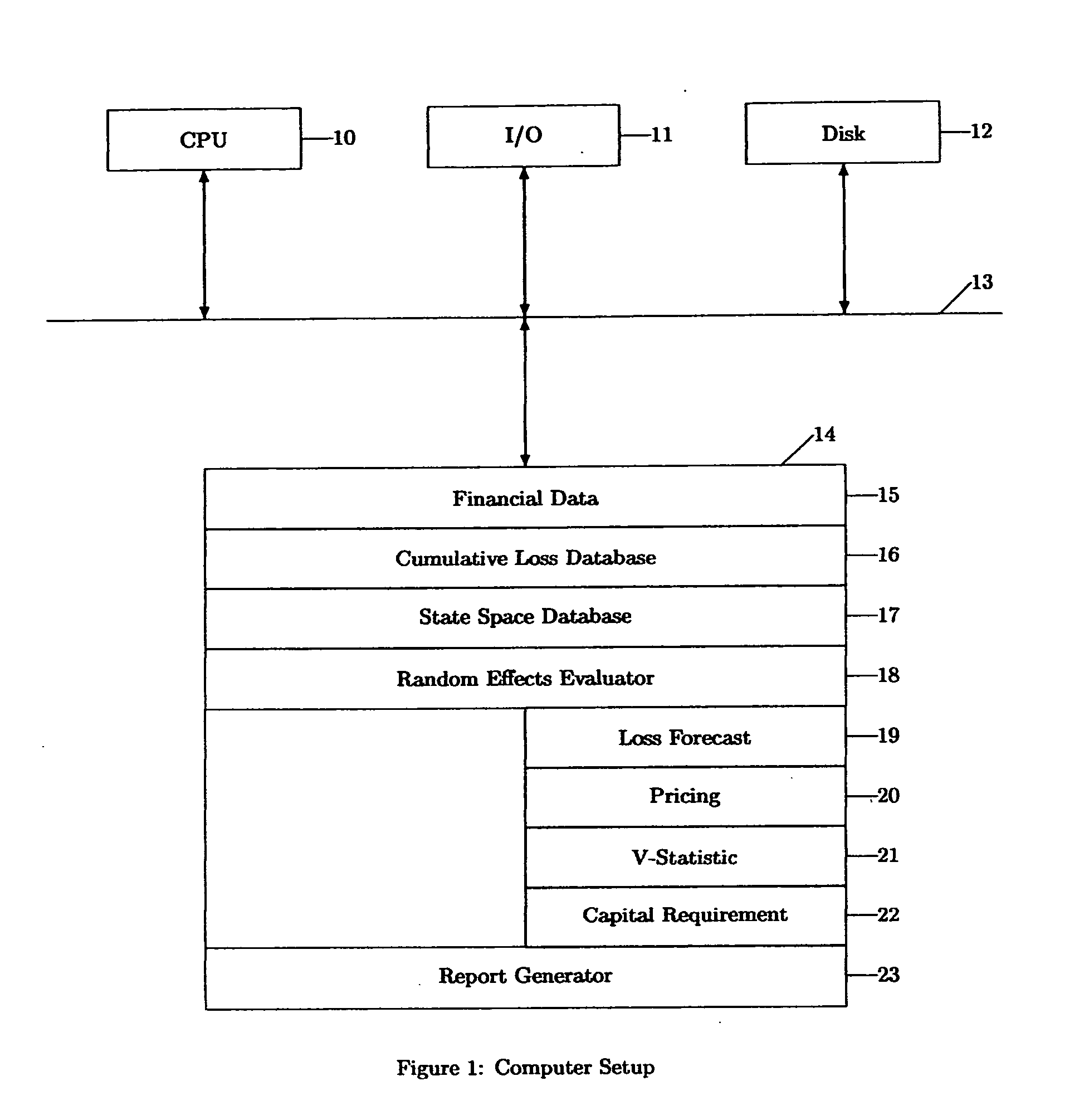
Modeling loss in a term structured financial portfolio
In accordance with the principles of the present invention, an apparatus, simulation method, and system for modeling loss in a term structured financial portfolio are provided. An historical date range, time unit specification, maturity duration, evaluation horizon, random effects specification, and set of portfolio covariates are selected. Historical data is then segmented into infinitely many cumulative loss curves according to a selected covariate predictive of risk. The s-shaped curves are modeled according to a nonlinear kernel. Nonlinear kernel parameters are regressed against time units up to the maturity duration and against selected portfolio covariates. The final regression equations represent the central moment models necessary for prior distribution specification in the hierarchical Bayes model to follow. Once the hierarchical Bayes model is executed, the finite samples generated by a Metropolis-Hastings within Gibbs sampling routine enable the inference of net dollar loss estimation and corresponding variance. In turn, the posterior distributions enable the risk analysis corresponding to lifetime loss estimates for routine risk management, the valuation of derivative financial instruments, risk-based pricing for secondary markets or new debt obligations, optimal holdings, and regulatory capital requirements. Posterior distributions and analytical results are dynamically processed and shared with other computers in a global network configuration.
Owner:STANELLE EVAN J
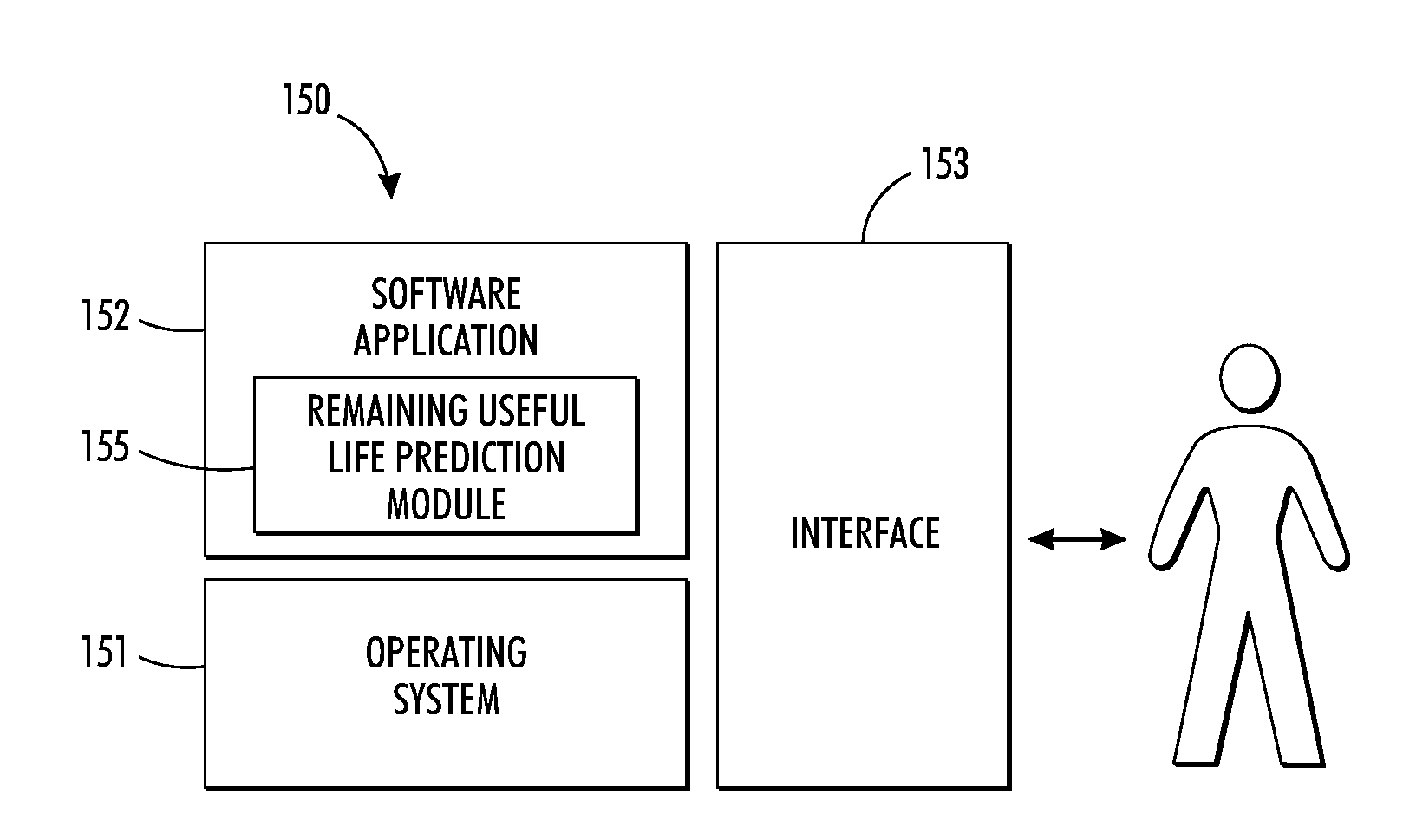
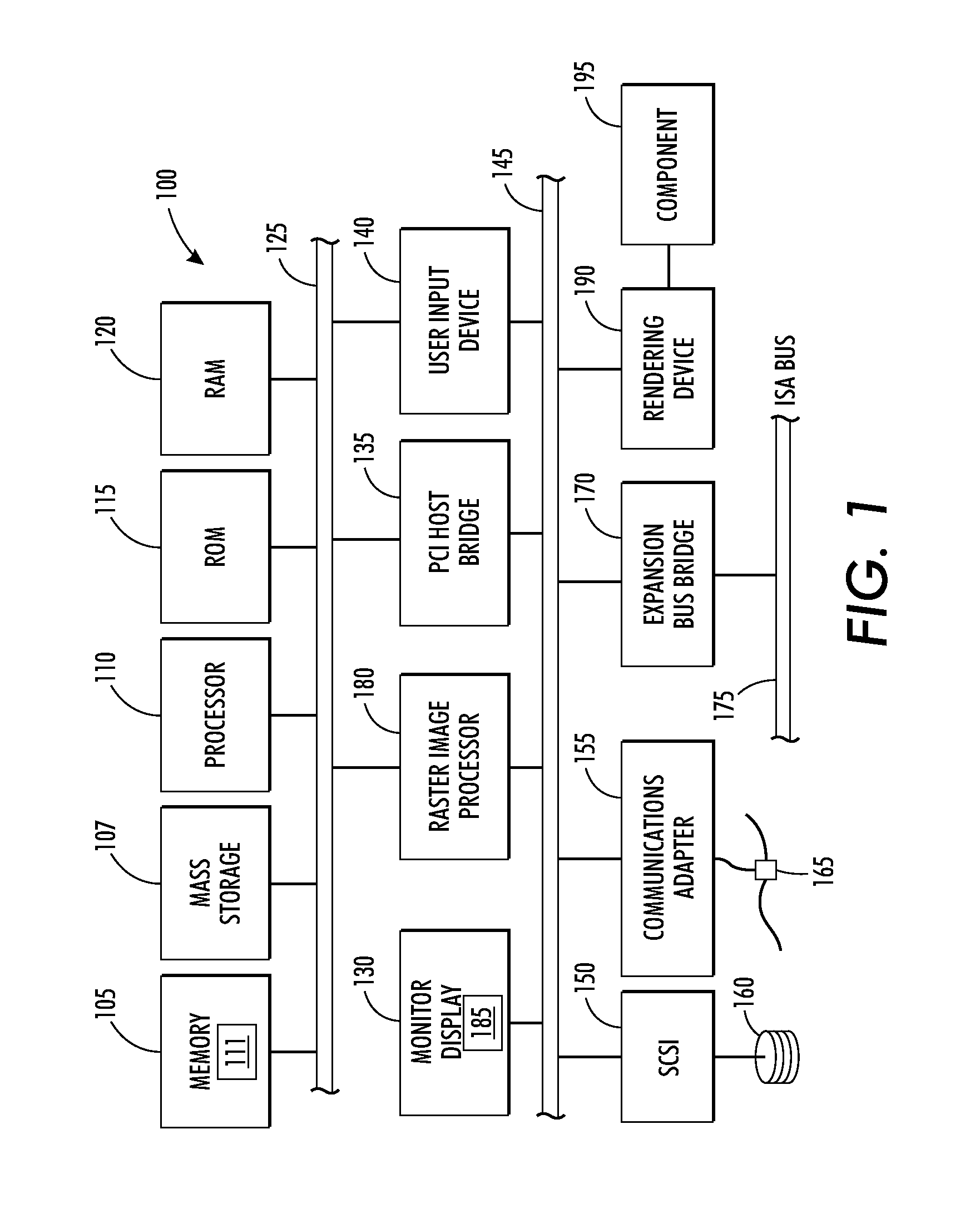
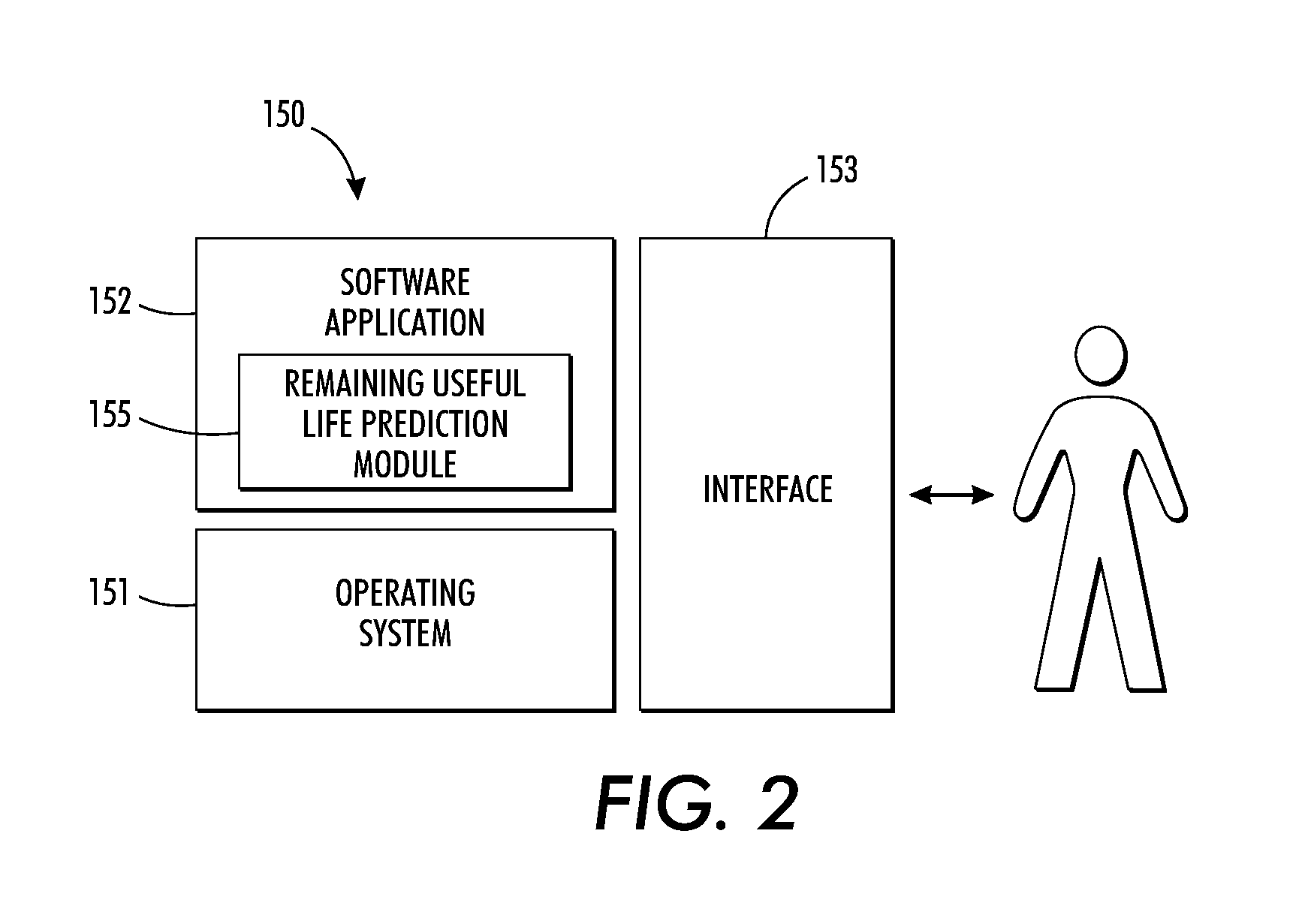
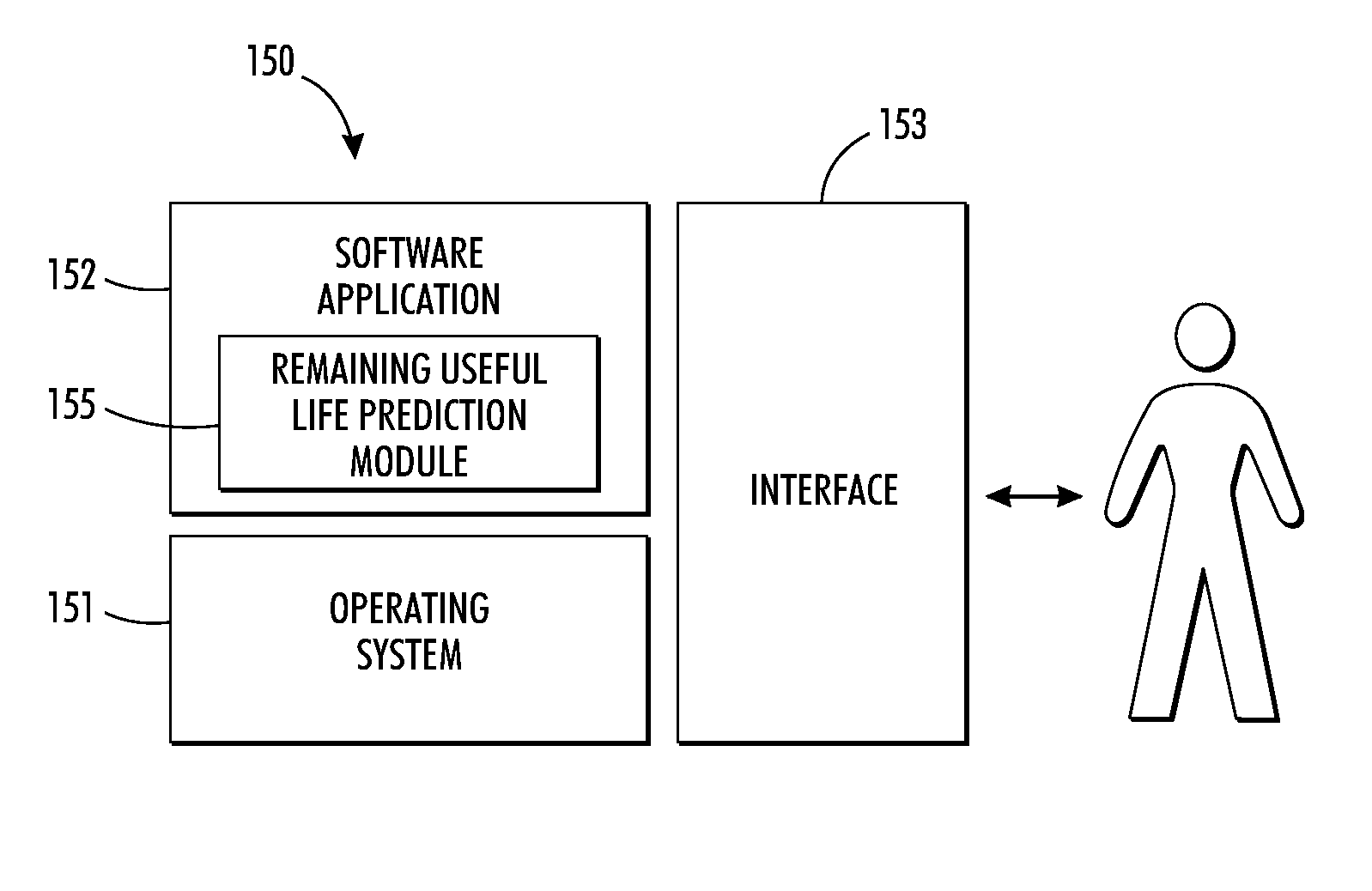
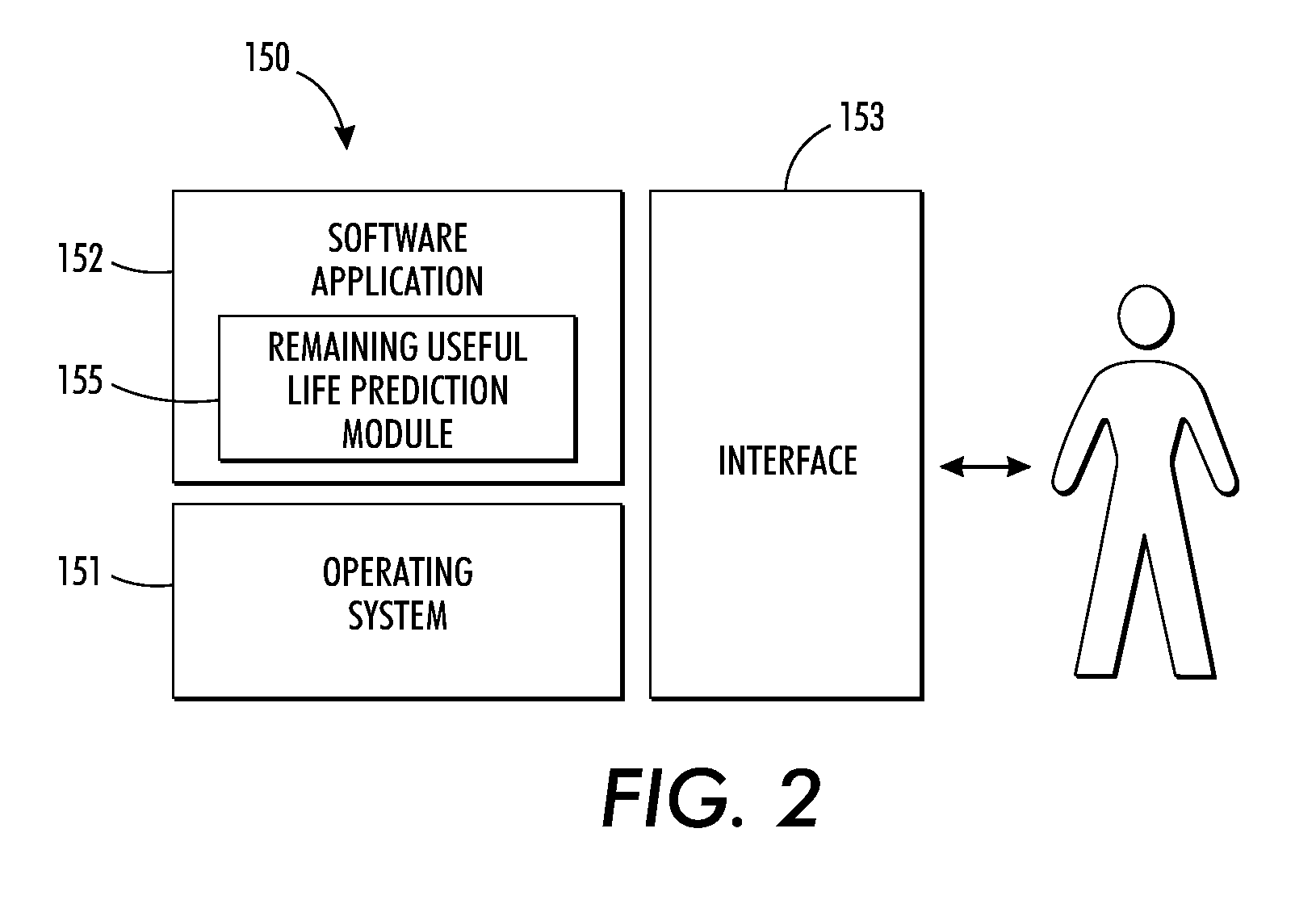
System and method for predicting remaining useful life of device components
InactiveUS20120143564A1Lower service costsAccurate predictionTesting/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsAnalysis dataStatistical analysis
A method and system for accurately predicting the remaining useful life of devices and device components based on rigorous statistical analysis data to reduce service costs by implementing condition-based maintenance is disclosed. One such rigorous statistical model is the general degradation path model. The General Path Model is used to generate simulated data that shares similar data characteristics of historical field failure data. This generated data can be used in a reliability study based on Monte Carlo techniques for RUL prediction. The study can be used to investigate the effects of influential factors such as suspension percentage and heavy-tailed behavior. The remaining useful life prediction is based on both the fixed-time predictors (such as the market segment) and the time-dependent covariates (e.g., dark decay, printing rate, etc.). The Random Forest Model can also be used for accurately predicting remaining useful life based on both fixed-time predictors and time-dependent covariates, which are both contained in the field data of a component. A relationship between component failure and amount of degradation makes it possible to use degradation models for accurate predictions of failure time.
