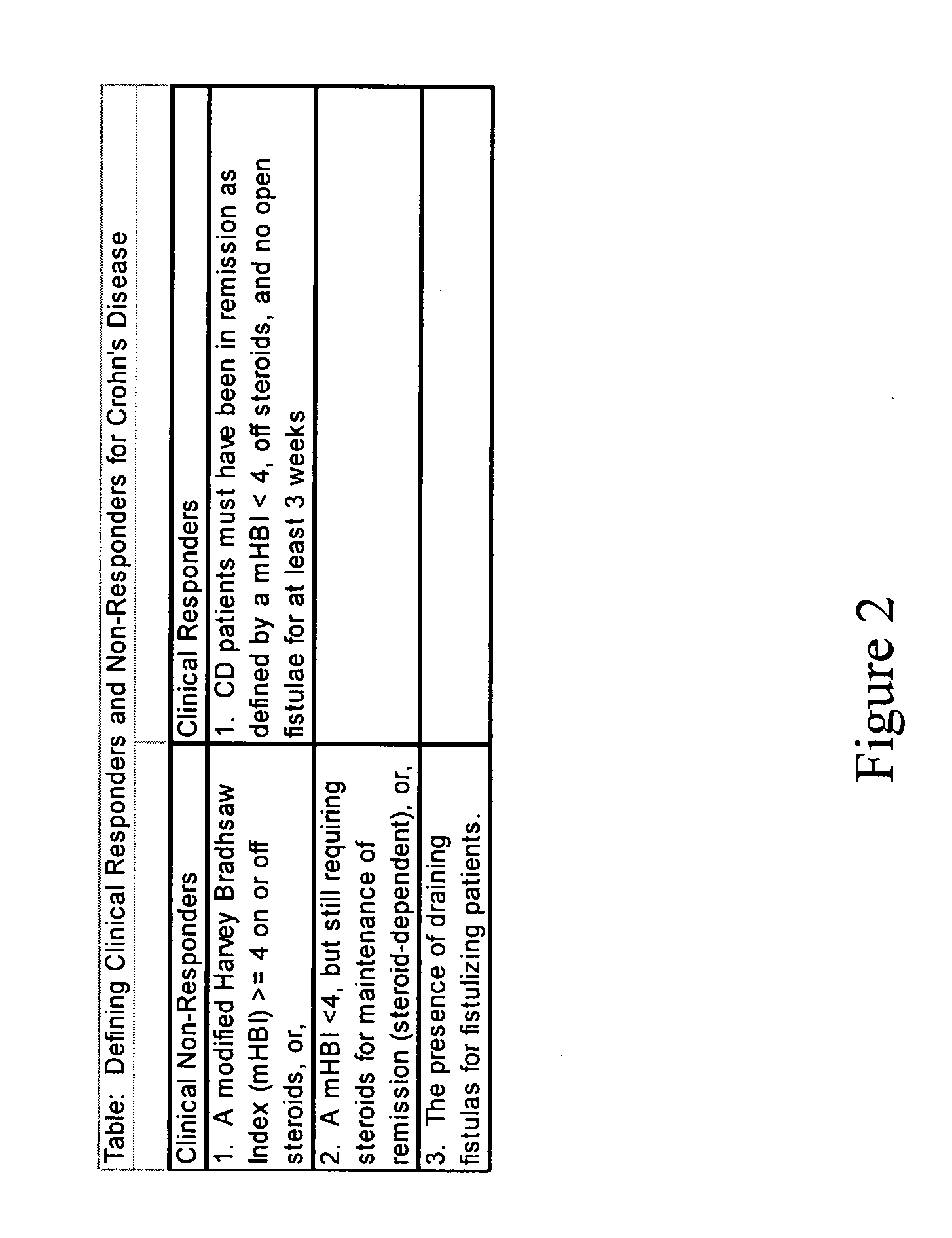
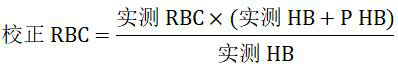Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Complete blood count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
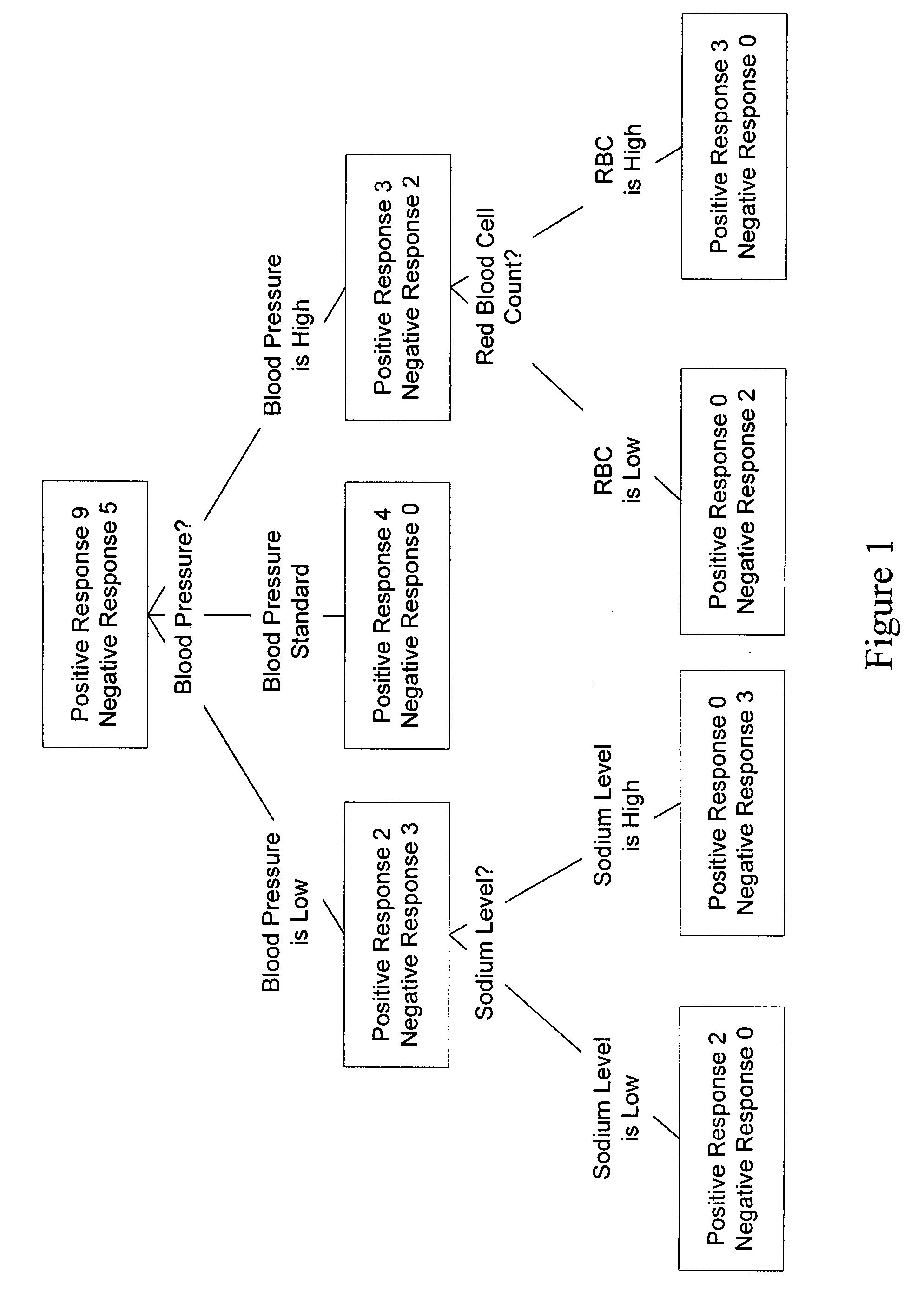
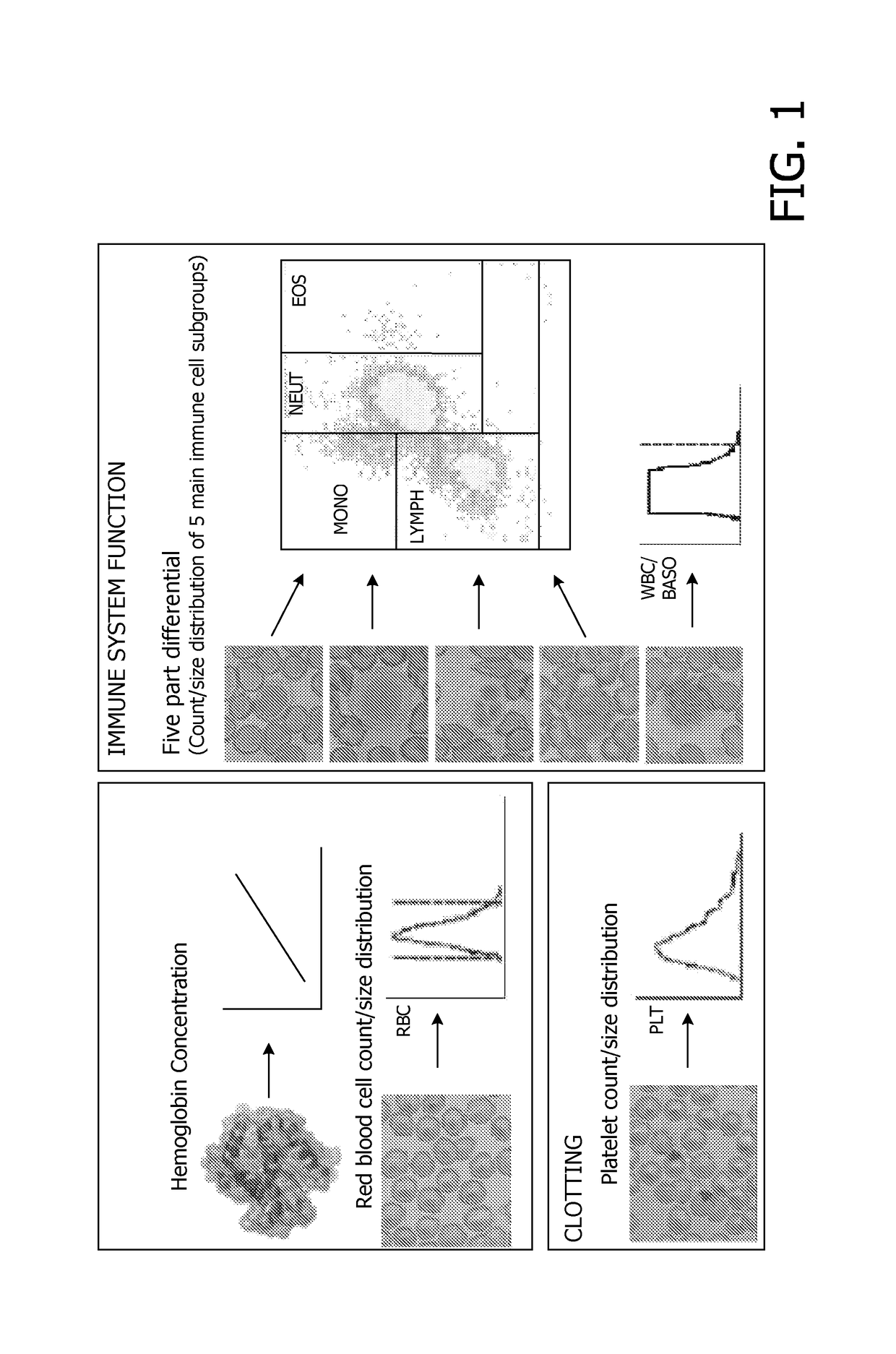
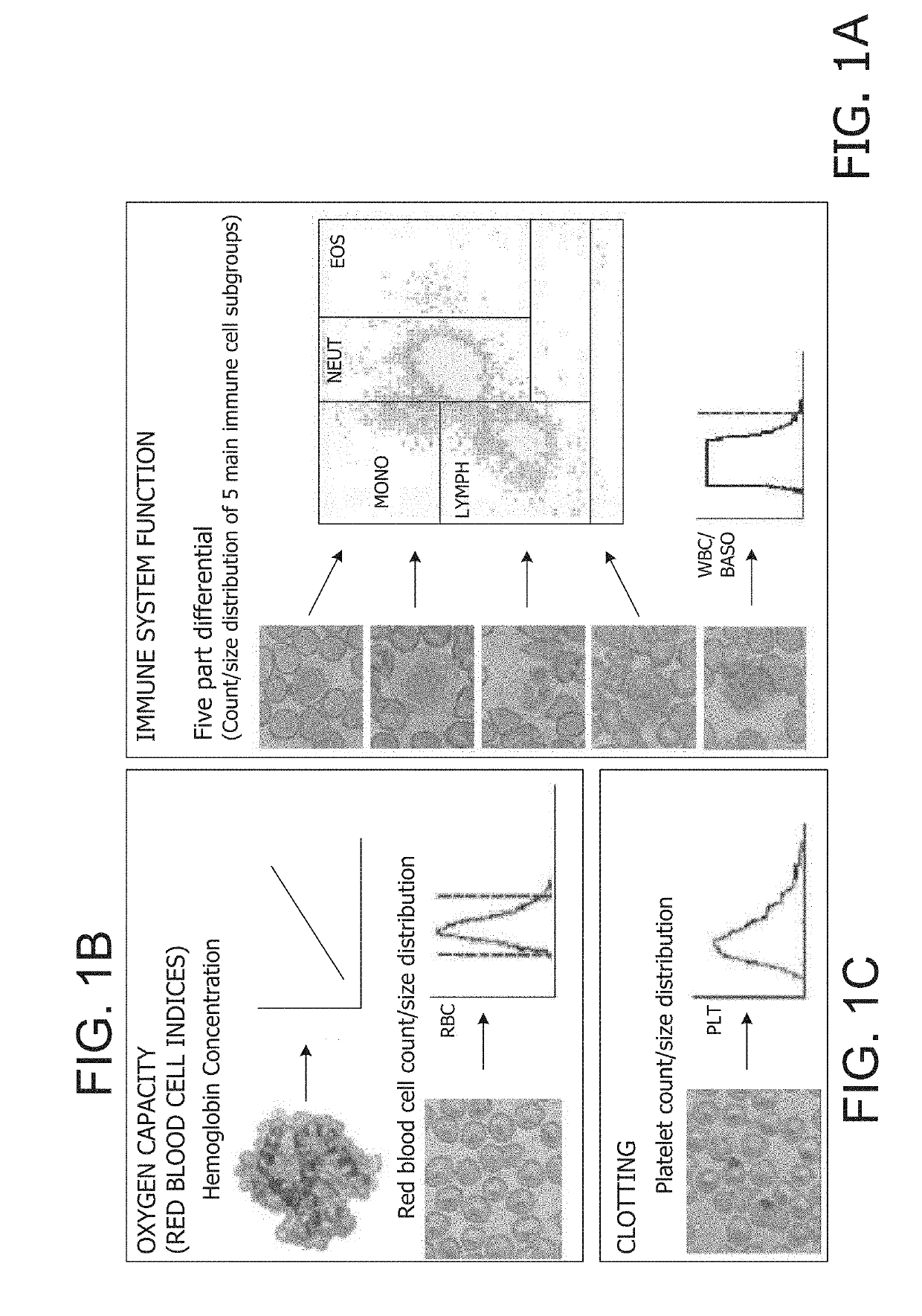
<ul><li>A low red blood cell count, hemoglobin or hematocrit indicates anemia.</li><li>A high red blood cell count may indicate underlying disease such as polycythemia vera or heart disease.</li><li>A low white blood cell count could be caused by autoimmune disease, cancer, conditions of the none marrow or medication side effects.</li><li>Abnormal platelet count could be a medication side effect or from an underlying disease.</li></ul>
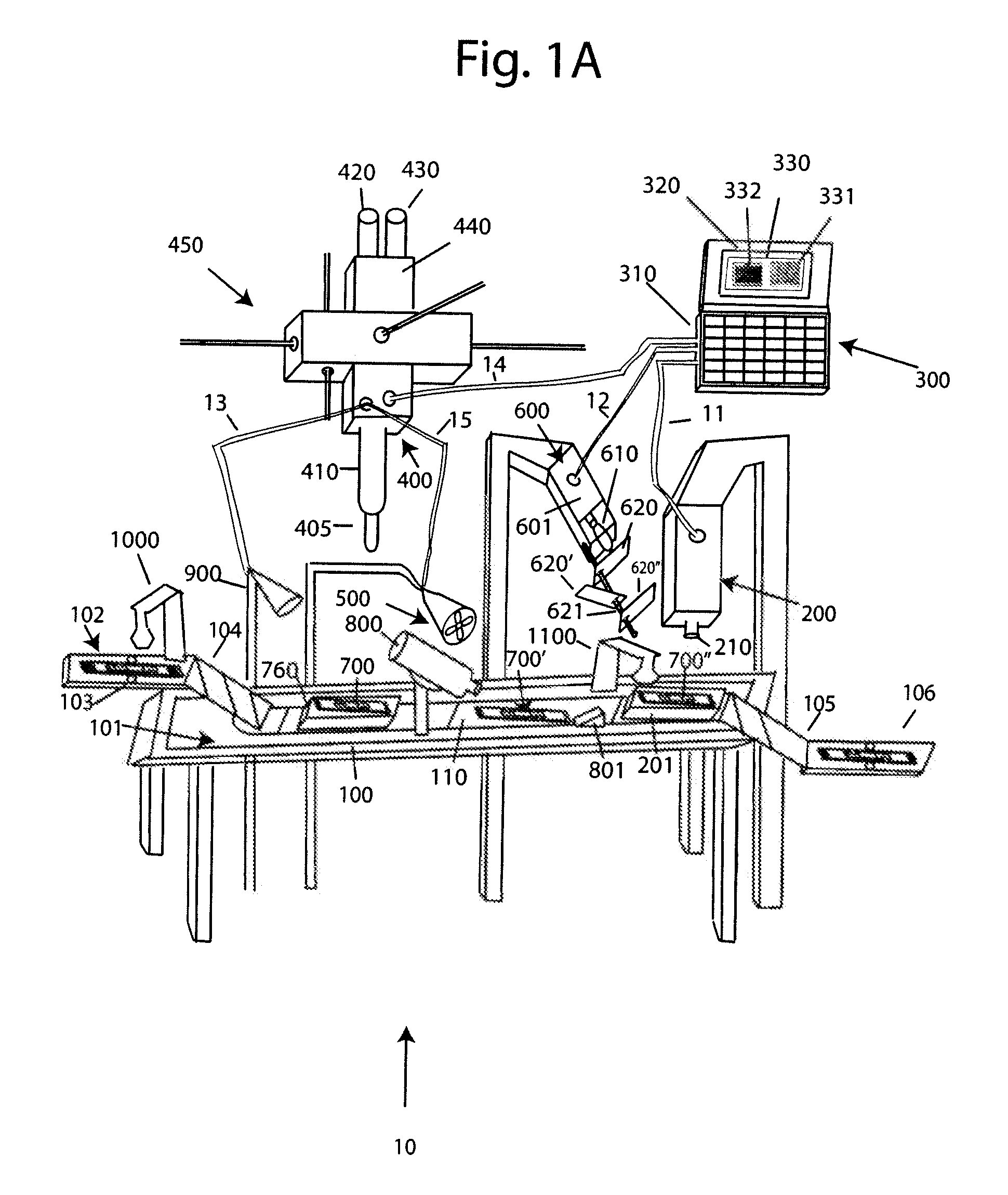
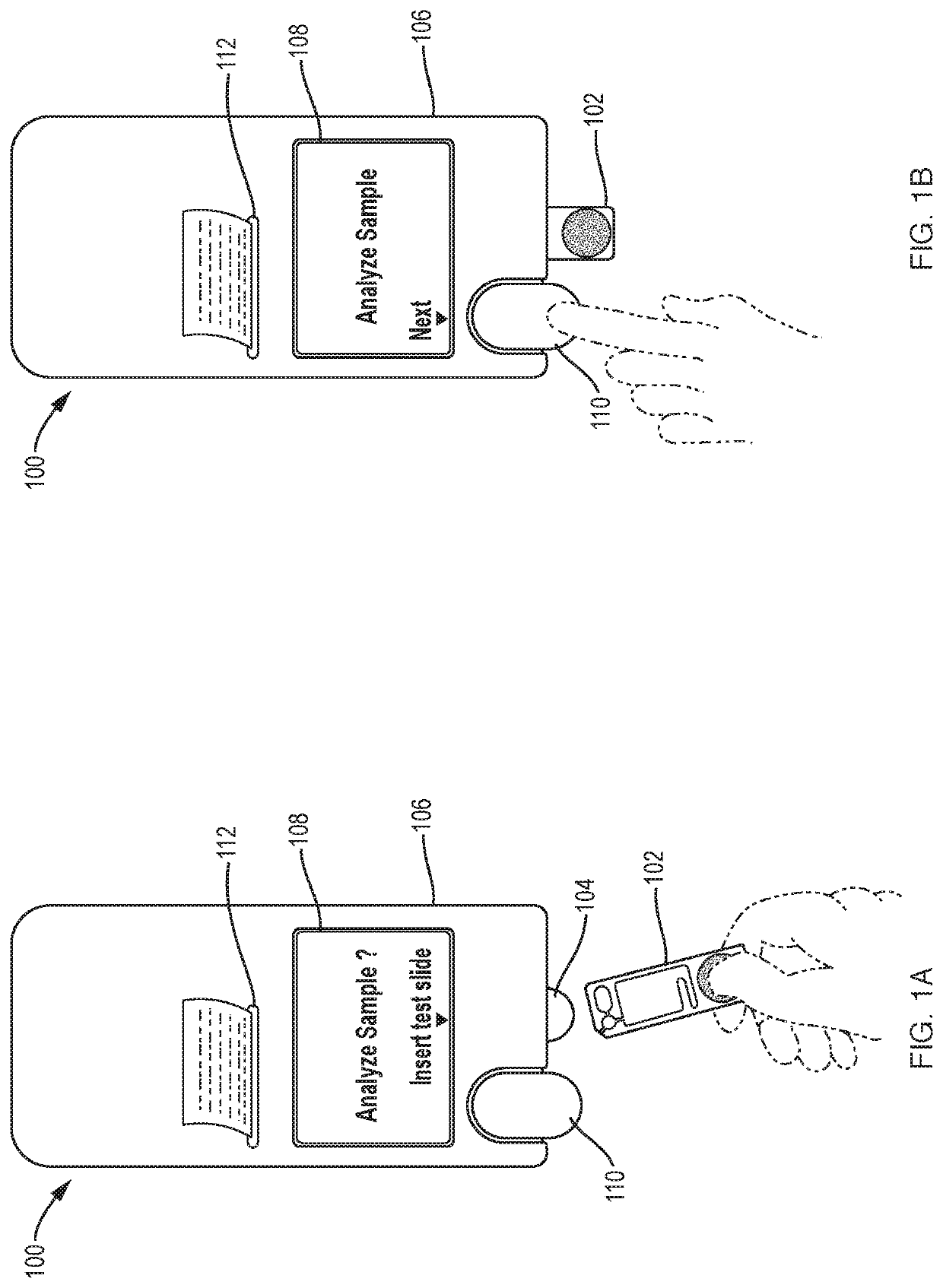
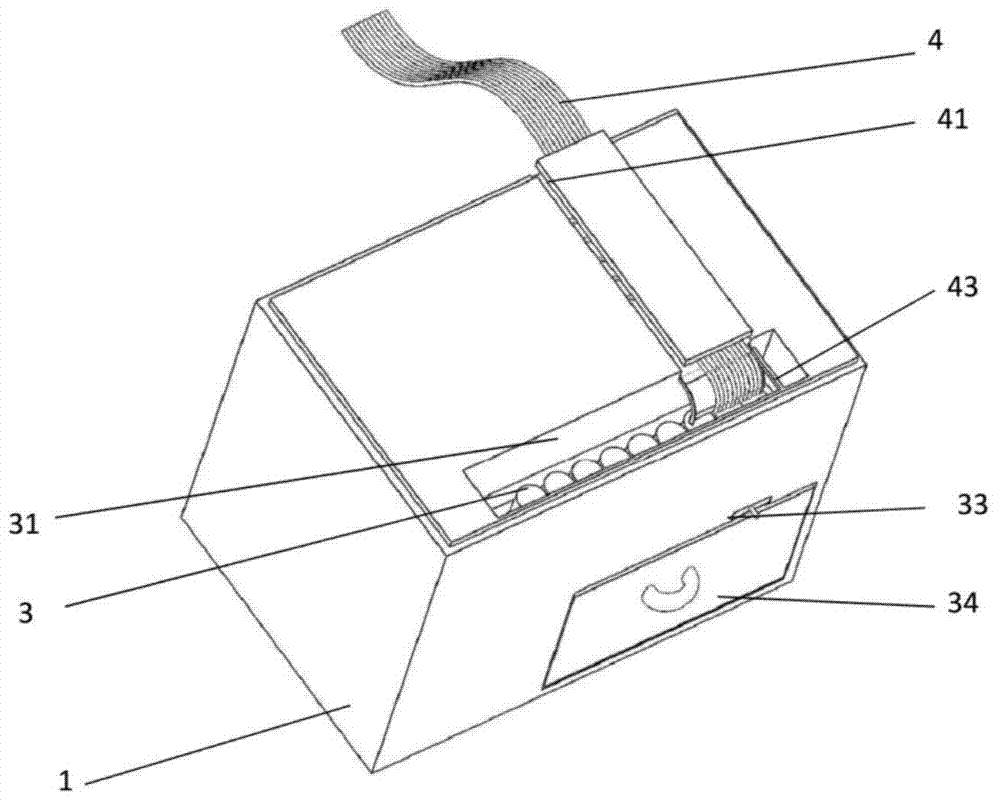
Method of determining a complete blood count and a white blood cell differential count
ActiveUS20090269799A1Improve accuracyLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsTelevision system detailsWhite blood cellBody fluid
Systems and methods analyzing body fluids such as blood and bone marrow are disclosed. The systems and methods may utilize an improved technique for applying a monolayer of cells to a slide to generate a substantially uniform distribution of cells on the slide. Additionally aspects of the invention also relate to systems and methods for utilizing multi color microscopy for improving the quality of images captured by a light receiving device.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS HEMATOLOGY INC
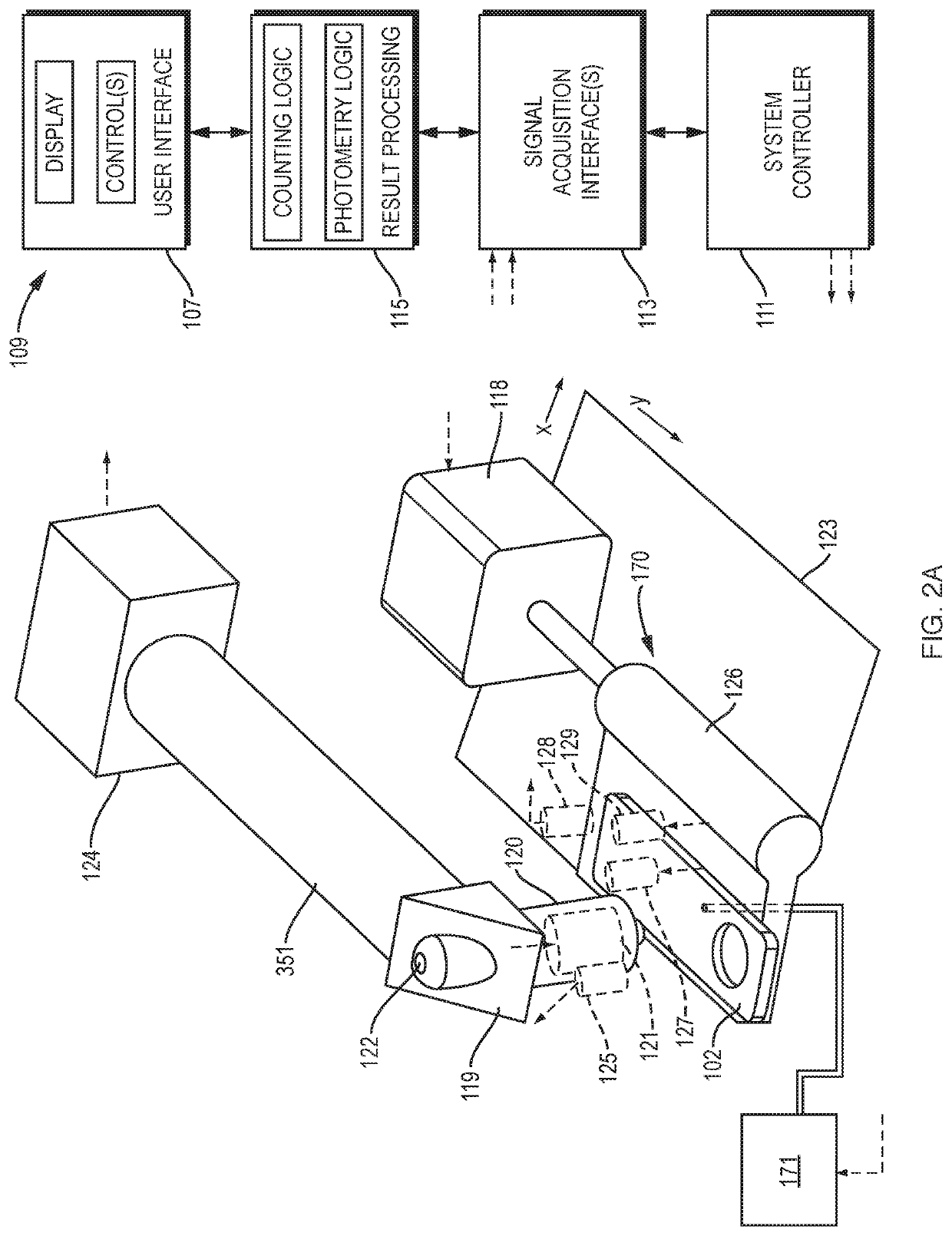
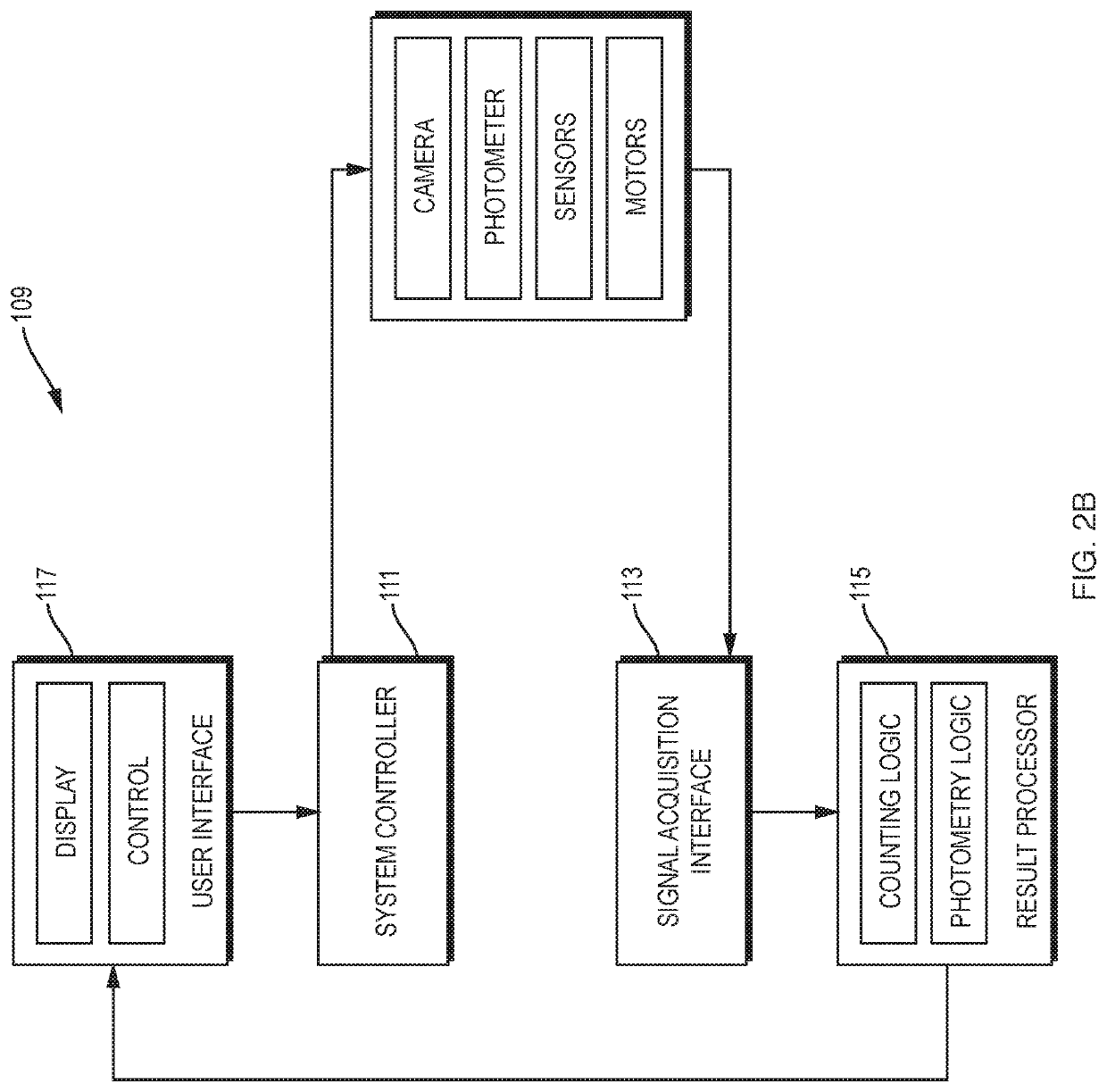
Consumable tube for use with a flow cytometry-based hematology system
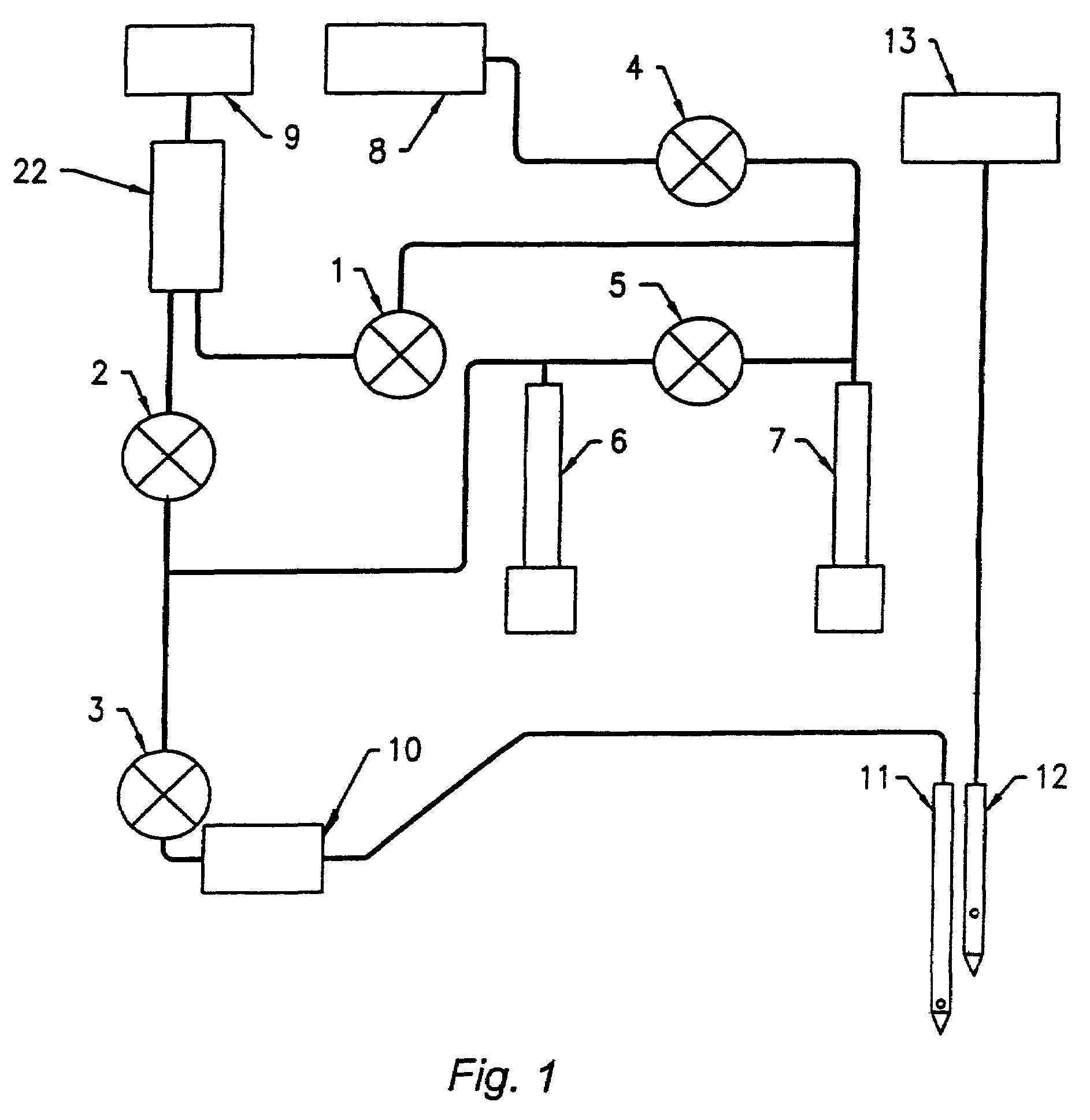
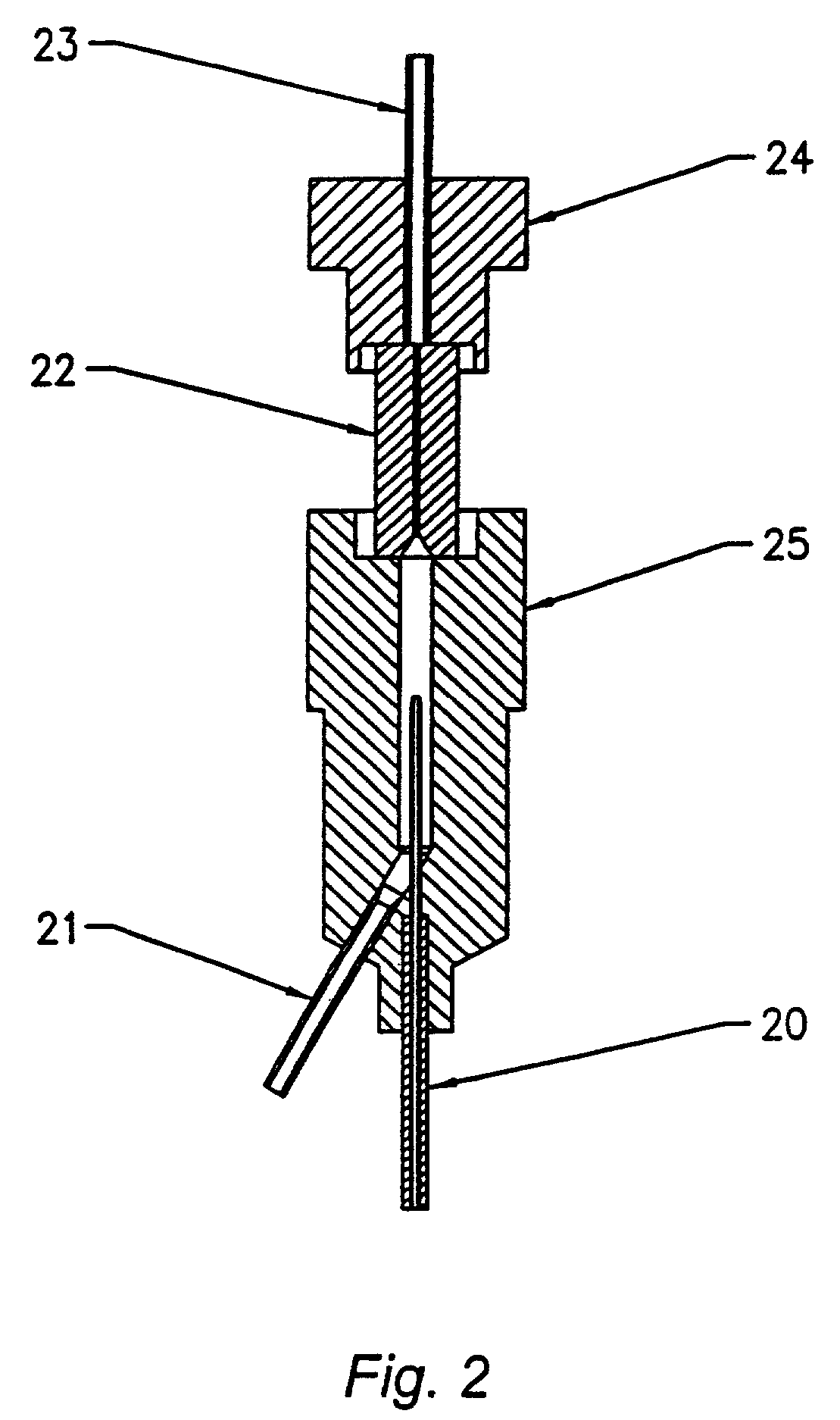
InactiveUS7064823B2Minimizes reagent wasteReduces systemWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationMedicine.hematologyFlow cell
The present invention is a flow cytometry-based hematology system useful in the analysis of biological samples, particularly whole blood or blood-derived samples. The system is capable of determining at least a complete blood count (CBC), a five-part white blood cell differential, and a reticulocyte count from a whole blood sample. The system preferably uses a laser diode that emits a thin beam to illuminate cells in a flow cell and a lensless optical detection system to measure one or more of axial light loss, low-angle forward scattered light, high-angle forward scattered light, right angle scattered light, and time-of-flight measurements produced by the cells. The lensless optical detection system contains no optical components, other than photoreactive elements, and does not include any moving parts. Finally, the system uses a unique system of consumable reagent tubes that act as reaction chambers, mixing chambers, and waste chambers for the blood sample analyses. The consumable tubes incorporate reference particles, which act as internal standards to ensure that the dilutions made during processing of the samples have been carried out correctly, and to ensure that the instrument is working properly. The present invention also relates to methods for using the system.
