Covariant initial value determination method for optimal landing track design
A trajectory design and determination method technology, applied in the field of deep space exploration, can solve problems such as difficult to determine the initial value of the covariate, difficult to determine the boundary value of two points, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
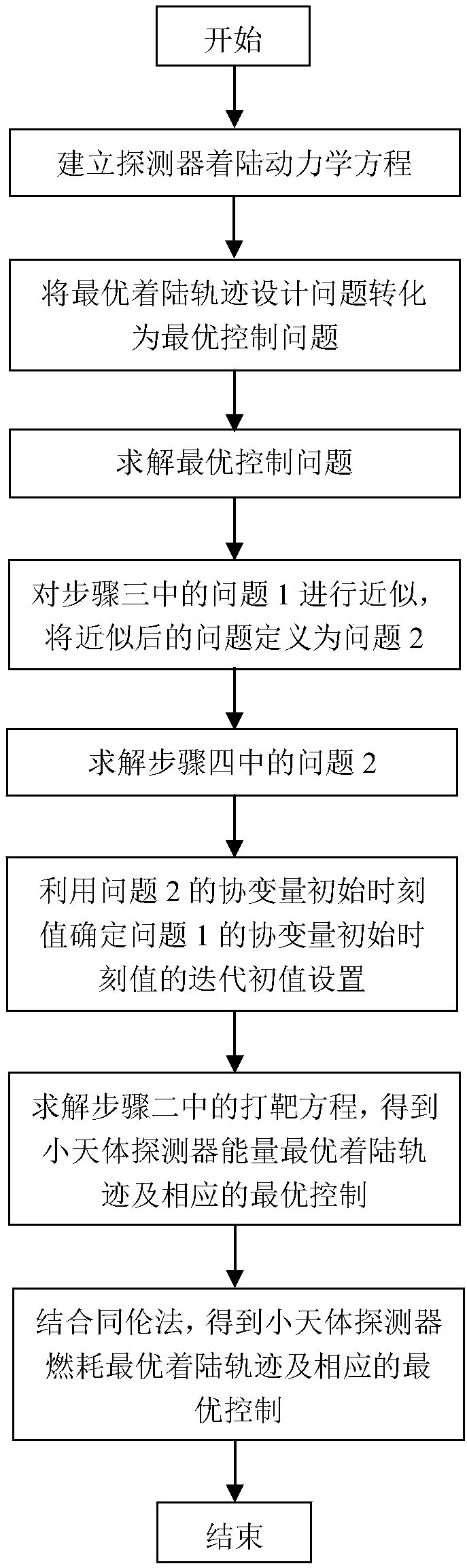
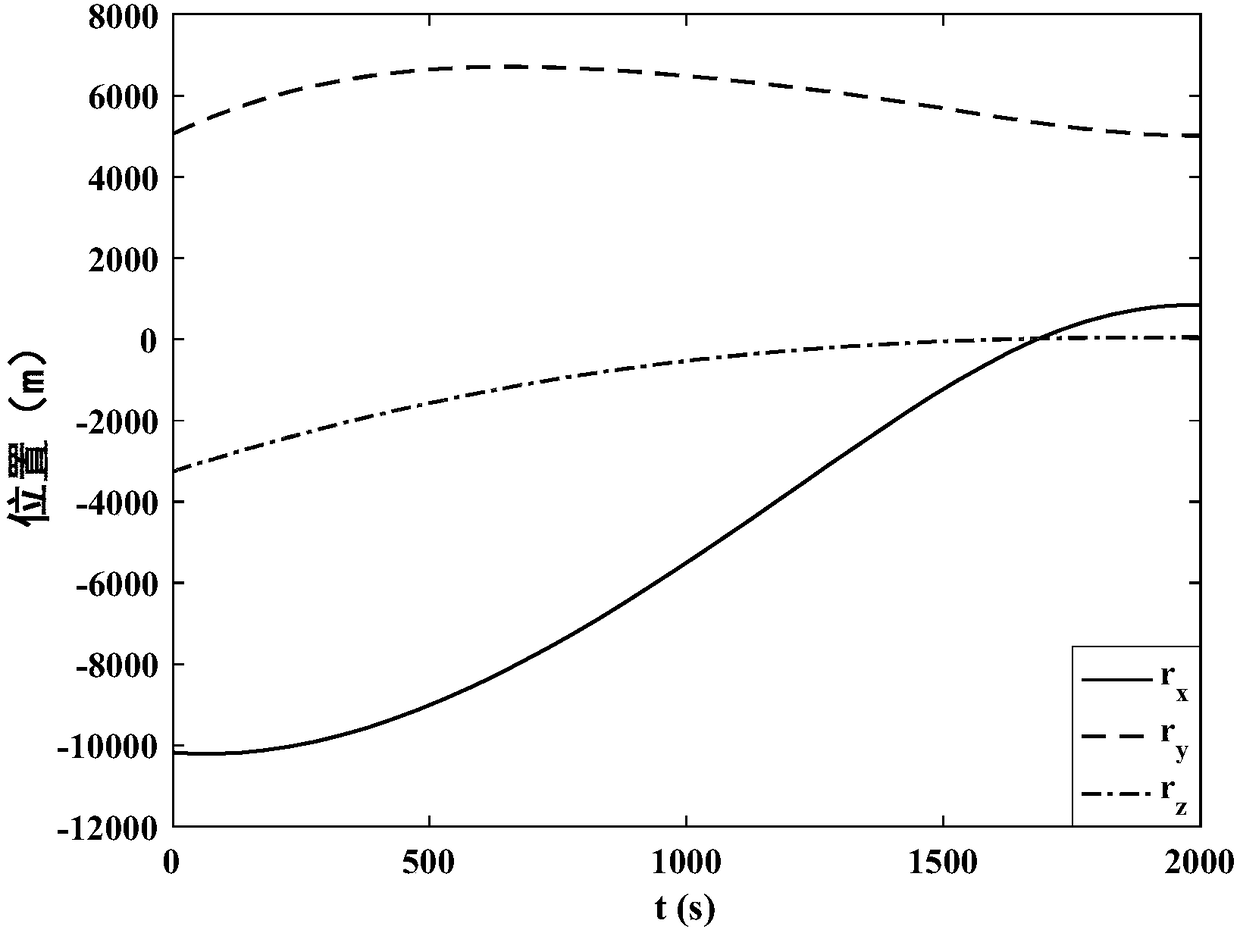
[0113] Such as figure 1 As shown, taking the design of the optimal landing trajectory of a small celestial body as an example, the method for determining the initial value of the covariates in the design of the optimal landing trajectory in this embodiment, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0114] Step 1. Establish the landing dynamic equation of the probe.
[0115] Define the small celestial body fixed coordinate system (x, y, z): the origin o is located at the center of mass of the small celestial body, the z axis coincides with the maximum inertia axis of the small celestial body, that is, the rotation axis, the x and y axes coincide with the minimum and intermediate inertia axes respectively, and x , y, z three axes satisfy the right-hand rule.
[0116] The landing dynamic equation of the probe in the small celestial body fixed coordinate system is:
[0117]
[0118] where r=[x,y,z] T is the position vector of the detector in the small celestial bod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com