Owner:XEROX CORP
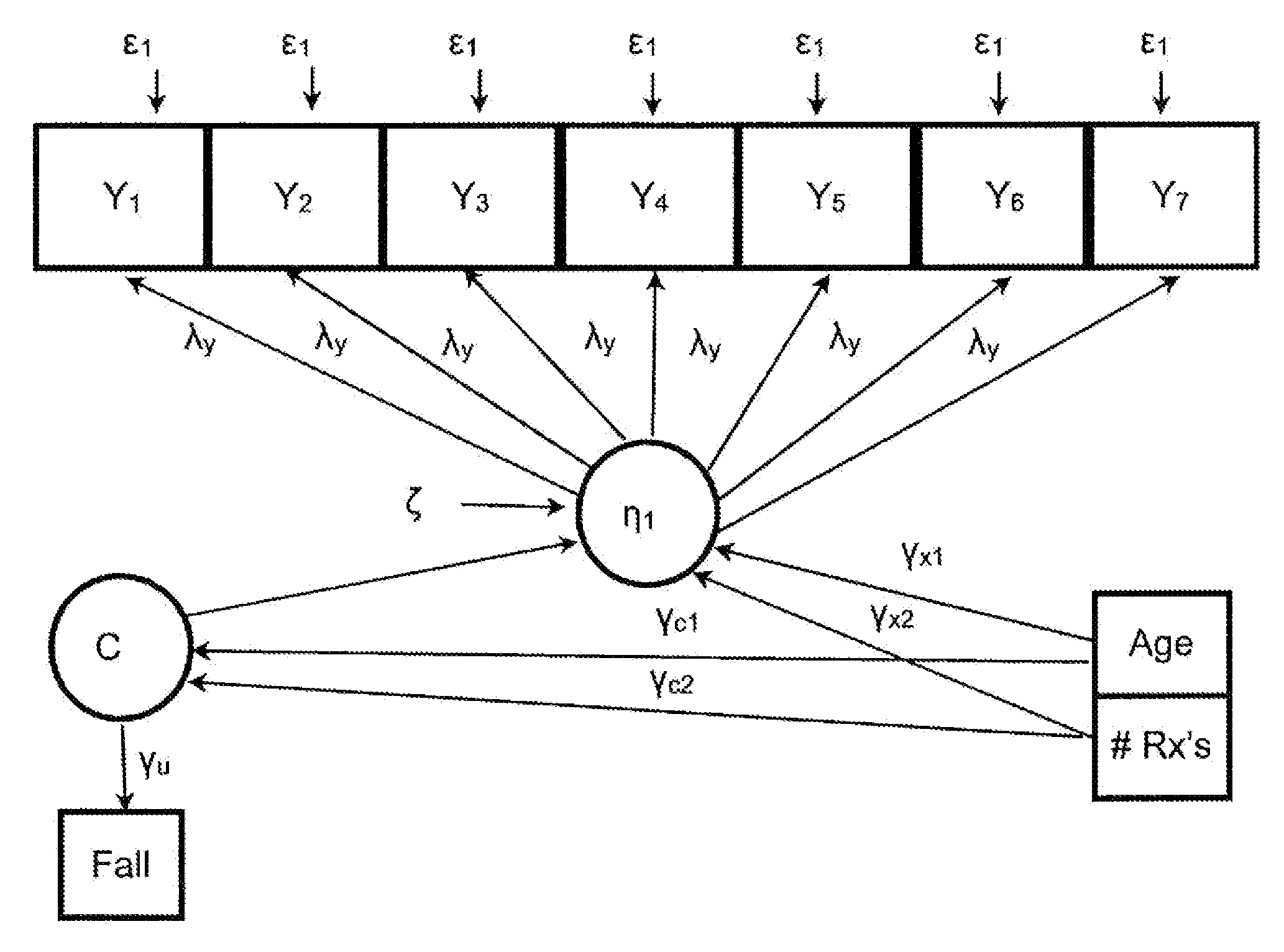
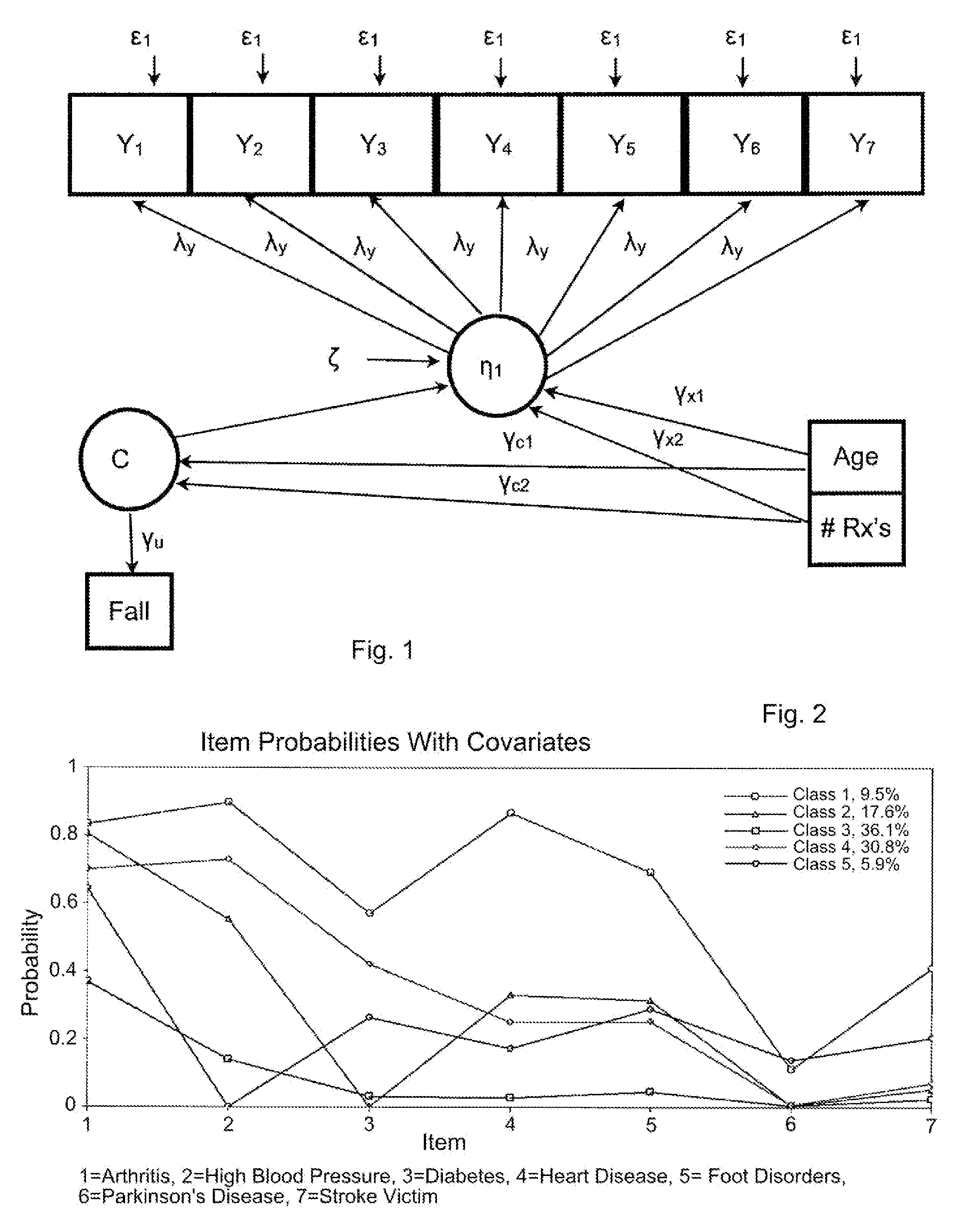
Statistical model for predicting falling in humans
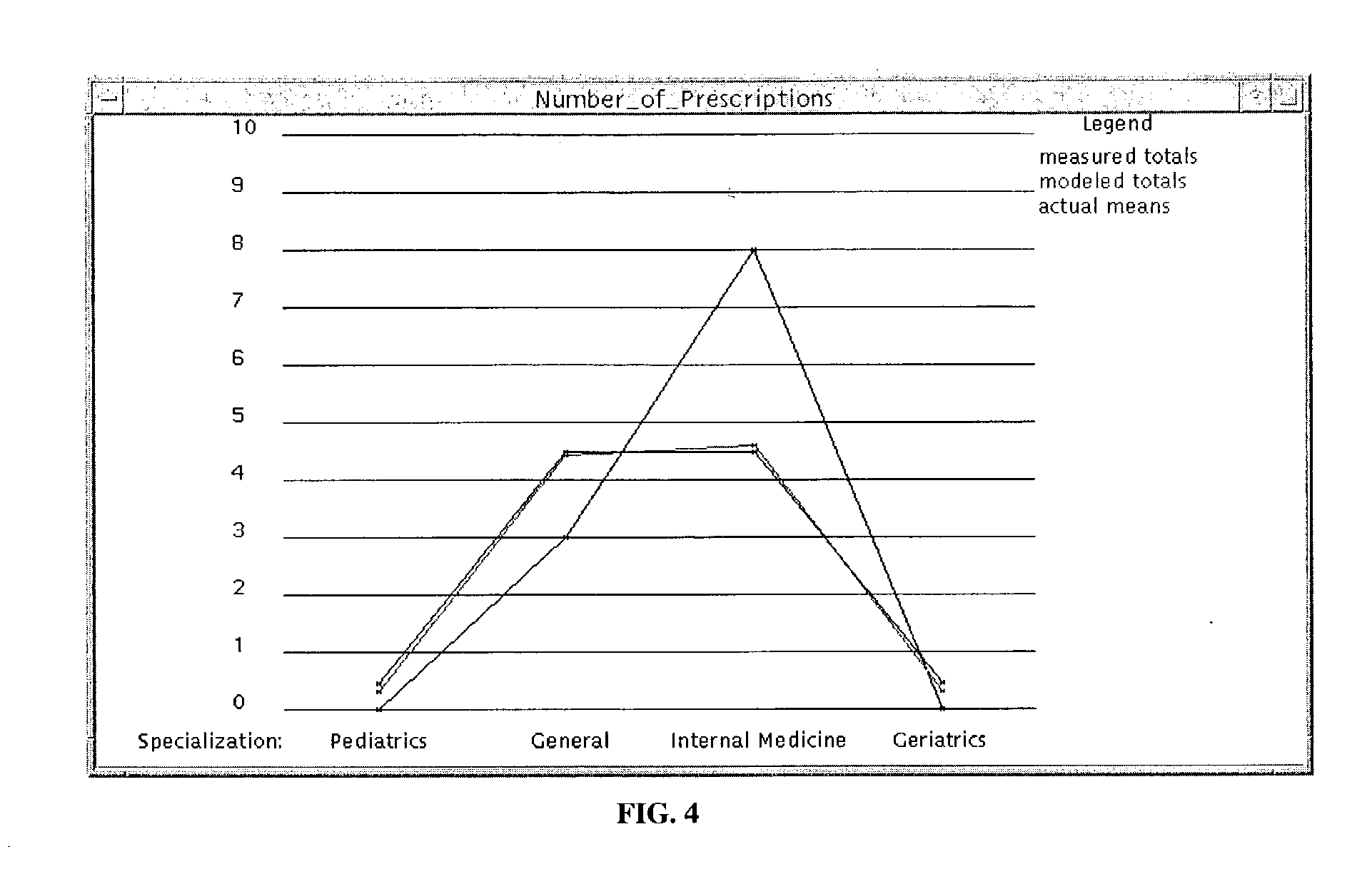
Dependent variables believed to contribute to a likelihood of falling are analyzed using a latent class analysis. The dependent variables are biomedical factors, which may include, for example, arthritis, high blood pressure, diabetes, foot disorders, Parkinson's Disease, stroke, eye disorder, limb disorder, or proprioceptive disorder. Data pertaining to the biomedical factors is gathered from a population of individuals at risk of falling. Covariate data, including for example age and the number of prescriptions taken, is further analyzed against latent class data. For a particular group of at risk individuals, a set of five classes produced useful results broadly corresponding to groups representing individuals who have: good health; a range of diseases; Parkinson's Disease; arthritis; and high blood pressure. A probability of falling is determined, relative to the group of individuals with good health.
Owner:NOVA SOUTHEASTERN UNIVERSITY
Automated generator of optimal models for the statistical analysis of data
ActiveUS20040220784A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusDigital computer detailsExact statisticsStatistical analysis
Provided is an automated process for producing accurate statistical models from sample data tables. The process solves for the optimal parameters of each statistical model considered, computes test statistics and degrees of freedom in the model, and uses these test statistics and degrees of freedom to establish a complete ordering of the statistical models. In cases where the sample data table is sufficiently small, the process constructs and analyzes all reasonable statistical models that might fit the data table provided. In cases where the number of possible models is prohibitively high, the process begins by constructing and solving more general models and then constructs and solves those more detailed models that are similar to those general models that achieved the highest ordering. In either of these two cases, the process arrives at a statistical model that is highest in the ordering and is thus deemed most suitable to model the sample data table. The result of this process is a statistical model deemed to be most suitable to model the sample data table and a set of average table values produced by this resulting model. This resulting table may include modeled values for table entries for which no initial data was supplied. This invention finds application in the area of credit scoring, where covariates such as age, profession, gender, and credit history are used to determine the likelihood that an individual will default on a loan. It also finds application in analyzing the effectiveness of many types of tools as they are used in various environments (e.g., the effectiveness of radar when used in different weather conditions). It also finds application in the area of insurance, where one wishes to estimate the future number of claims against a specific insurance policy based on a database of past insurance claims.
Owner:DANIEL H WAGNER ASSOCS
Squashed matrix factorization for modeling incomplete dyadic data
InactiveUS20100169158A1Character and pattern recognitionFuzzy logic based systemsTensor factorizationCovariate
Owner:OATH INC
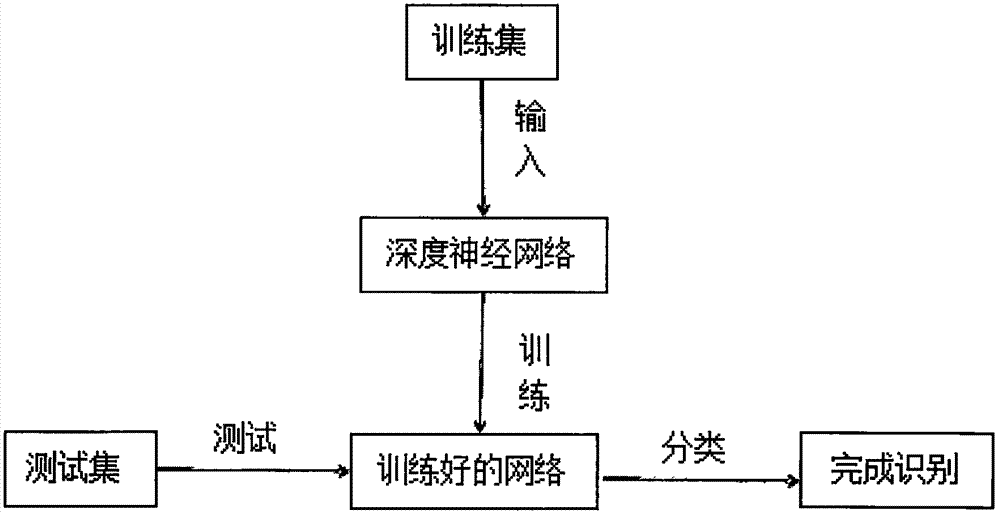
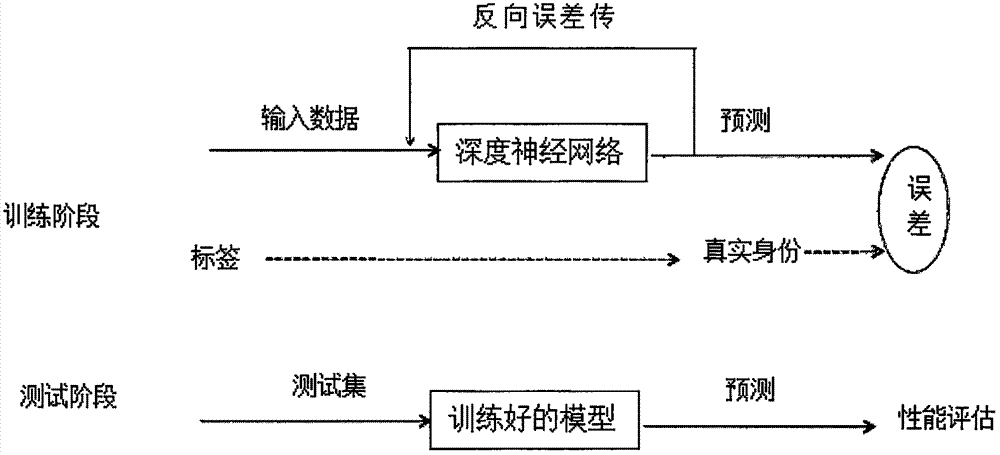
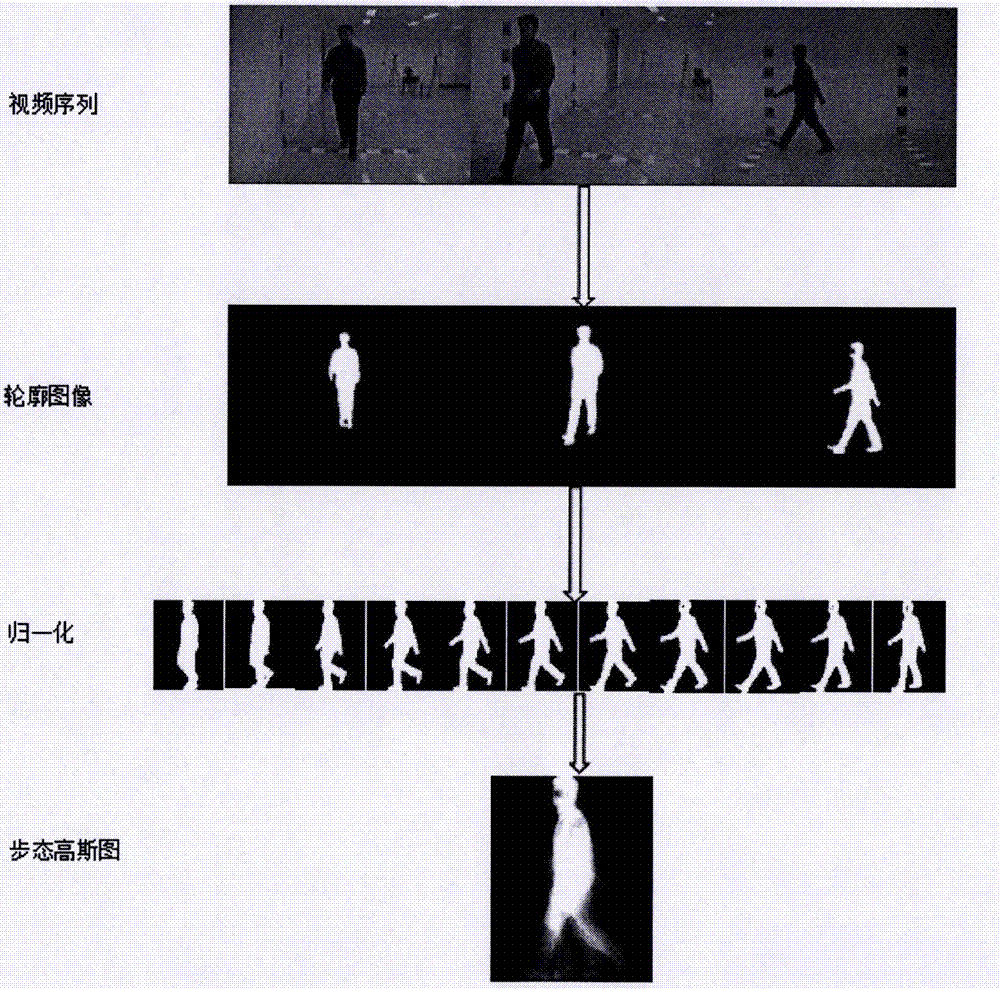
Gait recognition method based on depth neural network
InactiveCN107292250AFast convergenceAvoid the disadvantage of poor classification performanceImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionData setNetwork model
The invention discloses a gait recognition method based on a depth neural network, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the preprocessing of an original gait video image, extracting the gait Gaussian image of the original gait video image, and dividing a sample data set into a training set and a testing set at a proportion of 5: 1 according to a designed rule; building an eight-layer convolution neural network model consistent with an AlexNet structure, modifying the number of neurons of the last layer of the model, and enabling the model to adapt to a gait classification task; Carrying out the initialization of the parameters of a trained AlexNet model through the former seven layers of the model, and carrying out the random initialization of the last layer of the model; training the convolution neural network through the training set, and enabling the convolution neural network to effectively complete the gait recognition. The method is higher in robustness, can achieve the more effective recognition of the identity of a person under the condition of various types of concomitant variables, and can remarkably reduce the calculation resources and time of a training model.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Predictive discrete latent factor models for large scale dyadic data
InactiveUS7953676B2Accurate and interpretable predictive modelPrecision productionDigital computer detailsForecastingData setLocal structure
Owner:R2 SOLUTIONS
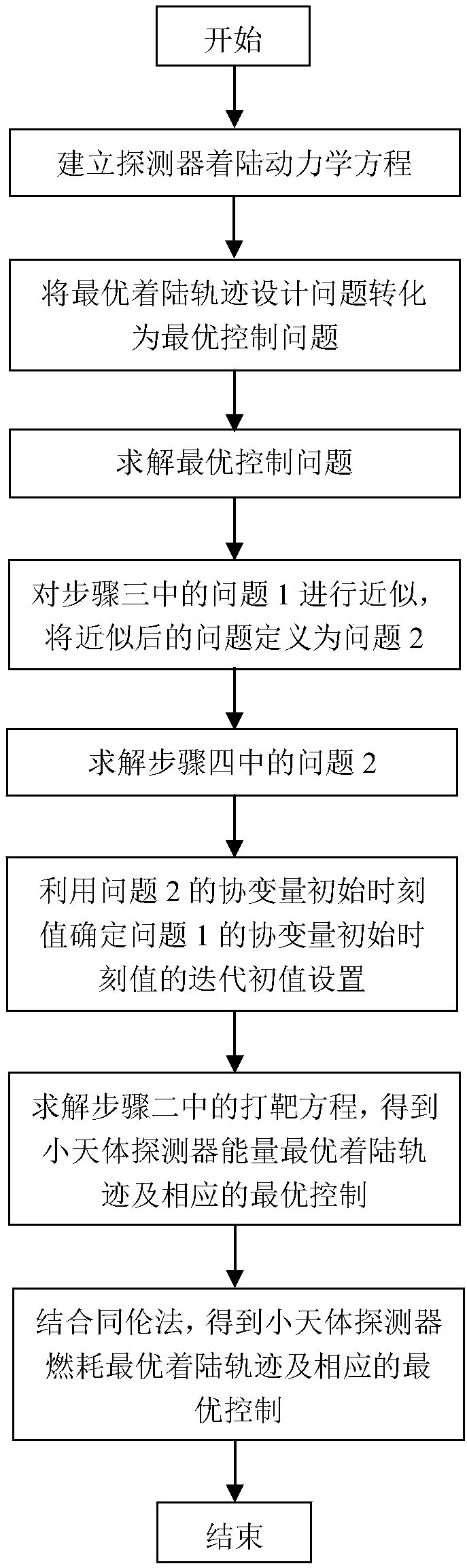
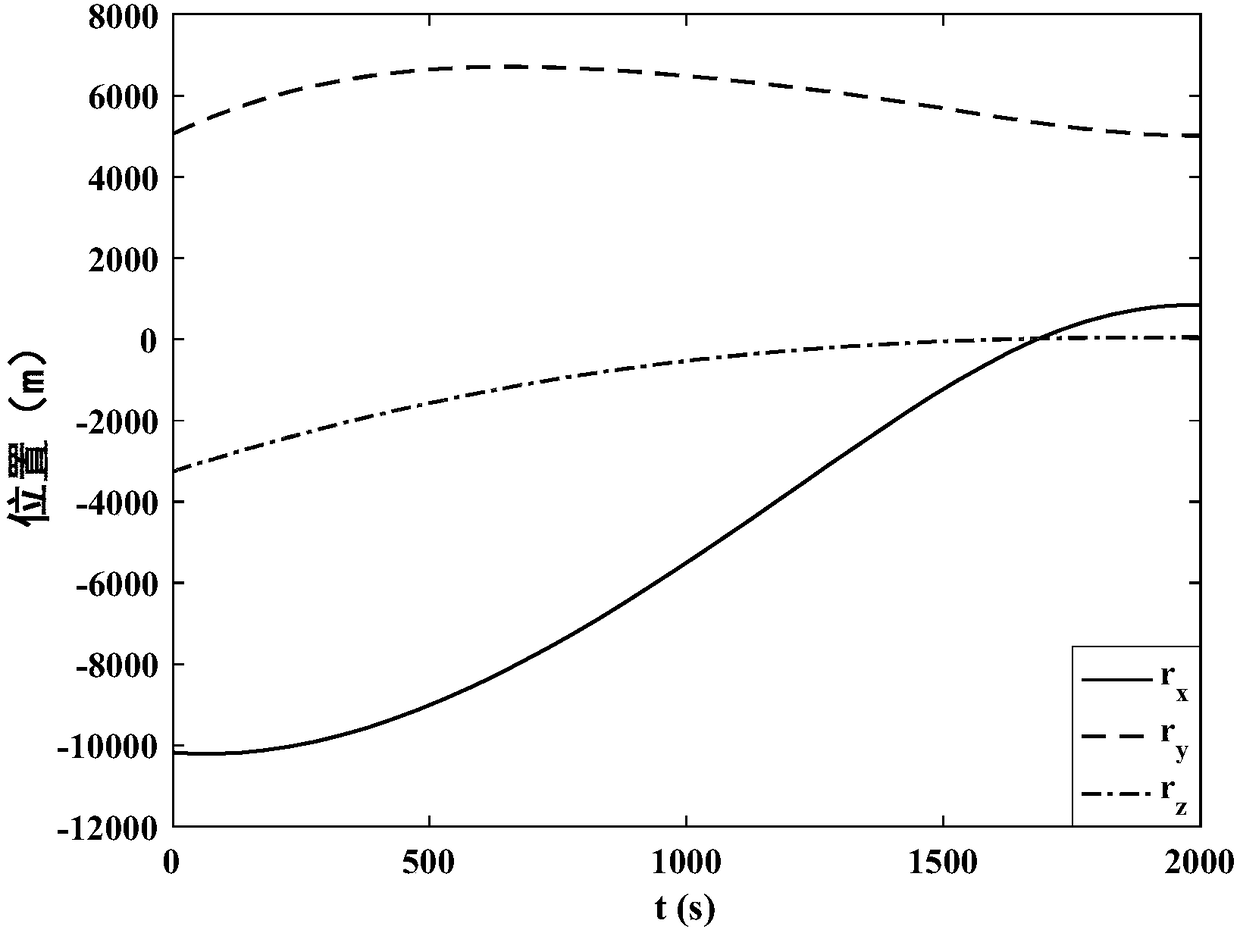
Covariant initial value determination method for optimal landing track design
ActiveCN108196449ASolve the defects that are not easy to solveSmall amount of calculationAdaptive controlDeep space explorationOptimal control