Owner:IDEXX LABORATORIES
Automated microscopic cell analysis
InactiveUS20170328924A1Eliminate Bubble ProblemsSolve insufficient capacityReagent containersPreparing sample for investigationWhite blood cellRed blood cell
Disclosed in one aspect is a method for performing a complete blood count (CBC) on a sample of whole blood by metering a predetermined amount of the whole blood and mixing it with a predetermined amount of diluent and stain and transferring a portion thereof to an imaging chamber of fixed dimensions and utilizing an automated microscope with digital camera and cell counting and recognition software to count every white blood cell and red blood corpuscle and platelet in the sample diluent / stain mixture to determine the number of red cells, white cells, and platelets per unit volume, and analyzing the white cells with cell recognition software to classify them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
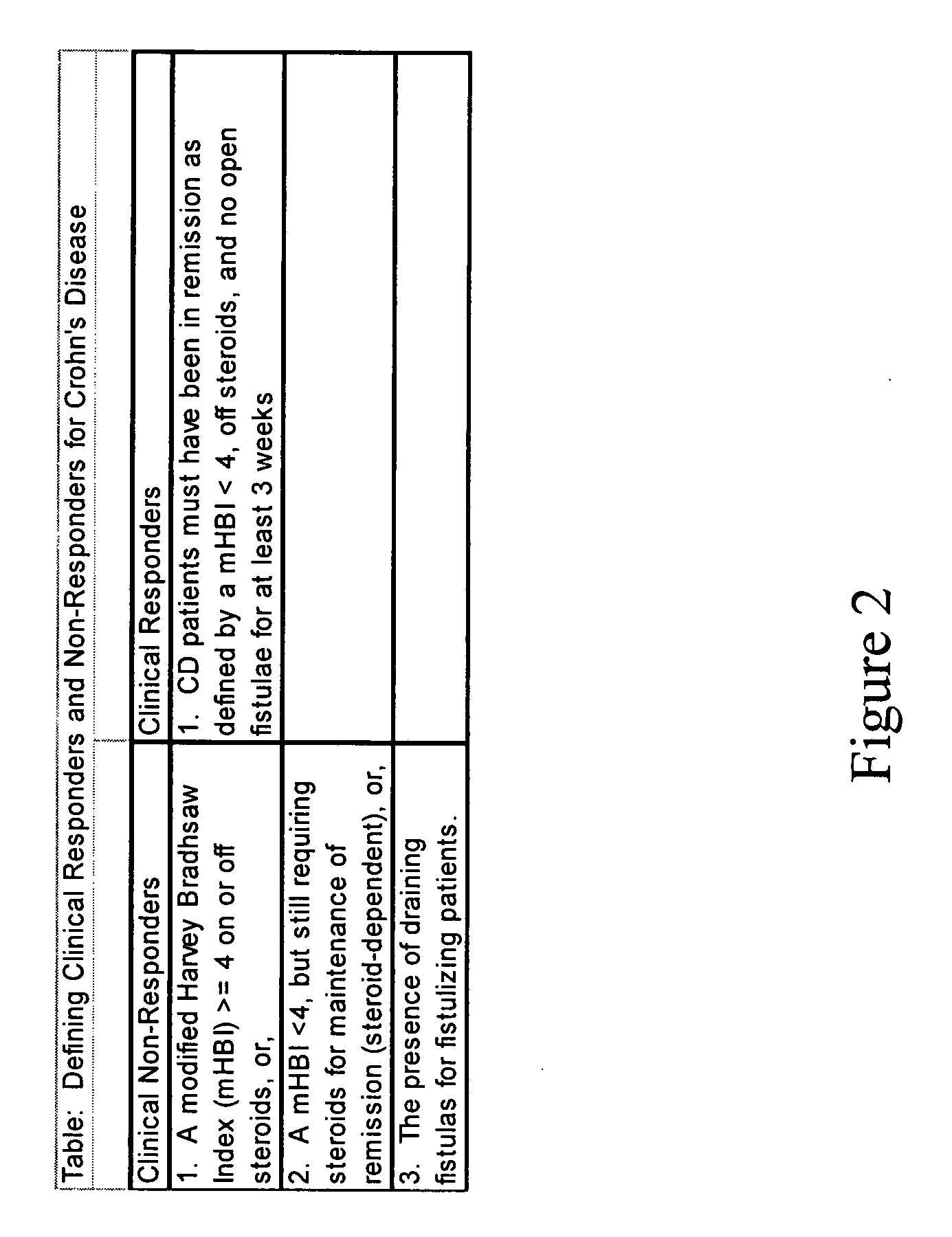
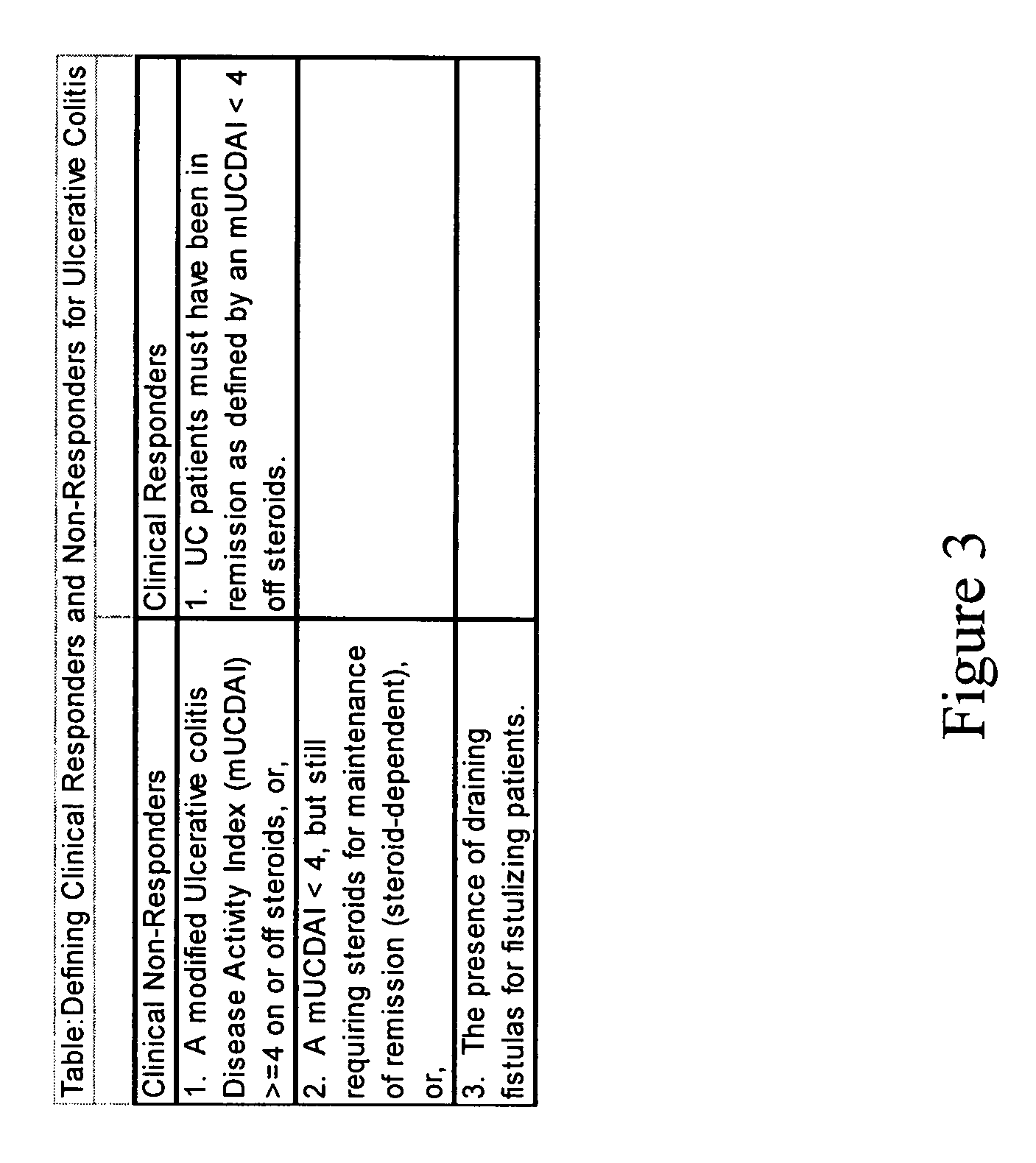
Algorithms to predict clinical response, adherence, and shunting with thiopurines
ActiveUS8126690B2Analogue computers for chemical processesMedical automated diagnosisTotal bloodInflammatory bowel disease
A method of using a variable set from complete blood counts and blood chemistry panels to generate a machine learned algorithm for determining the effectiveness of thiopurine treatment on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients using CART, boosted trees, random forest classification, RuleFit and / or logistic regression analysis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
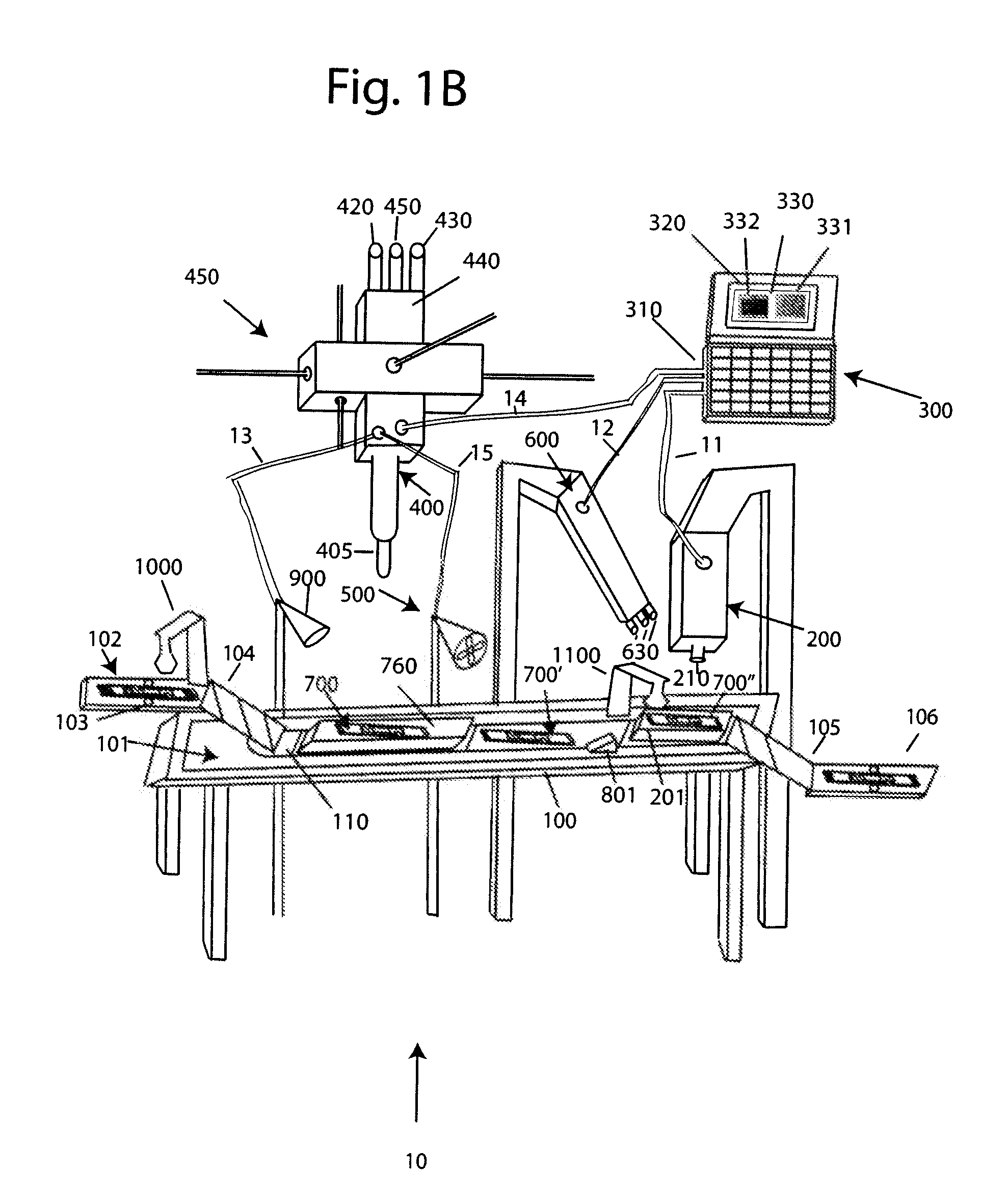
Method for determining a complete blood count on a white blood cell differential count
ActiveUS20100284602A1Improve accuracyLow costTelevision system detailsImage analysisWhite blood cellBody fluid
Systems and methods analyzing body fluids such as blood and bone marrow are disclosed. The systems and methods may utilize an improved technique for applying a monolayer of cells to a slide to generate a substantially uniform distribution of cells on the slide. Additionally aspects of the invention also relate to systems and methods for utilizing multi color microscopy for improving the quality of images captured by a light receiving device.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS HEMATOLOGY INC
Algorithms to predict clinical response, adherence, and shunting with thiopuriness
ActiveUS20080288227A1Increased likelihood of toxicityAnalogue computers for chemical processesMedical automated diagnosisInflammatory bowel diseaseBlood chemistry
A method of using a variable set from complete blood counts and blood chemistry panels to generate a machine learned algorithm for determining the effectiveness of thiopurine treatment on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients using CART, boosted trees, random forest classification, RuleFit and / or logistic regression analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF MICHIGAN THE