The invention discloses a covariant initial value determination method for the optimal landing track design and belongs to the field of deep space exploration. The covariant initial value determination method includes building a small body fixing coordinate system and corresponding detector landing kinetic equations; converting the optimal design problem of the small body landing track into the optimal control problem and the corresponding two-point boundary value problem, and defining the problems as the problem 1; approximating the problem 1, and defining the approximated problem 1 as the problem 2; solving the covariant initial values lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)> of the problem 2, setting the the covariant initial values lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)> of the problem 2 as iterative initial values of the covariant initial values lambda<r1(t0)> and lambda<v1(t0)> of the problem 1, determining the iterative initial value of the covariant initial value lambda<m1(t0)> of the problem 1 according to the setting of the iterative initial values, namely lambda<r2(t0)> and lambda<v2(t0)>, of the covariant initial values lambda<r1(t0)> and lambda<v1(t0)> of the problem 1, thereby achieving the iterative initial value setting of the covariant initial values for the optima landing track design. The defect that it is difficult to solve the two-point boundary value problem due to improper initial value setting can be avoided by application of the method.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
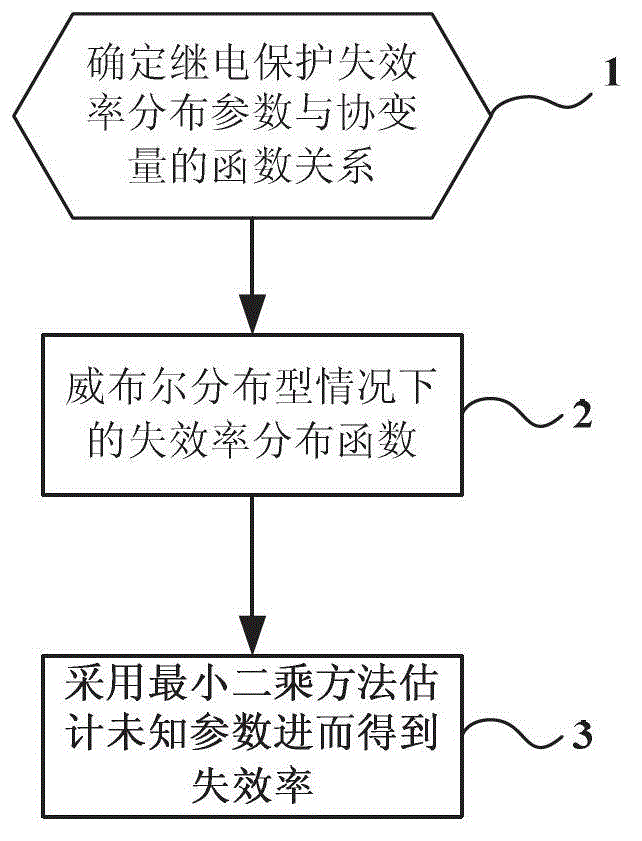
Failure rate calculation method for relay protection device in consideration of covariates
ActiveCN102945316AAccurately simulate failure behaviorImprove reliabilitySpecial data processing applicationsFailure rateElectric power system
A failure rate calculation method for a relay protection device in consideration of covariates belongs to the technical field of protection of electric power systems. The method comprises the following steps of: determining the function relationship between relay protection failure rate distribution parameters and the covariates by using a multiplication model; obtaining failure rate distribution functions under the Weibull distribution condition by the function relationship between the parameters and the covariates; and obtaining unknown parameters of the distribution functions through the formula (referring to the Specification) in order to calculate the failure rate of the relay protection device, wherein m and Eta in the formula respectively represent Weibull distribution shape parameters and scale parameters. According to the failure rate calculation method for the relay protection device in consideration of the covariates disclosed by the invention, the failure characteristics of the relay protection device are accurately simulated in consideration of the intrinsic characteristics of the relay protection and the external working conditions thereof, so that the covariates and failure rate calculation method for the relay protection is built. And the method is helpful to find out the principal factors which influence the reliability indexes of the method, and provides the guidance to improve the relay protection reliability.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
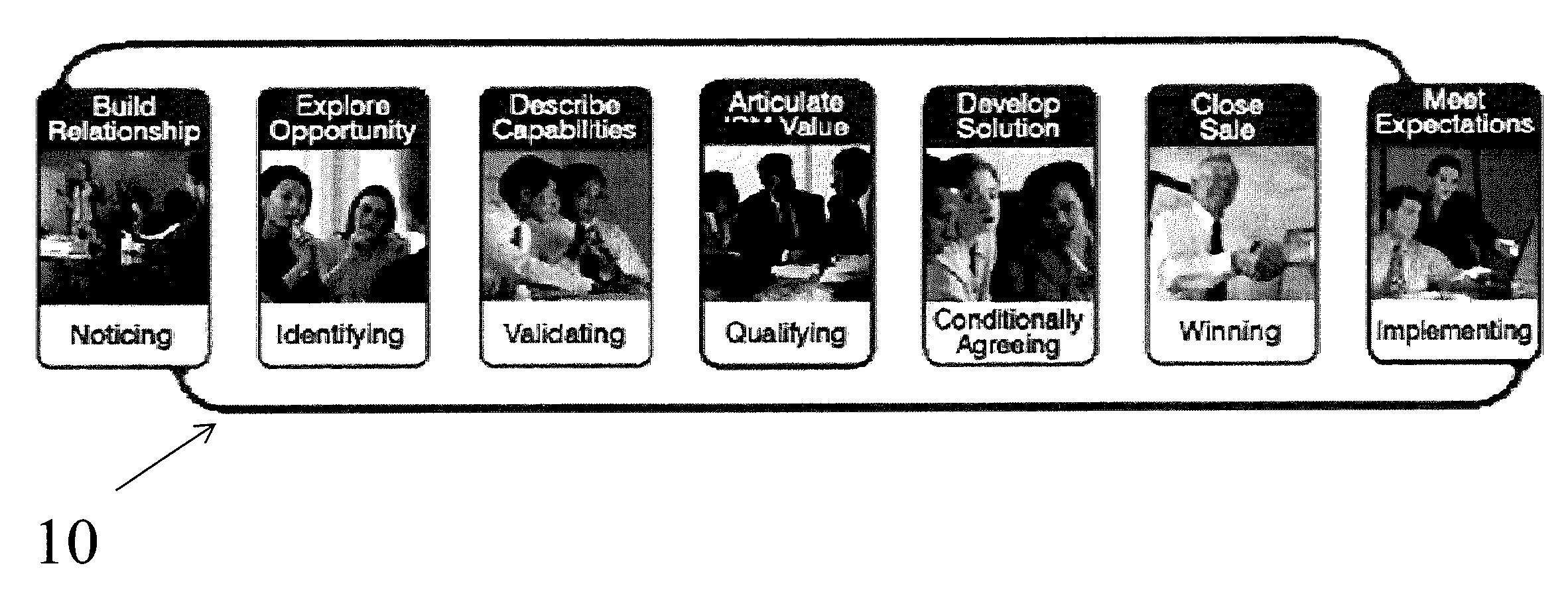
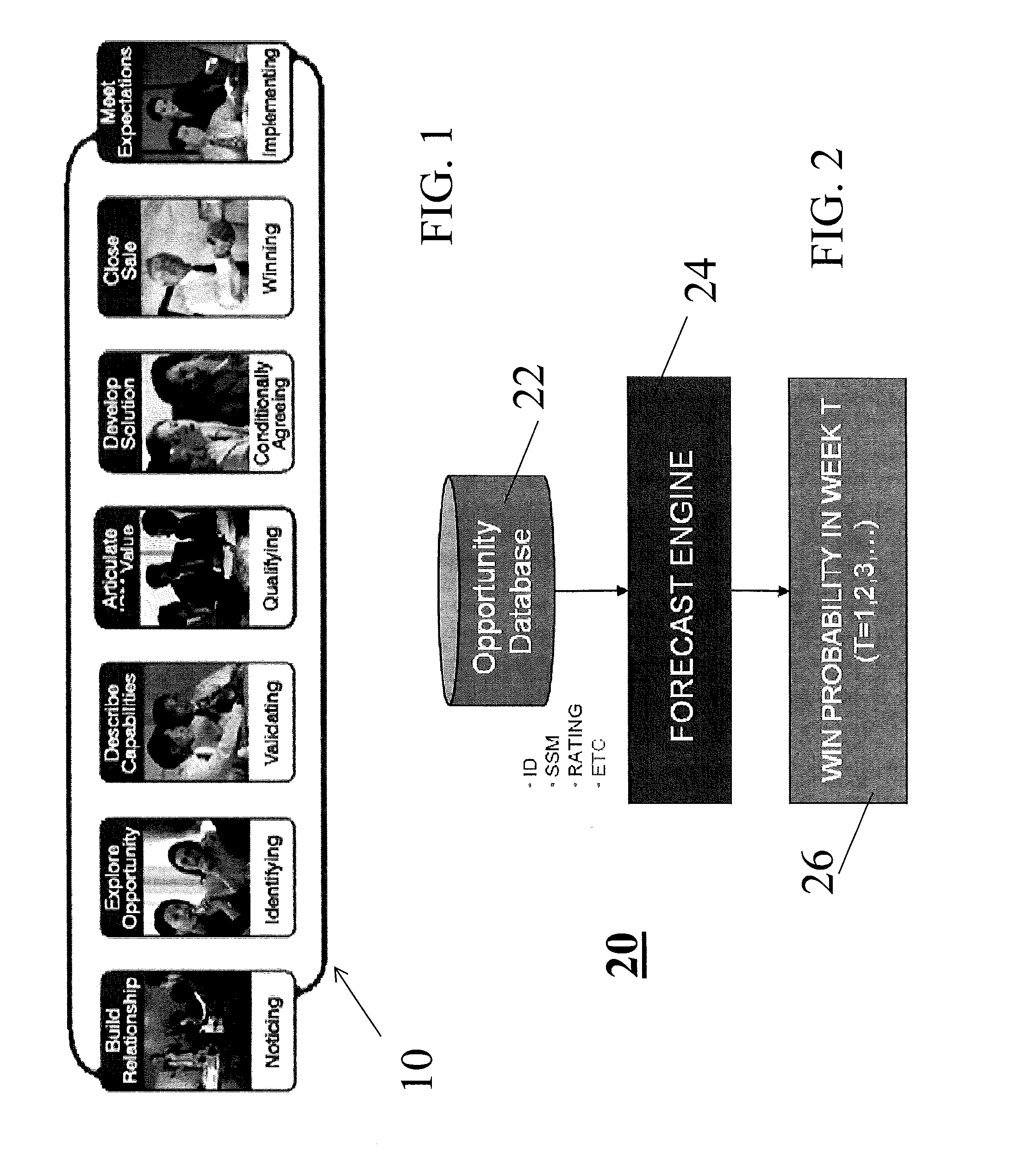
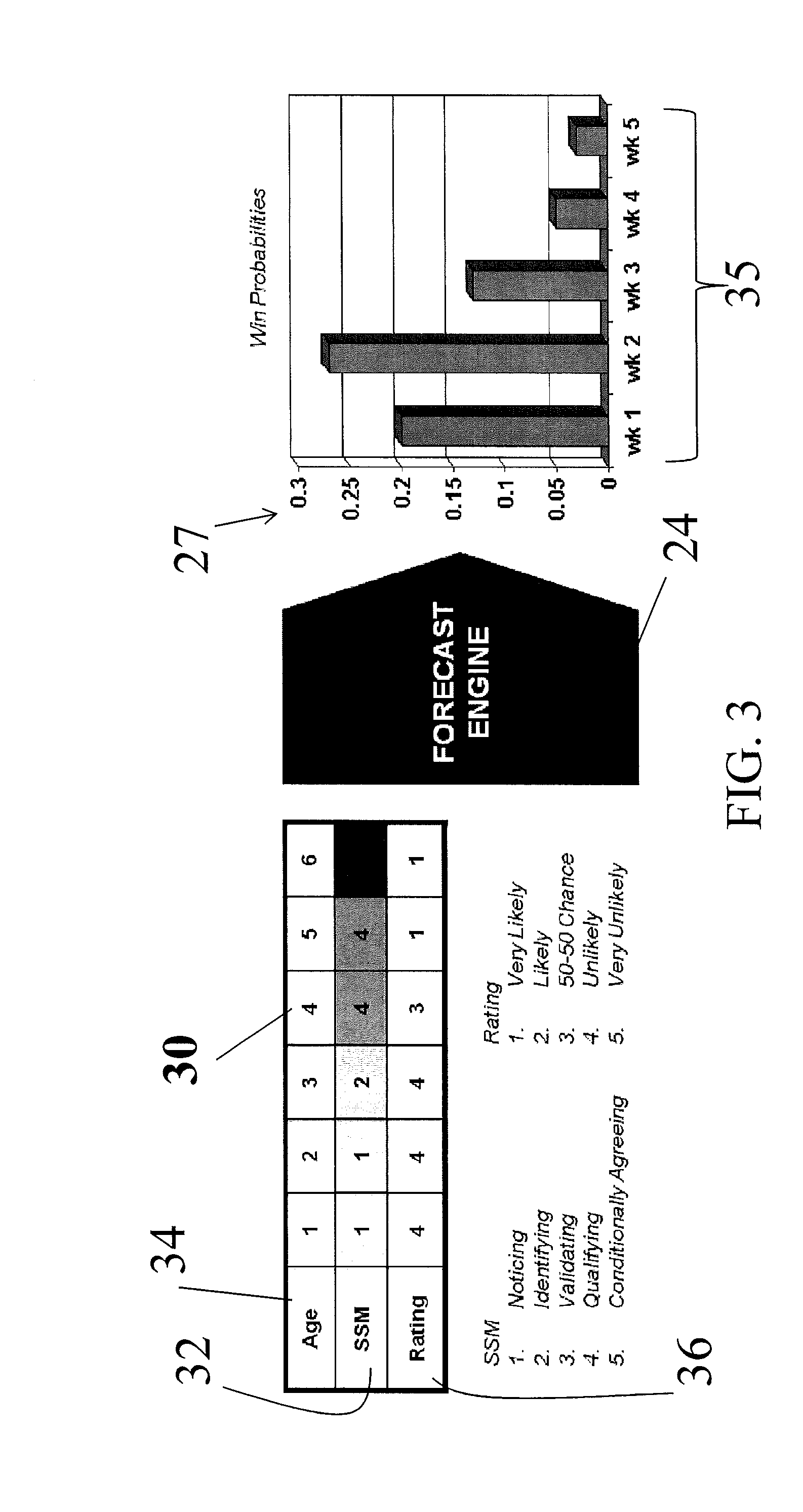
Business opportunity forecasting
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
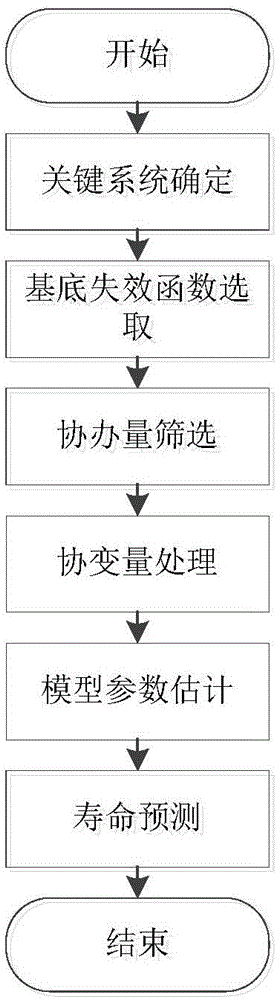
Method for predicting service life of key system of rail transit vehicles
InactiveCN105320797AImprove accuracyLife Prediction is AccurateSpecial data processing applicationsProportional hazards modelPrincipal component analysis
The invention discloses a method for predicting the service life of a key system of rail transit vehicles. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, determining the key system of urban rail vehicles, and bringing in a proportional hazard model to carry out service life prediction on the key system; secondly, screening historical overhauling data of the key system to obtain concomitant variable factors, and processing concomitant variables by applying a principal component analysis method so as to obtain a concomitant variable matrix; thirdly, solving a parameter estimation value in the proportional hazard model by adopting a maximum likelihood estimation method and a Newton iteration method; finally, calculating the predicted service life of the key system of the rail transit vehicles by utilizing the obtained proportional hazard model. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the influence of the concomitant variable factors on the service life of the key system of the rail transit vehicles is considered, and the defect that the service life prediction is inaccurate as only system failure is considered in traditional service life prediction is overcome.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for predicting remaining useful life of device components
InactiveUS8712726B2Improved condition-based maintenanceAccurately determine remaining useful lifeTesting/monitoring control systemsDigital computer detailsAnalysis dataStatistical analysis
A method and system for accurately predicting the remaining useful life of devices and components based on rigorous statistical analysis data to reduce service costs by implementing condition-based maintenance. One rigorous statistical model is the general degradation path model, which can be used to generate simulated data that shares similar data characteristics of historical field failure data. This generated data can be used in a reliability study based on, for example, Monte Carlo techniques for RUL prediction. The study can be used to investigate the effects of influential factors such as suspension percentage and heavy-tailed behavior. The remaining useful life prediction is based on both the fixed-time predictors and time-dependent covariates.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Electric spindle service life evaluation method without sudden failure information
ActiveCN109522650AImprove accuracyImprove reliability modeling accuracyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationElectricityFailure rate
The invention belongs to the technical field of reliability analysis of electric spindles, and relates to an electric spindle service life evaluation method without sudden failure information. The defect that sudden failure and the influence of degradation on the sudden failure are ignored when modeling is conducted according to degradation information in the prior art is overcome. The method comprises the following steps that 1, an electric spindle product timing truncation reliability test and electric spindle product degradation information collection are conducted; 2, index distribution product reliability modeling; 3, reliability modeling of Weibull distribution products; 4, carrying out partial distribution competition risk reliability modeling under the condition of no burst failureinformation in combination with the degradation information; And 5, evaluating the service life of the motorized spindle based on the partial distribution competition risk reliability model. The partial distribution competition risk modeling method based on the unilateral confidence limit modeling basic failure rate and with the multi-performance degradation amount as the covariable is provided from the perspective of competition failure, and the method has important significance for reasonably evaluating the reliability level of the electric spindle and perfecting the reliability technical system of the electric spindle.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
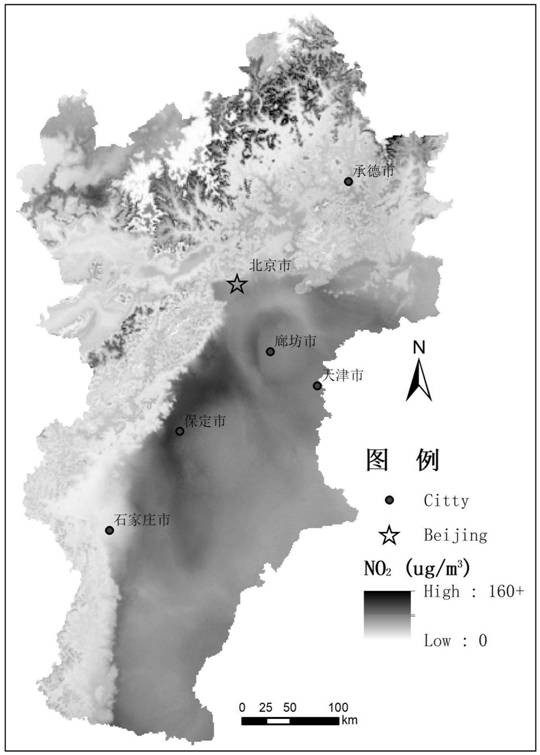
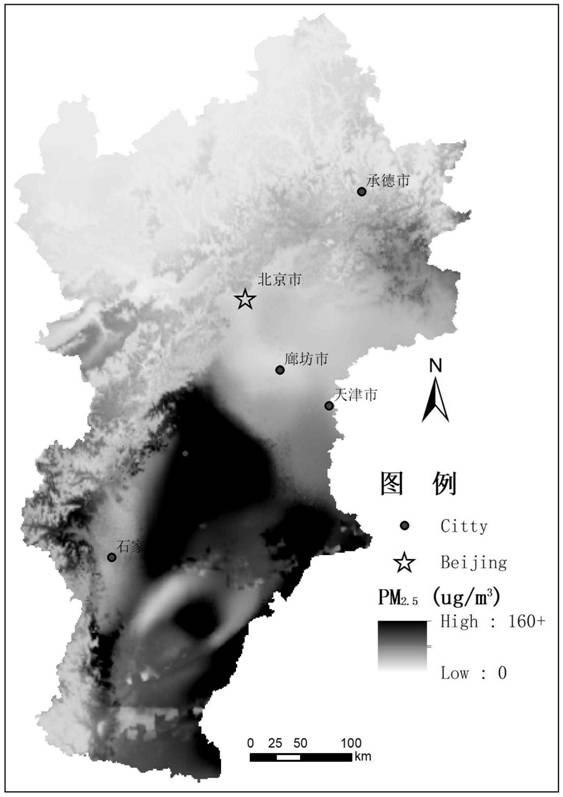
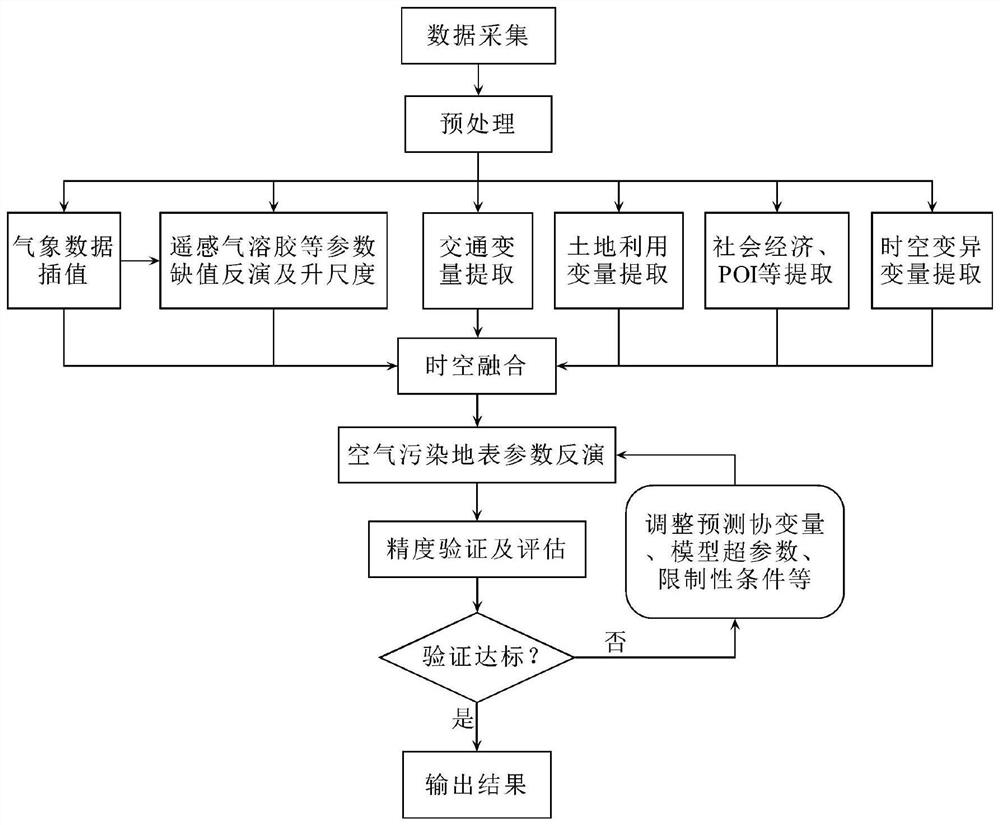
Air pollution prediction method based on deep fusion of multi-source space-time big data
ActiveCN112905560AWide range of time and spaceHigh spatio-temporal resolutionAnalysing gaseous mixturesNeural architecturesData setEngineering
The invention discloses an air pollution prediction method based on deep fusion of multi-source space-time big data. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and preprocessing multi-source big data; inverting the meteorological data to obtain high-resolution ground meteorological parameters; carrying out missing inversion and upscaling on aerosol parameters and NO2 remote sensing parameters; traffic variables, land utilization variables, social economy and POI variables and spatial-temporal variation variables are extracted; carrying out space-time fusion on covariable data of various kinds of space-time big data to form a data set with unified scale and space coordinates; inverting high-resolution earth surface parameters of the air pollution concentration; verifying and evaluating the precision; if the standard is reached, outputting a result; and if not, adjusting and circularly training until a reasonable model and prediction are obtained. According to the method, the space-time coverage is large, grid modeling of meteorological data and interpolation of satellite parameters are improved through an advanced optimization technology, high test precision and high generalization are achieved, estimation deviation is reduced through a result verification and circulating modeling mechanism, and the efficiency of practical application is improved.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
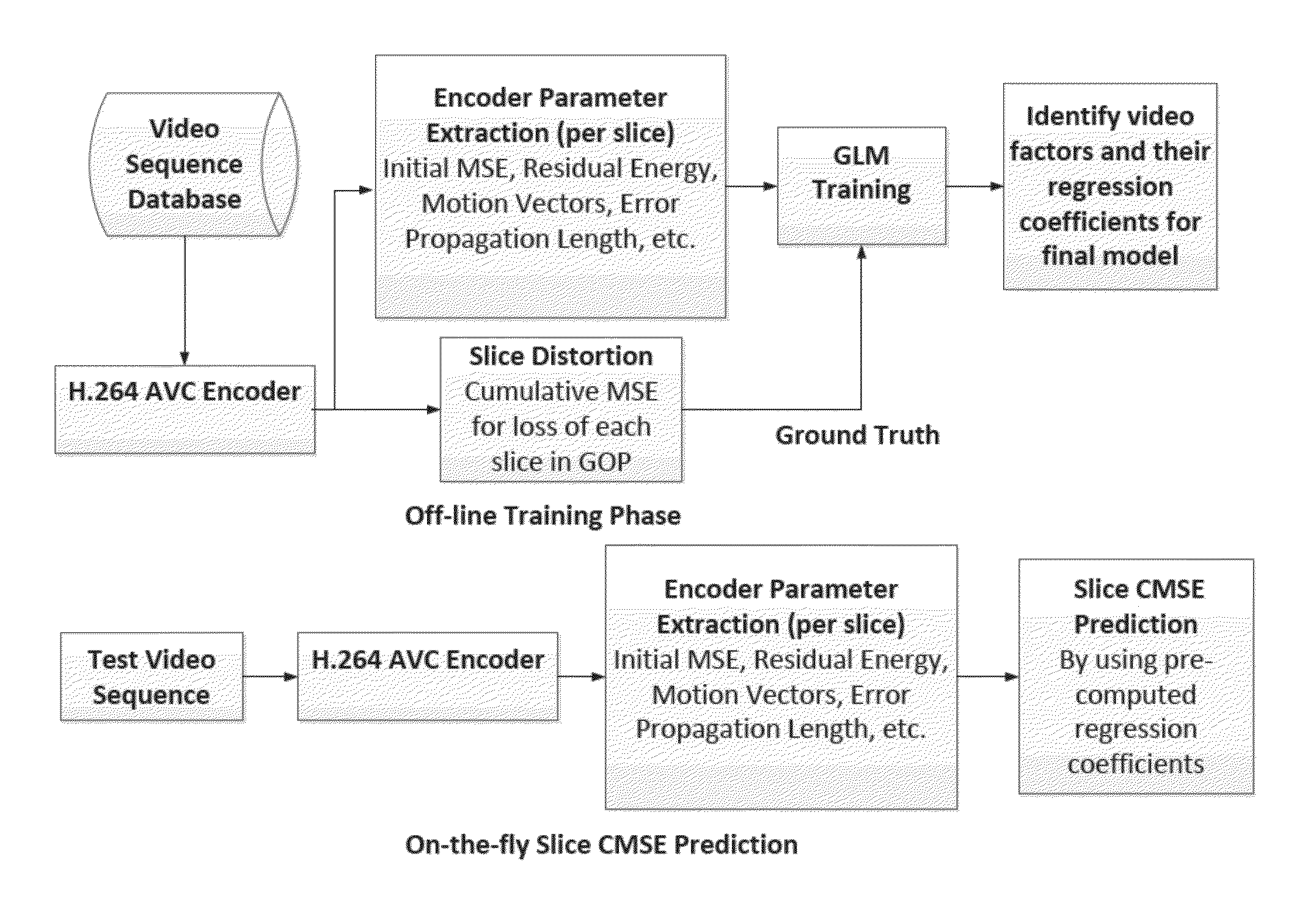
Slice priority prediction system for H.264 video
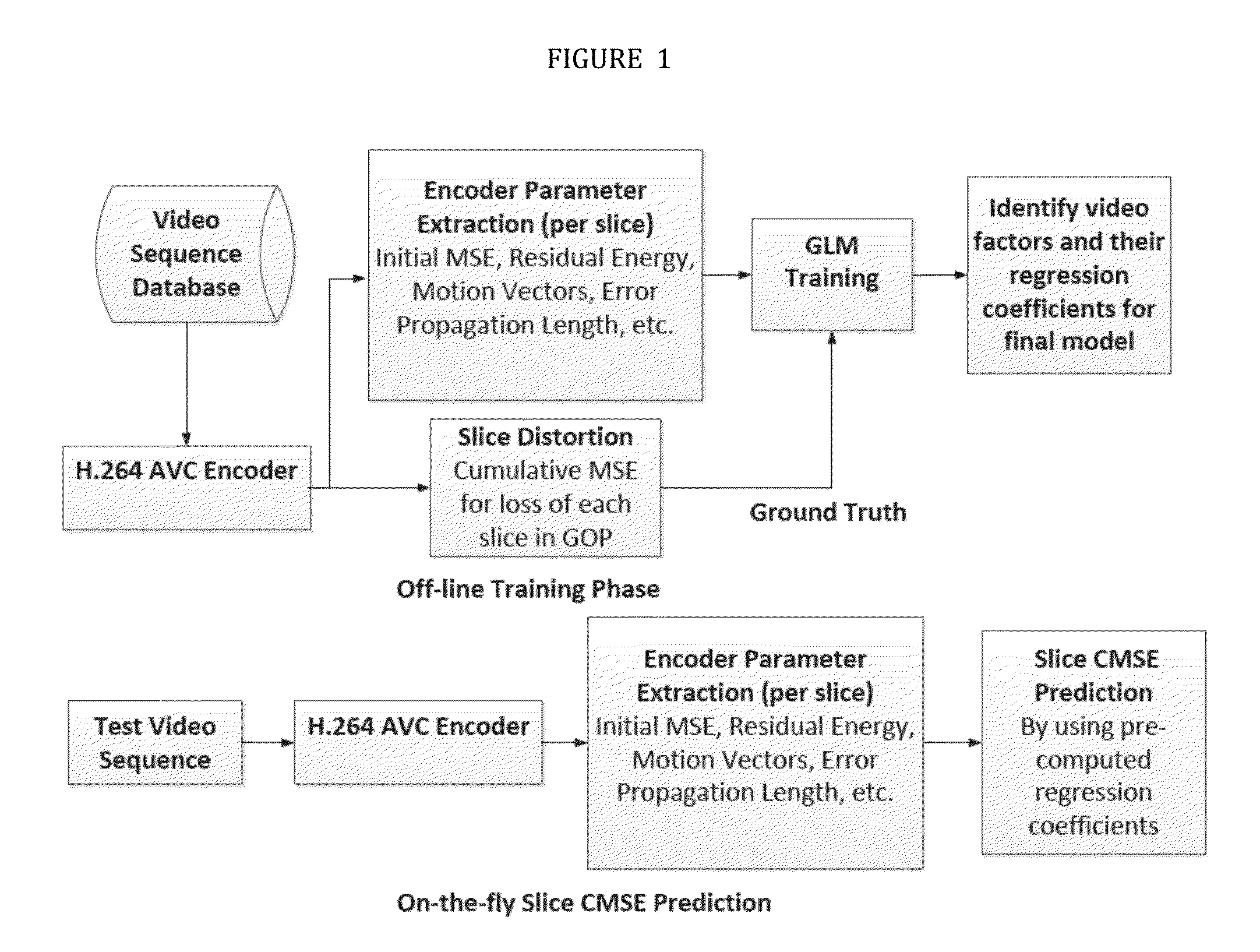
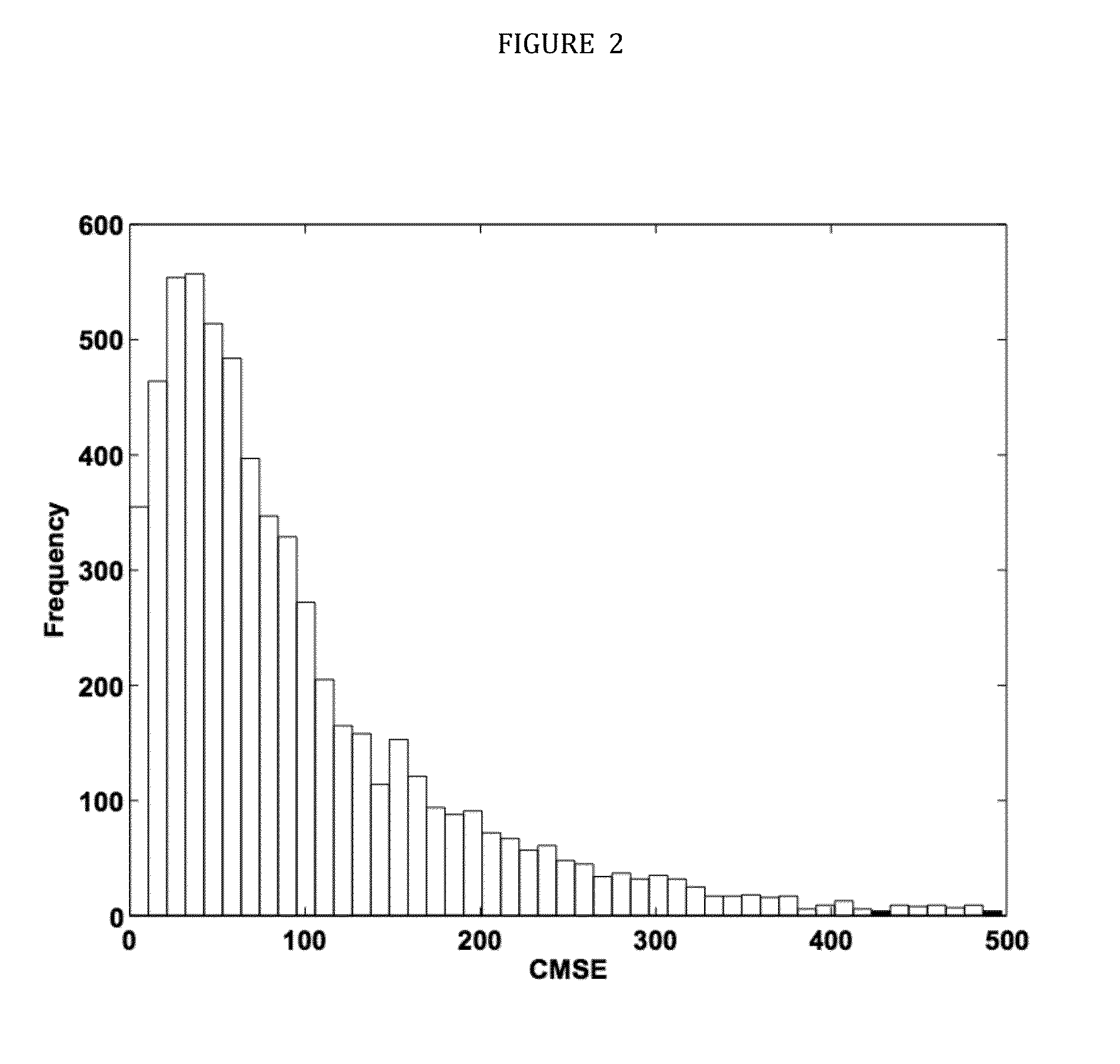
ActiveUS9210446B2Improve efficiencyReduce complexityDigital video signal modificationGuidelineForward selection
The invention relates to systems and methods for prioritizing video slices of H.264 video bitstream comprising: a memory storage and a processing unit coupled to the memory storage, wherein the processing unit operates to execute a low complexity scheme to predict the expected cumulative mean squared error (CMSE) contributed by the loss of a slice of H.264 video bitstream, wherein the processing unit operates to execute a series of actions comprising assigning each slice a predicted value according to the low complexity scheme; extracting video parameters during encoding process, said video parameters; and using a generalized linear model to model CMSE as a linear combination of the video parameters, wherein the video parameters are derived from analytical estimations by using a Generalized Linear Model (GLM) over a video database, encompassing videos of different characteristics such as high and low motion, camera panning, zooming and still videos, further comprising wherein the GLM is constructed in a training phase as follows: determining the distribution of the computed CMSE to be a Normal distribution with the Identity link function; sequentially adding covariates using the forward selection technique where by the best model is evaluated at each stage using the Akaike's Information Criterion (AIC); the training phase of the model generates regression coefficients; the final model is validated through the testing phase by predicting the CMSE for different video sequences, not in the training database; and by using the regression coefficients, the expected CMSE values are predicted for each slice.