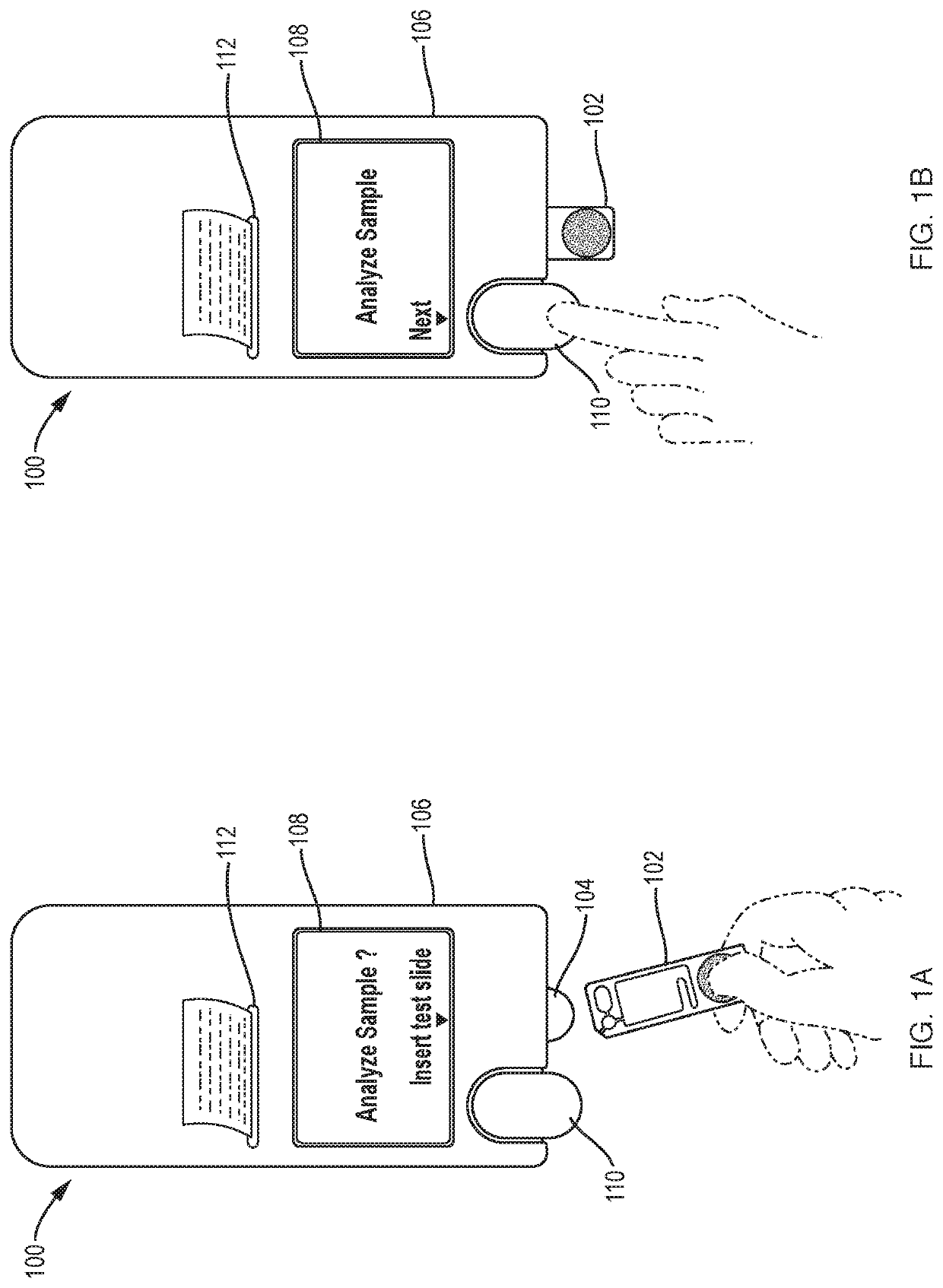
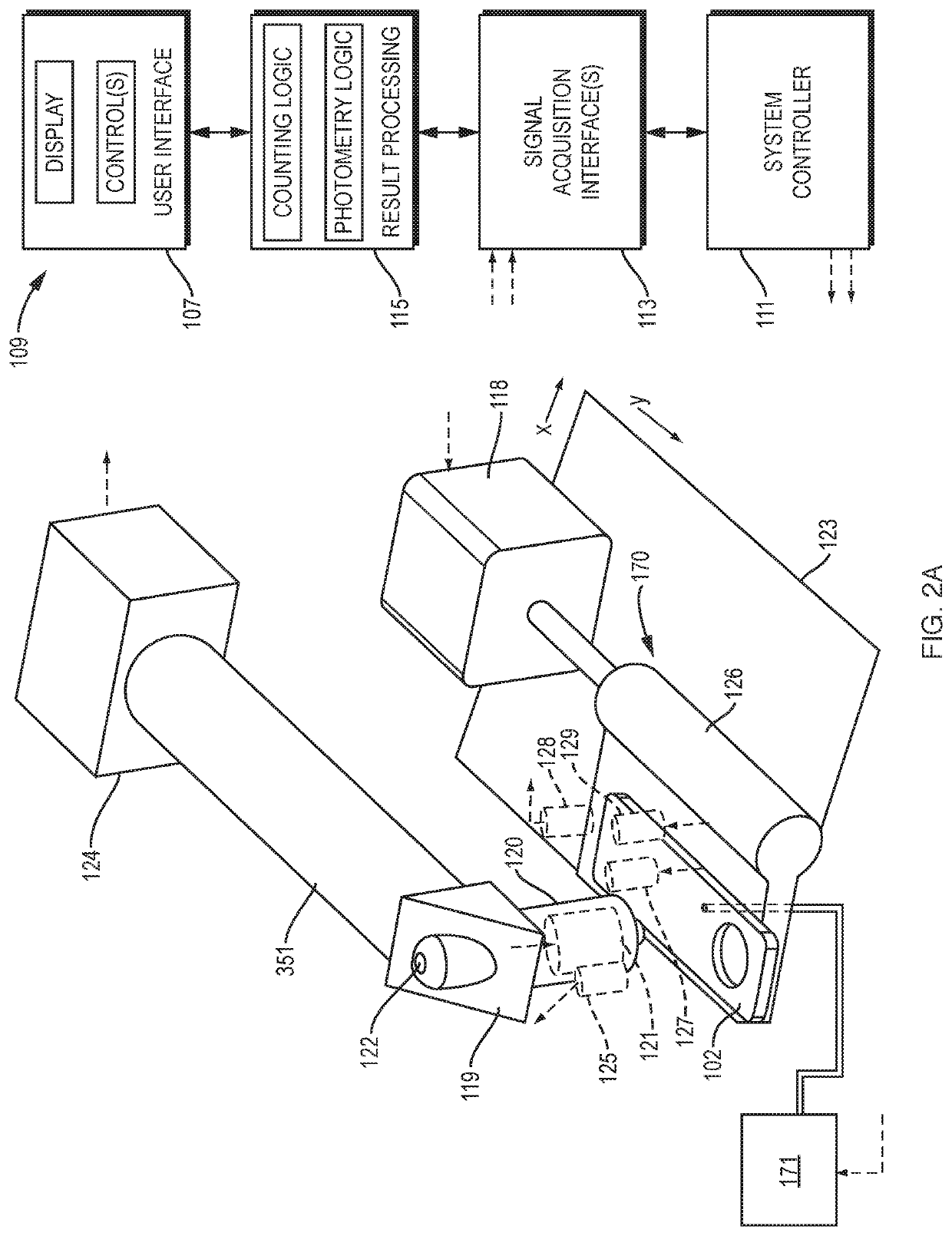
Methods for complete blood count measurement
ActiveUS20180095023A1Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsComplete blood countBiomedical engineering
The disclosure relates to devices and methods for analyzing blood cells in a sample. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods of performing complete blood count (CBC) testing. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a cartridge device and a reader instrument device, wherein the reader instrument device receives, operates, and / or actuates the cartridge device. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method of using a device as disclosed herein for analyzing blood cells in a sample.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
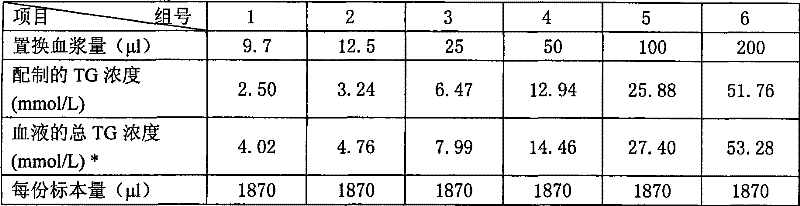
Method for eliminating interference of high riglyceride for detecting hemoglobin concentration
The invention provides an eliminating method of interference of the measurement of hypertriglyceride to the concentration of hemoglobin, comprising the following steps of: (1) carrying out complete blood count to blood containing the hypertriglyceride and obtaining the measuring value, HGB lipemia, of the concentration of the hemoglobin and the hematocrit, HCT lipemia, of the erythrocyte; (2) carrying out low-speed centrifugation to the blood containing the hypertriglyceride in the step (1) and leading the erythrocyte and the blood plasma in the blood to be separated; (3) aspirating the blood plasma separated out in the step (2), carrying out complete blood count to the blood plasma and obtaining the measuring value, HGB lipemia blood plasma, of the concentration of the hemoglobin in the blood plasma; and (4) carrying out correction to the measuring value, HGB lipemia, of the concentration of the hemoglobin obtained in the step (1), obtaining the corrected value of the concentration of the hemoglobin and the corrective formula is as follows: HGB corrected value is equal to HGB lipemia-(HGB lipemia blood plasma minus HGB lipemia blood plasma multiplied by HCT lipemia), in the formula, the HGB lipemia blood plasma multiplied by HCT lipemia is the percentage of the erythrocyte in the blood containing the hypertriglyceride.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS10625259B1High quantitative accuracySample preparation is improvedWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentHematological test
This disclosure describes single-use test cartridges, cell analyzer apparatus, and methods for automatically performing microscopic cell analysis tasks, such as counting and analyzing blood cells in biological samples. A small measured quantity of a biological sample, such as whole blood, is placed in a mixing bowl on the disposable test cartridge after being inserted into the cell analyzer. The analyzer also deposits a known amount of diluent / stain in the mixing bowl and mixes it with the blood. The analyzer takes a measured amount of the mixture and dispenses in a sample cup on the cartridge in fluid communication with an imaging chamber. The geometry of the imaging chamber is chosen to maintain the uniformity of the mixture, and to prevent cells from crowding or clumping as it is transferred into the imaging chamber by the analyzer. Images of all of the cellular components within the imaging chamber are counted and analyzed to obtain a complete blood count.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS11480778B2Minimizing any bubblingEliminate Bubble ProblemsPreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisWhite blood cellBiology
Disclosed in one aspect is a method for performing a complete blood count (CBC) on a sample of whole blood by metering a predetermined amount of the whole blood and mixing it with a predetermined amount of diluent and stain and transferring a portion thereof to an imaging chamber of fixed dimensions and utilizing an automated microscope with digital camera and cell counting and recognition software to count every white blood cell and red blood corpuscle and platelet in the sample diluent / stain mixture to determine the number of red cells, white cells, and platelets per unit volume, and analyzing the white cells with cell recognition software to classify them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Methods for complete blood count measurement
The disclosure relates to devices and methods for analyzing blood cells in a sample. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods of performing complete blood count (CBC) testing. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a cartridge device and a reader instrument device, wherein the reader instrument device receives, operates, and / or actuates the cartridge device. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method of using a device as disclosed herein for analyzing blood cells in a sample.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
Dry blood cell analytical method
InactiveCN103776768ARun fastImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansCamera lensBlood gas analysis
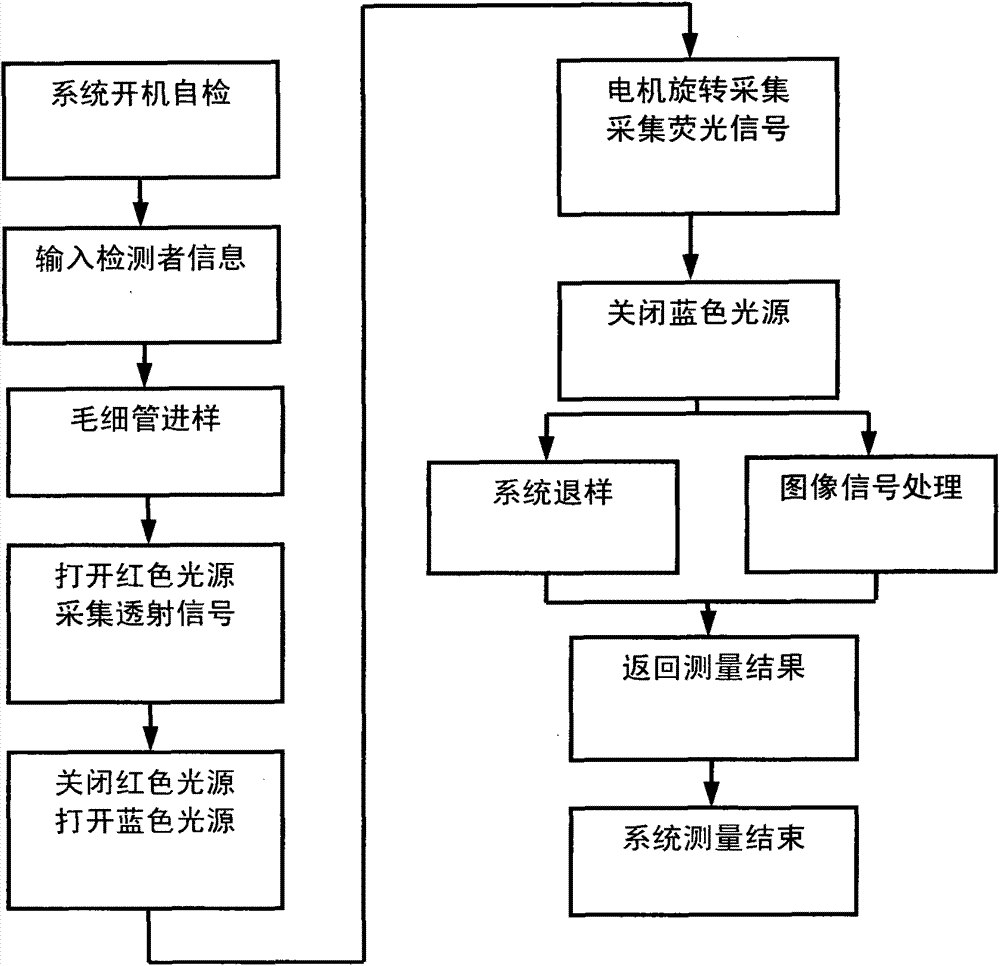
The invention discloses a dry blood cell analytical method. The technical principle of the method lies in that a specially-made centrifugal capillary tube is detected by a red light source and a blue light source, and an image is obtained through collection and analyzed, so that all the index parameters of complete blood cell count are obtained; during the analysis, the capillary tube is sequentially irradiated through the light sources of two colors, imaging for the capillary tube is carried out by a camera lens; images are collected by a colored thread CCD image sensor; the complete blood cell count subjected to data processing is displayed on a display screen and supports printout. The method consumes short time, is efficient, and can be used for quick and accurate whole blood cell analysis.