Owner:SAN DIEGO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Proportional hazard rate model method for estimating operation reliability of tool
InactiveCN102254100AEvaluation results are reliableImprove real-time performanceSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmEstimation methods
The invention relates to a proportional hazard rate model method for estimating operation reliability of a tool. Defects of difficulty in obtaining burn-out life data, incomplete matching with actual operation conditions of equipment and incapability of timely prevention and maintenance exist in the prior art. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the proportional hazard rate model method for estimating operation reliability of the tool comprises the following operation steps of: 1, using an effective value (RMS (Root Mean Square)) and a peak value (P) in a characteristic signal as covariates in a proportional hazard rate model; 2, calculating model parameters according to a nonlinear equation described in the specification; and 3, obtaining parameter results of maximum likelihood estimation of the tool working in different regressive states by applying a maximum likelihood estimation method of the proportional hazard rate model, and solving a current hazard rate according to state signals of the processing system tool working in different regressive states and finally obtaining the reliability. The method has the advantages of good instantaneity and reliable estimation result.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
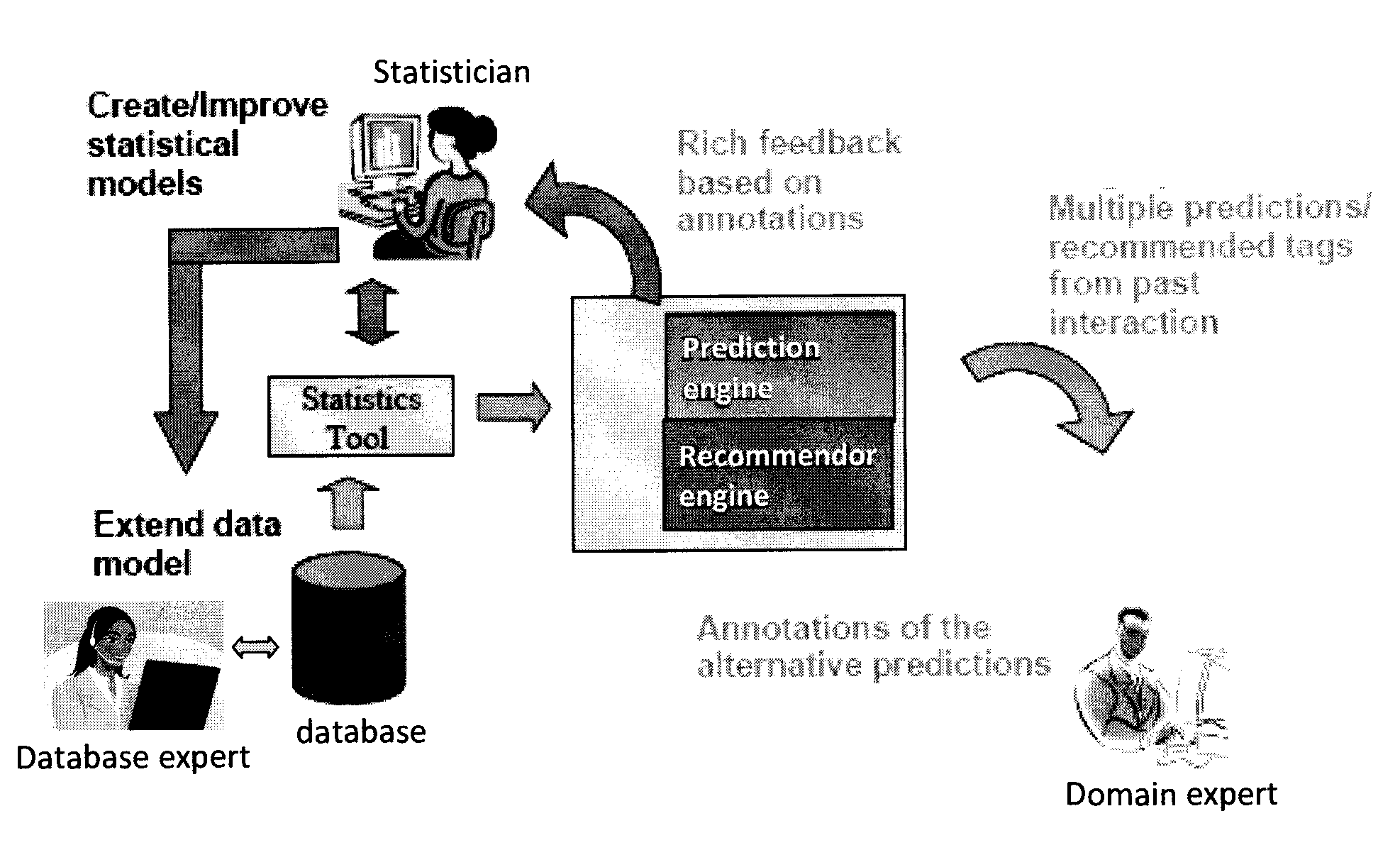
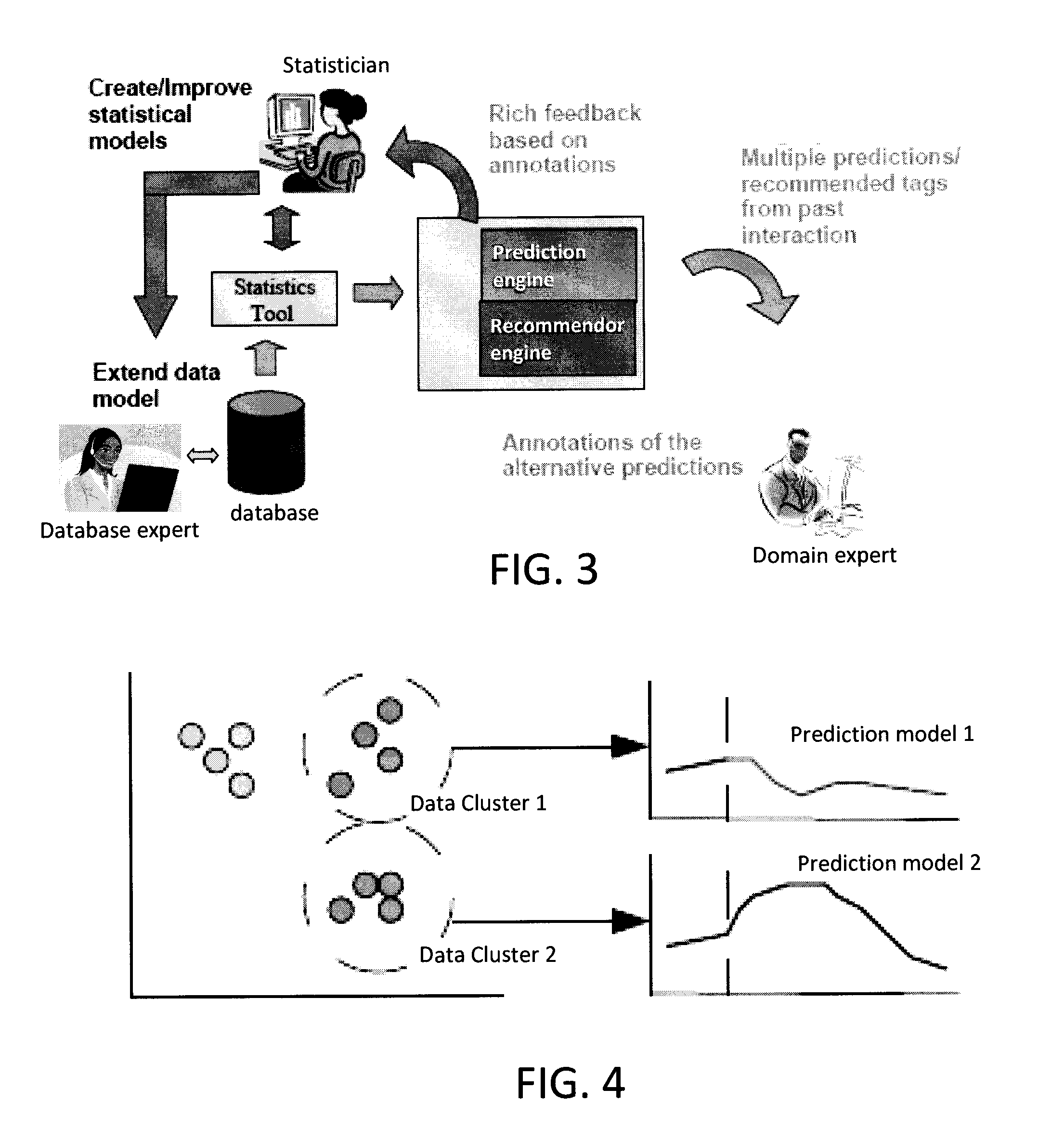
Iterative Active Feature Extraction
InactiveUS20140180992A1Improve accuracyMachine learningKnowledge representationFeature extractionData mining
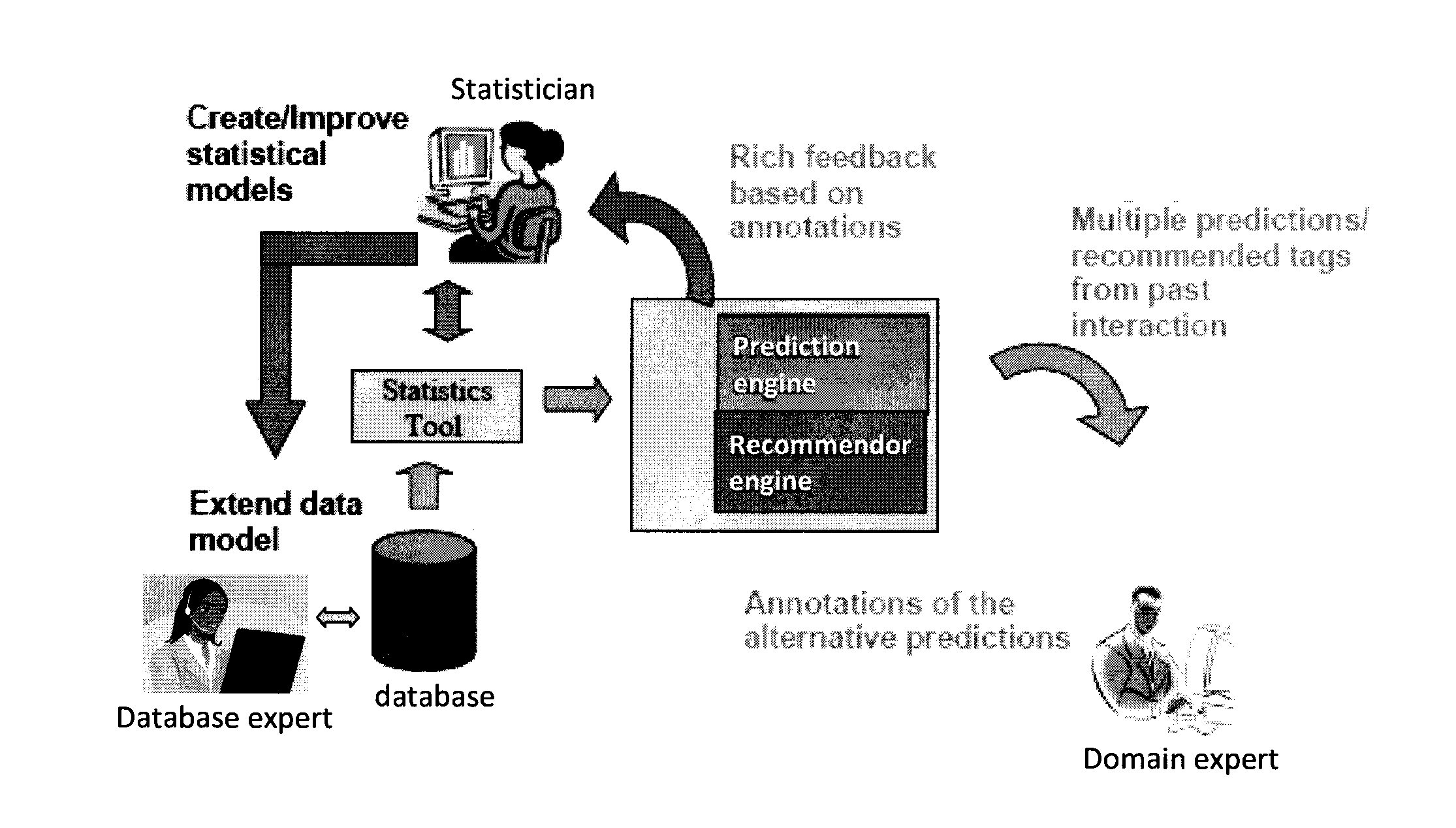
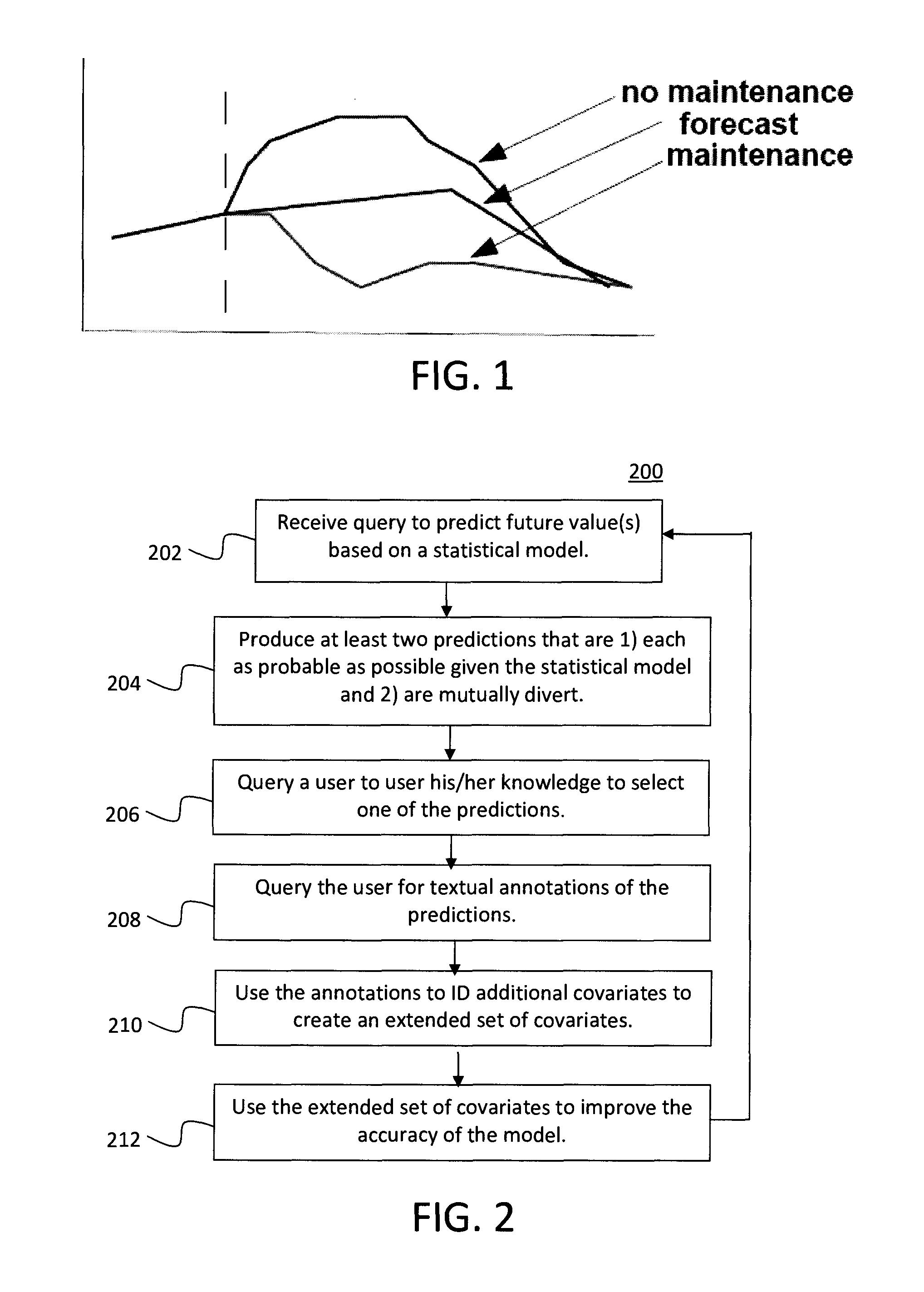
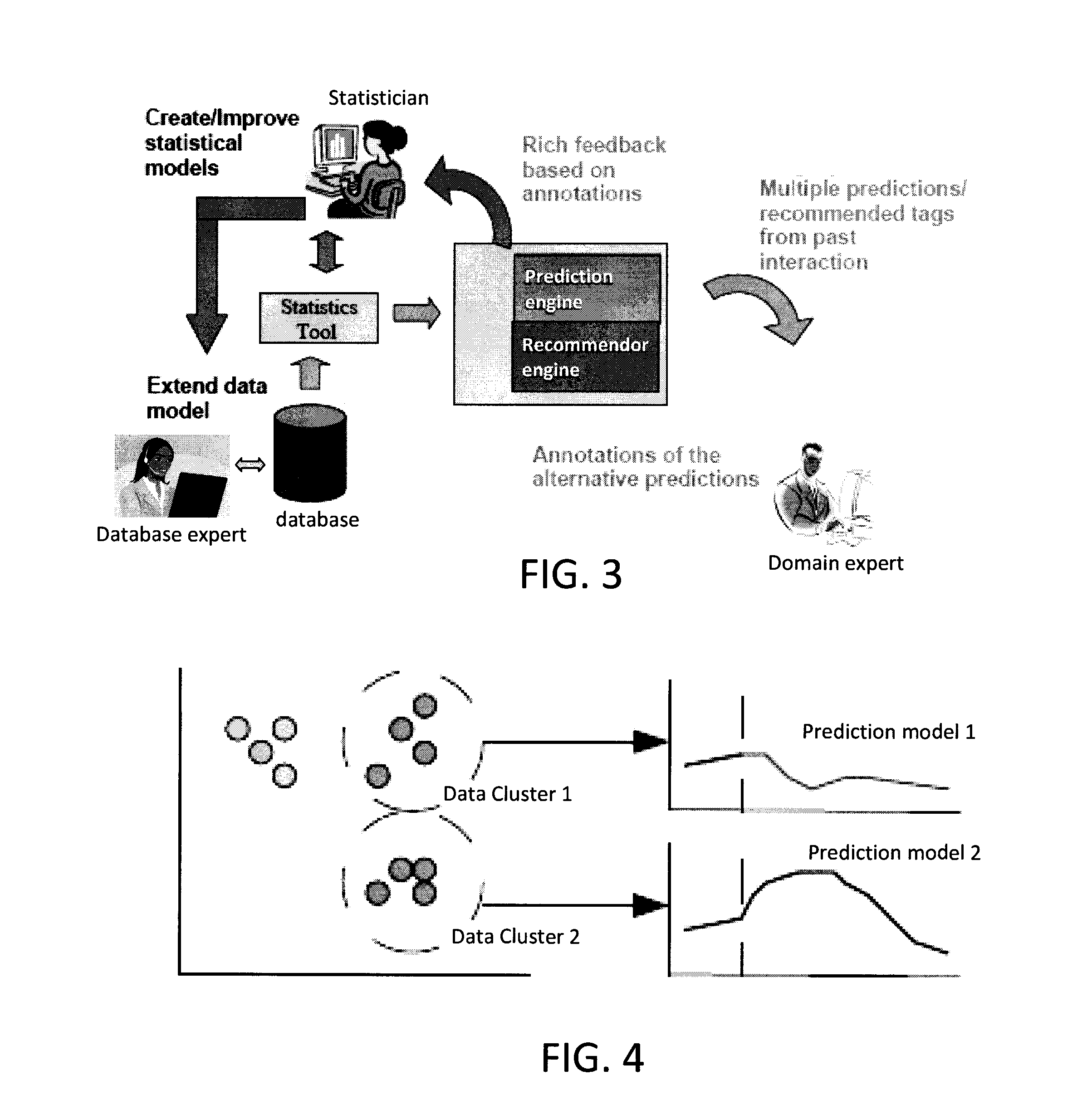
Techniques for iterative feature extraction using domain knowledge are provided. In one aspect, a method for feature extraction is provided. The method includes the following steps. At least one query to predict at least one future value of a given value series based on a statistical model is received. At least two predictions of the future value are produced fulfilling at least the properties of 1) each being as probable as possible given the statistical model and 2) being mutually divert (in terms of numerical distance measure). A user is queried to select one of the predictions. The user may be queried for textual annotations for the predictions. The annotations may be used to identify additional covariates to create an extended set of covariates. The extended set of covariates may be used to improve the accuracy of the statistical model.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods to predict a future outcome at a live sport event
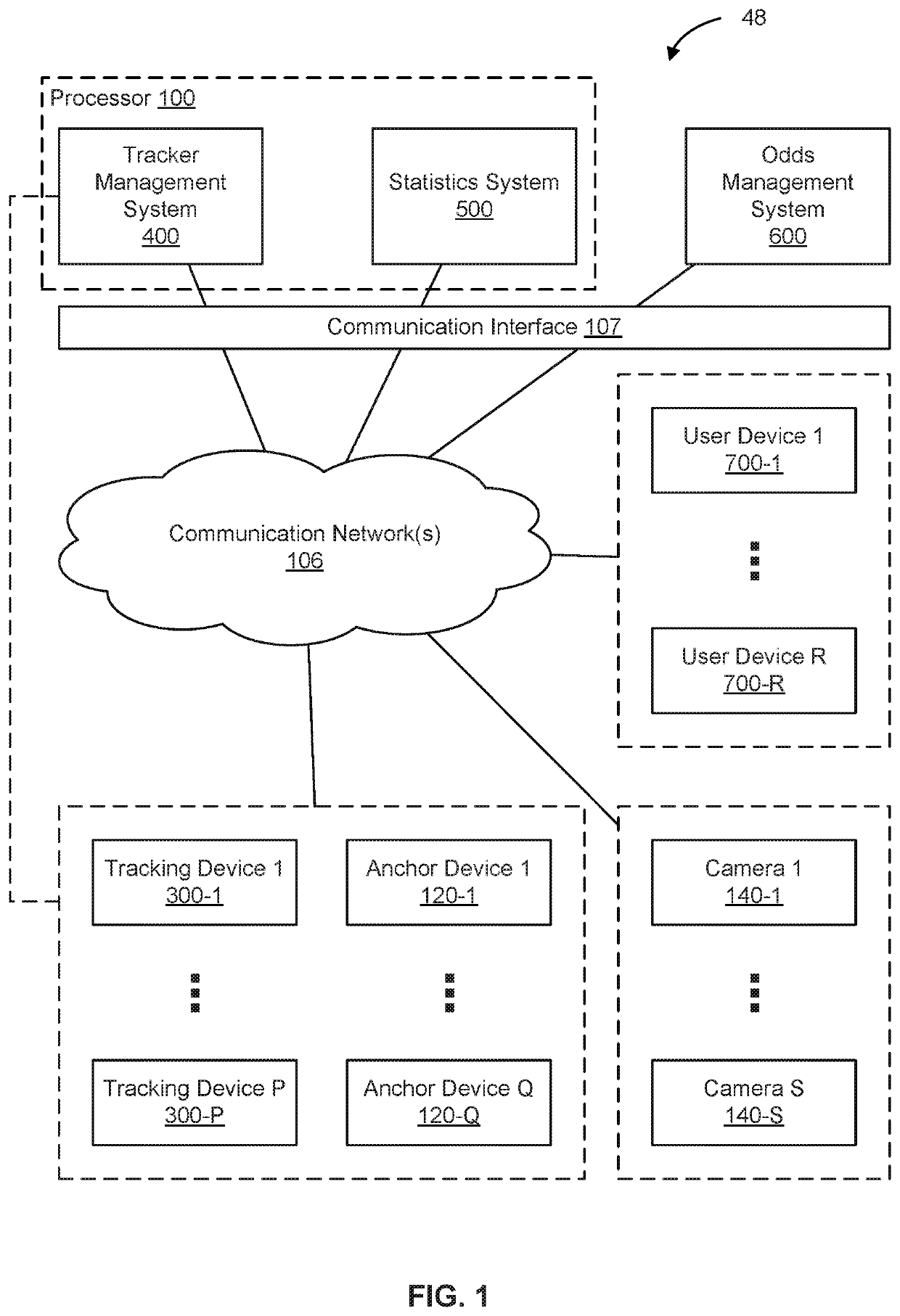
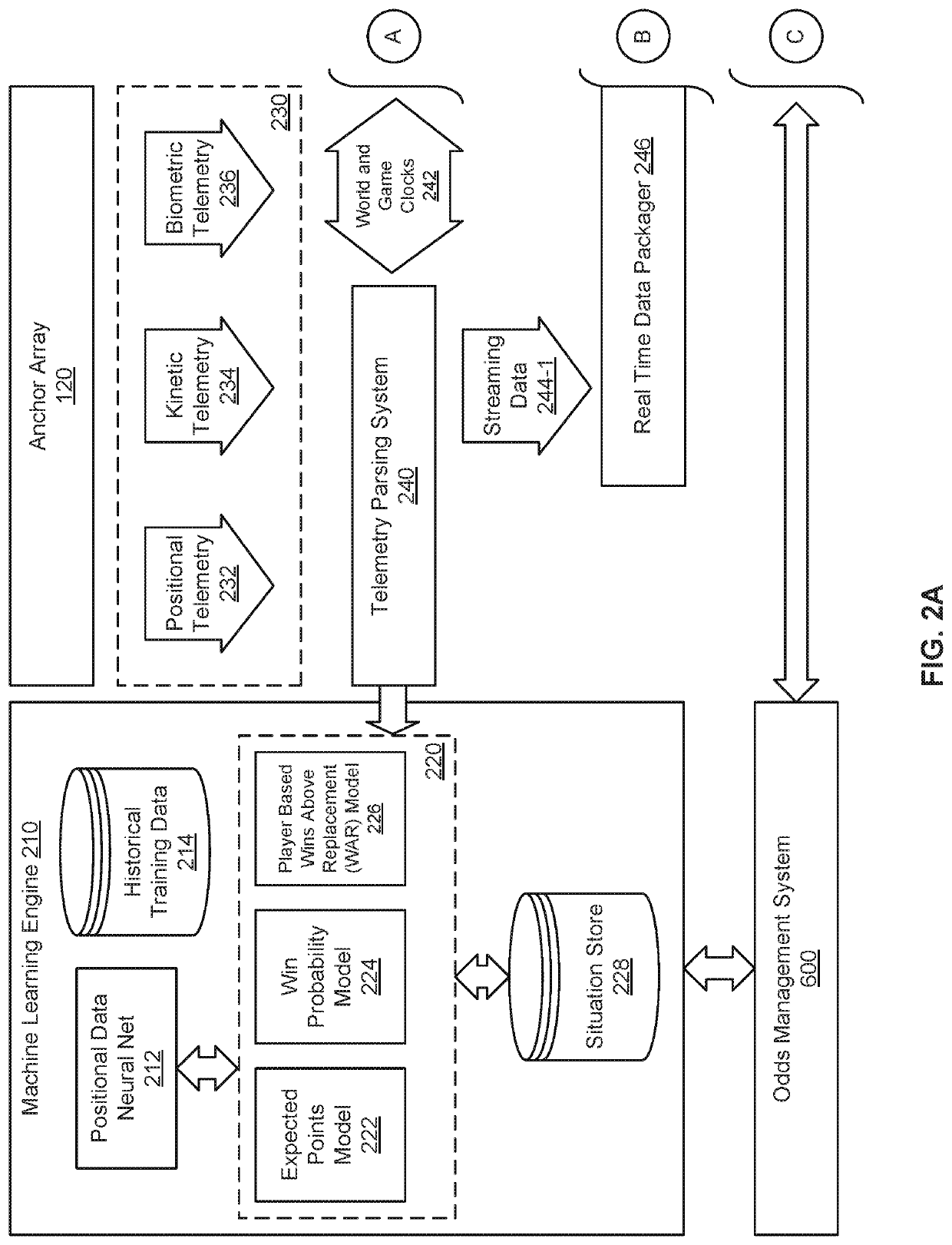
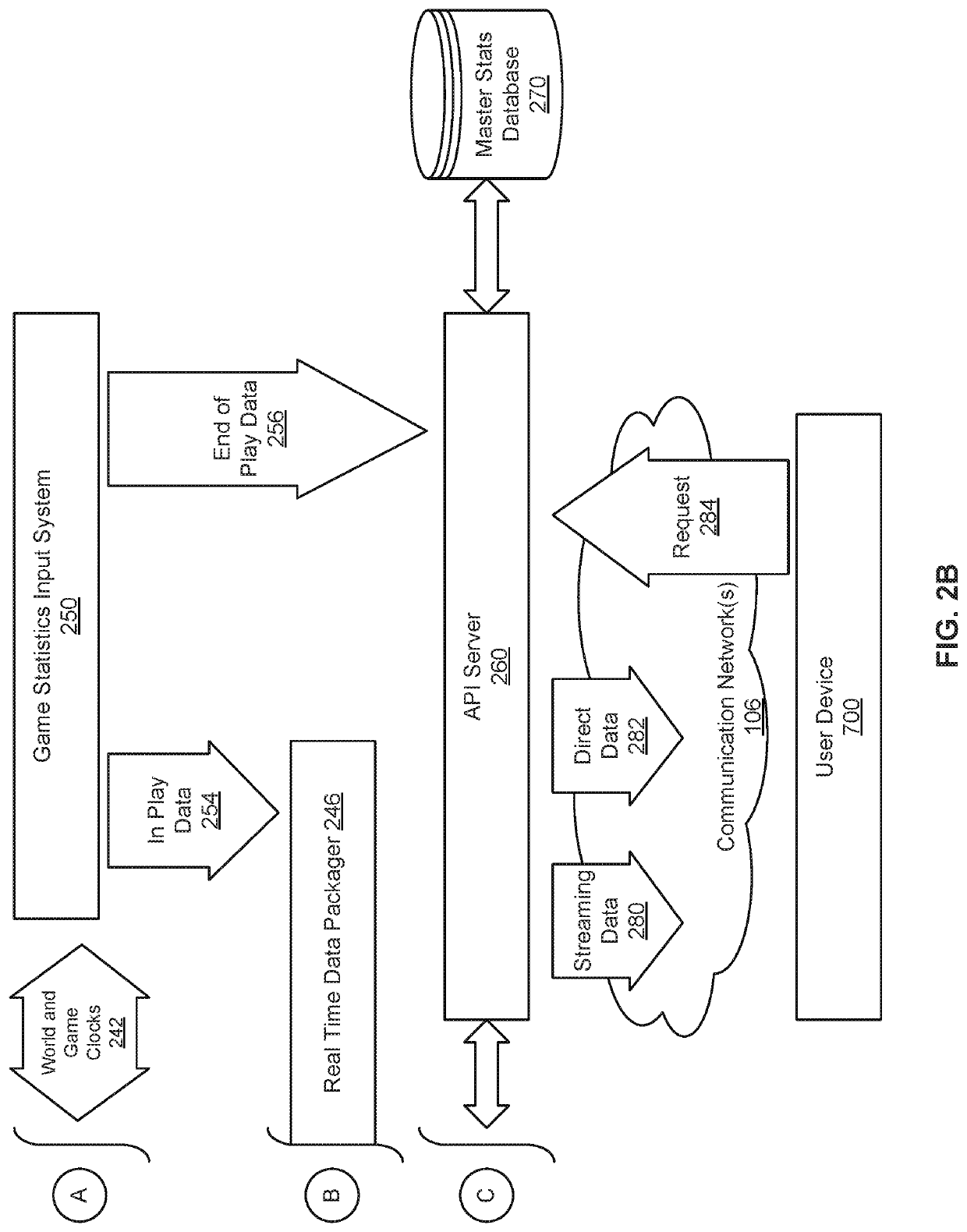
ActiveUS20200230501A1Accurately and efficiently predicting outcomeData processing applicationsVideo gamesTimestampEngineering
In an embodiment, a process to predict an outcome of a competition includes receiving time-stamped position information of participant(s), the time-stamped position information captured by a telemetry tracking system during the competition. The process includes calculating while the competition is ongoing a covariate parameter for each of one or more participants at a point in time, where each respective covariate parameter is derived from the time-stamped position information of a corresponding participant at the point in time. The process includes predicting the outcome of the competition, as of the point in time, based at least in part on (i) a difference between a calculated competitor strength of the first competitor the second competitor based on historical data associated with the competitors, and (ii) the calculated first covariate parameter(s).
Owner:TEMPUS EX MACHINA INC
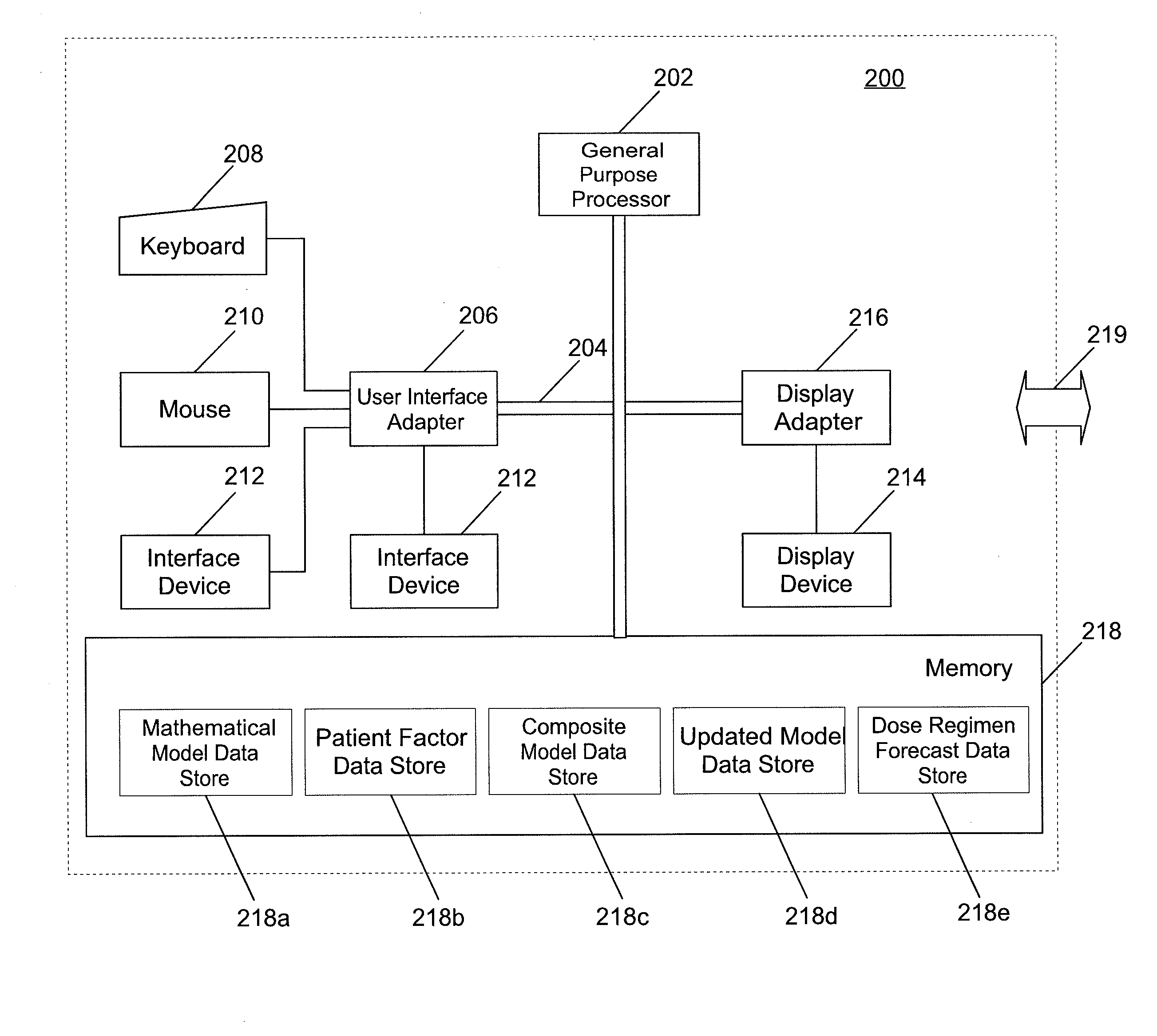
System and method for providing patient-specific dosing as a function of mathematical models updated to account for an observed patient response
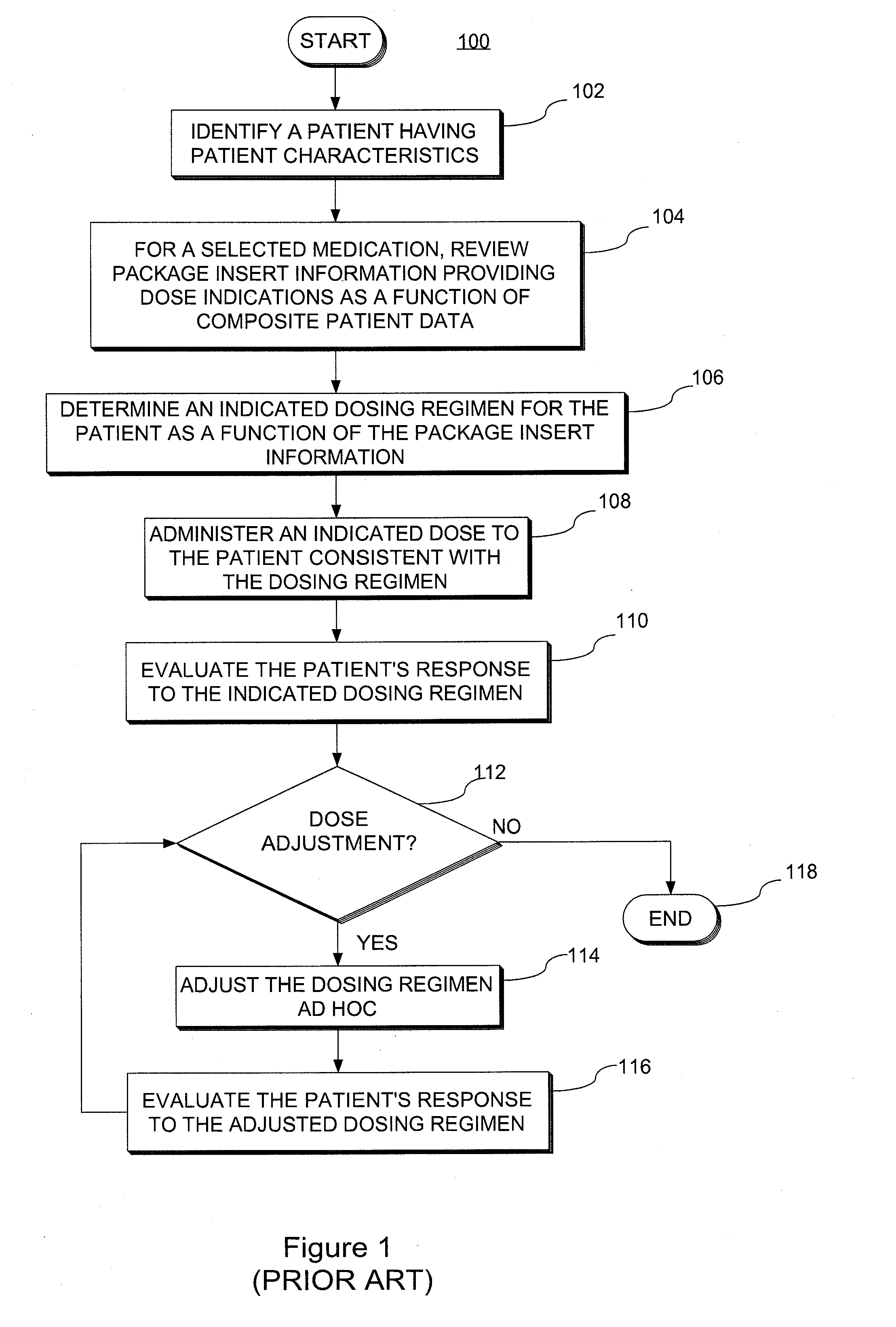
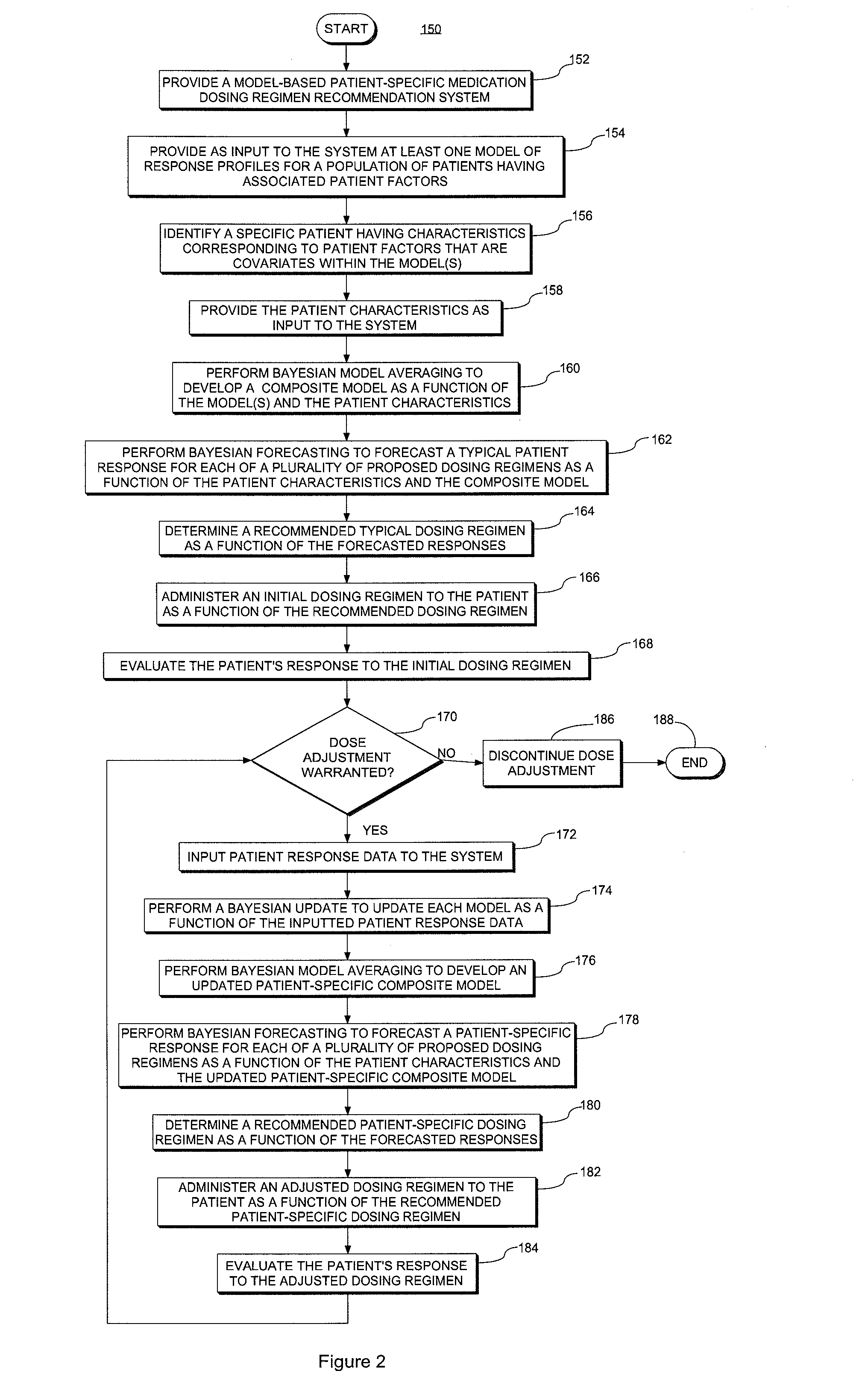
ActiveUS20140351197A1Good precisionEffectively personalize the modelsMedical simulationDrug and medicationsMedication doseRegimen
A system and method for predicting, proposing and / or evaluating suitable medication dosing regimens for a specific individual as a function of individual-specific characteristics and observed responses of the specific individual. Mathematical models of observed patient responses are used in determining an initial dose. The system and method use the patient's observed response to the initial dose to refine the model for use to forecast expected responses to proposed dosing regimens more accurately for a specific patient. More specifically, the system and method uses Bayesian averaging, Bayesian updating and Bayesian forecasting techniques to develop patient-specific dosing regimens as a function of not only generic mathematical models and patient-specific characteristics accounted for in the models as covariate patient factors, but also observed patient-specific responses that are not accounted for within the models themselves, and that reflect variability that distinguishes the specific patient from the typical patient reflected by the model.
Owner:MOLD DIANE R
Systems genetics network regulators as drug targets
InactiveUS20150252409A1Preventing and reducing incidencePreventing and reducing and severityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementHepatocellular carcinomaDrug target
The present invention provides for methods, processes and platforms to validate systems genetics networks to define their genetic regulators and to optimize translational applicability to humans for drug development. These systems genetics networks are sets of genes with a common function that demonstrate covariate expression that is genetically modulated by linked function network regulators (LFNRs) which comprise eQTLs in animals and GWAS SNPs in humans. LFNRs represent a new class of targets to identify drugs to prevent, ameliorate, and / or treat human diseases. LFNRs for the cell cycle-mitosis network have potential to be especially useful for anti-cancer therapies. The present invention provides for a drug that targets a specific LFNR for the cell cycle-mitosis network in Caucasian male liver to prevent the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in high risk patient populations.