Owner:北京倍肯恒业科技发展股份有限公司
Methods for complete blood count measurement
ActiveUS10641698B2Investigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsSurgeryComplete blood count
The disclosure relates to devices and methods for analyzing blood cells in a sample. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides devices and methods of performing complete blood count (CBC) testing. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a cartridge device and a reader instrument device, wherein the reader instrument device receives, operates, and / or actuates the cartridge device. In various embodiments, the present disclosure provides a method of using a device as disclosed herein for analyzing blood cells in a sample.
Owner:CYTOCHIP INC
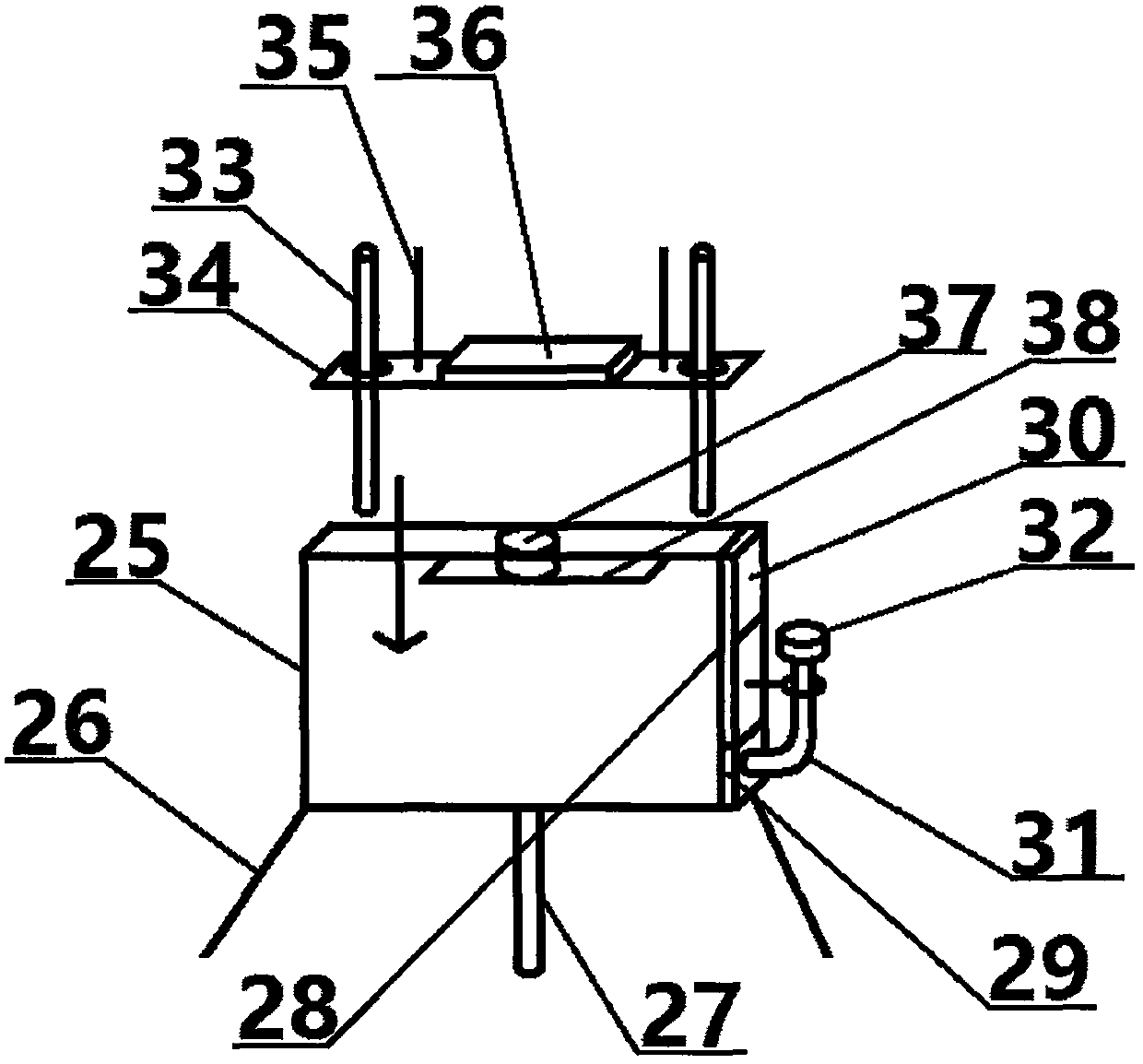
An intelligent blood collection device
ActiveCN105011948BGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed arrivalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBlood Collection TubeWorkload
The invention discloses an intelligent blood collection device, which comprises a box body, a vacuum storage blood vessel, and a blood collection tube. There is a control panel. When in use, the blood collection tube is connected to the vacuum storage vessel and the blood collector. A capacity detection device is installed at the vacuum storage vessel, and an alarm device is also provided on the box body. The control panel controls the capacity detection device and the blood collector. An alarm device, when the required blood volume is reached, the alarm device will alarm to complete the blood collection. The device can detect the amount of blood collected and actively collect blood samples during blood collection, reducing the workload of medical staff. In addition, the device can also record and transmit patient information, one-time information collection, and prevent errors.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
Hematid immunity function test method
The invention discloses a detection method for red blood cell immune function, comprising the following steps: (1) heparin anticoagulant blood is taken to carriy out centrifugalization, blood plasma is extracted for spare, and red blood cells are prepared into cell suspension of 1.25 multiplied by 10<7> / mL; (2) yeast is prepared into yeast solution of 1.0 multiplied by 10<8> / mL ; (3) the cell suspension and the yeast solution with the equal volume are mixed to be even, the blood plasma is added / not added, then water bath with the temperature of 37 DEG C is carried out for 30minutes, glutaric dialdehyde is fixed, smear, drying and dying are carried out, 100 red blood cells are counted, red blood cells stuck with two or more than two yeasts are one positive rosette, and the rosette rates of red blood cell C3bR and IC are calculated; the invention uses the self-blood plasma to carry out yeast sensitization with quick taking and using, no complement is inactive, no allogenic blood ingredients interfere, the preparation of the sensitized yeast reagent is not needed, complete blood cells are used for preparing the cell suspension after the blood plasma is extracted, thus truly reflecting the environment condition in the body, and leading the test cost to be reduced obviously and the detected result to be accurate and reliable.
Owner:常国良
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS20200174241A1Minimizing any bubblingEliminate Bubble ProblemsPreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisWhite blood cellBiology
Disclosed in one aspect is a method for performing a complete blood count (CBC) on a sample of whole blood by metering a predetermined amount of the whole blood and mixing it with a predetermined amount of diluent and stain and transferring a portion thereof to an imaging chamber of fixed dimensions and utilizing an automated microscope with digital camera and cell counting and recognition software to count every white blood cell and red blood corpuscle and platelet in the sample diluent / stain mixture to determine the number of red cells, white cells, and platelets per unit volume, and analyzing the white cells with cell recognition software to classify them.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Automated microscopic cell analysis
ActiveUS20210039093A1Easy to operateAvoid cross contaminationWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationCellular componentWhole blood units
This disclosure describes single-use test cartridges, cell analyzer apparatus, and methods for automatically performing microscopic cell analysis tasks, such as counting and analyzing blood cells in biological samples. A small measured quantity of a biological sample, such as whole blood, is placed in a mixing bowl on the disposable test cartridge after being inserted into the cell analyzer. The analayzer also deposits a known amount of diluent / stain in the mixing bowl and mixes it with the blood. The analyzer takes a measured amount of the mixture and dispenses in a sample cup on the cartridge in fluid communication with an imaging chamber. The geometry of the imaging chamber is chosen to maintain the uniformity of the mixture, and to prevent cells from crowding or clumping as it is transferred into the imaging chamber by the analyzer. Images of all of the cellular components within the imaging chamber are counted and analyzed to obtain a complete blood count.
Owner:MEDICA CORP
Master control data processing system of dry type blood cell analyzing apparatus
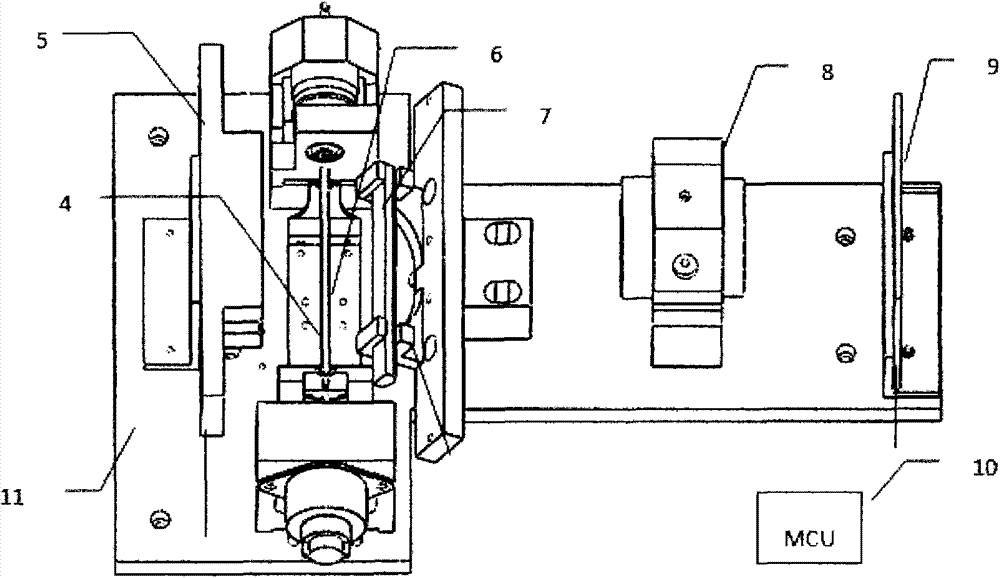
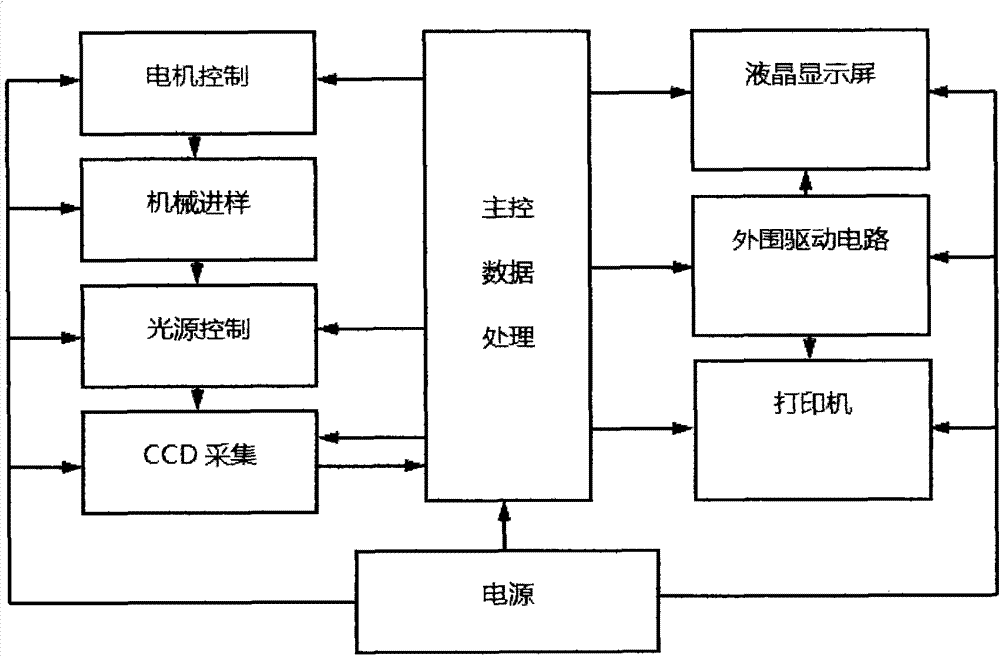
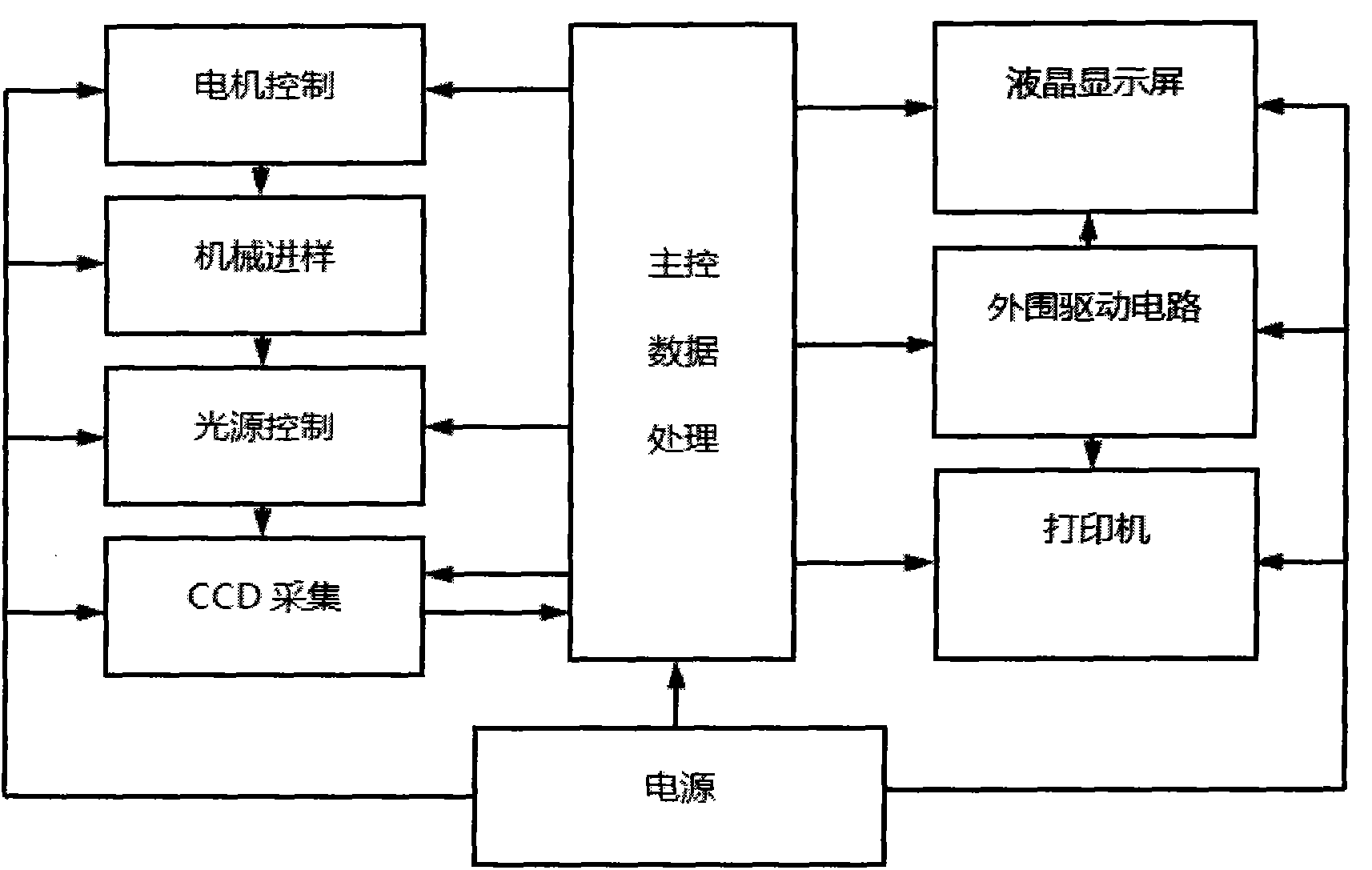
InactiveCN103558403ARun fastImprove detection efficiencyMaterial analysis by optical meansDigital signal processingData processing system
The invention discloses a master control data processing system of a dry type blood cell analyzing apparatus. The master control data processing system comprises a photoelectric sensor 6, a printer 1, a liquid crystal displayer 3 and a master control module 10. Through using the master control data processing system, functions of collecting data, processing images, driving the liquid crystal displayer and the like can be realized; a complete blood cell counting result is obtained after performing data processing on the collected image, displayed on a display screen, printed and output. The master control data processing system disclosed by the invention is equipped with a DSP (Digital Signal Processor) chip which is especially used for digital signal processing and is used for the image processing, so that the system operation speed is further increased, the time spent on analyzing is fully saved, and the detection efficiency is improved.