Owner:SCOTT ROBERT E
Prediction method and device
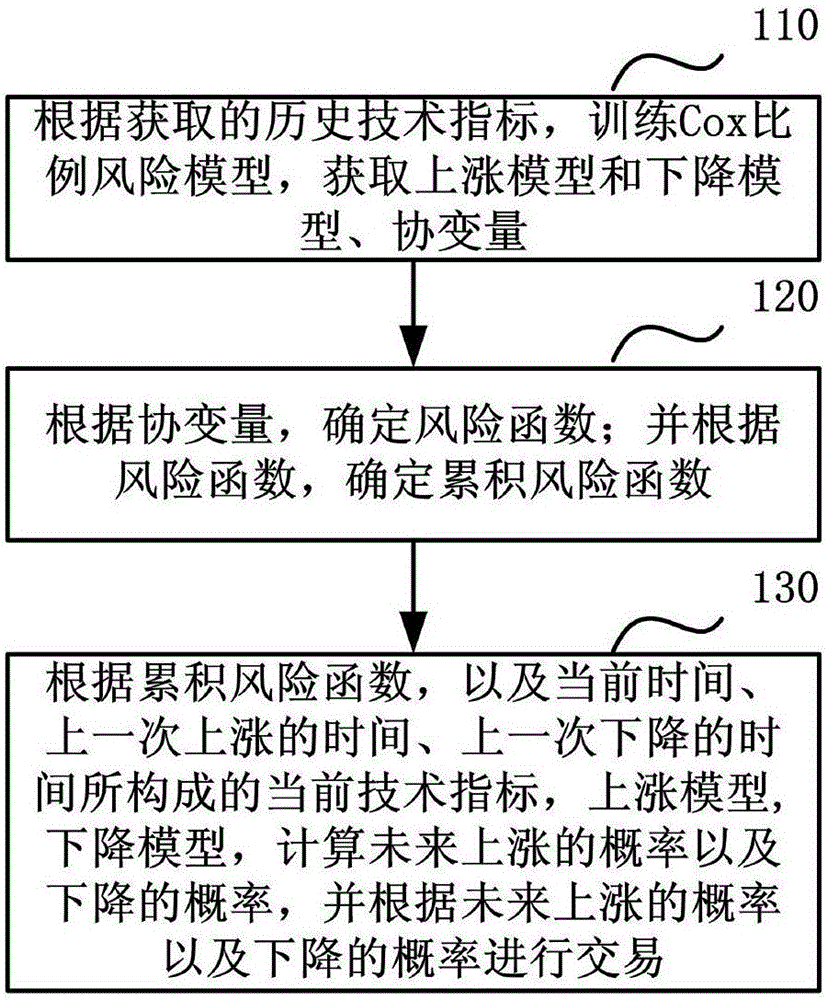
An embodiment of the invention relates to a prediction method and a prediction device. The prediction method comprises the steps of: training a Cox proportional hazard model according to acquired historical technical indexes, and acquiring a rising model, a declining model and a covariate; determining a risk function according to the covariate; determining an accumulative risk function according to the risk function; and calculating a probability of future rise and a probability of future decline according to the accumulative risk function, current technical indexes composed of time of previous rise and time of previous decline, the rising model and the declining model, and conducting a transaction based on the probability of future rise and the probability of future decline. Therefore, the prediction method and the prediction device are higher in precision of prediction results, are conductive to helping investors to make the most reasonable decision, increase profits and reduce the risks.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
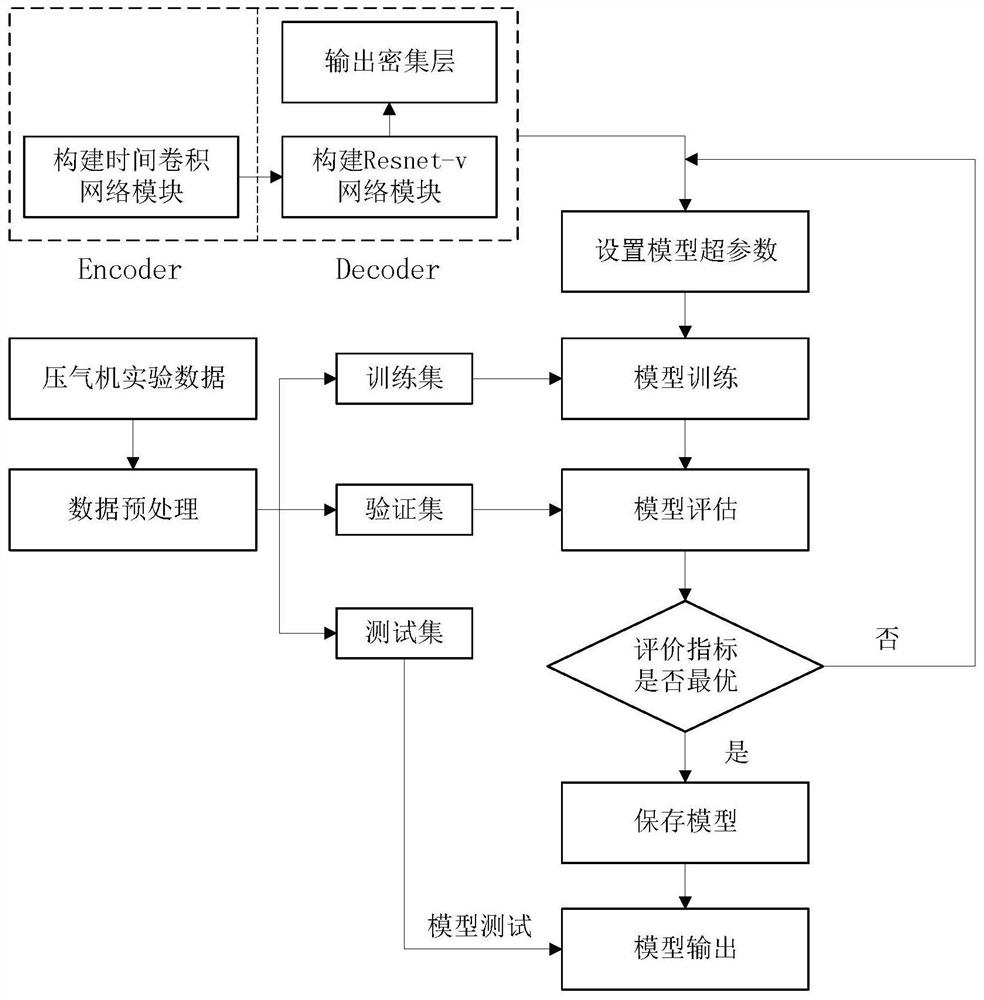
Gas compressor rotation stall early warning method based on time expansion convolutional network
ActiveCN113569338AImprove the performance of active controlImprove forecast accuracyGeometric CADSustainable transportationData setGas compressor
A gas compressor rotation stall early warning method based on a time expansion convolutional network comprises the following steps: firstly, preprocessing dynamic pressure data of an aero-engine, and dividing a test data set and a training data set from experimental data; secondly, sequentially constructing a time convolutional network module, constructing a Resnet-v network module, constructing a time expansion convolutional network prediction model, and storing an optimal prediction model; finally, performing real-time prediction on the test data: firstly, adjusting the data dimension of the test set according to the input requirement of the time convolutional network prediction model; according to a time sequence, calculating a surge prediction probability of each sample through a time expansion convolutional network prediction model; and calculating the real-time surge probability of a pair of samples containing covariables and not containing covariables through a time expansion convolutional network prediction model, and observing the improvement effect of the covariables on the model prediction effect. The time domain statistical characteristics and the change trend are integrated, and the prediction precision is improved; and the active control performance of the engine can be improved, and certain universality is achieved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
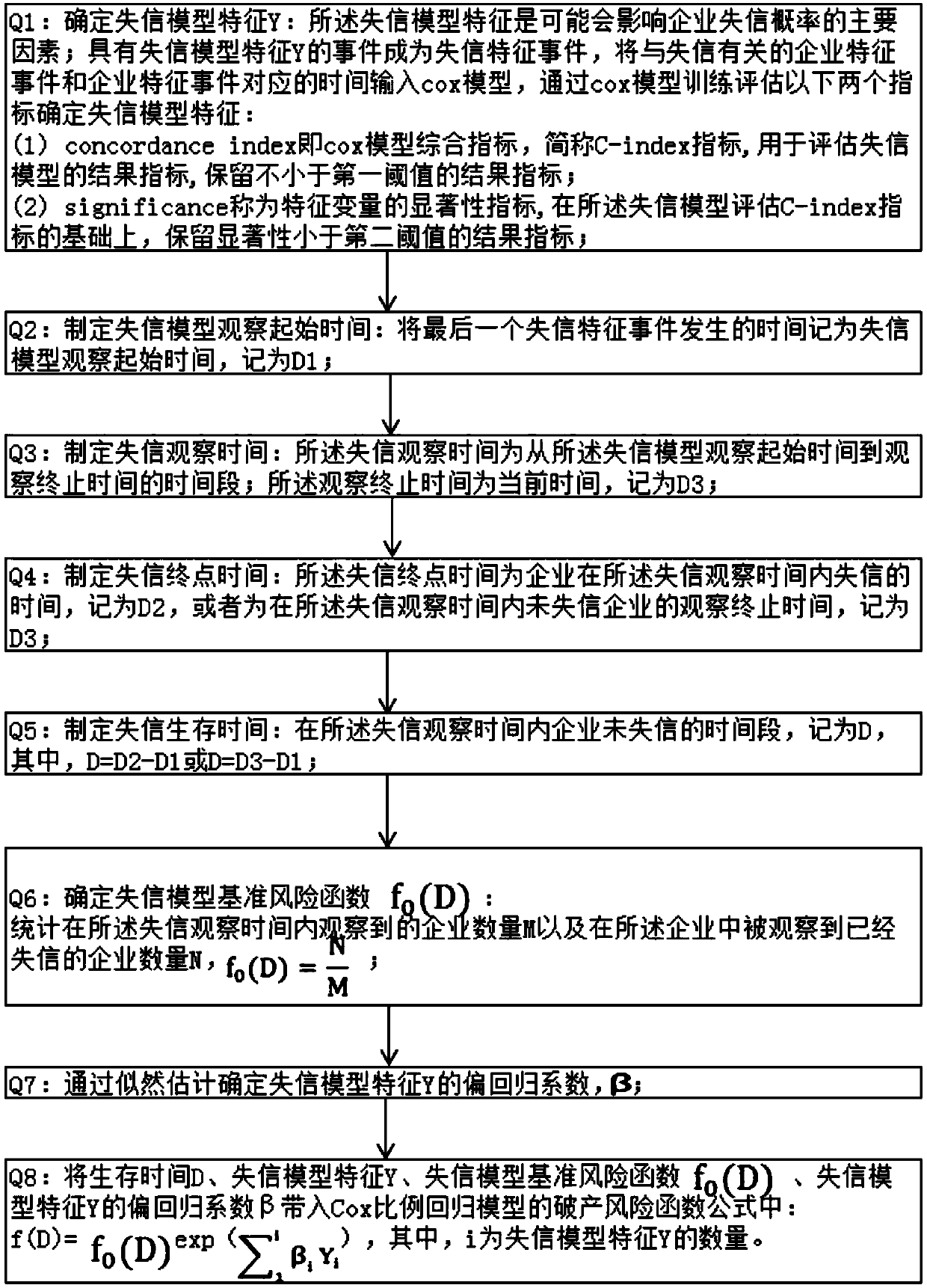
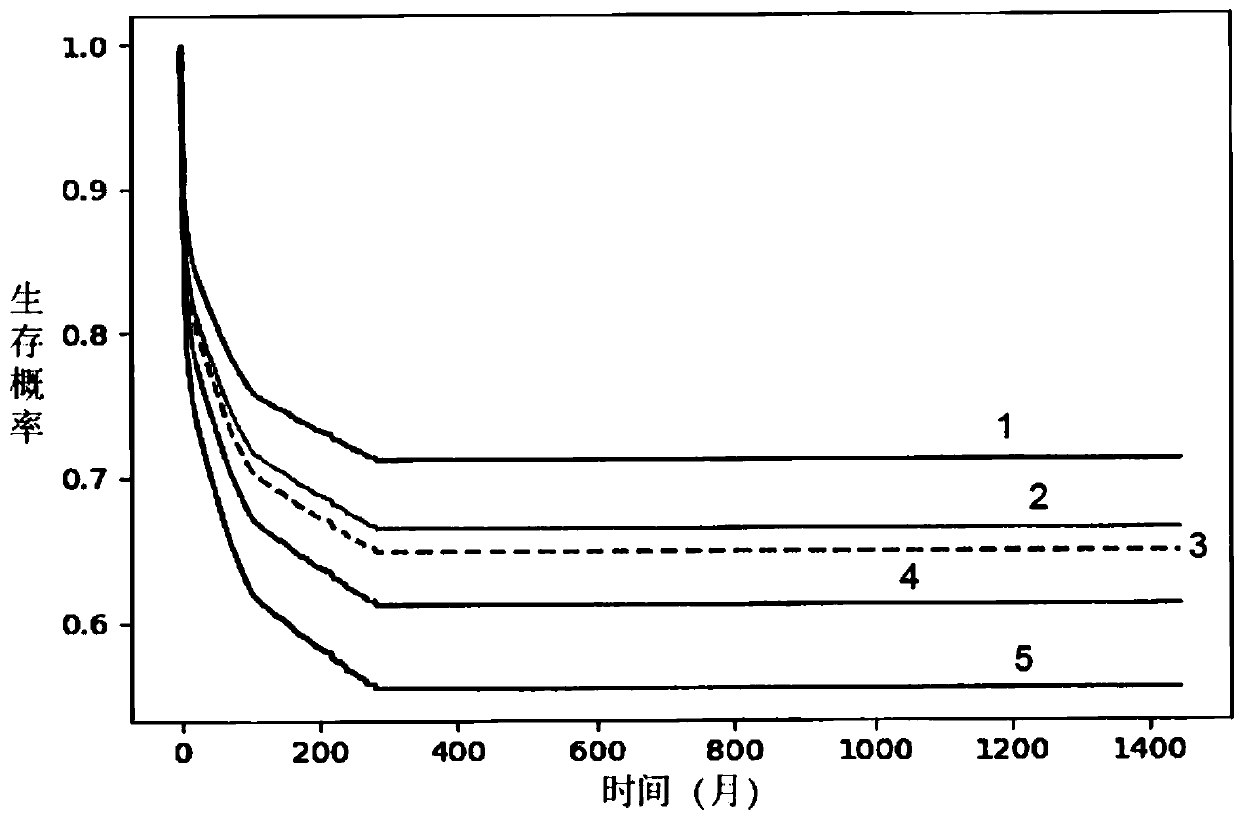
enterprise risk trust loss model based on Cox regression prediction
The invention discloses an enterprise risk trust loss model based on Cox regression prediction. the lost credit survival probability of the lost credit model is calculated; f (D), using an enterprisecredit model feature Y as a covariable or an interaction item; The construction method of the lost credit model comprises the following steps of: constructing a lost credit model; Q1, determining a feature Y of the lost credit model, Q2: formulating a lost credit model observation starting time D1; Q3: formulating a lost credit observation time D3; Q4: formulating a lost credit end point time D2 or D3; Q5, formulating a lost credit survival time D; Q6, determining a reference risk function f0 (D) of the lost trust model; Q7, determining a partial regression coefficient of the characteristic Yof the lost trust model through likelihood estimation; Q8, brining The survival time D, the untrustworthy model feature Y, the untrustworthy model reference risk function f0(D), and the partial regression coefficient Beta of the untrustworthy model feature Y into the unbalanced risk function formula of the Cox proportional regression model. According to the model disclosed by the invention, the future risk change trend of an enterprise can be predicted, so that the possibility of enterprise credit risk occurrence can be predicted. The model disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the risk change trend of the enterprise can be predicted.
Owner:重庆誉存科技有限公司
Iterative Active Feature Extraction
InactiveUS20140180973A1Improve accuracyDigital computer detailsMachine learningFeature extractionText annotation
Techniques for iterative feature extraction using domain knowledge are provided. In one aspect, a method for feature extraction is provided. The method includes the following steps. At least one query to predict at least one future value of a given value series based on a statistical model is received. At least two predictions of the future value are produced fulfilling at least the properties of 1) each being as probable as possible given the statistical model and 2) being mutually divert (in terms of numerical distance measure). A user is queried to select one of the predictions. The user may be queried for textual annotations for the predictions. The annotations may be used to identify additional covariates to create an extended set of covariates. The extended set of covariates may be used to improve the accuracy of the statistical model.
Owner:IBM CORP
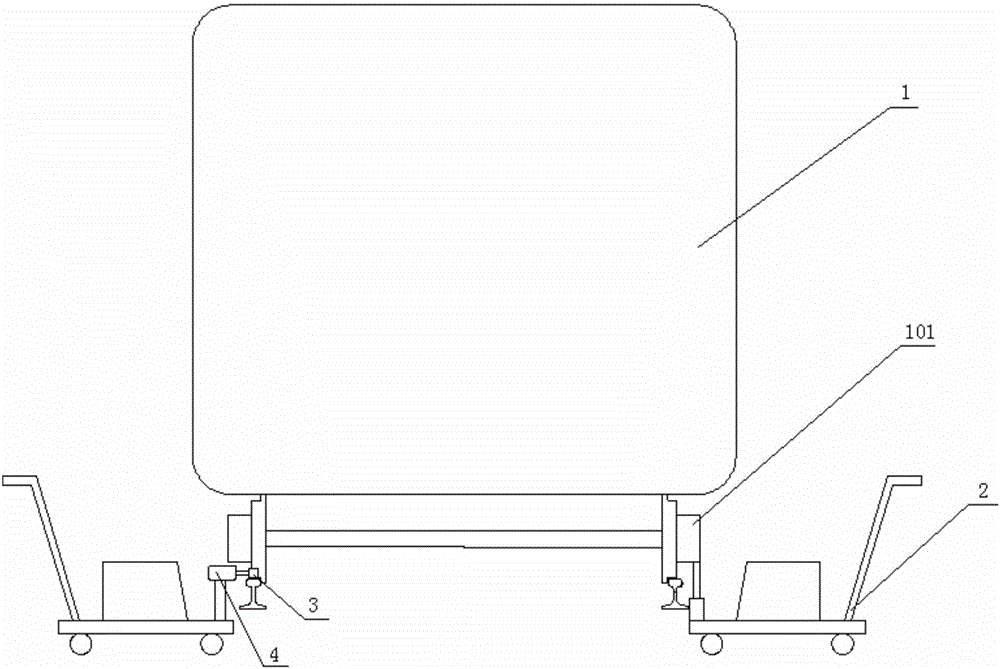
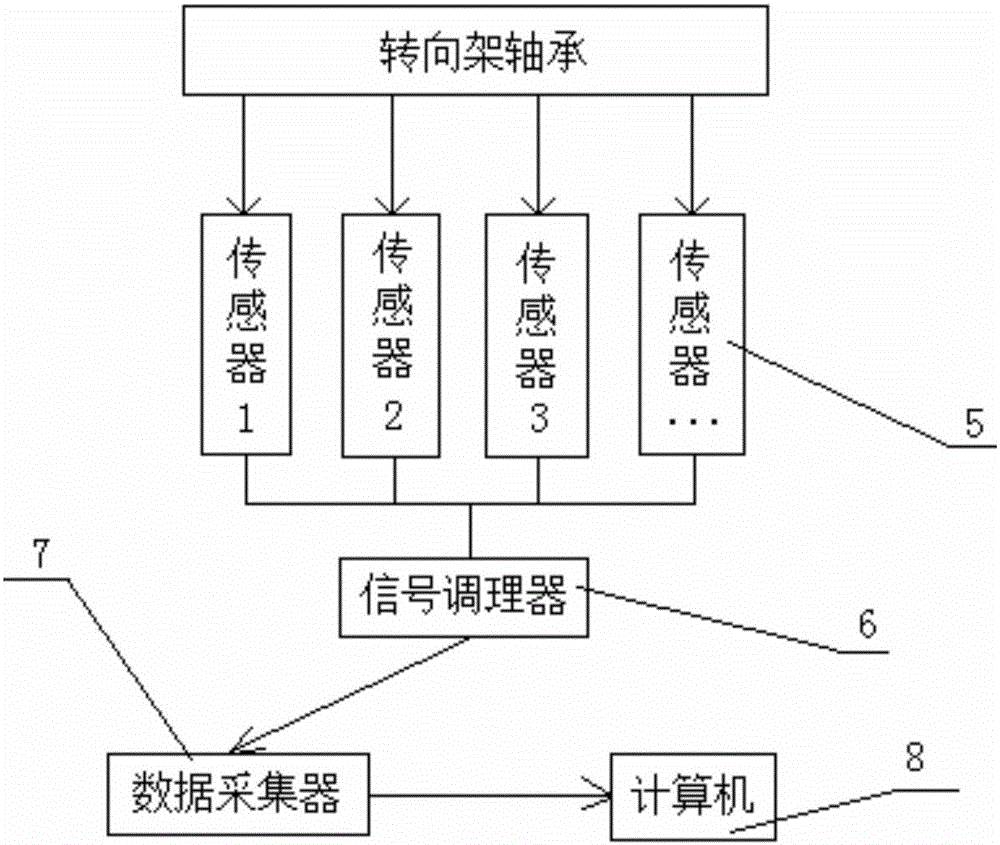
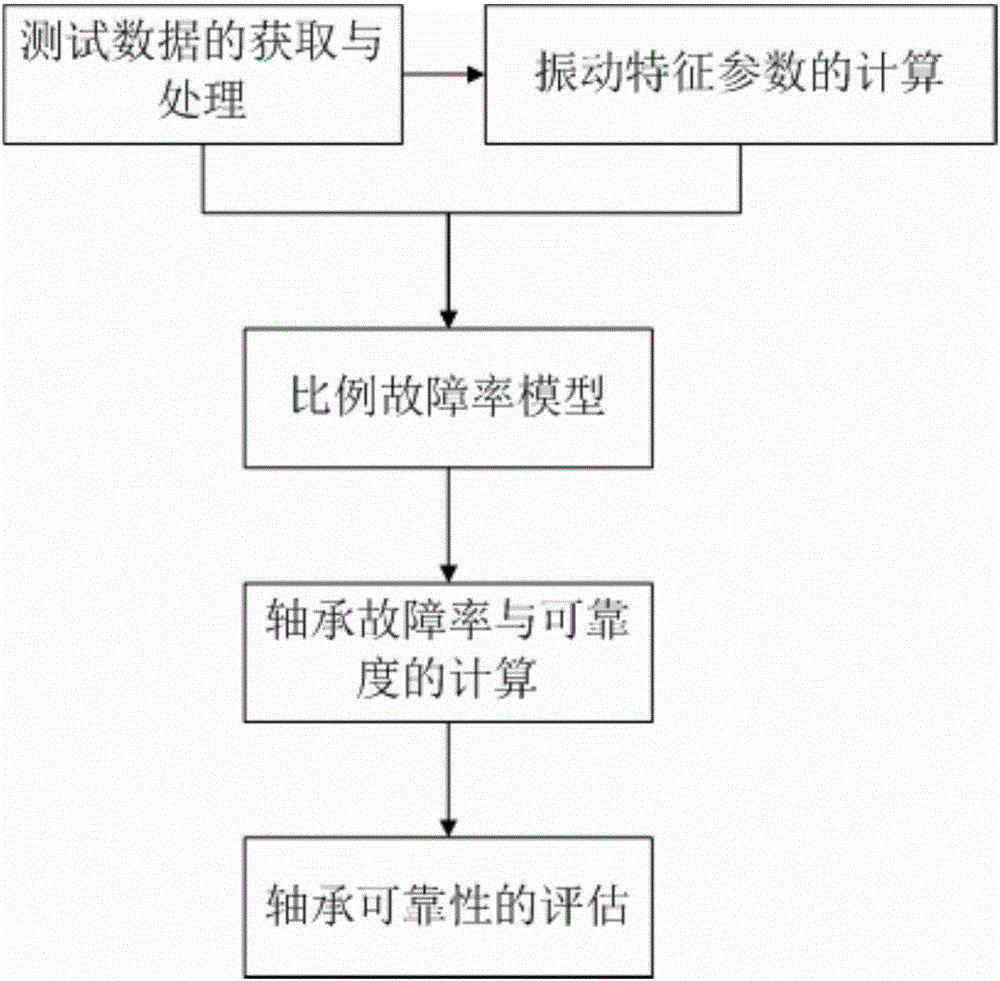
System for evaluating reliability of bogie rolling bearing based on offline state vibration characteristics
InactiveCN105910824ALow costAvoid problems such as high maintenanceMachine bearings testingBogieVibration acceleration
The invention provides a system for evaluating reliability of a bogie rolling bearing based on offline state vibration characteristics. The system comprises a jacking device, friction wheels, a sensor, a data collector and a computer, wherein the jacking device is used for jacking wheel pairs of a tested vehicle when the tested vehicle is in an offline state, so that the wheels are separated from rails; the friction wheels are in drive connection with the wheel pairs of the tested vehicle and are used for driving the wheel pairs of the tested vehicle to rotate; the sensor is arranged on a bogie of the tested vehicle and is used for determining vibration acceleration signals of an axial bearing and a traction motor bearing; the data collector is connected with the sensor and collects the collected vibration acceleration signals; the computer is connected with the data collector; the computer builds a proportion-fault rate model by statistical characteristic values, of the vibration acceleration signals as response covariate and reliability and calculates the fault rate and the reliability of the bearing through the proportion-fault rate model.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF ENG SCI
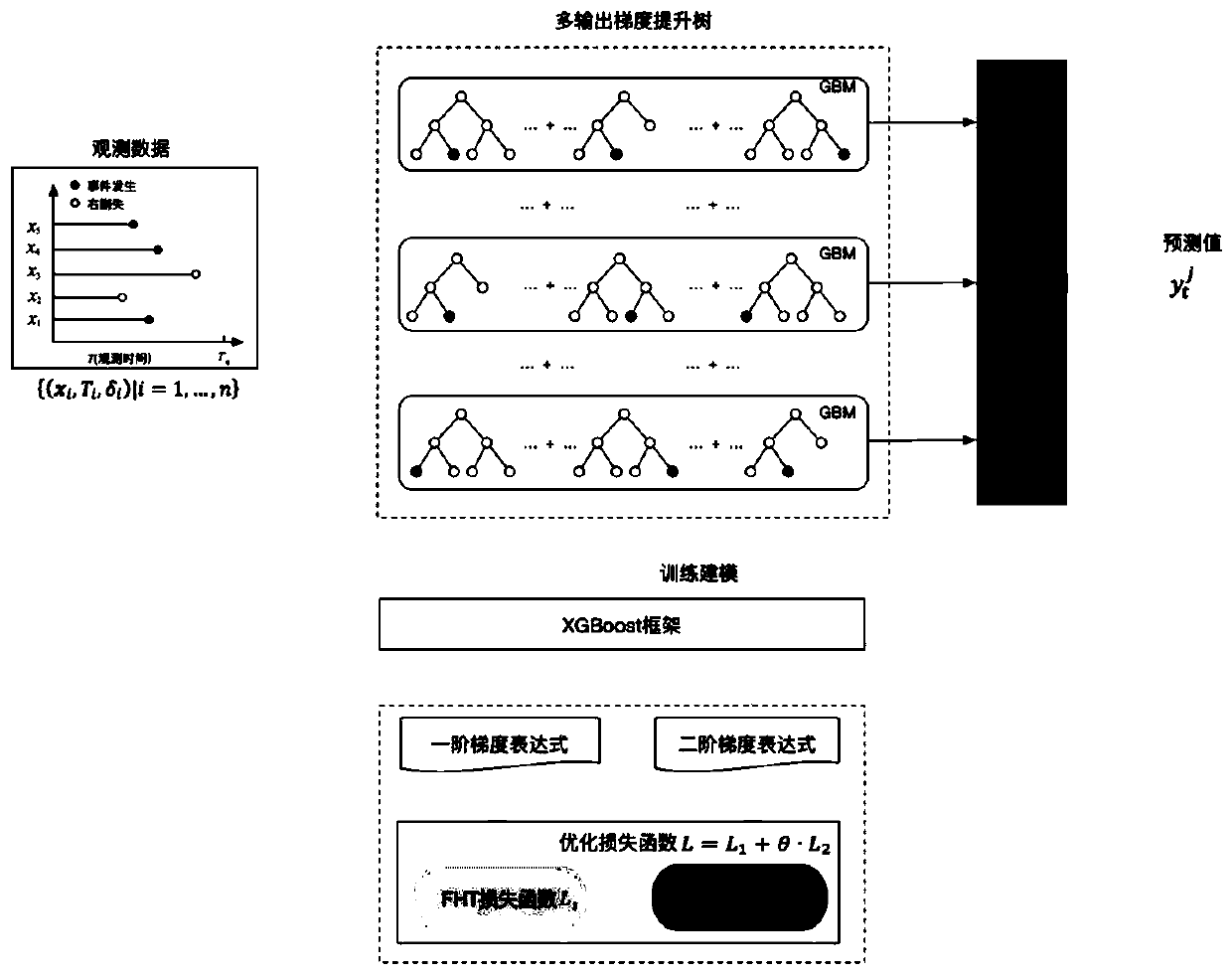
Multi-output gradient lifting tree modeling method for survival risk analysis
ActiveCN110119540AImprove accuracySolve the problem of insufficient explanationForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationRisk profilingSurvival analysis
The invention provides a multi-output gradient lifting tree modeling method for survival risk analysis, which comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing an expression of survival data for establishing a survival prediction model of financial, insurance, medical, traffic or industrial target industries under a model algorithm framework of an optimal gradient lifting tree (XGBoost); then defining and calculating a loss function corresponding to the survival data; then, defining and calculating a first step degree and a second step degree corresponding to the loss function; and finally,inputting the calculated loss function value and the first-order gradient value and the second-order gradient value of the loss function into an XGBoos model algorithm framework at the same time, andperforming automatic training to generate a survival prediction model of the target industry. The modeling method provided by the invention can better represent the relationship between the model covariable and the risk prediction value. The prediction performance and the generalization capability of the model are improved. The prediction performance and the risk distinguishing degree are better,and the application scene is wide.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
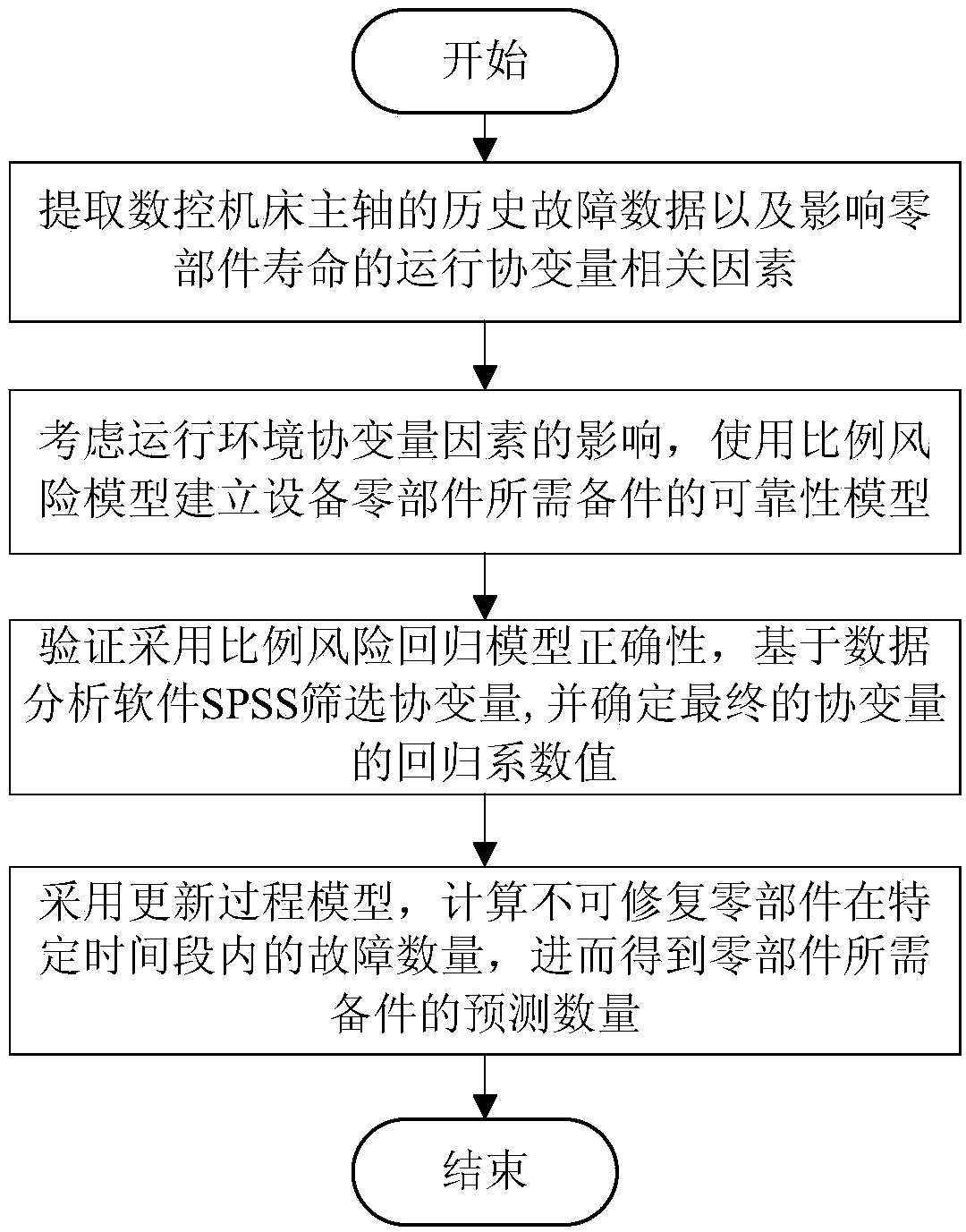
A prediction method of machine tool spindle spare parts based on running covariance analysis
InactiveCN109086945AReduce storageReduce operating costsForecastingResourcesNumerical controlOperational costs
The invention provides a machine tool spindle spare part prediction method based on operation covariance analysis, which relates to the technical field of numerical control machine tools. Firstly, thehistorical fault data of an NC machine tool spindle and the related factors of running covariates which affect the life of parts are extracted, and the reliability model of spare parts for equipmentparts is established by using a proportional risk model. Then the covariates are screened and the regression coefficients of the final covariates are determined based on the data analysis software SPSS. Finally, the update process model is used to calculate the number of faults in a specific period of time for the independently distributed parts with irreparable fault data, and then the forecast number of spare parts required for the parts is obtained. The machine tool spindle spare parts prediction method based on the operation covariance analysis provided by the invention improves the accuracy of the required spare parts prediction data, reduces the storage amount of the spare parts of the equipment, and greatly reduces the operation cost of the enterprise.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
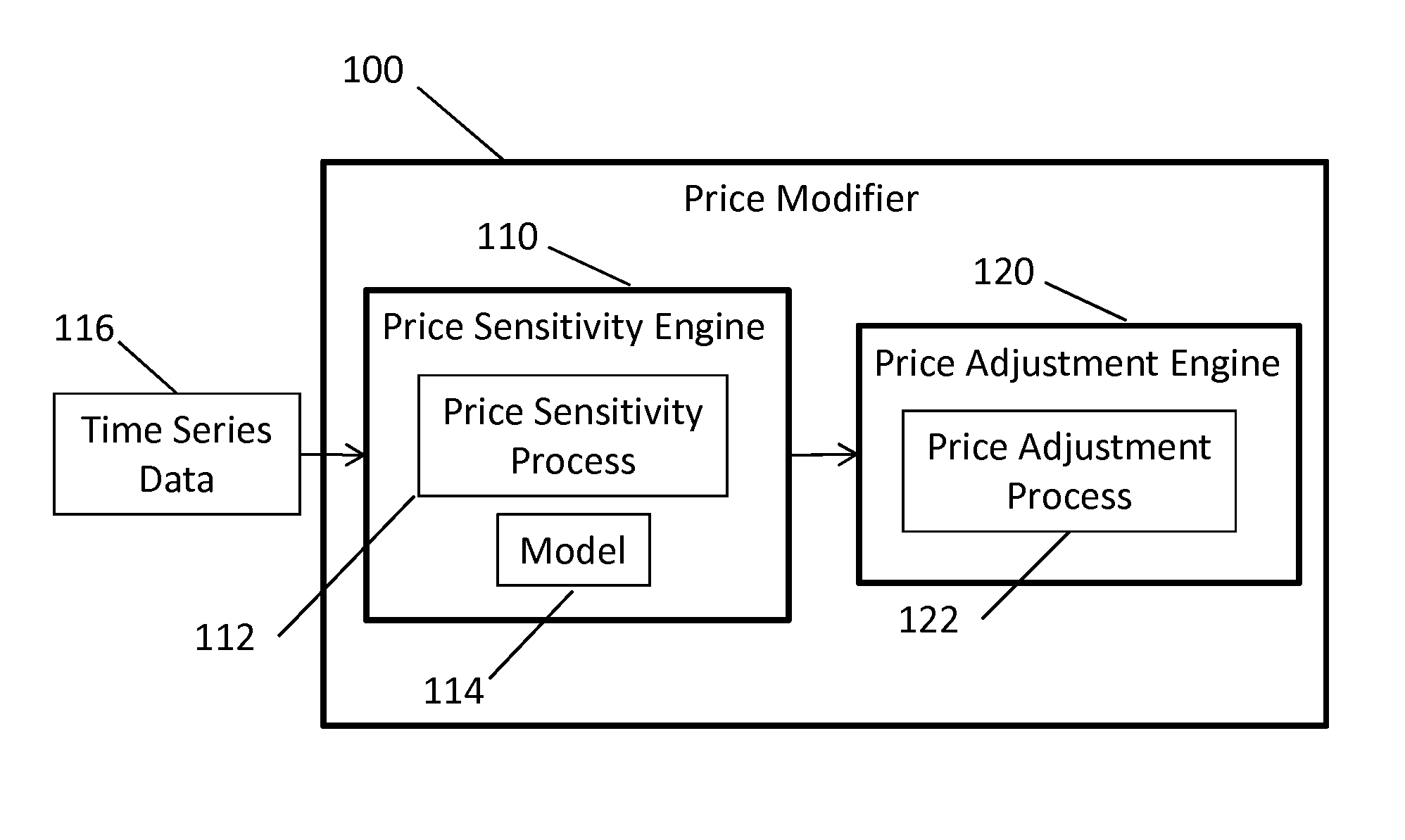
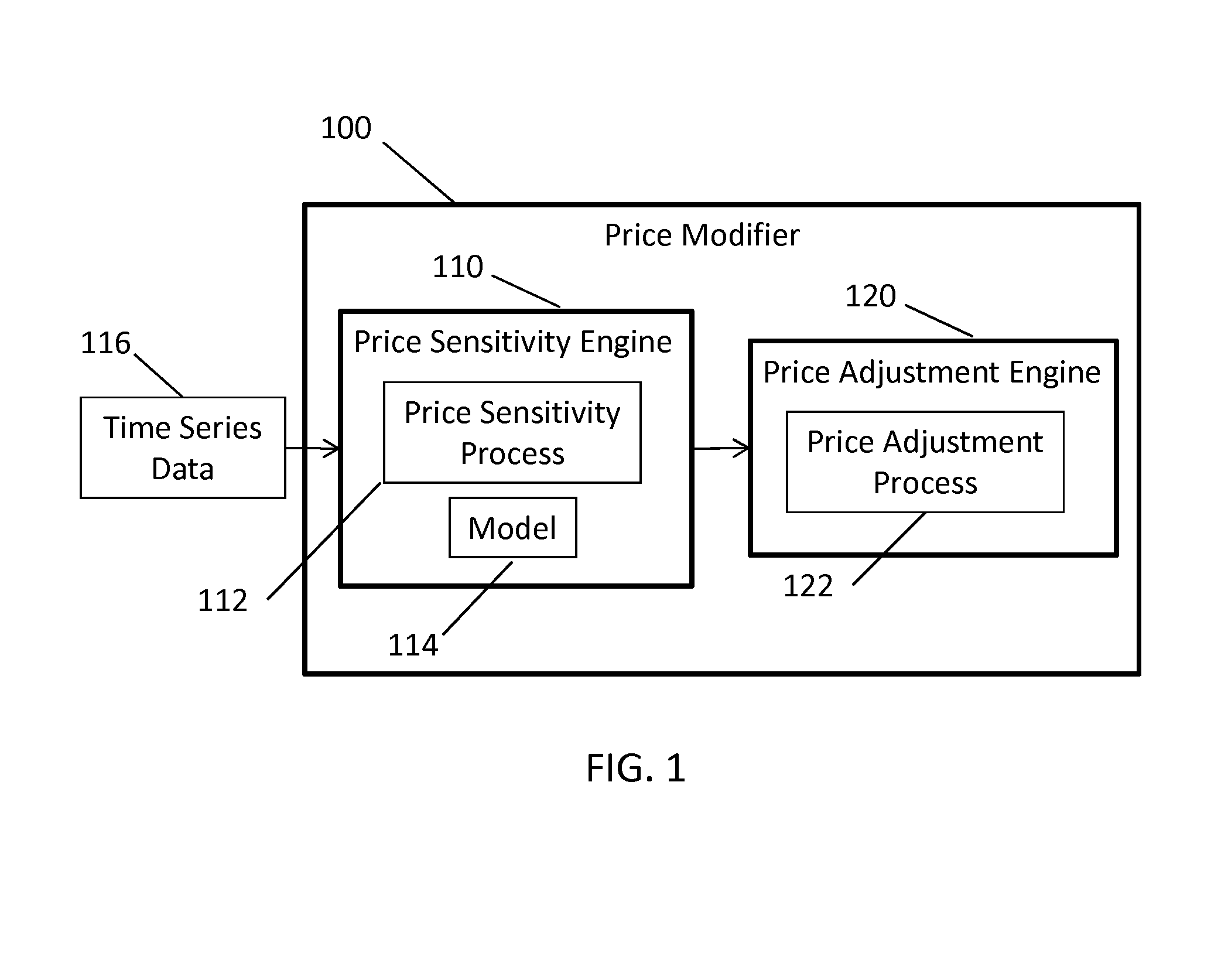
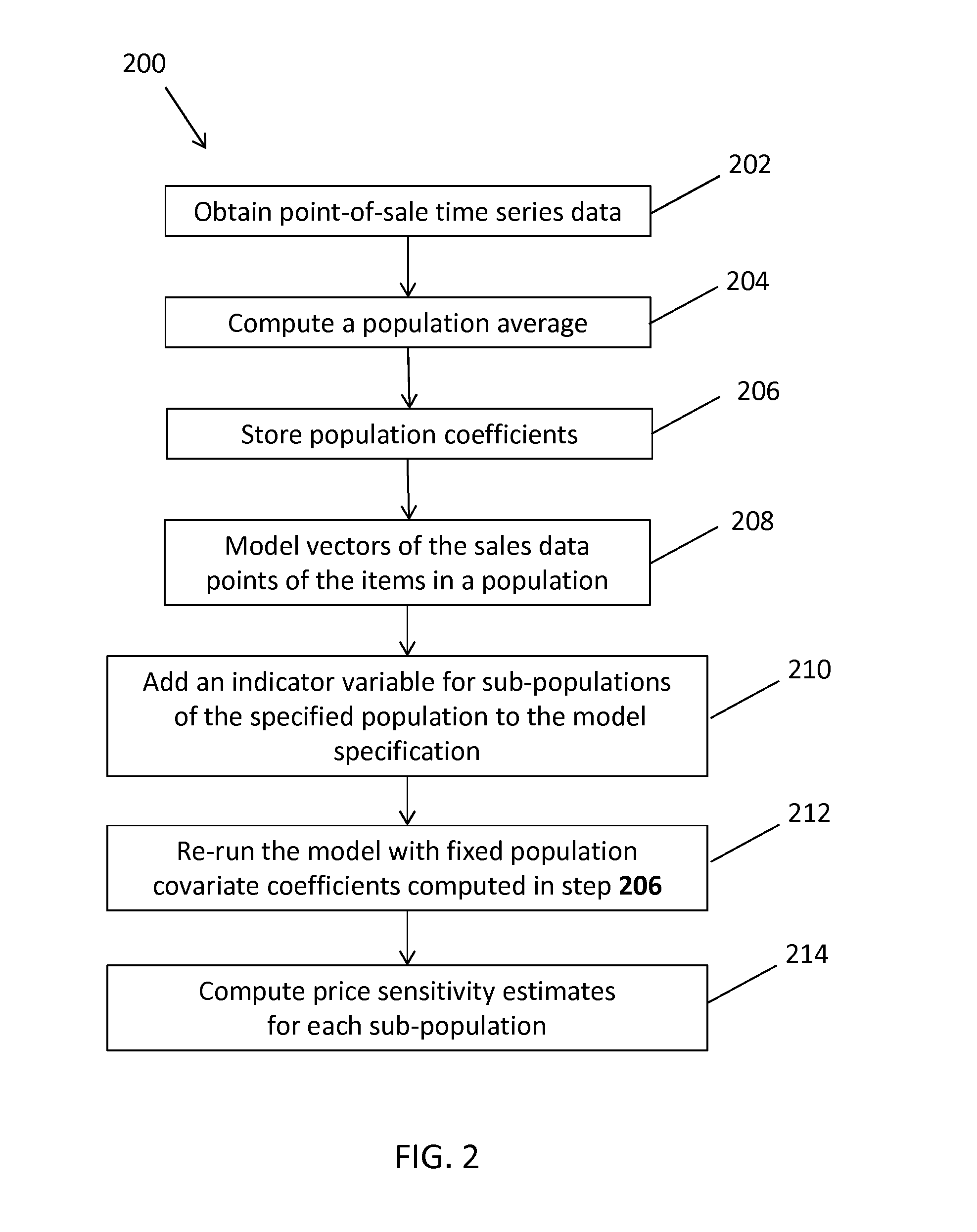
System and Method for Estimating Price Sensitivity and/or Price Aggregation for a Population Having a Collection of Items
Provided is a system for estimating price sensitivities and determining aggregate price adjustments for a population of items, the population comprising a plurality of sub-populations. More specifically, provided is a system comprising a computer executing a price sensitivity engine and a price aggregation engine, the price sensitivity engine receiving time-series information, determining covariate coefficients to estimate a population price sensitivity average, modeling a first set of vectors based on the covariate coefficients, modeling a second set of vectors based on the covariate coefficients and an indicator variable, and estimating sub-population price sensitivities based on the first and second sets of vectors; and the price aggregation engine comparing each of the sub-population price sensitivities to the population price sensitivity average and / or to other sub-population price sensitivities, ranking, ordering, and / or clustering the sub-populations, and determining aggregate price adjustments to items in the sub-populations.
Owner:OPERA SOLUTIONS
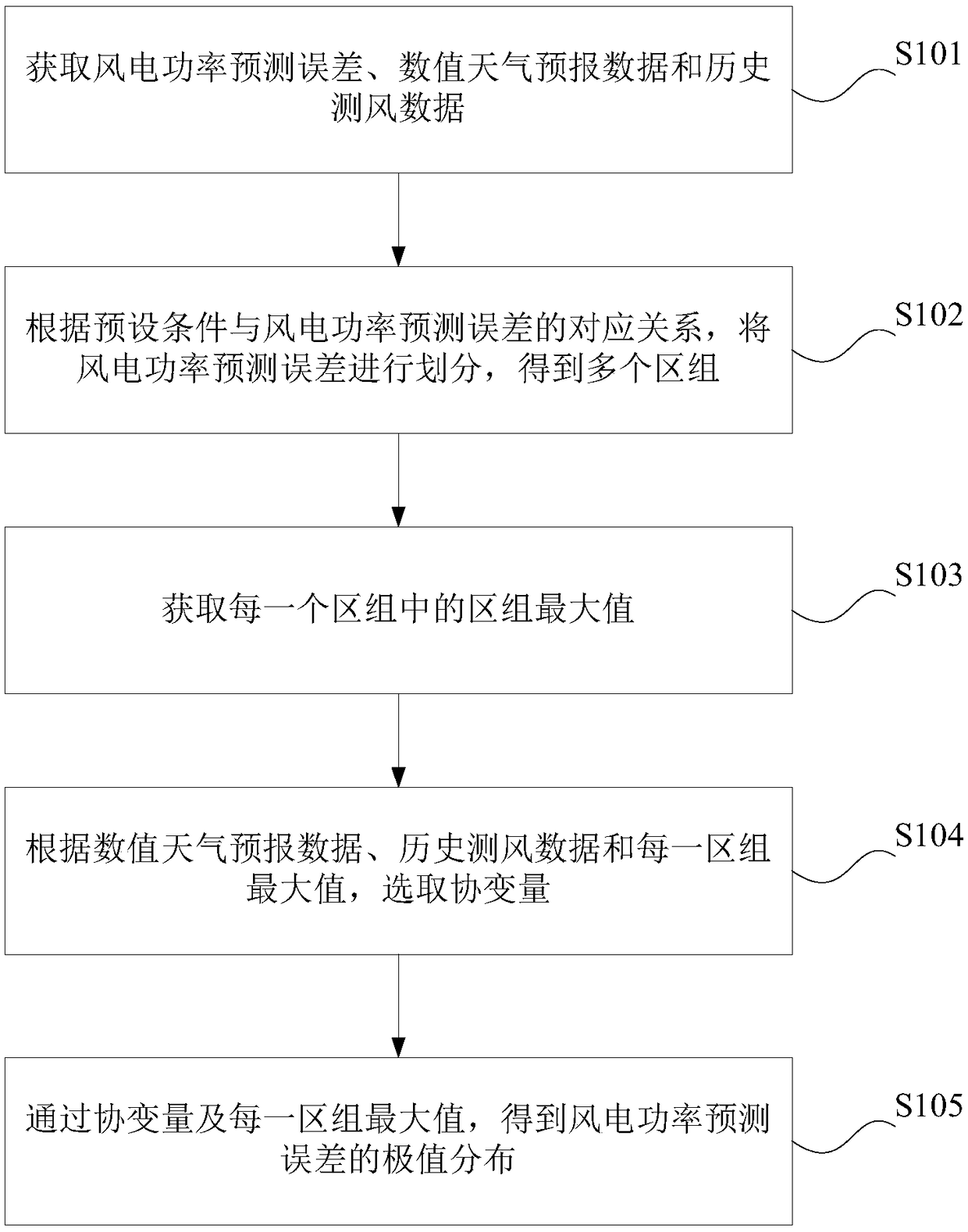
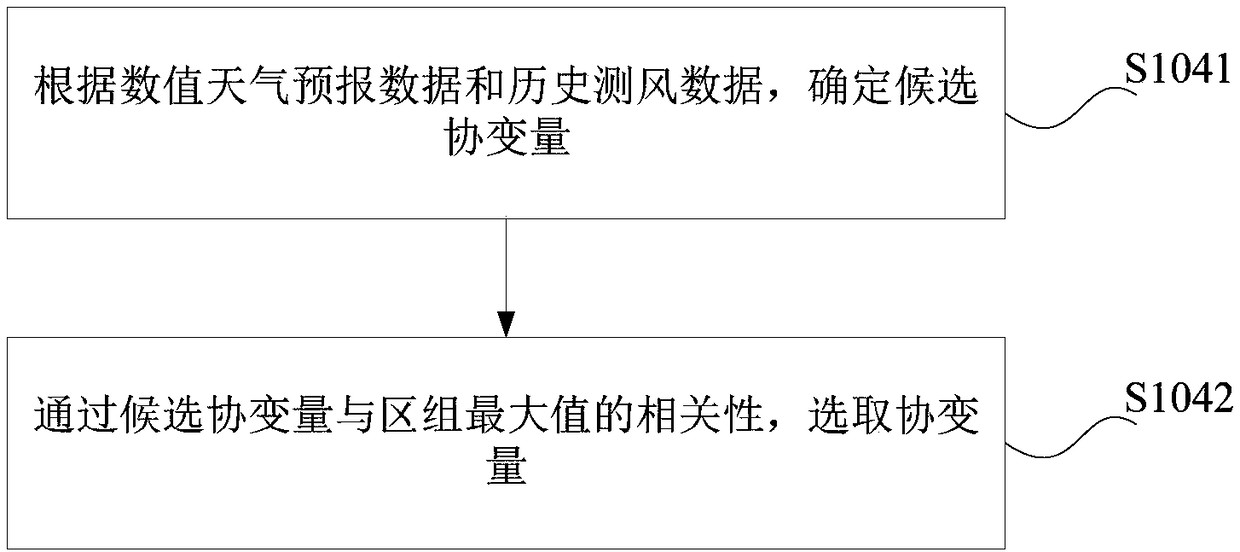
Prediction error extreme value analysis method and device, computer device and readable storage medium
ActiveCN108694472AImprove scheduling availabilitySolving the Maximum Cross-Correlation ProblemForecastingErrors and residualsAnalysis method
The invention provides a prediction error extreme value analysis method and device, a computer device and a readable storage medium. The method comprises: acquiring a wind power prediction errors, numerical weather forecast data and historical anemometry data, dividing the wind power prediction errors according to the corresponding relationship between the preset conditions and the wind power prediction errors, to obtain a plurality of blocks, obtaining the block maximum value in each block, selecting a concomitant variable according to the numerical weather forecast data, the historical anemometry data and the maximum value of each block, and obtaining the extreme value distribution of the wind power prediction errors through the concomitant variable and the maximum value of each block. By adopting the method, the extreme values of the day-ahead wind power prediction errors are analyzed, thus the accuracy of extreme value modeling is increased, and the scheduling availability of the day-ahead prediction result is improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com