Owner:北京倍肯恒业科技发展股份有限公司
Cytology counting device
InactiveCN107907471AImprove accuracyWill not affect judgmentBiological particle analysisIndividual particle analysisTransformerWear resistant
The invention discloses a cytology counting device which comprises a counting device body. A supporting platform is arranged on the lower side of the counting device body, a wear-resistant pad for preventing excessive wear is arranged on the lower side of the supporting platform, a lighting groove and a power source box for providing a power source are arranged inside the supporting platform, a lighting device is arranged inside the lighting groove, a power source line interface is arranged on the front side of the power source box, a power source line is arranged in the power source line interface, a power source plug and a transformer for regulating voltage are arranged on the power source line, and a display support is arranged on the right side of the counting device body. Compared with existing complete blood cell counting modes, the cytology counting device has the advantage that counting accuracy can be improved greatly; the cytology counting device adopts an integral counting mode, and a mode of using a counting plate for mathematical calculation is not needed, so that counting accuracy is improved greatly; medical staff is needed to implement complete blood cell counting modes, operation inevitably has certain errors, but manual operation needed by the cytology counting device is little, so that errors are extremely few and have no impact on judgment of disease conditions.
Owner:刘峰
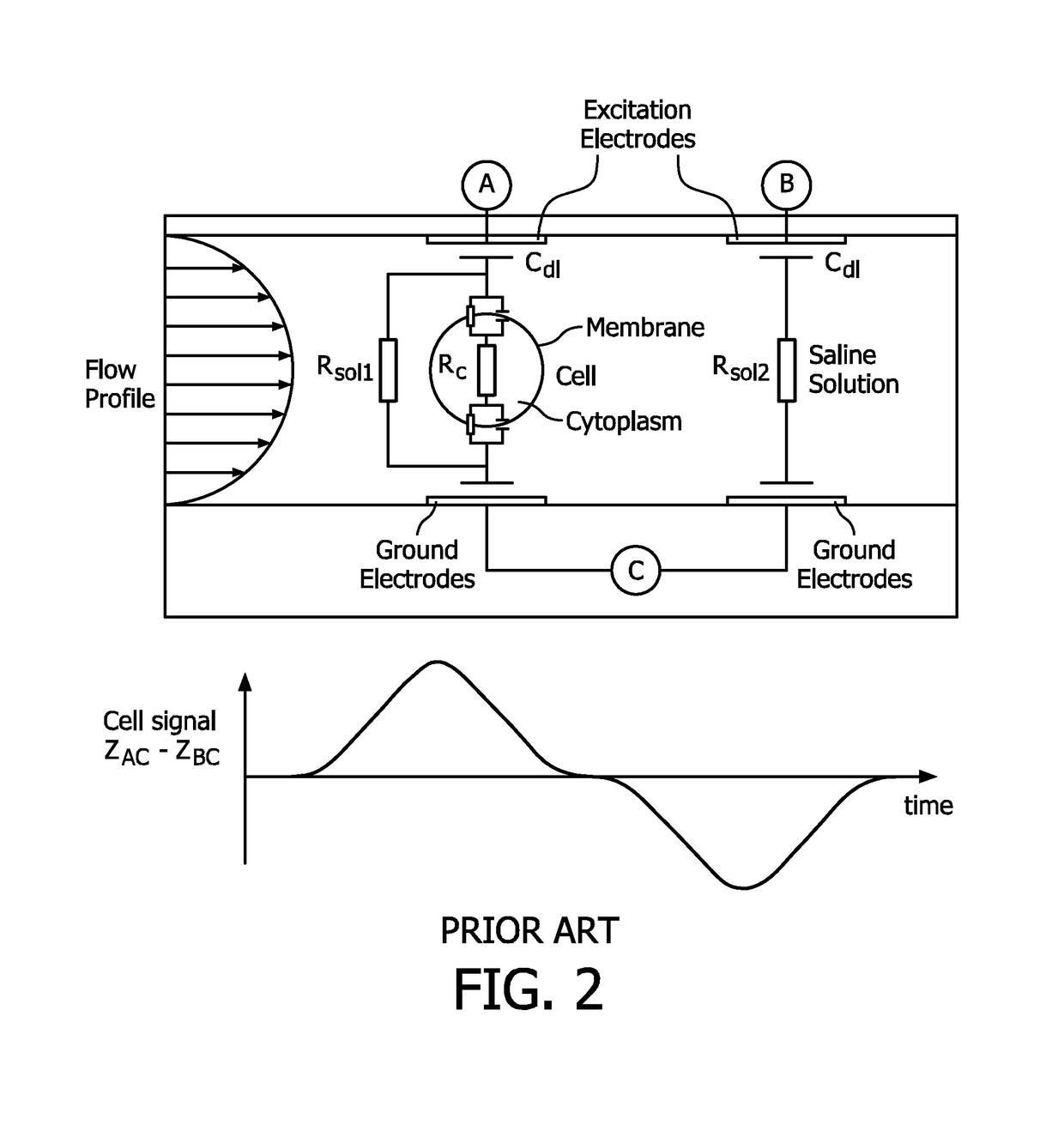
Microfluidic device for full blood count
ActiveUS10191054B2Accurate detectionSignificant dilutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLysisWhite blood cell
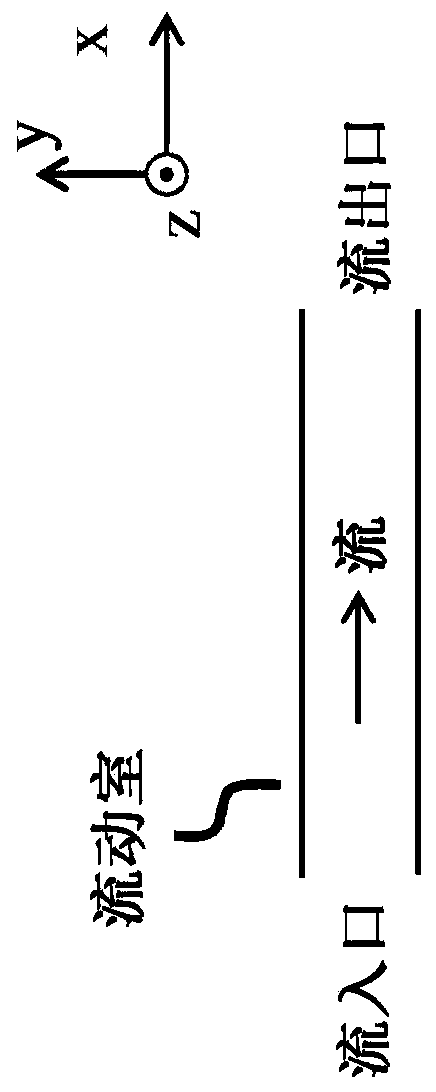
A device for full blood count includes first channel and second channels separated from each other. The device further includes a first inlet configured to provide a whole blood sample to the first and second channels, a second inlet configured to provide a lysis agent for white blood cell count in to the first channel, a third inlet configured to provide a quench solution to the first channel, and a fourth inlet configured to provide a lysis agent for hemoglobin measurement to the second channel.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for eliminating interference of high riglyceride for detecting hemoglobin concentration
The invention provides an eliminating method of interference of the measurement of hypertriglyceride to the concentration of hemoglobin, comprising the following steps of: (1) carrying out complete blood count to blood containing the hypertriglyceride and obtaining the measuring value, HGB lipemia, of the concentration of the hemoglobin and the hematocrit, HCT lipemia, of the erythrocyte; (2) carrying out low-speed centrifugation to the blood containing the hypertriglyceride in the step (1) and leading the erythrocyte and the blood plasma in the blood to be separated; (3) aspirating the bloodplasma separated out in the step (2), carrying out complete blood count to the blood plasma and obtaining the measuring value, HGB lipemia blood plasma, of the concentration of the hemoglobin in the blood plasma; and (4) carrying out correction to the measuring value, HGB lipemia, of the concentration of the hemoglobin obtained in the step (1), obtaining the corrected value of the concentration of the hemoglobin and the corrective formula is as follows: HGB corrected value is equal to HGB lipemia-(HGB lipemia blood plasma minus HGB lipemia blood plasma multiplied by HCT lipemia), in the formula, the HGB lipemia blood plasma multiplied by HCT lipemia is the percentage of the erythrocyte in the blood containing the hypertriglyceride.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
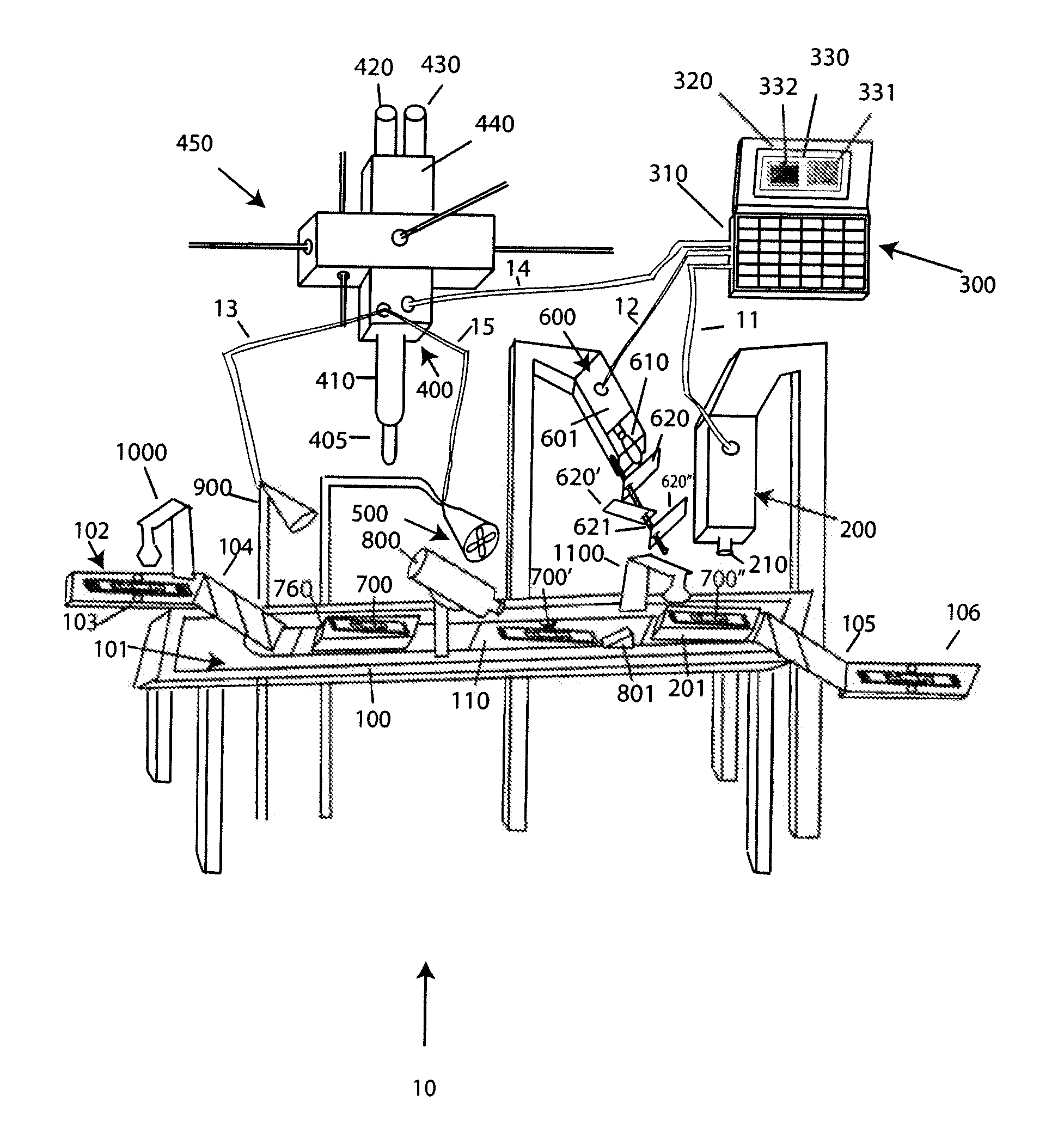
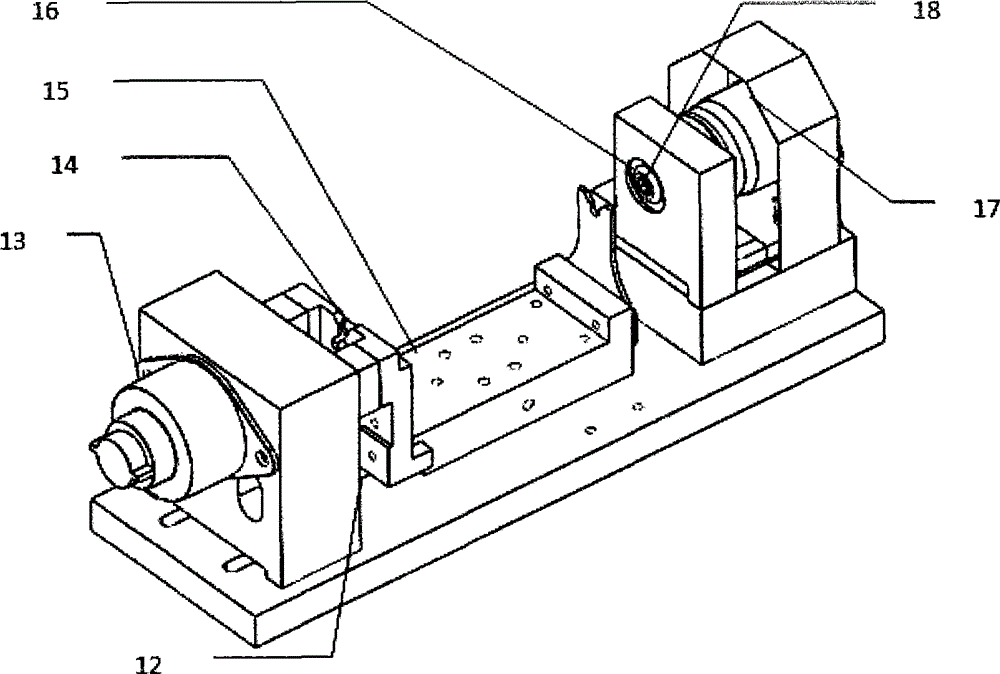
Mechanical sampling system of a dry blood cell analysis device
ActiveCN103529231BIncrease speedImprove seismic performanceMaterial analysisRed blood cellShock resistance
The invention discloses a mechanical sampling system of a dry-type blood cell analyzing device. The mechanical sampling system comprises a sampling groove 2, a capillary tube 4, a base 11, a supporting table 15, horizontal sliding rails 12, a spring clip 14, a bearing 16, a grip 18, a linear motor 13 for propulsion, a linear motor 17 for rotation, a permanent seat of the linear motor for propulsion, a permanent seat of the linear motor for rotation and a bearing permanent seat. The mechanical sampling system is suitable for the sampling of a complete blood cell analyzing device, is simple in structure and has good shock resistance, fast analysis speed and stable performance.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL SUPPORT TECH OF ACAD OF SYST ENG OF ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
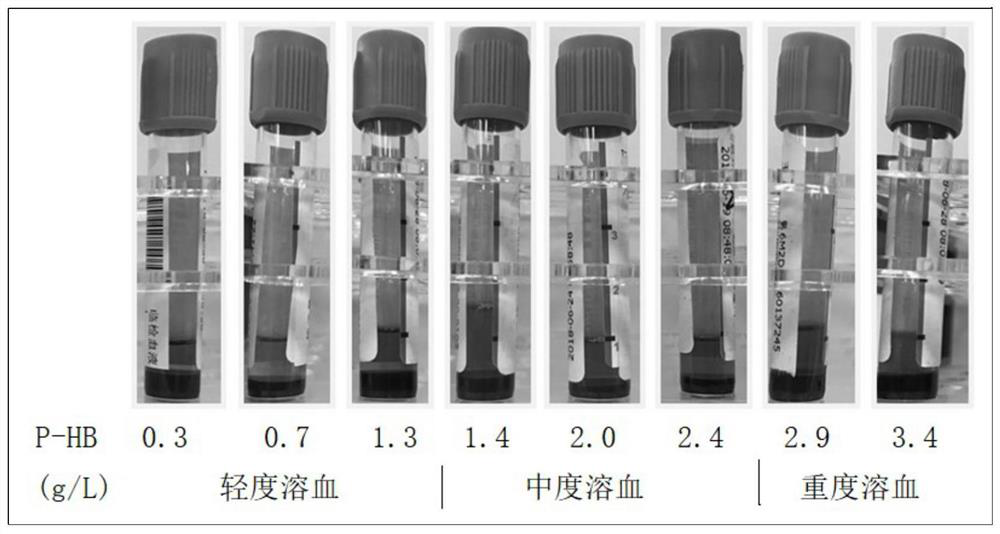
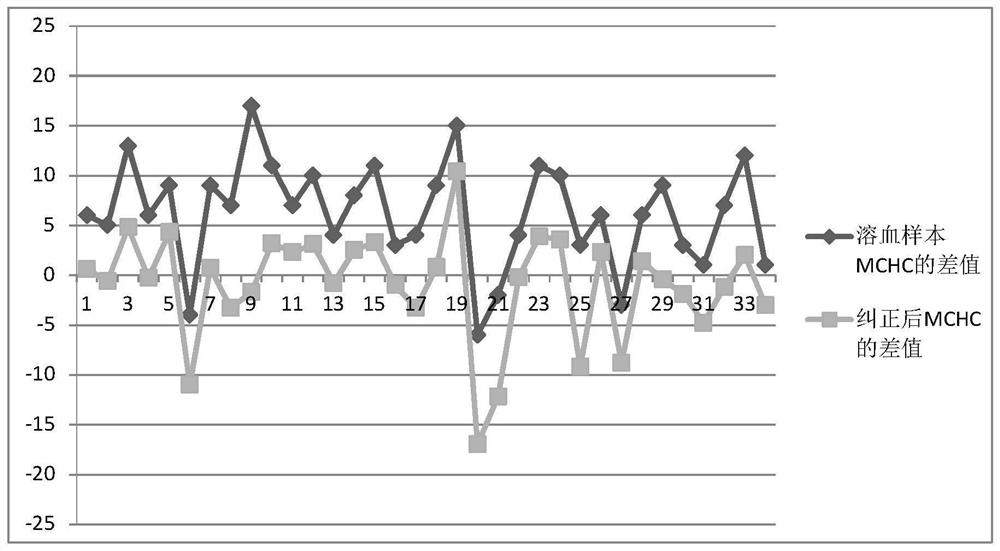
A method for correcting the influence of hemolysis on the detection of red blood cell series parameters
ActiveCN110187131BImprove accuracyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingHemolysisRed blood cell
The invention provides a method for correcting influence of hemolysis on detection of red blood cell series parameters, and the method comprises the following steps of obtaining a red blood cell countmeasurement value, a hemoglobin concentration measurement value, a blood cell specific product measurement value and an average red blood cell hemoglobin measurement value by complete blood cell count; separating the red blood cells and the plasma to obtain the hemoglobin concentration measurement value in the plasma, obtaining a corresponding correction value, and evaluating the result. The redblood cell series parameters of the hemolyzed blood obtained by the method provided by the invention have high numerical accuracy, and the difference from the true value is less than + / -0.5% on average. The method provided by the invention is simple in operation, and the detecting instrument and centrifuge used are laboratory routine equipment, thereby facilitating the popularization and application in various hospitals. The method provided by the invention requires a short time and can quickly obtain the detection result, that is, saving time and saving cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
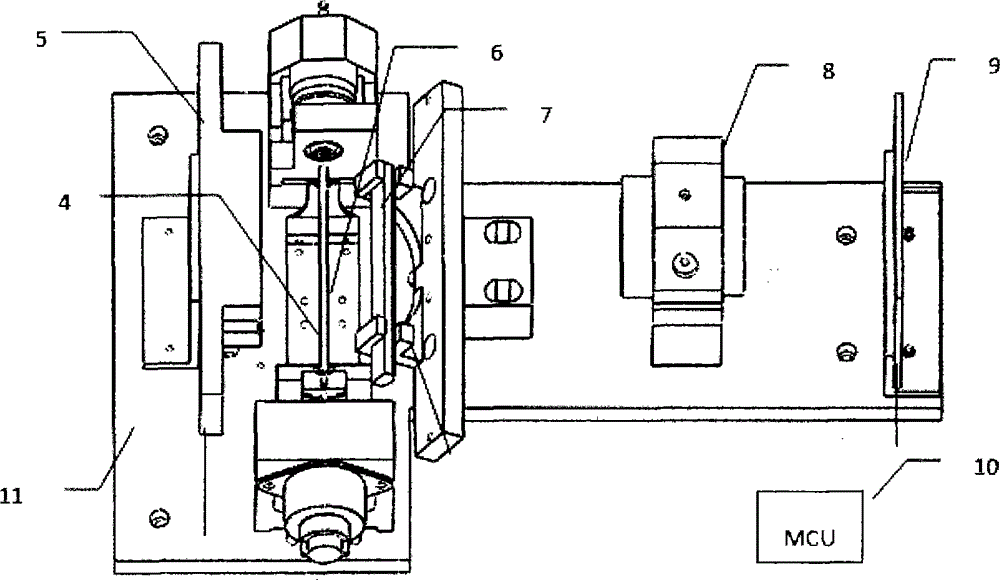
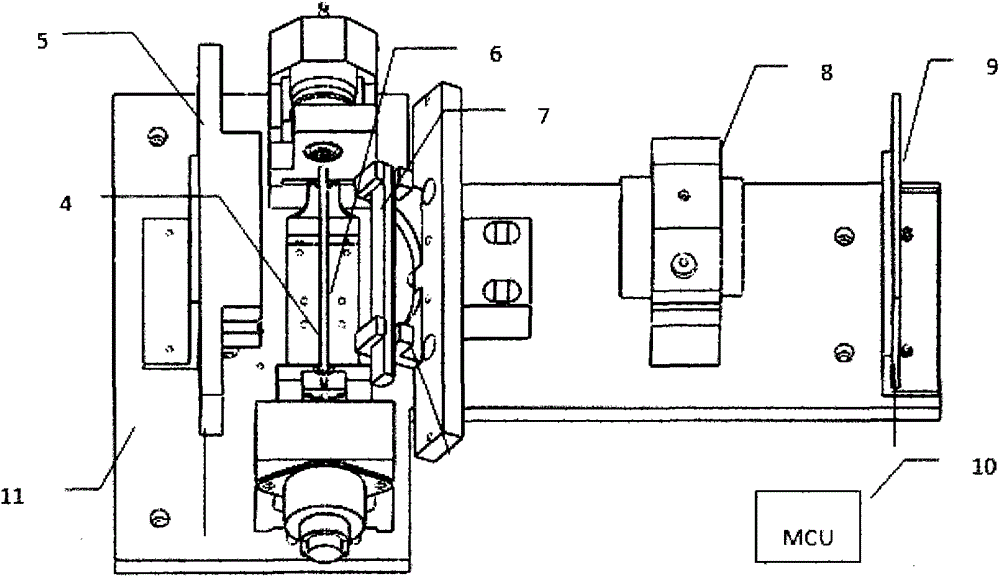
Optical detection system of dry-type blood cell analyzing device
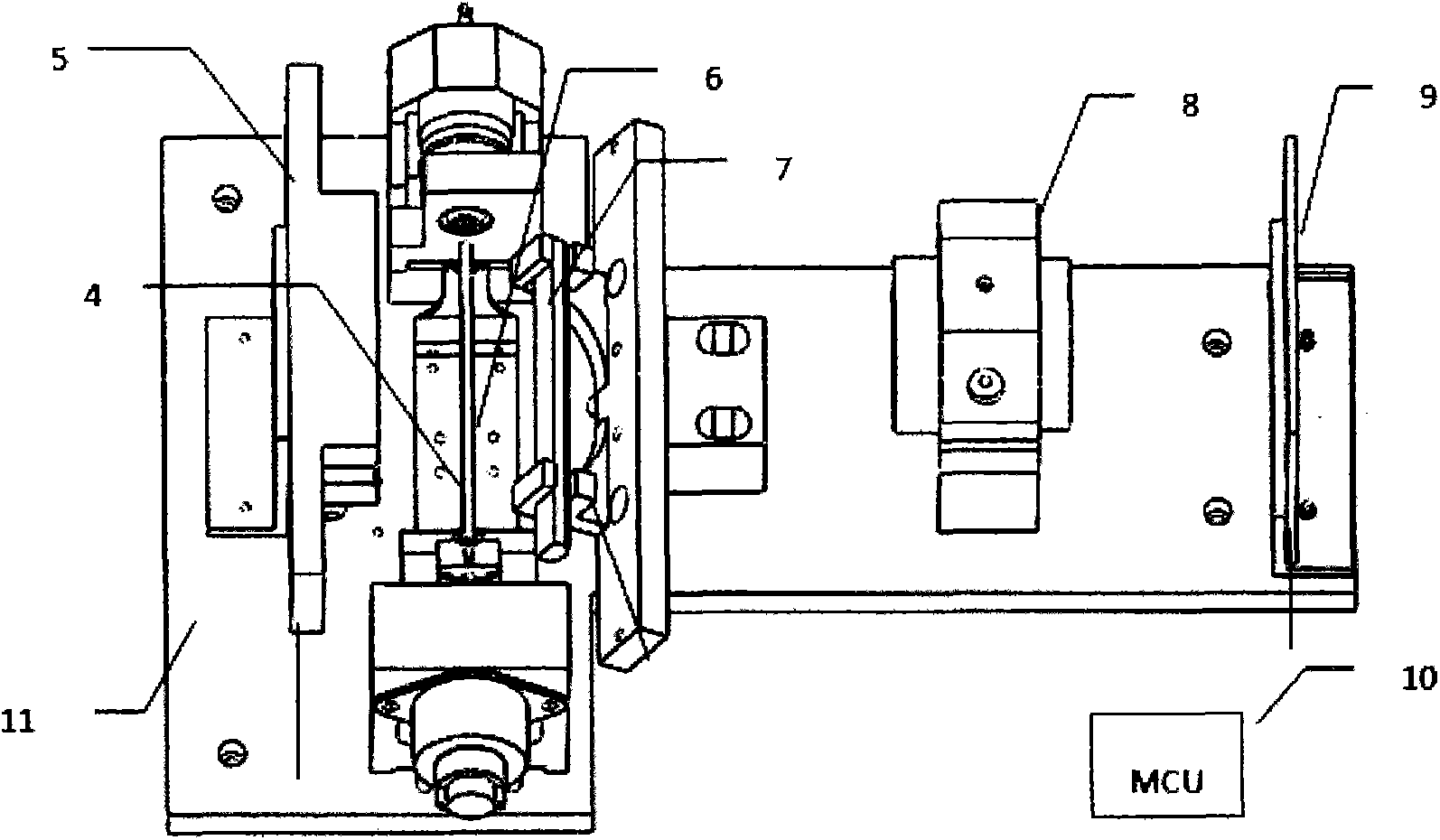
ActiveCN103528936AShort timeImprove efficiencyIndividual particle analysisComplete blood countCharge couple device
The invention discloses an optical detection system of a dry-type blood cell analyzing device. The optical detection system of the dry-type blood cell analyzing device comprises a red light source 5, a blue light source 7, a lens 8 and a colored linear array CCD (Charged Coupled Device) imaging sensor 9, wherein the two light sources are used for sequentially irradiating a to-be-detected capillary tube, the lens 8 is used for imaging the capillary tube, the colored linear array CCD imaging sensor 9 is used for collecting images, and complete blood cell counting results are obtained through data processing. The optical detection system is suitable for the optical detection of a complete blood cell analyzing device, is fast in speed and has stable performances.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL SUPPORT TECH OF ACAD OF SYST ENG OF ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Methods of diagnosing clostridium difficile infection or recurrence in a subject
ActiveUS20180164282A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsClostridial infectionBacteroides
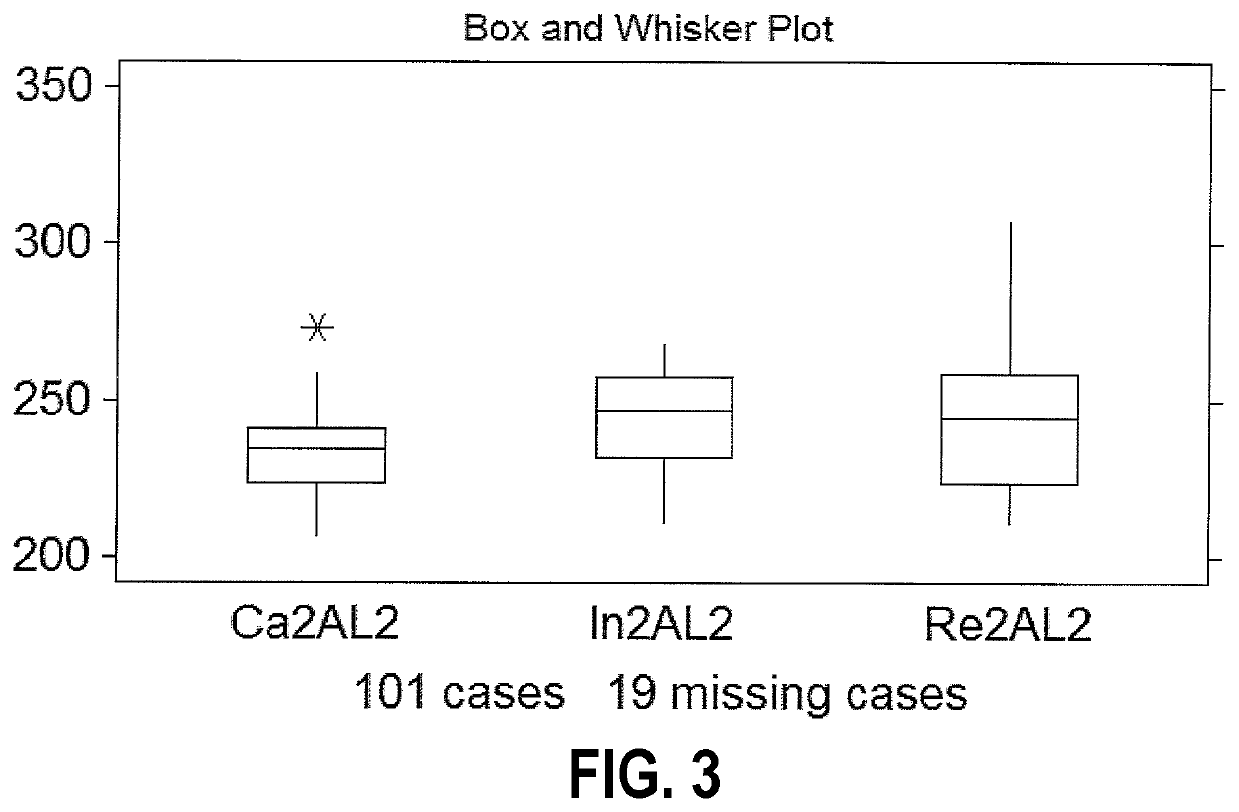
Methods are described for identifying CDI patients as well as CDI patients at risk for recurrence. Embodiments include: (1) flow cytometry of circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to phenotype for the less efficient immunoglobulin response to bacterial toxins and surface antigens that characterizes patients who will become recurrent; (2) stratification by means of complete blood count (CBC) using a Coulter counter to detect the differences in lower angle light scatter (LAL), which has a larger range in the recurrent population; and (3) stratification by means of complete blood count (CBC) using a Coulter counter to detect the lower axial light loss (AL2) exhibited in recurrent patients.
Owner:MUSIDORA BIOTECH LLC +1
Application of complete blood count in predicting sars-cov-2 infection
ActiveCN112525804BImprove performanceIncrease valueCharacter and pattern recognitionIndividual particle analysisHospitalized patientsData set
Owner:YANTAI ZHIYI MEDICINE TECH CO LTD +1
Methods of diagnosing Clostridium difficile infection or recurrence in a subject
ActiveUS11085912B2Increased speed and accuracy and reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsAntigenPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
Methods are described for identifying CDI patients as well as CDI patients at risk for recurrence. Embodiments include: (1) flow cytometry of circulating peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to phenotype for the less efficient immunoglobulin response to bacterial toxins and surface antigens that characterizes patients who will become recurrent; (2) stratification by means of complete blood count (CBC) using a Coulter counter to detect the differences in lower angle light scatter (LAL), which has a larger range in the recurrent population; and (3) stratification by means of complete blood count (CBC) using a Coulter counter to detect the lower axial light loss (AL2) exhibited in recurrent patients.
Owner:MUSIDORA BIOTECH LLC +1
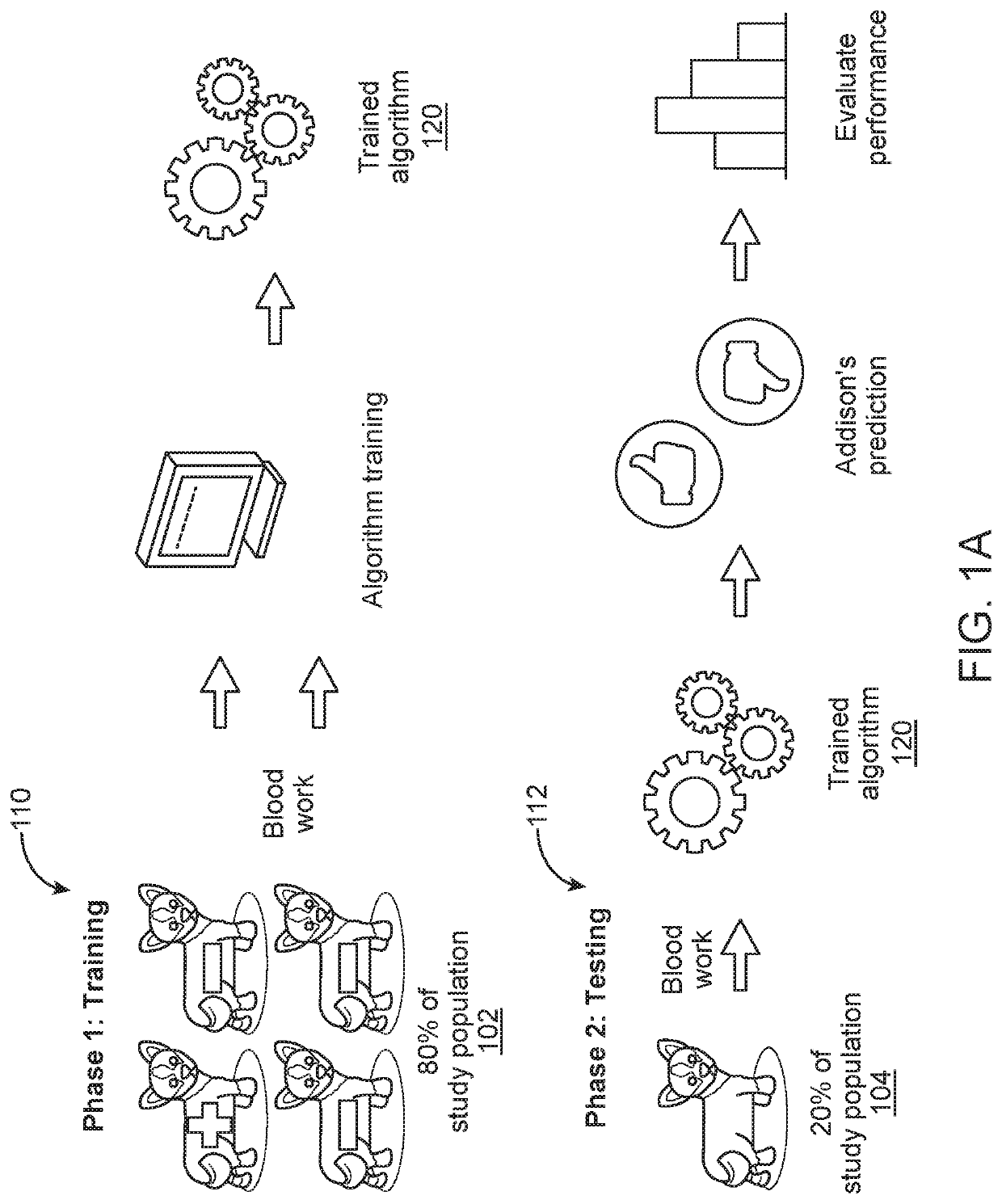
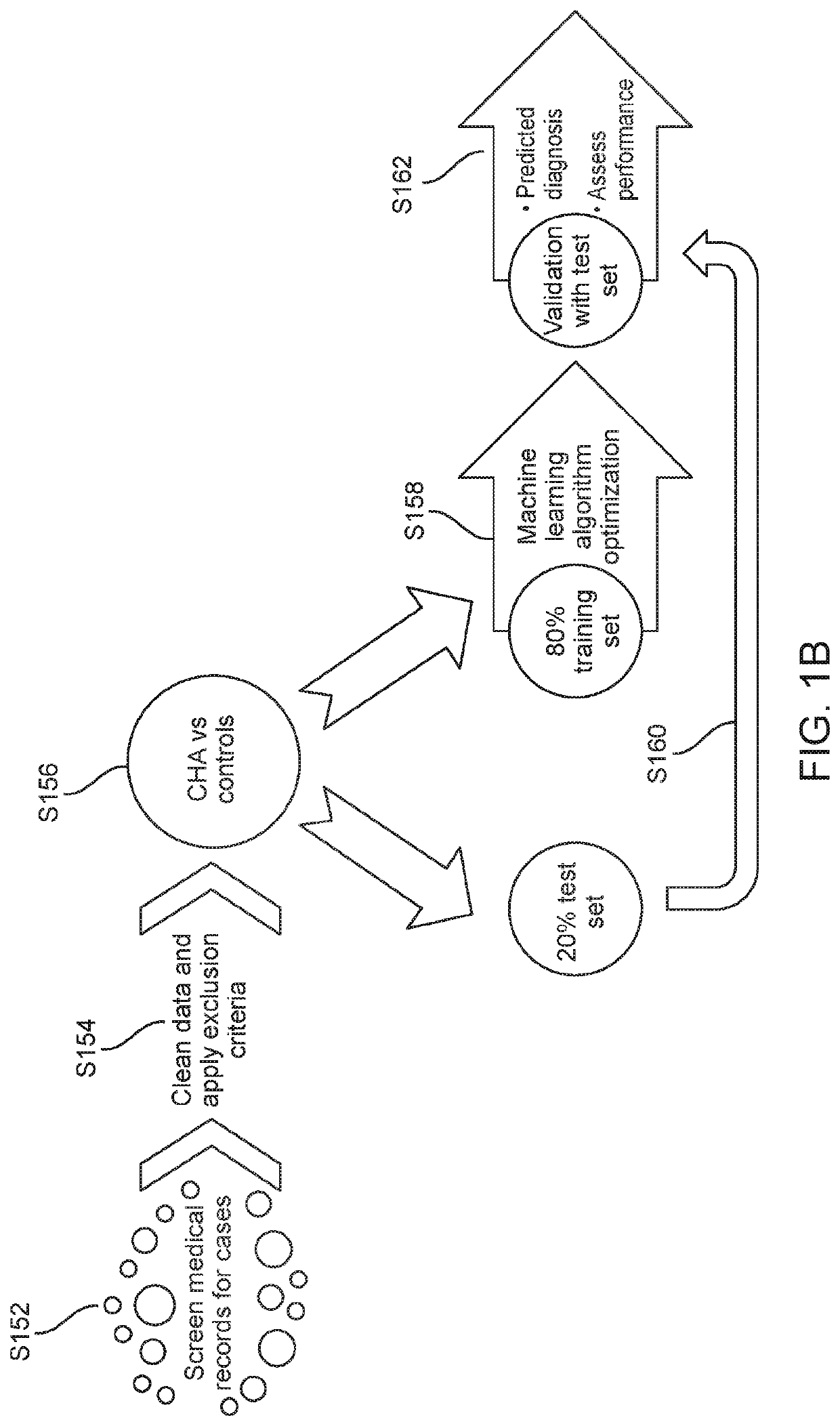
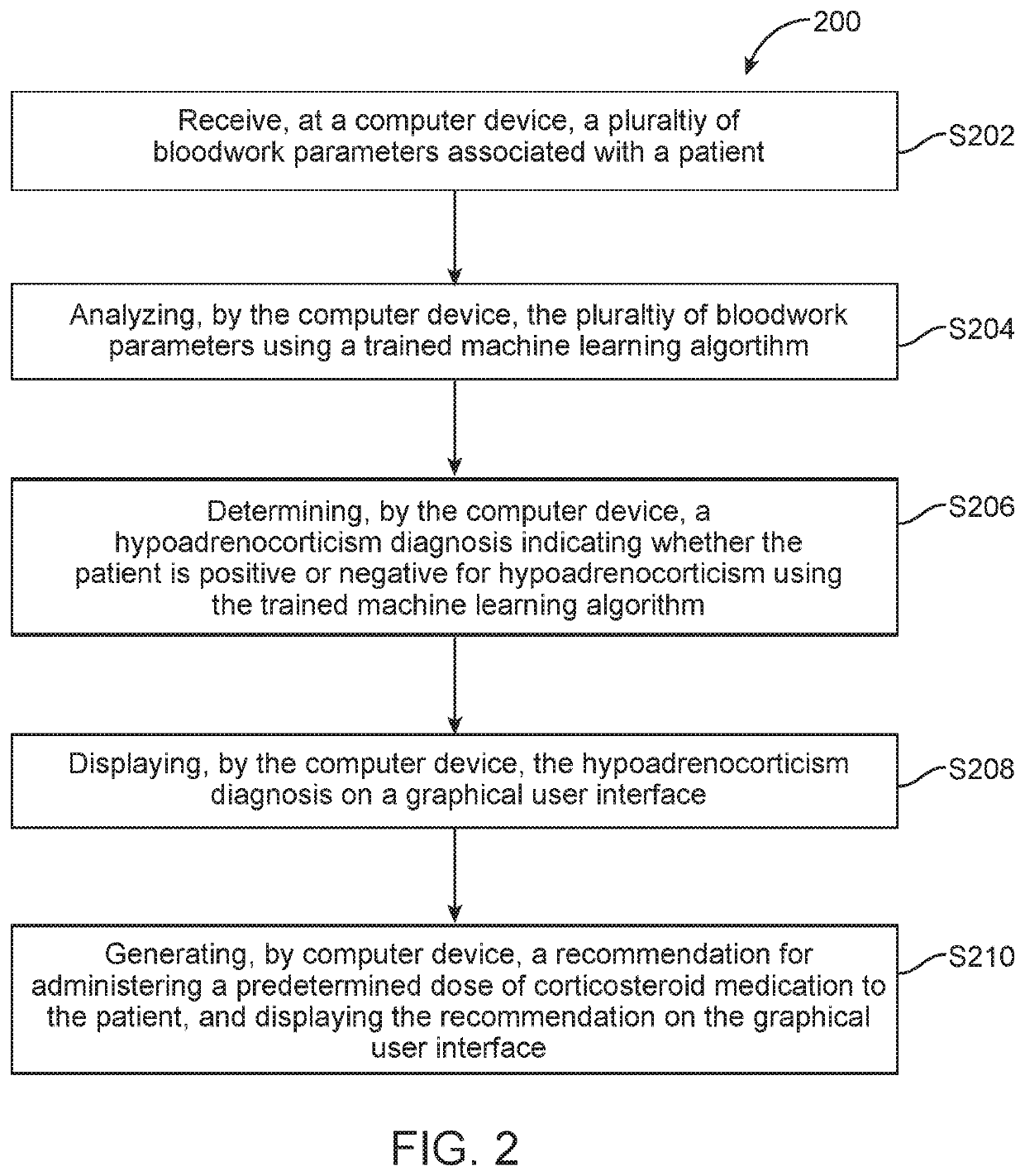
Diagnosing hypoadrenocorticism from hematologic and serum chemistry parameters using machine learning algorithm
PendingUS20210249136A1Efficient use ofBiostatisticsMedical automated diagnosisPattern recognitionAlgorithm
The invention is directed to a hypoadrenocorticism diagnostic tool including a computer device for executing a trained machine learning algorithm to analyze bloodwork parameters and determine a hypoadrenocorticism diagnosis based on the bloodwork parameters. The bloodwork parameters may include complete blood count and serum chemistry parameters. The computer device receives the bloodwork parameters associated with a patient and analyzes the bloodwork parameters using the trained machine learning algorithm. The computer device determines the hypoadrenocorticism diagnosis indicating whether the patient is positive or negative for hypoadrenocorticism using the trained machine learning algorithm, and displays the hypoadrenocorticism diagnosis on a graphical user interface.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
An optical detection system of a dry blood cell analysis device
ActiveCN103528936BShort timeImprove efficiencyIndividual particle analysisRed blood cellBlood cell analysis
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL SUPPORT TECH OF ACAD OF SYST ENG OF ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
Microfluidic device for full blood count
PendingUS20190120840A1Accurate detectionSignificant dilutionBiological particle analysisLaboratory glasswaresLysisWhite blood cell
A microfluidic device (10) for full blood count includes a first measurement channel (11) and a second measurement channel (12) separated from the first measurement channel (11). The microfluidic device (10) furthermore includes a first inlet (13) for providing a whole blood sample to the first and second measurement channel (11, 12), a second inlet (14) for providing a lysis agent for white blood cell count in to the first channel (11), a third inlet (15) for providing a quench solution to the first channel (11), and a fourth inlet (16) for providing a lysis agent for hemoglobin measurement to the second channel (12). A method for forming such a microfluidic device (10) and a method for performing a full blood count test using such a microfluidic device (10) are described.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com